
Affiliate 💸
Get started free
Literature Review

12 Best Tools For Perfect Research Summary Writing
Discover the 12 best tools to streamline your research summary writing, ensuring clarity and precision every time.
Aug 29, 2024

Consider you finally find the time to tackle that research paper for your class. You pull up your literature search and see dozens of articles and studies staring back at you. As you scroll through the titles and abstracts, you realize you need to figure out how to summarize the research to get started on your paper.
Writing a practical research summary can feel daunting, but it doesn’t have to. In this guide, we’ll break down what a research summary is, why it’s essential, and how to write one. This information lets you confidently write your research summary and finish your paper.
Otio’s AI research and writing partner can help you write efficient research summaries and papers. Our tool can summarize academic articles so you can understand the material and finish your writing.
Table Of Contents
What is a research summary, purpose of a research summary, how do you write a research summary in 10 simple steps, what is a phd research summary, examples of research summary, supercharge your researching ability with otio — try otio for free today.

A research summary is a piece of writing that summarizes your research on a specific topic. Its primary goal is to offer the reader a detailed study overview with critical findings. A research summary generally contains the structure of the article.
You must know the goal of your analysis before you launch a project. A research overview summarizes the detailed response and highlights particular issues. Writing it may be troublesome. You want to start with a structure in mind to write a good overview.
Related Reading
• Systematic Review Vs Meta Analysis • Impact Evaluation • How To Critique A Research Article • How To Synthesize Sources • Annotation Techniques • Skimming And Scanning • Types Of Literature Reviews • Literature Review Table • Literature Review Matrix • How To Increase Reading Speed And Comprehension • How To Read Research Papers • How To Summarize A Research Paper • Literature Gap

A research summary provides a brief overview of a study to readers. When searching for literature, a reader can quickly grasp the central ideas of a paper by reading its summary. It is also a great way to elaborate on the significance of the findings, reminding the reader of the strengths of your main arguments.
Having a good summary is almost as important as writing a research paper. The benefit of summarizing is showing the "big picture," which allows the reader to contextualize your words. In addition to the advantages of summarizing for the reader, as a writer, you gain a better sense of where you are going with your writing, which parts need elaboration, and whether you have comprehended the information you have collected.

1. Read The Entire Research Paper
Before writing a research summary , you must read and understand the entire research paper. This may seem like a time-consuming task, but it is essential to write a good summary. Make sure you know the paper's main points before you begin writing.
2. Take Notes As You Read
As you read, take notes on the main points of the paper. These notes will come in handy when you are writing your summary. Be sure to note any necessary information, such as the main conclusions of the author's writing. This helpful tip will also help you write a practical blog summary in less time.
3. Organize Your Thoughts
Once you have finished reading and taking notes on the paper, it is time to start writing your summary. Before you begin, take a few minutes to organize your thoughts. Write down the main points that you want to include in your summary. Then, arrange these points in a logical order.
4. Write The Summary
Now that you have organized your thoughts, it is time to start writing the summary. Begin by stating the author’s thesis statement or main conclusion. Then, briefly describe each of the main points from the paper. Be sure to write clearly and concisely. When you finish, reread your summary to ensure it accurately reflects the paper's content.
5. Write The Introduction
After you have written the summary, it is time to write the introduction. The introduction should include an overview of the paper and a summary description. It should also state the main idea.
6. Introduce The Report's Purpose
The summary of a research paper should include a brief description of the paper's purpose. It should state the paper's thesis statement and briefly describe each of the main points of the paper.
7. Use Keywords To Introduce The Report
When introducing the summary of a research paper, use keywords familiar to the reader. This will help them understand the summary and why it is essential.
8. State The Author's Conclusions
The summary of a research paper should include a brief statement of the author's conclusions. This will help your teacher understand what the paper is trying to achieve.
9. Keep It Concise
A summary should be concise and to the point. It should not include any new information or arguments. It should be one paragraph long at maximum.
10. Edit And Proofread
After you have written the summary, edit and proofread it to ensure it is accurate and precise. This will help ensure that your summary is effective and free of any grammar or spelling errors.

1. Otio: Your AI Research Assistant
Knowledge workers, researchers, and students today need help with content overload and are left to deal with it using fragmented, complex, and manual tooling. Too many settle for stitching together complicated bookmarking, read-it-later, and note-taking apps to get through their workflows. Now that anyone can create content with a button, this problem will only worsen. Otio solves this problem by providing researchers with one AI-native workspace. It helps them:
1. Collect a wide range of data sources, from bookmarks, tweets, and extensive books to YouTube videos.
2. extract key takeaways with detailed ai-generated notes and source-grounded q&a chat. , 3. create draft outputs using the sources you’ve collected. .
Otio helps you to go from a reading list to the first draft faster. Along with this, Otio also enables you to write research papers/essays faster. Here are our top features that researchers love: AI-generated notes on all bookmarks (Youtube videos, PDFs, articles, etc.), Otio enables you to chat with individual links or entire knowledge bases, just like you chat with ChatGPT, as well as AI-assisted writing.
Let Otio be your AI research and writing partner — try Otio for free today !
2. Hypotenuse AI: The Versatile Summarizer
Like all the AI text summarizers on this list, Hypotenuse AI can take the input text and generate a short summary. One area where it stands out is its ability to handle various input options: You can simply copy-paste the text, directly upload a PDF, or even drop a YouTube link to create summaries.
You can summarize nearly 200,000 characters (or 50,000 words) at once.
Hypotenuse AI summarizes articles, PDFs, paragraphs, documents, and videos.
With the AI tool, you can create engaging hooks and repurpose content for social media.
You'll need a paid plan after the 7-day free trial.
There needs to be a free plan available.
The AI tool majorly focuses on generating eCommerce and marketing content.
3. Scalenut: The Beginner-Friendly AI Summarizer
Scalenut is one of the powerful AI text summarizers for beginners or anyone starting out. While it's not as polished as some other business-focused apps, it's significantly easier to use — and the output is just as good as others. If you want a basic online text summarizer that lets you summarize the notes within 800 characters (not words), Scalenut is your app.
With Scalenut, you get a dedicated summary generation tool for more granular control.
The keyword planner available helps build content directly from the short and sweet summaries.
The AI tool integrates well with a whole suite of SEO tools, making it a more SEO-focused summarizer.
You only get to generate one summary per day.
Scalenut's paid plans are expensive compared to other AI tools.
You must summarize long-form articles or blogs at most the limit of 800 characters.
4. SciSummary: The Academic AI Summarizer
SciSummary is an AI summarizer that helps summarize single or multiple research papers. It combines and compares the content summaries from research papers, article links, etc.
It can save time and effort for scientists, students, and enthusiasts who want to keep up with the latest scientific developments.
It can provide accurate and digestible summaries powered by advanced AI models that learn from feedback and expert guidance.
It can help users read between the lines and understand complex scientific texts' main points and implications.
It may only capture some nuances and details of the original articles or papers, which may be necessary for some purposes or audiences.
Some types of scientific texts, such as highly technical, specialized, or interdisciplinary, may require more domain knowledge or context.
Some sources of scientific information, such as websites, videos, or podcasts not in text format, may need help summarizing.
5. Quillbot: The AI Summarizer for Academic Papers
QuillBot uses advanced neural network models to summarize research papers accurately and effectively. The tool leverages cutting-edge technology to condense lengthy papers into concise and informative summaries, making it easier for users to navigate vast amounts of literature.
You can upload the text for summarization directly from a document.
It's excellent for summarizing essays, papers, and lengthy documents.
You can summarize long texts up to 1200 words for free.
The free plan is limited to professionals.
There could have been some more output types.
QuillBot's Premium plan only gives you 6000 words for summaries per month.
6. Scribbr: The Research Paper Assistant
Scribbr is an AI-driven academic writing assistant with a summarization feature tailored for research papers. The tool assists users in the research paper writing process by summarizing and condensing information from various sources, offering support in structuring and organizing content effectively.
7. TLDR This: The Online Article Summarizer
TLDR This uses advanced AI to effectively filter out unimportant arguments from online articles and provide readers only with vital takeaways. Its streamlined interface eliminates ads and distractions while summarizing key points, metadata, images, and other crucial article details.
TLDR This condenses even very lengthy materials into compact summaries users can quickly consume, making it easier to process a vast range of internet content efficiently.
Ten free "AI" summaries
Summarization of long text
Basic summary extraction
Premium option cost
No significant improvement in premium options
8. AI Summarizer: The Text Document Summarizer
AI Summarizer harnesses artificial intelligence to summarize research papers and other text documents automatically. The tool streamlines the summarization process, making it efficient and accurate, enabling users to extract essential information from extensive research papers efficiently.
Easy-to-understand interface
1500-word limit
Multiple language support
Contains advertisements
Requires security captcha completion
Struggles with lengthy content summarization
9. Jasper: The Advanced Summarizer
Jasper AI is a robust summarizing tool that helps users generate AI-powered paper summaries quickly and effectively. The tool supports the prompt creation of premium-quality summaries, assisting researchers in distilling complex information into concise and informative outputs.
Jasper offers some advanced features, like generating a text from scratch and even summarizing it.
It integrates well with third-party apps like Surfer, Grammarly, and its own AI art generator.
It's versatile and can be used to create summaries of blogs, articles, website copy, emails, and even social media posts.
There's no free plan available — though you get a 7-day free trial.
You'll need to have a flexible budget to use Jasper AI.
The Jasper app has a steep learning curve.
10. Resoomer: The Summary Extractor
Resoomer rapidly analyzes textual documents to determine the essential sentences and summarizes these key points using its proprietary semantic analysis algorithm.
By automatically identifying what information matters most, Resoomer can condense elaborate texts across diverse subjects into brief overviews of their core message. With swift copy-and-paste functionality requiring no signup, this specialized tool simplifies the reading experience by extracting only vital details from complex writings.
Clear and accurate summaries
Creative sentence combining
Variety of modes and options
Lengthy text summarization without word limit in premium mode
Confusing interface with irrelevant features
Long-winded summaries spread across multiple pages
11. Anyword: The Marketing-Focused Summarizer
When I saw Anyword's summary, I could easily state that the content was unique and worth sharing, making this AI tool an excellent choice for marketers. Plus, it's very easy to use.
Once you've copied-pasted the text and chosen a summary type, paragraph, keywords, or TL;DR, it generates a summary in minutes. Approve it; you can share the text directly without worrying about plagiarized content.
You can test the AI tool with the 7-day free trial.
The Anyword's text generator and summarizer are perfect for creating long-form pieces like blog posts with snippets.
You can give detailed prompts to the AI tool to customize the generated text.
Any word is expensive for a more limited set of features than other AI summarizers.
It can sometimes be slower to use.
There is no free Anyword plan available.
12. Frase: The SEO Summarizer
Frase is a powerful AI-powered summarizer that focuses on SEO. This means it can generate summaries that attract audiences and rank higher. Its proprietary model stands out, providing more flexibility, competitive pricing, and custom features.
Frase uses BLUF and Reverse Pyramid techniques to generate summaries, improving ranking chances.
It's free to use Frase's summary generator.
Instead of GPT-3.5 or GPT-4, Frase uses its proprietary model.
There's no way to add links to the blog or article to generate a summary.
You can input up to 600-700 words for summarization.
It might not be an ideal article summarizer for those who don't care about SEO.

A research summary for a PhD is called a research statement . The research statement (or statement of research interests) is included in academic job applications. It summarizes your research accomplishments, current work, and future direction and potential. The statement can discuss specific issues such as funding history and potential requirements for laboratory equipment and space and other resources, possible research and industrial collaborations, and how your research contributes to your field's future research direction.
The research statement should be technical but intelligible to all department members, including those outside your subdiscipline. So keep the “big picture” in mind. The strongest research statements present a readable, compelling, and realistic research agenda that fits well with the department's needs, facilities, and goals. Research statements can be weakened by: overly ambitious proposals lack of apparent direction lack of big-picture focus, and inadequate attention to the needs and facilities of the department or position.
• Literature Search Template • ChatGPT Prompts For Research • How To Find Gaps In Research • Research Journal Example • How To Find Limitations Of A Study • How To Do A Literature Search • Research Concept Map • Meta-Analysis Methods • How To Identify Bias In A Source • Search Strategies For Research • Literature Search Template • How To Read A Research Paper Quickly • How To Evaluate An Article • ChatGPT Summarize Paper • How To Take Notes For A Research Paper

Research Summary Example 1: A Look at the Probability of an Unexpected Volcanic Eruption in Yellowstone
Introduction .
If the Yellowstone supervolcano erupted massively , the consequences would be catastrophic for the United States. The importance of analyzing the likelihood of such an eruption cannot be overstated.
Hypothesis
An eruption of the Yellowstone supervolcano would be preceded by intense precursory activity manifesting a few weeks up to a few years in advance.
Results
Statistical data from multiple volcanic eruptions happening worldwide show activity that preceded these events (in particular, how early each type of activity was detected).
Discussion and Conclusion
Given that scientists continuously monitor Yellowstone and that signs of an eruption are normally detected much in advance, at least a few days in advance, the hypothesis is confirmed. This could be applied to creating emergency plans detailing an organized evacuation campaign and other response measures.
Research Summary Example 2: The Frequency of Extreme Weather Events in the US from 2000-2008 as Compared to the ‘50s
Weather events bring immense material damage and cause human victims.
Extreme weather events are significantly more frequent nowadays than in the ‘50s.
Several categories of extreme events occur regularly now and then: droughts and associated fires, massive rainfall/snowfall and associated floods, hurricanes, tornadoes, Arctic cold waves, etc.
Discussion and Conclusion
Several extreme events have become significantly more frequent recently, confirming this hypothesis. This increasing frequency correlates reliably with rising CO2 levels in the atmosphere and growing temperatures worldwide.
In the absence of another recent significant global change that could explain a higher frequency of disasters, and knowing how growing temperature disturbs weather patterns, it is natural to assume that global warming (CO2) causes this increase in frequency. This, in turn, suggests that this increased frequency of disasters is not a short-term phenomenon but is here to stay until we address CO2 levels.
Researchers, students, and knowledge workers have long struggled with the initial stages of research projects. The early steps of gathering and organizing information , taking notes, and synthesizing the material into a coherent summary are vital for establishing a solid foundation for any research endeavor.
These steps can be tedious, overwhelming, and time-consuming. Otio streamlines this process so you can go from the reading list to the first draft faster. Along with this, Otio also helps you write research papers/essays faster. Here are our top features that researchers love:
AI-generated notes on all bookmarks (Youtube videos, PDFs, articles, etc.), Otio enables you to chat with individual links or entire knowledge bases, just like you chat with ChatGPT, as well as AI-assisted writing.
• Sharly AI Alternatives • AI For Summarizing Research Papers • Literature Review Tools • How To Identify Theoretical Framework In An Article • Graduate School Reading • Research Tools • AI For Academic Research • Research Paper Organizer • Best AI Tools For Research • Zotero Alternatives • Zotero Vs Endnote • ChatGPT For Research Papers • ChatGPT Literature Review • Mendeley Alternative • Unriddle AI Alternatives • Literature Matrix Generator • Research Assistant • Research Tools • Research Graphic Organizer • Good Websites for Research • Best AI for Research • Research Paper Graphic Organizer

Aug 31, 2024
15 Best AI For Research (Quick and Efficient)

Aug 28, 2024
22 Good Websites For Research Papers and Academic Articles
Join over 50,000 researchers changing the way they read & write

Chrome Extension
© 2024 Frontdoor Labs Ltd.
Terms of Service
Privacy Policy
Refund Policy
Join thousands of other scholars and researchers
Try Otio Free
© 2023 Frontdoor Labs Ltd.
arXiv's Accessibility Forum starts next month!
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: platypus: a generalized specialist model for reading text in various forms.
Abstract: Reading text from images (either natural scenes or documents) has been a long-standing research topic for decades, due to the high technical challenge and wide application range. Previously, individual specialist models are developed to tackle the sub-tasks of text reading (e.g., scene text recognition, handwritten text recognition and mathematical expression recognition). However, such specialist models usually cannot effectively generalize across different sub-tasks. Recently, generalist models (such as GPT-4V), trained on tremendous data in a unified way, have shown enormous potential in reading text in various scenarios, but with the drawbacks of limited accuracy and low efficiency. In this work, we propose Platypus, a generalized specialist model for text reading. Specifically, Platypus combines the best of both worlds: being able to recognize text of various forms with a single unified architecture, while achieving excellent accuracy and high efficiency. To better exploit the advantage of Platypus, we also construct a text reading dataset (called Worms), the images of which are curated from previous datasets and partially re-labeled. Experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed Platypus model. Model and data will be made publicly available at this https URL .
| Comments: | Accepted by ECCV2024 |
| Subjects: | Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV) |
| Cite as: | [cs.CV] |
| (or [cs.CV] for this version) | |
| Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration) |
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

Hubble Zooms into the Rosy Tendrils of Andromeda

Work Is Under Way on NASA’s Next-Generation Asteroid Hunter

NASA’s Roman Space Telescope to Investigate Galactic Fossils
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
NASA en Español
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Guest Program
- Image of the Day
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

NASA’s Europa Clipper Gets Set of Super-Size Solar Arrays

FAQ: NASA’s Boeing Crew Flight Test Return Status

NASA, Boeing Optimizing Vehicle Assembly Building High Bay for Future SLS Stage Production

NASA Seeks Input for Astrobee Free-flying Space Robots

NASA Funds Studies to Support Crew Performance on Long-Duration Missions

NASA JPL Developing Underwater Robots to Venture Deep Below Polar Ice

NASA Project in Puerto Rico Trains Students in Marine Biology

NASA Discovers a Long-Sought Global Electric Field on Earth

NASA, ESA Missions Help Scientists Uncover How Solar Wind Gets Energy
September’s Night Sky Notes: Marvelous Moons

Amendment 45: New Opportunity: A.60 Ecological Conservation
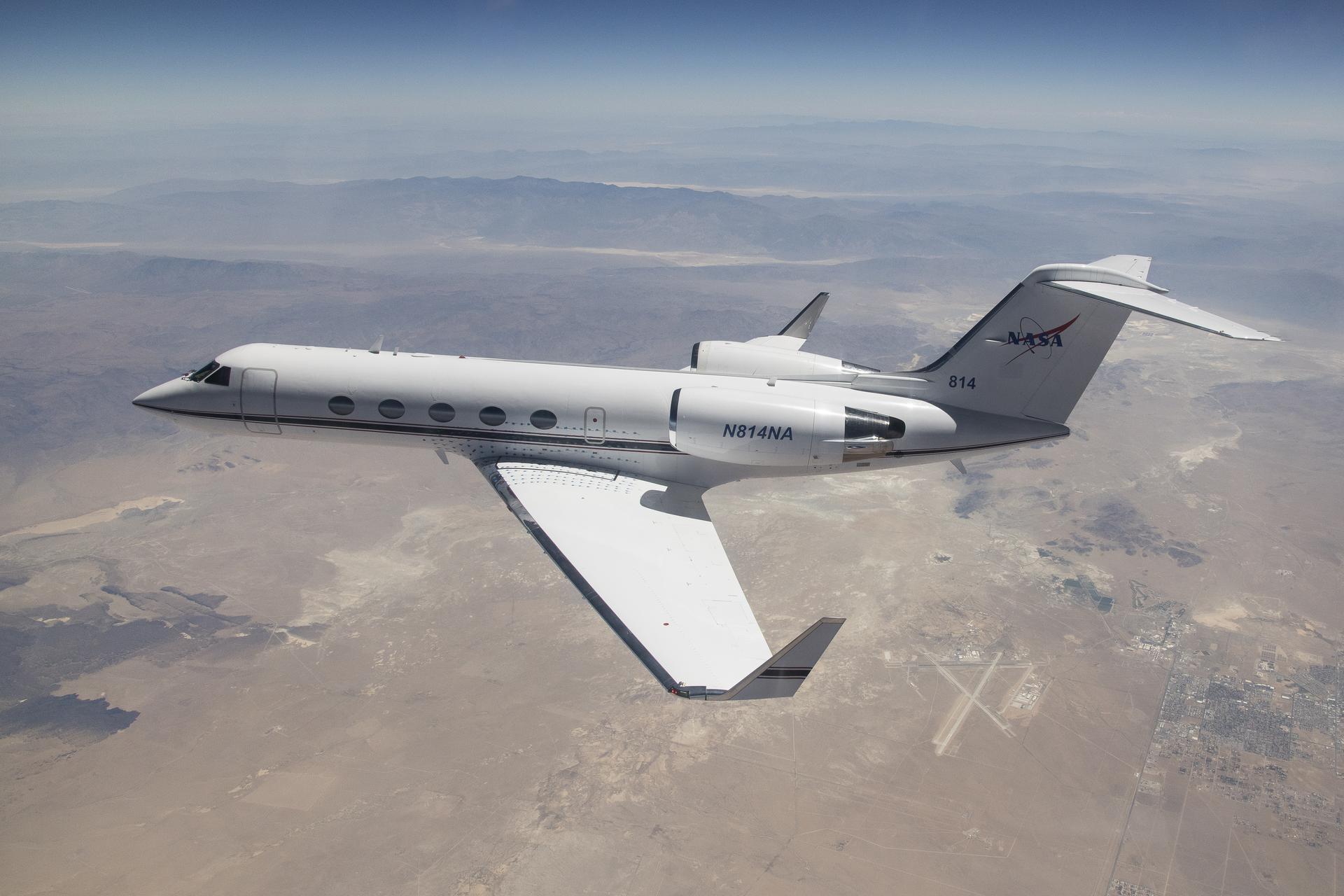

NASA G-IV Plane Will Carry Next-Generation Science Instrument

NASA Develops Pod to Help Autonomous Aircraft Operators

NASA Composite Manufacturing Initiative Gains Two New Members
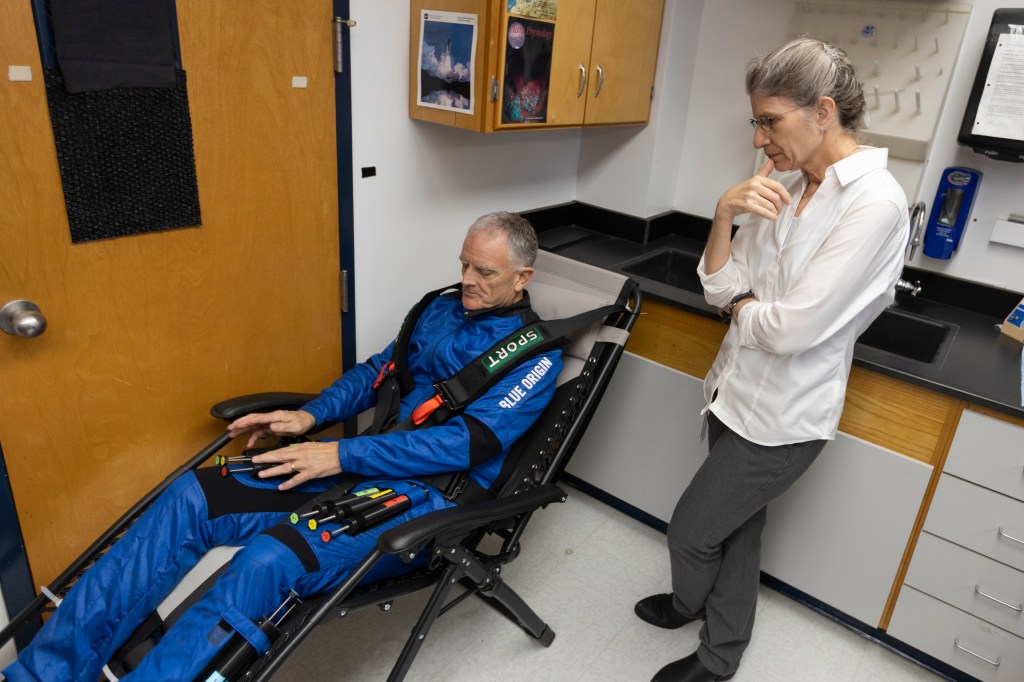

First NASA-Supported Researcher to Fly on Suborbital Rocket

How Do I Navigate NASA Learning Resources and Opportunities?

Aaron Vigil Helps Give SASS to Roman Space Telescope

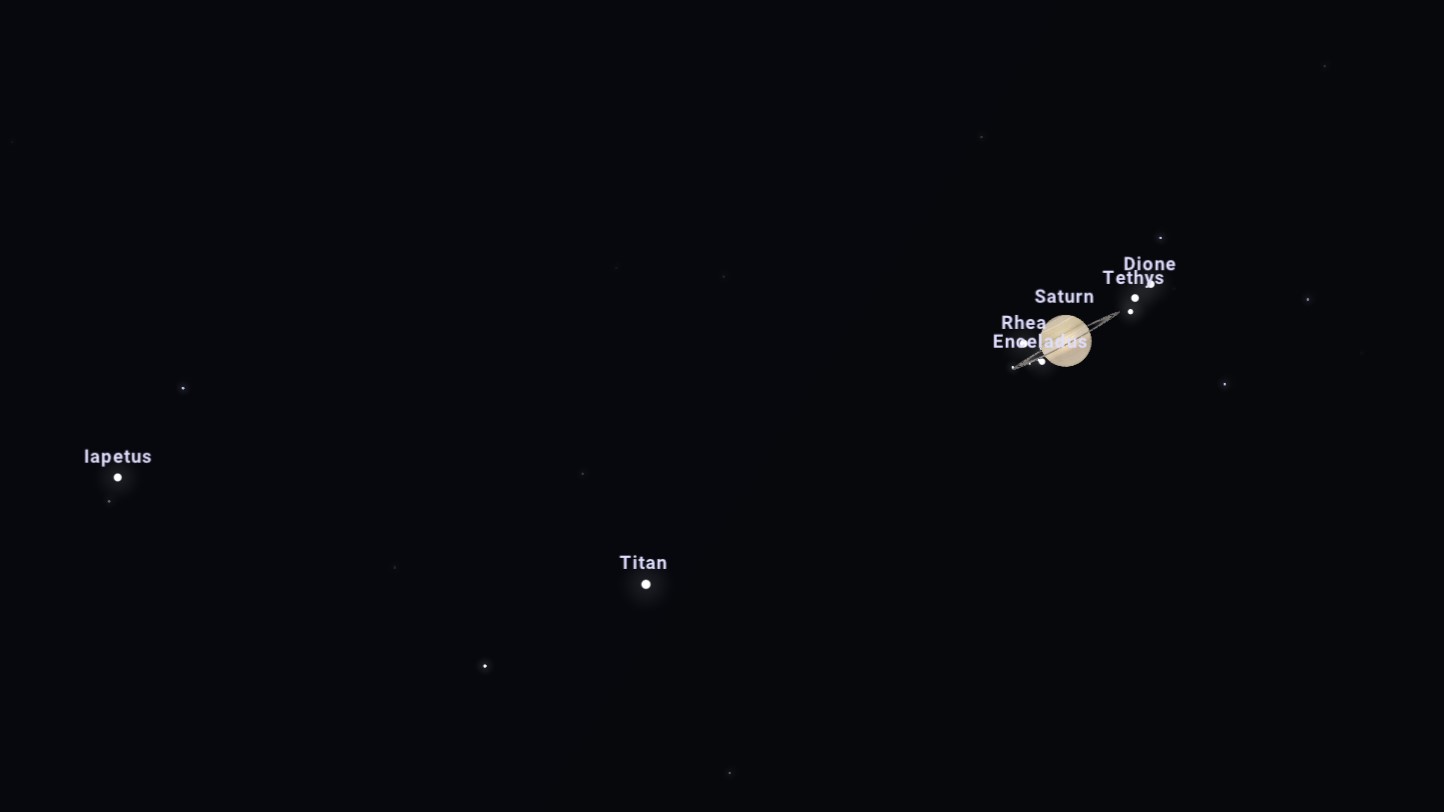
235 Years Ago: Herschel Discovers Saturn’s Moon Enceladus
Preguntas frecuentes: estado del retorno de la prueba de vuelo tripulado boeing de la nasa.

Astronauta de la NASA Frank Rubio

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas
For the first time, a NASA-funded researcher will fly with their experiment on a commercial suborbital rocket. The technology is one of two NASA-supported experiments, also known as payloads, funded by the agency’s Flight Opportunities program that will launch aboard Blue Origin’s New Shepard suborbital rocket system on a flight test no earlier than Thursday, Aug. 29.
The researcher-tended payload, from the University of Florida in Gainesville, seeks to understand how changes in gravity during spaceflight affect plant biology. Researcher Rob Ferl will activate small, self-contained tubes pre-loaded with plants and preservative to biochemically freeze the samples at various stages of gravity. During the flight, co-principal investigator Anna-Lisa Paul will conduct four identical experiments as a control. After the flight, Ferl and Paul will examine the preserved plants to study the effect of gravity transitions on the plants’ gene expression. Studying how changes in gravity affect plant growth will support future missions to the Moon and Mars.
The university’s flight test was funded by a grant awarded through the Flight Opportunities program’s TechFlights solicitation with additional support from NASA’s Division of Biological and Physical Sciences. This experiment builds on NASA’s long history of supporting plant research and aims to accelerate the pace and productivity of space-based research.
The other Flight Opportunities supported payload is from HeetShield, a small business in Flagstaff, Arizona. Two new thermal protection system materials will be mounted to the outside of New Shepard’s propulsion module to assess their thermal performance in a relevant environment, since conditions will be similar to planetary entry. After the flight, HeetShield will analyze the structure of the materials to determine how they were affected by the flight.
Flight Opportunities, within NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate, facilitates demonstration of technologies for space exploration and the expansion of space commerce through suborbital testing with industry flight providers. Through various mechanisms, the program funds flight tests for internal and external technology payloads.
To learn more, visit: https://www.nasa.gov/space-technology-mission-directorate/
Discover More Topics From NASA
- Space Technology Mission Directorate

STMD Solicitations and Opportunities
Access Flight Tests

STMD Small Spacecraft Technology

Related Terms
- Armstrong Flight Research Center
- Flight Opportunities Program
- Physical Sciences Program
- Technology for Space Travel
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Reading Research Effectively
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Reading a Scholarly Article or Research Paper
Identifying a research problem to investigate requires a preliminary search for and critical review of the literature in order to gain an understanding about how scholars have examined a topic. Scholars rarely structure research studies in a way that can be followed like a story; they are complex and detail-intensive and often written in a descriptive and conclusive narrative form. However, in the social and behavioral sciences, journal articles and stand-alone research reports are generally organized in a consistent format that makes it easier to compare and contrast studies and interpret their findings.
General Reading Strategies
W hen you first read an article or research paper, focus on asking specific questions about each section. This strategy can help with overall comprehension and with understanding how the content relates [or does not relate] to the problem you want to investigate. As you review more and more studies, the process of understanding and critically evaluating the research will become easier because the content of what you review will begin to coalescence around common themes and patterns of analysis. Below are recommendations on how to read each section of a research paper effectively. Note that the sections to read are out of order from how you will find them organized in a journal article or research paper.
1. Abstract
The abstract summarizes the background, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions of a scholarly article or research paper. Use the abstract to filter out sources that may have appeared useful when you began searching for information but, in reality, are not relevant. Questions to consider when reading the abstract are:
- Is this study related to my question or area of research?
- What is this study about and why is it being done ?
- What is the working hypothesis or underlying thesis?
- What is the primary finding of the study?
- Are there words or terminology that I can use to either narrow or broaden the parameters of my search for more information?
2. Introduction
If, after reading the abstract, you believe the paper may be useful, focus on examining the research problem and identifying the questions the author is trying to address. This information is usually located within the first few paragraphs of the introduction or in the concluding paragraph. Look for information about how and in what way this relates to what you are investigating. In addition to the research problem, the introduction should provide the main argument and theoretical framework of the study and, in the last paragraphs of the introduction, describe what the author(s) intend to accomplish. Questions to consider when reading the introduction include:
- What is this study trying to prove or disprove?
- What is the author(s) trying to test or demonstrate?
- What do we already know about this topic and what gaps does this study try to fill or contribute a new understanding to the research problem?
- Why should I care about what is being investigated?
- Will this study tell me anything new related to the research problem I am investigating?
3. Literature Review
The literature review describes and critically evaluates what is already known about a topic. Read the literature review to obtain a big picture perspective about how the topic has been studied and to begin the process of seeing where your potential study fits within the domain of prior research. Questions to consider when reading the literature review include:
- W hat other research has been conducted about this topic and what are the main themes that have emerged?
- What does prior research reveal about what is already known about the topic and what remains to be discovered?
- What have been the most important past findings about the research problem?
- How has prior research led the author(s) to conduct this particular study?
- Is there any prior research that is unique or groundbreaking?
- Are there any studies I could use as a model for designing and organizing my own study?
4. Discussion/Conclusion
The discussion and conclusion are usually the last two sections of text in a scholarly article or research report. They reveal how the author(s) interpreted the findings of their research and presented recommendations or courses of action based on those findings. Often in the conclusion, the author(s) highlight recommendations for further research that can be used to develop your own study. Questions to consider when reading the discussion and conclusion sections include:
- What is the overall meaning of the study and why is this important? [i.e., how have the author(s) addressed the " So What? " question].
- What do you find to be the most important ways that the findings have been interpreted?
- What are the weaknesses in their argument?
- Do you believe conclusions about the significance of the study and its findings are valid?
- What limitations of the study do the author(s) describe and how might this help formulate my own research?
- Does the conclusion contain any recommendations for future research?
5. Methods/Methodology
The methods section describes the materials, techniques, and procedures for gathering information used to examine the research problem. If what you have read so far closely supports your understanding of the topic, then move on to examining how the author(s) gathered information during the research process. Questions to consider when reading the methods section include:
- Did the study use qualitative [based on interviews, observations, content analysis], quantitative [based on statistical analysis], or a mixed-methods approach to examining the research problem?
- What was the type of information or data used?
- Could this method of analysis be repeated and can I adopt the same approach?
- Is enough information available to repeat the study or should new data be found to expand or improve understanding of the research problem?
6. Results
After reading the above sections, you should have a clear understanding of the general findings of the study. Therefore, read the results section to identify how key findings were discussed in relation to the research problem. If any non-textual elements [e.g., graphs, charts, tables, etc.] are confusing, focus on the explanations about them in the text. Questions to consider when reading the results section include:
- W hat did the author(s) find and how did they find it?
- Does the author(s) highlight any findings as most significant?
- Are the results presented in a factual and unbiased way?
- Does the analysis of results in the discussion section agree with how the results are presented?
- Is all the data present and did the author(s) adequately address gaps?
- What conclusions do you formulate from this data and does it match with the author's conclusions?
7. References
The references list the sources used by the author(s) to document what prior research and information was used when conducting the study. After reviewing the article or research paper, use the references to identify additional sources of information on the topic and to examine critically how these sources supported the overall research agenda. Questions to consider when reading the references include:
- Do the sources cited by the author(s) reflect a diversity of disciplinary viewpoints, i.e., are the sources all from a particular field of study or do the sources reflect multiple areas of study?
- Are there any unique or interesting sources that could be incorporated into my study?
- What other authors are respected in this field, i.e., who has multiple works cited or is cited most often by others?
- What other research should I review to clarify any remaining issues or that I need more information about?
NOTE: A final strategy in reviewing research is to copy and paste the title of the source [journal article, book, research report] into Google Scholar . If it appears, look for a "cited by" reference followed by a hyperlinked number under the record [e.g., Cited by 45]. This number indicates how many times the study has been subsequently cited in other, more recently published works. This strategy, known as citation tracking, can be an effective means of expanding your review of pertinent literature based on a study you have found useful and how scholars have cited it. The same strategies described above can be applied to reading articles you find in the list of cited by references.
Reading Tip
Specific Reading Strategies
Effectively reading scholarly research is an acquired skill that involves attention to detail and an ability to comprehend complex ideas, data, and theoretical concepts in a way that applies logically to the research problem you are investigating. Here are some specific reading strategies to consider.
As You are Reading
- Focus on information that is most relevant to the research problem; skim over the other parts.
- As noted above, read content out of order! This isn't a novel; you want to start with the spoiler to quickly assess the relevance of the study.
- Think critically about what you read and seek to build your own arguments; not everything may be entirely valid, examined effectively, or thoroughly investigated.
- Look up the definitions of unfamiliar words, concepts, or terminology. A good scholarly source is Credo Reference .
Taking notes as you read will save time when you go back to examine your sources. Here are some suggestions:
- Mark or highlight important text as you read [e.g., you can use the highlight text feature in a PDF document]
- Take notes in the margins [e.g., Adobe Reader offers pop-up sticky notes].
- Highlight important quotations; consider using different highlighting colors to differentiate between quotes and other types of important text.
- Summarize key points about the study at the end of the paper. To save time, these can be in the form of a concise bulleted list of statements [e.g., intro provides useful historical background; lit review has important sources; good conclusions].
Write down thoughts that come to mind that may help clarify your understanding of the research problem. Here are some examples of questions to ask yourself:
- Do I understand all of the terminology and key concepts?
- Do I understand the parts of this study most relevant to my topic?
- What specific problem does the research address and why is it important?
- Are there any issues or perspectives the author(s) did not consider?
- Do I have any reason to question the validity or reliability of this research?
- How do the findings relate to my research interests and to other works which I have read?
Adapted from text originally created by Holly Burt, Behavioral Sciences Librarian, USC Libraries, April 2018.
Another Reading Tip
When is it Important to Read the Entire Article or Research Paper
Laubepin argues, "Very few articles in a field are so important that every word needs to be read carefully." * However, this implies that some studies are worth reading carefully if they directly relate to understanding the research problem. As arduous as it may seem, there are valid reasons for reading a study from beginning to end. Here are some examples:
- Studies Published Very Recently . The author(s) of a recent, well written study will provide a survey of the most important or impactful prior research in the literature review section. This can establish an understanding of how scholars in the past addressed the research problem. In addition, the most recently published sources will highlight what is known and what gaps in understanding currently exist about a topic, usually in the form of the need for further research in the conclusion .
- Surveys of the Research Problem . Some papers provide a comprehensive analytical overview of the research problem. Reading this type of study can help you understand underlying issues and discover why scholars have chosen to investigate the topic. This is particularly important if the study was published recently because the author(s) should cite all or most of the important prior research on the topic. Note that, if it is a long-standing problem, there may be studies that specifically review the literature to identify gaps that remain. These studies often include the word "review" in their title [e.g., Hügel, Stephan, and Anna R. Davies. "Public Participation, Engagement, and Climate Change Adaptation: A Review of the Research Literature." Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change 11 (July-August 2020): https://doi.org/10.1002/ wcc.645].
- Highly Cited . If you keep coming across the same citation to a study while you are reviewing the literature, this implies it was foundational in establishing an understanding of the research problem or the study had a significant impact within the literature [either positive or negative]. Carefully reading a highly cited source can help you understand how the topic emerged and how it motivated scholars to further investigate the problem. It also could be a study you need to cite as foundational in your own paper to demonstrate to the reader that you understand the roots of the problem.
- Historical Overview . Knowing the historical background of a research problem may not be the focus of your analysis. Nevertheless, carefully reading a study that provides a thorough description and analysis of the history behind an event, issue, or phenomenon can add important context to understanding the topic and what aspect of the problem you may want to examine further.
- Innovative Methodological Design . Some studies are significant and should be read in their entirety because the author(s) designed a unique or innovative approach to researching the problem. This may justify reading the entire study because it can motivate you to think creatively about also pursuing an alternative or non-traditional approach to examining your topic of interest. These types of studies are generally easy to identify because they are often cited in others works because of their unique approach to examining the research problem.
- Cross-disciplinary Approach . R eviewing studies produced outside of your discipline is an essential component of investigating research problems in the social and behavioral sciences. Consider reading a study that was conducted by author(s) based in a different discipline [e.g., an anthropologist studying political cultures; a study of hiring practices in companies published in a sociology journal]. This approach can generate a new understanding or a unique perspective about the topic . If you are not sure how to search for studies published in a discipline outside of your major or of the course you are taking, contact a librarian for assistance.
* Laubepin, Frederique. How to Read (and Understand) a Social Science Journal Article . Inter-University Consortium for Political and Social Research (ISPSR), 2013
Shon, Phillip Chong Ho. How to Read Journal Articles in the Social Sciences: A Very Practical Guide for Students . 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2015; Lockhart, Tara, and Mary Soliday. "The Critical Place of Reading in Writing Transfer (and Beyond): A Report of Student Experiences." Pedagogy 16 (2016): 23-37; Maguire, Moira, Ann Everitt Reynolds, and Brid Delahunt. "Reading to Be: The Role of Academic Reading in Emergent Academic and Professional Student Identities." Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice 17 (2020): 5-12.
- << Previous: 1. Choosing a Research Problem
- Next: Narrowing a Topic Idea >>
- Last Updated: Aug 30, 2024 10:02 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Chess (Gr. 1-4)
- TV (Gr. 1-4)
- Metal Detectors (Gr. 2-6)
- Tetris (Gr. 2-6)
- Seat Belts (Gr. 2-6)
- The Coliseum (Gr. 2-6)
- The Pony Express (Gr. 2-6)
- Wintertime (Gr. 2-6)
- Reading (Gr. 3-7)
- Black Friday (Gr. 3-7)
- Hummingbirds (Gr. 3-7)
- Worst Game Ever? (Gr. 4-8)
- Carnivorous Plants (Gr. 4-8)
- Google (Gr. 4-8)
- Honey Badgers (Gr. 4-8)
- Hyperinflation (Gr. 4-8)
- Koko (Gr. 4-8)
- Mongooses (Gr. 5-9)
- Trampolines (Gr. 5-9)
- Garbage (Gr. 5-9)
- Maginot Line (Gr. 5-9)
- Asian Carp (Gr. 5-9)
- Tale of Two Countries (Gr. 6-10)
- Kevlar (Gr. 7-10)
- Tigers (Gr. 7-11)
- Statue of Liberty (Gr. 8-10)
- Submarines (Gr. 8-12)
- Castles (Gr. 9-13)
- Gutenberg (Gr. 9-13)
- Author's Purpose Practice 1
- Author's Purpose Practice 2
- Author's Purpose Practice 3
- Fact and Opinion Practice 1
- Fact and Opinion Practice 2
- Fact and Opinion Practice 3
- Idioms Practice Test 1
- Idioms Practice Test 2
- Figurative Language Practice 1
- Figurative Language Practice 2
- Figurative Language Practice 3
- Figurative Language Practice 4
- Figurative Language Practice 5
- Figurative Language Practice 6
- Figurative Language Practice 7
- Figurative Language Practice 8
- Figurative Language Practice 9
- Figurative Language of Edgar Allan Poe
- Figurative Language of O. Henry
- Figurative Language of Shakespeare
- Genre Practice 1
- Genre Practice 2
- Genre Practice 3
- Genre Practice 4
- Genre Practice 5
- Genre Practice 6
- Genre Practice 7
- Genre Practice 8
- Genre Practice 9
- Genre Practice 10
- Irony Practice 1
- Irony Practice 2
- Irony Practice 3
- Making Inferences Practice 1
- Making Inferences Practice 2
- Making Inferences Practice 3
- Making Inferences Practice 4
- Making Inferences Practice 5
- Main Idea Practice 1
- Main Idea Practice 2
- Point of View Practice 1
- Point of View Practice 2
- Text Structure Practice 1
- Text Structure Practice 2
- Text Structure Practice 3
- Text Structure Practice 4
- Text Structure Practice 5
- Story Structure Practice 1
- Story Structure Practice 2
- Story Structure Practice 3
- Author's Purpose
- Characterizations
- Context Clues
- Fact and Opinion
- Figurative Language
- Grammar and Language Arts
- Poetic Devices
- Point of View
- Predictions
- Reading Comprehension
- Story Structure
- Summarizing
- Text Structure
- Character Traits
- Common Core Aligned Unit Plans
- Teacher Point of View
- Teaching Theme
- Patterns of Organization
- Project Ideas
- Reading Activities
- How to Write Narrative Essays
- How to Write Persuasive Essays
- Narrative Essay Assignments
- Narrative Essay Topics
- Persuasive Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics
- Rubrics for Writing Assignments
- Learn About Sentence Structure
- Grammar Worksheets
- Noun Worksheets
- Parts of Speech Worksheets
- Punctuation Worksheets
- Sentence Structure Worksheets
- Verbs and Gerunds
- Examples of Allitertion
- Examples of Hyperbole
- Examples of Onomatopoeia
- Examples of Metaphor
- Examples of Personification
- Examples of Simile
- Figurative Language Activities
- Figurative Language Examples
- Figurative Language Poems
- Figurative Language Worksheets
- Learn About Figurative Language
- Learn About Poetic Devices
- Idiom Worksheets
- Online Figurative Language Tests
- Onomatopoeia Worksheets
- Personification Worksheets
- Poetic Devices Activities
- Poetic Devices Worksheets
- About This Site
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Understanding CCSS Standards
- What's New?
Ereading Worksheets
Free reading worksheets, activities, and lesson plans., site navigation.
- Learn About Author’s Purpose
- Author’s Purpose Quizzes
- Character Types Worksheets and Lessons
- List of Character Traits
- Differentiated Reading Instruction Worksheets and Activities
- Fact and Opinion Worksheets
- Irony Worksheets
- Animal Farm Worksheets
- Literary Conflicts Lesson and Review
- New Home Page Test
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 2 Worksheet
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 5 Worksheet
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 6 Worksheet
- Lord of the Flies Chapter 10 Worksheet
- Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass
- Sister Carrie
- The Count of Monte Cristo
- The Odyssey
- The War of the Worlds
- The Wizard of Oz
- Mood Worksheets
- Context Clues Worksheets
- Inferences Worksheets
- Main Idea Worksheets
- Making Predictions Worksheets
- Nonfiction Passages and Functional Texts
- Setting Worksheets
- Summarizing Worksheets and Activities
- Short Stories with Questions
- Story Structure Activities
- Story Structure Worksheets
- Tone Worksheets
- Types of Conflict Worksheets
- Reading Games
- Figurative Language Poems with Questions
- Hyperbole and Understatement Worksheets
- Simile and Metaphor Worksheets
- Simile Worksheets
- Hyperbole Examples
- Metaphor Examples
- Personification Examples
- Simile Examples
- Understatement Examples
- Idiom Worksheets and Tests
- Poetic Devices Worksheets & Activities
- Alliteration Examples
- Allusion Examples
- Onomatopoeia Examples
- Onomatopoeia Worksheets and Activities
- Genre Worksheets
- Genre Activities
- Capitalization Worksheets, Lessons, and Tests
- Contractions Worksheets and Activities
- Double Negative Worksheets
- Homophones & Word Choice Worksheets
- ‘Was’ or ‘Were’
- Simple Subjects & Predicates Worksheets
- Subjects, Predicates, and Objects
- Clauses and Phrases
- Type of Sentences Worksheets
- Sentence Structure Activities
- Comma Worksheets and Activities
- Semicolon Worksheets
- End Mark Worksheets
- Noun Worksheets, Lessons, and Tests
- Verb Worksheets and Activities
- Pronoun Worksheets, Lessons, and Tests
- Adverbs & Adjectives Worksheets, Lessons, & Tests
- Preposition Worksheets and Activities
- Conjunctions Worksheets and Activities
- Interjections Worksheets
- Parts of Speech Activities
- Verb Tense Activities
- Past Tense Worksheets
- Present Tense Worksheets
- Future Tense Worksheets
- Point of View Activities
- Point of View Worksheets
- Teaching Point of View
- Cause and Effect Example Paragraphs
- Chronological Order
- Compare and Contrast
- Order of Importance
- Problem and Solution
- Text Structure Worksheets
- Text Structure Activities
- Essay Writing Rubrics
- Narrative Essay Topics and Story Ideas
- Narrative Essay Worksheets & Writing Assignments
- Persuasive Essay and Speech Topics
- Persuasive Essay Worksheets & Activities
- Writing Narrative Essays and Short Stories
- Writing Persuasive Essays
- All Reading Worksheets
- Understanding Common Core State Standards
- Remote Learning Resources for Covid-19 School Closures
- What’s New?
- Ereading Worksheets | Legacy Versions
- Online Figurative Language Practice
- Online Genre Practice Tests
- Online Point of View Practice Tests
- 62 School Project Ideas
- 2nd Grade Reading Worksheets
- 3rd Grade Reading Worksheets
- 4th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 5th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 6th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 7th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 8th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 9th Grade Reading Worksheets
- 10th Grade Reading Worksheets
- Membership Billing
- Membership Cancel
- Membership Checkout
- Membership Confirmation
- Membership Invoice
- Membership Levels
- Your Profile
Want Updates?
101 research paper topics.
- Why do we sleep ?
- How do GPS systems work?
- Who was the first person to reach the North Pole ?
- Did anybody ever escape Alcatraz ?
- What was life like for a gladiator ?
- What are the effects of prolonged steroid use on the human body?
- What happened during the Salem witch trials ?
- Are there any effective means of repelling insects ?
- How did trains and railroads change life in America?
- What may have occurred during the Roswell UFO incident of 1947?
- How is bulletproof clothing made?
- What Olympic events were practiced in ancient Greece?
- What are the major theories explaining the disappearance of the dinosaurs ?
- How was the skateboard invented and how has it changed over the years?
- How did the long bow contribute to English military dominance?
- What caused the stock market crash of 2008?
- How did Cleopatra come to power in Egypt what did she do during her reign?
- How has airport security intensified since September 11 th , 2001?
- What is life like inside of a beehive ?
- Where did hip hop originate and who were its founders?
- What makes the platypus a unique and interesting mammal?
- How does tobacco use affect the human body?
- How do computer viruses spread and in what ways do they affect computers?
- What is daily life like for a Buddhist monk ?
- What are the origins of the conflict in Darfur ?
- How did gunpowder change warfare?
- In what ways do Wal-Mart stores affect local economies?
- How were cats and dogs domesticated and for what purposes?
- What do historians know about ninjas ?
- How has the music industry been affected by the internet and digital downloading?
- What were the circumstances surrounding the death of Osama Bin Laden ?
- What was the women’s suffrage movement and how did it change America?
- What efforts are being taken to protect endangered wildlife ?
- How much does the war on drugs cost Americans each year?
- How is text messaging affecting teen literacy?
- Are humans still evolving ?
- What technologies are available to home owners to help them conserve energy ?
- How have oil spills affected the planet and what steps are being taken to prevent them?
- What was the Magna Carta and how did it change England?
- What is the curse of the pharaohs?
- Why was Socrates executed?
- What nonlethal weapons are used by police to subdue rioters?
- How does the prison population in America compare to other nations?
- How did ancient sailors navigate the globe?
- Can gamblers ever acquire a statistical advantage over the house in casino games?
- What is alchemy and how has it been attempted?
- How are black holes formed?
- How was the assassination of Abraham Lincoln plotted and executed?
- Do the benefits of vaccination outweigh the risks?
- How do submarines work?
- Do lie detector tests accurately determine truthful statements?
- How did Cold War tension affect the US and the world?
- What happened to the lost settlers at Roanoke ?
- How does a hybrid car save energy?
- What ingredients can be found inside of a hotdog ?
- How did Julius Caesar affect Rome?
- What are some common sleep disorders and how are they treated?
- How did the Freedom Riders change society?
- How is internet censorship used in China and around the world?
- What was the code of the Bushido and how did it affect samurai warriors ?
- What are the risks of artificial tanning or prolonged exposure to the sun?
- What programs are available to help war veterans get back into society?
- What steps are involved in creating a movie or television show?
- How have the film and music industries dealt with piracy ?
- How did Joan of Arc change history?
- What responsibilities do secret service agents have?
- How does a shark hunt?
- What dangers and hardships did Lewis and Clark face when exploring the Midwest?
- Has the Patriot Act prevented or stopped terrorist acts in America?
- Do states that allow citizens to carry guns have higher or lower crime rates?
- How are the Great Depression and the Great Recession similar and different?
- What are the dangers of scuba diving and underwater exploration?
- How does the human brain store and retrieve memories ?
- What was the Manhattan Project and what impact did it have on the world?
- How does stealth technology shield aircraft from radar?
- What causes tornadoes ?
- Why did Martin Luther protest against the Catholic Church?
- How does a search engine work?
- What are the current capabilities and future goals of genetic engineers ?
- How did the Roman Empire fall?
- What obstacles faced scientists in breaking the sound barrier ?
- How did the black plague affect Europe?
- What happened to Amelia Earhart ?
- What are the dangers and hazards of using nuclear power ?
- How did Genghis Khan conquer Persia?
- What architectural marvels were found in Tenochtitlan, capital of the Aztec Empire ?
- From where does spam email come and can we stop it?
- How does night vision work?
- How did journalists influence US war efforts in Vietnam ?
- What are the benefits and hazards of medical marijuana ?
- What causes desert mirages and how do they affect wanderers?
- What was the cultural significance of the first moon landing ?
- What are sinkholes and how are they formed?
- Have any psychics ever solved crimes or prevented them from occurring?
- Who is Vlad the Impaler and what is his connection to Count Dracula ?
- What are the risks of climate change and global warming ?
- What treatments are available to people infected with HIV and are they effective?
- Who was a greater inventor, Leonardo di Vinci or Thomas Edison ?
- How are the Chinese and American economies similar and different?
- Why was communism unsuccessful in so many countries?
- In what ways do video games affect children and teenagers?

923 Comments
I like using this website when I assist kids with learning as a lot of these topics are quickly covered in the school systems. Thankyou
Mackenah Nicole Molina
Wow! I always have trouble deiciding what to do a research project on but this list has totally solved that. Now my only problem is choosing what idea on this list I should do first!
Most of these my teacher rejected because apparently ‘these aren’t grade level topics, and I doubt they interest you”
I’m sorry to hear that. Sounds like you will have a potentially valuable character-building experience in the short-term.
Edwin Augusto Galindo Cuba
THIS SITE IS AWESOME, THERE ARE LOTS OF TOPICS TO LEARN AND MASTER OUR SKILLS!
research kid
I need one about animals, please. I have been challenged to a animal research project, Due Friday. I have no clue what to research! somebody help, thanks for reading!
You can do one on bats
For international studies you can do Defense and Security.
This was very helpful.
Research on Ben Franklin? I think THAT will get a real charge out of everyone (hehehehegetit)
Mandy Maher
“Is it possible to colonize Mars?”
maddy burney
these are silly topics
thx for making this real.
more gaming questions!!!!!!
Is it still considered stealing if you don’t get caught?
Yes, yes it is still considered stealing.
I need topics on memes
Mary Nnamani
Please I need project topics on Language Literature
Marcella Vallarino
I would appreciate a list of survey questions for middle school grades 6-8
I need a research topics about public sector management
I NEED FIVE EXAMPLES EACH ON QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH (EDUCATION, HEALTH, TECHNOLOGY, ECONOMY AND ENGINEERING)
publish research that are interesting please……
hey can you do one on the burmiueda triangle
Anybody know video games effect kids,and,teens. There Fun!!
they’re
I need a topic about woman history if any of u can find 1 please that would be great!
You could research about the history of the astronauts, and of human past (WWI, WWII, etc.)
so about women? Manitoba Women Win the Right to Vote in Municipal Elections, The First Women, January 23, 1849: Elizabeth Blackwell becomes the first woman to graduate from medical school and become a doctor in the United States, Rosa Parks Civil Rights Equal Pay. I have way more. so if you need more just ask.
communism is good
what are you a communist?!?!
Did FDR know about the upcoming attack on Pearl Harbor on 07 DEC 1941.
do you know how babies are born
Christine Singu
kindly assist with a research topic in the field of accounting or auditing
need more about US army
Please can yiu give me a topic in education
I think one should be how can music/Video games can affect the life for people
or How Do Video Games Affect Teenagers?
zimbabwe leader
I think a good topic is supporting the confederate flag!
Need a research topic within the context of students union government and dues payments
do more weird ones plz
joyce alcantara
Hi pls po can you give me a topic relate for humanities pls thank u.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Subscribe Now
Popular content.
- Author's Purpose Worksheets
- Characterization Worksheets
- Common Core Lesson and Unit Plans
- Online Reading Practice Tests
- Plot Worksheets
- Reading Comprehension Worksheets
- Summary Worksheets
- Theme Worksheets
New and Updated Pages
- Capitalization Worksheets
- Contractions Worksheets
- Double Negatives Worksheets
- Homophones & Word Choice Worksheets
BECOME A MEMBER!
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Reading Research Effectively
- Purpose of Guide
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- The Research Problem/Question
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Evaluating Sources
- Reading Research Effectively
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Is it Peer-Reviewed?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism [linked guide]
- Annotated Bibliography
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
Reading a Scholarly Article or Research Paper
Reading Research Publications Effectively
It's easy to feel overwhelmed and frustrated when first reading a scholarly article or research paper. The text is dense and complex and often includes abstract or convoluted language . In addition, the terminology may be confusing or applied in a way that is unfamiliar. To help overcome these challenges w hen you first read an article or research paper, focus on asking specific questions about each section. This strategy can help with overall comprehension and understanding how the content relates [or does not relate] to the research problem you are investigating. This approach will also help identify key themes as you read additional studies on the same topic. As you review more and more studies about your topic, the process of understanding and critically evaluating the research will become easier because the content of what you review will begin to coalescence around common themes and patterns of analysis.
Think about the following in this general order:
1. Read the Abstract
An abstract summarizes the basic content of a scholarly article or research paper. Questions to consider when reading the abstract are: What is this article about? What is the working hypothesis or thesis? Is this related to my question or area of research? The abstract can be used to help filter out sources that may have appeared useful when you began searching for information but, in reality, are not relevant.
2. Identify the Research Problem and Underlying Questions?
If, after reading the abstract, you believe the paper may be useful, focus on examining the research problem and identifying the questions the author is trying to address. Look for information that is relevant to your research problem and make note of how and in what way this information relates to what you are investigating.
3. Read the Introduction and Discussion/Conclusion
The introduction provides the main argument and theoretical framework of the article. Questions to consider for the introduction include what do we already know about this topic and what is left to discover? What other research has been conducted about this topic? How is this research unique? Will this study tell me anything new related to the research problem I am investigating?
Questions to ask yourself while reading the discussion and conclusion sections include what does the study mean and why is it important? What are the weaknesses in their argument? Does the conclusion contain any recommendations for future research and do you believe conclusions about the significance of the study and its findings are valid?
4. Read about the Methods/Methodology
If what you have read so far closely relates to your research problem, then move on to reading about how the author(s) gathered information for their research. Questions to consider include how did the author do the research? Was it a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods project? What data is the study based on? Could I repeat their work and is all the information available to repeat the study?
5. Read about the Results and Analysis
Next, read the outcome the research and how it was discussed and analyzed. If any non-textual elements [e.g., graphs, charts, tables, etc.] are confusing, focus on the explanations about them in the text. Questions to consider are what did the author find and how did they find it? Are the results presented in a factual and unbiased way? Does their analysis of results agree with the data presented? Is all the data present? What conclusions do you formulate from this data and does it match with the author's conclusions?
6. Review the References
The list of references, or works cited, shows you the basis of prior research used by the author(s) to support their study. The references can be an effective way to identify additional sources of information on the topic. Questions to ask include what other research studies should I review? What other authors are respected in this field, i.e., who is cited most often by others? What other research should be explored to learn about issues I am unclear or need more information about?
Reading Tips
Preparing to Read a Scholarly Article or Research Paper for the First Time
Reading scholarly publications effectively is an acquired skill that involves attention to detail and the ability to comprehend complex ideas, data, and concepts in a way that applies logically to the research problem you are investigating. Here are some strategies to consider.
While You are Reading
- Focus on information in the publication that is most relevant to the research problem
- Think critically about what you read and seek to build your own arguments; not everything is 100% true or examined effectively
- Read out of order! This isn't a novel or movie; you want to start with the spoiler
- Look up the definitions of words you don't know as you read
There are any number of ways to take notes as you read, but use the method that you feel most comfortable with. Taking notes as you read will save time when you go back to examine your sources. Below are some suggestions:
- Print the article and highlight, circle, and/or underline text as you read [or, you can use the highlight text feature in a PDF document]
- Take notes in the margins [Adobe Reader offers pop-up sticky notes]
- Focus on highlighting important quotes; consider using a different color to differentiate between quotes and other types of text you want to return to when writing
- Quickly summarize the main or key points at the end of the paper
As you read, write down questions that come to mind that relate to or may clarify your research problem. Here are a few questions that might be helpful:
- Have I taken time to understand all the terminology?
- Am I spending too much time on the less important parts of this article?
- Are there any issues that the authors did not consider?
- Do I have any reason to question the credibility of this research?
- What specific problem does the research address and why is it important?
- How do these results relate to my research interests or to other works which I have read?
Adapted from text originally created by Holly Burt, USC Libraries, April 2018. Thank you, Holly!
- << Previous: Evaluating Sources
- Next: Primary Sources >>
- Last Updated: Aug 24, 2024 10:22 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.txstate.edu/socialscienceresearch


Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
113 Great Research Paper Topics
General Education

One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily find the best topic for you.
In addition to the list of good research topics, we've included advice on what makes a good research paper topic and how you can use your topic to start writing a great paper.
What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic?
Not all research paper topics are created equal, and you want to make sure you choose a great topic before you start writing. Below are the three most important factors to consider to make sure you choose the best research paper topics.
#1: It's Something You're Interested In
A paper is always easier to write if you're interested in the topic, and you'll be more motivated to do in-depth research and write a paper that really covers the entire subject. Even if a certain research paper topic is getting a lot of buzz right now or other people seem interested in writing about it, don't feel tempted to make it your topic unless you genuinely have some sort of interest in it as well.
#2: There's Enough Information to Write a Paper
Even if you come up with the absolute best research paper topic and you're so excited to write about it, you won't be able to produce a good paper if there isn't enough research about the topic. This can happen for very specific or specialized topics, as well as topics that are too new to have enough research done on them at the moment. Easy research paper topics will always be topics with enough information to write a full-length paper.
Trying to write a research paper on a topic that doesn't have much research on it is incredibly hard, so before you decide on a topic, do a bit of preliminary searching and make sure you'll have all the information you need to write your paper.
#3: It Fits Your Teacher's Guidelines
Don't get so carried away looking at lists of research paper topics that you forget any requirements or restrictions your teacher may have put on research topic ideas. If you're writing a research paper on a health-related topic, deciding to write about the impact of rap on the music scene probably won't be allowed, but there may be some sort of leeway. For example, if you're really interested in current events but your teacher wants you to write a research paper on a history topic, you may be able to choose a topic that fits both categories, like exploring the relationship between the US and North Korea. No matter what, always get your research paper topic approved by your teacher first before you begin writing.
113 Good Research Paper Topics
Below are 113 good research topics to help you get you started on your paper. We've organized them into ten categories to make it easier to find the type of research paper topics you're looking for.
Arts/Culture
- Discuss the main differences in art from the Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance .
- Analyze the impact a famous artist had on the world.
- How is sexism portrayed in different types of media (music, film, video games, etc.)? Has the amount/type of sexism changed over the years?
- How has the music of slaves brought over from Africa shaped modern American music?
- How has rap music evolved in the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of minorities in the media changed?

Current Events
- What have been the impacts of China's one child policy?
- How have the goals of feminists changed over the decades?
- How has the Trump presidency changed international relations?
- Analyze the history of the relationship between the United States and North Korea.
- What factors contributed to the current decline in the rate of unemployment?
- What have been the impacts of states which have increased their minimum wage?
- How do US immigration laws compare to immigration laws of other countries?
- How have the US's immigration laws changed in the past few years/decades?
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare in the US?
- What factors contributed to the UK deciding to leave the EU (Brexit)?
- What factors contributed to China becoming an economic power?
- Discuss the history of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies (some of which tokenize the S&P 500 Index on the blockchain) .
- Do students in schools that eliminate grades do better in college and their careers?
- Do students from wealthier backgrounds score higher on standardized tests?
- Do students who receive free meals at school get higher grades compared to when they weren't receiving a free meal?
- Do students who attend charter schools score higher on standardized tests than students in public schools?
- Do students learn better in same-sex classrooms?
- How does giving each student access to an iPad or laptop affect their studies?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Montessori Method ?
- Do children who attend preschool do better in school later on?
- What was the impact of the No Child Left Behind act?
- How does the US education system compare to education systems in other countries?
- What impact does mandatory physical education classes have on students' health?
- Which methods are most effective at reducing bullying in schools?
- Do homeschoolers who attend college do as well as students who attended traditional schools?
- Does offering tenure increase or decrease quality of teaching?
- How does college debt affect future life choices of students?
- Should graduate students be able to form unions?

- What are different ways to lower gun-related deaths in the US?
- How and why have divorce rates changed over time?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in education and/or the workplace?
- Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
- How has stem cell research impacted the medical field?
- How can human trafficking be reduced in the United States/world?
- Should people be able to donate organs in exchange for money?
- Which types of juvenile punishment have proven most effective at preventing future crimes?
- Has the increase in US airport security made passengers safer?
- Analyze the immigration policies of certain countries and how they are similar and different from one another.
- Several states have legalized recreational marijuana. What positive and negative impacts have they experienced as a result?
- Do tariffs increase the number of domestic jobs?
- Which prison reforms have proven most effective?
- Should governments be able to censor certain information on the internet?
- Which methods/programs have been most effective at reducing teen pregnancy?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Keto diet?
- How effective are different exercise regimes for losing weight and maintaining weight loss?
- How do the healthcare plans of various countries differ from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat depression ?
- What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
- Which methods are most effective for improving memory?
- What can be done to lower healthcare costs in the US?
- What factors contributed to the current opioid crisis?
- Analyze the history and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic .
- Are low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- How much exercise should the average adult be getting each week?
- Which methods are most effective to get parents to vaccinate their children?
- What are the pros and cons of clean needle programs?
- How does stress affect the body?
- Discuss the history of the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
- What were the causes and effects of the Salem Witch Trials?
- Who was responsible for the Iran-Contra situation?
- How has New Orleans and the government's response to natural disasters changed since Hurricane Katrina?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of British rule in India ?
- Was the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki necessary?
- What were the successes and failures of the women's suffrage movement in the United States?
- What were the causes of the Civil War?
- How did Abraham Lincoln's assassination impact the country and reconstruction after the Civil War?
- Which factors contributed to the colonies winning the American Revolution?
- What caused Hitler's rise to power?
- Discuss how a specific invention impacted history.
- What led to Cleopatra's fall as ruler of Egypt?
- How has Japan changed and evolved over the centuries?
- What were the causes of the Rwandan genocide ?

- Why did Martin Luther decide to split with the Catholic Church?
- Analyze the history and impact of a well-known cult (Jonestown, Manson family, etc.)
- How did the sexual abuse scandal impact how people view the Catholic Church?
- How has the Catholic church's power changed over the past decades/centuries?
- What are the causes behind the rise in atheism/ agnosticism in the United States?
- What were the influences in Siddhartha's life resulted in him becoming the Buddha?
- How has media portrayal of Islam/Muslims changed since September 11th?
Science/Environment
- How has the earth's climate changed in the past few decades?
- How has the use and elimination of DDT affected bird populations in the US?
- Analyze how the number and severity of natural disasters have increased in the past few decades.
- Analyze deforestation rates in a certain area or globally over a period of time.
- How have past oil spills changed regulations and cleanup methods?
- How has the Flint water crisis changed water regulation safety?
- What are the pros and cons of fracking?
- What impact has the Paris Climate Agreement had so far?
- What have NASA's biggest successes and failures been?
- How can we improve access to clean water around the world?
- Does ecotourism actually have a positive impact on the environment?
- Should the US rely on nuclear energy more?
- What can be done to save amphibian species currently at risk of extinction?
- What impact has climate change had on coral reefs?
- How are black holes created?
- Are teens who spend more time on social media more likely to suffer anxiety and/or depression?
- How will the loss of net neutrality affect internet users?
- Analyze the history and progress of self-driving vehicles.
- How has the use of drones changed surveillance and warfare methods?
- Has social media made people more or less connected?
- What progress has currently been made with artificial intelligence ?
- Do smartphones increase or decrease workplace productivity?
- What are the most effective ways to use technology in the classroom?
- How is Google search affecting our intelligence?
- When is the best age for a child to begin owning a smartphone?
- Has frequent texting reduced teen literacy rates?

How to Write a Great Research Paper
Even great research paper topics won't give you a great research paper if you don't hone your topic before and during the writing process. Follow these three tips to turn good research paper topics into great papers.
#1: Figure Out Your Thesis Early
Before you start writing a single word of your paper, you first need to know what your thesis will be. Your thesis is a statement that explains what you intend to prove/show in your paper. Every sentence in your research paper will relate back to your thesis, so you don't want to start writing without it!
As some examples, if you're writing a research paper on if students learn better in same-sex classrooms, your thesis might be "Research has shown that elementary-age students in same-sex classrooms score higher on standardized tests and report feeling more comfortable in the classroom."
If you're writing a paper on the causes of the Civil War, your thesis might be "While the dispute between the North and South over slavery is the most well-known cause of the Civil War, other key causes include differences in the economies of the North and South, states' rights, and territorial expansion."
#2: Back Every Statement Up With Research
Remember, this is a research paper you're writing, so you'll need to use lots of research to make your points. Every statement you give must be backed up with research, properly cited the way your teacher requested. You're allowed to include opinions of your own, but they must also be supported by the research you give.
#3: Do Your Research Before You Begin Writing
You don't want to start writing your research paper and then learn that there isn't enough research to back up the points you're making, or, even worse, that the research contradicts the points you're trying to make!
Get most of your research on your good research topics done before you begin writing. Then use the research you've collected to create a rough outline of what your paper will cover and the key points you're going to make. This will help keep your paper clear and organized, and it'll ensure you have enough research to produce a strong paper.
What's Next?
Are you also learning about dynamic equilibrium in your science class? We break this sometimes tricky concept down so it's easy to understand in our complete guide to dynamic equilibrium .
Thinking about becoming a nurse practitioner? Nurse practitioners have one of the fastest growing careers in the country, and we have all the information you need to know about what to expect from nurse practitioner school .
Want to know the fastest and easiest ways to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius? We've got you covered! Check out our guide to the best ways to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (or vice versa).
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
- Best Colleges
- Accelerated
- Bachelor’s
- Master’s
- Most Affordable
- Engineering
- Liberal Arts
- Certifications
- Best Online Community Colleges
- School Profiles
- Connecticut
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Washington D.C.
- West Virginia
- Choosing a Major
- Skills Interest Quiz
- ACT Testing Prep
- SAT Testing Prep
- CLEP Testing Guide
- Study Guides & Strategies
- Coalition App vs. Common App
- ROTC Programs
- Easiest College Majors
- Major vs. Minor
- Financial Aid & FAFSA
- Scholarships
- LGBTQ+ Guide
- Degree Specific Scholarships
- Military Scholarships
- Women Scholarships
- Career Quiz
- Get Hired Guide
- Cover Letter
- What are Job Skills?
- Resources by Major
- Student Mental Health
- Suicide Prevention
- Green Careers
- Business Administrator
- Financial Analyst
- Hospitality Manager
- Human Resources Manager
- Project Manager
- Supply Chain Manager
- Computer Programmer
- Cybersecurity Analyst
- Cybersecurity Engineer
- Database Administrator
- IT Specialist
- Software Developer
- Systems Analyst
- Web Developer
- Art Teacher
- Early Childhood Education Teacher
- Elementary School Teacher
- English Teacher
- ESL Teacher
- Preschool Teacher
- Special Education Teacher
- Civil Engineer
- Computer Engineer
- Electrical Engineer
- Mechanical Engineer
- Robotics Engineer
- Software Engineer
- Dental Assistant
- Healthcare Administrator
- Occupational Therapist
- Physical Therapist
- Veterinarian
- Correctional Officer
- Crime Scene Investigator
- Emergency Management Specialist
- Forensic Scientist
- Homeland Security Agent
- Homeland Security Investigator
- Police Officer
- Addictions Counselor
- Forensic Psychologist
- Marriage & Family Therapist
- Mental Health Counselor
- Psychologist
- School Counselor
- Social Worker
Reading and Research Strategy Guide
- Prereading Strategies
Reading Critically
Research strategies.
- SQ3R Reading
- KWL Reading
Interpretive Reading
Effective reading and research strategies are vital components of academic success, especially since they can improve comprehension and retention. Active reading is one of the key strategies you’re likely to learn - engaging readers by asking questions, making connections, and reflecting upon material they read.
Active reading has been shown to improve comprehension and retention by encouraging readers to actively think through what they are reading. Asking questions, making inferences, asking for clarification of material being presented, or simply reflecting upon it afterward are all proven methods of helping individuals connect new information with existing knowledge more readily. This type of active engagement with literature helps readers retain important details long-term.
Active strategies like asking questions, drawing connections, and reflecting can aid comprehension and retention. Practical tips such as discussing reading with others or taking breaks may further deepen understanding. Finally, changing reading speed as necessary may prove especially helpful when dealing with longer or more complex texts.
Reading for comprehension requires practice, but there are numerous practical strategies for doing it effectively. One such strategy is discussing reading material with others in order to gain new perspectives and deepen understanding. Also, taking short breaks while reading can help keep focus and prevent burnout. And taking notes while reading can also aid readers by helping retain key information better.
Changes to reading speed are another powerful strategy that can aid comprehension. At first, it may be advantageous to skim quickly over material to quickly gain an overview before returning more slowly to sections that need extra focus; this approach may prove especially helpful with longer or more complex texts as it enables readers to process it in manageable chunks. This guide can help you with reading strategies to help you plan for college and help you read more efficiently while pursing your college degree .
Study Guides and Strategy Resources
Study Guides & Strategies
Develop new skill-sets about a career you are interested in with a current curriculum to help you succeed.

Learning & Studying Techniques
Further your education and training in a field you are currently in and impress potential employers.
Project & Time Management
Make yourself stand out, bootcamps can help you stay up-to-date and relevant in your current field.

Reading & Research Strategies
Bootcamps are a cost-efficient way to start a new career or advance your current education without traditional degree costs.

Process & Types of Writing

Memorizing & Test Taking
Prereading strategies: how to maximize your reading material.
When it comes to reading, some people jump right in with both feet, while others opt for more strategic approaches, such as prereading strategies that can help them understand and retain what they read. Here are some effective prereading techniques to consider.
Before diving in to read, take some time to review text features such as headings, subheadings, and illustrations to gain an idea of what lies ahead. This will give you a basic understanding of what you’re about to read and what to expect from the text.
Recalling prior knowledge before reading can help create an initial framework for understanding text and make connections between what you already know and what is to come. This is especially helpful when reading textbooks or other works in which chapters may build upon previously learned information.
Establishing a clear purpose and expectations for reading can help keep you engaged during the reading process. You can ask yourself questions such as, "What am I hoping to gain from this text?" and "What knowledge or understanding do I already possess about its subject?"
One of the easiest and most efficient ways to comprehend what you are reading is to focus on each paragraph's main point. Search for words or phrases that reveal its topic sentence or use headings as guides in identifying this key concept.
Converting headings into questions can help keep you engaged and focused while reading and allows you to connect the text more closely to either your life experience or previously studied texts, making reading even more meaningful. Try making connections between what you are reading and your life experiences to make reading more personal.
After each page or section, take a moment to summarize what you have read. This can help ensure you retain information while reinforcing understanding. Creating an outline or concept map will also allow you to visually organize information while synthesizing multiple ideas into an easy-to-understand structure.
Pre-reading strategies can help you focus, organize, and retain information while reading. Implement them to get the most out of your reading material and become an insightful and proficient reader.
Critical reading is an integral skill that entails dissecting written material with greater insight and comprehension. Reading to gain understanding requires approaching a text from different perspectives - moving beyond its surface-level meaning to reveal hidden themes, biases, and assumptions. One way to enhance reading comprehension is by altering the text, engaging more actively with reading by questioning author messages, drawing connections among different ideas, or applying your prior knowledge in order to deepen understanding. No matter if it be journal articles, scientific literature, or news reports, creating effective reading strategies will enable you to become an adept reader.
Reading for Understanding
Teaching readers to comprehend is at the core of any successful reading instruction. Simply decoding individual words on a page won't do; to fully engage with text, they must comprehend its meaning behind those words and fully appreciate its context.
To better comprehend what you are reading, it’s vitally important to engage actively with the text. This may involve setting targets for what information you want from reading, making notes as you go along, underlining key points with highlighter pens when necessary, or writing summaries in margins - these strategies all serve to focus your attention on what's most vital while making retention simpler.
On top of employing these individual strategies, discussing reading material with others can be very helpful to gain multiple viewpoints on it and gain deeper understanding of its contents - this may uncover insights you might otherwise miss on your own!
Other effective reading strategies for comprehension include beginning by reading something that provides an overall view of a topic first, rather than diving straight into complex or technical material. Breaking reading up into short bursts of no more than twenty minutes at a time, with regular breaks between, can help you maintain focus and reduce mental fatigue, while changing speed while taking notes along the way allows readers to engage with texts more fully.
Reading comprehension is key for successful reading instruction. By actively engaging with text, setting targets, gaining multiple perspectives, and employing effective strategies, readers can improve their ability to comprehend what they read while also making the most out of their reading experiences.
Effective research strategies are key for anyone attempting to gain information and expand their understanding on any given subject matter. Selecting relevant information is the foundation of an effective research process. First, you must locate credible information sources relevant to your research question or topic. Journals can be invaluable tools in conducting research as they offer access to up to date and high-quality literature. When looking for sources, you should utilize all available resources such as academic databases, books, and online sources in your research process; critical reading skills are also key! Critical readers take an analytical approach to reading information by questioning its legitimacy, evaluating sources, and exploring alternative viewpoints. Employing critical reading can help researchers gain greater insight into their subject matter.
Selecting Relevant Information
Selecting information relevant to your research and reading is of utmost importance when conducting studies or gathering knowledge for research purposes. In order to select what will most effectively serve your needs, it's essential that a few key criteria be considered before choosing suitable sources.
First, establish the purpose or goal for reading or researching. Understanding why you're doing it will allow you to quickly filter out unnecessary information while keeping a keen eye on what matters.
Next, leverage your prior knowledge of the subject matter. This can help you quickly identify relevant information and assess source reliability - for instance, if researching something familiar such as politics, you may already possess an idea of which sources may be reliable and which aren't.
Consider the reliability and expertise of your sources when making decisions based on information gleaned from various sources. Look for authoritative figures with expertise in your chosen subject area while being wary of sources with hidden agendas that may distort their perspective.
At the forefront of selecting relevant information is making sure it's current. Information can quickly become outdated, making it important to find the newest sources. When gathering this type of data, it's advisable to note their dates so you can quickly assess whether they still provide accurate results or have become outdated.
Once you've amassed all the information required for your research, it’s critical that it is organized and manageable. You can take notes or print articles you find online. You should label your files clearly, making note of identifying information like ISBN or website addresses. Review your files regularly for anything which won't prove beneficial and remove anything unlikely to be used to keep all research organized and manageable.
By considering your purpose, evaluating sources for reliability and expertise, and keeping information current and manageable, you can select the most relevant and useful data for research or reading purposes.
The SQ3R Reading Method
The SQ3R Reading Method is a popular and effective technique used to improve reading comprehension and retention. SQ3R stands for Survey, Question, Read, Recite, and Review; these are the five steps that form this approach aimed at improving comprehension. Rather than passively taking in material and comprehending it all on one go, the goal of SQ3R is not simply reading material but actively engaging with it for full understanding and retention.
What is the SQ3R Reading Method?
Have you ever found yourself reading but unable to comprehend or retain the content? Unfortunately, this can be an everyday struggle that many face - particularly academic or professional environments where reading comprehension is vitally important. But there is a solution: SQ3R Reading Method can help. The SQ3R Reading Method is an effective strategy for increasing reading comprehension and retaining information. The five-step plan comprises Survey, Question, Read, Recite, and Review stages.
Survey is the initial step, in which readers examine a text visually by scanning headings, subheadings, and images to form an overall idea of its subject matter. This allows readers to develop an effective mental map that aids understanding and retention.
Question is the second step, in which readers engage with texts by actively interrogating them through inquiry. This encourages critical thinking and improves reading comprehension; by asking pertinent inquiries a reader will become better equipped to analyze and comprehend a text.
Step three of the SQ3R Reading Method requires readers to go deep, reading each concept thoroughly in their text. This requires concentration and focus from readers - this step being key in terms of its success.
Recite is the fourth step, in which readers use an interactive learning style by discussing text aloud as though teaching it to someone else. This step reinforces comprehension and retention as readers can use what they just learned immediately.
Review is the final and fifth step, focused on summarizing and reviewing key points of a text to reinforce what has been learned while long-term retention of information is attained.
The SQ3R Reading Method is an effective technique for reading comprehension and retention. Following this process is a holistic approach that helps to ensure that readers comprehend and remember what they read. Regular practice with this technique can lead to increased proficiency and become an essential skill in becoming a more successful reader.
The KWL Reading Method
The KWL Reading Method is an active reading strategy commonly utilized in classrooms to engage and focus students while reading. The acronym stands for "What I Know, Want to Know, and Learned." Students using this strategy activate prior knowledge, set goals for themselves as readers, and reflect upon what they have gained through reading. Here we will explain more about what the KWL Reading Method entails as well as provide advice on how you can utilize it effectively for reading practice.
What is the KWL Reading Method?
The KWL Reading Method is an efficient strategy for active reading that encourages readers to tackle challenging texts. Using three simple columns, readers can keep track of what they already know, what they would like to learn and what has been gained after reading.
“K” stands for what is already known to the reader about a topic - this could include any prior knowledge or experience that they already possess on this subject matter. "W" stands for what the reader wants to learn - possibly an inventory of questions related to said topic that the reader wants answered. Finally, "L" represents what has been learned or gained through reading.
This method can be especially helpful in academic settings where students are expected to read and comprehend complex texts. By engaging actively with a text using the KWL method, readers can retain key pieces of information more effectively and measure their learning progress more easily.
You start by recording what you know about a subject and record their ideas in the K column of a KWL Reading Method chart. This helps activate prior knowledge and make connections to what's written in the text before you begin listing questions or things you want to learn in the W column of the chart. This helps guide your reading and draw attention to relevant information in text. Upon finishing reading the text, you should record what you’ve learned by recording it in the L column. No matter your reading level , this tool can help to summarize and assess whether learning objectives have been fulfilled.
Overall, the KWL Reading Method is an effective strategy for active reading that can be implemented across academic and nonacademic environments alike. By engaging with challenging texts and monitoring their learning progress, readers can improve their retention of information, critical thinking skills, and overall reading comprehension.
Interpretive reading is another effective method of deepening comprehension and analyzing texts. Where literal reading merely seeks to comprehend surface-level meaning of texts, interpretive reading aims at unpacking authorial intent, tone, and any hidden messages contained therein.
To develop this skill, readers must actively read and question a text's purpose in relation to their background knowledge or the world. Doing this requires engaging with multiple layers of meaning within the text while critically analyzing its contents - all while paying close attention to word choice, sentence structure, themes, and symbols used by authors to fully grasp their message.
Once readers understand the meaning of a text, it’s important for them to consider its wider implications and how it fits within a larger context. This involves investigating its relationship to historical, social, and economic factors, as well as understanding why an author's message may still be applicable beyond immediate context.
Interpretive reading is a fundamental skill necessary to understanding and appreciating complex texts such as literary works, academic articles, and other forms of writing. By dissecting the author’s intent and message beyond what appears on the surface, readers can uncover deeper meanings and insights that lead to greater comprehension of what the author intended.
Interpretive reading is an invaluable method of comprehension and analysis, providing readers with access to the full depth and complexity of texts. By paying close attention to an author's intent, tone, and subtextual messages, they can broaden their own comprehension while connecting more intimately with the writing.
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

Research Reading: How to Make Reading Scientific Articles a Happy Habit
Scientific research reading is a complex endeavor that requires researchers to be able to choose an appropriate topic, create a project structure, select a study methodology, evaluate collected data, and write a comprehensive manuscript. All of this necessitates a knowledge of paper reviews and academic reports, as well as training and participation in the research process. One way to develop this knowledge is by inculcating regular research reading habits.
Table of Contents
The importance of research reading
Scholars require a set of very specific skills to navigate the often daunting task of writing a thesis or a research paper. Most researchers will acquire these skills over time – with experience, focused training, and most importantly by reading scientific articles in their field of research. Reading scientific journals and papers associated with their area of research helps academics develop a wider understanding of the subject and strengthen their ability to conduct a thorough scientific study.
Research reading is central to the scientific research process and the basis of skill development. Regardless of the research sources and methods you use, reading free scientific articles enables you to generate new ideas and become a more independent and creative researcher. Clearly, research reading is a practice that should not only be carried out during your doctoral journey but also throughout your research career. However, many academics and doctoral students do not take time to actively find and read scientific literature on a regular basis.
7 steps to make research reading a daily habit
Readers are not created overnight. Years of consistency and a genuine desire to learn new things are the two factors that shape our reading habits. This is something that develops gradually as you push yourself to read about topics outside your area of expertise. It takes time, constant effort and practice.
Here are some simple strategies you can adopt to make it easy to read scientific articles and incorporate research reading into your daily routine.
1. Create a reading list of relevant journals
Put together a comprehensive list of journals that regularly publish research in your field to kick-start your research reading. Be sure to include journals that publish new analysis or share details of experimental methods apart from those that publish primary research findings. Subscribe to online alerts so that you are informed of new reports as soon as they become available. This will ensure that you don’t miss out on the latest developments in your areas of interest. Finally, reassess your journal list regularly to account for any new journals that have been recently introduced and remove those that are phased out or not being published anymore.
2. Set a goal and schedule time for undisturbed reading
If you want to develop an appreciation and passion for scientific research, set a goal for yourself (it could be reading a set number of pages daily) to read free scientific articles in your chosen field. A great way to achieve your research reading goals is also setting aside dedicated time to read; this could be in the early mornings or even while travelling to and back from work.
3. Start with easy-to-read scientific articles beyond your discipline
Apart from only reading articles on your subject, mix it up by reading reports and articles on related research to broaden your knowledge. Reading scientific articles across fields can help you understand the scientific discovery process, develop critical reasoning skills, and empower you to think differently and outside the box. This lets you appreciate the variety and novelty in previously published science and can also help you come up with new research ideas, theories, and stories.

4. Actively read scientific articles and make notes where relevant
Researchers often end up passively reading scientific articles without absorbing the information provided, which could lead to a loss of genuine interest in reading. It is important to make an effort to develop the habit of actively reading scientific articles by highlighting key data, making notes, and critically thinking about the information provided.
5. Follow a chronological order for research reading
When researching about a new topic, consider reading existing literature in chronological order. This will give you an idea of how the scientific conversation developed over time, how different terms, concepts, and methods evolved, and even the names of leading researchers working on the topic.
6. Engage in intellectual conversations
In order to maintain an avid interest in research reading, actively engage with what you read and discuss scientific articles with your co-workers, and where possible, look to interact with the author to ask questions. You can also compare your own interpretations to those of your colleagues. This exchange of ideas enables you to gain a better understanding of scientific articles and helps you retain the information gleaned from them, which can be a motivating factor to keep reading.
7. Track your literature and reading
Use a reference manager to organize your literature and keep track of your reading. You can add papers and reports that you have read and store a list of the literature you want to read in a “Papers to read” folder, and you can further optimize this based on the topic. Researchers can also use Excel sheets or Word documents to keep notes on what they’ve read and the main findings from each paper. This will make it easy to refer to and retrieve data when you begin to write your own research manuscript.
Rather than reading scientific articles only when applying for funding, writing research proposals, analyzing data, and writing papers, research reading should become a continuous process of absorbing knowledge. Reading scientific literature and persuasive writing are inextricably linked because one cannot exist without the other.
Researching and reading scientific literature on a regular basis is essential for demystifying any topic of interest because it allows you to discuss complex and challenging issues with others, persuade and be persuaded, and most importantly enrich writing and learning in general.
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

Research in Shorts: R Discovery’s New Feature Helps Academics Assess Relevant Papers in 2mins

How Does R Discovery’s Interplatform Capability Enhance Research Accessibility

Research Topics & Ideas: Education
170+ Research Ideas To Fast-Track Your Dissertation, Thesis Or Research Project

I f you’re just starting out exploring education-related topics for your dissertation, thesis or research project, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll help kickstart your research topic ideation process by providing a hearty list of research topics and ideas , including examples from actual dissertations and theses..
PS – This is just the start…
We know it’s exciting to run through a list of research topics, but please keep in mind that this list is just a starting point . To develop a suitable education-related research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , and a viable plan of action to fill that gap.
If this sounds foreign to you, check out our free research topic webinar that explores how to find and refine a high-quality research topic, from scratch. Alternatively, if you’d like hands-on help, consider our 1-on-1 coaching service .
Overview: Education Research Topics
- How to find a research topic (video)
- List of 50+ education-related research topics/ideas
- List of 120+ level-specific research topics
- Examples of actual dissertation topics in education
- Tips to fast-track your topic ideation (video)
- Where to get extra help
Education-Related Research Topics & Ideas
Below you’ll find a list of education-related research topics and idea kickstarters. These are fairly broad and flexible to various contexts, so keep in mind that you will need to refine them a little. Nevertheless, they should inspire some ideas for your project.
- The impact of school funding on student achievement
- The effects of social and emotional learning on student well-being
- The effects of parental involvement on student behaviour
- The impact of teacher training on student learning
- The impact of classroom design on student learning
- The impact of poverty on education
- The use of student data to inform instruction
- The role of parental involvement in education
- The effects of mindfulness practices in the classroom
- The use of technology in the classroom
- The role of critical thinking in education
- The use of formative and summative assessments in the classroom
- The use of differentiated instruction in the classroom
- The use of gamification in education
- The effects of teacher burnout on student learning
- The impact of school leadership on student achievement
- The effects of teacher diversity on student outcomes
- The role of teacher collaboration in improving student outcomes
- The implementation of blended and online learning
- The effects of teacher accountability on student achievement
- The effects of standardized testing on student learning
- The effects of classroom management on student behaviour
- The effects of school culture on student achievement
- The use of student-centred learning in the classroom
- The impact of teacher-student relationships on student outcomes
- The achievement gap in minority and low-income students
- The use of culturally responsive teaching in the classroom
- The impact of teacher professional development on student learning
- The use of project-based learning in the classroom
- The effects of teacher expectations on student achievement
- The use of adaptive learning technology in the classroom
- The impact of teacher turnover on student learning
- The effects of teacher recruitment and retention on student learning
- The impact of early childhood education on later academic success
- The impact of parental involvement on student engagement
- The use of positive reinforcement in education
- The impact of school climate on student engagement
- The role of STEM education in preparing students for the workforce
- The effects of school choice on student achievement
- The use of technology in the form of online tutoring

Level-Specific Research Topics
Looking for research topics for a specific level of education? We’ve got you covered. Below you can find research topic ideas for primary, secondary and tertiary-level education contexts. Click the relevant level to view the respective list.
Research Topics: Pick An Education Level
Primary education.
- Investigating the effects of peer tutoring on academic achievement in primary school
- Exploring the benefits of mindfulness practices in primary school classrooms
- Examining the effects of different teaching strategies on primary school students’ problem-solving skills
- The use of storytelling as a teaching strategy in primary school literacy instruction
- The role of cultural diversity in promoting tolerance and understanding in primary schools
- The impact of character education programs on moral development in primary school students
- Investigating the use of technology in enhancing primary school mathematics education
- The impact of inclusive curriculum on promoting equity and diversity in primary schools
- The impact of outdoor education programs on environmental awareness in primary school students
- The influence of school climate on student motivation and engagement in primary schools
- Investigating the effects of early literacy interventions on reading comprehension in primary school students
- The impact of parental involvement in school decision-making processes on student achievement in primary schools
- Exploring the benefits of inclusive education for students with special needs in primary schools
- Investigating the effects of teacher-student feedback on academic motivation in primary schools
- The role of technology in developing digital literacy skills in primary school students
- Effective strategies for fostering a growth mindset in primary school students
- Investigating the role of parental support in reducing academic stress in primary school children
- The role of arts education in fostering creativity and self-expression in primary school students
- Examining the effects of early childhood education programs on primary school readiness
- Examining the effects of homework on primary school students’ academic performance
- The role of formative assessment in improving learning outcomes in primary school classrooms
- The impact of teacher-student relationships on academic outcomes in primary school
- Investigating the effects of classroom environment on student behavior and learning outcomes in primary schools
- Investigating the role of creativity and imagination in primary school curriculum
- The impact of nutrition and healthy eating programs on academic performance in primary schools
- The impact of social-emotional learning programs on primary school students’ well-being and academic performance
- The role of parental involvement in academic achievement of primary school children
- Examining the effects of classroom management strategies on student behavior in primary school
- The role of school leadership in creating a positive school climate Exploring the benefits of bilingual education in primary schools
- The effectiveness of project-based learning in developing critical thinking skills in primary school students
- The role of inquiry-based learning in fostering curiosity and critical thinking in primary school students
- The effects of class size on student engagement and achievement in primary schools
- Investigating the effects of recess and physical activity breaks on attention and learning in primary school
- Exploring the benefits of outdoor play in developing gross motor skills in primary school children
- The effects of educational field trips on knowledge retention in primary school students
- Examining the effects of inclusive classroom practices on students’ attitudes towards diversity in primary schools
- The impact of parental involvement in homework on primary school students’ academic achievement
- Investigating the effectiveness of different assessment methods in primary school classrooms
- The influence of physical activity and exercise on cognitive development in primary school children
- Exploring the benefits of cooperative learning in promoting social skills in primary school students
Secondary Education
- Investigating the effects of school discipline policies on student behavior and academic success in secondary education
- The role of social media in enhancing communication and collaboration among secondary school students
- The impact of school leadership on teacher effectiveness and student outcomes in secondary schools
- Investigating the effects of technology integration on teaching and learning in secondary education
- Exploring the benefits of interdisciplinary instruction in promoting critical thinking skills in secondary schools
- The impact of arts education on creativity and self-expression in secondary school students
- The effectiveness of flipped classrooms in promoting student learning in secondary education
- The role of career guidance programs in preparing secondary school students for future employment
- Investigating the effects of student-centered learning approaches on student autonomy and academic success in secondary schools
- The impact of socio-economic factors on educational attainment in secondary education
- Investigating the impact of project-based learning on student engagement and academic achievement in secondary schools
- Investigating the effects of multicultural education on cultural understanding and tolerance in secondary schools
- The influence of standardized testing on teaching practices and student learning in secondary education
- Investigating the effects of classroom management strategies on student behavior and academic engagement in secondary education
- The influence of teacher professional development on instructional practices and student outcomes in secondary schools
- The role of extracurricular activities in promoting holistic development and well-roundedness in secondary school students
- Investigating the effects of blended learning models on student engagement and achievement in secondary education
- The role of physical education in promoting physical health and well-being among secondary school students
- Investigating the effects of gender on academic achievement and career aspirations in secondary education
- Exploring the benefits of multicultural literature in promoting cultural awareness and empathy among secondary school students
- The impact of school counseling services on student mental health and well-being in secondary schools
- Exploring the benefits of vocational education and training in preparing secondary school students for the workforce
- The role of digital literacy in preparing secondary school students for the digital age
- The influence of parental involvement on academic success and well-being of secondary school students
- The impact of social-emotional learning programs on secondary school students’ well-being and academic success
- The role of character education in fostering ethical and responsible behavior in secondary school students
- Examining the effects of digital citizenship education on responsible and ethical technology use among secondary school students
- The impact of parental involvement in school decision-making processes on student outcomes in secondary schools
- The role of educational technology in promoting personalized learning experiences in secondary schools
- The impact of inclusive education on the social and academic outcomes of students with disabilities in secondary schools
- The influence of parental support on academic motivation and achievement in secondary education
- The role of school climate in promoting positive behavior and well-being among secondary school students
- Examining the effects of peer mentoring programs on academic achievement and social-emotional development in secondary schools
- Examining the effects of teacher-student relationships on student motivation and achievement in secondary schools
- Exploring the benefits of service-learning programs in promoting civic engagement among secondary school students
- The impact of educational policies on educational equity and access in secondary education
- Examining the effects of homework on academic achievement and student well-being in secondary education
- Investigating the effects of different assessment methods on student performance in secondary schools
- Examining the effects of single-sex education on academic performance and gender stereotypes in secondary schools
- The role of mentoring programs in supporting the transition from secondary to post-secondary education
Tertiary Education
- The role of student support services in promoting academic success and well-being in higher education
- The impact of internationalization initiatives on students’ intercultural competence and global perspectives in tertiary education
- Investigating the effects of active learning classrooms and learning spaces on student engagement and learning outcomes in tertiary education
- Exploring the benefits of service-learning experiences in fostering civic engagement and social responsibility in higher education
- The influence of learning communities and collaborative learning environments on student academic and social integration in higher education
- Exploring the benefits of undergraduate research experiences in fostering critical thinking and scientific inquiry skills
- Investigating the effects of academic advising and mentoring on student retention and degree completion in higher education
- The role of student engagement and involvement in co-curricular activities on holistic student development in higher education
- The impact of multicultural education on fostering cultural competence and diversity appreciation in higher education
- The role of internships and work-integrated learning experiences in enhancing students’ employability and career outcomes
- Examining the effects of assessment and feedback practices on student learning and academic achievement in tertiary education
- The influence of faculty professional development on instructional practices and student outcomes in tertiary education
- The influence of faculty-student relationships on student success and well-being in tertiary education
- The impact of college transition programs on students’ academic and social adjustment to higher education
- The impact of online learning platforms on student learning outcomes in higher education
- The impact of financial aid and scholarships on access and persistence in higher education
- The influence of student leadership and involvement in extracurricular activities on personal development and campus engagement
- Exploring the benefits of competency-based education in developing job-specific skills in tertiary students
- Examining the effects of flipped classroom models on student learning and retention in higher education
- Exploring the benefits of online collaboration and virtual team projects in developing teamwork skills in tertiary students
- Investigating the effects of diversity and inclusion initiatives on campus climate and student experiences in tertiary education
- The influence of study abroad programs on intercultural competence and global perspectives of college students
- Investigating the effects of peer mentoring and tutoring programs on student retention and academic performance in tertiary education
- Investigating the effectiveness of active learning strategies in promoting student engagement and achievement in tertiary education
- Investigating the effects of blended learning models and hybrid courses on student learning and satisfaction in higher education
- The role of digital literacy and information literacy skills in supporting student success in the digital age
- Investigating the effects of experiential learning opportunities on career readiness and employability of college students
- The impact of e-portfolios on student reflection, self-assessment, and showcasing of learning in higher education
- The role of technology in enhancing collaborative learning experiences in tertiary classrooms
- The impact of research opportunities on undergraduate student engagement and pursuit of advanced degrees
- Examining the effects of competency-based assessment on measuring student learning and achievement in tertiary education
- Examining the effects of interdisciplinary programs and courses on critical thinking and problem-solving skills in college students
- The role of inclusive education and accessibility in promoting equitable learning experiences for diverse student populations
- The role of career counseling and guidance in supporting students’ career decision-making in tertiary education
- The influence of faculty diversity and representation on student success and inclusive learning environments in higher education

Education-Related Dissertations & Theses
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a research topic in education, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual dissertations and theses in the education space to see how this all comes together in practice.
Below, we’ve included a selection of education-related research projects to help refine your thinking. These are actual dissertations and theses, written as part of Master’s and PhD-level programs, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- From Rural to Urban: Education Conditions of Migrant Children in China (Wang, 2019)
- Energy Renovation While Learning English: A Guidebook for Elementary ESL Teachers (Yang, 2019)
- A Reanalyses of Intercorrelational Matrices of Visual and Verbal Learners’ Abilities, Cognitive Styles, and Learning Preferences (Fox, 2020)
- A study of the elementary math program utilized by a mid-Missouri school district (Barabas, 2020)
- Instructor formative assessment practices in virtual learning environments : a posthumanist sociomaterial perspective (Burcks, 2019)
- Higher education students services: a qualitative study of two mid-size universities’ direct exchange programs (Kinde, 2020)
- Exploring editorial leadership : a qualitative study of scholastic journalism advisers teaching leadership in Missouri secondary schools (Lewis, 2020)
- Selling the virtual university: a multimodal discourse analysis of marketing for online learning (Ludwig, 2020)
- Advocacy and accountability in school counselling: assessing the use of data as related to professional self-efficacy (Matthews, 2020)
- The use of an application screening assessment as a predictor of teaching retention at a midwestern, K-12, public school district (Scarbrough, 2020)
- Core values driving sustained elite performance cultures (Beiner, 2020)
- Educative features of upper elementary Eureka math curriculum (Dwiggins, 2020)
- How female principals nurture adult learning opportunities in successful high schools with challenging student demographics (Woodward, 2020)
- The disproportionality of Black Males in Special Education: A Case Study Analysis of Educator Perceptions in a Southeastern Urban High School (McCrae, 2021)
As you can see, these research topics are a lot more focused than the generic topic ideas we presented earlier. So, in order for you to develop a high-quality research topic, you’ll need to get specific and laser-focused on a specific context with specific variables of interest. In the video below, we explore some other important things you’ll need to consider when crafting your research topic.
Get 1-On-1 Help
If you’re still unsure about how to find a quality research topic within education, check out our Research Topic Kickstarter service, which is the perfect starting point for developing a unique, well-justified research topic.

Find The Perfect Research Topic

How To Choose A Research Topic: 5 Key Criteria
How To Choose A Research Topic Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + Free Topic...
Research Topics & Ideas: Automation & Robotics
Research Topics & Ideas: Robotics 50 Topic Ideas To Kickstart Your Research...

Research Topics & Ideas: Sociology
Research Topics & Ideas: Sociology 50 Topic Ideas To Kickstart Your Research...

Research Topics & Ideas: Public Health & Epidemiology
Research Topics & Ideas: Public Health 50 Topic Ideas To Kickstart Your Research...

Research Topics & Ideas: Neuroscience
Research Topics & Ideas: Neuroscience 50 Topic Ideas To Kickstart Your Research...
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
70 Comments
This is an helpful tool 🙏
Special education
Really appreciated by this . It is the best platform for research related items
Research title related to school of students
How are you
I think this platform is actually good enough.
Research title related to students
My field is research measurement and evaluation. Need dissertation topics in the field
Assalam o Alaikum I’m a student Bs educational Resarch and evaluation I’m confused to choose My thesis title please help me in choose the thesis title
Good idea I’m going to teach my colleagues
You can find our list of nursing-related research topic ideas here: https://gradcoach.com/research-topics-nursing/
Write on action research topic, using guidance and counseling to address unwanted teenage pregnancy in school
Thanks a lot
I learned a lot from this site, thank you so much!
Thank you for the information.. I would like to request a topic based on school major in social studies
parental involvement and students academic performance
Science education topics?
plz tell me if you got some good topics, im here for finding research topic for masters degree
How about School management and supervision pls.?
Hi i am an Deputy Principal in a primary school. My wish is to srudy foe Master’s degree in Education.Please advice me on which topic can be relevant for me. Thanks.
Thank you so much for the information provided. I would like to get an advice on the topic to research for my masters program. My area of concern is on teacher morale versus students achievement.
Every topic proposed above on primary education is a starting point for me. I appreciate immensely the team that has sat down to make a detail of these selected topics just for beginners like us. Be blessed.
Kindly help me with the research questions on the topic” Effects of workplace conflict on the employees’ job performance”. The effects can be applicable in every institution,enterprise or organisation.
Greetings, I am a student majoring in Sociology and minoring in Public Administration. I’m considering any recommended research topic in the field of Sociology.
I’m a student pursuing Mphil in Basic education and I’m considering any recommended research proposal topic in my field of study
Research Defense for students in senior high
Kindly help me with a research topic in educational psychology. Ph.D level. Thank you.
Project-based learning is a teaching/learning type,if well applied in a classroom setting will yield serious positive impact. What can a teacher do to implement this in a disadvantaged zone like “North West Region of Cameroon ( hinterland) where war has brought about prolonged and untold sufferings on the indegins?
I wish to get help on topics of research on educational administration
I wish to get help on topics of research on educational administration PhD level
I am also looking for such type of title
I am a student of undergraduate, doing research on how to use guidance and counseling to address unwanted teenage pregnancy in school
the topics are very good regarding research & education .
Am an undergraduate student carrying out a research on the impact of nutritional healthy eating programs on academic performance in primary schools
Can i request your suggestion topic for my Thesis about Teachers as an OFW. thanx you
Would like to request for suggestions on a topic in Economics of education,PhD level
Would like to request for suggestions on a topic in Economics of education
Hi 👋 I request that you help me with a written research proposal about education the format
Am offering degree in education senior high School Accounting. I want a topic for my project work
l would like to request suggestions on a topic in managing teaching and learning, PhD level (educational leadership and management)
request suggestions on a topic in managing teaching and learning, PhD level (educational leadership and management)
I would to inquire on research topics on Educational psychology, Masters degree
I am PhD student, I am searching my Research topic, It should be innovative,my area of interest is online education,use of technology in education
request suggestion on topic in masters in medical education .
Look at British Library as they keep a copy of all PhDs in the UK Core.ac.uk to access Open University and 6 other university e-archives, pdf downloads mostly available, all free.
May I also ask for a topic based on mathematics education for college teaching, please?
Please I am a masters student of the department of Teacher Education, Faculty of Education Please I am in need of proposed project topics to help with my final year thesis
Am a PhD student in Educational Foundations would like a sociological topic. Thank
please i need a proposed thesis project regardging computer science
Greetings and Regards I am a doctoral student in the field of philosophy of education. I am looking for a new topic for my thesis. Because of my work in the elementary school, I am looking for a topic that is from the field of elementary education and is related to the philosophy of education.
Masters student in the field of curriculum, any ideas of a research topic on low achiever students
In the field of curriculum any ideas of a research topic on deconalization in contextualization of digital teaching and learning through in higher education
Amazing guidelines
I am a graduate with two masters. 1) Master of arts in religious studies and 2) Master in education in foundations of education. I intend to do a Ph.D. on my second master’s, however, I need to bring both masters together through my Ph.D. research. can I do something like, ” The contribution of Philosophy of education for a quality religion education in Kenya”? kindly, assist and be free to suggest a similar topic that will bring together the two masters. thanks in advance
Hi, I am an Early childhood trainer as well as a researcher, I need more support on this topic: The impact of early childhood education on later academic success.
I’m a student in upper level secondary school and I need your support in this research topics: “Impact of incorporating project -based learning in teaching English language skills in secondary schools”.
Although research activities and topics should stem from reflection on one’s practice, I found this site valuable as it effectively addressed many issues we have been experiencing as practitioners.
Your style is unique in comparison to other folks I’ve read stuff from. Thanks for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this site.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly

- Request new password
- Create a new account
Doing Research in Counselling and Psychotherapy
Student resources, reading research.
This chapter offers a grounding in the key research skill of reading research papers from a critical and affirmative stance. There is an emphasis on reading papers as a means of developing an appreciation of the diversity of research questions, methodologies and techniques that exist within the contemporary psychotherapy research literature. A further aim of the chapter is to explore strategies for finding interesting and relevant research papers.
The following learning activities offer starting points for developing critical reading skills:
PART 1. Reading Research Papers
Step 1. Read through this worksheet to support the development of skills in critically analysing a research paper and familiarise yourself with basic principles of critical analysis.
Step 2. Read the following research paper , and make notes on its strengths and weaknesses, in accordance with the questions in the worksheet.
Step 3. After (not before!) you have completed the previous step, read John McLeod’s notes on the Stephenson & Hale (2020) paper . Compare your perception of the paper with the analyses of your colleagues.
Step 4. Read the list of further questions to consider when critically analysing a research paper. Add to this list any additional questions that seem relevant to you, or that emerged when you were working on Stephenson & Hale (2020).
Step 5. Here are two additional papers to analyse, generated by a Google Scholar ‘cited by’ and ‘related articles’ search on the Stephenson & Hale (2020) article:
Rayner, M., & Vitali, D. (2016). Short-term existential psychotherapy in primary care: A quantitative report. Journal of Humanistic Psychology , 56(4), 357 – 372.
You are now in a position to go further, by including conclusions and insights arising from a comparison of this paper and Stephenson & Hale (2020).
Rayner, M., & Vitali, D. (2018). Existential experimentation: structure and principles for a short-term psychological therapy. Journal of Humanistic Psychology , 58(2), 194 – 213.
This more detailed understanding of a key aspect (i.e., the intervention) of these two studies makes it possible to consider other important questions, such as:
- How appropriate is the CORE outcome measure, as a tool for evaluating the effectiveness of existential therapy?
- What other methods of data collection, or research designs, might be appropriate?
- How would you describe existential therapy, if you were helping prospective clients to choose between this and CBT?
- What kind of rationale for existential therapy would be credible for health service managers and policy-makers – and what kind of research might be convincing to such stakeholders?
Step 6. Repeat this process, on a research topic that is particularly relevant to your own interests, or a topic that has been agreed by the members of your learning group. To get started, all you need is one relatively recent study. You can then work forwards and backwards, using the reference list in the article, Google Scholar, and search tools available through your university or college library or your workplace.
PART 2. Reviewing the research literature
In any research project, it is necessary to contextualise the proposed study by providing a rationale that shows how it builds on previous knowledge. This requires carrying out some kind of review of previous research. The extent and level of detail of such a review can vary widely.
A useful source of learning about the process of reviewing the research literature is to read published reviews. Doing Research in Counselling and Psychotherapy (4 th edn.) does not highlight completing a published review as part of the core skills set of a novice or practitioner researcher, because such research ‘products’ are too demanding for that stage of development as a researcher. However, reading reviews, and becoming a connoisseur of reviews, make it possible to appreciate the skills and strategies involved in conducting a high-quality review, as a basis for deciding which of them might be feasible or relevant to one’s own project.
The following sources provide an overview of some of the main types of review that have been implemented:
Munn, Z., Peters, M. D., Stern, C., Tufanaru, C., McArthur, A., & Aromataris, E. (2018). Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 18(1), 1 – 7.
A scoping review is basically a careful trawl of the research literature, to map and classify existing evidence. By contrast, a systematic review seeks to provide a rigorous answer to a specific question. This paper provides a clear explanation of this distinction.
Access to several downloadable scoping reviews of research is available at the following sites:
https://www.bacp.co.uk/events-and-resources/research/publications/ (British Association for Counselling and Psychotherapy)
https://www.pacfa.org.au/Portal/Publications-and-Research/Pub.aspx (Psychotherapy and Counselling Federation of Australia)
McPherson, S., Wicks, C., & Tercelli, I. (2020). Patient experiences of psychological therapy for depression: a qualitative metasynthesis. BMC Psychiatry , 20(1), 1 – 18.
This review is a good example of what is possible with qualitative metasynthesis (or meta-analysis). When reading it, pay particular attention to how these reviewers have handled the challenging task of comparing and making sense of different themes that have been identified in different studies.
It can be hard to conduct a systematic review on very large numbers of studies, because of the density and complexity of information that is available. A key strategy in such contexts is to identify a subset of studies that have examined a specific aspect of the topic.
The majority of reviews restrict themselves to establishing what is known – the facts of the matter – in as credible, unbiased and comprehensive a manner a possible. However, many reviews also make suggestions for further research (e.g., filling in the gaps, or concentrating on using research techniques that are associated with the most valid or reliable findings). In addition, some reviews are used to build theoretical understanding.
de Haan, A. M., Boon, A. E., de Jong, J. T., & Vermeiren, R. R. (2018). A review of mental health treatment dropout by ethnic minority youth. Transcultural Psychiatry , 55(1), 3 – 30.
This is a typical example of a review of quantitative studies. This particular review zooms in on that literature by applying two filters: age and ethnic minority status.
Miller, C. E., Townsend, M. L., Day, N. J., & Grenyer, B. F. (2020). Measuring the shadows: A systematic review of chronic emptiness in borderline personality disorder. PloS One , 15(7), e0233970.
This is even more highly focused in examining research on a single characteristic (chronic emptiness) of the experience of individuals seeking help for a specific problem.
Fernee, C. R., Gabrielsen, L. E., Andersen, A. J., & Mesel, T. (2017). Unpacking the black box of wilderness therapy: A realist synthesis. Qualitative Health Research , 27(1), 114 – 129.
Realist synthesis is a review approach that aims to develop a theoretical model of an area of practice. As well as providing an example of using the review process to develop a theoretical model, this article illustrates how a good review can be used to consolidate knowledge and provide a platform for further research in an area where relatively few studies have been published.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

How the Science of Reading Informs 21st‐Century Education
The science of reading should be informed by an evolving evidence base built upon the scientific method. Decades of basic research and randomized controlled trials of interventions and instructional routines have formed a substantial evidence base to guide best practices in reading instruction, reading intervention, and the early identification of at-risk readers. The recent resurfacing of questions about what constitutes the science of reading is leading to misinformation in the public space that may be viewed by educational stakeholders as merely differences of opinion among scientists. Our goals in this paper are to revisit the science of reading through an epistemological lens to clarify what constitutes evidence in the science of reading and to offer a critical evaluation of the evidence provided by the science of reading. To this end, we summarize those things that we believe have compelling evidence, promising evidence, or a lack of compelling evidence. We conclude with a discussion of areas of focus that we believe will advance the science of reading to meet the needs of all children in the 21st century.
For more than 100 years, the question of how best to teach children to read has been debated in what has been termed the “reading wars”. The debate cyclically fades into the background only to reemerge, often with the same points of conflict. We believe that this cycle is not helpful for promoting the best outcomes for children’s educational success. Our goal in this paper is to make an honest and critical appraisal of the science of reading, defining what it is, how we build a case for evidence, summarizing those things for which the science of reading has provided unequivocal answers, providing a discussion of things we do not know but that may have been “oversold,” identifying areas for which evidence is promising but not yet compelling, and thinking ahead about how the science of reading can better serve all stakeholders in children’s educational achievements.
At its core, scientific inquiry is the same in all fields. Scientific research, whether in education, physics, anthropology, molecular biology, or economics, is a continual process of rigorous reasoning supported by a dynamic interplay among methods, theories, and findings. It builds understandings in the form of models or theories that can be tested. Advances in scientific knowledge are achieved by the self-regulating norms of the scientific community over time, not, as sometimes believed, by the mechanistic application of a particular scientific method to a static set of questions (National Research Council, 2002, p. 2).
What is the Science of Reading and Why are we Still Debating it?
The “science of reading” is a phrase representing the accumulated knowledge about reading, reading development, and best practices for reading instruction obtained by the use of the scientific method. We recognize that the accrual of scientific knowledge related to reading is ever evolving, at times circuitous, and not without controversy. Nonetheless, the knowledge base on the science of reading is vast. In the last decade alone, over 14,000 peer-reviewed articles have been published in journals that included the keyword “reading” based on a PsycINFO search. Although many of these studies likely focused on a sliver of the reading process individually, collectively, research studies with a focus on reading have yielded a substantial knowledge base of stable findings based on the science of reading. Taken together, the science of reading helps a diverse set of educational shareholders across institutions (e.g., preschools, schools, universities), communities, and families to make informed choices about how to effectively promote literacy skills that foster healthy and productive lives ( DeWalt & Hink, 2009 ; Rayner et al., 2001 ).
An interesting question concerning the science of reading is “Why is there a debate surrounding the science of reading?” Although there are certainly disputes within the scientific community regarding best practices and new areas of research inquiry, most of the current debate seems to settle upon what constitutes scientific evidence, how much value we should place on scientific evidence as opposed to other forms of knowledge, and how preservice teachers should be instructed to teach reading ( Brady, 2020 ). The current disagreement in what constitutes the scientific evidence of reading (e.g., Calkins, 2020 ) is not new. During the last round of the “reading wars” in the late 1990’s and early 2000’s these same issues were discussed and debated. Much of the debate focused on conflicting views in epistemology between constructivists and positivists on the basic mechanisms associated with reading development. Constructivists, such as Goodman (1967) and Smith (1971) , believed that reading was a “natural act” akin to learning language and thus emphasized giving children the opportunity to discover meaning through experiences in a literacy-rich environment. In contrast, positivists, such as Chall (1967) and Flesch (1955) , made strong distinctions between innate language learning and the effortful learning required to acquire reading skills. Positivists argued for explicit instruction to help foster understanding of how the written code mapped onto language, whereas constructivists encouraged children to engage in a “psycholinguistic guessing game” in which readers use their graphic, semantic, and syntactic knowledge (known as the three cuing system) to guess the meaning of a printed word.
Research clearly indicates that skilled reading involves the consolidation of orthographic and phonological word forms ( Dehene, 2011 ). Work in cognitive neuroscience indicates that a small region of the left ventral visual cortex becomes specialized for this purpose. As children learn to read, they recruit neurons from a small region of the left ventral visual cortex within the left occipitotemporal cortex region (i.e., visual word form area) that are tuned to language-dependent parameters through connectivity to perisylvian language areas ( Dehaene-Lambertz et al., 2018 ). This provides an efficient circuit for grapheme-phoneme conversion and lexical access allowing efficient word-reading skills to develop. These studies provide direct evidence for how teaching alters the human brain by repurposing some visual regions toward the shapes of letters, suggesting that cultural inventions, such as written language, modify evolutionarily older brain regions. Furthermore, studies suggest that instruction focusing on the link between orthography and phonology promote this brain reorganization (e.g., Dehaene, 2011 ). Yet, arguments between philosophical constructivists and philosophical positivists on what constitutes the science of reading and how it informs instruction remain active today (e.g., Castles et al., 2018 ). In a recent interview with Emily Hanford, Ken Goodman defended his advocacy for the three cuing system saying that the three-cueing theory is based on years of observational research. In his view, three cueing is perfectly valid, drawn from a different kind of evidence than what scientists collect in their lab and later he stated that “my science is different” ( Hanford, 2019 ).
As scientists at the Florida Center for Reading Research, we are often frustrated when what we view to be the empirically supported evidence base about the reading process are distorted or denied in communications directed to the public and to teachers. However, Stanovich (2003) posited that “in many cases, the facts are secondary—what is being denied are the styles of reasoning that gave rise to the facts; what is being denied is closer to a worldview than an empirical finding. Many of these styles are implicit; we are not conscious of them as explicit rules of behavior” (pp. 106-107). Stanovich proposed five different dimensions that represent “styles” of generating knowledge about reading. For our purposes, here, we focus on the first dimension: the correspondence versus coherence theory of truth. It hits at the heart of how people believe something to be true. People who believe that a real world exists independent of their beliefs, and that interrogating this world using rigorous principles to gain knowledge is a fruitful activity are said to subscribe to the correspondence theory of truth. In contrast, those who subscribe to the coherence theory of truth believe that something is “true” if the beliefs about something fit together in a logical way. In essence, something is true if it makes sense.
Stanovich believed these differing truth systems might lie at the heart of the disagreements surrounding the science of reading. One side shouting, “Look at this mountain of evidence! How can you not believe it?” and the other side shouting, “It doesn’t make sense! It doesn’t match up with our experiences! Why should we value your knowledge above our own?!” By approaching the science of reading from the perspective of the correspondence theory of truth, we consider how compelling evidence can be generated, what we believe is the compelling evidence, what we think lacks evidence, and what we think is promising evidence.
How We Build a Case for Compelling Evidence
Research is the means by which we acquire and understand knowledge about the world ( Dane, 1990 ) to create scientific principles. Relatively few scientists would argue with the importance of using research evidence to support a principle or to make claims about reading development and the quality of reading instruction. Where significant divergence often occurs is in response to policy statements that categorize research claims and instructional strategies into those with greater or lesser levels of evidence. This divergence is typically rooted in applied epistemology, which can be understood as the study of whether the means by which we study evidence are themselves well designed to lead to valid conclusions. Researchers often frame the science of reading from divergent applied epistemological perspectives. Thus, two scientists who approach the science of reading with different epistemologies will both suggest that they have principled understandings and explanations for how children learn to read; yet, the means by which those understandings and explanations were derived are often distinct.
The correspondence and coherence theories of truth described above are examples of explanations from contrasting epistemological perspectives. Consistent with these perspectives, researchers approaching the science of reading using a correspondence theory typically prioritize deductive methods, which embed hypothesis testing, precise operationalization of constructs, and efforts to decouple the researchers’ beliefs from their interpretation and generalization of empirical evidence. Researchers approaching the science of reading using a coherence theory of truth typically prioritize more inductive methods, such as phenomenological, ethnographic, and grounded theory approaches that embed focus on the meaning and understanding that comes through a person’s lived experience and where the scientist’s own observations shape meaning and principles (e.g., Israel & Duffy, 2014 ).
When the National Research Council published Scientific Research in Education (2002), a significant amount of criticism levied against the report boiled down to differences in epistemological perspectives. Yet, these genuine contrasts can often obscure contributions to the science of reading that derive from multiple applied epistemologies. Observational research, using both inductive (e.g., case studies) and deductive (e.g., correlational studies) approaches, substantively informs the development of theories and of novel instructional approaches (e.g., Scruggs et al., 2007 ). Public health research offers a useful parallel. As it would be unethical to establish a causal link from smoking cigarettes to lung cancer through a randomized controlled trial, that field instead used well-designed observational studies to derive claims and principles. These findings then informed later stages in the broader program of research, including randomized controlled trials of interventions for smoking cessation.
In the science of reading, principles and instructional strategies should indeed capitalize on a program of research inclusive of multiple methodologies. Yet, as the public health domain ultimately takes direction from the efficacy of smoking cessation programs, so too must the science of reading take direction from theoretically informed and well-designed experimental and quasi-experimental studies of promising strategies when the intention is to evaluate instructional practices. The use of experimental (i.e., randomized trials) and quasi-experimental (e.g., regression discontinuity, propensity score matching, interrupted time series) designs, in which an intervention is competed against counterfactual conditions, such as typical practice or alternative interventions, provides the strongest causal credibility regarding which instructional strategies are effective. The What Works Clearinghouse (WWC) of the Institute of Education Sciences (e.g., What Works Clearinghouse, 2020) and the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA; Every Student Succeeds Act, 2015 ) are efforts by the US Department of Education to hierarchically characterize the levels of evidence currently available for instructional practices in education. The WWC uses a review framework, developed by methodological and statistical experts, for evaluating the quality and scope of evidence for specific instructional practices based on features of the design, implementation, and analysis of studies. Similarly, ESSA uses four tiers that focus on both the design of the study and the results of the study in which the tiers differ based on the quantity of evidence and quality of evidence supporting an approach. For both WWC and ESSA, quantity of evidence refers to the number of well-designed and well-implemented studies, and quality of evidence is defined by the ability of a study’s methods to allow for alternative explanations of a finding to be ruled out, for which the randomized controlled trial provides the strongest method.
As outlined above, the “science of reading” utilizes multiple research approaches to generate ideas about reading. Ultimately, the highest priority in the science of reading should be the replicable and generalizable knowledge from observational and experimental methods, rooted in a deductive research approach to knowledge generation that is framed in a correspondence theory of truth. In this manner, the accumulated evidence is built on a research foundation by which theories, principles, and hypotheses have been subjected to rigorous empirical scrutiny to determine the degree to which they hold up across variations in samples, measures, and contexts. In the following sections, we summarize issues related to the nature, development, and instruction of reading for which we believe the science of reading either has or has not yielded compelling evidence, identify what we believe are promising areas for which sufficient evidence has not yet accumulated, and suggest a number of areas that we believe will help move the science of reading forward, increasing knowledge and enhancing its positive impacts for a variety of stakeholders.
Compelling Evidence in the Science of Reading
In this section, we focus on a number of findings centrally important for understanding the development and teaching of reading in alphabetic languages. The evidence base provides answers varying across orthographic regularity (e.g., English vs. Spanish), reading subskill (i.e., decoding vs. comprehension), grade range or developmental level (e.g., early childhood, elementary, adolescence), and linguistic diversity (e.g., English language learners, dialect speakers).
There are large differences among alphabetic languages in the rules for how graphemes represent sounds in words (i.e., a language’s orthography). In languages like Spanish and Finnish there is a near one-to-one relation between letters and sounds. The letter-sound coding in these languages is transparent, and they have shallow orthographies. In other languages, most notably English, there is often not a one-to-one relation between letters and sounds. The letter-sound coding in these languages is opaque, and they have deep orthographies. Children must learn which words cannot be decoded based solely on letter-sound correspondence (e.g., two, knight, laugh) and learn to match these irregular spellings to the words they represent. Where a language’s orthography falls on the shallow-deep dimension affects how quickly children develop accurate and fluent word-reading skills ( Ellis et al., 2004 ; Ziegler & Goswami, 2005 ) and how much instruction on foundational reading skills is likely needed. Studies indicate that children learning to read in English are slower to acquire decoding skills (e.g., Caravolas et al., 2013 ). Ziegler et al. (1997) reported that 69% of monosyllabic words in English were consistent in spelling-to-phonology mappings and 31% of the phonology-to-spelling mappings were consistent. Thus, in teaching children to read in English, the “grain size” of phoneme, onset-rime, and whole word matters ( Ziegler & Goswami, 2005 ) and the preservation of morphological regularities in English spelling matters (e.g., vine vs. vineyard ).
Gough and Tunmer’s (1986) “simple view of reading” model, which is supported by a significant amount of research, provides a useful framework for conceptualizing the development of reading skills across time. It also frames the elements for which it is necessary to provide instructional support. The ultimate goal of reading is to extract and construct meaning from text for a purpose. For this task to be successful, however, the reader needs skills in both word decoding and linguistic comprehension. Weaknesses in either area will reduce the capacity to achieve the goal of reading. Decoding skills and linguistic comprehension make independent contributions to the prediction of reading comprehension across diverse populations of readers ( Kershaw & Schatschneider, 2012 ; Sabatini et al., 2010 ; Vellutino, et al., 2007 ). Results of several studies employing measurement strategies that allow modeling of each component as a latent variable indicate that decoding and linguistic comprehension account for almost all of the variance in reading comprehension (e.g., Foorman et al., 2015 ; Lonigan et al., 2018 ). The relative influence of these skill domains, however, changes across development. The importance of decoding skill in explaining variance in reading comprehension decreases across grades whereas the importance of linguistic comprehension increases (e.g., Catts et al., 2005 ; Foorman et al., 2018 ; García & Cain, 2014 ; Lonigan et al., 2018 ). By the time children are in high school linguistic comprehension and reading comprehension essentially form a single dimension (e.g., Foorman et al., 2018 ).
Children’s knowledge of the alphabetic principle (i.e., how letters and sounds connect) and knowledge of the morphophonemic nature of English are necessary to create the high-quality lexical representations essential to accurate and efficient decoding ( Ehri, 2005 ; Perfetti, 2007 ). Acquiring the alphabetic principle is dependent on understanding that words are composed of smaller sounds (i.e., phonological awareness, PA) and alphabet knowledge (AK). Both PA and AK are substantial correlates and predictors of decoding skills (e.g., Wagner & Torgesen, 1987 ; Wagner et al., 1994 ). Prior to formal reading instruction, children are developing PA and AK as well as other early literacy skills that are related to later decoding skills following formal reading instruction ( Lonigan et al., 2009 ; Lonigan et al., 1998 ; National Early Literacy Panel [NELP], 2008 ; Whitehurst & Lonigan, 1998 ). Reading comprehension takes advantage of the reader’s ability to understand language. In most languages, written language and spoken language have high levels of overlap in their basic structure. Longitudinal studies indicate that linguistic comprehension skills from early childhood predict reading comprehension at the end of elementary school ( Catts et al., 2015 ; Language and Reading Research Consortium & Chiu, 2018 ; Mancilla-Martinez & Lesaux, 2010 ; Storch & Whitehurst, 2002 ; Verhoeven & Van Leeuwe, 2008 ). The developmental precursors to skilled reading are present prior to school entry. Consequently, differences between children in the development of these skills forecast later differences in reading skills and are useful for identifying children at risk for reading difficulties.
The science of reading provides numerous clear answers about the type and focus of reading instruction for the subskills of reading, depending on where children are on the continuum of reading development and children’s linguistic backgrounds. Much of this knowledge is summarized in the practice guides produced by the Institute of Education Sciences ( Baker et al., 2014 ; Foorman et al., 2016a ; Gersten et al., 2007 , 2008 ; Kamil et al., 2008 ; Shanahan et al., 2010 ) and in meta-analytic summaries of research (e.g., Berkeley et al., 2012 ; Ehri, Nunes, Stahl et al., 2001 ; Ehri, Nunes, Willows et al., 2001 ; NELP, 2008 ; Therrien, 2004 ; Wanzek et al., 2013 , 2016 ). Whereas the practice guides list several best practices, here we emphasize those practices classified as supported by strong or moderate evidence based on WWC standards.
Since the publication of the Report of the National Reading Panel ( National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, 2000 ) and supported by subsequent research (e.g., Gersten et al., 2017a ; Foorman et al., 2016a ), it is clear that a large evidence base provides strong support for the explicit and systematic instruction of the component and foundational skills of decoding and decoding itself. That is, teaching children phonological awareness and letter knowledge, particularly when combined, results in improved word-decoding skills. Teaching children to decode words using systematic and explicit phonics instruction results in improved word-decoding skills. Such instruction is effective both for monolingual English-speaking children and children whose home language is other than English (i.e., dual-language learners; Baker et al., 2014 ; Gersten et al., 2007 ) as well as children who are having difficulties learning to read or who have an identified reading disability ( Ehri, Nunes, Stahl et al., 2001 ; Gersten et al., 2008 ). Additionally, providing children with frequent opportunities to read connected text supports the development of word-reading accuracy and fluency as well as comprehension skills ( Foorman et al., 2016a ; Therrien, 2004 ).
Similarly, a number of instructional activities to promote the development of reading comprehension have strong or moderate supporting evidence. For younger children, teaching children how to use comprehension strategies and how to utilize the organizational structure of a text to understand, learn, and retain content supports better reading comprehension ( Shanahan et al., 2010 ). For older children, teaching the use of comprehension strategies also enhances reading comprehension ( Kamil et al., 2008 ) as does explicit instruction in key vocabulary, providing opportunities for extended discussion of texts, and providing instruction on foundational reading skills when children lack these skills; such instructional approaches are also effective for children with significant reading difficulties ( Berkeley et al., 2012 ; Kamil et al., 2008 ).
Lack of Compelling Evidence in the Science of Reading
In the above section, practices were highlighted that have sufficient evidence to warrant their widespread use. In this section, we address reading practices for which there is a lack of compelling evidence. Some practices have simply not yet been scientifically evaluated. Other practices have been evaluated, but either the evidence does not support their use based on the generalizability of the results or the studies in which they were evaluated were not of sufficient quality to meet a minimal standard of evidence (e.g., WWC standards). Although we lack sufficient space to present a comprehensive list of practices that do not have compelling evidence, we provide examples of practices that are commonplace and vary in the degree to which they have been scientifically studied.
Evidence-based decision making regarding effective literacy programs and practices for classroom use can be difficult. Often, there is no evidence of effectiveness for a program or the evidence is of poor quality. For instance, of the five most popular reading programs used nationwide (i.e., Units of Study for Teaching Reading, Journeys, Into Reading, Leveled Literacy Intervention and Reading Recovery; Schwartz, 1999) only Leveled Literacy Intervention and Reading Recovery, both interventions for struggling readers, have studies that meet WWC standards. The evidence indicates that there were mixed effects across outcomes for Leveled Literacy Intervention and positive or potentially positive effects for Reading Recovery (e.g., Chapman & Tunmer, 2016 ). Classroom reading programs are typically built around the notion of evidence-informed practices – teaching approaches that are grounded in quality research – but have not been subjected to direct scientific evaluation. As a consequence, it is currently impossible for schools to select basal reading programs that adhere to strict evidence-based standards (e.g., ESSA, 2015 ). As an alternative, schools must develop selection criteria for choosing classroom reading programs informed by the growing scientific evidence on instructional factors that support early reading development (e.g., Castles et al., 2018 ; Foorman et al.2017 ; Rayner et al., 2001 ).
Common instructional approaches that lack generalizable empirical support include such practices as close reading ( Welsch et al., 2019 ), use of decodable text ( Jenkins et al., 2004 ), sustained silent reading ( NICHD, 2000 ), multisensory approaches ( Birsh, 2011 ), and the three-cueing system to support word recognition development (Seidenberg, 2017). Some of these instructional approaches rest on sound theoretical and pedagogical grounds. For example, giving beginning readers the opportunity to read decodable texts provides practice applying the grapheme-phoneme relations they have learned to successfully decode words ( Foorman et al., 2016a ), thus building lexical memory to support word reading accuracy and automaticity (Ehri, this issue). However, the only study to experimentally examine the impact of reading more versus less decodable texts as part of an early intervention phonics program for at risk first graders found no differences between the two groups on any of the posttest measures ( Jenkins et al., 2004 ). Such a result does not rule out the possibility of the usefulness of decodable texts but rather indicates the need to disentangle the active ingredients of effective interventions to specify what to use, when, how often, and for whom.
Similarly, multisensory approaches (e.g., Orton-Gillingham) that teach reading by using multiple senses (i.e., sight, hearing, touch, and movement) to help children make systematic connections between language, letters, and words ( Birsh, 2011 ) are commonplace and have considerable clinical support for facilitating reading development in children who struggle to learn to read. However, there is little scientific evidence that indicates that a multisensory approach is more effective than similarly structured phonological-based approaches that do not include a strong multisensory component (e.g., Boyer & Ehri, 2011 ; Ritchey & Goeke, 2006 ; Torgesen et al., 2001 ). With further research, we may find that a multisensory component is a critical ingredient of intervention for struggling readers, but we lack this empirical evidence currently.
Instruction in reading comprehension is another area where despite some studies showing moderate or strong support (see section on compelling evidence) other practices are employed despite limited support for them (e.g., Boulay et al., 2015 ). The complexity of reading comprehension relies on numerous cognitive resources and background knowledge; as a result, intervention directed exclusively at one component or another is not likely to be that impactful. For example, research shows a clear relation between breadth and depth of vocabulary and reading comprehension ( Wagner et al., 2007 ). One implication of this relation is that teaching vocabulary could improve reading comprehension. Numerous studies have tested this implication using instructional approaches that vary from teaching words in isolation to practices that involve instruction in the use of context to learn the meaning of unfamiliar words. Instruction has also included strategies to determine meaning of words through word study and morphological analysis (e.g., Beck & McKeown, 2007 ; Lesaux et al., 2014 ). Although these practices have been effective in increasing vocabulary knowledge of the words taught, there is limited evidence of transfer to untaught words (as measured by standardized measures) or to improvement in general reading comprehension ( Elleman et al., 2009 ; Lesaux et al., 2010 ). Such findings do not mean that vocabulary instruction is not a useful practice; rather, by itself, it is not sufficient to improve reading comprehension. To make meaningful gains, intervention for reading comprehension likely requires addressing multiple components of language as well as teaching content knowledge (see next section) to make sizable gains.
Other instructional practices go directly against what is known from the science of reading. For example, the three-cueing approach to support early word recognition (i.e., relying on a combination of semantic, syntactic, and graphophonic cues simultaneously to formulate an intelligent hypothesis about a word’s identity) ignores 40 years of overwhelming evidence that orthographic mapping involves the formation of letter-sound connections to bond spelling, pronunciation, and meaning of specific words in memory (see Ehri, this issue). Moreover, relying on alternative cuing systems impedes the building of automatic word-recognition skill that is the hallmark of skilled word reading ( Stanovich, 1990 ; 1991 ). The English orthography, being both alphabetic-phonemic and morpho-phonemic, clearly privileges the use of various levels of grapheme-phoneme correspondences to read words ( Frost, 2012 ), with rapid context-free word recognition being the process that most clearly distinguishes good from poor readers ( Perfetti, 1992 ; Stanovich, 1980 ). Guessing at a word amounts to a lost learning trial to help children learn the orthography of the word and thus reduce the need to guess the word in the future ( Castles et al., 2018 ; Share, 1995 ).
Similarly, alternative approaches to improving reading skills for struggling readers often fall well outside the scientific consensus regarding sources of reading difficulties. Some of these approaches are based on the tenet that temporal processing deficits in the auditory (e.g., Tallal, 1984 ) and visual (e.g., Stein, 2019 ) systems of the brain are causally related to poor word-reading development. Although there is some evidence that typically developing and struggling readers differ on measures tapping auditory ( Casini et al., 2018 ; Protopapas, 2014 ) and visual (e.g., Eden et al., 1995; Olson & Datta, 2002 ) processing skill, there is little evidence to support the use of instructional programs designed to improve auditory or visual systems to ameliorate reading problems ( Strong et al., 2011 ). Further, interventions designed to decrease visual confusion (e.g., Dyslexie font) or modify transient channel processing (e.g., Irlen lenses) to improve reading skill for children with reading disability have also failed to garner scientific support ( Hyatt et al., 2009 ; Iovino et al., 1998 ; Marinus et al., 2016 ). Similarly, although use of video games to improve reading via enhanced visual attention is reported to be an effective intervention for children with reading disability ( Peters et al., 2019 ), studies of this supplemental intervention approach have not compared it to standard supplemental approaches. Finally, studies of interventions designed to enhance other cognitive processes, such as working memory, also lack evidence effectiveness in terms of improved reading-related outcomes (e.g., Melby-Lervåg et al., 2016 ).
Promising but Not (Yet) Compelling Evidence in the Science of Reading
There are many promising areas of research that are poised to provide compelling evidence to inform the science of reading in the coming years. As we do not have space to provide a comprehensive list, we highlight only a few promising areas in prevention research and elementary education research.
Promising Directions in Prevention Research
Research on the prevention of reading problems is critical for our ability to reduce the number of children who struggle learning to read. One area of prevention research that has great promise but needs more evidence is how to more fully develop preschoolers’ language abilities that support later reading success. Both correlational and experimental findings indicate that providing children with opportunities to engage in high-quality conversations, coupled with exposure to advanced language models, matters for language development ( Cabell et al., 2015 ; Dickinson & Porche, 2011 ; Lonigan et al., 2011 ; Wasik & Hindman, 2018). Yet, most programs have a more robust impact on children’s proximal language learning (i.e., learning taught words) than on generalized language learning as measured with standardized assessments ( Marulis & Neuman, 2010 ).
Promising studies that have demonstrated significant effects on children’s general language development elucidate potential points of leverage. First, improving the connection between the school and home contexts by including parents as partners can promote synergistic learning for children as language-learning activities in school and home settings are increasingly aligned (e.g., Lonigan & Whitehurst, 1998 ). A second leverage point is increasing attention to children’s active use of language in the classroom to promote a rich dialogue between children and adults (e.g., Lonigan et al., 2011 ; Wasik & Hindman, 2018). A third leverage point is integrating content area instruction into early literacy instruction to improve language learning, for example, building children’s conceptual knowledge of the social and natural world and teaching vocabulary words within the context of related ideas (e.g., Gonzalez et al., 2011 ).
Promising Directions in Elementary Education Research
We present two promising areas in reading research with elementary-age students, one focused on improving linguistic comprehension and one focused on improving decoding, consistent with the simple view of reading.
The knowledge a reader brings to a text is the chief determinant of whether the reader will understand that text ( Anderson & Pearson, 1984 ). Thus, building knowledge is an essential, yet neglected, part of improving linguistic comprehension (Cabell & Hwang, this issue). Teaching reading is most often approached in early elementary classrooms as a subject that is independent from other subjects, such as science and social studies ( Palinscar & Duke, 2004 ). As such, reading is taught using curricula that do not systematically build children’s knowledge of the social and natural world. Instruction in reading and the content areas does not have to be an either/or proposition. Rather, the teaching of reading and of content-area learning can be simultaneously taught and integrated to powerfully impact children’s learning of both reading and content knowledge (e.g., Connor et al., 2017 ; Kim et al., 2020 ; Williams et al., 2014 ). This area of research is promising but not yet compelling, due to the small number of experimental and quasi-experimental studies that have examined either integrated content-area and literacy instruction or content-rich English Language Arts instruction in K-5 settings (approximately 31 studies). Through meta-analysis, this corpus of studies demonstrates that combining knowledge building and literacy approaches has a positive impact on both vocabulary and comprehension outcomes for elementary-age children ( Hwang et al., 2019 ). Further rigorous studies are needed that test widely used content-rich English Language Arts curricula (Cabell & Hwang, 2020, this issue); also required is new development of integrative and interdisciplinary approaches in this area.
There is also promising research on helping students to decode words more efficiently. It is widely accepted that students with reading difficulties often have underlying deficits in phonological processing (e.g., Brady & Schankweiler, 1991 ; Stanovich & Siegel, 1994 ; Torgesen, 2000 ; Vellutino et al., 1996 ) and these deficits are believed to disrupt the acquisition of spelling-to-sound translation routines that form the basis of early decoding-skill development (e.g., van IJzendoorn & Bus, 1994 ; Rack et al., 1992 ). For developing readers, decoding an unfamiliar letter string can result in either full or partial decoding. During partial decoding, the reader must match the assembled phonology from decoding with their lexical representation of a word ( Venezky, 1999 ). For example, encountering the word island might render the incorrect but partial decoding attempt, “izland”. A child’s flexibility with the partially decoded word is referred to as their “set for variability” or their ability to go from the decoded form to the correct pronunciation of a word. This skill serves as a bridge between decoding and lexical pronunciations and may be an important second step in the decoding process ( Elbro et al., 2012 ).
The matching of partial phonemic-decoding output is facilitated by the child’s decoding skills, the quality of the child’s lexical word representation, and by the potential contextual support of text ( Nation & Castles, 2017 ). Correlational studies indicate that students’ ability to go from a decoded form of a word to a correct pronunciation (their set for variability) predicts the reading of irregular words ( Tunmer & Chapman, 2012 ), regular words ( Elbro, et al., 2012 ), and nonwords ( Steacy et al., 2019a ). Set for variability has also been found to be a stronger predictor of word reading than phonological awareness in students in grades 2-5 (e.g., Steacy et al., 2019b ). Recent studies in this area suggest that children can benefit from being encouraged to engage with the irregularities of English ( Dyson et al., 2017 ) to promote the implicit knowledge structures needed to read and spell these complex words. Additional research suggests that set for variability training can be effective in promoting early word reading skills (e.g., Savage et al., 2018 ; Zipke, 2016 ). The work done in this area to date suggests that set for variability requires child knowledge structures and strategies, which can be developed through instruction, that allow successful matching of partial phonemic-decoding output with the corresponding phonological, morphological, and semantic lexical representations.
Where Do We Go Next in the Science of Reading?
Basic science research.
The science of reading has reached some consensus on the typical development of reading skill and how individual differences may alter this trajectory (e.g., Boscardin et al., 2008 ; Hjetland et al., 2019; Peng et al., 2019 ). Less is known about factors and mechanisms related to reading among diverse learners, a critical barrier to the field’s ability to address and prevent reading difficulty when it arises. Investigations with large and diverse participant samples are needed to improve understanding of how child characteristics additively and synergistically affect reading acquisition ( Hernandez, 2011 ; Lonigan et al., 2013 ). Insufficient research disentangles the influence of English-learner status for children who also have identified disabilities (Solari et al., 2014; Wagner et al., 2005 ). Greater attention to how language variation (e.g., dialect use) and differences in language experience affect reading development is crucial ( Patton Terry et al., 2010 ; Seidenberg & MacDonald, 2018; Washington et al., 2018). New realizations of the interaction between child characteristics and the depth of the orthography have also highlighted the importance of implicit learning in early reading ( Seidenberg, 2005 ; Steacy et al., 2019). Innovative cross-linguistic research is exploring how diverse methods of representing pronunciation and meaning within different orthographies, and children’s developing awareness of these methods, jointly predict reading skills (e.g., Kuo & Anderson, 2006 ; Wade-Woolley, 2016 ). Furthermore, a better understanding of the role of executive function, socio-emotional resilience factors, and biopsychosocial risk variables (e.g., poverty and trauma) on reading development is critical. Additional research like this, in English and across languages, is needed to develop effective instruction and assessments for all leaners.
A clearer understanding of child and contextual influences on the development of reading also will support improvements in how early and accurately children at risk for reading difficulties and disabilities are identified. Currently, numerous challenges remain in identifying children early enough to maximize benefits of interventions ( Colenbrander et al., 2018 ; Gersten et al., 2017b ). Investigators often use behavioral precursors or correlates of reading to estimate children’s risk for reading failure. Whereas this work has shown some promise ( Catts et al., 2015 ; Compton et al., 2006 , 2010 ; Lyytinen et al., 2015 ; Thompson et al., 2015 ), identification of risk typically involves high error rates, especially for preschoolers and kindergarteners who might benefit most from early identification and intervention. Similar challenges to accuracy have emerged when identifying older children with reading disabilities. Historically, this process has relied on discrepancy models (e.g., such as between reading skill and general cognitive aptitude), often yielding a just single comparison on which decisions are based (Waesche et al., 2011).
Challenges to identification for both younger and older children may be best met with frameworks that recognize the multifactorial casual basis of reading problems ( Pennington et al., 2012 ). Newer models of identification that combine across multiple indicators of risk derived from current skill, and that augment these indicators with other metrics of potential risk, may yield improved identification and interventions (e.g., Erbeli et al., 2018 ; Spencer et al., 2011). In particular, future research will need to consider and combine, while considering both additive and interactive effects, a wide array of measures, which may include genetic, neurological, and biopsychosocial indicators ( Wagner et al., 2019 ). Furthermore, more evaluation is needed of some new models of identification that integrate both risk and protective, or resiliency, factors, to see if these models increase the likelihood of correctly identifying those children most in need of additional instructional support (e.g., Catts & Petscher, 2020 ; Haft et al., 2016 ). Even if beneficial, it is likely that for early identification to be maximally effective, early risk assessments will need to be combined with progress monitoring of response to instruction ( Miciak & Fletcher, 2020 ). Of course, for such an approach to be successful, all children must receive high-quality reading instruction from the beginning and interventions need to be in place to address children who show varying levels of risk ( Foorman et al., 2016a ). Identifying children at risk and providing appropriate intervention early on has the potential to significantly improve reading outcomes and reduce the negative consequences of reading failure.
Intervention Innovations
Despite successes, too many children still struggle to read novel text with understanding, and intervention design efforts have not fully met this challenge ( Compton et al., 2014 ; Phillips et al., 2016 ; Vaughn et al., 2017 ). Greater creativity and integration of research from a broader array of complementary fields, including cognitive science and behavioral genetics may be required to deal with long-standing problems. For example, genetic information may have causal explanatory power; randomized trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy of using such information to select and individualize instruction and intervention ( Hart, 2016 ).
The field would benefit from increased attention to the problem of fading intervention effects over time. Although there can be detectable effects of interventions several years after they are completed (e.g., Blachman et al., 2014 ; Vadasy et al., 2011 ; Vadasy & Sanders, 2013 ), invariably effect sizes reduce over time. A meta-analysis of long-term effects of interventions for phonemic awareness, fluency, and reading comprehension found a 40 percent reduction in effect sizes within one year post-intervention ( Suggate, 2016 ). Perhaps reading interventions with larger initial effects or sequential reading interventions with smaller but cumulating effects would be more resistant to fade-out.
Solutions to the problem of diminishing effects may be inspired by examples from other fields. The field of memory includes examples of content that appears immune from forgetting. This phenomenon has been called permastore ( Bahrick, 1984 ). For example, people only meaningfully exposed to a foreign language in school classes will still retain some knowledge of the language 50 years later. Additionally, expertise in the form of world-class performance appears to result from cumulative effects of long-term deliberate practice ( Ericsson, 1996 ), and skilled reading can be viewed as an example of expert performance ( Wagner & Stanovich, 1996 ). Informed by these concepts and by advances in early math instruction (e.g., Sarama et al., 2012 ; Kang et al., 2019 ), reading intervention studies should prioritize follow-up evaluations, including direct comparisons of follow-through strategies aimed at sustaining benefits from earlier instruction. For example, studies should evaluate booster interventions, professional development that better aligns cross-grade instruction, and how re-teaching and cumulative review may consolidate skill acquisition across time (e.g., Cepeda et al., 2006 ; Smolen et al., 2016 ).
Translational and Implementation Science
If the science of reading is to be applied in a manner resulting in achievement for all learners, the field must increase its focus on processes supporting implementation of evidence-based reading practices in schools. The field can leverage its considerable evidence-base to systematically investigate, with replication, both the effectiveness of reading instructional practices with diverse learners and to investigate processes that facilitate or prevent adoption, implementation, and sustainability of these practices (National Research Council, 2002; Schneider, 2018 ; Slavin, 2002 ). Research on these processes in educational contexts may be best facilitated by making use of methodological and conceptual tools developed within the traditions of translation and implementation science research ( Gilliland et al., 2019 ; Eccles & Mittman, 2006 ). For example, these frameworks can support studies on whether and how educators and policymakers use information about evidence to inform decision making (e.g., Farley-Ripple et al., 2018 ) and studies on how institutional routines may need to be adapted to best integrate new procedures and practices (e.g., scheduling changes in the school day; Foorman et al., 2016b ).
Reading research that uses translational and implementation science frameworks and methodologies will make more explicit the processes of adoption, implementation and sustainability and how these interact within diverse settings and with multiple populations ( Brown et al., 2017 ; Fixsen et al., 2005 , 2013 ). This work will be guided by new questions, not only asking “what works” but also “what works for whom under what conditions” and “what factors promote sustainability of implementation.” Innovative studies would adhere to rigorous scientific standards, prioritize hypothesis testing within a deductive, experimental framework, and leverage qualitative methodologies to systematically explore implementation processes and factors ( Brown et al., 2017 ). Results could iteratively inform the breadth of scientific reading research, including basic mechanisms related to reading and the development of novel assessments and interventions to support achievement among diverse learners in diverse settings ( Cook & Odom, 2013 ; Douglas et al., 2015 ; Forman et al., 2013 ).
There has recently been a resurgence of the debate on the science of reading, and in this article, we described the existing evidence base and possible future directions. Compelling evidence is available to guide understanding of how reading develops and identify proven instructional practices that impact both decoding and linguistic comprehension. Whereas there is some evidence that is either not compelling or has yet to be generated for instructional practices and programs that are widely used, the scientific literature on reading is ever-expanding through contributions from the fields education, psychology, linguistics, communication science, neuroscience, and computational sciences. As these additions to the literature mature and contribute to an evidence base, we anticipate they will inform and shape the science of reading as well as the science of teaching reading.
Acknowledgments
First author was determined by group consensus. Authors equally contributed and are listed and alphabetically. The authors’ work was supported by funding from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, the Institute of Education Sciences (R305A160241, R305A170430, R305F100005, R305F100027, R324A180020, R324B19002) and Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (P50HD52120, P20HD091013, HD095193, HD072286).
- Anderson RC, & Pearson PD (1984). A schema-theoretic view of basic processes in reading comprehension. In Pearson PD, Barr R, Kamil ML, & Mosenthal P (Eds.), Handbook of reading research (1st ed., pp. 255–291). New York: Longman. [ Google Scholar ]
- Baker S, Lesaux N, Jayanthi M, Dimino J, Proctor CP, Morris J, … Newman-Gonchar R (2014). Teaching academic content and literacy to English learners in elementary and middle school (NCEE 2014-4012) . Washington, DC: National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance (NCEE), Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education. Retrieved from https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/Docs/PracticeGuide/english_learners_pg_040114.pdf . [ Google Scholar ]
- Bahrick HP (1984). Semantic memory content in permastore: Fifty years of memory for Spanish learned in school . Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 113 ,1–29. DOI: 10.1037//0096-3445.113.1.1 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beck IL, & McKeown MG (2007). Increasing young low-income children’s oral vocabulary repertoires through rich and focused instruction . The Elementary School Journal , 107 ( 3 ), 251–271. DOI: 10.1086/511706 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berkeley S, Scruggs TE, & Mastropier MA (2012). Reading comprehension instruction for student with learning disabilities, 1995-2006: A meta-analysis . Remedial and Special Education , 31 , 423–436. 10.1177/0741932509355988 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Birsh JR (2011). Multisensory teaching of basic language skills . Brookes Publishing Company. PO Box 10624, Baltimore, MD 21285. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blachman BA, Schatschneider C, Fletcher JM, Francis DJ, Clonan SM, Shaywitz BA, & Shaywitz SE (2004). Effects of intensive reading remediation for second and third graders and a 1-year follow-up . Journal of Educational Psychology , 96 ( 3 ), 444–461. doi: http://dx.doi.org.proxy.lib.fsu.edu/10.1037/0022-0663.96.3.444 [ Google Scholar ]
- Blachman BA, Schatschneider C, Fletcher JM, Murray MS, Munger KA, & Vaughn MG (2014). Intensive reading remediation in grade 2 or 3: Are there effects a decade later? Journal of Educational Psychology , 106 ( 1 ), 46–57. doi: http://dx.doi.org.proxy.lib.fsu.edu/10.1037/a0033663 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boscardin CK, Muthén B, Francis DJ, & Baker EL (2008). Early identification of reading difficulties using heterogeneous developmental trajectories . Journal of Educational Psychology , 100 , 192–208. 10.1037/0022-0663.100.1.192 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boulay B, Goodson B, Frye M, Blocklin M, & Price C (2015). Summary of Research Generated by Striving Readers on the Effectiveness of Interventions for Struggling Adolescent Readers. NCEE 2016-4001 . National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance. [ Google Scholar ]
- Boyer N, & Ehri LC (2011). Contribution of phonemic segmentation instruction with letters and articulation pictures to word reading and spelling in beginners . Scientific Studies of Reading , 15 ( 5 ), 440–470. 10.1080/10888438.2010.520778 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brady S (2020). Strategies used in education for resisting the evidence and implications of the science of reading . The Reading Journal , 1 ( 1 ), 33–40. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brady SA, & Shankweiler DP (Eds.). (1991). Phonological processes in literacy: A tribute to Isabelle Y. Liberman Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown CH, Curran G, Palinkas LA, Aarons GA, Wells KB, Jones L, Collins LM, Duan N, Mittman BS, Wallace A, Tabak RG, Ducharme L, Chambers DA, Neta G, Wiley T, Landsverk J, Cheung K, & Cruden G (2017). An overview of research and evaluation designs for dissemination and implementation . Annual Review of Public Health , 38 , 1–22. 10.1146/annurev-publhealth-031816-044215 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cabell SQ, Justice LM, McGinty AS, DeCoster J, & Forston L (2015). Teacher-child conversations in preschool classrooms: Contributions to children’s vocabulary development . Early Childhood Research Quarterly , 30 , 80–92. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecresq.2014.09.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Calkins L (2020). No one gets to own the term “The Science of Reading” . Retrieved from: https://readingandwritingproject.org/news/no-one-gets-to-own-the-term-the-science-of-reading [ Google Scholar ]
- Caravolas M, Lervåg A, Defior S, Málkova G,S, & Hulme C (2013). Different patterns, but equivalent predictors, of growth in reading in consistent and inconsistent orthographies . Psychological Science , 24 , 1398–1407. 10.1177/0956797612473122 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Casini L, Pech-Georgel C, & Ziegler JC (2018). It's about time: Revisiting temporal processing deficits in dyslexia . Developmental Science , 21 ( 2 ), 1–14. DOI: 10.1111/desc.12530 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Castles A, Rastle K, & Nation K (2018). Ending the reading wars: Reading acquisition from novice to expert . Psychological Science in the Public Interest , 19 ( 1 ), 5–51. 10.1177/1529100618772271 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Catts H, Adlof S, & Weismer SE (2006). Language deficits in poor comprehenders: A case for the simple view of reading . Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research , 49 , 278–293. 10.1044/1092-4388(2006/023) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Catts H, Herrera S, Nielsen D, & Bridges, 2015. Early prediction of reading comprehension within the simple view framework . Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal , 28 , 1407–1425. 10.1007/s11145-015-9576-x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Catts H, Hogan T, & Adlof S (2005). Developmental changes in reading and reading disabilities. In Catts H & Kamhi A, A. (Eds.). Connections between language and reading disabilities . Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum [ Google Scholar ]
- Catts HW, & Petscher Y (2020, March 25). A cumulative risk and protection model of dyslexia . 10.35542/osf.io/g57ph [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cepeda NJ, Pashler H, Vul E, Wixted JT, & Rohrer D (2006). Distributed practice in verbal recall tasks: A review and quantitative synthesis . Psychological Bulletin , 132 ( 3 ), 354–380. 10.1037/0033-2909.132.3.354 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chall J (1967). Learning to read: The great debate . New York: McGraw-Hill. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chapman JW, & Tunmer WE (2016). Is Reading Recovery an effective intervention for students with reading difficulties? A critique of the i3 scale-up study . Reading Psychology , 37 ( 7 ), 1025–1042. 10.1080/02702711.2016.1157538 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Colenbrander D, Ricketts J, & Breadmore HL (2018). Early identification of dyslexia: Understanding the issues . Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools , 49 , 817–828. 10.1044/2018_LSHSS-DYSLC-18-0007 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Compton DL, Fuchs D, Fuchs LS, & Bryant JD (2006). Selecting at-risk readers in first grade for early intervention: A two-year longitudinal study of decision rules and procedures . Journal of Educational Psychology , 98 , 394–409. [ Google Scholar ]
- Compton DL, Fuchs D, Fuchs LS, Bouton B, Gilbert JK, Barquero LA, Cho E, & Crouch RC (2010). Selecting at-risk readers in first grade for early intervention: Eliminating false positives and exploring the promise of a two-stage screening process . Journal of Educational Psychology . 102 , 327–340. 10.1037/0022-0663.98.2.394 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Compton DL, Miller AC, Elleman AM, & Steacy LM (2014). Have we forsaken reading theory in the name of “quick fix” interventions for children with reading disability? Scientific Studies of Reading , 18 ( 1 ), 55–73. doi: 10.1080/10888438.2013.836200 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Connor CMD, Dombek J, Crowe EC, Spencer M, Tighe EL, Coffinger S, … Petscher Y (2017). Acquiring science and social studies knowledge in kindergarten through fourth grade: Conceptualization, design, implementation, and efficacy testing of content-area literacy instruction (CALI) . Journal of Educational Psychology , 109 ( 3 ), 301–320. doi: 10.1037/edu0000128 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cook BG, & Odom SL (2013). Evidence-based practices and implementation science in special education . Exceptional Children , 79 , 135–144. 10.1177/001440291307900201 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dane FC (1990). Research methods (Vol. 120 ). Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole Publishing Company. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dehaene S (2011). The massive impact of literacy on the brain and its consequences for education . Human Neuroplascticity and Education , 117 , 19–32. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dehaene-Lambertz G, Monzalvo K, & Dehaene S (2018). The emergence of the visual word form: Longitudinal evolution of category-specific ventral visual areas during reading acquisition . PLoS biology , 16 ( 3 ), e2004103. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- DeWalt DA, & Hink A (2009). Health literacy and child health outcomes: a systematic review of the literature . Pediatrics , 124 ( Supplement 3 ), S265–S274. 10.1542/peds.2009-1162B [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dickinson DK, & Porche MV (2011). Relation between language experiences in preschool classrooms and children’s kindergarten and fourth-grade language and reading abilities . Child Development , 82 , 870–886. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.2011.01576.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Douglas NF, Campbell WN, & Hinckley J (2015). Implementation science: Buzzword or game changer? Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research , 58 , S1827–S1836. doi: 10.1044/2015_JSLHR-L-15-0302. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dyson H, Best W, Solity J, & Hulme C (2017). Training mispronunciation correction and word meanings improves children’s ability to learn to read words . Scientific Studies of Reading , 1–16. doi: 10.1080/10888438.2017.1315424 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eccles MP & Mittman BS (2006). Welcome to implementation science . Implementation Science , 1 , 1–3. 10.1186/1748-5908-1-1 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eden GF, VanMeter JW, Rumsey JM, Maisog JM, Woods RP, & Zeffiro TA (1996). Abnormal processing of visual motion in dyslexia revealed by functional brain imaging . Nature , 382 ( 6586 ), 66–69. DOI: 10.1038/382066a0 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ehri LC (2005). Learning to read words: Theory, findings, and issues . Scientific Studies of Reading , 9 , 167–188. 10.1207/s1532799xssr0902_4 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ehri LC (2014). Orthographic mapping in the acquisition of sight word reading, spelling memory, and vocabulary learning . Scientific Studies of Reading , 18 ( 1 ), 5–21. 10.1080/10888438.2013.819356 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ehri LC, Nunes SR, Stahl SA, & Willows DM (2001). Systematic phonics instruction helps students learn to read: Evidence from the National Reading Panel’s meta-analysis . Review of Educational Research , 71 , 393–447. 10.3102/00346543071003393 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ehri LC, Nunes SR, Willows D,M, Schuster BV, Yaghoub-Zadeh Z, & Shanahan T (2001). Phonemic awareness instruction helps children learn to read: Evidence from the National Reading Panel’s meta-analysis . Reading Research Quarterly , 36 , 250–287. 10.1598/RRQ.36.3.2 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elbro C, de Jong PF, Houter D, & Nielsen A (2012). From spelling pronunciation to lexical access: A second step in word decoding? Scientific Studies of Reading , 16 ( 4 ), 341–359. doi: 10.1080/10888438.2011.568556 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elleman A, Lindo E, Morphy P, & Compton D (2009). The impact of vocabulary instruction on passage-level comprehension of school-age children: A meta-analysis , Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness 2 , 1–44. 10.1080/19345740802539200 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ellis NC, Natsume I, Stavropoulou K, Hoxhallari L, van Daal VHP, Polyzoe N, et al. (2004). The effects of the orthographic depth on learning to read alphabetic, syllabic, and logographic scripts . Reading Research Quarterly , 39 , 438–468. doi: 10.1598/RRQ.39.4.5 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Erbeli F (2019). Translating research findings in genetics of learning disabilities to special education instruction . Mind, Brain, and Education , 13 ( 2 ), 74–79. 10.1111/mbe.12196 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Erbeli F, Hart SA, Wagner RW, & Taylor J (2018). Examining the etiology of reading disability as conceptualized by the hybrid model . Scientific Studies of Reading , 22 ( 2 ), 167–180. doi: 10.1080/10888438.2017.1407321. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ericsson KA (1996). The road to excellence: The acquisition of expert performance in the arts and sciences, sports, and games . Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Every Student Succeeds Act (2015). Pub. L. No. 114-95 § 114 Stat. 1177 (2015-2016) .
- Farley-Ripple, May H, Karpyn A, Tilley K, & McDonough K (2018). Rethinking connections between research and practice in education: A conceptual framework . Educational Researcher , 47 ( 4 ), 235–245. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fixsen D, Blase K, Metz A, & Van Dyke M (2013). Statewide implementation of evidence-based programs . Exceptional Children , 79 , 213–230. 10.1177/001440291307900206 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fixsen DL, Naoom SF, Blase KA, Friedman RM & Wallace F (2005). Implementation research: A synthesis of the literature . Tampa, FL: University of South Florida, Louis de la Parte Florida Mental Health Institute, The National Implementation Research Network (FMHI Publication #231). [ Google Scholar ]
- Flesch R (1955). Why Johnny can’t read - and what you can do about it . NY: Harper & Brothers. [ Google Scholar ]
- Foorman B, Beyler N, Borradaile K, Coyne M, Denton C, Dimino J, …Wissel S (2016a). Foundational skills to support reading for understanding in kindergarten through 3rd grade (NCEE 2016-4008) . Washington, DC: National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance (NCEE), Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education. Retrieved from https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/Docs/PracticeGuide/wwc_foundationalreading_070516.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Foorman B, Dombek J, & Smith K (2016b). Seven elements important to successful implementation of early literacy intervention . New Directions for Child and Adolescent Development , 2016 ( 154 ), 49–65. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Foorman BR, Koon S, Petscher Y, Mitchell A, & Truckenmiller A (2015). Examining general and specific factors in the dimensionality of oral language and reading in 4th–10th grades . Journal of Educational Psychology , 107 , 884–899. DOI: 10.1037/edu0000026 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Foorman B, Petscher Y, Herrera S (2018). Unique and common effects of decoding and language factors in predicting reading comprehension in grades 1-10 . Learning and Individual Differences , 63 , 12–23. 10.1016/j.lindif.2018.02.011 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Foorman BF, Smith KG, & Kosanovich ML (2017). Rubric for evaluating reading/language arts instructional materials for kindergarten to grade 5 (REL 2016-219) . Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences, National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance, Regional Educational Laboratory Southeast. [ Google Scholar ]
- Forman SG, Shapiro ES, Codding RS, Gonzales JE, Reddy LA, Rosenfield SA, Sanetti LMH, & Stoiber KC (2013). Implementation science and school psychology . School Psychology Quarterly , 28 , 77–100. 10.1037/spq0000019 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Frost R (2012). Toward a universal model of reading . Behavioral & Brain Sciences , 35 , 263–279. doi: 10.1017/S0140525X11001841 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- García JR, & Cain K (2014). Decoding and reading comprehension: A meta-analysis to identify which reader and assessment characteristics influence the strength of the relationship in English . Review of Educational Research , 84 ( 1 ), 74–111. 10.3102/0034654313499616 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gersten R, Baker SK, Shanahan T, Linan-Thompson S, Collins P, & Scarcella R (2007). Effective literacy and English language instruction for English learners in the elementary grades: A practice guide (NCEE 2007-4011) . Washington, DC: National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education. Retrieved from https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/Docs/PracticeGuide/20074011.pdf . [ Google Scholar ]
- Gersten R, Compton D, Connor CM, Dimino J, Santoro L, Linan-Thompson S, & Tilly WD (2008). Assisting students struggling with reading: Response to Intervention and multi-tier intervention for reading in the primary grades. A practice guide. (NCEE 2009-4045) . Washington, DC: National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education. Retrieved from https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/Docs/PracticeGuide/rti_math_pg_042109.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Gersten R, Jayanthi M, & Dimino J (2017a). Too much, too soon? Unanswered questions from national response to intervention evaluation . Exceptional Children , 83 , 244–254. 10.1177/0014402917692847 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gersten R, Newman-Gonchar R, Haymond K, & Dimino J (2017b). What is the evidence base for Response to Intervention in reading in grades 1–3? (REL 2016-129) . Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Education Sciences. National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance, Regional Educational Laboratory Southeast. Retrieved from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED573686.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Gillam RB, Loeb DF, Hoffman LM, Bohman T, Champlin CA, Thibodeau L, … & Friel-Patti S (2008). The efficacy of Fast ForWord language intervention in school-age children with language impairment: A randomized controlled trial . Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research , 51 ( 1 ), 97–119. 10.1044/1092-4388(2008/007) [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gilliland CT, White J, Gee B, Kreeftmeijer-Vegter R, Bietrix F, Ussi AE, Hajduch M, Kocis P, Chiba N, Hirasawa R, Suematsu M, Bryans J, Newman S, Hall MD, & Austin CP (2019). The fundamental characteristics of a translational scientist . ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science , 2 , 213–261. 10.1021/acsptsci.9b00022 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gonzalez JE, Pollard-Durodola S, Simmons DC, Taylor AB, Davis MJ, Kim M, & Simmons L (2011). Developing low-income preschoolers’ social studies and science vocabulary knowledge through content-focused shared book reading . Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness , 4 ( 1 ), 25–52. doi: 10.1080/19345747.2010.487927 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Goodman KS (1967). Reading: A psycholinguistic guessing game , Literacy Research and Instruction , 6 ( 4 ), 126–135, 10.1080/19388076709556976 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gough PB, & Tunmer WE (1986). Decoding, reading, and reading disability . Remedial and Special Education , 7 , 6–10. 10.1177/074193258600700104 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Haft SL, Myers CA, & Hoeft F (2016). Socio-emotional and cognitive resilience in children with reading disabilities . Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences , 10 , 133–141. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hanford E (2019). At a loss for words: How a flawed idea is teaching millions of kids to be poor readers . Retrieved from: https://www.apmreports.org/story/2019/08/22/whats-wrong-how-schools-teach-reading [ Google Scholar ]
- Hart SA (2016). Precision education initiative: Moving toward personalized education . Mind, Brain, and Education , 10 ( 4 ), 209–211.doi: 10.1111/mbe.12109 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hernandez DJ (2011). Double jeopardy: How third-grade reading skills and poverty influence high school graduation . Annie E. Casey Foundation. https://files-eric-ed-gov.proxy.lib.fsu.edu/fulltext/ED518818.pdf https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1097/00011363-200501000-00004 [ Google Scholar ]
- Hwang H, Cabell SQ, White TG, & Joiner R (2019, December). A systematic review of the research on the effect of knowledge building in literacy instruction on comprehension and vocabulary in the elementary years. Presentation at the annual meeting of the Literacy Research Association , Tampa, FL. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hyatt KJ, Stephenson J, & Carter M (2009). A review of three controversial educational practices: Perceptual motor programs, sensory integration, and tinted lenses . Education & Treatment of Children , 32 ( 2 ), 313–342. doi: 10.1353/etc.0.0054 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Iovino I, Fletcher JM, Breitmeyer BG, & Foorman BR (1998). Colored overlays for visual perceptual deficits in children with reading disability and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Are they differentially effective? Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology , 20 ( 6 ), 791–806. DOI: 10.1076/jcen.20.6.791.1113 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Israel SE, & Duffy GG (Eds.). (2014). Handbook of Research on Reading Comprehension . New York: Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jenkins JR, Peyton JA, Sanders EA, & Vadasy PF (2004). Effects of reading decodable texts in supplemental first-grade tutoring . Scientific Studies of Reading , 8 , 53–85. 10.1207/s1532799xssr0801_4 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Joyce E (2020, January 22). Scientific Racism 2.0 (SR2.0): An erroneous argument from genetics which inadvertently refines scientific racism . 10.35542/osf.io/f7jnh [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kamil ML, Borman GD, Dole J, Kral CC, Salinger T, & Torgesen J (2008). Improving adolescent literacy: Effective classroom and intervention practices: A practice guide (NCEE #2008-4027) . Washington, DC: National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education. Retrieved from https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/Docs/PracticeGuide/adlit_pg_082608.pdf . [ Google Scholar ]
- Kang CY, Duncan GJ, Clements DH, Sarama J, & Bailey DH (2019). The roles of transfer of learning and forgetting in the persistence and fadeout of early childhood mathematics interventions . Journal of Educational Psychology , 111 , 590–603. 10.1037/edu0000297 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kershaw S & Schatschneider C (2012). A latent variable approach to the simple view of reading . Reading and Writing , 25 , 433–464. 10.1177/0741932518764833 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim JS, Burkhauser MA, Mesite LM, Asher CA, Relyea JE, Fitzgerald J, & Elmore J (2020). Improving reading comprehension, science domain knowledge, and reading engagement through a first-grade content literacy intervention . Journal of Educational Psychology . Advance online publication. 10.1037/edu0000465. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuo LJ, & Anderson RC (2006). Morphological awareness and learning to read: A cross-language perspective . Educational Psychologist , 41 , 161–180. 10.1207/s15326985ep4103_3 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Language and Reading Research Consortium & Chiu YD (2018). The simple view of reading across development: Prediction of grade 3 reading comprehension from prekindergarten skills . Remedial and Special Education , 39 ( 5 ), 289–303. 10.1177/0741932518762055 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee JJ, Wedow R, Okbay A, Kong E, Maghzian O, Zacher M, … & Fontana MA (2018). Gene discovery and polygenic prediction from a 1.1-million-person GWAS of educational attainment . Nature Genetics , 50 ( 8 ), 1112–1121.doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0147-3 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lesaux NK, Kieffer MJ, Faller SE, & Kelley JG (2010). The effectiveness and ease of implementation of an academic vocabulary intervention for linguistically diverse students in urban middle schools . Reading Research Quarterly , 45 ( 2 ), 196–228. 10.1598/RRQ.45.2.3 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lesaux NK, Kieffer MJ, Kelley JG, & Harris JR (2014). Effects of academic vocabulary instruction for linguistically diverse adolescents: Evidence from a randomized field trial . American Educational Research Journal , 51 ( 6 ), 1159–1194. 10.3102/0002831214532165 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Little CW, Haughbrook R, & Hart SA (2017). Cross-study differences in the etiology of reading comprehension: A meta-analytical review of twin studies . Behavior Genetics , 47 ( 1 ), 52–76. 10.1007/s10519-016-9810-6 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lonigan CJ, Anthony JL, Phillips BM, Purpura DJ, Wilson SB, & McQueen J (2009). The nature of preschool phonological processing abilities and their relations to vocabulary, general cognitive abilities, and print knowledge . Journal of Educational Psychology , 101 , 345–358. 10.1037/a0013837 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lonigan CJ, Burgess SR, Anthony JL, & Barker TA (1998). Development of phonological sensitivity in two- to five-year-old children . Journal of Educational Psychology , 90 , 294–311. 10.1037/0022-0663.90.2.294 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lonigan C, Burgess S, & Schatschneider C (2018). Examining the Simple View of Reading with elementary school children: Still simple after all these years . Remedial and Special Education , 39 ( 5 ), 260–273. 10.1177/0741932518764833 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lonigan CJ, Farver JM, Nakamoto J, & Eppe S (2013). Developmental trajectories of preschool early literacy skills: A comparison of language-minority and monolingual-English children . Developmental Psychology , 49 , 1943–1957. 10.1037/a0031408 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lonigan CJ, Farver JM, Phillips BM, & Clancy-Menchetti J (2011). Promoting the development of preschool children’s emergent literacy skills: A randomized evaluation of a literacy-focused curriculum and two professional development models . Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal , 24 , 305–337. doi: 10.1007/s11145-009-9214-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lonigan CJ, & Whitehurst GJ (1998). Relative efficacy of parent and teacher involvement in a shared-reading intervention for preschool children from low-income backgrounds . Early Childhood Research Quarterly , 13 , 263–290. doi: 10.1016/S0885-2006(99)80038-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lyytinen H, Erskine J, Hämäläinen J, Torppa M & Ronimus M (2015). Dyslexia-early identification and prevention: Highlights of the Jyvaskyla longitudinal study of dyslexia . Current Developmental Disorders Report , 2 , 330–338. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maher B (2008). Personal genomes: The case of missing heritability . Nature , 456 , 18–21. doi: 10.1038/456018a. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mancilla-Martinez J, & Lesaux N (2010). Predictors of reading comprehension for struggling readers: The case of Spanish-speaking language minority children . Journal of Educational Psychology , 102 ( 3 ), 701–711. 10.1037/a0019135. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marinus E, Mostard M, Segers E, Schubert TM, Madelaine A, & Wheldall K (2016). A special font for people with dyslexia: Does it work and, if so, why? Dyslexia , 22 ( 3 ), 233–244. doi: 10.1002/dys.1527 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marulis LM, & Neuman SB (2010). The effects of vocabulary intervention on young children’s word learning: A meta-analysis . Review of Educational Research , 80 ( 3 ), 300–335. doi: 10.3102/0034654310377087 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Melby-Lervåg M, Redick TS, & Hulme C (2016). Working memory training does not improve performance on measures of intelligence or other measures of “far transfer” evidence from a meta-analytic review . Perspectives on Psychological Science , 11 ( 4 ), 512–534. doi: 10.1177/1745691616635612 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miciak J, & Fletcher JM (2020). The critical role of instructional response for identifying dyslexia and other learning disabilities . Journal of Learning Disabilities . Advance online publication. doi: 10.1177/0022219420906801 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nation K, & Castles A (2017). Putting the learning into orthographic learning . Theories of reading development , 148–168. [ Google Scholar ]
- National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (2000). National reading panel—Teaching children to read: Reports of the subgroups (NIH Pub. No. 00-4754) . Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Retrieved from https://www.nichd.nih.gov/sites/default/files/publications/pubs/nrp/Documents/report.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- National Institute for Literacy (2008). Developing early literacy: Report of the National Early Literacy Panel . Retrieved at https://lincs.ed.gov/publications/pdf/NELPReport09.pdf
- Neuman SB, & Kaefer T (2018). Developing low-income children’s vocabulary and content knowledge through a shared book reading program . Contemporary Educational Psychology , 52 , 15–24. doi: 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2017.12.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Olson R & Datta H (2002). Visual-temporal processing in reading-disabled and normal twins . Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal , 15 ( 1-2 ), 127–149. [ Google Scholar ]
- Palinscar AS, & Duke NK (2004). The role of text and text-reader interactions in young children’s reading development and achievement . The Elementary School Journal , 105 ( 2 ), 183–197. doi: 10.1086/428864 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Patton-Terry N, Connor CM, Thomas-Tate S, & Love M (2010). Examining relationships among dialect variation, literacy skills, and school context in first grade . Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research , 53 ( 1 ), 126–145. doi: 10.1044/1092-4388(2009/08-0058) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Peng P, Fuchs D, Fuchs LS, Elleman AM, Kearns DM, Gilbert JK, … & Patton S III (2019). A longitudinal analysis of the trajectories and predictors of word reading and reading comprehension development among at-risk readers . Journal of Learning Disabilities , 52 , 195–208. 10.1177/00222194188090 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pennington BF, Santerre-Lemmon L, Rosenberg J, MacDonald B, Boada R, et al. (2012). Individual prediction of dyslexia by single versus multiple deficit models . Journal of Abnormal Psychology , 121 , 212–224. doi: 10.1037/a0025823 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Perfetti C (2007). Reading ability: Lexical quality to comprehension . Scientific Studies of Reading , 11 ( 4 ), 357–383. 10.1080/10888430701530730 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Perfetti CA (1992). The representation problems in reading acquisition. In Gough PB, Ehri LC, & Treiman R (Eds.), Reading acquisition (pp. 145–174). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Peters JL, De Losa L, Bavin EL, & Crewther SG (2019). Efficacy of dynamic visuo-attentional interventions for reading in dyslexic and neurotypical children: A systematic review . Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews , 100 , 58–76. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.02.015 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Phillips BM, Connor CM, Lonigan CJ, Willis KB, & Crowe E (presented 2016, July). Supporting language and comprehension in second grade: Results from a Tier 2 efficacy trial. Presentation at Annual Meeting of the Society for the Scientific Study of Reading , Society for the Scientific Study of Reading, Porto, Portugal. [ Google Scholar ]
- Protopapas A (2014). From temporal processing to developmental language disorders: Mind the gap . Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences , 369 ( 1634 ), 20130090. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rack JP, Snowling MJ, & Olson RK (1992). The nonword reading deficit in developmental dyslexia: A review . Reading Research Quarterly , 27 ( 1 ), 28–53. doi: 10.2307/747832 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rayner K, Foorman BR, Perfetti CA, Pesetsky D, & Seidenberg MS (2001). How psychological science informs the teaching of reading . Psychological Science in the Public Interest , 2 ( 2 ), 31–74. doi: 10.1111/1529-1006.00004 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reutzel DR, Petscher Y, & Spichtig AN (2012). Exploring the value added of a guided, silent reading intervention: Effects on struggling third-grade readers’ achievement . The Journal of Educational Research , 105 ( 6 ), 404–415. 10.1080/00220671.2011.629693 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ritchey KD, & Goeke JL (2006). Orton-Gillingham and Orton-Gillingham—based reading instruction: A review of the literature . The Journal of Special Education , 40 ( 3 ), 171–183. 10.1177/00224669060400030501 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sabatini JP, Sawaki Y, Shore JR, & Scarborough HS (2010). Relationships among reading skills of adults with low literacy . Journal of Learning Disabilities , 43 , 122–138. 10.1177/0022219409359343 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sarama J, Clements DH, Wolfe CB, & Spitler ME (2012). Longitudinal evaluation of a scale-up model for teaching mathematics with trajectories and technologies . Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness , 5 , 105–135. 10.3102/0002831212469270 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Savage R, Georgiou G, Parrila R, & Maiorino K (2018). Preventative reading interventions teaching direct mapping of graphemes in texts and set-for-variability aid at-risk learners . Scientific Studies of Reading , 22 ( 3 ), 225–247. doi: 10.1080/10888438.2018.1427753 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schneider M (2018, December 17). A more systematic approach to replicating research . Institute of Education Sciences. https://ies.ed.gov/director/remarks/12-17-2018.asp [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwartz S (2019, December). The most popular reading programs aren't backed by science . Retrieved from EDWeek https://www.edweek.org/ew/articles/2019/12/04/the-most-popular-reading-programs-arent-backed.html [ Google Scholar ]
- Scruggs TE, Mastropieri MA, & McDuffie KA (2007). Co-teaching in inclusive classrooms: A meta-synthesis of qualitative research . Exceptional Children , 73 ( 4 ), 392–416. 10.1177/001440290707300401 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seidenberg MS (2005). Connectionist models of word reading . Current Directions in Psychological Science , 14 ( 5 ), 238–242. 10.1111/j.0963-7214.2005.00372.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Selzam S, Dale PS, Wagner RK, DeFries JC, Cederlöf M, O’Reilly PF, … & Plomin R (2017). Genome-wide polygenic scores predict reading performance throughout the school years . Scientific Studies of Reading , 21 ( 4 ), 334–349.doi: 10.1080/10888438.2017.1299152 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Seymour PH, Aro M, & Erskine JM (2003). Foundation literacy acquisition in european orthographies . British Journal of Psychology , 94 ( 2 ), 143–174. doi: http://dx.doi.org.proxy.lib.fsu.edu/10.1348/000712603321661859 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shanahan T, Callison K, Carriere C, Duke NK, Pearson PD, Schatschneider C, & Torgesen J (2010). Improving reading comprehension in kindergarten through 3rd grade: A practice guide (NCEE 2010-4038) . Washington, DC: National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance, Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education. Retrieved from https://ies.ed.gov/ncee/wwc/Docs/PracticeGuide/readingcomp_pg_092810.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Share DL (1995). Phonological recoding and self-teaching: Sine qua non of reading acquisition . Cognition , 55 , 151–218. 10.1016/0010-0277(94)00645-2 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Slavin RE (2002). Evidence-based education policies: Transforming educational practice and research . Educational Researcher , 31 , 15–21. 10.3102/0013189x031007015 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith (1971). Understanding Reading . New York: Holt, Rhinehart & Winston. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smolen P, Zhang Y, & Byrne JH (2016). The right time to learn: mechanisms and optimization of spaced learning . Nature Reviews Neuroscience , 17 ( 2 ), 77–88. 10.1038/nrn.2015.18 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stanovich KE (1980). Toward an interactive-compensatory model of individual differences in the development of reading fluency . Reading Research Quarterly , 16 ( 1 ), 32–71. DOI: 10.2307/747348 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stanovich KE (1990). Concepts in developmental theories of reading skill: Cognitive resources, automaticity, and modularity . Developmental Review , 10 ( 1 ), 72–100. 10.1016/0273-2297(90)90005-O [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stanovich KE (1991). Word recognition: Changing perspectives. In Barr R, Kamil ML, Mosenthal PB, & Pearson PD (Eds.), Handbook of reading research , Vol. 2 (p. 418–452). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stanovich KE (2000). Progress in understanding reading: Scientific foundations and new frontiers . Guilford Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stanovich (2003). Understanding the styles of science in the study of reading . Scientific Studies of Reading , 7 ( 2 ), 105–126, 10.1207/S1532799XSSR0702_1 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stanovich KE, & Siegel LS (1994). Phenotypic performance profile of children with reading disabilities: A regression-based test of the phonological-core variable-difference model . Journal of Educational Psychology , 86 ( 1 ), 24–53. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.86.1.24 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Steacy LM, Compton DL, Petscher Y, Elliott JD, Smith K, Rueckl JG, Sawi O, Frost SJ, & Pugh K (2019a). Development and prediction of context-dependent vowel pronunciation in elementary readers . Scientific Studies of Reading , 23 ( 1 ), 49–63. 10.1080/10888438.2018.1466303 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Steacy LM, Wade-Woolley L, Rueckl JG, Pugh KR, Elliott JD, & Compton DL (2019b). The role of set for variability in irregular word reading: Word and child predictors in typically developing readers and students at-risk for reading disabilities . Scientific Studies of Reading , 23 ( 6 ), 523–532. doi: 10.1080/10888438.2019.1620749 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stein J (2019). The current status of the magnocellular theory of developmental dyslexia . Neuropsychologia , 130 , 66–77. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.03.022 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Storch S, & Whitehurst GR (2002). Oral language and code-related precursors to reading: Evidence from a longitudinal, structural model . Developmental Psychology , 38 , 934–947 10.1037/0012-1649.38.6.934 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Strong GK, Torgerson CJ, Torgerson D, & Hulme C (2011). A systematic meta-analytic review of evidence for the effectiveness of the 'fast ForWord' language intervention program . Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry , 52 ( 3 ), 224–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02329.x [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suggate SP (2016). A meta-analysis of the long-term effect of phonemic awareness, phonics, fluency, and reading comprehension analyses . Journal of Learning Disabilities , 49 , 77–96. 10.1177/0022219414528540 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tallal P (1984). Temporal or phonetic processing deficit in dyslexia? That is the question . Applied Psycholinguistics , 5 ( 2 ), 167–169. 10.1017/S0142716400004963 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Therrien WJ (2004). Fluency and comprehension gains as a result of repeated reading: A meta-analysis . Remedial and Special Education , 25 , 253–261. 10.1177/07419325040250040801 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thompson PA, Hulme C, Nash HM, Gooch D, Hayiou-Thomas E & Snowling MJ (2015). Developmental dyslexia: Predicting risk . Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry , 56 , 976–987. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12412 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Torgesen JK (2000). Individual differences in response to early interventions in reading: The lingering problem of treatment resisters . Learning Disabilities Research & Practice , 15 ( 1 ), 55–64. doi: 10.1207/SLDRP1501_6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Torgesen JK, Alexander AW, Wagner RK, Rashotte CA, Voeller KK, & Conway T (2001). Intensive remedial instruction for children with severe reading disabilities: Immediate and long-term outcomes from two instructional approaches . Journal of Learning Disabilities , 34 ( 1 ), 33–58. doi: 10.1177/002221940103400104 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tunmer WE, & Chapman JW (2012). Does set for variability mediate the influence of vocabulary knowledge on the development of word recognition skills? Scientific Studies of Reading , 16 ( 2 ), 122–140. doi: 10.1080/10888438.2010.542527 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vadasy PF, Nelson JR, & Sanders EA (2011). Longer term effects of a tier 2 kindergarten vocabulary intervention for English learners . Remedial and Special Education , 34 , 91–101. 10.1177/0741932511420739 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vadasy PF, & Sanders EA (2013). Two-year follow-up of a code-oriented intervention for lower-skilled first graders: The influence of language status and word reading skills on third-grade literacy outcomes . Reading & Writing , 26 , 821–843. 10.1007/s11145-012-9393-4 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van IJzendoorn MH, & Bus AG (1994). Meta-analytic confirmation of the nonword reading deficit in developmental dyslexia . Reading Research Quarterly , 3 , 267–275. 10.2307/747877 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vaughn S, Martinez LR, Wanzek J, Roberts G, Swanson E, & Fall AM (2017). Improving content knowledge and comprehension for English language learners: Findings from a randomized control trial . Journal of Educational Psychology , 109 , 22–34. 10.1037/edu0000069 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vellutino FR, Scanlon DM, Sipay ER, Small SG, Pratt A, Chen R, & Denckla MB (1996). Cognitive profiles of difficult-to-remediate and readily remediated poor readers: Early intervention as a vehicle for distinguishing between cognitive and experiential deficits as basic causes of specific reading disability . Journal of Educational Psychology 88 , 601–638. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.88.4.601 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vellutino FR, Tunmer WE, Jaccard J, & Chen S (2007). Components of reading ability: Multivariate evidence for a convergent skills model of reading development . Scientific Studies of Reading , 11 , 3–32. DOI: 10.1080/10888430709336632 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Venezky RL (1999). The American way of spelling: The structure and origins of American English Orthography . New York, NY: Guilford Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Verhoeven L, & van Leeuwe J (2008). Prediction of the development of reading comprehension: A longitudinal study . Applied Cognitive Psychology , 22 , 407–423. 10.1002/acp.1414 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wade-Woolley L (2016). Prosodic and phonemic awareness in children’s reading of long and short words . Reading and Writing , 29 , 371–382. 10.1007/s11145-015-9600-1 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wagner RK, Edwards AA, Malkowski A, Schatschneider C, Joyner RE, Wood S, Zirps FA (2019). Combining old and new for better understanding and predicting dyslexia . New Directions for Child and Adolescent Development , 165 , 1–11. doi: 10.1002/cad.20289 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wagner RK, Francis DJ, & Morris RD (2005). Identifying English language learners with learning disabilities: Key challenges and possible approaches . Learning Disabilities Research & Practice , 20 ( 1 ), 6–15. 10.1111/j.1540-5826.2005.00115.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wagner RK, Muse AE, & Tannenbaum KR (2007). Promising avenues for better understanding implications of vocabulary development for reading comprehension. In Wagner R. Muse A, Tannenbaum K (Eds). Vocabulary acquisition: Implications for reading comprehension . New York: Guilford Press. pp. 276–291. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wagner RK, & Stanovich KE (1996). Expertise in reading. In Ericsson KA (Ed.), The road to excellence: The acquisition of expert performance in the arts and sciences, sports, and games (pp. 189–225). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wagner RK, & Torgesen JK (1987). The nature of phonological processing and its causal role in the acquisition of reading skills . Psychological Bulletin , 101 , 192–212. 10.1037/0033-2909.101.2.192 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wagner R, Torgesen J, & Rashotte C (1994). Development of reading-related phonological processing abilities: New evidence of bidirectional causality from a latent variable longitudinal study . Developmental Psychology , 30 , 73–87. 10.1037/0012-1649.30.1.73 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wanzek J, Vaughn S, Scammacca N, Gatlin B, Walker MA, & Capin P (2016). Meta-analyses of the effects of Tier 2 type reading interventions in grades K-3 . Educational Psychology Review , 28 , 551–576. 10.1007/s10648-015-9321-7 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wanzek J, Vaughn S, Scammacca NK, Metz K, Murray CS, Roberts G, & Danielson L (2013). Extensive reading interventions for students with reading difficulties after Grade 3 . Review of Educational Research , 83 , 163–195. 10.3102/0034654313477212 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wasik BA, & Hindman AH (2020). Increasing preschoolers’ vocabulary development through a streamlined teacher professional development intervention . Early Childhood Research Quarterly , 50 , 101–113. doi: 10.1016/j.ecresq.2018.11.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Welsch JG, Powell JJ, & Robnolt VJ (2019). Getting to the core of close reading: What do we really know and what remains to be seen? Reading Psychology , 40 ( 1 ), 95–116. 10.1080/02702711.2019.1571544 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Whitehurst GJ & Lonigan CJ (1998). Child development and emergent literacy . Child Development , 69 , 848–872. 10.2307/1132208 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Williams JP, Pollini S, Nubla-Kung AM, Snyder AE, Garcia A, Ordynans JG, & Atkins JG (2014). An intervention to improve comprehension of cause/effect through expository text structure instruction . Journal of Educational Psychology , 106 , 1–17. doi: 10.1037/a0033215 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ziegler J, & Goswami U (2005). Reading acquisition, developmental dyslexia, and skilled reading across languages: A psycholinguistic grain size theory . Psychological Bulletin , 131 ( 1 ), 3–29. 10.1037/0033-2909.131.1.3 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ziegler J, Stone G, & Jacobs A (1997). What is the pronunciation for –ough and the spelling for /u/? A database for computing feedforward and feedback consistence in English . Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers , 29 ( 4 ), 600–618. 10.3758/BF03210615 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zipke M (2016). The importance of flexibility of pronunciation in learning to decode: A training study in set for variability . First Language , 36 ( 1 ), 71–86. doi: 10.1177/0142723716639495 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER COLUMN
- 07 July 2022
How to find, read and organize papers
- Maya Gosztyla 0
Maya Gosztyla is a PhD student in biomedical sciences at the University of California, San Diego.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
“I’ll read that later,” I told myself as I added yet another paper to my 100+ open browser tabs.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-022-01878-7
This is an article from the Nature Careers Community, a place for Nature readers to share their professional experiences and advice. Guest posts are encouraged .
Competing Interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Related Articles

- Research management

Tales of a migratory marine biologist
Career Feature 28 AUG 24

Nail your tech-industry interviews with these six techniques
Career Column 28 AUG 24

How to harness AI’s potential in research — responsibly and ethically
Career Feature 23 AUG 24
Binning out-of-date chemicals? Somebody think about the carbon!
Correspondence 27 AUG 24

No more hunting for replication studies: crowdsourced database makes them easy to find
Nature Index 27 AUG 24

Partners in drug discovery: how to collaborate with non-governmental organizations
Tenure-track Associate Professor [Female Only]
Seeking tenure-track assoc. professor for interdisciplinary research in nanoprobe life sciences or related fields at WPI Nano Life Science Institute.
Kanazawa, Ishikawa, Japan (JP)
Nano Life Science Institute, Kanazawa University
Assistant/Associate Professor
Center for Virology and Vaccine Research at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center is seeking Assistant or Associate Professor.
Boston, Massachusetts (US)
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC)
OPEN FACULTY POSITION-INSTITUTE OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY, ACADEMIA SINICA, TAIWAN, ROC
One tenure-track faculty position is open to establish an active research program in all disciplines of molecular and cellular biology.
Taipei (TW)
The Institute of Molecular Biology, Academia Sinica, Taiwan
Global Faculty Recruitment of School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University
The School of Life Sciences at Tsinghua University invites applications for tenure-track or tenured faculty positions at all ranks (Assistant/Ass...
Beijing, China
Tsinghua University (The School of Life Sciences)
Tenure-Track/Tenured Faculty Positions
Tenure-Track/Tenured Faculty Positions in the fields of energy and resources.
Suzhou, Jiangsu, China
School of Sustainable Energy and Resources at Nanjing University
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

COMMENTS
What is A Research Summary. A research summary is a piece of writing that summarizes your research on a specific topic. Its primary goal is to offer the reader a detailed study overview with critical findings. A research summary generally contains the structure of the article. You must know the goal of your analysis before you launch a project.
Reading text from images (either natural scenes or documents) has been a long-standing research topic for decades, due to the high technical challenge and wide application range. Previously, individual specialist models are developed to tackle the sub-tasks of text reading (e.g., scene text recognition, handwritten text recognition and mathematical expression recognition). However, such ...
For the first time, a NASA-funded researcher will fly with their experiment on a commercial suborbital rocket. The technology is one of two NASA-supported experiments, also known as payloads, funded by the agency's Flight Opportunities program that will launch aboard Blue Origin's New Shepard suborbital rocket system on a flight test no earlier than Thursday, Aug. 29.
After research, citizen feedback and more, the Housing Action committee presented their findings and recommendations in an action plan with the final version to be brought back in September.
Reading Rockets offers a rich library of classroom strategies, articles, parent tip sheets, FAQs, videos, research briefs and more — providing research-based and best-practice information for educators, parents, and others who work with young readers. Browse by the topics listed below!
"Reading Research 101." ACSM's Health & Fitness Journal 20 (2016): 9-13; How to Read an Article in a Scholarly Journal (Research Guide Cayuga Community College Library, 2016; Jordan, C. H. And Zanna, M. P. "Appendix: How to Read a Journal Article in Social Psychology." ... should cite all or most of the important prior research on the topic ...
If you are interested in your topic, learning about it will be more pleasurable and you will write with greater passion, so choose your topic thoughtfully. Use the following list of 101 research paper topics as a starting point for your paper. As you begin learning and writing about your topic, you should revise or amend your research question ...
Despite decades of research in reading comprehension, international and national reading scores indicate stagnant growth for U.S. adolescents. In this article, we review the theoretical and empirical research in reading comprehension. We first explore different theoretical models for comprehension and then focus on components shown to be ...
Reading Research Publications Effectively. It's easy to feel overwhelmed and frustrated when first reading a scholarly article or research paper. The text is dense and complex and often includes abstract or convoluted language.In addition, the terminology may be confusing or applied in a way that is unfamiliar. To help overcome these challenges w hen you first read an article or research paper ...
Comprehension. Comprehension is the reason for reading. Good readers are both purposeful and active, and have the skills to absorb what they read, analyze it, make sense of it, and make it their own. Find out more about how to improve reading comprehension for all students. Home. Reading Topics A-Z. Comprehension. Reading 101.
As you research your topic, you'll need to read with different purposes and in different ways. These approaches to reading will help you to understand what is already known about your topic, to identify what isn't known or fully understood, and to identify your own contribution and to shape your argument. Reading for research isn't a ...
For many years, reading instruction was based on a concept of reading as the application of a set of isolated skills such as identifying words, finding main ideas, identifying cause and effect relationships, comparing and contrasting and sequencing. Comprehension was viewed as the mastery of these skills. One important classroom study conducted ...
113 Great Research Paper Topics. One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily ...
Effective research strategies are key for anyone attempting to gain information and expand their understanding on any given subject matter. Selecting relevant information is the foundation of an effective research process. First, you must locate credible information sources relevant to your research question or topic.
The following are journals that publish articles and research related to reading issues. The organization that publishes each journal is indicated in parentheses. Action in Teacher Education. (opens in a new window) (Association of Teacher Educators) American Educational Research Journal. (opens in a new window)
"The science of reading" is a phrase representing the accumulated knowledge about reading, reading development, and best practices for reading instruction obtained by the use of the scientific method.…Collectively, research studies with a focus on reading have yielded a substantial knowledge base of stable findings based on the science of reading.
Specific goals of this handbook are to help educators do the following: Define and explain Action Research. Demonstrate an understanding of how to use the recursive nature of Action Research to improve their teaching of instructional literacy. Provide examples of the Action Research process in action.
5. Follow a chronological order for research reading. When researching about a new topic, consider reading existing literature in chronological order. This will give you an idea of how the scientific conversation developed over time, how different terms, concepts, and methods evolved, and even the names of leading researchers working on the ...
The use of student data to inform instruction. The role of parental involvement in education. The effects of mindfulness practices in the classroom. The use of technology in the classroom. The role of critical thinking in education. The use of formative and summative assessments in the classroom.
11.1: The Reading Find and Develop a Research Topic. Page ID. Read: For more help and advice about learning how to choose a topic for your research essay, read the following short chapters from Cornell University Library via Quillbot (CC BY NA SA) and Excelsior OWL (CC-BY) SLO-Conduct inquiry-based research by formulating research questions ...
For commercial use, please contact [email protected]. Scientifically based reading research applies the scientific method to learn about about how young children develop reading skills, how children can be taught to read, and how children can overcome reading difficulties. Discover the basic elements to look for in science-based reading ...
This chapter offers a grounding in the key research skill of reading research papers from a critical and affirmative stance. There is an emphasis on reading papers as a means of developing an appreciation of the diversity of research questions, methodologies and techniques that exist within the contemporary psychotherapy research literature. A further aim of the chapter is to explore ...
The science of reading should be informed by an evolving evidence base built upon the scientific method. Decades of basic research and randomized controlled trials of interventions and instructional routines have formed a substantial evidence base to guide best practices in reading instruction, reading intervention, and the early identification of at-risk readers.
Published on behalf of the United Kingdom Literacy Association, Journal of Research in Reading is principally devoted to reports of original empirical research in reading and closely related fields (e.g., spoken language, writing), and to informed reviews of relevant literature. We publish papers from researchers in any relevant field on the learning, teaching, and use of literacy in adults or ...
The Science of Reading: Supports, Critiques, and Questions. In early 2020, the editors of Reading Research Quarterly issued a call for submissions examining research on the science of reading (SOR). The overwhelming response led to the publication of two special issues of the journal. The first issue, released in September 2020, examines ...
Reading motivation research. Researchers have identified a number of factors important to reading motivation including self-concept and value of reading, choice; time spent talking about books, types of text available, and the use of incentives. Students' self-concepts and the value they place on reading are critical to their success ...
Step 1: find. I used to find new papers by aimlessly scrolling through science Twitter. But because I often got distracted by irrelevant tweets, that wasn't very efficient. I also signed up for ...