

Present Simple Sentences With Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
The Present Simple tense is used to describe habitual actions, general truths, and fixed arrangements. It is formed using the base form of the verb, with an added “s” or “es” for the third person singular. Unlike the Present Continuous tense, which emphasizes the ongoing nature of an action, the Present Simple tense focuses on regular, repeated actions or facts.
The Present Simple tense in English is used to describe routines, facts, general truths, and timetabled events. The structure of a Present Simple sentence is:
Subject + Base Form of the Verb (add -s or -es for third person singular)
Let’s explore some examples to understand this better:
I walk to work every day. This sentence indicates that the speaker regularly walks to work. The action is a habitual routine.
She watches television in the evening. This example shows a regular action that occurs in the evenings. The action of watching television is a habit.
They play soccer every Saturday. This sentence describes an action that happens regularly on Saturdays. Playing soccer is a scheduled activity.
We do not go to the gym on Sundays. This sentence expresses a negative habitual action. The speaker and their companions do not go to the gym regularly on Sundays.
If you heat water to 100 degrees Celsius, it boils. This is an example of the Present Simple used to state a general truth. Heating water to 100 degrees Celsius always causes it to boil.
The Present Simple is formed by using the base form of the verb. It’s crucial to use the correct form of the verb, especially for the third person singular, to maintain the tense.
Incorrect: She walk to school every day.
We can see that the Present Simple is often used to talk about actions that happen regularly, general truths, and fixed schedules.
The words “ always ,” “ usually ,” “ often ,” “ sometimes ,” “ never ,” “ every day, ” and “ on Mondays ” are commonly used with the Present Simple to add context about the frequency of the action.
Present Simple Sentence Examples
- I read books every evening. (The action of reading is a daily habit.)
- She enjoys playing the piano. (She regularly finds pleasure in playing the piano.)
- They visit their grandparents every weekend. (Visiting grandparents is a regular activity.)
- We take the bus to school. (Taking the bus is a routine action.)
- He does not eat meat. (He regularly avoids eating meat.)
- The sun rises in the east. (This is a general truth about the sun.)
- Birds fly south for the winter. (This describes a regular migratory pattern of birds.)
- Water freezes at 0 degrees Celsius. (A scientific fact about water.)
- The train leaves at 9 AM every day. (A fixed schedule for the train.)
- She works at a bank. (Her regular job is at a bank.)
- He speaks four languages. (A general fact about his abilities.)
- The Earth orbits the Sun. (A scientific fact about the Earth’s movement.)
- Cats like to chase mice. (A general truth about cat behavior.)
- We celebrate Christmas on December 25th. (A fixed annual event.)
- She always forgets her keys. (A habitual action expressed with a hint of annoyance.)
- They play chess every Sunday. (A regular activity on Sundays.)
- He does not drink coffee. (A regular action of not drinking coffee.)
- The store opens at 8 AM. (A fixed schedule for the store’s opening.)
- I love to travel. (A general truth about my preferences.)
- She teaches English. (Her regular job is teaching English.)
The Present Simple tense is essential for describing routines, habits, general truths, and timetabled events. Using this tense allows for clear communication about regular activities and established facts. Mastering the Present Simple helps in expressing consistent actions and universal truths effectively.
Feel free to leave comments or ask questions if you need further clarification on any of the points discussed. Happy learning!
If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Modal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

Present Simple Tense Example & Exercises (Free PDF)
In this lesson you will learn about simple present tense with example, exercises and also you can get downloadable free PDF. The present simple tense is one of the fundamental tenses in English and allows you to describe habitual actions, general truths, and situations that are always or generally true, making it essential for expressing basic ideas and intentions in daily life.
Detailed Examples:
- I remember you.
- She reads books.
- They go to the gym.
- I do not (don’t) remember you.
- She does not (doesn’t) read books.
- They do not (don’t) go to the gym.
- Do I know you?
- Does she read books?
- Do they go to the gym?
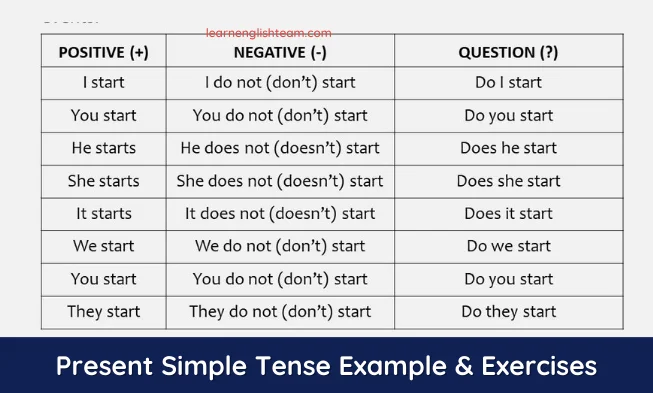
When to Use Present Simple Tense?
You use the present simple tense to talk about people’s routines and habits .
➜Tom goes for a walk every morning. ➜We always spend the summer in Turkey.
You use the present simple to talk about things that are permanent or always true , and in zero conditional sentences.
➜The office opens at seven every morning. ➜Water boils at 100c.
You use the present simple to talk about official scheduled or timetabled events, e.g. train timetables, television listing, etc.

You usually use the present simple (not the present continuous ) with certain verbs , e.g. agree, believe, feel, hate, hear, know, like, love, prefer, see, smell, taste, understand, etc.
➜ – She doesn’t understand the question. CORRECT X – She isn’t understanding the question. WRONG
➜ – I believe in life after death. CORRECT X – I am believing in life after death. WRONG
When to Add -S to Regular Verbs
In the present simple tense, you add “s” to the base form of the verb when the subject is a singular third person ( he , she , it ).
Here are the rules:
- He works at a bank.
- She runs every morning.
- It seems fine.
- He misses the bus.
- She washes the dishes.
- It catches the ball.
- He studies hard.
- She tries her best.
- It carries a lot of weight.
- He plays the piano.
- She enjoys the movie.
- It stays warm.

Simple Present Tense PDF
Present Simple Tense PDF – download
Learn Present Simple Tense PDF – download
You May Also Like

20 Useful Vocabulary & Phrases to Start Your Essay
English Time Expressions List & Examples (Free PDF)
The Eight Parts of Speech in English (PDF)
The Present Simple Tense
Perfect english grammar.

Also called the simple present tense
Download this explanation in PDF here. We need to use the Present Simple a lot in English, so it's really important to understand it well. Many students have problems with the form (or how to make it).
- If you'd prefer to learn about how to USE the Present Simple jump to this page.
- Or, click here for all the practice exercises about this tense.
Simple present tense with 'be'
Here's the positive form (positive means a normal sentence, not a negative or a question. This is sometimes called 'affirmative')
Click here to practise making the positive with 'be' . Next, here's the negative . It's very easy. You only add 'not' .
Click here to practise making the negative with 'be' . And finally let's talk about the question form of the present simple with 'be' .
Firstly, here's the 'yes / no' question form:
Click here to practise making yes / no questions with 'be' .
If you'd like to make a 'wh' question , you just put the question word at the front:
Click here to practise making 'wh' questions with 'be' .
Click here to practise making positive, negative and question forms with 'be' (exercise 1) Click here to practise making positive, negative and question forms with 'be' (exercise 2)
Present simple tense with other verbs
The positive is really easy. It's just the verb with an extra 's' if the subject is 'he', 'she', or 'it'. Let's take the verb 'play' as an example:
- Don't forget the 's' ! Even really advanced students do this!
- For a few verbs, there is a spelling change before the 's' . For example, 'study' becomes 'studies' . Click here for a list of these verbs
- 'have' becomes 'has'
- 'do' becomes 'does'
- 'go' becomes 'goes'
Click here to practise making the positive form for other verbs (exercise 1) Click here to practise making the positive form for other verbs (exercise 2)
To make the negative form, you need to use 'do not' (don't) or ' does not' (doesn't).
Click here to practise making the negative (exercise 1) Click here to practise making the negative (exercise 2)
How about the question form of the present simple tense?
We use 'do' or 'does' before the subject to make the 'yes / no' question :
Click here to practise making yes / no questions .
Just like with 'be', if you'd like to make a 'wh' question , you just put the question word at the front:
Click here to practise making 'wh' questions
Mixed exercise 1 Mixed exercise 2 Mixed exercise 3 Mixed exercise 4 using both 'be' and other verbs Click here for all the exercises about this tense

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

EnglishGrammarSoft
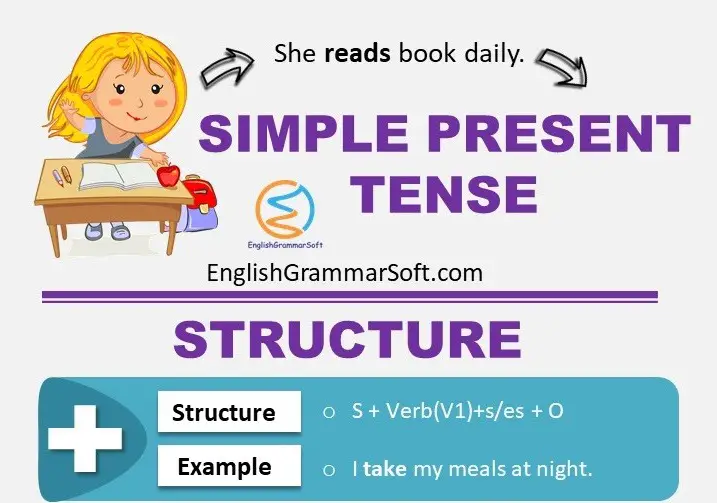
- Simple Present Tense (Formula, Examples & Exercises)
Simple Present Tense is one of the forms of verb tenses that refers to the present time. We will see its formula and usage with examples. Let’s start with the definition!
Simple present tense also called present indefinite tense, is used to express general statements and describe usual or habitual actions. In simple words, we can say that the simple present tense is used to describe routine acts.
Its formula is very simple as only base form of verb is used.
Affirmative Sentences
Formula for affirmative sentences.
Subject + Base form(V1) + “s/es” for third person + object
- I take my meals at night.
- It rains in winter.
Negative Sentences
Subject + do/does not + base form(V1) + object
- I do not take my meals at night.
- It does not rain in winter.
Interrogative Sentences
Do/does + subject + base form(V1) + object + ?
- Do I take my meals at night ?
- Does it rain in winter ?
Rules / Usage
- The sun sets in the west.
- I assent with your proposal.
- They work hard all day.
- Abuzar attributes his success to hard work.
- The cows graze in the field.
- Man clings to hope even on the deathbed.
- He conspires against his friends.
- The sun does not set in the west.
- I do not assent with your proposal.
- They do not work hard all day.
- Abuzar does not attribute his success to hard work.
- The cows do not graze in the field.
- Man does not cling to hope even on the deathbed.
- He does not conspire against his friends.
- Does the sun set in the west?
- Do I assent with your proposal?
- Do they work hard all day?
- Does Abuzar attribute his success to hard work?
- Do the cows graze in the field?
- Does man cling to hope even on the deathbed?
- Does he conspire against his friends?
- The government __________ five hour complete lock-down for one month. (announce)
- Tom __________ with his teacher on all matters. (consult)
- Our hostel __________ of 30 rooms. (consist)
- They __________ with each other. (not cooperate)
- She __________ after his mother. (not take)
- We __________ bath daily. (take)
- The old woman __________ beautiful flowers. (sell)
- I __________ the Holy Quran daily. (recite)
- He __________ his summer vacation at hill station. (spend)
- Jimmy __________ to eat fruits. (like)
Read also: 50 Sentences of Simple Present Tense
- do not cooperate
- does not take

Further Reading
- 50 Sentences of Simple Present Tense
- Simple Present Tense Worksheets
- Present Continuous Tense Formula, Examples & Usage
- 50 Sentences of Present Continuous Tense
- Present Continuous Tense Worksheets
- Present Perfect Tense with Examples
- 50 Sentences of Present Perfect Tense
- Present Perfect Tense Worksheets
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense Examples, Exercise, & Structure
- 50 Sentences of Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense Worksheets
Similar Posts

Future Continuous Tense Examples, Formula & Rules
Definition Future continuous/progressive tense is used to describe the action that will be taking place at some time in the future. In other words, it…

List of 50+ Collective Nouns for Food and Drink
Collective Nouns for Food, Drink and Vehetables Here is a list of nouns pertaining to different kinds of food items. Let’s dive into it! Collective…

Essay on Personality Development | Role of Education in Personality Development
Essay on Personality Development Education is an important factor in the personality development of individuals. The school, after the home, is one of the social…

Perfect Tenses of Verbs (20 Examples Each)
Perfect tenses are verb tenses that express actions or states that have been completed or will be completed. The three perfect tenses are the present…

Sentences with Juxtapose in them (as a verb)
These are 31 example sentences with juxtapose (as a verb) in them. Sentences with Juxtapose (as verb) My friend sent me a funny text that…

Countable and Uncountable Nouns (List, Examples & Exercise)
Countable and Uncountable Nouns The nouns are the names of things, people, or places. The nouns have different classifications. Countable and uncountable nouns are types…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Transcription Service for Your Academic Paper
Start Transcription now
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Stylistic devices
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources

Your Step to Success
Transcription Service for Your Paper
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Present Simple – Forms, Examples & Practice
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

To master any language, one of the most important rules is learning how to form tenses . They establish the backbone of how we express time in communication. A basic, yet fundamental tense in the English language is the present simple , an essential component of our language rules used to describe habitual actions, general truths, and fixed arrangements. In this article, we will dive into the rules and usage of this tense, shedding light on how to apply it correctly in numerous contexts.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Present simple in a nutshell
- 2 Definition: Present simple
- 3 Formula of present simple active voice
- 4 Active question form of present simple
- 5 Negative question form of present simple
- 6 Formula of present simple passive voice
- 7 Indicators for present simple
- 8 Short answers in present simple
- 9 Practice exercise
Present simple in a nutshell
This tense defines actions or events that express habits, general truths, and fixed arrangements. It is the most basic tense by adding an “s” to the infinitive of the verb, which makes it essential for effective communication about regular activities, timeless facts, and scheduled events.
Definition: Present simple
The present simple (also: simple present) tense is a common verb tense used to describe habits, facts, fixed arrangements, and unchanging situations, such as jokes and stories. As the name already indicates, it is an elementary tense, as it is formed by using the base form or infinitive of the verb . However, when using he, she, or it, a special verb conjugation is needed.
- So, I go to Eric and say , “Leave me alone.”
- They always walk to the park.
- He often plays games after he finishes dinner.
Formula of present simple active voice
The present simple tense is one of the three simple tenses – which include past simple and future simple – and plays a fundamental part in the English language. This tense is characterized by its clear-cut structure that relies simply on the base form (infinitive) of verbs.
Even though it is an easily memorizable tense, pronouns or subject-verb-agreement need to be considered to use it correctly. The only mistake one can make when forming the present simple in active voice is to forget the additional suffix “-s,” “-es,” or “ies,” which is added to the verb when the named or unnamed subject is in the third-person singular . In this section, we will explore the rules and patterns involved in creating the present simple tense for both regular and irregular verbs by providing clear examples and explanations.
Regular verbs
Regular verbs of the present simple tense in third-person singular adhere to a predictable conjugation pattern. This means that you simply add an “-s” at the end of the root form of the verb.
- She writes her a letter from jail.
- The kid plays soccer every week.
- He eats a full English breakfast.
In the table below, you can find more examples of regular verbs in 3rd person singular.
Irregular verbs
Most English verbs follow regular conjugation patterns, but there are a few irregular verbs that do not adhere to the standard rules. The concept of irregular verbs is more prominent in the past simple and past participle verb forms. However, in the present tense, the irregularities are seen in verbs that follow the following patterns:
- If the verb ends in – o , – ch , – sh , – ss , – x , or you add “-es.”
- If the verb ends in a consonant and – y , you drop the -y and add “-ies.”
Below are several example sentences.
- He goes to school at 8 o’clock.
- He washes his hands with soap.
- She tries very hard in school.
An example for each irregular verb pattern can be seen in the table below.
Auxiliary verbs
Primary auxiliary verbs are essential in forming various tenses and questions. They consist of “to be,” “to have,” and “to do.” As expected, their conjugations are very different from other verbs, which also applies to the present simple tense.
Note : To emphasize something, we may use the auxiliary verb “do.” For example, instead of saying “I want to go out,” one could say “I do want to go out.” The same emphasis can also be achieved by using “really.”
We have combined all regular and irregular verbs in a PDF document that you can obtain by clicking on the download box below.
Practice worksheet
Now that you know how to form the affirmative present simple tense, it is time for your first exercise. Below, you can find ten example sentences that include regular, irregular, and auxiliary verbs in numerous contexts. Let’s test if you can get them all correct.
Practice sentences
- They ____ soccer every Thursday and then ____ a movie. (To play, to watch)
- My name ____ Hanna, and I ____ 25 years old. (To be, to be)
- His dad ____ the car once a month. (To wash)
- He occasionally ____ a foam bath. (To take)
- She ____ in Munich, Germany. (To study)
- You ____ to the Bahamas every year. (To travel)
- The company ____ many birthday gifts. (To produce)
- I ____ on the roof and ____ the sunset disappear. (To go, to watch)
- I ____ we can ____ in a better world. (To believe, to live)
- This ____ my new dog. You can ____ him if you ____ . (To be, to pet, to want)
- They play soccer every Thursday and then watch a movie. (To play, to watch)
- My name is Hanna, and I am 25 years old. (To be, to be)
- His dad washes the car once a month. (To wash)
- He occasionally takes a foam bath. (To take)
- She studies in Munich, Germany. (To study)
- You travel to the Bahamas every year. (To travel)
- The company produces many birthday gifts. (To produce)
- I go on the roof and watch the sunset disappear. (To go, to watch)
- I believe we can live in a better world. (To believe, to live)
- This is my new dog. You can pet him if you like . (To be, to pet, to want)
Active question form of present simple
To form yes or no questions in the present simple tense, we use the auxiliary verb “do” or “does,” with the latter being used in the third-person singular. It is then followed by the subject, the base form of the main verb, and a question mark .
Do/Does + subject + infinitive + rest of the sentence?
Note : One-word time expressions, such as “always,” “often,” and “usually” may be added between the subject and the verb.
Questions with question words
When a simple yes or no is not enough, we use question words that require more elaboration in their answers. Those question words are: what, where, when, why, who, how, how many, and how much. They are then followed by “do” or “does,” the subject, and the base form of the main verb.
Question word + do/does + subject + infinitive + rest of the sentence?
- What do you need ?
- How much does the printed and bound thesis cost ?
- Why does he hate you?
- When do we want to go?
Negative question form of present simple
Negative questions in the present simple tense can be formed in two ways:
- Using “do not/does not” or its contraction “don’t/doesn’t.”
- Inverting the subject and auxiliary verb “do/does.”
Don’t/Doesn’t + subject + infinitive + rest of the sentence?
Do/Does + subject + not + infinitive + rest of the sentence?
The first question structure of present simple with the apostrophe is regularly used in spoken English and informal writing. It can convey a slight surprise or a need for confirmation of something the speaker believes to be true or is uncertain about.
The second question structure of present simple tends to be a bit more formal and is often found in written English. It emphasizes the negative aspect more clearly, which is typically used to indicate disbelief or surprise.
Note : The time expression “ever” may be added directly after the subject.
Negative questions with question words
When forming negative questions with question words in the present simple tense, the structure is the same, as you use “don’t/doesn’t” and the root form of the main verb.
Below, we have provided an image that contains the structures of the present simple active voice.
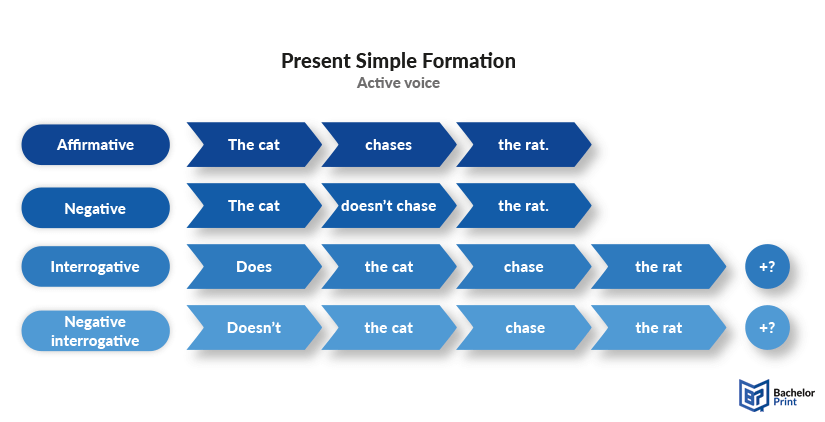
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
to the print shop
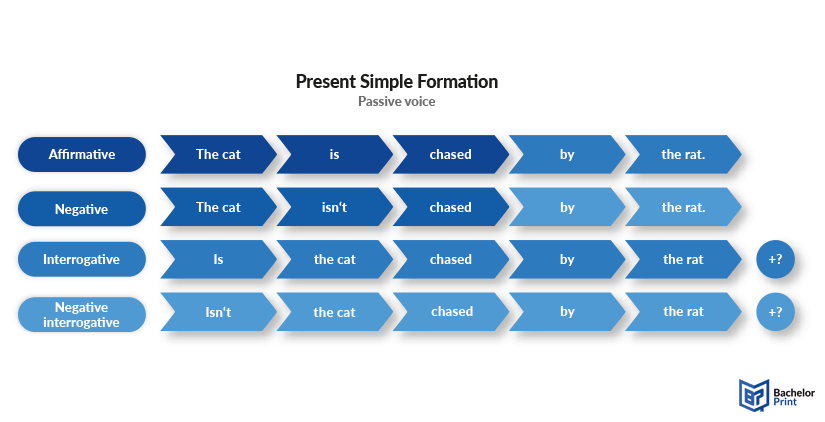
Formula of present simple passive voice
Now that we have explained the structure of the present simple’s active voice in the previous paragraphs , it is time to talk about the form of its passive voice. Passive is used when the focus is on the action rather than on the doer of the action. It is formed with the help of the auxiliary verb “to be” in its present simple form and the past participle (3 rd past form) of the main verb. When people are involved in a passive sentence, we use the agent “by” to show the subject of the action. Unlike with active voice, the object in a sentence becomes the subject of the passive sentence.
Interrogative
Negative interrogative.
Subject + am/is/are + past participle + (by agent) + object.
- The book is read by many people.
- The cake is eaten by me.
- Emails are sent every day.
Subject + isn’t/aren’t + past participle + (by agent) + object.
Subject + am/is/are + not + past participle + (by agent) + object.
- The book is not read by many people.
- The cake isn’t eaten by me.
- Emails are not sent every day.
Am/Is/Are + subject + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
- Is the book read by many people?
- Is the cake eaten by me?
- Are the emails sent every day?
Isn’t/Aren’t + subject + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
Am/Is/Are + subject + not + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
- Is the book not read by many people?
- Is the cake not eaten by me?
- Aren’t the emails sent every day?
Note : There is no contraction for the first-person pronoun “I.” Therefore, English speakers use “aren’t” in informal contexts, e.g., “Aren’t I funny?”. However, for academic writing and other formal contexts, this is not acceptable, thus using “am not” is the preferred choice.
Below, you can find an image that summarizes the formula of the present simple passive voice.
Indicators for present simple
The English language has many tenses and for each one, there are time expressions that simplify figuring out which tense to use. Here are common indicators for the present simple tense, along with numerous examples.
Adverbs of frequency
They provide information about the regularity or repetition of actions and are commonly used with the present simple tense to indicate habitual or regular actions. They include words like always, usually, frequently, rarely, never, etc.
- She always drinks tea in the morning.
- They often visit their grandparents.
- He never eats fast food.
Daily/Weekly/Monthly activities
Refers to regular activities that are daily/weekly/monthly.
- I go jogging every two days .
- They meet every week .
- She cleans her room every month .
Specific days
Refers to specific days when habitual actions take place.
- We go to the market on Saturdays .
- He attends yoga classes on Thursdays .
- They have a picnic on Sundays .
Short answers in present simple
Short answers in the present simple tense are concise responses that either confirm or deny the occurrence of an action or state, typically using auxiliary verbs. Here is how to form short answers in present simple, along with examples.
Active voice
A: Are you okay?
- Yes, I am .
- No, I am not .
A: Does she play the piano?
- Yes, she does .
- No, she doesn’t .
A: Do you have a car?
- Yes, I have .
- No, I have not .
Passive voice
A: Is the room cleaned by the staff?
- Yes, it is .
- No, it is not .
A: Are the reports written by Gina?
- Yes, they are .
- No, they aren’t .
A: Is the cat fed by you?
Practice exercise
To wrap up this article, you can fill in the gaps for this last practice exercise. The correct answers for present simple conjugations are provided in the second tab. Mastering English tenses can be challenging, so have fun, and don’t worry if you don’t get every correct the first time.
- The cake _____ my mom every Sunday. (To bake, passive)
- _____ she _____ the meeting regularly? (To attend, interrogative)
- The house _____ the maid every Monday. (To clean, passive)
- They _____ English every evening. (To study, active)
- The car _____ the mechanic twice a year. (To Service, passive)
- _____ you _____ your grandparents often? (To visit, interrogative)
- The project _____ on time by the team. (To complete, passive)
- He _____ the newspaper every morning. (To read, active)
- _____ the room _____ for the guests? (To prepare, interrogative)
- We _____ movies every Friday night. (To watch, active)
- The cake is baked by my mom every Sunday. (To bake, passive)
- Does she attend the meeting regularly? (To attend, interrogative)
- The house is cleaned by the maid every Monday. (To clean, passive)
- They study English every evening. (To study, active)
- The car is serviced by the mechanic twice a year. (To Service, passive)
- Do you visit your grandparents often? (To visit, interrogative)
- The project is completed on time by the team. (To complete, passive)
- He reads the newspaper every morning. (To read, active)
- Is the room prepared for the guests? (To prepare, interrogative)
- We watch movies every Friday night. (To watch, active)
What is a present simple example?
An example of present simple is the following:
- She walks to school every day.
What is the present simple form?
The present simple form of a verb consists of the base form (infinitive) for all subjects except the third-person singular, which typically adds an “-s,” “-es,” or “-ies” to the base form. For example:
- He walk s .
- He cr ies .
What are 10 examples of simple present tense?
- She reads books in the evening.
- They play tennis on weekends.
- He works at a bank.
- We go to the gym every morning.
- The sun rises in the east.
- I drink coffee every morning.
- It rains a lot in April.
- She teaches English.
- They live in New York.
- He studies French.
What is the rule for present simple?
The rule for present simple is to use the base form of the verb for all subjects, except the third-person singular (he, she, it), which adds an “-s,” “-es,” or “-ies” to the base form. This tense is used to express habitual actions, general truths, fixed arrangements, and scheduled events.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

COMMENTS
The simple present is used to refer to habits, unchanging situations or states, general truths, and scheduled events in the future. Most verbs in the simple present tense use the infinitive form (e.g., “run”). …
The Present Simple tense in English is used to describe routines, facts, general truths, and timetabled events. The structure of a Present Simple sentence is: Subject + Base …
We use the simple present tense when an action is happening right now, or when it happens regularly (or unceasingly, which is why it’s sometimes called present indefinite). …
This reference covers key areas such as what the Simple Present Tense is, its structure, and examples. It also explains how to use the Simple Present Tense, including its usage, notes, and time expressions. Find out …
The present simple tense is one of the fundamental tenses in English and allows you to describe habitual actions, general truths, and situations that are always …
Clear explanations about how to make the present simple tense (or simple present tense) in Englsih, with lots and lots of practice exercises.
Simple present tense also called present indefinite tense, is used to express general statements and to describe actions that are usual or habitual in nature.
Writing in the present tense means knowing its four aspects: the simple present (“she does” or “they do”), present continuous (“she is doing” or “they are doing”), present perfect (“she has done” or “they have done”), and …
The present simple (also: simple present) tense is a common verb tense used to describe habits, facts, fixed arrangements, and unchanging situations, such as jokes and stories. As the …