Trending Courses
Course Categories
Certification Programs
- Free Courses
Capital Budgeting Resources
- Free Practice Tests
- On Demand Webinars

Assignment Method
Published on :
21 Aug, 2024
Blog Author :
Edited by :
Reviewed by :
Dheeraj Vaidya
What Is The Assignment Method?
The assignment method is a strategic approach to allocating organizational resources, including tasks and jobs to various departments like people, machines, or teams. It aims to minimize total costs or completion time and gain maximum efficiency, by assigning resources to corresponding units.

The assignment procedure's importance stems from its capacity to optimize resource allocation procedures in a business. Organizations may guarantee that resources are used optimally, reducing waste and increasing productivity by implementing a systematic method. It facilitates the decision-making process for the efficient and economical use of resources by helping to make well-informed choices.
Table of contents
Assignment method explained, methodology, advantages & disadvantages, frequently asked questions (faqs), recommended articles.
- The assignment method strategically allocates resources to tasks, jobs or teams to minimize costs or completion time. It optimizes resource utilization, reduces waste, and improves operational efficiency.
- It involves using methods like complete enumeration, simplex, transportation, or the Hungarian method. It involves using the assignment method of linear programming .
- The Hungarian assignment method efficiently solves assignment problems by determining optimal assignments using a cost matrix.
- Advantages include structured resource allocation, enhanced resource utilization, and improved operational effectiveness. Limitations include data accuracy requirements and limited flexibility for dynamic changes.
The assignment method in operation research is a strategy for allocating organizational resources to tasks to increase profit via efficiency gains, cost reductions , and improved handling of operations that might create bottlenecks . It is an operations management tool that, by allocating jobs to the appropriate individual, minimizes expenses , time, and effort.
The technique is an essential tool for project management and cost accounting . It assists in allocating indirect expenses , such as overhead, to objects or cost centers according to predetermined standards, such as direct labor hours or required machine hours. The method helps determine the overall cost of every good or service, which helps with pricing, output, and resource distribution decisions. It also guarantees effective work allocation, on-time project completion, and economical use of resources. In short, it solves assignment problems.
Assignment problems involve assigning workers to specific roles, such as office workers or trucks on delivery routes, or determining which machines or products should be used in a plant during a specific period. Transportation problems involve distributing empty freight cars or assigning orders to factories. Allocation problems also involve determining which machines or products should be used to produce a given product or set of products. Unit costs or returns can be independent or interdependent, and if allocations affect subsequent periods, the problem is dynamic, requiring consideration of time in its solution.
The assignment problem can be solved using four methods: The complete enumeration method, the simplex method, the transportation method, and the Hungarian method.
The complete enumeration approach generates a list of potential assignments between resources and activities, from which the best option is chosen based on factors like cost, distance, time, or optimum profit. If the minimum cost, time, or distance for two or more assignments is the same, then this approach offers numerous optimal solutions. However If there are a lot of assignments, it is no longer appropriate for manual calculations. Assignment method calculators, if reliable, can be used for the same.
The simplex method can be solved as a linear programming problem using the simplex algorithm. The transportation method is a special case of the assignment problem. The method is, however, computationally inefficient for solving the assignment problem due to the solution's degeneracy problem.
The Hungarian assignment method problem, developed by mathematician D. Konig, is a faster and more efficient approach to solving assignment problems. It involves determining the cost of making all possible assignments using a matrix. Each problem has a row representing the objects to be assigned and columns representing assigned tasks. The cost matrix is square, and the optimum solution is to have only one assignment in a row or column. This method is a variation of the transportation problem, with the cost matrix being square and the optimum solution being one assignment in a row or column of the cost matrix.
Let us look into a few examples to understand the concept better.
TechLogistics Solutions, an imaginary delivery company, employs the assignment method to optimize the distribution of its delivery trucks. They meticulously consider distance, traffic conditions, and delivery schedules. TechLogistics efficiently allocates trucks to routes through strategic assignments, effectively reducing fuel costs and ensuring punctual deliveries. This method significantly enhances the company's operational efficiency and optimizes the utilization of its delivery resources.
Suppose XYZ Inc., a manufacturing company, is challenged to efficiently assign tasks to its machines (A, B, and C). Using the assignment method, XYZ calculates the cost matrix, reflecting the cost associated with each task assigned to each machine. Leveraging advanced algorithms like the Hungarian method, the company identifies optimal task-machine assignments, minimizing overall costs. This approach enables XYZ to streamline its production processes and enhance cost-effectiveness in manufacturing operations .
Advantages of the assignment method include:
- Resource allocation is carried out in a structured and organized manner.
- Enhancement of resource utilization to achieve optimal outcomes.
- Facilitation of efficient distribution of tasks.
- Improvement in operational effectiveness and productivity.
- Economical allocation of resources.
- Reduction in project completion time.
- Consideration of multiple factors and constraints for informed decision-making.
The disadvantages of the assignment method are as follows:
- Dependence on accurate and up-to-date data for effective decision-making.
- Complexity when dealing with resource allocation on a large scale.
- Subjectivity is involved in assigning values to the resource-requirement matrix.
- Limited flexibility in accommodating dynamic changes or unforeseen circumstances.
- Applicable primarily to quantitative tasks, with limitations in addressing qualitative aspects.
Johnson's rule is an operations research method that aims to estimate the optimal sequence of jobs in two work centers to reduce makespan. It optimizes the overall efficiency of the process. In contrast, the assignment method is useful for resource allocation, matching resources to specific tasks or requirements to optimize efficiency.
The study assignment method refers to the process of allocating students to specific courses or study programs based on their preferences, skills etc. It involves matching students with appropriate courses or programs to ensure optimal utilization of educational resources and meet individual student needs.
The assignment method is frequently employed when there is a requirement to allocate restricted resources like personnel, equipment, or budget to particular tasks or projects. It aids in enhancing resource utilization operational efficiency, and enables informed decision-making regarding resource allocation considering various factors and constraints.
This article has been a guide to what is Assignment Method. Here, we explain its methodologies, examples, advantages, & disadvantages. You may also find some useful articles here -
- Cost Allocation Methods
- Propensity Score Matching
- Regression Discontinuity Design
The Assignment Method: Definition, Applications, and Implementation Strategies
Last updated 03/15/2024 by
Fact checked by
Understanding the assignment method
Optimized resource utilization, enhanced production efficiency, maximized profitability, applications of the assignment method, workforce allocation, production planning, sales territory management, resource budgeting.
- Optimizes resource utilization
- Enhances production efficiency
- Maximizes profitability
- Requires thorough analysis of past performance and market conditions
- Potential for misallocation of resources if not executed properly
Frequently asked questions
How does the assignment method differ from other resource allocation methods, what factors should organizations consider when implementing the assignment method, can the assignment method be applied to non-profit organizations or public sector agencies, what role does technology play in implementing the assignment method, are there any ethical considerations associated with the assignment method, key takeaways.
- The assignment method optimizes resource allocation to enhance efficiency and profitability.
- Applications include workforce allocation, production planning, sales territory management, and resource budgeting.
- Effective implementation requires thorough analysis of past performance and market conditions.
- Strategic allocation of resources can drive overall performance and revenue growth.
Show Article Sources
You might also like.
Assignment Problem: Meaning, Methods and Variations | Operations Research
After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Assignment Problem 2. Definition of Assignment Problem 3. Mathematical Formulation 4. Hungarian Method 5. Variations.
Meaning of Assignment Problem:
An assignment problem is a particular case of transportation problem where the objective is to assign a number of resources to an equal number of activities so as to minimise total cost or maximize total profit of allocation.
The problem of assignment arises because available resources such as men, machines etc. have varying degrees of efficiency for performing different activities, therefore, cost, profit or loss of performing the different activities is different.
Thus, the problem is “How should the assignments be made so as to optimize the given objective”. Some of the problem where the assignment technique may be useful are assignment of workers to machines, salesman to different sales areas.
Definition of Assignment Problem:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Suppose there are n jobs to be performed and n persons are available for doing these jobs. Assume that each person can do each job at a term, though with varying degree of efficiency, let c ij be the cost if the i-th person is assigned to the j-th job. The problem is to find an assignment (which job should be assigned to which person one on-one basis) So that the total cost of performing all jobs is minimum, problem of this kind are known as assignment problem.
The assignment problem can be stated in the form of n x n cost matrix C real members as given in the following table:
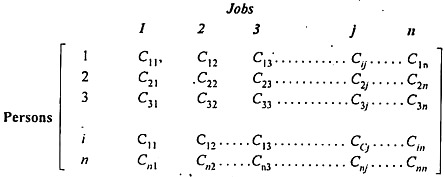
Hungarian Method Examples
Now we will examine a few highly simplified illustrations of Hungarian Method for solving an assignment problem .
Later in the chapter, you will find more practical versions of assignment models like Crew assignment problem , Travelling salesman problem , etc.
Example-1, Example-2
Example 1: Hungarian Method
The Funny Toys Company has four men available for work on four separate jobs. Only one man can work on any one job. The cost of assigning each man to each job is given in the following table. The objective is to assign men to jobs in such a way that the total cost of assignment is minimum.
| Job | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| A | 20 | 25 | 22 | 28 |
| B | 15 | 18 | 23 | 17 |
| C | 19 | 17 | 21 | 24 |
| D | 25 | 23 | 24 | 24 |
This is a minimization example of assignment problem . We will use the Hungarian Algorithm to solve this problem.
Identify the minimum element in each row and subtract it from every element of that row. The result is shown in the following table.
"A man has one hundred dollars and you leave him with two dollars, that's subtraction." -Mae West
On small screens, scroll horizontally to view full calculation
| Job | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| A | 0 | 5 | 2 | 8 |
| B | 0 | 3 | 8 | 2 |
| C | 2 | 0 | 4 | 7 |
| D | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Identify the minimum element in each column and subtract it from every element of that column.
| Job | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| A | 0 | 5 | 1 | 7 |
| B | 0 | 3 | 7 | 1 |
| C | 2 | 0 | 3 | 6 |
| D | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Make the assignments for the reduced matrix obtained from steps 1 and 2 in the following way:
- For every zero that becomes assigned, cross out (X) all other zeros in the same row and the same column.
- If for a row and a column, there are two or more zeros and one cannot be chosen by inspection, choose the cell arbitrarily for assignment.
An optimal assignment is found, if the number of assigned cells equals the number of rows (and columns). In case you have chosen a zero cell arbitrarily, there may be alternate optimal solutions. If no optimal solution is found, go to step 5.
Use Horizontal Scrollbar to View Full Table Calculation
| Job | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| A | 5 | 1 | 7 | |
| B | 3 | 7 | 1 | |
| C | 2 | 3 | 6 | |
| D | 2 | |||
Draw the minimum number of vertical and horizontal lines necessary to cover all the zeros in the reduced matrix obtained from step 3 by adopting the following procedure:
- Mark all the rows that do not have assignments.
- Mark all the columns (not already marked) which have zeros in the marked rows.
- Mark all the rows (not already marked) that have assignments in marked columns.
- Repeat steps 5 (ii) and (iii) until no more rows or columns can be marked.
- Draw straight lines through all unmarked rows and marked columns.
You can also draw the minimum number of lines by inspection.
Select the smallest element (i.e., 1) from all the uncovered elements. Subtract this smallest element from all the uncovered elements and add it to the elements, which lie at the intersection of two lines. Thus, we obtain another reduced matrix for fresh assignment.
| Job | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| A | 0 | 4 | 0 | 6 |
| B | 0 | 2 | 6 | 0 |
| C | 3 | 0 | 3 | 6 |
| D | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Now again make the assignments for the reduced matrix.
Final Table: Hungarian Method
| Job | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| A | 4 | 6 | ||
| B | 2 | 6 | ||
| C | 3 | 3 | 6 | |
| D | 3 | |||
Since the number of assignments is equal to the number of rows (& columns), this is the optimal solution.
The total cost of assignment = A1 + B4 + C2 + D3
Substituting values from original table: 20 + 17 + 17 + 24 = Rs. 78.
Share This Article
Operations Research Simplified Back Next
Goal programming Linear programming Simplex Method Transportation Problem
Your Article Library
Assignment problem in linear programming : introduction and assignment model.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Assignment problem is a special type of linear programming problem which deals with the allocation of the various resources to the various activities on one to one basis. It does it in such a way that the cost or time involved in the process is minimum and profit or sale is maximum. Though there problems can be solved by simplex method or by transportation method but assignment model gives a simpler approach for these problems.
In a factory, a supervisor may have six workers available and six jobs to fire. He will have to take decision regarding which job should be given to which worker. Problem forms one to one basis. This is an assignment problem.
1. Assignment Model :
Suppose there are n facilitates and n jobs it is clear that in this case, there will be n assignments. Each facility or say worker can perform each job, one at a time. But there should be certain procedure by which assignment should be made so that the profit is maximized or the cost or time is minimized.
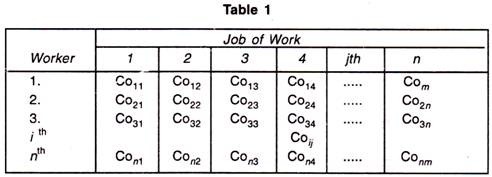
In the table, Co ij is defined as the cost when j th job is assigned to i th worker. It maybe noted here that this is a special case of transportation problem when the number of rows is equal to number of columns.
Mathematical Formulation:
Any basic feasible solution of an Assignment problem consists (2n – 1) variables of which the (n – 1) variables are zero, n is number of jobs or number of facilities. Due to this high degeneracy, if we solve the problem by usual transportation method, it will be a complex and time consuming work. Thus a separate technique is derived for it. Before going to the absolute method it is very important to formulate the problem.
Suppose x jj is a variable which is defined as
1 if the i th job is assigned to j th machine or facility
0 if the i th job is not assigned to j th machine or facility.
Now as the problem forms one to one basis or one job is to be assigned to one facility or machine.

The total assignment cost will be given by
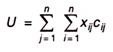
The above definition can be developed into mathematical model as follows:
Determine x ij > 0 (i, j = 1,2, 3…n) in order to
Subjected to constraints

and x ij is either zero or one.
Method to solve Problem (Hungarian Technique):
Consider the objective function of minimization type. Following steps are involved in solving this Assignment problem,
1. Locate the smallest cost element in each row of the given cost table starting with the first row. Now, this smallest element is subtracted form each element of that row. So, we will be getting at least one zero in each row of this new table.
2. Having constructed the table (as by step-1) take the columns of the table. Starting from first column locate the smallest cost element in each column. Now subtract this smallest element from each element of that column. Having performed the step 1 and step 2, we will be getting at least one zero in each column in the reduced cost table.
3. Now, the assignments are made for the reduced table in following manner.
(i) Rows are examined successively, until the row with exactly single (one) zero is found. Assignment is made to this single zero by putting square □ around it and in the corresponding column, all other zeros are crossed out (x) because these will not be used to make any other assignment in this column. Step is conducted for each row.
(ii) Step 3 (i) in now performed on the columns as follow:- columns are examined successively till a column with exactly one zero is found. Now , assignment is made to this single zero by putting the square around it and at the same time, all other zeros in the corresponding rows are crossed out (x) step is conducted for each column.
(iii) Step 3, (i) and 3 (ii) are repeated till all the zeros are either marked or crossed out. Now, if the number of marked zeros or the assignments made are equal to number of rows or columns, optimum solution has been achieved. There will be exactly single assignment in each or columns without any assignment. In this case, we will go to step 4.
4. At this stage, draw the minimum number of lines (horizontal and vertical) necessary to cover all zeros in the matrix obtained in step 3, Following procedure is adopted:
(iii) Now tick mark all the rows that are not already marked and that have assignment in the marked columns.
(iv) All the steps i.e. (4(i), 4(ii), 4(iii) are repeated until no more rows or columns can be marked.
(v) Now draw straight lines which pass through all the un marked rows and marked columns. It can also be noticed that in an n x n matrix, always less than ‘n’ lines will cover all the zeros if there is no solution among them.
5. In step 4, if the number of lines drawn are equal to n or the number of rows, then it is the optimum solution if not, then go to step 6.
6. Select the smallest element among all the uncovered elements. Now, this element is subtracted from all the uncovered elements and added to the element which lies at the intersection of two lines. This is the matrix for fresh assignments.
7. Repeat the procedure from step (3) until the number of assignments becomes equal to the number of rows or number of columns.
Related Articles:
- Two Phase Methods of Problem Solving in Linear Programming: First and Second Phase
- Linear Programming: Applications, Definitions and Problems
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Hungarian Method

The Hungarian method is a computational optimization technique that addresses the assignment problem in polynomial time and foreshadows following primal-dual alternatives. In 1955, Harold Kuhn used the term “Hungarian method” to honour two Hungarian mathematicians, Dénes Kőnig and Jenő Egerváry. Let’s go through the steps of the Hungarian method with the help of a solved example.
Hungarian Method to Solve Assignment Problems
The Hungarian method is a simple way to solve assignment problems. Let us first discuss the assignment problems before moving on to learning the Hungarian method.
What is an Assignment Problem?
A transportation problem is a type of assignment problem. The goal is to allocate an equal amount of resources to the same number of activities. As a result, the overall cost of allocation is minimised or the total profit is maximised.
Because available resources such as workers, machines, and other resources have varying degrees of efficiency for executing different activities, and hence the cost, profit, or loss of conducting such activities varies.
Assume we have ‘n’ jobs to do on ‘m’ machines (i.e., one job to one machine). Our goal is to assign jobs to machines for the least amount of money possible (or maximum profit). Based on the notion that each machine can accomplish each task, but at variable levels of efficiency.
Hungarian Method Steps
Check to see if the number of rows and columns are equal; if they are, the assignment problem is considered to be balanced. Then go to step 1. If it is not balanced, it should be balanced before the algorithm is applied.
Step 1 – In the given cost matrix, subtract the least cost element of each row from all the entries in that row. Make sure that each row has at least one zero.
Step 2 – In the resultant cost matrix produced in step 1, subtract the least cost element in each column from all the components in that column, ensuring that each column contains at least one zero.
Step 3 – Assign zeros
- Analyse the rows one by one until you find a row with precisely one unmarked zero. Encircle this lonely unmarked zero and assign it a task. All other zeros in the column of this circular zero should be crossed out because they will not be used in any future assignments. Continue in this manner until you’ve gone through all of the rows.
- Examine the columns one by one until you find one with precisely one unmarked zero. Encircle this single unmarked zero and cross any other zero in its row to make an assignment to it. Continue until you’ve gone through all of the columns.
Step 4 – Perform the Optimal Test
- The present assignment is optimal if each row and column has exactly one encircled zero.
- The present assignment is not optimal if at least one row or column is missing an assignment (i.e., if at least one row or column is missing one encircled zero). Continue to step 5. Subtract the least cost element from all the entries in each column of the final cost matrix created in step 1 and ensure that each column has at least one zero.
Step 5 – Draw the least number of straight lines to cover all of the zeros as follows:
(a) Highlight the rows that aren’t assigned.
(b) Label the columns with zeros in marked rows (if they haven’t already been marked).
(c) Highlight the rows that have assignments in indicated columns (if they haven’t previously been marked).
(d) Continue with (b) and (c) until no further marking is needed.
(f) Simply draw the lines through all rows and columns that are not marked. If the number of these lines equals the order of the matrix, then the solution is optimal; otherwise, it is not.
Step 6 – Find the lowest cost factor that is not covered by the straight lines. Subtract this least-cost component from all the uncovered elements and add it to all the elements that are at the intersection of these straight lines, but leave the rest of the elements alone.
Step 7 – Continue with steps 1 – 6 until you’ve found the highest suitable assignment.
|
|
|---|

Hungarian Method Example
Use the Hungarian method to solve the given assignment problem stated in the table. The entries in the matrix represent each man’s processing time in hours.
\(\begin{array}{l}\begin{bmatrix} & I & II & III & IV & V \\1 & 20 & 15 & 18 & 20 & 25 \\2 & 18 & 20 & 12 & 14 & 15 \\3 & 21 & 23 & 25 & 27 & 25 \\4 & 17 & 18 & 21 & 23 & 20 \\5 & 18 & 18 & 16 & 19 & 20 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
With 5 jobs and 5 men, the stated problem is balanced.
\(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}20 & 15 & 18 & 20 & 25 \\18 & 20 & 12 & 14 & 15 \\21 & 23 & 25 & 27 & 25 \\17 & 18 & 21 & 23 & 20 \\18 & 18 & 16 & 19 & 20 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Subtract the lowest cost element in each row from all of the elements in the given cost matrix’s row. Make sure that each row has at least one zero.
\(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}5 & 0 & 3 & 5 & 10 \\6 & 8 & 0 & 2 & 3 \\0 & 2 & 4 & 6 & 4 \\0 & 1 & 4 & 6 & 3 \\2 & 2 & 0 & 3 & 4 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Subtract the least cost element in each Column from all of the components in the given cost matrix’s Column. Check to see if each column has at least one zero.
\(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}5 & 0 & 3 & 3 & 7 \\6 & 8 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 2 & 4 & 4 & 1 \\0 & 1 & 4 & 4 & 0 \\2 & 2 & 0 & 1 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
When the zeros are assigned, we get the following:
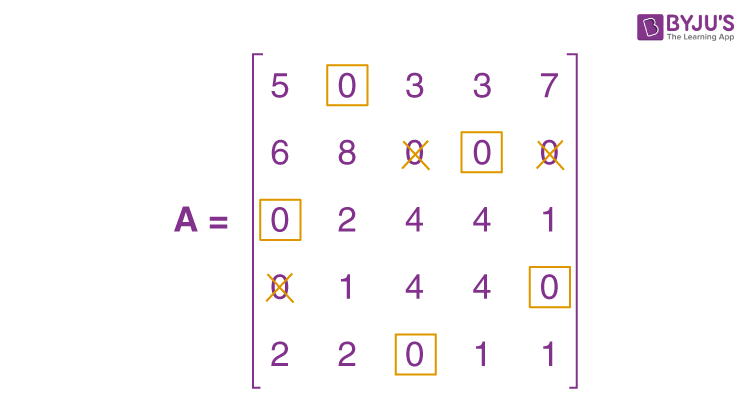
The present assignment is optimal because each row and column contain precisely one encircled zero.
Where 1 to II, 2 to IV, 3 to I, 4 to V, and 5 to III are the best assignments.
Hence, z = 15 + 14 + 21 + 20 + 16 = 86 hours is the optimal time.
Practice Question on Hungarian Method
Use the Hungarian method to solve the following assignment problem shown in table. The matrix entries represent the time it takes for each job to be processed by each machine in hours.
\(\begin{array}{l}\begin{bmatrix}J/M & I & II & III & IV & V \\1 & 9 & 22 & 58 & 11 & 19 \\2 & 43 & 78 & 72 & 50 & 63 \\3 & 41 & 28 & 91 & 37 & 45 \\4 & 74 & 42 & 27 & 49 & 39 \\5 & 36 & 11 & 57 & 22 & 25 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Stay tuned to BYJU’S – The Learning App and download the app to explore all Maths-related topics.
Frequently Asked Questions on Hungarian Method
What is hungarian method.
The Hungarian method is defined as a combinatorial optimization technique that solves the assignment problems in polynomial time and foreshadowed subsequent primal–dual approaches.
What are the steps involved in Hungarian method?
The following is a quick overview of the Hungarian method: Step 1: Subtract the row minima. Step 2: Subtract the column minimums. Step 3: Use a limited number of lines to cover all zeros. Step 4: Add some more zeros to the equation.
What is the purpose of the Hungarian method?
When workers are assigned to certain activities based on cost, the Hungarian method is beneficial for identifying minimum costs.
| MATHS Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- Google OR-Tools
- Español – América Latina
- Português – Brasil
- Tiếng Việt
Solving an Assignment Problem
This section presents an example that shows how to solve an assignment problem using both the MIP solver and the CP-SAT solver.
In the example there are five workers (numbered 0-4) and four tasks (numbered 0-3). Note that there is one more worker than in the example in the Overview .
The costs of assigning workers to tasks are shown in the following table.
| Worker | Task 0 | Task 1 | Task 2 | Task 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 | 80 | 75 | 70 | |
| 35 | 85 | 55 | 65 | |
| 125 | 95 | 90 | 95 | |
| 45 | 110 | 95 | 115 | |
| 50 | 100 | 90 | 100 |
The problem is to assign each worker to at most one task, with no two workers performing the same task, while minimizing the total cost. Since there are more workers than tasks, one worker will not be assigned a task.
MIP solution
The following sections describe how to solve the problem using the MPSolver wrapper .
Import the libraries
The following code imports the required libraries.
Create the data
The following code creates the data for the problem.
The costs array corresponds to the table of costs for assigning workers to tasks, shown above.
Declare the MIP solver
The following code declares the MIP solver.
Create the variables
The following code creates binary integer variables for the problem.
Create the constraints
Create the objective function.
The following code creates the objective function for the problem.
The value of the objective function is the total cost over all variables that are assigned the value 1 by the solver.
Invoke the solver
The following code invokes the solver.
Print the solution
The following code prints the solution to the problem.
Here is the output of the program.
Complete programs
Here are the complete programs for the MIP solution.
CP SAT solution
The following sections describe how to solve the problem using the CP-SAT solver.
Declare the model
The following code declares the CP-SAT model.
The following code sets up the data for the problem.
The following code creates the constraints for the problem.
Here are the complete programs for the CP-SAT solution.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License , and code samples are licensed under the Apache 2.0 License . For details, see the Google Developers Site Policies . Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2024-08-28 UTC.
- Practice Mathematical Algorithm
- Mathematical Algorithms
- Pythagorean Triplet
- Fibonacci Number
- Euclidean Algorithm
- LCM of Array
- GCD of Array
- Binomial Coefficient
- Catalan Numbers
- Sieve of Eratosthenes
- Euler Totient Function
- Modular Exponentiation
- Modular Multiplicative Inverse
- Stein's Algorithm
- Juggler Sequence
- Chinese Remainder Theorem
- Quiz on Fibonacci Numbers
Hungarian Algorithm for Assignment Problem | Set 1 (Introduction)
- For each row of the matrix, find the smallest element and subtract it from every element in its row.
- Do the same (as step 1) for all columns.
- Cover all zeros in the matrix using minimum number of horizontal and vertical lines.
- Test for Optimality: If the minimum number of covering lines is n, an optimal assignment is possible and we are finished. Else if lines are lesser than n, we haven’t found the optimal assignment, and must proceed to step 5.
- Determine the smallest entry not covered by any line. Subtract this entry from each uncovered row, and then add it to each covered column. Return to step 3.
Try it before moving to see the solution
Explanation for above simple example:
An example that doesn’t lead to optimal value in first attempt: In the above example, the first check for optimality did give us solution. What if we the number covering lines is less than n.
Time complexity : O(n^3), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm implements the Hungarian algorithm, which is known to have a time complexity of O(n^3).
Space complexity : O(n^2), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm uses a 2D cost matrix of size n x n to store the costs of assigning each worker to a job, and additional arrays of size n to store the labels, matches, and auxiliary information needed for the algorithm.
In the next post, we will be discussing implementation of the above algorithm. The implementation requires more steps as we need to find minimum number of lines to cover all 0’s using a program. References: http://www.math.harvard.edu/archive/20_spring_05/handouts/assignment_overheads.pdf https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQDZNHwuuOY
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Mathematical
- OpenAI o1 AI Model Launched: Explore o1-Preview, o1-Mini, Pricing & Comparison
- How to Merge Cells in Google Sheets: Step by Step Guide
- How to Lock Cells in Google Sheets : Step by Step Guide
- PS5 Pro Launched: Controller, Price, Specs & Features, How to Pre-Order, and More
- #geekstreak2024 – 21 Days POTD Challenge Powered By Deutsche Bank
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Operations Research by P. Mariappan
Get full access to Operations Research and 60K+ other titles, with a free 10-day trial of O'Reilly.
There are also live events, courses curated by job role, and more.
Assignment Problem
5.1 introduction.
The assignment problem is one of the special type of transportation problem for which more efficient (less-time consuming) solution method has been devised by KUHN (1956) and FLOOD (1956). The justification of the steps leading to the solution is based on theorems proved by Hungarian mathematicians KONEIG (1950) and EGERVARY (1953), hence the method is named Hungarian.
5.2 GENERAL MODEL OF THE ASSIGNMENT PROBLEM
Consider n jobs and n persons. Assume that each job can be done only by one person and the time a person required for completing the i th job (i = 1,2,...n) by the j th person (j = 1,2,...n) is denoted by a real number C ij . On the whole this model deals with the assignment of n candidates to n jobs ...
Get Operations Research now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.
Don’t leave empty-handed
Get Mark Richards’s Software Architecture Patterns ebook to better understand how to design components—and how they should interact.
It’s yours, free.

The Hungarian algorithm: An example
We consider an example where four jobs (J1, J2, J3, and J4) need to be executed by four workers (W1, W2, W3, and W4), one job per worker. The matrix below shows the cost of assigning a certain worker to a certain job. The objective is to minimize the total cost of the assignment.
| 82 | 83 | 69 | 92 | |
| 77 | 37 | 49 | 92 | |
| 11 | 69 | 5 | 86 | |
| 8 | 9 | 98 | 23 |
Below we will explain the Hungarian algorithm using this example. Note that a general description of the algorithm can be found here .
Step 1: Subtract row minima
We start with subtracting the row minimum from each row. The smallest element in the first row is, for example, 69. Therefore, we substract 69 from each element in the first row. The resulting matrix is:
| 13 | 14 | 0 | 23 | (-69) | |
| 40 | 0 | 12 | 55 | (-37) | |
| 6 | 64 | 0 | 81 | (-5) | |
| 0 | 1 | 90 | 15 | (-8) |
Step 2: Subtract column minima
Similarly, we subtract the column minimum from each column, giving the following matrix:
| 13 | 14 | 0 | 8 | |
| 40 | 0 | 12 | 40 | |
| 6 | 64 | 0 | 66 | |
| 0 | 1 | 90 | 0 | |
| (-15) |
Step 3: Cover all zeros with a minimum number of lines
We will now determine the minimum number of lines (horizontal or vertical) that are required to cover all zeros in the matrix. All zeros can be covered using 3 lines:
| 13 | 14 | 0 | 8 | ||
| 40 | 0 | 12 | 40 | ||
| 6 | 64 | 0 | 66 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 90 | 0 | ||
Step 4: Create additional zeros
First, we find that the smallest uncovered number is 6. We subtract this number from all uncovered elements and add it to all elements that are covered twice. This results in the following matrix:
| 7 | 8 | 0 | 2 | |
| 40 | 0 | 18 | 40 | |
| 0 | 58 | 0 | 60 | |
| 0 | 1 | 96 | 0 |
Now we return to Step 3.
Again, We determine the minimum number of lines required to cover all zeros in the matrix. Now there are 4 lines required:
| 7 | 8 | 0 | 2 | ||
| 40 | 0 | 18 | 40 | ||
| 0 | 58 | 0 | 60 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 96 | 0 |
Because the number of lines required (4) equals the size of the matrix ( n =4), an optimal assignment exists among the zeros in the matrix. Therefore, the algorithm stops.
The optimal assignment
The following zeros cover an optimal assignment:
This corresponds to the following optimal assignment in the original cost matrix:
Thus, worker 1 should perform job 3, worker 2 job 2, worker 3 job 1, and worker 4 should perform job 4. The total cost of this optimal assignment is to 69 + 37 + 11 + 23 = 140.
Solve your own problem online
HungarianAlgorithm.com © 2013-2024
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.

COMMENTS
The assignment method strategically allocates resources to tasks, jobs or teams to minimize costs or completion time. It optimizes resource utilization, reduces waste, and improves operational efficiency. It involves using methods like complete enumeration, simplex, transportation, or the Hungarian method.
Example of Assignment Method. A bank is allocating its sales force to grow its mortgage lending business. The bank has over 50 branches in New York but only ten in Chicago. Each branch has a staff ...
The assignment method is any technique used to assign organizational resources to activities. The best assignment method will maximize profits, typically through cost controls, increases in efficiency levels, and better management of bottleneck operations. The assignment method is incorporated into an organization's budgeting process, so that ...
The assignment method is a strategic approach for distributing organizational resources to specific tasks or areas. Its primary goal is to optimize resource allocation, enhance production efficiency, and maximize profits. This method finds applications in various aspects of business operations, including workforce allocation, production ...
The Hungarian method can be summarized in the following steps: Step 1: Develop the Cost Table from the given Problem: ADVERTISEMENTS: If the no of rows are not equal to the no of columns and vice versa, a dummy row or dummy column must be added. The assignment cost for dummy cells are always zero.
Solve an assignment problem online. Fill in the cost matrix of an assignment problem and click on 'Solve'. The optimal assignment will be determined and a step by step explanation of the hungarian algorithm will be given. Fill in the cost matrix ():
The assignment method finds applications in various fields, such as project management, workforce scheduling, transportation logistics, and resource allocation. ... The algorithm continues to iteratively improve the assignment by repeating the steps above until an optimal solution is found. 5. One important aspect of the Hungarian algorithm is ...
The assignment method is used to determine what resources are assigned to which department, machine, or center of operation in the production process. This method is used to allocate the proper number of employees to a machine or task, and the number of jobs that a given machine or factory can produce. The idea is to assign resources in such a ...
%PDF-1.3 %âãÏÓ 7 0 obj /Linearized 1 /O 11 /H [ 1265 213 ] /L 29034 /E 28238 /N 1 /T 28777 >> endobj xref 7 34 0000000016 00000 n 0000001024 00000 n 0000001174 00000 n 0000001227 00000 n 0000001478 00000 n 0000001631 00000 n 0000001764 00000 n 0000002044 00000 n 0000007679 00000 n 0000007847 00000 n 0000008158 00000 n 0000008379 00000 n 0000009834 00000 n 0000010173 00000 n 0000019094 ...
Example 1: Hungarian Method. The Funny Toys Company has four men available for work on four separate jobs. Only one man can work on any one job. The cost of assigning each man to each job is given in the following table. The objective is to assign men to jobs in such a way that the total cost of assignment is minimum. Job.
Assignment problem is a special type of linear programming problem which deals with the allocation of the various resources to the various activities on one to one basis. It does it in such a way that the cost or time involved in the process is minimum and profit or sale is maximum. Though there problems can be solved by simplex method or by ...
The Hungarian method is a computational optimization technique that addresses the assignment problem in polynomial time and foreshadows following primal-dual alternatives. In 1955, Harold Kuhn used the term "Hungarian method" to honour two Hungarian mathematicians, Dénes Kőnig and Jenő Egerváry. Let's go through the steps of the Hungarian method with the help of a solved example.
The following code creates the objective function for the problem. Python C++ Java C#. objective_terms = [] for i in range(num_workers): for j in range(num_tasks): objective_terms.append(costs[i][j] * x[i, j]) solver.Minimize(solver.Sum(objective_terms)) The value of the objective function is the total cost over all variables that are assigned ...
The Hungarian method is a combinatorial optimization algorithm that solves the assignment problem in polynomial time and which anticipated later primal-dual methods.It was developed and published in 1955 by Harold Kuhn, who gave it the name "Hungarian method" because the algorithm was largely based on the earlier works of two Hungarian mathematicians, Dénes Kőnig and Jenő Egerváry.
In this lesson we learn what is an assignment problem and how we can solve it using the Hungarian method.
Hungarian Algorithm Steps. To use the Hungarian Algorithm, we first arrange the activities and people in a matrix with rows being people, columns being activity, and entries being the costs. Once ...
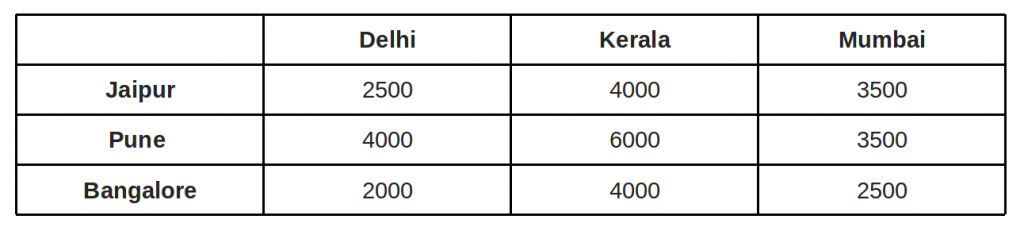
Step 3: Cover all zeroes with minimum number of. horizontal and vertical lines. Step 4: Since we need 3 lines to cover all zeroes, we have found the optimal assignment. 2500 4000 3500. 4000 6000 3500. 2000 4000 2500. So the optimal cost is 4000 + 3500 + 2000 = 9500. An example that doesn't lead to optimal value in first attempt: In the above ...
5.1 INTRODUCTION. The assignment problem is one of the special type of transportation problem for which more efficient (less-time consuming) solution method has been devised by KUHN (1956) and FLOOD (1956). The justification of the steps leading to the solution is based on theorems proved by Hungarian mathematicians KONEIG (1950) and EGERVARY ...
The six steps of the scientific method include: 1) asking a question about something you observe, 2) doing background research to learn what is already known about the topic, 3) constructing a hypothesis, 4) experimenting to test the hypothesis, 5) analyzing the data from the experiment and drawing conclusions, and 6) communicating the results ...
The Hungarian Method: The following algorithm applies the above theorem to a given n × n cost matrix to find an optimal assignment. Step 1. Subtract the smallest entry in each row from all the entries of its row. Step 2. Subtract the smallest entry in each column from all the entries of its column. Step 3.
The matrix below shows the cost of assigning a certain worker to a certain job. The objective is to minimize the total cost of the assignment. Below we will explain the Hungarian algorithm using this example. Note that a general description of the algorithm can be found here. Step 1: Subtract row minima.
2 6-2 Assignment: 12-Step Program Benefits The 12-Step Program, according to the American Addiction Centers, is a twelve-step framework that individuals can utilize or adhere to support one another in achieving and maintaining sobriety from the drug or behaviors to which they are addicted. It is frequently suggested and widely utilized for a variety of addictions (Addiction Centers in America ...
Precursor solution aging process can cause significant influence on the photovoltaic performance of perovskite solar cells (PVSCs). Notably, we first observe that the aging phenomenon is more severe in the precursor of two-step sequential method compared to that in one-step method due to that the protic solvent isopropanol facilitates amine-cation side reaction and iodide ions oxidation.