How to write the perfect design dissertation
Tutors and students from top design colleges share their advice.

Studying design is about crafting a great design portfolio that will wow potential employers, right? Well, yes. But don't discount the importance of astute creative thinking, and expressing yourself eloquently through the written word. In short, your design dissertation matters.
"I don't believe that design students should be focused entirely on portfolio work," argues Myrna MacLeod , programme leader for Graphic Design at Edinburgh Napier University. "They should also be able to demonstrate an interest in the contexts that underpin their work, and the histories and connections that have informed our practice."
- 5 top tips for graduate designers
"Think of a dissertation as an opportunity, not a burden," urges Craig Burston , Graphic and Media Design course leader at London College of Communication (LCC). "It gives us visually-minded people an opportunity to demonstrate that we too can construct arguments and distil complex notions."
As Burston points out, this is not just an academic exercise: the power of persuasion is often key to success as a commercial designer. "Clients seek clarity, and project concepts or proposals need to be put into context," he says.
Read on to discover some top tips from leading tutors and their students for nailing your design dissertation…

01. Treat it like a design brief
"A great dissertation should be a designed artefact, and portfolio-worthy in its own right," says Burston. And like a design brief, it should be about solving a problem: "Make sure it has clearly stated aims, strong focus, and doesn't lack opinion or rhetoric," he adds.
- Best laptops for graphic design
"The value of a designed dissertation as a portfolio piece is that it's a holistic view of the individual," agrees Sarah James , senior lecturer in Visual Communication at Arts University Bournemouth (AUB).
"It shows, type, editorial, research and aesthetic skill, as well as the personal interests and convictions of the individual."

James identifies AUB student Maarit Koobas , who investigated responsive type in both her dissertation and final project, as a particularly strong example of this. "Her design version was one of the most authentic, restrained and elegantly expressive I have ever received," she enthuses.
Koobas conducted a huge amount of initial research into both the contexts in which responsive type can be seen – such as advertising, product design, science and material cultures – and the theories behind its analysis, including semiotics, philosophy and politics. "Creating and analysing ideas, before they end up in your portfolio, is what design is all about," argues Koobas.
- 5 must-read books for design students
02. Write about your passion
"To develop essay questions, AUB students are asked to consider what they love, hate or are puzzled by in their practice – essentially, what moves them," says James.
"A poor dissertation is inauthentically chosen for ease as opposed to interest," she adds. "It rambles and blusters, using complex language to mask insufficient research."
"You can tell a mile off when the writer isn't interested," agrees Burston. "How can you expect the reader to care about it if you don't? Write about something that reflects your interests, focus and direction. I've read fascinating dissertations on topics as diverse as patterns in nature, and Brutalist car parks. Make me interested in what interests you."

For Edinburgh Napier graduate Fiona Winchester , this topic turned out to be typography in graphic novels. "I love reading them, but I think people still don't take them seriously as an art form, which is a shame," she says. For her dissertation, she conducted qualitative interviews using modified pages with and without imagery (shown above).
Her advice is simple: "Narrow down your idea to be as precise as possible. The smaller your question, the easier it is to research and try to answer it."
If you're struggling to get the ball rolling on the actual writing process, Winchester advocates starting with whichever bit you have ideas for. "If you're stuck, it's so much easier to write in whatever order it comes to you, and then edit it into a dissertation, than to try write straight through from beginning to end," she insists.
03. Don't be afraid to talk to people
"I always think my students get the most out of the new streams of knowledge they find from talking to people," says McLeod. "It breaks down barriers and allows them to find answers to problems. Hopefully they will adopt that approach when designing for people also."
In some cases, this can involve interviewing your design heroes. "Students are very surprised when they send a question to Stefan Sagmeister , Milton Glaser or Michael Wolff and they reply with the most precious nugget of knowledge," smiles McLeod.
But remember: it's your dissertation, so don't get lazy and expect your interview subject to do all the heavy lifting.

In other cases, it could be as simple as asking friends or family to help proofread. "It is quite daunting writing such a large body of text," admits Kaori Toh , a recent graduate from Central Saint Martins, whose dissertation explored the politics of design and technology.
"I often felt I'd get lost in all that text and research," she confesses. "Therefore, I would often send my drafts to a couple of friends to have them look through, and keep my writing cohesive."
04. Reflect on your design practice
Most of all, dissertations are an opportunity to reflect on, and develop, your creative process as a designer. "Ultimately, it's your job to make your work relevant and credible, and the dissertation helps you learn how to do this," adds Burston.
Of course, writing doesn't always come easily to visually minded people – and Burston highlights the fact that dyslexia is not uncommon amongst designers.
"You're not on your own – in our profession, quite the opposite in fact – so do seek academic support, and just enjoy thinking and writing about 'stuff' that informs your practice," is his advice.

One of Burston's stand-out students from this year, Tom Baber , welcomed support from the university to help with his dyslexia. Baber's dissertation focused on type design, and particularly the extent to which the longwinded design process is worth the effort, compared to using an existing typeface.
"I saw it as an opportunity to approach other type designers and see what they thought. Turns out I'm not the first to ask the question," he smiles. "Writing my dissertation helped me change from a 'maker' mentality to a 'designer' mentality, and be more critical of my ideas."
Related articles:
- 15 things they didn't teach you at design school
- The skills every design graduate needs
- 5 alternative routes into design education
Thank you for reading 5 articles this month* Join now for unlimited access
Enjoy your first month for just £1 / $1 / €1
*Read 5 free articles per month without a subscription
Join now for unlimited access
Try first month for just £1 / $1 / €1
Get the Creative Bloq Newsletter
Daily design news, reviews, how-tos and more, as picked by the editors.
Nick is a content strategist and copywriter. He has worked with world-class agencies including Superunion, Wolff Olins and Vault49 on brand storytelling, tone of voice and verbal strategy for global brands such as Virgin, Pepsi and TikTok. Nick launched the Brand Impact Awards in 2013 while editor of Computer Arts, and remains chair of judges. He's written for Creative Bloq on design and branding matters since the site's launch.
Related articles

- 2 Apple finally addresses its most infamous design crime
- 3 Logitech finally announced the iPad mini 6 keyboard I've been waiting for
- 4 How Still Wakes The Deep was made more terrifyingly beautiful with Unreal Engine 5
- 5 Federer’s iconic new ad is some of the best CGI marketing I’ve seen
- 2 Get started with Vision FX 2.0: the newest AI art plugin on the block
- 3 Harness AI for design and art using your very own workstation
- 5 A 3D artist is running Blender on a Nokia N95 (yes, really)
What’s Included: The Dissertation Template
If you’re preparing to write your dissertation, thesis or research project, our free dissertation template is the perfect starting point. In the template, we cover every section step by step, with clear, straightforward explanations and examples .
The template’s structure is based on the tried and trusted best-practice format for formal academic research projects such as dissertations and theses. The template structure reflects the overall research process, ensuring your dissertation or thesis will have a smooth, logical flow from chapter to chapter.
The dissertation template covers the following core sections:
- The title page/cover page
- Abstract (sometimes also called the executive summary)
- Table of contents
- List of figures /list of tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction (also available: in-depth introduction template )
- Chapter 2: Literature review (also available: in-depth LR template )
- Chapter 3: Methodology (also available: in-depth methodology template )
- Chapter 4: Research findings /results (also available: results template )
- Chapter 5: Discussion /analysis of findings (also available: discussion template )
- Chapter 6: Conclusion (also available: in-depth conclusion template )
- Reference list
Each section is explained in plain, straightforward language , followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover within each section. We’ve also included practical examples to help you understand exactly what’s required in each section.
The cleanly-formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX.
FAQs: Dissertation Template
What format is the template (doc, pdf, ppt, etc.).
The dissertation template is provided as a Google Doc. You can download it in MS Word format or make a copy to your Google Drive. You’re also welcome to convert it to whatever format works best for you, such as LaTeX or PDF.
What types of dissertations/theses can this template be used for?
The template follows the standard best-practice structure for formal academic research projects such as dissertations or theses, so it is suitable for the vast majority of degrees, particularly those within the sciences.
Some universities may have some additional requirements, but these are typically minor, with the core structure remaining the same. Therefore, it’s always a good idea to double-check your university’s requirements before you finalise your structure.
Will this work for a research paper?
A research paper follows a similar format, but there are a few differences. You can find our research paper template here .
Is this template for an undergrad, Masters or PhD-level thesis?
This template can be used for a dissertation, thesis or research project at any level of study. It may be slight overkill for an undergraduate-level study, but it certainly won’t be missing anything.
How long should my dissertation/thesis be?
This depends entirely on your university’s specific requirements, so it’s best to check with them. As a general ballpark, Masters-level projects are usually 15,000 – 20,000 words in length, while Doctoral-level projects are often in excess of 60,000 words.
What about the research proposal?
If you’re still working on your research proposal, we’ve got a template for that here .
We’ve also got loads of proposal-related guides and videos over on the Grad Coach blog .
How do I write a literature review?
We have a wealth of free resources on the Grad Coach Blog that unpack how to write a literature review from scratch. You can check out the literature review section of the blog here.
How do I create a research methodology?
We have a wealth of free resources on the Grad Coach Blog that unpack research methodology, both qualitative and quantitative. You can check out the methodology section of the blog here.
Can I share this dissertation template with my friends/colleagues?
Yes, you’re welcome to share this template. If you want to post about it on your blog or social media, all we ask is that you reference this page as your source.
Can Grad Coach help me with my dissertation/thesis?
Within the template, you’ll find plain-language explanations of each section, which should give you a fair amount of guidance. However, you’re also welcome to consider our dissertation and thesis coaching services .

- How it works

How to Structure a Dissertation – A Step by Step Guide
Published by Owen Ingram at August 11th, 2021 , Revised On September 20, 2023
A dissertation – sometimes called a thesis – is a long piece of information backed up by extensive research. This one, huge piece of research is what matters the most when students – undergraduates and postgraduates – are in their final year of study.
On the other hand, some institutions, especially in the case of undergraduate students, may or may not require students to write a dissertation. Courses are offered instead. This generally depends on the requirements of that particular institution.
If you are unsure about how to structure your dissertation or thesis, this article will offer you some guidelines to work out what the most important segments of a dissertation paper are and how you should organise them. Why is structure so important in research, anyway?
One way to answer that, as Abbie Hoffman aptly put it, is because: “Structure is more important than content in the transmission of information.”
Also Read: How to write a dissertation – step by step guide .
How to Structure a Dissertation or Thesis
It should be noted that the exact structure of your dissertation will depend on several factors, such as:
- Your research approach (qualitative/quantitative)
- The nature of your research design (exploratory/descriptive etc.)
- The requirements set for forth by your academic institution.
- The discipline or field your study belongs to. For instance, if you are a humanities student, you will need to develop your dissertation on the same pattern as any long essay .
This will include developing an overall argument to support the thesis statement and organizing chapters around theories or questions. The dissertation will be structured such that it starts with an introduction , develops on the main idea in its main body paragraphs and is then summarised in conclusion .
However, if you are basing your dissertation on primary or empirical research, you will be required to include each of the below components. In most cases of dissertation writing, each of these elements will have to be written as a separate chapter.
But depending on the word count you are provided with and academic subject, you may choose to combine some of these elements.
For example, sciences and engineering students often present results and discussions together in one chapter rather than two different chapters.
If you have any doubts about structuring your dissertation or thesis, it would be a good idea to consult with your academic supervisor and check your department’s requirements.
Parts of a Dissertation or Thesis
Your dissertation will start with a t itle page that will contain details of the author/researcher, research topic, degree program (the paper is to be submitted for), and research supervisor. In other words, a title page is the opening page containing all the names and title related to your research.
The name of your university, logo, student ID and submission date can also be presented on the title page. Many academic programs have stringent rules for formatting the dissertation title page.
Acknowledgements
The acknowledgments section allows you to thank those who helped you with your dissertation project. You might want to mention the names of your academic supervisor, family members, friends, God, and participants of your study whose contribution and support enabled you to complete your work.
However, the acknowledgments section is usually optional.
Tip: Many students wrongly assume that they need to thank everyone…even those who had little to no contributions towards the dissertation. This is not the case. You only need to thank those who were directly involved in the research process, such as your participants/volunteers, supervisor(s) etc.
Perhaps the smallest yet important part of a thesis, an abstract contains 5 parts:
- A brief introduction of your research topic.
- The significance of your research.
- A line or two about the methodology that was used.
- The results and what they mean (briefly); their interpretation(s).
- And lastly, a conclusive comment regarding the results’ interpretation(s) as conclusion .
Stuck on a difficult dissertation? We can help!
Our Essay Writing Service Features:
- Expert UK Writers
- Plagiarism-free
- Timely Delivery
- Thorough Research
- Rigorous Quality Control

“ Our expert dissertation writers can help you with all stages of the dissertation writing process including topic research and selection, dissertation plan, dissertation proposal , methodology , statistical analysis , primary and secondary research, findings and analysis and complete dissertation writing. “
Tip: Make sure to highlight key points to help readers figure out the scope and findings of your research study without having to read the entire dissertation. The abstract is your first chance to impress your readers. So, make sure to get it right. Here are detailed guidelines on how to write abstract for dissertation .
Table of Contents
Table of contents is the section of a dissertation that guides each section of the dissertation paper’s contents. Depending on the level of detail in a table of contents, the most useful headings are listed to provide the reader the page number on which said information may be found at.
Table of contents can be inserted automatically as well as manually using the Microsoft Word Table of Contents feature.
List of Figures and Tables
If your dissertation paper uses several illustrations, tables and figures, you might want to present them in a numbered list in a separate section . Again, this list of tables and figures can be auto-created and auto inserted using the Microsoft Word built-in feature.
List of Abbreviations
Dissertations that include several abbreviations can also have an independent and separate alphabetised list of abbreviations so readers can easily figure out their meanings.
If you think you have used terms and phrases in your dissertation that readers might not be familiar with, you can create a glossary that lists important phrases and terms with their meanings explained.
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with quantitative dissertations across a variety of STEM disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Introduction
Introduction chapter briefly introduces the purpose and relevance of your research topic.
Here, you will be expected to list the aim and key objectives of your research so your readers can easily understand what the following chapters of the dissertation will cover. A good dissertation introduction section incorporates the following information:
- It provides background information to give context to your research.
- It clearly specifies the research problem you wish to address with your research. When creating research questions , it is important to make sure your research’s focus and scope are neither too broad nor too narrow.
- it demonstrates how your research is relevant and how it would contribute to the existing knowledge.
- It provides an overview of the structure of your dissertation. The last section of an introduction contains an outline of the following chapters. It could start off with something like: “In the following chapter, past literature has been reviewed and critiqued. The proceeding section lays down major research findings…”
- Theoretical framework – under a separate sub-heading – is also provided within the introductory chapter. Theoretical framework deals with the basic, underlying theory or theories that the research revolves around.
All the information presented under this section should be relevant, clear, and engaging. The readers should be able to figure out the what, why, when, and how of your study once they have read the introduction. Here are comprehensive guidelines on how to structure the introduction to the dissertation .
“Overwhelmed by tight deadlines and tons of assignments to write? There is no need to panic! Our expert academics can help you with every aspect of your dissertation – from topic creation and research problem identification to choosing the methodological approach and data analysis.”
Literature Review
The literature review chapter presents previous research performed on the topic and improves your understanding of the existing literature on your chosen topic. This is usually organised to complement your primary research work completed at a later stage.
Make sure that your chosen academic sources are authentic and up-to-date. The literature review chapter must be comprehensive and address the aims and objectives as defined in the introduction chapter. Here is what your literature research chapter should aim to achieve:
- Data collection from authentic and relevant academic sources such as books, journal articles and research papers.
- Analytical assessment of the information collected from those sources; this would involve a critiquing the reviewed researches that is, what their strengths/weaknesses are, why the research method they employed is better than others, importance of their findings, etc.
- Identifying key research gaps, conflicts, patterns, and theories to get your point across to the reader effectively.
While your literature review should summarise previous literature, it is equally important to make sure that you develop a comprehensible argument or structure to justify your research topic. It would help if you considered keeping the following questions in mind when writing the literature review:
- How does your research work fill a certain gap in exiting literature?
- Did you adopt/adapt a new research approach to investigate the topic?
- Does your research solve an unresolved problem?
- Is your research dealing with some groundbreaking topic or theory that others might have overlooked?
- Is your research taking forward an existing theoretical discussion?
- Does your research strengthen and build on current knowledge within your area of study? This is otherwise known as ‘adding to the existing body of knowledge’ in academic circles.
Tip: You might want to establish relationships between variables/concepts to provide descriptive answers to some or all of your research questions. For instance, in case of quantitative research, you might hypothesise that variable A is positively co-related to variable B that is, one increases and so does the other one.
Research Methodology
The methods and techniques ( secondary and/or primar y) employed to collect research data are discussed in detail in the Methodology chapter. The most commonly used primary data collection methods are:
- questionnaires
- focus groups
- observations
Essentially, the methodology chapter allows the researcher to explain how he/she achieved the findings, why they are reliable and how they helped him/her test the research hypotheses or address the research problem.
You might want to consider the following when writing methodology for the dissertation:
- Type of research and approach your work is based on. Some of the most widely used types of research include experimental, quantitative and qualitative methodologies.
- Data collection techniques that were employed such as questionnaires, surveys, focus groups, observations etc.
- Details of how, when, where, and what of the research that was conducted.
- Data analysis strategies employed (for instance, regression analysis).
- Software and tools used for data analysis (Excel, STATA, SPSS, lab equipment, etc.).
- Research limitations to highlight any hurdles you had to overcome when carrying our research. Limitations might or might not be mentioned within research methodology. Some institutions’ guidelines dictate they be mentioned under a separate section alongside recommendations.
- Justification of your selection of research approach and research methodology.
Here is a comprehensive article on how to structure a dissertation methodology .
Research Findings
In this section, you present your research findings. The dissertation findings chapter is built around the research questions, as outlined in the introduction chapter. Report findings that are directly relevant to your research questions.
Any information that is not directly relevant to research questions or hypotheses but could be useful for the readers can be placed under the Appendices .
As indicated above, you can either develop a standalone chapter to present your findings or combine them with the discussion chapter. This choice depends on the type of research involved and the academic subject, as well as what your institution’s academic guidelines dictate.
For example, it is common to have both findings and discussion grouped under the same section, particularly if the dissertation is based on qualitative research data.
On the other hand, dissertations that use quantitative or experimental data should present findings and analysis/discussion in two separate chapters. Here are some sample dissertations to help you figure out the best structure for your own project.
Sample Dissertation
Tip: Try to present as many charts, graphs, illustrations and tables in the findings chapter to improve your data presentation. Provide their qualitative interpretations alongside, too. Refrain from explaining the information that is already evident from figures and tables.
The findings are followed by the Discussion chapter , which is considered the heart of any dissertation paper. The discussion section is an opportunity for you to tie the knots together to address the research questions and present arguments, models and key themes.
This chapter can make or break your research.
The discussion chapter does not require any new data or information because it is more about the interpretation(s) of the data you have already collected and presented. Here are some questions for you to think over when writing the discussion chapter:
- Did your work answer all the research questions or tested the hypothesis?
- Did you come up with some unexpected results for which you have to provide an additional explanation or justification?
- Are there any limitations that could have influenced your research findings?
Here is an article on how to structure a dissertation discussion .
Conclusions corresponding to each research objective are provided in the Conclusion section . This is usually done by revisiting the research questions to finally close the dissertation. Some institutions may specifically ask for recommendations to evaluate your critical thinking.
By the end, the readers should have a clear apprehension of your fundamental case with a focus on what methods of research were employed and what you achieved from this research.
Quick Question: Does the conclusion chapter reflect on the contributions your research work will make to existing knowledge?
Answer: Yes, the conclusion chapter of the research paper typically includes a reflection on the research’s contributions to existing knowledge. In the “conclusion chapter”, you have to summarise the key findings and discuss how they add value to the existing literature on the current topic.
Reference list
All academic sources that you collected information from should be cited in-text and also presented in a reference list (or a bibliography in case you include references that you read for the research but didn’t end up citing in the text), so the readers can easily locate the source of information when/if needed.
At most UK universities, Harvard referencing is the recommended style of referencing. It has strict and specific requirements on how to format a reference resource. Other common styles of referencing include MLA, APA, Footnotes, etc.
Each chapter of the dissertation should have relevant information. Any information that is not directly relevant to your research topic but your readers might be interested in (interview transcripts etc.) should be moved under the Appendices section .
Things like questionnaires, survey items or readings that were used in the study’s experiment are mostly included under appendices.
An Outline of Dissertation/Thesis Structure
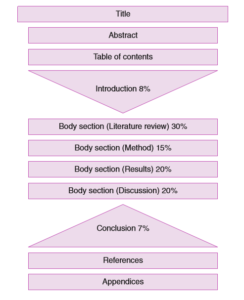
How can We Help you with your Dissertation?
If you are still unsure about how to structure a dissertation or thesis, or simply lack the motivation to kick start your dissertation project, you might be interested in our dissertation services .
If you are still unsure about how to structure a dissertation or thesis, or lack the motivation to kick start your dissertation project, you might be interested in our dissertation services.
Whether you need help with individual chapters, proposals or the full dissertation paper, we have PhD-qualified writers who will write your paper to the highest academic standard. ResearchProspect is UK-based, and a UK-registered business, which means the UK consumer law protects all our clients.
All You Need to Know About Us Learn More About Our Dissertation Services
FAQs About Structure a Dissertation
What does the title page of a dissertation contain.
The title page will contain details of the author/researcher, research topic , degree program (the paper is to be submitted for) and research supervisor’s name(s). The name of your university, logo, student number and submission date can also be presented on the title page.
What is the purpose of adding acknowledgement?
The acknowledgements section allows you to thank those who helped you with your dissertation project. You might want to mention the names of your academic supervisor, family members, friends, God and participants of your study whose contribution and support enabled you to complete your work.
Can I omit the glossary from the dissertation?
Yes, but only if you think that your paper does not contain any terms or phrases that the reader might not understand. If you think you have used them in the paper, you must create a glossary that lists important phrases and terms with their meanings explained.
What is the purpose of appendices in a dissertation?
Any information that is not directly relevant to research questions or hypotheses but could be useful for the readers can be placed under the Appendices, such as questionnaire that was used in the study.
Which referencing style should I use in my dissertation?
You can use any of the referencing styles such as APA, MLA, and Harvard, according to the recommendation of your university; however, almost all UK institutions prefer Harvard referencing style .
What is the difference between references and bibliography?
References contain all the works that you read up and used and therefore, cited within the text of your thesis. However, in case you read on some works and resources that you didn’t end up citing in-text, they will be referenced in what is called a bibliography.
Additional readings might also be present alongside each bibliography entry for readers.
You May Also Like
This brief introductory section aims to deal with the definitions of two paradigms, positivism and post-positivism, as well as their importance in research.
Your dissertation introduction chapter provides detailed information on the research problem, significance of research, and research aim & objectives.
Here are the steps to make a theoretical framework for dissertation. You can define, discuss and evaluate theories relevant to the research problem.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on 14 February 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 11 November 2022.
A dissertation proposal describes the research you want to do: what it’s about, how you’ll conduct it, and why it’s worthwhile. You will probably have to write a proposal before starting your dissertation as an undergraduate or postgraduate student.
A dissertation proposal should generally include:
- An introduction to your topic and aims
- A literature review of the current state of knowledge
- An outline of your proposed methodology
- A discussion of the possible implications of the research
- A bibliography of relevant sources
Dissertation proposals vary a lot in terms of length and structure, so make sure to follow any guidelines given to you by your institution, and check with your supervisor when you’re unsure.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Step 1: coming up with an idea, step 2: presenting your idea in the introduction, step 3: exploring related research in the literature review, step 4: describing your methodology, step 5: outlining the potential implications of your research, step 6: creating a reference list or bibliography.
Before writing your proposal, it’s important to come up with a strong idea for your dissertation.
Find an area of your field that interests you and do some preliminary reading in that area. What are the key concerns of other researchers? What do they suggest as areas for further research, and what strikes you personally as an interesting gap in the field?
Once you have an idea, consider how to narrow it down and the best way to frame it. Don’t be too ambitious or too vague – a dissertation topic needs to be specific enough to be feasible. Move from a broad field of interest to a specific niche:
- Russian literature 19th century Russian literature The novels of Tolstoy and Dostoevsky
- Social media Mental health effects of social media Influence of social media on young adults suffering from anxiety
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Like most academic texts, a dissertation proposal begins with an introduction . This is where you introduce the topic of your research, provide some background, and most importantly, present your aim , objectives and research question(s) .
Try to dive straight into your chosen topic: What’s at stake in your research? Why is it interesting? Don’t spend too long on generalisations or grand statements:
- Social media is the most important technological trend of the 21st century. It has changed the world and influences our lives every day.
- Psychologists generally agree that the ubiquity of social media in the lives of young adults today has a profound impact on their mental health. However, the exact nature of this impact needs further investigation.
Once your area of research is clear, you can present more background and context. What does the reader need to know to understand your proposed questions? What’s the current state of research on this topic, and what will your dissertation contribute to the field?
If you’re including a literature review, you don’t need to go into too much detail at this point, but give the reader a general sense of the debates that you’re intervening in.
This leads you into the most important part of the introduction: your aim, objectives and research question(s) . These should be clearly identifiable and stand out from the text – for example, you could present them using bullet points or bold font.
Make sure that your research questions are specific and workable – something you can reasonably answer within the scope of your dissertation. Avoid being too broad or having too many different questions. Remember that your goal in a dissertation proposal is to convince the reader that your research is valuable and feasible:
- Does social media harm mental health?
- What is the impact of daily social media use on 18– to 25–year–olds suffering from general anxiety disorder?
Now that your topic is clear, it’s time to explore existing research covering similar ideas. This is important because it shows you what is missing from other research in the field and ensures that you’re not asking a question someone else has already answered.
You’ve probably already done some preliminary reading, but now that your topic is more clearly defined, you need to thoroughly analyse and evaluate the most relevant sources in your literature review .
Here you should summarise the findings of other researchers and comment on gaps and problems in their studies. There may be a lot of research to cover, so make effective use of paraphrasing to write concisely:
- Smith and Prakash state that ‘our results indicate a 25% decrease in the incidence of mechanical failure after the new formula was applied’.
- Smith and Prakash’s formula reduced mechanical failures by 25%.
The point is to identify findings and theories that will influence your own research, but also to highlight gaps and limitations in previous research which your dissertation can address:
- Subsequent research has failed to replicate this result, however, suggesting a flaw in Smith and Prakash’s methods. It is likely that the failure resulted from…
Next, you’ll describe your proposed methodology : the specific things you hope to do, the structure of your research and the methods that you will use to gather and analyse data.
You should get quite specific in this section – you need to convince your supervisor that you’ve thought through your approach to the research and can realistically carry it out. This section will look quite different, and vary in length, depending on your field of study.
You may be engaged in more empirical research, focusing on data collection and discovering new information, or more theoretical research, attempting to develop a new conceptual model or add nuance to an existing one.
Dissertation research often involves both, but the content of your methodology section will vary according to how important each approach is to your dissertation.
Empirical research
Empirical research involves collecting new data and analysing it in order to answer your research questions. It can be quantitative (focused on numbers), qualitative (focused on words and meanings), or a combination of both.
With empirical research, it’s important to describe in detail how you plan to collect your data:
- Will you use surveys ? A lab experiment ? Interviews?
- What variables will you measure?
- How will you select a representative sample ?
- If other people will participate in your research, what measures will you take to ensure they are treated ethically?
- What tools (conceptual and physical) will you use, and why?
It’s appropriate to cite other research here. When you need to justify your choice of a particular research method or tool, for example, you can cite a text describing the advantages and appropriate usage of that method.
Don’t overdo this, though; you don’t need to reiterate the whole theoretical literature, just what’s relevant to the choices you have made.
Moreover, your research will necessarily involve analysing the data after you have collected it. Though you don’t know yet what the data will look like, it’s important to know what you’re looking for and indicate what methods (e.g. statistical tests , thematic analysis ) you will use.
Theoretical research
You can also do theoretical research that doesn’t involve original data collection. In this case, your methodology section will focus more on the theory you plan to work with in your dissertation: relevant conceptual models and the approach you intend to take.
For example, a literary analysis dissertation rarely involves collecting new data, but it’s still necessary to explain the theoretical approach that will be taken to the text(s) under discussion, as well as which parts of the text(s) you will focus on:
- This dissertation will utilise Foucault’s theory of panopticism to explore the theme of surveillance in Orwell’s 1984 and Kafka’s The Trial…
Here, you may refer to the same theorists you have already discussed in the literature review. In this case, the emphasis is placed on how you plan to use their contributions in your own research.
You’ll usually conclude your dissertation proposal with a section discussing what you expect your research to achieve.
You obviously can’t be too sure: you don’t know yet what your results and conclusions will be. Instead, you should describe the projected implications and contribution to knowledge of your dissertation.
First, consider the potential implications of your research. Will you:
- Develop or test a theory?
- Provide new information to governments or businesses?
- Challenge a commonly held belief?
- Suggest an improvement to a specific process?
Describe the intended result of your research and the theoretical or practical impact it will have:
Finally, it’s sensible to conclude by briefly restating the contribution to knowledge you hope to make: the specific question(s) you hope to answer and the gap the answer(s) will fill in existing knowledge:
Like any academic text, it’s important that your dissertation proposal effectively references all the sources you have used. You need to include a properly formatted reference list or bibliography at the end of your proposal.
Different institutions recommend different styles of referencing – commonly used styles include Harvard , Vancouver , APA , or MHRA . If your department does not have specific requirements, choose a style and apply it consistently.
A reference list includes only the sources that you cited in your proposal. A bibliography is slightly different: it can include every source you consulted in preparing the proposal, even if you didn’t mention it in the text. In the case of a dissertation proposal, a bibliography may also list relevant sources that you haven’t yet read, but that you intend to use during the research itself.
Check with your supervisor what type of bibliography or reference list you should include.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 11). How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved 18 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/proposal/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, what is a dissertation | 5 essential questions to get started, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.

by Yeonho Lee (MArch II ’24)…
Grace La and James Dallman , Faculty Advisors
Spring 2024

Learning from Quartzsite, AZ: Emerging Nomadic Spatial Practices in America
by Mojtaba Nabavi (MAUD ’24) Quartzsite, in Arizona, is a popular winter home base…
Rahul Mehrotra and Eve Blau , Faculty Advisors
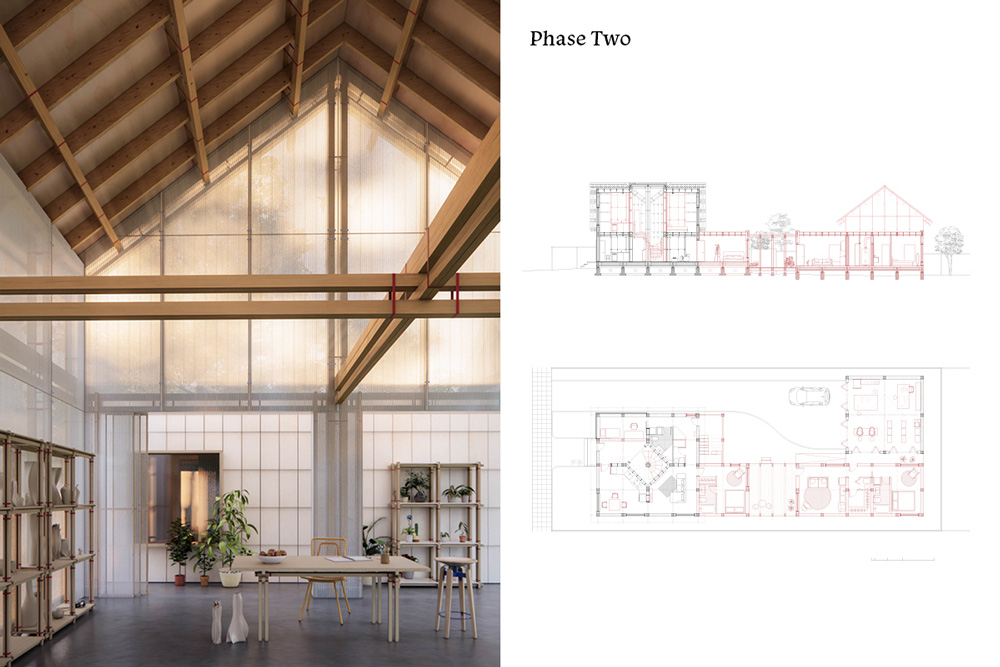
How to (Un)build a House? A Reinvention of Wood Framing
by Clara Mu He (MArch I…
Toshiko Mori , Faculty Advisor
Seeding Grounds: Working Beyond Arcadia in The Pyrocene
by Stewart Crane Sarris (MLA I ’24) From drought, to fire, Australia’s landscapes face multiple existential…
Craig Douglas , Faculty Advisor
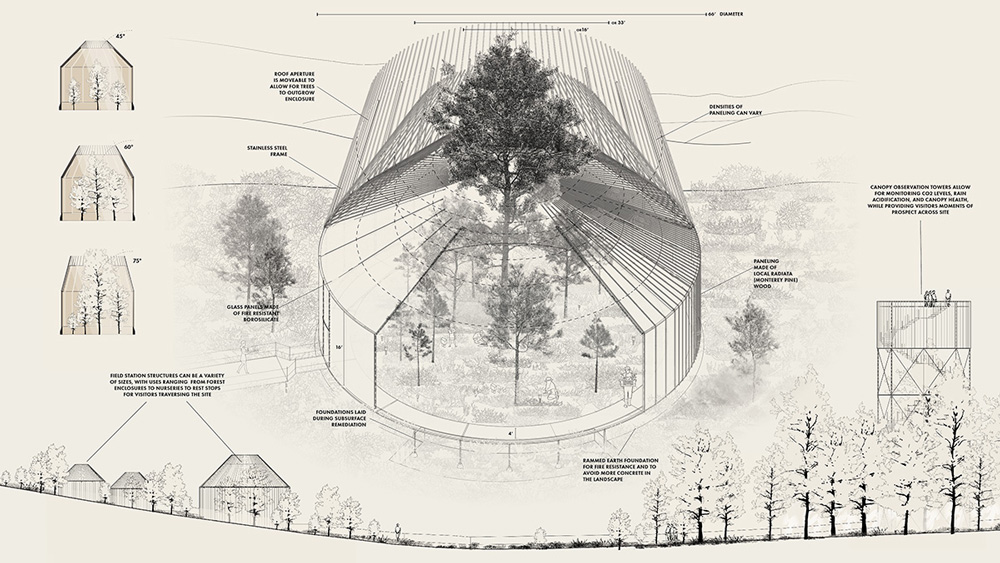
Reforesting Fort Ord
by Slide Kelly (MLA I AP, MDes ’24) This thesis examines the potential for…
Amy Whitesides , Faculty Advisor

Project Kin
by Priyanka Pillai (MDE ’24) and Julius Stein (MDE ’24) When conflict arises from humanitarian crises, families…
Kathleen Brandenburg and Karen Reuther , Faculty Advisors

INSURGENT GEOLOGY: Mineral Matters in the Arctic
by Melanie Louterbach (MLA I ’24) “Insurgent Geology” is about oil, fossils, power, and people.

KEUR FÀTTALIKU — The House of Recollection
by Mariama Muhammadou Modou Kah (MArch II…
Rahul Mehrotra , Faculty Advisor
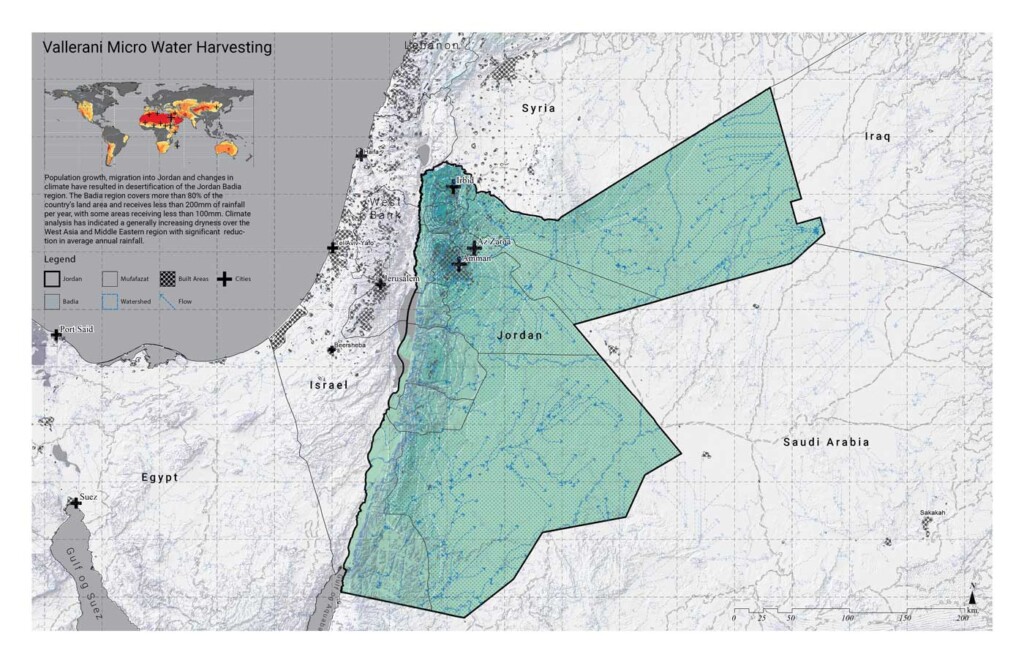
Vallerani Micro Water Harvesting
The Badia Region covers more than 80% of Jordan and receives less than 8 inches…
Amy Whitesides and Kira Clingen , Faculty Advisors
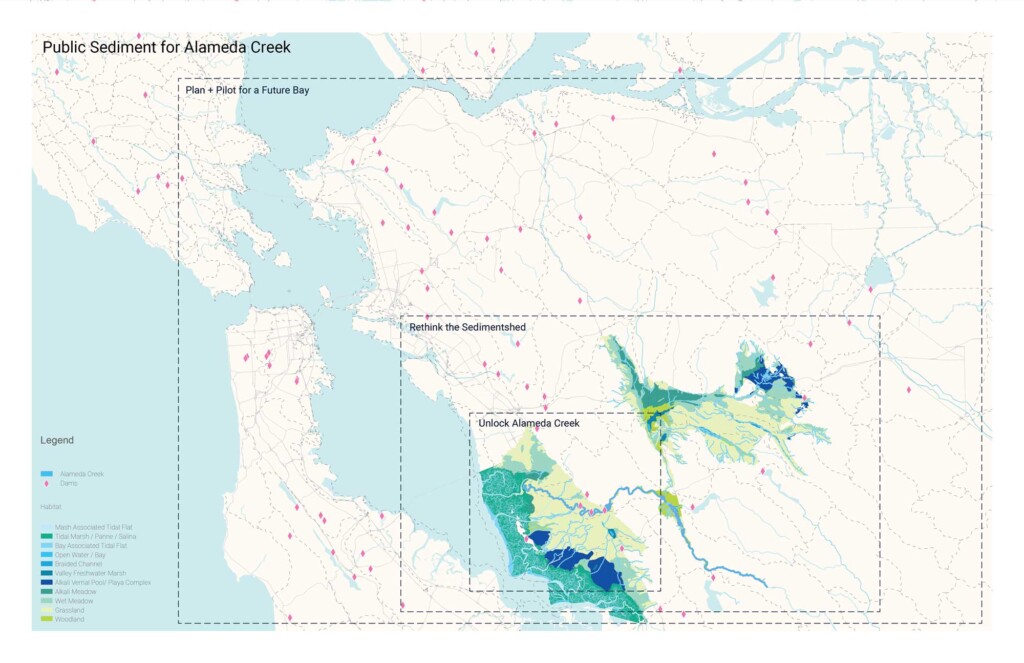
Public Sediment for Alameda Creek
Resilient by Design was the Bay Area’s year-long collaborative design challenge for resilience to sea…
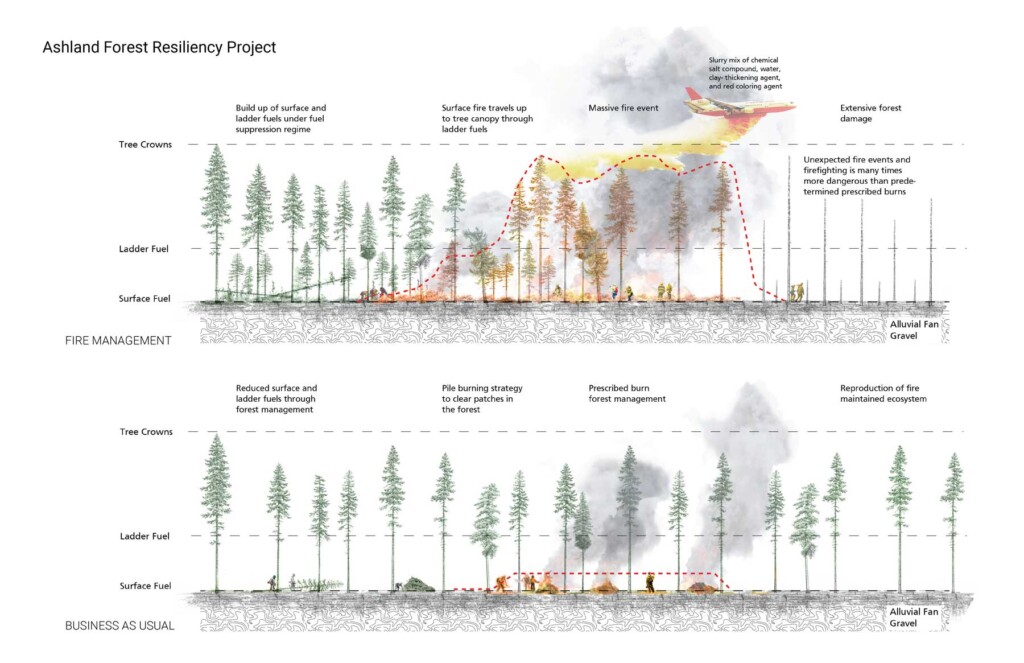
Ashland Forest Resiliency Project
The Ashland Forest Resiliency Stewardship Project is an ongoing collaboration since 2010 between the Lomakatsi…

TransMilenio and Bikeways
Enrique Peñalosa, was a two-term mayor of Bogotá. He served from 1998 to 2001 and…

Chagga Homegardens
Homegardens are subsistence gardens that provide a supplemental source of food and nutritional security in…
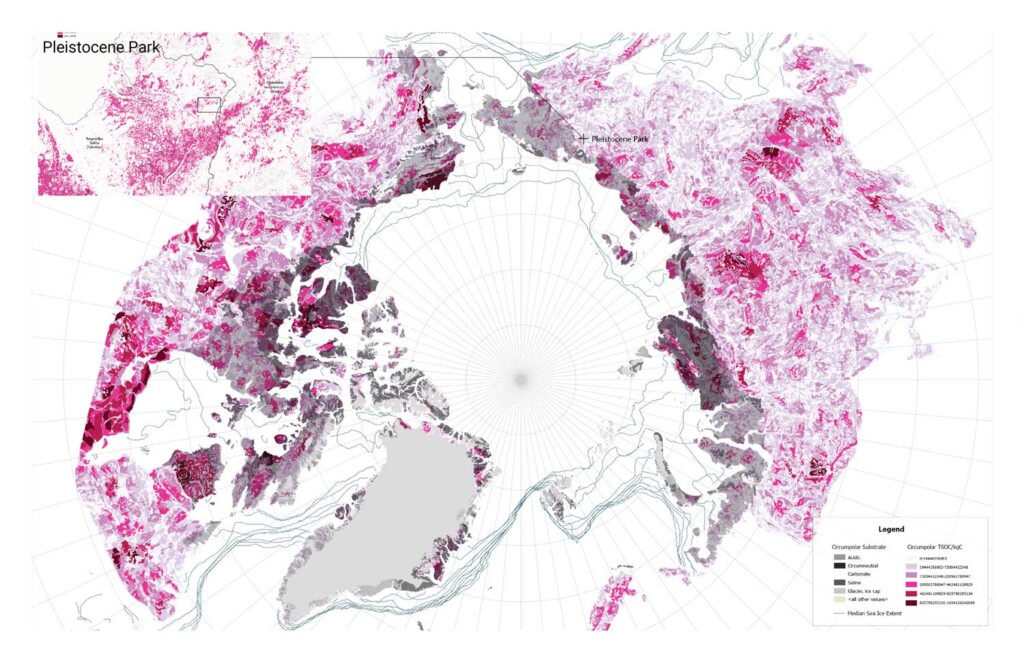
Pleistocene Park
At the end of the Pleistocene, the steppe ecosystem was dominant across the planet, with…
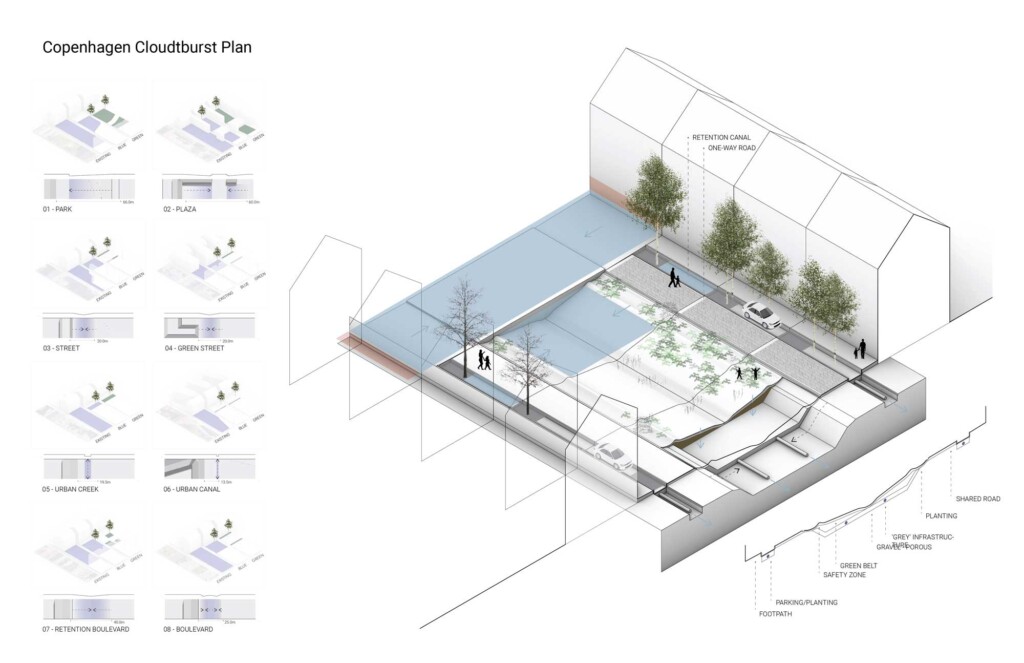
Copenhagen Cloudburst Plan
In 2011, Copenhagen was struck by a 1,000-year storm event, a Cloudburst, that flooded the…
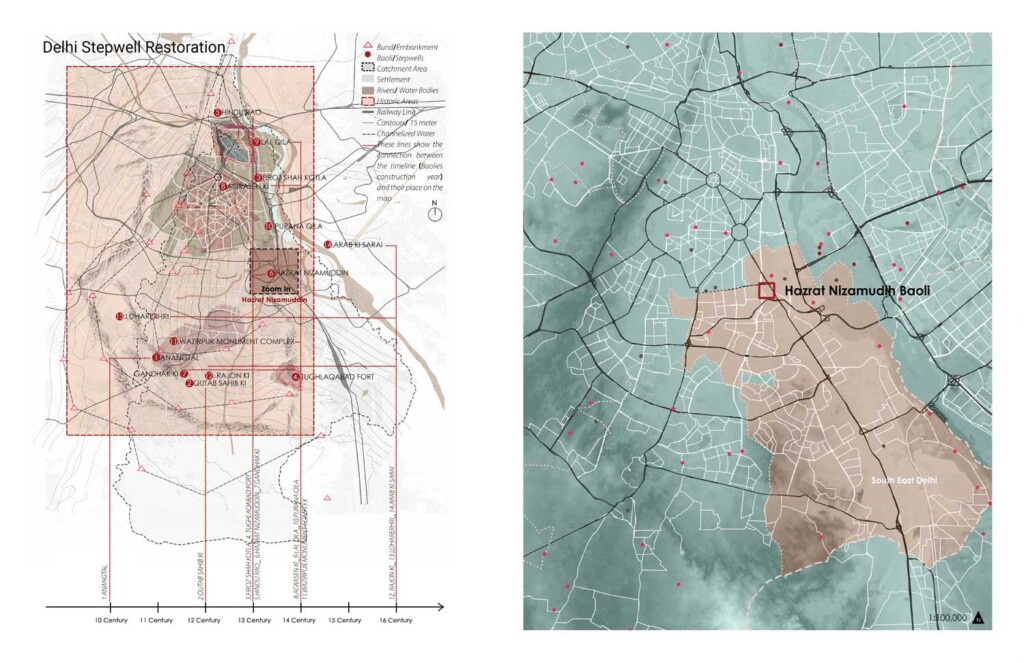
Delhi Stepwell Restoration
Baolis, or stepwells, are underground reservoirs where water can be stored close to the groundwater…
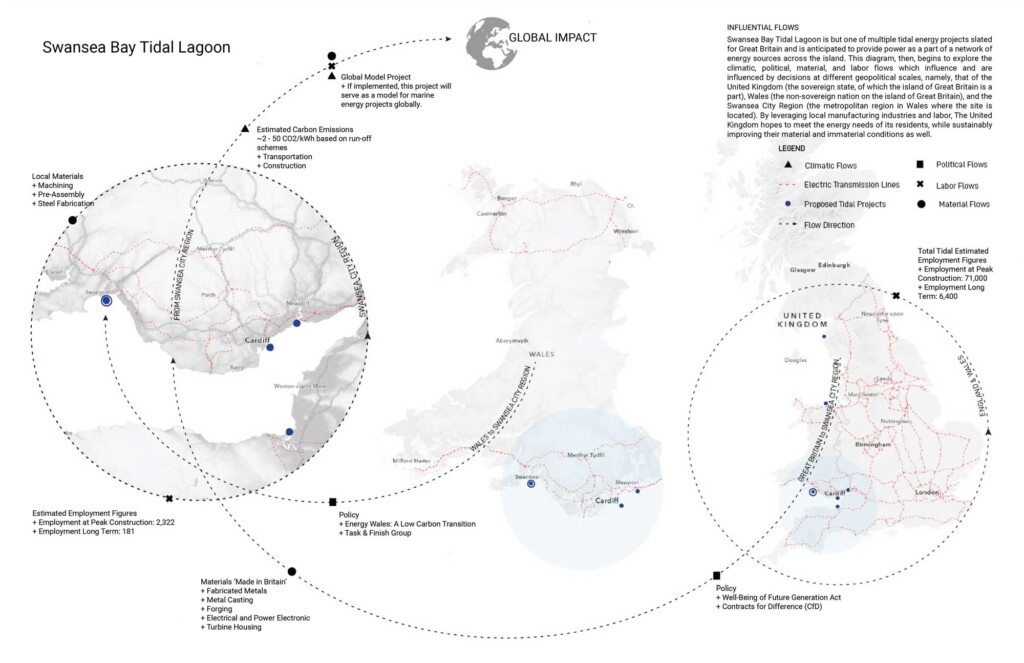
Swansea Bay Lagoon
Swansea Bay was once home to a thriving oyster industry that employed 600 residents in…

2023 Peter Rice Prize: Sujie Park’s “Material Alchemy”
by Sujie Park (MArch I ’23) — Recipient of the Peter Rice Prize. The history…
Andrew Witt and Martin Bechthold , Faculty Advisors
Spring 2023
Student Work
2023 Digital Design Prize: Amelia Gan’s “Place-Time: From Waste to 3D CAD, or, Framework for geographical and temporally conscious design”
by Amelia Gan (MDes ’23) — Recipient of the Digital Design Prize. The dominance of…
Andrew Witt and Allen Sayegh , Faculty Advisors

2023 Clifford Wong Prize in Housing Design: Randy Crandon and Maddie Farrer
Sidewalk Stuff: Adaptive Reuse Cohousing by Randy Crandon (MArch I ’25) and Maddie Farrer (MArch…
Jenny French , Instructor

2023 Urban Planning Thesis Prize: Michael Zajakowski Uhll’s “Our History is our Resource:” Historic Narrative as Urban Planning Strategy in Chicago’s Pullman Neighborhood
by Michael Zajakowski Uhll (MUP ’23) — Recipient of the Urban Planning Thesis Prize. How…
Rachel Meltzer , Faculty Advisor
2023 James Templeton Kelley Prize: Jacqueline Wong’s “An Intrinsic Model for a Non-Neutral Plural National School”
by Jacqueline Wong (MArch I ’23) — Recipient of the James Templeton Kelley Prize, Master…
Sergio Lopez-Pineiro, Faculty Advisor


2023 Urban Design Thesis Prize: Saad Boujane’s “Dwellings, Paths, Places: Configurative Habitat in Casablanca, Morocco “
by Saad Boujane (MAUD ’23) — Recipient of the Urban Design Thesis Prize. The Modernist…
Peter Rowe , Faculty Advisor

2023 Landscape Architecture AP Thesis Prize and 2023 Digital Design Prize: Sonia Sobrino Ralston’s “Uncommon Knowledge: Practices and Protocols for Environmental Information”
by Sonia Sobrino Ralston (MLA I AP ’23) — Recipient of the Landscape Architecture AP…
Rosalea Monacella , Faculty Advisor
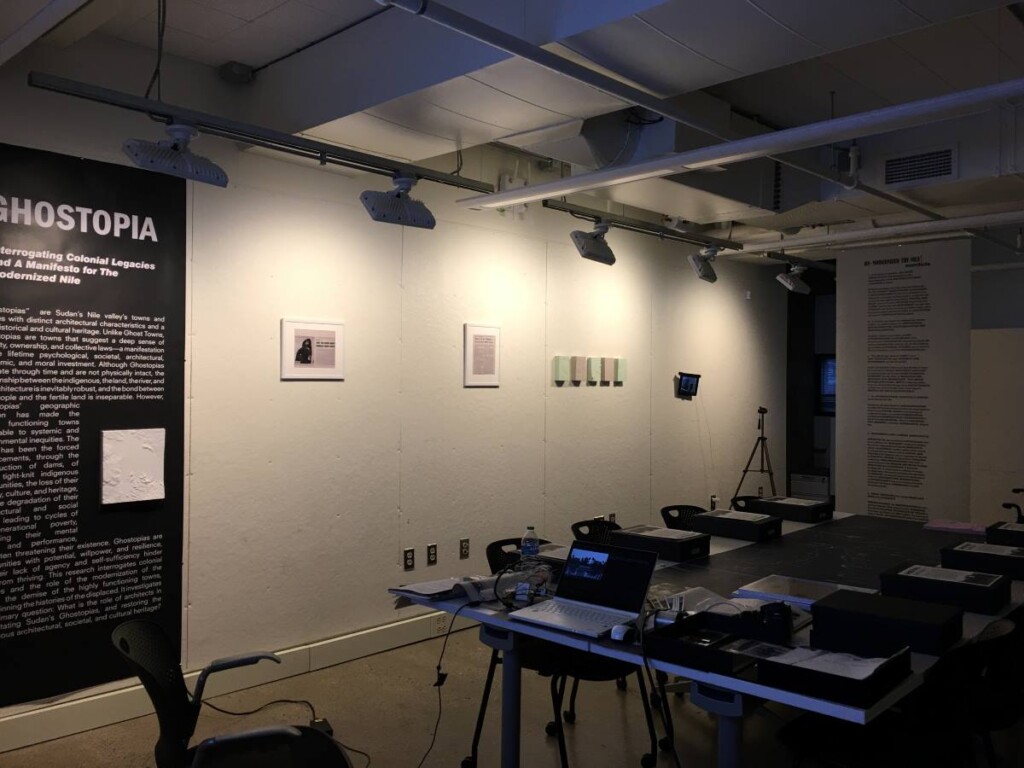

2023 Design Studies Thesis Prize: Alaa Suliman Eltayeb Mohamed Hamid’s Ghostopia: Interrogating Colonial Legacies and A Manifesto for The Modernized Nile
by Alaa Suliman Eltayeb Mohamed Hamid (MDes ’23) — Recipient of the Design Studies Thesis…
Montserrat Bonvehi Rosich, Faculty Advisor
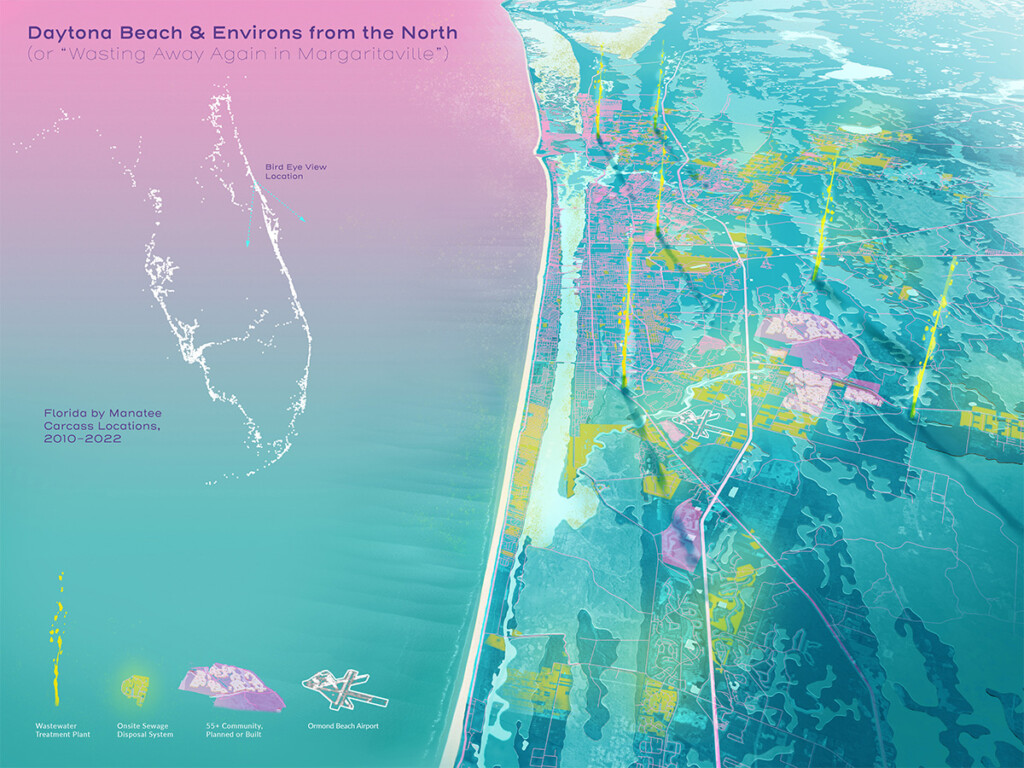
2023 Landscape Architecture Thesis Prize: Kevin Robishaw’s Manatees and Margaritas: Toward a Strange New Paradise
by Kevin Robishaw (MLA I ’23) — Recipient of the Landscape Architecture Thesis Prize.
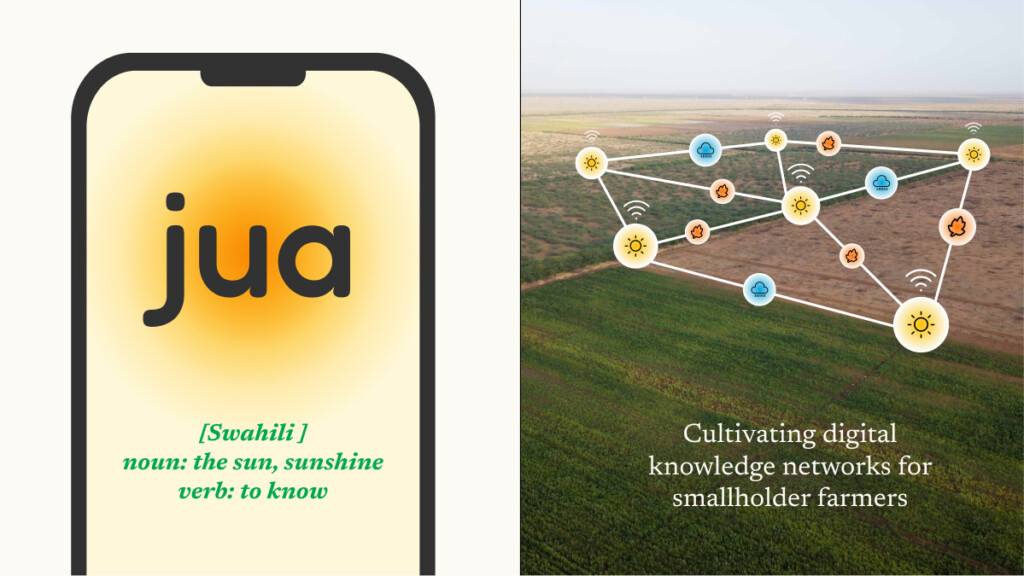
2023 Outstanding Design Engineering Project Award: Rebecca Brand and Caroline Fong’s Jua: Cultivating Digital Knowledge Networks for Smallholder Farmers
by Rebecca Brand (MDE ’23) and…
Jock Herron , Faculty Advisor
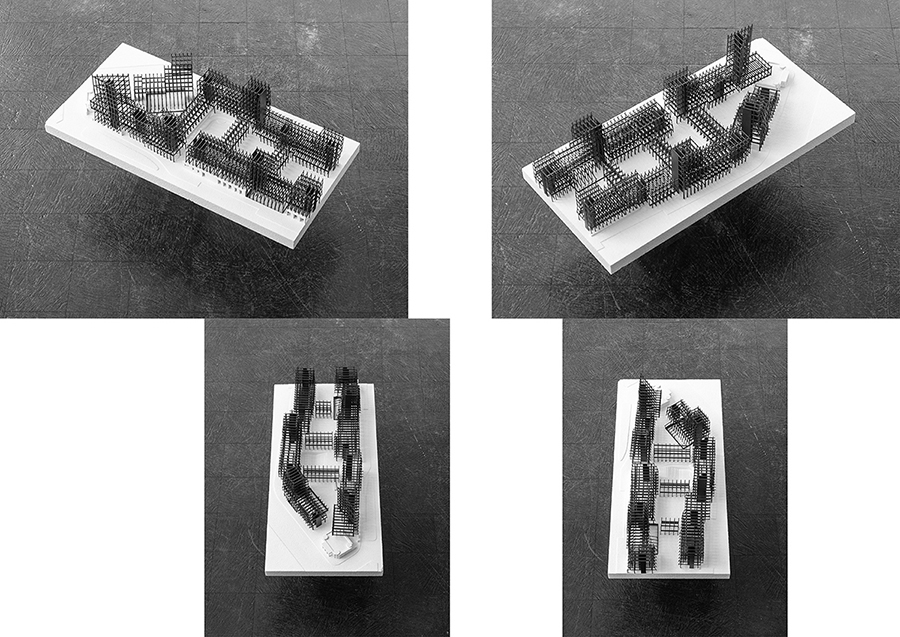
2023 James Templeton Kelley Prize: Deok Kyu Chung’s “Boundaries of Everyday: walls to voids, voids to solids, solids to walls”
by Deok Kyu Chung (MArch II ’23) — Recipient of the James Templeton Kelley Prize,…
Lyndon Neri and Rossana Hu, Faculty Advisors
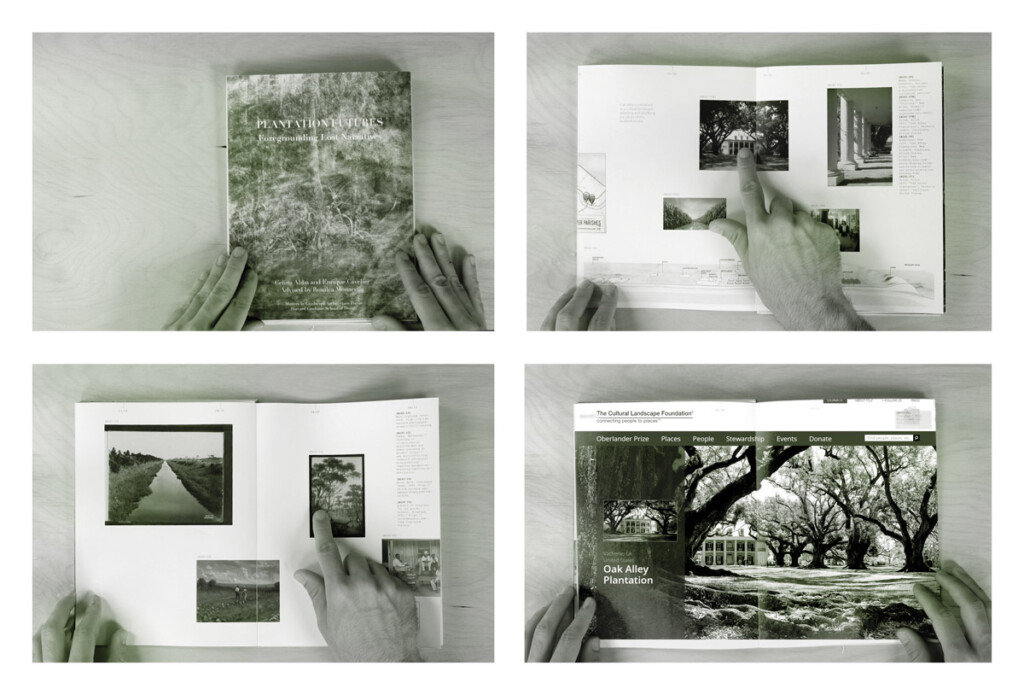

2023 Landscape Architecture AP Thesis Prize: Celina Abba and Enrique Cavelier’s Plantation Futures: Foregrounding Lost Narratives
by Celina Abba (MLA I AP ’23) and Enrique…
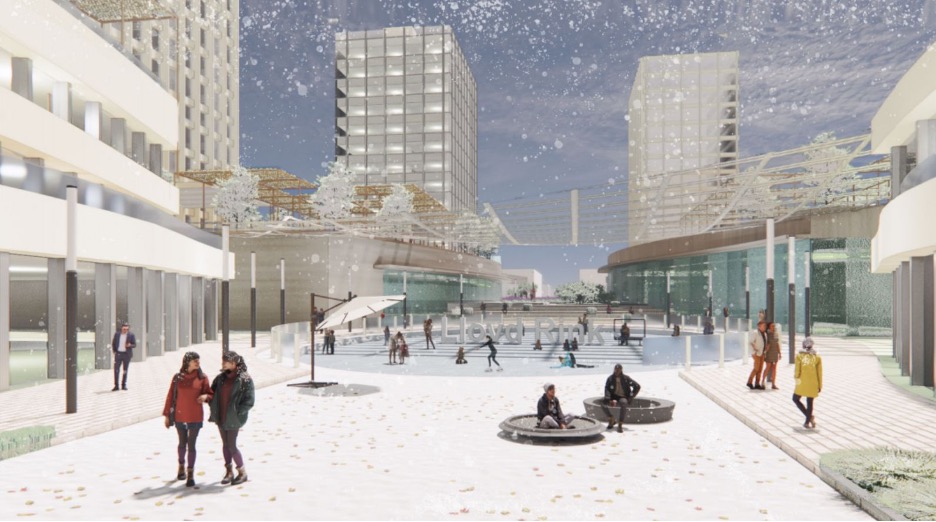

2023 Plimpton-Poorvu Design Prize, Honorable Mention: “Truly, Oregon! Empower Lloyd Center, Portland, OR”
by Heejin Park (MAUD ’23), Terry Kim (MUP ’23), Aelin Shaoyu Li (MDes ’24), Claire…
Richard Peiser , Instructor
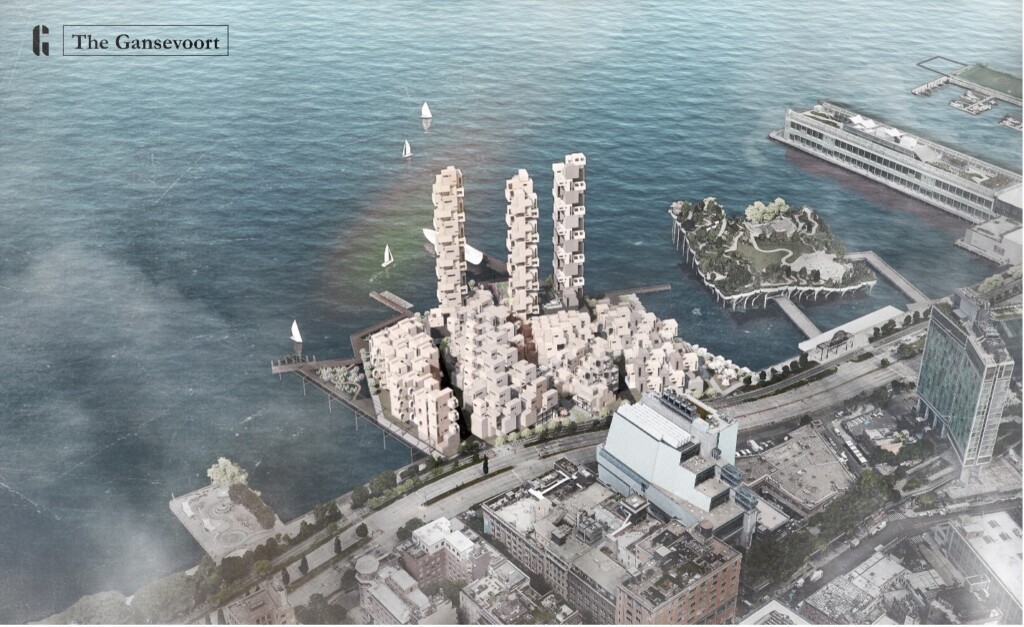

2023 Plimpton-Poorvu Design Prize, First Prize: “The Gansevoort: Design for Longevity”
by Xinxin Cheryl Lin (MArch II ’24), Vivian Cheng (MAUD ’23), and Pinyang Paul Chen…
Ben van Berkel and Dana Behrman, Instructors
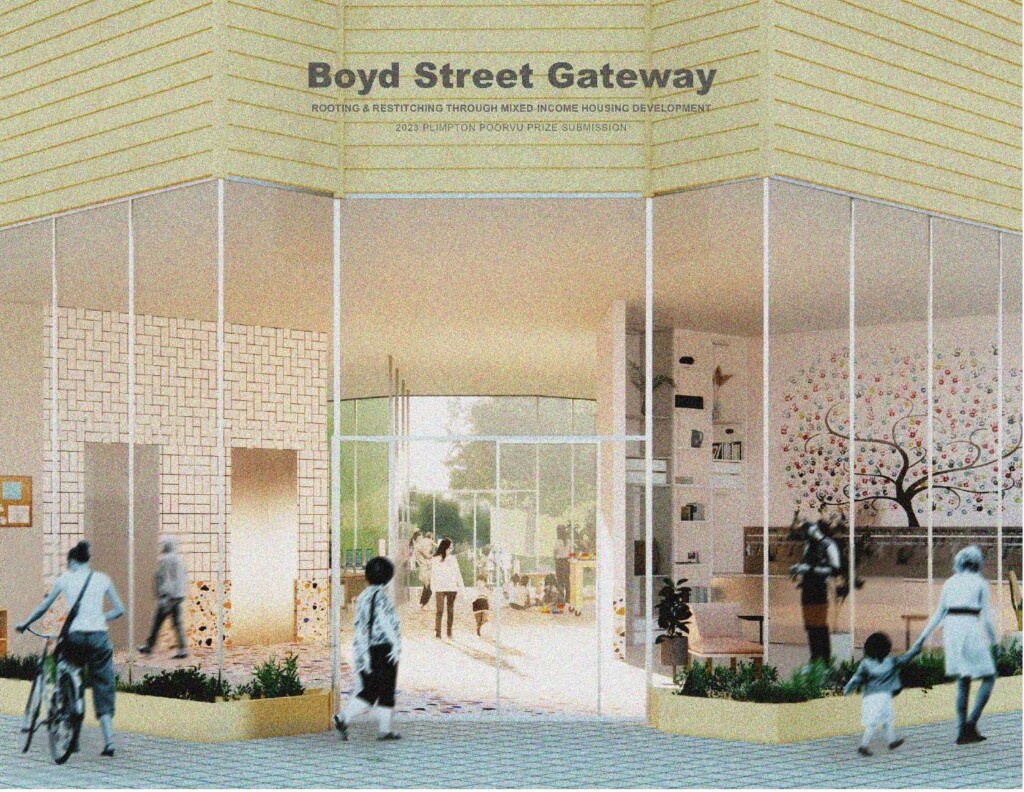

2023 Plimpton-Poorvu Design Prize, Second Prize: “Boyd Street Gateway”
by Maddie Farrer (MArch I ‘25), Madeleine Levin (MUP ‘23), and Arielle Rawlings (MUP ‘23)…
Edward Marchant, Instructor
Spring 2022
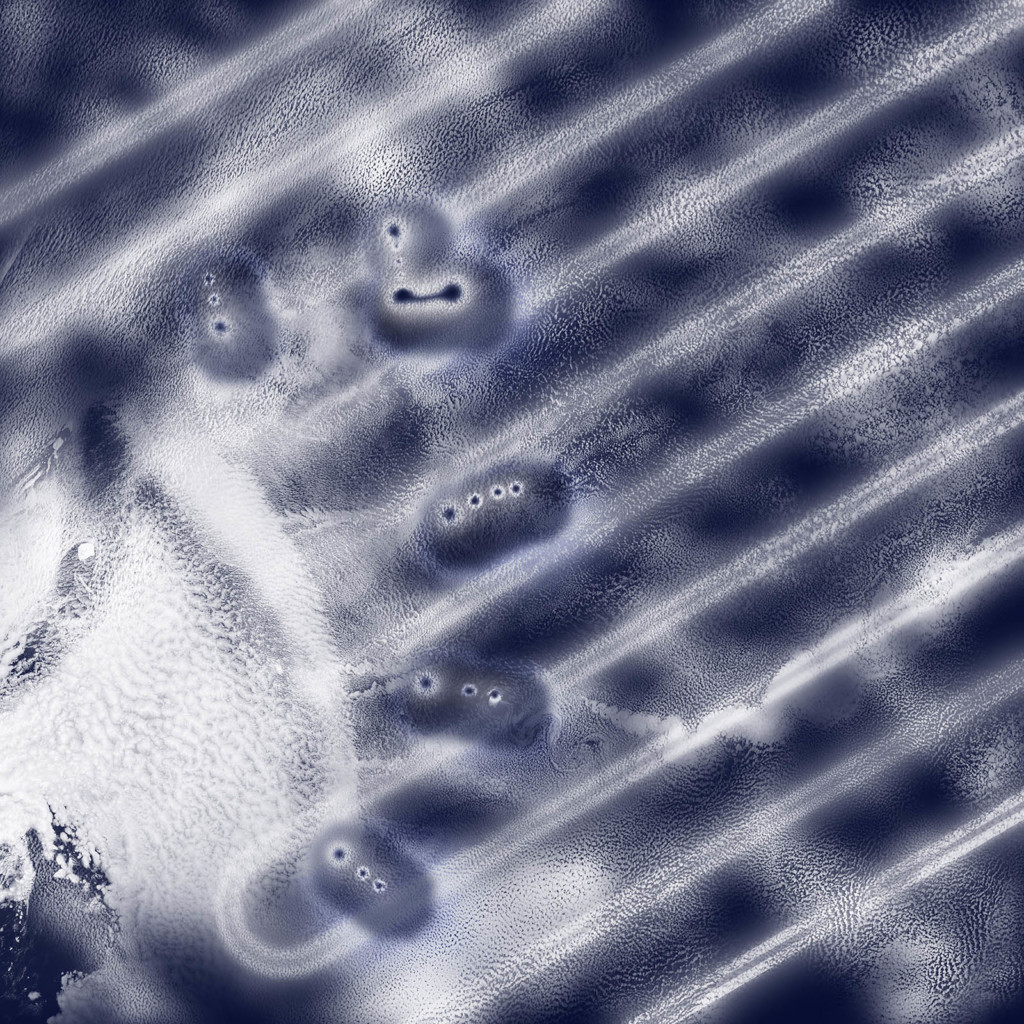
2022 Landscape Architecture Thesis Prize: Liwei Shen’s “The Echoes of Sky River – Two Pre-modern and Modern Atmospheric Assemblages”
by Liwei Shen (MLA I ’22) — Recipient of the Landscape Architecture Thesis Prize. The…

2022 James Templeton Kelley Prize: Remi McClain’s “There Goes the Neighborhood”
by Remi McClain (MArch II ’22) — Recipient of the James Templeton Kelley Prize, Master…
Mark Lee and Erika Naginski , Faculty Advisors
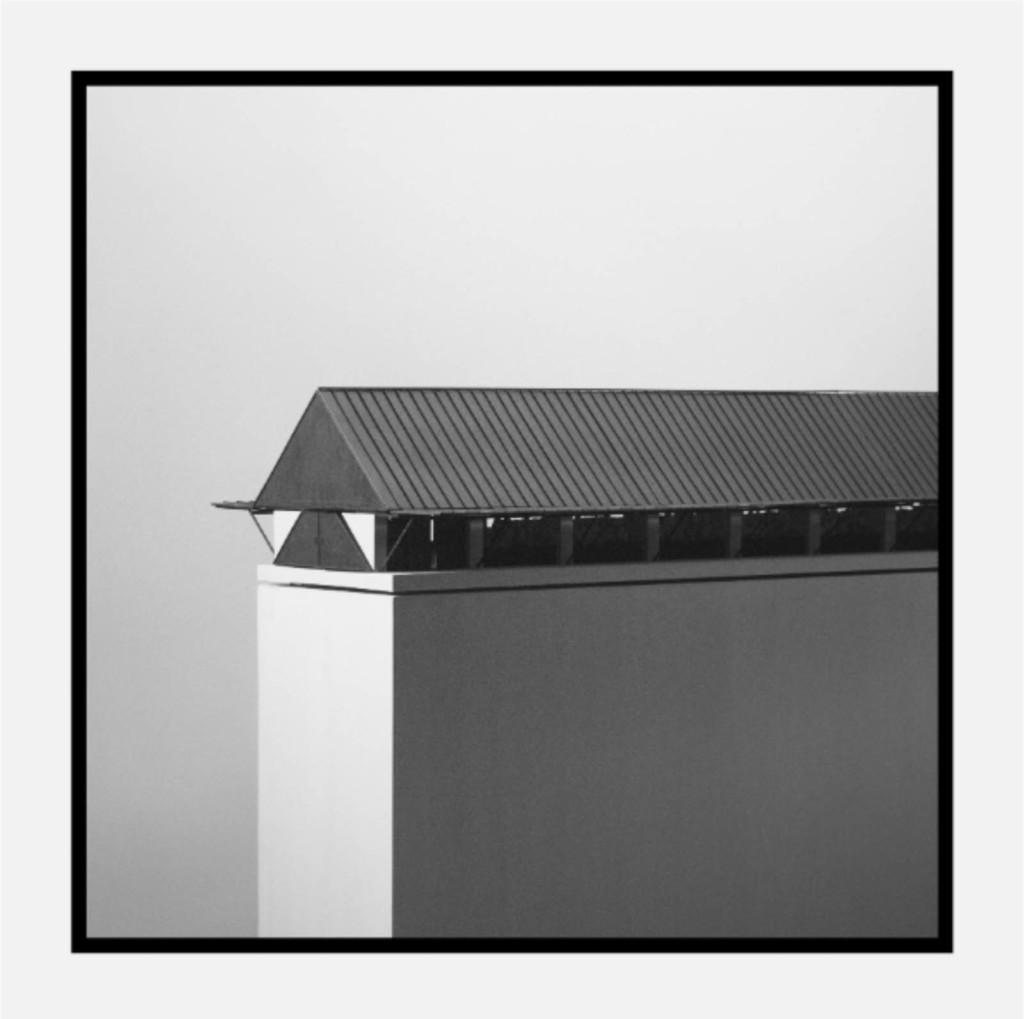

2022 James Templeton Kelley Prize: Isaac Henry Pollan’s “This Is Not A Firehouse”
by Isaac Henry Pollan (MArch I ’22) — Recipient of the James Templeton Kelley Prize,…
Sean Canty , Faculty Advisor

2022 Clifford Wong Prize in Housing Design: Brian Lee’s “People’s Park Complex: Repairing the Modern City”
by Brian Lee (MArch ’22) — Recipient of the 2021 Clifford Wong Prize in…
Grace La and Jenny French , Faculty Advisors

2022 Peter Rice Prize: Hangsoo Jeong’s “Upon Concrete: Retrofitting Architecture with Malleability”
by Hangsoo Jeong (MArch ’22) — Recipient of the Peter Rice Prize Upon Concrete:…
Mark Lee, Faculty Advisor
2022 Digital Design Prize: George Guida’s “Multimodal Architecture: Applications of Language in a Machine Learning Aided Design Process”
by George Guida (MArch II ’22) — Recipient of the Digital Design Prize. This thesis…
Andrew Witt and Jose Luis Garcia del Castillo Lopez , Faculty Advisors
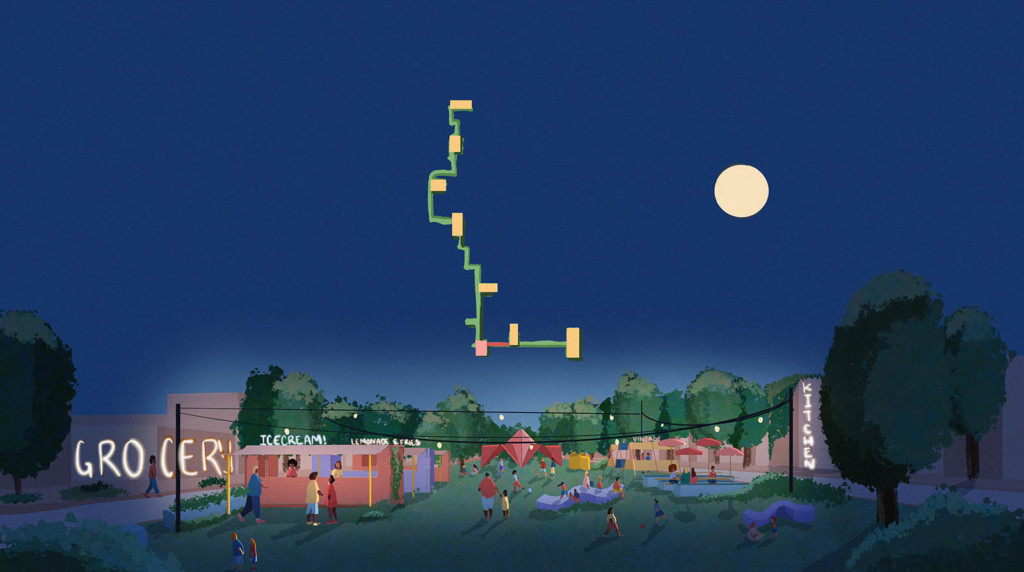

2022 Urban Design Thesis Prize: Rogelio Cadena’s “How Are ‘We’ Living? Reevaluating the Chicago Boulevard System”
by Rogelio Cadena (MAUD ’22) — Recipient of the Urban Design Thesis Prize. At its…
Stephen Gray , Faculty Advisor
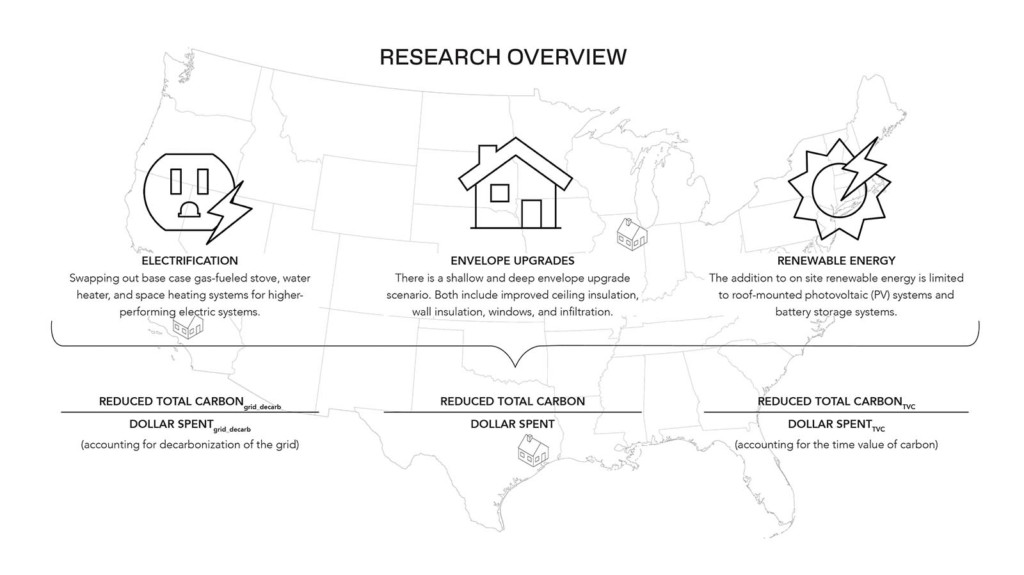
2022 Design Studies Thesis Prize: Allison Hyatt’s “Priorities in Building Decarbonization: Accounting for total carbon and the time value of carbon in cost-benefit analyses of residential retrofits”
by Allison Hyatt (MDes ’22) — Recipient of the Design Studies Thesis Prize. Energy consumption…
Holly Samuelson , Faculty Advisor
Pagination Links
- Go to page 2
- Go to page 3
- Go to page 4
- Go to page 5
- Go to page 6
- Go to page 7
- Go to page 8
- Go to page 9
- Page …
- Go to page 16

- Schools & departments

Dissertations / work based projects
Advice and resources to support you throughout your dissertation or work based project.
Dissertations and research projects
This is a general resource to help you with the basics of organising and writing a research-based dissertation or project. The Go further section at the end includes advice on work-based dissertations and signposts other resources.
You should consult your course or programme handbook, including online sources, and project supervisor or programme director for subject-specific guidance.
Dissertations and research projects are an opportunity to focus on particular question, and plan and undertake your own research to explore it further. Many students really enjoy being an independent researcher and becoming the expert on their work. The format varies depending on the disciplinary context, subject area, your research questions and the project. You may be reviewing the literature, analysing a novel, developing and testing a new method or doing a work-based project. However there are some common factors:
- They are an independent piece of work. You will be working under supervision to some extent and may be collaborating with others, but ultimately you are submitting a piece of independent thought and writing.
- They tend to have a large word count. This is to allow you to do sufficient in-depth analysis and discussion of the topic.
- They require a large investment of time, thought and energy throughout the process. As a significant body of academic work, you need to maintain effort whilst reading, researching, thinking, writing and redrafting it.
Choosing your dissertation or project
Whether you are choosing your dissertation from a selection of topics or you are proposing your own, there are a range of factors to consider. For example:
- What is the starting point for your work, i.e. previous or related research?
- How feasible is your project / proposal?
- Do you have enough time and resources to complete it?
- Will it be of an appropriate academic level?
A key questions to ask is “How interested am I in this topic?” You will be working on your dissertation or project for some time, so having a genuine interest in the topic will help to keep you motivated. If you have any questions specific to your topic or project, you should ask your supervisor, programme director or another member of staff who teaches you.
Planning your dissertation or research project
A research-based dissertation or project is a large piece of work requiring a high level of critical analysis. To achieve this you will have to allow time, not just for the researching phase, but also for the writing and editing stages. You will need to give yourself plenty of time to:
- Read around your topic and undertake background research;
- Digest and think about what you are learning and writing;
- Complete experiments, fieldwork, interviews or project placements;
- Analyse data, findings or results, and interpret them;
- Think about and decide on your conclusions.
Taking a project management approach to your dissertation or research project might be a more effective way to successfully complete it. The Time management page has tips and tools for organising your time.
Time management webpage and tools
The dissertation and project planner can be used to think about the different stages and help give you an overall view of the process. There are some general points and questions to act as prompts, spaces you can add your own notes in and some useful tips and resources.
Dissertation and project planner (pdf )
Dissertation and project planner (rtf)
Writing your dissertation
You should not underestimate the time that should be allocated to writing your dissertation. Writing will involve planning, background research, drafting, redrafting, and proof-reading and editing.
First draft : Your first draft is about getting words on the page. For example, it may sketch out your first thoughts, arguments and potential structure. You can review these and use them to check: are you focussed on the right topics and questions? Is your structure and line of thought sensible? This is also a good time to set up your format requirements (e.g. page layouts, references)
Redrafts : Redrafting is where you expand and refine your ideas and argument. You may also find that as you are writing the direction of your argument changes; for example this could be due to your literature research producing new avenues of thought or your experiments turning up unexpected results. This is a good time to review the focus of your initial question, and whether your arguments or conclusions are still sensible)
Final draft(s) : In your final draft(s) is where you cast a critical eye over your work and assess how effective it is in communicating your argument and conclusions - does it answer the question? You should also check that you presentation, spelling and grammar are appropriate and polished, all your references are included, and it follows the appropriate format guidance, etc.
It is a good idea to take a break between writing and reviewing your work. Try to leave at least a day between writing before you pick it up again, the longer the better. This allows you to look at your work with an analytical eye, looking for ways to improve. Imagine you are reading your work as someone who is not so familiar with the topic: would a reader be able to follow and understand your argument? Do your ideas link? Have you signposted on from one section to the next? Remember also to look back at your question/title, does your dissertation address it? Does it follow a logical structure?
There are a variety of study guides available on dissertation and project writing. Books aimed at postgraduate students can also be useful for undergraduates. Our IAD Resource List has a selection available in University libraries.
Study Skills Guide
Producing a professional document
Information Services have online courses available to help you produce a professional looking research report or dissertation. These are self-paced Learn courses using Lynda.com videos and lecture recordings.
Thesis Hub: Producing your thesis or dissertation in Word
A referencing management tool can help you to collect and organise and your source material to produce a bibliography or reference list.
Choosing a reference manager
Referencing and reference management
Work-based dissertations
Many courses and programmes, particularly at Postgraduate level, offer the opportunity to carry out a work-based dissertation. These opportunities vary between Schools and Programmes but will typically involve students tackling a research question identified by an organisation such as a business, a public sector organisation or a charity. A work based dissertation project can be invaluable for your employability and for career development.
If you are interested in carrying out a work-based dissertation you may need to start planning earlier than you would for a more traditional academic dissertation. If your Programme offers this opportunity, you will be given this information at the start of Semester 1. If you would like to source and set up a dissertation project with an external organisation yourself, you will need to speak with your Programme Director or Course Organiser first.
You can draw on resources developed by the Making the Most of Masters project.
Making the Most of Masters
Work-based projects – advice for students
Further information
Developing your English
Writing at postgraduate level
Critical thinking
Edinburgh Research Archive

- ERA Home
- Engineering, School of
Engineering thesis and dissertation collection
By Issue Date Authors Titles Subjects Publication Type Sponsor Supervisors
Search within this Collection:
Recent Submissions
Hvdc-scale modular multilevel converters with energy storage integration , liquid crystal dropelt lasers for chemical sensing , pathway towards the inverse design of all-composite honeycomb core sandwich panels , additive manufacturing of composites with tailored fibre architectures in fastened joint applications , next-generation valve actuation for digital displacement machines , investigating the effect of low feed water temperature on the organic fouling and cleaning of nanofiltration membranes , process modelling and optimisation of biomolecular reactions and separations for advanced biopharmaceutical manufacturing , application of optical flow for high-resolution velocity measurements in wall-bounded turbulence , asset maintenance of thick section fibre-reinforced composite structures , neural networks for channel estimation , design of new chemical sensors based on controlled morphologies of gold nanoparticles , big data analysis on long-span bridge structural health monitoring systems , investigation of a low-energy thermal energy recovery system for passive ventilation applications , nanostructured composite adsorbents and membranes for selective dye, oil and heavy metal ion separation , data-driven aerodynamic instabilities detection in centrifugal compressors , guided direct time-of-flight lidar for self-driving vehicles , properties and tunable nature of electrochemically-grown peptide-based hydrogels at single microelectrodes , thermal integration of waste to energy plants with post-combustion co₂ capture technologies , development and modelling of sustainable polymer–based membranes for gas separation and packaging , holographic single photon lidar for adaptive 3d imaging .

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Thesis / dissertation formatting manual (2024).
- Filing Fees and Student Status
- Submission Process Overview
- Electronic Thesis Submission
- Paper Thesis Submission
- Formatting Overview
- Fonts/Typeface
- Pagination, Margins, Spacing
- Paper Thesis Formatting
- Preliminary Pages Overview
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures (etc.)
- Acknowledgements
- Text and References Overview
- Figures and Illustrations
- Using Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Using Copyrighted Materials by Another Author
- Open Access and Embargoes
- Copyright and Creative Commons
- Ordering Print (Bound) Copies
- Tutorials and Assistance
- FAQ This link opens in a new window
UCI Libraries maintains the following templates to assist in formatting your graduate manuscript. If you are formatting your manuscript in Microsoft Word, feel free to download and use the template. If you would like to see what your manuscript should look like, PDFs have been provided. If you are formatting your manuscript using LaTex, UCI maintains a template on OverLeaf.
- Annotated Template (Dissertation) 2024 PDF of a template with annotations of what to look out for
- Word: Thesis Template 2024 Editable template of the Master's thesis formatting.
- PDF Thesis Template 2024
- Word: Dissertation Template 2024 Editable template of the PhD Dissertation formatting.
- PDF: Dissertation Template 2024
- Overleaf (LaTex) Template
- << Previous: Tutorials and Assistance
- Next: FAQ >>
- Last Updated: May 31, 2024 9:34 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/gradmanual
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
No notifications.
Dissertations on Design
Design is utilised in a broad range of industries and could include any number of different subjects from architecture and interior design, to products, packaging, logos, vehicles or anything in between.
View All Dissertation Examples

Latest Design Dissertations
Including full dissertations, proposals, individual dissertation chapters, and study guides for students working on their undergraduate or masters dissertation.
Effects of Packaging Colour on Consumer Behaviour
Dissertation Examples
Most buyers make the decision of purchasing because of the packaging, which is often considered as the silent salesman. This paper aims to investigate the effect of packaging colour in the soft drinks industry, on consumer behaviour....
Last modified: 23rd Dec 2021
Sensory Rooms and Withdrawal Rooms in Educational and Public Environments to Help Children with ASD
Dissertation Introductions
Introduction to a study that investigates the existent design principles for A.S.D. in Ireland, and aims to identify the necessary procedures that can be taken to improve such facilities, particularly in the education system....
Last modified: 6th Dec 2021
The Urban Street: A Conduit for Vitality and Multimodal Movement in the City
Example Literature Reviews
A study of Strøget, Copenhagen, analysing how the pioneering street design impacted the entire city's way of life. Through the exploration of factors which define the success of streets, their impact on the vitality and multimodal movement of the city can be assessed. ...
Appraisal of Formwork Types
The subject for this dissertation is the appraisal of formwork types and design and to identify the advantages of innovative materials, systems and design....
Last modified: 12th Nov 2021
Design and Construction of Class AB Audio Amplifier
This paper describes the design and the construction of the Class AB audio amplifier. A proposed approach is outlined and the challenges encountered during developing a well-designed circuit in this project are addressed in this report....
Last modified: 1st Nov 2021
Packaging Materials and Consumer Preferences
Consumer purchase decisions depend on the way a product is communicated at the store. The packaging becomes a major cause of the purchase decision because it is the first introduction of the product....
Last modified: 27th Oct 2021
Methodology: Clothing Quality Research
Dissertation Methodologies
The study was conducted to determine the types of informational cues used by consumers when evaluating clothing quality and their expectations of a high-quality garment....
Last modified: 20th Oct 2021
Analysis of Product Packaging Design
In this thesis I am trying to test whether a soup pot design communicates to the potential customer a series of qualitative attributes about its content, and triggers positive emotional responses....
Last modified: 24th Sep 2021
Juiced Life Smoothies Product Development Analysis
This report provides an analysis of the effectiveness of the innovative product system at Juice Life Smoothies and suggests improvements to maintain efficient product delivery and efficient business operations....
Last modified: 25th Aug 2021
Design Dissertation Topics
Dissertation Topics
We have provided a selection of example design dissertation topics below to help and inspire you when choosing a topic for your dissertation....
Last modified: 17th Aug 2021
Design Dissertation Titles
Dissertation Titles
Design Dissertation Titles. We have provided this selection of example design dissertation titles to help and inspire you....
Last modified: 16th Aug 2021
Design of a New Office Development that Inspires Workers
An innovative, unique, flexible and easy to use office development that allows users to be inspired by their work places....
Last modified: 11th Jun 2021
Effect of Workstation Lighting on Employee Performance
TITLE: Impacts of individually controlled dynamic task light and human centric task lighting solutions for office workstations in Bangalore (India). RESEARCH QUESTION: ...
Last modified: 18th May 2020
A Project Report on E-Decor
ABSTRACT E-Decor is the android application. There are many apps of online booking for movies, purchases goods or fashion but there is no app for Events and Wedding Decorators, Caterers, Photogr...
Last modified: 16th Dec 2019
Analysis of Three Instructional Design Models
This paper will briefly review and compare three instructional design models: Dick and Carey’s Systems Approach (DC) Model, the generic “Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation” (ADDIE) Model, and Michael Allen’s Successive Approximation (SAM) Model....
Last modified: 13th Dec 2019
Design, build and User-test a Curriculum Vitae Mobile Application for Software Developers
Table of Contents 1. Introduction 2. Review of Literature / Background 3. Methodology/Sources of data 4. Analysis 5. Discussion 6. Reflection 7. Conclusion 8. References 9. Appendices Projec...
Development of Luxury Products: Montblanc
Alongside this boom in the new luxury market there is a renewed interest from both academics and practitioners in luxury consumption research....
Last modified: 12th Dec 2019
Importance of Brands and Branding
Abstract Repetitive failures cost companies millions of dollars in redesign costs, liabilities, and transaction costs. However, by far the most serious cost of these failures is the lost business that...
Last modified: 11th Dec 2019
Design and Fabrication of All Terrain Vehicle
TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION ………………………………………………………………...
Design of Digital Platform for Assignment Submission
GETITDONE.COM Executive Summary GETITDONE.com is a digital platform which is designed to provide a complete environment to develop, manage and submit any assignment for the university students w...
Last modified: 10th Dec 2019
Development of a 3D Printed Robotic Limb for Prosthetics
Abstract In this project a 3D designed myoelectric prosthetic limb will be developed. The arm will be electronically stimulated, and the user will control the arm by flexing their muscles. An am...
Last modified: 9th Dec 2019
Popular Tags
- Browse All Tags
- Biomedical Science
- Business Analysis
- Business Strategy
- Computer Science
- Construction
- Consumer Decisions
- Criminology
- Cultural Studies
- Cyber Security
- Electronics
- Engineering
- Environmental Science
- Environmental Studies
- Food And Nutrition
- Health And Social Care
- Human Resources
- Information Systems
- Information Technology
- International Business
- International Relations
- International Studies
- Mental Health
- Pharmacology
- Social Policy
- Sustainability
- Young People

Dissertation Writing Service

Dissertation Proposal Service

Topic with Titles Service

Samples of our work
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
Hüsrev Cılasun, Alireza Khataei, and Siliang Zeng awarded doctoral dissertation fellowships

Doctoral candidates Hüsrev Cılasun, Alireza Khataei, and Siliang Zeng are recipients of the Graduate School’s 2024-2025 doctoral dissertation fellowship (DDF) award. The fellowship gives the University's most accomplished doctoral candidates an opportunity to devote full-time effort to an outstanding research project by providing time to finalize and write a dissertation during the fellowship year.

Hüsrev Cılasun is conducting his doctoral research under the guidance of Professor Ulya Karpuzcu, and is exploring novel and unconventional ways of computing with spin, the angular momentum of physical particles. He is working on two distinct aspects of such computation. The first one deals with using actual magnetic spins to enable several orders of magnitude higher performance and energy efficiency than conventional computers, while preserving data privacy and fault tolerance for emerging big data problems in, for instance, genomics. The second aspect uses abstract models of spins to solve large scale combinatorial optimization problems which are present in numerous applications in our lives, ranging from robotics, airline scheduling, logistics (determining ideal routes for package delivery) to chip design (finding the best way to draw a chip layout). All of these problems are hard to solve and characterized by several constraints. Cılasun’s research goal is to explore the design space of spin-based computing systems to solve existing problems more efficiently using significantly less resources (including energy) and to solve new problems that no conventional system can due to physical resource limitations.

Alireza Khataei has been working on his research under the guidance of Professor Kia Bazargan. Khataei’s research is located at the intersection of innovative data encoding and highly optimized hardware to perform computations with limited hardware resources. The goal is to accelerate compute-intensive applications such as neural networks and image processing. His work stems from the recent explosion of machine learning applications and the growth in AI computation complexity. These developments are the result of advances in hardware speed and innovations in neural network models. However, both the training of the network as well processing the many millions of user prompts entail massive amounts of computation, which requires the support of hardware that can stand up to the challenge. Hardware accelerators are specially designed computation units inside processors that target specific types of computation and are particularly critical for handling the anticipated growth and complexity of neural networks. Khataei’s research targets hardware acceleration, developing innovative solutions to improve the costs associated with computation in terms of time and power.

Siliang Zeng ’s research is focused on aligning artificial intelligence (AI) systems with human preferences, context, social norms, and other values. Working under the guidance of Professor Mingyi Hong, Zeng’s work develops a comprehensive framework, including formulation, algorithms, and customization to and for specific applications. This will allow AI systems to effectively learn from humans for a wide range of tasks. He addresses critical challenges such as the effective integration of diverse human generated data to build an aligned system, enabling AI systems to continuously learn and adapt to changing contexts and norms, and transparency of AI systems so users can understand and trust them.
Learn more about our graduate programs
Know more about our research areas
Additional student and alumni news
Related feature stories
- Alumnus Burhaneddin Yaman receives 2023 IEEE SPS Best PhD Dissertation Award
- Wen Zhou receives doctoral dissertation fellowship and Early Innovation Fund award
- Burhaneddin Yaman recognized with best dissertation award
- Alumnus Kejun Huang receives NSF CAREER Award
- Sai Sanjay Balaji awarded UMII-MnDRIVE Graduate Assistantship
- Future undergraduate students
- Future transfer students
- Future graduate students
- Future international students
- Diversity and Inclusion Opportunities
- Learn abroad
- Living Learning Communities
- Mentor programs
- Programs for women
- Student groups
- Visit, Apply & Next Steps
- Information for current students
- Departments and majors overview
- Departments
- Undergraduate majors
- Graduate programs
- Integrated Degree Programs
- Additional degree-granting programs
- Online learning
- Academic Advising overview
- Academic Advising FAQ
- Academic Advising Blog
- Appointments and drop-ins
- Academic support
- Commencement
- Four-year plans
- Honors advising
- Policies, procedures, and forms
- Career Services overview
- Resumes and cover letters
- Jobs and internships
- Interviews and job offers
- CSE Career Fair
- Major and career exploration
- Graduate school
- Collegiate Life overview
- Scholarships
- Diversity & Inclusivity Alliance
- Anderson Student Innovation Labs
- Information for alumni
- Get engaged with CSE
- Upcoming events
- CSE Alumni Society Board
- Alumni volunteer interest form
- Golden Medallion Society Reunion
- 50-Year Reunion
- Alumni honors and awards
- Outstanding Achievement
- Alumni Service
- Distinguished Leadership
- Honorary Doctorate Degrees
- Nobel Laureates
- Alumni resources
- Alumni career resources
- Alumni news outlets
- CSE branded clothing
- International alumni resources
- Inventing Tomorrow magazine
- Update your info
- CSE giving overview
- Why give to CSE?
- College priorities
- Give online now
- External relations
- Giving priorities
- CSE Dean's Club
- Donor stories
- Impact of giving
- Ways to give to CSE
- Matching gifts
- CSE directories
- Invest in your company and the future
- Recruit our students
- Connect with researchers
- K-12 initiatives
- Diversity initiatives
- Research news
- Give to CSE
- CSE priorities
- Corporate relations
- Information for faculty and staff
- Administrative offices overview
- Office of the Dean
- Academic affairs
- Finance and Operations
- Communications
- Human resources
- Undergraduate programs and student services
- CSE Committees
- CSE policies overview
- Academic policies
- Faculty hiring and tenure policies
- Finance policies and information
- Graduate education policies
- Human resources policies
- Research policies
- Research overview
- Research centers and facilities
- Research proposal submission process
- Research safety
- Award-winning CSE faculty
- National academies
- University awards
- Honorary professorships
- Collegiate awards
- Other CSE honors and awards
- Staff awards
- Performance Management Process
- Work. With Flexibility in CSE
- K-12 outreach overview
- Summer camps
- Outreach events
- Enrichment programs
- Field trips and tours
- CSE K-12 Virtual Classroom Resources
- Educator development
- Sponsor an event
University of Washington Links
- College of Arts & Sciences
- Directories
- Concentrations
- Photo/Media
- Painting + Drawing
- 3D4M: ceramics + glass + sculpture
- Field Studies
- Student Work
- Study Abroad
- Art History BA
- Art History Minor
- Art History MA Thesis
- Art History MA Practicum
- Art History PhD
- Student Research
- Interaction Design
- Visual Communication Design
- Industrial Design
- Laptop Requirement
- Master of Design
- BDes/MDes Shows
- COVID-19 Updates
- Voicing a Concern
- News + Events
- Exhibitions
Mobile Menu
- Graduate Students
- Visiting Artists + Lecturers
- Seattle Arts + Culture
- Jobs, Internships, and Opportunities
- First Day Attendance
- Final Exam Attendance
- Career Fair
- Design Travel Award Application
- Finding an Internship
- Finding a Job
- Portfolio Advice
- Resume Advice
- Alumni Blog
- Alumni Statistics
- Prevention Plan
- For Students
- Press Releases
- Stay Connected
- Undergraduate Students
- Jobs + Opportunities
- Academic Advising
- Student Voice Project
- Scholarships + Awards
- Advisory Board
- A-Z Directory
- Recent News
- News Archive
- Technology + Equipment
- Rome Center
- Exhibitions, 2022-2023
- Exhibitions, 2021-2022
- Exhibitions, 2020-2021
- Exhibitions, 2019–2020
- Exhibitions, 2018–2019
- Exhibitions, 2017–2018
- Exhibitions, 2016–2017
- Exhibitions, 2015–2016
- Exhibitions, 2014–2015
- Jacob Lawrence Legacy Residency
- The Black Embodiments Studio
- BIPOC Graduate Student Curatorial Fellowship
- Critical Art Writing Group

You are here
- News & Events
Core77 Design Awards 2024

The MDes thesis project of alum Claire Weizenegger (MDes 2023) on domestic voice assistants was selected for a Student Notable Speculative Design Award from Core77. Congraduations to Claire Weizenegger and project team member Wyatt Olson (MDes 2024) and thesis co-chairs Professors Audrey Desjardins and James Pierce.
Read on Core77
- Honors + Awards
- Student Success
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
Published on November 11, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 20, 2023.
Choosing your dissertation topic is the first step in making sure your research goes as smoothly as possible. When choosing a topic, it’s important to consider:
- Your institution and department’s requirements
- Your areas of knowledge and interest
- The scientific, social, or practical relevance
- The availability of data and resources
- The timeframe of your dissertation
- The relevance of your topic
You can follow these steps to begin narrowing down your ideas.
Table of contents
Step 1: check the requirements, step 2: choose a broad field of research, step 3: look for books and articles, step 4: find a niche, step 5: consider the type of research, step 6: determine the relevance, step 7: make sure it’s plausible, step 8: get your topic approved, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about dissertation topics.
The very first step is to check your program’s requirements. This determines the scope of what it is possible for you to research.
- Is there a minimum and maximum word count?
- When is the deadline?
- Should the research have an academic or a professional orientation?
- Are there any methodological conditions? Do you have to conduct fieldwork, or use specific types of sources?
Some programs have stricter requirements than others. You might be given nothing more than a word count and a deadline, or you might have a restricted list of topics and approaches to choose from. If in doubt about what is expected of you, always ask your supervisor or department coordinator.
Start by thinking about your areas of interest within the subject you’re studying. Examples of broad ideas include:
- Twentieth-century literature
- Economic history
- Health policy
To get a more specific sense of the current state of research on your potential topic, skim through a few recent issues of the top journals in your field. Be sure to check out their most-cited articles in particular. For inspiration, you can also search Google Scholar , subject-specific databases , and your university library’s resources.
As you read, note down any specific ideas that interest you and make a shortlist of possible topics. If you’ve written other papers, such as a 3rd-year paper or a conference paper, consider how those topics can be broadened into a dissertation.
After doing some initial reading, it’s time to start narrowing down options for your potential topic. This can be a gradual process, and should get more and more specific as you go. For example, from the ideas above, you might narrow it down like this:
- Twentieth-century literature Twentieth-century Irish literature Post-war Irish poetry
- Economic history European economic history German labor union history
- Health policy Reproductive health policy Reproductive rights in South America
All of these topics are still broad enough that you’ll find a huge amount of books and articles about them. Try to find a specific niche where you can make your mark, such as: something not many people have researched yet, a question that’s still being debated, or a very current practical issue.
At this stage, make sure you have a few backup ideas — there’s still time to change your focus. If your topic doesn’t make it through the next few steps, you can try a different one. Later, you will narrow your focus down even more in your problem statement and research questions .
There are many different types of research , so at this stage, it’s a good idea to start thinking about what kind of approach you’ll take to your topic. Will you mainly focus on:
- Collecting original data (e.g., experimental or field research)?
- Analyzing existing data (e.g., national statistics, public records, or archives)?
- Interpreting cultural objects (e.g., novels, films, or paintings)?
- Comparing scholarly approaches (e.g., theories, methods, or interpretations)?
Many dissertations will combine more than one of these. Sometimes the type of research is obvious: if your topic is post-war Irish poetry, you will probably mainly be interpreting poems. But in other cases, there are several possible approaches. If your topic is reproductive rights in South America, you could analyze public policy documents and media coverage, or you could gather original data through interviews and surveys .
You don’t have to finalize your research design and methods yet, but the type of research will influence which aspects of the topic it’s possible to address, so it’s wise to consider this as you narrow down your ideas.
It’s important that your topic is interesting to you, but you’ll also have to make sure it’s academically, socially or practically relevant to your field.
- Academic relevance means that the research can fill a gap in knowledge or contribute to a scholarly debate in your field.
- Social relevance means that the research can advance our understanding of society and inform social change.
- Practical relevance means that the research can be applied to solve concrete problems or improve real-life processes.
The easiest way to make sure your research is relevant is to choose a topic that is clearly connected to current issues or debates, either in society at large or in your academic discipline. The relevance must be clearly stated when you define your research problem .
Before you make a final decision on your topic, consider again the length of your dissertation, the timeframe in which you have to complete it, and the practicalities of conducting the research.
Will you have enough time to read all the most important academic literature on this topic? If there’s too much information to tackle, consider narrowing your focus even more.
Will you be able to find enough sources or gather enough data to fulfil the requirements of the dissertation? If you think you might struggle to find information, consider broadening or shifting your focus.
Do you have to go to a specific location to gather data on the topic? Make sure that you have enough funding and practical access.
Last but not least, will the topic hold your interest for the length of the research process? To stay motivated, it’s important to choose something you’re enthusiastic about!
Most programmes will require you to submit a brief description of your topic, called a research prospectus or proposal .
Remember, if you discover that your topic is not as strong as you thought it was, it’s usually acceptable to change your mind and switch focus early in the dissertation process. Just make sure you have enough time to start on a new topic, and always check with your supervisor or department.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly

You can assess information and arguments critically by asking certain questions about the source. You can use the CRAAP test , focusing on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
Ask questions such as:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert?
- Why did the author publish it? What is their motivation?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence?
A dissertation prospectus or proposal describes what or who you plan to research for your dissertation. It delves into why, when, where, and how you will do your research, as well as helps you choose a type of research to pursue. You should also determine whether you plan to pursue qualitative or quantitative methods and what your research design will look like.
It should outline all of the decisions you have taken about your project, from your dissertation topic to your hypotheses and research objectives , ready to be approved by your supervisor or committee.
Note that some departments require a defense component, where you present your prospectus to your committee orally.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 20). How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow. Scribbr. Retrieved June 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/dissertation-topic/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, what is a research design | types, guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Starting the Plan. Implementing the dissertation project plan begins with organizing your tasks and setting priorities based on your outlined timeline. Start by reviewing the project plan and identifying the first set of tasks to tackle. Ensure you have all necessary resources and materials before commencing each task.
Abstract or executive summary. The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report - in other words, it should be able to ...
01. Treat it like a design brief. "A great dissertation should be a designed artefact, and portfolio-worthy in its own right," says Burston. And like a design brief, it should be about solving a problem: "Make sure it has clearly stated aims, strong focus, and doesn't lack opinion or rhetoric," he adds. Best laptops for graphic design.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Example 1: Passive construction. The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise. Example: Passive construction.
Your project's validity depends on the data collection and interpretation techniques. A strong research design reflects a strong dissertation, scientific paper, or research proposal. The research design can be divided into five broad categories; descriptive, experimental, correlational, diagnostic, and explanatory.
Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples. Published on September 9, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on July 18, 2023. It can be difficult to know where to start when writing your thesis or dissertation.One way to come up with some ideas or maybe even combat writer's block is to check out previous work done by other students on a similar thesis or dissertation topic to yours.
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
Most dissertations run a minimum of 100-200 pages, with some hitting 300 pages or more. When editing your dissertation, break it down chapter by chapter. Go beyond grammar and spelling to make sure you communicate clearly and efficiently. Identify repetitive areas and shore up weaknesses in your argument.
The purpose of this document is to provide guidelines on writing a graduate project thesis. It is not intended to be used in writing a thesis describing theoretical research work. A graduate project thesis represents the culminating experience resulting from your graduate study.
If you're preparing to write your dissertation, thesis or research project, our free dissertation template is the perfect starting point. In the template, we cover every section step by step, with clear, straightforward explanations and examples.. The template's structure is based on the tried and trusted best-practice format for formal academic research projects such as dissertations and ...
3. The next section is the main body of the dissertation. There are several areas that this main body can include. Give a summary of the science behind your project. Provide a literature review of relevant work published in the area of your project. Summarise any key theoretical principles needed for your project.
The dissertation will be structured such that it starts with an introduction, develops on the main idea in its main body paragraphs and is then summarised in conclusion. However, if you are basing your dissertation on primary or empirical research, you will be required to include each of the below components.
Table of contents. Step 1: Coming up with an idea. Step 2: Presenting your idea in the introduction. Step 3: Exploring related research in the literature review. Step 4: Describing your methodology. Step 5: Outlining the potential implications of your research. Step 6: Creating a reference list or bibliography.
6. Project Design [included in in the Interim Document, and Final Dissertation] This section corresponds to the second stage of the software development process Citation Sommerville (2007): software design. Your design is most likely object-oriented. The design starts with a list of classes and their responsibilities.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
Student Work. 2023 Digital Design Prize: Amelia Gan's "Place-Time: From Waste to 3D CAD, or, Framework for geographical and temporally conscious design". by Amelia Gan (MDes '23) — Recipient of the Digital Design Prize. The dominance of…. Student Work. Andrew Wittand Allen Sayegh, Faculty Advisors. Spring 2023.
Dissertations and research projects. This is a general resource to help you with the basics of organising and writing a research-based dissertation or project. The Go further section at the end includes advice on work-based dissertations and signposts other resources. You should consult your course or programme handbook, including online ...
Next-generation valve actuation for digital displacement machines . Tkachuk Volodymyrovych, Andriy (The University of Edinburgh, 2024-06-05) A pump is the heart of a fluid-powered machine, which has a substantial impact on its efficiency. According to the state-of-the-art, the efficiency of a hydraulic excavator is about 16% due to a poor ...
UCI Libraries maintains the following templates to assist in formatting your graduate manuscript. If you are formatting your manuscript in Microsoft Word, feel free to download and use the template. If you would like to see what your manuscript should look like, PDFs have been provided.
We have provided a selection of example design dissertation topics below to help and inspire you when choosing a topic for your dissertation.... Last modified: 17th Aug 2021. ... A Project Report on E-Decor. Dissertation Examples. ABSTRACT E-Decor is the android application.
Writing a proposal or prospectus can be a challenge, but we've compiled some examples for you to get your started. Example #1: "Geographic Representations of the Planet Mars, 1867-1907" by Maria Lane. Example #2: "Individuals and the State in Late Bronze Age Greece: Messenian Perspectives on Mycenaean Society" by Dimitri Nakassis.
the dissertation project in several ways. •The first is through the series of required research courses that provide the foundation of knowledge needed both to assess the prior work of others and to develop work of one's own. In particular, a dissertation design seminar is offered in the third summer. (In
Doctoral candidates Hüsrev Cılasun, Alireza Khataei, and Siliang Zeng are recipients of the Graduate School's 2024-2025 doctoral dissertation fellowship (DDF) award. The fellowship gives the University's most accomplished doctoral candidates an opportunity to devote full-time effort to an outstanding research project by providing time to finalize and write a dissertation during the ...
The MDes thesis project of alum Claire Weizenegger (MDes 2023) on domestic voice assistants was selected for a Student Notable Speculative Design Award from Core77. Congraduations to Claire Weizenegger and project team member Wyatt Olson (MDes 2024) and thesis co-chairs Professors Audrey Desjardins and James Pierce. Read on Core77
Step 1: Check the requirements. Step 2: Choose a broad field of research. Step 3: Look for books and articles. Step 4: Find a niche. Step 5: Consider the type of research. Step 6: Determine the relevance. Step 7: Make sure it's plausible. Step 8: Get your topic approved. Other interesting articles.
Health & Wellness we have great resources available to assist students with their physical and mental health. like a student health center, counseling center and fitness center; Transition Programs we support students in their transition with programs like orientation, first-year experience, second-year experience, transfer student services, veteran student services, out-of-state student services