Role of Media in Society Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment

Introduction
Overview of the role of media in society, works cited.
In today’s society, the flow of information among the citizenry plays an important role towards the development of an informed society. To this effect, the media has been instrumental in ensuring that the population gets current news and information on different issues affecting various societies.
Arguably, without the media, the world would consist of an ignorant population devoid of any relevant information relating to issues affecting their environment. With this in mind, it could be argued that the media provides the backdrop against which we make sense of any new conditions and information that we encounter in a world that is increasingly becoming globalized.
Since its conception, the media has been hugely influential in the development of the society. The media can be used to drive public opinion, report on current news and advance some social values. The media is at best a complex genre which may be broken down into a large number of sub-genres such as news stories, opinion columns, advertisements, sports and horoscopes to name but a few.
As such, the role of the media in today’s society is important because it essentially helps individuals get access to valuable information, educate the people in the communities and is a useful, affordable and an economical tool for entertainment.
In today’s society, the social issue that has particularly struck individuals through the decades is that of the media. In this study, the various opinions held in regard to the media and how it operates shall be provided. Through the analysis of relevant literature, a brief yet informative discussion of the various benefits that have been enjoyed as a result of the media shall be presented. This shall be done by highlighting key areas where the media has been instrumental.
These areas include but are not limited to: provision of information, a source of education and knowledge, link between members of the global community and a source of entertainment. The differing opinions propagated by media critics shall also be presented. This shall at the end help us understand the roles that the media plays in society as well as the extent to which the media has been successful in performing its duties.
As such, it shall be a worthwhile endeavor to shed some light on the benefits as well as the costs that have risen due to the presence and effects of the media in our societies. This analysis shall help in the provision of a clearer understanding on how the media affects society.
The media is arguably one of the most powerful agents for change and the betterment of society. Its role as the society’s eyes; indeed a ‘watchdog’ constantly monitoring and critiquing the actions of those in authority for the betterment of society are some of the attributes that previously made the media seem as a positive influence to society.
The ability of media to so accurately reflect the mood of the society and advocate for people to fight against social injustices and vices portrays the media as a tool for promoting justice, equality and harmony among the masses.
In regards to this statement, the current states of affairs indicate that societies are ridden with selfishness and actions aimed at advancing individual goals. This can be derived from the argument raised by Michael Meyers who claims that today’s media does not educate the audience but train them (Kramer, Meyers and Rothstein 582).
This he attributes to the fact that the media outlets no longer providing credible information. In this regard, the audience does not buy the truth, but what prominent figures want them to believe. The author is trying to bring out the fact that media is biased.
The proposed biasness has its root in the anti-intellectual and anti-democratic media. In addition, the media’s advertisement of products and services is an act aimed at enabling the consumers to make informed choices. As Bernt explains, the skills and artistic nature used to present persuasive advertisements help consumers relate products to their lifestyle and preferences (193).
Texts and images represented in advertisement can signify a myriad of meanings to the viewer. All this is in an attempt by the creator of the advert to persuade the consumer to think, feel or act in a predetermined manner (Bernt 194). Advertisement is therefore more of an educative venture than a deliberate attempt to sway the consumer in any predetermined direction since in the end; the consumers are better informed of the variety of brands that are at their disposal.
Bernt suggests that the heavy emphasis of advertisements in media is due to the fact that advertisers are the dominant sources of revenue for most modern media (193). The influence that advertisements have on the people is colossal as can be inferred from the rise in sales for corporations that engage in large-scale advertisement.
Bernt further asserts that the persuasive nature of advertisements has had a great effect on American culture in regards to the relationship between working hard and purchasing power (193). Bernt asserts that advertisements have “replaced Puritanism or the Protestant work ethic as the driving force in American society that causes people to work hard in order to shop even harder (193).”
The various forms of entertainment availed e.g. Movies, sports, interactive programs and Music productions are very important means of relieving stress after a long day at work. In addition, they help alleviate boredom. As such, the sole agenda of such products is recreational and providing means for people to enjoy themselves and connect (Bellah et al 67).
For example, through satellite television providers like DSTV people all over the world are able to enjoy the entertainment genre that best suit their preferences. Examples include movies, sports, music and news. Truth be told, football clubs would never have gained such a strong and wide fan base were it not for the media.
In regards to change in journalism, Pavlik highlights on how journalism has been affected by the transformation of the new media (Fernback 163).
In his opinion, new media technologies have greatly affected the traditional perspective of journalism. This he explains by expounding on the new journalistic trends such as changes in the contents provided to the audience as news, changes in how journalists work, structural changes in news organizations and changes that have occurred in the correlations between media outlets, journalists and different audiences (Fernback 163).
These changes brought about by new media technologies have to a large extent led to the contextualization of journalism; a situation whereby journalism has become less objective and practical.
On the same note, Palvik (as cited by Fernback 163) further notes that these new trends perceive journalists as interpreters of current events who in their efforts “empower the audience and reconnect communities (Fernback 163).”
According to Palvik, the new transformations being experienced in media outlets can be attributed to the availability and emergence of online infrastructure, high degree of customization, instantaneity and interactivity that characterize new media. In his point of view, Palvik believes that such developments will at the end make journalism a better tool to promote democracy (Fernback 163).
Evidence of such developments can be derived from the emergence of the internet and the online architecture that supports this vast source of information. Through online encyclopedias such as Wikipedia and the various search engines, people are able to access information and learn about different issues that affect their lives.
In addition, students in all academic fields are able to do more research in their designated fields and as a result, they become more knowledgeable in these areas than they would have been while using the traditional means of acquiring knowledge. Similarly, the internet has also provided people with a global means of communicating and learning about each other through websites like “facebook” and “twitter”.
People from different countries globally are able to interact and socialize in the comfort of their homes without the inconveniencies caused by travelling as well as the enormous costs that would have otherwise been incurred. These facts prove Palvik’s assertion that new media is at the forefront in empowering the masses (by providing useful information) and connecting communities (interactive nature of the internet, radio and TV talk shows e. t. c.).
On the other hand, Preston (as cited by Fernback 163) contends that the transformations being experienced in media are as a result of political, social, economical and communication patterns rather than technological developments.
Preston asserts that the interrelation that exists between social and informational sciences accompanied by non-academic and industrial literatures can be used by media so as to develop an equitable society and ensure social order (Fernback 163). In his book reshaping communication , Preston uses the aforementioned aspects to develop a model that explores the social role of information and communication in societies today (Fernback 163).
In his opinion, Preston argues that our cultural, informational and social bearings are hinged not on technological advancements, but on the socioeconomic, political and communication trends that we adapt (Fernback 164). In this regard, it can arguably be stated that the role of the media in society is not determined by technological advancements, but by the socio-technical paradigm (Fernback 164).
The positive view of the media has greatly been challenged with time. No longer do the various media outlets stand out as the ‘last front were nobility and idealism still had a foothold.’ Instead, the media just like any other business has been influenced by competition and ratings. As such, it has been noted for a fact that media outlets do at times express their own biased opinions which may not always be ideal or noble at that.
For example, Gay Talese attests to the fact that the New York Times editor Gerald Boyd refused to print a story about an interracial wedding simply because it never emphasized on Black victimization (Kramer, Meyers and Rothstein 575). According to Gay Talese, any story that would soften the perception people had on such issues was disallowed and could not be printed (Kramer, Meyers and Rothstein 575).
In this case, the Media’s actions which were previously perceived as being selfless and socially motivated have been exposed to not always have been driven by benevolence. These actions are at times resounded with self interests and personal gains for the media houses and the corporations that sponsor them.
The previous view of the media’s ability to correctly reflect on the society’s mood has also been greatly questioned as the media does at time appear to affect the set the society’s mood as opposed to reflecting it through the use of propaganda. (Kramer, Meyers and Rothstein suggest that the one of the media’s greatest power is in its ability to subtly influence our opinion (575).
They further assert that in events that elicit a lot of public opinion, propaganda plays a great role and polarizes people along lines that they may not necessarily have taken had they not been “persuaded” to do so.
This subtle psychological nudges can be used to further the cause of big corporations in the form of advertisements or by politicians who want to sway public opinions for their own good. To this effect, the people’s previous trust in the media report has therefore been greatly clouded by this realization.
In terms of the unbiased reporting which had for a long time been viewed to be the hallmark of the popular media, it has been noted that some media reports are actually aimed at making the recipient of the information form a certain pre-determined opinion thus destroying any illusion of un-biasness (Kramer, Meyers and Rothstein 575).
Media outlets can therefore set out to further some social cause which they believe in. Using the cultivation theory, Burton propose that exposure to some kinds of media often cultivate certain attitudes and values (Steffen 455). As an example, Steffen sheds some light on how Arab media has in the recent past adopted the western form of journalism and media presentation (455).
In this regard, the author states that even journalists from countries such as Egypt and other Arabic countries which has stringent media policies accept western media values such as accuracy and balance (Steffen 455). As such, the reporter’s opinions and attitude will rub on the general population thus coloring their view of some events.
In addition, the aforementioned assertion that advertisement aired in different media outlets is aimed at making the consumer better informed has been changed by evidence which strongly suggests that advertisements are aimed at actively influencing the decision that the consumer makes or may make in future (Steffen 456).
What this means is that advertisement is no longer a primary tool for marketing, instead, it has been used to combat the aggressive competition. To this effect, only the consumers suffer because the advertisements no longer help them make informed decisions about the products but instead, the advertisements influence their judgments by giving half-truths.
An especially troubling fact that revealed through various research efforts is that uncontrolled media in some instances leads to desensitization of the population on issues such as violence.
Continuous exposure to media violence especially on the young and impressionable segment of the population can lead to catastrophic results as has been witnessed before in the various random shootouts that occur in our schools. Research shows that media violence encourages aggressive behavior and leads to pessimism in children (Burton 123; Steffen 456).
This information contradicts the aforementioned perception of the media as a guardian and propagator of social values since the compelling evidence presented by research showed that media also leads to breaking of social values and leads to a disruption of harmony through the violence it encourages.
On the same note, rampant advertisements through media outlets have in the recent past characterized modern media. These advertisements aim at influencing the consumer to maintain or develop some form of ideology (Bernt 194). This close relationship that media and advertising have developed raises concerns over the influences that the media may be willing to wield so as to achieve the advertising objectives.
A closer observation of the movies and other entertainment forms presented by the media revealed heavy advertisements therein. These rampant acts of branding were previously unknown to many and their effect though unconsciously administered is substantial.
The media’s promotion of social values is also at times only used as a cover to influence consumers by use of advertisement (Fernback 164). Due to these advertisements, naive recipients of the information presented are unwittingly influenced into buying the products that the particular advertisements promote.
This is at best a very irresponsible behavior by the media since most people are favorably disposed to agree with sentiments that are projected by the media. These misuses of social issues as a marketing tool have also changed the positive role that the media was supposed to deliver. This is mainly due to the fact that the media is being used as a tool for furthering the objectives of corporations at the cost of an unsuspecting population.
The role played by the media in today’s society cannot be understated. However, caution should be taken because as expressed in this study, not all media is healthy. Through this research, the knowledge that has been transferred herein should not make the public skeptical of the media but should help them become more skeptical about the issues being addressed through various media outlets.
This will invariably transform them from being passive, unquestioning and all-believing recipients, to active and questioning recipients of the information which is provided by the media. Nevertheless, a free and vibrant media is necessary for the good of the society. An unfettered media is the hallmark of a truly unbiased society. However, one should adopt a more questioning stance when dealing with any information provided by the media.
Bellah, Robert. ET AL.”Community, Commitment, and Individuality.” Literacies: Reading, Writing, Interpretation. New York: W.W. Norton, 2000. 65-74. Print.
Bernt, Joseph. P. “Ads, Fads, and Consumer Culture: Advertising’s Impact on American Character and Society.” Journalism and Mass Communication Quarterly 78.1 (2001): 193-194. Research Library, ProQuest. Web.
Fernback, Jan. “Journalism and New Media / Reshaping Communications: Technology, Information and Social Change.” Journalism & Mass Communication Educator 57.2 (2002): 162-164. Research Library, ProQuest. Web.
Kramer Hilton, Michael Meyers and Edward Rothstein. “The media and our country’s agenda.” Partisan Review 69.4 (2002): 574-606. Research Library, ProQuest. Web.
Steffen, Brian. J. “Media and Society: Critical Perspectives.” Journalism and Mass Communication Quarterly 83.2 (2006): 455-456. Research Library, ProQuest. Web.
- The Status of Journalism in Bahrain
- The Web Site for Online Journalism
- Social Media Replacing Traditional Journalism
- New Advertising Campaign of Crocs Company
- The Corporation & Our Media, Not Theirs
- Guns, Germs and Steel
- Functions and Power of Mass Media: Views of Two German Authors
- Chicken Run and The Nightmare Before Christmas
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, July 11). Role of Media in Society. https://ivypanda.com/essays/role-of-media/
"Role of Media in Society." IvyPanda , 11 July 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/role-of-media/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Role of Media in Society'. 11 July.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Role of Media in Society." July 11, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/role-of-media/.
1. IvyPanda . "Role of Media in Society." July 11, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/role-of-media/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Role of Media in Society." July 11, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/role-of-media/.

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Media: Short and Long Sample Essays

- Updated on
- Dec 18, 2023

Media plays an important role in shaping our perceptions, influencing public opinion, and connecting individuals across the globe. The role of media in today’s modern world is not limited to just providing information. There are three basic purposes of media; inform, educate, and entertain. A society with free media allows it to have a social and cultural impact on it. Media offers us information about every activity going on in the world. Our smartphones, laptops, televisions, radios, and even public transportation have access to media, where we can watch news anytime and anywhere. Media not only influence our thoughts but can often manipulate our understanding of a particular topic. Continue reading essay on media to know more. Stay tuned!
Also Read: Social Media Bane or Boon
Also Read: Essay on Colonialism
Short Essay on Media
‘Media plays an important role in shaping our perceptions, influencing public opinion, and connecting individuals across the globe. Media includes different platforms such as television, radio, newspapers, and the internet. Media is considered a powerful tool to disseminate information and have social, cultural, and political influences on the masses.’
Some of the roles played by the media are:
- Informing the public through newspapers, news channels, and online portals.
- At the push of a button, media can provide us with a large source of information.
- Media has a significant impact on public opinion by framing issues, influencing perceptions, and shaping narratives.
- Some media platforms are considered political watchdogs, scrutinizing the actions of government officials and institutions.
- Several media platforms rely on advertising revenue, and in turn, they provide a platform for businesses to promote their products and services.
Media can have both positive and negative impacts on an individual and society as a whole. Understanding the role of media and its limitations is important when watching or reading news. Media is meant for informational purposes. Its influence can vary from person to person. Media is a double-edged sword, which can have a negative or positive impact on our understanding, depending on how we perceive information.
Also Read: Essay on Social Issues
Long Essay on Media
‘Media is a great source of information. Some watch media for entertainment, while others for information or educational purposes. The way we perceive media can have a great impact on our understanding of a particular topic or information. In recent years, the influence of media has significantly increased. The role and influence of media is not limited and can take different forms. Newspapers and radio stations are some of the old and most preferred media sources as compared to television and internet media sources. The choices made by editors, the emphasis given to certain stories, and the narratives crafted can significantly impact how we perceive the world.
Types of Media
There are different types of media, which determine our choices.
News media comprises various platforms like SMS, blogs, email, internet, etc. These platforms are used to access and disseminate economic, social and political information. It offers new ways to develop business relationships with telecommunication companies that are capable of disseminating critical information that can change people’s lives.
Mass media includes print (newspapers, magazines), TV and radio. Due to the fast-paced TV and radio media platforms, there has been a significant decline in newspaper readership all over the world. However, there is a section of a group who still prefer newspapers as the best sources of information. On the other hand, TV and radio stations offer live information from different parts of the world.
Community Media
Community media focuses on the development and issues of a particular community. Some journalists work for community newspapers and radio stations within their community. They have their geographical limitations and sometimes are poorly resourced with immature journalists and editors.
What is the Role of Media?
‘Media plays multiple roles, educating and informing us about different fields. Media is not only there for news but also produces some amazing stories, documentaries, magazine programs and articles through its platforms.’
‘Media allows us to raise awareness and public voice against any unethical activity or decision of the government. Apart from sharing information, media has the power to be a catalyst for social change. It serves as a platform for advocacy, shedding light on injustices, and human rights violations, and inspiring collective action.
We have witnessed how movements for equality and justice have gained momentum through the amplifying effect of media. As responsible citizens, we should support and engage with media that contributes to positive social change.
Different Roles of People in Media
Different people play different roles in the media and mass communication sector.
- Board of Directors – Their job is to ensure that everyone within the organization fulfills their responsibilities within the given framework. They are the real policymakers within the organization. They are not responsible for day-to-day media programs. Their job is not to influence the work of editorial staff and junior journalists.
- Media Manager – They are responsible for the formulation and implementation of policies for employees. They keep a check on what their media covers, how they have to do it, and what resources are required for everyday media coverage.
- Editors – There are different editorial teams, based on their roles and responsibilities. It includes editor-in-chief, special projects, financial, business, assignment, entertainment, etc. They are the gatekeepers because they are the final decision-makers on what will be published. They also guide journalists on the sources they would like to see in the story.
- Sub-editors – They are an important part of a media house as they determine the ‘End product.’ Their role is to edit stories of structure, measure lengths of stories, check factual details, etc. They are responsible for writing news headlines and captions for photographs. These people have to work under strict deadlines. Because of this, their decision can be detrimental to the published stories.
- Reporter/ Journalist – They are the news hunters and gatherers. They make decisions on which stories to cover. It is critical to identify which journalists cover your type of issues and develop a relationship with them.
Related Articles
Ans: Media plays an important role in shaping our perceptions, influencing public opinion, and connecting individuals across the globe. Media includes different platforms such as television, radio, newspapers, and the internet.
Ans: There are three types of media: New media, Community media, and mass media.
Ans: Several people perform different roles in a media house, including reporters or journalists, sub-editors, editors, media managers, and the board of directors.
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu .
Shiva Tyagi
With an experience of over a year, I've developed a passion for writing blogs on wide range of topics. I am mostly inspired from topics related to social and environmental fields, where you come up with a positive outcome.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
The Significance and Impact of the Media in Contemporary Society
- First Online: 10 March 2018
Cite this chapter

- Faith Gordon 3
Part of the book series: Palgrave Socio-Legal Studies ((PSLS))
1187 Accesses
This chapter explores the significance of the media and the impact it has on the meaning-making processes in contemporary society. It draws on key national and international academic literature and previous studies on the role and functions of the media. This includes the key theoretical debates on deviancy amplification, folk devils and moral panics. It assesses the media’s impact on criminal justice policies and on public opinion of, and support for authoritarian ideologies and policies. In particular, it will focus on exploring how the media can influence popular culture and the impact of media portrayals of crime on societal perceptions, responses and reactions directed towards social groups, in particular children and young people ‘in conflict with the law’.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
It has long been acknowledged that the media are difficult to capture and define (Craig 2004 : 3). As outlined in Chap. 1 , the terms ‘media’ or ‘mass media’ refer to the traditional definition of the media, as consisting of newspapers (the print media), radio (broadcast media) and news bulletins and programs (televised media). While choosing to focus on the contemporary media, this book acknowledges from the outset that there is an extensive body of work existing on the historical origins of the media; mass communication and its impact, and the role of technological development (see Downing 1980 ; Frost 2000 ; Curran 2002 ).
There has been much criticism of pluralist theories on the media, including the arguments that pluralism is an ideological justification for the media and that the basis of the theory is not grounded in evidence. Rather the pluralist model assumes that the content of the media is diverse, without presenting evidence to reinforce or prove this theory (see Blumler and Gurevitch 1995 ).
Rupert Murdoch’s ownership of a range of media outlets in the United Kingdom (UK) and United States (US) is a prime example of the concentration of power and the influence of owners on media content (see Golding and Murdock 1991 ; Horrie 2003 ; Cole 2005 ). Further to this, academics such as Barker ( 1999 : 46) argue that conglomeration has aided a general concentration of media ownership, with research such as Bagdikian’s ( 2004 ) stating that the US media were controlled by 50 corporations in the 1980s, and by 2003 this had been reduced to five controlling the majority of the 178,000 media outlets. Significantly as Tait ( 2012 : 518) observes, the ‘scale and intensity’ of the phone hacking scandal in 2011, saw the resignation of the chief executive of one of the UK’s most influential newspaper groups, the resignation of one of the UK’s most senior police officers, the arrest of Andy Coulson, who had acted as the then Prime Minister, David Cameron’s head of communications, the resignation of two senior executives from key companies in the Murdoch empire, as well as the collapse of the takeover deal in relation to BSkyB and the closure of the News of the World (see also Keeble and Mair 2012 ; McKnight 2012 ; Watson and Hickman 2012 ).
As Barrat ( 1994 : 61) notes, the majority of media organisations are influenced by ‘a variety of commercial influences’, including the need to be profitable and also obtaining revenue through ‘advertising’. Some media outlets are part of the public sector, such as the BBC and they have the requirement ‘to provide a public service’, by ‘informing, educating, and entertaining audiences’ (Barrat 1994 : 61).
Tait’s ( 2012 : 520) analysis of the phone hacking scandal asserts that it has ‘revealed some fundamental issues in British political communications, the political system and the practice and regulation of journalism’. His analysis also documents ‘a secret history’ between Murdoch and British politics (Tait 2012 : 520–523).
Semiology provides a suitable vehicle for studying the meanings behind media content (see O’Connor 1989 ; Hall 1997 ; Berger 1998 ; Barker 2000 ; Schirato and Yell 2000 ). In contemporary literature it is now referred to as semiotics and was first developed by the Swiss linguist, Saussure, who proposed that meaning was ‘produced through … language systems’ (Schirato and Yell 2000 : 19). He focused on the ‘linguistic sign’, which he divided into the ‘signifier’, ‘the signified’ and the ‘sign’ (Schirato and Yell 2000 : 19).
As the findings of a number of content analysis studies highlight, the media exaggerate the levels of crime, in particular violent crime in the UK (see Ditton and Duffy 1983 ; Schlesinger and Murdock 1991 ; Williams and Dickinson 1993 ; Callanan 2005 ; Greer 2005 ; Reiner 2007 ).
Dorfman and Schiraldi’s ( 2001 ) research found that 76 percent of the public said they formed their opinions about crime from the media, whereas 22 percent reported that their knowledge of crime was formed through their personal experiences.
Bibliography
Aggleton, P. (1987) Deviance , London: Tavistock Publications.
Google Scholar
Albertazzi, D. and Cobley, P. (2010) The Media: An Introduction (Third Edition), Essex: Pearson Education Limited.
Allan, S. (1999) News Culture , Buckingham: Open University Press.
Ang, I. (1990a) ‘Culture and Communication’, European Journal of Communication , Volume 5, Number 2, pages 239–260.
Ang, I. (1990b) Desperately Seeking the Audience , London: Routledge.
Archers, J. and Jones, J. (2003) ‘Headlines from History: Violence in the Press, 1850–1914’, in E. A. Stanko (ed.) The Meanings of Violence , London: Routledge, pages 17–32.
Bagdikian, B. H. (2004) The New Media Monopoly , Boston, USA: Beacon Press.
Barker, C. (1999) Television, Globalization and Cultural Identities , Buckingham: Open University Press.
Barker, C. (2000) Cultural Studies: Theory and Practice , London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Barrat, D. (1994) Media Sociology (Fourth Edition), London: Routledge.
Barthes, R. (1977) ‘“The Photograph Message”, Translated by Stephen Heath, 1977, An Excerpt’, in V. Goldberg (ed.) Photography in Print: Writings from 1816 to Present , Albuquerque, New Mexico: University of New Mexico Press, pages 15–31.
Beck, U. (1992) Risk Society: Towards a New Modernity , Translation by Mark Ritter, London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Becker, H. (1963) Outsider: Studies in the Sociology of Deviance, New York and London: Free Press.
Becker, H. (1967) ‘Whose Side Are We On?’, Social Problems , Volume 14, Number 3, pages 234–247.
Berger, A. A. (1998) Media Analysis Techniques (Second Edition), London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Berrington, E. and Honkatukia, P. (2002) ‘An Evil Monster and a Poor Thing: Female Violence in the Media’, Journal of Scandinavian Studies in Criminology and Crime Prevention , Volume 3, pages 50–72.
Article Google Scholar
Bessant, J. and Hil, R. eds. (1997) Youth Crime and the Media: Media Representations of and Reactions to Young People in Relation to Law and Order , Hobart, Australia: Australian Clearinghouse for Youth Studies.
Bignell, J. (1997) Media Semiotics: An Introduction , Manchester: Manchester University Press.
Blumler, J. and Gurevitch, M. (1995) The Crisis of Public Communication , London: Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
Box, S. (1983) Power, Crime, and Mystification , New York, USA: Tavistock.
Braham, P. (1982) ‘How the Media Report Race’, in M. Gurevitch, T. Bennett, J. Curran and J. Woollacott (eds.) Culture, Society and the Media , London: Methuen, pages 274–275.
Branston, G. and Stafford, R. (2003) The Media Student’s Book (Third Edition), London: Routledge.
Briggs, A. and Cobley, P. eds. (1998) The Media: An Introduction , Essex: Addison Wesley Longman.
Briggs, A. and Cobley, P. eds. (2002) The Media: An Introduction (Second Edition), Essex: Addison Wesley Longman.
Brown, S. (1998) Understanding Youth and Crime: Listening to Youth? , Buckingham: Open University Press.
Bryant, J. and Zillmann, D. (2002) Media Effects: Advances in Theory and Research , London: Routledge.
Caliendo, S. M. (2011) ‘Race, Media and Popular Culture’, in S. M. Caliendo and C. D. Mcllwain (eds.) The Routledge Companion to Race and Ethnicity , Oxon: Routledge, pages 73–81.
Callanan, V. J. (2005) Feeding the Fear of Crime: Crime-related Media and Support for Three Strikes , New York, USA: LFB Scholarly.
Camargo Heck, M. (1980) ‘The Ideological Dimension of Media Messages’, in S. Hall, D. Hobson, A. Lowe and P. Willis (eds.) Culture, Media, Language , Oxon: Routledge, pages 122–127.
Chibnall, S. (1975) ‘The Crime Reporter: A Study in the Production of Commercial Knowledge’, Sociology , Volume 9, Number 1, pages 49–66.
Chibnall, S. (1977) Law and Order News: An Analysis of Crime Reporting in the British Press , London: Tavistock Publications.
Cicourel, A. (1968) The Social Organization of Juvenile Justice , New York: The Free Press.
Cohen, A. (1955) Delinquent Boys: The Culture of the Gang , London: Collier-Macmillan.
Cohen, S. (1972) Folk Devils and Moral Panics: The Creation of the Mods and Rockers (First Edition), Oxford: Martin Robertson.
Cohen, S. (1980) Folk Devils and Moral Panics: The Creation of the Mods and Rockers (Second Edition), Oxford: Martin Robertson.
Cohen, S. and Young, J. eds. (1981) The Manufacture of News: Social Problems, Deviance and the Mass Media (Second Revised Edition), London: Constable.
Cole, P. (2005) ‘The Structure of the Print Industry’, in R. Keeble (ed.) Print Journalism: A Critical Introduction , Oxon: Routledge, pages 21–38.
Conboy, M. (2006) Tabloid Britain: Constructing a Community Through Language , London: Routledge.
Cormack, M. (2000) ‘The Reassessment of Ideology’, in D. Fleming (ed.) 21st Century Media Studies Textbook , Manchester: Manchester University Press, pages 93–95.
Corner, J. and Hawthorn, J. eds. (1993) Communication Studies: An Introductory Reader (Fourth Edition), London: Arnold Publishers.
Cornwell, B. and Linders, A. (2002) ‘The Myth of “Moral Panic”: An Alternative Account of LSD Prohibition’, Deviant Behavior , Volume 23, Number 4, July–August, pages 307–330.
Craig, G. (2004) The Media, Politics and Public Life, New South Wales, Australia: Allen and Unwin.
Croteau, D. and Hoynes, W. (2003) Media Society: Industries, Imagery, and Audiences , London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Curran, J. (1998) ‘Newspapers: Beyond Policy Economy’, in A. Briggs and P. Cobley (eds.) The Media: An Introduction , Essex: Longman, pages 81–96.
Curran, J. (2002) Media and Power, London: Routledge.
Curran, J. and Seaton, J. (1992) Power Without Responsibility: The Press and Broadcasting in Britain (Fourth Edition), London: Routledge.
Curran, J., Douglas, A. and Whannel, G. (1980) ‘The Political Economy of the Human-Interest Story’, in A. Smith (ed.) Newspapers and Democracy , Cambridge: MIT Press, pages 288–347.
Curran, J., Gurevitch, M. and Woollacott, J. (1988) ‘The Study of the Media: Theoretical Approaches’, in M. Gurevitch, T. Bennett, J. Curran and J. Woollacott (eds.) Culture, Society and the Media , London: Routledge, pages 11–29.
Devereux, E. (2003) Understanding the Media , London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Devereux, E. (2007) Understanding the Media (Second Edition), London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Ditton, J. and Duffy, J. (1983) ‘Bias in the Newspaper Reporting of Crime News’, British Journal of Criminology , Volume 23, Number 2, pages 159–165.
Dorfman, L. and Schiraldi, V. (2001) Off Balance: Youth, Race and Crime in the News , New Hampshire, USA: The Police Policy Studies Council.
Downes, D. and Rock, P. (2007) Understanding Deviance , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Downing, J. (1980) The Media Machine , London: Pluto Press Limited.
Durham, A. M., Elrod, H. P. and Kinkade, P. T. (1995) ‘Images of Crime and Justice: Murder and the “True Crime” Genre’, Journal of Criminal Justice , Volume 23, Number 2, pages 143–152.
Dyer, R. (1993) The Matters of Images: Essays on Representations, London: Routledge.
Eldridge, J., Kitzinger, J. and Williams, K. (1997) The Mass Media Power in Modern Britain , London: Oxford University Press.
Entman, R. M. (1993) ‘Framing: Toward Clarification of a Fractured Paradigm’, Journal of Communication , Volume 43, Number 4, pages 51–58.
Ericson, R. V., Baranek, P.M. and Chan, J. B. L. (1987) Visualizing Deviance: A Study of News Organization , Milton Keynes: Open University Press.
Ericson, R. V., Baranek, P. M. and Chan, J. B. L. (1999) ‘Negotiating Control: A Study of News Sources’, in H. Tumber (ed.) News: A Reader , Oxford: Oxford University Press, pages 297–307.
Erikson, K. T. (1962) ‘Notes on the Sociology of Deviance’, Social Problems , Volume 9, Number 4, pages 307–314.
Erikson, K. T. (1966) Wayward Puritans: A Study in the Sociology of Deviance , New York, USA: John Wiley and Sons.
Farnen, R. F. (1990) ‘Decoding the Mass Media and Terrorism Connection: Militant Extremism As Systematic and Symbiotic Processes’, in C. R. Sander (ed.) Marginal Conventions, Popular Culture, Mass Media and Social Deviance, Ohio, USA: Bowling Green State University Popular Press, pages 98–116.
Farr, K. A. (2001) ‘Women on Death Row: Media Representations of Female Evil’, in D. E. Eber and A. G. Neal (eds.) Memory and Representation: Constructed Truths and Competing Realities , Ohio, USA: Bowling Green State University Popular Press, pages 73–87.
Fiske, J. and Hartley, J. (1989) Reading Television , London: Routledge.
Fowler, R. (1994) Language in the News: Discourse and Ideology in the Press , London: Routledge.
France, A. (2007) Understanding Youth in Late Modernity , Berkshire: Open University Press.
Franzese, R. J. (2009) The Sociology of Deviance: Differences, Tradition, and Stigma , Illinois, USA: Charles C. Thomas Publisher.
Frost, C. (2000) Media Ethics and Self-Regulation , Essex: Longman.
Gado, M. (2008) Death Row Women: Murder, Justice, and the New York Press , California, USA: Greenwood Publishing Group.
Gallagher, M. (1982) ‘Negotiation of Control in Media Organizations’, in M. Gurevitch, T. Bennett, J. Curran and J. Woollacott (eds.) Culture, Society and the Media , London: Routledge, pages 148–171.
Galtung, J. and Ruge, M. H. (1965) ‘The Structure of Foreign News: The Presentation of the Congo, Cuba and Cyprus Crises in Four Norwegian Newspapers’, Journal of Peace Research , Volume 2, Number 1, pages 64–91.
Galtung, J. and Ruge, M. H. (1982) ‘Structuring and Selecting News’, in S. Cohen and J. Young (eds.) The Manufacture of News: Deviance, Social Problems and the Mass Media (First Edition), London: Constable, pages 52–64.
Gieber, W. (1999) ‘News Is What Newspapermen Make It’, in H. Tumber (ed.) News: A Reader , Oxford: Oxford University Press, pages 218–223.
Glover, D. (1984) The Sociology of the Mass Media, Cornwall: Causeway Press Limited.
Golding, P. and Elliott, P. (1999) ‘Making the News’ (Excerpt), in H. Tumber (ed.) News: A Reader , Oxford: Oxford University Press, pages 102–111.
Golding, P. and Murdock, G. (1991) ‘Culture, Communications, and Political Economy’, in J. Curran and M. Gurevitch (eds.) Mass Media and Society , London: Edward Arnold, pages 15–32.
Goode, E. and Ben-Yehuda, N. (1994) Moral Panics: The Social Construction of Deviance , Oxford: Blackwell.
Goode, E. and Ben-Yehuda, N. (2009) Moral Panics: The Social Construction of Deviance (Second Edition), West Sussex: Wiley-Blackwell.
Goodwin, A. (1990) ‘TV News: Striking the Right Balance?’, in A. Goodwin and G. Whannel (eds.) Understanding Television , London: Routledge, pages 42–59.
Gorton, K. (2009) Media Audiences: Television, Meaning and Emotion . Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
Green, D. A. (2008a) ‘Suitable Vehicles: Framing Blame and Justice When Children Kill a Child’, Crime Media Culture , Volume 4, Number 2, August, pages 197–220.
Green, D. A. (2008b) When Children Kill Children: Penal Populism and Political Culture , Oxford: Clarendon Press.
Greenslade, R. (2003) Press Gang: How Newspapers Make Profits from Propaganda , London: Macmillan.
Greer, C. (2005) ‘Crime and Media’, in C. Hale, K. Hayward, A. Wahidin and E. Wincup (eds.) Criminology , Oxford: Oxford University Press, pages 152–182.
Gross, L. (1992) ‘Out of the Mainstream: Sexual Minorities and the Mass Media’, in E. Seiter, H. Borchers, G. Kreutzner and E. M. Warth (eds.) Remote Control: Television, Audiences and Cultural Power , London: Routledge, pages 130–149.
Hall, S., Critcher, C., Jefferson, T., Clarke, J., and Roberts, B. (1978) Policing the Crisis: Mugging, the State and Law and Order, London: Macmillan.
Hall, S. (1986) ‘Media Power and Class Power’, in J. Curran, J. Ecclestone, G. Oakley and A. Richardson (eds.) Bending Reality: The State of the Media , London: Pluto Press Limited, pages 5–14.
Hall, S. (1997) ‘Discourse, Power and the Subject’, in S. Hall (ed.) Representation: Cultural Representations and Signifying Practices , London: SAGE Publications Limited, pages 41–74.
Hall, S. and Scraton, P. (1981) ‘Law, Class and Control’, in M. Fitzgerald, G. McLennan and J. Pawson (eds.) Crime and Society , London: RKP, pages 460–498.
Hart, A. (1991) Understanding the Media: A Practical Guide , London: Routledge.
Haydon, D. and Scraton, P. (2000) ‘‘Condemn a Little More, Understand a Little Less’: The Political Context and Rights Implications of the Domestic and European Rulings in the Venables - Thompson Case’, Journal of Law and Society , Volume 27, Number 3, pages 416–448.
Herman, E. (1990) ‘Media in the U.S. Political Economy’, in J. Downing, A. Sreberny-Mohammadi and A. Mohammadi (eds.) Questioning the Media , London: SAGE Publications Limited, pages 75–87.
Herman, E. S. and Chomsky, N. (1988) The Political Economy of the Mass Media, New York, USA: Pantheon.
Horrie, C. (2003) Tabloid Nation: From the Birth of the Daily Mirror to the Death of the Tabloid , London: Carlton Publishing Group.
Jewkes, Y. (2004) Media and Crime , London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Keeble, R. L. and Mair, J. eds. (2012) The Phone Hacking Scandal: Journalism on Trial , Suffolk: Arima Publishing.
Khabaz, D. V. (2006) Manufactured Schema: Thatcher, the Miners and the Culture Industry , Leicester: Matador.
Kidd-Hewitt, D. (1995) ‘Crime and the Media: A Criminological Perspective’, pages 9–24, in D. Kidd-Hewitt and R. Osborne (eds.) Crime and the Media: The Post-Modern Spectacle , London: Pluto Press.
Kitsuse, J. I. (1962) ‘Social Reaction to Deviant Behavior: Problems of Theory and Method’, Social Problems , Volume 9, Number 1, pages 247–256.
Knight, V. (2016) Remote Control Television in Prison , Hampshire: Palgrave Macmillan.
Krinsky, C. ed. (2008) Moral Panics over Contemporary Children and Youth , Surrey: Ashgate Publishing Limited.
Lacey, N. (1998) Image and Representation: Key Concepts in Media Studies , Hampshire and London: Macmillan Press Limited.
Lashmar, P. (2010) ‘The Journalist, Folk Devil’, Paper Presented at the Moral Panics in the Contemporary World , International conference, Brunel University London, 10–12 December.
Lemert, E. M. (1951) Social Pathology: A Systematic Approach to the Theory of Sociopathic Behavior , New York: McGraw-Hill.
Lemert, E. M. (1967) Human Deviance, Social Problems, and Social Control , Englewood Cliffs, USA: Prentice Hall.
Lilly, J., Cullen, F. T. and Ball, R. A. (2011) Criminological Theory: Context and Consequences , (Fifth Edition), London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Machin, D. and Niblock, S. (2006) News Production: Theory and Practice , London: Routledge.
Marsh, I. and Melville, G. (2009) Crime, Justice and the Media , Oxon: Routledge.
Masterman, L. (1990) Teaching the Media , London: Routledge.
Mawby, R. C. (2010) ‘Chibnall Revisited: Crime Reporters, the Police and “Law-and-Order News”’, British Journal of Criminology , Volume 50, Number 6, pages 1060–1076.
McKnight, D. (2012) Rupert Murdoch: An Investigation of Political Power , UK: Allen and Unwin.
McNair, B. (1994) News and Journalism in the UK , London: Routledge.
McNair, B. (2009) News and Journalism in the UK (Fifth Edition), London: Routledge.
McQuail, D. (1972) Sociology of Mass Communications , Harmondsworth: Penguin Publishers.
McQuail, D. (1991) ‘Mass Media in the Public Interest: Towards a Framework of Norms for Media Performance’, in J. Curran and M. Gurevitch (eds.) Mass Media and Society , London: Edward Arnold, pages 68–81.
McQuail, D. (2000) McQuail’s Mass Communication Theory (Fourth Edition), London: SAGE Publications Limited.
McRobbie, A. (1994) Postmodernism and Popular Culture , London: Routledge.
McRobbie, A. and Thornton, S. (1995) ‘Rethinking “Moral Panic” for Multi-mediated Social Worlds’, British Journal of Sociology , Volume 46, pages 559–574.
McRobbie, A. and Thornton, S. (2002) ‘Rethinking “Moral Panic” for Multi-mediated Social Worlds’, in J. Muncie, G. Hughes and E. McLaughlin (eds.) Youth Justice: Critical Readings , London: SAGE Publications Limited, pages 68–79.
Mercer, C. (1992) ‘Regular Imaginings: The Newspaper and the Nation’, in T. Bennett, P. Buckridge, D. Carter and C. Mercer (eds.) Celebrating the Nation: A Critical Study of Australia’s Bicentenary , Sydney, Australia: Allen and Unwin, pages 26–46.
Merton, R. K. (1968) Social Theory and Social Structure , New York, USA: The Free Press.
Moores, S. (1993) Interpreting Audiences: The Ethnography of Media Consumption , London: SAGE.
Morley, D. (1997) Television, Audiences and Cultural Studies, London: Routledge.
Muncie, J. (2006) ‘Labelling’, in E. McLaughlin and J. Muncie (eds.) The SAGE Dictionary of Criminology (Second Edition), London: SAGE Publications Limited, pages 229–231.
Muraskin, R. and Domash, S. F. (2007). Crime and the Media: Headlines vs. Reality , New Jersey, USA: Pearson Education.
Murdock, P. and Golding, P. (1977) ‘Capitalism, Communication and Class Relations’, in J. Curran, M. Gurevitch and J. Woolacott (eds.) Mass Communication and Society , London: Edward Arnold, pages 12–43.
Naylor, B. (2001). ‘Reporting Violence in the British Print Media: Gendered Stories’, The Howard Journal , Volume 40, Number 2, pages 180–194.
Newburn, T. (2007) Criminology , Devon: Willan Publishing.
Nichols, B. (2010) Introduction to Documentary (Second Edition), Indiana, USA: Indiana University Press.
North, L. (2009) The Gendered Newsroom: How Journalists Experience the Changing World of Media , Cresskill, USA: Hampton Press, Inc.
O’Connor, A. (1989) ‘The Problem of American Cultural Studies’, Critical Studies in Mass Communication , December, pages 405–413.
O’Sullivan, T., Dutton, B. and Rayner, P. (2003) Studying the Media (Third Edition), London: Arnold Publishers.
Osgerby, B. (2004) Youth Media , Oxon: Routledge.
Pearson, G. (1983) Hooligan: A History of Respectable Fears , Basingstoke: Macmillan.
Perry, D. K. (2002) Theory and Research in Mass Communication Contexts and Consequences (Second Edition), New Jersey, USA: Laurence Erlbaum Associates Inc. Publisher.
Potter, W. J. (2010) Media Literacy , London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Poynting, S., Noble, G., Tabar, P. and Collins, J. (2004) Bin Laden in the Suburbs: Criminalising the Arab Other , Sydney Institute of Criminology Series, Number 18, Sydney: The Sydney Institute of Criminology.
Prus, R. and Grills, S. (2003) The Deviant Mystique: Involvements, Realities and Regulation , Westport, USA: Praeger Publishers.
Radway, J. (1984) Reading the Romance , Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
Regoli, R., Hewitt, J. and DeLisi, M. (2011) Delinquency in Society: The Essentials , London: Jones and Bartlett.
Reiner, R. (2007) ‘Media-made Criminality: The Representation of Crime in the Mass Media’, in M. Maguire, R. Morgan and R. Reiner (eds.) The Oxford Handbook of Criminology (Fourth Edition), Oxford: Oxford University Press, pages 302–340.
Robson, G. (2004) “No One Likes Us, We Don’t Care”: The Myth and Reality of Millwall Fandom , Oxford: Berg.
Schirato, T. and Yell, S. (2000) Communication and Culture: An Introduction , London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Schissel, B. (1997) Blaming Children: Youth Crime, Moral Panics and the Politics of Hate , Nova Scotia, Canada: Fernwood Publishing.
Schissel, B. (2006) Still Blaming Children: Youth Conduct and the Politics of Child Hating , Nova Scotia, Canada: Fernwood Publishing.
Schissel, B. (2008) ‘Justice Undone: Public Panic and the Condemnation of Children and Youth’, in C. Krinsky (ed.) Moral Panics Over Contemporary Children and Youth , Surrey: Ashgate Publishing Limited, pages 15–30.
Schlesinger, P. (1987) Putting ‘Reality’ Together: BBC News , London: Methuen and Company.
Schlesinger, P. and Tumber, H. (1994) Reporting Crime: The Media Politics of Criminal Justice , Oxford: Clarendon Press.
Schlesinger, P. and Murdock, G. (1991) ‘The Media Politics of Crime and Criminal Justice’, British Journal of Sociology , Volume 42, Number 3, pages 397–420.
Scraton, P. (2004) ‘Streets of Terror: Marginalisation, Criminalisation and Moral Renewal’, Social Justice , Volume 3, Numbers 1–2, pages 130–158.
Scraton, P. (2008) ‘The Criminalisation and Punishment of Children and Young People: Introduction’, in P. Scraton (ed.) Current Issues in Criminal Justice , Volume 20, Number 1, pages 1–13.
Shawcross, W. (1992) Rupert Murdoch: Ringmaster of the Information Circus , London: Random House.
Sheptycki, J. (2003) ‘Against Transnational Organized Crime’, in M. E. Beare (ed.) Critical Reflections on Transnational Organized Crime, Money Laundering and Corruption , Canada: University of Toronto Press, pages 120–144.
Shipman, M. (2002) ‘The Penalty Is Death’: US Newspaper Coverage of Women’s Executions , Missouri, USA: University of Missouri Press.
Silverstone, R. (1999a) Why Study the Media? London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Silverstone, R. (1999b) Television and Everyday Life . London: Routledge.
Simpson, B. (1997) ‘Youth Crime, the Media and Moral Panic’, in J. Bessant and R. Hil (eds.) Youth Crime and the Media: Media Representations of and Reactions to Young People in Relation to Law and Order , Hobart, Australia: Australian Clearinghouse for Youth Studies, pages 9–16.
Slattery, M. (2003) Key Ideas in Sociology , Cheltenham: Nelson Thornes Limited.
Springhall, J. (2008) ‘“The Monsters Next Door: What Made Them Do It?” Moral Panics Over the Causes of High School Multiple Shootings (Notably Columbine)’, in Krinsky, C. (ed.) Moral Panics Over Contemporary Children and Youth , Surrey: Ashgate Publishing Limited, pages 47–70.
Surette, R. (1998) Media, Crime and Criminal Justice: Images and Realities (Second Edition), California, USA: Wadsworth.
Tait, R. (2012) ‘Never Waste a Good Crisis: The British Phone Hacking Scandal and Its Implications for Politics and the Press’, in H. A. Semetko and M. Scammell (eds.) The SAGE Handbook of Political Communication , London: SAGE Publications Limited, pages 518–527.
Chapter Google Scholar
Tannebaum, F. (1938) Crime and the Community , New York: Columbia University Press.
Taylor, I., Walton, P. and Young, J. (1973) The New Criminology: For a Social Theory of Deviance , London: Routledge and Kegan Paul plc.
Thompson, K. ed. (1997) Media and Cultural Regulation , London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Thompson, K. (1998) Moral Panics: Key Ideas , London: Routledge.
Tierney, J. (2010) Criminology: Theory and Context (Third Edition), Harlow: Longman.
Tolson, A. (1996) Mediations: Text and Discourse in Media Studies , London: Arnold Publishers.
Unger, S. (2001) ‘Moral Panic Versus the Risk Society: The Implications of the Changing Sites of Social Anxiety’, British Journal of Society , Volume 52, June, pages 271–291.
van Dijk, T. A. (1991) Racism and the Press: Critical Studies in Racism and Migration , London: Routledge.
van Zoonen, L. (1996) Feminist Media Studies , London: SAGE Publications Limited.
Waddington, P. A. J. (1986) ‘Mugging as a Moral Panic: A Question of Proportion’, British Journal of Sociology , Volume 37, June, pages 245–259.
Waiton, S. (2008) The Politics of Antisocial Behaviour: Amoral Panics , London: Routledge.
Watson, T. and Hickman, M. (2012) Dial M for Murdoch: News Corporation and the Corruption of Britain , London, UK: Penguin.
West, D. J. (1976) The Young Offender , Middlesex: Penguin Books Limited.
Whale, J. (1980) The Politics of the Media (Revised Edition), Glasgow: William Collins Sons and Co. Limited.
White, R. (2002) Understanding Youth Gangs , Canberra, Australia: Australian Institute of Criminology.
Wilkins, L. T. (1964) Social Deviance: Social Policy, Action, and Research , London: Tavistock.
Williams, R. (1977) Marxism and Literature , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Williams, P. and Dickinson, J. (1993) ‘Fear of Crime: Read All About It? The Relationship Between Newspaper Crime Reporting and Fear of Crime’, British Journal of Criminology , Volume 33, Number 1, pages 33–56.
Wright Mills, C. (1976) The Sociological Imagination , New York: Oxford University Press.
Wykes, M. (2001) News, Crime, and Culture , London: Pluto.
Young, J. (1971) The Drugtakers: The Social Meaning of Drug Use , London: McGibbon and Kee.
Young, J. (2008) ‘Moral Panics’, in L. Kontos and D. C. Brotherton (eds.) Encyclopedia of Gangs , California, USA: Greenwood Publishing Group, pages 174–176.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Westminster History, Sociology and Criminology, London, UK
Faith Gordon
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Copyright information
© 2018 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Gordon, F. (2018). The Significance and Impact of the Media in Contemporary Society. In: Children, Young People and the Press in a Transitioning Society. Palgrave Socio-Legal Studies. Palgrave Macmillan, London. https://doi.org/10.1057/978-1-137-60682-2_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/978-1-137-60682-2_2
Published : 10 March 2018
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, London
Print ISBN : 978-1-137-60681-5
Online ISBN : 978-1-137-60682-2
eBook Packages : Law and Criminology Law and Criminology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Essay on Media Influence
Students are often asked to write an essay on Media Influence in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Media Influence
Introduction.
Media is a powerful tool that influences our lives daily. It includes television, radio, newspapers, and the internet.
Media’s Role
Positive influence.
Media can educate us, promote positive values, and inspire creativity. It can make us aware of social issues.
Negative Influence
However, media can also spread misinformation, promote harmful stereotypes, and influence unhealthy behaviors.
250 Words Essay on Media Influence
Media, in its various forms, plays a pivotal role in shaping public opinion and influencing our thoughts, attitudes, and behaviors. It has transformed into a powerful entity, capable of swaying public sentiment, steering political discourse, and even defining societal norms.
The Power of Media
Media’s power lies in its ability to disseminate information, educate masses, and stimulate conversations. It can frame narratives, highlight issues, and even influence policy making. It is not merely a passive channel of information, but an active participant in shaping public discourse.
Media and Perception
Media can significantly influence our perception of reality. It can shape our understanding of societal norms, political ideologies, and cultural values. It can subtly perpetuate stereotypes, reinforce biases, or challenge them. The portrayal of events and individuals in media often determines how they are perceived by the public.
Media and Behavior
Media also impacts our behaviors and choices. It influences our consumption patterns, lifestyle choices, and even our political leanings. The persuasive power of advertising and the influence of celebrity endorsements are classic examples of media’s impact on behavior.
In conclusion, media’s influence is profound and far-reaching. It is a double-edged sword, capable of both informing and misleading, empowering and manipulating. As consumers of media, it is crucial to critically evaluate the information we consume, understand the potential biases, and make informed decisions. The influence of media is an essential topic of study, given its significant role in shaping our society.
500 Words Essay on Media Influence
Media, in its various forms – print, broadcast, or digital – has emerged as a powerful tool that can shape public opinion and influence political, social, and economic outcomes. It has the capacity to reach millions of people simultaneously, making it an effective instrument for mass communication. The power of media lies in its ability to frame issues, set agendas, and shape narratives. It can highlight or downplay matters, thereby directing public attention and influencing the discourse.
Media as a Socializing Agent
Media plays a significant role in the socialization process, especially among the younger generation. It often serves as a primary source of information, shaping their worldview and values. Media content, whether news, entertainment, or advertising, exposes viewers to diverse perspectives and cultures, fostering tolerance and understanding. However, it can also perpetuate stereotypes, reinforce biases, and contribute to cultural homogenization.
Media and Consumerism
The media’s influence on consumer behavior is undeniable. Advertising, a prominent media function, persuades individuals to purchase products or services, often creating a perceived need. This potent tool can drive consumer trends and influence lifestyle choices, contributing to a culture of consumerism. While this can stimulate economic growth, it can also lead to overconsumption and environmental degradation.
The Dark Side of Media Influence
Media literacy: a necessary skill.
In the face of media’s pervasive influence, media literacy becomes crucial. It empowers individuals to critically analyze media content, discerning fact from fiction, and recognizing bias and manipulation. Media literacy fosters informed citizenship, enabling individuals to engage constructively in democratic processes.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

ADVERTISEMENTS:
Essay on the Role of Media in the Modern World
The importance and the impact of the media, written or electronic cannot be marginalized in the world of today. In the modern world of quick communication and quick information, media plays a very crucial role.
The original role of the media was and still is to give to the public all relevant information about occurrences in the country and the world. Now the written media includes a host of publications, dailies, fortnightly, weeklies, monthly all giving information about events with supplement of suggestions and comments by learned people. Today, the print media has acquired such proportions that, there is absolutely no avenue of knowledge or information that is left out.
Multifarious avenues are being touched upon, whether it be local, national or international. All avenues of news, business, health, sports, films and entertainment are being dwelt upon at great length. The great advantage of this media in spreading of news, knowledge and information through the length and breadth of the world.
Image Source: convergentdivergent.files.wordpress.com
In these days of awareness, even the remotest of villages of India get at least one daily newspaper in their local language. This keeps them abreast of the latest news and happenings of the world. Moreover, written media is the cheapest medium of collecting all important information of the district, city, country and the world.
Next in importance come the electronic media, i.e. the radio and the television. I call it second to the print media because it is more expensive and so, less common in far flung areas of the country. With ever so many channels on the radio and the television there is no information that is left untouched. This media specially caters more to urban areas as it is more expensive to buy and then to maintain.
Thus, the media, whatever it be print or the electronic media, its importance at least in the modern world cannot be denigrated. While we are sitting in our drawing rooms at home, we can get all the information of all happenings around the world. We get a sea of knowledge and all the information, relaxing at home.
So much so good, but, what we notice today, with the freedom of the press taking new proportions, the media is becoming slightly out of control and also partial. The latest trend in the media is that it has become tainted with signs of extreme partiality.
I personally feel that, the media is at times overstepping its limits and to some extent misusing its freedom. The job of the media is just to give information of what happens and not to add its own partial views to the information. The job of the media should remain restricted only to reporting facts as to when and how they occur, and leave the readers to form their own opinions. However, this is no more true of the modern trends of the media. They get news and paint them as per their own personal leanings and beliefs. This I’d say is not correct reporting as, it is likely to colour the views of the readers/ viewers. The task of the media is just to report and not colour the views of the people.
This is the position of the media because of the obvious political leanings and influences, and this I daresay should not be allowed to grow. It must be remembered that, the media plays a very important link between the people and organizations/Government. Thus, if a report is not correct or painted the common man gets a wrong picture of facts. In this way, the media is harming itself and tarnishing its image in front of the common man. If the common man loses faith in the truth of the media, it will be a bad symptom and a bad day for all.
It would be good if the media restricts itself only to passing On correct and exact information only, without any comments for or against any political party it would be doing its job correctly and sincerely. Political masters should be only heard and not followed by a media which is good and impartial.
Related Essays:
- 450 Words Short Essay on Alcoholism
- Essay on Reservation: Right or Wrong
- Short Essay on International Criminal Court
- Essay on Effects of Over Population
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
More Americans now see the media’s influence growing compared with a year ago
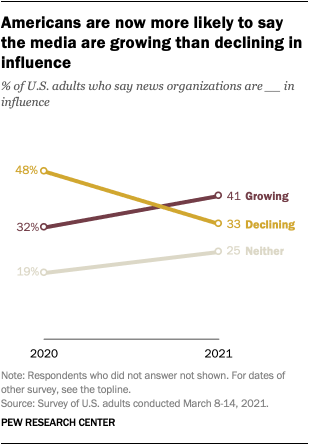
Americans’ views about the influence of the media in the country have shifted dramatically over the course of a year in which there was much discussion about the news media’s role during the election and post-election coverage , the COVID-19 pandemic and protests about racial justice . More Americans now say that news organizations are gaining influence than say their influence is waning, a stark contrast to just one year ago when the reverse was true.
When Americans were asked to evaluate the media’s standing in the nation, about four-in-ten (41%) say news organizations are growing in their influence, somewhat higher than the one-third (33%) who say their influence is declining, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted March 8-14, 2021. The remaining one-quarter of U.S. adults say they are neither growing nor declining in influence.
To examine Americans’ views about the influence of the news media, Pew Research Center surveyed 12,045 U.S. adults from March 8 to 14, 2021. Everyone who completed the survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology . See here to read more about the questions used for this analysis and the methodology .
This is the latest report in Pew Research Center’s ongoing investigation of the state of news, information and journalism in the digital age, a research program funded by The Pew Charitable Trusts, with generous support from the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation.
By comparison, Americans in early 2020 were far more likely to say the news media were declining in influence . Nearly half (48%) at that time said this, compared with far fewer (32%) who said news organizations were growing in influence.
The 2021 figures more closely resemble responses from 2011 – the next most recent time this was asked – and before, in that more Americans then said the news media were growing in influence than declining. Views could have shifted in the gap between 2011 and 2020, but if so, they have now shifted back. (It should be noted that prior to 2020, this question was asked on the phone instead of on the web.)
What’s more, this shift in views of the media’s influence in the country occurred among members of both political parties – and in the same direction.
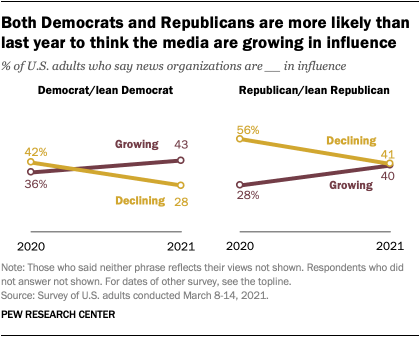
Republicans and Republican-leaning independents are about evenly split in whether they think news organizations are growing (40%) or declining in influence (41%). This is very different from a year ago, when Republicans were twice as likely to say their influence was declining than growing (56% vs. 28%).
And Democrats and Democratic leaners are now much more likely to say news organizations are growing (43%) than declining in influence (28%), while a year ago they were slightly more likely to say influence was declining (42% vs. 36% growing).
Overall, then, Republicans are still more likely than Democrats to say the news media are losing standing in the country, though the two groups are more on par in thinking that the media are increasing in their influence. (Democrats are somewhat more likely than Republicans to say news organizations are neither growing nor declining in influence – 29% vs. 19%.)
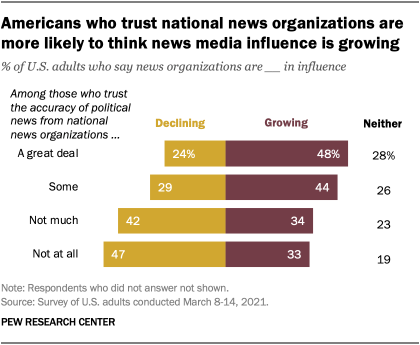
Trust in media closely ties to whether its influence is seen as growing or declining. Those who have greater trust in national news organizations tend to be more likely to see the news media gaining influence, while those with low levels of trust are generally more likely to see it waning.
Americans who say they have a great deal of trust in the accuracy of political news from national news organizations are twice as likely to say the news media are growing than declining in influence (48% vs. 24%, respectively). Conversely, those who have no trust at all are much more likely to think that news organizations are declining (47% vs. 33% who say they are growing).
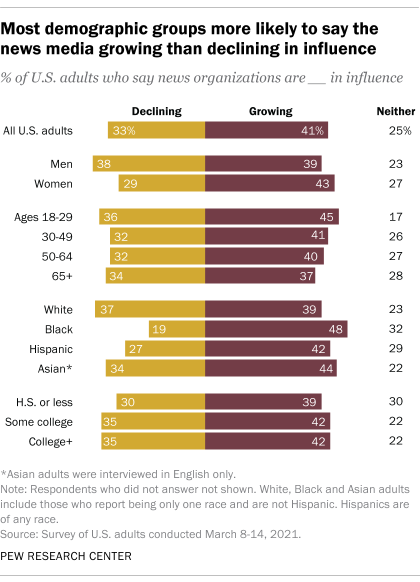
Black Americans are far more likely to think that the news media are growing in influence rather than declining (48% vs. 19%, respectively), as are Hispanic Americans though to a somewhat lesser degree. White Americans, on the other hand, are about evenly split in thinking the news media are growing or declining in influence (39% vs. 37%, respectively). And while men are about evenly split (39% growing vs. 38% declining), women are more likely to say news organizations are growing (43%) than declining (29%) in influence.
Note: Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology .
- Media Attitudes
- Politics & Media

Jeffrey Gottfried is an associate director focusing on internet and technology research at Pew Research Center .

Naomi Forman-Katz is a research analyst focusing on news and information research at Pew Research Center .
Americans’ Changing Relationship With Local News
Introducing the pew-knight initiative, 8 facts about black americans and the news, u.s. adults under 30 now trust information from social media almost as much as from national news outlets, u.s. journalists differ from the public in their views of ‘bothsidesism’ in journalism, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
“Role of Media in Our Society” || Essay on Role of Media
Role of Media: Today, the world is in the grip of media. Media has played a vital role in making the world well connected. Though media is not the only communication medium used to dispense the flow of information, its importance is huge.

Essay, Article, on Role of Media in Society
The ability of the media to reach a wide audience with a strong and influential message has the potential to have a strong social and cultural and political impact upon society as well as being the main source of entertainment. In the early times, print media has always been a dominant medium, but the television has become the main source of mass media since its emergence.
There are various sources of communication these days. With the evolution of digital technology, the role of mass media has taken a significant place in our lives and its role is changing at a rapid pace. In the present times, we cannot imagine our lives without mass media.

Essay About Role of Media Our Society
Mass media is any medium used to transmit mass communication i.e. a message created by a person or a group of people sent through a transmitting device to a large audience or market. In today’s connected society, it’s the media, that has become the most supply of knowledge With the advent of digitally enabled communication devices, the flow of information from one geographical location to another has increased in speed considerably.
Various types of sources like cell phones, computers, different network channels over cable or satellite TV, internet, newspapers, books, magazines, and radio channels are emerging at a very rapid pace providing the people with a medium to connect themselves with the outside world.
Through the internet, the connectivity with the world has become so strong through all the means that anything that happens anywhere, the information is passed within seconds. The people can receive information wherever they are
The radio and television channels to have become an important source of passing information in no time. Most of the cell phones have radio channels on it through which the user is connected to the world always.
Ta Media has a great impact on its user, especially through television and radio. Media has the supreme potential to educate, inform, and condition people’s mind. Through these sources, even the uneducated can have access to the world of knowledge and information.
Radio and television are widely used means of mass media that is useful for both literate and illiterate and has ability in spreading awareness in various fields to the mass. The persuasiveness of influential media such as television, Ghostwriter Schweiz and print media have been largely responsible for structuring people’s daily lives and routines.
This is because people have a tendency to follow what they see and believe. Media has thus played a great role in increasing consumerism and opting for universally accepted articles. This is also making people brand conscious.
Media also has a negative impact on the society. With the excess information available to be passed, sometimes unauthentic and irrelevant information is also communicated which is harmful to the society. It also damages the true essence of journalism.
Role of Media Essay in English
The negative propaganda results in violence, crimes, murders, etc. It is very common that certain things shown with the objective of entertainment is giving a wrong message to the society.
Vulgarism, violence, abuses shown with the purpose of entertainment are wrongly taken by the viewers and then followed in real life. All these are contributing to the moral downfall of society.
It has been also noticed that the politicians and other influential people manipulate the information and sources of media for their self-interest. Therefore, believing in all the information available is also not beneficial.
In today’s time, it is actually impossible to escape from any source of information available. These sources are all around us. We are completely in the grip of these sources of media and that is why it is difficult to cut off from the world.
Also, too much of information available through media is making people confused. It is, therefore, an individual’s own responsibility to access the required and relevant information partner Bachelorarbeit schreiben lassen . The people need to draw a line beyond which they do not allow the media to negatively influence their lives.
Easy Writing
Essay writing, subscribe to get the new updates, related articles.

First Day At My School : Essay For School Student All Class

Save Water Save Life Short an Essay Paragraph
Earth Day Essay: Earth Day Essay in English

My Favorite Author Essay on Short Words Paragraph

Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing

Why social media has changed the world — and how to fix it
Press contact :, media download.

*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."

Previous image Next image
Are you on social media a lot? When is the last time you checked Twitter, Facebook, or Instagram? Last night? Before breakfast? Five minutes ago?
If so, you are not alone — which is the point, of course. Humans are highly social creatures. Our brains have become wired to process social information, and we usually feel better when we are connected. Social media taps into this tendency.
“Human brains have essentially evolved because of sociality more than any other thing,” says Sinan Aral, an MIT professor and expert in information technology and marketing. “When you develop a population-scale technology that delivers social signals to the tune of trillions per day in real-time, the rise of social media isn’t unexpected. It’s like tossing a lit match into a pool of gasoline.”
The numbers make this clear. In 2005, about 7 percent of American adults used social media. But by 2017, 80 percent of American adults used Facebook alone. About 3.5 billion people on the planet, out of 7.7 billion, are active social media participants. Globally, during a typical day, people post 500 million tweets, share over 10 billion pieces of Facebook content, and watch over a billion hours of YouTube video.
As social media platforms have grown, though, the once-prevalent, gauzy utopian vision of online community has disappeared. Along with the benefits of easy connectivity and increased information, social media has also become a vehicle for disinformation and political attacks from beyond sovereign borders.
“Social media disrupts our elections, our economy, and our health,” says Aral, who is the David Austin Professor of Management at the MIT Sloan School of Management.
Now Aral has written a book about it. In “The Hype Machine,” published this month by Currency, a Random House imprint, Aral details why social media platforms have become so successful yet so problematic, and suggests ways to improve them.
As Aral notes, the book covers some of the same territory as “The Social Dilemma,” a documentary that is one of the most popular films on Netflix at the moment. But Aral’s book, as he puts it, "starts where ‘The Social Dilemma’ leaves off and goes one step further to ask: What can we do about it?”
“This machine exists in every facet of our lives,” Aral says. “And the question in the book is, what do we do? How do we achieve the promise of this machine and avoid the peril? We’re at a crossroads. What we do next is essential, so I want to equip people, policymakers, and platforms to help us achieve the good outcomes and avoid the bad outcomes.”
When “engagement” equals anger
“The Hype Machine” draws on Aral’s own research about social networks, as well as other findings, from the cognitive sciences, computer science, business, politics, and more. Researchers at the University of California at Los Angeles, for instance, have found that people obtain bigger hits of dopamine — the chemical in our brains highly bound up with motivation and reward — when their social media posts receive more likes.
At the same time, consider a 2018 MIT study by Soroush Vosoughi, an MIT PhD student and now an assistant professor of computer science at Dartmouth College; Deb Roy, MIT professor of media arts and sciences and executive director of the MIT Media Lab; and Aral, who has been studying social networking for 20 years. The three researchers found that on Twitter, from 2006 to 2017, false news stories were 70 percent more likely to be retweeted than true ones. Why? Most likely because false news has greater novelty value compared to the truth, and provokes stronger reactions — especially disgust and surprise.
In this light, the essential tension surrounding social media companies is that their platforms gain audiences and revenue when posts provoke strong emotional responses, often based on dubious content.
“This is a well-designed, well-thought-out machine that has objectives it maximizes,” Aral says. “The business models that run the social-media industrial complex have a lot to do with the outcomes we’re seeing — it’s an attention economy, and businesses want you engaged. How do they get engagement? Well, they give you little dopamine hits, and … get you riled up. That’s why I call it the hype machine. We know strong emotions get us engaged, so [that favors] anger and salacious content.”
From Russia to marketing
“The Hype Machine” explores both the political implications and business dimensions of social media in depth. Certainly social media is fertile terrain for misinformation campaigns. During the 2016 U.S. presidential election, Russia spread false information to at least 126 million people on Facebook and another 20 million people on Instagram (which Facebook owns), and was responsible for 10 million tweets. About 44 percent of adult Americans visited a false news source in the final weeks of the campaign.
“I think we need to be a lot more vigilant than we are,” says Aral.
We do not know if Russia’s efforts altered the outcome of the 2016 election, Aral says, though they may have been fairly effective. Curiously, it is not clear if the same is true of most U.S. corporate engagement efforts.
As Aral examines, digital advertising on most big U.S. online platforms is often wildly ineffective, with academic studies showing that the “lift” generated by ad campaigns — the extent to which they affect consumer action — has been overstated by a factor of hundreds, in some cases. Simply counting clicks on ads is not enough. Instead, online engagement tends to be more effective among new consumers, and when it is targeted well; in that sense, there is a parallel between good marketing and guerilla social media campaigns.
“The two questions I get asked the most these days,” Aral says, “are, one, did Russia succeed in intervening in our democracy? And two, how do I measure the ROI [return on investment] from marketing investments? As I was writing this book, I realized the answer to those two questions is the same.”
Ideas for improvement
“The Hype Machine” has received praise from many commentators. Foster Provost, a professor at New York University’s Stern School of Business, says it is a “masterful integration of science, business, law, and policy.” Duncan Watts, a university professor at the University of Pennsylvania, says the book is “essential reading for anyone who wants to understand how we got here and how we can get somewhere better.”
In that vein, “The Hype Machine” has several detailed suggestions for improving social media. Aral favors automated and user-generated labeling of false news, and limiting revenue-collection that is based on false content. He also calls for firms to help scholars better research the issue of election interference.
Aral believes federal privacy measures could be useful, if we learn from the benefits and missteps of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and a new California law that lets consumers stop some data-sharing and allows people to find out what information companies have stored about them. He does not endorse breaking up Facebook, and suggests instead that the social media economy needs structural reform. He calls for data portability and interoperability, so “consumers would own their identities and could freely switch from one network to another.” Aral believes that without such fundamental changes, new platforms will simply replace the old ones, propelled by the network effects that drive the social-media economy.
“I do not advocate any one silver bullet,” says Aral, who emphasizes that changes in four areas together — money, code, norms, and laws — can alter the trajectory of the social media industry.
But if things continue without change, Aral adds, Facebook and the other social media giants risk substantial civic backlash and user burnout.
“If you get me angry and riled up, I might click more in the short term, but I might also grow really tired and annoyed by how this is making my life miserable, and I might turn you off entirely,” Aral observes. “I mean, that’s why we have a Delete Facebook movement, that’s why we have a Stop Hate for Profit movement. People are pushing back against the short-term vision, and I think we need to embrace this longer-term vision of a healthier communications ecosystem.”
Changing the social media giants can seem like a tall order. Still, Aral says, these firms are not necessarily destined for domination.
“I don’t think this technology or any other technology has some deterministic endpoint,” Aral says. “I want to bring us back to a more practical reality, which is that technology is what we make it, and we are abdicating our responsibility to steer technology toward good and away from bad. That is the path I try to illuminate in this book.”
Share this news article on:
Press mentions.
Prof. Sinan Aral’s new book, “The Hype Machine,” has been selected as one of the best books of the year about AI by Wired . Gilad Edelman notes that Aral’s book is “an engagingly written shortcut to expertise on what the likes of Facebook and Twitter are doing to our brains and our society.”
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with Danny Crichton of TechCrunch about his new book, “The Hype Machine,” which explores the future of social media. Aral notes that he believes a starting point “for solving the social media crisis is creating competition in the social media economy.”
New York Times
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with New York Times editorial board member Greg Bensinger about how social media platforms can reduce the spread of misinformation. “Human-in-the-loop moderation is the right solution,” says Aral. “It’s not a simple silver bullet, but it would give accountability where these companies have in the past blamed software.”
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with Kara Miller of GBH’s Innovation Hub about his research examining the impact of social media on everything from business re-openings during the Covid-19 pandemic to politics.
Prof. Sinan Aral speaks with NPR’s Michael Martin about his new book, “The Hype Machine,” which explores the benefits and downfalls posed by social media. “I've been researching social media for 20 years. I've seen its evolution and also the techno utopianism and dystopianism,” says Aral. “I thought it was appropriate to have a book that asks, 'what can we do to really fix the social media morass we find ourselves in?'”
Previous item Next item
Related Links
- MIT Sloan School of Management
Related Topics
- Business and management
- Social media
- Books and authors
- Behavioral economics
Related Articles

The catch to putting warning labels on fake news

Our itch to share helps spread Covid-19 misinformation

Better fact-checking for fake news

Study: On Twitter, false news travels faster than true stories

Social networking
More mit news.

New computer vision method helps speed up screening of electronic materials
Read full story →

MIT Faculty Founder Initiative announces three winners of entrepreneurship awards

How a quantum scientist, a nurse, and an economist are joining the fight against global poverty

Catalyst Symposium helps lower “activation barriers” for rising biology researchers
Protein study could help researchers develop new antibiotics

Through econometrics, Isaiah Andrews is making research more robust
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
Role of Media Essay | Essay on Role of Media for Students and Children in English
February 14, 2024 by sastry
Role of Media Essay: Media is known as the fourth pillar of democracy due to its important role in shaping public opinion. Today, in this ultra modern world, the role of media has been augmenting day by day. It has been surving as a vigilant watch dog of India.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more.
Long and Short Essays on Role of Media for Kids and Students in English
Given below are two essays in English for students and children about the topic of ‘Role of Media’ in both long and short form. The first essay is a long essay on Role of Media of 400-500 words. This long essay about Role of Media is suitable for students of class 7, 8, 9 and 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants. The second essay is a short essay on Role of Media of 150-200 words. These are suitable for students and children in class 6 and below.
Long Essay on Role of Media 500 Words in English
Below we have given a long essay on Role of Media of 500 words is helpful for classes 7, 8, 9 and 10 and Competitive Exam Aspirants. This long essay on the topic is suitable for students of class 7 to class 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants.
Print Media has created an awareness among the people regarding their rights and duties. We can update ourselves just by going through the morning newspaper, getting each and every kind of news from every nook and corner of the world. Catering to all this, today mass media is well-established, wherein it is remarkable to see the All India Radio (AIR) now reaches 90% of the population, TV more than 80% and over 5,600 newspapers, 150 of these publications are published daily in over 100 languages.
There has been a worldwide growth of the Print Media even after the emergence of the electronic media. Moreover, there has been an increase in the circulation of newspapers around the world even after the emergence of electronic media and the internet. The newspapers play a very important role in the working of any democracy. Our Constitution too grants us the Right to Freedom of Expression which is manifested, in free press in our country. In a democracy, newspapers are the best way of educating people politically and socially. They play a decisive role no only in updating the public but also in formulating a well-balanced public opinion. The public read about the current events, interpret them and learn to intelligently participate in the political, social and economic affairs of the country.
Newspapers also reflect public opinion, thus formed through letters to the Editor which are usually published in a separate column. Moreover, Print Media provides great incentive to business by large number of advertisements on a variety of things s,uch as a house on sale, shops, electronic goods, stationary, cloth stores, glass ware, crockery shops etc. Matrimonial advertisements, job-opportunities, obituaries are all advertised through the Print Media.
Now-a-days, another very popular means of social interaction and propagation that has emerged along with the Print Media is the rise of Electronic Media. The birth of electronic media took place with the invention of radio, it further got spread through television, then through the laptops, computers via internet and now in every hand in I the form of mobile phones. Electronic Media has a very emphatic and motivating effect on the society today. The various news channels keep the vigilant citizens updated. Channels like Discovery and National Geographic keep the inquisitive mind busy and satisfy every intellectual query of a probing mind. Along with these, there are endless number of entertainment channels solely to amuse and tickle the audience. Now, quite a number of kids’ channels have come up to cater to this special section of the society. Television can help popularise technology and internationalise, and universalise our outlook.
These-days, the internet too is gaining a huge momentum, in terms of its role in media. This is because traditional ‘silent citizens’ for traditional media like newspaper often ‘speak out’ through the internet platform to let a society hear their voices. This has in turn increased the society’s level of democratic awareness wherein people of all age groups and sections formulate their opinion on the social networking sites. It is also because internet can be used by anybody, anywhere, at anytime easily to express themselves economically. Infact, these days there are many independent websites established which hope to monitor parliament activities and other crucial operations of society. The only major drawback internet is facing is that its spread is limited.
Yet, there is other side to media too, wherein it tries to cater to the transient needs of life and to appeal to the emotions of masses instead of maintaining an intellectual level. They even lower the moral tone and publish sub-standard materials to increase their readership.
Many times, newspapers try to ally themselves to particular ideology or a party instead of maintaining impartiality and indulge in mudslinging or even communal propaganda. These thoughtless means for easy money provides temporary financial benefits to a handful of people but prove to be extremely disastrous in the end for society at large.

Short Essay on Role of Media 200 Words in English
Below we have given a short essay on Role of Media is for Classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. This short essay on the topic is suitable for students of class 6 and below.
People involved in this profession should realise the massive responsibility they shoulder and sacredness of the duty that they perform. They should avoid personal bias and prejudice to cloud their good sense. Instead, they should try to combat social evils, communal forces and also keep the government on its toes, committed to its promises. It should try to make people politically conscious and keep patriotism and national pride alive in the people.
In today’s world media has become as necessary as food and clothing. In the earlier times, it united people for freedom struggle, today it is uniting people against social evils. It has always been a crucial part, a ‘mirror’ of society in every age, however it only differs in its approach, means and spread, from time to time. It has immense power which needs to be carefully harnessed. Moreover, it has also been seen that media is reduced to a commercialised sector, eying the news which are hot and good at selling. The goal is merely to gain the television rating points.
I believe, if the media identifies its responsibility and work sincerely and honestly, then it can serve as a great force in building the nation.
Role of Media Essay Word Meanings for Simple Understanding
- Augmenting – increasing, growing, raising
- Manifested – expressed, established
- Decisive – crucial, significant, critical
- Formulating – expressing, developing
- Obituaries – a published notice of a death, sometimes with a brief biography of the deceased
- Propagation – spreading, spread, promotion, communication, distribution
- Emphatic – forceful and positive; definite; direct
- Inquisitive – curious, questioning, inquiring
- Probing – searching
- Amuse – entertain, please, delight
- Transient – short-term, temporary
- Ally – associate, connect
- Mudslinging – efforts to discredit one’s opponent by malicious or scandalous attacks
- Propaganda – information, advertising, promotion
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education
Selected Essays/Role of Media
Media is known as the fourth pillar of democracy due to its important role in shaping public opinion. Today, in this ultra modern world, the role of media has been augmenting day by day. It has been serving as a vigilant watch dog of India. Print Media has created an awareness among the people regarding their rights and duties. We can update ourselves just by going through the morning newspaper, getting each and every kind of news from every nook and corner of the world. Catering to all this, today mass media is well-established, wherein it is remarkable to see the All India radio (AIR) now reaches 90% of the population, TV more than 80% and over 5,600 newspapers, 150 of these publications are published daily in over 100 languages.
There has been a worldwide growth of the Print Media even after the emergence of the electronic media. Moreover, there has been an increase in the circulation of newspapers around the world even after the emergence of electronic media and the internet. The newspapers play a very important role in the working of any democracy. Our Constitution too grants us the Right to Freedom of Expression which is manifested, in free press in our country. In a democracy, newspapers are the best way of educating people politically and socially. They play a decisive role not only in updating the public but also in formulating a well-balanced public opinion. The public read about the current events, interpret them and learn to intelligently participate in the political, social and economic affairs of the country.
Newspapers also reflect public opinion, thus formed through letters to the editor which are usually published in a separate column. Moreover, print Media provides great incentive to business by large number of advertisements on a variety of things such as a house on sale, shops, electronic goods, stationary, cloth stores,glass ware, crockery shops etc. Matrimonial advertisements, job-opportunities, obituaries are all advertised through the Print Media.
Nowadays, another very popular means of social interaction and propagation that has emerged along with the print Media is the rise of Electronic Media. The bit of electronic media took place with the invention of radio, it further got spread through television, then through the laptops, computers via internet and now in very hand in the form of mobile phones. Electronic Media has a very emphatic and motivating effect on the society today. The various news channels keep the vigilant citizens updated. Channels like Discovery and National Geographic keep the inquisitive mind busy and satisfy every intellectual query of a probing mind. Alongwith these, there are endless number of entertainment channels solely to amuse and tickle the audience. Now, quite a number of kids’ channels have come up to carter to this special section of the society. Television can help popularize technology and internationalise and universalize our outlook.
These days the internet too is gaining a huge momentum, in terms of its role in media. This is because traditional ‘silent citizens’ for traditional media like newspaper often ‘speak out’ through the internet platform to let a society hear their voices. This has fin turn increased the society’s level of democratic awareness wherein people of all age groups and sections formulate their opinion on the social networking sites. It is also because internet can be used by anybody, anywhere, at anytime easily to express themselves economically. Infact, these days there are many independent websites established which how to monitor parliament activities and other crucial operations of society. The only major drawback internet is facing is that its spread is limited. Yet, there is other side of media too, wherein it tries to carter to the transient needs of life and to appeal to the emotions of masses instead of maintaining an intellectual level. They even lower the moral tone and publish sub-standard materials to increase their readership.
Many a times, newspapers try to ally themselves to particular ideology or a party instead of maintaining impartiality and indulge in mudslinging or even communal propaganda. These thoughtless means of r easy money provides temporary financial benefits to a handful of people but prove to be extremely disastrous in the end or society at large.
People involved in this profession should realize the massive responsibility they shoulder and sacredness of the duty that they perform. They should avoid personal bias and prejudice to cloud their good sense. Instead, they should try to combat social evils ,communal forces and also keep the government on its toes, committed to its promises. It should try to make people politically conscious and keep patriotism and national pride alive in the people.
In today’s world media has become as necessary as food and clothing. In the earlier times, it united people for freedom struggle, today it is uniting people against social evils. It has always been a crucial part, a ‘mirror’ of society inn every age, however it only differs in its approach, means and spread, form time to time. It has immense power which needs to be carefully harnessed. Moreover, it has also been seen that media is reduced to a commercialized sector, eyeing the news which are hot and good at selling. The goal is merely to gain the television rating points.
I believe, if the media identifies its responsibility and work sincerely and honestly, then it can serve as a great force in building the nation.
- Book:Selected Essays
Navigation menu
Home / Essay Samples / Social Issues / Globalization / Media and Globalization: Shaping Our Perception of the World
Media and Globalization: Shaping Our Perception of the World
- Category: Sociology , Social Issues
- Topic: Effects of Social Media , Globalization , Media Influence
Pages: 5 (2221 words)
Views: 1144
- Downloads: -->
- Dixon, V. (2019). Understanding the Implications of a Global Village. Retrieved from http://www.inquiriesjournal.com/articles/1681/understanding-the-implications-of-a-global-village
- Fuchs, C. (2019). Capitalist Crisis, Communication, & Culture [Ebook]. Triple C.
- Georgidou, E. (2019). Marshall McLuhan’s ‘global village’ and the Internet [Ebook]. Canterbury: University of Kent at Canterbury.
- Gibson, T. (2019). Global Village. Retrieved from https://modernrhetoric.files.wordpress.com/2010/11/global-village.pdf
- Karr, N. (2019). How technology spawned a global village — and created a world of dissension & strife. Retrieved from https://mcluhangalaxy.wordpress.com/2017/04/23/how-technology-spawned-a-global-village-and-created-a-world-of-dissension-strife/
- Kaul, V. (2019). Globalisation and Media. Retrieved from https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access/globalisation-and-media-2165-7912.1000105.pdf
- Machado, K. (2019). Defining the global village [Powerpoint presentation]. Retrieved from www.umb.massonline.net
- Machado, K. (2019). Media and Economic Globalization [Powerpoint presentation]. Retrieved from www.umb.massonline.net
- Machado, K. (2019). Media and Cultural Globalization [Powerpoint presentation]. Retrieved from www.umb.massonline.net
- Machado, K. (2019). Global Village of Babel [Pdf]. Retrieved from www.umb.massonline.net
- Machado, K. (2019). “The Rise of Global Imaginary” [Pdf]. Retrieved from www.umb.massonline.net
- Machado, K. (2019). The role of media in Globalization [Pdf]. Retrieved from www.umb.massonline.net
- The Global Village: Media in the 21st Century. (2019). Retrieved from https://www.managementstudyguide.com/media-in-the-21st-century.htm
--> ⚠️ Remember: This essay was written and uploaded by an--> click here.
Found a great essay sample but want a unique one?
are ready to help you with your essay
You won’t be charged yet!
Privacy Essays
Malcolm X Essays
Affirmative Action Essays
2Nd Amendment Essays
Civil Rights Essays
Related Essays
We are glad that you like it, but you cannot copy from our website. Just insert your email and this sample will be sent to you.
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Your essay sample has been sent.
In fact, there is a way to get an original essay! Turn to our writers and order a plagiarism-free paper.
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->