TeacherHabits.com Becomes a Part of BetterWritingServices.com
TeacherHabits.com, a popular site for teachers with lots of great tips and ideas for educators, is now teaming up with BetterWritingServices.com, a site dedicated to helping students write awesome essays. This is a big deal for both sites and for everyone who uses them!

What’s Happening?
If you’ve been a fan of TeacherHabits.com, you know it’s a great place to find help for teaching, especially writing. Now that it’s joining forces with BetterWritingServices.com, you’ll get even more useful information!
The writing team at TeacherHabits.com will continue writing articles that focus on how to teach academic writing, especially essays and research papers, as well as share useful teaching tips to help other educators make their work lives easier.
Students, you’re not left out! This will help you better understand teachers and give you insight into what educators expect from you in writing assignments. Teachers, in turn, will be able to read about and understand students’ challenges.
What to Look Forward to
- More New Content: There will be more articles, reviews, videos, and tools that help both teachers and students.
- Personalized Help: If you’re really stuck on an essay, you can get one-on-one help from people who know their job.
As these two sites come together, watch for new content ideas coming your way. Whether you’re a teacher wanting to spice up your lessons or a student looking to ace your next college paper, the new combined site has got your back.
Apart from writing informational articles, BetterWritingServices.com can also help you find the best essay writing service for your specific needs, whether you’re looking for someone to proofread your work, assist with research, or even write an essay from scratch.
We have a separate team that is focused on writing reviews and helping students find the most effective tools to improve their studying process, from software and apps to textbooks and online courses.
P.S. We’ve also recently launched our forum, where you can discuss any topics related to education. This forum is a great place to share experiences, ask questions, and connect with others who have similar interests and challenges.
Students and teachers can create topics and join conversations like this one that discusses top research paper writing services , you can virtually discuss anything as long as it falls into the categories of education and academic development.
We’re really excited about what this partnership will bring. It’s a chance to make a big difference in the way we teach and learn. Stay tuned for more updates, and let’s make learning awesome together.
- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
- Explanatory Essay: Definition, Outline, Writing Steps & Samples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
Explanatory Essay: Definition, Outline, Writing Steps & Samples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
An explanatory essay is a type of essay that aims to explain or describe a particular topic or subject. The purpose of an explanatory essay is to provide readers with information and to educate them about a topic in a concise manner.
In this article, we will discuss an explanatory writing definition, provide an outline of key components, and guide you through how to write an explanatory essay. Additionally, we will provide a well-written explanatory essay example to further illustrate required structure and format of writing the paper. Whether you are a college student or a professional, this article will offer all the tools you need to write a clear and effective explanatory essay. Our professional essay writers did their best to share all essential details on an explanatory essay – beginning with an introduction and ending with a conclusion. Let’s get started!
What Is an Explanatory Essay: Definition
An explanatory essay is a type of academic writing in which the writer presents an explanation or analysis of a specific topic or idea. Its main goal is to provide the reader with a clear, unbiased and well-supported understanding of the subject matter, through use of evidence and logical reasoning. Instead of persuading or arguing with the reader, explanatory essays provide relevant information to them. Therefore, a writer must present information objectively, without injecting their own personal opinions or biases. Additionally, explanatory writing can be used in professional settings as well, for example, in a scientific report, or in a business proposal to explain the process of a product or service creation, or to provide data analysis. According to definition of explanatory writing, it explains why things happen the way they are.
What is the Purpose of an Explanatory Essay?
Explanatory essay purpose is to provide an explanation or clarification of a particular topic or subject. This type of assignment is used to inform or educate readers about a specific concept or idea. Similarly to writing an informative essay , the focus is on offering a clear and comprehensive understanding of topic, rather than arguing about a particular point of view. A writer should present information, define terms, and use evidence to support their explanations. Explanatory essay also aims to explain complex ideas in a clear and concise manner, making information accessible and understandable to reader.
Explanatory Essay Outline
Explanatory essay outline varies depending on information that author is trying to present. Aim of explanatory outline is to organize points into paragraphs and provide a framework on how to write an explanation paper. You can find an example of an essay outline online that can help guide you on what to do. Below is an example of an explanatory essay outline template.
- Background information on the topic.
- Thesis statement.
- First point supporting thesis statement.
- Evidence or examples to support this point.
- Explanation of evidence provided.
- Concluding statement.
- Second point supporting thesis statement.
- Evidence or examples to support point.
- Third point supporting thesis statement.
- Summarize main points
- Restate thesis statement
- Call to action or future implications.
Explanatory Essay Structure
Structure of an explanatory essay typically includes an introduction , body , and conclusion . Writing an explanatory essay begins with drafting an introduction . Introduction provides background information on topic and thesis statement in closing sentence. Thesis statement offers the main idea of paper. Subsequent parts of an explanatory essay support the developed thesis statement using valid evidence. Body of the paper is where writers present evidence, examples, and explanations to support their thesis statement. Body typically contains several paragraphs, each focusing on a specific aspect of topic and providing evidence to support it. Finally, conclusion summarizes main points and arguments of the writing, and restates thesis in different ways. It also provides a final perspective on topic, and may offer some recommendations or suggestions for further reading or research.
Explanatory Essay Introduction
Have you been wondering how to write an explanatory essay introduction? A good introduction for an explanatory essay should have three main elements:
- Background information
- Thesis statement
The hook is an attention-grabbing and interesting sentence that entices reader to continue reading. It can be a surprising fact, a quote, or a thought-provoking question. Background information provides context for the topic being discussed and helps readers to understand significance of the issue. This section should be brief and to the point. Last part of introduction paragraph for an explanatory essay is a thesis statement . This is a statement that author will support by using facts, quotes and examples throughout the body of paper before concluding with personal opinion based on provided evidence.
Explanatory Essay Thesis Statement
It is important to know what is an explanatory thesis statement before exploring its purpose. Thesis is a statement that presents main idea or topic in a clear and concise manner. Thesis statement for an explanatory essay is an essential element as it serves as a roadmap for the entire work. It should be specific and arguable. Thesis statement should be presented early in paper, typically in introduction, to guide reader's understanding of essay's main points. It should be specific enough to clearly convey a topic, but not so specific that it limits the paper’s scope. Additionally, it should be arguable, meaning that it should be open to interpretation and debate. With this information, you can practice how to write a thesis statement for an explanatory essay.
Explanatory Essay Body
Next step after introduction is to write a body paragraph for an explanatory essay . Explanatory essay body paragraph provides evidence that supports thesis statement. It should include facts, statistics, expert opinions, examples and other evidence that help to prove thesis statement is accurate. Body paragraphs should be written in a clear and logical manner, making a strong case for thesis statement. It should also be written in a way that is easy for readers to understand and follow, ensuring that evidence is presented in a clear and convincing manner. To effectively convey information in the body of an explanation essay, it is important to use a variety of different techniques and strategies. This may include use of images, infographics, examples, theories, quotes, and other relevant information. By incorporating these different elements, writers can more effectively engage readers and provide a more comprehensive understanding of topic at hand. Additionally, use of these different techniques can help to break up text and make it more visually appealing and easier to read.
Explanatory Essay Conclusion
An explanatory essay conclusion is the final section of the paper that summarizes main points and restates the thesis statement. Conclusion for explanatory essays should be written in a way that ties all of information presented in paper together, providing a clear and concise summary of main ideas. Steps on how to write a conclusion for an explanatory essay are as follows:
- Restate the thesis statement.
- Summarize main points: conclusion should sum up key points and evidence presented in paper, highlighting most important information.
- Provide a sense of closure: indicate that paper has come to an end and that main points have been fully discussed. Your conclusion must show that the ideas have been explored fully.
- Emphasize significance of the topic.
- Provide final thoughts or recommendations: give reader something to consider after reading your work.
How to Write an Explanatory Essay Step-by-Step?
Best way to understand how to write an explanatory essay is by practicing certain steps involved in the process. By following these steps, writer will have a clear understanding of process and be able to effectively present information in a logical and easy-to-understand manner. Subsequent section will discuss how to do an explanatory essay by covering some important tips and considerations for each step, to help you produce a high-quality writing. Details on each step are discussed below.
1. Produce an Idea
First step in producing an idea in an explanatory essay is by thinking about what you are passionate about or interested in. This will make writing process more enjoyable and will also make it easier for you to have a strong understanding of the topic. When brainstorming a topic in explanatory essay writing, you should consider your audience and what they may be interested in reading about. More ways to brainstorm new ideas include looking at current events or trending topics in your field of study or area of interest. Narrow down your list of ideas by evaluating which explanatory essay topics would make most interesting and informative writing. Once you have a topic in mind, do some preliminary research to ensure that there is enough information available to write a comprehensive paper.
2. Make a Detailed Research
Before writing an explanatory essay, you should do detailed research to collect relevant information. Here are some steps to follow when gathering information:
- Identify topic and focus of your research paper. This will help you determine what types of sources to look for and where to find them.
- Search for sources using a variety of methods, such as online databases, library catalogs, and search engines.
- Evaluate credibility of each source. Check for things like author's credentials, publisher, and date of publication.
- Take detailed notes as you read through your sources. Be sure to note author, title, and publication date for each source, as well as any key information or quotes that you plan to use in your paper.
- Finally, review all sources again, and make sure they are reliable and trustworthy before you use them in your explanatory paper.
3. Use Appropriate Examples
Examples in explanatory writing are an effective way to explain a concept or idea because they provide a concrete illustration of topic being discussed. They can make complex ideas easier to understand by providing a real-world context. Using an appropriate explanatory essay example can help to strengthen credibility of information being presented. Sources used in this paper should be applicable to the real world. Examples can be used to persuade readers to see a certain point of view. For instance, when discussing a controversial topic, providing examples can help to demonstrate validity of the writer's argument. Also, providing illustrations helps the reader to understand unfamiliar concepts.
4. Create an Explanatory Essay Outline
Best way to know how to write an explanatory essay outline is to consider the amount of information gathered through detailed research and obtaining logical arrangement to ensure flow of ideas. Created through identifying a specific idea from detailed research and ensuring readers can easily relate logical flow throughout the paper. Appropriate outline for explanatory essay entails introduction, body and conclusion each containing specific information arranged in a logical manner to provide flow of your paper. Example of an outline provided above follows a general structure and provides the best organization of communicating directly to readers. Moreover, a sample above shows a flawless way of obtaining information and opinion of an author. Besides, it provides an outline in a manner that is easy to follow and comprehend.
5. Write an Outstanding Beginning
Capturing attention of the reader to go ahead and read entire paper is dependent on the introduction. Therefore, providing a hook seems like the best way on how to start an explanatory essay. First step to capture your audience’s attention is usually to write an introduction paragraph for an explanatory essay. Introduction becomes the first paragraph in any type of writing, and it is important in capturing interest among readers. Writing an effective introduction involves providing a hook and general description of the topic, background information and thesis statement. These elements provide an overview of your paper and instigate readers to expect more detailed information about your topic throughout the writing.
Explanatory Essay Introduction Example
Introduction paragraph is the beginning of paper and helps to introduce general ideas about topic and to capture attention and interest of your readers to continue reading. Introduction must begin with a hook, followed by scope of the topic and closing sentence should include a debatable thesis statement. Revising explanatory essay introduction examples can help you understand the concept better. Below is an example of introduction paragraph.
6. Come Up With an Explanatory Essay Thesis Statement
Understanding how to write a thesis statement for an explanatory essay is essential in ensuring that the reader comprehends whole idea author is trying to prove. Thesis statement for explanatory essays provides main idea in a precise manner. It is usually written in concluding statement of introduction paragraph of explanation writing. Effective thesis statement should be specific but must consider scope of the work. In addition, an outstanding thesis statement doesn’t include your emotions or opinion. Save arguments and viewpoints for an argumentative essay .
Explanation Essay Thesis Statement Example
Thesis statement is written in the concluding sentence. It is supposed to be specific and concise in providing the main idea of your paper. Additionally, to make it effective, thesis statement should be outstanding and debatable with open interpretation. Thesis statement sums up central point of the writing, and should articulate it in a few words without providing too much information. However, reader has to note specific ideas that author is trying to relay. Example of an explanatory essay thesis statement is stated as follows:
7. Support Your Ideas With Evidence
The central idea that author intends to express can only be validated through relevant evidence from credible sources. Supporting thesis statement is based on how well one knows how to write an explanatory body paragraph. Body of an explanatory essay entails evidence to support your topic. Evidence supporting the idea is obtained from detailed research conducted after identifying a specific idea. Main aim of the body paragraph is to prove thesis statement. Some ways used to communicate in body include examples, facts and opinions among other evidence that are deemed relevant and credible. Having an effective body in writing requires presenting evidence in a clear and convincing way that will enable reader to easily relate important ideas to thesis statement. Including different techniques of presenting evidence in body of report, provides vivid understanding and wider perception of the topic.
Example of an Explanatory Essay Body Paragraph
Body paragraph provides evidence that supports thesis statement. Below is a perfect explanatory body paragraph example about factors that cause suicide among teenagers.
8. Summarize Your Explanatory Paper
Last section of the explanatory essay writing is to summarize your evidence to support the thesis statement. Explanatory summary restates thesis statement and highlights important information presented throughout the work. Main idea is to link all information in the paper together to provide a common relationship between main ideas and thesis statements. Opinion of author is provided in summary section, which is dependent on depth of evidence provided in body. Author can agree or disagree with thesis statement, if it is efficiently supported by credible and relevant sources. Besides, the summary provides necessity of the topic at hand and possible recommendations.
Example of Explanatory Essay Conclusion
Conclusion paragraph starts by restating thesis and summarizing main points. Sample of an explanatory essay conclusion as one provided below will help you understand concept better.
9. Proofread an Explanatory Essay
Final step in writing an explanatory article involves proofreading your work properly. It entails revising paper a couple of times to check if it has proper flow of thoughts, communicate to audience with the clear ideas, and understand if conclusion provides a concise value of the thesis statement. It is usually done a day after completion to easily spot mistakes. Moreover, proofreading explanatory essays aims at detecting minor errors and grammatical mistakes that might affect clarity and quality of the paper. During proofreading, any error or mistake is noted and necessary editing done to improve the value of the paper.
Explanatory Essay Format
Format for an explanatory essay depends on the discipline provided in the paper. There are different formats to write an explanatory essay including APA style format , MLA format and Chicago style paper format which are provided in instructions. Format provided in paper also dictates the style of structure and citation of sources used in the paper. The format does not have any influence on content of the paper and is usually based on a system preferred by the author. Writer uses the recommended format that seems easier and familiar. Therefore, explanatory papers can take any format with similar structure and enable the author to communicate effectively to readers.
Explanation Essay Examples
Explanatory writing examples provided below show the required structure of the essays. Under the structure there are possible sections with some clarifications to help the reader understand the main idea. Explanatory essay samples are necessary to readers because they help in understanding how to build up the topic under study. Moreover, each of the example of explanatory writing provided below is important in learning different formats of writing, conveying a general idea of the work.
Explanatory Essay Writing Tips
Writing tips are essential in ensuring an excellent explanation essay. Some of these writing tips are listed below:
- Take advantage of transition and linking words and write a hook for an explanatory essay.
- Cite sources from which facts were drawn. Sources should be credible and recent to ensure high value of paper. Following examples of explanatory essays is the best way of learning how to cite.
- Proofread the paper. This involves revising work to ensure topic is analyzed in a logical manner that follows correct explanatory essay layout which is easily understood by audience.
- Edit an essay. Follows after identifying and noting errors and mistakes during proofreading. It is done a day after completion of writing to ensure all mistakes are edited and paper’s value improved.
- Share the paper with a close person as a way of further improving its value and ensuring explanatory essay meaning is maintained. In addition, by sharing, authors can get feedback on where to make necessary corrections and changes to ensure writing is more understandable and clearly communicates to the audience.
Explanatory Essay Checklist
Before final submission of the explanatory essay, there are several checks it should go through first to ensure a proper flow in the paper and that the intended information is easily understood by the reader. The checklist enables one to write a good explanatory essay. The checklist includes the following:
Bottom Line on How to Write an Explanatory Essay
The question of what is explanatory writing has various definitions but generally, it is usually academic writing which provides analysis of a specific topic or idea to readers. Explanatory essay template provides the basic structure that can be followed in explanatory writing. Besides, explanatory essay examples provide vivid understanding on how to write a good explanatory paper. Through using templates and examples, one can master steps and structure of writing an explanatory essay. Structure of explanatory paper has three parts that are logically arranged to enable readers to easily understand what the author intends to prove. Besides, flow of ideas in a logical manner enables relating different evidence provided in body to thesis statement and accounting for correct conclusion. If you need more help on writing, feel free to seek more suggestions in our Blog. From guides on exemplification essay to tips on evaluation essay , you will find tutorial fitting any academic need.
If you are struggling with writing an expository essay, remember that you can always count on our expert academic writers. Let us know your assignment details and we will craft a custom paper in line with all requirements to your ‘ write my college essay for me ’ request.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

- checkbox My explanatory writing is clear.
- checkbox Provided information has required flow and is connected with transition words.
- checkbox Supporting evidence proves my thesis statement.
- checkbox I started an explanatory essay with a hook that grabs reader’s attention.
- checkbox My writing is understandable to the reader or doesn’t leave them confused.
- checkbox My summary ties key points to the thesis statement.
- checkbox The citation and referencing style is appropriate to the paper format.

Why do teenagers commit suicide? The rate of committing suicide among teenagers have been on rise. Some leave suicide notes while others left nothing to show the cause of their actions. Suicide has been linked with mental disorders. Nevertheless, there has been a need to investigate other underlying causes apart from mental disorder. Therefore, there are several underlying factors that lead to suicidal actions among youths that need to be investigated. Increase in suicide rates among teenagers can be attributed to a combination of societal pressures, mental health issues, and a lack of access to proper resources and support.
Increase in suicide rates among teenagers can be attributed to a combination of societal pressures, mental health issues, and a lack of access to proper resources and support.
Society plays a significant role in shaping mental health of teenagers. With constant pressure to fit in and meet societal expectations, many teens struggle with low self-esteem and feelings of inadequacy. Social media amplifies this pressure by providing a platform for teens to compare themselves to others and constantly measure themselves against impossible standards. This can lead to depression, anxiety, and ultimately, suicide. Mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety, are also major contributing factors to suicide among teenagers. These conditions are often left undiagnosed and untreated due to a lack of access to proper resources and support. Many teens may not have the means to seek out professional help or may not understand the severity of their condition. Additionally, the stigma surrounding mental health can prevent teens from seeking help, leaving them to struggle alone with their thoughts and feelings. This further increases the risk of suicide.
In conclusion, suicide among teenagers is a complex issue that is influenced by a combination of societal pressure, mental health issues, and a lack of access to proper resources and support. It is important that we take a holistic approach to addressing this issue by solving underlying causes and providing teens with support and resources they need to navigate challenges of adolescence. This includes providing mental health education, addressing societal pressures, and increasing access to professional help and support. By working together, we can help to reduce suicide rates among teenagers and give young people the chance to live happy and fulfilling lives.
FAQ About Explanatory Essays
1. how is an explanatory essay different from an argumentative essay.
Differences between explanatory and argumentative essay is that explanatory paper is about presenting information to explain something while an argumentative writing is about persuading the readers to agree with an opinion. In the explanatory paper, the author provides an open interpretation of the topic before finally providing links between main ideas that proves the thesis statement.
2. Is an explanatory essay the same as an informative essay?
No. An informative essay is based on detailed facts and data while an explanatory paper requires author’s opinion on some certain points. Explanatory essay meaning is drawn from author’s presentation of idea and how well it is supported. Despite having an open interpretation and debatable thesis statement, clear facts about topic in explanatory paper are not easily determined. Author makes rational decisions based on the weight of evidence provided.
3. What is included in explanatory essay?
Explanatory essay is a type of writing where author presents some points of view on a certain topic, event or situation. Opinion of author is generally the idea supported by most of the evidence provided in body. Remember to include introduction, body, and conclusion to adequately support your claims and understand the difference between those parts of your paper.
4. Is an explanatory essay objective or subjective?
Explanatory writing is about presenting a balanced, objective description of the topic. The paper is objective and provides an all around perception of topic both opposing and proposing evidence on thesis statement. General description provides the author's idea and reader can easily understand point of view based on provided sources and evidence.
5. How many paragraphs are in an explanatory essay?
Explanatory essay has five paragraphs though it can include more. Paragraphs vary with subheading the author decides to include in essay. General structure requires one paragraph for introduction, three for body and last one for conclusion. However, in case of extra evidence in body and long introduction, more paragraphs can be used.
7+ Explanatory Essay Examples That Get the Best Grades

Table of contents

Meredith Sell
Writing explanatory essays is hard, even for experienced scholars.
In this post, I want to try to tackle the major challenges students face when writing this type of essay, using examples of successful essays. These challenges include:
- Struggling to come up with the right idea . (solution: brainstorming techniques )
- Difficulty in organizing the essay. (solution: working on the outline of the essay)
- Not having enough evidence or sources to back up points. (solution: doing proper research )
- Failing to come up with a conclusion. (solution: following our guide to conclusions )
- Not having enough knowledge of the topic. (solution: summarizing key articles on the topic)
- Having trouble finding the right words. (solution: writing with Wordtune )
- Not having enough time to finish the essay. (solution: working on student time management )
- Not being able to present arguments effectively. (solution: learning essay persuasion techniques )
As you can see, for every issue there is the relevant solution, but it takes time to implement it. Another way of tackling this essay is to see other people's essay examples and getting inspiration from them.
Write your explanatory essay faster with this FREE AI tool > Write your explanatory essay faster with this FREE AI tool >

What Is an Explanatory Essay?

If you google “explanatory essay”, you’ll find a bunch of sites saying that an explanatory essay is the same as an expository essay, or that it’s totally different, or not even mentioning that expository essays exist. Who’s right?
Answer: Whoever your professor agrees with.
No, seriously. Your professor decides the parameters of your assignment. So if your professor defines an explanatory essay as one that describes a perspective or analyzes the efficacy of, for example, a local housing policy—that’s the definition you should work from.
But if your professor distinguishes between explanatory essays (which simply explain what something is and how it works or was developed) and expository essays (which expose the reality of a person, place, thing, or idea through investigation and evaluation), you should distinguish between them as well.
For the purposes of this piece, we’re going to use explanatory and expository interchangeably. The dividing line that some draw between these essay types is unnecessarily technical. What’s important is that both:
- Use an objective perspective
- Let the facts speak for themselves
As long as your essay does the same (and includes analysis if required by your professor), you should be in good shape.
Example of explanatory essay
We wrote a whole article on generating essay topic ideas , but here is a good example that can help you get an idea for your own essay:
Why is having a dog as a pet such a wonderful experience?
Dogs are one of the most popular pets in the world. They are beloved companions that bring joy and happiness into the lives of their owners. Dogs have been domesticated for thousands of years and have evolved to become the perfect pet for humans. In this essay, I will explain why having a dog as a pet is a wonderful experience.
One of the primary benefits of having a dog as a pet is the companionship they offer. Dogs are social animals that thrive on human interaction. They are loyal and loving creatures that are always there for their owners. Dogs can help alleviate feelings of loneliness and depression, and provide comfort and support during difficult times.
Another benefit of having a dog as a pet is the health benefits they offer. Studies have shown that owning a dog can help lower blood pressure, reduce stress, and improve overall health. Dogs require daily exercise, which encourages their owners to be more active and can lead to a healthier lifestyle. Additionally, having a dog can boost the immune system and reduce the risk of allergies and asthma in children.
Dogs are also great for families with children. They can help teach children about responsibility, compassion, and empathy. Children can learn to care for and nurture their pets, which can be beneficial for their emotional development. Dogs are also great playmates for children and can provide hours of entertainment and fun.
Training and caring for a dog can also be a rewarding experience. Dogs can be trained to perform a variety of tasks, such as fetching, obedience, and even therapy work. The process of training a dog can help strengthen the bond between the owner and the dog and can be a fulfilling experience. Additionally, caring for a dog requires daily attention and can provide a sense of purpose and fulfillment for the owner.
In conclusion, having a dog as a pet can be a wonderful experience. Dogs offer companionship, health benefits, and can be great for families with children. Caring for a dog can also be a rewarding experience and can provide a sense of purpose and fulfillment for the owner. Owning a dog is a big responsibility, but the rewards far outweigh the effort required.
Example of an explanatory paragraph, generated with AI:

A few subtypes of explanatory essays:
Description or definition essay example
Perhaps the most basic, this subtype does the deceptively simple work of, well, describing or defining a concept, place, person, etc.
Example: How Suspension Bridges Work
This essay explains: The way suspension bridges are constructed and how their design enables them to carry such immense weight.
Cause-and-effect essay example
This type of essay hones in on a particular phenomenon to show what caused it (i.e., where it came from) and how it influences other things.
Example: How Federally Funded Highways Transformed the United States
This essay explains: The history of federally funded highways in the U.S., when federal programs to fund highway construction started, why politicians and others thought highways were important, and what the effect has been on the landscapes, communities, economies, and ecosystems of the country.
Compare-and-contrast essay example
Take two or more things, gather the facts about them, and then write about their similarities and differences.
Example: Hybrid vs. Electric Cars
This essay explains: The various features of hybrid and electric cars, and shows how they are either different or similar in terms of: cost, energy consumption, size, drive time, ease of use, and so on.
How-to essay example
Walk your reader step-by-step through a procedure so they can do it for themselves. (We’re doing this later!)
Example: How to Prepare for an Intercontinental Bike Trip
This essay explains: How to get ready for a bike trip between nations and continents. Readers learn how to research their route, find out what travel documents they need, choose the right gear, and determine how much training they should do before leaving.
Problem and solution essay example
Explain a problem (along with its causes and effects) and then describe one or more potential solutions to that problem. This subtype could also be combined with compare-and-contrast to determine the most effective solution.
Example: How Bike Infrastructure Could Solve American Obesity
This essay explains: How American reliance on motorized vehicles promotes a sedentary lifestyle that drives obesity, whereas building bike lanes and trails could encourage Americans to be more active and improve their health one pedal at a time.
Chronology essay example
Explain the history or backstory of a person, place, thing, or idea in chronological order.
Example: The Evolution of the Bicycle
This essay explains: The initial invention of the bicycle and how its shape, frame, and size changed over the years.
What type of explanatory essay are you writing? Hopefully, this list helped you hone in. Now, let’s start the writing process.
5 Steps to Write Your Essay
Whether you’re writing an explanatory/expository essay or a persuasive essay, the process of researching and writing is pretty much the same. Both genres require research, organization, and thought . But with expository essays, the thought focuses on making sure you understand your topic inside-out and determining the best way to explain it, while with persuasive essays, you’re focused on crafting a convincing argument.
Follow these steps to turn that blank page into a final manuscript:
1. Choose topic and angle.
Do you have free rein to write about the topic of your choice? Make the most of it.
In college, my public speaking professor let us choose all of our own speech topics. A classmate gave an explanatory presentation on how to survive the zombie apocalypse . She brought props and had the class totally enchanted. Our professor encouraged creativity, so I’m sure she earned a winning grade—and had fun in the process.
You can’t use props or sound in a written essay, but you can still work some creative magic. That magic starts with choosing your topic and angle.
To choose well, first make sure you understand the assignment:
- What exactly has your professor asked you to write? Which of the subtypes should your piece be?
- Are there any parameters for what type of topic you can write about?
- What kind of class is this? An English composition class will offer more freedom than, say, a history class focused on the French Revolution.
If you’re allowed to write about anything, brainstorm a list of topics you’re curious about. Then think of smaller topics within that area.
Example: Transportation
- Electric cars
- The highway system
- Engineering
Any of these topics you could easily write volumes about, so next, narrow down to your specific angle. One way I like to come up with angles is to think of how two or three different topics intersect.
Example 1: electric cars + the highway system
Angle: How Much Will It Cost to Update Federal Highways with Charging Stations for Electric Cars
Notice that this angle includes a third element: cost
Example 2: bicycles + bridges
Angle: The Safest Bridges for Bicycles Have One Thing in Common: No Cars
Third element: safety
Example 3: electric cars + buses
Angle: Electric Cars vs. Buses: Which Is Better for the Environment?
Third element: environment
Your turn: Make a list of topics you’re interested in. Then, identify some intersecting topics. Based on your assignment parameters, develop an angle that narrows your focus to an intersection that interests you.
Not sure what angle to go with? Do some broad research on your topics and then return to this step.
2. Research, research, research.
Explanatory essays require solid research. These essays exist to lay out the facts for the reader so they can clearly understand the topic. Your opinion—what you think about electric cars or suspension bridges or transportation infrastructure—doesn’t matter. And it doesn’t belong here.
Where you should start your research depends on how much knowledge you already have.
If you’re writing about suspension bridges and you already know the Brooklyn Bridge and Golden Gate Bridge are suspension bridges, you probably don’t need to start with the encyclopedic entry for “suspension bridges”. But if you don’t know the basic facts about your topic, encyclopedias are a great place to start.
Thanks to the advances of technology—and this marvelous thing called the internet—you don’t have to go to a research library to gain that ground-level knowledge of your topic. But you do still need to make sure you’re drawing from credible sources.
For encyclopedias, try these to start:
- Encyclopedia.com
Dictionaries can be helpful too:
- Merriam-Webster
- Dictionary.com
Once you know your topics’ basic facts, focus on researching those topics in the context of your angle . It may help to make a list of questions you’re trying to answer so you can keep your research focused.
Example: Electric Cars vs. Buses: Which Is Better for the Environment?
- Are most buses gas-powered or electric?
- What’s the average emissions of greenhouse gas from gas-powered buses?
- How much energy do electric cars use? What’s the lifespan of their batteries? Are they just using electricity that was produced in a polluting way somewhere else? What about electric buses?
- How many people can ride a bus? How many people typically are transported by one car?
- What would be the average energy consumption per person in an electric car versus a bus?
Once you know the questions you need to answer, look for sources that address those questions. For an academic essay, you’ll probably want to stick with academic sources : peer-reviewed studies and research papers published by academic journals. But official government databases can also be useful. And news stories from reputable publications can provide some direction as well (check with your professor to see whether or not you can use news publications as sources for your essay). Your educational institution likely provides access to all of these kinds of sources through the university library.
Your turn: Think through your angle and make a list of questions your piece needs to answer. Next, start searching academic databases for the information you need. Take notes as you research, and be sure to save any links, titles, author names, page numbers, and publication information you’ll need to properly cite your sources.
3. Outline your essay.
Call me crazy, but I actually think this is the fun part. I hated writing outlines when I was in school, but since making my living as a professional writer, they’ve become the #1 way I beat writer’s block.
First: Throw out the idea that your outline should be a series of bullet points neatly organized into sections and subsections. Your outline only needs to make sense to you , so play around to find an approach that works with your brain. The idea here is simply to make a map you’ll follow when you sit down to write.
Here’s what I do:
- Identify the specific hook I’m going to use to start things off.
- List the different examples and details I need to include.
- Use the main focus or idea of my piece to order everything in a natural, logical way.
A lot of times, my outline becomes a combination of bullet points and sentences or paragraphs I write as I’m sketching out the piece. I’m basically just thinking the piece through, from beginning to end. Instead of getting stuck while I’m writing, I work through the tough spots in the outlining stage.
This is what my outline looked like for this piece:

Okay, that’s kind of long, so I cut it off early—but you get the point.
A lot of times, my outline starts as bare-bones bullets. As I work on it, ideas pop up that I stick in where they make sense. But when I write, those elements might move around ( notice how the examples of transportation essays got bumped up to the section on subtypes of essays ).
Your outline is just a guide. It’s not an architect’s blueprint that needs to be followed to the exact millimeter. There’s room for things to change.
But an outline keeps you on-track when you’re writing . If you find yourself stuck (or lost) in the writing step, reference your map. You might need to backtrack, move what you’ve written around, or adjust your route.
Your turn: Take a few minutes and sketch out your essay. Where does it start? What points does it hit? Are there any ways you see the different points connecting that should inform how you order them? As you think it through, scribble out any lines or paragraphs that come to you and stick them in the outline where they make the most sense. Even if you don’t use these exact words later, they’ll help prevent that deer-in-the-headlights stare that hits when you see a blank page.
Time to put everything together!
With your outline and research ready, start your intro and set up your piece. Your opening should briefly introduce your readers to the topic(s) you’re writing about and the questions you’re going to answer—but don’t give everything away. You want to stir up readers’ curiosity and give them a reason to keep reading.
Depending on the length of your essay, your intro may be one to three paragraphs long (longer pieces get longer intros). But it should be concise and to the point, and smoothly transition into the body of your essay.
The body is the meat and potatoes of your piece. Answer those questions, flesh out your explanation, and give readers a thorough understanding of your topic. Show off your research! Include those bizarre and fascinating facts you learned along the way. Use a tasteful metaphor or compelling anecdote to explain some of the more difficult aspects of your topic.
As you write, be sure to follow a consistent logic throughout your piece:
- If you’re detailing a history or an event, use chronological order: start at the beginning and write about the events in the order that they happened.
- Are you explaining how a machine or other invention works? Start with where the movement starts—the pedals of a bicycle, the wind turning the turbines—or with the feature doing the most significant work (e.g., the wires of the suspension bridge).
- Other logics include: size (small to large, large to small), significance (greatest to least), or space (left to right, right to left, outside to center, center to outside).
You don’t need to label everything you write about as the “next biggest” or “least significant”, but sticking to a logic helps your readers orient themselves—and helps you determine which paragraph or subtopic should go where. This way, your thoughts clearly flow from one paragraph to the next.
Quick note: If you can’t name the logic that’s guiding your piece, don’t worry. As long as your paragraphs naturally follow each other and all questions raised in the intro are answered by the end, your essay probably follows a logic just fine. But if you feel like your piece bounces around willy-nilly, play with a couple different logics and see if one smoothly orders your sentences and paragraphs.
Your turn: Get writing! If you’re stuck on the intro, try writing a working title for your piece to focus your attention. Then, follow your outline to work all the way from the beginning to a conclusion that sums everything up.
If you can, let your piece sit for at least a day. Then, for the editing process , open up that document and read through with these questions in mind:
- Does the essay fulfill the assignment? Review the assignment description from your professor. Does your essay tick all the boxes? If not, what’s missing? Can you weave that element into what you’ve already written? Revise as necessary.
- Are the sentences and paragraphs ordered in a way that makes logical sense? If your essay feels clunky in places, you might have switched logics (as explained above) or you might need to insert some more explanation that clearly ties the sentences or paragraphs together. Make sure your essay doesn’t just list facts, but also shows how they relate to each other.
- Does the hook catch your eye? The beginning of your piece should grab your reader’s attention. Check out our advice for prize-winning hooks here .
- Does the conclusion effectively sum things up? Instead of repeating everything your essay says, your conclusion should briefly distill the main takeaway or core idea for your reader. It should show that you’ve fulfilled the promise made in your intro, without being unnecessarily repetitive or redundant.
- Have you cited all your sources? Make sure to cross this off before hitting “submit.” Follow the citation style specified by your professor.
- Is spelling and grammar clean and correct? You are writing, after all, and these things matter. A bonus tip to help you catch those sneaky typos: Read your piece backwards. You might be surprised what you spot.
Did We Explain That Well Enough?
This blog was basically a long, non-academic explanatory essay, so hopefully, you’ve learned something new and are feeling less overwhelmed about your essay on medieval literature, transportation infrastructure, Persian history—or whatever you’re writing about.
Share This Article:
.webp)
How to Craft Your Ideal Thesis Research Topic

How to Craft an Engaging Elevator Pitch that Gets Results
.webp)
Eight Steps to Craft an Irresistible LinkedIn Profile
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
The Subtle Art of Writing an Explanatory Essay
21 July, 2020
10 minutes read
Author: Richard Pircher
When writing an explanatory essay, you may have many questions connected with this paper type. You might wonder how to craft it, structure it, represent your thoughts, and many more. But the main question will refer to the paper type you’re working on. And the first thing you have to remember is that it’s not a persuasive essay. In this paper, you only have to describe some event or subject and explain its major aspects and importance to a reader.

Our article contains exhaustive information on writing explanatory essays. Also, we’ve written the tips that will help you craft an excellent paper. So, keep on reading for more details.

What Is an Explanatory Essay?
Before you start writing your task, it’s necessary to find out what is an explanatory essay. Without a clear understanding of this paper type, it’s impossible to craft a brilliant paper and get excellent grades. An explanatory essay is a work in which you present a point of view on some subject and describe its main features, importance, or simply answer questions, “ Why? ” and “ How? ”
This paper type requires you to research, analyze facts, and explain the opinion of other people. Of course, you’ll have your thoughts concerning the subject, but you’ll have to avoid sharing them in your essay. The writer’s opinion remains neutral, and it doesn’t matter if you agree or disagree with the topic. Your goal is to help a reader understand the problem or subject by explaining details.
When crafting an essay, you can also add statistics and examples to become the guide leading the audience through the topic. The analysis of the subject and facts you’ve found during the research will help readers understand why and how things have happened. People don’t have to agree with the information from your article – they will only have to find answers to questions concerning the topic.
6 Types of an explanatory essay
Now that you know the definition of an explanatory essay, it’s necessary to learn its major types. We’ve prepared the list that will help you cope with a task correctly. Here are 6 explanatory essay types you need to know:
- Compare and contrast. This essay type requires you to describe differences and similarities between subjects, events, people, etc.
- Definition. This essay type is written to explain the idea, term, or subject.
- Classification. When crafting this essay type, you have to divide the characteristics of a subject or idea by groups and explain their features in detail.
- Cause and effect. It’s necessary to describe the situation that has happened and the event it’s caused.
- How-to. The explanation of this paper type is in its name – you have to explain how to do something or how things work.
- Problem and solution. This type of essay requires a writer to research, analyze, and evaluate a problem. It’s also necessary to provide suggestions on its solution.
How to Start an Explanatory Essay?
How to write an explanatory essay? If you haven’t ever crafted this paper, this question will disturb you most of all. Before you start writing an explanatory essay, it’s necessary to take a few preparatory steps. Comprehensive research, fact-checking, and analysis are the most important stages of task completion. When exploring the topic, write down all the relevant details because you’ll use them in your article.

Keep in mind that this essay should only contain facts and a few of your thoughts – it’s a perfect combination that will allow you to describe things without persuasion. You’ll have to find several credible resources to come up with truthful information. And our recommendations will help you craft an excellent paper:
- If a professor allows you to pick a topic, pick the neutral yet interesting one. For example, you can explain why people should learn more than two languages or how students can improve their writing skills.
- Look for credible sources. You can use Wikipedia, JSTOR, or Google Scholar to find the necessary information. Besides, the door of the college library is always open for students.
- Note essential details and quotes because you’ll use some of them in your paper.
- Create an outline.
- After researching the topic, collecting information, and writing an outline, it’s necessary to create a thesis statement. The latter explains what this topic is about. A thesis statement consists of one sentence and thoroughly describes a major idea of your essay.
- Check the data you’re planning to use and start writing an essay.
Explanatory Essay Outline
The best way to organize your thoughts and the collected details you’re planning to describe in your essay is to design an outline. It’s basically a summary of a paper and it will only contain major ideas and arguments. Typically, an explanatory essay outline has the following structure:
1) Introduction. This section is a combination of three important ingredients – it should contain a hook, a short explanation of the topic, and a thesis statement. At this stage, a writer engages the reader by adding a relevant quote, joke, fact, or question concerning the subject. A few sentences are enough for the introduction section.
2) Body text. The optimal size of this section is 3 paragraphs. However, it will depend on the complexity of your explanatory essay and the professor’s requirements. Start a new paragraph if you want to describe another thought. Write a topic sentence to explain the main idea of every section. Support your thoughts by adding the facts you’ve found. They will develop the reader’s confidence in the trustworthiness of your statements.
3) Conclusion. In this section, you have to mention your thesis statement again, summarize the information from your essay, and highlight the topic’s value. Finish a paper with a call to action to motivate readers to research the subject in the future.
Explanatory Essay Examples
Here are some online explanatory essay examples:
- http://www2.hawaii.edu/~davink/EXPOSITORY/Homesweet.html
- http://www2.hawaii.edu/~davink/EXPOSITORY/Housereturn.html
Useful Tips for Successful Explanatory Essay
Since writing an explanatory essay may be challenging, it’s necessary to start with preparation and research. We’ve created some tips on crafting an expository paper to help you impress your professor. Follow our guide to come up with an excellent essay:
1. Pick an understandable topic
If a professor allows you to choose explanatory essay topics, it’s better to focus on subjects that are easy to write about. There’s a thing called the “ writer’s block ” which doesn’t let you craft any sentence. You can’t find the necessary words, and writing turns into the impossible mission. Sometimes a complicated topic is a problem that causes the writer’s block. That’s why you have to pick it carefully. It should be neutral yet interesting to you. Here are a few examples of topics you can select:
- Why does everyone need friends?
- How to choose a career that is right for you?
- How do technologies shape your life?
- Why do Chinese people respect the symbol of the Dragon so much?
- What are the main stressors in students’ lives?
2. Conduct comprehensive research
It’s necessary to dedicate some time to research, fact-checking, and data analysis to come up with an excellent explanatory essay. Pick reputable resources to avoid providing misinformation. Write down all the relevant details and return to them later to choose the most important ones.
3. Craft an outline
An outline is a brief model of your future paper that will help you organize your ideas. As we’ve mentioned, it will consist of three sections, including an introduction, body text, and a conclusion. Divide your outline by sections, and you’ll see how many paragraphs your piece will have. A traditional explanatory essay format is a paper with 5 paragraphs. They include an introduction and conclusion. The body section usually has 3 paragraphs. However, a number of sections will depend on the complexity of a topic and the professor’s requirements.
4. Check your essay
After you’ve written an explanatory essay, it’s necessary to check it for grammar mistakes, punctuation errors, and miswording. We recommend you to read the text aloud to make sure it sounds natural. And you can use online tools like Grammarly and Thesaurus to improve your writing.
Write an Excellent Explanatory Essay with HandmadeWriting
Sometimes it’s better to ask for professional help rather than taking a risk and getting bad grades. HandmadeWriting is a reputable writing service offering the execution of high-quality papers. You can hire a professional essay writer specializing in your discipline, and they will help you complete the task excellently and improve your academic picture.
HandmadeWriting consists of more than 700 writers, which means that you’ll definitely find the one who’ll assist you even with a specific task. It’s fine if you have an urgent order because an experienced specialist will quickly craft an essay and deliver it even before the deadline. You’ll receive a professionally proofread paper meeting all your requirements,
When crafting an explanatory essay, follow such fundamental rules as picking an understandable topic, researching, using credible sources, writing an outline, and revising your paper. Hiring a professional writer from HandmadeWriting is another way to get an excellent writing piece done. So, choose the solution that works best for you and hurry up to improve your scores.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
explanatorythesis.com
Great Explanatory Thesis Esamples

How to Write an Explanatory Essay: Intro, Structure, Sample
Writing an explanatory essay appears to be quite easy for many writers. This is primarily because of the nature of an explanatory essay as an expository form of writing. However, many people may find difficulty properly structuring and beginning their writing. To top it off, they cross the boundary of informative writing and venture into argumentative writing. This article addresses everything that you need to know about how to start an explanatory essay. You’ll also find the most helpful tips on the ideal explanatory essay structure you should adopt.
The Proper Structure of an Explanatory Essay
To know how to write an exploratory essay, you must first understand the proper structure and arrangements of your work. You should know which parts of the writing come first, to guide you in your writing. The proper explanatory essay structure is outlined below:
The Introduction
An explanatory essay introduction is one of the most important parts of your write-up. Knowing how to write an explanatory essay introduction is very important. It has the power to encourage your reader to continue reading or dump your work for the next one. Hence, you must be crafty as you write this, to strongly captivate your reader. The introduction ushers readers into the body of your work and states what you aim to achieve with your writing. It shouldn’t be too long or boring, but prompt and detailed. In this stage, there is also the thesis statement of your work serving the purpose of briefly summarizing your work. Sometimes, people become confused about inputting the thesis and they wonder “where does the thesis go in the introduction, or how many sentences can a thesis be? ” The thesis often comes up towards the final parts of your introduction, just before you begin the next part of your writing and it could be one or multiple sentences.
The body of your essay is where you pour out all of your findings on the explanatory topic. You can achieve this by writing in paragraphs, fixing relatable points in one paragraph each. Your body could be a sum of about three to four paragraphs, each one housing important points. The body is often an expansion on the points of your thesis statement written in your introduction. One important feature of the body is your ability to make every paragraph connect and be uniform with the thesis statement.
The Conclusion
The conclusion of an explanatory essay is a summary of the body of the work. It is the final note that covers what has been discussed and what the essay has achieved at the end of the project. Like the introduction, your conclusion should not be too long, or boring. After writing a great essay, you want to wrap it up with the most interesting conclusion.
People would ask “there are how many paragraphs in an explanatory essay?” Paragraphing your essay depends on the complexity of your write-up. However, your total work should have at least five paragraphs.
How to Write an Explanatory Essay
It is not always enough to know how to properly structure your explanatory essay. It is also important that you put the right strategy in place to properly write your essay. From the point where you birth your writing idea, your choice of topic, and down to when you implement writing, there is a need for proper planning.
- Decide on your topic
The first step to writing your explanatory essay is deciding on the topic that you would like to work on. There are a variety of topics that you can choose from depending on your interest in the subject matter. You may be required to choose a topic from a set of themes, or upon recommendation from a supervisor. Either way, make sure that you develop an interest in whatever topic you choose.
- Gather resources
Resources for your writing include researching the topic for what you’d like to write. Some topics do not have many available materials and would require that you begin making your research from scratch. You may decide to utilize one or two quotes that relate to your topic. This is the process of getting unrefined data that you will have to rearrange for your work.
- Structure your information
Your data needs to be refined to become useful before you start writing. It might help if you get a raw sketch of what you expect your writeup to contain and which information should come first as you write.
- Begin writing
Now that you have everything you need to be lined up for you, you can begin writing. As you start to write, do not forget the draft that you have made to make your work easier and unique.
A Short Sample of an Explanatory Essay
Racism: why the disease of racial discrimination lingers.
Racism is a global problem that has been embedded in the history of man from time past. Every day, we see this plague raise its ugly head one way or the other. It exhibits itself in our interaction with one another, in the socio-political setting, and nearly every sphere of human existence. No matter how minute these discriminations may be, we cannot hide the fact that racism remains, and it affects the world negatively. The existing problem of racism lingers and is fueled by racial and ethnic identity, as well as inter-ethnic discrimination among the same people.
Racism is the superior-inferior relationship between two or more races. It is the belief that one race is superior to other races. This belief has been long existent in human history owing to different events. The direct consequence is the discrimination between colleagues, mates, or neighbors of different races. Racism exists between nearly all the races on earth and is not limited to the black and white races only.
There have been deliberate efforts by man to quell the global challenge of racism. This is evident through the enactment of stricter laws and educating people against racism in the workplace environment, international relations, etc. However, the problem persistently presents a tough front. One of the leading factors that contribute to this problem is ethnicity.
Ethnicity is the love for and recognition of one’s origin. This generally promotes oneness, unity, and also helps preserve the historical culture of different groups. The concept of ethnicity identifies not just the uniqueness of one’s ethnic background, but sometimes the need to be better than other ethnic groups. This idea is passed on from generation to generation and handed down to children in history classes. Hence, it isn’t unusual to find people of the same country, but from different ethnic identities having difficulties interacting with one another. In the same vein, the consciousness of their uniqueness becomes a reason to discriminate in more than one way.
Similarly, the already dividing factor between ethnic groups is bound to rub off on different races. For instance, America is historically known as the melting pot of the world. The unifying factor of being American by birth is often not enough to unite Asian Americans, African Americans, or Irish Americans. This is because the recognition of ethnicity becomes enough factor to recognize an “invading inferior” race.
Racism affects the world negatively in more than one way. The small seemingly innocent recognition of one’s ethnic group as the best among others has proven to be one of the primary reasons why racism still lingers. This ideology is bound to metamorphose into racial discrimination. Until the idea of ethnicity and racial consciousness is properly defined, racism and racial discrimination may continue to linger.
How to Write a Explanatory Essay
The process of writing an explanatory essay shouldn’t pose too much trouble for you if you do it right. The right way to go about how to write explanatory essay has been addressed here. Now that you know how to write exploratory essay, follow the steps and you’re on your way to having a stress-free writing journey.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- [email protected]
- Get 21% OFF . Use the code: FIRST21

The Art of Explanation: How to write an explanatory essay
Table of contents.
Welcome to our guide on how to write an explanatory essay! An explanatory essay is a type of writing that is used to explain a specific topic or concept. It is a useful tool for providing readers with a better understanding of a subject, whether it be a historical event, scientific principle, or even a personal experience. The ability to explain complex ideas clearly is an essential skill in today’s society, as it allows us to share our knowledge and understanding with others.
But before we dive into the nitty-gritty of writing an explanatory essay, let’s take a moment to talk about why it’s important. In today’s world, we are constantly bombarded with information from all different sources. It can be hard to sift through it all and make sense of what’s important. An explanatory essay is a way to help make sense of the information by breaking it down into smaller parts and providing a clear and accurate explanation of the topic.
Now that we understand the importance of explanatory essays, let’s talk about the steps involved in writing one. The process can be broken down into several manageable steps, including researching, planning, writing, and revising. By following these steps, you’ll be able to write a clear and effective explanatory essay that informs and educates your readers.
Enhance your writing skills with this informative piece, which is just one part of our comprehensive guide, “ Master the Art of Writing “.
In a hurry? Get a quick overview of the steps in our 2-minute summary
In this guide, we’ll take you through each of these steps in detail. We’ll talk about how to conduct thorough research, how to plan and organize your essay, and how to write an engaging and attention-grabbing introduction. We’ll also cover how to clearly and effectively explain complex ideas, how to write a strong conclusion, and how to revise and edit your explanatory essay to make it the best it can be.
So, grab a notebook and a pen and let’s get to the first step: researching. Conducting thorough research on your topic is essential for writing a clear and accurate explanatory essay. It allows you to identify key information and sources that will be used to support your main idea. When researching, it’s a good idea to use a variety of sources, including books, articles, and online resources. Make sure to take notes and organize your research so that you can easily access the information you need when writing your essay.
Next, we’ll move on to the planning stage. This includes outlining the main idea and key points of your essay, as well as organizing the information you have gathered. Creating an outline will serve as a roadmap for your essay , helping you to stay on track and ensure that your essay is logically structured.
With your research and planning complete, it’s time to start writing the introduction. The introduction is the first impression that readers will have of your essay, so it’s important to make it engaging and attention-grabbing. This can be done by using an interesting fact or statistic, asking a question, or providing a personal anecdote. The introduction should also establish the main idea and purpose of the essay.
The next step is writing the body of your essay. This is where you’ll provide a clear and detailed explanation of your topic or concept. It’s important to use evidence and examples to support the main idea, and to organize your information in a logical and easy-to-understand way. Use headings and subheadings to make the essay easy to follow and make sure to keep the tone friendly and engaging.
The conclusion of your essay is where you’ll summarize the main idea and key points of your essay. It’s also an opportunity to make a lasting impression on the reader. This can be done by providing a call to action, asking a thought-provoking question, or making a prediction. The conclusion should end the essay on a strong note and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
Finally, it’s time to revise and edit your essay. This is an essential step in the writing process and will help you to identify and fix any mistakes, and to polish your essay to make it the best it can be. Read through your essay several times, checking for grammar and punctuation errors, and making sure that the information is presented in a clear and logical way.
And there you have it! By following these steps, you’ll be able to write a clear and effective explanatory essay that informs and educates your readers. Remember, the ability to explain complex ideas clearly is an important skill and writing explanatory essays is a great way to practice and improve this skill. So, don’t be afraid to take on a challenging topic, and don’t be discouraged if your first draft isn’t perfect. Keep practicing and you’ll be writing great explanatory essays in no time!
Identify key information using research matrix
What is an explanatory essay.
An explanatory essay is a type of writing that explains or clarifies a certain topic . This is distinct from other forms of writing such as persuasive, narrative, and expository essays. While these other types of essays often revolve around making a certain argument, an explanatory essay is meant to explain a topic to readers in a concise and straightforward manner.
At its core, an explanatory essay is all about breaking down complex topics into more manageable and digestible chunks. Rather than trying to persuade readers to agree with a certain point, the goal of this form of writing is to impart knowledge on the specified topic. It typically follows the fundamental structure of an introduction, body paragraphs and conclusion.
The body of the essay is where the majority of the information is conveyed. Here, the writer must organize their thoughts and ideas into clear, concise points that can be easily understood by the reader. Additionally, the writer should use simple language to ensure that their points are easily followed by all audiences.
Explanatory essays differ from other forms of writing in that they do not require the author to take a specific stance on the subject. Rather, they are meant to simply provide information and educate the reader on the topic at hand. By presenting facts and data in an easily digestible format, the writer can help the audience gain a better understanding of the subject.
How to Choose a Topic
When it comes to writing an explanatory essay , the most important decision you will make is choosing your topic. Selecting the right topic can be crucial to the success of your essay as it should challenge you while also providing value to the reader. Here are some tips to help you choose the perfect topic.
Consider Your Audience
Take some time to think about who your readers will be and what they might be expecting from your essay. This will help narrow down the subject matter and allow you to focus on topics that your audience will find interesting and informative.
Ask Yourself Questions
Before you settle on a topic, consider the type of questions you can ask related to it. If the questions you come up with don’t have clear answers or invite further exploration, then it likely isn’t the right topic for you. Aim to select a topic that offers plenty of food for thought.
Narrow Down Your Choices
Once you have a few topics in mind, take some time to research each one and consider the amount of available materials. If there isn’t enough material to draw upon it might not be the best choice. Additionally, make sure your topic is neither too broad nor too narrow. Aim to strike a balance between the two.
Pick the Right Topic
Choosing the right topic is an important part of writing an explanatory essay . Spend some time considering your audience, asking yourself questions related to potential topics and doing research to narrow down your list of choices. Once you’ve done all this, you should have the perfect topic to write about.
Researching the Topic
Conducting research for an explanatory essay is a key step in the writing process. Research helps you to accurately and effectively support your argument, providing evidence and authority to back up your claims. To research effectively, follow these steps:
- Decide on your topic. Be sure that it’s specific and can be explored in depth.
- Gather resources. Use both online and offline sources such as books, articles, and interviews. Utilize reliable sources such as government websites and published materials.
- Organize your research. Utilize a spreadsheet or other visual tool to keep track of all the relevant information for your essay. This will help you better understand the material and quickly locate the information you need.
- Take notes. As you are researching and gathering information, take notes on the significant points of the material. It is important to stay organized and focused on the most important points so that you don’t get distracted while writing your essay.
- Cross-check sources. Be sure to double check your sources and make sure that the information you are citing is accurate. Don’t forget to cite any sources you use in the essay.
Research is an important step when writing an explanatory essay. By researching your topic ahead of time, you can ensure that you have enough information to accurately and effectively support your argument. Taking the time to properly research and organize your material will go a long way in helping you write a successful essay.
Constructing an Outline
Constructing an outline for an explanatory essay is an important step to ensure that the essay is organized and structured. An outline provides a starting point and framework for writing, while allowing you to keep track of the main points and arguments you wish to make in the essay. It also helps you set the tone of the essay and focus on the topic.
Writing an outline can seem daunting but it doesn’t have to be. To begin, think about the overall structure of the essay and the topics or ideas you would like to include in each section. From there, start to break those topics down into smaller points. Once you have outlined the main points you want to make, create an introduction, body and conclusion structure.
The introduction should present the main topic of the essay and why it is important. The main body should contain the evidence and arguments that support the main topic. Finally, the conclusion should summarize all the points made in the essay and provide a memorable takeaway for the reader.
An outline is also a great way to make sure you are keeping your sentences and paragraphs focused and on track. Thinking through the sequencing of the essay in advance will help you avoid any potential confusion or disjointedness in the finished product.
After creating the outline, you can use it as a guide for writing the essay. This step-by-step approach will help you stay organized and focused while generating ideas and composing the essay.
Overall, constructing an outline before writing an explanatory essay is a valuable tool that will help you create a well-structured and effective essay. Not only will it help you stay organized and focused while writing, but it will also give your readers a clear and organized essay to read.
Writing an Explanatory Essay
Using clear language, organizing your ideas, developing strong arguments, proofreading and editing, creating a strong body.
Once you have finished drafting your essay’s introduction and have an outline that you are satisfied with, it’s time to move onto the body paragraphs. The body of your essay is where you’re able to provide evidence, detail and further explain the points you make in your introduction. It’s important to structure each body paragraph in a logical and organized way to ensure they are strong and effective while supporting the main points of the argument.
Key Points To Consider:
- Structure each paragraph logically and clearly around one specific idea.
- Provide supporting facts, examples and quotes to back up your main point.
- Ensure you include a transition phrase at the start of each paragraph.
- Link the paragraphs appropriately using strong transitional words .
- Analyze and evaluate evidence to provide effective support for your argument.
- Maintain focus on the topic throughout the body paragraphs.
The first step in creating strong body paragraphs is to structure them properly. Each paragraph should cover one specific main idea or point and be made up of a single sentence. You should then elaborate on this point by providing evidence, facts and quotes to back up your claim. This will help to make your argument more convincing and compelling.
It is also important to ensure that you use appropriate transition phrases at the beginning of each paragraph to make sure they are connected effectively. This can be done through the use of connecting words and phrases such as ‘nevertheless’, ‘on the other hand’, ‘in addition to’, ‘as a result’ etc.
Throughout the body of your essay, you should analyze and evaluate the evidence you are providing to ensure it is effective. This involves discussing any counterarguments or opposing viewpoints and refuting these accordingly. By doing this, you show that your argument is well-rounded and demonstrate that you have thought about the issue thoroughly.
Finally, you should maintain focus throughout your body paragraphs. Making sure you stick to the main points of your argument and don’t drift off track is key to keeping the reader engaged. If you find yourself going off-topic, simply return to the main point and refocus on it.
Creating strong body paragraphs that support the main points of your argument is essential to writing an effective explanatory essay . With the right structure, evidence and analysis, you will be able to provide compelling arguments to your readers and ensure your essay has the desired impact.
Developing a Memorable Conclusion
Once you have written the body of your essay, it’s time to craft a memorable conclusion. This is often the most challenging part for many writers. It’s important that your conclusion not only summarizes the main points of your argument and leaves a lasting impact on the reader, but also ties together all the strands of your essay. Here are some tips for writing an effective conclusion:
- Restate the main points of your essay in a concise way. This can be done in one or two sentences.
- Reflect on the significance of your argument. Why is this topic worth discussing? What can the reader take away from your essay?
- Provide a thought-provoking statement or question. This can be used to stimulate the reader to think of potential solutions or implications.
- Avoid introducing new information. Your conclusion should only include information that has already been discussed in the essay.
- Connect the conclusion back to the introduction. This can help bring the essay full circle and create a sense of closure.
A well-crafted conclusion should leave the reader with something to think about and make them remember your essay. If you put in the effort to write a compelling conclusion that ties the entire essay together, you will be sure to make a lasting impression.
Editing the Essay
The editing phase of writing an explanatory essay is essential for achieving a successful final product. Editing allows writers to ensure that their essays are effective and make sense to the reader. It also provides writers with the opportunity to improve the flow and quality of their work.
When it comes to editing your essay, here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Check your essay for any spelling or grammar errors, and make sure all your facts are accurate.
- Make sure the essay has a strong introduction and conclusion that appropriately connect to each other.
- Be sure to eliminate any unnecessary language or passages that distract from the main point.
- Look for ways to make the essay more engaging and readable, such as using active voice, varying sentence structure, and including vivid narrative details.
- Read over the essay several times, paying attention to areas where more explanation or evidence may be needed.
- Have a friend or fellow student read over the essay, and ask them to provide feedback.
By making the most of the editing phase, you can create an explanatory essay that accurately expresses your message and impresses your readers. While this task may seem daunting, it’s important to remember that editing is an essential part of the writing process.
Staying Motivated and Pivoting When Challenges Arise
Writing an explanatory essay is a rewarding and challenging project. Although it can seem daunting, setting yourself up for success from the beginning will make the journey much easier. Here are some strategies for successfully completing your essay:
- Set goals and break your essay down into manageable chunks: Instead of overwhelming yourself with the entire essay, break the project down into smaller tasks such as research, outlining and drafting. Setting specific, achievable goals will help you stay motivated and track your progress.
- Reach out for help: Don’t be afraid to seek help when you need it. Ask friends, family or teachers for assistance if things start to feel overwhelming. Having a second set of eyes review your work can also be beneficial for catching mistakes.
- Find ways to stay inspired: If you find that you are getting burned out, take a break from your essay and do something else that inspires you. Take a walk, watch a movie or read a book to give yourself time to recharge.
- Be flexible: When challenges arise, be open to shifting gears and exploring different approaches. As you write, you may realize that your original plan was not the best course of action. Be prepared to pivot if a roadblock appears.
These strategies can help you stay motivated, focused and inspired while writing your essay. With the right amount of effort and the right attitude, you can create a successful explanatory essay .
Conclusion: Summarizing Our Guide to Writing an Explanatory Essay
Writing an explanatory essay is a great way to build your knowledge , strengthen your writing skills and present your point of view in a clear and concise manner. This guide has covered the essential steps of the process, from choosing a topic, researching the material and constructing an outline all the way to crafting a memorable conclusion.
We have discussed the importance of properly researching your topic and understanding the main points you want to make before structuring your essay. We also touched on the best practices for drafting, editing and proofreading your work for accuracy and clarity. Finally, we offered strategies for staying motivated throughout and finding balance in the creative process.
We hope that this guide has made the task of writing an explanatory essay much easier by providing all the information you need in one place. By following the steps outlined in this guide and utilizing the tips and techniques provided, you will be well on your way to successfully completing your next essay assignment.
- Last Edit 27 APR 2023

Nick Radlinsky
Nick Radlinsky is a devoted educator, marketing specialist, and management expert with more than 15 years of experience in the education sector. After obtaining his business degree in 2016, Nick embarked on a quest to achieve his PhD, driven by his commitment to enhancing education for students worldwide. His vast experience, starting in 2008, has established him as a reputable authority in the field.
Nick's article, featured in Routledge's " Entrepreneurship in Central and Eastern Europe: Development through Internationalization ," highlights his sharp insights and unwavering dedication to advancing the educational landscape. Inspired by his personal motto, "Make education better," Nick's mission is to streamline students' lives and foster efficient learning. His inventive ideas and leadership have contributed to the transformation of numerous educational experiences, distinguishing him as a true innovator in his field.

When to Submit TOK Essay? Deadlines
Understanding when to submit your TOK essay is crucial for success, as meeting these deadlines ensures you have ample time for revisions and reduces last-minute stress. This article offers a comprehensive guide on TOK essay deadlines, providing key insights from a seasoned IB writer.

What Are the IB IA Deadlines?
In this comprehensive guide, we discuss the essential dates and strategies for managing your submissions effectively. Understanding these deadlines is vital when preparing for the May or November exam sessions. From planning early and using digital tools to track your progress to communicating with teachers and handling unforeseen challenges, this article provides you with all the insights and tips you need to master the timing of your IAs.

2024 November TOK Essay Prompts | How to Write Them?
In this comprehensive guide, an experienced IB writer shares essential insights and strategies specifically tailored to mastering TOK essay prompts. From analyzing the nuances of knowledge acquisition in different areas of knowledge to considering the dynamic interplay between artistic creativity and scientific methodology, this article offers a deep immersion into each prompt.

How Long Is IB EE? Minimum and Maximum Word Count
Balancing word count limits requires careful planning and consideration of every word you write. In this guide, I’ll share strategies and insights from years of mentoring IB students to help you master the art of word count management in your extended essay.

TOK Essay Word Count. Min & Max
In this guide, we discuss the crucial parameters set by the International Baccalaureate for minimum and maximum word counts. Through the insights of an experienced IB writer, this article offers practical strategies for staying within these limits while improving the quality and depth of your essay.

How Long Is IB IA? Average IA Word Count
From my experience as IB tutor, a frequent question among students is, “How Long Is IB IA?” This question is crucial as the IA represents a significant component of the IB diploma, reflecting a student’s ability to apply classroom knowledge in a real-world context.
© 2024 I Bstudenthelp.com. This website is owned and operated by Udeepi OU Harju maakond, Tallinn, Lasnamäe linnaosa, Sepapaja tn 6, 15551. Disclaimer : Services we provide are only to assist the buyer like a guideline to complete any kind of writing assignment. Privacy Policy Terms and Conditions Cookie Policy Revision Policy Refund Policy

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
How to Write an Explanatory Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide
by Antony W
September 12, 2022

If you’re looking for a complete guide on how to write an explanatory essay, you’ve come to the right place.
In this guide, you’ll learn what an explanatory essay is, how to write the essay, and some tips to help you ace the assignment.
Key Takeaways
- An explanatory essay is a type of an essay that requires you to give your opinion about a process, a story, a person, or an event.
- You don’t make an argument in an explanatory essay. Rather than taking sides, you simply explain an issue to make it easy for a reader to understand.
- To write an explanatory essay, you choose a topic, conduct research, create an outline, write the essay, and then edit your final draft prior to submission.
What is an Explanatory Essay?
Also known as an expository essay, an explanatory assignment in which you give your opinion about an event, a story, a person, a subject, or a process.
You don’t necessarily have to agree with the view that you give. But your point of view must be thoroughly researched and logical.
An explanatory essay is different from an argumentative writing in that instead of taking a position and debating its validity, you simply explain the issue to make it easier for your audience (readers) to understand.
In other words, you have to take a neutral position on a topic and provide a clear analysis of the subject in question.
The primary objective of an explanatory essay is to help your reader to understand why something happened the way they did.
By the time they finish reading the essay, they should get a clear picture of your explanation, even if they don’t agree with it.
How to Write an Explanatory Essay Step-by-Step
Writing an expository essay shouldn’t be difficult if you have the right lead.
Continue reading this step-by-step guide to learn how to write the best explanatory essay fast.
1. Pick a Topic
Check the essay prompt to determine if your instructor has given you a topic to focus on.
If they have, write the essay according to the instructions that they provide.
If they haven’t, consider choosing an interesting topic that you can easily explore.
2. Research and Gather Evidence to Support Your Essay
Research your topic well and gather as much information about it as you possibly can.
Don’t worry if part of your explanatory essay will include merely opinions.
As long as the opinion is reasonably strong, your essay should stand out.
While there’s a wealth information that covers the topic under examination, it’s best to use reliable sources to write the essay.
Keep a record of your source somewhere in a separate notepad, because you need to cite and reference them at the bottom of the essay.
3. Create a Relevant Outline
All essays have one thing in common:
They follow a particular format to make ideas clear.
It follows then that your explanatory (expository) essay should also have a clear format.
Divide the essay into three parts: the introduction, body section, and the conclusion paragraph.
Don’t worry about writing the whole essay at this point. Just focus on organizing your main ideas in point form while keeling the three sections in mind.
Your instructor may ask to see the outline before you proceed with writing the essay.
But even if they don’t, you should make the outline as comprehensive as possible so that you have an easy time writing the expository.
4. Write the Body Paragraph
With a clear outline, writing the whole essay shouldn’t be difficult at all.
While it’s fine to start from the introduction, move to the body section, and then write the conclusion, writing the body of your paper makes your work a whole lot easier.
The consensus is that an expository essay should be at least five paragraphs .
That’s a good starting point.
So if your instructor hasn’t specifically stated that your assignment should be this short, you shouldn’t hesitate to make the essay longer .
The rule to getting the body paragraph right is to focus on one point or idea per paragraph.
Start that with a topic sentence, write your explanation, and then end with a conclusion that easily transitions to a new idea in a completely new paragraph.
6. Write Your Introduction
Your introduction can make or break the explanatory essay. So you shouldn’t take chances here.
Read the body of the article to get a clear idea for a hook. And then start the introduction with a statement that will attract eyeballs instantly.
Include a short background. Then, end the instruction of your expository essay with a strong thesis statement .
6. Write a Conclusion
Really, there’s no magic bullet to ending an essay and this part of the assignment should be a no brainer to complete.
The approach is to end the assignment on a very strong note.
Tie your idea together into a powerful statement that gives your readers something to think about.
Tips to Write a Good Expository Essay
Below are some tips you can use to write a good explanatory essay within the shortest time possible.
1. Use an Appropriate Writing Style
An explanatory essay uses the same three-part format used in all essays.
Beyond that, however, it doesn’t require you to take a side or persuade someone to do, say, or believe something.
As such, it’s important to use an appropriate writing style when writing this assignment.
Your explanation should be more of a discussion. And while you do have to present evidence to back your topic, you shouldn’t do so to put your reader in a position where they have to make a solid case.
2. Get Help from Professional Essay Writers
Still don’t have time to write an explanatory essay yourself even after reading this guide?
You can pay someone to write an essay for you and get the task completed in the shortest time possible.
You can use the essay you receive from us as reference to help you write your final draft, deliver the final copy to your teacher for review, and score good grades.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.1: Expository Essays
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 4531
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Understand the function and use of expository essays
- Identify eight types of expository essays
- Apply expository essay structure
What Is an Expository Essay?
An essay that explains a writer’s ideas by defining, explaining, informing, or elaborating on points to allow the reader to clearly understand the concept.
Many of your future academic workplace writing assignments will be expository–explaining your ideas or the significance of a concept or action. An expository essay allows the writer the opportunity to explain his or her ideas about a topic and to provide clarity for the reader by using:
- Explanations
- Definitions
It may also include the writer outlining steps of a procedure in a way that is straightforward for the reader to follow. It is purely informative and often contains elements of summary.
Imagine you need to verbally explain a concept to your classmates, maybe a behavioural theory. What are the key elements on which you would focus? How would you organize the information? You could explain who came up with the theory, the specific area of study to which it is related, its purpose, and the significant details to explain the theory. Telling these four elements to your classmates would give them a complete, yet summarized, picture of the theory, so they could apply the theory in future discussions.
Although you did this verbally, you were still fulfilling the elements of an expository essay by providing definition, details, explanations, and maybe even facts if you have a really good memory. This is the same process that you would use when you write an expository essay. You may actually be doing this all the time; for example, when you are giving someone directions to a place or explaining how to cook something. In the following sections of the chapter, you will practise doing this more in different expository written forms.
The Structure of an Expository Essay
Sections versus paragraphs.
Before looking at the general structure of an expository essay, you first need to know that in your post-secondary education, you should not consider your essay as writing being constructed with five paragraphs as you might have been used to in high school. You should instead think of your essay in terms of sections (there may be five), and each section may have multiple paragraphs.
To understand further why you need to think beyond the five-paragraph essay, imagine you have been asked to submit a six-page paper (approximately 1,500 words). You already know that each paragraph should be roughly 75 to 200 words long. If you divide the required word count by five paragraphs (1,500 by 5), you end with 300 words per paragraph, way above the number you should have in a paragraph. If your paragraphs are too long, they likely have too many ideas and your reader may become confused. Your paragraphs should be two-third of a page at most, and never longer than a page.
Instead, if you think of your essays being divided into sections (with possibly more than one paragraph per section), your writing will likely be more organized and allow your reader to follow your presentation of ideas without creating too much distance between your paragraph’s supporting points and its topic sentence.
As you will see in Section 4.5, some essay forms may require even more than five paragraphs or sections because of how many points are necessary to address. For the rest of this chapter, the term paragraph will also imply section.
Sections of an Expository Essay
An expository essay, regardless of its purpose, should have at least five sections, which are:
- Introduction
- First body section/paragraph
- Second body section/paragraph
- Third body section/paragraph
- Conclusion.
The introduction should state the topic of your paper: your thesis statement as well as brief signposts of what information the rest of the paper will include. That is, you only want to mention the content of the body paragraphs; you do not want to go in to a lot of detail and repeat what will be in the rest of the essay.
The first body section or paragraph should focus on one of your main points and provide evidence to support that point. There should be two to three supporting points: reasons, facts, statistics, quotations, examples, or a mix of these. Both the second and third body sections should follow the same pattern. Providing three body sections with one point each that supports the thesis should provide the reader with enough detail to be convinced of your argument or fully understand the concept you are explaining. However, remember that some sections will require more explanation, and you may need to separate this information into multiple paragraphs.
You can order your sections in the most logical way to explain your ideas. For example, if you are describing a process, you may use chronological order to show the definite time order in which the steps need to happen. You will learn about the different ways to organize your body paragraphs in the next chapter.
The concluding paragraph , or conclusion, can be a little tricky to compose because you need to make sure you give a concise summary of the body paragraphs, but you must be careful not to simply repeat what you have already written. Look back at the main idea of each section/paragraph, and try to summarize the point using words different from those you have already used. Do not include any new points in your concluding paragraph.
Consider Your Audience: How Much Do They Know?
Later in this chapter, you will work on determining and adapting to your audience when writing, but with an expository essay, since you are defining or informing your audience on a certain topic, you need to evaluate how much your audience knows about that topic (aside from having general common knowledge). You want to make sure you are giving thorough, comprehensive, and clear explanations on the topic. Never assume the reader knows everything about your topic (even if it is covered in the reader’s field of study). For example, even though some of your instructors may teach criminology, they may have specialized in different areas from the one about which you are writing; they most likely have a strong understanding of the concepts but may not recall all the small details on the topic. If your instructor specialized in crime mapping and data analysis for example, he or she may not have a strong recollection of specific criminological theories related to other areas of study. Providing enough background information without being too detailed is a fine balance, but you always want to ensure you have no gaps in the information, so your reader will not have to guess your intention. Again, we will practise this more in Section 4.9.

What Comes Next?
In the next eight sections (4.2 through 4.9), we will look at different expository modes, or rhetorical modes, you will often be assigned. These are:
- Illustration
- Description
- Classification
- Process analysis
- Compare and contrast
- Cause and effect
Rhetorical modes refers simply to the ways to communicate effectively through language. As you read about these modes, keep in mind that the rhetorical mode a writer chooses depends on his or her purpose for writing. Sometimes writers incorporate a variety of modes in any one essay. In this chapter, we also emphasize the rhetorical modes as a set of tools that will allow you greater flexibility and effectiveness in communicating with your audience and expressing your ideas.
In a few weeks, you will need to submit your first essay–an expository sample–and you will be given the choice of topic: one from each of the modes. Think about which types of expository essays are easier and which are more challenging for you. As mentioned, as you progress through your studies, you will be exposed to each of these types. You may want to explore a mode you find more challenging than the others in order to ensure you have a full grasp on developing each type. However, it is up to you. As you work through the sections, think about possible topics you may like to cover in your expository essay and start brainstorming as you work through the self-practice exercises.
After we explore each of the individual modes in the eight sections that follow, we will look at outlining and drafting; it is at this point you will want to fine tune and narrow the topic you will write about, so you can focus on that when doing the exercises.
Explanatory Essay Writing Guide

Before writing any type of assignment, you must understand its definition. The following approach can be applied to any other type of academic writing, including an explanatory essay.
In this article, our write my essay for me service professionals will try to explain what an explanatory essay is, its primary goal, and key features. Even though many people think that there is nothing more simple than writing an explanatory essay, for most students, it can still be a challenge to distinguish explanatory paper from other types of essays.
We highly recommend you read this article till the end. Guidelines outlined in our manual will help you gain new knowledge and enhance your writing skills. Designing explanatory essay will become an easy task for you once you put recommendations from our professional paper writing service into practice.
What is an Explanatory Essay?
An explanatory essay is a type of academic paper in which the author presents some point of view or opinion on a particular topic, subject, event or situation. It’s worth noting that explanatory essay is also known as expository essay.
When completing this kind of assignment you shouldn’t necessarily agree with the point of view you are writing about. Your goal is to report a certain event or situation and offer an analysis of a given subject. Try to present information or arguments of other people impartially. It’s also essential that you do not include any form of criticism in your explanatory essay. You shouldn’t argue or persuade while giving explanations. Let readers make their conclusions rather than persuading them to agree or disagree with the given point of view.
Explanatory essay is all about presenting a neutral view on the set topic by providing analysis from research. Its primary goal is to present a lucid explanation as to why things happened the way they did. After reading your essay, the audience should have a clear understanding of your point of view, even if they don’t pick your side.
Usually, the author of the explanatory essay decides upon a set topic and then approaches the issue from a specific angle. In most cases, this angle is complicated and gives room for discussion. The author presents a point of view of his or her choice that fairly explains why a certain outcome was reached.
Explanatory Essay Topics
In most cases, explanatory essay topics are pre-assigned to students by their teachers or college professors. For instance, you can be asked to explain how your brain works or outline the events that led to the 2008 financial crisis.

If you are asked to select the essay topic by yourself, remember that explanatory papers are based on facts. That’s why our custom essay writing professionals recommend that you choose a neutral topic that can be easily explained. The idea here is that the more controversial the topic, the more points of view you will need to explore in your essay, making it more complicated and time-consuming. Fortunately, we can explain almost everything as long as it falls within the parameters of the given assignment. Here are a couple of explanatory essay topics created by our paper topic generator you can choose from:
Beginner Explanatory Essay Topics
- Describe the day you came to school for the first time. How did it make you feel?
- What qualities do you believe make someone a good friend?
- Explain what makes dogs the best pet for a person.
- Who is your favorite superhero or movie/book character? Why?
- Describe your dream home.
- Who is that person you admire and look up to the most?
- Define what happiness means to you.
- Who is your favorite teacher?
- Tell what kind of food you love most and explain why you love it.
- What kind of job do you think will suit you the most?
Intermediate Explanatory Essay Topics
- What is the best lesson that parents can teach their kids?
- Describe your favorite kind of sport.
- What unique traditions does your family have?
- Tell about something you are really good at and could teach it to others.
- Does the word “responsibility” mean the same thing for adults and children?
- Describe what you believe makes a person truly rich.
- What is your favorite place on the planet?
- Explain how someone you know (a friend, teacher, parent) helped you become a better person.
- What is the school subject you enjoy the most?
- Describe how having a sibling can affect one’s personality.
Advanced Explanatory Essay Topics
- Explain one of the forms of cyberbullying and suggest ways to address it.
- Do you believe animals can really feel your fear?
- Describe a moral dilemma you have faced. How did you handle it?
- Do you believe in UFOs and aliens? Explain your point of view.
- Explain how your personality has changed as you were growing up.
- How can we measure happiness?
- Define your generation. What makes it different from other generations?
- Explain how you understand the universe.
- How do you imagine your perfect future?
- Describe your first work experience ever. What did it teach you, and how did you handle it?
College Level Explanatory Essay Topics
- Define the positive and harmful effects the Internet has on a human personality and life.
- What real-life lessons do you wish you’d learn 5 years ago?
- Tell about someone who has authority in your eyes and explain why.
- Do you think expressing the whole spectrum of emotions is better than suppressing them?
- Explain what experience was the most life-changing for you.
- How to cope with financial difficulties?
- Explain the benefits of social networks for modern students.
- What makes a person generous?
- Describe the technological advancement that took place over the last decade.
- Define what difference you see between “living” and “existing”.

Explanatory Essay Format
The typical format for an explanatory paper is the traditional 5-paragraph essay. Usually, this includes an introduction, three body paragraphs (limited to one subtopic each), and a conclusion. This is a basic essay format.
Keep in mind that the explanatory writing doesn’t need to be limited to five paragraphs — you can make it longer. No matter how many paragraphs you decide to include in your essay, be sure that your introduction includes a powerful thesis statement. Also, double-check if the paper is based on facts rather than personal opinion. Last but not least: make sure to connect paragraphs with transitions.
Explanatory Essay Outline
In simple terms, an explanatory essay outline is a plan for your explanatory paper. Usually, it varies based on the length of the topic and the information the author is trying to present. The goal of the outline is to organize the main points into paragraphs — it offers a so-called framework of how to write an explanatory essay. As it was mentioned in the paragraph above, most explanatory essays follow the basic essay structure. They consist of:
- Introduction;
- Body paragraphs;
- Conclusion.
Most explanatory essays tend to be a page or two in length. That's why the overall essay is usually around 5 paragraphs long. Remember that your introduction should present the topic to the audience. Also, it’s vital that you incorporate the thesis statement in the last paragraph. After you are done with it, try to develop the body paragraphs with the information detailed in the thesis statement. Finally, include a conclusion that summarizes your essay's key points after the restatement of the thesis. As you can see, creating an explanatory essay outline is not that difficult as it may seem at first glance. And now let’s dig deeper into the definition of the explanatory essay thesis.
Thesis Statement
When talking about a thesis statement, most people usually mean one or two sentences that summarize the main idea of their academic paper and clearly express what it is they are going to say about the given topic. Overall, your thesis statement identifies what topic will be discussed and the purpose of your essay. As the explanatory essay is tailored to explain or acquaint your readers with something, the goal of the explanatory thesis is to tell readers what it is you are going to explain and what aspects of the topic will be considered.
Introduction
Before you start writing your explanatory essay, there are some crucial tips to follow. The first recommendation is to carry out proper research and data collection. Explanatory essay authors should ensure that the information in their writing is a blend of personal views and ideas acquired from external sources. Explanatory essay relies heavily on solid research, focus on finding external sources that will supplement your personal opinion. Note down all the important information from those sources and use them as evidence in your essay. So, the first thing you should do is find multiple trusted sources that defend your thoughts. We suggest you look to online journals, historical dictionaries, or find relevant books in your college library to use them as trusted sources.
After collecting all the needed information, the next step is to develop a clear explanatory thesis. A concise thesis will make it easier for readers to understand the essence of the topic from a summarized point of view. In other words, explain what you will be showing to your audience. Be neutral — you are not arguing or criticizing, just stating facts. Remember, you are not supposed to take any side as that causes a loss in the outlook of an explanatory essay.
Another recommendation is to choose a neutral topic you'd like to explain. If your teacher or professor didn’t give you a specific topic, select the one that will be understandable for you. Just choose such a topic that is in line with your assignment.
Once you’ve chosen a suitable topic, it’s time to draft an outline of your explanatory essay. The best option here is to stick to five paragraphs that were mentioned above: draft an introduction, three main body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The outline helps students ensure that they follow a logical pattern to detail all their trains of thought. After completing all of the above steps - review your material and start writing your explanatory paper.
Each explanatory paper should start with an introduction. Try to capture your audience’s attention. No matter how you decide to do that - it may be a quote, rhetorical question, catchy motto, or anecdote. Feel free to improvise and use your imagination. Picking a hook thesis statement is also important. After presenting a thesis statement, include any necessary information that gives a background of the topic. The last sentence of your introduction should integrate a thesis statement to give a preview of the content in the body paragraphs.
Body Paragraphs
No matter how many paragraphs you decide to include in your explanatory essay, they all should follow a similar style. They all should be in-line with each other and maintain a certain flow in the paragraphs. Within each paragraph, you are to include a claim that is linked to the thesis statement. This way, it will be easier to connect all the points.
Try to support your claims with evidence from external sources. Make your readers feel confident about the information you present to them. Don’t forget to integrate a concluding statement that offers a summary of the claim's significance. Concluding statement should go along with the thesis statement. In simple terms, all body paragraphs in your explanatory paper should follow this format.
Conclusion Of Explanatory Essay
The explanatory essay must have a proper conclusion. When finishing your explanatory paper, follow these recommendations:
- Restate your thesis. This way you will bring your readers’ attention back to the main point as well as add strength to your presented point of view.
- Summarize your supporting points presented in each of the body paragraphs accordingly. Restate the importance of each one. This way you will logically defend your explanatory thesis.
- Provide an overall concluding statement. In other words, explain the value of the particular point of view chosen from a global perspective. Your goal here is to captivate your readers to study the subject further on.
How to Write an Explanatory Essay - Writing Tips
Some useful tips will help you write an excellent explanatory essay. Here are some of the most powerful ones:

Take advantage of transitions and linking words
While connecting all your body paragraphs, use transition words and sentences. They will make your explanatory paper flow more smoothly. Some of the words you can use to connect your sentences are:
- For instance;
- In comparison;
- Firstly, secondly, thirdly;
- On the other hand;
- In conclusion, to summarise.
Cite your sources
This one is an absolute requirement when writing an explanatory essay. You better try hard in this area. A successful explanatory essay will be factual and contain verifiable information. Cite your sources and make it easy for the audience to check where you drew your facts.
Revise your essay
After completing your explanatory paper, it’s always a good tip to revise it a couple of times. To make your revision phase more effective we advise you to answer the following questions:
- Does the essay give an objective analysis that unfolds logically? Did I use relevant facts and examples in your essay?
- Has the information in my paper been communicated to the audience? Is the word choice precise?
- Did I use transitions and linking words in the essay to help the reader’s understanding?
- Does the concluding paragraph communicate the value and meaning of the thesis statement and supporting ideas?
Edit your essay
Double-check your paper for different of mistakes and typos. When proofreading your paper, make sure that nobody distracts you. It would be perfect if you revise and proofread your essay in silence. If you notice any kinds of errors - edit your paper to improve both style and clarity. Even though your essay should be clear and concise, also think on how to make it engaging and lively as well.
Share your essay with a close person
Showing your essay to your parent, friend or other readers can be both useful and exciting. They can give you their opinion on what should be changed. They can also notice some grammar or punctual mistakes you missed while writing the essay. Overall, it always good to use the feedback to make your essay even better.
Explanatory Essay Example
Read the following essay sample to understand this type of essay better. If you need more examples, don’t hesitate to buy essay samples from our website.
What are the benefits of social networks for modern students?
According to the World Health Organization, people spend around 6 years and 8 months on various social media in their lifetime. These numbers are both impressive and terrifying. Given that the average lifespan across the world is 72 years, in 2020, the time spent on social networks makes up almost 10% of our entire life. And these figures keep changing and hitting higher points every year. Unsurprisingly, students are the largest group of active social network users. There always have been plenty of controversies concerning this matter. But, there is a belief that social media can actually have quite a few benefits for them.
One of the most obvious benefits of social media is that it keeps people connected. Clearly, many modern students are using these channels to make connections and communicate with their peers. Also, though it may not sound like too big of a deal, it can have a very positive effect on their lives in college. A recent study has shown that social media can play an integral role in the process of adjustment to college. The research found that student-centered networks can provide first-year students with so-needed support and help them adapt to the new environment faster, easier, and more effectively.
Another benefit of social networks for students is that such channels can boost students’ overall literacy and reading skills. Various literacy studies confirm that the general level of literacy and reading skills among younger generations is dropping. The biggest issue behind that is the fact that young people almost never pick up a book when they are outside of the class. They are just no longer interested in books as they make them bored. However, this does not mean that students don’t read at all. In fact, they do. It’s just that they are more inclined to read the information provided in smaller chunks and, preferably, containing some eye-catching animations, videos, or images. In other words, they are much more interested in reading publications on blogs, websites, and, of course, social networks. Keeping all that in mind, it shouldn’t surprise you that, according to the National Literacy Trust, social networks really can (and already do) help modern students enhance their reading skills and overall literacy.
Finally, the last significant benefit of social media is the accessibility of education. Such channels have provided us with plenty of opportunities for distance learning. The global quarantine has shown us that the effectiveness of distance learning can equal the effectiveness of traditional learning. But only if we integrate the right tools in the process. Among such tools are various social network channels. Numerous researches have found that social media can bring extra value in terms of education. It enables students to search for information, collaborate, and stay engaged and motivated through the learning process. Also, such channels make education more accessible. They can have a practical use in creating the right conditions for efficient distance learning. At the same time, they also streamline both learning and teaching processes and help deliver better results.
Based on what has been discussed earlier, we can conclude that social networks do have a number of weighty benefits for modern students. Such channels encourage continuous learning, create new opportunities for distance learning, boost students’ levels of literacy and skills, and also serve as great tools for communication and support. We can’t deny the fact that social media is invading our lives at a rapid pace, so the only thing we can do is to adapt to this and start making the most of it.
We hope we managed to explain how to write a great explanatory essay. Now you know how this type of academic paper differs from other essays and what writing style and topic to choose when preparing such kind of assignment.
We sincerely hope that the tips outlined in our guide will help you enhance your writing and get better grades. However, if you have difficulties with completing this kind of assignment, our team of professional writers is always ready to help you draft a top-notch explanatory essay from scratch. All you need to do is order an essay you need. We can also help you with other types of assignments, such as coursework, dissertation writing, or research paper. If you experience any kind of difficulties writing an explanatory essay — welcome to our first-class service!
Need some help with your explanatory essay? — Pay for essay online right now! Contact our experienced essay writers today!
Frequently asked questions
She was flawless! first time using a website like this, I've ordered article review and i totally adored it! grammar punctuation, content - everything was on point
This writer is my go to, because whenever I need someone who I can trust my task to - I hire Joy. She wrote almost every paper for me for the last 2 years
Term paper done up to a highest standard, no revisions, perfect communication. 10s across the board!!!!!!!
I send him instructions and that's it. my paper was done 10 hours later, no stupid questions, he nailed it.
Sometimes I wonder if Michael is secretly a professor because he literally knows everything. HE DID SO WELL THAT MY PROF SHOWED MY PAPER AS AN EXAMPLE. unbelievable, many thanks
You Might Also Like

New Posts to Your Inbox!
Stay in touch

Explanatory Essay
Explanatory essay generator.

Essays Writing For a lot of students this word seems to get them to react in a very informal manner. In a way that they perceive this word or this activity as punishment from their professors. When it should not be seen as such. But what about you? What is the first thing that you can think of when you hear the word essays? For those who have gone through this type of discussion, you may have a different type of reaction compared to the majority of the population. Going back, we know that each kind of essay plays a different role and each essay has its own definition and uses. Of course we are not here to talk about the other types of essays except for the explanatory essay, also known as an expository essay. You know that an explanatory essay is also called an expository essay, But what is it about this kind of essay that makes it different from the rest? We know that there are uses for each but what about this? Is it from its term to explain? Are you curious enough to know what do you think this is about? If you are, check the article right now for more.
What is an Explanatory Essay?
An explanatory essay is a type of writing that explains a certain viewpoint, situation, or event. Unlike argumentative essays, which aim to persuade, explanatory essays focus on presenting information in a clear and straightforward manner, allowing readers to understand the topic without the writer’s bias. The goal is to explore a topic in detail by examining various perspectives and providing evidence, such as facts, examples, and statistics, to support the explanation. This essay type encourages critical thinking and research skills, as the writer must thoroughly understand and convey complex information to the audience effectively.
How to Write an Explanatory Essay
Here’s how to craft an effective explanatory essay:
- Understand the Prompt: Begin by thoroughly understanding the essay prompt or question. Identify the key aspects of the topic you need to explain.
- Choose a Topic: If you have the freedom to choose your topic, select one that is interesting and has enough information available for exploration.
- Conduct Research: Gather information from credible sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of your topic. Take notes on significant facts, statistics, and perspectives.
- Create an Outline: Organize your main points and evidence into an outline. This will serve as a roadmap for your essay, ensuring a logical flow of information.
- Write the Introduction: Start with a hook to capture the reader’s interest, followed by background information on your topic. Conclude the introduction with a clear thesis statement that outlines the main points of your explanation.
- Develop Body Paragraphs: Each body paragraph should focus on a single aspect of your topic. Start with a topic sentence that introduces the paragraph’s main idea. Provide evidence and facts to support your points, and explain how this information contributes to understanding the topic.
- Craft a Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in your essay and restate how they contribute to a deeper understanding of the topic. Avoid introducing new information in the conclusion.
- Review and Revise: After completing your first draft, take time to review and revise your essay. Check for clarity, coherence, and logical progression of ideas. Ensure that your essay adequately explains the topic without expressing personal opinions.
- Edit for Grammar and Style: Carefully proofread your essay for grammatical errors, punctuation, and spelling mistakes. Use clear and concise language to maintain the reader’s interest and understanding.
- Cite Your Sources: Properly cite all the sources you used to gather information. This adds credibility to your essay and avoids plagiarism.
Tips for writting an Explanatory Essay
- Begin with a clear understanding of the essay prompt to ensure your essay remains focused and relevant.
- Choose a topic that is both interesting and has sufficient information available for comprehensive exploration.
- Conduct thorough research from credible sources to gather diverse perspectives and facts about your topic.
- Create a detailed outline to organize your ideas and evidence logically, ensuring a coherent flow of information throughout the essay.
- Craft a compelling introduction that includes a hook to grab the reader’s attention, followed by background information on the topic and a clear thesis statement.
- Develop each body paragraph around a single main idea, using facts, examples, and explanations to support your points and enhance understanding.
- Ensure smooth transitions between paragraphs to maintain the flow of your essay and guide the reader through your explanations.
- Write a conclusion that summarizes the main points discussed, reinforcing the understanding of the topic without introducing new information.
- Maintain an objective tone throughout your essay, focusing on explaining the topic without inserting personal opinions or arguments.
- Review and revise your essay to improve clarity, coherence, and organization, and to ensure it adequately addresses the essay prompt.
- Proofread your final draft for grammatical, punctuation, and spelling errors to ensure your essay is polished and professional.
- Properly cite all sources used in your research to lend credibility to your essay and avoid plagiarism.
- Use clear and concise language to convey your explanations, making complex information accessible and understandable to your audience.
Important Steps for a Strong Explanatory Essay Conclusion
Creating a compelling conclusion for an explanatory essay is crucial for leaving a lasting impression on your readers. It’s the final chance to reinforce your thesis and the insights you’ve shared throughout your paper. Here are essential steps to ensure your conclusion is powerful and effective:

Download This Image
Restate Your Thesis: Start by rephrasing your thesis statement. This reminds readers of the main argument of your essay without repeating it word for word. Ensure it reflects the discussion and evidence presented in your essay.
Summarize Key Points: Briefly summarize the key points you made throughout the essay. Highlight the most compelling evidence and how it supports your thesis. This recap helps readers recall your arguments and reinforces the essay’s overall message.
Connect to the Bigger Picture: Tie your essay’s insights to broader themes or implications. Discuss how your analysis contributes to understanding the topic at a deeper level or its relevance in a broader context. This can involve suggesting how your conclusions might apply to other situations or the implications for future research or policy.
Reflect or Project: Depending on your essay topic, you might choose to reflect on the significance of your findings or project future developments. Reflection can provide personal insights or lessons learned, while projection can speculate on how the topic might evolve.
End with a Strong Closing Sentence: Your final sentence should be memorable. It can be a call to action, a rhetorical question, or a profound statement that leaves the reader thinking. Aim for a closing line that encapsulates your essay’s essence while also pushing the reader to consider its implications further.
Avoid Introducing New Information: The conclusion is not the place to introduce new arguments or evidence. Stick to synthesizing the information already presented in your essay.
Personal Connection (Optional): If appropriate, you can briefly mention what the topic means to you or why it’s important on a personal level. This humanizes your conclusion, making it more relatable and impactful.
10+ Explanatory Essay Samples
- Explanatory Essay on My Favourite Sport
- Explanatory Essay on Road Safety
- Explanatory Essay on Responsibility
- Explanatory Essay on Time Management
- Explanatory Essay on Video Games
- Explanatory Essay on Value of Time
- Explanatory Essay on Tajmahal
- Explanatory Essay on Summer Vacation
- Explanatory Essay on Student Life
- Explanatory Essay on Trees
10+ Explanatory Essay Examples
1. animal explanatory essay.

2. Explanatory Essay Checklist

3. Internet Explanatory Essay

4. Explanatory Synthesis Essay

5. Explanatory Essay Sample

6. Informative Explanatory Essay

7. Baseball Explanatory Essay

8. Student Explanatory Essay

9. Education Explanatory Essay
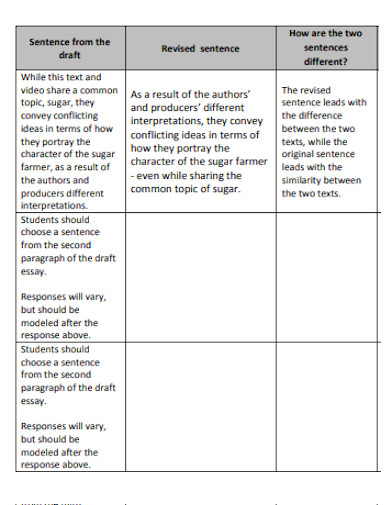
10. Explanatory Essay Analysis

11. Descriptive or Explanatory Essay

Purpose of an Explanatory Essay
An explanatory essay, often referred to as an expository essay, serves a dual purpose of exploring a topic and informing the audience. Its main goal is to provide a clear and detailed explanation of a subject, idea, process, or set of circumstances, based on facts and devoid of the writer’s personal opinions or biases. This type of essay is fundamental in academic settings as it fosters critical thinking, research skills, and the ability to communicate complex ideas in an accessible manner. Below are the key purposes of an explanatory essay:
- To Inform and Explain: The primary purpose is to educate the reader about a specific topic in a straightforward and logical manner. It aims to break down complex subjects into more understandable segments, ensuring the reader grasitates the full scope and context.
- To Analyze Concepts: Explanatory essays often delve into the analysis of ideas, processes, or phenomena. Through detailed examination, these essays present various perspectives and components of the topic, facilitating a deeper understanding.
- To Provide Clarity: One of the essay’s goals is to clarify any misconceptions or complexities surrounding the subject matter. It seeks to answer questions and resolve any ambiguities, making the topic accessible to all readers regardless of their prior knowledge.
- To Enhance Research and Writing Skills: Crafting an explanatory essay encourages students to conduct thorough research, evaluate sources for credibility, and organize their findings coherently. This process hones their ability to sift through information critically and present it in a structured and compelling manner.
- To Present a Neutral Viewpoint: Unlike persuasive or argumentative essays, the explanatory essay prioritizes neutrality and objectivity. It presents information without taking a stance, allowing readers to form their own opinions based on the facts provided.
- To Encourage Critical Thinking: By analyzing and explaining a topic from multiple angles, explanatory essays stimulate critical thinking in both the writer and the reader. They encourage questioning, exploration, and the synthesis of information into coherent understanding.
When writing the essay, what is best to avoid?
Avoid not editing your work, as well as avoid not doing extensive research. As this kind of essay requires the writer to do their research. Providing the fact and the ideas that an opinion from one writer is not enough to convince the readers. Regardless of what topic you may choose to write, you must have proof.
Is an expository essay and an explanatory essay the same?
Yes. An expository essay is also known as an explanatory essay. However, the term expository is more well known but they are the same type of essay.
This is all the information you may need as you plan to write your essay. Remember to always do extensive research on the topics you choose before you write. As well as ending your essays with a stronger statement or stronger opinion of the topic.
How Do You Write an Explanatory Research Paper?
To write an explanatory research paper, start with thorough research on your topic from credible sources. Organize your findings into a structured outline, categorizing information logically. Write your paper by explaining the research findings clearly, supporting your explanations with evidence, and maintaining an objective tone throughout.
How Do You Start an Explanatory Essay?
Start an explanatory essay with a hook to grab the reader’s attention, followed by a brief introduction to the topic that provides necessary background information. Conclude the introduction with a clear thesis statement that outlines the main points you will explain in the essay.
How Should I Start My Explanatory Essay?
Begin your explanatory essay with an engaging opening sentence or question that piques curiosity. Provide a concise overview or context for the topic, leading smoothly into a well-defined thesis statement that previews the essay’s key points or focus.
Can I Use “I” in an Explanatory Essay?
While it’s generally advised to maintain an objective tone in explanatory essays, using “I” might be acceptable if sharing personal experiences or observations directly relates to explaining the topic. However, this should be used sparingly and only when it enhances the explanation.
What Is the Difference Between Expository and Explanatory Essays?
Expository essays aim to inform and explain a topic to the reader, often involving a thorough analysis or breakdown of a concept. Explanatory essays focus on clarifying or elucidating a specific viewpoint, situation, or event, typically in a more straightforward and less analytical manner. Both share the goal of informing, but their approaches and focuses can vary
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write an Explanatory Essay on the process of photosynthesis
Discuss the causes and effects of global warming in an Explanatory Essay
How to research effectively for an explanatory essay.
Crafting a thesis statement for explanatory essays.
Organizing your explanatory essay: Outline essentials.
Writing introductions that captivate in explanatory essays.
Developing coherent body paragraphs in explanatory essays.
Concluding your explanatory essay: Summarizing key points.
Importance of revision in the explanatory essay process.
Citing sources correctly in explanatory essays.
What Is Expository Writing?
How to Write an Expository Essay
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Expository writing is used to convey factual information (as opposed to creative writing, such as fiction). It is the language of learning and understanding the world around us. If you've ever read an encyclopedia entry, a how-to article on a website, or a chapter in a textbook, then you've encountered examples of expository writing.
Key Takeaways: Expository Writing
- Just the facts, M'am: Expository writing is informational, not creative writing.
- Anytime you write to describe or explain, you use expository writing.
- Use a logical flow when planning an expository essay, report, or article: introduction, body text, and conclusion.
- It's often easier to write the body of your article first, before composing the introduction or conclusion.
Expository writing is everywhere in everyday life, not just academic settings, as it's present anytime there's information to be conveyed. It can take form in an academic paper, an article for a newspaper, a report for a business, or even book-length nonfiction. It explains, informs, and describes.
Types of Expository Writing
In composition studies , expository writing (also called exposition ) is one of the four traditional modes of discourse . It may include elements of narration , description , and argumentation . Unlike creative or persuasive writing , which can appeal to emotions and use anecdotes, expository writing's primary purpose is to deliver information about an issue, subject, method, or idea using facts.
Exposition may take one of several forms:
- Descriptive/definition: In this style of writing, topics are defined by characteristics, traits, and examples. An encyclopedia entry is a kind of descriptive essay.
- Process/sequential: This essay outlines a series of steps needed in order to complete a task or produce something. A recipe at the end of an article in a food magazine is one example.
- Comparative/contrast: This kind of exposition is used to demonstrate how two or more subjects are the same and different. An article that explains the difference between owning and renting a home and the benefits and drawbacks of each is one such an example.
- Cause/effect: This kind of essay describes how one step leads to a result. An example is a personal blog chronicling a workout regimen and documenting the results over time.
- Problem/solution: This type of essay presents a problem and possible solutions, backed by data and facts, not just opinion.
- Classification: A classification essay breaks down a broad topic into categories or groupings.
Tips for Expository Writing
As you write, keep in mind some of these tips for creating an effective expository essay:
Start where you know the information best. You don't have to write your introduction first. In fact, it might be easier to wait until the end for that. If you don't like the look of a blank page, move over the slugs from your outline for the main body paragraphs and write the topic sentences for each. Then start putting in your information according to each paragraph's topic.
Be clear and concise. Readers have a limited attention span. Make your case succinctly in language that the average reader can understand.
Stick to the facts. Although an exposition can be persuasive, it should not be based on opinion only. Support your case with facts, data, and reputable sources that can be documented and verified.
Consider voice and tone. How you address the reader depends on the kind of essay you're writing. An essay written in the first person is fine for a personal travel essay but is inappropriate if you're a business reporter describing a patent lawsuit. Think about your audience before you begin writing.
Planning Your Essay
- Brainstorm: Jot down ideas on a blank piece of paper. Connect them with arrows and lines, or just make lists. Rigor doesn't matter at this stage. Bad ideas don't matter at this stage. Just write down ideas, and the engine in your head will lead you to a good one. When you've got that idea, then repeat the brainstorming exercise with ideas that you want to pursue on that topic and information you could put in. From this list, you'll start to see a path emerge for your research or narrative to follow.
- Compose your thesis: When your ideas coalesce into a sentence in which you can summarize the topic you're writing about, you're ready to compose your thesis sentence. Write down in one sentence the main idea that you'll explore in your paper.
- Examine your thesis: Is it clear? Does it contain opinion? If so, revise that out. For this type of essay, you stick to the facts and evidence. This isn't an editorial. Is the thesis' scope manageable? You don't want your topic too narrow or too broad to be covered in the amount of space you have for your paper. If it's not a manageable topic, refine it. Don't be dismayed if you have to come back and tweak it if your research finds that your initial idea was off-kilter. It's all just part of the process of focusing the material.
- Outline: It may seem inconsequential, but making even a quick outline can save you time by organizing your areas of pursuit and narrowing them down. When you see your topics in an organized list, you may be able to discard off-topic threads before you research them—or as you're researching them and you find they just don't work.
- Research: Find your data and sources to back up the areas you want to pursue to support your thesis statement. Look for sources written by experts, including organizations, and watch for bias. Possible sources include statistics, definitions, charts and graphs, and expert quotes and anecdotes. Compile descriptive details and comparisons to make your topic clear to your reader, when applicable.
What Is an Expository Essay?
An expository essay has three basic parts: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. Each is crucial to writing a clear article or effective argument.
The introduction: The first paragraph is where you'll lay the foundation for your essay and give the reader an overview of your thesis. Use your opening sentence to get the reader's attention, and then follow up with a few sentences that give your reader some context for the information you're about to cover.
The body: At a minimum, include three to five paragraphs in the body of your expository essay. The body could be considerably longer, depending on your topic and audience. Each paragraph begins with a topic sentence where you state your case or objective. Each topic sentence supports your overall thesis statement. Then, each paragraph includes several sentences that expand on the information and/or support the topic sentence. Finally, a concluding sentence offers a transition to the following paragraph in the essay.
The conclusion: The final section of your expository essay should give the reader a concise overview of your thesis. The intent is not merely to summarize your argument but to use it as a means of proposing further action, offering a solution, or posing new questions to explore. Don't cover new material related to your thesis, though. This is where you wrap it all up.
Expository Examples
An expository article or report about a lake, for example, could discuss its ecosystem: the plants and animals that depend on it along with its climate. It could describe physical details about its size, depth, amount of rainfall each year, and the number of tourists it receives annually. Information on when it was formed, its best fishing spots, or its water quality could be included, depending on the audience for the piece.
An expository piece could be in third person or second person. Second-person examples could include, for example, how to test lake water for pollutants or how to kill invasive species. Expository writing is useful and informative.
In contrast, someone writing a creative nonfiction article about a lake might relate the place to a defining moment in his or her life, penning the piece in first person. It could be filled with emotion, opinion, sensory details, and even include dialogue and flashbacks. It's a much more evocative, personal type of writing than an expository piece, even though they're both nonfiction styles.
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Understanding Organization in Composition and Speech
- How to Structure an Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- Development in Composition: Building an Essay
- Tips for Writing an Art History Paper
- Definition and Examples of Body Paragraphs in Composition
- The Five Steps of Writing an Essay
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- Write an Attention-Grabbing Opening Sentence for an Essay
- Understanding What an Expository Essay Is
- How to Write a Research Paper That Earns an A
How to Write an Expository Essay: Definition, Outline, Writing Tips, and Examples

In the realm of academic writing, this type of essay stands as a beacon of clarity, demanding writers to illuminate a subject with precision and objectivity. Whether you're a seasoned essayist or a student embarking on your first exploration of this genre, mastering the art of expository writing is a valuable skill that transcends disciplines. This form of essay invites you to delve into expository essay topics, dissect their intricacies, and present your findings in a straightforward manner.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the terrain of expository writing, unraveling the techniques and strategies that transform a mere composition into a beacon of insight. From understanding the fundamental principles to honing your ability to craft a compelling thesis, join us on a journey that promises to demystify the process of writing, empowering you to articulate ideas with clarity and purpose. Or, you can get our essay writing help and take care of other important tasks set for today.
What Is an Expository Essay
An expository essay is a form of academic writing that aims to elucidate, clarify, and present a balanced analysis of a particular topic or idea. Unlike other essay types that may delve into personal opinions or narratives, the expository essay emphasizes objectivity and factual accuracy. The primary objective is to provide a clear and comprehensive explanation of the chosen subject, exploring its various facets, presenting evidence, and ensuring a logical progression of ideas.
.webp)
According to an expository essay definition, this genre requires the writer to delve into research, organize information systematically, and deliver a coherent and informative piece that educates the reader on the chosen topic. Whether investigating a scientific concept, historical event, or literary work, it serves as a vehicle for conveying knowledge in a concise, lucid manner.
Expository Essay Examples
An expository essay example serves as a valuable tool for students, offering a concrete illustration of the structure, style, and depth expected in this genre of writing. By studying examples, students gain insights into effective thesis formulation, organizing ideas within paragraphs, and integrating supporting evidence to bolster arguments.
Additionally, examples showcase how to balance factual accuracy and engaging prose, providing a model for clear and concise communication. Students can draw inspiration from the content and presentation of well-crafted expository essays, honing their own skills in research, analysis, and effective expression. By the way, we have an interesting autobiography example , so check it out!
Example 1: “The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence”
This expository essay explores the multifaceted evolution of artificial intelligence (AI), examining its historical roots, contemporary applications across various industries, and the consequential societal impact. It provides a comprehensive overview of AI's journey from philosophical debates and early computational developments to its current role as a transformative force in healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and entertainment. Additionally, the essay addresses ethical considerations surrounding the widespread adoption of AI, including concerns related to job displacement, privacy, and responsible development. Ultimately, it navigates the complex landscape of artificial intelligence, shedding light on its remarkable advancements and its challenges to our ever-changing society.
Example 2: “The Benefits of Outdoor Education for Children”
This essay highlights the advantages of outdoor education for children, emphasizing its positive impacts on their physical, mental, and social development. It argues that outdoor activities like hiking, camping, and team sports not only promote physical health by encouraging movement and reducing sedentary behavior but also contribute to mental well-being by providing a respite from everyday stressors and fostering a connection with nature. Furthermore, it suggests that exposure to outdoor environments cultivates environmental awareness and a sense of stewardship among children.
Need some help with your homework?
Get help from our expository essay writing service ! Leave us a notice and we'll make your tasks asap.
Types of Expository Essay
Expository essays come in several distinct types, each serving a unique purpose and requiring specific approaches to convey information effectively. One common categorization includes:
- Descriptive Expository Essay. This type focuses on painting a vivid picture of a subject, using sensory details to engage the reader's imagination. It aims to create a clear and sensory-rich portrayal of a person, place, object, or experience.
- Process Expository Essay. Here, the writer breaks down a complex process or procedure into manageable steps, providing a detailed and sequential explanation. This type of essay is instructional, guiding readers through a series of actions to achieve a specific outcome.
- Comparison and Contrast Expository Essay. This form involves analyzing similarities and differences between two or more subjects, offering insights into their shared characteristics or divergent qualities. It requires a careful examination of the chosen elements to highlight their relationships.
- Cause and Effect Expository Essay. Focused on exploring the reasons behind an occurrence and its subsequent consequences, this type delves into the cause-and-effect relationships within a given topic. Writers elucidate the connections between actions and outcomes, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Problem and Solution Expository Essay. Addressing real-world issues, this essay type identifies a specific problem, analyzes its root causes, and proposes viable solutions. It encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, compelling readers to consider alternative approaches to challenges.
- Definition Expository Essay. This essay seeks to clarify and explain the meaning of a particular term, concept, or idea. Writers provide a comprehensive definition, often including examples and illustrations to ensure readers grasp the essence of the subject.
- Cause and Effect Expository Essay. This type of essay examines the reasons behind a particular phenomenon or event and explores its subsequent effects. It aims to establish a clear cause-and-effect relationship, allowing readers to comprehend the interconnected elements of the topic.
Understanding these diverse types of essays empowers writers to choose the most suitable approach for effectively conveying information and achieving their communicative goals. Our experts can rewrite essay that you already did according to any of the above-mentioned types.
Expository Essay Topics
Selecting compelling expository essay topics requires thoughtful consideration of both personal interest and the potential engagement of the intended audience. Start by identifying subjects that genuinely captivate your curiosity or align with your expertise, as this enthusiasm will naturally infuse vigor into your writing. Additionally, assess the topic's relevance in the broader context, ensuring it addresses contemporary issues or timeless themes.
Consider the audience's interests, aiming for subjects that resonate with their experiences or evoke a sense of shared relevance. Striking a balance between uniqueness and accessibility is key—opt for topics that allow you to offer fresh perspectives while ensuring there is ample research material available. Ultimately, the best topics seamlessly blend your passion, the audience's interests, and the broader significance of the chosen subject, ensuring a captivating and informative exploration for both writer and reader alike. Here are expository essay ideas from our writers for your inspiration:
.webp)
- The influence of art on human emotions.
- Exploring the life cycle of a star.
- Tips for sustainable living in urban areas.
- The impact of social media on political awareness.
- How to cultivate a positive mindset in challenging times.
- The history and cultural significance of tattoos.
- The process of recycling electronic waste.
- Benefits of incorporating meditation into daily routines.
- The role of laughter in maintaining mental health.
- Understanding the psychology of decision-making.
- The impact of fashion on individual expression.
- Tips for effective conflict resolution in relationships.
- The science behind the sense of taste.
- The significance of biodiversity in ecosystems.
- Exploring the history of traditional folk music.
- How to foster a sense of community in a neighborhood.
- The benefits of learning a musical instrument.
- The evolution of communication technologies.
- The process of seed germination in plants.
- Tips for creating a productive home office space.
- The impact of artificial intelligence on job markets.
- Understanding the concept of emotional intelligence.
- The benefits of practicing gratitude daily.
- The history and cultural importance of tea.
- How to develop effective public speaking skills.
- Exploring the world of virtual reality technology.
- The significance of water purification methods.
- Tips for maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
- The process of making sustainable food choices.
- The role of literature in shaping societal norms.
Expository Essay Outline
An outline for expository essay is a structured plan that serves as a roadmap for organizing the main ideas and supporting details of the essay in a logical and coherent manner. While the specific structure may vary based on the assignment or preferences, a typical outline generally includes the following components, beginning with how to start an expository essay:
.webp)
Expository Essay Introduction
- Hook or attention-grabbing statement.
- Background information on the topic.
- Clear thesis statement that presents the main idea.
Body Paragraphs (usually three or more)
- Topic sentence for each paragraph, presenting a main point or supporting idea.
- Supporting evidence, facts, or examples to illustrate and explain the topic sentence.
- Analysis or interpretation of the evidence to connect it back to the thesis.
Expository Essay Conclusion
- Restatement of the thesis in different words.
- Summary of the main points discussed in the body paragraphs.
- Concluding thoughts or insights, possibly suggesting implications or future considerations.
Transitions
- Smooth transitions between paragraphs to ensure a cohesive flow of ideas.
- Clear connections between sentences and paragraphs to guide the reader through the essay.
Revising and Editing
- Space for notes on areas that may need revision or improvement.
- Consideration of clarity, coherence, and overall effectiveness.
By creating an expository essay outline, a college essay writer can organize their thoughts, ensure a logical progression of ideas, and maintain a clear and concise structure. This framework helps writers stay focused on the main purpose of the essay – to inform, explain, or analyze a particular subject – while providing a roadmap for readers to follow and comprehend the information presented.
How to Write an Expository Essay Step by Step
Writing an expository essay involves a systematic process that ensures clarity, coherence, and effectiveness in conveying information. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you craft an expository essay:
Choose a Topic
- Select a topic that interests you and aligns with the purpose of an expository essay – to inform, explain, or analyze a subject.
Conduct Research
- Gather relevant and credible information to support your chosen topic.
- Utilize reputable sources such as academic journals, books, and reliable websites.
Create an Outline
- Develop a clear and organized outline that includes the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
- Each section should have a specific purpose and contribute to the overall coherence of the essay.
Write the Introduction
- Start with an attention-grabbing hook that relates to your topic.
- Provide background information and context, leading to a concise and focused thesis statement that outlines the main idea.
Develop Body Paragraphs
- Each body paragraph should begin with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main point.
- Support the topic sentence with evidence, facts, or examples.
- Ensure a logical flow between paragraphs, using transitions to guide the reader.
Provide Evidence
- Support your points with credible evidence and examples.
- Ensure that each piece of evidence directly relates to the topic sentence and supports the overall thesis of the essay.
Analyze and Interpret
- After presenting evidence, analyze and interpret it.
- Explain the significance of the evidence and how it relates to your thesis.
- This step helps to ensure that your audience understands the relevance of the information presented.
Write the Conclusion
- Summarize the main points discussed in the body paragraphs without introducing new information.
- Restate the thesis in different words and offer concluding insights or implications related to the topic.
Revise and Edit
- Review your essay for clarity, coherence, and consistency.
- Check for grammatical errors and awkward phrasing, ensuring a smooth flow of ideas.
- Consider feedback from others or take a break before revising to gain a fresh perspective.
- Carefully proofread your essay to catch any remaining errors, typos, or issues.
- Pay attention to grammar and punctuation.
By following these steps, you can systematically approach the writing process and create a well-organized and informative expository essay. Remember to stay focused on the purpose of informing, explaining, or analyzing the chosen topic throughout the entire writing process.
Final Thoughts
Learning how to write an expository essay offers students several important advantages. First off, it helps them express their thoughts clearly and organize ideas effectively, skills that are useful not only in academics but also in various professional situations where clear communication is key.
Moreover, writing expository essays improves critical thinking as students practice analyzing information, connecting ideas, and presenting well-supported arguments. This skill is valuable in everyday decision-making and problem-solving scenarios.
Additionally, the process of crafting such essays enhances research abilities, teaching students how to find, evaluate, and use information effectively. Overall, mastering expository writing equips students with practical, transferable skills that can positively impact their academic and professional pursuits. You can use our research paper service to cope with assignments better and faster.
Want to Ace Your Expository Writing?
Your wish is our command - order now and experience the excellence of our expert writers!
What are the Different Types of Expository Essays?
What is the most important part of the expository essay structure, what is the main idea in expository writing.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)

Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident than in academia. From the quick scribbles of eager students to the inquisitive thoughts of renowned scholars, academic essays depict the power of the written word. These well-crafted writings propel ideas forward and expand the existing boundaries of human intellect.
What is an Academic Essay
An academic essay is a nonfictional piece of writing that analyzes and evaluates an argument around a specific topic or research question. It serves as a medium to share the author’s views and is also used by institutions to assess the critical thinking, research skills, and writing abilities of a students and researchers.
Importance of Academic Essays
4 main types of academic essays.
While academic essays may vary in length, style, and purpose, they generally fall into four main categories. Despite their differences, these essay types share a common goal: to convey information, insights, and perspectives effectively.
1. Expository Essay
2. Descriptive Essay
3. Narrative Essay
4. Argumentative Essay
Expository and persuasive essays mainly deal with facts to explain ideas clearly. Narrative and descriptive essays are informal and have a creative edge. Despite their differences, these essay types share a common goal ― to convey information, insights, and perspectives effectively.
Expository Essays: Illuminating ideas
An expository essay is a type of academic writing that explains, illustrates, or clarifies a particular subject or idea. Its primary purpose is to inform the reader by presenting a comprehensive and objective analysis of a topic.
By breaking down complex topics into digestible pieces and providing relevant examples and explanations, expository essays allow writers to share their knowledge.
What are the Key Features of an Expository Essay

Provides factual information without bias

Presents multiple viewpoints while maintaining objectivity
Uses direct and concise language to ensure clarity for the reader

Composed of a logical structure with an introduction, body paragraphs and a conclusion
When is an expository essay written.
1. For academic assignments to evaluate the understanding of research skills.
2. As instructional content to provide step-by-step guidance for tasks or problem-solving.
3. In journalism for objective reporting in news or investigative pieces.
4. As a form of communication in the professional field to convey factual information in business or healthcare.
How to Write an Expository Essay
Expository essays are typically structured in a logical and organized manner.
1. Topic Selection and Research
- Choose a topic that can be explored objectively
- Gather relevant facts and information from credible sources
- Develop a clear thesis statement
2. Outline and Structure
- Create an outline with an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion
- Introduce the topic and state the thesis in the introduction
- Dedicate each body paragraph to a specific point supporting the thesis
- Use transitions to maintain a logical flow
3. Objective and Informative Writing
- Maintain an impartial and informative tone
- Avoid personal opinions or biases
- Support points with factual evidence, examples, and explanations
4. Conclusion
- Summarize the key points
- Reinforce the significance of the thesis
Descriptive Essays: Painting with words
Descriptive essays transport readers into vivid scenes, allowing them to experience the world through the writer ‘s lens. These essays use rich sensory details, metaphors, and figurative language to create a vivid and immersive experience . Its primary purpose is to engage readers’ senses and imagination.
It allows writers to demonstrate their ability to observe and describe subjects with precision and creativity.
What are the Key Features of Descriptive Essay

Employs figurative language and imagery to paint a vivid picture for the reader

Demonstrates creativity and expressiveness in narration

Includes close attention to detail, engaging the reader’s senses

Engages the reader’s imagination and emotions through immersive storytelling using analogies, metaphors, similes, etc.
When is a descriptive essay written.
1. Personal narratives or memoirs that describe significant events, people, or places.
2. Travel writing to capture the essence of a destination or experience.
3. Character sketches in fiction writing to introduce and describe characters.
4. Poetry or literary analyses to explore the use of descriptive language and imagery.
How to Write a Descriptive Essay
The descriptive essay lacks a defined structural requirement but typically includes: an introduction introducing the subject, a thorough description, and a concluding summary with insightful reflection.
1. Subject Selection and Observation
- Choose a subject (person, place, object, or experience) to describe
- Gather sensory details and observations
2. Engaging Introduction
- Set the scene and provide the context
- Use of descriptive language and figurative techniques
3. Descriptive Body Paragraphs
- Focus on specific aspects or details of the subject
- Engage the reader ’s senses with vivid imagery and descriptions
- Maintain a consistent tone and viewpoint
4. Impactful Conclusion
- Provide a final impression or insight
- Leave a lasting impact on the reader
Narrative Essays: Storytelling in Action
Narrative essays are personal accounts that tell a story, often drawing from the writer’s own experiences or observations. These essays rely on a well-structured plot, character development, and vivid descriptions to engage readers and convey a deeper meaning or lesson.
What are the Key features of Narrative Essays
Written from a first-person perspective and hence subjective

Based on real personal experiences

Uses an informal and expressive tone

Presents events and characters in sequential order
When is a narrative essay written.
It is commonly assigned in high school and college writing courses to assess a student’s ability to convey a meaningful message or lesson through a personal narrative. They are written in situations where a personal experience or story needs to be recounted, such as:
1. Reflective essays on significant life events or personal growth.
2. Autobiographical writing to share one’s life story or experiences.
3. Creative writing exercises to practice narrative techniques and character development.
4. College application essays to showcase personal qualities and experiences.
How to Write a Narrative Essay
Narrative essays typically follow a chronological structure, with an introduction that sets the scene, a body that develops the plot and characters, and a conclusion that provides a sense of resolution or lesson learned.
1. Experience Selection and Reflection
- Choose a significant personal experience or event
- Reflect on the impact and deeper meaning
2. Immersive Introduction
- Introduce characters and establish the tone and point of view
3. Plotline and Character Development
- Advance the plot and character development through body paragraphs
- Incorporate dialog , conflict, and resolution
- Maintain a logical and chronological flow
4. Insightful Conclusion
- Reflect on lessons learned or insights gained
- Leave the reader with a lasting impression
Argumentative Essays: Persuasion and Critical Thinking
Argumentative essays are the quintessential form of academic writing in which writers present a clear thesis and support it with well-researched evidence and logical reasoning. These essays require a deep understanding of the topic, critical analysis of multiple perspectives, and the ability to construct a compelling argument.
What are the Key Features of an Argumentative Essay?

Logical and well-structured arguments

Credible and relevant evidence from reputable sources

Consideration and refutation of counterarguments

Critical analysis and evaluation of the issue
When is an argumentative essay written.
Argumentative essays are written to present a clear argument or stance on a particular issue or topic. In academic settings they are used to develop critical thinking, research, and persuasive writing skills. However, argumentative essays can also be written in various other contexts, such as:
1. Opinion pieces or editorials in newspapers, magazines, or online publications.
2. Policy proposals or position papers in government, nonprofit, or advocacy settings.
3. Persuasive speeches or debates in academic, professional, or competitive environments.
4. Marketing or advertising materials to promote a product, service, or idea.
How to write an Argumentative Essay
Argumentative essays begin with an introduction that states the thesis and provides context. The body paragraphs develop the argument with evidence, address counterarguments, and use logical reasoning. The conclusion restates the main argument and makes a final persuasive appeal.
- Choose a debatable and controversial issue
- Conduct thorough research and gather evidence and counterarguments
2. Thesis and Introduction
- Craft a clear and concise thesis statement
- Provide background information and establish importance
3. Structured Body Paragraphs
- Focus each paragraph on a specific aspect of the argument
- Support with logical reasoning, factual evidence, and refutation
4. Persuasive Techniques
- Adopt a formal and objective tone
- Use persuasive techniques (rhetorical questions, analogies, appeals)
5. Impactful Conclusion
- Summarize the main points
- Leave the reader with a strong final impression and call to action
To learn more about argumentative essay, check out this article .
5 Quick Tips for Researchers to Improve Academic Essay Writing Skills

Use clear and concise language to convey ideas effectively without unnecessary words

Use well-researched, credible sources to substantiate your arguments with data, expert opinions, and scholarly references

Ensure a coherent structure with effective transitions, clear topic sentences, and a logical flow to enhance readability

To elevate your academic essay, consider submitting your draft to a community-based platform like Open Platform for editorial review

Review your work multiple times for clarity, coherence, and adherence to academic guidelines to ensure a polished final product
By mastering the art of academic essay writing, researchers and scholars can effectively communicate their ideas, contribute to the advancement of knowledge, and engage in meaningful scholarly discourse.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![parts of an explanatory essay What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- AI in Academia
AI vs. AI: How to detect image manipulation and avoid academic misconduct
The scientific community is facing a new frontier of controversy as artificial intelligence (AI) is…

- Industry News
- Publishing News
Unified AI Guidelines Crucial as Academic Writing Embraces Generative Tools
As generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools like ChatGPT are advancing at an accelerating pace, their…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Need for Diversifying Academic Curricula: Embracing missing voices and marginalized perspectives
In classrooms worldwide, a single narrative often dominates, leaving many students feeling lost. These stories,…

- Reporting Research
How to Effectively Cite a PDF (APA, MLA, AMA, and Chicago Style)
The pressure to “publish or perish” is a well-known reality for academics, striking fear into…
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without…
Digital Citations: A comprehensive guide to citing of websites in APA, MLA, and CMOS…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?

วิธีการเขียนเรียงความอธิบาย
- ทีมบรรณาธิการ Smodin
- ที่เผยแพร่: May 24, 2024
การศึกษาจากวารสารการศึกษาการสอนภาษาอังกฤษ พบ ที่นักเรียนเผชิญความยากลำบากในการจัดระเบียบความคิด การสร้างความคิด และการทำความเข้าใจกระบวนการเขียนเมื่อเขียนเรียงความ [1] สิ่งเหล่านี้ล้วนเป็นองค์ประกอบสำคัญในการรวบรวมเรียงความที่มีคำอธิบายที่ดี หากฟังดูเหมือนคุณก็ไม่ต้องกังวล
ด้วยแนวทางที่ถูกต้อง คุณสามารถรวมส่วนประกอบเหล่านี้ทั้งหมดได้อย่างราบรื่น คู่มือนี้จะให้กลยุทธ์ง่ายๆ ทีละขั้นตอนในการเขียนเรียงความเชิงอธิบาย นอกจากนี้ยังให้คำแนะนำในการเขียนและคำแนะนำเครื่องมือที่เป็นประโยชน์ เช่น การใช้ปัญญาประดิษฐ์
ด้วยคู่มือนี้ คุณจะสามารถเขียนเรียงความอธิบายได้อย่างมั่นใจ
1. พัฒนาคำแถลงวิทยานิพนธ์ที่แข็งแกร่ง
การสร้างข้อความวิทยานิพนธ์ที่แข็งแกร่งถือเป็นรากฐานสำคัญของการเขียนเรียงความเชิงอธิบายที่เขียนมาอย่างดี มันช่วยปูทางว่าเรียงความของคุณจะพูดถึงอะไรและชี้แจงประเด็นหลักที่คุณจะอธิบาย ต่อไปนี้เป็นวิธีสร้างวิทยานิพนธ์:
- ค้นหาแนวคิดหลัก : เริ่มต้นด้วยการระบุแนวคิดหลักหรือคำถามที่คุณต้องการอธิบาย พัฒนาวัตถุประสงค์ที่ชัดเจนสำหรับเรียงความ สิ่งนี้จะเป็นแนวทางในการวิจัยและการเขียนบทความอธิบายของคุณ ใช้ตัวอย่างเรียงความอธิบายที่มีชื่อเสียงอื่นๆ เพื่อเป็นแนวทางในความคิดของคุณ ซึ่งอาจเกี่ยวข้องกับการสำรวจหัวข้อเรียงความเชิงอธิบายอื่นๆ ในสาขาเดียวกัน
- เฉพาะเจาะจง : วิทยานิพนธ์ที่คลุมเครืออาจทำให้ผู้อ่านสับสนได้ ดังนั้นโปรดตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าข้อความของคุณชัดเจน หากคุณกำลังอธิบายกระบวนการที่ซับซ้อน ให้แยกย่อยออกเป็นประเด็นสำคัญ หลังจากนั้นให้แบ่งเป็นข้อความที่ชัดเจน กระชับ เข้าใจง่าย
- สะท้อนความเป็นกลาง : เรียงความอธิบายให้ความรู้และแจ้ง พวกเขาไม่ได้โต้แย้งประเด็น ดังนั้น วิทยานิพนธ์ของคุณควรมีจุดยืนที่เป็นกลางในหัวข้อนี้ ควรนำเสนอข้อเท็จจริงตามที่เป็นอยู่ ไม่ใช่ตามที่คุณตีความ
- ใช้เครื่องมือเช่น นักเขียนสโมดิน : Smodin Writer ทำงานหนักทั้งหมดโดยใช้ประโยชน์จากพลังของปัญญาประดิษฐ์ ด้วยเครื่องมือนี้ คุณสามารถสร้างเรียงความพร้อมข้อความวิทยานิพนธ์ได้ คุณถามอย่างไร? ผ่านการทุ่มเทของมัน เครื่องกำเนิดวิทยานิพนธ์ - สามารถสร้างข้อความที่ทั้งชัดเจนและเกี่ยวข้องได้ นอกจากนี้ยังสามารถดึงข้อมูลที่น่าสนใจที่สุดทั้งหมดตามหัวข้อของคุณเพื่อเพิ่มคุณค่าให้กับข้อความวิทยานิพนธ์ของคุณ
ทำให้วิทยานิพนธ์ของคุณชัดเจน ให้ข้อมูล และเป็นกลาง นี่เป็นการวางรากฐานที่แข็งแกร่งสำหรับการเขียนเรียงความที่มีประสิทธิผล ต่อไป มาดูวิธีรวบรวมข้อมูลที่จำเป็นเพื่อสนับสนุนวิทยานิพนธ์นี้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
2. ค้นคว้าและรวบรวมข้อมูล
คุณต้องทำการวิจัยอย่างละเอียดเพื่อสนับสนุนวิทยานิพนธ์ของคุณด้วยแหล่งข้อมูลที่น่าเชื่อถือและหลักฐานที่เกี่ยวข้อง สิ่งนี้จะทำให้เรียงความเชิงอธิบายของคุณมีทั้งข้อมูลและโน้มน้าวใจ คำแนะนำทีละขั้นตอนในการทำวิจัยที่มีประสิทธิภาพ:
- เริ่มต้นด้วยแผน: รวบรวมโครงร่างเรียงความอธิบายที่มีข้อมูลที่คุณต้องการเพื่อสนับสนุนวิทยานิพนธ์ของคุณ แผนควรแสดงรายการแหล่งข้อมูลที่ดีที่สุด เช่น วารสารวิชาการ หนังสือ เว็บไซต์ที่มีชื่อเสียง หรือบทความทางวิชาการ
- ใช้แหล่งข้อมูลที่น่าเชื่อถือ: พวกเขารับประกันความถูกต้องของเรียงความของคุณ ห้องสมุด ฐานข้อมูลทางวิชาการ และเว็บไซต์ที่ได้รับการรับรองเป็นสถานที่ที่ดีเยี่ยมในการค้นหาข้อมูลที่น่าเชื่อถือ
- ค้นหาข้อมูลโดยละเอียด: มองหาแหล่งข้อมูลล่าสุดที่อธิบายหัวข้อของคุณได้ดี และให้ข้อมูลเชิงลึกที่ไม่ซ้ำใครที่เกี่ยวข้องหรือคัดค้านข้อความวิทยานิพนธ์ของคุณ ความลึกซึ้งนี้มีความสำคัญอย่างยิ่งในการอธิบายแนวคิดที่ซับซ้อนอย่างชัดเจนและทั่วถึงในเอกสารอธิบายของคุณ ให้ความสนใจกับโครงสร้างเรียงความที่อธิบายเพื่อเป็นแนวทางในหัวข้อที่คุณเลือก (เพิ่มเติมในภายหลัง)
- รวบรวมหลักฐานที่เกี่ยวข้อง: รวบรวมข้อมูล สถิติ และตัวอย่าง พวกเขาควรสนับสนุนประเด็นหลักของคุณโดยตรง ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าหลักฐานนี้เกี่ยวข้องโดยตรงกับหัวข้อของคุณและปรับปรุงการเล่าเรื่องของคุณ
- ใช้เครื่องมือดิจิทัล: เครื่องมืออย่างผู้ช่วยวิจัยของ Smodin สามารถเร่งกระบวนการวิจัยของคุณได้ เครื่องมือของ Smodin สามารถช่วยให้คุณค้นหาข้อมูลโดยละเอียดได้อย่างรวดเร็ว ทำให้มั่นใจได้ว่าข้อมูลที่คุณใช้เป็นข้อมูลล่าสุดและเกี่ยวข้อง
- เอกสารแหล่งที่มาของคุณ: ขณะที่คุณดำเนินการวิจัย ให้เก็บบันทึกอย่างพิถีพิถันว่าข้อมูลของคุณมาจากไหน การปฏิบัตินี้จะช่วยให้คุณสร้างบรรณานุกรมที่แม่นยำ สามารถช่วยประหยัดเวลาเมื่อคุณต้องการย้อนกลับไปดูรายละเอียดหรือตรวจสอบข้อเท็จจริง นี่เป็นสิ่งที่ต้องขอบคุณ Smodin's อีกครั้ง เครื่องอ้างอิง.
- ประเมินสิ่งที่คุณค้นพบ: ประเมินข้อมูลที่คุณรวบรวมอย่างมีวิจารณญาณ ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่ามีมุมมองที่สมดุลและครอบคลุมประเด็นที่จำเป็นของหัวข้อของคุณเพื่อให้ภาพรวมที่ครอบคลุมของเรียงความของคุณ
เมื่อทำตามขั้นตอนเหล่านี้ คุณจะสามารถรวบรวมข้อมูลมากมายที่เป็นกระดูกสันหลังที่แข็งแกร่งสำหรับการเขียนเรียงความเชิงอธิบายของคุณได้ ตอนนี้คุณสามารถเริ่มจัดโครงสร้างสิ่งที่คุณค้นพบลงในย่อหน้าเนื้อหาที่มีการจัดระเบียบอย่างดีได้แล้ว
3. โครงสร้างย่อหน้าเนื้อหา
เมื่อคุณรวบรวมหลักฐานที่เกี่ยวข้องผ่านการค้นคว้าอย่างละเอียดแล้ว ก็ถึงเวลาจัดระเบียบ คุณควรใส่ลงในย่อหน้าเนื้อหาที่มีโครงสร้างดีซึ่งเป็นไปตามลำดับตรรกะ ต่อไปนี้คือวิธีจัดโครงสร้างแต่ละย่อหน้าสำหรับเรียงความที่มีคำอธิบายที่ชัดเจน:
- ตัดสินใจว่าจะใช้กี่ย่อหน้า : ขึ้นอยู่กับความซับซ้อนของหัวข้อและรายละเอียดที่จำเป็น โดยทั่วไปแล้ว 3-5 ย่อหน้ามีความเหมาะสม แต่เรียงความที่ยาวกว่านั้นอาจต้องใช้มากกว่านั้น ตัวอย่างเรียงความอธิบายหัวข้อที่คุณเลือกจะเป็นประโยชน์
- เริ่มต้นด้วยประโยคหัวข้อ : แต่ละย่อหน้าเนื้อหาควรเริ่มต้นด้วยประโยคหัวข้อที่ชัดเจนซึ่งแนะนำแนวคิดหลักของย่อหน้า ประโยคนี้จะทำหน้าที่เป็นแผนงานสำหรับย่อหน้า ทำให้ผู้อ่านเข้าใจถึงสิ่งที่คาดหวัง
- ให้หลักฐานประกอบ : หลังประโยคหัวข้อ แบ่งปันหลักฐานจากงานวิจัยของคุณ ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าหลักฐานมีความเกี่ยวข้องและสนับสนุนประโยคหัวข้อของย่อหน้าโดยตรง
- ให้คำอธิบายโดยละเอียด : ติดตามหลักฐานพร้อมการวิเคราะห์หรือคำอธิบายที่เชื่อมโยงกับข้อความวิทยานิพนธ์ ขั้นตอนนี้สำคัญมากในการรักษาความลื่นไหลของตรรกะตลอดทั้งย่อหน้าเนื้อหา
- ใช้คำเชื่อมโยง : พวกเขาเชื่อมโยงย่อหน้าเนื้อหาได้อย่างราบรื่น ทำให้มั่นใจว่าผู้อ่านสามารถปฏิบัติตามข้อโต้แย้งของคุณได้
- ปิดท้ายเนื้อหาแต่ละย่อหน้าด้วยประโยคปิด : ควรสรุปประเด็นและก้าวไปสู่แนวคิดถัดไป
การปฏิบัติตามโครงสร้างนี้จะช่วยให้ย่อหน้าเนื้อหาของคุณสนับสนุนวิทยานิพนธ์ของคุณ ย่อหน้าเหล่านี้จะให้คำอธิบายที่ชัดเจนและละเอียดเกี่ยวกับหัวข้อเรียงความของคุณ ย่อหน้าที่มีเนื้อหาชัดเจนถือเป็นสิ่งสำคัญในการรักษาความเป็นกลางในการเขียนของคุณ
4. รักษาความเป็นกลาง
เรียงความอธิบายมีจุดมุ่งหมายเพื่อให้ข้อมูลและให้ความรู้ ซึ่งทำให้การรักษาความเป็นกลางเป็นสิ่งสำคัญ การรักษาความเป็นกลางทำให้ผู้อ่านสามารถแสดงความคิดเห็นของตนเองโดยอิงจากข้อเท็จจริง เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่างานเขียนมีความน่าเชื่อถือและให้ข้อมูล ต่อไปนี้เป็นวิธีการรักษาความเป็นกลาง:
- หลีกเลี่ยงความคิดเห็นส่วนตัว: เป้าหมายของคุณคือการให้ความเข้าใจที่ครอบคลุมในหัวข้อนี้ หลีกเลี่ยงการใส่ความคิดเห็นส่วนตัวหรืออคติของคุณ ให้ยึดการนำเสนอข้อมูลข้อเท็จจริงที่สนับสนุนวิทยานิพนธ์แทน
- ใช้หลักฐานที่เกี่ยวข้อง: ดังที่ได้กล่าวไปแล้ว ให้ยึดข้อโต้แย้งของคุณด้วยหลักฐานที่เกี่ยวข้องจากแหล่งที่มาที่น่าเชื่อถือ สำรองประเด็นหลักของคุณด้วยข้อมูลและใช้ผลการวิจัยและรายละเอียดที่ได้รับการตรวจสอบแล้ว ซึ่งจะทำให้บทความอธิบายน่าเชื่อถือ
- ให้มุมมองที่สมดุล: ในกรณีที่มีหลายมุมมอง ให้เสนอมุมมองที่สมดุล ปกปิดแต่ละด้านอย่างยุติธรรม แม้ว่ามุมมองหนึ่งจะมีมติเป็นเอกฉันท์ แต่การยอมรับความคิดเห็นอื่นๆ จะทำให้ผู้อ่านมีความเข้าใจที่กว้างขึ้น
- ใช้ภาษาที่เป็นกลาง: ระมัดระวังการเลือกคำและน้ำเสียง ภาษาที่เป็นกลางหมายถึงคำที่ไม่สนับสนุนหรือแสดงอคติ ซึ่งจะช่วยหลีกเลี่ยงวลีที่กระตุ้นอารมณ์และรักษาวัตถุประสงค์ในการเขียน
- อ้างอิงแหล่งที่มาอย่างถูกต้อง: การอ้างอิงแหล่งที่มาอย่างเหมาะสมทำให้เกิดความรับผิดชอบต่อหลักฐานที่นำเสนอ ความโปร่งใสนี้สร้างความน่าเชื่อถือและแสดงให้เห็นว่าคุณได้ดำเนินการวิจัยอย่างละเอียดถี่ถ้วน นอกจากนี้ ยังเป็นที่น่าสังเกตว่าสัญชาตญาณที่แตกต่างกันมีรูปแบบการอ้างอิงที่แตกต่างกัน เช่น APA และ Chicago ซึ่งเป็นสิ่งสำคัญที่ควรทราบก่อนเริ่มเรียงความ
- การตรวจสอบอคติ: หลังจากร่างเรียงความแล้ว ให้ทบทวนโดยคำนึงถึงอคติ ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าไม่มีส่วนใดเอนเอียงไปในมุมมองเดียวมากเกินไป และอย่ามองข้ามมุมมองที่ขัดแย้งกันโดยไม่มีสาเหตุ
การรักษาความเป็นกลางจะช่วยเพิ่มความชัดเจนและความน่าเชื่อถือของการเขียนอธิบาย ตอนนี้เรามาเน้นที่การสร้างคำนำและข้อสรุปที่จะช่วยรักษางานของคุณอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
5. จัดทำคำนำและบทสรุปที่มีประสิทธิภาพ
การแนะนำที่ดีและบทสรุปที่ชัดเจนเป็นกรอบของเรียงความที่อธิบายของคุณ โดยให้บริบทตั้งแต่เริ่มต้นและเสริมประเด็นหลักในตอนท้าย ต่อไปนี้คือวิธีการสร้างคำนำและบทสรุปที่มีประสิทธิภาพ
- ดึงดูดผู้อ่านของคุณในบทนำ : ใช้ข้อเท็จจริงที่น่าสนใจ คำพูดที่น่าสนใจ หรือสถิติที่น่าประหลาดใจ
- ให้ข้อมูลพื้นฐาน : กระชับและเสนอเฉพาะบริบทที่จำเป็นที่ผู้อ่านต้องการเพื่อทำความเข้าใจหัวข้ออย่างถ่องแท้ สิ่งนี้ควรทำให้ผู้ชมมีความเข้าใจพื้นฐานก่อนที่จะเจาะลึกประเด็นหลักของคุณ
- รวมข้อความวิทยานิพนธ์ด้วย : ระบุวิทยานิพนธ์ของคุณอย่างชัดเจนใกล้ส่วนท้ายของคำนำ ข้อความนี้จะสรุปทิศทางของเรียงความและให้ผู้อ่านได้ดูตัวอย่างย่อหน้าเนื้อหา
- สรุปประเด็นสำคัญ : เริ่มบทสรุปเรียงความเชิงอธิบายของคุณด้วยบทสรุป ควรครอบคลุมประเด็นหลักจากย่อหน้าเนื้อหา บทสรุปนี้ควรช่วยให้ผู้อ่านจดจำและเสริมข้อมูลที่พวกเขาเพิ่งอ่านได้
- ทบทวนวิทยานิพนธ์ : ทำซ้ำวิทยานิพนธ์ของคุณอีกครั้ง แต่ในรูปแบบใหม่ อธิบายว่าหลักฐานจากย่อหน้าเนื้อหาสนับสนุนหรือชี้แจงอย่างไร
- ให้ข้อสรุป : จบเรียงความด้วยข้อความที่สรุปข้อโต้แย้ง ข้อความนี้ควรสะท้อนกับผู้อ่าน ควรทิ้งความรู้สึกที่เน้นความสำคัญของหัวข้อนั้น
การแนะนำและการสรุปที่มีประสิทธิภาพจะทำให้โครงสร้างเรียงความและความสอดคล้องกัน พวกเขาแนะนำผู้อ่านตั้งแต่ต้นจนจบ ขั้นตอนต่อไปคือการแก้ไขและแก้ไขเรียงความทั้งหมดของคุณเพื่อความชัดเจนและแม่นยำ
6. แก้ไขและตรวจสอบความชัดเจน
การแก้ไขและแก้ไขเป็นกุญแจสำคัญในการเขียน พวกเขาทำให้แน่ใจว่าเรียงความของคุณชัดเจน สอดคล้อง และขัดเกลา ต่อไปนี้เป็นวิธีปรับแต่งงานเขียนของคุณโดยใช้รายการตรวจสอบเรียงความเชิงอธิบายและเทคนิคการเขียนเชิงวิชาการที่ได้รับการพิสูจน์แล้ว:
- หยุดพัก: ก่อนที่จะเริ่มการทบทวน ให้ถอยห่างจากการเขียนเรียงความสักสองสามชั่วโมงหรือหนึ่งวันเสียก่อน การหยุดพักนี้จะช่วยให้คุณกลับมามีดวงตาที่สดใส ทำให้มองเห็นข้อผิดพลาดหรือความไม่สอดคล้องกันได้ง่ายขึ้น
- ปฏิบัติตามรายการตรวจสอบเรียงความ: สร้างหรือใช้รายการตรวจสอบเพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าเรียงความของคุณมีส่วนที่จำเป็นทั้งหมด จำเป็นต้องมีคำนำที่ชัดเจนโดยมีวิทยานิพนธ์ที่ชัดเจน ย่อหน้าที่มีโครงสร้างดี แหล่งข้อมูลที่ดี และบทสรุปสั้นๆ ตรวจสอบว่าข้อโต้แย้งของคุณเป็นไปตามลำดับตรรกะ และหลักฐานที่เกี่ยวข้องทั้งหมดเชื่อมโยงโดยตรงกับข้อความวิทยานิพนธ์ของคุณ
- ตรวจสอบความชัดเจนและรัดกุม: การเขียนเชิงวิชาการจำเป็นต้องมีความชัดเจน ดังนั้น ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าแต่ละย่อหน้าและประโยคสื่อถึงประเด็นของคุณ อย่าใช้ศัพท์เฉพาะที่ไม่จำเป็นหรือภาษาที่ซับซ้อนจนเกินไป เขียนประโยคให้กระชับโดยยังคงคำอธิบายโดยละเอียดเกี่ยวกับประเด็นหลักของคุณ
- ตรวจสอบข้อเท็จจริงและการอ้างอิง: ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าข้อเท็จจริง ข้อมูล และคำพูดอ้างอิงในเรียงความทั้งหมดถูกต้อง นอกจากนี้ โปรดตรวจสอบว่ามีการอ้างอิงในรูปแบบวิชาการที่กำหนด (เช่น MLA, APA) การอ้างอิงที่ไม่เหมาะสมอาจบ่อนทำลายความน่าเชื่อถือของงานเขียนของคุณ
- ทบทวนไวยากรณ์และสไตล์: มองหาข้อผิดพลาดด้านไวยากรณ์ทั่วไป เครื่องหมายวรรคตอน และการใช้ถ้อยคำที่ไม่เหมาะสม การอ่านออกเสียงเรียงความสามารถช่วยเข้าใจโครงสร้างประโยคที่แปลกหรือการใช้ถ้อยคำที่สับสนได้
- ขอความคิดเห็น: แบ่งปันเรียงความของคุณกับเพื่อนหรือใช้เครื่องมือออนไลน์เพื่อรับคำวิจารณ์ที่สร้างสรรค์ มุมมองที่สองสามารถเน้นประเด็นที่คุณอาจพลาดไป
ขั้นตอนการแก้ไขเหล่านี้จะช่วยให้คุณสร้างเรียงความที่สวยงามซึ่งอธิบายประเด็นหลักของคุณอย่างชัดเจนและขึ้นอยู่กับการพิจารณาทางวิชาการ
รูปแบบเรียงความอธิบาย
การทำความเข้าใจรูปแบบเรียงความเชิงอธิบายเป็นกุญแจสำคัญในการเขียนเรียงความที่มีโครงสร้างที่ดีและมีเหตุผล ต่อไปนี้คือรายละเอียดพื้นฐานของรูปแบบการเขียนเรียงความเชิงอธิบาย:
- เริ่มต้นด้วยประโยคที่น่าสนใจเพื่อดึงดูดความสนใจของผู้อ่าน
- แนะนำตัวสั้นๆ ครับ ควรกำหนดหัวข้อและร่างวัตถุประสงค์ของเรียงความ
- นำเสนอข้อความวิทยานิพนธ์ที่ชัดเจนโดยสรุปแนวคิดหลักของเรียงความทั้งหมด
ย่อหน้าร่างกาย
- จัดระเบียบย่อหน้าเนื้อหาตามหัวข้อย่อยเชิงตรรกะที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อเรียงความ
- เริ่มต้นแต่ละย่อหน้าเนื้อหาด้วยประโยคหัวข้อที่สอดคล้องกับวิทยานิพนธ์
- แสดงหลักฐานจากแหล่งที่ดี นอกจากนี้ ให้รายละเอียดที่สำคัญสำหรับประเด็นหลักแต่ละประเด็นด้วย
- ใส่ข้อความสรุปที่มีประสิทธิภาพในแต่ละย่อหน้า ซึ่งจะช่วยขับเคลื่อนประเด็นของคุณ และเชื่อมโยงไปยังแนวคิดต่างๆ ในย่อหน้า/ส่วนถัดไป
- สรุปประเด็นสำคัญ
- จัดทำข้อความสุดท้ายที่สนับสนุนแนวคิดหลักโดยไม่ต้องนำเสนอข้อมูลใหม่
- เรียบเรียงข้อความสรุปที่ทำให้ครูหรืออาจารย์ของคุณประทับใจไม่รู้ลืม
การปฏิบัติตามโครงร่างเรียงความนี้ช่วยให้แน่ใจว่ารายงานของคุณมีลำดับขั้นตอนที่ชัดเจน ทำให้ผู้อ่านเข้าใจและปฏิบัติตามข้อโต้แย้งของคุณได้ง่าย
เขียนเรียงความเชิงอธิบายที่ดีขึ้นด้วย Smodin
เรียงความอธิบายสามารถครอบงำได้ การนำเสนอข้อโต้แย้งที่ชัดเจน ทำให้อาจารย์หรือครูสนใจ และการจดจำหลักเกณฑ์ เช่น การอ้างอิง อาจทำให้ปวดหัวได้
แต่วิทยานิพนธ์ที่แข็งแกร่งและการวิจัยอย่างละเอียดทำให้ง่ายขึ้น ย่อหน้าเนื้อหาที่มีโครงสร้างที่ดียังช่วยให้เขียนเรียงความที่ชัดเจนและลึกซึ้งซึ่งรักษาความเป็นกลางได้ เพียงอย่าลืมแก้ไขและตรวจสอบความถูกต้อง!
แพลตฟอร์มที่ขับเคลื่อนด้วย AI เช่น Smodin ลดความซับซ้อนและปรับปรุงกระบวนการเขียนเรียงความเชิงอธิบาย
เครื่องมือของ Smodin ช่วยสร้างเรียงความที่ชัดเจนและมีโครงสร้างที่ดีซึ่งตรงตามมาตรฐานการศึกษาของคุณ ด้วยความสามารถในการวิจัยขั้นสูงของ Smodin คุณสามารถรวบรวมข้อมูลที่มีรายละเอียดและเกี่ยวข้องได้อย่างรวดเร็ว สิ่งนี้จะช่วยคุณประหยัดเวลาและปรับปรุงงานของคุณ
- การคัดลอกผลงาน : ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าเรียงความของคุณยังคงความคิดริเริ่มด้วยเครื่องมือตรวจจับการลอกเลียนแบบของ Smodin คุณสมบัตินี้ช่วยรักษาความซื่อสัตย์ทางวิชาการโดยการตรวจสอบงานของคุณกับฐานข้อมูลขนาดใหญ่
- การอ้างอิงอัตโนมัติ : อ้างอิงแหล่งที่มาของคุณอย่างถูกต้องโดยไม่ต้องยุ่งยาก เครื่องมือการอ้างอิงอัตโนมัติของ Smodin ช่วยให้มั่นใจว่าการอ้างอิงของคุณอยู่ในรูปแบบที่ถูกต้องและเป็นไปตามกฎเกณฑ์ของสถาบันการศึกษาของคุณ
- ตัวย่อข้อความ : หากเรียงความอธิบายของคุณยาวเกินไป ให้ใช้นักเขียน AI ของ Smodin เป็นตัวย่อเรียงความ มันจะช่วยให้คุณตัดเนื้อหาของคุณโดยไม่สูญเสียรายละเอียดที่สำคัญ สิ่งนี้ช่วยให้เรียงความของคุณชัดเจนและเกี่ยวข้อง
- เขียนข้อความใหม่ : ช่วยถอดความเนื้อหาที่มีอยู่ ทำให้มั่นใจถึงความเป็นเอกลักษณ์และมุมมองที่สดใหม่
- ผู้สรุป : Summarizer ย่อบทความยาวๆ ให้เป็นบทสรุปสั้นๆ เหมาะสำหรับการทำโครงร่างหรือข้อสรุปที่มีประสิทธิภาพ
Advertisement
Supported by
The Interpreter
What the I.C.J. Ruling Actually Means for Israel’s Offensive in Rafah
There is a substantial consensus among legal experts that Israel cannot continue its current Rafah offensive without violating the court’s order.
- Share full article

By Amanda Taub
Reporting from London
I had two thoughts on Friday as I listened to the chief judge of the International Court of Justice tell Israel to halt its military offensive in Rafah, the city in southern Gaza to which more than a million displaced people fled earlier in the conflict.
The first was that the court’s ruling was unusually forceful: the judge said Israel “must halt” its military offensive in Rafah “immediately.” Many observers had not expected the court to issue such a direct order because it has no jurisdiction to impose similar requirements on Hamas, Israel’s opponent in the war.
My second thought was that the court’s use of punctuation was definitely going to provoke debate. Here’s the key part of the ruling:
The State of Israel shall, in conformity with its obligations under the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide, and in view of the worsening conditions of life faced by civilians in the Rafah Governorate: Immediately halt its military offensive, and any other action in the Rafah Governorate, which may inflict on the Palestinian group in Gaza conditions of life that could bring about its physical destruction in whole or in part.
Sure enough, for several days some legal scholars have been arguing about whether the clause that begins “which may inflict” put conditions on the order to “immediately halt.”
Has Israel been told to halt its offensive, or to do so only if that offensive is about to partly or completely destroy Palestinians as a group?
In some ways, the debate is a distraction. There is a substantial consensus among legal experts that Israel cannot continue its current offensive in Rafah without violating the court’s order. Five leading legal scholars I contacted said the order was clear on that point, and more said the same in interviews and social media posts online. (“The current offensive as currently planned and executed is prohibited under any reading,” wrote Adil Haque, an international law expert at Rutgers University. “This sentence means Israel must halt its current military offensive in Rafah,” wrote Janina Dill, the co-director of the Oxford Institute for Ethics, Law, and Armed Conflict.)
An earlier paragraph of the order offered vital context, these experts pointed out, and clearly explained the urgency of the court’s intervention:
“On the basis of the information before it, the Court is not convinced that the evacuation efforts and related measures that Israel affirms to have undertaken to enhance the security of civilians in the Gaza Strip, and in particular those recently displaced from the Rafah Governorate, are sufficient to alleviate the immense risk to which the Palestinian population is exposed as a result of the military offensive in Rafah.”
That, the court went on to explain, was the reason for the new order. Notice the use of the word “current” here: “The Court finds that the current situation arising from Israel’s military offensive in Rafah entails a further risk” to the rights of Palestinians in Gaza, the order says.
There is a wider range of disagreement about what Israel could legally do instead. But that is not immediately relevant, because all indications are that Israel is continuing the current offensive despite the court’s instructions to stop.
How did we get here?
To recap: Friday’s order was an interim decision in a case that South Africa filed in December, alleging that Israel’s military actions in Gaza violate the 1948 Genocide Convention. The court can only rule on Israel’s behavior, not that of Hamas, because Hamas is neither a state nor a party to the genocide convention. Israel has categorically denied that it is committing genocide.
A decision on the merits of the case is probably years away. In the meantime, the court has issued a series of “provisional measures” — essentially temporary injunctions — ordering Israel to proactively ensure genocide doesn’t occur while the broader case is pending.
The first, issued in January , ordered Israel to refrain from genocidal acts, to prevent and punish incitement and to enable the provision of humanitarian assistance. A subsequent order in March added a requirement that Israel take “ all necessary and effective measures ” to ensure the delivery of humanitarian aid “at scale.”
In early May, after Israel began its military operation in Rafah, South Africa urgently requested new provisional measures, arguing that the Rafah incursion would cause “irreparable harm to the rights of the Palestinian people in Gaza.” On Friday, by a majority of 13 to 2, the court’s judges found that the risks to civilians warned of in previous orders had now materialized, and that the situation had become “disastrous.”
“Israel has not provided sufficient information concerning the safety of the population during the evacuation process,” the court found, “or the availability in the Al-Mawasi area of the necessary amount of water, sanitation, food, medicine and shelter for the 800,000 Palestinians that have evacuated thus far.” (Al-Mawasi is a coastal area in Gaza to which many of the civilians in Rafah had been displaced.)
That created a risk of “irreparable prejudice to the plausible rights claimed by South Africa,” the court found, and so it ordered Israel to halt its military offensive in Rafah. It also ordered Israel to keep the Rafah crossing on the border with Egypt open “at scale” for the provision of humanitarian aid, and to allow U.N.-mandated investigators access to Gaza.
One order, two commas, many opinions
Some experts have noted that when the I.C.J. ordered Russia to halt its war in Ukraine in March 2022, the wording was more direct : “The Russian Federation shall immediately suspend the military operations that it commenced on 24 February 2022 in the territory of Ukraine,” that provisional measures order stated. (In that case, the ruling was also 13 to 2.)
So why would the court be even slightly ambiguous in this case? It may have been intentional, said Yuval Shany, an international law professor at Hebrew University in Jerusalem. Perhaps the vague language helped convince more judges to sign the order, he said, even if they did not all agree on a single interpretation of its meaning. There is actually a term for that phenomenon in international law, Shany noted. The term “constructive ambiguity” refers to when “you’re not able to actually reach a consensus formulation, so you use language that everyone can live with,” he said.
It might have been easier to convince a majority to agree to the unambiguous order in the Russia case, which followed the invasion of Ukraine, because invading another state’s territory is barred by international law. By contrast, Israel’s military operations came in response to Hamas’s attack on Israeli soil last October. Using force in self-defense is allowed under international law, though it is still subject to other laws of war and the prohibitions on genocide and other crimes.
Three of the judges who joined the majority in last week’s decision wrote separately to explain their interpretation of the order. Each indicated that there would be some circumstances in which certain types of military operations could continue: if the operations did not “inflict on the Palestinian group in Gaza conditions of life that could bring about its physical destruction in whole or in part” ( Judge Bogdan Aurescu ); if they did not prevent the provision of urgently needed basic services and humanitarian assistance ( Judge Georg Nolte ); or if they were limited to “defensive operations to repel specific attacks,” carried out in accordance with international law ( Judge Dire Tladi ).
But none appeared to say that the operation could continue in its current form — and Judge Tladi explicitly ruled that out.
“What would not be consistent is the continuation of the offensive military operation in Rafah, and elsewhere,” he wrote.
All of the experts I spoke to agreed that the order prohibited Israel from continuing its current operation in Rafah, but believed it allowed for Israel to take more limited defensive actions in the city in response to attacks from Hamas.
Pierre d’Argent, a professor at the University of Louvain in Belgium, initially appeared to take a relatively restrictive view of the court’s order in his posts on social media , where he argued that the court had ordered Israel only “to change course in its military operations, not to stop them all together in Rafah.”
But when I reached out to him, d’Argent told me via email that in fact “the issue is rather straightforward,” and that in his view Israel could not continue its current military operation.
“Since the court’s concern is the worsening humanitarian situation, aid cannot be distributed if the military operations continue as they are,” he said. “They must therefore cease as such (i.e. as they are currently being conducted), but the court is not prohibiting all military action in Rafah.”
Stefan Talmon, a professor of international law at the University of Bonn in Germany, said in an interview with Der Spiegel , a German newspaper, that the order only allowed for the military operation to continue if Israel ensured the civilian population could be supplied with food, water, and medicine. However, he believed that would be difficult to implement in practice. In effect, therefore, the offensive had to be halted.
Michael Becker, a law professor at Trinity College, Dublin, had a more categorical interpretation. “I interpret this language to mean the military offensive in Rafah needs to be halted, period,” he said. The order’s discussion of the worsening humanitarian disaster makes clear that the current military offensive “already creates a situation that may inflict on the Palestinian group in Gaza, conditions of life that could bring about its physical destruction in whole or in part,” he added.
Oona Hathaway, a law professor at Yale University, agreed. “The urgent request for additional provisional measures was in light of what was happening right then,” in the unfolding assault on Rafah, she said. “It just seems implausible that what the court meant was that it didn’t see that there was anything of concern, at present.”
The two judges who did not join the opinion also had narrow interpretations of what it required. Judge Aharon Barak wrote that the order mandated a halt to Israel’s operations in Rafah “only insofar as is necessary to protect the Palestinian group in Gaza” from possible genocide, and that Israel was already under that obligation. Judge Julia Sebutinde wrote that the order did not “entirely prohibit” Israel from operating in Rafah, but partially restricted the offensive “to the extent it implicates rights under the Genocide Convention.”
Israel has denied that its operation in Rafah risks the destruction of the Palestinian civilian population in Gaza.
“Israel has not and will not conduct military actions in the Rafah area which may inflict on the Palestinian civilian population in Gaza conditions of life that could bring about its physical destruction in whole or in part,” the head of the Israeli National Security Council and the spokesperson of the Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs said in a joint statement on Friday. (The Israeli military and Ministry of Defense did not respond to my request for comment.)
Overtaken by events
Even as legal scholars have pondered the semantics of the court’s order, the situation in Rafah has already moved on.
“In some ways, this debate among academics and the broader public about the precise contours of the I.C.J. order has been superseded by the weekend’s events,” Becker, the professor at Trinity College, Dublin, said, referring to an Israeli strike in Rafah on Sunday that killed at least 45 people, including children, and wounded 249.
“I think that the nature of what has happened in Rafah over the weekend demonstrates exactly the type of risk that the I.C.J. order was intended to prevent, under either reading,” he added.
Amanda Taub writes the Interpreter , an explanatory column and newsletter about world events. She is based in London. More about Amanda Taub
Our Coverage of the Israel-Hamas War
News and Analysis
Israel’s national security adviser said that he expected Israel’s military operations in Gaza to continue through at least the end of the year , appearing to reject the idea of a quick end to the war.
The bombs used in the Israeli strike that killed dozens of Palestinians in a camp for displaced people in Rafah were made in the United States , according to weapons experts and a Times visual analysis.
The Israeli military said that it had taken “tactical control” over the Philadelphi Corridor — a sensitive strip of Gaza along its border with Egypt.
U.S. Military Aid Project: The Pentagon predicted that a stream of humanitarian aid would be arriving in Gaza via the floating pier, but little relief has reached the besieged strip .
Ari Emanuel’s Condemnation: The media executive condemned Netanyahu for his leadership since the Hamas attack of Oct. 7, a conspicuous statement from one of Hollywood’s most powerful figures.
Amal Clooney Weighs In: The prominent human rights lawyer was on a panel that recommended arrest warrants for leaders of Israel and Hamas. She had been criticized earlier for not speaking out on the war.

COMMENTS
For example, you might explain the rise of obesity rates in the United States over the past few decades. State your thesis: A good explanatory thesis example should be clear, concise, and focused. It should state the main argument or point of your essay. For example, you might state, ' Regular exercise is crucial to maintaining a healthy weight ...
To write a five-paragraph explanatory essay, you must create an introduction that introduces the main topic and states the thesis, three body paragraphs to support the thesis, and a concluding paragraph to wrap up the points made in the essay. The tone should be formal throughout, with clear connections to the reader.
Writing an explanatory essay begins with drafting an introduction. Introduction provides background information on topic and thesis statement in closing sentence. Thesis statement offers the main idea of paper. Subsequent parts of an explanatory essay support the developed thesis statement using valid evidence.
A few subtypes of explanatory essays: Description or definition essay example Perhaps the most basic, this subtype does the deceptively simple work of, well, describing or defining a concept, place, person, etc. Example: How Suspension Bridges Work This essay explains: The way suspension bridges are constructed and how their design enables them to carry such immense weight.
Follow our guide to come up with an excellent essay: 1. Pick an understandable topic. If a professor allows you to choose explanatory essay topics, it's better to focus on subjects that are easy to write about. There's a thing called the " writer's block " which doesn't let you craft any sentence.
You should know which parts of the writing come first, to guide you in your writing. The proper explanatory essay structure is outlined below: The Introduction. An explanatory essay introduction is one of the most important parts of your write-up. Knowing how to write an explanatory essay introduction is very important.
Explanatory essays are common in academic settings, including high school and college courses. They can be assigned as a standalone writing assignment or as part of a larger research project. In addition, explanatory essays can be found in various forms of media, such as news articles, instructional manuals, and technical reports.
Organizing your thoughts in this manner gives you a framework to follow when writing your essay, and you'll find that it makes the entire process much easier. The general structure of an explanatory essay is as follows: introduction. body. main point #1. main point #2. main point #3. conclusion.
An explanatory essay is a way to help make sense of the information by breaking it down into smaller parts and providing a clear and accurate explanation of the topic. Now that we understand the importance of explanatory essays, let's talk about the steps involved in writing one.
Continue reading this step-by-step guide to learn how to write the best explanatory essay fast. 1. Pick a Topic. Check the essay prompt to determine if your instructor has given you a topic to focus on. If they have, write the essay according to the instructions that they provide.
The structure of your expository essay will vary according to the scope of your assignment and the demands of your topic. It's worthwhile to plan out your structure before you start, using an essay outline. A common structure for a short expository essay consists of five paragraphs: An introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
An essay that explains a writer's ideas by defining, explaining, informing, or elaborating on points to allow the reader to clearly understand the concept. Many of your future academic workplace writing assignments will be expository-explaining your ideas or the significance of a concept or action. An expository essay allows the writer the ...
Explanatory essay authors should ensure that the information in their writing is a blend of personal views and ideas acquired from external sources. Explanatory essay relies heavily on solid research, focus on finding external sources that will supplement your personal opinion. Note down all the important information from those sources and use ...
An explanatory essay, often referred to as an expository essay, serves a dual purpose of exploring a topic and informing the audience. Its main goal is to provide a clear and detailed explanation of a subject, idea, process, or set of circumstances, based on facts and devoid of the writer's personal opinions or biases.
An explanatory essay, also known as an expository essay, is a type of academic writing that aims to explain a particular topic or concept clearly and concisely. These essays are often used in academic settings but can also be found in newspapers, magazines, and online publications.
Key Takeaways: Expository Writing. Just the facts, M'am: Expository writing is informational, not creative writing. Anytime you write to describe or explain, you use expository writing. Use a logical flow when planning an expository essay, report, or article: introduction, body text, and conclusion. It's often easier to write the body of your ...
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you craft an expository essay: Choose a Topic. Select a topic that interests you and aligns with the purpose of an expository essay - to inform, explain, or analyze a subject. Conduct Research. Gather relevant and credible information to support your chosen topic.
Examples of essay outlines. Examples of outlines for different types of essays are presented below: an argumentative, expository, and literary analysis essay. Argumentative essay outline. This outline is for a short argumentative essay evaluating the internet's impact on education. It uses short phrases to summarize each point.
Expository Essay Part 1 Essay structure and the introductory paragraph Part 2 Body paragraphs, concluding paragraphs, and outlining Part 3 Improving your work. Cambridge University Press 978-1-107-62109-1 - Academic Writing Skills 2 Student's Book Peter Chin, Samuel Reid, Sean Wray, Yoko Yamazaki
The Type of writing is an explanatory essay. Then lead students through the topic-selection strategies. Point them also to pages 44-45 for more topic ideas. Afterward, download and distribute the KWL Chart to help students reflect on their prior knowledge of the topic and organize questions for research.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Narrative Essay. 4. Argumentative Essay. Expository and persuasive essays mainly deal with facts to explain ideas clearly. Narrative and descriptive essays are informal and have a creative edge. Despite their differences, these essay types share a common goal ― to convey information, insights, and perspectives effectively.
Parts of an Explanatory Synthesis Essay. Like any other academic essay, an explanatory synthesis essay will consist of: An introduction; A body; A conclusion; Introduction: The introduction should be brief. This section must also explain how it relates to the rest of the paper. This paragraph can also be used to introduce any necessary terms ...
Explanatory Essay Format. Understanding the explanatory essay format is key to a well-structured and logical paper. Here's a basic breakdown of the format for an explanatory essay: Introduction paragraph. Begin with an interesting sentence to capture the reader's attention. Give a short intro. It should set the topic and outline the essay ...
The Expository Times: Create email alert. Open access. Research article. First published online May 29, 2024. ... I argue, however, in this essay's second part, that the conceptual clarity we might first see is not the full story of universalism. In seeking a fuller story, I approach universalism from the perspective of its practical ...
May 30, 2024, 12:01 a.m. ET. I had two thoughts on Friday as I listened to the chief judge of the International Court of Justice tell Israel to halt its military offensive in Rafah, the city in ...