

Research Topics & Ideas: Healthcare

F inding and choosing a strong research topic is the critical first step when it comes to crafting a high-quality dissertation, thesis or research project. If you’ve landed on this post, chances are you’re looking for a healthcare-related research topic , but aren’t sure where to start. Here, we’ll explore a variety of healthcare-related research ideas and topic thought-starters across a range of healthcare fields, including allopathic and alternative medicine, dentistry, physical therapy, optometry, pharmacology and public health.
NB – This is just the start…
The topic ideation and evaluation process has multiple steps . In this post, we’ll kickstart the process by sharing some research topic ideas within the healthcare domain. This is the starting point, but to develop a well-defined research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , along with a well-justified plan of action to fill that gap.
If you’re new to the oftentimes perplexing world of research, or if this is your first time undertaking a formal academic research project, be sure to check out our free dissertation mini-course. In it, we cover the process of writing a dissertation or thesis from start to end. Be sure to also sign up for our free webinar that explores how to find a high-quality research topic.
Overview: Healthcare Research Topics
- Allopathic medicine
- Alternative /complementary medicine
- Veterinary medicine
- Physical therapy/ rehab
- Optometry and ophthalmology
- Pharmacy and pharmacology
- Public health
- Examples of healthcare-related dissertations
Allopathic (Conventional) Medicine
- The effectiveness of telemedicine in remote elderly patient care
- The impact of stress on the immune system of cancer patients
- The effects of a plant-based diet on chronic diseases such as diabetes
- The use of AI in early cancer diagnosis and treatment
- The role of the gut microbiome in mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety
- The efficacy of mindfulness meditation in reducing chronic pain: A systematic review
- The benefits and drawbacks of electronic health records in a developing country
- The effects of environmental pollution on breast milk quality
- The use of personalized medicine in treating genetic disorders
- The impact of social determinants of health on chronic diseases in Asia
- The role of high-intensity interval training in improving cardiovascular health
- The efficacy of using probiotics for gut health in pregnant women
- The impact of poor sleep on the treatment of chronic illnesses
- The role of inflammation in the development of chronic diseases such as lupus
- The effectiveness of physiotherapy in pain control post-surgery

Topics & Ideas: Alternative Medicine
- The benefits of herbal medicine in treating young asthma patients
- The use of acupuncture in treating infertility in women over 40 years of age
- The effectiveness of homoeopathy in treating mental health disorders: A systematic review
- The role of aromatherapy in reducing stress and anxiety post-surgery
- The impact of mindfulness meditation on reducing high blood pressure
- The use of chiropractic therapy in treating back pain of pregnant women
- The efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine such as Shun-Qi-Tong-Xie (SQTX) in treating digestive disorders in China
- The impact of yoga on physical and mental health in adolescents
- The benefits of hydrotherapy in treating musculoskeletal disorders such as tendinitis
- The role of Reiki in promoting healing and relaxation post birth
- The effectiveness of naturopathy in treating skin conditions such as eczema
- The use of deep tissue massage therapy in reducing chronic pain in amputees
- The impact of tai chi on the treatment of anxiety and depression
- The benefits of reflexology in treating stress, anxiety and chronic fatigue
- The role of acupuncture in the prophylactic management of headaches and migraines

Topics & Ideas: Dentistry
- The impact of sugar consumption on the oral health of infants
- The use of digital dentistry in improving patient care: A systematic review
- The efficacy of orthodontic treatments in correcting bite problems in adults
- The role of dental hygiene in preventing gum disease in patients with dental bridges
- The impact of smoking on oral health and tobacco cessation support from UK dentists
- The benefits of dental implants in restoring missing teeth in adolescents
- The use of lasers in dental procedures such as root canals
- The efficacy of root canal treatment using high-frequency electric pulses in saving infected teeth
- The role of fluoride in promoting remineralization and slowing down demineralization
- The impact of stress-induced reflux on oral health
- The benefits of dental crowns in restoring damaged teeth in elderly patients
- The use of sedation dentistry in managing dental anxiety in children
- The efficacy of teeth whitening treatments in improving dental aesthetics in patients with braces
- The role of orthodontic appliances in improving well-being
- The impact of periodontal disease on overall health and chronic illnesses

Topics & Ideas: Veterinary Medicine
- The impact of nutrition on broiler chicken production
- The role of vaccines in disease prevention in horses
- The importance of parasite control in animal health in piggeries
- The impact of animal behaviour on welfare in the dairy industry
- The effects of environmental pollution on the health of cattle
- The role of veterinary technology such as MRI in animal care
- The importance of pain management in post-surgery health outcomes
- The impact of genetics on animal health and disease in layer chickens
- The effectiveness of alternative therapies in veterinary medicine: A systematic review
- The role of veterinary medicine in public health: A case study of the COVID-19 pandemic
- The impact of climate change on animal health and infectious diseases in animals
- The importance of animal welfare in veterinary medicine and sustainable agriculture
- The effects of the human-animal bond on canine health
- The role of veterinary medicine in conservation efforts: A case study of Rhinoceros poaching in Africa
- The impact of veterinary research of new vaccines on animal health

Topics & Ideas: Physical Therapy/Rehab
- The efficacy of aquatic therapy in improving joint mobility and strength in polio patients
- The impact of telerehabilitation on patient outcomes in Germany
- The effect of kinesiotaping on reducing knee pain and improving function in individuals with chronic pain
- A comparison of manual therapy and yoga exercise therapy in the management of low back pain
- The use of wearable technology in physical rehabilitation and the impact on patient adherence to a rehabilitation plan
- The impact of mindfulness-based interventions in physical therapy in adolescents
- The effects of resistance training on individuals with Parkinson’s disease
- The role of hydrotherapy in the management of fibromyalgia
- The impact of cognitive-behavioural therapy in physical rehabilitation for individuals with chronic pain
- The use of virtual reality in physical rehabilitation of sports injuries
- The effects of electrical stimulation on muscle function and strength in athletes
- The role of physical therapy in the management of stroke recovery: A systematic review
- The impact of pilates on mental health in individuals with depression
- The use of thermal modalities in physical therapy and its effectiveness in reducing pain and inflammation
- The effect of strength training on balance and gait in elderly patients
Need a helping hand?
Topics & Ideas: Optometry & Opthalmology
- The impact of screen time on the vision and ocular health of children under the age of 5
- The effects of blue light exposure from digital devices on ocular health
- The role of dietary interventions, such as the intake of whole grains, in the management of age-related macular degeneration
- The use of telemedicine in optometry and ophthalmology in the UK
- The impact of myopia control interventions on African American children’s vision
- The use of contact lenses in the management of dry eye syndrome: different treatment options
- The effects of visual rehabilitation in individuals with traumatic brain injury
- The role of low vision rehabilitation in individuals with age-related vision loss: challenges and solutions
- The impact of environmental air pollution on ocular health
- The effectiveness of orthokeratology in myopia control compared to contact lenses
- The role of dietary supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, in ocular health
- The effects of ultraviolet radiation exposure from tanning beds on ocular health
- The impact of computer vision syndrome on long-term visual function
- The use of novel diagnostic tools in optometry and ophthalmology in developing countries
- The effects of virtual reality on visual perception and ocular health: an examination of dry eye syndrome and neurologic symptoms
Topics & Ideas: Pharmacy & Pharmacology
- The impact of medication adherence on patient outcomes in cystic fibrosis
- The use of personalized medicine in the management of chronic diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease
- The effects of pharmacogenomics on drug response and toxicity in cancer patients
- The role of pharmacists in the management of chronic pain in primary care
- The impact of drug-drug interactions on patient mental health outcomes
- The use of telepharmacy in healthcare: Present status and future potential
- The effects of herbal and dietary supplements on drug efficacy and toxicity
- The role of pharmacists in the management of type 1 diabetes
- The impact of medication errors on patient outcomes and satisfaction
- The use of technology in medication management in the USA
- The effects of smoking on drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics: A case study of clozapine
- Leveraging the role of pharmacists in preventing and managing opioid use disorder
- The impact of the opioid epidemic on public health in a developing country
- The use of biosimilars in the management of the skin condition psoriasis
- The effects of the Affordable Care Act on medication utilization and patient outcomes in African Americans
Topics & Ideas: Public Health
- The impact of the built environment and urbanisation on physical activity and obesity
- The effects of food insecurity on health outcomes in Zimbabwe
- The role of community-based participatory research in addressing health disparities
- The impact of social determinants of health, such as racism, on population health
- The effects of heat waves on public health
- The role of telehealth in addressing healthcare access and equity in South America
- The impact of gun violence on public health in South Africa
- The effects of chlorofluorocarbons air pollution on respiratory health
- The role of public health interventions in reducing health disparities in the USA
- The impact of the United States Affordable Care Act on access to healthcare and health outcomes
- The effects of water insecurity on health outcomes in the Middle East
- The role of community health workers in addressing healthcare access and equity in low-income countries
- The impact of mass incarceration on public health and behavioural health of a community
- The effects of floods on public health and healthcare systems
- The role of social media in public health communication and behaviour change in adolescents
Examples: Healthcare Dissertation & Theses
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a healthcare-related research topic, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual dissertations and theses to see how this all comes together.
Below, we’ve included a selection of research projects from various healthcare-related degree programs to help refine your thinking. These are actual dissertations and theses, written as part of Master’s and PhD-level programs, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- Improving Follow-Up Care for Homeless Populations in North County San Diego (Sanchez, 2021)
- On the Incentives of Medicare’s Hospital Reimbursement and an Examination of Exchangeability (Elzinga, 2016)
- Managing the healthcare crisis: the career narratives of nurses (Krueger, 2021)
- Methods for preventing central line-associated bloodstream infection in pediatric haematology-oncology patients: A systematic literature review (Balkan, 2020)
- Farms in Healthcare: Enhancing Knowledge, Sharing, and Collaboration (Garramone, 2019)
- When machine learning meets healthcare: towards knowledge incorporation in multimodal healthcare analytics (Yuan, 2020)
- Integrated behavioural healthcare: The future of rural mental health (Fox, 2019)
- Healthcare service use patterns among autistic adults: A systematic review with narrative synthesis (Gilmore, 2021)
- Mindfulness-Based Interventions: Combatting Burnout and Compassionate Fatigue among Mental Health Caregivers (Lundquist, 2022)
- Transgender and gender-diverse people’s perceptions of gender-inclusive healthcare access and associated hope for the future (Wille, 2021)
- Efficient Neural Network Synthesis and Its Application in Smart Healthcare (Hassantabar, 2022)
- The Experience of Female Veterans and Health-Seeking Behaviors (Switzer, 2022)
- Machine learning applications towards risk prediction and cost forecasting in healthcare (Singh, 2022)
- Does Variation in the Nursing Home Inspection Process Explain Disparity in Regulatory Outcomes? (Fox, 2020)
Looking at these titles, you can probably pick up that the research topics here are quite specific and narrowly-focused , compared to the generic ones presented earlier. This is an important thing to keep in mind as you develop your own research topic. That is to say, to create a top-notch research topic, you must be precise and target a specific context with specific variables of interest . In other words, you need to identify a clear, well-justified research gap.

Find The Perfect Research Topic

How To Choose A Research Topic: 5 Key Criteria
How To Choose A Research Topic Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + Free Topic...
Research Topics & Ideas: Automation & Robotics
A comprehensive list of automation and robotics-related research topics. Includes free access to a webinar and research topic evaluator.

Research Topics & Ideas: Sociology
Research Topics & Ideas: Sociology 50 Topic Ideas To Kickstart Your Research...

Research Topics & Ideas: Public Health & Epidemiology
A comprehensive list of public health-related research topics. Includes free access to a webinar and research topic evaluator.

Research Topics & Ideas: Neuroscience
Research Topics & Ideas: Neuroscience 50 Topic Ideas To Kickstart Your Research...
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
19 Comments
I need topics that will match the Msc program am running in healthcare research please
Hello Mabel,
I can help you with a good topic, kindly provide your email let’s have a good discussion on this.
Can you provide some research topics and ideas on Immunology?
Thank you to create new knowledge on research problem verse research topic
Help on problem statement on teen pregnancy
This post might be useful: https://gradcoach.com/research-problem-statement/
can you give me research titles that i can conduct as a school nurse
can you provide me with a research topic on healthcare related topics to a qqi level 5 student
Please can someone help me with research topics in public health ?
Hello I have requirement of Health related latest research issue/topics for my social media speeches. If possible pls share health issues , diagnosis, treatment.
I would like a topic thought around first-line support for Gender-Based Violence for survivors or one related to prevention of Gender-Based Violence
Please can I be helped with a master’s research topic in either chemical pathology or hematology or immunology? thanks
Can u please provide me with a research topic on occupational health and safety at the health sector
Good day kindly help provide me with Ph.D. Public health topics on Reproductive and Maternal Health, interventional studies on Health Education
may you assist me with a good easy healthcare administration study topic
May you assist me in finding a research topic on nutrition,physical activity and obesity. On the impact on children
I have been racking my brain for a while on what topic will be suitable for my PhD in health informatics. I want a qualitative topic as this is my strong area.
Hi, may I please be assisted with research topics in the medical laboratory sciences
How do i frame a qualitative topic that will be suitable for the use of calibrated drape among midwifes. this is a thesis for my master programme in midwifery education.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
Instant insights, infinite possibilities
77 interesting medical research topics for 2024
Last updated
25 November 2023
Reviewed by
Brittany Ferri, PhD, OTR/L
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Medical research is the gateway to improved patient care and expanding our available treatment options. However, finding a relevant and compelling research topic can be challenging.
Use this article as a jumping-off point to select an interesting medical research topic for your next paper or clinical study.
- How to choose a medical research topic
When choosing a research topic , it’s essential to consider a couple of things. What topics interest you? What unanswered questions do you want to address?
During the decision-making and brainstorming process, here are a few helpful tips to help you pick the right medical research topic:
Focus on a particular field of study
The best medical research is specific to a particular area. Generalized studies are often too broad to produce meaningful results, so we advise picking a specific niche early in the process.
Maybe a certain topic interests you, or your industry knowledge reveals areas of need.
Look into commonly researched topics
Once you’ve chosen your research field, do some preliminary research. What have other academics done in their papers and projects?
From this list, you can focus on specific topics that interest you without accidentally creating a copycat project. This groundwork will also help you uncover any literature gaps—those may be beneficial areas for research.
Get curious and ask questions
Now you can get curious. Ask questions that start with why, how, or what. These questions are the starting point of your project design and will act as your guiding light throughout the process.
For example:
What impact does pollution have on children’s lung function in inner-city neighborhoods?
Why is pollution-based asthma on the rise?
How can we address pollution-induced asthma in young children?
- 77 medical research topics worth exploring in 2023
Need some research inspiration for your upcoming paper or clinical study? We’ve compiled a list of 77 topical and in-demand medical research ideas. Let’s take a look.
- Exciting new medical research topics
If you want to study cutting-edge topics, here are some exciting options:
COVID-19 and long COVID symptoms
Since 2020, COVID-19 has been a hot-button topic in medicine, along with the long-term symptoms in those with a history of COVID-19.
Examples of COVID-19-related research topics worth exploring include:
The long-term impact of COVID-19 on cardiac and respiratory health
COVID-19 vaccination rates
The evolution of COVID-19 symptoms over time
New variants and strains of the COVID-19 virus
Changes in social behavior and public health regulations amid COVID-19
Vaccinations
Finding ways to cure or reduce the disease burden of chronic infectious diseases is a crucial research area. Vaccination is a powerful option and a great topic to research.
Examples of vaccination-related research topics include:
mRNA vaccines for viral infections
Biomaterial vaccination capabilities
Vaccination rates based on location, ethnicity, or age
Public opinion about vaccination safety
Artificial tissues fabrication
With the need for donor organs increasing, finding ways to fabricate artificial bioactive tissues (and possibly organs) is a popular research area.
Examples of artificial tissue-related research topics you can study include:
The viability of artificially printed tissues
Tissue substrate and building block material studies
The ethics and efficacy of artificial tissue creation
- Medical research topics for medical students
For many medical students, research is a big driver for entering healthcare. If you’re a medical student looking for a research topic, here are some great ideas to work from:
Sleep disorders
Poor sleep quality is a growing problem, and it can significantly impact a person’s overall health.
Examples of sleep disorder-related research topics include:
How stress affects sleep quality
The prevalence and impact of insomnia on patients with mental health conditions
Possible triggers for sleep disorder development
The impact of poor sleep quality on psychological and physical health
How melatonin supplements impact sleep quality
Alzheimer’s and dementia
Cognitive conditions like dementia and Alzheimer’s disease are on the rise worldwide. They currently have no cure. As a result, research about these topics is in high demand.
Examples of dementia-related research topics you could explore include:
The prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease in a chosen population
Early onset symptoms of dementia
Possible triggers or causes of cognitive decline with age
Treatment options for dementia-like conditions
The mental and physical burden of caregiving for patients with dementia
- Lifestyle habits and public health
Modern lifestyles have profoundly impacted the average person’s daily habits, and plenty of interesting topics explore its effects.
Examples of lifestyle and public health-related research topics include:
The nutritional intake of college students
The impact of chronic work stress on overall health
The rise of upper back and neck pain from laptop use
Prevalence and cause of repetitive strain injuries (RSI)
- Controversial medical research paper topics
Medical research is a hotbed of controversial topics, content, and areas of study.
If you want to explore a more niche (and attention-grabbing) concept, here are some controversial medical research topics worth looking into:
The benefits and risks of medical cannabis
Depending on where you live, the legalization and use of cannabis for medical conditions is controversial for the general public and healthcare providers.
Examples of medical cannabis-related research topics that might grab your attention include:
The legalization process of medical cannabis
The impact of cannabis use on developmental milestones in youth users
Cannabis and mental health diagnoses
CBD’s impact on chronic pain
Prevalence of cannabis use in young people
The impact of maternal cannabis use on fetal development
Understanding how THC impacts cognitive function
Human genetics
The Human Genome Project identified, mapped, and sequenced all human DNA genes. Its completion in 2003 opened up a world of exciting and controversial studies in human genetics.
Examples of human genetics-related research topics worth delving into include:
Medical genetics and the incidence of genetic-based health disorders
Behavioral genetics differences between identical twins
Genetic risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders
Machine learning technologies for genetic research
Sexual health studies
Human sexuality and sexual health are important (yet often stigmatized) medical topics that need new research and analysis.
As a diverse field ranging from sexual orientation studies to sexual pathophysiology, examples of sexual health-related research topics include:
The incidence of sexually transmitted infections within a chosen population
Mental health conditions within the LGBTQIA+ community
The impact of untreated sexually transmitted infections
Access to safe sex resources (condoms, dental dams, etc.) in rural areas
- Health and wellness research topics
Human wellness and health are trendy topics in modern medicine as more people are interested in finding natural ways to live healthier lifestyles.
If this field of study interests you, here are some big topics in the wellness space:
Gluten sensitivity
Gluten allergies and intolerances have risen over the past few decades. If you’re interested in exploring this topic, your options range in severity from mild gastrointestinal symptoms to full-blown anaphylaxis.
Some examples of gluten sensitivity-related research topics include:
The pathophysiology and incidence of Celiac disease
Early onset symptoms of gluten intolerance
The prevalence of gluten allergies within a set population
Gluten allergies and the incidence of other gastrointestinal health conditions
Pollution and lung health
Living in large urban cities means regular exposure to high levels of pollutants.
As more people become interested in protecting their lung health, examples of impactful lung health and pollution-related research topics include:
The extent of pollution in densely packed urban areas
The prevalence of pollution-based asthma in a set population
Lung capacity and function in young people
The benefits and risks of steroid therapy for asthma
Pollution risks based on geographical location
Plant-based diets
Plant-based diets like vegan and paleo diets are emerging trends in healthcare due to their limited supporting research.
If you’re interested in learning more about the potential benefits or risks of holistic, diet-based medicine, examples of plant-based diet research topics to explore include:
Vegan and plant-based diets as part of disease management
Potential risks and benefits of specific plant-based diets
Plant-based diets and their impact on body mass index
The effect of diet and lifestyle on chronic disease management
Health supplements
Supplements are a multi-billion dollar industry. Many health-conscious people take supplements, including vitamins, minerals, herbal medicine, and more.
Examples of health supplement-related research topics worth investigating include:
Omega-3 fish oil safety and efficacy for cardiac patients
The benefits and risks of regular vitamin D supplementation
Health supplementation regulation and product quality
The impact of social influencer marketing on consumer supplement practices
Analyzing added ingredients in protein powders
- Healthcare research topics
Working within the healthcare industry means you have insider knowledge and opportunity. Maybe you’d like to research the overall system, administration, and inherent biases that disrupt access to quality care.
While these topics are essential to explore, it is important to note that these studies usually require approval and oversight from an Institutional Review Board (IRB). This ensures the study is ethical and does not harm any subjects.
For this reason, the IRB sets protocols that require additional planning, so consider this when mapping out your study’s timeline.
Here are some examples of trending healthcare research areas worth pursuing:
The pros and cons of electronic health records
The rise of electronic healthcare charting and records has forever changed how medical professionals and patients interact with their health data.
Examples of electronic health record-related research topics include:
The number of medication errors reported during a software switch
Nurse sentiment analysis of electronic charting practices
Ethical and legal studies into encrypting and storing personal health data
Inequities within healthcare access
Many barriers inhibit people from accessing the quality medical care they need. These issues result in health disparities and injustices.
Examples of research topics about health inequities include:
The impact of social determinants of health in a set population
Early and late-stage cancer stage diagnosis in urban vs. rural populations
Affordability of life-saving medications
Health insurance limitations and their impact on overall health
Diagnostic and treatment rates across ethnicities
People who belong to an ethnic minority are more likely to experience barriers and restrictions when trying to receive quality medical care. This is due to systemic healthcare racism and bias.
As a result, diagnostic and treatment rates in minority populations are a hot-button field of research. Examples of ethnicity-based research topics include:
Cancer biopsy rates in BIPOC women
The prevalence of diabetes in Indigenous communities
Access inequalities in women’s health preventative screenings
The prevalence of undiagnosed hypertension in Black populations
- Pharmaceutical research topics
Large pharmaceutical companies are incredibly interested in investing in research to learn more about potential cures and treatments for diseases.
If you’re interested in building a career in pharmaceutical research, here are a few examples of in-demand research topics:
Cancer treatment options
Clinical research is in high demand as pharmaceutical companies explore novel cancer treatment options outside of chemotherapy and radiation.
Examples of cancer treatment-related research topics include:
Stem cell therapy for cancer
Oncogenic gene dysregulation and its impact on disease
Cancer-causing viral agents and their risks
Treatment efficacy based on early vs. late-stage cancer diagnosis
Cancer vaccines and targeted therapies
Immunotherapy for cancer
Pain medication alternatives
Historically, opioid medications were the primary treatment for short- and long-term pain. But, with the opioid epidemic getting worse, the need for alternative pain medications has never been more urgent.
Examples of pain medication-related research topics include:
Opioid withdrawal symptoms and risks
Early signs of pain medication misuse
Anti-inflammatory medications for pain control
- Identify trends in your medical research with Dovetail
Are you interested in contributing life-changing research? Today’s medical research is part of the future of clinical patient care.
As your go-to resource for speedy and accurate data analysis , we are proud to partner with healthcare researchers to innovate and improve the future of healthcare.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
151+ Public Health Research Topics [Updated 2024]

The important area of public health research is essential to forming laws, influencing medical procedures, and eventually enhancing community well-being. As we delve into the vast landscape of public health research topics, it’s essential to understand the profound impact they have on society.
This blog aims to provide a comprehensive guide to selecting and understanding the diverse array of public health research topics.
Overview of Public Health Research Topics
Table of Contents
Public health research encompasses a wide range of subjects, reflecting the interdisciplinary nature of the field. From epidemiology and health policy to environmental health and infectious diseases, researchers navigate through various dimensions to address complex health challenges.
Each category holds its own significance, contributing to the overall understanding of public health dynamics.
Key Considerations in Selecting Public Health Research Topics
- Current Relevance: Assess the timeliness of potential topics by considering recent health trends, emerging issues, and societal concerns.
- Impact on Public Health: Evaluate the potential impact of the research on improving health outcomes, addressing disparities, or influencing policy and interventions.
- Feasibility and Resources: Gauge the practicality of conducting research on a particular topic, considering available resources, data accessibility, and research infrastructure.
- Ethical Considerations: Scrutinize the ethical implications of the research, ensuring it aligns with ethical standards and guidelines, especially when dealing with vulnerable populations or sensitive topics.
Top 151+ Public Health Research Topics
Epidemiology.
- The Impact of Social Determinants on Disease Outcomes
- Patterns and Trends in Emerging Infectious Diseases
- Investigating Health Disparities among Different Ethnic Groups
- Childhood Obesity and its Long-Term Health Consequences
- Assessing the Effectiveness of Contact Tracing in Disease Control
Health Policy
- Universal Healthcare: Comparative Analysis of Global Models
- The Role of Telemedicine in Improving Healthcare Access
- Evaluating Mental Health Policies and Their Impact on Communities
- Assessing the Impact of Affordable Care Act on Public Health
- Vaccine Policies and Public Perception: A Comprehensive Study
Environmental Health
- Climate Change and Health: Adapting to the Challenges
- Air Quality and Respiratory Health in Urban Environments
- Waterborne Diseases and Strategies for Safe Water Supply
- Occupational Health Hazards: A Comprehensive Workplace Analysis
- The Impact of Green Spaces on Mental Health in Urban Areas
Infectious Diseases
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Strategies for Mitigation
- Vaccination Strategies and Herd Immunity
- Global Health Security: Preparedness for Pandemics
- The Impact of Vector-Borne Diseases on Public Health
- Emerging Trends in Antibiotic-Resistant Infections
Chronic Diseases
- Lifestyle Interventions for Preventing Cardiovascular Diseases
- Genetic Factors in the Development of Cancer: A Comprehensive Study
- Aging and Health: Addressing the Healthcare Needs of the Elderly
- Diabetes Prevention Programs: Efficacy and Implementation
- Mental Health in Chronic Disease Patients: Bridging the Gap
Maternal and Child Health
- Maternal Mortality: Understanding Causes and Prevention
- The Impact of Breastfeeding on Infant Health and Development
- Childhood Immunization: Barriers and Strategies for Improvement
- Teenage Pregnancy and Its Long-Term Health Consequences
- Mental Health Support for Postpartum Women: Current Gaps and Solutions
Health Behavior and Promotion
- Smoking Cessation Programs: Effectiveness and Challenges
- Physical Activity Promotion in Schools: Strategies for Success
- Nutrition Education and Its Impact on Healthy Eating Habits
- Mental Health Awareness Campaigns: Assessing Public Perceptions
- The Role of Social Media in Health Promotion
Global Health
- Assessing the Impact of International Aid on Global Health
- Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) Programs in Developing Countries
- The Role of Non-Governmental Organizations in Global Health
- Communicable Disease Control in Refugee Populations
- Global Access to Essential Medicines: Challenges and Solutions
Community Health
- Community-Based Participatory Research: Best Practices and Challenges
- The Impact of Community Health Workers on Health Outcomes
- Health Literacy and its Relationship to Health Disparities
- Assessing the Effectiveness of Mobile Health (mHealth) Interventions
- Community Resilience in the Face of Public Health Crises
Healthcare Quality and Patient Safety
- Hospital-Acquired Infections: Strategies for Prevention
- Patient Safety Culture in Healthcare Organizations
- Quality Improvement Initiatives in Primary Care Settings
- Healthcare Accreditation: Impact on Patient Outcomes
- Implementing Electronic Health Records: Challenges and Benefits
Mental Health
- Stigma Reduction Programs for Mental Health Disorders
- Integrating Mental Health into Primary Care Settings
- The Impact of COVID-19 on Mental Health: Long-Term Implications
- Mental Health in the Workplace: Strategies for Employee Well-being
- Suicide Prevention Programs: Effectiveness and Outreach
Health Disparities
- Racial Disparities in Healthcare: Addressing Systemic Inequities
- LGBTQ+ Health Disparities and Inclusive Healthcare Practices
- Socioeconomic Status and Access to Healthcare Services
- Geographical Disparities in Health: Rural vs. Urban
- The Impact of Gender on Health Outcomes and Access to Care
Public Health Education
- Evaluation of Public Health Education Programs
- Innovative Approaches to Teaching Public Health Concepts
- Online Health Education Platforms: Opportunities and Challenges
- Interdisciplinary Training in Public Health: Bridging Gaps
- Continuing Education for Public Health Professionals: Current Landscape
Digital Health
- The Role of Wearable Devices in Health Monitoring
- Telehealth Adoption: Barriers and Opportunities
- Health Apps for Chronic Disease Management: User Perspectives
- Blockchain Technology in Healthcare: Privacy and Security Implications
- Artificial Intelligence in Disease Diagnosis and Prediction
Health Economics
- Cost-Effectiveness of Preventive Health Interventions
- The Impact of Healthcare Financing Models on Access to Care
- Pharmaceutical Pricing and Access to Essential Medicines
- Economic Evaluation of Health Promotion Programs
- Health Insurance Coverage and Health Outcomes: A Global Perspective
Innovations in Public Health
- 3D Printing in Healthcare: Applications and Future Prospects
- Gene Editing Technologies and their Ethical Implications
- Smart Cities and Public Health: Integrating Technology for Well-being
- Nanotechnology in Medicine: Potential for Disease Treatment
- The Role of Drones in Public Health: Surveillance and Intervention
Food Safety and Nutrition
- Foodborne Illness Outbreaks: Investigating Causes and Prevention
- Sustainable Food Systems: Implications for Public Health
- Nutritional Interventions for Malnutrition in Developing Countries
- Food Labeling and Consumer Understanding: A Critical Review
- The Impact of Fast Food Consumption on Public Health
Substance Abuse
- Opioid Epidemic: Strategies for Prevention and Treatment
- Harm Reduction Approaches in Substance Abuse Programs
- Alcohol Consumption Patterns and Public Health Outcomes
- Smoking and Mental Health: Exploring the Connection
- Novel Psychoactive Substances: Emerging Threats and Strategies
Occupational Health
- Workplace Stress and Mental Health: Intervention Strategies
- Occupational Hazards in Healthcare Professions: A Comparative Analysis
- Ergonomics in the Workplace: Improving Worker Health and Productivity
- Night Shift Work and Health Consequences: Addressing Challenges
- Occupational Health and Safety Regulations: A Global Overview
Disaster Preparedness and Response
- Pandemic Preparedness and Lessons from COVID-19
- Natural Disasters and Mental Health: Post-Traumatic Stress
- Emergency Response Systems: Improving Timeliness and Efficiency
- Communicating Health Risks During Emergencies: Public Perception
- Collaborative Approaches to Disaster Response in Global Health
Cancer Research
- Precision Medicine in Cancer Treatment: Current Advancements
- Cancer Screening Programs: Efficacy and Challenges
- Environmental Factors and Cancer Risk: Exploring Connections
- Survivorship Care Plans: Enhancing Quality of Life after Cancer
- Integrative Therapies in Cancer Care: Complementary Approaches
Sexual and Reproductive Health
- Access to Contraception in Developing Countries: Challenges and Solutions
- Comprehensive Sex Education Programs: Impact on Teen Pregnancy
- Reproductive Health Rights: Global Perspectives and Challenges
- Infertility Treatment: Ethical Considerations and Societal Impact
- Maternal and Child Health in Conflict Zones: Addressing Challenges
Cardiovascular Health
- Hypertension Prevention Programs: Strategies and Effectiveness
- Cardiovascular Disease in Women: Gender-Specific Risk Factors
- Innovations in Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs
- Artificial Heart Technology: Advancements and Ethical Implications
- Impact of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Health: A Global Concern
Social Determinants of Health
- Educational Attainment and Health Outcomes: Exploring Links
- Income Inequality and its Impact on Population Health
- Social Support Networks and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Study
- Neighborhood Environments and Health Disparities
- Employment and Health: The Interplay of Work and Well-being
Genomics and Public Health
- Population Genomics and its Implications for Public Health
- Genetic Counseling and Education: Empowering Individuals and Families
- Ethical Issues in Genetic Research: Privacy and Informed Consent
- Pharmacogenomics: Tailoring Drug Therapies to Individual Genotypes
- Gene-Environment Interactions in Disease Risk: Unraveling Complexities
Public Health Ethics
- Informed Consent in Public Health Research: Current Practices
- Ethical Challenges in Global Health Research: Balancing Priorities
- Confidentiality in Public Health Reporting: Striking the Right Balance
- Research with Vulnerable Populations: Ethical Considerations
- Ethical Implications of Emerging Technologies in Healthcare
Health Communication
- The Role of Media in Shaping Public Health Perceptions
- Health Literacy Interventions: Improving Understanding of Health Information
- Social Media Campaigns for Public Health Promotion: Best Practices
- Tailoring Health Messages for Diverse Audiences: Cultural Competency
- Risk Communication in Public Health Emergencies: Lessons Learned
Nutrigenomics
- Personalized Nutrition Plans based on Genetic Makeup
- Impact of Nutrigenomics on Chronic Disease Prevention
- Ethical Considerations in Nutrigenomics Research
- Public Perceptions of Nutrigenomic Testing: A Qualitative Study
- Integrating Nutrigenomics into Public Health Policies
Public Health and Artificial Intelligence
- Predictive Analytics in Disease Surveillance: Harnessing AI for Early Detection
- Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Health Decision Support Systems
- Machine Learning in Epidemiology: Predicting Disease Outbreaks
- Natural Language Processing in Public Health: Text Mining for Insights
- Bias in AI Algorithms: Implications for Health Equity
Health Disparities in Aging
- Geriatric Health Disparities: Bridging the Gap in Elderly Care
- Ageism in Healthcare: Addressing Stereotypes and Discrimination
- Social Isolation and Health Consequences in Aging Populations
- Access to Palliative Care for Older Adults: A Global Perspective
- Alzheimer’s Disease and Ethnic Disparities in Diagnosis and Treatment
- Loneliness and Mental Health in the Elderly: Interventions and Support
Research Methodologies in Public Health
Public health research employs various methodologies, including quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods approaches. Each method brings its own strengths to the research process, allowing researchers to gain a comprehensive understanding of the complex issues they investigate.
Community-based participatory research is another valuable approach, emphasizing collaboration with communities to address their specific health concerns.
Challenges and Opportunities in Public Health Research
While public health research is immensely rewarding, it comes with its own set of challenges. Funding constraints, ethical dilemmas, the need for interdisciplinary collaboration, and the integration of technology pose both obstacles and opportunities.
Researchers must navigate these challenges to ensure their work has a meaningful impact on public health.
In conclusion, public health research topics are diverse and dynamic, reflecting the complex nature of the field. As researchers embark on their journeys, they must carefully consider the relevance, impact, and ethical implications of their chosen topics.
The collaborative and interdisciplinary nature of public health research positions it as a powerful tool in addressing the health challenges of our time. By exploring the depths of these topics, researchers contribute to the collective effort to build healthier and more equitable communities.
As we move forward, a continued exploration of relevant public health research topics is essential for shaping the future of healthcare and improving the well-being of populations worldwide.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
- Career Center
- Member Login
Transformative Research to Inform a High-Value Equitable Health Care System
In this blog post, the third in a series on AcademyHealth’s collaborative effort to develop a research agenda for high-value, equitable care, Kevin Fiscella and Deniz Naghibi, authors of the accompanying literature review, share their thoughts and reflections on what is needed for attaining a high-value, equitable health care system.
Why the U.S. Health Care System Lags Behind: A Call for Equitable, High-Value Care
The U.S. trails other wealthy nations in health care value. Compared to its peers, the U.S. faces higher health care disparities , avoidable hospitalizations, maternal morbidity and mortality, and a shorter life expectancy, all while incurring the world’s highest health care costs. U.S. health care delivers suboptimal value and equity.
Understanding Health Care Value and Equity
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services defines health care equity as “ensuring everyone has a fair and just opportunity to attain their optimal health, regardless of race, ethnicity, disability, sexual orientation, gender identity, socioeconomic status, geography, or other factors affecting access to care and health outcomes.” Patients experience equity based on perceived fairness in care processes and outcomes. Health care value and equity are inextricably intertwined, representing cornerstone s of high-value, equitable care.
AcademyHealth, funded by The Donaghue Foundation, assembled a diverse multistakeholder group to develop a research agenda toward achieving high-value, equitable care. The group developed a driver model to guide the assessment of evidence and gaps in the evidence. The first of the five drivers (listed below) is a “Fair and Just Culture of Whole-Person Health for All.” The summary report on the research agenda and drivers can be accessed here .
Key Drivers for Achieving High-Value, Equitable Care:
- A Fair and Just Culture of Whole-Person Health for All: The health care system is aligned to provide holistic care that addresses patients’ overall health and wellbeing
- Care That is Accessible to All Patients: All patients are able to receive the care they need.
- Health System Centered Around Primary Care: Primary care serves a key role in providing continuous and coordinated care within the broader health system
- Adequate Health System Capacity to Deliver Care: Health care organizations have appropriate policies, technologies, staffing and other resources to support patient needs.
- Health System Accountability for Outcomes: Health care organizations are held accountable to policies, payers, communities and patients for health outcomes.
A Fair and Just Culture of Whole-Person Health for All
Seventy-five years ago, the World Health Organization expanded the concept of health beyond a biomedical definition to include physical, mental, and social well-being. Yet, the biomedical “cultural imperative” persists today with health care payment based on the presence of disease, the performance of procedures, and treatment with drugs and devices. It reinforces an inequitable, often dehumanizing commodity-based health care system that fails to enable individuals, families, and communities to optimize their health and well-being.
A just, whole health model addresses these deficiencies . It is respectful and collaborative, centering care around what matters to the person/family, allowing investment in people’s capacity for healing and health. This model offers enablement for wellness, health optimization, disease management, and promotion of well-being. The word “culture” emphasizes that this health care transformation requires a culture change. The word “just” signals the critical role of equity in supporting whole health across the health care continuum from prevention, treatment, and disease management to end-of-life care. Achieving this transformation requires progress in the four other drivers. By integrating these elements, the whole health model aims to create a high-value, equitable health care system that rectifies current inequities and inefficiencies.
Research to Inform Novel Health Care Models
Research is needed to inform operationalization of these five drivers. This requires substantial investment in pragmatic research designed to demonstrate real-world generalizability , in addition to major investment in implementation research designed to promote the uptake and sustainability of high-impact, evidence-based interventions, including those that address equity . Research on optimal, equitable strategies for enabling people, families, and communities to live healthier lives and delay disease onset is foundational to improving population health, equity, and minimizing the costs of preventable disease and disparities in disease incidence. Access is a multidimensional construct that includes accommodations for affordability, distance, physical accessibility, language, and culture. Research is needed on addressing all dimensions in addition to fair and equitable access for those without insurance. Research on the design, implementation, and sustainment of high-quality, high-equity primary care models is lacking underscoring the need for research in this area . Addressing capacity for a high-value equitable system requires identifying core resources needed for an high-value, equitable system. One approach is demonstration models built from the ground up based on global payments that offer the flexibility for redesign. Accountability for outcomes requires clarifying and operationalizing core outcomes related to whole health, i.e. non-traditional quality measures, e.g. health outcomes including improved functioning or proxy measures for health such as the Life’s Essential 8 , well-being , and community health . The development of reliable, actionable whole health accountability measures is essential to progress towards a high-value equitable system.
Novel Research Partnerships
Three transformative changes in research partnerships are needed. First, existing funders must generate the evidence to inform new models . Second, much greater coordination between health systems and payers is needed in conducting pragmatic research including clinical trials . Third, equitable, sustainable models of research must be deployed, engaging communities in the entire process of designing, implementing, and evaluating models that address community-identified health problems . These fundamental changes involving the “what” and “how” of research are vital to health care transformation.
Read the first and second blog posts in this five-part series.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Global Health Research Topics
Subscribe to Fogarty's Global Health Matters newsletter , and weekly funding news for global health researchers .

The Fogarty International Center and its NIH partners invest in research on a variety of topics vital to global health. For each of these global health research topics, find an in-depth collection of news, resources and funding from Fogarty, the NIH, other U.S. government agencies, nongovernmental organizations and others.
- Chronic noncommunicable diseases (NCDs)
- Climate change
- Deafness and other communication disorders
- Diversity, equity, inclusion, and accessibility
- Eye disease, vision health and blindness
- Global health security
- Household air pollution
- Implementation science
- Infectious diseases
- Coronaviruses
- Ebola virus disease
- Tuberculosis (TB)
- Vector-borne diseases (malaria, dengue, Zika, etc.)
- Maternal and child health
- Mentoring and mentorship training
- Mobile health (mHealth)
- Neurological and mental disorders and diseases
- Oral and dental health
- Trauma and injury
- Tobacco control
- Women’s leadership in global health research
Health Topic Information
- NIH Health Topics
- MedlinePlus Health Topics
- Diseases and Conditions from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Updated January 3, 2024
Loading metrics
Open Access
Policy Forum
Policy Forum articles provide a platform for health policy makers from around the world to discuss the challenges and opportunities in improving health care to their constituencies.
See all article types »
Building the Field of Health Policy and Systems Research: Framing the Questions
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Public Health Foundation of India, New Delhi, India
Affiliations School of Public Health and Family Medicine, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, Department of Global Health and Development, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London, United Kingdom
Affiliation Ghana Health Service/University of Ghana School of Public Health, Accra, Ghana
Affiliation Department of Global Health and Development, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London, United Kingdom
Affiliation School of Public Health, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda
Affiliation Health Systems Programme, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland, United States of America
- Kabir Sheikh,
- Lucy Gilson,
- Irene Akua Agyepong,
- Kara Hanson,
- Freddie Ssengooba,
- Sara Bennett

Published: August 16, 2011
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001073
- Reader Comments
Citation: Sheikh K, Gilson L, Agyepong IA, Hanson K, Ssengooba F, Bennett S (2011) Building the Field of Health Policy and Systems Research: Framing the Questions. PLoS Med 8(8): e1001073. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001073
Copyright: © 2011 Sheikh et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Funding: No specific funding was received for writing this article.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Abbreviations: HPSR, Health Policy and Systems Research; LMIC, low- and middle-income country
Provenance: Commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
PLoS Medicine Series on HPSR
Following the First Global Symposium on Health Systems Research in Montreux in November 2010, PLoS Medicine commissioned three articles on the state-of-the-art in Health Policy and Systems Research (HPSR). Three Policy Forum articles, authored by a diverse group of global health academics, critically examine the current challenges to the field and lay out what is needed to build capacity in HPSR and support local policy development and health systems strengthening, especially in low- and middle-income countries.
Paper 1 . Kabir Sheikh and colleagues. Building the Field of Health Policy and Systems Research: Framing the Questions.
Paper 2 . Lucy Gilson and colleagues. Building the Field of Health Policy and Systems Research: Social Science Matters.
Paper 3 . Sara Bennett and colleagues. Building the Field of Health Policy and Systems Research: An Agenda for Action.
Summary Points
- This is the first of a series of three papers addressing the current challenges and opportunities for the development of Health Policy and Systems Research (HPSR). HPSR is a multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary field identified by the topics and scope of questions asked rather than by methodology. The focus of discussion is HPSR in low- and middle-income countries.
- Topics of research in HPSR include international, national, and local health systems and their interconnectivities, and policies made and implemented at all levels of the health system. Research questions in HPSR vary by the level of analysis (macro, meso, and micro) and intent of the question (normative/evaluative or exploratory/explanatory).
- Current heightened attention on HPSR contains significant opportunities, but also threats in the form of certain focus areas and questions being privileged over others; “disciplinary capture” of the field by the dominant health research traditions; and premature and inappropriately narrow definitions.
- We call for greater attention to fundamental, exploratory, and explanatory types of HPSR; to the significance of the field for societal and national development, necessitating HPSR capacity building in low- and middle-income countries; and for greater literacy and application of a wide spectrum of methodologies.
Introduction
The field of Health Policy and Systems Research (HPSR) is currently experiencing an unprecedented level of interest. The First Global Symposium on Health Systems Research, held in Montreux, Switzerland, in November 2010, is the most recent of a succession of conferences and task force deliberations that have spun off a series of debates about the nature of the field and the future directions it should take. Establishing the identity and terrain of HPSR is part of these debates, which is made difficult by the fact that it is an essentially multidisciplinary field delimited not by methodology but by the topic and scope of research questions asked. In this paper, the first of a series of three addressing the current challenges and opportunities for the development of HPSR, we introduce and map the types of research questions that it has addressed over its natural course of evolution, analyze the nature of current heightened attention, and highlight emerging opportunities and challenges for the development of the field.
We use the extended term Health Policy and Systems Research for a field that is often referred to simply as Health Systems Research. For us, the broader term better captures the terrain of work it encompasses because it explicitly identifies the interconnections between policy and systems, and highlights the social and political nature of the field. The geographical focus of our concern is low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) [1] , but we suggest that our approach also has value for high-income countries. Our understanding of the evolution of HPSR draws primarily from the English language literature, which we acknowledge as a limitation. However, this reflects global discussion about the field, which has tended to neglect literature in other languages.
Evolution of a Question-Driven Field
Compared to other health research traditions, HPSR has a short but eclectic history. Many of the researchers who have led its development have brought social science perspectives, including health economics, sociology, political science, and anthropology, complementing the contributions of individuals and institutions engaged in delivering health services. A rearview look at these diverse antecedents reveals that HPSR has taken form from, and continues to be shaped by, questions bubbling up from the field—whether those asked by curious social scientists and observers drawn to the complexity of health systems and seeking to support change within them, or by public health specialists and health systems actors impelled to resolve practical concerns of service delivery. The state of HPSR in terms of methodological sophistication and advances results both from the independent contributions of discrete traditions of enquiry, as well as from the mixing of disciplinary influences—it is simultaneously, therefore, a multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary field.
Focus Areas in HPSR
Figure 1 illustrates how understanding of subjects of inquiry in HPSR varies depending on the perspective taken [2] . Health policy is commonly seen as the formal written documents, rules, and guidelines that present policy makers' decisions about what actions are deemed legitimate and necessary to strengthen the health system and improve health. Increasingly, however, it has been understood to encompass, importantly, the processes of decision-making at all levels of the health system and the wider influences that underpin the prioritisation of policy issues, the formulation of policy, the processes of bringing them alive in practice, and their evaluation [3] .
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001073.g001
Definitions of health systems, meanwhile, have been based mainly on their utility in the achievement of health outcomes. The World Health Organization (WHO) building blocks approach is one such popular classification, which conceptualizes health systems in the functional or instrumental terms of its constituent “hardware”—finance, medical products, information systems, levels and types of human resources, forms of service delivery, and governance understood as organizational structures and legislation, for example. [4] . It also recognises that the system encompasses both the suppliers of policy, services, and interventions, and the communities and households intended to benefit from them who, as citizens, also play important roles in policy change. However, in addition to these concrete and tangible expressions of health systems, the “software”—by which we mean the ideas and interests, values and norms, and affinities and power that guide actions and underpin the relationships among system actors and elements—are also critical to overall health systems performance. Alternative formulations of complex health systems have been influenced by economic theories of markets and political institutionalism, drawing attention to non-linear and dynamic relationships between different parts of health systems, and to the role of software and its interplay with the visible and quantifiable hardware of systems [5] , [6] . Finally, the influence of discursive and critical theory, through contributions from policy analysis and sociology, have brought an emerging recognition that health systems and policies are artifices of human creation, embedded in social and political reality and shaped by particular, culturally determined ways of framing problems and solutions [7] , [8] . Acknowledgement of these influences was another reason for our choice of field name, and has radical implications for research, and also for how we envision change in systems.
International, national, subnational (provincial), and local arenas, as well as their respective intersections, are each equally part of this broader conception of the constructed reality of health systems, with the local arena encompassing not only delivery of services, but also the worlds of health providers; activities of provision, protection, and promotion of health in local communities and households; and systems of local health governance.
A Typology of Questions
The range of questions encompassed by HPSR is broad. In the first place, there are different levels of analysis—macro-level analysis analyzes the architecture and oversight of systems, meso-level analysis focuses on the functioning of organizations and systemic interventions, and micro-level analysis considers the roles of individuals involved in activities of health provision, utilization, and governance, and how systems respectively shape and are shaped by their decisions and behaviour. Research questions can also be classified by their intent , which may broadly be seen to be either 1) normative/evaluative or 2) exploratory/explanatory in nature [9] . Table 1 maps types of questions, with indicative examples, according to the level and intent of analysis—this may be seen as a step towards constructing a broad church (or mosque, or temple) for HPSR.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001073.t001
The New Interest in HPSR
The recent upsurge of interest in HPSR, whilst partly a culmination of the efforts of earlier generations of researchers, owes much to recognition of its importance for the success of health interventions and programmes, and the changing macroeconomic environment of international health. As funding for health scaled up during the period 2000–2008, it became evident that Millennium Development Goal targets would not be achieved due to weak health systems. This catalyzed interest in the health systems field by international alliances and donors, as well as a nascent advocacy movement, partly synergistic also with HIV/AIDS advocacy. Specific departments within international organizations, such as the Health Systems and Services cluster at WHO, were established and new research organizations focusing on health systems research, such as the Alliance for Health Policy and Systems Research and the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, emerged. During the past decade a series of conferences and task forces on health research, including the International Conference on Health Research for Development, Bangkok, 2000, and ministerial meetings in Mexico City in 2004 and Bamako in 2008, had a strong focus on practical, operational questions, and this was frequently framed as health systems research. In addition to these global trends, innovative health reforms in emerging economies such as Brazil, China, India, and Thailand have created enthusiasm around the scope for system-level interventions.
The upsurge in interest is a reflection of the wide-ranging relevance of HPSR, as well as a commentary on the overdue need for the elevation of this research field to the stature of the dominant traditions of health research. There are numerous potential benefits of the current concern, for the future of the field:
- New insights into key problems and focus areas, particularly resulting from the participation of actors representing the clinical and epidemiological sciences, and from reflection on operational and service delivery experiences.
- Opportunities for development of a range of new research methodologies drawing from diverse disciplinary perspectives.
- Expansion of funding platforms and increased funding for HPSR in LMIC contexts.
However, the combination of heightened attention in a short span of time with the differing interests of involved actors has altered how HPSR is perceived and framed in the present day. In itself this presents significant threats for the balanced and holistic development of the field—three of the most important threats are discussed here.
Skewed Balance in Focus Areas and Questions
HPSR has previously played an important role in exploring the societal relevance and purpose of systems and interventions, and helping shape systems values [10] , [11] . Another important potential function of HPSR is to examine software elements such as power and trust that have been demonstrated to be key determinants of health systems performance, and success of health policies [12] , [13] . However, the current focus of the field of research is frequently framed around the hardware of health systems, and less around its software (See Figure 1 ). This is underpinned by the dominance of the positivist paradigm of knowledge which, with its claims to value-neutrality, has led to health systems being seen primarily as vehicles for technological solutions rather than being grounded in political and social contexts with underlying power structures, interests, and interdependencies.
Secondly, particular arenas of health policy and systems remain poorly addressed. The current framing of HPSR has tended to foreground issues around the delivery of specific interventions and services (often specific programmes of disease control, and often driven by global actors and agendas) rather than the existing national and sub-national systems and institutions through which they are administered. The influence of local political cultures and practices over system performance is another critical area of neglect in HPSR—yet organizational ethos and inter-organizational relationships are key determinants of how and whether policies get implemented.
Finally, the current framing of HPSR has broadly been skewed towards short-term pragmatic and operational questions, rather than being oriented towards theoretical development. Within the predominantly normative/evaluative focus of current questions there has also been a particular emphasis on deriving generalizable solutions that can be applied internationally, rather than working towards resolving specific societal problems through engagement with national and subnational policy planners. The dominant trend of donor-driven HPSR with an emphasis on addressing operational needs could have the effect of undermining the capabilities of research and academic organizations to address more fundamental, exploratory, and explanatory questions around the character and relevance of health policies and systems in real-world social and political contexts [14] .
“Disciplinary Capture”
The stakeholders—including researchers, funders, and journal editors—who are converging on HPSR, come from diverse disciplinary backgrounds. In this plural field, probably the most significant risk to its development lies in the lack of mutual understanding and respect across the range of contributory disciplines. In HPSR, as in health research in general, the dominant group of actors (in terms of both volume and influence) are those involved in the delivery of health services (primarily medical professionals). These actors work mainly in the frame of the dominant health research traditions—including epidemiological, biomedical, and clinical research—and commonly employ a positivist paradigm of knowledge [15] .
Disciplinary capture may occur if this knowledge frame, with its attendant criteria of research quality, is superimposed on the entire field for want of a wider understanding of alternative paradigms of knowledge. The quantitative methods and measures commonly used in these dominant health research fields may be over-utilised in the service of HPSR questions, where qualitative, inductive, or participatory methods may work better. Frequently too, the rigour of HPSR is assessed with inappropriate standards, extrapolated from the dominant research traditions [15] .
Inappropriate Definitions
As HPSR is beginning to take shape from its multitude of influences, there is an undoubted and widely acknowledged need to enhance clarity and consensus on research methods, and deepen the theoretical foundations of the field. Prevailing attempts to characterize the field have broadly focused on offering definitions of HPSR, sometimes seeking to distinguish it from related areas of research [16] . It is argued that these definitional attempts have utility in guiding the allocation of global funds. However, for much the same reason, they risk constraining the understanding and natural development of the field, and may lead to the neglect and “crowding out” of particular types of HPSR that do not fit neatly into popular definitions, such as the examples of overlooked focus areas and types of questions cited above. In addition to militating against the hitherto inclusive, question-driven ethos of the field, such territorial approaches also present significant problems when definitions are inappropriately narrow or incomplete (Box 1).
Box 1. Narrow Definitions: Two Case Studies.
- Implementation Research: In the world of public policy analysis, research on implementation is a far-reaching terrain of work synonymous with the study of governance, clearly a central element of HPSR. Implementation research in this understanding is a four-decade-old field built on a wide foundation of empirical and theoretical work, propelled by vibrant debates between top-down and action-centered (or bottom-up) thinking. While top-down approaches analyze the ineffectiveness of public policies at all levels [22] , and aim to diagnose and resolve implementation deficits, action-centred theorists see implementation as a relationship between policy and action, involving negotiations and interactions in social and political contexts, and use social science research methods to understand “what actually happens, how and why” [23] . However, current definitions of Implementation Research (IR) in recent influential articles appear to overlook this entire paradigm and the extensive body of research within it [16] . IR in this interpretation focuses on the concerns of programme managers regarding the effectiveness of specific health interventions. In restricting IR to the objective of facilitating predetermined programmatic solutions, a broad terrain of understanding and research is effectively reduced to a topic area with a predominant top-down focus. The narrow enunciation of delivery of health interventions or programmes also excludes an understanding of implementation of other levels (e.g., global, sectoral, institutional) and domains of policy (e.g., health workforce, regulation, financing), each a significant area of research enquiry.
- Impact Evaluation: A related movement is the current ascendance of the field of “impact evaluation”, with its emphasis on a narrow range of “robust” methods that are believed to ensure an unbiased measure of intervention impact. This restriction on admissible study designs is also seen in Cochrane reviews of health system interventions undertaken through the Effective Practice and Organisation of Care (EPOC) group, which also holds the randomised design as the “gold standard”. Yet, such methods are often ill-suited to the evaluation of complex interventions (which would include many, if not all, health system strengthening interventions) where the causal mechanism is multifaceted and contextual factors play an important role. For instance, when there is a change in policy at the national level, there may be no obvious group against which change can be assessed, nor the opportunity to randomize units to intervention or control group. Even where it is possible to introduce variation in policy at the local level, reliance on randomised methods to rule out confounders in the measurement of impact may lead to a neglect of understanding of the specific elements of the context that are responsible for programme success or failure. For these interventions, it would seem wise to admit a wider variety of study designs for examining and interpreting programme impact, and for generating knowledge that can be generalised to other contexts.
Furthermore, LMIC health systems are also changing rapidly, and moves to delimit the field with narrow definitions may well be short-sighted. Emerging phenomena such as the changing roles of health care professionals, increasing health literacy, commercialization of health, and technological innovation—for information and communication, diagnosis, and treatment—will each pose new questions, necessitating a relatively open-ended outlook on the topics and approaches of enquiry constituting HPSR [17] – [20] .
Framing HPSR: A Balanced Agenda
HPSR owes much of its present-day prominence to its utility in supporting the effective implementation of health interventions and programmes. The key underlying assumption in this popular use of HPSR is that scientific-technical solutions for health concerns have previously been proven through epidemiological, biomedical, or clinical research, and the problem lies in actualization due to deficiencies in how the solution is administered by the health system, and necessitating enquiry into system “bottlenecks”. Consequently, in the broader schema of health research, research questions pertaining to health policy and systems have tended to occupy the position of being secondary or subsequent to the primary scientific-technical question.
It is important to recognize that HPSR does not exist only for reasons of its usefulness in addressing the constraints of specific health interventions, nor does it need to mimic the systems of knowledge generation prevalent in the dominant health research traditions. HPSR may logically be conceptualised in a complementary and equivalent , not subordinate, position to the other health research traditions in the quest for solutions to health concerns. It is a free-standing field of research with diverse, serious goals including supporting societal development and self-sufficiency of nations and communities in the long term, and examining the appropriateness of scientific-technical solutions when applied in real-world contexts [21] .
HPSR should have room for multiple foci of enquiry and types of research questions, and a wide spectrum of methodological approaches. The normative and evaluative functions of HPSR are well established, but there is also scope in HPSR for more fundamental, exploratory, and explanatory questions. Acceptance of and support for fundamental research is an important signifier of the maturation and wholeness of a field. Fundamental research has instrumental value in aiding health systems performance, and also serves long-term developmental goals. It is essential in shaping policy, and is the basis for a body of reference knowledge and a firm theoretical platform—baselines on which future researchers can build.
While the awakening of interest in HPSR contains great opportunities, we are also concerned that the disciplinary biases, premature enunciation of definitions, and the skewed balance of questions currently prioritised within HPSR weakens rather than strengthens the field, and so could undermine its potential to facilitate long-term goals of societal development. The practical challenges ahead, particularly as we seek to build capacity for HPSR in LMICs, include balanced growth and promoting wider literacy of the inherent diversity and varied potentialities of the field. These questions are addressed in the two forthcoming papers in this series.
Author Contributions
Wrote the first draft of the manuscript: KS LG IAA KH FS SB. Contributed to the writing of the manuscript: KS LG IAA KH FS SB. ICMJE criteria for authorship read and met: KS LG IAA KH FS SB. Agree with manuscript‚s results and conclusions: KS LG IAA KH FS SB.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 2. Gilson L (2011) Health systems and institutions. In: Smith R, Hanson K, editors. Health systems in low- and middle-income countries: an economic and policy perspective. Oxford: Oxford University Press. In press.
- 4. World Health Organization (2007) Everybody's business. Strengthening health systems to improve health outcomes: WHO's framework for action. Geneva: WHO.
- 6. De Savigny D, Adam T (2009) Systems thinking for health systems strengthening. Geneva: World Health Organization.
- 7. Illich I (2000) Limits to medicine: medical nemesis, the expropriation of health. London: Marion Boyars.
- 9. Thomas A, Chataway J, Wuyts M, editors. (1998) Finding out fast: investigative skills for policy and development. London: Thousand Oaks.
- 17. Sheikh K, George A (2010) India's health providers – diverse frontiers, disparate fortunes. In: Sheikh K, George A, editors. Health providers in India: on the frontlines of change. New Delhi: Routledge. pp. 1–13.
- 19. Mackintosh M, Koivusalo M, editors. (2005) Commercialization of health care: global and local dynamics and policy responses. Basingstoke, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
- 22. Pressman JL, Wildavsky AB (1973) Implementation: how great expectations in Washington are dashed in Oakland; or, Why it's amazing that Federal programs work at all, this being a saga of the Economic Development Administration as told by two sympathetic observers who seek to build morals on a foundation of ruined hopes. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- 23. Barrett S, Fudge C (1981) Policy and action: essays on the implementation of public policy. London: Methuen.
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Browse content in Art
- History of Art
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- History by Period
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Regional and National History
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Language Evolution
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Browse content in Religion
- Christianity
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Company and Commercial Law
- Comparative Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Financial Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Legal System and Practice
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Anaesthetics
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Forensic Medicine
- History of Medicine
- Medical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
Occupational Medicine
- Paediatrics
- Browse content in Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Physical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Browse content in Computing
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Environmental Sustainability
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Analysis
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Classical Mechanics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Browse content in Psychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Health Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Human Evolution
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Schools Studies
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Environment
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Economic Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Security Studies
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Research and Information
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Browse content in Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Migration Studies
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Journals A to Z
- Books on Oxford Academic
What are the trending topics in Public Health and related disciplines?
You can identify some of the most discussed and influential topics with the help of Altmetric attention scores, which take into account several outlets including social media, news articles, and policy documents.
Drawing from a selection of Public Health and Medicine journals, we have compiled a list of the articles that have been mentioned the most over the past few months.
Discover the articles that are trending right now, and catch up on current topics in Public Health and related disciplines. We will update our collection every few weeks; come back to this page to be on top of the latest conversations in Public Health and Medicine. Previously featured articles are listed here .
You can also sign up for e-alerts to make sure you never miss the latest research from our journals.
*Last updated October 2021*
Age and Ageing
Alcohol and alcoholism, american journal of epidemiology, annals of work exposures and health, epidemiologic reviews, european journal of public health, family practice, health education research, health policy and planning, health promotion international, international health, international journal of epidemiology, international journal for quality in health care, journal of public health, journal of travel medicine, journal of tropical pediatrics, nicotine & tobacco research, transactions of the royal society of tropical medicine & hygiene.
There is moderate-certainty evidence that behaviour change interventions are associated with increased physical activity levels among older hospitalised patients.
This study from Canada found that one in three young adults with ADHD had a lifetime alcohol use disorder, and that young adults with ADHD were also three times more likely to develop a substance use disorder. Targeted outreach and interventions for this extremely vulnerable population are warranted.
According to this study, resuming evictions in summer 2020 was associated with increased COVID-19 incidence and mortality in US states, with an estimated 433,700 excess cases and 10,700 excess deaths. Explore more research on COVID-19 in a curated collection from the AJE: https://academic.oup.com/aje/pages/covid-19
The British Occupational Hygiene Society (BOHS) developed a control banding matrix for employers and others to help assess the risks of COVID-19 infection, and calls for further work to validate the reliability of the tool. Browse the Annals' collection on occupational hygiene for virus protection: https://academic.oup.com/annweh/pages/covid-19
In 1777, George Washington ordered a mandatory inoculation program for his troops, in what would become the first mass immunization mandate in the US. This archival article discussess and contextualizes immunization practices for US Armed Forces.
Responding to concerns that that face mask use could elicit a false sense of security and lead to riskier behaviours, this study from Denmark found that mask use overall correlated positively with protective behaviours.
While medical practice is often undermined by subsequent investigation, randomized trials relevant to primary care generally hold up over time.
This study shows the potential for using social media influencers to inspire positive engagements on pro-vaccine health messaging. For more content on accurate information's importance for public health, browse the latest article collection from HER: https://academic.oup.com/her/pages/covid-19
Current emergency response planning does not have adequate coverage to maintain health systems functionality for essential health service delivery alongside emergency-specific interventions and healthcare. The findings from this study can help align health emergency planning with broader population health needs.
This case study shows that that ongoing efforts are needed to improve sustainability of nutrition policy and programmes to address all diet-related diseases.
This review article outlines evidence for a range of institutional measures and behaviour-change measures, and highlights research and knowledge gaps.
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered significant mortality increases in 2020 of a magnitude not witnessed since World War II in Western Europe or the breakup of the Soviet Union in Eastern Europe.
The authors propose an update to the Equator’s Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ) checklist, with the aim of enhancing inclusivity.
This study confirms previous findings on a low risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection. If confirmed, these findings suggest that more targeted restriction policies can be applied to the subjects that recovered after a first infection. Read highly cited papers on COVID-19 from the Journal of Public Health: https://academic.oup.com/jpubhealth/pages/covid-19
Given the Delta variant's high reproductive number associated with higher transmissibility, in a context of globally still low vaccine coverage rates and lower vaccine effectiveness, public health and social measures will need to be substantially strengthened. A high reproductive number also means that much higher vaccine coverage rates need to be achieved compared to the originally assumed.
Neurological complications are rare in children suffering from COVID-19. Still, these children are at risk of developing seizures and encephalopathy, more in those suffering from severe illness.
The researchers examined support for and perceived impact of e-cigarette sales restrictions. Findings suggest that bans on flavored vape products could have a positive impact on lower-risk users, but that other young adult user subgroups may not experience benefit.
An editorial from the earlier stages of the pandemic highlights the importance of properly fitted respirators for worker safety and outlines occupational hygiene measures.
Guidelines for safe mass drug administration for neglected tropical diseases were developed in a COVID-19 context; training and implementation were assessed through an observation checklist.
For more research on the impact of COVID-19 on NTDs, explore the March 2021 special issue: https://academic.oup.com/trstmh/issue/115/3
Previously featured
Age and frailty are independently associated with increased COVID-19 mortality and increased care needs in survivors: results of an international multi-centre study
Trajectories of Alcohol Use and Related Harms for Managed Alcohol Program Participants over 12 Months Compared with Local Controls: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Estimating the Effect of Social Distancing Interventions on COVID-19 in the United States
Selecting Controls for Minimizing SARS-CoV-2 Aerosol Transmission in Workplaces and Conserving Respiratory Protective Equipment Supplies
What Do We Know About the Association Between Firearm Legislation and Firearm-Related Injuries?
Denialism: what is it and how should scientists respond?
Acute cooling of the feet and the onset of common cold symptoms
The effect of falsely balanced reporting of the autism–vaccine controversy on vaccine safety perceptions and behavioral intentions
Climate change: an urgent priority for health policy and systems research
Power, control, communities and health inequalities I: theories, concepts and analytical frameworks
Research ethics in context: understanding the vulnerabilities, agency and resourcefulness of research participants living along the Thai–Myanmar border
Tobacco smoking and mortality among Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander adults in Australia
Quality and safety in the time of Coronavirus: design better, learn faster
Years of life lost associated with COVID-19 deaths in the United States
In-flight transmission of SARS-CoV-2: a review of the attack rates and available data on the efficacy of face masks
Stability of the Initial Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder by DSM-5 in Children: A Short-Term Follow-Up Study
Impact of Tobacco Smoking on the Risk of COVID-19: A Large Scale Retrospective Cohort Study
Mental health of staff working in intensive care during COVID-19
The benefits and costs of social distancing in high- and low-income countries
A classification tree to assist with routine scoring of the Clinical Frailty Scale
Recent Advances in the Potential of Positive Allosteric Modulators of the GABAB Receptor to Treat Alcohol Use Disorder
The recent oubreak of smallpox in Meschede, West Germany
Your Hair or Your Service: An Issue of Faith for Sikh Healthcare Professionals During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Emerging Infections: Pandemic Influenza
Identifying the views of adolescents in five European countries on the drivers of obesity using group model building
Novel multi-virus rapid respiratory microbiological point-of-care testing in primary care: a mixed-methods feasibility evaluation
Public health crisis in the refugee community: little change in social determinants of health preserve health disparities
In search of ‘community’: a critical review of community mental health services for women in African settings
COVID-19, a tale of two pandemics: novel coronavirus and fake news messaging
Disrupting vaccine logistics
Use of directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) to identify confounders in applied health research: review and recommendations
Measurement and monitoring patient safety in prehospital care: a systematic review
Black Lives Matter protests and COVID-19 cases: relationship in two databases
The positive impact of lockdown in Wuhan on containing the COVID-19 outbreak in China
Severe Malnutrition and Anemia Are Associated with Severe COVID in Infants
A Single-Arm, Open-Label, Pilot, and Feasibility Study of a High Nicotine Strength E-Cigarette Intervention for Smoking Cessation or Reduction for People With Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders Who Smoke Cigarettes
Healthcare workers and protection against inhalable SARS-CoV-2 aerosols
Affiliations
- Copyright © 2024
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Open access
- Published: 22 August 2018
Health policy and systems research: the future of the field
- David H. Peters ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8377-3444 1
Health Research Policy and Systems volume 16 , Article number: 84 ( 2018 ) Cite this article
16k Accesses
32 Citations
81 Altmetric
Metrics details
Health policy and systems research (HPSR) has changed considerably over the last 20 years, but its main purpose remains to inform and influence health policies and systems. Whereas goals that underpin health systems have endured – such as a focus on health equity – contexts and priorities change, research methods progress, and health organisations continue to learn and adapt, in part by using HPSR. For HPSR to remain relevant, its practitioners need to re-think how health systems are conceptualised, to keep up with rapid changes in how we diagnose and manage disease and use information, and consider factors affecting people’s health that go well beyond healthcare systems. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) represent a shifting paradigm in human development by seeking convergence across sectors. They also offer an opportunity for HPSR to play a larger role, given its pioneering work on applying systems thinking to health, its focus on health equity, and the strength of its multi-disciplinary approaches that make it a good fit for the SDG era.
Globally, population health is being challenged in different ways, from climate change and growing air pollution and toxic environmental exposure to food insecurity, massive population migration and refugee crises, to emerging and re-emerging diseases. Each of these trends reinforce each other and concentrate their harms on the most vulnerable populations. Multi-level governance, together with novel regulatory strategies and socially oriented investments, are key to successful action against many of the new challenges, with HPSR guiding their design and evolution.
The HPSR community cannot be complacent about its successful, yet short, history. Tensions remain about how different stakeholders use HPSR such as the contrast between embedding research within government institutions versus independently evaluating and holding decision-makers accountable. Such tensions are inevitable in the boundary-spanning field that HPSR has become. We should strive to enhance the influence of HPSR by staying relevant in a changing world and embracing the strength of our diversity of disciplines, the range of problems addressed, and the opportunity of the SDGs to ensure that health and social benefits are more inclusive for people within and across countries.
Peer Review reports
In 1962, Burnet, the Nobel prize-winning immunologist, wrote that the twentieth century would be witness to “ the virtual elimination of infectious disease as a significant factor in social life ” [ 1 ] – a reminder to be humble when predicting the future effects of health research. Nonetheless, the last 20 years has brought impressive change in the growth of health policy and systems research (HPSR), and the settings in which it is applied. One safe prediction is that the HPSR landscape will continue to change and grow in complexity.
The value of HPSR
The central idea behind HPSR is that research should inform and influence policies and systems to pursue health goals [ 2 ]. Health systems goals and the values that underpin them are enduring and should continue to be examined through HPSR. Contexts will change and new challenges will emerge, but research will still be needed to inform how to achieve the multiple health systems goals – improving effectiveness, equity and efficiency, expanding health services coverage, and enhancing people’s financial protection, while minimising costs and improving accountability and trust. HPSR provides the tools for Ministries of Health and other health organisations to become learning organisations, serving to lead and adapt to changes in the health sector.
Re-thinking health systems in a changing context
The changing context will also challenge how we think about health systems; HPSR should have a central role in understanding change and how to intervene. The social, political and environmental conditions for healthy living are rapidly shifting, as are expectations about the role of the state, civil society and business. Information communications and other technologies are transforming the diagnosis and management of disease, as well as the collection, analysis and sharing of individual and population health data. Additionally, there are growing population pressures due to environmental degradation, urbanisation and aging along with new threats due to emerging diseases and the failure of poorly organised market systems for health services, technologies and financial products. Each condition is both a driver of change and an effect of another; they are interdependent issues in an increasingly interconnected world.
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) represent a shifting paradigm in human development, moving from the building up of individual core sectors within countries to seeking convergence across co-influencing and co-dependent sectors. In a world where wealth inequality is escalating, the SDGs mark a shift from efforts to provide overall benefits to a nation to focusing on inclusive growth and tackling inequities as the core of development efforts. HPSR is well placed to take on these issues of the future since it has a traditional focus on understanding and addressing different types of disadvantage and inequity, taking advantage of various disciplines and approaches to address inequities, including social epidemiology, economics, participatory action research and ethics [ 3 ]. Further, HPSR has pioneered the application of systems thinking in health, providing a wide set of theories, frameworks and tools to examine and test how different elements of systems – actors, functions and their relationships – fit together to make an overall whole [ 4 ].
Efforts to strengthen health systems have been both facilitated and constrained by the dominance of the Health Systems Building Blocks model [ 5 ]. The model focuses on inputs and selected functions of a healthcare system, but was designed as a communication tool to indicate options for government investment, and not as an analytic or explanatory model of a complete health system. The building blocks model has especially neglected people (indeed the entire demand side of a health system) and institutions, the importance of dynamic linkages between stakeholders and functions in a health system, and connections between health systems and other related systems (e.g. education, economic development, ecology, etc.). To apply research to questions concerned with the linkages across sectors – as envisioned by the SDGs – it will be more important to consider the roles of people (as individuals, families, communities and larger populations) and the dynamic connections between policies and systems that affect people both inside the traditional health sector and through related sectors.
Growing challenges for HPSR
There are many new issues and evolving roles for different stakeholders in a health system, as well as novel ways in which we can study and influence health systems. Globally, population health is being challenged in different ways. Ambient air pollution in cities and indoor air pollution in rural homes have become important risk factors for chronic diseases. Food insecurity is again a critical public concern, as climate change is projected to decrease crop yields, particularly in South America, Africa, South Asia and Australia, while contributing to increased food price volatility [ 6 ]. Poor nutrition, exposure to environmental toxins and a resurgence of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue, are all consequences of environmental degradation. The poor are especially vulnerable, as they are most exposed to the direct and indirect shocks of environmental degradation, are more vulnerable because they lose relatively more wealth, and are less resilient because they do not have the financial and social safety nets required to manage them and recover [ 7 ].
The growing phenomenon of antimicrobial resistance is another major threat to global health that needs to be tackled in both the health and agricultural sectors at local, national and global levels. The failure to develop new antimicrobials or ensure equitable access to existing antibiotics, while counterfeit and substandard drugs flourish, represent major market failures [ 8 , 9 ]. New regulatory strategies, socially oriented investment and a realignment of incentives are needed at all levels. Multi-level governance is the key for successful action in containment strategies, supported by HPSR to assess how well they work and guide their evolution.
Population migration is another major social, political and health systems challenge. One billion individuals are now on the move globally, one-quarter of whom are crossing national borders. The estimated refugee population reached an unprecedented 19.6 million individuals worldwide in 2015, half of whom are children [ 10 ]. Health systems are at the forefront of the response to the ongoing crisis facing refugees and other migrants, both at first point of contact and later during resettlement. There is a need to develop more effective approaches that respond to the health needs of displaced populations, yet the evidence base regarding which interventions are effective is quite weak.
Opportunities for HPSR
HPSR has developed as a boundary-spanning field, not only crossing disciplinary lines, but also linking stakeholders with very different roles (e.g. policy-makers, health practitioners, researchers, civil society leaders, the media). As such, HPSR should continue to influence policy both within and across countries. HPSR has served in each of six types of research utilisation as described by Weiss [ 11 ], though in recent years it has tended to be used most directly in a problem-solving model (to facilitate decisions by policy-makers and managers) or to otherwise contribute to complex policy-making through an interactive model of health research. However, there is also a growing tension between new approaches that promote embedded and implementer-led research, which pursues problem-solving from ‘within’ [ 12 , 13 ] and research that takes an external perspective, seeking to independently evaluate policy effects, identify neglected problems or hold decision-makers accountable [ 14 , 15 ]. HPSR should be used to serve each of these perspectives, and not become captive to a single approach.
Encouraging diversity and equity has become part of the shared values of many practitioners and users of HPSR, crossing contexts and types of research utilisation. For example, the Alliance for Health Policy and Systems Research, along with many partners working in global health, have expressed a very clear set of values – “ to address problems of inequity, poverty and disadvantage ” [ 16 ] and to support partnerships and collaboration on an inclusive and participatory basis.
However, this set of values has come into conflict with recent policy and electoral decisions made around the world over the last few years. There has been a rise in electoral trends that seem to undermine the values of global citizenship and even the role of evidence in decision-making. Recent political events around the world, including in the Americas, Europe, Africa, and Asia, suggest that massive numbers of people are dissatisfied with incumbent policy-makers and their policies, and are voting for the politics of division. In contrast, HPSR can be a vehicle to learn from and promote the diversity of cultures, building of local capabilities and forging of international cooperation. The promise of research and its application to policy and public health practice can help people to overcome the divisions of nationalism, race, class, wealth and other obstacles to social justice and health equity.
Conclusions
This is a time when the technical skills, knowledge contributions and historical values of HPSR are needed more than ever. We need a HPSR agenda to better understand and meet peoples’ expectations, and to sharpen our science of communication, both issues within the remit of HPSR. However, the HPSR community cannot be complacent about its successful but short-lived history. We should strive to enhance the influence of HPSR by staying relevant in a changing world, embracing the strength of our diversity of disciplines, the range of problems addressed, and the opportunity of the SDGs to ensure that health and social benefits are more inclusive for people within and across countries. If we are to have policies and interventions that promote justice and good health whilst being grounded in evidence, then we must ensure that our thinking and practice of HPSR help us rise to these challenges.
Abbreviations
health policy and systems research
- Sustainable Development Goals
Burnet FM. Natural History of Infectious Disease. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1962.
Google Scholar
Alliance for Health Policy and Systems Research. World Report on Health Policy and Systems Research. Geneva: WHO; 2017.
Gilson L, editor. Health Policy and Systems Research: A Methodology Reader. Geneva: Alliance for Health Policy and Systems Research, World Health Organization; 2012.
Peters DH. The application of systems thinking in health: why use systems thinking? Health Res Policy Syst. 2014;12:51.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
World Health Organization. Everybody Business: Strengthening Health Systems to Improve Health Outcomes - WHO’s Framework for Action. Geneva: WHO; 2007.
Havlik P, Valin H, Gusti M, Schmid E, Leclère D, Forsell N, Herrero M, Khabarov N, Mosnier A, Cantele M, Obersteiner M. Climate change impacts and mitigation in the developing world: an integrated assessment of the agriculture and forestry sectors. Policy Research Working Paper No. WPS 7477. 2015. http://pure.iiasa.ac.at/11657 . Accessed 14 Aug 2018.
Hallegatte S, Bangalore M, Bonzanigo L, Fay M, Kane T, Narloch U, Rozenberg J, Treguer D, Vogt-Schilb A. Shock Waves: Managing the Impacts of Climate Change on Poverty. Climate Change and Development. Washington, DC: World Bank; 2016.
Cars O, Högberg LD, Murray M, Nordberg O, Sivaraman S, Lundborg CS, So AD, Tomson G. Meeting the challenge of antibiotic resistance. BMJ. 2008;337:a1438.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Peters DH, Bloom G. Developing world: bring order to unregulated health markets. Nature. 2012;487(7406):163–5.
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
United Nations Population Division. International Migrant Stock 2015. 2016. http://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/migration/data/estimates2/estimates15.shtml . Accessed 14 Aug 2018.
Weiss CH. The many meanings of research utilization. Public Adm Rev. 1979;39:426–31.
Article Google Scholar
MacGregor H, Bloom G. Health systems research in a complex and rapidly changing context: ethical implications of major health systems change at scale. Dev World Bioeth. 2016;16(3):158–67.
Tran N, Langlois EV, Reveiz L, Varallyay I, Elias V, Mancuso A, et al. Embedding research to improve program implementation in Latin America and the Caribbean. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2017;41:e75.
PubMed Google Scholar
Gaventa J, McGee R. The impact of transparency and accountability initiatives. Dev Policy Rev. 2013;31:s3–s28. https://doi.org/10.1111/dpr.12017 .
World Health Organization. Monitoring, Evaluation and Review of National Health Strategies: A Country-led Platform for Information and Accountability. Geneva: WHO; 2011.
Alliance for Health Policy and Systems Research. Investing in Knowledge for Resilient Health Systems: Strategic Plan 2016–2020. Geneva: WHO; 2016.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of International Health, Johns Hopkins University, Bloomberg School of Public Health, 615 N. Wolfe St, Suite E-8527, Baltimore, MD, 21205, United States of America
David H. Peters
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
DP was sole author. The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to David H. Peters .

Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethics approval was not required for this Commentary, as it does not involve human subjects research.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author declares that he has no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Peters, D.H. Health policy and systems research: the future of the field. Health Res Policy Sys 16 , 84 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-018-0359-0
Download citation
Received : 24 January 2018
Accepted : 12 March 2018
Published : 22 August 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-018-0359-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Health policy
- Health systems
- Health systems research
Health Research Policy and Systems
ISSN: 1478-4505
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Fact sheets
- Facts in pictures
Publications
- Questions and answers
- Tools and toolkits
- Endometriosis
- Excessive heat
- Mental disorders
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- All countries
- Eastern Mediterranean
- South-East Asia
- Western Pacific
- Data by country
- Country presence
- Country strengthening
- Country cooperation strategies
- News releases
- Feature stories
- Press conferences
- Commentaries
- Photo library
- Afghanistan
- Cholera
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- Greater Horn of Africa
- Israel and occupied Palestinian territory
- Disease Outbreak News
- Situation reports
- Weekly Epidemiological Record
- Surveillance
- Health emergency appeal
- International Health Regulations
- Independent Oversight and Advisory Committee
- Classifications
- Data collections
- Global Health Observatory
- Global Health Estimates
- Mortality Database
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Health Inequality Monitor
- Global Progress
- World Health Statistics
- Partnerships
- Committees and advisory groups
- Collaborating centres
- Technical teams
- Organizational structure
- Initiatives
- General Programme of Work
- WHO Academy
- Investment in WHO
- WHO Foundation
- External audit
- Financial statements
- Internal audit and investigations
- Programme Budget
- Results reports
- Governing bodies
- World Health Assembly
- Executive Board
- Member States Portal
- Science Division /
- Research for health
Research for Health
WHO’s goal: Forward looking and prioritized global health research
Research for health is a global endeavour, and WHO has a unique role to play in ensuring that these efforts can help improve health for all.
WHO provides leadership, calling on the wider scientific community to engage behind global health concerns. This is based on a deep understanding of the needs of countries, and rigorous assessment by international experts.
WHO has three key objectives to promote forward-looking and prioritized global health research:

Anticipating scientific, technological, and epidemiological shifts
To stay on top of scientific and technological advancements and epidemiological trends, WHO must anticipate new trends, technologies, research, and discoveries in medical and public health.
Through continuous, rigorous, and systematic horizon scanning, the Science Division assesses and identifies emerging issues, for early identification of potential health benefits or threats. It actively prospects for scientific and technological innovations that could change the equation on advancing health.
Science in action: the WHO Advisory Committee on Developing Global Standards for Governance and Oversight of Human Genome Editing
This committee examines the scientific, ethical, social, and legal challenges associated with human genome editing, and makes recommendations on the ethical framework for research and application of this technology.

Setting a global research agenda to address gaps, emerging areas, and country priorities
Truly useful innovations are not simply new; they are designed explicitly with the needs of the user in mind. By analyzing gaps, inequities, emerging areas and country priorities, the WHO research agenda anticipates the complex issues affecting people’s health and supports the discovery of innovative solutions to address them.
Science in action: R&D Blueprint for dementia research.
In 2017, the World Health Assembly adopted a Global Action Plan on the Public Health Response to Dementia. A key component of this plan was a call to action for research and innovation. To move this forward, the Science Division is developing an R&D Blueprint for dementia research.

Strengthening confidence in science
The Science Division supports countries in developing their scientific expertise and research capacities and facilitating the development of new and innovative research methodologies. This will improve understanding of the determinants of health, health systems, and the transformative potential of innovations in health.
Science in action: WHO Science Council
At WHO, Research for Health covers five key functions , which are integrated to apply research and innovation and achieve impact for people’s health around the world.

Foresight and emerging technologies
We try to get ahead of the curve by understanding what is needed to improve health for all in the future, and where the best new ideas are emerging.
Advances in science and technology hold great promise for new ways to address global health and support healthier populations worldwide. WHO engages in horizon scanning across the science and technology landscape. It also supports countries in doing their own futures and foresight exercises to understand their future needs. The aim of foresight is to identify and connect known, new, or emerging issues that could significantly impact global health within the next two decades.
Emerging technologies offer great health opportunities but also pose potentially significant challenges. The WHO Foresight function provides ongoing monitoring of emerging technologies to spot potential risks and come up with strategies for prevention and mitigation.

Research prioritization and support, R&D optimization
We identify gaps in current research priorities, and promote and support research that can best address unmet needs.
WHO has a unique role in supporting research for health , because we can help ensure health research is directed towards the biggest unmet needs in global health. We do this by sharing upstream research information from clinical trials , and research and development pipelines , and by providing guidance for research priority setting exercises.
WHO can determine strategic public health areas and identify key research and development needs. It then produces a clear target product profile to promote research and development that will be of most benefit. By mapping existing target product profiles in the Target Product Profile Directory and developing new ones based on identified public health needs, WHO steers innovation in support of improved health for all.
Product developers seek advice from WHO on whether or not their product likely has value for public health. In this way, WHO, expedites development of health related products, including novel therapeutics, diagnostics, and repurposing existing products.
Research for Health works with researchers and innovators to ensure they are aligned with the Prequalification Team and WHO’s technical departments on the package of evidence that will be needed to secure prequalification or a WHO policy recommendation. This process informs clinical trials on life-saving medical products, technologies and processes. A coordinated scientific advice process is currently in pilot phase.

Health ethics and governance
By putting ethics at the heart of decision-making and providing guidance on governance, WHO promotes this ethos within WHO and throughout the global health community.
In addition to supporting projects conducted by WHO, we are often called upon by development partners at country level for our expertise in global health ethics. Our Health Ethics and Governance unit produces guidance and tools for Member States on ethics in research and public health. Inside and outside WHO, it also helps researchers and public health specialists navigate ethical challenges posed by their projects.

Research policy for access
The best ideas are not just the brightest, but the one that actually get implemented and make an impact. WHO provides leadership on policies in research to ensure access and scale-up.
Having the right research policy is a key step towards ensuring health research has actual impact. This means that research priorities match real-world problems. At WHO, Research for Health works to ensure that the needs of countries are clearly articulated, and then communicated to the research community.
At WHO we promote an end-to-end approach in research policy. Working with local health systems and communities is needed to better understand the delivery and uptake of new products and to achieve widespread and equitable access. WHO can help broker multinational studies, foster regulatory harmonization, and promote dialogue among all stakeholders.

Taking knowledge from evidence to impact
Through a global network for evidence-informed health policy-making and tailored country support, WHO brings together researchers, policy-makers and implementers to translate evidence into improved health policies and programmes.
Public health problems are often complex and require nuanced, context-specific solutions and tailored implementation strategies. To make a difference for patients, communities and medical professionals, reliable evidence on how to tackle a health issue needs to be synthesized, reflected in a local context, and effectively communicated between researchers and decision-makers.
Through a set of field-tested and user-friendly tools, the Evidence to Policy and Impact Unit supports countries in bridging the gap between public health research, policy, and programme. Evidence briefs for policy and rapid response mechanisms put key research findings into context and place them at the fingertips of decision-makers. Policy dialogues provide researchers, policy-makers, and partner organizations with a forum to rally behind evidence-informed policy options and effective health interventions, discuss the findings, and share their own experiences and values. Citizen engagement strategies give voice to the beliefs and perspectives of individuals and communities, upholding accountability and democratic deliberation as core principles of equitable health care.
WHO’s global Evidence-informed Policy Network (EVIPNet) is a key initiative building sustainable and resilient capacity for evidence-informed decision-making and knowledge translation with Member States and in WHO offices at country, regional and international level. With over 15 years of experience and active teams in close to 50 countries, EVIPNet has successfully strengthened national health systems and emergency response capacity around the globe. The network also forms a vivid community of practice, facilitating decentralized peer-support among members and offering a treasure trove of successful strategies in evidence-informed health policy-making.
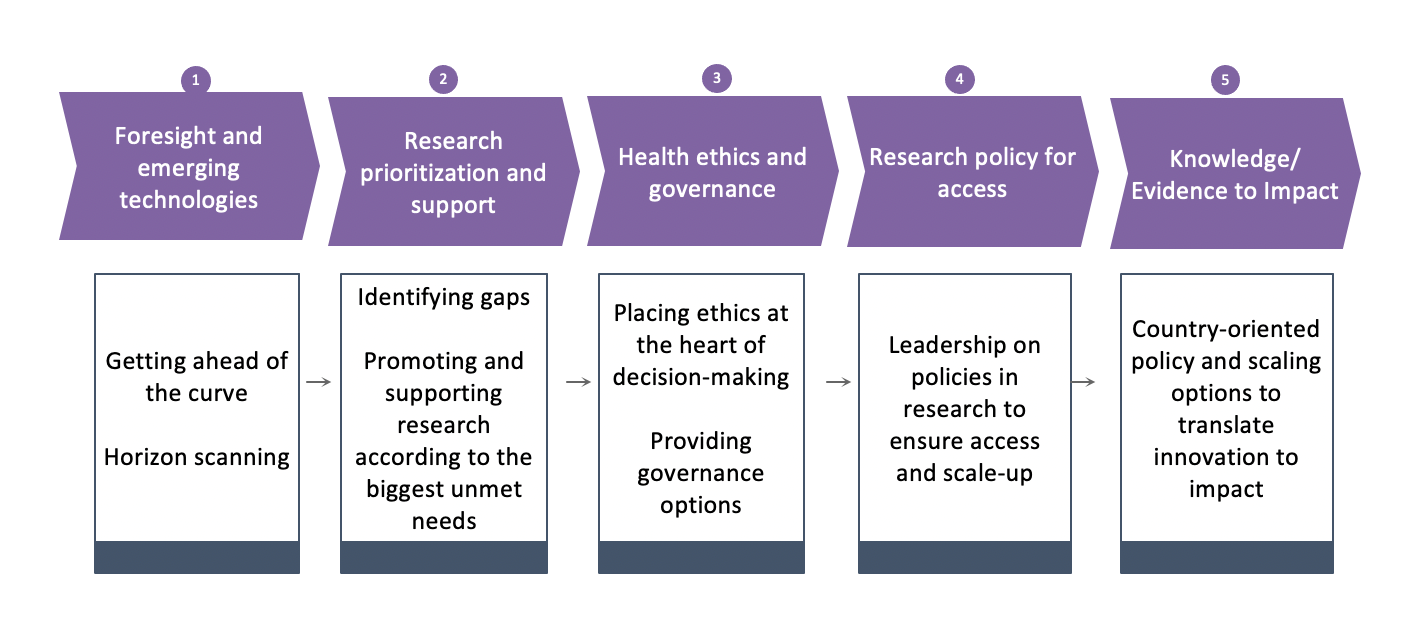
Research for Health within WHO
WHO’s Research for Health Department supports teams and units across the entire organization to establish their own research priorities . It helps people working in different parts of our global network connect the dots and create a better coordinated research response. This in turns helps keep WHO on track, ensuring that the research done within WHO is aligned with the health-related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and our own Triple Billion Targets of 1 billion more people benefitting from universal health coverage, 1 billion more people better protected from health emergencies, and 1 billion more people enjoying better health and well-being.
Research for Health: our role in the global public health research community
WHO’s technical units are just one part of a global web of research for health, encompassing academia, national and regional research bodies, product development partnerships and the private sector. WHO helps to provide global guidance for research priority setting. Our global, regional and country-level reach means we can help to clearly articulate the needs of the countries, and we are uniquely well-placed to broker multinational research efforts.
New global guidance puts forward recommendations for more effective and equitable clinical trials
Global Coalition for Evidence launched
What works to promote Evidence-Informed Decision-Making? A map of what we know
Public consultation
CLOSED - Call for Experts – Technical Advisory Group on the responsible use of the life sciences and dual-use research
Public consultation on WHO guidance for best practices for clinical trials

WHO global research priorities for sexually transmitted infections
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are widespread globally and negatively affect sexual and reproductive health. Gaps in evidence and in available...

Report of the sixth meeting of the WHO Diagnostic Technical Advisory Group for Neglected Tropical Diseases:...
The World Health Organization’s Global Neglected Tropical Diseases Programme (WHO/NTD) manages a diverse portfolio of 21 diseases and disease groups,1 ...

Protocol: using data to drive governance
This document introduces a collaboratively developed study protocol to identify what data and information is currently being collected by governments and...

Evidence generation for development of health products: a practical guide for WHO staff
This document describes the main elements that World Health Organization (WHO) technical departments should elaborate on when providing guidance on evidence...
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
The PMC website is updating on October 15, 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Health Res Policy Syst

How to strengthen a health research system: WHO’s review, whose literature and who is providing leadership?
Stephen r. hanney.
1 Health Economics Research Group, Institute of Health, Environment and Societies, Brunel University London, Uxbridge, UB8 3PH United Kingdom
2 Department of Health Policy, London School of Economics and Political Science, London, United Kingdom
Subhash Pokhrel
Teresa h. jones, annette boaz.
3 Faculty of Health, Social Care and Education, a partnership between Kingston University and St George’s, University of London, London, United Kingdom
Associated Data
The full details of the papers included in the Health Evidence Network Evidence Synthesis are provided in that report, which is cited in this paper as reference [ 30 ]. The additional analysis of papers from Health Research Policy and Systems was based on the open access publications.
Health research is important for the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals. However, there are many challenges facing health research, including securing sufficient funds, building capacity, producing research findings and using both local and global evidence, and avoiding waste. A WHO initiative addressed these challenges by developing a conceptual framework with four functions to guide the development of national health research systems. Despite some progress, more is needed before health research systems can meet their full potential of improving health systems. The WHO Regional Office for Europe commissioned an evidence synthesis of the systems-level literature. This Opinion piece considers its findings before reflecting on the vast additional literature available on the range of specific health research system functions related to the various challenges. Finally, it considers who should lead research system strengthening.
The evidence synthesis identifies two main approaches for strengthening national health research systems, namely implementing comprehensive and coherent strategies and participation in partnerships. The literature describing these approaches at the systems level also provides data on ways to strengthen each of the four functions of governance, securing financing, capacity-building, and production and use of research. Countries effectively implementing strategies include England, Ireland and Rwanda, whereas West Africa experienced effective partnerships. Recommended policy approaches for system strengthening are context specific. The vast literature on each function and the ever-growing evidence-base are illustrated by considering papers in just one key journal, Health Research Policy and Systems, and analysing the contribution of two national studies. A review of the functions of the Iranian system identifies over 200 relevant and mostly national records; an analysis of the creation of the English National Institute for Health Research describes the key leadership role played by the health department. Furthermore, WHO is playing leadership roles in helping coordinate partnerships within and across health research systems that have been attempting to tackle the COVID-19 crisis.
Conclusions
The evidence synthesis provides a firm basis for decision-making by policy-makers and research leaders looking to strengthen national health research systems within their own national context. It identifies five crucial policy approaches — conducting situation analysis, sustaining a comprehensive strategy, engaging stakeholders, evaluating impacts on health systems, and partnership participation. The vast and ever-growing additional literature could provide further perspectives, including on crucial leadership roles for health ministries.
Interest in strengthening health research systems has intensified following increasing recognition of the importance of research in achieving key goals such as universal health coverage [ 1 ] and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) [ 2 ]. However, achieving progress in health research faces many challenges, including securing sufficient funds [ 3 – 9 ], building and retaining capacity [ 3 , 7 , 10 – 14 ], producing research findings, and using both local and global evidence [ 1 , 15 – 20 ].
Chalmers and Glasziou [ 21 ] dramatically highlighted the extent of the challenges facing health research by claiming, in 2009, that even where there was funding and capacity, up to 85% of all biomedical research was wasted because it asked the wrong questions, was poorly designed, or was either not published or poorly reported, with only about 50% of studies being published in full.
Many of these challenges have long been recognised and the adoption of a systems approach advocated. In 2000, the Bangkok Declaration on Health Research for Development promoted the importance of a systems approach, following consideration of how a health research system could “be integrated with a nation’s health development plan” [ 15 ]. It suggested that establishing and strengthening an effective health research system needed coherent and coordinated health research strategies [ 15 ]. National strategies should have specific combinations of various health research system components, tailored to the country’s circumstances.
The WHO’s Knowledge for Better Health initiative involved further work on these issues [ 3 , 16 ]. The Mexico Statement on Health Research, issued in 2004 by a Ministerial Summit, called for nations to take actions to strengthen their national health research systems (NHRSs). It was endorsed in 2005 by the Fifty-eighth World Health Assembly in a resolution committing its Member States to strengthening their NHRSs as a pathway to improve their overall health system [ 22 ].
As part of the initiative, Pang et al. [ 3 ] developed a conceptual framework to guide the analysis and strengthening of health research systems, including development of a health research strategy. While this can be used for planning, monitoring and evaluation of health research systems, it did not claim to provide a precise blueprint. The framework defined a health research system as “the people, institutions, and activities whose primary purpose in relation to research is to generate high-quality knowledge that can be used to promote, restore, and/or maintain the health status of populations; it should include the mechanisms adopted to encourage the utilization of research” [ 3 ].
The framework indicates the range of constituent components and how they can best be brought together into a coherent system. It identified four main functions for an effective system, namely stewardship, financing, capacity-building (or creating and sustaining resources), and producing and using research [ 3 ]. Each function is defined by operational components and consists of one or more of a total of nine such components.
Since then, progress is evidenced by analyses of developments in individual countries, including the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) in England [ 23 – 25 ], and in repeat surveys conducted in various WHO regions, including Africa [ 4 , 26 , 27 ] and the Pan-American Health Organization (PAHO) [ 28 ]. However, as reported by those surveys and other publications, many challenges remain. For example, in February 2020 a new analysis by the WHO Global Observatory on Health R&D examined health research funding, concluding that “neglected diseases such as those on the WHO list of neglected tropical diseases remain very neglected in terms of R&D investments” [ 29 ].
Nevertheless, there are various initiatives underway, including in WHO’s Regional Office for Europe, which commissioned an evidence synthesis on the topic as part of its Action Plan to Strengthen the use of Evidence, Information and Research for Policy-making in the WHO European Region [ 18 ]. The synthesis is published in the WHO Region’s Health Evidence Network (HEN) report series and consists of a scoping review addressing the question “What is the evidence on policies, interventions and tools for establishing and/or strengthening NHRSs and their effectiveness?” [ 30 ].
The evidence synthesis focuses on the systems level and so primarily includes publications taking a systems approach at either the national or multi-national level. Not surprisingly, Health Research Policy and Systems ( HARPS ) is the single largest source of papers included in the HEN report. These were papers directly identified in the review’s search or papers included in the HEN report to illustrate a key point because they had been cited in one of the WHO reports or other systems-level collations of papers included in the synthesis.
While the system level papers did provide considerable data about each function, limited resources to conduct the scoping review meant that we had to exclude papers focusing solely on one specific function of a health research system or on just one field of health research. As acknowledged in the HEN report’s agenda for further research, there is a large number of publications (papers and grey literature) covering each function [ 30 ]. Therefore, reviewing all of these publications would be a major task but some exploration of the extent of the task, and the nature of such literature, could be informative. Furthermore, additional papers are continuously emerging, including from the various initiatives that are ongoing or just underway, for example, the European Health Research Network [ 31 ].
The three sections of this paper sequentially address the question of how to strengthen a health research system by:
- Describing key points and conclusions from WHO’s HEN report.
- Illustrating the nature of the ever-widening literature available on each function, or component, of a health research system by examining two sources in particular. First, the full range of papers published in HARPS in the 30 months up to February 2020. Second, the range of data gathered from publications or interviews that is included in detailed studies of the national health research systems in two countries – Iran [ 32 ] and England [ 33 ]; between them, these two papers also illustrate diverse aspects of the additional material that could be drawn upon.
- Considering a key question in the analysis of the current and future initiatives, namely who is going to steer the development of health research systems? Here, information and insights from the HEN about this sometimes-controversial issue, along with wider continuing analysis, are drawn on in the more flexible and speculative way that can be undertaken in an Opinion piece compared to a formal evidence synthesis.
WHO’s review, whose literature and who is providing leadership?
Who’s review.
The evidence synthesis described by the HEN report [ 30 ] starts by describing the importance of NHRSs in helping to achieve universal health coverage [ 1 ] and the SDGs [ 2 ]. It goes on to analyse the challenges facing health research and describes how issues remain unresolved despite the development and application of a systems approach including WHO’s framework for health research systems [ 3 ]. Many countries do not have comprehensive national health research policies or strategies that would facilitate the introduction of a systems approach. Therefore, challenges remain around two key and overlapping sets of issues. First, how to develop a systems approach to maximise the benefits from the research resources available – this can be a challenge even in high-income countries with considerable research funding. Second, how best to strengthen each specific function and component of a health research system [ 30 ].
The HEN identifies two main systems-level approaches to strengthening NHRSs. The first is comprehensive and coherent strategies, which can be contained in either policy documents, such as those from the English NIHR [ 34 ], the Irish Health Research Board (HRB) [ 35 ] and the Rwandan Ministry of Health [ 14 ], or in specific legislation as in the Philippines [ 36 ]. The second systems-level approach involves partnerships and multi-country initiatives, especially with international organisations. Two initiatives from the West African Health Organization (WAHO) are particularly important examples [ 5 , 37 ]. Here, the ministries of health of the 15 West African member countries worked together in a joint initiative covering all the countries and with funding and expertise from a range of partners, including the Council on Health Research for Development (COHRED), the Canadian International Research Centre, the Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases, and the Wellcome Trust. All WHO Regions have seen multi-country activities by WHO and/or COHRED to strengthen NHRSs, including the repeat surveys that identify areas for action [ 4 , 26 , 28 ].
Then, broadly using the WHO framework as the structure [ 3 ], the HEN identifies key points from systems-level literature on each of the four functions and nine components. The components of the stewardship and governance function include defining a vision, ethical review, research priority-setting, and appropriate monitoring and evaluation [ 3 ]. Consultation with health system stakeholders should enhance the relevance of the research priorities to the healthcare system, with examples of extensive priority-setting engagement activities sometimes being seen as a key aspect of building the NHRS as in Brazil [ 38 ]. Evaluating the impact of research on policy and practice should help researchers to focus on achieving such impact and was therefore promoted in the World Health Report 2013 [ 1 ].
Securing finance can involve obtaining funding from sources within the country and from external donors or multi-national organisations [ 30 ]. Targets for research expenditure, such as the 2% of national health expenditure set by the 1990 Commission on Health Research for Development [ 39 ], can usefully be brought into health research system strategies as in Rwanda [ 14 ]. Major health research strategies from countries within the European Union can highlight the importance of European Union funding as in France [ 40 ], Ireland [ 35 ] and Malta [ 41 ]. Requests for funding can be more effective when linked to other parts of the overall strategy, including identified priorities that need supporting through donor funding [ 42 ] and assessments of the benefits obtained from previous funding such as in England [ 24 ].
Capacity-building involves building, strengthening and sustaining the human and physical capacity to conduct, absorb and utilise health research [ 3 ]. In 2016, Santoro et al. [ 43 ] identified the generally low levels of research production in 17 countries of the former Soviet Union and south-eastern Europe and made recommendations for the sustained investment in training and career development of researchers, which should go beyond scholarships for training abroad and involve comprehensive strategies to ensure clear career structures. Strategies such as that from Inserm in France set out comprehensive plans for capacity-building [ 40 ] and strategies in both England and South Africa addressed priority gaps identified in the research capacity within the healthcare professions [ 34 , 44 ]. Donors can play an important part in building capacity but, recognising the need to avoid donor domination, often do so through partnerships. These can take diverse forms ranging from multi-country initiatives, such as that by WAHO, which included an initiative focusing on the challenges of post-conflict countries but was unable to meet all the needs [ 37 ], to accounts that focus on the partnership to address a broad range of capacity issues in a single country such as Malawi [ 7 ], to partnerships between individual institutions. Examples of the latter can feature particular challenges – the James Cook University in Australia worked with the Atoifi Adventist Hospital in Malaita, the most populous province of the Solomon Islands, to start establishing health research system capacity on the island using an inclusive, participatory approach [ 45 ]. Increasingly, there are also south–south partnerships, for example, an account of the Panamanian health research system described how the country’s first doctoral programme in biotechnology was established with support from Acharya Nagarjuna University in India [ 46 ]. The Rwandan strategy described plans to tackle the ‘brain drain’ through making the country an appealing place to conduct health research in terms of job requirements and providing opportunities for career advancement [ 14 ].
The three mutually reinforcing components of the producing and using research function encourage the production of scientifically valid findings that are relevant for users and communicated to them in an effective manner [ 30 ]. Major research funding bodies increasingly seek to address the waste issues raised by Chalmers and Glasziou [ 21 ] by working together in the Ensuring Value in Research (EViR) Funders’ Collaboration and Development Forum. It issued a consensus statement committing the organisations signing it to “require robust research design, conduct and analysis” [ 47 ]. The Forum is convened by the English NIHR, the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development, and the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (United States) with the active support of major research funding organisations from Australia, Ireland (HRB), Italy, Sweden and Wales, plus the Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases [ 48 ]. The first WAHO intervention also worked to boost research publications, including by creating a regional peer-reviewed, multilingual journal [ 5 ]. How research is produced can increase the chance that the evidence will be used in the health system, for example, the English NIHR strategy noted that leading medical centres with substantial funding to conduct translational research can act as “early adopters of new insights in technologies, techniques and treatments for improving health” [ 34 ].
Fostering the use of research requires specific knowledge translation and management approaches that draw on both locally produced and globally available evidence. Various health research strategies promote the role of Cochrane, including in England, where a unified knowledge management system to meet the needs of various stakeholders, including patients and their carers, involves funding both Cochrane and a review centre focusing on the needs of the National Health System [ 34 ]. In Ireland, the HRB strategy facilitated evidence-informed decisions through promoting access to the Cochrane Library and supporting training in conducting high-quality Cochrane reviews [ 35 ]. South Africa Cochrane featured as an important element in the NHRS [ 44 ]. The Rwandan strategy stated that “The Government of Rwanda is committed to using research findings to make evidence-based decisions that will improve health in Rwanda” [ 14 ]. It aimed to orientate various functions, including agenda-setting, monitoring and evaluation, and capacity-building, towards facilitating this challenging aim. The World Health Report 2013 highlighted various mechanisms that health research systems could adopt, including EVIPNet (Evidence-informed Policy Network), to promote the use of research [ 1 , 49 ].
The review also considers the effectiveness of approaches to strengthening NHRSs. Several reviews identified the effectiveness of the comprehensive approach taken by Professor Dame Sally Davies in creating the English NHRS [ 23 , 25 , 50 ]. The title of one analysis, ‘NIHR at 10: 100 examples, 10 themes, 1 transformation’, emphasises that the success of the NIHR depended on a range of elements being brought together in one transformation [ 25 , 50 ]. One of the 10 themes was the involvement of patients in decisions about research priorities and processes and, based on this, another recent analysis highlighted England and Alberta (Canada) as having health research systems that had made important progress [ 51 ]. Davies herself reflected on the success of the NIHR and stated: “What we envisaged was integrating a health research system into the health care delivery system so that the two would become interdependent and synergistic ” [ 24 ]. WHO’s Regional Office for Africa drew on their series of surveys of the performance of countries in building NHRSs and analysed the data from the 2014 and 2018 surveys using the NHRS barometer that they developed to score progress on a range of items linked to the list of NHRS functions [ 11 , 26 ]. In the 2014 survey, the Rwandan system was identified as the best performing and it, along with the majority of systems, was reported to have further improved in the 2018 survey; by then, South Africa was reported to have the best performance in Africa. The surveys also illustrate how the multi-country approach makes a useful contribution to strengthening NHRSs by helping to target action. Furthermore, the WAHO interventions made some progress but, while the evaluations identified the importance of political will and leadership provided by WAHO’s parent organisation of West African states, they also emphasised that building capacity for a whole NHRS is a significant task requiring commitment over the long-term [ 17 , 37 ].
The HEN review collated a range of examples of tools for NHRS strengthening. These were identified from the systems level discussions of NHRS strategies and partnerships and/or the major reports calling for NHRS strengthening such as the World Health Report 2013 [ 1 ]. The HEN lists these in an Annex [ 30 ].
The discussion in the HEN draws on the literature that was included to identify five key policies that those responsible for strengthening NHRSs could consider [ 30 ], namely conduct context, or situational, analyses to inform strengthening activities [ 5 , 34 , 35 , 37 , 52 – 54 ], develop a comprehensive and coherent strategy [ 14 , 34 – 36 ], engage stakeholders in the development and operation of the strategy [ 7 , 23 , 34 , 35 , 38 , 41 , 44 , 51 , 55 – 59 ], adopt monitoring and evaluation tools that focus on the objectives of the NHRS, including health improvement [ 1 , 14 , 24 , 60 , 61 ], and develop partnerships [ 5 , 11 , 28 , 37 , 62 ]. Examples of the evidence to support or illustrate each policy are given in Table 1 .
Policies to strengthen National Health Research Systems and supporting evidence
| Policy to strengthen National Health Research Systems | Examples of evidence supporting or illustrating each policy (selected from the body of evidence presented in the HEN [ ]) |
|---|---|
| Conduct context or situational analyses of current national position to inform strengthening activities | COHRED, in particular, has developed tools to assist countries in conducting situational analyses as part of wider advice [ ] and this approach was an important element in the WAHO interventions being successful to the extent that they were [ , , , ]. Strategies informed by analyses of their current situation include those for the English NIHR [ ] and the Irish HRB [ ] |
| Develop a comprehensive and coherent NHRS strategy | Comprehensive and coherent strategies with at least some degree of success (as seen in progress on some or all of the NIHR functions) had set out how they intended to take action on the range of health research system functions and components, even if not necessarily explicitly using the WHO framework [ ]; examples include the strategies for the English NIHR [ ], the Irish HRB [ ], and in the Philippines [ ] and Rwanda [ ] |
| Engage stakeholders in the development and operation of the NHRS strategy | Strategy documents such as those for the NIHR [ ] and HRB [ ], plus ones in British Columbia [ ], Malta [ ] and New Zealand [ ], describe the importance and/or range of stakeholders engaged in developing the strategy. Articles describing the approach in South Africa [ ] and Zambia [ ] also highlighted the importance of wide stakeholder engagement. An analysis of stakeholder engagement in the creation and operation of the NIHR identified it as making a key contribution to its success [ ]. There is increasing support for the engagement of stakeholders in setting the priorities for research as well as in research processes and translation [ , , , , ] |
| Adopt monitoring and evaluation tools that focus on the objectives of the NHRS, including health system improvement | A range of documents, including ones on the NIHR [ ], HRB [ ] and Rwandan strategies [ ], and the World Health Report 2013 [ ], demonstrate the importance of adopting monitoring and evaluation approaches that include a focus on assessing the impacts of research on health polices/practice and the economy, e.g. through application of the Payback Framework [ , ] |
| Develop/participate in partnerships across regions, bilaterally or within the NHRS | Examples of progress made by partnerships between countries, sometimes along with international organisations and donors, include the WAHO interventions [ , , , ] and the work of WHO regional offices for Africa [ , ] and the PAHO [ , ] |
Source: Data extracted from Health Evidence Network report 69 (Hanney et al., 2020) [ 30 ]
COHRED Council on Health Research for Development, HEN Health Evidence Network, HRB Health Research Board, NHRS National Health Research System, NIHR National Institute for Health Research, PAHO Pan-American Health Organization, WAHO West African Health Organization
In summary, therefore, this section shows that the WHO evidence synthesis, published as a HEN report [ 30 ], provides a firm basis for decision-making by policy-makers and research leaders looking to strengthen the health research system in their country. It analyses, in turn, the individual functions and components within a system and identifies a series of tools that can be used for strengthening many of them. Finally, this section highlights the five crucial policy approaches that the HEN report suggests can be applied as appropriate to the context of the country (Table (Table1 1 ).
Whose literature?
As noted above, the HEN was a scoping review and focused on the literature at the systems level rather than on publications (papers and grey literature) related solely to specific functions, types or fields of research [ 30 ]. Therefore, there is scope for further work to incorporate an even wider range of publications than the 112 included in the HEN review [ 30 ]. The discussion in the HEN suggests that further research could usefully take the form of a series of reviews on the extensive literature on each of the NHRS functions or components, which could then be collated [ 30 ]. Just two of the many available sources illustrate the nature of the vast literature available on each function, or component, of a health research system and the way the literature on that, and the system level developments, is ever-widening. First, we can examine the papers published in HARPS, the specialist journal in the field of building NHRSs. Second, we can focus on two very different but detailed studies of individual NHRSs – one conducted for a PhD thesis to show the 50 year history of the development of all the functions in the Iranian health research system [ 32 ] and the other an interview-based study to understand the factors behind the creation of the NIHR with its new strategy [ 33 ].
In terms of further reviews of the literature on specific functions or components, HARPS would probably be a key source. In the summer of 2017, an analysis by the retiring editors of the papers published in the journal from its inception in 2002 identified many papers that had been published on each of the functions or components of a health research system [ 63 ]. While this editors’ analysis was included in the HEN review because it organised its discussion of the papers at the systems level, the individual papers in it were, in general, only included in the HEN review if they, too, adopted a systems approach at the national or partnership level, or were also cited in a report such as the World Health Report 2013 [ 1 ]. Examples of such papers include Viergever et al. on priority-setting [ 59 ], Bates et al. on capacity-building [ 64 ], and Lavis et al. on the SUPPORT tools for evidence-informed policy-making [ 65 ]. Therefore, many additional papers related to specific functions (or fields) could be consulted, in a formal review or otherwise, in any future series of reviews, each with a narrow focus on strengthening a specific function.
To further inform this current Opinion piece, a quick ‘hand-search’ was conducted of the papers published in HARPS in the 30 months since the previous analysis in mid-2017 [ 63 ]. This again identified a wide range of papers on specific components, especially priority-setting, evaluation of research impacts, capacity-building and the translation of research (or knowledge mobilisation). Various papers linked the final two points and discussed capacity-building and knowledge translation [ 13 , 66 ]. Such a focus is entirely consistent with the aim described by the incoming editors in Autumn 2017 of bringing “all elements of the research–policy world together – such that the research which is done is useful and that it is used” [ 67 ]. In this more recent phase of HARPS , there have also been important papers on issues related to the policies ‘recommended’ at the end of the HEN and listed above, including the contribution of stakeholder engagement in research [ 68 ].
The more recent papers could sometimes provide useful further tools on specific functions. Their narrow focus meant they had not been directly included through the HEN search and, further, they had not been included in any of the major reports also used as sources for tools such as the World Health Report 2013 [ 1 ]. In some instances, this was because they were too recent, for example, the ISRIA statement by Adam et al. [ 69 ] describing the ten-point guidelines for an effective process of research impact assessment prepared by the International School on Research Impact Assessment (ISRIA). Even more recently, the Intervention Scalability Assessment Tool, developed by Milat et al. [ 70 ], was proposed for use not only by health policy-makers and practitioners for selecting interventions to scale up but also to help design research to fill evidence gaps. This analysis of the papers from just one journal reinforces the message that there is likely to be a plentiful supply of literature for a future review on any of the main specific components.
This message is further reinforced by a more detailed analysis of the papers in HARPS in the first 2 months of 2020. Articles on the main components of a NHRS were supplemented by some important papers on topics that are highly relevant but which feature less frequently in HARPS. These include a study aimed at reducing the research waste that arises from disproportionate regulation by examining the practices for exempting low-risk research from ethics review in four high-income countries [ 71 ], the Global Observatory’s paper on research funding described earlier [ 29 ], a study on the governance of national health research funding institutions [ 72 ], and one on a more recent topic of growing significance – an analysis of attempts to boost gender equality in health research [ 73 ]. Additionally, some of the papers on specific components, such as impact evaluation or use of evidence, are extending the analysis. Examples include consideration of how research impact assessments are implemented in practice within research organisations [ 74 ] and how evidence is used in decision-making in crisis zones [ 75 ]. To illustrate the volume of studies being produced, there has been a flurry of studies, in the first 2 months of 2020 alone, on the collaboration and coproduction of health research. The titles include ‘Building an integrated knowledge translation (IKT) evidence base: colloquium proceedings and research direction’ [ 76 ], ‘Using a ‘rich picture’ to facilitate systems thinking in research coproduction’ [ 77 ], ‘Exploring the evolution of engagement between academic public health researchers and decision-makers: from initiation to dissolution’ [ 78 ], ‘Research co-design in health: a rapid overview of reviews’ [ 79 ], and ‘Conceptualising the initiation of researcher and research user partnerships: a meta-narrative review’ [ 80 ].
Finally, another article in May 2020 presented a new conceptual model for health research systems to strengthen health inequalities research [ 81 ]. Here, we have focused on just one journal, HARPS, because it was the largest single source of papers in the HEN report, which totalled 140 publications (additional publications were included to the 112 in the review to help set the background, provide examples of key tools, etc). However, even with the review’s focus on the system level, HARPS only provided 22% (31 out of 140) of the publications; 31% (43 of 140) came from other journals and 47% (66 of 140) were other types of publication. If the focus was shifted to including papers on specific functions it is highly likely that there would be a higher proportion of papers from other journals.
The authors of two single-country papers on the development of the health research system, Mansoori [ 32 ] about Iran and Atkinson et al. [ 33 ] on the creation of the NIHR in England, both highlight the importance of context but also claim their findings could have wider application. Examining these two papers is also informative because of the differences between the studies, including one being located in a low- or middle-income country, and the other not.
Mansoori’s narrative review of studies addressing the health research system of Iran included 204 relevant and mostly national records, categorised using an approach informed by the functions and components of WHO’s NHRS framework [ 32 ]. The papers and grey literature documents included were all available in English or Persian, and mostly published in journals other than HARPS, and illustrate the vast literature available at a global level on the various components of a NHRS . They informed an impressively detailed account of the various NHRS components and the attempts to strengthen them. For example, the account of the development of the national level ethical overview includes a fully documented chronology of the progress over 25 years and some insightful analysis of how the progress was facilitated by the pivotal role of Professor Bagher Larijani, who was a prominent medical practitioner, leading researcher and founder of the Medical Ethics Research Centre in Iran. He was able to “use the confidence that Iranian authorities had in him as an opportunity” [ 32 ].
While Mansoori’s review was included in the HEN review, only a tiny fraction of the available data about Iran could be included, primarily in a brief description of the system’s effectiveness [ 30 ]. However, the full paper could usefully inform the approach of researchers and/or policy-makers planning a detailed analysis of their own NHRS prior to embarking on exercises to strengthen it, and “ [t] he findings emphasized that improvement of HRS functions requires addressing context-specific problems” [ 32 ]. As an illustration, Mansoori’s review identified a need for “ a more systematic, inclusive” approach to research priority-setting [ 32 ] and, in the same stream of research, she co-led just such a priority-setting exercise to help address the knowledge gaps related to achieving both Iran’s national health policies and the SDGs [ 82 ].
Atkinson et al. examined the creation of what might be viewed as the most successful attempt to strengthen a health research system in their paper ‘‘All the stars were aligned’? The origins of England’s National Institute for Health Research’ [ 33 ]. Compared with Mansoori, the authors adopted a different but equally detailed approach in their analysis, which was conducted principally through interviews and a witness seminar but also drew on the existing literature and documents [ 33 ]. They showed how the formation of the NIHR was led from the Department of Health by a key group driven by Sally Davies. They aimed to improve patient care through both the strengthening of evidence-based medicine and through boosting the infrastructure to facilitate pharmaceutical clinical trials that would also meet wider industrial and economic goals.
As with Mansoori’s study, consideration was given to how the full analysis could be informative to any planned detailed study or reforms in any other country. The key observations were similar to the recommendations from the HEN report with a focus on stakeholder engagement and building support: “ [t] wo measures likely to contribute to political support are to place the greatest emphasis on ‘problem’ rather than ‘investigation’ research, and to devote attention to measuring and reporting research ‘payback’ ” [ 33 ]. Atkinson et al.’s paper is also a link to the other main source considered here because it was a recent paper published in HARPS.
In summary, if further analysis and research beyond that in the WHO evidence synthesis [ 30 ] is thought to be relevant in the particular country looking to strengthen its health research system, this Opinion piece indicates some of the types of additional sources of information that are available and how they might be organised. The vast literature on each function and the ever-growing evidence base are illustrated by considering papers in just one key journal, HARPs, and analysing the contribution of two national studies. A review of the functions of the Iranian system identifies over 200 relevant, mostly national, records and an analysis of the creation of the English NIHR describes the key leadership role played from the health department.
Who is providing leadership?
The above analysis demonstrates that there is no shortage of useful material on which to draw when strengthening health research systems. However, key questions remain as to who might best lead or steer attempts to strengthen such a system.
The papers by both Mansoori [ 32 ] and Atkinson et al. [ 33 ] illustrate that, where a key committed individual has the capacity and opportunity to provide leadership, this can be a vital element in making progress. However, the institutional factors are also crucial.
The HEN developed the argument that a department or ministry of health will have a particular interest and perhaps experience in promoting research agendas that meet the needs of the healthcare system and in helping to develop mechanisms to use the findings from such research, where appropriate, to inform local policy and practice [ 30 ]. The health ministry or a research council responsible to it played an important role in the various systems identified above as being effective, as was also the case in the WAHO initiative [ 30 ]. In some cases, as with Zambia, more progress was made once the ministry of health elected to play a more important role, sometimes in place of other stakeholders [ 57 ]. Examples of the important role that health ministries can play were described in the 2013 World Health Report, including on Paraguay: “ the support of the Minister of Health backed by the President of Paraguay has been a key factor in the development of a national health research system” [ 1 ]. Additionally, naturally enough, the activities of the various WHO regional offices in boosting NHRSs tend to focus on working with the national ministries of health, including work in Europe [ 31 ] and by PAHO [ 28 ]. Conversely, several analyses illustrate that progress in strengthening the NHRS might be limited where key parts of the ministry of health, for whatever reason, do not provide support [ 9 , 83 ].
Nevertheless, some disadvantages or dangers were identified when the ministry of health plays the leading role. First, in England prior to the creation of the NIHR as well as in some other countries, the research funds controlled by the health ministry were sometimes appropriated by other parts of the health system when they were under particular pressure for resources [ 84 ]. Similarly, there have been a few reports that health research funding lost out when donor funds that had previously been allocated specifically for health research programmes were replaced by donations of funds to be allocated by the nation’s own health system according to its own priorities [ 85 , 86 ]. One way of attempting to mitigate the danger is, as undertaken by the NIHR and described by Atkinson, by building support for health research through measuring and reporting the payback from research [ 24 , 33 ].
The second danger arises because, traditionally, many researchers argued that the best science came when they had the freedom to identify the key research topics, rather than having priorities set by others [ 84 ]. Therefore, they argued, the responsibility for funding and organising health research should be left to organisations that are part of the research system and independent of the health system [ 84 ]. Furthermore, despite the growth of interest in coproduction approaches noted above, there have also been recent doubts raised about the assumption that coproduction is always the most appropriate approach [ 87 ]. This issue clearly requires sensitive handling. Indeed, Atkinson et al. [ 33 ] argue that one of the great successes of the NIHR is that this issue has been so skilfully handled by the NIHR that external input, or stakeholder engagement, in setting agendas has become widely accepted and the structures created give ministers a sense of ownership without sacrificing scientific independence.
The efforts of WAHO [ 5 , 37 ] and the WHO regional offices for Africa and PAHO [ 11 , 26 , 28 , 62 ] indicate that partnerships can be helpful. In Europe, the WHO regional office worked with Member States to create the European Health Research Network, which is intended to help nations with limited NHRSs who wish to make more progress [ 31 ].
Partnerships can provide important support and encouragement, but the evidence suggests there must be strong political will somewhere within the political and/or health systems for a health research system to be fully strengthened. The Central Asian countries in WHO’s European Region seem to provide an illustration of this point. A COHRED collaborative initiative successfully resulted in situation analyses being produced in each country and then jointly discussed as the basis for action [ 88 ], but according to the analysis by Santoro et al. [ 43 ], limited progress seems to have been made in the subsequent years.
The importance of partnerships and collaboration in focusing research efforts in an extreme crisis, with a leadership role for the WHO, has been seen in the race to find treatments for COVID-19 and vaccines against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which causes the COVID-19 disease [ 89 ]. In many NHRSs across the globe, including in the Philippines, scientists are coming together to participate in WHO’s Solidarity Trial, which will test the safety and effectiveness of various possible therapies for treating COVID-19 [ 90 ]. Sarah Gilbert, leader of Oxford University’s Jenner Institute’s work on developing one of the leading vaccine candidates explained that cooperation was vital for tackling the crisis: “Work is continuing at a very fast pace, and I am in no doubt that we will see an unprecedented spirit of collaboration and cooperation, convened by WHO, as we move towards a shared global goal of COVID-19 prevention through vaccination” [ 91 ]. A key issue going forward is how such cooperation can be built on in strengthening NHRSs into the future. For now, it is recommended that a prospective study be conducted to analyse all that is being done in different NHRSs to speed up research during the pandemic, with a view to taking lessons about cooperation, partnerships and other matters into strengthening NHRSs in the future [ 89 ].
The WHO evidence synthesis, published as a HEN report [ 30 ], provides a firm basis for decision-making by policy-makers and research leaders looking to strengthen the health research system in their country. It identifies five crucial policy approaches that can be applied as appropriate to the context of the country – conducting situation analyses, sustaining a comprehensive strategy, engaging stakeholders, evaluating impacts on health policies and practices, and partnership participation. It also analyses, in turn, the individual functions and components within a system and identifies a series of tools that can be used for strengthening many of them.
If further analysis and research is thought to be relevant in the particular country looking to strengthen its health research system, this Opinion piece indicates some of the types of additional sources of information that are available. The Opinion piece also discusses aspects of the sometimes-controversial question of who should lead or steer attempts to strengthen NHRSs. Again, the context of the particular nation will be crucial in determining the most appropriate course to take, as emphasised by both Mansoori [ 32 ] and Atkinson et al. [ 33 ], but at least some involvement of the ministry of health is likely to be beneficial; additionally, sometimes, key individuals can play a crucial leadership role in strengthening the whole system or one component. In countries with a less developed tradition of conducting health research, partnerships with other countries and/or with international organisations can help lead the progress and learning for all partners. The valuable role that international organisations, such as WHO, can play in leading partnerships and cooperation to strengthen health research systems is being highlighted during the COVID-19 crisis.
Overall, therefore, the full WHO HEN report not only provides a detailed analysis of NHRS strengthening, it also provides a structure within which an even wider and ongoing literature can be considered. Additionally, it contains a perhaps more nuanced account, on which this paper builds, of some aspects of the literature around the issue of who should provide leadership in developing NHRSs and identifies the importance of ministry of health involvement.
Acknowledgements
We thank colleagues at WHO’s Regional Office for Europe for the inputs to the original Health Evidence Network Evidence Synthesis. The authors are responsible for the content of this Opinion piece.
Abbreviations
| COHRED | Council on Health Research for Development |
| HARPS | Health Research Policy and Systems |
| HEN | Health Evidence Network |
| HRB | Health Research Board |
| NHRS | National Health Research System |
| NIHR | National Institute for Health Research |
| PAHO | Pan-American Health Organization |
| SDGs | Sustainable Development Goals |
| WAHO | West African Health Organization |
Authors’ contributions
SP, LK and SH planned the original phase of the WHO evidence synthesis, including the search strategy. LK led the original literature search and contributed article selection and data extraction and analysis. AB and SH planned the second phase of the evidence synthesis. TJ led the second phase of the literature search and contributed to the article selection and data extraction. AB contributed to the final version of the Health Evidence Network report. SH led the data extraction and analysis and drafting of the report. SH conducted the additional analysis of the literature and initial drafting for this Opinion piece. All authors commented on the Opinion piece and approved the final version.
The WHO’s Regional Office for Europe funded the Health Evidence Network Evidence Synthesis. The additional literature searching and analysis for this Opinion piece, along with its drafting, was unfunded. Annette Boaz, Kingston University and St George’s University of London, is supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Applied Research Collaboration South London (NIHR ARC South London) at King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NIHR or the Department of Health and Social Care.
Availability of data and materials
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The full version of the evidence synthesis was published by WHO’s Regional Office for Europe, and all the data used for the report and this Opinion piece are publicly available.
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare. AB is a member of the World Health Organization European Advisory Committee on Health Research. SH was co-editor of Health Research Policy and Systems from 2006 to 2017.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Stephen R. Hanney, Email: [email protected] .
Lucy Kanya, Email: [email protected] .
Subhash Pokhrel, Email: [email protected] .
Teresa H. Jones, Email: [email protected] .
Annette Boaz, Email: [email protected] .
Healthcare Research Paper Topics

In this page, we provide a comprehensive list of healthcare research paper topics , expert advice on selecting compelling topics, guidance on writing an impactful research paper, and information about iResearchNet’s writing services. By exploring these resources, students in the health sciences field can choose relevant and significant healthcare research paper topics, develop their papers effectively, and access professional writing assistance to excel in their academic endeavors.
100 Healthcare Research Paper Topics
The field of healthcare research encompasses a vast array of topics that are crucial for understanding, improving, and transforming healthcare practices. As students in the health sciences, you have the opportunity to explore these diverse areas and contribute to the knowledge base of healthcare research. This comprehensive list aims to inspire and guide you in selecting healthcare research paper topics that align with your interests and academic goals. The topics are divided into ten distinct categories, each containing ten thought-provoking and relevant research ideas. Let this list serve as a springboard for your exploration and a catalyst for impactful research in the dynamic field of healthcare.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
1. Healthcare Policy and Management
- The Impact of Health Policies on Access to Care
- Assessing the Effectiveness of Health Insurance Programs
- Analyzing the Role of Healthcare Leadership in Quality Improvement
- Exploring Strategies for Healthcare Cost Containment
- Investigating the Relationship Between Healthcare Regulations and Patient Outcomes
- Evaluating the Impact of Electronic Health Records on Healthcare Delivery
- Examining the Role of Public-Private Partnerships in Healthcare
- Analyzing the Influence of Political Factors on Healthcare Decision-Making
- Assessing the Ethical Implications of Resource Allocation in Healthcare
- Investigating the Effectiveness of Health Promotion Programs in Primary Care Settings
2. Healthcare Ethics and Legal Issues
- Analyzing the Ethical Challenges of Healthcare Research Involving Human Subjects
- Exploring the Impact of Cultural and Religious Beliefs on Healthcare Decision-Making
- Examining Legal Issues in End-of-Life Care and Advance Directives
- Investigating the Ethical Implications of Genetic Testing and Personalized Medicine
- Assessing the Ethical Dilemmas in Access to Experimental Treatments
- Exploring the Role of Ethics Committees in Healthcare Organizations
- Analyzing the Intersection of Healthcare Ethics and Artificial Intelligence
- Evaluating the Legal and Ethical Implications of Telemedicine
- Investigating the Ethics of Healthcare Resource Allocation during Public Health Emergencies
- Examining the Legal and Ethical Issues of Patient Privacy in the Digital Age
3. Healthcare Technology and Innovation
- Assessing the Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare Diagnostics
- Exploring the Potential of Wearable Devices for Remote Patient Monitoring
- Investigating the Role of Big Data Analytics in Healthcare Decision-Making
- Analyzing the Use of Robotics in Surgery and Patient Care
- Examining the Impact of Telehealth on Healthcare Access and Delivery
- Evaluating the Benefits and Challenges of Electronic Health Records Implementation
- Exploring the Applications of Virtual Reality in Healthcare Education and Training
- Investigating the Role of Mobile Health Applications in Health Behavior Change
- Assessing the Potential of Blockchain Technology in Healthcare Data Security
- Analyzing the Ethical and Social Implications of Genetic Engineering in Healthcare
4. Healthcare Quality and Patient Safety
- Evaluating the Impact of Patient-Centered Care on Health Outcomes
- Analyzing the Role of Quality Improvement Initiatives in Reducing Medical Errors
- Assessing the Effectiveness of Medication Safety Practices in Healthcare Settings
- Exploring Strategies to Improve Healthcare Communication and Interprofessional Collaboration
- Investigating the Relationship Between Nursing Workforce and Patient Safety
- Examining the Impact of Clinical Practice Guidelines on Healthcare Quality
- Analyzing the Role of Patient Engagement in Enhancing Healthcare Quality
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Lean Six Sigma in Healthcare Process Improvement
- Exploring the Role of Health Information Technology in Enhancing Patient Safety
- Investigating the Influence of Organizational Culture on Healthcare Quality and Safety
5. Mental Health and Psychological Well-being
- Analyzing the Impact of Stigma on Mental Health Help-Seeking Behavior
- Exploring the Effectiveness of Psychotherapy Approaches in Treating Mental Health Disorders
- Assessing the Role of Early Intervention in Preventing Mental Health Disorders
- Investigating the Relationship Between Adverse Childhood Experiences and Mental Health Outcomes
- Examining the Intersection of Mental Health and Substance Abuse Disorders
- Evaluating the Impact of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Psychological Well-being
- Exploring the Role of Social Support in Mental Health Recovery
- Analyzing the Effectiveness of Mental Health Awareness Campaigns
- Investigating the Influence of Cultural Factors on Mental Health Help-Seeking Behavior
- Examining the Mental Health Needs and Challenges among Specific Populations (e.g., LGBTQ+, Veterans, Refugees)
6. Chronic Diseases and their Management
- Assessing the Impact of Lifestyle Factors on Chronic Disease Prevention and Management
- Exploring the Role of Community-Based Interventions in Chronic Disease Control
- Investigating the Relationship Between Social Determinants of Health and Chronic Disease Burden
- Analyzing the Use of Digital Health Technologies in Chronic Disease Management
- Examining the Impact of Health Literacy on Chronic Disease Outcomes
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Self-Management Programs for Chronic Conditions
- Exploring the Role of Healthcare Providers in Chronic Disease Prevention and Management
- Analyzing the Impact of Health Policies on Chronic Disease Prevention Efforts
- Investigating the Relationship Between Mental Health and Chronic Disease Management
- Examining the Disparities in Access to Chronic Disease Care and Treatment
7. Healthcare Disparities and Access to Care
- Analyzing Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Healthcare Access and Quality
- Exploring the Role of Socioeconomic Factors in Healthcare Disparities
- Assessing the Impact of Geographic Location on Healthcare Access and Health Outcomes
- Investigating Gender Disparities in Healthcare Utilization and Treatment
- Examining the Influence of Health Insurance Status on Healthcare Disparities
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Culturally Competent Care in Reducing Disparities
- Exploring the Relationship Between Language Barriers and Healthcare Access
- Analyzing the Impact of Implicit Bias on Healthcare Disparities
- Investigating the Role of Health Literacy in Healthcare Disparities
- Examining the Disparities in Mental Health Services and Access to Mental Healthcare
8. Healthcare Education and Training
- Assessing the Effectiveness of Simulation-Based Training in Healthcare Education
- Exploring the Role of Interprofessional Education in Improving Collaborative Practice
- Investigating the Impact of Technology-Enhanced Learning in Healthcare Education
- Analyzing the Use of Gamification in Healthcare Training and Skill Development
- Examining the Role of Continuing Education in Enhancing Healthcare Providers’ Competence
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Mentorship Programs in Healthcare Education
- Exploring Strategies to Address Cultural Competence in Healthcare Education
- Analyzing the Role of Reflective Practice in Healthcare Professional Development
- Investigating the Use of Team-Based Learning in Healthcare Education
- Examining the Impact of Experiential Learning in Healthcare Training Programs
9. Public Health and Preventive Medicine
- Assessing the Impact of Vaccination Programs on Public Health Outcomes
- Exploring the Role of Health Promotion Campaigns in Preventing Non-communicable Diseases
- Investigating the Effectiveness of Community-Based Interventions in Disease Prevention
- Analyzing the Impact of Environmental Factors on Public Health
- Examining the Role of Social Determinants of Health in Health Disparities
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Public Health Policies in Tobacco Control
- Exploring Strategies for Preventing and Managing Infectious Diseases
- Analyzing the Role of Health Education in Promoting Healthy Lifestyles
- Investigating the Influence of Media on Public Health Perceptions and Behaviors
- Examining the Challenges and Opportunities in Global Health Initiatives
10. Emerging Topics in Healthcare Research
- Assessing the Implications of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- Exploring the Role of Precision Medicine in Personalized Healthcare
- Investigating the Impact of Genomic Research on Healthcare Delivery
- Analyzing the Use of Telemedicine in Rural and Underserved Areas
- Examining the Integration of Traditional and Complementary Medicine in Healthcare
- Evaluating the Potential of Digital Therapeutics in Disease Management
- Exploring the Ethical Considerations of Gene Editing Technologies in Healthcare
- Analyzing the Influence of Social Media on Healthcare Decision-Making
- Investigating the Role of Health Information Exchange in Coordinated Care
- Examining the Implications of Health Equity in Healthcare Research and Practice
This comprehensive list of healthcare research paper topics encompasses a wide range of areas within the healthcare field. Each category offers diverse research ideas that can inspire students in the health sciences to explore pressing issues, propose innovative solutions, and contribute to the advancement of healthcare knowledge. Whether you are interested in healthcare policy, ethics, technology, mental health, chronic diseases, healthcare disparities, education, public health, or emerging healthcare research paper topics, this list serves as a valuable resource to kickstart your research journey. Choose a topic that resonates with you, aligns with your academic goals, and enables you to make a meaningful impact in the field of healthcare research. Remember, the pursuit of knowledge and the drive to improve healthcare practices are at the heart of your journey as a student in the health sciences.
Choosing Healthcare Research Paper Topics
Choosing the right healthcare research paper topic is a crucial step in conducting a successful and impactful study. With the vast array of healthcare issues and areas to explore, it can be challenging to narrow down your focus. To help you navigate this process effectively, we have compiled expert advice and ten essential tips for selecting compelling healthcare research paper topics. Consider these insights as you embark on your research journey in the dynamic field of healthcare:
- Follow Your Passion : Choose a topic that genuinely interests you. Passion and enthusiasm will drive your motivation, ensuring that you remain engaged throughout the research process.
- Stay Informed : Keep up with the latest healthcare trends, emerging issues, and ongoing debates. Stay informed through reputable sources, academic journals, conferences, and professional networks to identify current and relevant research gaps.
- Identify a Research Gap : Conduct a thorough literature review to identify areas where there is a need for further research. Look for unanswered questions, controversies, or gaps in knowledge that you can address in your study.
- Consider Relevance and Significance : Choose a topic that is relevant to current healthcare challenges or contributes to improving healthcare practices, policies, or patient outcomes. Aim for a topic that has real-world implications and societal impact.
- Delve into Specific Areas : Narrow down your focus by selecting a specific aspect or subtopic within the broad field of healthcare. This allows for a more focused and in-depth analysis of the chosen area.
- Consult with Your Advisor or Faculty : Seek guidance from your research advisor or faculty members who specialize in healthcare research. They can provide valuable insights, help you refine your topic, and direct you to relevant literature and resources.
- Brainstorm with Peers : Engage in discussions with your peers and classmates to explore different perspectives and gain inspiration. Collaborative brainstorming sessions can generate new ideas and offer fresh insights.
- Consider Ethical Considerations : Take ethical considerations into account when selecting a healthcare research topic. Ensure that your research adheres to ethical guidelines and respects the rights and privacy of participants, especially in studies involving human subjects.
- Think Interdisciplinary : Consider interdisciplinary approaches to healthcare research. Explore how other disciplines, such as sociology, psychology, economics, or technology, intersect with healthcare, providing a broader perspective and enhancing the depth of your research.
- Feasibility and Available Resources : Assess the feasibility of your chosen topic, considering the resources, time, and data availability required for your research. Ensure that you have access to relevant data sources, research tools, and necessary support to carry out your study effectively.
By following these expert tips, you will be equipped to choose a healthcare research paper topic that aligns with your interests, is relevant to current healthcare challenges, and has the potential to make a meaningful impact in the field. Remember, selecting the right topic sets the foundation for a successful research endeavor, allowing you to contribute to the advancement of healthcare knowledge and practices.
How to Write a Healthcare Research Paper
Writing a healthcare research paper requires careful planning, organization, and attention to detail. To help you navigate the intricacies of the writing process, we have compiled ten essential tips to guide you towards crafting a well-written and impactful healthcare research paper. Follow these expert recommendations to enhance the quality and effectiveness of your research paper:
- Develop a Clear Research Question : Start by formulating a clear and concise research question that will serve as the central focus of your paper. Ensure that your question is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Conduct a Thorough Literature Review : Before diving into your research, conduct a comprehensive literature review to familiarize yourself with existing knowledge on the topic. Identify key theories, concepts, methodologies, and gaps in the literature that your research aims to address.
- Create a Solid Research Design : Design a robust research plan that aligns with your research question. Define your study population, sampling strategy, data collection methods, and statistical analyses. A well-designed research plan enhances the validity and reliability of your findings.
- Collect and Analyze Data : Implement your data collection methods, ensuring ethical considerations and adherence to research protocols. Once collected, analyze the data using appropriate statistical techniques and tools. Provide a clear description of your analytical methods.
- Structure your Paper Effectively : Organize your research paper into logical sections, including an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. Use headings and subheadings to enhance readability and guide the reader through your paper.
- Write a Compelling Introduction : Start your paper with a strong introduction that captures the reader’s attention and provides a concise overview of the research topic, objectives, and significance. Clearly state your research question and the rationale for your study.
- Present Clear and Concise Results : Present your research findings in a clear and concise manner. Use tables, graphs, and figures where appropriate to enhance the readability of your results. Provide a comprehensive interpretation of the results, highlighting key findings and their implications.
- Engage in Critical Analysis and Discussion : Analyze and interpret your findings in the context of existing literature. Discuss the strengths and limitations of your study, addressing potential biases or confounders. Consider alternative explanations and provide a thoughtful discussion of the implications of your findings.
- Follow Proper Citation and Referencing Guidelines : Adhere to the appropriate citation style (such as APA, MLA, or Chicago) consistently throughout your paper. Cite all sources accurately and include a comprehensive list of references at the end of your paper.
- Revise and Edit : Before finalizing your research paper, revise and edit it thoroughly. Pay attention to clarity, coherence, grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Ensure that your arguments flow logically and that your paper is well-structured and cohesive.
By following these tips, you will be well-equipped to write a high-quality healthcare research paper that effectively communicates your findings, contributes to the existing knowledge in the field, and engages readers with your insights and conclusions. Remember to seek feedback from your peers, professors, or research advisors to further refine your paper and ensure its overall excellence.
iResearchNet’s Custom Writing Services
At iResearchNet, we understand the challenges students face when it comes to writing healthcare research papers. To support you in your academic journey and ensure the highest quality of your work, we offer a comprehensive range of writing services. With a team of expert degree-holding writers and a commitment to excellence, we are dedicated to providing customized solutions tailored to your specific needs. Here are the features that set our writing services apart:
- Expert Degree-Holding Writers : Our team consists of highly qualified writers with advanced degrees in healthcare and related fields. They possess in-depth knowledge and expertise in various areas of healthcare, ensuring that your research paper is handled by professionals with subject matter expertise.
- Custom Written Works : We understand the importance of originality and uniqueness in academic writing. Our writers craft each research paper from scratch, tailoring it to your specific requirements and ensuring that it is entirely original and plagiarism-free.
- In-Depth Research : Our writers are skilled in conducting extensive research using reputable sources. They delve deep into the literature to gather the most relevant and up-to-date information, providing a solid foundation for your research paper.
- Custom Formatting : We offer custom formatting options to meet the specific guidelines of your institution and chosen citation style. Whether it’s APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, Harvard, or any other formatting style, our writers are well-versed in the intricacies of each.
- Top Quality : We are committed to delivering research papers of the highest quality. Our writers follow strict quality control measures to ensure that your paper meets the academic standards, including proper structure, clarity of writing, and logical flow of ideas.
- Customized Solutions : We recognize that every research paper is unique. Our writers work closely with you to understand your research objectives, guidelines, and preferences. They tailor their approach to ensure that your research paper reflects your vision and academic goals.
- Flexible Pricing : We offer flexible pricing options to accommodate students’ budgets. We understand the financial constraints students often face, and we strive to provide competitive and affordable pricing for our writing services.
- Short Deadlines : We understand that time is often a critical factor. We offer short turnaround times, allowing you to meet tight deadlines without compromising the quality of your research paper. With our dedicated team, we can handle urgent requests efficiently.
- Timely Delivery : We prioritize timely delivery to ensure that you receive your research paper well before your deadline. We understand the importance of submitting your work on time and offer our commitment to punctuality.
- 24/7 Support : Our customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you with any inquiries or concerns you may have. We are here to provide prompt and helpful assistance at any stage of the writing process.
- Absolute Privacy : We value your privacy and confidentiality. We have strict measures in place to protect your personal information and ensure that your identity remains anonymous throughout the process.
- Easy Order Tracking : We provide a user-friendly platform that allows you to track the progress of your order. You can stay updated on the status of your research paper and communicate directly with your assigned writer.
- Money-Back Guarantee : We are confident in the quality of our writing services. In the rare event that you are not satisfied with the final product, we offer a money-back guarantee, ensuring your peace of mind and commitment to your satisfaction.
At iResearchNet, we are dedicated to your success. We strive to exceed your expectations and provide you with a seamless and exceptional experience. Trust us with your healthcare research paper and let our expert writers bring your ideas to life with professionalism, accuracy, and academic excellence.
Customized Solutions for Your Research Needs
Are you a health sciences student in search of professional assistance for your healthcare research paper? Look no further than iResearchNet. We are here to empower your academic journey and help you excel in your research endeavors. With our comprehensive writing services and commitment to excellence, we provide the necessary tools and expert guidance to ensure your success.
At iResearchNet, we understand the unique challenges that come with writing healthcare research papers. Our team of expert degree-holding writers specializes in the health sciences field, allowing us to deliver customized solutions tailored to your specific research needs. Whether you need assistance in selecting a research topic, conducting in-depth literature reviews, analyzing data, or crafting a well-structured paper, we have the expertise to guide you every step of the way.
Take the next step in your healthcare research journey and unlock your academic potential with iResearchNet. Order your custom healthcare research paper today and let our expert writers bring your ideas to life with professionalism, accuracy, and academic excellence. Trust us to provide you with the guidance and support you need to achieve your research goals and make a meaningful impact in the field of healthcare.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

5 Critical Priorities for the U.S. Health Care System
by Marc Harrison

Summary .
The pandemic has starkly revealed the many shortcomings of the U.S. health care system — as well as the changes that must be implemented to make care more affordable, improve access, and do a better job of keeping people healthy. In this article, the CEO of Intermountain Healthcare describes five priorities to fix the system. They include: focus on prevention, not just treating sickness; tackle racial disparities; expand telehealth and in-home services; build integrated systems; and adopt value-based care.
Since early 2020, the dominating presence of the Covid-19 pandemic has redefined the future of health care in America. It has revealed five crucial priorities that together can make U.S. health care accessible, more affordable, and focused on keeping people healthy rather than simply treating them when they are sick.
Partner Center
- Mission and objectives
- History and achievements
- Secretariat
- Celebrating over two decades of advancing and supporting health policy and systems research
- Working in partnership
- Supporting the generation of knowledge
- Strengthening capacities
- Embedded research
- Evidence synthesis
- Gender and intersectionality
- Primary health care
- Systems thinking
- Subscribe to our newsletter »
- All publications
- Core documents
- Project documents
- Teaching and training material »
- Feature stories
- Current calls »
- Archive of past calls »
- What we do /
- What is Health Policy and Systems Research (HPSR)?
Section navigation
- How we work
- Thematic areas of focus
Health policy and systems research (HPSR) is an emerging field that seeks to understand and improve how societies organize themselves in achieving collective health goals, and how different actors interact in the policy and implementation processes to contribute to policy outcomes. By nature, it is inter-disciplinary, a blend of economics, sociology, anthropology, political science, public health and epidemiology that together draw a comprehensive picture of how health systems respond and adapt to health policies, and how health policies can shape − and be shaped by − health systems and the broader determinants of health.
Health policy and systems research can be employed at several points in the policy cycle, from getting an issue onto the policy agenda to evaluating and learning from implemented policies. In this way, HPSR is characterized not by any particular methodology, but the types of questions it addresses. It focuses primarily upon the more upstream aspects of health, organizations and policies, rather than clinical or preventive services or basic scientific research (for example into cell or molecular structures). It covers a wide range of questions − from financing to governance − and issues surrounding implementation of services and delivery of care in both the public and private sectors. It is a crucial policy analysis tool − of both policies and processes − including the role, interests and values of key actors at local, national and global levels.
The appropriate mix of disciplines to be used in HPSR depends largely on the nature of the research question being addressed. An evaluation of a health insurance scheme might draw upon economics to understand the financial consequences of the scheme and its impact upon demand for services, anthropology to understand various socio-cultural and organizational aspects as well as patterns of consumption, and epidemiology to understand its health consequences.
HPSR and the building blocks of a health system
HPSR can address any or several of the health systems building blocks (see graphic) and their ultimate objective to promote the coverage, quality, efficiency and equity of health systems. In doing so, it acknowledges the inherent connections and dynamics among the different building blocks in assessing and understanding how interventions might play out across them. It also seeks to unpack the behaviour, reactions, and interconnectedness of health systems and the people within those systems. The way HPSR conceptualizes and analyzes these interactions helps to illuminate not only what works, but for whom, and under what circumstances.
Linking health policy with health systems research
Why health policy and health systems research? Why are these two different domains fused into one? While seemingly separate − with health policy research principally studying how different actors interact in the policy and implementation processes and contribute to policy outcomes, and health systems research addressing questions such as the coverage, quality, efficiency and equity of health systems − the two have clear and multiple synergies:
- Health policies are subject to political processes that govern health systems. Understanding these processes is not only critical in the design of effective policies, but in the creation of evidence to inform those policies. Health policies and health systems are not separate entities: HPSR is a recognition that everything is connected.
- Understanding the processes and dynamics of health systems can directly inform policy- and decision-making.
- Active linkage and exchange between health system researchers, decision-makers and other research-users promotes evidence-informed policy and policy-informed research.
- A systems perspective is critical in evaluating and learning from implemented policies
- Removing both from their silos builds the capacities of key actors in health policy, in health systems research, and creates actors versed and able in both.

WHO Strategy on Health Policy and Systems Research
The WHO Strategy on Health Policy and Systems Research, Changing Mindsets, advocates for greater generation and use of research evidence in health policy...

Health Policy and Systems Research
Health Policy and Systems Research - A Methodology Reader is a collection of high quality papers that demonstrates the application of different health...

World Report on Health Policy and Systems Research
The report describes the evolution of the field and provides figures on the number of publications produced, funding trends and institutional capacity...
- Privacy Policy

Home » 500+ Medical Research Topic Ideas
500+ Medical Research Topic Ideas
Table of Contents

Medical research plays a crucial role in advancing healthcare and improving human health. It involves the scientific study of various aspects of medicine and health, including the causes, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases. Medical research is a dynamic and ever-evolving field, with new discoveries and breakthroughs happening all the time. It encompasses a wide range of disciplines, from basic science to clinical research, and involves collaboration between scientists, doctors, and other healthcare professionals. In this article, we will explore some exciting new and latest medical research topic ideas that are currently trending in the field. These Research Topics cover a variety of areas, including genetics, infectious diseases, mental health, and more.
Medical Research Topic Ideas
Medical Research Topic Ideas are as follows:
- The efficacy of mindfulness meditation in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety
- The effects of vitamin D supplementation on bone health in postmenopausal women
- The impact of social media on body image and eating disorders in adolescents
- The effectiveness of telemedicine in improving access to healthcare in rural communities
- The benefits and risks of long-term use of statins for cholesterol management
- The role of gut microbiota in the development of autoimmune diseases
- The potential of gene therapy for the treatment of genetic disorders
- The relationship between sleep disorders and cardiovascular disease
- The use of artificial intelligence in diagnosing and treating cancer
- The effect of exercise on cognitive function in older adults
- The impact of environmental factors on the development of asthma in children
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy for the treatment of PTSD in veterans
- The potential benefits of psychedelic-assisted therapy for the treatment of mental illness
- The relationship between diet and risk of developing type 2 diabetes
- The role of epigenetics in the development of psychiatric disorders
- The impact of COVID-19 on mental health and well-being
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction in improving quality of life in cancer patients
- The impact of childhood trauma on the development of mental illness in adulthood
- The benefits and risks of hormone replacement therapy for menopausal women
- The effect of music therapy on reducing symptoms of dementia in older adults
- The relationship between gut microbiota and obesity
- The impact of socioeconomic status on health outcomes
- The effectiveness of acupuncture in treating chronic pain
- The use of stem cells in regenerative medicine
- The impact of air pollution on respiratory health
- The potential of nanotechnology in drug delivery
- The relationship between social support and mental health
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions for addiction treatment
- The role of inflammation in the development of Alzheimer’s disease
- The use of virtual reality in pain management
- The impact of exercise on mental health in adolescents
- The effectiveness of group therapy for the treatment of substance abuse
- The relationship between sleep and weight management
- The benefits and risks of using medical marijuana for chronic pain management
- The role of the immune system in the development of autoimmune diseases
- The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation therapy for traumatic brain injury patients
- The impact of maternal stress on fetal development
- The relationship between physical activity and cardiovascular health
- The potential of gene editing for the treatment of genetic disorders
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions for reducing symptoms of postpartum depression.
- The impact of social media on mental health
- Investigating the use of virtual reality in pain management
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions for depression
- Exploring the relationship between sleep and anxiety
- Examining the efficacy of telemedicine in delivering mental health care
- Investigating the impact of environmental factors on the development of cancer
- The effect of exercise on cognitive function in elderly individuals
- Examining the potential benefits of psychedelic-assisted therapy for PTSD
- The relationship between diet and cardiovascular disease
- Investigating the impact of air pollution on respiratory health
- Examining the effects of social isolation on mental and physical health
- The use of machine learning in diagnosing medical conditions
- Investigating the effectiveness of acupuncture in pain management
- The impact of childhood trauma on mental and physical health outcomes in adulthood
- Examining the relationship between stress and autoimmune diseases
- The effect of music therapy on mental health outcomes
- Investigating the impact of gender on healthcare outcomes
- Examining the relationship between sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions for chronic pain
- Investigating the potential benefits of medical marijuana for chronic pain management
- Examining the impact of climate change on infectious disease transmission
- The use of robotics in surgery
- Investigating the relationship between alcohol consumption and cancer risk
- The effect of meditation on blood pressure control
- Examining the impact of social determinants of health on healthcare outcomes
- The role of genetics in the development of mental health conditions
- Investigating the efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy for anxiety disorders
- Examining the relationship between inflammation and depression
- The impact of shift work on sleep and circadian rhythms
- Investigating the potential benefits of probiotics in gut health
- Examining the relationship between diet and mental health outcomes
- The effectiveness of art therapy for individuals with dementia
- Investigating the relationship between chronic pain and mental health outcomes
- The impact of artificial intelligence on medical diagnosis and treatment
- Examining the effectiveness of exercise in treating depression
- Investigating the relationship between inflammation and cardiovascular disease
- The effect of aromatherapy on anxiety and stress
- Examining the impact of social support on mental health outcomes
- The effectiveness of hypnotherapy in pain management.
- The role of gut microbiota in immune system modulation
- Effects of intermittent fasting on insulin sensitivity in obese individuals
- Impact of smartphone usage on sleep quality and quantity
- The potential therapeutic effects of CBD on anxiety disorders
- Association between shift work and cardiovascular disease
- Efficacy and safety of psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy in treating depression
- The relationship between stress and autoimmune diseases
- Novel therapies for Alzheimer’s disease
- The effects of high-intensity interval training on metabolic syndrome
- The role of epigenetics in the development of cancer
- The effectiveness of virtual reality in pain management
- The effects of social media on body image and eating disorders
- The association between air pollution and respiratory diseases
- Effects of mindfulness meditation on stress and anxiety in healthcare workers
- The potential benefits of ketogenic diet in treating epilepsy
- The relationship between sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease
- The impact of climate change on infectious disease outbreaks
- The effectiveness of exercise in preventing falls in the elderly
- The effects of blue light exposure on circadian rhythm and sleep quality
- The association between alcohol consumption and liver disease
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating obsessive-compulsive disorder
- The role of gut-brain axis in mental health disorders
- The association between chronic inflammation and cancer
- The efficacy and safety of probiotics in treating irritable bowel syndrome
- The effects of social isolation on mental health in the elderly
- The impact of exercise on cognitive function in Parkinson’s disease patients
- The association between vitamin D deficiency and autoimmune diseases
- The potential therapeutic effects of music therapy in dementia patients
- The effects of second-hand smoke on cardiovascular health
- The association between maternal smoking and infant health outcomes
- The role of microbiome in the development of allergies
- The association between sleep duration and obesity
- The effects of blue light-blocking glasses on sleep quality and quantity
- The potential therapeutic effects of ketamine in treating depression
- The association between gut dysbiosis and inflammatory bowel disease
- The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation therapy in traumatic brain injury patients
- The impact of early childhood stress on adult mental health
- The role of inflammation in the development of type 2 diabetes
- The potential benefits of plant-based diets in preventing chronic diseases.
- The effects of exercise on cognitive function in aging adults
- The association between sleep disorders and cardiovascular disease
- The potential therapeutic effects of psilocybin in treating addiction
- The role of gut microbiota in the development of autism spectrum disorder
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in treating depression
- The effects of air pollution on cognitive function
- The association between maternal mental health and child development
- The potential therapeutic effects of cannabis in treating chronic pain
- The role of diet in the prevention and management of diabetes
- The effects of social support on mental health in cancer patients
- The association between shift work and mental health disorders
- The efficacy of antiviral therapies in treating COVID-19
- The effects of exercise on bone health in postmenopausal women
- The association between sleep disorders and obesity
- The potential therapeutic effects of mindfulness meditation in treating anxiety disorders
- The role of gut microbiota in the development of metabolic disorders
- The effectiveness of virtual reality therapy in treating phobias
- The association between social support and immune system function
- The impact of early life stress on adult cardiovascular health
- The potential benefits of intermittent fasting in cancer prevention
- The effects of air pollution on pregnancy outcomes
- The association between maternal obesity and child health outcomes
- The efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating post-traumatic stress disorder
- The effects of sedentary behavior on metabolic health
- The potential therapeutic effects of omega-3 fatty acids in treating depression
- The role of microbiome in the development of obesity
- The association between social isolation and cognitive decline in older adults
- The impact of environmental toxins on child development
- The potential benefits of plant-based diets in treating metabolic disorders
- The effects of sleep deprivation on cognitive function
- The association between maternal stress and fetal development
- The efficacy of pharmacological interventions in treating anxiety disorders
- The effects of air pollution on respiratory health in children
- The association between social support and cardiovascular health
- The potential therapeutic effects of mindfulness meditation in treating chronic pain
- The role of diet in the prevention and management of cardiovascular disease
- The effects of exercise on mental health in children and adolescents
- The association between social support and cancer survival rates
- The impact of environmental factors on epigenetic modifications and disease susceptibility.
- The effects of exercise on immune function
- The association between maternal obesity and infant health outcomes
- The impact of air pollution on cognitive function in children
- The association between sleep deprivation and mental health disorders
- The effectiveness of virtual reality in rehabilitation after stroke
- The role of the microbiome in the development of obesity
- The impact of noise pollution on cardiovascular health
- The association between depression and cardiovascular disease
- The association between periodontal disease and cardiovascular health
- The impact of social support on mental health outcomes in cancer patients
- The potential therapeutic effects of melatonin in treating sleep disorders
- The association between air pollution and cognitive decline in older adults
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating social anxiety disorder
- The impact of exercise on bone health in postmenopausal women
- The association between alcohol consumption and breast cancer risk
- The effects of blue light exposure on melatonin secretion and sleep quality
- The potential therapeutic effects of stem cells in treating Parkinson’s disease
- The role of inflammation in the development of depression
- The association between gut dysbiosis and depression
- The effectiveness of music therapy in reducing anxiety in cancer patients
- The impact of social media on mental health in adolescents
- The potential therapeutic effects of ketamine in treating post-traumatic stress disorder
- The association between vitamin D deficiency and cardiovascular disease
- The effects of chronic stress on immune function
- The potential benefits of Mediterranean diet in preventing cardiovascular disease
- The impact of noise pollution on sleep quality and quantity
- The association between sedentary behavior and depression
- The effects of air pollution on fetal development and pregnancy outcomes
- The potential therapeutic effects of acupuncture in treating anxiety disorders
- The role of microbiome in the development of multiple sclerosis
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction in treating chronic pain
- The impact of artificial sweeteners on metabolic health
- The association between sleep duration and cardiovascular disease
- The effects of social isolation on immune function in older adults
- The potential therapeutic effects of omega-3 fatty acids in treating depression.
- The effects of exercise on cognitive function in older adults
- The association between maternal mental health and infant development
- The potential therapeutic effects of probiotics in treating depression
- The impact of air pollution on lung health in children
- The association between sleep quality and academic performance in adolescents
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating insomnia
- The role of gut microbiota in the development of metabolic syndrome
- The potential therapeutic effects of ayahuasca in treating addiction
- The impact of green space on mental health in urban areas
- The association between sedentary behavior and cardiometabolic risk factors
- The effects of blue light on mood and cognitive performance in shift workers
- The potential benefits of vegan diets in preventing chronic diseases
- The impact of social support on mental health in older adults
- The association between air pollution and lung cancer risk
- The effects of exercise on mental health in cancer survivors
- The potential therapeutic effects of ketamine in treating bipolar disorder
- The role of the microbiome in the development of rheumatoid arthritis
- The association between maternal nutrition and fetal development
- The effects of sleep deprivation on immune function
- The potential benefits of mindfulness meditation in managing chronic pain
- The impact of noise pollution on sleep-disordered breathing
- The association between sedentary behavior and breast cancer risk
- The effects of blue light exposure on retinal health
- The potential therapeutic effects of deep brain stimulation in treating depression
- The role of gut microbiota in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- The association between air pollution and neurodegenerative diseases
- The effects of social support on immune function in cancer patients
- The potential therapeutic effects of acupuncture in treating migraines
- The impact of light pollution on sleep quality and quantity
- The association between sedentary behavior and type 2 diabetes risk
- The effects of mindfulness meditation on cognitive function in older adults
- The potential benefits of the DASH diet in preventing hypertension
- The impact of social media on body dissatisfaction and eating disorders in adolescents
- The association between air pollution and kidney disease
- The effects of chronic stress on cardiovascular health
- The potential therapeutic effects of gene therapy in treating inherited diseases
- The role of microbiome in the development of atopic dermatitis
- The association between maternal smoking and childhood obesity
- The effects of blue light exposure on visual function and eye health
- The potential therapeutic effects of electroconvulsive therapy in treating depression.
Healthcare Research Topics for College Students
- The impact of healthcare policies on patient outcomes
- The effectiveness of telemedicine in improving access to healthcare
- The role of cultural competency in healthcare delivery
- The impact of social determinants of health on healthcare outcomes
- The effectiveness of different types of healthcare interventions
- The role of genetics in predicting and preventing chronic diseases
- The impact of the opioid epidemic on healthcare delivery
- The effectiveness of alternative medicine in managing chronic conditions
- The role of technology in improving patient safety
- The impact of healthcare provider burnout on patient care
- The effectiveness of different healthcare models in managing chronic diseases
- The role of patient education in improving healthcare outcomes
- The impact of healthcare disparities on access to care and health outcomes
- The effectiveness of healthcare systems in responding to public health emergencies
- The role of nutrition in disease prevention and management
- The impact of healthcare policy on healthcare costs and spending
- The effectiveness of mental health interventions in improving overall health outcomes
- The role of healthcare systems in addressing health disparities
- The impact of healthcare data analytics on clinical decision making
- The effectiveness of healthcare interventions in reducing healthcare-associated infections
- The role of patient-centered care in improving healthcare outcomes
- The impact of healthcare regulations on patient safety
- The effectiveness of vaccination programs in preventing infectious diseases
- The role of healthcare systems in promoting healthy lifestyle behaviors
- The impact of chronic diseases on healthcare costs and quality of life
- The effectiveness of preventative healthcare in improving health outcomes
- The role of healthcare technology in improving healthcare delivery
- The impact of healthcare funding on healthcare outcomes
- The effectiveness of healthcare interventions in managing chronic pain
- The role of healthcare providers in promoting health equity.
Community Medicine Research Topics for Medical Students
- The impact of community-based interventions on reducing the burden of non-communicable diseases in low-income communities.
- The effectiveness of vaccination campaigns in preventing infectious diseases in marginalized communities.
- The relationship between air pollution and respiratory health in urban communities.
- The prevalence and risk factors of substance abuse among homeless populations.
- The impact of social determinants of health on health outcomes in rural communities.
- The role of community health workers in improving maternal and child health outcomes in low-resource settings.
- The association between food insecurity and obesity in low-income populations.
- The prevalence and risk factors of mental health disorders among adolescents in urban communities.
- The effectiveness of school-based health promotion programs in improving health behaviors among children and adolescents.
- The role of community-based participatory research in addressing health disparities in underserved populations.
- The impact of social support networks on mental health outcomes among elderly populations.
- The relationship between access to healthcare services and health outcomes in rural communities.
- The effectiveness of smoking cessation interventions in reducing the burden of tobacco-related diseases.
- The prevalence and risk factors of sexually transmitted infections among young adults in urban communities.
- The role of community-based organizations in promoting healthy behaviors and preventing chronic diseases.
- The impact of climate change on the incidence and distribution of infectious diseases.
- The prevalence and risk factors of intimate partner violence among women in low-income communities.
- The effectiveness of health education programs in improving health literacy and health outcomes in underserved populations.
- The relationship between social support and adherence to treatment among patients with chronic diseases.
- The prevalence and risk factors of hypertension and diabetes in urban communities.
- The impact of community-based interventions on reducing healthcare costs and improving health outcomes.
- The role of mobile health technologies in improving access to healthcare services in rural communities.
- The prevalence and risk factors of obesity among children and adolescents in low-income communities.
- The effectiveness of community-based interventions in promoting healthy behaviors among pregnant women.
- The impact of housing conditions on health outcomes in marginalized communities.
- The relationship between access to healthy food and health outcomes in urban communities.
- The prevalence and risk factors of depression among elderly populations in rural communities.
- The role of social media in promoting healthy behaviors and preventing diseases among young adults.
- The effectiveness of telemedicine in improving access to healthcare services in underserved populations.
- The prevalence and risk factors of infectious diseases among migrant populations in urban areas.
Surgery Research Topics for Medical Students
- The efficacy and safety of minimally invasive surgery for various conditions
- Comparison of laparoscopic and open surgery for common procedures
- The impact of surgeon experience on surgical outcomes
- Analysis of postoperative complications and their management
- The role of robotics in surgery
- Investigating the use of artificial intelligence in surgery
- The effectiveness of non-pharmacological pain management techniques after surgery
- The effect of preoperative anxiety on postoperative recovery
- Evaluation of different surgical approaches for breast cancer treatment
- The benefits and risks of surgical treatment for obesity
- Investigating the use of stem cells in tissue repair following surgery
- The influence of nutrition on postoperative recovery and wound healing
- Analysis of the psychological impact of surgery on patients
- The effect of different anesthesia methods on postoperative outcomes
- Comparison of outcomes between day surgery and inpatient surgery
- Evaluation of the use of surgical checklists in improving patient safety
- The impact of age on surgical outcomes and recovery
- Investigating the use of 3D printing in surgical planning and implant design
- The benefits and risks of bariatric surgery in patients with diabetes
- The role of surgery in the treatment of chronic pain
- The efficacy of arthroscopic surgery for joint conditions
- The use of lasers in surgery
- Investigating the use of virtual reality in surgical training and education
- The effect of preoperative counseling on patient satisfaction and outcomes
- The impact of comorbidities on surgical outcomes
- Analysis of the economic impact of different surgical approaches
- Investigating the use of telemedicine in surgical consultations and follow-up care
- The effectiveness of surgical treatment for endometriosis
- Comparison of outcomes between single-incision and multiport laparoscopic surgery
- The use of robotics in urologic surgery.
Research Projects for Undergraduate Medical Students
- Investigating the role of genetics in the development of cancer
- Analyzing the effectiveness of different types of pain management strategies in postoperative patients
- Evaluating the impact of diet and exercise on obesity-related health outcomes
- Examining the relationship between sleep quality and mental health in medical students
- Investigating the efficacy of different types of antibiotics in treating common bacterial infections
- Analyzing the impact of electronic medical record systems on patient care
- Evaluating the effectiveness of different types of vaccines in preventing infectious diseases
- Examining the relationship between maternal nutrition and fetal development
- Investigating the use of telemedicine in delivering healthcare services to rural populations
- Analyzing the impact of smoking on lung function and respiratory health
- Evaluating the effectiveness of different types of rehabilitation programs for stroke patients
- Examining the relationship between physical activity and cardiovascular health
- Investigating the use of stem cells in treating various medical conditions
- Analyzing the impact of stress on mental and physical health outcomes
- Evaluating the effectiveness of different types of medical interventions in managing chronic pain
- Examining the relationship between social support and mental health outcomes in patients with chronic illnesses
- Investigating the use of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing anxiety and depression
- Analyzing the impact of environmental factors on health outcomes in urban populations
- Evaluating the effectiveness of different types of cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery
- Examining the relationship between nutrition and mental health in older adults
- Investigating the use of mobile health technologies in promoting healthy behaviors
- Analyzing the impact of air pollution on respiratory health in children
- Evaluating the effectiveness of different types of treatments for substance use disorders
- Examining the relationship between socioeconomic status and health outcomes
- Investigating the use of music therapy in managing pain and anxiety in hospitalized patients
- Analyzing the impact of social media on mental health outcomes in adolescents
- Evaluating the effectiveness of different types of interventions in managing symptoms of depression and anxiety in cancer patients
- Examining the relationship between sleep and cognitive function in older adults
- Investigating the use of animal-assisted therapy in promoting physical and mental health
- Analyzing the impact of climate change on health outcomes in vulnerable populations
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

500+ Climate Change Research Topics

500+ Quantitative Research Titles and Topics

1100+ Research Paper Topics

500+ History Research Paper Topics

500+ Music Research Topics

300+ AP Research Topic Ideas

Major Areas of Research
IHSP’s research contributes to health system improvements worldwide by emphasizing six interrelated areas of focus. The combination of operations and academically-oriented research allow the findings and methodologies of Program members’ research to reach a wide audience and inform policymaking. A listing of peer-reviewed journal articles, project-related technical analyses and reports, and other material emanating from IHSP member research activities can be found on the publications page.
The six areas of IHSP research include the most relevant issues for low- and middle-income countries. These areas include :
- Institutional reforms and capacity building. Many challenges faced by governments around the world center around the management, organization and effectiveness of their health systems. IHSP’s research in this area emphasizes decentralization, organizational reform of ministries of health, human resource strategic planning, and case method management training.
- Politics and governance. Technical solutions to health systems deficiencies must take the political and governmental contexts into account to be effective and sustainable. IHSP’s research in this area emphasizes political strategies, advocacy and approaches to working in fragile states.
- Sustainability and Implementation Science. Pioneers in the study of sustainability and leaders in the new field of implementation science, IHSP faculty are involved in several projects to assess the sustainability of projects funded by donors and to provide effective recommendations to strengthen sustainability as well as develop useful evaluation research on the implementation of scale up and replication of innovations
- Health system financing: Strengthening the financial resources and reducing the financial risks of illness that drive many into poverty requires innovative approaches in different country contexts. IHSP’s research in this area emphasizes social health insurance, community financing and national health accounts.
- Public/Private partnerships: Involving and working with the private sector is crucial to long-term improvements in health systems quality and efficiency. IHSP’s research in this area emphasizes assessments of private markets and public/private partnerships.
- Building community capacities. Community involvement in delivery of health services is a key to promoting healthy behaviors and utilization of the health system. IHSP’s research in this area emphasizes the role of social capital in improving health systems delivery and innovative ways to make community health workers more effective.
- Reproductive health and HIV/AIDS projects. The Sustainable Development Goals and worldwide efforts to control the spread of HIV/AIDS have put a continuing concern on improving reproductive health services. IHSP’s research in this area emphasizes strengthening health system support for maternal and neonatal health, shifting family planning preferences from abortion to contraception and addressing economic and political aspects of HIV/AIDS programs. Recent studies of the Global Fund for HIV/AIDS and PEPFAR make recommendations to further health system strengthening by these funders.
Current Research Decentralization Human Resources Strategic Planning Politics of the Policy Process Health Sector Reform Sustainability and Implementation Science
Additional Research Topics Making Health Care Work Better through Reforms to Health Care Public and Private Provision Assessing the Impact of Aging Populations in Developing Countries on Health Expenditures Health Expenditures and the Elderly: A Survey of Issues in Forecasting, Methods Used, and Relevance for Developing Countries Developing National Health Accounts in Turkey The Role of Private Health Care Providers in Priority Public Health Programs Health Systems Resource Center Health System Reform Strategy for Andhra Pradesh State, India Executive Summary of India Andhra Pradesh Report Phase I HIV/AIDS and Health Expenditures in Nigeria Nigeria HIV/AIDS Accounts Report Out-of-pocket Payments and Informal Payments for Health in Middle Income European Countries
University Wide Publications through D.A.S.H. (Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard)
Please email us for more information at [email protected] .
We can also be reached by telephone at (USA) 617-432-0418
News from the School

Air pollution exposure in infancy may limit economic mobility in adulthood

Reducing health inequities in the Mississippi Delta

Climate change and planetary health concentration launches

Orientation 2024: New students encouraged to engage across differences
- Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
- Biostatistics
- Environmental Health and Engineering
- Epidemiology
- Health Policy and Management
- Health, Behavior and Society
- International Health
- Mental Health
- Molecular Microbiology and Immunology
- Population, Family and Reproductive Health
- Program Finder
- Admissions Services
- Course Directory
- Academic Calendar
- Hybrid Campus
- Lecture Series
- Convocation
- Strategy and Development
- Implementation and Impact
- Integrity and Oversight
- In the School
- In the Field
- In Baltimore
- Resources for Practitioners
- Articles & News Releases
- In The News
- Statements & Announcements
- At a Glance
- Student Life
- Strategic Priorities
- Inclusion, Diversity, Anti-Racism, and Equity (IDARE)
- What is Public Health?
- Recent Dissertation Titles
- MSPH Field Placements
- Master's Essays
- MAS Application Fee Waiver Requirements
- Master of Arts and Master of Science in Public Health (MA/MSPH)
- Master of Arts in Public Health Biology (MAPHB)
- Master of Bioethics (MBE)
- Mission, Vision, and Values
- Student Experience
- Program Outcomes
- For Hopkins Undergraduate Students
- Master of Health Science (MHS) - Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
- Master of Health Science (MHS) - Department of Epidemiology
- Alumni Update
- MHS Combined with a Certificate Program
- Master of Health Science (MHS) - Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology
- Bachelor's/MHS in Health Economics and Outcomes Research
- MHS HEOR Careers
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Master of Health Science (MHS)
- Concurrent School-Wide Master of Health Science Program in Biostatistics
- Master of Health Science - Department of Population, Family and Reproductive Health
- Master of Health Science Online (MHS) - Department of Population, Family and Reproductive Health
- Careers in Health Economics
- Core Competencies
- Meet the Director
- What is Health Economics
- MPH Capstone Schedule
- Concentrations
- Online/Part-Time Format
- Requirements
- Tuition and Funding
- Executive Board Faculty
- Master of Science (ScM) - Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
- Master of Science (ScM) - Department of Biostatistics
- Master of Science (ScM) - Department of Epidemiology
- Master of Science (ScM) - Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology
- Bachelor's/MSPH in Health Policy
- FAQ for MSPH in Health Policy
- Field Placement Experience
- MSPH Capstone
- MSPH Practicum
- Required and Elective Courses
- Student Timeline
- Career Opportunities
- 38-Week Dietetics Practicum
- Completion Requirements
- MSPH/RD Program FAQ
- Program Goals
- Biophysics and Structural Biology
- Cancer Biology
- Cell Biology
- Cellular Stress and Cell Signaling
- Chemical Biology and Proteomics
- Genetics, Genomics, and Gene Regulation
- Immunology and Infectious Diseases
- Translational Research
- Program Scope
- Application Fee Waiver Requirements
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) - Department of Biostatistics
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) - Department of Epidemiology
- Program Goals and Expectations
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) - Department of Molecular Microbiology and Immunology
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) - Department of Population, Family and Reproductive Health
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Clinical Investigation
- Recent Graduates and Dissertation Titles
- PhD Funding
- PhD TA Requirement
- JHU-Tsinghua Doctor of Public Health
- Prerequisites
- Concentration in Women’s and Reproductive Health
- Custom Track
- Concentration in Environmental Health
- Concentration in Global Health: Policy and Evaluation
- Concentration in Health Equity and Social Justice
- Concentration in Health Policy and Management
- Concentration in Implementation Science
- Combined Bachelor's / Master's Programs
- Concurrent MHS Option for BSPH Doctoral Students
- Concurrent MSPH Option for JHSPH Doctoral students
- Doctor of Medicine and Doctor of Philosophy (MD/PhD)
- Adolescent Health Certificate Program
- Bioethics Certificate Program
- Clinical Trials Certificate Program
- Community- Based Public Health Certificate Program
- Demographic Methods Certificate Program
- Epidemiology for Public Health Professionals Certificate Program
- Evaluation: International Health Programs Certificate Program
- Frequently Asked Questions for Certificate Programs
- Gender and Health Certificate Program
- Gerontology Certificate Program
- Global Digital Health Certificate Program
- Global Health Certificate Program
- Global Health Practice Certificate Program
- Health Communication Certificate Program
- Health Disparities and Health Inequality Certificate Program
- Health Education Certificate Program
- Health Finance and Management Certificate Program
- Health and Human Rights Certificate Program
- Healthcare Epidemiology and Infection Prevention and Control Certificate Program
- Humanitarian Health Certificate Program
- Implementation Science and Research Practice Certificate Program
- Injury and Violence Prevention Certificate Program
- International Healthcare Management and Leadership Certificate Program
- Leadership for Public Health and Healthcare Certificate Program
- Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, and Queer (LGBTQ) Public Health Certificate Program
- Maternal and Child Health Certificate Program
- Mental Health Policy, Economics and Services Certificate Program
- Non-Degree Students General Admissions Info
- Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety Certificate Program
- Population Health Management Certificate Program
- Population and Health Certificate Program
- Public Health Advocacy Certificate Program
- Public Health Economics Certificate Program
- Public Health Informatics Certificate Program
- Public Health Practice Certificate Program
- Public Health Training Certificate for American Indian Health Professionals
- Public Mental Health Research Certificate Program
- Quality, Patient Safety and Outcomes Research Certificate Program
- Quantitative Methods in Public Health Certificate Program
- Requirements for Successful Completion of a Certificate Program
- Rigor, Reproducibility, and Responsibility in Scientific Practice Certificate Program
- Risk Sciences and Public Policy Certificate Program
- Spatial Analysis for Public Health Certificate Program
- Training Certificate in Public Health
- Tropical Medicine Certificate Program
- Tuition for Certificate Programs
- Vaccine Science and Policy Certificate Program
- Online Student Experience
- MAS and Affiliated Certificate Programs
- Barcelona Information
- Registration, Tuition, and Fees
- Agency Scholarship Application
- General Scholarship Application
- UPF Scholarship Application
- Course Evaluations
- Online Courses
- Registration
- General Institute Tuition Information
- International Students
- Directions to the Bloomberg School
- All Courses
- Important Guidance for ONSITE Students
- D.C. Courses
- Registration and Fees
- Cancellation and Closure Policies
- Application Procedures
- Career Search
- Current Activities
- Current Trainees
- Related Links
- Process for Appointing Postdoctoral Fellows
- Message from the Director
- Program Details
- Admissions FAQ
- Current Residents
- Elective Opportunities for Visiting Trainees
- What is Occupational and Environmental Medicine?
- Admissions Info
- Graduates by Year
- Compensation and Benefits
- How to Apply
- Academic Committee
- Course Details and Registration
- Tuition and Fees
- ONLINE SOCI PROGRAM
- Principal Faculty
- General Application
- JHHS Application
- Our Faculty
- Descripción los Cursos
- Programa en Epidemiología para Gestores de Salud, Basado en Internet
- Consultants
- Britt Dahlberg, PhD
- Joke Bradt, PhD, MT-BC
- Mark R. Luborsky, PhD
- Marsha Wittink, PhD
- Rebekka Lee, ScD
- Su Yeon Lee-Tauler, PhD
- Theresa Hoeft, PhD
- Vicki L. Plano Clark, PhD
- Program Retreat
- Mixed Methods Applications: Illustrations
- Announcements
- 2023 Call for Applications
- Jennifer I Manuel, PhD, MSW
- Joke Bradt, PhD
- Josiemer Mattei, PhD, MPH
- Justin Sanders, MD, MSc
- Linda Charmaran, PhD
- Nao Hagiwara, PhD
- Nynikka R. A. Palmer, DrPH, MPH
- Olayinka O. Shiyanbola, BPharm, PhD
- Sarah Ronis, MD, MPH
- Susan D. Brown, PhD
- Tara Lagu, MD, MPH
- Theresa Hoft, PhD
- Wynne E. Norton, PhD
- Yvonne Mensa-Wilmot, PhD, MPH
- A. Susana Ramírez, PhD, MPH
- Animesh Sabnis, MD, MSHS
- Autumn Kieber-Emmons, MD, MPH
- Benjamin Han, MD, MPH
- Brooke A. Levandowski, PhD, MPA
- Camille R. Quinn, PhD, AM, LCSW
- Justine Wu, MD, MPH
- Kelly Aschbrenner, PhD
- Kim N. Danforth, ScD, MPH
- Loreto Leiva, PhD
- Marie Brault, PhD
- Mary E. Cooley, PhD, RN, FAAN
- Meganne K. Masko, PhD, MT-BC/L
- PhuongThao D. Le, PhD, MPH
- Rebecca Lobb, ScD, MPH
- Allegra R. Gordon, ScD MPH
- Anita Misra-Hebert, MD MPH FACP
- Arden M. Morris, MD, MPH
- Caroline Silva, PhD
- Danielle Davidov, PhD
- Hans Oh, PhD
- J. Nicholas Dionne-Odom, PhD RN ACHPN
- Jacqueline Mogle, PhD
- Jammie Hopkins, DrPH, MS
- Joe Glass, PhD MSW
- Karen Whiteman, PhD MSW
- Katie Schultz, PhD MSW
- Rose Molina, MD
- Uriyoán Colón-Ramos, ScD MPA
- Andrew Riley, PhD
- Byron J. Powell, PhD, LCSW
- Carrie Nieman MD, MPH
- Charles R. Rogers, PhD, MPH, MS, CHES®
- Emily E. Haroz, PhD
- Jennifer Tsui, Ph.D., M.P.H.
- Jessica Magidson, PhD
- Katherine Sanchez, PhD, LCSW
- Kelly Doran, MD, MHS
- Kiara Alvarez, PhD
- LaPrincess C. Brewer, MD, MPH
- Melissa Radey, PhD, MA, MSSW
- Sophia L. Johnson, PharmD, MPH, PhD
- Supriya Gupta Mohile, MD, MS
- Virginia McKay, PhD
- Andrew Cohen, MD, PhD
- Angela Chen, PhD, PMHNP-BC, RN
- Christopher Salas-Wright, PhD, MSW
- Eliza Park MD, MS
- Jaime M. Hughes, PhD, MPH, MSW
- Johanne Eliacin, PhD, HSPP
- Lingrui Liu ScD MS
- Meaghan Kennedy, MD
- Nicole Stadnick, PhD, MPH
- Paula Aristizabal, MD
- Radhika Sundararajan, MD
- Sara Mamo, AuD, PhD
- Tullika Garg, MD MPH FACS
- Allison Magnuson, DO
- Ariel Williamson PhD, DBSM
- Benita Bamgbade, PharmD, PhD
- Christopher Woodrell MD
- Hung-Jui (Ray) Tan, MD, MSHPM
- Jasmine Abrams, PhD
- Jose Alejandro Rauh-Hain, MD
- Karen Flórez, DrPH, MPH
- Lavanya Vasudevan, PhD, MPH, CPH
- Maria Garcia, MD, MPH
- Robert Brady, PhD
- Saria Hassan, MD
- Scherezade Mama, DrPH
- Yuan Lu, ScD
- 2021 Scholars
- Sign Up for Our Email List
- Workforce Training
- Cells-to-Society Courses
- Course/Section Numbers Explained
- Pathway Program with Goucher College
- The George G. Graham Lecture
Health systems management and health sector reform
- Performance-Based Payments, Provider Motivation and Quality of Care in Afghanistan
- Health Systems Strengthening in Post-Conflict Settings: Employee and Patient Satisfaction in Hospitals in Afghanistan
- The Use of Clinical Practice Guidelines to Improve Provider Performance of Well-Child Care in Armenia
- Quality Improvement and Its Effect on Patient Perceptions and Demand for Health Services-Evidence from Uttar Pradesh, India
- The Perception of Quality Among Users of Commune Health Centers and Users of Private Providers in Northern Vietnam
Health financing
- National Health Insurance in Ghana: Politics, Adverse Selection, and the Use of Child Health Services.
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of User Fee Increase in Improving The Quality of Care: Government Primary Health Care Services in Indonesia
- The Impact of Community-Based Health Insurance on Health Care Utilization and Financial Sustainability: The Example of Rwanda
- Impact of Health Insurance on Health Care Utilization in Vietnam
- Stimulating Demand: An Assessment of the Conditional Cash Transfer Project in Afghanistan
Health policy and resource allocation
- Exploring Attitudes and Perceptions of Policymakers and Health Researchers Towards Evidence-Based Health Policymaking in Argentina: A Mixed Methods Approach
- Dual Practice in Kampala, Uganda: A Mixed Methods Study of Management and Policy
- Understanding Political Priority Development for Public Health Issues in Turkey: Lessons from Tobacco Control & Road Safety
- Academic Knowledge Brokers in Kenya: A Mixed Methods Study of Relationships, Characteristics and Strategies
- Decision-Making for Allocation of Public Resources in Decentralized District Health Systems in Uganda
Maternal, neonatal and child health
- Antenatal and Delivery Care in Afghanistan Knowledge and Perceptions of Services, Decision Making for Service Use, and Determinants of Utilization
- Early Maternal Morbidity and Utilization of Delivery Services by Urban Slum Women of Dhaka, Bangladesh
- An Assessment of Maternal Health Service Needs of Immigrant Women Living in East Calgary, Canada
- Health Seeking Behavior of Women and Their Families During Pregnancy, Delivery and Postpartum Period in Nepal
Evaluation of health programs
- Comparison of Biomarker Surveillance of Measles Immunity to Conventional Indicators of Vaccination Coverage
- Qualitative Research to Develop a Framework for Evaluating the Sustainability of Community-Based Child Health Programs Implemented by Non-Government Organizations
- Evaluating the Delivery Huts Program for Promoting Maternal Health in Haryana, India
- Evaluating the Scale-Up of Community Case Management in Malawi: Health System Supports, Health Worker Attitudes, and Equity of Service Provision
Refugee and humanitarian assistance
- Family Relationships and Social Interaction in Post-Conflict South Kivu Province, Eastern Democratic Republic of Congo A Mixed Methods Study with Women from Rural Walungu Territory
- Utilization of Health Services for Children after the Tsunami in Aceh, Indonesia
- Factors Affecting School Enrollments in a Post-Repatriation Context: A Study of Household Roles, Attitudes and Forced Migration Processes in Urban Somaliland
- A Balanced Scorecard for Assessing the Quality and Provision of Health Services in UNHCR Refugee Camps
Injury prevention and control
- Road Traffic Injuries In China: Time Trends, Risk Factors and Economic Development
- Evaluating an Intervention to Prevent Motorcycle Injuries in Malaysia: Process Performance, and Policy
- Injuries and Socioeconomic Status in Iganga and Mayuge, Uganda: Inequities, Consequences and Impacts
- A neglected epidemic of childhood drowning in Bangladesh: Epidemiology, risk factors and potential interventions
Equity and fairness in distribution of health services
- Gender and Access to DOTS Program (Directly Observed Treatment, Short-Course) in a Poor, Rural and Minority Area of Gansu Province, China
- Empowering the Socially Excluded: A Study of Impact on Equity by Gender, Caste and Wealth in Access to Health Care in Rural Parts of Four North Indian States
- Gender, Empowerment, and Women's Health in India: Perceived Morbidity and Treatment-Seeking Behaviors for Symptoms of Reproductive Tract Infections among Women of Rural Gujarat
- Trust in Maternity Care: A Contextual Exploration of Meaning and Determinants in Peri-Urban Kenya
- The Effect of Contracting for Health Services on the Equity of Utilization and Out-of-Pocket Health Expenditure in Rural Afghanistan
Health economics
- The Equity and Cost-Effectiveness of HIV Voluntary Counseling and Testing in Tanzania
- Hospital Coding Practice, Data Quality, And DRG-Based Reimbursement Under the Thai Universal Coverage Scheme
- Willingness-to-Pay and Cost-Benefit Analysis on Introducing HIB Conjugate Vaccine into the Thai Expanded Program on Immunization
- Economic Evaluation of the Costs and Cost-Effectiveness of the Diarrhea Alleviation through Zinc and Oral Rehydration Therapy Program at Scale in Gujarat, India
- The Economics of Non-Communicable Diseases in Rural Bangladesh: Understanding Education Gradients in Mortality and Household Wealth Impacts from an Adult Death
Health outcomes and burden of disease methods
- Measuring the Burden of Disease: Introducing Healthy Life Years
- Measuring the Burden of Injuries in Pakistan Epidemiological and Policy Analysis
- Strengths and Limitations of Population-Based Health Surveys in Developing Countries: A Case Study of National Health Survey of Pakistan: 1990-94
- Approaches to Measuring Non-Fatal Health Outcomes: Disability at the Iganga-Mayuge Demographic Surveillance System in Uganda
- A National Burden of Disease Study for The United Arab Emirates (UAE): Quantifying Health Differentials Between Nationals and Migrants
- Open access
- Published: 24 September 2024
Barriers of Ukrainian refugees and migrants in accessing German healthcare
- Karina Davitian 1 ,
- Peter Noack 2 ,
- Katharina Eckstein 2 ,
- Jutta Hübner 1 &
- Emadaldin Ahmadi 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 1112 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
This study focused on Ukrainian refugees and migrants, a population that, with an ongoing war, is expected to grow in Germany. Over 1 million Ukrainians with exceptional legal status and access to public insurance in Germany significantly burden governmental services, especially German healthcare. It is thus essential to facilitate their integration into the healthcare system and ensure its proper usage. Identifying the obstacles Ukrainian refugees and migrants encounter while accessing healthcare services is crucial to ease their integration.
A qualitative study was conducted from February 2023 to April 2023. Thirty semi-structured interviews were performed with Ukrainian migrants and refugees. The interviews were transcribed verbatim, organized, and categorized. Thematic analysis was performed to identify barriers related to the use of German healthcare services. To assess possible differences in the experiences of Ukrainian refugees and migrants, the responses of these two groups for each topic were analysed separately.
Ukrainian migrants and refugees experience similar barriers while accessing German healthcare services. Predominantly, language barriers and a lack of understanding of the German healthcare system posed the main barriers in both groups. Additionally, structural challenges, such as differences in referral processes, appointment scheduling, and consultation duration, presented further challenges.
This research study emphasizes the importance of addressing cultural and structural barriers to improve healthcare accessibility and utilization for Ukrainian refugees and migrants in Germany to better facilitate their integration into the healthcare system.
Peer Review reports
With the Russian offensive war against Ukraine, Europe experienced one of the most significant movements of refugees since the Second World War. UNHCR estimates that as of July 2024, more than 6.5 million Ukrainians have fled since 24 February 2024. Many refugees have found shelter in neighbouring countries, mainly in Poland (more than 5.4 million people), Slovakia, Romania, and Moldova [ 1 ]. Germany has taken in a considerable number of those seeking protection, with 1,045,185 refugees from Ukraine recorded in the Central Register of Foreigners by the end of 2022 [ 2 ]. As martial law prohibits men between 18 and 60 from leaving Ukraine, most refugees are women, children, and the elderly.
Many of these people require medical care upon arrival and throughout the rest of their stay. Especially elderly and people with disabilities depend on continuous medical care [ 3 ]. With the activation of Directive 2001/55/EG on temporary protection, the legal status of Ukrainian refugees in Germany changed, so they do not have to go through the asylum procedure and can directly access social benefits and state insurance [ 4 ]. However, formal entitlement to the healthcare system often does not solve all healthcare problems.
Existing literature shows that refugees, asylum seekers, and migrants face significant challenges in accessing healthcare in host countries. Key barriers include legislative and administrative obstacles, language barriers, lack of cultural mediation, limited knowledge of the health care system, and breaks in the continuity of care [ 5 , 6 , 7 ]. Despite legal protections, access to healthcare varies across countries, influenced by national policies [ 8 , 9 ].
Recent studies assessed perceived barriers and healthcare needs among Ukrainian refugees in Romania. Common barriers encountered included language barriers and a general lack of understanding of the healthcare system. Especially vulnerable groups such as elderly refugees, people with disabilities, and pregnant women faced considerable obstacles in accessing health services [ 10 ]. Structural barriers reported were issues with insurance coverage, difficulties locating a specialised doctor, bureaucratic hurdles, long waiting lists, and a lack of trust in physicians [ 11 ].
A 2022 quantitative study investigated the challenges faced by general practitioners (GPs) in Germany when interacting with Ukrainian refugees. GPs identified several common challenges, including communication barriers due to a lack of language skills or lack of access to professional interpreters, missing information on refugees’ previous medical conditions, and unrealistic expectations of healthcare services such as routine unsubstantiated blood tests, thyroid tests, and multivitamin prescriptions [ 12 ].
Health care is fundamental to the successful integration of immigrants. People who are impaired or burdened by health problems are hindered in their integration. These can be their own conditions as well as illnesses of relatives or individuals from their close social environment. The illness promotes marginalization, and marginalization promotes the illness, creating a “vicious circle. " On the other hand, successful integration is essential for adequate healthcare, which is often compromised by insufficient access. Access to sufficient health care should be considered equally important as housing and education for the well-being and, thus, integration of migrants [ 13 ].
It is important to note that ‘access’ is a broad and ambiguous term. One component of this term concerns whether the person has the legal right to medical help. The other component concerns whether the person seeking help can interact with the health system. “Access” depends on many factors, some related to the health system, others to the person concerned. Factors that can complicate access include insufficient understanding of the healthcare system and lack of knowledge on how to claim healthcare services [ 13 ]. Studies of Polish labour migration to the United Kingdom and Norway show that migrants often do not know what medical services they are entitled to in the country of settlement [ 14 ]. According to Penchansky & Thomas, access to health care should be a “fit” between the patient and the health care system [ 15 ] whereby the patient identifies their health problems, searches for appropriate health care services, uses them and fulfils his medical needs.
On the other hand, health services should be accessible, suitable, available, and adequate [ 16 ]. Governments frequently depend on preexisting structures and communication channels, failing to adapt to the needs of refugee populations. Thus, formal entitlement to health services does not ensure that refugees have full access to existing services [ 17 , 18 ].
Among a growing body of literature on immigrants’ experiences with healthcare in host countries, little is known about Ukrainian refugees’ and migrants’ experiences with the German healthcare system. Since the beginning of the war, the number of Ukrainian citizens in Germany has increased dramatically. According to data from the Federal Statistical Office, approximately one Million Ukrainians were living in Germany as of 30 September 2022, almost seven times more than at the end of February 2022 [ 19 ]. Previous reports suggest that Ukrainian refugees have a low intention to permanently settle abroad, as they are hopeful of returning to their home country [ 20 ]. This may impact their integration motivations. However, a 2024 intentions survey indicates a growing uncertainty due to the ongoing war, as the proportion of refugees planning or hoping to return to Ukraine in the future has slightly decreased compared to one year ago [ 21 ] The unforeseeable end of the war suggests that integration is likely to become more relevant for Ukrainian refugees.
The aim of this article is to assess the challenges and barriers faced by Ukrainian refugees and migrants in accessing healthcare in Germany to identify potential means to improve policies and programs.
To assess the experience of Ukrainian migrants and refugees with the German healthcare system, we conducted 30 semi-structured interviews with members of the Ukrainian diaspora. The category “migrants” refers to individuals who had a residence permit and relocated to Germany before the outbreak of the war. This group includes permanent migrants, family reunification migrants, students, and labor migrants. The “refugee” group includes all participants under the temporary protection Directive. We analyzed the indicators for understanding the varied experiences and challenges faced by the two groups, allowing for a comprehensive comparison beyond healthcare access alone based on relevant literature including socioeconomic status [ 22 ], housing situation [ 23 , 24 ], social integration and support networks [ 25 ], access to employment opportunities [ 26 ]and cultural adaptation and identity [ 27 ]. The analysis showed no significant differences between the two groups across these domains, suggesting similar levels of integration and adaptation challenges in the German context.
During the interview process, data collection and analysis alternated. After each interview, the first author transcribed it verbatim, noting important themes before conducting subsequent interviews. Based on identifying novel topics, adjustments to the interview guide were made. The recruitment and interview process was concluded when subsequent interviews no longer introduced new themes or insights, indicating sufficient data saturation.
The English version of the interview guide is available in the supplementary files; see Additional file 1 .
Participants
The study was performed in Germany in 2023. Most participants were recruited online and volunteered in response to study listings posted throughout social media groups targeted at Ukrainian refugees and migrants. Another three participants self-selected in response to postings provided through NGOs, and three participants were recruited through snowball sampling. At the time of the interviews, most participants were residing in Berlin, while others lived in Hamburg and the federal states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Saxony, Thuringia, and North Rhine-Westphalia. Participation was voluntary; written informed consent to participate was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study. Before the interview, participants could choose to be interviewed in either Ukrainian or Russian language. All interviews were conducted by the first author, who is a native Ukrainian and Russian speaker. The interviews were primarily conducted online using the Platform Google Meets and telephone calls, and two interviews were performed in person.
Data analysis
Two out of 30 interviews were excluded from the final analysis due to the interviewee’s mental conditions, as the provided answers were unreliable for inclusion in the data set. The interviews lasted 20 to 60 min. All conversations were digitally recorded and transcribed verbatim. The data was organized using Microsoft Excel. The prior thematic categorization helped identify the core topics and classify the issues mentioned. During the data analysis, the four-eyes principle was applied to facilitate the reliability and accuracy of the research findings.
Four main themes emerged from our research: understanding the German healthcare system, barriers to accessing German healthcare, previous experience with the healthcare system and suggested improvements. Our findings demonstrate that Ukrainian migrants and refugees face similar obstacles when accessing German healthcare services; therefore, the results for these two groups are presented together. The demographics are presented in Table 1 .
The study findings show that language barriers and a lack of understanding of the German healthcare system posed the main obstacles. Additionally, adapting to the new healthcare system and structural challenges, such as differences in referral processes, appointment scheduling, and consultation duration, presented further challenges. We found that bureaucratic challenges in obtaining health insurance presented a unique challenge for the refugee group, especially among vulnerable individuals. Further elaboration of these findings will be provided below.
Obtaining information on health topics and understanding the German healthcare system
Participants were asked about their sources of health-related information and how they accessed it. Only a few respondents received medical information directly from their German healthcare providers. Respondents with limited knowledge of the German language used various strategies to obtain information and communicate with medical practitioners. Many participants consulted Russian-speaking specialists in Germany or contacted their general practitioners in Ukraine. One female refugee participant in her late 40s described her experience:
In the first place, if I have questions about my health, I call my Ukrainian GP. Considering my health issues, I can also talk to my friends who have been living in Germany for a long time, for about 20 years […] I don’t trust local doctors that much.
Several respondents sought information from Ukrainian friends or family members who spoke German and used their assistance as interpreters during consultations. The participants widely used the internet as a source of medical information and engaged with online Ukrainian communities on Facebook and other social media platforms for resources related to health, illness, and treatment. During the interview, a woman in her early thirties shared her challenges navigating the German healthcare system.
I am not aware of how the German medical system works; most of the information I get through internet forums or my own experience. Written blogs, YouTube blogs […] I started reading English-language articles, but they are irrelevant and do not describe what I need.
The lack of understanding of the German healthcare system was frequently cited as a significant challenge among the participants. A female participant in her late 40s highlighted this issue:
I don’t know how the system works; I feel insecure in any situation related to medicine.
Another female participant in her twenties described the challenges she encountered, particularly during the initial six months of her residency in Germany:
Very often, I found that I had unintentionally interrupted some processes because I was unaware they existed. For instance, I would arrive somewhere and be asked for a referral from my family doctor. And I didn’t even know that a referral was needed.
This statement emphasizes the importance of understanding how the healthcare system operates. It highlights the potential adverse effects of lacking knowledge about the system, such as ineffective engagement with healthcare services, which could result in failing to obtain necessary medical care. Many participants noted the necessity for more accessible information about the healthcare system. A woman in her thirties elaborated:
I realised that the German medical system is difficult for me because I don’t understand how it works. And I would still like to have some systemic information before the visit to understand where to go […] What I lack is an outline of what to do before going to the doctor […] it is organisational issues that cause me the most stress.
The lack of understanding of how health insurance works created additional barriers for some participants. It’s important to note that, unlike in Germany, there is no mandatory health insurance in Ukraine, and private health insurance, while available, is not widespread. A female participant in her mid-20s shared her experience:
Another barrier for me is that I don’t understand where, when and what my insurance covers, what tests or examinations are covered.
Participants often mentioned the difference between the healthcare systems in Germany and Ukraine. Several participants conveyed that the Ukrainian healthcare system concentrates more on providing preventive care and is usually perceived by Ukrainians as a service sector. Appointments are available on short notice, physicians spend at least an hour for a single appointment, and preventive lab testing and check-ups are accessible from an early age.
Trust was also a recurring theme among the participants, discussed in various contexts. Many participants expressed having trust in their physicians, although some specified that they trusted their doctors in Ukraine more than those in Germany. Several participants reported overall low levels of trust in medical professionals and expressed that they considered themselves to be their own best advisors. Due to previous negative experiences, some participants revealed trust issues and a lack of confidence in the German healthcare system. A Ukrainian student in her mid-20s explained that it was difficult to establish trust with the German doctors due to the short duration of the consultation:
What annoys me most is the minimal duration of consultations with the doctor. They are very brief, lacking thoroughness and interpersonal comfort […] When you visit a doctor, you want to feel trust, but here, it is difficult to build trust.
For some individuals, past negative experiences have led them to avoid the German healthcare and seek medical assistance in Ukraine. During an interview, a female participant in her late 20s, who had been residing in Germany for five years, shared her perspective.
Can I be honest with you? I’m not satisfied with the health care here, but I wouldn’t say that I often seek medical services. I usually try to either treat myself or go to Ukraine.
Previous contact with a different healthcare system can shape patients’ expectations, leading to frustration if they don’t receive the anticipated level of care. For example, a male respondent in his late 20s shared his experience contacting German healthcare:
After being accustomed to the Ukrainian healthcare system, where preventive treatment is common, I know that I need regular monitoring of my stomach, including annual blood tests and ultrasounds. I faced difficulties with this because here they said that I can’t have an ultrasound, only take some pills, but they didn’t explain why.
This experience underscores the challenges of adapting to a new healthcare system and highlights the participant’s unmet need for more information.
The reported differences in healthcare created significant barriers for some participants. A female participant in her late 40s summarized this issue as a clashing of expectations:
[…] Our people [Ukrainian] don’t always know what to expect when they visit a doctor here, and neither does a doctor know what a person might expect from the appointment, so this is probably the biggest problem. Sometimes, when a patient comes with different expectations from their home country and these expectations are not met, I think this is the biggest challenge for the patient and the doctor as well.
Barriers to accessing the health care system and using health care services
The language barrier was one of the most significant obstacles in accessing and interacting with the German healthcare system mentioned among the study participants. Some participants cited this as the reason why they only visited Russian-speaking physicians in Germany. A female refugee in her late 40s explained that she relies on her son to communicate with German-speaking practitioners:
The language barrier is definitely a problem; that’s why I mostly visit Russian-speaking doctors or take my son as a translator with me.
Some participants who assisted elderly refugees or their refugee parents with health-related issues and acted as interpreters during medical appointments emphasized the importance of language proficiency and familiarity with the healthcare system for accessing care. For example, a young Ukrainian student who accompanied an elderly refugee with cancer to physician appointments shared her perspective:
Honestly, she wouldn’t be able to access medical services on her own. GP who speaks Russian, yes, but everything other - no. Even with such mundane things as calling a practice and booking an appointment, even with Google Translate, it is challenging […] without language skills, there is no way. You need to have resources, not only language but also certain experience: who do I need to contact, how is it organised here? Apart from language, there is a need for certain familiarity with the system, not only medical but also social system in Germany.
Many participants faced structural barriers realted to the availability of health services, such as long waiting times, lack of appointments, short working hours of outpatient practices, a shortage of specialized doctors in rural areas, and limitations of state insurance. Several respondents reported that they couldn’t get an appointment with a doctor for several months or at all. Some participants described healthcare as theoretically accessible “on paper” through insurance but difficult to access in practice due to these barriers.
Several refugee respondents reported significant barriers in accessing healthcare due to issues with social services and difficulties obtaining health insurance. A refugee participant diagnosed with cancer shared her experience of contacting social services and obtaining health insurance in the early days of the war. She had to apply for social benefits multiple times before being approved, and the process required her to wait in long lines for hours, sometimes even an entire day:
Just to get registered, it took me eight trips there. I was in decent condition; I was a year out of treatment at that time. I had the strength and resources to do it, and those people who couldn’t do it didn’t manage [to do it] in the end […] So, these first two months were missed for people who needed treatment; it just was discontinued, and they didn’t get it, that’s a fact.
This participant, a social activist who volunteers to assist other refugees with cancer diagnoses, explained that these obstacles led to disruptions in therapy for many cancer patients. Another female refugee participant described her struggle with accessing healthcare due to issues with social services:
I spent my treatment voucher on this visit but did not receive any help […] they took this voucher at the reception desk, so I can’t go to another doctor. The next time, I didn’t have the strength to stand outside for six hours in line for this piece of paper, and I can’t bear to think about it now; I want to cry because it was incredibly torturous, especially for a sick person.
The participant referred to the issuance of treatment vouchers by the social authorities in Germany, a process established during the refugee crisis of 2015/16 that was applied to Ukrainian refugees during first months after activation of temporary protection Directive.
Previous experience with the German healthcare system
Participants shared various issues and personal stories regarding their medical history when asked about their experiences with the German healthcare system. In some cases, the patients subjectively experienced their acute health problem as more threatening and graver in comparison to the opinion of medical professionals. They expected comprehensive treatment and a more in-depth approach to their issues, leading to frustration upon not receiving the desired care. In a few instances, respondents felt that they had been prescribed the wrong therapy, and doctors did not perform diagnostics before the prescription. A female respondent in her early 20s described her experience:
I went to my GP, whom I eventually changed. I visited him regularly for a month, and each week, he prescribed me new antibiotics without doing any tests. So, for a whole month, I was on antibiotics without any betterment […] They haven’t had any interest in providing me with competent advice and told me to drink more tea.
In other instances, the patients revealed they did not receive any treatment and described physicians referring them to another specialist without trying to help. Some participants disclosed having a negative experience due to the rudeness of medical practitioners. A female participant in her middle 30s shared:
Yes, well, I had a miscarriage. The doctor traumatized me for a long time; she was very rude. She knew that I sought a second opinion from another doctor to check if there was a problem. When I returned to her, she was very rude to me […] it was very unpleasant.
Many participants heard at least one negative account of healthcare services in Germany from their friends or family. These respondents confirmed that such stories negatively influenced their expectations and opinions. Several participants mentioned that they put off or avoided doctor appointments because of negative expectations due to their friends’ poor experience with the healthcare system. A middle-aged female participant disclosed that such negative accounts led her to avoid seeking medical assistance in Germany:
Before I had any direct experience with the medical system in Germany, I heard that you couldn’t get to a doctor, so I put my problems on the back burner, thinking that as long as this is not an emergency, I don’t have to deal with it.
This experience underscores the complexity of building trust in a new healthcare system, highlighting that this process extends beyond individual experiences and is significantly shaped by collective perceptions and shared narratives.
Suggested improvements to the German healthcare system
During the interviews, most participants enthusiastically contributed their ideas and recommendations to improve the German healthcare system.
Many participants highlighted the importance of interpersonal communication and mentioned they would like to see a more attentive and patient-centric approach. Some respondents noted they would like more information about their illness and treatment from their physician, underscoring the significance of shared decision-making. A female respondent in her mid-30s conveyed that she would like physicians to take more time to listen and explain:
Well, I look for a personalized approach when the doctor is interested in your story, can offer you several treatment options or can explain. Here, you are often just given a piece of paper with a prescription and do not understand why you were prescribed these medicines.
The participant criticized that she often felt she was being processed on a conveyor belt without being heard due to a lack of time and many patients. This illustrates how structural barriers might make patients feel ignored or give an impression of superficial treatment.
Many respondents underscored the need to improve its accessibility and attributed the existing lack of access to the aforementioned structural barriers. Many respondents saw further digitalization of healthcare as a possible solution. Several participants acknowledged the general shortage of doctors and other medical professionals as a potential reason for current problems in German healthcare and the need to solve this problem in the long term. One respondent suggested the integration of Ukrainian physicians into the healthcare system as a possible solution.
Another important topic mentioned was including psychological help while treating refugees, while a few respondents noted they would appreciate more tolerance and understanding towards Ukrainian refugees from medical personnel. A young female refugee who works as an interpreter in a refugee center shared her opinion on this topic:
I think the only thing we need is more tolerance for Ukrainians who know nothing about this life. This means tolerance from nurses, service staff, and doctors. Understanding that it is necessary to explain and that the process of understanding takes some time.
This study aimed to identify the main challenges and barriers experienced by Ukrainian refugees and migrants in accessing and utilizing healthcare services in Germany.
We found that one of the main barriers to access health services in Germany was the language barrier. These findings are consistent with previous research, as the linguistic barrier is one of the most common obstacles quoted in studies of migrants’ access to health services in European countries [ 5 , 6 , 11 , 17 ].
Another prevalent barrier was the lack of understanding of the German healthcare system and the absence of sufficient information on the organization of the healthcare system. Though many participants found healthcare services in Germany accessible as covered by insurance, the lack of accessible information and understanding of the system posed a problem in accessing medical services. Similar findings were shown in the studies with Ukrainian refugees in Romania [ 10 , 11 ].
It has been demonstrated that language and information barriers can cause incorrect treatment, inadequate care, and underuse of outpatient services, particularly for patients in vulnerable situations. These recognized challenges create hardships for healthcare providers and patients, resulting in unfulfilled healthcare needs [ 5 , 28 ].
Following previous research on Ukrainian refugees [ 10 ], our study underscored the difficulties of adjusting to a different healthcare system. The Ukrainian system was the primary reference point for participants, and differences in referral processes, appointment scheduling, and consultation duration presented unique challenges. Previous research shows that the healthcare system’s structural aspects, such as variations in referral processes, can act as significant barriers, especially for individuals who have interacted with different healthcare systems [ 6 ]. Similar to other studies, perceived structural differences might prompt migrant and refugee participants to use transnational health services and seek help from healthcare providers in their home country [ 29 , 30 , 31 ].
Bureaucratic hurdles within the German healthcare system were a recurrent concern among participants. Several refugees, particularly those with severe conditions, faced a unique barrier in accessing healthcare due to difficulties in obtaining health insurance, possibly leading to delayed treatment and, consequently, poorer health outcomes. Similar structural hurdles were also reported within the Ukrainian refugee group in Romania [ 11 ]. This challenge may be related to the initial issue of treatment vouchers by the social authorities in Germany. Previous research has confirmed that this process creates additional barriers in accessing medical care [ 32 ]. As of 1 June 2022 Ukrainian refugees were granted unrestricted access to the German healthcare system through integration into the Social Code Book (Sozialgesetzbuch). This included access to electronic health cards, which replaced the problematic voucher system, eliminating additional barriers in accessing healthcare [ 33 ].
Another barrier to accessing healthcare services and patient satisfaction was a difference in treatment approaches and clashing perspectives towards healthcare. Similar results have been shown in studies with eastern European migrants in Scotland [ 29 ].
As Kleinman [ 34 ] observes, it is possible that healthcare providers do not always factor in their patient’s beliefs, past experiences, and values while giving advice or information. As a result, they might fail to understand that unconventional health-seeking behaviours, which could seem unreasonable or inconsistent, could stem from migrants’ previous experience with a different healthcare model or system shaped by different ideologies, values, and priorities. This mutual lack of comprehension can lead to mistrust between patients and healthcare providers. Consequently, migrants or refugees might feel ignored or unfairly treated.
As demonstrated in studies from other countries, there appears to be a complex interaction of factors at play when it comes to the reported lack of trust that Ukrainian refugees have in the German healthcare system. Cultural disparities lead to miscommunication and discontent, reflected in different patient expectations and healthcare procedures [ 29 ]. Effective interactions between immigrants and healthcare providers are hampered by communication challenges primarily caused by language barriers [ 35 ]. It has been shown that miscommunication can lead to multiple adverse consequences: disruption in ongoing care, risks to patient safety, dissatisfaction among patients [ 6 ], and an inefficient allocation of important resources, which may lead to economic losses [ 36 ]. Furthermore, a lack of consultation time may make it difficult for patients and medical professionals to communicate and understand one another. This might lead to distrust as the patient may feel not taken seriously [ 6 ]. A comprehensive strategy is required to guarantee a healthcare setting that is both culturally sensitive and helpful in building trust among Ukrainian refugees in Germany. Interventions should include language support services, cultural competency training for healthcare professionals, increases in the healthcare system’s efficiency to ensure optimal use of resources, patient-centred care, and communication initiatives, including providing better information about the healthcare system, to address these problems and restore trust [ 10 ]. Difficulties navigating the system and the alleged deficiency of individualized treatment also point to areas where healthcare service delivery could be improved. The intricate process of trust-building extends beyond personal experiences to encompass perceptions and narratives shared among individuals. Given this complexity, future research needs to delve deeper into and expand upon trust in healthcare professionals among the Ukrainian refugee population.
This study may offer relevant insights for other countries managing a significant influx of Ukrainian refugees. However, as inter-agency data exploration indicates [ 37 ], the implementation of the Directive on temporary protection varies by country as do health systems. Therefore, the findings may not apply to all Ukrainian refugees across Europe. It is also important to note that Ukrainian refugees have a unique legal status due to the temporary protection Directive. In Germany this grants them broader access to healthcare and social services compared to refugees/asylum seekers from other countries [ 4 , 38 ], making the legal context for policy and program solutions unique to this group.
Study limitations
The primary limitation of the study was the representativity of the sample. Recruitment through social media platforms may have led to the underrepresentation of the older population in our sample. Taking into consideration this cohort might be more prone to suffer chronic conditions and have different experiences with the healthcare system, further research is needed to assess barriers this group might face. Furthermore, as martial law prohibits adult men from leaving Ukraine, the male sex is underrepresented in our study population.
Given the relatively large sample of 30 participants for a qualitative study, we feel that we achieved sufficient data saturation. However, we acknowledge that other migrants and refugees may have different experiences with the German healthcare system.
This study underscores the importance of addressing cultural and structural barriers to improve healthcare accessibility and utilization for Ukrainian refugees and migrants in Germany. The findings also highlight the need for increased tolerance and understanding of the challenges faced by these individuals. It is recommended that improvements be made in communication, including interpretation services and the provision of comprehensive information about the healthcare system. Additionally, efforts to simplify bureaucratic procedures related to obtaining health insurance and facilitate more unrestricted access to primary care could prove beneficial.
This study contributes to a deeper understanding of the obstacles faced by Ukrainian refugees and migrants. These findings offer valuable insights for policymakers and healthcare providers to develop effective strategies for improving healthcare accessibility and utilization for migrant and refugee populations. However, additional research is necessary to explore these challenges and potential solutions further, particularly as the migrant and refugee populations evolve.
Availability of data and materials
Detailed interview guide is available in the supplementary information files.The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Kriegsflüchtlinge aus der Ukraine in Deutschland 2022. Statista Research Department. https://de.statista.com/statistik/daten/studie/1294820/umfrage/kriegsfluechtlinge-aus-der-ukraine-in-deutschland/ . Accessed 27 Jan 2023.
BAMF. Acht von zehn Schutzsuchenden kommen aus der Ukraine. Presemitteilung vom 11. Januar 2023. Pressemitteillung Bundesministerium des Innern und für Heimat. https://www.bmi.bund.de/SharedDocs/pressemitteilungen/DE/2023/01/asylantraege2022.html . Accessed 27 Jan 2023.
Murphy A, Fuhr D, Roberts B, Jarvis CI, Tarasenko A, McKee M. The health needs of refugees from Ukraine. BMJ. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.o864 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Aljadeeah S, Michielsen J, Ravinetto R, et al. Facilitating access to medicines and continuity of care for Ukrainian refugees: exceptional response or the promise of more inclusive healthcare for all migrants? BMJ Glob Heal. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjgh-2022-010327 .
Article Google Scholar
Nowak AC, Namer Y, Hornberg C. Health Care for refugees in Europe: a scoping review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031278 .
Scheppers E, van Dongen E, Dekker J, Geertzen J, Dekker J. Potential barriers to the use of health services among ethnic minorities: a review. Fam Pract. 2006. https://doi.org/10.1093/fampra/cmi113 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chiarenza A, Dauvrin M, Chiesa V, Baatout S, Verrept H. Supporting access to healthcare for refugees and migrants in European countries under particular migratory pressure. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-019-4353-1 .
Lebano A, Hamed S, Bradby H, et al. Migrants’ and refugees’ health status and healthcare in Europe: a scoping literature review. BMC Public Health. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-08749-8 .
Beauclercq I, Viello F, Petrova-Benedict R, Val E. Overview of Migration and Health in Europe. In: Krämer A, Fischer F, editors. Refugee Migration and Health Challenges for Germany and Europe. Springer International Publishing; 2019. pp. 19–39.
Chapter Google Scholar
World Health Organization. Behavioural insights on health service needs and access Results of a qualitative study among refugees from Ukraine in Romania. World Heal Organ Reg Off Eur. WHO/EURO:2023-7292-47058-68796.
Dumitrache L, Nae M, Mareci A, Tudoricu A, Cioclu A, Velicu A. Experiences and perceived barriers of Asylum seekers and people with Refugee backgrounds in Accessing Healthcare Services in Romania. Healthc. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10112162 .
Tillmann J, Weckbecker K, Wiesheu P, Bleckwenn M, Deutsch T, Münster E. Primary care of Ukrainian refugees: evaluation of challenges and information needs (RefUGe trial). Z Allgemeinmed. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s44266-022-00001-3 .
Ingleby D, Chimienti M, Hatziprokopiou P, Ormond MDFC. The role of health in integration. In: Fonseca LM, Jorge M, editors. Social Integration and mobility: Education, Housing and Health. IMISCOE Cluster B5. State of the Art Report. Centro de Estudos Geográficos, Univ. de Lisboa; 2005. pp. 101–37.
Google Scholar
Friberg JH. Working conditions for Polish construction workers and domestic cleaners in Oslo: segmentation, inclusion and the role of policy. In: Black R, Engbersen G, Okólski M, Panţîru C, editors. A continent moving West? EU Enlargement and Labour Migration from Central and Eastern Europe. Amsterdam University; 2010. pp. 23–51.
Penchansky R, Thomas JW. The concept of access: definition and relationship to consumer satisfaction. Med Care. 1981. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005650-198102000-00001 .
Levesque JF, Harris MF, Russell G. Patient-centred access to health care: Conceptualising access at the interface of health systems and populations. Int J Equity Health. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-9276-12-18 .
Nielsen MR, Jervelund SS. Experiences of access to healthcare among newly arrived immigrants in Denmark: examining the role of residence permit. Scand J Public Health. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/14034948231173473 .
Rechel B, Mladovsky P, Devillé W, Rijks B, Petrova-Benedict R, McKee M. Migration and Health in the European Union: an introduction. In: Rechel B, Mladovsky P, Devillé W, Rijks B, Petrova-Benedict R, McKee, editors. Migration and Health in the European Union. Open University; 2011. pp. 3–13.
Bevölkerung. Statistisches Bundesamt (Destatis). https://www.destatis.de/DE/Im-Fokus/Ukraine/Gesellschaft/_inhalt.html . Accessed 27 Jan 2023.
Adema J, Aksoy CG, Giesing Y, Poutvaara P. The effect of conflict on Ukrainian refugees’ Return and Integration. SSRN Electron J. 2024. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4758133 .
UNHCR. Lives on Hold: intentions and perspectives of refugees, refugee returnee’s and internally displaced people from Ukraine. 2024. https://data.unhcr.org/en/documents/details/106738 . Accessed 17 Jul 2024.
Castañeda H, Holmes SM, Madrigal DS, De Trinidad Young ME, Beyeler N, Quesada J. Immigration as a social determinant of health. Annu Rev Public Health. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-publhealth-032013-182419 .
Phillips D. Moving towards integration: the housing of asylum seekers and refugees in Britain. Hous Stud. 2006. https://doi.org/10.1080/02673030600709074 .
Aigner A. Housing entry pathways of refugees in Vienna, a city of social housing. Hous Stud. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/02673037.2018.1485882 .
Phillimore J. Refugees, acculturation strategies, stress and integration. J Soc Policy. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0047279410000929 .
Brell C, Dustmann C, Preston I. The labor market integration of refugee migrants in high-income countries. J Econ Perspect. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1257/JEP.34.1.94 .
Berry JW, Acculturation. Living successfully in two cultures. Int J Intercult Relations. 2005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijintrel.2005.07.013 .
Kullamaa L, Reile R. Socio-demographic and regional differences in unmet healthcare needs among migrants in Europe. PLoS ONE. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0285886 .
Sime D. I think that Polish doctors are better: newly arrived migrant children and their parents’ experiences and views of health services in Scotland. Heal Place. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthplace.2014.08.006 .
Migge B, Gilmartin M. Migrants and healthcare: investigating patient mobility among migrants in Ireland. Heal Place. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthplace.2011.05.002 .
Glinos IA, Baeten R, Helble M, Maarse H. A typology of cross-border patient mobility. Heal Place. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthplace.2010.08.001 .
Razum O, Bozorgmehr K. Restricted entitlements and access to health care for refugees and immigrants: the example of Germany. Glob Soc Policy. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468018116655267 .
Oliver R, Verena P, Amir M, Kayvan B. Covid-19 in Flüchtlingsunterkunften: GD jetzt weiter stärken. Gesundheitswesen. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1154-5063 .
Kleinman A. Patients and Healers in the Context of Culture: An Exploration of the Borderland between Anthropology, Medicine, and Psychiatry. University of California; 1980.
Book Google Scholar
Dias S, Gama A, Cargaleiro H, Martins MO. Health workers’ attitudes toward immigrant patients: a cross-sectional survey in primary health care services. Hum Resour Health. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1186/1478-4491-10-14 .
Vermeir P, Vandijck D, Degroote S, et al. Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. Int J Clin Pract. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.12686 .
UNHCR. Navigating health and well-being challenges for refugees from Ukraine an inter-agency exploration of data. 2024. https://data.unhcr.org/en/documents/details/108629 . Accessed 17 Jul 2024.
Bozorgmehr K, Razum O. Effect of restricting access to health care on health expenditures among asylum-seekers and refugees: a quasi-experimental study in Germany, 1994–2013. PLoS ONE. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0131483 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Klink für Innere Medizin II, Universitätsklinikum Jena, Am Klinikum 1, 07747, Jena, Germany
Karina Davitian, Jutta Hübner & Emadaldin Ahmadi
Lehrstuhl für pädagogische Psychologie, Humboldtstr. 27, 07743, Jena, Germany
Peter Noack & Katharina Eckstein
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
KD recruited the participants, performed the interviews, analysed, and interpreted the data, and was primarily responsible for writing the manuscript and incorporating feedback from co-authors. PN was involved in the conceptualisation and design of the study, the development of the methodology, and contributed to the writing of the original draft, as well as provided supervision and mentorship. KE assisted with the data collection strategy, implemented quality assurance protocols, and contributed to the writing through review and editing of the manuscript. JH was responsible for the original idea and overall study design, as well as performed critical revisions and contributed to the final version of the manuscript. EA developed the interview protocols, contributed to the methodological framework, and assisted in analysing and interpreting the data. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Karina Davitian .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The ethics committee of the university hospital at the Friedrich-Schiller-University Jena granted ethical approval in February 2023 (Nr.2023-2916-Bef). Written informed consent to participate was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. interview guide. the detailed interview guide used while performing the interviews., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Davitian, K., Noack, P., Eckstein, K. et al. Barriers of Ukrainian refugees and migrants in accessing German healthcare. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 1112 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11592-x
Download citation
Received : 14 April 2024
Accepted : 16 September 2024
Published : 24 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11592-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Healthcare system
- Accessibility
- Qualitative research
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Marshfield Clinic Health System intends to combine with Sanford Health. What does that mean for patients and rural health care?
Both systems announced wednesday plans to combine, creating an integrated health system in the rural midwest. what does it mean for employees, patients and rural health care.
MARSHFIELD – Marshfield Clinic Health System plans to combine with Sanford Health later this year.
The nonprofit health systems announced Wednesday morning in a joint release their intent to combine their assets and capabilities to create an integrated health system and advance health care in the rural Midwest. Sanford Health serves communities in South Dakota, North Dakota, Minnesota and Iowa, while Marshfield Clinic Health System serves in communities throughout Wisconsin and Michigan’s Upper Peninsula.
The partnership is expected to close by the end of the year, subject to regulatory processes and closing conditions. Both companies will remain separate and independent organizations until the deal is closed.
When the deal is complete, Sanford Health will serve as the parent company, headquartered in Sioux Falls, South Dakota. Marshfield Clinic Health System will be a region within Sanford Health and will maintain regional leadership and its flagship campus in Marshfield, keep its regional board of directors and regional physician executive council and maintain its brand, according to the release.
Sanford Health President and CEO Bill Gassen will serve as president and CEO of the combined system, and Marshfield Clinic Health System Interim CEO Dr. Brian Hoerneman will serve as president and CEO of the Marshfield Clinic Health System region.
Gassen and Hoerneman told a USA TODAY NETWORK-Wisconsin reporter there may be opportunities to co-brand certain services or programs in the future, but both Sanford Health and Marshfield Clinic Health System will maintain their existing branding and names.
According to the release, there are no immediate changes planned for employees or systems. When the two organizations combine, they will operate 56 hospitals with 56,000 employees and 4,300 providers. The organizations’ nationally recognized research institutions, specialty pharmacies and health plans — Sanford Health Plan and Security Health Plan — will be integrated, as well.
A ‘crisis’ in rural health care: Wisconsin hospital systems face increasing challenges in providing services in rural communities
What is Sanford Health?
According to the release, Sanford Health is the largest rural health system in the country. About 2,900 Sanford physicians and providers serve 1.4 million patients through 45 hospitals, 221 clinics and more than 160 Good Samaritan Society senior living centers. Sanford Health is running 540 active clinical trials and operates nine Sanford World Clinic locations around the world , offering broad primary care services, regenerative medicine, specialized procedures and more services to populations around the world.
According to its website, Sanford Health operates various Centers of Excellence, focusing on cancer care, children’s health, heart, women’s health and orthopedics and sports medicine.
According to the release, Sanford Health has invested more than $1.5 billion in communities across South Dakota, North Dakota, Minnesota and Iowa over the last 10 years, expanding access to specialty care and state-of-the-art facilities.
What is Marshfield Clinic Health System?
More than 1,400 providers serve Marshfield Clinic Health System across Wisconsin and Michigan’s Upper Peninsula, focusing on 170 specialties. Marshfield Clinic Health System operates research and education programs and its Security Health Plan.
Marshfield Clinic Health System operates more than 60 Marshfield Clinic sites, 11 hospitals, Marshfield Children’s Hospital, the Marshfield Clinic Research Institute and the Marshfield Clinic Health System Foundation.
What does this partnership mean for patients?
Hoerneman told a USA TODAY NETWORK-Wisconsin reporter patients will see very little change in service, especially at the beginning of the partnership. He said since Sanford Health and Marshfield Clinic Health System are closely aligned in their missions and the challenges they face, the connection between the two organizations will continue to prioritize continued and improved access to rural areas.
Gassen agreed, adding patients can expect to see continued investment in communities and expanded access in the years to come, both from Sanford Health and Marshfield Clinic Health System. They want to build on the decades of work each system has already brought to communities and work to meet changing demands in financially sustainable ways, he said.
How is this partnership different than other merger attempts?
Hoerneman told a USA TODAY NETWORK-Wisconsin reporter other attempts at mergers — like discussions Marshfield Clinic Health System had with Essentia Health — were lengthy discussions that ultimately ended with both organizations open to future collaborations on projects but weren’t a good fit to merge.
Discussions around the partnership with Sanford Health have been entirely different, Hoerneman said. Both organizations have similar missions and culture and have aligned priorities to focus on serving rural communities.
Gassen said there are many commonalities between the two organizations, from a shared mission and values to prioritizing communities while working to improve access, quality and availability of rural health care. He said a common sentiment shared as both organizations continued discussions was how natural the fit feels between the two.
In the news release, Hoerneman said the partnership offers an “incredible opportunity” to unify the organizations and establish a premier rural health system in the country.
“Together, we will ensure sustainable access to exceptional care for our communities for years to come,” Hoerneman said. “With a shared mission to serve, a mutual emphasis on research and education, and a strong tradition of physician leadership, Sanford Health is the ideal partner for this endeavor.”
How will this help address challenges in providing rural health care?
Hoerneman told a USA TODAY NETWORK-Wisconsin reporter there are many challenges both organizations have been facing when it comes to providing rural health care , including insufficient or declining reimbursement rates, increasing costs of pharmaceuticals, increasing costs related to attracting and retaining skilled staff, supply costs and more.
Hoerneman said the collaboration with Sanford Health will allow both organizations to address some of the biggest issues in providing rural health care head-on. Combined, both organizations reach rural communities on more of a national scale, and together, they can work to determine best practices and understand how they can offer better access and better care that is still cost-efficient. Some issues are bigger than any health system can solve on its own, Hoerneman said, but they’re important to discuss, as communities depend on systems like Sanford Health and Marshfield Clinic Health System.
One challenge in providing rural health care, especially in Wisconsin, has been serving an aging population. Sanford Health has been working with an affiliate, the Good Samaritan Society, since 2019, Gassen said. That partnership has allowed Sanford Health to invest in senior care locations and nursing and rehab facilities. When those two organizations merged, it created unique opportunities for Sanford Health to meet existing demands for acute and post-acute care.
Another challenge has been maintaining enough staffing to provide seamless care and transitions for patients. Many rural communities struggle with a nursing home “bottleneck,” causing patient backups all the way to emergency departments. Gassen said the Sanford locations in communities that work with the Good Samaritan Society are better staffed, have had more seamless transitions and are able to optimize care and efficiency. Locations without that partnership have seen similar struggles.
A benefit of partnering Sanford Health and Marshfield Clinic Health System will be listening to what programs and efforts are working and collaborating on ways to work together to create programs and opportunities to solve some of the biggest challenges, Gassen said.
What does this partnership mean for rural medical care and research?
According to the release, combining Sanford Health and Marshfield Clinic Health System will improve patient outcomes by providing broader health initiatives, care programs and innovative care delivery models. The partnership aims to utilize technology to focus on virtual care, digital health, data analytics and use artificial intelligence and genomic medicine to advance community health.
Combining Sanford Health and Marshfield Clinic Health System would also strengthen training, education and support for future physicians and caregivers through shared initiatives. According to the release, the combined organizations would create graduate medical education programs and establish strong partnerships with educational institutions across the shared region.
According to the release, the partnership would create new opportunities for research, collaboration, enhanced professional development and training and would create robust peer networks.
Gassen told a USA TODAY NETWORK-Wisconsin reporter there are already great opportunities in front of Sanford Health and Marshfield Clinic Health System, including offering more than 1,000 clinical trials neither organization could do on its own. Those trials bring more opportunities for more cures for more patients, he said. Together, the two organizations can work together to address challenges and advocate for the right programs that are needed in rural communities in sustainable ways, he said.
What about health insurance?
Hoerneman and Gassen said Sanford Health Plan and Security Health Plan will continue as separate and distinct legal entities but will share common governance. They said patients with these plans will see very little change as the partnership deal finalizes.
For patients who have outside health insurance coverage from other companies, both Hoerneman and Gassen said they don’t foresee any coverage changes for patients. Both said health insurance plans are important pieces of providing quality rural health care, and both organizations want to continue expanding patient access to care.
Contact Caitlin at [email protected] or follow her on Twitter @CaitlinShuda .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This page provides a comprehensive list of health thesis topics designed to help students select relevant and impactful research subjects for their academic work in health sciences. With 450 topics spread across 15 categories, including anatomy, epidemiology, nursing, and public health, the list covers a wide range of current issues, recent trends, and future directions in health and medicine.
Here, we'll explore a variety of healthcare-related research ideas and topic thought-starters across a range of healthcare fields, including allopathic and alternative medicine, dentistry, physical therapy, optometry, pharmacology and public health. NB - This is just the start….
Since 2020, COVID-19 has been a hot-button topic in medicine, along with the long-term symptoms in those with a history of COVID-19. Examples of COVID-19-related research topics worth exploring include: The long-term impact of COVID-19 on cardiac and respiratory health. COVID-19 vaccination rates.
151+ Public Health Research Topics [Updated 2024] The important area of public health research is essential to forming laws, influencing medical procedures, and eventually enhancing community well-being. As we delve into the vast landscape of public health research topics, it's essential to understand the profound impact they have on society.
Content last reviewed March 2023. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD. Health systems research provides evidence that, when applied can make healthcare affordable, safe, effective, equitable, accessible, and patient-centered. AHRQ invests in research to generate new evidence to help health care systems and health care ...
The Covid-19 pandemic has also necessitated and accelerated significant transformations. The authors discuss gaps and barriers in the current design of health and health systems, and the needed escalation of transformation including transition from hospital-based systems to primary care, community, and social care-based systems.
Health research entails systematic collection or analysis of data with the intent to develop generalizable knowledge to understand health challenges and mount an improved response to them. The full spectrum of health research spans five generic areas of activity: measuring the health problem; understanding its cause(s); elaborating solutions; translating the solutions or evidence into policy ...
Health system resilience is a prerequisite for effectively managing cataclysmic events adversely affecting health outcomes. The COVID-19 pandemic reasserted the importance of having resilient health systems and called for a relook at the existing framework that measures health system resilience. Mixed methods were used in this study. The review started with the measurement of health systems ...
RAND is a research organization that develops solutions to public policy challenges to help make communities throughout the world safer and more secure, healthier and more prosperous. RAND is nonprofit, nonpartisan, and committed to the public interest. Subscribe to the Policy Currents newsletter for RAND insights on the issues that matter most.
Why the U.S. Health Care System Lags Behind: A Call for Equitable, High-Value Care. The U.S. trails other wealthy nations in health care value. Compared to its peers, the U.S. faces higher health care disparities, avoidable hospitalizations, maternal morbidity and mortality, and a shorter life expectancy, all while incurring the world's highest health care costs.
The Fogarty International Center and its NIH partners invest in research on a variety of topics vital to global health. For each of these global health research topics, find an in-depth collection of news, resources and funding from Fogarty, the NIH, other U.S. government agencies, nongovernmental organizations and others. Bioethics.
Topic Selection. The initial topics were defined based on current developments in the health informatics field and an increasing number of published manuscripts between 2000 and 2021 (based on title-abstract-keyword screening in Scopus using the keywords "Health" AND "Informatics" AND "domain") in the respective subdomains (Figure 1 A).). After a first definition of the specific ...
Health Policy and Systems Research: A Methodology Reader / edited by Lucy Gilson - The Abridged Version 1.Health policy. 2.Health services research. 3.Delivery of health care. 4.Research. 5.Review literature. I.Gilson, Lucy. II.Alliance for Health Policy and Systems Research. III.World Health Organization.
This is the first of a series of three papers addressing the current challenges and opportunities for the development of Health Policy and Systems Research (HPSR). HPSR is a multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary field identified by the topics and scope of questions asked rather than by methodology. The focus of discussion is HPSR in low- and ...
Climate change: an urgent priority for health policy and systems research. Power, control, communities and health inequalities I: theories, concepts and analytical frameworks. Research ethics in context: understanding the vulnerabilities, agency and resourcefulness of research participants living along the Thai-Myanmar border
Health policy and systems research (HPSR) has changed considerably over the last 20 years, but its main purpose remains to inform and influence health policies and systems. Whereas goals that underpin health systems have endured - such as a focus on health equity - contexts and priorities change, research methods progress, and health organisations continue to learn and adapt, in part by ...
Research for health is a global endeavour, and WHO has a unique role to play in ensuring that these efforts can help improve health for all. WHO provides leadership, calling on the wider scientific community to engage behind global health concerns. This is based on a deep understanding of the needs of countries, and rigorous assessment by ...
These include a study aimed at reducing the research waste that arises from disproportionate regulation by examining the practices for exempting low-risk research from ethics review in four high-income countries , the Global Observatory's paper on research funding described earlier , a study on the governance of national health research ...
100 Healthcare Research Paper Topics. The field of healthcare research encompasses a vast array of topics that are crucial for understanding, improving, and transforming healthcare practices. As students in the health sciences, you have the opportunity to explore these diverse areas and contribute to the knowledge base of healthcare research.
They include: focus on prevention, not just treating sickness; tackle racial disparities; expand telehealth and in-home services; build integrated systems; and adopt value-based care. Since early ...
Overview. Health policy and systems research (HPSR) is an emerging field that seeks to understand and improve how societies organize themselves in achieving collective health goals, and how different actors interact in the policy and implementation processes to contribute to policy outcomes. By nature, it is inter-disciplinary, a blend of ...
Research. Strategy and Development; Implementation and Impact; Integrity and Oversight; Practice. In the School; ... Topics. Our topic pages offer a one-stop-shop for insights, experts, and offerings by areas of interest. ... Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health 615 N. Wolfe Street, Baltimore, MD 21205. Footer social. LinkedIn ...
Medical Research Topic Ideas. Medical Research Topic Ideas are as follows: The efficacy of mindfulness meditation in reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. The effects of vitamin D supplementation on bone health in postmenopausal women. The impact of social media on body image and eating disorders in adolescents.
IHSP's research contributes to health system improvements worldwide by emphasizing six interrelated areas of focus. The combination of operations and academically-oriented research allow the findings and methodologies of Program members' research to reach a wide audience and inform policymaking. A listing of peer-reviewed journal articles ...
Approaches to Measuring Non-Fatal Health Outcomes: Disability at the Iganga-Mayuge Demographic Surveillance System in Uganda. A National Burden of Disease Study for The United Arab Emirates (UAE): Quantifying Health Differentials Between Nationals and Migrants. Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Background This study focused on Ukrainian refugees and migrants, a population that, with an ongoing war, is expected to grow in Germany. Over 1 million Ukrainians with exceptional legal status and access to public insurance in Germany significantly burden governmental services, especially German healthcare. It is thus essential to facilitate their integration into the healthcare system and ...
Marshfield Clinic Health System operates more than 60 Marshfield Clinic sites, 11 hospitals, Marshfield Children's Hospital, the Marshfield Clinic Research Institute and the Marshfield Clinic ...