- AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
- TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
See how it works →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
- BY USE CASE
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
- 400+ Sample Business Plans

How to Write an Operations Plan Section of your Business Plan

Free Operations Plan Template
Ayush Jalan
- December 14, 2023

Your business plan is an elaborate set of instructions stating how to run your business to achieve objectives and goals. Each section describes a part of the process of reaching your desired goal. Similarly, the operations plan section of your business plan explains the production and supply of your product.
An operations plan is formed to turn plans into actions. It uses the information you gathered from the analysis of the market , customers, and competitors mentioned in the previous parts of your business plan and allows for the execution of relevant strategies to achieve desired results.
What Is an Operations Plan?
An operations plan is an in-depth description of your daily business activities centered on achieving the goals and objectives described in the previous sections of your business plan. It outlines the processes, activities, responsibilities of various departments and the timeframe of the execution.
The operations section of your business plan explains in detail the role of a team or department in the collective accomplishment of your goals. In other words, it’s a strategic allocation of physical, financial, and human resources toward reaching milestones within a specific timeframe.
A well-defined operational plan section of your business plan should be able to answer the following questions:
- Who is responsible for a specific task or department?
- What are the tasks that need to be completed?
- Where will these operations take place?
- When should the tasks be completed? What are the deadlines?
- How will the tasks be performed? Is there a standard procedure?
- How much is it going to cost to complete these tasks?

How to Write an Operations Plan Section?
Creating an operational plan has two major stages, both addressing different aspects of your company. The first stage includes the work that has been done so far, whereas the second stage describes it in detail.
1. Development Phase
In this stage, you mention what you’ve done to get your business operations up and running. Explain what you aim to change and improvise in the processes. These are the elements your development section will contain:
Production workflow
: Explain all the steps involved in creating your product. This should be a highly informative, elaborate description of the steps. Here, you also mention any inefficiencies that exist and talk about the actions that need to be taken to tackle them.
Supply chains
Quality control, 2. manufacturing phase.
The development stage acquaints the reader with the functioning of your business, while the manufacturing stage describes the day-to-day operation.
This includes the following elements:
Outline of daily activities:
Tools and equipment:, special requirements:, raw materials:, productions:, feasibility:, why do you need an operations plan.
An operations plan is essentially an instruction manual about the workings of your business. It offers insight into your business operations. It helps investors assess your credibility and understand the structure of your operations and predict your financial requirements.
An operations plan reflects the real-time application of a business plan.
Internally, an operations plan works as a guide, which helps your employees and managers to know their responsibilities. It also helps them understand how to execute their tasks in the desired manner—all whilst keeping account of deadlines.
The operations plan helps identify and cut the variances between planned and actual performance and makes necessary changes. It helps you visualize how your operations affect revenue and gives you an idea of how and when you need to implement new strategies to maximize profits.
Advantages of Preparing an Operations Plan:
- Offers Clarity: Operational planning, among other things, makes sure that everyone in the audience and team are aware of the daily, weekly, and monthly work. It improves concentration and productivity.
- Contains A Roadmap: Operational planning makes it much easier to reach long-term objectives. When members have a clear strategy to follow: productivity rises, and accountability is maintained.
- Sets A Benchmark: It sets a clear goal for everyone about what is the destination of the company and how to reach there.
Operations Plan Essentials
Now that you have understood the contents of an operations plan and how it should be written, you can continue drafting one for your business plan. But before doing so, take a look at these key components you need to remember while creating your operational plan.
- Your operations plan is fundamentally a medium for implementing your strategic plan. Hence, it’s crucial to have a solid strategic plan to write an effective operations plan.
- Focus on setting SMART goals and prioritizing the most important ones. This helps you create a clear and crisp operations plan. Focusing on multiple goals will make your plan complicated and hard to implement.
- To measure your goals, use leading indicators instead of lagging indicators. Leading indicators is a metric that helps you track your progress and predict when you will reach a goal. On the other hand, lagging indicators can only confirm a trend by taking the past as input but cannot predict the accomplishment of a goal.
- It is essential to choose the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) . It is a good practice to involve all your teams while you decide your KPIs.
- An operations plan should effectively communicate your goals, metrics, deadlines, and all the processes.
Now you’re all set to write an operations plan section for your business plan. To give you a headstart, we have created an operations plan example.
Operations Plan Example
Operations plan by a book publishing house
Track and Accomplish Goals With an Operations Plan
Drafting the operations plan section of your business plan can be tricky due to the uncertainties of the business environment and the risks associated with it. Depending on variables like your market analysis, product development, supply chain, etc., the complexity of writing an operations plan will vary.
The core purpose here is to put all the pieces together to create a synergy effect and get the engine of your business running. Create an effective operations plan to convey competence to investors and clarity to employees.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does the operations plan play in securing funding for a business.
The operations plan defines the clear goals of your business and what actions will be taken on a daily basis to reach them. So, investors need to know where your business stands, and it will prove the viability of the goals helping you in getting funded.
What are the factors affecting the operations plan?
- The mission of the company
- Goals to be achieved
- Finance and resources your company will need
Can an operations plan be created for both start-up and established businesses?
Yes, both a startup and a small business needs an operations plan to get a better idea of the roadmap they want for their business.
About the Author

Ayush is a writer with an academic background in business and marketing. Being a tech-enthusiast, he likes to keep a sharp eye on the latest tech gadgets and innovations. When he's not working, you can find him writing poetry, gaming, playing the ukulele, catching up with friends, and indulging in creative philosophies.
Related Articles

How to Write a Business Plan Complete Guide

Write Products and Services Section of a Business Plan

How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

An Ultimate Guide for Better Operations
- Operates towards success
- Describe business milestones
- Plan such as financials, budget planning
- Turn your goals into an actionable plan
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business 10+ Operational Planning Examples to Fulfill your Strategic Goals
10+ Operational Planning Examples to Fulfill your Strategic Goals
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Oct 25, 2023

An operational plan is a comprehensive, action-driven document that maps out how daily activities within an organization fuel the journey towards achieving strategic objectives.
Essentially acting as the nexus between high-level strategy and practical execution, this plan ensures that every department, from human resources to specific departments, operates in synchrony, aligning their day-to-day activities with the broader strategic goals.
By streamlining processes, it fosters cohesive efforts amongst diverse cross-functional teams, ensuring that both individual team members and entire departments work together harmoniously towards the company goals.
Ready to sculpt your organization’s future? Start your journey with venngage business plan maker and leverage their expertly crafted operational plan templates .
Click to jump ahead:
Why is an operational plan important?
10 operational plan examples, what should an operational plan include, how to write an operational plan.
- Strategic plan vs operational plan: What is the difference?
In summary
An operational plan is crucial because it serves as a bridge between a company’s high-level strategic planning and its day-to-day activities, ensuring that the business operations align with the strategic goals.
While a strategic plan provides a long-term vision, outlining the company’s objectives and goals to gain competitive advantages in the business environment, the operational plan outlines the specific actions, key elements and resource allocation required to achieve those objectives.
For example, while the strategic plan might set a goal for revenue growth over the fiscal year, the operational plan provides a detailed roadmap, breaking down major projects, assigning responsibilities to individual team members or specific departments and setting key performance indicators to monitor progress and ensure the entire organization works together effectively.
Operational planning, in essence, transforms the strategic objectives into actionable plans, ensuring that the entire team, from department heads to diverse cross-functional teams, is aligned and works in tandem to support revenue growth, increase productivity, and achieve the desired outcomes.
Operational plans, through a well-structured operational planning process, also provide a clear understanding of the day-to-day activities, allowing team members to know their roles, leading to better collaboration and synergy.
Moreover, by having clear operational plan examples or templates, businesses can ensure realistic expectations, manage their operating budget effectively and track progress through key performance metrics, thus ensuring that the company stays on course to realize its long-term vision.
Operational plans play a pivotal role in the business landscape, bridging the gap between strategic vision and tangible actions. They translate the overarching goals of an organization into detailed procedures, ensuring that daily operations are in line with the desired strategic outcomes.
In the section below, I will explore a few operational plan examples, shedding light on their structure and importance.
Business operational plan example
A business operational plan is a comprehensive document that elucidates the specific day-to-day activities of a company. It presents a detailed overview of the company’s organizational structure, management team, products or services and the underlying marketing and sales strategies.
For businesses, irrespective of their size, an operational plan can prove invaluable. By laying down the business goals and objectives, it acts as a blueprint, guiding entrepreneurs through the creation and implementation of strategies and action plans. The planning process also incorporates mechanisms to track progress and performance.
Additionally, for startups or companies looking to scale, a meticulously crafted operational plan can be pivotal in securing funds from potential investors and lenders.

Layered on this are details about the company’s organizational structure, its products or services and its marketing and sales strategies.
The document also delineates the roles and responsibilities of each team member, especially the management and key personnel. Given the dynamic nature of the business environment, it is imperative to revisit and update the operational plan regularly.
Related: 15+ Business Plan Templates for Strategic Planning
Simple operational plan example
A simple operational plan, often used by startups or smaller enterprises, emphasizes the basics, ensuring that the fundamental aspects of the business operations are captured succinctly. While it might not delve into the intricacies of every operation, it provides an overview of day-to-day activities, highlighting the goals and objectives the business aims to achieve in the short term.

In essence, this plan revolves around core elements like the company’s main objectives for the fiscal year, key responsibilities assigned to individual team members and basic resource allocation. A straightforward market analysis might also be included, offering insights into customer needs and competitive advantages the business hopes to leverage.

Though simple, this operational plan example remains pivotal for the organization. It provides a roadmap, guiding team members through their daily responsibilities while ensuring that everyone is working together towards shared goals. It becomes especially essential for diverse cross-functional teams, where clarity of roles can lead to increased productivity.

Modern operational plan example
In today’s fast-paced business environment, the emphasis on efficiency and innovative processes is paramount. The modern operational plan example caters precisely to this demand. Ideal for organizations aiming to streamline processes and highlight workflow, this type of operational plan emphasizes a more dynamic approach to planning.

It not only reflects the evolving nature of business operations but also provides a modern backdrop for content, ensuring that the presentation resonates with the current trends and technological advancements. The use of modern tools and platforms within this plan enables diverse cross-functional teams to work together seamlessly, ensuring that day-to-day activities are synchronized with the company’s long-term vision.

Furthermore, such an operational plan helps the entire organization stay agile, adapting rapidly to changes in the business environment and ensuring alignment with strategic goals.
Minimalist operational plan example
The minimalist operational plan example champions simplicity and clarity. By focusing on clear and concise business strategies, it eliminates any potential ambiguity, ensuring that team members and stakeholders have an unclouded understanding of the company’s objectives and goals.

The minimalist design not only promotes easy comprehension but also aligns with the modern trend of decluttering, ensuring that only the most vital components of the operational planning process are highlighted.
This approach leaves no room for confusion, streamlining the planning process and making sure that individual team members and departments are aligned with the business’s key objectives.

Moreover, the flexibility offered by a minimalist design allows businesses to craft an operational plan template that is not only functional but also accurately reflects their brand image and core values, ensuring cohesion across all aspects of the business strategy.

Clean operational plan example
The clean operational plan example stands as a testament to this principle. Ideal for businesses that prioritize clarity and directness, this format seeks to convey goals and strategies without overwhelming stakeholders.
While maintaining a neat and organized layout, it ensures that tasks are managed effectively, helping team members grasp their roles and responsibilities without getting lost in excessive details.

One of the primary advantages of a clean operational plan is its ability to eliminate distractions and focus solely on the critical aspects of operational planning.
Such a design aids in making sure that diverse cross-functional teams can work together harmoniously ensuring that day-to-day activities align seamlessly with the company’s long-term vision.
The simplicity of the clean operational plan not only supports revenue growth by ensuring efficiency but also reinforces the company’s strategic goals, making it an excellent tool in the arsenal of businesses that believe in clear communication and precise execution.
An effective operational plan acts as a roadmap, directing how resources should be allocated and tasks should be performed to meet the company’s objectives. Here’s what a comprehensive operational plan should encompass:
- Goals and objectives : Whether short-term or long-term, the operational plan should define clear goals and objectives that align with the company’s strategic plan. This gives direction to the entire organization, ensuring everyone is working towards a common aim.
- Clear responsibilities for team members : It’s essential that team members understand their roles within the operational plan. By outlining who is responsible for what, the plan ensures that there are no overlaps or gaps in duties and that everyone has clarity on their day-to-day activities.
- Assigned tasks: Alongside responsibilities, specific tasks need to be allocated to individual team members or specific departments. This granularity in assignment ensures that every aspect of the operational plan is covered.
- Timeline: This provides a clear schedule for when each task or objective should start and finish. A well-defined timeline assists in monitoring progress and ensures that the plan stays on track.
- Budget and resources : Every operational plan needs to factor in the budget and resources available. This includes everything from the operating budget to human resources, ensuring that the business has everything it needs to execute the plan effectively.
Read Also: 6 Steps to Create a Strategic HR Plan [With Templates]
As businesses evolve, it’s essential to have a comprehensive and adaptive operational plan in place to navigate the complexities of the business environment. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you craft an effective operational plan:
Step 1: Define your goals and objectives
Begin with a clear understanding of your strategic goals and objectives. This will act as a foundation for your operational plan. Ensure that these goals are in alignment with your company’s strategic plan and provide both short-term and long-term visions for the business.
Step 2: Determine roles and responsibilities
Identify the key stakeholders, department heads and team members who will play pivotal roles in executing the plan. Assign responsibilities to ensure that everyone knows their part in the planning process and day-to-day activities.
Step 3: Develop a timeline and milestones
Establish a clear timeline that breaks down the operational planning process. Include key milestones to track progress and ensure the plan remains on target.
Step 4: Allocate budget and resources
Determine the resources required to achieve your goals and objectives. This includes estimating the operating budget, identifying human resources needs and other resource allocations, ensuring you have everything in place to support revenue growth and other business needs.
Step 5: Outline day-to-day operations
Detail the day activities that are integral to the business operations. This will provide clarity on how different tasks and functions work together, ensuring efficiency across diverse cross-functional teams.
Step 6: Monitor and measure performance
Integrate key performance metrics and indicators to regularly monitor progress. Using both leading and lagging indicators will provide a comprehensive view of how well the operational plan is being executed and where improvements can be made.
Step 7: Review and adjust regularly
The business environment is dynamic and as such, your operational plan should be adaptable. Regularly review the plan, comparing actual outcomes with desired outcomes and adjust as necessary to account for changes in the business environment or company goals.
Step 8: Document and communicate
Create an operational plan document, potentially using operational plan examples or an operational plan template for guidance. Ensure that the entire team, from individual team members to the entire organization, is informed and aligned with the plan.
Related: 7 Best Business Plan Software for 2023
Strategic plan vs operational plan: What is the difference?
When running an organization, both strategic and operational planning play pivotal roles in ensuring success. However, each has a distinct purpose, time horizon and scope. Here’s a breakdown of the differences between these two essential business plans:
- Strategic plan : This plan sets the course for the organization’s future. It embodies the long-term vision and mission, detailing the objectives necessary to achieve it. The essence is how everyone, from C-suite executives to individual team members, collaborates towards realizing this vision.
- Operational plan : This is the roadmap for the day-to-day activities of the organization. While the strategic plan looks at the bigger picture, the operational plan hones in on the tactics and execution. It is crafted to support organizational goals with a focus on short-term activities specific to departments or functions.
Time horizon :
- Strategic plan : Long-term in nature, usually spanning three to five years.
- Operational plan : Concentrates on the short-term, with plans laid out yearly, quarterly, or even monthly.
Modification and updates :
- Strategic plan : This evolves over longer intervals, typically three to five years. There might be minor adjustments year over year based on changing business needs and the external business environment.
- Operational plan : Due to its short-term focus, it requires frequent assessments. Plans might be adjusted yearly, quarterly or even monthly to ensure alignment with the strategic objectives and current business environment.
Created by :
- Strategic plan : Crafted by the upper echelons of management – think CEO, CFO and other C-suite members.
- Operational plan : These plans come to life through mid-level management and department heads, ensuring alignment with the broader strategic vision while catering to specific departmental needs.
- Strategic plan : Broad in its outlook, it takes into account external factors like market trends, competition, customer needs and technological innovations.
- Operational plan : This narrows down the focus to the internal workings of the organization. It revolves around technology in use, key performance indicators, budgeting, projects, tasks and the allocation of responsibilities among team members.
As we’ve traversed through the importance of operational planning to various operational plan examples, it becomes evident that having a detailed and efficient operational plan is pivotal.
From the business-centric to the minimalist approach, every operational plan serves as the backbone, guiding team members and ensuring that day-to-day activities align with the long-term vision and strategic goals.
By knowing what should be included in these plans and how to craft them, businesses can navigate the complexities of their operational environment with greater confidence.
For those looking to refine their planning process or start from scratch, the world of digital tools has made it significantly easier. Venngage offers business plan maker and operational plan templates designed to simplify the process.
Whether you need to create an operational plan or draft a business strategy, their intuitive platform can guide you every step of the way.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How To Write the Operations Plan Section of the Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Stage of Development Section
Production process section, the bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs).
The operations plan is the section of your business plan that gives an overview of your workflow, supply chains, and similar aspects of your business. Any key details of how your business physically produces goods or services will be included in this section.
You need an operations plan to help others understand how you'll deliver on your promise to turn a profit. Keep reading to learn what to include in your operations plan.
Key Takeaways
- The operations plan section should include general operational details that help investors understand the physical details of your vision.
- Details in the operations plan include information about any physical plants, equipment, assets, and more.
- The operations plan can also serve as a checklist for startups; it includes a list of everything that must be done to start turning a profit.
In your business plan , the operations plan section describes the physical necessities of your business's operation, such as your physical location, facilities, and equipment. Depending on what kind of business you'll be operating, it may also include information about inventory requirements, suppliers, and a description of the manufacturing process.
Keeping focused on the bottom line will help you organize this part of the business plan.
Think of the operating plan as an outline of the capital and expense requirements your business will need to operate from day to day.
You need to do two things for the reader of your business plan in the operations section: show what you've done so far to get your business off the ground and demonstrate that you understand the manufacturing or delivery process of producing your product or service.
When you're writing this section of the operations plan, start by explaining what you've done to date to get the business operational, then follow up with an explanation of what still needs to be done. The following should be included:
Production Workflow
A high-level, step-by-step description of how your product or service will be made, identifying the problems that may occur in the production process. Follow this with a subsection titled "Risks," which outlines the potential problems that may interfere with the production process and what you're going to do to negate these risks. If any part of the production process can expose employees to hazards, describe how employees will be trained in dealing with safety issues. If hazardous materials will be used, describe how these will be safely stored, handled, and disposed.
Industry Association Memberships
Show your awareness of your industry's local, regional, or national standards and regulations by telling which industry organizations you are already a member of and which ones you plan to join. This is also an opportunity to outline what steps you've taken to comply with the laws and regulations that apply to your industry.
Supply Chains
An explanation of who your suppliers are and their prices, terms, and conditions. Describe what alternative arrangements you have made or will make if these suppliers let you down.
Quality Control
An explanation of the quality control measures that you've set up or are going to establish. For example, if you intend to pursue some form of quality control certification such as ISO 9000, describe how you will accomplish this.
While you can think of the stage of the development part of the operations plan as an overview, the production process section lays out the details of your business's day-to-day operations. Remember, your goal for writing this business plan section is to demonstrate your understanding of your product or service's manufacturing or delivery process.
When writing this section, you can use the headings below as subheadings and then provide the details in paragraph format. Leave out any topic that does not apply to your particular business.
Do an outline of your business's day-to-day operations, including your hours of operation and the days the business will be open. If the business is seasonal, be sure to say so.
The Physical Plant
Describe the type, site, and location of premises for your business. If applicable, include drawings of the building, copies of lease agreements, and recent real estate appraisals. You need to show how much the land or buildings required for your business operations are worth and tell why they're important to your proposed business.
The same goes for equipment. Besides describing the equipment necessary and how much of it you need, you also need to include its worth and cost and explain any financing arrangements.
Make a list of your assets , such as land, buildings, inventory, furniture, equipment, and vehicles. Include legal descriptions and the worth of each asset.
Special Requirements
If your business has any special requirements, such as water or power needs, ventilation, drainage, etc., provide the details in your operating plan, as well as what you've done to secure the necessary permissions.
State where you're going to get the materials you need to produce your product or service and explain what terms you've negotiated with suppliers.
Explain how long it takes to produce a unit and when you'll be able to start producing your product or service. Include factors that may affect the time frame of production and describe how you'll deal with potential challenges such as rush orders.
Explain how you'll keep track of inventory .
Feasibility
Describe any product testing, price testing, or prototype testing that you've done on your product or service.
Give details of product cost estimates.
Once you've worked through this business plan section, you'll not only have a detailed operations plan to show your readers, but you'll also have a convenient list of what needs to be done next to make your business a reality. Writing this document gives you a chance to crystalize your business ideas into a clear checklist that you can reference. As you check items off the list, use it to explain your vision to investors, partners, and others within your organization.
What is an operations plan?
An operations plan is one section of a company's business plan. This section conveys the physical requirements for your business's operations, including supply chains, workflow , and quality control processes.
What is the main difference between the operations plan and the financial plan?
The operations plan and financial plan tackle similar issues, in that they seek to explain how the business will turn a profit. The operations plan approaches this issue from a physical perspective, such as property, routes, and locations. The financial plan explains how revenue and expenses will ultimately lead to the business's success.
Want to read more content like this? Sign up for The Balance's newsletter for daily insights, analysis, and financial tips, all delivered straight to your inbox every morning!

Business Plan Operational Plan - Everything You Need to Know
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the business plan operational plan. A fundamental component of any effective business plan and a key component of growth As a business owner, executive, or manager, you understand that a well-articulated strategy is crucial for the success and growth of your venture. But have you ever stopped to ponder how this strategy is executed on a day-to-day basis? How do we transform those lofty goals into tangible, everyday actions? This is where an operational plan comes into play. An operational plan outlines the practical details of how your business will operate and deliver on its strategic goals. It describes the inner workings of your business, detailing everything from your daily operations and production processes to your team's roles and responsibilities. In this guide we will delve into the purpose and scope of an operational plan, its essential elements, and how to develop one effectively. We'll also share valuable tips, best practices, and common pitfalls to avoid.
Table of Contents
- Operational Plan - The Purpose
- The Essential Elements
- Description of Operations
- Steps for Creating Operational Plan
- Tips & Best Practices
Real-Life Case Study
- Common Pitfalls
- Final Thoughts
Business Plan Operational Plan - The Purpose
The role of an operational plan in a business cannot be overstated. This fundamental document is a strategic guide that outlines the direction, timelines, and resources necessary to achieve specific objectives within an organisation. An operational plan is the driving force behind the execution of your business strategy. It allows you to map out clear and attainable operational goals that align with your overall strategic objectives, breaking them down into manageable, actionable steps. Whilst acting as a map for your business you can also use to track performance via measurable objectives.

Scope of an Operational Plan in Day-to-Day Operations
The business plan operational plan should detail key elements such as the operational processes, resource allocation, tasks, and timelines. From personnel and location to inventory, suppliers, and operating hours - the operational plan touches every aspect of your business. It's a living document, evolving and changing as your business grows and adapts to market dynamics and industry trends.
Remember, the opening of your Executive Summary sets the tone for the entire document. Make it memorable and compelling to encourage the reader to continue exploring.
Business Plan Operational Plan - The Essential Elements
Creating an operational plan requires thoughtful consideration of several vital components that collectively represent the full breadth of your company's operations. Each one plays a crucial role in defining the day-to-day activities that will lead to the fulfilment of your strategic objectives.
Description of the Business Operations
Every operational plan starts with a comprehensive description of the business operations. This includes outlining your production process, operations workflow, and supply chain management. Defining these processes in clear terms provides a concrete vision of how products or services will be created and delivered, identifying the necessary resources and potential bottlenecks along the way.
People are the lifeblood of your business, and it's essential to define their roles and responsibilities within the operational plan. This involves outlining the team's structure, detailing who is responsible for what, and defining key performance indicators (KPIs) for each role. By assigning clear responsibilities, you ensure the efficient use of human resources and promote accountability.
Your business location and the physical resources at your disposal play a crucial role in your operational plan. Detail the premises your business will operate from, the equipment required, and any associated costs. Whether you're operating from a single office, managing multiple retail outlets, or running a home-based online business, defining your operational space is crucial.
Effective inventory management is crucial for maintaining smooth operations, particularly for businesses dealing with physical products. Your operational plan should outline how you will manage your supplies, including how often you'll restock, which vendors you'll use, and how you'll handle storage and distribution. Remember, balancing supply with demand is key to avoiding unnecessary costs or stockouts.
Your operational plan needs to address your suppliers - who they are, what terms and agreements you have with them, and how you will manage these relationships. The reliability and quality of your suppliers can greatly affect your operations, making this a critical consideration in your planning process.
When constructed effectively, these elements come together to form an operational plan that is clear, comprehensive, and actionable. In the next section, we'll explore the steps to develop such a plan, and later, we'll offer some tips and best practices for bringing your operational plan to life. Stay tuned! Looking an industry specific guide to business plans, then check out our business plan guides homepage .

Steps for Developing an Operational Plan
Creating a comprehensive and effective operational plan involves careful planning, clear communication, and continuous monitoring and evaluation. Let's explore these steps in detail:
- 1. Setting Clear Operational Goals and Objectives: The first step towards developing an operational plan is defining what you want to achieve operationally within a given period. These goals should align with your strategic business objectives and be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).For instance, if your strategic goal is to increase market share, your operational objective might be to ramp up production by a certain percentage within the next quarter. Or, if you aim to improve customer satisfaction, you might focus on improving the quality and durability of the product.
- Regular Monitoring and Evaluation: With your operational goals in place, the next step is to monitor progress and evaluate performance regularly. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics should be set for each operational goal. These could range from production volumes and delivery times to quality measures and cost efficiency.Consistently monitoring these metrics allows you to measure progress, identify any potential issues or bottlenecks early on, and adjust your operational plan as necessary.
- Communication: This is a crucial when implementing your operational plan. Ensure all stakeholders, including team members, suppliers, and partners, are aware of the plan and understand their roles within it.Hold regular meetings to update everyone on progress and address any challenges or changes in the plan. Remember, your operational plan should be a living document, flexible enough to adapt to changes and updates as required.

Business Plan Operational Plan - Tips and Best Practices
Creating an operational plan that works requires more than just defining goals and setting performance metrics. There are nuances and best practices that can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your operational plan. Here are a few tips to guide you:
- Involve Your Team : The people responsible for executing the operational plan should also contribute to its creation. Encourage your team to share their ideas, challenges, and insights. Their first-hand experience can lead to more practical, achievable operational plans. Besides, team involvement promotes ownership and commitment to the plan's execution.
- Keep It Flexible : Operational plans need to be adaptable to accommodate changes in the business environment, such as market dynamics, customer preferences, or new regulations. Regularly review and update your plan to ensure it remains relevant and effective. Remember, the operational plan is a guide, not a set-in-stone document.
- Be Specific : Avoid ambiguity in your operational plan. Use clear, concise language and provide detailed action plans, including what needs to be done, by whom, when, and with what resources. This clarity reduces misunderstanding and keeps everyone on the same page.
- Use Technology : Leverage the power of technology to enhance your operational efficiency. There are numerous tools and software available that can help with project management, process automation, data analysis, and more. Use these tools to streamline your operations, track performance, and improve communication.
- Consistency with the Business Plan : Ensure your operational plan aligns with your broader business strategy. This alignment ensures that your day-to-day operations contribute effectively to achieving your long-term business objectives.
By applying these tips and best practices, you can create an operational plan that's not only effective but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and strategic alignment in your organisation.
To further illustrate the importance of a well-executed operational plan, let's look at a real-life case study - the global tech giant, Apple Inc. Apple's operational plan is a testament to the company's relentless focus on precision, quality, and groundbreaking innovation. One key operational strategy that Apple uses is its tight control over its supply chain.
- Description of Business Operations: Apple's business operations are highly integrated and efficient. They manufacture and market a variety of products, including iPhones, iPads, Macs, and services like iCloud and Apple Music. Their production process is complex, involving design, prototyping, manufacturing, and distribution, often happening across different continents.
- Personnel: Apple's workforce is highly specialised. Each team and department has clearly defined roles and responsibilities, whether it's designing new products, managing supplier relationships, or ensuring quality control. Employees at Apple are encouraged to think differently, fostering a culture of innovation.
- Location: Apple operates in multiple locations worldwide, including its iconic headquarters, Apple Park, in Cupertino, California. The company also has a network of retail stores across the globe and contracts with manufacturing facilities, primarily in Asia.
- Inventory: Apple's inventory management is legendary for its efficiency. Through just-in-time inventory practices, Apple reduces storage costs and minimises the risk of stock obsolescence, contributing to its streamlined operations and impressive profit margins.
- Suppliers: Apple has a vast network of suppliers from around the world. It maintains strong relationships with these suppliers and holds them to strict standards of quality and ethical business practices, ensuring the integrity and excellence of its products.
Apple's operational plan aligns seamlessly with its business strategy, focusing on innovation, quality, and customer experience. This has allowed the company to maintain its status as a market leader and pioneer in the tech industry. This case study illustrates how an effective operational plan can turn a strategic vision into a successful reality. In the next section, we'll delve into common pitfalls to avoid when creating your operational plan.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
As you embark on developing an operational plan for your business, it's crucial to be aware of some common pitfalls that can hinder your plan's effectiveness. Here, we outline these potential obstacles and provide advice on how to avoid them.
- Lack of Alignment with Strategic Goals: One of the most common mistakes is a disconnect between the operational plan and the company's strategic goals. Your operational plan should directly support and drive towards achieving these objectives. Ensure all operational goals, processes, and tasks align with your overarching business vision.
- Overly Complex or Unrealistic Plans: While an operational plan needs to be comprehensive, it also needs to be practical and achievable. Avoid creating overly complex plans that your team cannot implement or that require resources beyond your means. Strike a balance between thoroughness and simplicity for a more manageable plan.
- Neglecting to Involve the Team: Your team members are the ones who will execute the operational plan, and neglecting to involve them in its creation can lead to resistance or confusion. Make sure your team is part of the planning process, understands the plan, and is committed to its implementation.
- Ignoring Market Changes: A business doesn't operate in a vacuum. Failing to consider external factors such as market trends, customer behaviour, and economic conditions can derail your operational plan. Ensure your plan is flexible and adaptable to respond to changing circumstances.
- Insufficient Monitoring and Evaluation: An operational plan is not a set-and-forget document. Regular monitoring and evaluation are critical to assess progress, identify bottlenecks, and make necessary adjustments. Make sure you set measurable KPIs and allocate resources to track and review them.Avoiding these common pitfalls will significantly enhance the effectiveness of your business plan operational plan. With a solid operational plan in place, your business is well-positioned to achieve its strategic objectives, driving growth, and success.
Wrapping It All Up
Operational planning plays a vital role in any business, acting as a roadmap to direct daily operations and align them with the strategic goals of the company. As we have seen in this blog post, creating an operational plan involves several important components and steps, from defining clear goals to continuous monitoring and evaluation. Remember, the key to an effective operational plan is to keep it flexible, involve your team and maintain alignment with your business plan. If you implement those principles and regularly review and update you will have set a solid foundation for future business growth. We wish you all the best on your operational planning journey, and remember - every step you take towards detailed and thoughtful planning is a step towards long-term success and growth for your business. If you require any further help on other sections of your business plan, visit our Learning Zone for several in-depth guides.
Business Plan Operational Plan - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
To wrap up this guide, let's address some frequently asked questions about operational plans in business.
- What is the difference between a strategic plan and an operational plan? A strategic plan outlines a company's long-term vision, objectives, and strategies for achieving those objectives. It's a high-level roadmap for the direction the company intends to go. On the other hand, an operational plan details the day-to-day activities and resources necessary to achieve the strategic goals. It's the 'action plan' that brings the strategic plan to life.
- How often should an operational plan be reviewed? The frequency of review may vary depending on your business size, type, and industry, but generally, it is a good idea to review your operational plan at least quarterly. The regular review ensures that the plan is still relevant and effective, allowing for adjustments as business conditions change.
- How long should an operational plan be? There is no set length for an operational plan, as it will depend on the complexity of the operations. It needs to be comprehensive enough to cover all operational aspects of the business but concise enough to be understandable and manageable.
- Who is responsible for creating an operational plan? While the business owner or top management usually leads the creation of an operational plan, it should involve input from all levels of the organisation. Each department or team can provide valuable insights into their operations, challenges, and opportunities, leading to a more realistic and effective plan.
- How can I measure the success of my operational plan? The success of an operational plan is measured by how effectively it helps achieve the strategic objectives. Regular monitoring of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) related to your operational goals will provide a clear indication of your plan's success. If these KPIs are consistently met, your operational plan is likely successful. If not, adjustments may be needed.
- Grasshopper
Operations Plan
- Lesson Materials Operations Plan Worksheet
- Completion time About 40 minutes
The operations section of your business plan is where you explain – in detail – you company's objectives, goals, procedures, and timeline. An operations plan is helpful for investors, but it's also helpful for you and employees because it pushes you to think about tactics and deadlines.
In the previous course, you outlined your company's strategic plan, which answers questions about your business mission. An operational plan outlines the steps you'll take to complete your business mission.
Your operations plan should be able to answer the following:
- Who – The personnel or departments who are in charge of completing specific tasks.
- What – A description of what each department is responsible for.
- Where – The information on where daily operations will be taking place.
- When –The deadlines for when the tasks and goals are to be completed.
- How much – The cost amount each department needs to complete their tasks.
In this session, we explain each item to include in your operations plan.
Goals and Objectives
The key to an operations plan is having a clear objective and goal everyone is focused on completing. In this section of your plan, you'll clearly state what your company's operational objective is.
Your operational objective is different than your company's overall objective. In Course One , you fleshed out what your strategic objective was. Your operational objective explains how you intend to complete your strategic objective.
In order to create an efficient operational objective, think SMART:
- Specific – Be clear on what you want employees to achieve.
- Measurable – Be able to quantify the goal in order to track progress.
- Attainable & Realistic – It's great to be ambitious but make sure you aren't setting your team up for failure. Create a goal that everyone is motivated to complete with the resources available.
- Timely – Provide a deadline so everyone has a date they are working towards.
Different departments will have different operational objectives. However, each department objective should help the company reach the main objective. In addition, operational objectives change; the objectives aren't intended to be permanents or long term. The timeline should be scheduled with your company's long-term goals in mind.
Let's look at the following example for a local pizza business objective:
- Strategic objective : To deliver pizza all over Eastern Massachusetts.
- Technology department operational objective : To create a mobile app by January 2017 to offer a better user experience.
- Marketing department operational objective : To increase website visitors by 50% by January 2017 by advertising on radio, top local food websites, and print ads.
- Sales department operational objective : To increase delivery sales by 30%, by targeting 3 of Massachusetts's largest counties.
Sales department operational objective: To increase delivery sales by 30%, by targeting 3 of Massachusetts's largest counties.
Production Process
After you create your objectives, you have to think strategically on how you're going to meet them. In order to do this, each department (or team) needs to have all the necessary resources for the production process.
Resources you should think about include the following:
- Suppliers – do you have a supplier (or more) to help you produce your product?
- Technology team: app developing software
- Marketing team: software licenses for website analytical tools
- Sales team: headsets, phone systems or virtual phone system technology
- Cost – what is the budget for each department?
In addition to the production process, you'll also need to describe in detail your operating process. This will demonstrate to investors that you know exactly how you want your business to run on a day-to-day basis.
Items to address include:
- Location – where are employees working? Will you need additional facilities?
- Work hours – will employees have a set schedule or flexible work schedule?
- Personnel – who is in charge of making sure department tasks are completed?
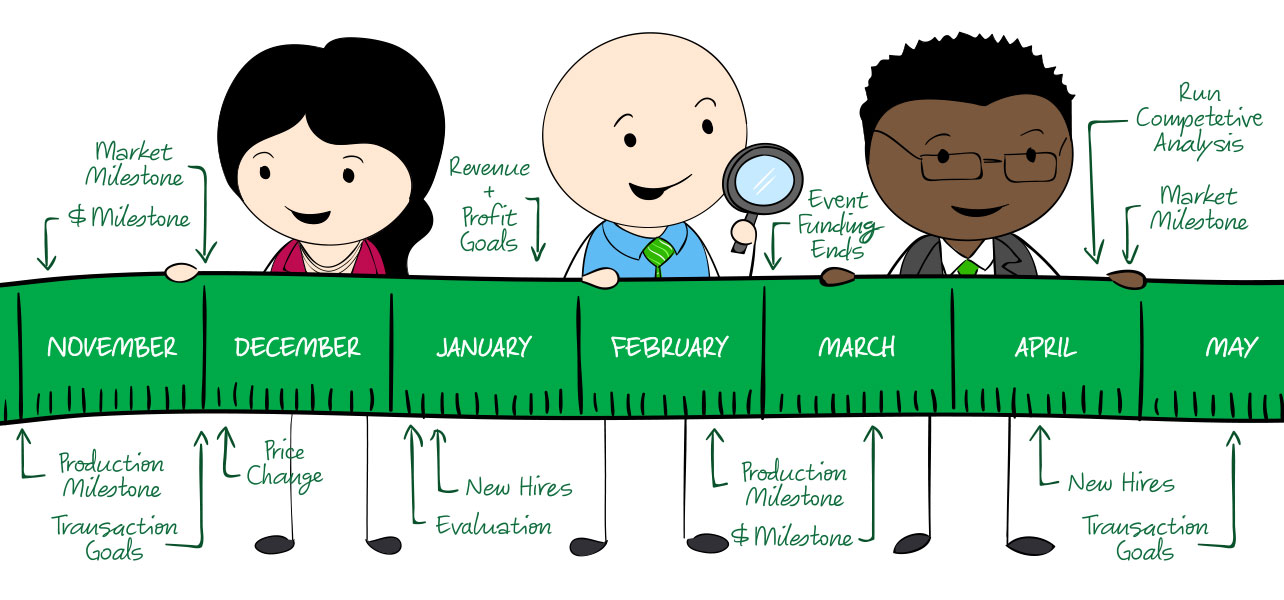
Creating a timeline with milestones is important for your new business. It keeps everyone focused and is a good tracking method for efficiency. For instance, if milestones aren’t being met, you'll know that it's time to re-evaluate your production process or consider new hires.
Below are common milestones new businesses should plan for.
When you completed your Management Plan Worksheet in the previous course, you jotted down which key hires you needed right away and which could wait. Make sure you have a good idea on when you would like those key hires to happen; whether it’s after your company hits a certain revenue amount or once a certain project takes off.
Production Milestones
Production milestones keep business on track. These milestones act as "checkpoints" for your overall department objectives. For instance, if you want to create a new app by the end of the year, product milestones you outline might include a beta roll out, testing, and various version releases.
Other product milestones to keep in mind:
- Design phase
- Product prototype phase
- Product launch
- Version release
Market Milestones
Market milestones are important for tracking efficiency and understanding whether your operations plan is working. For instance, a possible market milestone could be reaching a certain amount of clients or customers after a new product or service is released.
A few other market milestones to consider:
- Gain a certain amount of users/clients by a certain time
- Signing partnerships
- Running a competitive analysis
- Performing a price change evaluation
Financial Milestones
Financial milestones are important for tracking business performance. It's likely that a board of directors or investors will work with you on creating financial milestones. In addition, in startups, it's common that financial milestones are calculated for 12 months.
Typical financial milestones include:
- Funding events
- Revenue and profit goals
- Transaction goals
In summary, your operations plan gives you the chance to show investors you know how you want your business to run. You know who you want to hire, where you want to work, and when you expect projects to be completed.
Download the attached worksheet and start putting your timelines and milestones together on paper.

Talk about this lesson
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Operational Planning: How to Make an Operations Plan

The operations of your business can be defined as the sum of all the daily activities that you and your team execute to create products or services and engage with your customers, among other critical business functions. While organizing these moving parts might sound difficult, it can be easily done by writing a business operational plan. But before we learn how to make one, let’s first understand what’s the relationship between strategic and operational planning.
Operational Planning vs. Strategic Planning
Operational planning and strategic planning are complementary to each other. This is because strategic plans define the business strategy and the long-term goals for your organization, while operational plans define the steps required to achieve them.

Get your free
Operational Plan Template
Use this free Operational Plan Template for Word to manage your projects better.
What Is a Strategic Plan?
A strategic plan is a business document that describes the business goals of a company as well as the high-level actions that will be taken to achieve them over a time period of 1-3 years.
What Is an Operational Plan?
Operational plans map the daily, weekly or monthly business operations that’ll be executed by the department to complete the goals you’ve previously defined in your strategic plan. Operational plans go deeper into explaining your business operations as they explain roles and responsibilities, timelines and the scope of work.
Operational plans work best when an entire department buys in, assigning due dates for tasks, measuring goals for success, reporting on issues and collaborating effectively. They work even better when there’s a platform like ProjectManager , which facilitates communication across departments to ensure that the machine is running smoothly as each team reaches its benchmark. Get started with ProjectManager for free today.
What Is Operational Planning?
Operational planning is the process of turning strategic plans into action plans, which simply means breaking down high-level strategic goals and activities into smaller, actionable steps. The main goal of operational planning is to coordinate different departments and layers of management to ensure the whole organization works towards the same objective, which is achieving the goals set forth in the strategic plan .
How to Make an Operational Plan
There’s no single approach to follow when making an operation plan for your business. However, there’s one golden rule in operations management : your strategic and operational plans must be aligned. Based on that principle, here are seven steps to make an operational plan.
- Map business processes and workflows: What steps need to be taken at the operations level to accomplish long-term strategic goals?
- Set operational-level goals: Describe what operational-level goals contribute to the achievement of larger strategic goals.
- Determine the operational timeline: Is there any time frame for the achievement of the operational plan?
- Define your resource requirements: Estimate what resources are needed for the execution of the operational plan.
- Estimate the operational budget: Based on your resource requirements, estimate costs and define an operational budget.
- Set a hiring plan: Are there any skills gaps that need to be filled in your organization?
- Set key performance indicators: Define metrics and performance tracking procedures to measure your team’s performance.
Free Operational Plan Template
Leverage everything you’ve learned today with our template. This free operational plan template for Word will help you define your budget, timeline, KPIs and more. It’s the perfect first step in organizing and improving your operations. Download it today.
What Should be Included in an Operational Plan?
Your operational plan should describe your business operations as accurately as possible so that internal teams know how the company works and how they can help achieve the larger strategic objectives. Here’s a list of some of the key elements that you’ll need to consider when writing an operational plan.
Executive Summary
An executive summary is a brief document that summarizes the content of larger documents like business plans, strategic plans or operation plans. Their main purpose is to provide a quick overview for busy stakeholders.
Operational Budget
An operational budget is an estimation of the expected operating costs and revenues for a given time period. As with other types of budget, the operational budget defines the amount of money that’s available to acquire raw materials, equipment or anything else that’s needed for business operations.
It’s important to limit your spending to stay below your operational budget, otherwise, your company could run out of resources to execute its normal activities. You can use our free operating budget template for Excel to track your operating costs.
Operational Objectives
It’s essential to align your operational objectives with your strategic objectives. For example, if one of your strategic objectives is to increase sales by 25 percent over the next three years, one possible operational objective would be to hire new sales employees. You should always grab your strategic plan objectives and turn them into one or multiple action items .
Processes & Workflows
Explain the various business processes, workflows and tasks that need to be executed to achieve your operational objectives. Make sure to explain what resources are needed, such as raw materials, equipment or human resources.
Operational Timeline
It’s important to establish a timeline for your operational plan. In most cases, your operational plan will have the same length as your strategic plan, but in some scenarios, you might create multiple operational plans for specific purposes. Not all operational plans are equal, so the length of your operational timeline will depend on the duration of your projects , workflows and processes.
Hiring Plan
Find any skills gap there might be in your team. You might need to hire a couple of individuals or even create new departments in order to execute your business processes .
Quality Assurance and Control
Most companies implement quality assurance and control procedures for a variety of reasons such as customer safety and regulatory compliance. In addition, quality assurance issues can cost your business millions, so establishing quality management protocols is a key step in operational planning.
Key Performance Indicators
It’s important to establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the productivity of your business operations. You can define as many KPIs as needed for all your business processes. For example, you can define KPIs for marketing, sales, product development and other key departments in your company. This can include product launch deadlines, number of manufactured goods, number of customer service cases closed, number of 5-star reviews received, number of customers acquired, revenue increased by a certain percentage and so on.
Risks, Assumptions and Constraints
Note any potential risks, assumptions and time or resource constraints that might affect your business operations.
What Are the Benefits of Operational Planning?
Every plan has a massive effect on all team members involved, and those can be to your company’s benefit or to their detriment. If it’s to their detriment, it’s best to find out as soon as possible so you can modify your operational plan and pivot with ease.
But that’s the whole point of operational planning: you get to see the effect of your operations on the business’s bottom line in real time, or at every benchmark, so you know exactly when to pivot. And with a plan that’s as custom to each department as an operational plan, you know exactly where things go wrong and why.
How ProjectManager Can Help with Operational Planning
Creating and implementing a high-quality operational plan is the best way to ensure that your organization starts out a project on the right foot. ProjectManager has award-winning project management tools to help you craft and execute such a plan.
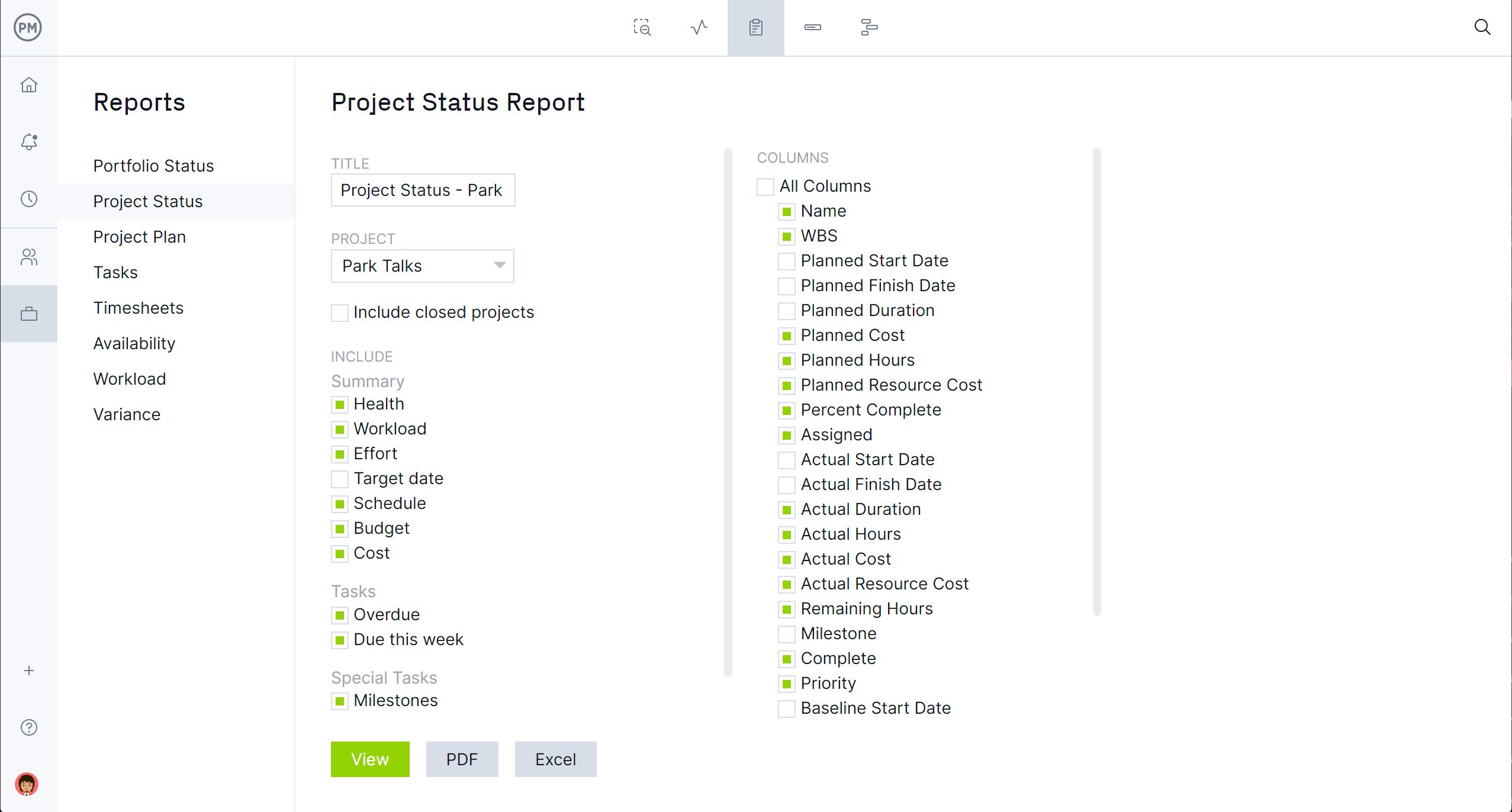
Gantt charts are essential to create and monitor operational plans effectively. ProjectManager helps you access your Gantt chart online so you can add benchmarks for operational performance reviews. You can also create tasks along with dependencies to make the operation a surefire success.
Whether you’re a team of IT system administrators, marketing experts, or engineers, ProjectManager includes robust planning and reporting tools. Plan in sprints, assign due dates, collaborate with team members and track everything with just the click of a button. Plus, we have numerous ready-made project reports that can be generated instantly, including status reports, variance reports, timesheet reports and more.
Related Operations Management Content
- Operational Strategy: A Quick Guide
- Operations Management: Key Functions, Roles and Skills
- Operational Efficiency: A Quick Guide
- Using Operational Excellence to Be More Productive
Operational planning isn’t done in a silo, and it doesn’t work without the full weight of the team backing it up. Ensure that your department is successful at each benchmark. ProjectManager is an award-winning pm software dedicated to helping businesses smooth out their operational plans for a better year ahead. Sign up for our free 30-day trial today.

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.
Operational planning: 5 steps to create a better business operational plan
Learn how to conduct operational planning to enhance collaboration, streamline workflows, and unlock peak productivity in all your company’s teams.

Webflow Enterprise gives your teams the power to build, ship, and manage sites collaboratively at scale.

Operational planning enhances collaboration and streamlines workflows to unlock peak efficiency.
Transforming a strategic vision into business success demands meticulous planning. It requires navigating unexpected obstacles, coordinating team activities with long-term goals, and implementing practical steps to realize organizational objectives.
Organizational planning plays a pivotal role in this context by translating high-level strategies into actionable day-to-day tasks.
But an operational plan is more than a structured to-do list — it’s a comprehensive framework that outlines roles, responsibilities, and timelines. By breaking down grand strategies into executable actions, operational planning ensures cohesive teamwork and transforms ambiguous business strategies into achievable realities.
What’s operational planning?
Operational planning is how companies organize day-to-day tasks to align with broader strategic goals. It’s a road map guiding teams through operational decisions about daily operations, ensuring every task contributes to the company’s long-term and high-level objectives. This typically involves setting short-term objectives, defining key activities, and establishing clear timelines.
In practice, operational planning often blends traditional and innovative methods to maximize efficiency. Conventional strategies like Gantt charts and flowcharts help leaders visualize data , tasks, and timelines to make complex projects more manageable. And digital tools like enterprise project management software introduce automation, real-time collaboration, and data analytics into the mix. These platforms enable agile plan adjustments and offer insights through predictive analytics.
By integrating these mixed methodologies, operational planning helps enterprises build a system that’s efficient and responsive to evolving business needs. It bridges the gap between meticulous organization and the agility needed in a fast-paced business environment.
Benefits of operational planning
Operational planning offers a structured approach to decision-making, but its advantages extend beyond planning. Here’s why it’s a crucial tool for achieving organizational goals.
Clarifies goals
Operational planning turns abstract ideas into concrete objectives. It encourages setting explicit goals with definitive timelines. This clarity benefits leadership and the entire team, ensuring everyone understands what needs doing, who’s doing it, and by when.
Enhances productivity
An operational plan enhances productivity by establishing timelines, outlining objectives, and allocating resources. This structure helps team members prioritize their work and manage their time efficiently because they have clear deadlines to guide them.
By defining precise objectives, the plan ensures every team member understands their specific tasks and expected outcomes, preventing unnecessary work and deviations from the plan. And knowing what resources are available helps team members prepare realistically for their taskwork.
Improves efficiency
A well-crafted operational plan boosts efficiency by optimizing workflows and streamlining organizational processes . By mapping out immediate and long-term objectives, the plan establishes a clear blueprint for task execution. As team members better understand their roles, task sequence, and the rationale behind each, they can execute them more seamlessly. This clarity and structure are also invaluable for onboarding new team members and allow them to integrate and understand the workflow with less friction.
Strategic planning vs. operational planning
Both plan types are distinct yet essential components of an organization’s overall planning process. Let’s break down the primary differences:
- A strategic plan defines your company’s “what,” outlines your business’s direction, and sets broad, long-term objectives. It’s a high-level overview that articulates your mission statement, establishes key business objectives, and outlines strategies for achieving them. This plan typically spans several years into the future and aligns the company’s efforts with its overarching vision.
- An operational plan focuses on the “how” by detailing how to execute the strategies and goals laid out in the strategic plan. This is where you get into the specifics — setting milestones, crafting a detailed road map, and establishing short-term, incremental goals that steer your company toward achieving strategic objectives. And at this point, you’ll focus on more immediate factors, like dealing with daily management and task implementation, that are necessary to achieve strategic organizational goals.
Types of operational plans
Departmental goals and needs vary significantly, and tailored operational plans ensure you optimally manage each area. While a sales department might need a plan focused on customer engagement and retention, an IT department might emphasize technology upgrades and cybersecurity . Combining various plan types — like a couple of those that follow — ensures optimal management and effectiveness in each area, aligning departmental activities with broader objectives.
Project operation plans
Project operation plans are indispensable documents for breaking projects into actionable milestones and assigning teams to relevant tasks. A well-developed project plan organizes tasks and anticipates resource requirements such as personnel, infrastructure, and time. By identifying these requirements early on, project operation plans provide planning foresight that helps avoid resource shortages and last-minute scrambles to ensure projects progress smoothly and stay on track.
Say you’re designing a website . Your project operation plan will outline key steps, such as user research , wireframing , user testing , and launch. Each step would have assigned teams, deadlines, and specific objectives, like establishing focus groups by a certain date and finalizing prototypes. The project manager would monitor progress to ensure resource availability and timeline adherence.
Enterprise operation plans
Enterprise operation plans translate broader strategic goals into smaller, manageable milestones. They involve assigning responsibility for these milestones to department directors to ensure accountability for each plan segment.
When creating an enterprise operational plan, it’s vital to identify resource gaps, dependencies, and other potential obstacles to ensure seamless execution. This lets you set realistic, achievable milestones and achieve smooth interdepartmental coordination. Involving directors from the start is also crucial because their insights can reveal critical aspects you might otherwise overlook.
Consider a web design agency planning to expand their service offerings to include mobile app development over the next year. The enterprise operational plan might include milestones such as hiring app developers, training current staff in responsive mobile design , and marketing these new services to potential leads. You might also ask the development head to oversee recruitment and training and involve the marketing director in developing strategies to promote the new services.
IT operation plans
IT departments confront unique challenges due to rapid cybersecurity threats and their critical role in every business sector. Unlike other departments focusing on sales and marketing, IT departments must ensure the organization’s technological structure is robust, secure, and current.
IT operation plans typically outline how the department will adapt to business changes, like scaling up for new hires, migrating from a legacy system to a new one, and safeguarding the organization against evolving cybersecurity threats.
If you’re preparing for a major server infrastructure upgrade, for instance, an IT operation plan will outline steps like evaluating current server and hosting capacities, selecting new hardware and infrastructure, and scheduling website migration to new servers. The plan would include specific timelines — such as completing server evaluations by the end of the first quarter and starting the migration in the second quarter — to ensure minimal downtime and a smooth transition for all hosted websites.

Discover how the right CMS can allow teams to efficiently scale rich, complex content – all without writing code.
Key elements of an operational plan
No matter the type you’re creating, most operational plans include the following core traits.
Operational plans should be clear and to the point. While comprehensive coverage is important, elaborating too much risks misinterpretation and becoming bogged down in the details. Focus on concise, direct explanations and allow the details to unfold during project execution.
Team buy-in is essential for success. Instead of leaving the executive team to dictate the plan exclusively, involve team members in its creation. A collaborative approach helps garner buy-in and fosters feelings of ownership and responsibility toward the plan’s objectives. This involvement translates to increased motivation and commitment because team members feel more likely to invest effort in a plan they helped shape.
Consistency
Consistency in operational plans is crucial for their effectiveness and for establishing organizational trust. It involves applying the same standards and procedures uniformly across all departments and teams. By consistently applying rules and policies, you ensure every organizational element operates under the same guidelines, enhancing fairness and reducing confusion. Consistent execution of your operational plan also streamlines progress and success tracking because the criteria and methods used for each remain uniform.
Specify the processes and methodologies each department should use. If the design team uses an agile, iterative process , for instance, implement similar practices in other departments like IT. This standardization enables smoother collaboration and operational harmony.
Key performance indicators
Every operational plan needs well-defined key performance indicators (KPIs) from the outset. These should include:
- Leading indicators provide early insights into your strategy’s effectiveness by signaling shifts and trends ahead of their full realization. By monitoring these indicators, you can gauge your strategy’s immediate impact and proactively adjust your approach. Indicator examples include customer satisfaction levels, changes in market share, and fluctuations in sales figures.
- Lagging indicators reflect the outcomes of your operational efforts by providing historical data on your plan’s efficacy after execution. Key lagging indicators include metrics like the time taken to complete projects, support ticket volumes, and total expenses incurred. Analyzing these metrics also helps identify improvement areas, like optimizing resource allocation, enhancing customer support processes, and streamlining operational workflows.
Constraints
Acknowledge any assumptions and constraints within your plan, such as technological limitations, tight deadlines, and regulatory requirements. Being upfront about these factors is essential for setting realistic expectations and guiding effective task execution. And it ensures everyone involved understands the framework they’re operating in.
Say you’re building an agency website in the European Union (EU). A critical constraint would be compliance with data protection regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). You must keep this constraint in mind as you develop your operational plan because it affects the technology and processes used for data handling and shapes your website’s design and functionality. For instance, you’ll likely need to integrate clear consent mechanisms for data collection, prominent user data management tools into the website’s layout, and GDPR-compliant technologies for data processing and storage.
The 5 steps of the operational planning process
Enterprises develop operational plans through five strategic steps, each essential for shaping an actionable and effective strategy. Let’s explore what this planning process looks like.
1. Set goals
Establish specific, immediate business goals that align with your strategic plan. This might include launching a redesigned website, increasing online sales by a specific percentage, or reducing digital marketing expenses.
Make these goals ambitious yet adaptable, allowing for flexible responses to unexpected challenges. This step lays the foundation for your operational strategy and aligns every subsequent action toward these well-defined objectives.
2. Allocate resources
After establishing your goals, evaluate your capacity to achieve them. Analyze your current resources and identify what additional expertise, technology, and budget you require. This step isn’t just about highlighting what’s missing — it’s about strategizing how to scale your business to accommodate these needs.
3. Define KPIs
Select KPIs that align closely with your operational goals and ensure they reflect key aspects of your strategy. These KPIs should include leading indicators, like website traffic and user engagement rates for predictive analytics, and lagging indicators, such as satisfaction scores post-launch, to evaluate past performance. Consistently apply these KPIs throughout your project to monitor progress and keep the team focused on core objectives.
Consider using digital analytic platforms like Google Analytics to track KPIs. These tools offer detailed insights into traffic and user behavior. And you can set up dashboards to visually represent these metrics to help spot trends and patterns without combing through data.
Suppose you notice rising bounce rates on a specific webpage — this might indicate user disinterest or navigational issues. In response, you might pivot to revise the page’s copy, restructure its visual hierarchy , or simplify the navigation structure to make it more engaging and user-friendly.
4. Prescribe processes
Develop clear and detailed plans for how your teams should execute tasks. This clarity guides them through each stage, reducing confusion, ensuring consistency, and enhancing productivity.
To communicate these procedures to your team, use tools like flowcharts. They simplify and clarify each operational plan phase and help ensure everyone understands their responsibilities.
For large-scale projects, consider using project management software like Asana, Trello, or Jira. These platforms offer features like task assignment, deadline tracking, and real-time communication, and they provide a centralized platform for monitoring progress and maintaining team alignment.
5. Determine milestones
Create a road map that outlines clear, measurable goals and specific objectives. This map transforms your operational plan into achievable targets, helping teams visualize where they’re headed and the benchmarks they need to hit. Host regular meetings when outlining your milestones — this consistent evaluation ensures everyone moves forward in sync, maintaining the necessary momentum to achieve the plan’s goals.
In a web development project, for example, these evaluations might reveal if certain phases, like design or development, have too few or surplus resources. Identifying these imbalances lets you efficiently reallocate resources to ensure each department has what it needs to meet its milestones effectively and on schedule.
Get started with Webflow
Operational planning thrives on agility, and Webflow has the tools you need to effectively navigate this dynamic environment. With Webflow, you can build flexible websites that keep pace with your operational goals and integrate with analytics and targeting tools for informed operational decision-making .
Learn how Webflow Enterprise can be a part of your operational strategy, and harness a visual-first design platform that lets you create and adapt web content in real time.
Loved by designers. Trusted by enterprises. Bring Webflow in-house at your company with advanced security, custom traffic scaling, guaranteed uptime, and much more.
Subscribe to Webflow Inspo
Get the best, coolest, and latest in design and no-code delivered to your inbox each week.
Related articles

A step-by-step guide to strategic planning (and what makes it unique)
Discover how strategic planning differs from other project management approaches and learn how to draft a strategy that benefits your organization.

The ultimate step-by-step guide to streamlining your business processes
Learn the benefits of streamlining business processes and implement best practices to improve productivity and output at all organizational levels.

Website project management best practices: 10 fundamentals for success
Learn how to implement project management best practices, streamline organizational workflows, and adopt a proactive approach to delivering projects.

How hidden (but vital) operational decisions affect your business strategy
Discover the most important factors affecting operational decisions and learn how to make informed, data-driven choices for your business.

How to create a strategy map for project success
If you’ve ever been confused about strategic planning, we’ve got you covered. Discover the benefits of a strategy map and the best ways to make one.

Navigating desirability, feasibility, and viability in web design
Implement design thinking in web development by balancing desirability, feasibility, and viability, and learn how they help you build powerful sites.
Get started for free
Try Webflow for as long as you like with our free Starter plan. Purchase a paid Site plan to publish, host, and unlock additional features.
Transforming the design process at
- Interactions
- Localization
- Figma to Webflow Labs
- DevLink Labs
- Feature index
- Accessibility
- Webflow vs WordPress
- Webflow vs Squarespace
- Webflow vs Shopify
- Webflow vs Contentful
- Webflow vs Sitecore
- Careers We're Hiring
- Webflow Shop
- Accessibility statement
- Terms of Service
- Privacy policy
- Cookie policy
- Cookie preferences
- Freelancers
- Global alliances
- Marketplace
- Libraries Beta
- Hire an Expert
- Made in Webflow
- Become an Expert
- Become a Template Designer
- Become an Affiliate
What is an Operational Plan? A Complete Playbook (+ Examples, Tips & More)
Introduction.
Without a plan, your business operations are as good as a children’s playground—everyone’s doing their own thing with no care in the world.
An operational plan brings order to your organization. It defines the functional aspects of your long-term strategy, like goals, milestones, responsibilities and timelines, to build collaboration and make real progress toward your vision.
Teams often overlook the importance of operational plan management, leading to miscommunication, unnecessary roadblocks and slow growth.
If you don't want to end up in a chaotic playground with everything going south, read this start-to-finish guide on operational planning. We'll share a 6-step process of making your own operational plan with a few examples to inspire you.
TL;DR: What is an operational plan?
- An operational plan clarifies the details of your strategy, assigns responsibilities, and sets milestones and timelines.
- Use an operational plan to create a roadmap, assign roles, track progress, establish criteria for success, and minimize errors.
- To develop an operational plan, create a fail-proof strategic plan, establish clear goals and budgets, define the project scope, create the operational plan, get stakeholders' buy-in, and publish the plan using the right tool.
What is an operational plan?
An operational plan is a roadmap designed to implement your business strategies. It operationalizes your strategic plan by defining:
- Vision and objectives behind a strategy.
- Budget and resources required for execution.
- Weekly, monthly and quarterly milestones.
- Relevant metrics to track progress consistently.
An operational plan clarifies all the finer details about your strategy—like what, who, when and how—to help you realize the bigger vision. It’s a work plan for transferring the available inputs into the desired outputs.
Operational planning vs. strategic planning
While operational and strategic planning might sound the same, they have significantly different meanings. Let's take a quick look at these differences to understand what an operational plan stacks up against a strategic plan.
5 reasons why you need an operational plan
Only setting goals without a solid operational plan to implement them is like making new year’s resolutions that never come true.
Without a clear direction of what to do and how, you’d end up wasting your resources with little to no progress to show for it. An operational plan helps move the needle for your company by clarifying the steps to success and bringing more accountability.
Still wondering how an operational plan can keep you on track? These five benefits will clue you in:
1. Creating an airtight roadmap
If a strategic plan defines the destination, an operational plan chalks out the itinerary to reach that destination. This actionable roadmap covers all bases to streamline collaboration within the team and set up the right systems to hit your milestones.
2. Attributing roles to all stakeholders
Making an operational plan allows you to assign responsibilities to all internal and external stakeholders. It clarifies who’s responsible for what and sets expectations from the start. This is key for bringing everyone on the same page and avoiding roadblocks once the work is underway.
3. Tracking progress & making strategic changes
Timelines and milestones are two of the most crucial components of an operational plan in business. They empower teams to analyze their performance and review progress objectively. You can use these insights to tweak your game plan for greater success and to improve operational efficiency .
4. Establishing criteria & metrics for success
An operational plan outlines the parameters for success and metrics to monitor the same. These metrics give you a clear picture of your progress at every stage to ensure you’re moving as per the plan. They also highlight any potential red flags that can potentially derail the plan and need your attention.
5. Minimizing discrepancies & errors
One of the most important benefits of making an operational plan is the clarity it brings to everyone. Instead of leaving your team clueless about the next steps, this work plan clarifies how and where they can start. It also reduces errors by laying down the ground rules for every task and process.
📌 Related resource: Operations Teams: How to Assemble and Lead a High-Performing Team
How to develop an operational plan strategy
There’s no standard rulebook for creating an operational plan. It’s a fully customizable document that depends entirely on your company’s goals, resources, timelines and overall approach.
For example, a fast-paced team can work with shorter timelines and hit more goals than a large-scale organization with more levels of checks and a bigger hierarchy.
So, instead of replicating other companies’ operational plans, let’s help you create your own plan with this 6-step process:
- Draw out a fail-proof strategic plan.
- Establish clear goals and budgets.
- Dig deeper into the project scope.
- Create your operational plan.
- Get all stakeholders’ buy-in for the plan.
- Publish the plan using the right tool.
1. Draw out a fail-proof strategic plan
A strategic plan is to an operational plan what a storyline is to a movie—it conveys the essence and creates a direction for the operational plan to become a masterpiece.
So, naturally, the first step to operational planning is creating a strategic plan; here’s how:
- Define what success looks like for the entire organization.
- Evaluate organizational readiness to implement this strategy.
- Take inputs from people in the senior leadership.
- Assign responsibilities to different stakeholders.
- Prioritize goals against timelines.
Once done, you can rely on this strategic plan throughout the operational planning process to prepare for what lies ahead.
💡 Use these 14 free customizable project plan templates to enhance communication, save time and achieve your strategic planning goals.
2. Establish clear goals & budgets
The next step is breaking your high-level goals into shorter, more actionable objectives. For example, you can divide the goal of achieving an X% growth in revenue into smaller targets, like increasing inbound leads, doubling down on cold outreach and rolling out a referral program. Implementing effective referral tracking within the program will allow you to monitor and optimize the success of your referral initiatives, providing valuable insights into the sources and impact of referred business.
Goal-setting makes your operational plan realistic and feasible. You're ideating the means to realize the long-term vision by hitting the right milestones.
More importantly, once you have a list of goals, it's easier to determine the budget and resources required to achieve them. Before moving ahead, do your homework to set a solid budget that allows you to implement your strategy without splurging too much.
3. Dig deeper into the project scope
Once you’re clear about your goals and resources, it’s time to define the finer details of your plan—specifying who’ll do what, when and how.
Create a comprehensive project scope by outlining:
- Department-wise goals and tasks according to the goals.
- Different stakeholders involved within and outside your company.
- Responsibilities for each stakeholder with primary KPIs for their role.
- SOPs and workflows to perform a task or complete a process.
This step brings more specificity to your operational plan. It concretely spells out each goal with details about milestones within each goal, roles and teams responsible for fulfilling these milestones and how they will work toward the end goals.
💡 Scribe top tip: Creating a project scope document is a breeze when you use Scribe. You can use Scribe's project scope template to get cracking at the earliest.
4. Create your operational plan
By this point, you've done all the legwork to get to work and start writing your operational plan finally.
Make it as actionable and value-packed as possible by answering these five main questions:
- Who: People involved in different tasks. Include a list of teams and specific roles involved in the business operations and clarify what’s expected of them.
- What: Plan of action and targets to pursue. Create a milestone-based roadmap of the high-level goals to achieve and the smaller goals involved in the process.
- Where: Platform(s) where daily operations will happen. Add all the tools and frameworks you'll use to run business operations through this plan seamlessly.
- When: Deadlines for different tasks and activities. Map out the timelines for each job to ensure your team is on track for timely completion.
- How much: Costs involved in hitting the designated goals. Mention your final budget and resource allocation for different tasks.
Use Scribe's free AI Writer for Operations tool to capture and document operational procedures.
Additionally, a good operational plan also lists the metrics to track your progress. Pick and explain relevant metrics in your plan to show employees how you'll analyze their efforts.
5. Get all stakeholders’ buy-in for the plan
No plan is perfect and there's always scope for improving your operational plan to make it perfect. So, once you've drafted the plan, don't forget to run it by a few select stakeholders to identify the gaps you can cover.
Actively seek feedback from people in different ranks and departments to understand the missing links in your plan. Your plan will go through 2-3 rounds of iterations before it’s finally ready to roll out.
6. Publish the plan using the right tool
The final step in the process is publishing the plan. The most important thing to remember is that your plan should be:
- Reader-friendly.
- Easily accessible.
- Quickly shareable.
Clueless about the best way to hit all three points to roll out your operational plan? We have just the solution you need — Scribe .
Scribe is a documentation tool designed to create intuitive documents, like an operational plan, in a few seconds. It significantly reduces the time spent on creating such documents and improves team efficiency in more ways than one.
You can create a single Scribe to explain a process or compile instructions with SOPs in a single place with Pages. You can even ask the AI to write your operational plan — just add a simple prompt and your Scribes, and the AI will build a customized document!
It's the easiest way to bring your team on the same page and power up your operations!
✨ See how operations teams use Scribe to tackle even the most daunting operational challenges.
3 operational plan examples (& why they work)
If you’re looking for some inspiration to get cracking with your planning process, looking at a few operations plan examples can help big time! Let’s look at three great examples, see why they work and how you can replicate the results.
1. Carter Supply’s risk management plan
This detailed risk management plan by Carter Supply covers several aspects of managing risk at the organization. This 10-page document lists the key components of this plan, like a summary, the approval process and the end-to-end risk management process.
As an operational plan, it gives the entire team clear insights into the risk management plan, highlights why it’s in place and explains how this plan will be used.
This plan also covers different aspects of the plan and lays down the process of working on each element. For example, for risk quantification, the plan specifies that the risk manager will work with the risk owner to understand the exposure.
2. Upscope’s go-to-market plan
Upscope ’s go-to-market (GTM) plan is another excellent example of operational planning. The SaaS company created this plan to execute its strategy for breaking into the co-browsing market.
Pursuing this goal, the team created an airtight plan with a rundown of its target audience, pain points the product solves and the buyer journey.
The Upscope marketing and sales teams could use this GTM plan to launch targeted campaigns and reach the right people. They were also well aware of the main value propositions to share with the target buyers, nudging them towards a purchase.
📌 Related resource: How Product Operations Can Help Your Team Build Better Products 📌
3. SmartNet’s project quality management plan
The quality management plan by SmartNet is a detailed document explaining the company’s entire operations framework, from the management structure to project reporting, risk assessment, deliverable production and more.
Instead of a single department, this operational plan documents the complete business operations. Despite being so lengthy, the document is easy to read and understand—exactly how the plan should look like.
It also includes all the critical information to guide new employees about the company's operations from scratch.
Make operational planning your road to success
When done right, operational planning can be a game-changer for streamlining your operations. It’s an in-depth roadmap to work toward your vision and hit all goals.
Even though making an operational plan isn’t the most exciting task and it can get extremely time-consuming, the right process and tools can do the trick for you. Follow the six steps we’ve highlighted in this guide and when you’re ready to roll, use Scribe to put the plan in place.
Scribe takes the pain out of documentation to empower teams for seamless operational planning. Try it today to see how it works!
Ready to try Scribe?
Related content
- Scribe Gallery
- Help Center
- What's New
- Careers We're Hiring!
- Contact Sales
How to Write the Operations Plan Section of Your Business Plan
- Written By Dave Lavinsky

The Operations Plan is a component of your business plan that is like the engine of your car. The operations plan holds the key parts of your business and it shows how those parts work together to keep the business running. If you are starting a business or your business is growing, the operations plan also shows that your business is more than just a good concept. It shows why the business is running smoothly and how key milestones ahead will be met as the business grows. The operations plan is the powerhouse engine in your business plan . Let’s start that engine together.
What is the Operations Plan in a Business Plan?
The key to putting your operations plan together is choosing which processes show how your business works and what the expected outcomes will be as a result. Include the processes that you believe are most important even if they are basic or simple. And, if you think your business is too new to create an operations plan, think again. Every business has processes, no matter how large or small they may be. Your operations plan may be considered by potential investors or lenders; make it the best it can be.
Components of a Comprehensive Operations Plan
The best operations plan includes a list of key processes with short explanations that detail each process. Some explanations will also include a brief sentence explaining how the key process will help the business meet the expected key milestones. For example, “Our Marketing team will post on social media each time our product sales reach one of our sales goals. This will drive new customers to our product offering.”
Main components of an operations plan:
Product Development
Describe how the product is being developed and if it is currently offered or is on target for launch. Include the production process for testing, improvements or revisions.
Key milestone : Note the forecast for new product development to expand the product line.
Manufacturing
Describe the process of manufacturing, from the first step to the delivery of products. This may include several bullet points. Add facilities maintenance in this section. Also, include the management processes of the staff.
Key milestone : Include a brief forecast with plans to increase manufacturing capabilities.
Administration/Human Resources
Include a description of day-to-day activities that are overseen by staff members, including facilities management, safety, reports and compliance, hiring staff and training.
Key milestone : Add a sentence regarding staff training for leadership as the business grows.
List the process of purchasing parts, services, products, and raw materials. Include a sentence about financial oversight of expenditures to control costs.
Key milestone : Indicate how the staff is preparing for purchasing increases to meet higher manufacturing demands.
Customer Service
List the processes that comprise customer service, including any customer relationship management software (CRM) or other processes that interact with customers. Provide details on processes for customer retention.
Key milestone : Add a sentence describing staff training to build customer relationships.
Describe how your business conducts sales, whether through online channels, via wholesale or retail sales, or by other means. Explain why the process works for your business and how it is positioned to be successful because of the sales process.
Key milestone : Indicate how planned sales strategies will expand to meet key milestones.
Note the process of current marketing campaigns and the response of the target audience. Note how responses are scored on social media.
Key milestone : Include operational plans for building brand awareness, key selling points, and entry positions.
At this stage of business, the finance process should be clearly outlined, with current and any expected funding included. Also, include a sentence about how the business has structured a repayment plan for any loans and is making on-time payments.
Key milestone : Describe any anticipated funding options that have already been put into place.
Accounting/Payroll:
Describe in a few sentences how timely accounting is completed on a regular basis. Add a sentence about the payroll system and the software that runs it.
Key milestone : Add a note about increasing software programs in accounting to increase performance during growth.
Include a sentence about the process of oversight for the business. Add the process of documentation, filings, and oversight of any copyrights, patents, or trademarks. Include any licensing payments that add revenue to the business.
Key milestone : Include a description of the legal process already in place to accommodate expansion and long-term growth.
How to Write the Operations Plan For Your Business
Now that you’ve read about the main components in a business operations plan, it’s time to connect them in writing your own operations plan. To do this, you can follow the easy steps ahead as you construct each process.
Remember, you may not need all of the processes listed here. You will want to choose those that make sense for your business and, if needed, add some others. When completed, your operations plan will flow smoothly from start to finish.
- Consider your Business Goals . Write out each goal. Read them as you decide which processes to include in your operations plan and think about how soon you will want to meet the company goals.
- Create a Process List . Look at the list of components and decide how to make them into a list for your own business. Don’t write out full descriptions yet. We’re building the list first. How do processes start in your business?
- Finance (get funding)
- Product Development (buy a truck, provide services, equipment, tools)
- Manufacturing (maintain the garage and tow truck)
- Sales (make sales calls)
- Customer Service (answering texts, and emails)
- Marketing (getting referrals from friends)
- Accounting/Payroll (paying yourself and the bookkeeper)
- Legal (risk management assistance)
- Start filling in the Process Descriptions . Use the examples above to describe the processes of your business. A few sentences that explain each process are all you need in the operations plan.
- For example, key milestones for your tow truck business might be:
- Tow at least five vehicles daily during each week (sales/marketing)
- Buy a second tow truck within 6 months (finance)
- Add a second tow truck driver within 6 months (human resources)
- Buy a commercial truck within 12 months (finance/product development)
- Finish your Operations Plan . Re-read each Process Description and complete the Key Milestones for each operations section.
Sample Operations Plan for Badger Drains & Plumbing
Badger Drains & Plumbing, based in Milwaukee, WI, is dedicated to providing top-notch residential and commercial plumbing services. Our operations plan outlines the key processes that make our business run smoothly and how we plan to meet our key milestones as we grow.
Our services, instead of physical products, are continuously refined based on customer feedback and technological advancements in plumbing. This includes adopting newer, more efficient ways to conduct pipe repairs, installations, and maintenance services.
Key milestone : To introduce environmentally friendly and cost-effective plumbing solutions within the next year.
Our staff handle day-to-day operational tasks, prioritizing safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. This includes everything from scheduling service calls to conducting routine safety checks and equipment maintenance.
Key milestone : Implement a leadership development program for senior technicians to prepare them for managerial roles as the company expands.
We procure high-quality plumbing materials, tools, and technologies from reputable suppliers, ensuring we have the necessary inventory to meet customer demand without excessive expenditure.
Key milestone : Strengthen relationships with key suppliers to negotiate better prices and ensure priority fulfillment as service demand increases.
Customer service is a pillar of our operations, involving not just resolving issues but proactively enhancing customer satisfaction through follow-ups and feedback collection using CRM software.
Key milestone : Introduce a loyalty program by the end of the next quarter to increase customer retention rates.
Sales efforts are directed through personal client interactions and digital marketing to generate leads, with a strong focus on the benefits of choosing Badger Drains & Plumbing for reliability and professionalism.
Key milestone : Achieve a 20% increase in annual contracts by targeting commercial entities in the Milwaukee area.
Our marketing is focused on local SEO, targeted ads, and social media engagement to connect with the Milwaukee community, emphasizing our quick response times and quality service.
Key milestone : Launch a community-oriented campaign to increase brand visibility and customer engagement by participating in local events and sponsorships.
Our current financing includes business revenue and a small business loan, with a diligent approach to budgeting and a clear plan for loan repayment and future investments.
Key milestone : Secure a line of credit to fund an expansion of services within the next two years.
Accounting/Payroll
We use modern software solutions to ensure accurate and timely financial and payroll management, allowing us to focus more on serving our customers and less on back-office tasks.
Key milestone : Transition to a more comprehensive software suite that integrates CRM and finance for better overall management efficiency.
Our legal framework encompasses regular reviews of compliance, documentations, and the management of any intellectual property, ensuring all operations are above board.
Key milestone : Establish a retainer partnership with a legal firm specializing in small businesses to prepare for interstate licensing and expansion.
By following this operations plan, Badger Drains & Plumbing aims to enhance its service offerings, optimize operational efficiency, increase productivity, and achieve sustainable growth, maintaining its commitment to being Milwaukee’s trusted plumbing service provider.
If You Aren’t a Writer or Have No Time to Write…
The truth is, not all of us are writers and some of us don’t have time to spare. The good news is that we have a solution for you in the newest software designed for entrepreneurs and business owners who need a complete business plan–without having to write one.
If you would like to easily create a comprehensive business plan, you can join over 100,000 entrepreneurs and business leaders who’ve created their business plans with PlanBuildr.
Why do we offer PlanBuildr? We are business owners. We know your time is valuable. And, we know a comprehensive business plan is vital when it’s time to obtain funding or secure investors. Not all of us are writers, but we all know good value when we see it. Try PlanBuildr for free !

- Business Planning
- Venture Funding
Filter by Keywords
10 Simple Operational Plan Templates in Word & ClickUp
Praburam Srinivasan
Growth Marketing Manager
February 15, 2024
Every business starts with an idea, but it takes disciplined execution to bring it to life. That’s why operational plans are indispensable—they require you to think about the steps and resources you need to make your vision come true. By writing down these processes, you create a roadmap for your organization and empower your teams to work together towards the same goal.
There are lots of components that make up an operational plan—from your business objectives and market analysis to your operational strategy and budget. You need to add clear details, tasks, and assignments for your plan to be useful.
The good news is you don’t need to start from scratch. Use an operational plan template to outline and manage the day-to-day activities and processes of your business, ensuring that you have the capacity to complete tasks efficiently and on time. With the right tools in hand, like Word or ClickUp templates, businesses of any size can create effective operational plans tailored to their individual needs.
In this article, we’ll explore 10 customizable and simple operational plan templates.
What is an Operational Plan Template?
What makes a good operational plan template, 1. clickup operational plan template, 2. clickup business plan template, 3. clickup business requirements template, 4. clickup business continuity plan template, 5. clickup business development plan template, 6. clickup business roadmap template, 7. clickup compliance project plan template, 8. clickup contingency plan template, 9. clickup action plan template, 10. microsoft word operational plan template.
An operational plan template is a document designed to help you turn your business strategy into action. It includes pre-designed pages, lists, and tables that you can fill in with details like:
- The day-to-day operations that need to be implemented to reach your business objectives
- What you need in terms of space, human resources, and equipment
- Roles, responsibilities, and scope of work
- Operational budget and financial limitations
- Project timelines
- Metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) for success
Depending on the size and scope of your organization, operational plans can vary in complexity and length. That’s why you need to find a template that gives you flexibility in making it your own—and we’re here to help you do just that.
A good operational plan template is customizable to fit your specific needs. It offers you several ways to view, sort, and organize your data, and makes it easy for you to track responsibilities and progress. It provides visual cues and clear and concise instructions on how to fill out each section and page.
The best operational plan templates offer an intuitive, user-friendly experience so that anyone using them for the first time can easily navigate them. Think of how people in your organization will use the plan: Will they want to see your progress at a glance? Do they need to see workload distribution among your team? Choose a template with features that support those needs.
You also want your operational plan template to be able to scale with your organization as you grow. Choose a template that lets you adjust and update your plans without needing to start from scratch every time.
10 Operational Plan Templates
Whether you’re looking for an annual operational plan template or a simple project tracker , there are plenty of options available. Here we’ve rounded up 10 of the best templates in Word and ClickUp that you can use to create effective operational plans.

This simple operation plan template by ClickUp helps you strategically plan your business by outlining processes , clearly defining individual responsibilities, and tracking your progress toward your goals. It’s designed to help you monitor all the moving parts of setting up a business.
With this ClickUp operation plan template, you get a range of view options. Use the List view for maximum flexibility in grouping and sorting tasks, and arranging tasks by priority.
Switch to Board View to examine Plan Phases: planning, implementation, monitoring, and management. Use other views like Gantt, Timeline, and Workload to visualize dependencies, keep track of schedules, and spread out work across your team.
Do more with this template using custom fields. These fields let you assign responsibilities to a team, add information and resources to a task, and update a project’s progress.
The ClickUp Business Plan Template is an excellent tool to help entrepreneurs move from ideation to launch. Start documenting your business strategy by going through the topics provided in the Topics List View. Add notes, files, and tasks to sections on your company background, market analysis, sales and marketing strategy, operational strategy, and milestones.
Each section has pre-filled tasks with short descriptions to help you flesh out the details of your business plan. For example, under the Company Background section, you have four “tasks” to fill out—The Team, Overview, Mission, and Vision.
Launching a business gets hectic pretty quickly, so use the Board and Timeline views to keep track of tasks and deadlines. And when you’re ready to zoom out and see what you’ve written, head over to the Business Plan Doc view, which presents the outputs of each section and task in one clean, professional document.
The ClickUp Business Requirements Template outlines the necessary steps and resources for an end solution to fulfill your business needs. For example, if you’re looking for an agency to help you build an app, you’d use a Business Requirements Document (BRD) to explain what you need, why you need it, and how the agency can help you. This helps you get buy-in from your company’s decision-makers, determine the project’s scope, and get all parties aligned on timelines, budgets, goals, and expectations.
This useful business requirements template starts with a list of subpages, and each one comes with brief instructions for filling it out. For example, the Project Objectives subpage comes with a note asking you to include the project’s purpose, current processes, challenges, and reasons for the undertaking.
It recommends using the SMART goals format (specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-bound). Other subpages also come with tables that you can easily fill out.
When the unexpected happens, don’t be caught without a plan. The ClickUp Business Continuity Plan Template helps you plan how to manage risks in the event of a disruption to your business operations. This includes mapping out the steps you need to take in the event of a natural disaster, power outage, cyber attack, or other unforeseen (and unfortunate) events.
This template covers the core parts of a business continuity system—priorities, continuity coverage, and guiding principles. Dive into the details of your plan with a Priorities List view, a consolidated List view, and a Board view. Quickly spot tasks across different categories and progress stages with the use of distinct color coding.
With this template’s intuitive and minimalist design, you can focus on the crucial steps and resources to keep your business sailing through a storm (literal or figurative!).

Track your short-term and long-term business goals with this ClickUp Business Development Plan Template for beginners. The template dedicates one subpage each for operations, marketing, finance, and people, as well as an executive summary.
Each subpage gives you a structure to guide you in writing down your plans. For example, the Operations subpage comes with tables for facilities and equipment costs and also shares an example of a process map. The Financial Plan subpage gives you a template for projecting cash flow, forecasting your balance sheet, and running a break-even analysis.
Make this template your own, whether you’re planning for a short-term or long-term business development goal.
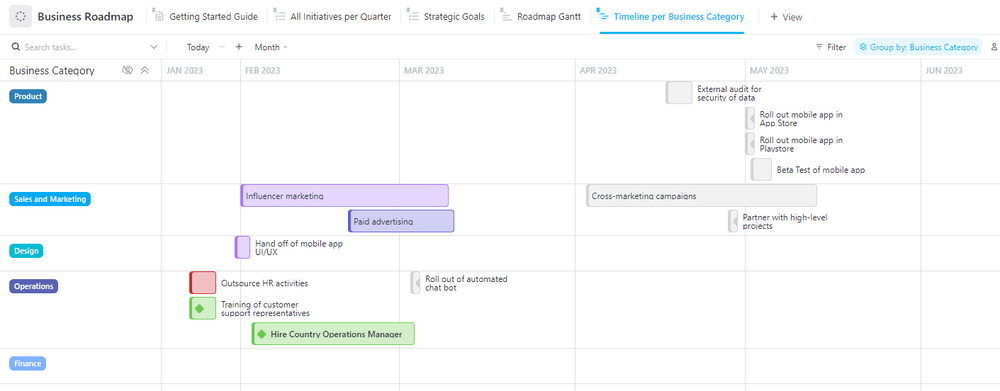
Avoid falling prey to fuzzy strategy syndrome by documenting your business roadmap . Use this ClickUp Business Roadmap Template to record your strategy, focus on your North Star, and say “no” to tactics that don’t align with your vision .
The ClickUp Business Roadmap Template helps you create a high-level strategic document that communicates your goal and how you plan to get there. It sets expectations for every team in your business and maps out project initiatives to strategic goals. Your team can collaborate on projects in List, Gantt, and Timeline views, helping to streamline communication and collaboration.
When you’re ready to dive into the details of your roadmap, use this template’s custom fields to add long text descriptions and upload files. And whenever you complete a subtask, checklist, or comment, the template automatically updates a progress bar, showing you how close you’re getting to reaching your goal.

Complying with legal and industry rules and standards involves keeping track of a lot of documents and tasks. This ClickUp Compliance Project Plan Template ensures nothing slips through the cracks as you work on your compliance project.
The template is organized into sections for regulatory, HR, and data compliance. Start by using forms for collecting information on various compliance requirements. You can use the form’s preset questions and add or delete items as you need. The answers will show up in the List view, where you can group, sort, explain, and assign each requirement. Track priorities, task statuses, point persons, and due dates in Board view as your compliance project progresses.
To provide more context to each requirement, use custom fields to fill in details like performance metrics and consequences of non-compliance. The template also has dropdown fields with pre-filled options—for example, fields for compliance threat category and degree of compliance.
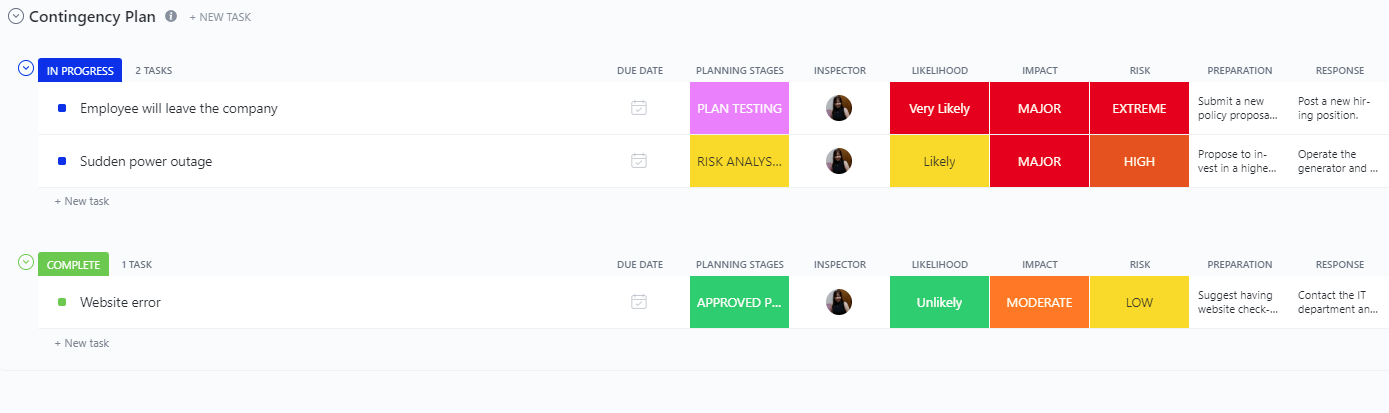
No project goes off exactly as you imagine—even when you follow your plan to the letter. An employee goes on emergency leave, your website crashes and the WiFi stops working. For times like these, you need a plan B. And you can create it using the ClickUp Contingency Plan Template .
The ClickUp Contingency Plan Template offers three views that let you list down events, prioritize them based on risk level, and track progress across planning stages. When you add a task, the template automatically creates custom fields, such as the event’s risk level, likelihood, and potential impact on your organization. There are also fields for you to describe the preparations you’ve made to mitigate risk internally and provide details about your response plan.
Bonus: Contingency planning templates !
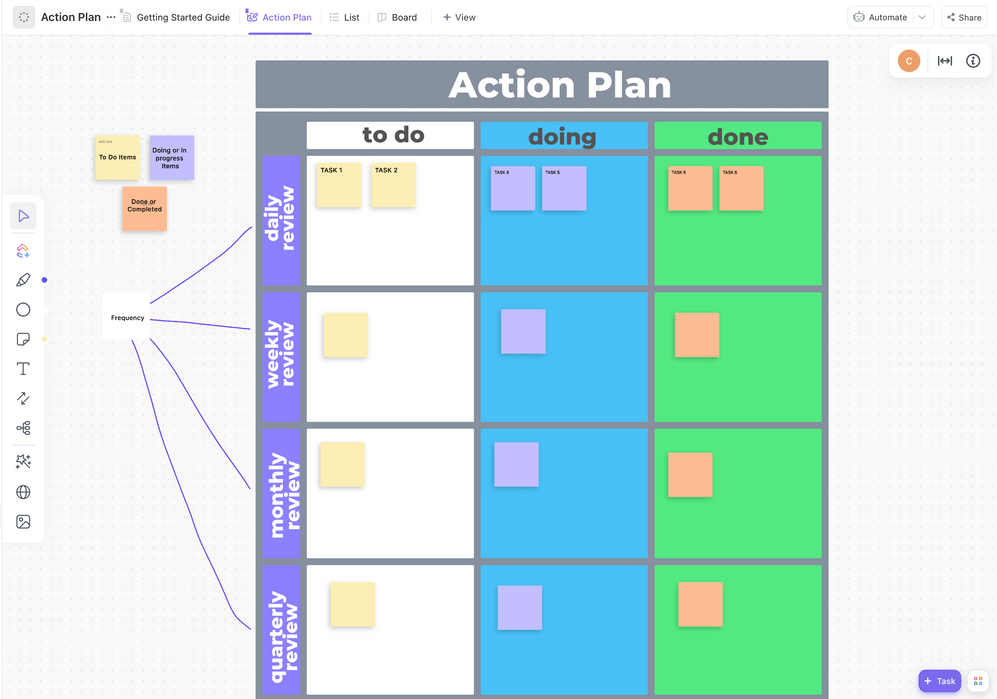
The ClickUp Action Plan Template is a colorful whiteboard template for reviewing an action plan daily, weekly, monthly, and quarterly. You can add files from within ClickUp or from your device, or import them from G Suite or Figma. You can also embed YouTube videos and ClickUp tasks, making this template interactive, collaborative, and anything but boring!
This media-rich template gives you the space and flexibility you need for creating action plans that come with lots of contextual information. Zoom out for a bird’s eye view of your progress or zoom in to break down action plans into small steps. You can also use this Action Plan Template to assign tasks, track progress, set deadlines, and add notes.

Create a professional document with a Microsoft Word Operational Plan Template, such as this business plan template that gives you step-by-step instructions for creating a comprehensive plan. It comes with formatted text and simple layouts so you can focus on the content more than the presentation.
If you want more creative control, though, this template is completely customizable. Plus, it lets you add animations and transitions, as well as photos, videos, and graphics. Once you’re done, you can share and publish the doc with a few quick clicks.
Streamline Your Operational Planning Process
Boost your chances of reaching your business goals by creating an effective operational plan. With the right tools and templates, you can easily create a tailored document that helps you track your operational planning process and projects.
We hope our list of 10 simple operational plan templates has helped you find the perfect template for your needs!
Try them out by setting up a free ClickUp Workspace !
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
- Professional Services
- Creative & Design
- See all teams
- Project Management
- Workflow Management
- Task Management
- Resource Management
- See all use cases
Apps & Integrations
- Microsoft Teams
- See all integrations
Explore Wrike
- Book a Demo
- Take a Product Tour
- Start With Templates
- Customer Stories
- ROI Calculator
- Find a Reseller
- Mobile & Desktop Apps
- Cross-Tagging
- Kanban Boards
- Project Resource Planning
- Gantt Charts
- Custom Item Types
- Dynamic Request Forms
- Integrations
- See all features
Learn and connect
- Resource Hub
- Educational Guides
Become Wrike Pro
- Submit A Ticket
- Help Center
- Premium Support
- Community Topics
- Training Courses
- Facilitated Services
Operational Planning: How to Make an Operational Plan
June 6, 2022 - 10 min read
Having a strategic plan is essential to any company, but it’s not enough. To ensure that the broader organizational goals are within reach, you need an operational plan for day-to-day work.
Using templates to manage your operation plan can help simplify your complex processes and save you time. You know how a shopping list helps you remember what to buy at the store? Templates are like that for your work. And Wrike has many templates ready to go for different kinds of jobs.
For example, you can use the retail trade template to see what step comes next when adding something new for customers to buy. Then there’s the business operations templates , which helps you and your team keep track of your business plan without getting wires crossed. And when you need to manage bills, you can use the invoice tracking template . All these templates are great tools for keeping an operational plan ticking over.
In this blog post, we’ll explain what an operational plan is, show you how to create one without feeling overwhelmed, and provide you with an example of an operational plan. We’ll also share our prebuilt templates to get you up and running quickly.
What is an operational plan?
An operational plan is a document that outlines the key objectives and goals of an organization and how to reach them.
The document includes short-term or long-term goals in a clear way so that team members know their responsibilities and have a clear understanding of what needs to be done.
Crafting an operational plan keeps teams on track while guiding them in making crucial decisions about the company's long-term strategy.
Operational planning vs strategic planning
Though related to each other, these two planning strategies differ in their focus.
Operational planning is the process of the day-to-day work to execute your strategy. It ensures you have all the resources and staff necessary to get work done efficiently.
On the other hand, strategic planning is about looking ahead into the future, identifying the upcoming pipeline, and figuring out how you can prepare for it.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor, nearly 7 million Americans are self-employed, with an additional 10 million employed by small businesses.
If you're working at a large corporation, chances are your company will have some form of strategic goals in place. However, if you're one of the millions who work remotely and independently, your success will rely on operational planning instead.
What are the key elements of an operational plan?
The success of operational planning largely depends on setting realistic expectations for all teams.

Here are the key elements of a functional operational plan:
- Clearly define the ultimate vision or objective for the plan
- Review and break down the smaller goals for the operating budget, team, and resources required to put the plan into action
- Assign budgets, team members, key stakeholders, and resources
- Monitor progress with consistent reports
- Refine the operational plan and be ready to pivot if needed
Ensure all teams understand the parameters of success. Doing this shows how their work contributes to wider company goals and ensures better decision-making for the business operation.
How to create an operational planning process
Think of an operational plan as a key component in a team puzzle. It provides employees with a manual on how to operate the company.
It should be created in tandem with other foundational documents like an organizational mission statement, vision document, or business strategy. Daily, it can help answer questions such as:
- Who should be working on what?
- How can we mitigate those risks?
- How will resources be assigned for different tasks?
- Are there any internal and external risks facing the business?
To create a successful operational plan, it's important to define goals clearly. Here are several steps that will help you develop a functional operating plan:
Start with the strategic plan
Before defining an operational goal, make sure your strategic objectives are in place and relevant.
Prioritize the most critical activities first
Once these goals have been decided on, prioritize the most critical activities required to achieve these aims.
Stop diluting team efforts and let them focus on the most important goals first. Doing this means everyone works on a smaller set of tasks, instead of spreading themselves thin in multiple areas. It also helps in optimizing available resources.

Use predictive indicators
For a robust operational plan, consider using key performance metrics or indicators that can help you determine project progress and lend visibility to team activities.
While lagging indicators look backward, leading indicators look to the future. Think of the plan as a car — the rear-view mirror would be a lagging indicator, while the windshield would be the leading indicator.
A leading indicator could be a new product, higher customer satisfaction levels, or new markets. Examples of lagging indicators include the number of people who attended an event or the monthly operating expenses for specific departments.
Instead of lagging indicators, use leading indicators. Lagging metrics will show that your efforts are falling short only after you execute the operations.
Leading KPIs include predictive measures that allow early identification of problems before they become critical and impact business performance negatively.

Get team buy-in
The key to defining appropriate KPIs is involving the whole team in the process. Meet to discuss the business goals and figure out what measurements are right for the team instead of working independently or outsourcing them.
Ensure consistent communication
Communication is key. By understanding your company's metrics and what they mean, you'll be able to work together more effectively with colleagues to reach common goals.

Operational plan example
Let’s say that a company plans to increase production volume by 50% at the end of a fiscal year.
When the company goal is clear, the team will make a strategic plan with three main components: marketing, sales, and operations.
This can be further broken down into an operational plan, which will assign resources, teams, budgets, and timelines for different departments such as manufacturing, sourcing, accounts, finance, and logistics to achieve the increase in production. Such a plan should include a financial summary and financial projections as well.
Operational plan template
Think about the example above. The goals and parties involved are clear as part of the operational plan. At the same time, to remain on track, the plan requires continuous analysis and reviews. An operational plan template can be extremely helpful to achieve that.
An operational template can be a simple document that is reused for different plans by the same organization. However, it is also possible and extremely helpful to make use of project management software tools to create one.
For instance, Gantt charts can serve exactly that purpose. Using a Gantt chart as an operational plan template, it is possible to create and manage plans, track changes and edit project-related activities in real time. The chart allows clear visibility for timelines, tasks, responsibilities, and team members.
Operational planning advantages and disadvantages
Most businesses utilize an operational plan to keep track of their daily tasks.
The plan outlines the day-to-day activities for running the organization — teams, managers, and employees are then able to visualize their contribution, which is crucial for reaching company goals.
But every process has two sides. Let’s review the operational planning advantages and disadvantages in more detail.
Operational planning advantages
Clarifies organizational goals.
An operational plan helps managers and department heads define their daily tasks, responsibilities, and activities in detail.
It also illustrates how individual team members contribute to the overall company or department goals. Without a clearly defined plan, managers and employees have no way to measure their daily tasks against predefined outcomes.
Boosts team productivity
Business owners are always looking for ways to increase productivity, which in turn translates into higher profits. One of the best and easiest ways to boost efficiency is through an operational plan.
Employees are more productive when they know their daily objectives and responsibilities. Conversely, if they're unsure of what is required of them, chances are their productivity will suffer.
An operational plan provides this vital information to employees in each department and across the company as a whole.
Enhance organizational profitability
Having a plan helps in keeping projects and teams on track.
When operations are managed properly, teams are able to consistently increase revenue and develop new products.
Innovation pays off. A BCG survey points out that 60% of companies that are committed to innovation report steadily increasing revenues year after year. With an operational plan in place, teams are able to innovate better and faster.
Improves competitive advantages
Competitive advantages are made up of multiple levels and components.
Coordinating the different parts with an operational plan will make your workflows run more smoothly. This allows you to deliver high-quality deliverables on time, creating an outstanding customer experience and keeping you ahead of the competition.
Operational planning disadvantages
Possibility of human error.
Human error is a common problem in manufacturing that can often occur when transitioning from production to sale.
Operations management teams will need to coordinate effectively with diverse cross-functional teams such as finance, accounting, engineering, and human resources. In doing so, each team will have a clear understanding of the end goals of each department.
Interdependency amongst parts
One of the main disadvantages of implementing an operations planning process is that its success depends on coordination across parts.
Plans end up failing due to one part not working, which can have an adverse impact on the subsequent process. Disruptions in one process can end up affecting the entire process, making the entire operational plan useless.
Using Wrike for operational planning
Boost your organization’s efficiency by ensuring every project starts off on the right foot. Wrike’s award-winning project management tools can help you create and execute operational plans with various prebuilt templates .
Establish your plan, monitor progress, and be prepared to pivot if necessary. With Wrike, you can share real-time data, making all milestones crystal clear for your team and helping them stay updated and on track.
These templates keep processes running smoothly so you can focus on doing your work well. Want to try them out? They’re just a click away.
Choose the most suitable template and start a free two-week trial of Wrike today!

Yuvika Iyer
Yuvika is a freelance writer who specializes in recruitment and resume writing.
Related articles

What Is a PMIS and How Does it Work?
Discover how a PMIS can help your team deliver high-quality projects faster in this in-depth guide. Learn what is PMIS and how you can set one up.

Google Workspace for Project Management Guide
Google project management tools include Google Sheets, Docs, and Slides. Read on to discover everything you need to know about Google project management.

Work Skills You Need on Your Resume in 2021
Navigating the highly competitive job market can be brutal. In a recent Jobvite survey, nearly three in four respondents said they believe finding a job has become much harder following the pandemic. It’s clearer now more than ever how important it is for your resume to stand out. In fact, nearly 24% of hiring managers spend 30 seconds or less reviewing a resume to determine whether a candidate is qualified for a position or not. You quite literally have seconds to catch their attention before your resume ends up in the recycling bin with the rest of the candidates that didn’t make the cut. So, how exactly do you set yourself apart and stand out from the crowd? Highlighting your work skills on your resume is the best place to start. We did some digging and pulled together some work skills examples in various categories to inspire you to revitalize your resume. Important social work skills for the workplace What are social work skills? Social skills, otherwise known as interpersonal skills, are essential in helping us communicate with one another in the workplace. These skills allow us to build relationships, interact, and communicate with those around us in a meaningful and effective way. This includes verbal and nonverbal cues. Social work skills are essential in every job. Whether you work on a team, are in a client-facing role, or are an individual contributor reporting to a direct manager, solid social skills will help you succeed in your position. Let’s take a look at some of the most important social work skills for the workplace: 1. Empathy One of the best ways to interact well with others is to put yourself in their shoes and understand how they feel. Empathetic people can understand how others are feeling and can identify with those feelings in some way. Having empathy is a vital trait, especially for those who hold leadership positions. Being empathetic isn’t something you can force, and it doesn’t happen overnight if it doesn’t come naturally to you. This skill takes a conscious effort to build and will help you forge and maintain stronger workplace relationships. 2. Active listening Have you ever been in the middle of a conversation with a colleague and felt like they weren’t paying attention to a single word you were saying? Or have you ever been chatting with a coworker and felt like they heard you and gave you their utmost attention? The latter is known as active listening. Active listening involves giving someone your full, undivided attention and it allows you to build trust and strong relationships with your colleagues and clients. Active listening requires practice, but it is a skill that can be acquired with proper training and effort. 3. Emotional intelligence At a high level, emotional intelligence refers to recognizing and being aware of the emotions of both yourself and other people. Those with high emotional intelligence are known for being self-aware and can practice self-regulation, particularly in stressful and potentially overwhelming situations at work. Emotional intelligence is critical in the workplace because it contributes to strong, long-term relationships and can help you manage and appropriately tailor your reactions. 4. Conflict resolution According to recent research, 65% of workers experienced conflict with another coworker. Conflict is inevitable in the workplace, which means developing a solid set of conflict resolution skills can help you manage and navigate these situations efficiently. Conflict resolution is the ability to address the root cause of disagreements and devise a solution that works for all parties involved. You can use various techniques to help resolve conflicts, so it’s essential to learn and understand how to address different disputes. 5. Written communication Social skills refer to how we communicate with one another, which means written skills are a must. Some forms of written communication include emails, instant messages, documents, reports, slide decks, and your resume. Using appropriate grammar, proper spelling, and following formatting guidelines will allow you to communicate effectively with others. 6. Nonverbal communication When it comes to communication, it’s easy to think about what we are saying, but we don’t always focus on how we are saying it. Nonverbal skills can dramatically impact the way your message is received. Your body language, eye contact, facial expressions, and tone can completely change the message you are trying to deliver to your coworkers. It’s important to be aware of these subtle cues so that you can make sure your message isn’t misconstrued or misinterpreted. Work-related skills for virtual environments You might not be working with your colleagues side-by-side in the same office. In addition to the skills we discussed above, remote work requires some different skills and disciplines. Below are a few competencies that you’ll definitely want to have when collaborating in virtual work environments: Self-motivation: There’s a big difference between in-person office environments and virtual workplace settings. At the office, your manager can simply stop by your desk or quickly check in to see how things are going. While your supervisor can technically do the same via email or instant message, you ultimately don’t have anyone looking over your shoulder 24/7 at your home office (unless you have pets, children, or spouses nearby!). That means self-motivation and knowing how to hold yourself accountable to get your work done are vital to helping you thrive in a virtual role. Adaptability: Adaptability is beneficial in any setting, but it’s a particularly beneficial skill in virtual environments. Whether you’re working with a distributed team and constantly trying to navigate time zones or your presentation gets interrupted due to an unreliable internet connection, adaptability is an important skill to help you navigate the unexpected and ever-changing conditions you may find yourself running up against. Digital and technical knowledge: In virtual environments, employees work remotely and generally rely on several tools to collaborate and tackle their to-do lists. Between project management software, instant messaging, video conferencing, document sharing, and email, there are many different technologies to navigate daily. If you’re working in a virtual environment, it’s essential to feel comfortable using these platforms if you want to keep up with the pace of your work. It’s also worth mentioning that, while you still may be able to reach the IT help desk, you may not receive assistance as quickly as you would in an office setting. That means you might have to do some troubleshooting and problem-solving on your own. What teamwork skills are important for 2021? Teamwork makes the dream work, right? Teamwork skills are a subset of skills that enable us to work well with groups of people (meaning, our teams) to achieve a shared goal or outcome. In 2021 and beyond, as we see a shift toward hybrid work models, honing in on your teamwork skills can help you land your dream gig. Here are the teamwork skills that are important to develop for 2021 and beyond: 1. Reliability Being reliable is arguably the most crucial teamwork skill. Those who are reliable can be depended on and trusted to do their part time and time again. They show a certain level of commitment to their work and colleagues, meet deadlines (or even get work in early), and follow through on any action or task they say they will do. You want to be a reliable teammate so your colleagues and your employer will have faith in you. And the more trustworthy you are, the more responsibility you will be trusted with over time, which may boost your career growth in the long run. It’s even more important to showcase your reliability in a virtual workplace environment through clear and frequent communication. 2. Accountability Accountability goes hand-in-hand with reliability. But beyond being reliable, accountability is all about taking responsibility for one’s work — even when that includes mistakes or failures. There’s no room for the blame game or pointing fingers on teams that work well with one another, which means you have to hold yourself accountable and take fault when necessary. Your teammates will likely think more of you if you’re willing to admit you’re wrong, as opposed to constantly shifting blame or pointing fingers when issues arise. 3. Respectfulness A little bit of respect goes a long way, especially at work. According to Indeed, respectfulness in the workplace reduces stress, increases productivity and collaboration, improves employee satisfaction, and creates a fair environment. You need to respect your team members, manager, and clients to do your best work together. Acts of respect include acknowledging others and calling them by name, encouraging and exchanging opinions and ideas without judgment, giving credit where it’s due, and listening to and understanding your teammates. 4. Collaboration There is no successful teamwork without collaboration. Collaboration is working together with one or more people on a project or toward a shared goal. When employees can work together and collaborate successfully, they can share ideas and come up with practical solutions to complex problems. Brainstorming, open discussions, workshops, and knowledge sharing sessions are all examples of collaboration that lead to great teamwork. 5. Persuasion Have you ever worked with a teammate who insists on working their way, even if the rest of the team agrees to pursue another route? How do you keep making progress on your project or goal if one team member isn’t on the same page? That’s where your skills of persuasion come in handy. Sometimes you might have to persuade a team member to see another point of view and change their mind to benefit the rest of the group. But persuasive skills are more than just getting someone to change their mind and see your perspective — it’s about doing so in an empathetic and respectful way in order to maintain a healthy working relationship. 6. Constructive feedback for improvement You should be able to offer your teammate constructive feedback to help them improve and vice versa. Exchanging feedback not only benefits individuals and the team as a whole but also adds value to your organization by creating an opportunity for constant growth. Giving feedback requires offering suggestions for improvement in a positive way, while receiving feedback requires listening with an open mind and a willingness to change. Work skills that work on any resume Sure, there are specialized skills for different roles and industries. Engineers add their programming skills to their resume, project managers add project management certifications and relevant skills, and HR professionals add the performance management and HRIS systems they’ve previously used. While there are specialized skills you’ll want to emphasize on your resume based on your industry and role (and trust us, those are important), there are also some work skills that are relevant on any resume. These include: Creativity: Creativity is an essential component of innovation and complex problem-solving. In its most basic form, creativity requires thinking about a problem or task differently and using your imagination to form and test new ideas. Problem-solving: All employers value problem-solving abilities because they want to hire people who can break down problems and develop effective solutions. To showcase your problem-solving skills, you might possess a range of qualities such as analysis, evaluation, decision-making, and communication. Time management: No employer wants to hire someone who doesn’t make good use of their time and will have a hard time getting their work done. Your future employer wants to know that you’ll be able to meet deadlines, effectively use your workday to get tasks accomplished, and handle your workload without a lot of babysitting. Examples of specific time management responsibilities include goal setting, prioritizing tasks, meeting deadlines, and minimizing or eliminating distractions for optimal focus. Leadership: Showcasing how you’ve demonstrated leadership in your previous roles can demonstrate to your future potential employer what type of employee you are. Being an effective leader can increase your advancement opportunities within your organization. Use specific examples of successful leadership on your resume for the most significant impact. So how do you showcase these skills on your resume? Now that you know what work skills for resumes employers want to see, you’re bound to have this question: Where do you put them? Keep in mind that the goal of your resume is to prove that you’re a qualified, no-brainer fit for the role you’re applying for. That’s why your smartest move is to tailor your resume to a specific job. Take a fine-tooth comb to the job description and identify words or skills that are repeated or emphasized. Those are traits that you should be incorporating in your own resume (provided you honestly possess them, of course). The most important skills should go as close to the top of your document as possible, because remember, hiring managers are only skimming for a few seconds. As for where you can work these skills in, you have a number of options, including: Your professional summary at the top of your document A dedicated key skills section where you can bullet out your most relevant abilities Your past positions, where you can demonstrate how you applied your skills in previous jobs Finally, remember that many of your work skills and social work skills — from communication and time management to problem-solving and active listening — will be on display throughout the hiring process and your interviews. So, it should go without saying, but show up on time, respond to messages promptly and respectfully, and treat everybody respectfully. After all, when it comes to your work skills, employers want you to show — and not just tell.

Get weekly updates in your inbox!
You are now subscribed to wrike news and updates.
Let us know what marketing emails you are interested in by updating your email preferences here .
Sorry, this content is unavailable due to your privacy settings. To view this content, click the “Cookie Preferences” button and accept Advertising Cookies there.

Expertly Writing the Operations Plan Section of Your Business Plan
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Operational plans are important for any effective business plan . They provide a roadmap for how the company will operate on a day-to-day basis. The operational strategic plan should outline the company’s goals and objectives, as well as the strategies and actions that will be taken to achieve them.
Business Operations Section of a Business Plan
The operational plan or operations section of a business plan is where you describe how your business will function on a day-to-day basis. This includes everything from the resources you’ll need to run your business, to the people who will be responsible for carrying out various tasks, to the processes and procedures you’ll use to get work done.
Purpose of the Operational Plan Section of a Business Plan
An operational plan is essential for any business because it provides a roadmap for how it will function. It ensures that everyone involved in the business is on the same page and knows what their roles and responsibilities are. Having an operational plan also makes it easier to track and accomplish goals, while driving cost reduction and improving overall results. Finally, your operations plan section helps show readers that you can turn your vision and goals into reality.
Benefits of an Operations Plan Include:
- Identifying the key processes your company must perform to achieve its goals
- Mapping out short-term and long-term milestones so you have specific goals and a roadmap for achieving them
- Understanding the human and other resources required to execute your vision
Writing an Operations Section of a Business Plan
When writing the operations section of a business plan, there are a few things you’ll want to keep in mind. First, be sure to describe the resources that will be required to run your business. This includes everything from office space and equipment to human resources. Next, detail the processes and procedures that will be used to get work done. Be as specific as possible so that there is no confusion about how things should be done. Finally, identify the people who will be responsible for carrying out various tasks. This includes both employees and contractors.
Tracking Key Performance Indicators with Operational Planning
As a business owner, it’s important to track your progress against your company goals. This is where KPIs come in. KPIs are performance indicators and an important part of creating a strategic plan that can help you track your progress and identify areas of improvement. You should document your KPIs in the operation plan of your business plan
There are a few things to keep in mind when choosing KPIs for your business:
- Make sure that the KPIs you choose are relevant to your company’s goals.
- Choose KPIs that can be easily measured.
- Avoid choosing too many KPIs, as this can be overwhelming. Stick to a few key ones that will give you the most insights into your business’s progress.
- Set realistic targets for each KPI. This will help you track your progress and identify areas of improvement.
- Review your KPIs on a regular basis to ensure that they are still relevant and accurate, while also being in line with strategic plans.
Some Examples of KPIs that You Could Track with an Operational Plan
When creating an operations plan, it’s important to track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure your progress against your company goals. Some examples of KPIs that you could track are:
- Sales growth
- Delivery times
- Customer satisfaction ratings
- Product Quality
- Production Process
- Employee retention
- Operational costs
Creating an operational plan with KPIs will help you track your progress, identify areas of improvement, improve strategic planning and make necessary changes to reach your company’s strategic objective.
Example of an Operations Section of a Business Plan
Here is what an operations plan example might look like:
The XYZ Company will require the following resources to operate:
- 1,000 square feet of office space
- $10,000 for office furniture and equipment
- 3 full-time employees
- 2 part-time employees
- 1 contractor
The XYZ Company will use the following processes and procedures to get work done:
- All new clients will be contacted within 24 hours of the initial inquiry
- Initial consultations will be scheduled within 48 hours of contact
- Proposals will be presented within 10 days of the initial consultation
- Work will begin within 2 weeks of proposal acceptance
The following people will be responsible for carrying out these tasks:
- John Smith, full-time employee, will contact new clients
- Jane Doe, full-time employee, will schedule initial consultations
- John Smith and Jane Doe will conduct initial consultations
- John Smith and Jane Doe will prepare proposals
- John Smith and Jane Doe will manage projects
- Joe Johnson, contractor, will provide support as needed
An operations plan is a critical part of any business planning work. It provides a roadmap for how the business will function on a day-to-day basis. This includes everything from the resources you’ll need to run your business, to the people who will be responsible for carrying out various tasks, to the processes and procedures you’ll use to get work done. Having operational plans in place will ensure that everyone involved in the business is on the same page and knows what their roles and responsibilities are. It will also make it easier to track and accomplish goals.
Key Takeaways
A few key things to remember when writing your operations plan:
- Describe the resources that will be required to run your business
- Detail the processes and procedures that will be used to get work done
- Identify the people who will be responsible for carrying out various tasks
Following these tips will help you create a comprehensive and effective operations plan for your business.
A strategic plan is one of the critical components of any successful company. The operations plan outlines the roadmap for your business, outlining the steps you need to take to achieve your goals. If you’re not sure where to start, we can help. Our team of experts has created a comprehensive business plan template that will guide you through the process of creating an operational plan tailored to your specific business needs. Ready to get started? Download our template today and get access to all the tools and information you need to create a thriving business.
How to Finish Your Business Plan Template in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan template?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!


Operational Plan: Everything You Need To Know (2024 Guide)

The old way of planning no longer works in complex and unpredictable business environments, and companies are struggling to find their feet on shaky ground. As we’ve seen with many of our customers and strategies in Cascade, organizations can no longer count on executing three or even five-year strategic plans.
The new reality forces companies and their operations teams to adapt their operational plans more frequently and within shorter time frames if they want to reap benefits faster than their competitors. Organizations need to work on their strategic instinct and fast adaptability to enhance their operational efficiency .
And that requires big changes—including building a flexible operational plan, supported by the right tools and systems that help you achieve real-time centralized observability and empower a strategic response to external disruptions.
Read this article to build a bulletproof operational plan that includes all the key elements necessary to overcome unpredictable business chaos. You’ll also get free templates that will help you rapidly adapt and align your teams.
✨Bonus: We’ve included pro tips from business leaders in our network to help you identify gaps in your strategy execution and build resilient business operations.

What Is An Operational Plan?
An operational plan is action and detail-oriented; it needs to focus on short-term strategy execution and outline an organization's day-to-day operations. If your operations strategy is a promise, your operational plan is the action plan for how you will deliver on it every day, week, and month.
Put simply, an operational plan helps you bridge the gap between business strategy and on-the-ground execution and ensures that the organization is on track to achieve its long-term goals.
Benefits of operational planning
- Clear definition of relationships between cross-functional teams in different departments and responsibilities for each to eliminate duplicated efforts.
- Tighter alignment between corporate or business unit strategic plans and on-the-ground execution, helping the organization meet its business targets.
- Strong operating system that enables the company to quickly adapt, deliver operations goals, and monitor performance.
Operational planning vs. strategic planning
Operational planning deals with the day-to-day details and short-term goals, while strategic planning focuses on the big picture and long-term direction of an organization.
To put it in simpler terms, operational planning is about the "how" of daily tasks, while strategic planning defines the "what" and "why" for future success.
📚Recommended reading: Strategic vs. Operational Planning
Kickstart Your Operational Planning Process: Lay The Foundation
The quality of your operational plan will depend on your input. A successful operational planning initiative will consider these aspects:
- Who will be involved? Identify and include employees, customers, and the management team in the planning process to gain valuable insights from the front lines, ensuring better strategy and execution buy-in.
- What are your internal capabilities? Assess internal capabilities by conducting an internal analysis , including resource requirements, operating budget, and talent skills. Talent management and employee engagement are just a few of the many challenges that COOs will have on their operations agenda.
- What environment are you operating in? Conduct an external analysis (e.g., PESTLE or Porter’s 5 Forces ) to inform your approach and identify optimization opportunities and risks, keeping you agile in a changing market.
- Is it aligned with your organization’s strategy? Ensure alignment of your operational plan with your organization’s strategic plan to actively support the company's long-term vision and contribute to key business metrics.
👉🏻 Once you’ve gathered this information, you can develop an operational plan to help you execute business strategies.
Key Elements Of Your Operational Plan
Enough chit-chat; it’s time to put your operational plan together. We've built this based on our proven and tested approach, used by over +45,000 Cascade users.
See how Cascade Strategy Execution Platform enhances operational efficiency by reducing duplication and aligning teams toward common goals. It effectively eliminates waste resulting from misalignment, fostering smoother operations and improved performance.
Here’s a recap of the five key elements your plan must consider:
Choose key metrics aligned with the company goals
Selecting your operational plan's key metrics isn't a mere exercise in tracking numbers; it's about laser-focused alignment with your business needs and objectives. These metrics are the tangible indicators of your organization's efficiency and performance. They serve as the compass, guiding your daily decisions and actions toward achieving concrete results.
By precisely aligning these metrics with your company's core objectives, you ensure that every initiative and action within your operational plan directly contributes to achieving tangible results.
An aligned operational plan makes it easier to:
- Communicate roles and responsibilities to all employees so they know how their efforts contribute to overall business success.
- Identify and address operational bottlenecks and inefficiencies that could derail strategy execution.
- Motivate and engage employees to work toward strategic objectives and deliver on business outcomes.
Remember that the role of operations is to close the gap between your organization's strategic goals and what is being done on a daily basis to make them happen.
👉🏻 How Cascade can help:
With Cascade’s Metrics Library , you can bring your operating and financial business-level goals together with your strategy under one single roof. This makes reporting & governance easy, accurate, and less time-consuming by connecting your business data to your key business initiatives.
.png)
Through Cascade’s integrations , you can consolidate your metrics in one place, importing your data directly from business systems, data lakes, BI tools, or even spreadsheets.
Define the focus areas of your operational plan
The focus areas of your operational plan are the key areas of the business that the plan will address.
This will depend on your business plan. Think about how the business operates and how it succeeds. Do you need to pursue short-term cost reductions while simultaneously pursuing longer-term growth and transformation initiatives? Your operational plans must be built on these strategic priorities.
For example, you can prioritize your focus areas based on the most relevant business strategies or by specific departments. Some examples of focus areas could be:
- Administration
- Human Resources
💡Tips to help define the focus areas of your operational plan:
- Identify the business's key challenges and opportunities.
- Consider the business's overall long-term strategy and key metrics and how the operational plan's focus areas can support these objectives.
- Bring other people on board to help you identify what needs to be addressed by the operations plan.
Create strategic objectives for your operational plan
Strategic objectives are specific goals aligned with the operation’s strategy and focus areas. They represent what you want to achieve in each focus area and will serve as the building blocks of your plan, ensuring that it’s focused and actionable.
Some examples of strategic objectives:
- Reduce costs by 10% within the next year by implementing more efficient processes and streamlining the supply chain over the next year.
- Launch three new products in the next fiscal year to expand your product lines and increase revenue.
- Increase customer satisfaction scores by 5% within the next six months.
💡Tips for defining strategic objectives include:
- Ensure your objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Consistently align objectives with your operational plan's focus areas and the company's goals.
- Don’t be afraid to get input from other people about your objectives.
Identify and prioritize projects
It’s time to identify and prioritize the projects that need to be executed. Remember, projects are action plans to help you achieve your strategic objectives.
Project planning should include thinking about time frames, task assignments, and deliverables (and prioritizing).
Here are some examples of project ideas:
- Localize sourcing for critical semi-finished materials.
- Streamline the supply chain to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Find and develop an alternative logistics channel.
- Implement a new customer service training program to improve customer satisfaction scores.
- Implement a new technology that will enable end-to-end supply chain visibility.
💡Tips for defining and prioritizing projects:
- Identify the specific actions and activities needed to achieve each strategic objective.
- Prioritize the projects based on their importance, feasibility, and potential impact on the business.
- Involve stakeholders in defining and prioritizing the projects to ensure their needs and concerns are heard.
Identify and track key performance indicators (KPIs)
Finally, you’ll need to know if your operational plan and day-to-day activities result in outcomes.
Set KPIs for key initiatives and strategic objectives to measure success, ensure alignment, and identify performance gaps in your operational plan.
Some examples of operations KPIs are:
- Inventory costs
- Costs of goods sold
- Revenue growth
- Employee retention rate
- Customer satisfaction score
💡Tips for defining and tracking KPIs:
- Align KPIs with your strategic objectives and focus areas so that you can track the plan's progress against these specific goals.
- Add both lagging and leading indicators .
- Instead of using multiple disconnected spreadsheets and project management tools, consider live dashboards or reporting systems to track the KPIs and monitor progress over time.
👉🏻 How Cascade can help build your plan:
Cascade’s planner feature enables you to build your operational plan with structure and ease by breaking down the complexity from high-level initiatives to executable outcomes. Define your key elements (focus areas, objectives, projects, and KPIs), and share the plan with your teams. You’ll get full visibility of the plan’s progress in real-time, allowing you to identify gaps, quickly update the plan, and communicate the change with your team with a single click.
%20(1).png)
👉🏻 If you don’t want to start building the plan from scratch, use our free Operational Plan Template pre-filled with examples of focus areas, objectives, projects, and KPIs that you can customize to meet your organization’s needs.
Operational Plan Examples & Templates
Here are five operational plan examples to help you create plans for your teams. You can use one master operational plan or set up an operational plan for each department.

Master Operational Plan Example
.png)
This Operational Plan Template will help you close the gap between business goals and day-to-day operations. You'll be able to set goals and KPIs for your top priorities and work with the operations team to deliver operational excellence and business results.
HR Plan Example
This HR Operational Plan Template can be used to meet staffing requirements, manage human capital and align human resources activities with your strategy. HR managers in any industry can create a clear operational plan that can be constantly monitored, adapted, and improved.
IT Plan Example
If you’re in the IT team, try out this IT Plan Template to get your IT operational planning up and running fast. It comes prefilled with focus areas and KPIs relevant to IT operations; you can easily customize workflows and deliverables to your needs.
Marketing Plan Example
This Marketing Plan Template can help you efficiently understand and plan your digital marketing operations using best practices. Use it to quickly set up priorities and get your social media and marketing teams moving on tasks that will make an impact.
Finance Plan Example
This finance-focused template is ideal if you want to get on top of your finance operations plan. Use it to allocate and distribute financial resources across your organization and get real-time updates through your dashboard and reports—which are great tools to create a visually compelling financial summary that clearly shows your key metrics.
💡Pro Tip: To ensure successful execution, it's crucial to align not just your master operational plan with your overarching strategic plan, but also all the operational department plans.
With the Alignment Maps feature, you’ll be able to visualize how your top-level business strategy breaks down into functional and operational plans. This empowers COOs and CFOs to consolidate their operational plans in one place, creating tighter alignment between the finance and operations teams and improving cross-collaboration to build more resilient operations.

Want to dig deeper? Use the Relationships feature to see the relationships between connected objectives from your plans and understand how your different department goals contribute to the core business metrics and goals. This view will allow you to clearly map dependencies, blockers, and risks that may lie along your journey.
%20(1).png)
5 Tips For An Effective Operational Plan And Its Execution
1. don’t underestimate the power of transparent communication.
Regularly communicate the operational plan and progress to all relevant stakeholders to build the necessary buy-in and support. Your employees must know your goals and the roadmap, and team members should understand their role in its execution. This business transparency will help everyone row in the same direction.
“Clarity regarding strategy is one of the key drivers of autonomous execution. If people understand what you’re working toward and have guardrails in place, they can be empowered to make their own decisions and don’t need everything to be ‘run up the chain’ to get approved. This allows you to move fast and at scale.” — Sam Sterling , Chief Strategy Officer, Akqa
2. Keep moving forward and adopt a growth mindset
Keep the momentum going and ensure that the plan is executed effectively. Regular monitoring and reviews can help identify and address any challenges or obstacles that may arise.
Schedule regular reviews and check-ins and provide the necessary support to ensure projects are on track and moving forward.
“I think adopting a growth mindset is super important. This means having the confidence to fail fast, try something new and empower people to do that.” — Ken Miller , General Manager, Azure Intelligent Cloud at Microsoft
With the Team Updates functionality, every team member can post updates on key measures, actions, and objectives. This will give you real-time visibility into performance and help you identify possible risks before it’s too late—without having to schedule extra meetings or nag your team members for updates.
3. Make strategic moves and change fast when you need to
Your operational plan should be flexible, adaptable, and open to adjustments. This means keeping an eye on progress, making corrections if needed, and being willing to adapt the plan to changing circumstances or new opportunities. As McKinsey suggests, you can consider creating a team that will be able to collect data, link analysis with action, and offer quick responses to rapid changes.
“Traditionally, companies would have taken that piece of paper and gone out and said: we're going to execute it, start to finish. Then get into the formulation of the strategy, what we need to hit, and what the end product result will be like. But what we do know is that’s never the case. Along the way, you're going to have bumps, and inevitably, you’ll need to change from that original picture.” — Annie Lucchitti , Marketing Manager, Unilever
4. Empower your operations team and boost efficiency
Effective operational planning requires the engagement and empowerment of your team. Involve stakeholders in the planning process and provide them with the necessary resources. Give them context and an opportunity to set goals and prioritize initiatives. This will help you boost engagement and hold them accountable for progress.
“I think it just works at every single level. Are people allowed to be themselves at work? Personally, are they at peace? Are they happy? Productivity happens when people have the right skills, but also when they are engaged and happy. If one of those fails a bit, productivity will start decreasing.” — Joan Torrents , Global Sourcing Manager, TESCO.
5. If it isn’t measured, it isn’t managed
Don’t underestimate the importance of tracking and measuring progress against the operational plan's goals and objectives. Set milestones, enforce KPIs, and stay on top of progress. Doing this will help you stay on course, empower you to act quickly, and provide valuable insights into what is going wrong.
“Data is a foundational element in the strategy definition phase as well as in the strategy execution phase as it helps create a baseline, identify key priorities, set goals, and measure progress.” — Erica Santoni , Principal, Diversity Equity & Inclusion, Intuit
Use Cascade’s Dashboards to monitor your day-to-day progress on key metrics and critical business and strategic information in real-time.
.jpg)
Compile the information in powerful reports and executive summaries in seconds with pre-built templates. Share them with your key stakeholders —internal and external— and invite them to collaborate on your strategy together.
Execute Your Operational Plan With Cascade 🚀
What good is an operational plan if no one executes it? If your organization wants to operate at a higher level, static tools like Excel spreadsheets, PowerPoints, Google Docs, and/or project management tools aren’t the solution.
❌They aren’t designed for adaptive strategy and planning.
❌They often lead to siloing and hinder effective cross-collaboration.
❌They make it challenging to measure progress and slow down decision-making.
With Cascade as your central operating system, you can stop running business operations blindfolded and embrace rapid, coordinated, and data-driven decision-making.
Get your Operational Plan Template to get started with a dynamic plan that will lead to actual outcomes for your business and see faster results from your strategy.
Or take Cascade for a spin! Start today for free or book a 1:1 product tour with Cascade’s in-house strategy expert.
Popular articles

Viva Goals Vs. Cascade: Goal Management Vs. Strategy Execution

What Is A Maturity Model? Overview, Examples + Free Assessment
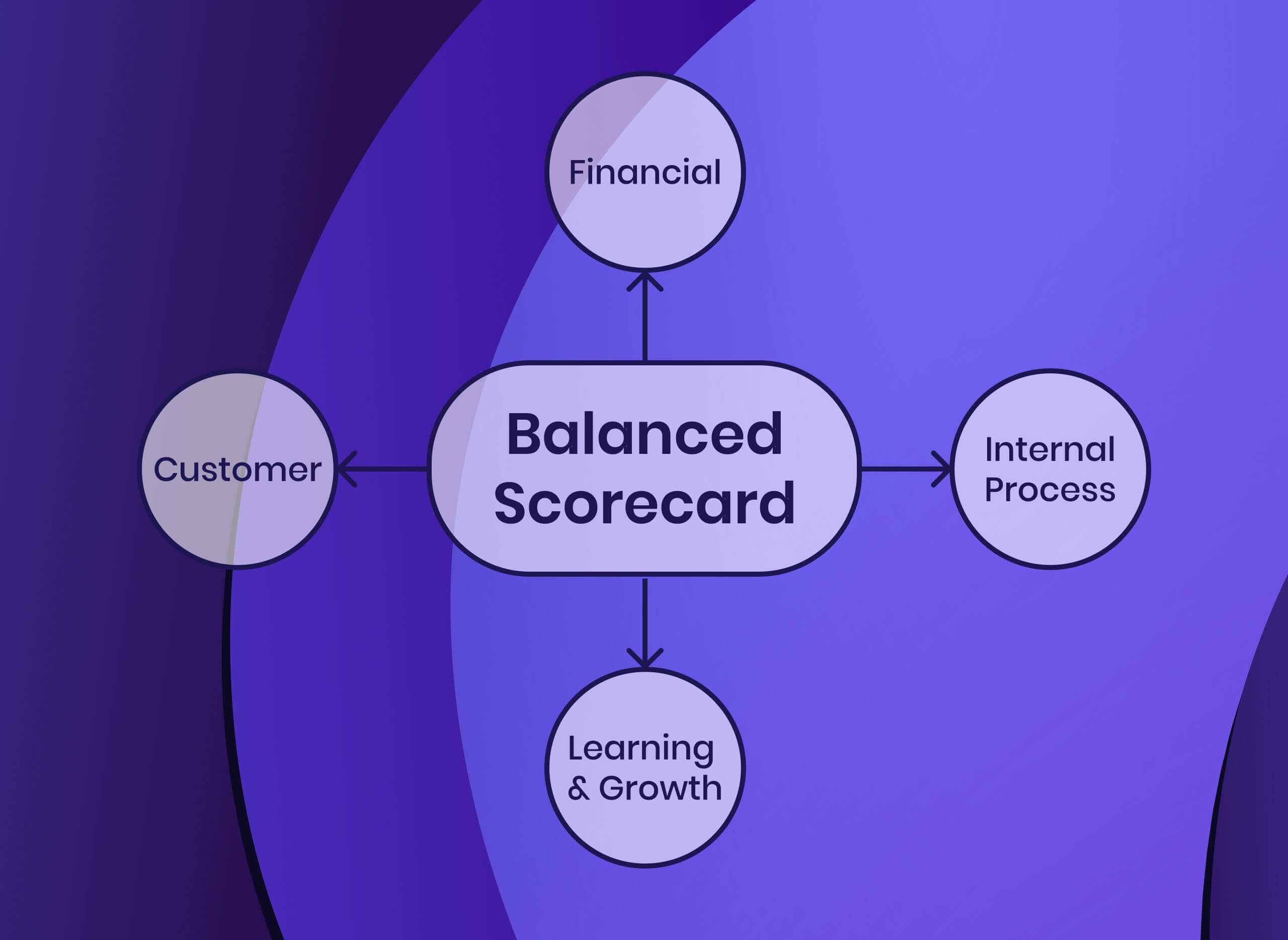
How To Implement The Balanced Scorecard Framework (With Examples)

The Best Management Reporting Software For Strategy Officers (2024 Guide)
Your toolkit for strategy success.

Operating Procedures in Business Plan
The operating procedures in a business plan help employees carry out an organization's daily operations. 4 min read updated on February 01, 2023
The operating procedures in a business plan help employees carry out an organization's daily operations. Essentially, it is a step-by-step instructional guide detailing how workers should complete any complex activities related to the business. It also helps keep companies stay in compliance with the regulations within their industry.
Standard Operating Procedures For a Business
A standard operating procedure (SOP) details the daily procedures for an entity. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends that SOPs should always be written in an easy, step-by-step manner. Additionally, SOPs should be supported with flowcharts to clarify the relationship between departments and activities or interdepartmental relationships.
There are many potential components outlined in an SOP, such as:
- Legal expenses.
- Property tax assessments.
- Directives for the management of accounting documentation.
- Confidentiality agreements.
- Bank account reconciliations .
- Policies for wire transfers and credit cards.
- How to handle travel and entertainment expenses.
Information regarding financial directives can also constitute as a component of an SOP. This may entail information regarding the directives for the board of directors or stockholder meetings and the company's financial reporting. Additionally, specifics regarding the release of any financial documents related to analysis, reporting, and forecasting may be included.
Sometimes information regarding computer and information technology (IT) may be outlined in the SOP. This would detail company policies regarding the following:
- Hardware and software evaluations.
- Training plans.
- Company policy regarding internet use .
- IT troubleshooting methods.
- Standards to assess security risk breaches.
Human resource information is often part of an SOP. This includes guidelines for the following areas:
- Background checks .
- Outlining job descriptions.
- Policies for job applications processes.
- Describing the employee benefits and compensation policies.
- Employee health insurance directives.
- Retirement benefits.
- Payroll policies.
With regards to the operations section, the basic rule is to simply cover the major areas and provide the most relevant details. This would include areas such as materials, equipment, labor, facilities, and processes. These are all components that are critical to the operations of a business and may offer a competitive advantage. Last, measures for maintaining security and safety may be detailed in an SOP. Generally, this would include emergency plans, ethic statements, and employee code of conduct manuals.
Writing the Operations Section of Your Business Plan
There are some steps to consider when writing the operations section of your business plan . First, remember that service and retail firms have very different operation requirements from manufacturers. Therefore, you will want to devote a considerable amount of time to outlining staffing and describing employment contracts for key service providers such as marketing experts, buyers, and designers.
Do not go into too much detail in your operations section. It is important to stick to the processes that are the most significant to the business, such as those that provide a significant advantage over your competitors or those that are essential to your production. Be sure to estimate the need for the materials required and adequately describe any agreements with suppliers. In your SOP, make a list of every potential piece of equipment you may need, including a description of its function, features, and cost.
Business Plan Procedure
The procedures of a business plan describe how to:
- Prioritize short and long-term goals.
- Manage the organization's growth.
- Develop successful objectives and strategies.
The strategy team is responsible for developing the organization's business plan. A well thought out business plan helps employees understand how their daily responsibilities and tasks relate to the overall goals of the company strategy.
How to Write Business Standard Operating Procedures
The purpose of a standard operating procedure is to identify the tasks that will require detailed instructions in order to run the business smoothly. A well-written SOP should describe the activity and any necessary tasks involved acting in accordance with industry regulations, provincial laws, or even just the standards for running the business. Be descriptive when explaining how to complete the task. For example, in a clothing retailer operation, the instructions may be:
- Verify all locks on the premises.
- Hang or fold all disorganized clothes.
- Make sure the floor is free from any debris.
Remember, it's important to identify the scope for each role in the organization. Also, make sure that the information that is supplied to each employee is relevant to their overall role in the business. All managers should:
- Clearly understand the standard operating procedures.
- Make sure standard operating procedures are followed.
- Understand the significance of the standard operating procedures.
The standard operating procedures should be regularly reviewed at the business level to ensure that all updates in the operations are properly accounted for.
If you need help with operating procedures in business plan, you can post your legal need to UpCounsel's marketplace. Upcounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- What Is the Operational Plan Section of the Business Plan?
- Management Plan in a Business Plan
- Business Plan Management Structure: What You Need to Know
- Business Operations Definition
- How to Make a Business Plan Format
- How Does a Business Operate: Everything You Need To Know
- Details of a Business Plan
- Service Business Plan
- Parts of Business Plan and Definition
- Creating a Business Plan

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Business Operational Plan Templates with Samples and Examples

Aditya Chakraborty
Are you aspiring for the best outcomes from your business model? Do you want to set the pace of the organization in the right direction?
The right kind of business operational plan will set teams in motion to achieve desired organizational goals. With the assistance of powerful PPT models, businesses are able to direct the process’s blueprint to the employee and all stakeholders. A clearer picture of the state of operations and targets always helps teams be comfortable with what they are doing. They also know what success looks like.
Running, and even thriving in you business, could be a greater challenge when the marketplace is tough. If your enterprise can be taken as a ship, a business operation plan can be considered as its lighthouse. It (the business operational plan) reminds teams & stakeholders of the way to go and highlights potholes or obstructions the path ahead.
A well-designed PPT Presentation is the answer to ensure your venture prospers and has answers to most problems that will come your way. Start your business operational plan today with help of suitable presentations that suit your requirements. SlideTeam offers you PPT templates that assist in shaping business operational plans. Download slides that assist businesses to tackle operational challenges with flair and effectiveness.
Why Do You Need Business Operational Plan?
Companies often tend to spend time and resources in strategic planning for long-term goals. While it is necessary to make strategic plans, most of these miss out on a key strategic element: a business operating plan.
“The proper outlining of business operational plan for daily needs leads to best outcomes for the organizations. Research has indicated better allocation of resources in organizations with well-laid operating plans.”
The operator should be able to answer these questions:
- What are the operational strategies in line with the vision of the organization?
- How to perform and outshine in changing business environment?
- What are the tasks to be completed on regular basis?
- How to prevent risks associated with the implementation of plans?
Let us look at the list of PPT models to fit business operating models:
Template 1: Business Operational Plan
This PPT Template is meant to ensure a pictorial depiction of the company’s sales & marketing goals. Use this presentation deck to highlight the executive summary, company vision, company strategy, changes in the competitive environment, revenue sources, objective for the next 12 months, milestones, financial summary, and others. The deck also contains slides related to acquisition of new customers, customer lifetime Value, and risk mitigation strategies to fit sales requirement.

Download Now
Template 2: Business Plan Operational Strategy
The PPT slide deck is helping businesses overcome fears and tackle challenges. It displays the company mission and objective, KPIs, business problems & solutions, changes in the competitive environment, financial summary, revenue growth, and others. Businesses are able to optimize their performance with information related to gross margin improvement, operating expenses, product roadmap , and more.

Download now
Template 3: Business Operational Planning Process
The specific kind of PowerPoint Deck is focusing on the condition of the company, key performance indicators, operating highlights, hiring plans, and more to boost the overall outcome. It will help businesses devise top strategies to support product roadmap, operational challenges, risk & mitigation plans, and others. Put forth all details in the respective slides to make the presentation fruitful and result-oriented.

Template 4: Business Operation Planning
If you’re planning to set long-term business goals, then this PowerPoint Deck will be a desirable option. It includes slides related to the executive summary, business solutions, details related to key stakeholders, analysis of competitors, budget, source of revenue, and more. Highlight milestones of the company through visuals, establishing operational highlights.

Template 5: Business Operational Plan PPT Infographics
The business operational plan PPT infographic will help companies establish their goals efficiently. It includes details related to mission & objectives, strategic intent, budget, performance indicators, time, responsibility, and progress. We provide thousands of editable icons on each topic and adjust sizes easily. Companies can use their own icons in the PPT Slides and edit the color of the graphics. Highlight details accurately through infographics and boost the overall output of presentations.
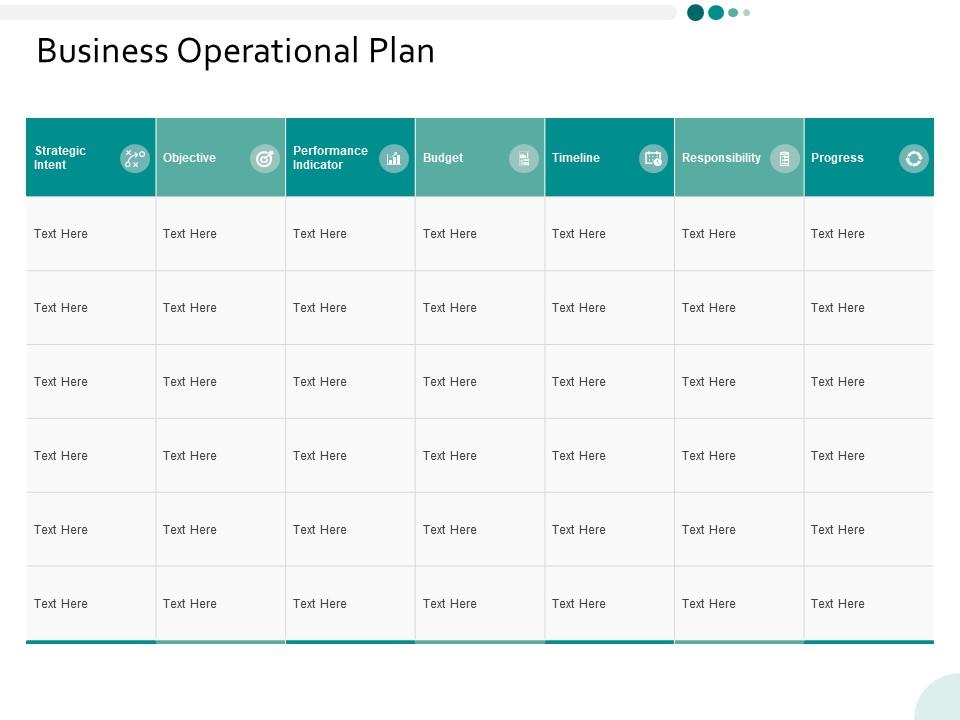
Template 6: Business Operational Plan Pie Charts
Graphical presentation of data assists in easier understanding of key business indicators. The business operational plan pie charts are creating huge impact on business meetings through the guided presentation. We provide thousands of editable icons for each category to make business presentations successful. Our pie charts are easy to understand, and comparison in the meeting rooms become easier with this.
Template 7: Business Operational Plan Timeline Pictures Infographics
Plan the best moves for the company with a business operational plan timeline PowerPoint Deck. The infographics used in the PPT will help businesses analyze present costs and plan future timeline. Use the editable infographics and pictures to highlight details related to the strategic intent of the company, performance indicators, budget, progression, risks mitigation, and others.
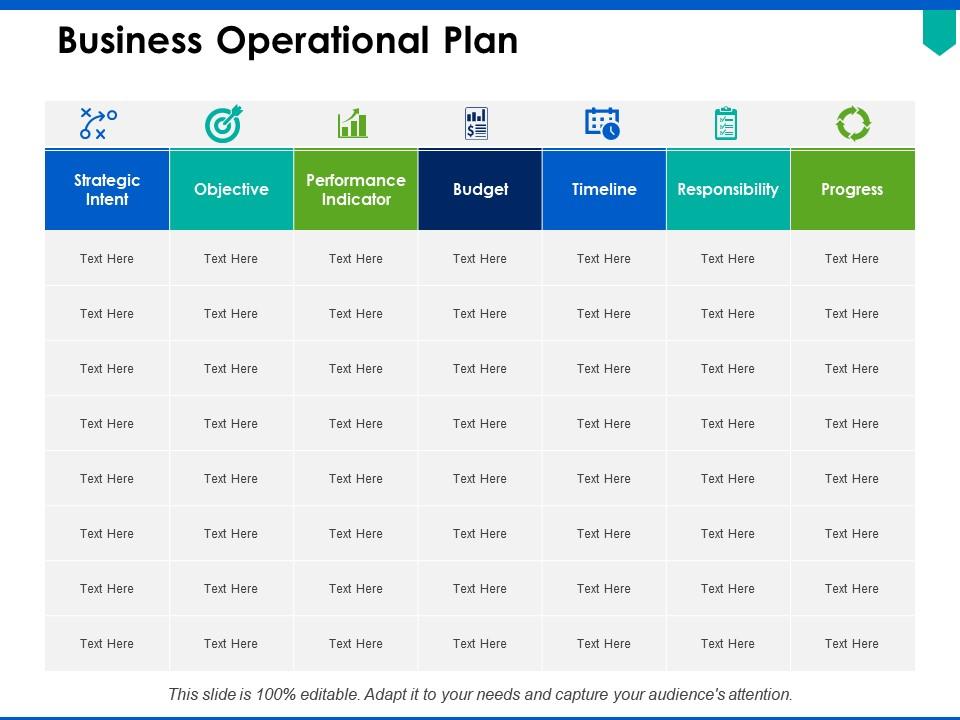
Template 8: Business Operational Readiness Plan with Multiple Tasks
Select Business Operational Readiness Plan with Multiple Tasks PPT to describe aspects of operations minutely. It is the best option for businesses looking for pro-presentation solutions to highlight essential details. The slides can be easily edited, as per the preferred size and color to fit the business presentation requirements.
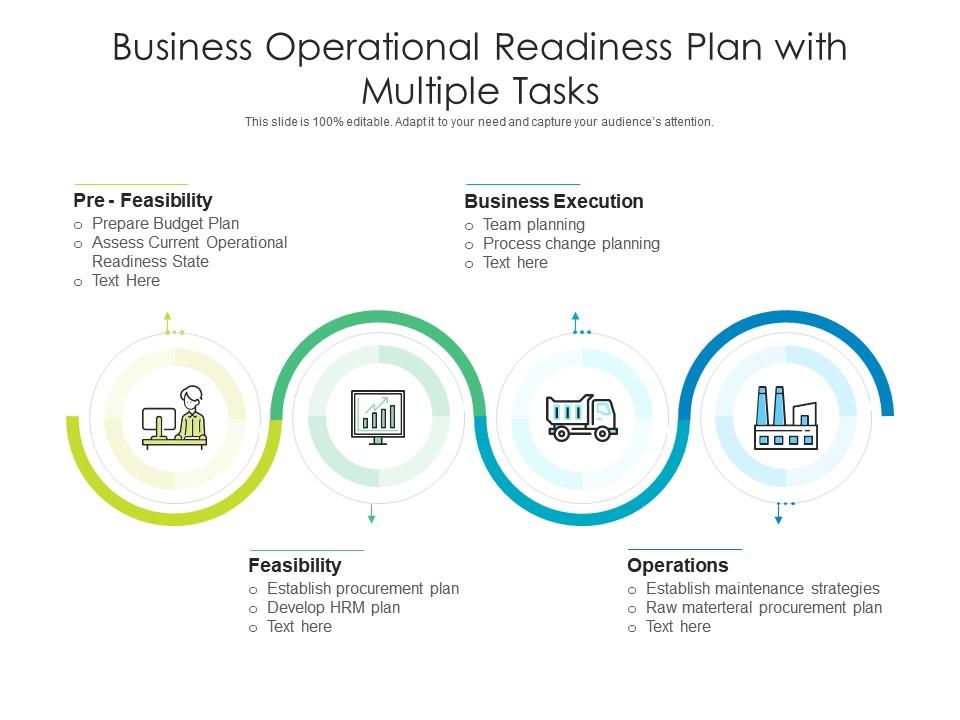
Template 9: Essential Elements of Business Operational Readiness Plan
Businesses need to add backdrops in their presentations to describe subjects minutely. The Essential Elements of Business Operational Readiness Plan PPT deck is designed by our experts to make the teams ready for efficient operations. Edit the slides as per choice and improve the output of business meetings. Download the PPT deck today to ensure the completion of business pro presentations timely.
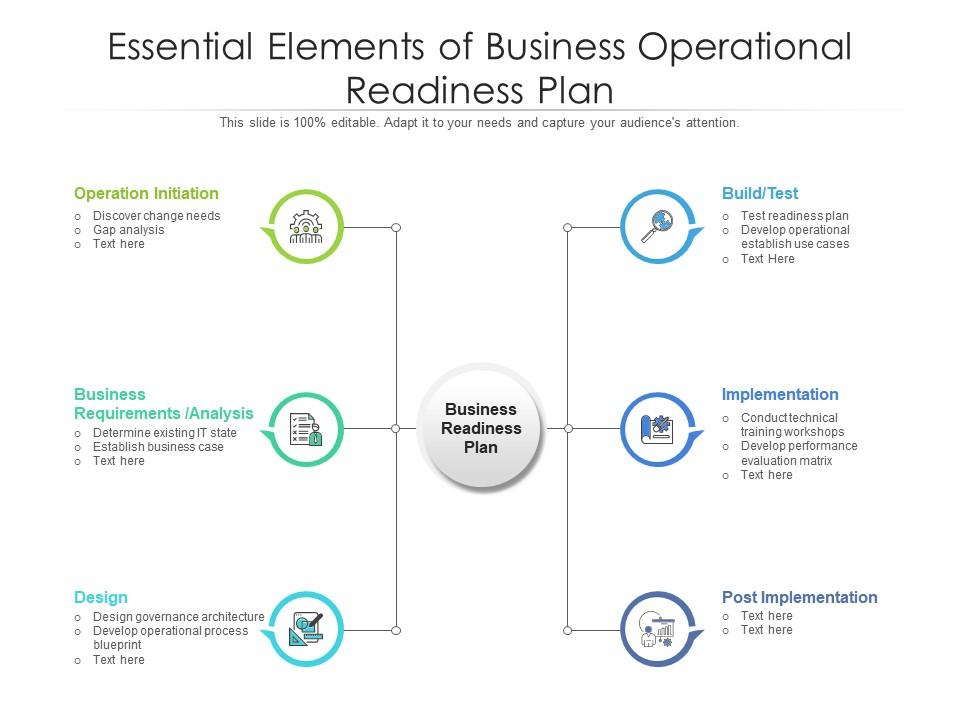
Template 10: Business Operational Plan for Organizational Governance Infographic Template
The governance of organizations needs to be chalked out accurately for optimal output. Our Business Operational Plan for Organizational Governance Infographics Template provides you detailed-reports on specific subjects. The editable slides suit pro-business presentation requirements and incorporate icons that fit business needs. Download it today to present detailed reports on the company’s progression and govern the organization suitably.
Final Thoughts!
The operational plan templates prove to be the idle option to develop the presentations to be showcased in business conferences. Such plans should be in line with the strategic plans of the company and ensure focus on specific goals. Take the stakeholders & business partners in the loop to focus on the right objective of the business. The templates will work as the top option to solve specific problems in company operations and achieve long-term goals.
What is an example of an operational plan?
An operational plan focuses on the future of the business and identifies its activities. It helps in better outlining of the purpose of businesses and understand specific activities to achieve desired goals. If you desire to grow your business by 25%, over the next few years, then the creation of an operational plan becomes critical to meeting targets. An example is given below:
Goal: 25% growth in business by evaluating the revenues.
Timeline: 2-5 years.
Tasks: Engaging with customers and advertising brand products to generate leads for business.
Resources: Specific skills and customer servicing needs.
Budget: $5,000-$10,000 for each year.
Output Monitoring: Revenue analysis for the next few years
How do you write a business operational plan?
Write business plans in templates to ensure a simple understanding of facts that help in getting desirable output at all levels. Plan presentations critically as the checklist for dealing with business problems & solutions.
A business operational plan includes
- Defining employee roles and contributing to the business outcomes.
- Detailed instructions on daily operations within organizations.
- Creation of risk and mitigation plans.
- Defining short and long-term business operational goals.
- Detailed reporting on financial summary of businesses.
- Providing realistic goals to key stakeholders for achievement of goals.
- Create transparency to earn the trust and loyalty of employees.
What are the seven things an operational plan should contain?
A business operational plan helps in decide on a strategy that will deliver the best results. If you want to run projects successfully, then prepare operational plans that help to build revenues. The operational strategy of a company is future-oriented and set the plans that fit the requirements.
Let us look at the seven things to be included in a business operational plan:
- Precise objective
- Delivery of activities
- Quality standards
- Best outcomes
- Staffing & resourceful needs
- Milestone tracking
- Keep revising and updating monitoring procedures
What are the three types of business operational plans?
The business operational plan is acting as the blueprint for business procedures and helps your reach your milestones with both speed and ease. The three types of business operational plans include
Single-use plans: It is meant for a specific purpose in business operations and handle challenges promptly. The development of single-use plans helps deal with problems for top outcomes.
Multi-use plans: It includes plans for stages of the business operation and implements these accurately. These work at many level with accuracy and efficacy.
Ongoing plans: It is the best way to solve repetitive, assembly-line like issues in daily operations. Such plans help in business growth and thus eliminate prevailing troubles.
Related posts:
- 11 Must Have Slides in your Business Operational Challenges PowerPoint Deck
- [Updated 2023] Top 25 Brainstorming PowerPoint Templates for Stimulating Out-of-the-box Thinking!
- [Updated 2023] Top 20 Balanced Scorecard Templates in PowerPoint PPT for Business Management
- Top 10 Free Business Google Slides Templates for Entrepreneurs
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Non-profit Business Plan Templates with Examples and Samples

Business Strategic Planning: 11 PowerPoint Templates You Must Have
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
How to create an operating plan: Examples with template

In today’s business environment, clear and consistent communication enables your team to have a shared understanding of the status and direction of your product. To this end, an operating plan collects your strategic objectives in one place, allowing everyone to grasp what they need to do, and how the product will remain successful.

In this article you will learn what a product operating plan is, how it can help you achieve your objectives, and best practices for effectively implementing one within your project team.
What is an operating plan and why is it important for product managers?
A product operating plan is a document that outlines the strategic actions your team will take to achieve a specific goal. Most operating plans only cover a period of one to two years and serve a crucial role in the product development process . You can expect your operating plan to include budgets, resource allocation, timelines, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
The operating plan moves away from the big picture vantage point of vision and strategy, towards a more granular and tactical plan for the execution of product strategy.
The operating plan helps product managers assess the impact of changing business priorities and customer needs on the product roadmap . Product managers can use the operating plan as a tool to factor in and communicate changes across the organization, allowing the product development process to remain agile.
What goes into an operating plan?
An operating plan seeks to outline your product strategy to guide decisions and deliver on your stated goals. The operating plan comprises of the following:
- Product goals and objectives — Define the product goals and objectives based on your product vision. Objectives should have clear deadlines and measurable outcomes that align with the business strategy
- Milestone based plan — Create a milestone oriented plan to map your goals and objectives that can be tracked and measured against target
- Structure of team, budget, resource, and timeline — Design your team, resources for the project, and budget allocation in order to work on the scope of the project and adhere to the milestones
- Product metrics to measure progress — Identify and create the product metrics which can be used to measure the success of the product once it goes live to customers
- Status check and interactive corrections — Iterate to customer requirements and watch for opportunities to make changes to the product
How to develop an effective operating plan
To better understand what goes into an effective operating plan we will breakdown each step and discuss best practices for approaching the following:
Identifying the product goals and objectives
Aligning with the strategy and vision of the product, selecting and tracking the product metrics.
The product goals derive from the product vision and strategy. To define these you should:
- Break your vision into executable tasks (include the ‘what’ and not the ‘how’)
- Ensure consistency with the product vision
- Make you have a way to measure success
In order to align with the product strategy and vision, one should:
- Infuse the product strategy and vision into all the steps of the product life cycle
- Align the product vision with customer and business needs, as well as the values and principles of the company
- Check alignment and correct any deviations with the vision
Identifying and tracking the right metrics is key to the success of any product and therefore the product team. Below are the steps to identify and track the right product metrics:
- Identify the goal of your business and business strategy
- Ask the right questions to help determine which goals would help track the success of your product against the business goals
- Assign metrics as acquisition, engagement, retention, revenue, or referral
- Create a platform to visualize and track the metrics
Implementing and monitoring an operating plan
A product operating plan provides you with an instrument to ensure your product will deliver on the stated vision, strategy, and goals. However, the success of your operating plan depends upon your ability to manage and monitor it throughout the course of the product lifecycle. Proper management of the operating plan includes:
Tracking success
Adjusting and/or pivoting course, keeping stakeholders aligned.
You can measure the success of a product operating plan by developing product metrics which allow you to quantify and track the progress of the plan. Also, having a visual representation of the metrics allows you to make better interpretations and display your progress visually.
Product metrics let you determine whether a product operates to plan or not. When your team performs as planned, there’s no need for further adjustment.
However, when the team misses, or finds themselves falling short of the agreed upon target, you need to take corrective action and pivot course.
Here, corrective action could come from aligning or augmenting resources, changing the budget allocation, or moving around the tasks based on the dependencies in the plan.
Because the operating plan has many moving parts and stakeholders involved, you need to ensure that you have the buy-in from all the stakeholders involved.
The best practices for ensuring stakeholder buy-in include:
- Communication — Constant and consistent communication with all stakeholders will allow all everyone to be on board and aligned with the operating plan
- Transparency — Being transparent with all stakeholders in terms of progress updates and any challenges/roadblocks that crop up during the course of executing the operating plan will ensure all stakeholders are are able to provide their full support
- Status updates — Providing status updates to leadership and obtaining regular status communication from other stakeholder teams will ensure everyone remains aware of the state of your product
Common challenges and how to overcome them
As with anything, challenges will arise while working with a product operating plan. Rather than allowing these to grow into a bigger problem, you should work to mitigate following issues before they impact the health of your product:
Lack of authority
Communication challenges, visibility restraints.
Similar to the product manager role, the product operations or operating plan team has to work without direct authority, or people management responsibilities. You should be aware of this while trying to push the team towards your deliverables and use the operating plan as an influencing tool.
Communication is key to maintaining the flow of delivery across the product lifecycle. Insufficient communication or communication gaps can result in teams and stakeholders missing out on necessary changes or tasks. These knowledge gaps could result in misalignment, which impacts the product delivery timelines, as well as the scope.
Since the product operations team is a level above the product management, the product operations team may have limited visibility of the roadmap, customer needs, or the technical architecture/design information.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Operating plan example
Below is an example of an operating plan that provides an illustration of what the process might look like for you. The operating plan focuses on two main steps:
Product vision and strategy
Product operating plan components.
To provide a mobile based shopping experience for a retail grocery store shopper (in addition to in store shopping which is currently available)
Product goal(s):
- Complete an end-to-end customer journey on a mobile app (viewing inventory by categories, adding to cart or wish list, checkout, and completing payment)
- Seamless experience in terms of navigation on the site, as well as understanding the pricing and assortment to the mobile platform users
- Additional benefits of the mobile shopping experience in terms of reordering items, mobile based return/refund for eligible items
- Discuss the scope of work needed to deliver complete functionality in terms of the mobile shopping experience to the mobile platform users
- Create the plan for delivering the identified scope (e.g., to have the first version of the mobile grocery shopping platform released to customer within the next six months)
- Identify the data engineering needs to provide a seamless mobile platform experience for grocery shopping (e.g., identify what categories of products will be available for user selection in the first version of mobile application and how many concurrent users can shop on the platform)
- Determine the structure of the team and resourcing needs to deliver to scope and planned timelines (e.g., scrum team would develop the mobile platform in terms of frontend and backend and user experience engineers)
- Identify the success metrics for the product (e.g., how many users were activated on the mobile platform, how many users could complete one successful workflow of the mobile grocery shopping experience, or the time taken to complete a checkout in store checkout)
Operating plan template
To help you get started on your own operating plan, use this template . The template includes all the key parameters that need to be tracked and mobilized in order to make the product operating plan successful.
The product operating plan is a key component of the product development and delivery lifecycle. Having a product operating plan allows you to outline the tactical steps and ensure successful product delivery and tracking of your product.
The product operating plan also fosters alignment with the vision, stakeholder buy-in, and sets the product and the product organization up for success.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #product strategy
- #project management

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

The PR/FAQ method for product innovation
The PR/FAQ (press release/frequently asked questions) helps you to envision and define a new product before it’s developed.
Leader Spotlight: Transforming retail with GenAI, with Russell Goldman
Russell Goldman talks about the possibilities and challenges associated with bringing GenAI into a combined retail and software space.

A guide to product-led marketing
Product-led marketing is a strategy that focuses on the product itself as the main driver of customer acquisition, conversion, and retention.

A guide to asynchronous communication
Asynchronous communication is a style of communication where participants don’t need to be simultaneously present.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Operational Plan for Business Plan

It is important for a business plan to have an operational plan. Your business functions will not be complete if you will not set action plans and strategies that will be used for your operations.
- 19+ Hotel Operational Business Plan Examples
- 11+ Operational Plan For Cleaning Services Examples
Business Operational Plan Template

- Google Docs
Size: US, A4
Operational Plan Template

Startup Operational Plan Template

Having an operational plan can help you look into the quality standards and metrics that you need to consider to attain operational successes and other business goals and objectives. May it be a monthly, quarterly, or annual operational plan that you would like to develop or update as a part of your business plan, you always have to ensure that you are fully aware of the purposes of the document and how its usage can affect the actual operations of your business.
We have listed a number of operational plan for business plan examples that you can browse through and download in this post. Refer to these downloadable examples if you want to be more specific with the formatting and content development of your own operational plan.
Operational Plan and Budget for Business Plan Example

Size: 871 KB
Operational Plan for Business Plan Elements Example

Size: 172 KB
Operational Business Plan Example

Size: 91 KB
What Is an Operational Plan for Business Plan?
Just like a project operational plan , an operational plan for business plan promotes organization within all the processes that concerned stakeholders will be involved in. Every business should have an operational plan as this document can help point out operational goals, the gap that is needed to be filled during business operations, and the business condition that is needed to be achieved with the help of a proactive and productive workforce.
Here are some ways on how an operational plan for business plan can be defined:
1. An operational plan for simple business plan deals with the daily activities of the business. It helps prepare specific action plans that can be used to support the requirements, needs, and demands of the operations. This can help the workplace become more organized, functional, and appropriate for all the work processes that are needed to be done on a day-to-day basis.
2. An operational plan for business plan is an extremely detailed document that presents the tactics and strategies necessary to be implemented for operational growth and development.
For an operational plan to be highly usable, it needs to present the entities who will be responsible for the execution of particular call-to-actions, the details of the operational plan activities, the location where specific work functions will be implemented, and the time frames that are necessary to be considered when executing general action plans .
3. An operational plan for business plan ensures that the lower management is fully aware of the desired and demands of the upper management. With this document, there will be clarity with the direction where the operations will be brought which should be relevant and aligned with the objectives of the business. You may also see operational plan for restaurant examples .
4. An operational plan for business plan adheres to low-level management. This means that this document is helpful for single-area units like specific departments. As an example, a sales operational plan can help the sales team associate its professional goals , work processes, and action plans with the objectives of the business.
Annual Operational Plan for a Business Example

Size: 310 KB
Farm Operational Plan for Business Plan Example

Size: 350 KB
Bank Group Operational Plan for Business Plan Example

Size: 565 KB
Key Elements of an Operational Plan for Business Plan Example
Using an operational plan for business plan can help you define all the factors, elements, and components that you need to consider to ensure that all the objectives and goals of the upper management for its operations can be achieved. The same goes with how event management teams use an event operational plan to ensure that the workforce is well aware of what is expected from them.
Especially when dealing with potential operational successes, it is important for you to know how strategies and tactics can help business processes, operational workloads, and stakeholders’ relationships to be better. Here are the key elements that you should not forget to include in your own operational plan for general business plan :
- The desired output of the upper management and the operational guidelines that the workforce can refer to so that they can provide all their deliverable needed during operations.
- The strategies and tactics that you will incorporate in your business operations for you to yield better results and return of investments.
- The tasks, obligations, and responsibilities that are needed to be done in a timely manner to ensure that specific operational goals and objectives will be realized.
- The particular entities who will be assigned to take ownership of the incorporation of strategies or the execution of call-to-actions.
- The timeline that will serve as guide within the entire execution of the operational plan for business plan.
- The time frames or duration where particular operational activities are expected to be done, completed, and/or provided.
- The amount that will be used for the implementation of the operational plan for business plan and the financial resources where the required budget will be coming from. You may also see event operational plan examples .
- The performance indicators that can assess the quality of the results given by the workforce and other stakeholders with the help of the operational plan.
Operations and Maintenance Business Plan Draft Example

Business Plan Outline with a Thorough Operational Plan Example

Size: 12 KB
Things That You Need to Focus on When Developing an Operational Plan for Business Plan
It is essential for you to know the phases of the business management planning processes where you will incorporate the operational plan. You have to consider the different setups within various business areas so you can develop an operational plan that works for every department and division while still considering the overall corporate goal of the company. With this, you have to be keen with the development of your own operational plan for business plan.
Here are some of the things that you always need to look into when drafting the specified document:
1. Ensure that there is clarity with your objectives. You have to be aware of what it is that you truly want to achieve. If you can present the better goals that you have in mind for the operations of the business, then it will be easier for you to come up with strategies and process guides that can help your objectives be a reality.
2. Particularly and specifically present all the activities and functions that the operations team is expected to be delivered. The people that you will be working with must be knowledgeable of what you expect from them so that they can execute work processes accordingly. Having an operational plan for a business plan can also help the operations become more sensitive with the quality standards that they need to meet.
3. Speaking about quality standards, you have to set the measures and metrics that you will use for assessment and evaluation. It is essential for you to have a thorough process of identifying whether the operational plan is working for the benefit of the business, and not against the direction where the upper management would like the business to be at. You may also see annual operational plan examples .
4. List down all your desired outcomes. This should be based on your long-term and short-term goals . Specify the things that you would like to achieve in different time frames and periods. Through this, you can be aware of whether there is growth and development that is happening to the business and its operations with the usage of the operational plan that you have created.
5. It is important for you to consider the staffing needs of the operational plan for business plan that you will develop. You have to look into the current workforce pool of the company so that you can identify whether the plans that you have are realistic and attainable based on the number of people that you can work with. You may also like IT operational plan examples .
6. Present all the resource requirements, needs, and demands that are essential to be supplied within the actual implementation of the operational plan for business plan. You have to be aware of the resources that you will be needing, from the budget that you need up to the equipment and materials that are expected to be at hand and readily available, so that there will be a smooth execution of all your simple action plans for the business operations.
7. Develop an implementation timetable that can ensure the timeliness of all your work processes. You have to keep in mind that the daily operations of the business have particular requirements.
Hence, you have to make sure that all your listed work functions are time-sensitive. If you can present all the time frames for every operational action plan, then it will be easier for all point persons to execute their responsibilities in a timely manner. You may also checkout project operational plan examples .
8. Include all the processes, activities, programs, and efforts that are relevant to the operations of the business. You have to incorporate a particular success measure for monitoring the progress and growth of the business operations. Your b usiness operational plan should be evaluated and updated from time to time so you can ensure that the usage of the document is still effective.
Food Truck Operational Plan for Business Plan Example
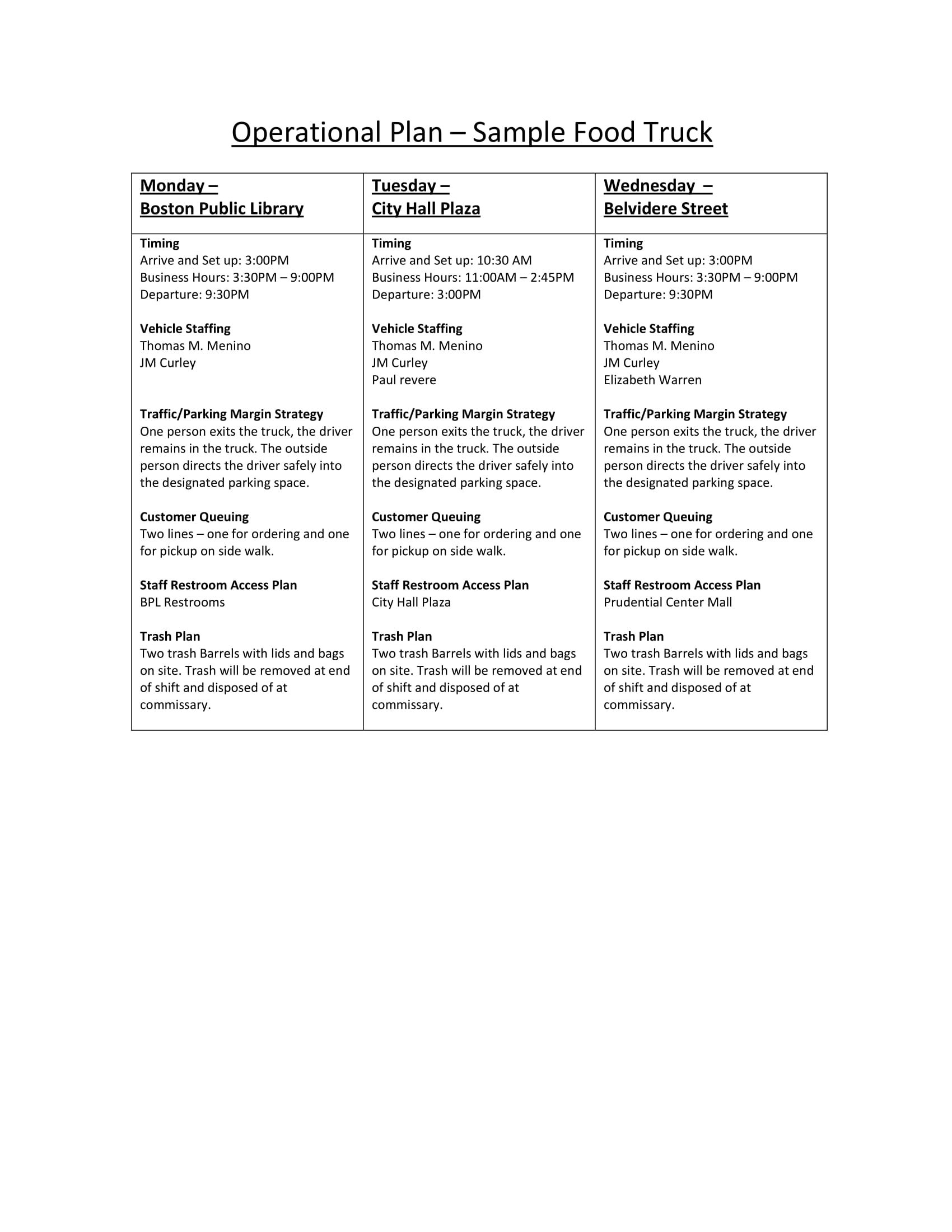
Size: 45 KB
Business Planning: Operating Plan or Operations and Maintenance Plan

Size: 54 KB
Operational Plan for Business Plan Example

Size: 116 KB
Guidelines and Instructions for an Operational Plan for a Business Plan Example

Tips and Guidelines for the Creation of an Operational Plan for Business Plan
Whether you are making an operational plan for a restaurant or any other kinds of businesses, you always have to ensure that the document that you will come up with is understandable, specific, direct to the point, and complete with all the details that you would like to disseminate to your target audience. A few of the useful tips and guidelines that you can refer to if you want to start drafting your own operational plan for business plan are as follows:
1. Ensure that the discussion in the operational plan for formal business plan are divided into clauses or segments. You have to present key points and areas of consideration in an organized manner so that it will be easier for the document to be understood and interpreted accordingly.
2. Know the nature of your business operations and how your performance as a corporate entity pars up with your competition. Having the knowledge about your current operational conditions can give you an idea on how you can develop formal action plans that can bridge the gap between the state of the business right now and the condition that you would like to experience, business operations wise.
3. Browse through a selection of operational plan for business plan examples especially those that have been used by successful businesses in the same industry. Being able to see the trends or common denominators in the development of this document can help you come up with an effective operational plan of your own. You may also see importance of business plan .
4. Be specific with your plan discussion. Limit the content of the document to its bare minimum ensuring that your operational plan only contains relevant and necessary information.
With the help and guidance of the operational plan for business plan examples that we have compiled just for you, we hope that you can have an easier and faster time in developing your operational plan for sample business plan . You can always go back to the discussion specified above if you need to refresh your mind about the proper and efficient creation of an operational plan.
Download any of our examples and try to create a well-formatted and comprehensive operational plan for business plan now.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.
Create an Operational Plan that Makes an Impact

Companies often confuse strategic, tactical, and operational planning. Strategic planning sets your organization’s long-term vision and goals. Tactical planning is the process of figuring out how to achieve your strategic plan. And operational planning links the two, outlining the procedural steps you’ll take to meet your goals. A sound operational plan is critical for achieving success in your organization.
What Is Operational Planning?
Operational planning is the process of creating actionable steps that your team can take to meet the goals in your strategic plan. An operational plan outlines daily, weekly, and monthly tasks for each department or employee. During operational planning, you’ll also create milestones that help you achieve your strategic plan. For example, if your strategic plan aims to grow your customer base by 20%, your operational plan will include incremental steps to gain new leads and customers.
What Are the Benefits of an Operational Plan?
A well-constructed operational plan makes everyone’s jobs easier. The benefits include:
- Clear guidance: With actionable steps for each department, operational plans help teams understand if they are performing well or need to improve.
- Better workflow : Each team knows what they’ll be working on over the month or quarter, and they can adjust their workflow as needed.
- Improves morale : All employees can see how their day-to-day work connects to the company’s broader goals.
Creating an Effective Operational Plan
Operational plans help you hit strategic goals, so start by reviewing your strategic plan. Your operational plan should be specific to a department or team, so your organization will likely have more than one operational plan. Identify the key stakeholders for a particular team: they’ll be best suited to develop the plan, which should include:
- Departmental objectives
- Key performance indicators
- Staffing and budget needs
- Process for tracking and reporting on progress
Once the plan is complete, you can replicate this process for each department. Plans should be shared department-wide for feedback and questions.
Operational Goals
Also referred to as departmental goals or objectives, operational goals are the short-term targets that your organization wants to hit. An operational plan includes operational goals and the steps to achieve them. Typically, organizational goals are:
- Tied to a specific department or team
- Tied to a budget line or item
- Tied to a specific short time frame, such as a month or a quarter
Operational Goals Examples
All operational goals should be measurable and actionable. Actionable means your team can achieve them – so the goal cannot be dependent on an outside factor. For example, your IT team may be tasked with training 10 new employees on security best practices each quarter. But if 10 employees aren’t hired in a particular quarter, that operational goal is not actionable.
To be measurable, there must be a clear way to tell if you met your operational goal or not. For example, one operational goal for an accounting team might be to process invoices more quickly. Their accounting software should be able to collect data on how quickly invoices are processed and paid, so the team can measure their performance over time and see if they are working more efficiently.
Share Your Operational Plan
An operational plan shouldn’t be static – it’s a living document. As time goes on, you may need to adjust your operational goals. That isn’t a sign of failure – it means you’re doing a better job of understanding how each team functions and setting your targets accordingly. You should keep your plan up to date and revisit it regularly, whether once a year or at the end of each fiscal quarter. Include key stakeholders in this process so that the plan works for everyone.
Start Your Operational Plan with Spider Impact
Creating an operational plan might seem challenging at first – but once you get started, it can help all your teams run more smoothly. See how Spider Impact helps you define, measure, manage and report on your operational goals. Click for a free test drive or demo .
Share this post
Newest articles, what are smart kpis and why are they important, unlocking business success through strategic partnerships, mitigating spreadsheet errors: a guide to reliable data management, previous articles, the difference between goals and objectives in business planning, mission statement vs vision statement: do you know the difference, executive reporting 101: best practices and what's expected, kpi software.
Learn how software brings your KPIs to life with Dashboards, Reports, and performance alerts.
Help from Experts
If your organization hasn’t defined its KPIs, we've partnered with world-class experts to fast-track your strategy.
VIP Content
The latest on strategy execution, KPIs, and business intelligence, straight to your inbox.
Experience Spider Impact for Free
Schedule a live demo or claim your free 30-day trial. We’re standing by to either show off Spider Impact or turn your data into a prototype for free.
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Strategic planning |
Operational plan template
Operational planning is simpler when you have a system. Learn how Asana’s operations team uses standardized processes to streamline strategic planning—no matter how many stakeholders are involved.
Sign up to create your own template.
INTEGRATED FEATURES
Recommended apps.
Operational planning is highly cross-functional. It touches every team and can drive real change—but it also involves lots of coordination. For it to work, you need to bring together almost every team in the company, including executives, finance, product, legal, human resources, and more.
With so many relationships to manage, templatized workflows are key. Templates give stakeholders a plan for how to work together—so instead of constant back-and-forth conversations, you can make plans and take action quickly. At Asana, we use predefined workflows to streamline our operational planning processes—from annual planning to business planning meetings.
What is operational planning?
Operational planning is the process of organizing how your company comes together to make strategic decisions. It’s similar to project management, except instead of looking at a single project, you’re charting the course for the entire company. The goal of operational planning is to drive alignment and clarity across all business divisions—so company leaders can work together to make decisions, and the rest of the company can understand and take action on those decisions.
For example, operational planning involves:
Organizing monthly and quarterly business reviews
Annual planning
Project management for strategic initiatives
What is an operational plan template?
An operational plan template is a pre-made workflow for any essential operational planning process—like annual planning or quarterly business reviews. The template lays out each step of the process, so stakeholders know exactly how to collaborate with each other. For example, if you build an annual planning template , you no longer have to start from scratch for each new planning cycle. Instead, you can just copy the template and follow a predefined workflow.
Why use a digital operations plan template?
Since operational planning involves so many stakeholders, it’s common to run into pitfalls like long and confusing email chains, too many meetings, and losing information in the shuffle. There’s a lot to keep track of, and static tools like email and Google Docs often add to the confusion.
Using a work management platform solves these problems by centralizing your strategic planning process in one place. That way, everyone has a single source of truth where they can communicate, share updates, and make plans in real time.
Here’s what you can do with a digital operations plan template:
Create a single system of record for operational planning work.
Centralize conversations with stakeholders in one place, so no information is lost.
Share status reports with stakeholders without scheduling extra meetings.
View project reports and graphs to quickly understand how initiatives are performing.
Automate operations workflows—so teams can spend less time coordinating work and more time on high-impact initiatives.
Easily update project schedules, tasks, and owners as circumstances change.
Use forms to standardize how teams share information.
Switch between project views to visualize operations workflows in different ways—including task lists , Gantt charts , calendars , or Kanban boards .
Types of operational planning templates
When creating operational planning templates, it’s best to focus on a single use case at a time. Below, we’ve outlined two specific use cases we utilize at Asana—plus the key elements of each.
Annual planning template
With everything streamlined and the busywork automated, we can focus on the work of planning, collaborating, and creative problem-solving—instead of the busywork of coordinating planning, and wishing we had more time to collaborate and think creatively.”
Annual planning is a highly cross-functional process. There are top-down company goals and bottom-up team and department plans, all happening at the same time. At Asana, our strategic planning team uses predefined workflows to streamline the planning process, share information across teams, and help everything come together into a coherent, integrated plan. Here’s how.
Create a single system of record for all annual planning tasks. During annual planning, you need to coordinate tasks across many different teams. Make sure nothing gets lost by centralizing everything in one project, so you can see what each team is responsible for and by when.
Define each annual planning phase. At Asana, we break the annual planning process into phases, each with a specific goal and time frame. When building your template, create a section at the top to define each annual planning phase—including the goal of that phase and when it occurs. By clearly defining what you want to achieve by when, stakeholders can understand how their individual annual planning tasks fit into the overarching process.
Create sections for each department or team. Organize each team’s tasks into a single section, so they can easily see what they’re responsible for accomplishing during the annual planning cycle.
Use custom tags to add additional information. At Asana, we use custom tags to view important details about each task. For example, we use tags to identify which team is responsible, which planning workstream the task falls under, whether it’s a concrete deliverable or a decision to be made, and whether a meeting is required.
Identify key milestones in your plan. Create milestones to identify important checkpoints throughout the annual planning process. This helps teams understand what they’re working toward and how it fits into the overall planning roadmap.
Once you’ve created your annual plan, share and track it with Asana’s Goals feature. Goals is an organization-wide tool that can help your entire company set, monitor, and communicate about goals.
Business planning meeting template
Bringing together the leaders of our business org across sales, marketing, biz tech, people ops, customer success, and business strategy is critical to ensure ongoing cross-functional clarity and alignment. But, it can also be extremely costly if it’s not done so effectively and efficiently.”
Business leaders need to stay aligned. One way to keep executives on the same page is by hosting regular business planning meetings—where leaders can share updates, align on action items, and create plans.
At Asana, we’ve created a standardized workflow to streamline business planning meetings and ensure we’re using meeting time as efficiently as possible. Thanks to this workflow, we no longer have to scramble to pull together and prioritize the right topics. Instead, presenters have plenty of lead time, and meeting attendees can focus on what’s most important for the business—not just what’s top of mind. Here’s how.
Create a single source of truth for meeting planning and follow-up. Centralize planning tasks in one place, so stakeholders can easily see what’s coming up and who’s responsible for each presentation. Create a single task for each agenda item—and then when the meeting is over, add that same task to other projects (like meeting notes or action items) without duplicating work.
Use sections to organize information. Make tasks easier to find by bucketing them into sections, like upcoming topics, new topic submissions, and meeting agendas.
Submit new discussion topics with forms. Create a topic request form to standardize how new agenda items are added. Forms ensure you have all the information you need to plan agenda topics—like a brief description of the agenda item, goals for the discussion, the facilitator, and time required.
Create custom tags to see key information at-a-glance. Add custom tags to get a quick view of each task’s category and status. For example, use custom tags to identify whether agenda items are set or still open.
Recommended features and integrations
As you build out your operational planning templates, customize your team’s workflows with these features and app integrations.
Integrated features
Custom fields . Custom fields are the best way to tag, sort, and filter work. Create unique custom fields for any information you need to track—from priority and status to email or phone number. Use custom fields to sort and schedule your to-dos so you know what to work on first. Plus, share custom fields across tasks and projects to ensure consistency across your organization.
Adding tasks to multiple projects . The nature of work is cross-functional. Teams need to be able to work effectively across departments. But if each department has their own filing system, work gets stalled and siloed. Asana makes it easy to track and manage tasks across multiple projects. This doesn't just reduce duplicative work and increase cross-team visibility. It also helps your team see tasks in context, view who’s working on what, and keep your team and tasks connected.
Automation . Automate manual work so your team spends less time on the busy work and more time on the tasks you hired them for. Rules in Asana function on a basis of triggers and actions—essentially “when X happens, do Y.” Use Rules to automatically assign work, adjust due dates, set custom fields, notify stakeholders, and more. From ad hoc automations to entire workflows, Rules gives your team time back for skilled and strategic work.
Forms . When someone fills out a Form, it shows up as a new task within an Asana project. By intaking information via a Form, you can standardize the way work gets kicked off, gather the information you need, and ensure no work falls through the cracks. Instead of treating each request as an ad hoc process, create a standardized system and set of questions that everyone has to answer. Or, use branching logic to tailor questions based on a user’s previous answer. Ultimately, Forms help you reduce the time and effort it takes to manage incoming requests so your team can spend more time on the work that matters.
Zoom . Asana and Zoom are partnering up to help teams have more purposeful and focused meetings. The Zoom + Asana integration makes it easy to prepare for meetings, hold actionable conversations, and access information once the call is over. Meetings begin in Asana, where shared meeting agendas provide visibility and context about what will be discussed. During the meeting, team members can quickly create tasks within Zoom, so details and action items don’t get lost. And once the meeting is over, the Zoom + Asana integration pulls meeting transcripts and recordings into Asana, so all collaborators and stakeholders can review the meeting as needed.
Google Workplace . Attach files directly to tasks in Asana with the Google Workplace file chooser, which is built into the Asana task pane. Easily attach any My Drive file with just a few clicks.
Microsoft Teams . With the Microsoft Teams + Asana integration, you can search for and share the information you need without leaving Teams. Easily connect your Teams conversations to actionable items in Asana. Plus, create, assign, and view tasks during a Teams Meeting without needing to switch to your browser.
Vimeo . Text may get the point across, but written words lack tone, emotion, and expression. With video messaging in Asana, powered by Vimeo, you can give your team all the context they need, without having to schedule another meeting. Record short video messages of yourself, your screen—or both—then embed the videos in tasks, projects, messages, and comments to provide additional clarity and context. A transcript of the recording is automatically created by Asana, making it readable and searchable. Give feedback, ask questions, and assign tasks—all without leaving Asana.
What other operational planning templates can I use to streamline workflows for my business? .css-i4fobf{-webkit-transition:-webkit-transform 200ms ease-in-out;transition:transform 200ms ease-in-out;-webkit-transform:rotateZ(0);-moz-transform:rotateZ(0);-ms-transform:rotateZ(0);transform:rotateZ(0);}
With Asana you can create—and customize—templates to fit any business operations use case. Here are some places to start:
Business plan template
Operations project plan template
All company meeting template
Startup checklist template
Business continuity plan template
Team goals and objectives planning template
Can a project management platform help my business achieve strategic goals faster?
Project management platforms like Asana can significantly improve team efficiency, allowing you to accomplish more with fewer resources. According to an independent report , Asana cuts the time it takes to complete a project by up to 50%—meaning it could help your team get work done in half the time. With less time wasted day-to-day, your team can focus on high-impact work, like driving revenue and achieving strategic goals.
What’s the best way to monitor all operational workflows in one place?
With Asana Portfolios , you can see a high-level view of all operational planning initiatives—including project status, progress, and owners. If an initiative is off track, it’s easy to click in, identify the blocker, and create an action plan to get things back on track.
Related templates
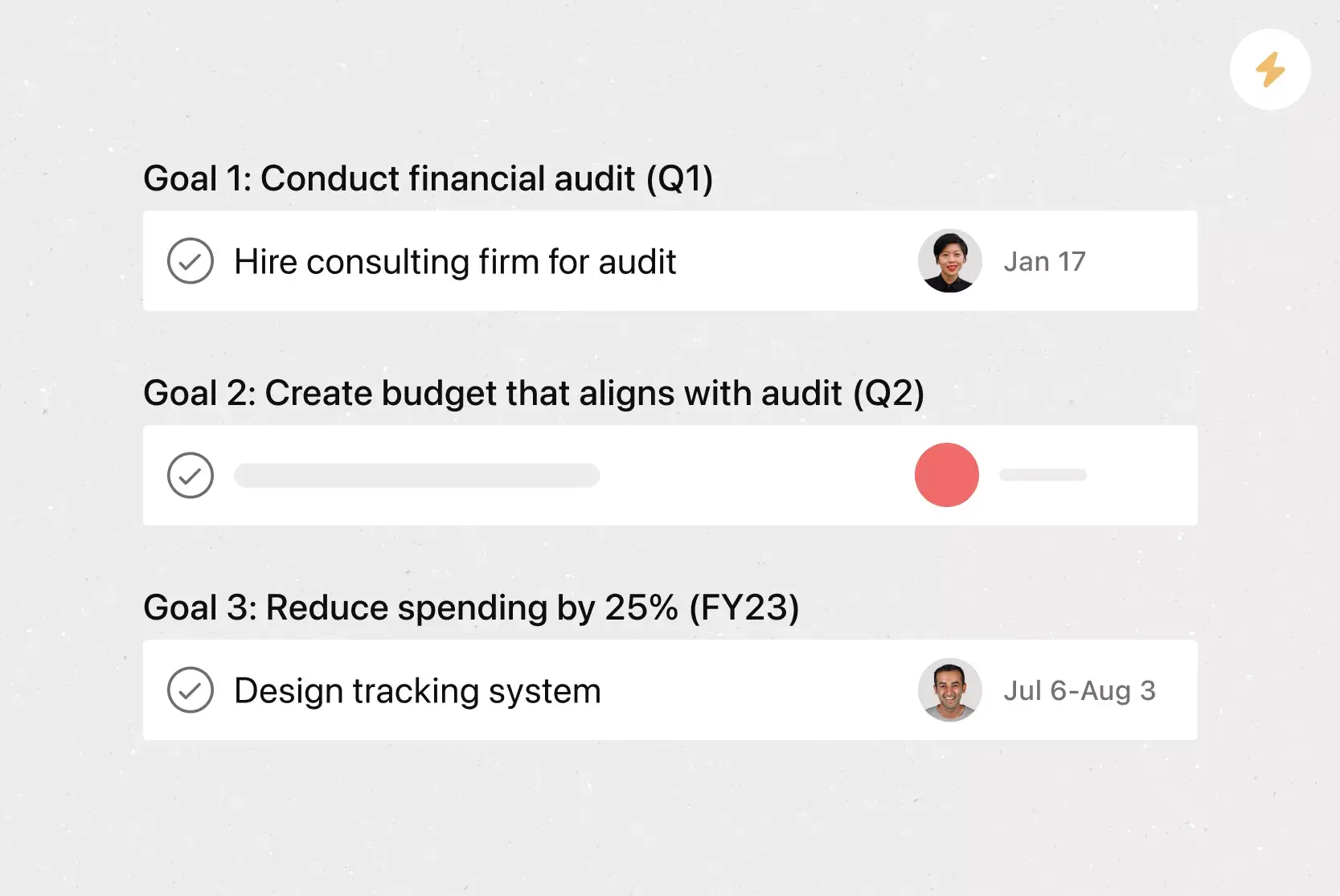
Action plan template
Taking action has never been easier. Learn how to create a reusable action plan template in Asana to take the guesswork out of strategic planning.

Marketing strategy
A marketing strategy template is a useful tool that helps your marketing team achieve their goals. Learn how to create your marketing strategy with Asana.

PEST analysis
A PEST analysis template helps compile info on the external environment affecting your business. Learn how to prevent risk with a PEST analysis template.
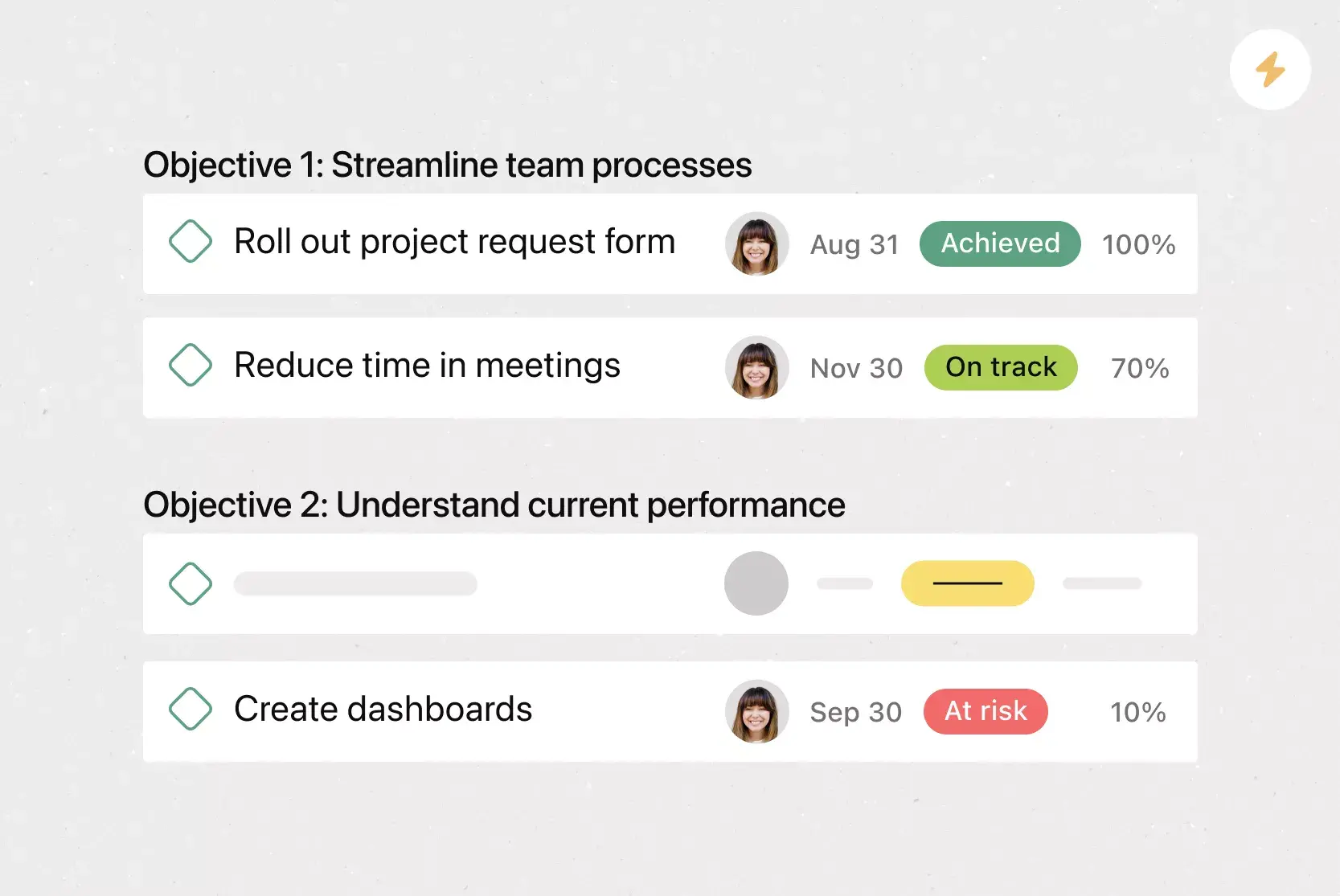
Objectives and key results (OKR) template
Learn how to create an OKR template in Asana so you can standardize the goal-setting process for everyone.
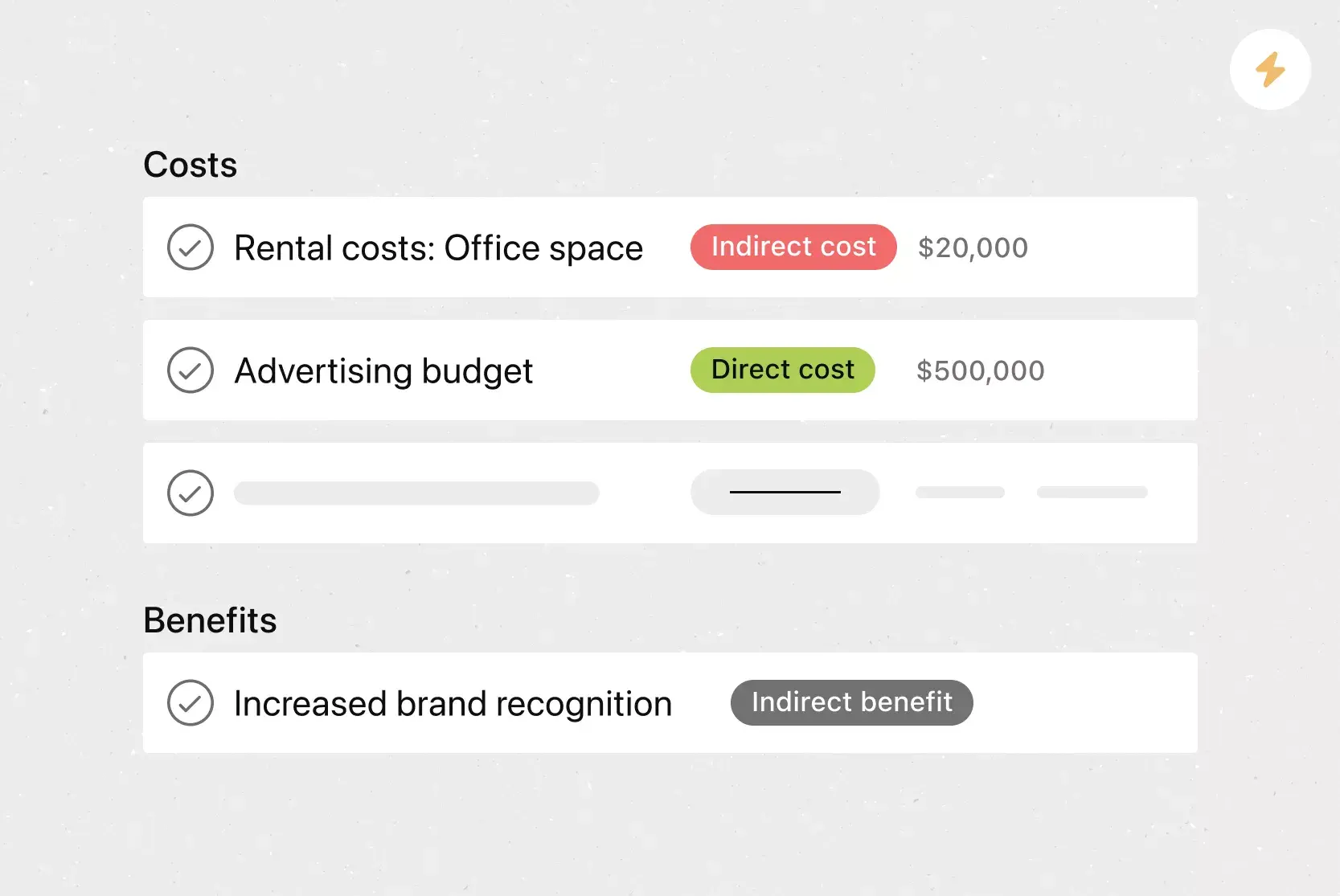
Cost benefit analysis template
Digital cost benefit analysis templates are a useful framework to see if a new project or idea is viable. Learn how to create your own in a few simple steps, with Asana.
Nonprofit business plan template
Success doesn’t just happen—it’s planned. Stay focused on your most crucial work with a custom nonprofit business plan template.
Contingency plan
Using a contingency plan template will help you create well-developed strategies to help you protect your business from potential risk. Learn how Asana can help.

Requirements traceability matrix
A requirements traceability matrix template is a tool to help organize project requirements in a concise manner. Learn how to create one for your team.
Creating a digital punch list template can help streamline the final bits of a project for your team. Here’s how to create one.
Go-to-market strategy template
Simplify your GTM strategy with a go-to-market strategy template that aligns teams and keeps work on track. Learn how in Asana.
Project closure template
Endings are important. Create a project closure template to help your team tie up loose ends and finish their projects with confidence.
Project reporting
Stay on top of your project’s performance. Keep everyone on the same page about what’s been completed and where your project is headed.
![operational process in business plan example [Templates] Product Roadmap (Card image)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/2728edf4-eb35-4dd5-8d03-25ba8cbe5864/TG23-web-thumbnail-028-scrumban-feature-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Product roadmap
What if you could create, share, and update your product roadmap in one place? Everyone could see you’re tackling the right priorities. Start planning your product roadmap with this template.

Program roadmap
Create a program roadmap template and know the exact structure of each program, how they operate, and their future plans—company-wide.
Strategic planning template
When you’re launching a new product, team, or even a new business, strategic planning templates keep you laser-focused and on task.

Set clear goals and streamline your planning process—so every level of your company is aligned on what’s important.
Competitive analysis template
The more you know about your competitors, the better your strategy will be. Competitive analysis templates use a data-driven approach to see exactly how your business, products, and features compare to your competition.

Crisis management plan
Does your team know what to do during a crisis? Using a crisis management plan template can help keep all your employees on the same page.
Business plan
A business plan is the first step to start your business and secure financing. Use our business plan template so you don’t have to start from scratch.
SIPOC template
Use your SIPOC template to ensure that the processes outlined in your SIPOC diagrams are consistent and up to your standards.
Create templates with Asana
Learn how to create a customizable template in Asana. Get started today.
Blog Center
Productivity
Comparisons
Product Updates

Operations Management: Definition, Examples, Benefits, and More

Ethan Miller
May 3, 2024
13 min read.

Excellent operations management makes a difference you can both see and feel. It's the reason some businesses run like clockwork.
Sure, you may understand the basics of running a business, but how do you take your operations to the next level? In this article, we uncover the secrets to exceptional operations management and offer examples and tips to help you refine your approach.
What is operations management?
Struggling with late deliveries, stockouts, or unhappy customers? Operations management is your solution. It’s the process of planning, organizing, directing, and overseeing business activities to deliver the best possible products and services to customers.
Essentially, operations management is what gets a product from an idea to your doorstep.
What does operations management cover?
Think of everything it takes to get your product or service into a customer's hands. Without effective planning, you’re likely to waste time, effort, and money.
That's where operations management comes in. With a strong operations foundation, you ensure:
On-time deliveries: Operations management streamlines production schedules to meet customer deadlines.
Optimized resources: Efficient supply chain and inventory management means you always have what you need without unnecessary waste.
Consistent quality: Good and reliable quality control processes guarantee your products or services always meet customer expectations.
Seamless workflow: Operations management maximizes efficiency across departments.
Increased productivity: Get more done with the same resources through process improvements.
What doesn’t operations management cover?
While operations management takes on many important tasks, it doesn’t include responsibilities outside the production and delivery of goods or services, such as:
Strategic direction: Setting the company's big-picture goals isn't part of operations management.
External analysis: Operations management doesn't focus on external factors like market trends, the economy, or competitors.
Non-operational investments: Financial decisions unrelated to daily activities aren't handled by operations management.
Brand and marketing: Brand image and marketing fall outside the scope of operations management.
Compliance and governance: Operations management doesn’t involve setting company-wide rules or legal policies

Get started with Lark’s Operations Plan template
10 operations management examples
Operations management takes different forms across industries. Whether it's a healthcare or manufacturing organization or a local restaurant, successful businesses rely on well-designed operational processes.
Here’s what operations management means for 10 different business sectors:
1. Healthcare
In healthcare, miscommunication and delays can jeopardize patient care and drive up costs. Operations management ensures the right care is delivered at the right time, all while optimizing resources. This means coordinating patient care seamlessly, keeping wait times down, and managing costs effectively.
Doctors, nurses, and medical staff need to be able to share information quickly and accurately to provide the best possible patient care. Many hospitals have turned to technology to improve communication, reduce wait times, and keep costs down.
Take WhiteCoat , a leading telehealth provider. They used Lark's video conferencing platform, which offers AI translation, to help their Singapore and Vietnam divisions communicate more effectively. Lark Drive also became a central hub for their regional employees to collaborate and share important documents and knowledge, leading to more efficient and higher-quality care.
2. Manufacturing
Production delays, quality issues, and supply chain problems can lead to lost revenue and unfulfilled customers. Operations management oversees and controls production to ensure everything runs smoothly and all products reach your customers perfectly.
It includes making sure assembly lines work, spotting and addressing production bottlenecks, and performing frequent quality checks. Another key job is managing supply chain logistics to keep production on track. The correct inventory level is critical. A delicate balance needs to be struck between having all the raw materials arrive at the factory at the right time and not having excessive unused inventory that costs money to store or leads to waste.
A successful manufacturing operation guarantees on-time deliveries, satisfied customers, and a more profitable bottom line.
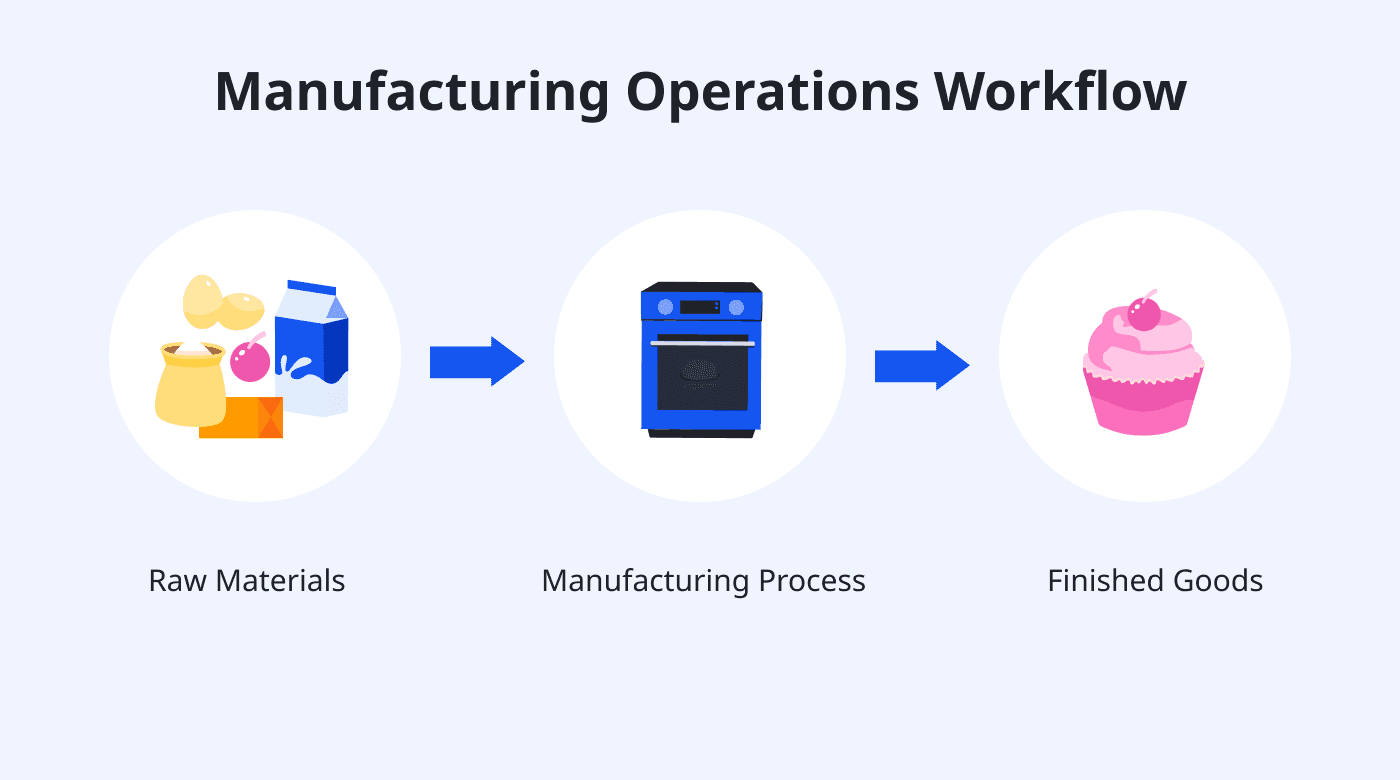
3. Restaurant
The chaotic yet captivating hit series “The Bear” is a great example of the contrast between the hectic behind-the-scenes world of restaurant operations and the polished dining experience those same restaurants give their customers.
There are so many aspects that go into restaurant management , including daily food preparation, managing food inventory, safety protocols, maintaining cleanliness, and optimizing kitchen workflow.
Operations management streamlines your kitchen workflow, ensures consistent food quality, and helps you optimize staffing for peak periods.
Mama Lou’s , a family-run Italian-Filipino restaurant, knows this well. By using Lark Base to centralize their daily sales reports and create a more organized workflow, they were able to not only improve customer satisfaction but also create a more positive work environment for their employees.
Learn how Lark can help your food and beverage businesses. Contact us now .
In the fast-paced IT industry, downtime and slow response times lead to lost productivity and frustrated clients. Since customers rely on your IT services to keep everything from websites to customer databases up and running, operations management brings reliable support and proactive problem-solving.
This means having the right technicians available to troubleshoot, monitoring IT systems for potential problems, and gathering client feedback to improve your service.
When unplanned outages or issues occur, IT operations management has procedures in place to quickly restore service and minimize downtime.
From global retail giants to local boutique shops, retail operations management keeps everything in check. But mismanaged inventory, inefficient staffing, and poor customer service can really hurt your business.
With effective operations management, you can better manage in-store operations, such as staffing, visual merchandising, and providing excellent customer service — all while driving sales.
Workforce scheduling is a major consideration in retail operations management. You need to make sure the right number of people are working to help customers during the busiest times and stay cost-effective when things are slower.
Use Lark’s employee schedule template to simplify workforce scheduling.
Additionally, analyzing sales data gives you a better idea of how to staff employees, what to stock, and where to concentrate your marketing efforts.

Image Source
Milan-based designer furniture brand REAL Home & Fashion used Lark to streamline their retail management and procurement processes. With Lark Anycross, they could see all past purchases in one place. As a result, their procurement team was able to better allocate resources and budgets to optimize their procurement process.
Explore Lark's retail solutions today.
6. Financial services
Banks, investment firms, and insurance providers are all institutions that we put our trust in. Even a small operational error or security breach can cause devastating damage to both your reputation and finances.
Think of the number of financial transactions that happen every second — there’s a lot that needs to be managed effectively and securely.
The three primary goals in the financial sector are to 1) protect customer information and funds, 2) optimize operations for efficiency, and 3) keep clients satisfied with quality service.
Operations management in the finance industry carries immense responsibility, as it involves creating secure processes and streamlining transactions. It also ensures your business is up-to-date on the latest regulatory compliance guidelines to protect both you and your customers.
7. E-commerce
E-commerce has made it easier than ever to find what we need to buy online. But, to run a successful e-commerce operation, you need to face the challenges of juggling orders, inventory, and deliveries across multiple online platforms.
Inefficient processes can cause delays in deliveries and unhappy consumer experiences. Operations management streamlines your e-commerce workflow, helping you process orders quickly, maintain accurate inventory, and ensure on-time deliveries.
Heptaco , a digital innovation company that builds e-commerce systems, understands the importance of efficient operations. By switching to Lark’s all-in-one platform, they were able to consolidate all key business communication and collaboration tools. This streamlined their operations, helping them to better collaborate with and support their customers and even save on costs.
8. Construction
Construction projects face tight deadlines, unexpected delays, and strict compliance regulations. Unforeseen costs and scheduling conflicts can seriously derail a project. Operations management keeps your construction projects on track with careful planning, efficient resource use, and regular quality checks.

You’ll need to consider your budget, scheduling, and compliance with local building codes. This means creating a realistic timeline, outlining the necessary expenses, and staying updated on legal requirements.
Operations management makes sure these standards are upheld throughout the construction process, helping ensure that each project is completed on time and within budget.
9. Transportation
Rarely do we think about the operations that make our commute to work or deliveries possible. A successful transportation business needs a good operations strategy to deal with delays, routing inefficiencies, and vehicle breakdowns.
Operations management coordinates logistics for timely deliveries, plans vehicle routes, and sets up maintenance schedules to minimize delays, wasted fuel, and sudden breakdowns.
When Seryu Cargo , a logistics company specializing in e-commerce, needed a solution to improve efficiency and collaboration among their team, they turned to Lark. Lark's collaboration tools and mobile-friendly platform helped them automate routine administrative tasks and allowed drivers to update their main office on the go. This led to a more efficient deployment of resources and, as a result, improved operations as a whole.
10. Agriculture
The unpredictability of agricultural operations, like managing water, land, and livestock in variable weather conditions, is a unique challenge.
Effective operations management keeps your business running smoothly so that you can provide the food and resources customers need. It helps you optimize resources and make informed decisions. This leads to higher crop yields and a stronger business overall.
Many agriculture businesses are also focusing more on sustainability in farming. Agriculture operations management also helps reduce environmental impact.
Streamline your operations workflow with Lark Base
What is the role of an operations manager?
Operations managers are the backbone of a business. They are in charge of the following:
Inventory management
An operations manager needs to manage stock so that the business can meet customer demands without overstocking or running out of inventory.
To do so, they usually use systems to track inventory levels, predict future needs, and organize restocking efforts.
Personnel management
Staffing and training are key parts of an operations manager's job. Hiring the right people and providing them with top-notch training helps you build a collaborative team that can do their jobs well and handle unexpected situations with ease.

Another aspect of the job is to help maintain a positive work environment. While operations managers aren't human resources professionals, they can do their part to address staff issues quickly and fairly.
Delivery planning
Operations managers carefully plan delivery routes and schedule timely deliveries to customers.
If sudden delivery issues arise, such as delays, wrong orders, or damaged goods, they need to jump in and address the problems to help prevent them from happening again. Their role here is to help ensure a smooth customer experience and build customer trust.
Process optimization
Think of operations managers as expert mechanics — constantly fine-tuning the engine of a business, even when it's already running well. They conduct regular reviews of current workflows to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize processes for more efficiency and cost savings.
Generally, this means testing and adopting new methods or technologies to enhance daily operations and performance. Adopting this approach keeps businesses competitive and agile.
Optimize your processes and workflows with Lark
4 operations management best practices
Figuring out the nitty-gritty of operations and workflows can get tricky and even overwhelming. We've compiled four best practices to help make it easier:
1. Automate routine business processes
There are so many tasks and processes involved in running a business. But the good news is you don’t have to do everything yourself.
As many as 89% of business owners and managers report that their businesses have grown due to process automation, and 92% say that automation has freed up their employees to take on more strategy-focused jobs.

Automation technologies like robotic process automation and artificial intelligence (AI) can help make your operations more efficient. They can also reduce the number of mistakes made and make sure tasks are done in the most optimal way possible.
It’s estimated that AI will boost employee productivity by approximately 40% by 2035. But with so many tools, choosing the right ones is essential. Analyze your current processes and identify which are best suited for automation. AI can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy for repetitive, rules-based tasks, such as data entry and invoice processing.
Use Lark’s cost-savings calculator to find out how much you can save by automating your processes.
2. Adopt a consumer-centric approach
Your connection with a customer shouldn't end after you deliver a product or service. Gather and review customer feedback to find areas for improvement and new ways to customize products based on customer preferences.
For example, if a customer has a negative experience due to a delayed shipment, look at your delivery processes to see where you can strengthen them.
Take a page out of Amazon's playbook by making your operations consumer-centric. Align your operations strategy with customer needs to ensure they get the experience and value they expect from your products or services.
3. Prioritize continuous improvement
How do you know how well your business is performing? Start by setting key performance indicators (KPIs) to track operational performance and identify areas for improvement. A good tip is to set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) KPIs.
Additionally, motivate employees to suggest improvements based on their experience. Since employees are typically the ones in the field, their insights can be valuable.
You can use Lark’s Survey Template to customize a feedback mechanism for employees and let them easily share their ideas.
4. Build a strong line of communication across departments
We all know how important communication is in the workplace. In fact, 26% of leaders believe that poor cross-team collaboration is the biggest challenge in business management.
To build a smooth-running operation, you need high-functioning and collaborative teams. But how do you do that across departments? By prioritizing clear and consistent communication.
Hosting regular inter-departmental meetings and using collaborative platforms can help your different teams share information, problem-solve, and align their objectives. It’s equally important to encourage a culture of transparency and teamwork to bridge operational silos.
The challenges of collaboration multiply with teams spread across different time zones. Tools designed for global teams make all the difference. Choose platforms with features like video chatting, real-time translation, and clear task management to ensure seamless collaboration no matter where you are.
Master cross-departmental communication with Lark
Lark Suite improves operations management for all businesses
Operations management can be complicated, time-consuming, and expensive. Lark has you covered with helpful tools to automate your processes, boost efficiency, and reduce operational costs .
Looking for a quick approval process or a streamlined task tracker? Done. Lark's no-code automation means you can create custom workflows and SOPs within minutes. With Lark Flow, tasks move forward automatically, saving you time and effort.
You can also customize permissions for cross-departmental teams so that everyone can access the relevant information they need while also protecting sensitive data.
Additionally, take advantage of Lark’s template library , which includes a customer service management & tracking base template and an order and inventory management template , among many others.
Lark Meetings
Powered by AI tech, Lark Meetings allows you to connect from anywhere and collaborate on documents in-call. You can share feedback and make edits instantly, keeping your team up to date.

Plus, Lark Minutes automatically transcribes video meetings into transcripts that you can view, search, and collaborate on. No more taking notes — now, you can fully focus on your discussions.
The best part? Lark’s video chat supports subtitles that can be translated in real time. This is especially helpful for global teams since everyone can express themselves in their native language.
If you're curious about just how powerful Lark’s video translator is, give it a try here .
Lark Approval
Do you wish you had an easier way to approve processes? Well, Lark Approval acts as a central approvals hub. You can submit and process all types of approvals with one click. Plus, you can customize your approval processes to perfectly suit your business needs.
Try out our versatile Approval Matrix Whiteboard template to create your own approval workflow.
Lark OKR helps you go beyond simply setting goals by giving you the tools you need to achieve them. You can easily organize your teams around strategic objectives to stay aligned.
On each team member’s Lark profile, you’ll find OKRs to help with cross-departmental alignment and personal accountability.
And when it’s time to update your OKRs, you can simply insert them into Lark Docs so your team can update them collectively and then sync them back to the OKR system.
Moreover, determine your team’s “state of health.” Through data analysis, you can monitor team progress in real time, identify potential problems early on, and make data-driven decisions to optimize your strategy.
Lark’s Team Weekly Report (OKR) template can help you track your team's weekly progress and align with organizational objectives.

Manage OKRs and KPIs on Lark
Manage your business operations with Lark’s all-in-one platform
Give your operations a productivity and efficiency boost. Try Lark for free today!
Table of Contents

Interested in Lark?
Contact us to get a customized demo today
Schedule a demo
Try for free
Keep reading
Back to all posts

From Meta Workplace to New Horizons: Navigating the Future of Communication
The Meta workplace closure marks a shift in enterprise communication, urging businesses to explore new, integrated tools to improve productivity.
May 17, 2024

10 Best Rostering Software Tools to Simplify Your Job
Find the perfect solution to simplify employee rostering, boost efficiency, improve communication, and optimize your workforce management.
May 6, 2024
16 min read
Pay less to get more today
No more redundant tools. Save time and costs.
Get Lark today
Download Lark

Users love us

Open Platform
Savings Calculator
Lark vs. Slack
Lark vs. Zoom
Lark vs. Whatsapp
Lark vs. Teams
Lark vs. ClickUp
Lark vs. monday.com
Lark vs. Airtable
Lark vs. Trello
Lark vs. Wrike
Lark vs. DingTalk
Lark vs. Base.vn
Become a Partner
Partner Directory
Alternatives
Slack alternatives
Zoom alternatives
Discord alternatives
Airtable alternatives
Notion alternatives
Lattice alternatives
Project Management
Human Resources
Sales & Marketing
Students & Educators
IT Managers
Build with Us
Developers/Applications
Integrations/APIs
Property Management
Manufacturing
Media & Entertainment
Lark for Startups
Global Collaboration
Food & Beverages
Professional Services
Customer Stories
Help Center
Lark Academy
Lark Topics
Security & Compliance
Privacy Policy
Customer Terms of Services
User Terms of Services
Acceptable Use Policy
Cookie Policy
Cookie Settings
© 2024 Lark Technologies Pte. Ltd. Headquartered in Singapore with offices worldwide.
Defining your ‘true north’: A road map to successful transformation
At every turn, companies are grappling with unprecedented disruption. At a time when macroeconomic and geopolitical turbulence has become the norm, and businesses are deeply technology dependent and globally entwined, yesterday’s recipe for success falls short of even ensuring survival tomorrow. The imperative to adapt, evolve, and transform is clear. But business leaders must also shift their mindsets and approaches if they are to create sustainable, transformative change and meet the demands of today’s hypercompetitive environment.
“Transformation,” a well-worn term in the corporate vernacular, has come to mean many things to many people, diluting its significance and leading to transformation fatigue. Many organizations have grown used to viewing transformations as short-term efforts to “cut the way to greatness.” Such undertakings lack clear connections to a business’s longer-term strategic priorities. In extreme cases, they can lead to shortsighted decisions that compromise an enterprise’s competitive position and even viability.
Real transformative change goes beyond episodic efficiency efforts or organizational restructurings. It instead aims to reprogram an organization’s very DNA and embed a new operating model, guided by a bold strategy, to reach a company’s full potential. When done right, a transformation becomes a source of continual renewal, evolving and even revolutionizing a business over a series of horizons.
In 2016, McKinsey laid out transformation elements in “ Transformation with a capital T ,” defining transformation as an intense program to significantly enhance performance (an earnings improvement of 25 percent or more, for example) and boost the health of the entire organization. 1 Michael Bucy, Stephen Hall, and Doug Yakola, “ Transformation with a capital T ,” McKinsey Quarterly , November 7, 2016. Since then, our view has evolved. While cost reductions and operational excellence remain table stakes, best-in-class companies are expanding the scope of their transformations to include the reassessment and resetting of their strategies. They’re placing the focus on innovation and growth to take enterprise-wide performance to a new level.
Best-in-class companies are expanding the scope of their transformations to include the reassessment and resetting of their strategies.
To achieve this bigger impact, a transformation must be guided by what a company wants to become—a bold aspiration encapsulated in its strategy. This strategic “true north” should then determine the sequence of initiatives, along with the performance metrics used to track them, across four distinct work streams: cost optimization, growth, organizational effectiveness, and digital enablement. Finally, business leaders must fully integrate the transformation approach into the company’s day-to-day operations. This means making the transformation the new business as usual rather than treating it as a limited-scope side project.
Treating strategy as the true north
In McKinsey’s early experience in transformation work, going back to 2010, the majority of efforts revolved around delivering rapid performance improvement at companies facing significant operational and financial challenges. The focus was on survival—freeing up cash and resources to resolve liquidity and balance sheet issues. With cost efficiency as the primary aim, strategy rarely entered the discussion. Indeed, in the 2016 article, the word “strategy” appears only twice. 2 Michael Bucy, Stephen Hall, and Doug Yakola, “ Transformation with a capital T ,” McKinsey Quarterly , November 7, 2016. Today, CEOs are expanding the definition of transformation, aiming to turn middle-of-the-pack performers into dominant industry titans. In these ambitious transformations, strategy plays a leading role.
In ambitious transformations, strategy plays a leading role.
As the scope of the transformation grows, the approach to execution must also change. Most successful change programs move through several distinct horizons over multiple years. With each horizon comes a set of objectives plus defined resources and investments in capability building. The full strategic agenda is also sequenced in stages. This helps ensure that the organization isn’t overburdened at the start, which could stifle its ability to deliver the rapid impact critical to building internal momentum, as well as external confidence and support.
While each transformation context is distinct, the journey often begins with a focus on stabilizing and improving the fundamentals of the business. This is followed by accelerating growth, organizational design, and digital enablement, all of which lay the foundation for a strategic and operational repositioning:
- Horizon one: all about the fundamentals (first three to 12 months). The priorities during this period are typically grounded in tactical improvements, including cost optimization, cash flow generation, and filling capability gaps. Speed is of the essence : our research shows that in successful transformations, initiatives executed within the first six months deliver 57 percent of the total program’s value. 3 Kevin Laczkowski, Tao Tan, and Matthias Winter, “ The numbers behind successful transformations ,” McKinsey Quarterly , October 17, 2019. Companies must quickly prove to their boards and investors that their strategic plans have substance and can generate bottom-line impact. Being able to celebrate early improvements is also essential to building momentum and mobilizing the entire organization.
- Horizon two: growth and scalability (next 12 to 24 months). Having established early momentum, business leaders shift their focus from driving incremental improvements to fortifying their companies’ operating systems and setting up the conditions to fully realize the long-term strategic vision. Such initiatives typically have longer implementation road maps and timelines and substantial investment requirements. It’s critical to remain vigilant about timely execution and to validate impact. This is often the stage at which performance can regress, as the initiatives tend to be more complex and nuanced. Reacting quickly to correct the course as needed and invigorate the transformation plan with new ideas is essential to realizing the commitments and goals of the transformation.
- Horizon three: repositioning and reinvention (24 months and beyond). Achieving a company’s full potential typically involves a mix of specific actions executed in horizons one and two along with one or two strategy-guided big bets. These bets are likely to materially reshape, or even reinvent, the business over the longer term. Such initiatives might include geographic expansion, product innovation, or strategic M&A activity. This work requires a higher level of effort and resources than the first two phases do.
Setting out four performance work streams
We have learned over the past decade that companies have a better chance of reaching their full potential when transformations are directly linked to strategy. Companies should define the objectives based on an organization’s capabilities and performance across a set of impact and business reinvention metrics . The core transformation should focus on four aspects of performance:
- Cost optimization. Leading companies treat efficiency measures as merely a jumping-off point to the transformation—a way to free up capital to reinvest in the business. By eliminating waste and adjusting cost structure to support the vision of the future organization, the company can improve its operating margins while also generating the funds to invest in higher-ROI projects across the other three work streams.
- Growth. Our latest internal analysis suggests that more than 50 percent of transformation value comes from growth initiatives, up from less than 40 percent two years ago. Companies undertaking transformations need to set clear priorities for how and where they will pursue profitable revenue growth , looking at organic paths, such as launching new products or entering new segments; M&A; and business building. To support such moves, leaders should constantly monitor the return on growth investments and relentlessly reprioritize and reallocate resources based on demonstrated results. Committing to a bold growth agenda can not only reshape the performance trajectory of the business but also energize the organization to persevere toward the transformation’s broader goal.
- Organizational effectiveness. At its core, transformation is about people. In the more than 15 years that McKinsey has conducted transformation surveys , respondents consistently put getting the people part right among the top predictors of success. Additionally, internal analysis suggests that the likelihood of transformation success increases 3.2 times when the full organization is focused on the right priorities. This focus should go beyond rethinking the organizational chart. It should include thoughtfully challenging the status quo and creating a culture that is nimble, embraces cross-enterprise collaboration, and does it all with speed.
- Digital enablement. Technology plays a role in every successful transformation. At a time when 85 percent of companies believe that they need to build digital businesses or technologically enable their existing businesses to survive, strong digital capabilities are critical to staying competitive. 4 “ The new digital edge: Rethinking strategy for the postpandemic era ,” McKinsey, May 26, 2021. Yet most organizations have been underinvesting in technology , particularly in the cloud, agile operating models, technology talent, and generative AI. This work stream requires establishing a state-of-the-art enterprise-resource-planning system that can facilitate the execution of all the other performance work streams. Leading companies focus on improving the accuracy and speed of information and developing new customer and product insights from their data. Those that use digital transformations to fully rewire their organizations improve their shareholder returns, P/E ratios, and returns on tangible equity more than competitors do, our research shows. 5 Eric Lamarre, Kate Smaje, and Rodney Zemmel, “ Rewired to outcompete ,” McKinsey Quarterly , June 20, 2023.
The core transformation should focus on four aspects of performance: cost optimization, growth, organizational effectiveness, and digital enablement.
Consider one consumer product company that followed this four-work-stream path to chart a successful new course. Historically, it focused on incremental improvements as part of its annual planning cycle. But as nimbler competitors with stronger balance sheets rapidly gained market share, the company’s leaders realized they needed to fundamentally rethink how they operated. The company expanded its manufacturing footprint through acquisitions, revamped its production and logistics operations, and leveraged data to predict changes in consumer demand. It also empowered executives and line managers to adopt an owner’s mindset that raised individual impact on the business. The transformation doubled the company’s EBITDA while reestablishing its standing as an industry shaper.
Making transformation business as usual
It’s common to see a transformation achieve its milestones and stated objectives only to have the underlying business underperform, eroding the delivered value. Too often, management views a transformation as separate and distinct from day-to-day operations, failing to maintain the same high bar of rigor and accountability across the enterprise. We have seen companies tackle this issue head-on by leveraging the transformation as a catalyst for improving performance, essentially creating a new operating model that applies to each aspect of the business.
The integration of transformation and daily operations fosters a mindset of one goal and one mission. It encourages impact-based prioritization of initiatives and resources and ensures alignment across the organization through consistent messaging. To achieve this alignment, the operating model and the performance management system should serve as the hardwiring that links a company’s transformation goals to its strategy. Without clear KPIs, for instance, executives won’t be able to determine how or whether the transformation investments create value.
The operating model and the performance management system should serve as the hardwiring that links a company’s transformation goals to its strategy.
This approach requires a shift in the execution cadence under the leadership of a chief transformation officer (CTO). The role of the CTO was originally an extension of the CEO (perhaps even a possible successor), with full authority to work across the entire organization and guide the business agenda. Over time, the role’s scope has diminished, with CTOs now tending to be two or three levels below the executive suite, serving as process managers rather than true change agents. In that structure, the day-to-day operations fall outside the CTO’s purview, separating the transformation agenda from the ordinary course of business. Additionally, with the CTO having to run most decisions through a committee of more senior leaders, the pace and impact of the transformation slows.
We believe that the role should expand even beyond its original incarnation, turning the CTO into a chief performance officer focused on not only setting the transformation agenda but also integrating it into the daily business operations. The CTO should ensure, for example, that any governance process, supported by the CEO and cascaded throughout the organization, covers all business activities—transformation related or otherwise. A single set of metrics should cover the full scope of financial and operational performance.
The chief transformation officer role should expand into a chief performance officer focused on not only setting the transformation agenda but also integrating it into the daily business operations.
The experience of an industrial company with operations in more than 150 countries bears out the value of this approach. A messy merger, on top of hundreds of previous acquisitions, had created a highly fragmented organization that lacked a clear strategy. After a 30 percent slump in stock price over 18 months, the company decided to launch a transformation. The CTO mobilized the entire organization, from top leaders to more than 7,000 frontline employees, and implemented rigorous weekly performance checks.
The initial phase of the program delivered more than $2 billion in bottom-line impact, and the company is now in horizon two. Those who led the work in horizon one are serving as recruiting and coaching leaders for the next phase, helping pass on the lessons that they learned. The company’s free-cash-flow conversion has improved to 90 percent, from 60 percent. And the organization has gone from an industry laggard to a leader, with its share price outperforming those of its peers by roughly 20 percent.
In an environment of deep uncertainty, companies need to constantly monitor their competitive positions and evolve to match changing conditions. By ensuring that transformation objectives reflect business strategies, pursuing four core performance work streams, and staying vigilant about embedding the changes into business as usual, business leaders can reap long-term benefits from their transformation investments.
Kevin Carmody is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Chicago office, Louisa Greco is a partner in the Toronto office, and Rob Montgomery is a partner in the Bay Area office.
The authors wish to thank Colleen Baum, Mary Lass Stewart, Meagan Hill, Michael Bucy, Michael Dillon, Rick Gold, Rob Cain, and Stephan Görner for their contributions to this article.
This article was edited by Joanna Pachner, an executive editor in the Toronto office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Transformation with a capital T

Driving long-term business transformation

How to gain and sustain a competitive edge through transformation
- Professional Services
- Multiple Users
- Admin Console
- White Labeling
- Local Data Residency
- Single Sign-On
- Jotform Sign
- Business Services
- Field Service Management
- Financial Services
- Lunch & Learn Sessions
- White Papers
- Contact Sales
- Sign Up for Free

- Business Process Management
What is a business process? A complete guide
Whether you’re a line manager or individual contributor, you’ve undoubtedly heard the term business process thrown around in meetings and emails. Chances are you have a pretty good idea of what the term refers to, but this guide will ensure you have a definitive, clear understanding of its meaning.
We’ll go beyond simply defining what a business process is (and is not) to explore related terms and give examples of how each concept plays out in real life.
You’ll also hear from two business leaders, Aaron Alpeter and Stephen Roethe, on how they regularly create, refine, and implement processes at their companies to keep work on track, employees on task, and customers happy. Alpeter is the founder of izba , a supply-chain consulting, outsourcing, and technology firm. Roe is the founder and head of digital strategy at Grow Atom , an SEO agency for e-commerce stores.
Here’s an in-depth look at five key business-process terms and how to apply business-process concepts to your organization.
1. Business process
A business process is a set of connected tasks that an organization performs to achieve a specific goal, such as manufacturing a product or delivering a service.
“Business processes require you to create workflows and systemic methods to handle recurring tasks that give you a desired result,” says Roe. Consider what it takes to write an article or deliver an invoice to a customer. To produce those results, you have to take certain steps.
“When creating or refining a process, I recommend working backward,” says Roe. “Define the end result you want and walk through what it takes to get there.”
A process may be formal or informal. Organizations often record formal processes and perform them in the same manner every time. Informal processes are rarely codified, and their exact steps tend to vary depending on who’s performing them.
“Many people don’t realize that the work they do, even if it’s not formalized, is part of a process,” says Alpeter. “If there’s a defined outcome the person is trying to achieve, how they achieve that outcome is the process, regardless of whether it’s written down or performed differently by a coworker.”
Sometimes, informal processes may become formalized after a manager, external consultant, or other authority reviews them. For example, let’s say two employees, Janet and David, both have the same job and create the same work outputs every day. However, Janet routinely completes her work more quickly than David, making her more productive.
Their manager takes note of this discrepancy and calls for a review of how both employees complete their work. The review reveals that the set of steps Janet takes — her informal process — is more efficient than David’s.
Subsequently, the manager asks Janet to record her process and walk through it with David and the rest of the team. Janet’s informal process then becomes the team’s formal business process.
Types of business processes
The term business process is broad and encompasses many kinds of outcomes, so it can be helpful to categorize processes into these three types.
This type of process is tied directly to how you generate value for customers (and income for your company). Consider the products and services your customers purchase. How you create and deliver these items and experiences are your core processes.
For example, Alpeter’s company provides consulting expertise on matters related to supply chains. Clients pay for this expertise in the form of consultations, negotiations, strategic planning, forecasting, and other services. The activities that go into developing and delivering these services to clients are core processes.
“Clients buy our experience and problem-solving capabilities — our ability to resolve their issues and educate them on the why and how to avoid the same types of pitfalls as they scale,” Alpeter explains. “Each process that results in generating value for our clients is core to our business.”
Consider another example. Let’s say your company produces a software as a service (SaaS) product. After customers make a purchase, you need to onboard them so they know how to use the product effectively — which ensures they’ll maintain their subscription. “This is a core process because it’s generating value for customers and aiding in continued revenue generation,” Alpeter explains.
You can also find core processes in fast-casual restaurants, like those offering burritos or sandwiches. There’s a clear production line — a process — for making these food items that you can watch take place. “The steps for making the burrito or sandwich are a clear-cut core process, as customers will purchase the food item immediately after it’s created,” says Alpeter.
Unlike core processes, support processes do not generate income or direct value for customers — though that’s not to say they don’t have value. Most support processes are internal and tied to areas that are cost centers, such as HR and IT. The activities of these departments may not make money, but they’re important for supporting the company’s ability to do so — that is, they support core processes.
For example, talent management is an important aspect of any successful organization, and HR typically leads these efforts. They have to find the right people to fill the roles you’ve identified as necessary for sales, operations, and other key functional areas.
They accomplish this by posting job openings, asking current employees to refer friends and professional connections, reviewing applicants, and eventually hiring and training approved candidates. All these actions are considered support processes.
Similarly, IT provides technical leadership and support to all areas of the organization. They help implement and maintain software that employees use in their work, fix these tools when they break, and troubleshoot when employees have technical difficulties. Again, the internal nature of these actions means they don’t directly generate client value or revenue — hence, they’re support processes.
3. Management
Like support processes, management processes don’t generate revenue for the company or direct value for customers, but they’re necessary. These processes are high-level activities that set the direction of the company and focus on planning, monitoring, and controlling core and support processes.
For example, company executives regularly perform strategic planning and goal-setting, which helps guide the organization down the desired path. They also keep track of company results and report to a board or shareholders. These activities are management processes.
Consider also how an organization improves processes over time. There’s typically a process in place for identifying and addressing activities that aren’t generating revenue, result in poor customer perception, lead to errors, or negatively affect employees performance. This type of process controls core and support activities, which makes it a management process.
2. Business process management
Business process management (BPM) is the practice of reviewing, analyzing, measuring, and identifying opportunities to automate and optimize business processes. You can think of it as the discipline behind management-type processes.
“With BPM, you’re taking a high-level view of processes, considering how they work both independently and together,” Roe explains. Instead of allowing employees to haphazardly accomplish tasks in whatever way they deem fit, practicing this management discipline ensures your organization is creating and maintaining processes that consistently deliver desired outcomes.
Alpeter recommends a few ways to ensure effective BPM:
- Define clear success criteria for each business process.
- Ensure core and support processes tie together well.
- Formalize processes whenever possible by creating templates and standard operating procedures (SOPs).
Roe notes that many small business owners forgo practicing BPM, mostly because it takes time away from other priorities. But he says it’s important for any organization, regardless of size, to ensure its processes are in order. For busy owners, his recommendation is to loop in other employees and assign them process areas to manage.
“Too many business owners abdicate when they need to delegate,” Roe explains. “Someone needs to be accountable for keeping processes in line and up to date. But you don’t have to do it all yourself. Lean on your workforce to lighten the load and ensure your company’s processes are working as intended.”
How often to review business processes
While organizations should certainly review their business processes regularly, the exact time frame will vary based on several factors: the importance and complexity of the process, available time and resources, and so on.
“For example, we review some of our core processes — such as writing articles — every week to ensure our customers are receiving the value we promise,” says Roe. “However, nonessential processes like vacation requests don’t get nearly the same level of attention.”
Clearly, Roe takes BPM seriously. In fact, he blocks out time every business day to review one or more processes, depending on the priority level he’s assigned to them and what his schedule will allow.
“I keep a tight schedule,” he says, “so I like to batch tasks to limit mental fatigue from switching back and forth between dissimilar to-do items. So I do all my process reviews at once.”
Revising a process
Keep an eye out for indications that your business may need to review and revise a process. For example, a particular process might be prone to human error. A review may find that a step of the process is ambiguous and leads to different interpretations, depending on the person using the process.
“If a problem happens once, it’s most likely a people issue,” says Roe. “However, if a problem rears its head consistently, chances are it’s a process issue that needs to be addressed. Even a few occurrences of a problem may indicate the process should be thoroughly reviewed.”
3. Business process modeling
Business process modeling is a structured approach to recording a set of expected activities, including who is responsible for performing them. It’s a map of what’s happening in a company — a set of living documents that define how work gets done.
Modeling is essentially how you create or develop your processes from beginning to end. “It helps you see the big picture,” says Roe.
“In business process modeling, you’re figuring out and recording interdependencies — the inputs and outputs needed to move from step to step,” Alpeter explains. “It’s a value stream map that shows how something is created. For example, you could produce a product flow that illustrates how a product goes from the factory to the warehouse to the customer.”
There are a number of techniques you can use for business process modeling. Roe likes to use kanban boards because they allow him and his team to quickly grasp the order of steps from a visual representation of tasks.
“The boards tie nicely to our writing phases,” he says, “and we can easily add columns and cards to represent new phases in the process. For example, we recently reviewed our process and determined that having the writer review their article a second time helped improve output quality. So we added an extra column to the board to capture the new step.”
Returning to the burrito-making example, Alpeter notes how fast-casual restaurants have created processes that reflect the need for efficiency. After all, speed is important in these businesses.
“For example,” he says, “you often see that employees will start with a tortilla, move to proteins, then vegetables, and pass off the finished product to the cashier. There’s obviously solid reasoning for this specific set of steps because many burrito places model their building process in the same order.”
4. Business process improvement
Business process improvement is the practice of using different methods to analyze, redesign, and optimize existing processes to reduce task completion time, improve quality, reduce friction, or some combination of these.
“It’s about determining how you can complete a process faster, cheaper, and better,” says Roe. “Just keep in mind you need someone leading the improvement effort, or it won’t get done.”
Process improvement falls under the umbrella of business process management, with the focus on optimization being the key differentiator. BPM says which processes need review and optimization. Business process improvement says how to optimize them.
“What you optimize for depends on what’s important to your company,” says Alpeter. “We try to optimize for client value because that’s one of our primary focuses. We want to ensure we’re doing something better — not just different — than competitors.”
By comparison, Alpeter notes that other consulting companies may optimize processes for profit, which may result in companies billing as much as possible without delivering as much value in their work. “Clients may still achieve their goals,” he says, “but with some drawbacks. The work may take longer, they may not be as informed, the experience may be less than ideal, and so on.”
He cites another example: “Everyone knows Chick-fil-A and Popeyes — they both sell chicken, but the customer experience is different. Chick-fil-A regularly has long lines, but customers happily wait because the restaurant has clearly reviewed its processes and determined that ‘improvement’ for them means optimizing around the customer experience. In contrast, Popeyes tends to be quicker, but the experience can be less than ideal because they’re optimizing for something else.”
5. Business process automation
Business process automation is the practice of using technology to automate repeatable tasks to save time and effort, increase scalability, minimize human error, and reduce costs.
While many have lauded automation in recent years as a beneficial practice, especially for larger organizations where scale is important, Alpeter cautions against automating every part of a business process just because you can.
“Too many business leaders get caught up in automation because of the promised benefits — which are often very real — but neglect to first identify whether automation is even necessary,” Alpeter explains. “You may find there are parts of your process that need to be changed or eliminated altogether, rendering automation an unnecessary task.”
Alpeter provides three examples where business process automation often occurs.
- Meeting scheduling
Everyone knows the headache of trying to wrangle schedules to see what time works for a meeting. SaaS products such as Calendly, ScheduleOnce, and Jotform provide the tools to automate how organizations schedule meetings .
“Instead of emailing back and forth, you can just provide a link for someone to find a time that works for them,” Alpeter explains. “These solutions automatically sync with your calendar to ensure that invitees can only choose times when you’re available.”
- Email drip campaigns
Automation also comes in handy in the marketing realm, where marketers value the ability to connect with a large number of customers automatically. Take email drip campaigns — software solutions can automatically send emails to customers based on certain events. “For example, you may want to send customers a thank-you email immediately after they make a purchase or an exclusive offer X days later,” says Alpeter.
- Ridesharing
The rideshare space has been transformed by automation. Previously, the manual process of calling a taxi led to long wait times and ambiguous fares. Popular apps like Uber and Lyft brought automation into the picture, remedying these inconvenient aspects of the rideshare experience.
“Now you can simply request a ride on your smartphone and be notified when it arrives,” Alpeter explains. “Plus, fares are presented up front so you have a clear estimate of how much you’ll pay.”
Organizational success depends heavily on your business processes. Refining those processes requires taking a multifaceted, thoughtful approach. For best results, your organization should evaluate its processes on an ongoing basis to truly reap the benefits.
Photo by cottonbro studio
Thank you for helping improve the Jotform Blog. 🎉
RECOMMENDED ARTICLES

Business Process Management (BPM): A Guide

Business activity monitoring

5 best business process improvement software tools

10 best BPM software programs and tools

How to use process mapping symbols

Process vs procedure: How they differ and why it matters

Low-code vs BPM: What’s the difference?

Business process reengineering vs continuous improvement

9 benefits of business process automation

Business process model and notation (BPMN) diagrams tutorial

Business process automation

The 4 best enterprise BPM solutions

Business process reengineering guide: Tools and examples

BPM vs workflow

A brief, tactical guide to agile business process management

Workflow vs process

10 ways to improve interdepartmental communication

How BPI enhances employee performance

5 benefits of process mapping

11 Laserfiche alternatives to achieve maximum productivity for 2024

BPM vs RPA: Which should you use to boost efficiency?
Send Comment :
10 min read
Improving a business is about more than just increasing efficiencies or maximizing ROI. Today’s global economy also requires the flexibility to adjust to changing markets, conditions and technologies. Operational excellence is a way for organizations to create a roadmap toward continuous improvement in a complex business environment.
Its goal is to give companies a competitive advantage. If done right, operational excellence helps business leaders make better decisions and employees show continuous improvement. Companies that are better at problem-solving and process improvement, the theory goes, will ultimately exceed their competition in profitability.
Here, we’ll explore the core principles of operational excellence and how companies are using technology to implement these methodologies.
Operational excellence (OpEx) is an approach to business management that emphasizes continuous improvement across all aspects of the business and within all business processes by creating a culture where management and employees are invested in business outcomes and empowered to implement change. When implemented well, every member of an organization sees the flow of value to the customer and, if problems arise, finds a solution before any disruptions occur.
Operational excellence begins with a culture shift, where all leaders and employees are dedicated to creating not only a quality product but also providing great customer experiences. Businesses that use operational excellence methodologies clearly define leadership and workforce roles and how they work together to improve operations. At all levels, employees can initiate change and drive toward efficiency, effectiveness and agility.
The definition of operational excellence has its roots in the Shingo Model, an approach to business that emphasizes quality at the source, value to the customers, a zero-inventory supply chain and an understanding of the workplace at all levels. It was created by Dr. Shigeo Shingo, a business leader who published 18 books on his philosophy and closely collaborated with Toyota executives to apply his principles in their manufacturing operations.
Shingo is also the inspiration for the Shingo Prize, awarded annually by the Shingo Institute for Operational Excellence at Utah State University. This prize defines the 10 Shingo Guiding Principles, often referred to as the core principles of operational excellence:
- Respect every individual: When people feel respected and valued by an organization, they are more likely to give more. Respect seeks to draw the best from individual contributors.
- Lead with humility: When decisions are made unilaterally, frontline employees are less likely to respect the decisions being made. To lead with humility, companies must implement a management system where leaders seek input and buy-in from stakeholders at all levels.
- Seek perfection: This principle is similar to the adage, “You have to believe it to achieve it.” By seeking ways to continuously improve, you can open the door to new ways of thinking and innovation.
- Embrace scientific thinking: This principle is not just about being data-driven. Creating a culture where employees are able to “experiment” and test new ideas based on observations and data fosters innovation.
- Focus on process: If something goes wrong, instead of blaming people (which can be counterproductive), look for ways the process can be improved.
- Assure quality at the source: Much like good food is made with good ingredients, assuring quality in business relies on doing work right the first time, using the right people and the right components.
- Improve flow and pull: Providing value to the customer means having the products that they demand when they need them and nothing more, which is exemplified in lean supply chains.
- Think systemically: Instead of focusing on individual players or departments for improvement, think of ways to improve the entire system.
- Create constancy of purpose: Communication of goals, purpose, commitment to the customer and the “why” behind the company are key to operational excellence.
- Create value for the customer: Ultimately, all businesses are all about the customer, so operations should reflect the value customers hold and should be provided.
As the Shingo Model gained popularity within the business world, others developed methodologies based on this approach and the core principles of operational excellence. These include:
- Lean manufacturing: Lean manufacturing is a systematic method designed to minimize waste while keeping productivity constant.
- Six Sigma: Six Sigma is a set of methodologies, tools and techniques used to improve processes and minimize defects. It’s sometimes combined with lean manufacturing principles and then known as “lean Six Sigma.”
- Kaizen: Focused on continuous improvement, Kaizen emphasizes teamwork and proactively taking responsibility for designated areas within the organization to make incremental improvements.
When implementing operational excellence within an organization, it can be helpful to view the process as an ongoing journey rather than a final destination. Because the focus is on continuous improvement, business leaders and employees should always strive for ways to get better at what they do.
That being said, organizations need to establish goals and define metrics to understand if and how they are improving. These metrics include key performance indicators (KPIs), such as sales increases, health and safety performance and workforce retention rates.
Here are the types of goals that are often included in operational excellence-based processes:
- Operational goals: How the company operates, including efficiency and safety. For example, an organization might seek to accelerate order to cash, solve problems with the supply chain or improve the delivery of services.
- Financial goals: Metrics related to sales and losses. These goals could be to lower churn, efficiently enter new markets or improve the marketing-to-sales pipeline.
- Culture and workforce goals: These include measuring worker satisfaction, offering professional development and investing in worker retention. This could entail initiatives to create a more inclusive culture, creating a more equitable compensation package or incentivizing professional development.
Value flow to customers
Operational excellence goals are typically focused on delivering value to the customer. What is value? Essentially, it’s what the customer demands and is willing to pay for.
Within the operational excellence methodology, companies provide this value by creating value streams. A value stream refers to the processes and initiatives that an organization creates to deliver the products and services the customers’ need in the time it takes to meet that demand.
For example, a data center that can keep up with customer demand and has the compute, storage and networking resources needed to service online transactions without overprovisioning is seen as a value stream that is running smoothly.
Communicating operational excellence
Communication is another key element for reaching operational excellence goals. If employees aren’t aware of company goals, have no idea how to deliver value to the customer or feel leadership is not invested in their professional success, it makes it difficult to achieve goals and continuously improve.
Implementation often includes a plan for communicating all aspects of the program, such as the mission, goals and those impacted to all employees. Companies that excel in operational excellence often have a well-designed internal communication system, as well as a forum for receiving and addressing feedback.
Operational excellence requires organizations to look critically at their operations and how they manage employees. In some cases, they must be willing to shift their culture. Being open to continuous change helps companies better implement methodologies and reach these benefits:
- Optimized workflows: Part of creating an unhindered flow of value to the customer is being able to see and address roadblocks, supply chain issues and misaligned priorities. When using business management tools, companies can gain visibility into workflows and business processes to make them more efficient. For example, with better workflow modeling, they can get to the root cause of bottlenecks and redundancies and eliminate overproduction or waste.
- Lower operational risk: Reducing risk is a primary goal of any business strategy, and a primary benefit of operational excellence. With the efficiencies that it brings, companies can also lower operating costs and increase revenues, especially when compared to competitors.
- Standardized work and outcomes: Having standards of how work should be done and what the end product looks like improves efficiency and overall business outcomes.
- Accountability: Defining roles and providing performance evaluations at all levels ensures that people have clear expectations.
- Employee empowerment: Instead of a “top-down” culture where the CEO has a hand in business decisions throughout all departments, operational excellence strives to create a model where leadership makes strategic decisions and empowers frontline employees with the resources and decision-making abilities they need to succeed.
Operational excellence can benefit just about every industry and business model, however, there are some industries where operational excellence has become a standard in operations:
- Manufacturing: Companies like Motorola and BAE Systems have employed operational excellence methodologies to enhance productivity, decrease downtime and cut out waste.
- IT: Using the core principles of operational excellence gives IT teams a way to minimize development rework and improve workflow efficiency in a fast-paced environment.
- Healthcare: With a focus on customer experience, operational excellence helps healthcare providers reduce wait times, improve patient portals and better track patient outcomes.
- Construction: Using operational excellence helps construction companies ensure worker safety, efficient workforce management and cost-effective sourcing of materials.
Automation, process analysis, observability and data and business management tools can help companies more quickly implement—and stick with—continuous improvement.
Business automation
Companies have been looking to automation for decades to create efficiencies and harness the power of digital technology. This could include automating hands-on tasks on the assembly line with machinery or automating back-office tasks like accounting and billing with software solutions.
There are many tasks that require creative thinking, intuition and strategy planning that only people can perform. However, automation tools can be used to perform the repetitive and mundane tasks, such as prepopulating invoices with account information and transferring data to multiple back-end systems that can save people time:
- Business process management software: The business process management approach is iterative; you don’t implement it once, never to be touched again. Instead, you design, model, create, simulate, monitor and optimize your processes on a regular basis. Business process management tools help companies maintain this iterative process to create, analyze and improve business processes for continuous improvement.
- Process modeling: A key concept in operational excellence is identifying abnormal flow—where the process has broken down—and figure out how to fix it. Process modeling gives a visual representation of business processes or workflows that companies can use to identify opportunities for efficiencies and better workflow. If a company wants to know what’s happening at every step of their supply chain process, it would use data modeling.
- Process mapping: Organizations gather information from employees to create a visualized model of the workflows. If a company wants to clarify which departments own each part of the procurement process, it would use data mapping .
- Decision management: Companies recognize that streamlined, automated decision-making is key to being able to respond quickly to market pressures and pivot without losing momentum. When policies and business logic are embedded directly into application code, it can take weeks or even months for IT to recode. Decision management software allows business users to model and manage operational decisions that are repeatable, automated and in compliance with business guidelines and regulations.
- Robotic process automation: Robotic process automation , also known as software robotics, uses automation technologies to mimic back-office tasks of human workers, such as extracting data, filling in forms, moving files, et cetera. It combines APIs and user interface (UI) interactions to integrate and perform repetitive tasks between enterprise and productivity applications. By deploying scripts which emulate human processes, RPA tools complete autonomous execution of various activities and transactions across unrelated software systems.
IT automation
In today’s digital-first age, customer satisfaction depends on the performance and availability of business-critical applications and infrastructure. As such, IT operations (ITOps) teams are under immense pressure to deliver operational excellence and must move at the pace of increasing business demands. AIOps drives efficiency and optimization in a modern, dynamic IT environment to accelerate necessary digital transformation.
Using software to create processes that reduce or replace manual interaction with IT systems, AIOps brings real-time insights to IT environments so that IT operations teams can assure proactive, continuous application performance that enables exceptional customer experiences, while increasing compliance and safely reducing cost across high variability of demand:
- Full-stack enterprise observability: Modern applications, services and environments are continuously becoming more complex, and traditional monitoring tools lack the visibility that’s required to achieve the operational excellence needed in these new environments. Enterprise observability platforms, powered by automated APM, deliver full visibility by automatically ingesting observability metrics, tracing every request and profiling all processes across microservice platforms and the CI/CD pipeline . Enterprise observability enables ITOps teams to discover, map and monitor the full application stack, including all interdependencies, providing immediate feedback after any change.
- Application resource management (ARM) and optimization: Businesses often face the challenge of balancing the right number of resources for business applications while limiting as much overallocation as possible. When organizations come to terms with overallocating any of their applications, it is often unsustainable and costly. Modern applications are separated by multiple layers of abstraction, making it difficult to understand which underlying physical server, storage and networking resources are supporting which applications. Application resource management drives OpEx by automatically assuring applications get the resources they need to perform, no matter where they run or how they are built. ARM eliminates resource congestion at every level of the application stack, from the business application to the underlying hybrid and multicloud environment.
- Proactive incident resolution, remediation and avoidance: A few seconds of application downtime can cost millions in lost revenue, reputational damage or regulatory penalties. To avoid these pitfalls, enterprises want to better predict IT outages and resolve them more quickly. With proactive incident resolution and remediation, ITOps teams gather new insights faster and with context, transforming user experiences and improving business outcomes. Proactive incident management platforms use explainable AI to help CIOs and ITOps teams detect and diagnose complex issues by connecting the dots between structured and unstructured data in real-time to give users a holistic understanding of IT incidents, enabling businesses to drive toward operational excellence within their IT estate.
Integration
As transformation efforts quicken across the globe, they also introduce a serious side effect—pushing data out into silos and impeding access to information that business teams need to be successful. Organizations that can quickly and securely connect applications and systems will outperform those that don’t. Without the right integration tools, data stays locked away, hampering your ability to make informed business decisions and implement scalable automations that uncover new efficiencies:
- API management: APIs are in use everywhere. They connect your systems and applications so you can access and expose your data in a secure way. Having a strong API management strategy and toolset is critical to being able to create, manage, secure and socialize APIs with internal and external consumers.
- Application integration: To make effective business decisions, you need to ensure you can trust your data. With application integration , you can move and transform data between applications and systems—no matter where it resides—so existing and newly deployed applications are seamlessly integrated throughout your organization.
- Event streaming: To optimize value flow to customers, businesses need to gain insights from real-time data to make informed choices that improve operations and act quickly in response to shifting customer needs. Event streaming allows you to capture and integrate streaming event data from your applications so you can automate customer-facing and backend actions based on defined triggers.
- Enterprise messaging: With an explosion in the number and types of systems within a typical enterprise, cost-effective, scalable system-to-system integration has become a challenge. Enterprise messaging is a proven technology that connects systems and their data in the most flexible, highly available and secure way. Critical data, like a financial transaction, is sent between systems in the form of messages and held in a queue if it can’t be delivered immediately (like in the case of a system outage) to ensure it’s sent successfully, never lost and never sent more than once.
- High-speed file transfer: Companies that need to transfer very large files over long distances under varying network conditions are challenged by the Internet’s underlying transfer technology, Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). Fast, Adaptive and Secure Protocol (FASP) takes a different approach to file transfer, allowing businesses to achieve transfer speeds of 100x faster than traditional methods.
Seven ways IBM can help companies achieve operational excellence using intelligent automation:
- Completely understand your processes before you automate with process mining.
- Put automation in the hands of your employees with digital workers.
- Improve productivity and reduce errors with RPA.
- Assure application performance with smarter resource management.
- Improve application performance monitoring with observability.
- Connect your apps and data to automate your business.
- Manage your API lifecycle with API management.
Get the latest tech insights and expert thought leadership in your inbox.
Get our newsletters and topic updates that deliver the latest thought leadership and insights on emerging trends.
- AI Meeting Assistant
- Communication and collaboration
- Contact center tips
- Tips and best practices
- App tutorials
How to Write A Meeting Agenda Template + Examples
Improved Teamwork
Design and format, key takeaways from this meeting agenda template guide.
Play the article
Spread the word
Meetings are an integral part of any organization’s operations these days. It is impossible for a business to collaborate effectively without meaningful meetings, no matter what the meeting format – physical or virtual. Nonetheless, 95% of meeting attendees worldwide report missing portions of meetings, which demonstrates the importance of a well-planned meeting agenda template.
The latter is a powerful tool for ensuring that meetings stay on track, achieve their objectives, and make the most of everyone’s time. By following a structured approach, teams can facilitate focused discussions, encourage active participation, and drive meaningful outcomes.
Why Create a Meeting Agenda Template?
There are fundamental reasons why planning meeting agenda template can save the outcome of your meeting. Let’s discuss them one by one!
Meeting Transparency and Clarity
A meeting agenda template provides transparency and clarity for all attendees. It outlines the purpose, goals, and topics to be discussed, ensuring that everyone is aligned and aware of the meeting’s intended outcomes.
This clarity helps participants prepare adequately, contributing to more productive discussions and better decision-making.
Better Time-Management
Effective time management is crucial in meetings, and a well-designed agenda template can help achieve this goal.
By allocating specific time frames for each agenda item, participants can stay focused and ensure that critical topics receive the attention they deserve. This approach prevents meetings from running over or getting sidetracked by tangential discussions.
Efficient Decision-Making
Meetings often revolve around making important decisions that impact the organization. An agenda template helps facilitate efficient decision-making by providing a structured meeting format for presenting information, discussing options, and reaching consensus.
With a clear roadmap, teams can move through agenda items systematically, ensuring that all relevant factors are considered before finalizing decisions.
Collaboration and teamwork are essential for successful meetings, especially in a work-from-home environment , where strategic and transparent communication is key for good outcomes. A meeting agenda template encourages active engagement and ownership by involving all participants in the agenda-setting process.
When team members contribute to the agenda, they feel valued and are more likely to participate actively during the meeting, fostering a collaborative and inclusive environment.
Essential Components of a Practical Team Meeting Agenda Template
Now that we understand the role planning meeting agenda template can play in our busy lives, let’s examine what it consists of.
- Date, Time, and Location
The most basic components of a meeting agenda template include the meeting’s date, time, and location. This information ensures that all attendees are aware of when and where the meeting will take place, allowing them to plan and take notes during meetings accordingly and avoid scheduling conflicts.
Purpose & Goals of the Meeting
Clearly stating the purpose and goals of the meeting is crucial for maintaining focus and achieving desired outcomes. This section should outline the specific objectives or topics to be addressed, ensuring that everyone is on the same page from the start.
Agenda Items and Allocate Time Frames Per Topic
The heart of any meeting agenda template lies in the agenda items themselves.

These should be listed in a logical order, with each item accompanied by a realistic time allocation. This structure helps ensure that all relevant topics are covered while maintaining a reasonable meeting duration.
Talking Points
Some templates may include talking points or discussion prompts for each agenda item in addition to listing agenda items. These prompts can help guide the conversation and ensure that all critical aspects of a topic are addressed, promoting productive and focused discussions .
A List of Supporting Documents
Many meetings require participants to review and discuss supporting documents, such as reports, presentations, or proposals. Including these documents in the agenda template allows attendees to access and review them in advance, maximizing the meeting’s productivity.
How to Write A Meeting Agenda Template
Having said all of the above, let’s dive into the practical tips on how to plan and write a meeting agenda template.
Identify the Type
Before creating a meeting agenda template, it’s essential to identify the type of meeting you’re planning. Different types of meetings, such as status updates, brainstorming sessions, or decision-making meetings, may require different structures and approaches. Understanding the meeting’s purpose will help you tailor the agenda template accordingly.
Set the Standard Sections
Most meeting agenda templates share common sections, such as the meeting title, date, attendees, and objectives. Establish these standard sections as the foundation for your template, ensuring that essential information is consistently included.
Fix Time for Each Section
Allocating appropriate time frames for each agenda item is crucial for effective time management during the meeting. Consider the complexity of each topic and the level of discussion required, and assign realistic time slots accordingly. This approach will help ensure that all items are covered without running over the scheduled meeting duration.
Highlight the Purpose
At the top of the agenda template, clearly state the meeting’s purpose or objective. This will help attendees understand the meeting’s context and ensure that discussions remain focused on achieving the desired outcomes.
Clarify the Expectations
In some cases, the agenda template may need to include specific expectations or requirements for attendees. For example, if participants need to prepare materials or come prepared with specific insights, clearly communicate these expectations to ensure everyone is adequately prepared.
List Responsibilities
Assign specific roles or responsibilities to attendees for each agenda item. This approach fosters accountability and ensures that everyone understands their contributions to the meeting’s success. Additionally, it can help prevent confusion or overlap during discussions.
Attach Necessary Files
If the meeting requires the review or discussion of supporting documents, such as reports, presentations, or proposals, attach or link to these files within the agenda template. This step allows attendees to access and review the materials in advance, promoting informed discussions and saving valuable meeting time.
While the content of the agenda template is crucial, its visual presentation can also impact its effectiveness. Use clear headings, bullet points, and appropriate formatting to create an organized and easy-to-follow structure. Additionally, consider incorporating your organization’s branding or visual elements to create a consistent and professional appearance.
Examples of Meeting Agendas
To further illustrate the application of meeting agenda templates, let’s explore a few examples tailored to different types of meetings. However, these are editable meeting agenda template examples , so take them with a grain of salt and customize according to your needs.
Weekly Team Meeting Agenda Template:
Date: [Date]
Duration: [Time]
- Provide updates from each team.
- Highlight notable achievements and key milestones.
- Recognize significant individual or team accomplishments.
- Discuss any barriers hindering progress.
- Brainstorm solutions and assign follow-up actions.
- Review the action items from the previous meeting.
- Delegate tasks and responsibilities for upcoming assignments.
- Outline goals and targets for the following week.
- Ensure alignment with overall team objectives.
- Open the floor for any additional topics.
- Address urgent matters or new updates.
Brainstorming Session Agenda Template:
- Meeting Objectives [x minutes]
- Icebreaker or Warm-up Activity [x minutes]
- Problem Statement or Objective [x minutes]
- Brainstorming Techniques and Ground Rules [x minutes]
- Individual Brainstorming [x minutes]
- Group Brainstorming and Discussion [x minutes]
- Idea Evaluation and Selection [x minutes]
- Action Items and Next Steps [x minutes]
These examples showcase how meeting agenda templates can be tailored to specific meeting types, ensuring that all relevant components are covered and discussions remain focused on achieving the desired outcomes.
By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this article, you can create agenda templates that promote productivity, collaboration, and successful outcomes for your team.
Krisp Can Help You Take the Next Step In Your Meetings
Krisp is an exceptional tool for enhancing the productivity and efficiency of meetings, particularly when used in conjunction with a well-structured meeting agenda template.
With its advanced AI Meeting Assistant , Krisp ensures noise-free virtual meetings, seamlessly transcribing, summarizing, and recording every detail. This simplifies the collaboration process and makes follow-ups more effective. Users can enjoy free unlimited transcriptions with 96% accuracy, regardless of the conferencing app they use, eliminating the hassle of manual note-taking.

Krisp’s real-time editing and collaboration features enable users to capture and share essential meeting points effortlessly. AI-powered noise cancellation ensures clear communication, regardless of the location, while the automatic recording and transcription provide a comprehensive record of the meeting. This helps in assigning tasks, planning meeting agenda template with action items in the future, and setting deadlines efficiently.
By integrating with your calendar, Krisp automates note-taking and sharing, making it that much easier to create your next meeting agenda template. With Krisp, every meeting becomes a well-documented, productive session, allowing teams to focus on meaningful discussions and decision-making.
Try Krisp For Free!
Creating a well-structured meeting agenda template is essential for ensuring productive and efficient meetings. Here are the key tips and messages to remember:
Maintain Clarity and Transparency A meeting agenda template provides clear objectives and topics, enabling all participants to prepare effectively and contribute meaningfully.
Manage Time Effectively
Allocate specific time frames to each agenda item to keep discussions focused and prevent meetings from running over.
Facilitate Decision-Making
Use a structured meeting format to present information and options clearly, making it easier for teams to reach well-informed decisions.
Encourage Teamwork and Participation
Involve all participants in setting the agenda, fostering a sense of ownership and active engagement.
Include Essential Components
Ensure your agenda template includes the date, time, location, purpose, goals, agenda items, talking points, and any necessary supporting documents.
By implementing these practices, you can transform your meetings into organized, productive sessions that drive meaningful outcomes.
In conclusion, a thoughtfully designed meeting agenda template is more than just a schedule—it’s a strategic tool that enhances collaboration, ensures efficient time use, and leads to better decision-making. Tools like Krisp can further enhance your meetings by providing noise-free virtual environments and automating note-taking and transcription. Embrace these best practices and tools to elevate your meetings from mundane to impactful, fostering a culture of productivity and engagement within your team.
Related Articles


COMMENTS
The first stage includes the work that has been done so far, whereas the second stage describes it in detail. 1. Development Phase. In this stage, you mention what you've done to get your business operations up and running. Explain what you aim to change and improvise in the processes.
Step 1: Define your goals and objectives. Begin with a clear understanding of your strategic goals and objectives. This will act as a foundation for your operational plan. Ensure that these goals are in alignment with your company's strategic plan and provide both short-term and long-term visions for the business.
How To Write the Operations Plan Section of the Business Plan. Stage of Development Section. Production Process Section. The Bottom Line. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Photo: Daniel Ingold / Getty Images. How to write the operations plan section of the business plan, including details on writing the development and production process sections.
The business plan operational plan should detail key elements such as the operational processes, resource allocation, tasks, and timelines. From personnel and location to inventory, suppliers, and operating hours - the operational plan touches every aspect of your business. It's a living document, evolving and changing as your business grows ...
Operations Plan. Lesson Materials Operations Plan Worksheet; Completion time About 40 minutes; The operations section of your business plan is where you explain - in detail - you company's objectives, goals, procedures, and timeline. An operations plan is helpful for investors, but it's also helpful for you and employees because it pushes ...
Operational plans go deeper into explaining your business operations as they explain roles and responsibilities, timelines and the scope of work. Operational plans work best when an entire department buys in, assigning due dates for tasks, measuring goals for success, reporting on issues and collaborating effectively.
The 5 steps of the operational planning process. Enterprises develop operational plans through five strategic steps, each essential for shaping an actionable and effective strategy. Let's explore what this planning process looks like. 1. Set goals. Establish specific, immediate business goals that align with your strategic plan.
Without a plan, your business operations are as good as a children's playground—everyone's doing their own thing with no care in the world.. An operational plan brings order to your organization. It defines the functional aspects of your long-term strategy, like goals, milestones, responsibilities and timelines, to build collaboration and make real progress toward your vision.
Consider your Business Goals. Write out each goal. Read them as you decide which processes to include in your operations plan and think about how soon you will want to meet the company goals. Create a Process List. Look at the list of components and decide how to make them into a list for your own business.
Free operations project plan template Operational planning vs. strategic planning. A strategic plan is a business-level plan of your long-term strategy for the next three to five years. An operational plan is smaller in both scope and timeline. The goal of operational planning is to outline the daily actions you need to take to hit your ...
Here we've rounded up 10 of the best templates in Word and ClickUp that you can use to create effective operational plans. 1. ClickUp Operational Plan Template. Get your operations in order with this simple ClickUp template. This simple operation plan template by ClickUp helps you strategically plan your business by outlining processes ...
An operational plan is a document that outlines the key objectives and goals of an organization and how to reach them. The document includes short-term or long-term goals in a clear way so that team members know their responsibilities and have a clear understanding of what needs to be done. Crafting an operational plan keeps teams on track ...
Operational plans are important for any effective business plan.They provide a roadmap for how the company will operate on a day-to-day basis. The operational strategic plan should outline the company's goals and objectives, as well as the strategies and actions that will be taken to achieve them.
Here are a few steps you can take to create an effective operations plan: 1. Create a strategic plan. Creating a strategic plan before an operational plan can help you clearly outline long-term goals and expectations to ensure alignment with business processes, values and initiatives. Your operations plan can then help you accomplish the goals ...
Example of Cascade's Metrics Library view. Through Cascade's integrations, you can consolidate your metrics in one place, importing your data directly from business systems, data lakes, BI tools, or even spreadsheets.. Define the focus areas of your operational plan . The focus areas of your operational plan are the key areas of the business that the plan will address.
The operating procedures in a business plan help employees carry out an organization's daily operations. Essentially, it is a step-by-step instructional guide detailing how workers should complete any complex activities related to the business. It also helps keep companies stay in compliance with the regulations within their industry.
Strategy. Most business strategies have an operations component. For example, if a train manufacturer develops a plan to expand revenue by 50% that plan will include a marketing, sales and operations component. The operations component of the plan would include procurement, manufacturing and logistics strategies that enable the firm to boost ...
Template 2: Business Plan Operational Strategy. The PPT slide deck is helping businesses overcome fears and tackle challenges. It displays the company mission and objective, KPIs, business problems & solutions, changes in the competitive environment, financial summary, revenue growth, and others.
The operating plan comprises of the following: Product goals and objectives — Define the product goals and objectives based on your product vision. Objectives should have clear deadlines and measurable outcomes that align with the business strategy. Milestone based plan — Create a milestone oriented plan to map your goals and objectives ...
Here are some ways on how an operational plan for business plan can be defined: 1. An operational plan for simple business plan deals with the daily activities of the business. It helps prepare specific action plans that can be used to support the requirements, needs, and demands of the operations.
Updated 1 March 2023. An operational plan is a plan that outlines the key objectives and goals of a company while also outlining how the company can achieve them. A clear and concise operational plan can help to ensure that projects stay on track and can help to improve day-to-day operations. If you're planning a career in business or ...
Operational planning is the process of creating actionable steps that your team can take to meet the goals in your strategic plan. An operational plan outlines daily, weekly, and monthly tasks for each department or employee. During operational planning, you'll also create milestones that help you achieve your strategic plan.
Operational planning is the process of organizing how your company comes together to make strategic decisions. It's similar to project management, except instead of looking at a single project, you're charting the course for the entire company. The goal of operational planning is to drive alignment and clarity across all business divisions ...
Key components of a business process include process objectives, inputs and outputs, activities or tasks, resources, responsibilities, controls and timeline. The three types of business processes are core, support and management. The lifecycle of a business process has these key stages: design, modeling, execution, monitoring and optimization.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
Here's what operations management means for 10 different business sectors: 1. Healthcare. In healthcare, miscommunication and delays can jeopardize patient care and drive up costs. Operations management ensures the right care is delivered at the right time, all while optimizing resources.
The CTO should ensure, for example, that any governance process, supported by the CEO and cascaded throughout the organization, covers all business activities—transformation related or otherwise. A single set of metrics should cover the full scope of financial and operational performance.
Business process. A business process is a set of connected tasks that an organization performs to achieve a specific goal, such as manufacturing a product or delivering a service. "Business processes require you to create workflows and systemic methods to handle recurring tasks that give you a desired result," says Roe.
Operational excellence (OpEx) is an approach to business management that emphasizes continuous improvement across all aspects of the business and within all business processes by creating a culture where management and employees are invested in business outcomes and empowered to implement change. When implemented well, every member of an ...
A meeting agenda template provides clear objectives and topics, enabling all participants to prepare effectively and contribute meaningfully. Manage Time Effectively. Allocate specific time frames to each agenda item to keep discussions focused and prevent meetings from running over. Facilitate Decision-Making.