- Review article
- Open access
- Published: 09 November 2022

Shifting online during COVID-19: A systematic review of teaching and learning strategies and their outcomes
- Joyce Hwee Ling Koh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5626-4927 1 &
- Ben Kei Daniel 1
International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education volume 19 , Article number: 56 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
11k Accesses
22 Citations
9 Altmetric
Metrics details
This systematic literature review of 36 peer-reviewed empirical articles outlines eight strategies used by higher education lecturers and students to maintain educational continuity during the COVID-19 pandemic since January 2020. The findings show that students’ online access and positive coping strategies could not eradicate their infrastructure and home environment challenges. Lecturers’ learning access equity strategies made learning resources available asynchronously, but having access did not imply that students could effectively self-direct learning. Lecturers designed classroom replication, online practical skills training, online assessment integrity, and student engagement strategies to boost online learning quality, but students who used ineffective online participation strategies had poor engagement. These findings indicate that lecturers and students need to develop more dexterity for adapting and manoeuvring their online strategies across different online teaching and learning modalities. How these online competencies could be developed in higher education are discussed.
Introduction
Higher education institutions have launched new programmes online for three decades, but their integration of online teaching and learning into on-campus programmes remained less cohesive (Kirkwood & Price, 2014 ). Since early 2020, educational institutions have been shifting online in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Some consider this kind of emergency remote teaching a temporary online shift during a crisis, whereas online learning involves purposive design for online delivery (Hodges et al., 2020 ). Two years into the pandemic, fully online, blended or hybridised modalities are still being used in response to evolving COVID-19 health advisories (Jaschik, 2021 ). Even though standards for the pedagogical, social, administrative, and technical requirements of online learning have already been published before the pandemic (e.g. Bigatel et al., 2012 ; Goodyear et al., 2001 ), the online competencies of lecturers and students remain critical challenges for higher education institutions during the pandemic (Turnbull et al., 2021 ). Emerging systematic literature reviews about higher education online teaching and learning during the pandemic focus on the clinical aspects of health science programmes (see Dedeilia et al., 2020 ; Hao et al., 2022 ; Papa et al., 2022 ). Understanding the strategies used in other programmes and disciplines is critical for outlining higher education lecturers’ and students’ future online competency needs.
This study, therefore, presents a systematic literature review of the teaching and learning strategies that lecturers and students used to shift online in response to the pandemic and their consequent outcomes. The review was conducted through content analysis and thematic analysis of 36 peer-reviewed articles published from January 2020 to December 2021. It discusses how relevant online competencies for lecturers and students can be further developed in higher education.
Methodology
A Systematic and Tripartite Approach (STA) (Daniel & Harland, 2017 ) guided the review process. STA draws from systematic review approaches such as the Cochrane Review Methods, widely used in application-based disciplines such as the health sciences (Chandler & Hopewell, 2013 ). It develops systematic reviews through description (providing a summary of the review), synthesis (logically categorising research reviewed based on related ideas, connections and rationales), and critique (providing evidence to support, discard or offer new ideas about the literature).
Framing the review
The following research questions guided the review:
What strategies did higher education lecturers and students use when they shifted teaching and learning online in response to the pandemic?
What were the outcomes arising from these strategies?
Search strategy
Peer-reviewed articles were identified from databases indexing leading educational journals—Educational Database (ProQuest), Education Research Complete (EBSCOhost), ERIC (ProQuest), Scopus, Web of Science (Core Collection), and ProQuest Central. The following search terms were used to locate articles with empirical evidence of lecturers’ and/or students’ shifting online strategies:
(remote OR virtual OR emergency remote OR online OR digital OR eLearning) AND (teaching strateg* OR learning strateg* OR shifting online) AND (higher education OR tertiary OR university OR college) AND (covid*) AND (success OR challenge OR outcome OR effect OR case OR lesson or evidence OR reflection)
The following were the inclusion and exclusion criteria:
Review period—From January 2020 to December 2021, following the first reported case of COVID-19 (WHO, 2020 ).
Language—Only articles published in the English language were included.
Type of article—In order maintain rigour in the findings, only peer-reviewed journal articles and conference proceedings were included, and non-refereed articles and conference proceedings were excluded. Peer-reviewed articles reporting empirical data from the lecturer and/or student perspectives were included. Editorials and literature reviews were examined to deepen conceptual understanding but excluded from the review.
The article’s focus—Articles with adequate descriptions and evaluation of lecturers’ and students’ online teaching and learning strategies undertaken because of health advisories during the COVID-19 pandemic were included. K-12 studies, higher education studies with data gathered prior to January 2020, studies describing general online learning experiences that did not arise from COVID-19, studies describing the functionalities of online learning technologies, studies about tips and tricks for using online tools during COVID-19, studies about the public health impact of COVID-19, or studies purely describing online learning attitudes or successes and challenges during COVID-19 without corresponding descriptions of teaching and learning strategies and their outcomes were excluded.
A list of 547 articles published between January 2020 and December 2021 were extracted using keyword and manual search with a final list of 36 articles selected for review (see Fig. 1 ). The inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied to the PRISMA process (Moher et al., 2009 ). The articles and a summary of coding are found in Appendix .
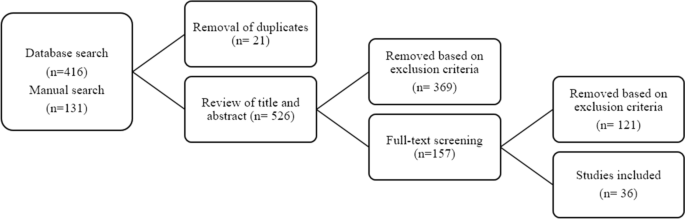
Article screening with the PRISMA process
Data analysis
Content analysis (Weber, 1990 ) and thematic analysis (Braun & Clarke, 2006 ) were used to answer the research questions. Pertinent sections of each article outlining lecturers’ and/or students’ shifting online strategies were identified, read and re-read for data familiarisation. The first author used content analysis to generate eight teaching and learning strategies. These were verified through an inter-rater analysis where a random selection of eight articles was recoded by a second-rater (22.22% of total articles) and confirmed with adequate Cohen’s kappas (Teaching strategies: 0.88, Learning strategies: 0.78). Frequency counts were analysed to answer research question 1.
For the second research question, we first categorised the various shifting online outcomes described in each article and coded each outcome as “success”, “challenge”, or “mixed”. Successful outcomes include favourable descriptions of teaching, learning, or assessment experiences, minimal issues with technology/infrastructure, favourable test scores, or reasonable attendance/course completion rates, whereas challenging outcomes suggest otherwise. Mixed outcomes were not a success or challenge, for example, positive and negative experiences during learning, assessment or with learning infrastructure, or mixed learning outcomes such as positive test scores but lower ratings of professional confidence. Frequency distributions were used to compare the overall successes and challenges of shifting online (see Tables 1 and 2 of “ Findings ” section). Following this, the pertinent outcomes associated with each of the eight shifting online strategies were pinpointed through thematic analysis and critical relationships were visualised as theme maps. These were continually reviewed for internal homogeneity and external heterogeneity (Patton, 1990 ). To ensure trustworthiness and reliability (Creswell, 1998 ), there was frequent debriefing between the authors to refine themes and theme maps, followed by critical peer review with another lecturer specialising in higher education educational technology practices. Throughout this process, an audit trail was maintained to document the evolution of themes. These processes completed the description and synthesis aspects of the systematic literature review prior to critique and discussion (Daniel & Harland, 2017 ).
Descriptive characteristics
Descriptive characteristics of the articles are summarised in Table 1 .
Table 1 shows that articles about shifting online during the pandemic were published steadily between August 2020 and December 2021. About two-thirds of the articles were based on data from the United States of America, Asia, or Australasia, with close to 45% of the articles analysing shifting online strategies used in the disciplines of Natural Sciences and Medical and Health Sciences and around 60% focusing on degree programmes. While there was an exact representation of studies with sample sizes from below 50 to above 150, the majority were descriptive studies, with close to half based on quantitative data gathered through surveys. About half of the articles focused on teaching strategies, while around 40% also examined students' learning strategies. However, only about 20% of the articles had theoretical framing for their teaching strategies. Besides using self-developed theories, the authors also used established theories such as the Community of Inquiry Theory by Garrison et. al. ( 2010 ), the Interaction Framework for Distance Education by Moore ( 1989 ), self-regulated learning by Zimmerman ( 2002 ) and the 5E model of Bybee et. al. ( 2006 ). Different types of shifting online outcomes were reported in the articles. The majority documented the positive and negative experiences associated with synchronous or asynchronous online learning activities, online learning technology and infrastructure, or online assessment. A quarter of the articles reported data on student learning outcomes and attendance/completion rates, while a minority also described teaching workload effects. Table 2 shows other successes and challenges associated with shifting online. Of the articles that examined online learning experiences, over a quarter reported clear successes in terms of positive experiences while about half reported mixed experiences. Majority of the articles examining technology and infrastructure experiences or assessment experiences either reported challenging or mixed experiences. All the articles examining learning outcomes reported apparent successes but only half of those investigating attendance/completion rates found these to be acceptable. Only challenges were reported for teaching workload.
Teaching strategies and outcomes
Lecturers used five teaching strategies to shift online during the pandemic (see Table 3 ).
Online practical skills training
Lecturers had to create online practical skills training . With limited access to clinical, field-based, or laboratory settings, lecturers taught only the conceptual aspects of practical skills through online guest lectures, live skill demonstration sessions, video recordings of field trips, conceptual application exercises, or by substituting skills practice with new theoretical topics (Chan et al., 2020 ; de Luca et al., 2021 ; Dietrich et al., 2020 ; Dodson & Blinn, 2021 ; Garcia-Alberti et al., 2021 ; Gomez et al., 2020 ; Xiao et al., 2020 ). Only in three studies about forest operations, ecology, and nursing was it possible to practice hand skills in alternative locations such as public parks and students’ homes (Dodson & Blinn, 2021 ; Gerhart et al., 2021 ; Palmer et al., 2021 ).
Outcomes : Online practical skills training had different effects on learning experiences, test scores, and attendance/completion rates. Students can attain expected test scores through conceptual learning of practical skills (Garcia-Alberti et al., 2021 ; Gomez et al., 2020 ; Xiao et al., 2020 ). However, not all students had positive learning experiences as some appreciated deeper conceptual learning, but others felt disconnected from peers, anxious about losing hand skills proficiency, and could not maintain class attendance (de Luca et al., 2021 ; Dietrich et al., 2020 ; Gomez et al., 2020 ). Positive learning experiences, reasonable course attendance/completion rates, and higher confidence in content mastery were more achievable when students had opportunities to practice hand skills in alternative locations (Gerhart et al., 2021 ).
Online assessment integrity
Lecturers had to devise strategies to maintain online assessment integrity , primarily through different ways of preventing cheating (see Reedy et al., 2021 ). Pass/Fail grading, reducing examination weightage through a higher emphasis on daily work and class participation, and asking students to make academic integrity declarations were some changes to examination policies (e.g. Ali et al., 2020 ; Dicks et al., 2020 ). Randomising and scrambling questions, administering different versions of examination papers, using proctoring software, open-book examinations, and replacing multiple choice with written questions were other ways of preventing cheating during online examinations (Hall et al., 2021 ; Jaap et al., 2021 ; Reedy et al., 2021 ).
Outcomes : There was concern that shifting to online assessment had detrimental effects on learning outcomes, but several studies reported otherwise (Garcia-Alberti et al., 2021 ; Gomez et al., 2020 ; Hall et al., 2021 ; Jaap et al., 2021 ; Lapitan et al., 2021 ). Nevertheless, there were mixed assessment experiences. When lecturers changed multiple-choice to written critical thinking questions, it made students perceive that examinations have become harder (Garcia-Alberti et al., 2021 ; Khan et al., 2022 ). Some students were anxious about encountering technical problems during online examinations, while others felt less nervous taking examinations at home (Jaap et al., 2021 ). Students also became less confident about the integrity of assessment processes when lecturers failed to set clear rules for open-book examinations (Reedy et al., 2021 ). While Pass/Fail grading alleviated students’ test performance anxiety, some lecturers felt that this lowered academic standards (Dicks et al., 2020 ; Khan et al., 2022 ). More emphasis on daily work alleviated student anxiety as examination weightage was reduced, but students also perceived a corresponding increase in course workload as they had more assignments to complete (e.g. Dietrich et al., 2020 ; Swanson et al., 2021 ).
Classroom replication
Lecturers used classroom replication strategies to foster regularity, primarily through substituting classroom sessions with video conferencing under pre-pandemic timetables (Palmer et al., 2021 ; Simon et al., 2020 ; Zhu et al., 2021 ). Lecturers also annotated their presentation materials and decorated their teaching locations with content-related backdrops to emulate the ‘chalk and talk’ of physical classrooms (e.g. Chan et al., 2020 ; Dietrich et al., 2020 ; Xiao et al., 2020 ).
Outcomes : Regular video conferencing classes helped students to maintain course attendance/completion rates (e.g. Ahmed & Opoku, 2021 ; Garcia-Alberti et al., 2021 ; Gerhart et al., 2021 ). Student engagement improved when lecturers annotated on Powerpoint™ or digital whiteboards during video conferencing (Hew et al., 2020 ). However, screen fatigue commonly affected concentration, and lecturers had challenges assessing social cues effectively, especially when students turned off their cameras (Khan et al., 2022 ; Lapitan et al., 2021 ; Marshalsey & Sclater, 2020 ). Lecturers tried to shorten class duration with asynchronous activities, only to find students failing to complete their assigned tasks (Grimmer et al., 2020 ).
Learning access equity
Lecturers implemented learning access equity strategies so that those without stable network connections or conducive home environments could continue studying (Abou-Khalil et al., 2021 ; Ahmed & Opoku, 2021 ; Dodson & Blinn, 2021 ; Garcia-Alberti et al., 2021 ; Grimmer et al., 2020 ; Kapasia et al., 2020 ; Khan et al., 2022 ; Marshalsey & Sclater, 2020 ; Pagoto et al., 2021 ; Swanson et al., 2021 ; Yeung & Yau, 2021 ). They equalised learning access by making lecture recordings available, using chat to communicate during live classes, and providing supplementary asynchronous activities (e.g. Gerhart et al., 2021 ; Grimmer et al., 2020 ). Some lecturers only delivered lessons asynchronously through pre-recorded lectures and online resources (e.g. de Luca et al., 2021 ; Dietrich et al., 2020 ). In developing countries, lecturers created access opportunities by sending learning materials through both learning management systems and WhatsApp™ (Kapasia et al., 2020 ).
Outcomes : Learning access strategies maintained some level of student equity through asynchronous learning but created challenging student learning experiences. There is evidence that students could achieve expected test scores through asynchronous learning (Garcia-Alberti et al., 2021 ) but maintaining learning consistency was a challenge, especially for freshmen (e.g. Grimmer et al., 2020 ; Khan et al., 2022 ). Some students found it hard to understand difficult concepts without in-person lectures but they also did not actively attend the live question-and-answer sessions organised by lecturers (Ali et al., 2020 ; Dietrich et al., 2020 ; Gomez et al., 2020 ). Poorly designed lecture recordings and unclear online learning instructions from lecturers compounded these problems (Gomez et al., 2020 ; Yeung & Yau, 2021 ).
Student engagement
Lecturers used two kinds of student engagement strategies, one of which was through active learning. Hew et. al. ( 2020 ) fostered active learning through 5E activities (Bybee et al., 2006 ) that encouraged students to Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, and Evaluate. Lapitan et. al. ( 2021 ) implemented active learning through their DLPCA process, where students Discover, Learn and Practice outside of class with content resources and Collaborate in class before Assessment. Chan et. al. ( 2020 ) used their Theory of Change to support active learning through shared meaning-making. Other studies emphasised active learning but did not reference theoretical frameworks (e.g. Martinelli & Zaina, 2021 ). Many described how lecturers used interactive tools such as Nearpod™, and Padlet™, online polling, and breakout room discussions to encourage active learning (e.g. Ali et al., 2020 ; Gomez et al., 2020 ).
Another student engagement strategy was through regular communication and support, where lecturers sent emails, announcements, and reminders to keep students in pace with assignments (e.g. Abou-Khalil et al., 2021 ). Support was also provided through virtual office hours, social media contact after class hours and uploading feedback over shared drives (e.g. Khan et al., 2022 ; Xiao et al., 2020 ).
Outcomes : Among the student engagement strategies, success in test scores tends to be associated with the use of active learning (Garcia-Alberti et al., 2021 ; Gomez et al., 2020 ; Hew et al., 2020 ; Lapitan et al., 2021 ; Lau et al., 2020 ; Xiao et al., 2020 ). On the other hand, positive learning experiences were more often reported when lecturers emphasised care and empathy through their communication (e.g. Chan et al., 2020 ; Conklin & Dikkers, 2021 ). Students felt this more strongly when lecturers used humour, conversational and friendly tone, provided assurance, set clear expectations, exercised flexibility, engaged their feedback to improve online lessons, and responded swiftly to their questions (e.g. Chan et al., 2020 ; Swanson et al., 2021 ). These interactions fostered the social presence of Garrison et. al.’s ( 2010 ) Community of Inquiry Theory (Conklin & Dikkers, 2021 ). However, keeping up with multiple communication channels increased teaching workload, especially when support requests arrived through social media after work hours (Garcia-Alberti et al., 2021 ; Khan et al. 2022 ; Marshalsey & Sclater, 2020 ).
Learning strategies and outcomes
Students used three learning strategies during the pandemic (see Table 4 ).
Online access
Students had to maintain online access , as institutional support for data and technology was rarely reported (Ahmed & Opoku, 2021 ; Laher et al., 2021 ). Students did so by switching to more reliable internet service providers, purchasing more data, borrowing computing equipment, or switching off webcams during class (Kapasia et al., 2020 ; Mahmud & German, 2021 ).
Outcomes : Unstable internet connections, noisy home environments, tight study spaces, and disruptions from family duties were challenges often reported in students’ learning environments (e.g. Castelli & Sarvary, 2021 ; Yeung & Yau, 2021 ). The power supply was unstable in developing countries and students also had limited financial resources to purchase data. To keep studying, these students relied on materials shared through WhatsApp™ groups or Google Drive™ and learnt using mobile phones even though their small screen sizes affected students’ learning quality (Kapasia et al., 2020 ).
Online participation
Students had to maintain online participation by redesigning study routines according to when lecturers posted lecture recordings, identifying personal productive hours, changing work locations at home to improve focus and concentration, and devising study strategies to use online resources effectively, such as through note-taking (e.g. Abou-Khalil et al., 2021 ; Mahmud & German, 2021 ; Marshalsey & Sclater, 2020 ). Students also adjusted their online communication style by taking the initiative to contact lecturers through email, discussion forums, or chat for support, and learning new etiquette for video conferencing (Abou-Khalil et al., 2021 ; Dietrich et al., 2020 ; Mahmud & German, 2021 ; Simon et al., 2020 ; Yeung & Yau, 2021 ). Students recognised the need for active online participation (Yeung & Yau, 2021 ) but most tended to switch off webcams and avoided speaking up during class (Ahmed & Opoku, 2021 ; Castelli & Sarvary, 2021 ; Dietrich et al., 2020 ; Khan et al., 2022 ; Lapitan et al., 2021 ; Marshalsey & Sclater, 2020 ; Munoz et al., 2021 ; Rajab & Soheib, 2021 ).
Outcomes : Mahmud and German ( 2021 ) found that students lack the confidence to plan their study strategies, seek help, and manage time. Students also lacked confidence and switched off webcams out of privacy concerns or because they felt self-conscious about their appearances and home environments (Marshalsey & Sclater, 2020 ; Rajab & Soheib, 2021 ). Too many turned off webcams and this became a group norm (Castelli & Sarvary, 2021 ). Classes eventually became dominated by more vocal students, making the quieter ones feel left out (Dietrich et al., 2020 ).
Positive coping
Students’ positive coping strategies included family support, rationalising their situation, focusing on their future, self-motivation, and making virtual social connections with classmates (Ando, 2021 ; Laher et al., 2021 ; Mahmud & German, 2021 ; Reedy et al., 2021 ; Simon et al., 2020 ).
Outcomes : Positive coping strategies helped students to improve learning experiences, maintain attendance/completion rates, and avoid academic integrity violations during online examinations (Ando, 2021 ; Reedy et al., 2021 ; Simon et al., 2020 ). However, these strategies cannot circumvent technology and infrastructure challenges (Mahmud & German, 2021 ), while the realities of economic, family, and health pressures during the pandemic threatened their educational continuity and caused some to manifest negative coping behaviours such as despondency and overeating (Laher et al., 2021 ).
Higher education online competencies
This systematic review outlined eight teaching and learning strategies for shifting online during the pandemic. Online teaching competency frameworks published before the pandemic advocate active learning, social interaction, and prompt feedback as critical indicators of online teaching quality (e.g. Bigatel et al., 2012 ; Crews et al., 2015 ). The findings suggest that lecturers’ student engagement strategies aligned with these standards, but they also needed to adjust practical skills training, assessment, learning access channels, and classroom teaching strategies. Students’ online participation and positive coping strategies reflected how online learners could effectively manage routines, schedules and their sense of isolation (Roper, 2007 ). Since most students had no choice over online learning during the pandemic (Dodson & Blinn, 2021 ), those lacking personal motivation or adequate infrastructure had to develop online participation and online access strategies to cope with the situation.
The eight teaching and learning strategies effectively maintained test scores and attendance/completion rates, but many challenges surfaced during teaching, learning, and assessment. Turnbull et. al. ( 2021 ) attribute lecturers’ and students’ pandemic challenges to online competency gaps, particularly in digital literacy or competencies for accessing information, analysing data, and communicating with technology (Blayone et al., 2018 ). However, the study findings show that digital literacy may not be enough for students to overcome infrastructure and home environment challenges in their learning environment. Lecturers can try helping students mitigate these challenges by providing asynchronous resource access through access equity strategies. Yet, students may not successfully learn asynchronously unless they can effectively self-direct learning. Lecturers may have pedagogical knowledge to create engaging active online learning experiences. How these strategies effectively counteract students’ inhibitions to turn on webcams and speak up during class remains challenging. Lectures may also have the skills to set up different online communication channels, but students may not actively engage if care and empathy are perceived to be lacking. Furthermore, lecturers’ online assessment strategies may not always balance academic integrity with test validity.
These findings show that online competencies are not just standardised technical or pedagogical skills (e.g. Goodyear et al., 2001 ) but “socially situated” (Alvarez et al., 2009 , p. 322) abilities for manoeuvring strategies according to situation and context (Hatano & Inagaki, 1986 ). It encompasses “dexterity” or finesse with skill performance (Merriam-Webster, n.d.). The pandemic demands one to be “flexible and adaptable” (Ally, 2019 , p. 312) amidst shifting national, institutional and learning contexts. Online dexterity is needed in several areas. Online learning during the pandemic is rarely unimodal. Establishing the appropriate synchronous-asynchronous blend is a critical pedagogical decision for lecturers. They need dexterity across learning modalities to create the “right” blend in different student, content, and technological contexts (Baran et al., 2013 ; Martin et al., 2019 ). Lecturers also need domain-related dexterity to preserve authentic learning experiences while converting subject content online (Fayer, 2014 ). Especially when teaching skill-based content under different social distancing requirements, competencies to maintain learning authenticity through simulations, alternative locations, or equipment may be critical (e.g. Schirmel, 2021 ). Dexterity with online assessment is also essential. Besides preventing cheating, lecturers need to ensure that online assessments retain test validity, improve learning processes and are effective for performance evaluation (AERA, 2014 ; Sadler & Reimann, 2018 ). Another area is the dexterity to engage in online communication that appropriately manifests care and empathy (Baran et al., 2013 ). Since online teaching increases lecturers’ workload (Watermeyer et al., 2021 ), dexterity to balance student care and self-care without compromising learning quality is also crucial.
Access to conducive learning environments critically affects students’ online learning success (Kapasia et al., 2020 ). While some infrastructure challenges cannot be prevented, students should have the dexterity to mitigate their effects. For example, when disconnected from class because of bandwidth fluctuations, students should be able to find alternative ways of catching up with the lecturer rather than remaining passive and frustrated (Ezra et al., 2021 ). Self-direction is critical during online learning because it is the ability to set learning goals, self-manage learning processes, self-monitor, self-motivate, and adjust learning strategies (Garrison, 1997 ). Students need the dexterity to manage self-direction processes across different courses, learning modalities, and learning schedules. Dexterity to create an active learning presence through using appropriate learning etiquette and optimising the affordances of text, audio, video, and shared documents during class is also essential. This can support students' cognitive, social, and emotional engagement across synchronous and asynchronous modalities, individually or in groups (Zilvinskis et al., 2017 ).
Future directions
Online learning is highly diverse and increasingly dynamic, making it challenging to cover all published work for review. In this study, we have analysed pandemic-related teaching and learning strategies and their outcomes but recognise that a third of the studies were from the United States and close to half from natural or health science programmes. The findings cannot fully elucidate the strategies implemented in unrepresented countries or disciplines. Recognising these limitations, we propose the following as future directions for higher education:
Validate post-pandemic relevance of online teaching and learning strategies
The eight strategies can be validated through longitudinal empirical studies, theoretical analyses or meta-synthesis of literature to establish their relevance for post-pandemic teaching and learning. Studies outside the United States and the natural and health science disciplines are especially needed. This could address the paucity of theoretical framing in the articles reviewed, even with theories developed before the pandemic (e.g. Garrison et al., 2010 ; Moore, 1989 ; Zimmerman, 2002 ).
Demarcate post-pandemic online competencies
The plethora of descriptive studies in the articles reviewed is inadequate for understanding the online competencies driving lecturers’ pedagogical decision-making and students’ learning processes. In situ studies adopting qualitative methods such as grounded theory or phenomenology can better demarcate lecturers’ and students’ competencies for “why and under which conditions certain methods have to be used, or new methods have to be devised” (Bohle Carbonell et al., 2014 , p. 15). A longitudinal comparison of these studies can provide a better understanding of relevant post-pandemic competencies.
Develop dexterity with respect to application of online competencies
Higher education institutions use technology workshops, mentoring, and instructional consultation to develop competencies in technology-enhanced learning (e.g. Baran, 2016 ). However, dexterity to manoeuvre contextual differences may be better fostered through exploration, discovery, and exposure to varied contexts of practice (Mylopoulos et al., 2018 ). Innovative ways of developing dexterity with respect to how online competencies can be applied and the efficacy of these methodologies are areas for further research.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly increased the adoption and utilisation of online learning. While the present review findings suggest that the strategies lecturers and students employed to shift online during the pandemic have contributed to maintaining educational continuity and test scores but many outstanding issues remained unresolved. These include failure for students to gain an enhanced learning experience, problems encountered in designing and implementing robust assessment and online examinations, cases of academic misconduct, inequitable access to digital technologies, and increased faculty workload. Lecturers and institutions need to tackle these issues to fully leverage the opportunities afforded by online teaching and learning. Further, our findings revealed that the level of online dexterity for both students and teachers need to be enhanced. Therefore, higher education institutions must understand and develop online dexterity institutional frameworks to ensure that pedagogical innovation through online learning can be continually sustained, both during the pandemic and beyond.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Abou-Khalil, V., Helou, S., Khalife, E., Chen, M. A., Majumdar, R., & Ogata, H. (2021). Emergency online learning in low-resource settings: Effective student engagement strategies. Education Sciences, 11 (24), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11010024
Article Google Scholar
AERA. (2014). Standards for educational and psychological testing. https://www.testingstandards.net/uploads/7/6/6/4/76643089/standards_2014edition.pdf
Ahmed, V., & Opoku, A. (2021). Technology supported learning and pedagogy in times of crisis: The case of COVID-19 pandemic. Education and Information Technologies . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10706-w
Ali, I., Narayan, A. K., & Sharma, U. (2020). Adapting to COVID-19 disruptions: Student engagement in online learning of accounting. Accounting Research Journal, 34 (3), 261–269. https://doi.org/10.1108/arj-09-2020-0293
Ally, M. (2019). Competency profile of the digital and online teacher in future education. International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 20 (2), 302–318. https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v20i2.4206
Alvarez, I., Guasch, T., & Espasa, A. (2009). University teacher roles and competencies in online learning environments: A theoretical analysis of teaching and learning practices. European Journal of Teacher Education, 32 (3), 321–336. https://doi.org/10.1080/02619760802624104
Ando, S. (2021). University teaching and learning in a time of social distancing: A sociocultural perspective. Journal of Human Behavior in the Social Environment, 31 (1–4), 435–448. https://doi.org/10.1080/10911359.2020.1814928
Baran, E. (2016). Investigating faculty technology mentoring as a university-wide professional development model. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 28 (1), 45–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12528-015-9104-7
Baran, E., Correia, A.-P., & Thompson, A. (2013). Tracing successful online teaching in higher education: Voices of exemplary online teachers. Teachers College Record, 115 (3), 1–41.
Bigatel, P. M., Ragan, L. C., Kennan, S., May, J., & Redmond, B. F. (2012). The identification of competencies for online teaching success. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks, 16 (1), 59–77.
Google Scholar
Blayone, T. J. B., Mykhailenko, O., Kavtaradze, M., Kokhan, M., vanOostveen, R., & Barber, W. (2018). Profiling the digital readiness of higher education students for transformative online learning in the post-soviet nations of Georgia and Ukraine. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 15 , 37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-018-0119-9
Bohle Carbonell, K., Stalmeijer, R. E., Könings, K. D., Segers, M., & van Merriënboer, J. J. G. (2014). How experts deal with novel situations: A review of adaptive expertise. Educational Research Review, 12 , 14–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2014.03.001
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology, 3 (2), 77–101. https://doi.org/10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Bybee, R., Taylor, J., Gardner, A., Van Scotter, P., Powell, J., Westbrook, A., & Landes, N. (2006). The BSCS 5E instructional model: Origins, effectiveness, and applications. Colorado Springs: BSCS. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies, 29 , 407–427.
Castelli, F. R., & Sarvary, M. A. (2021). Why students do not turn on their video cameras during online classes and an equitable and inclusive plan to encourage them to do so. Ecology and Evolution, 11 (8), 3565–3576. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.7123
Chan, B. C., Baker, J. L., Bunagan, M. R., Ekanger, L. A., Gazley, J. L., Hunter, R. A., O’Connor, A. R., & Triano, R. M. (2020). Theory of change to practice: How experimentalist teaching enabled faculty to navigate the COVID-19 disruption. Journal of Chemical Education, 97 (9), 2788–2792. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00731
Chandler, J., & Hopewell, S. (2013). Cochrane methods—Twenty years experience in developing systematic review methods. Systematic Reviews, 2 (1), 76. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-2-76
Conklin, S., & Dikkers, A. G. (2021). Instructor social presence and connectedness in a quick shift from face-to-face to online instruction. Online Learning, 25 (1), 135–150. https://doi.org/10.24059/olj.v25i1.2482
Creswell, J. W. (1998). Qualitative inquiry and research design . SAGE Publications.
Crews, T. B., Wilkinson, K., & Neill, J. K. (2015). Principles for good practice in undergraduate education: Effective online course design to assist students’ success. Journal of Online Learning and Teaching, 11 (1), 87–103.
Daniel, B. K., & Harland, T. (2017). Higher education research methodology: A step-by-step guide to the research process . Routledge.
Book Google Scholar
de Luca, K., McDonald, M., Montgomery, L., Sharp, S., Young, A., Vella, S., Holmes, M. M., Aspinall, S., Brousseau, D., Burrell, C., Byfield, D., Dane, D., Dewhurst, P., Downie, A., Engel, R., Gleberzon, B., Hollandsworth, D., Nielsen, A. M., O’Connor, L., … French, S. D. (2021). COVID-19: How has a global pandemic changed manual therapy technique education in chiropractic programs around the world? Chiropractic & Manual Therapies, 29 (1), 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12998-021-00364-7
Dedeilia, A., Sotiropoulos, M. G., Hanrahan, J. G., Janga, D., Dedeilias, P., & Sideris, M. (2020). Medical and surgical education challenges and innovations in the COVID-19 era: A systematic review. In Vivo, 34 (3 suppl), 1603. https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.11950
Dicks, A. P., Morra, B., & Quinlan, K. B. (2020). Lessons learned from the COVID-19 crisis: Adjusting assessment approaches within introductory organic courses. Journal of Chemical Education, 97 (9), 3406–3412. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00529
Dietrich, N., Kentheswaran, K., Ahmadi, A., Teychene, J., Bessiere, Y., Alfenore, S., Laborie, S., Bastoul, D., Loubiere, K., Guigui, C., Sperandio, M., Barna, L., Paul, E., Cabassud, C., Line, A., & Hebrard, G. (2020). Attempts, successes, and failures of distance learning in the time of COVID-19. Journal of Chemical Education, 97 (9), 2448–2457. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00717
Dodson, E. M., & Blinn, C. R. (2021). Forest operations instructor and student perspectives on rapid transition from face-to-face to online learning in the US. International Journal of Forest Engineering . https://doi.org/10.1080/14942119.2021.1907109
Ezra, O., Cohen, A., Bronshtein, A., Gabbay, H., & Baruth, O. (2021). Equity factors during the COVID-19 pandemic: Difficulties in emergency remote teaching (ert) through online learning. Education and Information Technologies, 26 , 7657–7681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10632-x
Fayer, L. (2014). A multi-case study of student perceptions of online course design elements and success. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching & Learning, 8 (1), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.20429/ijsotl.2014.080113
Garcia-Alberti, M., Suarez, F., Chiyon, I., & Feijoo, J. C. M. (2021). Challenges and experiences of online evaluation in courses of civil engineering during the lockdown learning due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Education Sciences, 11 (2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11020059
Garrison, D. R. (1997). Self-directed learning: Toward a comprehensive model. Adult Education Quarterly , 48 (1), 18–33. https://doi.org/10.1177/074171369704800103
Garrison, D. R., Anderson, T., & Archer, W. (2010). The first decade of the community of inquiry framework: A retrospective. The Internet and Higher Education, 13 (1), 5–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2009.10.003
Gerhart, L. M., Jadallah, C. C., Angulo, S. S., & Ira, G. C. (2021). Teaching an experiential field course via online participatory science projects: A COVID-19 case study of a UC California Naturalist course. Ecology and Evolution, 11 (8), 3537–3550. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.7187
Gomez, E., Azadi, J., & Magid, D. (2020). Innovation born in isolation: Rapid transformation of an in-person medical student radiology elective to a remote learning experience during the COVID-19 pandemic. Academic Radiology, 27 (9), 1285–1290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2020.06.001
Goodyear, P., Salmon, G., Spector, J. M., Steeples, C., & Tickner, S. (2001). Competences for online teaching: A special report. Educational Technology Research and Development, 49 (1), 65–72.
Grimmer, R., Pollard, A., & Rolls, N. (2020). COVID-19 induced change in higher education: Reflections on rapidly transitioning a first-year undergraduate academic literacies unit from face-to-face to online. Journal of Academic Language and Learning, 14 , 95–105.
Hall, E. A. P., Spivey, C. P., Kendrex, H. P., & Havrda, D. E. P. (2021). Effects of remote proctoring on composite examination performance among Doctor of pharmacy students. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 85 (8), 824–828. https://doi.org/10.5688/ajpe8410
Hao, X., Peng, X., Ding, X., Qin, Y., Lv, M., Li, J., & Li, K. (2022). Application of digital education in undergraduate nursing and medical interns during the COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review. Nurse Education Today, 108 , 105183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2021.105183
Hatano, G., & Inagaki, K. (1986). Two courses of expertise. In H. A. H. Stevenson & K. Hakuta (Eds.), Child development and education in Japan (pp. 262–272). Freeman.
Hew, K. F., Jia, C., Gonda, D. E., & Bai, S. (2020). Transitioning to the “new normal” of learning in unpredictable times: Pedagogical practices and learning performance in fully online flipped classrooms. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 17 (1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-020-00234-x
Hodges, C. B., Moore, S., Lockee, B. B., Trust, T., & Bond, M. A. (2020). The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning . Educause Review. https://er.educause.edu/articles/2020/3/the-difference-between-emergency-remote-teaching-and-online-learning
Jaap, A., Dewar, A., Duncan, C., Fairhurst, K., Hope, D., & Kluth, D. (2021). Effect of remote online exam delivery on student experience and performance in applied knowledge tests. BMC Medical Education, 21 , 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-021-02521-1
Jaschik, S. (2021, 16 August). Delta variant raises questions as campuses start semester. Inside Higher Ed. https://www.insidehighered.com/news/2021/08/16/delta-variant-raises-questions-colleges-about-reopening-plans
Kapasia, N., Paul, P., Roy, A., Saha, J., Zaveri, A., Mallick, R., Barman, B., Das, P., & Chouhan, P. (2020). Impact of lockdown on learning status of undergraduate and postgraduate students during COVID-19 pandemic in West Bengal, India. Children and Youth Services Review, 116 (5), 105194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105194
Khan, S., Kambris, M. E., & Alfalahi, H. (2022). Perspectives of university students and faculty on remote education experiences during COVID-19—A qualitative study. Education and Information Technologies . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10784-w
Kirkwood, A., & Price, L. (2014). Technology-enhanced learning and teaching in higher education: What is ‘enhanced’ and how do we know? A critical literature review. Learning, Media and Technology, 39 (1), 6–36. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439884.2013.770404
Laher, S., Bain, K., Bemath, N., de Andrade, V., & Hassem, T. (2021). Undergraduate psychology student experiences during COVID-19: Challenges encountered and lessons learnt. South African Journal of Psychology . https://doi.org/10.1177/0081246321995095
Lapitan, L. D., Jr., Tiangco, C. E., Sumalinog, D. A. G., Sabarillo, N. S., & Diaz, J. M. (2021). An effective blended online teaching and learning strategy during the COVID-19 pandemic. Education for Chemical Engineers, 35 , 116–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ece.2021.01.012
Lau, P. N., Chua, Y. T., Teow, Y., & Xue, X. J. (2020). Implementing alternative assessment strategies in chemistry amidst COVID-19: Tensions and reflections. Education Sciences, 10 (11), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10110323
Mahmud, Y. S., & German, E. (2021). Online self-regulated learning strategies amid a global pandemic: Insights from Indonesian university students. Malaysian Journal of Learning and Instruction, 18 (2), 45–68. https://doi.org/10.32890/mjli2021.18.2.2
Marshalsey, L., & Sclater, M. (2020). Together but apart: Creating and supporting online learning communities in an era of distributed studio education. International Journal of Art & Design Education, 39 (4), 826–840. https://doi.org/10.1111/jade.12331
Martin, F., Ritzhaupt, A., Kumar, S., & Budhrani, K. (2019). Award-winning faculty online teaching practices: Course design, assessment and evaluation, and facilitation. The Internet and Higher Education, 42 , 34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2019.04.001
Martinelli, S. R., & Zaina, L. A. M. (2021). Learning HCI from a virtual flipped classroom: Improving the students’ experience in times of COVID-19. In ACM international conference proceeding series, virtual event. https://doi.org/10.1145/3472301.3484326
Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Dexterity . Retrieved December 8, 2021, from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/dexterity
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & The, P. G. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLOS Medicine, 6 (7), e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Moore, M. G. (1989). Three types of interaction. The American Journal of Distance Education, 3 (2), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923648909526659
Munoz, K. E., Wang, M. J., & Tham, A. (2021). Enhancing online learning environments using social presence: Evidence from hospitality online courses during COVID-19. Journal of Teaching in Travel & Tourism . https://doi.org/10.1080/15313220.2021.1908871
Mylopoulos, M., Kulasegaram, K., & Woods, N. N. (2018). Developing the experts we need: Fostering adaptive expertise through education. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice, 24 (3), 674–677. https://doi.org/10.1111/jep.12905
Pagoto, S., Lewis, K. A., Groshon, L., Palmer, L., Waring, M. E., Workman, D., De Luna, N., & Brown, N. P. (2021). STEM undergraduates’ perspectives of instructor and university responses to the COVID-19 pandemic in Spring 2020. PLoS ONE, 16 (8), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256213
Palmer, T. J., Chisholm, L. J., Rolf, C. G., & Morris, C. R. (2021). Deliberate practice and self-recorded demonstration of skill proficiency: One baccalaureate nursing school’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Nurse Education in Practice, 53 , 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nepr.2021.103071
Papa, V., Varotto, E., Galli, M., Vaccarezza, M., & Galassi, F. M. (2022). One year of anatomy teaching and learning in the outbreak: Has the Covid-19 pandemic marked the end of a century-old practice? A systematic review. Anatomical Sciences Education, 15 (2), 261–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.2162
Patton, M. Q. (1990). Qualitative evaluation and research methods . SAGE Publications.
Rajab, M. H., & Soheib, M. (2021). Privacy concerns over the use of webcams in online medical education during the COVID-19 pandemic. Cureus, 13 (2), 8. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.13536
Reedy, A., Pfitzner, D., Rook, L., & Ellis, L. (2021). Responding to the COVID-19 emergency: Student and academic staff perceptions of academic integrity in the transition to online exams at three Australian universities. International Journal for Educational Integrity, 17 (1), 1–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40979-021-00075-9
Roper, A. R. (2007). How students develop online learning skills. Educause Quarterly, 30 (1), 62–65.
Sadler, I., & Reimann, N. (2018). Variation in the development of teachers’ understandings of assessment and their assessment practices in higher education. Higher Education Research & Development, 37 (1), 131–144. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2017.1344199
Schirmel, J. (2021). COVID-19 pandemic turns life-science students into “citizen scientists”: Data indicate multiple negative effects of urbanization on biota. Sustainability, 13 (5), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052992
Simon, L. E., Genova, L. E., Kloepper, M. L. O., & Kloepper, K. D. (2020). Learning postdisruption: Lessons from students in a fully online nonmajors laboratory course. Journal of Chemical Education, 97 (9), 2430–2438. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00778
Swanson, S. R., Davis, J. C., Gonzalez-Fuentes, M., & Robertson, K. R. (2021). In these unprecedented times: A critical incidents technique examination of student perceptions’ of satisfying and dissatisfying learning experiences. Marketing Education Review, 31 (3), 209–225. https://doi.org/10.1080/10528008.2021.1952082
Turnbull, D., Chugh, R., & Luck, J. (2021). Transitioning to e-learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: How have higher education institutions responded to the challenge? Education and Information Technologies, 26 (5), 6401–6419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10633-w
Watermeyer, R., Crick, T., Knight, C., & Goodall, J. (2021). COVID-19 and digital disruption in UK universities: Afflictions and affordances of emergency online migration. Higher Education, 81 (3), 623–641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-020-00561-y
Weber, R. P. (1990). Basic content analysis . SAGE Publications.
WHO. (2020). Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) situation report -1 . World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200121-sitrep-1-2019-ncov.pdf?sfvrsn=20a99c10_4
Xiao, C. L., Cai, H., Su, Y. J., & Shen, L. M. (2020). Online teaching practices and strategies for inorganic chemistry using a combined platform based on DingTalk, Learning@ZJU, and WeChat. Journal of Chemical Education, 97 (9), 2940–2944. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00642
Yeung, M. W. L., & Yau, A. H. Y. (2021). A thematic analysis of higher education students’ perceptions of online learning in Hong Kong under COVID-19: Challenges, strategies and support. Education and Information Technologies . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10656-3
Zhu, X. Q., Shek, D. T. L., & Chan, C. H. M. (2021). Promoting service leadership qualities and well-being among university students through an online course during COVID-19 pandemic. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18 (15), 8162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18158162
Zilvinskis, J., Masseria, A. A., & Pike, G. R. (2017). Student engagement and student learning: Examining the convergent and discriminant validity of the revised national survey of student engagement. Research in Higher Education, 58 (8), 880–903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11162-017-9450-6
Zimmerman, B. J. (2002). Becoming a self-regulated learner: An overview. Theory into Practice, 41 (2), 64.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
The University of Otago Research Grant was used for research support in article searching and inter-rater analysis.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Higher Education Development Centre, University of Otago, 65-75 Union Place West, PO Box 56, Dunedin, 9054, New Zealand
Joyce Hwee Ling Koh & Ben Kei Daniel
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The authors conceptualised the paper together. JK coded the data and drafted the paper. BD provided critical review of methodology, coding and thematic analysis, and edited the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Joyce Hwee Ling Koh .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix: Selected articles and coding
SN | Author and article information | Teaching strategies
| Learning strategies
| Outcomes
C—Challenge S—Success M—Mixed outcome | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ST | AI | CR | AE | SE | OA | OP | PC | LE | TIN | ASS | LO | AC | TW | ||
1 | Abou-Khalil et. al. ( ) Site: Multiple Level: Multiple Subject: Multiple Methodology: Survey N: 300–349 Published: Jan-21 Theory: Moore’s interaction framework | √ | √ | √ | √ | M | C | ||||||||
2 | Ahmed and Opoku ( ) Site: Middle East Level: Multiple Subject: Engineering or Computer Science Methodology: Mixed methods N: 300–349 Published: Aug-21 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | M | M | M | S | ||||
3 | Ali et. al. ( ) Site: Australasia Level: Multiple Subject: Commerce Methodology: Qualitative N: ≤ 50 Published: Oct-20 | √ | √ | √ | √ | M | M | ||||||||
4 | Ando ( ) Site: Asia Level: Postgrad Subject: Multiple Methodology: Qualitative N: ≤ 50 Published: Oct-20 | √ | √ | M | C | S | |||||||||
5 | Castelli and Sarvary ( ) Site: USA Level: Degree Subject: Natural Sciences Methodology: Survey—Student N: 250–299 Published: Nov-20 | √ | √ | √ | C | ||||||||||
6 | Chan et. al. ( ) Site: USA Level: Degree Subject: Natural Sciences Methodology: Qualitative N ≤ 50 Published: Aug-20 Theory: Theory of Change (ToC) | √ | √ | √ | √ | M | |||||||||
7 | Conklin and Dikkers ( ) Site: USA Level: Multiple Subject: Multiple Methodology: Survey N: 400–449 Published: Mar-21 Theory: COI | √ | S | ||||||||||||
8 | de Luca et. al. ( ) Site: Multiple Level: Degree Subject: Medical and Health Sciences Methodology: Survey—Teacher N: ≤ 50 Published: Jan-21 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | C | C | |||||||
9 | Dicks et. al. ( ) Site: Others Level: Degree (1st yr) Subject: Natural Sciences Methodology: Mixed methods N: ≤ 50 Published: Aug-20 | √ | S | S | |||||||||||
10 | Dietrich et. al. ( ) Site: Europe Level: Degree Subject: Natural Sciences Methodology: Survey N: 100–149 Published: Aug-20 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | S | |||||||
11 | Dodson and Blinn ( ) Site: USA Level: Degree Subject: Natural Sciences Methodology: Survey N: 51–99 Published: Apr-21 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | M | C | |||||||
12 | Garcia-Alberti et. al. ( ) Site: Latin America Level: Multiple Subject: Engineering or Computer Science Methodology: Mixed methods N: ≤ 50 Published: Feb-21 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | C | C | C | S | S | C | |||
13 | Gerhart et. al. ( ) Site: USA Level: Degree Subject: Natural Sciences Methodology: Mixed methods N: ≤ 50 Published: Dec-20 | √ | √ | √ | S | S | S | ||||||||
14 | Gomez et. al. ( ) Site: USA Level: Degree Subject: Medical and Health Sciences Methodology: Mixed methods N: ≤ 50 Published: Sep-20 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | M | S | |||||||
15 | Grimmer et. al. ( ) Site: Australasia Level: Degree (1st yr) Subject: Others Methodology: Qualitative N: 300–349 Published: Nov-20 | √ | √ | √ | M | C | M | ||||||||
16 | Hall et. al. ( ) Site: USA Level: Postgrad Subject: Medical and Health Sciences Methodology: Quasi-experiment/correlational N: ≥ 450 Published: Sep-21 | √ | S | ||||||||||||
17 | Hew et. al. ( ) Site: Asia Level: Postgrad Subject: Education Methodology: Quasi-experiment/correlational N: 51–99 Published: Dec-20 Theory: 5E | √ | √ | S | S | ||||||||||
18 | Jaap et. al. ( ) Site: Europe Level: Degree Subject: Medical and Health Sciences Methodology: Quasi-experiment/correlational N: 100–149 Published: Feb-21 | √ | √ | S | M | S | |||||||||
19 | Kapasia et. al. ( ) Site: Others Level: Multiple Subject: Multiple Methodology: Survey N: 200–249 Published: Sep-20 | √ | √ | √ | C | ||||||||||
20 | Khan et. al. ( ) Site: Middle East Level: Degree Subject: Natural Sciences Methodology: Qualitative N: 51–99 Published: Oct-21 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | M | M | C | M | C | ||||
21 | Laher et. al. ( ) Site: Others Level: Degree Subject: Arts and Social Sciences Methodology: Survey N: 150–199 Published: Jun-21 | √ | √ | √ | C | C | |||||||||
22 | Lapitan et. al. ( ) Site: Asia Level: Degree Subject: Engineering or Computer Science Methodology: Survey N: 150–199 Published: Jan-21 Theory: Discover, Learn, Practice, Collaborate and Assess (DLPCA) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | M | M | S | ||||||
23 | Lau et. al. ( ) Site: Asia Level: Diploma Subject: Natural Sciences Methodology: Mixed methods N: 350–399 Published: Nov-20 | √ | √ | √ | √ | S | C | S | |||||||
24 | Mahmud and German ( ) Site: Asia Level: Degree Subject: Others Methodology: Mixed methods N: 300–349 Published: Jul-21 Theory: Self-regulated Learning | √ | √ | √ | M | C | M | ||||||||
25 | Marshalsey and Sclater ( ) Site: Australasia Level: Degree Subject: Arts and Social Sciences Methodology: Qualitative N: 51–99 Published: Nov-20 | √ | √ | √ | √ | M | C | C | |||||||
26 | Martinelli and Zaina ( ) Site: Latin America Level: Multiple Subject: Engineering or Computer Science Methodology: Mixed M: < 51 Published: Oct-21 | √ | S | S | |||||||||||
27 | Munoz et. al. ( ) Site: Asia Level: Postgrad Subject: Commerce Methodology: Qualitative N: ≤ 50 Published: Apr-21 Theory: COI | √ | √ | √ | M | ||||||||||
28 | Pagoto et. al. ( ) Site: USA Level: Degree Subject: Multiple Methodology: Qualitative N: 51–99 Published: Aug-21 | √ | √ | √ | √ | M | M | ||||||||
29 | Palmer et. al. ( ) Site: USA Level: Degree Subject: Medical and Health Sciences Methodology: Survey N: ≤ 50 Published: May-21 | √ | √ | S | |||||||||||
30 | Rajab and Soheib ( ) Site: Middle East Level: Multiple Subject: Medical and Health Sciences Methodology: Survey N: 300–349 Published: Feb-21 | √ | C | ||||||||||||
31 | Reedy et. al. ( ) Site: Australasia Level: Multiple Subject: Multiple Methodology: Survey N: ≥ 450 Published: Mar-21 | √ | √ | √ | √ | M | |||||||||
32 | Simon et. al. ( ) Site: USA Level: Degree Subject: Natural Sciences Methodology: Survey N: ≤ 50 Published: Aug-20 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | S | |||||||
33 | Swanson et. al. ( ) Site: USA Level: Degree Subject: Commerce Methodology: Survey N: 300–349 Published: Jul-21 | √ | √ | √ | M | C | M | ||||||||
34 | Xiao et. al. ( ) Site: Asia Level: Degree (1st yr) Subject: Natural Sciences Methodology: Mixed methods N: ≤ 50 Published: Aug-20 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | S | S | |||||||
35 | Yeung and Yau ( ) Site: Asia Level: Multiple Subject: Multiple Methodology: Survey N: 100–149 Publication month: Jun-21 | √ | √ | √ | C | C | C | ||||||||
36 | Zhu et. al. ( ) Site: Asia Level: Degree Subject: Others Methodology: Quasi-experiment/correlational N: 200–249 Published: Aug-21 | √ | √ | √ | S | ||||||||||
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Koh, J.H.L., Daniel, B.K. Shifting online during COVID-19: A systematic review of teaching and learning strategies and their outcomes. Int J Educ Technol High Educ 19 , 56 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-022-00361-7
Download citation
Received : 04 April 2022
Accepted : 12 August 2022
Published : 09 November 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-022-00361-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Online learning
- Emergency response teaching
- Online dexterity
- Online pedagogy
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
COVID-19’s impacts on the scope, effectiveness, and interaction characteristics of online learning: A social network analysis
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing
¶ ‡ JZ and YD are contributed equally to this work as first authors.
Affiliation School of Educational Information Technology, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft
Affiliations School of Educational Information Technology, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China, Hangzhou Zhongce Vocational School Qiantang, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
Roles Data curation, Writing – original draft
Roles Data curation
Roles Writing – original draft
Affiliation Faculty of Education, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Roles Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected] (JH); [email protected] (YZ)
- Junyi Zhang,
- Yigang Ding,
- Xinru Yang,
- Jinping Zhong,
- XinXin Qiu,
- Zhishan Zou,
- Yujie Xu,
- Xiunan Jin,
- Xiaomin Wu,

- Published: August 23, 2022
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016
- Reader Comments
The COVID-19 outbreak brought online learning to the forefront of education. Scholars have conducted many studies on online learning during the pandemic, but only a few have performed quantitative comparative analyses of students’ online learning behavior before and after the outbreak. We collected review data from China’s massive open online course platform called icourse.163 and performed social network analysis on 15 courses to explore courses’ interaction characteristics before, during, and after the COVID-19 pan-demic. Specifically, we focused on the following aspects: (1) variations in the scale of online learning amid COVID-19; (2a) the characteristics of online learning interaction during the pandemic; (2b) the characteristics of online learning interaction after the pandemic; and (3) differences in the interaction characteristics of social science courses and natural science courses. Results revealed that only a small number of courses witnessed an uptick in online interaction, suggesting that the pandemic’s role in promoting the scale of courses was not significant. During the pandemic, online learning interaction became more frequent among course network members whose interaction scale increased. After the pandemic, although the scale of interaction declined, online learning interaction became more effective. The scale and level of interaction in Electrodynamics (a natural science course) and Economics (a social science course) both rose during the pan-demic. However, long after the pandemic, the Economics course sustained online interaction whereas interaction in the Electrodynamics course steadily declined. This discrepancy could be due to the unique characteristics of natural science courses and social science courses.
Citation: Zhang J, Ding Y, Yang X, Zhong J, Qiu X, Zou Z, et al. (2022) COVID-19’s impacts on the scope, effectiveness, and interaction characteristics of online learning: A social network analysis. PLoS ONE 17(8): e0273016. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016
Editor: Heng Luo, Central China Normal University, CHINA
Received: April 20, 2022; Accepted: July 29, 2022; Published: August 23, 2022
Copyright: © 2022 Zhang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: The data underlying the results presented in the study were downloaded from https://www.icourse163.org/ and are now shared fully on Github ( https://github.com/zjyzhangjunyi/dataset-from-icourse163-for-SNA ). These data have no private information and can be used for academic research free of charge.
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
1. Introduction
The development of the mobile internet has spurred rapid advances in online learning, offering novel prospects for teaching and learning and a learning experience completely different from traditional instruction. Online learning harnesses the advantages of network technology and multimedia technology to transcend the boundaries of conventional education [ 1 ]. Online courses have become a popular learning mode owing to their flexibility and openness. During online learning, teachers and students are in different physical locations but interact in multiple ways (e.g., via online forum discussions and asynchronous group discussions). An analysis of online learning therefore calls for attention to students’ participation. Alqurashi [ 2 ] defined interaction in online learning as the process of constructing meaningful information and thought exchanges between more than two people; such interaction typically occurs between teachers and learners, learners and learners, and the course content and learners.
Massive open online courses (MOOCs), a 21st-century teaching mode, have greatly influenced global education. Data released by China’s Ministry of Education in 2020 show that the country ranks first globally in the number and scale of higher education MOOCs. The COVID-19 outbreak has further propelled this learning mode, with universities being urged to leverage MOOCs and other online resource platforms to respond to government’s “School’s Out, But Class’s On” policy [ 3 ]. Besides MOOCs, to reduce in-person gatherings and curb the spread of COVID-19, various online learning methods have since become ubiquitous [ 4 ]. Though Lederman asserted that the COVID-19 outbreak has positioned online learning technologies as the best way for teachers and students to obtain satisfactory learning experiences [ 5 ], it remains unclear whether the COVID-19 pandemic has encouraged interaction in online learning, as interactions between students and others play key roles in academic performance and largely determine the quality of learning experiences [ 6 ]. Similarly, it is also unclear what impact the COVID-19 pandemic has had on the scale of online learning.
Social constructivism paints learning as a social phenomenon. As such, analyzing the social structures or patterns that emerge during the learning process can shed light on learning-based interaction [ 7 ]. Social network analysis helps to explain how a social network, rooted in interactions between learners and their peers, guides individuals’ behavior, emotions, and outcomes. This analytical approach is especially useful for evaluating interactive relationships between network members [ 8 ]. Mohammed cited social network analysis (SNA) as a method that can provide timely information about students, learning communities and interactive networks. SNA has been applied in numerous fields, including education, to identify the number and characteristics of interelement relationships. For example, Lee et al. also used SNA to explore the effects of blogs on peer relationships [ 7 ]. Therefore, adopting SNA to examine interactions in online learning communities during the COVID-19 pandemic can uncover potential issues with this online learning model.
Taking China’s icourse.163 MOOC platform as an example, we chose 15 courses with a large number of participants for SNA, focusing on learners’ interaction characteristics before, during, and after the COVID-19 outbreak. We visually assessed changes in the scale of network interaction before, during, and after the outbreak along with the characteristics of interaction in Gephi. Examining students’ interactions in different courses revealed distinct interactive network characteristics, the pandemic’s impact on online courses, and relevant suggestions. Findings are expected to promote effective interaction and deep learning among students in addition to serving as a reference for the development of other online learning communities.
2. Literature review and research questions
Interaction is deemed as central to the educational experience and is a major focus of research on online learning. Moore began to study the problem of interaction in distance education as early as 1989. He defined three core types of interaction: student–teacher, student–content, and student–student [ 9 ]. Lear et al. [ 10 ] described an interactivity/ community-process model of distance education: they specifically discussed the relationships between interactivity, community awareness, and engaging learners and found interactivity and community awareness to be correlated with learner engagement. Zulfikar et al. [ 11 ] suggested that discussions initiated by the students encourage more students’ engagement than discussions initiated by the instructors. It is most important to afford learners opportunities to interact purposefully with teachers, and improving the quality of learner interaction is crucial to fostering profound learning [ 12 ]. Interaction is an important way for learners to communicate and share information, and a key factor in the quality of online learning [ 13 ].
Timely feedback is the main component of online learning interaction. Woo and Reeves discovered that students often become frustrated when they fail to receive prompt feedback [ 14 ]. Shelley et al. conducted a three-year study of graduate and undergraduate students’ satisfaction with online learning at universities and found that interaction with educators and students is the main factor affecting satisfaction [ 15 ]. Teachers therefore need to provide students with scoring justification, support, and constructive criticism during online learning. Some researchers examined online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. They found that most students preferred face-to-face learning rather than online learning due to obstacles faced online, such as a lack of motivation, limited teacher-student interaction, and a sense of isolation when learning in different times and spaces [ 16 , 17 ]. However, it can be reduced by enhancing the online interaction between teachers and students [ 18 ].
Research showed that interactions contributed to maintaining students’ motivation to continue learning [ 19 ]. Baber argued that interaction played a key role in students’ academic performance and influenced the quality of the online learning experience [ 20 ]. Hodges et al. maintained that well-designed online instruction can lead to unique teaching experiences [ 21 ]. Banna et al. mentioned that using discussion boards, chat sessions, blogs, wikis, and other tools could promote student interaction and improve participation in online courses [ 22 ]. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Mahmood proposed a series of teaching strategies suitable for distance learning to improve its effectiveness [ 23 ]. Lapitan et al. devised an online strategy to ease the transition from traditional face-to-face instruction to online learning [ 24 ]. The preceding discussion suggests that online learning goes beyond simply providing learning resources; teachers should ideally design real-life activities to give learners more opportunities to participate.
As mentioned, COVID-19 has driven many scholars to explore the online learning environment. However, most have ignored the uniqueness of online learning during this time and have rarely compared pre- and post-pandemic online learning interaction. Taking China’s icourse.163 MOOC platform as an example, we chose 15 courses with a large number of participants for SNA, centering on student interaction before and after the pandemic. Gephi was used to visually analyze changes in the scale and characteristics of network interaction. The following questions were of particular interest:
- (1) Can the COVID-19 pandemic promote the expansion of online learning?
- (2a) What are the characteristics of online learning interaction during the pandemic?
- (2b) What are the characteristics of online learning interaction after the pandemic?
- (3) How do interaction characteristics differ between social science courses and natural science courses?
3. Methodology
3.1 research context.
We selected several courses with a large number of participants and extensive online interaction among hundreds of courses on the icourse.163 MOOC platform. These courses had been offered on the platform for at least three semesters, covering three periods (i.e., before, during, and after the COVID-19 outbreak). To eliminate the effects of shifts in irrelevant variables (e.g., course teaching activities), we chose several courses with similar teaching activities and compared them on multiple dimensions. All course content was taught online. The teachers of each course posted discussion threads related to learning topics; students were expected to reply via comments. Learners could exchange ideas freely in their responses in addition to asking questions and sharing their learning experiences. Teachers could answer students’ questions as well. Conversations in the comment area could partly compensate for a relative absence of online classroom interaction. Teacher–student interaction is conducive to the formation of a social network structure and enabled us to examine teachers’ and students’ learning behavior through SNA. The comment areas in these courses were intended for learners to construct knowledge via reciprocal communication. Meanwhile, by answering students’ questions, teachers could encourage them to reflect on their learning progress. These courses’ successive terms also spanned several phases of COVID-19, allowing us to ascertain the pandemic’s impact on online learning.
3.2 Data collection and preprocessing
To avoid interference from invalid or unclear data, the following criteria were applied to select representative courses: (1) generality (i.e., public courses and professional courses were chosen from different schools across China); (2) time validity (i.e., courses were held before during, and after the pandemic); and (3) notability (i.e., each course had at least 2,000 participants). We ultimately chose 15 courses across the social sciences and natural sciences (see Table 1 ). The coding is used to represent the course name.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.t001
To discern courses’ evolution during the pandemic, we gathered data on three terms before, during, and after the COVID-19 outbreak in addition to obtaining data from two terms completed well before the pandemic and long after. Our final dataset comprised five sets of interactive data. Finally, we collected about 120,000 comments for SNA. Because each course had a different start time—in line with fluctuations in the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases in China and the opening dates of most colleges and universities—we divided our sample into five phases: well before the pandemic (Phase I); before the pandemic (Phase Ⅱ); during the pandemic (Phase Ⅲ); after the pandemic (Phase Ⅳ); and long after the pandemic (Phase Ⅴ). We sought to preserve consistent time spans to balance the amount of data in each period ( Fig 1 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.g001
3.3 Instrumentation
Participants’ comments and “thumbs-up” behavior data were converted into a network structure and compared using social network analysis (SNA). Network analysis, according to M’Chirgui, is an effective tool for clarifying network relationships by employing sophisticated techniques [ 25 ]. Specifically, SNA can help explain the underlying relationships among team members and provide a better understanding of their internal processes. Yang and Tang used SNA to discuss the relationship between team structure and team performance [ 26 ]. Golbeck argued that SNA could improve the understanding of students’ learning processes and reveal learners’ and teachers’ role dynamics [ 27 ].
To analyze Question (1), the number of nodes and diameter in the generated network were deemed as indicators of changes in network size. Social networks are typically represented as graphs with nodes and degrees, and node count indicates the sample size [ 15 ]. Wellman et al. proposed that the larger the network scale, the greater the number of network members providing emotional support, goods, services, and companionship [ 28 ]. Jan’s study measured the network size by counting the nodes which represented students, lecturers, and tutors [ 29 ]. Similarly, network nodes in the present study indicated how many learners and teachers participated in the course, with more nodes indicating more participants. Furthermore, we investigated the network diameter, a structural feature of social networks, which is a common metric for measuring network size in SNA [ 30 ]. The network diameter refers to the longest path between any two nodes in the network. There has been evidence that a larger network diameter leads to greater spread of behavior [ 31 ]. Likewise, Gašević et al. found that larger networks were more likely to spread innovative ideas about educational technology when analyzing MOOC-related research citations [ 32 ]. Therefore, we employed node count and network diameter to measure the network’s spatial size and further explore the expansion characteristic of online courses. Brief introduction of these indicators can be summarized in Table 2 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.t002
To address Question (2), a list of interactive analysis metrics in SNA were introduced to scrutinize learners’ interaction characteristics in online learning during and after the pandemic, as shown below:
- (1) The average degree reflects the density of the network by calculating the average number of connections for each node. As Rong and Xu suggested, the average degree of a network indicates how active its participants are [ 33 ]. According to Hu, a higher average degree implies that more students are interacting directly with each other in a learning context [ 34 ]. The present study inherited the concept of the average degree from these previous studies: the higher the average degree, the more frequent the interaction between individuals in the network.
- (2) Essentially, a weighted average degree in a network is calculated by multiplying each degree by its respective weight, and then taking the average. Bydžovská took the strength of the relationship into account when determining the weighted average degree [ 35 ]. By calculating friendship’s weighted value, Maroulis assessed peer achievement within a small-school reform [ 36 ]. Accordingly, we considered the number of interactions as the weight of the degree, with a higher average degree indicating more active interaction among learners.
- (3) Network density is the ratio between actual connections and potential connections in a network. The more connections group members have with each other, the higher the network density. In SNA, network density is similar to group cohesion, i.e., a network of more strong relationships is more cohesive [ 37 ]. Network density also reflects how much all members are connected together [ 38 ]. Therefore, we adopted network density to indicate the closeness among network members. Higher network density indicates more frequent interaction and closer communication among students.
- (4) Clustering coefficient describes local network attributes and indicates that two nodes in the network could be connected through adjacent nodes. The clustering coefficient measures users’ tendency to gather (cluster) with others in the network: the higher the clustering coefficient, the more frequently users communicate with other group members. We regarded this indicator as a reflection of the cohesiveness of the group [ 39 ].
- (5) In a network, the average path length is the average number of steps along the shortest paths between any two nodes. Oliveres has observed that when an average path length is small, the route from one node to another is shorter when graphed [ 40 ]. This is especially true in educational settings where students tend to become closer friends. So we consider that the smaller the average path length, the greater the possibility of interaction between individuals in the network.
- (6) A network with a large number of nodes, but whose average path length is surprisingly small, is known as the small-world effect [ 41 ]. A higher clustering coefficient and shorter average path length are important indicators of a small-world network: a shorter average path length enables the network to spread information faster and more accurately; a higher clustering coefficient can promote frequent knowledge exchange within the group while boosting the timeliness and accuracy of knowledge dissemination [ 42 ]. Brief introduction of these indicators can be summarized in Table 3 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.t003
To analyze Question 3, we used the concept of closeness centrality, which determines how close a vertex is to others in the network. As Opsahl et al. explained, closeness centrality reveals how closely actors are coupled with their entire social network [ 43 ]. In order to analyze social network-based engineering education, Putnik et al. examined closeness centrality and found that it was significantly correlated with grades [ 38 ]. We used closeness centrality to measure the position of an individual in the network. Brief introduction of these indicators can be summarized in Table 4 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.t004
3.4 Ethics statement
This study was approved by the Academic Committee Office (ACO) of South China Normal University ( http://fzghb.scnu.edu.cn/ ), Guangzhou, China. Research data were collected from the open platform and analyzed anonymously. There are thus no privacy issues involved in this study.
4.1 COVID-19’s role in promoting the scale of online courses was not as important as expected
As shown in Fig 2 , the number of course participants and nodes are closely correlated with the pandemic’s trajectory. Because the number of participants in each course varied widely, we normalized the number of participants and nodes to more conveniently visualize course trends. Fig 2 depicts changes in the chosen courses’ number of participants and nodes before the pandemic (Phase II), during the pandemic (Phase III), and after the pandemic (Phase IV). The number of participants in most courses during the pandemic exceeded those before and after the pandemic. But the number of people who participate in interaction in some courses did not increase.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.g002
In order to better analyze the trend of interaction scale in online courses before, during, and after the pandemic, the selected courses were categorized according to their scale change. When the number of participants increased (decreased) beyond 20% (statistical experience) and the diameter also increased (decreased), the course scale was determined to have increased (decreased); otherwise, no significant change was identified in the course’s interaction scale. Courses were subsequently divided into three categories: increased interaction scale, decreased interaction scale, and no significant change. Results appear in Table 5 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.t005
From before the pandemic until it broke out, the interaction scale of five courses increased, accounting for 33.3% of the full sample; one course’s interaction scale declined, accounting for 6.7%. The interaction scale of nine courses decreased, accounting for 60%. The pandemic’s role in promoting online courses thus was not as important as anticipated, and most courses’ interaction scale did not change significantly throughout.
No courses displayed growing interaction scale after the pandemic: the interaction scale of nine courses fell, accounting for 60%; and the interaction scale of six courses did not shift significantly, accounting for 40%. Courses with an increased scale of interaction during the pandemic did not maintain an upward trend. On the contrary, the improvement in the pandemic caused learners’ enthusiasm for online learning to wane. We next analyzed several interaction metrics to further explore course interaction during different pandemic periods.
4.2 Characteristics of online learning interaction amid COVID-19
4.2.1 during the covid-19 pandemic, online learning interaction in some courses became more active..
Changes in course indicators with the growing interaction scale during the pandemic are presented in Fig 3 , including SS5, SS6, NS1, NS3, and NS8. The horizontal ordinate indicates the number of courses, with red color representing the rise of the indicator value on the vertical ordinate and blue representing the decline.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.g003
Specifically: (1) The average degree and weighted average degree of the five course networks demonstrated an upward trend. The emergence of the pandemic promoted students’ enthusiasm; learners were more active in the interactive network. (2) Fig 3 shows that 3 courses had increased network density and 2 courses had decreased. The higher the network density, the more communication within the team. Even though the pandemic accelerated the interaction scale and frequency, the tightness between learners in some courses did not improve. (3) The clustering coefficient of social science courses rose whereas the clustering coefficient and small-world property of natural science courses fell. The higher the clustering coefficient and the small-world property, the better the relationship between adjacent nodes and the higher the cohesion [ 39 ]. (4) Most courses’ average path length increased as the interaction scale increased. However, when the average path length grew, adverse effects could manifest: communication between learners might be limited to a small group without multi-directional interaction.
When the pandemic emerged, the only declining network scale belonged to a natural science course (NS2). The change in each course index is pictured in Fig 4 . The abscissa indicates the size of the value, with larger values to the right. The red dot indicates the index value before the pandemic; the blue dot indicates its value during the pandemic. If the blue dot is to the right of the red dot, then the value of the index increased; otherwise, the index value declined. Only the weighted average degree of the course network increased. The average degree, network density decreased, indicating that network members were not active and that learners’ interaction degree and communication frequency lessened. Despite reduced learner interaction, the average path length was small and the connectivity between learners was adequate.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.g004
4.2.2 After the COVID-19 pandemic, the scale decreased rapidly, but most course interaction was more effective.
Fig 5 shows the changes in various courses’ interaction indicators after the pandemic, including SS1, SS2, SS3, SS6, SS7, NS2, NS3, NS7, and NS8.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.g005
Specifically: (1) The average degree and weighted average degree of most course networks decreased. The scope and intensity of interaction among network members declined rapidly, as did learners’ enthusiasm for communication. (2) The network density of seven courses also fell, indicating weaker connections between learners in most courses. (3) In addition, the clustering coefficient and small-world property of most course networks decreased, suggesting little possibility of small groups in the network. The scope of interaction between learners was not limited to a specific space, and the interaction objects had no significant tendencies. (4) Although the scale of course interaction became smaller in this phase, the average path length of members’ social networks shortened in nine courses. Its shorter average path length would expedite the spread of information within the network as well as communication and sharing among network members.
Fig 6 displays the evolution of course interaction indicators without significant changes in interaction scale after the pandemic, including SS4, SS5, NS1, NS4, NS5, and NS6.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.g006
Specifically: (1) Some course members’ social networks exhibited an increase in the average and weighted average. In these cases, even though the course network’s scale did not continue to increase, communication among network members rose and interaction became more frequent and deeper than before. (2) Network density and average path length are indicators of social network density. The greater the network density, the denser the social network; the shorter the average path length, the more concentrated the communication among network members. However, at this phase, the average path length and network density in most courses had increased. Yet the network density remained small despite having risen ( Table 6 ). Even with more frequent learner interaction, connections remained distant and the social network was comparatively sparse.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.t006
In summary, the scale of interaction did not change significantly overall. Nonetheless, some course members’ frequency and extent of interaction increased, and the relationships between network members became closer as well. In the study, we found it interesting that the interaction scale of Economics (a social science course) course and Electrodynamics (a natural science course) course expanded rapidly during the pandemic and retained their interaction scale thereafter. We next assessed these two courses to determine whether their level of interaction persisted after the pandemic.
4.3 Analyses of natural science courses and social science courses
4.3.1 analyses of the interaction characteristics of economics and electrodynamics..
Economics and Electrodynamics are social science courses and natural science courses, respectively. Members’ interaction within these courses was similar: the interaction scale increased significantly when COVID-19 broke out (Phase Ⅲ), and no significant changes emerged after the pandemic (Phase Ⅴ). We hence focused on course interaction long after the outbreak (Phase V) and compared changes across multiple indicators, as listed in Table 7 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.t007
As the pandemic continued to improve, the number of participants and the diameter long after the outbreak (Phase V) each declined for Economics compared with after the pandemic (Phase IV). The interaction scale decreased, but the interaction between learners was much deeper. Specifically: (1) The weighted average degree, network density, clustering coefficient, and small-world property each reflected upward trends. The pandemic therefore exerted a strong impact on this course. Interaction was well maintained even after the pandemic. The smaller network scale promoted members’ interaction and communication. (2) Compared with after the pandemic (Phase IV), members’ network density increased significantly, showing that relationships between learners were closer and that cohesion was improving. (3) At the same time, as the clustering coefficient and small-world property grew, network members demonstrated strong small-group characteristics: the communication between them was deepening and their enthusiasm for interaction was higher. (4) Long after the COVID-19 outbreak (Phase V), the average path length was reduced compared with previous terms, knowledge flowed more quickly among network members, and the degree of interaction gradually deepened.
The average degree, weighted average degree, network density, clustering coefficient, and small-world property of Electrodynamics all decreased long after the COVID-19 outbreak (Phase V) and were lower than during the outbreak (Phase Ⅲ). The level of learner interaction therefore gradually declined long after the outbreak (Phase V), and connections between learners were no longer active. Although the pandemic increased course members’ extent of interaction, this rise was merely temporary: students’ enthusiasm for learning waned rapidly and their interaction decreased after the pandemic (Phase IV). To further analyze the interaction characteristics of course members in Economics and Electrodynamics, we evaluated the closeness centrality of their social networks, as shown in section 4.3.2.
4.3.2 Analysis of the closeness centrality of Economics and Electrodynamics.
The change in the closeness centrality of social networks in Economics was small, and no sharp upward trend appeared during the pandemic outbreak, as shown in Fig 7 . The emergence of COVID-19 apparently fostered learners’ interaction in Economics albeit without a significant impact. The closeness centrality changed in Electrodynamics varied from that of Economics: upon the COVID-19 outbreak, closeness centrality was significantly different from other semesters. Communication between learners was closer and interaction was more effective. Electrodynamics course members’ social network proximity decreased rapidly after the pandemic. Learners’ communication lessened. In general, Economics course showed better interaction before the outbreak and was less affected by the pandemic; Electrodynamics course was more affected by the pandemic and showed different interaction characteristics at different periods of the pandemic.
(Note: "****" indicates the significant distinction in closeness centrality between the two periods, otherwise no significant distinction).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273016.g007
5. Discussion
We referred to discussion forums from several courses on the icourse.163 MOOC platform to compare online learning before, during, and after the COVID-19 pandemic via SNA and to delineate the pandemic’s effects on online courses. Only 33.3% of courses in our sample increased in terms of interaction during the pandemic; the scale of interaction did not rise in any courses thereafter. When the courses scale rose, the scope and frequency of interaction showed upward trends during the pandemic; and the clustering coefficient of natural science courses and social science courses differed: the coefficient for social science courses tended to rise whereas that for natural science courses generally declined. When the pandemic broke out, the interaction scale of a single natural science course decreased along with its interaction scope and frequency. The amount of interaction in most courses shrank rapidly during the pandemic and network members were not as active as they had been before. However, after the pandemic, some courses saw declining interaction but greater communication between members; interaction also became more frequent and deeper than before.
5.1 During the COVID-19 pandemic, the scale of interaction increased in only a few courses
The pandemic outbreak led to a rapid increase in the number of participants in most courses; however, the change in network scale was not significant. The scale of online interaction expanded swiftly in only a few courses; in others, the scale either did not change significantly or displayed a downward trend. After the pandemic, the interaction scale in most courses decreased quickly; the same pattern applied to communication between network members. Learners’ enthusiasm for online interaction reduced as the circumstances of the pandemic improved—potentially because, during the pandemic, China’s Ministry of Education declared “School’s Out, But Class’s On” policy. Major colleges and universities were encouraged to use the Internet and informational resources to provide learning support, hence the sudden increase in the number of participants and interaction in online courses [ 46 ]. After the pandemic, students’ enthusiasm for online learning gradually weakened, presumably due to easing of the pandemic [ 47 ]. More activities also transitioned from online to offline, which tempered learners’ online discussion. Research has shown that long-term online learning can even bore students [ 48 ].
Most courses’ interaction scale decreased significantly after the pandemic. First, teachers and students occupied separate spaces during the outbreak, had few opportunities for mutual cooperation and friendship, and lacked a sense of belonging [ 49 ]. Students’ enthusiasm for learning dissipated over time [ 50 ]. Second, some teachers were especially concerned about adapting in-person instructional materials for digital platforms; their pedagogical methods were ineffective, and they did not provide learning activities germane to student interaction [ 51 ]. Third, although teachers and students in remote areas were actively engaged in online learning, some students could not continue to participate in distance learning due to inadequate technology later in the outbreak [ 52 ].
5.2 Characteristics of online learning interaction during and after the COVID-19 pandemic
5.2.1 during the covid-19 pandemic, online interaction in most courses did not change significantly..
The interaction scale of only a few courses increased during the pandemic. The interaction scope and frequency of these courses climbed as well. Yet even as the degree of network interaction rose, course network density did not expand in all cases. The pandemic sparked a surge in the number of online learners and a rapid increase in network scale, but students found it difficult to interact with all learners. Yau pointed out that a greater network scale did not enrich the range of interaction between individuals; rather, the number of individuals who could interact directly was limited [ 53 ]. The internet facilitates interpersonal communication. However, not everyone has the time or ability to establish close ties with others [ 54 ].
In addition, social science courses and natural science courses in our sample revealed disparate trends in this regard: the clustering coefficient of social science courses increased and that of natural science courses decreased. Social science courses usually employ learning approaches distinct from those in natural science courses [ 55 ]. Social science courses emphasize critical and innovative thinking along with personal expression [ 56 ]. Natural science courses focus on practical skills, methods, and principles [ 57 ]. Therefore, the content of social science courses can spur large-scale discussion among learners. Some course evaluations indicated that the course content design was suboptimal as well: teachers paid close attention to knowledge transmission and much less to piquing students’ interest in learning. In addition, the thread topics that teachers posted were scarcely diversified and teachers’ questions lacked openness. These attributes could not spark active discussion among learners.
5.2.2 Online learning interaction declined after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Most courses’ interaction scale and intensity decreased rapidly after the pandemic, but some did not change. Courses with a larger network scale did not continue to expand after the outbreak, and students’ enthusiasm for learning paled. The pandemic’s reduced severity also influenced the number of participants in online courses. Meanwhile, restored school order moved many learning activities from virtual to in-person spaces. Face-to-face learning has gradually replaced online learning, resulting in lower enrollment and less interaction in online courses. Prolonged online courses could have also led students to feel lonely and to lack a sense of belonging [ 58 ].
The scale of interaction in some courses did not change substantially after the pandemic yet learners’ connections became tighter. We hence recommend that teachers seize pandemic-related opportunities to design suitable activities. Additionally, instructors should promote student-teacher and student-student interaction, encourage students to actively participate online, and generally intensify the impact of online learning.
5.3 What are the characteristics of interaction in social science courses and natural science courses?
The level of interaction in Economics (a social science course) was significantly higher than that in Electrodynamics (a natural science course), and the small-world property in Economics increased as well. To boost online courses’ learning-related impacts, teachers can divide groups of learners based on the clustering coefficient and the average path length. Small groups of students may benefit teachers in several ways: to participate actively in activities intended to expand students’ knowledge, and to serve as key actors in these small groups. Cultivating students’ keenness to participate in class activities and self-management can also help teachers guide learner interaction and foster deep knowledge construction.
As evidenced by comments posted in the Electrodynamics course, we observed less interaction between students. Teachers also rarely urged students to contribute to conversations. These trends may have arisen because teachers and students were in different spaces. Teachers might have struggled to discern students’ interaction status. Teachers could also have failed to intervene in time, to design online learning activities that piqued learners’ interest, and to employ sound interactive theme planning and guidance. Teachers are often active in traditional classroom settings. Their roles are comparatively weakened online, such that they possess less control over instruction [ 59 ]. Online instruction also requires a stronger hand in learning: teachers should play a leading role in regulating network members’ interactive communication [ 60 ]. Teachers can guide learners to participate, help learners establish social networks, and heighten students’ interest in learning [ 61 ]. Teachers should attend to core members in online learning while also considering edge members; by doing so, all network members can be driven to share their knowledge and become more engaged. Finally, teachers and assistant teachers should help learners develop knowledge, exchange topic-related ideas, pose relevant questions during course discussions, and craft activities that enable learners to interact online [ 62 ]. These tactics can improve the effectiveness of online learning.
As described, network members displayed distinct interaction behavior in Economics and Electrodynamics courses. First, these courses varied in their difficulty: the social science course seemed easier to understand and focused on divergent thinking. Learners were often willing to express their views in comments and to ponder others’ perspectives [ 63 ]. The natural science course seemed more demanding and was oriented around logical thinking and skills [ 64 ]. Second, courses’ content differed. In general, social science courses favor the acquisition of declarative knowledge and creative knowledge compared with natural science courses. Social science courses also entertain open questions [ 65 ]. Natural science courses revolve around principle knowledge, strategic knowledge, and transfer knowledge [ 66 ]. Problems in these courses are normally more complicated than those in social science courses. Third, the indicators affecting students’ attitudes toward learning were unique. Guo et al. discovered that “teacher feedback” most strongly influenced students’ attitudes towards learning social science courses but had less impact on students in natural science courses [ 67 ]. Therefore, learners in social science courses likely expect more feedback from teachers and greater interaction with others.
6. Conclusion and future work
Our findings show that the network interaction scale of some online courses expanded during the COVID-19 pandemic. The network scale of most courses did not change significantly, demonstrating that the pandemic did not notably alter the scale of course interaction. Online learning interaction among course network members whose interaction scale increased also became more frequent during the pandemic. Once the outbreak was under control, although the scale of interaction declined, the level and scope of some courses’ interactive networks continued to rise; interaction was thus particularly effective in these cases. Overall, the pandemic appeared to have a relatively positive impact on online learning interaction. We considered a pair of courses in detail and found that Economics (a social science course) fared much better than Electrodynamics (a natural science course) in classroom interaction; learners were more willing to partake in-class activities, perhaps due to these courses’ unique characteristics. Brint et al. also came to similar conclusions [ 57 ].
This study was intended to be rigorous. Even so, several constraints can be addressed in future work. The first limitation involves our sample: we focused on a select set of courses hosted on China’s icourse.163 MOOC platform. Future studies should involve an expansive collection of courses to provide a more holistic understanding of how the pandemic has influenced online interaction. Second, we only explored the interactive relationship between learners and did not analyze interactive content. More in-depth content analysis should be carried out in subsequent research. All in all, the emergence of COVID-19 has provided a new path for online learning and has reshaped the distance learning landscape. To cope with associated challenges, educational practitioners will need to continue innovating in online instructional design, strengthen related pedagogy, optimize online learning conditions, and bolster teachers’ and students’ competence in online learning.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- PubMed/NCBI
- 30. Serrat O. Social network analysis. Knowledge solutions: Springer; 2017. p. 39–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0983-9_9
- 33. Rong Y, Xu E, editors. Strategies for the Management of the Government Affairs Microblogs in China Based on the SNA of Fifty Government Affairs Microblogs in Beijing. 14th International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management 2017.
- 34. Hu X, Chu S, editors. A comparison on using social media in a professional experience course. International Conference on Social Media and Society; 2013.
- 35. Bydžovská H. A Comparative Analysis of Techniques for Predicting Student Performance. Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Educational Data Mining; Raleigh, NC, USA: International Educational Data Mining Society2016. p. 306–311.
- 40. Olivares D, Adesope O, Hundhausen C, et al., editors. Using social network analysis to measure the effect of learning analytics in computing education. 19th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies 2019.
- 41. Travers J, Milgram S. An experimental study of the small world problem. Social Networks: Elsevier; 1977. p. 179–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-442450-0.50018–3
- 43. Okamoto K, Chen W, Li X-Y, editors. Ranking of closeness centrality for large-scale social networks. International workshop on frontiers in algorithmics; 2008; Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
- 47. Ding Y, Yang X, Zheng Y, editors. COVID-19’s Effects on the Scope, Effectiveness, and Roles of Teachers in Online Learning Based on Social Network Analysis: A Case Study. International Conference on Blended Learning; 2021: Springer.
- 64. Boys C, Brennan J., Henkel M., Kirkland J., Kogan M., Youl P. Higher Education and Preparation for Work. Jessica Kingsley Publishers. 1988. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079612331381467
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Published: 27 September 2021
Why lockdown and distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic are likely to increase the social class achievement gap
- Sébastien Goudeau ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7293-0977 1 ,
- Camille Sanrey ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3158-1306 1 ,
- Arnaud Stanczak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2596-1516 2 ,
- Antony Manstead ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7540-2096 3 &
- Céline Darnon ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2613-689X 2
Nature Human Behaviour volume 5 , pages 1273–1281 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
117k Accesses
162 Citations
128 Altmetric
Metrics details
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced teachers and parents to quickly adapt to a new educational context: distance learning. Teachers developed online academic material while parents taught the exercises and lessons provided by teachers to their children at home. Considering that the use of digital tools in education has dramatically increased during this crisis, and it is set to continue, there is a pressing need to understand the impact of distance learning. Taking a multidisciplinary view, we argue that by making the learning process rely more than ever on families, rather than on teachers, and by getting students to work predominantly via digital resources, school closures exacerbate social class academic disparities. To address this burning issue, we propose an agenda for future research and outline recommendations to help parents, teachers and policymakers to limit the impact of the lockdown on social-class-based academic inequality.
Similar content being viewed by others

Large socio-economic, geographic and demographic disparities exist in exposure to school closures
Elementary school teachers’ perspectives about learning during the COVID-19 pandemic
Uncovering Covid-19, distance learning, and educational inequality in rural areas of Pakistan and China: a situational analysis method
The widespread effects of the COVID-19 pandemic that emerged in 2019–2020 have drastically increased health, social and economic inequalities 1 , 2 . For more than 900 million learners around the world, the pandemic led to the closure of schools and universities 3 . This exceptional situation forced teachers, parents and students to quickly adapt to a new educational context: distance learning. Teachers had to develop online academic materials that could be used at home to ensure educational continuity while ensuring the necessary physical distancing. Primary and secondary school students suddenly had to work with various kinds of support, which were usually provided online by their teachers. For college students, lockdown often entailed returning to their hometowns while staying connected with their teachers and classmates via video conferences, email and other digital tools. Despite the best efforts of educational institutions, parents and teachers to keep all children and students engaged in learning activities, ensuring educational continuity during school closure—something that is difficult for everyone—may pose unique material and psychological challenges for working-class families and students.
Not only did the pandemic lead to the closure of schools in many countries, often for several weeks, it also accelerated the digitalization of education and amplified the role of parental involvement in supporting the schoolwork of their children. Thus, beyond the specific circumstances of the COVID-19 lockdown, we believe that studying the effects of the pandemic on academic inequalities provides a way to more broadly examine the consequences of school closure and related effects (for example, digitalization of education) on social class inequalities. Indeed, bearing in mind that (1) the risk of further pandemics is higher than ever (that is, we are in a ‘pandemic era’ 4 , 5 ) and (2) beyond pandemics, the use of digital tools in education (and therefore the influence of parental involvement) has dramatically increased during this crisis, and is set to continue, there is a pressing need for an integrative and comprehensive model that examines the consequences of distance learning. Here, we propose such an integrative model that helps us to understand the extent to which the school closures associated with the pandemic amplify economic, digital and cultural divides that in turn affect the psychological functioning of parents, students and teachers in a way that amplifies academic inequalities. Bringing together research in social sciences, ranging from economics and sociology to social, cultural, cognitive and educational psychology, we argue that by getting students to work predominantly via digital resources rather than direct interactions with their teachers, and by making the learning process rely more than ever on families rather than teachers, school closures exacerbate social class academic disparities.
First, we review research showing that social class is associated with unequal access to digital tools, unequal familiarity with digital skills and unequal uses of such tools for learning purposes 6 , 7 . We then review research documenting how unequal familiarity with school culture, knowledge and skills can also contribute to the accentuation of academic inequalities 8 , 9 . Next, we present the results of surveys conducted during the 2020 lockdown showing that the quality and quantity of pedagogical support received from schools varied according to the social class of families (for examples, see refs. 10 , 11 , 12 ). We then argue that these digital, cultural and structural divides represent barriers to the ability of parents to provide appropriate support for children during distance learning (Fig. 1 ). These divides also alter the levels of self-efficacy of parents and children, thereby affecting their engagement in learning activities 13 , 14 . In the final section, we review preliminary evidence for the hypothesis that distance learning widens the social class achievement gap and we propose an agenda for future research. In addition, we outline recommendations that should help parents, teachers and policymakers to use social science research to limit the impact of school closure and distance learning on the social class achievement gap.
Economic, structural, digital and cultural divides influence the psychological functioning of parents and students in a way that amplify inequalities.
The digital divide
Unequal access to digital resources.
Although the use of digital technologies is almost ubiquitous in developed nations, there is a digital divide such that some people are more likely than others to be numerically excluded 15 (Fig. 1 ). Social class is a strong predictor of digital disparities, including the quality of hardware, software and Internet access 16 , 17 , 18 . For example, in 2019, in France, around 1 in 5 working-class families did not have personal access to the Internet compared with less than 1 in 20 of the most privileged families 19 . Similarly, in 2020, in the United Kingdom, 20% of children who were eligible for free school meals did not have access to a computer at home compared with 7% of other children 20 . In 2021, in the United States, 41% of working-class families do not own a laptop or desktop computer and 43% do not have broadband compared with 8% and 7%, respectively, of upper/middle-class Americans 21 . A similar digital gap is also evident between lower-income and higher-income countries 22 .
Second, simply having access to a computer and an Internet connection does not ensure effective distance learning. For example, many of the educational resources sent by teachers need to be printed, thereby requiring access to printers. Moreover, distance learning is more difficult in households with only one shared computer compared with those where each family member has their own 23 . Furthermore, upper/middle-class families are more likely to be able to guarantee a suitable workspace for each child than their working-class counterparts 24 .
In the context of school closures, such disparities are likely to have important consequences for educational continuity. In line with this idea, a survey of approximately 4,000 parents in the United Kingdom confirmed that during lockdown, more than half of primary school children from the poorest families did not have access to their own study space and were less well equipped for distance learning than higher-income families 10 . Similarly, a survey of around 1,300 parents in the Netherlands found that during lockdown, children from working-class families had fewer computers at home and less room to study than upper/middle-class children 11 .
Data from non-Western countries highlight a more general digital divide, showing that developing countries have poorer access to digital equipment. For example, in India in 2018, only 10.7% of households possessed a digital device 25 , while in Pakistan in 2020, 31% of higher-education teachers did not have Internet access and 68.4% did not have a laptop 26 . In general, developing countries lack access to digital technologies 27 , 28 , and these difficulties of access are even greater in rural areas (for example, see ref. 29 ). Consequently, school closures have huge repercussions for the continuity of learning in these countries. For example, in India in 2018, only 11% of the rural and 40% of the urban population above 14 years old could use a computer and access the Internet 25 . Time spent on education during school closure decreased by 80% in Bangladesh 30 . A similar trend was observed in other countries 31 , with only 22% of children engaging in remote learning in Kenya 32 and 50% in Burkina Faso 33 . In Ghana, 26–32% of children spent no time at all on learning during the pandemic 34 . Beyond the overall digital divide, social class disparities are also evident in developing countries, with lower access to digital resources among households in which parental educational levels were low (versus households in which parental educational levels were high; for example, see ref. 35 for Nigeria and ref. 31 for Ecuador).
Unequal digital skills
In addition to unequal access to digital tools, there are also systematic variations in digital skills 36 , 37 (Fig. 1 ). Upper/middle-class families are more familiar with digital tools and resources and are therefore more likely to have the digital skills needed for distance learning 38 , 39 , 40 . These digital skills are particularly useful during school closures, both for students and for parents, for organizing, retrieving and correctly using the resources provided by the teachers (for example, sending or receiving documents by email, printing documents or using word processors).
Social class disparities in digital skills can be explained in part by the fact that children from upper/middle-class families have the opportunity to develop digital skills earlier than working-class families 41 . In member countries of the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), only 23% of working-class children had started using a computer at the age of 6 years or earlier compared with 43% of upper/middle-class children 42 . Moreover, because working-class people tend to persist less than upper/middle-class people when confronted with digital difficulties 23 , the use of digital tools and resources for distance learning may interfere with the ability of parents to help children with their schoolwork.
Unequal use of digital tools
A third level of digital divide concerns variations in digital tool use 18 , 43 (Fig. 1 ). Upper/middle-class families are more likely to use digital resources for work and education 6 , 41 , 44 , whereas working-class families are more likely to use these resources for entertainment, such as electronic games or social media 6 , 45 . This divide is also observed among students, whereby working-class students tend to use digital technologies for leisure activities, whereas their upper/middle-class peers are more likely to use them for academic activities 46 and to consider that computers and the Internet provide an opportunity for education and training 23 . Furthermore, working-class families appear to regulate the digital practices of their children less 47 and are more likely to allow screens in the bedrooms of children and teenagers without setting limits on times or practices 48 .
In sum, inequalities in terms of digital resources, skills and use have strong implications for distance learning. This is because they make working-class students and parents particularly vulnerable when learning relies on extensive use of digital devices rather than on face-to-face interaction with teachers.
The cultural divide
Even if all three levels of digital divide were closed, upper/middle-class families would still be better prepared than working-class families to ensure educational continuity for their children. Upper/middle-class families are more familiar with the academic knowledge and skills that are expected and valued in educational settings, as well as with the independent, autonomous way of learning that is valued in the school culture and becomes even more important during school closure (Fig. 1 ).
Unequal familiarity with academic knowledge and skills
According to classical social reproduction theory 8 , 49 , school is not a neutral place in which all forms of language and knowledge are equally valued. Academic contexts expect and value culture-specific and taken-for-granted forms of knowledge, skills and ways of being, thinking and speaking that are more in tune with those developed through upper/middle-class socialization (that is, ‘cultural capital’ 8 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 ). For instance, academic contexts value interest in the arts, museums and literature 54 , 55 , a type of interest that is more likely to develop through socialization in upper/middle-class families than in working-class socialization 54 , 56 . Indeed, upper/middle-class parents are more likely than working-class parents to engage in activities that develop this cultural capital. For example, they possess more books and cultural objects at home, read more stories to their children and visit museums and libraries more often (for examples, see refs. 51 , 54 , 55 ). Upper/middle-class children are also more involved in extra-curricular activities (for example, playing a musical instrument) than working-class children 55 , 56 , 57 .
Beyond this implicit familiarization with the school curriculum, upper/middle-class parents more often organize educational activities that are explicitly designed to develop academic skills of their children 57 , 58 , 59 . For example, they are more likely to monitor and re-explain lessons or use games and textbooks to develop and reinforce academic skills (for example, labelling numbers, letters or colours 57 , 60 ). Upper/middle-class parents also provide higher levels of support and spend more time helping children with homework than working-class parents (for examples, see refs. 61 , 62 ). Thus, even if all parents are committed to the academic success of their children, working-class parents have fewer chances to provide the help that children need to complete homework 63 , and homework is more beneficial for children from upper-middle class families than for children from working-class families 64 , 65 .
School closures amplify the impact of cultural inequalities
The trends described above have been observed in ‘normal’ times when schools are open. School closures, by making learning rely more strongly on practices implemented at home (rather than at school), are likely to amplify the impact of these disparities. Consistent with this idea, research has shown that the social class achievement gap usually greatly widens during school breaks—a phenomenon described as ‘summer learning loss’ or ‘summer setback’ 66 , 67 , 68 . During holidays, the learning by children tends to decline, and this is particularly pronounced in children from working-class families. Consequently, the social class achievement gap grows more rapidly during the summer months than it does in the rest of the year. This phenomenon is partly explained by the fact that during the break from school, social class disparities in investment in activities that are beneficial for academic achievement (for example, reading, travelling to a foreign country or museum visits) are more pronounced.
Therefore, when they are out of school, children from upper/middle-class backgrounds may continue to develop academic skills unlike their working-class counterparts, who may stagnate or even regress. Research also indicates that learning loss during school breaks tends to be cumulative 66 . Thus, repeated episodes of school closure are likely to have profound consequences for the social class achievement gap. Consistent with the idea that school closures could lead to similar processes as those identified during summer breaks, a recent survey indicated that during the COVID-19 lockdown in the United Kingdom, children from upper/middle-class families spent more time on educational activities (5.8 h per day) than those from working-class families (4.5 h per day) 7 , 69 .
Unequal dispositions for autonomy and self-regulation
School closures have encouraged autonomous work among students. This ‘independent’ way of studying is compatible with the family socialization of upper/middle-class students, but does not match the interdependent norms more commonly associated with working-class contexts 9 . Upper/middle-class contexts tend to promote cultural norms of independence whereby individuals perceive themselves as autonomous actors, independent of other individuals and of the social context, able to pursue their own goals 70 . For example, upper/middle-class parents tend to invite children to express their interests, preferences and opinions during the various activities of everyday life 54 , 55 . Conversely, in working-class contexts characterized by low economic resources and where life is more uncertain, individuals tend to perceive themselves as interdependent, connected to others and members of social groups 53 , 70 , 71 . This interdependent self-construal fits less well with the independent culture of academic contexts. This cultural mismatch between interdependent self-construal common in working-class students and the independent norms of the educational institution has negative consequences for academic performance 9 .
Once again, the impact of these differences is likely to be amplified during school closures, when being able to work alone and autonomously is especially useful. The requirement to work alone is more likely to match the independent self-construal of upper/middle-class students than the interdependent self-construal of working-class students. In the case of working-class students, this mismatch is likely to increase their difficulties in working alone at home. Supporting our argument, recent research has shown that working-class students tend to underachieve in contexts where students work individually compared with contexts where students work with others 72 . Similarly, during school closures, high self-regulation skills (for example, setting goals, selecting appropriate learning strategies and maintaining motivation 73 ) are required to maintain study activities and are likely to be especially useful for using digital resources efficiently. Research has shown that students from working-class backgrounds typically develop their self-regulation skills to a lesser extent than those from upper/middle-class backgrounds 74 , 75 , 76 .
Interestingly, some authors have suggested that independent (versus interdependent) self-construal may also affect communication with teachers 77 . Indeed, in the context of distance learning, working-class families are less likely to respond to the communication of teachers because their ‘interdependent’ self leads them to respect hierarchies, and thus perceive teachers as an expert who ‘can be trusted to make the right decisions for learning’. Upper/middle class families, relying on ‘independent’ self-construal, are more inclined to seek individualized feedback, and therefore tend to participate to a greater extent in exchanges with teachers. Such cultural differences are important because they can also contribute to the difficulties encountered by working-class families.
The structural divide: unequal support from schools
The issues reviewed thus far all increase the vulnerability of children and students from underprivileged backgrounds when schools are closed. To offset these disadvantages, it might be expected that the school should increase its support by providing additional resources for working-class students. However, recent data suggest that differences in the material and human resources invested in providing educational support for children during periods of school closure were—paradoxically—in favour of upper/middle-class students (Fig. 1 ). In England, for example, upper/middle-class parents reported benefiting from online classes and video-conferencing with teachers more often than working-class parents 10 . Furthermore, active help from school (for example, online teaching, private tutoring or chats with teachers) occurred more frequently in the richest households (64% of the richest households declared having received help from school) than in the poorest households (47%). Another survey found that in the United Kingdom, upper/middle-class children were more likely to take online lessons every day (30%) than working-class students (16%) 12 . This substantial difference might be due, at least in part, to the fact that private schools are better equipped in terms of online platforms (60% of schools have at least one online platform) than state schools (37%, and 23% in the most deprived schools) and were more likely to organize daily online lessons. Similarly, in the United Kingdom, in schools with a high proportion of students eligible for free school meals, teachers were less inclined to broadcast an online lesson for their pupils 78 . Interestingly, 58% of teachers in the wealthiest areas reported having messaged their students or their students’ parents during lockdown compared with 47% in the most deprived schools. In addition, the probability of children receiving technical support from the school (for example, by providing pupils with laptops or other devices) is, surprisingly, higher in the most advantaged schools than in the most deprived 78 .
In addition to social class disparities, there has been less support from schools for African-American and Latinx students. During school closures in the United States, 40% of African-American students and 30% of Latinx students received no online teaching compared with 10% of white students 79 . Another source of inequality is that the probability of school closure was correlated with social class and race. In the United States, for example, school closures from September to December 2020 were more common in schools with a high proportion of racial/ethnic minority students, who experience homelessness and are eligible for free/discounted school meals 80 .
Similarly, access to educational resources and support was lower in poorer (compared with richer) countries 81 . In sub-Saharan Africa, during lockdown, 45% of children had no exposure at all to any type of remote learning. Of those who did, the medium was mostly radio, television or paper rather than digital. In African countries, at most 10% of children received some material through the Internet. In Latin America, 90% of children received some remote learning, but less than half of that was through the internet—the remainder being via radio and television 81 . In Ecuador, high-school students from the lowest wealth quartile had fewer remote-learning opportunities, such as Google class/Zoom, than students from the highest wealth quartile 31 .
Thus, the achievement gap and its accentuation during lockdown are due not only to the cultural and digital disadvantages of working-class families but also to unequal support from schools. This inequality in school support is not due to teachers being indifferent to or even supportive of social stratification. Rather, we believe that these effects are fundamentally structural. In many countries, schools located in upper/middle-class neighbourhoods have more money than those in the poorest neighbourhoods. Moreover, upper/middle-class parents invest more in the schools of their children than working-class parents (for example, see ref. 82 ), and schools have an interest in catering more for upper/middle-class families than for working-class families 83 . Additionally, the expectation of teachers may be lower for working-class children 84 . For example, they tend to estimate that working-class students invest less effort in learning than their upper/middle-class counterparts 85 . These differences in perception may have influenced the behaviour of teachers during school closure, such that teachers in privileged neighbourhoods provided more information to students because they expected more from them in term of effort and achievement. The fact that upper/middle-class parents are better able than working-class parents to comply with the expectations of teachers (for examples, see refs. 55 , 86 ) may have reinforced this phenomenon. These discrepancies echo data showing that working-class students tend to request less help in their schoolwork than upper/middle-class ones 87 , and they may even avoid asking for help because they believe that such requests could lead to reprimands 88 . During school closures, these students (and their families) may in consequence have been less likely to ask for help and resources. Jointly, these phenomena have resulted in upper/middle-class families receiving more support from schools during lockdown than their working-class counterparts.
Psychological effects of digital, cultural and structural divides
Despite being strongly influenced by social class, differences in academic achievement are often interpreted by parents, teachers and students as reflecting differences in ability 89 . As a result, upper/middle-class students are usually perceived—and perceive themselves—as smarter than working-class students, who are perceived—and perceive themselves—as less intelligent 90 , 91 , 92 or less able to succeed 93 . Working-class students also worry more about the fact that they might perform more poorly than upper/middle-class students 94 , 95 . These fears influence academic learning in important ways. In particular, they can consume cognitive resources when children and students work on academic tasks 96 , 97 . Self-efficacy also plays a key role in engaging in learning and perseverance in the face of difficulties 13 , 98 . In addition, working-class students are those for whom the fear of being outperformed by others is the most negatively related to academic performance 99 .
The fact that working-class children and students are less familiar with the tasks set by teachers, and less well equipped and supported, makes them more likely to experience feelings of incompetence (Fig. 1 ). Working-class parents are also more likely than their upper/middle-class counterparts to feel unable to help their children with schoolwork. Consistent with this, research has shown that both working-class students and parents have lower feelings of academic self-efficacy than their upper/middle-class counterparts 100 , 101 . These differences have been documented under ‘normal’ conditions but are likely to be exacerbated during distance learning. Recent surveys conducted during the school closures have confirmed that upper/middle-class families felt better able to support their children in distance learning than did working-class families 10 and that upper/middle-class parents helped their children more and felt more capable to do so 11 , 12 .
Pandemic disparity, future directions and recommendations
The research reviewed thus far suggests that children and their families are highly unequal with respect to digital access, skills and use. It also shows that upper/middle-class students are more likely to be supported in their homework (by their parents and teachers) than working-class students, and that upper/middle-class students and parents will probably feel better able than working-class ones to adapt to the context of distance learning. For all these reasons, we anticipate that as a result of school closures, the COVID-19 pandemic will substantially increase the social class achievement gap. Because school closures are a recent occurrence, it is too early to measure with precision their effects on the widening of the achievement gap. However, some recent data are consistent with this idea.
Evidence for a widening gap during the pandemic
Comparing academic achievement in 2020 with previous years provides an early indication of the effects of school closures during the pandemic. In France, for example, first and second graders take national evaluations at the beginning of the school year. Initial comparisons of the results for 2020 with those from previous years revealed that the gap between schools classified as ‘priority schools’ (those in low-income urban areas) and schools in higher-income neighbourhoods—a gap observed every year—was particularly pronounced in 2020 in both French and mathematics 102 .
Similarly, in the Netherlands, national assessments take place twice a year. In 2020, they took place both before and after school closures. A recent analysis compared progress during this period in 2020 in mathematics/arithmetic, spelling and reading comprehension for 7–11-year-old students within the same period in the three previous years 103 . Results indicated a general learning loss in 2020. More importantly, for the 8% of working-class children, the losses were 40% greater than they were for upper/middle-class children.
Similar results were observed in Belgium among students attending the final year of primary school. Compared with students from previous cohorts, students affected by school closures experienced a substantial decrease in their mathematics and language scores, with children from more disadvantaged backgrounds experiencing greater learning losses 104 . Likewise, oral reading assessments in more than 100 school districts in the United States showed that the development of this skill among children in second and third grade significantly slowed between Spring and Autumn 2020, but this slowdown was more pronounced in schools from lower-achieving districts 105 .
It is likely that school closures have also amplified racial disparities in learning and achievement. For example, in the United States, after the first lockdown, students of colour lost the equivalent of 3–5 months of learning, whereas white students were about 1–3 months behind. Moreover, in the Autumn, when some students started to return to classrooms, African-American and Latinx students were more likely to continue distance learning, despite being less likely to have access to the digital tools, Internet access and live contact with teachers 106 .
In some African countries (for example, Ethiopia, Kenya, Liberia, Tanzania and Uganda), the COVID-19 crisis has resulted in learning loss ranging from 6 months to more 1 year 107 , and this learning loss appears to be greater for working-class children (that is, those attending no-fee schools) than for upper/middle-class children 108 .
These findings show that school closures have exacerbated achievement gaps linked to social class and ethnicity. However, more research is needed to address the question of whether school closures differentially affect the learning of students from working- and upper/middle-class families.
Future directions
First, to assess the specific and unique impact of school closures on student learning, longitudinal research should compare student achievement at different times of the year, before, during and after school closures, as has been done to document the summer learning loss 66 , 109 . In the coming months, alternating periods of school closure and opening may occur, thereby presenting opportunities to do such research. This would also make it possible to examine whether the gap diminishes a few weeks after children return to in-school learning or whether, conversely, it increases with time because the foundations have not been sufficiently acquired to facilitate further learning 110 .
Second, the mechanisms underlying the increase in social class disparities during school closures should be examined. As discussed above, school closures result in situations for which students are unevenly prepared and supported. It would be appropriate to seek to quantify the contribution of each of the factors that might be responsible for accentuating the social class achievement gap. In particular, distinguishing between factors that are relatively ‘controllable’ (for example, resources made available to pupils) and those that are more difficult to control (for example, the self-efficacy of parents in supporting the schoolwork of their children) is essential to inform public policy and teaching practices.
Third, existing studies are based on general comparisons and very few provide insights into the actual practices that took place in families during school closure and how these practices affected the achievement gap. For example, research has documented that parents from working-class backgrounds are likely to find it more difficult to help their children to complete homework and to provide constructive feedback 63 , 111 , something that could in turn have a negative impact on the continuity of learning of their children. In addition, it seems reasonable to assume that during lockdown, parents from upper/middle-class backgrounds encouraged their children to engage in practices that, even if not explicitly requested by teachers, would be beneficial to learning (for example, creative activities or reading). Identifying the practices that best predict the maintenance or decline of educational achievement during school closures would help identify levers for intervention.
Finally, it would be interesting to investigate teaching practices during school closures. The lockdown in the spring of 2020 was sudden and unexpected. Within a few days, teachers had to find a way to compensate for the school closure, which led to highly variable practices. Some teachers posted schoolwork on platforms, others sent it by email, some set work on a weekly basis while others set it day by day. Some teachers also set up live sessions in large or small groups, providing remote meetings for questions and support. There have also been variations in the type of feedback given to students, notably through the monitoring and correcting of work. Future studies should examine in more detail what practices schools and teachers used to compensate for the school closures and their effects on widening, maintaining or even reducing the gap, as has been done for certain specific literacy programmes 112 as well as specific instruction topics (for example, ecology and evolution 113 ).
Practical recommendations
We are aware of the debate about whether social science research on COVID-19 is suitable for making policy decisions 114 , and we draw attention to the fact that some of our recommendations (Table 1 ) are based on evidence from experiments or interventions carried out pre-COVID while others are more speculative. In any case, we emphasize that these suggestions should be viewed with caution and be tested in future research. Some of our recommendations could be implemented in the event of new school closures, others only when schools re-open. We also acknowledge that while these recommendations are intended for parents and teachers, their implementation largely depends on the adoption of structural policies. Importantly, given all the issues discussed above, we emphasize the importance of prioritizing, wherever possible, in-person learning over remote learning 115 and where this is not possible, of implementing strong policies to support distance learning, especially for disadvantaged families.
Where face-to face teaching is not possible and teachers are responsible for implementing distance learning, it will be important to make them aware of the factors that can exacerbate inequalities during lockdown and to provide them with guidance about practices that would reduce these inequalities. Thus, there is an urgent need for interventions aimed at making teachers aware of the impact of the social class of children and families on the following factors: (1) access to, familiarity with and use of digital devices; (2) familiarity with academic knowledge and skills; and (3) preparedness to work autonomously. Increasing awareness of the material, cultural and psychological barriers that working-class children and families face during lockdown should increase the quality and quantity of the support provided by teachers and thereby positively affect the achievements of working-class students.
In addition to increasing the awareness of teachers of these barriers, teachers should be encouraged to adjust the way they communicate with working-class families due to differences in self-construal compared with upper/middle-class families 77 . For example, questions about family (rather than personal) well-being would be congruent with interdependent self-construals. This should contribute to better communication and help keep a better track of the progress of students during distance learning.
It is also necessary to help teachers to engage in practices that have a chance of reducing inequalities 53 , 116 . Particularly important is that teachers and schools ensure that homework can be done by all children, for example, by setting up organizations that would help children whose parents are not in a position to monitor or assist with the homework of their children. Options include homework help groups and tutoring by teachers after class. When schools are open, the growing tendency to set homework through digital media should be resisted as far as possible given the evidence we have reviewed above. Moreover, previous research has underscored the importance of homework feedback provided by teachers, which is positively related to the amount of homework completed and predictive of academic performance 117 . Where homework is web-based, it has also been shown that feedback on web-based homework enhances the learning of students 118 . It therefore seems reasonable to predict that the social class achievement gap will increase more slowly (or even remain constant or be reversed) in schools that establish individualized monitoring of students, by means of regular calls and feedback on homework, compared with schools where the support provided to pupils is more generic.
Given that learning during lockdown has increasingly taken place in family settings, we believe that interventions involving the family are also likely to be effective 119 , 120 , 121 . Simply providing families with suitable material equipment may be insufficient. Families should be given training in the efficient use of digital technology and pedagogical support. This would increase the self-efficacy of parents and students, with positive consequences for achievement. Ideally, such training would be delivered in person to avoid problems arising from the digital divide. Where this is not possible, individualized online tutoring should be provided. For example, studies conducted during the lockdown in Botswana and Italy have shown that individual online tutoring directly targeting either parents or students in middle school has a positive impact on the achievement of students, particularly for working-class students 122 , 123 .
Interventions targeting families should also address the psychological barriers faced by working-class families and children. Some interventions have already been designed and been shown to be effective in reducing the social class achievement gap, particularly in mathematics and language 124 , 125 , 126 . For example, research showed that an intervention designed to train low-income parents in how to support the mathematical development of their pre-kindergarten children (including classes and access to a library of kits to use at home) increased the quality of support provided by the parents, with a corresponding impact on the development of mathematical knowledge of their children. Such interventions should be particularly beneficial in the context of school closure.
Beyond its impact on academic performance and inequalities, the COVID-19 crisis has shaken the economies of countries around the world, casting millions of families around the world into poverty 127 , 128 , 129 . As noted earlier, there has been a marked increase in economic inequalities, bringing with it all the psychological and social problems that such inequalities create 130 , 131 , especially for people who live in scarcity 132 . The increase in educational inequalities is just one facet of the many difficulties that working-class families will encounter in the coming years, but it is one that could seriously limit the chances of their children escaping from poverty by reducing their opportunities for upward mobility. In this context, it should be a priority to concentrate resources on the most deprived students. A large proportion of the poorest households do not own a computer and do not have personal access to the Internet, which has important consequences for distance learning. During school closures, it is therefore imperative to provide such families with adequate equipment and Internet service, as was done in some countries in spring 2020. Even if the provision of such equipment is not in itself sufficient, it is a necessary condition for ensuring pedagogical continuity during lockdown.
Finally, after prolonged periods of school closure, many students may not have acquired the skills needed to pursue their education. A possible consequence would be an increase in the number of students for whom teachers recommend class repetitions. Class repetitions are contentious. On the one hand, class repetition more frequently affects working-class children and is not efficient in terms of learning improvement 133 . On the other hand, accepting lower standards of academic achievement or even suspending the practice of repeating a class could lead to pupils pursuing their education without mastering the key abilities needed at higher grades. This could create difficulties in subsequent years and, in this sense, be counterproductive. We therefore believe that the most appropriate way to limit the damage of the pandemic would be to help children catch up rather than allowing them to continue without mastering the necessary skills. As is being done in some countries, systematic remedial courses (for example, summer learning programmes) should be organized and financially supported following periods of school closure, with priority given to pupils from working-class families. Such interventions have genuine potential in that research has shown that participation in remedial summer programmes is effective in reducing learning loss during the summer break 134 , 135 , 136 . For example, in one study 137 , 438 students from high-poverty schools were offered a multiyear summer school programme that included various pedagogical and enrichment activities (for example, science investigation and music) and were compared with a ‘no-treatment’ control group. Students who participated in the summer programme progressed more than students in the control group. A meta-analysis 138 of 41 summer learning programmes (that is, classroom- and home-based summer interventions) involving children from kindergarten to grade 8 showed that these programmes had significantly larger benefits for children from working-class families. Although such measures are costly, the cost is small compared to the price of failing to fulfil the academic potential of many students simply because they were not born into upper/middle-class families.
The unprecedented nature of the current pandemic means that we lack strong data on what the school closure period is likely to produce in terms of learning deficits and the reproduction of social inequalities. However, the research discussed in this article suggests that there are good reasons to predict that this period of school closures will accelerate the reproduction of social inequalities in educational achievement.
By making school learning less dependent on teachers and more dependent on families and digital tools and resources, school closures are likely to greatly amplify social class inequalities. At a time when many countries are experiencing second, third or fourth waves of the pandemic, resulting in fresh periods of local or general lockdowns, systematic efforts to test these predictions are urgently needed along with steps to reduce the impact of school closures on the social class achievement gap.
Bambra, C., Riordan, R., Ford, J. & Matthews, F. The COVID-19 pandemic and health inequalities. J. Epidemiol. Commun. Health 74 , 964–968 (2020).
Google Scholar
Johnson, P, Joyce, R & Platt, L. The IFS Deaton Review of Inequalities: A New Year’s Message (Institute for Fiscal Studies, 2021).
Education: from disruption to recovery. https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse (UNESCO, 2020).
Daszak, P. We are entering an era of pandemics—it will end only when we protect the rainforest. The Guardian (28 July 2020); https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2020/jul/28/pandemic-era-rainforest-deforestation-exploitation-wildlife-disease
Dobson, A. P. et al. Ecology and economics for pandemic prevention. Science 369 , 379–381 (2020).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Harris, C., Straker, L. & Pollock, C. A socioeconomic related ‘digital divide’ exists in how, not if, young people use computers. PLoS ONE 12 , e0175011 (2017).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zhang, M. Internet use that reproduces educational inequalities: evidence from big data. Comput. Educ. 86 , 212–223 (2015).
Article Google Scholar
Bourdieu, P. & Passeron, J. C. Reproduction in Education, Society and Culture (Sage, 1990).
Stephens, N. M., Fryberg, S. A., Markus, H. R., Johnson, C. S. & Covarrubias, R. Unseen disadvantage: how American universities’ focus on independence undermines the academic performance of first-generation college students. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 102 , 1178–1197 (2012).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Andrew, A. et al. Inequalities in children’s experiences of home learning during the COVID-19 lockdown in England. Fisc. Stud. 41 , 653–683 (2020).
Bol, T. Inequality in homeschooling during the Corona crisis in the Netherlands. First results from the LISS Panel. Preprint at SocArXiv https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/hf32q (2020).
Cullinane, C. & Montacute, R. COVID-19 and Social Mobility. Impact Brief #1: School Shutdown (The Sutton Trust, 2020).
Bandura, A. Self-efficacy: toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychol. Rev. 84 , 191–215 (1977).
Prior, D. D., Mazanov, J., Meacheam, D., Heaslip, G. & Hanson, J. Attitude, digital literacy and self efficacy: low-on effects for online learning behavior. Internet High. Educ. 29 , 91–97 (2016).
Robinson, L. et al. Digital inequalities 2.0: legacy inequalities in the information age. First Monday https://doi.org/10.5210/fm.v25i7.10842 (2020).
Cruz-Jesus, F., Vicente, M. R., Bacao, F. & Oliveira, T. The education-related digital divide: an analysis for the EU-28. Comput. Hum. Behav. 56 , 72–82 (2016).
Rice, R. E. & Haythornthwaite, C. In The Handbook of New Media (eds Lievrouw, L. A. & Livingstone S. M.), 92–113 (Sage, 2006).
Yates, S., Kirby, J. & Lockley, E. Digital media use: differences and inequalities in relation to class and age. Sociol. Res. Online 20 , 71–91 (2015).
Legleye, S. & Rolland, A. Une personne sur six n’utilise pas Internet, plus d’un usager sur trois manques de compétences numériques de base [One in six people do not use the Internet, more than one in three users lack basic digital skills] (INSEE Première, 2019).
Green, F. Schoolwork in lockdown: new evidence on the epidemic of educational poverty (LLAKES Centre, 2020); https://www.llakes.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/RP-67-Francis-Green-Research-Paper-combined-file.pdf
Vogels, E. Digital divide persists even as americans with lower incomes make gains in tech adoption (Pew Research Center, 2021); https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2021/06/22/digital-divide-persists-even-as-americans-with-lower-incomes-make-gains-in-tech-adoption/
McBurnie, C., Adam, T. & Kaye, T. Is there learning continuity during the COVID-19 pandemic? A synthesis of the emerging evidence. J. Learn. Develop. http://dspace.col.org/handle/11599/3720 (2020).
Baillet, J., Croutte, P. & Prieur, V. Baromètre du numérique 2019 [Digital barometer 2019] (Sourcing Crédoc, 2019).
Giraud, F., Bertrand, J., Court, M. & Nicaise, S. In Enfances de Classes. De l’inégalité Parmi les Enfants (ed. Lahire, B.) 933–952 (Seuil, 2019).
Ahamed, S. & Siddiqui, Z. Disparity in access to quality education and the digital divide (Ideas for India, 2020); https://www.ideasforindia.in/topics/macroeconomics/disparity-in-access-to-quality-education-and-the-digital-divide.html
Soomro, K. A., Kale, U., Curtis, R., Akcaoglu, M. & Bernstein, M. Digital divide among higher education faculty. Int. J. Educ. Tech. High. Ed. 17 , 21 (2020).
Meng, Q. & Li, M. New economy and ICT development in China. Inf. Econ. Policy 14 , 275–295 (2002).
Chinn, M. D. & Fairlie, R. W. The determinants of the global digital divide: a cross-country analysis of computer and internet penetration. Oxf. Econ. Pap. 59 , 16–44 (2006).
Lembani, R., Gunter, A., Breines, M. & Dalu, M. T. B. The same course, different access: the digital divide between urban and rural distance education students in South Africa. J. Geogr. High. Educ. 44 , 70–84 (2020).
Asadullah, N., Bhattacharjee, A., Tasnim, M. & Mumtahena, F. COVID-19, schooling, and learning (BRAC Institute of Governance & Development, 2020); https://bigd.bracu.ac.bd/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/COVID-19-Schooling-and-Learning_June-25-2020.pdf
Asanov, I., Flores, F., McKenzie, D., Mensmann, M. & Schulte, M. Remote-learning, time-use, and mental health of Ecuadorian high-school students during the COVID-19 quarantine. World Dev. 138 , 105225 (2021).
Kihui, N. Kenya: 80% of students missing virtual learning amid school closures—study. AllAfrica (18 May 2020); https://allafrica.com/stories/202005180774.html
Debenedetti, L., Hirji, S., Chabi, M. O. & Swigart, T. Prioritizing evidence-based responses in Burkina Faso to mitigate the economic effects of COVID-19: lessons from RECOVR (Innovations for Poverty Action, 2020); https://www.poverty-action.org/blog/prioritizing-evidence-based-responses-burkina-faso-mitigate-economic-effects-covid-19-lessons
Bosumtwi-Sam, C. & Kabay, S. Using data and evidence to inform school reopening in Ghana (Innovations for Poverty Action, 2020); https://www.poverty-action.org/blog/using-data-and-evidence-inform-school-reopening-ghana
Azubuike, O. B., Adegboye, O. & Quadri, H. Who gets to learn in a pandemic? Exploring the digital divide in remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Nigeria. Int. J. Educ. Res. Open 2 , 100022 (2021).
Attewell, P. Comment: the first and second digital divides. Sociol. Educ. 74 , 252–259 (2001).
DiMaggio, P., Hargittai, E., Neuman, W. R. & Robinson, J. P. Social implications of the Internet. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 27 , 307–336 (2001).
Hargittai, E. Digital na(t)ives? Variation in Internet skills and uses among members of the ‘Net Generation’. Sociol. Inq. 80 , 92–113 (2010).
Iivari, N., Sharma, S. & Ventä-Olkkonen, L. Digital transformation of everyday life—how COVID-19 pandemic transformed the basic education of the young generation and why information management research should care? Int. J. Inform. Manag. 55 , 102183 (2020).
Wei, L. & Hindman, D. B. Does the digital divide matter more? Comparing the effects of new media and old media use on the education-based knowledge gap. Mass Commun. Soc. 14 , 216–235 (2011).
Octobre, S. & Berthomier, N. L’enfance des loisirs [The childhood of leisure]. Cult. Études 6 , 1–12 (2011).
Education at a glance 2015: OECD indicators (OECD, 2015); https://doi.org/10.1787/eag-2015-en
North, S., Snyder, I. & Bulfin, S. Digital tastes: social class and young people’s technology use. Inform. Commun. Soc. 11 , 895–911 (2008).
Robinson, L. & Schulz, J. Net time negotiations within the family. Inform. Commun. Soc. 16 , 542–560 (2013).
Bonfadelli, H. The Internet and knowledge gaps: a theoretical and empirical investigation. Eur. J. Commun. 17 , 65–84 (2002).
Drabowicz, T. Social theory of Internet use: corroboration or rejection among the digital natives? Correspondence analysis of adolescents in two societies. Comput. Educ. 105 , 57–67 (2017).
Nikken, P. & Jansz, J. Developing scales to measure parental mediation of young children’s Internet use. Learn. Media Technol. 39 , 250–266 (2014).
Danic, I., Fontar, B., Grimault-Leprince, A., Le Mentec, M. & David, O. Les espaces de construction des inégalités éducatives [The areas of construction of educational inequalities] (Presses Univ. de Rennes, 2019).
Goudeau, S. Comment l'école reproduit-elle les inégalités? [How does school reproduce inequalities?] (Univ. Grenoble Alpes Editions/Presses Univ. de Grenoble, 2020).
Bernstein, B. Class, Codes, and Control (Routledge, 1975).
Gaddis, S. M. The influence of habitus in the relationship between cultural capital and academic achievement. Soc. Sci. Res. 42 , 1–13 (2013).
Lamont, M. & Lareau, A. Cultural capital: allusions, gaps and glissandos in recent theoretical developments. Sociol. Theory 6 , 153–168 (1988).
Stephens, N. M., Markus, H. R. & Phillips, L. T. Social class culture cycles: how three gateway contexts shape selves and fuel inequality. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 65 , 611–634 (2014).
Lahire, B. Enfances de classe. De l’inégalité parmi les enfants [Social class childhood. Inequality among children] (Le Seuil, 2019).
Lareau, A. Unequal Childhoods: Class, Race, and Family Life (Univ. of California Press, 2003).
Bourdieu, P. La distinction. Critique sociale du jugement [Distinction: a social critique of the judgement of taste] (Éditions de Minuit, 1979).
Bradley, R. H., Corwyn, R. F., McAdoo, H. P. & Garcia Coll, C. The home environments of children in the United States part I: variations by age, ethnicity, and poverty status. Child Dev. 72 , 1844–1867 (2001).
Blevins‐Knabe, B. & Musun‐Miller, L. Number use at home by children and their parents and its relationship to early mathematical performance. Early Dev. Parent. 5 , 35–45 (1996).
LeFevre, J. A. et al. Pathays to mathematics: longitudinal predictors of performance. Child Dev. 81 , 1753–1767 (2010).
Lareau, A. Home Advantage. Social Class and Parental Intervention in Elementary Education (Falmer Press, 1989).
Guryan, J., Hurst, E. & Kearney, M. Parental education and parental time with children. J. Econ. Perspect. 22 , 23–46 (2008).
Hill, C. R. & Stafford, F. P. Allocation of time to preschool children and educational opportunity. J. Hum. Resour. 9 , 323–341 (1974).
Calarco, J. M. A Field Guide to Grad School: Uncovering the Hidden Curriculum (Princeton Univ. Press, 2020).
Daw, J. Parental income and the fruits of labor: variability in homework efficacy in secondary school. Res. Soc. Strat. Mobil. 30 , 246–264 (2012).
Rønning, M. Who benefits from homework assignments? Econ. Educ. Rev. 30 , 55–64 (2011).
Alexander, K. L., Entwisle, D. R. & Olson, L. S. Lasting consequences of the summer learning gap. Am. Sociol. Rev. 72 , 167–180 (2007).
Cooper, H., Nye, B., Charlton, K., Lindsay, J. & Greathouse, S. The effects of summer vacation on achievement test scores: a narrative and meta-analytic review. Rev. Educ. Res. 66 , 227–268 (1996).
Stewart, H., Watson, N. & Campbell, M. The cost of school holidays for children from low income families. Childhood 25 , 516–529 (2018).
Pensiero, N., Kelly, A. & Bokhove, C. Learning inequalities during the Covid-19 pandemic: how families cope with home-schooling (University of Southampton, 2020); https://doi.org/10.5258/SOTON/P0025
Stephens, N. M., Markus, H. R. & Townsend, S. S. Choice as an act of meaning: the case of social class. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 93 , 814–830 (2007).
Kraus, M. W., Piff, P. K. & Keltner, D. Social class, sense of control, and social explanation. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 97 , 992–1004 (2009).
Dittmann, A. G., Stephens, N. M. & Townsend, S. S. Achievement is not class-neutral: working together benefits pople from working-class contexts. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 119 , 517–539 (2020).
Zimmerman, B. J. Investigating self-regulation and motivation: historical background, methodological developments, and future prospects. Am. Educ. Res. J. 45 , 166–183 (2008).
Backer-Grøndahl, A., Nærde, A., Ulleberg, P. & Janson, H. Measuring effortful control using the children’s behavior questionnaire–very short form: modeling matters. J. Pers. Assess. 98 , 100–109 (2016).
Johnson, S. E., Richeson, J. A. & Finkel, E. J. Middle class and marginal? Socioeconomic status, stigma, and self-regulation at an elite university. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 100 , 838–852 (2011).
Størksen, I., Ellingsen, I. T., Wanless, S. B. & McClelland, M. M. The influence of parental socioeconomic background and gender on self-regulation among 5-year-old children in Norway. Early Educ. Dev. 26 , 663–684 (2015).
Brady, L. et al. 7 ways for teachers to truly connect with parents. Education Week (31 December 2020); https://www.edweek.org/leadership/opinion-7-ways-for-teachers-to-truly-connect-with-parents/2020/12
Montacute, R. Social mobility and Covid-19: implications of the Covid-19 crisis for educational inequality (Sutton Trust, 2020); https://dera.ioe.ac.uk/35323/2/COVID-19-and-Social-Mobility-1.pdf
Dorn, E., Hancock, B., Sarakatsannis, J. & Viruleg, E. COVID-19 and student learning in the United States: the hurt could last a lifetime (McKinsey & Company, 2020); https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/public-and-social-sector/our-insights/covid-19-and-student-learning-in-the-united-states-the-hurt-could-last-a-lifetime
Parolin, Z. & Lee, E. K. Large socio-economic, geographic and demographic disparities exist in exposure to school closures. Nat. Hum. Behav. 5 , 522–528 (2021).
Saavedra, J. A silent and unequal education crisis. And the seeds for its solution (World Bank, 2021); https://blogs.worldbank.org/education/silent-and-unequal-education-crisis-and-seeds-its-solution
Murray, B., Domina, T., Renzulli, L. & Boylan, R. Civil society goes to school: parent–teacher associations and the equality of educational opportunity. Russell Sage Found. J. Soc. Sci. 5 , 41–63 (2019).
Calarco, J. M. Avoiding us versus them: how schools’ dependence on privileged ‘helicopter’ parents influences enforcement of rules. Am. Sociol. Rev. 85 , 223–246 (2020).
Rist, R. Student social class and teacher expectations: the self-fulfilling prophecy in ghetto education. Harv. Educ. Rev. 40 , 411–451 (1970).
Tobisch, A. & Dresel, M. Negatively or positively biased? Dependencies of teachers’ judgments and expectations based on students’ ethnic and social backgrounds. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 20 , 731–752 (2017).
Brantlinger, E. Dividing Classes: How the Middle-class Negotiates and Rationalizes School Advantage (Routledge, 2003).
Calarco, J. M. ‘I need help!’ Social class and children’s help-seeking in elementary school. Am. Sociol. Rev. 76 , 862–882 (2011).
Calarco, J. M. The inconsistent curriculum: cultural tool kits and student interpretations of ambiguous expectations. Soc. Psychol. Quart. 77 , 185–209 (2014).
Goudeau, S. & Cimpian, A. How do young children explain differences in the classroom? Implications for achievement, motivation, and educational equity. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 16 , 533–552 (2021).
Croizet, J. C., Goudeau, S., Marot, M. & Millet, M. How do educational contexts contribute to the social class achievement gap: documenting symbolic violence from a social psychological point of view. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 18 , 105–110 (2017).
Goudeau, S. & Croizet, J.-C. Hidden advantages and disadvantages of social class: how classroom settings reproduce social inequality by staging unfair comparison. Psychol. Sci. 28 , 162–170 (2017).
Kudrna, L., Furnham, A. & Swami, V. The influence of social class salience on self-assessed intelligence. Soc. Behav. Personal. 38 , 859–864 (2010).
Wiederkehr, V., Darnon, C., Chazal, S., Guimond, S. & Martinot, D. From social class to self-efficacy: internalization of low social status pupils’ school performance. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 18 , 769–784 (2015).
Jury, M., Smeding, A., Court, M. & Darnon, C. When first-generation students succeed at university: on the link between social class, academic performance, and performance-avoidance goals. Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 41 , 25–36 (2015).
Jury, M., Quiamzade, A., Darnon, C. & Mugny, G. Higher and lower status individuals’ performance goals: the role of hierarchy stability. Motiv. Sci. 5 , 52–65 (2019).
Autin, F. & Croizet, J.-C. Improving working memory efficiency by reframing metacognitive interpretation of task difficulty. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 141 , 610–618 (2012).
Schmader, T., Johns, M. & Forbes, C. An integrated process model of stereotype threat effects on performance. Psychol. Rev. 115 , 336–356 (2008).
Usher, E. L. & Pajares, F. Self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: a validation study. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 68 , 443–463 (2008).
Bruno, A., Jury, M., Toczek-Capelle, M.-C. & Darnon, C. Are performance-avoidance goals always deleterious for academic achievement in college? The moderating role of social class. Soc. Psychol. Educ. 22 , 539–555 (2019).
Holloway, S. D. et al. Parenting self-efficacy and parental involvement: mediators or moderators between socioeconomic status and children’s academic competence in Japan and Korea? Res. Hum. Dev. 13 , 258–272 (2016).
Tazouti, Y. & Jarlégan, A. The mediating effects of parental self-efficacy and parental involvement on the link between family socioeconomic status and children’s academic achievement. J. Fam. Stud. 25 , 250–266 (2019).
Andreu, S. et al. Évaluations 2020, repères CP, CE1: premiers résultats [2020 assessments, first and second grades benchmarks: first results] (Ministère de l’Éducation nationale, de la Jeunesse et des Sports, 2020); https://www.education.gouv.fr/evaluations-2020-reperes-cp-ce1-premiers-resultats-307122
Engzell, P., Frey, A. & Verhagen, M. D. Learning loss due to school closures during the COVID-19 pandemic. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118 , e2022376118 (2021).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Maldonado, J. E. & De Witte, K. The effect of school closures on standardized student test outcomes (KU Leuven—Faculty of Economics and Business, 2020); https://limo.libis.be/primo-explore/fulldisplay?docid=LIRIAS3189074&context=L&vid=Lirias&search_scope=Lirias&tab=default_tab&lang=en_US
Domingue, B., Hough, H. J., Lang, D. & Yeatman, J. Changing patterns of growth in oral reading fluency during the COVID-19 pandemic (PACE, 2021); https://edpolicyinca.org/publications/changing-patterns-growth-oral-reading-fluency-during-covid-19-pandemic
Dorn, E., Hancock, B., Sarakatsannis, J. & Viruleg, E. COVID-19 and learning loss—disparities grow and students need help (McKinsey & Company, 2020); https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/public-and-social-sector/our-insights/covid-19-and-learning-loss-disparities-grow-and-students-need-help
Angrist, N. et al. Building back better to avert a learning catastrophe: estimating learning loss from COVID-19 school shutdowns in Africa and facilitating short-term and long-term learning recovery. Int. J. Educ. Dev. 84 , 102397 (2021).
Reddy, V., Soudien, C. & Winnaar, L. Disrupted learning during COVID-19: the impact of school closures on education outcomes in South Africa (The Conversation, 2020); https://theconversation.com/impact-of-school-closures-on-education-outcomes-in-south-africa-136889
Entwisle, D. R. & Alexander, K. L. Summer setback: race, poverty, school composition, and mathematics achievement in the first two years of school. Am. Sociol. Rev. 57 , 72–84 (1992).
Kieffer, M. J. Catching up or falling behind? Initial English proficiency, concentrated poverty, and the reading growth of language minority learners in the United States. J. Educ. Psychol. 100 , 851–868 (2008).
Calarco, J. M., Horn, I. & Chen, G. A. ‘You need to be more responsible’: how math homework operates as a status-reinforcing process in school. Preprint at SocArXiv https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/xf96q (2020).
Kaiper-Marquez, A. et al. On the fly: adapting quickly to emergency remote instruction in a family literacy program. Int. Rev. Educ. 66 , 1–23 (2020).
Barton, D. C. Impacts of the COVID‐19 pandemic on field instruction and remote teaching alternatives: results from a survey of instructors. Ecol. Evol. 10 , 12499–12507 (2020).
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
IJzerman, H. et al. Use caution when applying behavioural science to policy. Nat. Hum. Behav. 4 , 1092–1094 (2020).
Taylor, J. & Mallery, J. In person and online learning go together (Stanford Institute for Economic Policy Research, 2020); https://siepr.stanford.edu/research/publications/person-and-online-learning-go-together
Dietrichson, J., Bøg, M., Filges, T. & Klint Jørgensen, A. M. Academic interventions for elementary and middle school students with low socioeconomic status: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Educ. Res. 87 , 243–282 (2017).
Núñez, J. C. et al. Teachers’ feedback on homework, homework-related behaviors, and academic achievement. J. Educ. Res. 108 , 204–216 (2015).
Singh, R. et al. In Artificial Intelligence in Education (eds Biswas, G.et al.) 328–336 (Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2011).
Harackiewicz, J. M., Rozek, C. S., Hulleman, C. S. & Hyde, J. S. Helping parents to motivate adolescents in mathematics and science: an experimental test of a utility-value intervention. Psychol. Sci. 23 , 899–906 (2012).
Jeynes, W. A meta-analysis of the efficacy of different types of parental involvement programs for urban students. Urban Educ. 47 , 706–742 (2012).
Mol, S. E., Bus, A. G., De Jong, M. T. & Smeets, D. J. Added value of dialogic parent–child book readings: a meta-analysis. Early Educ. Dev. 19 , 7–26 (2008).
Angrist, N., Bergman, P. & Matsheng, M. School’s out: experimental evidence on limiting learning loss using “low-tech” in a pandemic (National Bureau of Economic Research, 2021); https://www.nber.org/papers/w28205
Carlana, M. & La Ferrara, E. Apart but connected: online tutoring and student outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic (Institute of Labor Economics, 2021); http://hdl.handle.net/10419/232846
Pagan, S. & Sénéchal, M. Involving parents in a summer book reading program to promote reading comprehension, fluency, and vocabulary in grade 3 and grade 5 children. Can. J. Educ. 37 , 1–31 (2014).
Sénéchal, M. & LeFevre, J. A. Parental involvement in the development of children’s reading skill: a five‐year longitudinal study. Child Dev. 73 , 445–460 (2002).
Starkey, P. & Klein, A. Fostering parental support for children’s mathematical development: an intervention with Head Start families. Early Educ. Dev. 11 , 659–680 (2000).
Buheji, M. et al. The extent of Covid-19 pandemic socio-economic impact on global poverty: a global integrative multidisciplinary review. Am. J. Econ. 10 , 213–224 (2020).
The world economy on a tightrope (OECD, 2020); http://www.oecd.org/economic-outlook/june-2020/
Martin, A., Markhvida, M., Hallegatte, S. & Walsh, B. Socio-economic impacts of COVID-19 on household consumption and poverty. Econ. Disasters Clim. Change 4 , 453–479 (2020).
Jetten, J., Mols, F. & Selvanathan, H. P. How economic inequality fuels the rise and persistence of the Yellow Vest movement. Int. Rev. Soc. Psychol. 33 , 2 (2020).
Wilkinson, R. G. & Pickett, K. E. Income inequality and social dysfunction. Annu. Rev. Sociol. 35 , 493–511 (2009).
Sommet, N., Morselli, D. & Spini, D. Income inequality affects the psychological health of only the people facing scarcity. Psychol. Sci. 29 , 1911–1921 (2018).
Hattie, J. Visible Learning: A Synthesis of over 800 Meta-analyses Relating to Achievement (Routledge, 2008).
Cooper, H., Charlton, K., Valentine, J. C., Muhlenbruck, L. & Borman, G. D. Making the most of summer school: a meta-analytic and narrative review. Monogr. Soc. Res. Child 65 , 1–127 (2000).
Heyns, B. Schooling and cognitive development: is there a season for learning? Child Dev. 58 , 1151–1160 (1987).
McCombs, J. S., Augustine, C. H. & Schwartz, H. L. Making Summer Count: How Summer Programs can Boost Children’s Learning (Rand Education, 2011).
Borman, G. D. & Dowling, N. M. Longitudinal achievement effects of multiyear summer school: evidence from the teach Baltimore randomized field trial. Educ. Eval. Policy 28 , 25–48 (2006).
Kim, J. S. & Quinn, D. M. The effects of summer reading on low-income children’s literacy achievement from kindergarten to grade 8: a meta-analysis of classroom and home interventions. Rev. Educ. Res. 83 , 386–431 (2013).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank G. Reis for editing the figure. The writing of this manuscript was supported by grant ANR-19-CE28-0007–PRESCHOOL from the French National Research Agency (S.G.).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Université de Poitiers, CNRS, CeRCA, Centre de Recherches sur la Cognition et l’Apprentissage, Poitiers, France
Sébastien Goudeau & Camille Sanrey
Université Clermont Auvergne, CNRS, LAPSCO, Laboratoire de Psychologie Sociale et Cognitive, Clermont-Ferrand, France
Arnaud Stanczak & Céline Darnon
School of Psychology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, UK
Antony Manstead
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sébastien Goudeau .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Human Behaviour thanks Daniele Checchi and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Goudeau, S., Sanrey, C., Stanczak, A. et al. Why lockdown and distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic are likely to increase the social class achievement gap. Nat Hum Behav 5 , 1273–1281 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01212-7
Download citation
Received : 15 March 2021
Accepted : 06 September 2021
Published : 27 September 2021
Issue Date : October 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01212-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Advertisement
Students’ online learning challenges during the pandemic and how they cope with them: The case of the Philippines
- Published: 28 May 2021
- Volume 26 , pages 7321–7338, ( 2021 )

Cite this article

- Jessie S. Barrot ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8517-4058 1 ,
- Ian I. Llenares 1 &
- Leo S. del Rosario 1
942k Accesses
267 Citations
4 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Recently, the education system has faced an unprecedented health crisis that has shaken up its foundation. Given today’s uncertainties, it is vital to gain a nuanced understanding of students’ online learning experience in times of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although many studies have investigated this area, limited information is available regarding the challenges and the specific strategies that students employ to overcome them. Thus, this study attempts to fill in the void. Using a mixed-methods approach, the findings revealed that the online learning challenges of college students varied in terms of type and extent. Their greatest challenge was linked to their learning environment at home, while their least challenge was technological literacy and competency. The findings further revealed that the COVID-19 pandemic had the greatest impact on the quality of the learning experience and students’ mental health. In terms of strategies employed by students, the most frequently used were resource management and utilization, help-seeking, technical aptitude enhancement, time management, and learning environment control. Implications for classroom practice, policy-making, and future research are discussed.
Explore related subjects
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Education and Educational Technology
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Since the 1990s, the world has seen significant changes in the landscape of education as a result of the ever-expanding influence of technology. One such development is the adoption of online learning across different learning contexts, whether formal or informal, academic and non-academic, and residential or remotely. We began to witness schools, teachers, and students increasingly adopt e-learning technologies that allow teachers to deliver instruction interactively, share resources seamlessly, and facilitate student collaboration and interaction (Elaish et al., 2019 ; Garcia et al., 2018 ). Although the efficacy of online learning has long been acknowledged by the education community (Barrot, 2020 , 2021 ; Cavanaugh et al., 2009 ; Kebritchi et al., 2017 ; Tallent-Runnels et al., 2006 ; Wallace, 2003 ), evidence on the challenges in its implementation continues to build up (e.g., Boelens et al., 2017 ; Rasheed et al., 2020 ).
Recently, the education system has faced an unprecedented health crisis (i.e., COVID-19 pandemic) that has shaken up its foundation. Thus, various governments across the globe have launched a crisis response to mitigate the adverse impact of the pandemic on education. This response includes, but is not limited to, curriculum revisions, provision for technological resources and infrastructure, shifts in the academic calendar, and policies on instructional delivery and assessment. Inevitably, these developments compelled educational institutions to migrate to full online learning until face-to-face instruction is allowed. The current circumstance is unique as it could aggravate the challenges experienced during online learning due to restrictions in movement and health protocols (Gonzales et al., 2020 ; Kapasia et al., 2020 ). Given today’s uncertainties, it is vital to gain a nuanced understanding of students’ online learning experience in times of the COVID-19 pandemic. To date, many studies have investigated this area with a focus on students’ mental health (Copeland et al., 2021 ; Fawaz et al., 2021 ), home learning (Suryaman et al., 2020 ), self-regulation (Carter et al., 2020 ), virtual learning environment (Almaiah et al., 2020 ; Hew et al., 2020 ; Tang et al., 2020 ), and students’ overall learning experience (e.g., Adarkwah, 2021 ; Day et al., 2021 ; Khalil et al., 2020 ; Singh et al., 2020 ). There are two key differences that set the current study apart from the previous studies. First, it sheds light on the direct impact of the pandemic on the challenges that students experience in an online learning space. Second, the current study explores students’ coping strategies in this new learning setup. Addressing these areas would shed light on the extent of challenges that students experience in a full online learning space, particularly within the context of the pandemic. Meanwhile, our nuanced understanding of the strategies that students use to overcome their challenges would provide relevant information to school administrators and teachers to better support the online learning needs of students. This information would also be critical in revisiting the typology of strategies in an online learning environment.
2 Literature review
2.1 education and the covid-19 pandemic.
In December 2019, an outbreak of a novel coronavirus, known as COVID-19, occurred in China and has spread rapidly across the globe within a few months. COVID-19 is an infectious disease caused by a new strain of coronavirus that attacks the respiratory system (World Health Organization, 2020 ). As of January 2021, COVID-19 has infected 94 million people and has caused 2 million deaths in 191 countries and territories (John Hopkins University, 2021 ). This pandemic has created a massive disruption of the educational systems, affecting over 1.5 billion students. It has forced the government to cancel national examinations and the schools to temporarily close, cease face-to-face instruction, and strictly observe physical distancing. These events have sparked the digital transformation of higher education and challenged its ability to respond promptly and effectively. Schools adopted relevant technologies, prepared learning and staff resources, set systems and infrastructure, established new teaching protocols, and adjusted their curricula. However, the transition was smooth for some schools but rough for others, particularly those from developing countries with limited infrastructure (Pham & Nguyen, 2020 ; Simbulan, 2020 ).
Inevitably, schools and other learning spaces were forced to migrate to full online learning as the world continues the battle to control the vicious spread of the virus. Online learning refers to a learning environment that uses the Internet and other technological devices and tools for synchronous and asynchronous instructional delivery and management of academic programs (Usher & Barak, 2020 ; Huang, 2019 ). Synchronous online learning involves real-time interactions between the teacher and the students, while asynchronous online learning occurs without a strict schedule for different students (Singh & Thurman, 2019 ). Within the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, online learning has taken the status of interim remote teaching that serves as a response to an exigency. However, the migration to a new learning space has faced several major concerns relating to policy, pedagogy, logistics, socioeconomic factors, technology, and psychosocial factors (Donitsa-Schmidt & Ramot, 2020 ; Khalil et al., 2020 ; Varea & González-Calvo, 2020 ). With reference to policies, government education agencies and schools scrambled to create fool-proof policies on governance structure, teacher management, and student management. Teachers, who were used to conventional teaching delivery, were also obliged to embrace technology despite their lack of technological literacy. To address this problem, online learning webinars and peer support systems were launched. On the part of the students, dropout rates increased due to economic, psychological, and academic reasons. Academically, although it is virtually possible for students to learn anything online, learning may perhaps be less than optimal, especially in courses that require face-to-face contact and direct interactions (Franchi, 2020 ).
2.2 Related studies
Recently, there has been an explosion of studies relating to the new normal in education. While many focused on national policies, professional development, and curriculum, others zeroed in on the specific learning experience of students during the pandemic. Among these are Copeland et al. ( 2021 ) and Fawaz et al. ( 2021 ) who examined the impact of COVID-19 on college students’ mental health and their coping mechanisms. Copeland et al. ( 2021 ) reported that the pandemic adversely affected students’ behavioral and emotional functioning, particularly attention and externalizing problems (i.e., mood and wellness behavior), which were caused by isolation, economic/health effects, and uncertainties. In Fawaz et al.’s ( 2021 ) study, students raised their concerns on learning and evaluation methods, overwhelming task load, technical difficulties, and confinement. To cope with these problems, students actively dealt with the situation by seeking help from their teachers and relatives and engaging in recreational activities. These active-oriented coping mechanisms of students were aligned with Carter et al.’s ( 2020 ), who explored students’ self-regulation strategies.
In another study, Tang et al. ( 2020 ) examined the efficacy of different online teaching modes among engineering students. Using a questionnaire, the results revealed that students were dissatisfied with online learning in general, particularly in the aspect of communication and question-and-answer modes. Nonetheless, the combined model of online teaching with flipped classrooms improved students’ attention, academic performance, and course evaluation. A parallel study was undertaken by Hew et al. ( 2020 ), who transformed conventional flipped classrooms into fully online flipped classes through a cloud-based video conferencing app. Their findings suggested that these two types of learning environments were equally effective. They also offered ways on how to effectively adopt videoconferencing-assisted online flipped classrooms. Unlike the two studies, Suryaman et al. ( 2020 ) looked into how learning occurred at home during the pandemic. Their findings showed that students faced many obstacles in a home learning environment, such as lack of mastery of technology, high Internet cost, and limited interaction/socialization between and among students. In a related study, Kapasia et al. ( 2020 ) investigated how lockdown impacts students’ learning performance. Their findings revealed that the lockdown made significant disruptions in students’ learning experience. The students also reported some challenges that they faced during their online classes. These include anxiety, depression, poor Internet service, and unfavorable home learning environment, which were aggravated when students are marginalized and from remote areas. Contrary to Kapasia et al.’s ( 2020 ) findings, Gonzales et al. ( 2020 ) found that confinement of students during the pandemic had significant positive effects on their performance. They attributed these results to students’ continuous use of learning strategies which, in turn, improved their learning efficiency.
Finally, there are those that focused on students’ overall online learning experience during the COVID-19 pandemic. One such study was that of Singh et al. ( 2020 ), who examined students’ experience during the COVID-19 pandemic using a quantitative descriptive approach. Their findings indicated that students appreciated the use of online learning during the pandemic. However, half of them believed that the traditional classroom setting was more effective than the online learning platform. Methodologically, the researchers acknowledge that the quantitative nature of their study restricts a deeper interpretation of the findings. Unlike the above study, Khalil et al. ( 2020 ) qualitatively explored the efficacy of synchronized online learning in a medical school in Saudi Arabia. The results indicated that students generally perceive synchronous online learning positively, particularly in terms of time management and efficacy. However, they also reported technical (internet connectivity and poor utility of tools), methodological (content delivery), and behavioral (individual personality) challenges. Their findings also highlighted the failure of the online learning environment to address the needs of courses that require hands-on practice despite efforts to adopt virtual laboratories. In a parallel study, Adarkwah ( 2021 ) examined students’ online learning experience during the pandemic using a narrative inquiry approach. The findings indicated that Ghanaian students considered online learning as ineffective due to several challenges that they encountered. Among these were lack of social interaction among students, poor communication, lack of ICT resources, and poor learning outcomes. More recently, Day et al. ( 2021 ) examined the immediate impact of COVID-19 on students’ learning experience. Evidence from six institutions across three countries revealed some positive experiences and pre-existing inequities. Among the reported challenges are lack of appropriate devices, poor learning space at home, stress among students, and lack of fieldwork and access to laboratories.
Although there are few studies that report the online learning challenges that higher education students experience during the pandemic, limited information is available regarding the specific strategies that they use to overcome them. It is in this context that the current study was undertaken. This mixed-methods study investigates students’ online learning experience in higher education. Specifically, the following research questions are addressed: (1) What is the extent of challenges that students experience in an online learning environment? (2) How did the COVID-19 pandemic impact the online learning challenges that students experience? (3) What strategies did students use to overcome the challenges?
2.3 Conceptual framework
The typology of challenges examined in this study is largely based on Rasheed et al.’s ( 2020 ) review of students’ experience in an online learning environment. These challenges are grouped into five general clusters, namely self-regulation (SRC), technological literacy and competency (TLCC), student isolation (SIC), technological sufficiency (TSC), and technological complexity (TCC) challenges (Rasheed et al., 2020 , p. 5). SRC refers to a set of behavior by which students exercise control over their emotions, actions, and thoughts to achieve learning objectives. TLCC relates to a set of challenges about students’ ability to effectively use technology for learning purposes. SIC relates to the emotional discomfort that students experience as a result of being lonely and secluded from their peers. TSC refers to a set of challenges that students experience when accessing available online technologies for learning. Finally, there is TCC which involves challenges that students experience when exposed to complex and over-sufficient technologies for online learning.
To extend Rasheed et al. ( 2020 ) categories and to cover other potential challenges during online classes, two more clusters were added, namely learning resource challenges (LRC) and learning environment challenges (LEC) (Buehler, 2004 ; Recker et al., 2004 ; Seplaki et al., 2014 ; Xue et al., 2020 ). LRC refers to a set of challenges that students face relating to their use of library resources and instructional materials, whereas LEC is a set of challenges that students experience related to the condition of their learning space that shapes their learning experiences, beliefs, and attitudes. Since learning environment at home and learning resources available to students has been reported to significantly impact the quality of learning and their achievement of learning outcomes (Drane et al., 2020 ; Suryaman et al., 2020 ), the inclusion of LRC and LEC would allow us to capture other important challenges that students experience during the pandemic, particularly those from developing regions. This comprehensive list would provide us a clearer and detailed picture of students’ experiences when engaged in online learning in an emergency. Given the restrictions in mobility at macro and micro levels during the pandemic, it is also expected that such conditions would aggravate these challenges. Therefore, this paper intends to understand these challenges from students’ perspectives since they are the ones that are ultimately impacted when the issue is about the learning experience. We also seek to explore areas that provide inconclusive findings, thereby setting the path for future research.
3 Material and methods
The present study adopted a descriptive, mixed-methods approach to address the research questions. This approach allowed the researchers to collect complex data about students’ experience in an online learning environment and to clearly understand the phenomena from their perspective.
3.1 Participants
This study involved 200 (66 male and 134 female) students from a private higher education institution in the Philippines. These participants were Psychology, Physical Education, and Sports Management majors whose ages ranged from 17 to 25 ( x̅ = 19.81; SD = 1.80). The students have been engaged in online learning for at least two terms in both synchronous and asynchronous modes. The students belonged to low- and middle-income groups but were equipped with the basic online learning equipment (e.g., computer, headset, speakers) and computer skills necessary for their participation in online classes. Table 1 shows the primary and secondary platforms that students used during their online classes. The primary platforms are those that are formally adopted by teachers and students in a structured academic context, whereas the secondary platforms are those that are informally and spontaneously used by students and teachers for informal learning and to supplement instructional delivery. Note that almost all students identified MS Teams as their primary platform because it is the official learning management system of the university.
Informed consent was sought from the participants prior to their involvement. Before students signed the informed consent form, they were oriented about the objectives of the study and the extent of their involvement. They were also briefed about the confidentiality of information, their anonymity, and their right to refuse to participate in the investigation. Finally, the participants were informed that they would incur no additional cost from their participation.
3.2 Instrument and data collection
The data were collected using a retrospective self-report questionnaire and a focused group discussion (FGD). A self-report questionnaire was considered appropriate because the indicators relate to affective responses and attitude (Araujo et al., 2017 ; Barrot, 2016 ; Spector, 1994 ). Although the participants may tell more than what they know or do in a self-report survey (Matsumoto, 1994 ), this challenge was addressed by explaining to them in detail each of the indicators and using methodological triangulation through FGD. The questionnaire was divided into four sections: (1) participant’s personal information section, (2) the background information on the online learning environment, (3) the rating scale section for the online learning challenges, (4) the open-ended section. The personal information section asked about the students’ personal information (name, school, course, age, and sex), while the background information section explored the online learning mode and platforms (primary and secondary) used in class, and students’ length of engagement in online classes. The rating scale section contained 37 items that relate to SRC (6 items), TLCC (10 items), SIC (4 items), TSC (6 items), TCC (3 items), LRC (4 items), and LEC (4 items). The Likert scale uses six scores (i.e., 5– to a very great extent , 4– to a great extent , 3– to a moderate extent , 2– to some extent , 1– to a small extent , and 0 –not at all/negligible ) assigned to each of the 37 items. Finally, the open-ended questions asked about other challenges that students experienced, the impact of the pandemic on the intensity or extent of the challenges they experienced, and the strategies that the participants employed to overcome the eight different types of challenges during online learning. Two experienced educators and researchers reviewed the questionnaire for clarity, accuracy, and content and face validity. The piloting of the instrument revealed that the tool had good internal consistency (Cronbach’s α = 0.96).
The FGD protocol contains two major sections: the participants’ background information and the main questions. The background information section asked about the students’ names, age, courses being taken, online learning mode used in class. The items in the main questions section covered questions relating to the students’ overall attitude toward online learning during the pandemic, the reasons for the scores they assigned to each of the challenges they experienced, the impact of the pandemic on students’ challenges, and the strategies they employed to address the challenges. The same experts identified above validated the FGD protocol.
Both the questionnaire and the FGD were conducted online via Google survey and MS Teams, respectively. It took approximately 20 min to complete the questionnaire, while the FGD lasted for about 90 min. Students were allowed to ask for clarification and additional explanations relating to the questionnaire content, FGD, and procedure. Online surveys and interview were used because of the ongoing lockdown in the city. For the purpose of triangulation, 20 (10 from Psychology and 10 from Physical Education and Sports Management) randomly selected students were invited to participate in the FGD. Two separate FGDs were scheduled for each group and were facilitated by researcher 2 and researcher 3, respectively. The interviewers ensured that the participants were comfortable and open to talk freely during the FGD to avoid social desirability biases (Bergen & Labonté, 2020 ). These were done by informing the participants that there are no wrong responses and that their identity and responses would be handled with the utmost confidentiality. With the permission of the participants, the FGD was recorded to ensure that all relevant information was accurately captured for transcription and analysis.
3.3 Data analysis
To address the research questions, we used both quantitative and qualitative analyses. For the quantitative analysis, we entered all the data into an excel spreadsheet. Then, we computed the mean scores ( M ) and standard deviations ( SD ) to determine the level of challenges experienced by students during online learning. The mean score for each descriptor was interpreted using the following scheme: 4.18 to 5.00 ( to a very great extent ), 3.34 to 4.17 ( to a great extent ), 2.51 to 3.33 ( to a moderate extent ), 1.68 to 2.50 ( to some extent ), 0.84 to 1.67 ( to a small extent ), and 0 to 0.83 ( not at all/negligible ). The equal interval was adopted because it produces more reliable and valid information than other types of scales (Cicchetti et al., 2006 ).
For the qualitative data, we analyzed the students’ responses in the open-ended questions and the transcribed FGD using the predetermined categories in the conceptual framework. Specifically, we used multilevel coding in classifying the codes from the transcripts (Birks & Mills, 2011 ). To do this, we identified the relevant codes from the responses of the participants and categorized these codes based on the similarities or relatedness of their properties and dimensions. Then, we performed a constant comparative and progressive analysis of cases to allow the initially identified subcategories to emerge and take shape. To ensure the reliability of the analysis, two coders independently analyzed the qualitative data. Both coders familiarize themselves with the purpose, research questions, research method, and codes and coding scheme of the study. They also had a calibration session and discussed ways on how they could consistently analyze the qualitative data. Percent of agreement between the two coders was 86 percent. Any disagreements in the analysis were discussed by the coders until an agreement was achieved.
This study investigated students’ online learning experience in higher education within the context of the pandemic. Specifically, we identified the extent of challenges that students experienced, how the COVID-19 pandemic impacted their online learning experience, and the strategies that they used to confront these challenges.
4.1 The extent of students’ online learning challenges
Table 2 presents the mean scores and SD for the extent of challenges that students’ experienced during online learning. Overall, the students experienced the identified challenges to a moderate extent ( x̅ = 2.62, SD = 1.03) with scores ranging from x̅ = 1.72 ( to some extent ) to x̅ = 3.58 ( to a great extent ). More specifically, the greatest challenge that students experienced was related to the learning environment ( x̅ = 3.49, SD = 1.27), particularly on distractions at home, limitations in completing the requirements for certain subjects, and difficulties in selecting the learning areas and study schedule. It is, however, found that the least challenge was on technological literacy and competency ( x̅ = 2.10, SD = 1.13), particularly on knowledge and training in the use of technology, technological intimidation, and resistance to learning technologies. Other areas that students experienced the least challenge are Internet access under TSC and procrastination under SRC. Nonetheless, nearly half of the students’ responses per indicator rated the challenges they experienced as moderate (14 of the 37 indicators), particularly in TCC ( x̅ = 2.51, SD = 1.31), SIC ( x̅ = 2.77, SD = 1.34), and LRC ( x̅ = 2.93, SD = 1.31).
Out of 200 students, 181 responded to the question about other challenges that they experienced. Most of their responses were already covered by the seven predetermined categories, except for 18 responses related to physical discomfort ( N = 5) and financial challenges ( N = 13). For instance, S108 commented that “when it comes to eyes and head, my eyes and head get ache if the session of class was 3 h straight in front of my gadget.” In the same vein, S194 reported that “the long exposure to gadgets especially laptop, resulting in body pain & headaches.” With reference to physical financial challenges, S66 noted that “not all the time I have money to load”, while S121 claimed that “I don't know until when are we going to afford budgeting our money instead of buying essentials.”
4.2 Impact of the pandemic on students’ online learning challenges
Another objective of this study was to identify how COVID-19 influenced the online learning challenges that students experienced. As shown in Table 3 , most of the students’ responses were related to teaching and learning quality ( N = 86) and anxiety and other mental health issues ( N = 52). Regarding the adverse impact on teaching and learning quality, most of the comments relate to the lack of preparation for the transition to online platforms (e.g., S23, S64), limited infrastructure (e.g., S13, S65, S99, S117), and poor Internet service (e.g., S3, S9, S17, S41, S65, S99). For the anxiety and mental health issues, most students reported that the anxiety, boredom, sadness, and isolation they experienced had adversely impacted the way they learn (e.g., S11, S130), completing their tasks/activities (e.g., S56, S156), and their motivation to continue studying (e.g., S122, S192). The data also reveal that COVID-19 aggravated the financial difficulties experienced by some students ( N = 16), consequently affecting their online learning experience. This financial impact mainly revolved around the lack of funding for their online classes as a result of their parents’ unemployment and the high cost of Internet data (e.g., S18, S113, S167). Meanwhile, few concerns were raised in relation to COVID-19’s impact on mobility ( N = 7) and face-to-face interactions ( N = 7). For instance, some commented that the lack of face-to-face interaction with her classmates had a detrimental effect on her learning (S46) and socialization skills (S36), while others reported that restrictions in mobility limited their learning experience (S78, S110). Very few comments were related to no effect ( N = 4) and positive effect ( N = 2). The above findings suggest the pandemic had additive adverse effects on students’ online learning experience.
4.3 Students’ strategies to overcome challenges in an online learning environment
The third objective of this study is to identify the strategies that students employed to overcome the different online learning challenges they experienced. Table 4 presents that the most commonly used strategies used by students were resource management and utilization ( N = 181), help-seeking ( N = 155), technical aptitude enhancement ( N = 122), time management ( N = 98), and learning environment control ( N = 73). Not surprisingly, the top two strategies were also the most consistently used across different challenges. However, looking closely at each of the seven challenges, the frequency of using a particular strategy varies. For TSC and LRC, the most frequently used strategy was resource management and utilization ( N = 52, N = 89, respectively), whereas technical aptitude enhancement was the students’ most preferred strategy to address TLCC ( N = 77) and TCC ( N = 38). In the case of SRC, SIC, and LEC, the most frequently employed strategies were time management ( N = 71), psychological support ( N = 53), and learning environment control ( N = 60). In terms of consistency, help-seeking appears to be the most consistent across the different challenges in an online learning environment. Table 4 further reveals that strategies used by students within a specific type of challenge vary.
5 Discussion and conclusions
The current study explores the challenges that students experienced in an online learning environment and how the pandemic impacted their online learning experience. The findings revealed that the online learning challenges of students varied in terms of type and extent. Their greatest challenge was linked to their learning environment at home, while their least challenge was technological literacy and competency. Based on the students’ responses, their challenges were also found to be aggravated by the pandemic, especially in terms of quality of learning experience, mental health, finances, interaction, and mobility. With reference to previous studies (i.e., Adarkwah, 2021 ; Copeland et al., 2021 ; Day et al., 2021 ; Fawaz et al., 2021 ; Kapasia et al., 2020 ; Khalil et al., 2020 ; Singh et al., 2020 ), the current study has complemented their findings on the pedagogical, logistical, socioeconomic, technological, and psychosocial online learning challenges that students experience within the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Further, this study extended previous studies and our understanding of students’ online learning experience by identifying both the presence and extent of online learning challenges and by shedding light on the specific strategies they employed to overcome them.
Overall findings indicate that the extent of challenges and strategies varied from one student to another. Hence, they should be viewed as a consequence of interaction several many factors. Students’ responses suggest that their online learning challenges and strategies were mediated by the resources available to them, their interaction with their teachers and peers, and the school’s existing policies and guidelines for online learning. In the context of the pandemic, the imposed lockdowns and students’ socioeconomic condition aggravated the challenges that students experience.
While most studies revealed that technology use and competency were the most common challenges that students face during the online classes (see Rasheed et al., 2020 ), the case is a bit different in developing countries in times of pandemic. As the findings have shown, the learning environment is the greatest challenge that students needed to hurdle, particularly distractions at home (e.g., noise) and limitations in learning space and facilities. This data suggests that online learning challenges during the pandemic somehow vary from the typical challenges that students experience in a pre-pandemic online learning environment. One possible explanation for this result is that restriction in mobility may have aggravated this challenge since they could not go to the school or other learning spaces beyond the vicinity of their respective houses. As shown in the data, the imposition of lockdown restricted students’ learning experience (e.g., internship and laboratory experiments), limited their interaction with peers and teachers, caused depression, stress, and anxiety among students, and depleted the financial resources of those who belong to lower-income group. All of these adversely impacted students’ learning experience. This finding complemented earlier reports on the adverse impact of lockdown on students’ learning experience and the challenges posed by the home learning environment (e.g., Day et al., 2021 ; Kapasia et al., 2020 ). Nonetheless, further studies are required to validate the impact of restrictions on mobility on students’ online learning experience. The second reason that may explain the findings relates to students’ socioeconomic profile. Consistent with the findings of Adarkwah ( 2021 ) and Day et al. ( 2021 ), the current study reveals that the pandemic somehow exposed the many inequities in the educational systems within and across countries. In the case of a developing country, families from lower socioeconomic strata (as in the case of the students in this study) have limited learning space at home, access to quality Internet service, and online learning resources. This is the reason the learning environment and learning resources recorded the highest level of challenges. The socioeconomic profile of the students (i.e., low and middle-income group) is the same reason financial problems frequently surfaced from their responses. These students frequently linked the lack of financial resources to their access to the Internet, educational materials, and equipment necessary for online learning. Therefore, caution should be made when interpreting and extending the findings of this study to other contexts, particularly those from higher socioeconomic strata.
Among all the different online learning challenges, the students experienced the least challenge on technological literacy and competency. This is not surprising considering a plethora of research confirming Gen Z students’ (born since 1996) high technological and digital literacy (Barrot, 2018 ; Ng, 2012 ; Roblek et al., 2019 ). Regarding the impact of COVID-19 on students’ online learning experience, the findings reveal that teaching and learning quality and students’ mental health were the most affected. The anxiety that students experienced does not only come from the threats of COVID-19 itself but also from social and physical restrictions, unfamiliarity with new learning platforms, technical issues, and concerns about financial resources. These findings are consistent with that of Copeland et al. ( 2021 ) and Fawaz et al. ( 2021 ), who reported the adverse effects of the pandemic on students’ mental and emotional well-being. This data highlights the need to provide serious attention to the mediating effects of mental health, restrictions in mobility, and preparedness in delivering online learning.
Nonetheless, students employed a variety of strategies to overcome the challenges they faced during online learning. For instance, to address the home learning environment problems, students talked to their family (e.g., S12, S24), transferred to a quieter place (e.g., S7, S 26), studied at late night where all family members are sleeping already (e.g., S51), and consulted with their classmates and teachers (e.g., S3, S9, S156, S193). To overcome the challenges in learning resources, students used the Internet (e.g., S20, S27, S54, S91), joined Facebook groups that share free resources (e.g., S5), asked help from family members (e.g., S16), used resources available at home (e.g., S32), and consulted with the teachers (e.g., S124). The varying strategies of students confirmed earlier reports on the active orientation that students take when faced with academic- and non-academic-related issues in an online learning space (see Fawaz et al., 2021 ). The specific strategies that each student adopted may have been shaped by different factors surrounding him/her, such as available resources, student personality, family structure, relationship with peers and teacher, and aptitude. To expand this study, researchers may further investigate this area and explore how and why different factors shape their use of certain strategies.
Several implications can be drawn from the findings of this study. First, this study highlighted the importance of emergency response capability and readiness of higher education institutions in case another crisis strikes again. Critical areas that need utmost attention include (but not limited to) national and institutional policies, protocol and guidelines, technological infrastructure and resources, instructional delivery, staff development, potential inequalities, and collaboration among key stakeholders (i.e., parents, students, teachers, school leaders, industry, government education agencies, and community). Second, the findings have expanded our understanding of the different challenges that students might confront when we abruptly shift to full online learning, particularly those from countries with limited resources, poor Internet infrastructure, and poor home learning environment. Schools with a similar learning context could use the findings of this study in developing and enhancing their respective learning continuity plans to mitigate the adverse impact of the pandemic. This study would also provide students relevant information needed to reflect on the possible strategies that they may employ to overcome the challenges. These are critical information necessary for effective policymaking, decision-making, and future implementation of online learning. Third, teachers may find the results useful in providing proper interventions to address the reported challenges, particularly in the most critical areas. Finally, the findings provided us a nuanced understanding of the interdependence of learning tools, learners, and learning outcomes within an online learning environment; thus, giving us a multiperspective of hows and whys of a successful migration to full online learning.
Some limitations in this study need to be acknowledged and addressed in future studies. One limitation of this study is that it exclusively focused on students’ perspectives. Future studies may widen the sample by including all other actors taking part in the teaching–learning process. Researchers may go deeper by investigating teachers’ views and experience to have a complete view of the situation and how different elements interact between them or affect the others. Future studies may also identify some teacher-related factors that could influence students’ online learning experience. In the case of students, their age, sex, and degree programs may be examined in relation to the specific challenges and strategies they experience. Although the study involved a relatively large sample size, the participants were limited to college students from a Philippine university. To increase the robustness of the findings, future studies may expand the learning context to K-12 and several higher education institutions from different geographical regions. As a final note, this pandemic has undoubtedly reshaped and pushed the education system to its limits. However, this unprecedented event is the same thing that will make the education system stronger and survive future threats.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Adarkwah, M. A. (2021). “I’m not against online teaching, but what about us?”: ICT in Ghana post Covid-19. Education and Information Technologies, 26 (2), 1665–1685.
Article Google Scholar
Almaiah, M. A., Al-Khasawneh, A., & Althunibat, A. (2020). Exploring the critical challenges and factors influencing the E-learning system usage during COVID-19 pandemic. Education and Information Technologies, 25 , 5261–5280.
Araujo, T., Wonneberger, A., Neijens, P., & de Vreese, C. (2017). How much time do you spend online? Understanding and improving the accuracy of self-reported measures of Internet use. Communication Methods and Measures, 11 (3), 173–190.
Barrot, J. S. (2016). Using Facebook-based e-portfolio in ESL writing classrooms: Impact and challenges. Language, Culture and Curriculum, 29 (3), 286–301.
Barrot, J. S. (2018). Facebook as a learning environment for language teaching and learning: A critical analysis of the literature from 2010 to 2017. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 34 (6), 863–875.
Barrot, J. S. (2020). Scientific mapping of social media in education: A decade of exponential growth. Journal of Educational Computing Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633120972010 .
Barrot, J. S. (2021). Social media as a language learning environment: A systematic review of the literature (2008–2019). Computer Assisted Language Learning . https://doi.org/10.1080/09588221.2021.1883673 .
Bergen, N., & Labonté, R. (2020). “Everything is perfect, and we have no problems”: Detecting and limiting social desirability bias in qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research, 30 (5), 783–792.
Birks, M., & Mills, J. (2011). Grounded theory: A practical guide . Sage.
Boelens, R., De Wever, B., & Voet, M. (2017). Four key challenges to the design of blended learning: A systematic literature review. Educational Research Review, 22 , 1–18.
Buehler, M. A. (2004). Where is the library in course management software? Journal of Library Administration, 41 (1–2), 75–84.
Carter, R. A., Jr., Rice, M., Yang, S., & Jackson, H. A. (2020). Self-regulated learning in online learning environments: Strategies for remote learning. Information and Learning Sciences, 121 (5/6), 321–329.
Cavanaugh, C. S., Barbour, M. K., & Clark, T. (2009). Research and practice in K-12 online learning: A review of open access literature. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 10 (1), 1–22.
Cicchetti, D., Bronen, R., Spencer, S., Haut, S., Berg, A., Oliver, P., & Tyrer, P. (2006). Rating scales, scales of measurement, issues of reliability: Resolving some critical issues for clinicians and researchers. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 194 (8), 557–564.
Copeland, W. E., McGinnis, E., Bai, Y., Adams, Z., Nardone, H., Devadanam, V., & Hudziak, J. J. (2021). Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on college student mental health and wellness. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 60 (1), 134–141.
Day, T., Chang, I. C. C., Chung, C. K. L., Doolittle, W. E., Housel, J., & McDaniel, P. N. (2021). The immediate impact of COVID-19 on postsecondary teaching and learning. The Professional Geographer, 73 (1), 1–13.
Donitsa-Schmidt, S., & Ramot, R. (2020). Opportunities and challenges: Teacher education in Israel in the Covid-19 pandemic. Journal of Education for Teaching, 46 (4), 586–595.
Drane, C., Vernon, L., & O’Shea, S. (2020). The impact of ‘learning at home’on the educational outcomes of vulnerable children in Australia during the COVID-19 pandemic. Literature Review Prepared by the National Centre for Student Equity in Higher Education. Curtin University, Australia.
Elaish, M., Shuib, L., Ghani, N., & Yadegaridehkordi, E. (2019). Mobile English language learning (MELL): A literature review. Educational Review, 71 (2), 257–276.
Fawaz, M., Al Nakhal, M., & Itani, M. (2021). COVID-19 quarantine stressors and management among Lebanese students: A qualitative study. Current Psychology , 1–8.
Franchi, T. (2020). The impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on current anatomy education and future careers: A student’s perspective. Anatomical Sciences Education, 13 (3), 312–315.
Garcia, R., Falkner, K., & Vivian, R. (2018). Systematic literature review: Self-regulated learning strategies using e-learning tools for computer science. Computers & Education, 123 , 150–163.
Gonzalez, T., De La Rubia, M. A., Hincz, K. P., Comas-Lopez, M., Subirats, L., Fort, S., & Sacha, G. M. (2020). Influence of COVID-19 confinement on students’ performance in higher education. PLoS One, 15 (10), e0239490.
Hew, K. F., Jia, C., Gonda, D. E., & Bai, S. (2020). Transitioning to the “new normal” of learning in unpredictable times: Pedagogical practices and learning performance in fully online flipped classrooms. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 17 (1), 1–22.
Huang, Q. (2019). Comparing teacher’s roles of F2F learning and online learning in a blended English course. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 32 (3), 190–209.
John Hopkins University. (2021). Global map . https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/
Kapasia, N., Paul, P., Roy, A., Saha, J., Zaveri, A., Mallick, R., & Chouhan, P. (2020). Impact of lockdown on learning status of undergraduate and postgraduate students during COVID-19 pandemic in West Bengal. India . Children and Youth Services Review, 116 , 105194.
Kebritchi, M., Lipschuetz, A., & Santiague, L. (2017). Issues and challenges for teaching successful online courses in higher education: A literature review. Journal of Educational Technology Systems, 46 (1), 4–29.
Khalil, R., Mansour, A. E., Fadda, W. A., Almisnid, K., Aldamegh, M., Al-Nafeesah, A., & Al-Wutayd, O. (2020). The sudden transition to synchronized online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia: A qualitative study exploring medical students’ perspectives. BMC Medical Education, 20 (1), 1–10.
Matsumoto, K. (1994). Introspection, verbal reports and second language learning strategy research. Canadian Modern Language Review, 50 (2), 363–386.
Ng, W. (2012). Can we teach digital natives digital literacy? Computers & Education, 59 (3), 1065–1078.
Pham, T., & Nguyen, H. (2020). COVID-19: Challenges and opportunities for Vietnamese higher education. Higher Education in Southeast Asia and beyond, 8 , 22–24.
Google Scholar
Rasheed, R. A., Kamsin, A., & Abdullah, N. A. (2020). Challenges in the online component of blended learning: A systematic review. Computers & Education, 144 , 103701.
Recker, M. M., Dorward, J., & Nelson, L. M. (2004). Discovery and use of online learning resources: Case study findings. Educational Technology & Society, 7 (2), 93–104.
Roblek, V., Mesko, M., Dimovski, V., & Peterlin, J. (2019). Smart technologies as social innovation and complex social issues of the Z generation. Kybernetes, 48 (1), 91–107.
Seplaki, C. L., Agree, E. M., Weiss, C. O., Szanton, S. L., Bandeen-Roche, K., & Fried, L. P. (2014). Assistive devices in context: Cross-sectional association between challenges in the home environment and use of assistive devices for mobility. The Gerontologist, 54 (4), 651–660.
Simbulan, N. (2020). COVID-19 and its impact on higher education in the Philippines. Higher Education in Southeast Asia and beyond, 8 , 15–18.
Singh, K., Srivastav, S., Bhardwaj, A., Dixit, A., & Misra, S. (2020). Medical education during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single institution experience. Indian Pediatrics, 57 (7), 678–679.
Singh, V., & Thurman, A. (2019). How many ways can we define online learning? A systematic literature review of definitions of online learning (1988–2018). American Journal of Distance Education, 33 (4), 289–306.
Spector, P. (1994). Using self-report questionnaires in OB research: A comment on the use of a controversial method. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 15 (5), 385–392.
Suryaman, M., Cahyono, Y., Muliansyah, D., Bustani, O., Suryani, P., Fahlevi, M., & Munthe, A. P. (2020). COVID-19 pandemic and home online learning system: Does it affect the quality of pharmacy school learning? Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 11 , 524–530.
Tallent-Runnels, M. K., Thomas, J. A., Lan, W. Y., Cooper, S., Ahern, T. C., Shaw, S. M., & Liu, X. (2006). Teaching courses online: A review of the research. Review of Educational Research, 76 (1), 93–135.
Tang, T., Abuhmaid, A. M., Olaimat, M., Oudat, D. M., Aldhaeebi, M., & Bamanger, E. (2020). Efficiency of flipped classroom with online-based teaching under COVID-19. Interactive Learning Environments , 1–12.
Usher, M., & Barak, M. (2020). Team diversity as a predictor of innovation in team projects of face-to-face and online learners. Computers & Education, 144 , 103702.
Varea, V., & González-Calvo, G. (2020). Touchless classes and absent bodies: Teaching physical education in times of Covid-19. Sport, Education and Society , 1–15.
Wallace, R. M. (2003). Online learning in higher education: A review of research on interactions among teachers and students. Education, Communication & Information, 3 (2), 241–280.
World Health Organization (2020). Coronavirus . https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_1
Xue, E., Li, J., Li, T., & Shang, W. (2020). China’s education response to COVID-19: A perspective of policy analysis. Educational Philosophy and Theory , 1–13.
Download references
No funding was received in the conduct of this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Education, Arts and Sciences, National University, Manila, Philippines
Jessie S. Barrot, Ian I. Llenares & Leo S. del Rosario
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Jessie Barrot led the planning, prepared the instrument, wrote the report, and processed and analyzed data. Ian Llenares participated in the planning, fielded the instrument, processed and analyzed data, reviewed the instrument, and contributed to report writing. Leo del Rosario participated in the planning, fielded the instrument, processed and analyzed data, reviewed the instrument, and contributed to report writing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jessie S. Barrot .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval.
The study has undergone appropriate ethics protocol.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was sought from the participants.
Consent for publication
Authors consented the publication. Participants consented to publication as long as confidentiality is observed.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Barrot, J.S., Llenares, I.I. & del Rosario, L.S. Students’ online learning challenges during the pandemic and how they cope with them: The case of the Philippines. Educ Inf Technol 26 , 7321–7338 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10589-x
Download citation
Received : 22 January 2021
Accepted : 17 May 2021
Published : 28 May 2021
Issue Date : November 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10589-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Remote learning
- Online learning
- Online learning strategies
- Higher education
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Impact of the covid-19 pandemic on online learning in higher education: a bibliometric analysis.

- 1 Faculty of Public Administration, University of Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia
- 2 Department of Primary Level Education, University of the Aegean, Rhodes, Greece
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted higher education by forcing the transition to online learning, which became a mandatory teaching process during the lockdowns. Although the epidemiological situation has gradually improved since then, online learning is becoming ever more popular as it provides new learning opportunities. Therefore, the paper aims to present recent research trends concerning online learning in higher education during the COVID-19 pandemic by using selected bibliometric approaches. The bibliometric analysis is based on 8,303 documents from the Scopus database published between January 2020 and March 2022, when repeated lockdowns meant most countries were experiencing constant disruptions to the educational process. The results show that the COVID-19 pandemic increased interest in online learning research, notably in English-speaking and Asian countries, with most research being published in open-access scientific journals. Moreover, the topics most frequently discussed in the online learning research during the COVID-19 pandemic were ICT and pedagogy, technology-enhanced education, mental health and well-being, student experience and curriculum and professional development. Finally, the COVID-19 pandemic encouraged explorations of emergency remote learning approaches like e-learning, distance learning and virtual learning, which are intended to limit physical contact between teachers and students, where the specific requirements of a given field of study often guide which online learning approach is the most suitable. The findings add to the existing body of scientific knowledge and support the evidence-based policymaking needed to ensure sustainable higher education in the future.
1. Introduction
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted higher education by forcing the transition to online learning, which became a mandatory teaching process during the lockdowns ( Aristovnik et al., 2020a ). Despite the educational process saw disruptions on all levels of education, i.e., primary, secondary and tertiary ( Tang, 2023 ), as well as in adult education ( James and Thériault, 2020 ), worker education ( Dedeilia et al., 2023 ) and lifelong education ( Waller et al., 2020 ), higher education students proved to be one of the worst affected groups because the social distancing measures, on top of their education, challenged their financial and housing situation ( Aristovnik et al., 2020a ). Challenges arising from the density of students in educational facilities (e.g., campuses, faculties, dormitories etc.) meant higher education institutions were forced to offer education relying on various information and communication technologies (ICTs) and tried to ensure education comparable in quality to traditional learning, noting that the quality of online learning delivery holds important implications for student satisfaction and student performance ( Keržič et al., 2021 ). Nevertheless, the lockdown periods were devastating for many students also in terms of their emotional functioning ( Raccanello et al., 2022 ). The COVID-19 pandemic eventually grew more predictable and manageable, allowing higher education institutions to gradually shift back to traditional learning approaches. Although the epidemiological situation has improved over time, online learning is becoming increasingly popular as it provides new learning opportunities, especially when combined with traditional learning.
The rapid, yet from the health protection point of view necessary ( Aristovnik et al., 2020b ), shift from traditional learning to online learning considerably affected teaching and learning. The transition to online learning was made without adequate consideration of whether the study materials and teaching methods were suitable for this mode of higher education delivery. This was an ad hoc shift in a situation of great uncertainty for both teachers and students. The transition to online learning has also brought to the surface gaps in higher education providers’ preparedness and their lack of ICT infrastructure, resulting in unequal access to quality education for all, particularly students from rural areas and regions with lower socio-economic development. It is important to note here that the rapid shift to an online learning environment in emergency circumstances should not be confused with properly planned online education equipped with appropriate infrastructure that enables and supports pedagogical work and study in an online environment ( Hodges et al., 2020 ; Fuchs, 2022 ; Misiejuk et al., 2023 ). Apart from the changes in teaching and learning, the social aspect of students’ lives has been affected as well. The most worrying consequence has been social isolation leading to a lack of crucial social interaction for students ( Elmer et al., 2020 ; Bonsaksen et al., 2021 ; Fried et al., 2021 ; Van der Graaf et al., 2021 ) and in some cases also in coronavirus-related post-traumatic stress syndrome (PTSD) ( Ochnik et al., 2021 ). According to Gavriluţă et al. (2022) , three dimensions affected students during the COVID-19 pandemic: educational, social, and emotional. The transition from traditional to online learning entailed a significant transformation in education, requiring changes in teaching practices and new learning approaches. Further, the social aspect of the COVID-19 pandemic and associated lockdowns is evident in the absence of relational, economic and professional problems (in)directly affecting the transition to adulthood. The new reality changed attitudes to various aspects of life and, in turn, also affected emotional responsiveness. Briefly, substantial changes to everyday student lives were made during the COVID-19 pandemic that may hold far-reaching effects of currently unknown scope in the near and distant future ( Campos et al., 2022 ; Gao et al., 2022 ; Keržič et al., 2022 ; Rasli et al., 2022 ).
Therefore, the educational community requires greater insights into different aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic’s impact on online learning, e.g., students, teachers, pedagogy, ICT technology, online learning approaches and implications for various fields of study. In the context of higher education, some bibliometric studies (e.g., Gurcan et al., 2022 ; Saqr et al., 2023 ) have already sought to address issues involving online learning during the pandemic. Yet, they relied on a limited and narrow bibliographic dataset of peer-reviewed literature or lacked a qualitative synthesis of the results beyond the metrics, thereby neglecting some general comprehensive outlines of the global research into the topic ( Saqr et al., 2023 ). Moreover, despite some bibliometric studies focusing on technical aspects (e.g., Navarro-Espinosa et al., 2021 ; Bozkurt, 2022 ; Tlili et al., 2022 ), the identification of the most effective ICT tools for specific online learning approaches remains unclear. Finally, there are also some bibliometric studies that attempt to determine the effectiveness of online learning in providing higher education ( Brika et al., 2021 ; Baber et al., 2022 ; Bilal et al., 2022 ; Bozkurt, 2022 ; Fauzi, 2022 ; Küçük-Avci et al., 2022 ; Yan et al., 2022 ), however, they often overlook the specific requirements of individual fields of study, thereby neglecting the crucial aspect of tailoring online learning provision to different disciplines.
The bibliometric study presented in the paper accordingly aims to fill the presented gaps in the literature. Specifically, it aims to present a global overview of the recent research trends in online learning in higher education using a comprehensive dataset of literature encompassing different varieties of online learning approaches that can facilitate online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic, provide some relevant qualitative synthesis of the results beyond the metrics and examine the relationships between ICT tools, online learning approaches and fields of study. Thus, the present bibliometric study, focusing on higher education, tries to answer the following three research questions:
• RQ1: What is the current state of the online learning research by conducting a descriptive overview and identifying top-cited documents?
• RQ2: What is the scientific production of online learning research across countries and sources?
• RQ3: Which are the main research hotspots and concepts in online learning research?
The remainder of the paper is structured as follows. The next section provides a literature review of recent bibliometric studies. The following section outlines the materials and methods applied in the study before the results of the present bibliometric analysis are described in the next section. At the end, the final section provides a discussion and conclusion while summarizing the main findings and implications.
2. Literature review
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic led many governments to expand the use of online learning approaches as a solution to the global health challenge. Researchers thus showed rising interest in investigating the field of online learning, its dimensions, and its trends on all levels of education, particularly higher education. Such research relied heavily on bibliometric approaches to analyzing scientific research in the higher education context. Pham et al. (2022) concluded based on the 414 articles that although in the decades prior, there was an increase in the number of articles touching on the components of e-learning, such as the learning management system, this rise was accelerated during the pandemic in both developed and developing countries. This may be attributed to the attention of governmental policies that considered the topic of e-learning to be critical and worthy of priority. Similarly, Fauzi (2022) investigated 1,496 articles and concluded that the research focused on a few specific topics. The first is the delivery factor, which refers to selecting the appropriate learning practices. The second is the health and safety factor that relates to minimizing any risk that e-learning could bring to the mental and physical health of learners or teachers, such as stress, anxiety or even depression. The third topic refers to the field of study and the impact of e-learning. In areas like medical education, where clinical activities and labs have to be attended in person, some online learning approaches might be less appropriate than when used in other areas, such as social studies, where the requirements are less complex or different. Zhang et al. (2022) confirmed this finding after performing bibliometric research on 1,061 articles published between January 2020 and August 2021. They explained that theorists and researchers showed a growing interest in ways to respond to crises, such as the pandemic, and how to develop the best practices to ensure the quality and efficiency of e-learning. Examples of such practices might be inquiry-oriented learning and hands-on activities. This could derive from the already existing tendency of education researchers to respond to unprecedented global challenges or changes. The authors explain that this conclusion addresses interest in e-learning practices holistically.
In the same context, Yan et al. (2022) employed a bibliometric approach and identified that various digital tools are used in e-learning in the field of health studies. After investigating 132 studies, they concluded that selecting appropriate tools depends on many factors, including the field of a given course, the aims, and their effectiveness. They add that these findings can be significant for groups of people such as experts or trainee teachers. Okoro et al. (2022) researched 1,722 articles published between 2012 and 2021 and detected a surge in interest in the mental health of postgraduate students, as revealed by the research trends discussed in these articles. Still, they describe this surge as having been greater between 2020 and 2021, which may be attributed to the COVID-19 restrictions and their implications. Moreover, they believe that this research focus will likely continue soon.
After looking at 2,307 articles published between 2017 and 2021, Baber et al. (2022) detected an increasing trend in researching digital literacy. While this was underway before the pandemic, the latter caused a statistically significant further surge. Digital literacy is approached in the studied articles through parameters like instruction, teachers, learners, ICT and its applications, content knowledge, competencies, skills, perceptions, and higher education. It is also associated with acquiring the qualities required to deal with topics such as misinformation, fake news, technological content knowledge, health literacy, COVID-19, and distance education. The authors state that their study identified dynamics hidden in these research trends, which will likely continue in the next few years.
In higher education specifically, based on 602 articles, Brika et al. (2021) corroborated the growing trend of publishing articles on e-learning during the pandemic and outlined certain sub-topics of it, namely: motivation and students’ attitudes; blended and virtual learning comparison; types of online assessment; stress, anxiety and mental health; strategies to improve learners’ skills; quality; performance of the education delivered; challenges; and the potential of technology to lead to change and reform of higher education syllabi or curricula. The scope of those articles was to paint a bigger picture of how higher education communities and institutions use and treat online learning. This is expected to help with efficient decision-making in the future in order to have better results and functions in higher education and appropriate response to crises.
The bibliometric studies carried out during the pandemic identified a trend among researchers in higher education institutions to investigate more the technology factor and how the progress of the Internet, along with information and communication technologies generally, can further assist new modes of learning, such as online learning and distance learning. This might be attributed to a vision for a better means for new types of learning, as Küçük-Avci et al. (2022) claimed after carrying out a bibliometric analysis of 1,547 articles published between 2020 and 2021. The authors detected certain trends regarding distance learning in higher education. A main finding of their study, along with the increase in studies on distance education and e-learning in higher education, is that before the pandemic, the fact that these approaches were not so mandatory meant there was greater efficiency, probably due to the learners’ motivation. The authors further claim that researchers show a stronger interest in the technological means that can assist these types of learning. In addition, while researching 1,986 articles, Bozkurt (2022) established an increase in the implementation of blended learning by researchers who also aim to investigate the relationship between technological applications and learning institutions. Within these tendencies, researchers consider four thematic fields: a comparison of online and onsite learning with regard to effectiveness and efficiency; the experience, impressions and attitudes of stakeholders and learning community members with respect to blended learning; teacher training and curriculum development that will assure the appropriate and challenge-free implementation of blended learning; and the use of mostly a quantitative approach to research of blended learning.
Bilal et al. (2022) also examined research trends concerned with e-learning in higher education during the COVID-19 period by researching 1,595 studies published between 2020 and 2021. The four main trends they identified were supplementary to those mentioned by other authors: the first is about the challenges regarding online learning or blended learning along with the appropriate strategies in response; the second is student-centered collaborative learning and appropriate curriculum design; the third concerns home-based learning through a type of laboratory and the general conditions surrounding it; and the fourth addresses teachers’ background, training, professional competencies and interdisciplinary learning.
Tlili et al. (2022) focused on mapping COVID-19’s impact on Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs). The overall finding from the 108 articles they considered is that there has been growing interest in these courses generally, and more specifically in research around their function and quality. This interest encompasses the main features of such courses, which provide easy accessibility and flexibility. However, they noted that this interest followed another trend among researchers in the context. In other words, the countries that published on MOOCs before the pandemic are the same countries that published during the period under study. Moreover, they stated that there is interest in the technical characteristics and requirements of such courses. Finally, the authors concluded that although most MOOCs were ICT courses, research has escalated into courses that refer to business, personal development or the humanities.
Several conclusions can be drawn from the above bibliometric studies. First, the series of bibliometric studies conducted during the pandemic demonstrates the rise of interest in online learning in higher education during the pandemic. Of course, there was a tendency toward e-learning before the pandemic, but between 2020 and 2022, this seems to have accelerated. The phenomenon is more intense in countries such as the USA, Canada, Australia, the UK, India and China. Concerning the area of study, the focus of researchers appears to be greater in fields such as Engineering, Sciences, and Health Sciences, albeit all fields seem to be investigated ( Djeki et al., 2022 ; Pham et al., 2022 ; Vaicondam et al., 2022 ; Zhang et al., 2022 ). Various studies have focused on determining the effectiveness of e-learning classes and courses or pointing out parameters that influence their effectiveness. These could be the appropriate conditions or subtopics like motivation, blended learning, learning tools, teacher training, cooperation between different institutions or efficient practices ( Brika et al., 2021 ; Baber et al., 2022 ; Bilal et al., 2022 ; Bozkurt, 2022 ; Fauzi, 2022 ; Küçük-Avci et al., 2022 ; Yan et al., 2022 ). A specific trend of authors is to examine virtual classes and laboratories ( Kartimi et al., 2022 ; Rojas-Sánchez et al., 2022 ; Zhang et al., 2022 ). Finally, there is a focus on the technology factor. Namely, researchers have concentrated on technical issues and conditions related to e-learning courses and their proper functioning ( Navarro-Espinosa et al., 2021 ; Bozkurt, 2022 ; Tlili et al., 2022 ).
3. Materials and methods
Comprehensive bibliometric data on online learning research during the COVID-19 pandemic were retrieved on 1 March 2022 from Scopus, a world-leading bibliographic database of peer-reviewed literature. The Scopus database was preferred because it has a broader coverage of scientific research than other databases such as Web of Science ( Falagas et al., 2008 ). This was confirmed by an initial search using the same search query in each database, revealing that Scopus provided more relevant documents than Web of Science. Moreover, compared to the Scopus database, the Web of Science has been found to be a database that significantly underrepresents the scientific disciplines of the Social Sciences and the Arts and Humanities ( Mongeon and Paul-Hus, 2016 ). Although English dominates in both Scopus and Web of Science, Scopus generally offers wider coverage of non-English documents, given that the titles, abstracts, and keywords are in English ( Vera-Baceta et al., 2019 ). According to the basic statistical theory, which can also be applied in the context of bibliometric analysis, larger samples lead to analytical outcomes that are likely to be more accurate ( Rogers et al., 2020 ). Therefore, Scopus appears to be a more relevant bibliographic database meeting the specifics of online learning research during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The search strategy was based on title, abstract, and keywords search using the advanced search engine and the search query covered keywords related to different online learning types (using the Boolean operator ‘OR’) and the COVID-19 pandemic (using the Boolean operator ‘AND’). The search was further limited to the period 2020–2022 (using the Boolean operator ‘AND’) to capture documents published between January 2020 and March 2022, when most countries were experiencing constant disruptions in the educational process imposed by repeated lockdowns. As the search query had no language restrictions, the full text of the obtained documents can be in any language, provided that the titles, abstracts, and keywords are in English. Therefore, the language has no impact on the results, as the bibliometric analysis is conducted solely based on the titles, abstracts, and keywords of the documents. According to the presented search query, 9,921 documents were obtained. After further revising the obtained documents, it was identified that some of them are not explicitly related to the context of higher education. By machine screening of documents by title, abstract, and keywords, those related to lower levels of education (i.e., primary and secondary education), as well as adult and worker education (i.e., lifelong education), were excluded from the database. There were 1,618 or 16% of such documents. The remaining 8,303 documents were identified as eligible for further bibliometric examination of online learning research during the COVID-19 pandemic. The bibliometric analysis utilized several bibliometric approaches ( Figure 1 ).
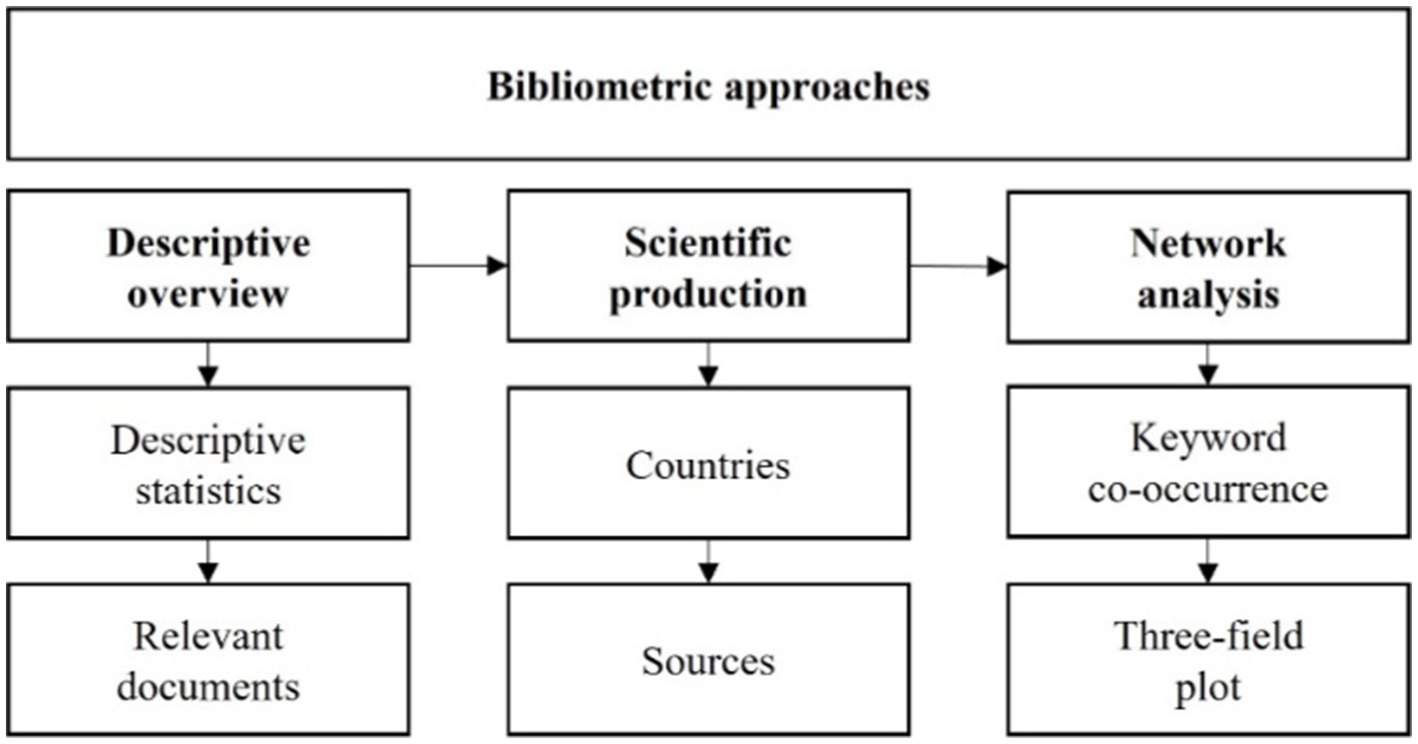
Figure 1 . Bibliometric approaches used in the bibliometric analysis. Own elaboration.
First, a descriptive overview was conducted to examine particular general bibliometric items, including timespan, number of (all, cited, single-authored) documents, authors, sources and author keywords and authors, references, and citations per document as well as to identify the most relevant documents. Scientific production was also examined to determine the most relevant countries and sources. Finally, network analysis was performed to identify the research hotspots according to the keyword co-occurrence network and examine the relationship between the main concepts based on a three-field plot analysis. The presented bibliometric approaches required the use of several different software tools. The descriptive overview was conducted using the Python Data Analysis Library Pandas ( McKinney, 2012 ), scientific production was visualized by the Python Visualization Library Matplotlib ( Hunter, 2007 ), while network analysis was performed using VOSviewer (keyword co-occurrence) ( Van Eck and Waltman, 2010 ) and the Python Visualization Library Plotly (a three-field plot) ( Pandey and Panchal, 2020 ). Specifically, the calculation for the three-field plot analysis included the following steps. Suppose that C 1 , C 2 , … , C m are analysed concepts where each concept C i is defined by a set of keywords and represented by binary indicators W i 1 , W i 2 , … , W i k i , expressed as C i = max j = 1 , … , k i W i j for i = 1 , … , m (matrix column). Using this notation, the relationship between C i and C j can be defined as C 1 T ∗ C j (matrix multiplication) where i and j are from three different sets (ICT tools, online learning approaches, fields of study).
The descriptive overview presented in Table 1 shows the main characteristics of online learning and COVID-19 research in the higher education context. This research area covers a total of 8,303 documents (of which 7,922 (95%) have the full text in English) published in 2,447 sources between January 2020 and March 2022. Slightly less than half (46%) of these documents have at least one citation, while a relatively small number (15%) were written by a single author. The average number of references per document in this research area is 31.39, which is below the general scientific area of Educational Research (44.00) ( Patience et al., 2017 ), suggesting that online learning research during the COVID-19 pandemic is grounded on fewer existing studies than general research. Finally, 3.50 citations per document can be observed for this research area. Due to the potential benefits of online learning, especially when combined with the traditional learning approaches and hence the development of the blended learning environment, this research is expected to further develop and be extended in the ensuing years ( Fauzi, 2022 ). Further, upon analyzing the documents, it is evident that the average year of references is 2014.03, with an h-index of 60 (indicating at least 60 papers with 60 or more citations each) and a g-index of 94 (denoting that the top 94 publications have accumulated citations equal to or greater than the square of 94). Finally, it was found that within the examined dataset, a total of 1,334 documents (16%) have achieved a minimum of 5 citations (C5), while 691 documents (8%) have attained at least 10 citations (C10), 302 documents (4%) have obtained a minimum of 20 citations (C20), 79 documents (1%) have acquired at least 50 citations (C50), and 31 documents (0.4%) have obtained more than 100 citations (C100).
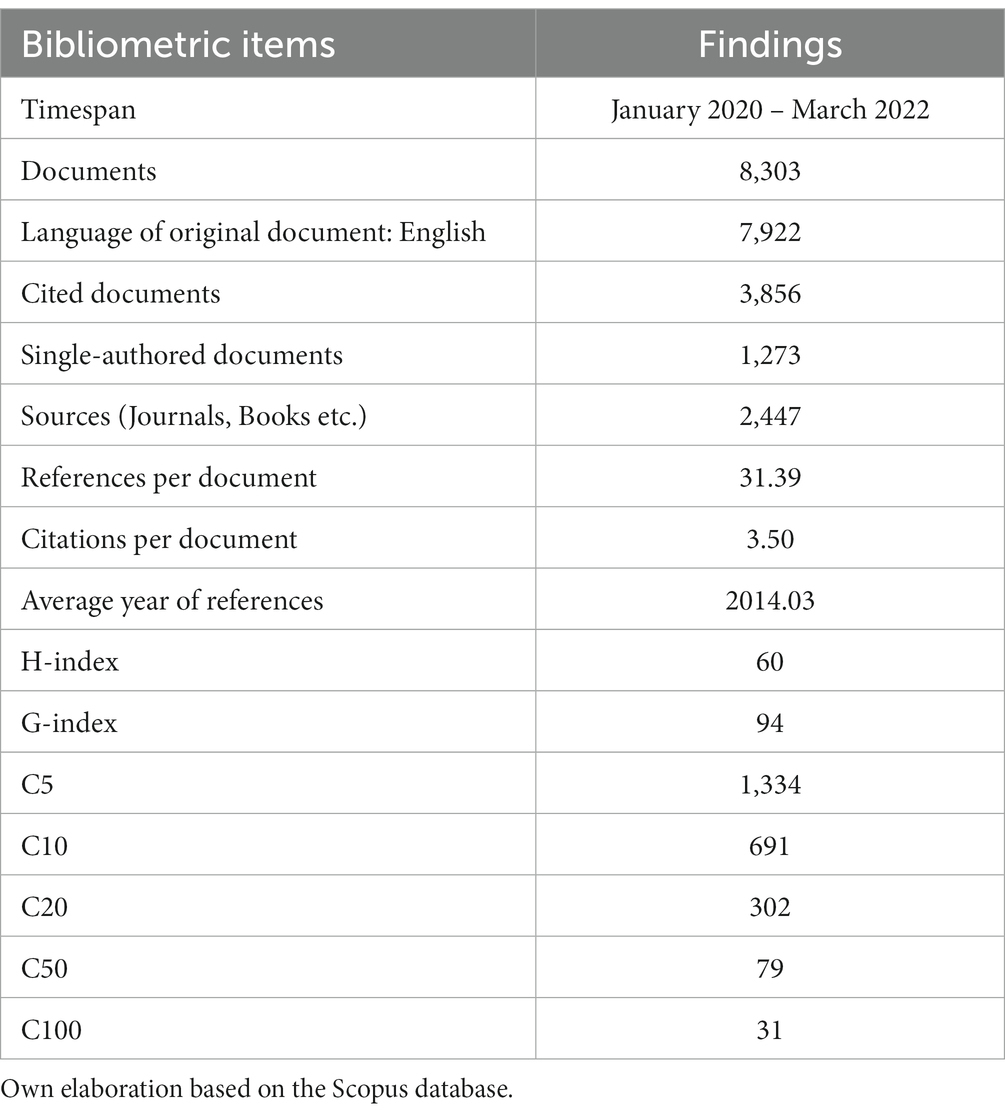
Table 1 . Descriptive overview of online learning and COVID-19 research (2020–2022).
The most relevant (top-10) highly cited documents in online learning and COVID-19 research in the context of higher education are shown in Table 2 . The overview of the most relevant documents reveals several important topics that were intensively discussed. The first most relevant topic concerns ICT. The COVID-19 pandemic has created significant challenges for higher education, especially for medical and surgical education, which requires personal attendance in clinical activities and labs. Accordingly, several innovative ICT tools (i.e., videoconferencing, social media, and telemedicine) and online learning approaches (i.e., flipped classroom or blended learning and virtual learning) were proposed to address this challenge. It is also stressed that by using appropriately established ICT solutions, online learning can lead to more sustainable education ( Adedoyin and Soykan, 2020 ; Chick et al., 2020 ; Dedeilia et al., 2020 ).
Table 2 . Most relevant documents in online learning and COVID-19 research (2020–2022).
The next top-cited topic relates to pedagogy. The disruption of education around the world due to the COVID-19 pandemic required teachers to possess specific pedagogical content knowledge related to designing and organizing better learning experiences with digital technologies. At the same time, challenges for online assessment and post-pandemic pedagogy are also highlighted ( García Peñalvo et al., 2020 ; Iyer et al., 2020 ; Murphy, 2020 ; Rapanta et al., 2020 ). Finally, life and work is another of the most cited topics. Namely, the COVID-19 pandemic has considerably reshaped education and other aspects of life and work, often also through the perspective of mental health or emotional well-being ( Dwivedi et al., 2020 ; Kapasia et al., 2020 ; Aristovnik et al., 2020a ).
Furthermore, it is noteworthy that all of the highly cited documents were published in 2020. However, it is also evident that there are notable and highly relevant publications that emerged in the second year of the COVID-19 pandemic. Accordingly, there are two documents with a minimum of 100 citations published in 2021. In the COVID-19 pandemic context, Watermeyer et al. (2021) , with 148 citations, examined the implications of digital disruption in universities within the United Kingdom, highlighting the challenges and opportunities arising from the emergency shift to online learning. Meanwhile, Pokhrel and Chhetri (2021) conducted a literature review to assess the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on teaching and learning.
The scientific production across countries and sources is presented in terms of the number of documents and citations, whereby additional information is provided by a circle’s size, revealing the h-index as a measure of the scientific impact ( Harzing and Van Der Wal, 2009 ) and by its color, presenting the time dimension in scientific production. The most relevant (top-10) highly cited countries in online learning and COVID-19 research are shown in Figure 2 . While the United States of America stands out among all countries, the United Kingdom, China and India have a relatively large number of documents and citations. The findings are similar to those of other bibliometric studies on this topic ( Saqr et al., 2023 ).
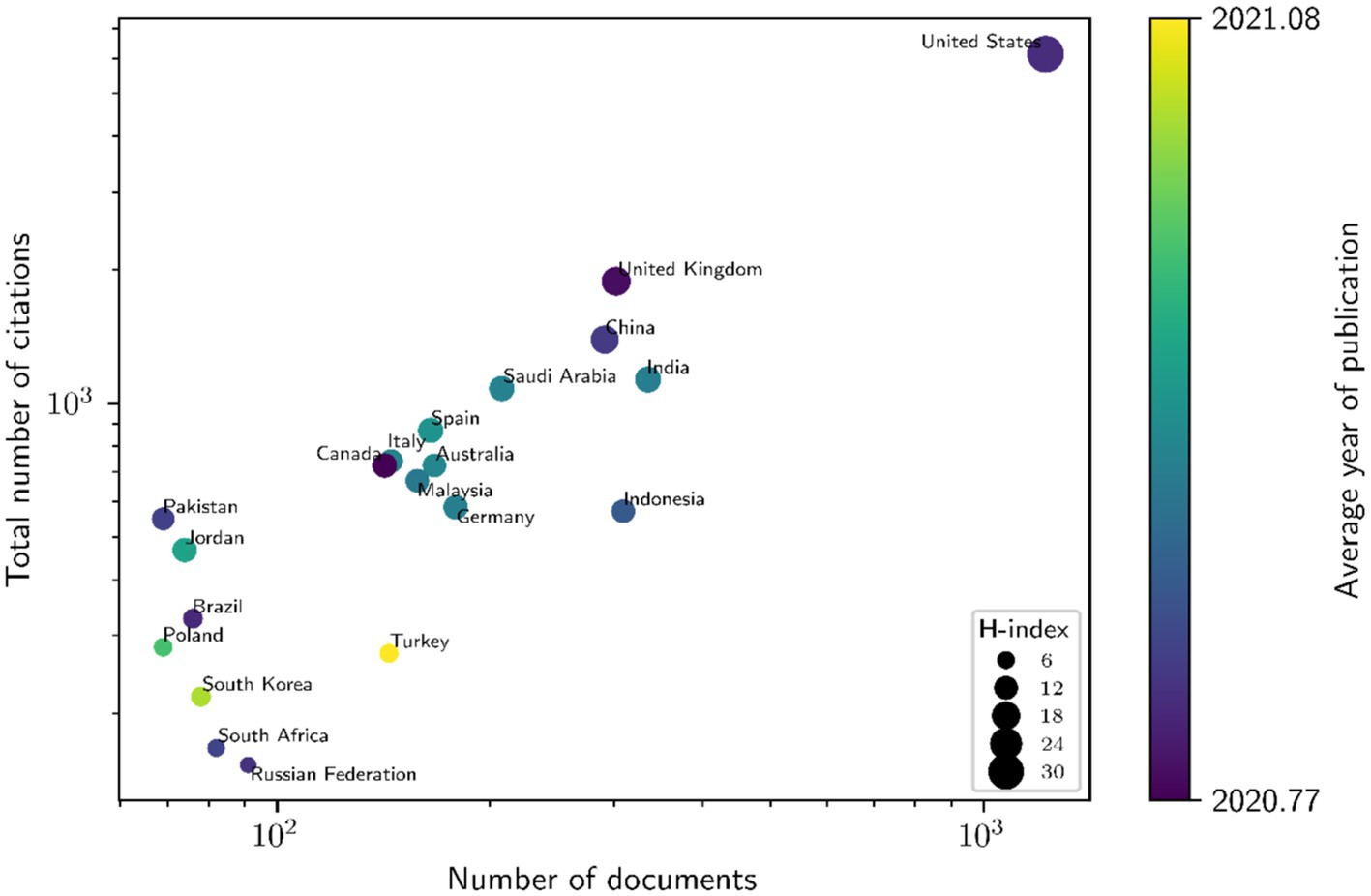
Figure 2 . Most relevant countries in online learning and COVID-19 research (2020–2022). Own elaboration based on the Scopus database.
The most relevant (top-10) highly cited sources in online learning and COVID-19 research in the context of higher education are presented in Figure 3 . Despite conference proceedings being prominent in terms of the relatively high number of documents, the most prominent journals, considering the number of citations, are Journal of Chemical Education, with the highest number of citations as well as documents, followed by Sustainability, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, and Education Sciences. More specifically, the most relevant journals address different topics. First, Journal of Chemical Education covers the attempts, successes and failures of distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in chemistry education. It covers various topics, including the development of at-home practical activities ( Schultz et al., 2020 ), student engagement and learning ( Perets et al., 2020 ), online assessments ( Nguyen et al., 2020 ) and virtual reality labs ( Williams et al., 2021 ). Further, Sustainability is focused on student and teacher perceptions of e-learning and related challenges ( Khan et al., 2020 ; Aristovnik et al., 2020a ) and sustainability in education during the COVID-19 pandemic ( Sobaih et al., 2020 ) to improve online learning and sustain higher education during uncertain times. Further, the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health covers various topics like the health and psychological implications of the COVID-19 pandemic ( Sundarasen et al., 2020 ), including well-being and changes in behavior and habits. Finally, Education Sciences publishes some general research on the challenges and opportunities for online learning ( Almazova et al., 2020 ), including student and teacher experiences ( García-Alberti et al., 2021 ; Müller et al., 2021 ).
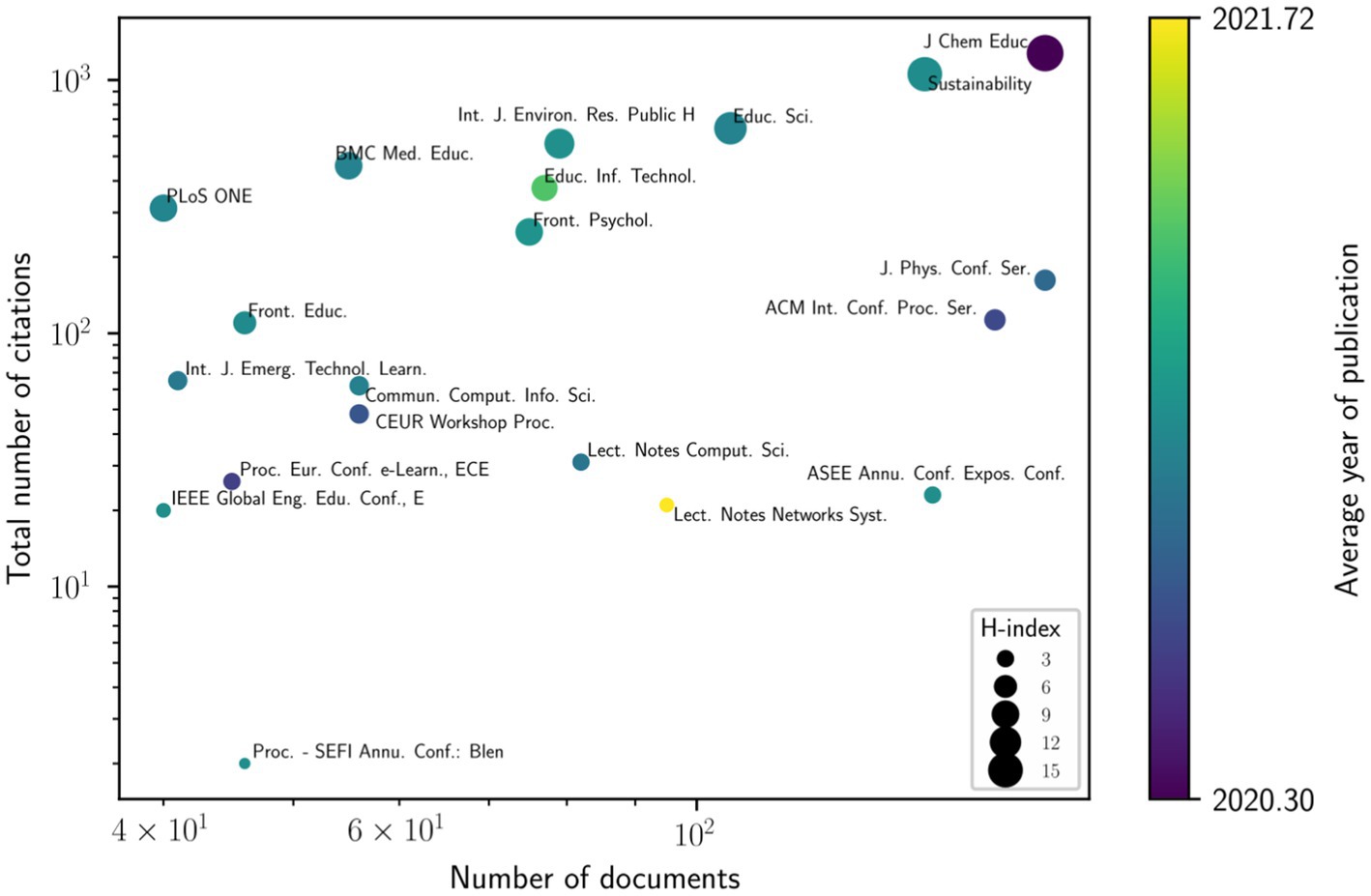
Figure 3 . Most relevant sources in online learning and COVID-19 research (2020–2022). Own elaboration based on the Scopus database.
The keyword co-occurrence network is presented in Figure 4 . Note that the nodes indicate keywords and the links the relations of co-occurrence between them. The node size is proportional to the number of keyword occurrences, showing the research intensity (node degree), while the link width is proportional to the co-occurrences between keywords (edge weight). In addition, the node color indicates the cluster to which a particular keyword belongs ( Wang et al., 2020 ; Ravšelj et al., 2022 ). The keyword co-occurrence analysis reveals five research hotspots in online learning in higher education research during the COVID-19 pandemic. These are ICT and pedagogy (red cluster), technology-enhanced education (green cluster), mental health and well-being (blue cluster), student experience (yellow cluster) and curriculum and professional development (purple cluster).
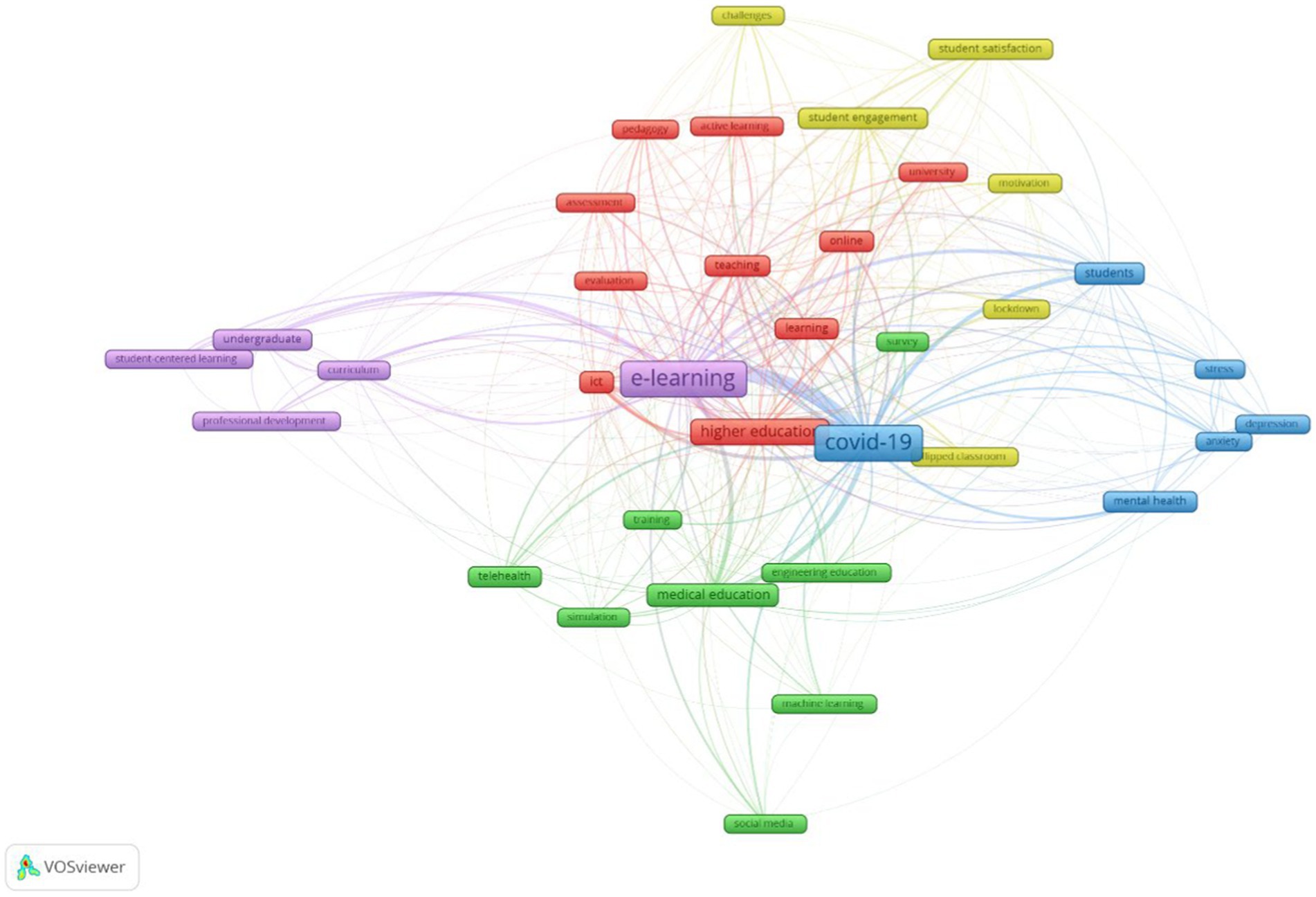
Figure 4 . Keyword co-occurrence network in online learning and COVID-19 research (2020–2022). Own elaboration based on the Scopus database.
A detailed synopsis of the research hotspots, including representative (the most frequent) keywords and documents (with several representative keywords), is presented in Table 3 . The first research hotspot highlights the relevance of ICT and pedagogy in higher education during the COVID-19 pandemic. The most representative documents looked at the quality of online learning mechanisms ( Gritsova and Tissen, 2021 ), active learning activities ( Yan et al., 2021 ) and the role of e-learning departments in controlling the quality of academic processes ( Hamdan et al., 2021 ). The second research hotspot refers to technology-enhanced education from different perspectives, such as opportunities to incorporate technological and curricular innovations ( Shapiro and Reza, 2021 ), the adoption of different virtual experiences such as telehealth and virtual learning ( Kahwash et al., 2021 ), and the utilization of social media to reach higher education students ( Leighton et al., 2021 ). The third research hotspot emphasizes the problem of mental health and well-being issues that became a prevalent topic of discussion during the COVID-19 pandemic. Namely, several studies showed an increase in depression, anxiety and stress levels among higher education students in response to the COVID-19 pandemic ( Abu Kwaik et al., 2021 ; Keskin, 2021 ; Yaghi, 2022 ). The fourth cluster is about student experience during the COVID-19 pandemic with specific focus on the between interaction and online learning satisfaction ( Bawa'aneh, 2021 ; Bismala and Manurung, 2021 ; She et al., 2021 ). The fifth research hotspot underscores the relevance of curriculum and professional development. Several studies described the ways in which courses were adapted to online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic as well as the related challenges and strategies ( Chen et al., 2020 ; Gonzalez and Knecht, 2020 ; Rhile, 2020 ).
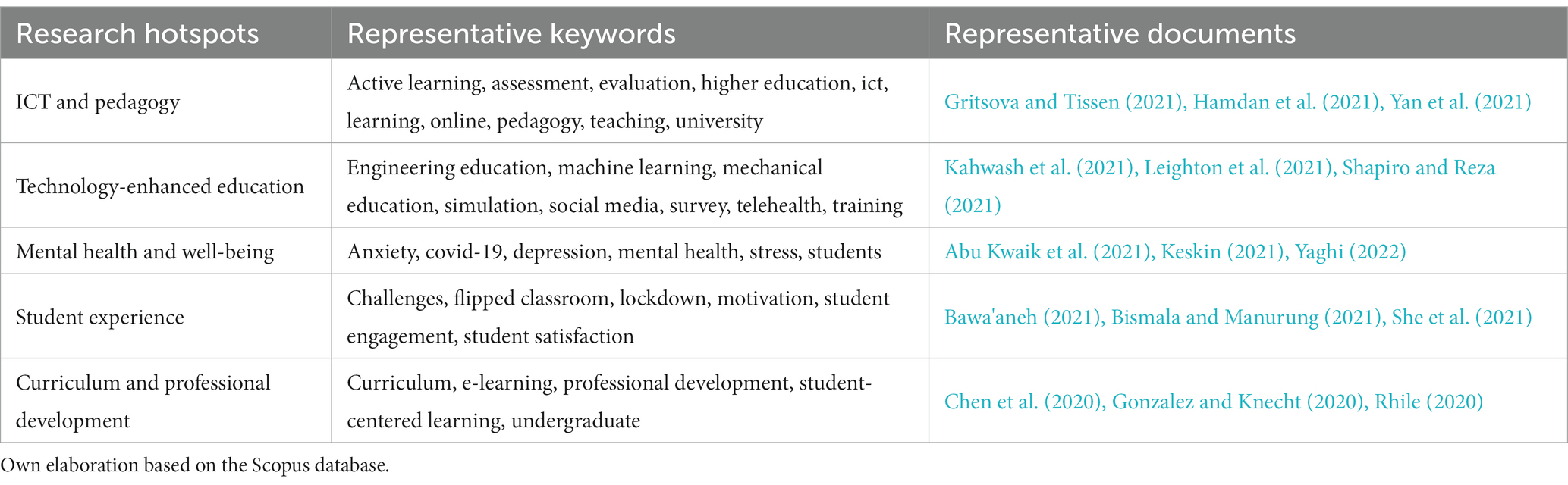
Table 3 . Research hotspots based on the author keyword co-occurrence network in online learning and COVID-19 research (2020–2022).
Finally, the three-field plot analysis of the relationship between the main concepts (i.e., ICT tools, online learning approaches, fields of study) is presented in a Sankey diagram shown in Figure 5 . The size of a rectangle corresponds to the number of documents for each theme, while the edge width reflects the inclusion index for connected themes ( Wang et al., 2020 ; Ravšelj et al., 2022 ). These three concepts have been proven to be relevant in the context of online learning. Namely, ICT tools are a precondition for delivering course content through different online learning approaches, while the choice of online learning approaches may depend on the field of study ( Ferri et al., 2020 ). During the COVID-19 pandemic, most attention was devoted to exploring e-learning (a combination of asynchronous and synchronous learning), distance learning (pre-recorded online lectures), followed by virtual learning (real-time online lectures). Since all these online learning approaches limit physical contact between teachers and students, they have been referred to as emergency remote learning approaches ( Hodges et al., 2020 ; Fauzi, 2022 ; Fuchs, 2022 ), while other online learning approaches (computer-based learning, blended learning, m-learning) do not necessarily take place in an online learning environment. The emergency remote learning approaches were primarily supported by several ICT tools, particularly by social media (e.g., Facebook), gamification/simulation and virtual reality (integration of game-like elements into online learning platforms, mobile applications, or virtual reality simulations), Zoom and other videoconferencing platforms, as well as telehealth (for educating health professionals). Regarding the fields of study, e-learning, distance learning and virtual learning were mostly addressed in the context of medical/health education, while computer-based learning (i.e., specific engineering software programs etc.) was examined in the context of engineering education. This implies that the specific requirements of a given field of study often guide the selection of the most suitable online learning approaches ( Fauzi, 2022 ).
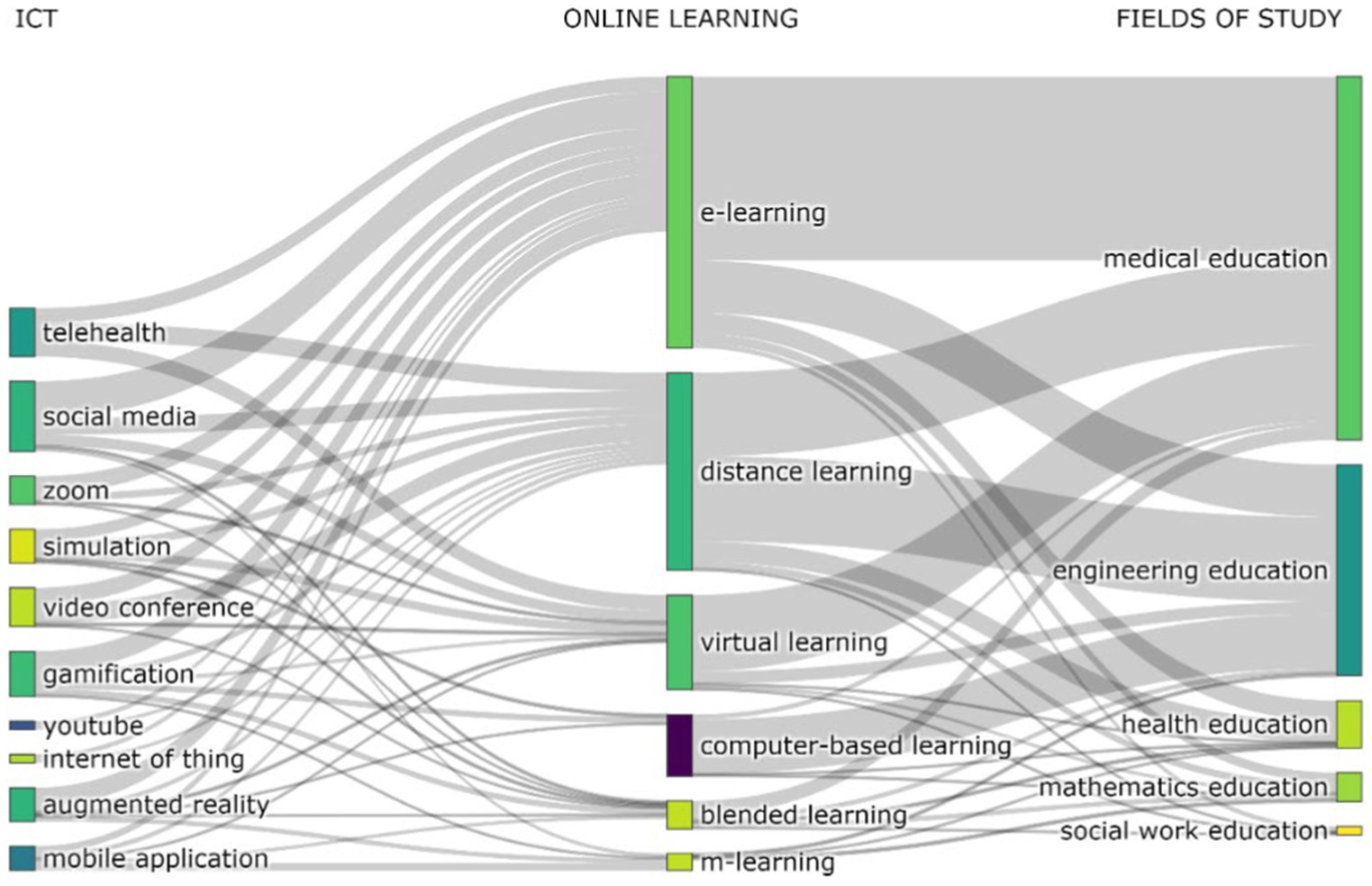
Figure 5 . Three-field plot showing the network between ICT tools (left), online approaches (middle), and fields of study (right) (2020–2022). Own elaboration based on the Scopus database.
5. Conclusion
The presented bibliometric study provides several important insights arising from research into online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. In this period, a large volume of scientific knowledge was produced in the context of education that considered a range of aspects ( Saqr et al., 2023 ). Therefore, a combination of selected bibliometric approaches was utilized to extract some general comprehensive outlines of the global research. The bibliometric analysis revealed the following.
As suggested by the descriptive overview of the state of Educational Research ( Patience et al., 2017 ), the research into online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic is characterized by greater cooperation between authors, which coincides with the general observation that (international) scientific collaboration grew significantly during the pandemic ( Duan and Xia, 2021 ). Further, online learning research during the COVID-19 pandemic is grounded on fewer studies than Educational Research ( Patience et al., 2017 ), which may be explained by the absence of COVID-19-related literature at the time these documents were published. Nevertheless, noting the potential benefits of online learning approaches also when the epidemiological conditions are favorable, this line of research is expected to further develop and be extended in the ensuing years ( Fauzi, 2022 ). The potential benefits refer especially to the development of a blended learning environment, which combines online and traditional learning approaches ( Rasheed et al., 2020 ). The overview of the most relevant documents revealed three topics that were intensively discussed in the academic community, i.e., ICT, pedagogy, and life and work. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance and role of reliable ICT infrastructure for ensuring effective pedagogy in the online environment, as was needed to prevent the spread of the virus and to protect public health. Apart from the devastating health consequences for those directly affected by the virus and the disrupted educational process, the COVID-19 pandemic also dramatically affected students’ social life and work ( Aristovnik et al., 2020a ). The educational community is increasingly interested in finding ways to respond to crises like the COVID-19 pandemic and develop effective pedagogical practices that assure high-quality and efficient education in the online learning environment ( Zhang et al., 2022 ).
The scientific production of online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic was geographically uneven. The greatest scientific production in terms of citations and number of documents can be observed in the United States, followed by the United Kingdom, China and India. Besides developed English-speaking countries, emerging Asian economies also seem to have played a crucial role in online learning research. Similar findings also emerged from other bibliometric studies on this topic ( Saqr et al., 2023 ). Moreover, despite conference proceedings being prominent in terms of the relatively high number of documents, the most prominent journals, considering the number of citations, are Journal of Chemical Education, Sustainability, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health and Education Sciences, indicating that online learning research at the time of the COVID-19 pandemic was primarily published in open-access journals, as already observed in other research ( Zhang et al., 2022 ).
The network analysis revealed five research hotspots in online learning research during the COVID-19 pandemic in the context of higher education: (1) ICT and pedagogy, focused on the quality of online learning mechanisms ( Gritsova and Tissen, 2021 ), active learning activities ( Yan et al., 2021 ) and the role of e-learning departments in controlling the quality of academic processes ( Hamdan et al., 2021 ); technology-enhanced education concentrated on opportunities to incorporate technological and curricular innovations ( Shapiro and Reza, 2021 ), the adoption of different virtual experiences such as telehealth and virtual learning ( Kahwash et al., 2021 ), and the utilization of social media to reach higher education students ( Leighton et al., 2021 ); (2) mental health and well-being issues facing higher education students, including depression, anxiety, and stress levels ( Abu Kwaik et al., 2021 ; Keskin, 2021 ; Yaghi, 2022 ); student experience with specific focus on the between interaction and online learning satisfaction ( Bawa'aneh, 2021 ; Bismala and Manurung, 2021 ; She et al., 2021 ) and (3) curriculum and professional development, focused on the ways in which courses were adapted to online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic as well as the related challenges and strategies ( Chen et al., 2020 ; Gonzalez and Knecht, 2020 ; Rhile, 2020 ).
Further, the COVID-19 pandemic led to the exploration of emergency remote learning approaches such as e-learning, distance learning and virtual learning, which are intended to limit physical contact between teachers and students. These approaches were chiefly supported by several ICT tools, including social media, gamification/simulation, virtual reality, videoconferencing platforms, and telehealth. While computer-based learning, blended learning and m-learning do not necessarily occur in an online learning environment, they may still be suitable for certain fields of study, especially in the post-COVID-19 pandemic period. This implies that the determination of which online learning approach is the most suitable is often guided by the specific requirements of a given field of study ( Fauzi, 2022 ).
Before generalizing these conclusions, it is important to note the limitations of the paper. First, the bibliometric analysis relied on documents indexed in the Scopus database, which might not cover the entire collection of research. Namely, documents that are published in journals indexed in other databases such as Web of Science, Education Research Index, Educational Resources Information Centre, etc. are not included in the analysis. However, to achieve the comparability of bibliometric metrics across documents, the bibliometric metrics are obtained from the single and, in general, broader Scopus database. Given the substantial overlap of documents across different databases of peer-reviewed literature, this limitation might not significantly affect the general observations on global research trends. Nevertheless, to check the robustness of the findings, it is still valuable to consider other bibliometric databases for future research. Second, the bibliometric analysis is conducted the bibliometric is based on a short time period (January 2020 – March 2022), which may also impact the metrics of documents published in closed-access (subscription-based) journals, placing them at a disadvantage compared to documents published in open-access journals. While it is not possible to overcome this limitation at present, conducting a bibliometric study with a longer time span would provide further time-dimensional insights. This would also be beneficial in terms of achieving better comparability between documents published in closed-access and open-access journals. Finally, despite the detailed search queries, some other relevant keywords may have been overlooked in the document search. Finally, the bibliometric method, as a method based on big data analysis, may miss certain highlights from the scientific literature that a systematic literature review would otherwise capture. Therefore it would be beneficial for future bibliometric studies also to incorporate a systematic literature review methodology, as the combined approach can provide a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the implications of the COVID-19 pandemic on online learning in higher education.
The bibliometric study provides some possible avenues for future research. First, in future bibliometric studies, it would be beneficial to conduct in-depth analyses of the relevant contexts that have emerged as highly significant in online learning during the pandemic. These include ICT and innovation, mental health and well-being, online learning and engagement, and curriculum and professional development. Examining these contexts more comprehensively can provide valuable insights into the specific dynamics and trends within each area, contributing to a deeper understanding of the implications of online learning during the pandemic. Second, it would be beneficial to conduct separate bibliometric analyses and comparisons to examine the differences between developed and developing countries. This approach can shed light on the unique research trends, contributions, and challenges faced by each group of countries in the context of online learning during the pandemic. This can provide a more nuanced understanding of the global landscape and identify potential areas for collaboration and knowledge sharing between developed and developing countries. Finally, it would be valuable to investigate the long-term impact of rapid publishing in open-access journals on the recognition and dissemination of scholarly findings in the field of online learning in higher education during the pandemic.
From the practical perspective, the COVID-19 pandemic has significantly disrupted higher education, but at the same time, it also accelerated the use of online learning tools in the educational process. Although the COVID-19 pandemic has gradually subsided over time, online learning approaches developed during this period continue to hold relevance and value for future education. Therefore, higher education institutions should prioritize leveraging ICT tools and innovative solutions in their educational delivery, which proved effective during the pandemic. Moreover, higher education institutions should also prioritize adapting appropriate online learning approaches and curricula to align with modern realities and the corresponding fields of study. This adaptation is crucial for enhancing student engagement and ensuring that educational programs remain relevant and responsive to the evolving needs of students in various disciplines.
The findings may help not only the scientific community in detecting research gaps in online learning research during the COVID-19 pandemic but also evidence-based policymaking by assisting in identifying appropriate educational practices in emergency circumstances. Specifically, the findings may help higher education policymakers to address the underlying shortcomings of the existing educational framework exposed by the COVID-19 pandemic and to design proactive mechanisms to deal effectively with such disruptions, thereby enabling them to create a more resilient and adaptable education system that can successfully navigate unforeseen challenges and ensure the continuity of quality higher education in the future.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
AA contributed to the design of the study. DR and LU assisted with the data identification, cleaning, and analysis. DR and KK wrote the manuscript in consultation with AA. All authors contributed to the manuscript’s revision and read and approved the submitted version.
This research and the APC were funded by the Slovenian Research Agency under grant numbers P5-0093 and Z5-4569.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Slovenian Research Agency (research core funding no. P5-0093 and project no. Z5-4569). A preliminary version of the paper was presented at the International Conference on Information, Communication Technologies in Education (ICICTE) in July 2022. The authors are grateful to colleagues who attended the presentation and provided interesting comments and suggestions. Further, they wish to thank the reviewers for their valuable suggestions and comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abu Kwaik, A., Saleh, R., Danadneh, M., and Kateeb, E. (2021). Stress, anxiety and depression among dental students in times of covid-19 lockdown. Int. J. Dentist. Oral Sci. 8, 1560–1564. doi: 10.19070/2377-8075-21000310
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Adedoyin, O. B., and Soykan, E. (2020). COVID-19 pandemic and online learning: the challenges and opportunities. Interact. Learn. Environ. 31, 863–875. doi: 10.1080/10494820.2020.1813180
Almazova, N., Krylova, E., Rubtsova, A., and Odinokaya, M. (2020). Challenges and opportunities for Russian higher education amid COVID-19: teachers’ perspective. Educ. Sci. 10:368. doi: 10.3390/educsci10120368
Aristovnik, A., Keržič, D., Ravšelj, D., Tomaževič, N., and Umek, L. (2020a). Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on life of higher education students: a global perspective. Sustainability 12:8438. doi: 10.3390/su12208438
Aristovnik, A., Ravšelj, D., and Umek, L. (2020b). A bibliometric analysis of COVID-19 across science and social science research landscape. Sustainability 12:9132. doi: 10.3390/su12219132
Baber, H., Fanea-Ivanovici, M., Lee, Y. T., and Tinmaz, H. (2022). A bibliometric analysis of digital literacy research and emerging themes pre-during COVID-19 pandemic. Inform. Learn. Sci. 123, 214–232. doi: 10.1108/ILS-10-2021-0090
Bawa'aneh, M. S. (2021). Distance learning during COVID-19 pandemic in UAE public schools: student satisfaction, attitudes and challenges. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 13:10872. doi: 10.30935/cedtech/10872
Bilal, H., Hysa, E., Akbar, A., Yasmin, F., Rahman, A. u., and Li, S. (2022). Virtual learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: a bibliometric review and future research agenda. Risk Manag. Healthcare Policy 15, 1353–1368. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S355895
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Bismala, L., and Manurung, Y. H. (2021). Student satisfaction in E-learning along the COVID-19 pandemic with importance performance analysis. Int. J. Eval. Res. Educ. 10, 753–759. doi: 10.11591/ijere.v10i3.21467
Bonsaksen, T., Leung, J., Schoultz, M., Thygesen, H., Price, D., Ruffolo, M., et al. (2021). Cross-National Study of worrying, loneliness, and mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: a comparison between individuals with and without infection in the family. Healthcare 9:903. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9070903
Bozkurt, A. (2022). A retro perspective on blended/hybrid learning: systematic review, mapping and visualization of the scholarly landscape. J. Interact. Media Educ. 2022, 1–15. doi: 10.5334/jime.751
Brika, S. K. M., Chergui, K., Algamdi, A., Musa, A. A., and Zouaghi, R. (2021). E-learning research trends in higher education in light of COVID-19: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Psychol. 12:762819. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.762819
Campos, E., Daruich, S. D. N., Escamilla, J., and Hosseini, S. (2022). Educational model transition: student evaluation of teaching amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Educ. 7:991654. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2022.991654
Chen, K., Chen, Y., Ling, Y., and Lin, J. (2020). The individual experience of online chemistry teacher education in China: coping with COVID-19 pandemic. J. Chem. Educ. 97, 3265–3270. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00581
Chick, R. C., Clifton, G. T., Peace, K. M., Propper, B. W., Hale, D. F., Alseidi, A. A., et al. (2020). Using technology to maintain the education of residents during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Surg. Educ. 77, 729–732. doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2020.03.018
Dedeilia, A., Papapanou, M., Papadopoulos, A. N., Karela, N. R., Androutsou, A., Mitsopoulou, D., et al. (2023). Health worker education during the COVID-19 pandemic: global disruption, responses and lessons for the future—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum. Resour. Health 21, 13–35. doi: 10.1186/s12960-023-00799-4
Dedeilia, A., Sotiropoulos, M. G., Hanrahan, J. G., Janga, D., Dedeilias, P., and Sideris, M. (2020). Medical and surgical education challenges and innovations in the COVID-19 era: a systematic review. In Vivo 34, 1603–1611. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11950
Djeki, E., Dégila, J., Bondiombouy, C., and Alhassan, M. H. (2022). E-learning bibliometric analysis from 2015 to 2020. J. Comput. Educ. 9, 727–754. doi: 10.1007/s40692-021-00218-4
Duan, D., and Xia, Q. (2021). Evolution of scientific collaboration on COVID-19: a bibliometric analysis. Learn. Publish. 34, 429–441. doi: 10.1002/leap.1382
Dwivedi, Y. K., Hughes, D. L., Coombs, C., Constantiou, I., Duan, Y., Edwards, J. S., et al. (2020). Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on information management research and practice: transforming education, work and life. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 55:102211. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102211
Elmer, T., Mepham, K., and Stadtfeld, C. (2020). Students under lockdown: comparisons of students' social networks and mental health before and during the COVID-19 crisis in Switzerland. PLoS One 15:e0236337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236337
Falagas, M. E., Pitsouni, E. I., Malietzis, G. A., and Pappas, G. (2008). Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, web of science, and Google scholar: strengths and weaknesses. FASEB J. 22, 338–342. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-9492LSF
Fauzi, M. A. (2022). E-learning in higher education institutions during COVID-19 pandemic: current and future trends through bibliometric analysis. Heliyon 8:e09433. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09433
Ferri, F., Grifoni, P., and Guzzo, T. (2020). Online learning and emergency remote teaching: opportunities and challenges in emergency situations. Societies 10:86. doi: 10.3390/soc10040086
Fried, E. I., Papanikolaou, F., and Epskamp, S. (2021). Mental health and social contact during the COVID-19 pandemic: an ecological momentary assessment study. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 10, 340–354. doi: 10.1177/21677026211017839
Fuchs, K. (2022). The difference between emergency remote teaching and e-learning. Front. Educ. 7:921332. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2022.921332
Gao, Y., Wong, S. L., Khambari, M. N., and Noordin, N. (2022). A bibliometric analysis of the scientific production of e-learning in higher education (1998-2020). Int. J. Inform. Educ. Technol. 12, 390–399. doi: 10.18178/ijiet.2022.12.5.1632
García Peñalvo, F. J., Corell Almuzara, A., Abella García, V., and Grande de Prado, M. (2020). La evaluación online en la educación superior en tempos’ de la COVID-19. Educ. Knowl. Soc. 21:23086. doi: 10.14201/eks.23086
García-Alberti, M., Suárez, F., Chiyón, I., and Mosquera Feijoo, J. C. (2021). Challenges and experiences of online evaluation in courses of civil engineering during the lockdown learning due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Educ. Sci. 11:59. doi: 10.3390/educsci11020059
Gavriluţă, C., Dalban, C. M., and Ioan, B. G. (2022). Educational, emotional, and social impact of the emergency state of COVID-19 on Romanian university students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:3990. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19073990
Gonzalez, C., and Knecht, L. D. (2020). Strategies employed in transitioning multi-instructor, multisection introductory general and organic chemistry courses from face-to-face to online learning. J. Chem. Educ. 97, 2871–2877. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00670
Gritsova, O. A., and Tissen, E. V. (2021). Quality assessment of online learning in regional higher education systems. Econ. Regions 17, 929–943. doi: 10.17059/ekon.reg.2021-3-15
Gurcan, F., Dalveren, G. G. M., and Derawi, M. (2022). COVID-19 and E-learning: an exploratory analysis of research topics and interests in E-learning during the pandemic. IEEE Access 10, 123349–123357. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3224034
Hamdan, R., Ashour, W., and Daher, W. (2021). The role of the e-learning departments in controlling the quality of electronic assessments in Palestinian universities during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sustainability 13:12021. doi: 10.3390/su132112021
Harzing, A. W., and Van Der Wal, R. (2009). A Google scholar h-index for journals: an alternative metric to measure journal impact in economics and business. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 60, 41–46. doi: 10.1002/asi.20953
Hodges, C. B., Moore, S., Lockee, B. B., Trust, T., and Bond, M. A. (2020). The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning. Virginia Tech Online Available online at: http://hdl.handle.net/10919/104648 (Accessed February 15, 2023).
Google Scholar
Hunter, J. D. (2007). Matplotlib: a 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 9, 90–95. doi: 10.1109/MCSE.2007.55
Iyer, P., Aziz, K., and Ojcius, D. M. (2020). Impact of COVID-19 on dental education in the United States. J. Dent. Educ. 84, 718–722. doi: 10.1002/jdd.12163
James, N., and Thériault, V. (2020). Adult education in times of the COVID-19 pandemic: inequalities, changes, and resilience. Stud. Educ. Adults 52, 129–133. doi: 10.1080/02660830.2020.1811474
Kahwash, B. M., Deshpande, D. R., Guo, C., Panganiban, C. M., Wangberg, H., and Craig, T. J. (2021). Allergy/immunology trainee experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic: AAAAI work group report of the fellows-in-training committee. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 9, 1–6.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.09.036
Kapasia, N., Paul, P., Roy, A., Saha, J., Zaveri, A., Mallick, R., et al. (2020). Impact of lockdown on learning status of undergraduate and postgraduate students during COVID-19 pandemic in West Bengal, India. Child Youth Serv. Rev. 116:105194. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105194
Kartimi, K., Yunita, Y., Addiin, I., and Shidiq, A. S. (2022). A bibliometric analysis on chemistry virtual laboratory. Educación Química 33:194. doi: 10.22201/fq.18708404e.2022.2.80579
Keržič, D., Alex, J. K., Pamela Balbontín Alvarado, R., da Silva Bezerra, D., Cheraghi, M., Dobrowolska, B., et al. (2021). Academic student satisfaction and perceived performance in the e-learning environment during the COVID-19 pandemic: evidence across ten countries. PLoS One 16:e0258807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258807
Keržič, D., Umek, L., Tomaževič, N., and Aristovnik, A. (2022). E-learning acceptance of public administration students in Slovenia in comparison with Europe: differences between the first and second waves of the COVID-19 pandemic. EGPA 2022 Conference, 6–9 September 2022, Lisbon, Portugal.
Keskin, G. (2021). Self-report measurement of depression, anxiety, and stress caused by covid-19 pandemic in senior undergraduate dental students. Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada 21:102. doi: 10.1590/pboci.2021.102
Khan, M. A., Nabi, M. K., Khojah, M., and Tahir, M. (2020). Students’ perception towards e-learning during COVID-19 pandemic in India: an empirical study. Sustainability 13:57. doi: 10.3390/su13010057
Küçük-Avci, Ş., Topal, M., and İstanbullu, A. (2022). The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on distance education in higher education: a bibliometric analysis study. Croatian J. Educ. 24, 457–488. doi: 10.15516/cje.v24i2.4534
Leighton, K., Kardong-Edgren, S., Schneidereith, T., and Foisy-Doll, C. (2021). Using social media and snowball sampling as an alternative recruitment strategy for research. Clin. Simul. Nurs. 55, 37–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ecns.2021.03.006
McKinney, W. (2012). Python for data analysis: Data wrangling with pandas, NumPy, and IPython . Sebastopol, CA: O'Reilly Media, Inc.
Misiejuk, K., Ness, I. J., Gray, R., and Wasson, B. (2023). Changes in online course designs: before, during, and after the pandemic. Front. Educ. 7:996006. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2022.996006
Mongeon, P., and Paul-Hus, A. (2016). The journal coverage of web of science and Scopus: a comparative analysis. Scientometrics 106, 213–228. doi: 10.1007/s11192-015-1765-5
Müller, A. M., Goh, C., Lim, L. Z., and Gao, X. (2021). COVID-19 emergency elearning and beyond: experiences and perspectives of university educators. Educ. Sci. 11:19. doi: 10.3390/educsci11010019
Murphy, M. P. (2020). COVID-19 and emergency eLearning: consequences of the securitization of higher education for post-pandemic pedagogy. Contemp. Security Policy 41, 492–505. doi: 10.1080/13523260.2020.1761749
Navarro-Espinosa, J. A., Vaquero-Abellán, M., Perea-Moreno, A.-J., Pedrós-Pérez, G., Aparicio-Martínez, P., and Martínez-Jiménez, M. P. (2021). The influence of technology on mental well-being of STEM teachers at university level: COVID-19 as a stressor. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:9605. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18189605
Nguyen, J. G., Keuseman, K. J., and Humston, J. J. (2020). Minimize online cheating for online assessments during COVID-19 pandemic. J. Chem. Educ. 97, 3429–3435. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00790
Ochnik, D., Rogowska, A. M., Kuśnierz, C., Jakubiak, M., Wierzbik-Strońska, M., Schütz, A., et al. (2021). Exposure to COVID-19 during the first and the second wave of the pandemic and coronavirus-related PTSD risk among university students from six countries-a repeated cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Med. 10:5564. doi: 10.3390/jcm10235564
Okoro, C., Owojori, O. M., and Umeokafor, N. (2022). The developmental trajectory of a decade of research on mental health and well-being amongst graduate students: a bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:4929. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19094929
Pandey, K., and Panchal, R. (2020). A study of real world data visualization of COVID-19 dataset using Python. Int. J. Manag. Human. 4, 104–107. doi: 10.35940/ijmh.H0834.044820
Patience, G. S., Patience, C. A., Blais, B., and Bertrand, F. (2017). Citation analysis of scientific categories. Heliyon 3:e00300. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2017.e00300
Perets, E. A., Chabeda, D., Gong, A. Z., Huang, X., Fung, T. S., Ng, K. Y., et al. (2020). Impact of the emergency transition to remote teaching on student engagement in a non-STEM undergraduate chemistry course in the time of COVID-19. J. Chem. Educ. 97, 2439–2447. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00879
Pham, P. T., Lien, D. T. H., Kien, H. C., Chi, N. H., Tinh, P. T., Do, T., et al. (2022). Learning management system in developing countries: a bibliometric analysis between 2005 and 2020. Europ. J. Educ. Res. 11, 1363–1377. doi: 10.12973/eu-jer.11.3.1363
Pokhrel, S., and Chhetri, R. (2021). A literature review on impact of COVID-19 pandemic on teaching and learning. High. Educ. Future 8, 133–141. doi: 10.1177/234763112098348
Raccanello, D., Balbontín-Alvarado, R., da Silva Bezerra, D., Burro, R., Cheraghi, M., Dobrowolska, B., et al. (2022). Higher education students’ achievement emotions and their antecedents in e-learning amid COVID-19 pandemic: a multi-country survey. Learn. Instr. 80:101629. doi: 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2022.101629
Rapanta, C., Botturi, L., Goodyear, P., Guàrdia, L., and Koole, M. (2020). Online university teaching during and after the COVID-19 crisis: refocusing teacher presence and learning activity. Postdigital Sci. Educ. 2, 923–945. doi: 10.1007/s42438-020-00155-y
Rasheed, R. A., Kamsin, A., and Abdullah, N. A. (2020). Challenges in the online component of blended learning: a systematic review. Comput. Educ. 144:103701. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103701
Rasli, A., Tee, M., Ling, L. Y., Cheak, T. Z., and Hui, S. E. (2022). Post COVID-19 strategies for higher education institutions in dealing with unknown and uncertainties. Front. Educ. 7:992063. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2022.992063
Ravšelj, D., Umek, L., Todorovski, L., and Aristovnik, A. (2022). A review of digital era governance research in the first two decades: a bibliometric study. Future Internet 14:126. doi: 10.3390/fi14050126
Rhile, I. J. (2020). Course redesign for college general chemistry during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Chem. Educ. 97, 2857–2862. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00618
Rogers, G., Szomszor, M., and Adams, J. (2020). Sample size in bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 125, 777–794. doi: 10.1007/s11192-020-03647-7
Rojas-Sánchez, M. A., Palos-Sánchez, P. R., and Folgado-Fernández, J. A. (2022). Systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis on virtual reality and education. Educ. Inf. Technol. 28, 155–192. doi: 10.1007/s10639-022-11167-5
Saqr, M., Raspopovic Milic, M., Pancheva, K., Jovic, J., Peltekova, E. V., and Conde, M. Á. (2023). A multimethod synthesis of COVID-19 education research: the tightrope between covidization and meaningfulness. Univ. Access Inf. Soc. 1-14, 1–14. doi: 10.1007/s10209-023-00989-w
Schultz, M., Callahan, D. L., and Miltiadous, A. (2020). Development and use of kitchen chemistry home practical activities during unanticipated campus closures. J. Chem. Educ. 97, 2678–2684. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00620
Shapiro, H., and Reza, N. (2021). Cardiovascular medical education during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic: challenges, adaptations, and considerations for the future. US Cardiol. 15:25. doi: 10.15420/usc.2020.25
She, L., Ma, L., Jan, A., Sharif Nia, H., and Rahmatpour, P. (2021). Online learning satisfaction during COVID-19 pandemic among Chinese university students: the serial mediation model. Front. Psychol. 12:743936. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.743936
Sobaih, A. E. E., Hasanein, A. M., and Abu Elnasr, A. E. (2020). Responses to COVID-19 in higher education: social media usage for sustaining formal academic communication in developing countries. Sustainability 12:6520. doi: 10.3390/su12166520x
Sundarasen, S., Chinna, K., Kamaludin, K., Nurunnabi, M., Baloch, G. M., Khoshaim, H. B., et al. (2020). Psychological impact of COVID-19 and lockdown among university students in Malaysia: implications and policy recommendations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17:6206. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17176206
Tang, K. H. D. (2023). Impacts of COVID-19 on primary, secondary and tertiary education: a comprehensive review and recommendations for educational practices. Educ. Res. Policy Prac. 22, 23–61. doi: 10.1007/s10671-022-09319-y
Tlili, A., Altınay, F., Altınay, Z., Aydın, C. H., Huang, R., and Sharma, R. (2022). Reflections on massive open online courses (Moocs) during the COVID-19 pandemic: a bibliometric mapping analysis. Turk. Online J. Dist. Educ. 23, 1–17. doi: 10.17718/tojde.1137107
Vaicondam, Y., Sikandar, H., Irum, S., Khan, N., and Qureshi, M. I. (2022). Research landscape of digital learning over the past 20 years: a bibliometric and visualisation analysis. Int. J. Online Biomed. Eng. 18, 4–22. doi: 10.3991/ijoe.v18i08.31963
Van der Graaf, L., Dunajeva, J., Siarova, H., and Bankauskaite, R. (2021). Research for CULT committee – Education and youth in post-COVID-19 Europe – Crisis effects and policy recommendations. European Parliament, Policy Department for Structural and Cohesion Policies, Brussels. Available at: http://www.europarl.europa.eu/thinktank/en/document.html?reference=IPOL_STU(2021)690872 (Accessed February 15, 2023).
Van Eck, N., and Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84, 523–538. doi: 10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Vera-Baceta, M. A., Thelwall, M., and Kousha, K. (2019). Web of science and Scopus language coverage. Scientometrics 121, 1803–1813. doi: 10.1007/s11192-019-03264-z
Waller, R., Hodge, S., Holford, J., Milana, M., and Webb, S. (2020). Lifelong education, social inequality and the COVID-19 health pandemic. Int. J. Lifelong Educ. 39, 243–246. doi: 10.1080/02601370.2020.1790267
Wang, C., Lim, M. K., Zhao, L., Tseng, M. L., Chien, C. F., and Lev, B. (2020). The evolution of omega-the international journal of management science over the past 40 years: a bibliometric overview. Omega 93:102098. doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2019.08.005
Watermeyer, R., Crick, T., Knight, C., and Goodall, J. (2021). COVID-19 and digital disruption in UK universities: afflictions and affordances of emergency online migration. High. Educ. 81, 623–641. doi: 10.1007/s10734-020-00561-y
Williams, N. D., Gallardo-Williams, M. T., Griffith, E. H., and Bretz, S. L. (2021). Investigating meaningful learning in virtual reality organic chemistry laboratories. J. Chem. Educ. 99, 1100–1105. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.1c00476
Yaghi, A. (2022). Impact of online education on anxiety and stress among undergraduate public affairs students: a longitudinal study during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Public Affairs Educ. 28, 91–108. doi: 10.1080/15236803.2021.1954469
Yan, Y., Cheng, X., Zhou, C., Yang, X., and Li, Y. Q. (2021). The perceptions of anatomy teachers for different majors during the COVID-19 pandemic: a national Chinese survey. Med. Educ. Online 26:1897267. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2021.1897267
Yan, H., Rahgozar, A., Sethuram, C., Karunananthan, S., Archibald, D., Bradley, L., et al. (2022). Natural language processing to identify digital learning tools in postgraduate family medicine: protocol for a scoping review. JMIR Res. Protocols 11:e34575. doi: 10.2196/34575
Zhang, L., Carter, R. A. Jr., Qian, X., Yang, S., Rujimora, J., and Wen, S. (2022). Academia’s responses to crisis: a bibliometric analysis of literature on online learning in higher education during COVID-19. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 53, 620–646. doi: 10.1111/bjet.13191
Keywords: online learning, e-learning, higher education, bibliometrics, mapping, visualization, VOSviewer, COVID-19
Citation: Aristovnik A, Karampelas K, Umek L and Ravšelj D (2023) Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on online learning in higher education: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Educ . 8:1225834. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2023.1225834
Received: 19 May 2023; Accepted: 14 July 2023; Published: 03 August 2023.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2023 Aristovnik, Karampelas, Umek and Ravšelj. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Aleksander Aristovnik, [email protected] ; Dejan Ravšelj, [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
By providing an email address. I agree to the Terms of Use and acknowledge that I have read the Privacy Policy .
The struggle for connection and other challenges in online distance learning
Blended learning has introduced a unique set of challenges for both teachers and students in public schools. The shift to online distance learning, initially adopted to continue education during the pandemic, has proven to be a complex adjustment for many. A significant issue encountered by teachers is the insufficient internet data available to students. Many learners start a lesson only to run out of data midway, causing them to drop out of class. This struggle for connection is further compounded by poor signal quality, which students often claim as the reason for not participating in recitations, or for the choppy communication during online classes. These technical difficulties create a barrier to effective learning and meaningful interaction.
Moreover, the flexibility of online learning can sometimes work against student engagement. Some learners are tempted to skip classes, citing poor internet connectivity as an excuse, while others are distracted by the comfort of their homes. The home environment, filled with potential distractions, competes with the focus required for schoolwork. This situation is exacerbated by the temptation to manage other personal matters during school hours, leading to further disengagement from the learning process.
In many schools across the country, the struggle for online connection is even more pronounced. Numerous public schools were asked to offer senior high school programs despite lacking the necessary facilities. Without adequate classrooms and resources, these schools resorted to blended learning as a solution. However, the lack of infrastructure makes it difficult to deliver quality education through this mode. Said one learner: “I feel like I’m not learning as much as those in schools that have full face-to-face classes. It’s frustrating because I want to do well, but it feels like I’m missing out on a lot.”
As a teacher, I can personally attest that this mode of learning is not effective and cannot be a substitute for face-to-face interaction. The in-person classroom experience is crucial for helping learners become engaged with and understand the material better. There is no replacement for the dynamic interactions and immediate feedback that occur in a physical classroom, where students are more focused and less prone to distractions. The investment in classrooms and physical infrastructure is essential to ensure that education is effective, and that students can learn in an environment conducive to their academic and personal development.
This struggle for connection highlights the difficulties teachers face in maintaining student participation and engagement in a blended learning setup. The lack of direct supervision and the myriad distractions at home make it difficult for students to remain committed to their studies, posing a significant hurdle to the success of blended learning in public schools.
Teachers are tasked not only with delivering educational content, but also with finding innovative ways to keep students engaged and accountable in a learning environment that is far less structured than the traditional classroom. Investing in classroom infrastructure and returning to face-to-face learning is a step toward ensuring that students receive the best possible education. While technology has its place, it should complement rather than replace the traditional classroom experience, which remains vital for student success.
Maria Teresa B. Macasinag, Rizal National High School, Baguio City
Subscribe to our daily newsletter

Fearless views on the news
Disclaimer: Comments do not represent the views of INQUIRER.net. We reserve the right to exclude comments which are inconsistent with our editorial standards. FULL DISCLAIMER
© copyright 1997-2024 inquirer.net | all rights reserved.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. By continuing, you are agreeing to our use of cookies. To find out more, please click this link.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Academic and emotional effects of online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic on engineering students
Rosó baltà-salvador.
1 Department of Graphic and Design Engineering, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya C, Colom 11, 08222 Terrassa, Spain
Noelia Olmedo-Torre
2 Department of Graphic and Design Engineering, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Av, Eduard Maristany 16, 08019 Barcelona, Spain
Marta Peña
3 Department of Mathematics, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya Av. Diagonal 647, 08028 Barcelona, Spain
Ana-Inés Renta-Davids
4 Department of Pedagogy, Universitat Rovira i Virgili Ctra. de Valls, 43007 Tarragona, Spain
Associated Data
The data and materials that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
The unprecedented situation of the COVID-19 pandemic has caused the closure of universities worldwide and has forced the transition to online learning. This exceptional context compels us to understand students' experience with online learning. Previous literature identifies relevant factors that intervene in the online education experience and can affect students' academic development. One of the main concerns is the students' mental health, given the lockdown restrictions under which classes have been conducted. Furthermore, the impact of the prolonged lockdown and the pandemic fatigue on university students and their academic experience is still unclear. This study delves into engineering undergraduate students’ online education experience during the COVID-19 pandemic and its emotional impact across time. With this aim, a questionnaire was distributed to second, third, and fourth-year engineering undergraduate students at two time points, approximately six months apart. The results show significant differences in students' connection with other students and teachers, workspace conditions, and boredom between time points. Besides, the findings indicate significant correlations between academic development and quality of online classes, adaptation of the course, workspace conditions, and connection with other students and teachers, and also between students' emotions and connection with other students and teachers. Finally, the study identifies best practices carried out during online teaching that will be of value for future courses and engineering education beyond the pandemic situation, amongst which those related to effective communication with teachers stand out.
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has posed an unprecedented challenge in education, leading to the suspension of face-to-face teaching (UNESCO, 2020 ). This change has been particularly challenging in university undergraduate engineering degrees since much of the learning process is based on practical applications, laboratory classes, and direct contact with teachers and other students. Being an exceptional and novel situation, the potential impact of the health crisis and the prolonged lockdown on students' academic development and emotional state is still unknown.
Recent work has identified some variables that intervene in the online education process, such as the correct adaptation of teaching to the online format, including classes, assessment methods, and teacher support (Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ); the quality of the classes received (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ); the conditions of students' workspace (Gelles et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ); and the connection with other students and teachers (Elmer et al., 2020 ; Radu et al., 2020 ). However, there is a knowledge gap in how these variables are related to students' academic development and whether having been in a prolonged lockdown might have affected them.
Furthermore, educational and psychological research has raised concerns about students' mental health as they have had to suddenly switch to online learning systems and follow classes under lockdown restrictions. Investigations pointed out that students have experienced an increase in stress, anxiety, and depression (Aslan et al., 2020 ; Odriozola-González et al., 2020 ; Saravanan et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ), and have felt some negative feelings intensified, such as fear, worry, or boredom (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Several studies have highlighted the protective effect that the connection with the rest of the academic community can have on anxiety, depression, and stress (Elmer et al., 2020 ; Magson et al., 2021 ; Procentese et al., 2020 ). Although mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic has received much attention in the academic field, studies have focused on analyzing adverse mental states such as depression, stress, or anxiety, but a broader perspective on the emotional state of the students, including a wider range of emotions and considering positive emotions such as calm or trust, is still missing.
Within this context, the present study carried out at the Polytechnic University of Catalonia (UPC), Spain, investigates how the COVID-19 pandemic and the lockdown has affected the academic experience of students and their emotional state across time. Two measurements taken six months apart were compared to detect changes potentially caused by a prolonged public health crisis and lockdown, providing new knowledge about pandemic fatigue in university students. Moreover, we assessed the correlations between the variables related to online education and the academic development of students to understand how the change to online teaching may have affected the performance of engineering students. Also, based on Plutchik’s theoretical framework on emotions (Plutchik, 1994 ), a study has been carried out to understand the impact of the pandemic on students' emotional state and how the connection with other students and teachers can help not only to reduce adverse emotions, but also to enhance positive emotions such as calm or confidence. To the best of our knowledge, no prior studies on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on engineering university students have considered such a wide spectrum of emotions and have observed the impact of being in contact with the rest of the academic community on these emotions. Furthermore, our research is novel as it encompasses the different variables involved in online education identified in previous studies, and conducts a longitudinal study to understand the impact of time and pandemic fatigue on these variables and students' academic development. Finally, this investigation identifies best practices carried out during distance teaching that can help improve the online learning experience in engineering studies beyond the pandemic situation.
Understanding the academic and emotional effects of the pandemic on engineering students is essential for several reasons. There is a growing trend for universities to offer online courses. However, in engineering, this transition is still a challenge since traditional engineering studies are based fundamentally on the practical application of scientific and technological principles. The unexpected situation generated by COVID-19 has forced engineering universities to offer their studies online, even for students who would not have proactively chosen to learn online. Therefore, it is an opportunity to analyze students' academic experience in distance engineering studies since they are rarely offered online. This information will contribute to the design of remote engineering courses to make them more accessible. On the other hand, the pandemic's scope during the next few years is unclear, so it is essential to understand its impact on learning to develop support actions for students. Also, all these lessons will be relevant if we face a similar situation that requires the confinement of the population in the coming years.
Impact of COVID-19 on students’ learning experience
The COVID-19 pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus began in late 2019 and spread around the world rapidly within months (Du Toit, 2020 ; Zhou et al., 2020 ). On March 11th, 2020, The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the public health emergency caused by the new coronavirus an international pandemic. Due to the high transmission rate of SARS-CoV-2, most countries took measures to stop the spread, including the blockade of cities, strict implementation of contact isolation, and strict medical system precaution (World Health Organization, 2021 ). This reduction in population mobility caused higher education institutions to cancel in-person classes and move towards remote learning (UNESCO, 2020 ). In the case of traditional engineering studies, this posed a significant challenge since it is a field in which a large part of the curriculum is based on the practical application of knowledge and relies heavily on face-to-face practical and laboratory classes (Jacques et al., 2020 ). This unexpected change in the teaching format has forced engineering students to adapt to new ways of learning under the conditions of the health crisis, potentially affecting their academic development. Furthermore, while previous research has revealed the impact of online education on those students who proactively chose distance learning, the current pandemic situation allows studying the impact on all students and in degrees that are generally not available online, as it is the case for engineering studies. Due to the exceptional nature of the situation, the effect of online classes derived from the emergence of COVID-19 on students is yet unknown, so work providing empirical data is crucial to understand the scope of its impact and to be able to propose support actions for students.
Although literature is still limited in this regard, several studies have tried to explain the impact of the rapid transition to online models during COVID-19 on students’ academic development. However, the results of these investigations are not homogeneous and show remarkable differences in the results. These variations may be due to the start and end dates of the academic years and school holidays, the timing and impact of the pandemic in each country, and the corresponding measures implemented to manage the health crisis. For example, in some countries face-to-face classes were suspended from the beginning of the pandemic while others were less restrictive and just reduced face-to-face teaching or postponed the beginning of the semester (Gonzalez et al., 2020 ). These contrasts can also be related to other factors like the differences between academic fields, the resources available for students, and the methodologies implemented by teachers during online teaching, among others. This lack of consistency opens the door to new studies that provide complementary evidence which might allow for a better understanding of the impact of online teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic on university students from different countries and academic fields.
To study the way in which the lockdown and distance teaching have affected engineering students during the COVID-19 pandemic, it is necessary to identify the variables that intervene in the online educational experience. Previous research in psychology and education has identified four relevant constructs in distance education, which have also received attention in studies on remote education in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
First, previous research on online teaching highlighted the courses’ quality as a significant factor in students’ satisfaction and learning (Piccoli et al., 2001 ; Sun et al., 2008 ) and pointed out that the effective switch toward online teaching models is influenced by the perceived quality of the classes (Ibrahim et al., 2013 ). When designing online courses, classes cannot simply be transferred from a face-to-face to an online environment. Content, pedagogy, methodology, and technology need to be adapted for successful online teaching (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ). The quality of online teaching has received considerable attention in studies on the effects of COVID-19 on higher education. In some of the studies conducted during the lockdown, university students reported low satisfaction with the quality of online teaching (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Alnusairat et al., 2020 ) and higher learning satisfaction in face-to-face learning than in distance learning (Amir et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ). According to the UNESCO ( 2020 ), this disaffection with the online classes stems from the fact that the content offered was never designed within the framework of a distance course but instead tried to make up for the absence of face-to-face classes with virtual classes without sufficient preparation. However, the results of other studies showed that students were satisfied with the overall e-learning provided thus far in their university studies (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Jacques et al., 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ). More specifically, in a study with a sample that included engineering students, 85% of the respondents indicated that online teaching quality during the COVID-19 pandemic was good or very good (Radu et al., 2020 ). Since the quality of teaching is one of the main constructs in the evaluation of distance teaching, it has been included in this research as a study variable. Also, as there is a lack of consistency in the results of previous studies regarding the satisfaction with the online course’s quality during COVID-19, it is necessary to provide more data from samples of engineering students.
Second, there are considerable differences in results among research regarding specific aspects, such as classes, exams, or teachers’ support, in adaptation to distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. Nevertheless, the results differ across the investigations. On the one hand, previous research reported students’ low satisfaction with the support received from their teachers (Alnusairat et al., 2020 ) and less satisfaction with the classes and assessment methods in distance education compared to classroom learning (Linh & Trang, 2020 ). This low satisfaction with how teaching was adapted to the online format is associated with an increase in the perceived workload (Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Gelles et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Furthermore, Khalil et al. ( 2020 ) pointed out that the issues related to the implementation and quality of online courses can become barriers to the engagement and acquisition of knowledge. On the other hand, there are studies in university settings in which students were satisfied with the teacher support received and the content of their online classes during the COVID-19 pandemic (Jacques et al., 2020 ; Rodríguez-Rodríguez et al., 2020 ). Also, in Puljak et al.’s ( 2020 ) investigation, students reported that the assessment methods and materials used in their classes during the lockdown were tailored to e-learning. Similar to the courses’ quality, current studies show contradictory results regarding student satisfaction on how their courses were adapted to the remote format. Moreover, adaptation to online teaching was a highly discussed construct during the COVID-19 health crisis due to the short time in which classes, evaluation methods, and teachers' support and guidance had to be readjusted to the online format (UNESCO, 2020 ).
Third, another major challenge on distance education are the feelings of isolation and disconnection in online courses due to lack of face-to-face contact with other students and teachers (Mcinnerney & Roberts, 2004 ). Numerous studies prior to the COVID-19 pandemic indicated that interactions with other students and teachers were essential for student satisfaction and played a decisive role in academic development and students’ achievements (Arbaugh, 2000 ; Hong, 2002 ; Mcinnerney & Roberts, 2004 ; Piccoli et al., 2001 ; Sun et al., 2008 ). Hence, when designing online courses, the interaction mechanisms must be considered to offer enriching and thriving learning environments. Concerning the perceived connection with other students and teachers during the lockdown, previous research indicated that students felt less connected with fellow students and teachers than in face-to-face education (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Overall, university students indicated that they have missed in-person contact with other students and professors during the lockdown (Puljak et al., 2020 ) and that communication has been more complicated than in face-to-face education (Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Radu et al., 2020 ). In Elmer et al. ( 2020 ) investigation on students enrolled in engineering and natural science programs, students reported fewer study partners and felt significantly more socially isolated. Also, in the study by Tang et al. ( 2020 ) on undergraduate students from engineering majors, almost 70% thought that they had not communicated often with their teachers from the online courses during the pandemic. This lack of contact is worrisome since social contact and socialization routines are part of the daily experience of higher education students and can affect their academic development (UNESCO, 2020 ). In the context of online classes during the pandemic, a greater connection with the community has been related to greater self-efficacy and engagement and lower academic stress (Luan et al., 2020 ; Procentese et al., 2020 ). Connection with fellow students and teachers is one of the variables that has received the most attention in the academic community concerning the experience in online education. Social isolation of students during the pandemic has further increased the importance of this factor and hence, we have included connection with other students and teachers as a variable in this study.
Finally, although it had not received much attention in distance education literature before the pandemic, learning environment conditions, its ergonomics, and access to a quality internet connection are additional and indeed important variables to consider in distance learning. A workspace that does not offer the appropriate conditions represents a risk factor for comfort, well-being, and students’ academic performance (Braat-Eggen et al., 2017 ; Hviid et al., 2020 ; Parvez et al., 2019 ; Zhong et al., 2019 ). The unexpected change to online education due to the COVID-19 pandemic has made researchers and academic staff wonder whether students were prepared to take classes from their home and whether they had an adequate workspace, equipment, and facilities for effective learning. In addition, the lockdown situation has prevented students from going to libraries or study halls and, in many cases, has forced family members to share the spaces of their houses, which might have worsened student workplace conditions by increasing noise and distractions (Driessen et al., 2020 ). In several studies, university students reported that their home has been a distractive environment and mentioned that they were more prone to be interrupted by roommates or family members (Gelles et al., 2020 ; Kyne & Thompson, 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Moreover, Realyvásquez-Vargas et al. ( 2020 ) pointed out that environmental factors such as noise, temperature, and lighting had a significant effect on university students’ academic performance during online classes in the pandemic context. These issues were associated with more difficulties in focusing and concentrating while learning (Amir et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ) and can become a barrier to the acquisition of knowledge through online courses (Khalil et al., 2020 ). Another drawback identified in online classes during the pandemic has been inadequate internet access (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Kyne & Thompson, 2020 ). Several studies have reported that a significant percentage of university students, especially those from disadvantaged families, have had problems accessing internet services (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ). Due to the unexpected lockdown situation and the rapid transition to online learning, students did not have time to adapt their workspace, which may have had an impact on their academic development. Thus, we included workspace conditions as a variable for this study.
All these factors should be considered when designing online courses to avoid detrimental effects on students’ academic development (Braat-Eggen et al., 2017 ; Hviid et al., 2020 ; Mcinnerney & Roberts, 2004 ; Piccoli et al., 2001 ; Sun et al., 2008 ; Zhong et al., 2019 ). Numerous studies predicted that the change in teaching methods during the pandemic affected students’ academic development and their outcomes, although the results are inconsistent. Some of the studies have shown that confinement had positively affected students’ academic performance and their learning efficiency (Gonzalez et al., 2020 ; Khalil et al., 2020 ). The study by Jacques et al. ( 2020 ) carried out with engineering students showed that distance learning did not reduce students’ performance and that the grades obtained were similar to those expected in face-to-face teaching. Contrarily, previous research revealed that students perceived worse performance upon face-to-face classes being canceled (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ) and showed concerns about the negative impact that the pandemic situation will have on their academic outcomes (Nassr et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). The study by Hamann et al. ( 2020 ) suggested that students who followed the course entirely online were significantly less likely to be successful than students who also, or exclusively, attended face-to-face courses during the pandemic. Furthermore, Tang et al. ( 2020 ) indicated in their study during the COVID-19 lockdown that students felt generally dissatisfied with the effects of online engineering courses on their learning.
Based on these assumptions, we expect to find a positive correlation between students' academic development with the variables of quality of teaching, adaptation of the classes to the online format, connection with other students and professors, and workspace conditions (Hypothesis 1). Since many of the studies done so far in the context of the pandemic have identified these variables separately, few correlational studies have analyzed their associations and identified the factors that may have had the greatest impact on students' academic development during COVID-19. Knowing how the variables related to the online experience have affected the performance of the students will allow us to identify relevant points that should be considered in the design of online courses. To complement this information, we also identified the best practices carried out by instructors in online teaching during the pandemic that have helped students transition to this new learning environment. This information can help instructors and institutions improve online teaching beyond the pandemic situation. This approach is aligned with the conclusions of Anderson et al. ( 2011 ), which showed that receiving feedback from students about the online lessons is vital to improve the courses offered.
Emotional effects of COVID-19
Studies before the COVID-19 pandemic already reported the negative psychological effects that lockdown can cause on people (Blendon et al., 2004 ). Quarantine is often described as an unpleasant experience for those who suffer it, and can involve uncertainty about the situation and boredom (Brooks et al., 2020 ; Cava et al., 2005 ). It is also associated with significant psychological distress, depressive symptoms, post-traumatic stress, and aversive emotional states such as anger, confusion, anguish, disgust, fear, or nervousness, among others (Brooks et al., 2020 ; Hawryluck et al., 2004 ). In the studies carried out during the COVID-19 lockdown, university students reported negative effects on their mental health and emotions. Generally, students have experienced an increase in their stress, anxiety, and depression during the COVID-19 pandemic (Aslan et al., 2020 ; Odriozola-González et al., 2020 ; Saravanan et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Besides, they reported feeling some negative emotions intensified, such as fear, worry, or boredom (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ).
Despite the proven adverse effects that lockdown can have on people, in cases like a public health emergency due to an infectious disease, imposing measures on the population to stop the spread of such disease is needed. Studying which elements can minimize the negative impact and aversive feelings during isolation are of great importance in this context. Some studies have indicated that contact with the academic community can act as a protector and decrease the negative impact of lockdown on students’ mental health (Elmer et al., 2020 ; Magson et al., 2021 ; Procentese et al., 2020 ). Others have shown that the lack of relationships and connection with other students and teachers is associated with an increase in academic stress (Zurlo et al., 2020 ).
Most studies during the COVID-19 pandemic on the emotional state of university students have only analyzed negative emotional states such as anxiety, stress, or depression. However, there is a lack of research with a more global perspective on the emotional state of university students that also includes positive emotions to study whether these have decreased during the pandemic. In the study of emotions, psychological theories have proposed some dimensions to measure people’s emotional state, although they have hardly been contemplated in studies on the emotional impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. One of the best known and widely used is Plutchik’s ( 1994 ) theory, which presents eight emotional dimensions in opposite pairs. Compared with other theories such as Ekman ( 1992 ) or Parrot ( 2001 ), Plutchik’s framework is well-founded in psychological studies, presents a good balance between positive and negative emotions, and offers a broader subset of emotional dimensions (Wang et al., 2019 ), the aforementioned reasons being why it has been used as a reference to measure the emotions of the students in this study.
Based on the results of the previous literature, we hypothesize that there is an association between the perceived connection with other students and teachers and the emotional state of the students, so a greater connection with other students and teachers will be associated with a decrease in negative emotions and an increase in positive emotions (Hypothesis 2).
Effects of pandemic fatigue
One of the great unknowns related to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic are the effects of a prolonged lockdown situation. The entire world population has been exposed to a state of exceptionality generated by the COVID-19 pandemic that has required the implementation of invasive measures with unprecedented impact on daily lives. When these measures are prolonged for an extended period of time, it can cause what is known as pandemic fatigue, which is the mental exhaustion caused by a public health crisis and the restrictions derived from it. This state can affect the mental health of those who suffer it, causing boredom, demotivation, alienation, and hopelessness (World Health Organization & Regional Office for Europe, 2020 ). Given the unusual nature of the situation, the literature on the impact of the pandemic and the lockdown implemented is still limited, and there is little evidence to indicate whether the academic and psychological effects of lockdown are greater at the beginning of the pandemic because of the uncertainty of the situation or may become more significant as the pandemic continues due to the feeling of burnout during the prolonged lockdown (Canet-Juric et al., 2020 ). Additionally, most longitudinal studies in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic in university students assessed only the psychological impact, so more research is required to analyze the academic impact. As Odriozola-González et al. ( 2020 ) pointed out, more longitudinal studies are needed to analyze the long-term impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and to draw conclusions about the cause and effect relationships between the variables involved.
In the current literature there is substantial debate about the detrimental effects of pandemic fatigue. In particular, there are two major views: some longitudinal studies supported the theory that adverse effects have intensified as time in lockdown increased and showed significant increments in negative symptoms such as depression, anxiety, or stress (Ausín et al., 2021 ; Cecchini et al., 2021 ; Gopal et al., 2020 ). In contrast, other studies argued that the effects did not increase over time and, in any case, were are greater at the beginning of the pandemic due to uncertainty and fear of the unknown situation (Canet-Juric et al., 2020 ). Regarding this theory, the study by Ramos-Morcillo et al. ( 2020 ) identified two phases as a pandemic progresses. The first is the so-called shock phase, which occurs during the first weeks, and disorientation and mental performance decreases, along with the ability to concentrate. The second is the normalization phase, in which conditions of confinement start to be assimilated, and the new everyday life is normalized. Thus, based on this second theory, we hypothesize that there is an association between time in lockdown and academic experience, and students will have a worst online learning experience at the beginning of lockdown (Hypothesis 3). We also expect an association between the time in lockdown and students’ emotional state, and we hypothesize that negative feelings will be greater at the beginning of lockdown, and positive feelings will be greater as time progresses (Hypothesis 4). Knowing when the impact of a confinement situation or health crisis is greater and which feelings increase over time will help to develop support plans for students and plan corrective measures in similar situations like climate, political, or security crises that can restrict people’s movement and prevent regular university access.
Context of the current study
In the current study carried out at the UPC, we made two measurements at different time points and compared data collected in spring and fall semesters, 2020, to evaluate the effects of prolonged lockdown and pandemic fatigue on the educational experience and emotional state of engineering students. Regarding the restrictions derived from the pandemic in Spain, the first state of alarm was decreed on March 14th, and the free movement of citizens was limited to essential activities resulting in the confinement of the population in their places of residence and the suspension of face-to-face education. Consequently, educational institutions had to switch the teaching to the online format, and many held the classes and academic activities remotely until the end of the course in June 2020. Due to the increase in cases, on October 16th, all face-to-face activity in universities was suspended again, although many higher education institutions had already started the academic year online after the summer. On October 25th, after exceeding half a million infected countywide, the second state of alarm was established to face the pandemic’s second wave. In this case, a curfew was imposed between 10 p.m. and 6 a.m., and later the population was confined again in their municipalities and social gatherings were restricted.
Participants
The participants of this study were students enrolled in the second, third, and fourth-year of the Bachelor’s Degree in Industrial Design and Product Development Engineering. First-year students were excluded from the sample due to the short time they had been in engineering studies and the inability to compare the impact of the lockdown on their academic activity with previous courses. All students enrolled in the other three courses were invited to participate, that is, a total of 339 students, 168 at Time 1 (T1) and 171 at Time 2 (T2). The required sample size calculated based on a confidence level of 95% and a margin of error of 5% was 181 students for the total sample, 119 for each measurement. Finally, a total of 254 students participated in the study, 122 at T1 and 132 at T2, so the study sample meets the intended size. Participants were self-selected and no incentive was given to students to participate in the study. The protection of personal data was duly taken into account, ensuring that all recipients agreed to receive communications. Both anonymity of the participants and confidentiality of the data to be collected were guaranteed. Data did not include personal characteristics of the students. Table Table1 1 shows the academic year and the conditions in which the participants took the online classes during the pandemic, type of residence and workspace conditions.
Academic course and lockdown conditions of the participants
| Baseline characteristic | Time 1 | Time 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | % | |||
| Academic course | ||||
| Second-year | 22 | 18.0 | 41 | 31.1 |
| Third-year | 62 | 50.8 | 52 | 39.4 |
| Fourth-year | 38 | 31.1 | 39 | 29.5 |
| Residence | ||||
| Family home | 119 | 97.5 | 112 | 85 |
| Student flat | 3 | 2.5 | 12 | 9 |
| University residence | 0 | 0 | 8 | 6 |
| Workspace | ||||
| Personal bedroom | 79 | 64.8 | 92 | 69.7 |
| Home office | 25 | 20.5 | 18 | 13.6 |
| Common area | 18 | 14.8 | 22 | 16.7 |
Due to the exceptional nature of the situation a questionnaire was designed for this study with measures derived from previous literature and adapted to fit the research context. In previous investigations on the impact of online teaching on students' academic experience during the COVID-19 pandemic, these constructs were measured using questionnaires addressed to students. In these questionnaires, students were asked about their perception of the quality of teaching (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Radu et al., 2020 ), the adaptation of classes to the online format (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Rodríguez-Rodríguez et al., 2020 ), the perceived connection with other students and teachers (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Radu et al., 2020 ; Tang et al., 2020 ), their workspace conditions (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Driessen et al., 2020 ; Kyne & Thompson, 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ; Realyvásquez-Vargas et al., 2020 ), and the impact on students' academic development (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ; Realyvásquez-Vargas et al., 2020 ; Tang et al., 2020 ). These investigations have been used as a foundation to build the measuring instrument for this study.
The quality of the online classes that students received during the lockdown was assessed with a 4-point scale (1 = Very bad to 4 = Very good). To measure students’ perceptions about the adaptation of the course to the online format, a set of 4 items was designed (α = .76) rated on a 4-point scale (1 = Strongly disagree to 4 = Strongly agree). Students were asked to indicate if the classes and the assessment methods had been adapted correctly to the online format, if they had been able to follow the course correctly, and if they had received the necessary support from teachers. To assess the level of connection that students felt with other students and teachers a set of 4 items was designed (α = .65) rated on a 4-point scale (1 = Strongly disagree to 4 = Strongly agree). Students were asked to indicate if they felt connected with other students and teachers and if they had missed having contact with fellow students and teachers. To measure the workspace conditions, students were asked about the place and the type of room from where they followed the online classes with two multiple-choice questions of three options each (e.g., from a student flat) and an open field. Students also had to indicate if their workspace conditions had been suitable on a 4-point scale (1 = Strongly disagree to 4 = Strongly agree). To determine how students perceived the impact of the switch to online classes on their academic development, they were asked to rate on a 3-point scale (1 = It has worsened to 3 = It has improved) if they believed that their academic development had been affected by online teaching.
To measure the emotions students felt during online classes while they were in lockdown, a measure based on Plutchik’s ( 1994 ) wheel of emotions was designed using a multiple-choice question. Students were asked to select their feelings during the lockdown from 8 options adapted from Plutchik’s classification.
Finally, an optional open question was added in which students could share if there was something that teachers did during the online teaching that helped them especially.
For the present study, students completed the exact same questionnaire at two points, approximately six months apart. The first time the questionnaire was distributed was on June 3rd, 2020 (T1), during the spring semester and almost three months after the first lockdown was established and all classes went online. Consequently, students had a reasonable exposure to the online learning experience and the lockdown to answer the questionnaire. The second measurement was made in the fall semester on November 18th, 2020 (T2), approximately one month after the second state of alarm was decreed and the new lockdown was applied to face the second COVID-19 outbreak. Therefore, both measurements were made while students were taking classes online.
The questionnaire, which was anonymous and drawn up using Google Forms, was sent by email together with a motivational letter explaining the purpose of the study. Both times, students had up to 1 week to complete it, and took approximately fifteen minutes to finish. Participants were recruited via email messages sent by the authors of this research and faculty members, and were encouraged to answer all the questions accordingly to their opinions. Before being sent, the questionnaire was submitted to a validation process to identify whether it omitted some question areas, determine whether the questions were clear and well-formulated, and detect possible errors in its preparation.
No outliers were identified, and no missing values were found either since all the questions in the questionnaire were mandatory. Descriptive statistics and frequency analyses were applied to characterize the sample. Spearman's rank correlation coefficient was used to test the first hypothesis on how the variables related to the online academic experience affected students' academic development. Although the intercorrelations were calculated between all the variables of the online academic experience, the analysis was done using academic development as the independent variable and the variables of connection with other students and teachers, workspace conditions, quality of online classes, and adaptation of the course as dependent variables. To evaluate our second hypothesis about whether the connection with other students and teachers can affect students' emotional state, a Chi-Square Test for Independence was performed using connection with other students and teachers as the independent variable and emotions as the dependent variables. To fulfill the assumption concerning the minimum expected cell frequency, the measure of connection with other students and teachers was transformed into a dichotomous variable combining the negative and positive values, respectively. To assess our third hypothesis on how the time in lockdown affected the academic experience of the students, we performed a Mann-Whitney U Test using the time in which the measurements were made as the independent variable and the variables of academic development, connection with other students and teachers, workspace conditions, quality of online classes, and adaptation of the course as dependent variables. Since the emotion variables were dichotomous, for the fourth hypothesis about how time in lockdown affected the emotional state of the students, a Chi-Square Test for Independence was carried out using the time in which the measurements were taken as the independent variable and the different emotions as dependent variables. In the analyzes, p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant, and the effect size was assessed using Cohen’s ( 1988 ) criteria. For the qualitative data, an abductive methodology was used to identify the codes. First, half of the dataset was analyzed, and a preliminary code list was obtained. Next, the entire dataset was processed with the identified codes, and the rest of the codes emerged from the data iteratively, adding new codes if practices not identified in the preliminary list were found.
Descriptive analyses indicated that about half of the students reported that the quality of the online classes received during the pandemic was bad or very bad (T1 = 54.1%, T2 = 46.2%), and more than a half thought that their academic development worsened during online classes compared to face-to-face classes (T1 = 66.4%, T2 = 68.9%). Also, more than half of the students indicated that their workspace conditions had been adequate, especially at T2 (T1 = 58.2%, T2 = 73.5%). Regarding the single items that compose the variable adaptation of the course variable, over half of the students reported that classes were correctly adapted to the online format (T1 = 57.4%, T2 = 68.2%) and that the evaluation methods were also properly adapted (T1 = 56.6%, T2 = 54.5%). Furthermore, the majority indicated that they had been able to follow the course correctly (T1 = 63.9%, T2 = 78.8%) and had the necessary support from teachers (T1 = 57.4%, T2 = 67.4%). Remarkable differences can be observed between the two time points regarding the 4-items that compose the variable connection with other students and teachers. Students felt less connected to other students and teachers in T2 than in T1 (T1 = 67.2%, T2 = 27.3%; and T1 = 51.6%, T2 = 40.1%; respectively) and the vast majority missed having contact with other students and teachers (T1 = 82.0%, T2 = 95.5%; and T1 = 81.1%, T2 = 91.7%; respectively).
As shown in Table Table2, 2 , the workspace conditions in which students took the online classes improved significantly from T1 to T2 with a small effect size. On the other hand, the perceived connection with fellow students and teachers worsened significantly from T1 to T2 with a medium effect size, so that in T2 they felt less connected with other students and teachers. Although the quality of online classes and the adaptation of the course improved at T2 compared with T1, no significant differences were found.
Descriptive Statistics and Mann-Whitney Test at Time 1 and Time 2
| Variables | No. of items | Range | Time 1 | Time 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality of online classes | 1 | 1-4 | 2.5 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 0.7 | 7540 | 0.97 | .334 |
| Academic development | 1 | 1-3 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 7909 | -0.30 | .765 |
| Workspace conditions | 1 | 1-4 | 2.7 | 0.8 | 2.9 | 0.7 | 6864 | 2.23 | .026 |
| Adaptation of the course | 4 | 1-4 | 2.6 | 0.6 | 2.7 | 0.5 | 7146 | 1.57 | .116 |
| Connection with other students and teachers | 4 | 1-4 | 2.2 | 0.5 | 1.8 | 0.5 | 4361 | -6.38 | .000 |
At both times, correlations between academic development and quality of online classes and adaptation to the course were relatively high and positive with a medium effect size (see Table Table3). 3 ). Also, the workspace conditions had a positive significant correlation with academic development with a small effect at T1 and T2. Therefore, those students who perceived a better quality and adaptation of the online classes and had better workspace conditions were those who reported a better academic development. On the other hand, academic development had a significant positive correlation with connection with other students and teachers with a small effect size at T2, the time point when they felt more disconnected with fellow students and teachers.
Intercorrelations for Study Variables at Time 1 and Time 2
| Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Academic development | - | .176 | .403*** | .358*** | .237** |
| 2. Connection with other students and teachers | .282** | - | .274** | .340*** | .118 |
| 3. Quality of online classes | .496*** | .265** | - | .409*** | .258** |
| 4. Adaptation of the course | .435*** | .298** | .571*** | - | .313*** |
| 5. Workspace conditions | .243** | .188* | .423*** | .393*** |
The results for the Time 1 sample ( n = 122) are shown above the diagonal. The results for the Time 2 sample ( n = 132) are shown below the diagonal
* p < .05; ** p < .01; *** p < .001
As illustrated in Fig. 1 , the emotions that students felt the most during the lockdown were discouragement (22.6% T1, 23.0% T2), boredom (T1 = 17.5%, T2 = 21.8%), confusion (T1 = 18.3%, T2 = 15.7%), worry (T1 = 15.4%, T2 = 14.3%), and annoyance (T1 = 10.8%, T2 = 10.3%). Contrary, the least common were vigilance (T1 = 8.2%, T2 = 7.3%), calm (T1 = 5.7%, T2 = 6.1%), and trust (T1 = 1.5%, T2 = 1.6%). Regarding the differences between T1 and T2, students felt slightly less worried and confused at T2, although no statistically significant difference was found (X2 (1, N = 254) = 0.12, p = .728, phi = -.030; and X2 (1, N = 254) = 1.13, p = .288, phi = -.075; respectively). Besides, they felt more bored at T2 than T1, with a statistically significant difference (X2 (1, N = 254) = 5.30, p = .021, phi = .153) with a small effect.

Changes in Students’ Emotions between Time 1 and Time 2
As shown in Table Table4, 4 , a significant association with small effect was found between the connection with other students and teachers and the emotions felt by the students, with the exception of boredom, which did not present significant differences. Those students who felt more connected with other students and teachers were more likely to feel calm and trust. Otherwise, those students who felt more disconnected were the ones who felt more worry, confusion, discouragement, annoyance, and vigilance.
Chi-Square Results for Connection with Other Students and Teachers in Students’ Emotions
| Variable | Disconnected | Connected | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | % | ||||||
| Calm | 30 | 15.3% | 18 | 31.0% | 6.23 | .013 | .169 |
| Worry | 101 | 51.5% | 20 | 34.5% | 4.55 | .033 | -.143 |
| Confusion | 115 | 58.7% | 23 | 39.7% | 5.78 | .016 | -.160 |
| Discouragement | 153 | 78.1% | 33 | 56.9% | 9.18 | .002 | -.201 |
| Boredom | 127 | 64.8% | 34 | 58.6% | 0.49 | .482 | -.054 |
| Annoyance | 74 | 37.8% | 12 | 20.7% | 5.08 | .024 | -.151 |
| Trust | 5 | 2.6% | 8 | 13.8% | 9.45 | .002 | .214 |
| Vigilance | 55 | 28.1% | 8 | 13.8% | 4.15 | .042 | -.139 |
The open question regarding best practices carried out during the online teaching received 117 responses, 63 from T1 and 54 from T2. From these responses, 21 best practices were identified, plus the “other practices” code (Table (Table5). 5 ). As some answers referred to more than one code, the total number of best practices identified ( n = 182) is greater than the total number of responses. The codes were classified into four categories: communication, classes, course adaptation to the online format, and teachers.
Best Practices in Online Teaching During COVID-19 Lockdown
| Category | Code | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication | Instant messaging | 10 | 5.3 |
| 9 | 4.8 | ||
| Forum | 2 | 1.1 | |
| Social networks | 2 | 1.1 | |
| Classes | Record and share classes | 37 | 19.6 |
| Individual or small group tutoring | 18 | 9.5 | |
| Sessions to resolve doubts | 9 | 4.8 | |
| Live problem solving | 3 | 1.6 | |
| Synchronous learning | 3 | 1.6 | |
| Asynchronous learning | 3 | 1.6 | |
| Course adaptation to the online format | Provide solved problems | 10 | 5.3 |
| Provide support videos | 10 | 5.3 | |
| Adapt the statement of the projects | 5 | 2.6 | |
| Provide extra support documentation | 5 | 2.6 | |
| Make assignment deadlines more flexible | 4 | 2.1 | |
| Small workgroups | 4 | 2.1 | |
| Adapt evaluation methods | 4 | 2.1 | |
| Follow-up activities (as questionnaires or discussions) | 3 | 1.6 | |
| Teachers | Fast answers | 20 | 10.6 |
| Supportive attitude | 19 | 10.1 | |
| Frequent contact | 2 | 1.1 | |
| Other practices | 7 | 3.7 | |
| Total | 189 | 100 |
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought a global change in educational systems, forcing the transition from face-to-face to online learning due to the restrictions and lockdowns imposed in most countries. This study has examined university engineering students’ academic experience and the emotional impact of online education during the COVID-19 pandemic using a longitudinal approach. The results provide novel information and extend prior research on the impact of distance education during the COVID-19 lockdown on engineering students.
Effects of the prolonged lockdown on students’ learning experience
The majority of students in our sample reported that their academic development worsened during online learning, and a high percentage considered that the online teaching they received was of a bad quality. Therefore, students have perceived a negative impact regarding the change to online teaching during COVID-19 in their academic experience, especially in their academic development and the quality of the teaching they have received. These findings are consistent with some studies on university students during the COVID-19 pandemic regarding the quality of teaching received (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Linh & Trang, 2020 ) and the impact on students’ learning outcomes (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Nassr et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ; Tang et al., 2020 ). As UNESCO ( 2020 ) has pointed out, this may be because the change towards online learning has been sudden and consequently the content offered in the classes was not designed to be taught in an online course and online classes were given with limited preparation.
Contrary to our hypothesis (Hypothesis 3), there are no significant differences between T1 and T2 regarding the quality of online classes, the adaptation of teaching to the online format, and the academic development of students. However, we observed a slight increase in the perception of the online classes’ quality and the adaptation of the course, though this difference is not statistically significant. These results suggest that although there may have been an improvement in some aspects of teaching, probably due to enhancements introduced by teachers in the subjects after the first months of the pandemic, these have not been enough to make a significant change in students’ perception. On the other hand, our data show significant differences between T1 and T2 on the workspace conditions and the perceived contact with fellow students and professors. The conditions of the workspace have significantly improved as time progressed in lockdown. This result suggests that students, foreseeing that the new course would also be online, prepared their workspace conditions to suit their needs. As UNESCO ( 2020 ) argues, student's expectations differ if they expect to enroll from the beginning in a distance course or a regular course. So, it is relevant that academic institutions inform students in advance on possible changes in teaching, so that they can adapt their expectations and prepare properly. Contrary to what was expected, the perception of connection with other students and teachers is significantly lower at T2, so the feeling of isolation worsens significantly as the time in lockdown passes and online classes become regular. Students who reported having missed the contact with other students at T2 reach 95.5% and with teachers 91.7%. Similarly, previous studies have highlighted the lack of social contact and the feelings of isolation and disconnection during the COVID-19 lockdown (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Elmer et al., 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Radu et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). These studies indicate that students have felt less connected to the academic community than in face-to-face teaching (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Our findings reveal that not only do students feel less connected to their peers and teachers in online learning compared to face-to-face classes, but also that this feeling increases as time in lockdown lengthens. This finding reaffirms the importance of social contact and communication mechanisms in online education and suggests that if these mechanisms are not properly implemented in the online education systems, the lack of social contact and its negative effects on students’ educational experience may get worse (Luan et al., 2020 ; Procentese et al., 2020 ).
The results of this study indicate that the effects of the prolonged lockdown may impact differently on the variables involved in the online educational experience, and raise new hypotheses regarding the impact of a prolonged lockdown. On the one hand, the impact on variables related to pedagogical aspects of online teaching, such as quality and adaptation of the course, may be more negative at the beginning of the pandemic due to the uncertainty of the situation (Canet-Juric et al., 2020 ; Ramos-Morcillo et al., 2020 ). However, these aspects may improve as time passes due to teaching improvements on the online practices and students’ preparation of their workspace environment foreseeing that they will continue the classes remotely (Scull et al., 2020 ). This hypothesis is supported by studies such as Van Nuland et al. ( 2020 ), which indicates that many teachers have been asked, almost overnight, to implement classes remotely in response to the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic. Many of these teachers had no or little prior experience in online teaching and that they lacked the pedagogical content knowledge needed for online teaching. As the pandemic has progressed, teachers and universities have been adapting and have implemented several innovations to improve the online teaching experience of students (Scull et al., 2020 ). On the other hand, the variables related to the social aspects of the academic experience, such as the contact with other students and teachers, may be negatively affected by the feeling of burnout as time in lockdown passes (Ausín et al., 2021 ; Cecchini et al., 2021 ; Gopal et al., 2020 ). As other studies have reported, the lockdown situation has triggered the feeling of isolation and disconnection of students (Al-Balas et al., 2020 ; Puljak et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ), feelings already identified in pedagogical research on the challenges of e-learning (Mcinnerney & Roberts, 2004 ). Understandably, this feeling strengthens while students remain locked in their homes, and as the time without seeing their classmates and teachers increases. Therefore, it will be crucial for academic institutions and faculty members to put mechanisms in place that help students feel connected to each other and to their teachers, such as discussion forums or instant messaging channels (Moorhouse, 2020 ; Rosenberg & Asterhan, 2018 ). The study by Scull et al. ( 2020 ) shares some learnings from universities and teachers that might help strengthen the connection and communication with students during the pandemic, such as providing channels through which they can ask for help or by opening the debate to more personal day-to-day issues to relax the atmosphere and enhance engagement.
In line with what was predicted in our first hypothesis (Hypothesis 1), we find significant relationships between academic development and the rest of the variables related to the online academic experience of students. Specifically, students’ academic development is associated with the quality of the classes received, the adaptation of the courses to the distance format, and the workspace conditions. Also, a positive correlation was found in T2 between students’ academic development and contact with other students and teachers. Previous literature already pointed out the relationship between the variables studied and the academic development of students (Braat-Eggen et al., 2017 ; Hviid et al., 2020 ; Mcinnerney & Roberts, 2004 ; Piccoli et al., 2001 ; Sun et al., 2008 ; Zhong et al., 2019 ). In this line, our results confirm these relationships between the variables under the conditions of a pandemic and lockdown in engineering students. Considering the direction of the correlations, offering students classes of high quality, adapting the class contents, assessing teaching methods properly, and giving support from teachers to the online format relate to a better academic development. Therefore, it is important to offer teachers training and pedagogical tools needed to provide adequate distance teaching (Van Nuland et al., 2020 ). Moreover, having better workspace conditions can enhance students’ academic development. In this regard, academic institutions can ask students about their conditions and offer support, for example, temporarily borrowing computers from the university or granting access to online learning platforms through mobile phones (UNESCO et al., 2020 ).
Furthermore, previous literature has focused on the positive effects that contact with teachers and other students can have on academic development, such as greater self-efficacy and learning engagement, and less academic stress (Luan et al., 2020 ; Procentese et al., 2020 ). Our study suggests that having good connections with other students and teachers is not necessarily associated with academic development (as observed at T1), but if this lack of contact is extended in time (as observed at T2), it may negatively impact students’ academic development. This new finding supports the previous observation that it is necessary to work on the relationships between students themselves and with their teachers in online learning; otherwise, if these connections are lacking, it may have a negative effect on the educational experience and students’ outcomes.
Emotional impact of prolonged lockdown
Students’ most-reported emotions during the lockdown are discouragement, boredom, confusion, and worry, all of them negative emotions. On the contrary, those less prevalent are the positive emotions of calm and trust. Despite previous articles mainly focusing on negative emotions (Aslan et al., 2020 ; Odriozola-González et al., 2020 ; Saravanan et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ), future studies on students’ mental health should also include positive feelings to understand to what extent these decrease due to the pandemic situation. Assessing positive feelings during a public health crisis is essential as it has been shown that positive emotions can help maintain and improve human mental health (Yamaguchi et al., 2020 ). Thus, using a theoretical framework as Plutchik's ( 1994 ), which includes a broad subset of emotional dimensions, can give a more detailed picture of the emotional state of students and can help detect which feelings teachers and academic institutions need to reinforce, such as students' confidence and calm. Based on this information, institutions can work on messages and communications towards their students to counteract the emotional impact and enhance these positive emotions (Heffner et al., 2021 ).
Contrary to what was expected regarding the differences in the emotional state of the students as the lockdown elapses (Hypothesis 2), most emotions do not show significant changes from T1 to T2. However, worry and confusion are less reported in T2. The fact that students feel more concerned and confused at the beginning of confinement is aligned with the phases of the pandemic identified by Ramos-Morcillo et al. ( 2020 ), in which there is a first phase when disorientation prevails due to the novelty of the situation and a second phase as time progresses when the situation is assimilated and normalized. The only emotion that shows a significant increase from T1 to T2 is boredom, a feeling also present in other studies in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic (Aristovnik et al., 2020 ; Son et al., 2020 ). Although this result is not consistent with our hypothesis, it is aligned with the effect of mental exhaustion and demotivation the WHO ( 2020 ) claims that pandemic fatigue can cause. These results suggest that burnout does not affect all emotional states in the same way, and while some may not increase as time progresses or even decrease, such as worry or confusion, others such as boredom may increase (Canet-Juric et al., 2020 ). This information is relevant for teachers and academic institutions to understand how their students feel in each phase of the pandemic and to adapt the type of support provided at each moment.
In line with hypothesis 4 and the results of prior research (Elmer et al., 2020 ; Magson et al., 2021 ; Procentese et al., 2020 ), the connection with other students and teachers is correlated with students’ emotions. As expected, connection with others acts as a protector and, as the perception of contact with the academic community increases, the negative feelings of worry, confusion, discouragement, annoyance, and vigilance decrease. Besides, it has also been found that contact with fellow students and teachers is positively associated with the feelings of calm and trust, which suggests that social contact is not only a protector against negative emotions, but that it can also enhance positive emotions. Since positive emotions are the least reported by students during the lockdown, it is essential to identify which actions can enhance these emotions to improve students' mood. This finding reinforces the need to create alternative ways to stay in contact, so students can feel more connected with their classmates and teachers. Fostering social contact and communication will improve students’ mental health during online learning in the public health crisis and, as indicated by other studies, even beyond the pandemic situation (Holen et al., 2018 ).
Best practices in online teaching
In addition to validating the hypotheses raised, this study explores best practices carried out by the teaching staff during distance classes that have helped engineering students during online teaching. Although these practices have been identified in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic during the lockdown, they can also be initiatives of interest for regular teaching in university studies or in the design of online courses beyond the pandemic. Concerning the communication between students and teachers, the two most mentioned communication channels are instant messages and emails. Students have highly appreciated those teachers who have opened instant messaging channels such as WhatsApp to communicate with them in a faster and more accessible way. During the classes, the practice that helped students the most was the recording of the online classes allowing students to review them later. Besides, individual or small group video calls with the professor to clarify doubts more closely and in a more comfortable environment were also highly appreciated. Regarding the course adaptation, the two most relevant initiatives have been sharing problems already solved so students have guidelines to self-correct their exercises and sharing support videos with complementary explanations to the subjects’ content. Finally, it was highly appreciated that teachers gave quick answers to students’ questions and that they had a supportive attitude and were attentive to students’ needs. Some students reported on teachers having asked them for feedback to know how they were doing and improve their classes accordingly. Previous research has already highlighted the importance for teachers of receiving feedback from students in order to improve teaching (Anderson et al., 2011 ). The results of our study suggest that the benefits of the feedback are bi-directional, and it is not only helpful for teachers, but also makes students feel heard and valued. Previous research indicates that communication between students and teachers can be more complicated online than in face-to-face teaching (Alnusairat et al., 2020 ; Amir et al., 2020 ; Radu et al., 2020 ). Our study supports this claim, showing that most of the outstanding initiatives have been those practices that allowed students to solve their doubts more efficiently, such as faster communication methods, individual or small group tutoring sessions or having problems already solved in order to self-solve possible doubts autonomously. Although other studies already identified some of the initiatives undertaken by teachers to improve the experience during online teaching (Scull et al., 2020 ), our work collects those practices most valued from the students’ perspective and the ones that have been most helpful for them.
Limitations and future directions
The results of this study should be interpreted in the context of some limitations, which can be addressed in future research.
The study was conducted during an exceptional public health crisis, so it is not easily replicable. Also, the results of this study are influenced by the actions to face the COVID-19 pandemic taken by both the state and local governments and the academic institution in which the study was carried out. The measures adopted by the different countries and universities have differed, adapting them to the possibilities and characteristics of each case (Gonzalez et al., 2020 ). These differences may make the results of this study difficult to extrapolate to other countries or university degrees in which different solutions to the COVID-19 crisis have been implemented. For this reason, while it is expected that some of the results may be of value beyond the pandemic situation, it will be necessary to validate their applicability in other contexts.
Participants of this research were recruited from second, third and fourth year from a specific engineering degree, so the lack of random sampling and the representation of a student population limited to one engineering degree seem to be a limitation in generalizing the results to all engineering studies or all academic courses. As the field of engineering is vast and there are many different specializations, it would be interesting to expand the study and validate the results in other engineering degrees and in other courses. For example, the academic experience of first-year students who have started their studies in a pandemic situation may be different from those students from second, third and fourth year. It would also be interesting to extend the sample to other universities and countries since the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has not been the same everywhere. Furthermore, we have only included students in the study sample and not teachers. Perspectives of teachers regarding the switch to online learning would be valuable and should be explored in future studies. The samples of this study have been treated as independent. However, since it is a longitudinal study, it would be interesting to validate the observations with paired samples to compare the changes between time points on an individual basis.
Regarding the instruments used in the research, one limitation is that we created a new questionnaire for this study. Although the questions are based on previous studies, we could not find a similar questionnaire in the literature that incorporated all the measurements. Also, the reliability value of the scale used to measure the contact with other students and teachers is a bit low (α = 0.65) although Cronbach’s alpha is quite sensitive to the number of items in the scale, and short scales often have low Cronbach alpha values. Future research should validate these results and the instrument used and expand the number of items of the proposed scales to improve the scale’s reliability. Moreover, we did not collect participants’ personal data, such as gender or demographic information to preserve participants’ anonymity and favor the predisposition of students to answer the questionnaire.
As the study was conducted using a questionnaire, the results studied are based on students’ perceptions. However, perceptions do not always match reality. For example, while in our study students indicated that their academic development worsened during online teaching, the study of Jacques et al. ( 2020 ) found no differences between the grades of engineering students in online education and those expected in a face-to-face teaching. Thus, it would be interesting for future research to compare students’ perceptions regarding their academic development with their academic qualifications to validate the impact of the lockdown and distance classes on students’ outcomes. Also, we phrased the questions to collect the opinion of students regarding the majority of teachers and courses. We acknowledge that they may be differences between different teachers and courses that may impact individual experiences. However, we were interested in analyzing overall collective students’ opinion towards the online learning experience.
Despite these limitations, the results of this study offer valuable information on the academic and emotional effects that online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic had on engineering students and raises new hypotheses which can be examined in more detail in subsequent work. Moreover, a more specific analysis can be carried out to know how much of the variance in academic development can be explained by the quality of the classes, the adaptation of the teaching to the online format, the conditions of students’ workspace and the connection with other students and teachers.
Conclusions
The findings of this study highlight that the majority of students were not satisfied with the quality of their online education enforced during the lockdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and that they believe that it has negatively affected their academic performance. Moreover, students' academic development is correlated with the quality of the teaching, the adaptation of the assignments, workspace conditions, and the contact with other students and professors. Regarding their emotional state, students reported feeling discouragement, boredom, confusion, and worry to a greater extent, and calm and trust to a lesser extent. Except for boredom, all emotions are associated with the connection with classmates and teachers perceived by students, hence the students who have perceived a higher level of connection are those who reported more positive emotions and less negative ones. Additionally, we find significant improvements as time in lockdown elapsed regarding the students’ workspace conditions, while perceived contact with other students and teachers and boredom worsened significantly as the pandemic progressed. These results indicate that it is necessary to consider how the courses should be adapted to the online format since their quality and their correct adaptation will have an impact on the students' academic development. Furthermore, it is essential to work on connection and communication mechanisms among students and between students and teachers since these can improve students’ emotional state. These conclusions, along with the good practices that teachers have carried out during online classes in the pandemic and that we have identified in this study, will hopefully help in the design of future online courses and in the implementation of support plans to improve the student learning experience and their emotional state.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all the students from the Bachelor's Degree in Industrial Design and Product Development Engineering of the UPC who took part in answering the questionnaire and the teachers who facilitated the distribution of the questionnaire.
Authors’ contributions
Conceptualization, R.B.-S.; Methodology, R.B.-S., N.O.-T. and M.P.; Software, R.B.-S and A.-I.R.-D.; Validation, N.O.-T. and M.P.; Formal analysis, R.B.-S and A.-I.R.-D.; Investigation, R.B.-S.; Resources, N.O.-T. and M.P.; Writing—original draft preparation, R.B.-S., N.O.-T., M.P. and A.-I.R.-D.; Writing—review and editing, R.B.-S, N.O.-T., M.P. and A.-I.R.-D.; Supervision, R.B.-S., N.O.-T. and M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
This research received no external funding.
Availability of data and material
Declarations.
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
The participants have consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Rosó Baltà-Salvador, Email: [email protected] .
Noelia Olmedo-Torre, Email: [email protected] .
Marta Peña, Email: [email protected] .
Ana-Inés Renta-Davids, Email: [email protected] .
- Al-Balas M, Al-Balas HI, Jaber HM, Obeidat K, Al-Balas H, Aborajooh EA, Al-Taher R, Al-Balas B. Distance learning in clinical medical education amid COVID-19 pandemic in Jordan: Current situation, challenges, and perspectives. BMC Medical Education. 2020; 20 :341. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02257-4. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alnusairat, S., Al Maani, D., & Al-Jokhadar, A. (2020). Architecture students’ satisfaction with and perceptions of online design studios during COVID-19 lockdown: the case of Jordan universities. International Journal of Architectural Research , ahead - of - p . 10.1108/ARCH-09-2020-0195
- Amir LR, Tanti I, Maharani DA, Wimardhani YS, Julia V, Sulijaya B, Puspitawati R. Student perspective of classroom and distance learning during COVID-19 pandemic in the undergraduate dental study program Universitas Indonesia. BMC Medical Education. 2020; 20 :392. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02312-0. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderson D, Imdieke S, Standerford NS. Feedback Please: Studying Self in the Online Classroom. International Journal. 2011; 4 (1):3–15. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arbaugh JB. Virtual Classroom Characteristics and Student Satisfaction with Internet-Based MBA Courses. Journal of Management Education. 2000; 24 (1):32–54. doi: 10.1177/105256290002400104. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aristovnik A, Keržič D, Ravšelj D, Tomaževič N, Umek L. Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on life of higher education students: A global perspective. Sustainability. 2020; 12 (20):8438. doi: 10.3390/su12208438. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aslan I, Ochnik D, Çınar O. Exploring perceived stress among students in Turkey during the covid-19 pandemic. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17 (23):8961. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17238961. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ausín B, González-Sanguino C, Castellanos MÁ, Muñoz M. Gender-related differences in the psychological impact of confinement as a consequence of COVID-19 in Spain. Journal of Gender Studies. 2021; 30 (1):29–38. doi: 10.1080/09589236.2020.1799768. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blendon RJ, Benson JM, DesRoches CM, Raleigh E, Taylor-Clark K. The public’s response to severe acute respiratory syndrome in Toronto and the United States. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2004; 38 (7):925–931. doi: 10.1086/382355. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Braat-Eggen PE, van Heijst A, Hornikx M, Kohlrausch A. Noise disturbance in open-plan study environments: a field study on noise sources, student tasks and room acoustic parameters. Ergonomics. 2017; 60 (9):1297–1314. doi: 10.1080/00140139.2017.1306631. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brooks SK, Webster RK, Smith LE, Woodland L, Wessely S, Greenberg N, Rubin GJ. The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: rapid review of the evidence. The Lancet. 2020; 395 (10227):912–920. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30460-8. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Canet-Juric L, Andrés ML, del Valle M, López-Morales H, Poó F, Galli JI, Yerro M, Urquijo S. A Longitudinal Study on the Emotional Impact Cause by the COVID-19 Pandemic Quarantine on General Population. Frontiers in Psychology. 2020; 11 :565688. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.565688. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cava MA, Fay KE, Beanlands HJ, McCay EA, Wignall R. The experience of quarantine for individuals affected by SARS in Toronto. Public Health Nursing. 2005; 22 (5):398–406. doi: 10.1111/j.0737-1209.2005.220504.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cecchini, J. A., Carriedo, A., Fernández-Río, J., Méndez-Giménez, A., González, C., Sánchez-Martínez, B., & Rodríguez-González, P. (2021). A longitudinal study on depressive symptoms and physical activity during the Spanish lockdown. International Journal of Clinical and Health Psychology , 21 (1). 10.1016/j.ijchp.2020.09.001 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (2nd edn) . Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. 10.4324/9780203771587
- Driessen E, Beatty A, Stokes A, Wood S, Ballen C. Learning principles of evolution during a crisis: An exploratory analysis of student barriers one week and one month into the COVID-19 pandemic. Ecology and Evolution. 2020; 10 (22):12431–12436. doi: 10.1002/ece3.6741. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Du Toit, A. (2020). Outbreak of a novel coronavirus. Nature Reviews Microbiology , 18 (3), 123. 10.1038/s41579-020-0332-0 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Ekman P. An Argument for Basic Emotions. Cognition and Emotion. 1992; 6 (3):169–200. doi: 10.1080/02699939208411068. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elmer T, Mepham K, Stadtfeld C. Students under lockdown: Comparisons of students’ social networks and mental health before and during the COVID-19 crisis in Switzerland. PLoS ONE. 2020; 15 (7):e0236337. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236337. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gelles LA, Lord SM, Hoople GD, Chen DA, Mejia JA. Compassionate flexibility and self-discipline: Student adaptation to emergency remote teaching in an integrated engineering energy course during COVID-19. Education Sciences. 2020; 10 :304. doi: 10.3390/educsci10110304. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gonzalez T, De la Rubia MA, Hincz KP, Comas-Lopez M, Subirats L, Fort S, Sacha GM. Influence of COVID-19 confinement on students’ performance in higher education. PLoS ONE. 2020; 15 (10):e0239490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239490. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gopal A, Sharma AJ, Subramanyam MA. Dynamics of psychological responses to COVID-19 in India: A longitudinal study. PLoS ONE. 2020; 15 (10):e0240650. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240650. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hamann K, Glazier RA, Wilson BM, Pollock PH. Online teaching, student success, and retention in political science courses. European Political Science. 2020 doi: 10.1057/s41304-020-00282-x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hawryluck L, Gold WL, Robinson S, Pogorski S, Galea S, Styra R. SARS control and psychological effects of quarantine, Toronto. Canada. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2004; 10 (7):1206–1212. doi: 10.3201/eid1007.030703. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heffner J, Vives M-L, FeldmanHall O. Emotional responses to prosocial messages increase willingness to self-isolate during the COVID-19 pandemic. Personality and Individual Differences. 2021; 170 :110420. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2020.110420. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Holen S, Waaktaar T, Sagatun Å. A Chance Lost in the Prevention of School Dropout? Teacher-Student Relationships Mediate the Effect of Mental Health Problems on Noncompletion of Upper-Secondary School. Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research. 2018; 62 (5):737–753. doi: 10.1080/00313831.2017.1306801. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hong KS. Relationships between students’ and instructional variables with satisfaction and learning from a Web-based course. Internet and Higher Education. 2002; 5 (3):267–281. doi: 10.1016/S1096-7516(02)00105-7. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hviid CA, Pedersen C, Dabelsteen KH. A field study of the individual and combined effect of ventilation rate and lighting conditions on pupils’ performance. Building and Environment. 2020; 171 :106608. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2019.106608. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ibrahim A, Al Kaabi A, El Zaatari W. Teacher resistance to educational change in the United Arab Emirates. International Journal of Research Studies in Education. 2013; 2 (3):25–36. doi: 10.5861/ijrse.2013.254. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jacques S, Ouahabi A, Lequeu T. Remote Knowledge Acquisition and Assessment During the COVID-19 Pandemic. International Journal of Engineering Pedagogy. 2020; 10 (6):120. doi: 10.3991/ijep.v10i6.16205. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Khalil R, Mansour AE, Fadda WA, Almisnid K, Aldamegh M, Al-Nafeesah A, Alkhalifah A, Al-Wutayd O. The sudden transition to synchronized online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia: A qualitative study exploring medical students’ perspectives. BMC Medical Education. 2020; 20 :285. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02208-z. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kyne SH, Thompson CD. The COVID cohort: Student transition to university in the face of a global pandemic. Journal of Chemical Education. 2020; 97 (9):3381–3385. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00769. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Linh PD, Trang TN. Pandemic, social distancing, and social work education: students’ satisfaction with online education in Vietnam. Social Work Education. 2020; 39 (8):1074–1083. doi: 10.1080/02615479.2020.1823365. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Luan L, Hong J-C, Cao M, Dong Y, Hou X. Exploring the role of online EFL learners’ perceived social support in their learning engagement: a structural equation model. Interactive Learning Environments. 2020 doi: 10.1080/10494820.2020.1855211. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Magson NR, Freeman JYA, Rapee RM, Richardson CE, Oar EL, Fardouly J. Risk and Protective Factors for Prospective Changes in Adolescent Mental Health during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Youth and Adolescence. 2021; 50 :44–57. doi: 10.1007/s10964-020-01332-9. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mcinnerney JM, Roberts TS. Online Learning: Social Interaction and the Creation of a Sense of Community. Journal of Educational Technology & Society. 2004; 7 (3):73–81. [ Google Scholar ]
- Moorhouse BL. Adaptations to a face-to-face initial teacher education course ‘forced’ online due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Education for Teaching. 2020; 46 (4):1–3. doi: 10.1080/02607476.2020.1755205. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nassr RM, Aborujilah A, Aldossary DA, Aldossary AAA. Understanding Education Difficulty During COVID-19 Lockdown: Reports on Malaysian University Students’ Experience. IEEE Access. 2020; 8 :186939–186950. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3029967. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Odriozola-González P, Planchuelo-Gómez Á, Irurtia MJ, de Luis-García R. Psychological effects of the COVID-19 outbreak and lockdown among students and workers of a Spanish university. Psychiatry Research. 2020; 290 :113108. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113108. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Parrott WG. Emotions in social psychology. Psychology Press; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Parvez MS, Rahman A, Tasnim N. Ergonomic mismatch between students anthropometry and university classroom furniture. Theoretical Issues in Ergonomics Science. 2019; 20 (5):603–631. doi: 10.1080/1463922X.2019.1617909. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Piccoli G, Ahmad R, Ives B. Web-based virtual learning environments: A research framework and a preliminary assessment of effectiveness in basic it skills training. MIS Quarterly: Management Information Systems. 2001; 25 (4):401–426. doi: 10.2307/3250989. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Plutchik, R. (1994). The Psychology and Biology of Emotion . Harper Collins College Publishers.
- Procentese F, Capone V, Caso D, Donizzetti AR, Gatti F. Academic community in the face of emergency situations: Sense of responsible togetherness and sense of belonging as protective factors against academic stress during covid-19 outbreak. Sustainability. 2020; 12 (22):9718. doi: 10.3390/su12229718. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Puljak L, Čivljak M, Haramina A, Mališa S, Čavić D, Klinec D, Aranza D, Mesarić J, Skitarelić N, Zoranić S, Majstorović D, Neuberg M, Mikšić Š, Ivanišević K. Attitudes and concerns of undergraduate university health sciences students in Croatia regarding complete switch to e-learning during COVID-19 pandemic: a survey. BMC Medical Education. 2020; 20 :416. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02343-7. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Radu MC, Schnakovszky C, Herghelegiu E, Ciubotariu VA, Cristea I. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of educational process: A student survey. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17 (21):7770. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17217770. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ramos-Morcillo AJ, Leal-Costa C, Moral-García JE, Ruzafa-Martínez M. Experiences of nursing students during the abrupt change from face-to-face to e-learning education during the first month of confinement due to COVID-19 in Spain. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17 (15):5519. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17155519. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Realyvásquez-Vargas, A., Maldonado-Macías, A. A., Arredondo-Soto, K. C., Baez-Lopez, Y., Carrillo-Gutiérrez, T., & Hernández-Escobedo, G. (2020). The Impact of Environmental Factors on Academic Performance of University Students Taking Online Classes during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Mexico. Sustainability , 12 (21), 9194. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/21/9194
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez E, Sánchez-Paniagua M, Sanz-Landaluze J, Moreno-Guzmán M. Analytical Chemistry Teaching Adaptation in the COVID-19 Period: Experiences and Students’ Opinion. Journal of Chemical Education. 2020; 97 (9):2556–2564. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00923. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenberg, H., & Asterhan, C. S. C. (2018). “WhatsApp, Teacher?” Student Perspectives on Teacher-Student WhatsApp Interactions in Secondary Schools. Journal of Information Technology Education Research , 4081 , 205–226. 10.28945/4081
- Saravanan C, Mahmoud I, Elshami W, Taha MH. Knowledge, Anxiety, Fear, and Psychological Distress About COVID-19 Among University Students in the United Arab Emirates. Frontiers in Psychiatry. 2020; 11 :582189. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.582189. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scull J, Phillips M, Sharma U, Garnier K. Innovations in teacher education at the time of COVID19: an Australian perspective. Journal of Education for Teaching. 2020; 46 (4):497–506. doi: 10.1080/02607476.2020.1802701. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Son C, Hegde S, Smith A, Wang X, Sasangohar F. Effects of COVID-19 on college students’ mental health in the United States: Interview survey study. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2020; 22 (9):e21279. doi: 10.2196/21279. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sun PC, Tsai RJ, Finger G, Chen YY, Yeh D. What drives a successful e-Learning? An empirical investigation of the critical factors influencing learner satisfaction. Computers and Education. 2008; 50 (4):1183–1202. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2006.11.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tang T, Abuhmaid AM, Olaimat M, Oudat DM, Aldhaeebi M, Bamanger E. Efficiency of flipped classroom with online-based teaching under COVID-19. Interactive Learning Environments. 2020 doi: 10.1080/10494820.2020.1817761. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- UNESCO. (2020). COVID-19 and higher education: Today and tomorrow. Impact analysis, policy responses and recommendations . http://www.iesalc.unesco.org/en/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/COVID-19-EN-090420-2.pdf
- UNESCO, UNICEF, & The World Bank. (2020). What Have We Learnt? : Overview of Findings from a Survey of Ministries of Education on National Responses to COVID-19 . https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/34700
- Van Nuland S, Mandzuk D, Tucker Petrick K, Cooper T. COVID-19 and its effects on teacher education in Ontario: a complex adaptive systems perspective. Journal of Education for Teaching. 2020; 46 (4):442–451. doi: 10.1080/02607476.2020.1803050. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang X, Tang L, (Rebecca), & Kim, E. More than words: Do emotional content and linguistic style matching matter on restaurant review helpfulness? International Journal of Hospitality Management. 2019; 77 :438–447. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.08.007. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organization. (2021). Looking back at a year that changed the world. Who’s Response To COVID-19 . https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/looking-back-at-a-year-that-changed-the-world-who-s-response-to-covid-19
- World Health Organization & Regional Office for Europe. (2020). Pandemic fatigue: reinvigorating the public to prevent COVID-19: policy framework for supporting pandemic prevention and management . https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/337574
- Yamaguchi K, Takebayashi Y, Miyamae M, Komazawa A, Yokoyama C, Ito M. Role of Focusing on the Positive Side During COVID-19 Outbreak: Mental Health Perspective From Positive Psychology. Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy. 2020; 12 (S1):S49–S50. doi: 10.1037/tra0000807. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhong, L., Yuan, J., & Fleck, B. (2019). Indoor environmental quality evaluation of lecture classrooms in an institutional building in a cold climate. Sustainability , 11 (23). 10.3390/su11236591
- Zhou P, Yang X. Lou, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, Si HR, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang CL, Chen HD, Chen J, Luo Y, Guo H, Jiang R. Di, Liu MQ, Chen Y, Shen XR, Wang X, Shi ZL. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020; 579 (7798):270–273. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zurlo MC, Volta Cattaneo Della, M. F., & Vallone, F. COVID-19 Student Stress Questionnaire: Development and Validation of a Questionnaire to Evaluate Students’ Stressors Related to the Coronavirus Pandemic Lockdown. Frontiers in Psychology. 2020; 11 :576758. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.576758. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

Capturing the benefits of remote learning
How education experts are applying lessons learned in the pandemic to promote positive outcomes for all students
Vol. 52 No. 6 Print version: page 46
- Schools and Classrooms

With schools open again after more than a year of teaching students outside the classroom, the pandemic sometimes feels like a distant memory. The return to classrooms this fall brings major relief for many families and educators. Factors such as a lack of reliable technology and family support, along with an absence of school resources, resulted in significant academic setbacks, not to mention stress for everyone involved.
But for all the downsides of distance learning, educators, psychologists, and parents have seen some benefits as well. For example, certain populations of students found new ways to be more engaged in learning, without the distractions and difficulties they faced in the classroom, and the general challenges of remote learning and the pandemic brought mental health to the forefront of the classroom experience.
Peter Faustino, PsyD, a school psychologist in Scarsdale, New York, said the pandemic also prompted educators and school psychologists to find creative new ways of ensuring students’ emotional and academic well-being. “So many students were impacted by the pandemic, so we couldn’t just assume they would find resources on their own,” said Faustino. “We had to work hard at figuring out new ways to connect with them.”
Here are some of the benefits of distance learning that school psychologists and educators have observed and the ways in which they’re implementing those lessons post-pandemic, with the goal of creating a more equitable, productive environment for all students.
Prioritizing mental health
Faustino said that during the pandemic, he had more mental health conversations with students, families, and teachers than ever. “Because COVID-19 affected everyone, we’re now having mental health discussions as school leaders on a daily and weekly basis,” he said.
This renewed focus on mental health has the potential to improve students’ well-being in profound ways—starting with helping them recover from the pandemic’s effects. In New York City, for example, schools are hiring more than 600 new clinicians, including psychologists , to screen students’ mental health and help them process pandemic-related trauma and adjust to the “new normal” of attending school in person.
Educators and families are also realizing the importance of protecting students’ mental health more generally—not only for their health and safety but for their learning. “We’ve been seeing a broader appreciation for the fact that mental health is a prerequisite for learning rather than an extracurricular pursuit,” said Eric Rossen, PhD, director of professional development and standards at the National Association of School Psychologists.
As a result, Rossen hopes educators will embed social and emotional learning components into daily instruction. For example, teachers could teach mindfulness techniques in the classroom and take in-the-moment opportunities to help kids resolve conflicts or manage stress.
Improved access to mental health resources in schools is another positive effect. Because of physical distancing guidelines, school leaders had to find ways to deliver mental health services remotely, including via online referrals and teletherapy with school psychologists and counselors.
Early in the pandemic, Faustino said he was hesitant about teletherapy’s effectiveness; now, he hopes to continue offering a virtual option. Online scheduling and remote appointments make it easier for students to access mental health resources, and some students even enjoy virtual appointments more, as they can attend therapy in their own spaces rather than showing up in the counselor’s office. For older students, Faustino said that level of comfort often leads to more productive, open conversations.
Autonomy as a key to motivation
Research suggests that when students have more choices about their materials and activities, they’re more motivated—which may translate to increased learning and academic success. In a 2016 paper, psychology researcher Allan Wigfield, PhD, and colleagues make the case that control and autonomy in reading activities can improve both motivation and comprehension ( Child Development Perspectives , Vol. 10, No. 3 ).
During the period of online teaching, some students had opportunities to learn at their own pace, which educators say improved their learning outcomes—especially in older students. In a 2020 survey of more than 600 parents, researchers found the second-most-valued benefit of distance learning was flexibility—not only in schedule but in method of learning.
In a recent study, researchers found that 18% of parents pointed to greater flexibility in a child’s schedule or way of learning as the biggest benefit or positive outcome related to remote learning ( School Psychology , Roy, A., et al., in press).
This individualized learning helps students find more free time for interests and also allows them to conduct their learning at a time they’re most likely to succeed. During the pandemic, Mark Gardner, an English teacher at Hayes Freedom High School in Camas, Washington, said he realized how important student-centered learning is and that whether learning happens should take precedence over how and when it occurs.
For example, one of his students thrived when he had the choice to do work later at night because he took care of his siblings during the day. Now, Gardner posts homework online on Sundays so students can work at their own pace during the week. “Going forward, we want to create as many access points as we can for kids to engage with learning,” he said.
Rosanna Breaux , PhD, an assistant professor of psychology and assistant director of the Child Study Center at Virginia Tech, agrees. “I’d like to see this flexibility continue in some way, where—similar to college—students can guide their own learning based on their interests or when they’re most productive,” she said.
During the pandemic, many educators were forced to rethink how to keep students engaged. Rossen said because many school districts shared virtual curricula during the period of remote learning, older students could take more challenging or interesting courses than they could in person. The same is true for younger students: Megan Hibbard, a teacher in White Bear Lake, Minnesota, said many of her fifth graders enjoyed distance learning more than in-person because they could work on projects that aligned with their interests.
“So much of motivation is discovering the unique things the student finds interesting,” said Hunter Gehlbach, PhD, a professor and vice dean at the Johns Hopkins School of Education. “The more you can facilitate students spending more time on the things they’re really interested in, the better.”
Going forward, Rossen hopes virtual curricula will allow students greater opportunities to pursue their interests, such as by taking AP classes, foreign languages, or vocational electives not available at their own schools.
Conversely, Hibbard’s goal is to increase opportunities for students to pursue their interests in the in-person setting. For example, she plans to increase what she calls “Genius Hours,” a time at the end of the school day when students can focus on high-interest projects they’ll eventually share with the class.
Better understanding of children's needs
One of the most important predictors of a child’s success in school is parental involvement in their education. For example, in a meta-analysis of studies, researchers linked parental engagement in their middle schoolers’ education with greater measures of success (Hill, N. E., & Tyson, D. F., Developmental Psychology , Vol. 45, No. 3, 2009).
During the pandemic, parents had new opportunities to learn about their kids and, as a result, help them learn. According to a study by Breaux and colleagues, many parents reported that the pandemic allowed them a better understanding of their child’s learning style, needs, or curriculum.
James C. Kaufman , PhD, a professor of educational psychology at the University of Connecticut and the father of an elementary schooler and a high schooler, said he’s had a front-row seat for his sons’ learning for the first time. “Watching my kids learn and engage with classmates has given me some insight in how to parent them,” he said.
Stephen Becker , PhD, a pediatric psychologist at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, said some parents have observed their children’s behavior or learning needs for the first time, which could prompt them to consider assessment and Individualized Education Program (IEP) services. Across the board, Gehlbach said parents are realizing how they can better partner with schools to ensure their kids’ well-being and academic success.
For example, Samantha Marks , PsyD, a Florida-based clinical psychologist, said she realized how much help her middle school daughter, a gifted and talented student with a 504 plan (a plan for how the school will offer support for a student’s disability) for anxiety, needed with independence. “Bringing the learning home made it crystal clear what we needed to teach our daughter to be independent and improve executive functioning” she said. “My takeaway from this is that more parents need to be involved in their children’s education in a healthy, helpful way.”
Marks also gained a deeper understanding of her daughter’s mental health needs. Through her 504 plan, she received help managing her anxiety at school—at home, though, Marks wasn’t always available to help, which taught her the importance of helping her daughter manage her anxiety independently.
Along with parents gaining a deeper understanding of their kids’ needs, the pandemic also prompted greater parent participation in school. For example, Rossen said his kids’ school had virtual school board meetings; he hopes virtual options continue for events like back-to-school information sessions and parenting workshops. “These meetings are often in the evening, and if you’re a single parent or sole caregiver, you may not want to pay a babysitter in order to attend,” he said.
Brittany Greiert, PhD, a school psychologist in Aurora, Colorado, says culturally and linguistically diverse families at her schools benefited from streamlined opportunities to communicate with administrators and teachers. Her district used an app that translates parent communication into 150 languages. Parents can also remotely participate in meetings with school psychologists or teachers, which Greiert says she plans to continue post-pandemic.
Decreased bullying
During stay-at-home orders, kids with neurodevelopmental disorders experienced less bullying than pre-pandemic (McFayden, T. C., et al., Journal of Rural Mental Health , No. 45, Vol. 2, 2021). According to 2019 research, children with emotional, behavioral, and physical health needs experience increased rates of bullying victimization ( Lebrun-Harris, L. A., et al., ), and from the U.S. Department of Education suggests the majority of bullying takes place in person and in unsupervised areas (PDF) .
Scott Graves , PhD, an associate professor of educational studies at The Ohio State University and a member of APA’s Coalition for Psychology in Schools and Education (CPSE), said the supervision by parents and teachers in remote learning likely played a part in reducing bullying. As a result, he’s less worried his Black sons will be victims of microaggressions and racist behavior during online learning.
Some Asian American families also report that remote learning offered protection against racism students may have experienced in person. Shereen Naser, PhD, an associate professor of psychology at Cleveland State University and a member of CPSE, and colleagues found that students are more comfortable saying discriminatory things in school when their teachers are also doing so; Naser suspects this trickle-down effect is less likely to happen when students learn from home ( School Psychology International , 2019).
Reductions in bullying and microaggressions aren’t just beneficial for students’ long-term mental health. Breaux said less bullying at school results in less stress, which can improve students’ self-esteem and mood—both of which impact their ability to learn.
Patricia Perez, PhD, an associate professor of international psychology at The Chicago School of Professional Psychology and a member of CPSE, said it’s important for schools to be proactive in providing spaces for support and cultural expression for students from vulnerable backgrounds, whether in culture-specific clubs, all-school assemblies that address racism and other diversity-related topics, or safe spaces to process feelings with teachers.
According to Rossen, many schools are already considering how to continue supporting students at risk for bullying, including by restructuring the school environment.
One principal, Rossen said, recently switched to single-use bathrooms to avoid congregating in those spaces once in-person learning commences to maintain social distancing requirements. “The principal received feedback from students about how going to the bathroom is much less stressful for these students in part due to less bullying,” he said.
More opportunities for special needs students
In Becker and Breaux’s research, parents of students with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), particularly those with a 504 plan and IEP, reported greater difficulties with remote learning. But some students with special learning needs—including those with IEPs and 504 plans—thrived in an at-home learning environment. Recent reporting in The New York Times suggests this is one reason many students want to continue online learning.
According to Cara Laitusis, PhD, a principal research scientist at Educational Testing Service ( ETS ) and a member of CPSE, reduced distractions may improve learning outcomes for some students with disabilities that impact attention in a group setting. “In assessments, small group or individual settings are frequently requested accommodations for some students with ADHD, anxiety, or autism. Being in a quiet place alone without peers for part of the instructional day may also allow for more focus,” she said. However, she also pointed out the benefits of inclusion in the classroom for developing social skills with peers.
Remote learning has improved academic outcomes for students with different learning needs, too. Marks said her seventh-grade daughter, a visual learner, appreciated the increase in video presentations and graphics. Similarly, Hibbard said many of her students who struggle to grasp lessons on the first try have benefited from the ability to watch videos over again until they understand. Post-pandemic, she plans to record bite-size lessons—for example, a 1-minute video of a long division problem—so her students can rewatch and process at their own rate.
Learners with anxiety also appreciate the option not to be in the classroom, because the social pressures of being surrounded by peers can make it hard to focus on academics. “Several of my students have learned more in the last year simply due to the absence of anxiety,” said Rosie Reid, an English teacher at Ygnacio Valley High School in Concord, California, and a 2019 California Teacher of the Year. “It’s just one less thing to negotiate in a learning environment.”
On online learning platforms, it’s easier for kids with social anxiety or shyness to participate. One of Gardner’s students with social anxiety participated far more in virtual settings and chats. Now, Gardner is brainstorming ways to encourage students to chat in person, such as by projecting a chat screen on the blackboard.
Technology has helped school psychologists better engage students, too. For example, Greiert said the virtual setting gave her a new understanding of her students’ personalities and needs. “Typing out their thoughts, they were able to demonstrate humor or complex thoughts they never demonstrated in person,” she said. “I really want to keep incorporating technology into sessions so kids can keep building on their strengths.”
Reid says that along with the high school students she teaches, she’s seen her 6-year-old daughter benefit from learning at her own pace in the familiarity of her home. Before the pandemic, she was behind academically, but by guiding her own learning—writing poems, reading books, playing outside with her siblings—she’s blossomed. “For me, as both a mother and as a teacher, this whole phenomenon has opened the door to what education can be,” Reid said.
Eleanor Di Marino-Linnen, PhD, a psychologist and superintendent of the Rose Tree Media School District in Media, Pennsylvania, says the pandemic afforded her district a chance to rethink old routines and implement new ones. “As challenging as it is, it’s definitely an exciting time to be in education when we have a chance to reenvision what schools have looked like for many years,” she said. “We want to capitalize on what we’ve learned.”
Further reading
Why are some kids thriving during remote learning? Fleming, N., Edutopia, 2020
Remote learning has been a disaster for many students. But some kids have thrived. Gilman, A., The Washington Post , Oct. 3, 2020
A preliminary examination of key strategies, challenges, and benefits of remote learning expressed by parents during the COVID-19 pandemic Roy, A., et al., School Psychology , in press
Remote learning during COVID-19: Examining school practices, service continuation, and difficulties for adolescents with and without attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder Becker S. P., et al., Journal of Adolescent Health , 2020
Recommended Reading

Contact APA
You may also like.
Challenges and Opportunities of Online Learning in the Philippine Context: Thriving in the New Normal
New citation alert added.
This alert has been successfully added and will be sent to:
You will be notified whenever a record that you have chosen has been cited.
To manage your alert preferences, click on the button below.
New Citation Alert!
Please log in to your account
Information & Contributors
Bibliometrics & citations, recommendations, challenges and opportunities for international students in graduate education.
International students pursuing graduate education in U.S. institutes have been rapidly increasing in recent years. Students from all over the world remarkably contribute to the advancement of U.S. economy and technology. This article addresses the ...
Opportunities and Challenges of online learning in China
With the impact of the COVID-19, online education is more and more mentioned and concerned. Online education is getting more and more popular due to its advantages of breaking through the limitations of field and time, fully and effectively allocating ...
Compensating Learning Losses in Online Learning: Teachers and Students' Performance in Virtual Classrooms
The study demonstrates the learning losses in remote online learning during the Covid-19 pandemic and how online teaching can mitigate these losses. The findings were analyzed using descriptive statistics and theme analysis based on online surveys and ...
Information
Published in.

Association for Computing Machinery
New York, NY, United States
Publication History
Permissions, check for updates, author tags.
- covid-19 pandemic
- online learning
- opportunities
- Research-article
- Refereed limited
Contributors
Other metrics, bibliometrics, article metrics.
- 0 Total Citations
- 154 Total Downloads
- Downloads (Last 12 months) 17
- Downloads (Last 6 weeks) 1
View Options
Login options.
Check if you have access through your login credentials or your institution to get full access on this article.
Full Access
View options.
View or Download as a PDF file.
View online with eReader .
HTML Format
View this article in HTML Format.
Share this Publication link
Copying failed.
Share on social media
Affiliations, export citations.
- Please download or close your previous search result export first before starting a new bulk export. Preview is not available. By clicking download, a status dialog will open to start the export process. The process may take a few minutes but once it finishes a file will be downloadable from your browser. You may continue to browse the DL while the export process is in progress. Download
- Download citation
- Copy citation
We are preparing your search results for download ...
We will inform you here when the file is ready.
Your file of search results citations is now ready.
Your search export query has expired. Please try again.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Is Online Learning Effective?
A new report found that the heavy dependence on technology during the pandemic caused “staggering” education inequality. What was your experience?

By Natalie Proulx
During the coronavirus pandemic, many schools moved classes online. Was your school one of them? If so, what was it like to attend school online? Did you enjoy it? Did it work for you?
In “ Dependence on Tech Caused ‘Staggering’ Education Inequality, U.N. Agency Says ,” Natasha Singer writes:
In early 2020, as the coronavirus spread, schools around the world abruptly halted in-person education. To many governments and parents, moving classes online seemed the obvious stopgap solution. In the United States, school districts scrambled to secure digital devices for students. Almost overnight, videoconferencing software like Zoom became the main platform teachers used to deliver real-time instruction to students at home. Now a report from UNESCO , the United Nations’ educational and cultural organization, says that overreliance on remote learning technology during the pandemic led to “staggering” education inequality around the world. It was, according to a 655-page report that UNESCO released on Wednesday, a worldwide “ed-tech tragedy.” The report, from UNESCO’s Future of Education division, is likely to add fuel to the debate over how governments and local school districts handled pandemic restrictions, and whether it would have been better for some countries to reopen schools for in-person instruction sooner. The UNESCO researchers argued in the report that “unprecedented” dependence on technology — intended to ensure that children could continue their schooling — worsened disparities and learning loss for hundreds of millions of students around the world, including in Kenya, Brazil, Britain and the United States. The promotion of remote online learning as the primary solution for pandemic schooling also hindered public discussion of more equitable, lower-tech alternatives, such as regularly providing schoolwork packets for every student, delivering school lessons by radio or television — and reopening schools sooner for in-person classes, the researchers said. “Available evidence strongly indicates that the bright spots of the ed-tech experiences during the pandemic, while important and deserving of attention, were vastly eclipsed by failure,” the UNESCO report said. The UNESCO researchers recommended that education officials prioritize in-person instruction with teachers, not online platforms, as the primary driver of student learning. And they encouraged schools to ensure that emerging technologies like A.I. chatbots concretely benefited students before introducing them for educational use. Education and industry experts welcomed the report, saying more research on the effects of pandemic learning was needed. “The report’s conclusion — that societies must be vigilant about the ways digital tools are reshaping education — is incredibly important,” said Paul Lekas, the head of global public policy for the Software & Information Industry Association, a group whose members include Amazon, Apple and Google. “There are lots of lessons that can be learned from how digital education occurred during the pandemic and ways in which to lessen the digital divide. ” Jean-Claude Brizard, the chief executive of Digital Promise, a nonprofit education group that has received funding from Google, HP and Verizon, acknowledged that “technology is not a cure-all.” But he also said that while school systems were largely unprepared for the pandemic, online education tools helped foster “more individualized, enhanced learning experiences as schools shifted to virtual classrooms.” Education International, an umbrella organization for about 380 teachers’ unions and 32 million teachers worldwide, said the UNESCO report underlined the importance of in-person, face-to-face teaching. “The report tells us definitively what we already know to be true, a place called school matters,” said Haldis Holst, the group’s deputy general secretary. “Education is not transactional nor is it simply content delivery. It is relational. It is social. It is human at its core.”
Students, read the entire article and then tell us:
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
1. Introduction. Recently, advances in modern computer and network technology have driven the development of distance education [].In addition, the COVID-19 pandemic, a public health crisis of worldwide importance, announced by the World Health Organization (WHO) in January 2020 as an outbreak, has made distance education through the E-learning system an urgent and irreplaceable requirement.
This systematic literature review of 36 peer-reviewed empirical articles outlines eight strategies used by higher education lecturers and students to maintain educational continuity during the COVID-19 pandemic since January 2020. The findings show that students' online access and positive coping strategies could not eradicate their infrastructure and home environment challenges.
The COVID-19 outbreak brought online learning to the forefront of education. Scholars have conducted many studies on online learning during the pandemic, but only a few have performed quantitative comparative analyses of students' online learning behavior before and after the outbreak. We collected review data from China's massive open online course platform called icourse.163 and ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced the world to engage in the ubiquitous use of virtual learning. And while online and distance learning has been used before to maintain continuity in education ...
The article presents some challenges faced by teachers and learners, supplemented with the recommendations to remove them. JEL Code: A20. The COVID-19 pandemic has led to an expansion in the demand for online teaching and learning across the globe. Online teaching and learning is attracting many students for enhanced learning experiences.
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in nearly all universities switching courses to online formats. We surveyed the online learning experience of undergraduate students ( n = 187) at a large, public research institution in course structure, interpersonal interaction, and academic resources. Data was also collected from course evaluations.
Full article: Online Teaching and Learning under COVID-19: Challenges and Opportunities. Computers in the Schools. Interdisciplinary Journal of Practice, Theory, and Applied Research. Volume 38, 2021 - Issue 4: Technology's Challenge in K-12 and Higher Education to Deal with a Worldwide Pandemic. Free access.
The COVID-19 pandemic led to school closures and distance learning that are likely to exacerbate social class academic disparities. This Review presents an agenda for future research and outlines ...
The sudden transition to synchronized online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Saudi Arabia: A qualitative study exploring medical students' perspectives. BMC Medical Education. 2020; 20 (1):1-10. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02208-z. [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] Matsumoto K. Introspection, verbal reports and second language ...
This pandemic has most severely hit the education system in developing countries, which do not have the educational technologies and online learning platforms required to shift to online learning. Citation 9 Moreover, there is a scarcity of studies on how the educational system in underdeveloped and impoverished countries has responded to this ...
Recently, the education system has faced an unprecedented health crisis that has shaken up its foundation. Given today's uncertainties, it is vital to gain a nuanced understanding of students' online learning experience in times of the COVID-19 pandemic. Although many studies have investigated this area, limited information is available regarding the challenges and the specific strategies ...
1. Introduction. The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted higher education by forcing the transition to online learning, which became a mandatory teaching process during the lockdowns (Aristovnik et al., 2020a).Despite the educational process saw disruptions on all levels of education, i.e., primary, secondary and tertiary (), as well as in adult education (James and ...
The sudden outbreak of a deadly disease called Covid-19 caused by a Corona Virus (SARS-CoV-2) shook the entire world. The World Health Organization declared it as a pandemic. This situation challenged the education system across the world and forced educators to shift to an online mode of teaching overnight.
However, there has been a lack of information on university students' perspectives regarding online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. This study assessed the perspectives, satisfaction and experiences with online and classroom learning among human health students at the University of Zambia.
Students' perception of online learning during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A survey study of Polish medical students. Medicine, 100 (7), e24821. 10.1097/MD.0000000000024821 [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] Barbour, M. K. (2013). The landscape of k‐12 online learning: Examining what is known.
This study explores how students at different stages of their K-12 education reacted to the mandatory full-time online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. For this purpose, we conducted a province-wide survey study in which the online learning experience of 1,170,769 Chinese students was collected from the Guangdong Province of China.
The shift to online distance learning, initially adopted to continue education during the pandemic, has proven to be a complex adjustment for many. A significant issue encountered by teachers is the insufficient internet data available to students. Many learners start a lesson only to run out of data midway, causing them to drop out of class.
Introduction. The COVID-19 pandemic has posed an unprecedented challenge in education, leading to the suspension of face-to-face teaching (UNESCO, 2020).This change has been particularly challenging in university undergraduate engineering degrees since much of the learning process is based on practical applications, laboratory classes, and direct contact with teachers and other students.
Why are some kids thriving during remote learning? Fleming, N., Edutopia, 2020. Remote learning has been a disaster for many students. But some kids have thrived. Gilman, A., The Washington Post, Oct. 3, 2020. A preliminary examination of key strategies, challenges, and benefits of remote learning expressed by parents during the COVID-19 pandemic
This study compares university students' performance in traditional learning to that of online learning during the pandemic, and analyses the implications of the shift to online learning from a faculty's perspective. The Quick-Response Research method using Google Documents was used with 104 faculty members chosen on convenience sampling in ...
Simamora, R. M. (2020). The Challenges of Online Learning during the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Essay Analysis of Performing Arts Education Students. Studies in Learning and Teaching, 1(2). Retrieved from https://scie-journal.com ... The study demonstrates the learning losses in remote online learning during the Covid-19 pandemic and how online ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed education forever. This is how. Apr 29, 2020. With schools shut across the world, millions of children have had to adapt to new types of learning. Image: REUTERS/Gonzalo Fuentes. The COVID-19 has resulted in schools shut all across the world. Globally, over 1.2 billion children are out of the classroom.
219. A UNESCO report says schools' heavy focus on remote online learning during the pandemic worsened educational disparities among students worldwide. Amira Karaoud/Reuters. By Natalie Proulx ...