For a better website experience, please confirm you are in:
Are you trying to review or purchase products for a school based in New York City?


A Teacher-Led K–8 Math Program

Ready Common Core Mathematics
Ready Common Core Mathematics helps teachers create a rich classroom environment in which students at all levels become active, real-world problem solvers. Through teacher-led instruction, students develop mathematical reasoning, engage in discourse, and build strong mathematical habits. This math program’s instructional framework supports educators as they strengthen their teaching practices and facilitate meaningful discourse that encourages all learners.
Ready Common Core Mathematics :
- Encourages students to develop a deeper understanding of mathematics concepts through the embedded Standards for Mathematical Practice
- Builds on students’ prior knowledge with lessons that make connections within and across grade levels and directly address the major focus of the grade
- Ready Mathematics 6–8, ©2020 Edition provides additional features for supporting English Learners, such as:
- English Language Development guidelines on scaffolding language use during instruction to benefit students at different levels of English proficiency
- Language routines that integrate language and mathematics
- Concept development activities that allow students of varying mathematical and English language abilities to build on familiar concepts
Proven Math Programs for All Students
Ready Common Core Mathematics can be used as your core curriculum or to enhance your math instruction. Designed to develop strong mathematical thinkers, our math programs focus on conceptual understanding using real-world problem solving and help students become active participants in their own learning.
Proven to Work
Third-party research provides evidence that students using the Ready Mathematics programs perform significantly better than students not using the program.
See Ready Mathematics at Work in the Classroom
See how students collaborate and share problem-solving strategies with the Think–Share–Compare routine.
Get to Know Ready Common Core Mathematics
Making mathematics work for you.
- Sample Lessons

Student Solution
The two-part student edition consists of a Student Instruction Book and a Practice and Problem Solving book, a powerful combination of thoughtful instruction, real-world problem solving, and fluency practice.
- VIEW SAMPLE LESSONS

Teacher Solution
The Teacher Resource Book features embedded, point-of-use professional support in every lesson, such as learning progressions, prerequisite skills, and prompts for promoting mathematical discourse.

Assessment Solution
Robust formative and summative assessment tools closely match the rigor and expectations of the state assessments and include lessons, mid- and end-of-unit assessments, and performance tasks at the end of each unit (Grades 2–5 only).
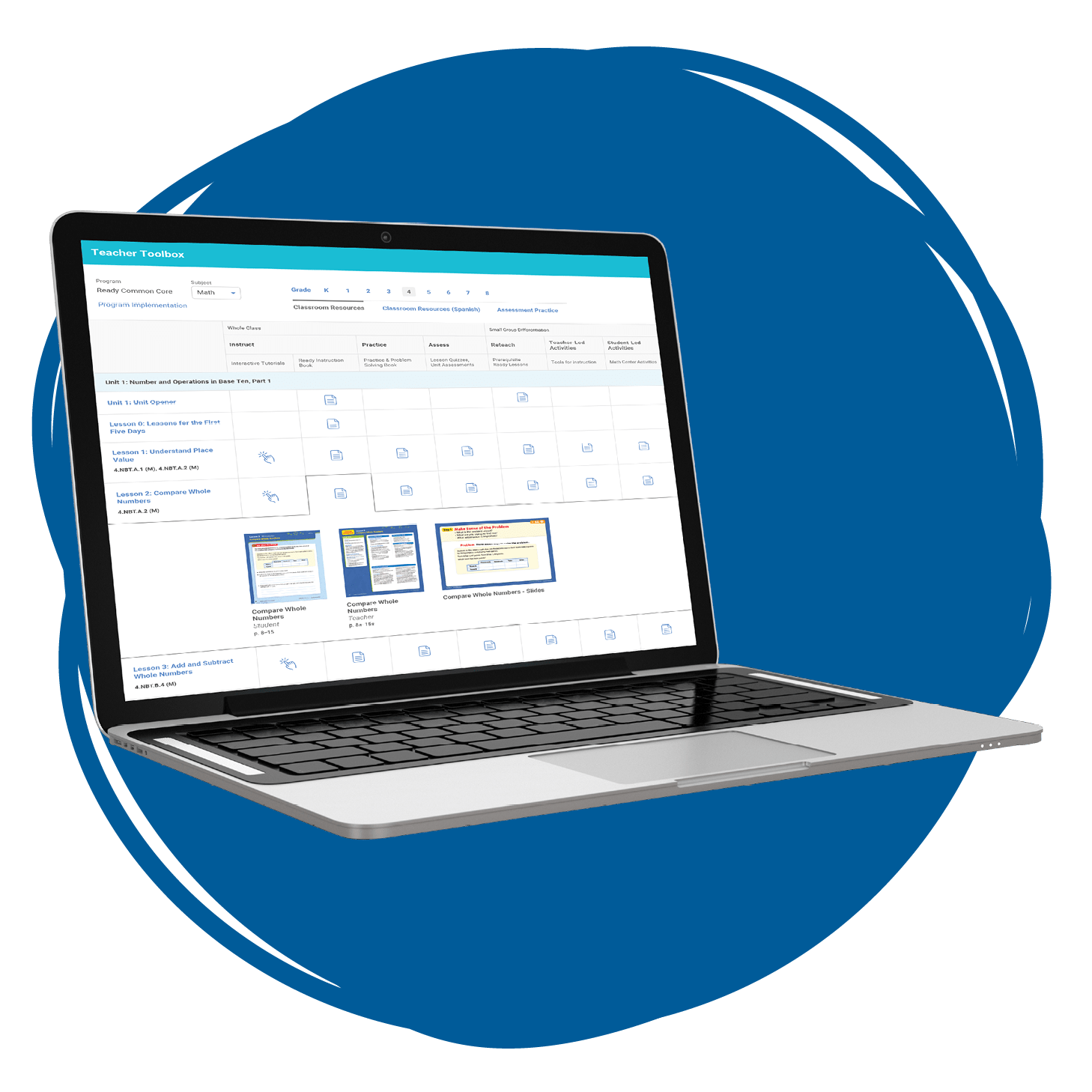
Teacher Toolbox for Mathematics
A perfect complement to Ready Common Core Mathematics , Teacher Toolbox for Mathematics is a digital collection of K–8 instructional resources that supports educators in differentiating instruction for students performing on, below, or above grade level. Regardless of the grade they teach, subscribers get access to the full range of Ready Common Core Mathematics resources for all grade levels, in addition to multimedia content, assessment practice, discourse supports, and more.
*For educators from K–12 educational institutions only.
- TEST DRIVE*

Robust formative and summative assessment tools closely match the rigor and expectations of the state assessments and include lessons, mid- and end-of-unit assessments, and performance tasks at the end of each unit (Grades 2–8 only).
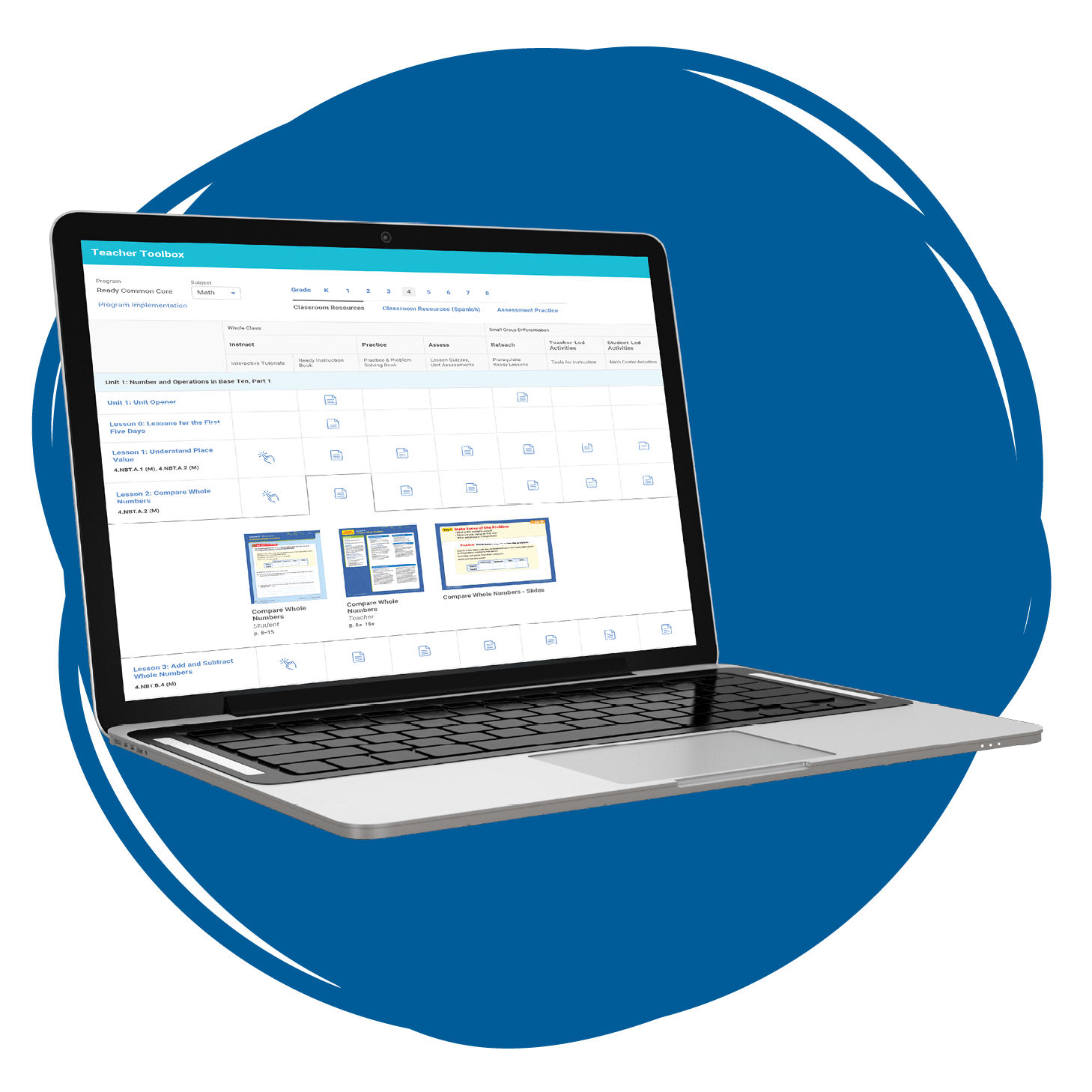
A perfect complement to Ready Common Core Mathematics , Teacher Toolbox for Mathematics is a digital collection of K–8 instructional resources that supports educators in differentiating instruction for students performing on, below, or above grade level. Regardless of the grade they teach, subscribers get access to the full range of Ready Common Core Mathematics K–8 resources for all grade levels, in addition to multimedia content, assessment practice, discourse supports, and more.
*For educators from K–12 educational institutions only.
Behind Our Program
Orchestrating Mathematical Discourse to Enhance Student Learning
Discover strategies that support student collaboration and mathematical discussion.
Selecting and Sequencing Student Solutions
Know more about strategies to facilitate productive mathematics discussions.
Fostering Student Engagement in the Mathematical Practices
Read how to implement discourse that encourages instructional routines in the classroom.
Mathematical Discourse Cards
Use these cards to facilitate and support organic discussions within class.
Curriculum / Math / 6th Grade / Unit 6: Equations and Inequalities / Lesson 6
Equations and Inequalities
Lesson 6 of 14
Criteria for Success
Tips for teachers, anchor problems, problem set, target task, additional practice.
Lesson Notes
There was an error generating your document. Please refresh the page and try again.
Generating your document. This may take a few seconds.
Are You Sure?
Are you sure you want to delete this note? This action cannot be undone.
Solve percent problems using equations.
Common Core Standards
Core standards.
The core standards covered in this lesson

Expressions and Equations
6.EE.B.7 — Solve real-world and mathematical problems by writing and solving equations of the form x + p = q and px = q for cases in which p, q and x are all nonnegative rational numbers.
Ratios and Proportional Relationships
6.RP.A.3.C — Find a percent of a quantity as a rate per 100 (e.g., 30% of a quantity means 30/100 times the quantity); solve problems involving finding the whole, given a part and the percent.
Foundational Standards
The foundational standards covered in this lesson
6.RP.A.1 — Understand the concept of a ratio and use ratio language to describe a ratio relationship between two quantities. For example, "The ratio of wings to beaks in the bird house at the zoo was 2:1, because for every 2 wings there was 1 beak." "For every vote candidate A received, candidate C received nearly three votes."
6.RP.A.2 — Understand the concept of a unit rate a/b associated with a ratio a:b with b ≠ 0, and use rate language in the context of a ratio relationship. Expectations for unit rates in this grade are limited to non-complex fractions. For example, "This recipe has a ratio of 3 cups of flour to 4 cups of sugar, so there is 3/4 cup of flour for each cup of sugar." "We paid $75 for 15 hamburgers, which is a rate of $5 per hamburger."
The essential concepts students need to demonstrate or understand to achieve the lesson objective
- Determine, through repeated reasoning, an equation to represent the relationship between percent, whole, and part: $$percent\times{whole}=part$$ (MP.8).
- Write an equation to represent a percent situation when given a part and a percent.
- Write and solve equations to find the whole, given the part and percent.
Suggestions for teachers to help them teach this lesson
In Unit 2, students solved percent problems by reasoning about diagrams, double number lines, and tables. Now having learned about equations in the form $${px=q}$$ , students revisit percent problems to see how they can be modeled and solved efficiently using an equation (MP.4).
Unlock features to optimize your prep time, plan engaging lessons, and monitor student progress.
Problems designed to teach key points of the lesson and guiding questions to help draw out student understanding
25-30 minutes
- 30% of 120?
In general, if you’re given a percent and a whole, how can you find the part? Write this as an equation.
Guiding Questions
Student response.
Upgrade to Fishtank Plus to view Sample Response.
30% of what number is 12?
Solve this problem first by drawing a diagram. Then write and solve an equation to verify your solution.
For each situation below, write and solve an equation to answer the question.
a. There are 6 liters of water in a bucket, which is 20% of the maximum number of liters the bucket can hold. What is the maximum number of liters the bucket can hold?
b. A softball team won 18 games, which was 60% of the games they played this season. How many games did the softball team play this season?
A set of suggested resources or problem types that teachers can turn into a problem set
15-20 minutes
Give your students more opportunities to practice the skills in this lesson with a downloadable problem set aligned to the daily objective.
A task that represents the peak thinking of the lesson - mastery will indicate whether or not objective was achieved
5-10 minutes
Paula is saving money to buy a tablet. So far, she has saved $54, which is 45% of what she needs to buy the tablet.
Write and solve an equation to find the price of the tablet.
The following resources include problems and activities aligned to the objective of the lesson that can be used for additional practice or to create your own problem set.
- Challenge: In a choir, there are 28 female singers which is 40% of the choir. How many female singers would have to be added to the group so exactly 50% of the choir were females?
- EngageNY Mathematics Grade 6 Mathematics > Module 1 — Lessons 27–29 (Revisit these lessons from Unit 2 and have students write equations to solve.)
- Open Up Resources Grade 6 Unit 6 Practice Problems — Lesson 7 #1–3
Topic A: Reasoning About and Solving Equations
Represent equations in the form $${ x+p=q }$$ and $${px=q}$$ using tape diagrams and balances.
6.EE.B.6 6.EE.B.7
Define and identify solutions to equations.
Write equations for real-world situations.
Solve one-step equations with addition and subtraction.
Solve one-step equations with multiplication and division.
6.EE.B.7 6.RP.A.3.C
Solve multi-part equations leading to the form $${x+p=q }$$ and $${px=q}$$ .
Create a free account to access thousands of lesson plans.
Already have an account? Sign In
Topic B: Reasoning About and Solving Inequalities
Define and identify solutions to inequalities.
6.EE.B.5 6.EE.B.8
Write and graph inequalities for real-world conditions. (Part 1)
Write and graph inequalities for real-world conditions. (Part 2)
Solve one-step inequalities.
6.EE.B.6 6.EE.B.8
Topic C: Representing and Analyzing Quantitative Relationships
Write equations for and graph ratio situations. Define independent and dependent variables.
6.EE.C.9 6.RP.A.3.A
Represent the relationship between two quantities in graphs, equations, and tables. (Part 1)
Represent the relationship between two quantities in graphs, equations, and tables. (Part 2)
Request a Demo
See all of the features of Fishtank in action and begin the conversation about adoption.
Learn more about Fishtank Learning School Adoption.
Contact Information
School information, what courses are you interested in, are you interested in onboarding professional learning for your teachers and instructional leaders, any other information you would like to provide about your school.

We Handle Materials So You Can Focus on Students
We've got you covered with rigorous, relevant, and adaptable math lesson plans for free
Problem Solving - Make a Table

Description
Questions & answers.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
- 888-309-8227
- 732-384-0146
New User Registration
Forgot Password
Go Math! 6 Common Core Edition, Grade: 6 Publisher: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Go math 6 common core edition, title : go math 6 common core edition, publisher : houghton mifflin harcourt, isbn : 547587783, isbn-13 : 9780547587783, use the table below to find videos, mobile apps, worksheets and lessons that supplement go math 6 common core edition..
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| --> |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
textbook resources
- Call us toll-free
- FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
- Contact Lumos Learning – Proven Study Programs by Expert Teachers
Follow us: Lumos Learning -->
- 2024 © Lumos Learning
- Privacy Policy - Terms of Service - Disclaimers
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc... Read More
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc., the Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any state of the Union. Neither PARCC, Inc., nor The Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any member state has endorsed this product. No portion of any fees or charges paid for any products or services Lumos Learning offers will be paid or inure to the benefit of PARCC, Inc., or any state of the Union
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not aff... Read More
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC, was not... Read More
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC,was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved... Read More
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the prod... Read More
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved... Read More
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved... Read More
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved... Read More
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved... Read More
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Report an Error
| | > >
|
Chapter 6, Lesson 7: Problem-Solving Strategy: Make a Table
- Extra Examples
- Self-Check Quizzes
The resource you requested requires you to enter a username and password below:
| Password: | |
Please read our Terms of Use and Privacy Notice before you explore our Web site. To report a technical problem with this Web site, please contact the site producer .

- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 1 Lesson 27 Answer Key
Engage ny eureka math 6th grade module 1 lesson 27 answer key, eureka math grade 6 module 1 lesson 27 example answer key.
Example 1. Solve the following three problems. Write the words PERCENT, WHOLE, or PART under each problem to show which piece you were solving for. 60% of 300 = ____________ 60% of ____________ = 300 60 out of 300 = ____________ %
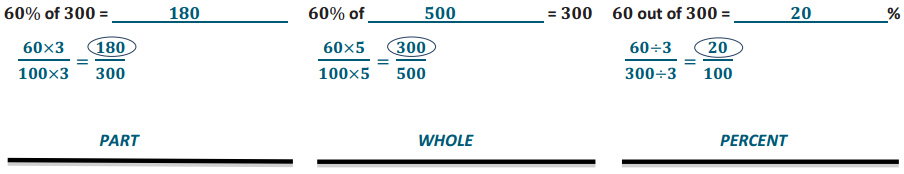
How did your solving method differ with each problem? Answer: Solutions will vary. A possible answer may include: When solving for the part, I need to find the missing number in the numerator. When solving for the whole, I solve for the denominator. When I solve for the percent, I need to find the numerator when the denominator is 100.
Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 1 Lesson 27 Exercise Answer Key
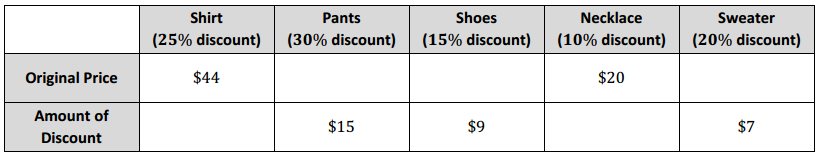
What is the total cost of Priya’s outfit? Answer: Shirt 25% = \(\frac{25}{100}=\frac{1}{4}=\frac{11}{44}\) The discount is $11. The cost of the shirt is $33 because $44 – $11 = $33.
Pants 30% = \(\frac{30}{100}=\frac{15}{50}\) The original price is $50. The price of the pants is $35 because $50 – $15 = $35.
Shoes 15% = \(\frac{15}{100}=\frac{3}{20}=\frac{9}{60}\) The original price is $60. The cost of the shoes is $51 because $60 – $9 = $51.
Necklace 10% = \(\frac{1}{10}=\frac{2}{20}\) The discount is $2. The cost of the necklace is $18 because $20 – $2 = $18.
Sweater 20% = \(\frac{20}{100}=\frac{1}{5}=\frac{7}{35}\) The original price is $35. The cost of the sweater is $28 because $35 – $7 = $28. The total outfit would cost the following: $33 + $35 + $51 + $18 + $28 = $165.
Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 1 Lesson 27 Problem Set Answer Key
Question 1. Mr. Yoshi has 75 papers. He graded 60 papers, and he had a student teacher grade the rest. What percent of the papers did each person grade? Answer: Mr. Yoshi graded 80% of the papers, and the student teacher graded 20%.
Question 2. Mrs. Bennett has graded 20% of her 150 student’s papers. How many papers does she still need to finish grading? Answer: Mrs. Bennett has graded 30 papers. 150 – 30 = 120. Mrs. Bennett has 120 papers left to grade.
Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 1 Lesson 27 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Jane paid $40 for an item after she received a 20% discount. Jane’s friend says this means that the original price of the item was $48.
a. How do you think Jane’s friend arrived at this amount? Answer: Jane’s friend found that 20% of 40 is 8. Then she added $8 to the sale price: 40 + 8 = 48. Then she determined that the original amount was $48.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- enVision Math
- EngageNY Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

Texas Go Math Grade 6 Lesson 8.2 Answer Key Ratios, Rates, Tables, and Graphs
Refer to our Texas Go Math Grade 6 Answer Key Pdf to score good marks in the exams. Test yourself by practicing the problems from Texas Go Math Grade 6 Lesson 8.2 Answer Key Ratios, Rates, Tables, and Graphs.
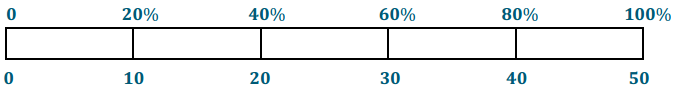
Question 1. Look for a Pattern When the amount of solvent increases by 1 milliliter, the amount of distilled water increases by ____________ milliliters. So 6 milliliters of solvent requires ____________ milliliters of distilled water. Answer: 1 ∙ 50 = 50 6 ∙ 50 = 300 50 milliliters, 300 milliliters.
Go Math Grade 6 Lesson 8.2 Ratio Tables Answer Key Question 2. Communicate Mathematical Ideas How can you use the graph to find the amount of distilled water to use for 4.5 milliliters of solvent? Answer: Locate the point x = 4.5 on the graph and then study its corresponding value of y. This value of y is the amount of distilled water required for 4.5 ml of ammonia and will be equal to 4.5 × 50 = 225 ml.
| time | gallon |
| 2 | 8 |
| 3 | 12 |
| 3.5 | 14 |
| 5 | 20 |
| 6.5 | 26 |
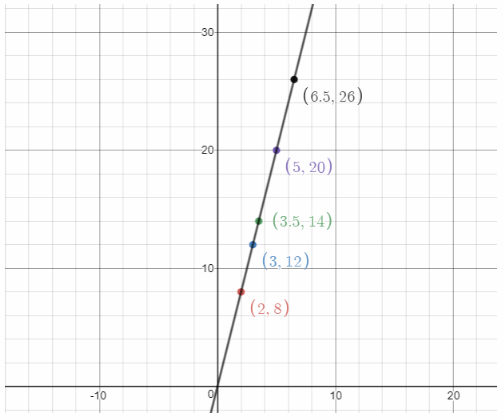
The shower uses 4 gallons per minute.
Texas Go Math Grade 6 Lesson 8.2 Guided Practice Answer Key
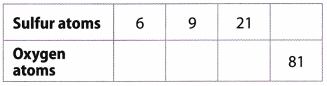
| Sulfur | Oxygen |
| 6 | 18 |
| 9 | 27 |
| 21 | 63 |
| 27 | 81 |
Equivalent ratios are: \(\frac{6}{18}=\frac{9}{27}=\frac{21}{63}=\frac{27}{81}\)
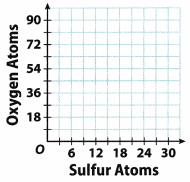
List the ordered pairs from the table: (6, 18), (9, 27), (21, 63), (27, 81) and graph them on a coordinate plane.
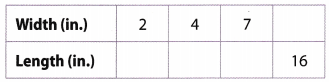
| Width (in) | Length (in) |
| 2 | 4 |
| 4 | 8 |
| 7 | 14 |
| 8 | 16 |
| For every 2 inches of width the length is 4 inches. | This implies that there is \( \frac{4}{2} \) = 2 inches of length per inch of width. |
Equivalent ratio of width to length is 1 : 2
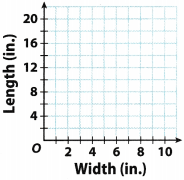
List the ordered pairs from the table: (2, 4), (4, 8), (7, 14), (8, 16) and graph them on a coordinate plane.
Essential Question Check-In
Question 6. How do you represent real-world problems involving ratios and rates with tables and graphs? Answer: Real-world problems involving ratios and rates are represented with tables as ordered pairs and then these ordered pairs are graphed to study the relation between the 2 given variables or quantities.
We can study the relation between the two given variables or quantities.
The table shows information about the number of sweatshirts sold and the money collected at a fund raiser for school athletic programs. For Exercises 7 – 12, use the table.
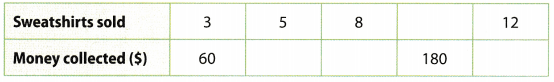
Question 7. Find the rate of money collected per sweatshirt sold. Show your work. Answer: According to the given data, the sale of 3 sweatshirts collected $60, so this means that 1 sweatshirt collected \(\frac{\$ 60}{3}\) = $20 $20 is collected per sweatshirt sold.
Question 8. Use the unit rate to complete the table. Answer: $20 is collected per sweatshirt sold, so the sale of 5 sweatshirts will generate 5 × $20 = $100. $20 is collected per sweatshirt sold, so the sale of 8 sweatshirts will generate 8 × $20 = $160. $20 is collected per sweatshirt sold, so the sale of 12 sweatshirts will generate 12 × $20 = $240. $20 is collected per sweatshirt sold, so $180 was collected by selling \(\frac{\$ 180}{\$ 20}\) = 9 sweatshirts.
Go Math 6th Grade Ratios and Rates Answer Key Question 9. Explain how to graph Information from the table. Answer: List the ordered pairs from the table: (3, 60), (5, 100), (8, 160), (9, 180), (12. 240) and graph them on a coordinate plane.
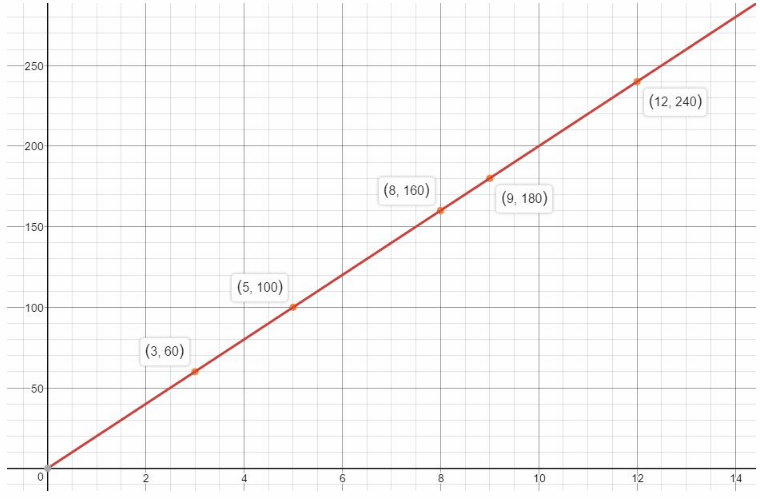
The sale of 24 sweatshirts will collect $480.
Question 12. Analyze Relationships Does the point (5.5, 110) make sense in this context? Explain. Answer: The point (5.5, 110) does not make sense in this context because the independent variable x, the number of shirts sold is discrete and not continuous. This means that selling 5.5 sweatshirts does not make sense, the number of sweatshirts sold MUST be a whole number.
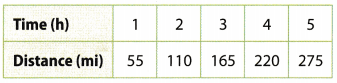
She would have covered a distance of 330 miles.
Use the graph for Exercises 14 – 15.
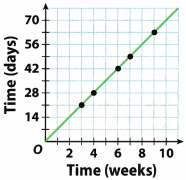
Question 14. Analyze Relationships Does the relationship show a ratio or a rate? Explain. Answer: The ratio because it represents the relationship between the two numbers.
Go Math Grade 6 Lesson 8.2 Ratios and Rates Question 15. Represent Real-World Problems What is a real-life relationship that might be described by the graph? Answer: We can find out how many days are in, for example, one, two, or three weeks. Ordered pair on the graph (4, 28) tells us there are 28 days in 4 weeks.
H.O.T. Focus On Higher Order Thinking
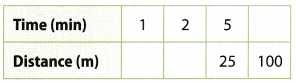
| Time | Distance |
| 1 | 5 |
| 2 | 10 |
| 5 | 25 |
| 20 | 100 |
\(\frac{\text { distance }}{\text { time }}\) = \(\frac{5}{1}\) \(\frac{\text { time }}{\text { distance }}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
a. Are the \(\frac{\text { time }}{\text { distance }}\) rates equivalent? Explain. Answer: They are equivalent because \(\frac{1}{5} \cdot \frac{2}{2}=\frac{2}{10}\) \(\frac{1}{5} \cdot \frac{5}{5}=\frac{5}{25}\) \(\frac{1}{5} \cdot \frac{20}{20}=\frac{20}{100}\)
b. Suppose you graph the points (time, distance) and your friend graphs (distance, time). How will your graphs be different? Answer: The graph of (time, distance) will grow slower than the graph of (distance, time)
Lesson 8.2 Answer Key 6th Grade Go Math Question 17. Communicate Mathematical Ideas To graph a rate or ratio from a table, how do you determine the scales to use on each axis? Answer: The maximum values of the 2 given quantities are considered and based on that, the scales of the axes of the graphs are decided.
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Lesson 6 Problem-Solving Practice Slope and Similar Triangles 1. The slope of a roof line is also called the pitch. Find the pitch of the roof shown. y O x B A 2. A carpenter is building a set of steps for a bunk bed. The plan for the steps is shown below. Using points A and B, find the slope of the line up the steps. Then
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Ready Mathematics Practice and Problem Solving Grade 6 - 9781495704833, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Fluency Table of Contents. Section 1: Compute with Percents. Section 2: Divide Fractions. Section 3: Add Decimals.
2. $7.20, because each baseball card costs 60 cents, and 0.6 times 12 is 7.2. 3. Answers vary. Sample response: A table would be more convenient, because the rows of the table can be listed in any order, and not all values between the ones needed have to be filled in. Problem 7 (from Unit 2, Lesson 9) Jada traveled 135 miles in 3 hours.
Scott Foresman-Addison Wesley enVisionMATH 6 grade 6 workbook & answers help online. Grade: 6, Title: Scott Foresman-Addison Wesley enVisionMATH 6, Publisher: Pearson, ISBN: 032827285x ... Lesson 9: Problem Solving: Make a Table and Look for a Pattern. apps. videocam. create. Chapter 12: Ratios, Rates, and Proportions: Apps Videos Practice Now ...
$1/year; Sample answer: Jing starts at a higher wage, but gets a smaller raise each year. They both must work 6 years for Max to make more than Jing. Practice and Problem Solving: D 1. f slope =1; g slope = 2; f y-intercept =−1; g y-intercept = 4; The slope of f(x) is less steep than the slope of g(x). Both slopes are positive.
Ready Common Core Mathematics helps teachers create a rich classroom environment in which students at all levels become active, real-world problem solvers. Through teacher-led instruction, students develop mathematical reasoning, engage in discourse, and build strong mathematical habits. This math program's instructional framework supports ...
Solve each problem by making a table. Problem Solving • Customary and Metric Conversions 1. Thomas is making soup. His soup pot holds 8 quarts of soup. How many 1-cup servings of soup will Thomas make? 2. Paulina works out with a 2.5-kilogram mass. What is the mass of the 2.5-kilogram mass in grams? 3. Alex lives 500 yards from the park. How ...
6.EE.B.7 — Solve real-world and mathematical problems by writing and solving equations of the form x + p = q and px = q for cases in which p, q and x are all nonnegative rational numbers. 6.RP.A.3.C — Find a percent of a quantity as a rate per 100 (e.g., 30% of a quantity means 30/100 times the quantity); solve problems involving finding ...
30 minutes. Report this resource to TPT. Reported resources will be reviewed by our team. Report this resource to let us know if this resource violates TPT's content guidelines. This page teaches students how to use the Make a Table strategy when solving a problem. I created it in my class for studetns to use during a guided practice lesson.
A manatee eats an average of 70 pounds of wet vegetation each day. 9. Make a table to show the relationship between the number of p pounds of wet vegetation a manatee eats in d days. 10. Write an equation to find p, the number of pounds of wet vegetation a manatee eats in d days.
Lesson Resources Extra Examples Group Activity Cards Personal Tutor Self-Check Quizzes. Hotmath Homework Help ... Concepts, Skills, and Problem Solving, Course 3. Chapter 11, Lesson 1: Problem-Solving Investigation: Make a Table. Extra Examples; Group Activity Cards; Personal Tutor; Self-Check Quizzes; Log In. The resource you requested ...
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Khanmigo is now free for all US educators! Plan lessons, develop exit tickets, and so much more with our AI teaching assistant. ... If this problem persists, tell us. Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to ...
Problem 3 (from Unit 6, Lesson 22) Complete the equation with a number that makes the expression on the right side of the equal sign equivalent to the expression on the left side. Solution 5.5 Problem 4 (from Unit 2, Lesson 4) Match each table with the equation that represents the same proportional relationship. 2. Name three angles that sum to ...
Use the table below to find videos, mobile apps, worksheets and lessons that supplement enVision MATH Common Core 6. enVision MATH Common Core 6 grade 6 workbook & answers help online. Grade: 6, Title: enVision MATH Common Core 6, Publisher: Scott Foresman Addison Wesley, ISBN: 328672645.
Use the table below to find videos, mobile apps, worksheets and lessons that supplement Go Math! 6 Common Core Edition. Go Math! 6 Common Core Edition grade 6 workbook & answers help online. Grade: 6, Title: Go Math! 6 Common Core Edition, Publisher: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, ISBN: 547587783.
Lesson Resources Extra Examples Self-Check Quizzes Personal Tutor. Math Review ... Mathematics. Home > Chapter 6 > Lesson 7. California Algebra Readiness: Concepts, Skills, and Problem Solving. Chapter 6, Lesson 7: Problem-Solving Strategy: Make a Table. Extra Examples; Self-Check Quizzes; Log In.
Lesson 12 Summary. Finding a row containing a "1" is often a good way to work with tables of equivalent ratios. For example, the price for 4 lbs of granola is $ 5. At that rate, what would be the price for 62 lbs of granola? Here are tables showing two different approaches to solving this problem. Both of these approaches are correct.
Solve each inequality. Graph the solution set on a number line. 5.s + 8 < 9 6. -3 ≤ d - 2 Lesson 6 Solve Inequalities by Addition or Subtraction Solving an inequality means fi nding values for the variable that make the inequality true. You can use the Addition and Subtraction Properties of Inequality to help solve an inequality. When you add or
All the solutions provided in McGraw Hill Math Grade 4 Answer Key PDF Chapter 5 Lesson 6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Make a Table will give you a clear idea of the concepts. McGraw-Hill My Math Grade 4 Answer Key Chapter 5 Lesson 6 Problem-Solving Investigation: Make a Table. Learn the Strategy Each roller coaster car holds 18 people.
Answer: How did your solving method differ with each problem? Answer: Solutions will vary. A possible answer may include: When solving for the part, I need to find the missing number in the numerator. When solving for the whole, I solve for the denominator. When I solve for the percent, I need to find the numerator when the denominator is 100 ...
Read the ordered pairs from the graph to make a table. Answer: x from the graph Corresponding value of y from the graph 0 20. 5 25. 10 30. 15 35. 20 40. Grade 6 Independent Practice Answer Key Texas Go Math Lesson 14.4 Question 6. Write an equation that expresses the total hours in terms of the additional hours. Answer:
Question 2. Graph the relationship between sulfur atoms and oxygen atoms. Answer: List the ordered pairs from the table: (6, 18), (9, 27), (21, 63), (27, 81) and graph them on a coordinate plane. Ratio Tables and Graphs Answer Key Lesson 8.2 Question 3. Stickers are made with the same ratio of width to length.