Limitations and Weaknesses of Quantitative Research
- Post author: Edeh Samuel Chukwuemeka ACMC
- Post published: August 16, 2021
- Post category: Scholarly Articles
Limitations and Weaknesses of Quantitative Research: Research entails the collection of materials for academic or other purposes. It is a process of gathering information and data to solve or existing problem or prevent future problems. Research works can be done via two methods. Qualitative research or quantitative research.
Qualitative research involves the carrying out of research by gathering non-numerical data. For example, gathering of video evidence, texts or messages for analysis. On the other hand, quantitative research is the process where by numerical data are collected and analyzed. It is effectively used to find patterns and averages as well as generalising a finding or result to a wider population. Quantitative research is mostly used in natural and social sciences such as biology, psychology, economics, among others.

Quantitative research could be carried out using any four methods of researching which are descriptive research, correlational research, experimental research or survey research. In descriptive, one seeks to know the ‘what’ of a thing rather than the ‘why’ of such thing. It tries to describe the various components of an information.
Correlational research involves the research between two variables to ascertain the relationship between the variables. It understudies the impact of one variable on the other. On the other hand, an experimental research is one that uses scientific methods to establish the relationship between groups of variables. That is, it tries to establish a cause-effect relationship between the various variables under study.

Recommended: How to become a good researcher: 5 qualities you need to have.
Finally, the survey research which is most widely used involves the preparation of set questionnaires, interviews and polls to which answers are provided by a segment of the target population and then, conclusions are drawn from such answers given. Survey research studies the relationship between various variables in a given research.
One of the major benefit of quantitative research method is that it makes one arrive at a well considered conclusion since samples are collected from those who are directly affected by the research. The data collected are majorly converted to a numerical form which aids in statistical analysis. Also, quantitative research is more convenient for projects with scientific and social science inclinations.
Also see: Advantages and Disadvantages of quantitative and qualitative Research

Weaknesses of Quantitative Research
Notwithstanding the benefits of quantitative research, the research method has its own weaknesses and limitations. This is because the method is not applicable and convenient in all cases of research. Thus, using a quantitative research method in a research where qualitative research method should be used will not produce the needed result.

To this end, some of the weaknesses and limitations of quantitative research are highlighted below.
1. It Requires a Large Number of Respondents: In the course of carrying out a quantitative research, recourse has to be made to a large number of respondents. This is because you are sampling a section of a population to get their views, which views will be seen as that of the general population. In doing this, a huge number of respondents have to be consulted so as to get a fair view or percentage of the target population.
For example, if one wishes to carry out a quantitative research in Nigeria as to her acceptance of a policy of the government, one will need to consult wider. This is because Nigeria has a population of over 200 million people and the opinions of a few thousands cannot pass out as that of 200 million people. In the light of this, more respondents will be required to be interviewed so as to enable one get a fair view of the population.
Large number of respondents is thus, one of the weaknesses or limitations of quantitative research as a small sampling of a section of the target population might not be of much help to the research.
2. It is time consuming: Unlike qualitative research which has to do with analysis of already prepared data, quantitative research demands that you source for and collate the data yourself while converting such data collected into a numerical form for proper analysis. This process is time consuming. Again, the task of sending out questionnaires to respondents and waiting for answers to such questionnaires might be time consuming as most respondents will reply late or may not even reply at all.
Great patience is therefore needed in carrying out a quantitative research. It is therefore not always a good method of research in cases of urgencies as the time to get responses might take too long.
Also see: Major characteristics of customary laws
3. It requires huge resources: Quantitative research requires huge investment of time, money and energy. It is time consuming just as it also involve huge financial commitments.
In carrying out quantitative research, one needs to get your questions prepared, sent out and also followed up to ensure that such is answered. Also, some respondents might demand to be paid before giving their inputs to such a research. An example is the trending online surveys in which the target respondents are paid for every survey they carry out for a researcher.
4. Difficulty in Analyzing the Data Collected: Data are collected from respondents and then converted into statistics. This usually poses as a limitation to a researcher who is not an expert in statistics. Analysis of collected data is also demanding and time consuming. A researcher needs to make such information collected into numerical data and correlate them with the larger population. Where this is not properly done, it means that the outcome might be false or misleading.
Also, due to the fact that a researcher might not have control over the environment he is researching in, as any such environment is susceptible to change at any point in time, the outcome of his research might be inconsistent.
Recommended: Problems and criticism of democracy
5. Outcomes of quantitative research is usually limited: In quantitative research, the outcomes are usually limited. This is because the outcome is usually based on what the researcher wants. This limited outcome is due to the structured pattern of the questionnaires. Questionnaires usually have close ended questions which gives a respondent little or no opportunity of explanations. Thus, the answers provided are limited to the questions asked and nothing more.
6. Data outcomes are usually generalised : As noted earlier, quantitative research is usually conducted on a section of a target population and not on the whole population. The outcome of this research is then generalised as the view of the entire population. What this portends is that the views of few respondents in that research is seen as that of the general populace. Such views from them might be biased or insincere, yet they are seen as that of the entire population.
In the light of this, the fallacy of hasty generalisation is prone to be committed in a quantitative research. Generalisation of the views of a section of the population might not be the best as their views may be biased.
Recommended: Advantages and Disadvantages of Capitalism
In conclusion, quantitative research is a veritable means of conducting research especially in the fields of natural sciences and social sciences. This is because it mostly has a one on one interaction between the researcher and the various respondents as it majorly studies behavior. This advantage notwithstanding, the research method has its own limitations and weaknesses. These limitations and weaknesses often times affect the quality of a research which is done using the quantitative method of research.

Edeh Samuel Chukwuemeka, ACMC, is a lawyer and a certified mediator/conciliator in Nigeria. He is also a developer with knowledge in various programming languages. Samuel is determined to leverage his skills in technology, SEO, and legal practice to revolutionize the legal profession worldwide by creating web and mobile applications that simplify legal research. Sam is also passionate about educating and providing valuable information to people.

13 Pros and Cons of Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research utilizes mathematical, statistical, and computational tools to derive results. This structure creates a conclusiveness to the purposes being studied as it quantifies problems to understand how prevalent they are.
It is through this process that the research creates a projectable result which applies to the larger general population.
Instead of providing a subjective overview like qualitative research offers, quantitative research identifies structured cause-and-effect relationships. Once the problem is identified by those involved in the study, the factors associated with the issue become possible to identify as well. Experiments and surveys are the primary tools of this research method to create specific results, even when independent or interdependent factors are present.
These are the quantitative research pros and cons to consider.
List of the Pros of Quantitative Research
1. Data collection occurs rapidly with quantitative research. Because the data points of quantitative research involve surveys, experiments, and real-time gathering, there are few delays in the collection of materials to examine. That means the information under study can be analyzed very quickly when compared to other research methods. The need to separate systems or identify variables is not as prevalent with this option either.
2. The samples of quantitative research are randomized. Quantitative research uses a randomized process to collect information, preventing bias from entering into the data. This randomness creates an additional advantage in the fact that the information supplied through this research can then be statistically applied to the rest of the population group which is under study. Although there is the possibility that some demographics could be left out despite randomization to create errors when the research is applied to all, the results of this research type make it possible to glean relevant data in a fraction of the time that other methods require.
3. It offers reliable and repeatable information. Quantitative research validates itself by offering consistent results when the same data points are examined under randomized conditions. Although you may receive different percentages or slight variances in other results, repetitive information creates the foundation for certainty in future planning processes. Businesses can tailor their messages or programs based on these results to meet specific needs in their community. The statistics become a reliable resource which offer confidence to the decision-making process.
4. You can generalize your findings with quantitative research. The issue with other research types is that there is no generalization effect possible with the data points they gather. Quantitative information may offer an overview instead of specificity when looking at target groups, but that also makes it possible to identify core subjects, needs, or wants. Every finding developed through this method can go beyond the participant group to the overall demographic being looked at with this work. That makes it possible to identify trouble areas before difficulties have a chance to start.
5. The research is anonymous. Researchers often use quantitative data when looking at sensitive topics because of the anonymity involved. People are not required to identify themselves with specificity in the data collected. Even if surveys or interviews are distributed to each individual, their personal information does not make it to the form. This setup reduces the risk of false results because some research participants are ashamed or disturbed about the subject discussions which involve them.
6. You can perform the research remotely. Quantitative research does not require the participants to report to a specific location to collect the data. You can speak with individuals on the phone, conduct surveys online, or use other remote methods that allow for information to move from one party to the other. Although the number of questions you ask or their difficulty can influence how many people choose to participate, the only real cost factor to the participants involves their time. That can make this option a lot cheaper than other methods.
7. Information from a larger sample is used with quantitative research. Qualitative research must use small sample sizes because it requires in-depth data points to be collected by the researchers. This creates a time-consuming resource, reducing the number of people involved. The structure of quantitative research allows for broader studies to take place, which enables better accuracy when attempting to create generalizations about the subject matter involved. There are fewer variables which can skew the results too because you’re dealing with close-ended information instead of open-ended questions.
List of the Cons of Quantitative Research
1. You cannot follow-up on any answers in quantitative research. Quantitative research offers an important limit: you cannot go back to participants after they’ve filled out a survey if there are more questions to ask. There is a limited chance to probe the answers offered in the research, which creates fewer data points to examine when compared to other methods. There is still the advantage of anonymity, but if a survey offers inconclusive or questionable results, there is no way to verify the validity of the data. If enough participants turn in similar answers, it could skew the data in a way that does not apply to the general population.
2. The characteristics of the participants may not apply to the general population. There is always a risk that the research collected using the quantitative method may not apply to the general population. It is easy to draw false correlations because the information seems to come from random sources. Despite the efforts to prevent bias, the characteristics of any randomized sample are not guaranteed to apply to everyone. That means the only certainty offered using this method is that the data applies to those who choose to participate.
3. You cannot determine if answers are true or not. Researchers using the quantitative method must operate on the assumption that all the answers provided to them through surveys, testing, and experimentation are based on a foundation of truth. There are no face-to-face contacts with this method, which means interviewers or researchers are unable to gauge the truthfulness or authenticity of each result.
A 2011 study published by Psychology Today looked at how often people lie in their daily lives. Participants were asked to talk about the number of lies they told in the past 24 hours. 40% of the sample group reported telling a lie, with the median being 1.65 lies told per day. Over 22% of the lies were told by just 1% of the sample. What would happen if the random sampling came from this 1% group?
4. There is a cost factor to consider with quantitative research. All research involves cost. There’s no getting around this fact. When looking at the price of experiments and research within the quantitative method, a single result mist cost more than $100,000. Even conducting a focus group is costly, with just four groups of government or business participants requiring up to $60,000 for the work to be done. Most of the cost involves the target audiences you want to survey, what the objects happen to be, and if you can do the work online or over the phone.
5. You do not gain access to specific feedback details. Let’s say that you wanted to conduct quantitative research on a new toothpaste that you want to take to the market. This method allows you to explore a specific hypothesis (i.e., this toothpaste does a better job of cleaning teeth than this other product). You can use the statistics to create generalizations (i.e., 70% of people say this toothpaste cleans better, which means that is your potential customer base). What you don’t receive are specific feedback details that can help you refine the product. If no one likes the toothpaste because it tastes like how a skunk smells, that 70% who say it cleans better still won’t purchase the product.
6. It creates the potential for an unnatural environment. When carrying out quantitative research, the efforts are sometimes carried out in environments which are unnatural to the group. When this disadvantage occurs, the results will often differ when compared to what would be discovered with real-world examples. That means researchers can still manipulate the results, even with randomized participants, because of the work within an environment which is conducive to the answers which they want to receive through this method.
These quantitative research pros and cons take a look at the value of the information collected vs. its authenticity and cost to collect. It is cheaper than other research methods, but with its limitations, this option is not always the best choice to make when looking for specific data points before making a critical decision.

10 Advantages & Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a powerful tool for those looking to gather empirical data about their topic of study. Using statistical models and math, researchers evaluate their hypothesis.

Quantitative Research
When researchers look at gathering data, there are two types of testing methods they can use: quantitative research, or qualitative research. Quantitative research looks to capture real, measurable data in the form of numbers and figures; whereas qualitative research is concerned with recording opinion data, customer characteristics, and other non-numerical information.
Quantitative research is a powerful tool for those looking to gather empirical data about their topic of study. Using statistical models and math, researchers evaluate their hypothesis. An integral component of quantitative research - and truly, all research - is the careful and considered analysis of the resulting data points.
There are several key advantages and disadvantages to conducting quantitative research that should be considered when deciding which type of testing best fits the occasion.
5 Advantages of Quantitative Research
- Quantitative research is concerned with facts & verifiable information.
Quantitative research is primarily designed to capture numerical data - often for the purpose of studying a fact or phenomenon in their population. This kind of research activity is very helpful for producing data points when looking at a particular group - like a customer demographic. All of this helps us to better identify the key roots of certain customer behaviors.
Businesses who research their customers intimately often outperform their competitors. Knowing the reasons why a customer makes a particular purchasing decision makes it easier for companies to address issues in their audiences. Data analysis of this kind can be used for a wide range of applications, even outside the world of commerce.
- Quantitative research can be done anonymously.
Unlike qualitative research questions - which often ask participants to divulge personal and sometimes sensitive information - quantitative research does not require participants to be named or identified. As long as those conducting the testing are able to independently verify that the participants fit the necessary profile for the test, then more identifying information is unnecessary.
- Quantitative research processes don't need to be directly observed.
Whereas qualitative research demands close attention be paid to the process of data collection, quantitative research data can be collected passively. Surveys, polls, and other forms of asynchronous data collection generate data points over a defined period of time, freeing up researchers to focus on more important activities.
- Quantitative research is faster than other methods.
Quantitative research can capture vast amounts of data far quicker than other research activities. The ability to work in real-time allows analysts to immediately begin incorporating new insights and changes into their work - dramatically reducing the turn-around time of their projects. Less delays and a larger sample size ensures you will have a far easier go of managing your data collection process.
- Quantitative research is verifiable and can be used to duplicate results.
The careful and exact way in which quantitative tests must be designed enables other researchers to duplicate the methodology. In order to verify the integrity of any experimental conclusion, others must be able to replicate the study on their own. Independently verifying data is how the scientific community creates precedent and establishes trust in their findings.
5 Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
- Limited to numbers and figures.
Quantitative research is an incredibly precise tool in the way that it only gathers cold hard figures. This double edged sword leaves the quantitative method unable to deal with questions that require specific feedback, and often lacks a human element. For questions like, “What sorts of emotions does our advertisement evoke in our test audiences?” or “Why do customers prefer our product over the competing brand?”, using the quantitative research method will not derive a meaningful answer.
- Testing models are more difficult to create.
Creating a quantitative research model requires careful attention to be paid to your design. From the hypothesis to the testing methods and the analysis that comes after, there are several moving parts that must be brought into alignment in order for your test to succeed. Even one unintentional error can invalidate your results, and send your team back to the drawing board to start all over again.
- Tests can be intentionally manipulative.
Bad actors looking to push an agenda can sometimes create qualitative tests that are faulty, and designed to support a particular end result. Apolitical facts and figures can be turned political when given a limited context. You can imagine an example in which a politician devises a poll with answers that are designed to give him a favorable outcome - no matter what respondents pick.
- Results are open to subjective interpretation.
Whether due to researchers' bias or simple accident, research data can be manipulated in order to give a subjective result. When numbers are not given their full context, or were gathered in an incorrect or misleading way, the results that follow can not be correctly interpreted. Bias, opinion, and simple mistakes all work to inhibit the experimental process - and must be taken into account when designing your tests.
- More expensive than other forms of testing.
Quantitative research often seeks to gather large quantities of data points. While this is beneficial for the purposes of testing, the research does not come free. The grander the scope of your test and the more thorough you are in it’s methodology, the more likely it is that you will be spending a sizable portion of your marketing expenses on research alone. Polling and surveying, while affordable means of gathering quantitative data, can not always generate the kind of quality results a research project necessitates.
Key Takeaways

Numerical data is a vital component of almost any research project. Quantitative data can provide meaningful insight into qualitative concerns. Focusing on the facts and figures enables researchers to duplicate tests later on, and create their own data sets.
To streamline your quantitative research process:
Have a plan. Tackling your research project with a clear and focused strategy will allow you to better address any errors or hiccups that might otherwise inhibit your testing.
Define your audience. Create a clear picture of your target audience before you design your test. Understanding who you want to test beforehand gives you the ability to choose which methodology is going to be the right fit for them.
Test, test, and test again. Verifying your results through repeated and thorough testing builds confidence in your decision making. It’s not only smart research practice - it’s good business.
About Author

Send Your First Survey Today!
Set up and begin receiving results within minutes. Sign up for free, no contract required.
Helpfull is the easiest way to get feedback from thousands of people in minutes. Our online focus group platform provides a pool of qualified panelists to give you their real detailed opinions helping you make better, more informed decisions.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Table of Contents

Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a type of research that collects and analyzes numerical data to test hypotheses and answer research questions . This research typically involves a large sample size and uses statistical analysis to make inferences about a population based on the data collected. It often involves the use of surveys, experiments, or other structured data collection methods to gather quantitative data.
Quantitative Research Methods

Quantitative Research Methods are as follows:
Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design is used to describe the characteristics of a population or phenomenon being studied. This research method is used to answer the questions of what, where, when, and how. Descriptive research designs use a variety of methods such as observation, case studies, and surveys to collect data. The data is then analyzed using statistical tools to identify patterns and relationships.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to investigate the relationship between two or more variables. Researchers use correlational research to determine whether a relationship exists between variables and to what extent they are related. This research method involves collecting data from a sample and analyzing it using statistical tools such as correlation coefficients.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This research method is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks full control over the independent variable. Researchers use quasi-experimental research designs when it is not feasible or ethical to manipulate the independent variable.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This research method involves manipulating the independent variable and observing the effects on the dependent variable. Researchers use experimental research designs to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships.
Survey Research
Survey research involves collecting data from a sample of individuals using a standardized questionnaire. This research method is used to gather information on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors of individuals. Researchers use survey research to collect data quickly and efficiently from a large sample size. Survey research can be conducted through various methods such as online, phone, mail, or in-person interviews.
Quantitative Research Analysis Methods
Here are some commonly used quantitative research analysis methods:
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis is the most common quantitative research analysis method. It involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis can be used to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze the relationship between one dependent variable and one or more independent variables. Researchers use regression analysis to identify and quantify the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is a statistical technique used to identify underlying factors that explain the correlations among a set of variables. Researchers use factor analysis to reduce a large number of variables to a smaller set of factors that capture the most important information.
Structural Equation Modeling
Structural equation modeling is a statistical technique used to test complex relationships between variables. It involves specifying a model that includes both observed and unobserved variables, and then using statistical methods to test the fit of the model to the data.
Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze data that is collected over time. It involves identifying patterns and trends in the data, as well as any seasonal or cyclical variations.
Multilevel Modeling
Multilevel modeling is a statistical technique used to analyze data that is nested within multiple levels. For example, researchers might use multilevel modeling to analyze data that is collected from individuals who are nested within groups, such as students nested within schools.
Applications of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research has many applications across a wide range of fields. Here are some common examples:
- Market Research : Quantitative research is used extensively in market research to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform marketing strategies, product development, and pricing decisions.
- Health Research: Quantitative research is used in health research to study the effectiveness of medical treatments, identify risk factors for diseases, and track health outcomes over time. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze data from clinical trials, surveys, and other sources to inform medical practice and policy.
- Social Science Research: Quantitative research is used in social science research to study human behavior, attitudes, and social structures. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform social policies, educational programs, and community interventions.
- Education Research: Quantitative research is used in education research to study the effectiveness of teaching methods, assess student learning outcomes, and identify factors that influence student success. Researchers use experimental and quasi-experimental designs, as well as surveys and other quantitative methods, to collect and analyze data.
- Environmental Research: Quantitative research is used in environmental research to study the impact of human activities on the environment, assess the effectiveness of conservation strategies, and identify ways to reduce environmental risks. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze data from field studies, experiments, and other sources.
Characteristics of Quantitative Research
Here are some key characteristics of quantitative research:
- Numerical data : Quantitative research involves collecting numerical data through standardized methods such as surveys, experiments, and observational studies. This data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns and relationships.
- Large sample size: Quantitative research often involves collecting data from a large sample of individuals or groups in order to increase the reliability and generalizability of the findings.
- Objective approach: Quantitative research aims to be objective and impartial in its approach, focusing on the collection and analysis of data rather than personal beliefs, opinions, or experiences.
- Control over variables: Quantitative research often involves manipulating variables to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships. Researchers aim to control for extraneous variables that may impact the results.
- Replicable : Quantitative research aims to be replicable, meaning that other researchers should be able to conduct similar studies and obtain similar results using the same methods.
- Statistical analysis: Quantitative research involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis allows researchers to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories.
- Generalizability: Quantitative research aims to produce findings that can be generalized to larger populations beyond the specific sample studied. This is achieved through the use of random sampling methods and statistical inference.
Examples of Quantitative Research
Here are some examples of quantitative research in different fields:
- Market Research: A company conducts a survey of 1000 consumers to determine their brand awareness and preferences. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify trends and patterns that can inform marketing strategies.
- Health Research : A researcher conducts a randomized controlled trial to test the effectiveness of a new drug for treating a particular medical condition. The study involves collecting data from a large sample of patients and analyzing the results using statistical methods.
- Social Science Research : A sociologist conducts a survey of 500 people to study attitudes toward immigration in a particular country. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify factors that influence these attitudes.
- Education Research: A researcher conducts an experiment to compare the effectiveness of two different teaching methods for improving student learning outcomes. The study involves randomly assigning students to different groups and collecting data on their performance on standardized tests.
- Environmental Research : A team of researchers conduct a study to investigate the impact of climate change on the distribution and abundance of a particular species of plant or animal. The study involves collecting data on environmental factors and population sizes over time and analyzing the results using statistical methods.
- Psychology : A researcher conducts a survey of 500 college students to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify correlations and potential causal relationships.
- Political Science: A team of researchers conducts a study to investigate voter behavior during an election. They use survey methods to collect data on voting patterns, demographics, and political attitudes, and analyze the results using statistical methods.
How to Conduct Quantitative Research
Here is a general overview of how to conduct quantitative research:
- Develop a research question: The first step in conducting quantitative research is to develop a clear and specific research question. This question should be based on a gap in existing knowledge, and should be answerable using quantitative methods.
- Develop a research design: Once you have a research question, you will need to develop a research design. This involves deciding on the appropriate methods to collect data, such as surveys, experiments, or observational studies. You will also need to determine the appropriate sample size, data collection instruments, and data analysis techniques.
- Collect data: The next step is to collect data. This may involve administering surveys or questionnaires, conducting experiments, or gathering data from existing sources. It is important to use standardized methods to ensure that the data is reliable and valid.
- Analyze data : Once the data has been collected, it is time to analyze it. This involves using statistical methods to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables. Common statistical techniques include correlation analysis, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing.
- Interpret results: After analyzing the data, you will need to interpret the results. This involves identifying the key findings, determining their significance, and drawing conclusions based on the data.
- Communicate findings: Finally, you will need to communicate your findings. This may involve writing a research report, presenting at a conference, or publishing in a peer-reviewed journal. It is important to clearly communicate the research question, methods, results, and conclusions to ensure that others can understand and replicate your research.
When to use Quantitative Research
Here are some situations when quantitative research can be appropriate:
- To test a hypothesis: Quantitative research is often used to test a hypothesis or a theory. It involves collecting numerical data and using statistical analysis to determine if the data supports or refutes the hypothesis.
- To generalize findings: If you want to generalize the findings of your study to a larger population, quantitative research can be useful. This is because it allows you to collect numerical data from a representative sample of the population and use statistical analysis to make inferences about the population as a whole.
- To measure relationships between variables: If you want to measure the relationship between two or more variables, such as the relationship between age and income, or between education level and job satisfaction, quantitative research can be useful. It allows you to collect numerical data on both variables and use statistical analysis to determine the strength and direction of the relationship.
- To identify patterns or trends: Quantitative research can be useful for identifying patterns or trends in data. For example, you can use quantitative research to identify trends in consumer behavior or to identify patterns in stock market data.
- To quantify attitudes or opinions : If you want to measure attitudes or opinions on a particular topic, quantitative research can be useful. It allows you to collect numerical data using surveys or questionnaires and analyze the data using statistical methods to determine the prevalence of certain attitudes or opinions.
Purpose of Quantitative Research
The purpose of quantitative research is to systematically investigate and measure the relationships between variables or phenomena using numerical data and statistical analysis. The main objectives of quantitative research include:
- Description : To provide a detailed and accurate description of a particular phenomenon or population.
- Explanation : To explain the reasons for the occurrence of a particular phenomenon, such as identifying the factors that influence a behavior or attitude.
- Prediction : To predict future trends or behaviors based on past patterns and relationships between variables.
- Control : To identify the best strategies for controlling or influencing a particular outcome or behavior.
Quantitative research is used in many different fields, including social sciences, business, engineering, and health sciences. It can be used to investigate a wide range of phenomena, from human behavior and attitudes to physical and biological processes. The purpose of quantitative research is to provide reliable and valid data that can be used to inform decision-making and improve understanding of the world around us.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
There are several advantages of quantitative research, including:
- Objectivity : Quantitative research is based on objective data and statistical analysis, which reduces the potential for bias or subjectivity in the research process.
- Reproducibility : Because quantitative research involves standardized methods and measurements, it is more likely to be reproducible and reliable.
- Generalizability : Quantitative research allows for generalizations to be made about a population based on a representative sample, which can inform decision-making and policy development.
- Precision : Quantitative research allows for precise measurement and analysis of data, which can provide a more accurate understanding of phenomena and relationships between variables.
- Efficiency : Quantitative research can be conducted relatively quickly and efficiently, especially when compared to qualitative research, which may involve lengthy data collection and analysis.
- Large sample sizes : Quantitative research can accommodate large sample sizes, which can increase the representativeness and generalizability of the results.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
There are several limitations of quantitative research, including:
- Limited understanding of context: Quantitative research typically focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, which may not provide a comprehensive understanding of the context or underlying factors that influence a phenomenon.
- Simplification of complex phenomena: Quantitative research often involves simplifying complex phenomena into measurable variables, which may not capture the full complexity of the phenomenon being studied.
- Potential for researcher bias: Although quantitative research aims to be objective, there is still the potential for researcher bias in areas such as sampling, data collection, and data analysis.
- Limited ability to explore new ideas: Quantitative research is often based on pre-determined research questions and hypotheses, which may limit the ability to explore new ideas or unexpected findings.
- Limited ability to capture subjective experiences : Quantitative research is typically focused on objective data and may not capture the subjective experiences of individuals or groups being studied.
- Ethical concerns : Quantitative research may raise ethical concerns, such as invasion of privacy or the potential for harm to participants.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Quantitative Methods
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Quantitative methods emphasize objective measurements and the statistical, mathematical, or numerical analysis of data collected through polls, questionnaires, and surveys, or by manipulating pre-existing statistical data using computational techniques . Quantitative research focuses on gathering numerical data and generalizing it across groups of people or to explain a particular phenomenon.
Babbie, Earl R. The Practice of Social Research . 12th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage, 2010; Muijs, Daniel. Doing Quantitative Research in Education with SPSS . 2nd edition. London: SAGE Publications, 2010.
Need Help Locating Statistics?
Resources for locating data and statistics can be found here:
Statistics & Data Research Guide
Characteristics of Quantitative Research
Your goal in conducting quantitative research study is to determine the relationship between one thing [an independent variable] and another [a dependent or outcome variable] within a population. Quantitative research designs are either descriptive [subjects usually measured once] or experimental [subjects measured before and after a treatment]. A descriptive study establishes only associations between variables; an experimental study establishes causality.
Quantitative research deals in numbers, logic, and an objective stance. Quantitative research focuses on numeric and unchanging data and detailed, convergent reasoning rather than divergent reasoning [i.e., the generation of a variety of ideas about a research problem in a spontaneous, free-flowing manner].
Its main characteristics are :
- The data is usually gathered using structured research instruments.
- The results are based on larger sample sizes that are representative of the population.
- The research study can usually be replicated or repeated, given its high reliability.
- Researcher has a clearly defined research question to which objective answers are sought.
- All aspects of the study are carefully designed before data is collected.
- Data are in the form of numbers and statistics, often arranged in tables, charts, figures, or other non-textual forms.
- Project can be used to generalize concepts more widely, predict future results, or investigate causal relationships.
- Researcher uses tools, such as questionnaires or computer software, to collect numerical data.
The overarching aim of a quantitative research study is to classify features, count them, and construct statistical models in an attempt to explain what is observed.
Things to keep in mind when reporting the results of a study using quantitative methods :
- Explain the data collected and their statistical treatment as well as all relevant results in relation to the research problem you are investigating. Interpretation of results is not appropriate in this section.
- Report unanticipated events that occurred during your data collection. Explain how the actual analysis differs from the planned analysis. Explain your handling of missing data and why any missing data does not undermine the validity of your analysis.
- Explain the techniques you used to "clean" your data set.
- Choose a minimally sufficient statistical procedure ; provide a rationale for its use and a reference for it. Specify any computer programs used.
- Describe the assumptions for each procedure and the steps you took to ensure that they were not violated.
- When using inferential statistics , provide the descriptive statistics, confidence intervals, and sample sizes for each variable as well as the value of the test statistic, its direction, the degrees of freedom, and the significance level [report the actual p value].
- Avoid inferring causality , particularly in nonrandomized designs or without further experimentation.
- Use tables to provide exact values ; use figures to convey global effects. Keep figures small in size; include graphic representations of confidence intervals whenever possible.
- Always tell the reader what to look for in tables and figures .
NOTE: When using pre-existing statistical data gathered and made available by anyone other than yourself [e.g., government agency], you still must report on the methods that were used to gather the data and describe any missing data that exists and, if there is any, provide a clear explanation why the missing data does not undermine the validity of your final analysis.
Babbie, Earl R. The Practice of Social Research . 12th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage, 2010; Brians, Craig Leonard et al. Empirical Political Analysis: Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods . 8th ed. Boston, MA: Longman, 2011; McNabb, David E. Research Methods in Public Administration and Nonprofit Management: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches . 2nd ed. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, 2008; Quantitative Research Methods. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Singh, Kultar. Quantitative Social Research Methods . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2007.
Basic Research Design for Quantitative Studies
Before designing a quantitative research study, you must decide whether it will be descriptive or experimental because this will dictate how you gather, analyze, and interpret the results. A descriptive study is governed by the following rules: subjects are generally measured once; the intention is to only establish associations between variables; and, the study may include a sample population of hundreds or thousands of subjects to ensure that a valid estimate of a generalized relationship between variables has been obtained. An experimental design includes subjects measured before and after a particular treatment, the sample population may be very small and purposefully chosen, and it is intended to establish causality between variables. Introduction The introduction to a quantitative study is usually written in the present tense and from the third person point of view. It covers the following information:
- Identifies the research problem -- as with any academic study, you must state clearly and concisely the research problem being investigated.
- Reviews the literature -- review scholarship on the topic, synthesizing key themes and, if necessary, noting studies that have used similar methods of inquiry and analysis. Note where key gaps exist and how your study helps to fill these gaps or clarifies existing knowledge.
- Describes the theoretical framework -- provide an outline of the theory or hypothesis underpinning your study. If necessary, define unfamiliar or complex terms, concepts, or ideas and provide the appropriate background information to place the research problem in proper context [e.g., historical, cultural, economic, etc.].
Methodology The methods section of a quantitative study should describe how each objective of your study will be achieved. Be sure to provide enough detail to enable the reader can make an informed assessment of the methods being used to obtain results associated with the research problem. The methods section should be presented in the past tense.
- Study population and sampling -- where did the data come from; how robust is it; note where gaps exist or what was excluded. Note the procedures used for their selection;
- Data collection – describe the tools and methods used to collect information and identify the variables being measured; describe the methods used to obtain the data; and, note if the data was pre-existing [i.e., government data] or you gathered it yourself. If you gathered it yourself, describe what type of instrument you used and why. Note that no data set is perfect--describe any limitations in methods of gathering data.
- Data analysis -- describe the procedures for processing and analyzing the data. If appropriate, describe the specific instruments of analysis used to study each research objective, including mathematical techniques and the type of computer software used to manipulate the data.
Results The finding of your study should be written objectively and in a succinct and precise format. In quantitative studies, it is common to use graphs, tables, charts, and other non-textual elements to help the reader understand the data. Make sure that non-textual elements do not stand in isolation from the text but are being used to supplement the overall description of the results and to help clarify key points being made. Further information about how to effectively present data using charts and graphs can be found here .
- Statistical analysis -- how did you analyze the data? What were the key findings from the data? The findings should be present in a logical, sequential order. Describe but do not interpret these trends or negative results; save that for the discussion section. The results should be presented in the past tense.
Discussion Discussions should be analytic, logical, and comprehensive. The discussion should meld together your findings in relation to those identified in the literature review, and placed within the context of the theoretical framework underpinning the study. The discussion should be presented in the present tense.
- Interpretation of results -- reiterate the research problem being investigated and compare and contrast the findings with the research questions underlying the study. Did they affirm predicted outcomes or did the data refute it?
- Description of trends, comparison of groups, or relationships among variables -- describe any trends that emerged from your analysis and explain all unanticipated and statistical insignificant findings.
- Discussion of implications – what is the meaning of your results? Highlight key findings based on the overall results and note findings that you believe are important. How have the results helped fill gaps in understanding the research problem?
- Limitations -- describe any limitations or unavoidable bias in your study and, if necessary, note why these limitations did not inhibit effective interpretation of the results.
Conclusion End your study by to summarizing the topic and provide a final comment and assessment of the study.
- Summary of findings – synthesize the answers to your research questions. Do not report any statistical data here; just provide a narrative summary of the key findings and describe what was learned that you did not know before conducting the study.
- Recommendations – if appropriate to the aim of the assignment, tie key findings with policy recommendations or actions to be taken in practice.
- Future research – note the need for future research linked to your study’s limitations or to any remaining gaps in the literature that were not addressed in your study.
Black, Thomas R. Doing Quantitative Research in the Social Sciences: An Integrated Approach to Research Design, Measurement and Statistics . London: Sage, 1999; Gay,L. R. and Peter Airasain. Educational Research: Competencies for Analysis and Applications . 7th edition. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Merril Prentice Hall, 2003; Hector, Anestine. An Overview of Quantitative Research in Composition and TESOL . Department of English, Indiana University of Pennsylvania; Hopkins, Will G. “Quantitative Research Design.” Sportscience 4, 1 (2000); "A Strategy for Writing Up Research Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper." Department of Biology. Bates College; Nenty, H. Johnson. "Writing a Quantitative Research Thesis." International Journal of Educational Science 1 (2009): 19-32; Ouyang, Ronghua (John). Basic Inquiry of Quantitative Research . Kennesaw State University.
Strengths of Using Quantitative Methods
Quantitative researchers try to recognize and isolate specific variables contained within the study framework, seek correlation, relationships and causality, and attempt to control the environment in which the data is collected to avoid the risk of variables, other than the one being studied, accounting for the relationships identified.
Among the specific strengths of using quantitative methods to study social science research problems:
- Allows for a broader study, involving a greater number of subjects, and enhancing the generalization of the results;
- Allows for greater objectivity and accuracy of results. Generally, quantitative methods are designed to provide summaries of data that support generalizations about the phenomenon under study. In order to accomplish this, quantitative research usually involves few variables and many cases, and employs prescribed procedures to ensure validity and reliability;
- Applying well established standards means that the research can be replicated, and then analyzed and compared with similar studies;
- You can summarize vast sources of information and make comparisons across categories and over time; and,
- Personal bias can be avoided by keeping a 'distance' from participating subjects and using accepted computational techniques .
Babbie, Earl R. The Practice of Social Research . 12th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage, 2010; Brians, Craig Leonard et al. Empirical Political Analysis: Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods . 8th ed. Boston, MA: Longman, 2011; McNabb, David E. Research Methods in Public Administration and Nonprofit Management: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches . 2nd ed. Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, 2008; Singh, Kultar. Quantitative Social Research Methods . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2007.
Limitations of Using Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods presume to have an objective approach to studying research problems, where data is controlled and measured, to address the accumulation of facts, and to determine the causes of behavior. As a consequence, the results of quantitative research may be statistically significant but are often humanly insignificant.
Some specific limitations associated with using quantitative methods to study research problems in the social sciences include:
- Quantitative data is more efficient and able to test hypotheses, but may miss contextual detail;
- Uses a static and rigid approach and so employs an inflexible process of discovery;
- The development of standard questions by researchers can lead to "structural bias" and false representation, where the data actually reflects the view of the researcher instead of the participating subject;
- Results provide less detail on behavior, attitudes, and motivation;
- Researcher may collect a much narrower and sometimes superficial dataset;
- Results are limited as they provide numerical descriptions rather than detailed narrative and generally provide less elaborate accounts of human perception;
- The research is often carried out in an unnatural, artificial environment so that a level of control can be applied to the exercise. This level of control might not normally be in place in the real world thus yielding "laboratory results" as opposed to "real world results"; and,
- Preset answers will not necessarily reflect how people really feel about a subject and, in some cases, might just be the closest match to the preconceived hypothesis.
Research Tip
Finding Examples of How to Apply Different Types of Research Methods
SAGE publications is a major publisher of studies about how to design and conduct research in the social and behavioral sciences. Their SAGE Research Methods Online and Cases database includes contents from books, articles, encyclopedias, handbooks, and videos covering social science research design and methods including the complete Little Green Book Series of Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences and the Little Blue Book Series of Qualitative Research techniques. The database also includes case studies outlining the research methods used in real research projects. This is an excellent source for finding definitions of key terms and descriptions of research design and practice, techniques of data gathering, analysis, and reporting, and information about theories of research [e.g., grounded theory]. The database covers both qualitative and quantitative research methods as well as mixed methods approaches to conducting research.
SAGE Research Methods Online and Cases
- << Previous: Qualitative Methods
- Next: Insiderness >>
- Last Updated: May 25, 2024 4:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Quantitative Research
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 13 January 2019
- Cite this reference work entry

- Leigh A. Wilson 2 , 3
4426 Accesses
4 Citations
Quantitative research methods are concerned with the planning, design, and implementation of strategies to collect and analyze data. Descartes, the seventeenth-century philosopher, suggested that how the results are achieved is often more important than the results themselves, as the journey taken along the research path is a journey of discovery. High-quality quantitative research is characterized by the attention given to the methods and the reliability of the tools used to collect the data. The ability to critique research in a systematic way is an essential component of a health professional’s role in order to deliver high quality, evidence-based healthcare. This chapter is intended to provide a simple overview of the way new researchers and health practitioners can understand and employ quantitative methods. The chapter offers practical, realistic guidance in a learner-friendly way and uses a logical sequence to understand the process of hypothesis development, study design, data collection and handling, and finally data analysis and interpretation.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Writing Quantitative Research Studies

Qualitative Research Methods
Babbie ER. The practice of social research. 14th ed. Belmont: Wadsworth Cengage; 2016.
Google Scholar
Descartes. Cited in Halverston, W. (1976). In: A concise introduction to philosophy, 3rd ed. New York: Random House; 1637.
Doll R, Hill AB. The mortality of doctors in relation to their smoking habits. BMJ. 1954;328(7455):1529–33. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.328.7455.1529 .
Article Google Scholar
Liamputtong P. Research methods in health: foundations for evidence-based practice. 3rd ed. Melbourne: Oxford University Press; 2017.
McNabb DE. Research methods in public administration and nonprofit management: quantitative and qualitative approaches. 2nd ed. New York: Armonk; 2007.
Merriam-Webster. Dictionary. http://www.merriam-webster.com . Accessed 20th December 2017.
Olesen Larsen P, von Ins M. The rate of growth in scientific publication and the decline in coverage provided by Science Citation Index. Scientometrics. 2010;84(3):575–603.
Pannucci CJ, Wilkins EG. Identifying and avoiding bias in research. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(2):619–25. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181de24bc .
Petrie A, Sabin C. Medical statistics at a glance. 2nd ed. London: Blackwell Publishing; 2005.
Portney LG, Watkins MP. Foundations of clinical research: applications to practice. 3rd ed. New Jersey: Pearson Publishing; 2009.
Sheehan J. Aspects of research methodology. Nurse Educ Today. 1986;6:193–203.
Wilson LA, Black DA. Health, science research and research methods. Sydney: McGraw Hill; 2013.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Science and Health, Western Sydney University, Penrith, NSW, Australia
Leigh A. Wilson
Faculty of Health Science, Discipline of Behavioural and Social Sciences in Health, University of Sydney, Lidcombe, NSW, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Leigh A. Wilson .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Pranee Liamputtong
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Wilson, L.A. (2019). Quantitative Research. In: Liamputtong, P. (eds) Handbook of Research Methods in Health Social Sciences. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_54
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_54
Published : 13 January 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-10-5250-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-10-5251-4
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

My Account
Donate
Research Methods
Quantitative research methods.
- Qualitative Research Methods
- Mixed Methods
- Books on Research Methods
Need Help?
- Ask us a question
- Schedule a research appointment
Quantitative research methods involve the collection of numerical data and the use of statistical analysis to draw conclusions. This method is suitable for research questions that aim to measure the relationship between variables, test hypotheses, and make predictions. Here are some tips for choosing quantitative research methods:
Identify the research question: Determine whether your research question is best answered by collecting numerical data. Quantitative research is ideal for research questions that can be quantified, such as questions that ask how much, how many, or how often.
Choose the appropriate data collection methods: Select data collection methods that allow you to collect numerical data, such as surveys, experiments, or observational studies. Surveys involve asking participants to respond to a set of standardized questions, while experiments involve manipulating variables to determine their effect on an outcome. Observational studies involve observing and recording behaviors or events in a natural setting.
When choosing a data collection method, it's important to consider the feasibility, reliability, and validity of the method. Feasibility refers to whether the method is practical and achievable within the available resources, while reliability refers to the consistency of the results over time and across different observers or settings. Validity refers to whether the method accurately measures what it's intended to measure.
The sample size: Decide on the sample size that is needed to produce statistically significant results. The sample size is the number of participants in the study. The larger the sample size, the more reliable the results are likely to be. However, a larger sample size also requires more resources and time. Therefore, it's important to determine the appropriate sample size based on the research question and available resources.
Statistical test: Choose the appropriate statistical analysis techniques based on the type of data you have collected and the research question. Common statistical analysis techniques include descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, regression analysis, and t-tests. Descriptive statistics summarize the data using measures such as mean, standard deviation, and frequency. Correlation analysis examines the relationship between two or more variables. Regression analysis examines the relationship between one dependent variable and one or more independent variables. T-tests compare the means of two groups.
When selecting a statistical analysis technique, it's important to consider the assumptions of the technique and whether they are appropriate for the data being analyzed. It's also important to consider the level of statistical significance required to draw meaningful conclusions.
Strength and Limitations
Strength and limitations of quantitative research methods:.
- The use of statistical analysis allows for the identification of patterns and relationships between variables.
- Provides a structured and standardized approach to data collection, allowing for replication of studies and comparisons across studies.
- It can produce reliable and valid results which are generalizable to larger populations.
- Allows for hypothesis testing, making it suitable for research questions that require a cause-and-effect relationship.
- It can produce numerical data, making it easy to summarize and communicate results.
Limitations:
- It may oversimplify complex phenomena by reducing them to numerical data.
- It may not capture the context and subjective experiences of individuals.
- It may not allow for the exploration of new ideas or unexpected findings.
- It may be influenced by researcher bias or the use of inappropriate statistical techniques.
- It may not account for variables that are difficult to measure or control.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Qualitative Research Methods >>
- Seton Hall University
- 400 South Orange Avenue
- South Orange, NJ 07079
- (973) 761-9000
- Student Services
- Parents and Families
- Career Center
- Web Accessibility
- Visiting Campus
- Public Safety
- Disability Support Services
- Campus Security Report
- Report a Problem
- Login to LibApps

Limitations and weakness of quantitative research methods
According to Saunders et al. (2009), research methodology serves as the backbone of a research study. Quantitative research’s main purpose is the quantification of the data. It allows generalisations of the results by measuring the views and responses of the sample population. Every research methodology consists of two broad phases namely planning and execution (Younus 2014). Therefore, it is evident that within these two phases, there are likely to have limitations which are beyond our control (Simon 2011).
Improper representation of the target population
As mentioned in the article , improper representation of the target population might hinder the researcher from achieving its desired aims and objectives. Despite applying an appropriate sampling plan representation of the subjects is dependent on the probability distribution of observed data. This may lead to a miscalculation of probability distribution and lead to falsity in the proposition.
A study purports to check the proportion of females aged between 20-30 years who are applying make-up ranges of international brands. The target population, in this case, is the women belonging to the said age group, with both professional and non-professional backgrounds, residing in Delhi. The sampled population based on the probability distribution has to be calculated against the total females residing in the city (e.g. 400 sampled out of 7,800,615 female populations). However, there is a scope of getting partial information about the range of makeup products from the sampled, owing to its meagre form against the total population. Hence, the results of the study cannot be generalised in context to a larger population, but rather be suggested.
Lack of resources for data collection
Quantitative research methodology usually requires a large sample size. However, due to the lack of resources, this large-scale research becomes impossible. In many developing countries, interested parties (e.g., government or non-government organisations, public service providers, educational institutions, etc.) may lack knowledge and especially the resources needed to conduct thorough quantitative research (Science 2001).
Inability to control the environment
Sometimes researchers face problems to control the environment where the respondents provide answers to the questions in the survey (Baxter 2008). Responses often depend on a particular time which again is dependent on the conditions occurring during that particular time frame.
For example, if data for a study is collected on residents’ perception of development works conducted by the municipality, the results presented for a specific year (say, 2009), will be held redundant or of limited value in 2015. The reasons are, that either the officials have changed or the development scenario has changed (from too effective to minimal effective or vice versa).
Limited outcomes in a quantitative research
The quantitative research method involves a structured questionnaire with close-ended questions. It leads to limited outcomes outlined in the research proposal. So the results cannot always represent the actual occurrence, in a generalised form. Also, the respondents have limited options for responses, based on the selection made by the researcher.
“Does your manager motivates you to take up challenges”
The answer can be Yes / No / Can’t say or Strongly Agree to Strongly disagree. But to know what strategies are applied by the manager to motivate the employee or on what parameters the employee does not feel motivated (if responded no), the researcher has to ask broader questions which somewhat has limited scope in close-ended questionnaires
Expensive and time-consuming
Quantitative research is difficult, expensive and requires a lot of time to perform the analysis. This type of research is planned carefully in order to ensure complete randomization and correct designation of control groups (Morgan 1980). A large proportion of respondents is appropriate for the representation of the target population. So, to achieve in-depth responses on an issue, data collection in quantitative research methodology is often too expensive than the qualitative approach.
To understand the influence of advertising on the propensity of purchase decision of baby foods parents of 5-year old and below in Bangalore, the researcher needs to collect data from 200 respondents. This is time-consuming and expensive, given the approach needed for each of these parents to explain the study’s purpose.
Difficulty in data analysis
The quantitative study requires extensive statistical analysis , which can be difficult to perform for researchers from non-statistical backgrounds. Statistical analysis is based on scientific discipline and hence is difficult for non-mathematicians to perform.
Quantitative research is a lot more complex for social sciences, education, anthropology and psychology. The effective response should depend on the research problem rather than just a simple yes or no response.
To understand the level of motivation perceived by Grade 5 students from the teaching approach taken by their class teachers, mere yes and no might lead to ambiguity in data collection and hence improper results. Instead, a detailed interview or focus group technique might develop in-depth views and perspectives of both the teachers and children.
Requirement of extra resources to analyse the results
The requirements for the successful statistical confirmation of the result are very tough in quantitative research. A hypothesis is proven with few experiments due to which there is ambiguity in the results. Results are retested and refined several times for an unambiguous conclusion (Ong 2003). So it requires extra time, investment and resources to refine the results.
- Barbour, R.S., 2000. The role of qualitative research in broadening the “evidence base” for clinical practice. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice , 6(2), pp.155–163.
- Baxter, P., 2008. Qualitative Case Study Methodology: Study Design and Implementation for Novice Researchers. The Qualitative Report , 13(4), pp.544–559.
- Bowen, G.A., 2006. Document Analysis as a Qualitative Research Method. Qualitative Research Journal , 9(2), pp.27 – 40.
- Elo, S. & Kyngäs, H., 2008. The qualitative content analysis process. Journal of Advanced Nursing , 62(1), pp.107–115.
- Maxwell, J.A., 2005. Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach , SAGE Publications. Available at: https://books.google.co.in/books/about/Qualitative_Research_Design.html?id=XqaJP-iehskC&pgis=1 [Accessed May 20, 2015].
- Morgan, G., 1980. The Case for Qualitative Research. Academy of Management Journal , 5(4), pp.491–500.
- Ong, S.-E., 2003. Mass spectrometric-based approaches in quantitative proteomics. Methods , 29(2), pp.124–130.
- Saunders, M., Lewis, P. & Thornhill, A., 2009. Research Methods for Business Students 5th ed., Essex, England: Pearson Education Limited.
- Science, J. of D., 2001. Invited Review: Integrating Quantitative Findings from Multiple Studies Using Mixed Model Methodology. Journal of Dairy Science , 84(4), pp.741–755.
- Simon, M.K., 2011. Dissertation and scholarly research: Recipes for success , Seattle, W.A.: Dissertation Success LLC.
- Younus, M.A.F., 2014. Research Methodology. In Vulnerability and Adaptation to Climate Change in Bangladesh: Processes, Assessment and Effects (Springer Theses) . Springer, pp. 35–76. Available at: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-94-007-5494-2_2 [Accessed August 1, 2016].
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
19 thoughts on “Limitations and weakness of quantitative research methods”
Proofreading.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research Methods & Data Analysis
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative?
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze.
Quantitative research collects numerical data and analyzes it using statistical methods. The aim is to produce objective, empirical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms. Quantitative research is often used to test hypotheses, identify patterns, and make predictions.
Qualitative research , on the other hand, collects non-numerical data such as words, images, and sounds. The focus is on exploring subjective experiences, opinions, and attitudes, often through observation and interviews.
Qualitative research aims to produce rich and detailed descriptions of the phenomenon being studied, and to uncover new insights and meanings.
Quantitative data is information about quantities, and therefore numbers, and qualitative data is descriptive, and regards phenomenon which can be observed but not measured, such as language.
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical data, such as language. Qualitative research can be used to understand how an individual subjectively perceives and gives meaning to their social reality.
Qualitative data is non-numerical data, such as text, video, photographs, or audio recordings. This type of data can be collected using diary accounts or in-depth interviews and analyzed using grounded theory or thematic analysis.
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretive, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 2)
Interest in qualitative data came about as the result of the dissatisfaction of some psychologists (e.g., Carl Rogers) with the scientific study of psychologists such as behaviorists (e.g., Skinner ).
Since psychologists study people, the traditional approach to science is not seen as an appropriate way of carrying out research since it fails to capture the totality of human experience and the essence of being human. Exploring participants’ experiences is known as a phenomenological approach (re: Humanism ).
Qualitative research is primarily concerned with meaning, subjectivity, and lived experience. The goal is to understand the quality and texture of people’s experiences, how they make sense of them, and the implications for their lives.
Qualitative research aims to understand the social reality of individuals, groups, and cultures as nearly as possible as participants feel or live it. Thus, people and groups are studied in their natural setting.
Some examples of qualitative research questions are provided, such as what an experience feels like, how people talk about something, how they make sense of an experience, and how events unfold for people.
Research following a qualitative approach is exploratory and seeks to explain ‘how’ and ‘why’ a particular phenomenon, or behavior, operates as it does in a particular context. It can be used to generate hypotheses and theories from the data.
Qualitative Methods
There are different types of qualitative research methods, including diary accounts, in-depth interviews , documents, focus groups , case study research , and ethnography.
The results of qualitative methods provide a deep understanding of how people perceive their social realities and in consequence, how they act within the social world.
The researcher has several methods for collecting empirical materials, ranging from the interview to direct observation, to the analysis of artifacts, documents, and cultural records, to the use of visual materials or personal experience. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 14)
Here are some examples of qualitative data:
Interview transcripts : Verbatim records of what participants said during an interview or focus group. They allow researchers to identify common themes and patterns, and draw conclusions based on the data. Interview transcripts can also be useful in providing direct quotes and examples to support research findings.
Observations : The researcher typically takes detailed notes on what they observe, including any contextual information, nonverbal cues, or other relevant details. The resulting observational data can be analyzed to gain insights into social phenomena, such as human behavior, social interactions, and cultural practices.
Unstructured interviews : generate qualitative data through the use of open questions. This allows the respondent to talk in some depth, choosing their own words. This helps the researcher develop a real sense of a person’s understanding of a situation.
Diaries or journals : Written accounts of personal experiences or reflections.
Notice that qualitative data could be much more than just words or text. Photographs, videos, sound recordings, and so on, can be considered qualitative data. Visual data can be used to understand behaviors, environments, and social interactions.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative research is endlessly creative and interpretive. The researcher does not just leave the field with mountains of empirical data and then easily write up his or her findings.
Qualitative interpretations are constructed, and various techniques can be used to make sense of the data, such as content analysis, grounded theory (Glaser & Strauss, 1967), thematic analysis (Braun & Clarke, 2006), or discourse analysis.
For example, thematic analysis is a qualitative approach that involves identifying implicit or explicit ideas within the data. Themes will often emerge once the data has been coded .
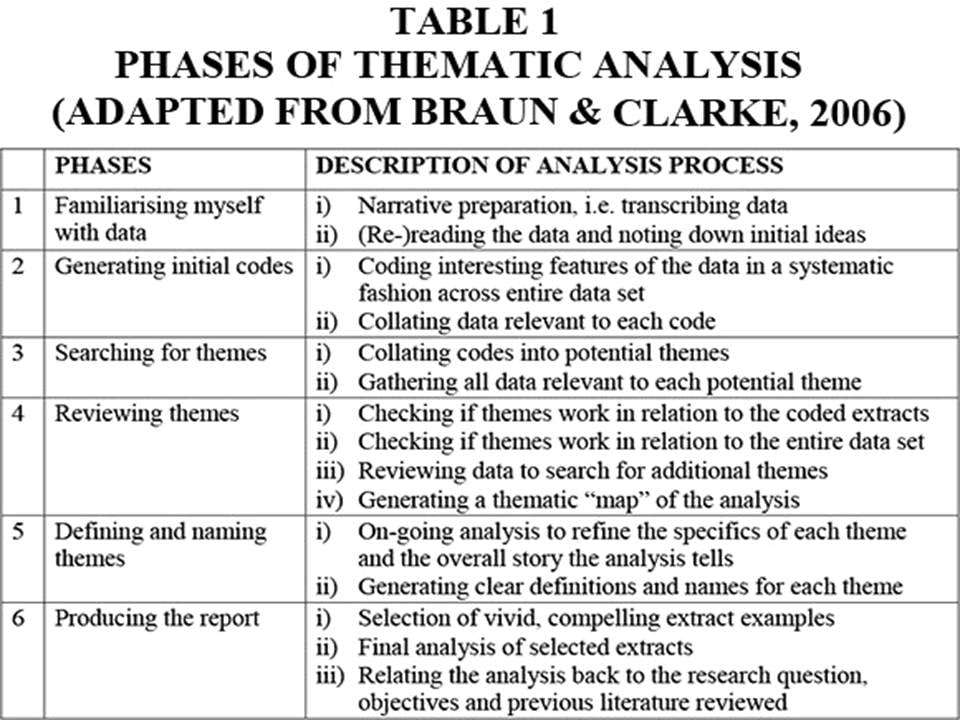
Key Features
- Events can be understood adequately only if they are seen in context. Therefore, a qualitative researcher immerses her/himself in the field, in natural surroundings. The contexts of inquiry are not contrived; they are natural. Nothing is predefined or taken for granted.
- Qualitative researchers want those who are studied to speak for themselves, to provide their perspectives in words and other actions. Therefore, qualitative research is an interactive process in which the persons studied teach the researcher about their lives.
- The qualitative researcher is an integral part of the data; without the active participation of the researcher, no data exists.
- The study’s design evolves during the research and can be adjusted or changed as it progresses. For the qualitative researcher, there is no single reality. It is subjective and exists only in reference to the observer.
- The theory is data-driven and emerges as part of the research process, evolving from the data as they are collected.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
- Because of the time and costs involved, qualitative designs do not generally draw samples from large-scale data sets.
- The problem of adequate validity or reliability is a major criticism. Because of the subjective nature of qualitative data and its origin in single contexts, it is difficult to apply conventional standards of reliability and validity. For example, because of the central role played by the researcher in the generation of data, it is not possible to replicate qualitative studies.
- Also, contexts, situations, events, conditions, and interactions cannot be replicated to any extent, nor can generalizations be made to a wider context than the one studied with confidence.
- The time required for data collection, analysis, and interpretation is lengthy. Analysis of qualitative data is difficult, and expert knowledge of an area is necessary to interpret qualitative data. Great care must be taken when doing so, for example, looking for mental illness symptoms.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
- Because of close researcher involvement, the researcher gains an insider’s view of the field. This allows the researcher to find issues that are often missed (such as subtleties and complexities) by the scientific, more positivistic inquiries.
- Qualitative descriptions can be important in suggesting possible relationships, causes, effects, and dynamic processes.
- Qualitative analysis allows for ambiguities/contradictions in the data, which reflect social reality (Denscombe, 2010).
- Qualitative research uses a descriptive, narrative style; this research might be of particular benefit to the practitioner as she or he could turn to qualitative reports to examine forms of knowledge that might otherwise be unavailable, thereby gaining new insight.
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research involves the process of objectively collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest.
The goals of quantitative research are to test causal relationships between variables , make predictions, and generalize results to wider populations.
Quantitative researchers aim to establish general laws of behavior and phenomenon across different settings/contexts. Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Quantitative Methods
Experiments typically yield quantitative data, as they are concerned with measuring things. However, other research methods, such as controlled observations and questionnaires , can produce both quantitative information.
For example, a rating scale or closed questions on a questionnaire would generate quantitative data as these produce either numerical data or data that can be put into categories (e.g., “yes,” “no” answers).
Experimental methods limit how research participants react to and express appropriate social behavior.
Findings are, therefore, likely to be context-bound and simply a reflection of the assumptions that the researcher brings to the investigation.
There are numerous examples of quantitative data in psychological research, including mental health. Here are a few examples:
Another example is the Experience in Close Relationships Scale (ECR), a self-report questionnaire widely used to assess adult attachment styles .
The ECR provides quantitative data that can be used to assess attachment styles and predict relationship outcomes.
Neuroimaging data : Neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI and fMRI, provide quantitative data on brain structure and function.
This data can be analyzed to identify brain regions involved in specific mental processes or disorders.
For example, the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) is a clinician-administered questionnaire widely used to assess the severity of depressive symptoms in individuals.
The BDI consists of 21 questions, each scored on a scale of 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe depressive symptoms.
Quantitative Data Analysis
Statistics help us turn quantitative data into useful information to help with decision-making. We can use statistics to summarize our data, describing patterns, relationships, and connections. Statistics can be descriptive or inferential.
Descriptive statistics help us to summarize our data. In contrast, inferential statistics are used to identify statistically significant differences between groups of data (such as intervention and control groups in a randomized control study).
- Quantitative researchers try to control extraneous variables by conducting their studies in the lab.
- The research aims for objectivity (i.e., without bias) and is separated from the data.
- The design of the study is determined before it begins.
- For the quantitative researcher, the reality is objective, exists separately from the researcher, and can be seen by anyone.
- Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
- Context: Quantitative experiments do not take place in natural settings. In addition, they do not allow participants to explain their choices or the meaning of the questions they may have for those participants (Carr, 1994).
- Researcher expertise: Poor knowledge of the application of statistical analysis may negatively affect analysis and subsequent interpretation (Black, 1999).
- Variability of data quantity: Large sample sizes are needed for more accurate analysis. Small-scale quantitative studies may be less reliable because of the low quantity of data (Denscombe, 2010). This also affects the ability to generalize study findings to wider populations.
- Confirmation bias: The researcher might miss observing phenomena because of focus on theory or hypothesis testing rather than on the theory of hypothesis generation.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
- Scientific objectivity: Quantitative data can be interpreted with statistical analysis, and since statistics are based on the principles of mathematics, the quantitative approach is viewed as scientifically objective and rational (Carr, 1994; Denscombe, 2010).
- Useful for testing and validating already constructed theories.
- Rapid analysis: Sophisticated software removes much of the need for prolonged data analysis, especially with large volumes of data involved (Antonius, 2003).
- Replication: Quantitative data is based on measured values and can be checked by others because numerical data is less open to ambiguities of interpretation.
- Hypotheses can also be tested because of statistical analysis (Antonius, 2003).
Antonius, R. (2003). Interpreting quantitative data with SPSS . Sage.
Black, T. R. (1999). Doing quantitative research in the social sciences: An integrated approach to research design, measurement and statistics . Sage.
Braun, V. & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology . Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3, 77–101.
Carr, L. T. (1994). The strengths and weaknesses of quantitative and qualitative research : what method for nursing? Journal of advanced nursing, 20(4) , 716-721.
Denscombe, M. (2010). The Good Research Guide: for small-scale social research. McGraw Hill.
Denzin, N., & Lincoln. Y. (1994). Handbook of Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA, US: Sage Publications Inc.
Glaser, B. G., Strauss, A. L., & Strutzel, E. (1968). The discovery of grounded theory; strategies for qualitative research. Nursing research, 17(4) , 364.
Minichiello, V. (1990). In-Depth Interviewing: Researching People. Longman Cheshire.
Punch, K. (1998). Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches. London: Sage
Further Information
- Designing qualitative research
- Methods of data collection and analysis
- Introduction to quantitative and qualitative research
- Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog?
- Qualitative research in health care: Analysing qualitative data
- Qualitative data analysis: the framework approach
- Using the framework method for the analysis of
- Qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research
- Content Analysis
- Grounded Theory
- Thematic Analysis
Related Articles

Research Methodology
Qualitative Data Coding

What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches to Generalization and Replication–A Representationalist View
In this paper, we provide a re-interpretation of qualitative and quantitative modeling from a representationalist perspective. In this view, both approaches attempt to construct abstract representations of empirical relational structures. Whereas quantitative research uses variable-based models that abstract from individual cases, qualitative research favors case-based models that abstract from individual characteristics. Variable-based models are usually stated in the form of quantified sentences (scientific laws). This syntactic structure implies that sentences about individual cases are derived using deductive reasoning. In contrast, case-based models are usually stated using context-dependent existential sentences (qualitative statements). This syntactic structure implies that sentences about other cases are justifiable by inductive reasoning. We apply this representationalist perspective to the problems of generalization and replication. Using the analytical framework of modal logic, we argue that the modes of reasoning are often not only applied to the context that has been studied empirically, but also on a between-contexts level. Consequently, quantitative researchers mostly adhere to a top-down strategy of generalization, whereas qualitative researchers usually follow a bottom-up strategy of generalization. Depending on which strategy is employed, the role of replication attempts is very different. In deductive reasoning, replication attempts serve as empirical tests of the underlying theory. Therefore, failed replications imply a faulty theory. From an inductive perspective, however, replication attempts serve to explore the scope of the theory. Consequently, failed replications do not question the theory per se , but help to shape its boundary conditions. We conclude that quantitative research may benefit from a bottom-up generalization strategy as it is employed in most qualitative research programs. Inductive reasoning forces us to think about the boundary conditions of our theories and provides a framework for generalization beyond statistical testing. In this perspective, failed replications are just as informative as successful replications, because they help to explore the scope of our theories.
Introduction
Qualitative and quantitative research strategies have long been treated as opposing paradigms. In recent years, there have been attempts to integrate both strategies. These “mixed methods” approaches treat qualitative and quantitative methodologies as complementary, rather than opposing, strategies (Creswell, 2015 ). However, whilst acknowledging that both strategies have their benefits, this “integration” remains purely pragmatic. Hence, mixed methods methodology does not provide a conceptual unification of the two approaches.
Lacking a common methodological background, qualitative and quantitative research methodologies have developed rather distinct standards with regard to the aims and scope of empirical science (Freeman et al., 2007 ). These different standards affect the way researchers handle contradictory empirical findings. For example, many empirical findings in psychology have failed to replicate in recent years (Klein et al., 2014 ; Open Science, Collaboration, 2015 ). This “replication crisis” has been discussed on statistical, theoretical and social grounds and continues to have a wide impact on quantitative research practices like, for example, open science initiatives, pre-registered studies and a re-evaluation of statistical significance testing (Everett and Earp, 2015 ; Maxwell et al., 2015 ; Shrout and Rodgers, 2018 ; Trafimow, 2018 ; Wiggins and Chrisopherson, 2019 ).
However, qualitative research seems to be hardly affected by this discussion. In this paper, we argue that the latter is a direct consequence of how the concept of generalizability is conceived in the two approaches. Whereas most of quantitative psychology is committed to a top-down strategy of generalization based on the idea of random sampling from an abstract population, qualitative studies usually rely on a bottom-up strategy of generalization that is grounded in the successive exploration of the field by means of theoretically sampled cases.
Here, we show that a common methodological framework for qualitative and quantitative research methodologies is possible. We accomplish this by introducing a formal description of quantitative and qualitative models from a representationalist perspective: both approaches can be reconstructed as special kinds of representations for empirical relational structures. We then use this framework to analyze the generalization strategies used in the two approaches. These turn out to be logically independent of the type of model. This has wide implications for psychological research. First, a top-down generalization strategy is compatible with a qualitative modeling approach. This implies that mainstream psychology may benefit from qualitative methods when a numerical representation turns out to be difficult or impossible, without the need to commit to a “qualitative” philosophy of science. Second, quantitative research may exploit the bottom-up generalization strategy that is inherent to many qualitative approaches. This offers a new perspective on unsuccessful replications by treating them not as scientific failures, but as a valuable source of information about the scope of a theory.
The Quantitative Strategy–Numbers and Functions
Quantitative science is about finding valid mathematical representations for empirical phenomena. In most cases, these mathematical representations have the form of functional relations between a set of variables. One major challenge of quantitative modeling consists in constructing valid measures for these variables. Formally, to measure a variable means to construct a numerical representation of the underlying empirical relational structure (Krantz et al., 1971 ). For example, take the behaviors of a group of students in a classroom: “to listen,” “to take notes,” and “to ask critical questions.” One may now ask whether is possible to assign numbers to the students, such that the relations between the assigned numbers are of the same kind as the relations between the values of an underlying variable, like e.g., “engagement.” The observed behaviors in the classroom constitute an empirical relational structure, in the sense that for every student-behavior tuple, one can observe whether it is true or not. These observations can be represented in a person × behavior matrix 1 (compare Figure 1 ). Given this relational structure satisfies certain conditions (i.e., the axioms of a measurement model), one can assign numbers to the students and the behaviors, such that the relations between the numbers resemble the corresponding numerical relations. For example, if there is a unique ordering in the empirical observations with regard to which person shows which behavior, the assigned numbers have to constitute a corresponding unique ordering, as well. Such an ordering coincides with the person × behavior matrix forming a triangle shaped relation and is formally represented by a Guttman scale (Guttman, 1944 ). There are various measurement models available for different empirical structures (Suppes et al., 1971 ). In the case of probabilistic relations, Item-Response models may be considered as a special kind of measurement model (Borsboom, 2005 ).

Constructing a numerical representation from an empirical relational structure; Due to the unique ordering of persons with regard to behaviors (indicated by the triangular shape of the relation), it is possible to construct a Guttman scale by assigning a number to each of the individuals, representing the number of relevant behaviors shown by the individual. The resulting variable (“engagement”) can then be described by means of statistical analyses, like, e.g., plotting the frequency distribution.
Although essential, measurement is only the first step of quantitative modeling. Consider a slightly richer empirical structure, where we observe three additional behaviors: “to doodle,” “to chat,” and “to play.” Like above, one may ask, whether there is a unique ordering of the students with regard to these behaviors that can be represented by an underlying variable (i.e., whether the matrix forms a Guttman scale). If this is the case, we may assign corresponding numbers to the students and call this variable “distraction.” In our example, such a representation is possible. We can thus assign two numbers to each student, one representing his or her “engagement” and one representing his or her “distraction” (compare Figure 2 ). These measurements can now be used to construct a quantitative model by relating the two variables by a mathematical function. In the simplest case, this may be a linear function. This functional relation constitutes a quantitative model of the empirical relational structure under study (like, e.g., linear regression). Given the model equation and the rules for assigning the numbers (i.e., the instrumentations of the two variables), the set of admissible empirical structures is limited from all possible structures to a rather small subset. This constitutes the empirical content of the model 2 (Popper, 1935 ).

Constructing a numerical model from an empirical relational structure; Since there are two distinct classes of behaviors that each form a Guttman scale, it is possible to assign two numbers to each individual, correspondingly. The resulting variables (“engagement” and “distraction”) can then be related by a mathematical function, which is indicated by the scatterplot and red line on the right hand side.
The Qualitative Strategy–Categories and Typologies
The predominant type of analysis in qualitative research consists in category formation. By constructing descriptive systems for empirical phenomena, it is possible to analyze the underlying empirical structure at a higher level of abstraction. The resulting categories (or types) constitute a conceptual frame for the interpretation of the observations. Qualitative researchers differ considerably in the way they collect and analyze data (Miles et al., 2014 ). However, despite the diverse research strategies followed by different qualitative methodologies, from a formal perspective, most approaches build on some kind of categorization of cases that share some common features. The process of category formation is essential in many qualitative methodologies, like, for example, qualitative content analysis, thematic analysis, grounded theory (see Flick, 2014 for an overview). Sometimes these features are directly observable (like in our classroom example), sometimes they are themselves the result of an interpretative process (e.g., Scheunpflug et al., 2016 ).
In contrast to quantitative methodologies, there have been little attempts to formalize qualitative research strategies (compare, however, Rihoux and Ragin, 2009 ). However, there are several statistical approaches to non-numerical data that deal with constructing abstract categories and establishing relations between these categories (Agresti, 2013 ). Some of these methods are very similar to qualitative category formation on a conceptual level. For example, cluster analysis groups cases into homogenous categories (clusters) based on their similarity on a distance metric.
Although category formation can be formalized in a mathematically rigorous way (Ganter and Wille, 1999 ), qualitative research hardly acknowledges these approaches. 3 However, in order to find a common ground with quantitative science, it is certainly helpful to provide a formal interpretation of category systems.
Let us reconsider the above example of students in a classroom. The quantitative strategy was to assign numbers to the students with regard to variables and to relate these variables via a mathematical function. We can analyze the same empirical structure by grouping the behaviors to form abstract categories. If the aim is to construct an empirically valid category system, this grouping is subject to constraints, analogous to those used to specify a measurement model. The first and most important constraint is that the behaviors must form equivalence classes, i.e., within categories, behaviors need to be equivalent, and across categories, they need to be distinct (formally, the relational structure must obey the axioms of an equivalence relation). When objects are grouped into equivalence classes, it is essential to specify the criterion for empirical equivalence. In qualitative methodology, this is sometimes referred to as the tertium comparationis (Flick, 2014 ). One possible criterion is to group behaviors such that they constitute a set of specific common attributes of a group of people. In our example, we might group the behaviors “to listen,” “to take notes,” and “to doodle,” because these behaviors are common to the cases B, C, and D, and they are also specific for these cases, because no other person shows this particular combination of behaviors. The set of common behaviors then forms an abstract concept (e.g., “moderate distraction”), while the set of persons that show this configuration form a type (e.g., “the silent dreamer”). Formally, this means to identify the maximal rectangles in the underlying empirical relational structure (see Figure 3 ). This procedure is very similar to the way we constructed a Guttman scale, the only difference being that we now use different aspects of the empirical relational structure. 4 In fact, the set of maximal rectangles can be determined by an automated algorithm (Ganter, 2010 ), just like the dimensionality of an empirical structure can be explored by psychometric scaling methods. Consequently, we can identify the empirical content of a category system or a typology as the set of empirical structures that conforms to it. 5 Whereas the quantitative strategy was to search for scalable sub-matrices and then relate the constructed variables by a mathematical function, the qualitative strategy is to construct an empirical typology by grouping cases based on their specific similarities. These types can then be related to one another by a conceptual model that describes their semantic and empirical overlap (see Figure 3 , right hand side).

Constructing a conceptual model from an empirical relational structure; Individual behaviors are grouped to form abstract types based on them being shared among a specific subset of the cases. Each type constitutes a set of specific commonalities of a class of individuals (this is indicated by the rectangles on the left hand side). The resulting types (“active learner,” “silent dreamer,” “distracted listener,” and “troublemaker”) can then be related to one another to explicate their semantic and empirical overlap, as indicated by the Venn-diagram on the right hand side.
Variable-Based Models and Case-Based Models
In the previous section, we have argued that qualitative category formation and quantitative measurement can both be characterized as methods to construct abstract representations of empirical relational structures. Instead of focusing on different philosophical approaches to empirical science, we tried to stress the formal similarities between both approaches. However, it is worth also exploring the dissimilarities from a formal perspective.
Following the above analysis, the quantitative approach can be characterized by the use of variable-based models, whereas the qualitative approach is characterized by case-based models (Ragin, 1987 ). Formally, we can identify the rows of an empirical person × behavior matrix with a person-space, and the columns with a corresponding behavior-space. A variable-based model abstracts from the single individuals in a person-space to describe the structure of behaviors on a population level. A case-based model, on the contrary, abstracts from the single behaviors in a behavior-space to describe individual case configurations on the level of abstract categories (see Table 1 ).
Variable-based models and case-based models.
From a representational perspective, there is no a priori reason to favor one type of model over the other. Both approaches provide different analytical tools to construct an abstract representation of an empirical relational structure. However, since the two modeling approaches make use of different information (person-space vs. behavior-space), this comes with some important implications for the researcher employing one of the two strategies. These are concerned with the role of deductive and inductive reasoning.
In variable-based models, empirical structures are represented by functional relations between variables. These are usually stated as scientific laws (Carnap, 1928 ). Formally, these laws correspond to logical expressions of the form
In plain text, this means that y is a function of x for all objects i in the relational structure under consideration. For example, in the above example, one may formulate the following law: for all students in the classroom it holds that “distraction” is a monotone decreasing function of “engagement.” Such a law can be used to derive predictions for single individuals by means of logical deduction: if the above law applies to all students in the classroom, it is possible to calculate the expected distraction from a student's engagement. An empirical observation can now be evaluated against this prediction. If the prediction turns out to be false, the law can be refuted based on the principle of falsification (Popper, 1935 ). If a scientific law repeatedly withstands such empirical tests, it may be considered to be valid with regard to the relational structure under consideration.
In case-based models, there are no laws about a population, because the model does not abstract from the cases but from the observed behaviors. A case-based model describes the underlying structure in terms of existential sentences. Formally, this corresponds to a logical expression of the form
In plain text, this means that there is at least one case i for which the condition XYZ holds. For example, the above category system implies that there is at least one active learner. This is a statement about a singular observation. It is impossible to deduce a statement about another person from an existential sentence like this. Therefore, the strategy of falsification cannot be applied to test the model's validity in a specific context. If one wishes to generalize to other cases, this is accomplished by inductive reasoning, instead. If we observed one person that fulfills the criteria of calling him or her an active learner, we can hypothesize that there may be other persons that are identical to the observed case in this respect. However, we do not arrive at this conclusion by logical deduction, but by induction.
Despite this important distinction, it would be wrong to conclude that variable-based models are intrinsically deductive and case-based models are intrinsically inductive. 6 Both types of reasoning apply to both types of models, but on different levels. Based on a person-space, in a variable-based model one can use deduction to derive statements about individual persons from abstract population laws. There is an analogous way of reasoning for case-based models: because they are based on a behavior space, it is possible to deduce statements about singular behaviors. For example, if we know that Peter is an active learner, we can deduce that he takes notes in the classroom. This kind of deductive reasoning can also be applied on a higher level of abstraction to deduce thematic categories from theoretical assumptions (Braun and Clarke, 2006 ). Similarly, there is an analog for inductive generalization from the perspective of variable-based modeling: since the laws are only quantified over the person-space, generalizations to other behaviors rely on inductive reasoning. For example, it is plausible to assume that highly engaged students tend to do their homework properly–however, in our example this behavior has never been observed. Hence, in variable-based models we usually generalize to other behaviors by means of induction. This kind of inductive reasoning is very common when empirical results are generalized from the laboratory to other behavioral domains.
Although inductive and deductive reasoning are used in qualitative and quantitative research, it is important to stress the different roles of induction and deduction when models are applied to cases. A variable-based approach implies to draw conclusions about cases by means of logical deduction; a case-based approach implies to draw conclusions about cases by means of inductive reasoning. In the following, we build on this distinction to differentiate between qualitative (bottom-up) and quantitative (top-down) strategies of generalization.
Generalization and the Problem of Replication
We will now extend the formal analysis of quantitative and qualitative approaches to the question of generalization and replicability of empirical findings. For this sake, we have to introduce some concepts of formal logic. Formal logic is concerned with the validity of arguments. It provides conditions to evaluate whether certain sentences (conclusions) can be derived from other sentences (premises). In this context, a theory is nothing but a set of sentences (also called axioms). Formal logic provides tools to derive new sentences that must be true, given the axioms are true (Smith, 2020 ). These derived sentences are called theorems or, in the context of empirical science, predictions or hypotheses . On the syntactic level, the rules of logic only state how to evaluate the truth of a sentence relative to its premises. Whether or not sentences are actually true, is formally specified by logical semantics.
On the semantic level, formal logic is intrinsically linked to set-theory. For example, a logical statement like “all dogs are mammals,” is true if and only if the set of dogs is a subset of the set of mammals. Similarly, the sentence “all chatting students doodle” is true if and only if the set of chatting students is a subset of the set of doodling students (compare Figure 3 ). Whereas, the first sentence is analytically true due to the way we define the words “dog” and “mammal,” the latter can be either true or false, depending on the relational structure we actually observe. We can thus interpret an empirical relational structure as the truth criterion of a scientific theory. From a logical point of view, this corresponds to the semantics of a theory. As shown above, variable-based and case-based models both give a formal representation of the same kinds of empirical structures. Accordingly, both types of models can be stated as formal theories. In the variable-based approach, this corresponds to a set of scientific laws that are quantified over the members of an abstract population (these are the axioms of the theory). In the case-based approach, this corresponds to a set of abstract existential statements about a specific class of individuals.
In contrast to mathematical axiom systems, empirical theories are usually not considered to be necessarily true. This means that even if we find no evidence against a theory, it is still possible that it is actually wrong. We may know that a theory is valid in some contexts, yet it may fail when applied to a new set of behaviors (e.g., if we use a different instrumentation to measure a variable) or a new population (e.g., if we draw a new sample).
From a logical perspective, the possibility that a theory may turn out to be false stems from the problem of contingency . A statement is contingent, if it is both, possibly true and possibly false. Formally, we introduce two modal operators: □ to designate logical necessity, and ◇ to designate logical possibility. Semantically, these operators are very similar to the existential quantifier, ∃, and the universal quantifier, ∀. Whereas ∃ and ∀ refer to the individual objects within one relational structure, the modal operators □ and ◇ range over so-called possible worlds : a statement is possibly true, if and only if it is true in at least one accessible possible world, and a statement is necessarily true if and only if it is true in every accessible possible world (Hughes and Cresswell, 1996 ). Logically, possible worlds are mathematical abstractions, each consisting of a relational structure. Taken together, the relational structures of all accessible possible worlds constitute the formal semantics of necessity, possibility and contingency. 7
In the context of an empirical theory, each possible world may be identified with an empirical relational structure like the above classroom example. Given the set of intended applications of a theory (the scope of the theory, one may say), we can now construct possible world semantics for an empirical theory: each intended application of the theory corresponds to a possible world. For example, a quantified sentence like “all chatting students doodle” may be true in one classroom and false in another one. In terms of possible worlds, this would correspond to a statement of contingency: “it is possible that all chatting students doodle in one classroom, and it is possible that they don't in another classroom.” Note that in the above expression, “all students” refers to the students in only one possible world, whereas “it is possible” refers to the fact that there is at least one possible world for each of the specified cases.
To apply these possible world semantics to quantitative research, let us reconsider how generalization to other cases works in variable-based models. Due to the syntactic structure of quantitative laws, we can deduce predictions for singular observations from an expression of the form ∀ i : y i = f ( x i ). Formally, the logical quantifier ∀ ranges only over the objects of the corresponding empirical relational structure (in our example this would refer to the students in the observed classroom). But what if we want to generalize beyond the empirical structure we actually observed? The standard procedure is to assume an infinitely large, abstract population from which a random sample is drawn. Given the truth of the theory, we can deduce predictions about what we may observe in the sample. Since usually we deal with probabilistic models, we can evaluate our theory by means of the conditional probability of the observations, given the theory holds. This concept of conditional probability is the foundation of statistical significance tests (Hogg et al., 2013 ), as well as Bayesian estimation (Watanabe, 2018 ). In terms of possible world semantics, the random sampling model implies that all possible worlds (i.e., all intended applications) can be conceived as empirical sub-structures from a greater population structure. For example, the empirical relational structure constituted by the observed behaviors in a classroom would be conceived as a sub-matrix of the population person × behavior matrix. It follows that, if a scientific law is true in the population, it will be true in all possible worlds, i.e., it will be necessarily true. Formally, this corresponds to an expression of the form
The statistical generalization model thus constitutes a top-down strategy for dealing with individual contexts that is analogous to the way variable-based models are applied to individual cases (compare Table 1 ). Consequently, if we apply a variable-based model to a new context and find out that it does not fit the data (i.e., there is a statistically significant deviation from the model predictions), we have reason to doubt the validity of the theory. This is what makes the problem of low replicability so important: we observe that the predictions are wrong in a new study; and because we apply a top-down strategy of generalization to contexts beyond the ones we observed, we see our whole theory at stake.
Qualitative research, on the contrary, follows a different strategy of generalization. Since case-based models are formulated by a set of context-specific existential sentences, there is no need for universal truth or necessity. In contrast to statistical generalization to other cases by means of random sampling from an abstract population, the usual strategy in case-based modeling is to employ a bottom-up strategy of generalization that is analogous to the way case-based models are applied to individual cases. Formally, this may be expressed by stating that the observed qualia exist in at least one possible world, i.e., the theory is possibly true:
This statement is analogous to the way we apply case-based models to individual cases (compare Table 1 ). Consequently, the set of intended applications of the theory does not follow from a sampling model, but from theoretical assumptions about which cases may be similar to the observed cases with respect to certain relevant characteristics. For example, if we observe that certain behaviors occur together in one classroom, following a bottom-up strategy of generalization, we will hypothesize why this might be the case. If we do not replicate this finding in another context, this does not question the model itself, since it was a context-specific theory all along. Instead, we will revise our hypothetical assumptions about why the new context is apparently less similar to the first one than we originally thought. Therefore, if an empirical finding does not replicate, we are more concerned about our understanding of the cases than about the validity of our theory.
Whereas statistical generalization provides us with a formal (and thus somehow more objective) apparatus to evaluate the universal validity of our theories, the bottom-up strategy forces us to think about the class of intended applications on theoretical grounds. This means that we have to ask: what are the boundary conditions of our theory? In the above classroom example, following a bottom-up strategy, we would build on our preliminary understanding of the cases in one context (e.g., a public school) to search for similar and contrasting cases in other contexts (e.g., a private school). We would then re-evaluate our theoretical description of the data and explore what makes cases similar or dissimilar with regard to our theory. This enables us to expand the class of intended applications alongside with the theory.
Of course, none of these strategies is superior per se . Nevertheless, they rely on different assumptions and may thus be more or less adequate in different contexts. The statistical strategy relies on the assumption of a universal population and invariant measurements. This means, we assume that (a) all samples are drawn from the same population and (b) all variables refer to the same behavioral classes. If these assumptions are true, statistical generalization is valid and therefore provides a valuable tool for the testing of empirical theories. The bottom-up strategy of generalization relies on the idea that contexts may be classified as being more or less similar based on characteristics that are not part of the model being evaluated. If such a similarity relation across contexts is feasible, the bottom-up strategy is valid, as well. Depending on the strategy of generalization, replication of empirical research serves two very different purposes. Following the (top-down) principle of generalization by deduction from scientific laws, replications are empirical tests of the theory itself, and failed replications question the theory on a fundamental level. Following the (bottom-up) principle of generalization by induction to similar contexts, replications are a means to explore the boundary conditions of a theory. Consequently, failed replications question the scope of the theory and help to shape the set of intended applications.
We have argued that quantitative and qualitative research are best understood by means of the structure of the employed models. Quantitative science mainly relies on variable-based models and usually employs a top-down strategy of generalization from an abstract population to individual cases. Qualitative science prefers case-based models and usually employs a bottom-up strategy of generalization. We further showed that failed replications have very different implications depending on the underlying strategy of generalization. Whereas in the top-down strategy, replications are used to test the universal validity of a model, in the bottom-up strategy, replications are used to explore the scope of a model. We will now address the implications of this analysis for psychological research with regard to the problem of replicability.
Modern day psychology almost exclusively follows a top-down strategy of generalization. Given the quantitative background of most psychological theories, this is hardly surprising. Following the general structure of variable-based models, the individual case is not the focus of the analysis. Instead, scientific laws are stated on the level of an abstract population. Therefore, when applying the theory to a new context, a statistical sampling model seems to be the natural consequence. However, this is not the only possible strategy. From a logical point of view, there is no reason to assume that a quantitative law like ∀ i : y i = f ( x i ) implies that the law is necessarily true, i.e.,: □(∀ i : y i = f ( x i )). Instead, one might just as well define the scope of the theory following an inductive strategy. 8 Formally, this would correspond to the assumption that the observed law is possibly true, i.e.,: ◇(∀ i : y i = f ( x i )). For example, we may discover a functional relation between “engagement” and “distraction” without referring to an abstract universal population of students. Instead, we may hypothesize under which conditions this functional relation may be valid and use these assumptions to inductively generalize to other cases.
If we take this seriously, this would require us to specify the intended applications of the theory: in which contexts do we expect the theory to hold? Or, equivalently, what are the boundary conditions of the theory? These boundary conditions may be specified either intensionally, i.e., by giving external criteria for contexts being similar enough to the ones already studied to expect a successful application of the theory. Or they may be specified extensionally, by enumerating the contexts where the theory has already been shown to be valid. These boundary conditions need not be restricted to the population we refer to, but include all kinds of contextual factors. Therefore, adopting a bottom-up strategy, we are forced to think about these factors and make them an integral part of our theories.
In fact, there is good reason to believe that bottom-up generalization may be more adequate in many psychological studies. Apart from the pitfalls associated with statistical generalization that have been extensively discussed in recent years (e.g., p-hacking, underpowered studies, publication bias), it is worth reflecting on whether the underlying assumptions are met in a particular context. For example, many samples used in experimental psychology are not randomly drawn from a large population, but are convenience samples. If we use statistical models with non-random samples, we have to assume that the observations vary as if drawn from a random sample. This may indeed be the case for randomized experiments, because all variation between the experimental conditions apart from the independent variable will be random due to the randomization procedure. In this case, a classical significance test may be regarded as an approximation to a randomization test (Edgington and Onghena, 2007 ). However, if we interpret a significance test as an approximate randomization test, we test not for generalization but for internal validity. Hence, even if we use statistical significance tests when assumptions about random sampling are violated, we still have to use a different strategy of generalization. This issue has been discussed in the context of small-N studies, where variable-based models are applied to very small samples, sometimes consisting of only one individual (Dugard et al., 2012 ). The bottom-up strategy of generalization that is employed by qualitative researchers, provides such an alternative.
Another important issue in this context is the question of measurement invariance. If we construct a variable-based model in one context, the variables refer to those behaviors that constitute the underlying empirical relational structure. For example, we may construct an abstract measure of “distraction” using the observed behaviors in a certain context. We will then use the term “distraction” as a theoretical term referring to the variable we have just constructed to represent the underlying empirical relational structure. Let us now imagine we apply this theory to a new context. Even if the individuals in our new context are part of the same population, we may still get into trouble if the observed behaviors differ from those used in the original study. How do we know whether these behaviors constitute the same variable? We have to ensure that in any new context, our measures are valid for the variables in our theory. Without a proper measurement model, this will be hard to achieve (Buntins et al., 2017 ). Again, we are faced with the necessity to think of the boundary conditions of our theories. In which contexts (i.e., for which sets of individuals and behaviors) do we expect our theory to work?
If we follow the rationale of inductive generalization, we can explore the boundary conditions of a theory with every new empirical study. We thus widen the scope of our theory by comparing successful applications in different contexts and unsuccessful applications in similar contexts. This may ultimately lead to a more general theory, maybe even one of universal scope. However, unless we have such a general theory, we might be better off, if we treat unsuccessful replications not as a sign of failure, but as a chance to learn.
Author Contributions
MB conceived the original idea and wrote the first draft of the paper. MS helped to further elaborate and scrutinize the arguments. All authors contributed to the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Annette Scheunpflug for helpful comments on an earlier version of the manuscript.
1 A person × behavior matrix constitutes a very simple relational structure that is common in psychological research. This is why it is chosen here as a minimal example. However, more complex structures are possible, e.g., by relating individuals to behaviors over time, with individuals nested within groups etc. For a systematic overview, compare Coombs ( 1964 ).
2 This notion of empirical content applies only to deterministic models. The empirical content of a probabilistic model consists in the probability distribution over all possible empirical structures.
3 For example, neither the SAGE Handbook of qualitative data analysis edited by Flick ( 2014 ) nor the Oxford Handbook of Qualitative Research edited by Leavy ( 2014 ) mention formal approaches to category formation.
4 Note also that the described structure is empirically richer than a nominal scale. Therefore, a reduction of qualitative category formation to be a special (and somehow trivial) kind of measurement is not adequate.
5 It is possible to extend this notion of empirical content to the probabilistic case (this would correspond to applying a latent class analysis). But, since qualitative research usually does not rely on formal algorithms (neither deterministic nor probabilistic), there is currently little practical use of such a concept.
6 We do not elaborate on abductive reasoning here, since, given an empirical relational structure, the concept can be applied to both types of models in the same way (Schurz, 2008 ). One could argue that the underlying relational structure is not given a priori but has to be constructed by the researcher and will itself be influenced by theoretical expectations. Therefore, abductive reasoning may be necessary to establish an empirical relational structure in the first place.
7 We shall not elaborate on the metaphysical meaning of possible worlds here, since we are only concerned with empirical theories [but see Tooley ( 1999 ), for an overview].
8 Of course, this also means that it would be equally reasonable to employ a top-down strategy of generalization using a case-based model by postulating that □(∃ i : XYZ i ). The implications for case-based models are certainly worth exploring, but lie beyond the scope of this article.
- Agresti A. (2013). Categorical Data Analysis, 3rd Edn. Wiley Series In Probability And Statistics . Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. [ Google Scholar ]
- Borsboom D. (2005). Measuring the Mind: Conceptual Issues in Contemporary Psychometrics . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 10.1017/CBO9780511490026 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Braun V., Clarke V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology . Qual. Res. Psychol . 3 , 77–101. 10.1191/1478088706qp063oa [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Buntins M., Buntins K., Eggert F. (2017). Clarifying the concept of validity: from measurement to everyday language . Theory Psychol. 27 , 703–710. 10.1177/0959354317702256 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carnap R. (1928). The Logical Structure of the World . Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Coombs C. H. (1964). A Theory of Data . New York, NY: Wiley. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell J. W. (2015). A Concise Introduction to Mixed Methods Research . Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dugard P., File P., Todman J. B. (2012). Single-Case and Small-N Experimental Designs: A Practical Guide to Randomization Tests 2nd Edn . New York, NY: Routledge; 10.4324/9780203180938 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Edgington E., Onghena P. (2007). Randomization Tests, 4th Edn. Statistics. Hoboken, NJ: CRC Press; 10.1201/9781420011814 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Everett J. A. C., Earp B. D. (2015). A tragedy of the (academic) commons: interpreting the replication crisis in psychology as a social dilemma for early-career researchers . Front. Psychol . 6 :1152. 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01152 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Flick U. (Ed.). (2014). The Sage Handbook of Qualitative Data Analysis . London: Sage; 10.4135/9781446282243 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Freeman M., Demarrais K., Preissle J., Roulston K., St. Pierre E. A. (2007). Standards of evidence in qualitative research: an incitement to discourse . Educ. Res. 36 , 25–32. 10.3102/0013189X06298009 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ganter B. (2010). Two basic algorithms in concept analysis , in Lecture Notes In Computer Science. Formal Concept Analysis, Vol. 5986 , eds Hutchison D., Kanade T., Kittler J., Kleinberg J. M., Mattern F., Mitchell J. C., et al. (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; ), 312–340. 10.1007/978-3-642-11928-6_22 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ganter B., Wille R. (1999). Formal Concept Analysis . Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 10.1007/978-3-642-59830-2 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Guttman L. (1944). A basis for scaling qualitative data . Am. Sociol. Rev . 9 :139 10.2307/2086306 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hogg R. V., Mckean J. W., Craig A. T. (2013). Introduction to Mathematical Statistics, 7th Edn . Boston, MA: Pearson. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hughes G. E., Cresswell M. J. (1996). A New Introduction To Modal Logic . London; New York, NY: Routledge; 10.4324/9780203290644 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Klein R. A., Ratliff K. A., Vianello M., Adams R. B., Bahník Š., Bernstein M. J., et al. (2014). Investigating variation in replicability . Soc. Psychol. 45 , 142–152. 10.1027/1864-9335/a000178 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krantz D. H., Luce D., Suppes P., Tversky A. (1971). Foundations of Measurement Volume I: Additive And Polynomial Representations . New York, NY; London: Academic Press; 10.1016/B978-0-12-425401-5.50011-8 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Leavy P. (2014). The Oxford Handbook of Qualitative Research . New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199811755.001.0001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maxwell S. E., Lau M. Y., Howard G. S. (2015). Is psychology suffering from a replication crisis? what does “failure to replicate” really mean? Am. Psychol. 70 , 487–498. 10.1037/a0039400 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles M. B., Huberman A. M., Saldaña J. (2014). Qualitative Data Analysis: A Methods Sourcebook, 3rd Edn . Los Angeles, CA; London; New Delhi; Singapore; Washington, DC: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Open Science, Collaboration (2015). Estimating the reproducibility of psychological science . Science 349 :Aac4716. 10.1126/science.aac4716 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Popper K. (1935). Logik Der Forschung . Wien: Springer; 10.1007/978-3-7091-4177-9 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ragin C. (1987). The Comparative Method : Moving Beyond Qualitative and Quantitative Strategies . Berkeley, CA: University Of California Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rihoux B., Ragin C. (2009). Configurational Comparative Methods: Qualitative Comparative Analysis (Qca) And Related Techniques . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, Inc; 10.4135/9781452226569 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scheunpflug A., Krogull S., Franz J. (2016). Understanding learning in world society: qualitative reconstructive research in global learning and learning for sustainability . Int. Journal Dev. Educ. Glob. Learn. 7 , 6–23. 10.18546/IJDEGL.07.3.02 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schurz G. (2008). Patterns of abduction . Synthese 164 , 201–234. 10.1007/s11229-007-9223-4 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shrout P. E., Rodgers J. L. (2018). Psychology, science, and knowledge construction: broadening perspectives from the replication crisis . Annu. Rev. Psychol . 69 , 487–510. 10.1146/annurev-psych-122216-011845 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith P. (2020). An Introduction To Formal Logic . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 10.1017/9781108328999 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suppes P., Krantz D. H., Luce D., Tversky A. (1971). Foundations of Measurement Volume II: Geometrical, Threshold, and Probabilistic Representations . New York, NY; London: Academic Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tooley M. (Ed.). (1999). Necessity and Possibility. The Metaphysics of Modality . New York, NY; London: Garland Publishing. [ Google Scholar ]
- Trafimow D. (2018). An a priori solution to the replication crisis . Philos. Psychol . 31 , 1188–1214. 10.1080/09515089.2018.1490707 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Watanabe S. (2018). Mathematical Foundations of Bayesian Statistics. CRC Monographs On Statistics And Applied Probability . Boca Raton, FL: Chapman And Hall. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiggins B. J., Chrisopherson C. D. (2019). The replication crisis in psychology: an overview for theoretical and philosophical psychology . J. Theor. Philos. Psychol. 39 , 202–217. 10.1037/teo0000137 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
André Queirós Higher Polytechnic Institute of Gaya, V. N. Gaia, Portugal
Daniel Faria Higher Polytechnic Institute of Gaya, V. N. Gaia, Portugal
Fernando Almeida Faculty of Engineering of Oporto University, INESC TEC, Porto, Portugal
.................................................
..................................................
Education Journals
European Journal Of Physical Education and Sport Science
European Journal of Foreign Language Teaching
European Journal of English Language Teaching
European Journal of Special Education Research
European Journal of Alternative Education Studies
European Journal of Open Education and E-learning Studies
Public Health Journals
European Journal of Public Health Studies
European Journal of Fitness, Nutrition and Sport Medicine Studies
European Journal of Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation Studies
Social Sciences Journals
European Journal of Social Sciences Studies
European Journal of Economic and Financial Research
European Journal of Management and Marketing Studies
European Journal of Human Resource Management Studies
European Journal of Political Science Studies
Literature, Language and Linguistics Journals
European Journal of Literature, Language and Linguistics Studies
European Journal of Literary Studies
European Journal of Applied Linguistics Studies
European Journal of Multilingualism and Translation Studies
...................................................

- Other Journals
- ##Editorial Board##
- ##Indexing and Abstracting##
- ##Author's guidelines##
- ##Covered Research Areas##
- ##Announcements##
- ##Related Journals##
- ##Manuscript Submission##
STRENGTHS AND LIMITATIONS OF QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH METHODS
Scientific research adopts qualitative and quantitative methodologies in the modeling and analysis of numerous phenomena. The qualitative methodology intends to understand a complex reality and the meaning of actions in a given context. On the other hand, the quantitative methodology seeks to obtain accurate and reliable measurements that allow a statistical analysis. Both methodologies offer a set of methods, potentialities and limitations that must be explored and known by researchers. This paper concisely maps a total of seven qualitative methods and five quantitative methods. A comparative analysis of the most relevant and adopted methods is done to understand the main strengths and limitations of them. Additionally, the work developed intends to be a fundamental reference for the accomplishment of a research study, in which the researcher intends to adopt a qualitative or quantitative methodology. Through the analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of each method, it becomes possible to formulate a more accurate, informed and complete choice.
Article visualizations:
Acocella, I. (2012). The focus group in social research: advantages and disadvantages. Quality & Quantity, 46(4), 1125-1136.
Almeida, F., & Monteiro, J. (2017). Approaches and principles for UX web experiences. International Journal of Information Technology and Web Engineering, 12(2), 49-65.
Alshenqeeti, H. (2014). Interviewing as a data collection method: a critical review. English Linguistics Research, 3(1), 39-45.
Atieno, O. (2009). An analysis of the strengths and limitation of qualitative and quantitative research paradigms. Problems of Education in the 21st Century, 13, 13-18.
Baxter, P., & Jack, S. (2008). Qualitative case study methodology: study design and implementation for novice researchers. The Qualitative Report, 13(4), 544-559.
Blackstone, A. (2012). Principles of sociological inquiry: qualitative and quantitative methods. Retrieved from https://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/sociological-inquiry-principles-qualitative-and-quantitative-methods/index.html
Borrego, M., Douglas, E., & Amelink, C. (2009). Quantitative, qualitative, and mixed research methods in engineering education. Journal of Engineering Education, 98(1), 53-66.
Castellan, C. (2010). Quantitative and qualitative research: a view for clarity. International Journal of Education, 2(2), 1-14.
Charmaz, K. (2006). Constructing grounded theory: a practical guide through qualitative analysis. London, United Kingdom: Sage.
Choy, L. (2014). The strengths and weaknesses of research methodology: comparison and complimentary between qualitative and quantitative approaches. IOSR Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 19(4), 99-104.
Coughlan, M., Cronin, P, & Ryan, F. (2007). Step-by-step guide to critiquing research. Part 1: quantitative research. British Journal of Nursing, 16(11), 658-663.
Crescentini, A. & Mainardi, G. (2009). Qualitative research articles: guidelines, suggestions and needs. Journal of Workplace Learning, 21(5), 431-439.
Creswell, J. (2013). Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. London, United Kingdom: Sage.
Creswell, J. & Poth, C. (2017). Qualitative inquiry and research design: choosing among five approaches. London, United Kingdom: Sage.
Davies, M. (2011). Concept mapping, mind mapping and argument mapping: what are the differences and do they matter? Higher Education, 62(3), 279-301.
Etikan, I., Musa, S., & Alkassim, R. (2016). Comparison convenience sampling and purposive sampling. American Journal of Theoretical and Applied Statistics, 5(1), 1-4.
Flanagan, T. (2013). The scientific method and why it matters. C2C Journal, 7(1), 4-6.
Felix, E. (2015). The implications of parametric and non-parametric statistics in data analysis in marketing research. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science, 5(6), 74-83.
Hoy, W. & Adams, C. (2015). Quantitative research in education. London, United Kingdom: Sage.
Jamshed, S. (2014). Qualitative research method - interviewing and observation. Journal of Basic and Clinical Pharmacy, 5(4), 87-88.
Kelley, K., Clark, B., Brown, V., & Sitzia, J. (2003). Good practice in the conduct and reporting of survey research. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 15(3), 261-266.
Kothari, C. (2013). Research methodology: methods and techniques. New Delhi, India: New Age International.
Maher, J., Markey, J., & Ebert-May, D. (2013). The other half of the story: effect size analysis in quantitative research. CBE Life Sciences Education, 12(3), 345-351.
Martin, W., & Bridgmon, K. (2012). Quantitative and statistical research methods: from hypothesis to results. New Jersey, USA: Jossey-Bass.
Maxwell, J. (2013). Qualitative research design: an interactive approach. London, United Kingdom: Sage.
Merriam, S. & Tisdell, E. (2015). Qualitative research: a guide to design and implementation. New Jersey, USA: Jossey-Bass.
Mori, H. & Nakayama, T. (2013). Academic impact of qualitative studies in healthcare: bibliometric analysis. Plos One, 8(3), 1-7.
Moriarty, J. (2011). Qualitative methods overview. London, UK: NIHR School for Social Care Research.
Noble, H., & Smith, J. (2015). Issues of validity and reliability in qualitative research. Evidence-Based Nursing, 18(2), 34-5.
Nurani, L. (2008). Critical review of ethnographic approach. Jurnal Sosioteknologi, 7(14), 441-447.
Oppong, S. (2013). The problem of sampling in qualitative research. Asian Journal of Management Sciences and Education, 2(2), 202-210.
Polit, D., & Beck C. (2006). Essentials of nursing research: methods, appraisal and utilization. Philadelphia, USA: Lippincott Willaims and Wilkins.
Ponelis, S. (2015). Using interpretive qualitative case studies for exploratory research in doctoral studies: a case of information systems research in small and medium enterprises. International Journal of Doctoral Studies, 10, 535-550.
Rahman, S. (2017). The advantages and disadvantages of using qualitative and quantitative approaches and methods in language "testing and assessment" research: a literature review. Journal of Education and Learning, 6(1), 102-112.
Roshan, B. & Deeptee, P. (2009). Justifications for qualitative research in organisations: a step forward. The Journal of Online Education, 1, 1-7.
Schneider, J. (2013). Caveats for using statistical significance tests in research assessment. Journal of Informetrics, 7(1), 50-62.
Starman, A. (2013). The case study as a type of qualitative research. Journal of Contemporary Educational Studies, 1, 28-43.
Williams, C. (2007). Research methods. Journal of Business & Economic Research, 5(3), 65-72.
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright © 2015-2023. European Journal of Education Studies (ISSN 2501 - 1111) is a registered trademark of Open Access Publishing Group . All rights reserved.
This journal is a serial publication uniquely identified by an International Standard Serial Number ( ISSN ) serial number certificate issued by Romanian National Library ( Biblioteca Nationala a Romaniei ). All the research works are uniquely identified by a CrossRef DOI digital object identifier supplied by indexing and repository platforms. All authors who send their manuscripts to this journal and whose articles are published on this journal retain full copyright of their articles. All the research works published on this journal are meeting the Open Access Publishing requirements and can be freely accessed, shared, modified, distributed and used in educational, commercial and non-commercial purposes under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0) .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Problems of quantitative research method. To this end, some of the weaknesses and limitations of quantitative research are highlighted below. 1. It Requires a Large Number of Respondents: In the course of carrying out a quantitative research, recourse has to be made to a large number of respondents.
List of the Pros of Quantitative Research. 1. Data collection occurs rapidly with quantitative research. Because the data points of quantitative research involve surveys, experiments, and real-time gathering, there are few delays in the collection of materials to examine. That means the information under study can be analyzed very quickly when ...
5 Disadvantages of Quantitative Research. Limited to numbers and figures. Quantitative research is an incredibly precise tool in the way that it only gathers cold hard figures. This double edged sword leaves the quantitative method unable to deal with questions that require specific feedback, and often lacks a human element.
Quantitative research methods. You can use quantitative research methods for descriptive, correlational or experimental research. In descriptive research, you simply seek an overall summary of your study variables.; In correlational research, you investigate relationships between your study variables.; In experimental research, you systematically examine whether there is a cause-and-effect ...
Jamshed (2014) advocates the use of interviewing and observation as two main methods. to have an in depth and extensive understanding of a complex reality. Qualitative studies ha ve been used in a ...
Quantitative Research Methods are as follows: Descriptive Research Design. Descriptive research design is used to describe the characteristics of a population or phenomenon being studied. This research method is used to answer the questions of what, where, when, and how. ... Limitations of Quantitative Research. There are several limitations of ...
Quantitative methods emphasize objective measurements and the statistical, mathematical, or numerical analysis of data collected through polls, questionnaires, and surveys, or by manipulating pre-existing statistical data using computational techniques.Quantitative research focuses on gathering numerical data and generalizing it across groups of people or to explain a particular phenomenon.
Keywords: Quantitative methods, advantages, disadvantages, data collection, research design, ethical standards. Discover the world's research 25+ million members
Quantitative research methods are concerned with the planning, design, and implementation of strategies to collect and analyze data. Descartes, the seventeenth-century philosopher, suggested that how the results are achieved is often more important than the results themselves, as the journey taken along the research path is a journey of discovery. . High-quality quantitative research is ...
Quantitative . Research Methods. T. his chapter focuses on research designs commonly used when conducting . quantitative research studies. The general purpose of quantitative research is to investigate a particular topic or activity through the measurement of variables in quantifiable terms. Quantitative approaches to conducting educational ...
Mixed-methods research is a flexible approach, where the research design is determined by what we want to find out rather than by any predetermined epistemological position. In mixed-methods research, qualitative or quantitative components can predominate, or both can have equal status. 1.4. Units and variables.
Quantitative research methods involve the collection of numerical data and the use of statistical analysis to draw conclusions. This method is suitable for research questions that aim to measure the relationship between variables, test hypotheses, and make predictions. ... Strength and Limitations of Quantitative Research Methods: Strengths ...
consuming. Quantitative research methods, on the other hand, involve a larger sample, and do not require relatively a longer time for data collection. Some limitations are that quantitative research methods take snapshots of a phenomenon: not in-depth, and overlook test-takers' and testers' experiences as well as what they mean by something.
Quantitative research is a way to conduct studies and examine data for trends and patterns. Researchers using quantitative methods often attempt to interpret the meaning of the data to find potential causal relationships between different variables. If you want to work in research, understanding this style can help you study issues through data ...
Limitations and weakness of quantitative research methods. According to Saunders et al. (2009), research methodology serves as the backbone of a research study. Quantitative research's main purpose is the quantification of the data. It allows generalisations of the results by measuring the views and responses of the sample population.
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge. Quantitative research. Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions.
Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes.2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed ...
CONCLUSION. Siddaway 16 noted that, "The best reviews synthesize studies to draw broad theoretical conclusions about what the literature means, linking theory to evidence and evidence to theory" (p. 747). To that end, high quality systematic reviews are explicit, rigorous, and reproducible. It is these three criteria that should guide authors seeking to write a systematic review or editors ...
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze. Quantitative research collects numerical data and analyzes it using statistical methods. The aim is to produce objective, empirical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms.
Hence, mixed methods methodology does not provide a conceptual unification of the two approaches. Lacking a common methodological background, qualitative and quantitative research methodologies have developed rather distinct standards with regard to the aims and scope of empirical science (Freeman et al., 2007). These different standards affect ...
On the other hand, the quantitative methodology seeks to obtain accurate and reliable measurements that allow a statistical analysis. Both methodologies offer a set of methods, potentialities and limitations that must be explored and known by researchers. This paper concisely maps a total of seven qualitative methods and five quantitative methods.
Quantitative research methods, on the other hand, involve a larger sample, and do not require relatively a longer time for data collection. Some limitations are that quantitative research methods take snapshots of a phenomenon: not in-depth, and overlook test-takers' and testers' experiences as well as what they mean by something.
The article discusses previous quantitative LL research and introduces a quantitative approach developed by the author during a data gathering and annotation of 6016 items. Quantitative methods can provide valuable insight to the ordering of reality and the materialized discourses. Furthermore, they can mitigate personal bias.
With the advancement of information technology, the Internet is pivotal in today's society, serving as a global connectivity platform. Leveraging Internet technology within an enterprise can improve operational efficiency and curtail costs. However, traditional Internet platform selection methods cannot simultaneously handle quantitative and qualitative information, fuzzy semantics, and ...