An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Environ Res Public Health


The Effectiveness of an Evidence-Based Practice (EBP) Educational Program on Undergraduate Nursing Students’ EBP Knowledge and Skills: A Cluster Randomized Control Trial
Daniela cardoso.
1 Health Sciences Research Unit: Nursing, Nursing School of Coimbra, Portugal Centre for Evidence-Based Practice: A Joanna Briggs Institute Centre of Excellence, 3004-011 Coimbra, Portugal; tp.cfnese@osodracf (A.F.C.); tp.cfnese@oiregor (R.R.); moc.liamg@7ramed (M.A.R.); tp.cfnese@olotsopa (J.A.)
2 FMUC—Faculty of Medicine, University of Coimbra, 3000-370 Coimbra, Portugal
Filipa Couto
3 Alfena Hospital—Trofa Health Group, Health Sciences Research Unit: Nursing, Nursing School of Coimbra, 3000-232 Coimbra, Portugal; moc.liamg@otuoccdapilif
Ana Filipa Cardoso
Elzbieta bobrowicz-campos.
4 Health Sciences Research Unit: Nursing, Nursing School of Coimbra, 3004-011 Coimbra, Portugal; [email protected] (E.B.-C.); tp.cfnese@stnasasiul (L.S.); tp.cfnese@ohnituocv (V.C.); tp.cfnese@otnipaleinad (D.P.)
Luísa Santos
Rogério rodrigues, verónica coutinho, daniela pinto, mary-anne ramis.
5 Mater Health, Evidence in Practice Unit & Queensland Centre for Evidence Based Nursing and Midwifery: A Joanna Briggs Institute Centre of Excellence, 4101 Brisbane, Australia; [email protected]
Manuel Alves Rodrigues
João apóstolo, associated data.
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available because this issue was not considered within the informed consent signed by the participants of the study.
Evidence-based practice (EBP) prevents unsafe/inefficient practices and improves healthcare quality, but its implementation is challenging due to research and practice gaps. A focused educational program can assist future nurses to minimize these gaps. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of an EBP educational program on undergraduate nursing students’ EBP knowledge and skills. A cluster randomized controlled trial was undertaken. Six optional courses in the Bachelor of Nursing final year were randomly assigned to the experimental (EBP educational program) or control group. Nursing students’ EBP knowledge and skills were measured at baseline and post-intervention. A qualitative analysis of 18 students’ final written work was also performed. Results show a statistically significant interaction between the intervention and time on EBP knowledge and skills ( p = 0.002). From pre- to post-intervention, students’ knowledge and skills on EBP improved in both groups (intervention group: p < 0.001; control group: p < 0.001). At the post-intervention, there was a statistically significant difference in EBP knowledge and skills between intervention and control groups ( p = 0.011). Students in the intervention group presented monographs with clearer review questions, inclusion/exclusion criteria, and methodology compared to students in the control group. The EBP educational program showed a potential to promote the EBP knowledge and skills of future nurses.
1. Introduction
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is defined as “clinical decision-making that considers the best available evidence; the context in which the care is delivered; client preference; and the professional judgment of the health professional” [ 1 ] (p. 2). EBP implementation is recommended in clinical settings [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ] as it has been attributed to promoting high-value health care, improving the patient experience and health outcomes, as well as reducing health care costs [ 6 ]. Nevertheless, EBP is not the standard of care globally [ 7 , 8 , 9 ], and some studies acknowledge education as an approach to promote EBP adoption, implementation, and sustainment [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ].
It has been recommended that educational curricula for health students should be based on the five steps of EBP in order to support developing knowledge, skills, and positive attitudes toward EBP [ 16 ]. These steps are: translation of uncertainty into an answerable question; search for and retrieval of evidence; critical appraisal of evidence for validity and clinical importance; application of appraised evidence to practice; and evaluation of performance [ 16 ].
To respond to this recommendation, undergraduate nursing curricula should include courses, teaching strategies, and training that focus on the development of research and EBP skills for nurses to be able to incorporate valid and relevant research findings in practice. Nevertheless, teaching research and EBP to undergraduate nursing students is a challenging task. Some studies report that undergraduate students have negative attitudes/beliefs toward research and EBP, especially toward the statistical components of the research courses and the complex terminology used. Additionally, students may not understand the importance of the link between research and clinical practice [ 17 , 18 , 19 ]. In fact, a lack of EBP and research knowledge is commonly reported by nurses and nursing students as a barrier to EBP. It is imperative to provide the future nurses with research and EBP skills in order to overcome the barriers to EBP use in clinical settings.
At an international level, several studies have been performed with undergraduate nursing students to assess the effectiveness of EBP interventions on multiple outcomes, such as EBP knowledge and skills [ 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 ]. The Classification Rubric for EBP Assessment Tools in Education (CREATE) [ 24 ] suggests EBP knowledge should be assessed cognitively using paper and pencil tests, as EBP knowledge is defined as “learners’ retention of facts and concepts about EBP” [ 24 ] (p. 5). Additionally, the CREATE framework suggests EBP skills should be assessed using performance tests, as skills are defined as “the application of knowledge” [ 24 ] (p. 5). Despite these recommendations, few studies have assessed EBP knowledge and skills using both cognitive and performance instruments.
Therefore, this study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of an EBP educational program on undergraduate nursing students’ EBP knowledge and skills using a specific cognitive and performance instrument. The intervention used in this study was recently developed [ 25 ], and this is the first study designed to assess its effectiveness in undergraduate EBP.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. design.
A cluster randomized controlled trial with two-armed parallel group design was undertaken (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: {"type":"clinical-trial","attrs":{"text":"NCT03411668","term_id":"NCT03411668"}} NCT03411668 ).
2.2. Sample Size Calculation
The sample size was calculated using the software G*Power 3.1.9.2. (Heinrich-Heine-Universität Dusseldorf, Düsseldorf, Germany) Recognizing that there were no studies performed a priori using a cognitive and performance instrument to assess the effectiveness of an EBP educational program on undergraduate nursing students’ EBP knowledge and skills, we used an effect size of 0.25, which is a small effect size as proposed by Cohen [ 26 ]. A power analysis based on a type I error of 0.05; power of 0.80; effect size f = 0.25; and ANOVA repeated measures between factors determined a sample size of 98 as total.
Taking into account that our study used clusters (optional courses) and that each one had an average of 25 students, we needed at least four clusters to cover the total sample size of 98. However, to cover potential losses to follow-up, we included a total of six optional courses.
2.3. Participants’ Recruitment and Randomization
We recruited participants from one Portuguese nursing school in 2018. From the 12 optional clinical nursing courses (such as Community Nursing Intervention in Vulnerable Groups; Ageing; Health and Citizenship; The Child with Special Needs: Diagnoses and Interventions in Pediatric Nursing; Liaison Psychiatry Nursing; Nursing in the Emergency Room; etc.) in the 8th semester of the nursing program (last year before graduation), students from three clinical nursing courses were randomly assigned to the experimental group (EBP educational program) and students from another three clinical nursing courses were randomly assigned to the control group (no intervention— education as usual ) before the baseline assessment. An independent researcher performed this assignment using a random number generator from the random.org website [ 27 ]. This assignment was performed based on a list of the 12 optional courses provided through the nursing school’s website.
2.4. Intervention Condition
The participants in the intervention group received education as usual plus the EBP educational program, which was developed by Cardoso, Rodrigues, and Apóstolo [ 25 ]. This intervention included EBP contents regarding models of thinking about EBP, systematic reviews types, review question development, searching for studies, study selection process, data extraction, and data synthesis.
This program was implemented in 6 sessions over 17 weeks:
- Sessions 1–3—total of 12 h (4 h per session) during the first 7 weeks using expository methods with practice tasks to groups of 20–30 students.
- Sessions 4–6—total of 6 h (2 h per session) during the last 10 weeks using active methods through mentoring to groups of 2–3 students.
Due to the nature of the intervention, it was not possible to blind participants regarding treatment assignment nor was it feasible to blind the individuals delivering treatment.
2.5. Control Condition
The participants in the control group received only education as usual; i.e., students allocated to this control condition received the standard educational contents (theoretical, theoretical–practical, practical) delivered by the nursing educators of the selected nursing school.
2.6. Assessment
All participants were assessed before (week 0) and after the intervention (week 18) using a self-report instrument. EBP knowledge and skills were assessed by the Adapted Fresno Test for undergraduate nursing students [ 28 ]. This instrument was adapted from the Fresno Test, which was originally developed in 2003 to measure knowledge and skills on EBP in family practice residents [ 29 ]. The Adapted Fresno Test for undergraduate nursing students has seven short answer questions and two fill-in-the-blank questions [ 28 ]. At the beginning of the instrument, two scenarios, which suggest clinical uncertainty, are presented. These two scenarios are used to guide the answers to questions 1 to 4: (1) write a clinical question; (2) identify and discuss the strengths and weaknesses of information sources as well as the advantages and disadvantages of information sources; (3) identify the type of study most suitable for answering the question of one of the clinical scenarios and justify the choice; and (4) describe a possible search strategy in Medline for one of the clinical scenarios, explaining the rationale. The next three short answer questions require that the students identify topics for determining the relevance and validity of a research study and address the magnitude and value of research findings. The last two questions are fill-in-the-blank questions. The answers are scored using a modified standardized grading system [ 28 ], which was adapted from the original [ 29 ]. The instrument has a total minimum score of 0 and a maximum score of 101. The inter-rater correlation for the total score of the Adapted Fresno Test was 0.826 [ 28 ]. The rater that graded the answers to the Adapted Fresno Test was blinded to treatment assignment.
Despite the fact that in the study proposal we did not consider any kind of qualitative analysis in order to assess EBP knowledge and skills in a more practical context, we decided during the development of the study to perform a qualitative analysis of monographs at the posttest. The monographs were developed by small groups of nursing students and were the final written work submitted by the students for their bachelor’s degree course. In this work, the students were asked to define a review question regarding the context of clinical practice where they were performing their clinical training. Students then proceeded to answer the review question through a systematic process of searching and selecting relevant studies and extracting and synthesizing the data. From the 58 submitted monographs (30 from the control group and 28 from the intervention group), 18 were randomized for evaluation (nine from the control group and nine from the intervention group) by an independent researcher using the random.org website [ 27 ] based on a list provided by the research team. Three independent experts (one psychologist with a doctoral qualification and two qualified nurses, one with a master’s degree) performed a qualitative analysis of the selected monographs. All experts had experience with the EBP approach and were blinded to treatment assignment. The experts independently used an evaluation form to guide the qualitative analysis of each monograph. This form presented 11 guiding criteria regarding review questions, inclusion/exclusion criteria, methodology (namely search strategy, study selection process, data extraction, and data synthesis), results presentation, and congruency between the review questions and the answers to them that were provided in the conclusion section. Thereafter, the experts met to discuss any discrepancies in their qualitative analysis until consensus was reached.
2.7. Statistical Analyses
The data were analyzed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS; version 24.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Differences in sociodemographic characteristics of study participants and outcome data at baseline were analyzed using Pearson’s chi-squared test for nominal data and independent the t -test for continuous data.
Taking into account the central limit theorem and that ANOVA tests are robust to violation of assumptions [ 30 ], we decided to perform two-way mixed ANOVA to compare the outcome between and within groups. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to analyze how many participants had improved their EBP knowledge and skills item-by-item, how many remained the same, and how many had decreased performance within each group. Statistical significance was determined by p -values less than 0.05.
To minimize the noncompliance impact, an intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis was used to analyze participants in the groups that they were initially randomized to [ 31 ] by using the last observation carried forward imputation method.
2.8. Ethics
This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Coimbra (Reference: CE-037/2017). The institution where the study was carried out provided written approval. All participants gave informed consent, and the data were managed in a confidential way.
Twelve potential clusters (optional courses in the 8th semester of the nursing program) were identified as eligible for this study. Of these, three were randomized for the intervention group and three for the control group. During the intervention, eight participants (two in the intervention group and six in the control group) were lost to follow-up because they did not fill-in the instrument in the post-intervention. Figure 1 shows the flow of participants through each stage of the trial.

Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) diagram showing the flow of participants through each stage of the trial. ITT: intention-to-treat.
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
As Table 1 displays, 148 undergraduate nursing students with an average age of 21.95 years (SD = 2.25; range: 21–41) participated in the study. A large majority of the sample were female ( n = 118, 79.7%), had a 12th grade educational level ( n = 144, 97.3%), and had participated in some form of EBP training ( n = 121, 81.8%).
Socio-demographic characterization of the sample—ITT analysis.
* Defined as any kind and duration of evidence-based practice (EBP) training, such as EBP contents in a course, a workshop, a seminar.
At baseline, the experimental and control groups were comparable regarding sex, age, education, EBP training, and performance on the Adapted Fresno Test ( Table 1 and Table 3). The baseline data were similar with dropouts excluded; therefore, only ITT analysis results are presented.
3.2. EBP Knowledge and Skills
3.2.1. adapted fresno test.
The two-way mixed ANOVA showed a statistically significant interaction between the intervention and time on EBP knowledge and skills, F (1, 146) = 9.550, p = 0.002, partial η 2 = 0.061 ( Table 2 ). Excluding the dropouts, the two-way mixed ANOVA analysis was similar. Thus, only the ITT analysis results are presented.
Main effects of time and group and interaction effects on EBP knowledge and skills—ITT analysis.
To determine the difference between groups at baseline and post-intervention, two separate between-subjects ANOVAs (i.e., two separate one-way ANOVAs) were performed. At the pre-intervention, there was no statistically significant difference in EBP knowledge and skills between groups: F (1,146) = 0.221, p = 0.639, partial η 2 = 0.002. At the post-intervention, there was a statistically significant difference in EBP knowledge and skills between groups: F (1,146) = 6.720, p = 0.011, partial η 2 = 0.044 ( Table 3 ).
Repeated measures ANOVA and between-subjects ANOVA—ITT analysis.
To determine the differences within groups from the baseline to post-intervention, two separate within-subjects ANOVAs (repeated measures ANOVAs) were performed. There was a statistically significant effect of time on EBP knowledge and skills for the intervention group: F (1,73) = 53.028, p < 0.001, partial η 2 = 0.421 and for the control group: F (1,73) = 13.832, p < 0.001, partial η 2 = 0.159 ( Table 3 ).
The results of repeated measures ANOVA and between-subjects ANOVA analysis are similar if we exclude the dropouts; therefore, only ITT analysis results are presented.
The results of the Wilcoxon signed-rank test for each item of the Adapted Fresno Test are presented in Table 4 . The results of this analysis revealed that students in both the intervention and control groups significantly improved their knowledge and skills in writing a focused clinical question (Item 1) (intervention group: Z = −4.572, p < 0.000; control group: Z = −2.338, p = 0.019), in building a search strategy (item 3) (intervention group: Z = −4.740, p < 0.000; control group: Z = −4.757, p < 0.000), in identifying and justifying the study design most suitable for answering the question of one of the clinical scenarios (item 4) (intervention group: Z = −4.508, p < 0.000; control group: Z = −3.738, p < 0.000), and in describing the characteristics of a study to determine its relevance (item 5) (intervention group: Z = −2.699, p = 0.007; control group: Z = −1.980, p = 0.048).
Within groups comparison with Wilcoxon signed-rank test for each item of the Adapted Fresno Test—ITT analysis.
The students in the control group significantly improved their knowledge and skills in describing the characteristics of a study to determine its validity (item 6) ( Z = −2.714, p = 0.007). The students in the intervention group significantly improved their knowledge and skills in describing the characteristics of a study to determine its magnitude and significance (item 7) ( Z = −2.543, p = 0.011). No other significant differences were detected.
The results of the within groups comparison with the Wilcoxon signed-rank test are similar if we exclude the dropouts; therefore, only ITT analysis results are presented.
3.2.2. Qualitative Analysis of Monographs
Based on the experts’ consensus report of each monograph, the analysis of the intervention group monographs showed that the students’ groups clearly defined their review questions and inclusion/exclusion criteria. These groups of students effectively searched for studies using appropriate databases, keywords, Boolean operators, and truncation. Additionally, we found thorough descriptions from students concerning the selection process, data extraction, and data synthesis. However, only three students’ groups provided a good description of the review findings with an appropriate data synthesis as well as a clear answer to the review question in the conclusion section of their monographs. It is noted that the criteria for the results and conclusion sections were more difficult to successfully achieve, even in the intervention group.
The monographs of the control groups showed weaknesses throughout. From the nine monographs of the control group, only two presented the review question in a way that was clearly defined. In all of the monographs, the inclusion/exclusion criteria were either not very informative, unclear, or did not match with the defined review questions. Additionally, the search strategies were not clear and demonstrated limited understanding, such as lack of use of appropriate synonyms, absent truncations, and no definition of the search field for each word or expression to be searched. None of the monographs from the control group reported information about the methods used to study the selection process, to extract data, or to synthesize data. In the conclusion section, students from the control group also demonstrated difficulties in synthesizing the data and limitations by providing a clear answer to the review question.
4. Discussion
This study sought to evaluate the effectiveness of an EBP educational program on undergraduate nursing students’ EBP knowledge and skills. Even though both groups improved after the intervention in EBP knowledge and skills, the study results showed that the improvement was greater in the intervention group. This result was reinforced by the results of the qualitative analysis of monographs.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to use a cognitive and performance assessment instrument (Adapted Fresno Test) with undergraduate nursing students, as suggested by CREATE [ 24 ]. Additionally, it is the first study conducted using the EBP education program [ 25 ]. Therefore, comparison of our findings with similar studies in terms of the type of assessment instrument and intervention is limited.
However, comparing our study with other previous research using other types of instruments and interventions demonstrates similar results [ 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 ]. In a quasi-experimental study [ 20 ], it was found that an EBP educational teaching strategy showed positive results in improving EBP knowledge in undergraduate nursing students. A study showed that undergraduate nursing students who received an EBP-focused interactive teaching intervention improved their EBP knowledge [ 21 ]. Another study indicated that a 15-week educational intervention in undergraduate nursing students (second- and third-year) significantly improved their EBP knowledge and skills [ 22 ]. In addition, a study by Zhang, Zeng, Chen, and Li revealed a significant improvement in undergraduate nursing students’ EBP knowledge after participating in a two-phase intervention: a self-directed learning process and a workshop for critical appraisal of literature [ 23 ].
Despite the effectiveness of the program in improving EBP knowledge and skills, the students included in the present study had low levels of EBP knowledge and skills as assessed by the Adapted Fresno Test at the pretest and posttest. These low levels of EBP knowledge and skills, especially at the pretest, might have influenced our study results. As a matter of fact, the Adapted Fresno Test is a demanding test since it requires that students retrieve and apply knowledge while doing a task associated with EBP based on scenarios involving clinical uncertainty. Consequently, this kind of test is very useful to truly assess EBP knowledge retention and abilities in clinical scenarios that do not allow guessing the answers. Notwithstanding, due to these characteristics, the Adapted Fresno Test may possibly be less sensitive when small changes occur or when students have low levels of EBP knowledge and skills. Nevertheless, even using instruments with Likert scales, other studies also showed that students have low levels of EBP knowledge and skills [ 21 , 22 , 23 ].
The low levels of EBP knowledge and skills of the undergraduate nursing students may be a reflection of a persistent, traditional education with regard to research. By this we mean that the focus of training remains on primary research—preparing students to be “research generators” instead of preparing them to be “evidence users” [ 32 ]. Furthermore, the designed and tested intervention used in this study was limited in time (only 17 weeks), was provided by only two instructors, and was delivered to fourth-year undergraduate nursing students, which are limitations for curriculum-wide integration of EBP.
Indeed, a curriculum that promotes EBP should facilitate students’ acquisition of EBP knowledge and skills over time and with levels of increasing complexity through their participation in EBP courses and during their clinical practice experiences [ 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 ]. As Moch, Cronje, and Branson suggest, “It is only in such practical settings that students can experience the challenges intrinsic to applying scientific evidence to the care of real patients. In these clinical settings, students can experience both the frustrations and the triumphs inevitable to integrating scientific knowledge into patient care.” [ 35 ] (p. 11). Therefore, in future studies, other broad approaches for curriculum-wide integration of EBP as well as its long-term effects should be evaluated.
Previously in the Discussion, we highlighted the limitations of the proposed intervention in terms of time constraints (only 17 weeks), instructors’ constraints (only two instructors provided the intervention), and participants’ constraints (fourth-year undergraduate nursing students). In addition, the study was also restricted to one Portuguese nursing school, which can limit the generalization of the results. However, our study tried to address some of the fragilities identified in other studies [ 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 ] on the effectiveness of EBP educational interventions by including a control group and by measuring EBP knowledge and skills with an objective measure and not a self-reported measure.
Bearing this in mind, future studies in multiple sites should assess the long-term effects of the EBP educational intervention and the impact on EBP knowledge and skills of potential variations in contents and teaching methods. In addition, studies using more broad interventions for curriculum-wide integration of EBP should also be performed.
5. Conclusions
Our findings show that the EBP educational program was effective in improving the EBP knowledge and skills of undergraduate nursing students. Therefore, the use of an EBP approach as a complement to the research education of undergraduate nursing students should be promoted by nursing schools and educators. This will help to prepare the future nurses with the EBP knowledge and skills that are essential to overcome the barriers to EBP use in clinical settings, and consequently, to contribute to better health outcomes.
Acknowledgments
This paper contributed toward the D.C. PhD in Health Sciences—Nursing. The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the Health Sciences Research Unit: Nursing (UICISA: E), hosted by the Nursing School of Coimbra (ESEnfC) and funded by the Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT). Moreover, the authors gratefully thank Catarina Oliveira for all the support as a Ph.D. supervisor and Isabel Fernandes, Maria da Nazaré Cerejo, and Irma Brito for help and facilitation of data collection.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.C., M.A.R., and J.A.; methodology, D.C., M.A.R., and J.A.; validation, D.C., M.A.R., and J.A.; formal analysis, D.C., F.C., and A.F.C.; investigation, D.C., F.C., A.F.C., E.B.-C., L.S., R.R., V.C., D.P., M.-A.R., M.A.R., and J.A.; resources, D.C., M.A.R., and J.A.; data curation, D.C., F.C., and A.F.C.; writing—original draft preparation, D.C.; writing—review and editing, F.C., A.F.C., E.B.-C., L.S., R.R., V.C., D.P., M.-A.R., M.A.R., and J.A.; supervision, M.A.R. and J.A.; project administration, D.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
This work was funded by National Funds through the FCT—Foundation for Science and Technology, I.P., within the scope of the project Ref. UIDP/00742/2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Ethical Committee of Faculty of Medicine of the University of Coimbra (protocol code: CE-037/2017 and date of approval: 22 May 2017).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Psychology: Research and Review
- Open access
- Published: 19 March 2021
Appraising psychotherapy case studies in practice-based evidence: introducing Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE)
- Greta Kaluzeviciute ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1197-177X 1
Psicologia: Reflexão e Crítica volume 34 , Article number: 9 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
7263 Accesses
5 Citations
5 Altmetric
Metrics details
Systematic case studies are often placed at the low end of evidence-based practice (EBP) due to lack of critical appraisal. This paper seeks to attend to this research gap by introducing a novel Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE). First, issues around knowledge generation and validity are assessed in both EBP and practice-based evidence (PBE) paradigms. Although systematic case studies are more aligned with PBE paradigm, the paper argues for a complimentary, third way approach between the two paradigms and their ‘exemplary’ methodologies: case studies and randomised controlled trials (RCTs). Second, the paper argues that all forms of research can produce ‘valid evidence’ but the validity itself needs to be assessed against each specific research method and purpose. Existing appraisal tools for qualitative research (JBI, CASP, ETQS) are shown to have limited relevance for the appraisal of systematic case studies through a comparative tool assessment. Third, the paper develops purpose-oriented evaluation criteria for systematic case studies through CaSE Checklist for Essential Components in Systematic Case Studies and CaSE Purpose-based Evaluative Framework for Systematic Case Studies. The checklist approach aids reviewers in assessing the presence or absence of essential case study components (internal validity). The framework approach aims to assess the effectiveness of each case against its set out research objectives and aims (external validity), based on different systematic case study purposes in psychotherapy. Finally, the paper demonstrates the application of the tool with a case example and notes further research trajectories for the development of CaSE tool.
Introduction
Due to growing demands of evidence-based practice, standardised research assessment and appraisal tools have become common in healthcare and clinical treatment (Hannes, Lockwood, & Pearson, 2010 ; Hartling, Chisholm, Thomson, & Dryden, 2012 ; Katrak, Bialocerkowski, Massy-Westropp, Kumar, & Grimmer, 2004 ). This allows researchers to critically appraise research findings on the basis of their validity, results, and usefulness (Hill & Spittlehouse, 2003 ). Despite the upsurge of critical appraisal in qualitative research (Williams, Boylan, & Nunan, 2019 ), there are no assessment or appraisal tools designed for psychotherapy case studies.
Although not without controversies (Michels, 2000 ), case studies remain central to the investigation of psychotherapy processes (Midgley, 2006 ; Willemsen, Della Rosa, & Kegerreis, 2017 ). This is particularly true of systematic case studies, the most common form of case study in contemporary psychotherapy research (Davison & Lazarus, 2007 ; McLeod & Elliott, 2011 ).
Unlike the classic clinical case study, systematic cases usually involve a team of researchers, who gather data from multiple different sources (e.g., questionnaires, observations by the therapist, interviews, statistical findings, clinical assessment, etc.), and involve a rigorous data triangulation process to assess whether the data from different sources converge (McLeod, 2010 ). Since systematic case studies are methodologically pluralistic, they have a greater interest in situating patients within the study of a broader population than clinical case studies (Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ). Systematic case studies are considered to be an accessible method for developing research evidence-base in psychotherapy (Widdowson, 2011 ), especially since they correct some of the methodological limitations (e.g. lack of ‘third party’ perspectives and bias in data analysis) inherent to classic clinical case studies (Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ). They have been used for the purposes of clinical training (Tuckett, 2008 ), outcome assessment (Hilliard, 1993 ), development of clinical techniques (Almond, 2004 ) and meta-analysis of qualitative findings (Timulak, 2009 ). All these developments signal a revived interest in the case study method, but also point to the obvious lack of a research assessment tool suitable for case studies in psychotherapy (Table 1 ).
To attend to this research gap, this paper first reviews issues around the conceptualisation of validity within the paradigms of evidence-based practice (EBP) and practice-based evidence (PBE). Although case studies are often positioned at the low end of EBP (Aveline, 2005 ), the paper suggests that systematic cases are a valuable form of evidence, capable of complimenting large-scale studies such as randomised controlled trials (RCTs). However, there remains a difficulty in assessing the quality and relevance of case study findings to broader psychotherapy research.
As a way forward, the paper introduces a novel Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE) in the form of CaSE Purpose - based Evaluative Framework for Systematic Case Studies and CaSE Checklist for Essential Components in Systematic Case Studies . The long-term development of CaSE would contribute to psychotherapy research and practice in three ways.
Given the significance of methodological pluralism and diverse research aims in systematic case studies, CaSE will not seek to prescribe explicit case study writing guidelines, which has already been done by numerous authors (McLeod, 2010 ; Meganck, Inslegers, Krivzov, & Notaerts, 2017 ; Willemsen et al., 2017 ). Instead, CaSE will enable the retrospective assessment of systematic case study findings and their relevance (or lack thereof) to broader psychotherapy research and practice. However, there is no reason to assume that CaSE cannot be used prospectively (i.e. producing systematic case studies in accordance to CaSE evaluative framework, as per point 3 in Table 2 ).
The development of a research assessment or appraisal tool is a lengthy, ongoing process (Long & Godfrey, 2004 ). It is particularly challenging to develop a comprehensive purpose - oriented evaluative framework, suitable for the assessment of diverse methodologies, aims and outcomes. As such, this paper should be treated as an introduction to the broader development of CaSE tool. It will introduce the rationale behind CaSE and lay out its main approach to evidence and evaluation, with further development in mind. A case example from the Single Case Archive (SCA) ( https://singlecasearchive.com ) will be used to demonstrate the application of the tool ‘in action’. The paper notes further research trajectories and discusses some of the limitations around the use of the tool.
Separating the wheat from the chaff: what is and is not evidence in psychotherapy (and who gets to decide?)
The common approach: evidence-based practice.
In the last two decades, psychotherapy has become increasingly centred around the idea of an evidence-based practice (EBP). Initially introduced in medicine, EBP has been defined as ‘conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients’ (Sackett, Rosenberg, Gray, Haynes, & Richardson, 1996 ). EBP revolves around efficacy research: it seeks to examine whether a specific intervention has a causal (in this case, measurable) effect on clinical populations (Barkham & Mellor-Clark, 2003 ). From a conceptual standpoint, Sackett and colleagues defined EBP as a paradigm that is inclusive of many methodologies, so long as they contribute towards clinical decision-making process and accumulation of best currently available evidence in any given set of circumstances (Gabbay & le May, 2011 ). Similarly, the American Psychological Association (APA, 2010 ) has recently issued calls for evidence-based systematic case studies in order to produce standardised measures for evaluating process and outcome data across different therapeutic modalities.
However, given EBP’s focus on establishing cause-and-effect relationships (Rosqvist, Thomas, & Truax, 2011 ), it is unsurprising that qualitative research is generally not considered to be ‘gold standard’ or ‘efficacious’ within this paradigm (Aveline, 2005 ; Cartwright & Hardie, 2012 ; Edwards, 2013 ; Edwards, Dattilio, & Bromley, 2004 ; Longhofer, Floersch, & Hartmann, 2017 ). Qualitative methods like systematic case studies maintain an appreciation for context, complexity and meaning making. Therefore, instead of measuring regularly occurring causal relations (as in quantitative studies), the focus is on studying complex social phenomena (e.g. relationships, events, experiences, feelings, etc.) (Erickson, 2012 ; Maxwell, 2004 ). Edwards ( 2013 ) points out that, although context-based research in systematic case studies is the bedrock of psychotherapy theory and practice, it has also become shrouded by an unfortunate ideological description: ‘anecdotal’ case studies (i.e. unscientific narratives lacking evidence, as opposed to ‘gold standard’ evidence, a term often used to describe the RCT method and the therapeutic modalities supported by it), leading to a further need for advocacy in and defence of the unique epistemic process involved in case study research (Fishman, Messer, Edwards, & Dattilio, 2017 ).
The EBP paradigm prioritises the quantitative approach to causality, most notably through its focus on high generalisability and the ability to deal with bias through randomisation process. These conditions are associated with randomised controlled trials (RCTs) but are limited (or, as some argue, impossible) in qualitative research methods such as the case study (Margison et al., 2000 ) (Table 3 ).
‘Evidence’ from an EBP standpoint hovers over the epistemological assumption of procedural objectivity : knowledge can be generated in a standardised, non-erroneous way, thus producing objective (i.e. with minimised bias) data. This can be achieved by anyone, as long as they are able to perform the methodological procedure (e.g. RCT) appropriately, in a ‘clearly defined and accepted process that assists with knowledge production’ (Douglas, 2004 , p. 131). If there is a well-outlined quantitative form for knowledge production, the same outcome should be achieved regardless of who processes or interprets the information. For example, researchers using Cochrane Review assess the strength of evidence using meticulously controlled and scrupulous techniques; in turn, this minimises individual judgment and creates unanimity of outcomes across different groups of people (Gabbay & le May, 2011 ). The typical process of knowledge generation (through employing RCTs and procedural objectivity) in EBP is demonstrated in Fig. 1 .
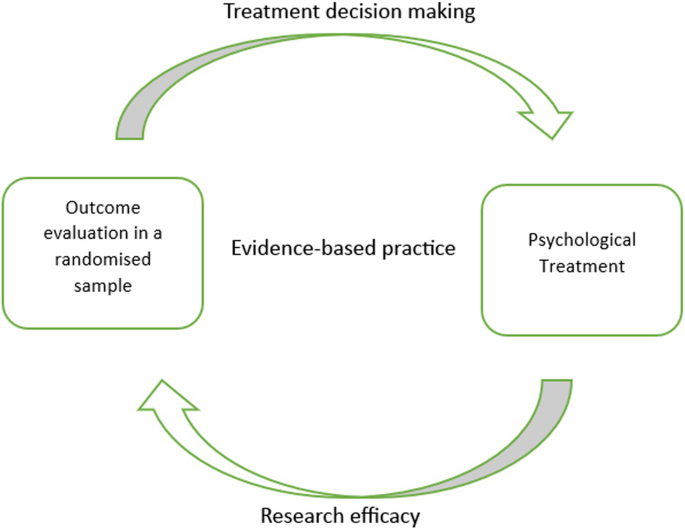
Typical knowledge generation process in evidence–based practice (EBP)
In EBP, the concept of validity remains somewhat controversial, with many critics stating that it limits rather than strengthens knowledge generation (Berg, 2019 ; Berg & Slaattelid, 2017 ; Lilienfeld, Ritschel, Lynn, Cautin, & Latzman, 2013 ). This is because efficacy research relies on internal validity . At a general level, this concept refers to the congruence between the research study and the research findings (i.e. the research findings were not influenced by anything external to the study, such as confounding variables, methodological errors and bias); at a more specific level, internal validity determines the extent to which a study establishes a reliable causal relationship between an independent variable (e.g. treatment) and independent variable (outcome or effect) (Margison et al., 2000 ). This approach to validity is demonstrated in Fig. 2 .
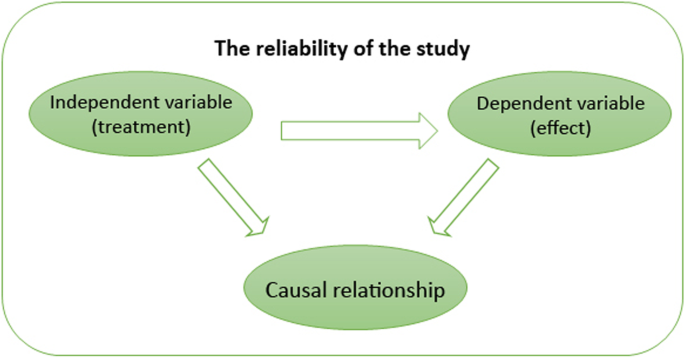
Internal validity
Social scientists have argued that there is a trade-off between research rigour and generalisability: the more specific the sample and the more rigorously defined the intervention, the outcome is likely to be less applicable to everyday, routine practice. As such, there remains a tension between employing procedural objectivity which increases the rigour of research outcomes and applying such outcomes to routine psychotherapy practice where scientific standards of evidence are not uniform.
According to McLeod ( 2002 ), inability to address questions that are most relevant for practitioners contributed to a deepening research–practice divide in psychotherapy. Studies investigating how practitioners make clinical decisions and the kinds of evidence they refer to show that there is a strong preference for knowledge that is not generated procedurally, i.e. knowledge that encompasses concrete clinical situations, experiences and techniques. A study by Stewart and Chambless ( 2007 ) sought to assess how a larger population of clinicians (under APA, from varying clinical schools of thought and independent practices, sample size 591) make treatment decisions in private practice. The study found that large-scale statistical data was not the primary source of information sought by clinicians. The most important influences were identified as past clinical experiences and clinical expertise ( M = 5.62). Treatment materials based on clinical case observations and theory ( M = 4.72) were used almost as frequently as psychotherapy outcome research findings ( M = 4.80) (i.e. evidence-based research). These numbers are likely to fluctuate across different forms of psychotherapy; however, they are indicative of the need for research about routine clinical settings that does not isolate or generalise the effect of an intervention but examines the variations in psychotherapy processes.
The alternative approach: practice-based evidence
In an attempt to dissolve or lessen the research–practice divide, an alternative paradigm of practice-based evidence (PBE) has been suggested (Barkham & Mellor-Clark, 2003 ; Fox, 2003 ; Green & Latchford, 2012 ; Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ; Laska, Motulsky, Wertz, Morrow, & Ponterotto, 2014 ; Margison et al., 2000 ). PBE represents a shift in how we think about evidence and knowledge generation in psychotherapy. PBE treats research as a local and contingent process (at least initially), which means it focuses on variations (e.g. in patient symptoms) and complexities (e.g. of clinical setting) in the studied phenomena (Fox, 2003 ). Moreover, research and theory-building are seen as complementary rather than detached activities from clinical practice. That is to say, PBE seeks to examine how and which treatments can be improved in everyday clinical practice by flagging up clinically salient issues and developing clinical techniques (Barkham & Mellor-Clark, 2003 ). For this reason, PBE is concerned with the effectiveness of research findings: it evaluates how well interventions work in real-world settings (Rosqvist et al., 2011 ). Therefore, although it is not unlikely for RCTs to be used in order to generate practice-informed evidence (Horn & Gassaway, 2007 ), qualitative methods like the systematic case study are seen as ideal for demonstrating the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions with individual patients (van Hennik, 2020 ) (Table 4 ).
PBE’s epistemological approach to ‘evidence’ may be understood through the process of concordant objectivity (Douglas, 2004 ): ‘Instead of seeking to eliminate individual judgment, … [concordant objectivity] checks to see whether the individual judgments of people in fact do agree’ (p. 462). This does not mean that anyone can contribute to the evaluation process like in procedural objectivity, where the main criterion is following a set quantitative protocol or knowing how to operate a specific research design. Concordant objectivity requires that there is a set of competent observers who are closely familiar with the studied phenomenon (e.g. researchers and practitioners who are familiar with depression from a variety of therapeutic approaches).
Systematic case studies are a good example of PBE ‘in action’: they allow for the examination of detailed unfolding of events in psychotherapy practice, making it the most pragmatic and practice-oriented form of psychotherapy research (Fishman, 1999 , 2005 ). Furthermore, systematic case studies approach evidence and results through concordant objectivity (Douglas, 2004 ) by involving a team of researchers and rigorous data triangulation processes (McLeod, 2010 ). This means that, although systematic case studies remain focused on particular clinical situations and detailed subjective experiences (similar to classic clinical case studies; see Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ), they still involve a series of validity checks and considerations on how findings from a single systematic case pertain to broader psychotherapy research (Fishman, 2005 ). The typical process of knowledge generation (through employing systematic case studies and concordant objectivity) in PBE is demonstrated in Fig. 3 . The figure exemplifies a bidirectional approach to research and practice, which includes the development of research-supported psychological treatments (through systematic reviews of existing evidence) as well as the perspectives of clinical practitioners in the research process (through the study of local and contingent patient and/or treatment processes) (Teachman et al., 2012 ; Westen, Novotny, & Thompson-Brenner, 2004 ).
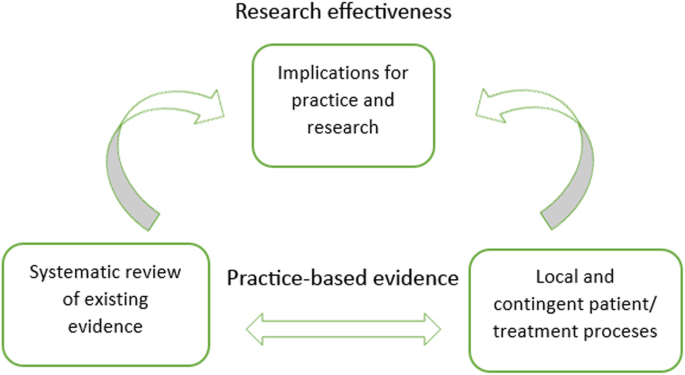
Typical knowledge generation process in practice-based evidence (PBE)
From a PBE standpoint, external validity is a desirable research condition: it measures extent to which the impact of interventions apply to real patients and therapists in everyday clinical settings. As such, external validity is not based on the strength of causal relationships between treatment interventions and outcomes (as in internal validity); instead, the use of specific therapeutic techniques and problem-solving decisions are considered to be important for generalising findings onto routine clinical practice (even if the findings are explicated from a single case study; see Aveline, 2005 ). This approach to validity is demonstrated in Fig. 4 .
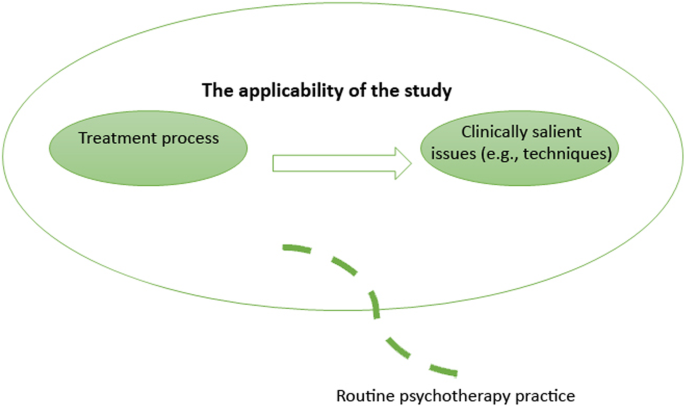
External validity
Since effectiveness research is less focused on limiting the context of the studied phenomenon (indeed, explicating the context is often one of the research aims), there is more potential for confounding factors (e.g. bias and uncontrolled variables) which in turn can reduce the study’s internal validity (Barkham & Mellor-Clark, 2003 ). This is also an important challenge for research appraisal. Douglas ( 2004 ) argues that appraising research in terms of its effectiveness may produce significant disagreements or group illusions, since what might work for some practitioners may not work for others: ‘It cannot guarantee that values are not influencing or supplanting reasoning; the observers may have shared values that cause them to all disregard important aspects of an event’ (Douglas, 2004 , p. 462). Douglas further proposes that an interactive approach to objectivity may be employed as a more complex process in debating the evidential quality of a research study: it requires a discussion among observers and evaluators in the form of peer-review, scientific discourse, as well as research appraisal tools and instruments. While these processes of rigour are also applied in EBP, there appears to be much more space for debate, disagreement and interpretation in PBE’s approach to research evaluation, partly because the evaluation criteria themselves are subject of methodological debate and are often employed in different ways by researchers (Williams et al., 2019 ). This issue will be addressed more explicitly again in relation to CaSE development (‘Developing purpose-oriented evaluation criteria for systematic case studies’ section).
A third way approach to validity and evidence
The research–practice divide shows us that there may be something significant in establishing complementarity between EBP and PBE rather than treating them as mutually exclusive forms of research (Fishman et al., 2017 ). For one, EBP is not a sufficient condition for delivering research relevant to practice settings (Bower, 2003 ). While RCTs can demonstrate that an intervention works on average in a group, clinicians who are facing individual patients need to answer a different question: how can I make therapy work with this particular case ? (Cartwright & Hardie, 2012 ). Systematic case studies are ideal for filling this gap: they contain descriptions of microprocesses (e.g. patient symptoms, therapeutic relationships, therapist attitudes) in psychotherapy practice that are often overlooked in large-scale RCTs (Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ). In particular, systematic case studies describing the use of specific interventions with less researched psychological conditions (e.g. childhood depression or complex post-traumatic stress disorder) can deepen practitioners’ understanding of effective clinical techniques before the results of large-scale outcome studies are disseminated.
Secondly, establishing a working relationship between systematic case studies and RCTs will contribute towards a more pragmatic understanding of validity in psychotherapy research. Indeed, the very tension and so-called trade-off between internal and external validity is based on the assumption that research methods are designed on an either/or basis; either they provide a sufficiently rigorous study design or they produce findings that can be applied to real-life practice. Jimenez-Buedo and Miller ( 2010 ) call this assumption into question: in their view, if a study is not internally valid, then ‘little, or rather nothing, can be said of the outside world’ (p. 302). In this sense, internal validity may be seen as a pre-requisite for any form of applied research and its external validity, but it need not be constrained to the quantitative approach of causality. For example, Levitt, Motulsky, Wertz, Morrow, and Ponterotto ( 2017 ) argue that, what is typically conceptualised as internal validity, is, in fact, a much broader construct, involving the assessment of how the research method (whether qualitative or quantitative) is best suited for the research goal, and whether it obtains the relevant conclusions. Similarly, Truijens, Cornelis, Desmet, and De Smet ( 2019 ) suggest that we should think about validity in a broader epistemic sense—not just in terms of psychometric measures, but also in terms of the research design, procedure, goals (research questions), approaches to inquiry (paradigms, epistemological assumptions), etc.
The overarching argument from research cited above is that all forms of research—qualitative and quantitative—can produce ‘valid evidence’ but the validity itself needs to be assessed against each specific research method and purpose. For example, RCTs are accompanied with a variety of clearly outlined appraisal tools and instruments such as CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme) that are well suited for the assessment of RCT validity and their implications for EBP. Systematic case studies (or case studies more generally) currently have no appraisal tools in any discipline. The next section evaluates whether existing qualitative research appraisal tools are relevant for systematic case studies in psychotherapy and specifies the missing evaluative criteria.
The relevance of existing appraisal tools for qualitative research to systematic case studies in psychotherapy
What is a research tool.
Currently, there are several research appraisal tools, checklists and frameworks for qualitative studies. It is important to note that tools, checklists and frameworks are not equivalent to one another but actually refer to different approaches to appraising the validity of a research study. As such, it is erroneous to assume that all forms of qualitative appraisal feature the same aims and methods (Hannes et al., 2010 ; Williams et al., 2019 ).
Generally, research assessment falls into two categories: checklists and frameworks . Checklist approaches are often contrasted with quantitative research, since the focus is on assessing the internal validity of research (i.e. researcher’s independence from the study). This involves the assessment of bias in sampling, participant recruitment, data collection and analysis. Framework approaches to research appraisal, on the other hand, revolve around traditional qualitative concepts such as transparency, reflexivity, dependability and transferability (Williams et al., 2019 ). Framework approaches to appraisal are often challenging to use because they depend on the reviewer’s familiarisation and interpretation of the qualitative concepts.
Because of these different approaches, there is some ambiguity in terminology, particularly between research appraisal instruments and research appraisal tools . These terms are often used interchangeably in appraisal literature (Williams et al., 2019 ). In this paper, research appraisal tool is defined as a method-specific (i.e. it identifies a specific research method or component) form of appraisal that draws from both checklist and framework approaches. Furthermore, a research appraisal tool seeks to inform decision making in EBP or PBE paradigms and provides explicit definitions of the tool’s evaluative framework (thus minimising—but by no means eliminating—the reviewers’ interpretation of the tool). This definition will be applied to CaSE (Table 5 ).
In contrast, research appraisal instruments are generally seen as a broader form of appraisal in the sense that they may evaluate a variety of methods (i.e. they are non-method specific or they do not target a particular research component), and are aimed at checking whether the research findings and/or the study design contain specific elements (e.g. the aims of research, the rationale behind design methodology, participant recruitment strategies, etc.).
There is often an implicit difference in audience between appraisal tools and instruments. Research appraisal instruments are often aimed at researchers who want to assess the strength of their study; however, the process of appraisal may not be made explicit in the study itself (besides mentioning that the tool was used to appraise the study). Research appraisal tools are aimed at researchers who wish to explicitly demonstrate the evidential quality of the study to the readers (which is particularly common in RCTs). All forms of appraisal used in the comparative exercise below are defined as ‘tools’, even though they have different appraisal approaches and aims.
Comparing different qualitative tools
Hannes et al. ( 2010 ) identified CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme-tool), JBI (Joanna Briggs Institute-tool) and ETQS (Evaluation Tool for Qualitative Studies) as the most frequently used critical appraisal tools by qualitative researchers. All three instruments are available online and are free of charge, which means that any researcher or reviewer can readily utilise CASP, JBI or ETQS evaluative frameworks to their research. Furthermore, all three instruments were developed within the context of organisational, institutional or consortium support (Tables 6 , 7 and 8 ).
It is important to note that neither of the three tools is specific to systematic case studies or psychotherapy case studies (which would include not only systematic but also experimental and clinical cases). This means that using CASP, JBI or ETQS for case study appraisal may come at a cost of overlooking elements and components specific to the systematic case study method.
Based on Hannes et al. ( 2010 ) comparative study of qualitative appraisal tools as well as the different evaluation criteria explicated in CASP, JBI and ETQS evaluative frameworks, I assessed how well each of the three tools is attuned to the methodological , clinical and theoretical aspects of systematic case studies in psychotherapy. The latter components were based on case study guidelines featured in the journal of Pragmatic Case Studies in Psychotherapy as well as components commonly used by published systematic case studies across a variety of other psychotherapy journals (e.g. Psychotherapy Research , Research In Psychotherapy : Psychopathology Process And Outcome , etc.) (see Table 9 for detailed descriptions of each component).
The evaluation criteria for each tool in Table 9 follows Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) ( 2017a , 2017b ); Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) ( 2018 ); and ETQS Questionnaire (first published in 2004 but revised continuously since). Table 10 demonstrates how each tool should be used (i.e. recommended reviewer responses to checklists and questionnaires).
Using CASP, JBI and ETQS for systematic case study appraisal
Although JBI, CASP and ETQS were all developed to appraise qualitative research, it is evident from the above comparison that there are significant differences between the three tools. For example, JBI and ETQS are well suited to assess researcher’s interpretations (Hannes et al. ( 2010 ) defined this as interpretive validity , a subcategory of internal validity ): the researcher’s ability to portray, understand and reflect on the research participants’ experiences, thoughts, viewpoints and intentions. JBI has an explicit requirement for participant voices to be clearly represented, whereas ETQS involves a set of questions about key characteristics of events, persons, times and settings that are relevant to the study. Furthermore, both JBI and ETQS seek to assess the researcher’s influence on the research, with ETQS particularly focusing on the evaluation of reflexivity (the researcher’s personal influence on the interpretation and collection of data). These elements are absent or addressed to a lesser extent in the CASP tool.
The appraisal of transferability of findings (what this paper previously referred to as external validity ) is addressed only by ETQS and CASP. Both tools have detailed questions about the value of research to practice and policy as well as its transferability to other populations and settings. Methodological research aspects are also extensively addressed by CASP and ETQS, but less so by JBI (which relies predominantly on congruity between research methodology and objectives without any particular assessment criteria for other data sources and/or data collection methods). Finally, the evaluation of theoretical aspects (referred to by Hannes et al. ( 2010 ) as theoretical validity ) is addressed only by JBI and ETQS; there are no assessment criteria for theoretical framework in CASP.
Given these differences, it is unsurprising that CASP, JBI and ETQS have limited relevance for systematic case studies in psychotherapy. First, it is evident that neither of the three tools has specific evaluative criteria for the clinical component of systematic case studies. Although JBI and ETQS feature some relevant questions about participants and their context, the conceptualisation of patients (and/or clients) in psychotherapy involves other kinds of data elements (e.g. diagnostic tools and questionnaires as well as therapist observations) that go beyond the usual participant data. Furthermore, much of the clinical data is intertwined with the therapist’s clinical decision-making and thinking style (Kaluzeviciute & Willemsen, 2020 ). As such, there is a need to appraise patient data and therapist interpretations not only on a separate basis, but also as two forms of knowledge that are deeply intertwined in the case narrative.
Secondly, since systematic case studies involve various forms of data, there is a need to appraise how these data converge (or how different methods complement one another in the case context) and how they can be transferred or applied in broader psychotherapy research and practice. These systematic case study components are attended to a degree by CASP (which is particularly attentive of methodological components) and ETQS (particularly specific criteria for research transferability onto policy and practice). These components are not addressed or less explicitly addressed by JBI. Overall, neither of the tools is attuned to all methodological, theoretical and clinical components of the systematic case study. Specifically, there are no clear evaluation criteria for the description of research teams (i.e. different data analysts and/or clinicians); the suitability of the systematic case study method; the description of patient’s clinical assessment; the use of other methods or data sources; the general data about therapeutic progress.
Finally, there is something to be said about the recommended reviewer responses (Table 10 ). Systematic case studies can vary significantly in their formulation and purpose. The methodological, theoretical and clinical components outlined in Table 9 follow guidelines made by case study journals; however, these are recommendations, not ‘set in stone’ case templates. For this reason, the straightforward checklist approaches adopted by JBI and CASP may be difficult to use for case study researchers and those reviewing case study research. The ETQS open-ended questionnaire approach suggested by Long and Godfrey ( 2004 ) enables a comprehensive, detailed and purpose-oriented assessment, suitable for the evaluation of systematic case studies. That said, there remains a challenge of ensuring that there is less space for the interpretation of evaluative criteria (Williams et al., 2019 ). The combination of checklist and framework approaches would, therefore, provide a more stable appraisal process across different reviewers.
Developing purpose-oriented evaluation criteria for systematic case studies
The starting point in developing evaluation criteria for Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE) is addressing the significance of pluralism in systematic case studies. Unlike RCTs, systematic case studies are pluralistic in the sense that they employ divergent practices in methodological procedures ( research process ), and they may include significantly different research aims and purpose ( the end - goal ) (Kaluzeviciute & Willemsen, 2020 ). While some systematic case studies will have an explicit intention to conceptualise and situate a single patient’s experiences and symptoms within a broader clinical population, others will focus on the exploration of phenomena as they emerge from the data. It is therefore important that CaSE is positioned within a purpose - oriented evaluative framework , suitable for the assessment of what each systematic case is good for (rather than determining an absolute measure of ‘good’ and ‘bad’ systematic case studies). This approach to evidence and appraisal is in line with the PBE paradigm. PBE emphasises the study of clinical complexities and variations through local and contingent settings (e.g. single case studies) and promotes methodological pluralism (Barkham & Mellor-Clark, 2003 ).
CaSE checklist for essential components in systematic case studies
In order to conceptualise purpose-oriented appraisal questions, we must first look at what unites and differentiates systematic case studies in psychotherapy. The commonly used theoretical, clinical and methodological systematic case study components were identified earlier in Table 9 . These components will be seen as essential and common to most systematic case studies in CaSE evaluative criteria. If these essential components are missing in a systematic case study, then it may be implied there is a lack of information, which in turn diminishes the evidential quality of the case. As such, the checklist serves as a tool for checking whether a case study is, indeed, systematic (as opposed to experimental or clinical; see Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 for further differentiation between methodologically distinct case study types) and should be used before CaSE Purpose - based Evaluative Framework for Systematic Case Studie s (which is designed for the appraisal of different purposes common to systematic case studies).
As noted earlier in the paper, checklist approaches to appraisal are useful when evaluating the presence or absence of specific information in a research study. This approach can be used to appraise essential components in systematic case studies, as shown below. From a pragmatic point view (Levitt et al., 2017 ; Truijens et al., 2019 ), CaSE Checklist for Essential Components in Systematic Case Studies can be seen as a way to ensure the internal validity of systematic case study: the reviewer is assessing whether sufficient information is provided about the case design, procedure, approaches to inquiry, etc., and whether they are relevant to the researcher’s objectives and conclusions (Table 11 ).
CaSE purpose-based evaluative framework for systematic case studies
Identifying differences between systematic case studies means identifying the different purposes systematic case studies have in psychotherapy. Based on the earlier work by social scientist Yin ( 1984 , 1993 ), we can differentiate between exploratory (hypothesis generating, indicating a beginning phase of research), descriptive (particularising case data as it emerges) and representative (a case that is typical of a broader clinical population, referred to as the ‘explanatory case’ by Yin) cases.
Another increasingly significant strand of systematic case studies is transferable (aggregating and transferring case study findings) cases. These cases are based on the process of meta-synthesis (Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ): by examining processes and outcomes in many different case studies dealing with similar clinical issues, researchers can identify common themes and inferences. In this way, single case studies that have relatively little impact on clinical practice, research or health care policy (in the sense that they capture psychotherapy processes rather than produce generalisable claims as in Yin’s representative case studies) can contribute to the generation of a wider knowledge base in psychotherapy (Iwakabe, 2003 , 2005 ). However, there is an ongoing issue of assessing the evidential quality of such transferable cases. According to Duncan and Sparks ( 2020 ), although meta-synthesis and meta-analysis are considered to be ‘gold standard’ for assessing interventions across disparate studies in psychotherapy, they often contain case studies with significant research limitations, inappropriate interpretations and insufficient information. It is therefore important to have a research appraisal process in place for selecting transferable case studies.
Two other types of systematic case study research include: critical (testing and/or confirming existing theories) cases, which are described as an excellent method for falsifying existing theoretical concepts and testing whether therapeutic interventions work in practice with concrete patients (Kaluzeviciute, 2021 ), and unique (going beyond the ‘typical’ cases and demonstrating deviations) cases (Merriam, 1998 ). These two systematic case study types are often seen as less valuable for psychotherapy research given that unique/falsificatory findings are difficult to generalise. But it is clear that practitioners and researchers in our field seek out context-specific data, as well as detailed information on the effectiveness of therapeutic techniques in single cases (Stiles, 2007 ) (Table 12 ).
Each purpose-based case study contributes to PBE in different ways. Representative cases provide qualitatively rich, in-depth data about a clinical phenomenon within its particular context. This offers other clinicians and researchers access to a ‘closed world’ (Mackrill & Iwakabe, 2013 ) containing a wide range of attributes about a conceptual type (e.g. clinical condition or therapeutic technique). Descriptive cases generally seek to demonstrate a realistic snapshot of therapeutic processes, including complex dynamics in therapeutic relationships, and instances of therapeutic failure (Maggio, Molgora, & Oasi, 2019 ). Data in descriptive cases should be presented in a transparent manner (e.g. if there are issues in standardising patient responses to a self-report questionnaire, this should be made explicit). Descriptive cases are commonly used in psychotherapy training and supervision. Unique cases are relevant for both clinicians and researchers: they often contain novel treatment approaches and/or introduce new diagnostic considerations about patients who deviate from the clinical population. Critical cases demonstrate the application of psychological theories ‘in action’ with particular patients; as such, they are relevant to clinicians, researchers and policymakers (Mackrill & Iwakabe, 2013 ). Exploratory cases bring new insight and observations into clinical practice and research. This is particularly useful when comparing (or introducing) different clinical approaches and techniques (Trad & Raine, 1994 ). Findings from exploratory cases often include future research suggestions. Finally, transferable cases provide one solution to the generalisation issue in psychotherapy research through the previously mentioned process of meta-synthesis. Grouped together, transferable cases can contribute to theory building and development, as well as higher levels of abstraction about a chosen area of psychotherapy research (Iwakabe & Gazzola, 2009 ).
With this plurality in mind, it is evident that CaSE has a challenging task of appraising research components that are distinct across six different types of purpose-based systematic case studies. The purpose-specific evaluative criteria in Table 13 was developed in close consultation with epistemological literature associated with each type of case study, including: Yin’s ( 1984 , 1993 ) work on establishing the typicality of representative cases; Duncan and Sparks’ ( 2020 ) and Iwakabe and Gazzola’s ( 2009 ) case selection criteria for meta-synthesis and meta-analysis; Stake’s ( 1995 , 2010 ) research on particularising case narratives; Merriam’s ( 1998 ) guidelines on distinctive attributes of unique case studies; Kennedy’s ( 1979 ) epistemological rules for generalising from case studies; Mahrer’s ( 1988 ) discovery oriented case study approach; and Edelson’s ( 1986 ) guidelines for rigorous hypothesis generation in case studies.
Research on epistemic issues in case writing (Kaluzeviciute, 2021 ) and different forms of scientific thinking in psychoanalytic case studies (Kaluzeviciute & Willemsen, 2020 ) was also utilised to identify case study components that would help improve therapist clinical decision-making and reflexivity.
For the analysis of more complex research components (e.g. the degree of therapist reflexivity), the purpose-based evaluation will utilise a framework approach, in line with comprehensive and open-ended reviewer responses in ETQS (Evaluation Tool for Qualitative Studies) (Long & Godfrey, 2004 ) (Table 13 ). That is to say, the evaluation here is not so much about the presence or absence of information (as in the checklist approach) but the degree to which the information helps the case with its unique purpose, whether it is generalisability or typicality. Therefore, although the purpose-oriented evaluation criteria below encompasses comprehensive questions at a considerable level of generality (in the sense that not all components may be required or relevant for each case study), it nevertheless seeks to engage with each type of purpose-based systematic case study on an individual basis (attending to research or clinical components that are unique to each of type of case study).
It is important to note that, as this is an introductory paper to CaSE, the evaluative framework is still preliminary: it involves some of the core questions that pertain to the nature of all six purpose-based systematic case studies. However, there is a need to develop a more comprehensive and detailed CaSE appraisal framework for each purpose-based systematic case study in the future.
Using CaSE on published systematic case studies in psychotherapy: an example
To illustrate the use of CaSE Purpose - based Evaluative Framework for Systematic Case Studies , a case study by Lunn, Daniel, and Poulsen ( 2016 ) titled ‘ Psychoanalytic Psychotherapy With a Client With Bulimia Nervosa ’ was selected from the Single Case Archive (SCA) and analysed in Table 14 . Based on the core questions associated with the six purpose-based systematic case study types in Table 13 (1 to 6), the purpose of Lunn et al.’s ( 2016 ) case was identified as critical (testing an existing theoretical suggestion).
Sometimes, case study authors will explicitly define the purpose of their case in the form of research objectives (as was the case in Lunn et al.’s study); this helps identifying which purpose-based questions are most relevant for the evaluation of the case. However, some case studies will require comprehensive analysis in order to identify their purpose (or multiple purposes). As such, it is recommended that CaSE reviewers first assess the degree and manner in which information about the studied phenomenon, patient data, clinical discourse and research are presented before deciding on the case purpose.
Although each purpose-based systematic case study will contribute to different strands of psychotherapy (theory, practice, training, etc.) and focus on different forms of data (e.g. theory testing vs extensive clinical descriptions), the overarching aim across all systematic case studies in psychotherapy is to study local and contingent processes, such as variations in patient symptoms and complexities of the clinical setting. The comprehensive framework approach will therefore allow reviewers to assess the degree of external validity in systematic case studies (Barkham & Mellor-Clark, 2003 ). Furthermore, assessing the case against its purpose will let reviewers determine whether the case achieves its set goals (research objectives and aims). The example below shows that Lunn et al.’s ( 2016 ) case is successful in functioning as a critical case as the authors provide relevant, high-quality information about their tested therapeutic conditions.
Finally, it is also possible to use CaSE to gather specific type of systematic case studies for one’s research, practice, training, etc. For example, a CaSE reviewer might want to identify as many descriptive case studies focusing on negative therapeutic relationships as possible for their clinical supervision. The reviewer will therefore only need to refer to CaSE questions in Table 13 (2) on descriptive cases. If the reviewed cases do not align with the questions in Table 13 (2), then they are not suitable for the CaSE reviewer who is looking for “know-how” knowledge and detailed clinical narratives.
Concluding comments
This paper introduces a novel Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE) for systematic case studies in psychotherapy. Unlike most appraisal tools in EBP, CaSE is positioned within purpose-oriented evaluation criteria, in line with the PBE paradigm. CaSE enables reviewers to assess what each systematic case is good for (rather than determining an absolute measure of ‘good’ and ‘bad’ systematic case studies). In order to explicate a purpose-based evaluative framework, six different systematic case study purposes in psychotherapy have been identified: representative cases (purpose: typicality), descriptive cases (purpose: particularity), unique cases (purpose: deviation), critical cases (purpose: falsification/confirmation), exploratory cases (purpose: hypothesis generation) and transferable cases (purpose: generalisability). Each case was linked with an existing epistemological network, such as Iwakabe and Gazzola’s ( 2009 ) work on case selection criteria for meta-synthesis. The framework approach includes core questions specific to each purpose-based case study (Table 13 (1–6)). The aim is to assess the external validity and effectiveness of each case study against its set out research objectives and aims. Reviewers are required to perform a comprehensive and open-ended data analysis, as shown in the example in Table 14 .
Along with CaSE Purpose - based Evaluative Framework (Table 13 ), the paper also developed CaSE Checklist for Essential Components in Systematic Case Studies (Table 12 ). The checklist approach is meant to aid reviewers in assessing the presence or absence of essential case study components, such as the rationale behind choosing the case study method and description of patient’s history. If essential components are missing in a systematic case study, then it may be implied that there is a lack of information, which in turn diminishes the evidential quality of the case. Following broader definitions of validity set out by Levitt et al. ( 2017 ) and Truijens et al. ( 2019 ), it could be argued that the checklist approach allows for the assessment of (non-quantitative) internal validity in systematic case studies: does the researcher provide sufficient information about the case study design, rationale, research objectives, epistemological/philosophical paradigms, assessment procedures, data analysis, etc., to account for their research conclusions?
It is important to note that this paper is set as an introduction to CaSE; by extension, it is also set as an introduction to research evaluation and appraisal processes for case study researchers in psychotherapy. As such, it was important to provide a step-by-step epistemological rationale and process behind the development of CaSE evaluative framework and checklist. However, this also means that further research needs to be conducted in order to develop the tool. While CaSE Purpose - based Evaluative Framework involves some of the core questions that pertain to the nature of all six purpose-based systematic case studies, there is a need to develop individual and comprehensive CaSE evaluative frameworks for each of the purpose-based systematic case studies in the future. This line of research is likely to enhance CaSE target audience: clinicians interested in reviewing highly particular clinical narratives will attend to descriptive case study appraisal frameworks; researchers working with qualitative meta-synthesis will find transferable case study appraisal frameworks most relevant to their work; while teachers on psychotherapy and counselling modules may seek out unique case study appraisal frameworks.
Furthermore, although CaSE Checklist for Essential Components in Systematic Case Studies and CaSE Purpose - based Evaluative Framework for Systematic Case Studies are presented in a comprehensive, detailed manner, with definitions and examples that would enable reviewers to have a good grasp of the appraisal process, it is likely that different reviewers may have different interpretations or ideas of what might be ‘substantial’ case study data. This, in part, is due to the methodologically pluralistic nature of the case study genre itself; what is relevant for one case study may not be relevant for another, and vice-versa. To aid with the review process, future research on CaSE should include a comprehensive paper on using the tool. This paper should involve evaluation examples with all six purpose-based systematic case studies, as well as a ‘search’ exercise (using CaSE to assess the relevance of case studies for one’s research, practice, training, etc.).
Finally, further research needs to be developed on how (and, indeed, whether) systematic case studies should be reviewed with specific ‘grades’ or ‘assessments’ that go beyond the qualitative examination in Table 14 . This would be particularly significant for the processes of qualitative meta-synthesis and meta-analysis. These research developments will further enhance CaSE tool, and, in turn, enable psychotherapy researchers to appraise their findings within clear, purpose-based evaluative criteria appropriate for systematic case studies.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Almond, R. (2004). “I Can Do It (All) Myself”: Clinical technique with defensive narcissistic self–sufficiency. Psychoanalytic Psychology , 21 (3), 371–384. https://doi.org/10.1037/0736-9735.21.3.371 .
Article Google Scholar
American Psychological Association (2010). Evidence–based case study. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/pst/evidence–based–case–study.
Google Scholar
Aveline, M. (2005). Clinical case studies: Their place in evidence–based practice. Psychodynamic Practice: Individuals, Groups and Organisations , 11 (2), 133–152. https://doi.org/10.1080/14753630500108174 .
Barkham, M., & Mellor-Clark, J. (2003). Bridging evidence-based practice and practice-based evidence: Developing a rigorous and relevant knowledge for the psychological therapies. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy , 10 (6), 319–327. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.379 .
Berg, H. (2019). How does evidence–based practice in psychology work? – As an ethical demarcation. Philosophical Psychology , 32 (6), 853–873. https://doi.org/10.1080/09515089.2019.1632424 .
Berg, H., & Slaattelid, R. (2017). Facts and values in psychotherapy—A critique of the empirical reduction of psychotherapy within evidence-based practice. Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice , 23 (5), 1075–1080. https://doi.org/10.1111/jep.12739 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bower, P. (2003). Efficacy in evidence-based practice. Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy , 10 (6), 328–336. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.380 .
Cartwright, N., & Hardie, J. (2012). What are RCTs good for? In N. Cartwright, & J. Hardie (Eds.), Evidence–based policy: A practical guide to doing it better . Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:osobl/9780199841608.003.0008 .
Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP). (2018). Qualitative checklist. Retrieved from https://casp–uk.net/wp–content/uploads/2018/01/CASP–Qualitative–Checklist–2018.pdf .
Davison, G. C., & Lazarus, A. A. (2007). Clinical case studies are important in the science and practice of psychotherapy. In S. O. Lilienfeld, & W. T. O’Donohue (Eds.), The great ideas of clinical science: 17 principles that every mental health professional should understand , (pp. 149–162). Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group.
Douglas, H. (2004). The irreducible complexity of objectivity. Synthese , 138 (3), 453–473. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SYNT.0000016451.18182.91 .
Duncan, B. L., & Sparks, J. A. (2020). When meta–analysis misleads: A critical case study of a meta–analysis of client feedback. Psychological Services , 17 (4), 487–496. https://doi.org/10.1037/ser0000398 .
Edelson, M. (1986). Causal explanation in science and in psychoanalysis—Implications for writing a case study. Psychoanalytic Study of Child , 41 (1), 89–127. https://doi.org/10.1080/00797308.1986.11823452 .
Edwards, D. J. A. (2013). Collaborative versus adversarial stances in scientific discourse: Implications for the role of systematic case studies in the development of evidence–based practice in psychotherapy. Pragmatic Case Studies in Psychotherapy , 3 (1), 6–34.
Edwards, D. J. A., Dattilio, F. M., & Bromley, D. B. (2004). Developing evidence–based practice: The role of case–based research. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice , 35 (6), 589–597. https://doi.org/10.1037/0735-7028.35.6.589 .
Erickson, F. (2012). Comments on causality in qualitative inquiry. Qualitative Inquiry , 18 (8), 686–688. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077800412454834 .
Fishman, D. B. (1999). The case for pragmatic psychology . New York University Press.
Fishman, D. B. (2005). Editor’s introduction to PCSP––From single case to database: A new method for enhancing psychotherapy practice. Pragmatic Case Studies in Psychotherapy , 1 (1), 1–50.
Fishman, D. B., Messer, S. B., Edwards, D. J. A., & Dattilio, F. M. (Eds.) (2017). Case studies within psychotherapy trials: Integrating qualitative and quantitative methods . Oxford University Press.
Fox, N. J. (2003). Practice–based evidence: Towards collaborative and transgressive research. Sociology , 37 (1), 81–102. https://doi.org/10.1177/0038038503037001388 .
Gabbay, J., & le May, A. (2011). Practice–based evidence for healthcare: Clinical mindlines . Routledge.
Green, L. W., & Latchford, G. (2012). Maximising the benefits of psychotherapy: A practice–based evidence approach . Wiley–Blackwell. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119967590 .
Hannes, K., Lockwood, C., & Pearson, A. (2010). A comparative analysis of three online appraisal instruments’ ability to assess validity in qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research , 20 (12), 1736–1743. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732310378656 .
Hartling, L., Chisholm, A., Thomson, D., & Dryden, D. M. (2012). A descriptive analysis of overviews of reviews published between 2000 and 2011. PLoS One , 7 (11), e49667. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0049667 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hill, A., & Spittlehouse, C. (2003). What is critical appraisal? Evidence–Based Medicine , 3 (2), 1–8.
Hilliard, R. B. (1993). Single–case methodology in psychotherapy process and outcome research. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology , 61 (3), 373–380. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-006X.61.3.373 .
Horn, S. D., & Gassaway, J. (2007). Practice–based evidence study design for comparative effectiveness research. Medical Care , 45 (10), S50–S57. https://doi.org/10.1097/MLR.0b013e318070c07b .
Iwakabe, S. (2003, May). Common change events in stages of psychotherapy: A qualitative analysis of case reports. In Paper presented at the 19th Annual Conference of the Society for Exploration of Psychotherapy Integration, New York .
Iwakabe, S. (2005). Pragmatic meta–analysis of case studies. Annual Progress of Family Psychology , 23 , 154–169.
Iwakabe, S., & Gazzola, N. (2009). From single–case studies to practice–based knowledge: Aggregating and synthesizing case studies. Psychotherapy Research , 19 (4-5), 601–611. https://doi.org/10.1080/10503300802688494 .
Jimenez-Buedo, M., & Miller, L. (2010). Why a Trade–Off? The relationship between the external and internal validity of experiments. THEORIA: An International Journal for Theory History and Foundations of Science , 25 (3), 301–321.
Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI). (2017a). Critical appraisal checklist for qualitative research. Retrieved from https://joannabriggs.org/sites/default/files/2019–05/JBI_Critical_Appraisal–Checklist_for_Qualitative_Research2017_0.pdf
Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI). (2017b). Checklist for case reports. Retrieved from https://joannabriggs.org/sites/default/files/2019–05/JBI_Critical_Appraisal–Checklist_for_Case_Reports2017_0.pdf
Kaluzeviciute, G. (2021). Validity, Evidence and Appraisal in Systematic Psychotherapy Case Studies . Paper presented at the Research Forum of Department of Psychosocial and Psychoanalytic Studies, University of Essex, Colchester, UK. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.33502.15683
Kaluzeviciute, G., & Willemsen, J. (2020). Scientific thinking styles: The different ways of thinking in psychoanalytic case studies. The International Journal of Psychoanalysis , 101 (5), 900–922. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207578.2020.1796491 .
Katrak, P., Bialocerkowski, A. E., Massy-Westropp, N., Kumar, S. V. S., & Grimmer, K. (2004). A systematic review of the content of critical appraisal tools. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 4 (1), 22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-4-22 .
Kennedy, M. M. (1979). Generalising from single case studies. Evaluation Quarterly , 3 (4), 661–678. https://doi.org/10.1177/0193841X7900300409 .
Laska, K. M., Gurman, A. S., & Wampold, B. E. (2014). Expanding the lens of evidence–based practice in psychotherapy: A common factors perspective. Psychotherapy , 51 (4), 467–481. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0034332 .
Levitt, H. M., Motulsky, S. L., Wertz, F. J., Morrow, S. L., & Ponterotto, J. G. (2017). Recommendations for designing and reviewing qualitative research in psychology: Promoting methodological integrity. Qualitative Psychology , 4 (1), 2–22. https://doi.org/10.1037/qup0000082 .
Lilienfeld, S. O., Ritschel, L. A., Lynn, S. J., Cautin, R. L., & Latzman, R. D. (2013). Why many clinical psychologists are resistant to evidence–based practice: root causes and constructive remedies. Clinical Psychology Review , 33 (7), 883–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2012.09.008 .
Long, A. F., & Godfrey, M. (2004). An evaluation tool to assess the quality of qualitative research studies. International Journal of Social Research Methodology , 7 (2), 181–196. https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000045302 .
Longhofer, J., Floersch, J., & Hartmann, E. A. (2017). Case for the case study: How and why they matter. Clinical Social Work Journal , 45 (3), 189–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10615-017-0631-8 .
Lunn, S., Daniel, S. I. F., & Poulsen, S. (2016). Psychoanalytic psychotherapy with a client with bulimia nervosa. Psychotherapy , 53 (2), 206–215. https://doi.org/10.1037/pst0000052 .
Mackrill, T., & Iwakabe, S. (2013). Making a case for case studies in psychotherapy training: A small step towards establishing an empirical basis for psychotherapy training. Counselling Psychotherapy Quarterly , 26 (3–4), 250–266. https://doi.org/10.1080/09515070.2013.832148 .
Maggio, S., Molgora, S., & Oasi, O. (2019). Analyzing psychotherapeutic failures: A research on the variables involved in the treatment with an individual setting of 29 cases. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 1250. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01250 .
Mahrer, A. R. (1988). Discovery–oriented psychotherapy research: Rationale, aims, and methods. American Psychologist , 43 (9), 694–702. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.43.9.694 .
Margison, F. B., et al. (2000). Measurement and psychotherapy: Evidence–based practice and practice–based evidence. British Journal of Psychiatry , 177 (2), 123–130. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.177.2.123 .
Maxwell, J. A. (2004). Causal explanation, qualitative research, and scientific inquiry in education. Educational Researcher , 33 (2), 3–11. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X033002003 .
McLeod, J. (2002). Case studies and practitioner research: Building knowledge through systematic inquiry into individual cases. Counselling and Psychotherapy Research: Linking research with practice , 2 (4), 264–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/14733140212331384755 .
McLeod, J. (2010). Case study research in counselling and psychotherapy . SAGE Publications. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781446287897 .
McLeod, J., & Elliott, R. (2011). Systematic case study research: A practice–oriented introduction to building an evidence base for counselling and psychotherapy. Counselling and Psychotherapy Research , 11 (1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/14733145.2011.548954 .
Meganck, R., Inslegers, R., Krivzov, J., & Notaerts, L. (2017). Beyond clinical case studies in psychoanalysis: A review of psychoanalytic empirical single case studies published in ISI–ranked journals. Frontiers in Psychology , 8 , 1749. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01749 .
Merriam, S. B. (1998). Qualitative research and case study applications in education . Jossey–Bass Publishers.
Michels, R. (2000). The case history. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association , 48 (2), 355–375. https://doi.org/10.1177/00030651000480021201 .
Midgley, N. (2006). Re–reading “Little Hans”: Freud’s case study and the question of competing paradigms in psychoanalysis. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association , 54 (2), 537–559. https://doi.org/10.1177/00030651060540021601 .
Rosqvist, J., Thomas, J. C., & Truax, P. (2011). Effectiveness versus efficacy studies. In J. C. Thomas, & M. Hersen (Eds.), Understanding research in clinical and counseling psychology , (pp. 319–354). Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group.
Sackett, D. L., Rosenberg, W. M., Gray, J. A. M., Haynes, R. B., & Richardson, W. S. (1996). Evidence based medicine: what it is and what it isn’t. BMJ , 312 (7023), 71–72. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.312.7023.71 .
Stake, R. E. (1995). The art of case study research . SAGE Publications.
Stake, R. E. (2010). Qualitative research: Studying how things work . The Guilford Press.
Stewart, R. E., & Chambless, D. L. (2007). Does psychotherapy research inform treatment decisions in private practice? Journal of Clinical Psychology , 63 (3), 267–281. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.20347 .
Stiles, W. B. (2007). Theory–building case studies of counselling and psychotherapy. Counselling and Psychotherapy Research , 7 (2), 122–127. https://doi.org/10.1080/14733140701356742 .
Teachman, B. A., Drabick, D. A., Hershenberg, R., Vivian, D., Wolfe, B. E., & Goldfried, M. R. (2012). Bridging the gap between clinical research and clinical practice: introduction to the special section. Psychotherapy , 49 (2), 97–100. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0027346 .
Thorne, S., Jensen, L., Kearney, M. H., Noblit, G., & Sandelowski, M. (2004). Qualitative metasynthesis: Reflections on methodological orientation and ideological agenda. Qualitative Health Research , 14 (10), 1342–1365. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732304269888 .
Timulak, L. (2009). Meta–analysis of qualitative studies: A tool for reviewing qualitative research findings in psychotherapy. Psychotherapy Research , 19 (4–5), 591–600. https://doi.org/10.1080/10503300802477989 .
Trad, P. V., & Raine, M. J. (1994). A prospective interpretation of unconscious processes during psychoanalytic psychotherapy. Psychoanalytic Psychology , 11 (1), 77–100. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0079522 .
Truijens, F., Cornelis, S., Desmet, M., & De Smet, M. (2019). Validity beyond measurement: Why psychometric validity is insufficient for valid psychotherapy research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 . https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00532 .
Tuckett, D. (Ed.) (2008). The new library of psychoanalysis. Psychoanalysis comparable and incomparable: The evolution of a method to describe and compare psychoanalytic approaches . Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203932551 .
van Hennik, R. (2020). Practice based evidence based practice, part II: Navigating complexity and validity from within. Journal of Family Therapy , 43 (1), 27–45. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-6427.12291 .
Westen, D., Novotny, C. M., & Thompson-Brenner, H. (2004). The empirical status of empirically supported psychotherapies: Assumptions, findings, and reporting in controlled clinical trials. Psychological Bulletin , 130 (4), 631–663. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.130.4.631 .
Widdowson, M. (2011). Case study research methodology. International Journal of Transactional Analysis Research & Practice , 2 (1). https://doi.org/10.29044/v2i1p25 .
Willemsen, J., Della Rosa, E., & Kegerreis, S. (2017). Clinical case studies in psychoanalytic and psychodynamic treatment. Frontiers in Psychology , 8 (108). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00108 .
Williams, V., Boylan, A., & Nunan, D. (2019). Critical appraisal of qualitative research: Necessity, partialities and the issue of bias. BMJ Evidence–Based Medicine . https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjebm-2018-111132 .
Yin, R. K. (1984). Case study research: Design and methods . SAGE Publications.
Yin, R. K. (1993). Applications of case study research . SAGE Publications.
Download references
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank Prof Jochem Willemsen (Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences, Université catholique de Louvain-la-Neuve), Prof Wayne Martin (School of Philosophy and Art History, University of Essex), Dr Femke Truijens (Institute of Psychology, Erasmus University Rotterdam) and the reviewers of Psicologia: Reflexão e Crítica / Psychology : Research and Review for their feedback, insight and contributions to the manuscript.
Arts and Humanities Research Council (AHRC) and Consortium for Humanities and the Arts South-East England (CHASE) Doctoral Training Partnership, Award Number [AH/L50 3861/1].
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychosocial and Psychoanalytic Studies, University of Essex, Wivenhoe Park, Colchester, CO4 3SQ, UK
Greta Kaluzeviciute
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
GK is the sole author of the manuscript. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Greta Kaluzeviciute .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kaluzeviciute, G. Appraising psychotherapy case studies in practice-based evidence: introducing Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE). Psicol. Refl. Crít. 34 , 9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41155-021-00175-y
Download citation
Received : 12 January 2021
Accepted : 09 March 2021
Published : 19 March 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41155-021-00175-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Systematic case studies
- Psychotherapy research
- Research appraisal tool
- Evidence-based practice
- Practice-based evidence
- Research validity
Evidence-Based Practice
- EBP resources
- Apply & Assess

Example questions
Case study: complementary & alternative medicine, databases to search.
- Additional resources
Your next patient is a 72-year-old woman with osteoarthritis of the knees and moderate hypertension, accompanied by her daughter, a lab tech from the hospital. The daughter wants you to give her mother a prescription for one of the new COX-2 inhibitors. She has heard that they cause less GI bleeding. Her mother is concerned that the new drugs will mean more out-of-pocket costs each month.
Specific Question:
In a 72-year-old woman with osteoarthritis of the knee, can COX-2 Inhibitor use decrease the risk of GI Bleeding compared with other NSAIDs?
You have been treating a 54-year-old woman for many years and despite the excellence of your fixed partial denture restorations, the intense routine maintenance by her periodontist, and good homecare, she has been experiencing a continued deterioration of her periodontal tissues. Her attempts to quit smoking have been unsuccessful; otherwise she is in good health and taking no medications. Because you are her primary care dentist, she has questioned you about her current dilemma. The periodontist has suggested a 3-week course of doxycycline therapy to control her latest exacerbation of periodontal disease, but she is concerned about Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reports asking for prudent use of antibiotics. How do you advise this patient?
For a 54-year-old woman with periodontal disease, how effective is the therapeutic use of doxcyline in decreasing gum bleeding and recession compared with no treatment?
Case Study Scenario: Diabetes and Fenugreek
Mrs. Hernandez, a 45-year-old Spanish-speaking woman, has been recently diagnosed with Diabetes Type 2.
- She is admitted to UWMC with uncontrolled hypertension.
- She takes fenugreek.
- Prescribed medications include Lisinopril, Clonidine, and Metformin.
Search the databases below for evidence-based information on fenugreek used for diabetes.
For more information on each database, see Find Articles/Databases.
Filter to Article Type
Case Study example:
- In the PubMed Search box, type: (fenugreek OR trigonella) AND diabetes
- Then filter from left sidebar to: English, Human
- For evidence-based articles, filter by Article Type to: Randomized controlled trial, meta-analysis, clinical trial
Filter to Subject
- In the PubMed Search box, type: Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/th
- Then filter to: Complementary Medicine and/or Dietary Supplements under Subjects.
- This strategy will produce results about alternative treatments for diabetes.
- For evidence-based articles, filter under Article Type to: Randomized controlled trial, meta-analysis, clinical trial
Search PubMed Clinical Queries
Search By Clinical Study Category
- Type: (fenugreek OR trigonella) AND diabetes
- Select Therapy and Narrow (specific) search.
Find Systematic Reviews

Limit to Research Article
- Type in the Search box: (fenugreek OR trigonella) and diabetes
- Click on Research Article under Limit your Results.
Limit by Publication Type
- Type in Search box: (fenugreek OR trigonella) and diabetes
- In Limit your Results, select Clinical Trial or Systematic Review or Research under Publication Type.
Limit by Clinical Query
- Select any of the choices under Clinical Queries limits.
Limit by Journal Subset
- In Limit your Results, select Alternative/Complementary Therapies under Journal Subset.
Limit by Evidence-Based Practice
- Click on Evidence-Based Practice under Limit your Results.
- In the Search box, type: fenugreek AND diabetes
- In this case, there are no systematic reviews on this topic. You do retrieve, however, some citations to clinical trials.
- Type fenugreek in Search box and then click on Professional Monograph: Fenugreek.
- Note the diabetes evidence grade under Clinical Bottom Line/Effectiveness.
IBIDS (International Bibliographic Information on Dietary Supplements)
- Type in Search box: +fenugreek +diabetes
- Change drop-down menu to Peer-reviewed References instead of All IBIDS References .
- look under Treatment>Diet for use of fenugreek
- OR, click on Search Within Text link and follow directions to find fenugreek
- Type in Search box: fenugreek and diabetes and ('clinical trial'/exp or 'controlled study'/exp or 'controlled clinical trial' or 'randomized controlled trial')
- << Previous: Apply & Assess
- Next: Additional resources >>
- Last Updated: Feb 23, 2024 12:11 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uw.edu/hsl/ebp
Be boundless
1959 NE Pacific Street | T334 Health Sciences Building | Box 357155 | Seattle, WA 98195-7155 | 206-543-3390
© 2024 University of Washington | Seattle, WA


Everyday Evidence-Based Practice in Academic Libraries: Case Studies and Reflections
November 30, 2023 Erin Nevius Publications 0

ACRL announces the publication of Everyday Evidence-Based Practice in Academic Libraries: Case Studies and Reflections , edited by Claire Walker Wiley, Amanda B. Click, and Meggan Houlihan. This new book collects excellent, thorough examples of evidence-based practice across functional areas of academic libraries and includes many evidence types in a variety of contexts.
Learn more about Everyday Evidence-Based Practice in Academic Libraries in this excerpt from the Introduction, © the editors.
The most important part of the title of this book, Everyday Evidence-Based Practice in the Academic Library: Case Studies and Reflections , is the word “everyday.” We believe that these chapters contain excellent, thorough examples of evidence-based practice (EBP) in numerous functional areas of academic libraries. It is possible that you may read one of these chapters and feel discouraged, or that you don’t have the skills, resources, or time to engage with evidence-based practice in an effective way. This is absolutely not our intent. The goal of this book is to emphasize the importance of everyday EBP while highlighting well-designed projects to inspire the work of others. An EBP project might look like a yearlong study with many types of evidence collected, or it might look like a simple assessment that helps you make a small adjustment to your work. EBP is a way of operating day-to-day. It’s not just something to turn off or on—it is embedded in the way that we approach our work.
Let’s say that you’re interested in making improvements to your information literacy program assessment process. You could conduct a review of the literature, analyze instruction statistics, run focus groups with students, survey faculty, and schedule one-on-one conversations with every teaching librarian. But it’s crucial that your EBP process fits your reality. Perhaps you don’t have the time to collect all of this evidence. You may face institutional hurdles when collecting student data. Maybe your faculty suffer from survey fatigue. Once you’ve considered your context, adapt an EBP cycle to your needs. We like the evidence-based library and information practice (EBLIP) cycle developed by Brettle and Koufogiannakis (2016), and you will see it referenced many times in these pages. Perhaps you could spend some time with instruction statistics this semester and/or recruit a colleague to help you scan the literature. Next semester (or next year!), have coffee with some targeted faculty to get their perspectives and collect feedback from your colleagues using the process that works best in your library culture. EBP doesn’t have to be exhaustive (or exhausting), and it doesn’t have to move lightning fast. It does, however, need to be flexible and appropriate for your context.
EBP Foundations
Denise Koufogiannakis and Alison Brettle’s 2016 book, Being Evidence Based in Library and Information Practice , provides the foundation for our work. Their book introduced a new framework for EBLIP including a “holistic and cyclical approach to considering evidence” (2016, p. 4). Koufogiannakis and Brettle also encourage librarians to take the principles of EBLIP and “emphasize an overall approach to practice that is about being evidence based ” (2016, p. 3). Everyday Evidence-Based Practice in the Academic Library: Case Studies and Reflections aims to provide real-world examples of librarians who embody this call. LaFitte (formerly Koufogiannakis) and Brettle also graciously contributed to this edited volume, writing the first chapter titled “The Evolving Model of EBLIP in Research and Practice” that explains the history of EBP in libraries, describes the ways that the scholarship and practice in this area have evolved and grown over the years, and makes predictions for the future.
The cyclical approach to the EBLIP process proposed by Koufogiannakis and Brettle includes five steps: articulate , assemble , assess , agree , and adapt (2016, p. 4). The authors emphasize that this process is designed to foster a “continual cycle of improvement” (2016, p. 7). In the following chapter, they provide additional insight into the cycle. In addition, the EBLIP framework encourages librarians to consider three categories of evidence to be used in combination (pp. 29–43):
- Research Evidence: Literature reporting on the previous research that is related to the question at hand.
- Local Evidence: Forms of data specific to your institution or context, either that you already have or that you specifically gather in order to answer your question.
- Professional Knowledge: What we learned in school and on the job and from mentors, peers, and professional development opportunities.
Each category encompasses many types of evidence in order to allow for the process to be “as broad and complete as possible, depending on the problem faced or question posed” (p. 28). Table 1 includes examples of different types of evidence that are described in chapters from this book. These examples provide a preview of the “everyday” focus of this book. You won’t find any randomized control trials or meta-analyses here! We acknowledge that these are valuable types of evidence for many research questions, but they are less commonly used to answer questions in library and information science practice.
Table 1. Examples from Chapters of Everyday Evidence by Evidence Type
Building the Evidence Base
Thorpe’s (2021) proposed sixth step in the EBLIP cycle is announce/advocate, which involves communicating the EBP work that we do. She proposed four benefits that could result from more announcing, advocating, and communicating as part of the EBP cycle: “to advocate and influence, to contribute to the profession’s evidence base, to demonstrate professional expertise, and to build organizational capacity and maturity” (Thorpe, 2021, p. 121). This book is our announcement , our attempt at contributing high-quality evidence from a variety of perspectives to the library and information science evidence base.
It is our hope that this book inspires a commitment to evidence-based practice in your day-to-day work and perhaps even in your library culture. We look forward to seeing many announcements of your work as the evidence base grows.
Koufogiannakis, D., & Brettle, A. (Eds.). (2016). Being evidence based in library and information practice . Facet Publishing.
Thorpe, C. (2021). Announcing and advocating: The missing step in the EBLIP model. Evidence Based Library and Information Practic e, 16 (4), 118–125. http://doi.10.18438/eblip30044 .
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Case Studies
Now that you’ve learned what goes into a good clinical question, why not give it a try?
Select one of the following case studies to practice identifying PICO elements and forming a research question.
Evidence-Based Practice Copyright © by Various Authors - See Each Chapter Attribution is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Open access
- Published: 03 June 2024
The use of evidence to guide decision-making during the COVID-19 pandemic: divergent perspectives from a qualitative case study in British Columbia, Canada
- Laura Jane Brubacher ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2806-9539 1 , 2 ,
- Chris Y. Lovato 1 ,
- Veena Sriram 1 , 3 ,
- Michael Cheng 1 &
- Peter Berman 1
Health Research Policy and Systems volume 22 , Article number: 66 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
69 Accesses
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
The challenges of evidence-informed decision-making in a public health emergency have never been so notable as during the COVID-19 pandemic. Questions about the decision-making process, including what forms of evidence were used, and how evidence informed—or did not inform—policy have been debated.
We examined decision-makers' observations on evidence-use in early COVID-19 policy-making in British Columbia (BC), Canada through a qualitative case study. From July 2021- January 2022, we conducted 18 semi-structured key informant interviews with BC elected officials, provincial and regional-level health officials, and civil society actors involved in the public health response. The questions focused on: (1) the use of evidence in policy-making; (2) the interface between researchers and policy-makers; and (3) key challenges perceived by respondents as barriers to applying evidence to COVID-19 policy decisions. Data were analyzed thematically, using a constant comparative method. Framework analysis was also employed to generate analytic insights across stakeholder perspectives.
Overall, while many actors’ impressions were that BC's early COVID-19 policy response was evidence-informed, an overarching theme was a lack of clarity and uncertainty as to what evidence was used and how it flowed into decision-making processes. Perspectives diverged on the relationship between 'government' and public health expertise, and whether or not public health actors had an independent voice in articulating evidence to inform pandemic governance. Respondents perceived a lack of coordination and continuity across data sources, and a lack of explicit guidelines on evidence-use in the decision-making process, which resulted in a sense of fragmentation. The tension between the processes involved in research and the need for rapid decision-making was perceived as a barrier to using evidence to inform policy.
Conclusions
Areas to be considered in planning for future emergencies include: information flow between policy-makers and researchers, coordination of data collection and use, and transparency as to how decisions are made—all of which reflect a need to improve communication. Based on our findings, clear mechanisms and processes for channeling varied forms of evidence into decision-making need to be identified, and doing so will strengthen preparedness for future public health crises.
Peer Review reports
The challenges of evidence-informed decision-making Footnote 1 in a public health emergency have never been so salient as during the COVID-19 pandemic, given its unprecedented scale, rapidly evolving virology, and multitude of global information systems to gather, synthesize, and disseminate evidence on the SARS-CoV-2 virus and associated public health and social measures [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, rapid decision-making became central for governments globally as they grappled with crucial decisions for which there was limited evidence. Critical questions exist, in looking retrospectively at these decision-making processes and with an eye to strengthening future preparedness: Were decisions informed by 'evidence'? What forms of evidence were used, and how, by decision-makers? [ 4 , 5 , 6 ].
Scientific evidence, including primary research, epidemiologic research, and knowledge synthesis, is one among multiple competing influences that inform decision-making processes in an outbreak such as COVID-19 [ 7 ]. Indeed, the use of multiple forms of evidence has been particularly notable as it applies to COVID-19 policy-making. Emerging research has also documented the important influence of ‘non-scientific’ evidence such as specialized expertise and experience, contextual information, and level of available resources [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the politics of evidence-use in policy-making [ 11 ]; what evidence is used and how can be unclear, and shaped by political bias [ 4 , 5 ]. Moreover, while many governments have established scientific advisory boards, the perspectives of these advisors were reportedly largely absent from COVID-19 policy processes [ 6 ]. How evidence and public health policy interface—and intersect—is a complex question, particularly in the dynamic context of a public health emergency.
Within Canada, a hallmark of the public health system and endorsed by government is evidence-informed decision-making [ 12 ]. In British Columbia (BC), Canada, during the early phases of COVID-19 (March—June 2020), provincial public health communication focused primarily on voluntary compliance with recommended public health and social measures, and on supporting those most affected by the pandemic. Later, the response shifted from voluntary compliance to mandatory enforceable government orders [ 13 ]. Like many other jurisdictions, the government’s public messaging in BC asserted that the province took an approach to managing the COVID-19 pandemic and developing related policy that was based on scientific evidence, specifically. For example, in March 2021, in announcing changes to vaccination plans, Dr. Bonnie Henry, the Provincial Health Officer, stated, " This is science in action " [ 14 ]. As a public health expert with scientific voice, the Provincial Health Officer has been empowered to speak on behalf of the BC government across the COVID-19 pandemic progression. While this suggests BC is a jurisdiction which has institutionalized scientifically-informed decision-making as a core tenet of effective public health crisis response, it remains unclear as to whether BC’s COVID-19 response could, in fact, be considered evidence-informed—particularly from the perspectives of those involved in pandemic decision-making and action. Moreover, if evidence-informed, what types of evidence were utilized and through what mechanisms, how did this evidence shape decision-making, and what challenges existed in moving evidence to policy and praxis in BC’s COVID-19 response?
The objectives of this study were: (1) to explore and characterize the perspectives of BC actors involved in the COVID-19 response with respect to evidence-use in COVID-19 decision-making; and (2) to identify opportunities for and barriers to evidence-informed decision-making in BC’s COVID-19 response, and more broadly. This inquiry may contribute to identifying opportunities for further strengthening the synthesis and application of evidence (considered broadly) to public health policy and decision-making, particularly in the context of future public health emergencies, both in British Columbia and other jurisdictions.
Study context
This qualitative study was conducted in the province of British Columbia (BC), Canada, a jurisdiction with a population of approximately five million people [ 15 ]. Within BC’s health sector, key actors involved in the policy response to COVID-19 included: elected officials, the BC Government’s Ministry of Health (MOH), the Provincial Health Services Authority (PHSA), Footnote 2 the Office of the Provincial Health Officer (PHO), Footnote 3 the BC Centre for Disease Control (BCCDC), Footnote 4 and Medical Health Officers (MHOs) and Chief MHOs at regional and local levels.
Health research infrastructure within the province includes Michael Smith Health Research BC [ 16 ] and multiple post-secondary research and education institutions (e.g., The University of British Columbia). Unlike other provincial (e.g., Ontario) and international (e.g., UK) jurisdictions, BC did not establish an independent, formal scientific advisory panel or separate organizational structure for public health intelligence in COVID-19. That said, a Strategic Research Advisory Council was established, reporting to the MOH and PHO, to identify COVID-19 research gaps and commission needed research for use within the COVID-19 response [ 17 ].
This research was part of a multidisciplinary UBC case study investigating the upstream determinants of the COVID-19 response in British Columbia, particularly related to institutions, politics, and organizations and how these interfaced with, and affected, pandemic governance [ 18 ]. Ethics approval for this study was provided by the University of British Columbia (UBC)’s Institutional Research Ethics Board (Certificate #: H20-02136).
Data collection
From July 2021 to January 2022, 18 semi-structured key informant interviews were conducted with BC elected officials, provincial and regional-level health officials, and civil society actors (e.g., within non-profit research organizations, unions) (Table 1 ). Initially, respondents were purposively sampled, based on their involvement in the COVID-19 response and their positioning within the health system organizational structure. Snowball sampling was used to identify additional respondents, with the intent of representing a range of organizational roles and actor perspectives. Participants were recruited via email invitation and provided written informed consent to participate.
Interviews were conducted virtually using Zoom® videoconferencing, with the exception of one hybrid in-person/Zoom® interview. Each interview was approximately one hour in duration. One to two research team members led each interview. The full interview protocol focused on actors’ descriptions of decision-making processes across the COVID-19 pandemic progression, from January 2020 to the date of the interviews, and they were asked to identify key decision points (e.g., emergency declaration, business closures) [see Additional File 1 for the full semi-structured interview guide]. For this study, we used a subset of interview questions focused on evidence-use in the decision-making process, and the organizational structures or actors involved, in BC's early COVID-19 pandemic response (March–August 2020). Questions were adapted to be relevant to a respondent’s expertise and particular involvement in the response. ‘Evidence’ was left undefined and considered broadly by the research team (i.e., both ‘scientific’/research-based and ‘non-scientific’ inputs) within interview questions, and therefore at the discretion of the participant as to what inputs they perceived and described as ‘evidence’ that informed or did not inform pandemic decision-making. Interviews were audio-recorded over Zoom® with permission and transcribed using NVivo Release 1.5© software. Each transcript was then manually verified for accuracy by 1–2 members of the research team.
Data analysis
An inductive thematic analysis was conducted, using a constant comparative method, to explore points of divergence and convergence across interviews and stakeholder perspectives [ 19 ]. Transcripts were inductively coded in NVivo Release 1.5© software, which was used to further organize and consolidate codes, generate a parsimonious codebook to fit the data, and retrieve interview excerpts [ 20 ]. Framework analysis was also employed as an additional method for generating analytic insights across stakeholder perspectives and contributed to refining the overall coding [ 21 ]. Triangulation across respondents and analytic methods, as well as team collaboration in reviewing and refining the codebook, contributed to validity of the analysis [ 22 ].
How did evidence inform early COVID-19 policy-making in BC?
Decision-makers described their perceptions on the use of evidence in policy-making; the interface between researchers and policy-makers; and specific barriers to evidence-use in policy-making within BC’s COVID-19 response. In discussing the use of evidence, respondents focused on ‘scientific’ evidence; however, they noted a lack of clarity as to how and what evidence flowed into decision-making. They also acknowledged that ‘scientific’ evidence was one of multiple factors influencing decisions. The themes described below reflect the narrative underlying their perspectives.
Perceptions of evidence-use
Multiple provincial actors generally expressed confidence or had an overall impression that decisions were evidence-based (IDI5,9), stating definitively that, "I don’t think there was a decision we made that wasn’t evidence-informed" (IDI9) and that "the science became a driver of decisions that were made" (IDI5). However, at the regional health authority level, one actor voiced skepticism that policy decisions were consistently informed by scientific evidence specifically, stating, "a lot of decisions [the PHO] made were in contrast to science and then shifted to be by the science" ( IDI6). The evolving nature of the available evidence and scientific understanding of the virus throughout the pandemic was acknowledged. For instance, one actor stated that, "I’ll say the response has been driven by the science; the science has been changing…from what I’ve seen, [it] has been a very science-based response" (IDI3).
Some actors narrowed in on certain policy decisions they believed were or were not evidence-informed. Policy decisions in 2020 that actors believed were directly informed by scientific data included the early decision to restrict informal, household gatherings; to keep schools open for in-person learning; to implement a business safety plan requirement across the province; and to delay the second vaccine dose for maximum efficacy. One provincial public health actor noted that an early 2020 decision made, within local jurisdictions, to close playgrounds was not based on scientific evidence. Further, the decision prompted public health decision-makers to centralize some decision-making to the provincial level, to address decisions being made 'on the ground' that were not based on scientific evidence (IDI16). Similarly, they added that the policy decision to require masking in schools was not based on scientific evidence; rather, "it's policy informed by the noise of your community." As parents and other groups within the community pushed for masking, this was "a policy decision to help schools stay open."
Early in the pandemic response, case data in local jurisdictions were reportedly used for monitoring and planning. These "numerator data" (IDI1), for instance case or hospitalization counts, were identified as being the primary mode of evidence used to inform decisions related to the implementation or easing of public health and social measures. The ability to generate epidemiological count data early in the pandemic due to efficient scaling up of PCR testing for COVID-19 was noted as a key advantage (IDI16). As the pandemic evolved in 2020, however, perspectives diverged in relation to the type of data that decision-makers relied on. For example, it was noted that BCCDC administered an online, voluntary survey to monitor unintended consequences of public health and social measures and inform targeted interventions. Opinions varied on whether this evidence was successfully applied in decision-making. One respondent emphasized this lack of application of evidence and perceived that public health orders were not informed by the level and type of evidence available, beyond case counts: "[In] a communicable disease crisis like a pandemic, the collateral impact slash damage is important and if you're going to be a public health institute, you actually have to bring those to the front, not just count cases" (IDI1).
There also existed some uncertainty and a perceived lack of transparency or clarity as to how or whether data analytic ‘entities’, such as BCCDC or research institutions, fed directly into decision-making. As a research actor shared, "I’m not sure that I know quite what all those channels really look like…I’m sure that there’s a lot of improvement that could be driven in terms of how we bring strong evidence to actual policy and practice" (IDI14). Another actor explicitly named the way information flowed into decision-making in the province as "organic" (IDI7). They also noted the lack of a formal, independent science advisory panel for BC’s COVID-19 response, which existed in other provincial and international jurisdictions. Relatedly, one regional health authority actor perceived that the committee that was convened to advise the province on research, and established for the purpose of applying research to the COVID-19 response, "should have focused more on knowledge translation, but too much time was spent commissioning research and asking what kinds of questions we needed to ask rather than looking at what was happening in other jurisdictions" (IDI6). Overall, multiple actors noted a lack of clarity around application of evidence and who is responsible for ensuring evidence is applied. As a BCCDC actor expressed, in relation to how to prevent transmission of COVID-19:
We probably knew most of the things that we needed to know about May of last year [2020]. So, to me, it’s not even what evidence you need to know about, but who’s responsible for making sure that you actually apply the evidence to the intervention? Because so many of our interventions have been driven by peer pressure and public expectation rather than what we know to be the case [scientifically] (IDI1).
Some described the significance of predictive disease modelling to understand the COVID-19 trajectory and inform decisions, as well as to demonstrate to the public the effectiveness of particular measures, which "help[ed] sustain our response" (IDI2). Others, however, perceived that "mathematical models were vastly overused [and] overvalued in decision-making around this pandemic" (IDI1) and that modellers stepped outside their realm of expertise in providing models and policy recommendations through the public media.
Overall, while many actors’ impressions were that the response was evidence-informed, an overarching theme was a lack of clarity and uncertainty with respect to how evidence actually flowed into decision-making processes, as well as what specific evidence was used and how. Participants noted various mechanisms created or already in place prior to COVID-19 that fed data into, and facilitated, decision-making. There was an acknowledgement that multiple forms of evidence—including scientific data, data on public perceptions, as well as public pressure—appeared to have influenced decision-making.
Interface between researchers and policy-makers
There was a general sense that the Ministry supported the use of scientific and research-based evidence specifically. Some actors identified particular Ministry personnel as being especially amenable to research and focused on data to inform decisions and implementation. More broadly, the government-research interface was characterized by one actor as an amicable one, a "research-friendly government", and that the Ministry of Health (MOH), specifically, has a research strategy whereby, "it’s literally within their bureaucracy to become a more evidence-informed organization" (IDI11). The MOH was noted to have funded a research network intended to channel evidence into health policy and practice, and which reported to the research side of the MOH.
Other actors perceived relatively limited engagement with the broader scientific community. Some perceived an overreliance on 'in-house expertise' or a "we can do that [ourselves] mentality" within government that precluded academic researchers’ involvement, as well as a sense of "not really always wanting to engage with academics to answer policy questions because they don’t necessarily see the value that comes" (IDI14). With respect to the role of research, an actor stated:
There needs to be a provincial dialogue around what evidence is and how it gets situated, because there’s been some tension around evidence being produced and not used or at least not used in the way that researchers think that it should be (IDI11).
Those involved in data analytics within the MOH acknowledged a challenge in making epidemiological data available to academic researchers, because "at the time, you’re just trying to get decisions made" (IDI7). Relatedly, a research actor described the rapid instigation of COVID-19 research and pivoting of academic research programs to respond to the pandemic, but perceived a slow uptake of these research efforts from the MOH and PHSA for decision-making and action. Nevertheless, they too acknowledged the challenge of using research evidence, specifically, in an evolving and dynamic pandemic:
I think we’ve got to be realistic about what research in a pandemic situation can realistically contribute within very short timelines. I mean, some of these decisions have to be made very quickly...they were intuitive decisions, I think some of them, rather than necessarily evidence-based decisions (IDI14).
Relatedly, perspectives diverged on the relationship between 'government' and public health expertise, and whether or not public health actors had an independent voice in articulating evidence to inform governance during the pandemic. Largely from Ministry stakeholders, and those within the PHSA, the impressions were that Ministry actors were relying on public health advice and scientific expertise. As one actor articulated, "[the] government actually respected and acknowledged and supported public health expertise" (IDI9). Others emphasized a "trust of the people who understood the problem" (IDI3)—namely, those within public health—and perceived that public health experts were enabled "to take a lead role in the health system, over politics" (IDI12). This perspective was not as widely held by those in the public health sector, as one public health actor expressed, "politicians and bureaucrats waded into public health practice in a way that I don't think was appropriate" and that, "in the context of a pandemic, it’s actually relatively challenging to bring true expert advice because there’s too many right now. Suddenly, everybody’s a public health expert, but especially bureaucrats and politicians." They went on to share that the independence of public health to speak and act—and for politicians to accept independent public health advice—needs to be protected and institutionalized as "core to good governance" (IDI1). Relatedly, an elected official linked this to the absence of a formal, independent science table to advise government and stated that, "I think we should have one established permanently. I think we need to recognize that politicians aren't always the best at discerning scientific evidence and how that should play into decision-making" (IDI15).
These results highlight the divergent perspectives participants had as to the interface between research and policy-making and a lack of understanding regarding process and roles.
Challenges in applying evidence to policy decisions
Perspectives converged with respect to the existence of numerous challenges with and barriers to applying evidence to health policy and decision-making. These related to the quality and breadth of available data, both in terms of absence and abundance. For instance, as one public health actor noted in relation to health policy-making, "you never have enough information. You always have an information shortage, so you're trying to make the best decisions you can in the absence of usually really clear information" (IDI8). On the other hand, as evidence emerged en masse across jurisdictions in the pandemic, there were challenges with synthesizing evidence in a timely fashion for 'real-time' decision-making. A regional health authority actor highlighted this challenge early in the COVID-19 pandemic and perceived that there was not a provincial group bringing new synthesized information to decision-makers on a daily basis (IDI6). Other challenges related to the complexity of the political-public health interface with respect to data and scientific expertise, which "gets debated and needs to be digested by the political process. And then decisions are made" (IDI5). This actor further expressed that debate among experts needs to be balanced with efficient crisis response, that one has to "cut the debate short. For the sake of expediency, you need to react."
It was observed that, in BC’s COVID-19 response, data was gathered from multiple sources with differing data collection procedures, and sometimes with conflicting results—for instance, 'health system data' analyzed by the PHSA and 'public health data' analyzed by the BCCDC. This was observed to present challenges from a political perspective in discerning "who’s actually getting the 'right' answers" (IDI7). An added layer of complexity was reportedly rooted in how to communicate such evidence to the public and "public trust in the numbers" (IDI7), particularly as public understanding of what evidence is, how it is developed, and why it changes, can influence public perceptions of governance.
Finally, as one actor from within the research sector noted, organizationally and governance-wise, the system was "not very well set up to actually use research evidence…if we need to do better at using evidence in practice, we need to fix some of those things. And we actually know what a lot of those things are." For example , "there’s no science framework for how organizations work within that" and " governments shy away from setting science policy " (IDI11). This challenge was framed as having a macro-level dimension, as higher-level leadership structures were observed to not incentivize the development and effective use of research among constituent organizations, and also micro-level implications. From their perspective, researchers will struggle without such policy frameworks to obtain necessary data-sharing agreements with health authorities, nor will they be able to successfully navigate other barriers to conducting action-oriented research that informs policy and practice.
Similarly, a research actor perceived that the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted pre-existing fragmentation, "a pretty disjointed sort of enterprise" in how research is organized in the province:
I think pandemics need strong leadership and I think pandemic research response needed probably stronger leadership than it had. And I think that’s to do with [how] no one really knew who was in charge because no one really was given the role of being truly in charge of the research response (IDI14).
This individual underscored that, at the time of the interview, there were nearly 600 separate research projects being conducted in BC that focused on COVID-19. From their perspective, this reflected the need for more centralized direction to provide leadership, coordinate research efforts, and catalyze collaborations.
Overall, respondents perceived a lack of coordination and continuity across data sources, and a lack of explicit guidelines on evidence-use in the decision-making process, which resulted in a sense of fragmentation. The tension between the processes involved in research and the need for rapid decision-making was perceived as a barrier to using evidence to inform policy.
This study explored the use of evidence to inform early COVID-19 decision-making within British Columbia, Canada, from the perspectives of decision-makers themselves. Findings underscore the complexity of synthesizing and applying evidence (i.e., ‘scientific’ or research-based evidence most commonly discussed) to support public health policy in 'real-time', particularly in the context of public health crisis response. Despite a substantial and long-established literature on evidence-based clinical decision-making [ 23 , 24 ], understanding is more limited as to how public health crisis decision-making can be evidence-informed or evidence-based. By contributing to a growing global scholarship of retrospective examinations of COVID-19 decision-making processes [ 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ], our study aimed to broaden this understanding and, thus, support the strengthening of public health emergency preparedness in Canada, and globally.
Specifically, based on our findings on evidence-based public health practice, we found that decision-makers clearly emphasized ‘evidence-based’ or ‘evidence-informed’ as meaning ‘scientific’ evidence. They acknowledged other forms of evidence such as professional expertise and contextual information as influencing factors. We identified four key points related to the process of evidence-use in BC's COVID-19 decision-making, with broader implications as well:
Role Differences: The tensions we observed primarily related to a lack of clarity among the various agencies involved as to their respective roles and responsibilities in a public health emergency, a finding that aligns with research on evidence-use in prior pandemics in Canada [ 29 ]. Relatedly, scientists and policy-makers experienced challenges with communication and information-flow between one another and the public, which may reflect their different values and standards, framing of issues and goals, and language [ 30 ].
Barriers to Evidence-Use: Coordination and consistency in how data are collected across jurisdictions reportedly impeded efficiency and timeliness of decision-making. Lancaster and Rhodes (2020) suggest that evidence itself should be treated as a process, rather than a commodity, in evidence-based practice [ 31 ]. Thus, shifting the dialogue from 'barriers to evidence use' to an approach that fosters dialogue across different forms of evidence and different actors in the process may be beneficial.
Use of Evidence in Public Health versus Medicine: Evidence-based public health can be conflated with the concept of evidence-based medicine, though these are distinct in the type of information that needs to be considered. While ‘research evidence’ was the primary type of evidence used, other important types of evidence informed policy decisions in the COVID-19 public health emergency—for example, previous experience, public values, and preferences. This concurs with Brownson’s (2009) framework of factors driving decision-making in evidence-based public health [ 32 ]. Namely, that a balance between multiple factors, situated in particular environmental and organizational context, shapes decision-making: 1) best available research evidence; 2) clients'/population characteristics, state, needs, values, and preferences; and 3) resources, including a practitioner’s expertise. Thus, any evaluation of evidence-use in public health policy must take into consideration this multiplicity of factors at play, and draw on frameworks specific to public health [ 33 ]. Moreover, public health decision-making requires much more attention to behavioural factors and non-clinical impacts, which is distinct from the largely biology-focused lens of evidence-based medicine.
Transparency: Many participants emphasized a lack of explanation about why certain decisions were made and a lack of understanding about who was involved in decisions and how those decisions were made. This point was confirmed by a recent report on lessons learned in BC during the COVID-19 pandemic in which the authors describe " the desire to know more about the reasons why decisions were taken " as a " recurring theme " (13:66). These findings point to a need for clear and transparent mechanisms for channeling evidence, irrespective of the form used, into public health crisis decision-making.
Our findings also pointed to challenges associated with the infrastructure for utilizing research evidence in BC policy-making, specifically a need for more centralized authority on the research side of the public health emergency response to avoid duplication of efforts and more effectively synthesize findings for efficient use. Yet, as a participant questioned, what is the realistic role of research in a public health crisis response? Generally, most evidence used to inform crisis response measures is local epidemiological data or modelling data [ 7 ]. As corroborated by our findings, challenges exist in coordinating data collection and synthesis of these local data across jurisdictions to inform 'real-time' decision-making, let alone to feed into primary research studies [ 34 ].
On the other hand, as was the case in the COVID-19 pandemic, a 'high noise' research environment soon became another challenge as data became available to researchers. Various mechanisms have been established to try and address these challenges amid the COVID-19 pandemic, both to synthesize scientific evidence globally and to create channels for research evidence to support timely decision-making. For instance: 1) research networks and collaborations are working to coordinate research efforts (e.g., COVID-END network [ 35 ]); 2) independent research panels or committees within jurisdictions provide scientific advice to inform decision-making; and 3) research foundations, funding agencies, and platforms for knowledge mobilization (e.g., academic journals) continue to streamline funding through targeted calls for COVID-19 research grant proposals, or for publication of COVID-19 research articles. While our findings describe the varied forms of evidence used in COVID-19 policy-making—beyond scientific evidence—they also point to the opportunity for further investments in infrastructure that coordinates, streamlines, and strengthens collaborations between health researchers and decision-makers that results in timely uptake of results into policy decisions.
Finally, in considering these findings, it is important to note the study's scope and limitations: We focused on evidence use in a single public health emergency, in a single province. Future research could expand this inquiry to a multi-site analysis of evidence-use in pandemic policy-making, with an eye to synthesizing lessons learned and best practices. Additionally, our sample of participants included only one elected official, so perspectives were limited from this type of role. The majority of participants were health officials who primarily referred to and discussed evidence as ‘scientific’ or research-based evidence. Further work could explore the facilitators and barriers to evidence-use from the perspectives of elected officials and Ministry personnel, particularly with respect to the forms of evidence—considered broadly—and other varied inputs, that shape decision-making in the public sphere. This could include a more in-depth examination of policy implementation and how the potential societal consequences of implementation factor into public health decision-making.
We found that the policy decisions made during the initial stages of the COVID-19 pandemic were perceived by actors in BC's response as informed by—not always based on—scientific evidence, specifically; however, decision-makers also considered other contextual factors and drew on prior pandemic-related experience to inform decision-making, as is common in evidence-based public health practice [ 32 ]. The respondents' experiences point to specific areas that need to be considered in planning for future public health emergencies, including information flow between policy-makers and researchers, coordination in how data are collected, and transparency in how decisions are made—all of which reflect a need to improve communication. Furthermore, shifting the discourse from evidence as a commodity to evidence-use as a process will be helpful in addressing barriers to evidence-use, as well as increasing understanding about the public health decision-making process as distinct from clinical medicine. Finally, there is a critical need for clear mechanisms that channel evidence (whether ‘scientific’, research-based, or otherwise) into health crisis decision-making, including identifying and communicating the decision-making process to those producing and synthesizing evidence. The COVID-19 pandemic experience is an opportunity to reflect on what needs to be done to guild our public health systems for the future [ 36 , 37 ]. Understanding and responding to the complexities of decision-making as we move forward, particularly with respect to the synthesis and use of evidence, can contribute to strengthening preparedness for future public health emergencies.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are not publicly available to maintain the confidentiality of research participants.
The terms 'evidence-informed' and 'evidence-based' decision-making are used throughout this paper, though are distinct. The term 'evidence-informed' suggests that evidence is used and considered, though not necessarily solely determinative in decision-making [ 38 ].
The Provincial Health Services Authority (PHSA) works with the Ministry of Health (MOH) and regional health authorities to oversee the coordination and delivery of programs.
The Office of the Provincial Health Officer (PHO) has binding legal authority in the case of an emergency, and responsibility to monitor the health of BC’s population and provide independent advice to Ministers and public offices on public health issues.
The British Columbia Centre for Disease Control (BCCDC) is a program of the PHSA and provides provincial and national disease surveillance, detection, treatment, prevention, and consultation.
Abbreviations
British Columbia
British Columbia Centre for Disease Control
Coronavirus Disease 2019
Medical Health Officer
Ministry of Health
Provincial Health Officer
Provincial Health Services Authority
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus—2
University of British Columbia
Rubin O, Errett NA, Upshur R, Baekkeskov E. The challenges facing evidence-based decision making in the initial response to COVID-19. Scand J Public Health. 2021;49(7):790–6.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Williams GA, Ulla Díez SM, Figueras J, Lessof S, Ulla SM. Translating evidence into policy during the COVID-19 pandemic: bridging science and policy (and politics). Eurohealth (Lond). 2020;26(2):29–48.
Google Scholar
Vickery J, Atkinson P, Lin L, Rubin O, Upshur R, Yeoh EK, et al. Challenges to evidence-informed decision-making in the context of pandemics: qualitative study of COVID-19 policy advisor perspectives. BMJ Glob Heal. 2022;7(4):1–10.
Piper J, Gomis B, Lee K. “Guided by science and evidence”? The politics of border management in Canada’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Front Polit Sci. 2022;4
Cairney P. The UK government’s COVID-19 policy: what does “Guided by the science” mean in practice? Front Polit Sci. 2021;3(March):1–14.
Colman E, Wanat M, Goossens H, Tonkin-Crine S, Anthierens S. Following the science? Views from scientists on government advisory boards during the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative interview study in five European countries. BMJ Glob Heal. 2021;6(9):1–11.
Salajan A, Tsolova S, Ciotti M, Suk JE. To what extent does evidence support decision making during infectious disease outbreaks? A scoping literature review. Evid Policy. 2020;16(3):453–75.
Article Google Scholar
Cairney P. The UK government’s COVID-19 policy: assessing evidence-informed policy analysis in real time. Br Polit. 2021;16(1):90–116.
Lancaster K, Rhodes T, Rosengarten M. Making evidence and policy in public health emergencies: lessons from COVID-19 for adaptive evidence-making and intervention. Evid Policy. 2020;16(3):477–90.
Yang K. What can COVID-19 tell us about evidence-based management? Am Rev Public Adm. 2020;50(6–7):706–12.
Parkhurst J. The politics of evidence: from evidence-based policy to the good governance of evidence. Abingdon: Routledge; 2017.
Office of the Prime Minister. Minister of Health Mandate Letter [Internet]. 2021. https://pm.gc.ca/en/mandate-letters/2021/12/16/minister-health-mandate-letter
de Faye B, Perrin D, Trumpy C. COVID-19 lessons learned review: Final report. Victoria, BC; 2022.
First Nations Health Authority. Evolving vaccination plans is science in action: Dr. Bonnie Henry. First Nations Health Authority. 2021.
BC Stats. 2021 Sub-provincial population estimates highlights. Vol. 2021. Victoria, BC; 2022.
Michael Smith Health Research BC [Internet]. 2023. healthresearchbc.ca. Accessed 25 Jan 2023.
Michael Smith Health Research BC. SRAC [Internet]. 2023. https://healthresearchbc.ca/strategic-provincial-advisory-committee-srac/ . Accessed 25 Jan 2023.
Brubacher LJ, Hasan MZ, Sriram V, Keidar S, Wu A, Cheng M, et al. Investigating the influence of institutions, politics, organizations, and governance on the COVID-19 response in British Columbia, Canada: a jurisdictional case study protocol. Heal Res Policy Syst. 2022;20(1):1–10.
Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3:77–101.
DeCuir-Gunby JT, Marshall PL, McCulloch AW. Developing and using a codebook for the analysis of interview data: an example from a professional development research project. Field Methods. 2011;23(2):136–55.
Gale NK, Heath G, Cameron E, Rashid S, Redwood S. Using the framework method for the analysis of qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13(117):1–8.
Creswell JW, Miller DL. Determining validity in qualitative inquiry. Theory Pract. 2000;39(3):124–30.
Sackett D. How to read clinical journals: I. Why to read them and how to start reading them critically. Can Med Assoc J. 1981;1245:555–8.
Evidence Based Medicine Working Group. Evidence-based medicine: a new approach to teaching the practice of medicine. JAMA Netw. 1992;268(17):2420–5.
Allin S, Fitzpatrick T, Marchildon GP, Quesnel-Vallée A. The federal government and Canada’s COVID-19 responses: from “we’re ready, we’re prepared” to “fires are burning.” Heal Econ Policy Law. 2022;17(1):76–94.
Bollyky TJ, Hulland EN, Barber RM, Collins JK, Kiernan S, Moses M, et al. Pandemic preparedness and COVID-19: an exploratory analysis of infection and fatality rates, and contextual factors associated with preparedness in 177 countries, from Jan 1, 2020, to Sept 30, 2021. Lancet. 2022;6736(22):1–24.
Kuhlmann S, Hellström M, Ramberg U, Reiter R. Tracing divergence in crisis governance: responses to the COVID-19 pandemic in France, Germany and Sweden compared. Int Rev Adm Sci. 2021;87(3):556–75.
Haldane V, De Foo C, Abdalla SM, Jung AS, Tan M, Wu S, et al. Health systems resilience in managing the COVID-19 pandemic: lessons from 28 countries. Nat Med. 2021;27(6):964–80.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Rosella LC, Wilson K, Crowcroft NS, Chu A, Upshur R, Willison D, et al. Pandemic H1N1 in Canada and the use of evidence in developing public health policies—a policy analysis. Soc Sci Med. 2013;83:1–9.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Saner M. A map of the interface between science & policy. Ottawa, Ontario; 2007. Report No.: January 1.
Lancaster K, Rhodes T. What prevents health policy being “evidence-based”? New ways to think about evidence, policy and interventions in health. Br Med Bull. 2020;135(1):38–49.
Brownson RC, Fielding JE, Maylahn CM. Evidence-based public health: a fundamental concept for public health practice. Annu Rev Public Health. 2009;30:175–201.
Rychetnik L, Frommer M, Hawe P, Shiell A. Criteria for evaluating evidence on public health interventions. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2002;56:119–27.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Khan Y, Brown A, Shannon T, Gibson J, Généreux M, Henry B, et al. Public health emergency preparedness: a framework to promote resilience. BMC Public Health. 2018;18(1):1–16.
COVID-19 Evidence Network to Support Decision-Making. COVID-END [Internet]. 2023. https://www.mcmasterforum.org/networks/covid-end . Accessed 25 Jan 2023.
Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Moving forward from the COVID-19 pandemic: 10 opportunities for strengthening Canada’s public health systems. 2022.
Di Ruggiero E, Bhatia D, Umar I, Arpin E, Champagne C, Clavier C, et al. Governing for the public’s health: Governance options for a strengthened and renewed public health system in Canada. 2022.
Adjoa Kumah E, McSherry R, Bettany-Saltikov J, Hamilton S, Hogg J, Whittaker V, et al. Evidence-informed practice versus evidence-based practice educational interventions for improving knowledge, attitudes, understanding, and behavior toward the application of evidence into practice: a comprehensive systematic review of undergraduate studen. Campbell Syst Rev. 2019;15(e1015):1–19.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to extend our gratitude to current and former members of the University of British Columbia Working Group on Health Systems Response to COVID-19 who contributed to various aspects of this study, including Shelly Keidar, Kristina Jenei, Sydney Whiteford, Dr. Md Zabir Hasan, Dr. David M. Patrick, Dr. Maxwell Cameron, Mahrukh Zahid, Dr. Yoel Kornreich, Dr. Tammi Whelan, Austin Wu, Shivangi Khanna, and Candice Ruck.
Financial support for this work was generously provided by the University of British Columbia's Faculty of Medicine (Grant No. GR004683) and Peter Wall Institute for Advanced Studies (Grant No. GR016648), as well as a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Operating Grant (Grant No. GR019157). These funding bodies were not involved in the design of the study, the collection, analysis or interpretation of data, or in the writing of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Population and Public Health, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada
Laura Jane Brubacher, Chris Y. Lovato, Veena Sriram, Michael Cheng & Peter Berman
School of Public Health Sciences, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Canada
Laura Jane Brubacher
School of Public Policy and Global Affairs, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada
Veena Sriram
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
CYL, PB, and VS obtained funding for and designed the study. LJB, MC, and PB conducted data collection. LJB and VS analyzed the qualitative data. CYL and LJB collaboratively wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Laura Jane Brubacher .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This case study received the approval of the UBC Behavioural Research Ethics Board (Certificate # H20-02136). Participants provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Semi-structured interview guide [* = questions used for this specific study]
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Brubacher, L.J., Lovato, C.Y., Sriram, V. et al. The use of evidence to guide decision-making during the COVID-19 pandemic: divergent perspectives from a qualitative case study in British Columbia, Canada. Health Res Policy Sys 22 , 66 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-024-01146-2
Download citation
Received : 08 February 2023
Accepted : 29 April 2024
Published : 03 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-024-01146-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Decision-making
- Public health
- Policy-making
- Qualitative
Health Research Policy and Systems
ISSN: 1478-4505
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Enhancing drug therapy in ostomy patients: Best practice recommendations for medication management
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Hospital Pharmacy, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany
Roles Validation, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Department of General, Abdominal, Thoracic and Vascular Surgery, Katholisches Marienkrankenhaus, Hamburg, Germany
Affiliation Department of General Practice and Primary Care, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing
Roles Resources, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Department of Urology, University Medical Centre Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany
Roles Writing – review & editing
Contributed equally to this work with: Annika van der Linde, Claudia Langebrake
Roles Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing
Roles Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing
Affiliations Hospital Pharmacy, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany, Department of Stem Cell Transplantation, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany
- Vivien Berger,
- Matthias Reeh,
- Martin Scherer,
- Steffen Härterich,
- Sven Möller,
- Eva-Maria Anette Wansing,
- Annika van der Linde,
- Claudia Langebrake

- Published: June 6, 2024
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305047
- Reader Comments
Ostomy surgery is a common procedure that poses various challenges for patients and healthcare professionals. There are numerous guidelines addressing different ostomy-related problems (ORPs) and supporting an interdisciplinary approach for ostomy care, but evidence-based literature for optimizing drug therapy after ostomy surgery is lacking.
To investigate and characterize typical ORPs in relation to drug therapy and provide best practice recommendations from a pharmaceutical point of view.
Patients with an ileo- or colostomy were consecutively enrolled in a prospective, interventional monocentric cohort study during hospitalization, with particular attention to medication. A clinical pharmacist assessed DRPs by performing level 3 medication reviews and patient interviews. Pharmacists’ interventions (PIs) were evaluated by two senior clinical pharmacists and documented in DokuPIK (Documentation of Pharmacists’ Interventions in the Hospital). Following interdisciplinary discussions, physicians either accepted or rejected the proposed changes in drug therapy. Comparisons were made between ileostomy and colostomy patients regarding type and extent of PIs.
Out of the 80 patients included in the cohort, 54 (67.5%) had an ileostomy and 26 (32.5%) a colostomy. In this study, 288 PIs were documented (234 ileostomy vs . 54 colostomy), of wich 94.0% were accepted and implemented by the physicians. The most common reason for PIs in both subgroups (29.6% ileostomy vs . 26.1% colostomy) was a missing drug although indicated (e.g. no loperamide, but high stoma output). The proportion of PIs associated with the ostomy was higher in ileostomy patients (48.3% ileostomy vs . 31.5% colostomy; p = 0.025). Typical ORPs were extracted and analyzed as case studies including recommendations for their respective management and prevention.
This study highlights the importance of clinical pharmacists being a part of interdisciplinary teams to collaboratively improve ostomy care and patient safety. Especially ileostomy patients are more vulnerable for ORPs in the context of drug therapy and need to be monitored carefully.
Citation: Berger V, Reeh M, Scherer M, Härterich S, Möller S, Wansing E-MA, et al. (2024) Enhancing drug therapy in ostomy patients: Best practice recommendations for medication management. PLoS ONE 19(6): e0305047. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305047
Editor: Mert Tanal, Acibadem Maslak Hospital: Acibadem Maslak Hastanesi, TURKEY
Received: March 23, 2024; Accepted: May 23, 2024; Published: June 6, 2024
Copyright: © 2024 Berger et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.
Funding: This study was sponsored by Coloplast GmbH ( https://www.coloplast.de/ ) with a research grant for the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
Have you ever been confronted with the problem that a tablet appeared undissolved in the ostomy bag of an ostomy patient? In this case, what have you done? Do you remember which drug it might have been? Did you find a solution for this problem?
In some cases, these questions reach clinical pharmacists–whether it is a phone call of the surgeon/physician, the WOC (Wound, Ostomy and Continence) nurse, nurses in general, dietitians or the patient himself who is facing this problem. If a whole tablet becomes visible in the ostomy bag, liberation and absorption of the drug is very likely to be impaired. As a result, the drug therapy can lose its effect. Especially during the first weeks and months after ostomy surgery, complications occur more frequently [ 1 , 2 ].
The limited absorption of drugs in ostomy patients is a relevant problem which is often underestimated as it is rarely detected plus there is a lack of awareness. In contrast, there are international guidelines providing recommendations on the supplementation of nutrients and vitamins [ 3 – 6 ] and nutrition counseling representing an essential part of ostomy care [ 7 , 8 ].
According to Nightingale et al., especially in patients with a short bowel syndrome, malabsorption of vitamins and nutrients as well as a reduced absorption of drugs needs to be considered [ 9 ]. Zanni et al. concluded that jejunostomy and ileostomy patients are more likely to have drug-related problems regarding to drug absorption than colostomy patients [ 10 ]. There are some studies and reports that have attempted to point out the absorption problems in ostomy patients [ 9 – 16 ], but evidence-based literature for drug therapy after ostomy surgery is still lacking. The Association of Stoma Care Nurses has developed a summary of guidelines addressing common complications and challenges regarding ostomy care [ 17 ]. The summary refers in different sections to the need for daily medication reviews.
Pharmacists encounter ostomy patients in both inpatient and outpatient settings, but the information about the patient’s ostomy and potential absorption problems are often insufficient. By improving the flow of information and involving pharmacists more actively, they can provide added value in terms of drug therapy. This has been recognized by the Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario (RNAO), which names pharmacists as key members of the interprofessional team in their best practice guideline for ostomy care [ 18 ]. For comprehensive ostomy care, patients need access to expert healthcare professionals. While other healthcare professionals are already involved in ostomy care, there is still a lack of cooperation with clinical pharmacists. In recent years, various professional societies have recognized the importance and impact of involving clinical pharmacists in interdisciplinary teams. This is particularly true for areas such as emergency departments, intensive care units, stem cell transplantation and as a member of the antimicrobial stewardship program [ 19 – 22 ]. Clinical pharmacists can identify and solve drug-related problems (DRPs) through pharmacists’ interventions (PIs), thereby improving patient safety [ 23 – 29 ].
The aim of the study was to systematically investigate DRPs in ostomy patients and evaluate the potential impact of PIs within the subgroups of ileo- and colostomy patients. The primary objective was to raise awareness among healthcare professionals regarding absorption problems, to take action, adapt drug therapy and improve patient safety. In order to enhance drug therapy in ostomy patients, we aimed to provide useful recommendations for the management and prevention of typical DRPs.
Material and methods
Setting and study design.
This prospective, interventional cohort study was conducted at the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE), Germany. The study was approved by the local ethics committee of the Ärztekammer Hamburg (2021-100645-BO-ff) and registered within the German Clinical Trials Register (DRKS 00027291).
We consecutively included adult ileo- or colostomy patients with an inpatient stay between February 14, 2022 and March 16, 2023. The study participants either had an existing ostomy or a new ostomy was created during the hospital stay. Further inclusion criteria were age ≥ 18 years, written informed consent as well as sufficient German language skills. The aim of the study was to improve the drug therapy for ostomy patients through an intensified pharmaceutical medication management. As the primary outcome we defined the extent of PIs to solve DRPs. Secondary endpoints were the classification of DRPs as well as the assessment of pharmaceutical management from the patients’ perspective.
The medication process at the UKE is referred to as Closed Loop Medication Management (CLMM) consisting of four elements [ 30 ]. In the first step, physicians prescribe medications in the electronic prescribing software (computerized physician order entry with clinical decision support: CPOE/CDSS). These prescriptions are reviewed and validated by clinical pharmacists. Afterwards, the medications are packaged individually for each patient in the hospital pharmacy as part of the unit-dose logistics. As a final step, the administration of the medications is documented in the electronic prescribing software. Within the CLMM, clinical pharmacists perform a large number of medication reviews every day. In this study, in addition to the routine process, a clinical pharmacist performed level 3 medication reviews [ 31 ] for ostomy patients during their hospital stay, with a specific focus on ostomy-related problems (ORPs). Proposals for therapy modifications were discussed interdisciplinary with physicians and the WOC nurse. As part of an individual comprehensive consultation, patients were informed about modifications of their drug therapy and special aspects of drug formulations in the context of ostomy therapy in general. To evaluate the outpatient setting patients received a phone call at two points–one week and three months after discharge. From the patient’s point of view, pharmaceutical management was surveyed by a pseudonymized questionnaire (online or handwritten). The results of the questionnaire and the challenges in the outpatient setting will be presented in a separate publication. This paper focuses on the results of an intensified medication management during inpatient care and resulting recommendations for the prevention and management of typical ORPs in clinical practice.
Patient and medication data
For the characterization of the patient population, demographic and clinical data including age, sex, type of ostomy (ileo- vs . colostomy and temporary vs . permanent), diagnoses, surgical procedures, date of surgery and length of hospital stay were assessed. All patient data were collected from the electronic patient record system Soarian Clinicals® (Cerner Health Services Deutschland GmbH, Berlin, Germany, version 4.5.200). Additional information, including serum electrolytes (creatinine, potassium, sodium and magnesium), was accessible in the patient’s record for the medication review.
Both home medication and inpatient prescriptions were evaluated by drug, ATC (Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical) classification, dosage, interval, route of administration, formulation and duration. The medication data were retrieved from the electronic prescribing software ID MEDICS® (ID Information und Dokumentation im Gesundheitswesen GmbH & Co. KgaA, Berlin, Germany, version 7.8.39).
The home medication was obtained from at least two different sources of information: Scanned medication lists, previous hospital discharge reports, information from the community healthcare provider, and always verified by a patient interview.
Pharmacists’ interventions (PIs)
For all PIs, the involved drug(s), the reason for PIs (e.g. dose adjustment, initiation/discontinuation, modification of the dosage form), the resulting action and the acceptance rate were documented according to the DokuPIK criteria (Documentation of Pharmacists’ interventions [ 32 ]).
Furthermore, we classified PIs into two categories: (a) ostomy-related or (b) regular (independent of an existing ostomy). The classification into ostomy-related PIs was based on a list of drugs from a previous project (see S1 Table ). The list includes commonly used drugs for ORPs [ 33 ], along with specific reasons for PIs: advice on the selection and dosage or evaluation of a (no longer) existing indication for these drugs. Irrespective of the drug, PIs were assessed as ostomy-related if changing a drug formulation for better absorption was recommended. The classification into (b) regular refers to all PIs that were independent of the ostomy (e.g. discontinued home medication or necessary dose adjustments). The classification of PIs was reviewed by two independent senior clinical pharmacists and consensus was reached.
Definitions
- Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) Classification
The ATC classification is a hierarchical system by the World Health Organization (WHO) to divide the active substances of drugs into different groups according to the organ or system which they affect. There are five different levels from the main anatomical group (1 st level) to the chemical substance (5 th level) [ 34 ].
- Drug-related problems (DRPs)
Drug-related problems are events or circumstances relating to drug therapy that actually or potentially interfere with the intended outcome and can cause harm to the patient [ 35 ].
High Output Syndrome (HOS)
A small bowel ostomy output greater than 1.5 L to 2.0 L within 24 hours is usually considered as a high output syndrome (HOS) [ 9 ]. The consequences of a HOS are electrolyte and fluid imbalance up to acute renal failure in severe cases [ 36 ]. The type of ostomy, the amount and composition of enteral intake and the volume of gastrointestinal secretion are relevant factors influencing the ostomy output.
- Medication review
A medication review is a structured analysis of the patient’s drug therapy. The aim is to identify and manage drug-related problems (DRPs) to increase effectiveness and minimize potential risks associated with drug therapy [ 37 ]. In the present study, medication review is classified as level 3 (clinical medication review). In addition to medication and clinical data, there is a face-to-face collaboration between the clinical pharmacist, physicians, nursing staff and the patient [ 31 ].
- Ostomy-related problems (ORPs)
Ostomy-related problems generally refer to all problems that may occur in association with ostomy care, from physical (e.g. peristomal skin complications, constipation, sexual problems) to psychological changes in everyday life [ 38 ]. In this study, ostomy-related problems mainly refer to drug therapy from a pharmaceutical point of view, considering the absorption site and drug formulations.
- Pharmacists interventions (PIs)
Regarding DokuPIK PIs are defined as "any communication/action solving and/or avoiding DRPs" and includes the "management of existing DRPs as well as any proactive approach avoiding potential DRPs within the medication use process" [ 39 ]. (a) Physicians can accept PIs as a proposal and consequently implement them, (b) they can reject PIs for reasons of risk-benefit assessment or non-acceptance or (c) the outcome is not known.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed anonymously using MS Excel (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, United States, version 2016) and IBM® SPSS Statistics (IBM, Armonk, United States, version 27). Patient characteristics were summarized using median and range. Percentages and frequencies were calculated to characterize prescribed drugs and the associated ATC classification system (considering the 1 st and 3 rd levels). The acceptance rate of PIs was calculated based on all PIs except those, where only information was provided to physicians, nurses or patients. For group comparisons, categorical variables were examined using chi-square text (χ 2 ) or Fisher’s exact test. Continuous variables were expressed as the median and range and compared using the Mann-Whitney U test. The level of significance was defined as α = 0.05.
Patient characteristics
A total of 80 patients were recruited and included in the study, comprising 54 ileo- and 26 colostomy patients. The median age was 63 years with a range of 26 to 84 years. Females accounted for 54.0% of patients. There were no significant differences regarding age and sex between the ileostomy and the colostomy subgroup.
In almost two-thirds of patients, there was a surgical indication for new ostomy formation within the current hospital stay. In 74.0% of these patients, surgery was performed because of a cancer diagnosis. While the reasons for surgical indications were similar, the incidence of new ostomies was found to be significantly higher in the ileostomy group than in the colostomy group ( p = 0.04). The median number of home medication was three (range 0 to 19) and raised to nine prescriptions (range 3 to 19) during the hospital stay.
Further comparability data is shown in Table 1 .
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305047.t001
Medication data and pharmacists’ interventions
The prescribed drugs were cumulated for the entire hospital stay and classified according to ATC groups. Table 2 summarizes the most relevant ATC groups 1 st level and the associated 3 rd level subgroups with the most frequently prescribed drugs. In relation to the ATC group, the proportion of patients of the total study population treated with at least one drug was assessed. Within each ATC group, the two most common drugs were evaluated. For example, within the ATC subgroup "N02B Other analgesics" and antipyretics, 72 patients (90.0% of the total study population) were treated with at least one drug of this subgroup. Here, the top two drugs were metamizole sodium for 68 and paracetamol for 40 patients.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305047.t002
Classification of drugs
Classification and acceptance of pis.
A total of 288 PIs, including 234 in the ileostomy and 54 in the colostomy group were carried out as part of the pharmaceutical medication management focusing on ostomy. Overall, the intervention rate was 3.6 PIs per patient. Considering the different ostomy types, the intervention rate in the ileostomy group was 4.3 PIs per patient versus 2.1 PIs in the colostomy group ( p = 0.006).
The five most frequent reasons for PIs are listed in Table 3 and refer to the main categories "drugs", "other" and "dose". The most common reason accounting for a quarter of all PIs (26.4%) was performed, because a drug was not prescribed even though there was an indication. Altogether, the top five reasons were responsible for more than two-thirds of the PIs (68.8%). All other reasons were involved in less than 5.0% of the PIs. The overall acceptance rate for all PIs was 94.0%, with the highest acceptance rate in the category "other" at 100.0% and the lowest in the category "drugs" at 91.4%.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305047.t003
Ostomy-related PIs
Fig 1 illustrates the distribution of PIs (n = 288) among the subgroups of ileo- and colostomy patients. More than half of the PIs (n = 158; 54.9%) were classified as regular PIs (ostomy-independent). Within the category ostomy-related PIs (n = 130; 45.1%), approximately 86.9% (n = 113) were related to the ileostomy subgroup, while the proportion in the colostomy subgroup was 13.1% (n = 17). There was a statistically significant difference between the subgroups regarding the ostomy-related PIs (p = 0.025). The most frequently involved drugs were loperamide (n = 26; 20.0%) and pectin powder (n = 15; 11.5%), respectively.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305047.g001
Best practice: Medication-associated ostomy-related problems (ORPs)
Within our study, we identified drugs that are frequently associated with ORPs. We elaborated recommendations to solve these problems with a focus on adverse drug effect profile and drug formulation. Typical clinical cases from the study highlighting potential scenarios and recommendations for optimizing drug therapy are listed in Table 4 . Especially for ileostomy patients, the high output syndrome (HOS) is a clinically relevant problem, which requires early diagnosis and appropriate drug treatment. The internal hospital standard for the management of a HOS is shown in Fig 2 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305047.g002
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305047.t004
The three-stage medication standard for ostomy patients with HOS ( Fig 2 ) developed and implemented at the UKE is shown here as an example for a systematic approach. Apart from the recommendations for fluid and electrolyte (e.g. potassium, magnesium) management, the standard is based on thickening measures (pectin powder) and anti-motility measures (loperamide and opium tincture). Our data demonstrate that the three-step HOS ladder is well implemented, as at least one drug of the HOS standard was prescribed to 45 patients (56.0%) during hospitalization. Primarily, these were ileostomy patients, except for one colostomy patient with a short bowel syndrome. The majority of patients (n = 18) received pectin powder in combination with loperamide (level 2). The triple therapy (level 3) was indicated in 13 patients. There was no patient with opium as a monotherapy.
The current study, conducted in a German university hospital, evaluated an intensified medication management of ostomy patients to determine the extent of PIs and to identify DRPs in this special group of patients. Typical, recurring problems from clinical practice were outlined along with the pharmaceutical recommendations as best practice examples. We identified more PIs with a relation to the ostomy for ileostomy patients. The findings of our study suggest that both ileo- and colostomy patients benefit from a pharmaceutical medication management, but ileostomy patients in particular are more vulnerable for problems of drug absorption or HOS.
Intestinal ostomy surgery is a common surgical procedure, with more than 30,000 cases performed annually in Germany [ 40 ]. Nevertheless, we are unable to derive the actual number of ostomy patients. Over ten years ago, the number of stoma (ileo-, colo- or urostomies) patients in Germany was estimated at 160,000 [ 41 ], but there are no reliable updated numbers. Within our study, cancer was the main indication for ostomy formation, which is consistent with other studies [ 12 , 42 ]. The number of prescriptions increased by a median of five drugs during hospitalization in both ileo- and colostomy group. In this context, the risk of DRPs increases with a higher number of medications [ 43 ].
To the best of our knowledge, there is no study or systematic approach, which focuses on PIs performed within a group of ostomy patients. A first exploratory analysis within our hospital demonstrated beneficial effects of an intensified medication management for ostomy patients [ 14 ]. While the literature advocates interdisciplinary collaboration in pre- and postoperative education, focusing on ostomy care, ostomy complications, diet plans or quality of life concerns, there is little information on the role of pharmacists in supporting the evaluation of drug therapy [ 9 , 11 , 17 , 44 ]. Based on a nationwide survey in Germany, 91.0% of ostomy patients seek advice from their physician when they have problems with their medication [ 14 ]. Only a few sources mention pharmacists in connection with DRPs or switching drug formulations [ 11 , 12 , 45 ]. However, the Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario (RNAO) best practice guideline, which recognizes pharmacists as key members of the interprofessional team, is an exception [ 18 ]. As a topic outside of the scope of that document pharmacists’ interventions for the prevention and management of ostomy-related complications are mentioned. The simple remark in the RNAO guideline indicates that it is a relevant problem in clinical practice.
The importance of medication management for ostomy patients is shown by the evaluation of the PIs. Compared to the median number of PIs performed as part of the routine CLMM process, there were over three additional PIs per ostomy patient case, with a higher proportion for ileostomy patients. Medication reviews were performed on at least two days during the study. In more complex patient cases with a long hospital stay, PIs were still carried out in the following weeks due to queries or problems. The high intervention rate is comparable to the study by Hilgarth et al., where clinical pharmacy services were performed in critical care units in Germany and the intervention rate was 1 PI per patient case [ 46 ]. In the PROTECTED-UK study, which also analyzed PIs in critical care units in UK, the average intervention rate was 1.2 per patient [ 47 ]. Here, the higher intervention rate is likewise explained by the more complex patient population. A recent study from Vietnam, which included a defined patient population of hypertensive outpatients and likewise provided patient education, reported 1.9 PIs per patient–without reporting how often each patient was seen [ 48 ]. The considerably higher intervention rate within our study can be explained by two aspects: Firstly, the special patient population and secondly, the intensified management over several days including level 3 medication reviews and patient interviews.
For the classification of PIs, the database DokuPIK provides differentiated reasons for PIs [ 49 ]. The proportion of PIs targeting suboptimal drug formulation is much higher in ostomy patients, particularly in ileostomy patients, compared to nationwide data on general PIs in Germany (14.9% vs . 4.31%) [ 29 ]. In terms of indication, literature data varies between 9.5% and 19.1% for a missing indication and in contrast for an untreated indication from 4.5% to 20.3% [ 24 , 29 , 50 , 51 ]. Due to direct patient interviews, the rate of patient counseling is considerably high in our study. Patients had the chance to ask questions regarding their medication with no need to focus on ORPs. The category patient counseling is not included in all classification tools for PIs used in other countries [ 52 ]. The MEDAP study has demonstrated that communication-based interventions are more prevalent in outpatient settings [ 53 ]. While the proportion of interventions involving direct communication with patients was consistent with our data (8.0% vs . 10.0%), it is important to highlight that both inpatient and outpatient PIs were assessed in the MEDAP study. The high acceptance rate of PIs in our study results from close collaboration with physicians and a long-established clinical pharmacy service in our hospital. Working together with the WOC nurse was also essential to obtain information about problems such as increased ostomal output.
At the same time, it is important to differentiate how many PIs were exclusively related to the ostomy. A national survey of 107 ostomy patients in Germany revealed that more than half of the patients already had observed a tablet in their ostomy bag [ 14 ]. Over 70.0% of these were ileostomy patients. The occurrence of a tablet in the ostomy bag is a common problem described in the literature, especially for ileostomies, but with a lack of incidence data [ 9 , 54 , 55 ]. In ostomy patients, the question often arises as to what extent the absorption of drugs is impaired, due to most oral drugs being absorbed in the small intestine [ 56 ]. Zanni et al. examined the absorption profile of drugs, as well as medications that influence intestinal functioning and the risk of vitamin and mineral deficiencies [ 10 ]. Especially patients with a small bowel ostomy are more likely to have problems regarding drug absorption [ 57 , 58 ]. The problem of absorption especially in ileostomy patients with regard to enteric coated or extended release tablets is also addressed by Prinz et al. in their best practice guidelines for discharge planning for patients with a new ostomy [ 11 ]. In summary, the higher proportion of ostomy-related PIs in ileostomy patients in our study confirms prior findings that ileostomy patients are more likely to suffer from problems related to drug therapy.
Furthermore, mainly ileostomy patients often experience increased ostomy output or even a high output syndrome, HOS. While clinical management of a HOS is often based on empiric data and small studies, there are no national or international guidelines. Besides fluid and electrolyte management, drug therapy is a key element in reported trials. There are only published practical approaches concerning the management of a HOS [ 59 – 64 ], but there is no guideline. A recent meta-analysis by Lederhuber et al. shows that there are inconsistent definitions of HOS and only limited evidence for a preferable treatment [ 65 ]. The most frequently used drugs in included studies were loperamide, somatostatin analogues and omeprazole, but there was no overall effect on stomal output to determine which intervention was most effective. The effect of opium tincture was not evaluated in the meta-analysis of Lederhuber et al., since there were no existing studies at that time. A recently published prospective, noninterventional study (CLARIFY) evaluated the therapeutic effect of opium tincture over a period of six months [ 66 ]. Main findings showed a rapid decrease of stool frequency and no observed risk for dependency after discontinuation of opium tincture. A recent randomized controlled trial by Okdahl et al. confirmed that opium tincture prolongs gastrointestinal transit time and reduces motility without signs of sedation during treatment [ 67 ]. These results are consistent with our observations from clinical practice with the internal HOS standard ( Fig 2 ). While pectin powder in combination with loperamide was most frequently prescribed, a triple therapy with additional opium tincture was only necessary for a few patients. Although opium tincture and loperamide have the same mechanism of action (activation of intestinal μ-opioid receptors), synergistic effects have been discussed [ 68 , 69 ]. The HOS standard was developed based on prescription data at our hospital [ 14 ] and is intended to function as a practical approach for other hospitals.
Several limitations of our study need to be addressed. Firstly, we included both patients with a new ostomy and patients with an existing ostomy, regardless of how long ago the ostomy was created. There was no differentiation between emergency vs . planned ostomy surgery. The proportion of new ostomies within our study was higher, because patients were identified in collaboration with the WOC nurse, who focuses particularly on this subgroup. In addition, more problems happen to occur in the first few weeks after ostomy formation, so here the intervention rate may be higher than in patients who have been living with an ostomy for several months or even years. However, due to the small number of patients and the very heterogeneous timespan since ostomy surgery, this trend could not be observed in our data. We categorized all ostomies as existing if they were not performed during the current hospital stay. No distinction was made about how long the patient had been living with the ostomy–whether it was one week or several years–which would be important to analyze the differences between the groups more precisely. The number of ileostomy patients was higher than the one of colostomy patients, which means that typical problems in colostomy patients may be underrepresented. Secondly, the number of medications at discharge was not recorded in detail. The patients were only asked about changes in their medication one week after discharge during interviews via telephone. After discharge, there were no medical records, only verbal information from the patients. However, the new prescriptions are particularly relevant for patients because further questions may arise in the outpatient setting.
From clinical practice, we know that problems regarding drug absorption are frequently experienced by ostomy patients. For this reason, it will be even more important to involve clinical pharmacists for medication management and patient education. Based on best practice examples obtained in this study, we aim to provide specific recommendations for frequently occurring problems in the clinical setting from a pharmaceutical perspective regarding drug therapy. Additional evaluations of data from the study regarding the relevance of pharmaceutical management and the patient’s perspective from questionnaires and interviews after discharge will be analyzed to investigate problems in the outpatient setting. The implementation of an intensified medication management to a larger number of hospitals and the measurement of patient-reported outcome are key elements for future trials.
Conclusions
Many patients are facing problems due to ostomy formation in the context of drug therapy. However, there are options and solutions to address these problems. As specialists for drug therapy, clinical pharmacists can help to analyze and optimize the medication. Each patient, each ostomy as well as each drug therapy must be considered individually, but standards can be implemented for both the PIs and the therapeutic approaches (e.g. high output syndrome, HOS). Raising awareness amongst healthcare professionals and patients should be the first step to an overall improvement in patient safety. Subsequently, the collaboration between physicians, WOC nurses and clinical pharmacists should be enhanced. Especially, ileostomy patients benefit from an intensified medication management by clinical pharmacists.
Supporting information
S1 table. list of drugs and reasons for classification into ostomy-related pis..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305047.s001
Acknowledgments
First of all, we would like to express our gratitude to all the study participants who dedicated their time to participate in the interviews, without whom this research would not have been possible. Additionally, we would like to thank two clinical pharmacists from the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf: Nina Michalowski for her assistance in identifying ostomy patients during the routine process, and Alexander Runkel for his contributions to refining the figures.
- View Article
- PubMed/NCBI
- Google Scholar
- 14. Van der Linde A. Bedeutung der Intensivierung der Pharmazeutischen Betreuung von Stomapatienten.: [Hamburg]: Universität Hamburg; 2019.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introduction to Evidence-Based Practice. What is Evidence-Based Practice? Why is EBP Important? EBP can help you find the best evidence quickly. The five steps of EBP. ... Next, apply the evidence to one of the following case studies. Dentistry Case Study: Medicine Case Study: Nursing Case Study: Occupational Therapy Case Study: Pharmacy Case ...
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply… 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units'.1 A case study has also been described as an intensive, systematic investigation of a ...
This study provided an opportunity for a group of six practitioners working at the Aotearoa/New Zealand Ministry of Education to engage in an evidence-based review within the Waikato context. The evaluative process used in this study was consistent with the Ministry's practice principle for an EBP approach where professional knowledge is shared.
Evidence-based practice (EBP) is a problem-solving approach to the delivery of health care that integrates the best evidence from studies and patient care data with clinician expertise and patient preferences and values. When delivered in a context of caring and in a supportive organizational culture, the highest quality of care and best ...
Evidence Based Practice (EBP) has proven to be a reliable framework for making these types of important decisions. EBP provides a sequential and structured approach for integrating the best available evidence into the decision-making process. Typically, this process entails formulating an answerable question, searching for the best available ...
A case study on using evidence-based practice to reinvigorate performance management practices. Case studies. Fair selection: Surrey Police and Sussex Police. A case study on using evidence-based practice to review selection processes for promoting police officers. Explore our other factsheets.
The Case Study and Its Maligned Account. Evidence-based practice (EBP) is the integration of the best available research, clinical expertise, and a patient's values when making clinical decisions. 1 The central principle of EBP is that each patient is unique, and decisions for the patient's care must be made at the individual, "n-of-1" level. 2, 3 As more evidence is presented to the ...
Research studies show that evidence-based practice (EBP) leads to higher quality care, improved patient outcomes, reduced costs, and greater nurse satisfaction than traditional approaches to care. 1-5 Despite these favorable findings, many nurses remain inconsistent in their implementation of evidence-based care. Moreover, some nurses, whose education predates the inclusion of EBP in the ...
1. Introduction. Evidence-based practice (EBP) is defined as "clinical decision-making that considers the best available evidence; the context in which the care is delivered; client preference; and the professional judgment of the health professional" [] (p. 2).EBP implementation is recommended in clinical settings [2,3,4,5] as it has been attributed to promoting high-value health care ...
Systematic case studies are often placed at the low end of evidence-based practice (EBP) due to lack of critical appraisal. This paper seeks to attend to this research gap by introducing a novel Case Study Evaluation-tool (CaSE). First, issues around knowledge generation and validity are assessed in both EBP and practice-based evidence (PBE) paradigms. Although systematic case studies are more ...
5 Steps of EBP. Ask: Convert the need for information into an answerable question. Find: Track down the best evidence with which to answer that question. Appraise: Critically appraise that evidence for its validity and applicability. Apply: Integrate the critical appraisal with clinical expertise and with the patient's unique biology, values ...
Limit by Evidence-Based Practice. Case Study example: ... Click on Evidence-Based Practice under Limit your Results. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR) Case Study example: In the Search box, type: fenugreek AND diabetes; In this case, there are no systematic reviews on this topic. You do retrieve, however, some citations to clinical ...
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply... 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units' .1 A case study has also been described ...
Koufogiannakis and Brettle also encourage librarians to take the principles of EBLIP and "emphasize an overall approach to practice that is about being evidence based" (2016, p. 3). Everyday Evidence-Based Practice in the Academic Library: Case Studies and Reflections aims to provide real-world examples of librarians who embody this call ...
Using Stake's Qualitative Case Study Approach to Explore Implementation of Evidence-Based Practice. Sheryl L. Boblin, Sandra Ireland, […], Helen Kirkpatrick, and ... (2012). The real world journey of implementing fall prevention best practices in three acute care hospitals: A case study. Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing, 10(2), 95-103 ...
Evidence-based case study guidelines. The clinical case study may be defined as a detailed analysis of the therapy conducted with a couple or family that will be instructive, may be exemplary or cautionary, and stresses factors contributing to either success or failure of the treatment. Because evidence-based clinical case studies can be ...
Evidence-based practice among speech-language pathologists: Attitudes, utilization, and barriers. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology , 14 , 208-220. ASHAWire Google Scholar
Introduction to Evidence-Based Practice. What is Evidence-Based Practice? Why is EBP Important? EBP can help you find the best evidence quickly. The five steps of EBP. ... Select one of the following case studies to practice identifying PICO elements and forming a research question. Dentistry Case Study: Medicine Case Study: Nursing Case Study:
Evidence-Based Case Study. Parallel in purpose to the Practice Review articles, I would like to issue an open invitation for authors to submit an Evidence-Based Case Study for possible publication in Psychotherapy. I believe developing such a series of Evidence-Based Case Studies will be extremely useful in several ways.
The challenges of evidence-informed decision-making in a public health emergency have never been so notable as during the COVID-19 pandemic. Questions about the decision-making process, including what forms of evidence were used, and how evidence informed—or did not inform—policy have been debated. We examined decision-makers' observations on evidence-use in early COVID-19 policy-making in ...
Background Ostomy surgery is a common procedure that poses various challenges for patients and healthcare professionals. There are numerous guidelines addressing different ostomy-related problems (ORPs) and supporting an interdisciplinary approach for ostomy care, but evidence-based literature for optimizing drug therapy after ostomy surgery is lacking. Aim To investigate and characterize ...
Clinicians are encouraged to become familiar with each of the different interventions to determine which of these might be consistent with their practice, to develop a plan for additional training and professional development, and to become informed about the range of evidence-based treatment options in order to help patients with decision ...