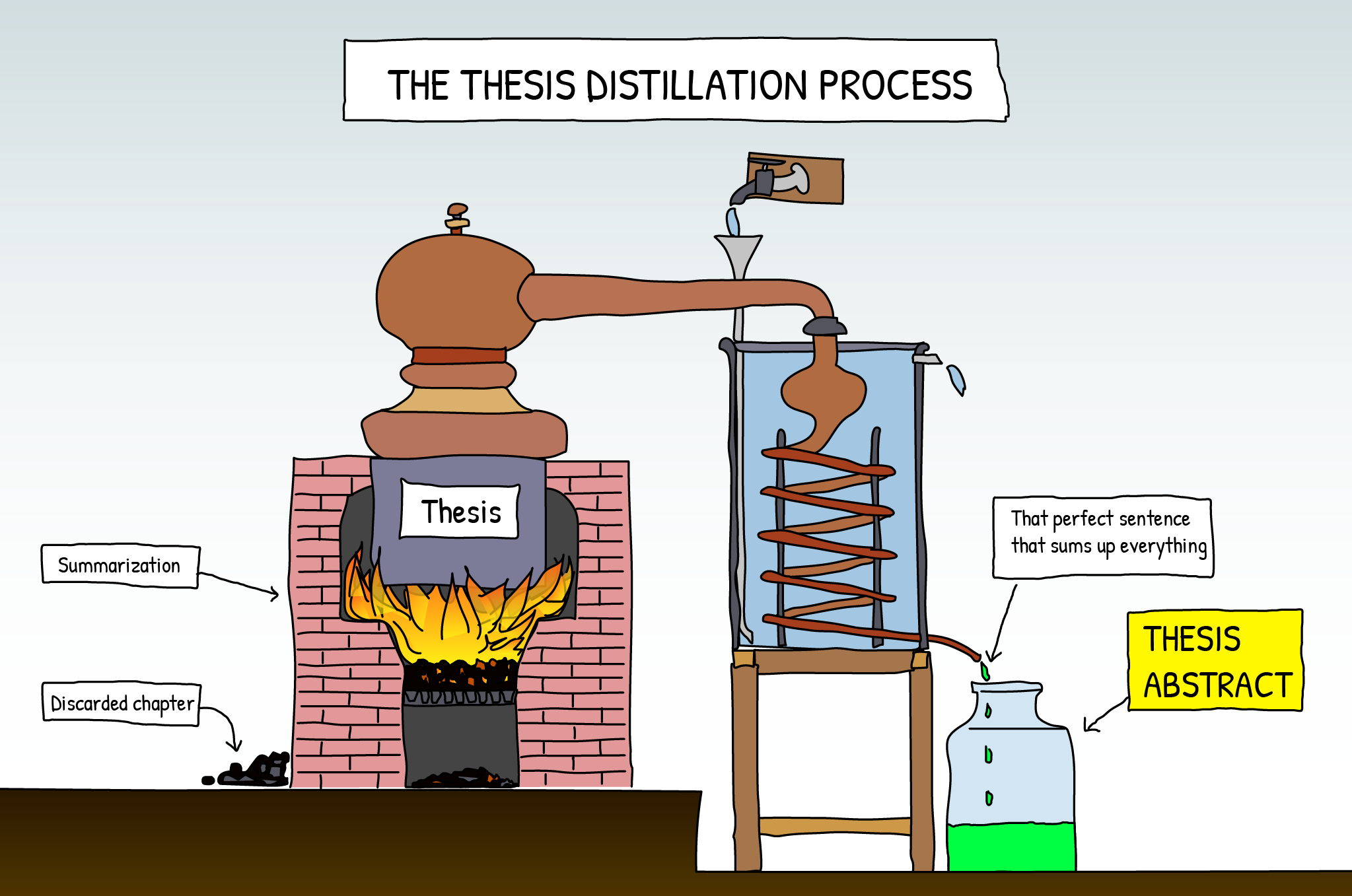
How to Write a Great Synopsis for Thesis
A synopsis is a structured outline of a research thesis and the steps followed to answer the research question. The goal of writing a synopsis is to clearly and thoroughly explain the need to investigate a certain problem using particular practical methods to conduct the study. One of the main components of this written work is an extensive literature review containing strong evidence that the proposed research is feasible.

Establishing the Background
A supervisor may ask you to write a synopsis for one or more reasons:
- to help you improve your critical thinking and writing skills
- to help you understand how to design a comprehensive synopsis
- to encourage you to write a comprehensive literature review to make sure that the research problem has not been answered yet
- to make you conduct a logical analysis of the steps that should be followed to meet the objectives of the research
A synopsis should be coherent in terms of research design. Thus, you should ensure that the research problem, aims, and research methods are logically linked and well-considered. Note that all synopses should contain answers for several crucial questions:
- Why should research on the proposed problem be undertaken?
- What is expected to be achieved?
- What has been done by other researchers on the proposed topic?
- How will the objectives of the study be achieved?
The Writing Process
Before proceeding, consider answering the following questions:
- Why am I going to study this topic?
- Why do I consider it to be important?
- Have I conducted an extensive literature review on the topic?
- What problem will the research help to solve?
- How do I incorporate previous studies on the topic?
The structure of a synopsis should correspond to the structure of qualifying research work, and the word count should be 2,500–3,000 words (Balu 38). The basic elements of a synopsis include a title page, contents page, an introduction, background, literature review, objectives, methods, experiments and results, conclusions, and references.
Introduction
As this comprises the first part of the main text, the introduction should convince readers that the study addresses a relevant topic and that the expected outcomes will provide important insights. Also, this section should include a brief description of the methods that will be used to answer the research question. Usually, the introduction is written in 1–3 paragraphs and answers the following questions:
- What is the topic of the research?
- What is the research problem that needs to be meaningfully understood or investigated?
- Why is the problem important?
- How will the problem be studied?
In this section, you should set the scene and better introduce the research topic by proving its scientific legitimacy and relevance. It is important to establish a clear focus and avoid broad generalizations and vague statements. If necessary, you may explain key concepts or terms. Consider covering the following points in this section:
- Discuss how the research will contribute to the existing scientific knowledge.
- Provide a detailed description of the research problem and purpose of the research.
- Provide a rationale for the study.
- Explain how the research question will be answered.
- Be sure to discuss the methods chosen and anticipated implications of the research.
Literature Review
A review of existing literature is an important part of a synopsis, as it:
- gives a more detailed look at scientific information related to the topic
- familiarizes readers with research conducted by others on a similar subject
- gives insight into the difficulties faced by other researchers
- helps identify variables for the research based on similar studies
- helps double-check the feasibility of the research problem.
When writing the literature review, do not simply present a list of methods researchers have used and conclusions they have drawn. It is important to compare and contrast different opinions and be unafraid to criticize some of them. Pay attention to controversial issues and divergent approaches used to address similar problems. You may discuss which arguments are more persuasive and which methods and techniques seem to be more valid and reliable. In this section, you are expected not to summarize but analyze the previous research while remembering to link it to your own purpose.
Identify the objectives of the research based on the literature review. Provide an overall objective related to the scientific contribution of the study to the subject area. Also include a specific objective that can be measured at the end of the research.
When writing this section, consider that the aim of the research is to produce new knowledge regarding the topic chosen. Therefore, the research methodology forms the core of your project, and your goal is to convince readers that the research design and methods chosen will rationally answer the research questions and provide effective tools to interpret the results correctly. It may be appropriate to incorporate some examples from your literature review into the description of the overall research design.
When describing the research methodology, ensure that you specify the approaches and techniques that will be used to answer the research question. In addition, be specific about applying the chosen methods and what you expect to achieve. Keep in mind that the methods section allows readers to evaluate the validity and feasibility of the study. Therefore, be sure to explain your decision to adopt specific methods and procedures. It is also important to discuss the anticipated barriers and limitations of the study and how they will be addressed. Specify what kind of contribution to the existing knowledge on the topic is expected, and discuss any ethical considerations that are relevant to the research.
Experiments and Results
Logically present and analyze the results of the study using tables or figures.
In this section, you should again state the significance of the research and summarize the study. Be sure to mention the study objectives and methods used to answer the research questions. Also, discuss how the results of the study contribute to the current knowledge on the problem.
A synopsis should contain a list of all references used. Make sure the references are formatted according to the chosen citation style and each source presented in this section is mentioned within the body of the synopsis.
The purpose of writing a synopsis is to show a supervisor a clear picture of a proposed project and allow him or her to find any gaps that have not been considered previously. A concisely written synopsis will help you gain approval to proceed with the actual research. While no rigid rules for writing this type of paper have been established, a synopsis should be constructed in a manner to help a supervisor understand the proposed research at first glance.
Balu, R. “Writing a Good Ph.D Research Synopsis.” International Journal of Research in Science and Technology, vol. 5, no. 4, 2015, pp. 38–48.
Unfortunately, your browser is too old to work on this site.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Research Synopsis: Template, Examples, & More
Last Updated: May 9, 2024 Fact Checked
- Organizing & Formatting
- Writing Your Synopsis
- Reviewing & Editing
Research Synopsis Template
This article was reviewed by Gerald Posner and by wikiHow staff writer, Raven Minyard, BA . Gerald Posner is an Author & Journalist based in Miami, Florida. With over 35 years of experience, he specializes in investigative journalism, nonfiction books, and editorials. He holds a law degree from UC College of the Law, San Francisco, and a BA in Political Science from the University of California-Berkeley. He’s the author of thirteen books, including several New York Times bestsellers, the winner of the Florida Book Award for General Nonfiction, and has been a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize in History. He was also shortlisted for the Best Business Book of 2020 by the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 279,230 times.
A research synopsis describes the plan for your research project and is typically submitted to professors or department heads so they can approve your project. Most synopses are between 3,000 and 4,000 words and provide your research objectives and methods. While the specific types of information you need to include in your synopsis may vary depending on your department guidelines, most synopses include the same basic sections. In this article, we’ll walk you step-by-step through everything you need to know to write a synopsis for research.
Things You Should Know
- Begin your research synopsis by introducing the question your research will answer and its importance to your field.
- List 2 or 3 specific objectives you hope to achieve and how they will advance your field.
- Discuss your methodology to demonstrate why the study design you chose is appropriate for your research question.

Organizing Your Research Synopsis

- Find out what citation format you’re supposed to use, as well as whether you’re expected to use parenthetical references or footnotes in the body of your synopsis.
- If you have questions about anything in your guidelines, ask your instructor or advisor to ensure you follow them correctly.

- Title: the title of your study
- Abstract: a summary of your research synopsis
- Introduction: identifies and describes your research question
- Literature Review: a review of existing relevant research
- Objectives: goals you hope to accomplish through your study
- Hypotheses: results you expect to find through your research
- Methodology and methods: explains the methods you’ll use to complete your study
- References: a list of any references used in citations
Tip: Your synopsis might have additional sections, depending on your discipline and the type of research you're conducting. Talk to your instructor or advisor about which sections are required for your department.

- Keep in mind that you might not end up using all the sources you initially found. After you've finished your synopsis, go back and delete the ones you didn't use.
Writing Your Research Synopsis

- Your title should be a brief and specific reflection of the main objectives of your study. In general, it should be under 50 words and should avoid unneeded phrases like “an investigation into.”
- On the other hand, avoid a title that’s too short, as well. For example, a title like “A Study of Urban Heating” is too short and doesn’t provide any insight into the specifics of your research.

- The introduction allows you to explain to your reader exactly why the question you’re trying to answer is vital and how your knowledge and experience make you the best researcher to tackle it.
- Support most of the statements in your introduction with other studies in the area that support the importance of your question. For example, you might cite a previous study that mentions your problem as an area where further research needs to be done.
- The length of your introduction will vary depending on the overall length of your synopsis as well as the ultimate length of your eventual paper after you’ve finished your research. Generally, it will cover the first page or two of your synopsis.

- For example, try finding relevant literature through educational journals or bulletins from organizations like WHO and CDC.
- Typically, a thorough literature review discusses 8 to 10 previous studies related to your research problem.
- As with the introduction, the length of your literature review will vary depending on the overall length of your synopsis. Generally, it will be about the same length as your introduction.
- Try to use the most current research available and avoid sources over 5 years old.

- For example, an objective for research on urban heating could be “to compare urban heat modification caused by vegetation of mixed species considering the 5 most common urban trees in an area.”
- Generally, the overall objective doesn’t relate to solving a specific problem or answering a specific question. Rather, it describes how your particular project will advance your field.
- For specific objectives, think in terms of action verbs like “quantify” or “compare.” Here, you’re hoping to gain a better understanding of associations between particular variables.

- Specify the sources you used and the reasons you have arrived at your hypotheses. Typically, these will come from prior studies that have shown similar relationships.
- For example, suppose a prior study showed that children who were home-schooled were less likely to be in fraternities or sororities in college. You might use that study to back up a hypothesis that home-schooled children are more independent and less likely to need strong friendship support networks.

- Expect your methodology to be at least as long as either your introduction or your literature review, if not longer. Include enough detail that your reader can fully understand how you’re going to carry out your study.
- This section of your synopsis may include information about how you plan to collect and analyze your data, the overall design of your study, and your sampling methods, if necessary. Include information about the study setting, like the facilities and equipment that are available to you to carry out your study.
- For example, your research work may take place in a hospital, and you may use cluster sampling to gather data.

- Use between 100 and 200 words to give your readers a basic understanding of your research project.
- Include a clear statement of the problem, the main goals or objectives of your study, the theories or conceptual framework your research relies upon, and the methods you’ll use to reach your goals or objectives.
Tip: Jot down a few notes as you draft your other sections that you can compile for your abstract to keep your writing more efficient.
Reviewing and Editing Your Research Synopsis

- If you don’t have that kind of time because you’re up against a deadline, at least take a few hours away from your synopsis before you go back to edit it. Do something entirely unrelated to your research, like taking a walk or going to a movie.

- Eliminate sentences that don’t add any new information. Even the longest synopsis is a brief document—make sure every word needs to be there and counts for something.
- Get rid of jargon and terms of art in your field that could be better explained in plain language. Even though your likely readers are people who are well-versed in your field, providing plain language descriptions shows you know what you’re talking about. Using jargon can seem like you’re trying to sound like you know more than you actually do.
Tip: Free apps, such as Grammarly and Hemingway App, can help you identify grammatical errors as well as areas where your writing could be clearer. However, you shouldn't rely solely on apps since they can miss things.

- Reference list formatting is very particular. Read your references out loud, with the punctuation and spacing, to pick up on errors you wouldn’t have noticed if you’d just read over them.
- Compare your format to the one in the stylebook you’re using and make sure all of your entries are correct.

- Read your synopsis backward by starting on the last word and reading each word separately from the last to the first. This helps isolate spelling errors. Reading backward sentence by sentence helps you isolate grammatical errors without being distracted by the content.
- Print your synopsis and circle every punctuation mark with a red pen. Then, go through them and focus on whether they’re correct.
- Read your synopsis out loud, including the punctuation, as though you were dictating the synopsis.

- Have at least one person who isn’t familiar with your area of study look over your synopsis. If they can understand your project, you know your writing is clear. If any parts confuse them, then that’s an area where you can improve the clarity of your writing.

Expert Q&A
- If you make significant changes to your synopsis after your first or second round of editing, you may need to proofread it again to make sure you didn’t introduce any new errors. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://admin.umt.edu.pk/Media/Site/iib1/FileManager/FORMAT%20OF%20SYNOPSIS%2012-10-2018.pdf
- ↑ https://www.scientificstyleandformat.org/Tools/SSF-Citation-Quick-Guide.html
- ↑ https://numspak.edu.pk/upload/media/Guidelines%20for%20Synopsis%20Writing1531455748.pdf
- ↑ https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279917593_Research_synopsis_guidelines
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ https://www.cornerstone.edu/blog-post/six-steps-to-really-edit-your-paper/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jul 25, 2022
Did this article help you?
Wave Bubble
Aug 31, 2021

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
- How it works
- Homework answers

How to Write a Good Synopsis for Thesis

After countless hours studying, hundreds of exams and tests, millions of words written in essays and projects, here you are at the final boss of your PhD or MBA program; your thesis. This is what stands between you and your degree and nothing may be more daunting a task than this one. Luckily for you, there are several ways of attacking this, and one of the major steps in doing so is writing a clear and effective synopsis for your thesis.
For those of you unfamiliar or wanting to know more, a thesis is a scholarly essay based upon your own personal research on a topic you have discovered or learned about during your time at school. In order to receive a Master’s degree or a PhD, a thesis is required, as it proves that you have critical thinking skills about your area of expertise and can prove your thesis through the research you have done. This is what separates you from the rest, your professors will see all the work you have done and the knowledge you have acquired throughout your journey to this point.
What is a Synopsis?
Generally speaking, a synopsis is a general discussion or survey of a piece of work, explaining only the essential information in an easy, readable way. The function is to explain the main idea before a reader begins to read the thesis. Beyond that, a synopsis for a thesis has more function and importance than just a brief summary.
The synopsis first of all, is not so brief. It gives a detailed description of your thesis, including the purpose of your research and methods you used as well as the process you used to explore the topic in depth. It introduces your thesis in a way that your readers know what to expect, but still surprised at the amount of work and detail presented within.
This helps your supervisor see the possible strengths and weaknesses of your thesis and can give you helpful ideas on how to fill in those gaps. It’s a protocol used by your supervisor to ensure that you are on the right track to completing your thesis and you’ll finish on time. This is an essential step before writing your actual thesis. Make sure you complete your synopsis before you begin your research, as you may not need all the information you think you need.
So, what makes a good Synopsis?
A good synopsis details everything related to your topic, but a great synopsis ensures that not only is the content there, but it is presented in a logical manner and easy to follow. Your outlined thesis should include the following:
- The title of the topic
- The abstract
- The necessity of the topic – the background
- All related literature concerning the topic
- Methods and Materials of your research
Once these headings are established, it helps you to go through each stage, making sure that no information is left off or missed. The scope of your thesis is broad, but has a direction. As you progress through your synopsis, the details fall into place and allows you to start doing your research and collecting your data.
Establish your background
Your loose thoughts should be filtered and sorted and should be organized based on how they are all linked together. The aims and goals of your topic should be apparent, so make sure to ask yourself these questions:
“Why should someone research this topic” “What are my expectations of this topic” “What have others contributed to the research of this topic” “How will I reach the goals and objectives of my topic”
Once the background is established, you can start thinking about the actual content.
Identify your Objectives
The background can help you decide the main reasons why you are undergoing this research into this topic. What good will this do for the world? What good will this do for professionals in this field? What good will it do for the communities surrounding this field? Having a measurable objective will pave the way to a better thesis.
Consider your Methods
The aim of the thesis is to provide novel information about your topic, something original or groundbreaking. This is important as it gives the reader something to analyze and think about. The way you deliver your information should provoke thoughts, or leave a trail to be followed into a thought process. Your approach should be able to answer any and all questions regarding your thesis, whether or not your ideas hold validity and some substance. Explaining your decisions and thought processes are much easier if you set your boundaries and barriers that you can address in your synopsis.
Present your Experiments and Analysis
This is an important step once everything else has been established. Detail the research you will do and the experiments you will be observing and analyze them in detail. You should link the results to your findings and your knowledge about the topic. This is where you earn your money, the way you can tie in numbers and facts to the knowledge you already know to solidify your thesis. The better your analysis is, the more your reader will understand.
Conclude and Summarize
Your supervisor should have already read your synopsis up to this point and understood the concept and scope of your thesis. But you should reiterate your main idea in case your supervisor got lost or that you had a different idea than they had. Once you’ve summed it up, your supervisor can give you helpful hints and tips to solidify the rest of your thesis and smooth out the potential problems or holes in your thesis.
So, what now?
Begin writing your synopsis with these key facts in mind. Know that your synopsis is a tool for you to organize your thoughts and for your supervisor to advise you on your direction and objectives. Be concise and be knowledgeable, so that you may get the best possible feedback on your synopsis.
- More Networks

LAW COLLOQUY

You Must Know Yourself, To Grow Yourself
How to write Dissertation and synopsis
What is the importance of your research?
Which type of problem your dissertation is going to challenge or raise?
Why is it a problem for the research, academic, scientific, technical, the management, or legal community?
Why is it important for you to find a solution?
How are you going to search for the answers?
YouTube video on the topic is shared below:
A step before the Dissertation - How to write a synopsis
Dissertation topic - The topic is the most important thing for research, which should be selected wisely, e.g.:-
It should be specific, unambiguous, and explicit.
It should not be vague or prolonged.
It should concern general, legal, informative, or technical issues at the national or international level.
Introduction —This section should provide a brief description of the area of the proposed research work in a very concrete, concise, and accurate manner. It must be clear rather than fuzzy and general.
Review of Literature – ' Research' means ‘to search again’. That’s why a ‘review of the literature’ is an essential and very important part of any research work, which explicitly the research work was done previously in the same area of the proposed research. It is essential to plan further research efficiently and appropriately. References should support the information given in the review.
Objectives of research - There must be comprehensive objectives of the research work. These objectives will indicate the aim, major aspects, and the study's overall purpose. It should be clearly and concisely defined. These are broad statements of desired outcomes, or the general intentions of the research, which 'paint a picture' of your research work. The maximum aim or objectives should be up to three. If should not be too extensive. Make accurate use of concepts, which must be sensible and precisely described.
Justification of the problem - Every objective needs justification. In research, it is essential to justify your objective in a concrete and impressive and remarkable manner. You may take help from previous research work, cases, reports, etc. There is a possibility to predict the specific and general benefits likely to be achieved as a result of the completion of the proposed research by comparing and citing references of the previous works.
The hypothesis of Study- Hypothesis is a statement to be tested for possible acceptance or rejection. Hypothesis are of two types, i.e.:-
Null (Ho) - The null hypothesis is tested for possible rejection.
Alternative (H1)., which is tested for possible acceptance.
Significance of Study —It emphasises the significance/ importance of the research work/study, i.e., the reason and aim of the selection of the topic of research.
Statement of Problem —The researcher must clearly identify the problem/issue selected for the thesis/ dissertation.
Research Methodology - It means a plan of work describing the various aspects of the study in a logical sequence along with the methodologies to be employed. It helps to validate that the researcher has a fairly good idea about the nature of the work likely to be involved. The methodology includes the following:-
Sources of data : Factual information is called quantitative data. Information collected about opinions and views is called qualitative data. There are two methods for this:
Primary research (field research) involves gathering new data that has not been collected before. Examples include surveys using questionnaires, interviews with focus groups, and observations.
Secondary research (desk research) involves gathering existing data that has already been produced. For example, research newspapers and company reports, case studies, diaries, critical incidents, portfolios, books, journals, periodicals, abstracts, indexes, directories, research reports, conference papers, market reports, annual reports, internal records of organisations, newspapers and magazines, CD-ROMs, online databases, the Internet, videos, and broadcasts.
References and Bibliography —The synopsis should include a list of references and a bibliography if required. These should follow a standard pattern.
Length of a synopsis —It will be difficult to define an overall length for a synopsis for legal research in such varied fields of study. However, it should be as concise as possible and avoid repetitions. A synopsis's total length may range from 1500 to a few thousand words.
Click YouTube video link for Structure of footnote and bibliography below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AUnbGpOctLk
Introduction - The first chapter should include a background of the problem and a statement of the issue. The purpose of the study must be clearly stated, followed by the research questions. Your whole research work and other chapters should be the answers to the research question you raised. You should provide clear definitions of the terms related to the work. You will also be able to expose your assumptions and expectations of the final results.
Literature Review –This is the most significant part of your research. In this chapter of the dissertation, you will review the research process in the same manner as described earlier. This part reflects your work and efforts.
Methodology -This part of the dissertation focuses on how you located the resources and the methods of implementation of the results. If you're writing a qualitative dissertation, you will expose the research questions, setting, participants, data collection, and data analysis processes. If, on the other hand, you're writing a quantitative dissertation, you will focus this chapter on the research questions and hypotheses, information about the population and sample, instrumentation, collection of data, and analysis of data.
Sample size: The sample size should be normal neither too small nor too large.
Data Collection Techniques : (Registration, Questionnaires, interviews, Direct Observations) Analysis of Data: The data will be analysed according to the topic's requirements. After collecting the data, it is to be tabulated. The total number of variables used will be included in the study, and then the relationship between variables will be analysed.
Findings —This is again a very important point in the whole research process because it reflects your cerebral aptitude or intellectual ability. In the findings, you reiterate the research questions and discuss the outcomes.
Conclusions - In the dissertation's final chapter, you will summarise the study and briefly report the results and outcomes. You should focus on explaining how your findings make a difference in the academic community and how they are implied in practice.
Recommendations/ Suggestions - This part is the end chapter of your research, which includes "Recommendations for future research“, where you propose future research to clarify the issues further. Explain why you suggest this research and what form it should take.
Bibliography : Use the recommended citation style for your field of study and include all sources you used during the research and writing stages.
Difference between footnotes, references, and bibliography
Footnotes, endnotes, references, and bibliographies are the sources and references of the materials used in the research work which is mandatory to acknowledge. If the sources are not acknowledged than it falls under the category of plagiarism.
Footnotes - These are always mentioned at the bottom of the page only under the footer. It reflects references for each page separately.
References/ endnotes - These are located at the end of articles or in chapters.
Bibliography - It is always located at the end of research which is the list of all the sources and references.
BLUE BOOK (19th ed.) CITATION FORMAT EXAMPLES
Times New Roman, Size 10/12, 1 line spacing, Justified.
Add full stop after every footnote.
Months should be written in abbreviated forms: Jan., Feb., Mar., Apr., May, June, July, Aug., Sept., Oct., Nov., Dec.
Volume No. (if any) NAME OF AUTHOR, TITLE OF THE BOOK pg. cited (Editors/Translators Name, edition cited year). Eg:
2, FREDERICK POLLOCK & FREDERIC WILLIAM MAITLAND, THE HISTORY OF ENGLISH LAW 205-06 (2d ed. 1911).
CHARLES DICKENS, BLEAK HOUSE 49-55 (Norman Page ed., Penguin Books 1971) (1853).
Rules & Exceptions
Follow the font format illustrated above. For example, the author's name must be in SMALL CAPS.
The first name must always be written before the surname.
For two authors, write both their names separated by „&?.
In case of citing a book that has been edited, write „ed. or „eds. after the editor's name. If translated, write trans after the name of the translator. If both, write the editor’s name first and then the translator’s name.
For more than two authors, editors or translators write the name of the author, editor, or translator that appears first, followed by “ et al.”
Do not add „p? or „pp? before the page number. Just write the numerical.
In case the book is being published by more than one publishing house, write the name of the publisher cited after the name of the editor in sentence case.
JOURNAL ARTICLE
a) For consecutively paginated journals (Where the periodical is organised by volume and page numbers continue throughout the volume, it is a consecutively paginated periodical) Name of Author, “Title of Article”, Journal volume no. ABBREVIATION OF JOURNAL Page on which Article Begins, Page Cited (Year). Eg.
Charles A. Reich, “The New Property”, 73 YALE L.J. 733, 737-38 (1964).
For more than two authors, write the name of the author who appears first, followed by “et al.”
b) For non-consecutively paginated journals (works appearing in periodicals that are separately paginated within each issue)
Name of Author, “Title of Article”, ABBREVIATION OF JOURNAL, date of issue as appears in the cover, at the first page of work, page cited. E.g.
Barbara Ward,” Progress for a Small Planet”, HARV. BUS. REV., Sept.-Oct. 1979, at 89, 90.
NEWSPAPER ARTICLE
Author's name, Name of Article/ news report, ABBRV. OF NAME OF NEWSPAPER, Month Date, Year, at pg. no. Eg.
Ari L. Goldman, O'Connor Warns Politicians Risk Excommunication over Abortion, N.Y. TIMES, June 15, 1990, at A1.
When an authenticated official or exact copy of the source is available online, citation can be made as if to the original print source without any URL info appended.)
Name of the Author, Name of the article, INSTITUTIONAL OWNER OF DOMAIN (Month date, year, time), URL. Visited on a date. Eg:
Eric Posner, More on Section 7 of the Torture Convention, THE VOLOKH CONSPIRACY (Jan. 29, 2009, 10:04 AM), http://www.volokh.com/posts/1233241458.html. visited on 21/01/18.
Format for a time as illustrated.
Don’t write available at or before the URL.
Write the entire URL as appears in the address bar of the browser, remove the hyperlink.
a) U.S. cases:
First Party v. Second Party, Reporter Vol. No., Reporter Abbreviation, First Page of Case, Specific Page Reference (Year).
Eg: Meritor Sav. Bank v. Vinson, 477 U.S. 57, 60 (1986).
b) Indian cases:
Case name, (year of a reporter) Vol No. Reporter Abbreviation, First page (year of a decision if different from year of a reporter (India, if not evident from context) Eg:
Charan Lal Sahu v Union Carbide, (1989) 1 S.C.C. 674 (India). Reporters that depart from this format shall be written in their own format. Eg:
Jabalpur v. Shukla, A.I.R. 1976 S.C. 1207 (India).
Rules & Exceptions:
Do not italicize the case name.
If there is more than one party, list only the first party.
Italicize the procedural phrases, e.g., In re, Ex parte , etc.
a) U.S. Law
The official name of the act, U.S.C. title number Abbreviation of Code cited sections symbols and span of sections containing statute (Date of Code edition cited). Eg:
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act, 42 U.S.C. §§ 9601-9675 (2006).
b) U.S. Constitution
Abbreviation of Constitution cited Abbreviation for Amendment No of amendment cited, section symbol and no. of section cited. Eg
U.S. CONST. amend. XIV, § 2.
LA. CONST. art. X, pt. IV. c)
c) Indian Law
Act name, Act No., Acts of Parliament, Year of Volume (India, if not evident from context). Eg:
The Copyright (Amendment) Act, 1992, No. 13, Acts of Parliament, 1992 (India).
d) Indian Constitution
INDIA CONST. art. 1, cl. 2.
Abbreviations
"Ibid and Op.cit"
Ibid. (abbreviation for the Latin Ibidem, meaning "The same").
Refers to the same author and source (e.g., book, journal) in the immediately preceding reference.
op. cit. (abbreviation for the Latin opus citatum, meaning "the work cited").
This refers to the reference listed earlier by the same author.
Ibid. refers to the immediately preceding reference; op. cit. refers to the prior reference by the same author.
R. Poirer, "Learning physics," (Academic, New York, 1993), p. 4.
Ibid., p. 9.
T. Eliot, "Astrophysics," (Springer, Berlin, 1989), p. 141.
R. Builder, J Phys Chem 20(3) 1654-57, 1991.
Eliot, op. cit., p.148.
"Id." is an all-purpose short form citation that may be used for any cited authority except internal cross-references.
"Id." always refers to the immediately preceding cited authority, either in the same footnote or the previous footnote so long as it is the only authority cited in the proceeding footnote.
Sweatt v. Painter, 339 U.S. 629, 632 (1950).
NOTE: Sources cited in explanatory parentheticals or phrases or as part of the case prior or subsequent history are not counted as intervening authorities preventing the use of "Id."
Any change in what is cited, such as page numbers, must be indicated after "Id."
"Supra" may be used to refer to certain types of previously cited materials as well as internal cross-references. Rule 4.2 contains a complete, detailed list of which materials may and may not be cited to using "Supra." Note, however, that in general most forms of primary legal authority (cases, statutes, etc.) should not be referred to using "Supra."
NOTE: This is also true for materials such as restatements, legislative documents (other than hearings), and model codes that typically have similar citation formats.
"Supra" citations, such as books and periodicals, are most commonly used for secondary authority. Therefore, the most common format for a Supra short-form citation consists of the author's last name followed by "supra," offset by a comma. Immediately after "supra" is the word "note" in ordinary type, followed by the number of the footnote in which the authority was first cited in full:
15. Philip D. O'Neill, Jr., Verification in an Age of Insecurity: The Future of Arms Control Compliance 45 (2010).
25. O'neil, supra note 15.
A pincite offset by a comma should indicate changes in what portion of the authority is being cited. An "at" is typically necessary to avoid confusion:
28. O'neil, supra note 15, at 52.
Suppose a work has an institutional author, use the complete institutional name. In that case, works without an author may be cited by the title, while unsigned student-authored law journal works should be cited by the appropriate designation such as "Note" or "Comment."
NOTE: The typeface convention from the source should be used for the author's name or title in a "supra" citation.
"hereinafter"
The term 'hereinafter' is used when using another short form would be impractical, cumbersome, or confusing.
Two typical circumstances where a "hereinafter" is appropriate are when an author name or title is long and unwieldy for a normal "supra" short-form citation and to distinguish between two or more authorities cited originally in the same footnote, which could easily be confused with each other.
To use "hereinafter," at the end of the first full citation and enclosed in square brackets, but before any explanatory parenthetical, and write "hereinafter" followed by a shortened form of the authority, typically a paraphrase of the title or designation of the type of document as long as unambiguous.
NOTE: The shortened hereinafter form should be in the same typeface as the original.
Subsequent citations to the authority will function as supra citations but will use the hereinafter designation in place of the full author or title.
- Law Colloquy
- Dissertation
- Research Methodology
- Research Problem
- Review Of Litereature
- # Law Colloquy
- # Arbitration
- #Conciliation
- #Consumerprotection
- #Lawcolloquy
- #Legalprocedure
- # Bhartiya Nyaya Sanhita
- # Exceptions In Ipc
- #Privatedefence
- #Triflingact
- #Criminalintend
- #Volentinonfiitinjuria
- #Actdonebyconsent
- #Justifiedact
- #Excusableact
- #Actofanintoxicatedperson
- #Actofaninsaneperson
- #Doliincapax
- # Commonintention
- #Commonobject
- #Section149
- # Section 3(5)
- # Section 190
- #Legalsystem
- #Coronavirus
- #Criminology
- #Punishment
- #Theoriesofpunishment
- #Indianpenalcode
- #Expiatorytheory
- #Reformativetheory
- #Preventivetheory
- #Retributivetheory
- #Deterrenttheory
- # Detention
- # Criminal Law
- # Female Lawyers
- # Indian Legal Sysytem
- # Intraterritorial
- # Extraterritorial
- # Kerala Development Model
- # Higher Literacy Rate
- # Priya Sepaha
- # Organisedcrime
- #Racketeering
- #Syndicatecrime
- #Whitecollarcrime
- # Priyal Sepaha
- # Gender Pay Gap
- # Womenempowerment
- # Womenrights
- # Reformatory
- #Jurisprudence
- #Rehabilitation
- # Socieconomicoffences
- #Organisedcrime
- # Stages Of Crime
- #Publichealth
- #Criminaljustice
- #Coronavirusindia
- #Covid19lockdown
- #Criminalprocdurecode
- #Criminallaw
- # Dissertation
- # Research Methodology
- # Hypothesis
- # Research Problem
- # Review Of Litereature
- #Lawoftorts
- #Breachofcontract
- #Breachoftrust
- #Briefoftorts
- #Meaningoftorts
- # Wrongfulrestraint
- #Wrongfulconfinement
- #Differences
- #Distinction
- #Abortioninindia
- #Human Rights
- #International Law
- # Acid Attack
- # Ordinance
- # Differences
- #Arbitration
- #Career In Law
- # Law School
- # Legal News
- # Legal Updates
- #Childrights
- # Governance
- # Governmentality
- # Historicity
- # Enactment
- # Normatively
- # Conversion
- # Legal Blog
- # Law Students
- #Constitution
- # Indian Constitution
- # Constitutional Law
- # Article 19(1)
- #Credit Cards
- # Economics
- #E- Contracts
- # Intention
- # Actusreus
- # Female Genital Mutilation
- # Hervoicematters
- # Zero Tolerance
- # First Information Report
- # Code Of Criminal Procedure
- # Investigation
- #Fundamental Rights
- # Human Rights
- # Difference
- # Constitution
- # Similarities
- #How To Write An Abstract
- # Abstract For Research Paper
- # How To Write An Abstract For A Project
- # How To Write An Abstract For A Conference
- # How To Write An Abstract For A Presentation
- #Indian Penal Code
- # Amendments
- # New Criminal Law
- # International Humanitarian Law
- # Geneva Convention
- # Armed Conflict
- # United Nations
- # Un Charter
- #Investigation
- # Criminallaw
- # Categories Of Law
- # Sources Of Law
- # Constitutionalism.
- #Kidnapping
- #Wrongfullyconceals
- #Importationofgirl
- #Procuration
- #Law Colloquy
- # Criminal Trial
- # Indian Law
- # Bhartiya Nagrik Suraksha Sanhita
- # Stockexchange
- # Corporate
- #Investment
- # Marriage Certificate
- # Court Marriage
- # Hindu Marriage Act
- # Special Marriage Act
- # Education Policy
- # No Confidence Motion
- # Parliament
- # Constitution Of India
- # Structure Of Parliament
- # Online Dispute Resolution
- # Amicuscuriae
- #Supremecourt
- # Dihonestly
- #Fraudulently
- #Indianpnalcode
- #Manusmriti
- #Legislation
- #Law Of Crime
- # General Exceptions
- # Sections Of Code
- #Good Faith
- # Mental Element
- # Indian Laws
- # Case Analysis
- # Kompetenz-kompetenz Doctrine
- # Cyber Crime
- # International Law
- # Law Career
- # Pranshu Yadav
- # Cyber Bulling
- # Awareness
- # Municipal Law
- # Personal Bill
- # Personal Bill Data Protection Bill
- # Supreme Court
- # High Court
- # Women Impresario
- # Amendment
- # Proposed Bill Criminal Law
- # Election Process
- # Election In India
- # Suo Moto Cognizance
- # Manipur Violence
- # Women Empowerment
- # Amendmen For Female
- # Women Supporting Women
- # Supreme Court Of India
- # New Legal Terminology For Women In The Court
- #Formal Sources Of Law
- # Informal Sources Of Law
- # Legislation
- # Precedent
- # Solicitor
- #Lawadvocate
- #Advocateonrecord
- #Attorneygeneralinindia
- #Attorneygeneralinengland
- #Attorneygeneralinus
- #Solicitorsolicitorgeneral
- #Awcolloquy
- #Lawstudents
- #Registration
- #Artificial Intelligence
- #Intellectual Property
- #Healthcare
- #Educationpolicy
- #Lawstudent
- #Womenrights
- #Womenabuse
- #Unitednation
- #Hinduschooloflaw
- #Schooloflaw
- #Succesionact
- #Succestion
- #Daughtersright
- #Propertyrights
- #Biologicalage
- #Mentalillness
- #Criminaljusticesystem
- #Parliament
- #Parliamentaryssystem
- #Government
- #Selfreliantindia
- #Aatmnirbharbharat
- #Onlinearbitration
- # Narayani Sepaha
- # Convertiontheory
- #Homosexuality
- #Constitutionallaw
- #Insolvency
- #Bankruptcycode
- #Interimrelief
- #Emergencyarbitration
- #Internationalarbitration
- #Consumerprotectionact
- #Pecuniaryjurisdiction
- #Probationofoffender
- #Guiltymind
- #Rapevictim
- #Reservation
- #Transgender
- #Genderbias
- #Gendersensitivity
- #Genderissue
- #Legal Entity
- # Legal Entity Identifier
- # What Is Legal Entity
- # Legal Entity Meaning
- #Legal Method
- # Dissenting Opinions
- # Distinguishing Opinions
- # Concurring Opinions
- #Legal News
- # Legal Headlines
- # Judiciary
- # Decisions
- # Judgements
- # Headlines
- # Same Sex Marriage
- # Conciliation
- # Arbitraion
- #Mental Illness
- # Mental Health
- # Psychopaths
- # Schizophrenia
- #Misuse Of Laws
- # Gender Oriented Laws
- # Sexual Harassment
- # Dowry Harassment
- # Eve-teasing
- # Loopholes
- # Indian Legal System
- #Moblynching
- #Mouth Publicity
- # Social Media
- # Marketing
- # Censor Board Of India
- # Certificate
- #High Court
- #Supreme Court
- #Pedagogy Model
- # Ukraine Lawyer
- # Anatoliy Kosturb
- # Pedagogy Model Of Lawyer
- # Ukraine Law Professor
- #Police Commissioner Sysytem
- # Collector
- #Presumption
- #Evidenceact
- #Maypresume
- #Shallpresume
- #Conclusiveproof
- #Presumptionoffact
- #Presumptionoflaw
- #Mixedpresumption
- #Public Interest Litigation
- # Legal Education
- # Frivolous Pil
- #Research Papers
- # How To Write Legal Research Paper
- # Research Requirements
- #Right To Information
- # Transparency
- # E-government
- # Accountability
- #Right To Know
- # Right To Information
- # Public Disclosure
- # Judicial Independence
- #Sc Verdict
- # Supreme Court Today Judgement
- # Judgement Order
- # Supreme Court Of India Judgements
- # Lawcolloquy
- # War Crime
- # Prosecution
- # United Nation
- # Women Laws
Not a member? Sign Up
Forgot Password?
Already have an account? Log In
- Forgot Password
Login/Signup?
- Member Login
Become Member
How to Write a Thesis Summary
Your thesis summary is the distilled essence of your thesis: a tool to underline the strengths of your research and make yourself recognizable as a competent scholar.

The importance of writing a good thesis summary is often underestimated and it is not too difficult to understand why. Even in the cases where a student has seriously engaged in writing his thesis, the summary is usually the last thing that gets done. The typical scenario is therefore the following: the bulk of the work has finally been done, the deadline to submit the thesis is imminent. Time is running out and, consequently, when it comes to set the summary down, this is written in a very hasty way… I am pretty sure that you can relate to this situation and – trust me – you are not the only one. Yet, this is a pity! Your thesis summary deserves to be written with a certain care for several good reasons. An effective summary is the best way to impress your readers. It will be the first thing to be read and – as hard as it is to admit – the first impression is what really counts. You should therefore think of the summary as a distilled and concentrated essence of your thesis: a tool to underline the strengths of your research and make yourself recognizable as a competent scholar.
Especially if your thesis is written in another language, setting down an accurate, compelling summary in English can be the first step to internationally disseminate your work. In this regard, keep also in mind that an English summary of your thesis may be required for a job application or a PhD-position. Having said that, how to proceed? Here you are some useful steps to write an effective summary.
Elaborate a thesis statement
The thesis statement . is the most important part. This is a sentence usually placed at the beginning of the summary and it is aimed at clarifying the main research questions of your work. The thesis statement must be clear and concise. MA theses, but also PhD dissertations, usually concern very narrow topics. So, avoid being vague and explain the central idea of your research as specific as possible. Let’s do some practical examples. A sentence like:
“the aim of the present study is to show how English skills can be improved in several ways” is certainly too vague.
Instead, a statement like:
“the aim of the present research is to show how the use of Ludwig can improve English writing skills, by providing reliable texts to get inspiration”
defines a narrower field of research. In addition, as the last example demonstrates, a good thesis statement can be enforced with further arguments.
For example, one could state that:
taking inspiration from a database of 300 million English sentences can indeed help a student to perfect their phrasing, by seeing words in the context of real sentences. A mere automatic correction tool, instead, carries the risk of worsening the student performance, for example by favouring the memorization of wrong phrases and expressions.

Explain the structure of the thesis
Each thesis is usually divided into diverse chapters, such as an introduction, a section dedicated to explaining the terminology, a chapter for the methodology, the discussion of the data, the results of the research etc. A good summary must give a clear idea of how you have organized your research step by step. So be very clear and use sentences like “in the first chapter of my thesis I treated”, “while in the second…”, “the analysis of the data has shown that” etc. And, of course, do not hesitate to use Ludwig if you need examples to take inspiration from. Keep in mind, you may have made the discovery of the century… but if you are not able to explain how you achieved such a result, you will be considered a charlatan.
How to write a thesis summary: a practical example
In this regard, it is good practice to read a number of thesis summaries and to analyse how they are written. Nowadays all the most prestigious universities offer free access to their online repositories, where one can find great inspirational models. See, for example, this website by Cambridge University. Now, let's analyse the structure of one of them:
The Italian giallo film was a type of thriller that was produced in huge numbers between the early 1960s and the late 1980s. This thesis contributes to recent scholarly attempts to situate the giallo within its socio-cultural historical context but resists the critical tendency to read these films as passive and transparent reflections of social attitudes in post-war Italy. Rather, I attend concretely to the form of these films and, specifically, to their critically neglected sound designs . I argue that the giallo’s voice tracks were conditioned by the commercial imperatives of Italy’s post-war popular film industry and that these commercial imperatives were in turn shaped by wider social, economic and political phenomena. By theorising the voice as a mediator between the giallo text and its industrial and social contexts, I show that these films both registered and reified social change. Chapter 1 demonstrates that the anonymous narrator of Mario Bava’s The Girl Who Knew Too Much (1963) adopts a range of sonorous modes throughout the film. Each of these sonorous modes invokes a specific set of intertexts which are vital to tracing both the giallo’s cultural origins and the increasingly globalised socio- cultural landscape from which it emerged. This chapter then shows that Dario Argento’s The Bird with the Crystal Plumage (1970) uses the model of the cinematic voice-over to explore the subjective experience of urban space in post-war Italy. The film suggests that by 1970 the ability to vocally ‘narrate’ and thus control space had become a fundamental assumption of the modern, cosmopolitan subject. Chapter 2 analyses Lucio Fulci’s Don’t Torture a Duckling (1972) and Sergio Martino’s Torso (1973). Both films draw on longstanding Italian cultural stereotypes to pitch the silence of the rural against the vocality of the urban. The films use silence and the voice as ‘cartographic’ tools to delineate the profound socio-economic divisions between Italy’s rural South and its more urban North, but they also illustrate the giallo’s underlying affinities with its silent cinema ancestors and so challenge the assumed temporal borders between cinematic eras. Chapter 3 argues that Argento’s Tenebrae (1982) and Fulci’s The New York Ripper (1982) variously mimic the vocal aesthetics of television. These films lay bare both the increasing dominance of the Italian cultural landscape by imported commercial television in the 1980s and the neoliberal economic project that underpinned that trend. Ultimately, they question the stability of the nation itself, precisely because the voice — now fractured across a global mediascape — is unable to signal national specificity.
The sentences in bold highlight how the author carefully organized the structure of the text. He started with a well elaborate thesis statement. As you can see, the object of the research is well defined and narrow: the study focuses on Italian thrillers , produced during a specific historical period between the early 1960s and the late 1980s. Moreover, the investigation depeens a specific aspect: the use of sounds in this movie genre. Then, the scholar explains in detail how he organized his work step by step, by summarizing the content of each chapter.

Ultimately, we can say that to write a theis summary is a less daunting task than one might imagine at first sight!
Keep in mind why and for whom you are writing
There is a huge difference between writing a summary for the theses database of your university and to write a summary for a more ambitious purpose. As mentioned above, a summary of your thesis may be required for a job application or to get a PhD position. So, if you are facing this kind of situation, you must “use” your summary in a smart way. Are there any points of contact between your thesis and the position you hope to get? If yes which ones? Is it the topic? Or, perhaps, in order to undertake your research, you have used a tool/method/program that could be pertinent with this position? So, tailor your summary in order to highlight what you need to stand out from the crowd and… good luck!
Others from Academic English

MLA, APA, Chicago, IEEE - What’s the best citation style for your paper?

The Fall of the Five-Paragraph Essay

Should I publish it in English? About the role of English in the scientific community

How to write the perfect abstract: do not displease your reviewers and get published
Subscribe to new posts.
- Log in / Register

- Getting started
- Criteria for a problem formulation
- Find who and what you are looking for
- Too broad, too narrow, or o.k.?
- Test your knowledge
- Lesson 5: Meeting your supervisor
- Getting started: summary
- Literature search
- Searching for articles
- Searching for Data
- Databases provided by your library
- Other useful search tools
- Free text, truncating and exact phrase
- Combining search terms – Boolean operators
- Keep track of your search strategies
- Problems finding your search terms?
- Different sources, different evaluations
- Extract by relevance
- Lesson 4: Obtaining literature
- Literature search: summary
- Research methods
- Combining qualitative and quantitative methods
- Collecting data
- Analysing data
- Strengths and limitations
- Explanatory, analytical and experimental studies
- The Nature of Secondary Data
- How to Conduct a Systematic Review
- Directional Policy Research
- Strategic Policy Research
- Operational Policy Research
- Conducting Research Evaluation
- Research Methods: Summary
- Project management
- Project budgeting
- Data management plan
- Quality Control
- Project control
- Project management: Summary
- Writing process
- Title page, abstract, foreword, abbreviations, table of contents
- Introduction, methods, results
- Discussion, conclusions, recomendations, references, appendices, layout
- Use citations correctly
- Use references correctly
- Bibliographic software
- Writing process – summary
- Getting started /
Lesson 4: Synopsis
In order to clarify your thoughts about the purpose of your thesis and how you plan to reach your research goals, you should prepare a synopsis. A synopsis is a short, systematic outline of your proposed thesis, made in preparation for your first meeting with your supervisor. It serves to ensure that your supervisor gets a clear picture of your proposed project and allows him or her to spot whether there are gaps or things that you have not taken into account.
Your synopsis will work as a kind of protocol for the further steps you need to take to ensure that your thesis reaches the required academic level – and that you finish on time.
Although there are no rigid rules for how a synopsis should look, it must contain:
- Rationale – should address the gaps/problems/issues observed as part of the background section and thus present the argument/justification for completing the study – as described in the lesson of the same name.
- Problem formulation – the problem you aim to address in your thesis,as described in the lesson of the same name.
- Overall and specific objectives – the actions to be taken in order to address the problem, as described in the lesson of the same name.
- Method outline: What type of study is best suited to support the actions stated in the specific objectives? What kind of data (qualitative, quantitative) will your study require? What is your geographical study area and who is your target group(s)? Are there ethical considerations you have to make? Etc.
- Time plan: In the beginning, a rough timeline showing a plan on how your work will be divided over time. When is your deadline for e.g. literature search, potential fieldwork (e.g. interviews and/or questionnaire administration), data analysis, writing and layout? Once your problem formulation and objectives are approved by your supervisor, all details should be added to your time plan.
- References : Create a short list of the major references on which your rationale is based. Make sure that your in-text citations and reference list are completed correctly, both in support of your subsequent work, but also to demonstrate that you have a serious, scientific and methodical approach to your work. See how to use references correctly in the lesson of the same name in the module: Writing process.
At the beginning of your thesis period, your synopsis will be limited in scope and detail, but as you work your way deeper into your topic and you get a clearer picture of your objectives, methods and references, the more complete and detailed your synopsis will become.
A rule of thumb is that the length of your synopsis can vary from two to five pages, but the precise length and exact requirements of your synopsis can vary from institute to institute and from supervisor to supervisor.
Most study programmes will require that you present a final synopsis before starting data collection. However, the first version of your synopsis for discussion with your supervisor should not be an informal draft. Carefully performed work creates respect and motivation and saves a lot of you and your supervisor’s time.
A good approach from the very beginning is to establish a practice of how to write headings, references, names of species, etc. And be consistent. This will help you save time and importantly, lead to a better overall assessment of your final work.
Do you now know how to write a synopsis. Test yourself in the following.
Your friend's e-mail
Message (Note: The link to the page is attached automtisk in the message to your friend)

Did you know...

Dissertation Structure & Layout 101: How to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | July 2019
So, you’ve got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is , you’ve chosen your topic and hopefully you’ve received approval for your research proposal . Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey.
To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure . In this post, we’ll walk you through the generic dissertation structure and layout, step by step. We’ll start with the big picture, and then zoom into each chapter to briefly discuss the core contents. If you’re just starting out on your research journey, you should start with this post, which covers the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis .

*The Caveat *
In this post, we’ll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
So, always check with your university if they have a prescribed structure or layout that they expect you to work with. If not, it’s safe to assume the structure we’ll discuss here is suitable. And even if they do have a prescribed structure, you’ll still get value from this post as we’ll explain the core contents of each section.
Overview: S tructuring a dissertation or thesis
- Acknowledgements page
- Abstract (or executive summary)
- Table of contents , list of figures and tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results
- Chapter 5: Discussion
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
As I mentioned, some universities will have slight variations on this structure. For example, they want an additional “personal reflection chapter”, or they might prefer the results and discussion chapter to be merged into one. Regardless, the overarching flow will always be the same, as this flow reflects the research process , which we discussed here – i.e.:
- The introduction chapter presents the core research question and aims .
- The literature review chapter assesses what the current research says about this question.
- The methodology, results and discussion chapters go about undertaking new research about this question.
- The conclusion chapter (attempts to) answer the core research question .
In other words, the dissertation structure and layout reflect the research process of asking a well-defined question(s), investigating, and then answering the question – see below.

To restate that – the structure and layout of a dissertation reflect the flow of the overall research process . This is essential to understand, as each chapter will make a lot more sense if you “get” this concept. If you’re not familiar with the research process, read this post before going further.
Right. Now that we’ve covered the big picture, let’s dive a little deeper into the details of each section and chapter. Oh and by the way, you can also grab our free dissertation/thesis template here to help speed things up.
The title page of your dissertation is the very first impression the marker will get of your work, so it pays to invest some time thinking about your title. But what makes for a good title? A strong title needs to be 3 things:
- Succinct (not overly lengthy or verbose)
- Specific (not vague or ambiguous)
- Representative of the research you’re undertaking (clearly linked to your research questions)
Typically, a good title includes mention of the following:
- The broader area of the research (i.e. the overarching topic)
- The specific focus of your research (i.e. your specific context)
- Indication of research design (e.g. quantitative , qualitative , or mixed methods ).
For example:
A quantitative investigation [research design] into the antecedents of organisational trust [broader area] in the UK retail forex trading market [specific context/area of focus].
Again, some universities may have specific requirements regarding the format and structure of the title, so it’s worth double-checking expectations with your institution (if there’s no mention in the brief or study material).

Acknowledgements
This page provides you with an opportunity to say thank you to those who helped you along your research journey. Generally, it’s optional (and won’t count towards your marks), but it is academic best practice to include this.
So, who do you say thanks to? Well, there’s no prescribed requirements, but it’s common to mention the following people:
- Your dissertation supervisor or committee.
- Any professors, lecturers or academics that helped you understand the topic or methodologies.
- Any tutors, mentors or advisors.
- Your family and friends, especially spouse (for adult learners studying part-time).
There’s no need for lengthy rambling. Just state who you’re thankful to and for what (e.g. thank you to my supervisor, John Doe, for his endless patience and attentiveness) – be sincere. In terms of length, you should keep this to a page or less.

Abstract or executive summary
The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report – in other words, it should be able to stand alone .
For it to stand alone, your abstract should cover the following key points (at a minimum):
- Your research questions and aims – what key question(s) did your research aim to answer?
- Your methodology – how did you go about investigating the topic and finding answers to your research question(s)?
- Your findings – following your own research, what did do you discover?
- Your conclusions – based on your findings, what conclusions did you draw? What answers did you find to your research question(s)?
So, in much the same way the dissertation structure mimics the research process, your abstract or executive summary should reflect the research process, from the initial stage of asking the original question to the final stage of answering that question.
In practical terms, it’s a good idea to write this section up last , once all your core chapters are complete. Otherwise, you’ll end up writing and rewriting this section multiple times (just wasting time). For a step by step guide on how to write a strong executive summary, check out this post .
Need a helping hand?
Table of contents
This section is straightforward. You’ll typically present your table of contents (TOC) first, followed by the two lists – figures and tables. I recommend that you use Microsoft Word’s automatic table of contents generator to generate your TOC. If you’re not familiar with this functionality, the video below explains it simply:
If you find that your table of contents is overly lengthy, consider removing one level of depth. Oftentimes, this can be done without detracting from the usefulness of the TOC.
Right, now that the “admin” sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you’ll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter – as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
It’s important to understand that even though you’ve provided an overview of your research in your abstract, your introduction needs to be written as if the reader has not read that (remember, the abstract is essentially a standalone document). So, your introduction chapter needs to start from the very beginning, and should address the following questions:
- What will you be investigating (in plain-language, big picture-level)?
- Why is that worth investigating? How is it important to academia or business? How is it sufficiently original?
- What are your research aims and research question(s)? Note that the research questions can sometimes be presented at the end of the literature review (next chapter).
- What is the scope of your study? In other words, what will and won’t you cover ?
- How will you approach your research? In other words, what methodology will you adopt?
- How will you structure your dissertation? What are the core chapters and what will you do in each of them?
These are just the bare basic requirements for your intro chapter. Some universities will want additional bells and whistles in the intro chapter, so be sure to carefully read your brief or consult your research supervisor.
If done right, your introduction chapter will set a clear direction for the rest of your dissertation. Specifically, it will make it clear to the reader (and marker) exactly what you’ll be investigating, why that’s important, and how you’ll be going about the investigation. Conversely, if your introduction chapter leaves a first-time reader wondering what exactly you’ll be researching, you’ve still got some work to do.
Now that you’ve set a clear direction with your introduction chapter, the next step is the literature review . In this section, you will analyse the existing research (typically academic journal articles and high-quality industry publications), with a view to understanding the following questions:
- What does the literature currently say about the topic you’re investigating?
- Is the literature lacking or well established? Is it divided or in disagreement?
- How does your research fit into the bigger picture?
- How does your research contribute something original?
- How does the methodology of previous studies help you develop your own?
Depending on the nature of your study, you may also present a conceptual framework towards the end of your literature review, which you will then test in your actual research.
Again, some universities will want you to focus on some of these areas more than others, some will have additional or fewer requirements, and so on. Therefore, as always, its important to review your brief and/or discuss with your supervisor, so that you know exactly what’s expected of your literature review chapter.

Now that you’ve investigated the current state of knowledge in your literature review chapter and are familiar with the existing key theories, models and frameworks, its time to design your own research. Enter the methodology chapter – the most “science-ey” of the chapters…
In this chapter, you need to address two critical questions:
- Exactly HOW will you carry out your research (i.e. what is your intended research design)?
- Exactly WHY have you chosen to do things this way (i.e. how do you justify your design)?
Remember, the dissertation part of your degree is first and foremost about developing and demonstrating research skills . Therefore, the markers want to see that you know which methods to use, can clearly articulate why you’ve chosen then, and know how to deploy them effectively.
Importantly, this chapter requires detail – don’t hold back on the specifics. State exactly what you’ll be doing, with who, when, for how long, etc. Moreover, for every design choice you make, make sure you justify it.
In practice, you will likely end up coming back to this chapter once you’ve undertaken all your data collection and analysis, and revise it based on changes you made during the analysis phase. This is perfectly fine. Its natural for you to add an additional analysis technique, scrap an old one, etc based on where your data lead you. Of course, I’m talking about small changes here – not a fundamental switch from qualitative to quantitative, which will likely send your supervisor in a spin!
You’ve now collected your data and undertaken your analysis, whether qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. In this chapter, you’ll present the raw results of your analysis . For example, in the case of a quant study, you’ll present the demographic data, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics , etc.
Typically, Chapter 4 is simply a presentation and description of the data, not a discussion of the meaning of the data. In other words, it’s descriptive, rather than analytical – the meaning is discussed in Chapter 5. However, some universities will want you to combine chapters 4 and 5, so that you both present and interpret the meaning of the data at the same time. Check with your institution what their preference is.
Now that you’ve presented the data analysis results, its time to interpret and analyse them. In other words, its time to discuss what they mean, especially in relation to your research question(s).
What you discuss here will depend largely on your chosen methodology. For example, if you’ve gone the quantitative route, you might discuss the relationships between variables . If you’ve gone the qualitative route, you might discuss key themes and the meanings thereof. It all depends on what your research design choices were.
Most importantly, you need to discuss your results in relation to your research questions and aims, as well as the existing literature. What do the results tell you about your research questions? Are they aligned with the existing research or at odds? If so, why might this be? Dig deep into your findings and explain what the findings suggest, in plain English.
The final chapter – you’ve made it! Now that you’ve discussed your interpretation of the results, its time to bring it back to the beginning with the conclusion chapter . In other words, its time to (attempt to) answer your original research question s (from way back in chapter 1). Clearly state what your conclusions are in terms of your research questions. This might feel a bit repetitive, as you would have touched on this in the previous chapter, but its important to bring the discussion full circle and explicitly state your answer(s) to the research question(s).

Next, you’ll typically discuss the implications of your findings . In other words, you’ve answered your research questions – but what does this mean for the real world (or even for academia)? What should now be done differently, given the new insight you’ve generated?
Lastly, you should discuss the limitations of your research, as well as what this means for future research in the area. No study is perfect, especially not a Masters-level. Discuss the shortcomings of your research. Perhaps your methodology was limited, perhaps your sample size was small or not representative, etc, etc. Don’t be afraid to critique your work – the markers want to see that you can identify the limitations of your work. This is a strength, not a weakness. Be brutal!
This marks the end of your core chapters – woohoo! From here on out, it’s pretty smooth sailing.
The reference list is straightforward. It should contain a list of all resources cited in your dissertation, in the required format, e.g. APA , Harvard, etc.
It’s essential that you use reference management software for your dissertation. Do NOT try handle your referencing manually – its far too error prone. On a reference list of multiple pages, you’re going to make mistake. To this end, I suggest considering either Mendeley or Zotero. Both are free and provide a very straightforward interface to ensure that your referencing is 100% on point. I’ve included a simple how-to video for the Mendeley software (my personal favourite) below:
Some universities may ask you to include a bibliography, as opposed to a reference list. These two things are not the same . A bibliography is similar to a reference list, except that it also includes resources which informed your thinking but were not directly cited in your dissertation. So, double-check your brief and make sure you use the right one.
The very last piece of the puzzle is the appendix or set of appendices. This is where you’ll include any supporting data and evidence. Importantly, supporting is the keyword here.
Your appendices should provide additional “nice to know”, depth-adding information, which is not critical to the core analysis. Appendices should not be used as a way to cut down word count (see this post which covers how to reduce word count ). In other words, don’t place content that is critical to the core analysis here, just to save word count. You will not earn marks on any content in the appendices, so don’t try to play the system!
Time to recap…
And there you have it – the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows:
- Acknowledgments page
Most importantly, the core chapters should reflect the research process (asking, investigating and answering your research question). Moreover, the research question(s) should form the golden thread throughout your dissertation structure. Everything should revolve around the research questions, and as you’ve seen, they should form both the start point (i.e. introduction chapter) and the endpoint (i.e. conclusion chapter).
I hope this post has provided you with clarity about the traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout. If you have any questions or comments, please leave a comment below, or feel free to get in touch with us. Also, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
36 Comments
many thanks i found it very useful
Glad to hear that, Arun. Good luck writing your dissertation.
Such clear practical logical advice. I very much needed to read this to keep me focused in stead of fretting.. Perfect now ready to start my research!
what about scientific fields like computer or engineering thesis what is the difference in the structure? thank you very much
Thanks so much this helped me a lot!
Very helpful and accessible. What I like most is how practical the advice is along with helpful tools/ links.
Thanks Ade!
Thank you so much sir.. It was really helpful..
You’re welcome!
Hi! How many words maximum should contain the abstract?
Thank you so much 😊 Find this at the right moment
You’re most welcome. Good luck with your dissertation.
best ever benefit i got on right time thank you
Many times Clarity and vision of destination of dissertation is what makes the difference between good ,average and great researchers the same way a great automobile driver is fast with clarity of address and Clear weather conditions .
I guess Great researcher = great ideas + knowledge + great and fast data collection and modeling + great writing + high clarity on all these
You have given immense clarity from start to end.
Morning. Where will I write the definitions of what I’m referring to in my report?
Thank you so much Derek, I was almost lost! Thanks a tonnnn! Have a great day!
Thanks ! so concise and valuable
This was very helpful. Clear and concise. I know exactly what to do now.
Thank you for allowing me to go through briefly. I hope to find time to continue.
Really useful to me. Thanks a thousand times
Very interesting! It will definitely set me and many more for success. highly recommended.
Thank you soo much sir, for the opportunity to express my skills
Usefull, thanks a lot. Really clear
Very nice and easy to understand. Thank you .
That was incredibly useful. Thanks Grad Coach Crew!
My stress level just dropped at least 15 points after watching this. Just starting my thesis for my grad program and I feel a lot more capable now! Thanks for such a clear and helpful video, Emma and the GradCoach team!
Do we need to mention the number of words the dissertation contains in the main document?
It depends on your university’s requirements, so it would be best to check with them 🙂
Such a helpful post to help me get started with structuring my masters dissertation, thank you!
Great video; I appreciate that helpful information
It is so necessary or avital course
This blog is very informative for my research. Thank you
Doctoral students are required to fill out the National Research Council’s Survey of Earned Doctorates
wow this is an amazing gain in my life
This is so good
How can i arrange my specific objectives in my dissertation?
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Current Students
- News & Press
- Exam Technique for In-Person Exams
- Revising for 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Introduction to 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Before the 24 Hour Take Home Exam
- Exam Technique for 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Structuring a Literature Review
- Writing Coursework under Time Constraints
- Reflective Writing
- Writing a Synopsis
- Structuring a Science Report
- Presentations
- How the University works out your degree award
- Accessing your assignment feedback via Canvas
- Inspera Digital Exams
- Writing Introductions and Conclusions
- Paragraphing
- Reporting Verbs
- Signposting
- Proofreading
- Working with a Proofreader
- Writing Concisely
- The 1-Hour Writing Challenge
- Editing strategies
- Apostrophes
- Semi-colons
- Run-on sentences
- How to Improve your Grammar (native English)
- How to Improve your Grammar (non-native English)
- Independent Learning for Online Study
- Reflective Practice
- Academic Reading
- Strategic Reading Framework
- Note-taking Strategies
- Note-taking in Lectures
- Making Notes from Reading
- Using Evidence to Support your Argument
- Integrating Scholarship
- Managing Time and Motivation
- Dealing with Procrastination
- How to Paraphrase
- Quote or Paraphrase?
- How to Quote
- Referencing
- Responsible and Ethical use of AI
- Acknowledging use of AI
- Numeracy, Maths & Statistics
- Library Search
- Search Techniques
- Keeping up to date
- Evaluating Information
- Managing Information
- Understanding Artificial Intelligence
- Getting started with prompts
- Thinking Critically about AI
- Using Information generated by AI
- SensusAccess
- Develop Your Digital Skills
- Digital Tools to Help You Study

Learn how to prepare and write a synopsis assignment.
- Newcastle University
- Academic Skills Kit
- Assignment Types
A synopsis is a brief summary which gives readers an overview of the main points. In an academic context, this is usually a summary of a text (a journal article, book, report etc) but in some instances you might be writing a synopsis of a talk, film or other form of presentation. A synopsis is a neutral summary, objectively capturing the main points, rather than your own perspective or critique, and it focusses directly on the text you’re summarising rather than being a wider discussion of a topic, as an essay might be.
A synopsis aims to give the reader a full, if brief, account of the whole text so that they can follow its main points without having to read it themselves. It’s not a ‘trailer’ designed to tempt your audience to read the text itself, so you don’t have to worry about ‘hooking’ them in with hints and high points or ‘spoiling the ending’ - give the whole text equal coverage, including the conclusions. You could add some commentary which gives the reader a bit of context about the text, including the authors and circumstances it was written in (for example, if it is part of a debate, particular school of thought or its significance and what impact it’s had).
Writing a good synopsis is a skill, and there are a number of challenges:
- Separating the main points from the minor detail
- Knowing what to leave out as well as what to include
- Giving a sense of the overall narrative as well as listing the key points
- Covering the whole text within a small word limit
- Knowing how closely to stick to the original, especially in terms of the wording
- Whether to give all key points equal treatment, or cover some more briefly, even combining them
- Rephrasing things concisely without losing the meaning or misrepresenting it
- Not leaving out anything crucial to understanding the whole overall message
A good synopsis will allow the reader to feel as if they’d skimread the whole text themselves, understanding the overall gist and highlighting what they need to know. A poor synopsis will get bogged down in detail, giving a confused account of the whole story by just listing points, miss out major points or give an inaccurate or one-sided account or stick so closely to the original that it becomes plagiarism without demonstrating a real understanding by the person summarising it.
How to prepare a synopsis
Boiling down the key points and overall narrative of the original means good reading and note-taking skills which aim to identify and boil down key points to their essence. You could try some of the following approaches:
- Read the whole text, and afterwards, without re-reading, jot down your first initial summary in 50 words to capture its overall point. You can check it back for accuracy or anything you left out, but stick within ca 50 words
- Read the introduction and first line of each paragraph to get a sense of the overall structure and key points within it
- Highlight one sentence in each paragraph that you think is essential detail to understanding that section
- Alternatively, with a marker pen, cross out anything that isn’t essential to an understanding of the whole section or text
- Jot down only key words as a summary of each point rather than whole sentences
- Read each paragraph and summarise it without looking, in one sentence of your own
- Consider how many points you can make within your word count, and reduce or combine your list of summarised points down to this number
You could start small, identifying just keywords or sentences at first and then work them up into phrases, bullet points and sentences as a rough plan or draft, or you could start big with the original text and reduce each section, paragraph and sentence summary again and again until you have boiled it down to its essence.
When you start to prepare your first plan or draft, try to use your notes or memory and step away from the original as much as you can. You can go back and check it afterwards, but you need to create some distance to be able to create your own account and have confidence in the points you have identified as essential.
Writing a synopsis
The main decisions facing you as you write up your summary are about how closely to stick to the original in terms of structure and style, and how much attention to give to each point.
- You could begin your synopsis with a brief context, explaining who the authors are, the context and significance of their work, as well as anything you think might help the reader to understand the following summary
- The most common structure is to follow that of the original text, to give a sense of its narrative flow as well as the key points within it. You could choose to depart from it a little though, perhaps glossing over some points faster than others, combining two sections which go together or aren’t enough in their own right, possibly even changing the order a little where it helps to combine two similar points. Careful use of signposting language will help the reader clearly follow the structure (and note anywhere you’ve changed it from the original) so they can identify the bit you’re talking about in the original if they want to
- The style will naturally be strongly influenced by the original wording, but you should phrase it in your own words wherever possible. It’s harder to nibble away words from a much longer original than it is to start again and use your own concise phrasing, and you want to demonstrate your own understanding to the reader. You could use the odd original phrase or quotation here or there, but the synopsis needs to be more than a collage of quotations; it’s a thing in its own right rather than a cut-down version of the original
- You can also show your own response to the text in the way you use language to guide the reader to what you feel are the key points and (briefly) why. Your own voice doesn’t need to be very obvious in the synopsis, as it’s about the text rather than your reaction to it, but you have made analytical decisions about what is important, and might want to explain to the reader why these points are significant in understanding the whole
- What is the main purpose of this text? What did it aim to discover, explain or prove?
- Why was this research done? How significant is it?
- How was the research conducted? What kind of research is it?
- What were the three (or four, five) main things I should be aware of from this paper?
- What is their line of argument?
- What is their overall conclusion, recommendation, finding? Why is that important?
Managing word count
The trick to writing a concise synopsis which keeps within your word limit is not to start from the much bigger original text, but from your own boiled down notes. If you’re over the word count, you could start cutting out words that don’t seem essential, but if you go too far, you end up with a text which does not read well and doesn’t hang together. It might be better to remove whole sentences and perhaps whole points, than nibble away at words here and there.
Download this guide as a PDF
Learn how to prepare and write a synopsis assignment. **PDF Download**
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
Published on September 9, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
It can be difficult to know where to start when writing your thesis or dissertation . One way to come up with some ideas or maybe even combat writer’s block is to check out previous work done by other students on a similar thesis or dissertation topic to yours.
This article collects a list of undergraduate, master’s, and PhD theses and dissertations that have won prizes for their high-quality research.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Award-winning undergraduate theses, award-winning master’s theses, award-winning ph.d. dissertations, other interesting articles.
University : University of Pennsylvania Faculty : History Author : Suchait Kahlon Award : 2021 Hilary Conroy Prize for Best Honors Thesis in World History Title : “Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the “Noble Savage” on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807”
University : Columbia University Faculty : History Author : Julien Saint Reiman Award : 2018 Charles A. Beard Senior Thesis Prize Title : “A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man”: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947
University: University College London Faculty: Geography Author: Anna Knowles-Smith Award: 2017 Royal Geographical Society Undergraduate Dissertation Prize Title: Refugees and theatre: an exploration of the basis of self-representation
University: University of Washington Faculty: Computer Science & Engineering Author: Nick J. Martindell Award: 2014 Best Senior Thesis Award Title: DCDN: Distributed content delivery for the modern web
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
University: University of Edinburgh Faculty: Informatics Author: Christopher Sipola Award: 2018 Social Responsibility & Sustainability Dissertation Prize Title: Summarizing electricity usage with a neural network
University: University of Ottawa Faculty: Education Author: Matthew Brillinger Award: 2017 Commission on Graduate Studies in the Humanities Prize Title: Educational Park Planning in Berkeley, California, 1965-1968
University: University of Ottawa Faculty: Social Sciences Author: Heather Martin Award: 2015 Joseph De Koninck Prize Title: An Analysis of Sexual Assault Support Services for Women who have a Developmental Disability
University : University of Ottawa Faculty : Physics Author : Guillaume Thekkadath Award : 2017 Commission on Graduate Studies in the Sciences Prize Title : Joint measurements of complementary properties of quantum systems
University: London School of Economics Faculty: International Development Author: Lajos Kossuth Award: 2016 Winner of the Prize for Best Overall Performance Title: Shiny Happy People: A study of the effects income relative to a reference group exerts on life satisfaction
University : Stanford University Faculty : English Author : Nathan Wainstein Award : 2021 Alden Prize Title : “Unformed Art: Bad Writing in the Modernist Novel”
University : University of Massachusetts at Amherst Faculty : Molecular and Cellular Biology Author : Nils Pilotte Award : 2021 Byron Prize for Best Ph.D. Dissertation Title : “Improved Molecular Diagnostics for Soil-Transmitted Molecular Diagnostics for Soil-Transmitted Helminths”
University: Utrecht University Faculty: Linguistics Author: Hans Rutger Bosker Award: 2014 AVT/Anéla Dissertation Prize Title: The processing and evaluation of fluency in native and non-native speech
University: California Institute of Technology Faculty: Physics Author: Michael P. Mendenhall Award: 2015 Dissertation Award in Nuclear Physics Title: Measurement of the neutron beta decay asymmetry using ultracold neutrons
University: Stanford University Faculty: Management Science and Engineering Author: Shayan O. Gharan Award: Doctoral Dissertation Award 2013 Title: New Rounding Techniques for the Design and Analysis of Approximation Algorithms
University: University of Minnesota Faculty: Chemical Engineering Author: Eric A. Vandre Award: 2014 Andreas Acrivos Dissertation Award in Fluid Dynamics Title: Onset of Dynamics Wetting Failure: The Mechanics of High-speed Fluid Displacement
University: Erasmus University Rotterdam Faculty: Marketing Author: Ezgi Akpinar Award: McKinsey Marketing Dissertation Award 2014 Title: Consumer Information Sharing: Understanding Psychological Drivers of Social Transmission
University: University of Washington Faculty: Computer Science & Engineering Author: Keith N. Snavely Award: 2009 Doctoral Dissertation Award Title: Scene Reconstruction and Visualization from Internet Photo Collections
University: University of Ottawa Faculty: Social Work Author: Susannah Taylor Award: 2018 Joseph De Koninck Prize Title: Effacing and Obscuring Autonomy: the Effects of Structural Violence on the Transition to Adulthood of Street Involved Youth
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/examples/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, checklist: writing a dissertation, thesis & dissertation database examples, what is your plagiarism score.
ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
How to generate, capture, and collect ideas to realize creative projects., writing a synopsis for a bachelor, master or phd thesis in media and computer science.
2020-06-17 Daniel Community Aspects , Doing Science , Feedback , General Tips , Generating Ideas , Improving your Creativity , Infrastructure , Learning to do Science , Science , Something to Think About 1
The development of ‘Balance Of Power’ reminds me if the use of paratroops in WW2. After much trial and error, the strategists eventually learned that the real value of paratroops lay in their powers to motivate regular troops to fight to rescue the paras. Its difficult to inspire soldiers to risk their lives to win a patch of ground, but when they know that their comrades are just ahead, surrounded by the enemy, counting on the regular troops to save them, the regular troops will fight with unparalleled determination. Paratroops, then, allow the commander to set a clear and tough goal for his troops to reach. Using paratroops is like putting yourself in a deep hole to see if you can dig yourself out of it. Chris Crawford, «Balance Of Power»
At the university I work for, students have to write a synopsis prior to the start of their bachelor or masters thesis. It’s got a particular structure:
- Motivation/Goal of the Thesis
- Research Questions (only needed for a Masters Thesis)
- Starting Scenario
- Goal Scenario
- Approach / Time Table
To be honest, the differentiation in starting scenario and goal scenario is already a clarification. It’s not fleshed out in the usual template, so many students miss it. I would also add the following tips:
General issues about writing a synopsis:
Planning of the human-centered design process: The synopsis covers the first step of the human-centered design process — the planning stage. You determine what you want to develop using a HCD process.
The synopsis determine the evaluation criteria — for your work: There’s a reason for the quote at the beginning of this posting. The synopsis determines the standard by which your work will be evaluated. It states clearly what you have promised, and it will be compared against what you have achieved. So invest some thought into what you actually write down. Your advisors will remember … it’s written down, after all … and they will grade you accordingly. Don’t shot yourself in the leg, don’t promise anything you cannot (realistically) achieve.
Open Issues vs. Outlook: In our theses, there are two distinct sections. Open Issues vs. Outlook (future research). Open issues is what you did promise but could not achieve. This section should be as short as possible. And then there is the outlook or future research, things you did find out during your work which would be interesting to explore. That can be longer. Just make sure you deliver what you did promise. The old adage applies here: Under-promise but over-deliver.
Write so I can see you: The synopsis is the first work with which to evaluate whether a person can already write for a mature audience, or whether this person has to learn a lot. Few if any students write well (even though many think they do, oh sweet summer children …). Thing is, it’s a process, so yeah, use the opportunity to take the feedback to your writing seriously. If there are problems with your synopsis, these problems will be — unless actively addressed (you’re too old for it to be a fluke) — in your thesis text. And this applies to the style, the use of sources, and your argumentation. If you speak German, perhaps this video might be useful: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_ID7q7pXzyc
Ad 1: Motivation/Goal of the Thesis
Answers the most important question: This section answers the crucial question: “Why should I care?”. You need to met the reader where he is and show (not just tell ) why the problem is important and why your product should be developed with a human-centered development process. And to go deeper into the “show (not just tell )” issue — almost all cases in which people mention that something is “important”, it really isn’t. If it is, you don’t have to mention it. People see it based on the overall situation. So, show, don’t just tell.
State of the Art: This is actually something that is dealt with quite differently depending on the advisor. Given that it is part of the introduction, I think the state of the art should only include what you did get before starting with the thesis. Once you do an analysis — e.g., search in databases — it’s an active, creative process. Then it should be in the analysis, because other people might act differently. So, in my view, the state of the art should only include an existing system for which you do — e.g., develop another module. But there are different perspectives. Some people see the results of a literature/app research here.
State of the research: In contrast to the mere technology (caveat: I’m a psychologist) the underlying theories you are going to use. E.g., which psychological theories will you use to influence the target behavior? What are the overall goals? The work will continue iteratively and does contain creative elements, but the overall goal should remain the same, so what is known about it? You should state the goal quite clearly, e.g., developing an application which allows every citizen to get a clear view on how much money the government spends on which projects.
Ad 2: Research Questions (only needed for a Masters Thesis)
This section can be removed for Bachelor theses.
In a master’s thesis, clear research questions which the master’s thesis will answer. Specific questions , and you should be damn sure you can answer those questions, you will be graded by how well you can answer them.
Master’s Thesis about User Modeling in Ability-Based Design:
- How does a user model look like when abilities (instead of disabilities) are considered?
- Which parameters are required for an ability-based perspective and how can they be assessed?
- What are the differences of user modeling of abilities compared with other user models?
Master’s Thesis about Designing for Dyslexic People:
- Which commonalities and differences exist in the laws and design guidelines for developing accessible websites in different countries?
- Are those guidelines sufficient for specific user groups, e.g., dyslexic people?
- Which enhancements to the current guidelines would support dyslexic people?
Master’s Thesis about a Catastrophe and Neighborly-Help-App:
- How must a catastrophe app be designed to achieve a high acceptance prior to a crisis?
- Which smart city innovations can be used with a crisis-support-app?
Master’s Thesis to develop a competitive Learning App with Moodle:
- How can the learning success when preparing for written exams be positively influenced via a competitive learning app?
- Can a learning app be used to change extrinsic to intrinsic motivation?
Ad 3: Scenarios
The scenario section is used to provide some life to the rather abstract goals: Students describe two conditions, first without the developed solution. Just how does the situation present itself now . Then how could the situation look like when the app is implemented. Just provide a vivid scenario of how the world looks like. Something vivid but realistic. And if you have different user groups, describe the goal scenario for those different user groups.
Ad 4: Approach / Time Table
Now it gets to how you will achieve that goal: Just decide for an overall development strategy (e.g., an human-centered design process according to DIN EN ISO 9241-210, or scenario-based design, or whatever). Describe what you will do in each phase.
Details of the time table: Sure, a time table is fiction, but it still helps to check whether the project is actually doable. Just jot down how much time you will need for the analysis, conceptual phase, realization (programming! *gasp* it has to compile *gasp^2*), evaluation and actually finishing writing the damn thing. Schedule buffer time.
Realistic time plan: Consider the time periods during the next (usually six months) during which you will be occupied by something else, be it vacation, exams, or whatever. And no, people usually don’t work during xmas or exams.
Availability of the user groups: You need actual users to get accurate feedback. Usually during the analysis, formative evaluation and summative evaluation time periods. Check wether they are actually available. Evaluating a learning app for students during the semester break is rather difficult, and there are time during which most of the people in a country take their vacation.
When to officially start your thesis: If you have any influence on when to start the actual work period (usually limited to six months), do not start it during the time from mid-December to the start of January. Not much if any work will be done during that time. And if you get sick during your thesis, make sure you check whether you can get that time added to your thesis. Usually that’s possible, if you take the time to actually inform the right people about it.
Ad 5: Literature
At my university, we use the APA standard, i.e., the citation standard of the American Psychological Association. Of course, you’ll only cite the literature you have actually used in your synopsis, and to cite it, a literature manager is really helpful. Personally, I like Zotero. Just make sure you add all the required information (you need to know which information actually is required, strangely enough, Zotero does not complain if something is missing, it just follows the old Garbage in — Garbage Out rule (GIGO). So make damn sure you have added the necessary information. And yeah, Zotero also works with Word and other apps.
In the text it’s ASSERTION (Brandstätter, Schüler, Puca, & Lozo, 2013)
In the Reference list it’s:
Brandstätter, V., Schüler, J., Puca, R. M., & Lozo, L. (2013). Motivation und Emotion. Springer-Verlag.
(As a heuristic, the stuff you see on the spine — of books or of bound journal/conference papers — is in italics.)
Or for a journal paper:
In the test it’s: ASSERTION (Franke, Attig, & Wessel, 2019)
In the reference list it’s:
Franke, T., Attig, C., & Wessel, D. (2019). A Personal Resource for Technology Interaction: Development and Validation of the Affinity for Technology Interac-tion (ATI) Scale. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 35 (6), 456–467. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2018.1456150
Final Remarks
So, that’s it for a thesis synopsis. For a bachelor or master’s thesis, the synopsis takes around 3 toi 6 back and forth between the student and the advisor. For a PhD thesis … it takes about a year to really nail down what you want to examine (and how).
Research takes some time, but it shouldn’t take too much time.
As usual, constructive feedback and questions are greatly appreciated.
- stimulation
- task_management
- think_differently
1 Trackback / Pingback
- Thesis Template – Media and Computer Science – Medieninformatik [German Template] | ORGANIZING CREATIVITY
Comments are closed.

Thesis Summary
Ai generator.
Considering that you have finished writing your thesis, it is high time that you started working on your thesis summary or abstract as the last and final part of your research paper before submitting it to your instructor. Writing an abstract is actually the simplest way for your audience, the teachers and the panel of publishers (if you wish for it to be published) to know what your research paper is about without going through the bulk of your paper.
What is an Abstract?
According to an article found in the Simon Fraser University database, the abstract is deemed a critical part of your thesis and it is presented at the beginning of the thesis, as it is a summary of the whole thesis. The thesis summary is a substantive description of your work read by an external examiner by presenting all the major elements of your work in a highly condensed form.
Size and Structure
Normally, a thesis summary would only contain 120 or less (for undergraduate theses), 150 words (for Masters theses) and 350 words (for a doctoral dissertation).
- For doctoral dissertations, it is best to limit it to only 280 words with a format of one double-spaced page, to preserve visual coherence.
- The structure of the abstract should mirror the structure of the whole thesis, and should represent all its major elements.
- For instance, if your thesis has five chapters (rationale, literature review, methodology, results, conclusion), limit each chapter to only a sentence or two for each chapter in order to maximize some parts that need more substantial backing.
Clearly Specify Your Research Questions
- Research questions are important in making sure that the abstract is coherent and logically structured as they form the backbone to which other elements adhere; they should be presented near the beginning of the abstract.
- Depending on the length of your research paper, there is only room for one to three questions. If there are more than three major research questions in your thesis, try to rearrange them by reducing some to subsidiary status.
Don’t Forget the Results
- One of the most common mistakes in writing abstracts is the failure to indicate the results.
- The primary function of your thesis (and by extension your abstract) is not to tell readers what you did, it is to tell them what you discovered. Other information, such as the account of your research methods, is needed mainly to back the claims you make about your results.
- The final part of your thesis should be about summarizing your results as well as interpreting them.
- Although it is sometimes not necessary, you can choose to add keywords below your abstract as the most important terms that can be found in the thesis.
Listed below are some thesis summary examples:
This study aimed to analyze and identify the most frequent news category and rhetoric of the three local English dailies as well as assess whether they align to the readers’ news preference. These factors served as the sources of the data gathered by the researchers: ninety tertiary students, each local publication’s respective editorial board, and banner stories. Findings indicated that even though the editors would usually select their stories based on impact, the banner story content however focused more on news like crime and politics which are mostly conflict-based issues, instead of human interest stories that readers prefer the most. In conclusion, the respective editorial boards of each publication are not presenting the readers with their main interests in the banner story. Keywords: banner stories, news values, news categories, gatekeeping/gatekeepers, and readers’ preference
An example of a summary format The aim or goal or purpose of this graduation thesis (title) is to … (analyse, characterize, compare, examine, illustrate, present, survey, design, reconstruct) … The graduation thesis is composed of five chapters, each of them dealing with different aspect of … Chapter 1 is introductory and (defines, describes, reviews, deals with) … The chapter is subdivided into two parts. Part 1 describes … and explains … . Part 2 deals with … Chapter 2 examines … . The chapter consists of three parts. Part 1 focuses on … . Part 2 investigates … . Part 3 addresses the issue of … . Chapter 3 is subdivided into two parts and provides an outline of relevant … Part 1 illustrates … . Part 2 looks at … . Chapter 4 concentrates on problems resulting from … Part 1 describes …. Part 2 recommends changes to be made in legislation … Conclusions are drawn in Chapter 5. The main aim of the graduation thesis has been reached. The author suggests that …………………… should be changed/introduced/applied.
The aim of this graduation thesis entitled Development of Yamakawa Technologies to Ascertain the Existence of Cheese on the Moon is to test the use of Yamakawa technologies in ascertaining the existence of cheese on the moon. Yamakawa technologies have been successfully used to test the existence of water in Wakanda, but to date no further applications are known. For this reason the author decided to test further applications, with the aim of describing the technology’s suitability for further development. This thesis first examines the testing procedures for the water in Wakanda experiment, and presents the results. In a second stage several adaptations to Yamakawa for the testing of the existence of cheese on the moon are undertaken. Finally the technology is applied to the question of cheese on the moon, within a six-week testing phase. At the end of each week the testing apparatus is fine tuned, and experiment results are charted every twenty-four hours. The results of the experiment show that Yamakawa technologies are well suited to ascertaining the presence of water in Wakanda, but were unable to be sufficiently modified for the purpose of ascertaining the existence of cheese on the moon. The author recommends further modification to the technology before any other uses are considered.
After writing the said abstract in your research paper, then congratulations! You are now ready to move to the next step of your thesis journey, defending it. Just remember this, always know your thesis by heart. Believe me, if you do, you will not have a hard time and eventually, you will learn to enjoy it too. Good luck!
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Architecture Student Chronicles
Guide to writing a Synopsis for the Thesis Project
How to write synopsis for a thesis project.
This article would be of great interest to the Final year Architecture students. Writing a Synopsis determines your level of understanding of the chosen topic as your thesis project. We will list out and discuss different steps in which one should proceed with writing a Synopsis.

Introduction
Objectives and scope and limitations, description of the research work, conclusions/summary of the work, list of case studies.
- List of references/literature case studies for thesis research work
- Identification of the project site
Briefly explain the Architectural/technological/social relevance or significance of the research work of your thesis topic. Be precise and include only relevant background material in the introduction. Provide information on past works by way of giving appropriate references.
It should not exceed two pages.
Develop further on the background material provided in the introduction and bring the subject of thesis in the chosen area of research in to focus. Emphasize, based on the content status, the importance of the research problem identified. Should broadly indicate the existing drawbacks and why further research is required to eliminate the drawbacks and find new architectural solutions. Identification of these should be brief and can be out of the scope of the Thesis subject but has to be relevant. You can enumerate those technical challenges one has to address to solve the problems/drawbacks posed herein to place emphasis on the quality of the research work.
I came across a very interesting piece of article on motivation for writing thesis . This reading should be helpful to all.
This should not exceed two pages.
State precisely the questions for which the answers are sought through this thesis work. Define the conceptual, analytical, experimental and/or methodological boundaries within which the exercise will be carried out.
Admit with clarity the limitation of such a research and difficulties involved.
Keeping in mind the limitations and difficulties, identify the precise architecturally relevant area and extent of research that is attempted by you.
Detailed explanations of the drawbacks/problems identified for which you are seeking possible architectural solutions.
Explain in detail how the case studies will help in resolving the drawbacks/problems identified.
Clear the role of literature studies/observations/experiments/questionnaires.
Define with clarity the detailed methodology to be adopted that will lead you towards the Architectural solutions.
Explain in detail how you are specifically equipped to deal with the research and find Architectural solutions.
It should not exceed 10-12 pages.
Highlight major conclusions you are working towards. Clearly bring out not only the generally useful advantages arising out of the work but also the architectural advancement you are seeking through this Thesis work. If there are no conclusions at the moment, then enumerate the possible contributions of the work.
Maximum two pages.
List the probable Case Studies and the relevant areas of study possible in them. Indicate clearly why you have chosen the particular case for study. Make a mention of the ease/difficulty of approach and obtaining information from the case studies. Also give the time frame required for each case study.
It should not exceed one page.
(Also, it is important to know all the factors to be considered for conducting a successful case study .)
List of references/literature studies for thesis research work
List the publications/books you have already identified for your literature study. List only published or accepted books/papers.
Never claim contents of the publications/books as your own. Always give credit where it is due.
Maximum one page.
Identification of Project site
The student has to identify a possible and suitable site for the proposal where the conclusions and solutions can be carried out. The project site may or may not be a live project but should definitely be suitable for the chosen project.
30 thoughts on “Guide to writing a Synopsis for the Thesis Project”
great job…!
dear sir iam a final year architecture student.i am entering 9th semester now.i am supposed to give a synopsis of my thesis project.could you please guide me how to choose topics for my thesis. regards nandheni
hi i am a 9th sem student!!i m completely at my wits end in going ahead with my topic!!althou not a topic my idea is like”to represent space in terms of all 5 elements,’air,water,fire,earth,space(sky)’.which form d very essence of life,present in everything but r disguised!i really dunno how to translate this into a built space!!n wat it l b!can anybody throw some light on this..
Hi Neha This is Arun, i myself am a final year student of architecture and we are also supposed to give synopsis on the thesis topics. and i guess that i am pretty lost. it would be gr8 if u could share in yhing that u have come across regarding the synopsis, how it is done or made.
regards Arun
Hello friends, I hope you have gone through the guidelines for writing the Synopsis. This will definitely be of help to you. Inspite of the guidelines, if you are unable to understand as to what is to be included in your thesis synopsis, you could tell us your topic through our comment section and then we shall have a discussion so that all the readers benefit from it.
Also check out the following link. You will find various articles that will benefit you. Guidelines for a Thesis Project
its so helpful to me,…thanks ..
want to no a certain source to grasp latest architectural updates
Hello Siddhant, We have now made it possible for you to subscribe for FREE updates of Architecture Student Blog!
Subscribe for Architecture Updates
Look forward to see you on our Subscription list. Cheers 🙂
i m architecture final year student i want to take topic related to our cultural in terms of family entertainment but i m confused how to proceed that topic and how to write synopsis for that particular topic plz guide me as i have to submitt ny synopsis on coming tuesday
Hello Farah,
Apologies for the delay in replying. I hope your synopsis writing went well. I can definitely give you feedback and guide you through your thesis project. Do get back in touch and we can discuss your project on the blog.
hi, i’m a final year architecture student. i’m supposed to give my synopsis on the 9th of December. as of now i am planning to do an apparel house( as my school prefers only pure architectural projects at the under graduate level)..kindly suggest a few live case studies in India ..:D regards gayathri.
Hello there,
There is an apparel house in Gurgaon, Haryana.
Such a gr8 help in taking my initial steps towards thesis
I am a architecture 9th semister student and i am working on marble industry thesis ,I have problems in my thesis methodology hope you will guide me
It would be useful if you could post your questions regarding your thesis here so that we can all have a look at it and help you with your thesis.
Hello sir, I m a student of architecture in my final sem. I have choose a juvenile center as my thesis topic. So please sir can u help me out with this. U can mail me on my mail id:[email protected]
Hello,am a student of architecture,I have choose hotel as my thesis topic.really need your help on how to start.
Hello Joshua,
Here is the link to a number of articles on how you could progress with your thesis project. http://architecture-student.com/category/thesis-project/
I am sure this will be useful.
Hi sir I m in my final semester and my topic is institute of game developing and animation. Can you please guide me through.
- Pingback: Architecture Thesis Synopsis | Great Architecture Fan
hello sir, i have just got into my 9th semester of arch. and wanted to know if you could suggest me some case studies regarding my thesis topic i.e. Hospice care center for terminally ill or cancer patients, in india.anything outside india would also be helpfull for literature study.
Hiii frnds… i m architecture final year student, i have choosed my thesis topic as RIVER FRONT DEVELOPMENT ..it will be a gr8 help to me if u give the related data which u have
Hi, I’m architecture 9th sem student. We are supposed to give our synopsis so can u elaborate me further about the topic aqua marine park. The factors considered for choosing the site and will it be a big project or I can work in details in time. Please help.
Hello Shashi,
This will be an interesting design topic but the casestudies would be difficult because i dont think we have good marine parks in India. If you are willing to go to Dubai for a casestudy then I am sure this would be a fantastic project.
Hi, I am architecture final year student..hav opted the church as a topic for thesis.. i want to reinterpret the design methadology biblicaly ..can you help with this.. is there any church in india that i can opt for case study
Hi I am currently working on my design project and masters thesis: Fruits Processing plant, with emphasis on integrating environmental and human factors. I would be greatly appreciate any relevant materials that could aid my work. Thank you……..
Hi am a final year student I hv choose my topic as orphanage nd old-age homes combined . Help me to develop my topic Case study regarding this Will this work out
Hello, I’m a currently working on my final year thesis :Event Centre.I will love to get materials that would aid my work.Thank you…..
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

- ---Citations---
Translate this page into:
Guidelines for writing a research project synopsis or protocol
| Betkerur J. Guidelines for writing a research project synopsis or protocol. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2008;74:687-690 |
"Success is often the result of taking a mis - step in the right direction. "
Al Bernstein
A protocol or a synopsis of a research project is a document submitted to an authority or an institution for the purpose of
- Ethical clearance
- Formal registration to universities for the award of a degree or doctorate
- Peer review
- Financial assistance from organizations like ICMR, DST, NACO, DGHS, and MHRD
Synopsis is the gist of your planned project submitted for approval from competent authorities. It gives a panoramic view of your research for quick analysis by the reviewers.
Thus, a protocol or a synopsis forms an integral part of a research project or a thesis. Many universities have made it mandatory for the postgraduate degree student to prepare a thesis as a part of their postgraduate training. A good knowledge about how a protocol or a synopsis is written is imperative to all people involved in medical research.
Literally, protocol (Greek word, protokollon - first page) means a format procedure for carrying out a scientific research. Synopsis (Greek word, sun - together, opsis - seeing) means brief summary of something. Frequently, both the terms are used as synonyms but the term ′synopsis′ is used more often.
A synopsis should be constructed in a manner that facilitates the reviewer to understand the research project at a glance. It should be brief but precise. A synopsis can be structured in the following manner:
- Statement of the problem and hypothesis
- Aims and objectives
- Review of literature
- Research methodology
- Official requirements
Title The title of the research project should be brief but informative; sensationalization of the title is best avoided. It should neither be too short nor too long. Any name of the institution, the number of cases to be studied should not be included. The hypothesis to be studied can be included.
a. "Study of ectopic pregnancy"
This was a title chosen for university registration. The title is too short. It does not state the problem or the hypothesis and is least informative. More meaningful title shall be, "Study of ectopic pregnancy in relation to morbidity, mortality, and intervention in a referral hospital".
b. "A novel sustained release matrix based on biodegradable poly (esteramides) and, impregnated with bacteriophages and an antibiotic shows promise in management of infected venous stasis ulcer and other poorly healing wounds", (Int. J Dermat vol 8 2002). The title is long and ill conceived. It gives a confusing picture about the study problem. Such long titles are best avoided. Certain amount of sensationalization is also present by using term ′novel′. More meaningful title shall be, "Response of venous stasis ulcers and other poorly healing wounds to a biodegradable matrix impregnated with bacteriophages and an antibiotic". The other details about the new method can be mentioned while stating the problem.
c. "Fine needle aspiration, as a diagnostic tool for papulonodular skin lesions". This is an acceptable, informative, and precise title. It states the hypothesis correctly.
Statement of the problem or hypothesis The problem being studied should be mentioned in precise and clear terms. Understanding the problem aids the researcher in constructing the research proposal. It also allows the person to formulate the hypothesis. The problem under study should be relevant to the present. A brief account of its utility at the local or national level has to be discussed. The present status of the problem and the necessity for taking up the study needs to be mentioned.
Hypothesis is mentioned as a tentative prediction or explanation of the relationship between two or more variables. Hypothesis should not be a haphazard guess but should reflect the knowledge, imagination, and experience of the investigator. Hypothesis can be formulated by understanding the problem, reviewing the literature on it, and considering other factors. A researcher can state the problem and the hypothesis in about 200 words covering all the aspects described above.
Aims and objectives All research projects should have objectives and aims and every effort should be made to achieve them. The objectives and aims should be only a few (2-3). They must pertain to the study problem. Usages of terms like "first study", "the only study", etc. should be avoided.
Review of literature Review of literature is a very important part of a research project. It achieves the following:
- Familiarizes the reader to the problem under study.
- It describes the work done by others either at local or international level on it or similar subject.
- It helps the researcher to understand the difficulties faced by others and the corrective steps taken or modifications made by them. The researcher can anticipate similar or additional problems during the study and review of literature helps him in anticipating them.
- Research methodology of the researcher can be structured and modified after reviewing the literature.
- The review assists in identifying various variables in the research project and conceptualizes their relationship.
- Review of literature in a synopsis helps the reviewer in assessing the knowledge of the researcher. The reviewer can assess the work put in by the researcher and also assists in assessing the feasibility of the study.
The review of literature in a synopsis need not be exhaustive. The relevant information should be covered in about 300 words quoting 8-10 authentic, easily retrievable references. Literature can be reviewed by using various scientific-information-gathering methods. These are journals, national or international; bulletins of organizations like WHO, CDC, and ICMR; books; computer-assisted searches like Medline and Medlar; and personal communications with other researchers. Internet provides a vast avenue for information gathering. Care must be taken to retrieve only relevant information. In this era of information technology review of literature is literally "just a click away".
Research methodology In a synopsis the research methodology adopted should be mentioned in about 150-200 words. The research methodology forms the core of the research project. The methodology should cover the following aspects:
- Study design
Study settings
- Study methods - examinations or investigations
- Data collection
- Data analysis
Study design The methodology starts with selection of study design. A single study design or a combination can be selected e.g.:
Descriptive designs
Cross-sectional study or survey
Epidemiological description of disease occurrence
Community diagnosis
Study of natural history of a disease
Observational analytical designs
Prospective study
Retrospective study
Follow-up study
Experimental designs
Animal studies
Therapeutic clinical trials - drugs
Prophylactic clinical trials- vaccines
Field trials
Operational designs
A mention about the research setting should be made. This includes information about the institution, facilities available, time of study, and population of study.
Sampling Sampling is selecting a sample of appropriate size for the study. The sample size depends on the study design. The study population can be population of cases, population of people, or population of recipients of certain treatment.
There are many methods for sampling like simple random, systemic and stratified sampling, cluster sampling, etc. Care should be taken to ensure that the sample size is adequate to produce meaningful results. The sample size should be adequate to apply all relevant tests of statistical significance. The samples should be representative of the population and should be reliable. This minimizes sampling errors.
Variables Variables are the factors that can change. These changes can affect the outcome of a research project. Thus, it is important to identify the variables at the planning stage. They should be quantified with a measurable unit. Knowledge of the various variables in a research project will assist in refining the objectives. Usually, objectives of a research will be to see the effect of independent variables on dependent variables. There are four types of variables.
Independent variables
These are the variables that can be manipulated by the researcher and the effects of that are observed on the other variables. For example, predisposing factors, risk factors and cause.
Dependent variables
The changes occur as a result of independent variables. For example, disease and outcome.
Intervening variables
These may influence the effect of independent variables on the dependent variables. For example, while studying the response of HIV-AIDS to HAART the outcome may be influenced by the presence of antitubercular drugs.
Background variables
These are changes that are relevant in the groups or population under study. These need to be included in the study. For example, age, sex, and ethnic origin.
Controls Control groups increase the validity of the research project. They usually consist of units of same population but differ in some respects. Controls are not necessary for all research projects. As far as possible they should be used in all analytical studies, drug trials, and intervention programs.
Study methods Here the researcher will have to describe the method of data collection, which may be in the form of:
- Questionnaire
- Medical examination
- Laboratory investigations
- Screening procedures
A sample of the proforma should be prepared and attached. The possible cost involved and any financial assistance received must be mentioned.
Data collection A brief note on how data are collected should be included. The information should be about:
- The organizational setup
- Training to data collecting team
- Logistic support
- Plans for collaboration with other organization should be included
Data analysis Data analysis is an important part of a research project. A good analysis leads to good results. The plans for data analysis should be mentioned under the following heads Statistical methods, Computer program used, and Data sorting method. A general statement "appropriate statistical methods will be used." must be avoided.
Ethical clearance Wherever necessary, ethical committee clearance from the institute should be obtained. The certificate must be attached. Ethical clearance is required in all human and animal studies.
References All references quoted in review of literature and anywhere else in the synopsis should be listed here. There are two styles for writing references, Vancouver style and Harvard style. Vancouver style is easy to follow as it depends on the numbers as quoted in text.
Official requirements A synopsis is incomplete if it does not contain the following information:
- Name of the researcher and designation
- Name and designation of the guide
- Name and designation of head of department\institution
- Name of the institution
- Signatures of all with official seal
Synopsis writing is an important step in a research project. A good synopsis will give maximum information in minimum words. A well-conceived synopsis will go a long way in convincing the reviewer about the ability of the researcher to conduct the project. In cases of need for financial assistance, the request will be considered favorably. Thus, all research workers should make efforts to prepare a well-structured synopsis.
Acknowledgments
The author is thankful to M/s Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers for their permission to reproduce this article from the "Handbook on Health Professional Education" published by them. [21] [Table 1]
| ed. London: Pergmon Press; 1994. | |
| ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1983. | |
| ed. New Delhi: 1985. | |
| ed. Churchill Livingstone; 2000. | |
Suggested read for related articles:
- Eat Coat, Eat! Writing style and Indian Dermatology… October 28, 2023
- Illustrated synopsis of dermatology &… June 21, 2024
- Equipoise: Where does it stand in current clinical research February 25, 2022
ISSN (Print): 0378-6323 ISSN (Online): 0973-3922

Research guidance, Research Journals, Top Universities

Format of synopsis for PhD | Download Sample.
Guidelines for writing ph. d synopsis..
FORMAT OF SYNOPSIS (MS/MPHIL & PHD). Given below is an outline for synopsis writing. It provides guidelines for organization and presentation of research.
INTRODUCTION OF 2-3 PAGES
- Identify a real world problem
- Describe the undesirable symptoms
- Identify the knowledge gap that needs to be filled in order to help solve the problem
- Support your discussion with solid peer-reviewed references
LITERATURE REVIEW
- Create an Outline or “mindmap” of the key theories and concepts.
- Dig deep into the “ Peer-reviewed” literature for each theory and concept and create an annotated bibliography and literature map
- Write literature review
- Map out the research gap
- Identify the “type(s)” of question that need to be answer to fulfill the purpose
- Develop the main research question and sub-questions
- Develop hypotheses as appropriate
- Identify and diagram the key variables in the research question
- Identify and diagram the key relationships between the variables
- Identify and diagram the key context factors
- Describe the framework
- Research Process
- Based on the research questions, the overall approach (Data Collection, Analysis methods, Validity and Reliability test process)
POSSIBLE OUTCOME AND LIMITATIONS OF YOUR STUDY
- Identify the larger application(s) and meaning(s) of the findings.
- Identify the limitations associated with the findings and conclusion.
BIBLIOGRAPHY OR REFERENCES
Most preferable format:
Font: Times New Roman
Title of the thesis: 18
Main Heading: 14 Bold
Sub Heading: 12 Bold
Spacing 1.5
Reference style: APA/IEEE/Harvard
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

SYNOPSIS FORMAT FOR DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO ……… LAW SCHOOL IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT OF THE REQUIREMENT FOR THE DEGREE OF LL.B./ LL. M.

INDIAN UNIVERSITIES DISSERTATION FORMAT, SYNOPSIS FORMAT
Related Papers
Sidharth Patel
Reetam Singh
Gazi Md. Muidul Haque
The programme of study for the degree of Bachelor of Laws with Honours (LL.B. Honours) will extend over a period of four (4) academic years and eight (8) semesters. It comprises studies on variety of areas of law and other related courses. LL.B. Honours programme will be an integrated course, carrying 4200 marks and 138 credit points
Tamanna Goyal
Talwant Singh
Prabhash Ranjan
Interdisciplinary Studies on The Indian Legal System (Seminar Course)
Sidharth Chauhan
This seminar course was taught to upper-level students at NALSAR Hyderabad. It was delivered four times, that is during the January-April 2015, January-April 2016, January-April 2017 and January-April 2018 terms. The instructor was Mr. Sidharth Chauhan.
Law and Literature
This is a course plan for a required course on 'Law and Literature' that was taught to 2nd year B.A.,LL.B. students at NALSAR Hyderabad. Mr. Sidharth Chauhan taught this course during the January-April 2015 and January-April 2016 semesters. It was later re-assigned to other instructors who can be contacted for the most recent versions of this course.
Kaustav Saha
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
prity mukherjee
Saphy Bullu
Ankit Kumar
Gowtham Krishna Madugula
Vysakh Chingath
Mahendra Kumar Bhandari
Shikhar Tiwari
ashu dahiya
LRK Krishnan
Indian Society for Legal Research
Mohd Imran , Indian Research
Taylor & Francis Online
Pragyanshu Gautam
Meghna Mittal
Lalchand Jorasiya
Dhiraj Sarmah
Saleem Marsoof
chaitanya krishna
Anjan Datta
Dr. Sultan Haidar Alam
kewfilsjhfkjsf
Ravi Prakash
Prabir Datta
Gregory T Papanikos
Ishimwe Rosine
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The structure of a synopsis should correspond to the structure of qualifying research work, and the word count should be 2,500-3,000 words (Balu 38). The basic elements of a synopsis include a title page, contents page, an introduction, background, literature review, objectives, methods, experiments and results, conclusions, and references.
1. Format your title page following your instructor's guidelines. In general, the title page of a research synopsis includes the title of the research project, your name, the degree and discipline for which you're writing the synopsis, and the names of your supervisor, department, institution, and university.
A good synopsis details everything related to your topic, but a great synopsis ensures that not only is the content there, but it is presented in a logical manner and easy to follow. Your outlined thesis should include the following: The title of the topic. The abstract. The necessity of the topic - the background.
Alternative (H1)., which is tested for possible acceptance. —It emphasises the significance/ importance of the research work/study, i.e., the reason and aim of the selection of the topic of research. —The researcher must clearly identify the problem/issue selected for the thesis/ dissertation. - It means a plan of work describing the ...
Answer: The synopsis for a thesis is basically the plan for a research project, typically done when pursuing a doctorate. It outlines the focus areas and key components of the research in order to obtain approval for the research. Here is a listing of the sections that typically are a part of the synopsis. Do check with your guide/supervisor ...
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
Elaborate a thesis statement. The thesis statement. is the most important part. This is a sentence usually placed at the beginning of the summary and it is aimed at clarifying the main research questions of your work. The thesis statement must be clear and concise. MA theses, but also PhD dissertations, usually concern very narrow topics.
Lesson 4: Synopsis. In order to clarify your thoughts about the purpose of your thesis and how you plan to reach your research goals, you should prepare a synopsis. A synopsis is a short, systematic outline of your proposed thesis, made in preparation for your first meeting with your supervisor. It serves to ensure that your supervisor gets a ...
Abstract or executive summary. The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report - in other words, it should be able to ...
Writing a Synopsis. A synopsis is a brief summary which gives readers an overview of the main points. In an academic context, this is usually a summary of a text (a journal article, book, report etc) but in some instances you might be writing a synopsis of a talk, film or other form of presentation. A synopsis is a neutral summary, objectively ...
Synopsis is a short summary of your Ph.D thesis work. This paper suggests some ideas to motivate the young researchers for effectively writing the Ph.D synopsis with essential tips and tricks.This can act as a reference and help young researcher to ... Sample of a literature review 3. OBJECTIVES Objectives should be identified on the basis of ...
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
Sample Dissertation Overview. The problem generally is addressed in two related parts: The problem statement is contained in Chapter 1, and a review of the related research, theory, and professional literature is described in Chapter 2. The methods used for investigating the problem are usually included in Chapter 3.
Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples. Published on September 9, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on July 18, 2023. It can be difficult to know where to start when writing your thesis or dissertation.One way to come up with some ideas or maybe even combat writer's block is to check out previous work done by other students on a similar thesis or dissertation topic to yours.
Examples: In the text it's ASSERTION (Brandstätter, Schüler, Puca, & Lozo, 2013) ... So, that's it for a thesis synopsis. For a bachelor or master's thesis, the synopsis takes around 3 toi 6 back and forth between the student and the advisor. For a PhD thesis … it takes about a year to really nail down what you want to examine (and ...
LMANUAL FOR PREPARATION OF Ph.D. SYNOPSIS (Prescribed Format and Specification)GENERAL:The synopsis is to be considered as a detailed summary of the work wit. important results highlighting the orig. nal contributions in the thesis to be submitted. It should give an outline of the thesis. The review of earlier work is to be minimized with jus.
The research synopsis is the plan for your research project. It provides the rationale for the research, the research objectives, the proposed methods for data collection and recording formats and ...
Sample 2. An example of a summary format. The aim or goal or purpose of this graduation thesis (title) is to … (analyse, characterize, compare, examine, illustrate, present, survey, design, reconstruct) …. The graduation thesis is composed of five chapters, each of them dealing with different aspect of …. Chapter 1 is introductory and ...
The student has to identify a possible and suitable site for the proposal where the conclusions and solutions can be carried out. The project site may or may not be a live project but should definitely be suitable for the chosen project. Maximum one page. Writing a Synopsis requires research and understanding of the project you have chosen for ...
1. The length of a synopsis for the Ph.D. Thesis should normally be 1000 to 4000 words including tables and figures. The Synopsis should be on A4 size paper. Four copies of the synopsis are required to be submitted. 2. There exists, at present, a wide variation in the subject matter and style of presentation of the synopsis.
Thus, a protocol or a synopsis forms an integral part of a research project or a thesis. Many universities have made it mandatory for the postgraduate degree student to prepare a thesis as a part of their postgraduate training. A good knowledge about how a protocol or a synopsis is written is imperative to all people involved in medical research.
FORMAT OF SYNOPSIS (MS/MPHIL & PHD). Given below is an outline for synopsis writing. It provides guidelines for organization and presentation of research. Figure 1: Format of Synopsis. THE TITLE OF RESEARCH OR THESIS. CERTIFICATE. INDEX. INTRODUCTION OF 2-3 PAGES. Identify a real world problem.
(batch) * the same format will be used both for submission of synopsis and dissertation synopsis format table of contents introduction literature review statement of problem objectives of the study research questions hypothesis methodology chapterization (tentatively as follows) introduction nature, meaning and scope &historical development ...