
- Schools & departments


Writing your PhD research proposal
Find guidance on how to write your PhD research proposal and a template form for you to use to submit your research proposal.
By asking you for an outline research proposal we hope to get a good picture of your research interests and your understanding of what such research is likely to entail.
The University's application form is designed to enable you to give an overview of your academic experience and qualifications for study at postgraduate level. Your outline research proposal then gives us an idea of the kind of research you want to undertake. This, together with information from your referees, will help us assess whether the Moray House School of Education and Sport would be the appropriate place for you to pursue your research interests.
At the application stage, you are unlikely to be in a position to provide a comprehensive research proposal; the detailed shaping up of a research plan would be done in conjunction with your supervisor(s). But it is important for us to appreciate what you are hoping to investigate, how you plan to carry out the research, and what the results might be expected to contribute to current knowledge and understanding in the relevant academic field(s) of study. In writing your proposal, please indicate any prior academic or employment experience relevant to your planned research.
In your research proposal, please also ensure that you clearly identify the Moray House research cluster your proposal falls under, as well as two to three staff members with expertise in this area. We also encourage you to contact potential supervisors within your area of proposed research before submitting your application to gauge their interest and availability.
How to write your research proposal
The description of your proposed research should consist of 4-5 typed A4 sheets. It can take whatever form seems best, but should include some information about the following:
- The general area within which you wish to conduct research, and why (you might find it helpful to explain what stimulated your interest in your chosen research field, and any study or research in the area that you have already undertaken)
- The kind of research questions that you would hope to address, and why (in explaining what is likely to be the main focus of your research, it may be helpful to indicate, for example, why these issues are of particular concern and the way in which they relate to existing literature)
- The sources of information and type of research methods you plan to use (for example, how you plan to collect your data, which sources you will be targeting and how you will access these data sources).
In addition to the above, please include any comments you are able to make concerning:
- The approach that you will take to analyse your research data
- The general timetable you would follow for carrying out and writing up your research
- Any plans you may have for undertaking fieldwork away from Edinburgh
- Any problems that might be anticipated in carrying out your proposed research
Please note: This guidance applies to all candidates, except those applying to conduct PhD research as part of a larger, already established research project (for example, in the Institute for Sport, Physical Education & Health Sciences).
In this case, you should provide a two- to three-page description of a research project you have undertaken, to complement information in the application form. If you are in any doubt as to what is appropriate, please contact us:
Email: Education@[email protected]
All doctoral proposals submitted as part of an application will be run through plagiarism detection software.
Template form for your research proposal
All applicants for a PhD or MSc by Research must submit a research proposal as part of their application. Applicants must use the template form below for their research proposal. This research proposal should then be submitted online as part of your application. Please use Calibri size 11 font size and do not change the paragraph spacing (single, with 6pt after each paragraph) or the page margins.
- Log in
- Site search
How to write a successful research proposal
As the competition for PhD places is incredibly fierce, your research proposal can have a strong bearing on the success of your application - so discover how to make the best impression
What is a research proposal?
Research proposals are used to persuade potential supervisors and funders that your work is worthy of their support. These documents set out your proposed research that will result in a Doctoral thesis. They are typically between 1,500 and 3,000 words.
Your PhD research proposal must passionately articulate what you want to research and why, convey your understanding of existing literature, and clearly define at least one research question that could lead to new or original knowledge and how you propose to answer it.
Professor Leigh Wilson, head of the graduate school at the University of Westminster , explains that while the research proposal is about work that hasn't been done yet, what prospective supervisors and funders are focusing on just as strongly is evidence of what you've done.
This includes how well you know existing literature in the area, including very recent publications and debates, and how clearly you've seen what's missing from this and so what your research can do that's new. Giving a strong sense of this background or frame for the proposed work is crucial.
'Although it's tempting to make large claims and propose research that sweeps across time and space, narrower, more focused research is much more convincing,' she adds. 'To be thorough and rigorous in the way that academic work needs to be, even something as long as a PhD thesis can only cover a fairly narrow topic. Depth not breadth is called for.'
The structure of your research proposal is therefore important to achieving this goal, yet it should still retain sufficient flexibility to comfortably accommodate any changes you need to make as your PhD progresses.
Layout and formats vary, so it's advisable to consult your potential PhD supervisor before you begin. Here's what to bear in mind when writing a research proposal.
Your provisional title should be around ten words in length, and clearly and accurately indicate your area of study and/or proposed approach. It should be catchy, informative and interesting.
The title page should also include personal information, such as:
- academic title
- date of birth
- nationality
- contact details.
Aims and objectives
This is a summary of your project. Your aims should be two or three broad statements that emphasise what you want to achieve, complemented by several focused, feasible and measurable objectives - the steps that you'll take to answer each of your research questions.
You'll need to clearly and briefly outline:
- how your research addresses a gap in, or builds upon, existing knowledge
- how your research links to the department that you're applying to
- the academic, cultural, political and/or social significance of your research questions.
Literature review
This section of your PhD proposal discusses the most important theories, models and texts that surround and influence your research questions, conveying your understanding and awareness of the key issues and debates.
It should focus on the theoretical and practical knowledge gaps that your work aims to address, as this ultimately justifies and provides the motivation for your project.
Methodology
Here, you're expected to outline how you'll answer each of your research questions. A strong, well-written methodology is crucial, but especially so if your project involves extensive collection and significant analysis of primary data.
In disciplines such as humanities, the research proposal methodology identifies the data collection and analytical techniques available to you, before justifying the ones you'll use in greater detail. You'll also define the population that you're intending to examine.
You should also show that you're aware of the limitations of your research, qualifying the parameters you plan to introduce. Remember, it's more impressive to do a fantastic job of exploring a narrower topic than a decent job of exploring a wider one.
Concluding or following on from your methodology, your timetable should identify how long you'll need to complete each step - perhaps using bi-weekly or monthly timeslots. This helps the reader to evaluate the feasibility of your project and shows that you've considered how you'll go about putting the PhD proposal into practice.
Bibliography
Finally, you'll provide a list of the most significant texts, plus any attachments such as your academic CV .
Demonstrate your skills in critical reflection by selecting only those resources that are most appropriate.
Final checks
Before submitting this document along with your PhD application, you'll need to ensure that you've adhered to the research proposal format. This means that:
- every page is numbered
- it's professional, interesting and informative
- the research proposal has been proofread by both an experienced academic (to confirm that it conforms to academic standards) and a layperson (to correct any grammatical or spelling errors)
- it has a contents page
- you've used a clear and easy-to-read structure, with appropriate headings.
Research proposal examples
To get a better idea of how your PhD proposal may look, some universities have provided examples of research proposals for specific subjects, including:
- The Open University - Social Policy and Criminology
- Queen's University Belfast - Nursing and Midwifery
- University of Sheffield - Sociological Studies
- University of Sussex
- University of York - Politics
- York St John University
Find out more
- Explore PhD studentships .
- For tips on writing a thesis, see 7 steps to writing a dissertation .
- Consider your PhD, what next?
How would you rate this page?
On a scale where 1 is dislike and 5 is like
- Dislike 1 unhappy-very
- Like 5 happy-very
Thank you for rating the page

How to write a research proposal
Drafting your first research proposal can be intimidating if you’ve never written (or seen) one before. Our grad students and admissions staff have some advice on making a start.
Before you make a start
Is it a requirement for your course.
For some research courses in sciences you’ll join an existing research group so you don’t need to write a full research proposal, just a list of the groups and/or supervisors you want to work with. You might be asked to write a personal statement instead, giving your research interests and experience.
Still, for many of our research courses — especially in humanities and social sciences — your research proposal is one of the most significant parts of your application. Grades and other evidence of your academic ability and potential are important, but even if you’re academically outstanding you’ll need to show you’re a good match for the department’s staff expertise and research interests. Every course page on the University website has detailed information on what you’ll need to send with your application, so make sure that’s your first step before you continue:
There are many ways to start, I’ve heard stories about people approaching it totally differently. Yannis (DPhil in Computer Science)
How to begin?
There isn’t one right way to start writing a research proposal. First of all, make sure you’ve read your course page - it’ll have instructions for what to include in your research proposal (as well as anything to avoid), how your department will assess it, and the required word count.
Start small, think big
A research degree is a big undertaking, and it’s normal to feel a bit overwhelmed at first. One way to start writing is to look back at the work you’ve already done. How does your proposed research build on this, and the other research in the area? One of the most important things you’ll be showing through your research project is that your project is achievable in the time available for your course, and that you’ve got (or know how you’ll get) the right skills and experience to pull off your plan.
They don’t expect you to be the expert, you just have to have good ideas. Be willing to challenge things and do something new. Rebecca (DPhil in Medieval and Modern Languages)
However, you don’t have to know everything - after all, you haven’t started yet! When reading your proposal, your department will be looking at the potential and originality of your research, and whether you have a solid understanding of the topic you’ve chosen.
But why Oxford?
An Admissions Officer at one of our colleges says that it’s important to explain why you’re applying to Oxford, and to your department in particular:
“Really, this is all dependent on a department. Look at the department in depth, and look at what they offer — how is it in line with your interests?”
Think about what you need to successfully execute your research plans and explain how Oxford’s academic facilities and community will support your work. Should I email a potential supervisor? Got an idea? If your course page says it’s alright to contact a supervisor (check the top of the How to apply section), it’s a good idea to get in touch with potential supervisors when you come to write your proposal.
You’re allowed to reach out to academics that you might be interested in supervising you. They can tell you if your research is something that we can support here, and how, and give you ideas. Admissions Officer
You’ll find more information about the academics working in your area on your department’s website (follow the department links on your course page ). John (DPhil in Earth Sciences) emailed a professor who had the same research interests as he did.
“Luckily enough, he replied the next day and was keen to support me in the application.”
These discussions might help you to refine your ideas and your research proposal.
Layal says, “I discussed ideas with my supervisor — what’s feasible, what would be interesting. He supported me a lot with that, and I went away and wrote it.”
It’s also an opportunity to find out more about the programme and the department:
“Getting in touch with people who are here is a really good way to ask questions.”
Not sure how to find a potential supervisor for your research? Visit our How-to guide on finding a supervisor .
Asking for help
My supervisors helped me with my research proposal, which is great. You don’t expect that, but they were really helpful prior to my application. Nyree (DPhil in Archaeological Science)
Don’t be afraid to ask for advice and feedback as you go. For example, you could reach out to a supervisor from your current or previous degree, or to friends who are also studying and could give you some honest feedback.
More help with your application
You can find instructions for the supporting documents you’ll need to include in your application on your course page and in the Application Guide.
- Application Guide: Research proposal
Can't find what you're looking for?
If you have a query about graduate admissions at Oxford, we're here to help:
Ask a question
Privacy Policy
Postgraduate Applicant Privacy Policy
- Skip to content
- Skip to footer
- Accessibility options

- Business and employers
- Alumni and supporters
- For students

- Postgraduate research degrees
- Apply for a PhD
- Writing a research proposal for a PhD application
How to write a research proposal for a PhD application
What is a research proposal.
A research proposal gives details of the direction of your future research, usually based on a research question and a chapter-by-chapter approach to answering it.
For PhD applications, this proposal will be assessed to see:
- whether the project is likely to be completed within three years of full-time research
- whether it can be effectively supervised at the university
- whether you are competent and keen enough to complete it.
There may be other factors affecting whether you get a place at the University of Brighton:
- whether the project fits a growing or established research priority of the university
- how the proposal fits with a current cohort and the research environment
A successful proposal will leave the panel in no doubt on these, and you should prepare to show the strength of your idea and demonstrate your suitability.
Within the proposal, you should take the opportunity to clearly outline your research idea; your research methodology and critical approaches; your experience in this field of research where you can; and how your work will be offering an original contribution to knowledge, theories and/or practice.
Find more details about a PhD in your discipline at the University of Brighton
How to get a prospective supervisor's help with your proposal
The strongest proposals are often ones that have been written jointly between a prospective student and prospective supervisor.
As Professor Pollen states in our film, supervisors have an understanding of the language used in proposals and the skillsets that asessors will want to see -- whether for a university position or a funding application.
To develop a strong proposal, we recommend you work with a possible supervisor at the University of Brighton who can help shape your project for feasibility and suitability within our institution. This person may then become your lead supervisor.
Please enable targeting cookies in order to view this video content on our website, or you can watch the video on YouTube .
What journey leads to a PhD application? This film was made by the University of Brighton for UKRI and features University of Brighton students and academics as well as those from other partner universities.
Finding a PhD theme and understanding the university research environment
You may be responding to an advertised call for a particular project that has already achieved funding. Alternatively, you may want to propose a personally developed project.
If you are responding to a call then the advertisement will have clear guidance as to what research experience and interest a candidate will need. This should help you structure your PhD research proposal.
If you are proposing a personally developed project then it should be carefully written to show the viability within the university's current research environment and a specific supervisory possibility at the university.
Some applicants have found our repository of theses helpful for the development and refinement of their research idea. You can find over 1000 theses completed at the University of Brighton over the past 40 years at our repository of successful PhD student theses .
Our research database has useful leads to potential supervisory staff and a strong idea of the university's current research priorities online:
- Explore our PhD disciplinary programme search tools including free search and A-Z
- Explore our research centres (COREs) or our research groups (REGs)
- Visit our research database of staff, projects and organisational units.
Once you have identified a potential lead researcher of a research project most aligned to yours, do not hesitate to email them.
Explain who you are, your motivation to do a PhD in their field of study and with them. They will let you know if they are interested in your project and would be interested in potentially supervising your PhD. If they cannot commit, they may be able to help you identify another researcher who could be available and interested.
By liaising with a suitable supervisor, your proposal will benefit from expert help and be channelled towards the appropriate disciplinary environment.
If you are in doubt about whether we can offer the appropriate supervision, please contact the Doctoral College .
Find out more about your opportunities for a PHD on our FAQ page
What should a research proposal contain?
A research proposal should include the following:
1. Indicative title of the topic area
This should accurately reflect what it is that you want to study and the central issues that you are going to address.
It may be useful to present this in the format of a statement (perhaps a quote) and a question, separated by a colon. For example: '"The tantalising future of research": how are research proposals developed and assessed?'
2. Context / rationale / why is this study important? (300 – 500 words)
Introduce your specific area of study. You should identify the theoretical context within which your research will be developed by discussing the discipline(s) and or field/s of study relevant to your research.
This means outlining the key theoretical area(s) you will draw upon to enable you to find out what it is that you want to know (for example, how it is underpinned from methods in the social sciences; arts and humanities; life, health and physical sciences).
What we are looking for here is an indication that you understand and have done some research into the wider theoretical context.
Developing the context is just one part of this section; you are building a case / rationale for the study area. Why is this study important, which theoretical areas support this? Can you identify any gaps in current understanding that help you build the case for this research study?
For example, this section might take the form of: a series of statements on the current landmark areas of thought; a recognition of what has not yet been done thoroughly enough or where there is territory for research between these landmark studies; and where your study will fill the gaps you have identified.
3. Literature review (approximately 700 – 900 words)
Here you are demonstrating that you are aware of what has been and what is currently being written about your topic.
It will certainly include the up-to-date and relevant past landmark academic literature. It may also include other evidence of current thought and attitude, for example, government documents or media coverage. Practice-led PhD studies may make reference to innovation and trends in industry or professional practice.
We are looking for you to make links between this body of literature and your proposed area of study. This will support the ways you have identified gaps in the current global knowledge-base. A PhD thesis arises from original research leading to new knowledge or a significant contribution to existing knowledge. If, at this stage, you have some thoughts on how your research is likely to contribute to knowledge then include details in your proposal.
This section should include citations which are compiled into a reference list at the end of the document (see point 7).
4. The research questions or hypotheses (approximately 200 words)
Having told us what you want to study and why, and then illustrated these ideas with reference to a body of literature, the next task is to distil your ideas into a tentative set of research questions, hypotheses, aims and objectives (as per the underpinning discipline requires) that are manageable and achievable within a normal PhD timeframe (see 6 below). There are typically between three and ten questions/aims of this kind.
5. Research approach/ methodologies / methods (approximately 400 words)
There will be many research approaches open to you. In your proposal, suggest the methodological approach that you might take and make a reasoned case as to why the research questions you have posed are best addressed by this approach.
You might also suggest what methods you would use to generate data that can help you address your research questions.
6. Timescale/research planning (approximately 200 words)
A full-time PhD should take three years to complete, although you may require more time to acquire the relevant skills prior to commencing your research. Part-time study will take longer (up to five - six years). Within this timeframe, you will need to demonstrate your awareness of time management and planning, for example the length of time for primary research/ fieldwork.
7. Reference list
You should include a reference list of all the sources that you referred to in the text using a recognised referencing style appropriate to your discipline (for example Harvard or Vancouver for Sciences).
Evidence of thorough background reading might include between ten and twenty citations at this point. They should demonstrate to an expert that you are knowledgeable of the landmark work in your field.
There are a number of books widely available that may help in preparing your research proposal (as well as in completing your research degree), here are a couple to point you in the right direction:
Bell, J (2010, 5th edn) Doing Your Research Project: A Guide for First-time Researchers in Education & Social Science , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Baxter, L, Hughes, C and Tight, M (2007, 3rd edn) How to Research , Buckingham: Open University Press.

Research proposals in practice-led and professionally-based disciplines
The University of Brighton prides itself on the quality of its research in areas that intersect with professional practices and direct impact through in-the-field relationships with co-producers.
We are very supportive of doctoral projects that bring positive results from these methodolgies and practices.
Some of the subject areas that have supported personal practice as research include: design, art, architecture, media production and creative writing, with successful approaches including autoethnographic methods and public participation or site-specific interventions.
Some of the areas that have benefited from significant professional practice and industry relationship-focused research have included: engineering, nursing, business administration and teaching.
The research proposal will still need to demonstrate your capability as a researcher with a project that is workable and fits with the university's interests and capacities.
You should, however, adapt your proposal to demonstrate the value that your practice can bring to the research. This should be in tandem with a clear understanding of the relationship between practice and research.
A clear competence in practice should be evidenced, but do be aware that your proposal will be judged on its research and the new knowledge that is developed and shared, rather than the quality of practice in and of itself.
Personal practices, experiences and data gained through professional relationships may form part of a standard PhD thesis and proposal as description of work and resulting data. You will only be appyling for a practice-led component to be taken into account if this will form a significant part of the representation and examination of the knowledge-base. In such cases, the thesis is signficantly shorter.
Some pitfalls in the applications for practice-led or practice-focused research include:
- An imbalance between the practical and theoretical elements
- Too arbitrary a divide between the practice and theory
- Using practice to simply provide personal illustrations of established theories or concepts
- Insufficient sense of how the research knowledge will be held and disseminated
- Insufficiently contained scope for a three-year project – for example, where the practice is described as a life-long investigation – with no clarity on an end-point
- A project that could be better or similarly tackled through a standard PhD in terms of efficient response to the research questions. For example where the practice element might be represented as data or results instead of examined practice.
Your potential supervisor will be able to advise where a proposal will include significant elements beyond the traditional thesis. For further information, please contact the Doctoral College .

A set of designed objects submitted as part of a practice-led PhD project in medical therapeutic design, by Dr Tom Ainsworth, who went on to become a teacher, researcher and supervisor at the University of Brighton.
- Postgraduate Research

How to write a PhD research proposal
Creating a focused and well-written research proposal - a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research - is an essential part of a successful PhD application.
A research proposal is normally required for self-funded PhDs (where you develop your own idea for a thesis), but isn't usually needed for funded studentships or pre-defined research projects.
What is a research proposal?
A research proposal sets out the central issues or questions that you intend to address. It outlines the general area of study within which your research falls, referring to the current state of knowledge and any recent debates on the topic. It should also demonstrate the originality of your proposed research.
What it should include
As a guide, research proposals should be around 2,000-3,000 words and contain:
- A title – this is just tentative and can be revised over the course of your research
- An abstract – a concise statement of your intended research
- Context - a brief overview of the general area of study within which your proposed research falls, summarising the current state of knowledge and recent debates on the topic
- Research questions - central aims and questions that will guide your research
- Research methods - outline of how you are going to conduct your research, for example, visiting particular libraries or archives, field work or interviews
- Research significance - demonstrate the originality of your intended research
- A bibliography.
Crucially, it is also an opportunity for you to communicate your passion for the subject area and to make a persuasive argument about the impact your project can achieve.
Your research proposal will be assessed by our academic schools to assess the quality of your proposed research and to establish whether they have the expertise to support your proposed area of PhD study.
Thesis writing classes and support for international research students
The University’s English Language Centre (ELC) provides thesis writing support for international PhD students. Classes run throughout semesters one and two and are designed to help develop the academic writing skills needed to write up research effectively.
The sessions are taught by tutors with their own research experience. They have PhDs themselves and have many years of experience in analysing writing in different disciplines.
The course also provides an opportunity for students to receive individual feedback on samples of their own writing.
The following classes are available:
- Thesis Writing for Science, Technology, Engineering and Medicine
- Thesis Writing for Humanities and Social Sciences
In addition to these thesis writing classes, the ELC also provides a 1:1 Academic Writing Consultation service.
Back to: Study
Find a course
- A-Z of courses /
- Studentship vacancies
Undergraduate enquiries
International enquiries
Postgraduate taught enquiries
Postgraduate research enquiries
Ask the University of Liverpool a question
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate Taught
- Online programmes
- Welcome to Liverpool
Learn about...
- Visits and Open Days
- Accommodation
- Student support
- Careers and Employability
- Continuing Education
- Continuing Professional Development
Information for...
- International students
- Mature students and access courses
- Parents and supporters
- School and careers advisors
- Postgraduate
- PhD and Professional Doctorates
- How to apply
Writing a research proposal
Your research proposal is the most important part of your doctoral application. Find out how to write a proposal for your own research, for advertised PhD projects, and for Professional Doctorates.
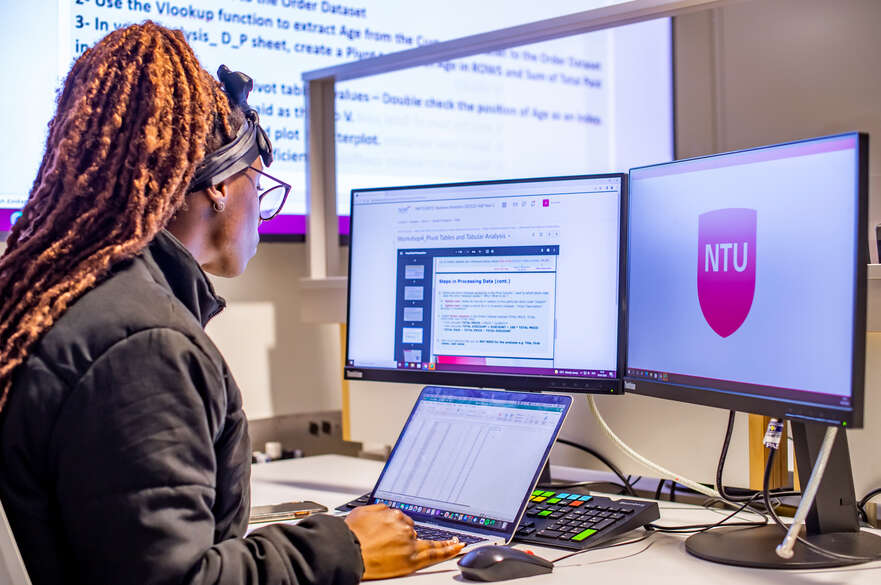

What is a research proposal?
A research proposal is the beginning of your doctoral project. The proposal outlines the intended focus of your research and the possibilities. It will also include your research question, which is the question your project will explore and aim to answer. A good research question will guide your process and should be feasible, specific and relevant to your topic.
Doctoral research should be an original contribution to an academic field, and your proposal should demonstrate that.
Research proposal structure
A proposal should be concise and direct - the panel won’t be expecting you to know all the answers yet, but they need to see the need for the project, your planned approach or methodology, and its potential impact. Make sure your research proposal structure includes these elements:
- a relevant title for the project - the first step in writing your proposal is to decide on a title that clearly indicates the focus of your research.
- an outline of your chosen research question or focus - this should be outlined at the beginning of your proposal, clearly stating any factors that make the project unique.
- a brief overview of existing academic work on or connected to your topic - all proposals should include this, and a clear reason as to why your project will differ or add something new.
- details of the methodology you intend to use - your proposal should also include your plan for the research over the course of your degree and what's called your 'research impact' - the effect your research will have beyond academia.
Your proposal should be no more than 1500 words (not including references). Once you’ve drafted your proposal, ask your potential supervisor for feedback and work on any edits alongside them. Once both you and your supervisor are happy with the proposal, you can submit your application.
Top three tips for your research proposal
1. be distinct.
Amplify the originality of your research, particularly if your work will spotlight an underrepresented area of research or offer a new perspective on a major issue. Outline the need for your research and any elements that might facilitate real-world change.
2. Maximise the potential
How will your project contribute to the research community? Will it have potential for public engagement or be of benefit to a certain community? What could the outcomes be?
Demonstrate your project's scope in your proposal to help it stand out to a decision panel, and to highlight your potential as a researcher.
3. Show your skill
Use your proposal to demonstrate your knowledge of the field, your grasp of methodologies and key concepts, and your abilities as a researcher. Make sure your research plan is feasible and shows your understanding of research practice. The panel will be looking out for good planning and project management.
Research proposals for named PhD projects
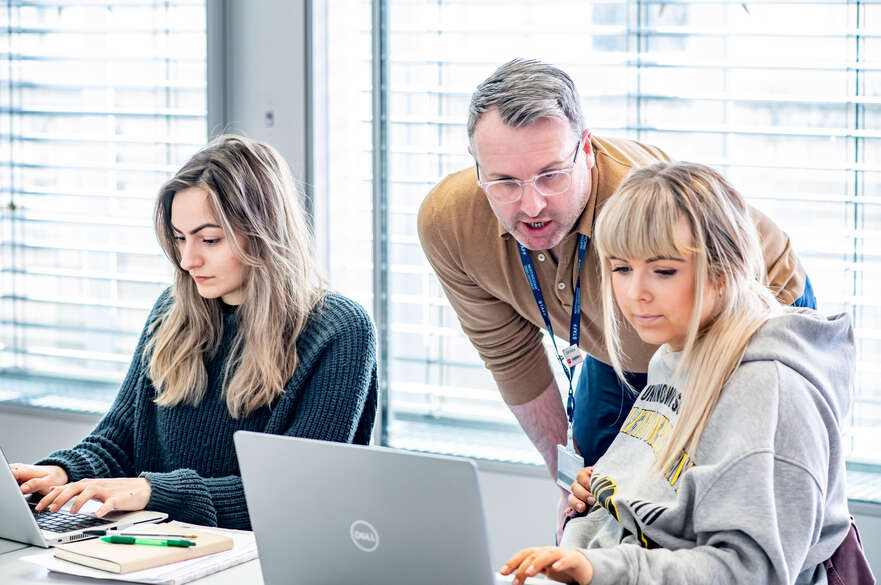

Make sure you state which of the projects you are choosing to apply for. Your statement should be concise, with your key points clearly emphasised and detailed. This will help you make a strong impression on the application panel.
Your proposal should provide an outline that demonstrates your understanding of the research project you are applying for, its goals and potential impact, and the approach that you would take as a doctoral candidate. Demonstrate your knowledge of the field and current academic work on the topic and outline what sort of methodology you would choose.
For example, what do you think would be the best way to collect data for the project, and why? Include any potential avenues you would pursue, sharing the project’s research outcomes and possible long-term impacts you could facilitate. Make sure that your proposal has a clear plan for undertaking the research in the proposed timeframe. Your potential supervisor may be able to offer guidance on this.
The statement should be 1500 words, not including any references or appendices.
Personal statements for Professional Doctorates
The researcher is at the heart of any research project - what is about this research that inspires you? Does your personal or professional background give you a unique insight?
Your personal statement should be a snapshot of you as an individual, your professional identity and your experience. The purpose is to demonstrate to the panel that you have the potential to be an excellent researcher and that you are the right person for your proposed project.
Ready to apply?
When you’ve thought about your proposal, the next step is to submit your application. Read our guide on how to apply.

School of Social Sciences
How to write a research proposal
You will need to submit a research proposal with your PhD application. This is crucial in the assessment of your application and it warrants plenty of time and energy.
Your proposal should outline your project and be around 1,500 words.
Your research proposal should include a working title for your project.
Overview of the research
In this section, you should provide a short overview of your research. You should also state how your research fits into the research priorities of your particular subject area.
Here you can refer to the research areas and priorities of a particular research grouping or supervisor.
You must also state precisely why you have chosen to apply to the discipline area and how your research links into our overall profile.
Positioning of the research
This should reference the most important texts related to the research, demonstrate your understanding of the research issues, and identify existing gaps (both theoretical and practical) that the research is intended to address.
Research design and methodology
This section should identify the information that is necessary to carry out the analysis and the possible research techniques that could deliver the information.
Ethical considerations
You should identify and address any potential ethical considerations in relation to your proposed research. Please discuss your research with your proposed supervisor to see how best to progress your ideas in line with University of Manchester ethics guidance, and ensure that your proposed supervisor is happy for you to proceed with your application.
Your research proposal will be used to assess the quality and originality of your ideas, whether you are able to think critically and whether you have a grasp of the relevant literature. It also gives us important information about the perspectives you intend to take on your research area, and how you fit into the department's research profile overall. This is helpful when assigning a supervisor.
If you are applying to study an Economics postgraduate research programme, our advice and requirements are slightly different:
- How to write an economics proposal
Supervisors
We encourage you to discuss your proposal informally with a potential supervisor before making a formal application to ensure it is of mutual interest.
Please note that we cannot guarantee that we will be able to allocate you to the supervisor you initially contact and that we may allocate you to another expert in the area.
- Find a supervisor
Flexibility
You will not be forced to follow the proposal exactly once you have started to study. It is normal for students to refine their original proposal, in light of detailed literature review, further consideration of research approaches and comments received from your supervisors (and other academic staff).
Pitfalls to avoid
We sometimes have to reject students who meet the academic requirements but have not produced a satisfactory research proposal, therefore:
- Make sure that your research idea, question or problem is very clearly stated and well-grounded in academic research.
- Make sure that your proposal is well focused and conforms exactly to the submission requirements described here.
- Poorly specified, jargon-filled or rambling proposals will not convince us that you have a clear idea of what you want to do.
The University uses electronic systems to detect plagiarism and other forms of academic malpractice and for assessment. All Humanities PhD programmes require the submission of a research proposal as part of the application process. The Doctoral Academy upholds the principle that where a candidate approaches the University with a project of study, this should be original. While it is understandable that research may arise out of previous studies, it is vital that your research proposal is not the subject of plagiarism.
Example proposals
- Philosophy - Example 1
- Philosophy - Example 2
- Politics - Example 1
- Politics - Example 2
- Social Anthropology - Example 1
- Social Anthropology - Example 2
- Social Statistics - Example 1
- Social Statistics - Example 2
- Sociology - Example 1
- Sociology - Example 2
Further help
The following books may help you to prepare your research proposal (as well as in doing your research degree).
- Bell, J. (1999): Doing Your Research Project: A Guide for First-time Researchers in Education & Social Science , (Oxford University Press, Oxford).
- Baxter, L, Hughes, C. and Tight, M. (2001): How to Research , (Open University Press, Milton Keynes).
- Cryer, P. (2000): The Research Student's Guide to Success , (Open University, Milton Keynes).
- Delamont, S., Atkinson, P. and Parry, O. (1997): Supervising the PhD , (Open University Press, Milton Keynes).
- Philips, E. and Pugh, D. (2005): How to get a PhD: A Handbook for Students and their Supervisors , (Open University Press, Milton Keynes).
If you need help and advice about your application, contact the Postgraduate Admissions Team.
Admissions contacts
University guidelines
You may also find it useful to read the advice and guidance on the University website about writing a proposal for your research degree application.
Visit the University website
Imperial College London Imperial College London
Latest news.

Neutrino discoveries and academic awards for excellence: News from Imperial

Imperial joins European discussion on accelerating innovation

Imperial to strengthen Transatlantic tech cooperation with new hub
- Postgraduate doctoral
- Application process
Writing a research proposal
If your supervisor asks you to formalise your idea as a research proposal (this is not always a requirement) this needs to define a clear research question.
You should also be prepared to explain how this contributes to and develops (or challenges) any existing theories in the field.
It’s important to tailor your proposal to the department you’re applying to.
Different departments may also have different format requirements (e.g. word limit, content) so it’s important to discuss these with your potential supervisor in advance.
For more general advice on how to write a good proposal, see FindaPhd.com .
- Postgraduate
Research degrees
- Examples of Research proposals
- Find a course
- Accessibility
Examples of research proposals
How to write your research proposal, with examples of good proposals.

Research proposals
Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use.
We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
In your proposal, please tell us if you have an interest in the work of a specific academic at York St John. You can get in touch with this academic to discuss your proposal. You can also speak to one of our Research Leads. There is a list of our Research Leads on the Apply page.
When you write your proposal you need to:
- Highlight how it is original or significant
- Explain how it will develop or challenge current knowledge of your subject
- Identify the importance of your research
- Show why you are the right person to do this research
- Research Proposal Example 1 (DOC, 49kB)
- Research Proposal Example 2 (DOC, 0.9MB)
- Research Proposal Example 3 (DOC, 55.5kB)
- Research Proposal Example 4 (DOC, 49.5kB)
Subject specific guidance
- Writing a Humanities PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- Writing a Creative Writing PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- About the University
- Our culture and values
- Academic schools
- Academic dates
- Press office
Our wider work
- Business support
- Work in the community
- Donate or support
Connect with us
York St John University
Lord Mayor’s Walk
01904 624 624
York St John London Campus
6th Floor Export Building
1 Clove Crescent
01904 876 944
- Policies and documents
- Module documents
- Programme specifications
- Quality gateway
- Admissions documents
- Access and Participation Plan
- Freedom of information
- Accessibility statement
- Modern slavery and human trafficking statement
© York St John University 2024
Colour Picker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Dui id ornare arcu odio.
Felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis ipsum. Et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Faucibus pulvinar elementum integer enim neque volutpat ac. Hac habitasse platea dictumst vestibulum rhoncus.
Nec ullamcorper sit amet risus nullam eget felis eget. Eget felis eget nunc lobortis mattis aliquam faucibus purus.
University of Bristol Law School
How to write a phd proposal.
We are delighted to consider applications for PhD research. We have a fantastic, diverse and energetic student body who are making the most of fabulous resources for postgraduate students. We welcome you to join us.
In order to help you with your application, the information below aims to give some guidance on how a typical research proposal might look.
Please be aware that if you are applying for ESRC funding then the proposal must be no longer than 1,300 words , and if you are applying for University of Bristol Postgraduate Research Scholarship then the proposal must be no longer than 1,000 words (incl. footnotes).
Your aim here is to showcase your ability to carry out postgraduate research. PhD research often travels and what you apply to study for may differ from your ultimate PhD. It is perfectly acceptable for research to move over time in response to findings or changes in preference/supervision.
Please note: we do not generally have the expertise to supervise PhD proposals that are exclusively in a jurisdiction outside UK, EU or international law. We have many expert supervisors in comparative, international and regional law but if your proposal is only to study the law in your home country, we may not be able to offer you supervision even if you meet the admission requirements.
Title. A short, indicative title is best.
Abstract. This is a succinct summary of your research proposal that will present a condensed outline, enabling the reader to get a very quick overview of your proposed project, lines of inquiry and possible outcomes. An abstract is often written last, after you have written the proposal and are able to summarise it effectively.
Rationale for the research project. This might include a description of the question/debate/phenomenon of interest, and the context(s) and situation in which you think the research will take place; an explanation of why the topic is of interest to you; and an outline of the reasons why the topic should be of interest to research and/ or practice (the 'so what?' question).
Issues and initial research question. What legal or governance question(s) do you intend to investigate? (This may be quite imprecise at the application stage); what might be some of the key literatures that might inform the issues (again, indicative at the application stage); and, as precisely as you can, what is the question you are trying to answer? A research proposal can and should make a positive and persuasive first impression and demonstrate your potential to become a good researcher. In particular, you need to demonstrate that you can think critically and analytically as well as communicate your ideas clearly.
Intended methodology. How do you think you might go about answering the question? At Bristol we supervise an incredibly wide range of PhDs, including doctrinal, theoretical, empirical, historical, comparative or policy-focused work. Even if your methods are, for example, doctrinal, please do make this clear and give some indication why you think this is the best methodology for your proposed study. If you have a key theorist in mind, do please outline this in your application, together with some understanding of any critiques that have been raised. If you are planning to do empirical work, do please give some indication of what your methods might be (quantitative (surveys, statistics etc); qualitative (interviews, ethnography etc)
Expected outcomes and impact. How do you think the research might add to existing knowledge; what might it enable organisations or interested parties to do differently? Increasingly in academia (and this is particularly so for ESRC-funded studentships) PhD students are being asked to consider how their research might contribute to both academic impact and/or economic and societal impact . This is well explained on the ESRC website if you would like to find out more.
Timetable. What is your initial estimation of the timetable of the dissertation? When will each of the key stages start and finish (refining proposal; literature review; developing research methods; fieldwork; analysis; writing the draft; final submission). There are likely to overlaps between the stages.
Why Bristol? Why –specifically - do you want to study for your PhD at Bristol? How would you fit into our research themes and research culture (please see the ’10 reasons to study for a PhD at Bristol’ section on the website for more information). You do not need to identify supervisors at the application stage.
Bibliography. Do make sure that you cite what you see as the key readings in the field. This does not have to be comprehensive but you are illustrating the range of sources you might use in your research.
Scholarships
A number of scholarships are available to study for a PhD at Bristol. You can see more information regarding scholarships on our fees and funding page. If you have any questions about which scholarship to apply for and how your research might fit in please contact the PGR Director, Yvette Russell [email protected] .
Tips on writing a successful application
- School of Law
- Postgraduate
Writing a PhD research proposal
The following guidance has been compiled to help you submit a high quality application that is targeted to the research strengths of The School of Law.

Choosing a research topic
PhDs are supposed to contain an element of originality and innovation. Originality need not mean that you explore a wholly new concept. For instance, it might also include applying new methods or new theories to existing scholarship on the topic. They also need to be backed up by logically reasoned evidence and argument – whether that is provided by theoretical or empirical sources.
The types of thesis that could be constructed:
An analysis of a specific area of law or criminology on which there is no significant existing literature. The lack of existing literature may be explained by the relative newness of the body of law and/or creation of institutions; or the previous lack of attention given to the practical impact of the chosen area of study. A thesis in this area might attempt to describe, explain and rationalise the development of this particular area of law and/ or critically analyse the content of the legal system being researched.
An analysis applying, analysing, or evaluating existing studies in a new context. For instance, one might extend a study of one jurisdiction to another, providing comparative evidence that tests the applicability of existing research and enables the existing theory to be challenged, reconsidered, or expanded upon.
An empirical study of an area of law or criminology where there is existing doctrinal, conceptual, or theoretical literature, but limited empirical evidence to test those doctrines, concepts, or theories. Such an empirical study would still require a degree of originality but would be academically interesting if it offers a view of the area of study not previously attempted and/or allowed for an appraisal of the effectiveness of the law as it currently stands and is organised.
An in-depth critical study of a specific aspect of law or criminology. Such an examination may consist solely or mainly of library based or theoretical work, or include an element of socio-legal research. As well as recognising existing literature, such an approach needs to make clear how this project would build on and add to that work. The answer may be that the area of law or criminology has evolved or the work itself takes a very different approach to analysing the problem.
Before drafting a research proposal it is a good idea to consult with any academic contacts you already have for their feedback.
The Research Proposal
Applications must include an outline research proposal. If a proposal is submitted without a proposal it will be automatically rejected.
The application asks you to give a description of your research project, including the research questions to be addressed, the methodology to be used, the sources to be consulted and a brief timetable. Your proposal should be included in the application as a separate attachment, and distinguished from your supporting statement (if you include one).
There is no set format or page length for proposals, although to keep the proposal concise and clear while still providing enough information, we recommend limiting yourself to 1,500-2,500 words. Within your application it is useful to identify and bear in mind some or all of the following points:
It is important that you demonstrate clearly the area that you intend to research and provide some indication that you are already knowledgeable in the area that you intend to research. This can be achieved through suitable references and/or by supplying a bibliography to support your application.
Research is about more than collating knowledge already in the public domain. Within your application you should indicate how you intend to add to the knowledge that you will be uncovering. Examples of potential aims include: adding to existing theory; disproving previous understandings; a critique of the current legal position; a defended positive/negative prognosis of the impact of a new legal provision; new empirically obtained findings. You may find it helpful to express your research aims as questions to be answered, or as aims to fulfil by doing the research. Try to limit the number of aims of your study as much as possible.
A research application is more likely to be accepted if you can demonstrate that it has relevance and academic merit. Ultimately PhDs are awarded where a piece of work can demonstrate some originality and innovation. This should be explained within your application.
It is rare for an entirely original piece of research to be written. Therefore, the links with existing research should be made clear, as should the possibilities your work might open up for future research. You should provide some background to the research, exploring the wider literature and making as clear as possible what makes your proposed research original in the context of that literature.
In other words, how do you intend to undertake the research? Methods may include reviewing library-based resources or empirical research. If the latter, then what form – e.g. quantitative or qualitative analysis, and what evidence can you provide that you have the skills to undertake such research. These methods should be carefully considered in relation to the research aims and questions you are seeking to address in the proposed research.
You must consider the partnerships, knowledge exchange and impacts associated with your proposed research. If you already have collaborative arrangements in place with relevant external stakeholders then you should describe these and potentially also provide letters of support, in principle, if you have them. You should consider the likely impacts of your proposed research and how these will be achieved, as well as your plans for disseminating your research findings beyond academia.
If you are applying for WRDTP or WRoCAH scholarships, it is essential that you consider how your proposed research fits in with the research pathways or clusters of these two funders. The quality of your scholarship application will be judged partly by the fit of your research within these pathways or clusters.
Your application should not be too unrealistic as to what can be delivered. It is also wise to predict the likely challenges that you will face in undertaking the research and suggest ways in which those challenges can be overcome.
What to avoid
Research proposals should not be viewed as binding contracts. Most first-year PhD students adapt their research proposal once they start studying the topic in more depth and working with their supervisor. Nevertheless, a PhD proposal should amount to a coherent, intelligent, realistic and relatively well thought-out idea of an area of potential research.
The following errors should be avoided if possible:
Simplistic descriptions of an area of study should be avoided – eg ‘I want to research EU law’. The specific focus of the research must be clear.
Offer to review or analyse an area of law on which there is already a significant existing literature. PhDs should be attempting something more than bringing together knowledge that already exists.
Develop a research proposal primarily because the topic is or has been fashionable. Topics such as the legality of the war in Iraq, the operation of the International Criminal Court or the Human Rights Act 1998 remain extremely important areas of academic study, but as a PhD student it is going to be very difficult to say anything interesting, new or original about these topics.
Avoid trying to resolve grand problems in one thesis. The best research proposals tend to focus on discrete and well-confined subject areas.
Relying upon a comparison to provide the intellectual component of the proposal, whether that is a comparison between different institutions, different bodies of law or different countries. Comparative research proposals are worthy if properly thought out. If the comparison is between different legal systems for instance, in the submission it needs to be made clear why that comparison could be a useful one and what can be learnt from the comparison. For instance, you may be undertaking research in the UK and from Botswana, but that does not mean that there are any valid reasons why comparing the UK to Botswana is actually worthwhile in your subject area.
Relatedly, you should consider the research expertise of supervisors at the University of Sheffield, and the value that studying at Sheffield adds to your research. Generally a PhD submitted in a UK university should contribute to knowledge about the UK, or about global/international issues. If you want to research another country of jurisdiction, you need to provide a credible reason for why Sheffield is a good place to undertake that study, as opposed to an institution in that country.
Make sure that your methodology is as clear and specific as you can make it at this early stage. Proposals that say, “I will use qualitative methods” are unlikely to succeed because they suggest an ignorance of the diversity of qualitative methods. Ideally, you should be able to say something about:
the methods you will use (e.g. surveys, documentary analysis, interviews, observation, ethnography, audio-visual methods...);
the target populations of your research (eg, a study of criminal courts might seek to recruit judges, lawyers, ushers, defendants, police officers, or other actors. Which groups do you want to participate in your research, and why? The answer to this question should bear some relation to your research aims); and,
If possible, the approximate number of participants you want to recruit for each method (for instance, you might want to conduct 10-15 interviews with each of two groups of participants, or to survey 500 people) and how they will be accessed/recruited. Try to be realistic about how long empirical research takes, and how many research participants it is possible to study.
How these chosen methods are likely to illuminate the research questions of the proposed research
Ethical considerations of the research in relation to things like informed consent, anonymity, the safeguarding of researchers and participants
It may not be possible to say much at this stage, but the more details you can provide, the clearer it will be that you have thought seriously about your research project, and the easier it will be for the School of Law to evaluate its feasibility.
Positive steps to take
When we make an offer we will do so on the basis of various considerations. Making an effort to foreshadow those considerations in your application is a good idea. It is advisable to submit a supporting statement alongside the research proposal. Issues to consider include:
Why did you choose to apply to the University of Sheffield?
Can you provide any evidence to suggest that you are capable of completing an extensive piece of research and have the character to undertake three years of study, on a relatively low income and with only supervisory support?
Does the research proposal fit into one of the areas in which the Law School has a speciality ? Often a proposal only needs minor adaptation to fall within an area the School can supervise, but to improve your chances of success it is worthwhile reviewing the academic profile of the various staff in the Law School before you submit an application.
If you are able, it would be helpful to have a look at some past PhD theses in your own area of interest which have been successfully submitted at a UK university. Most UK universities have copies in the library of all past successful PhDs, either as physical copies or in an online repository.
The online application form requires you to provide some standard information about yourself and your past academic performance. Please ensure that this information is correct and that you provide evidence to support your qualifications.
The references that your referees provide are important sources of information for us. Wherever possible, it is helpful to provide (where possible) a reference from at least one academic who is aware of your research potential and has read some of your work.
Search for PhD opportunities at Sheffield and be part of our world-leading research.
Department of Politics and International Relations
University | A to Z | Departments
- Politics and International Relations
- PhD research proposal
- Undergraduate study
- Postgraduate taught degrees
- PhD in Politics
- PhD in Politics Distance Learning
- PhD in Environment and Politics
- PhD in Global Development
- Fees and funding
- How to apply
- Training and facilities
- Postgraduate Research studentships
- About our research
- Research - Information for Staff (login required)
- News & events
- Current students
- Careers and Student Employability
- International students
- Equality, Diversity and Inclusion
- Wellbeing, welfare and support
Writing a research proposal

The research proposal is the main way in which we evaluate the quality of your research plans. You should aim to make your proposal about 1500-2000 words long.
Your proposal should include the following:
The title indicates the overall question or topic of the PhD. It should include any key concepts, empirical focus, or lines of inquiry that you aim to pursue, and it should be concise and descriptive. You can normally discuss changes in the title with your supervisor(s) should you be successful but it is important to try to choose a clear and engaging title.
Research questions
What are the questions or problems for politics or international relations that you are trying to understand and solve? In explaining these, it will be helpful to spell out what else we need to know in order to understand why you are framing the problem this way.
Research aims
In answering these questions, what will your research project do? What will it shed light on or help us to understand that we don’t really understand better?
Contribution
Why this project? Explain why your project is interesting, what its broader implications are, and – if you think this is relevant – why you are particularly well placed to tackle it. It is also valuable to reflect on who has worked on the topic before and to provide a brief literature review. Are there any good approaches to the topic, or particular articles or books, that you are drawing on or bad ones you want to push back against?
What are the sources you plan to use to answer your research questions? These will vary according to the nature of your research but may include study of particular texts, interviews, published or unpublished data, archival or policy documents, or field site visits, among others. Try to be as specific as you can and assess the possibility of access to relevant sources.
This includes thinking about the research methods you will use to analyse empirical sources (e.g., sampling, survey or interview design, data collection, discourse analysis) but may also include setting out the kind of theoretical framework you will employ or your approach to history or political ideas. What prior knowledge and skills do you bring to the project? What extra training may you need?
Structure and timetable
Include a provisional chapter structure and timetable to completion, covering the three years of the full-time programme or six years of the part-time programme, as appropriate.
To help you with your application here are some examples of PhD proposals which were successful in obtaining funding: PhD sample research proposal 1 (PDF , 96kb) PhD sample research proposal 2 (PDF , 79kb) PhD sample research proposal 3 (PDF , 197kb)
Apply for a PhD now
Department of Politics and International Relations University of York , York , YO10 5DD , UK Tel: work +44 (0) 1904 323542 | Fax: fax 01904 323563
Legal statements | Privacy | Cookies | Accessibility © University of York | Modify | Direct Edit
Browser does not support script.
Go to…
- Undergraduate
- Our students
- Postgraduate
- PhD research
- Publications
- Research Centres and Groups
- Our connections
- Student societies
EIS PhD Research Proposal Guidelines
The research proposal is the most important part of your PhD application. We do not expect the proposal to be perfect at this stage, nor do we expect you to stick to it rigidly, as your ideas will almost certainly change once you start to study. However, we do expect it to show convincing evidence of your ability to plan and organise independent research. Please read and follow the guidelines carefully.
Your proposal should be 2,000-3,000 words long , plus bibliography, using the following sections:
- Title – The best titles are simple and descriptive, identifying the topic and approach that will be taken.
- Central research question and objectives – The question your research seeks to answer should be stated simply, then fleshed out to show to show why it is timely and important – both intellectually and politically – for you to be writing a PhD on this topic. After that, you should state, in straightforward terms, how the PhD will answer the research question.
- Literature review – Here you must show how your central research question relates to existing academic studies in your field. This requires a short literature review which will situate your proposed research within the framework of the dominant perspectives on similar issues in the existing literature. Ideally, you should be able to demonstrate how your proposed research fills a gap in the literature and therefore adds substantively and can make a lasting contribution to academic debates. One key criterion for writing a successful PhD is that it is original work, so you must try to avoid setting up your analysis in a way which simply replicates work which can already be found within the literature.
- Theoretical framework – Here, you should detail what theoretical framework(s) will underpin the analysis in your PhD, why that framework has been chosen, and what advantages it gives you for addressing your central research question.
- Case studies and methodology – Here, you should discuss the type of empirical research (statistical work, interviews, surveys etc.) that you will be doing and the case study/case studies that you have chosen. This is essential in all cases except for abstract political theory PhDs. You should show how your theoretical framework informs the methodology that you will use and why that methodology is particularly advantageous for answering the research question.
- Problems – Here, you should reflect on any problems you think you may encounter whilst undertaking your research and indicate how they might be overcome or mitigated. These might include, for example, access to data.
- Bibliography – You should include a complete bibliography for the proposal.
The above draws on the advice issued by the Political and International Studies department at Warwick University.
- View all courses
- Taught postgraduate study
- Postgraduate taught degree courses
- Postgraduate taught tuition fees
- Pre-masters for international students
- Funding your postgraduate taught studies
- How to apply for a postgraduate taught degree
- Postgraduate offer holders - prepare for your studies
- Pre-sessional English courses
- PhDs and research degrees
- Create your own research project
- Find a PhD project
- Funding your research degree
- How to apply for a PhD or research degree
- How to make a PhD enquiry
- Support while studying your PhD or research degree
- Exchanges and studying abroad
- Undergraduate study
- Undergraduate degree courses
- Foundation year programmes
- Undergraduate tuition fees
- Customise your degree
- Funding undergraduate studies
- How to apply
- Tuition fees and funding
- Short courses
- Lunchtime evening and weekend courses
- Summer schools
- Get a prospectus
- Student life
- Accommodation
- Choose your halls of residence
- Apply for accommodation
- Guaranteed accommodation
- Your accommodation options
- Accommodation for those with additional requirements
- International and pre-sessional students
- Postgraduate accommodation
- Couples and students with children
- Renting privately
- Our accommodation areas
- Privacy notice
- Terms and conditions
- Fees and contracts
- Southampton
- Sports and gyms
- Sports facilities
- Sports clubs
- Watersports centres
- Our campuses
- Avenue Campus
- Boldrewood Innovation Campus
- City Centre Campus
- Highfield Campus
- University Hospital Southampton
- Waterfront Campus
- Winchester Campus
- Join our student community
- What's on
- Clubs and societies
- Sports teams
- SUSU places
- Representing you
- SUSU support and advice
- Support and money
- Living costs
- Academic and mental health support
- Support for disabled students
- Part-time work
- Health services
- Research projects
- Research areas
- Research facilities
- Collaborate with us
- Institutes, centres and groups
- Support for researchers
- Faculties, schools and departments
- Research jobs
- Find people and expertise
- Why work with us?
- Collaboration
- Consultancy
- Commercialisation
- Use our facilities
- Connect with our students
- How we operate
- Make a business enquiry
- International students
- International Office
- Partnerships and initiatives
- Visiting delegations
- Visiting fellowships
- University of Southampton Delhi
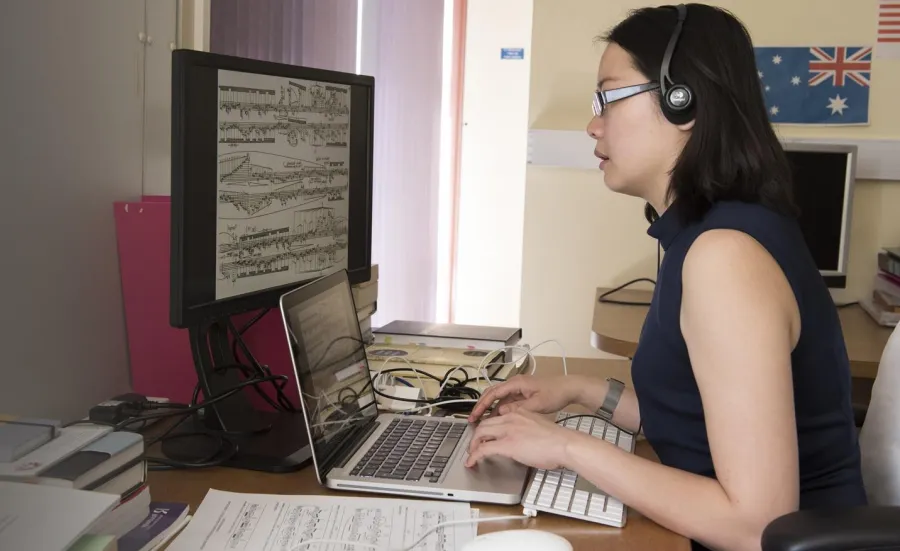

Create your own research proposal
A research proposal is a short document that summarises the research you want to undertake. If you cannot find a suitable advertised project, this is a route to create your own.
When creating a research proposal, you’ll need to consider the question or issue you want to address with your project. Think about the background of the subject and how your research will be an original contribution to the field. You’ll also need to think about the methods you'll use to conduct this research. Your proposal helps us assess your suitability for a research degree and decide if we can offer you the right supervision.
Preparation
You may want to make contact with 1 or more potential supervisors to discuss project ideas. They may also be able to help with funding your degree .
You can search our academics to find a supervisor whose research interests align to yours. When you find a match, contact them to discuss your proposals. Allow time for responses and to consider their feedback.
Learn how to make a supervisor enquiry
Writing your research proposal
You should keep it clear, objective and realistic. Include:
- an outline of your research interests
- your initial thoughts about your topic
- clear objectives of what you aim to achieve or the question you want to address
- references to previous work
- why the research is relevant and original
- your proposed method and general approach
- why you believe the research should be funded
- how your skills will help to conduct the research
- any training you may need to undertake the project
How to structure your proposal
Your research proposal should include:
- a working title for your project
- up to 1,500 words (excluding a bibliography)
It’s best to write with short paragraphs and sentences. You can use images and diagrams if it’s appropriate.
Example structure:
- introduction statement (200 words)
- your background reading and the area you want to contribute to (400 words)
- your research question or issue to investigate (200 words)
- data sources, research methods and critical approaches to use (500 words)
- conclusion on how your project will contribute to the field (200 words)
- bibliography
Submit your proposal
Your potential supervisor will inform you of when to start the application process and how to include the details of your agreed project.
More about how to apply
- Course modules
- Acoustical engineering
- Biomedical and medical engineering
- Civil engineering
- Every day I’m completely immersed in an environment that’s creative in all aspects
- Everything I learn feels so relevant, even If it’s a subject rooted in the past
- Maritime engineering
- Photonics and optoelectronics
- Social statistics and demography
- A missing link between continental shelves and the deep sea: Have we underestimated the importance of land-detached canyons?
- A seismic study of the continent-ocean transition southwest of the UK
- A study of rolling contact fatigue in electric vehicles (EVs)
- Acoustic monitoring of forest exploitation to establish community perspectives of sustainable hunting
- Acoustic sensing and characterisation of soil organic matter
- Advancing intersectional geographies of diaspora-led development in times of multiple crises
- Aero engine fan wake turbulence – Simulation and wind tunnel experiments
- Against Climate Change (DACC): improving the estimates of forest fire smoke emissions
- All-in-one Mars in-situ resource utilisation (ISRU) system and life-supporting using non-thermal plasma
- An electromagnetic study of the continent-ocean transition southwest of the UK
- An investigation of the relationship between health, home and law in the context of poor and precarious housing, and complex and advanced illness
- Antibiotic resistance genes in chalk streams
- Being autistic in care: Understanding differences in care experiences including breakdowns in placements for autistic and non-autistic children
- Biogeochemical cycling in the critical coastal zone: Developing novel methods to make reliable measurements of geochemical fluxes in permeable sediments
- Bloom and bust: seasonal cycles of phytoplankton and carbon flux
- British Black Lives Matter: The emergence of a modern civil rights movement
- Building physics for low carbon comfort using artificial intelligence
- Building-resolved large-eddy simulations of wind and dispersion over a city scale urban area
- Business studies and management: accounting
- Business studies and management: banking and finance
- Business studies and management: decision analytics and risk
- Business studies and management: digital and data driven marketing
- Business studies and management: human resources (HR) management and organisational behaviour
- Business studies and management: strategy, innovation and entrepreneurship
- Carbon storage in reactive rock systems: determining the coupling of geo-chemo-mechanical processes in reactive transport
- Cascading hazards from the largest volcanic eruption in over a century: What happened when Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai erupted in January 2022?
- Characterisation of cast austenitic stainless steels using ultrasonic backscatter and artificial intelligence
- Climate Change effects on the developmental physiology of the small-spotted catshark
- Climate at the time of the Human settlement of the Eastern Pacific
- Collaborative privacy in data marketplaces
- Compatibility of climate and biodiversity targets under future land use change
- Cost of living in modern and fossil animals
- Creative clusters in rural, coastal and post-industrial towns
- Deep oceanic convection: the outsized role of small-scale processes
- Defect categories and their realisation in supersymmetric gauge theory
- Defining the Marine Fisheries-Energy-Environment Nexus: Learning from shocks to enhance natural resource resilience
- Design and fabrication of next generation optical fibres
- Developing a practical application of unmanned aerial vehicle technologies for conservation research and monitoring of endangered wildlife
- Development and evolution of animal biomineral skeletons
- Development of all-in-one in-situ resource utilisation system for crewed Mars exploration missions
- Ecological role of offshore artificial structures
- Effect of embankment and subgrade weathering on railway track performance
- Efficient ‘whole-life’ anchoring systems for offshore floating renewables
- Electrochemical sensing of the sea surface microlayer
- Engagement with nature among children from minority ethnic backgrounds
- Enhancing UAV manoeuvres and control using distributed sensor arrays
- Ensuring the Safety and Security of Autonomous Cyber-Physical Systems
- Environmental and genetic determinants of Brassica crop damage by the agricultural pest Diamondback moth
- Estimating marine mammal abundance and distribution from passive acoustic and biotelemetry data
- Evolution of symbiosis in a warmer world
- Examining evolutionary loss of calcification in coccolithophores
- Explainable AI (XAI) for health
- Explaining process, pattern and dynamics of marine predator hotspots in the Southern Ocean
- Exploring dynamics of natural capital in coastal barrier systems
- Exploring the mechanisms of microplastics incorporation and their influence on the functioning of coral holobionts
- Exploring the potential electrical activity of gut for healthcare and wellbeing
- Exploring the trans-local nature of cultural scene
- Facilitating forest restoration sustainability of tropical swidden agriculture
- Faulting, fluids and geohazards within subduction zone forearcs
- Faulting, magmatism and fluid flow during volcanic rifting in East Africa
- Fingerprinting environmental releases from nuclear facilities
- Flexible hybrid thermoelectric materials for wearable energy harvesting
- Floating hydrokinetic power converter
- Glacial sedimentology associated subglacial hydrology
- Green and sustainable Internet of Things
- How do antimicrobial peptides alter T cell cytokine production?
- How do calcifying marine organisms grow? Determining the role of non-classical precipitation processes in biogenic marine calcite formation
- How do neutrophils alter T cell metabolism?
- How well can we predict future changes in biodiversity using machine learning?
- Hydrant dynamics for acoustic leak detection in water pipes
- If ‘Black Lives Matter’, do ‘Asian Lives Matter’ too? Impact trajectories of organisation activism on wellbeing of ethnic minority communities
- Illuminating luciferin bioluminescence in dinoflagellates
- Imaging quantum materials with an XFEL
- Impact of neuromodulating drugs on gut microbiome homeostasis
- Impact of pharmaceuticals in the marine environment in a changing world
- Impacts of environmental change on coastal habitat restoration
- Improving subsea navigation using environment observations for long term autonomy
- Information theoretic methods for sensor management
- Installation effect on the noise of small high speed fans
- Integrated earth observation mapping change land sea
- Interconnections of past greenhouse climates
- Investigating IgG cell depletion mechanisms
- Is ocean mixing upside down? How mixing processes drive upwelling in a deep-ocean basin
- Landing gear aerodynamics and aeroacoustics
- Lightweight gas storage: real-world strategies for the hydrogen economy
- Long-term change in the benthos – creating robust data from varying camera systems
- Machine learning for multi-robot perception
- Marine ecosystem responses to past climate change and its oceanographic impacts
- Mechanical effects in the surf zone - in situ electrochemical sensing
- Microfluidic cell isolation systems for sepsis
- Migrant entrepreneurship, gender and generation: context and family dynamics in small town Britain
- Miniaturisation in fishes: evolutionary and ecological perspectives
- Modelling high-power fibre laser and amplifier stability
- Modelling soil dewatering and recharge for cost-effective and climate resilient infrastructure
- Modelling the evolution of adaptive responses to climate change across spatial landscapes
- Nanomaterials sensors for biomedicine and/or the environment
- New high-resolution observations of ocean surface current and winds from innovative airborne and satellite measurements
- New perspectives on ocean photosynthesis
- Novel methods of detecting carbon cycling pathways in lakes and their impact on ecosystem change
- Novel technologies for cyber-physical security
- Novel transparent conducting films with unusual optoelectronic properties
- Novel wavelength fibre lasers for industrial applications
- Ocean circulation and the Southern Ocean carbon sink
- Ocean influence on recent climate extremes
- Ocean methane sensing using novel surface plasmon resonance technology
- Ocean physics and ecology: can robots disentangle the mix?
- Ocean-based Carbon Dioxide Removal: Assessing the utility of coastal enhanced weathering
- Offshore renewable energy (ORE) foundations on rock seabeds: advancing design through analogue testing and modelling
- Optical fibre sensing for acoustic leak detection in buried pipelines
- Optimal energy transfer in nonlinear systems
- Optimizing machine learning for embedded systems
- Oxidation of fossil organic matter as a source of atmospheric CO2
- Partnership dissolution and re-formation in later life among individuals from minority ethnic communities in the UK
- Personalized multimodal human-robot interactions
- Preventing disease by enhancing the cleaning power of domestic water taps using sound
- Quantifying riparian vegetation dynamics and flow interactions for Nature Based Solutions using novel environmental sensing techniques
- Quantifying the response and sensitivity of tropical forest carbon sinks to various drivers
- Quantifying variability in phytoplankton electron requirements for carbon fixation
- Resilient and sustainable steel-framed building structures
- Resolving Antarctic meltwater events in Southern Ocean marine sediments and exploring their significance using climate models
- Robust acoustic leak detection in water pipes using contact sound guides
- Silicon synapses for artificial intelligence hardware
- Smart photon delivery via reconfigurable optical fibres
- The Gulf Stream control of the North Atlantic carbon sink
- The Mayflower Studentship: a prestigious fully funded PhD studentship in bioscience
- The calming effect of group living in social fishes
- The duration of ridge flank hydrothermal exchange and its role in global biogeochemical cycles
- The evolution of symmetry in echinoderms
- The impact of early life stress on neuronal enhancer function
- The oceanic fingerprints on changing monsoons over South and Southeast Asia
- The role of iron in nitrogen fixation and photosynthesis in changing polar oceans
- The role of singlet oxygen signaling in plant responses to heat and drought stress
- Time variability on turbulent mixing of heat around melting ice in the West Antarctic
- Triggers and Feedbacks of Climate Tipping Points
- Uncovering the drivers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progression using patient derived organoids
- Understanding recent land-use change in Snowdonia to plan a sustainable future for uplands: integrating palaeoecology and conservation practice
- Understanding the role of cell motility in resource acquisition by marine phytoplankton
- Understanding the structure and engagement of personal networks that support older people with complex care needs in marginalised communities and their ability to adapt to increasingly ‘digitalised’ health and social care
- Unpicking the Anthropocene in the Hawaiian Archipelago
- Unraveling oceanic multi-element cycles using single cell ionomics
- Unravelling southwest Indian Ocean biological productivity and physics: a machine learning approach
- Using acoustics to monitor how small cracks develop into bursts in pipelines
- Using machine learning to improve predictions of ocean carbon storage by marine life
- Vulnerability of low-lying coastal transportation networks to natural hazards
- Wideband fibre optical parametric amplifiers for Space Division Multiplexing technology
- Will it stick? Exploring the role of turbulence and biological glues on ocean carbon storage
- X-ray imaging and property characterisation of porous materials
- Postgraduate Taught Diversity Scholarship (Environmental and Life Sciences)
- Southampton Business School Postgraduate UK Scholarship
- Southampton Genomics Talent Scholarship
- Southampton History Patricia Mather and Helen Patterson Scholarship
- Southampton MA Holocaust scholarships
- Southampton Philosophy David Humphris-Norman Scholarship
- Southampton UK Alumni Music Scholarship
- The National Institute for Health and care Research South Central INSIGHT Programme
- Winchester School of Art Progression Scholarship
- Southampton Physics and Astronomy Achievement Scholarship
- GREAT Scholarships 2024 – Greece
- Engineering Excellence Scholarship
- Winchester School of Art Postgraduate Global Talent Scholarship
- Engineering Global Talent Scholarship
- Southampton University Corporate Civil Engineering Scholarship Scheme
- Merit scholarships for international postgraduates
- Merit scholarships for international undergraduates
- Scholarships, awards and funding opportunities
- Becas Chile Scholarship
- Chevening Scholarships
- China Scholarship Council Scholarships
- COLFUTURO Scholarships
- Commonwealth Distance Learning Scholarships
- Commonwealth Master's Scholarships
- Commonwealth PhD Scholarships
- Commonwealth PhD Scholarships for high income countries
- Commonwealth Shared Scholarships
- Commonwealth Split-Site Scholarships
- FIDERH Scholarships
- Fulbright Awards
- FUNED Scholarships
- Great Scholarships 2024 – India
- Great Scholarships 2024 – Bangladesh
- Great Scholarships 2024 – Mexico
- Great Scholarships 2024 – Nigeria
- Marshall Scholarship
- Saïd Foundation Scholarships
- British Council Scholarships for Women in STEM
- Xiamen University PhD Scholarships
- GREAT scholarships for justice and law 2024 – Indonesia
- Scholarship terms and conditions
- Southampton Education Civic Scholarship
- Southampton Ageing and Gerontology Talent Scholarship
- Southampton Canadian Prestige Scholarship for Law
- Southampton Presidential International Scholarship
- Continuing professional development
- Archers Road
- City Gateway
- Erasmus Park
- Highfield Hall
- Orion Point
- Wessex Lane
- Cancer Sciences Protein Facility
- Geotechnical Centrifuge
- Maritime Robotics and Instrumentation Laboratory (MRIL)
- Active Living
- Advanced Fibre Applications
- Advanced Laser Laboratory
- Advanced Project Management Research Centre
- Antibody and Vaccine Group
- Astronomy Group
- Autism Community Research Network @ Southampton (ACoRNS)
- Bioarchaeology and Osteoarchaeology at Southampton (BOS)
- Bladder and Bowel Management
- Cell and Developmental Biology
- Centre for Defence and Security Research
- Centre for Developmental Origins of Health and Disease
- Centre for Digital Finance
- Centre for Eastern European and Eurasian Studies (CEEES)
- Centre for Empirical Research in Finance and Banking (CERFIB)
- Centre for Geometry, Topology, and Applications
- Centre for Global Englishes
- Centre for Global Health and Policy (GHaP)
- Centre for Health Technologies
- Centre for Healthcare Analytics
- Centre for Human Development, Stem Cells and Regeneration
- Centre for Imperial and Postcolonial Studies
- Centre for Inclusive and Sustainable Entrepreneurship and Innovation (CISEI)
- Centre for International Film Research (CIFR)
- Centre for International Law and Globalisation
- Centre for Internet of Things and Pervasive Systems
- Centre for Justice Studies
- Centre for Linguistics, Language Education and Acquisition Research
- Centre for Machine Intelligence
- Centre for Maritime Archaeology
- Centre for Medieval and Renaissance Culture (CMRC)
- Centre for Modern and Contemporary Writing (CMCW)
- Centre for Music Education and Social Justice
- Centre for Political Ethnography (CPE)
- Centre for Research in Accounting, Accountability and Governance
- Centre for Research on Work and Organisations
- Centre for Resilient Socio-Technical Systems
- Centre for Transnational Studies
- Child and Adolescent Research Group
- Clinical Ethics, Law and Society (CELS)
- Computational Nonlinear Optics
- Cyber Security Academy
- Data Science Group
- Digital Oceans
- EPSRC and MOD Centre for Doctoral Training in Complex Integrated Systems for Defence and Security
- Economic Theory and Experimental Economics
- Economy, Society and Governance
- Electrical Power Engineering
- Environmental Hydraulics
- Gas Photonics in Hollow Core Fibres
- Geochemistry
- Global Health (Demography)
- Global Health Community of Practice
- Gravity group
- Healthy Oceans
- High Power Fibre Lasers
- Hollow Core Fibre
- Human Genetics and Genomic Medicine
- Infrastructure Group
- Institute of Developmental Sciences
- Institute of Maritime Law (IML)
- Integrated Photonic Devices
- Integrative Molecular Phenotyping Centre
- Interdisciplinary Musculoskeletal Health
- International Centre for Ecohydraulics Research (ICER)
- Language Assessment and Testing Unit (LATU)
- Laser-Direct-Write (LDW) Technologies for Biomedical Applications
- Law and Technology Centre
- Long Term Conditions
- Magnetic Resonance
- Mathematical Modelling
- Medicines Management
- Molecular and Precision Biosciences
- Multiwavelength Accretion and Astronomical Transients
- National Biofilms Innovation Centre (NBIC)
- National Centre for Research Methods
- National Infrastructure Laboratory
- Nature-Based Ocean Solutions
- Nonlinear Semiconductor Photonics
- Ocean Perception Group
- Operational Research
- Optical Engineering and Quantum Photonics Group
- Paediatrics and Child Health - Clinical and Experimental Sciences
- People, Property, Community
- Photonic Systems, Circuits and Sensors Group
- Physical Optics
- Primary Care Research Centre
- Product Returns Research Group (PRRG)
- Quantum, Light and Matter Group
- Silica Fibre Fabrication
- Silicon Photonics
- Skin Sensing Research Group
- Southampton Centre for Nineteenth-Century Research
- Southampton Ethics Centre
- Southampton Health Technology Assessments Centre (SHTAC)
- Southampton High Energy Physics group
- Southampton Imaging
- Southampton Theory Astrophysics and Gravity (STAG) Research Centre
- Stefan Cross Centre for Women, Equality and Law
- String theory and holography
- The India Centre for Inclusive Growth and Sustainable Development
- The Parkes Institute
- Tony Davies High Voltage Laboratory
- Ultrafast X-ray Group
- Vision Science
- WSA Exchange
- Work Futures Research Centre (WFRC)
- Departments
Cookies on our website
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We'd like to set additional cookies to understand how you use our site so we can improve it for everyone. Also, we'd like to serve you some cookies set by other services to show you relevant content.
Writing your research proposal
Your proposal is your chance to tell us why you want to study your PhD at Sussex. Follow our guide to making your research proposal as strong as possible.
Your research proposal
If you are considering studying a PhD, there are two options available to you.
- apply for a funded PhD where you research a set project
- design your own research project, which you can either fund yourself, or apply for external funding.
If you decide to design your own research project, you need to write a research proposal which will form a central part of your PhD application.
Follow our step-by-step guide below to help you through the process of writing your research proposal.
Plan your research proposal
You should contact the relevant academic department before applying to Sussex and check if there are any additional requirements for your research proposal.
Even at this early stage, you may be asked questions regarding your research, and so you should start thinking about:
- the questions driving your research
- how your research makes 'an original contribution' to your field and how will you achieve this
- if your research provides new knowledge, or reinterprets existing ideas in an original way
- how you intend to do the research i.e. the methodology you'll use and how you'll structure your work
- how Sussex can aid you in your research and what you want to study here.
Ask for advice
If you need further advice you can contact our academic staff working in your field.
You can also ask research students and academic staff at your current university for help. It is good practice to discuss your ideas with others in your research area and use their suggestions to further your understanding and strengthen your proposal.
During this process you should start making detailed notes. You might also want to start planning your research proposal. If so, breaking it down into the traditional sections below may help you organise and manage your thoughts:
- introduction
- research background
- research methods
- bibliography.
Find a supervisor
Choosing the right supervisor is one of the most important steps towards a successful and rewarding PhD.
Before approaching a supervisor, you'll need to have a clear idea of the research you hope to undertake.
Once you have established a relationship with a potential supervisor, you can ask them to read the first draft of your research proposal. They can give you valuable feedback and help you refine your ideas before you submit your application.
Discover how to find a supervisor
Write your proposal
You may now be in a position to start writing your proposal. This is central to your final application.
A strong research proposal:
- formulates a precise, interesting research question
- establishes the relevance and value of the proposed research question in the context of current academic thinking
- describes the data or source material your research requires
- outlines a clear and practical methodology, which enables you to answer the research question
- states clearly what you hope to discover at the end of your research and what new areas it might open up.
The exact content and structure of your research proposal will depend on your subject area.
Below you can see information from each academic school which shows what they expect a research proposal to contain:
Length: 8-10 pages
Your research proposal should include the following sections:
Introduction
You should:
- include a short summary of the central question behind your research
- explain the background of your proposed project
- describe the expected outcome of your project.
Thesis statement
Write a summary of your overarching research question and include:
- why your research area is of academic and practical interest
- how your research builds on existing work
- what has inspired you to pursue your area of research
- your knowledge of the research area.
Literature review
You must show you have the ability to review current research (literature and papers) within your field of study. Your literature review should demonstrate that your research question is relevant, you are aware of the work of others in your field, and how your research will contribute new findings to the subject area.
Theoretical Framework
The theoretical framework provides the rationale behind your research proposal. You must provide a critical review of existing theories, which are closely related to your research topic. Show how these theories frame your research questions and the overall structure of your research proposal.
Methodology
You must show how you will carry out the research and analyse your findings. Include potential sources, how data will be collected, and any difficulties there may be in conducting your research.
Ethical considerations
Outline any ethical concerns which arise from your research topic or your proposed methods. Read the existing codes of conduct in the social sciences before writing this part of your research proposal.
Bibliography
List the sources you have used in your literature review and any potential sources you may use for your research.
For more information visit the Business School .
Length: 2,000 - 3,000 words excluding references
Your research proposal should describe what you want to research, why it is important to do this research, and how you plan to conduct your study. Here is a suggested structure:
Provide a clear working title for your research.
The introduction will indicate the focus of your research and your main research question. It should also address:
- why this topic is an important area of research
- why the subject is important to you
- how your research will contribute to our knowledge and understanding.
Research context
Provide a concise overview of the context in which you plan to conduct your research.
This section provides a concise review of related research within your field of study. It demonstrates that you are aware of the work of others and how your research will contribute new knowledge. It should also demonstrate critical engagement with relevant conceptual and theoretical frameworks and make clear your theoretical position about the issues you are researching, how this frames your research questions and your methodological approach.
Methodology and methods
Indicate your methodological approach, followed by details of how you plan to answer your research questions. This should include information about:
- how you plan to collect data (through which research methods)
- how you plan to select participants
- how you plan to analyse the data
- how you will address ethical considerations.
Provide a timeline, including time to conduct the research, process and analyse your data and write your final thesis.
Provide a bibliography of all citations used in your proposal.
For more information visit the School of Education and Social Work .
Length: 2,000 words
You should identify which research group you want to work with and check that we can support your area of research before writing your research proposal.
Your research proposal should include:
- your interest in the particular research area and the topic you want to study
- the specific research questions you want to investigate
- a description of your knowledge of the subject
- the relevant research literature you have read
- the methods and techniques you will use for your research
- an explanation of your motivations for applying for a PhD degree and an outline of your career aspirations
- a timetable for your project (monthly for the first year, and quarterly for subsequent years).
For more information visit the School of Engineering and Informatics
Length: about 2,000 words
You must provide a working title for your research. This is likely to change over time, but provides a good starting point.
You should introduce the questions and issues central to your research and explain how your research will benefit the field.
Research background
Expand on the information you have given in your introduction and try to answer the following questions:
- what are the key texts already existing in your field?
- how does your proposal differ from existing research?
- what will your project contribute to existing work in the field?
- how does your project expand our understanding and knowledge of the subject?
You must set out your research questions as clearly as possible and explain the problems you want to explore.
Research methods
Show how you plan to carry out your research:
- does your project involve archives, databases or specialist libraries?
- is your study interdisciplinary?
- what are the theoretical resources you intend to use and why?
- is your research based on a single author or a group of writers and texts?
Set out your timescale for completing your study. You need to think about dividing your research into sections and indicate how you plan to write up each section.
Include a bibliography, which lists the books and articles, you have referred to in the proposal.
Extra information
Some of these sections will be easier to write than others at this preliminary stage. The selectors who read your proposal know that it is a provisional statement and that your ideas, questions, and approaches will change during the course of your research.
You should treat the proposal as an opportunity to show that you have begun to explore an important area of study and that you have a question, or questions, that challenge and develop that area. It is also necessary to demonstrate that you can express your ideas in clear and precise English, accessible to a non-specialist.
For more information visit the Department of English
Length: 1,000-2,000 words
Include a short summary of your central question. You should tell us what you are attempting to research and why it is significant.
Thesis statement and literature review
Explain the subject matter of your project, and why you think the issues raised are important. You should also show us you are familiar with texts in the field, and can show how your research area is relevant, and in context to current academic thinking.
You must explain how your proposed project is original and will increase our understanding of the subject matter.
You must state clearly what you hope to discover at the end of your research.
Theoretical framework
Show how you plan to carry out your research and how you will analyse the findings.
Outline any ethical concerns which arise from either your research topic or your proposed methods of collating data.
List the sources you have used in your literature review and point to potential sources for your research.
For more information visit the School of Global Studies
You must provide a working title for your research, this is likely to change over time, but provides a good starting point for your proposal.
Include a bibliography, which lists the books and articles you have referred to in the proposal.
For more information visit the School of History, Art History and Philosophy
Length: 2000-3500 words (excluding bibliography)
Your title should give a clear indication of your proposed research approach or key question.
Include a short summary of your central question. You should tell us what you are attempting to research and why it is significant. You must state clearly what you hope to discover at the end of your research.
Explain the subject matter of your project and why you think the issues raised are important. Provide a summary of the key debates and developments in your chosen area and demonstrate your knowledge and grasp of the specific literature (global) that you will be engaging with during your research. You should show that you are familiar with texts in your chosen area, and what are the gaps in the literature that your research is attempting to fill, i.e., how your proposed research is original and will increase our understanding of the subject matter. Through this, you should detail how your research area fits into current academic thinking and/or policy discourse.
The theoretical framework provides the rationale behind your research proposal. You must provide a critical review of existing theories or concepts (global), which are closely related to your research topic. Show how these theories/concepts frame your research questions and the overall structure of your research proposal, and clearly state the specific theoretical concepts/analytical frameworks that you are engaging with.
You should outline your draft overall research question and any relevant sub-research questions and hypotheses through engagement with the theoretical literature.
State to what extent your approach is distinctive or new or builds on/deepens existing theoretical literature in your chosen area.
Research Design
Show how you plan to carry out your research (including fieldwork) and how you will analyse the findings. You should also show how this relates to your hypothesis. Put details of your research design in terms of approaches, methods and tools, along with some indication of specifics such as sample size (i.e., give an idea of the scope of your research project).
Outline any ethical concerns that arise from either your research topic or your proposed methods of collecting and collating data.
List the sources you have used in your literature review. Also, separately, point to potential sources that will be appropriate for your proposed research.
For more information about the PhD in Development Studies by Research visit the Institute of Development Studies website .
Length: 2,000-3,000 words
- what has inspired you to pursue your area of research.
You must show you have the ability to review current research within your field of study. Your literature review should demonstrate that your research question is relevant, you are aware of the work of others in your field, and show how your research will contribute new findings to the subject area.
Outline any ethical concerns which arise from your research topic or your proposed methods.
For more information visit the School of Law, Politics and Sociology
Length: 1,500-2,000 words
You should identify the research group you want to work with and ensure that we can support your area of research before writing your research proposal.
- a general personal statement, which describes a broad topic of interest to you and how your areas of academic strength would benefit the topic
- a specific personal statement, which shows us why you are the right person for one of our advertised research projects
- explain your motivation for applying for a PhD degree and outline your career aspirations
- your knowledge of the subject and relevant research literature you have read
- the methods and techniques you will use for your research.
If you are applying for an advertised research project you should tell us:
- which project or PhD scholarship you want to be considered for in the financial information session
- if you have another way of funding your studies if we are unable to offer you a place on a funded project
- the name of your sponsor, if you will be funded by a third party.
For more information visit the School of Life Sciences
You should identify the research area (and/or the researchers) you want to be involved with.
You should either:
- write a new research proposal
- write a general personal statement, which describes a broad topic of interest to you and how your areas of academic strength would benefit the topic
- write a specific personal statement, which shows us why you are the right person for one of our advertised research projects.
- explain your interest in the research area, your motivation for carrying out the research and your career aspirations
- describe the questions you want to investigate
- describe your knowledge of the subject and relevant previous research experience and skills
- tell us about the relevant research literature you've read
- describe the methods and techniques you will use to achieve your aims.
If you are applying for advertised funding you should tell us:
- which project or PhD scholarship you want to be considered for in the financial information section
For more information visit the School of Mathematical and Physical Sciences
Length: about 2,000 words (not including bibliography)
You must provide a working title for your research. This is likely to change over time but provides a good starting point for your proposal.
Brief abstract
Write a paragraph summarising your proposed project.
Research questions and rationale
Introduce your main research questions and why you think your research matters. Indicate how you think your research will be an original contribution to the knowledge and understanding of the subject. Describe the form of your anticipated outputs if your proposal includes creative practice. You may want to explain how you think your research will connect with existing research interests at Sussex.
Conceptual framework
The conceptual framework should elaborate the rationale behind your research proposal. You should demonstrate a critical engagement with theories and secondary literature or other artefacts that are relevant to your research topic. Show how these theories frame your research questions and the overall structure of your research proposal. If relevant, reflect on the research dimension of your creative practice.
Methodology and Research Ethics
Show us how you intend to achieve your research aims and outcomes and how you will answer your research questions. Include information about specific methods and access to relevant sources. If your project involves creative practice in some way, it is important that you describe what facilities you will need and indicate your experience in the relevant production techniques. You may want to include a practice portfolio, or provide links to online examples of your work. Reflect on any ethical considerations relevant to the conduct of your research.
Indicative timeline
Provide an account of how you envisage conducting your research to completion within the period of registration. Note that we fully expect proposals and attendant timelines to evolve in practice, but we are keen to see your ability to design a research project, bearing this in mind.
Include any literature, audiovisual or online resources you have referenced in the proposal.
For more information visit the School of Media, Film and Music
Length: 1,000-1,500 words Your research proposal should contain the following sections:
- why your research topic is interesting and important
- what we know already about the research area and how your study will expand our knowledge of it.
You should assume you are writing your research proposal for someone who has a good understanding of psychology, but not an expert in your area of research.
You should identify any gaps in our knowledge in your research area, and how your research will fill them. At the end of the section outline your aims and hypotheses.
We are interested in your ability to think critically. You should answer the following questions:
- what kind of control conditions are needed for your research?
- what do you need to measure and how?
- do you need to run any pilot studies?
- what difficulties might you have carrying out your research, and how can these be overcome?
You are expected to show how your initial idea can be developed and expanded over the duration of your PhD degree.
Reference list
You must add in a reference list in American Psychological Association format.
For more information visit the School of Psychology.
Proofread your research proposal
Once you have completed your proposal, check it through thoroughly. You should make sure all the information you have cited is accurate. Correct spelling and punctuation is also essential.
Write in clear sentences and structure your research proposal in a logical format that is easy for the reader to follow.
It is easy to miss errors in your own work, so ask someone else to proofread your research proposal before submitting it to Sussex.
You might also be interested in:
- finding a supervisor
- using our postgraduate application system
- how to apply for a PhD
This site uses cookies
We use necessary cookies to make our sites work. We'd also like to set additional cookies to analyse how our sites are performing, to improve the relevance of our ads and to optimise your experience. These will be set only if you accept. To learn more, view our privacy policy .
Privacy Preferences
Necessary cookies.
These cookies are necessary for the website to function normally and cannot be turned off. They are usually set in response to actions made by you which amount to a request for services, such as setting your privacy preferences, logging in or filling in forms. You can block or delete them in your browser settings, but this may affect how the website functions.
Analytics cookies
These cookies allow us to monitor how our websites and services are performing by collecting data about how visitors interact with our sites. The data is collected in a way that does not directly identify anyone.
Marketing cookies
These cookies are set through our site by our advertising partners. They may be used by those companies to build a profile of your interests and show you relevant ads on other sites. If you disable this setting, you will experience less targeted advertising.
Functionality cookies
These cookies enable us to provide enhanced functionality and personalisation. They may be set by us or by third party providers whose services we have added to our pages.
Research proposal guidelines
Your research proposal is an essential part of your application that will be used to assess your suitability for the PhD programme, and link you to an appropriate academic colleague who can support you throughout your studies.
Proposal requirements
When submitting your proposal please make sure it meets the following requirements so we can properly assess your suitability for the programme. It should:
- Have a title
- Explain your particular topic or question you wish to study
- Briefly summarise existing research on the topic, making reference to publications as appropriate
- Give a clear outline of the research you intend to do, with a timeframe where possible
Please ensure your proposal meets our word limit requirements. These are different depending on which PhD programme you are applying for, so please ensure you check this carefully.
For those applying to PhD with Integrated Study in Accounting/Finance/Management or to the MSc by Research in Management, the research proposal must be between 1,000 and 1,500 words (excluding references and appendices).
For those applying to PhD Business Economics/Financial Technology/Management Science and Analytics the research proposal must be between 3,000 and 5,000 words (excluding references and appendices).
If you have any questions about the proposal word limit please contact the PGR Admissions Team at [email protected]
Important points
- If accepted, you are not committed to following your research proposal exactly, although any major changes must be agreed with your supervisory team
- Applications received without a research proposal will not be considered
- A personal statement does not meet the requirements of a research proposal
- Your research proposal may be submitted to the Turnitin plagiarism detection system
Writing an effective proposal
A weak proposal can lead to an application being unsuccessful. To help you stand out from the crowd we have created a detailed guide on how to get started.
How to write a good research proposal
For students
- Current Students website
- Email web access
- Make a payment
- MyExeter (student app)
- Programme and module information
- Current staff website
- Room Bookings
- Finance Helpdesk
- IT Service Desk
Popular links
- Accommodation
- Job vacancies
- Temporary workers
- Future Leaders & Innovators Graduate Scheme
New and returning students
- New students website
- Returning Students Guide
Wellbeing, Inclusion and Culture
- Wellbeing services for students
- Wellbeing services for staff
- Equality, Diversity and Inclusion
- Israel, Palestine, and the Middle East
Postgraduate Study - PhD and Research Degrees
- Postgraduate Research home
- How to apply
Research proposal
- After you apply
- Admission terms, conditions and policies
- Immigration and visas
What is a research proposal?
For comprehensive advice please download our How to write a research proposal guide.
What is a research proposal
Your research proposal needs to outline the nature of your proposed research project and give some indication of how you will conduct your research. It is an integral part of the postgraduate research application process, so it is certainly worth investing time and energy into it.
Your research proposal should leave a positive first impression upon the reader about your ‘fitness’ to study a PhD. It is your project, so it is important to demonstrate leadership in this first stage of the application process. An ideal proposal should leave the reader feeling in no doubt that you have done some preliminary research about your subject and that you are knowledgeable and ready to tackle the challenges of a PhD. Give your proposal your utmost attention and time, but also be realistic ‐ you are not expected to know everything at this stage. Your proposal can also be flexible. It is not a contract. Always ask someone else to read your proposal before you submit it, and to offer you some critical but supportive feedback. Remember that a research proposal is about what you want to study; it immediately reflects your initial understanding of, and commitment to, PhD study. A research proposal can and should make a positive and powerful first impression about your potential to become a good researcher. Importantly, the main purpose is to enable the university to assess whether you are a good ‘match’ for our supervisors and our areas of research expertise. Therefore, in a good research proposal you will need to demonstrate two main things:
- that you are capable of independent critical thinking and analysis
- that you are capable of communicating your ideas clearly
Applying for a PhD is like applying for a job, you are not applying for a taught programme. When you start a PhD you will become a valued researcher in an academic department. Through your research proposal your colleagues want to know whether they can work with you, and whether your ideas are focussed, interesting and realistic. Try and impress them! Your proposal should be indicative and it should outline your areas of interest and your general insight into the research topic. You are not expected to be an expert and to be familiar with all the specific details of your subject. However, you are expected to have a good level of knowledge about the subject and where you might make a valuable contribution to research. The perfect research proposal should leave the reader interested, excited and wanting to find out more about your ideas, and about you!
Preparing a research proposal
Before you write a research proposal, the first step should be to provide a 500-word outline of your proposed research project. You should then forward this to any academic you feel would best suit your proposed project – you can find contact details for staff on the individual subject websites. If you receive a positive response, you can then plan to submit a formal application in the form of a research proposal.
Your proposal must specify the area of your proposed research and should cover relevance, theoretical perspectives, research methodology, and sources of data. Your proposal is your calling card. It is your chance to sell yourself and your research to prospective supervisors. Competition for places is fierce, and many students apply to us with excellent Bachelors and Masters degrees from around the world. Your proposal is your way of setting yourself apart from the crowd. So, you should work hard to submit the best possible application.
Putting together your document
There is no set formula for your research proposal in terms of length or what you include in it. It is quality, not quantity, that counts to demonstrate that you have a clear and concise way of thinking. Your proposal should explain your project, establish its importance, and set out how you are going to complete it in the time allowed.
PhD-level study, quite literally, encompasses an almost infinite variety of topics and projects. It is for this reason that prescribing a ‘one-size-fits-all’ method for research proposal writing is a difficult task, but the strongest proposals are likely to contain many of the following:
Background – You should establish the context to, and rationale for, your research based on a reading of the relevant academic and/or practitioner literature. Where possible, cite relevant authors and studies, and explain how this research builds on your previous academic work or professional experience. You should discuss the intellectual importance of your work, its contribution to your subject area, and its originality, which, in time, form three of the four main criteria for assessing your PhD.
Aims and objectives – Set out the central aims and research questions that guide your research. What hypothesis or argument are you trying to explore and what questions are you trying to answer? Set out your terms of reference clearly and precisely. These may cover what you intend to achieve by the research in general and, more specifically, how the research fits the background and the outcomes from the project.
Methods and techniques – Explain how your approach to collecting and analysing information will help you satisfy your aims and objectives. Potential data collection methods and possible analytical techniques give a sense of the direction of the research. Explain the choices behind case study organisations or locations, as well as sampling strategies or particular computer-based techniques.
Rationale - contextualise your questions/aims in a broader field of study, identifying the main literature that you are addressing. You need to explain why your research questions/hypotheses are important and topical.
Project management – You don’t need to produce a detailed time plan because research projects evolve. However, it is extremely useful to explain in general terms what you are proposing to do, and when, in order to get a sense of the scale of the task. This is especially important if you are proposing to undertake case study work or fieldwork.
Ethics – Almost inevitably your research will raise some ethical issues and you should aspire to conduct your research with the highest ethical standards.
Health and safety – All types of research have implications for health and safety, albeit some types of work are more risky than others. Where appropriate your proposal should seek to identify any issues and explain how you may address them.
References – Please enter a reference list using Harvard Notation. It is useful for potential supervisors to better understand the breadth and depth of your reading to date.
Appendices – These are a useful way of including additional supporting material while keeping the main body of the proposal succinct.
Timeline – You don’t need to produce a detailed time plan, but it is helpful to provide a summary of what you are planning to do and when. You will be expected to submit your thesis within three years (six years for part-time students) so it is important you have a feasible timeline. This section is especially important if you are proposing to undertake case study work or fieldwork. Bibliography – a short bibliography of relevant works in your research area.
Guidelines and advice
How long should a good research proposal be?
A good research proposal is as long as it takes, but a guide would be 1,500-2,500 words. Remember that it is meant to be an accurate overview, not a thesis, so you need to provide enough detail for the reader to understand it. A paragraph would not be enough and 5,000 words likely too much.
The '3Cs' rule
When you have written your research proposal, ask a friend to read it critically and provide you with feedback. Also, ask yourself whether it follows the '3Cs' rule:
- Clear - is what you have written intelligible and clearly articulated? Does it make sense, or is it vague and confusing? Does your proposal leave the reader with a clear sense of the purpose and direction of your research project?
- Concise - have you written your proposal in a succinct and focused way?
- Coherent - does your proposal link together well so that it tells the reader a short story about what you want to do, why you want to do it and how you will do it?
If you can answer all of these questions with confidence, you have probably put together a good proposal.
Dissemination
Depending on your project and the wider field it is a part of, you may want to include a paragraph on how you would go about spreading the ideas discussed in your research to the academic community, and in some cases the organisation arranging your funding. This could be anything, from traditional sources such as publications and seminars, to more contemporary methods such as blogs, vlogs and exhibitions.
To protect yourself from accusations of plagiarism please make sure that all your references are present, correct and up-to-date at the time of submission. In order to ensure you have correctly referenced, it is sensible to include publications in your bibliography that influenced your thoughts and arguments in any way, even if they are not quoted from directly. If you have used quotations from other academics, please check you have used quotation marks and a citation.
6 steps to a successful research proposal
A good research proposal should not be complicated. However, it can be challenging to write and it is important to get right. A PhD is challenging, so it is good training working on your research proposal. Although there is no exact prescribed format for a general research proposal (across all subjects), a research proposal should generally include six main sections, as detailed below:
1: A clear working title for your research project
- What will you call your project?
- What key words would describe your proposal?
2: A clear statement about what you want to work on and why it is important, interesting, relevant and realistic
- What are your main research objectives? These could be articulated as hypotheses, propositions, research questions, or problems to solve
- What difference do you think your research will make?
- Why does this research excite you?
- What research ‘gaps’ will you be filling by undertaking your project?
- How might your research ‘add value’ to the subject?
- Is your research achievable in the time allocated? (e.g. 3 years full‐time)
3: Some background knowledge and context of the area in which you wish to work, including key literature, key people, key research findings
- How does your work link to the work of others in the same field or related fields?
- Would your work support or contest the work of others?
- How does your work relate to the expertise within the department you are applying to?
4: Some consideration of the methods/approach you might use
- How will you conduct your research?
- Will you use existing theories, new methods/approaches or develop new methods/approaches?
- How might you design your project to get the best results/findings?
5: Some indication of the strategy and timetable for your research project and any research challenges you may face
- What would be the main stages of your project?
- What would you be expecting to do in each year of your PhD?
- What challenges might you encounter and how might your overcome these?
6: A list of the key references which support your research proposal
- References should be listed in the appropriate convention for your subject area (e.g. Harvard). Such references should be used throughout your research proposal to demonstrate that you have read and understood the work of others
- Other relevant material that you are aware of, but not actually used in writing your proposal, can also be added as a bibliography
All of the above six sections are important but section 2 is particularly important because in any research project, establishing your main purpose represents the whole basis for completing the research programme. Therefore, the value of your proposed research is assessed in relation to your research aims and objectives.
Connect with us
Information for:
- Current students
- New students
- Alumni and supporters
Quick links
Streatham Campus
St Luke's Campus
Penryn Campus
Truro Campus
- Using our site
- Accessibility
- Freedom of Information
- Modern Slavery Act Statement
- Data Protection
- Copyright & disclaimer
- Cookie settings

London Centre for Nanotechnology Research Groups
- CDT-AMR Project Proposals

How to Propose a Project
Propose a phd project .
Our PhD projects are supervised by academic staff from various backgrounds and of all levels of seniority from across UCL, supported by non-academic partners where appropriate. Projects are submitted and selected in autumn for a start in the autumn of the next calendar year.
Proposals are ranked per research theme, with a maximum of 5 projects selected per research theme, to be proposed to candidate students (~10 in total per cohort) during the PhD recruitment process.
Projects can only be submitted by UCL supervisors, are expected to be interdisciplinary, and must be (for at least 50%) in the EPSRC remit .
Selection criteria are:
Fit to remit of the CDT and one of the three main CDT research themes
Quality of the proposed research
Quality of the supervision and research environment
Strength of contributions from non-academic partners (if applicable)
Project selection and allocation will take into account matched funding contributions made by different UCL departments to the CDT, and where appropriate favour supervisors from those departments. Furthermore, project selection may favour proposals with matched funding from external partners provided all other selection criteria are met.
For information on the matched funding required and how studentships with external partners will be set up, please consult the “ Matched funding - info for supervisors.docx " document.
Academics will not be allowed to be first supervisor for more than one on-going CDT PhD project or to be second supervisor for more than one on-going CDT PhD project; and should not submit more than one CDT PhD project as first supervisor or more than one CDT PhD project as second supervisor any year. Projects with significant matched funding (cash contribution) are exempt from these limitations.
Confirmation of initial project selection may be pending on additional information provided by supervisors.
Supervisors of selected projects are expected to participate in the student recruitment process.
Submit a Project Now:
* The deadline to submit a project is midnight on Sunday 6 th October 2024
Submit a Project
Please find here a Word document including all fields to be completed in the online submission form

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Find guidance on how to write your PhD research proposal and a template form for you to use to submit your research proposal.
Get guidance on how to write an original, high quality PhD research proposal for study at the School of Sociology, Politics and International Studies.
Research proposals are used to persuade potential supervisors and funders that your work is worthy of their support. These documents set out your proposed research that will result in a Doctoral thesis. They are typically between 1,500 and 3,000 words. Your PhD research proposal must passionately articulate what you want to research and why ...
Writing a PhD research proposal: A 6‐step general guide for prospective PhD researchers Introduction This short guide is aimed at helping you to write a good research proposal. It is intended to help you to think about your proposed PhD research in a clear, structured and meaningful way.
For some research courses in sciences you'll join an existing research group so you don't need to write a full research proposal, just a list of the groups and/or supervisors you want to work with. You might be asked to write a personal statement instead, giving your research interests and experience. Still, for many of our research courses ...
What is a research proposal? A research proposal gives details of the direction of your future research, usually based on a research question and a chapter-by-chapter approach to answering it. For PhD applications, this proposal will be assessed to see:
Guidance for PhD applicants Faculty of Education, University of Cambridge The 1,500 word research proposal is an important element of your application to doctoral study, whether full-time or part-time. It offers you the opportunity to outline the research you intend to conduct, including how you plan to go about it, and how your research might make a contribution to a theoretical or empirical ...
How to write a PhD research proposal Creating a focused and well-written research proposal - a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research - is an essential part of a successful PhD application.
Writing a research proposal Your research proposal is the most important part of your doctoral application. Find out how to write a proposal for your own research, for advertised PhD projects, and for Professional Doctorates.
A PhD proposal is an outline of your proposed project. It needs to: Define a clear question and approach to answering it. Highlight its originality and/or significance. Explain how it adds to, develops (or challenges) existing literature in the field. Persuade potential supervisors of the importance of the work, and why you are the right person ...
How to write a research proposal. You will need to submit a research proposal with your PhD application. This is crucial in the assessment of your application and it warrants plenty of time and energy. Your proposal should outline your project and be around 1,500 words.
The research proposal - an outline. Your proposal should be typed double-spaced, if possible, and be between 1,000 and 2,000 words. Your PhD proposal can be added under the 'Supporting Documents' section of the Postgraduate Applications Online System. Your proposal should contain at least the following elements:
Information about writing a research proposal as part of an application for postgraduate doctoral study at Imperial
Research proposals. Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use. We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
How to write a PhD proposal We are delighted to consider applications for PhD research. We have a fantastic, diverse and energetic student body who are making the most of fabulous resources for postgraduate students. We welcome you to join us.
Nevertheless, a PhD proposal should amount to a coherent, intelligent, realistic and relatively well thought-out idea of an area of potential research. The following errors should be avoided if possible: Simplistic descriptions of an area of study should be avoided - eg 'I want to research EU law'.
The research proposal is the main way in which we evaluate the quality of your research plans. You should aim to make your proposal about 1500-2000 words long. Your proposal should include the following: Show all / Hide all.
EIS PhD Research Proposal Guidelines The research proposal is the most important part of your PhD application. We do not expect the proposal to be perfect at this stage, nor do we expect you to stick to it rigidly, as your ideas will almost certainly change once you start to study. However, we do expect it to show convincing evidence of your ability to plan and organise independent research ...
A research proposal is a project outline of around 3000 words that you write as part of the process of applying to study for an MPhil or PhD research degree.
Writing your research proposal Your proposal is your chance to tell us why you want to study your PhD at Sussex. Follow our guide to making your research proposal as strong as possible.
Your research proposal is an essential part of your application that will be used to assess your suitability for the PhD programme, and link you to an appropriate academic colleague who can support you throughout your studies.
Below you will find a research proposal template you can use to write your own PhD proposal, along with examples of specific sections. Note that your own research proposal should be specific and carefully tailored to your own project and no two proposals look the same. Use the template and examples below with that in mind.
Research proposal. Postgraduate Research home. How to apply. After you apply. Admission terms, conditions and policies. Research proposal. Immigration and visas.
Proposals are ranked per research theme, with a maximum of 5 projects selected per research theme, to be proposed to candidate students (~10 in total per cohort) during the PhD recruitment process. Projects can only be submitted by UCL supervisors, are expected to be interdisciplinary, and must be (for at least 50%) in the EPSRC remit.