- Top Articles
- Experiences
This topic encompasses the business of UX, as well as the business contexts in which UX professionals work.
- Big Data (12)
- Business of UX (51)
- Careers in UX (33)
- Case Studies (16)
- Consulting (29)
- Content Development (10)
- Content Management (1)
- Culture Change (29)
- DesignOps (4)
- Design Thinking (21)
- Digital Governance (4)
- Digital Transformation (1)
- Evangelizing UX (3)
- Hiring UX Professionals (12)
- Industry Report (2)
- Innovation (21)
- Localization (8)
- Product Management (15)
- Project Management (7)
- Remote Work (10)
- Requirements (6)
- ResearchOps (1)
- Role of UX (15)
- Search-Engine Optimization (SEO) (3)
- Soft Skills (44)
- Stakeholders (13)
- UX Leadership (66)
- UX Maturity (9)
- UX Professions (30)
- UX Roles (12)
- UX Skills (9)
- UX Teams (12)
- Value of User Experience (24)
This topic is about developing software user experiences for the Web and mobile devices.
- Frameworks (4)
- Front-End Development (16)
- Mobile App Development (4)
- Performance Optimization (3)
- Prototyping (12)
- Responsive Web Design (5)
- Web App Development (1)
- Web Site Development (1)
This topic includes both communications to the UXmatters community and information about the broader UX community.
- Conferences (3)
- Editorials (25)
- Education (8)
- Information Resources (8)
- Interviews (32)
- Professional Development (81)
- Professional Organizations (3)
- Sample Chapters (61)
- Thought Leaders (104)
- User Experience (97)
- UXmatters (1)
- UX News (18)
This topic comprehends every aspect of product and Web user experience design.
- Accessibility (37)
- Animation Design (2)
- Artificial Intelligence Design (37)
- Customer Experience Design (5)
- Data-Informed Design (19)
- Data Visualization (2)
- Decision Architecture (13)
- Designing for Children (7)
- Designing for Senior Citizens (2)
- Design Systems (3)
- eCommerce Design (14)
- Enterprise UX Design (28)
- Experience Design (16)
- Extended Reality Design (6)
- Graphic Design (4)
- Guidelines & Standards (3)
- Industrial Design (3)
- Information Architecture (56)
- Information Design (32)
- Instructional Design (2)
- Interaction Design (51)
- Internet of Things Design (2)
- Mobile UX Design (104)
- Patterns & Antipatterns (19)
- Philosophy (5)
- Portfolio Design (2)
- Principles (34)
- Process Design (1)
- Responsive Design (5)
- Service Design (35)
- Software Design (4)
- Survey Design (3)
- Trends (17)
- Typography (1)
- Universal Design (6)
- User Assistance Design (43)
- User Interface Design (16)
- UX Design (227)
- Voice User Interface Design (11)
- Visual Interface Design (49)
- Wearables Design (2)
- Web Application Design (45)
- Web Form Design (18)
- Web Site Design (77)
- Writing User-Interface Text (19)
This topic explores various types of user and customer experiences, accessibility and usability challenges, and product and technology trends.
- Augmented Reality (2)
- Consumer Experiences (6)
- Cross-Channel Experiences (2)
- Customer Experiences (10)
- eCommerce Experiences (10)
- Employee Experiences (4)
- Enterprise Experiences (19)
- Experience Trends (10)
- Future User Experiences (6)
- Global User Experiences (6)
- Healthcare Experiences (2)
- Internet of Things (2)
- Learning Experiences (3)
- Mixed Reality (3)
- Mobile Experiences (21)
- Product Experiences (5)
- Search Experiences (5)
- Service Experiences (9)
- Software User Experiences (71)
- Technology Trends (18)
- Usability Challenges (1)
- User Experiences (24)
- Virtual Reality (3)
- Voice User Interfaces (8)
- Wearables Experiences (1)
- Web Experiences (12)
This topic encompasses the entire product design and development process, including best practices for deliverables and collaborative work.
- Agile Development (15)
- Agile UX (42)
- Collaboration (38)
- Communicating Design (56)
- Content Analysis (2)
- Deliverables (43)
- Design Critique (5)
- DesignOps (7)
- Design Process (114)
- Development Process (14)
- Envisioning (4)
- Ideation (6)
- Journey Mapping (7)
- Lean UX (19)
- Mapping User Experiences (1)
- Persona Development (2)
- Prototyping (20)
- Requirements Definition (23)
- Sketching (5)
- Task Modeling (4)
- Teamwork (91)
- Testing (2)
- User-Centered Design (75)
- User Modeling (5)
This topic covers generative UX research, usability evaluation, and pure research that pertains to UX design.
- A/B Testing (3)
- Analysis (20)
- Analytics (14)
- Card Sorts (3)
- Consumer Research (3)
- Contextual Inquiry (1)
- Diary Studies (1)
- Ethnography (3)
- Expert Reviews (8)
- Eyetracking (3)
- Facilitating Workshops (1)
- HCI Research (4)
- Human Factors Research (29)
- Interviewing Users (4)
- Metrics (13)
- Remote UX Research (20)
- ResearchOps (2)
- Stakeholder Research (4)
- Testing AI (1)
- User Feedback (3)
- Usability Testing (152)
- User Research (281)
- UX Research (26)
This topic includes reviews of products, services, training, and publications for UX professionals.
- Book Reviews (68)
- Conference Reviews (92)
- Course Reviews (1)
- Product Reviews (19)
- Software Reviews (7)
- Training Program Reviews (1)
This topic comprehends strategy and planning for business, design, products, and UX teams.
- Brand Strategy (8)
- Business Strategy (28)
- Content Strategy (46)
- CX Strategy (8)
- Design Strategy (22)
- Enterprise UX Strategy (23)
- Experience Strategy (6)
- Innovation Strategy (4)
- Mobile UX Strategy (5)
- Planning (2)
- Product Strategy (14)
- Service Design Strategy (1)
- UX Strategy (283)
- Web Strategy (1)

New on UXmatters
- Designing Technology: Backtracking to Meet Users’ Needs While Innovating
- Engaging Your Audience Through a Seamless Happy Path
- Mastering User-Centered Design, with 5 Advanced Tips
- Inclusive Digital Experiences: Redesign Strategies for Addressing Diverse Abilities and Accessibility Challenges, Part 2
- Designing Mobile Apps with Accessibility in Mind
Share this article

What Is User Research, and What Is Its Purpose?

User research, or UX research, is an absolutely vital part of the user experience design process.
Typically done at the start of a project, it encompasses different types of research methodologies to gather valuable data and feedback. When conducting user research, you’ll engage with and observe your target users, getting to know their needs, behaviors, and pain points in relation to the product or service you’re designing.
Ultimately, user research means the difference between designing based on guesswork and assumptions, and actually creating something that solves a real user problem. In other words: Do not skip the research phase!
If you’re new to user research, fear not. We’re going to explain exactly what UX research is and why it’s so important. We’ll also show you how to plan your user research and introduce you to some key user research methods .
We’ve divided this rather comprehensive guide into the following sections. Feel free to skip ahead using the menu below:
- What is user research?
- What is the purpose of user research?
- How to plan your user research.
- An introduction to different research methods—and when to use them.
Ready? Let’s jump in.
1. What is user research?
User experience research is the systematic investigation of your users in order to gather insights that will inform the design process. With the help of various user research techniques, you’ll set out to understand your users’ needs, attitudes, pain points, and behaviors (processes like task analyses look at how users actually navigate the product experience —not just how they should or how they say they do).
Typically done at the start of a project—but also extremely valuable throughout—it encompasses different types of research methodology to gather both qualitative and quantitative data in relation to your product or service.
Before we continue, let’s consider the difference between qualitative and quantitative data .
Qualitative vs. Quantitative data: What’s the difference?
Qualitative UX research results in descriptive data which looks more at how people think and feel. It helps to find your users’ opinions, problems, reasons, and motivations. You can learn all about in-depth in this video by professional UX designer Maureen Herben:
Quantitative UX research , on the other hand, generally produces numerical data that can be measured and analyzed, looking more at the statistics. Quantitative data is used to quantify the opinions and behaviors of your users.
User research rarely relies on just one form of data collection and often uses both qualitative and quantitative research methods together to form a bigger picture. The data can be applied to an existing product to gain insight to help improve the product experiences, or it can be applied to an entirely new product or service, providing a baseline for UX, design, and development.
From the data gathered during your user research phase, you should be able to understand the following areas within the context of your product or service:
- Who your users are
- What their needs are
- What they want
- How they currently do things
- How they’d like to do them
As you consider the why of user research, remember that it’s easier than you might realize to overlook entire groups of users. It’s important to ensure that you’re conducting inclusive UX research and that starts in the earliest stages!
2. What is the purpose of user research?
The purpose of user research is to put your design project into context. It helps you understand the problem you’re trying to solve; it tells you who your users are, in what context they’ll be using your product or service, and ultimately, what they need from you, the designer! UX research ensures that you are designing with the user in mind, which is key if you want to create a successful product.
Throughout the design process, your UX research will aid you in many ways. It’ll help you identify problems and challenges, validate or invalidate your assumptions, find patterns and commonalities across your target user groups, and shed plenty of light on your users’ needs, goals, and mental models.
Why is this so important? Let’s find out.
Why is it so important to conduct user research?
Without UX research, you are essentially basing your designs on assumptions. If you don’t take the time to engage with real users, it’s virtually impossible to know what needs and pain-points your design should address.
Here’s why conducting user research is absolutely crucial:
User research helps you to design better products!
There’s a misconception that it’s ok to just do a bit of research and testing at the end of your project. The truth is that you need UX research first, followed by usability testing and iteration throughout.
This is because research makes the design better. The end goal is to create products and services that people want to use. The mantra in UX design is that some user research is always better than none .
It’s likely at some point in your UX career that you will come across the first challenge of any UX designer—convincing a client or your team to include user research in a project.
User research keeps user stories at the center of your design process.
All too often, the user research phase is seen as optional or merely “nice-to-have”—but in reality, it’s crucial from both a design and a business perspective. This brings us to our next point…
User research saves time and money!
If you (or your client) decide to skip the research phase altogether, the chances are you’ll end up spending time and money developing a product that, when launched, has loads of usability issues and design flaws, or simply doesn’t meet a real user need. Through UX research, you’ll uncover such issues early on—saving time, money, and lots of frustration!
The research phase ensures you’re designing with real insights and facts — not guesswork! Imagine you release a product that has the potential to fill a gap in the market but, due to a lack of user research, is full of bugs and usability issues. At best, you’ll have a lot of unnecessary work to do to get the product up to scratch. At worst, the brand’s reputation will suffer.
UX research gives the product a competitive edge. Research shows you how your product will perform in a real-world context, highlighting any issues that need to be ironed out before you go ahead and develop it.
User research can be done on a budget
There are ways that you can conduct faster and less costly user research , utilizing Guerrilla research outlined later on in this article (also handy if budget and time are an issue). Even the smallest amount of user research will save time and money in the long run.
The second challenge is how often businesses think they know their users without having done any research. You’ll be surprised at how often a client will tell you that user research is not necessary because they know their users!
In a 2005 survey completed by Bain, a large global management consulting firm, they found some startling results. 80% of businesses thought they knew best about what they were delivering. Only 8% of those businesses’ customers agreed.
The survey may be getting old, but the principle and misperception still persist.
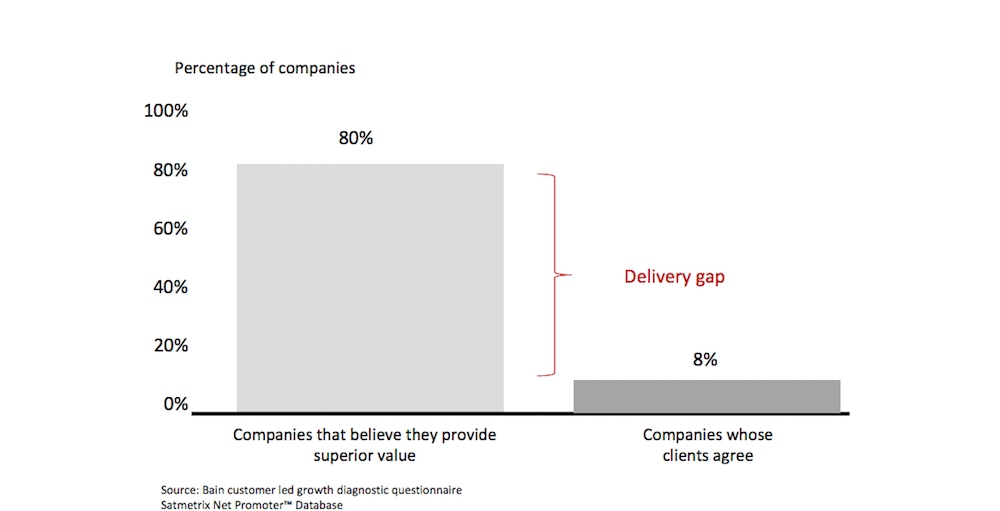
In some cases, businesses genuinely do know their customers and there may be previous data on hand to utilize. However, more often than not, ‘knowing the users’ comes down to personal assumptions and opinions.
“It’s only natural to assume that everyone uses the Web the same way we do, and—like everyone else—we tend to think that our own behavior is much more orderly and sensible than it really is.” (Don’t Make Me Think ‘Revisited’, Steve Krug, 2014.) A must on every UX Designer’s bookshelf!
What we think a user wants is not the same as what a user thinks they want. Without research, we inadvertently make decisions for ourselves instead of for our target audience. To summarize, the purpose of user research is to help us design to fulfill the user’s actual needs, rather than our own assumptions of their needs.
In a nutshell, UX research informs and opens up the realm of design possibilities. It saves time and money, ensures a competitive edge, and helps you to be a more effective, efficient, user-centric designer.
3. How to plan your user research
When planning your user research , it’s good to have a mix of both qualitative and quantitative data to draw from so you don’t run into issues from the value-action gap, which can at times make qualitative data unreliable.
The value-action gap is a well-known psychology principle outlining that people genuinely don’t do what they say they would do, and is commonly referred to as what people say vs. what people do.
More than 60% of participants said they were “likely” or “very likely” to buy a kitchen appliance in the next 3 months. 8 months later, only 12% had. How Customers Think, Gerald Zaltman, 2003
When planning your user research, you need to do more than just User Focus Groups—observation of your users really is the key. You need to watch what your users do.
Part of being a great user researcher is to be an expert at setting up the right questions and getting unbiased answers from your users.
To do this we need to think like the user.
Put yourself in your user’s shoes without your own preconceptions and assumptions on how it should work and what it should be. For this, we need empathy (and good listening skills) allowing you to observe and challenge assumptions of what you already think you know about your users.
Be open to some surprises!
4. When to use different user research methods
There’s a variety of different qualitative and quantitative research methods out there. If you’ve been doing the CareerFoundry UX Design course , you may have already covered some of the list below in your course.
It isn’t an exhaustive list, but covers some of the more popular methods of research. Our student team lead runs through many of them in the video below.
Qualitative Methods:
- Guerrilla testing: Fast and low-cost testing methods such as on-the-street videos, field observations, reviews of paper sketches, or online tools for remote usability testing.
- Interviews: One-on-one interviews that follow a preset selection of questions prompting the user to describe their interactions, thoughts, and feelings in relation to a product or service, or even the environment of the product/service.
- Focus groups: Participatory groups that are led through a discussion and activities to gather data on a particular product or service. If you’ve ever watched Mad Men you’ll be familiar with the Ponds’ cold cream Focus Group !
- Field Studies: Heading into the user’s environment and observing while taking notes (and photographs or videos if possible).
- In-lab testing: Observations of users completing particular tasks in a controlled environment. Users are often asked to describe out loud their actions, thoughts, and feelings and are videoed for later analysis
- Card sorting : Used to help understand Information Architecture and naming conventions better. Can be really handy to sort large amounts of content into logical groupings for users.
Quantitative Methods:
- User surveys: Questionnaires with a structured format, targeting your specific user personas. These can be a great way to get a large amount of data. Surveymonkey is a popular online tool.
- First click testing: A test set up to analyse what a user would click on first in order to complete their intended task. This can be done with paper prototypes, interactive wireframes or an existing website.
- Eye tracking: Measures the gaze of the eye, allowing the observer to ‘see’ what the user sees. This can be an expensive test and heatmapping is a good cheaper alternative.
- Heatmapping: Visual mapping of data showing how users click and scroll through your prototype or website. The most well-known online tool to integrate would be Crazyegg.
- Web analytics: Data that is gathered from a website or prototype it is integrated with, allowing you to see the demographics of users, page views, and funnels of how users move through your site and where they drop off. The most well-known online tool to integrate would be Google Analytics .
- A/B testing: Comparing two versions of a web page to see which one converts users more. This is a great way to test button placements, colors, banners, and other elements in your UI.
Further reading
Now you know what user research is and why it’s so important. If you’re looking for a way to get trained in this particular discipline, there’s good news—owing to demand and popularity, there’s a growing number of UX research bootcamps out there.
If you’d like to learn more about UX research, you may find the following articles useful:
- What Does A UX Researcher Actually Do? The Ultimate Career Guide
- How to Conduct User Research Like a Professional
- How to Build a UX Research Portfolio (Step-by-Step Guide)
User research is the process of understanding the needs, behaviors, and attitudes of users to inform the design and development of products or services. It involves collecting and analyzing data about users through various methods such as surveys, interviews, and usability testing.
2. How to conduct user research?
User research can be conducted through various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, and usability testing. The method chosen depends on the research goals and the resources available. Typically, user research involves defining research objectives, recruiting participants, creating research protocols, conducting research activities, analyzing data, and reporting findings.
3. Is user research the same as UX?
User research is a part of the broader UX (User Experience) field, but they are not the same. UX encompasses a wide range of activities such as design, testing, and evaluation, while user research specifically focuses on understanding user needs and behaviors to inform UX decisions.
4. What makes good user research?
Good user research is characterized by clear research goals, well-defined research protocols, appropriate sampling methods, unbiased data collection, and rigorous data analysis. It also involves effective communication of research findings to stakeholders, as well as using the findings to inform design and development decisions.
5. Is user research a good career?
User research is a growing field with many opportunities for career growth and development. With the increasing importance of user-centered design, there is a high demand for skilled user researchers in various industries such as tech, healthcare, and finance. A career in user research can be fulfilling for those interested in understanding human behavior and designing products that meet user needs.
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
User Research: A 10-step Guide. Just for you
UX research is the most essential part of the UX design process. If you do not have a clear idea of who your target user is and what they want (or need); it is nearly impossible to provide them with the right user experience.
To make your work easier for you, we have crafted a 10-step guide to make your work easier and to help you communicate user research to your clients and boss.
- Evangelize. With a bit of luck, your company or client is already aware of the importance of user research in a design project. If not, make sure you find ways to communicate your points and put all team members and stakeholders on the same page. Find examples, case studies, or any other resources to help you evangelize the importance of user research upfront. Just take one of our courses and we will equip you with lots of good arguments.
- Rewind. It is likely that your client or boss has come to you with a pre-made solution, design, or service. At this point, he/she wants you to do user research to fully understand this solution/design/service in a usage context. It could also be yourself who have a ready-made design that you want to research from a UX perspective. In this situation, danger lurks.If you have a pre-designed solution, you need to resist the temptation to push it onto your users. The goal of UXresearch is to find out what someone thinks – as opposed to hand them something and say; “This is great! Isn’t it?” A leading question like that may get you the answers you want but not the answers you need. In other words, be very mindful of your own biases – or those of your client and boss.
- Team up. Team diversity is really important and we mean both academic and professional diversity. You want researchers with experience of the topic in hand and also those without. Why? Those with experience may be able to drill down in-depth with your users to get a deep understanding of their issues/needs/wants/etc. Those without, on the other hand, may pick up on issues/needs/wants/etc that more experienced people miss because they make assumptions based on their experience.
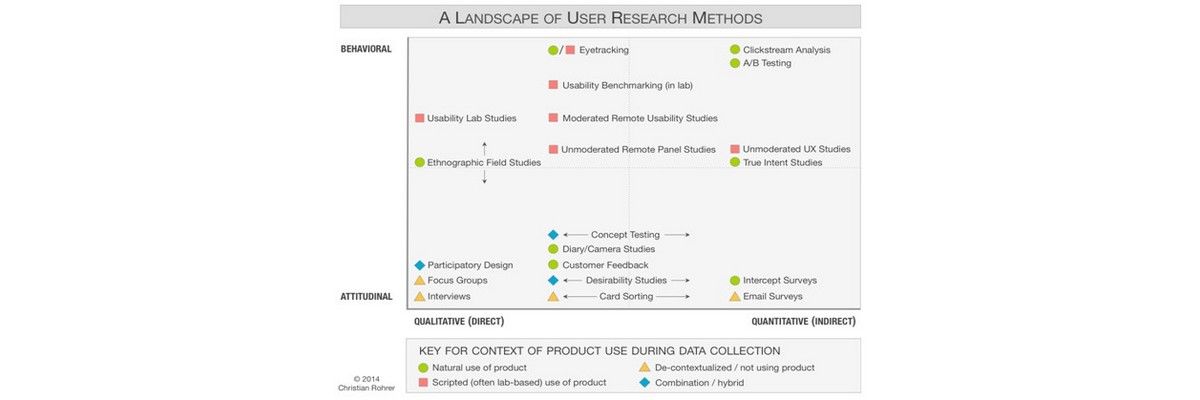
- Choose. The toolbox for user research methods is large and they all have pros and cons; the best option depends on the needs of your project. In order to select the right one(s) consider elements such as: budget, time frame, access to target users, results from desk research, etc. With all these in mind – and above all with a clear question or problem to answer or solve – choose a user research method. The image above made by Christian Rohrer is very helpful to have nearby. For the full article: http://www.nngroup.com/articles/which-ux-research-methods/
- Plan. This short word involves many tasks that need be taken care of before reaching out to users. By now, the target audience is clear but you still need to 1) prepare a screener to recruit the most appropriate users, 2) hire a recruiting company or do it yourself, 3) schedule the interviews, focus groups , contextual inquiry or the method of your choice. More at: https://www.interaction-design.org/ux-daily/121/the-basics-of-recruiting-users-for-usability-testing . Besides the recruitment, do not forget to prepare your script for the interview!
- Equip yourself. It is really difficult to observe someone properly when you’re talking to them. You’re trying to listen to them, you’re trying to make notes, and you’re trying to ask relevant questions – you’re basically overloaded. If you video-record your interviews, you’ll be amazed at how much they reveal when you play them back afterward. They can help inform not just the current research but also help you optimize your behavior for the next interview. In addition, we recommend a team of two for each interview. More interviewers would be too much but two people listening to a user is just the right amount. One to ask questions and lead the interview, the other one to take notes and take care of the video camera.
- Introduce yourself and what you do
- Explain that the user should treat you like you don’t know anything at all about the product
- Ask some simple questions to start off. Even if the questions are simple, direct themat some details of the product. That will encourage the user to follow your example and go into details.
- Be curious. Learn how to ask more questions and listen. You are there to learn from the user. It can be hard to work out what someone means by their words and even body language alone. In other cases it can be hard for someone to express what they mean in words. The more questions you ask, the easier it becomes to find out what someone means. “Why?” is a very handy question to ask and you can ask it often to drill down further.
- Analyze. Debrief with your fellow interviewer as soon as possible and take notes so that you do not rely only in your memory and that you use these insights to improve the next interview. Once you have done all your meetings with users, consolidate results and prepare the necessary documentation to communicate about the findings.
- Share. The more the rest of the team members and stakeholders are aware and incorporate, the easier it will be from now on. Ensure that all of you are on the same page and that the key takeaways from the research phase are always present.
How are you feeling after reading this list? If you want one word – just one single word – which is the most essential word in user research, then it is empathy . You need empathy to understand your client or boss and drive him/her where you want in terms of UX design. You need empathy to put yourself in the target users’ shoes and find a solution that fits them.
If you want to learn more, we have a new course on User Research – Methods and Good Practices ( https://www.interaction-design.org/courses/user_research_-_methods_and_best_practices.html ).
10 User research steps: Evangelize, Rewind, Team Up, Choose, Plan, Equip Yourself, Connect, Be Curious, Analyze and share. Or just Empathy. [ Tweet this ]
Design for Thought and Emotion

Get Weekly Design Insights
Topics in this article, what you should read next, apple’s product development process – inside the world’s greatest design organization.

- 1.4k shares
How to Change Your Career from Graphic Design to UX Design
What is Interaction Design?

Shneiderman’s Eight Golden Rules Will Help You Design Better Interfaces

- 1.3k shares
The Principles of Service Design Thinking - Building Better Services

- 10 mths ago
A Simple Introduction to Lean UX
- 3 years ago
Dieter Rams: 10 Timeless Commandments for Good Design

How to Do a Thematic Analysis of User Interviews

- 1.2k shares
The 7 Factors that Influence User Experience
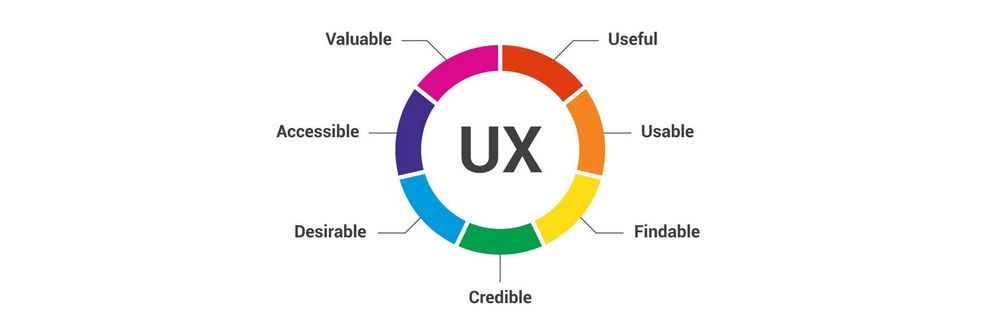
Adaptive vs. Responsive Design
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!
UX Research Techniques and Their Applications
UX research techniques and their applications will result in better designs that avoid costly mistakes such as cost overruns, guesswork, following best practices, and reliance on industry knowledge.

By Michael Craig
Michael is an experienced designer whose research-driven design process has resulted in purposeful user experiences that delight users.
PREVIOUSLY AT
If we knew what it was we were doing, it would not be called research, would it? —Albert Einstein
User research existed long before it became a part of the user experience (UX) process. In the early 1900s, Frank and Lillian Gilbreth pioneered motion study . In order to gain a better understanding of efficiency, they observed how people moved in space by watching bricklayers at construction sites. Motion study consisted of a variety of procedures for the description, systematic analysis, and means of improving work methods.
These observations led to the infamous time and motion studies, which paved the way for modern-day user research as a means to improve products through methodical and investigative user observations.
User research has improved vastly since then. Everything from an app to a kitchen blender has a design team with an embedded researcher trying to figure out ways to attract attention and improve the user experience.
Prior to the influence of user research, products were made to be utilitarian with no attention being paid to UX. And while this may have resulted in designs that worked (sometimes), the lack of a user-centric approach led to failed products which were the result of guesswork and best practices.
“We’re reducing risk, which is ultimately what user research does,” says Ashley Sewall , Senior User Researcher at Cvent. “We make sure designers, product managers, and developers have enough information to make effective decisions that are going to decrease their risk.”
There’s a lot of information on how to conduct UX research and create UX research assets, but little on how to use these assets. It’s not about the technique, it’s knowing how to apply the results that lead to better user experiences and improved product designs.
UX Research Methods and Frameworks
Let’s take a look at some popular user research methods before diving into how they are applied.
Personas and Empathy Maps
Without knowledge of who our users are, the following UX research techniques will not be as effective. This is where personas and empathy maps play an important role.
Personas and empathy maps serve as guides to better understand who the core users are and what is going on in their minds. They are typically used when a designer is seeking to address tasks that need to be performed, pain points that are blocks, how users feel, and what they are trying to achieve.

User Interviews
User interviews are one-on-one sessions that can be conducted in a variety of ways (in-person, focus groups, etc.), though increasingly they are performed remotely using video apps such as Skype or Zoom. Another popular method is the guerrilla style of interview where a user researcher performs “drop-in” style interviews on a random selection of users (such as at a coffee shop).
User interviews require a lot of skill in order to obtain valuable information. The UX researcher is attempting to learn how a user feels about a specific topic, product, service, etc., and it’s important they do more listening than talking, record qualitative feedback, observe, and avoid leading questions.
Research has shown that five user interviews will uncover 80% of issues , and selecting these five users will give more accurate results if we remember to use the personas developed prior to performing the research.
Surveys are scalable, inexpensive, and a quick way to collect specific information from users who fit the personas we defined early on in the research process.
The strength of surveys can also be their weakness. Because they are easy and less costly, there is a danger in using surveys and avoiding any further UX research methods. While surveys are certainly a great tool, they shouldn’t be used exclusively.
Card Sorting
Card sorts are another popular UX research method and are useful in determining the information architecture of websites and apps. They can be open, closed, or hybrid. A user is presented with a set of ideas/topics which they arrange into categories, either of their own choosing (open card sort), or pre-made (closed card sort) by the researcher.

As with surveys and interviews, card sorts should be performed with users who fit the user personas.
A/B Testing
When there is a need to test designs variations in order to find the most effective one, A/B testing , used primarily for conversion optimization, can also be used as a quantitative UX research method.
Users are presented with two different versions of a design, and pick which one they prefer; this also works to determine which features a user finds most useful, such as a button vs. a link.
With A/B testing, it’s a good idea to switch out the pool of testers. Over time, due to their familiarity with the product, the same people testing the same products can become biased and complacent.
Usability Testing
Usability testing is performed when designers want to observe how products are used by a representative user group.
During a usability test, users complete tasks while the UX researcher observes and takes notes. The researcher gathers both qualitative and quantitative data in order to find usability issues.

To run an effective usability test, it’s good practice to think about which user personas would be a good fit, and recruit early in the process. Incentives are often offered to users, but some UX researchers believe this adds a strong element of bias to the test, i.e., are the users only doing this for the incentive?
Practical Applications of UX Research Results
Unless there is an effort to analyze and act on the results of the UX research data, all of the work that went into the research loses its effectiveness.
If we think of UX research as part of the scientific method, then it will follow this format:
- Make an observation – Interviews, surveys
- Form a hypothesis – Make an assumption and draft a prototype
- Perform the experiment – Usability studies, A/B testing, card sorts
- Analyze the data – Perform analysis on the qualitative/quantitative feedback
- Report the findings – Discuss with the team and the client
- Invite others to reproduce the results – Collaborate and iterate
Using each of the above UX research methods, let’s look at a few ways to apply actionable insights from the research data gathered.
Applying Personas and Empathy Maps
Personas and empathy maps are a powerful set of tools that UX researchers can use for usage scenarios, characters for experience maps and storyboards, and as a focal point for ideation.
For example, if we have a persona attribute that signals “impatient/busy/always in a hurry,” we can make certain design decisions which enable this user to take shortcuts within the product and thus save them time.
Another use of personas is getting everyone (product, engineering, marketing, sales, and customer service) on the same page about who the users are, thereby facilitating a more unified user experience.
Implementing User Interview Data
User interviews result in qualitative data. With this data, we can use frameworks such as thematic analysis , which is the process of identifying patterns and themes using qualitative data.

An example is a user interview with the goal of getting feedback for a set of reports produced by an application.
The user interviews are completed and the data is analyzed using thematic analysis which shows a theme of customization . We can make an assumption that our users want to be able to customize their reports and have more control over them. This assumption can then be tested with further UX research.
Another practical use of user interviews is the opportunity to listen and observe. Users tend to give a lot of clues during an interview, such as making verbal side-comments, or non-verbal gestures. These observations can give insights into how users are truly feeling and thinking.
Employing Survey Results
Surveys provide a flexible set of data to work with. For example, we could have an idea to build a car-buying application that automatically calculates the car insurance rate for each listing.
Before spending the time and money to build out the application, surveys can be used to quickly gather information from a large number of users to see if it’s something people actually need.
If surveys are combined with usability testing, they can help find the answers to questions that pure analytical methods of UX research can’t tell us. For example, heat maps (a form of usability test), can tell us where users are interacting the most (and least) with an app or website, but they don’t tell us why.
Use surveys to ask why the user takes the actions they do, and then use this information to improve the product.
Using Card Sorting Data
A practical use of card sorting is to help determine how users would classify and organize topics for a website or app. The results of the card sort can then be used to construct an information architecture that fits their needs and goals.
An example is a florist website. We may have an idea of how users will want to navigate the site; however, when we do a card sort and ask users to provide categories, we learn that they look for flowers based mainly on color, not seasonality or special occasion.
Practical Use of A/B Testing Data
The data from an A/B test is mostly quantitative and binary; the user likes one version of something, or the other version.
One practical application which received a lot of coverage was Spotify testing their “burger menu.” Spotify used the standard three-line menu icon on their mobile app for a long time but decided to do an A/B test. To their surprise, this popular design was not a winner with their audience. Instead, users preferred a tab bar.
This had a major impact since there are millions of users who use the app daily. Changing to the new tab bar resulted in a better user experience and decreased subscription churn.
Applying Usability Testing
Usability testing produces both qualitative and quantitative data. There are several advantages that can be had with this data depending on the type of testing done and the presumed outcomes.
An example is a moderated usability test in which we observe a user during the checkout process of a new shopping app. What we see is the user trying to add a product to the cart several times, but unable to do so, finally abandoning the process altogether. Taking this feedback, we would go back to the drawing board to revise the checkout flow.
A second way of applying usability tests is validation of a prototype or MVP. For example, we might be redesigning a mobile coupon app and realize that there is no way for a user to perform a search for deals because they get stuck in the category they initially chose. This realization leads the design team to focus on the user flow within the app and improve the user experience.
Today’s experience economy shapes industries, transforms businesses, and helps companies build deeper, more meaningful, and more profitable relationships with their customers. By selecting appropriate UX research techniques and applying them diligently, designers can come up with products that serve both customers and businesses more effectively.
Further Reading on the Toptal Blog:
- UX Research Methods and the Path to User Empathy
- How to Conduct Effective UX Research: A Guide
- If You’re Not Using UX Data, It’s Not UX Design
- Design Talks: Research in Action with UX Researcher Caitria O'Neill
- The Value of User Research
Understanding the basics
How do you do ux research.
UX research is done using certain methods and frameworks which is decided based on the project and needs of the researcher. It is done by first identifying a specific type of user, then picking a research method, performing the research, and then analyzing the results.
What's a UX researcher?
A UX researcher is someone, usually from the UX field, who specializes in doing research using a methodical and investigative set of procedures to learn more about users needs, wants, and behaviors.
Why is UX research important?
UX research is important to both the design process and the business. It helps avoid guesswork, costly mistakes, and not creating products which are delightful and actually used by the audience intended.
What is a heat map chart?
A heat map chart shows where users interact the most and least with an interface, such as a web page. Heat map charts use both color and percentages to indicate where users have either clicked or scrolled to the most and the least.
What does a heat map tell you?
A heat map tells you where users interact with a web page or app the most or least using color and percentages. They are used to help researchers make more informed decisions to improve the user experience.
- Product Design
Michael Craig
Albany, GA, United States
Member since November 7, 2016
About the author
World-class articles, delivered weekly.
By entering your email, you are agreeing to our privacy policy .
Toptal Designers
- Adobe Creative Suite Experts
- Agile Designers
- AI Designers
- Art Direction Experts
- Augmented Reality Designers
- Axure Experts
- Brand Designers
- Creative Directors
- Dashboard Designers
- Digital Product Designers
- E-commerce Website Designers
- Full-Stack Designers
- Information Architecture Experts
- Interactive Designers
- Mobile App Designers
- Mockup Designers
- Presentation Designers
- Prototype Designers
- SaaS Designers
- Sketch Experts
- Squarespace Designers
- User Flow Designers
- User Research Designers
- Virtual Reality Designers
- Visual Designers
- Wireframing Experts
- View More Freelance Designers
Join the Toptal ® community.
- Get started Get started for free
Figma design
Design and prototype in one place
Collaborate with a digital whiteboard
Translate designs into code
Get the desktop, mobile, and font installer apps
See the latest features and releases
- Prototyping
- Design systems
- Wireframing
- Online whiteboard
- Team meetings
- Strategic planning
- Brainstorming
- Diagramming
- Product development
- Web development
- Design handoff
- Product managers
Organizations
Config 2024
Register to attend in person or online — June 26–27

Creator fund
Build and sell what you love
User groups
Join a local Friends of Figma group
Learn best practices at virtual events
Customer stories
Read about leading product teams
Stories about bringing new ideas to life
Get started
- Developer docs
- Best practices
- Reports & insights
- Resource library
- Help center
UX design research methods

Effective user experience design is intuitive, accessible, and engaging. But how do you design a delightful experience that meets your target audience’s needs? Conducting user experience research gives you a glimpse inside your users’ heads, so you can understand what they care about and the challenges they face.
In this article, Figma Designer Advocate Ana Boyer weighs in on:
- What user experience research is, and why your team needs it
- Different types of UX research that support product development
- UX design research methods made easier with Figma
What is user experience research?
User experience research helps design teams identify areas of opportunity to improve user interfaces and enhance the overall user experience. According to Ana, UX research can reveal insights about target users across all phases of product development—from strategy and planning to product launch and post-launch improvements. A robust UX research framework includes both quantitative and qualitative research.
Quantitative research
Using information gathered from larger sample sizes, quantitative research yields concrete numerical data that reveals what users are doing. Researchers run statistical analyses and review analytics to gain insights into user behavior. For example, Ana says, “you might try tracking the number of times users clicked a CTA button on a newly designed web page, compared to an old version."
Qualitative research
For qualitative research, researchers collect subjective and descriptive feedback directly from users, tapping into users’ personal feelings and experiences with a product or design. "Qualitative research gives you a more thorough explanation of why someone is doing something in the context of a flow,” Ana says.
User-centered design research often covers two types of qualitative research: attitudinal and behavioral. Attitudinal research examines users’ self-reported beliefs and perceptions related to a user experience, while behavioral research focuses on observing first-hand what users do with a product.
Sign up for Figma today
With Figma, you can create low or high fidelity designs for free. Sign up today.
3 benefits of user experience research
According to Ana, with UX research you can:
- Validate your design. "You can learn whether or not your design is hitting project goals and your users are able to accomplish a task—for example, ordering an item from your platform.”
- Put your users front and center. UX research uncovers what users want and need, so you can deliver a product that delights customers.
- Save time and resources. Doing user research and testing early and often allows you to make smaller adjustments quickly and easily. That way, Ana says, “you can take a more iterative approach to design—without having to backtrack and redo your entire UX design.”
How to conduct UX research
Most common UX research methodologies break down into these essential activities:
- Observe how users act and react . This not only includes clicks and scrolling onscreen, but also their body language and facial expressions. Careful observation helps you understand how users normally perform a task, what interactions users pick up easily or enjoy, where they get stuck in a flow, and more.
- Empathize with your users . To create a useful and usable product, you need to consider how users' context influences them as they interact with your design.
- Analyze information to surface common themes. “Tagging key user responses helps you pinpoint what needs the most work and refinement to improve the user experience," Ana advises
When to use key UX research methods—at a glance
Given all the UX research methods you can use for product development, when is each most useful? Ana offers these pro tips.
- User personas help you understand your core users in the early stages of development. “If you don’t know who you’re building for, then the time you invest in building and creating something will be wasted,” Ana explains. FigJam’s user persona template will help you get the ball rolling.
- Interviews gather in-depth information directly from users to test your ideas, so you can lower the risk of building a product that misses the target. FigJam’s user interview template will help you lay the groundwork.
- Card sorting invites users to show you what they think is the most intuitive way to organize high-level information in your design. Try FigJam’s card-sorting tool to shape your product’s information architecture.
- Task analysis studies users as they use your site or app to complete tasks, or jobs to be done. Use it to validate your design, and ensure users can quickly and easily accomplish their goals. Get started with FigJam’s jobs to be done template .
- Eye tracking analyzes where users look, when, and how long as they interact with your product.
- Surveys indicate how useful and usable your design is. Surveys can provide useful insights at any phase of product development, pinpointing where users are struggling with an interface, and revealing user sentiment about a product’s colors, fonts, and overall design.
Launch & post-launch
- A/B testing shows which version or iteration of a webpage, app screen, or CTA button performs better with your users.
- Analytics track KPIs like time spent on page, bounce rate, number of clicks on key CTAs, and more to see what’s working—and what isn’t. Analytics may also reveal useful insights about your users, including location, device usage, age, and gender.
- Usability bug testing identifies and helps fix usability issues that affect your product’s quality and ease of use. “Teams struggle to invest the time and process in doing this, but it can have a huge impact on quality,” Ana says.
- Diaries captured in writing or on video track users’ thoughts and impressions over a certain time period. This self-reporting approach reveals how a product fits into and enhances users’ daily lives.
Kick off user experience research with Figma
No matter where you are in the product development process, FigJam’s research plan template can help you define your research goals. Figma’s research and design templates help you conduct research with user interviews , user personas , card sorting , and Sprig study integration .
With the insights gained from your research, you're ready to design, develop, and prototype engaging user experiences. Use Figma’s UX design tool to:
- Give and receive instant feedback on designs or prototypes—and enjoy real-time collaboration with your team. Figma's Maze integration makes testing prototypes easy.
- Set up design libraries to quickly launch user research projects and improve UX design.
- Easily share assets between Figma and FigJam to help keep your projects moving forward.
To jumpstart your UX research, browse inspiring UX research resources shared by the Figma community .
Now you're ready to roll with UX research!
Go to next section
[1] https://www.nngroup.com/articles/which-ux-research-methods/
[2] https://www.uxbooth.com/articles/complete-beginners-guide-to-design-research/
Integrations
What's new?
Prototype Testing
Live Website Testing
Feedback Surveys
Interview Studies
Card Sorting
Tree Testing
In-Product Prompts
Participant Management
Automated Reports
Templates Gallery
Choose from our library of pre-built mazes to copy, customize, and share with your own users
Browse all templates
Financial Services
Tech & Software
Product Designers
Product Managers
User Researchers
By use case
Concept & Idea Validation
Wireframe & Usability Test
Content & Copy Testing
Feedback & Satisfaction
Content Hub
Educational resources for product, research and design teams
Explore all resources
Question Bank
Research Maturity Model
Guides & Reports
Help Center
Future of User Research Report
The Optimal Path Podcast
Maze Guides | Resources Hub
What is UX Research: The Ultimate Guide for UX Researchers
0% complete
11 Key UX research methods: How and when to use them
After defining your objectives and planning your research framework, it’s time to choose the research technique that will best serve your project's goals and yield the right insights. While user research is often treated as an afterthought, it should inform every design decision. In this chapter, we walk you through the most common research methods and help you choose the right one for you.

What are UX research methods?
A UX research method is a way of generating insights about your users, their behavior, motivations, and needs. You can use methods like user interviews, surveys, focus groups, card sorting, usability testing to identify user challenges and turn them into opportunities to improve the user experience.
More of a visual learner? Check out this video for a speedy rundown. If you’re ready to get stuck in, jump straight to our full breakdown .

The most common types of user research
First, let’s talk about the types of UX research. Every individual research method falls under these types, which reflect different goals and objectives for conducting research.
Here’s a quick overview:

Qualitative vs. quantitative
All research methods are either quantitative or qualitative . Qualitative research focuses on capturing subjective insights into users' experiences. It aims to understand the underlying reasons, motivations, and behaviors of individuals. Quantitative research, on the other hand, involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and significance. It aims to quantify user behaviors, preferences, and attitudes, allowing for generalizations and statistical insights.
Qualitative research also typically involves a smaller sample size than quantitative research (40 participants, as recommended by Nielsen Norman Group ).
Attitudinal vs. behavioral
Attitudinal research is about understanding users' attitudes, perceptions, and beliefs. It delves into the 'why' behind user decisions and actions. It often involves surveys or interviews where users are asked about their feelings, preferences, or perceptions towards a product or service. It's subjective in nature, aiming to capture people's emotions and opinions.
Behavioral research is about what users do rather than what they say they do or would do. This kind of research is often based on observation methods like usability testing, eye-tracking, or heat maps to understand user behavior.
Generative vs. evaluative
Generative research is all about generating new ideas, concepts, and insights to fuel the design process. You might run brainstorming sessions with groups of users, card sorting, and co-design sessions to inspire creativity and guide the development of user-centered solutions.
On the other hand, evaluative research focuses on assessing the usability, effectiveness, and overall quality of existing designs or prototypes. Once you’ve developed a prototype of your product, it's time to evaluate its strengths and weaknesses. You can compare different versions of a product design or feature through A/B testing—ensuring your UX design meets user needs and expectations.
Remove the guesswork from product decisions
Collect both quantitative and qualitative insights from your customers and build truly user-centric products with Maze.
11 Best UX research methods and when to use them
There are various UX research techniques—each method serves a specific purpose and can provide unique insights into user behaviors and preferences. In this section, we’ll highlight the most common research techniques you need to know.
Read on for an at-a-glance table, and full breakdown of each method.
User interviews
User interviews are a qualitative research method that involves having open-ended and guided discussions with users to gather in-depth insights about their experiences, needs, motivations, and behaviors.
Typically, you would ask a few questions on a specific topic and analyze participants' answers. The results you get will depend on how well you form and ask questions, as well as follow up on participants’ answers.
“As a researcher, it's our responsibility to drive the user to their actual problems,” says Yuliya Martinavichene , User Experience Researcher at Zinio. She adds, “The narration of incidents can help you analyze a lot of hidden details with regard to user behavior.”
That’s why you should:
- Start with a wide context : Make sure that your questions don’t start with your product
- Ask questions that focus on the tasks that users are trying to complete
- Invest in analysis : Get transcripts done and share the findings with your team
Tanya Nativ , Design Researcher at Sketch recommends defining the goals and assumptions internally. “Our beliefs about our users’ behavior really help to structure good questions and get to the root of the problem and its solution,” she explains.
It's easy to be misunderstood if you don't have experience writing interview questions. You can get someone to review them for you or use our Question Bank of 350+ research questions .
When to conduct user interviews
This method is typically used at the start and end of your project. At the start of a project, you can establish a strong understanding of your target users, their perspectives, and the context in which they’ll interact with your product. By the end of your project, new user interviews—often with a different set of individuals—offer a litmus test for your product's usability and appeal, providing firsthand accounts of experiences, perceived strengths, and potential areas for refinement.
Field studies
Field studies are research activities that take place in the user’s environment rather than in your lab or office. They’re a great method for uncovering context, unknown motivations, or constraints that affect the user experience.
An advantage of field studies is observing people in their natural environment, giving you a glimpse at the context in which your product is used. It’s useful to understand the context in which users complete tasks, learn about their needs, and collect in-depth user stories.
When to conduct field studies
This method can be used at all stages of your project—two key times you may want to conduct field studies are:
- As part of the discovery and exploration stage to define direction and understand the context around when and how users interact with the product
- During usability testing, once you have a prototype, to evaluate the effectiveness of the solution or validate design assumptions in real-world contexts
3. Focus groups
A focus group is a qualitative research method that includes the study of a group of people, their beliefs, and opinions. It’s typically used for market research or gathering feedback on products and messaging.
Focus groups can help you better grasp:
- How users perceive your product
- What users believe are a product’s most important features
- What problems do users experience with the product
As with any qualitative research method, the quality of the data collected through focus groups is only as robust as the preparation. So, it’s important to prepare a UX research plan you can refer to during the discussion.
Here’s some things to consider:
- Write a script to guide the conversation
- Ask clear, open-ended questions focused on the topics you’re trying to learn about
- Include around five to ten participants to keep the sessions focused and organized
When to conduct focus groups
It’s easier to use this research technique when you're still formulating your concept, product, or service—to explore user preferences, gather initial reactions, and generate ideas. This is because, in the early stages, you have flexibility and can make significant changes without incurring high costs.
Another way some researchers employ focus groups is post-launch to gather feedback and identify potential improvements. However, you can also use other methods here which may be more effective for identifying usability issues. For example, a platform like Maze can provide detailed, actionable data about how users interact with your product. These quantitative results are a great accompaniment to the qualitative data gathered from your focus group.
4. Diary studies
Diary studies involve asking users to track their usage and thoughts on your product by keeping logs or diaries, taking photos, explaining their activities, and highlighting things that stood out to them.
“Diary studies are one of the few ways you can get a peek into how users interact with our product in a real-world scenario,” says Tanya.
A diary study helps you tell the story of how products and services fit into people’s daily lives, and the touch-points and channels they choose to complete their tasks.
There’s several key questions to consider before conducting diary research, from what kind of diary you want—freeform or structured, and digital or paper—to how often you want participants to log their thoughts.
- Open, ‘freeform’ diary: Users have more freedom to record what and when they like, but can also lead to missed opportunities to capture data users might overlook
- Closed, ‘structured; diary: Users follow a stricter entry-logging process and answer pre-set questions
Remember to determine the trigger: a signal that lets the participants know when they should log their feedback. Tanya breaks these triggers down into the following:
- Interval-contingent trigger : Participants fill out the diary at specific intervals such as one entry per day, or one entry per week
- Signal-contingent trigger : You tell the participant when to make an entry and how you would prefer them to communicate it to you as well as your preferred type of communication
- Event-contingent trigger : The participant makes an entry whenever a defined event occurs
When to conduct diary studies
Diary studies are often valuable when you need to deeply understand users' behaviors, routines, and pain points in real-life contexts. This could be when you're:
- Conceptualizing a new product or feature: Gain insights into user habits, needs, and frustrations to inspire your design
- Trying to enhance an existing product: Identify areas where users are having difficulties or where there are opportunities for better user engagement
Although surveys are primarily used for quantitative research, they can also provided qualitative data, depending on whether you use closed or open-ended questions:
- Closed-ended questions come with a predefined set of answers to choose from using formats like rating scales, rankings, or multiple choice. This results in quantitative data.
- Open-ended question s are typically open-text questions where test participants give their responses in a free-form style. This results in qualitative data.
Matthieu Dixte , Product Researcher at Maze, explains the benefit of surveys: “With open-ended questions, researchers get insight into respondents' opinions, experiences, and explanations in their own words. This helps explore nuances that quantitative data alone may not capture.”
So, how do you make sure you’re asking the right survey questions? Gregg Bernstein , UX Researcher at Signal, says that when planning online surveys, it’s best to avoid questions that begin with “How likely are you to…?” Instead, Gregg says asking questions that start with “Have you ever… ?” will prompt users to give more specific and measurable answers.
Make sure your questions:
- Are easy to understand
- Don't guide participants towards a particular answer
- Include both closed-ended and open-ended questions
- Respect users and their privacy
- Are consistent in terms of format
To learn more about survey design, check out this guide .
When to conduct surveys
While surveys can be used at all stages of project development, and are ideal for continuous product discovery , the specific timing and purpose may vary depending on the research goals. For example, you can run surveys at:
- Conceptualization phase to gather preliminary data, and identify patterns, trends, or potential user segments
- Post-launch or during iterative design cycles to gather feedback on user satisfaction, feature usage, or suggestions for improvements
6. Card sorting
Card sorting is an important step in creating an intuitive information architecture (IA) and user experience. It’s also a great technique to generate ideas, naming conventions, or simply see how users understand topics.
In this UX research method, participants are presented with cards featuring different topics or information, and tasked with grouping the cards into categories that make sense to them.
There are three types of card sorting:
- Open card sorting: Participants organize topics into categories that make sense to them and name those categories, thus generating new ideas and names
- Hybrid card sorting: Participants can sort cards into predefined categories, but also have the option to create their own categories
- Closed card sorting: Participants are given predefined categories and asked to sort the items into the available groups
You can run a card sorting session using physical index cards or digitally with a UX research tool like Maze to simulate the drag-and-drop activity of dividing cards into groups. Running digital card sorting is ideal for any type of card sort, and moderated or unmoderated sessions.
Read more about card sorting and learn how to run a card sorting session here .
When to conduct card sorting
Card sorting isn’t limited to a single stage of design or development—it can be employed anytime you need to explore how users categorize or perceive information. For example, you may want to use card sorting if you need to:
- Understand how users perceive ideas
- Evaluate and prioritize potential solutions
- Generate name ideas and understand naming conventions
- Learn how users expect navigation to work
- Decide how to group content on a new or existing site
- Restructure information architecture
7. Tree testing
During tree testing a text-only version of the site is given to your participants, who are asked to complete a series of tasks requiring them to locate items on the app or website.
The data collected from a tree test helps you understand where users intuitively navigate first, and is an effective way to assess the findability, labeling, and information architecture of a product.
We recommend keeping these sessions short, ranging from 15 to 20 minutes, and asking participants to complete no more than ten tasks. This helps ensure participants remain focused and engaged, leading to more reliable and accurate data, and avoiding fatigue.
If you’re using a platform like Maze to run remote testing, you can easily recruit participants based on various demographic filters, including industry and country. This way, you can uncover a broader range of user preferences, ensuring a more comprehensive understanding of your target audience.
To learn more about tree testing, check out this chapter .
When to conduct tree testing
Tree testing is often done at an early stage in the design or redesign process. That’s because it’s more cost-effective to address errors at the start of a project—rather than making changes later in the development process or after launch.
However, it can be helpful to employ tree testing as a method when adding new features, particularly alongside card sorting.
While tree testing and card sorting can both help you with categorizing the content on a website, it’s important to note that they each approach this from a different angle and are used at different stages during the research process. Ideally, you should use the two in tandem: card sorting is recommended when defining and testing a new website architecture, while tree testing is meant to help you test how the navigation performs with users.
8. Usability testing
Usability testing evaluates your product with people by getting them to complete tasks while you observe and note their interactions (either during or after the test). The goal of conducting usability testing is to understand if your design is intuitive and easy to use. A sign of success is if users can easily accomplish their goals and complete tasks with your product.
There are various usability testing methods that you can use, such as moderated vs. unmoderated or qualitative vs. quantitative —and selecting the right one depends on your research goals, resources, and timeline.
Usability testing is usually performed with functional mid or hi-fi prototypes . If you have a Figma, InVision, Sketch, or prototype ready, you can import it into a platform like Maze and start testing your design with users immediately.
The tasks you create for usability tests should be:
- Realistic, and describe a scenario
- Actionable, and use action verbs (create, sign up, buy, etc)
Be mindful of using leading words such as ‘click here’ or ‘go to that page’ in your tasks. These instructions bias the results by helping users complete their tasks—something that doesn’t happen in real life.
Product tip ✨
With Maze, you can test your prototype and live website with real users to filter out cognitive biases, and gather actionable insights that fuel product decisions.
When to conduct usability testing
To inform your design decisions, you should do usability testing early and often in the process . Here are some guidelines to help you decide when to do usability testing:
- Before you start designing
- Once you have a wireframe or prototype
- Prior to the launch of the product
- At regular intervals after launch
To learn more about usability testing, check out our complete guide to usability testing .
9. Five-second testing
In five-second testing , participants are (unsurprisingly) given five seconds to view an image like a design or web page, and then they’re asked questions about the design to gauge their first impressions.
Why five seconds? According to data , 55% of visitors spend less than 15 seconds on a website, so it;s essential to grab someone’s attention in the first few seconds of their visit. With a five-second test, you can quickly determine what information users perceive and their impressions during the first five seconds of viewing a design.
Product tip 💡
And if you’re using Maze, you can simply upload an image of the screen you want to test, or browse your prototype and select a screen. Plus, you can star individual comments and automatically add them to your report to share with stakeholders.
When to conduct five-second testing
Five-second testing is typically conducted in the early stages of the design process, specifically during initial concept testing or prototype development. This way, you can evaluate your design's initial impact and make early refinements or adjustments to ensure its effectiveness, before putting design to development.
To learn more, check out our chapter on five-second testing .
10. A/B testing
A/B testing , also known as split testing, compares two or more versions of a webpage, interface, or feature to determine which performs better regarding engagement, conversions, or other predefined metrics.
It involves randomly dividing users into different groups and giving each group a different version of the design element being tested. For example, let's say the primary call-to-action on the page is a button that says ‘buy now’.
You're considering making changes to its design to see if it can lead to higher conversions, so you create two versions:
- Version A : The original design with the ‘buy now’ button positioned below the product description—shown to group A
- Version B : A variation with the ‘buy now’ button now prominently displayed above the product description—shown to group B
Over a planned period, you measure metrics like click-through rates, add-to-cart rates, and actual purchases to assess the performance of each variation. You find that Group B had significantly higher click-through and conversion rates than Group A. This indicates that showing the button above the product description drove higher user engagement and conversions.
Check out our A/B testing guide for more in-depth examples and guidance on how to run these tests.
When to conduct A/B testing
A/B testing can be used at all stages of the design and development process—whenever you want to collect direct, quantitative data and confirm a suspicion, or settle a design debate. This iterative testing approach allows you to continually improve your website's performance and user experience based on data-driven insights.
11. Concept testing
Concept testing is a type of research that evaluates the feasibility, appeal, and potential success of a new product before you build it. It centers the user in the ideation process, using UX research methods like A/B testing, surveys, and customer interviews.
There’s no one way to run a concept test—you can opt for concept testing surveys, interviews, focus groups, or any other method that gets qualitative data on your concept.
*Dive into our complete guide to concept testing for more tips and tricks on getting started. *
When to conduct concept testing
Concept testing helps gauge your audience’s interest, understanding, and likelihood-to-purchase, before committing time and resources to a concept. However, it can also be useful further down the product development line—such as when defining marketing messaging or just before launching.
Which is the best UX research type?
The best research type varies depending on your project; what your objectives are, and what stage you’re in. Ultimately, the ideal type of research is one which provides the insights required, using the available resources.
For example, if you're at the early ideation or product discovery stage, generative research methods can help you generate new ideas, understand user needs, and explore possibilities. As you move to the design and development phase, evaluative research methods and quantitative data become crucial.
Discover the UX research trends shaping the future of the industry and why the best results come from a combination of different research methods.
How to choose the right user experience research method
In an ideal world, a combination of all the insights you gain from multiple types of user research methods would guide every design decision. In practice, this can be hard to execute due to resources.
Sometimes the right methodology is the one you can get buy-in, budget, and time for.

Gregg Bernstein , UX Researcher at Signal
UX research tools can help streamline the research process, making regular testing and application of diverse methods more accessible—so you always keep the user at the center of your design process. Some other key tips to remember when choosing your method are:
Define the goals and problems
A good way to inform your choice of user experience research method is to start by considering your goals. You might want to browse UX research templates or read about examples of research.
Michael Margolis , UX Research Partner at Google Ventures, recommends answering questions like:
- “What do your users need?”
- “What are your users struggling with?”
- “How can you help your users?”
Understand the design process stage
If your team is very early in product development, generative research —like field studies—make sense. If you need to test design mockups or a prototype, evaluative research methods—such as usability testing—will work best.
This is something they’re big on at Sketch, as we heard from Design Researcher, Tanya Nativ. She says, “In the discovery phase, we focus on user interviews and contextual inquiries. The testing phase is more about dogfooding, concept testing, and usability testing. Once a feature has been launched, it’s about ongoing listening.”
Consider the type of insights required
If you're looking for rich, qualitative data that delves into user behaviors, motivations, and emotions, then methods like user interviews or field studies are ideal. They’ll help you uncover the ‘why’ behind user actions.
On the other hand, if you need to gather quantitative data to measure user satisfaction or compare different design variations, methods like surveys or A/B testing are more suitable. These methods will help you get hard numbers and concrete data on preferences and behavior.
*Discover the UX research trends shaping the future of the industry and why the best results come from a combination of different research methods. *
Build a deeper understanding of your users with UX research
Think of UX research methods as building blocks that work together to create a well-rounded understanding of your users. Each method brings its own unique strengths, whether it's human empathy from user interviews or the vast data from surveys.
But it's not just about choosing the right UX research methods; the research platform you use is equally important. You need a platform that empowers your team to collect data, analyze, and collaborate seamlessly.
Simplifying product research is simple with Maze. From tree testing to card sorting, prototype testing to user interview analysis—Maze makes getting actionable insights easy, whatever method you opt for.
Meanwhile, if you want to know more about testing methods, head on to the next chapter all about tree testing .
Get valuable insights from real users
Conduct impactful UX research with Maze and improve your product experience and customer satisfaction.
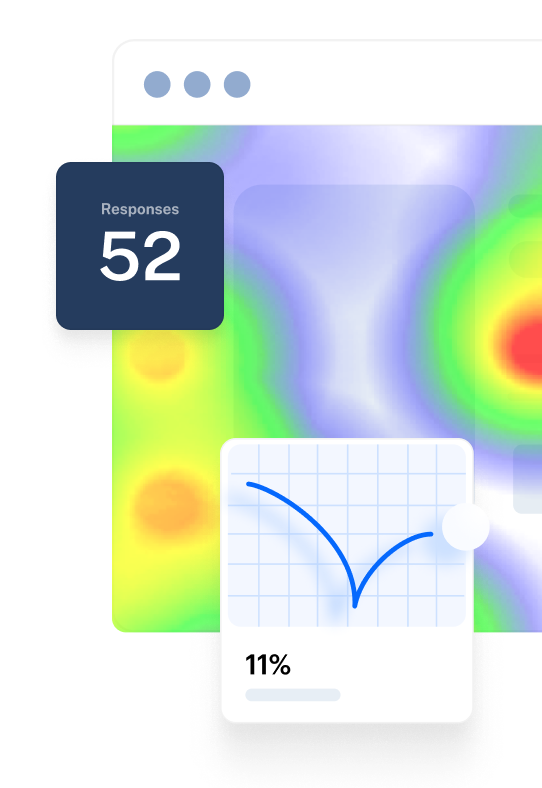
Frequently asked questions
How do you choose the right UX research method?
Choosing the right research method depends on your goals. Some key things to consider are:
- The feature/product you’re testing
- The type of data you’re looking for
- The design stage
- The time and resources you have available
What is the best UX research method?
The best research method is the one you have the time, resources, and budget for that meets your specific needs and goals. Most research tools, like Maze, will accommodate a variety of UX research and testing techniques.
When to use which user experience research method?
Selecting which user research method to use—if budget and resources aren’t a factor—depends on your goals. UX research methods provide different types of data:
- Qualitative vs quantitative
- Attitudinal vs behavioral
- Generative vs evaluative
Identify your goals, then choose a research method that gathers the user data you need.
Tree Testing: Your Guide to Improve Navigation and UX

Pulse UX Blog
Theory, Analysis and Reviews on UX User Experience Research and Design
Home Mission About Charles L. Mauro CHFP
« Updates From Mauro Usability Science - Critical Analysis of Maeda Design in Tech Report 2017 »
User Interface Design and UX Design: 80+ Important Research Papers Covering Peer-Reviewed and Informal Studies
Charles Mauro CHFP
Important peer-reviewed and informally published recent research on user interface design and user experience (UX) design.
For the benefit of clients and colleagues we have culled a list of approximately 70 curated recent research publications dealing with user interface design, UX design and e-commerce optimization.
In our opinion these publications represent some of the best formal research thinking on UI and UX design. These papers are also among the most widely downloaded and cited formal research on UI / UX design. We have referenced many of these studies in our work at MauroNewMedia.

Pay walls: As you will note in reviewing the following links and abstracts, most of the serious research on UI / UX design and optimization is located behind pay walls controlled by major publishers. However, in the end, good data is well worth the investment. Many links and other cited references are, of course, free.
Important disclaimer: We do not receive any form of compensation for citing any of the following content. Either Charles L Mauro CHFP or Paul Thurman MBA has personally reviewed all papers and links in this list. Some of these references were utilized in the recent NYTECH UX talk given by Paul Thurman MBA titled: Critical New UX Design Optimization Research
In addition to historical research papers, we frequently receive requests from colleagues, clients and journalists for recommended reading lists on topics covering our expertise in UX design, usability research and human factors engineering. These requests prompted us to pull from our research library (yes, we still have real books) 30+ books which our professional staff felt should be considered primary conceptual literature for anyone well-read in the theory and practice of UX design and research. Please follow the for PulseUX’s compilation of the 30+ Best UX Design and Research Books of All Time
Title: The influence of hedonic and utilitarian motivations on user engagement: The case of online shopping experiences
Abstract User experience seeks to promote rich, engaging interactions between users and systems. In order for this experience to unfold, the user must be motivated to initiate an interaction with the technology. This study explored hedonic and utilitarian motivations in the context of user engagement with online shopping. Factor analysis was performed to identify a parsimonious set of factors from the Hedonic and Utilitarian Shopping Motivation Scale and the User Engagement Scale based on responses from 802 shoppers. Multiple linear regression was used to test hypotheses with hedonic and utilitarian motivations (Idea, Social, Adventure/Gratification, Value and Achievement Shopping) and attributes of user engagement (Aesthetics, Focused Attention, Perceived Usability, and Endurability). Results demonstrate the salience of Adventure/Gratification Shopping and Achievement Shopping Motivations to specific variables of user engagement in the e-commerce environment and provide considerations for the inclusion of different types of motivation into models of engaging user experiences. Abstract Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: New Support for Marketing Analytics
Abstract Consumer surveys and myriad other forms of research have long been the grist for marketing decisions at large companies. But many firms have been reluctant to embrace the high-tech approach to data gathering and number crunching that falls under the rubric of marketing analytics, which uses advanced techniques to transform the tracking of promotional efforts, customer preferences, and industry developments into sophisticated branding and advertising campaigns. Fueled in part by Tom Peters and Robert Waterman’s seminal 1982 book In Search of Excellence , which coined the phrase “paralysis through analysis,” skepticism about the approach remains widespread, even in the face of a number of positive research results over the years. This new study, involving Fortune 1000 companies, offers yet more ammunition for supporters of marketing analytics. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Booz & Company Inc. All rights reserved.
Title: Video game values: Human-computer interaction and games
Abstract Current human–computer interaction (HCI) research into video games rarely considers how they are different from other forms of software. This leads to research that, while useful concerning standard issues of interface design, does not address the nature of video games as games specifically. Unlike most software, video games are not made to support external, user-defined tasks, but instead define their own activities for players to engage in. We argue that video games contain systems of values which players perceive and adopt, and which shape the play of the game. A focus on video game values promotes a holistic view of video games as software, media, and as games specifically, which leads to a genuine video game HCI. Abstract Copyright © 2006 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: When fingers do the talking: a study of text messaging
Abstract SMS or text messaging is an area of growth in the communications field. The studies described below consisted of a questionnaire and a diary study. The questionnaire was designed to examine texting activities in 565 users of the mobile phone. The diary study was carried out by 24 subjects over a period of 2 weeks. The findings suggest that text messaging is being used by a wide range of people for all kinds of activities and that for some people it is the preferred means of communication. These studies should prove interesting for those examining the use and impact of SMS. Abstract Copyright © 2004 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Understanding factors affecting trust in and satisfaction with mobile banking in Korea: A modified DeLone and McLean’s model perspective
Abstract As mobile technology has developed, mobile banking has become accepted as part of daily life. Although many studies have been conducted to assess users’ satisfaction with mobile applications, none has focused on the ways in which the three quality factors associated with mobile banking – system quality, information quality and interface design quality – affect consumers’ trust and satisfaction. Our proposed research model, based on DeLone and McLean’s model, assesses how these three external quality factors can impact satisfaction and trust. We collected 276 valid questionnaires from mobile banking customers, then analyzed them using structural equation modeling. Our results show that system quality and information quality significantly influence customers’ trust and satisfaction, and that interface design quality does not. We present herein implications and suggestions for further research. Abstract Copyright © 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.

Title: What is beautiful is usable
Abstract An experiment was conducted to test the relationships between users’ perceptions of a computerized system’s beauty and usability. The experiment used a computerized application as a surrogate for an Automated Teller Machine (ATM). Perceptions were elicited before and after the participants used the system. Pre-experimental measures indicate strong correlations between system’s perceived aesthetics and perceived usability. Post-experimental measures indicated that the strong correlation remained intact. A multivariate analysis of covariance revealed that the degree of system’s aesthetics affected the post-use perceptions of both aesthetics and usability, whereas the degree of actual usability had no such effect. The results resemble those found by social psychologists regarding the effect of physical attractiveness on the valuation of other personality attributes. The findings stress the importance of studying the aesthetic aspect of human–computer interaction (HCI) design and its relationships to other design dimensions. Abstract Copyright © 2000 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: UX Curve: A method for evaluating long-term user experience
Abstract The goal of user experience design in industry is to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty through the utility, ease of use, and pleasure provided in the interaction with a product. So far, user experience studies have mostly focused on short-term evaluations and consequently on aspects relating to the initial adoption of new product designs. Nevertheless, the relationship between the user and the product evolves over long periods of time and the relevance of prolonged use for market success has been recently highlighted. In this paper, we argue for the cost-effective elicitation of longitudinal user experience data. We propose a method called the “UX Curve” which aims at assisting users in retrospectively reporting how and why their experience with a product has changed over time. The usefulness of the UX Curve method was assessed in a qualitative study with 20 mobile phone users. In particular, we investigated how users’ specific memories of their experiences with their mobile phones guide their behavior and their willingness to recommend the product to others. The results suggest that the UX Curve method enables users and researchers to determine the quality of long-term user experience and the influences that improve user experience over time or cause it to deteriorate. The method provided rich qualitative data and we found that an improving trend of perceived attractiveness of mobile phones was related to user satisfaction and willingness to recommend their phone to friends. This highlights that sustaining perceived attractiveness can be a differentiating factor in the user acceptance of personal interactive products such as mobile phones. The study suggests that the proposed method can be used as a straightforward tool for understanding the reasons why user experience improves or worsens in long-term product use and how these reasons relate to customer loyalty. Abstract Copyright 2011 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Heuristic evaluation: Comparing ways of finding and reporting usability problems
Abstract Research on heuristic evaluation in recent years has focused on improving its effectiveness and efficiency with respect to user testing. The aim of this paper is to refine a research agenda for comparing and contrasting evaluation methods. To reach this goal, a framework is presented to evaluate the effectiveness of different types of support for structured usability problem reporting. This paper reports on an empirical study of this framework that compares two sets of heuristics, Nielsen’s heuristics and the cognitive principles of Gerhardt-Powals, and two media of reporting a usability problem, i.e. either using a web tool or paper. The study found that there were no significant differences between any of the four groups in effectiveness, efficiency and inter-evaluator reliability. A more significant contribution of this research is that the framework used for the experiments proved successful and should be reusable by other researchers because of its thorough structure. Abstract Copyright © 2006 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Socio-technical systems: From design methods to systems engineering
Abstract It is widely acknowledged that adopting a socio-technical approach to system development leads to systems that are more acceptable to end users and deliver better value to stakeholders. Despite this, such approaches are not widely practised. We analyse the reasons for this, highlighting some of the problems with the better known socio-technical design methods. Based on this analysis we propose a new pragmatic framework for socio-technical systems engineering (STSE) which builds on the (largely independent) research of groups investigating work design, information systems, computer-supported cooperative work, and cognitive systems engineering. STSE bridges the traditional gap between organisational change and system development using two main types of activity: sensitisation and awareness; and constructive engagement. From the framework, we identify an initial set of interdisciplinary research problems that address how to apply socio-technical approaches in a cost-effective way, and how to facilitate the integration of STSE with existing systems and software engineering approaches. Abstract Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Five reasons for scenario-based design
Abstract Scenarios of human–computer interaction help us to understand and to create computer systems and applications as artifacts of human activity—as things to learn from, as tools to use in one’s work, as media for interacting with other people. Scenario-based design of information technology addresses five technical challenges: scenarios evoke reflection in the content of design work, helping developers coordinate design action and reflection. Scenarios are at once concrete and flexible, helping developers manage the fluidity of design situations. Scenarios afford multiple views of an interaction, diverse kinds and amounts of detailing, helping developers manage the many consequences entailed by any given design move. Scenarios can also be abstracted and categorized, helping designers to recognize, capture and reuse generalizations and to address the challenge that technical knowledge often lags the needs of technical design. Finally, scenarios promote work-oriented communication among stakeholders, helping to make design activities more accessible to the great variety of expertise that can contribute to design, and addressing the challenge that external constraints designers and clients face often distract attention from the needs and concerns of the people who will use the technology. Abstract Copyright © 2000 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Needs, affect, and interactive products – Facets of user experience
Abstract Subsumed under the umbrella of User Experience (UX), practitioners and academics of Human–Computer Interaction look for ways to broaden their understanding of what constitutes “pleasurable experiences” with technology. The present study considered the fulfilment of universal psychological needs, such as competence, relatedness, popularity, stimulation, meaning, security, or autonomy, to be the major source of positive experience with interactive technologies. To explore this, we collected over 500 positive experiences with interactive products (e.g., mobile phones, computers). As expected, we found a clear relationship between need fulfilment and positive affect, with stimulation, relatedness, competence and popularity being especially salient needs. Experiences could be further categorized by the primary need they fulfil, with apparent qualitative differences among some of the categories in terms of the emotions involved. Need fulfilment was clearly linked to hedonic quality perceptions, but not as strongly to pragmatic quality (i.e., perceived usability), which supports the notion of hedonic quality as “motivator” and pragmatic quality as “hygiene factor.” Whether hedonic quality ratings reflected need fulfilment depended on the belief that the product was responsible for the experience (i.e., attribution). Abstract Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: The role of social presence in establishing loyalty in e-Service environments
Abstract Compared to offline shopping, the online shopping experience may be viewed as lacking human warmth and sociability as it is more impersonal, anonymous, automated and generally devoid of face-to-face interactions. Thus, understanding how to create customer loyalty in online environments (e-Loyalty) is a complex process. In this paper a model for e-Loyalty is proposed and used to examine how varied conditions of social presence in a B2C e-Services context influence e-Loyalty and its antecedents of perceived usefulness, trust and enjoyment. This model is examined through an empirical study involving 185 subjects using structural equation modeling techniques. Further analysis is conducted to reveal gender differences concerning hedonic elements in the model on e-Loyalty. Abstract Copyright © 2006 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: A framework for evaluating the usability of mobile phones based on multi-level, hierarchical model of usability factors
Abstract As a mobile phone has various advanced functionalities or features, usability issues are increasingly challenging. Due to the particular characteristics of a mobile phone, typical usability evaluation methods and heuristics, most of which are relevant to a software system, might not effectively be applied to a mobile phone. Another point to consider is that usability evaluation activities should help designers find usability problems easily and produce better design solutions. To support usability practitioners of the mobile phone industry, we propose a framework for evaluating the usability of a mobile phone, based on a multi-level, hierarchical model of usability factors, in an analytic way. The model was developed on the basis of a set of collected usability problems and our previous study on a conceptual framework for identifying usability impact factors. It has multi-abstraction levels, each of which considers the usability of a mobile phone from a particular perspective. As there are goal-means relationships between adjacent levels, a range of usability issues can be interpreted in a holistic as well as diagnostic way. Another advantage is that it supports two different types of evaluation approaches: task-based and interface-based. To support both evaluation approaches, we developed four sets of checklists, each of which is concerned, respectively, with task-based evaluation and three different interface types: Logical User Interface (LUI), Physical User Interface (PUI) and Graphical User Interface (GUI). The proposed framework specifies an approach to quantifying usability so that several usability aspects are collectively measured to give a single score with the use of the checklists. A small case study was conducted in order to examine the applicability of the framework and to identify the aspects of the framework to be improved. It showed that it could be a useful tool for evaluating the usability of a mobile phone. Based on the case study, we improved the framework in order that usability practitioners can use it more easily and consistently. Abstract Copyright © 2011 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Understanding the most satisfying and unsatisfying user experiences: Emotions, psychological needs, and context
Abstract The aim of this research was to study the structure of the most satisfying and unsatisfying user experiences in terms of experienced emotions, psychological needs, and contextual factors. 45 university students wrote descriptions of their most satisfying and unsatisfying recent user experiences and analyzed those experiences using the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS) method for experienced emotions, a questionnaire probing the salience of 10 psychological needs, and a self-made set of rating scales for analyzing context. The results suggested that it was possible to capture variations in user experiences in terms of experienced emotions, fulfillment of psychological needs, and context effectively by using psychometric rating scales. The results for emotional experiences showed significant differences in 16 out of 20 PANAS emotions between the most satisfying and unsatisfying experiences. The results for psychological needs indicated that feelings of autonomy and competence emerged as highly salient in the most satisfying experiences and missing in the unsatisfying experiences. High self-esteem was also notably salient in the most satisfying experiences. The qualitative results indicated that most of the participants’ free-form qualitative descriptions, especially for the most unsatisfying user experiences, gave important information about the pragmatic aspects of the interaction, but often omitted information about hedonic and social aspects of user experience. Abstract Copyright © 2011 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: The Usability Metric for User Experience
Abstract The Usability Metric for User Experience (UMUX) is a four-item Likert scale used for the subjective assessment of an application’s perceived usability. It is designed to provide results similar to those obtained with the 10-item System Usability Scale, and is organized around the ISO 9241-11 definition of usability. A pilot version was assembled from candidate items, which was then tested alongside the System Usability Scale during usability testing. It was shown that the two scales correlate well, are reliable, and both align on one underlying usability factor. In addition, the Usability Metric for User Experience is compact enough to serve as a usability module in a broader user experience metric. Abstract Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.

Title: User acceptance of mobile Internet: Implication for convergence technologies
Abstract Using the Technology Acceptance Model as a conceptual framework and a method of structural equation modeling, this study analyzes the consumer attitude toward Wi-Bro drawing data from 515 consumers. Individuals’ responses to questions about whether they use/accept Wi-Bro were collected and combined with various factors modified from the Technology Acceptance Model.
The result of this study show that users’ perceptions are significantly associated with their motivation to use Wi-Bro. Specifically, perceived quality and perceived availability are found to have significant effect on users’ extrinsic and intrinsic motivation. These new factors are found to be Wi-Bro-specific factors, playing as enhancing factors to attitudes and intention. Abstract Copyright © 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Understanding purchasing behaviors in a virtual economy: Consumer behavior involving virtual currency in Web 2.0 communities
Abstract This study analyzes consumer purchasing behavior in Web 2.0, expanding the technology acceptance model (TAM), focusing on which variables influence the intention to transact with virtual currency. Individuals’ responses to questions about attitude and intention to transact in Web 2.0 were collected and analyzed with various factors modified from the TAM. The results of the proposed model show that subjective norm is a key behavioral antecedent to using virtual currency. In the extended model, the moderating effects of subjective norm on the relations among the variables were found to be significant. The new set of variables is virtual environment-specific, acting as factors enhancing attitudes and behavioral intentions in Web 2.0 transactions. Abstract Copyright © 2008 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Fundamentals of physiological computing
Abstract This review paper is concerned with the development of physiological computing systems that employ real-time measures of psychophysiology to communicate the psychological state of the user to an adaptive system. It is argued that physiological computing has enormous potential to innovate human–computer interaction by extending the communication bandwidth to enable the development of ‘smart’ technology. This paper focuses on six fundamental issues for physiological computing systems through a review and synthesis of existing literature, these are (1) the complexity of the psychophysiological inference, (2) validating the psychophysiological inference, (3) representing the psychological state of the user, (4) designing explicit and implicit system interventions, (5) defining the biocybernetic loop that controls system adaptation, and (6) ethical implications. The paper concludes that physiological computing provides opportunities to innovate HCI but complex methodological/conceptual issues must be fully tackled during the research and development phase if this nascent technology is to achieve its potential. Abstract Copyright © 2008 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Modelling user experience with web sites: Usability, hedonic value, beauty and goodness
Abstract Recent research into user experience has identified the need for a theoretical model to build cumulative knowledge in research addressing how the overall quality or ‘goodness’ of an interactive product is formed. An experiment tested and extended Hassenzahl’s model of aesthetic experience. The study used a 2 × 2 × (2) experimental design with three factors: principles of screen design, principles for organizing information on a web page and experience of using a web site. Dependent variables included hedonic perceptions and evaluations of a web site as well as measures of task performance, navigation behaviour and mental effort. Measures, except Beauty, were sensitive to manipulation of web design. Beauty was influenced by hedonic attributes (identification and stimulation), but Goodness by both hedonic and pragmatic (user-perceived usability) attributes as well as task performance and mental effort. Hedonic quality was more stable with experience of web-site use than pragmatic quality and Beauty was more stable than Goodness. Abstract Copyright © 2008 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Sample Size In Usability Studies
Abstract Usability studies are a cornerstone activity for developing usable products. Their effectiveness depends on sample size, and determining sample sizehas been a research issue in usability engineering for the past 30 years. In 2010, Hwang and Salvendy reported a meta study on the effectiveness of usability evaluation, concluding that a sample size of 10±2 is sufficient for discovering 80% of usability problems (not five, as suggested earlier by Nielsen in 2000). Here, I show the Hwang and Salvendy study ignored fundamental mathematical properties of the problem, severely limiting the validity of the 10±2 rule, then look to reframe the issue of effectiveness and sample-size estimation to the practices and requirements commonly encountered in industrial-scale usability studies. Abstract Copyright © 2013 ACM, Inc. Title: An experimental study of learner perceptions of the interactivity of web-based instruction
Abstract An effectively designed interaction mechanism creates a shortcut for human–computer interaction. Most studies in this area have concluded that the higher the level of interactivity, the better, especially regarding interactive websites applied in the fields of business and education. Previous studies have also suggested that designs with a higher level of interactivity result in higher learner evaluations of websites. However, little research has examined learner perceptions as they interact with web-based instruction (WBI) systems in a situation with limited time. To assist learners in acquiring knowledge quickly, the interactivity design must make the web learning environment easier to use by reducing the complexity of the interface. The aim of the present study is to explore learner perceptions of three WBI systems with different interaction levels under time limitations. This study was therefore designed to provide a new framework to design systems with different degrees of interactivity, and to examine learners’ perceptions of these interaction elements. Three WBI systems were developed with different degrees of interactivity from high to low, and a between-subject experiment was conducted with 45 subjects. The results of the experiment indicate that a higher level of interactivity does not necessarily guarantee a higher perception of interactivity in a short-term learning situation. Therefore, the instructors must pay attention to modifying or selecting appropriate interactive elements that are more suitable for various learning stages. The findings provide insights for designers to adopt different degrees of interactivity in their designs that will best fulfill various learners’ needs. Abstract Copyright © 2011 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.

Title: Age differences in the perception of social presence in the use of 3D virtual world for social interaction
Abstract 3D virtual worlds are becoming increasingly popular as tool for social interaction, with the potential of augmenting the user’s perception of physical and social presence. Thus, this technology could be of great benefit to older people, providing home-bound older users with access to social, educational and recreational resources. However, so far there have been few studies looking into how older people engage with virtual worlds, as most research in this area focuses on younger users. In this study, an online experiment was conducted with 30 older and 30 younger users to investigate age differences in the perception of presence in the use of virtual worlds for social interaction. Overall, we found that factors such as navigation and prior experience with text messaging tools played a key role in older people’s perception of presence. Both physical and social presence was found to be linked to the quality of social interaction for users of both age groups. In addition, older people displayed proxemic behavior which was more similar to proxemic behavior in the physical world when compared to younger users. Abstract Copyright © 2012 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Human error and information systems failure: the case of the London ambulance service computer-aided despatch system project
Abstract Human error and systems failure have been two constructs that have become linked in many contexts. In this paper we particularly focus on the issue of failure in relation to that group of software systems known as information systems. We first review the extant theoretical and empirical work on this topic. Then we discuss one particular well-known case — that of the London ambulance service computer-aided despatch system (Lascad) project — and use it as a particularly cogent example of the features of information systems failure. We maintain that the tendency to analyse information systems failure solely from a technological standpoint is limiting, that the nature of information systems failure is multi-faceted, and hence cannot be adequately understood purely in terms of the immediate problems of systems construction. Our purpose is also to use the generic material on IS failure and the specific details of this particular case study to critique the issues of safety, criticality, human error and risk in relation to systems not currently well considered in relation to these areas. Abstract Copyright © 1999 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.

Title: Feminist HCI meets facebook: Performativity and social networking sites
Abstract In this paper, I reflect on a specific product of interaction design, social networking sites. The goals of this paper are twofold. One is to bring a feminist reflexivity, to HCI, drawing on the work of Judith Butler and her concepts of peformativity, citationality, and interpellation. Her approach is, I argue, highly relevant to issues of identity and self-representation on social networking sites; and to the co-constitution of the subject and technology. A critical, feminist HCI must ask how social media and other HCI institutions, practices, and discourses are part of the processes by which sociotechnical configurations are constructed. My second goal is to examine the implications of such an approach by applying it to social networking sites (SNSs) drawing the empirical research literature on SNSs, to show how SNS structures and policies help shape the subject and hide the contingency of subject categories. Abstract Copyright © 2011 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: A survey of methods for data fusion and system adaptation using autonomic nervous system responses in physiological computing
Abstract Physiological computing represents a mode of human–computer interaction where the computer monitors, analyzes and responds to the user’s psychophysiological activity in real-time. Within the field, autonomic nervous system responses have been studied extensively since they can be measured quickly and unobtrusively. However, despite a vast body of literature available on the subject, there is still no universally accepted set of rules that would translate physiological data to psychological states. This paper surveys the work performed on data fusion and system adaptation using autonomic nervous system responses in psychophysiology and physiological computing during the last ten years. First, five prerequisites for data fusion are examined: psychological model selection, training set preparation, feature extraction, normalization and dimension reduction. Then, different methods for either classification or estimation of psychological states from the extracted features are presented and compared. Finally, implementations of system adaptation are reviewed: changing the system that the user is interacting with in response to cognitive or affective information inferred from autonomic nervous system responses. The paper is aimed primarily at psychologists and computer scientists who have already recorded autonomic nervous system responses and now need to create algorithms to determine the subject’s psychological state. Abstract Copyright © 2012 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Positive mood induction procedures for virtual environments designed for elderly people
Abstract Positive emotions have a significant influence on mental and physical health. Their role in the elderly’s wellbeing has been established in numerous studies. It is therefore worthwhile to explore ways in which elderly people can increase the number of positive experiences in their daily lives. This paper describes two Virtual Environments (VEs) that were used as mood induction procedures (MIPs) for this population. In addition, the VEs’ efficacy at increasing joy and relaxation in elderly users is analyzed. The VEs contain exercises for generating positive-autobiographic memories, mindfulness and slow breathing rhythms. The total sample comprised 18 participants over 55 years old who used the VEs on two occasions. Twelve of them used the joy environment, while 16 used the relaxation environment. Moods before and after each session were assessed using Visual Analogical Scales. After using both VEs, results indicated significant increases in joy and relaxation and significant decreases in sadness and anxiety. The participants also indicated low levels of difficulty of use and high levels of satisfaction and sense of presence. Hence, the VEs demonstrate their usefulness at promoting positive affects and enhancing the wellbeing of elderly people. Abstract Copyright © 2012 British Informatics Society Limited. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: The effects of trust, security and privacy in social networking: A security-based approach to understand the pattern of adoption
Abstract Social network services (SNS) focus on building online communities of people who share interests and/or activities, or who are interested in exploring the interests and activities of others. This study examines security, trust, and privacy concerns with regard to social networking Websites among consumers using both reliable scales and measures. It proposes an SNS acceptance model by integrating cognitive as well as affective attitudes as primary influencing factors, which are driven by underlying beliefs, perceived security, perceived privacy, trust, attitude, and intention. Results from a survey of SNS users validate that the proposed theoretical model explains and predicts user acceptance of SNS substantially well. The model shows excellent measurement properties and establishes perceived privacy and perceived security of SNS as distinct constructs. The finding also reveals that perceived security moderates the effect of perceived privacy on trust. Based on the results of this study, practical implications for marketing strategies in SNS markets and theoretical implications are recommended accordingly. Abstract Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Usability testing: what have we overlooked?
Abstract For more than a decade, the number of usability test participants has been a major theme of debate among usability practitioners and researchers keen to improve usability test performance. This paper provides evidence suggesting that the focus be shifted to task coverage instead. Our data analysis of nine commercial usability test teams participating in the CUE-4 study revealed no significant correlation between the percentage of problems found or of new problems and number of test users, but correlations of both variables and number of user tasks used by each usability team were significant. The role of participant recruitment on usability test performance and future research directions are discussed. Abstract Copyright © 2013 ACM, Inc.
Title: Predicting online grocery buying intention: a comparison of the theory of reasoned action and the theory of planned behavior
Abstract This paper tests the ability of two consumer theories—the theory of reasoned action and the theory of planned behavior—in predicting consumer online grocery buying intention. In addition, a comparison of the two theories is conducted. Data were collected from two web-based surveys of Danish ( n =1222) and Swedish ( n =1038) consumers using self-administered questionnaires. These results suggest that the theory of planned behavior (with the inclusion of a path from subjective norm to attitude) provides the best fit to the data and explains the highest proportion of variation in online grocery buying intention. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Decomposition and crossover effects in the theory of planned behavior: A study of consumer adoption intentions
Abstract The Theory of Planned Behavior, an extension of the well-known Theory of Reasoned Action, is proposed as a model to predict consumer adoption intention. Three variations of the Theory of Planned Behavior are examined and compared to the Theory of Reasoned Action. The appropriateness of each model is assessed with data from a consumer setting. Structural equation modelling using maximum likelihood estimation for the four models revealed that the traditional forms of the Theory of Reasoned Action and the Theory of Planned Behavior fit the data adequately. Decomposing the belief structures and allowing for crossover effects in the Theory of Planned Behavior resulted in improvements in model prediction. The application of each model to theory development and management intervention is explored. Abstract Copyright © 1995 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Title: Knowledge and the Prediction of Behavior: The Role of Information Accuracy in the Theory of Planned Behavior
Abstract The results of the present research question the common assumption that being well informed is a prerequisite for effective action to produce desired outcomes. In Study 1 ( N = 79), environmental knowledge had no effect on energy conservation, and in Study 2 ( N = 79), alcohol knowledge was unrelated to drinking behavior. Such disappointing correlations may result from an inappropriate focus on accuracy of information at the expense of its relevance to and support for the behavior. Study 3 ( N = 85) obtained a positive correlation between knowledge and pro-Muslim behavior, but Study 4 ( N = 89) confirmed the proposition that this correlation arose because responses on the knowledge test reflected underlying attitudes. Study 4 also showed that the correlation could become positive or negative by appropriate selection of questions for the knowledge test. The theory of planned behavior (Ajzen, 1991 ), with its focus on specific actions, predicted intentions and behavior in all four studies. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Informa plc

Link: h ttp://www.businessinsider.com/ron-johnson-apple-store-j-c-penney-2011-11
People come to the Apple Store for the experience — and they’re willing to pay a premium for that. There are lots of components to that experience, but maybe the most important — and this is something that can translate to any retailer — is that the staff isn’t focused on selling stuff, it’s focused on building relationships and trying to make people’s lives better. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Business Insider, Inc. All rights reserved.
Title : Naturalizing aesthetics: Brain areas for aesthetic appraisal across sensory modalities
Abstract We present here the most comprehensive analysis to date of neuroaesthetic processing by reporting the results of voxel-based meta-analyses of 93 neuroimaging studies of positive-valence aesthetic appraisal across four sensory modalities. The results demonstrate that the most concordant area of activation across all four modalities is the right anterior insula, an area typically associated with visceral perception, especially of negative valence (disgust, pain, etc.). We argue that aesthetic processing is, at its core, the appraisal of the valence of perceived objects. This appraisal is in no way limited to artworks but is instead applicable to all types of perceived objects. Therefore, one way to naturalize aesthetics is to argue that such a system evolved first for the appraisal of objects of survival advantage, such as food sources, and was later co-opted in humans for the experience of artworks for the satisfaction of social needs. Abstract Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Link: http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=the-neuroscience-of-beauty
Studies from neuroscience and evolutionary biology challenge this separation of art from non-art. Human neuroimaging studies have convincingly shown that the brain areas involved in aesthetic responses to artworks overlap with those that mediate the appraisal of objects of evolutionary importance, such as the desirability of foods or the attractiveness of potential mates. Hence, it is unlikely that there are brain systems specific to the appreciation of artworks; instead there are general aesthetic systems that determine how appealing an object is, be that a piece of cake or a piece of music. Abstract © 2013 Scientific American, a Division of Nature America, Inc.
Link: http://blogs.scientificamerican.com/symbiartic/2011/10/03/need-proof-that-were-visual-beings/
This video offers proof that humans are visual beings. Abstract © 2013 Scientific American, a Division of Nature America, Inc.
Link: http://hbr.org/web/slideshows/five-charts-that-changed-business/1-slide
Once in a while, a chart so deftly captures an important strategic insight that it becomes an iconic part of management thinking and a tool that shows up in MBA classrooms and corporate boardrooms for years to come. As HBR prepares for its 90th anniversary, in 2012, their editors have combed the magazine archives and other sources to select five charts that changed the shape of strategy. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved.
Link: http://www.strategy-business.com/article/04412
It is a widely accepted and rarely challenged tenet of marketing that companies can sustain competitive advantage only through “new and improved” product differentiation based on unique features and benefits. What a mistake. By paying attention to what consumers really want, companies can attract new customers and create a distinctive brand. Abstract © 2013 Booz & Company Inc. All rights reserved.
Link: http://www.economist.com/node/17723028
If you can have everything in 57 varieties, making decisions becomes hard work. Many of these options have improved life immeasurably in the rich world, and to a lesser extent in poorer parts. They are testimony to human ingenuity and innovation. Free choice is the basis on which markets work, driving competition and generating economic growth. It is the cornerstone of liberal democracy. The 20th century bears the scars of too many failed experiments in which people had no choice. But amid all the dizzying possibilities, a nagging question lurks: is so much extra choice unambiguously a good thing? Abstract Copyright © The Economist Newspaper Limited 2013. All rights reserved.
Link: http://e.businessinsider.com/public/1099804
Mobile apps are becoming more important to people, not less important, according to this chart plucked from a big presentation on the internet. It’s an interesting trend because it shows how mobile behavior is different than traditional desktop computing behavior when it comes to the web. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Business Insider, Inc. All rights reserved.
Link: http://blogs.scientificamerican.com/scicurious-brain/2012/07/30/you-want-that-well-i-want-it-too-the-neuroscience-of-mimetic-desire/
Mimetic desire is more than jealously wanting something because someone else has it. Rather, it’s about valuing something because someone else values it . And it’s pretty easy to transmit the value. Just writing about Person A’s activities and habits and showing it to Person B will make Person B start to think Person A must have seen something good about the Toyota Camry…maybe his next car…
But what is behind this contagion of desires? Abstract © 2013 Scientific American, a Division of Nature America, Inc.

Link: http://www.united-academics.org/magazine/27212/visual-memory-blindness/
A well-known pheonomenon in psychology has been the ‘inattentional blindness’ principle. In fact, you might know it from experience: it means that people tend to fail seeing things in their visible fields when they have to focus on a task. Until now, it was thought that in order to cause the effect, a cluttered visual field is required. Recent research shows that the effect is present though in many more situations. Abstract Copyright United Academics 2012 Coypright – All rights Reserved
Link: http://www.businessinsider.com/18-24-texting-2011-9
Chart of the Day: According to the Pew Internet project , people in the 18-24 year-old range are sending and receiving 110 texts per day on average. The median number of texts sent/received by that group is 50 per day. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Business Insider, Inc. All rights reserved.
Link: http://www.businessinsider.com/chart-of-the-day-facebook-time-2011-9
Chart of the Day: A new report on social media from Nielsen shows U.S. users spent 53.5 billion minutes on Facebook in May, which is more time than was spent on the next four biggest sites. Abstract Copyright © 2013 Business Insider, Inc. All rights reserved.
Link: http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=your-brain-on-facebook
A recent study showed that certain brain areas expand in people who have greater numbers of friends on Facebook . There was a problem, though. The study, in Proceedings of the Royal Society B , was unable to resolve the question of whether “friending” plumps up the brain areas or whether people with a type of robustness in brain physiology are just natural social butterflies. But with the help of a few monkeys in England, teenagers everywhere may now have more ammunition to use against parents. Abstract © 2013 Scientific American, a Division of Nature America, Inc.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/3/196.abstract.html?etoc
Although advances in technology now enable people to communicate ‘anytime, anyplace’, it is not clear how citizens can be motivated to actually do so. This paper evaluates the impact of three principles of psychological empowerment, namely perceived self-efficacy, sense of community and causal importance, on public transport passengers’ motivation to report issues and complaints while on the move. A week-long study with 65 participants revealed that self-efficacy and causal importance increased participation in short bursts and increased perceptions of service quality over longer periods. Finally, we discuss the implications of these findings for citizen participation projects and reflect on design opportunities for mobile technologies that motivate citizen participation. Abstract 2013 Oxford University Press.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/3/208.abstract.html?etoc
This review paper argues that users of personal information management systems have three particularly pressing requirements, for which current systems do not fully cater: (i) To combat information overload, as the volume of information increases. (ii) To ease context switching, in particular, for users who face frequent interrupts in their work. (iii) To be supported in information integration, across a variety of applications. To meet these requirements, four broad technological approaches should be adopted in an incremental fashion: (i) The deployment of a unified file system to manage all information objects, including files, emails and webpage URLs. (ii) The use of tags to categorize information; implemented in a way which is backward-compatible with existing hierarchical file systems. (iii) The use of context to aid information retrieval; built upon existing file and tagging systems rather than creating a parallel context management system. (iv) The deployment of semantic technologies, coupled with the harvesting of all useful metadata. Abstract 2013 Oxford University Press.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/3/238.abstract.html?etoc
Projective techniques are used in psychology and consumer research to provide information about individuals’ motivations, thoughts and feelings. This paper reviews the use of projective techniques in marketing research and user experience (UX) research and discusses their potential role in understanding users, their needs and values, and evaluating UX in practical product development contexts. A projective technique called sentence completion is evaluated through three case studies. Sentence completion produces qualitative data about users’ views in a structured form. The results are less time-consuming to analyze than interview results. Compared with quantitative methods such as AttrakDiff, the results are more time consuming to analyze, but more information is retrieved on negative feelings. The results show that sentence completion is useful in understanding users’ perceptions and that the technique can be used to complement other methods. Sentence completion can also be used online to reach wider user groups. Abstract 2013 Oxford University Press.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/3/256.abstract.html?etoc
Cognitive load (CL) is experienced during critical tasks and also while engaged emotional states are induced either by the task itself or by extraneous experiences. Emotions irrelevant to the working memory representation may interfere with the processing of relevant tasks and can influence task performance and behavior, making the accurate detection of CL from nonverbal information challenging. This paper investigates automatic CL detection from facial features, physiology and task performance under affective interference. Data were collected from participants (n=20) solving mental arithmetic tasks with emotional stimuli in the background, and a combined classifier was used for detecting CL levels. Results indicate that the face modality for CL detection was more accurate under affective interference, whereas physiology and task performance were more accurate without the affective interference. Multimodal fusion improved detection accuracies, but it was less accurate under affective interferences. More specifically, the accuracy decreased with an increasing intensity of emotional arousal. Abstract 2013 Oxford University Press.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/3/269.abstract.html?etoc
In the field of virtual reality (VR), many efforts have been made to analyze presence, the sense of being in the virtual world. However, it is only recently that functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has been used to study presence during an automatic navigation through a virtual environment. In the present work, our aim was to use fMRI to study the sense of presence during a VR-free navigation task, in comparison with visualization of photographs and videos (automatic navigations through the same environment). The main goal was to analyze the usefulness of fMRI for this purpose, evaluating whether, in this context, the interaction between the subject and the environment is performed naturally, hiding the role of technology in the experience. We monitored 14 right-handed healthy females aged between 19 and 25 years. Frontal, parietal and occipital regions showed their involvement during free virtual navigation. Moreover, activation in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex was also shown to be negatively correlated to sense of presence and the postcentral parietal cortex and insula showed a parametric increased activation according to the condition-related sense of presence, which suggests that stimulus attention and self-awareness processes related to the insula may be linked to the sense of presence. Abstract 2013 Oxford University Press.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/3/285.abstract.html?etoc
Unlike visual stimuli, little attention has been paid to auditory stimuli in terms of emotion prediction with physiological signals. This paper aimed to investigate whether auditory stimuli can be used as an effective elicitor as visual stimuli for emotion prediction using physiological channels. For this purpose, a well-controlled experiment was designed, in which standardized visual and auditory stimuli were systematically selected and presented to participants to induce various emotions spontaneously in a laboratory setting. Numerous physiological signals, including facial electromyogram, electroencephalography, skin conductivity and respiration data, were recorded when participants were exposed to the stimulus presentation. Two data mining methods, namely decision rules and k-nearest neighbor based on the rough set technique, were applied to construct emotion prediction models based on the features extracted from the physiological data. Experimental results demonstrated that auditory stimuli were as effective as visual stimuli in eliciting emotions in terms of systematic physiological reactivity. This was evidenced by the best prediction accuracy quantified by the F1 measure (visual: 76.2% vs. auditory: 76.1%) among six emotion categories (excited, happy, neutral, sad, fearful and disgusted). Furthermore, we also constructed culture-specific (Chinese vs. Indian) prediction models. The results showed that model prediction accuracy was not significantly different between culture-specific models. Finally, the implications of affective auditory stimuli in human–computer interaction, limitations of the study and suggestions for further research are discussed. Abstract 2013 Oxford University Press.
Link: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160289614000087
The deliberate practice view has generated a great deal of scientific and popular interest in expert performance. At the same time, empirical evidence now indicates that deliberate practice, while certainly important, is not as important as Ericsson and colleagues have argued it is. In particular, we (Hambrick, Oswald, Altmann, Meinz, Gobet, & Campitelli, 2014) found that individual differences in accumulated amount of deliberate practice accounted for about one-third of the reliable variance in performance in chess and music, leaving the majority of the reliable variance unexplained and potentially explainable by other factors. Ericsson’s (2014) defense of the deliberate practice view, though vigorous, is undercut by contradictions, oversights, and errors in his arguments and criticisms, several of which we describe here. We reiterate that the task now is to develop and rigorously test falsifiable theories of expert performance that take into account as many potentially relevant constructs as possible. Abstract © 2014 Elsevier Inc.
Link: http://techcrunch.com/2013/02/05/amazon-to-launch-virtual-currency-amazon-coins-in-its-appstore-in-may/
Amazon has just announced a new virtual currency for Kindle Fire owners to use on in-app purchases, app purchases, etc. in the Amazon Appstore. Abstract © 2013 AOL Inc. All rights reserved.
Link: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smj.2284/abstract
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2014/05/09/iwc.iwu016.abstract.html?papetoc
Wizard of Oz (WOZ) is a well-established method for simulating the functionality and user experience of future systems. Using a human wizard to mimic certain operations of a potential system is particularly useful in situations where extensive engineering effort would otherwise be needed to explore the design possibilities offered by such operations. The WOZ method has been widely used in connection with speech and language technologies, but advances in sensor technology and pattern recognition as well as new application areas such as human–robot interaction have made it increasingly relevant to the design of a wider range of interactive systems. In such cases, achieving acceptable performance at the user interface level often hinges on resource-intensive improvements such as domain tuning, which are better done once the overall design is relatively stable. Although WOZ is recognized as a valuable prototyping technique, surprisingly little effort has been put into exploring it from a methodological point of view. Starting from a survey of the literature, this paper presents a systematic investigation and analysis of the design space for WOZ for language technology applications, and proposes a generic architecture for tool support that supports the integration of components for speech recognition and synthesis as well as for machine translation. This architecture is instantiated in WebWOZ—a new web-based open-source WOZ prototyping platform. The viability of generic support is explored empirically through a series of evaluations. Researchers from a variety of backgrounds were able to create experiments, independent of their previous experience with WOZ. The approach was further validated through a number of real experiments, which also helped to identify a number of possibilities for additional support, and flagged potential issues relating to consistency in wizard performance. Abstract 2014 Oxford University Press
Link: http://www.thinkwithgoogle.com/insights/library/studies/the-new-multi-screen-world-study/
This paper studies how business models can be designed to tap effectively into open innovation labor markets with heterogeneously motivated workers. Using data on open source software, we show that motivations are diverse, and demonstrate how managers can strategically influence the flow of code contributions and their impact on project performance. Unlike previous literature using survey data, we exploit the observed pattern of project membership and code contributions—the “revealed preference” of developers—to infer the motivations driving their decision to contribute. Developers strongly sort along key dimensions of the business model chosen by project managers, especially the degree of openness of the project license. The results indicate an important role for intrinsic motivation, reputation, and labor market signaling, and a more limited role for reciprocity. Abstract 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
updated on 5/13
Title: Developing elements of user experience for mobile phones and services: survey, interview, and observation approaches
Abstract The term user experience (UX) encompasses the concepts of usability and affective engineering. However, UX has not been defined clearly. In this study, a literature survey, user interview and indirect observation were conducted to develop definitions of UX and its elements. A literature survey investigated 127 articles that were considered to be helpful to define the concept of UX. An in-depth interview targeted 14 hands-on workers in the Korean mobile phone industry. An indirect observation captured daily experiences of eight end-users with mobile phones. This study collected various views on UX from academia, industry, and end-users using these three approaches. As a result, this article proposes definitions of UX and its elements: usability, affect, and user value. These results are expected to help design products or services with greater levels of UX. Abstract Copyright 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Title: Why different people prefer different systems for different tasks: An activity perspective on technology adoption in a dynamic user environment
Abstract In a contemporary user environment, there are often multiple information systems available for a certain type of task. Based on the premises of Activity Theory, this study examines how user characteristics, system experiences, and task situations influence an individual’s preferences among different systems in terms of user readiness to interact with each. It hypothesizes that system experiences directly shape specific user readiness at the within-subject level, user characteristics and task situations make differences in general user readiness at the between-subject level, and task situations also affect specific user readiness through the mediation of system experiences. An empirical study was conducted, and the results supported the hypothesized relationships. The findings provide insights on how to enhance technology adoption by tailoring system development and management to various task contexts and different user groups. Abstract Copyright 2011 ASIS&T
Title: A review of factors influencing user satisfaction in information retrieval
Abstract The authors investigate factors influencing user satisfaction in information retrieval. It is evident from this study that user satisfaction is a subjective variable, which can be influenced by several factors such as system effectiveness, user effectiveness, user effort, and user characteristics and expectations. Therefore, information retrieval evaluators should consider all these factors in obtaining user satisfaction and in using it as a criterion of system effectiveness. Previous studies have conflicting conclusions on the relationship between user satisfaction and system effectiveness; this study has substantiated these findings and supports using user satisfaction as a criterion of system effectiveness. Abstract Copyright 2010 ASIS&T
Title: The development and evaluation of a survey to measure user engagement
Abstract Facilitating engaging user experiences is essential in the design of interactive systems. To accomplish this, it is necessary to understand the composition of this construct and how to evaluate it. Building on previous work that posited a theory of engagement and identified a core set of attributes that operationalized this construct, we constructed and evaluated a multidimensional scale to measure user engagement. In this paper we describe the development of the scale, as well as two large-scale studies (N=440 and N=802) that were undertaken to assess its reliability and validity in online shopping environments. In the first we used Reliability Analysis and Exploratory Factor Analysis to identify six attributes of engagement: Perceived Usability, Aesthetics, Focused Attention, Felt Involvement, Novelty, and Endurability. In the second we tested the validity of and relationships among those attributes using Structural Equation Modeling. The result of this research is a multidimensional scale that may be used to test the engagement of software applications. In addition, findings indicate that attributes of engagement are highly intertwined, a complex interplay of user-system interaction variables. Notably, Perceived Usability played a mediating role in the relationship between Endurability and Novelty, Aesthetics, Felt Involvement, and Focused Attention. Abstract Copyright 2009 ASIS&T
Title: Exploring user engagement in online news interactions
Abstract This paper describes a qualitative study of online news reading and browsing. Thirty people participated in a quasi-experimental study in which they were asked to browse a news website and select three stories to discuss at a social gathering. Semi-structured interviews were conducted post-task to understand participants’ perceptions of what makes online news reading and browsing engaging or non-engaging. Findings as presented within the experience-based framework of user engagement and demonstrate the complexity of users’ interactions with information content and systems in online news environments. This study extends the model of user engagement and contributes new insights into user’s experience in casual-leisure settings, such as online news, which has implications for other information domains. Abstract Copyright 2011 by American Society for Information Science and Technology
Abstract This chapter of The Fabric of Mobile Services: Software Paradigms and Business Demands contains sections titled: New Services and User Experience, User-Centered Simplicity and Experience, Methodologies for Simplicity and User Experience, and Case Studies: Simplifying Paradigms Abstract Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Title: The Right Angle: Visual Portrayal of Products Affects Observers’ Impressions of Owners
Abstract Consumer products have long been known to influence observers’ impressions of product owners. The angle at which products are visually portrayed in advertisements, however, may be an overlooked factor in these effects. We hypothesize and find that portrayals of the same product from different viewpoints can prime different associations that color impressions of product and owner in parallel ways. In Study 1, automobiles were rated higher on status- and power-related traits (e.g., dominant , powerful ) when portrayed head-on versus in side profile, an effect found for sport utility vehicles (SUVs)—a category with a reputation for dominance—but not sedans. In Study 2, these portrayal-based associations influenced the impressions formed about the product’s owner: a target person was rated higher on status- and power-related traits when his SUV was portrayed head-on versus in side profile. These results suggest that the influence of visual portrayal extends beyond general evaluations of products to affect more specific impressions of products and owners alike, and highlight that primed traits are likely to influence impressions when compatible with other knowledge about the target. Abstract Copyright 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc
Title: The Counterfeit Self: The Deceptive Costs of Faking It
Abstract Although people buy counterfeit products to signal positive traits, we show that wearing counterfeit products makes individuals feel less authentic and increases their likelihood of both behaving dishonestly and judging others as unethical. In four experiments, participants wore purportedly fake or authentically branded sunglasses. Those wearing fake sunglasses cheated more across multiple tasks than did participants wearing authentic sunglasses, both when they believed they had a preference for counterfeits (Experiment 1a) and when they were randomly assigned to wear them (Experiment 1b). Experiment 2 shows that the effects of wearing counterfeit sunglasses extend beyond the self, influencing judgments of other people’s unethical behavior. Experiment 3 demonstrates that the feelings of inauthenticity that wearing fake products engenders—what we term the counterfeit selfmediate the impact of counterfeits on unethical behavior. Finally, we show that people do not predict the impact of counterfeits on ethicality; thus, the costs of counterfeits are deceptive. Abstract Copyright 2010 Francesca Gino, Michael I. Norton, and Dan Ariely3
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/5/389.full.html?etoc
Menus are a key mechanism for organizing different commands in graphical user interfaces. Nowadays low-cost devices that allow using different interaction techniques in remote interfaces have become widespread. Nevertheless, their corresponding menus are direct adaptations from traditional ones. As a consequence, they are inaccurate and slow, and also produce tiredness. In this paper, we design, implement and evaluate a menu selection technique for remote interfaces, the Body Menu. This technique permits whole-body interaction and is specifically designed to take advantage of the proprioception sense. The Body Menu attaches virtual menu items to different parts of the body and selects them when the users reach these zones with their hands. We use the Microsoft Kinect to implement this system. Additionally, we compared it with the most representative menus, studied the best number of body parts to be used and analyzed how children interact with it. Abstract © 2013 Oxford University Publishing.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/5/403.full.html?etoc
We present the evaluation of an interactive audio map system that enables blind and partially sighted users to explore and navigate city maps from the safety of their home using simulated 3D audio and synthetic speech alone. We begin with a review of existing literature in the areas of spatial knowledge and wayfinding, auditory displays and auditory map systems, before describing how this research builds on and differentiates itself from this body of work. One key requirement was the ability to quantify the effectiveness of the audio map, so we describe the design and implementation of the evaluation, which took the form of a game downloaded by participants to their own computers. The results demonstrate that participants (blind, partially sighted and sighted) have acquired detailed spatial knowledge and also that the availability of positional audio cues significantly improves wayfinding performance. Abstract © 2013 Oxford University Publishing.
Link: http://iwc.oxfordjournals.org/content/26/5/417.full.html?etoc
Delegation is the practice of sharing authority with another individual to enable them to complete a specific task as a proxy. Practices to permit delegation can range from formal to informal arrangements and can involve spontaneous yet finely balanced notions of trust between people. This paper argues that delegation is a ubiquitous yet an unsupported feature of socio-technical computer systems and that this lack of support illustrates a particular neglect to the everyday financial practices of the more vulnerable people in society. Our contribution is to provide a first exploration of the domain of person-to-person delegation in digital payments, a particularly pressing context. We first report qualitative data collected across several studies concerning banking practices of individuals over 80 years of age. We then use analytical techniques centred upon identification of stakeholders, their concerns and interactions, to characterize the delegation practices we observed. We propose a Concerns Matrix as a suitable representation to capture conflicts in the needs of individuals in such complex socio-technical systems, and finally propose a putative design response in the form of a Helper Card. Abstract © 2013 Oxford University Publishing..
Link: Why We Love Beautiful Things
Great design, the management expert Gary Hamel once said, is like Justice Potter Stewart’s famous definition of pornography — you know it when you see it. You want it, too: brain scan studies reveal that the sight of an attractive product can trigger the part of the motor cerebellum that governs hand movement. Instinctively, we reach out for attractive things; beauty literally moves us. © 2013 New York Times
Link: http://www.bris.ac.uk/news/2013/9478.html
A new study has analysed tens of thousands of articles available to readers of online news and created a model to find out ‘what makes people click’. The aim of the study was to model the reading preferences for the audiences of 14 online news outlets using machine learning techniques. The models, describing the appeal of an article to each audience, were developed by linear functions of word frequencies. The models compared articles that became “most popular” on a given day in a given outlet with articles that did not. The research dentified the most attractive keywords, as well as the least attractive ones, and explained the choices readers made. Abstract © 2013 University of Bristol.
Title: Pointing and Selecting with Facial Activity
Abstract The aim of this paper was to evaluate the use of three facial actions (i.e. frowning, raising the eyebrows, and smiling) in selecting objects on a computer screen when gaze was used for pointing. Dwell time is the most commonly used selection technique in gaze-based interaction, and thus, a dwell time of 400 ms was used as a reference selection technique. A wireless, head-mounted prototype device that carried out eye tracking and contactless, capacitive measurement of facial actions was used for the interaction task. Participants (N=16) performed point-and-select tasks with three pointing distances (i.e. 60, 120 and 240 mm) and three target sizes (i.e. 25, 30 and 40 mm). Task completion times, pointing errors and throughput values based on Fitts’ law were used to compare the selection techniques. The participants also rated the techniques with subjective ratings scales. The results showed that the different techniques performed equally well in many respects. However, throughput values varied from 8.38 bits/s (raising the eyebrows) to 15.33 bits/s (smiling) and were comparable to or, in the case of smiling, better than in earlier research with similar interaction techniques. The dwell time was found to be the least accurate selection technique in terms of the magnitudes of point-and-select errors. Smiling technique was rated as more accurate to use than the frowning or the raising techniques. The results give further support for methods that combine facial behavior to eye tracking when interacting with technology.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Outi Tuisku1, Ville Rantanen, Oleg Špakov, Veikko Surakka and Jukka Lekkala
Title: Modeling Traditional Literacy, Internet Skills and Internet Usage: An Empirical Study
Abstract This paper focuses on the relationships among traditional literacy (reading, writing and understanding text), medium-related Internet skills (consisting of operational and formal skills), content-related Internet skills (consisting of information and strategic skills) and Internet usage types (information- and career-directed Internet use and entertainment use). We conducted a large-scale survey that resulted in a dataset of 1008 respondents. The results reveal the following: (i) traditional literacy has a direct effect on formal and information Internet skills and an indirect effect on strategic Internet skills and (ii) differences in types of Internet usage are indirectly determined by traditional literacy and directly affected by Internet skills, such that higher levels of strategic Internet skills result in more information- and career-directed Internet use. Traditional literacy is a pre-condition for the employment of Internet skills, and Internet skills should not be considered an easy means of disrupting historically grounded inequalities caused by differences in traditional literacy.
Abstract Copyright 2014 A.J.A.M. van Deursen and J.A.G.M. van Dijk
Title: Life Is Too Short to RTFM: How Users Relate to Documentation and Excess Features in Consumer Products
Abstract This paper addresses two common problems that users of various products and interfaces encounter—over-featured interfaces and product documentation. Over-featured interfaces are seen as a problem as they can confuse and over-complicate everyday interactions. Researchers also often claim that users do not read product documentation, although they are often exhorted to ‘RTFM’ (read the field manual). We conducted two sets of studies with users which looked at the issues of both manuals and excess features with common domestic and personal products. The quantitative set was a series of questionnaires administered to 170 people over 7 years. The qualitative set consisted of two 6-month longitudinal studies based on diaries and interviews with a total of 15 participants. We found that manuals are not read by the majority of people, and most do not use all the features of the products that they own and use regularly. Men are more likely to do both than women, and younger people are less likely to use manuals than middle-aged and older ones. More educated people are also less likely to read manuals. Over-featuring and being forced to consult manuals also appears to cause negative emotional experiences. Implications of these findings are discussed.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Alethea L. Blackler, Rafael Gomez, Vesna Popovic and M. Helen Thompson
Title: Effect of Age on Human–Computer Interface Control Via Neck Electromyography
Abstract The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of age on visuomotor tracking using submental and anterior neck surface electromyography (sEMG) to assess feasibility of computer control via neck musculature, which allows people with little remaining motor function to interact with computers. Thirty-two healthy adults participated: 16 younger adults aged 18–29 years and 16 older adults aged 69–85 years. Participants modulated sEMG to achieve targets presented at different amplitudes using real-time visual feedback. Root mean squared (RMS) error was used to quantify tracking performance. RMS error was increased for older adults relative to younger adults. Older adults demonstrated more RMS error than younger adults as a function of increasing target amplitude. The differential effects of age found on static tracking performance in anterior neck musculature suggest more difficult translation of human–computer interfaces controlled using anterior neck musculature for static tasks to older populations.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Gabrielle L. Hands and Cara E. Stepp
Title: Should I Stay or Should I Go? Improving Event Recommendation in the Social Web
Abstract This paper focuses on the recommendation of events in the Social Web, and addresses the problem of finding if, and to which extent, certain features, which are peculiar to events, are relevant in predicting the users’ interests and should thereby be taken into account in recommendation. We consider, in particular, three ‘additional’ features that are usually shown to users within social networking environments: reachability from the user location, the reputation of the event in the community and the participation of the user’s friends. Our study is aimed at evaluating whether adding this information to the description of the event type and topic, and including in the user profile the information on the relevance of these factors, can improve our capability to predict the user’s interest. We approached the problem by carrying out two surveys with users, who were asked to express their interest in a number of events. We then trained, by means of linear regression, a scoring function defined as a linear combination of the different factors, whose goal was to predict the user scores. We repeated this experiment under different hypotheses on the additional factors, in order to assess their relevance by comparing the predictive capabilities of the resulting functions. The compared results of our experiments show that additional factors, if properly weighted, can improve the prediction accuracy with an error reduction of 4.1%. The best results were obtained by combining content-based factors and additional factors in a proportion of ∼10:4.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Federica Cena, Silvia Likavec, Ilaria Lombardi and Claudia Picardi
Title: “I Need to Be Explicit: You’re Wrong”: Impact of Face Threats on Social Evaluations in Online Instructional Communication
Abstract Online instructional communication, as found in ask-an-expert forums, e-learning discussion boards or online help desks, creates situations that threaten the recipient’s face. This study analyzed the evaluation of face-threatening acts with a 1×3 design. An online forum thread confronted a layperson with an expert who either (a) addressed the layperson’s misconceptions directly and frankly, (b) mitigated face threats through explicit hints about the need to be direct or (c) communicated politely and indirectly. College students read these dialogues and assessed the expert communicator’s facework, recipient orientation, credibility and likability. Results showed that polite experts were evaluated most positively; explicit hints did not improve perceptions of face-threatening acts. This implies that users of instructional forums prefer communicators to be polite even when face threats are necessary. We discuss practical implications for different online instruction contexts and make suggestions for further research.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Regina Jucks, Lena Päuler and Benjamin Brummernhenrich
Title: The Potential of a Text-Based Interface as a Design Medium: An Experiment in a Computer Animation Environment
Abstract Since the birth of the concept of direct manipulation, the graphical user interface has been the dominant means of controlling digital objects. In this research, we hypothesize that the benefits of a text-based interface involve multiple tradeoffs, and we explore the potential of text as a medium of design from three perspectives: (i) the perceived level of control of the designed object, (ii) a tool for realizing creative ideas and (iii) an effective form for a highly learnable user interface. Our experiment in a computer animation environment shows that (i) participants did feel a high level of control of characters, (ii) creativity was both restricted and facilitated depending on the task and (iii) natural language expedited the learning of a new interface language. Our research provides experimental proof of the effect of a text-based interface and offers guidelines for the design of future computer-aided design applications.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Sangwon Lee and Jin Yan
Title: Framing a Set: Understanding the Curatorial Character of Personal Digital Bibliographies
Abstract We articulate a model of curatorship that emphasizes framing the character of the curated set as the focus of curatorial activity. This curatorial character is structured through the articulation, via mechanisms of selection, description and arrangement, of coherent classificatory principles. We describe the latest stage of a continuing project to examine the curatorial character of personal digital bibliographies, such as Pinterest boards, Flickr galleries and GoodReads shelves, and to support the design of such curatorially expressive personal collections. In the study reported here, 24 participants created personal bibliographies using either a structured design process, with explicit tasks for selecting, describing and arranging collection items, or an unstructured process that did not separate these activities. Our findings lead to a more complex understanding of personal collections as curatorial, expressive artifacts. We explore the role of cohesion as a quality that facilitates expression of the curatorial frame, and we find that when designers read source materials as a part of a set, they are more likely to write cohesive collections. Our findings also suggest that the curatorial act involves both the definition of abstract classificatory principles and their instantiation in a specific material environment. We describe various framing devices that facilitate these reading and writing activities, and we suggest design directions for supporting curatorial reading and writing tasks.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Melanie Feinberg, Ramona Broussard and Eryn Whitworth
Title: Identifying Problems Associated with Focus and Context Awareness in 3D Modelling Tasks
Abstract Creating complex 3D models is a challenging process. One of the main reasons for this is that 3D models are usually created using software developed for conventional 2D displays which lack true depth perspective, and therefore do not support correct perception of spatial placement and depth-ordering of displayed content. As a result, modellers often have to deal with many overlapping components of 3D models (e.g. vertices, edges, faces, etc.) on a 2D display surface. This in turn causes them to have difficulties in distinguishing distances, maintaining position and orientation awareness, etc. To better understand the nature of these problems, which can collectively be defined as ‘focus and context awareness’ problems, we have conducted a pilot study with a group of novice 3D modellers, and a series of interviews with a group of professional 3D modellers. This article presents these two studies, and their findings, which have resulted in identifying a set of focus and context awareness problems that modellers face in creating 3D models using conventional modelling software. The article also provides a review of potential solutions to these problems in the related literature.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Masood Masoodian, Azmi bin Mohd Yusof and Bill Rogers
Abstract The goal of user experience design in industry is to improve customer satisfaction and loyalty through the utility, ease of use, and pleasure provided in the interaction with a product. So far, user experience studies have mostly focused on short-term evaluations and consequently on aspects relating to the initial adoption of new product designs. Nevertheless, the relationship between the user and the product evolves over long periods of time and the relevance of prolonged use for market success has been recently highlighted. In this paper, we argue for the cost-effective elicitation of longitudinal user experience data. We propose a method called the “UX Curve” which aims at assisting users in retrospectively reporting how and why their experience with a product has changed over time. The usefulness of the UX Curve method was assessed in a qualitative study with 20 mobile phone users. In particular, we investigated how users’ specific memories of their experiences with their mobile phones guide their behavior and their willingness to recommend the product to others. The results suggest that the UX Curve method enables users and researchers to determine the quality of long-term user experience and the influences that improve user experience over time or cause it to deteriorate. The method provided rich qualitative data and we found that an improving trend of perceived attractiveness of mobile phones was related to user satisfaction and willingness to recommend their phone to friends. This highlights that sustaining perceived attractiveness can be a differentiating factor in the user acceptance of personal interactive products such as mobile phones. The study suggests that the proposed method can be used as a straightforward tool for understanding the reasons why user experience improves or worsens in long-term product use and how these reasons relate to customer loyalty.
Abstract Copyright 2011 Sari Kujalaa, Virpi Rotob, Kaisa Väänänen-Vainio-Mattilaa, Evangelos Karapanosc and Arto Sinneläa
Title: Researching Young Children’s Everyday Uses of Technology in the Family Home
Abstract Studies of the everyday uses of technology in family homes have tended to overlook the role of children and, in particular, young children. A study that was framed by an ecocultural approach focusing on children’s play and learning with toys and technologies is used to illustrate some of the methodological challenges of conducting research with young children in the home. This theoretical framework enabled us to identify and develop a range of methods that illuminated the home’s unique mix of inhabitants, learning opportunities and resources and to investigate parents’ ethnotheories, or cultural beliefs, that gave rise to the complex of practices, values and attitudes and their intersections with technology and support for learning in the home. This resulted in a better understanding of the role of technology in the lives of these 3- and 4-year-old children.
Abstract Copyright 2014 Lydia Plowman
Title: Measuring web usability using item response theory: Principles, features and opportunities
Abstract Usability is considered a critical issue on the web that determines either the success or the failure of a company. Thus, the evaluation of usability has gained substantial attention. However, most current tools for usability evaluation have some limitations, such as excessive generality and a lack of reliability and validity. The present work proposes the construction of a tool to measure usability in e-commerce websites using item response theory (IRT). While usability issues have only been considered in theoretical or empirical contexts, in this study, we discuss them from a mathematical point of view using IRT. In particular, we develop a standardised scale to measure usability in e-commerce websites. This study opens a new field of research in the ergonomics of interfaces with respect to the development of scales using IRT.
Abstract Copyright 2011 Rafael Tezzaa, Antonio Cezar Borniaa and Dalton Francisco de Andrade
Title: Everything Science Knows Right Now About Standing Desks
Abstract If it wasn’t already clear through common sense, it’s become painfully clear through science that sitting all day is terrible for your health. What’s especially alarming about this evidence is that extra physical activity doesn’t seem to offset the costs of what researchers call “prolonged sedentary time.” Just as jogging and tomato juice don’t make up for a night of smoking and drinking, a little evening exercise doesn’t erase the physical damage done by a full work day at your desk.
In response some people have turned to active desks—be it a standing workspace or even a treadmill desk—but the research on this recent trend has been too scattered to draw clear conclusions on its benefits (and potential drawbacks). At least until now. A trio of Canada-based researchers has analyzed the strongest 23 active desk studies to draw some conclusions on how standing and treadmill desks impact both physiological health and psychological performance. Abstract Copyright 2015 Eric Jaffe
Send Us Your Research References: If you have interesting and relevant research references post, post content as comment below for possible inclusion in next year’s updated list.
Other Content from PulseUX: Here are 2 other references from widely read and quoted long-form posts you may find interesting.

Angry Birds UX: Why Angry Birds is so successful and popular: a cognitive teardown of the user experience (1.5 million page views). https://live-mauro-usability-science.pantheonsite.io/blog/why-angry-birds-is-so-successful-a-cognitive-teardown-of-the-user-experience/

Apple v. Samsung: Impact and Implications for Product Design, User Interface Design (UX), Software Development and the Future of High-Technology Consumer Products https://live-mauro-usability-science.pantheonsite.io/blog/apple-v-samsung-implications-for-product-design-user-interface-ux-design-software-development-and-the-future-of-high-technology-consumer-products/
Charles L Mauro CHFP President / Founder MauroNewMedia
Find out more about Charles L Mauro Find out more about MauroNewMedia Follow Pulse>UX on Twitter @PulseUX
Subscribe to email updates
- Pingback: Why Flappy Bird Is / Was So Successful And Popular But So Difficult To Learn: A Cognitive Teardown Of The User Experience (UX)
- Pingback: Wishing You and Your Technology Success in 2014… and Goodbye to Engelbart from MauroNewMedia
Fantastic site. A lot of helpful info here. I’m sending it to some buddies ans additionally sharing in delicious. And naturally, thanks on your sweat!
you are truly a just right webmaster. The site loading speed is incredible. It kind of feels that you’re doing any distinctive trick. In addition, The contents are masterwork. you have done a great activity in this matter!
This is such an intriguing post, thank you for sharing it!
This is a comment from Bing using Python.
pelicula mexicana red social hi5 red social the social network en español red social mas usada en mexico
Thanks, I have just been looking for information about this subject for a long time and yours is the best I’ve discovered till now. However, what in regards to the bottom line? Are you certain in regards to the supply?
Post a Comment
Subscribe to email updates.

UX Beginner

The Ultimate List of UX Topics All Beginners Should Know
When entering a new field, there’s usually a standard curriculum to learn. Front-end developers learn HTML & CSS . Content producers learn the basics of copywriting. But…
What are UX skills UX designers should learn?
Since everything about a product is technically tied to the user’s experience, it can be confusing to determine the most important topics for beginners to learn. That’s what we’re going to cover today.
The methodology – I compiled this list of topics using this rough approach:
- My personal experience working as a UX Designer and interviewing for different UX teams
- Analyzing most written-about topics from top UX publications: UXMag, UXBooth, UXMatters and Alistapart. I distill the main UX categories that overlap from each blog.
- Knowledge gleaned from UX books. Jesse James Garrett’s 5 Elements was especially instrumental.
TL;DR version of the these UX topics and skills are:
UX Strategy / User Research / Information Architecture / Interaction Design / Usability Testing / Visual Design / Content Strategy / SEO / Coding
Without further ado, let’s dive into the full list of UX topics to learn!
UX Strategy
User experience strategy is a blend of business, process and design. If a digital product is a house, then UX strategy is asking why that house should be built in the first place, and how it should be built. And it also involves convincing others (stakeholders) along the way.

Who Does This?
This is the bread and butter of Chief Experience Officers (CXOs), UX Directors and UX Managers. But every UX Designer should be aware of UX strategy because it is an invisible force that’ll affect how you design whether you like it or not (continue below…)
This is also the domain of:
- digital business analysts
- project managers.
Why You Should Know It
UX is not just about cranking out wireframes . Interviewers will ask for your thoughts on designing in a Waterfall Compared to agile or lean, waterfall is a software development method with a relatively linear, sequential process. Originating from heavy manufacturing and automotive industries, waterfall is now see as a less flexible and iterative way of design. For proven, repeatable projects, waterfall may still have a place. ” >waterfall vs agile/Lean process. In project kickoff meetings the factors of budget, resources and schedule will impact your designs.
Business requirements are also a standard requirement when working on digital products. Whether working solo or with a business analyst, much of a product’s user experience does start at the requirements level.
It’s about striking a balance between user needs and business goals, all while executing projects in a resourceful manner.
The more that a UX Designer advances in her career, the more she has to deal with strategy and partner with business. Actually, that happens across every industry and every role.
Solid Resources On This Topic :
- Applied UX Strategy Part 1 and Part 2 are good primer articles from UXMatters. They are a long read but will give you a very good overview of UX strategy, as well as useful links to other strategic frameworks.
- User Experience Strategy by Jaime Levy is by far the most definitive book on UX strategy. Having sat in on Jaime’s UX class myself, she is the real deal and has a knack for blending the vital parts of business strategy into the UX design practice.
- Lean UX is an award-winning book about applying Lean principles to designing the UX of products and services. This is the way that most startups and companies now aspire to validate, test and design products.
- UXStrat is an entire conference dedicated to the craft of UX Strategy!
User Research
User Research is the practice of identifying your users, distilling knowledge and insights from them, and determining their real-world behaviors. A design that is user-centric means that it was designed in a way to solve those users’ pain points in a way that feels natural to them.

User Research is different from Market Research. UX Research is concerned with evaluating the behaviors, pain points, and number of touchpoints that users experience with a given product/service.
Below is a quick breakdown of Market Research vs User Research by Momentology :
Most large product/digital companies now have at least one User Researcher on their teams.
Since UX research is an integral part of an organization’s larger UX Strategy, that means most UX Designers do need to conduct some form of user research to make sure that they’re building something users actually want.
User research makes the difference between making what you think users want versus gathering insights to create something that users will actually enjoy.
Research done right is also a humbling, learning experience. It teaches you empathy and to put aside assumptions for the greater good of your users.
It’s the difference between knowing that most of your users are age 19-25 (market research) vs observing that all your younger users ignore the “Buy Button” when asked to make a purchase (behavior from user research).
- Just Enough Research by Erika Hall is built on the premise that research is “something every member of your team can and should do, and which everyone can learn, quickly.” And the book delivers. It’s my #1 recommendation for UX Designers need a quick start guide to user research. Practical, to the point, and full of research useful methods.
- Observing the User Experience is the consummate text on User Research. This is the textbook we were assigned to read in the Cal State Fullerton UX Certificate program. While it is a giant book and can be a bit try, the text is sprinkled with tons of real-life examples from the three authors. A good one to keep at your desk.
- List of User Research Methods by Usability .gov is a quick rundown of popular UX research methods
Information Architecture
Information Architecture, or “ IA ,” is the practice of organizing information to be clear, understandable and findable. If you’ve ever had trouble finding the info on a website, there’s a chance it’s an IA problem. Confusing label here. Weird category name there.

The job title “ Information Architect ” dates back before “ User Experience Designer ” came into being. Today, IAs are now seen as a specialty, and there aren’t as many jobs with strict IA responsibilities because many jobs now demand a broader UX skillset.
UX Designers do not necessarily deal with information architecture with as much depth as a dedicated IA professional, but this is a foundational stage of design for any project regardless of job title.
Why You Should Know It :
Much of design is organizing information. Those with strong IA skills can create sensible, flexible structures that scale. Information architects thrive with content heavy sites, e-commerce, and any situation where lots of (meta)data is required,
Knowledge in Information Architecture will not only help you become a UX Designer, but also assist in all facets of life – writing emails, organizing your files and beyond.
Solid Resources On This Topic :
- Information Architecture for the Web and Beyond is the consummate text on the topic. Now in its 4th edition, this big reference book is the best starting point for building IA knowledge.
- How to Make Sense of Any Mess by Abby Covert lives up to its tagline – Information Architecture for Everybody . It’s a refreshing approach that lowers the barrier to IA with plain language and great examples. The blog at AbbyTheIA is also chock full of educational diagrams and posts on Information Architecture.
- The Complete Beginner’s Guide to Information Architecture by UXBooth is a great introduction into the world of IA with links and references to many resources. It’s a very comprehensive list that I’ve bookmarked myself!
Interaction Design

“Interaction Designer” and “UX Designer” are often interchangeable job titles. If there is a core skill that UX Designers are expected to know, interaction design is that core skill. IxD applies to anyone who prototypes interactive experiences.
Anecdotally, as of this writing (Jan 2016), I find that job descriptions are often more accurate for Interaction Designer roles compared to UX Designer roles, because the latter can include any number of skillsets (pixel-perfect visual design, front-end programming, etc).
Why You Should Know It:
The field of Interaction Design demands that designers elevate their thinking from static to interactive. A sample group of questions that IxDs concern themselves with:
- What’s the flow of the system?
- What if this could be reduced from 6 steps to 3?
- How can we prevent users from making errors?
If this sounds similar to usability , you’re also right. From load times to ensuring your design’s touch targets are large enough, usability is a huge focus of User Experience at large. There’s a reason why UPA changed its name to UXPA 2012 .
Solid Resources On This Topic:
- Complete Guide to Interaction Design – UXBooth does it again with another solid beginners resource. Chock full of useful links and people to follow.
- About Face (4th Edition) by Alan Cooper is your bible for Interaction Design. The chapter on “Metaphors, Idioms, Affordances” is damn interesting, and “Digital Etiquette” will make you rethink how to treat users with your design.
- Don’t Make Me Think is the most popular introductory text onusability. Steve Krug’s Rocket Surgery Made Easy is a great companion handbook on how to identify and solve usability problems.
- The Design of Everyday Things by Don Norman is the standard textbook in this field for a good reason. It’s hard not to become a more considerate and observant designer after reading this book.
- Web Form Design by Luke Wroblewsi is probably the most underrated and immediately useful text you can pick up today. His book is full of examples (good and bad) of how to handle user input. A designer ends up making many forms in her lifetime, and so reading this book provides an immediate return on investment
Visual Design
Visuals make the “top” layer of the design stack, and good visual design helps users connect with products. As far as digital UI design is concerned, the main subtopics include typography, layout, color, and increasingly animation.

Those with training in traditional graphic design typically make a great transition into designing high fidelity interfaces for digital products, with job titles like Visual Designer , User Interface Designer and occasionally Product Designer.
Employers are understanding more and more now that UI is not UX , but having Visual design skills is often seen as a must for UX Designer positions. UXers might not be required to make the hottest graphic design, but they’ll need to create clean designs that look good.
Good visual design enables a designer to go from concept (low-fi) to product (high-fidelity). Almost every UX Designer will feel immediately more powerful with visual & UI design in their tool belt.
And let’s not forget that visual design engenders trust and confidence in users. From behavior specialist, BJ Fogg:
“… looking good is often interpreted as being good—and being credible…This basic human processing bias— “looking good is being good” —also seems to hold true for evaluating the credibility of Web sites, especially since design look is highly noticeable.”
- The Non-Designers Design Book (4th Ed) is the best bang-for-buck book on visual design I’ve ever read. Knowing “C.R.A.P.” (you’ll find out) alone is worth the cost of this book; to this day I still apply these principles to all my designs.
- Practical Typography is a beautiful free guide on typography. Since designs are 90% text (look at any web design and strip out the text…what are you left with?), knowing a few good typography rules will immediately enhance your designs. Start with Butterick’s Typography in Ten Minutes for a quick primer.
- Design for Hackers by David Kadavy is a surprisingly deep book that teaches design from a historical perspective, analyzing how we arrive at design today through architecture, the development of the alphabet and beyond. The book does a great job explaining the “why” behind visual design principles.
Other topics of consideration
I don’t consider the following topics core to a UX curriculum for beginners; they don’t come up as often on-the-job as the aforementioned topics. With that said, the following topics are all industries onto themselves, and knowledge in them will prove very useful for UX Designers.
UX Metrics / Analytics
How do you know if your design is successful? How do you measure a product’s user experience?
User Experience metrics help provide “ objective, persuasive data on which to base your design recommendations” ( NNGroup ).

There is a “data” person/team at most companies and they come in several forms:
- Data Analyst
- Business analyst
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization) professionals
- SEM (Search Engine Marketing) professionals
- Analytics (web and/or marketing)
It’s smart for UX designers to partner with and learn from those who own metrics in order to measure the user experience.
But with services like Google Analytics, Optimizely and CrazyEgg, UX designers can get started measuring UX on their own.
Why You Should Consider It :
When working with stakeholders – especially those in the business realm – metrics help designers get buy-in. Numbers help explain how designers arrive at certain decisions.
Analytics are powerful when paired with user testing to strike a balance between qualitative and quantitative factors. It’s the difference between knowing how many people clicked a button (quantitative) versus reasons why people clicked that button (qualitative).
Peter Drucker, management guru, is known for saying “What gets measured gets managed.” Measuring the user experience with the right metrics helps designers stay objective and work towards a goal.
- How to Choose the Right UX Metrics for your Product is a beautiful introduction to UX metrics. The HEART framework, used by Google, is a clever way to remember groups of important UX metrics.
- UX Booth’s An Analytics-First Approach to UX Part 1 and Part 2 are both great starting points of looking at UX through an analytics lens
- MeasuringU is the blog of Jeff Sauro, who’s basically the god of UX metrics. His blog article 10 Benchmarks for UX Metrics is a good introduction. If you have a mind for numbers and want to dig deep, Quantifying the User Experience is the most comprehensive guide on this topic.
Content Strategy
Bless Wikipedia for having the simplest definition of content strategy:
Content strategy refers to the planning, development, and management of content—written or in other media.

Just as “UX Designers” used to be called by other names ( cough web designer cough ), “Content Strategists” have come into their own in recent years.
Due to the recent formalization of the field, those who hold titles like “web content writer” and “copywriter” often do content strategy.
Anyone who writes words or creates media for consumption can leverage content strategy to their benefit.
Why You Should Consider It:
Designers who have a sense of content strategy can design better sites that feel natural and conversational , as opposed to cold and transactional.
There’s a saying in the digital business that “content is king.” Think of any website or app and strip out just the text, and you remove 90% of its meaning. Then take out other media like images and you pretty much just have a skeleton of a layout.
You may have heard of content-first design , which sounds like exactly what it is: starting a design with the content first. It’s a great way to prioritize designs, because changing the words is much easier than changing a design.
Some of my articles like The Text First Portfolio and Minimum Viable UX Portfolio have a content-first bent to them.
Solid Resources on the Topic:
- The Discipline of Content Strategy by AListApart is where you should start to get your bearings on the content strategy industry and how it came to be.
- UX and Content Strategy – The Project Guide by GatherContent is a free action-packed, how-to guide that teaches content strategy through an example project.
- The Content Strategy Toolkit by Meghan Casey is one of the newest, best-reviewed, and actionable books on Content Strategy today.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of making your content get found by search engines.

Here’s the formal definition:
The process of affecting the visibility of a website or a web page in a search engine’s unpaid results—often referred to as ‘natural,” “organic,” or “earned” results.
Many SEO Professionals refer to themselves as SEOs, or search engine optimizers . Here are some job titles you might be working with:
- SEO Professional
- SEO Specialist
- Search Specialist
- SEO/SEM/Analytics Specialist
The last bullet points shows how SEOs are often responsible for digital marketing and analytics efforts.
You’ve designed a great website and made it live. Other than notifying friends on your Facebook and Twitter, how do strangers find your new creation? In one word, Google (okay, and other search engines.)
Aside: my SEO friends joke that they don’t work at Google, but Google keeps them employed.
More and more, user experience factors like mobile-friendly sites and loading time affect how high websites rank on search engines.
SEO practices also cross-pollinate with information architecture and content strategy – if people search for a certain term, why not use that same content on your page when designing?
- Beginner’s Guide to SEO – the massive free guide to SEO from Moz, a leading SEO company
- Marketing Guru Neil Patel’s The On-Page SEO Cheatsheet is an action-packed post with practical tips for designers
- Stick to blogs like Moz and Search Engine Land to stay updated; Google can make changes to their search algorithms at any point, so even books 1 year old may be outdated
Coding and Front-End Development (FED)
At a certain point, designs need to be made into real working products. Prototypes and new design-to-code tools are getting better each day, but they still don’t come close to manipulating code.

This is the longest ongoing debate in the design community: should designers code? The answer to that question is “it depends.”
In The Last Post You’ll Read On Whether UX Designers Need to Learn Code , I argue that the contexts of work environment and team structure are vital. For example, someone who wants to work in a leaner environment that requires wearing more hats (startups) may have to pick up front-end web development, whereas another person who wants to focus purely on UX can specialize in larger teams.
People who code for a living go by just as many names as designers, so I’ll list the job titles with the most cross-over with UX roles:
- Web Designer
- UX/UI Developer
- Digital Designer
- Front-end developer
- Product Designer (more and more so associated with a “ unicorn ” skillset)
Even a little front-end knowledge can help UX Designers communicate with developers. Given 2 equally good designs, knowing that one solution is easier to implement in code will save you and the developer a lot of time.
There’s one camp arguing that knowing the realities of code can stifle the most creative, user-centric designs. While that might apply for some people, I don’t know a single designer who regrets their coding ability.
- Codecademy is the de-facto beginner’s resource on learning code through interactive lessons. I highly recommend following up with General Assembly’s free Dash interactive tutorials, which help you build more fun mini-projects.
- Shay Howe’s Learn to Code HTML & CSS is a beautiful resource that covers both Beginner and Advanced topics for free :-)
- Check out A Smarter Way to Learn HTML & CSS and A Smarter Way to Learn Javascript , a series that helps beginners learn coding concepts quick. “The learner spends two to three times as long practicing as he does reading. Based on cognitive research showing that retention increases 400 percent when learners are challenged to retrieve the information they just read.” Sounds promising, and the Amazon reviews are near-perfect!
- Codepen is the Dribbble of code. It not only allows you to explore interesting designs from a thriving community of coders, but you can easily see how designs are implemented in HTML/CSS/Javascript.
- Macaw and Webflow are two of the most formidable design-to-code products on the market today. They aren’t perfect and come with their own learning curves, but I’ve heard that the actual code output quality is quite impressive.
Do I have to learn all that?
If you feel a bit overwhelmed right now, then what’d you expect from an Ultimate List ?? Just kidding. This industry is huge and I stress again that you don’t have to master all of these topics .
But knowing about these topics helps make you into a more complete UX Designer, because they are all different facets of building a product/service. This is especially true when you interview with an entire digital team (not just with the UX team).
Try reading through one or 2 links in each topic’s Solid Resources and you’ll be ahead of most UX Beginners.
- Term: Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)
- Term: Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)
- Term: User Experience (UX)
- Term: User Experience Design
- Term: Usability Testing
- Term: Graphic Design
- Term: Content Strategy
- Term: Wireframes
- Term: Usability
- Term: Information Architecture (IA)
- Term: Information Architect
- Term: Interaction Designer
- Term: Interaction Design (IxD)
- Term: User Interface
- Term: Graphic Designer
- Term: User Testing
- Term: Full Stack Designer
- Term: Waterfall
3 responses to “The Ultimate List of UX Topics All Beginners Should Know”

We stand with Ukraine and our team members from Ukraine. Here are ways you can help

A Community Of Over 800,000
- 3D Graphics and Interfaces
- Accessibility
- Adobe Flash
- Agile and Iterative Process
- Analytics and Tracking
- Artificial Intelligence
- Augmented Reality
- Behavioral Science
- Business UX Leaders
- Business Value and ROI
- Cloud Computing
- Conferences
- Consumer products
- Content and Copy
- Content Strategy
- Contests and Giveaways
- Contextual User Studies
- Conversational Design
- Customer Experience
- Data visualization
- Decision Architecture
- Defining AI
- Design for Experience Awards
- Design Theory
- Design Tools and Software
- Development
- Digital Publishing and eBooks
- Direct Observation Research
- Employee Experience
- Employment and Hiring
- Enterprise Products
- Entertainment and Humor
- Ethnography
- Eye tracking
- Flow and Immersion
- Form design
- Global Products and Localization
- Government and Public Services
- Human factors
- Information Design and Architecture
- Input devices
- Interaction Design
- Interface and Navigation Design
- Internal Company Dynamics
- Internal Company Systems and Intranets
- Language Learning Models
- Location-Based Services
- Machine Learning
- Marketing and Brand
- Media Contour
- Microsoft Silverlight
- Microsoft Windows
- Mobile Applications
- Mobile Technology
- Motion and Animation
- Neuroscience
- New and Emerging Technologies
- Nomenclature
- Open source
- Operating Systems
- Patents and Closed Systems
- Patterns and Components
- Personal and Professional Development
- Persuasive Design
- Presentations
- Privacy and Data Security
- Product design
- Product Releases and Redesigns
- Project Management
- Psychology and Human Behavior
- Remote Research
- Requirements and Specifications
- Research Methods and Techniques
- Research Tools and Software
- Rich Internet applications
- Ruby on Rails
- Search, SEO, and SEM
- Semantic Technology
- Social Media Marketing
- Social Networking
- Software as a Service
- Sound and Audio
- Storytelling
- Team Dynamics
- Technology for the Common Good
- The Business of UX
- The Business of UX Page Banner
- The Evolution of Research
- The rise of design
- The UX of cars
- Things UX People Like
- Ubiquitous Computing
- User Acceptance Testing
- User Adoption
- User Reported Feedback
- UX Business News
- UX Education
- UX Magazine
- UX World Changing Ideas
- Vendor-Client Relationships
- Visual Design
- Voice & Natural Language
- Windows Phone
- Working With Stakeholders
- Workshops and Brainstorming
Did you know UX Magazine hosts the most popular podcast about conversational AI?
Join 740,000 designers, thinkers, and doers.
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. check our privacy policy and.
How To Run UX Research Without Access To Users
May 7, 2024 — How do we conduct UX research when there is no or only limited access to users? Here are some workarounds to run UX research or make a strong case for it. An upcoming part of Smart Interface Design Patterns . Read more…
No need to be sad!
Unfortunately, there are no more articles in this category. But you can subscribe to our lovely email newsletter to not miss the next one.
On front-end & UX . Trusted by 200,000+ folks.
Get a free custom homepage design for your new website.
Design, UI, UX , Inspiration
15 excellent ux case studies every creative should read.
- By Sandra Boicheva
- October 21st, 2021
In a previous article, we talked about UX portfolios and how they carefully craft a story of how designers work. Interestingly enough, recruiters decide if a UX freelance designer or an agency is a good match within 5 minutes into the portfolio . In order to persuade these recruiters, the portfolio needs to present an appealing story that showcases the skill, the thought process, and the choices taken for key parts of the designs. With this in mind, today we’ll talk about UX case studies and give 15 excellent examples of case studies with compelling stories.
The Storytelling Approach in UX Case Studies
An essential part of the portfolio of a UX designer is the case studies that pack a showcase of the designer’s skills, way of thinking, insights in the form of compelling stories. These case studies are often the selling point as recruiters look for freelancers and agencies who can communicate their ideas through design and explain themselves in a clear and appealing way. So how does this work?
Photography by Alvaro Reyes
Just like with every other story, UX case studies also start with an introduction, have a middle, and end with a conclusion .
- Introduction: This UX case study example starts with a design brief and presents the main challenges and requirements. In short, the UX designer presents the problem, their solution, and their role.
- Middle: The actual story of the case study example explains the design process and the techniques used. This usually starts with obstacles, design thinking, research, and unexpected challenges. All these elements lead to the best part of the story: the action part. It is where the story unveils the designer’s insights, ideas, choices, testing, and decisions.
- Conclusion: The final reveal shows the results and gives space for reflection where the designer explains what they’ve learned, and what they’ve achieved.
Now as we gave you the introduction, let’s get to the main storyline and enjoy 15 UX case studies that tell a compelling story.
1. Car Dealer Website for Mercedes-Benz Ukraine by Fulcrum
This case study is a pure pleasure to read. It’s well-structured, easy to read, and still features all the relevant information one needs to understand the project. As the previous client’s website was based on the official Mercedes Benz template, Fulcrum had to develop an appealing and functional website that would require less time to maintain, be more user-friendly, and increase user trust.
- Intro: Starts with a summary of the task.
- Problem: Lists the reasons why the website needs a redesign.
- Project Goals: Lists the 4 main goals with quick summaries.
- Project: Showcases different elements of the website with desktop and mobile comparison.
- Functionality: Explains how the website functionality helps clients to find, and order spare parts within minutes.
- Admin Panel: Lists how the new admin panel helps the client customize without external help.
- Elements: Grid, fonts, colors.
- Tech Stack: Shows the tools used for the backend, mobile, admin panel, and cloud.
- Client review: The case study ends with a 5-star review by the marketing director of Mercedes Benz Ukraine, Olga Belova.
This case study is an example of a detailed but easy to scan and read story from top to bottom, featuring all relevant information and ending on the highest note: the client’s review.
Advertisement
2. Galaxy Z Flips 5G Website by DFY
This is a big project that covers every aspect of the website, including the UX strategy. The creative studio aimed to fully illustrate and demonstrate the significant upgrades over previous models and to enable two-way communication with the customers through an interactive experience.
- Intro: Summary of the project and roles.
- Interactive Experience: The main project goal.
- Demonstration: Explains the decision to feature 360-degree views and hands-on videos instead of technical terms.
- Screens: Includes high-quality screenshots of significant pages and features.
- Ecosystem: Highlight a page with easy navigation across different products as a marketing decision that makes cross-selling seamless.
- Essentials: Showcases a slider of all products with key features that provide ample information.
- Showroom: Interactive experience that helps the user “play around” with the product.
- Credits: As a conclusion, DFY features the stakeholders involved.
A strong presentation of a very ambitious project. It keeps the case study visual while still providing enough insight into the thought process and the most important decisions.
3. Jambb Social Platform by Finna Wang
Here we have a beautiful case study for a platform that aims to help creators grow their communities by recognizing and rewarding their base of supporters. It tackles a curious problem that 99% of fans who contribute in non-monetary ways don’t get the same content, access, and recognition they deserve. This means the creators need a way to identify their fans across all social platforms to grow their business and give recognition. To get a clear picture of what the design has to accomplish, Finna Wang conducted stakeholder interviews with the majority of the client’s team.
- Intro: Listing roles, dates, team, and used tools.
- Project Overview: The main concept and the reasons behind it.
- Exploration: What problem will the platform solve, preliminary research, and conclusions from the research. The section includes the project scope and problem statement.
- Design Process: A thorough explanation of the discoveries and the exact steps.
- User Flows: 3 user flows based on common tasks that the target user/fan would do on the site.
- Design Studio: Visualization process with wireframes, sitemap, prototypes.
- Design Iterations: The designer highlights the iterations they were primary behind.
- Style Guide: Typography, colors, visual elements breakdown.
- Usability Testing: Beta site vs Figma prototype; usertesting.com, revised problem statement.
- Prototype: Features an accessible high fidelity prototype in Figma you can view.
- Takeaways: Conclusions.
An extremely detailed professionally made and well-structured UX case study. It goes a step further by listing specific conclusions from the conducted research and featuring an accessible Figma prototype.
4. Memento Media by Masha Keyhani
This case study is dedicated to a very interesting project for saving family stories. It aims to help users capture and record memories from their past. To do so, the design team performed user research and competitive analysis. The entire project took a 6-week sprint.
- Overview: Introducing the client and the purpose of the app.
- My Role: Explaining the roles of the designer and their team.
- Design Process: A brief introduction of the design process and the design toolkit
- Home: The purpose of the Homepage and the thought process behind it.
- Question Selection: The decision behind this screen.
- Recording Process: Building the recording feature and the decisions behind it.
- User research: a thorough guide with the main focuses, strategies, and competitor analysts, including interviews.
- Research Objectives: The designer gives the intent of their research, the demographics, synthesis, and usability testing insights.
- Propositions: Challenges and solutions
- User Flow: Altering the user flow based on testing and feedback.
- Wireframes: Sketches, Lo-Fi wireframing.
- Design System: Typography, colors, iconography, design elements.
- The Prototype: It shows a preview of the final screens.
This UX study case is very valuable for the insights it presents. The design features a detailed explanation of the thinking process, the research phase, analysts, and testing which could help other creatives take some good advice from it for their future research.
5. Perfect Recipes App by Tubik
Here we have a UX case study for designing a simple mobile app for cooking, recipes, and food shopping. It aims to step away from traditional recipe apps by creating something more universal for users who love cooking with extended functionality. The best idea behind it is finding recipes based on what supplies the user currently has at home.
- Intro: Introducing the concept and the team behind it.
- Project: What they wanted to make and what features would make the app different than the competitors.
- UI design: The decisions behind the design.
- Personalization: Explaining how the app gives the user room for personalization and customizing the features according to their personal preferences.
- Recipe Cards and Engaging Photos: The decisions behind the visuals.
- Cook Now feature: Explaining the feature.
- Shopping List: Explaining the feature.
- Pantry feature: The idea to sync up the app with AmazonGo services. This case study section features a video.
- Bottom Line: What the team learned.
This UX case study is a good example of how to present your concept if you have your own idea for an app. You could also check the interactive preview of the app here .
6. SAM App by Mike Wilson
The client is the Seattle Art Museum while the challenge is to provide engaging multimedia content for users as well as self-guided tours. Mile Wilson has to create an experience that will encourage repeat visits and increase events and exhibition attendance.
- Intro: Listing time for the project, team members, and roles.
- The Client: A brief introduction of Seattle Art Museum
- The Challenge: What the app needs to accomplish.
- Research and Planning: Explaining the process for gathering insights, distributing surveys, interviews, and identifying specific ways to streamline the museum experience.
- Sloane: Creating the primary persona. This includes age, bio, goals, skills, and frustrations.
- Designing the Solution: Here the case study features the results of their research, information architecture, user flows, early sketching, paper prototypes, and wireframes.
- Conclusion: Explaining the outcome, what the team would have done differently, what’s next, and the key takeaways.
What we can take as a valuable insight aside from the detailed research analysis, is the structure of the conclusion. Usually, most case studies give the outcome and preview screens. However, here we have a showcase of what the designer has learned from the project, what they would do differently, and how they can improve from the experience.
7. Elmenus Case Study
This is a case study by UX designers Marwa Kamaleldin, Mario Maged, Nehal Nehad, and Abanoub Yacoub for redesigning a platform with over 6K restaurants. It aims to help users on the territory of Egypt to find delivery and dine-out restaurants.
- Overview: What is the platform, why the platform is getting redesigned, what is the target audience. This section also includes the 6 steps of the team’s design process.
- User Journey Map: A scheme of user scenarios and expectations with all phases and actions.
- Heuristic Evaluation: Principles, issues, recommendations, and severity of the issues of the old design.
- First Usability Testing: Goals, audience, and tasks with new user scenarios and actions based on the heuristic evaluation. It features a smaller section that lists the most severe issues from usability for the old design.
- Business Strategy: A comprehensive scheme that links problems, objectives, customer segment, measurements of success, and KPIs.
- Solutions: Ideas to solve all 4 issues.
- Wireframes: 4 directions of wireframes.
- Styleguide: Colors, fonts, typeface, components, iconography, spacing method.
- Design: Screens of the different screens and interactions.
- Second Usability Testing: Updated personas, scenarios, and goals. The section also features before-and-after screenshots.
- Outcome: Did the team solve the problem or not.
A highly visual and perfectly structured plan and process for redesigning a website. The case study shows how the team discovers the issues with the old design and what decisions they made to fix these issues.
8. LinkedIn Recruiter Tool by Evelynma
A fresh weekend project exploring the recruiting space of LinkedIn to find a way to help make it easier for recruiters to connect with ideal candidates.
- Background Info: What made the designer do the project.
- Problem and Solution: A good analysis of the problem followed by the designer’s solution.
- Process: This section includes an analysis of interviewing 7 passive candidates, 1 active candidate, 3 recruiters, and 1 hiring manager. The designer also includes their journey map of the recruiting experience, a sketch of creating personas, and the final 3 personas.
- Storyboard and User Flow Diagrams: The winning scenario for Laura’s persona and user flow diagram.
- Sketches and Paper Prototypes: Sticky notes for paper prototypes for the mobile experience.
- Visual Design: Web and mobile final design following the original LinkedIn pattern.
- Outcome: Explaining the opportunity.
This is an excellent UX case study when it comes to personal UX design projects. creating a solution to a client’s problem aside, personal project concepts is definitely something future recruiters would love to see as it showcases the creativity of the designers even further.
9. Turbofan Engine Diagnostics by Havana Nguyen
The UX designer and their team had to redesign some legacy diagnostics software to modernize the software, facilitate data transfers from new hardware, and improve usability. They built the desktop and mobile app for iOS and Android.
- Problem: The case study explain the main problem and what the team had to do to solve it.
- My Role: As a lead UX designer on a complicated 18-month project, Havana Nguyen had a lot of work to do, summarized in a list of 5 main tasks.
- Unique Challenges: This section includes 4 main challenges that made the project so complex. ( Btw, there’s a photo of sketched wireframes literally written on the wall.)
- My Process: The section includes a description of the UX design process highlighted into 5 comprehensive points.
- Final Thoughts: What the designer has learned for 18 months.
The most impressive thing about this case study is that it manages to summarize and explain well an extremely complex project. There are no prototypes and app screens since it’s an exclusive app for the clients to use.
10. Databox by FireArt
A very interesting project for Firearts’s team to solve the real AL & ML challenges across a variety of different industries. The Databox project is about building scalable data pipeline infrastructure & deploy machine learning and artificial intelligence models.
- Overview: The introduction of the case study narrows down the project goal, the great challenge ahead, and the solution.
- How We Start: The necessary phases of the design process to get an understanding of a product.
- User Flow: The entire scheme from the entry point through a set of steps towards the final action of the product.
- Wireframes: A small selection of wireframe previews after testing different scenarios.
- Styleguide: Typography, colors, components.
- Visual Design: Screenshots in light and dark mode.
A short visual case study that summarizes the huge amount of work into a few sections.
11. Travel and Training by Nikitin Team
Here’s another short and sweet case study for an app with a complete and up-to-date directory of fitness organizations in detailed maps of world cities.
- Overview: Explaining the project.
- Map Screen : Outlining the search feature by categories.
- Profiles: Profile customization section.
- Fitness Clubs: Explaining the feature.
- Icons: A preview of the icons for the app.
- App in Action: A video of the user experience.
This case study has fewer sections, however, it’s very easy to read and comprehend.
12. Carna by Ozmo
Ozmo provides a highly visual case study for a mobile application and passing various complexities of courses. The main goal for the UX designer is to develop a design and recognizable visual corporate identity with elaborate illustrations.
- Intro: A visual project preview with a brief description of the goal and role.
- Identity: Colors, fonts, and logo.
- Wireframes: The thinking process.
- Interactions: Showcase of the main interactions with animated visuals.
- Conclusion: Preview of the final screens.
The case study is short and highly visual, easy to scan and comprehend. Even without enough insight and text copy, we can clearly understand the thought process behind and what the designer was working to accomplish.
13. An Approach to Digitization in Education by Moritz Oesterlau
This case study is for an online platform for challenge-based learning. The designer’s role was to create an entire product design from research to conception, visualization, and testing. It’s a very in-depth UX case study extremely valuable for creatives in terms of how to structure the works in their portfolio.
- Intro: Introducing the client, project time, sector, and the designer’s role.
- Competitive Analysis: the case study starts off with the process of creating competitive profiles. It explains the opportunities and challenges of e-learning that were taken into consideration.
- Interviews and Surveys: Listing the goals of these surveys as well as the valuable insights they found.
- Building Empathy: The process and defining the three target profiles and how will the project cater to their needs. This section includes a PDF of the user personas.
- Structure of the Course Curriculum: Again with the attached PDF files, you can see the schemes of the task model and customer experience map.
- Information Architecture: The defined and evaluated sitemap for TINIA
- Wireframing, Prototyping, and Usability Testing : An exploration of the work process with paper and clickable prototypes.
- Visual Design: Styleguide preview and detailed PDF.
- A/B and Click Tests: Reviewing the usability assumptions.
- Conclusion: A detailed reflection about the importance of the project, what the designer learned, and what the outcome was.
This is a very important case study and there’s a lot to take from it. First, the project was too ambitious and the goal was too big and vague. Although the result is rather an approximation and, above all, at the conceptual level requires further work, the case study is incredibly insightful, informative, and insightful.
14. In-class Review Game by Elizabeth Lin
This project was never realized but the case study remains and it’s worth checking out. Elizabeth Lin takes on how to create an engaging in-class review game with a lot of research, brainstorming, and a well-structured detailed process.
- Intro: What makes the project special.
- Research: Explaining how they approached the research and what they’ve learned.
- Brainstorming: the process and narrowing all How Might We questions to one final question: How might we create an engaging in-class math review game.
- Game Loop and Storyboarding: Sketch of the core game loop and the general flow of the game.
- Prototyping: Outlining basic game mechanics and rounds in detail.
- Future Explorations: The case study goes further with explorations showing how the product could look if we expanded upon the idea even further.
- What Happened?: The outcome of the project.
This case study tells the story of the project in detail and expands on it with great ideas for future development.
15. Virtual Makeup Studio by Zara Dei
And for our last example, this is a case study that tells the story of an app-free shippable makeover experience integrated with the Covergirl website. The team has to find a way to improve conversion by supporting customers in their purchase decisions as well as to increase basket size by encouraging them to buy complementary products.
- Intro: Introducing the project and the main challenges.
- Discovery and Research: Using existing product information on the website to improve the experience.
- Onboarding and Perceived Performance: Avoiding compatibility issues and the barrier of a user having to download an app. The section explains the ideas for features that will keep users engaged, such as a camera with face scan animation.
- Fallback Experience and Error States: Providing clear error messaging along with troubleshooting instructions.
- Interactions: explaining the main interactions and the decisions behind them.
- Shared Design Language: Explaining the decision to provide links on each product page so users could be directed to their preferred retailer to place their order. Including recommended products to provide users with alternatives.
- Outcome and Learning: The good ending.
- Project Information: Listing all stakeholders, the UX designer’s role in a bullet list, and design tools.
In Conclusion
These were the 15 UX case studies we wanted to share with you as they all tell their story differently. If we can take something valuable about what are the best practices for making an outstanding case study, it will be something like this.
Just like with literature, storytelling isn’t a blueprint: you can write short stories, long in-depth analyses, or create a visual novel to show your story rather than tell. The detailed in-depth UX case studies with lots of insights aren’t superior to the shorter visual ones or vice versa. What’s important is for a case study to give a comprehensive view of the process, challenges, decisions, and design thinking behind the completed project .
In conclusion, a UX case study should always include a summary; the challenges; the personas; roles and responsibilities; the process; as well as the outcomes, and lessons learned.
Video Recap
Take a look at the special video we’ve made to visualize and discuss the most interesting and creative ideas implemented in the case studies.

In the meantime, why not browse through some more related insights on web development and web design?
- The 30 Best UX Books Every Creative Should Read in 2022
- Great UI Animation Examples to Make Your Jaw Drop [+Tips and Freebies]
- 60 Superb App Design Inspiration Examples
Popular Posts
- 20 UI/UX Design Trends that will Rock 2023 [Updated]
- Best 15 UI Color Palette & Scheme Generators for the Perfect Interface Design
- 10 Golden UI Design Principles and How To Use Them
- GET A QUICK QUOTE
Subscribe for our newsletter
We hate boring. Our newsletters are relevant and on point. Excited? Let’s do this!
Skip navigation

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
Cookie permissions: 6 design guidelines.
Summary: Design cookie permissions that strike the balance between respecting user privacy and being user-friendly.
5 minute video by 2024-05-01 5
- Samhita Tankala
- Design Patterns Design Patterns
Share this article:
- Share this video:
You must have javascript and cookies enabled in order to display videos.
Related Article
Cookie Permissions 101
Cookie permissions need to follow the law and strike the balance between respecting user privacy and being user-friendly.
Video Author
Samhita Tankala is a User Experience Specialist with Nielsen Norman Group. With her background in consulting, education and UX Research, Samhita’s expertise include executing and delivering UX research with a range of stakeholders and training teams. Some of her research focuses on cognitive behavior, human behavior and the learning sciences.
- Share:
Subscribe to the weekly newsletter to get notified about future articles.

How to Present UX Research Results Responsibly
3 minute video

Accordions: 5 Scenarios to Avoid Them

User Feedback: 5 Guidelines

3 Alternatives to Infinite Scrolling
4 minute video
- Deceptive Patterns in UX: How to Recognize and Avoid Them
- Passwordless Accounts: One-Time Passwords (OTPs) and Passkeys
- Bottom Sheets: Definition and UX Guidelines
- Skeleton Screens 101
- Maintaining the Privacy and Security of Research Participants’ Data
Research Reports
- Intranet Design Annual: 2020
- Intranet Design Annual: 2019
- Intranet Design Annual: 2022
- Intranet Design Annual: 2018

COMMENTS
UX (user experience) research is the systematic study of target users and their requirements, to add realistic contexts and insights to design processes. UX researchers adopt various methods to uncover problems and design opportunities. Doing so, they reveal valuable information which can be fed into the design process.
What is UX research? Research is a disciplined, methodical investigation into a topic. Let's see how Jane Suri, Executive Design Director @ Ideo defines design research."Design research both inspires imagination and informs intuition through a variety of methods with related intents: to expose patterns underlying the rich reality of people's behaviors and experiences, to explore reactions ...
The Complete Guide to UX Research Methods. UX research provides invaluable insight into product users and what they need and value. Not only will research reduce the risk of a miscalculated guess, it will uncover new opportunities for innovation. authors are vetted experts in their fields and write on topics in which they have demonstrated ...
UX Research Cheat Sheet. Susan Farrell. February 12, 2017. Summary: User research can be done at any point in the design cycle. This list of methods and activities can help you decide which to use when. User-experience research methods are great at producing data and insights, while ongoing activities help get the right things done.
This topic covers generative UX research, usability evaluation, and pure research that pertains to UX design. A/B Testing (3) Analysis (20) Analytics (14) Card Sorts (3) Consumer Research (3) Contextual Inquiry (1) Diary Studies (1) Ethnography (3) Expert Reviews (8) Eyetracking (3) Facilitating Workshops (1) HCI Research (4) Human Factors ...
User research is the parent of UX research; it's a broader research effort that aims to understand the demographics, behaviors, and sentiments of your users and personas. UX research, on the other hand, is a type of user research that's specific to your product or platform. Where user research focuses on the user as a whole, UX research ...
Take a deep dive into User Research Methods with our course AI for Designers . In an era where technology is rapidly reshaping the way we interact with the world, understanding the intricacies of AI is not just a skill, but a necessity for designers. The AI for Designers course delves into the heart of this game-changing field, empowering you ...
User research, or UX research, is an absolutely vital part of the user experience design process. Typically done at the start of a project, it encompasses different types of research methodologies to gather valuable data and feedback. When conducting user research, you'll engage with and observe your target users, getting to know their needs ...
To make your work easier for you, we have crafted a 10-step guide to make your work easier and to help you communicate user research to your clients and boss. Evangelize. With a bit of luck, your company or client is already aware of the importance of user research in a design project. If not, make sure you find ways to communicate your points ...
UX research is a fundamental requirement of the design process. Through methodical and investigative procedures, designers can gain a better understanding of user expectations, behaviors, and needs. But it is the application of the results that will lead to better user experiences and improved product designs.
Use Figma's UX design tool to: Give and receive instant feedback on designs or prototypes—and enjoy real-time collaboration with your team. Figma's Maze integration makes testing prototypes easy. Set up design libraries to quickly launch user research projects and improve UX design. Easily share assets between Figma and FigJam to help keep ...
What is desk research? Desk research, or secondary research, is vital to UX research. It involves analyzing existing data, reports, and papers to understand a subject, identify trends, and pinpoint gaps in knowledge. It's cost-effective and time-efficient, informing primary research and guiding decisions in UX design.
11. Concept testing. Concept testing is a type of research that evaluates the feasibility, appeal, and potential success of a new product before you build it. It centers the user in the ideation process, using UX research methods like A/B testing, surveys, and customer interviews.
User interviews are a fundamental technique in UX research that let designers get qualitative information straight from users. Designers may acquire profound insights into user demands, motivations, behaviors, and pain spots by having one-on-one dialogues with users. Here, we'll explore the essential elements of user interviews, including ...
Important peer-reviewed and informally published recent research on user interface design and user experience (UX) design. ... PulseUX BLOG Visit our blog for insightful and interesting posts on a wide-range of design research topics. Some posts have had millions of page views. A Division of MauroNewMedia Contact: MauroNewMedia, 23 East 73rd ...
The term "user experience" (UX/UE) is extensively adopted but interpreted in various ways. Broadly, it describes the interaction between users and products and has become a topic of the general concern in human-computer interaction and other areas, but there is no consensus on its meaning (Park et al., 2013).The multidisciplinary nature of UX has led to multiple definitions and research ...
Jesse James Garrett's 5 Elements was especially instrumental. TL;DR version of the these UX topics and skills are: UX Strategy / User Research / Information Architecture / Interaction Design / Usability Testing / Visual Design / Content Strategy / SEO / Coding. Without further ado, let's dive into the full list of UX topics to learn! _ _ _.
Windows Phone. Wireframes. Working With Stakeholders. Workshops and Brainstorming. Yahoo! Discover the diverse range of topics covered on UX magazine. Our list of categories includes everything from AI to UX, making it easy to find the content that matters to you. Browse our topics and stay informed on the latest news and ideas.
Magazine on CSS, JavaScript, front-end, accessibility, UX and design. For developers, designers and front-end engineers.
This UX study case is very valuable for the insights it presents. The design features a detailed explanation of the thinking process, the research phase, analysts, and testing which could help other creatives take some good advice from it for their future research. View The Full UX Case Study 5. Perfect Recipes App by Tubik
Here are they👇. Redesign of a website or app. Photo by KOBU Agency on Unsplash. This is a classic topic for a UI/UX case study. The redesign could be focused on improving usability, accessibility, or visual design. The case study could include research, user testing, and iterations of the design. 2.
User Experience (UX) Research is a critical component of interaction design, focusing on understanding user behaviors, needs, and motivations through observation techniques, task analysis, and ...
Samhita Tankala is a User Experience Specialist with Nielsen Norman Group. With her background in consulting, education and UX Research, Samhita's expertise include executing and delivering UX research with a range of stakeholders and training teams. Some of her research focuses on cognitive behavior, human behavior and the learning sciences.