

Why is it important to do a literature review in research?
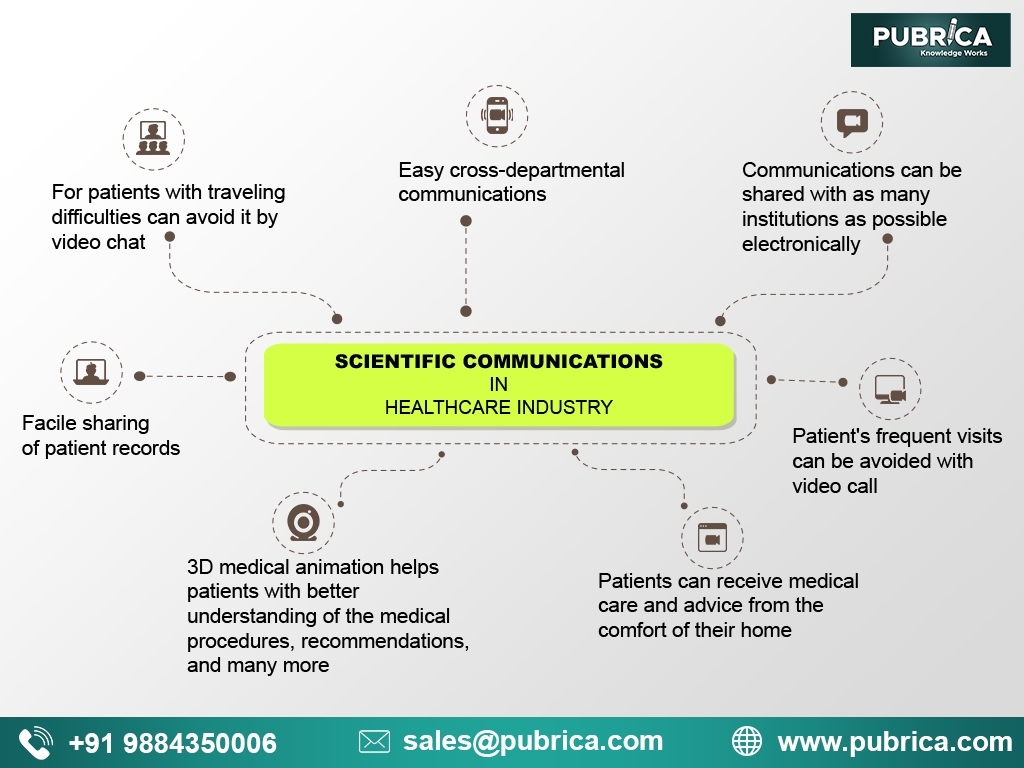
The importance of scientific communication in the healthcare industry
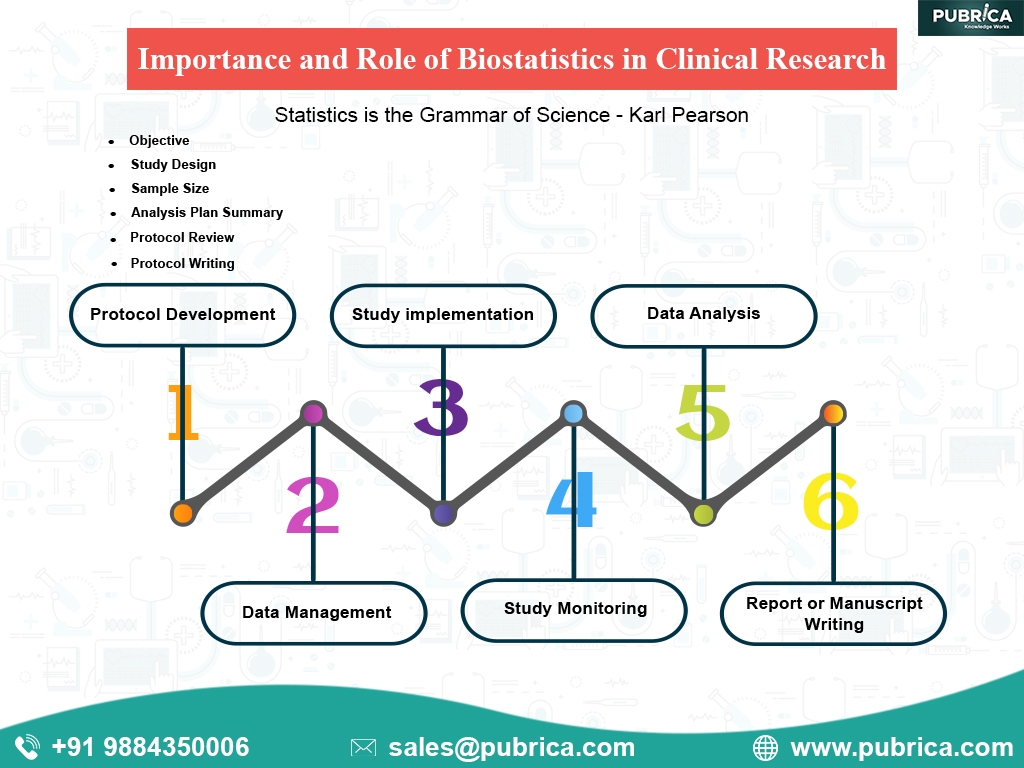
The Importance and Role of Biostatistics in Clinical Research
“A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research”. Boote and Baile 2005
Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review. Since it is one of the basic needs for researches at any level, they have to be done vigilantly. Only then the reader will know that the basics of research have not been neglected.
The aim of any literature review is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of existing knowledge in a particular field without adding any new contributions. Being built on existing knowledge they help the researcher to even turn the wheels of the topic of research. It is possible only with profound knowledge of what is wrong in the existing findings in detail to overpower them. For other researches, the literature review gives the direction to be headed for its success.
The common perception of literature review and reality:
As per the common belief, literature reviews are only a summary of the sources related to the research. And many authors of scientific manuscripts believe that they are only surveys of what are the researches are done on the chosen topic. But on the contrary, it uses published information from pertinent and relevant sources like
- Scholarly books
- Scientific papers
- Latest studies in the field
- Established school of thoughts
- Relevant articles from renowned scientific journals
and many more for a field of study or theory or a particular problem to do the following:
- Summarize into a brief account of all information
- Synthesize the information by restructuring and reorganizing
- Critical evaluation of a concept or a school of thought or ideas
- Familiarize the authors to the extent of knowledge in the particular field
- Encapsulate
- Compare & contrast
By doing the above on the relevant information, it provides the reader of the scientific manuscript with the following for a better understanding of it:
- It establishes the authors’ in-depth understanding and knowledge of their field subject
- It gives the background of the research
- Portrays the scientific manuscript plan of examining the research result
- Illuminates on how the knowledge has changed within the field
- Highlights what has already been done in a particular field
- Information of the generally accepted facts, emerging and current state of the topic of research
- Identifies the research gap that is still unexplored or under-researched fields
- Demonstrates how the research fits within a larger field of study
- Provides an overview of the sources explored during the research of a particular topic
Importance of literature review in research:
The importance of literature review in scientific manuscripts can be condensed into an analytical feature to enable the multifold reach of its significance. It adds value to the legitimacy of the research in many ways:
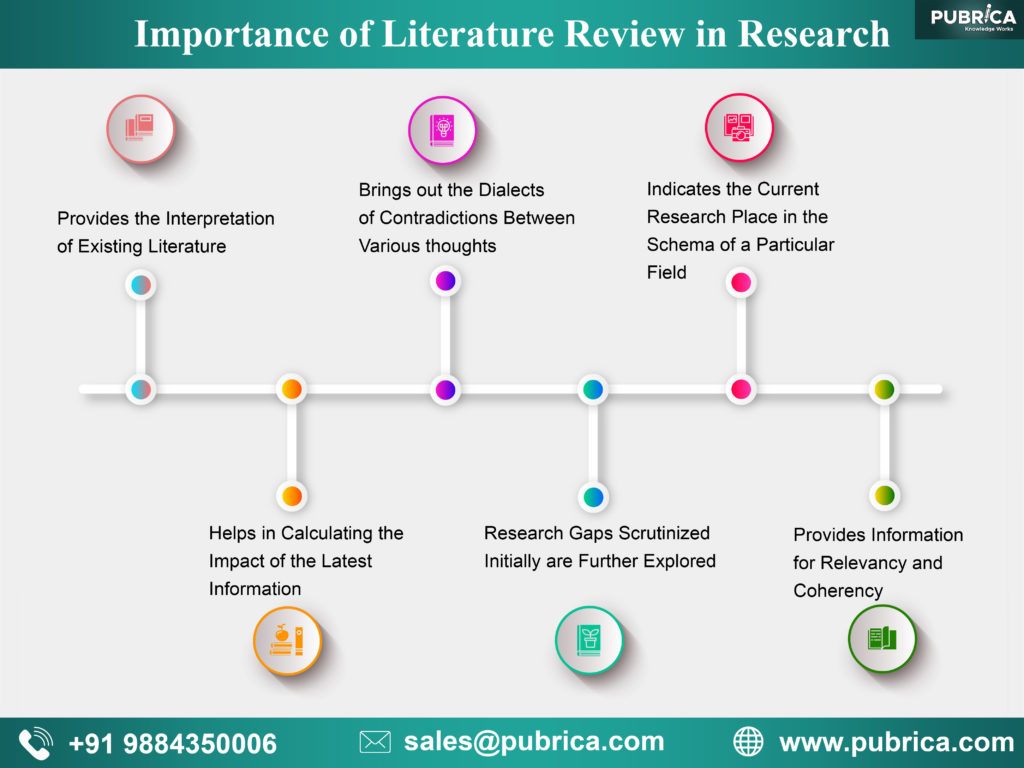
- Provides the interpretation of existing literature in light of updated developments in the field to help in establishing the consistency in knowledge and relevancy of existing materials
- It helps in calculating the impact of the latest information in the field by mapping their progress of knowledge.
- It brings out the dialects of contradictions between various thoughts within the field to establish facts
- The research gaps scrutinized initially are further explored to establish the latest facts of theories to add value to the field
- Indicates the current research place in the schema of a particular field
- Provides information for relevancy and coherency to check the research
- Apart from elucidating the continuance of knowledge, it also points out areas that require further investigation and thus aid as a starting point of any future research
- Justifies the research and sets up the research question
- Sets up a theoretical framework comprising the concepts and theories of the research upon which its success can be judged
- Helps to adopt a more appropriate methodology for the research by examining the strengths and weaknesses of existing research in the same field
- Increases the significance of the results by comparing it with the existing literature
- Provides a point of reference by writing the findings in the scientific manuscript
- Helps to get the due credit from the audience for having done the fact-finding and fact-checking mission in the scientific manuscripts
- The more the reference of relevant sources of it could increase more of its trustworthiness with the readers
- Helps to prevent plagiarism by tailoring and uniquely tweaking the scientific manuscript not to repeat other’s original idea
- By preventing plagiarism , it saves the scientific manuscript from rejection and thus also saves a lot of time and money
- Helps to evaluate, condense and synthesize gist in the author’s own words to sharpen the research focus
- Helps to compare and contrast to show the originality and uniqueness of the research than that of the existing other researches
- Rationalizes the need for conducting the particular research in a specified field
- Helps to collect data accurately for allowing any new methodology of research than the existing ones
- Enables the readers of the manuscript to answer the following questions of its readers for its better chances for publication
- What do the researchers know?
- What do they not know?
- Is the scientific manuscript reliable and trustworthy?
- What are the knowledge gaps of the researcher?
22. It helps the readers to identify the following for further reading of the scientific manuscript:
- What has been already established, discredited and accepted in the particular field of research
- Areas of controversy and conflicts among different schools of thought
- Unsolved problems and issues in the connected field of research
- The emerging trends and approaches
- How the research extends, builds upon and leaves behind from the previous research
A profound literature review with many relevant sources of reference will enhance the chances of the scientific manuscript publication in renowned and reputed scientific journals .
References:
http://www.math.montana.edu/jobo/phdprep/phd6.pdf
journal Publishing services | Scientific Editing Services | Medical Writing Services | scientific research writing service | Scientific communication services
Related Topics:
Meta Analysis
Scientific Research Paper Writing
Medical Research Paper Writing
Scientific Communication in healthcare
pubrica academy
Related posts.
Importance Of Proofreading For Scientific Writing Methods and Significance

Statistical analyses of case-control studies

Selecting material (e.g. excipient, active pharmaceutical ingredient, packaging material) for drug development
Comments are closed.
A Guide to Literature Reviews
Importance of a good literature review.
- Conducting the Literature Review
- Structure and Writing Style
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Citation Management Software This link opens in a new window
- Acknowledgements
A literature review is not only a summary of key sources, but has an organizational pattern which combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
The purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
- << Previous: Definition
- Next: Conducting the Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 3:13 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mcmaster.ca/litreview
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: Jul 8, 2024 11:22 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews

Literature Review - what is a Literature Review, why it is important and how it is done
What are literature reviews, goals of literature reviews, types of literature reviews, about this guide/licence.
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Literature Reviews and Sources
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
- Useful Resources
Help is Just a Click Away
Search our FAQ Knowledge base, ask a question, chat, send comments...
Go to LibAnswers
What is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries. " - Quote from Taylor, D. (n.d) "The literature review: A few tips on conducting it"
Source NC State University Libraries. This video is published under a Creative Commons 3.0 BY-NC-SA US license.
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review?
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
- Baumeister, R.F. & Leary, M.R. (1997). "Writing narrative literature reviews," Review of General Psychology , 1(3), 311-320.
When do you need to write a Literature Review?
- When writing a prospectus or a thesis/dissertation
- When writing a research paper
- When writing a grant proposal
In all these cases you need to dedicate a chapter in these works to showcase what have been written about your research topic and to point out how your own research will shed a new light into these body of scholarship.
Literature reviews are also written as standalone articles as a way to survey a particular research topic in-depth. This type of literature reviews look at a topic from a historical perspective to see how the understanding of the topic have change through time.
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
- Narrative Review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Book review essays/ Historiographical review essays : This is a type of review that focus on a small set of research books on a particular topic " to locate these books within current scholarship, critical methodologies, and approaches" in the field. - LARR
- Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L.K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . San Diego, CA: Plural Publishing.
- Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M.C. & Ilardi, S.S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Malden, MA: Blackwell Pub.
- Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). "Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts," Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53(3), 311-318.
Guide adapted from "Literature Review" , a guide developed by Marisol Ramos used under CC BY 4.0 /modified from original.
- Next: Strategies to Find Sources >>
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 10:56 AM
- URL: https://lit.libguides.com/Literature-Review
The Library, Technological University of the Shannon: Midwest
Service update: Some parts of the Library’s website will be down for maintenance on August 11.
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Conducting a literature review: why do a literature review, why do a literature review.
- How To Find "The Literature"
- Found it -- Now What?
Besides the obvious reason for students -- because it is assigned! -- a literature review helps you explore the research that has come before you, to see how your research question has (or has not) already been addressed.
You identify:
- core research in the field
- experts in the subject area
- methodology you may want to use (or avoid)
- gaps in knowledge -- or where your research would fit in
It Also Helps You:
- Publish and share your findings
- Justify requests for grants and other funding
- Identify best practices to inform practice
- Set wider context for a program evaluation
- Compile information to support community organizing
Great brief overview, from NCSU
Want To Know More?
- Next: How To Find "The Literature" >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 1:10 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/litreview
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Jul 15, 2024 10:34 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Aug 13, 2024 1:52 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
What is the Purpose of a Literature Review?

4-minute read
- 23rd October 2023
If you’re writing a research paper or dissertation , then you’ll most likely need to include a comprehensive literature review . In this post, we’ll review the purpose of literature reviews, why they are so significant, and the specific elements to include in one. Literature reviews can:
1. Provide a foundation for current research.
2. Define key concepts and theories.
3. Demonstrate critical evaluation.
4. Show how research and methodologies have evolved.
5. Identify gaps in existing research.
6. Support your argument.
Keep reading to enter the exciting world of literature reviews!
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical summary and evaluation of the existing research (e.g., academic journal articles and books) on a specific topic. It is typically included as a separate section or chapter of a research paper or dissertation, serving as a contextual framework for a study. Literature reviews can vary in length depending on the subject and nature of the study, with most being about equal length to other sections or chapters included in the paper. Essentially, the literature review highlights previous studies in the context of your research and summarizes your insights in a structured, organized format. Next, let’s look at the overall purpose of a literature review.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Literature reviews are considered an integral part of research across most academic subjects and fields. The primary purpose of a literature review in your study is to:
Provide a Foundation for Current Research
Since the literature review provides a comprehensive evaluation of the existing research, it serves as a solid foundation for your current study. It’s a way to contextualize your work and show how your research fits into the broader landscape of your specific area of study.
Define Key Concepts and Theories
The literature review highlights the central theories and concepts that have arisen from previous research on your chosen topic. It gives your readers a more thorough understanding of the background of your study and why your research is particularly significant .
Demonstrate Critical Evaluation
A comprehensive literature review shows your ability to critically analyze and evaluate a broad range of source material. And since you’re considering and acknowledging the contribution of key scholars alongside your own, it establishes your own credibility and knowledge.
Show How Research and Methodologies Have Evolved
Another purpose of literature reviews is to provide a historical perspective and demonstrate how research and methodologies have changed over time, especially as data collection methods and technology have advanced. And studying past methodologies allows you, as the researcher, to understand what did and did not work and apply that knowledge to your own research.
Identify Gaps in Existing Research
Besides discussing current research and methodologies, the literature review should also address areas that are lacking in the existing literature. This helps further demonstrate the relevance of your own research by explaining why your study is necessary to fill the gaps.
Support Your Argument
A good literature review should provide evidence that supports your research questions and hypothesis. For example, your study may show that your research supports existing theories or builds on them in some way. Referencing previous related studies shows your work is grounded in established research and will ultimately be a contribution to the field.
Literature Review Editing Services
Ensure your literature review is polished and ready for submission by having it professionally proofread and edited by our expert team. Our literature review editing services will help your research stand out and make an impact. Not convinced yet? Send in your free sample today and see for yourself!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template (2024)
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.

APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jun 20, 2024 9:08 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
- Library Homepage
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide: Literature Reviews?
- Literature Reviews?
- Strategies to Finding Sources
- Keeping up with Research!
- Evaluating Sources & Literature Reviews
- Organizing for Writing
- Writing Literature Review
- Other Academic Writings
What is a Literature Review?
So, what is a literature review .
"A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available or a set of summaries." - Quote from Taylor, D. (n.d)."The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting it".
- Citation: "The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting it"
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Each field has a particular way to do reviews for academic research literature. In the social sciences and humanities the most common are:
- Narrative Reviews: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific research topic and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weaknesses, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section that summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Book review essays/ Historiographical review essays : A type of literature review typical in History and related fields, e.g., Latin American studies. For example, the Latin American Research Review explains that the purpose of this type of review is to “(1) to familiarize readers with the subject, approach, arguments, and conclusions found in a group of books whose common focus is a historical period; a country or region within Latin America; or a practice, development, or issue of interest to specialists and others; (2) to locate these books within current scholarship, critical methodologies, and approaches; and (3) to probe the relation of these new books to previous work on the subject, especially canonical texts. Unlike individual book reviews, the cluster reviews found in LARR seek to address the state of the field or discipline and not solely the works at issue.” - LARR
What are the Goals of Creating a Literature Review?
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
- Baumeister, R.F. & Leary, M.R. (1997). "Writing narrative literature reviews," Review of General Psychology , 1(3), 311-320.
When do you need to write a Literature Review?
- When writing a prospectus or a thesis/dissertation
- When writing a research paper
- When writing a grant proposal
In all these cases you need to dedicate a chapter in these works to showcase what has been written about your research topic and to point out how your own research will shed new light into a body of scholarship.
Where I can find examples of Literature Reviews?
Note: In the humanities, even if they don't use the term "literature review", they may have a dedicated chapter that reviewed the "critical bibliography" or they incorporated that review in the introduction or first chapter of the dissertation, book, or article.
- UCSB electronic theses and dissertations In partnership with the Graduate Division, the UC Santa Barbara Library is making available theses and dissertations produced by UCSB students. Currently included in ADRL are theses and dissertations that were originally filed electronically, starting in 2011. In future phases of ADRL, all theses and dissertations created by UCSB students may be digitized and made available.
Where to Find Standalone Literature Reviews
Literature reviews are also written as standalone articles as a way to survey a particular research topic in-depth. This type of literature review looks at a topic from a historical perspective to see how the understanding of the topic has changed over time.
- Find e-Journals for Standalone Literature Reviews The best way to get familiar with and to learn how to write literature reviews is by reading them. You can use our Journal Search option to find journals that specialize in publishing literature reviews from major disciplines like anthropology, sociology, etc. Usually these titles are called, "Annual Review of [discipline name] OR [Discipline name] Review. This option works best if you know the title of the publication you are looking for. Below are some examples of these journals! more... less... Journal Search can be found by hovering over the link for Research on the library website.
Social Sciences
- Annual Review of Anthropology
- Annual Review of Political Science
- Annual Review of Sociology
- Ethnic Studies Review
Hard science and health sciences:
- Annual Review of Biomedical Data Science
- Annual Review of Materials Science
- Systematic Review From journal site: "The journal Systematic Reviews encompasses all aspects of the design, conduct, and reporting of systematic reviews" in the health sciences.
- << Previous: Overview
- Next: Strategies to Finding Sources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 5, 2024 11:44 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucsb.edu/litreview
A systematic literature review of sustainable water management in South Africa
- August 2024
- Sustainable Water Resources Management 10(5)
- This person is not on ResearchGate, or hasn't claimed this research yet.

- Bournemouth University

Abstract and Figures

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Pumzile Shikwambane

- SCI TOTAL ENVIRON

- Hansheng Wang
- Thobekile Zikhali-Nyoni

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
Systematic literature review of gender equity and social inclusion in primary education for teachers in Tanzania: assessing status and future directions
- Open access
- Published: 13 August 2024
- Volume 3 , article number 122 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Henry Nkya 1 &
- Isack Kibona 2
Gender equity and social inclusion (GESI) are crucial for creating inclusive and equitable educational environments in primary schools. This systematic literature review aimed to interpret and synthesize the findings of previous studies on GESI interventions and programs in primary schools in Tanzania, identified gaps in the knowledge, and provided recommendations for policy and practice. A systematic literature review search identified 22 relevant studies that met the inclusion criteria. The studies conducted between 2010 and 2021, and the sample sizes of participants were above 50. More than 50% of the studies were conducted in rural areas and used a quasi-experimental design. The interventions evaluation included teacher training, community engagement, and curriculum reform. The systematic literature review employed statistical methods to measure effect sizes and employed traditional univariate systematic literature review to synthesize the results. A table summarizing the literature that met the inclusion criteria was created to ensure transparency and clarity in the data coding process. The systematic literature review found a positive effect of GESI interventions on various outcomes, including improved academic performance, reduced gender-based violence, and increased social inclusion. However, variations in effect sizes and study designs across the studies were noted. Several gaps were identified, such as the lack of long-term follow-up and the need for more rigorous study designs. The implications of the findings for policy and practice in promoting GESI in primary schools in Tanzania were discussed, and recommendations for future research were provided. This systematic literature review highlighted the importance of addressing GESI in primary school education in Tanzania and underscored the critical role of teachers in promoting these values. It calls for targeted interventions, policy enhancements, and further research to bridge the gaps identified in the literature.
Explore related subjects
- Artificial Intelligence
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
GESI are critical components of education that ensure equitable access to education for all individuals, regardless of their gender, socioeconomic status, ethnicity, or other backgrounds. In Tanzania, GESI has become a significant concern, particularly in primary schools, where gender and social inequalities often lead to disparities in educational outcomes.
Research has shown that girls are more likely to face barriers in education than boys, including poverty, early marriages, and cultural bias that prioritize boys’ education over girls [ 28 ]. Furthermore, children from marginalized groups, such as children with disabilities, children from ethnic minority groups, and children from low-income families, often experience unequal access to quality education [ 38 ].
Addressing GESI issues in primary schools is crucial for ensuring that all children have access to quality education, which is essential for their personal development and future success. GESI initiatives can promote equity and inclusion in schools and create an environment where all children feel valued and supported [ 13 ].
Addressing gender stereotypes in teacher education programs can play a vital role in promoting GESI in primary schools [ 32 ]. Similarly, Okkolin et al. [ 27 ] suggest that interventions that address GESI can improve educational outcomes for girls and marginalized groups.
Overall, promoting GESI in primary schools is essential for creating a more equitable and inclusive education system that benefits all children [ 2 ]. It requires a concerted effort from policymakers, educators, parents, and communities to work together to create a learning environment that is supportive, respectful, and inclusive for all children.
1.1 Theoretical framework
This study is guided by the Social Justice Theory, which emphasizes the need for equitable treatment, opportunities, and outcomes for all individuals, particularly those from marginalized and disadvantaged backgrounds [ 10 ]. This framework is crucial in understanding the components of GESI and their impact on educational outcomes. The Social Justice Theory aligns with the goals of GESI by promoting fairness and the elimination of disparities in education [ 1 ].
1.1.1 Components of GESI
The key components of GESI in this study include [ 24 ]:
Gender equity: ensuring that girls and boys have equal access to education and opportunities.
Social inclusion: creating an inclusive environment where all students, regardless of their backgrounds, can participate and succeed.
Teacher training: educating teachers on gender-sensitive and inclusive teaching practices.
Community engagement: involving communities in promoting GESI.
Curricula reform: developing and implementing curricula that address GESI issues.
1.2 Justification for focusing on Tanzania
Tanzania provides a unique context for examining GESI due to its diverse population and the significant challenges it faces in achieving GESI in education [ 18 ]. Despite efforts to promote GESI, disparities persist, making it an important area of study to identify effective interventions and inform policy and practice.
1.3 Rationale for conducting a systematic literature review
A Systematic literature review is an essential tool for synthesizing research findings from different studies and summarizing the overall effect size of an intervention or variable of interest [ 34 ]. Conducting a systematic literature review on GESI in primary school education is critical for providing an overview of the existing research and identifying gaps that need to be addressed in future research. It also helps establish the overall effect of interventions aimed at promoting GESI in primary schools in Tanzania [ 9 ]. The results of the Systematic literature review can inform policies and practices aimed at promoting GESI in primary school education, thereby improving learning outcomes for all children, regardless of their gender, social, and economic backgrounds.
By addressing the GESI issues and synthesizing the existing literature, this systematic literature review aims to contribute to a more equitable and inclusive educational environment in Tanzania [ 22 ].
1.4 Research objectives
To identify the state of GESI in primary schools. This objective aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how GESI issues manifest in primary schools, considering various social and educational contexts.
To number factors that contribute to gender GESI in primary schools. This shall allow informed decisions on the effort to contain the issues of GESI.
To synthesize the findings of previous studies on GESI in primary schools. This objective focuses on aggregating and interpreting the results of existing research to offer a clear and cohesive picture of what is known about GESI interventions and their effectiveness.
To identify gaps in the knowledge of GESI in primary schools. By evaluating the existing literature, this objective seeks to highlight areas where further research is needed, identifying shortcomings in study designs, populations, or intervention strategies.
To provide recommendations for improving GESI in primary schools. Based on the synthesis of previous studies and identified gaps, this objective aims to propose actionable strategies and policies to enhance GESI in primary education.
2 Methodology
Having set the study objectives, the search-strategy for the study involved conducting a comprehensive literature review of studies on GESI in primary schools. The search was conducted using electronic databases such as Google Scholar, JSTOR, and EBSCOhost. The search terms used were “gender equity,” “social inclusion,” “primary schools,” “Tanzania,” and “teachers.” Additionally, hand searching was conducted by reviewing the reference lists of identified studies to identify any relevant studies that may have been missed during the initial search.
Inclusion criteria:
The study must be conducted in primary schools.
The study must focus on gender equity and/or social inclusion in education.
The study must involve teachers as the primary participants or focus on the teacher’s role in promoting GESI.
The study must be published in English between 2010 and 2022.
Exclusion criteria:
Studies conducted outside Tanzania.
Studies not related to gender equity and/or social inclusion in education.
Studies not involving teachers or not focusing on the teacher’s role in promoting GESI.
Studies published before 2010 or after 2022.
The search process was conducted by two independent reviewers to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the search results. The reviewers screened the titles and abstracts of the identified studies for relevance and then reviewed the full text of potentially relevant studies. Any discrepancies between the reviewers were resolved through discussion and consensus. Reviewers made necessary steps to ensure a justified systematic review. Overall, the Authors reviewed 22 papers considered to have met the set criteria.
2.1 Choice of the effect size measure and analytical methods
The effect size measure used in this study was generated by statistical tools, making it suitable for systematics review that synthesize findings across multiple studies. For similar research questions, the study employed traditional univariate meta-analysis. This method was chosen because it is suitable for synthesizing the results of multiple studies that investigate similar research questions. Traditional univariate meta-analysis allows for the calculation of an overall effect size, providing a comprehensive summary of the impact of GESI interventions across different studies.
2.2 Choice of software
We used R software, specifically the ‘metafor’ package, for our analysis. This software was selected due to its robustness and versatility in conducting analytical procedures. The ‘metafor’ package supports a wide range of meta-analytic models and methods, making it a comprehensive tool for this type of analysis.
2.3 Coding of effect sizes
Table 1 summarizes the literature included that meets the inclusion criteria. This table includes information such as study design, sample size, effect sizes, and any other relevant variables. This step ensures transparency and clarity in the data coding process.
3 Results and analysis
The layout of the manuscript has been organized accordingly, so that headings and subheadings clearly demarcates each step of the systematic literature review process.
3.1 Status of GESI in primary schools in Tanzania
3.1.1 persistent gender disparities.
One of the major findings in this study was that gender disparities in primary education persist in Tanzania. This was evident in the lower enrollment and completion rates for girls in primary schools compared to boys [ 36 ]. Girls are less likely to attend school than boys, with enrollment rates lower for girls at both the primary and secondary levels. Additionally, girls are more likely to drop out of school due to various reasons, including early marriage, household responsibilities, and financial constraints [ 5 ]. These disparities highlight the ongoing challenges faced by girls in accessing and completing primary education.
3.1.2 Cultural and societal beliefs
Several studies have identified cultural and societal beliefs as a major factor contributing to gender disparities in primary education. In many Tanzanian communities, girls are expected to prioritize domestic responsibilities over their education, which can lead to low enrollment rates and high drop-out rates [ 39 ]. Furthermore, gender-based violence and sexual harassment are prevalent in schools, with girls facing discrimination and harassment from both male students and teachers [ 4 ]. These issues underscore the need for targeted interventions to create a safer and more supportive educational environment for girls.
Furthermore, Losioki and Mdee [ 12 ] found that gender stereotypes perpetuated in teacher education programs in Tanzania, which can affect the ability of teachers to create a gender-equitable and socially inclusive classroom environment. Teachers may unconsciously reinforce gender stereotypes in the classroom, leading to further marginalization of girls and other vulnerable groups.
3.1.3 Underrepresented minorities
In addition, limited access to education for children with disabilities or those from low-income families and marginalized communities can perpetuate social inequalities in primary schools [ 30 ]. These students often face significant barriers, including inadequate school facilities, lack of appropriate learning materials, and insufficient support services, which hinder their educational progress.
3.2 Strategies addressing the challenge
Despite these challenges, there have been government efforts to improve GESI in primary schools. The government of Tanzania has committed to providing equal access to education for all children, regardless of gender, ethnicity, or socio-economic status. The government has implemented policies such as free primary education and affirmative action programs to promote equal access to education for all children, regardless of gender or social status [ 15 , 26 ]. These initiatives aim to reduce financial barriers to education and encourage the enrollment and retention of girls and children from marginalized groups. This includes initiatives such as the Tanzania Education Sector Development Plan (ESDP) and the Primary Education Development Program (PEDP) [ 6 , 16 ]. These programs aim to address systemic barriers in education and promote inclusive practices in schools. The government also is open to collaborate with external forces like international interventions, community development agencies and NGO to work toward enhancing GESI. Some Strategies Addressing GESI Challenges. For instance, projects that focus on community engagement and parental involvement have shown positive impacts in changing attitudes towards girls’ education and promoting inclusive practices [ 17 ].
3.2.1 International and community-based programs
In recent years, there have been an increase in programs and initiatives aimed at promoting GESI in primary education. For example, the “Let Girls Learn” program, launched by the US government in partnership with the Tanzanian government, aimed to increase access to education for girls and reduce gender disparities in education [ 7 ]. Similarly, the Tanzania Gender Networking Programme (TGNP) has been working to promote GESI in education through community mobilization, advocacy, and capacity building [ 14 ].
3.2.2 Interventions with recorded impact
Previous studies identified several approaches that have been successful in improving GESI in primary schools. Among others, at least two are discussed. One such approach is the use of gender-responsive pedagogy, which involves incorporating gender-sensitive teaching practices and materials into the classroom [ 17 ]. This method helps create a more inclusive learning environment that acknowledges and addresses the different needs of boys and girls. Another effective intervention is the provision of sanitary pads and menstrual hygiene education to girls, which has been shown to improve school attendance and reduce drop-out rates [ 35 ]. By addressing menstrual hygiene needs, schools can help ensure that girls do not miss out on education due to a lack of resources or stigma associated with menstruation.
3.2.3 Intervention recommendations
GESI are essential components of a quality education system, and there is a need to address the persistent gender disparities in primary education. While cultural and societal beliefs continue to be major barriers, efforts to improve GESI through government policies and initiatives, as well as community-based programs, showed promise. The use of gender-responsive pedagogy and the provision of menstrual hygiene education and supplies were promising approaches that showed positive results [ 21 ]. However, more research and investment are needed to ensure that all children have access to primary education. Continued collaboration between the government, NGOs, and communities is essential to sustain and expand these efforts, ensuring that all students can benefit from a supportive and equitable educational environment [ 29 ].
Overall, there is still much work to be done to ensure GESI in primary schools [ 33 ]. It will require continued efforts and collaboration from the government, educators, and communities to address cultural and traditional beliefs, promote teacher education that challenges gender stereotypes, and provide equal access to education for all children. Policymakers must prioritize the allocation of resources to support GESI initiatives and ensure that schools are equipped to meet the diverse needs of all students [ 3 ].
By addressing these systemic issues, Tanzania can make significant strides towards achieving an inclusive and equitable education system that benefits all children, irrespective of their gender or socioeconomic background. Continued research and monitoring are essential to evaluate the effectiveness of existing interventions and identify new strategies to overcome persistent challenges in promoting GESI in primary education [ 31 ].
3.2.4 Gaps in the knowledge about GESI in primary schools
While the literature have provided valuable insights into the state of GESI in primary schools in Tanzania, several gaps in the knowledge still need to be addressed.
One major gap is the lack of research on the experiences of marginalized groups, including children with disabilities and those from low-income households. Studies have shown that these groups face significant barriers to accessing education and are often excluded from educational opportunities. For example, a study by Mwaijande [ 20 ] found that children with disabilities faced challenges such as lack of access to assistive devices and negative attitudes from teachers and other students. Similarly, research by Pak et al. [ 30 ] and Thomas and Rugambwa [ 36 ] revealed that children from poor families often struggle to pay school fees and may not have access to basic learning materials.
Another gap in the Tanzanian knowledge is the lack of research on the experiences of female teachers in primary schools. While studies have examined gender stereotypes and biases among teacher education programs, Thomas and Rugambwa [ 36 ] stressed that there is limited research on the experiences of female teachers in the classroom. Research on female teachers could shed light on the ways in which gender intersects with other forms of marginalization, such as age and socioeconomic status.
Furthermore, there is a need for more research on effective interventions and strategies for promoting GESI in primary schools. While some studies have evaluated the impact of interventions such as teacher training programs [ 19 , 25 ] , more rigorous evaluations of these interventions are needed to determine their effectiveness and sustainability.
Additionally, there is a lack of longitudinal studies that follow the long-term impact of GESI interventions. Many studies focus on short-term outcomes, but understanding the lasting effects of interventions is crucial for developing sustainable policies and practices.
In summary, while previous research has provided valuable insights into GESI in primary schools, several gaps in the knowledge need to be addressed. Future research should focus on the experiences of marginalized groups, including children with disabilities and those from low-income households, as well as female teachers. Additionally, the study showed more need for more rigorous evaluations of interventions and strategies aimed at promoting GESI in primary schools. Longitudinal studies that assess the long-term impact of these interventions would also be beneficial.
3.3 Patterns observed across the studies
As observed in the study, there were some patterns and trends identified across the studies. Firstly, there was a consistent finding that gender disparities persist in primary schools, particularly in terms of access to education and academic achievement. Despite efforts to promote GESI, girls and marginalized groups continue to face significant barriers that hinder their educational progress.
Secondly, there was a growing recognition of the importance of addressing GESI in primary education, as evidenced by the increasing number of interventions and programs aimed at promoting these values. This trend indicates a positive shift towards acknowledging and addressing GESI issues within the education system.
Thirdly, the systematic literature review revealed that the role of teachers is critical in promoting GESI in primary schools. Teacher training and support are essential for equipping educators with the skills and knowledge needed to foster an inclusive and equitable learning environment. Studies consistently highlighted the need for gender-sensitive pedagogy and teacher professional development programs.
Finally, there were some gaps in the current knowledge base, particularly with regard to the long-term impact of interventions and the effectiveness of different approaches to promoting GESI in primary education. While some interventions showed promising results, more research was needed to determine their sustainability and broader applicability.
By addressing these gaps and building on the patterns observed across studies, future research could contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of GESI in primary schools and inform the development of policies and practices to promote equity and inclusion for all students.
To sum up, analysis revealed that GESI interventions have a positive effect on various outcomes such as academic performance, reduced gender-based violence, and increased social inclusion. However, variations in effect sizes and study designs were observed across the studies. The studies included in the systematic literature review used various designs, such as randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-experimental designs, which contributed to the diversity in effect sizes.
4 Discussion
GESI is a critical components of a better-quality education system over otherwise. In Tanzania, primary education is the foundation for future academic and professional success [ 23 ], making it essential to ensure that all students, regardless of gender or social status, have access to an inclusive and equitable education. Previous studies explored the state of GESI in primary schools and identified areas for improvement.
The findings of the study highlighted the state of GESI in primary schools. The analysis of some 10 included studies revealed that significant disparities in access to education and academic performance among genders persist, with girls being more disadvantaged. Additionally, children from marginalized backgrounds, such as those from low-income families or those with disabilities, face substantial barriers to education.
To sum up, the study suggests a holistic approach involving teachers, schools, communities, and policymakers. Thus, multifaceted approach is necessary to create a more inclusive and equitable education system. Therefore, Recommendations include:
Providing comprehensive teacher training on gender-sensitive teaching methods.
Implementing community-based initiatives to address social and cultural barriers.
Developing policies and programs prioritizing marginalized students’ needs.
4.1 Implications of the study
Overall, the systematic literature review provided important insights into the state of GESI in primary schools. While progress has been made, significant challenges remain. Continued efforts and investments are necessary to promote a more equitable and inclusive education system. Future research should address the identified gaps and build on the promising interventions highlighted in this study. Based on the evidence synthesized, it is clear that targeted interventions are necessary to address the barriers that girls and other marginalized groups face in accessing and completing primary education. The study has the following recommendations on policy and practice and the areas for future research.
4.1.1 Addressing school issues related to GESI
Teacher training: policies should mandate comprehensive training for teachers on gender-sensitive teaching practices. Educators need to be equipped with the skills and knowledge to foster an inclusive classroom environment that supports both boys and girls. This includes understanding how to address and counteract gender stereotypes and biases.
Providing resources: schools should be equipped with resources to support girls’ education. This includes the provision of sanitary pads, access to clean and safe gender-segregated toilets, and gender-sensitive teaching materials. These resources are essential in reducing barriers to attendance and participation for girls.
Reviewing curricula: the school curriculum should be reviewed and revised to promote GESI. Curricula should reflect the diversity of Tanzanian society and challenge existing gender stereotypes. Including content that promotes GESI will help inculcate these values in students from a young age.
4.1.2 Addressing structural and socio-economic barriers
Financial support: there should be policies to provide financial support to families who cannot afford school fees. This can include scholarships, free school meals, and other financial incentives that alleviate the economic burden on families and keep girls in school.
Cultural norms and attitudes: interventions must focus on changing cultural norms and attitudes that limit girls’ access to education. Community engagement and awareness campaigns are crucial in shifting perceptions and promoting the value of girls’ education. Programs should aim to involve parents and community leaders in promoting gender equity.
Reducing gender-based violence: schools should implement strict policies against gender-based violence and harassment. Providing a safe and supportive environment is crucial for retaining girls in school. Support services for victims of violence and harassment should be readily available.
4.1.3 Promoting girls’ participation and leadership
Extracurricular activities: schools should create opportunities for girls to engage in extracurricular activities. Programs such as sports, arts, and clubs can enhance girls’ skills and confidence, providing a platform for them to express themselves and develop leadership qualities.
Leadership training: providing leadership training for girls to support their involvement in decision-making processes within schools and communities is essential. This training can empower girls to take active roles in their schools and communities, fostering a sense of agency and leadership.
4.1.4 Comprehensive and integrated approach
Involving multiple stakeholders: a comprehensive approach to promoting GESI should involve multiple stakeholders, including the government, civil society, and communities. Collaboration among these groups is essential for creating a supportive environment for GESI.
Evidence-based interventions: policies and practices should be guided by evidence-based interventions tailored to the specific needs and contexts of different regions and populations. Utilizing data and research to inform practices ensures that efforts are effective and impactful.
Monitoring and evaluation: continuous monitoring and evaluation of interventions are necessary to assess their effectiveness and make necessary adjustments. This helps in ensuring the sustainability and scalability of successful initiatives.
The study highlights the importance of a comprehensive and integrated approach to promoting GESI in primary schools. It underscores the need for targeted interventions, policy enhancements, and continued efforts to address the persistent barriers that girls and marginalized groups face. By implementing these recommendations, Tanzania can make significant strides towards achieving a more inclusive and equitable education system for all children.
4.2 Areas for future research
Future research and policy efforts should focus on sustaining and scaling successful interventions, ensuring that all children, regardless of gender or socio-economic background, have access to quality education. Future research should address these gaps:
Experiences of marginalized groups: more high-quality research is needed on the experiences of marginalized groups, including children with disabilities and those from low-income households.
Female teachers: investigate the experiences of female teachers in primary schools to understand how gender intersects with other forms of marginalization, such as age and socioeconomic status.
Effectiveness of interventions: conduct more rigorous evaluations of specific interventions and strategies for promoting GESI, including long-term impact studies.
Intersectionality: explore the intersectionality of factors such as gender, socioeconomic status, and ethnicity to provide a more comprehensive
5 Conclusion
GESI is crucial for improving access to education, ensuring equal opportunities, and promoting positive social outcomes. Teachers play a critical role in promoting these values and must receive appropriate training and support to create inclusive learning environments. Policymakers and education leaders must prioritize efforts to address GESI in primary schools, including investing in research to understand the factors contributing to gender and social equality and identifying effective strategies for promoting GESI.
The systematic literature review examined the state of GESI in primary schools and revealed significant challenges, particularly in terms of teacher training and the implementation of policies and programs. The review highlighted persistent gender disparities and the barriers faced by marginalized groups, such as children with disabilities and those from low-income families.
The findings suggest that targeted interventions are needed to address these barriers, recommended interventions include:
Increasing access to education: efforts to increase access to education for marginalized groups, such as scholarships and school feeding programs.
Policy development: implementing policies that address gender-based violence and discrimination.
Community engagement: involving multiple stakeholders, including government, civil society, and communities, in promoting GESI.
Develop and implement teacher training programs: focus on GESI principles, awareness of gender biases, strategies for promoting inclusivity, and the use of gender-sensitive teaching materials.
Develop and implement gender-sensitive curricula: address gender biases and stereotypes across all subject areas.
Strengthen policies and regulations: enforce policies that promote GESI in school governance, teacher recruitment, and student enrollment.
Increase participation of girls: provide incentives for girls to attend school, such as scholarships and school feeding programs, and improve school infrastructure.
The study provides crucial insights into the state of GESI in primary schools and underscores the need for coordinated and sustained efforts to address these challenges. By implementing the recommended strategies and involving all stakeholders, Tanzania can ensure that all children have access to quality primary education that promotes GESI.
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Adipat S, Chotikapanich R. Sustainable development goal 4: an education goal to achieve equitable quality education. Acad J Interdiscip Stud. 2022;11(6):174–83.
Article Google Scholar
Cavicchioni V, Motivans A. Monitoring educational disparities in less developed countries. In: In pursuit of equity in education: using international indicators to compare equity policies. New York: Springer; 2001. p. 217–40.
Google Scholar
Clancy J, Barnett A, Cecelski E, Pachauri S, Dutta S, Oparaocha S, Kooijman A. Gender in the transition to sustainable energy for all: from evidence to inclusive policies. 2019.
Colclough C, Rose P, Tembon M. Gender inequalities in primary schooling: the roles of poverty and adverse cultural practice. Int J Educ Dev. 2000;20(1):5–27.
Esteves M. Gender equality in education: a challenge for policy makers. Int J Soc Sci. 2018;4(2):893–905.
Fenech M, Skattebol J. Supporting the inclusion of low-income families in early childhood education: an exploration of approaches through a social justice lens. Int J Incl Educ. 2021;25(9):1042–60.
Frank A. Understanding the “success” of an all girls’ boarding school in rural Tanzania: perspectives of graduates, teachers, and administrators, PhD thesis. The Florida State University; 2019.
Group WB. Malawi systematic country diagnostic: breaking the cycle of low growth and slow poverty reduction. Washington, DC: World Bank; 2018.
Book Google Scholar
Guthridge M, Kirkman M, Penovic T, Giummarra MJ. Promoting gender equality: a systematic review of interventions. Soc Justice Res. 2022;35(3):318–43.
Kaur B. Equity and social justice in teaching and teacher education. Teach Teach Educ. 2012;28(4):485–92.
Lokina RB, Nyoni J, Kahyarara G. Social policy, gender and labour in Tanzania. Dar es Salaam: Economic and Social Research Foundation (ESRF); 2016.
Losioki BE, Mdee HK. The contribution of the hidden curriculum to gender inequality in teaching and learning materials: experiences from Tanzania. Asian J Educ Train. 2023;9(2):54–8.
Lovell E. Gender equality, social inclusion and resilience in Malawi. In: Building resilience and adapting to climate change. 2021.
Makulilo AB, Bakari M. Building a transformative feminist movement for women empowerment in Tanzania: the role of the Tanzania gender networking programme (TGNP-Mtandao). Afr Rev. 2021;13(2):155–74.
Malelu AM. Institutional factors influencing career advancement of women faculty: a case of, PhD thesis. Kenyatta University; 2015.
Mashala YL. The impact of the implementation of free education policy on secondary education in Tanzania. Int J Acad Multidiscip Res. 2019;3(1):6–14.
Mhewa, M. M., Bhalalusesa, E. P., & Kafanabo, E. (2021). Secondary school teachers’ understanding of gender-responsive pedagogy in bridging inequalities of students’ learning in tanzania. Papers in Education and Development, 38(2).
Mohun R, Biswas S, Jacobson J, Sajjad F. Infrastructure: a game changer for women’s economic empowerment. Background paper. UN Secretary-General’s High-Level Panel on Women’s Economic Empowerment; 2016.
Mondal S, Joe W, Akhauri S, Sinha I, Thakur P, Kumar V, Kumar T, Pradhan N, Kumar A. Delivering PACE++ curriculum in community settings: impact of TARA intervention on gender attitudes and dietary practices among adolescent girls in Bihar, India. PLoS ONE. 2023;18(11): e0293941.
Mwaijande VT. Access to education and assistive devices for children with physical disabilities in Tanzania, Master’s thesis. Oslo and Akershus University College; 2014.
Mwakabenga RJ, Komba SC. Gender inequalities in pedagogical classroom practice: what influence do teachers make? J Educ Humanit Sci. 2021;10(3):66–82.
Nazneen S, Cole N. Literature review on socially inclusive budgeting. 2018.
Ndijuye LG, Mligo IR, Machumu MAM. Early childhood education in Tanzania: views and beliefs of stakeholders on its status and development. Global Educ Rev. 2020;7(3):22–39.
Nelly S. Gender equality and social inclusion (GESI) in village development. Legal Brief. 2021;10(2):245–52.
Nkya HE, Bimbiga I. Unlocking potential: the positive impact of in-service training on science and mathematics teachers teaching strategies. Res Humanit Soc Sci. 2023. https://doi.org/10.7176/RHSS/13-16-04 .
Nyoni WP, He C, Yusuph ML. Sustainable interventions in enhancing gender parity in senior leadership positions in higher education in Tanzania. J Educ Pract. 2017;8(13):44–54.
Okkolin M-A, Lehtomäki E, Bhalalusesa E. The successful education sector development in Tanzania—comment on gender balance and inclusive education. Gend Educ. 2010;22(1):63–71.
Omari CK, Mbilinyi DA. Born to be less equal: the predicament of the girl child in Tanzania. In: Gender, family and work in Tanzania. London: Routledge; 2018. p. 292–314.
Chapter Google Scholar
Opini B, Onditi H. Education for all and students with disabilities in Tanzanian primary schools: challenges and successes. Int J Educ Stud. 2016;3(2):65–76.
Pak K, Desimone LM, Parsons A. An integrative approach to professional development to support college-and career-readiness standards. Educ Policy Anal Arch. 2020;28(111): n111.
Palmary I. Back2School gender mainstreaming guidelines. 2024.
Prasetyo P, Azwardi A, Kistanti N. Gender equality and social inclusion (GESI) and institutions as key drivers of green entrepreneurship. Int J Data Netw Sci. 2023;7(1):391–8.
Shelley J. Identifying and overcoming barriers to gender equality in Tanzanian schools: educators’ reflections. Int J Pedagog Innov New Technol. 2019;6(1):9–27.
Siddaway AP, Wood AM, Hedges LV. How to do a systematic review: a best practice guide for conducting and reporting narrative reviews, meta-analyses, and meta-syntheses. Annu Rev Psychol. 2019;70(1):747–70.
Stoilova D, Cai R, Aguilar-Gomez S, Batzer NH, Nyanza EC, Benshaul-Tolonen A. Biological, material and socio-cultural constraints to effective menstrual hygiene management among secondary school students in Tanzania. PLOS Global Public Health. 2022;2(3): e0000110.
Thomas MA, Rugambwa A. Equity, power, and capabilities: constructions of gender in a Tanzanian secondary school. Fem Form. 2011;23(3):153–75.
Tieng’o EWB. Community perception on public primary schools: implications for sustainable fee free basic education in Rorya district, Tanzania. East Afr J Educ Soc Sci. 2019;1(1):32–47.
Wapling L. Inclusive education and children with disabilities: quality education for all in low and middle income countries. 2016. https://eajess.ac.tz/2020/05/26/community-perception-on-public-primary-schools-implications-for-sustainable-fee-free-basic-education-in-rorya-district-tanzania/ .
Zacharia L. Factors causing gender inequality in education in Tanzania: a case of Korogwe district secondary schools, PhD thesis. The Open University of Tanzania; 2014.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Tanzania Institute of Accountancy, Mwanza, Tanzania
Mbeya University of Science and Technology, Mbeya, Tanzania
Isack Kibona
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
H.E was collecting the literatures and read and write major parts I.K was good on drafting conclusion and analysis part. But we work hand on hand together.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Henry Nkya .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Nkya, H., Kibona, I. Systematic literature review of gender equity and social inclusion in primary education for teachers in Tanzania: assessing status and future directions. Discov Educ 3 , 122 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44217-024-00221-8
Download citation
Received : 26 March 2024
Accepted : 02 August 2024
Published : 13 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s44217-024-00221-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Equitable education
- Inclusive education
- Targeted intervention
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
- DOI: 10.1002/mar.22099
- Corpus ID: 271851461
Humanlike service robots: A systematic literature review and research agenda
- Wenzhen Zhang , Emma L. Slade , Eleonora Pantano
- Published in Psychology & Marketing 10 August 2024
- Business, Sociology
- Psychology & Marketing
178 References
How does the anthropomorphism of ai chatbots facilitate users' reuse intention in online health consultation services the moderating role of disease severity, when anthropomorphized brands push their gender boundaries, the role of anthropomorphism and racial homophily of virtual influencers in encouraging low‐ versus high‐cost pro‐environmental behaviors, is her (his) gender matched or not matched with me gender (dis)match effect between customers and gendered service robots, engaging consumers through artificially intelligent technologies: systematic review, conceptual model, and further research, avoiding excessive ai service agent anthropomorphism: examining its role in delivering bad news, service robots: the dynamic effects of anthropomorphism and functional perceptions on consumers’ responses, social cognition of humanoid robots on customer tolerance of service failure, the negative effect of service robots’ affective human-likeness on consumer satisfaction in frontline service encounters, consumers' responses to personalized service from medical artificial intelligence and human doctors, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers

IMAGES
COMMENTS
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. ... Literature reviews play an important role as a foundation for all types of research. They can serve as a basis for ...
"A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research". Boote and Baile 2005 . Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review.
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
A literature review is not only a summary of key sources, but has an organizational pattern which combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem.
Example: Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398 ; Systematic review: "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139).
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the ...
Mapping the gap. The purpose of the literature review section of a manuscript is not to report what is known about your topic. The purpose is to identify what remains unknown—what academic writing scholar Janet Giltrow has called the 'knowledge deficit'—thus establishing the need for your research study [].In an earlier Writer's Craft instalment, the Problem-Gap-Hook heuristic was ...
The systematic literature review (SLR) is one of the important review methodologies which is increasingly becoming popular to synthesize literature in any discipline in general and management in particular. ... Snyder H. (2019). Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 104, 333-339 ...
As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." - Quote from Taylor, D. (n.d) "The literature review: A few tips on ...
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
Besides the obvious reason for students -- because it is assigned! -- a literature review helps you explore the research that has come before you, to see how your research question has (or has not) already been addressed. You identify: core research in the field. experts in the subject area. methodology you may want to use (or avoid)
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic. A literature review is important because it: Explains the background of research on a topic. Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area. Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
What is a Literature Review? A literature review is a critical summary and evaluation of the existing research (e.g., academic journal articles and books) on a specific topic. It is typically included as a separate section or chapter of a research paper or dissertation, serving as a contextual framework for a study.
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
Most literature reviews are embedded in articles, books, and dissertations. In most research articles, there are set as a specific section, usually titled, "literature review", so they are hard to miss.But, sometimes, they are part of the narrative of the introduction of a book or article. This section is easily recognized since the author is engaging with other academics and experts by ...
Purpose and Importance of the Literature Review. An understanding of the current literature is critical for all phases of a research study. Lingard 9 recently invoked the "journal-as-conversation" metaphor as a way of understanding how one's research fits into the larger medical education conversation. As she described it: "Imagine yourself joining a conversation at a social event.
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing ...
Maria Watson is a PhD candidate in the Urban and Regional Science program at Texas A&M University. Her research interests include disaster recovery, public policy, and economic development. Literature reviews establish the foundation of academic inquires. However, in the planning field, we lack rigorous systematic reviews.
Abstract. The process of literature review in research is explained in detail with llustrations. Content may be subject to copyright. 1. A literature review may be an end in itself to. 2. It can ...
literature review of 57 scientific papers published in the W eb of Science database between 1995 and 2021 this study aims . ... In response, research highlights the importance of .
The study takes the form of a systematic literature review, to allow the maximum combination and critical, reflective and synthetic assessment of a large number of results regarding the subject studied [].Tranfield et al. [] proposed a clear, reproducible methodology to summarise scientific research in a systematic review, aiming to produce reliable, impartial knowledge of a given topic.
This systematic literature review highlighted the importance of addressing GESI in primary school education in Tanzania and underscored the critical role of teachers in promoting these values. It calls for targeted interventions, policy enhancements, and further research to bridge the gaps identified in the literature. Gender equity and social ...
Selecting the Topic and the Literature 1. Select a topic - Before a researcher conducts literature review, he/she must identify the research problem first. However, in some cases, literature review is the source of research problem. 2. Selecting the literature - Once a topic is chosen, literature search follows. Any literature that carries topics, variables, and terms that are related to the ...
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. ... Boote DN, Beile P (2005) Scholars before researchers: on the centrality of the dissertation literature review in research preparation. Educ Res 34: 3-15 doi:10.3102 ...
Section "Literature review" focuses on the literature background of biomimicry, ... suggesting a gradual but increasing recognition of its importance. Research on exosomes has significantly ...
Checks were done for literature review studies to ensure research previously highlighted in the literature was omitted. Finally, 143 studies were chosen, as shown in Figure 7. FIGURE 7. ... It is important to note that the energy yield is influenced by the location's climatic conditions, mounting configuration, and system parameters. ...
Humanlike robots are increasingly employed to provide frontline services. They are frequently designed with stereotypically feminine or masculine humanlike features which affect or bias consumer behavior in service encounters. This systematic review of 118 peer‐reviewed journal papers aims to comprehensively capture the current status of the field and identify important research gaps ...
This approach is important as critically analyzing the literature on leadership-UPB holds promise for providing deeper empirical and theoretical insights and facilitating the development of this important area of research. Second, our review provides a novel summary of statistical findings with respect to the leadership-UPB literature.