What is the importance of research in everyday life?
Chemotherapy. Browsing the internet. Predicting hurricanes and storms. What do these things have in common? For one, they all exhibit the importance of research in everyday life; we would not be able to do these today without preceding decades of trial and error. Here are three top reasons we recognise the importance of research in everyday life, and why it is such an integral part of higher education today.

Research increases the quality of life
According to Universities Canada , “Basic research has led to some of the most commercially successful and life-saving discoveries of the past century, including the laser, vaccines and drugs, and the development of radio and television.” Canadian universities, for example, are currently studying how technology can help breed healthier livestock, how dance can provide long-term benefits to people living with Parkinson’s, and how to tackle affordable student housing in Toronto.
We know now that modern problems require modern solutions. Research is a catalyst for solving the world’s most pressing issues, the complexity of which evolves over time. The entire wealth of research findings throughout history has led us to this very point in civilisation, which brings us to the next reason why research matters.
What does a university’s research prowess mean for you as a student? Source: Shutterstock
Research empowers us with knowledge
Though scientists carry out research, the rest of the world benefits from their findings. We get to know the way of nature, and how our actions affect it. We gain a deeper understanding of people, and why they do the things they do. Best of all, we get to enrich our lives with the latest knowledge of health, nutrition, technology, and business, among others.
On top of that, reading and keeping up with scientific findings sharpen our own analytical skills and judgment. It compels us to apply critical thinking and exercise objective judgment based on evidence, instead of opinions or rumours. All throughout this process, we are picking up new bits of information and establishing new neural connections, which keeps us alert and up-to-date.
Research drives progress forward
Thanks to scientific research, modern medicine can cure diseases like tuberculosis and malaria. We’ve been able to simplify vaccines, diagnosis, and treatment across the board. Even COVID-19 — a novel disease — could be studied based on what is known about the SARS coronavirus. Now, the vaccine Pfizer and BioNTech have been working on has proven 90% effective at preventing COVID-19 infection.
Mankind has charted such progress thanks to the scientific method. Beyond improving healthcare, it is also responsible for the evolution of technology, which in turn guides the development of almost every other industry in the automation age. The world is the way it is today because academics throughout history have relentlessly sought answers in their laboratories and faculties; our future depends on what we do with all this newfound information.
Popular stories
Student protests in the us: how to attend and keep your visa safe as an international student, boarding schools in america providing an excellent education to inspire the next generation of leaders, how to increase productivity by at least 12%: 8 tips to help you crush deadlines, get a job in the us, uk, or australia with these companies that sponsor visas for international students, international phd students now eligible for uk research and innovation scholarships, international scholars make lasting contributions to the us: report.

10 Importance of Research in Our Daily Life
Table of Contents
In a world filled with information, it’s really important to understand the importance of research in our daily life . Whether you’re a professional in business, a scientist striving for breakthroughs, or a student navigating the academic landscape, research plays a crucial role in shaping your understanding and decisions. We need to conduct research to continually expand our knowledge base and stay informed in an ever-evolving world. In this article, we’ll discuss the reasons why research is important and its importance in our daily life.
Reasons Why Research is Important in Our Daily Life
The reasons why research is important in our daily lives are different and significant. From expanding knowledge to staying updated with the latest advancements, research provides the foundation for progress and knowledge that empowers us in various aspects of our everyday existence.
In addition, understanding how research plays an important role in our life is important, as it not only enhances our ability to gather information but also empowers us to make informed decisions. In jobs and work, research helps us think of new ideas, solve problems, and keep up with what’s happening in different areas.
It helps people learn more, ask questions, and develop a smart way of thinking. Also, doing research encourages us to be curious and keep learning all the time. It helps us see things from different angles and get better at adapting to a world that’s always changing. In the end, research is essential because it helps us improve ourselves and makes society better as a whole.

What is the Role of Research in Our Life?
Research plays an important role in our lives by helping us understand the world around us and make informed decisions. It is like detective work that scientists, scholars, and experts do to discover new things and find solutions to problems. In simple terms, research helps us answer questions and solve puzzles.
Imagine you have a question like, “How can we make our environment cleaner?” Researchers would study different aspects, like pollution, recycling, and renewable energy, to find the best solutions. This way, research helps us find ways to improve our lives and the world we live in.
Here are the following 10 importance of research in our daily life:
1. Expanding Knowledge Base
Research acts as a door to education and continuous learning. Regardless of your expertise, there is always more to discover about a subject. The process of research opens new paths for learning and personal growth, providing opportunities to build on existing knowledge.
2. Accessing the Latest Information
Staying informed is crucial, especially in dynamic fields. Research encourages the pursuit of the most recent information, preventing the risk of falling behind in rapidly evolving areas. This ensures that your insights are up-to-date and contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
3. Understanding the Competitive Landscape
In business and various other domains, understanding what you’re up against is vital. Researching competitors helps in formulating effective plans and strategies, identifying unique selling points, and staying ahead in the market. Beyond business, the research identifies challenges and adversaries, offering solutions and strategies for overcoming them.
4. Building Credibility
Credibility is the foundation of effective communication. Thorough research provides a solid base for ideas and opinions, making it difficult for others to question your knowledge. By relying on reputable sources, your credibility is enhanced, ensuring that your contributions are taken seriously.
5. Economic Development
Research plays a crucial role in driving economic growth. From market trends to consumer behavior, businesses rely on research to make strategic decisions that contribute to their success and, consequently, the economic development of a nation.
6. Exploring New Ideas
Research is the engine of innovation, driving the exploration of new ideas. It fuels creativity and pushes the boundaries of what is possible, leading to breakthroughs in various fields and shaping the world of tomorrow. Research is like a treasure hunt for smart solutions to problems, making life better for everyone. Without research, we might miss out on incredible inventions that could change the way we live!
7. Exploring New Ideas
Research introduces individuals to diverse perspectives and ideas. While individuals may enter the research process with preconceived notions, exposure to various viewpoints encourages openness to new ideas. This dynamic exploration may lead to shifts in opinions or the refinement of existing ones.
8. Facilitating Problem-Solving
Research is a valuable tool for problem-solving . Whether addressing personal or professional challenges, informed decisions are crucial. Through thorough research, individuals gain the necessary information to devise effective solutions, boosting confidence in decision-making.
9. Raising Awareness
The importance of research in raising awareness lies in its ability to provide valuable information and insights about various issues. Through systematic investigation and analysis, research helps uncover facts, trends, and challenges related to critical issues. This information serves as a foundation for creating awareness campaigns, educational initiatives, and advocacy efforts.
10. Cultivating Curiosity
Curiosity is the driving force behind continuous learning. Research nurtures curiosity by exposing individuals to different opinions, ideas, and possibilities. It rewards the innate human desire to explore, ensuring a perpetual state of intellectual growth.
In conclusion, the importance of research in our daily life is deep and complex. It’s not just about school or learning; it becomes a part of how we live every day. Research expands our knowledge base, keeping us in tune with the latest information and helping us understand the competitive landscape, be it in business or personal challenges. Furthermore, recognizing the reasons why research is important in our daily life empowers us to make informed decisions, solve problems effectively, and navigate the complexities of the modern world with confidence.
Moreover, it builds credibility, narrows the overwhelming scope of information, and enhances discernment. Research isn’t just about fixing problems; it helps us understand important things happening in society. It keeps us curious and always learning new stuff. Choosing to study isn’t just a choice; it’s a way to have a smarter, stronger, and more interesting life.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- About This Blog
- Official PLOS Blog
- EveryONE Blog
- Speaking of Medicine
- PLOS Biologue
- Absolutely Maybe
- DNA Science
- PLOS ECR Community
- All Models Are Wrong
- About PLOS Blogs
A Guide to Using the Scientific Method in Everyday Life

The scientific method —the process used by scientists to understand the natural world—has the merit of investigating natural phenomena in a rigorous manner. Working from hypotheses, scientists draw conclusions based on empirical data. These data are validated on large-scale numbers and take into consideration the intrinsic variability of the real world. For people unfamiliar with its intrinsic jargon and formalities, science may seem esoteric. And this is a huge problem: science invites criticism because it is not easily understood. So why is it important, then, that every person understand how science is done?
Because the scientific method is, first of all, a matter of logical reasoning and only afterwards, a procedure to be applied in a laboratory.
Individuals without training in logical reasoning are more easily victims of distorted perspectives about themselves and the world. An example is represented by the so-called “ cognitive biases ”—systematic mistakes that individuals make when they try to think rationally, and which lead to erroneous or inaccurate conclusions. People can easily overestimate the relevance of their own behaviors and choices. They can lack the ability to self-estimate the quality of their performances and thoughts . Unconsciously, they could even end up selecting only the arguments that support their hypothesis or beliefs . This is why the scientific framework should be conceived not only as a mechanism for understanding the natural world, but also as a framework for engaging in logical reasoning and discussion.
A brief history of the scientific method
The scientific method has its roots in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. Philosophers Francis Bacon and René Descartes are often credited with formalizing the scientific method because they contrasted the idea that research should be guided by metaphysical pre-conceived concepts of the nature of reality—a position that, at the time, was highly supported by their colleagues . In essence, Bacon thought that inductive reasoning based on empirical observation was critical to the formulation of hypotheses and the generation of new understanding : general or universal principles describing how nature works are derived only from observations of recurring phenomena and data recorded from them. The inductive method was used, for example, by the scientist Rudolf Virchow to formulate the third principle of the notorious cell theory , according to which every cell derives from a pre-existing one. The rationale behind this conclusion is that because all observations of cell behavior show that cells are only derived from other cells, this assertion must be always true.
Inductive reasoning, however, is not immune to mistakes and limitations. Referring back to cell theory, there may be rare occasions in which a cell does not arise from a pre-existing one, even though we haven’t observed it yet—our observations on cell behavior, although numerous, can still benefit from additional observations to either refute or support the conclusion that all cells arise from pre-existing ones. And this is where limited observations can lead to erroneous conclusions reasoned inductively. In another example, if one never has seen a swan that is not white, they might conclude that all swans are white, even when we know that black swans do exist, however rare they may be.
The universally accepted scientific method, as it is used in science laboratories today, is grounded in hypothetico-deductive reasoning . Research progresses via iterative empirical testing of formulated, testable hypotheses (formulated through inductive reasoning). A testable hypothesis is one that can be rejected (falsified) by empirical observations, a concept known as the principle of falsification . Initially, ideas and conjectures are formulated. Experiments are then performed to test them. If the body of evidence fails to reject the hypothesis, the hypothesis stands. It stands however until and unless another (even singular) empirical observation falsifies it. However, just as with inductive reasoning, hypothetico-deductive reasoning is not immune to pitfalls—assumptions built into hypotheses can be shown to be false, thereby nullifying previously unrejected hypotheses. The bottom line is that science does not work to prove anything about the natural world. Instead, it builds hypotheses that explain the natural world and then attempts to find the hole in the reasoning (i.e., it works to disprove things about the natural world).
How do scientists test hypotheses?
Controlled experiments
The word “experiment” can be misleading because it implies a lack of control over the process. Therefore, it is important to understand that science uses controlled experiments in order to test hypotheses and contribute new knowledge. So what exactly is a controlled experiment, then?
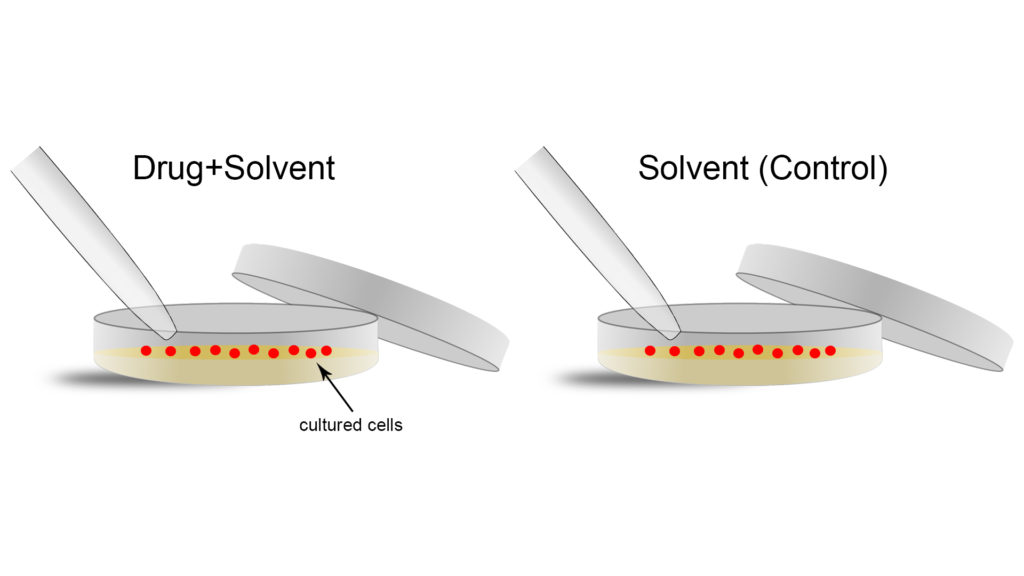
Let us take a practical example. Our starting hypothesis is the following: we have a novel drug that we think inhibits the division of cells, meaning that it prevents one cell from dividing into two cells (recall the description of cell theory above). To test this hypothesis, we could treat some cells with the drug on a plate that contains nutrients and fuel required for their survival and division (a standard cell biology assay). If the drug works as expected, the cells should stop dividing. This type of drug might be useful, for example, in treating cancers because slowing or stopping the division of cells would result in the slowing or stopping of tumor growth.
Although this experiment is relatively easy to do, the mere process of doing science means that several experimental variables (like temperature of the cells or drug, dosage, and so on) could play a major role in the experiment. This could result in a failed experiment when the drug actually does work, or it could give the appearance that the drug is working when it is not. Given that these variables cannot be eliminated, scientists always run control experiments in parallel to the real ones, so that the effects of these other variables can be determined. Control experiments are designed so that all variables, with the exception of the one under investigation, are kept constant. In simple terms, the conditions must be identical between the control and the actual experiment.
Coming back to our example, when a drug is administered it is not pure. Often, it is dissolved in a solvent like water or oil. Therefore, the perfect control to the actual experiment would be to administer pure solvent (without the added drug) at the same time and with the same tools, where all other experimental variables (like temperature, as mentioned above) are the same between the two (Figure 1). Any difference in effect on cell division in the actual experiment here can be attributed to an effect of the drug because the effects of the solvent were controlled.
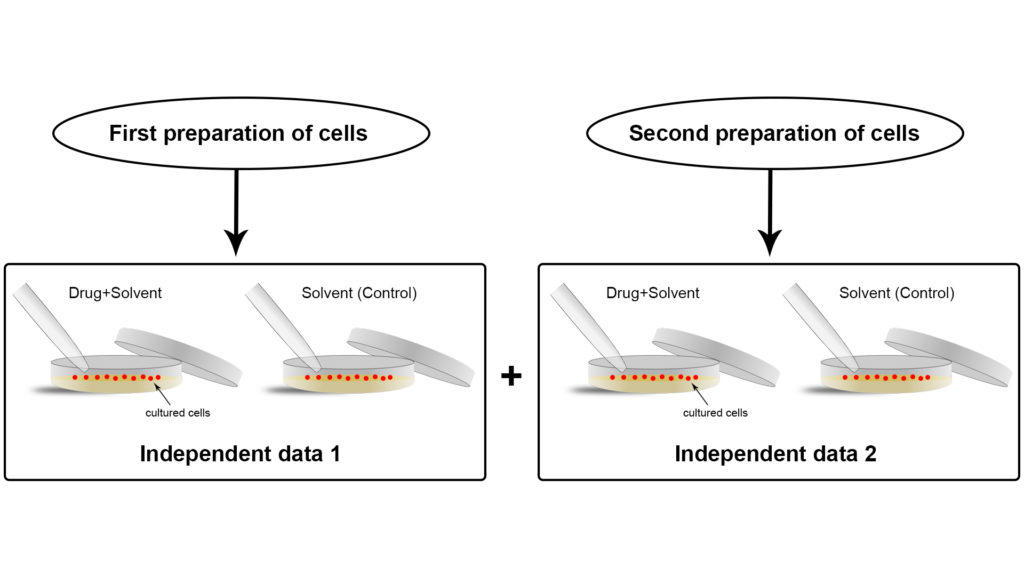
In order to provide evidence of the quality of a single, specific experiment, it needs to be performed multiple times in the same experimental conditions. We call these multiple experiments “replicates” of the experiment (Figure 2). The more replicates of the same experiment, the more confident the scientist can be about the conclusions of that experiment under the given conditions. However, multiple replicates under the same experimental conditions are of no help when scientists aim at acquiring more empirical evidence to support their hypothesis. Instead, they need independent experiments (Figure 3), in their own lab and in other labs across the world, to validate their results.

Often times, especially when a given experiment has been repeated and its outcome is not fully clear, it is better to find alternative experimental assays to test the hypothesis.
Applying the scientific approach to everyday life
So, what can we take from the scientific approach to apply to our everyday lives?
A few weeks ago, I had an agitated conversation with a bunch of friends concerning the following question: What is the definition of intelligence?
Defining “intelligence” is not easy. At the beginning of the conversation, everybody had a different, “personal” conception of intelligence in mind, which – tacitly – implied that the conversation could have taken several different directions. We realized rather soon that someone thought that an intelligent person is whoever is able to adapt faster to new situations; someone else thought that an intelligent person is whoever is able to deal with other people and empathize with them. Personally, I thought that an intelligent person is whoever displays high cognitive skills, especially in abstract reasoning.
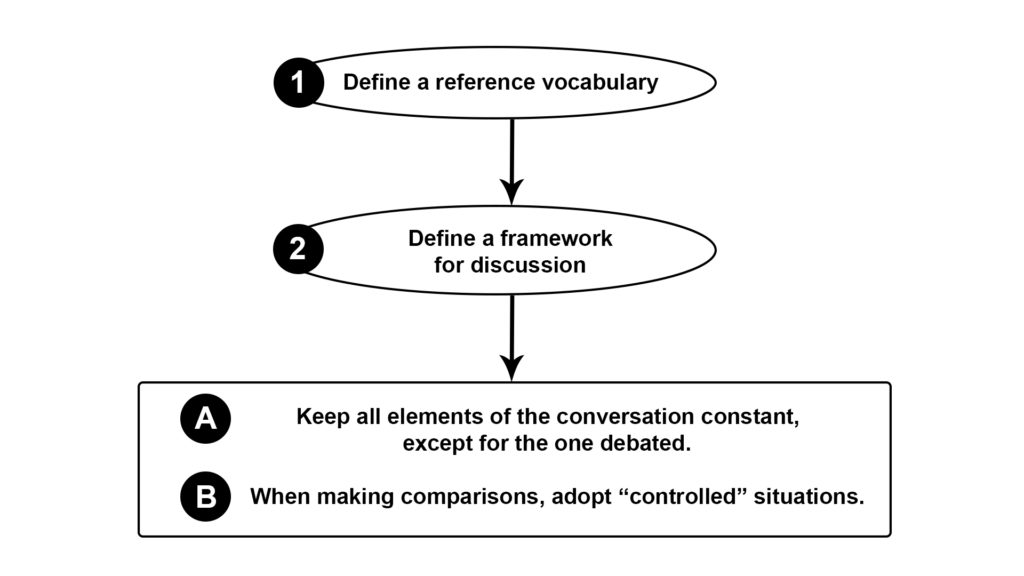
The scientific method has the merit of providing a reference system, with precise protocols and rules to follow. Remember: experiments must be reproducible, which means that an independent scientists in a different laboratory, when provided with the same equipment and protocols, should get comparable results. Fruitful conversations as well need precise language, a kind of reference vocabulary everybody should agree upon, in order to discuss about the same “content”. This is something we often forget, something that was somehow missing at the opening of the aforementioned conversation: even among friends, we should always agree on premises, and define them in a rigorous manner, so that they are the same for everybody. When speaking about “intelligence”, we must all make sure we understand meaning and context of the vocabulary adopted in the debate (Figure 4, point 1). This is the first step of “controlling” a conversation.
There is another downside that a discussion well-grounded in a scientific framework would avoid. The mistake is not structuring the debate so that all its elements, except for the one under investigation, are kept constant (Figure 4, point 2). This is particularly true when people aim at making comparisons between groups to support their claim. For example, they may try to define what intelligence is by comparing the achievements in life of different individuals: “Stephen Hawking is a brilliant example of intelligence because of his great contribution to the physics of black holes”. This statement does not help to define what intelligence is, simply because it compares Stephen Hawking, a famous and exceptional physicist, to any other person, who statistically speaking, knows nothing about physics. Hawking first went to the University of Oxford, then he moved to the University of Cambridge. He was in contact with the most influential physicists on Earth. Other people were not. All of this, of course, does not disprove Hawking’s intelligence; but from a logical and methodological point of view, given the multitude of variables included in this comparison, it cannot prove it. Thus, the sentence “Stephen Hawking is a brilliant example of intelligence because of his great contribution to the physics of black holes” is not a valid argument to describe what intelligence is. If we really intend to approximate a definition of intelligence, Steven Hawking should be compared to other physicists, even better if they were Hawking’s classmates at the time of college, and colleagues afterwards during years of academic research.
In simple terms, as scientists do in the lab, while debating we should try to compare groups of elements that display identical, or highly similar, features. As previously mentioned, all variables – except for the one under investigation – must be kept constant.
This insightful piece presents a detailed analysis of how and why science can help to develop critical thinking.
In a nutshell
Here is how to approach a daily conversation in a rigorous, scientific manner:
- First discuss about the reference vocabulary, then discuss about the content of the discussion. Think about a researcher who is writing down an experimental protocol that will be used by thousands of other scientists in varying continents. If the protocol is rigorously written, all scientists using it should get comparable experimental outcomes. In science this means reproducible knowledge, in daily life this means fruitful conversations in which individuals are on the same page.
- Adopt “controlled” arguments to support your claims. When making comparisons between groups, visualize two blank scenarios. As you start to add details to both of them, you have two options. If your aim is to hide a specific detail, the better is to design the two scenarios in a completely different manner—it is to increase the variables. But if your intention is to help the observer to isolate a specific detail, the better is to design identical scenarios, with the exception of the intended detail—it is therefore to keep most of the variables constant. This is precisely how scientists ideate adequate experiments to isolate new pieces of knowledge, and how individuals should orchestrate their thoughts in order to test them and facilitate their comprehension to others.
Not only the scientific method should offer individuals an elitist way to investigate reality, but also an accessible tool to properly reason and discuss about it.
Edited by Jason Organ, PhD, Indiana University School of Medicine.

Simone is a molecular biologist on the verge of obtaining a doctoral title at the University of Ulm, Germany. He is Vice-Director at Culturico (https://culturico.com/), where his writings span from Literature to Sociology, from Philosophy to Science. His writings recently appeared in Psychology Today, openDemocracy, Splice Today, Merion West, Uncommon Ground and The Society Pages. Follow Simone on Twitter: @simredaelli
- Pingback: Case Studies in Ethical Thinking: Day 1 | Education & Erudition
This has to be the best article I have ever read on Scientific Thinking. I am presently writing a treatise on how Scientific thinking can be adopted to entreat all situations.And how, a 4 year old child can be taught to adopt Scientific thinking, so that, the child can look at situations that bothers her and she could try to think about that situation by formulating the right questions. She may not have the tools to find right answers? But, forming questions by using right technique ? May just make her find a way to put her mind to rest even at that level. That is why, 4 year olds are often “eerily: (!)intelligent, I have iften been intimidated and plain embarrassed to see an intelligent and well spoken 4 year old deal with celibrity ! Of course, there are a lot of variables that have to be kept in mind in order to train children in such controlled thinking environment, as the screenplay of little Sheldon shows. Thanking the author with all my heart – #ershadspeak #wearescience #weareallscientists Ershad Khandker
Simone, thank you for this article. I have the idea that I want to apply what I learned in Biology to everyday life. You addressed this issue, and have given some basic steps in using the scientific method.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email for the next time I comment.
By Ashley Moses, edited by Andrew S. Cale Each year, millions of scientific research papers are published. Virtually none of them can…
By Ana Santos-Carvalho and Carolina Lebre, edited by Andrew S. Cale Excessive use of technical jargon can be a significant barrier to…
By Ryan McRae and Briana Pobiner, edited by Andrew S. Cale In 2023, the field of human evolution benefited from a plethora…
Jacks Of Science
Simple Answers to Scientific Questions
Importance Of Research In Daily Life
Whether we are students, professionals, or stay-at-home parents, we all need to do research on a daily basis.
The reason?
Research helps us make informed decisions.
It allows us to learn about new things, and it teaches us how to think critically.
There is an importance of research in daily life.
Let’s discuss the importance of research in our daily lives and how it can help us achieve our goals!
6 ways research plays an important role in our daily lives.

- It leads to new discoveries and innovations that improve our lives. Many of the technologies we rely on today are the result of research in fields like medicine, computer science, engineering, etc. Things like smartphones, wifi, GPS, and medical treatments were made possible by research.
- It informs policy making. Research provides data and evidence that allows policymakers to make more informed decisions on issues that impact society, whether it’s related to health, education, the economy, or other areas. Research gives insights into problems.
- It spreads knowledge and awareness. The research contributes new information and facts to various fields and disciplines. The sharing of research educates people on new topics, ideas, social issues, etc. It provides context for understanding the world.
- It drives progress and change. Research challenges existing notions, tests new theories and hypotheses, and pushes boundaries of what’s known. Pushing the frontiers of knowledge through research is key for advancement. Even when research invalidates ideas, it leads to progress.
- It develops critical thinking skills. The research process itself – asking questions, collecting data, analyzing results, drawing conclusions – builds logic, problem-solving, and cognitive skills that benefit individuals in their professional and personal lives.
- It fuels innovation and the economy. Research leads to the development of new products and services that create jobs and improve productivity in the marketplace. Private sector research drives economic growth.
So while not always visible, research underlies much of our technological, social, economic, and human progress. It’s a building block for society.

Conducting quality research and using it to maximum benefit is key.
Research is important in everyday life because it allows us to make informed decisions about the things that matter most to us.
Whether we’re researching a new car before making a purchase, studying for an important test, or looking into different treatment options for a health issue, research allows us to get the facts and make the best choices for ourselves and our families.
- In today’s world, there’s so much information available at our fingertips, and research is more accessible than ever.
- The internet has made it possible for anyone with an interest in doing research to access vast amounts of information in a short amount of time.
This is both a blessing and a curse; while it’s great that we have so much information available to us, it can be overwhelming to try to sort through everything and find the most reliable sources.
What is the importance of research in our daily life?
Research is essential to our daily lives.

- It helps us to make informed decisions about everything from the food we eat to the medicines we take.
- It also allows us to better understand the world around us and find solutions to problems.
In short, research is essential for our health, safety, and well-being. Without it, we would be living in a world of ignorance and misinformation.
What is the importance of research in our daily lives as a student?

As a student, research plays an important role in our daily life. It helps us to gain knowledge and understanding of the world around us.
- It also allows us to develop new skills and perspectives.
- In addition, research helps us to innovate and create new things.
- Research is essential for students because it helps us to learn about the world around us. Without research, we would be limited to our own personal experiences and observations.
- Research allows us to go beyond our personal bubble and explore new ideas and concepts.
- It also gives us the opportunity to develop new skills and perspectives.
- In addition, research is important because it helps us to innovate and create new things. When we conduct research , we are constantly learning new information that can be used to create something new.
This could be anything from a new product or service to a new way of doing things.
Research is essential for students because it allows us to be innovative and create new things that can make a difference in the world.
Consequently, while each person’s daily life routine might differ based on their unique circumstances, the role that research plays in our lives as students is an integral one nonetheless.
Different though our routines might be, the value of research in our lives shines through brightly regardless. And that importance cannot be overstated .
How does research affect your daily life?

Every day, we benefit from the countless hours of research that have been conducted by scientists and scholars around the world.
- From the moment we wake up in the morning to the time we go to bed at night, we rely on research to improve our lives in a variety of ways.
- For instance, many of the items we use every day, such as our phones and laptops, are the result of years of research and development.
- And when we see a news story about a new medical breakthrough or a natural disaster, it is often the result of research that has been conducted over a long period of time.
In short, research affects our daily lives in countless ways, both big and small. Without it, we would be living in a very different world.
What are the purposes of research?

The word “research” is used in a variety of ways. In its broadest sense, research includes any gathering of data, information, and facts for the advancement of knowledge.
Whether you are looking for a new recipe or trying to find a cure for cancer, the process of research is the same.
You start with a question or an area of interest and then use different sources to find information that will help you answer that question or learn more about that topic.
“The purpose of research is to find answers to questions, solve problems, or develop new knowledge.”
It is an essential tool in business , education, science, and many other fields. By conducting research, we can learn about the world around us and make it a better place.
How to do effective research

Research is a process of uncovering facts and information about a subject.
It is usually done when preparing for an assignment or project and can be either primary research, which involves collecting data yourself, or secondary research, which involves finding existing data.
Regardless of the type of research you do, there are some effective strategies that will help you get the most out of your efforts:
- First, start by clearly defining your topic and what you hope to learn. This will help you to focus your search and find relevant information more quickly.
- Once you know what you’re looking for, try using keyword searches to find websites, articles, and other resources that are relevant to your topic.
- When evaluating each source, be sure to consider its reliability and biases.
- Finally, take good notes as you read, and make sure to keep track of where each piece of information came from so that you can easily cite it later.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your research is both thorough and accurate.
How to use research to achieve your goals.
Achieving your goals requires careful planning and a lot of hard work.
But even the best-laid plans can sometimes go awry.
That’s where research comes in.
By taking the time to do your homework, you can increase your chances of success while also learning more about your topic of interest.
When it comes to goal-setting, research can help you to identify realistic targets and develop a roadmap for achieving them.
It can also provide valuable insights into potential obstacles and how to overcome them.
In short, research is an essential tool for anyone who wants to achieve their goals.
So if you’re serious about reaching your target, be sure to do your homework first.
So the next time you are faced with a decision, don’t forget to do your research!
It could very well be the most important thing you do all day.
Jacks of Science sources the most authoritative, trustworthy, and highly recognized institutions for our article research. Learn more about our Editorial Teams process and diligence in verifying the accuracy of every article we publish.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Understanding Science
How science REALLY works...
- Understanding Science 101
- Misconceptions
Science affects our everyday lives in many ways.
Misconception: Science isn’t important in my life.
Correction: Science is deeply interwoven with our everyday lives. Read more about it.
What has science done for you lately?
Plenty. If you think science doesn’t matter much to you, think again. Science affects us all, every day of the year, from the moment we wake up, all day long, and through the night. Your digital alarm clock, the weather report, the asphalt you drive on, the bus you ride in, your decision to eat a baked potato instead of fries, your cell phone, the antibiotics that treat your sore throat, the clean water that comes from your faucet, and the light that you turn off at the end of the day have all been brought to you courtesy of science. The modern world would not be modern at all without the understandings and technology enabled by science.
To make it clear how deeply science is interwoven with our lives, just try imagining a day without scientific progress. Just for starters, without modern science, there would be:
- no plastic. The first completely synthetic plastic was made by a chemist in the early 1900s, and since then, chemistry has developed a wide variety of plastics suited for all sorts of jobs, from blocking bullets to making slicker dental floss.
- no modern agriculture. Science has transformed the way we eat today. In the 1940s, biologists began developing high-yield varieties of corn, wheat, and rice, which, when paired with new fertilizers and pesticides developed by chemists, dramatically increased the amount of food that could be harvested from a single field, ushering in the Green Revolution. These science-based technologies triggered striking changes in agriculture, massively increasing the amount of food available to feed the world and simultaneously transforming the economic structure of agricultural practices.
- no modern medicine. In the late 1700s, Edward Jenner first convincingly showed that vaccination worked. In the 1800s, scientists and doctors established the theory that many diseases are caused by germs. And in the 1920s, a biologist discovered the first antibiotic. From the eradication of smallpox, to the prevention of nutritional deficiencies, to successful treatments for once deadly infections, the impact of modern medicine on global health has been powerful. In fact, without science, many people alive today would have instead died of diseases that are now easily treated.
Scientific knowledge can improve the quality of life at many different levels — from the routine workings of our everyday lives to global issues. Science informs public policy and personal decisions on energy, conservation, agriculture, health, transportation, communication, defense, economics, leisure, and exploration. It’s almost impossible to overstate how many aspects of modern life are impacted by scientific knowledge. Here we’ll discuss just a few of these examples. You can investigate:
Fueling technology
- Making strides in medicine
- Getting personal
- Shaping society
Or just click the Next button to dive right in!
- Take a sidetrip
Learn more about innovation on the Understanding Global Change site .
Summing up science and society
Subscribe to our newsletter
- The science flowchart
- Science stories
- Grade-level teaching guides
- Teaching resource database
- Journaling tool

Improving Research Use in the World We Actually Live In
How to maximize research use in education policy and practice..
Posted September 20, 2021 | Reviewed by Devon Frye
Researchers often believe, or at least have the hope, that rigorous peer-reviewed work will find its way into practice. However, as Carrie Conaway , who is one of the rare people who has worked for years in an education policy or practice setting who understands what rigorous research is, explains :
"Research influences policy more often than much of the academic community thinks, and more frequently every day as we learn how to do this work better. But its influence is less linear than researchers expect, and it is driven as much by relationships and organizational capacity as by the actual information studies produce. Research use operates through conversations, not code; structures in organizations, not standard errors; relationships, not randomized controlled trials."
Carrie kindly replied to my questions about her work on maximizing research in the real world, how “research-practice partnerships” might be one useful way of linking practice and rigorous research, and how her book Common-Sense Evidence can be used by education leaders and scholars more broadly to improve the use of research in practice.
How can we maximize research use in the world we actually live in?
First, by recognizing that research use doesn’t always look how we expect it to. People often envision research use as a linear, one-directional process: An educator or policymaker is sitting at their desk, waiting to make a decision, when some research comes across their desk. They read it and then decide to implement whatever that research says. But the reality is a lot more complex.

The research on research use shows that it’s a process that extends over time, not an event or a single moment. It’s embedded in organizations, and it’s inherently social. And the most important way research matters for practice is probably its influence on how people frame problems, rather than how it informs any specific decision or choice.
If you think of research use that way, then it becomes obvious that the way to maximize research use isn’t just to get more research in front of practitioners. We need to create opportunities for practitioners to integrate research use into their daily work and make meaning together from data and evidence. Without attention to these social mechanisms, any effort to increase research use will fall flat.
What are research-practice partnerships and how do you think these are helpful for research to play a more influential role in practice?
A research-practice partnership is “a long-term collaboration aimed at educational improvement or equitable transformation through engagement with research” ( Farrell et al, 2021 ). Concretely, RPPs put researchers and practitioners into the same conversation, on equal footing when it comes to defining what research needs to be done and interpreting its meaning for practice. This is a radical shift from traditional research production models, which envision researchers developing and testing interventions and then “translating” them or scaling them up, with little or no interaction with practitioners in the process.
Practitioners benefit from RPPs because they create a structure for the social mechanisms that enable research use: regular interactions with researchers about individual research projects, larger events where findings can be shared and interpreted, and so on. These structures allow research use to flourish. But researchers benefit too, through a deeper understanding of the context and local priorities that influence their work and deeper relationships with the practitioners who can most directly benefit from their findings.
Why did you write the book Common-Sense Evidence ? Do you think this could be a useful book not only for education leaders but also researchers and practitioners from other disciplines?
My co-author Nora Gordon and I wrote the book because using evidence is an essential skill for educators, and because no other book helps educators learn that skill and apply it in a practical way. Few educators receive any training about how to use evidence effectively in practice—what kinds of questions to ask, how to know what type of evidence you need to answer a specific question, what makes for stronger or weaker evidence, how to know if a particular finding is relevant to their own context. Nora and I hope that our book empowers educators to use evidence to improve their own work, by helping them to cull the prior research findings that are most convincing and relevant for their own practice and giving them a structured way to learn from and improve their work over time. While the book is written with education leaders as the intended audience, the skills and techniques we describe are broadly applicable to anyone who wants to learn how to use evidence in a policy or practice setting.
Booker, L., Conaway, C., & Schwartz, N. (2019). Five ways RPPs can fail and how to avoid them: Applying conceptual frameworks to improve RPPs . William T. Grant Foundation .
Conaway, C. (2020). Maximizing research use in the world we actually live in: Relationships, organizations, and interpretation . Education Finance & Policy, 15 (1), 1-10.
Farrell, C. C., Penuel, W. R., Coburn, C. E., Daniel, J., & Steup, L. (2021). Research-practice partnerships in education: The state of the field . William T. Grant Foundation .
Gordon, N., & Conaway, C. (2020). Common sense evidence: The education leader’s guide to using data and research . Cambridge, MA: Harvard Education Press.

Jonathan Wai, Ph.D. , is Assistant Professor of Education Policy and Psychology and the 21st Century Endowed Chair in Education Policy at the University of Arkansas.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Research Methods for Studying Daily Life
Introduction, general overviews.
- Study Designs and Sampling Methods
- Advantages and Limitations of Daily-Life Methods
- Sampling and Measurement Considerations
- Technology/Equipment for Daily Assessments
- Additional Considerations and Future Directions
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Action Research
- Ambulatory Assessment in Behavioral Science
- Item Response Theory
- Meta-Analysis
- Protocol Analysis
- Replication Initiatives in Psychology
- Research Methods
- Signal Detection Theory and its Applications
- Single-Case Experimental Designs
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Data Visualization
- Remote Work
- Workforce Training Evaluation
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Research Methods for Studying Daily Life by Carla Arredondo , Gloria Luong LAST REVIEWED: 24 April 2019 LAST MODIFIED: 24 April 2019 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199828340-0243
Methods for studying daily life have blossomed since the 1980s. Although these methods have been around for years, their popularity is always increasing as technological innovations have made the use of these methods easier and more reliable to employ. Methods for studying daily life typically include taking repeated real-time assessments of individual behaviors, physiology, and/or psychological experiences, over the course of an individual’s everyday life. These methods include experience sampling methodology (ESM), ecological momentary assessments (EMA), ambulatory assessments (AA), and daily diary or day reconstruction methods. All of these methods include repeated or detailed assessments of daily- life experiences but vary in terms of the frequency of assessments, technological tools to administer assessments, and timing of assessments (e.g., real time assessments versus retrospective recall). Given that these methods are intended to capture observations of psychological experiences in daily life, they require careful consideration of study design, measurements, and assessment tools. This article will provide a general overview of daily-life methods, including discussions about the different study designs and sampling methods. Furthermore, it will describe the advantages and limitations of using these methods along with examples of empirical studies that illustrate the usefulness of these techniques. It will also provide information on important considerations for sampling and measuring experiences in daily life and provide examples of the technology available for daily-life assessments.
Mehl and Conner 2012 is an all-encompassing review that discusses theoretical, methodological, and statistical considerations for conducting daily-life studies. Conner and Lehman 2012 focuses on providing practical advice for designing and conducting daily-life studies, while Stone and Shiffman 2002 outlines standardized reporting guidelines for researchers and provides recommendations for the information that should be included in study reports. Broderick, et al. 2003 and Green, et al. 2006 discuss issues of participant compliance and provide examples of how to monitor and improve participant compliance in daily-life studies. Barta, et al. 2012 discusses issues of measurement reactivity, whereby measurements bring about changes in study participants, and Conner and Reid 2012 is an example of testing for measurement reactivity. Lastly, Bolger, et al. 2003 provides an outline of areas of research that will need further investigation as intensive longitudinal designs become more prevalent.
Barta, W. D., H. Tennen, and M. D. Litt. 2012. Measurement reactivity in diary research. In Handbook of research methods for studying daily life . Edited by M. R. Mehl and T. S. Conner, 89–107. New York: Guildford Press.
Reviews factors that can affect measurement of constructs in daily-life studies. Discusses some of the sources of measurement reactivity, such as social desirability of the construct under investigation and conditions that influence reactivity of self-monitoring, such as participant motivation. They conclude with a review of studies demonstrating mixed findings on measurement reactivity and recommend that more daily-life studies explicitly test for measurement reactivity.
Bolger, N., A. Davis, and E. Rafaeli. 2003. Diary methods: Capturing life as it is lived. Annual Review of Psychology 54:579–616.
DOI: 10.1146/annurev.psych.54.101601.145030
Discusses areas of research that will need further consideration as intensive longitudinal study designs become more common. The article also discusses using technology to monitor objective measurements, such as heart rate, in conjunction with subjective experiences (i.e., mood). Also covered is the need to develop and test measures that can capture within-person changes and ideas for formulating research questions to further understand how these processes unfold in everyday life.
Broderick, J., J. Schwartz, S. Shiffman, M. Hufford, and A. Stone. 2003. Signaling does not adequately improve diary compliance. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 26:139–148.
DOI: 10.1207/S15324796ABM2602_06
Tested the extent to which signaling participants, via a programmed wristwatch, improved compliance in a twenty-four-day experience sampling study of individuals with chronic pain. The study used photo sensors to detect when diaries were opened and closed by participants to make an entry, and this information was cross-referenced with participant self-reports of compliance.
Conner, T. S., and B. Lehman. 2012. Getting started: Launching a study in daily life. In Handbook of research methods for studying daily life . Edited by M. R. Mehl and T. S. Conner, 89–107. New York: Guildford Press.
Provides an overview of important considerations for designing and conducting daily-life studies. It begins with preliminary considerations, such as participant characteristics, and moves into sampling strategies and platforms. Practical concerns, such as ethical considerations, are also discussed.
Conner, T. S., and K. A. Reid. 2012. Effects of intensive mobile happiness reporting in daily life. Social Psychology and Personality Science 3:315–323.
DOI: 10.1177/1948550611419677
An example of an experience sampling study that explicitly tested measurement reactivity. The study examined the extent to which there was measurement reactivity in a measure of happiness. Results demonstrate that overall the measure in question did not show reactivity. However, participant characteristics, such as depressive symptoms and trait neuroticism, contributed to measurement reactivity.
Green, A. S., E. Rafaeli, N. Bolger, P. E. Shrout, and H. T. Reis. 2006. Paper or plastic? Data equivalence in paper and electronic diaries. Psychological Methods 11:87–105.
DOI: 10.1037/1082-989X.11.1.87
See this article for a brief review of concerns regarding participant compliance in diary studies (pp. 87–88). The article also discusses other issues such as important considerations for improving the data quality from diary studies, recommendations for defining compliance, and individual differences in compliance (pp. 102–104). The article concludes with recommendations for improving diary studies.
Mehl, M. R., and T. S. Conner, eds. 2012. Handbook of research methods for studying daily life . New York: Guildford Press.
This book provides an all-encompassing review for researchers conducting daily-life studies. It is a resource for conducting high-quality research and provides guidelines to select and implement methods for studying daily life. The book begins with fundamental theoretical and methodological considerations for conducting these studies and then reviews statistical techniques that can be used to analyze these data. The book concludes with examples of these methods and techniques across different sub-fields in psychology.
Stone, A. A., and S. Shiffman. 2002 Capturing momentary, self-report data: A proposal for reporting guidelines. Guidelines for Momentary Research 24:236–243.
Proposes criteria for collecting momentary data. Argues that strategies for sampling daily-life data should be based on theoretical, statistical, and practical considerations of the phenomena in question that allow researchers to adequately collect data for hypothesis testing. The article also provides recommendations on reporting guidelines to facilitate study replication.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Psychology »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Abnormal Psychology
- Academic Assessment
- Acculturation and Health
- Action Regulation Theory
- Addictive Behavior
- Adolescence
- Adoption, Social, Psychological, and Evolutionary Perspect...
- Advanced Theory of Mind
- Affective Forecasting
- Affirmative Action
- Ageism at Work
- Allport, Gordon
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA)
- Animal Behavior
- Animal Learning
- Anxiety Disorders
- Art and Aesthetics, Psychology of
- Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Psychology
- Assessment and Clinical Applications of Individual Differe...
- Attachment in Social and Emotional Development across the ...
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Adults
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Childre...
- Attitudinal Ambivalence
- Attraction in Close Relationships
- Attribution Theory
- Authoritarian Personality
- Bayesian Statistical Methods in Psychology
- Behavior Therapy, Rational Emotive
- Behavioral Economics
- Behavioral Genetics
- Belief Perseverance
- Bereavement and Grief
- Biological Psychology
- Birth Order
- Body Image in Men and Women
- Bystander Effect
- Categorical Data Analysis in Psychology
- Childhood and Adolescence, Peer Victimization and Bullying...
- Clark, Mamie Phipps
- Clinical Neuropsychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Consistency Theories
- Cognitive Dissonance Theory
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Communication, Nonverbal Cues and
- Comparative Psychology
- Competence to Stand Trial: Restoration Services
- Competency to Stand Trial
- Computational Psychology
- Conflict Management in the Workplace
- Conformity, Compliance, and Obedience
- Consciousness
- Coping Processes
- Correspondence Analysis in Psychology
- Counseling Psychology
- Creativity at Work
- Critical Thinking
- Cross-Cultural Psychology
- Cultural Psychology
- Daily Life, Research Methods for Studying
- Data Science Methods for Psychology
- Data Sharing in Psychology
- Death and Dying
- Deceiving and Detecting Deceit
- Defensive Processes
- Depressive Disorders
- Development, Prenatal
- Developmental Psychology (Cognitive)
- Developmental Psychology (Social)
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM...
- Discrimination
- Dissociative Disorders
- Drugs and Behavior
- Eating Disorders
- Ecological Psychology
- Educational Settings, Assessment of Thinking in
- Effect Size
- Embodiment and Embodied Cognition
- Emerging Adulthood
- Emotional Intelligence
- Empathy and Altruism
- Employee Stress and Well-Being
- Environmental Neuroscience and Environmental Psychology
- Ethics in Psychological Practice
- Event Perception
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Expansive Posture
- Experimental Existential Psychology
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Eyewitness Testimony
- Eysenck, Hans
- Factor Analysis
- Festinger, Leon
- Five-Factor Model of Personality
- Flynn Effect, The
- Forensic Psychology
- Forgiveness
- Friendships, Children's
- Fundamental Attribution Error/Correspondence Bias
- Gambler's Fallacy
- Game Theory and Psychology
- Geropsychology, Clinical
- Global Mental Health
- Habit Formation and Behavior Change
- Health Psychology
- Health Psychology Research and Practice, Measurement in
- Heider, Fritz
- Heuristics and Biases
- History of Psychology
- Human Factors
- Humanistic Psychology
- Implicit Association Test (IAT)
- Industrial and Organizational Psychology
- Inferential Statistics in Psychology
- Insanity Defense, The
- Intelligence
- Intelligence, Crystallized and Fluid
- Intercultural Psychology
- Intergroup Conflict
- International Classification of Diseases and Related Healt...
- International Psychology
- Interviewing in Forensic Settings
- Intimate Partner Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Introversion–Extraversion
- Law, Psychology and
- Lazarus, Richard
- Learned Helplessness
- Learning Theory
- Learning versus Performance
- LGBTQ+ Romantic Relationships
- Lie Detection in a Forensic Context
- Life-Span Development
- Locus of Control
- Loneliness and Health
- Mathematical Psychology
- Meaning in Life
- Mechanisms and Processes of Peer Contagion
- Media Violence, Psychological Perspectives on
- Mediation Analysis
- Memories, Autobiographical
- Memories, Flashbulb
- Memories, Repressed and Recovered
- Memory, False
- Memory, Human
- Memory, Implicit versus Explicit
- Memory in Educational Settings
- Memory, Semantic
- Metacognition
- Metaphor, Psychological Perspectives on
- Microaggressions
- Military Psychology
- Mindfulness
- Mindfulness and Education
- Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
- Money, Psychology of
- Moral Conviction
- Moral Development
- Moral Psychology
- Moral Reasoning
- Nature versus Nurture Debate in Psychology
- Neuroscience of Associative Learning
- Nonergodicity in Psychology and Neuroscience
- Nonparametric Statistical Analysis in Psychology
- Observational (Non-Randomized) Studies
- Obsessive-Complusive Disorder (OCD)
- Occupational Health Psychology
- Olfaction, Human
- Operant Conditioning
- Optimism and Pessimism
- Organizational Justice
- Parenting Stress
- Parenting Styles
- Parents' Beliefs about Children
- Path Models
- Peace Psychology
- Perception, Person
- Performance Appraisal
- Personality and Health
- Personality Disorders
- Personality Psychology
- Person-Centered and Experiential Psychotherapies: From Car...
- Phenomenological Psychology
- Placebo Effects in Psychology
- Play Behavior
- Positive Psychological Capital (PsyCap)
- Positive Psychology
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Prejudice and Stereotyping
- Pretrial Publicity
- Prisoner's Dilemma
- Problem Solving and Decision Making
- Procrastination
- Prosocial Behavior
- Prosocial Spending and Well-Being
- Psycholinguistics
- Psychological Literacy
- Psychological Perspectives on Food and Eating
- Psychology, Political
- Psychoneuroimmunology
- Psychophysics, Visual
- Psychotherapy
- Psychotic Disorders
- Publication Bias in Psychology
- Reasoning, Counterfactual
- Rehabilitation Psychology
- Relationships
- Reliability–Contemporary Psychometric Conceptions
- Religion, Psychology and
- Risk Taking
- Role of the Expert Witness in Forensic Psychology, The
- Sample Size Planning for Statistical Power and Accurate Es...
- Schizophrenic Disorders
- School Psychology
- School Psychology, Counseling Services in
- Self, Gender and
- Self, Psychology of the
- Self-Construal
- Self-Control
- Self-Deception
- Self-Determination Theory
- Self-Efficacy
- Self-Esteem
- Self-Monitoring
- Self-Regulation in Educational Settings
- Self-Report Tests, Measures, and Inventories in Clinical P...
- Sensation Seeking
- Sex and Gender
- Sexual Minority Parenting
- Sexual Orientation
- Simpson's Paradox in Psychology
- Single People
- Skinner, B.F.
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Small Groups
- Social Class and Social Status
- Social Cognition
- Social Neuroscience
- Social Support
- Social Touch and Massage Therapy Research
- Somatoform Disorders
- Spatial Attention
- Sports Psychology
- Stanford Prison Experiment (SPE): Icon and Controversy
- Stereotype Threat
- Stereotypes
- Stress and Coping, Psychology of
- Student Success in College
- Subjective Wellbeing Homeostasis
- Taste, Psychological Perspectives on
- Teaching of Psychology
- Terror Management Theory
- Testing and Assessment
- The Concept of Validity in Psychological Assessment
- The Neuroscience of Emotion Regulation
- The Reasoned Action Approach and the Theories of Reasoned ...
- The Weapon Focus Effect in Eyewitness Memory
- Theory of Mind
- Therapy, Cognitive-Behavioral
- Thinking Skills in Educational Settings
- Time Perception
- Trait Perspective
- Trauma Psychology
- Twin Studies
- Type A Behavior Pattern (Coronary Prone Personality)
- Unconscious Processes
- Video Games and Violent Content
- Virtues and Character Strengths
- Women and Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math (STEM...
- Women, Psychology of
- Work Well-Being
- Wundt, Wilhelm
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|195.158.225.230]
- 195.158.225.230
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How Psychology Can Improve Your Life
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
How can psychology apply to your everyday life? Do you think that psychology is just for students, academics, and therapists? Think again. Because psychology is both an applied and a theoretical subject, it can be used in a number of ways.
While research studies aren't exactly light reading material for the average person, the results of these experiments and studies can have significant applications in daily life. The following are some practical uses for psychology in everyday life.
Whether your goal is to quit smoking, lose weight, or learn a new language, lessons from psychology offer tips for getting motivated. To increase your motivational levels when approaching a task, use strategies derived from research in cognitive and educational psychology .
- Introduce new or novel elements to keep your interest high.
- Vary repetitive sequences to help stave off boredom.
- Learn new things that build on your existing knowledge.
- Set clear goals that are directly related to the task.
- Reward yourself for a job well done.
It doesn’t matter if you’re an office manager or a volunteer at a local youth group: Having good leadership skills will probably be essential at some point in your life. Not everyone is a born leader, but a few simple tips gleaned from psychological research can help you be a better leader.
One of the most famous studies on this topic looked at three distinct leadership styles . Based on the findings of this study and subsequent research, practice some of the following when you are in a leadership position.
- Offer clear guidance, but allow group members to voice opinions.
- Talk about possible solutions with members of the group.
- Focus on stimulating ideas and be willing to reward creativity.
Communication
Communication involves much more than how you speak or write. Research suggests that nonverbal signals make up a huge portion of our interpersonal communications. To communicate your message effectively, you need to learn how to express yourself nonverbally and to read the nonverbal cues of those around you.
- Use good eye contact.
- Start noticing nonverbal signals in others.
- Learn to use your tone of voice to reinforce your message.
Emotional Intelligence
Much like nonverbal communication, the ability to understand your emotions and the emotions of those around you plays an important role in your relationships and professional life. The term emotional intelligence refers to your ability to understand both your own emotions and those of other people.
Your emotional intelligence quotient is a measure of this ability. According to psychologist Daniel Goleman, your EQ may actually be more important than your IQ. To become more emotionally intelligent, consider some of the following strategies.
- Carefully assess your own emotional reactions.
- Record your experiences and emotions in a journal.
- Try to see situations from the perspective of another person.
Decision-Making
Research in cognitive psychology has provided a wealth of information about decision making. By applying these strategies to your life, you can learn to make wiser choices. The next time you need to make a big decision, try using some of these techniques.
- Use the “six thinking hats” approach by looking at the situation from multiple points of view, including rational, emotional, intuitive, creative, positive, and negative perspectives.
- Consider the potential costs and benefits of a decision.
- Employ a grid analysis technique that gives a score for how a particular decision will satisfy specific requirements you may have.
Press Play for Advice On Dealing With Decision Fatigue
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how to manage feelings of decision fatigue and how you can avoid it. Click below to listen now.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
Have you ever wondered why you can remember the exact details of childhood events, yet forget the name of the new client you met yesterday? Research on how we form new memories as well as how and why we forget has led to a number of findings that can be applied directly in your daily life. To increase your memory power:
- Focus on the information.
- Rehearse what you have learned.
- Eliminate distractions.
Money Management
Nobel Prize-winning psychologist Daniel Kahneman and his colleague Amos Tversky conducted a series of studies that looked at how people manage uncertainty and risk when making decisions. Subsequent research in this area, known as behavior economics, has yielded some key findings that you can use to manage your money more wisely.
One study found that workers could more than triple their savings by using some of the following strategies.
- Don’t procrastinate. Start investing in savings now.
- Commit in advance to devote portions of your future earnings to your retirement savings.
- Try to be aware of personal biases that may lead to poor money choices.
Academic Success
The next time you're tempted to complain about pop quizzes, midterms, or final exams, consider that research has demonstrated that taking tests actually helps you better remember what you've learned, even if it wasn't covered on the test.
A study found that repeated test-taking may be a better memory aid than studying. Students who were tested repeatedly were able to recall 61% of the material, while those in the study group recalled only 40%. How can you apply these findings to your own life? When trying to learn new information, self-test frequently in order to cement what you have learned into your memory.
Productivity
There are thousands of books and magazine articles telling us how to get more done, but how much of this advice is founded on actual research? Take the belief that multitasking can help you be more productive. In reality, research has found that trying to perform more than one task at a time seriously impairs speed, accuracy, and productivity. Use lessons from psychology to increase your productivity more effectively.
- Avoid multitasking when working on complex or dangerous tasks.
- Focus on the task at hand.
Psychology can also be a useful tool for improving your overall health. From ways to encourage exercise and better nutrition to new treatments for depression, the field of health psychology offers a wealth of beneficial strategies that can help you to be healthier and happier.
- Studies have shown that both sunlight and artificial light can reduce the symptoms of seasonal affective disorder.
- Research has demonstrated that exercise can contribute to greater psychological well-being.
- Studies have found that helping people understand the risks of unhealthy behaviors can lead to healthier choices.
Thaler RH, Benartzi S. Save More Tomorrow™: Using behavioral economics to increase employee saving . J Political Econ . 2004;112(S1):S164-187. doi:10.1086/380085
Chan JC, McDermott KB, Roediger HL. Retrieval-induced facilitation: initially nontested material can benefit from prior testing of related material . J Exp Psychol Gen . 2006;135(4):553-71. doi:10.1037/0096-3445.135.4.553
Ophir E, Nass C, Wagner AD. Cognitive control in media multitaskers . Proc Natl Acad Sci USA . 2009;106(37):15583-7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903620106
Solberg PA, Halvari H, Ommundsen Y, Hopkins WG. A 1-year follow-up of effects of exercise programs on well-being in older adults . J Aging Phys Act . 2014;22(1):52-64. doi:10.1123/japa.2012-0181
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Achieving Goals
You need these 7 things to thrive, research says, by dr. ryan niemiec.

Do you feel like you’re thriving-really thriving-or are you just going through the motions every day? Do you bounce back quickly from adversity and problems, and feel strong physically and psychologically? If you don’t feel like you’re truly thriving yet, the latest research can help you get there.
In a recent study, researchers reviewed what was known about how human beings thrive. They examined personal factors and environmental factors. Here are the main seven personal factors, or enablers of thriving, that they discovered. These are parts of yourself that you can attend to and improve upon, so you can move from surviving to fully thriving.
7 Things You Need To Thrive
1. Positive perspective: “I see the good in the future.” Research shows that having hopeful future expectations, an optimistic attitude, and positive views of your future are linked with greater thriving. This approach helps you cope with stress and adversity by sticking with activities or tasks rather than quitting or avoiding.
Character strengths: The central strength here is hope , which means to look positively toward the future, to set your goals, and to feel confident you can reach them. Researchers also link this to being honest about one’s values. Honesty might be considered a secondary character strength here, meaning you have integrity with your values, practice what you preach, and are authentic along the journey forward.
2. Religiosity and spirituality: “I am connected with the universe in a meaningful way.” For some people, religious coping, faith, a relationship with a higher power, and having a spiritual community are connected with thriving. Other research has shown the importance of practicing one’s religion/spirituality, as opposed to merely having a religion.
Character strengths: The strength of spirituality is broadly viewed as having a sense of meaning and purpose in life, which may or may not include formal religion. Personal practices such as meditation and prayer, spending time in nature, and reflecting on the universe are sources of spiritual sustenance for many. When this is connected with other people in community, other strengths emerge such as gratitude, and the gateway to thriving may widen further.
3. Proactive personality: “I try to challenge myself.” Proactive people seek out opportunities to be challenged. This is an internal desire you feel when you want to pursue something and to challenge yourself. One example found in research is teachers who engage in purposeful career decision-making; they are more likely to thrive.
Character strengths: Facing challenges and obstacles is the work of the bravery and perseverance strengths. In addition, I have observed that when I am proactive in pursuing a new work project, I tap into my zest strength while maintaining levels of self-regulation strength to take on the right task and not take on too much. No doubt when you are being proactive you are using more than one character strength in that effort.
4. Motivation: “I am motivated to grow.” Research shows people are motivated by their naturally occurring strengths, talents, and interests. These serve as sparks for fueling interest, growth, and learning. Thriving in the workplace is connected with work that is meaningful.
Character strengths: Curiosity and love of learning are central to our pursuit of knowledge, ideas, and the development of new skills. Individuals can turn to their highest strengths–signature strengths–as a central source of personal motivation to take action in relationships, work, or play.
5. Knowledge and learning: “I learn, therefore I know.” Research shows the desire and commitment to learning is important to thriving not just for certain people but across groups of people.
Character strengths: Here researchers suggest a number of strengths that have been found to support thriving under hardship in academic and vocational domains. These include creativity , perspective , appreciation of excellence , and especially love of learning.
6. Psychological resilience: “I overcome, rise up, and benefit from my struggles.” When stress and adversity arise, those who thrive are able to be flexible and adaptable and even benefit from the problem. The idea here is to move beyond surviving to thriving. Extra workloads, colleague difficulties, new demands–these become sources not to overcome and “ride out” but to benefit from.
Character strengths: What helps you become more resilient? In researching this area I’ve found links between all 24 character strengths and resilience. The strength with the most immediate resonance would be perseverance–the capacity to keep going, to overcome obstacles. Other important strengths include hope, gratitude , forgiveness , spirituality, curiosity, and kindness .
7. Social competence: “It matters that I connect with others.” An important enabler of thriving is to access others, connect with them, and benefit from their social support. The building of social competence matters here, such as skills of peaceful conflict resolution, awareness and appreciation of other cultures, and interpersonal skills.
Character strengths: The strength of social intelligence helps us assess situations and people, and respond appropriately. It serves us in sensing what is going on within both ourselves and others and to share those feelings in the spirit of cooperation or connection. Also important here is the strength of love which involves bonding with others, being warm and genuine with them, and giving/receiving that caring support. The justice-oriented character strengths of leadership, fairness, and teamwork are important for building social competence.
Brown, D. J., Arnold, R., Fletcher, D., & Standage, M. (2017). Human thriving A conceptual debate and literature review. European Psychologist, 22(3), 167–179. DOI: 10.1027/1016-9040/a000294
Discover Tips For Using Your Strengths In New Ways

Your in-depth Total 24 Character Strengths Report provides research-based guidance on using your strengths in new ways in your daily life. Learn simple ways to use more of your best qualities to improve your life. Get your personalized Total 24 Report and discover what makes you, uniquely YOU!

Learn more about the author
Dr. ryan niemiec.

Science In Everyday Life: 50 Examples Showing How Science Impacts Our Daily Activities
Science plays a vital role in our daily lives, even if we don’t always realize it. From the alarm that wakes us up to the phones we scroll through before bed, advancements in science, technology, engineering, and math touch every aspect of our routines.
If you’re short on time, here’s a quick answer on examples of science in daily life: Science gives us technology like smartphones, WiFi, microwaves, and virtual assistants . It brings us medical treatments, weather forecasts, and green energy solutions.
Fields like chemistry, biology, and physics explain the world around us and advancements that enhance how we live.
This comprehensive guide provides over 50 examples demonstrating the many amazing ways science impacts our lives. We’ll cover common technologies, healthcare innovations, environmental applications, and insights science provides into the world around us.
Read on to gain appreciation for just how integral STEM is to our modern lives.
Technology Innovations from Science
Smartphones and wifi.
Smartphones have become an integral part of our lives, and we can thank science for their existence. These devices combine various technologies, such as wireless communication, touchscreen displays, and powerful processors, all made possible through scientific advancements.
With the advent of WiFi technology, we can now connect our smartphones to the internet seamlessly, allowing us to access information, communicate with others, and stay connected wherever we go. According to a report by Statista, there are over 3.8 billion smartphone users worldwide, highlighting the widespread impact of this technology.
Virtual Assistants and AI
Virtual assistants, like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, have become an integral part of our daily lives. These AI-powered technologies are the result of extensive research and development in the field of artificial intelligence.
They can perform a wide range of tasks, from answering questions and setting reminders to controlling smart home devices. Virtual assistants have revolutionized the way we interact with technology and have made our lives more convenient.
According to a study by Pew Research Center, around 46% of Americans use voice assistants, showcasing the widespread adoption of this technology.
Streaming Entertainment
Gone are the days when we had to wait for our favorite TV shows or movies to air on traditional television networks. Thanks to scientific advancements, we now have streaming platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video that allow us to enjoy a vast library of entertainment content on demand.
Streaming services rely on technologies like high-speed internet connections and video compression algorithms, which have made it possible to deliver high-quality content to our devices. According to a report by Conviva, global streaming hours increased by 57% in 2020, highlighting the growing popularity of streaming entertainment.
Kitchen Appliances
Science has also revolutionized our kitchens with innovative appliances that make cooking and food preparation easier and more efficient. From microwave ovens and induction cooktops to smart refrigerators and programmable coffee makers, these appliances utilize scientific principles to enhance our culinary experiences.
For example, microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly, while induction cooktops use magnetic fields to generate heat directly in the cookware. These advancements have saved us time and energy in the kitchen, allowing us to focus on creating delicious meals.
Healthcare and Medicine
Medical treatments and drugs.
Science plays a crucial role in the development of medical treatments and drugs. Through extensive research and experimentation, scientists are able to discover new medications and therapies that help treat diseases and improve the quality of life for patients.
From antibiotics to cancer-fighting drugs, science has revolutionized the field of medicine. For instance, in recent years, breakthroughs in immunotherapy have provided hope for patients with previously untreatable cancers, offering them a chance at a longer and healthier life.
Medical Imaging and Scans
The advancement of medical imaging technology has greatly contributed to the field of healthcare. X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds are all examples of medical imaging techniques that allow doctors to visualize the internal structures of the body without invasive procedures.
These imaging tools aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of various conditions, such as broken bones, tumors, and organ abnormalities. With the help of these technologies, doctors can make more accurate and timely diagnoses, leading to better treatment outcomes for patients.
Prosthetics and Implants
Science has also revolutionized the field of prosthetics and implants, providing individuals with enhanced mobility and improved quality of life. With advancements in materials science and robotics, prosthetic limbs have become increasingly sophisticated, allowing amputees to regain functionality and perform daily activities with greater ease.
Additionally, advancements in medical implants, such as pacemakers and artificial joints, have significantly improved the lives of individuals with chronic conditions, enabling them to live longer and more fulfilling lives.
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing is another area where science has had a significant impact on healthcare. With advancements in DNA sequencing technology, scientists are now able to analyze an individual’s genetic makeup and identify potential genetic disorders or predispositions to certain diseases.
This information can be used for early detection and prevention, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their health. Genetic testing has also paved the way for personalized medicine, where treatments can be tailored to an individual’s specific genetic profile, leading to more effective and targeted therapies.
Energy and Environment
Renewable energy.
Renewable energy plays a crucial role in reducing our carbon footprint and preserving the environment. Solar power, for example, harnesses the energy from the sun and converts it into electricity, providing a sustainable and clean alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
Wind power is another example, where the kinetic energy of the wind is converted into electricity through wind turbines. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), renewable energy accounted for 26% of global electricity generation in 2018, and this number is expected to rise significantly in the coming years.
Harnessing the power of renewable energy sources not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also leads to economic growth and job creation in the renewable energy sector.
Water Filtration and Conservation
Science has greatly contributed to improving water filtration systems and promoting water conservation. Advanced technologies such as reverse osmosis and ultraviolet (UV) disinfection are used to remove impurities and pathogens from water, making it safe for consumption.
These filtration systems are essential in areas where access to clean drinking water is limited. Additionally, scientific research has led to the development of water-saving devices and techniques, such as low-flow showerheads and rainwater harvesting systems.
These innovations help conserve water resources and reduce water wastage, ultimately benefiting both the environment and our daily lives.
Weather Forecasting
Weather forecasting relies heavily on scientific advancements to accurately predict and analyze weather patterns. Meteorologists use a variety of tools and technologies, including satellites, radar systems, and computer models, to collect data and make predictions about future weather conditions.
By understanding atmospheric phenomena and analyzing historical data, scientists can provide crucial information regarding upcoming storms, hurricanes, and other weather events. Accurate weather forecasts not only help us plan our daily activities but also play a vital role in disaster preparedness and mitigation efforts, potentially saving lives and minimizing damage.
Recycling and Waste Management
In today’s world, proper waste management and recycling have become essential for the health of our environment. Science has played a significant role in developing efficient recycling processes and waste management systems.
Recycling helps reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills and conserves valuable resources. Through various scientific methods, materials such as paper, plastic, glass, and metal can be recycled and used for the production of new products.
Furthermore, advancements in waste management technologies, such as waste-to-energy systems, enable the conversion of waste materials into renewable energy sources. These innovations not only reduce the environmental impact of waste but also contribute to a more sustainable and circular economy.
Science continues to drive innovations and advancements in the energy and environmental sectors. By embracing renewable energy, implementing efficient water filtration and conservation methods, improving weather forecasting accuracy, and promoting recycling and waste management, we can create a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
Transportation Innovations
Aircraft technology.
Aircraft technology has come a long way since the Wright brothers’ first flight. Today, we have advanced and sophisticated airplanes that allow us to travel to any corner of the world in a matter of hours.
From the use of composite materials to improve fuel efficiency, to the development of quieter engines and advanced navigation systems, science has played a crucial role in revolutionizing air travel. The aerodynamic design of modern airplanes allows them to achieve incredible speeds while maintaining stability and safety.
This not only makes air travel more convenient for passengers but also reduces the environmental impact of aviation.
Automotive Engineering
The field of automotive engineering has witnessed tremendous advancements, making our cars safer, more efficient, and more comfortable. Science has enabled the development of innovative safety features such as airbags, ABS brakes, and collision avoidance systems, which have significantly reduced the number of accidents and saved countless lives.
The use of lightweight materials and aerodynamic designs has made cars more fuel-efficient, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the integration of GPS technology and smart infotainment systems has made navigation and entertainment more convenient for drivers and passengers alike.
Traffic Optimization Systems
With the increasing number of vehicles on the road, traffic congestion has become a major issue in many cities around the world. Science has played a vital role in developing traffic optimization systems that help manage and reduce congestion.
These systems use advanced algorithms and real-time data to analyze traffic patterns and suggest the most efficient routes for drivers. By optimizing traffic flow, these systems not only save time for commuters but also reduce fuel consumption and air pollution.
Examples of such systems include smart traffic lights, intelligent transportation systems, and traffic management apps.
Supply Chain Logistics
Supply chain logistics involves the management and coordination of the flow of goods and services from the point of origin to the point of consumption. Science has revolutionized this field by introducing innovative technologies and processes that improve efficiency and reduce costs.
For example, the use of barcode scanning, RFID tags, and GPS tracking has made inventory management more accurate and streamlined. Advanced analytics and predictive modeling help optimize routing and scheduling, ensuring timely delivery while minimizing transportation costs.
These innovations have transformed the way goods are transported, making supply chains more efficient and responsive to customer demands.
Insights into Our World
Science plays a fundamental role in our daily lives, often in ways we may not even realize. From the stars in the sky to the products we use, science provides us with valuable insights and understanding. Let’s explore some examples of how science impacts our everyday activities.
Astronomy and Space Science
Have you ever looked up at the night sky and marveled at the stars? Astronomy, the study of celestial objects and phenomena, helps us understand the vastness of the universe. Through telescopes and satellites, scientists have made groundbreaking discoveries about galaxies, planets, and even the origins of the universe itself.
Websites like NASA offer a wealth of information and breathtaking images that bring the wonders of space closer to us.
Physics Principles at Work
Physics is the study of matter and energy, and its principles can be found in many aspects of our daily lives. For example, the laws of motion explain why objects fall to the ground, why vehicles move, and why we can ride a bicycle.
Understanding these principles allows us to design safer cars, build sturdy bridges, and even enjoy thrilling roller coaster rides. Physics is not just for scientists in labs; it’s all around us!
Earth Sciences – Climate, Seismology
Earth sciences, such as climatology and seismology, provide us with valuable knowledge about our planet. Climate science helps us understand the changes happening in our environment and the impact of human activities on the Earth’s climate.
Seismology, the study of earthquakes, allows us to monitor and predict seismic activity, helping to save lives and minimize damage. Websites like climate.gov and USGS offer comprehensive information on these topics.
Chemistry in Everyday Products
Chemistry is present in countless products we use every day, from cleaning supplies to personal care items. For instance, the chemical reactions that occur in batteries power our smartphones and other electronic devices.
Additionally, the development of new materials and pharmaceuticals relies heavily on chemical research. Understanding the principles of chemistry allows us to create safer and more efficient products. Websites like American Chemical Society provide valuable resources on the role of chemistry in our daily lives.
Science is an integral part of our lives, providing us with knowledge and improving our understanding of the world around us. Whether it’s exploring the mysteries of space, harnessing the power of physics, studying our planet’s climate, or utilizing chemistry in everyday products, science impacts our daily activities in profound ways.
As this extensive list of examples shows, science fundamentally shapes our daily lives in modern society. Cutting-edge innovations that enhance how we live, work, communicate, travel, stay healthy, and understand the world all stem from scientific discovery.
Fields like physics, chemistry, biology, astronomy, and engineering create astounding technologies, life-saving medications, and solutions for sustainability. They also unlock deeper insights into our own bodies, the environment, and the universe around us.
So whether you’re video chatting on your phone, cooking dinner, driving your car, or just breathing – you have science to thank! Our modern world simply would not function without the dedicated work of scientists pushing boundaries every day.
Similar Posts
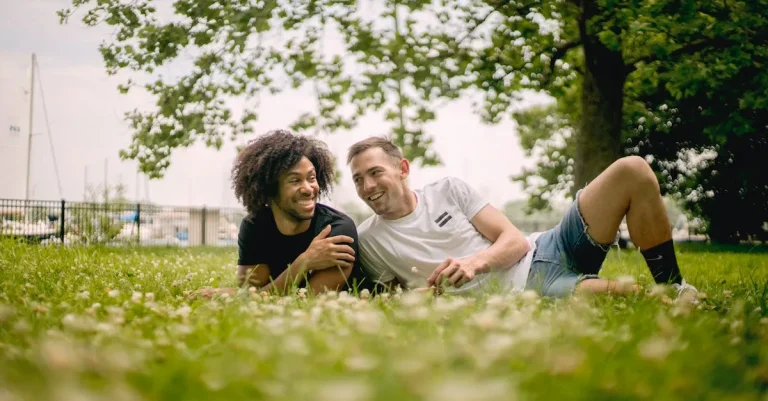

The Best Age To Get Married According To Science
Deciding when to get married is a major life decision. You want to make sure you and your partner are ready for the commitment. But is there an ideal age range scientifically shown to lead to the most successful marriages? If you’re short on time, here’s a quick answer: While people can have happy marriages…

University Of Utah Computer Science Program
The University of Utah boasts one of the top computer science programs in the nation, offering undergraduates hands-on learning opportunities, access to groundbreaking research, and pathways to start careers at top tech companies. If you’re considering University of Utah computer science, here’s a quick look at some of the program’s standout features. This in-depth guide…

Is Political Science A Humanities Subject?
Political science is a fascinating field that examines how power is distributed and exercised in society. But is it considered a humanities subject? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll analyze political science’s classification and relationship to the humanities. If you’re short on time, here’s a quick answer: political science occupies a middle ground between the humanities…

Which Fields Of Science Provide Evidence For Evolution?
The theory of evolution is a unifying framework in biology, supported by evidence from a wide range of scientific disciplines. Understanding which fields provide insights into evolution gives a broader perspective on the foundations of this powerful explanatory model. If you’re short on time, here’s a quick answer to your question: Key scientific fields that…

Master’S In Computer Science Salary Guide
Pursuing a Master’s degree in Computer Science can significantly boost your earning potential in tech careers. But how much can you expect to make with an advanced CS degree? If you’re short on time, here’s the quick answer: The average starting salary for MS in Computer Science graduates is $95,000, with mid-career salaries reaching $140,000….
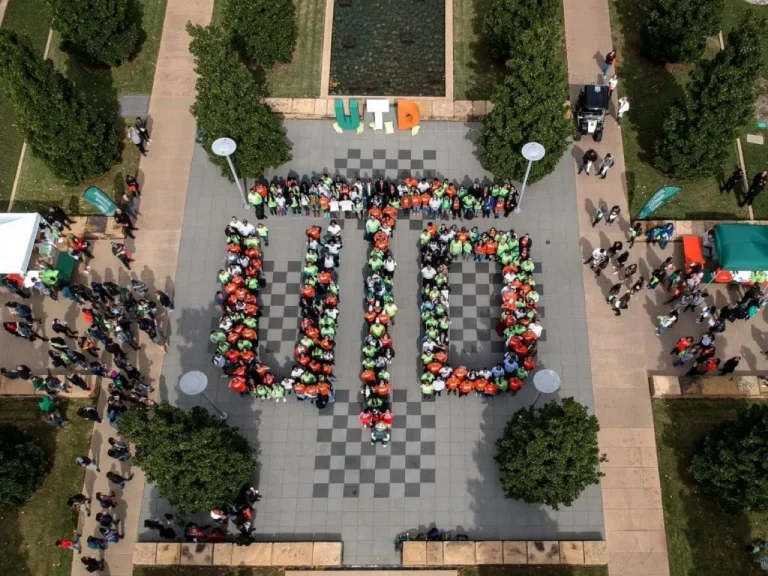

Ut Dallas Computer Science Ranking And Program Overview
The University of Texas at Dallas (UT Dallas) is well-known for its technology-focused academics and research. Its computer science program, in particular, has developed an excellent reputation over the years. If you’re considering UT Dallas for computer science, you probably want to know – how does its program rank compared to other schools? If you’re…
Research and Its Importance for Daily Life Essay
Introduction, impact of research, qualities of effective research, role of beliefs and values.
Research plays an important role in science. This is normally done to obtain detailed knowledge about certain aspects before an invention. Scientific research involves the study of diseases and other parameters to invent medicine and vaccines. Therefore, without research, there will be no inventions and therefore a big blow to health. Essentially research fulfils purposes that are designed before the exercise. However, apart from that, research has other implications on reality and daily lives. As a result, the effects of research go beyond the purpose it is meant for. This paper aims to take an analytical look at the concept of research. The paper will begin with a detailed look at the concept of research. Thereafter, the several similarities between different aspects of research will be analyzed. The impact of research on our daily life will also be reviewed.
Research has a lot of impact on the daily functioning of life. First and foremost, research leads to a better life by producing results that can be used to make life better. Especially as far as scientific research is concerned, the invention of vaccines and medicines makes diseases to be less of a threat to society (Calderon & Slavin 2001). Therefore, through the process of research, various methods of handling life’s problems and making the world a better place to live in are facilitated. Secondly, the very process of research affects society in several ways. The impact of the process of research has two dimensions.
The first part is the negative part in which the process of research has certain consequences for society. Unethical practices harm society. Since research is done on people in society, the practices adopted by the researchers have a lot of impacts. Scientific research has left some people with serious illnesses and injuries sometimes; it is like experimenting with people’s life. However, the process of research also has positive effects on society (McGill 1981). This is mainly because of employment opportunities, awareness and education. Research offers vast opportunities to the members of society to learn and obtain understanding about certain issues. At the same time, the participants of the research are remunerated making them earn a living from the same.
Several factors denote effective and valid research. To conduct valid or effective research, therefore, several considerations must be in place. First is the aspect of ethics, for research to be valid it must be conducted ethically. This involves the practices adopted for the research (Cresswell 2003). If the research involves risks, this must be communicated to the participants in advance. At the same time plans must be in place to compensate all those that will be affected in the course of the research. The disbursing of information is necessary before the research. This is important to take care of deception which is rampant in research. In general, proper preparation and education of the participants is the key to successful research. Another crucial requirement is the availability of resources for research.
Several forms of research involve a different processes. As a result, not all forms of research involve vigour. For instance, scientific research on diseases is more demanding than research on recreational issues. This is due to the context of the studies and the parameters involved. For instance, scientific research involves several processes and procedures which tend to take more resources. Recreational issues, on the other hand, are less involved due to the nature of the subject. The research can therefore be conducted with much ease.
Beliefs and values have a lot of impact on the process of research. People’s beliefs, therefore, influence the outcome and process of research. This is due to the relevance that beliefs and values have on people’s perception and philosophy of life. For instance, certain topics are considered sacred and secret in certain societies (Bryant 2005). Their beliefs don’t allow them to discuss certain things. Therefore in the process of collecting information from such people, it becomes very difficult to deal with them. People’s values also play a huge role. Some people are flexible in certain areas than others. Therefore, when conducting research one must understand the values of all participants. This is because their values determine how they approach certain issues. Religion plays a great role in determining the beliefs and values of people.
Research is part and parcel of life, in fact without research life will not be as it is. To live better life research is necessary; this is because research leads to innovation and invention. As far as science is concerned research leads to the invention of vaccines and drugs. Other areas of research also lead to a better understanding of the concepts involved. However, it is not only the results of research that benefit society but also the process of research. Some several opportunities and benefits that come with the process of research. As a result, the role of research in society goes beyond its real purpose. For research to be effective and valid several factors must be considered. Chief among them is the aspect of ethics. Different forms of research involve different forms of approaches. As a result, certain forms of research are more demanding than others. The influence of values and beliefs is notable as far as research is concerned. The paper has discussed the concept of research in detail. The process and impact of research have also been discussed.
Bryant, M. (2005). Managing an Effective and Ethical Research Project . London: Berrett-Koehler Publishers.
Calderon, M. & Slavin, R. (2001). Effective programs for Latino students. New York: Routledge.
Cresswell, J. (2003). Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-method approaches. New York: SAGE.
McGill, N. (1981). Effective research: a handbook for health planners. Washington: Institute for Health Planning.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, December 29). Research and Its Importance for Daily Life. https://ivypanda.com/essays/research-and-its-importance-for-daily-life/
"Research and Its Importance for Daily Life." IvyPanda , 29 Dec. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/research-and-its-importance-for-daily-life/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Research and Its Importance for Daily Life'. 29 December.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Research and Its Importance for Daily Life." December 29, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/research-and-its-importance-for-daily-life/.
1. IvyPanda . "Research and Its Importance for Daily Life." December 29, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/research-and-its-importance-for-daily-life/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Research and Its Importance for Daily Life." December 29, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/research-and-its-importance-for-daily-life/.
- Targeting of Coronavirus Vaccines’ Distribution
- Do Vaccines Cause Autism?
- The Companies Investing Heavily in Vaccine
- Market Condition Survey and Grading
- Dynamic Nature of Discovery: Crystal Skulls
- The Indispensability Argument Putting Forward by Quine and Putnam
- Problems of Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
- Pressure in Work, University and Life
Premium Content
Can scientists ‘solve’ stress? They’re trying.
From cardiovascular disease and obesity to a weakened immune system, the side effects of stress can be life-altering. But there may be a way to prevent those outcomes.

As modern-day stress ratchets up to what feels like unbearable levels, researchers are striving to learn more about the precise mechanisms through which it affects our body and mind. The hope is that by unlocking more about how stress works physiologically, we can find ways to prevent it from permanently harming people.
Over the last five decades, scientists have established beyond doubt that persistent stress really can poison our overall health. In addition to increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease , stress plays a role in obesity and diabetes and can weaken the immune system , leaving us more vulnerable to infectious diseases. You can recover swiftly from an episode of acute stress—for example, the alarm one might feel when caught unprepared for a presentation. Chronic stress, on the other hand, is more toxic as it is an unrelenting circumstance that offers little chance for a return to normalcy. Financial strain, having a bully for a boss, and social isolation are all examples.

Today chronic stress seems to be increasing worldwide, as people grapple with rapid socioeconomic and environmental change. A 2023 national survey by the American Psychological Association found that stress has taken a serious toll since the start of the pandemic , with the incidence of chronic illnesses and mental health problems going up significantly, especially among those ages 35 to 44.
( Do you have chronic stress? Look for these signs. )
So far, one of the major realizations among scientists is that stress harms all of us in different and powerful ways. But is there any way to avoid it—or at least recover more quickly? Some promising avenues of research offer hope for the future.

Preventing chronic stress from harming you in the first place
Groundbreaking studies in orphans showed how stress in early life can leave an indelible mark on the brain.
For Hungry Minds
“Chronic stress in early life has more serious and lasting effects, because that’s when a lot of connections are being laid down in the brain,” says Aniko Korosi, a researcher at the University of Amsterdam who has been conducting experiments on mice to elucidate that link between early-life stress and brain development.
Korosi may have found a surprising link between stress and the resulting nutrient composition in the brain . She and her colleagues noticed that mouse pups that had been exposed to stress in the first week of their lives—having been moved from their mother’s care to a cage—had lower levels of certain fatty acids and amino acids in their brains compared with pups being raised in a stress-free environment.
She wondered if it was possible to normalize a stressed pup’s development by feeding it a diet rich in the specific nutrients its brain would be lacking. To find out, the researchers first fed a supplemented diet to the mothers so it would pass through their milk, then continued to provide it in the pups’ feed for two weeks after they were weaned. A few months later, the researchers tested the now adult mice in learning and memory. Unlike stressed mice that had never received an enriched diet, these mice did not display cognitive impairments.
( How wild animals cope with stress—from overeating to sleepless nights. )

“I was surprised that changing the nutrition could have such a powerful effect, because it’s such an easy intervention,” Korosi says.
If further studies provide more evidence of the nutritional pathway, she says, there would be a strong basis for supplementing the diets of infants born to mothers living in stressful conditions.
Developing an early warning system for stress
Katie McLaughlin, a psychologist at the University of Oregon, is investigating how mental health problems arise in adolescents as they’re going through a particularly vulnerable time in their lives, transitioning to adulthood.
She and her colleagues are still collecting data , but a smaller, precursor study tracking 30 teenagers offers clues about what the researchers might learn—and how it might help them identify stress before it goes too far.

In that study, McLaughlin found that the extent of stress experienced by a subject in the month before their lab visit changed how their brain responded to emotionally impactful information such as when they were shown a picture of a threatening face. The brain’s prefrontal cortex, which helps regulate emotions, showed less activation when the subject had experienced higher levels of stress.
McLaughlin is optimistic that data from the ongoing study will help pinpoint changes in behavior as well as brain activity that predict the emergence of mental health problems like anxiety and depression. This could enable the development of targeted interventions delivered to teenagers at just the right time, she says. If the identified marker of stress were a sudden decrease in sleep duration or a sharp decline in social interactions, for example, it would be possible to push the intervention out to the individual on their smartphone.
“Like, here’s a reminder about good sleep hygiene, or this might be a good time to check in with your counselor at school about what’s been going on in your life,” McLaughlin explains.
( ‘Hysterical strength’? Fight or flight? This is how your body reacts to extreme stress. )

Learn more about stress and how to manage it
Preventing inflammation caused by chronic stress.
Gaining a deeper understanding of how stress affects the immune system may also help find a way to reverse those effects.
You May Also Like

Does meditation actually work? Here’s what the science says.

How to cope with stress at work—and avoid burning out

20 stress-relief gifts for the frazzled friend in your life
In the 1980s, psychologist Janice Kiecolt-Glaser and her virologist husband, Ronald Glaser, began exploring the physiological impact of stress on two notably stressed segments of society: medical students and older caregivers. The researchers found the students’ immune systems were less robust when they were taking exams than during non-exam times—and that stress altered the body’s response to vaccines.

Researchers then administered the flu and pneumonia vaccines to individuals responsible for a spouse with dementia. Unlike medical students taking exams, who were likely stressed only in the short term, these people were experiencing unrelenting stress. When tested at set periods after inoculation, they had fewer antibodies compared with a control group —they couldn’t maintain their protective response. “That gave us good evidence that the changes brought on by stress were biologically meaningful,” says Kiecolt-Glaser, now an emeritus professor at the Ohio State University.
Around the same time, researchers led by Sheldon Cohen, now emeritus professor of psychology at Carnegie Mellon University, delivered cold-causing viruses into the nostrils of about 400 adult volunteers in the U.K. “The more stress they reported prior to our exposing them to a virus, the higher the risk was for them to develop a cold,” says Cohen. The duration and type of stress mattered: Chronic economic or interpersonal stress were what really put people at high risk—and the longer it went on, the greater the susceptibility to falling sick.

Cohen and his colleagues also learned that when exposed to viruses, chronically stressed people tended to produce an excess of cytokines—proteins that serve as messengers of the immune system, traveling to sites of infection and injury and activating inflammation and other cellular processes to protect the body. Too many cytokines cause an excess of inflammation.
Researchers still don’t know enough about how stress alters the immune system’s ability to regulate cytokines to devise an intervention to reduce the inflammation, but in one way, these findings signal some hope: There are clear targets for more work to be done.
Understanding stress on a cellular level
The future of understanding and combating stress may lie in our DNA.
In 2023, Ursula Beattie, then a doctoral student at Tufts University, and her colleagues found possible evidence that stress can overwhelm DNA’s repair mechanisms . In their study, researchers repeatedly tapped on sparrow cages with pens, played the radio loudly, and other actions designed to cause distress but no physical harm. Blood and tissue samples from the sparrows after three weeks of this unpleasant treatment revealed damage to the DNA. “It’s like if you had two pieces of string coiled up, just like DNA, and you took a pair of scissors and cut them,” Beattie says.

While these kinds of double-strand breaks in DNA occur all the time in sparrows and other species, including humans, the damage is typically reversed through self-repair mechanisms. In a chronic-stress setting, “those repair mechanisms get overwhelmed, which is how we see a buildup of DNA damage,” Beattie explains. The damage in the birds appears to be the most severe in cells of the liver, she adds, suggesting that for humans, too, the extent and type of damage inflicted by stress might be different for different tissues of the body.
Separately, Kiecolt-Glaser and psychologist Lisa Christian at OSU are conducting a longitudinal study to determine whether chronic stress ages you more quickly. If results support a smaller, earlier study, it appears that chronically stressed caregivers not only are more likely to get sick and heal more slowly but they also show signs of accelerated aging.
We’re still learning how deep stress goes into our bodies. But these exploratory findings mean we’re getting closer to solving the puzzle that is stress, which promises a future where we can better meet the ongoing demand for change.
( 20 stress-relief gifts for the frazzled friend in your life. )

Related Topics
- MENTAL HEALTH
- PUBLIC HEALTH

‘Hysterical strength’? Fight or flight? This is how your body reacts to extreme stress

The benefits—and downsides—of taking ashwagandha

Many people wean off antidepressants too quickly. That can be dangerous.

Do you really need 10,000 steps a day? Here’s what the science says.
Fungi could be the key to major cancer research breakthroughs
- Environment
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Feeling loved in everyday life linked with improved well-being
Poets and songwriters may tend to focus their artistry on passion and romance, but it may be those unsung, brief feelings of love throughout the day that are connected with psychological well-being, according to a team of researchers led by two Penn State Institute for Computational and Data Sciences (ICDS) researchers. They added that the findings could one day lead to interventions aimed at boosting well-being.
In two studies, the researchers found that people who experienced higher "felt love" -- brief experiences of love and connection in everyday life -- also had significantly higher levels of psychological well-being, which includes feelings of purpose and optimism, compared to those who had lower felt love scores. They also found that people with higher felt love tended to have higher extraversion personality scores, while people with lower felt love scores were more likely to show signs of neuroticism.
"We took a very broad approach when we looked at love," said Zita Oravecz, assistant professor of human development and family studies and ICDS faculty co-hire. "Everyday felt love is conceptually much broader than romantic love. It's those micro-moments in your life when you experience resonance with someone. For example, if you're talking to a neighbor and they express concern for your well-being, then you might resonate with that and experience it as a feeling of love, and that might improve your well-being."
According to the researchers, the baseline of the subjects' felt love experiences, in general, rose throughout the study, suggesting that the nudges to recognize examples of love and connection during the study may also have gradually increased the subjects' overall sense of being loved. Stronger experiences of felt love, in turn, are associated with improvements in psychological well-being.
"It's something that we've seen in the literature on mindfulness, when people are reminded to focus attention on positive things, their overall awareness of those positive things begins to rise," said Oravecz. "Similarly, just by paying attention to those everyday moments of felt love, we may also increase our awareness of the overall positive aspects of love in our daily lives. This effect replicates in both studies, implying that raising awareness of felt love in day-to-day life may itself be an intervention that raises levels of felt love over a longer period of time."
The researchers, who report their findings in the current issue of Personality and Individual Differences , added that because the studies have only shown a correlation between felt love and well-being, more research would be needed to establish a causal relationship. If a firmer connection is established, the researchers said possible interventions could be designed, such as sending regular reminders to a person's smartphone to draw attention to the felt love that they may be experiencing in that moment to raise psychological well-being. Similar interventions have been designed for mindfulness and gratitude.
The team relied on smartphone technology to gather data from participants throughout their everyday lives. In the first study, they recruited 52 people of various ages. The second study consisted of 160 undergraduate students. Participants received six random prompts throughout the day over a four-week period to assess felt love and well-being, according to Timothy Brick, assistant professor of human development and family studies and ICDS co-hire. He added that sending these messages randomly throughout the day was critical to manage the possible effects of expectation bias.
"It's important from a research point-of-view," said Brick. "If the participants expect a call or a text at a certain time of day, they are no longer reacting to what's going on in their daily life, but are expecting the prompt and reacting to that expectation."
Gathering data multiple times throughout the day from more than 200 subjects over a month can produce a lot of data, said Brick. Also, these everyday experiences of love tend to fluctuate during the study, which can result in what the researchers termed "noisy" data.
"It's often very difficult to measure psychological quantities because we don't always have a great idea about what's going on in our own heads," said Brick.
Oravecz added, "But with the right statistical methods, we can start to get at questions about difficult constructs like love or compassion, and hopefully build interventions to promote them."
To analyze this large amount of noisy data, the researchers used nuanced statistical tools. According to Oravecz, the researchers specifically used a Bayesian latent stochastic differential equations model to cut through the noise in the data and identify processes happening underneath. This method is especially suited to help scientists investigate intricate social systems, which often involve relationships that generate complex, highly variable data, she said.
According to the researchers, this statistical method may be used more as social scientists begin to gather large amounts of real-world data from sensors on wearable devices. The researchers used computational resources of ICDS's advanced computer infrastructure for their analysis.
The team also included Jessica Dirsmith, clinical assistant professor of education, Duquesne University; Saeideh Heshmati, assistant professor of psychology, Claremont Graduate University; and Joachim Vandekerckhove, associate professor of cognitive sciences, University of California Irvine.
This research was supported by the John Templeton Foundation.
- Social Psychology
- Relationships
- Intelligence
- Child Development
- Spirituality
- Learning Disorders
- Platonic love
- Intellectual giftedness
- Maternal bond
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
Story Source:
Materials provided by Penn State . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Zita Oravecz, Jessica Dirsmith, Saeideh Heshmati, Joachim Vandekerckhove, Timothy R. Brick. Psychological well-being and personality traits are associated with experiencing love in everyday life . Personality and Individual Differences , 2020; 153: 109620 DOI: 10.1016/j.paid.2019.109620
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Nature's 3D Printer: Bristle Worms
- Giant ' Cotton Candy' Planet
- A Young Whale's Journey
- No Inner Voice Linked to Poorer Verbal Memory
- Bird Flu A(H5N1) Transmitted from Cow to Human
- Universe's Oldest Stars in Our Galactic Backyard
- Polygenic Embryo Screening for IVF: Opinions
- VR With Cinematoghraphics More Engaging
- 2023 Was the Hottest Summer in 2000 Years
- Fastest Rate of CO2 Rise Over Last 50,000 Years
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
Everyday life and its variability influenced human evolution at least as much as rare activities like big-game hunting
Professor and Chair of Biology at Seattle Pacific University and Affiliate Assistant Professor of Anthropology, University of Washington
Disclosure statement
Cara Wall-Scheffler does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
University of Washington provides funding as a member of The Conversation US.
View all partners

Think about taking a walk: where you need to go, how fast you need to move to get there, and whether you need to bring something along to carry the results of your errand.
Are you going on this walk with someone else? Does walking with a friend change your preparation? If you’re walking with a child, do you remember to bring an extra sweater or a snack? You probably did – because people intuitively vary their plan depending on their current needs and situations.
In my research as an anthropologist , I’ve focused on the evolution of human walking and running because I love the flexibility people bring to these behaviors. Humans in all kinds of environments across space and time vary how far they go, when they go and what they go for – whether food, water or friends – based on a multitude of factors, including season, daylight, rituals and family.
Anthropologists split their studies of human activity into two broad categories: what people need to do – including eat, keep their kids alive and so on – and what solutions they come up with to accomplish these needs.
How people keep their children alive is a key issue in my research because it has a direct impact on whether a population survives. It turns out that kids stay alive if they’re with adults. To this end, it is a human universal that women carry heavy loads every day , including kids and their food. This needs-based behavior seems to have been an important part of our evolutionary history and explains quite a few aspects of human physiology and female morphology , such as women’s lower center of mass .

The solutions to other key problems, like specifically which food women will be carrying, vary across time and space. I suggest that these variations are as integral to explaining human biology and culture as the needs themselves.
Impacts of uncommon activities
Evolutionary scientists often focus on how beneficial heritable traits get passed on to offspring when they provide a survival advantage. Eventually a trait can become more common in a population when it provides a useful solution.
For example, researchers have made big claims about how influential persistence hunting via endurance running has been on the way the human body evolved. This theory suggests that taking down prey by running them to exhaustion has led to humans’ own abilities to run long distances – by increasing humans’ ability to sweat, strengthening our head support and making sure our lower limbs are light and elastic.
But persistence hunting occurs in fewer than 2% of the recorded instances of hunting in one major ethnographic database , making it an extremely rare solution to the need to find food. Could such a rare and unusual form of locomotion have had a strong enough impact to select for the suite of adaptive traits that make humans such excellent endurance athletes today?
Maybe persistence hunting is actually a fallback strategy, providing a solution only at key moments when survivorship is on the edge. Or maybe these capabilities are just side effects of the loaded walking done every day . I think a better argument is that the ability to predict how to move between common and uncommon strategies has been the driver of human endurance capacity.

Everyday life’s influence on evolution
Hunting itself, especially of large mammals, is hardly ubiquitous , despite how frequently it is discussed. For example, anthropologists tend to generalize that people who lived in the Arctic even up to a hundred years ago consumed only animal meat hunted by men. But actually, the original ethnographic work reveals a far more nuanced picture .
Women and children were actively involved in hunting, and it was a strongly seasonal activity. Coastal fishing, berry picking and the use of plant materials were all vital to Arctic people’s day-to-day sustenance. Small family groups used canoes for coastal foraging for part of the year.
During other seasons, the whole community participated in hunting large mammals by herding them into dangerous situations where they were more easily killed. Sometimes family groups were together, and sometimes large communities were together. Sometimes women hunted with rifles, and sometimes children ran after caribou.
The dynamic nature of daily life means that the relatively uncommon activity of hunting large terrestrial vertebrates is unlikely to be the main behavior that helps humans solve the key problems of food, water and keeping children alive.
Anthropologist Rebecca Bliege Bird has investigated how predictable food is throughout the day and the year . She’s noted that for most communities, big game is rarely caught, especially when a person is hunting alone. Even among the Hadza in Tanzania, generally considered a big-game hunting community, a hunter acquires 0.03 prey per day on average – essentially 11 animals a year for that person.
Bird and others clearly argue that the planning and flexible coordination done by females is the crucial aspect of how humans survive on a daily basis. It’s the daily efforts of females that allow people to be spontaneous a few times a year to accomplish high-risk activities such as hunting – persistence or otherwise. Therefore it is female flexibility that allows communities to survive between the rare big-game opportunities.

Changing roles and contributions
Some anthropologists argue that in some parts of the world, behavior varies more for cultural reasons , like what tools you make, than for environmental ones, such as how much daylight there is during winter. The importance of culture means that the solutions vary more than the needs.
One of the aspects of culture that varies is the role assigned to specific genders. Varying gender roles are related to the distribution of labor and when people take on certain solution-based tasks . In most cultures, these roles change across a female’s life span. In American culture, this would be like a grandparent going back to college to hone a childhood passion in order to take on a new job to send their grandchildren to college.
In many places, females go from youth when they might carry their siblings and firewood, to early parenthood where they might go hunting with a baby on their back , to older parenthood where they might carry water on their head, a baby on their back and tools in their hands, to postmenopausal periods when they might carry giant loads of mangoes and firewood to and from camp.
Even though always load carrying , our capacity to plan and change our behavior for diverse environments is part of what drives Homo sapiens ’ success, which means that the behavior of females across their different life stages has been a major driver of this capability.
- Anthropology
- Human evolution
- Ethnography
- Women's bodies

Compliance Lead

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Global Cognition
Critical thinking in everyday life.
by Winston Sieck updated September 19, 2021

Have you ever been listening to one of your teacher’s lessons and thought that it had no relevance to your own life?
You’re not alone. Just about every student has felt the same way.
Sure, you use critical thinking skills in the classroom to solve word problems in math, write essays in English, and create hypotheses in science.
But how will you use critical thinking in everyday life?
First, keep in mind that critical thinking is simply a “deliberate thought process.”
Basically, it means that you are using reason and logic to come to a conclusion about an issue or decision you are tangling with.
And clear, sound reasoning is something that will help you every day.
To help you make the leap from classroom to real world, here are 3 concrete examples of critical thinking in everyday life.
Fake News vs. Real News
Take a moment to reflect on your media skills. Do you think you have what it takes to sort out a real news source from a piece of clever advertising?
According to a recent study from Stanford University, a whopping 82% of the teens surveyed could not distinguish between an ad labeled “sponsored content” and a legitimate news story.
Part of the problem may come from schools cutting back on formal instruction of critical thinking skills and an assumption that today’s “digital native” teens can automatically tell the difference without practice or instruction.
You are good at lots of things. But, you know, you’ve practiced those things you’re good at. So, how can you practice telling fact from fiction?
One way (outside of school) is to chat with your family and friends about media sources. Find out how they stay informed, and why they choose those outlets. Ask each other routine questions for evaluating sources .
Do your Friends Know Everything?
It’s tempting to believe that the world begins and ends with your friends. Don’t get me wrong. Friends are definitely important. However, it pays to reflect a little on how a group influences our lives.
To practice critical thinking in everyday life, take a close look at your group of friends. Are there things that are “forbidden” in your social circle? Are you expected to act a certain way, dress a certain way?
Think a certain way?
It’s natural that when a group defines something as “cool”, all the people in the group work to fit into that definition. Regardless of what they individually believe.
The problem is that virtually every situation can be defined in multiple ways. What is “dumb” to one person may be “cool” to another.
Develop your ability to redefine the way you see the world around you. On your own terms.
Find a time when your friend group sees the negative in a situation. Is there a positive way to view it instead? Or at least a way that makes it seem not quite so bad?
You may not be ready to speak up with your independent view. And that’s ok. Just practice thinking differently from the group to strengthen your mind.
Critical Thinking in the Driver’s Seat
One of the core critical thinking skills you need every day is the ability to examine the implications and consequences of a belief or action. In its deepest form, this ability can help you form your own set of beliefs in everything from climate change to religion.
But this skill can also save your life (and your car insurance rate) behind the wheel.
Imagine you are cruising down the freeway when your phone alerts you to an incoming text message. The ability to examine your potential actions and their accompanying consequences will help you make the best choice for how to handle the situation.
Do you look at the text and risk getting into an accident? Do you wait and risk not responding to an urgent matter? Or do you pull over to look at the text and risk being late for your appointment?
The same skill can be applied when you are looking for a place to park, when to pull onto a busy street, or whether to run the yellow light.
Better yet, the more practiced you are at looking at the implications of your driving habits, the faster you can make split second decisions behind the wheel.
Why Critical Thinking in Everyday Life Matters
Literally everyone can benefit from critical thinking because the need for it is all around us.
In a philosophical paper , Peter Facione makes a strong case that critical thinking skills are needed by everyone, in all societies who value safety, justice, and a host of other positive values:
“Considered as a form of thoughtful judgment or reflective decision-making, in a very real sense critical thinking is pervasive. There is hardly a time or a place where it would not seem to be of potential value. As long as people have purposes in mind and wish to judge how to accomplish them, as long as people wonder what is true and what is not, what to believe and what to reject, strong critical thinking is going to be necessary.”
So, in other words, as long as you remain curious, purposeful, and ambitious, no matter what your interests, you’re going to need critical thinking to really own your life.
About Winston Sieck
Dr. Winston Sieck is a cognitive psychologist working to advance the development of thinking skills. He is founder and president of Global Cognition, and director of Thinker Academy .
Reader Interactions
July 27, 2019 at 7:20 am
Wonderful article.. Useful in daily life… I have never imagined the way critical thinking is useful to make judgments
December 9, 2020 at 9:38 pm
My name is Anthony Lambert I am student at miller Motte. Critical Thinking is one my classes. I thank you for giving me the skills of critical thinking.
- Save Your Ammo
- Publications
GC Blog Topics
- Culture & Communication
- Thinking & Deciding
- Learning Skills
- Learning Science
Online Courses
- Thinker Academy
- Study Skills Course
- For Parents
- For Teachers
share this!
May 7, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
What can early Earth teach us about the search for life?
by Evan Gough, Universe Today
Earth is the only life-supporting planet we know of, so it's tempting to use it as a standard in the search for life elsewhere. But the modern Earth can't serve as a basis for evaluating exoplanets and their potential to support life. Earth's atmosphere has changed radically over its 4.5 billion years.
A better way is to determine what biomarkers were present in Earth's atmosphere at different stages in its evolution and judge other planets on that basis.
That's what a group of researchers from the UK and the U.S. did. Their research is titled " The early Earth as an analogue for exoplanetary biogeochemistry ," and it appears on the pre-print server arXiv . The lead author is Eva E. Stüeken, a Ph.D. student at the School of Earth & Environmental Sciences, University of St Andrews, UK.
When Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago, its atmosphere was nothing like it is today. At that time, the atmosphere and oceans were anoxic. About 2.4 billion years ago, free oxygen began to accumulate in the atmosphere during the Great Oxygenation Event, one of the defining periods in Earth's history. But the oxygen came from life itself, meaning life was present when the Earth's atmosphere was much different.
This isn't the only example of how Earth's atmosphere has changed over geological time . But it's an instructive one and shows why searching for life means more than just searching for an atmosphere like modern Earth's. If that's the way we conducted the search, we'd miss worlds where photosynthesis hadn't yet appeared.
In their research, the authors point out how Earth hosted a rich and evolving population of microbes under different atmospheric conditions for billions of years.
"For most of this time, Earth has been inhabited by a purely microbial biosphere albeit with seemingly increasing complexity over time," the authors write. "A rich record of this geobiological evolution over most of Earth's history thus provides insights into the remote detectability of microbial life under a variety of planetary conditions."
It's not just life that's changed over time. Plate tectonics have changed and may have been 'stagnant lid' tectonics for a long time. In stagnant lid tectonics, plates don't move horizontally. That can have consequences for atmospheric chemistry.
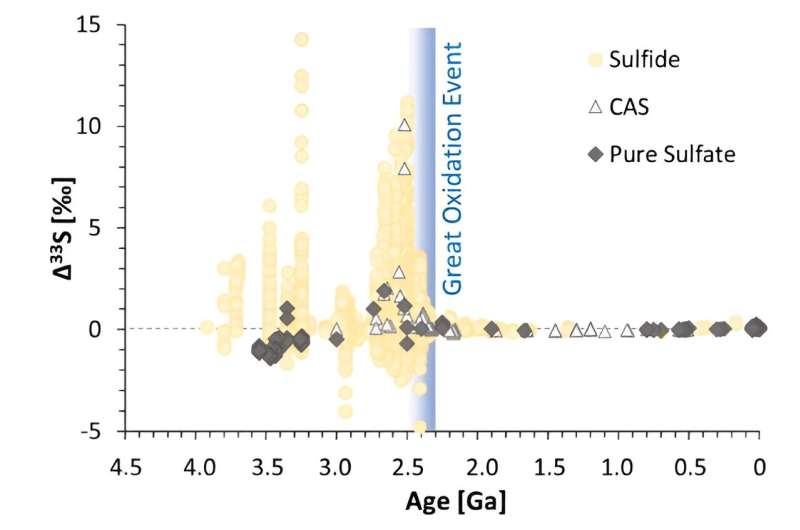
The main point is that Earth's atmosphere does not reflect the solar nebula the planet formed in. Multiple intertwined processes have changed the atmosphere over time. The search for life involves not only a better understanding of these processes, but how to identify what stage exoplanets might be in.
It's axiomatic that biological processes can have a dramatic effect on planetary atmospheres. "On the modern Earth, the atmospheric composition is very strongly controlled by life," the researchers write. "However, any potential atmospheric biosignature must be disentangled from a backdrop of abiotic (geological and astrophysical) processes that also contribute to planetary atmospheres and would be dominating on lifeless worlds and on planets with a very small biosphere."
The authors outline what they say are the most important lessons that the early Earth can teach us about the search for life.
The first is that the Earth has actually had three different atmospheres throughout its long history. The first one came from the solar nebula and was lost soon after the planet formed. That's the primary atmosphere. The second one formed from outgassing from the planet's interior.
The third one, Earth's modern atmosphere, is complex. It's a balancing act involving life, plate tectonics, volcanism, and even atmospheric escape. A better understanding of how Earth's atmosphere has changed over time gives researchers a better understanding of what they see in exoplanet atmospheres.
The second is that the further we look back in time, the more the rock record of Earth's early life is altered or destroyed. Our best evidence suggests life was present by 3.5 billion years ago, maybe even by 3.7 billion years ago. If that's the case, the first life may have existed on a world covered in oceans, with no continental land masses and only volcanic islands.
If there had been abundant volcanic and geological activity between 3.5 and 3.7 billion years ago, there would've been large fluxes of CO 2 and H 2 . Since these are substrates for methanogenesis, then methane may have been abundant in the atmosphere and detectable.
The third lesson the authors outline is that a planet can host oxygen-producing life for a long time before oxygen can be detected in an atmosphere. Scientists think that oxygenic photosynthesis appeared on Earth in the mid-Archean eon. The Archean spanned from 4 billion to 2.5 billion years ago, so mid-Archean is sometime around 3.25 billion years ago. But oxygen couldn't accumulate in the atmosphere until the Great Oxygenation Event about 2.4 billion years ago.
Oxygen is a powerful biomarker, and if it is found in an exoplanet's atmosphere, it would be cause for excitement. But life on Earth was around for a long time before atmospheric oxygen would've been detectable.
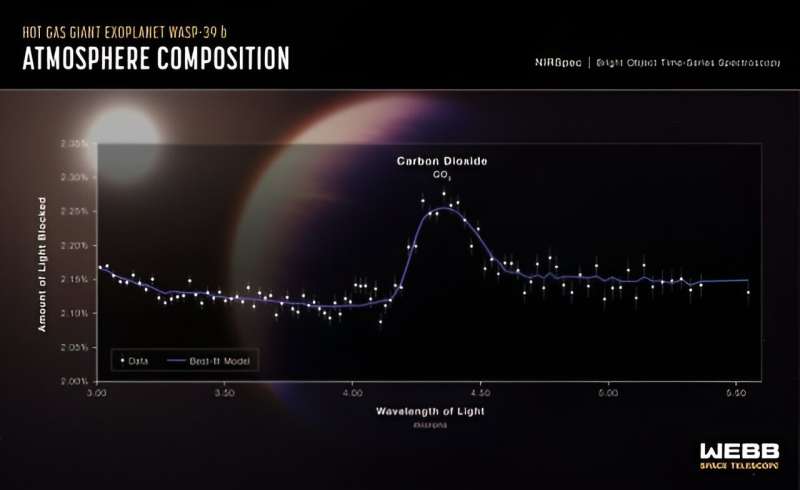
The fourth lesson involves the appearance of horizontal plate tectonics and its effect on chemistry. "From the GOE onwards, the Earth looked tectonically similar to today," the authors write. The oceans were likely stratified into an anoxic layer and an oxygenated surface layer. However, hydrothermal activity constantly introduced ferrous iron into the oceans. That increased the sulfate levels in the seawater which reduced the methane in the atmosphere. Without that methane, Earth's biosphere would've been much less detectable.
"Planet Earth has evolved over the past 4.5 billion years from an entirely anoxic planet with possibly a different tectonic regime to the oxygenated world with horizontal plate tectonics that we know today," the authors explain. All that complex evolution allowed life to appear and to thrive, but it also makes detecting earlier biospheres on exoplanets more complicated.
We're at a huge disadvantage in the search for life on exoplanets. We can literally dig into Earth's ancient rock to try to untangle the long history of life on Earth and how the atmosphere evolved over billions of years. When it comes to exoplanets, all we have is telescopes. Increasingly powerful telescopes, but telescopes nonetheless. While we are beginning to explore our own solar system, especially Mars and the tantalizing ocean moons orbiting the gas giants, other solar systems are beyond our physical reach.
"We must instead remotely recognize the presence of alien biospheres and characterize their biogeochemical cycles in planetary spectra obtained with large ground- and space-based telescopes," the authors write. "These telescopes can probe atmospheric composition by detecting absorption features associated with specific gases." Probing atmospheric gases is our most powerful approach right now, as the JWST shows.
But as scientists get better tools, they'll start to go beyond atmospheric chemistry. "We might also be able to recognize global-scale surface features, including light interaction with photosynthetic pigments and 'glint' arising from specular reflection of light by a liquid ocean."
Understanding what we're seeing in exoplanet atmospheres parallels our understanding of Earth's long history. Earth could be the key to our broadening and accelerating search for life.
"Unraveling the details of Earth's complex biogeochemical history and its relationship with remotely observable spectral signals is an important consideration for instrument design and our own search for life in the universe," the authors write.
Provided by Universe Today
Explore further
Feedback to editors

From roots to resilience: Investigating the vital role of microbes in coastal plant health
6 hours ago
Temperature, time and blueberry wine: Researchers examine fermentation's effects on health-promoting compounds
7 hours ago
Heating proteins to body temperature reveals new drug targets

What fire ants can teach us about making better self-healing materials
8 hours ago

Robotic 'superlimbs' could help moonwalkers recover from falls
A novel multifunctional catalyst turns methane into valuable hydrocarbons
9 hours ago

NASA's Juno provides high-definition views of Europa's icy shell

New research addresses alleged benefits of a vegan diet for dogs

Trees on a university campus endure droughts with help from leaky pipes

First direct imaging of radioactive cesium atoms in environmental samples
Relevant physicsforums posts, light curving around vortex simulating a black hole.
20 hours ago
Solar Activity and Space Weather Update thread
May 14, 2024
Our Beautiful Universe - Photos and Videos
Strange cosmic particles in my detector.
May 13, 2024
U.S. Solar Eclipses - Oct. 14, 2023 (Annular) & Apr. 08, 2024 (Total)
May 12, 2024
Exploring the Sun: Amateur Solar Imaging Techniques
More from Astronomy and Astrophysics
Related Stories

Webb telescope probably didn't find life on an exoplanet—yet
May 2, 2024
Will we know if TRAPPIST-1e has life?
Apr 23, 2024

Is it life, or is it volcanoes?
Sep 29, 2023

Life might be easiest to find on planets that match an earlier Earth
Nov 17, 2023

Earth holds the key to detecting life beyond our solar system
Feb 19, 2018

If a planet has a lot of methane in its atmosphere, life is the most likely cause
Dec 24, 2020
Recommended for you

Astronomers discover new Earth-sized world orbiting an ultra-cool star
19 hours ago

Sun shoots out biggest solar flare in almost 2 decades, but Earth should be out of the way this time

Astronomers discover WASP-193b, a giant planet with a density similar to that of cotton candy

Astronomers find the biggest known batch of planet ingredients swirling around young star

Discovery of biomarkers in space—conditions on Saturn's moon Enceladus simulated in the laboratory
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

Glimpse of next-generation internet

Epic science inside a cubic millimeter of brain

What is ‘original scholarship’ in the age of AI?

Venki Ramakrishnan.
Niles Singer/Harvard Staff Photographer
Science is making anti-aging progress. But do we want to live forever?
Nobel laureate details new book, which surveys research, touches on larger philosophical questions
Anne J. Manning
Harvard Staff Writer
Mayflies live for only a day. Galapagos tortoises can reach up to age 170. The Greenland shark holds the world record at over 400 years of life.
Venki Ramakrishnan, Nobel laureate and author of the newly released “ Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for Immortality ,” opened his packed Harvard Science Book Talk last week by noting the vast variabilities of lifespans across the natural world. Death is certain, so far as we know. But there’s no physical or chemical law that says it must happen at a fixed time, which raises other, more philosophical issues.
The “why” behind these enormous swings, and the quest to harness longevity for humans, have driven fevered attempts (and billions of dollars in research spending) to slow or stop aging. Ramakrishnan’s book is a dispassionate journey through current scientific understanding of aging and death, which basically comes down to an accumulation of chemical damage to molecules and cells.
“The question is whether we can tackle aging processes, while still keeping us who we are as humans,” said Ramakrishnan during his conversation with Antonio Regalado, a writer for the MIT Technology Review. “And whether we can do that in a safe and effective way.”
Even if immortality — or just living for a very, very long time — were theoretically possible through science, should we pursue it? Ramakrishnan likened the question to other moral ponderings.
“There’s no physical or chemical law that says we can’t colonize other galaxies, or outer space, or even Mars,” he said. “I would put it in that same category. And it would require huge breakthroughs, which we haven’t made yet.”
In fact, we’re a lot closer to big breakthroughs when it comes to chasing immortality. Ramakrishnan noted the field is moving so fast that a book like his can capture but a snippet. He then took the audience on a brief tour of some of the major directions of aging research. And much of it, he said, started in unexpected places.
Take rapamycin, a drug first isolated in the 1960s from a bacterium on Easter Island found to have antifungal, immunosuppressant, and anticancer properties. Rapamycin targets the TOR pathway, a large molecular signaling cascade within cells that regulates many functions fundamental to life. Rapamycin has garnered renewed attention for its potential to reverse the aging process by targeting cellular signaling associated with physiological changes and diseases in older adults.
Other directions include mimicking the anti-aging effects of caloric restriction shown in mice, as well as one particularly exciting area called cellular reprogramming. That means taking fully developed cells and essentially turning back the clock on their development.
The most famous foundational experiment in this area was by Kyoto University scientist and Nobel laureate Shinya Yamanaka, who showed that just four transcription factors could revert an adult cell all the way back to a pluripotent stem cell, creating what are now known as induced pluripotent stem cells.
Ramakrishnan , a scientist at England’s MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, won the 2009 Nobel Prize in chemistry for uncovering the structure of the ribosome. He said he felt qualified to write the book because he has “no skin in the game” of aging research. As a molecular biologist who has studied fundamental processes of how cells make proteins, he had connections in the field but wasn’t too close to any of it.
While researching the book, he took pains to avoid interviewing scientists with commercial ventures tied to aging.
The potential for conflicts of interest abound.
The world has seen an explosion in aging research in recent decades, with billions of dollars spent by government agencies and private companies . And the consumer market for products is forecast to hit $93 billion by 2027 .
As a result, false or exaggerated claims by companies promising longer life are currently on the rise, Ramakrishnan noted. He shared one example: Supplements designed to lengthen a person’s telomeres, or genetic segments that shrink with age, are available on Amazon.
“Of course, these are not FDA approved. There are no clinical trials, and it’s not clear what their basis is,” he said.
But still there appears to be some demand.
Get the best of the Gazette delivered to your inbox
By subscribing to this newsletter you’re agreeing to our privacy policy
Share this article
You might like.
Physicists demo first metro-area quantum computer network in Boston

Researchers publish largest-ever dataset of neural connections

Symposium considers how technology is changing academia
How far has COVID set back students?
An economist, a policy expert, and a teacher explain why learning losses are worse than many parents realize
Excited about new diet drug? This procedure seems better choice.
Study finds minimally invasive treatment more cost-effective over time, brings greater weight loss
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Manage Your Subscription
- Give a Gift Subscription
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
Psychiatrist Dr. David Pruder on Everyday Habits That May Be Affecting Your Mental Health
The psychiatrist and mental health podcaster breaks down ways to break bad habits, from limiting your phone usage before going to bed to exercising
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SeanNeumann-PEOPLE-718cf3b51a4648c98dd8bbd62d70796e.jpg)
Daily routines can help provide structure and certainty in a person’s life. But some of the little things we do every day – especially in an increasingly modern world – can negatively impact our mental health.
Dr. David Pruder , a licensed psychiatrist who hosts the “ Psychiatry & Psychotherapy Podcast ,” recently spoke with PEOPLE about some everyday habits that can lead to negative mental health and ways you can start training your brain to break those routines to avoid micro negativities throughout your day. Here are four areas of focus where you can cut down on daily habits you might not realize are impacting your mental health.
Limiting Screen Time
Pruder suggests one major change people can make in their daily lives is to limit their screen time.
“There have been a lot of studies that show more than two hours a day of screen time increases risk of depression, suicidal thoughts, all sorts of different poor mental health outcomes,” the psychiatrist says. “And part of that is: What are people not doing when they're on their screens? They're not interacting with real humans, they're not doing exercise.”
One specific time of day to focus on limiting your screen usage is late at night, Pruder says.
“Your brain capacity, your ability to focus, concentrate, move forward in life, all of that is going to be impacted by your sleep,” Pruder notes.
Not only does staring at a screen right before you go to bed – whether your phone, a television, or another device – impact how much melatonin your body is producing, but the psychiatrist says most peoples’ brains become more impulsive at night, allowing anxieties and fears to more easily dominate a person’s headspace. This can also disrupt your ability to fall asleep, and evidence shows that consistent sleep is key to good mental health. The psychiatrist says it’s a good idea to begin dimming your lights and avoid using your phone about an hour before going to bed. Pruder suggests putting your phone in another room to avoid being woken up intermittently when a notification rings, or to reach for their phone when they wake up in the middle of the night.
“It's hard though,” Pruder admits. “I empathize with anyone who has a hard time doing it and wants to binge on Netflix or something. I've been there.”
Routine strength training and cardio workouts can both positively impact different hormone systems and brain systems in complimentary ways, Pruder says.
Many people who stop routinely exercising develop anxiety and depression, the mental health professional points out.
“I see a lot of that with bikers when they stop,” Pruder says. “They stop [routinely biking and working out] and they just feel awful.” This pattern also is evident with many college-aged students once they stop playing sports after high school. Pruder recommends getting together with friends to do outdoor activities, or looking into joining a local recreational sports team to stay active and on top of your physical health, which will ultimately impact your mental health as well. “Being a part of a sports team is great for ADHD, depression, anxiety, pretty much every mental health condition,” Pruder says.
Paying Attention to Your Diet
Eating healthier is another major change people can make to their daily lives that will have a positive impact on their mental health, Pruder says.
Pruder recommends limiting processed foods and points to a 2017 study that shows how adopting a Mediterranean diet can lead to a reduction in depression for many people.
He also notes that studies about how bodies change over time as healthier eating habits are adopted show that there are measurable impacts on mental health as well.
“It's not like one thing has changed in your body,” the psychiatrist says. “It's like tens of thousands of changes happen just by making that one change. That’s where the magic happens.”
Connecting with Others
Lastly, Pruder says focusing on our connection with others is another major category to work on every day – whether that’s seeking out positive relationships, or starting psychotherapy, which can help people better connect with others.
“A lot of people I meet who have significant mental health concerns have progressively become more detached from the world to the point that maybe they have one person they have some connection with. Some people have zero,” Pruder says. “And that's for many, many reasons, but as they progress out into the world, they always end up inevitably connected to more people.”
Pruder implores people to “invest in good friendships, value good friendships, and pursue good friendships” or consider therapy to help replenish and build social skills. “If psychotherapy is accomplished well, and you are more empathetic, generous, a better listener, a better friend, then you go on in life and it impacts thousands of future relationships,” he says.
Staying Motivated
It’s hard to make positive changes to your life once you’re settled into a routine.
“But focus on the meaning and the purpose,” Pruder recommends. “Think about ‘why’ you’re doing the things you’re doing. I think that’s essential. Then you can start to make decisions based on what you really value in your life.”

Social online training can help against loneliness and depression
M ental health problems, loneliness among young people, and polarization are rapidly increasing, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. A new large-scale research study, the CovSocial project, led by Tania Singer from the Max Planck Society, is helping people to reconnect with themselves, others and society at large.
Recent findings reveal that a ten-week, partner-based mental online training program boosted resilience, empathy and compassion, and deepened social connections. At the same time, these short daily, app-based practices done with another person, so-called Dyads, decreased loneliness, depression, anxiety and a negative outlook in life. Researchers hope that this training can be scaled worldwide to overcome loneliness and social divisions.
The work is published in the Journal of Affective Disorders .
Singer, a psychologist, social neuroscientist and scientific head of the Max Planck Society's Social Neuroscience Lab in Berlin, Germany, has for many years been developing mental intervention programs based on partner-based daily exercises, known as "Contemplative Dyads" as they resemble a mindfulness meditation done together with a partner in your daily life.
Unlike solitary mindfulness-based meditation practices, Dyads involve structured interactions between pairs of individuals who are taking turn in exploring loudly specific questions while the other is empathically listening without judging and interrupting in any way. The basic Affect Dyad for example consists of two questions that are aiming at both exploring and cultivating a deeper understanding and acceptance of challenging emotions as well as building resilience through the cultivation of gratitude and care.
More tolerance and less prejudice
These daily Dyads are done over ten weeks as a social skill learning program and the practice is supported by teacher-led weekly coaching sessions to help deepen the daily practice. People are randomly paired every week with a new partner to help increase tolerance, help reduce prejudice, overcome boundaries, and foster a sense of common humanity. With roots in ancient meditation traditions and recent advancements in social neuroscience, dyadic practices have emerged as a powerful tool for cultivating social skills and promoting resilience in diverse populations.
Science is now revealing the benefits of such social practices. The CovSocial Project, a large-scale mental health study spearheaded by Singer at the Social Neuroscience Lab of the Max Planck Society and performed during the years of the COVID-19 pandemic, has revealed in its first phase--by tracking thousands of Berliners recruited from a random draw of the Berlin city register--that loneliness, stress, depression and anxiety increased, with each lockdown showing severe lockdown fatigue effects.
To reduce this suffering, the team therefore decided to offer a second-phase mental online training program to those still participating in the study. The team compared the efficiency of two 10-week online mental training programs: a classic mindfulness-based and a partner-based socio-emotional Dyad intervention program.
Daily contemplative exercises are effective
A growing body of research is now published, giving impressive evidence that these daily social contemplative exercises done with another person are indeed effective in supporting participants mental well-being and health by reducing depression, anxiety and emotion regulation difficulties while at the same time increasing social skills such as empathy, self and other-related compassion. These findings give hope that such social mental practices could help overcome social divides, reducing loneliness, and improving human-to-human social connection.
The recently published paper showed that the ten-week online Dyad program could indeed reduce depression, anxiety and emotion-regulation difficulties while at the same time improving resilience. Interestingly, participants also showed a significant reduction in their "negative interpretation bias"—the likelihood of interpreting other people or situations in a negative way—and this decrease in negativity could actually account for the observed mental health benefits.
This means that internalized knee-jerk anxieties about life or different groups or individuals can be tackled and a more positive worldview and outlook on life can be trained.
Singer comments on these findings, "While both interventions could decrease mental health problems, it was interesting to see that only in the dyadic social practices the reduction in negative interpretation bias was a strong candidate mechanism underlying the observed decrease in depression. We think that practicing daily gratitude during a Dyad with a partner may help boost this more positive outlook onto life and in turn strengthen one's resilience and mental health."
Increasing social connections
In another mental training study from the CovSocial project just published, first author Hannah Matthaeus and colleagues revealed that again only the socio-emotional Dyad practice program, but not the classic mindfulness practice program focusing on meditations done alone, could significantly reduce loneliness.
Singer concludes, "As in a previous large-scale mental training study, the ReSource project, we could confirm again that these daily relational practices are a powerful tool to increase social connections and facilitate people to share their difficulties and vulnerability.
"In the recent study, we could extend these previous findings in showing that even if practicing Dyads only online and only for ten weeks, we can find this deepening of social connections and even reduce loneliness. This offers real hope that recent alarming trends towards social isolation, loneliness and division can be reversed by scaling such interrelational mental training programs based on Dyads."
As the evidence for the effectiveness of this Dyad intervention builds, the study's authors hope that they can develop ways to scale it so that these Dyad training programs can be brought to society at large and especially to domains which suffer mostly under high burn-out rates and stress such as the health-care or educational systems. Their next programs, Edu:Social School and Health will focus on exactly this: testing the effects of such Dyad programs in the context of the classroom and hospitals in the hope to increase not only the resilience of teachers and health care providers but also boost classroom climate and team spirits and social cohesion.
Singer, the principal investigator of the CovSocial study, concludes, "At a time when policymakers are grappling with a rising tide of poor public mental health and increasing loneliness and social divisions, our study shows it is possible to bring communities back together and promote positive, healthy human interactions. This is what our societies need urgently. People are crying out for a sense of belonging, community, care, and true social connections.
"I hope we can take the lessons of this study and begin to scale and amplify such interrelation mental training programs to benefit society. This is why we started now a follow-up study, the Edu:Social project, to bring these practices into the fields of education and health care."
More information: Malvika Godara et al, Training-related improvements in mental well-being through reduction in negative interpretation bias: A randomized trial of online socio-emotional dyadic and mindfulness interventions, Journal of Affective Disorders (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.03.037
Provided by Max Planck Society

Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
Image credit: Claire Scully
New advances in technology are upending education, from the recent debut of new artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots like ChatGPT to the growing accessibility of virtual-reality tools that expand the boundaries of the classroom. For educators, at the heart of it all is the hope that every learner gets an equal chance to develop the skills they need to succeed. But that promise is not without its pitfalls.
“Technology is a game-changer for education – it offers the prospect of universal access to high-quality learning experiences, and it creates fundamentally new ways of teaching,” said Dan Schwartz, dean of Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE), who is also a professor of educational technology at the GSE and faculty director of the Stanford Accelerator for Learning . “But there are a lot of ways we teach that aren’t great, and a big fear with AI in particular is that we just get more efficient at teaching badly. This is a moment to pay attention, to do things differently.”
For K-12 schools, this year also marks the end of the Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) funding program, which has provided pandemic recovery funds that many districts used to invest in educational software and systems. With these funds running out in September 2024, schools are trying to determine their best use of technology as they face the prospect of diminishing resources.
Here, Schwartz and other Stanford education scholars weigh in on some of the technology trends taking center stage in the classroom this year.
AI in the classroom
In 2023, the big story in technology and education was generative AI, following the introduction of ChatGPT and other chatbots that produce text seemingly written by a human in response to a question or prompt. Educators immediately worried that students would use the chatbot to cheat by trying to pass its writing off as their own. As schools move to adopt policies around students’ use of the tool, many are also beginning to explore potential opportunities – for example, to generate reading assignments or coach students during the writing process.
AI can also help automate tasks like grading and lesson planning, freeing teachers to do the human work that drew them into the profession in the first place, said Victor Lee, an associate professor at the GSE and faculty lead for the AI + Education initiative at the Stanford Accelerator for Learning. “I’m heartened to see some movement toward creating AI tools that make teachers’ lives better – not to replace them, but to give them the time to do the work that only teachers are able to do,” he said. “I hope to see more on that front.”
He also emphasized the need to teach students now to begin questioning and critiquing the development and use of AI. “AI is not going away,” said Lee, who is also director of CRAFT (Classroom-Ready Resources about AI for Teaching), which provides free resources to help teach AI literacy to high school students across subject areas. “We need to teach students how to understand and think critically about this technology.”
Immersive environments
The use of immersive technologies like augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality is also expected to surge in the classroom, especially as new high-profile devices integrating these realities hit the marketplace in 2024.
The educational possibilities now go beyond putting on a headset and experiencing life in a distant location. With new technologies, students can create their own local interactive 360-degree scenarios, using just a cell phone or inexpensive camera and simple online tools.
“This is an area that’s really going to explode over the next couple of years,” said Kristen Pilner Blair, director of research for the Digital Learning initiative at the Stanford Accelerator for Learning, which runs a program exploring the use of virtual field trips to promote learning. “Students can learn about the effects of climate change, say, by virtually experiencing the impact on a particular environment. But they can also become creators, documenting and sharing immersive media that shows the effects where they live.”
Integrating AI into virtual simulations could also soon take the experience to another level, Schwartz said. “If your VR experience brings me to a redwood tree, you could have a window pop up that allows me to ask questions about the tree, and AI can deliver the answers.”
Gamification
Another trend expected to intensify this year is the gamification of learning activities, often featuring dynamic videos with interactive elements to engage and hold students’ attention.
“Gamification is a good motivator, because one key aspect is reward, which is very powerful,” said Schwartz. The downside? Rewards are specific to the activity at hand, which may not extend to learning more generally. “If I get rewarded for doing math in a space-age video game, it doesn’t mean I’m going to be motivated to do math anywhere else.”
Gamification sometimes tries to make “chocolate-covered broccoli,” Schwartz said, by adding art and rewards to make speeded response tasks involving single-answer, factual questions more fun. He hopes to see more creative play patterns that give students points for rethinking an approach or adapting their strategy, rather than only rewarding them for quickly producing a correct response.
Data-gathering and analysis
The growing use of technology in schools is producing massive amounts of data on students’ activities in the classroom and online. “We’re now able to capture moment-to-moment data, every keystroke a kid makes,” said Schwartz – data that can reveal areas of struggle and different learning opportunities, from solving a math problem to approaching a writing assignment.
But outside of research settings, he said, that type of granular data – now owned by tech companies – is more likely used to refine the design of the software than to provide teachers with actionable information.
The promise of personalized learning is being able to generate content aligned with students’ interests and skill levels, and making lessons more accessible for multilingual learners and students with disabilities. Realizing that promise requires that educators can make sense of the data that’s being collected, said Schwartz – and while advances in AI are making it easier to identify patterns and findings, the data also needs to be in a system and form educators can access and analyze for decision-making. Developing a usable infrastructure for that data, Schwartz said, is an important next step.
With the accumulation of student data comes privacy concerns: How is the data being collected? Are there regulations or guidelines around its use in decision-making? What steps are being taken to prevent unauthorized access? In 2023 K-12 schools experienced a rise in cyberattacks, underscoring the need to implement strong systems to safeguard student data.
Technology is “requiring people to check their assumptions about education,” said Schwartz, noting that AI in particular is very efficient at replicating biases and automating the way things have been done in the past, including poor models of instruction. “But it’s also opening up new possibilities for students producing material, and for being able to identify children who are not average so we can customize toward them. It’s an opportunity to think of entirely new ways of teaching – this is the path I hope to see.”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research empowers us with knowledge. Though scientists carry out research, the rest of the world benefits from their findings. We get to know the way of nature, and how our actions affect it. We gain a deeper understanding of people, and why they do the things they do. Best of all, we get to enrich our lives with the latest knowledge of health ...
9. Raising Awareness. 10. Cultivating Curiosity. Conclusion. In a world filled with information, it's really important to understand the importance of research in our daily life. Whether you're a professional in business, a scientist striving for breakthroughs, or a student navigating the academic landscape, research plays a crucial role in ...
In this article, we delve into the importance of research in daily life, making tangible the link between the seemingly abstract world of research and our everyday experiences. The Hidden Guide in Our Decision Making. One of the most immediate ways research impacts our lives is by informing our daily decision-making.
A brief history of the scientific method. The scientific method has its roots in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. Philosophers Francis Bacon and René Descartes are often credited with formalizing the scientific method because they contrasted the idea that research should be guided by metaphysical pre-conceived concepts of the nature of reality—a position that, at the time, was ...
Research is essential to our daily lives. It helps us to make informed decisions about everything from the food we eat to the medicines we take. It also allows us to better understand the world around us and find solutions to problems. In short, research is essential for our health, safety, and well-being.
Why Research Is Necessary and Valuable in Our Daily Lives. It's a tool for building knowledge and facilitating learning. It's a means to understand issues and increase public awareness. It helps us succeed in business. It allows us to disprove lies and support truths. It is a means to find, gauge, and seize opportunities.
Benefits of science. The process of science is a way of building knowledge about the universe — constructing new ideas that illuminate the world around us. Those ideas are inherently tentative, but as they cycle through the process of science again and again and are tested and retested in different ways, we become increasingly confident in them.
Plenty. If you think science doesn't matter much to you, think again. Science affects us all, every day of the year, from the moment we wake up, all day long, and through the night. Your digital alarm clock, the weather report, the asphalt you drive on, the bus you ride in, your decision to eat a baked potato instead of fries, your cell phone, the antibiotics that treat your sore throat, the ...
The research on research use shows that it's a process that extends over time, not an event or a single moment. It's embedded in organizations, and it's inherently social.
Handbook of research methods for studying daily life. New York: Guildford Press. This book provides an all-encompassing review for researchers conducting daily-life studies. It is a resource for conducting high-quality research and provides guidelines to select and implement methods for studying daily life.
Science is one of many factors that can help inform decisions. Scientific studies can help people make many types of decisions. For example, science can help us learn which products are safe to use or which foods are healthy to eat. Doctors use science to decide how to diagnose and treat disease.
The book takes researchers through the process of designing and conducting a daily life project. It focuses on the classic, prototypical kinds of projects—studies that sample at least once a day and collect self-report data. On the design side, the authors emphasize daily diaries and within-day experience sampling.
Psychology's Impact. Psychologists use scientific research to better understand how people learn, interpret events and make decisions. They then translate that knowledge into techniques to help people make smarter choices in their daily lives. Based on a deep knowledge of how lifestyles are affected by factors related to biology, mental ...
A step-by-step guide to researching what people do in their everyday lives. This practical, beginner-friendly book teaches readers how to do daily life research, which is the study of what people do in their ordinary environments in their everyday lives. The basic approach is to collect data intensively over time, at least once a day for many ...
Research on how we form new memories as well as how and why we forget has led to a number of findings that can be applied directly in your daily life. To increase your memory power: Focus on the information. Rehearse what you have learned. Eliminate distractions.
Other important strengths include hope, gratitude, forgiveness, spirituality, curiosity, and kindness. 7. Social competence: "It matters that I connect with others.". An important enabler of thriving is to access others, connect with them, and benefit from their social support.
Understanding the principles of chemistry allows us to create safer and more efficient products. Websites like American Chemical Society provide valuable resources on the role of chemistry in our daily lives. Science is an integral part of our lives, providing us with knowledge and improving our understanding of the world around us.
Research has a lot of impact on the daily functioning of life. First and foremost, research leads to a better life by producing results that can be used to make life better. Especially as far as scientific research is concerned, the invention of vaccines and medicines makes diseases to be less of a threat to society (Calderon & Slavin 2001).
May 14, 2024. As modern-day stress ratchets up to what feels like unbearable levels, researchers are striving to learn more about the precise mechanisms through which it affects our body and mind ...
Sociologists evaluate and examine subject matter such as crime, religion, family relationships, racial and gender identity, class divisions, communities, cultures, and social stability. Understandably, there are many examples of sociology in everyday life. Sociology provides a unique and illuminating perspective on how we, as complex human ...
Researchers find that people who experience higher 'felt love' -- brief experiences of love and connection in everyday life -- also have significantly higher levels of psychological well-being ...
The dynamic nature of daily life means that the relatively uncommon activity of hunting large terrestrial vertebrates is unlikely to be the main behavior that helps humans solve the key problems ...
First, keep in mind that critical thinking is simply a "deliberate thought process.". Basically, it means that you are using reason and logic to come to a conclusion about an issue or decision you are tangling with. And clear, sound reasoning is something that will help you every day. To help you make the leap from classroom to real world ...
The second is that the further we look back in time, the more the rock record of Earth's early life is altered or destroyed. Our best evidence suggests life was present by 3.5 billion years ago ...
The world has seen an explosion in aging research in recent decades, with billions of dollars spent by government agencies and private companies. And the consumer market for products is forecast to hit $93 billion by 2027. As a result, false or exaggerated claims by companies promising longer life are currently on the rise, Ramakrishnan noted.
Daily routines can help provide structure and certainty in a person's life. But some of the little things we do every day - especially in an increasingly modern world - can negatively impact ...
Recent findings reveal that a ten-week, partner-based mental online training program boosted resilience, empathy and compassion, and deepened social connections. At the same time, these short ...
With new technologies, students can create their own local interactive 360-degree scenarios, using just a cell phone or inexpensive camera and simple online tools. "This is an area that's ...