Top five research articles of 2020
Despite the significant challenges this year has posed, The Pharmaceutical Journal has continued to publish high-quality peer-reviewed research.
Our researchers have made a range of investigations — from evaluating pharmacist interventions using the Simpler tool in Malaysia , to a pharmacist-led virtual thiopurine clinic to support people with inflammatory bowel disease and auto-immune hepatitis, here in the UK.
We have some exciting research coming up in 2021, but in case you missed them the first time around, here are the top five most popular research articles of 2020:

5. Misuse of prescription and over-the-counter drugs to obtain illicit highs: how pharmacists can prevent abuse
Use of prescription and over-the-counter drugs for recreational purposes is increasing, and this perspective article collates the existing literature to provide an in-depth overview of the misuse and diversion of a range of drugs with psychoactive potential, including gabapentinoids, antihistamine drugs and loperamide.
4. Effective detection and management of hypertension through community pharmacy in England
Community pharmacists can play a big role in managing hypertension — from the identification of medication-related problems, to providing lifestyle advice. Despite this, they are not routinely involved in structured hypertension management or screening programmes. So, this review summarises the evidence to recommend the roll-out of a community pharmacy-led hypertension management service.
3. Recent advances in the oral delivery of biologics
Oral administration of medicines is often preferred by patients for its convenience, but, for biologics, the gastrointestinal tract poses challenges for administering in this way. This review discusses the advantages and limitations of several novel drug delivery strategies, and highlights the work to be done to put this technology into clinical practice.
2. Immuno-oncology agents for cancer therapy
Immuno-oncology is a novel treatment that works by conditioning the body’s immune cells to recognise and kill cancer cells — combining this treatment with conventional therapies has led to promising improvements in patient outcomes. This review looks at the range of immuno-oncology agents, and how problems such as their toxicity and high cost can be overcome.
1. Investigational treatments for COVID-19
The emergence of COVID-19 resulted in a global research effort to find effective treatment options to relieve healthcare burdens and, ultimately, save lives. In June 2020, this rapid review summarised the clinical trials and treatment evidence at the time.
Check out The Pharmaceutical Journal’ s ‘Everything you should know about the coronavirus outbreak’ for the latest on this continually evolving situation.
Find the full catalogue of articles in our research section .
Call for submissions
In 2021, The Pharmaceutical Journal will keep adding to the evidence base with review, perspective and research articles. If you have undertaken research into innovations and initiatives that can improve pharmacy services and administration, the pharmacological management of disease, or advances in drug development, please submit your article for consideration by email to: [email protected]
You may also be interested in
Artificial intelligence: act or be acted upon — staying relevant in the ai era, equality, diversity and inclusion: why true allyship must shift words into action, pharmacy needs to be at the forefront of shaping digital health — but how do we get there.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Medicinal chemistry articles from across Nature Portfolio
Medicinal chemistry deals with the design, optimization and development of chemical compounds for use as drugs. It is inherently a multidisciplinary topic — beginning with the synthesis of potential drugs followed by studies investigating their interactions with biological targets to understand the medicinal effects of the drug, its metabolism and side-effects.
Related Subjects
- Chemical libraries
- Cheminformatics
- Computational chemistry
- Drug delivery
- Drug discovery and development
- Lead optimization
- Pharmacology
- Structure-based drug design
- Target identification
- Target validation
Latest Research and Reviews
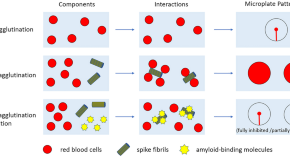
Reduction of hemagglutination induced by a SARS-CoV-2 spike protein fragment using an amyloid-binding benzothiazole amphiphile
- Sascha Castro Lingl

Computer-aided pattern scoring – A multitarget dataset-driven workflow to predict ligands of orphan targets
- Katja Stefan
- Vigneshwaran Namasivayam
- Sven Marcel Stefan
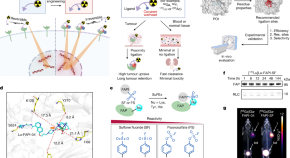
Covalent targeted radioligands potentiate radionuclide therapy
Radiopharmaceuticals engineered with click chemistry to selectively bind to tumour-specific proteins can be used to successfully target tumour cells, boosting the pharmacokinetics of radionuclide therapy and improving tumour regression.
- Xi-Yang Cui
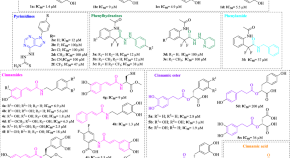
Py-CoMFA, docking, and molecular dynamics simulations of Leishmania (L.) amazonensis arginase inhibitors
- Priscila Goes Camargo
- Carine Ribeiro dos Santos
- Camilo Henrique da Silva Lima
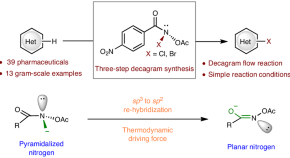
Discovery of N–X anomeric amides as electrophilic halogenation reagents
Electrophilic halogenation approaches often suffer from low reactivity and chemoselectivity when it comes to complex compounds. Now a class of halogenating reagents based on anomeric amides that can halogenate complex bioactive molecules with diverse functional groups and heterocycles has been developed. The higher reactivity of these anomeric amide reagents is attributed to the energy stored in the pyramidalized nitrogen.
- Phil S. Baran
Exploring SureChEMBL from a drug discovery perspective
- Yojana Gadiya
- Simran Shetty
- Andrea Zaliani
News and Comment
Trapping the helicase.
- Grant Miura
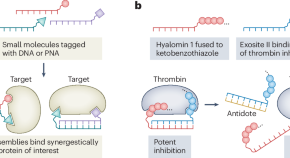
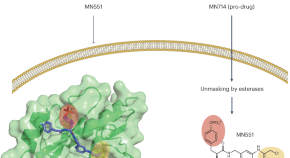
Designing drugs with reversible activity
A strategy for creating drugs that can be quickly neutralized is demonstrated for anticoagulants.
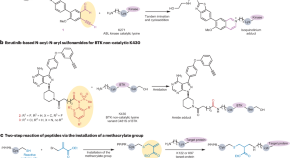
Tying the knot with lysine
Targeted covalent inhibitors (TCIs) can react irreversibly with lysine in kinases and other proteins. Small molecule TCIs can have both broad or specific lysine targeting whereas peptide- and protein-based TCIs were shown to provide high target specificity for lysines in shallow protein surfaces.
- Ana Koperniku
- Nicholas A. Meanwell
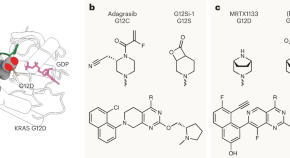
Another KRAS variant trapped
Inhibitors of KRAS G12C have shown that directly targeting RAS is possible, but G12C is only one of many RAS driver mutations. Covalent targeting of another major variant, G12D, raises hope for treating other groups of patients with KRAS-mutant tumors.
- Kenneth Westover
The druggability of SH2 domains unmasked
Developing inhibitors for SH2 domains is challenging due to their shallow pockets and highly charged ligands. Structure-guided drug design has enabled the discovery of a cell-permeable covalent inhibitor of the SOCS2 SH2 domain, a key regulator of cytokine signaling pathways.
- Oliver Hantschel
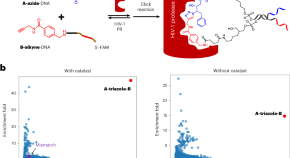
A protein-templated selection approach for the identification of full ligands from DNA-encoded libraries
A protein-templated selection approach has been developed for the discovery of full ligands from dual-pharmacophore DNA-encoded libraries by incorporating fragment linking into the selection process. The performance of this method was demonstrated with selections against protein–protein interaction and protein–DNA interaction targets, through which potent and selective inhibitors were identified.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal
- Presents the full spectrum of new drug research, including synthesis methods, rational drug design and pharmacological, toxicological, modelling, docking and biochemical studies.
- Describes the properties and applications of new medicinal products, drug delivery, targeting, and multifunctional nanosystems.
- Discusses proteomics metabolonomics, and pharmacogenomics of new pharmaceutical agents, along with nanobiotechnology of SiRNA, microRNAs, antibodies, and nanoparticles.
- Applies new physicochemical methods to identification, quantitative determination, uncover molecular details of condensed media and control of solid particle surface chemistry.
- Reviews international literature to report on recent developments in the field.
- Nikolai Shimanovskii

Latest issue
Volume 57, Issue 12
Latest articles
Effect of formulation parameters and physiological environment on amlodipine release kinetics encapsulated in biodegradable polymers and optimized by design methodology.
- Naima Ifourah
- Sandrine Cammas-Marion
- Hayet Belkacemi

Phytochemical Profiling and In Vitro Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, Cytotoxicity Effects of Some Glycyrrhiza Species from Turkey
- Faruk Karahan
- Musa Türkmen
- Sevgi Gezici

Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 7-Azaindole Analogues as Novel Antiproliferative Agent and Tyrosine Protein Kinase SRC Inhibitors
- Neha Sharma
- Monika Sachdeva
Alternative Synthesis of Cobimetinib
- Mikayel L. Movsisyan
- Mariam H. Gharibyan
- Frank Porstmann
Sodium Selenite Through Targeting NRF2/STAT3 Pathway Attenuates Testicular Damage in Irradiated Rats
- Rania A. Gawish
- Hanan A. Fahmy
- Ahmed S. Nada
Journal updates
Read highlighted articles from pharmaceutical chemistry journald articles.
Check out most welcome articles from 2020-2022
Journal information
- Biological Abstracts
- Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS)
- Google Scholar
- Japanese Science and Technology Agency (JST)
- OCLC WorldCat Discovery Service
- Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE)
- TD Net Discovery Service
- UGC-CARE List (India)
Rights and permissions
Editorial policies
© The Editorial Board of the Khimico-Farmatsevticheskii Zhurnal
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Elsevier - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Research Designs and Methodologies Related to Pharmacy Practice
The need for evidence to inform policy and practice in pharmacy is becoming increasingly important. In parallel, clinical pharmacy and practice research is evolving. Research evidence should be used to identify new areas for improved health service delivery and rigorously evaluate new services in pharmacy. The generation of such evidence through practice-based research should be predicated on appropriate use of robust and rigorous methodologies. In addition to the quantitative and qualitative approaches used in pharmacy practice research, mixed methods and other novel approaches are increasingly being applied in pharmacy practice research. Approaches such as discrete choice experiments, Delphi techniques, and simulated client technique are now commonly used in pharmacy practice research. Therefore, pharmacy practice researchers need to be competent in the selection, application, and interpretation of these methodological and analytical approaches. This chapter focuses on introducing traditional and novel study designs and methodologies that are particularly pertinent to contemporary clinical pharmacy and practice research. This chapter will introduce the fundamentals and structures of these methodologies, but more details regarding the different approaches may be found within the Encyclopedia.
Learning Objectives
- • Discuss the value of pharmacy practice research to evidence-based practice and policy.
- • Describe the classifications and types of study designs commonly used in pharmacy practice research.
- • Discuss the concepts and structure of common study designs used in pharmacy practice research including experimental, quasi-experimental, observational, qualitative, and mixed method designs.
- • Discuss the important considerations for conducting pharmacy practice research in terms of study design, data collection, data analyses, and ethical considerations.
Introduction to Research Methodologies Used in Pharmacy Practice
The mission of pharmacy profession and the role of pharmacists in healthcare have evolved toward patient-centered care in the last few decades. Pharmacists with their expertise in drug therapy and accessibility to the public have unprecedented opportunities to assume increasing responsibility for direct patient care ( Bond, 2006 ). New cognitive pharmaceutical services and new roles for pharmacists continue to emerge.
In the era of evidence-based practice and health services, it is not just adequate to propose those new pharmacy services or new roles without evidence of their benefit ( Awaisu and Alsalimy, 2015 , Bond, 2006 ). New pharmacy services and new roles must be proven to be feasible, acceptable, cost-effective, and increase health outcomes. Pharmacy practice research provides such evidence and can confirm the value of a new service, inform policy, and result in practice changes ( Bond, 2006 , Chen and Hughes, 2016 ). Research evidence should be used to identify new areas for improved health service delivery and rigorously evaluate new services. The research used to generate such evidence should be grounded in robust and rigorous methodologies ( Chen and Hughes, 2016 ). Traditionally, common quantitative and qualitative methods such as randomized controlled trials, cohort study, case control study, questionnaire-based surveys, and phenomenology using qualitative interviews have been used in pharmacy. However, in recent years, novel and more complex methods are being developed and utilized. Pharmacy practice researchers need to know how these old and new methodological approaches should be selected, applied, and interpreted in addressing research problems.
Various study designs, including, but not limited to experimental, quasi-experimental, observational, qualitative, and mixed method designs, have been used in pharmacy practice research. Furthermore, different classification systems (e.g., quantitative vs. qualitative, experimental vs. observational, descriptive vs. analytical study designs) have been used in the literature. The choice of a study design to answer a research question in pharmacy practice research is driven by several factors, including the type of the research question or the research hypothesis, expertise of the investigator, availability of data, and funding opportunities. Pharmacy practice researchers need to be competent in the selection, design, application, and interpretation of these methodological and analytical approaches. Today, many of the research methods used in pharmacy practice research have been adapted from fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, economics, and other disciplines. This paradigm shift has led to a greater emphasis on the appropriate choice of a specific research design or method to answer a specific research question ( Chen and Hughes, 2016 ). Consequently, pharmacy practice researchers should place an emphasis on the reliability of the methods selected, the correct interpretation of their findings, the testing of a specific hypothesis, and the internal validity of their data, among other considerations. Novice and early career researchers should be familiar and have sound foundation in a variety of methods applied in pharmacy practice research, which will be covered in this chapter and other chapters in this Encyclopedia. We do believe that more experienced researchers should focus on certain methods in order to advance research in our discipline.
Core Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches Used in Pharmacy Practice Research
Traditionally, core quantitative approaches used in pharmacy practice research include nonexperiments, quasi-experimental designs, and true experimental designs such as prospective randomized controlled intervention trials. Nonexperiments also include observational study designs that are often described as pharmacoepidemiologic study designs such as case–control study, cohort study, nested case–control study, and cross-sectional study ( Etminan, 2004 , Etminan and Samii, 2004 ). In recent years, conventional qualitative approaches and their philosophical paradigms are increasingly been used in pharmacy. These include the five qualitative approaches to inquiry: narrative research, phenomenology, grounded theory, ethnography, and case study. These qualitative methods are often difficult for pharmacy practice researchers to comprehend, and researchers tend to describe the methods of data collection such as individual interviews and focus group discussions as qualitative methods of inquiry. These data collection methods are briefly described later in this chapter, among others. Furthermore, there is an increasing importance on the appropriate selection and use of mixed method approach ( Hadi et al., 2013 ; Hadi and Closs, 2016a , Hadi and Closs, 2016b ), which are often designed and applied wrongly. Finally, it is worthwhile to be familiar with novel research methodologies such as discrete choice experiments, Delphi techniques, simulated client technique, and nominal group techniques, which fall between quantitative and qualitative approaches, often with no clear differentiation on where they belong. Although called “novel” in the context of this chapter, these methods are not new in other relevant disciplines, but new and not commonly used in pharmacy practice research.

Research Question and Selection of Study Design
Pharmacy practice researchers begin by conception of a research idea or identifying a research question and defining a hypothesis based on the question. The researcher then selects a study design that will be suitable to answer the research question. The study design should be appropriately selected prior to initiation of any research investigation. Selecting an inappropriate study design may potentially undermine the validity of a study in its entirety. Investigators are encouraged to critically think about the possible study designs to ensure that the research question is adequately addressed and should be able to adequately justify their choice. These study designs have been variously classified and one common classification system is quantitative vs. qualitative study designs. Study designs play a major role in determining the scientific value of research studies. Inappropriate choice of a study design is impossible to correct after completion of the study. Therefore, thorough planning is required to avoid unconvincing results and invalid conclusions. Good understanding of basic study design concepts will aid researchers in conducting robust and rigorous practice-based research. This chapter introduces the structure and the fundamentals of common study designs used in pharmacy practice research and discusses the important considerations for conducting pharmacy practice research in terms of study design, data collection, data analyses, and ethical considerations.
Classification of Research Methodologies Used in Pharmacy Practice
Various classifications for research designs and methods used in pharmacy practice have been used in the literature. The following are some of the approaches for the classification of research designs:
Case example: Investigators were looking for the association between acute myocardial infarction and smoking status, type of tobacco, amount of smoke, etc. ( Teo et al., 2006 ). Another example of a case–control study from published literature is the study investigating the association between the use of phenylpropanolamine and the risk of hemorrhagic stroke ( Kernan et al., 2000 ).
Case example: Investigators were interested to determine the long-term effectiveness of influenza vaccines in elderly people; they recruited cohorts of vaccinated and unvaccinated community-dwelling elderly ( Nichol et al., 2007 ).
Case example: A case report was written by a physician who contracted Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) during an outbreak in Hong Kong ( Wu and Sung, 2003 ). Another example is an ecological study examining diet and sunlight as risks for prostate cancer mortality ( Colli and Colli, 2006 ). Chim et al. conducted a large population-based survey in Australia to determine what community members think about the factors that do and should influence government spending on prescribed medicines ( Chim et al., 2017 ).
Case example: A group of investigators carried out a study to establish an association between the use of traditional eye medicines (TEM) and corneal ulcers. In this case, both case–control and cohort study designs are applicable. In an example of a case control study, Archibugi et al. aimed to investigate the association between aspirin and statin exclusive and combined and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma occurrence ( Archibugi et al., 2017 ). Another example of a cohort study is a study carried out by Wei et al. in which they investigated whether or not acid-suppression medicines increased the risk of bacterial gastroenteritis ( Wei et al., 2017 ).
Case examples: Investigators conducted a study about the newer versus older antihypertensive agents in African hypertensive patients (NOAAH) trial (nct01030458) to compare the efficacy of single-pill combinations of newer versus older antihypertensive agents (i.e., a single-pill combination of newer drugs, not involving a diuretic, with a combination of older drugs including a diuretic) ( Odili et al., 2012 ). In a crossover design, a group of investigators evaluated the effect of spironolactone on nonresolving central serous chorioretinopathy ( Bousquet et al., 2015 ).
Case examples: Prashanth et al. aimed to understand if (and how) a package of interventions targeting primary health centers and community participation platforms affect utilization and access to generic medicines for people with noncommunicable diseases using quasi-experimental design approach ( Prashanth et al., 2016 ).
- c. Observational design—It involves only observation of natural phenomena and does not involve investigator intervention. Typically, this study design investigates associations and not causation. Examples include cohort study and case–control study. These studies can explore an association between a pharmacologic agent and a disease of interest. Case examples: Please see previous examples of these.
Case examples: Please see experimental studies, and case–control and cohort study designs.
Case examples: Investigators in Canada explored the lived experiences of youth who are prescribed antipsychotics by conducting interpretative phenomenology study ( Murphy et al., 2015 ).
Case examples: Shiyanbola et al. combined focus group discussion with a survey tool to investigate patients' perceived value and use of quality measures in evaluating and choosing community pharmacies ( Shiyanbola and Mort, 2015 ).
Below is a brief description of traditional and novel pharmacoepidemiologic study designs. Several examples of pharmacoepidemiologic study designs are provided above. Some descriptive studies including case reports, case series, and ecological studies will not be described in this chapter.
- a. Case–control studies—In this design, patients (those who develop the disease or outcome of interest) are identified and control patients (those who do not develop the disease or outcome of interest) are sampled at random from the original cohort that gives rise to the cases ( Etminan and Samii, 2004 , Newman et al., 2013 ). The distribution of exposure to certain risk factors between the cases and the controls is then explored, and an odds ratio (OR) is calculated.
- b. Cohort studies—This can be described as a study in which a group of exposed subjects and a group of unexposed subjects are followed over time and the incidence of the disease or outcome of interest in the exposed group is compared with that in the unexposed group ( Etminan and Samii, 2004 , Hulley et al., 2013 ).
- c. Case-crossover studies—The case-crossover may be considered comparable to a crossover randomized controlled trial in which the patients act as their own control ( Etminan and Samii, 2004 ). Pattern of exposure among the cases is compared between event time and control time. The between-patient confounding that occurs in a classic case-control study is circumvented in this design. Tubiana et al. evaluated the role of antibiotic prophylaxis and assessed the relation between invasive dental procedures and oral streptococcal infective endocarditis, using a nationwide population-based cohort and a case-crossover study design ( Tubiana et al., 2017 ).
- d. Case–time control studies—This design is an extension of the case-crossover design, but includes a control group ( Etminan and Samii, 2004 ). A group of researchers assessed medication-related hospitalization. They used the case–time control study design to investigate the associations between 12 high risk medication categories (e.g., antidiabetic agents, diuretics, benzodiazepine hypnotics) and unplanned hospitalizations ( Lin et al., 2017 ).
- e. Nested case–control studies—In this design, a cohort of individuals is followed during certain time periods until a certain outcome is reached and the analysis is conducted as a case–control study in which cases are matched to only a sample of control subjects ( Etminan, 2004 ). de Jong et al. examined the association between interferon-β (IFN-β) and potential adverse events using population-based health administrative data in Canada ( De Jong et al., 2017 ).
- f. Cross-sectional studies—In this type of study, the investigator measures the outcome of interest and the exposures among the study participants at the same time ( Hulley et al., 2013 , Setia, 2016b ). It provides a snapshot of a situation for a particular period.
Quantitative Research Designs in Pharmacy Practice
A wide range of quantitative methods are commonly applied in pharmacy practice research. These methods are widely used in published pharmacy practice literature to explore appropriateness of medicines use, appropriateness and quality of prescribing, and medication safety, through analyzing existing datasets, direct observation, or self-report ( Green and Norris, 2015 ). Pharmacy practice research questions also seek to determine the knowledge, behaviors, attitudes, and practices of pharmacists, other healthcare providers, patients, policy-makers, regulators, and the general public. Quantitative methods are also used in evaluating the effect of new pharmacy services and interventions to improve medicines use. These practice research projects provide valuable insights about how medicines are used, and how to maximize their benefits and minimize their harmful effects. In the context of this chapter, quantitative study designs will be broadly classified into three: (1) observational, (2) experimental and quasi experimental, and (3) other designs.
Observational Study Designs
Pharmacoepidemiology is a “relatively new science that explores drug efficacy or toxicity using large observational study designs” ( Etminan, 2004 , Etminan and Samii, 2004 ). These study designs explore drug use studies that usually cannot be answered using randomized controlled trials or other experimental designs. In several instances, experimental study designs may not be suitable or feasible; in such circumstances, observational study designs are applied ( Cummings et al., 2013 ). As the name implies, observational studies involve merely observing the subjects in a noncontrolled setting, without investigator intervention or manipulating other aspects of the study. Therefore, observational studies are nonexperimental. The observation of the variables of interest can be prospective, retrospective, or current depending on the type of the observational study.
In pharmacoepidemiology and other areas of pharmacy practice, researchers are often interested in measuring the relationships between exposure to a drug and its efficacy, toxicity, or other outcomes of interest using observational study designs. It is worthwhile to note that observational study designs investigate association, but, in most cases, not causation. Here, we provide descriptions of some commonly used study designs in pharmacoepidemiology and pharmacy practice research in general.
Case–Control Studies
Case–control study design is used to determine association between risk factors or exposures and outcomes. It is a useful design to study exposures in rare diseases or diseases that take long time to develop ( Newman et al., 2013 ). It investigates exposures in individuals with and those without the outcome of interest. Nevertheless, case–control studies can help to identify harmful or beneficial exposures. Furthermore, the outcome of interest can be undesirable (e.g., mortality) or desirable (e.g., microbiological cure). As the name suggests, in a case–control study design, there are two groups of subjects: (1) cases (individuals with the outcome of interest) and (2) controls (individuals without the outcome of interest) ( Newman et al., 2013 ). Cases are randomly selected based on prespecified eligibility criteria from a population of interest. Appropriate representative controls for the cases selected are then identified. The researchers then retrospectively investigate possible exposures to the risk factor. Fig. 1 represents a schematic diagram of a case–control study.

Case–control study design.
Case–control studies are relatively inexpensive, less time-consuming to conduct, allow investigation of several possible exposures or associations, and are suitable for rare diseases. Selection of the control group is a critical component of case–control studies. Case–control studies have several drawbacks: confounding must be controlled, subject to recall, observation, and selection biases.
OR is the measure of association used for the analysis of case–control studies. This is defined as the odds of exposure to a factor in those with a condition or disease compared with those who do not have the condition or disease.
Cohort Studies
Similar to case–control studies, cohort studies determine an association between exposures/factors and development of an outcome of interest. As previously described, a cohort study is a study in which a group of exposed subjects and a group of unexposed subjects are followed over time to measure and compare the rate of a disease or an outcome of interest in both groups ( Etminan and Samii, 2004 , Hulley et al., 2013 ). A cohort study can be prospective (most common) or retrospective. While a case–control study begins with patients with and those without the outcome of interest (e.g., diseased and nondiseased patients), a cohort study begins with exposed and unexposed patients (e.g., patients with and those without certain risk factor) ( Hulley et al., 2013 , Setia, 2016a ). In a cohort study, both the exposed and the unexposed subjects are members of a larger cohort in which subjects may enter and exit the cohort at different periods in time ( Etminan and Samii, 2004 , Hulley et al., 2013 ).
Typically, a cohort study should have a defined time zero, which is defined as the time of entry into the cohort ( Etminan and Samii, 2004 ). The cohort (a group of exposed and unexposed subjects, who are free of the outcome at time zero) is followed for a certain period until the outcome of interest occurs. In addition, information or data related to all potential confounders or covariates should also be collected as failure to account for these can bias the results and over- or underestimates the risk estimate. There are two types of cohort studies: retrospective cohort and prospective cohort studies.
Retrospective cohort study, also known as historical cohort study, begins and ends in the present, while looking backward to collect information about exposure that occurred in the past ( Fig. 2 ). Historical cohort studies are relatively less time-consuming and less expensive than prospective cohort studies ( Etminan and Samii, 2004 , Hulley et al., 2013 , Setia, 2016a ). In addition, there is no loss to follow-up and researchers can investigate issues not amenable to intervention study designs. However, these studies are only as good as the data available, the investigator has limited control of confounding variables, and it is prone to recall bias.

Retrospective (historical) cohort study design.
On the other hand, prospective cohort study, also known as longitudinal cohort study, begins in the present and progresses forward, collecting data from enrolled subjects whose outcomes fall in the future ( Etminan and Samii, 2004 , Hulley et al., 2013 , Setia, 2016a ) ( Fig. 3 ). Prospective cohort studies are easier to plan for data collection, have low recall bias, and the researcher has a better control of confounding factors. On the other hand, it is difficult to study rare conditions; they are more prone to selection bias, more time-consuming, expensive, and loss of subjects to follow-up is common.

Prospective (longitudinal) cohort study design.
Relative risk (RR) is the measure of association used for the analysis of a cohort study. This is defined as the risk of an event or development of an event relative to exposure (i.e., the risk of subjects developing a condition when exposed to a risk factor compared with subjects who have not been exposed to the risk factor).
Case-Crossover Studies
This is a relatively new design in the field of epidemiology in which the patients act as their own controls ( Maclure, 1991 ). In this design, there is a case and a control element both of which come from the same subject. In other words, each case serves as its own control. It can be considered equivalent to a crossover RCT with a washout period ( Etminan and Samii, 2004 ). Pattern of exposure to the risk factor is compared between the event time and the control time ( Etminan and Samii, 2004 ). Case-crossover study design is useful to investigate triggers within an individual. For instance, it is applicable when studying a transient exposure or risk factor. However, determination of the period of the control and case components is a crucial and challenging aspect of a case-crossover study design. Since the patients serve as their own controls, the interindividual variability that is inherent in classic case–control studies is eliminated. This is important in studies involving progressive disease states in which disease severity may differ between patients such as multiple sclerosis. OR is estimated using techniques such as Mantel–Haenszel statistics and logistic regression.
Cross-Sectional Studies
Cross-sectional studies also known as prevalence studies identify the prevalence or characteristics of a condition in a group of individuals. This design provides a snapshot of the prevalence or the characteristics of the study subjects in a single time point. The study investigator measures the outcomes and the exposures in the study subjects simultaneously ( Etminan and Samii, 2004 , Hulley et al., 2013 , Setia, 2016b ). Hence, cross-sectional studies do not follow up patients to observe outcomes or exposures of interest. Data are often collected through surveys. Cross-sectional design cannot provide cause and effect relationships between certain exposures and outcomes of interest.
Experimental and Quasi-Experimental Study Designs
In a typical experimental study design, the investigator assigns subjects to the intervention and control/comparison groups in an effort to determine the effects of the intervention ( Cummings et al., 2013 ). Since the investigator has the opportunity to control various aspects of the experiment, this allows the researcher to determine the causal link between exposure to the intervention and outcome of interest. The researcher either randomly or conveniently assigns the subjects to an experimental group and a control group. When the investigator performs randomization, the study is considered a true experiment (see Fig. 4 ). On the other hand, if subjects are assigned into groups without randomization, the study is considered a quasi-experiment (refer to Fig. 5 ). As with experimental designs, quasi-experimental designs also attempt to demonstrate a causal link between the intervention and the outcome of interest. Due to the challenges of conducting a true experimental design, the quasi-experimental study designs have been consistently used in pharmacist intervention research.

True experimental study design.

Quasi experimental study design.
RCTs are considered the gold standard of experimental study designs in pharmacy practice and evidence-based research ( Cummings et al., 2013 ). The investigator randomly assigns a representative sample of the study population into an experimental group and a control group ( Fig. 4 ). Randomization in RCT is to minimize confounding and selection bias; it enables attainment of similar experimental and control groups, thereby isolating the effect of the intervention. The experimental group receives the treatment or intervention (e.g., a new drug or pharmaceutical care for treatment of a certain disease), while the control group receives a placebo treatment, no treatment, or usual care treatment depending on the objective of the study ( Cummings et al., 2013 ). These groups are then followed prospectively over time to observe the outcomes of interest that are hypothesized to be affected by the treatment or intervention. The result of the study is considered to have high internal validity if significant changes on the outcome variable occur in the experimental group, but not the control group. The investigator can infer that the treatment or intervention is the most probable cause of the changes observed in the intervention group. The unit of randomization in RCTs is usually the patient, but can sometimes be clusters to circumvent the drawbacks of contamination.
RCTs are very challenging to undertake and pharmacy practice researchers should ensure design of robust experiments, while considering all essential elements and adhering to best practices. For instance, to determine the impact of a cognitive pharmaceutical service, the selection of a representative sample of the population is a prime consideration in an RCT. Moreover, RCTs are expensive, labor-intensive, and highly prone to attrition bias or loss to follow-up.
In pharmacy practice research, it is often difficult to comply with the stringent requirements of true experimental designs such as RCTs, due to logistic reasons and/or ethical considerations ( Grady et al., 2013 , Krass, 2016 ). Whenever true experimental models are not feasible to be applied in pharmacy practice research, the researcher should endeavor to use a more robust quasi-experimental design. For instance, when randomization is not feasible, the researcher can choose from a range of quasi-experimental designs that are non-randomized and often noncontrolled ( Grady et al., 2013 , Krass, 2016 ). Quasi-experimental studies used in pharmacy literature may be classified into five major categories: (1) quasi-experimental design without control groups (i.e., one group pre–posttest design); (2) quasi-experimental design that use control groups with no pretest; (3) quasi-experimental design that use control groups and pretests (i.e., nonequivalent control group design with dependent pretests and posttests) (see Fig. 5 ); (4) interrupted time series and; (5) stepped wedge designs ( Brown and Lilford, 2006 , Grady et al., 2013 , Harris et al., 2006 ).
The one group pretest posttest design and the nonequivalent control group design ( Fig. 5 ) are the most commonly applied quasi-experimental designs in practice-based research literature. These designs have been commonly used to evaluate the effect of pharmacist interventions in medications management in general and specific disease states management. The lack of randomization and/or the lack of control group is a major weakness and a threat to internal validity in quasi-experimental designs ( Grady et al., 2013 ). The observed changes could be due to some effects other than the treatment.
Other Quantitative Study Designs
In addition to the common observational, experimental, and quasi-experimental designs described above, there are other designs that are used in pharmacy. These research methods include, but are not limited to, simulated client technique, discrete choice experiments, and Delphi techniques. These methods, which are considered relatively new to pharmacy, are now commonly used in pharmacy practice research. In this chapter, we briefly describe these methods and their application in pharmacy. However, a more detailed description of their components and the nitty gritty of their application in pharmacy practice are available elsewhere within this textbook.
Simulated Client Method
The use of simulated client or simulated patient (mystery shopper) method to assess practices or behaviors in pharmacy practice has received much attention in recent times ( Watson et al., 2004 , Watson et al., 2006 ). “A simulated patient is an individual who is trained to visit a pharmacy (or drug store) to enact a scenario that tests a specific behavior of the pharmacist or pharmacy staff” ( Watson et al., 2006 ). A review by Watson et al. demonstrated the versatility and applicability of this method to pharmacy practice research in both developing and developed countries ( Watson et al., 2006 ). The investigators also identified some important characteristics that should be taken into consideration in designing studies that use this technique.
This method can be used to assess wide range of cognitive pharmacy services including counseling and advice provision, treatment of minor ailments, provision of nonprescription medicines, and public health pharmacy, among other things. This method can be a robust and rigorous method of assessing pharmacy practice if used appropriately ( Watson et al., 2006 , Xu et al., 2012 ). More recent developments have documented that the simulated patient methods have been used to provide formative feedback in addition to assessing practice behavior of pharmacists and their staff ( Xu et al., 2012 ).
In a case example, a group of investigators evaluated Qatari pharmacists' prescribing, labeling, dispensing, and counseling practices in response to acute community-acquired gastroenteritis ( Ibrahim et al., 2016 ). In another example, the investigators documented the state of insomnia management at community pharmacies in Pakistan ( Hussain et al., 2013 ).
Discrete Choice Experiments
Evidence in healthcare suggests that understanding consumers' preferences can help policy-makers to design services to match their views and preferences ( Ryan, 2004 ). Traditionally, studies to understand patients' and consumers' preferences for pharmaceutical services used opinion or satisfaction survey instruments. Nevertheless, such satisfaction surveys lack the ability to identify the drivers of satisfaction or the relative importance of the different characteristics of the service ( Vass et al., 2016 ). Discrete choice experiments are a novel survey-based method in pharmacy that are predicated on economic theories that allow systematic quantification of preferences to help identify which attributes of a good or service consumers like, the relative value of each attribute, and the balance between the different attributes ( Naik Panvelkar et al., 2010 , Ryan, 2004 , Vass et al., 2016 ). In-depth description of this method and its essential elements are described in another chapter in the Encyclopedia.
Qualitative Research Designs in Pharmacy Practice
Qualitative research methodology is applied to investigate a problem that has unmeasurable variables, to get a comprehensive understanding of the topic, through discussing it with the involved individuals, and to recognize the natural context in which the investigated issue takes place ( Creswell, 2013 ). The use of qualitative research methodology is becoming increasingly common across diverse health-related disciplines, including pharmacy practice. This is because of its ability to describe social processes and behaviors associated with patients or healthcare professionals, which strengthen the research impact ( McLaughlin et al., 2016 ). Therefore, pharmacy researchers and practitioners need to be better oriented to qualitative research methods ( Behar-Horenstein et al., 2018 ).
In the following section, interpretative frameworks and philosophical orientations, methodologies, data collection and analysis methods, approaches to ensure rigor, and ethical considerations in qualitative research are briefly discussed ( Cohen et al., 2013 , Creswell, 2013 ).
Interpretative Framework and Philosophical Assumptions of Qualitative Research
Interpretative frameworks.
Interpretative frameworks are the conceptual structures for comprehension, which form researcher's reasoning and views of truth and knowledge ( Babbie, 2015 ). Different scholars have categorized qualitative research paradigms or interpretative frameworks differently. The following are examples of interpretative framework categories that are used in health science research based on the categorization of Creswell (2013) : (1) social constructivism (interpretivism) framework; (2) post-positivism framework; (3) transformative, feminist, critical frameworks and disabilities theories; (4) postmodern frameworks; (5) pragmatism frameworks.
Philosophical Assumptions
Philosophical assumptions are theories and perspectives about ontology, epistemology, axiology, and methodology, which underpin the interpretative frameworks selected by qualitative researchers ( Cohen et al., 2013 ). As with interpretative framework, there are numerous means to categorize the philosophical assumptions that are folded within interpretative framework. The following are explanations of philosophical assumptions based on the categorization of Creswell (2013) :
- 1. Ontological assumptions, which define the nature of reality
- 2. Epistemological assumptions, which clarify means for knowing reality
- 3. Axiological assumptions, which explain the role and influence of researcher values
- 4. Methodological assumptions, which identify approaches to inquiry
It is important that a qualitative researcher understands how interpretative frameworks (e.g., social constructivism, post-positivism, and pragmatic interpretative frameworks) are differentiated because of their underpinning philosophical assumptions (i.e., ontological, epistemological, axiological, and methodological assumptions).
Approaches to Inquiry (Methodology)
It is important that qualitative researchers understand the differences between the characteristics of the five qualitative approaches to inquiry, in order to select an approach to inquiry and attain methodological congruence ( Creswell, 2013 ). The five approaches to qualitative research inquiry are:
- a. Narrative research: Describes participants' written and spoken stories about their experiences with a phenomenon being investigated, while considering the chronological connection of the phenomenon's series of events ( Anderson and Kirkpatrick, 2016 , Creswell, 2013 , Czarniawska, 2004 ).
- b. Phenomenological research: Describes the essence of participants' common experiences of a phenomenon, so that the description is a general essence rather than an individual experience ( Creswell, 2013 , Giorgi, 1997 , Moustakas, 1994 ).
- c. Grounded theory research: Aims to generate a theory grounded in participants' data that conceptually explain a social phenomenon, which could involve social processes, or actions or interactions ( Creswell, 2013 , Strauss and Corbin, 1990 , Woods et al., 2016 ).
- d. Ethnographic research: Involves describing the shared patterns of values, behaviors, and beliefs of culture-sharing participants ( Creswell, 2013 , Harris, 1968 , Rosenfeld et al., 2017 ).
- e. Case study research: Provides an in-depth examination of a real-life contemporary phenomenon that researchers cannot change over time, to illustrate the significance of another general topic ( Baker, 2011 , Creswell, 2013 , de León-Castañeda et al., 2018 , Mukhalalati, 2016 , Yin, 2014 ).
Data Collection and Analysis Methods in Qualitative Research
Data collection tools in qualitative research can be categorized into the following fundamental categories ( Creswell, 2013 ):
- a. Observation
- b. Documents
- c. Individual semi-structured interviews
- d. Focus groups (FGs)
- e. Audio-visual materials
- f. Emails chat rooms, weblogs, social media, and instant messaging.
- a. Topic guides: Topic guides guide the discussions in focus groups and individual interviews, and contain open-ended questions and probes, to enable the researcher to understand the complete picture, based on participant views and experiences. They are developed based on the literature review, aim and objectives, research questions, and propositions ( Kleiber, 2004 ).
- b. Audio recording of FGs and interviews: Audio recording of discussions that take place in interviews and FGs is essential for managing and analyzing data, and for increasing the accuracy of data collection and analysis, and ultimately enhancing the dependability and credibility of the research ( Rosenthal, 2016 , Tuckett, 2005 ).
- c. Transcription of FGs and interviews recording: Verbatim transcription refers to the word-for-word conversion of oral words from an audio-recorded format into a scripted text format. Transcribing data is considered as the first data reduction step because it generates texts that can be examined and rechecked ( Miles et al., 2014 , Grossoehme, 2014 ).
Data analysis comprises several fundamental steps, including reading the transcribed text, arranging data, coding data deductively based on prefigured themes or inductively to produce emergent themes, and then summarizing the codes into themes, and finally presenting the analyzed data as results ( Cohen et al., 2013 , Crabtree and Miller, 1999 , Pope et al., 2000 ).
The most commonly used data analysis methods in health science research are:
Thematic analysis is characterized by identifying, analyzing, and reporting themes that are available in the data ( Braun and Clarke, 2006 , Castleberry and Nolen, 2018 ).
Content analysis comprises systematic coding followed by quantification of the analyzed data in a logical and unbiased way ( Berelson, 1952 , Vaismoradi et al., 2013 ).
Discourse analysis emphasizes the core format and the structure of texts to examine the assumptions and concealed aspirations behind discourses ( Brown and Yule, 1983 , Gee, 2004 ).
Quality Perspectives in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research validation involves ensuring the rigor of the utilized data collection, management, and analysis methods, by utilizing approaches to ensure the quality. In pharmacy practice research, Hadi and Closs, 2016a , Hadi and Closs, 2016b argued that quality in qualitative research topic has not been discussed widely in the literature, and therefore Hadi and Closs, 2016a , Hadi and Closs, 2016b suggested using several trustworthiness criteria to ensure the rigor of qualitative study. The trustworthiness criteria for ensuring quality in qualitative research ( Lincoln and Guba, 1985 ) are:
This criterion aims to ensure that the results are true and increases the possibility that the conclusions are credible ( Cohen and Crabtree, 2008 ).
This criterion aims to indicate that the research results are repeatable and consistent, in order to support the conclusions of the research ( Cohen and Crabtree, 2008 ).
This criterion aims to confirm the neutrality in interpretation by ensuring that the perspectives of participants, not the bias of researchers, influence the results ( Krefting, 1991 ).
This criterion involves identifying the contexts to which the study results can be generalized, and indicating if the study conclusions can be applied in similar setting ( Yin, 2014 ).
Reflexivity implies revealing and evaluating the effect and biases that researchers can possibly bring to research process, by explaining the researcher's opinion, feelings, and experience with the phenomenon in question, and explaining the influence of this experience on research methods, findings, and write-ups ( Creswell, 2013 , Krefting, 1991 , Lincoln and Guba, 1985 ).
Ethical Considerations
Obtaining an ethical approval from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) is required before conducting the qualitative research ( Creswell, 2013 ). The key ethical issues that need to be considered are:
Informed consent refers to the decision taken by a competent individual to voluntarily participate in a research, after adequately understanding the research. Participant information leaflet is usually distributed to participants before they consent to participate in the research to clarify them the voluntary nature of research participation, the aim and objectives of the research, the rights of the respondents and the potential risks and harms, the data collection, management and storage conditions, and the right of participants to withdraw from the research ( Jefford and Moore, 2008 ).
The anonymity is usually ensured by not disclosing names of participants and by utilizing a code system to identify them during data collection, management, analysis, and in the writing up of the research. The confidentiality of participants and data is ensured by using a code system to identify participants, and by storing all data in a locked cabinet and a password-protected computer for a specified period of time ( Creswell, 2013 ).
Power imbalance is caused by the fact that participants have the experience about the investigated phenomenon, and researchers need to obtain information about these experiences. The power imbalance is usually associated with interaction between the researcher and participants during recruitment stage, and during data collection, analysis, interpretation, and validation stages. Hence, researchers should take suitable measures at each stage to decrease the influence of possible power imbalance, and should enhance trust with participants ( Karnieli-Miller et al., 2009 , Yardley, 2000 ).
Mixed Methods in Pharmacy Practice Research
Research studies in pharmacy practice usually utilize single-method research designs. However, often these report numerous limitations and may not adequately answer the research question. Therefore, the combination of more than one research method to answer certain research questions has become increasingly common in pharmacy practice research ( Ryan et al., 2015 ). Mixed methods research design is now a popular and widely used research paradigm in pharmacy practice research fields ( Hadi et al., 2013 , Hadi et al., 2014 ; Hadi and Closs, 2016a , Hadi and Closs, 2016b , Ryan et al., 2015 ). Mixed methods research allows the expansion of the scope of research to offset the weaknesses of using either quantitative or qualitative approach alone ( Creswell et al., 2004 , Hadi et al., 2013 ; Hadi and Closs, 2016a , Hadi and Closs, 2016b , Pluye and Hong, 2014 ). Typically, qualitative and quantitative data are collected concurrently or sequentially in order to increase the validity and the comprehensiveness of the study findings ( Creswell et al., 2004 , Hadi et al., 2013 ; Hadi and Closs, 2016a , Hadi and Closs, 2016b , Pluye and Hong, 2014 , Ryan et al., 2015 ). The mixed method approach provides an expanded understanding of phenomenon under investigation through the comparison between qualitative and quantitative data ( Hadi et al., 2013 ; Hadi and Closs, 2016a , Hadi and Closs, 2016b , Pluye and Hong, 2014 ).
This section provides an overview and application of mixed method research in pharmacy practice. However, considerations in selecting, designing, and analyzing mixed methods research studies as well as the various typologies of mixed methods research are discussed elsewhere. Johnson et al. (2007) proposed the following definition for mixed methods research: “The type of research in which a researcher or team of researchers combines elements of qualitative and quantitative research approaches (e.g., use of qualitative and quantitative viewpoints, data collection, analysis, inference techniques) for the broad purpose of breadth and depth of understanding and corroboration.”
Mixed methods design allows the viewpoints of participants to be reflected, enables methodological flexibility, and promotes multidisciplinary teamwork ( Ryan et al., 2015 ). Furthermore, the approach allows a more holistic understanding of the research question. However, its major limitations include: need for wide range of research expertise across the research team members, highly labor-intensive, and the complexity of data integration.
Scholars believe that it is challenging to provide researchers with a step-by-step guide on how to undertake a mixed methods study and that this is driven by the specific research question ( Ryan et al., 2015 ). Nevertheless, the investigator should precisely determine the type of qualitative and quantitative methods to be employed, the order of data collection to be undertaken, the data collection instruments to be used, and the method of data analysis ( Ryan et al., 2015 ). This approach encompasses a synthesis of findings from both quantitative and qualitative components, which is achieved through integration of the findings from each approach ( Hadi et al., 2013 ; Hadi and Closs, 2016a , Hadi and Closs, 2016b , Pluye and Hong, 2014 ).
Different models or typologies for mixed methods research have been described in the literature. The most common typologies used in pharmacy practice and health services research include: concurrent or convergent parallel design, exploratory sequential design, explanatory sequential design, and the embedded design ( Hadi et al., 2013 , Pluye and Hong, 2014 ). Scholars believe that there are several factors to consider when selecting the typology or model of mixed methods research to use. These factors include: the order of qualitative and quantitative data collection (concurrent vs. sequential); priority of data (i.e., which type of data has priority between quantitative and qualitative data); purpose of integration of the data (e.g., triangulation); and number of data strands ( Hadi et al., 2013 , Pluye and Hong, 2014 ). In mixed methods research, integration of qualitative and quantitative findings is critical, and this research approach does not simply involve the collection of these data ( Ryan et al., 2015 ).
Summary and Take-Home Messages
- • In the era of evidence-based practice, it is not sufficient to propose new pharmacy services or roles without evidence of their benefit.
- • New pharmacy services and new roles must be proven to be feasible, acceptable, beneficial, and cost-effective.
- • Practice-based research provides such evidence and can inform policy, confirm the value of the new service, and change practice.
- • Various study designs, including, but not limited to experimental, quasi-experimental, observational, qualitative, and mixed-methods designs, have been used in pharmacy practice research.
- • Pharmacy practice researchers need to be competent in the selection, design, application, and interpretation of these methodological and analytical approaches.
- • The choice of any study design in pharmacy practice research is driven by the expertise of the investigator, type of research question or hypothesis, data availability, time orientation, ethical issues, and availability of funding.
There is a great demand for innovation and quality in pharmacy practice. These can be achieved partly through robust and well-designed pharmacy practice research. Pharmacy students, practitioners, educators, and policy-makers are exposed to a variety of research designs and methods. We need to have the best evidence (e.g., in policy, regulation, practice) for making decisions about the optimal research design that ensures delivering an ultimate pharmacy practice and a quality patient care.
- Anderson C., Kirkpatrick S. Narrative interviewing. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2016; 38 :631–634. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Archibugi L., Piciucchi M., Stigliano S., Valente R., Zerboni G., Barucca V., …, Capurso G. Exclusive and combined use of statins and aspirin and the risk of pancreatic cancer: a case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2017; 7 :13024. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Awaisu A., Alsalimy N. Pharmacists' involvement in and attitudes toward pharmacy practice research: a systematic review of the literature. Res. Social Adm. Pharm. 2015; 11 :725–748. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Babbie E. Nelson Education; 2015. The Practice of Social Research. [ Google Scholar ]
- Baker G.R. The contribution of case study research to knowledge of how to improve quality of care. BMJ Quality Safety. 2011; 20 :i30–i35. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Behar-Horenstein L.S., Beck D.E., Su Y. Perceptions of pharmacy faculty need for development in educational research. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2018; 10 :34–40. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Berelson, B., 1952. Content analysis in communication research.
- Bond C. The need for pharmacy practice research. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2006; 14 :1–2. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bousquet E., Beydoun T., Rothschild P.-R., Bergin C., Zhao M., Batista R., …, Behar-Cohen F. Spironolactone for nonresolving central serous chorioretinopathy: a Randomized Controlled Crossover Study. Retina (Philadelphia, PA) 2015; 35 (12):2505–2515. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Braun V., Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006; 3 :77–101. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown C.A., Lilford R.J. The stepped wedge trial design: a systematic review. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2006; 6 :54. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown G., Yule G. Cambridge University Press; 1983. Discourse Analysis. [ Google Scholar ]
- Castleberry A., Nolen A. Thematic analysis of qualitative research data: is it as easy as it sounds? Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2018; 10 (6):807–815. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen T.F., Hughes C.M. Why have a special issue on methods used in clinical pharmacy practice research? Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2016; 38 :599–600. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chim L., Salkeld G., Kelly P., Lipworth W., Hughes D.A., Stockler M.R. Societal perspective on access to publicly subsidised medicines: a cross sectional survey of 3080 adults in Australia. PLoS ONE. 2017; 12 (3):e0172971. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen D.J., Crabtree B.F. Evaluative criteria for qualitative research in health care: controversies and recommendations. Ann. Fam. Med. 2008; 6 :331–339. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen L., Manion L., Morrison K. Routledge; 2013. Research Methods in Education. [ Google Scholar ]
- Colli J.L., Colli A. International comparison of prostate cancer mortality rates with dietary practices and sunlight levels. Urologic Oncol. 2006; 24 :184–194. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Crabtree B.F., Miller W.L. Sage Publications; 1999. Doing Qualitative Research. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell J.W. Sage; 2013. Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing Among Five Approaches. [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell J.W., Fetters M.D., Ivankova N.V. Designing a mixed methods study in primary care. Ann. Fam. Med. 2004; 2 :7–12. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cummings S.R., Grady D., Hulley S.B. Designing a randomized blinded trial. In: Hulley S.B., Cummings S.R., Browner W.S., Grady D., Newman T.B., editors. Designing Clinical Research. fourth ed. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Czarniawska B. Sage; 2004. Narratives in Social Science Research. [ Google Scholar ]
- De Jong H.J.I., Kingwell E., Shirani A., Cohen Tervaert J.W., Hupperts R., Zhao Y., …, Tremlett H. Evaluating the safety of β-interferons in MS: a series of nested case-control studies. Neurology. 2017; 88 (24):2310–2320. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- de León-Castañeda C.D., Gutiérrez-Godínez J., Colado-Velázquez J., III, Toledano-Jaimes C. Healthcare professionals' perceptions related to the provision of clinical pharmacy services in the public health sector of Mexico: a case study. Res. Soc. Administr. Pharm. 2018; 15 (3):321–329. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Etminan M., Samii A. Pharmacoepidemiology I: a review of pharmacoepidemiologic study designs. Pharmacotherapy. 2004; 24 :964–969. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Etminan M. Pharmacoepidemiology II: the nested case-control study—a novel approach in pharmacoepidemiologic research. Pharmacotherapy. 2004; 24 :1105–1109. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gee J.P. Routledge; 2004. An Introduction to Discourse Analysis: Theory and Method. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. The theory, practice, and evaluation of the phenomenological method as a qualitative research procedure. J. Phenomenol. Psychol. 1997; 28 :235–260. [ Google Scholar ]
- Grady D., Cummings S.R., Hulley S.B. Alternative trial designs and implementation issues. In: Hulley S.B., Cummings S.R., Browner W.S., Grady D., Newman T.B., editors. Designing Clinical Research. fourth ed. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Green J.A., Norris P. Quantitative methods in pharmacy practice research. In: Babar Z.-U.-D., editor. Pharmacy Practice Research Methods. first ed. Springer International Publishing; Switzerland: 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- Grossoehme D.H. Overview of qualitative research. J. Health Care Chaplaincy. 2014; 20 :109–122. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hadi M.A., Closs S.J. Applications of mixed-methods methodology in clinical pharmacy research. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2016; 38 :635–640. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hadi M.A., Closs S.J. Ensuring rigour and trustworthiness of qualitative research in clinical pharmacy. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2016; 38 :641–646. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hadi M.A., Alldred D.P., Closs S.J., Briggs M. Mixed-methods research in pharmacy practice: basics and beyond (part 1) Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2013; 21 :341–345. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hadi M.A., Alldred D.P., Closs S.J., Briggs M. Mixed-methods research in pharmacy practice: recommendations for quality reporting (part 2) Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2014; 22 :96–100. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harris A.D., Mcgregor J.C., Perencevich E.N., Furuno J.P., Zhu J., Peterson D.E., Finkelstein J. The use and interpretation of quasi-experimental studies in medical informatics. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2006; 13 :16–23. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harris M. Routledge and Kegan Paul; London: 1968. Emics, Etics, and the New Ethnography. The Rise of Anthropological Theory: a History of Theories of Culture. pp. 568–604. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hulley S.B., Cummings S.R., Newman T.B. Designing cross-sectional and cohort studies. In: Hulley S.B., Cummings S.R., Browner W.S., Grady D., Newman T.B., editors. Designing Clinical Research. fourth ed. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hussain A., Ibrahim M.I., Malik M. Assessment of disease management of insomnia at community pharmacies through simulated visits in Pakistan. Pharm. Pract. 2013; 11 (4):179–184. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ibrahim M.I., Palaian S., Al-Sulaiti F., El-Shami S. Evaluating community pharmacy practice in Qatar using simulated patient method: acute gastroenteritis management. Pharm. Pract. 2016; 14 (4):800. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jefford M., Moore R. Improvement of informed consent and the quality of consent documents. Lancet Oncol. 2008; 9 :485–493. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson R.B., Onwuegbuzie A.J., Turner L.A. Toward a definition of mixed methods research. J. Mixed Methods Res. 2007; 1 :112–133. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaae S., Traulsen J.M. Qualitative methods in pharmacy practice research. In: Babar Z.-U.-D., editor. Pharmacy Practice Research Methods. first ed. Springer International Publishing; Switzerland: 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- Karnieli-Miller O., Strier R., Pessach L. Power relations in qualitative research. Qual. Health Res. 2009; 19 :279–289. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kernan W.N., Viscoli C.M., Brass L.M., Broderick J.P., Brott T., Feldmann E., Morgenstern L.B., Wilterdink J.L., Horwitz R.I. Phenylpropanolamine and the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000; 343 :1826–1832. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kleiber P.B. Focus groups: More than a method of qualitative inquiry. Foundations Res. 2004:87–102. [ Google Scholar ]
- Koshman S.L., Blais J. What is pharmacy research? Can. J. Hosp. Pharm. 2011; 64 :154–155. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krass I. Quasi experimental designs in pharmacist intervention research. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2016; 38 :647–654. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krefting L. Rigor in qualitative research: the assessment of trustworthiness. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1991; 45 :214–222. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lin C.-W., Wen Y.-W., Chen L.-K., Hsiao F.-Y. Potentially high-risk medication categories and unplanned hospitalizations: a case–time–control study. Sci. Rep. 2017; 7 :41035. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lincoln Y.S., Guba E.G. Sage; 1985. Naturalistic Inquiry. [ Google Scholar ]
- Maclure M. The case-crossover design: a method for studying transient effects on the risk of acute events. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1991; 133 :144–153. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McLaughlin J.E., Bush A.A., Zeeman J.M. Mixed methods: expanding research methodologies in pharmacy education. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2016; 8 :715–721. [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles M.B., Huberman A.M., Saldana J. Sage Publications; CA, USA: 2014. Qualitative Data Analysis: A Method Sourcebook. [ Google Scholar ]
- Moustakas C. Sage; 1994. Phenomenological Research Methods. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mukhalalati, B., 2016. Examining the disconnect between learning theories and educational practices in the PharmD programme at Qatar University: a case study.
- Murphy A.L., Gardner D.M., Kisely S., Cooke C., Kutcher S.P., Hughes J. A qualitative study of antipsychotic medication experiences of youth. J. Can. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry. 2015; 24 :61. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naik Panvelkar P., Armour C., Saini B. Community pharmacy-based asthma service-what do patients prefer? J. Asthma. 2010; 47 :1085–1093. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Newman T.B., Browner W.S., Cummings S.R., Hulley S.B. Designing case-control studies. In: Hulley S.B., Cummings S.R., Browner W.S., Grady D., Newman T.B., editors. Designing Clinical Research. fourth ed. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nichol K.L., Nordin J.D., Nelson D.B., Mullooly J.P., Hak E. Effectiveness of influenza vaccine in the community-dwelling elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007; 357 (14):1373–1381. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Odili A.N., Ezeala-Adikaibe B., Ndiaye M.B., Anisiuba B.C., Kamdem M.M., Ijoma C.K., …, Ulasi I.I. Progress report on the first sub-Saharan Africa trial of newer versus older antihypertensive drugs in native black patients. Trials. 2012; 13 :59. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pluye P., Hong Q.N. Combining the power of stories and the power of numbers: mixed methods research and mixed studies reviews. Annu. Rev. Public Health. 2014; 35 :29–45. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pope C., Ziebland S., Mays N. Qualitative research in health care: analysing qualitative data. Br. Med. J. 2000; 320 :114. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Prashanth N.S., Elias M.A., Pati M.K., Aivalli P., Munegowda C.M., Bhanuprakash S., …, Devadasan N. Improving access to medicines for non-communicable diseases in rural India: a mixed methods study protocol using quasi-experimental design. BMC Health Services Res. 2016; 16 (1):421. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenfeld E., Kinney S., Weiner C., Newall F., Williams A., Cranswick N., Wong I., Borrott N., Manias E. Interdisciplinary medication decision making by pharmacists in pediatric hospital settings: an ethnographic study. Res. Social Adm. Pharm. 2018; 14 :269–278. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosenthal M. Qualitative research methods: why, when, and how to conduct interviews and focus groups in pharmacy research. Curr. Pharm. Teach. Learn. 2016; 8 :509–516. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan C.A., Cadogan C., Hughes C. Mixed methods research in pharmacy practice. In: Babar Z.U.D., editor. Pharmacy Practice Research Methods. first ed. Springer International Publishing; Switzerland: 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan M. Discrete choice experiments in health care. BMJ. 2004; 328 :360–361. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Setia M.S. Methodology series module 1: Cohort studies. Indian J. Dermatol. 2016; 61 :21–25. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Setia M.S. Methodology series module 3: Cross-sectional studies. Indian J. Dermatol. 2016; 61 :261–264. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shiyanbola O.O., Mort J.R. Patients' perceived value of pharmacy quality measures: a mixed-methods study. BMJ Open. 2015; 5 (1):e006086. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Strauss A., Corbin J.M. Sage Publications, Inc.; CA, USA: 1990. Basics of Qualitative Research: Grounded Theory Procedures and Techniques. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tashakkori A., Creswell J.W. Editorial: The new era of mixed methods. J. Mixed Methods Res. 2007; 1 :3–7. [ Google Scholar ]
- Teo K.K., Ounpuu S., Hawken S., Pandey M., Valentin V., Hunt D. Tobacco use and risk of myocardial infarction in 52 countries in the INTERHEART study: a case-control study. Lancet. 2006; 368 (9536):647–658. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tubiana S., Blotière P.-O., Hoen B., Lesclous P., Millot S., Rudant J., …, Duval X. Dental procedures, antibiotic prophylaxis, and endocarditis among people with prosthetic heart valves: nationwide population based cohort and a case-crossover study. BMJ. 2017; 358 :j3776. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tuckett A.G. Part II. Rigour in qualitative research: complexities and solutions: Anthony G Tuckett outlines the strategies and operational techniques he used to attain rigour in a qualitative research study through relying on Guba and Lincoln's trustworthiness criterion. Research strategies such as use of personal journals, audio recording and transcript auditing, and operational techniques including triangulation strategies and peer review, are examined. Nurse Researcher. 2005; 13 :29–42. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vaismoradi M., Turunen H., Bondas T. Content analysis and thematic analysis: implications for conducting a qualitative descriptive study. Nurs. Health Sci. 2013; 15 :398–405. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vass C., Gray E., Payne K. Discrete choice experiments of pharmacy services: a systematic review. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2016; 38 :620–630. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Watson M.C., Skelton J.R., Bond C.M., Croft P., Wiskin C.M., Grimshaw J.M., Mollison J. Simulated patients in the community pharmacy setting – Using simulated patients to measure practice in the community pharmacy setting. Pharm. World Sci. 2004; 26 :32–37. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Watson M., Norris P., Granas A. A systematic review of the use of simulated patients and pharmacy practice research. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2006; 14 :83–93. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wei L., Ratnayake L., Phillips G., Mcguigan C.C., Morant S.V., Flynn R.W., …, Macdonald T.M. Acid-suppression medications and bacterial gastroenteritis: a population-based cohort study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017; 83 (6):1298–1308. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Woods A., Cashin A., Stockhausen L. Communities of practice and the construction of the professional identities of nurse educators: a review of the literature. Nurse Educ. Today. 2016; 37 :164–169. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu E.B., Sung J.J.Y. Haemorrhagic-fever-like changes and normal chest radiograph in a doctor with SARS. Lancet. 2003; 361 (9368):1520–1521. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu T., De Almeida Neto A.C., Moles R.J. A systematic review of simulated-patient methods used in community pharmacy to assess the provision of non-prescription medicines. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2012; 20 :307–319. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yardley L. Dilemmas in qualitative health research. Psychol. Health. 2000; 15 :215–228. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R.K. Sage Publications; 2014. Case Study Research: Design and Methods. [ Google Scholar ]
Further Reading
- Baxter P., Jack S. Qualitative case study methodology: study design and implementation for novice researchers. Qual. Rep. 2008; 13 :544–559. [ Google Scholar ]
- Boyatzis R.E. Sage; 1998. Transforming Qualitative Information: Thematic Analysis and Code Development. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bryman A. Oxford University Press; 2015. Social Research Methods. [ Google Scholar ]
- Easton K.L., Mccomish J.F., Greenberg R. Avoiding common pitfalls in qualitative data collection and transcription. Qual. Health Res. 2000; 10 :703–707. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eisner E.W. Teachers College Press; 2017. The Enlightened Eye: Qualitative Inquiry and the Enhancement of Educational Practice. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gibbs A. Thousand Oaks; 2012. Focus groups and group interviews. Research Methods and Methodologies in Education. pp. 186–192. [ Google Scholar ]
- Grodstein F., Manson J.E., Stampfer M.J. Postmenopausal hormone use and secondary prevention of coronary events in the nurses' health study. a prospective, observational study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001; 135 :1–8. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Halcomb E.J., Davidson P.M. Is verbatim transcription of interview data always necessary? Appl. Nurs. Res. 2006; 19 :38–42. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hanson J.L., Balmer D.F., Giardino A.P. Qualitative research methods for medical educators. Acad. Pediatr. 2011; 11 :375–386. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jonsson P., Jakobsson A., Hensing G., Linde M., Moore C.D., Hedenrud T. Holding on to the indispensable medication—a grounded theory on medication use from the perspective of persons with medication overuse headache. J. Headache Pain. 2013; 14 (1):43. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kruijtbosch M., Göttgens-Jansen W., Floor-Schreudering A., Van Leeuwen E., Bouvy M.L. Moral dilemmas of community pharmacists: a narrative study. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2018; 40 :74–83. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Landier W., Hughes C.B., Calvillo E.R., Anderson N.L.R., Briseño-Toomey D., Dominguez L., Martinez A.M., Hanby C., Bhatia S. A grounded theory of the process of adherence to oral chemotherapy in Hispanic and Caucasian children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Pediatr. Oncol. Nurs. 2011; 28 :203–223. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lecompte M.D., Goetz J.P. Problems of reliability and validity in ethnographic research. Rev. Educ. Res. 1982; 52 :31–60. [ Google Scholar ]
- Maclean L.M., Meyer M., Estable A. Improving accuracy of transcripts in qualitative research. Qual. Health Res. 2004; 14 :113–123. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan D.L. Sage; 1997. Focus Groups as Qualitative Research. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morse J.M. Sage Publications Sage CA; Thousand Oaks, CA: 1998. The Contracted Relationship: Ensuring Protection of Anonymity and Confidentiality. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Myers G. Cambridge University Press; 2004. Matters of Opinion: Talking about Public Issues. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nisbet, J., Watt, J., 1984. Case Study, Chapter 5 in Bell, K., et al. Conducting Small-Scale Investigations in Educational Management.
- Nunkoosing K. The problems with interviews. Qual. Health Res. 2005; 15 :698–706. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pearce R. University of Birmingham; 2014. Learning How to Lead through Engagement with Enquiry Based Learning as a Threshold Process: A Study of How Post-graduate Certificate in Education Healthcare Professional Students Learn to Lead. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ping W.L. Data analysis in health-related qualitative research. Singapore Med. J. 2008; 49 :435–1435. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Polit D.F., Beck C.T. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2013. Essentials of Nursing Research: Appraising Evidence for Nursing Practice. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rivas C., Sohanpal R., Macneill V., Steed L., Edwards E., Antao L., …, Walton R. Determining counselling communication strategies associated with successful quits in the National Health Service community pharmacy Stop Smoking programme in East London: a focused ethnography using recorded consultations. BMJ Open. 2017; 7 (10):e015664. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rubin H.J., Rubin I.S. Sage; 2012. Qualitative Interviewing: The Art of Hearing Data. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryan K., Patel N., Lau W.M., Abu-Elmagd H., Stretch G., Pinney H. Pharmacists in general practice: a qualitative interview case study of stakeholders' experiences in a West London GP federation. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2018; 18 :234. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Santiago-Delefosse M., Gavin A., Bruchez C., Roux P., Stephen S.L. Quality of qualitative research in the health sciences: analysis of the common criteria present in 58 assessment guidelines by expert users. Soc. Sci. Med. 2016; 148 :142–151. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shiyanbola O.O., Brown C.M., Ward E.C. “I did not want to take that medicine”: African-Americans' reasons for diabetes medication nonadherence and perceived solutions for enhancing adherence. Patient Prefer. Adherence. 2018; 12 :409. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shoemaker S.J., Ramalho D.E., Oliveira D. Understanding the meaning of medications for patients: the medication experience. Pharm. World Sci. 2008; 30 (1):86–91. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Silverman D. SAGE Publications Limited; 2013. Doing Qualitative Research: A Practical Handbook. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sim J. Informed consent: ethical implications for physiotherapy. Physiotherapy. 1986; 72 :584–587. [ Google Scholar ]
- Skukauskaite, A., 2012. Transparency in Transcribing: Making Visible Theoretical Bases Impacting Knowledge Construction from Open-Ended Interview Records.
- Sofaer S. Qualitative methods: what are they and why use them? Health Serv. Res. 1999; 34 :1101. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tobin G.A., Begley C.M. Methodological rigour within a qualitative framework. J. Adv. Nurs. 2004; 48 :388–396. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Todd A., Holmes H., Pearson S., Hughes C., Andrew I., Baker L., Husband A. I don't think I'd be frightened if the statins went': a phenomenological qualitative study exploring medicines use in palliative care patients, carers and healthcare professionals. BMC Palliat Care. 2016; 15 :13. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Pharmacology Research Paper Topics

In this page on pharmacology research paper topics , we explore the diverse and dynamic field of pharmacology and provide valuable resources for students who are tasked with writing research papers in this discipline. Pharmacology, as a branch of science, encompasses the study of how drugs interact with biological systems, aiming to understand their mechanisms of action, therapeutic uses, and potential side effects. With the growing importance of pharmacology in healthcare and drug development, it is crucial for students to delve into relevant pharmacology research paper topics that contribute to advancing knowledge and addressing current challenges in the field. Additionally, we highlight iResearchNet’s writing services, offering students the opportunity to order custom pharmacology research papers tailored to their specific needs. Our team of expert writers, equipped with in-depth knowledge of pharmacology and related fields, ensures high-quality, well-researched papers that adhere to the highest academic standards.
In the field of pharmacology, research plays a critical role in advancing our understanding of drugs, their mechanisms of action, and their impact on human health. As students of pharmacology, you may be tasked with writing research papers that explore various aspects of this dynamic discipline. To assist you in your research journey, we have curated a comprehensive list of pharmacology research paper topics that cover a wide range of subfields and emerging areas of interest. Whether you are interested in drug discovery, clinical pharmacology, pharmacogenomics, or drug safety, this list provides a wealth of ideas to inspire and guide your research endeavors.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Drug Discovery and Development
- Role of Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Drug Therapy to Individual Patients
- Drug Repurposing: Exploring New Indications for Existing Drugs
- Pharmacogenomics and Drug Response Prediction
- Nanomedicine: Applications in Drug Delivery and Targeting
- Innovative Approaches for Drug Formulation and Delivery
- Drug Combinations: Synergistic Effects and Therapeutic Opportunities
- Natural Products as Sources of Novel Therapeutic Agents
- Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking in Drug Design
- Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of New Drug Entities
Clinical Pharmacology
- Precision Dosing: Optimizing Drug Therapy for Individual Patients
- Pharmacokinetic Variability in Special Populations (Pediatrics, Geriatrics, Pregnant Women)
- Drug-Drug Interactions: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications
- Adverse Drug Reactions: Identification, Prevention, and Management
- Pharmacovigilance and Drug Safety Monitoring
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring: Rationale and Practical Considerations
- Clinical Trials in Pharmacology: Design, Implementation, and Analysis
- Drug Development and Regulatory Approval Processes
- Pharmacoeconomics: Evaluating the Cost-Effectiveness of Drug Therapy
- Ethical Considerations in Clinical Pharmacology Research
Neuropharmacology and Psychopharmacology
- Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Applications of Antidepressant Drugs
- Neurotransmitter Systems and Their Role in Mental Health Disorders
- Psychotropic Drugs and Their Impact on Cognitive Functioning
- Novel Approaches for Targeting Neurodegenerative Disorders
- Pharmacological Management of Substance Use Disorders
- Pharmacogenetics in Psychiatry: Implications for Individualized Treatment
- Role of Neuroinflammation in Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders
- Neuropharmacology of Sleep and Wakefulness
- Pharmacotherapy for Schizophrenia: Current Trends and Future Directions
- Novel Treatments for Anxiety and Mood Disorders
Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism
- Drug Transporters and Their Role in Drug Disposition
- Pharmacogenetics and Personalized Drug Therapy
- Pharmacokinetic Variability and Its Impact on Drug Response
- Drug Metabolism Pathways and Enzyme Polymorphisms
- Drug-Drug Interactions: Mechanisms and Clinical Significance
- Predictive Modeling in Pharmacokinetics and Dose Optimization
- Pharmacokinetics in Special Populations: Pediatrics and Geriatrics
- Impact of Genetic Variation on Drug Clearance and Toxicity
- Role of Pharmacokinetics in Individualizing Drug Dosage
- Strategies for Improving Oral Bioavailability of Drugs
Pharmacology of Infectious Diseases
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Mechanisms, Epidemiology, and Strategies
- Development of Novel Antiviral Agents: Challenges and Opportunities
- Pharmacotherapy for Bacterial Infections: Current Approaches and Future Directions
- Antifungal Drugs: Mechanisms of Action and Resistance
- Host-Pathogen Interactions and Their Implications for Drug Development
- Pharmacokinetic Considerations in the Treatment of Viral Infections
- Targeting Virulence Factors in Bacterial Pathogens
- Drug Combination Therapy for Multidrug-Resistant Infections
- Pharmacogenomics of Antimicrobial Agents
- New Approaches for Antiparasitic Drug Development
Cardiovascular Pharmacology
- Novel Antiplatelet Agents: Mechanisms and Clinical Applications
- Antihypertensive Therapy: Current Strategies and Future Perspectives
- Pharmacotherapy for Heart Failure: Advancements and Challenges
- Role of Pharmacogenomics in Cardiovascular Drug Therapy
- Therapeutic Potential of Antiarrhythmic Agents
- Pharmacological Management of Dyslipidemia and Atherosclerosis
- Emerging Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension
- Pharmacological Approaches to Preventing Thromboembolic Disorders
- Cardiotoxicity of Chemotherapeutic Agents: Mechanisms and Cardioprotective Strategies
- Targeting Inflammatory Pathways in Cardiovascular Disease
Pharmacology and Aging
- Geriatric Pharmacotherapy: Challenges and Approaches
- Age-Related Changes in Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
- Polypharmacy and Its Impact on Older Adults
- Adverse Drug Reactions in the Elderly: Recognition and Prevention
- Pharmacological Management of Age-Related Neurodegenerative Disorders
- Geriatric Pharmacogenomics: Implications for Personalized Medicine
- Drug-Related Falls and Fractures in the Elderly: Prevention and Intervention
- Medication Adherence in Older Adults: Barriers and Strategies
- Geriatric Pain Management: Balancing Efficacy and Safety
- Optimizing Drug Therapy in Older Adults with Multiple Comorbidities
Pharmacology of Cancer
- Targeted Therapies for Solid Tumors: Recent Advances and Future Directions
- Immunotherapy in Cancer Treatment: Current Approaches and Challenges
- Pharmacogenomics of Chemotherapy: Implications for Personalized Treatment
- Drug Resistance in Cancer: Mechanisms and Strategies for Overcoming Resistance
- Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Anticancer Agents
- Combination Therapies in Oncology: Rationale and Clinical Outcomes
- Oncolytic Viruses: Exploiting Viral Infections for Cancer Treatment
- Cancer Stem Cells: Targeting Tumor Initiation and Progression
- Development of Novel Imaging Agents for Cancer Diagnosis and Monitoring
- Pharmacological Interventions for Cancer-Associated Pain Management
Pharmacology and Immunology
- Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Immunotherapy
- Autoimmune Diseases: Novel Pharmacological Approaches and Therapies
- Immunomodulatory Effects of Drugs: Implications for Therapeutic Interventions
- Role of Pharmacogenomics in Immunomodulatory Drug Therapy
- Immunopharmacology of Allergic Reactions: Mechanisms and Treatment Strategies
- Immunosuppressive Drugs in Transplantation: Balancing Efficacy and Safety
- Targeting Inflammatory Pathways in Autoimmune Disorders
- Immunopharmacological Interventions for Infectious Diseases
- Pharmacological Modulation of Cytokines in Inflammatory Disorders
- Vaccines: Advancements in Development and Delivery
Pharmacovigilance and Drug Safety
- Post-Marketing Surveillance: Detecting and Evaluating Adverse Drug Reactions
- Signal Detection in Pharmacovigilance: Methods and Applications
- Risk Management Strategies in Drug Development and Marketing
- Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers for Predicting Drug Safety
- Pharmacovigilance in Special Populations: Pregnant Women and Pediatrics
- Drug Safety Communication: Enhancing Patient Awareness and Education
- Role of Pharmacovigilance in Drug Regulatory Affairs
- Pharmacovigilance Data Mining: Leveraging Big Data for Drug Safety
- Pharmacovigilance Systems and Reporting Structures
- Pharmacogenetic Testing in Drug Safety Assessment
This comprehensive list of pharmacology research paper topics provides a broad range of ideas and areas to explore within the field of pharmacology. From drug discovery and development to clinical pharmacology, neuropharmacology, and pharmacokinetics, each category offers multiple topics for students to delve into and contribute to the advancement of pharmacological knowledge. Whether you are interested in the impact of pharmacogenomics on drug therapy, exploring novel treatment strategies, or investigating drug safety and pharmacovigilance, there is a wealth of research possibilities awaiting exploration. By selecting a topic of interest and following the expert advice on topic selection and research paper writing, students can embark on an enriching journey of discovery and make meaningful contributions to the field of pharmacology.
Pharmacology: Exploring the Range of Research Paper Topics
Pharmacology is a captivating and dynamic scientific discipline that focuses on the study of drugs and their effects on living organisms. It plays a crucial role in improving human health by advancing our understanding of how medications interact with biological systems. Within the field of pharmacology, there is a vast array of pharmacology research paper topics that offer students an opportunity to delve into various aspects of drug discovery, development, clinical application, and safety. In this article, we will explore the breadth and depth of pharmacology as a scientific field, highlighting the range of research paper topics it encompasses.
Drug Discovery and Development: One exciting area of pharmacology research is drug discovery and development. This field involves the identification and development of new therapeutic agents to treat a wide range of diseases. Students interested in this area can explore topics such as the exploration of novel drug targets and therapeutic approaches, investigating natural products for drug development, advancements in targeted drug delivery systems, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of new drug entities, and understanding and overcoming drug resistance mechanisms.
Clinical Pharmacology: Clinical pharmacology focuses on the application of pharmacological principles in the clinical setting. It plays a vital role in optimizing drug therapy and ensuring patient safety. Pharmacology research paper topics in this area may include pharmacogenomics, which explores the relationship between an individual’s genetic makeup and their response to medication. Other topics of interest include the identification, prevention, and management of adverse drug reactions, the design and ethical considerations in clinical trials, pharmacovigilance, and optimizing drug regimens for special populations such as pediatrics, geriatrics, and pregnant women.
Neuropharmacology and Psychopharmacology: The field of neuropharmacology examines how drugs interact with the central nervous system and influence brain function. Pharmacology research paper topics in this area may involve investigating the mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications of psychotropic drugs, exploring neurotransmitter systems and their role in neurological disorders, pharmacological interventions for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders, the psychopharmacology of substance use disorders, and the pharmacological management of mental health disorders.
Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism: Pharmacokinetics and drug metabolism focus on understanding how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and eliminated by the body. Pharmacology research paper topics in this area may include studying drug interactions, such as the mechanisms, predictions, and clinical implications of drug-drug interactions. Other topics of interest include pharmacogenetics and individual variations in drug response, the role of drug transporters in drug disposition, drug metabolism and its impact on drug-drug interactions, and the use of predictive modeling in pharmacokinetics and dosing optimization.
Pharmacology of Infectious Diseases: The pharmacology of infectious diseases involves studying how drugs can effectively treat and prevent infections. Research topics in this area may include exploring antimicrobial resistance, including its mechanisms, epidemiology, and strategies to combat it. Additionally, students may investigate the development of new antiviral agents, the pharmacological management of bacterial infections, host-pathogen interactions, and the pharmacokinetic considerations in the treatment of infectious diseases.
Cardiovascular Pharmacology: Cardiovascular pharmacology focuses on understanding the effects of drugs on the cardiovascular system. Research topics in this area may include exploring drug therapy for hypertension and current guidelines for treatment, novel anticoagulants in the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic disorders, pharmacological approaches to managing heart failure, drug-induced cardiotoxicity and strategies for prevention, and emerging pharmacotherapies for atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease.
Pharmacology and Aging: Pharmacology and aging is a specialized field that investigates how drug therapy can be optimized in older adults. Research topics in this area may include exploring geriatric pharmacotherapy, age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, the impact of polypharmacy on older adults, the recognition and prevention of adverse drug reactions, pharmacological management of age-related neurodegenerative disorders, and strategies for improving medication adherence in the elderly.
The field of pharmacology offers a wide range of exciting research paper topics that span from drug discovery and development to clinical pharmacology, neuropharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and beyond. By exploring these topics, students can contribute to the advancement of pharmacological knowledge and make meaningful contributions to the field. Remember to choose a research topic that aligns with your interests and career aspirations, and be sure to consult with your instructors or mentors for guidance throughout your research journey. With dedication, curiosity, and a passion for improving patient care, you have the opportunity to shape the future of pharmacology research.
How to Choose a Pharmacology Research Topic
Choosing the right research paper topic is crucial for a successful academic journey in pharmacology. It allows you to explore your interests, contribute to the field, and showcase your knowledge and skills. However, with the vast scope of pharmacology, selecting a research topic can be a daunting task. In this section, we will provide you with expert advice on how to choose pharmacology research paper topics that are engaging, relevant, and have the potential for significant contribution.
- Identify Your Interests : Start by identifying your areas of interest within pharmacology. Reflect on the topics that have captivated your attention during your coursework or sparked your curiosity. Consider whether you are more inclined towards drug discovery, clinical applications, pharmacokinetics, neuropharmacology, or any other subfield of pharmacology. This self-reflection will help you narrow down your options and select a topic that resonates with your passion.
- Stay Updated with Current Research : To choose a compelling research topic, it is essential to stay updated with the latest advancements and trends in pharmacology. Follow reputable scientific journals, attend conferences, and engage with the pharmacological community to gain insights into the ongoing research and emerging areas of interest. This will help you identify gaps in the current knowledge and select a topic that offers the potential for novel discoveries or addressing existing challenges.
- Consult with Faculty and Experts : Seek guidance from your faculty members, mentors, or experts in the field of pharmacology. They can provide valuable insights and suggest potential research areas based on their expertise and experience. Discuss your interests, goals, and research aspirations with them, and they can help you refine your research topic, provide relevant literature references, and offer valuable advice on the feasibility and scope of your chosen topic.
- Consider Practicality and Resources : When selecting a research topic, consider the practicality and availability of resources. Assess whether the necessary laboratory facilities, equipment, or access to clinical data are readily accessible to conduct your research. Additionally, consider the time and resources required to complete the research within the given timeframe. Choosing a topic that aligns with the available resources will enhance the feasibility and success of your research endeavor.
- Address Current Challenges or Gaps : Pharmacology is a field that constantly evolves, presenting new challenges and unanswered questions. Consider selecting a research topic that addresses current challenges or explores gaps in the existing knowledge. This could involve investigating the mechanisms of drug resistance, exploring novel drug targets, or optimizing drug regimens for specific patient populations. By tackling these challenges, you can contribute to the advancement of pharmacological science and make a meaningful impact.
- Collaborate with Peers : Consider collaborating with fellow students or researchers who share similar research interests. Collaborative research projects can provide a broader perspective, foster knowledge sharing, and enhance the overall quality of your research. Collaborating with peers also allows you to divide the workload, share resources, and receive feedback and support throughout the research process.
- Seek Ethical Considerations : When selecting a pharmacology research topic, it is essential to consider ethical considerations and adhere to the principles of research ethics. Ensure that your chosen topic respects patient confidentiality, follows the guidelines for the ethical use of animal subjects (if applicable), and aligns with the ethical principles outlined by regulatory bodies. Consulting with your institution’s ethics committee or research advisor can help ensure that your research project meets the required ethical standards.
- Evaluate Feasibility and Novelty : Evaluate the feasibility and novelty of your chosen research topic. Consider whether the research question is answerable within the available resources and time constraints. Additionally, assess whether your topic brings something new to the field, whether it fills a knowledge gap, or offers a fresh perspective on an existing topic. A balance between feasibility and novelty is essential for a successful research paper.
- Consult Literature Reviews : Conduct thorough literature reviews on your chosen topic to gain a comprehensive understanding of the existing research. Literature reviews help you identify gaps in the current knowledge and provide a foundation for your research question. They also enable you to build on previous findings, develop a robust research methodology, and position your research within the context of the broader field of pharmacology.
- Remain Flexible : Lastly, remain flexible throughout the process of choosing a research topic. As you delve deeper into the literature and research process, you may discover new avenues of interest or encounter unexpected challenges. It is essential to remain open to refining or adjusting your research topic based on new insights, emerging data, or feedback from your research advisors. Flexibility allows you to adapt and ensure that your research remains relevant and impactful.
Choosing a pharmacology research paper topic is an exciting and important step in your academic journey. By following expert advice, identifying your interests, staying updated with current research, seeking guidance, considering practicality and resources, addressing current challenges or gaps, collaborating with peers, adhering to ethical considerations, evaluating feasibility and novelty, consulting literature reviews, and remaining flexible, you can select a research topic that is engaging, relevant, and has the potential to contribute to the field of pharmacology. Remember, this is your opportunity to explore, innovate, and make a lasting impact in the dynamic field of pharmacology research.
How to Write a Pharmacology Research Paper
Writing a pharmacology research paper requires careful planning, organization, and attention to detail. It is an opportunity for you to showcase your understanding of the subject matter, critical thinking skills, and ability to communicate scientific information effectively. In this section, we will provide you with expert guidance on how to write a pharmacology research paper that is well-structured, informative, and compelling.
- Choose a Well-Defined Research Question : Start by formulating a clear and well-defined research question. Your research question should be focused, specific, and address a gap in the existing knowledge. Consider the significance of your research question in the context of pharmacology and how it contributes to the overall understanding of the field. A well-defined research question sets the foundation for your entire research paper.
- Conduct a Thorough Literature Review : Before diving into your research, conduct a thorough literature review on the chosen topic. Familiarize yourself with the existing research, theories, and findings related to your research question. This will provide you with a solid understanding of the current state of knowledge and help you identify gaps or areas for further investigation. Additionally, the literature review will inform your research methodology and discussion of results.
- Develop a Clear Structure : A well-structured research paper is essential for effectively conveying your ideas and findings. Begin with an engaging introduction that provides background information, context, and clearly states your research question. Follow with a comprehensive literature review that supports your research question and highlights the gaps in knowledge. Next, present your research methodology, including details on sample selection, data collection, and analysis methods. In the results section, present your findings in a clear and organized manner using tables, graphs, or figures as necessary. Finally, discuss your results, interpret their significance, and relate them back to your research question in the discussion section. Conclude with a concise summary of your findings and their implications.
- Use Reliable and Credible Sources : Ensure that the sources you use for your research paper are reliable, credible, and peer-reviewed. Consult reputable scientific journals, textbooks, and conference proceedings. Avoid relying solely on internet sources or non-scholarly publications. Citations are critical to acknowledge the work of other researchers and to support your claims and arguments. Use a consistent citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, and follow the guidelines carefully.
- Analyze and Interpret Your Data : If your research involves collecting and analyzing data, ensure that your data analysis is thorough and accurate. Use appropriate statistical methods to analyze your data and present the results in a clear and meaningful way. Interpret the findings in the context of your research question and discuss any limitations or potential sources of bias. Remember to relate your findings back to the existing literature and explain how they contribute to the broader understanding of pharmacology.
- Write Clearly and Concisely : Effective scientific writing is clear, concise, and free of unnecessary jargon. Use language that is precise and straightforward, avoiding ambiguous or vague statements. Clearly articulate your ideas and ensure that your arguments are logical and well-supported by evidence. Use appropriate scientific terminology, but also consider your target audience and strive to communicate your findings in a way that is accessible to readers who may not have expertise in pharmacology.
- Pay Attention to Formatting and Style : Follow the formatting and style guidelines specified by your instructor or the target journal. Pay attention to details such as font size, line spacing, margins, and headings. Use subheadings to organize your content and make it easier for readers to navigate. Adhere to the specific citation style required for your paper and ensure that your references are complete and accurate.
- Revise and Edit : Revision and editing are essential steps in the writing process. Take the time to review your research paper for clarity, coherence, and accuracy. Check for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and punctuation errors. Ensure that your ideas flow logically and that your paper is well-structured. Consider seeking feedback from peers, instructors, or mentors to gain different perspectives and improve the overall quality of your paper.
- Proofread : Before submitting your research paper, thoroughly proofread it to ensure that it is error-free. Check for any typos, inconsistencies, or formatting issues. Read your paper aloud to catch any awkward phrasing or unclear sentences. It can also be helpful to have someone else read your paper to identify any errors or areas that need improvement.
- Ethical Considerations : Ensure that your research paper adheres to ethical considerations. If your research involved human subjects, ensure that you have obtained the necessary approvals and informed consent. Respect patient confidentiality and anonymity when presenting your research findings. Adhere to the ethical guidelines set by your institution or the relevant regulatory bodies.
Writing a pharmacology research paper requires careful planning, thorough research, effective communication, and attention to detail. By following the expert advice provided in this section, you can develop a well-structured and informative research paper that contributes to the field of pharmacology. Remember to choose a well-defined research question, conduct a thorough literature review, use reliable sources, analyze and interpret your data, write clearly and concisely, pay attention to formatting and style, revise and edit your paper, proofread for errors, and ensure ethical considerations are met. With diligence and commitment, your pharmacology research paper has the potential to make a meaningful impact in the field of pharmacology.
iResearchNet’s Writing Services
At iResearchNet, we understand the challenges that students face when it comes to writing high-quality pharmacology research papers. We recognize the importance of delivering well-researched, well-written, and timely papers that meet the rigorous standards of academic institutions. That’s why we offer a comprehensive range of writing services tailored specifically for students studying pharmacology. With our expertise and commitment to excellence, we are here to provide you with customized solutions to all your research paper needs.
- Expert Degree-Holding Writers : At iResearchNet, we have a team of expert writers who hold advanced degrees in pharmacology and related fields. They have in-depth knowledge of the subject matter and are well-versed in the latest research trends and methodologies. Our writers are experienced in crafting research papers that adhere to the highest academic standards and follow the guidelines provided by your institution.
- Custom Written Works : We understand that each research paper is unique, and that’s why we offer custom-written works tailored to your specific requirements. Our writers will collaborate with you to understand your research question, objectives, and any specific instructions provided by your instructor. This ensures that the final paper is original, well-researched, and meets your expectations.
- In-Depth Research : Our writers are skilled in conducting thorough and comprehensive research on pharmacology topics. They have access to reputable scientific databases, journals, and other reliable sources of information. By utilizing the latest research findings, our writers ensure that your research paper is based on current and relevant literature, enhancing the credibility and academic rigor of your work.
- Custom Formatting : We understand the importance of adhering to specific formatting styles in academic writing. Whether it’s APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, or Harvard, our writers are well-versed in these formatting styles and will ensure that your research paper is formatted correctly. This includes citing sources, creating reference lists, and formatting headings, margins, and page numbers according to the required style.
- Top Quality : At iResearchNet, we are committed to delivering top-quality research papers. Our writers pay meticulous attention to detail, ensuring that the content is accurate, coherent, and well-structured. They employ critical thinking skills to analyze and interpret data, present logical arguments, and provide insightful discussions. Our rigorous quality assurance process includes multiple levels of review and editing to ensure that the final paper meets the highest standards of academic excellence.
- Customized Solutions : We understand that every student’s research paper requirements are unique. That’s why we offer customized solutions to meet your specific needs. Whether you require assistance with topic selection, literature review, methodology, data analysis, or any other aspect of your research paper, our writers are here to provide personalized support and guidance.
- Flexible Pricing : We believe that quality academic assistance should be accessible to all students. That’s why we offer flexible pricing options to accommodate different budgetary constraints. Our pricing is competitive and transparent, without compromising on the quality of our services. We offer affordable rates tailored to the specific requirements of your research paper.
- Short Deadlines : We understand that students often face tight deadlines for submitting their research papers. At iResearchNet, we offer short deadlines as quick as 3 hours, ensuring that you receive your paper on time. Our writers are experienced in working under pressure without compromising the quality of the work. We prioritize timely delivery to help you meet your academic deadlines.
- Timely Delivery : We value your time and understand the importance of meeting deadlines. Our writers are committed to delivering your research paper on time, allowing you ample time for review and any necessary revisions. We have a proven track record of timely delivery, ensuring that you can submit your research paper without any concerns.
- 24/7 Support : We provide 24/7 customer support to address any questions or concerns you may have throughout the process. Our friendly and knowledgeable support team is available round the clock to assist you with any queries, provide updates on your paper, or address any issues that may arise. We are dedicated to ensuring a smooth and positive experience for our clients.
- Absolute Privacy : We understand the importance of confidentiality when it comes to academic assistance. At iResearchNet, we prioritize your privacy and guarantee absolute confidentiality. We have strict security measures in place to protect your personal information and ensure that your identity remains anonymous. Your research paper and personal details will be handled with the utmost confidentiality and professionalism.
- Easy Order Tracking : We have developed a user-friendly platform that allows you to easily track the progress of your research paper. You can communicate directly with your assigned writer, provide additional instructions or clarifications, and monitor the status of your paper throughout the writing process. Our streamlined order tracking system ensures transparency and enables effective collaboration.
- Money Back Guarantee : We are confident in the quality of our services and the expertise of our writers. In the unlikely event that you are not satisfied with the final research paper, we offer a money-back guarantee. We are committed to ensuring your complete satisfaction and will work with you to resolve any issues or concerns. Your academic success is our top priority.
At iResearchNet, we are dedicated to providing top-quality writing services tailored to meet the unique needs of students studying pharmacology. Our team of expert writers, in-depth research capabilities, custom formatting, top-quality papers, flexible pricing, timely delivery, 24/7 support, absolute privacy, easy order tracking, and money-back guarantee ensure that your research paper is in capable hands. We are here to support you throughout your academic journey and help you excel in your pharmacology studies. Place your order with iResearchNet and experience the difference of working with a trusted and reliable academic writing service.
Unlock Your Potential with iResearchNet
Are you struggling to write a compelling and well-researched pharmacology research paper? Do you find yourself overwhelmed with the demands of your academic workload? Don’t worry, iResearchNet is here to help you excel in your pharmacology studies and achieve the academic success you deserve.
At iResearchNet, we understand the challenges that students face when it comes to writing high-quality research papers in pharmacology. Our team of expert writers, in-depth research capabilities, and commitment to excellence make us the perfect partner to assist you in your academic journey. Whether you need assistance with topic selection, literature review, methodology, data analysis, or the entire writing process, we are here to provide you with a custom pharmacology research paper that meets your unique requirements.
Don’t let the challenges of writing a pharmacology research paper hinder your academic progress. Unlock your potential and achieve your goals with the support of iResearchNet’s pharmacology writing services. Place your order today and experience unparalleled excellence in academic writing. Our team of expert writers is ready to assist you in crafting a high-quality research paper that will impress your instructors and elevate your academic performance. Trust iResearchNet to be your reliable partner in pharmacology writing.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER


- FREE WHITEPAPERS
- FEATURED ARTICLES
- FREE RESOURCES
- FREE eNEWSLETTER

Healthcare Technology Featured Article
The power of ai in pharma r&d.

According to a recent McKinsey study, pharmaceutical businesses were already employing AI in many cases before the general public became aware of generative AI. Even yet, multimodal AI in healthcare has enormous potential – $60 billion to $110 billion in new economic value for the sector each year. Expect AI-powered technologies to have a significant impact on medicine discovery and development, time to market, and other elements of R&D. Keep reading to know how corporations use AI to reduce the cost of pharmaceutical R&D and what's on the horizon.
Key Functions of AI in Pharmaceutical Research and Development
The pharmaceutical sector has generally been hesitant about embracing new technology. There are many reasons explaining this hesitance. The potentially life-changing nature of pharmaceutical products, stringent restrictions, and significant financial risks associated with drug development were always the main constraints. Nevertheless, industry executives realize the enormous potential of AI, particularly generative AI, in pharmaceutical R&D. These technologies are changing the way new pharmaceuticals are found, produced, tested, and introduced to the market. That’s why more and more companies are starting to use AI.
Applications of AI in Pharma
Modern AI solutions can help firms access information quicker, enhance processes, and unleash creativity. The potential applications of AI in the pharmaceutical and life sciences sectors are only limited by creativity and technological boundaries. Here are some of the most common applications of AI in pharmaceuticals, which will continue to expand as new capabilities emerge.
#1 — Target Identification
Target identification is critical in drug development, especially for complicated diseases such as colorectal and pancreatic malignancies. Companies such as Phenomic AI and Boehringer Ingelheim are using AI to better identify cancer targets. This AI-driven technique enables researchers to leverage digital screening and experimental validation to enhance assessments of these particular tumors, perhaps revealing better therapeutic targets.
Virtual AI screening is an effective method for comparing chemical structures to targets, estimating binding probabilities, and finding potential targets for future investigation. All of this can be done on a larger scale and faster than earlier computational or manual efforts.
#2 — Drug Design
AI technology is speeding up conventional drug design methods. For example, Cradle, a biotech firm, is employing generative AI to accelerate protein design and optimization. The business has a large number of industrial partners and is working on more than ten R&D projects that concentrate on generative AI capabilities for protein modalities.
Separately, university academics are using AI techniques to accelerate their study of Parkinson's illness. An AI engine swiftly analyzed a library of chemical compounds and selected a small number of intriguing compounds for future investigation.
#3 — Knowledge Management
Roche has used artificial intelligence to ensure fast and easy access to essential information throughout its worldwide network for further verification and insights. This artificial intelligence-driven strategy has changed Roche's communication and innovation. The changes have impacted not only operations; Roche is fostering an integrated culture of information sharing that benefits both corporate success and patient outcomes.
Roche has witnessed significant growth in platform engagement after implementing Starmind in 2020, with user numbers expected to increase from 1,000 to over 9,000 by 2024. The platform's AI capabilities have saved over 91,000 hours previously spent looking for information, demonstrating a considerable improvement in operational efficiency.
#4 — Clinical Trial Documentation
Clinical trial documentation is an essential yet time-consuming procedure that may cause delays in medication development. Generative AI techniques are being utilized to generate complicated texts including clinical trial reports, patient narratives, and summary clinical safety records. Employees spend less time creating, evaluating, and approving these critical components.
For example, Yseo employs pre-trained big language models designed exclusively for biopharma applications. These artificial intelligence systems compile clinical documentation automatically, producing over 10,000 reports by 2023 and saving thousands of hours of human work. The startup plans to automate other areas of document processing, such as FDA clearances.
#5 — Manufacturing
AI can help pharmaceutical companies like Amgen increase operational efficiency and speed up the manufacturing of critical drugs. The company collaborated with Amazon Web Services to improve the throughput and reliability of pharmaceutical manufacturing. The new production facility of Amgen will use Amazon SageMaker and other machine learning technology to evaluate manufacturing data in real-time.
It Is Just the Beginning
AI in pharmaceutical research and development is revolutionizing the whole process, from drug discovery and design to clinical trials and production. Companies are already using AI to reduce the cost of pharmaceutical R&D, optimize processes, and reduce time to market. Taking into account how AI impacts the development of custom-branded apps , more is to come in the pharma industry in the future.
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Healthcare technology related articles.
- Strategies for Success: 5 Ways of Improving Hospital Efficiency and Patient Outcomes
- Smoothening Healthcare Revenue Cycle Management: Addressing Staffing Shortfalls
- The Role of Assistive Technology in Enhancing Independence for People with Disabilities
- Explore the Advantages of Using Telehealth Video Calls
- Medical Record Evolution: The Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud-based Solutions in Patient Information Management
- Transforming Healthcare: The Power of Software Development in Medical Field
From White Paper Library
- The language of innovation: Why and how to gain your customers' trust with your AI and digital
- Exploring CX strategy and technology adoption: A decision-maker's chart
- Transforming Customer Experience
- RingCentral RingCX overview
- RingCX Digital Engagement Datasheet
MedHealth RSS
- Healthcare Providers
- IT Professionals
- Electronic Records
- Healthcare Innovation
- Medical Devices
- Mobile & Connected Health

- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My Portfolio
- Latest News
- Stock Market
- Premium News
- Biden Economy
- EV Deep Dive
- Stocks: Most Actives
- Stocks: Gainers
- Stocks: Losers
- Trending Tickers
- World Indices
- US Treasury Bonds
- Top Mutual Funds
- Highest Open Interest
- Highest Implied Volatility
- Stock Comparison
- Advanced Charts
- Currency Converter
- Basic Materials
- Communication Services
- Consumer Cyclical
- Consumer Defensive
- Financial Services
- Industrials
- Real Estate
- Mutual Funds
- Credit cards
- Balance Transfer Cards
- Cash-back Cards
- Rewards Cards
- Travel Cards
- Student Loans
- Personal Loans
- Car Insurance
- Morning Brief
- Market Domination
- Market Domination Overtime
- Asking for a Trend
- Opening Bid
- Stocks in Translation
- Lead This Way
- Good Buy or Goodbye?
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Yahoo Finance
Global pharmaceutical industry outlook 2024: key growth opportunities in scaling precision oncology in asia-pacific through public-private partnership models.
Dublin, May 27, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- The "Global Pharmaceutical Industry Outlook, 2024" report has been added to ResearchAndMarkets.com's offering. The leading trends shaping the global pharmaceutical landscape are covered in this analysis.
After a plateaued growth in 2023 due to the biologics segment slowdown and a decrease in the uptake of COVID-19 vaccines and therapeutics, the industry will likely realign its growth to record a 5.9% CAGR between 2023 and 2028. Year-on-year (YoY) growth will remain low in developed economies, including the United States and Europe. In contrast, emerging economies in APAC, LATAM, and the rest of the world will register comparatively stronger single-digit YoY growth. The recession and ongoing inflation will remain pressing challenges for the pharmaceutical industry in 2024, affecting returns on investment. Pharmaceutical companies will continue to shift toward regional rather than global suppliers to ensure geographic proximity and a smoother, more reliable supply chain. There continues to be a strong focus on environmental, social, and governance commitments and supply-chain digitalization through lighthouse manufacturing techniques, decentralized clinical trial approaches, and the application of artificial intelligence.
The industry is also witnessing a healthy mergers and acquisitions landscape, with several successful transactions recently. In addition, the publisher expects a rebound in initial public offerings (IPOs), with 5 IPOs completed by February 2024.
Key Growth Opportunities:
Scale Precision Oncology in Asia-Pacific Through Public-private Partnership Models
Target Undruggable Proteins with Emerging Biotech Platforms
Develop Agile Partnership Models for Drug Discovery and Development
Key Topics Covered:
Top Predictions for 2024
Industry Trends
Trend 1: Increasing M&As in Biopharma
Trend 2: Higher Focus on Precision Medicine
Trend 3: More RWE Integration in Drug R&D
Global Pharmaceutical Industry - R&D Expenditure Outlook
Global Drug Development Pipeline by Development Phase
Key Therapeutic Area Outlook
Macroeconomic Factors
Top 10 Trends for 2024
Top 10 Growth Opportunities
Global GDP Growth - Global Growth will See a Mild Slowdown from 3% in 2023 to 2.6% in 2024 as Major Economies Lose Momentum
Inflation and Interest Rates - Headline Inflation will Continue to Decline. H2 2024 will Shift Toward Rate Cuts for Advanced Economies
Currency Trajectory - The Dollar will Remain Strong in H1 2024. Emerging Market Currencies will Receive a Boost From Q3 2024
Oil Markets - OPEC+ will Cut Oil Production in Q1. Non-OPEC Production will Increase
Labor Market - Unemployment will See a Moderate Uptick. Positive Expectations Over Market Sentiment will Support Labor Hoarding
Critical Mineral Supplies - The Need for Economic Resiliency will Bolster Cross-border and Cross-industry Partnerships
North America - The Region will See an Economic Slowdown Amidst a Discretionary Spending Pullback and Elevated Interest Rates
Western Europe - The Region will See a Moderate Growth Pick-up as Inflation Headwinds Ease. Rebuilding Fiscal Buffers will Take Precedence
The Middle East - Economic Diversification will Drive Non-oil Growth to Limit the Pullback From a Slowdown in Global oil Markets
Asia - Emerging Economies will Drive Growth Momentum. Fiscal Measures will Support CHINESE Economic Recovery
High Inflation and Global Recession
Intensification of Supply Chain Resilience Strategies
Sustainability Across the Pharma Value Chain
Growth Generator
Global Pharmaceutical Industry - Historic Sales and Forecast
Segment Performance - Historic Sales and Forecast
Revenue Forecast by Region
Revenue Forecast Analysis by Region
Regional Regulatory Trends - North America
Regional Regulatory Trends - Europe
Regional Regulatory Trends - APAC
Regional Regulatory Trends - APAC, LATAM, the Caribbean, the Middle East, and Africa
Growth Generator: Small Molecules
Small Molecules Snapshot - 2024
Small-molecule Companies to Watch
Growth Generator: Biologics
Biologics Snapshot - 2024
Biologics Companies to Watch
For more information about this report visit https://www.researchandmarkets.com/r/aft3ed
About ResearchAndMarkets.com ResearchAndMarkets.com is the world's leading source for international market research reports and market data. We provide you with the latest data on international and regional markets, key industries, the top companies, new products and the latest trends.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Hot Topics in Pharmaceutical Research. In this virtual issue, we highlight some of the most impactful recent articles in the journal as reflected by citations in 2022. Highly cited articles provide insight into which research topics are attracting the most attention and reflect innovative new discoveries, or timely reviews and perspectives on ...
We have some exciting research coming up in 2021, but in case you missed them the first time around, here are the top five most popular research articles of 2020: 5. Misuse of prescription and over-the-counter drugs to obtain illicit highs: how pharmacists can prevent abuse. Use of prescription and over-the-counter drugs for recreational ...
Pharmaceutical Research is an official journal of the American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists, covering innovative research in drug discovery, development, evaluation, and regulatory approval.. Current emphasis of the journal includes: preformulation; drug delivery and targeting; formulation design, engineering, and processing; pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacogenomics ...
Pharmaceutics is the scientific discipline concerned with the process of creating the dosage form (such as a pill for oral administration or a powder for intravenous injection) of a therapeutic ...
Assessment of Tunable Resistive Pulse Sensing (TRPS) Technology for Particle Size Distribution in Vaccine Formulations - A Comparative Study with Dynamic Light Scattering. Rahul Misra. Ginny Fung. Marina Kirkitadze. Original Research Article 22 April 2024 Pages: 1021 - 1029.
The Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences will publish original research papers, original research notes, invited topical reviews (including Minireviews), and editorial commentary and news. The area of focus shall be concepts in basic pharmaceutical science and such topics as chemical processing of pharmaceuticals, including crystallization ...
Research Highlights 08 Sept 2023 Neuropsychopharmacology. Volume: 48, P: 1703-1704. All News & Comment. Search. Search articles by subject, keyword or author. Show results from.
Treating chronic conditions to prevent cognitive decline and dementia. The most cited pharmacology and pharmacy journal advances access to pharmacological discoveries to prevent and treat human disease.
Molecular docking and synthesis of N-alkyl-isatin-3-imino aromatic amine derivatives and their antileishmanial and cytotoxic activities. Hassanzadeh, Farshid; Hejazi, Seyed Hossein; Jafari, Elham; More. Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences. 19 (2):238-250, Mar-Apr 2024. Abstract.
Medicinal chemistry deals with the design, optimization and development of chemical compounds for use as drugs. It is inherently a multidisciplinary topic — beginning with the synthesis of ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review ...
Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal, a peer-reviewed journal, is dedicated to scientific and technical research on the creation and manufacturing improvement of medicines and intermediates.. Presents the full spectrum of new drug research, including synthesis methods, rational drug design and pharmacological, toxicological, modelling, docking and biochemical studies.
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature ...
Bridging across disciplines. An IUPHAR-affiliated journal, International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology Pharmacological Research publishes cutting-edge articles in biomedical sciences to cover a broad range of topics that move the pharmacological field forward. We provide a venue through which specialists across disciplines can rapidly exchange information in health sciences that ...
Drug development and formulation. | Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on PHARMACEUTICS. Find methods information, sources, references or ...
Current Research in Pharmacology and Drug Discovery (CRPHAR) is a new primary research, gold open access journal from Elsevier. CRPHAR publishes original papers, reviews, graphical reviews, short communications and follow-up manuscripts resulting from research in pharmacology and drug discovery that cover aspects of drug action at the cellular, molecular, and biochemical level.
Various classifications for research designs and methods used in pharmacy practice have been used in the literature. The following are some of the approaches for the classification of research designs: 1. Classification based on time orientation: Retrospective vs. prospective designs. a.
New Advances in the Pharmacology and Toxicology of Lithium: A Neurobiologically Oriented Overview
In this page on pharmacology research paper topics, we explore the diverse and dynamic field of pharmacology and provide valuable resources for students who are tasked with writing research papers in this discipline.Pharmacology, as a branch of science, encompasses the study of how drugs interact with biological systems, aiming to understand their mechanisms of action, therapeutic uses, and ...
The pharmaceutical industry plays an essential role in the financial development and social care of any society (Singh et al., 2016).It has been defined by Shah (2004) as a complex industry concerned with the invention, evolution, and production of medicines and remedies. Indeed, improvements in the pharmaceutical industry and suitable supply have ensured that people can access medications ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on PHARMACEUTICAL BIOTECHNOLOGY. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature ...
Strategy and Drug Research. D.J. Triggle, in Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry II, 2007 2.02.7 Conclusions. Medicinal chemistry is a discipline firmly grounded in organic chemistry. Traditionally, in fact, a subdiscipline of synthetic organic chemistry, medicinal chemistry has increasingly expanded at both the physical and biological interfaces of organic chemistry.
AI in pharmaceutical research and development is revolutionizing the whole process, from drug discovery and design to clinical trials and production. Companies are already using AI to reduce the cost of pharmaceutical R&D, optimize processes, and reduce time to market. Taking into account how AI impacts the development of custom-branded apps ...
Dublin, May 27, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- The "Global Pharmaceutical Industry Outlook, 2024" report has been added to ResearchAndMarkets.com's offering.The leading trends shaping the global ...
positive impact to health care outcomes in India and. other developing as well as developed countries. The. pharmaceuticals market in India is expected to grow. at CAGR of ~16% and reach USD 55 ...