- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works

110+ Exceptional Education Research Topics Ideas

Topics for education research usually comprise school research topics, research problems in education, qualitative research topics in education, and concept paper topics about education to mention a few.
If you’re looking for research titles about education, you’re reading the right post! This article contains 110 of the best education research topics that will come in handy when you need to choose one for your research. From sample research topics in education, to research titles examples for high school students about education – we have it all.
Educational Research Topics
Research title examples for college students, quantitative research titles about education, topics related to education for thesis, research titles about school issues, ph.d. research titles in education, elementary education research topics, research title examples about online class, research titles about modular learning, examples of research questions in education, special education research titles.
The best research titles about education must be done through the detailed process of exploring previous works and improving personal knowledge.
Here are some good research topics in education to consider.
What Are Good Research Topics Related to Education?
- The role of Covid-19 in reinvigorating online learning
- The growth of cognitive abilities through leisure experiences
- The merits of group study in education
- Merits and demerits of traditional learning methods
- The impact of homework on traditional and modern education
- Student underdevelopment as a result of larger class volumes
- Advantages of digital textbooks in learning
- The struggle of older generations in computer education
- The standards of learning in the various academic levels
- Bullying and its effects on educational and mental health
- Exceptional education tutors: Is the need for higher pay justifiable?
The following examples of research titles about education for college students are ideal for a project that will take a long duration to complete. Here are some education topics for research that you can consider for your degree.
- Modern classroom difficulties of students and teachers
- Strategies to reform the learning difficulties within schools
- The rising cost of tuition and its burden on middle-class parents
- The concept of creativity among public schools and how it can be harnessed
- Major difficulties experienced in academic staff training
- Evaluating the learning cultures of college students
- Use of scientific development techniques in student learning
- Research of skill development in high school and college students
- Modern grading methods in underdeveloped institutions
- Dissertations and the difficulties surrounding their completion
- Integration of new gender categories in personalized learning
These research topics about education require a direct quantitative analysis and study of major ideas and arguments. They often contain general statistics and figures to back up regular research. Some of such research topics in education include:
- The relationship between poor education and increased academic fees
- Creating a social link between homeschool and traditional schoolgoers
- The relationship between teacher satisfaction and student performance
- The divide between public and private school performance
- The merits of parental involvement in students’ cognitive growth.
- A study on child welfare and its impact on educational development
- The relationship between academic performance and economic growth
- Urbanization in rural areas and its contribution to institutional growth
- The relationship between students and professors in dissertation writing
- The link between debt accumulation and student loans
- Boarding schools and regular schools: The role these two school types play in cognitive development
Educational-related topics used for a thesis normally require a wide aspect of study and enough educational materials. Here are some education research topics you can use for write my thesis .
- The difficulties of bilingual education in private universities
- Homework and its impact on learning processes in college education
- Dissertation topic selection: Key aspects and research obligations
- Social media research topics and their educational functions
- A detailed educational review of student learning via virtual reality techniques
- Ethnicities in universities and their participation in group activities
- The modern approach to self-studying for college students
- Developing time management skills in modern education
- Guidelines for teacher development in advanced educational institutions
- The need for religious education in boarding schools
- A measure of cognitive development using digital learning methods
A research title about school issues focuses on activities surrounding the school environment and its effects on students, teachers, parents, and education in general. Below are some sample research titles in education, relating to school issues.
- Learning English in bilingual schools
- A study of teachers’ role as parent figures on school grounds
- Addressing the increased use of illegal substances and their effects in schools
- The benefits of after-class activities for foreign students
- Assessing student and teacher relationships
- A study of the best methods to implement safety rules in school
- Major obstacles in meeting school schedules using boarding students as a case study
- The need for counseling in public and private schools: Which is greater?
- Academic volunteering in understaffed public schools
- Modern techniques for curbing school violence among college students
- The advantages and disadvantages of teacher unions in schools
As you create your proposed list of research topics in education, consider scientific journals for referencing purposes. Here are some Ph.D. research titles for education.
- The modern methods of academic research writing
- The role of colleges in advanced mental care
- The merits and demerits of Ph.D. studies in Europe and Africa
- Interpersonal relationships between students and professors in advanced institutions
- A review of community colleges: merits and demerits
- Assessing racism in academic ethnic minorities
- The psychological changes of students in higher education
- The questionable standards of student loan provisions
- The merits of personalized teaching techniques in colleges
- The wage gap between private and public university teachers
- Teacher responsibilities in private universities versus public universities
The research topics in elementary education in 2023 are very different from the elementary education research topics from five or ten years ago. This creates interesting grounds for different research titles for elementary education.
Here are some elementary education title research ideas.
- Assessing quick computer literacy among elementary school pupils.
- The role of video games in childhood brain development
- Male vs female role models in early education periods
- The advantages of digital textbooks in elementary schools
- The impact of modern curriculums on elementary education
- Lack of proper school grooming is a cause of violence.
- Should elementary school children be taught about LGBTQ?
- A review of the need for sexual education in elementary schools
- The effects of emotional dependence in early childhood learners.
- The need for constant technology supervision of elementary school students
- Advantages of computer-guided education in elementary schools
Here are some research title examples for students taking online classes.
- The academic difficulties experienced by online students.
- A study of decreased attention in online classes
- The upsides and downsides of online education
- The rising fees of online and traditional education in universities
- A detailed study on the necessity of college internships
- The need to provide college scholarships based on environmental achievements
- How online education terminates university fraternities and sororities.
- The role of academic supervisors in career selection
- Why interactive assignments improved learning capabilities during the pandemic
- Merits of education in online learning environments
- Why online lessons are the least effective for some college students
The modular learning approach focuses primarily on learning outcomes. Here are some examples of research titles about modular learning.
- Modular learning and the role of teachers in its execution
- Teaching techniques of religious institutions
- Potential risks of accelerated learning
- Modular learning on students’ future performances
- The general overview of modular learning amongst students
- The modern Advantages and disadvantages of inclusive classes
- Observing student developments in modular learning
- Music therapy for fostering modular learning techniques
- The creation of a personalized curriculum for students.
- Applications of modular learning both in home-schooling?
- The benefits of modular learning towards creating a more holistic educational system
These research title examples about education answer important questions and they can also be argumentative essay topics .
Here are some titles of research about education questions.
- What impacts do learning approaches provide for students?
- How can schools manage their increasing gender differences?
- What fosters the provision of learning needs?
- What are the best educational recruitment methods?
- How can cognitive development improve education?
- How can you assess the moral growth of institutions?
- What are the primary causes of educational differences in geographical locations?
- How can institutions address increasing mental health needs?
- Why is early intervention essential in students with mental health setbacks?
- What are the characteristics of mental health deterioration among students?
- What techniques are acceptable in regulating the violence of students in institutions
Some of the research title examples about education include:
- How do schools create more personalized learning methods?
- Evaluating mental health setbacks during education
- The impact of modern technology on special education
- The cognitive improvements via specialized learning in dyslexic children
- The psychological link between dyslexia and bullying in high school
- Impact of social isolation in special education classes
- The difficulties in providing specialized learning environments
- A study of orphan students with disabilities and their aptitudes for learning
- How special classes improve the self-esteem of disabled students.
- How to use modern teaching techniques in unique learning environments.
- A study of the application of digital games to autistic learning
Final words about education research topics
We have provided some reliable examples of a research topic about education you can use for write my thesis . You can use these research titles in education to cultivate your ideas, create inspiration, or for online research. Remember always to select a topic that you’re naturally passionate about and do diligent research, and reach out to our professional writing services if you need any help.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
383 Exciting Education Research Topics
Education is vital to every person’s career and life success. People enrolled in higher education programs are 48% less likely to be incarcerated. Moreover, individuals with at least a Bachelor’s degree have the highest employment rates ( 86% ). Thus, investing time and effort in proper education is the best decision you can make in your young years.
Whether you’re interested in studying education or researching this subject for your classes, you will surely benefit from our detailed list of education research topics. Our experts have prepared research suggestions for students of all levels to aid you at every step of your education studies. Read on to find the best pick for your assignment.
- 🔝 Top-15 Research Titles about Education
- #️⃣ Quantitative Research Topics
- ️📋 Qualitative Research Topics
- 🎒 Titles about School Issues in 2024
- 🦼 Research Topics on Special Education
- 👶 Early Childhood Education
- 🧠 Educational Psychology
- 🧸 Child Development Topics
- 👩🏻💼 Educational Management Research Topics
- 📑 Dissertation Topics
🏫 Ideas of a Quantitative Research Title about School Problems
🔗 references, 🔝 top-15 research titles about education for 2024.
If you want to write a compelling paper, select an appropriate topic . You can find a unique research title about education in our list below and simplify your writing process.
- The role of education in eradicating poverty.
- The impact of technology on modern learning.
- The influence of social media on effective learning.
- A comparative analysis of student loans and debt accumulation.
- Effective approaches to student privacy and safety in schools.
- How does the school leadership experience shape a student’s personality?
- Evaluate the significance of assistive technology in special education.
- The role of parents in education.
- The importance of multicultural education.
- Homeschooling vs. regular schooling.
- The role of teachers as moral mediators.
- Approaches to prevent mental health issues among college students.
- The effectiveness of standardized tests in graduate schools.
- Should the government ban boarding schools?
- The importance of preschool education.
️#️⃣ 30 Quantitative Research Topics in Education
Quantitative research topics in education require extensive quantitative analysis and assessment of stats and figures. They involve doing calculations to support the research findings and hypotheses . The following are exciting topics on quantitative research you can use:
- The link between the e-learning environment and students’ social anxiety levels.
- Work hours and academic success relationship.
- The correlation between homeschooling and GPA.
- The effectiveness of parental involvement in child education: Statistical evidence.
- Motivation and learning relationship analysis.
- An analysis of the divide between tuition rates in private and public universities.
- The relationship between high tuition fees and poor education.
- Intervention strategies addressing six negative emotions.
- The connection between the national debt and student loans.
- Comparing students’ cognitive development scores in boarding and day schools.
- Formative assessments and raising attainment levels.
- The link between student well-being and teacher fulfillment.
- The correlation between students’ academic workload and mental wellness.
- Traditional or online education: which is better?
- The impact of socioeconomic status on academic performance.
- The link between urbanization and education development.
- The impact of school uniforms on school safety .
- The effects of teaching methods on student performance.
- A correlation between higher education attainment rates and unemployment rates.
- The race and class impact on academic performance.
- The impact of government policies on educational quality.
- The correlation between coding courses and a child’s cognitive development score.
- COVID-19 impact on student academic performance.
- Comparing the outcomes of data science programs for students of various specialties.
- The impact of student leadership on academic performance.
- Video games and their impact on students’ motivation.
- The link between social media use and psychological disorders’ incidence among students.
- The effects of students’ educational attainment on their post-graduation economic position.
- Time management: impact on the academic performance.
- The impact of educational field experiences on students’ career preparedness.
📋 30 Qualitative Research Topics in Education
Numerous issues in education need extensive research. Qualitative research is a way to gain an in-depth understanding of problems facing students and teachers. Below are qualitative research topics in education you can use for your academic project:
- Internet use among elementary school children.
- Educational challenges of students with autism.
- Teachers’ perspectives on the best learning strategies for autistic children.
- A case study of the significance of mental health education in schools.
- Inclusive classroom case study.
- The effects of learning conditions in developing countries.
- Early childhood educators’ perspectives on critical preschool classroom experiences.
- A case study examining why new teachers leave the profession.
- Students’ perceptions of their computer literacy skills.
- Coping strategies of schoolchildren’s parents from food-insecure households.
- Case study of a gifted student.
- High school students’ experiences of virtual learning.
- Students’ perceptions of lockdown browsers.
- Case study of learning disabilities: autism.
- The impact of alcoholism on student performance: A case study.
- A qualitative study of adult learners’ self-regulation in a digital learning environment.
- Human resources challenges in the higher education sphere.
- Academic leadership challenges in nursing schools.
- Students’ motivation to learn a rare foreign language.
- Challenges and barriers to equal opportunities in education.
- The role of teachers in improving learning for disabled children.
- Student loans: The effects on student career life.
- Korean Americans’ challenges in education.
- Teachers’ beliefs about their role in shaping the personalities of students.
- How to curb bullying in schools: Educators’ perspectives.
- Challenges and benefits of today’s student life.
- Remote learning: Advantages and disadvantages from students’ perspective.
- Interviews with teachers on the persistence of racism in schools.
- Learning challenges among people of color in public schools.
- Are students from lower social classes stigmatized in schools?
🎒 Research Titles about School Issues in 2024
Education research is vital in explaining and addressing fundamental issues affecting schools. It explores learning approaches, teaching practices , or educational changes after the pandemic. Choose your ideal research title about school issues from this list:
- The importance of standardized tests. Analyze the pros and cons of standardized tests and the consequences for students who fail the test.
- Government policy on education funding. Examine the flaws in the formula for financing schools and assess whether it is constitutional.
- Computer literacy in schools. Conduct a comparative assessment of effective methods to ensure all schools have enough resources to teach computer studies.
- Digital transformation in education. Analyze issues associated with online learning. Talk about the instructional tools that improve remote education.
- The effects of homeschooling. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of homeschooling and its cognitive impact on young children. Examine its sustainability in modern education.
- School safety in the 21st century. Explore the government policies on gun violence and approaches to prevent school shootings.
- Disciplinary policies in schools. Analyze the leading causes of suspensions and expulsions in schools. Examine the impact of reform policies on preventing undisciplined students’ transition into the juvenile system.
- The teaching of evolution. The is an ongoing debate about how to teach students about the origins of life. You can conduct a qualitative study examining parents’ or teachers’ attitudes toward this question.
- Student loans in higher education. Conduct a case study of students who are beneficiaries of student loans. Assess the effects of debt accumulation on their present careers.
- Bullying in schools. Study the causes and effects of bullying on students. Explore viable solutions to prevent bullying and discipline bullies.
🦼 53 Research Topics on Special Education
Special education is vital in modern society since many students have different disabilities and special needs. Teachers adopt accommodative practices to ensure total inclusivity for effective learning. Special education entails attending to students’ special needs using appropriate resources and accessible learning tools.
The following are research topics on special education to inspire your academic paper :
- Government policies on special education. Explore the policy frameworks and implementation guidelines that advocate special needs education. Talk about learning resources, accessibility, and transition rates to higher education and career life.
- Disabled children in early childhood education. Analyze the impact of special education on young children and determine strategies for effective teaching. Identify the challenges and possible solutions for enhancing seamless learning.
- The role of a school principal in improving special education. Discuss the approaches a principal can introduce to support disabled students. Talk about the instructions that teachers should adopt to guarantee inclusivity.
- Global impact of learning disabilities . Evaluate strategic approaches to special education in different countries. Analyze students’ responses to these methods and possible career paths in various countries.
- Coping mechanisms of special needs children. Investigate stress reactions and emotional security among children with disabilities. Explore methods that teachers can adopt to help students cope with new environments.
- The role of workshops on special educators’ mental wellness. Explore the causes and effects of stress and burnout on teachers in special education. Talk about acceptance and commitment therapy in alleviating depressive episodes.
- Social-emotional development in special education. Explain effective ways to promote social and emotional engagement of special needs children. Discuss parent and teacher training interventions and evaluate the results and implications for future research.
- Impact of technology on special education. Analyze the benefits of assistive technology in improving learning and give examples of tools used in special education. Talk about the barriers faced by special needs children, which result in learning exclusion.
- Discrimination and stigmatization. Conduct a case study of physically disabled children attending regular schools. Explore the psychological impact and trauma faced by special needs children. Present possible recommendations for better learning conditions.
- Effects of parenting style on special needs children. Analyze how different parenting styles can affect the behavior of special needs children. Explore a group of high school students with various disabilities.
- Behavioral issues in early childhood special education. Explore the influence of negative parent-child interactions on the behavior of children with disabilities. Discuss problem-solving models for correcting behavior and creating a positive learning environment.
- Patterns of language acquisition in children with disabilities. Compare language development in healthy and special needs children. Discuss the significance of communication skills in the early years and their effects on future learning.
- Social participation barriers. Compare the barriers to social participation in school faced by students with hearing and visual impairment. Talk about the assistive technologies that offer solutions and prevent social obstacles.
- Teaching strategies for special needs children. Analyze the effectiveness of various teaching approaches regarding their impact on the academic performance of special needs children.
- Disciplining students with disabilities. Explore appropriate methods of enforcing discipline among special needs students without raising controversies. Address the rights of students and ways of encouraging good behavior.
Here are other themes you can consider when writing on a special education topic:
- Discuss collaborative teaching strategies for special educators.
- Special education and teacher burnout.
- Speech-language therapists: The benefits of working in an inclusive environment.
- Discuss the challenges faced by special needs children.
- Special education disability categories.
- Why should special needs children learn in a special school, not a mainstream one?
- Effects of positive social interactions on children with disabilities.
- Teaching strategies for pupils with special educational needs.
- How to prevent bullying of special children?
- Analyze the history of early childhood education for special needs children.
- The inclusion of learners with special educational needs.
- Should the government make special education free for all students?
- The role of parents in instilling self-confidence in their children with disabilities.
- Exceptional children: introduction to special education.
- Why do students with autism face bullying more often than regular students?
- Should teachers be trained in handling special needs children?
- Field experience report and reflection: special education.
- Discuss effective teaching practices in special schools.
- Inclusive learning environment: Does it hinder or promote academic performance?
- Learning disability: special education strategies.
- Government policies on special education.
- A comparative analysis of special education in different countries.
- American special education and early intervention.
- Why are parents of children with disabilities prone to stress?
- Standardized tests for evaluating special needs children in early childhood education.
- Technology integration in special education.
- How to identify gifted children with different disabilities?
- An analysis of education equality for children with disabilities.
- The effect of training employees to work with special education children.
- The effects of teachers’ attitudes on students with dyslexia.
- Special needs children should have equal access to education.
- Special education: parent–professional collaboration.
- Is distance learning effective in special education?
- Evaluate digital literacy in special schools.
- Teacher leadership in special education.
- The importance of peer support in special education.
- Discuss strategies to motivate and retain special educators.
- Autism spectrum disorder and special education issues.
👶 53 Research Topics for Early Childhood Education
Early childhood education is a vital phase that sets the proper academic foundation for students. The early years of a child are essential since education provides a base for future learning abilities and social development .
Below are research topics for early childhood education to inspire your thesis:
- Child development stages. Compare different theories of child development. Analyze the role of the environment and genetics or explain the changes that occur from conception until a child is fully developed.
- The role of parents in early childhood education. Explore parents’ contribution to a child’s cognitive development and behavioral patterns . Discuss the importance of consistent communication with children for their proper development.
- The significance of field activities in preschool. Evaluate the effects of singing, dancing, drawing, painting, and physical exercise on cognitive development. Discuss the teachers’ attitudes toward child performance.
- The history of early childhood theorists. Assess the contribution of Maria Montessori to early childhood education. Describe her approach and explain why multi-sensory learning is essential.
- Computer literacy in young learners. Explore the reasons for introducing computer lessons in preschools. Discuss why young learners need to embrace technology but with strict limitations. Talk about the pros and cons of screen time for young children.
- Development of cognitive abilities in the early years. Analyze how children acquire knowledge, develop skills, and learn to solve problems. You can also focus on the brain development in the early years.
- The importance of play in child development. Explain how playing stimulates the brain and encourages social and emotional development. Give examples of child play and toys and discuss their impact.
- Early detection of special needs children. Explain how preschool educators can detect signs of learning disabilities. Talk about the symptoms of autism, ADHD, and other conditions affecting young learners.
- Teaching strategies in early childhood education. Explore the different teaching approaches used by educators for effective learning. Discuss play-based , inquiry, direct instruction, and project methods and assess their impact on young learners.
- Diversity in preschool. Compare opportunities to learn about cultural differences in homeschooling and regular schooling. Highlight the benefits of diversity for a child’s cognitive development.
- Child trauma. Explain how educators are trained to detect trauma in preschool kids. Talk about the signs of traumatic stress and its impact on a child’s development.
- Legal regulations in early childhood education. Explore the objective of public regulation of education. Discuss children’s rights to education and the regulatory bodies that ensure their protection.
- Contribution of Friedrich Froebel. Explore Froebel’s advocacy of an activity-based approach to early childhood education. Talk about the importance of creative and structured learning for developing minds.
- Effects of social interaction. Discuss the significance of socializing on a child’s cognitive development. Explain why educators should incorporate social activities in preschool to boost a child’s confidence.
- Importance of childcare centers. Evaluate their significance in developing emotional, social, and communication skills. Talk about the safety and health of children in preschool.
Here are some more exciting topics about early childhood education:
- The significance of physical books for preschool children.
- Best practices in early childhood education.
- The effects of divorce on the cognitive development of a preschool child.
- The influence of parents on young children’s moral development .
- Interview with an early childhood professional.
- Teachers’ attitudes toward children with ADHD in preschool.
- Effects of technology in an early childhood class.
- Impact of early childhood experience on the development of the personality .
- The significance of kindergarten in children’s development.
- How does unlimited screen time affect a child’s brain?
- Arts and play in early childhood development.
- Discuss the environmental factors that influence a child’s development.
- What is the observational strategy in early childhood training?
- Early childhood education: leadership and management.
- Significance of outdoor play in kindergarten learners.
- The role of vision therapy in young autistic children.
- Teaching philosophy in early childhood development.
- The influence of video games on young children’s learning outcomes.
- Discuss Vygotsky’s theory of socio-cultural learning.
- Early childhood profession in Australia.
- An analysis of the practical implications of early childhood learning.
- Discuss the objectives of international agreements on early childhood education.
- Environment in early childhood education.
- The barriers and challenges hindering young children’s effective learning.
- Genetic influences on a child’s behavior.
- Curricular issues in early childhood education.
- The significance of play in enhancing social skills.
- How does storytelling improve cognitive development?
- Early childhood safety considerations.
- Does early childhood development affect an individual’s personality?
- The effect of green classroom environment on young children.
- Early childhood education standards and practices.
- The role of diet on child development.
- The influence of culture on a child’s behavior.
- Overcoming stereotypes in early childhood education.
- The impact of bullying on young children.
- Emotional development in early childhood education.
- Stress in early childhood education.
🧠 53 Educational Psychology Research Topics
Educational psychology studies human learning processes, such as memory, conceptual understanding, and social-emotional skills. It covers both cognitive and behavioral aspects. Below are interesting educational psychology research topics to inspire your academic project:
- History of educational psychology. Explore the origin of educational psychology and the contributions made by its founders. Discuss the formal learning steps according to Johann Herbart.
- Young learners vs. adult learners. Explain the difference between learning as a child and an adult. Describe the challenges encountered and problem-solving skills demonstrated by children and adults in different situations.
- Significance of inspirational teaching. Explore the gender differences in teaching strategies. Discuss the pros and cons of incorporating emotions when teaching. Present the findings and implications for student performance.
- Emotion-based learning. Conduct a comparative study among autistic children and regular children in preschool. Explain how emotion-based teaching influences cognitive development and corrects learning impairments in autistic children.
- Importance of discipline models. Construct a case study of high-school students engaging in extra-curricular activities. Establish a connection between discipline models and high achievements. Talk about the psychological impact of a strict routine on shaping an individual’s personality.
- Effects of language challenges. Explore how language impacts the learning abilities of young children and how it may affect a student’s personality and performance later.
- Philosophers of education. Present a comparative evaluation of the history of education philosophers. Talk about the approaches of Juan Vives, Johann Herbart, and Johann Pestalozzi and their contribution to educational psychology.
- Impact of culture on education. Explore how culture can strongly influence an individual’s perception of education. Discuss the positive and negative aspects of culture from modern and historical angles.
- Educational psychology in rural schools. Evaluate the ethical, professional, and legal frameworks of education in rural contexts. Talk about the challenges faced by educators in rural areas.
- Effects of motivation on student performance. Explain the importance of motivation in students. You can focus on high-school learners and assess the effectiveness of a particular system of rewards for good performance.
- Language and literacy in education. Identify and define language issues during early years and the implications for future achievements. Talk about reading and language barriers affecting young children.
- Bell curve approach. Explore the fairness of the bell curve system of grading. Discuss the history of this method and its pros and cons. Explain its educational relevance and role in motivating students.
- Positive psychology in education. Evaluate the role of positive psychology in encouraging student performance. Analyze how schools can integrate mental health education into teaching achievement and accomplishment.
- Stress management techniques. Suggest the best approach to managing academic stress and preventing depression among students. Talk about the leading causes and effects of stress among college students and effective coping techniques.
- Impact of peer pressure. Explain the upsides and downsides of peer groups in school-going children. Discuss the effects of peer pressure on the moral conduct of students.
Here are some more examples of educational psychology topics for your research writing:
- The importance of educational psychology.
- Educational psychology: theory and practice.
- How does a child’s brain develop during learning?
- The risk factors and outcomes of bullying.
- Educational psychology: changing students’ behavior.
- The significance of peer interaction in adolescents.
- Effects of substance abuse on student performance.
- Using educational psychology in teaching.
- The influence of cartoons on a child’s mental state.
- Discuss teenage rebellion against parents.
- Reinforcers in classrooms: educational psychology in teaching.
- The relationship between speech disorders and cognitive development.
- An analysis of psychological theories in education.
- Educational psychology: behaviorism.
- The impact of media violence on child development.
- Explore the trends in educational psychology.
- School facilities in educational psychology.
- The effect of gender stereotyping in schools.
- Autism spectrum : the perspectives of parents and teachers.
- Psychology of learning and memory .
- The influence of the authoritarian parenting style on student performance.
- The impact of single parenting on children’s cognitive development.
- Cognitive learning and IQ tests.
- Discuss major challenges in mathematical thinking.
- An analysis of social-emotional development in children.
- Pathways of adult learning.
- The influence of modern technology on educational psychology.
- The importance of critical thinking in learners.
- Learning styles and their importance .
- Should schools teach moral behavior?
- A comparative study of psychological disorders.
- Anxiety causes and effects on language learning.
- Leading causes of mental health issues among students.
- The significance of professional educators.
- Student motivation and ways to enhance it.
- Discipline approaches for moral development.
- The mechanism of character development in young children.
- Learning and memory relations.
🧸 53 Child Development Topics to Explore
Child development is an important field of study since it investigates the changes a person undergoes from conception to adolescence. Finding a unique topic on child development may be challenging. We offer a comprehensive list of child development topics to simplify your research project:
- Child development theories. Explore significant theories and their importance in explaining children’s social and emotional development. For example, talk about the contributions of Jean Piaget to understanding children’s cognition.
- The significance of social interaction. Evaluate the importance of socialization in a child’s behavior. Present the outcomes of interacting with peers and its influence on a child’s personality.
- Mental health in early childhood development. Explain why mental health is often overlooked in young children. Discuss the signs of psychological problems in children.
- Jean Piaget’s perspective on child development. Explore the history of Piaget’s philosophy and the importance of child psychology in the modern world. Talk about the relevance of each developmental stage.
- Early childhood personality. Study personality development at a young age. Discuss how childhood shapes an individual’s personality throughout their life.
- The impact of gender roles in child development. Explore what part parents and educators play in teaching children about gender roles. Discuss the possible effects of learning gender roles on shaping a child’s perception and actions as an adult.
- The significance of the environment. Explain the role of the environment in developing the human mind during childhood. Consider such environmental factors as friends, housing, climate, and access to basic needs.
- Communication skills in language development. Explain the importance of consistent communication with a child from conception to the early years. Talk about parent-child bonding through communication and how it influences language development.
- The influence of culture on child development. Conduct a comprehensive study of how cultural differences impact a child’s development. Talk about the cultural norms that children are trained to accept as they grow from infancy to adulthood.
- Importance of child observation . Explain why observing a child during the early years is crucial to identify issues in achieving developmental milestones. Discuss the role of parents and educators in child development.
- Attachment theory by John Bowlby. Explore the attachment theory and why interpersonal relationships are essential among humans. Talk about the significance of an emotional bond between a child and a parent to facilitate normal development.
- Erickson’s stages of development. Analyze the eight phases of human development. Discuss the importance of each stage and how it affects an individual’s future behavior and personality.
- Asynchronous development. Explore the challenges of asynchronous development to parents, educators, and the child. Talk about the possible causes and effects of asynchronous development.
- Child research methods. Conduct a comparative analysis of infant research methods. Discuss the key challenges when studying infants. Talk about such approaches as eye tracking, the sucking technique, or brain imaging technology.
- Ethical considerations in child research. Explore the ethical dilemmas when conducting studies on children. Describe the verbal and non-verbal indicators that researchers can use as a child’s consent to participation.
Here are more exciting topics on child development:
- Discuss Piaget’s theory of child development.
- Child development from birth to three wears and the role of adults.
- Importance of play in improving gross motor skills.
- Why do parents need to understand child development theories?
- Attachment and its role in child development.
- The role of music in increasing focus in children.
- Discuss the five steps of cognitive development.
- Child development and education: physical exercise.
- Ego formation in a child.
- Discuss positive parenting styles.
- Cognitive domain of child development: activity plan.
- Effects of food insecurity on child development.
- Explore Vygotsky’s social-cultural theory.
- Gifted students: child development.
- Child development: The role of a mother .
- Importance of language stimulation in young children.
- Physical education: impact on child development.
- Significance of movement in child development.
- An analysis of effective parenting styles.
- Child development theories.
- The influence of genetics on child development.
- The role of a balanced diet in child development.
- Educative toys’ role in child development.
- Why are children more creative than adults?
- The importance of pretend-play on development.
- Connection between screen time and child development.
- Discuss social development theory in relation to children.
- A comparative analysis of Vygotsky’s and Piaget’s theories.
- Child development: ages one through three.
- Discuss the impact of literate communities on child development.
- How can parents deal with stress in children and teenagers?
- Child development and environmental influences.
- The environmental influences on a child’s behavior.
- Pros and cons of imaginary friends.
- The impact of dyslexia on child development.
- Effective approaches in language development.
- The role of books in child development.
- Child development during the COVID-19 pandemic.
👩🏻💼 53 Educational Management Research Topics
Educational management is a collection of various components of education. Research topics cover multiple concepts ranging from administrative to financial aspects of education. Here are inspiring educational management research topics for your perusal:
- Higher education leadership. Explore the qualifications of higher education leaders in developed countries. Discuss their implications for pursuing a career in educational management.
- A review of the educational ecosystem. Explore the governing bodies in education. Talk about the government ministries, statutory bodies, principals, administrative personnel, educators, and non-teaching staff. Explain why management is vital at all levels.
- Significance of extra-curricular activities. Explore the role of co-curricular activities in maintaining a holistic education approach. Discuss the types of activities and their benefits for student performance.
- Curriculum planning. Explore the strategies used in curriculum planning and the factors affecting its development, evaluation, and implementation. Discuss the three stages involved in this process.
- Friedrich Frobel’s approach to curriculum development. Explore the key educational components at the preschool level and describe the forms of knowledge. Explain Frobel’s focus on life, knowledge, and beauty.
- The impact of technology. Explore the significance of technology in education management. Investigate such issues as budget limitations, data security concerns, and poor network infrastructure.
- Importance of financial policies in schools. Explain how economic policies offer administrative support to ensure seamless operations. Talk about the revenue streams, school funds, government subsidies, grants, and allowances.
- Health and physical development. Explain why institutions need a health and physical education department. Talk about healthy living and the importance of exercise.
- Significance of human resources. Discuss the role of the HR department in educational institutions. Present the benefits of specific organizational structures and operational policies in ensuring smooth functioning.
- The objectives of educators. Explore the strategies for planning and implementing lessons. Talk about the importance of pedagogical practices in educational management. Discuss the effects of the classroom-management approach.
- National examples of educational management. Conduct a comparative study on Australia, Finland, and Singapore. Discuss the school structure, curriculum, and government policies and involvement.
- Parents’ perception of educational administrative policies. Discuss the parents’ attitudes toward policies from preschool to the university level. Explore both private and public institutions.
- The goals of education ministries. Explore the objectives of the education ministry, such as designing, implementing, monitoring, and evaluating educational legislation. Discuss the leadership roles in ensuring smooth operations of learning institutions.
- Challenges of educators. Explore the leadership styles of educators in high school. Talk about the discipline strategies for dealing with rebellious teenagers and cases of indiscipline.
- Special education. Analyze the features of education management in special schools. Discuss the process of developing individual education plans and dealing with special education issues, such as budgeting or parent education.
Here are some more engaging topics in educational management you can check out to get inspiration:
- Discuss the critical issues of classroom management.
- Why is the UK education system successful?
- Effects of guidance on student performance.
- The effectiveness of standardized tests for measuring student performance.
- Corruption in the education sector: Democratic Republic of Congo.
- The features of managing distance learning systems.
- The role of a principal in school functioning.
- The financial issues in the secondary education area in the US.
- The relationship between a principal’s leadership style and teachers’ satisfaction.
- The link between classroom management and student behavior.
- School principals as agents of change.
- Effects on instructional-based learning on academic performance.
- An analysis of interactive teaching methods.
- School-community partnership and its benefits.
- The influence of government policies in educational administration.
- Discuss educational leadership in the digital age.
- Program quality assessment: teaching and learning.
- The role of educators in moral discipline.
- The impact of a poor educational system.
- The lack of sex education in the Thai educational system.
- An analysis of Montessori education.
- Importance of curriculum planning.
- Teachers’ certification: is it necessary?
- The effects of progressive education.
- The influence of the environment on academic performance.
- How can a principal improve the quality of special education?
- Discuss the impact of teacher motivation.
- Does strict school supervision translate to high academic performance?
- Effectiveness of educational leadership management skills.
- Can poor management of schools result in increased student indiscipline?
- The influence of good administrative leadership in education.
- Educational leadership and instruction differentiation.
- Factors preventing effective school management.
- Explore biases in educational administration.
- The use of standardized tests in college admissions.
- The link between academic performance and school accountability.
- Gender equality in educational management.
- Financial issues facing US higher education.
📑 15 Dissertation Topics in Education
Dissertation research is more complex than usual research for college or university assignments. It requires more originality and extends over a longer period. Here are some dissertation topics in education you can consider for your forthcoming dissertation project:
- Examine the impact of COVID-19 social isolation on students of your university.
- Social media impact on English language learning.
- Cross-cultural communication and conflict management at your chosen online study course.
- Principals’ concerns and attitudes toward social distancing policies in Texas schools.
- Formative assessment: impact on student achievement.
- A case study of children’s first and second language use in play-based interactions in a private kindergarten.
- The impact of present-day economic pressures on the K-12 curriculum development in the US: Teachers’ and policymakers’ perspectives.
- How does inclusion impact autistic children?
- Collaborative inquiry and video documentation to facilitate school teachers’ critical thinking competencies: Analysis of the INSIGHT project at a public school.
- Using computer-based reading interventions for at-risk preschoolers: Teachers’ perspectives.
- Homeschooling and its impact on learners.
- Relationship between the Math assessment method and student self-esteem.
- Parents’ attitudes toward the use of technology in elementary school.
- Impact of classroom technology on learner attitudes.
- Impact of teacher training on student attainment: An EU study.
- The link between homework load and student stress levels.
- How common are shootings in American schools?
- The impact of classroom size on academic performance in elementary schools.
- The relationship between school safety measures and student psychological well-being.
- How effective is an inclusive school environment in fostering better academic outcomes?
- The impact of socioeconomic factors on school dropout rates.
- What is the role of school policies in addressing cyberbullying among students?
- The influence of socioeconomic aspects on the quality of education in public schools.
- How prevalent is bullying in public schools?
- The influence of standardized testing on student success.
- How important is parent involvement in the learning process?
- The effect of extracurricular overload on student anxiety development.
- How does peer pressure affect student decision-making?
- The influence of inclusive education on the performance of students with learning disabilities.
- How can AI technology in education engage students in more active learning?
- The link between socioeconomic background and access to educational resources.
- The impact of government funding on the education system.
- How limited is access to mental health support in high schools?
Now that you have a comprehensive list of educational research topics of all complexity levels, you can easily ace any assignment for your Pedagogy course. Don’t hesitate to share this article with your peers and post a commentary if any topic has been helpful to you.
❓ Education Research Topics FAQ
What are some good research topics in education.
Well-chosen topics for educational research should be carefully scoped and relevant to your academic level and context. It’s vital to cover hot issues by linking theory and practice, thus ensuring that your study is valuable and related to present-day education.
What is an example of educational research?
Educational research covers many subjects and subdisciplines, so you may focus on any area important to you. It may be a special education class where you can approach teachers or observe students with special needs . Or it can be educational leadership research, where you will search for new, efficient ways of school administration for principals.
What topics should be addressed in sex education?
Sex education is a pressing issue in many schools worldwide, as teenage pregnancy rates are increasing. You may approach this subject by examining the attitudes to sex education among parents with different religious affiliations. Or you can compare the rates of teenage abortion and pregnancies in states with and without sex education in the formal curriculum.
What is action research in education?
Action research is a combination of practice and research in one endeavor. You should first study theory, develop an assumption that can be applied in practice, and then implement that method in your educational setting. After the intervention, you measure the outcomes and present findings in your research paper, thus concluding whether your assumption was valid.
- Child Development Basics | CDC
- Issues and Challenges in Special Education | Southeast Asia Early Childhood Journal
- Social Issues That Special Education Teachers Face | Chron
- Problems in Educational Administration | Classroom
- Early Childhood Development: The Promise, the Problem, and the Path Forward | Brookings
- Educational Psychology and Research | University of South Carolina
- 5 Big Challenges for Schools in 2023 | EducationWeek
- Quantitative Methods in Education | University of Minnesota
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | American University
414 Proposal Essay Topics for Projects, Research, & Proposal Arguments
725 research proposal topics & title ideas in education, psychology, business, & more.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 02 December 2020
Enhancing senior high school student engagement and academic performance using an inclusive and scalable inquiry-based program
- Locke Davenport Huyer ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1526-7122 1 , 2 na1 ,
- Neal I. Callaghan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8214-3395 1 , 3 na1 ,
- Sara Dicks 4 ,
- Edward Scherer 4 ,
- Andrey I. Shukalyuk 1 ,
- Margaret Jou 4 &
- Dawn M. Kilkenny ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3899-9767 1 , 5
npj Science of Learning volume 5 , Article number: 17 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
43k Accesses
5 Citations
13 Altmetric
Metrics details
The multi-disciplinary nature of science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) careers often renders difficulty for high school students navigating from classroom knowledge to post-secondary pursuits. Discrepancies between the knowledge-based high school learning approach and the experiential approach of future studies leaves some students disillusioned by STEM. We present Discovery , a term-long inquiry-focused learning model delivered by STEM graduate students in collaboration with high school teachers, in the context of biomedical engineering. Entire classes of high school STEM students representing diverse cultural and socioeconomic backgrounds engaged in iterative, problem-based learning designed to emphasize critical thinking concomitantly within the secondary school and university environments. Assessment of grades and survey data suggested positive impact of this learning model on students’ STEM interests and engagement, notably in under-performing cohorts, as well as repeating cohorts that engage in the program on more than one occasion. Discovery presents a scalable platform that stimulates persistence in STEM learning, providing valuable learning opportunities and capturing cohorts of students that might otherwise be under-engaged in STEM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Subject integration and theme evolution of STEM education in K-12 and higher education research
Skill levels and gains in university STEM education in China, India, Russia and the United States
Academic ecosystems must evolve to support a sustainable postdoc workforce
Introduction.
High school students with diverse STEM interests often struggle to understand the STEM experience outside the classroom 1 . The multi-disciplinary nature of many career fields can foster a challenge for students in their decision to enroll in appropriate high school courses while maintaining persistence in study, particularly when these courses are not mandatory 2 . Furthermore, this challenge is amplified by the known discrepancy between the knowledge-based learning approach common in high schools and the experiential, mastery-based approaches afforded by the subsequent undergraduate model 3 . In the latter, focused classes, interdisciplinary concepts, and laboratory experiences allow for the application of accumulated knowledge, practice in problem solving, and development of both general and technical skills 4 . Such immersive cooperative learning environments are difficult to establish in the secondary school setting and high school teachers often struggle to implement within their classroom 5 . As such, high school students may become disillusioned before graduation and never experience an enriched learning environment, despite their inherent interests in STEM 6 .
It cannot be argued that early introduction to varied math and science disciplines throughout high school is vital if students are to pursue STEM fields, especially within engineering 7 . However, the majority of literature focused on student interest and retention in STEM highlights outcomes in US high school learning environments, where the sciences are often subject-specific from the onset of enrollment 8 . In contrast, students in the Ontario (Canada) high school system are required to complete Level 1 and 2 core courses in science and math during Grades 9 and 10; these courses are offered as ‘applied’ or ‘academic’ versions and present broad topics of content 9 . It is not until Levels 3 and 4 (generally Grades 11 and 12, respectively) that STEM classes become subject-specific (i.e., Biology, Chemistry, and/or Physics) and are offered as “university”, “college”, or “mixed” versions, designed to best prepare students for their desired post-secondary pursuits 9 . Given that Levels 3 and 4 science courses are not mandatory for graduation, enrollment identifies an innate student interest in continued learning. Furthermore, engagement in these post-secondary preparatory courses is also dependent upon achieving successful grades in preceding courses, but as curriculum becomes more subject-specific, students often yield lower degrees of success in achieving course credit 2 . Therefore, it is imperative that learning supports are best focused on ensuring that those students with an innate interest are able to achieve success in learning.
When given opportunity and focused support, high school students are capable of successfully completing rigorous programs at STEM-focused schools 10 . Specialized STEM schools have existed in the US for over 100 years; generally, students are admitted after their sophomore year of high school experience (equivalent to Grade 10) based on standardized test scores, essays, portfolios, references, and/or interviews 11 . Common elements to this learning framework include a diverse array of advanced STEM courses, paired with opportunities to engage in and disseminate cutting-edge research 12 . Therein, said research experience is inherently based in the processes of critical thinking, problem solving, and collaboration. This learning framework supports translation of core curricular concepts to practice and is fundamental in allowing students to develop better understanding and appreciation of STEM career fields.
Despite the described positive attributes, many students do not have the ability or resources to engage within STEM-focused schools, particularly given that they are not prevalent across Canada, and other countries across the world. Consequently, many public institutions support the idea that post-secondary led engineering education programs are effective ways to expose high school students to engineering education and relevant career options, and also increase engineering awareness 13 . Although singular class field trips are used extensively to accomplish such programs, these may not allow immersive experiences for application of knowledge and practice of skills that are proven to impact long-term learning and influence career choices 14 , 15 . Longer-term immersive research experiences, such as after-school programs or summer camps, have shown successful at recruiting students into STEM degree programs and careers, where longevity of experience helps foster self-determination and interest-led, inquiry-based projects 4 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 .
Such activities convey the elements that are suggested to make a post-secondary led high school education programs successful: hands-on experience, self-motivated learning, real-life application, immediate feedback, and problem-based projects 20 , 21 . In combination with immersion in university teaching facilities, learning is authentic and relevant, similar to the STEM school-focused framework, and consequently representative of an experience found in actual STEM practice 22 . These outcomes may further be a consequence of student engagement and attitude: Brown et al. studied the relationships between STEM curriculum and student attitudes, and found the latter played a more important role in intention to persist in STEM when compared to self-efficacy 23 . This is interesting given that student self-efficacy has been identified to influence ‘motivation, persistence, and determination’ in overcoming challenges in a career pathway 24 . Taken together, this suggests that creation and delivery of modern, exciting curriculum that supports positive student attitudes is fundamental to engage and retain students in STEM programs.
Supported by the outcomes of identified effective learning strategies, University of Toronto (U of T) graduate trainees created a novel high school education program Discovery , to develop a comfortable yet stimulating environment of inquiry-focused iterative learning for senior high school students (Grades 11 & 12; Levels 3 & 4) at non-specialized schools. Built in strong collaboration with science teachers from George Harvey Collegiate Institute (Toronto District School Board), Discovery stimulates application of STEM concepts within a unique term-long applied curriculum delivered iteratively within both U of T undergraduate teaching facilities and collaborating high school classrooms 25 . Based on the volume of medically-themed news and entertainment that is communicated to the population at large, the rapidly-growing and diverse field of biomedical engineering (BME) were considered an ideal program context 26 . In its definition, BME necessitates cross-disciplinary STEM knowledge focused on the betterment of human health, wherein Discovery facilitates broadening student perspective through engaging inquiry-based projects. Importantly, Discovery allows all students within a class cohort to work together with their classroom teacher, stimulating continued development of a relevant learning community that is deemed essential for meaningful context and important for transforming student perspectives and understandings 27 , 28 . Multiple studies support the concept that relevant learning communities improve student attitudes towards learning, significantly increasing student motivation in STEM courses, and consequently improving the overall learning experience 29 . Learning communities, such as that provided by Discovery , also promote the formation of self-supporting groups, greater active involvement in class, and higher persistence rates for participating students 30 .
The objective of Discovery , through structure and dissemination, is to engage senior high school science students in challenging, inquiry-based practical BME activities as a mechanism to stimulate comprehension of STEM curriculum application to real-world concepts. Consequent focus is placed on critical thinking skill development through an atmosphere of perseverance in ambiguity, something not common in a secondary school knowledge-focused delivery but highly relevant in post-secondary STEM education strategies. Herein, we describe the observed impact of the differential project-based learning environment of Discovery on student performance and engagement. We identify the value of an inquiry-focused learning model that is tangible for students who struggle in a knowledge-focused delivery structure, where engagement in conceptual critical thinking in the relevant subject area stimulates student interest, attitudes, and resulting academic performance. Assessment of study outcomes suggests that when provided with a differential learning opportunity, student performance and interest in STEM increased. Consequently, Discovery provides an effective teaching and learning framework within a non-specialized school that motivates students, provides opportunity for critical thinking and problem-solving practice, and better prepares them for persistence in future STEM programs.
Program delivery
The outcomes of the current study result from execution of Discovery over five independent academic terms as a collaboration between Institute of Biomedical Engineering (graduate students, faculty, and support staff) and George Harvey Collegiate Institute (science teachers and administration) stakeholders. Each term, the program allowed senior secondary STEM students (Grades 11 and 12) opportunity to engage in a novel project-based learning environment. The program structure uses the problem-based engineering capstone framework as a tool of inquiry-focused learning objectives, motivated by a central BME global research topic, with research questions that are inter-related but specific to the curriculum of each STEM course subject (Fig. 1 ). Over each 12-week term, students worked in teams (3–4 students) within their class cohorts to execute projects with the guidance of U of T trainees ( Discovery instructors) and their own high school teacher(s). Student experimental work was conducted in U of T teaching facilities relevant to the research study of interest (i.e., Biology and Chemistry-based projects executed within Undergraduate Teaching Laboratories; Physics projects executed within Undergraduate Design Studios). Students were introduced to relevant techniques and safety procedures in advance of iterative experimentation. Importantly, this experience served as a course term project for students, who were assessed at several points throughout the program for performance in an inquiry-focused environment as well as within the regular classroom (Fig. 1 ). To instill the atmosphere of STEM, student teams delivered their outcomes in research poster format at a final symposium, sharing their results and recommendations with other post-secondary students, faculty, and community in an open environment.
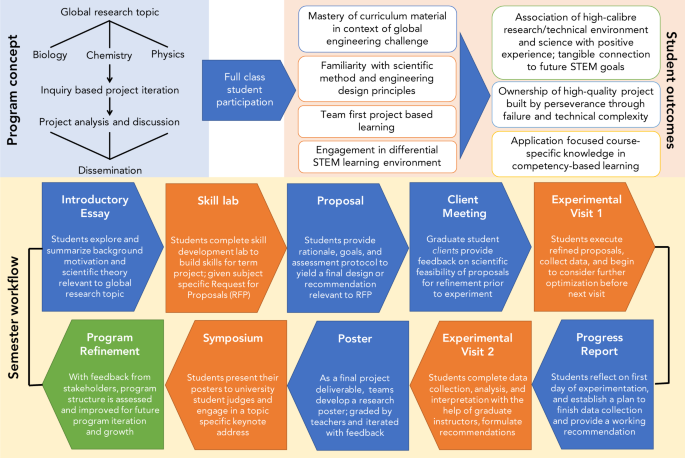
The general program concept (blue background; top left ) highlights a global research topic examined through student dissemination of subject-specific research questions, yielding multifaceted student outcomes (orange background; top right ). Each program term (term workflow, yellow background; bottom panel ), students work on program deliverables in class (blue), iterate experimental outcomes within university facilities (orange), and are assessed accordingly at numerous deliverables in an inquiry-focused learning model.
Over the course of five terms there were 268 instances of tracked student participation, representing 170 individual students. Specifically, 94 students participated during only one term of programming, 57 students participated in two terms, 16 students participated in three terms, and 3 students participated in four terms. Multiple instances of participation represent students that enrol in more than one STEM class during their senior years of high school, or who participated in Grade 11 and subsequently Grade 12. Students were surveyed before and after each term to assess program effects on STEM interest and engagement. All grade-based assessments were performed by high school teachers for their respective STEM class cohorts using consistent grading rubrics and assignment structure. Here, we discuss the outcomes of student involvement in this experiential curriculum model.
Student performance and engagement
Student grades were assigned, collected, and anonymized by teachers for each Discovery deliverable (background essay, client meeting, proposal, progress report, poster, and final presentation). Teachers anonymized collective Discovery grades, the component deliverable grades thereof, final course grades, attendance in class and during programming, as well as incomplete classroom assignments, for comparative study purposes. Students performed significantly higher in their cumulative Discovery grade than in their cumulative classroom grade (final course grade less the Discovery contribution; p < 0.0001). Nevertheless, there was a highly significant correlation ( p < 0.0001) observed between the grade representing combined Discovery deliverables and the final course grade (Fig. 2a ). Further examination of the full dataset revealed two student cohorts of interest: the “Exceeds Expectations” (EE) subset (defined as those students who achieved ≥1 SD [18.0%] grade differential in Discovery over their final course grade; N = 99 instances), and the “Multiple Term” (MT) subset (defined as those students who participated in Discovery more than once; 76 individual students that collectively accounted for 174 single terms of assessment out of the 268 total student-terms delivered) (Fig. 2b, c ). These subsets were not unrelated; 46 individual students who had multiple experiences (60.5% of total MTs) exhibited at least one occasion in achieving a ≥18.0% grade differential. As students participated in group work, there was concern that lower-performing students might negatively influence the Discovery grade of higher-performing students (or vice versa). However, students were observed to self-organize into groups where all individuals received similar final overall course grades (Fig. 2d ), thereby alleviating these concerns.
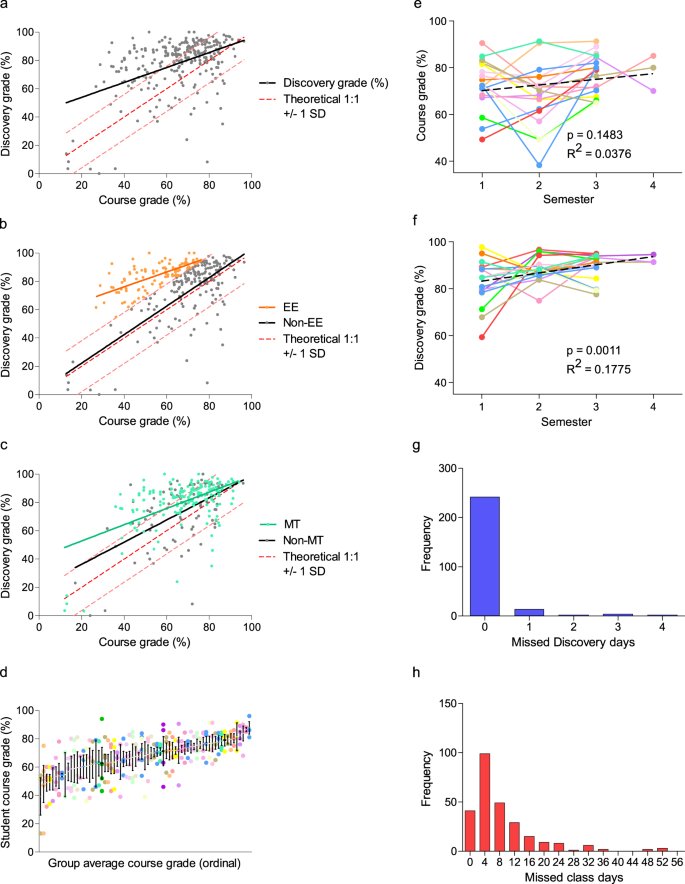
a Linear regression of student grades reveals a significant correlation ( p = 0.0009) between Discovery performance and final course grade less the Discovery contribution to grade, as assessed by teachers. The dashed red line and intervals represent the theoretical 1:1 correlation between Discovery and course grades and standard deviation of the Discovery -course grade differential, respectively. b , c Identification of subgroups of interest, Exceeds Expectations (EE; N = 99, orange ) who were ≥+1 SD in Discovery -course grade differential and Multi-Term (MT; N = 174, teal ), of which N = 65 students were present in both subgroups. d Students tended to self-assemble in working groups according to their final course performance; data presented as mean ± SEM. e For MT students participating at least 3 terms in Discovery , there was no significant correlation between course grade and time, while ( f ) there was a significant correlation between Discovery grade and cumulative terms in the program. Histograms of total absences per student in ( g ) Discovery and ( h ) class (binned by 4 days to be equivalent in time to a single Discovery absence).
The benefits experienced by MT students seemed progressive; MT students that participated in 3 or 4 terms ( N = 16 and 3, respectively ) showed no significant increase by linear regression in their course grade over time ( p = 0.15, Fig. 2e ), but did show a significant increase in their Discovery grades ( p = 0.0011, Fig. 2f ). Finally, students demonstrated excellent Discovery attendance; at least 91% of participants attended all Discovery sessions in a given term (Fig. 2g ). In contrast, class attendance rates reveal a much wider distribution where 60.8% (163 out of 268 students) missed more than 4 classes (equivalent in learning time to one Discovery session) and 14.6% (39 out of 268 students) missed 16 or more classes (equivalent in learning time to an entire program of Discovery ) in a term (Fig. 2h ).
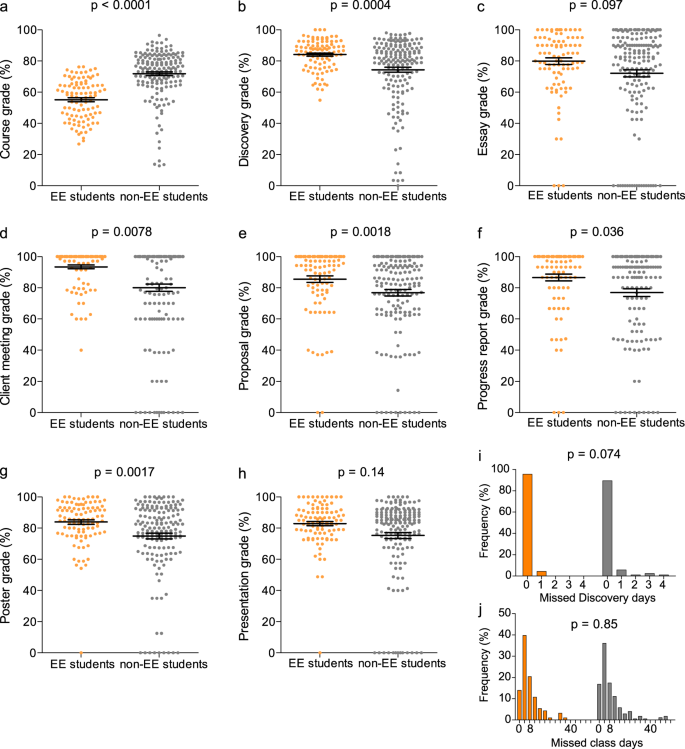
Discovery EE students (Fig. 3 ), roughly by definition, obtained lower course grades ( p < 0.0001, Fig. 3a ) and higher final Discovery grades ( p = 0.0004, Fig. 3b ) than non-EE students. This cohort of students exhibited program grades higher than classmates (Fig. 3c–h ); these differences were significant in every category with the exception of essays, where they outperformed to a significantly lesser degree ( p = 0.097; Fig. 3c ). There was no statistically significant difference in EE vs. non-EE student classroom attendance ( p = 0.85; Fig. 3i, j ). There were only four single day absences in Discovery within the EE subset; however, this difference was not statistically significant ( p = 0.074).
The “Exceeds Expectations” (EE) subset of students (defined as those who received a combined Discovery grade ≥1 SD (18.0%) higher than their final course grade) performed ( a ) lower on their final course grade and ( b ) higher in the Discovery program as a whole when compared to their classmates. d – h EE students received significantly higher grades on each Discovery deliverable than their classmates, except for their ( c ) introductory essays and ( h ) final presentations. The EE subset also tended ( i ) to have a higher relative rate of attendance during Discovery sessions but no difference in ( j ) classroom attendance. N = 99 EE students and 169 non-EE students (268 total). Grade data expressed as mean ± SEM.
Discovery MT students (Fig. 4 ), although not receiving significantly higher grades in class than students participating in the program only one time ( p = 0.29, Fig. 4a ), were observed to obtain higher final Discovery grades than single-term students ( p = 0.0067, Fig. 4b ). Although trends were less pronounced for individual MT student deliverables (Fig. 4c–h ), this student group performed significantly better on the progress report ( p = 0.0021; Fig. 4f ). Trends of higher performance were observed for initial proposals and final presentations ( p = 0.081 and 0.056, respectively; Fig. 4e, h ); all other deliverables were not significantly different between MT and non-MT students (Fig. 4c, d, g ). Attendance in Discovery ( p = 0.22) was also not significantly different between MT and non-MT students, although MT students did miss significantly less class time ( p = 0.010) (Fig. 4i, j ). Longitudinal assessment of individual deliverables for MT students that participated in three or more Discovery terms (Fig. 5 ) further highlights trend in improvement (Fig. 2f ). Greater performance over terms of participation was observed for essay ( p = 0.0295, Fig. 5a ), client meeting ( p = 0.0003, Fig. 5b ), proposal ( p = 0.0004, Fig. 5c ), progress report ( p = 0.16, Fig. 5d ), poster ( p = 0.0005, Fig. 5e ), and presentation ( p = 0.0295, Fig. 5f ) deliverable grades; these trends were all significant with the exception of the progress report ( p = 0.16, Fig. 5d ) owing to strong performance in this deliverable in all terms.
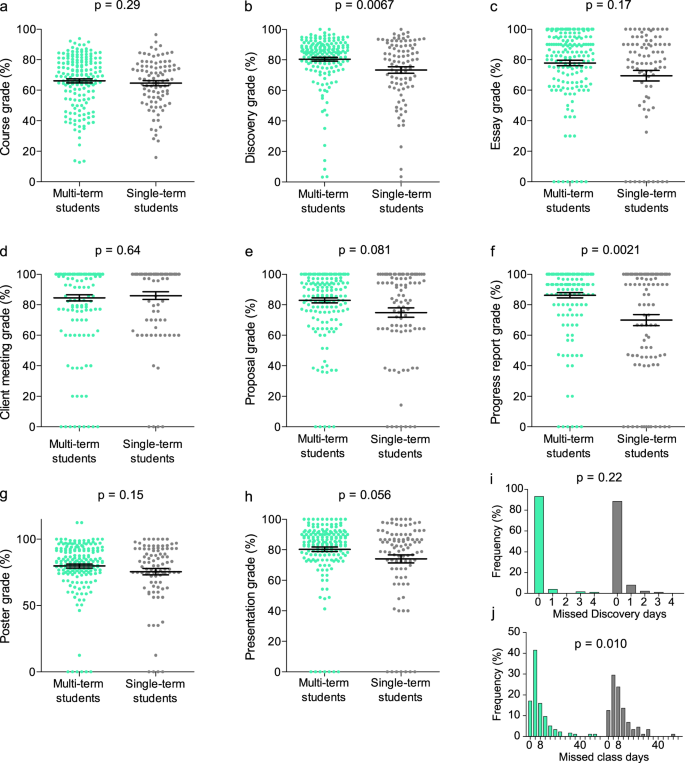
The “multi-term” (MT) subset of students (defined as having attended more than one term of Discovery ) demonstrated favorable performance in Discovery , ( a ) showing no difference in course grade compared to single-term students, but ( b outperforming them in final Discovery grade. Independent of the number of times participating in Discovery , MT students did not score significantly differently on their ( c ) essay, ( d ) client meeting, or ( g ) poster. They tended to outperform their single-term classmates on the ( e ) proposal and ( h ) final presentation and scored significantly higher on their ( f ) progress report. MT students showed no statistical difference in ( i ) Discovery attendance but did show ( j ) higher rates of classroom attendance than single-term students. N = 174 MT instances of student participation (76 individual students) and 94 single-term students. Grade data expressed as mean ± SEM.
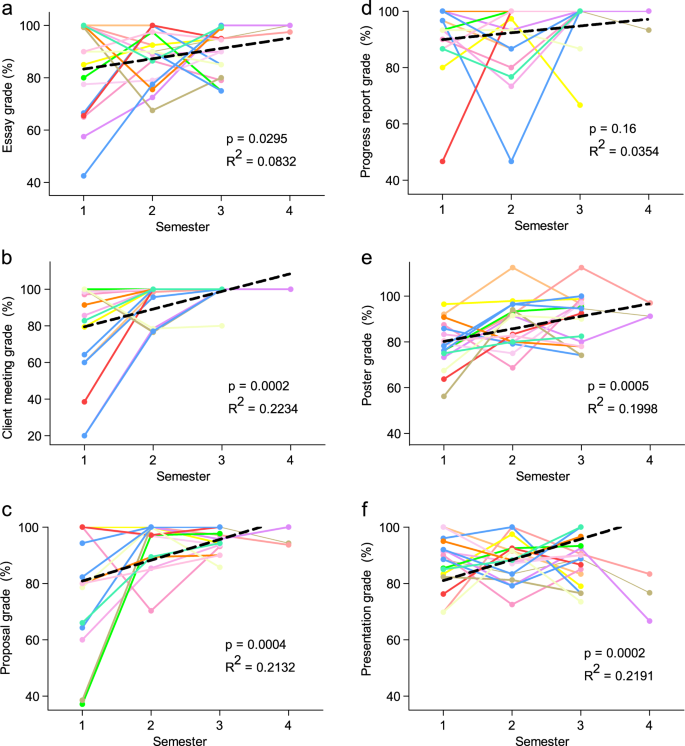
Longitudinal assessment of a subset of MT student participants that participated in three ( N = 16) or four ( N = 3) terms presents a significant trend of improvement in their ( a ) essay, ( b ) client meeting, ( c ) proposal, ( e ) poster, and ( f ) presentation grade. d Progress report grades present a trend in improvement but demonstrate strong performance in all terms, limiting potential for student improvement. Grade data are presented as individual student performance; each student is represented by one color; data is fitted with a linear trendline (black).
Finally, the expansion of Discovery to a second school of lower LOI (i.e., nominally higher aggregate SES) allowed for the assessment of program impact in a new population over 2 terms of programming. A significant ( p = 0.040) divergence in Discovery vs. course grade distribution from the theoretical 1:1 relationship was found in the new cohort (S 1 Appendix , Fig. S 1 ), in keeping with the pattern established in this study.
Teacher perceptions
Qualitative observation in the classroom by high school teachers emphasized the value students independently placed on program participation and deliverables. Throughout the term, students often prioritized Discovery group assignments over other tasks for their STEM courses, regardless of academic weight and/or due date. Comparing within this student population, teachers spoke of difficulties with late and incomplete assignments in the regular curriculum but found very few such instances with respect to Discovery -associated deliverables. Further, teachers speculated on the good behavior and focus of students in Discovery programming in contrast to attentiveness and behavior issues in their school classrooms. Multiple anecdotal examples were shared of renewed perception of student potential; students that exhibited poor academic performance in the classroom often engaged with high performance in this inquiry-focused atmosphere. Students appeared to take a sense of ownership, excitement, and pride in the setting of group projects oriented around scientific inquiry, discovery, and dissemination.
Student perceptions
Students were asked to consider and rank the academic difficulty (scale of 1–5, with 1 = not challenging and 5 = highly challenging) of the work they conducted within the Discovery learning model. Considering individual Discovery terms, at least 91% of students felt the curriculum to be sufficiently challenging with a 3/5 or higher ranking (Term 1: 87.5%, Term 2: 93.4%, Term 3: 85%, Term 4: 93.3%, Term 5: 100%), and a minimum of 58% of students indicating a 4/5 or higher ranking (Term 1: 58.3%, Term 2: 70.5%, Term 3: 67.5%, Term 4: 69.1%, Term 5: 86.4%) (Fig. 6a ).
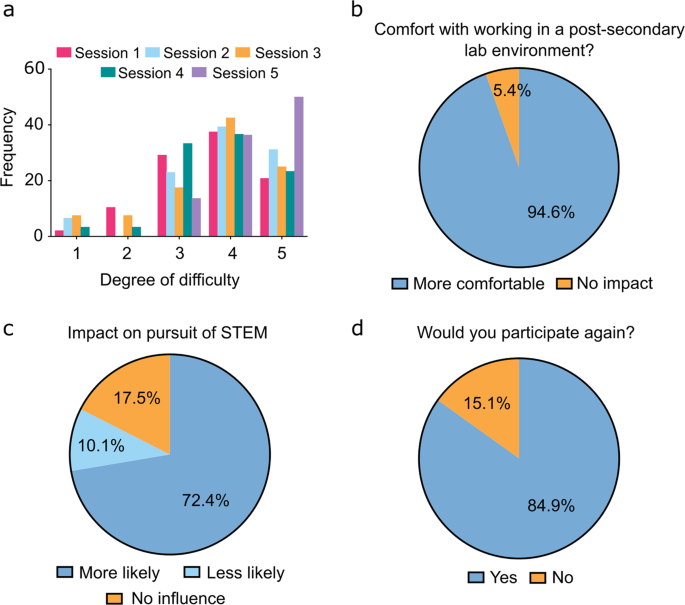
a Histogram of relative frequency of perceived Discovery programming academic difficulty ranked from not challenging (1) to highly challenging (5) for each session demonstrated the consistently perceived high degree of difficulty for Discovery programming (total responses: 223). b Program participation increased student comfort (94.6%) with navigating lab work in a university or college setting (total responses: 220). c Considering participation in Discovery programming, students indicated their increased (72.4%) or decreased (10.1%) likelihood to pursue future experiences in STEM as a measure of program impact (total responses: 217). d Large majority of participating students (84.9%) indicated their interest for future participation in Discovery (total responses: 212). Students were given the opportunity to opt out of individual survey questions, partially completed surveys were included in totals.
The majority of students (94.6%) indicated they felt more comfortable with the idea of performing future work in a university STEM laboratory environment given exposure to university teaching facilities throughout the program (Fig. 6b ). Students were also queried whether they were (i) more likely, (ii) less likely, or (iii) not impacted by their experience in the pursuit of STEM in the future. The majority of participants (>82%) perceived impact on STEM interests, with 72.4% indicating they were more likely to pursue these interests in the future (Fig. 6c ). When surveyed at the end of term, 84.9% of students indicated they would participate in the program again (Fig. 6d ).
We have described an inquiry-based framework for implementing experiential STEM education in a BME setting. Using this model, we engaged 268 instances of student participation (170 individual students who participated 1–4 times) over five terms in project-based learning wherein students worked in peer-based teams under the mentorship of U of T trainees to design and execute the scientific method in answering a relevant research question. Collaboration between high school teachers and Discovery instructors allowed for high school student exposure to cutting-edge BME research topics, participation in facilitated inquiry, and acquisition of knowledge through scientific discovery. All assessments were conducted by high school teachers and constituted a fraction (10–15%) of the overall course grade, instilling academic value for participating students. As such, students exhibited excitement to learn as well as commitment to their studies in the program.
Through our observations and analysis, we suggest there is value in differential learning environments for students that struggle in a knowledge acquisition-focused classroom setting. In general, we observed a high level of academic performance in Discovery programming (Fig. 2a ), which was highlighted exceptionally in EE students who exhibited greater academic performance in Discovery deliverables compared to normal coursework (>18% grade improvement in relevant deliverables). We initially considered whether this was the result of strong students influencing weaker students; however, group organization within each course suggests this is not the case (Fig. 2d ). With the exception of one class in one term (24 participants assigned by their teacher), students were allowed to self-organize into working groups and they chose to work with other students of relatively similar academic performance (as indicated by course grade), a trend observed in other studies 31 , 32 . Remarkably, EE students not only excelled during Discovery when compared to their own performance in class, but this cohort also achieved significantly higher average grades in each of the deliverables throughout the program when compared to the remaining Discovery cohort (Fig. 3 ). This data demonstrates the value of an inquiry-based learning environment compared to knowledge-focused delivery in the classroom in allowing students to excel. We expect that part of this engagement was resultant of student excitement with a novel learning opportunity. It is however a well-supported concept that students who struggle in traditional settings tend to demonstrate improved interest and motivation in STEM when given opportunity to interact in a hands-on fashion, which supports our outcomes 4 , 33 . Furthermore, these outcomes clearly represent variable student learning styles, where some students benefit from a greater exchange of information, knowledge and skills in a cooperative learning environment 34 . The performance of the EE group may not be by itself surprising, as the identification of the subset by definition required high performers in Discovery who did not have exceptionally high course grades; in addition, the final Discovery grade is dependent on the component assignment grades. However, the discrepancies between EE and non-EE groups attendance suggests that students were engaged by Discovery in a way that they were not by regular classroom curriculum.
In addition to quantified engagement in Discovery observed in academic performance, we believe remarkable attendance rates are indicative of the value students place in the differential learning structure. Given the differences in number of Discovery days and implications of missing one day of regular class compared to this immersive program, we acknowledge it is challenging to directly compare attendance data and therefore approximate this comparison with consideration of learning time equivalence. When combined with other subjective data including student focus, requests to work on Discovery during class time, and lack of discipline/behavior issues, the attendance data importantly suggests that students were especially engaged by the Discovery model. Further, we believe the increased commute time to the university campus (students are responsible for independent transit to campus, a much longer endeavour than the normal school commute), early program start time, and students’ lack of familiarity with the location are non-trivial considerations when determining the propensity of students to participate enthusiastically in Discovery . We feel this suggests the students place value on this team-focused learning and find it to be more applicable and meaningful to their interests.
Given post-secondary admission requirements for STEM programs, it would be prudent to think that students participating in multiple STEM classes across terms are the ones with the most inherent interest in post-secondary STEM programs. The MT subset, representing students who participated in Discovery for more than one term, averaged significantly higher final Discovery grades. The increase in the final Discovery grade was observed to result from a general confluence of improved performance over multiple deliverables and a continuous effort to improve in a STEM curriculum. This was reflected in longitudinal tracking of Discovery performance, where we observed a significant trend of improved performance. Interestingly, the high number of MT students who were included in the EE group suggests that students who had a keen interest in science enrolled in more than one course and in general responded well to the inquiry-based teaching method of Discovery , where scientific method was put into action. It stands to reason that students interested in science will continue to take STEM courses and will respond favorably to opportunities to put classroom theory to practical application.
The true value of an inquiry-based program such as Discovery may not be based in inspiring students to perform at a higher standard in STEM within the high school setting, as skills in critical thinking do not necessarily translate to knowledge-based assessment. Notably, students found the programming equally challenging throughout each of the sequential sessions, perhaps somewhat surprising considering the increasing number of repeat attendees in successive sessions (Fig. 6a ). Regardless of sub-discipline, there was an emphasis of perceived value demonstrated through student surveys where we observed indicated interest in STEM and comfort with laboratory work environments, and desire to engage in future iterations given the opportunity. Although non-quantitative, we perceive this as an indicator of significant student engagement, even though some participants did not yield academic success in the program and found it highly challenging given its ambiguity.
Although we observed that students become more certain of their direction in STEM, further longitudinal study is warranted to make claim of this outcome. Additionally, at this point in our assessment we cannot effectively assess the practical outcomes of participation, understanding that the immediate effects observed are subject to a number of factors associated with performance in the high school learning environment. Future studies that track graduates from this program will be prudent, in conjunction with an ever-growing dataset of assessment as well as surveys designed to better elucidate underlying perceptions and attitudes, to continue to understand the expected benefits of this inquiry-focused and partnered approach. Altogether, a multifaceted assessment of our early outcomes suggests significant value of an immersive and iterative interaction with STEM as part of the high school experience. A well-defined divergence from knowledge-based learning, focused on engagement in critical thinking development framed in the cutting-edge of STEM, may be an important step to broadening student perspectives.
In this study, we describe the short-term effects of an inquiry-based STEM educational experience on a cohort of secondary students attending a non-specialized school, and suggest that the framework can be widely applied across virtually all subjects where inquiry-driven and mentored projects can be undertaken. Although we have demonstrated replication in a second cohort of nominally higher SES (S 1 Appendix , Supplementary Fig. 1 ), a larger collection period with more students will be necessary to conclusively determine impact independent of both SES and specific cohort effects. Teachers may also find this framework difficult to implement depending on resources and/or institutional investment and support, particularly if post-secondary collaboration is inaccessible. Offerings to a specific subject (e.g., physics) where experiments yielding empirical data are logistically or financially simpler to perform may be valid routes of adoption as opposed to the current study where all subject cohorts were included.
As we consider Discovery in a bigger picture context, expansion and implementation of this model is translatable. Execution of the scientific method is an important aspect of citizen science, as the concepts of critical thing become ever-more important in a landscape of changing technological landscapes. Giving students critical thinking and problem-solving skills in their primary and secondary education provides value in the context of any career path. Further, we feel that this model is scalable across disciplines, STEM or otherwise, as a means of building the tools of inquiry. We have observed here the value of differential inclusive student engagement and critical thinking through an inquiry-focused model for a subset of students, but further to this an engagement, interest, and excitement across the body of student participants. As we educate the leaders of tomorrow, we suggest that use of an inquiry-focused model such as Discovery could facilitate growth of a data-driven critical thinking framework.
In conclusion, we have presented a model of inquiry-based STEM education for secondary students that emphasizes inclusion, quantitative analysis, and critical thinking. Student grades suggest significant performance benefits, and engagement data suggests positive student attitude despite the perceived challenges of the program. We also note a particular performance benefit to students who repeatedly engage in the program. This framework may carry benefits in a wide variety of settings and disciplines for enhancing student engagement and performance, particularly in non-specialized school environments.
Study design and implementation
Participants in Discovery include all students enrolled in university-stream Grade 11 or 12 biology, chemistry, or physics at the participating school over five consecutive terms (cohort summary shown in Table 1 ). Although student participation in educational content was mandatory, student grades and survey responses (administered by high school teachers) were collected from only those students with parent or guardian consent. Teachers replaced each student name with a unique coded identifier to preserve anonymity but enable individual student tracking over multiple terms. All data collected were analyzed without any exclusions save for missing survey responses; no power analysis was performed prior to data collection.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the University of Toronto Health Sciences Research Ethics Board (Protocol # 34825) and the Toronto District School Board External Research Review Committee (Protocol # 2017-2018-20). Written informed consent was collected from parents or guardians of participating students prior to the acquisition of student data (both post-hoc academic data and survey administration). Data were anonymized by high school teachers for maintenance of academic confidentiality of individual students prior to release to U of T researchers.
Educational program overview
Students enrolled in university-preparatory STEM classes at the participating school completed a term-long project under the guidance of graduate student instructors and undergraduate student mentors as a mandatory component of their respective course. Project curriculum developed collaboratively between graduate students and participating high school teachers was delivered within U of T Faculty of Applied Science & Engineering (FASE) teaching facilities. Participation allows high school students to garner a better understanding as to how undergraduate learning and career workflows in STEM vary from traditional high school classroom learning, meanwhile reinforcing the benefits of problem solving, perseverance, teamwork, and creative thinking competencies. Given that Discovery was a mandatory component of course curriculum, students participated as class cohorts and addressed questions specific to their course subject knowledge base but related to the defined global health research topic (Fig. 1 ). Assessment of program deliverables was collectively assigned to represent 10–15% of the final course grade for each subject at the discretion of the respective STEM teacher.
The Discovery program framework was developed, prior to initiation of student assessment, in collaboration with one high school selected from the local public school board over a 1.5 year period of time. This partner school consistently scores highly (top decile) in the school board’s Learning Opportunities Index (LOI). The LOI ranks each school based on measures of external challenges affecting its student population therefore schools with the greatest level of external challenge receive a higher ranking 35 . A high LOI ranking is inversely correlated with socioeconomic status (SES); therefore, participating students are identified as having a significant number of external challenges that may affect their academic success. The mandatory nature of program participation was established to reach highly capable students who may be reluctant to engage on their own initiative, as a means of enhancing the inclusivity and impact of the program. The selected school partner is located within a reasonable geographical radius of our campus (i.e., ~40 min transit time from school to campus). This is relevant as participating students are required to independently commute to campus for Discovery hands-on experiences.
Each program term of Discovery corresponds with a five-month high school term. Lead university trainee instructors (3–6 each term) engaged with high school teachers 1–2 months in advance of high school student engagement to discern a relevant overarching global healthcare theme. Each theme was selected with consideration of (a) topics that university faculty identify as cutting-edge biomedical research, (b) expertise that Discovery instructors provide, and (c) capacity to showcase the diversity of BME. Each theme was sub-divided into STEM subject-specific research questions aligning with provincial Ministry of Education curriculum concepts for university-preparatory Biology, Chemistry, and Physics 9 that students worked to address, both on-campus and in-class, during a term-long project. The Discovery framework therefore provides students a problem-based learning experience reflective of an engineering capstone design project, including a motivating scientific problem (i.e., global topic), subject-specific research question, and systematic determination of a professional recommendation addressing the needs of the presented problem.
Discovery instructors were volunteers recruited primarily from graduate and undergraduate BME programs in the FASE. Instructors were organized into subject-specific instructional teams based on laboratory skills, teaching experience, and research expertise. The lead instructors of each subject (the identified 1–2 trainees that built curriculum with high school teachers) were responsible to organize the remaining team members as mentors for specific student groups over the course of the program term (~1:8 mentor to student ratio).
All Discovery instructors were familiarized with program expectations and trained in relevant workspace safety, in addition to engagement at a teaching workshop delivered by the Faculty Advisor (a Teaching Stream faculty member) at the onset of term. This workshop was designed to provide practical information on teaching and was co-developed with high school teachers based on their extensive training and experience in fundamental teaching methods. In addition, group mentors received hands-on training and guidance from lead instructors regarding the specific activities outlined for their respective subject programming (an exemplary term of student programming is available in S 2 Appendix) .
Discovery instructors were responsible for introducing relevant STEM skills and mentoring high school students for the duration of their projects, with support and mentorship from the Faculty Mentor. Each instructor worked exclusively throughout the term with the student groups to which they had been assigned, ensuring consistent mentorship across all disciplinary components of the project. In addition to further supporting university trainees in on-campus mentorship, high school teachers were responsible for academic assessment of all student program deliverables (Fig. 1 ; the standardized grade distribution available in S 3 Appendix ). Importantly, trainees never engaged in deliverable assessment; for continuity of overall course assessment, this remained the responsibility of the relevant teacher for each student cohort.
Throughout each term, students engaged within the university facilities four times. The first three sessions included hands-on lab sessions while the fourth visit included a culminating symposium for students to present their scientific findings (Fig. 1 ). On average, there were 4–5 groups of students per subject (3–4 students per group; ~20 students/class). Discovery instructors worked exclusively with 1–2 groups each term in the capacity of mentor to monitor and guide student progress in all project deliverables.
After introducing the selected global research topic in class, teachers led students in completion of background research essays. Students subsequently engaged in a subject-relevant skill-building protocol during their first visit to university teaching laboratory facilities, allowing opportunity to understand analysis techniques and equipment relevant for their assessment projects. At completion of this session, student groups were presented with a subject-specific research question as well as the relevant laboratory inventory available for use during their projects. Armed with this information, student groups continued to work in their classroom setting to develop group-specific experimental plans. Teachers and Discovery instructors provided written and oral feedback, respectively , allowing students an opportunity to revise their plans in class prior to on-campus experimental execution.
Once at the relevant laboratory environment, student groups executed their protocols in an effort to collect experimental data. Data analysis was performed in the classroom and students learned by trial & error to optimize their protocols before returning to the university lab for a second opportunity of data collection. All methods and data were re-analyzed in class in order for students to create a scientific poster for the purpose of study/experience dissemination. During a final visit to campus, all groups presented their findings at a research symposium, allowing students to verbally defend their process, analyses, interpretations, and design recommendations to a diverse audience including peers, STEM teachers, undergraduate and graduate university students, postdoctoral fellows and U of T faculty.
Data collection
Teachers evaluated their students on the following associated deliverables: (i) global theme background research essay; (ii) experimental plan; (iii) progress report; (iv) final poster content and presentation; and (v) attendance. For research purposes, these grades were examined individually and also as a collective Discovery program grade for each student. For students consenting to participation in the research study, all Discovery grades were anonymized by the classroom teacher before being shared with study authors. Each student was assigned a code by the teacher for direct comparison of deliverable outcomes and survey responses. All instances of “Final course grade” represent the prorated course grade without the Discovery component, to prevent confounding of quantitative analyses.
Survey instruments were used to gain insight into student attitudes and perceptions of STEM and post-secondary study, as well as Discovery program experience and impact (S 4 Appendix ). High school teachers administered surveys in the classroom only to students supported by parental permission. Pre-program surveys were completed at minimum 1 week prior to program initiation each term and exit surveys were completed at maximum 2 weeks post- Discovery term completion. Surveys results were validated using a principal component analysis (S 1 Appendix , Supplementary Fig. 2 ).
Identification and comparison of population subsets
From initial analysis, we identified two student subpopulations of particular interest: students who performed ≥1 SD [18.0%] or greater in the collective Discovery components of the course compared to their final course grade (“EE”), and students who participated in Discovery more than once (“MT”). These groups were compared individually against the rest of the respective Discovery population (“non-EE” and “non-MT”, respectively ). Additionally, MT students who participated in three or four (the maximum observed) terms of Discovery were assessed for longitudinal changes to performance in their course and Discovery grades. Comparisons were made for all Discovery deliverables (introductory essay, client meeting, proposal, progress report, poster, and presentation), final Discovery grade, final course grade, Discovery attendance, and overall attendance.
Statistical analysis
Student course grades were analyzed in all instances without the Discovery contribution (calculated from all deliverable component grades and ranging from 10 to 15% of final course grade depending on class and year) to prevent correlation. Aggregate course grades and Discovery grades were first compared by paired t-test, matching each student’s course grade to their Discovery grade for the term. Student performance in Discovery ( N = 268 instances of student participation, comprising 170 individual students that participated 1–4 times) was initially assessed in a linear regression of Discovery grade vs. final course grade. Trends in course and Discovery performance over time for students participating 3 or 4 terms ( N = 16 and 3 individuals, respectively ) were also assessed by linear regression. For subpopulation analysis (EE and MT, N = 99 instances from 81 individuals and 174 instances from 76 individuals, respectively ), each dataset was tested for normality using the D’Agostino and Pearson omnibus normality test. All subgroup comparisons vs. the remaining population were performed by Mann–Whitney U -test. Data are plotted as individual points with mean ± SEM overlaid (grades), or in histogram bins of 1 and 4 days, respectively , for Discovery and class attendance. Significance was set at α ≤ 0.05.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author DMK. These data are not publicly available due to privacy concerns of personal data according to the ethical research agreements supporting this study.
Holmes, K., Gore, J., Smith, M. & Lloyd, A. An integrated analysis of school students’ aspirations for STEM careers: Which student and school factors are most predictive? Int. J. Sci. Math. Educ. 16 , 655–675 (2018).
Article Google Scholar
Dooley, M., Payne, A., Steffler, M. & Wagner, J. Understanding the STEM path through high school and into university programs. Can. Public Policy 43 , 1–16 (2017).
Gilmore, M. W. Improvement of STEM education: experiential learning is the key. Mod. Chem. Appl. 1, e109. https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-6798.1000e109 (2013).
Roberts, T. et al. Students’ perceptions of STEM learning after participating in a summer informal learning experience. Int. J. STEM Educ. 5 , 35 (2018).
Gillies, R. M. & Boyle, M. Teachers’ reflections on cooperative learning: Issues of implementation. Teach. Teach. Educ. 26 , 933–940 (2010).
Nasir, M., Seta, J. & Meyer, E.G. Introducing high school students to biomedical engineering through summer camps. Paper presented at the ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition, Indianapolis, IN. https://doi.org/10.18260/1-2-20701 (2014).
Sadler, P. M., Sonnert, G., Hazari, Z. & Tai, R. Stability and volatility of STEM career interest in high school: a gender study. Sci. Educ. 96 , 411–427 (2012).
Sarikas, C. The High School Science Classes You Should Take . https://blog.prepscholar.com/the-high-school-science-classes-you-should-take (2020).
Ontario, G. o. The ontario curriculum grades 11 and 12. Science http://www.edu.gov.on.ca/eng/curriculum/secondary/2009science11_12.pdf (2008).
Scott, C. An investigation of science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) focused high schools in the US. J. STEM Educ.: Innov. Res. 13 , 30 (2012).
Google Scholar
Erdogan, N. & Stuessy, C. L. Modeling successful STEM high schools in the United States: an ecology framework. Int. J. Educ. Math., Sci. Technol. 3 , 77–92 (2015).
Pfeiffer, S. I., Overstreet, J. M. & Park, A. The state of science and mathematics education in state-supported residential academies: a nationwide survey. Roeper Rev. 32 , 25–31 (2009).
Anthony, A. B., Greene, H., Post, P. E., Parkhurst, A. & Zhan, X. Preparing university students to lead K-12 engineering outreach programmes: a design experiment. Eur. J. Eng. Educ. 41 , 623–637 (2016).
Brown, J. S., Collins, A. & Duguid, P. Situated cognition and the culture of learning. Educ. researcher 18 , 32–42 (1989).
Reveles, J. M. & Brown, B. A. Contextual shifting: teachers emphasizing students’ academic identity to promote scientific literacy. Sci. Educ. 92 , 1015–1041 (2008).
Adedokun, O. A., Bessenbacher, A. B., Parker, L. C., Kirkham, L. L. & Burgess, W. D. Research skills and STEM undergraduate research students’ aspirations for research careers: mediating effects of research self-efficacy. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 50 , 940–951 (2013).
Boekaerts, M. Self-regulated learning: a new concept embraced by researchers, policy makers, educators, teachers, and students. Learn. Instr. 7 , 161–186 (1997).
Honey, M., Pearson, G. & Schweingruber, H. STEM Integration in K-12 Education: Status, Prospects, and An Agenda for Research . (National Academies Press, Washington, DC, 2014).
Moote, J. K., Williams, J. M. & Sproule, J. When students take control: investigating the impact of the crest inquiry-based learning program on self-regulated processes and related motivations in young science students. J. Cogn. Educ. Psychol. 12 , 178–196 (2013).
Fantz, T. D., Siller, T. J. & Demiranda, M. A. Pre-collegiate factors influencing the self-efficacy of engineering students. J. Eng. Educ. 100 , 604–623 (2011).
Ralston, P. A., Hieb, J. L. & Rivoli, G. Partnerships and experience in building STEM pipelines. J. Professional Issues Eng. Educ. Pract. 139 , 156–162 (2012).
Kelley, T. R. & Knowles, J. G. A conceptual framework for integrated STEM education. Int. J. STEM Educ. 3 , 11 (2016).
Brown, P. L., Concannon, J. P., Marx, D., Donaldson, C. W. & Black, A. An examination of middle school students’ STEM self-efficacy with relation to interest and perceptions of STEM. J. STEM Educ.: Innov. Res. 17 , 27–38 (2016).
Bandura, A., Barbaranelli, C., Caprara, G. V. & Pastorelli, C. Self-efficacy beliefs as shapers of children’s aspirations and career trajectories. Child Dev. 72 , 187–206 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Davenport Huyer, L. et al. IBBME discovery: biomedical engineering-based iterative learning in a high school STEM curriculum (evaluation). Paper presented at ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition, Salt Lake City, UT. https://doi.org/10.18260/1-2-30591 (2018).
Abu-Faraj, Ziad O., ed. Handbook of research on biomedical engineering education and advanced bioengineering learning: interdisciplinary concepts: interdisciplinary concepts. Vol. 2. IGI Global (2012).
Johri, A. & Olds, B. M. Situated engineering learning: bridging engineering education research and the learning sciences. J. Eng. Educ. 100 , 151–185 (2011).
O’Connell, K. B., Keys, B. & Storksdieck, M. Taking stock of oregon STEM hubs: accomplishments and challenges. Corvallis: Oregon State University https://ir.library.oregonstate.edu/concern/articles/hq37vt23t (2017).
Freeman, K. E., Alston, S. T. & Winborne, D. G. Do learning communities enhance the quality of students’ learning and motivation in STEM? J. Negro Educ. 77 , 227–240 (2008).
Weaver, R. R. & Qi, J. Classroom organization and participation: college students’ perceptions. J. High. Educ. 76 , 570–601 (2005).
Chapman, K. J., Meuter, M., Toy, D. & Wright, L. Can’t we pick our own groups? The influence of group selection method on group dynamics and outcomes. J. Manag. Educ. 30 , 557–569 (2006).
Hassaskhah, J. & Mozaffari, H. The impact of group formation method (student-selected vs. teacher-assigned) on group dynamics and group outcome in EFL creative writing. J. Lang. Teach. Res. 6 , 147–156 (2015).
Ma, V. J. & Ma, X. A comparative analysis of the relationship between learning styles and mathematics performance. Int. J. STEM Educ. 1 , 3 (2014).
Weinstein, C. E. & Hume, L. M. Study Strategies for Lifelong Learning . (American Psychological Association, 1998).
Toronto District School Board. The 2017 Learning Opportunities Index: Questions and Answers. https://www.tdsb.on.ca/Portals/research/docs/reports/LOI2017v2.pdf (2017).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This study has been possible due to the support of many University of Toronto trainee volunteers, including Genevieve Conant, Sherif Ramadan, Daniel Smieja, Rami Saab, Andrew Effat, Serena Mandla, Cindy Bui, Janice Wong, Dawn Bannerman, Allison Clement, Shouka Parvin Nejad, Nicolas Ivanov, Jose Cardenas, Huntley Chang, Romario Regeenes, Dr. Henrik Persson, Ali Mojdeh, Nhien Tran-Nguyen, Ileana Co, and Jonathan Rubianto. We further acknowledge the staff and administration of George Harvey Collegiate Institute and the Institute of Biomedical Engineering (IBME), as well as Benjamin Rocheleau and Madeleine Rocheleau for contributions to data collation. Discovery has grown with continued support of Dean Christopher Yip (Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering, U of T), and the financial support of the IBME and the National Science and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) PromoScience program (PROSC 515876-2017; IBME “Igniting Youth Curiosity in STEM” initiative co-directed by DMK and Dr. Penney Gilbert). LDH and NIC were supported by Vanier Canada graduate scholarships from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and NSERC, respectively . DMK holds a Dean’s Emerging Innovation in Teaching Professorship in the Faculty of Engineering & Applied Science, U of T.
Author information
These authors contributed equally: Locke Davenport Huyer, Neal I. Callaghan.
Authors and Affiliations
Institute of Biomedical Engineering, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Locke Davenport Huyer, Neal I. Callaghan, Andrey I. Shukalyuk & Dawn M. Kilkenny
Chemical Engineering and Applied Chemistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Locke Davenport Huyer
Translational Biology and Engineering Program, Ted Rogers Centre for Heart Research, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Neal I. Callaghan
George Harvey Collegiate Institute, Toronto District School Board, Toronto, ON, Canada
Sara Dicks, Edward Scherer & Margaret Jou
Institute for Studies in Transdisciplinary Engineering Education & Practice, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Dawn M. Kilkenny
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
LDH, NIC and DMK conceived the program structure, designed the study, and interpreted the data. LDH and NIC ideated programming, coordinated execution, and performed all data analysis. SD, ES, and MJ designed and assessed student deliverables, collected data, and anonymized data for assessment. SD assisted in data interpretation. AIS assisted in programming ideation and design. All authors provided feedback and approved the manuscript that was written by LDH, NIC and DMK.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Dawn M. Kilkenny .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplemental material, reporting summary, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Davenport Huyer, L., Callaghan, N.I., Dicks, S. et al. Enhancing senior high school student engagement and academic performance using an inclusive and scalable inquiry-based program. npj Sci. Learn. 5 , 17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41539-020-00076-2
Download citation
Received : 05 December 2019
Accepted : 08 October 2020
Published : 02 December 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41539-020-00076-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Advertisement
Active Student Participation in Whole-School Interventions in Secondary School. A Systematic Literature Review
- REVIEW ARTICLE
- Open access
- Published: 04 May 2023
- Volume 35 , article number 52 , ( 2023 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Sara Berti ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5238-1077 1 ,
- Valentina Grazia 1 &
- Luisa Molinari 1
5832 Accesses
4 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This review presents a reasoned synthesis of whole-school interventions seeking to improve the overall school environment by fostering active student participation (ASP) in school activities and decision-making processes. The aims are to describe the selected programs, assess their methodological quality, and analyze the activities soliciting ASP. Among the 205 publications initially provided by the literature search in the academic databases PsycINFO and Education Research Complete, 22 reports met the inclusion criteria of presenting whole-school interventions that solicit ASP in secondary schools, and were thus included in the review. Such publications referred to 13 different whole-school programs, whose implemented activities were distinguished on a 5-point scale of ASP levels, ranging from Very high ASP , when students were involved in a decision-making role, to Very low ASP , when students were the passive recipients of content provided by adults. This review contributes to the literature by proposing an organizing structure based on different levels of ASP, which provides clarity and a common ground for future studies on student participation. Overall, the in-depth description of activities offers a framework to researchers and practitioners for planning interventions aimed at improving the learning environment and contributing meaningfully to the far-reaching goal of encouraging student participation in school life.
Similar content being viewed by others

Play-Based Learning: Evidence-Based Research to Improve Children’s Learning Experiences in the Kindergarten Classroom
The role of school in adolescents’ identity development. a literature review.
Teachers’ Beliefs About Inclusive Education and Insights on What Contributes to Those Beliefs: a Meta-analytical Study
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Research in educational psychology is consistent in showing that the quality of the school environment largely affects student well-being. Indeed, students’ experiences of a supportive school context have a significant impact on positive behaviors, such as academic achievement (Brand et al., 2008 ; Hoy, 2012 ) and good relationships among students and between students and staff (Cohen et al., 2009 ; Thapa et al., 2013 ). Conversely, the poor quality of the learning environment predicts negative outcomes, such as substance use (Weatherson et al., 2018 ) or bullying (Låftman et al., 2017 ).
In view of this, schools need to face the challenge of implementing interventions aimed at changing and improving the learning environment in the direction of promoting positive behaviors and reducing negative outcomes. One of the most promising directions in this regard is based on the adoption of whole-school approaches whose key features are the focus on overall school systems instead of on specific problems (Bonell et al., 2018 ).
The literature on whole-school interventions is broad (see, for example, Charlton et al., 2021 , for an extensive review on whole-school interventions focused on school climate), but it suffers from two major gaps. First, it relies primarily on programs applicable to elementary schools, while studies on high school populations are rarer, presumably because of the multiple challenges derived from the implementation of programs in such complex contexts (Estrapala et al., 2021 ; Vancel et al., 2016 ). Second, despite the importance generally attributed to the active involvement of students in the programs, to our knowledge, no previous reviews have specifically investigated the degree and the characteristics of student participation in such interventions. To address these limitations, in this article, we present a systematic literature review on whole-school interventions carried out in secondary schools and based on programs that envisage students’ active participation and involvement.
Whole-School Interventions for Improving the Learning Environment
In educational research, some reviews and meta-analyses (Charlton et al., 2021 ; Merrell et al., 2008 ; Voight & Nation, 2016 ) have critically synthesized and discussed studies on school interventions aimed at improving the learning environment. These programs have considered different outcomes of improvement, ranging from a general focus on school climate dimensions—e.g., relational aspects, institutional organization, and safety—to more specific aspects, such as bullying, violence, or substance use. However, the degree of effectiveness of such programs remains controversial. For example, a meta-analysis by Ttofi et al. ( 2008 ) indicated that school-based bullying prevention programs were able to bring about positive results, while another meta-analysis on the same topic (Merrel et al., 2008 ) concluded that evidence in this direction was only modest.
More positive results concerning the effectiveness of interventions were reported by Allen ( 2010 ) with reference to programs conducted by means of a whole-school approach. In her literature overview of studies designed to reduce bullying and victimization, the author concluded that whole-school interventions generally showed at least marginal evidence of improvement. Despite these encouraging findings, the studies conducted with a whole-school approach in secondary education contexts were rare. Among these, a well-established framework of whole-school interventions mostly implemented in middle schools is the School-Wide Positive Behavior Support program (for reviews, see Gage et al., 2018 ; Noltemeyer et al., 2019 ), which is a multi-tiered framework engaging students, school staff, and families for the delivery of evidence-based behavioral support aligned to students’ needs (Horner et al., 2004 ). By and large, the study results in this framework are again promising in suggesting a connection between such programs and school improvement, although the evidence is generally moderate and only regards a few of the considered outcome measures.
The mixed or weak results reported in the cited reviews solicit further exploration of the specific characteristics of whole-school interventions. In particular, a major limitation of the literature is the lack of an in-depth analysis of the types of activities proposed to students in each program, especially as far as their direct involvement is concerned. Given the importance attributed to student engagement in school life (Markham & Aveyard, 2003 ), this is a relevant area of inquiry that can inform researchers and practitioners willing to design and conduct whole-school interventions calling for students’ involvement.
Student Involvement in School Intervention
The importance of students’ involvement and participation finds a theoretical ground in the self-determination theory (see Ryan & Deci, 2017 ), according to which people who are self-determined perceive themselves as causal agents in life experiences, being proactive and engaged in the social environment. Studies examining such human disposition in adolescence supported the relevance of self-determination for quality of life and identity development (Griffin et al., 2017 ; Nota et al., 2011 ) and as a full mediator in the negative association between stress and school engagement (Raufelder et al., 2014 ).
In the light of these assumptions, educational and school psychologists have launched scientific and professional debates on the ways in which schools can implement favorable conditions for students to feel active and co-responsible for their educational and academic pathways (Carpenter & Pease, 2013 ; Helker & Wosnitza, 2016 ; Schweisfurth, 2015 ). These debates have reached consensus across-the-board on the recognition that school change and improvement are best fostered by intervention programs in which students are offered opportunities to get actively involved in school life (Baeten et al., 2016 ; Voight & Nation, 2016 ). For this goal to be achieved, all educational agencies are called upon to promote interventions capable of supporting activities that require student involvement and participation (Antoniou & Kyriakides, 2013 ).
The importance of students’ active participation in the school environment has also been confirmed by a substantial amount of literature investigating over time the association between high student involvement and positive learning environments. Mitchell ( 1967 ) reported that school climate is related to the extent of student participation and interaction during school life. Epstein and McPartland ( 1976 ) showed that student opportunities for school involvement were related to satisfactory outcomes. In a 1982 review published, Anderson claimed that “the type and extent of student interaction that is possible within a school appears to be a significant climate variable” (Anderson, 1982 ; p.401). A few years later, Power et al. ( 1989 ) described a program implemented in several contexts and characterized by high student involvement, whose results showed that a high rate of student participation led to their capacity to take on responsibility for building an effective learning environment and positive climate. More recent studies (Vieno et al., 2005 ) have confirmed that democratic school practices, such as student participation in decision-making processes, play a significant role in the development of a sense of community at individual, class, and school levels. The review by Thapa et al. ( 2013 ) confirmed the importance of student classroom participation as a variable affecting school climate and academic achievement.
On these theoretical and empirical grounds, providing space to student voices in decision-making and school change emerges as a powerful strategy for improving school environments and enforcing the success of programs (Mitra, 2004 ). The construct of student agency fits in well with this approach, as it refers to the students’ willingness and skill to act upon activities and circumstances in their school lives (Lipponen & Kumpulainen, 2011 ). Representing adolescents’ authentic, proactive, and transformative contributions to school life (Grazia et al., 2021 ), agency is fostered by school environments capable of soliciting and valorizing students’ active participation in educational practices and school decisions (Makitalo, 2016 ) and encouraging them to feel co-responsible with teachers and staff for their school lives (Mameli et al., 2019 ). The value of agency has been confirmed by research showing its positive associations with motivation and the fulfilment of basic psychological needs (Jang et al., 2012 ) as well as with the perception of supportive teaching (Matos et al., 2018 ).
Despite the agreement on student participation as a crucial feature for the success of programs capable of improving students’ school life, to our knowledge, previous literature reviews on school interventions have not focused specifically on the extent and way in which students are given a voice and are involved in the programs. In view of this, in the present work, we set out to search, in the existing literature, for interventions specifically based on activities in which students were not just the recipients of activities but rather took on an active and decision-making role. For our purposes, we use the notion of active student participation (ASP) to include the variety of ways in which students are given the opportunity to participate actively in school activities and decisions that will shape their own lives and those of their peers.
Review’s Aims
Previous reviews (Charlton et al., 2021 ; Estrapala et al., 2021 ; Voight & Nation, 2016 ) have provided extensive descriptions of whole-school interventions aimed at improving school environments or reducing school problems, suggesting their effectiveness. Moreover, a growing amount of literature has found that students’ active involvement in their school life is a crucial feature for improvement. Our general goal was to move forward by conducting an in-depth examination of existing whole-school interventions based on activities promoting ASP in secondary schools, by providing a reasoned synthesis of their characteristics and implementation. The choice to focus on secondary schools was driven by the evidence that this developmental stage has so far received less attention in whole-school intervention research (Estrapala et al., 2021 ; Vancel et al., 2016 ).
Given the large heterogeneity of existing intervention programs, both in terms of participants (specific subgroups vs general student population) and targets of improvement (specific abilities vs general school environment), it was essential to set clear boundaries for the study selection. As this was a novel undertaking, we chose to focus on whole-school interventions directed to the overall student population and aimed at improving the school climate as a whole. This allowed us to select a reasonably homogeneous sample of studies, with the confidence that future reviews will advance our knowledge by considering more specific fields and populations.
The review’s aims were (a) to describe the selected programs on the basis of their focus, country, duration, age of participants, and research design; (b) to assess the soundness of the research design and methodologies adopted in each study in order to provide evidence of the methodological quality of the selected programs; and (c) to differentiate among various levels of ASP in the program’s activities and, for each of these levels, to describe methods and activities carried out in the programs.
The present review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses 2020 updated statement (PRISMA 2020; Page et al., 2021 ). In line with the terminology proposed by the authors, in the following sections, we use the term study for every investigation that includes a well-defined group of participants and one or more interventions and outcomes, report for every document supplying information about a particular study (a single study might have multiple reports), and record for the title and/or abstract of a report indexed in a database. In addition, for the specific purposes of the present review, we use the term program when referring to an implemented whole-school intervention that has specific characteristics and is usually named, since more than one study may be conducted with the same program.
Eligibility Criteria
Studies were eligible for inclusion in the review if they were (i) written in English language; (ii) published in peer-reviewed academic journals; and (iii) aimed at assessing psychological effects of whole-school interventions that solicit ASP in secondary schools; thus, studies in which students were involved solely as recipients of activities delivered by adults were excluded. Moreover, in line with the review’s aims described above, studies were excluded from the review if they were (i) focused on specific subgroups of students (e.g., ethnical minorities or LGBTQ students); (ii) solely aimed at improving specific skills (e.g., literacy or mathematics); and (iii) solely focused on physical health (e.g., nutrition or physical activity).
Information Sources and Search Strategy
A literature search was conducted via EBSCO, including the academic databases PsycINFO and Education Research Complete, last consulted on April 9, 2022. The entered search terms were school-wide interventions OR whole-school interventions OR school-wide programs OR whole-school programs OR school-wide trainings OR whole-school trainings AND secondary school OR high school OR secondary education. By means of the software’s automated procedure, we searched these terms in the abstracts and filtered the results according to the first two inclusion criteria, selecting articles in English and published in peer-reviewed academic journals.
Selection and Data Collection Process
The records of each study were screened by two researchers, and the potentially relevant studies were further assessed for eligibility by three researchers, who read the full text independently. Moreover, some records relevant to the purposes of the research were identified through the references of the included documents ( forward snowballing ; Wohlin, 2014 ). Data from each included report were searched by two researchers, who worked independently to extrapolate the information relevant to the review, which were (a) the study characteristics; (b) the indicators of methodological quality; and (c) the program activities.
Detailed information about the selection process is provided in the PRISMA flow diagram (Fig. 1 ). The literature search provided 205 total records, and reduced to 169 after the automatic deduplication provided by EBSCO. After the application of our inclusion and exclusion criteria, 62 records were selected for full text reading. Of the 107 excluded records, 37 did not report interventions (e.g., they presented only school surveys), 25 were informative papers on initiatives and/or interventions without assessments, 15 focused only on academic skills attainment, 11 referred to primary schools, 10 focused on minorities, 6 were reviews of books or DVDs, and 3 only evaluated physical health as an outcome. After the full text reading of the 62 selected reports, 48 were excluded as they only discussed aspects related to implementation (e.g., feasibility or fidelity) without assessing the psychological effects of the intervention on students ( n = 23) or did not solicit ASP during the intervention ( n = 25). Thus, 14 reports were included in the sample. In addition, 10 reports were identified by sifting through the references of the selected documents ( forward snowballing ; Wohlin, 2014 ). After the full text reading, two of them were excluded as they did not assess the effects of the intervention. At the end of the selection process, the final sample of the present review included 22 reports, which referred to 16 studies and 13 programs.
PRISMA flow diagram
Study Characteristics
The main information about each study is reported in Table 1 . As for the focus of the interventions, three macro-areas were identified: (a) prevention of violence (nine studies and twelve reports), including programs for less bullying, cyberbullying, dating violence, sexual violence, and aggression; (b) promotion of mental health (five studies and seven reports), including programs for addressing depression and suicide risk and for promoting general psychological health; (c) promotion of positive emotional and relational school climate (two studies and three reports), including programs for enhancing school connectedness and school climate.
Within each macro-area, in Table 1 , the programs are listed following the alphabetical order of the program name. Out of the studies focused on preventing violence, three referred to unnamed anti-bullying programs, which in the present review were labeled Anti-bullying_1 , Anti-bullying_2 , and Anti-bullying_3 ; the other studies on the topic referred to an anti-cyberbullying program named Cyber Friendly School ; an anti-bullying program named Friendly School ; a bystander program aimed at preventing dating violence and sexual violence, named Green Dots ; a program aimed at preventing bullying and aggression, named Learning Together ; and an anti-bullying program named STAC , which stands for Stealing the show, Turning it over, Accompanying others, Coaching compassion. The studies focused on promoting mental health comprised a school research initiative aimed at preventing depression, named Beyond blue ; an intervention aimed at promoting mental health, named Gatehouse Project ; and a program to prevent suicide risk, named Sources of Strengths . Out of the studies focused on promoting positive emotional and relational school climate, one referred to the Restorative Justice program, aimed at promoting healthy and trusting relationships within the school, and the other referred to a program aimed at the promotion of a good school climate, named SEHER , which stands for Strengthening Evidence base on scHool-based intErventions for pRomoting adolescent health.
A large majority of the studies were conducted in the USA, some were carried out in Australia and the UK, and a few studies in India and China. The studies varied in duration, ranging from one to seven school years, and the number of schools involved in the intervention, ranging from 1 to 75. About half of the studies involved students from all grades while the other half was targeted only for some grades. Lastly, the reports varied in its research design: the majority conducted experimental group comparisons (EGC), but also other quantitative research designs (O) were present along with some qualitative designs (QUAL). To make text and tables more readable, the 13 included programs were renamed with a program ID consisting of the initials of the program name. Similarly, the 22 included reports were renamed with a report ID , consisting in the program ID followed by the surname of the first author and the publication year, all separated by underscores. Report ID and Program ID are reported in Table 1 .
Assessment of Methodological Quality
To assess each report’s methodological quality, we searched in the literature for a rigorous and comprehensive set of indicators and eventually decided to use as a reference the standards for evidence-based practices identified by the Council for Exceptional Children (CEC, 2014 ), which include indicators on setting and program description, fidelity, and reliability of outcome measures. Although the standards were originally recommended for the specific field of special education, they are considered appropriate to evaluate studies in all educational settings and were previously used by Charlton et al. ( 2021 ) in a systematic review studying the effects of school-wide interventions on school climate perceptions. Given that our aim was not to identify evidence-based practices but more generally to assess the methodological quality of the reports included in the review, some of the identified indicators were not applicable to our material. For this reason, among all the indicators described in the document (CEC, 2014), we selected those that provided a general overview of each report’s methodological quality. The selected indicators, their corresponding number in the CEC document, and a short description for each are reported in Table 2 .
In more detail, we applied a more extensive set of indicators to reports which fit the CEC definition of experimental group comparison design (EGC, as reported in Table 1 ), where participants were divided into two or more groups, both randomly and non-randomly, to test the effects of the interventions. For reports based on qualitative analyses and on quantitative analyses not consistent with the EGC design (QUAL and O, as reported in Table 1 ), we used a more limited set of indicators (indicators 1 to 6, as described in Table 2 ) and included a brief description of the research aims and methods. In the assessment of methodological quality, interrater reliability was achieved as three independent researchers read each report in detail, and the attribution of each indicator was discussed and agreed upon.
The assessment of methodological quality for the EGC reports is summarized in Table 3 . The findings show that most studies were strong in contextualizing the research, clearly describing the intervention program (either directly or with references to previous work) and conducting quality analyses. Weak points emerged to be related to the assessment of fidelity implementation (indicators 4 and 5 in Table 3 ), both with reference to adherence to the intervention program and to the dosage received by participants. Results for studies with qualitative analyses or quantitative analyses not EGC are reported in Table 4 . Like the ECG reports, most of these studies appeared strong in contextualizing the research and describing the intervention program, while fidelity of implementation received less attention (indicators 4 and 5 in Table 4 ).
Levels of Active Student Participation
As required by our inclusion criteria, all the selected programs were based on interventions that solicited ASP. However, from the careful analysis of the studies, we realized that the program activities promoted very different forms of ASP. Three independent researchers thus considered in detail each activity described in the programs and eventually agreed to score it on a 5-point scale (see Table 5 ), distinguishing among activities that solicit various levels of ASP. The scale partly followed the school participation scale of the HBSC questionnaire as defined by De Róiste et al. ( 2012 ). It ranged from Very high levels of ASP, attributed to activities in which students were given a fully decision-making role, to Very low levels of ASP, given to activities in which students were just the recipients of activities delivered by adults. In line with our inclusion criteria, in no programs, students were involved solely as recipients of activities delivered by adults (Very low ASP). Moreover, levels were not mutually exclusive, so that each program might include different levels of ASP.
In Table 5 , we report all the considered ASP levels, with the specifically related activities, and the coding of each program. It should be specified that the distribution of activities in the various levels was based on a qualitative accurate analysis of the role attributed to students and not on the number of students involved in each program’s activities, which varied to a great extent. In more detail, Very high ASP was attributed to interventions in which students were involved in processes with a direct organizational impact on school roles, curricula, and policies; this included two types of activities, i.e., student involvement in decision-making processes and the formation of school action teams comprising students. High ASP was recognized when students were still involved in organizational activities, but their role was limited to the implementation of activities and did not directly impact on school curricula and policies; it consisted of three activities, i.e., presentation of students’ works, leading of activities for peers, and leading of activities for adults. Moderate ASP was attributed when students were asked to express their viewpoints and opinions, without having a decision-making power, however; it comprised activities in which students were called to express their points of view on various school issues, either by the provision of platforms to share ideas, concerns, or suggestions, or by the organization of interactive school assemblies, or by their involvement in surveys based on data collection (e.g., by means of questionnaires) on specific aspects of their school life. Low ASP was attributed when the students’ activation was limited to a specific task required within a structured format designed by other people, including training for student leaders, interactive group activities, and individual activities. Finally, activities were coded as Very low ASP when students were involved as the passive recipients of contents provided by adults, through lecture-style lessons, viewing of videos, or distribution of didactic material. The activities provided for in each program are described at length in the following paragraphs, considering activities scored in every specific level of ASP.
For the sake of completeness, in Table 5 , we added a final column in which we indicated additional program activities that involved the staff. They comprised the formation of school action teams made up of adults, training, and the provision of materials for the staff. As the description of these activities goes beyond the scope of our investigation, we will not describe them in detail.
Very High ASP: Making School Rules
As can be seen in Table 5 , activities implying involvement of students in decision-making processes were identified in six programs. In AB3, during a school assembly, students were invited to develop a whole-school anti-bullying policy, while in later activities, they were asked to identify strategies to be implemented in the school to prevent bullying. In CFS, school staff and student leaders conducted whole-school activities helping students to review school policies to promote a positive use of technology. In FS, the intervention aimed to help the transition between primary and secondary school was co‐developed with students who had already made such a transition. In GP, the use of peer support and leadership was encouraged to increase opportunities and skills for students to participate in decision-making processes within the school; in addition, at a classroom level, rules were negotiated by teachers and students and displayed in each classroom. In RJ, during the first year of implementation, staff and students developed a plan for pathways of primary, secondary, and tertiary restorative interventions; in the following years, students’ leadership roles and collective decision-making activities increased, so that students themselves were able to advance whole-school initiatives and activities, to map out course goals and determine which projects they would embrace. Finally, in SE, some health policies were discussed with the principal, teachers, and students before being finalized in a school action team meeting and disseminated at whole-school level.
Activities consisting in the creation of school action teams (or school action groups) including students and teachers were identified in three programs (see Table 5 ). In AB2, a school action group with both students and staff was formed to define action plans and training for staff on restorative practices at whole-school level and to implement a new school curriculum focusing on social and emotional skills. In LT, a school action group comprising around six students and six staff was formed to lay down school policies and coordinate interventions, based on the feedback from the student data collection. In SE, a school health promotion committee, consisting of representatives from the school board, parents, teachers, and students, was formed to discuss issues submitted by the students and to plan the activities for the future years based on the feedback from the activities already carried out. In addition, a peer group of 10 and 15 students from each class discussed health topics and student concerns with adult facilitators, in order to develop an action plan and to help in organizing various activities, such as contests and school assemblies.
High ASP: Organizing School Events
Three types of activities were included in this level of ASP. As reported in Table 5 , five programs solicited the creation of different student artifacts . AB1 included a student-made video on bullying to be presented to all the students. In GP, student artifacts were presented to audiences such as parents, other students, teachers, and members of the community. In SS, student leaders made presentations for peers to share personal examples of using the strengths provided by the program. In RJ, students engaged in collaborative, interactive writing activities based on analytical reflection for the realization of a rubric co-developed by students. SE included the contribution of all the students, teachers, and the principal in the realization of works like write-ups, poems, pictures, or artwork, on specific topics for a monthly wall magazine publication. SE also envisaged contests among students, such as poster-making and essay writing, linked to the monthly topic of the wall magazine.
Activities regarding the organization of student-led activities for peers were found in four programs (see Table 5 ). In CFS, student leaders (four to six in each intervention school) conducted at least three important whole-school activities to promote students’ positive use of technology for raising students’ awareness of their rights and responsibilities online; they also provided cyberbullying prevention trainings for peers. In SS, student leaders (up to six in the school) conducted activities aimed at raising awareness of Sources of Strengths , generating conversations with other students, providing presentations about the strengths proposed by the program, and engaging peers to identify their own trusted adults. RJ included student-led restorative circles with students, workshops for students, and peer-to-peer mentorship on restorative practices. In SE, student leaders (between 10 and 15 in each class) conducted peer group meetings to discuss on relevant health topics.
In two programs, student-led activities for adults were organized (see Table 5 ). In CFS, student-led activities provided information to the teaching staff about the technologies used by students and cyberbullying prevention training given to parents. In RJ, circles and workshops on restorative practices were implemented by the students for the staff.
Moderate ASP: Expressing Personal Views
Three types of activities were included in this level of ASP. As can be seen in Table 5 , two programs provided platforms where students could express their personal views on various topics. In BB, students, families, and school staff were provided with platforms to share information and communication on mental health issues. In SE, platforms were used to raise concerns, make complaints, and give suggestions, either anonymously or by self-identifying, on the intervention topics.
Interactive assemblies for students to discuss on the main intervention topics were organized in three programs (see Table 5 ). AB1 provided a first interactive school assembly to discuss respect and bullying, and later assemblies at class level to further discuss the themes emerged during the whole-school assembly. Similarly, AB3 included a school assembly where students were encouraged to get involved in the development of a whole-school anti-bullying policy, followed by three lessons during which the class teacher facilitated a discussion in each class aimed to raise awareness about bullying and to think about school-based solutions. SE included group discussions for generating awareness about health issues, to be discussed during the school assemblies that took place four times a month.
In six programs, students were given a voice by data collections to be used in the process of school changes (see Table 5 ). AB1 included a bullying report form that students, in addition to staff and parents, filled in to report bullying incidents. AB3 provided feedback from student data collection during the school assembly as a basis for discussing whole-school anti-bullying strategies. In LT, annual reports on students’ needs, drawing from student surveys in relation to bullying, aggression, and school experiences, guided the action teams to define school policies and coordinate interventions. In BB, summaries of student and staff data on current school structures, policies, programs, and practices related to student well-being, collected annually, were used by the team to create an “action plan” for changes across the school, both at the classroom and whole-school level. In GP, the profile emerging from the student surveys on school environment guided school teams in the definition of priority areas and strategies within each school, both by coordinating existing health promotional work and introducing new strategies that met the needs of a specific school. In SE, the school action team planned school activities based on reports and discussions on issues presented by the students.
Low ASP: Trainings
A low level of ASP was identified in three types of activities. As can be seen in Table 5 , four programs included trainings for student peer leaders . CFS provided a 10-h training for peer leaders to lead whole-school activities on the positive use of technology. GD provided a 5-h bystander training for student leaders to recognize situations and behaviors that could lead to violence or abuse and to identify active bystander behaviors to be performed either individually or collectively to reduce the risk or effect of violence. ST provided a 90-min training session and two 15-min booster sessions on bullying, which included icebreaker exercises, hands-on activities, and role plays. SS provided a 4-h interactive training for peer leaders aimed at developing protective resources in themselves and encouraging peers to grow such resources as well.
Eight programs included interactive group activities (see Table 5 ). In AB3, students worked in small groups to identify the types of bullying in the school and to discuss strategies to prevent bullying, with the support of bullying scenarios with discussion questions. In CFS, interactive activities included problem-solving, quizzes, and case studies on the use of technology to prevent cyberbullying. LT included various interactive activities aimed at preventing violence, ranging from informal practice, for example, using “affective” statements to communicate feelings, to formal practices, for example hosting a restorative “circle” where participants were encouraged to express emotions and create emotional bonds after problematic or disruptive behavior. BB provided a range of interactive teaching methods, such as small-group exercises, role plays, and quizzes, for reflecting on mental health issues. GP provided activities as small group work and class discussion, by also implementing interactive teaching strategies, such as using questions to kindle discussions and emphasizing the importance to consider different perspectives on a topic, encourage challenges, and debate ideas. SS included peer-to-peer messages and activities wherein student leaders shared examples of strengths that have helped them to overcome personal challenges and invited their peers to participate in interactive tasks. RJ included many interactive practices, such as restorative circles, interactive writing activities, and peer-to-peer mentorship to broaden the impact of restorative practices. SE included monthly contests for students, such as elocution, debates, and quiz games.
Finally, in BB program, some individual activities , in addition to group tasks, were conducted (see Table 5 ). Such activities consisted of individual writings and self-reflection on specific topics, aimed at building or enhancing sense of self-worth, belonging, control, purpose, future, and humor, which were considered to protect against mental health problems.
Very Low ASP: Students as Recipients
Activities in which student’s role was overall that of the recipients of actions taken from adults were of three types. As can be seen in Table 5 , six programs included lecture-style lessons . AB1 included the speech by a nationally known speaker about respect and bullying and the presentation of the Social Support System to students by their English teachers. AB3 included the presentation of summary feedback from the pre-test questionnaires during a school assembly and three lessons, delivered by the class teachers, on school bullying. CFS included lessons led by class teachers, aimed at improving online social skills, focusing, in particular, on positive communication, resilience, self-management, conflict resolution, and social responsibility. GD included a 50-min persuasive lesson led by adults focused on violence victimization, perpetration, and prosocial behaviors. LT included adult-led lessons on social and emotional skills. SE organized workshops led by teachers or program facilitators on effective study skills, such as time management, learning style, note-taking, reading comprehension, memorization techniques, and concentration techniques.
Three programs included the viewing of videos during the implementation (see Table 5 ). AB1 and AB3 provided a video on school bullying for all the students. BB provided video or DVD materials on mental health issues.
Finally, three programs provided students with informative materials (see Table 5 ). AB1 provided a form with several responses for intervening against bullying, which offered alternatives to the traditional method of apportioning blame and punishing bullies. Similarly, AB3 provided a worksheet on possible responses to bullying. FS provided educational magazines on bullying issues. BB provided many materials, such as individual student workbooks, a review poster, master copies of resources for all activities, and homework worksheets.
The aim of this systematic review was to provide a reasoned synthesis of whole-school interventions in secondary school capable of improving the school environment by assigning an active role to students. The first result that warrants consideration regards the number of publications that met our eligibility criteria to select whole-school interventions based on activities soliciting ASP in secondary schools. Despite the wide interest of researchers on the topic of whole-school interventions in general (see Bonell et al., 2018 ; Charlton et al., 2021 ), our selection and data collection process eventually provided only 22 reports referring to 16 studies that fostered ASP during the intervention. This result calls for further work in the field. Based on the emphasis given by educational and political agendas about the importance of empowering students in their role as active participants in schools, first of all, and in societies, subsequently, research should not overlook the question of how to improve their participatory skills by involving them in school activities and decisions (Markham & Aveyard, 2003 ). More investment in this direction is needed to evaluate the consistency and efficacy of the existing programs, to eventually reach consensus on the intervention protocols that schools can implement to improve their learning environment. Results related to each of our specific aims will be discussed in the following paragraphs.
Characteristics of the Selected Programs
As for the first aim of the review, concerning the description of the identified literature, several reflections arise from our results. Considering the year of publication, we found growing interest by researchers in the field, as most reports were published in the last few years, i.e., from 2018 to 2021. This may be considered positive indication that research has identified student participation in school interventions as a crucial topic on which to invest for future works. As for the focus of the selected literature, most of the included studies concerned the reduction of violent behaviors, referring for the most part to bullying, while the promotion of a more general positive emotional and relational school climate is the less investigated topic. Notwithstanding the overall need to fill in this limitation of research, these results suggest that future studies should address the issue of how it is possible to create better school environments for students starting from their own involvement and decision-making roles. This is consistent with the direction indicated by Bonell et al. ( 2018 ), who upheld the importance of focusing more on overall school systems rather than on specific problems. The implementation of a larger number of programs fostering ASP in order to improve school climate and learning environments would thus be important to understand how to support students in dealing with the variety of non-specific problems that can arise during school life. Indeed, as confirmed by the literature, a positive school climate is related to higher academic achievement (Berkowitz et al., 2017 ; Kutsyuruba et al., 2015 ) and fewer problematic behaviors, violence (Reaves et al., 2018 ), and psychological malaise at school (Aldridge and McChesney, 2018 ). Finally, looking at the country of the selected program implementation, most of the studies were conducted in the USA, some in Australia and the UK, and a few in India and China. To our knowledge, with the exception of the two anti-bullying programs carried out in the UK and included in the current review, no other studies were conducted in European countries. With caution, as in many other countries researchers may have developed programs that could not be included in this review due to the inclusion criteria, we consider this as a gap in the literature that future work should fill, especially considering that school policies and organizations are very different between continents. In this regard, it would be interesting both to replicate existing programs and to develop revisited or new interventions specifically adapted to the context of the country’s school system, a work that would also fulfil the aim to increase the ecological validity of the proposed activities.
Methodological Quality of the Selected Reports
The second aim of the review was to assess the soundness of the research design and methodologies adopted in the selected studies. In this regard, we found that the considered reports were robust overall, as they met most of the considered indicators of methodological quality. In particular, most of the studies, based both on EGC or on other designs, described and contextualized the intervention and provided adequate analyses. Beyond the generally good methodological quality of the included studies, consistently with previous examinations of intervention programs (Charlton et al., 2021 ), we found a weakness concerning the fidelity of implementation, as this indicator was observed in only about half of the considered programs. Given that fidelity is a fundamental aspect for the evaluation of the intervention efficacy (O’Donnell, 2008 ), future studies should consider this important factor, by adding it to the evaluation of the programs for providing adequate monitoring tools that include qualitative and process indicators. Overall, however, the literature on the interventions meeting the criteria for our review, albeit limited, relies on methodologically sound grounds that allow us to draw some conclusions on programs and activities actively involving students and to offer suggestions for researchers and practitioners in the field.
Program Activities and Levels of ASP
As for the third and last aim of the review, i.e., concerning the analysis and description of ASP activities proposed in the various programs, our results offer material for an innovative way to look at the programs and points the way to future research in the field. In particular, some points should be highlighted. First, we were able to show that a variety of ASP activities can be used in interventions, from those requiring students to directly act on school programs and policies to those in which students are merely involved as recipients of contents delivered by school staff. From the careful and independently conducted analysis of all program activities, we were also able to grade such activities on a scale ranging from very high to very low levels of ASP. This may be a useful tool for researchers, as it advances a way to develop and organize interventions fostering different levels of ASP activities, to be selected on the basis of the research focus and aims. The effort to identify different levels of ASP also has the merit of introducing some degree of clarity and order in the great variability of program activities. While the importance of student involvement and participation was generally recognized in the literature (Baeten et al., 2016 ; Schweisfurth, 2015 ), our in-depth description shows that not all forms of participation are equal, and thus offers a tool to differentiate between them. This advances our understanding of the concept of student participation both on a theoretical and methodological level.
Beyond this general picture of ASP activities, our findings show that the interventions based on the highest levels of ASP are those aimed at generally improving the school environment, i.e., the Restorative Justice and SEHER programs. These programs included all but one of the activities defined as Very High ASP or High ASP , while all other programs usually provided only one or two of them. This result can offer interesting insights if taken together with the above-reported considerations on the importance to promote overall school improvement, and not to restrict the focus on one or few specific problems. On the basis of this result, we tentatively advance that when the study scope is broad and the theoretical approach is systemic, interventions are more directly centered on lending a voice to students and assigning to them a decision-making role. This again supports the importance of promoting whole-school interventions targeted toward the general learning environment.
Limitations and Conclusion
We are aware that the findings of the present literature review should be considered in the light of certain limitations. First of all, our choice to include only studies published in peer-reviewed journals in English requires some caution. While this selection criteria allowed us to provide a picture of the international literature, this might entail the loss of programs published in other languages that nonetheless contribute to the issue and deserve to be explored in future reviews. Secondly, in the present work, we did not address the issue of cross-cultural similarities and differences in schooling and education, which may influence the way ASP is conceived and valorized in the school context. However, the levels of ASP activities we proposed have the strength of resulting from the analysis of programs from several countries and may thus offer a basis for future discussions on the cross-cultural validity of practices fostering ASP. Furthermore, the present review has focused only on secondary school programs. While this choice was needed for guaranteeing clear references and boundaries to our findings, it also leaves to be explored whether our proposed classification of ASP activities could also be applied to younger students. Given the developmental and organizational differences between primary and secondary levels of education, this issue certainly merits further exploration in future reviews.
As the aim of our review was to provide an in-depth and reasoned description of existing studies based on ASP and of the activities adopted to promote the active role of students, testing the efficacy of these studies was beyond the scope of the present work. While future research may advance this line of inquiry, based on the evidence that different outcomes are considered in such a small number of studies, it seems premature to move toward extensive efficacy testing such as meta-analyses. Rather, at present, it is probably more feasible and desirable to have an increasing amount of literature focusing on ASP in whole-school interventions, to collect further evidence of robust programs and activities, especially with regard to high ASP. As a possible further research question in this direction, we suggest it would also be useful to assess whether the ways of actively involving students may change depending on the intervention target outcomes or on the number of students taking part in the activities. Lastly, while this is true for any review of the literature, it should nonetheless be acknowledged that our syntheses and reflections are dependent upon the choices made in the article selection process. For example, our inclusion and exclusion criteria (i.e., focusing on general participants and targets of intervention) may have restricted our sample. With this in mind, we followed closely the PRISMA guidelines and detailed each step of the process, so that readers can be well informed and future research may build as seamlessly as possible from our work.
Despite the mentioned limitations, this review provides a literature advance in its in-depth examination of existing whole-school interventions that include active student participation in secondary school. Their description and reasoned synthesis make available to researchers and practitioners an overview of specific programs and activities that are being used to actively involve students in processes of change. This in turn can inform reflections and experimentations as to how to integrate and improve the existing provision. In this direction, the major effort and contribution of the present review is the proposal of an organizing structure based on different levels of ASP for analyzing interventions, which allows to classify the specific activities included in each program. Such an effort provides a common ground for reflections and future studies on active student participation, as a shared classification can be instrumental for planning new interventions or evaluating the actual degree of students’ active involvement in the implemented programs. Overall, this work significantly contributes to the far-reaching goal of encouraging student participation in school life, and more specifically in the transformation of their learning environment, so that they can be empowered in shaping it to be increasingly responsive to their insights, ideas, and needs.
Aldridge, J. M., & McChesney, K. (2018). The relationships between school climate and adolescent mental health and wellbeing: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Educational Research, 88 , 121–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2018.01.012
Article Google Scholar
Allen, K. P. (2010). A bullying intervention system in high school: A two-year school-wide follow-up. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 36 (3), 83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2011.01.002
Anderson, C. S. (1982). The search for school climate: A review of the research. Review of Educational Research, 52 (3), 368–420. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543052003368
Antoniou, P., & Kyriakides, L. (2013). A dynamic integrated approach to teacher professional development: Impact and sustainability of the effects on improving teacher behavior and student outcomes. Teaching and Teacher Education, 29 (1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2012.08.001
Baeten, M., Dochy, F., Struyven, K., Parmentier, E., & Vanderbruggen, A. (2016). Student-centred learning environments: An investigation into student teachers’ instructional preferences and approaches to learning. Learning Environments Research, 19 (1), 43–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-015-9190-5
Berkowitz, R., Moore, H., Astor, R. A., & Benbenishty, R. (2017). A research synthesis of the associations between socioeconomic background, inequality, school climate, and academic achievement. Review of Educational Research, 87 (2), 425–469. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654316669821
Bond, L., Patton, G., Glover, S., Carlin, J. B., Butler, H., Thomas, L., & Bowes, G. (2004). The Gatehouse Project: Can a multilevel school intervention affect emotional wellbeing and health risk behaviours? Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health, 58 (12), 997–1003. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.2003.009449
Bonell, C., Allen, E., Warren, E., McGowan, J., Bevilacqua, L., Jamal, F., ... & Viner, R. M. (2018). Effects of the Learning Together intervention on bullying and aggression in English secondary schools (INCLUSIVE): A cluster randomised controlled trial. The Lancet , 392 (10163), 2452–2464. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31782-3
Brand, S., Felner, R. D., Seitsinger, A., Burns, A., & Bolton, N. (2008). A large scale study of the assessment of the social environment of middle and secondary schools: The validity and utility of teachers’ ratings of school climate, cultural pluralism, and safety problems for understanding school effects and school improvement. Journal of School Psychology, 46 (5), 507–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2007.12.001
Carpenter, J. P., & Pease, J. S. (2013). Preparing students to take responsibilities for learning: The role of non-curricular learning strategies. Journal of Curriculum and Instruction, 7 (2), 38–55. https://doi.org/10.3776/joci.2013.v7n2p38-55
Charlton, C. T., Moulton, S., Sabey, C. V., & West, R. (2021). A systematic review of the effects of schoolwide intervention programs on student and teacher perceptions of school climate. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 23 (3), 185–200. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300720940168
Cohen, J., Mccabe, E. M., Michelli, N. M., & Pickeral, T. (2009). School climate: Research, policy, practice, and teacher education. Teachers College Record, 111 (1), 180–213. https://doi.org/10.1177/016146810911100108
Coker, A. L., Bush, H. M., Brancato, C. J., Clear, E. R., & Recktenwald, E. A. (2019). Bystander program effectiveness to reduce violence acceptance: RCT in high schools. Journal of Family Violence, 34 (3), 153–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-018-9961-8
Council for Exceptional Children (CEC): Standards for evidence-based practices in special education. (2014). Exceptional Children, 80 (4), 504–511. https://doi.org/10.1177/0014402914531388
Cross, D., Shaw, T., Hadwen, K., Cardoso, P., Slee, P., Roberts, C., Thomas, L., & Barnes, A. (2016). Longitudinal impact of the cyber friendly schools program on adolescents’ cyberbullying behavior. Aggressive Behavior, 42 (2), 166–180. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.21609
Cross, D., Shaw, T., Epstein, M., Pearce, N., Barnes, A., Burns, S., Waters, S., Lester, L., & Runions, K. (2018). Impact of the friendly schools whole-school intervention on transition to secondary school and adolescent bullying behaviour. European Journal of Education, 53 (4), 495–513. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejed.12307
De Róiste, A., Kelly, C., Molcho, M., Gavin, A., & Gabhainn, S. N. (2012). Is school participation good for children? Associations with health and wellbeing. Health Education, 112 (2), 88–104. https://doi.org/10.1108/09654281211203394
Doumas, D. M., Midgett, A., & Watts, A. D. (2019a). The impact of a brief, bullying bystander intervention on internalizing symptoms: Is gender a moderator of intervention effects? School Psychology International, 40 (3), 275–293. https://doi.org/10.1177/0143034319830149
Doumas, D. M., Midgett, A., & Watts, A. D. (2019b). A pilot evaluation of the social validity of a bullying bystander program adapted for high school students. Psychology in the Schools, 56 (7), 1101–1116. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.22249
Epstein, J. L., & McPartland, J. M. (1976). The concept and measurement of the quality of school life. American Educational Research Journal, 13 (1), 15–30. https://doi.org/10.1037/e435912004-001
Estrapala, S., Rila, A., & Bruhn, A. L. (2021). A systematic review of Tier I PBIS implementation in high schools. Journal of Positive Psychology, 23 (4), 288–302. https://doi.org/10.1177/1098300720929684
Fletcher, A., Fitzgerald-Yau, N., Wiggins, M., Viner, R. M., & Bonell, C. (2015). Involving young people in changing their school environment to make it safer: Findings from a process evaluation in English secondary schools. Health Education, 115 (3–4), 322–338. https://doi.org/10.1108/HE-04-2014-0063
Gage, N., Whitford, D. K., & Katsiyannis, A. (2018). A review of schoolwide positive behavior interventions and supports as a framework for reducing disciplinary exclusions. The Journal of Special Education, 52 , 142–151. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022466918767847
González, T., Sattler, H., & Buth, A. J. (2019). New directions in whole-school restorative justice implementation. Conflict Resolution Quarterly, 36 (3), 207–220. https://doi.org/10.1002/crq.21236
Grazia, V., Mameli, C., & Molinari, L. (2021). Adolescents’ profiles based on student agency and teacher autonomy support: Does interpersonal justice matter? European Journal of Psychology of Education, 36 (4), 1117–1134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-020-00504-2
Griffin, L. K., Adams, N., & Little, T. D. (2017). Self determination theory, identity development, and adolescence. Development of self-determination through the life-course , 189–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-1042-6_14
Helker, K., & Wosnitza, M. (2016). The interplay of students’ and parents’ responsibility judgements in the school context and their associations with student motivation and achievement. International Journal of Educational Research, 76 , 34–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2016.01.001
Horner, R. H., Todd, A. W., Lewis-Palmer, T., Irvin, L., Sugai, G., & Boland, J. B. (2004). The school-wide evaluation tool (SET): A research instrument for assessing school-wide positive behavior support. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 6 , 3–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/10983007040060010201
Hoy, W. K. (2012). School characteristics that make a difference for the achievement of all students: A 40-year odyssey. Journal of Educational Administration, 50 (1), 76–97. https://doi.org/10.1108/09578231211196078
Jang, H., Kim, E. J., & Reeve, J. (2012). Longitudinal test of self-determination theory’s motivation mediation model in a naturally occurring classroom context. Journal of Educational Psychology, 104 , 1175–1188. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0028089
Johnston, A. D., Midgett, A., Doumas, D. M., & Moody, S. (2018). A mixed methods evaluation of the “aged-up” STAC bullying bystander intervention for high school students. The Professional Counselor, 8 (1), 73–87. https://doi.org/10.15241/adj.8.1.73
Kutsyuruba, B., Klinger, D. A., & Hussain, A. (2015). Relationships among school climate, school safety, and student achievement and well-being: A review of the literature. Review of Education, 3 , 103–135. https://doi.org/10.1002/rev3.3043
Låftman, S. B., Östberg, V., & Modin, B. (2017). School climate and exposure to bullying: A multilevel study. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 28 (1), 153–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/09243453.2016.1253591
Lipponen, L., & Kumpulainen, K. (2011). Acting as accountable authors: Creating interactional space for agency work in teacher education. Teaching and Teachers Education, 27 (5), 821–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tate.2011.01.001
Makitalo, A. (2016). On the notion of agency in studies of interaction and learning. Learning, Culture, and Social Interaction, 10 , 64–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lcsi.2016.07.003
Mameli, C., Molinari, L., & Passini, S. (2019). Agency and responsibility in adolescent students: A challenge for the societies of tomorrow. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 89 (1), 41–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12215
Markham, W. A., & Aveyard, P. (2003). A new theory of health promoting schools based on human functioning, school organization and pedagogic practices. Social Sciences & Medicine, 56 , 1209–1220. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0277-9536(02)00120-x
Matos, L., Reeve, J., Herrera, D., & Claux, M. (2018). Students’ agentic engagement predicts longitudinal increases in perceived autonomy-supportive teaching: The squeaky wheel gets the grease. The Journal of Experimental Education, 86 (4), 579–596. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2018.1448746
Melendez-Torres, G. J., Allen, E., Viner, R., & Bonell, C. (2021). Effects of a whole-school health intervention on clustered adolescent health risks: Latent transition analysis of data from the inclusive trial. Prevention Science, 23 , 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11121-021-01237-4
Merrell, K. W., Gueldner, B. A., Ross, S. W., & Isava, D. M. (2008). How effective are school bullying intervention programs? A meta-analysis of intervention research. School Psychology Quarterly, 23 (1), 26–42. https://doi.org/10.1037/1045-3830.23.1.26
Midgett, A., & Doumas, D. M. (2019). The impact of a brief bullying bystander intervention on depressive symptoms. Journal of Counseling & Development, 97 (3), 270–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcad.12267
Mitchell, J. V. (1967). A study of high school learning environments and their impact on students. Report, U.S. Office of Education, Project No. 5–8032. University of Rochester.
Mitra, D. L. (2004). The significance of students: Can increasing “student voice” in schools lead to gains in youth development? Teacher College Record, 106 (4), 651–688. https://doi.org/10.1177/016146810410600402
Noltemeyer, A., Palmer, K., James, A. G., & Wiechman, S. (2019). School-wide positive behavioral interventions and supports (SWPBIS): A synthesis of existing research. International Journal of School & Educational Psychology, 7 , 253–262. https://doi.org/10.1080/21683603.2018.1425169
Nota, L., Soresi, S., Ferrari, L., & Wehmeyer, M. L. (2011). A multivariate analysis of the self-determination of adolescents. Journal of Happiness Studies, 12 , 245–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-010-9191-0
O’Donnell, C. L. (2008). Defining, conceptualizing, and measuring fidelity of implementation and its relationship to outcomes in K–12 curriculum intervention research. Review of Educational Research, 78 (1), 33–84. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654307313793
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., ... & Moher, D. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. International Journal of Surgery , 88 , 105906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906
Patton, G. C., Bond, L., Carlin, J. B., Thomas, L., Butler, H., Glover, S., ... & Bowes, G. (2006). Promoting social inclusion in schools: A group-randomized trial of effects on student health risk behavior and well-being. American journal of public health, 96(9) , 1582–1587. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.2004.047399
Petrova, M., Wyman, P. A., Schmeelk-Cone, K., & Pisani, A. R. (2015). Positive-themed suicide prevention messages delivered by adolescent peer leaders: Proximal impact on classmates’ coping attitudes and perceptions of adult support. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior, 45 (6), 651–663. https://doi.org/10.1111/sltb.12156
Pickering, T. A., Wyman, P. A., Schmeelk-Cone, K., Hartley, C., Valente, T. W., Pisani, A. R., Rulison, K. L., Brown, C. H., & LoMurray, M. (2018). Diffusion of a peer-led suicide preventive intervention through school-based student peer and adult networks. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 9 , 598. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00598
Power, F. C., Higgins, A., & Kohlberg, L. (1989). Lawrence Kohlberg’s approach to moral education . Columbia University Press.
Google Scholar
Raufelder, D., Kittler, F., Braun, S. R., Lätsch, A., Wilkinson, R. P., & Hoferichter, F. (2014). The interplay of perceived stress, self-determination and school engagement in adolescence. School Psychology International, 35 (4), 405–420. https://doi.org/10.1177/0143034313498953
Reaves, S., McMahon, S. D., Duffy, S. N., & Ruiz, L. (2018). The test of time: A meta-analytic review of the relation between school climate and problem behavior. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 39 , 100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2018.01.006
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2017). Self-determination theory. Basic psychological needs in motivation, development, and wellness. Guilford Publications.
Sawyer, M. G., Pfeiffer, S., Spence, S. H., Bond, L., Graetz, B., Kay, D., ... & Sheffield, J. (2010). School‐based prevention of depression: A randomised controlled study of the beyondblue schools research initiative. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry , 51 (2), 199–209. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2009.02136.x
Schweisfurth, M. (2015). Learner-centred pedagogy: Towards a post-2015 agenda for teaching and learning. International Journal of Educational Development, 40 , 259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedudev.2014.10.011
Shinde, S., Weiss, H. A., Varghese, B., Khandeparkar, P., Pereira, B., Sharma, A., Gupta, R., Ross, D. A., Patton, G., & Patel, V. (2018). Promoting school climate and health outcomes with the SEHER multi-component secondary school intervention in Bihar, India: A cluster-randomised controlled trial. The Lancet, 392 (10163), 2465–2477. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31615-5
Singla, D. R., Shinde, S., Patton, G., & Patel, V. (2021). The mediating effect of school climate on adolescent mental health: Findings from a randomized controlled trial of a school-wide intervention. Journal of Adolescent Health, 69 (1), 90–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2020.09.030
Thapa, A., Cohen, J., Guffey, S., & Higgins-D’Alessandro, A. (2013). A review of school climate research. Review of Educational Research, 83 (3), 357–385. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654313483907
Ttofi, M. M., Farrington, D. P., & Baldry, A. C. (2008). Effectiveness of programmes to reduce school bullying . Swedish Council for Crime Prevention, Information, and Publications.
Vancel, S. M., Missall, K. N., & Bruhn, A. L. (2016). Teacher ratings of the social validity of Schoolwide Positive Behavior Interventions and Supports: A comparison of school groups. Preventing School Failure, 60 , 320–328. https://doi.org/10.1080/1045988x.2016.1157784
Vieno, A., Perkins, D. D., Smith, T. M., & Santinello, M. (2005). Democratic school climate and sense of community in school: A multilevel analysis. American Journal of Community Psychology, 36 (3–4), 327–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10464-005-8629-8
Voight, A., & Nation, M. (2016). Practices for improving secondary school climate: A systematic review of research literature. American Journal of Community Psychology, 58 , 174–191. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajcp.12074
Weatherson, K. A., O’Neill, M., Lau, E. Y., Qian, W., Leatherdale, S. T., & Faulkner, G. E. (2018). The protective effects of school connectedness on substance use and physical activity. Journal of Adolescent Health, 63 (6), 724–731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.07.002
Williford, A., Yoder, J., Fulginiti, A., Ortega, L., LoMurray, S., Duncan, D., & Kennedy, N. (2021). Peer leaders as gatekeepers and agents of change: Understanding how sources of strength reduces suicide risk and promotes wellness. Child & Youth Care Forum, 51 (3), 539–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-021-09639-9
Wohlin, C. (2014, May). Guidelines for snowballing in systematic literature studies and a replication in software engineering. In Proceedings of the 18th international conference on evaluation and assessment in software engineering (1–10). https://doi.org/10.1145/2601248.2601268
Wurf, G. (2012). High school anti-bullying interventions: An evaluation of curriculum approaches and the method of shared concern in four Hong Kong international schools. Australian Journal of Guidance and Counselling, 22 (1), 139–149. https://doi.org/10.1017/jgc.2012.2
Wyman, P. A., Brown, C. H., LoMurray, M., Schmeelk-Cone, K., Petrova, M., Yu, Q., ... & Wang, W. (2010). An outcome evaluation of the Sources of Strength suicide prevention program delivered by adolescent peer leaders in high schools. American journal of public health , 100 (9), 1653–1661. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.2009.190025
Download references
Open access funding provided by Università degli Studi di Parma within the CRUI-CARE Agreement. The research leading to these results received funding from the Program “FIL-Quota Incentivante” of the University of Parma co-sponsored by Fondazione Cariparma.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Humanities, Social Sciences and Cultural Industries, University of Parma, Borgo Carissimi 10, 43121, Parma, PR, Italy
Sara Berti, Valentina Grazia & Luisa Molinari
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Literature search was conducted by Sara Berti; assessment of methodological quality was supervised by Valentina Grazia; draft of the introduction and overall supervision were performed by Luisa Molinari. All the authors contributed to data analyses, draft of the manuscript, and critical revisions of the work and they eventually approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sara Berti .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Berti, S., Grazia, V. & Molinari, L. Active Student Participation in Whole-School Interventions in Secondary School. A Systematic Literature Review. Educ Psychol Rev 35 , 52 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-023-09773-x
Download citation
Accepted : 19 April 2023
Published : 04 May 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-023-09773-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Active student participation
- Whole-school intervention
- Secondary school
- Student involvement
- Program activities
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Research Skills
50 Mini-Lessons For Teaching Students Research Skills
Please note, I am no longer blogging and this post hasn’t updated since April 2020.
For a number of years, Seth Godin has been talking about the need to “ connect the dots” rather than “collect the dots” . That is, rather than memorising information, students must be able to learn how to solve new problems, see patterns, and combine multiple perspectives.
Solid research skills underpin this. Having the fluency to find and use information successfully is an essential skill for life and work.
Today’s students have more information at their fingertips than ever before and this means the role of the teacher as a guide is more important than ever.
You might be wondering how you can fit teaching research skills into a busy curriculum? There aren’t enough hours in the day! The good news is, there are so many mini-lessons you can do to build students’ skills over time.
This post outlines 50 ideas for activities that could be done in just a few minutes (or stretched out to a longer lesson if you have the time!).
Learn More About The Research Process
I have a popular post called Teach Students How To Research Online In 5 Steps. It outlines a five-step approach to break down the research process into manageable chunks.

This post shares ideas for mini-lessons that could be carried out in the classroom throughout the year to help build students’ skills in the five areas of: clarify, search, delve, evaluate , and cite . It also includes ideas for learning about staying organised throughout the research process.
Notes about the 50 research activities:
- These ideas can be adapted for different age groups from middle primary/elementary to senior high school.
- Many of these ideas can be repeated throughout the year.
- Depending on the age of your students, you can decide whether the activity will be more teacher or student led. Some activities suggest coming up with a list of words, questions, or phrases. Teachers of younger students could generate these themselves.
- Depending on how much time you have, many of the activities can be either quickly modelled by the teacher, or extended to an hour-long lesson.
- Some of the activities could fit into more than one category.
- Looking for simple articles for younger students for some of the activities? Try DOGO News or Time for Kids . Newsela is also a great resource but you do need to sign up for free account.
- Why not try a few activities in a staff meeting? Everyone can always brush up on their own research skills!
- Choose a topic (e.g. koalas, basketball, Mount Everest) . Write as many questions as you can think of relating to that topic.
- Make a mindmap of a topic you’re currently learning about. This could be either on paper or using an online tool like Bubbl.us .
- Read a short book or article. Make a list of 5 words from the text that you don’t totally understand. Look up the meaning of the words in a dictionary (online or paper).
- Look at a printed or digital copy of a short article with the title removed. Come up with as many different titles as possible that would fit the article.
- Come up with a list of 5 different questions you could type into Google (e.g. Which country in Asia has the largest population?) Circle the keywords in each question.
- Write down 10 words to describe a person, place, or topic. Come up with synonyms for these words using a tool like Thesaurus.com .
- Write pairs of synonyms on post-it notes (this could be done by the teacher or students). Each student in the class has one post-it note and walks around the classroom to find the person with the synonym to their word.

- Explore how to search Google using your voice (i.e. click/tap on the microphone in the Google search box or on your phone/tablet keyboard) . List the pros and cons of using voice and text to search.
- Open two different search engines in your browser such as Google and Bing. Type in a query and compare the results. Do all search engines work exactly the same?
- Have students work in pairs to try out a different search engine (there are 11 listed here ). Report back to the class on the pros and cons.
- Think of something you’re curious about, (e.g. What endangered animals live in the Amazon Rainforest?). Open Google in two tabs. In one search, type in one or two keywords ( e.g. Amazon Rainforest) . In the other search type in multiple relevant keywords (e.g. endangered animals Amazon rainforest). Compare the results. Discuss the importance of being specific.
- Similar to above, try two different searches where one phrase is in quotation marks and the other is not. For example, Origin of “raining cats and dogs” and Origin of raining cats and dogs . Discuss the difference that using quotation marks makes (It tells Google to search for the precise keywords in order.)
- Try writing a question in Google with a few minor spelling mistakes. What happens? What happens if you add or leave out punctuation ?
- Try the AGoogleADay.com daily search challenges from Google. The questions help older students learn about choosing keywords, deconstructing questions, and altering keywords.
- Explore how Google uses autocomplete to suggest searches quickly. Try it out by typing in various queries (e.g. How to draw… or What is the tallest…). Discuss how these suggestions come about, how to use them, and whether they’re usually helpful.
- Watch this video from Code.org to learn more about how search works .
- Take a look at 20 Instant Google Searches your Students Need to Know by Eric Curts to learn about “ instant searches ”. Try one to try out. Perhaps each student could be assigned one to try and share with the class.
- Experiment with typing some questions into Google that have a clear answer (e.g. “What is a parallelogram?” or “What is the highest mountain in the world?” or “What is the population of Australia?”). Look at the different ways the answers are displayed instantly within the search results — dictionary definitions, image cards, graphs etc.
- Watch the video How Does Google Know Everything About Me? by Scientific American. Discuss the PageRank algorithm and how Google uses your data to customise search results.
- Brainstorm a list of popular domains (e.g. .com, .com.au, or your country’s domain) . Discuss if any domains might be more reliable than others and why (e.g. .gov or .edu) .
- Discuss (or research) ways to open Google search results in a new tab to save your original search results (i.e. right-click > open link in new tab or press control/command and click the link).
- Try out a few Google searches (perhaps start with things like “car service” “cat food” or “fresh flowers”). A re there advertisements within the results? Discuss where these appear and how to spot them.
- Look at ways to filter search results by using the tabs at the top of the page in Google (i.e. news, images, shopping, maps, videos etc.). Do the same filters appear for all Google searches? Try out a few different searches and see.
- Type a question into Google and look for the “People also ask” and “Searches related to…” sections. Discuss how these could be useful. When should you use them or ignore them so you don’t go off on an irrelevant tangent? Is the information in the drop-down section under “People also ask” always the best?
- Often, more current search results are more useful. Click on “tools” under the Google search box and then “any time” and your time frame of choice such as “Past month” or “Past year”.
- Have students annotate their own “anatomy of a search result” example like the one I made below. Explore the different ways search results display; some have more details like sitelinks and some do not.
- Find two articles on a news topic from different publications. Or find a news article and an opinion piece on the same topic. Make a Venn diagram comparing the similarities and differences.
- Choose a graph, map, or chart from The New York Times’ What’s Going On In This Graph series . Have a whole class or small group discussion about the data.
- Look at images stripped of their captions on What’s Going On In This Picture? by The New York Times. Discuss the images in pairs or small groups. What can you tell?
- Explore a website together as a class or in pairs — perhaps a news website. Identify all the advertisements .
- Have a look at a fake website either as a whole class or in pairs/small groups. See if students can spot that these sites are not real. Discuss the fact that you can’t believe everything that’s online. Get started with these four examples of fake websites from Eric Curts.
- Give students a copy of my website evaluation flowchart to analyse and then discuss as a class. Read more about the flowchart in this post.
- As a class, look at a prompt from Mike Caulfield’s Four Moves . Either together or in small groups, have students fact check the prompts on the site. This resource explains more about the fact checking process. Note: some of these prompts are not suitable for younger students.
- Practice skim reading — give students one minute to read a short article. Ask them to discuss what stood out to them. Headings? Bold words? Quotes? Then give students ten minutes to read the same article and discuss deep reading.

All students can benefit from learning about plagiarism, copyright, how to write information in their own words, and how to acknowledge the source. However, the formality of this process will depend on your students’ age and your curriculum guidelines.
- Watch the video Citation for Beginners for an introduction to citation. Discuss the key points to remember.
- Look up the definition of plagiarism using a variety of sources (dictionary, video, Wikipedia etc.). Create a definition as a class.
- Find an interesting video on YouTube (perhaps a “life hack” video) and write a brief summary in your own words.
- Have students pair up and tell each other about their weekend. Then have the listener try to verbalise or write their friend’s recount in their own words. Discuss how accurate this was.
- Read the class a copy of a well known fairy tale. Have them write a short summary in their own words. Compare the versions that different students come up with.
- Try out MyBib — a handy free online tool without ads that helps you create citations quickly and easily.
- Give primary/elementary students a copy of Kathy Schrock’s Guide to Citation that matches their grade level (the guide covers grades 1 to 6). Choose one form of citation and create some examples as a class (e.g. a website or a book).
- Make a list of things that are okay and not okay to do when researching, e.g. copy text from a website, use any image from Google images, paraphrase in your own words and cite your source, add a short quote and cite the source.
- Have students read a short article and then come up with a summary that would be considered plagiarism and one that would not be considered plagiarism. These could be shared with the class and the students asked to decide which one shows an example of plagiarism .
- Older students could investigate the difference between paraphrasing and summarising . They could create a Venn diagram that compares the two.
- Write a list of statements on the board that might be true or false ( e.g. The 1956 Olympics were held in Melbourne, Australia. The rhinoceros is the largest land animal in the world. The current marathon world record is 2 hours, 7 minutes). Have students research these statements and decide whether they’re true or false by sharing their citations.
Staying Organised

- Make a list of different ways you can take notes while researching — Google Docs, Google Keep, pen and paper etc. Discuss the pros and cons of each method.
- Learn the keyboard shortcuts to help manage tabs (e.g. open new tab, reopen closed tab, go to next tab etc.). Perhaps students could all try out the shortcuts and share their favourite one with the class.
- Find a collection of resources on a topic and add them to a Wakelet .
- Listen to a short podcast or watch a brief video on a certain topic and sketchnote ideas. Sylvia Duckworth has some great tips about live sketchnoting
- Learn how to use split screen to have one window open with your research, and another open with your notes (e.g. a Google spreadsheet, Google Doc, Microsoft Word or OneNote etc.) .
All teachers know it’s important to teach students to research well. Investing time in this process will also pay off throughout the year and the years to come. Students will be able to focus on analysing and synthesizing information, rather than the mechanics of the research process.
By trying out as many of these mini-lessons as possible throughout the year, you’ll be really helping your students to thrive in all areas of school, work, and life.
Also remember to model your own searches explicitly during class time. Talk out loud as you look things up and ask students for input. Learning together is the way to go!
You Might Also Enjoy Reading:
How To Evaluate Websites: A Guide For Teachers And Students
Five Tips for Teaching Students How to Research and Filter Information
Typing Tips: The How and Why of Teaching Students Keyboarding Skills
8 Ways Teachers And Schools Can Communicate With Parents

10 Replies to “50 Mini-Lessons For Teaching Students Research Skills”
Loving these ideas, thank you
This list is amazing. Thank you so much!
So glad it’s helpful, Alex! 🙂
Hi I am a student who really needed some help on how to reasearch thanks for the help.
So glad it helped! 🙂
seriously seriously grateful for your post. 🙂
So glad it’s helpful! Makes my day 🙂
How do you get the 50 mini lessons. I got the free one but am interested in the full version.
Hi Tracey, The link to the PDF with the 50 mini lessons is in the post. Here it is . Check out this post if you need more advice on teaching students how to research online. Hope that helps! Kathleen
Best wishes to you as you face your health battler. Hoping you’ve come out stronger and healthier from it. Your website is so helpful.
Comments are closed.
1000+ FREE Research Topics & Title Ideas
If you’re at the start of your research journey and are trying to figure out which research topic you want to focus on, you’ve come to the right place. Select your area of interest below to view a comprehensive collection of potential research ideas.

Research Topic FAQs
What (exactly) is a research topic.
A research topic is the subject of a research project or study – for example, a dissertation or thesis. A research topic typically takes the form of a problem to be solved, or a question to be answered.
A good research topic should be specific enough to allow for focused research and analysis. For example, if you are interested in studying the effects of climate change on agriculture, your research topic could focus on how rising temperatures have impacted crop yields in certain regions over time.
To learn more about the basics of developing a research topic, consider our free research topic ideation webinar.
What constitutes a good research topic?
A strong research topic comprises three important qualities : originality, value and feasibility.
- Originality – a good topic explores an original area or takes a novel angle on an existing area of study.
- Value – a strong research topic provides value and makes a contribution, either academically or practically.
- Feasibility – a good research topic needs to be practical and manageable, given the resource constraints you face.
To learn more about what makes for a high-quality research topic, check out this post .
What's the difference between a research topic and research problem?
A research topic and a research problem are two distinct concepts that are often confused. A research topic is a broader label that indicates the focus of the study , while a research problem is an issue or gap in knowledge within the broader field that needs to be addressed.
To illustrate this distinction, consider a student who has chosen “teenage pregnancy in the United Kingdom” as their research topic. This research topic could encompass any number of issues related to teenage pregnancy such as causes, prevention strategies, health outcomes for mothers and babies, etc.
Within this broad category (the research topic) lies potential areas of inquiry that can be explored further – these become the research problems . For example:
- What factors contribute to higher rates of teenage pregnancy in certain communities?
- How do different types of parenting styles affect teen pregnancy rates?
- What interventions have been successful in reducing teenage pregnancies?
Simply put, a key difference between a research topic and a research problem is scope ; the research topic provides an umbrella under which multiple questions can be asked, while the research problem focuses on one specific question or set of questions within that larger context.
How can I find potential research topics for my project?
There are many steps involved in the process of finding and choosing a high-quality research topic for a dissertation or thesis. We cover these steps in detail in this video (also accessible below).
How can I find quality sources for my research topic?
Finding quality sources is an essential step in the topic ideation process. To do this, you should start by researching scholarly journals, books, and other academic publications related to your topic. These sources can provide reliable information on a wide range of topics. Additionally, they may contain data or statistics that can help support your argument or conclusions.
Identifying Relevant Sources
When searching for relevant sources, it’s important to look beyond just published material; try using online databases such as Google Scholar or JSTOR to find articles from reputable journals that have been peer-reviewed by experts in the field.
You can also use search engines like Google or Bing to locate websites with useful information about your topic. However, be sure to evaluate any website before citing it as a source—look for evidence of authorship (such as an “About Us” page) and make sure the content is up-to-date and accurate before relying on it.
Evaluating Sources
Once you’ve identified potential sources for your research project, take some time to evaluate them thoroughly before deciding which ones will best serve your purpose. Consider factors such as author credibility (are they an expert in their field?), publication date (is the source current?), objectivity (does the author present both sides of an issue?) and relevance (how closely does this source relate to my specific topic?).
By researching the current literature on your topic, you can identify potential sources that will help to provide quality information. Once you’ve identified these sources, it’s time to look for a gap in the research and determine what new knowledge could be gained from further study.
How can I find a good research gap?
Finding a strong gap in the literature is an essential step when looking for potential research topics. We explain what research gaps are and how to find them in this post.
How should I evaluate potential research topics/ideas?
When evaluating potential research topics, it is important to consider the factors that make for a strong topic (we discussed these earlier). Specifically:
- Originality
- Feasibility
So, when you have a list of potential topics or ideas, assess each of them in terms of these three criteria. A good topic should take a unique angle, provide value (either to academia or practitioners), and be practical enough for you to pull off, given your limited resources.
Finally, you should also assess whether this project could lead to potential career opportunities such as internships or job offers down the line. Make sure that you are researching something that is relevant enough so that it can benefit your professional development in some way. Additionally, consider how each research topic aligns with your career goals and interests; researching something that you are passionate about can help keep motivation high throughout the process.
How can I assess the feasibility of a research topic?
When evaluating the feasibility and practicality of a research topic, it is important to consider several factors.
First, you should assess whether or not the research topic is within your area of competence. Of course, when you start out, you are not expected to be the world’s leading expert, but do should at least have some foundational knowledge.
Time commitment
When considering a research topic, you should think about how much time will be required for completion. Depending on your field of study, some topics may require more time than others due to their complexity or scope.
Additionally, if you plan on collaborating with other researchers or institutions in order to complete your project, additional considerations must be taken into account such as coordinating schedules and ensuring that all parties involved have adequate resources available.
Resources needed
It’s also critically important to consider what type of resources are necessary in order to conduct the research successfully. This includes physical materials such as lab equipment and chemicals but can also include intangible items like access to certain databases or software programs which may be necessary depending on the nature of your work. Additionally, if there are costs associated with obtaining these materials then this must also be factored into your evaluation process.
Potential risks
It’s important to consider the inherent potential risks for each potential research topic. These can include ethical risks (challenges getting ethical approval), data risks (not being able to access the data you’ll need), technical risks relating to the equipment you’ll use and funding risks (not securing the necessary financial back to undertake the research).
If you’re looking for more information about how to find, evaluate and select research topics for your dissertation or thesis, check out our free webinar here . Alternatively, if you’d like 1:1 help with the topic ideation process, consider our private coaching services .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
193 Education Research Topics & Ideas
Developing healthcare, engineering, and IT is undoubtedly useful. However, the professionals in these areas do not grow on their own. The education system is the birthplace of all the science geniuses who change our world.
If you’re looking for a research title about education, you’re in the right place! This article contains 193 best education research topics that Custom-writing.org experts have prepared for you.
School issues, educational management, special education, child development, and even the new normal education in this pandemic – everything is collected here!
No matter if you’re a high school, an undergraduate, or a graduate college student, this list of research topics in education will be helpful. Find the perfect idea for your paper, discussion, presentation, or even a dissertation below.
- 🔝 Top 10 Topics
- 👓 How to Choose a Topic
🎓 Education Research Topics List
- 🚌 Special Education
- 👶 Child Development
🔍 References
🔝 research topics in education 2024.
- The future of didactics
- Teaching digital literacy
- What is “learning loss”?
- Augmented reality in the classroom
- Real-time performance data in education
- Cognitive science and learning environments
- Ways of monitoring students’ mental health
- Girls’ education and empowerment
- Mental effects of distance learning
- Online teacher-parent communication
- Distant education in the era of COVID-19 pandemic
- The role of technology in distant learning
- Student-student communication in distance education
👓 How to Choose an Education Research Topic?
If you have decided to start working on an educational research, you can definitely benefit from the following list of tips on how to choose a topic. It is the first writing step on your way to the successful paper.
- Review your previous works. Take a look at the essays and research projects you finished earlier. You may have mentioned an issue there that would be worth a more detailed examination.
- Stay informed about the latest updates in education. You might find some government reports saying about their plan of action. It is an excellent source of the most relevant topics that need to be developed in the nearest future.

- “Go out into the field.” If you don’t work in the area of education, it can be beneficial to visit some schools and colleges. Seeing how all the methods are applied in real life gives some food for thought.
- Dig into literature. You might as well get inspired by reading some acknowledged authors’ works.
- Check out international practices. Don’t be afraid to go out of the limits of the national education system. There are thousands of new approaches applied in different areas of education.
Try at least one of the suggested tips if you feel stuck. Be creative while working on your paper! Use our great collection of funny quotes about education . And keep in mind that we’ve also prepared some speech and research proposal ideas on education.
We made a list of educational research topics to make your life easier and save your time! There are 113 great ideas about which way you can start moving:
- Early childhood education : learning through play. We already discussed the importance of education in the development of our society. You see, the personality and mindset of a person are developed in the first years of their lives. Early childhood education is the foundation for the rest of the child’s life.
- Evaluation of the ability grouping method effectiveness. Ability grouping is creating groups of pupils with the same abilities, unlike the more popular age grouping strategy. However, there might be some challenges. For instance, the group should be rearranged if one child starts developing faster. You can research its effectiveness.
- How does the blended learning approach affect students’ performance? Blended learning has been getting more and more popular recently. It is a modern learning approach that combines traditional classes with online materials. It requires strong management skills from students but gives more opportunities in the age of technologies.
- Growing classes: do learning outcomes suffer from it? It looks like there are fewer and fewer professionals willing to teach at schools. But the demand is growing, which results in bigger classes. Teachers can’t possibly split and attend to each and every student with the same level of individual approach. So how does it affect students’ performance ?
- The trends in computer literacy. Nowadays, no one is surprised by a toddler using a tablet or a smartphone without any trouble. Technologies are also incorporated into the learning process. You may write on it with an argumentative approach or see what trends there are and compare them.
- How to recognize which learning style a student needs? There are four learning styles based on different ways students perceive information. For some, it is easier to visualize information; for others, it is all about reading. Look into how schools apply this knowledge, how the best teachers find individual approaches, or how can a study styles quiz help in determining the best educational strategy.
- Should all teachers receive merit pay ? Let’s talk about finances now! Being a teacher is an essential but sometimes tough job. Most teachers overwork and don’t even have weekends. However, they would still receive a standard paycheck. Is it fair? Or should they be paid according to their performance ?
- From homeschooling to successful careers: an overview. There are many reasons why mothers would prefer homeschooling to public education. However, only one thing matters – its effectiveness. If you know anyone who was studying at home, take this chance to analyze how it affected their current life. It is one of the experimental research topics in education.
- How do children benefit from bilingual education? At the times of globalization, this question is undoubtedly relevant. There are more and more advocates for bilingual education. Studies have shown that kids who study in two or more languages have better cognitive abilities and overall academic achievement.
- Single-sex education vs. mixed-sex education. The division started to honor traditions and religion. You might think that it is in the past… But, today, there are still plenty of separate schools for boys and girls. There are many debates on this issue and an excellent chance to research it from the scientific point of view.
- Where is the line for parental involvement ? It is easily one of the best education research topics. Maybe it is too biased for a thesis but could be excellent as a research paper for majors like psychology and communication. Parental involvement is undoubtedly essential, but is there a limit? Parents sometimes overdo it!
- Boarding schools: advantages & disadvantages. Sometimes parents send their kids to the boarding schools to get rid of them. But often they underestimate the stress that students go under there. Spending all their time on the school premises, even at the weekend. It can be psychologically exhausting.
- How should a proper sex education program look like? Let’s leave the Netflix show aside, though… In real life, it is much less dramatic. But just as important! In many schools, there is a lack of sex ed classes. And even if there are some, they don’t seem to be working… However, this topic is vital for youth health and is worth researching.
- Reforming the school schedule: the most efficient solution. This education research topic list would not be complete without this highlighting this issue. There is no way to satisfy all students’ needs regarding the schedule. But that is what compromises for! Maybe your research can become the next universal solution.
- How can career counseling support high school students? Career counseling might be a good investment for schools. Counselors analyze students’ unique abilities and skills based on the scores as well as their passions. It is also a great chance for students to evaluate their real prospects for a specific career path.
- The benefits of the flipped classroom approach. The flipped classroom approach is kinda a type of blended learning. Students are asked to learn the new material at home. When they get to school, they work through it with a teacher and create discussion groups. But does it really work?
- How does Race to the Top program affect students’ outcomes? Race to the Top is an initiative that helps to reform the education system by giving grants to states. It provides multiple opportunities, such as creating data systems and organizing training for teachers. However, it met a wave of criticism.
- The new solutions to prevent violence at schools . Education is good, but children can be mean to each other. Whenever kids get together, there are always fights. It is hard even dealing with and preventing sounds impossible. But you only need to study some cases of educational institutions in countries like Sweden.
- Why should teachers join teacher unions? Teacher unions are organizations that connect professionals who want to stand for their rights. It may be extremely beneficial if a teacher seeks legal advice. But is it the only advantage of joining the union? You can elaborate on this topic, which is relevant at all times.
- Adapted physical education vs. usual physical education
- Is busing still relevant, and should it be stopped?
- How to avoid plagiarism?
- Charter schools vs. public schools: compare & contrast
- Online courses interaction: types and effects
- The inclusivity in charter schools
- High school students and vocational education
- Should collaborative learning be applied more in high school?
- Comparing education in USA and in Saudi Arabia
- Do Common Core State Standards succeed in preparing students for college ?
- Evidence-based model and solving problems with school funding
- Why is computer-assisted instruction also necessary for non-IT students?
- Personal lecture results
- Data-based decision making in assessment
- The role of teachers and parents in the discipline : compare & contrast
- Education: qualitative research study roles
- Should time management be taught in schools?
- Education: peer evaluation system
- Do dual enrollment programs put more pressure on high school students?
- College student life: participation, perceptions and satisfaction
- DACA and DREAM act : compare & contrast
- Impacts of teaching detective stories to esl students
- Can Kalamazoo Promise initiative be applied in other states?
- Liberal arts: Otis College of Arts and Design
- Using Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences to create a new learning approach
- Where and how sex education should be conducted among the young people?
- Where is the limit of self-improvement: the case of the No Child Left Behind Act ?
- Homeschooling: argumentation for and against
- School sex education and teenage pregnancy in the United States
- The effect of outcomes-based education on children’s mental health
- Education: financial aid for college students
- The benefits of peer-counseling
- Learning methods: online learning
- School uniform in learning institutions
- Improving oral reading skills to enhance reading comprehension
- The root causes of plagiarism in high school
- Religion in schools: is there a place for it? Pros and cons
- Are plagiarism and dishonesty in childhood connected?
- Should a school choice be a usual practice?
- Education issues: differentiation and technology
- The best school-to-career programs in the country: an overview
- The concept of lifelong learning
- Studying abroad: pros and cons
- Is there still a need for school-to-career programs?
- Addressing bullying in elementary and middle school classrooms
- What is STEM lacking?
- STEAM vs. STEM: compare & contrast
- Peer evaluation system in education
- The ways of integrating technology into the classroom
- College education: arguments for and against
- How to prevent students from being distracted by smartphones ?
- Continuing nursing education: a 3-5 year plan
- Psychology of the high school: why do students become bullies ?
- Adult education: reasons to continue studying
- How to prevent cyberbullying among teenagers?
- Flipped classroom in nursing schools
- Do virtual classrooms lack a personal connection between students and teachers?
- Classroom management and techniques to incorporate in student’s reinforcement plan
- Will virtual classrooms substitute real-life classes in the future?
- Children’s bullying in school
- Is the whole brain teaching method effective for college students?
- Gamification in education practice
- Uniforms : killing individuality or improving discipline?

- Perceptions about relationships around schooling
- Does the zero-tolerance policy violate the law?
- Academic dishonesty and its detrimental effects
- Online education and e-learning: potential and benefits
- The approaches to emotional development in early childhood education
- Understanding student’s professionalism
- Importance of sex education
- Sex education curricula as the factor that reduced the number of pregnancies in Fayette and Shelby counties
- School communication
- Encouraging students in reading and literacy
- The correct ways to minimize plagiarism and cheating
- The role of textbooks in education
- Why do college students drop out of school?
- Social skills vs. general knowledge: what is more important in early childhood education?
- Distance learning and social change
- A school without homework: a case study
- The role of history learning in society
- Public vs. private schools : what affects academic achievement?
- The impact of education on life quality
- Educational experiences and significant career goals
- The most advanced best practices in adult ESL instruction
- College entrance exams in the US and China: the competitiveness
- Information technologies & online learning
- An information overload: what are high school students’ limits?
- The impact of education on life qualityEducation: Internet courses versus traditional courses
- Multicultural education : how does it promote a positive attitude?
- Course evaluation methods
- Critical thinking in education
- Criterion and norm-referenced tests in education
🚌 Special Education Research Topics & Ideas
Special education makes it possible for students with special needs to receive all the individual support they require. There are plenty of interesting special education research topics you can choose from:
- Practical approaches to teaching students with an auditory processing disorder. The percentage of children diagnosed with an auditory processing disorder (APD) is rising. Despite the difficulty in diagnosing, there is believed to be at least 5% of students having this learning disorder. It doesn’t affect the hearing itself but makes it hard for children to process what they hear.
- Music therapy for children on the autism spectrum : what instruments are the most effective? Children on the autism spectrum find it difficult to interact socially. Some studies show that music therapy helps them become more flexible and responsive. In turn, it promotes the development of their social skills. For example, the didgeridoo playing showed significant results.
- Karaoke as a way to help children with learning disorders. Kids with learning disabilities need special care. It is one of the research paper topics on education which can bring a brilliant solution! It has been shown that children with learning disorders did much better in reading tests after doing karaoke-based exercises.

- How does peer support help children with disabilities socialize in the classroom? We have already mentioned a topic related to peer review, which is quite a good one for the thesis. Here, you can study how peers can help their classmates with special needs. It is especially relevant for schools with inclusivity policies.
- Cooperative learning & students with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder . Cooperative learning is vital in early childhood. Most schools choose this approach because of its apparent benefits. However, kids with ADHD might see it as a real challenge. Look into the best ways to engage them in cooperative learning activities without harm.
- Social skills: the best time for children with EBD to learn them. It is one of the research topics in social studies education. Secondary school becomes a tough period for students with emotional and behavioral disorders. It is the time when social skills training is as relevant for them as never before. However, what is the best time to start SST?
- How to develop self-determination in children with disabilities? Self-determination is one of the most vital components of growing up. Every independent human being needs to have it developed. But what about children with special needs? Since they rely heavily on support, it is the educators’ responsibility to help them build self-determination.
- What are the negative sides of the response to intervention approach? Response to intervention is not a new method. However, it has appeared to be controversial. It not only focuses on children with special needs but on every student who struggles to achieve a specific level. Some evaluations show its ineffectiveness, though.
- Inclusive classes vs. special education. It is one of the most relevant child development research paper topics. Special education classes were created out of fear that students with learning disabilities cannot reach the same level of academic achievement in usual courses. However, it seems that the performance is the same in both approaches.
- How does grade retention affect children with learning disabilities ? Even frequent testing can be a stress for any student. How do children with learning disorders feel then? What’s more, they are put under more pressure if they need to repeat the year? Therefore, some particular approaches need to be applied to prevent it.
- Why should students with learning disabilities be included in the Adequate Yearly Progress evaluation?
- Is a foreign language learning disability a real thing?
- Learning disabilities: when is a child’s communication considered delayed?
- Are students more engaged in self-directed IEP classes?
- Teaching communication skills for students with autism
- Zero-tolerance policy & students with special needs
- Assessing students with learning problems
- Strategies for addressing individual needs in special education
- How effective is the Reading Recovery program?
- Inquiry in the field of education: critical and historical analysis of inclusion of students with disabilities
- Early intervention & students with hearing disabilities
- Inclusive classes & bullying prevention
- Technology integration for children with learning disabilities
- Education for students with autism in Saudi Arabia
- Blended learning & children on the autism spectrum: pros and cons
- Special education & trauma-informed learning
- Should twice-exceptional students still get a special education approach?
- What are the causes of disproportionality in special education?
- Self-monitoring & students with learning disabilities
- How does virtual reality help students with autism adapt to stressful real-life situations?
- Homeschooling children with learning disorders
- How to prevent special education teachers from burnouts?
- Co-teaching & special education
- Is full inclusion a good idea?
- Student-led planning to promote independence in special education
- Early detection & learning disabilities
👶 Child Development Research Topics & Ideas
Child development is a vast area since it covers both the physical and mental development of a child from birth to adulthood. Below you can find 30 child development research topics suitable for your project or even a dissertation!
- Mother-child connection: how does stress affect a child’s wellbeing? Everyone knows about the mother-child connection, but not many know how deep it is. During pregnancy, a woman can get into a stressful situation. It may cause chemical reactions in the brain of a child, which, in turn, affects its future health.
- What role do genes play in child development ? Some of us are used to blaming genes for one thing or another. However, it appears that the environment in which we grow up is much more critical. You can debate on how a child’s environment cases chemical modifications in genes.
- How does living in a community affect child development ? Of course, parents are the primary caregivers for small children. On the other hand, there are advocates for shared responsibilities. In communities, kids interact mostly with close neighbors. A child is open to more experience this way. Elaborate on this topic.

- Child development : does it slow down after the third birthday? It is true that in the first three years of life, children develop the most basic brain functions very actively. However, it doesn’t mean that after that they can’t learn anything new! So what areas of the brain stop active development after the child’s third birthday, if any?
- How is neglecting and ignoring your child worse than physical punishment? Physical violence against children is addressed as one of the main issues in child development. Undoubtedly, it has incredibly adverse effects on a child’s mental health. However, neglect is often omitted. It may cause severe disruptions in the healthy social life and development of a child.
- Childhood trauma & happy life. Children who faced violence or any other unpleasant experience have a higher risk of developing stress-related disorders. On the other hand, it is not a rule. If a child gets sufficient support as soon as possible, traumas may just become a neutral life experience for them.
- What care should traumatized children be provided? It is not enough to just save a child from a traumatizing environment. They can still feel insecure even in safe and predictable surroundings. This situation would require more than one action. A child needs therapeutic care for sooner recovery.
- Child development: coping with troubles alone or in a team? Usually, parents try to teach their children to become more independent. Being brave and only relying on yourself is promoted as socially acceptable behavior. But scientists found out that it’s not individualism that helps to overcome obstacles but supportive relationships.
- Responsive relationships & child development . It appears that having a healthy relationship with parents in childhood is related to having good mental health. Parents should practice responsive relationships with their children. It promotes healthy brain development and resilience in kids. You can research this connection.
- Why should parents teach core life skills to their children? Children are capable of learning how to adapt to life on their own. But researchers highlight that parents can significantly help in this process by teaching core life skills to children. This scaffolding process helps kids learn, develop, and make healthy life choices.
- Why is reducing stress essential for child development?
- Family factors that shape children’s behavior
- How does the process of building neural connections change with time?
- Why is it essential to respond to the child’s interaction actions?
- Child development: using the early plasticity at full
- How emotional health and social skills affect a child’s future career?
- Toxic stress & child development
- What effect does divorce cause in child development?
- Video games & child development: pros and cons
- What does single parenting mean for the development of a child?
- Can a child develop normally without a father’s love?
- Can food supplements help to develop a child’s cognitive abilities?
- Postpartum depression & child development
- Does verbal abuse have the same effect on a child as physical punishment ?
- Should beauty pageants be banned as a threat to healthy child development?
- How soon should mothers end maternity leave?
- Child development in low-income families
- How does graphic violence in animations and movies affect child development ?
- Child development & mother’s mental illness
- Is daycare right for child development ?
- Child development : how do children adopt parents’ beliefs?
🤔 Education Research FAQs
Research in education is important because it contributes to the development in the field. Proving theories, creating new methodologies, and practical solutions are all the outcomes of the research in the education area. It plays a vital role – bringing innovation and progress. It also enables teachers to perfect the learning processes for the benefit of the students.
Research is important in child development because it helps find ways to improve children’s quality of life. Environment, teachers, and relationships have a profound impact on child development. All the children’s basic needs should be met to secure their healthy development. Therefore, it is crucial to find the best solutions for any issues arising in those three aspects. That is why the research is done in child development.
It may not be easy to design and evaluate research in education, but comprehensive guidelines make the process much smoother. First of all, choose the topic you want to work on. Then think about the research methodologies and pick the one which works best. After that, be ready to spend quite a while on the steps like data analysis and writing research proposals.
Action research in education is anything related to evaluating and analyzing issues and weak spots in the learning process. Unlike other types of research, this one is very practical. It may help teachers transition from the old methodologies to newer and more effective ones. Teachers get practical solutions to solve problems in the education process and meet the special needs of their students.
Both culture and ethics influence child development research in many ways. It is especially important if your research is done internationally. Cultural differences should be taken into consideration while collecting and analyzing data. Ethics, on the other hand, influences the whole process. While researching early childhood development, for example, remember about consent and anonymity of the groups.
Learn more on this topic:
- 280 Good Nursing Research Topics & Questions
- 226 Research Topics on Criminal Justice & Criminology
- 204 Research Topics on Technology & Computer Science
- 178 Best Research Titles about Cookery & Food
- 497 Interesting History Topics to Research
- 110+ Micro- & Macroeconomics Research Topics
- 417 Business Research Topics for ABM Students
- 190+ Research Topics on Psychology & Communication
- 512 Research Topics on HumSS
- 281 Best Health & Medical Research Topics
- 501 Research Questions & Titles about Science
- A List of Research Topics for Students. Unique and Interesting
- Good Research Topics, Titles and Ideas for Your Paper
- Databases for Research & Education: Gale
- Top Tips on Choosing a Topic for Your Education Research Project: Acedemia
- InBrief: The Science of Early Childhood Development (Harvard University)
- Child Development: Research (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
- Topics in Early Childhood Special Education: SAGE Journals
- PhD Research Topics: Department of Education, University of York
- Early childhood education: UNICEF
- Early Childhood Education: Australian Council for Educational Research
- Do the Effects of Early Childhood Programs on Academic Outcomes Vary by Gender? A Meta-Analysis (2011 SREE Conference Abstract Template)
- Research in Education: Ontario Ministry of Education
- Center for Education Policy Research: Harvard University
- Research: School of Education, University of Queensland
- Faculty & Research: School of Education, University of Pittsburgh
- Education Research Section: Princeton University
- Engaging with educational research: free course (OpenLearn)
- Education in a Changing World: NSW Government
- Research areas: The University of Sydney, School of Education and Social Work
- Faculty & Research: Stanford, Graduate School of Education
- Special Education: UW College of Education
- Special Education: Michigan State University
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

A history class can become a jumble of years, dates, odd moments, and names of people who have been dead for centuries. Despite this, you’ll still need to find history topics to write about. You may have no choice! But once in a while, your instructor may let you pick...
![research title about school activities 150 Argumentative Research Paper Topics [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-magnifier-glass-yellow-background-284x153.jpg)
Argumentative research paper topics are a lot easier to find than to come up with. We always try to make your life easier. That’s why you should feel free to check out this list of the hottest and most controversial argumentative essay topics for 2024. In the article prepared by...

One of the greatest problems of the scholarly world is the lack of funny topics. So why not jazz it up? How about creating one of those humorous speeches the public is always so delighted to listen to? Making a couple of funny informative speech topics or coming up with...
![research title about school activities Gun Control Argumentative Essay: 160 Topics + How-to Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/bullets-gun-black-velvet-desk-284x153.jpg)
After the recent heartbreaking mass shootings, the gun control debate has reached its boiling point. Do we need stricter gun control laws? Should everyone get a weapon to oppose crime? Or should guns be banned overall? You have the opportunity to air your opinion in a gun control argumentative essay....
![research title about school activities Best Childhood Memories Essay Ideas: 94 Narrative Topics [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/child-working-in-cambodia-284x153.jpg)
Many people believe that childhood is the happiest period in a person’s life. It’s not hard to see why. Kids have nothing to care or worry about, have almost no duties or problems, and can hang out with their friends all day long. An essay about childhood gives an opportunity...
![research title about school activities 435 Literary Analysis Essay Topics and Prompts [2024 Upd]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/girl-having-idea-with-copy-space-284x153.jpg)
Literature courses are about two things: reading and writing about what you’ve read. For most students, it’s hard enough to understand great pieces of literature, never mind analyzing them. And with so many books and stories out there, choosing one to write about can be a chore. But you’re in...
![research title about school activities 335 Unique Essay Topics for College Students [2024 Update]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/smiling-students-walking-after-lessons1-284x153.jpg)
The success of any college essay depends on the topic choice. If you want to impress your instructors, your essay needs to be interesting and unique. Don’t know what to write about? We are here to help you! In this article by our Custom-Writing.org team, you will find 335 interesting...

Social studies is an integrated research field. It includes a range of topics on social science and humanities, such as history, culture, geography, sociology, education, etc. A social studies essay might be assigned to any middle school, high school, or college student. It might seem like a daunting task, but...

If you are about to go into the world of graduate school, then one of the first things you need to do is choose from all the possible dissertation topics available to you. This is no small task. You are likely to spend many years researching your Master’s or Ph.D....

Looking for a good argumentative essay topic? In need of a persuasive idea for a research paper? You’ve found the right page! Academic writing is never easy, whether it is for middle school or college. That’s why there are numerous educational materials on composing an argumentative and persuasive essay, for...

Persuasive speech is the art of convincing the audience to understand and trust your opinion. Are you ready to persuade someone in your view? Our list of sports persuasive speech topics will help you find a position to take and defend. If you need more options quick, apart from contents...

Can there possibly be anything fun about academic writing? It seems there is – what are all those fun persuasive speech topics then for, after all? However, creating a bunch of good topics might seem hard the first time around. No need to worry though – there’s always plenty of...
I need research topic on Education in Mountainous community In Northern Pakistan
This is wonderful, got some ideas.
Thanks got some ideas here.
Can you help me for our Research Title po, BSED MAJOR IN VALUES. THANYOU😊❤
Please help me with the research topic also the source of research topic
Can you help me . About the education research papr share me ?
Can you help me with literature review on this topic the importance of developing a learners literacy skills in foundation phase South Africa
can you help me some research paper?
200+ Research Title Ideas To Explore In 2024

Choosing a compelling research title is a critical step in the research process, as it serves as the gateway to capturing the attention of readers and potential collaborators. A well-crafted research title not only encapsulates the essence of your study but also entices readers to delve deeper into your work.
In this blog post, we will explore the significance of research title ideas, the characteristics of an effective title, strategies for generating compelling titles, examples of successful titles, common pitfalls to avoid, the importance of iterative refinement, and ethical considerations in title creation.
Characteristics of a Good Research Title
Table of Contents
Clarity and Precision
A good research title should communicate the core idea of your study clearly and precisely. Avoid vague or overly complex language that might confuse readers.

Relevance to the Research Topic
Ensure that your title accurately reflects the content and focus of your research. It should provide a clear indication of what readers can expect from your study.
Conciseness and Avoidance of Ambiguity
Keep your title concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary words or phrases that may add ambiguity. Aim for clarity and directness to make your title more impactful.
Use of Keywords
Incorporating relevant keywords in your title can enhance its visibility and accessibility. Consider the terms that researchers in your field are likely to search for and integrate them into your title.
Reflecting the Research Methodology or Approach
If your research employs a specific methodology or approach, consider incorporating that information into your title. This helps set expectations for readers and indicates the uniqueness of your study.
What are the Strategies for Generating Research Title Ideas?
- Brainstorming
- Individual Brainstorming: Set aside time to generate title ideas on your own. Consider different angles, perspectives, and aspects of your research.
- Group Brainstorming: Collaborate with peers or mentors to gather diverse perspectives and insights. Group brainstorming can lead to innovative and multidimensional title ideas.
- Keyword Analysis
- Identifying Key Terms and Concepts: Break down your research into key terms and concepts. These will form the foundation of your title.
- Exploring Synonyms and Related Terms: Expand your search by exploring synonyms and related terms. This can help you discover alternative ways to express your research focus.
- Literature Review
- Examining Existing Titles in the Field: Review titles of relevant studies in your field to identify common patterns and effective strategies.
- Analyzing Successful Titles for Inspiration: Analyze successful research titles to understand what makes them stand out. Look for elements that resonate with your own research.
- Consultation with Peers and Mentors
- Seek feedback from peers and mentors during the title creation process. External perspectives can offer valuable insights and help refine your ideas.
- Use of Online Tools and Title Generators
- Explore online tools and title generators designed to aid in the generation of creative and relevant research titles. While these tools can be helpful, exercise discretion and ensure the generated titles align with the essence of your research.
200+ Research Title Ideas: Category-Wise
Technology and computer science.
- “Cybersecurity Measures in the Age of Quantum Computing”
- “Machine Learning Applications for Predictive Maintenance”
- “The Impact of Augmented Reality on Learning Outcomes”
- “Blockchain Technology: Enhancing Supply Chain Transparency”
- “Human-Computer Interaction in Virtual Reality Environments”
Environmental Science and Sustainability
- “Evaluating the Efficacy of Green Infrastructure in Urban Areas”
- “Climate Change Resilience Strategies for Coastal Communities”
- “Biodiversity Conservation in Tropical Rainforests”
- “Renewable Energy Adoption in Developing Economies”
- “Assessing the Environmental Impact of Plastic Alternatives”
Health and Medicine
- “Precision Medicine Approaches in Cancer Treatment”
- “Mental Health Interventions for Youth in Urban Settings”
- “Telemedicine: Bridging Gaps in Rural Healthcare Access”
- “The Role of Gut Microbiota in Metabolic Disorders”
- “Ethical Considerations in Genetic Editing Technologies”
Social Sciences and Psychology
- “Social Media Influence on Body Image Perception”
- “Impact of Cultural Diversity on Team Performance”
- “Psychological Resilience in the Face of Global Crises”
- “Parental Involvement and Academic Achievement in Adolescents”
- “Exploring the Dynamics of Online Communities and Identity”
Business and Economics
- “Sustainable Business Practices and Consumer Behavior”
- “The Role of Big Data in Financial Decision-Making”
- “Entrepreneurship and Innovation in Emerging Markets”
- “Corporate Social Responsibility and Brand Loyalty”
- “Economic Implications of Remote Work Adoption”
Education and Pedagogy
- “Inclusive Education Models for Diverse Learning Needs”
- “Gamification in STEM Education: A Comparative Analysis”
- “Online Learning Effectiveness in Higher Education”
- “Teacher Training for Integrating Technology in Classrooms”
- “Assessment Strategies for Measuring Critical Thinking Skills”
Psychology and Behavior
- “The Influence of Social Media on Adolescent Well-being”
- “Cognitive Biases in Decision-Making: A Cross-Cultural Study”
- “The Role of Empathy in Conflict Resolution”
- “Positive Psychology Interventions for Workplace Satisfaction”
- “Exploring the Relationship Between Sleep Patterns and Mental Health”
Biology and Genetics
- “Genetic Markers for Predisposition to Neurodegenerative Diseases”
- “CRISPR-Cas9 Technology: Ethical Implications and Future Prospects”
- “Evolutionary Adaptations in Response to Environmental Changes”
- “Understanding the Microbiome’s Impact on Immune System Function”
- “Epigenetic Modifications and Their Role in Disease Development”
Urban Planning and Architecture
- “Smart Cities: Balancing Technological Innovation and Privacy”
- “Revitalizing Urban Spaces: Community Engagement in Design”
- “Sustainable Architecture: Integrating Nature into Urban Designs”
- “Transit-Oriented Development and Its Impact on City Dynamics”
- “Assessing the Cultural Significance of Urban Landscapes”
Linguistics and Communication
- “The Influence of Language on Cross-Cultural Communication”
- “Language Development in Multilingual Environments”
- “The Impact of Nonverbal Communication on Interpersonal Relationships”
- “Digital Communication and the Evolution of Language”
- “Language Processing in Bilingual Individuals: A Neuroscientific Approach”
Political Science and International Relations
- “The Role of Social Media in Political Mobilization”
- “Global Governance in the Era of Transnational Challenges”
- “Human Rights and the Ethics of Intervention in International Affairs”
- “Political Polarization: Causes and Consequences”
- “Climate Change Diplomacy: Assessing International Agreements”
Physics and Astronomy
- “Dark Matter: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Universe”
- “Quantum Entanglement and Its Potential Applications”
- “The Search for Exoplanets in Habitable Zones”
- “Astrophysical Phenomena: Exploring Black Holes and Neutron Stars”
- “Advancements in Quantum Computing Algorithms”
Education Technology (EdTech)
- “Adaptive Learning Platforms: Personalizing Education for Every Student”
- “The Impact of Virtual Reality Simulations on STEM Education”
- “E-Learning Accessibility for Students with Disabilities”
- “Gamified Learning: Enhancing Student Engagement and Retention”
- “Digital Literacy Education: Navigating the Information Age”
Sociology and Anthropology
- “Cultural Shifts in Modern Society: An Anthropological Exploration”
- “Social Movements in the Digital Age: Activism and Connectivity”
- “Gender Roles and Equality: A Cross-Cultural Perspective”
- “Urbanization and Its Effects on Traditional Societal Structures”
- “Cultural Appropriation: Understanding Boundaries and Respect”
Materials Science and Engineering
- “Nanostructured Materials: Innovations in Manufacturing and Applications”
- “Biodegradable Polymers: Towards Sustainable Packaging Solutions”
- “Materials for Energy Storage: Advancements and Challenges”
- “Smart Materials in Healthcare: From Diagnosis to Treatment”
- “Robust Coatings for Extreme Environments: Applications in Aerospace”
History and Archaeology
- “Digital Reconstruction of Historical Sites: Preserving the Past”
- “Trade Routes in Ancient Civilizations: A Comparative Study”
- “Archaeogenetics: Unraveling Human Migrations Through DNA Analysis”
- “Historical Linguistics: Tracing Language Evolution Over Millennia”
- “The Archaeology of Conflict: Studying War through Artifacts”
Marketing and Consumer Behavior
- “Influencer Marketing: Impact on Consumer Trust and Purchasing Decisions”
- “The Role of Brand Storytelling in Consumer Engagement”
- “E-commerce Personalization Strategies: Balancing Customization and Privacy”
- “Cross-Cultural Marketing: Adapting Campaigns for Global Audiences”
- “Consumer Perceptions of Sustainable Products: A Market Analysis”
Neuroscience and Cognitive Science
- “Neuroplasticity and Cognitive Rehabilitation: Implications for Therapy”
- “The Neuroscience of Decision-Making: Insights from Brain Imaging”
- “Cognitive Aging: Understanding Memory Decline and Cognitive Resilience”
- “The Role of Neurotransmitters in Emotional Regulation”
- “Neuroethical Considerations in Brain-Computer Interface Technologies”
Public Health and Epidemiology
- “Epidemiological Trends in Infectious Diseases: Lessons from Global Outbreaks”
- “Public Health Interventions for Reducing Non-Communicable Diseases”
- “Health Disparities Among Marginalized Communities: Addressing the Gaps”
- “The Impact of Climate Change on Vector-Borne Diseases”
- “Community-Based Approaches to Promoting Health Equity”
Robotics and Automation
- “Human-Robot Collaboration in Manufacturing: Enhancing Productivity and Safety”
- “Autonomous Vehicles: Navigating the Path to Mainstream Adoption”
- “Soft Robotics: Engineering Flexibility for Real-World Applications”
- “Ethical Considerations in the Development of AI-powered Robotics”
- “Bio-Inspired Robotics: Learning from Nature to Enhance Machine Intelligence”
Literature and Literary Criticism
- “Postcolonial Narratives: Deconstructing Power Structures in Literature”
- “Digital Storytelling Platforms: Changing the Landscape of Narrative Arts”
- “Literature and Cultural Identity: Exploring Representations in Global Contexts”
- “Eco-Critical Perspectives in Contemporary Literature”
- “Feminist Literary Criticism: Reinterpreting Classic Texts Through a New Lens”
Chemistry and Chemical Engineering
- “Green Chemistry: Sustainable Approaches to Chemical Synthesis”
- “Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery: Innovations in Biomedical Applications”
- “Chemical Process Optimization: Towards Energy-Efficient Production”
- “The Chemistry of Taste: Molecular Insights into Food Flavors”
- “Catalytic Converters: Advancements in Pollution Control Technologies”
Cultural Studies and Media
- “Media Representations of Social Movements: Framing and Impact”
- “Pop Culture and Identity: Exploring Trends in a Globalized World”
- “The Influence of Social Media on Political Discourse”
- “Reality Television and Perceptions of Reality: A Cultural Analysis”
- “Media Literacy Education: Navigating the Digital Information Age”
Astronomy and Astrophysics
- “Gravitational Waves: Probing the Cosmos for New Discoveries”
- “The Life Cycle of Stars: From Birth to Supernova”
- “Astrobiology: Searching for Extraterrestrial Life in the Universe”
- “Dark Energy and the Accelerating Expansion of the Universe”
- “Cosmic Microwave Background: Insights into the Early Universe”
Social Work and Community Development
- “Community-Based Mental Health Interventions: A Social Work Perspective”
- “Youth Empowerment Programs: Fostering Resilience in Vulnerable Communities”
- “Social Justice Advocacy in Contemporary Social Work Practice”
- “Intersectionality in Social Work: Addressing the Complex Needs of Individuals”
- “The Role of Technology in Enhancing Social Services Delivery”
Artificial Intelligence and Ethics
- “Ethical Considerations in AI Decision-Making: Balancing Autonomy and Accountability”
- “Bias and Fairness in Machine Learning Algorithms: A Critical Examination”
- “Explainable AI: Bridging the Gap Between Complexity and Transparency”
- “The Social Implications of AI-Generated Content: Challenges and Opportunities”
- “AI and Personal Privacy: Navigating the Ethical Dimensions of Data Usage”
Linguistics and Computational Linguistics
- “Natural Language Processing: Advancements in Understanding Human Communication”
- “Multilingualism in the Digital Age: Challenges and Opportunities”
- “Cognitive Linguistics: Exploring the Relationship Between Language and Thought”
- “Speech Recognition Technologies: Applications in Everyday Life”
- “Syntax and Semantics: Unraveling the Structure of Language”
Geology and Earth Sciences
- “Geological Hazards Assessment in Urban Planning: A Case Study”
- “Paleoclimatology: Reconstructing Past Climate Patterns for Future Predictions”
- “Geomorphological Processes in Coastal Landscapes: Implications for Conservation”
- “Volcanic Activity Monitoring: Early Warning Systems and Mitigation Strategies”
- “The Impact of Human Activities on Soil Erosion: An Ecological Perspective”
Political Economy and Global Governance
- “Global Trade Agreements: Assessing Economic Impacts and Equity”
- “Political Economy of Energy Transition: Policies and Socioeconomic Effects”
- “The Role of International Organizations in Global Governance”
- “Financial Inclusion and Economic Development: A Comparative Analysis”
- “The Political Economy of Pandemics: Governance and Crisis Response”
Food Science and Nutrition
- “Nutrigenomics: Personalized Nutrition for Optimal Health”
- “Functional Foods: Exploring Health Benefits Beyond Basic Nutrition”
- “Sustainable Food Production: Innovations in Agriculture and Aquaculture”
- “Dietary Patterns and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Review”
- “Food Allergies and Sensitivities: Mechanisms and Management Strategies”
Sociology and Technology
- “Digital Inequalities: Examining Access and Usage Patterns Across Demographics”
- “The Impact of Social Media on Social Capital and Community Building”
- “Technological Surveillance and Privacy Concerns: A Sociological Analysis”
- “Virtual Communities: An Exploration of Identity Formation in Online Spaces”
- “The Social Dynamics of Online Activism: Mobilization and Participation”
Materials Science and Nanotechnology
- “Nanomaterials for Biomedical Imaging: Enhancing Diagnostic Precision”
- “Self-Healing Materials: Advances in Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure”
- “Smart Textiles: Integrating Nanotechnology for Enhanced Functionality”
- “Multifunctional Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery: Targeted Therapies and Beyond”
- “Nanocomposites for Energy Storage: Engineering Efficient Capacitors”
Communication and Media Studies
- “Media Convergence: The Evolution of Content Delivery in the Digital Age”
- “The Impact of Social Media Influencers on Consumer Behavior”
- “Crisis Communication in a Hyperconnected World: Lessons from Global Events”
- “Media Framing of Environmental Issues: A Comparative Analysis”
- “Digital Detox: Understanding Media Consumption Patterns and Well-being”
Developmental Psychology
- “Early Childhood Attachment and Its Long-Term Impact on Adult Relationships”
- “Cognitive Development in Adolescence: Challenges and Opportunities”
- “Parenting Styles and Academic Achievement: A Cross-Cultural Perspective”
- “Identity Formation in Emerging Adulthood: The Role of Social Influences”
- “Interventions for Promoting Resilience in At-Risk Youth Populations”
Aerospace Engineering
- “Advancements in Aerodynamics: Redefining Flight Efficiency”
- “Space Debris Management: Mitigating Risks in Earth’s Orbit”
- “Aerodynamic Design Optimization for Supersonic Flight”
- “Hypersonic Propulsion Technologies: Pushing the Boundaries of Speed”
- “Materials for Space Exploration: Engineering Solutions for Harsh Environments”
Political Psychology
- “Political Polarization and Public Opinion: Exploring Cognitive Biases”
- “Leadership Styles and Public Perception: A Psychological Analysis”
- “Nationalism and Identity: Psychological Factors Shaping Political Beliefs”
- “The Influence of Emotional Appeals in Political Communication”
- “Crisis Leadership: The Psychological Dynamics of Decision-Making in Times of Uncertainty”
Marine Biology and Conservation
- “Coral Reef Restoration: Strategies for Biodiversity Conservation”
- “Ocean Plastic Pollution: Assessing Impacts on Marine Ecosystems”
- “Marine Mammal Communication: Insights from Bioacoustics”
- “Sustainable Fisheries Management: Balancing Ecological and Economic Concerns”
- “The Role of Mangrove Ecosystems in Coastal Resilience”
Artificial Intelligence and Creativity
- “Generative AI in Creative Industries: Challenges and Innovations”
- “AI-Enhanced Creativity Tools: Empowering Artists and Designers”
- “Machine Learning for Music Composition: Bridging Art and Technology”
- “Creative AI in Film and Entertainment: Transforming Storytelling”
- “Ethical Considerations in AI-Generated Art and Content”
Cultural Anthropology
- “Cultural Relativism in Anthropological Research: Opportunities and Challenges”
- “Rituals and Symbolism: Unraveling Cultural Practices Across Societies”
- “Migration and Cultural Identity: An Ethnographic Exploration”
- “Material Culture Studies: Understanding Societies through Objects”
- “Indigenous Knowledge Systems: Preserving and Promoting Cultural Heritage”
Quantum Computing and Information Science
- “Quantum Information Processing: Algorithms and Applications”
- “Quantum Cryptography: Securing Communication in the Quantum Era”
- “Quantum Machine Learning: Enhancing AI through Quantum Computing”
- “Quantum Computing in Finance: Opportunities and Challenges”
- “Quantum Internet: Building the Next Generation of Information Networks”
Public Policy and Urban Planning
- “Smart Cities and Inclusive Urban Development: A Policy Perspective”
- “Public-Private Partnerships in Infrastructure Development: Lessons Learned”
- “The Impact of Transportation Policies on Urban Mobility Patterns”
- “Housing Affordability: Policy Approaches to Addressing Urban Challenges”
- “Data-Driven Decision-Making in Urban Governance: Opportunities and Risks”
Gerontology and Aging Studies
- “Healthy Aging Interventions: Promoting Quality of Life in Older Adults”
- “Social Isolation and Mental Health in Aging Populations: Interventions and Support”
- “Technology Adoption Among Older Adults: Bridging the Digital Divide”
- “End-of-Life Decision-Making: Ethical Considerations and Legal Frameworks”
- “Cognitive Resilience in Aging: Strategies for Maintaining Mental Sharpness”
Examples of Effective Research Titles
Illustrative Examples from Various Disciplines
Here are examples of effective research titles from different disciplines:
- “Unlocking the Mysteries of Neural Plasticity: A Multidisciplinary Approach”
- “Sustainable Urban Development: Integrating Environmental and Social Perspectives”
- “Quantum Computing: Navigating the Path to Practical Applications”
Analysis of What Makes Each Title Effective
- Clear indication of the research focus.
- Inclusion of key terms relevant to the field.
- Incorporation of a multidisciplinary or integrated approach where applicable.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Research Title Creation
A. Vagueness and Ambiguity
Vague or ambiguous titles can deter readers from engaging with your research. Ensure your title is straightforward and leaves no room for misinterpretation.
B. Overuse of Jargon
While technical terms are essential, excessive jargon can alienate readers who may not be familiar with the specific terminology. Strike a balance between precision and accessibility.
C. Lack of Alignment with Research Objectives
Your title should align seamlessly with the objectives and findings of your research. Avoid creating titles that misrepresent the core contributions of your study.
D. Lengthy and Complicated Titles
Lengthy titles can be overwhelming and may not effectively convey the essence of your research. Aim for brevity while maintaining clarity and informativeness.
E. Lack of Creativity and Engagement
A bland title may not capture the interest of potential readers. Inject creativity where appropriate and strive to create a title that sparks curiosity.
Ethical Considerations in Research Title Creation
- Avoiding Sensationalism and Misleading Titles
Ensure that your title accurately represents the content of your research. Avoid sensationalism or misleading language that may compromise the integrity of your work.
- Ensuring Accuracy and Integrity in Representing Research Content
Your title should uphold the principles of accuracy and integrity. Any claims or implications in the title should be supported by the actual findings of your research.
Crafting a captivating research title is a nuanced process that requires careful consideration of various factors. From clarity and relevance to creativity and ethical considerations, each element plays a crucial role in the success of your title.
By following the outlined strategies and avoiding common pitfalls for research title ideas, researchers can enhance the visibility and impact of their work, contributing to the broader scholarly conversation. Remember, your research title is the first impression readers have of your work, so make it count.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently

100 Qualitative Research Titles For High School Students
Are you brainstorming for excellent qualitative research titles for your high school curriculum? If yes, then this blog is for you! Academic life throws a lot of thesis and qualitative research papers and essays at you. Although thesis and essays may not be much of a hassle. However, when it comes to your research paper title, you must ensure that it is qualitative, and not quantitative.
Qualitative research is primarily focused on obtaining data through case studies, artifacts, interviews, documentaries, and other first-hand observations. It focuses more on these natural settings rather than statistics and numbers. If you are finding it difficult to find a topic, then worry not because the high schooler has this blog post curated for you with 100 qualitative research titles that can help you get started!
Qualitative research prompts for high schoolers
Qualitative research papers are written by gathering and analyzing non-numerical data. Generally, teachers allot a list of topics that you can choose from. However, if you aren’t given the list, you need to search for a topic for yourself.
Qualitative research topics mostly deal with the happenings in society and nature. There are endless topics that you can choose from. We have curated a list of 100 qualitative research titles for you to choose from. Read on and pick the one that best aligns with your interests!
- Why is there a pressing need for wildlife conservation?
- Discuss the impacts of climate change on future generations.
- Discuss the impact of overpopulation on sustainable resources.
- Discuss the factors considered while establishing the first 10 engineering universities in the world.
- What is the contribution of AI to emotional intelligence? Explain.
- List out the effective methods to reduce the occurrences of fraud through cybercrimes.
- With case studies, discuss some of the greatest movements in history leading to independence.
- Discuss real-life scenarios of gender-based discrimination.
- Discuss disparities in income and opportunities in developing nations.
- How to deal with those dealing with ADHD?
- Describe how life was before the invention of the air conditioner.
- Explain the increasing applications of clinical psychology.
- What is psychology? Explain the career opportunities it brings forth for youngsters.
- Covid lockdown: Is homeschooling the new way to school children?
- What is the role of army dogs? How are they trained for the role?
- What is feminism to you? Mention a feminist and his/her contributions to making the world a better place for women.
- What is true leadership quality according to you? Explain with a case study of a famous personality you admire for their leadership skills.
- Is wearing a mask effective in preventing covid-19? Explain the other practices that can help one prevent covid-19.
- Explain how teachers play an important role in helping students with disabilities improve their learning.
- Is ‘E business’ taking over traditional methods of carrying out business?
- What are the implications of allowing high schoolers to use smartphones in classes?
- Does stress have an effect on human behavior?
- Explain the link between poverty and education.
- With case studies, explain the political instability in developing nations.
- Are ‘reality television shows’ scripted or do they showcase reality?
- Online vs Offline teaching: which method is more effective and how?
- Does there exist an underlying correlation between education and success? Explain with case studies.
- Explain the social stigma associated with menstruation.
- Are OTT entertainment platforms like Netflix and Amazon Prime beneficial in any other way?
- Does being physically active help reverse type 2 diabetes?
- Does pop culture influence today’s youth and their behavior?
- ‘A friend in need is a friend in deed.’ Explain with case studies of famous personalities.
- Do books have greater importance in the lives of children from weaker economic backgrounds? Explain in detail.
- Give an overview of the rise of spoken arts.
- Explain the problem of food insecurity in developing nations.
- How related are Windows and Apple products?
- Explore the methods used in schools to promote cultural diversity.
- Has social media replaced the physical social engagement of children in society?
- Give an overview of allopathic medicine in treating mental disorders.
- Explain if and how willpower plays a role in overcoming difficulties in life.
- Are third-world countries seeing a decline in academic pursuit? Explain with real-life scenarios.
- Can animals predict earthquakes in advance? Explain which animals have this ability and how they do it.
- Discuss if the education system in America needs to improve. If yes, list out how this can be achieved.
- Discuss democracy as a government of the people, by the people, and for the people.’
- Discuss the increasing rate of attention deficit disorder among children.
- Explain fun games that can help boost the morale of kids with dyslexia.
- Explain the causes of youth unemployment.
- Explain some of the ways you think might help in making differently-abled students feel inclusive in the mainstream.
- Explain in detail the challenges faced by students with special needs to feel included when it comes to accessibility to education.
- Discuss the inefficiency of the healthcare system brought about by the covid-19 pandemic.
- Does living in hostels instill better life skills among students than those who are brought up at home? Explain in detail.
- What is Advanced Traffic Management? Explain the success cases of countries that have deployed it.
- Elaborate on the ethnic and socioeconomic reasons leading to poor school attendance in third-world nations.
- Do preschoolers benefit from being read to by their parents? Discuss in detail.
- What is the significance of oral learning in classrooms?
- Does computer literacy promise a brighter future? Analyze.
- What people skills are enhanced in a high school classroom?
- Discuss in detail the education system in place of a developing nation. Highlight the measures you think are impressive and those that you think need a change.
- Apart from the drawbacks of UV rays on the human body, explain how it has proven to be beneficial in treating diseases.
- Discuss why or why not wearing school uniforms can make students feel included in the school environment.
- What are the effective ways that have been proven to mitigate child labor in society?
- Explain the contributions of arts and literature to the evolving world.
- How do healthcare organizations cope with patients living with transmissive medical conditions?
- Why do people with special abilities still face hardships when it comes to accessibility to healthcare and education?
- What are the prevailing signs of depression in small children?
- How to identify the occurrences and onset of autism in kids below three years of age?
- Explain how SWOT and PESTLE analysis is important for a business.
- Why is it necessary to include mental health education in the school curriculum?
- What is adult learning and does it have any proven benefits?
- What is the importance of having access to libraries in high school?
- Discuss the need for including research writing in school curriculums.
- Explain some of the greatest non-violent movements of ancient history.
- Explain the reasons why some of the species of wildlife are critically endangered today.
- How is the growing emission of co2 bringing an unprecedented change in the environment?
- What are the consequences of an increasing population in developing nations like India? Discuss in detail.
- Are remote tests as effective as in-class tests?
- Explain how sports play a vital role in schools.
- What do you understand about social activities in academic institutions? Explain how they pose as a necessity for students.
- Are there countries providing free healthcare? How are they faring in terms of their economy? Discuss in detail.
- State case studies of human lives lost due to racist laws present in society.
- Discuss the effect of COVID-19 vaccines in curbing the novel coronavirus.
- State what according to you is more effective: e-learning or classroom-based educational systems.
- What changes were brought into the e-commerce industry by the COVID-19 pandemic?
- Name a personality regarded as a youth icon. Explain his or her contributions in detail.
- Discuss why more and more people are relying on freelancing as a prospective career.
- Does virtual learning imply lesser opportunities? What is your take?
- Curbing obesity through exercise: Analyze.
- Discuss the need and importance of health outreach programs.
- Discuss in detail how the upcoming generation of youngsters can do its bit and contribute to afforestation.
- Discuss the 2020 budget allocation of the United States.
- Discuss some of the historic ‘rags to riches’ stories.
- What according to you is the role of nurses in the healthcare industry?
- Will AI actually replace humans and eat up their jobs? Discuss your view and also explain the sector that will benefit the most from AI replacing humans.
- Is digital media taking over print media? Explain with case studies.
- Why is there an increasing number of senior citizens in the elderly homes?
- Are health insurances really beneficial?
- How important are soft skills? What role do they play in recruitment?
- Has the keto diet been effective in weight loss? Explain the merits and demerits.
- Is swimming a good physical activity to curb obesity?
- Is work from home as effective as work from office? Explain your take.

Tips to write excellent qualitative research papers
Now that you have scrolled through this section, we trust that you have picked up a topic for yourself from our list of 100 brilliant qualitative research titles for high school students. Deciding on a topic is the very first step. The next step is to figure out ways how you can ensure that your qualitative research paper can help you grab top scores.
Once you have decided on the title, you are halfway there. However, deciding on a topic signals the next step, which is the process of writing your qualitative paper. This poses a real challenge!
To help you with it, here are a few tips that will help you accumulate data irrespective of the topic you have chosen. Follow these four simple steps and you will be able to do justice to the topic you have chosen!
- Create an outline based on the topic. Jot down the sub-topics you would like to include.
- Refer to as many sources as you can – documentaries, books, news articles, case studies, interviews, etc. Make a note of the facts and phrases you would like to include in your research paper.
- Write the body. Start adding qualitative data.
- Re-read and revise your paper. Make it comprehensible. Check for plagiarism, and proofread your research paper. Try your best and leave no scope for mistakes.
Wrapping it up!
To wrap up, writing a qualitative research paper is almost the same as writing other research papers such as argumentative research papers , English research papers , Biology research papers , and more. Writing a paper on qualitative research titles promotes analytical and critical thinking skills among students. Moreover, it also helps improve data interpretation and writing ability, which are essential for students going ahead.

Having a 10+ years of experience in teaching little budding learners, I am now working as a soft skills and IELTS trainers. Having spent my share of time with high schoolers, I understand their fears about the future. At the same time, my experience has helped me foster plenty of strategies that can make their 4 years of high school blissful. Furthermore, I have worked intensely on helping these young adults bloom into successful adults by training them for their dream colleges. Through my blogs, I intend to help parents, educators and students in making these years joyful and prosperous.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

A Behind-the-Scenes Guide to School-Based Research
Benjamin d. plummer.
University of Pennsylvania
Brian M. Galla
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Sarah D. Patrick
David meketon, julia leonard, calvin goetz, elizabeth fernandez-vina.
Northeast High School, Philadelphia PA
Sara Bartolino
National Center for Time and Learning, Boston MA
Rachel E. White
Angela l. duckworth.
Schools are an important context for both basic and applied scientific research. Unlike the laboratory, however, the physical and social conditions of schools are not under the exclusive control of scientists. In this article, we liken collecting data in schools to putting on a theatrical production. We begin by describing the large cast of characters whose collaborative efforts make school-based research possible. Next, we address the critics, including the university Institutional Review Board (IRB) and school administrators, whose feedback often improves the final study design. We then turn our attention to set building, stage directions, and rehearsals – key steps in the iterative process of refining study procedures. We end with a discussion of the day of data collection itself and activities that take place after the curtain drops. Throughout, we make recommendations based on our recent experience collecting data at several high schools.
All the world’s a stage ~William Shakespeare, As You Like It , 2.7.139
Most researchers collect their data in laboratories. By definition, laboratories are physical spaces whose features can be carefully controlled. Schools, in contrast, are not institutions whose primary purpose is to provide a carefully controlled setting for scientific experimentation or observation. Nevertheless, the importance of schools as a context for scientific research cannot be overstated. Most obviously, translational research at the intersection of educational practice and basic science depends on in vivo data collection from students and teachers.
Motivations for conducting school-based research are diverse. For instance, scientists interested in youth between the ages of 5 and 18 understand that their subjects are too young or too busy to travel to laboratories on their own. Some researchers are particularly interested in representative samples and, thus, eager to expand their recruitment beyond the upper middle class families who are most commonly involved in lab studies. Given the importance of developmental research in this age range and, in particular, the potential for translational research to inform both basic science and educational practice ( Donovan, 2013 ; Brabeck, 2008 ), what can be done?
Recently, several researchers have shared observations from their own school-based studies. For instance, Alibali and Nathan (2010) provide an overview of the research cycle, beginning with approvals from school district officials and concluding with how to show appreciation to the school community after data collection is completed. More recently, Glennon and colleagues (2013) describe a successful lab school partnership, a tradition advocated by Dewey (1899) entailing a deep, long-term commitment between researchers and educational practitioners. Their insights are particularly helpful in understandings collaborations in which the topics for research are decided upon in equal partnership.
Recently, the last author of this article joined a small group of psychologists to discuss how to increase the quality and quantity of school-based research ( Radcliffe Workshop, 2013 ). A major constraint, the group agreed, was simply lack of procedural knowledge. Indeed, all of the group members had learned what to do (and, just as important, what not to do) from a relatively inefficient process of trial and error. None of them felt that their graduate training had adequately prepared them for the unique challenges of conducting research in schools. Like most human endeavors, learning from mistakes is inevitable. Still, the consensus among those present at the workshop was that a field guide to school-based research could be helpful.
In the current article, we liken school-based research to putting on a play. See Figure 1 . Drawing from our recent experience conducting a multi-site study of cognitive skills and personality traits in high school seniors, we begin by describing the large cast of characters whose separate contributions are essential to a successful performance. Next, we consider the critics, most notably the university Institutional Review Board (IRB) and school administrators. Once their scrutiny has been satisfied, researchers can proceed with the iterative process of rehearsing and refining procedures in preparation for the day of the show: collecting data. Finally, we discuss post-show activities including managing data and debriefing all stakeholders in the research process, including students, parents, teachers, and administrators. We conclude that the considerable challenges inherent in school-based research are surmountable with careful planning, clear communication, and a readiness to continuously iterate, learn, and improve.

The process by which a research idea becomes a viable school-based research study.
Cast of Characters
Our core research team included a principal investigator, post-doctoral fellow, research coordinator, and school liaison. As with conventional laboratory research, the principal investigator took final responsibility for all aspects of the research program, meeting weekly with the full research team to review milestones and troubleshoot as necessary. Specific to the school-based design of our study, the principal investigator also strove to meet periodically with school administrators, faculty, and parents to communicate the overall goals of the research as well as to update them on progress and problems. In our study, the post-doctoral fellow was responsible for day-to-day leadership of all study activities, responsibilities for which he particularly suited for given his prior experience as a classroom teacher and, while earning his doctorate in psychology, studying self-control in school-age children. Our research coordinator, a recent college graduate with more computer experience than anyone else on our team, took primary responsibility for setting up and troubleshooting the technology-related components of our research, which, given our plan to collect data exclusively online from students and teachers using school computers, were extensive. Finally, our school liaison was a retired 37-year veteran school teacher and administrator who managed communication with students, parents, teachers, and administrators. We recruited additional personnel as needed for the day of the show, but the above mentioned core team was responsible for day to day operations.
Our study of cognitive and non-cognitive traits included over 2,000 students from 5 high schools spanning 4 different public school districts. During preliminary meetings with school district administrators (e.g., superintendents and principals), we asked that a primary contact be designated to coordinate all aspects of the project. For most schools, this contact was an assistant principal or grade-level dean, whose respect and familiarity among teachers, students, and parents proved essential to successfully advocating for our research project. Critical to the success of the study, our primary contacts were especially conscientious and energetic, attending to innumerable details of the study including communicating with parents and teachers, distributing consent forms, scheduling data collection sessions, troubleshooting problems on the day of data collection, and coordinating the transfer of school records. Our research funding made it possible to offer an honorarium to each primary contact in recognition of the many hours they devoted to the project. Crucially, at all sites, our school contacts were reachable by cell phone during the entire data collection session and reachable via email virtually any time during the days leading up to data collection. Their accessibility proved crucial when we faced unexpected events both before and during data collection. Obstacles which threatened the success of the study were, on several occasions, surmounted with the quick and responsive assistance of the primary school contact.
Because our study design included several computer-based tasks, we also worked closely with the technology director at each of our partner schools. The technology director and her team ensured that the necessary infrastructure (e.g., Internet connectivity) was in place and, in addition, worked with our team to pilot and troubleshoot administration issues (e.g., firewalls). Finally, classroom teachers supported our project by being present and maintaining discipline during data collection sessions, correcting roster errors, and arranging student seating. In addition, a subset of these teachers completed online informant-report questionnaires rating students on a range of behaviors relevant to our research project. While the majority of teachers responded within two weeks, some teachers with higher class loads took much longer. Via our primary school contact, we thanked teachers for their time with small gifts (e.g., chocolates, their choice of gift card). In future studies, however, we plan to follow the recommendations of Groves, Cialdini, and Couper (1992) and provide these gifts before rather than after survey completion.
By meeting in person frequently, maintaining candid and transparent communication (both when things were going well and when, inevitably, obstacles were encountered), castmates on both the researcher and school practitioner sides developed positive relationships characterized by trust and respect. Considering prior research projects that were decidedly less successful in their execution, we have concluded that these relationships are essential and their importance cannot be overestimated. Indeed, we realize in hindsight that we could have done more to communicate the study goals and procedures to teachers prior to the day of data collection. In future work, we aim to give a short presentation at a faculty meeting at the start of the research collaboration and again after data have been collected and analyzed. Such interactions provide teachers a crucial opportunity to ask questions, raise concerns, make suggestions, and otherwise engage actively in the research process.
The Critics
Every production has its critics. First and foremost, our study procedures were scrutinized by our university’s Institutional Review Board (IRB), a committee tasked with overseeing and approving all protocols for human research. A complete IRB protocol includes a brief background section; detailed descriptions of all measures, data collection procedures, data management and confidentiality practices; a signed letter of support from each school partner; and verbatim copies of parent consent and child assent forms. Each time the protocol is substantively changed, an amendment must be submitted. In our experience, the review process can extend to weeks and even months depending on changes requested by the IRB (e.g., to improve data confidentiality practices) as well as modifications proposed by the research team (e.g., changes in measures as a result of piloting).
Since requiring signed consent forms from parents can result in a biased sample of participants ( Anderman, 1995 ), we emphasized in our IRB protocol that procedures posed minimal risks to participants and therefore justified implied parent consent procedures. This enabled us to send letters home to parents (initially drafted by the research team and then edited by our primary school contact) describing the planned research. In these letters, parents were told that not returning the letter or otherwise contacting the school or our research team implied their consent for their children to participate. In retrospect, we realize that we should have asked schools to use their automated phone message system to alert parents about the mailing, thus providing two rather than one occasion on which parents were notified. We intend to do so in future studies.
In addition to parent consent, our IRB deemed the high school seniors involved in our research as old enough to understand the procedures and make an independent judgment as to whether they wanted to participate. Thus, on the first day of data collection, we provided students with information about the study and offered them the opportunity to either participate or, alternatively, to complete a non-research activity during data collection sessions. For example, students who declined participation could read their own books quietly or go to the library to do homework. Following these procedures, participation in our project exceeded 90% of eligible students, and there was no evidence of selection bias on demographic variables including gender, ethnicity, and free/reduced-price lunch status.
School administrators comprise a second set of critics whose feedback is critical. For instance, our primary contact reviewed all study measures and procedures in advance, ensuring that questions were both comprehensible and non-sensitive (e.g., no questions about drug and alcohol use). Our primary contact for each school made every effort to schedule data collection sessions during non-academic periods (e.g., study hall or advisory periods) and on dates that did not conflict with important school events (e.g., assemblies, standardized testing). Because scheduling constraints varied widely by school, we had to be flexible, particularly in the duration and number of data collection sessions. For instance, in one school, we collected data in four separate sessions, each lasting about 50 minutes. In another school, we collected data in one extended session lasting more than an hour and two shorter sessions lasting about 30 minutes each. Similarly, at different schools, we collected data in different locations, including classrooms, the school library, the school computer lab, and the cafeteria. One common feature of all our school sites was the necessity of at least one make-up session, planned in advance, for students who were absent on their originally scheduled date.
Building the Set and Writing the Script
A performance is only as good as the preparation that precedes it. Accordingly, prior to collecting data in schools, a tremendous amount of time and effort must be devoted to the study design (set building), the procedures that are followed on the day of data collection (scripting), and rehearsing, over and over again, each time making improvements. A codebook, which we updated throughout the study, included documentation of final study materials and procedures, as well as the specific dates that parent consent forms were distributed, testing dates including which measures were administered and to whom, a full copy of the IRB protocol, and syntax for questionnaire scoring and data analysis.
Our study involved questionnaires and tasks which, ultimately, we decided to administer via websites accessed by school computers. Like any decision, there were trade-offs to consider. On the one hand, online administration meant managing computer lab firewalls, equipment failures, Internet connectivity problems, and related technology issues. On the other hand, collecting data online obviated the need to transport and store questionnaires, thereby reducing cost, hassle, and the possibility of a breach of confidentiality. Likewise, we had to make difficult choices between longer, more accurate measures and shorter, less precise ones. At each school, we made the decision between erecting cardboard dividers, which kept students on-task and enhanced their sense of privacy, and forgoing those benefits in order to reduce set-up time and maximize desk space.
To ensure that data were collected in the same way across classrooms and schools, we wrote a script for research team members to follow closely on the day of data collection. This script included both what to say aloud to students (dialogue), where to stand, and when to pause, etc. (stage directions). The script also contained a reference section with all study website URLs as well as wireless network information and an administrator logon for the school computers. Finally, a troubleshooting section included solutions for common technology problems, cell phone numbers for the primary contact and other research team members, and responses to frequently asked questions. We provided teachers who were present in the classroom during data collection sessions with their own script. Namely, at the earliest opportunity, we introduced ourselves to the classroom teacher and asked for their help in maintaining classroom discipline.
Rehearsals, Rehearsals, Rehearsals
No matter how good the script, the cast must rehearse frequently. For us, piloting was an iterative process carried out over several months. These rehearsals, though time and effort intensive, enabled us to improve the script dramatically. Usability studies in engineering suggest that a surprisingly small number of participants can efficiently identify problems during piloting ( Daniel, 2012 ). Accordingly, we typically asked between five and seven individuals to pilot measures before using their feedback to make improvements. Whenever changes were necessary, we conducted additional pilots to ensure that our solutions did not precipitate further problems.
Initially, we piloted measures in our lab to identify technological glitches, spelling and grammar errors, and similar “obvious” problems. In addition to lab members directly involved in this project, we included other willing volunteers (e.g., graduate students working on other projects). Naïve pilot subjects proved an especially critical and, therefore, especially helpful audience. Their many suggestions vastly improved the clarity of directions and the overall task flow (e.g., transitions between questionnaires). To identify potential problems associated with multiple users accessing our server at once, we then ran an online pilot with several hundred adults recruited from Amazon.com’s Mechanical Turk marketplace. Finally, we conducted pilots with high school juniors who, though they attended our partner schools, were not seniors and therefore ineligible for study participation. During these “full dress rehearsals,” we followed scripts for administering measures exactly as we would during actual data collection, using both the data collected and verbal feedback (e.g., regarding unclear directions or unfamiliar terminology) to make final improvements.
Both piloting and detailed discussions with our school contact enabled us to foresee possible problems with task administration and to develop contingency plans accordingly. For example, occasional disruptions of Internet connectivity during piloting prompted us to bring hard-copy versions of online questionnaires on the day of data collection which, at one of our partner schools, we ended up using. Similarly, the variety and novelty of problems encountered led us to add an extra researcher to our team. In one school, this “extra” researcher helped move laptops when, without warning, we were asked to move from classroom to another. At another school, this individual helped relay messages (e.g., information about schedule changes) from one classroom to another.
Day of the Show
Even with adequate preparation, show time can be hectic. We have learned the hard way that while members of the cast (researchers and school practitioners) may rehearse their routines to fluency, members of the audience (students themselves) most certainly do not. For instance, even though teachers at every school site in our study announced to students exactly where they were to show up on the day of data collection, at least a few students at each school reported to the wrong classroom and had to be redirected to their assigned location. Once seated, it was typical for one or two students in the classroom to forget their computer login or password, thus requiring a researcher to use an administrator password to grant them access. On average, we found that it took up to fifteen minutes for all students to arrive to their assigned classroom, take a seat, put away their cell phones and books, settle down, and log in to their computers.
Once students were settled and on task, maintaining a controlled environment was paramount. We found the best way to do so was to circle the classroom frequently, passing by students slowly but, to maximize their sense of privacy, deliberately maintaining a disinterested demeanor and directing our gaze away from their screens. When not pacing about the room, we liked to stand where we could scan the entire room for raised hands or disruptive behavior. If a student was talking or otherwise off-task, we gently reminded them to turn their attention to the study activities. In rare instances of serious misbehavior, we asked the classroom teacher to intervene. Notwithstanding these precautions, we kept meticulous notes about administration, foreseeing correctly that some data would be excluded because of technological problems or student misbehavior.
Another lesson learned was to expect the unexpected. In our study, we were surprised by fire alarms, field trips, and all-school assemblies, among other events which, in most cases, had been arranged by school administrators other than our primary contact. On one occasion, we were forced to reschedule the entire data collection session when, on the originally scheduled morning, we awoke to discover that schools were closed for severe weather. In another school, entire classes of students showed up late (or not at all) to their assigned classrooms for reasons we never figured out. In all of these cases, the study was rescued by our ability to reach our school contact by cell phone and to make alternative plans accordingly.
After the Curtain Comes Down: Following Through with Cast and Audience
Unlike a dramatic production, much of the work of a research study goes on after the curtain comes down. Data collection sessions spanned several days at each of our school sites, and at the end of each day, we met with our primary school contact to discuss attendance and behavioral problems, unexpected events, technological glitches, and anything else that prompted changes in procedures for the next day. We also examined our data, scrutinizing files for missing or impossible values and completing preliminary analyses to ensure that data had been collected properly. In tandem, we updated our list of opt-outs with the names of students whose parents had provided consent but who themselves elected not to participate in the study. We also consolidated our notes about anomalies during administration (e.g., students starting a survey over at its midpoint, students who came late to test administration, sessions that ended early because of a fire alarm, Internet connectivity problems). All notes were included verbatim in the codebook which, as mentioned before, was a living document that we constantly updated as the study progressed.
In the weeks following data collection, we completed more detailed analyses of the data, following a standard protocol defined by our lab. Among the more mundane post-production activities were the unpacking of supplies (e.g., extra ear buds, cardboard dividers, handouts) and repacking for the next scheduled data collection. During this period, we also followed up with our primary school contact to obtain school records (e.g., report card grades) relevant to our study hypotheses.
While preparing data for analysis and fitting statistical models can take a long time, school faculty, parents, and the students are understandably eager to learn how the research turned out as soon as possible. We therefore distributed a one-page newsletter with at least a few confirmed study findings before the end of the school year, posting an electronic version on our website and making sure each primary contacts sent printed versions to their entire school communities. In future studies, we hope to do even better, preparing longer reports with more substantive information, perhaps supplementing study findings with additional information on topics of special interest to the school community. In addition to newsletters, we made presentations in person to faculty and parents at school sites that were located near our campus. In the future, we intend to film presentations for school partners we cannot visit in person at the conclusion of data collection. As a final gesture of gratitude, we sent thank you notes and candy baskets to each school at the very end of the school year.
Conducting a school-based research study, like performing a play, can be daunting. The challenges associated with collecting data from students in vivo are numerous and qualitatively different, in some ways, than those encountered in standard laboratory research. Our strong belief is that school-based research is nevertheless viable. Success depends in large part on a cast which collectively exemplifies enthusiasm, conscientiousness, and flexibility. Each member of the cast, both at the research institution and the school site, plays a special and important role. The feedback of critics, in this case the university IRB and school administrators, must be received and incorporated into the study design. Many months before data collection itself, the cast of a school-based research study is hard at work designing the set, writing the script, and making refinements based on pilot work. At long last, there is the much anticipated and often hectic day of data collection itself. Despite dress rehearsals and careful planning, data collection inevitably comes with at least a few surprises, demanding that cast members troubleshoot on the spot and maintain open and clear lines of communication. Finally, after the curtain comes down, there is yet more work to do. In particular, data need to be analyzed, results need to be communicated, and gestures of gratitude need to be made in recognition of the substantial contributions made by all concerned.
The urgent need for more inquiry at the intersection of science and education ( Donovan, 2013 ) motivated us to pen this article. The study of cognitive and non-cognitive traits in high school seniors to which we allude throughout our remarks is, of course, just one example of school-based research. Other studies, using different methods and different samples to answer different research questions, will have their own particular challenges. Still, we hope others can learn from our experience, including things we are proud to have done reasonably well and, in addition, the mistakes we hope other researchers (and ourselves) will avoid in the future.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by funding from the National Institute of Health (5-K01-AG033182-02), and the Bill and Melina Gates Foundation (OPP1046454). The authors are grateful to the students, teachers, and school administrators who made this research possible.
Contributor Information
Benjamin D. Plummer, University of Pennsylvania.
Brian M. Galla, University of Pennsylvania.
Amy Finn, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Sarah D. Patrick, University of Pennsylvania.
David Meketon, University of Pennsylvania.
Julia Leonard, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Calvin Goetz, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Elizabeth Fernandez-Vina, Northeast High School, Philadelphia PA.
Sara Bartolino, National Center for Time and Learning, Boston MA.
Rachel E. White, University of Pennsylvania.
Angela L. Duckworth, University of Pennsylvania.
- Alibali MW, Nathan MJ. Conducting research in schools: A practical guide. Journal of Cognition and Development. 2010; 11 (4):397–407. [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderman C, Cheadle A, Curry S, Diehr P, Shultz L, Wagner E. Selection bias related to parental consent in school-based survey research. Evaluation Review. 1995; 19 (6):663–674. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brabeck M. Why we need translational research: Putting clinical findings to work in classrooms. Education Week. 2008; 27 (38):28, 36. [ Google Scholar ]
- Daniel DB. Promising principles: Translating the science of learning to educational practice. Journal of Applied Research in Memory and Cognition. 2012; 1 (4):251–253. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dewey J. The school and society. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press; 1899. [ Google Scholar ]
- Donovan MS. Generating improvement through research and development in education systems. Science. 2013; 340 (6130):317–319. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Glennon C, Hinton C, Callahan T, Fischer KW. School-based research. Mind, Brain, and Education. 2013; 7 (1):30–34. [ Google Scholar ]
- Groves RM, Cialdini RB, Couper MP. Understanding the decision to participate in a survey. Public Opinion Quarterly. 1992; 56 (4):475–495. [ Google Scholar ]
- Radcliffe Workshop. Social pathways to improving education. Cambridge, MA: 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Find My Rep
You are here
100 Activities for Teaching Research Methods
- Catherine Dawson - Self-employed researcher and writer
- Description
A sourcebook of exercises, games, scenarios and role plays, this practical, user-friendly guide provides a complete and valuable resource for research methods tutors, teachers and lecturers.
Developed to complement and enhance existing course materials, the 100 ready-to-use activities encourage innovative and engaging classroom practice in seven areas:
- finding and using sources of information
- planning a research project
- conducting research
- using and analyzing data
- disseminating results
- acting ethically
- developing deeper research skills.
Each of the activities is divided into a section on tutor notes and student handouts. Tutor notes contain clear guidance about the purpose, level and type of activity, along with a range of discussion notes that signpost key issues and research insights. Important terms, related activities and further reading suggestions are also included.
Not only does the A4 format make the student handouts easy to photocopy, they are also available to download and print directly from the book’s companion website for easy distribution in class.
Supplements
Catherine's book is a fantastic resource for anyone who is teaching research methods in the social sciences. Covering all aspects of the research process, it is packed full of innovative ideas, useful tips, and structured activities for use within the classroom. If you are a tutor, teacher, or lecturer who is looking to provide interesting and engaging content for your students, this book is an absolute 'must have'.
Every university with a Social Science department has to deliver research methods in some capacity, but there is no need for us all to sit in our institutional silos and reinvent the wheel. Dawson provides a huge and varied list of pre-designed activities for methods teachers to draw upon covering the whole research process and an eclectic range of methodological approaches. The activities are pedagogically engaging, comprehensively resourced and provide us with an opportunity to rethink how social science research methods can be taught in a more interactive and engaging way.
Preview this book
Sample materials & chapters.
100 Activities for Teaching Research Methods: Listening to Interviewees
For instructors
Select a purchasing option, order from:.
- VitalSource
- Amazon Kindle
- Google Play
Related Products

Get the Reddit app
Reddit's home for wholesome discussion related to pre-medical studies.
My thoughts on how to write the activity section to get the most bang for your experiences and writing
Arnold's back with more advice and The Arnold Guide TM that will focus on both how to write your activity section.
As always everything here is simply my opinion and should not be taken as law-- please seek out multiple resources to make a well-rounded and informed decision when you work on your own applications. Come see the rest of my advice here on extra curriculars , the personal statement , the application timeline , and interviewing .
Let's start.
What is the activity section?
The activity section is a part of your primary application where you list all your activities (commonly referred to here as ECs). You have up to 15 entries to fill out (not necessarily meaning you can only use 15 activities. More on this later). Your primary consists of your GPA and MCAT (intellectual aptitude for medical school), your personal statement (your personal reasons of why you're applying to medical school), and your activities (how you're qualified beyond your academics for a career in medicine and why your experiences are unique as compared to others). Now I've already written about the activities themselves-- this post is about how to WRITE about them.
What I will be doing is going through each entry of 1 AMCAS activity. The following is what the entries of an activity look like. In the next section I'll break it down.
Experience Type: You can only classify it as one
Artistic Endeavor
Community Service - Nonclinical
Community service - Clinical
Conferences Attended
Extracurricular Activities
Honors Awards Recognition
Intercollegiate Athletics
Leadership - Not listed elsewhere
Paid Employment - clinical
Paid Employment - nonclinical
Physician Shadowing
Presentations/Posters
Publications
Teaching/ Tutor/ Teaching Assistant
Experience Name:
Start Date:
Total Hours:
Repeated? this is for activities that you did multiple times but did not do the entire year. So, for an example, an activity you did all 4 years of college in the month of April can be "repeated" every April for 4 year"
Organization Name:
Contact’s name:
Contact’s title:
Contact phone or email:
Experience Description (700 characters including spaces):
Most Meaningful: yes/no You can only designate 3 activities as most meaningful and you get an extra 1325 characters so discuss it. Choose wisely. You are quite literally telling schools what to focus on
Experience Summary (1325 characters including spaces):
Ok there are a lot of categories to pick from... how do I pick one?
Picking the category of of your activity is as important as what you write about them. This is one of your main ways of telling the Admissions Committee how you'd like your experience to be viewed as. Look at your application as a whole and try to fill in holes. For example-- if you're a leader of a volunteering club on campus, one of the heads of your schools peer-reviewed scientific journal, and leader of a random club (say a robotics club), how you'd categorize each is important. What I personally would do is list the leader of the volunteering club as non-clinical volunteering and the other two as leadership. Why? Because it is very easy in the description of the volunteering club to say you led it, but it's more important on a statistic basis to boost your non-volunteering hours. I know this is silly but there are legit schools that will break down your app into hours of each category and will go off what YOU say!
Another example is research versus clinical experience sometimes. Now if you have a ton of research and little clinical experience, it may be better to put that clinical research position you had working with patients as clinical experience. Alternatively, if you have a lot of clinical experience and little research experience, doing the opposite can help. Your goal is to be well-rounded and have as many categories hit as possible.
This is the name of your experience. You want to be as specific as possible while giving the most important information. Let's take being an emergency department volunteer at Arnold's Hospital for the Swole. I would put the experience name as "Emergency Department Volunteer" and in the organization name put the hospital name. You have limited space (not sure how many characters but it's not a lot). It's more specific than "Volunteer." I know this seems obvious, but sometimes people view this as what your specific title is but it's not-- it's the name of the experience!
This can also be used as an umbrella experience! So for example say you were really involved in a club on campus and held 4 different leadership rules throughout your time. Do NOT make 4 different activities -- it's silly. What I would do is have the experience name be "Leadership roles of X Club" and in the experience write the titles, duties, and hours of each position.
This is also a good place for athletics or hobbies. A good way is to simply have an activity devoted to one.
This is the date you started.
This is the date you ended. Now this is important-- COUNT YOUR HOURS THAT YOU WILL COMPLETE OVER YOUR APPLICATION YEAR. Seriously. On SDN all the adcom's agree there are 3 legit ways to list your end date and your total hours. 1) simply put the end date as the day you submit your application and your hours up until that point. 2) put the end date as the day you submit your application and include current and future hours. 3) put the end date as when you envision stopping that activity (the latest you should do is the following summer when school starts) and just including all hours into your total hours. I am a fan of 3. The process is so unnecessarily wrong that I did not want to be punished for it. So I wasn't. So what I did was activities that were completed before and during my gap years I just estimated the hours that would be done, put it in the total hours section (see below), and then didn't mention hours again. People focus too much on hours and I never EVER mentioned hours outside of the total hours slot (unless it was multiple activities and I was specifying which hours went into what) because the more you mention it the more it comes across as box checking and not doing it for genuine purposes. This is NOT lying and this is NOT inflating your numbers-- you genuinely do plan to complete these hours, so list them. DO NOT LIE AND SAY YOU'LL DO 1000 HOURS in 1 MONTH.
See above. List all hours completed and planning to complete. Moreover, if you have multiple experiences in one activity just add them all up and specify in the description.
This is for activities that you did multiple times but did not do the entire year. So, for an example, an activity you did all 4 years of college in the month of April can be "repeated" every April for 4 year"
This is the name of whatever organization you had. IIRC activities like publications and hobbies do not have this.
Wherever your experience was in!
I'm just gonna group these all together. Your contact is someone that can verify what you wrote on your application is true. It is NOT a reference and they do NOT have to comment on anything you did-- simply that it was done. If in a club just list the highest leadership you can (or if you're president, list a vice president). If it's a personal activity, just list yourself. If it's a job, list a supervisor, boss, etc. What I recommend though, regardless of who you choose, TELL them you're choosing them and say how many hours you are putting down. The last thing you want is any miscommunication and on the off chance they do get contacted to not be on the same page as you. Ouch lol.
Alright this experience description is different depending if you choose it as a most meaningful experience or not.
If designated as a most meaningful experience :
Keep this strictly based on what you did. You only have 700 characters which is nothing. You're choosing this as most meaningful for a reason so I would assume what you did was very interesting/you have a lot of responsibility/ etc. Moreover (and this applies regardless of the designation) focus on the important aspect of your duties. They limit your space, so you need to limit what you tell them. For example if you have 15 duties as a clinical volunteer but only have room to list 7, choose the 7 that is most pertinent to patient care and is most clinical in nature even if they're not the 7 most high yield things you did. They're giving you 700 characters--use it wisely. No one cares if you changed the patients beds or helped stock IV carts if you also hung out with patients, transported them, helped place IVs, etc.
If NOT designated as a most meaningful experience :
You have the unfortunate duty, in 700 characters, to somehow write about what you did and why it's important. Defintely write about why it's important to you (whether you simply love it [i.e. sports], exposed you to different types of people, or your career in medicine). DO NOT FORCE MEDICINE. You did NOT play basketball with your friends because medicine requires teamwork lol. You also did not do research in your free time because you just love it so much. Don't bullshit the Adcom's. Small stuff like this pisses them off.
Most Meaningful: yes/no
You can only designate 3 activities as most meaningful and you get an extra 1325 characters so discuss it. Choose wisely. You are quite literally telling schools what to focus on*
How do I pick which 3 to choose?!
I wanted to give a well-rounded view of what I personally thought was most meaningful in my own personal journey to medicine. I chose one clinical experience, one research experience, and one non-clinical volunteering/leadership experience. To me those were my most meaningful as it fostered many attributes and motivations for seeking out this career. Be well-rounded but stay true to yourself-- if basketball truly was one of your most meaningful experiences, list it. If you're forcing something it'll be quite obvious it was forced.
Arguably the most important part of the activity section is this. Not only have you specifically told the admissions committee WHAT to focus on, now you're telling them WHY to. I treated this part much like my personal statement-- I made it VERY personal with stories of why this is important to me and why (for the activities that it works for) why this helps me for medicine. For my clinical experience I focused on 2 things. 1) exposure to patients and patient care. I told a story of one of my favorite patients and going above and beyond for that specific patient. and 2) exposure to being a physician and exposure to medicine. For research I spoke about WHY I thought the specific clinical research was important and how it affected me on a personal level as I saw it in practice affecting patient care in front of my eyes. These were the easiest for me to write-- I thought to myself "Why is this important?" and wrote that. If you're struggling a lot to write this section you need to evaluate why you think it's so meaningful to you.
Ok now that I've gone through each section, now some FAQs I see a lot
Do I list my fraternity or sorority?!
Here's the rule of thumb on Greek life-- if you had leadership roles, especially President, VP (or any executive member), risk reduction, or ESPECIALLY philanthropy, definitely list it. It's a super valuable experience and it shows you as both a social person and someone who can lead your peers (A VERY VALUABLE TRAIT IN MEDICINE). But if you were simply a brother or sister for all 4 years and didn't do anything, don't list it. Unfortunately people still view Greek life as alcohol filled sex clubs.
How constitutes a publication and how do I list it? How do I list co-author number?
Publications as AMCAS and medical schools are concerned about is the publications that are in peer-reviewed professional scientific journals (not your local student run one). Do NOT put your pubs in your research activity-- make an extra activity with the tab "publications" and put in the citation as is appeared in pubmed. I never specified what number co-author I was (cause I was never first or second lol if you are then specify it). In my research section I wrote I was a co-author and in the publication tabs I copy and pasted exactly how it appeared-- and it's 100% obvious which number co-author I am, but there's no need to specify it unless it helps you.
What about my quirky ECs?!
Ask yourself how you want an adcom to view you. This is important. Really important. Adcom's are mostly older physicians from a different time. I will leave it at that.
Should I include that I worked for LGBT organizations? Should I include that I'm gay/lesbian?
As with the personal statement only write about things that you are ok with discussing. If you're not openly out and want to stay in, then don't write about it. If it's a major part of who you are and you can discuss it, then definitely list it.
How do I list shadowing?
I simply listed each doctors name, specialty, hours shadowed, hospital or clinic name, and contact information. Doing this for 5 physicians was essentially exactly 700 characters. It's not as important to mention what you saw or what it meant for you-- that's good secondary and/or interview material.
How do I classify research?
There are 2 major types of research: basic science research and clinical research.
Basic science research: A general rule of thumb is if you're working in a lab and doing typical lab work (fume hood work, PCR, splitting cells, etc. actually working with specimens and samples) it's basic science research and can simply be listed as research. You'll list yourself as either of 2 things: if you're involved ONLY in the lab and have absolutely no say in the research aspect, research design, statistically analysis, etc then you're a laboratory assistant. If you're involved with any part of the actual research, statistical analysis, etc then you're a research assistant.
Clinical research: If you're working with data, retrospective chart data, interviewing patients, etc then it's clinical research.
I think that's it for now. As always any and all questions please ask :). If anyone with more experience has better/ more correct information, please let me know and I will update as needed. I will try and add commonly asked questions to this OP eventually.
Thanks all! Good vibes to everyone. Stay classy r/premed
- Privacy Policy

Home » 500+ Quantitative Research Titles and Topics
500+ Quantitative Research Titles and Topics
Table of Contents

Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships among variables. This method is widely used in social sciences, psychology , economics , and other fields where researchers aim to understand human behavior and phenomena through statistical analysis. If you are looking for a quantitative research topic, there are numerous areas to explore, from analyzing data on a specific population to studying the effects of a particular intervention or treatment. In this post, we will provide some ideas for quantitative research topics that may inspire you and help you narrow down your interests.
Quantitative Research Titles
Quantitative Research Titles are as follows:
Business and Economics
- “Statistical Analysis of Supply Chain Disruptions on Retail Sales”
- “Quantitative Examination of Consumer Loyalty Programs in the Fast Food Industry”
- “Predicting Stock Market Trends Using Machine Learning Algorithms”
- “Influence of Workplace Environment on Employee Productivity: A Quantitative Study”
- “Impact of Economic Policies on Small Businesses: A Regression Analysis”
- “Customer Satisfaction and Profit Margins: A Quantitative Correlation Study”
- “Analyzing the Role of Marketing in Brand Recognition: A Statistical Overview”
- “Quantitative Effects of Corporate Social Responsibility on Consumer Trust”
- “Price Elasticity of Demand for Luxury Goods: A Case Study”
- “The Relationship Between Fiscal Policy and Inflation Rates: A Time-Series Analysis”
- “Factors Influencing E-commerce Conversion Rates: A Quantitative Exploration”
- “Examining the Correlation Between Interest Rates and Consumer Spending”
- “Standardized Testing and Academic Performance: A Quantitative Evaluation”
- “Teaching Strategies and Student Learning Outcomes in Secondary Schools: A Quantitative Study”
- “The Relationship Between Extracurricular Activities and Academic Success”
- “Influence of Parental Involvement on Children’s Educational Achievements”
- “Digital Literacy in Primary Schools: A Quantitative Assessment”
- “Learning Outcomes in Blended vs. Traditional Classrooms: A Comparative Analysis”
- “Correlation Between Teacher Experience and Student Success Rates”
- “Analyzing the Impact of Classroom Technology on Reading Comprehension”
- “Gender Differences in STEM Fields: A Quantitative Analysis of Enrollment Data”
- “The Relationship Between Homework Load and Academic Burnout”
- “Assessment of Special Education Programs in Public Schools”
- “Role of Peer Tutoring in Improving Academic Performance: A Quantitative Study”
Medicine and Health Sciences
- “The Impact of Sleep Duration on Cardiovascular Health: A Cross-sectional Study”
- “Analyzing the Efficacy of Various Antidepressants: A Meta-Analysis”
- “Patient Satisfaction in Telehealth Services: A Quantitative Assessment”
- “Dietary Habits and Incidence of Heart Disease: A Quantitative Review”
- “Correlations Between Stress Levels and Immune System Functioning”
- “Smoking and Lung Function: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Influence of Physical Activity on Mental Health in Older Adults”
- “Antibiotic Resistance Patterns in Community Hospitals: A Quantitative Study”
- “The Efficacy of Vaccination Programs in Controlling Disease Spread: A Time-Series Analysis”
- “Role of Social Determinants in Health Outcomes: A Quantitative Exploration”
- “Impact of Hospital Design on Patient Recovery Rates”
- “Quantitative Analysis of Dietary Choices and Obesity Rates in Children”
Social Sciences
- “Examining Social Inequality through Wage Distribution: A Quantitative Study”
- “Impact of Parental Divorce on Child Development: A Longitudinal Study”
- “Social Media and its Effect on Political Polarization: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “The Relationship Between Religion and Social Attitudes: A Statistical Overview”
- “Influence of Socioeconomic Status on Educational Achievement”
- “Quantifying the Effects of Community Programs on Crime Reduction”
- “Public Opinion and Immigration Policies: A Quantitative Exploration”
- “Analyzing the Gender Representation in Political Offices: A Quantitative Study”
- “Impact of Mass Media on Public Opinion: A Regression Analysis”
- “Influence of Urban Design on Social Interactions in Communities”
- “The Role of Social Support in Mental Health Outcomes: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Examining the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Employment Status”
Engineering and Technology
- “Performance Evaluation of Different Machine Learning Algorithms in Autonomous Vehicles”
- “Material Science: A Quantitative Analysis of Stress-Strain Properties in Various Alloys”
- “Impacts of Data Center Cooling Solutions on Energy Consumption”
- “Analyzing the Reliability of Renewable Energy Sources in Grid Management”
- “Optimization of 5G Network Performance: A Quantitative Assessment”
- “Quantifying the Effects of Aerodynamics on Fuel Efficiency in Commercial Airplanes”
- “The Relationship Between Software Complexity and Bug Frequency”
- “Machine Learning in Predictive Maintenance: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Wearable Technologies and their Impact on Healthcare Monitoring”
- “Quantitative Assessment of Cybersecurity Measures in Financial Institutions”
- “Analysis of Noise Pollution from Urban Transportation Systems”
- “The Influence of Architectural Design on Energy Efficiency in Buildings”
Quantitative Research Topics
Quantitative Research Topics are as follows:
- The effects of social media on self-esteem among teenagers.
- A comparative study of academic achievement among students of single-sex and co-educational schools.
- The impact of gender on leadership styles in the workplace.
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic performance of students.
- The effect of mindfulness meditation on stress levels in college students.
- The relationship between employee motivation and job satisfaction.
- The effectiveness of online learning compared to traditional classroom learning.
- The correlation between sleep duration and academic performance among college students.
- The impact of exercise on mental health among adults.
- The relationship between social support and psychological well-being among cancer patients.
- The effect of caffeine consumption on sleep quality.
- A comparative study of the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy in treating depression.
- The relationship between physical attractiveness and job opportunities.
- The correlation between smartphone addiction and academic performance among high school students.
- The impact of music on memory recall among adults.
- The effectiveness of parental control software in limiting children’s online activity.
- The relationship between social media use and body image dissatisfaction among young adults.
- The correlation between academic achievement and parental involvement among minority students.
- The impact of early childhood education on academic performance in later years.
- The effectiveness of employee training and development programs in improving organizational performance.
- The relationship between socioeconomic status and access to healthcare services.
- The correlation between social support and academic achievement among college students.
- The impact of technology on communication skills among children.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction programs in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- The relationship between employee turnover and organizational culture.
- The correlation between job satisfaction and employee engagement.
- The impact of video game violence on aggressive behavior among children.
- The effectiveness of nutritional education in promoting healthy eating habits among adolescents.
- The relationship between bullying and academic performance among middle school students.
- The correlation between teacher expectations and student achievement.
- The impact of gender stereotypes on career choices among high school students.
- The effectiveness of anger management programs in reducing violent behavior.
- The relationship between social support and recovery from substance abuse.
- The correlation between parent-child communication and adolescent drug use.
- The impact of technology on family relationships.
- The effectiveness of smoking cessation programs in promoting long-term abstinence.
- The relationship between personality traits and academic achievement.
- The correlation between stress and job performance among healthcare professionals.
- The impact of online privacy concerns on social media use.
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating anxiety disorders.
- The relationship between teacher feedback and student motivation.
- The correlation between physical activity and academic performance among elementary school students.
- The impact of parental divorce on academic achievement among children.
- The effectiveness of diversity training in improving workplace relationships.
- The relationship between childhood trauma and adult mental health.
- The correlation between parental involvement and substance abuse among adolescents.
- The impact of social media use on romantic relationships among young adults.
- The effectiveness of assertiveness training in improving communication skills.
- The relationship between parental expectations and academic achievement among high school students.
- The correlation between sleep quality and mood among adults.
- The impact of video game addiction on academic performance among college students.
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating eating disorders.
- The relationship between job stress and job performance among teachers.
- The correlation between mindfulness and emotional regulation.
- The impact of social media use on self-esteem among college students.
- The effectiveness of parent-teacher communication in promoting academic achievement among elementary school students.
- The impact of renewable energy policies on carbon emissions
- The relationship between employee motivation and job performance
- The effectiveness of psychotherapy in treating eating disorders
- The correlation between physical activity and cognitive function in older adults
- The effect of childhood poverty on adult health outcomes
- The impact of urbanization on biodiversity conservation
- The relationship between work-life balance and employee job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) in treating trauma
- The correlation between parenting styles and child behavior
- The effect of social media on political polarization
- The impact of foreign aid on economic development
- The relationship between workplace diversity and organizational performance
- The effectiveness of dialectical behavior therapy in treating borderline personality disorder
- The correlation between childhood abuse and adult mental health outcomes
- The effect of sleep deprivation on cognitive function
- The impact of trade policies on international trade and economic growth
- The relationship between employee engagement and organizational commitment
- The effectiveness of cognitive therapy in treating postpartum depression
- The correlation between family meals and child obesity rates
- The effect of parental involvement in sports on child athletic performance
- The impact of social entrepreneurship on sustainable development
- The relationship between emotional labor and job burnout
- The effectiveness of art therapy in treating dementia
- The correlation between social media use and academic procrastination
- The effect of poverty on childhood educational attainment
- The impact of urban green spaces on mental health
- The relationship between job insecurity and employee well-being
- The effectiveness of virtual reality exposure therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between childhood trauma and substance abuse
- The effect of screen time on children’s social skills
- The impact of trade unions on employee job satisfaction
- The relationship between cultural intelligence and cross-cultural communication
- The effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy in treating chronic pain
- The correlation between childhood obesity and adult health outcomes
- The effect of gender diversity on corporate performance
- The impact of environmental regulations on industry competitiveness.
- The impact of renewable energy policies on greenhouse gas emissions
- The relationship between workplace diversity and team performance
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating substance abuse
- The correlation between parental involvement and social skills in early childhood
- The effect of technology use on sleep patterns
- The impact of government regulations on small business growth
- The relationship between job satisfaction and employee turnover
- The effectiveness of virtual reality therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic motivation in adolescents
- The effect of social media on political engagement
- The impact of urbanization on mental health
- The relationship between corporate social responsibility and consumer trust
- The correlation between early childhood education and social-emotional development
- The effect of screen time on cognitive development in young children
- The impact of trade policies on global economic growth
- The relationship between workplace diversity and innovation
- The effectiveness of family therapy in treating eating disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and college persistence
- The effect of social media on body image and self-esteem
- The impact of environmental regulations on business competitiveness
- The relationship between job autonomy and job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of virtual reality therapy in treating phobias
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic achievement in college
- The effect of social media on sleep quality
- The impact of immigration policies on social integration
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee well-being
- The effectiveness of psychodynamic therapy in treating personality disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and executive function skills
- The effect of parental involvement on STEM education outcomes
- The impact of trade policies on domestic employment rates
- The relationship between job insecurity and mental health
- The effectiveness of exposure therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and social mobility
- The effect of social media on intergroup relations
- The impact of urbanization on air pollution and respiratory health.
- The relationship between emotional intelligence and leadership effectiveness
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between early childhood education and language development
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in STEM fields
- The impact of trade policies on income inequality
- The relationship between workplace diversity and customer satisfaction
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and civic engagement in adolescents
- The effect of social media on mental health among teenagers
- The impact of public transportation policies on traffic congestion
- The relationship between job stress and job performance
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between early childhood education and cognitive development
- The effect of parental involvement on academic motivation in college
- The impact of environmental regulations on energy consumption
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee engagement
- The effectiveness of art therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in vocational education
- The effect of social media on academic achievement in college
- The impact of tax policies on economic growth
- The relationship between job flexibility and work-life balance
- The effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and social competence
- The effect of parental involvement on career readiness in high school
- The impact of immigration policies on crime rates
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee retention
- The effectiveness of play therapy in treating trauma
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in online learning
- The effect of social media on body dissatisfaction among women
- The impact of urbanization on public health infrastructure
- The relationship between job satisfaction and job performance
- The effectiveness of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between early childhood education and social skills in adolescence
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in the arts
- The impact of trade policies on foreign investment
- The relationship between workplace diversity and decision-making
- The effectiveness of exposure and response prevention therapy in treating OCD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in special education
- The impact of zoning laws on affordable housing
- The relationship between job design and employee motivation
- The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation therapy in treating traumatic brain injury
- The correlation between early childhood education and social-emotional learning
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in foreign language learning
- The impact of trade policies on the environment
- The relationship between workplace diversity and creativity
- The effectiveness of emotion-focused therapy in treating relationship problems
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in music education
- The effect of social media on interpersonal communication skills
- The impact of public health campaigns on health behaviors
- The relationship between job resources and job stress
- The effectiveness of equine therapy in treating substance abuse
- The correlation between early childhood education and self-regulation
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in physical education
- The impact of immigration policies on cultural assimilation
- The relationship between workplace diversity and conflict resolution
- The effectiveness of schema therapy in treating personality disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in career and technical education
- The effect of social media on trust in government institutions
- The impact of urbanization on public transportation systems
- The relationship between job demands and job stress
- The correlation between early childhood education and executive functioning
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in computer science
- The effectiveness of cognitive processing therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in homeschooling
- The effect of social media on cyberbullying behavior
- The impact of urbanization on air quality
- The effectiveness of dance therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and math achievement
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in health education
- The impact of global warming on agriculture
- The effectiveness of narrative therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in character education
- The effect of social media on political participation
- The impact of technology on job displacement
- The relationship between job resources and job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of art therapy in treating addiction
- The correlation between early childhood education and reading comprehension
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in environmental education
- The impact of income inequality on social mobility
- The relationship between workplace diversity and organizational culture
- The effectiveness of solution-focused brief therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in physical therapy education
- The effect of social media on misinformation
- The impact of green energy policies on economic growth
- The relationship between job demands and employee well-being
- The correlation between early childhood education and science achievement
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in religious education
- The impact of gender diversity on corporate governance
- The relationship between workplace diversity and ethical decision-making
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in dental hygiene education
- The effect of social media on self-esteem among adolescents
- The impact of renewable energy policies on energy security
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in social studies
- The impact of trade policies on job growth
- The relationship between workplace diversity and leadership styles
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in online vocational training
- The effect of social media on self-esteem among men
- The impact of urbanization on air pollution levels
- The effectiveness of music therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between early childhood education and math skills
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in language arts
- The impact of immigration policies on labor market outcomes
- The effectiveness of hypnotherapy in treating phobias
- The effect of social media on political engagement among young adults
- The impact of urbanization on access to green spaces
- The relationship between job crafting and job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of exposure therapy in treating specific phobias
- The correlation between early childhood education and spatial reasoning
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in business education
- The impact of trade policies on economic inequality
- The effectiveness of narrative therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in nursing education
- The effect of social media on sleep quality among adolescents
- The impact of urbanization on crime rates
- The relationship between job insecurity and turnover intentions
- The effectiveness of pet therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and STEM skills
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in culinary education
- The impact of immigration policies on housing affordability
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee satisfaction
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction in treating chronic pain
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in art education
- The effect of social media on academic procrastination among college students
- The impact of urbanization on public safety services.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

500+ Astronomy Research Topics

1000+ Sociology Research Topics

500+ Qualitative Research Titles and Topics

500+ Statistics Research Topics

500+ History Research Paper Topics

300+ Social Media Research Topics
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to content
- Skip to footer
Research-based feedback for students and insights for teachers, within minutes
June 10, 2024 By Chidi Chiemelu 1 Min Read

I found the color coding on each student extremely helpful. Assessing their tone meant I could immediately see the type of day each student was having.
Kim Sharp | Kleb Intermediate School, Klein ISD
Build reflective skills and improve writing outcomes
Instructional Specialist in Digital Learning
School/District:
Kleb Intermediate School, Klein ISD
Grade: middle school
As an innovative Instructional Specialist in Digital Learning for Kleb Intermediate School, Kim Sharp wanted to find new ways to gain insights into her students’ learning and growth. She decided to explore tech solutions that qualified for Title 1 funding . Her research led to Swivl’s new interactive reflection station, Mirror.
After receiving Mirror, Kim put the device to the test. Kim had her humanities co-teaching partner, Christy Stewart, create custom reflections in Mirror for each of her students to reflect on their writing processes. Their goal was to determine whether offering an option for students to record verbal reflections would help the students improve their written outcomes.
When setting up custom reflections for students to complete with Mirror, teachers have the choice to type out the “goal” of a reflection or to record themselves as they say the goal out loud. Kim and Christy decided to record the goal so the students would hear their teacher’s voice.
Students were initially hesitant about recording verbal reflections with Mirror, but after demoing how to use it, and hearing their teachers’ voices stating the goal, they quickly warmed up. The students even named their Mirror, Siggy after Sigmund Freud.
Improving students’ reflective skills
The more Kim and Christy used Mirror with their students the more they realized that their students don’t know how to reflect on their own. This made them realize that Mirror needed a dedicated place in their classroom. This newly minted reflection station helps students easily build their reflective skills.
After a student records a reflection with Mirror, Mirror’s AI generates immediate feedback based on the student’s response. Each piece of feedback includes something a student did well, and offers an unbiased insight into how students can improve.
Data grounded in education research and theory
As part of the feedback Mirror offers, teachers can access a dashboard containing individualized reflection cards for each student reflection. To generate the data on each card Mirror’s AI measures the student’s reflection against education research and theories from Piaget, Kegan, Erikson, Vygotsky, CASEL, and more.
Minutes after a student completes a reflection, teachers are able to dive into the data. Mirror presents an overall reflection score comprising sentiment, tone, and mindset scoring. It clearly lays out how a student understood the objective of the reflection, to name a few of the data points.
“I found the teacher dashboard extremely helpful! The color coding on each student’s reflection that assessed their tone meant I could easily see the students that were having a really good day. On the students where the analysis was red, I immediately knew where I needed to focus more one-on-one time.”
Helping students demonstrate how they are thinking
Mirror is helping Christy and Kim better understand the thinking patterns of each of their students. Mirror isn’t a linear assessment. Mirror is enabling Kim and Christy to see a better representation of their students’ thinking processes – in their words, “We’re able to see the students who always think outside of the box, and the students who need more support to think outside of the box.” For Kleb Intermediate School they have found a solution that provides better opportunities for students to process concepts and themes while expressing the depth of their thinking.
Read more about how Klein ISD educators are using Mirror
- Klein ISD – Monica Shallenberger, the Instructional Specialist in Digital Learning for the Klein Independent School District, uses Mirror to support her teachers amidst stringent state budgets.
- Hildebrandt Intermediate School – Sarah Marin uses Mirror in her 7th-grade English classroom for project-based learning assessments.
Interested in seeing how Mirror can support your students and teachers? Sign up to participate in a 30-day, free demo of Mirror.
- International information
- Early childhood education
- New teacher programs
- 30-Day Mirror demo
Senior Director for Research, Medical School Office of Research
How to apply.
A cover letter is required for consideration for this position and should be attached as the first page of your resume. The cover letter should address your specific interest in the position and outline skills and experience that directly relate to this position.
Mission Statement
Michigan Medicine improves the health of patients, populations and communities through excellence in education, patient care, community service, research and technology development, and through leadership activities in Michigan, nationally and internationally. Our mission is guided by our Strategic Principles and has three critical components; patient care, education and research that together enhance our contribution to society.
Responsibilities*
Reporting directly to the Executive Vice Dean for Research/Chief Scientific Officer (CSO), the Senior Director for Research will serve as the chief administrator and business manager of the Medical School Office of Research. This individual will be a key member of the Office of Research leadership team and advisor to the Executive Vice Dean for Research/CSO and will have additional accountability to the Executive Director of Administration and Chief Operating Officer for the Medical School.
The Senior Director is responsible for the operational and fiscal management of the Medical School Office of Research, strategic programs, and reporting units, with a cumulative operation totaling nearly $90M and greater than 600 FTEs. The Senior Director oversees the fiscal, personnel, operational, and administrative activities of the Office of Research and its units. Examples of responsibilities include, but are not limited to, sound financial management (budget preparation and management); human resource management of managers and staff (including hiring, terminating, professional development, and conflict resolution); operational and administrative management; and designing business plans to cost-effectively sustain the infrastructure and offerings of the Office of Research. The selected candidate will be responsible for strategic planning, development, implementation, and assessment of short- and long-range objectives. They will also provide direct supervision, mentorship, and professional development for research directors.
The Senior Director will develop and implement:
- Research services and infrastructure to enable leading-edge research.
- Models of research productivity and impact using traditional and non-traditional measures to aid in the identification of research strengths and opportunities.
- Initiatives and service offerings, including review and evaluation of outcomes.
- Administrative and research policies, procedures, and operational issues for the research enterprise.
- Innovative strategies to support faculty, streamline research processes, and reduce administrative burden.
- Key performance indicators.
They will oversee micro and macro assessments of the economic drivers that impact the research enterprise to inform strategic and tactical planning and lead change to facilitate adoption of new initiatives, policies, and practices.
The Senior Director is expected to manage complex situations and multiple responsibilities simultaneously, mixing longer-term projects with the urgency of immediate demands. They must exercise discretion and demonstrate the ability to respect highly confidential information and act as a liaison between the Executive Vice Dean for Research/CSO and other internal and external constituencies.
The selected candidate will possess the skills to collaborate with and achieve actionable results through others, demonstrate the ability to build strong sustainable relationships, and exhibit the capability to interact with colleagues at all levels of the institution.
The Senior Director represents the Office of Research on institutional working groups and committees to advance the mission of the Medical School and university. Additionally, they will work closely with the Administrative Senior Directors of the Medical School as part of the Senior Administrative Staff team, on institution wide initiatives and deliverables. They are expected to be a strong, effective communicator with the ability to distill complex information into actionable steps, including the ability to collect and analyze data, interpret results, and prepare subsequent communications to inform Medical School leadership.
As a member of a greater team, the selected candidate will be called upon to perform other duties as assigned.
Required Qualifications*
- A bachelor's degree, or equivalent combination of education and experience, with practical work experience in the biomedical sciences and deep knowledge of a large research enterprise such as at an academic health center or equivalent.
- A minimum of five years of senior management experience with proven business acumen, preferably in a biomedical research or health care-related setting.
- Demonstrated experience with responsibility and accountability for the daily operations of many units, including priority setting and financial and human resources management.
- Successful experience leading and managing a complex team of multiple professionals, including hiring, setting direction and expectations, coaching and developing, assessing, and providing formal and informal performance feedback.
- Demonstrated leadership and change management skills needed to successfully develop new initiatives, change culture, and foster strong partnerships and collaborations across all levels of the university.
- Ability to build strong interpersonal relationships and trust with all constituents.
- Excellent written, verbal, and presentation skills.
- Competency in organizational navigation and ability to deal effectively and persuasively with individuals of varying levels of institutional authority.
- Ability to use astute judgment, think strategically, analyze logically, and cogently present summaries and recommendations.
- Demonstrated poise, tact, diplomacy, and unquestionable integrity.
Desired Qualifications*
- Substantial familiarity with university standard practices and guidelines.
- Experience within an academic medical center, research institution, or healthcare related setting.
- Creates value for a diverse community by fostering a climate of service excellence.
- Leads in the alignment of Michigan Medicine culture by being organizationally astute and leveraging processes and relationships to succeed.
- Fosters and supports diverse teams and provides a work climate that is inclusive and elicits a high level of team engagement.
Background Screening
Michigan Medicine conducts background screening and pre-employment drug testing on job candidates upon acceptance of a contingent job offer and may use a third party administrator to conduct background screenings. Background screenings are performed in compliance with the Fair Credit Report Act. Pre-employment drug testing applies to all selected candidates, including new or additional faculty and staff appointments, as well as transfers from other U-M campuses.
Application Deadline
Job openings are posted for a minimum of seven calendar days. The review and selection process may begin as early as the eighth day after posting. This opening may be removed from posting boards and filled anytime after the minimum posting period has ended.
U-M EEO/AA Statement
The University of Michigan is an equal opportunity/affirmative action employer.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Abstract. Extra-curricular activities including clubs, fraternities and societies have been part of the fabric of higher level institutions since their origin. A significant body of educational research has investigated the impact of these activities on academic performance and the acquisition of discipline complementary skills and competencies.
A research title about school issues focuses on activities surrounding the school environment and its effects on students, teachers, parents, and education in general. Below are some sample research titles in education, relating to school issues.
A comprehensive list of research topics and ideas in education, along with a list of existing dissertations & theses covering education.
Looking for education research topics? 🎓 Here, you'll find qualitative quantitative research topics in education, including child development & more.
The multi-disciplinary nature of science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) careers often renders difficulty for high school students navigating from classroom knowledge to post-secondary ...
Schools offer a unique environment to influence children's physical activity (PA) levels positively. This study aims to systematically review the evidence surrounding how PA affects academic performance by analysing how the frequency, intensity, ...
PDF | On Jan 1, 2020, Roden Torrena Lacanilao published Stakeholders' Participation in School Activities in Public Secondary Schools in Los Baños, Laguna | Find, read and cite all the research ...
This review presents a reasoned synthesis of whole-school interventions seeking to improve the overall school environment by fostering active student participation (ASP) in school activities and decision-making processes.
In this paper, we aim to describe the potential benefits of conducting research on the impact of physically active high school classrooms and to highlight the challenges and possible misconceptions related to conducting this research. The following paper discusses (1) the role of physical activity in supporting adolescent neurocognitive and ...
Learn how to teach research skills to primary students, middle school students, or high school students. 50 activities that could be done in just a few minutes a day. Lots of Google search tips and research tips for kids and teachers.
Title: The Graduate School University of Wisconsin-Stout Menomonie, WI Wilson, Nikki L. Impact of Extracurricular Activities on Students Graduate Degree/ Major: MS School Counseling Research Adviser: Carol Johnson, Ph.D. MonthfVear: May, 2009 Number of Pages: 39 Style Manual Used: American Psychological Association, 5th edition ABSTRACT
This article serves as a quantitative review of classroom physical activity interventions in terms of their physical activity, health and learning outcomes for students, with implications of ...
The aims and objectives of this action research are to: To improve students' active participation in classroom teaching and learning. To explore the reasons why students hardly take part in ...
Find the perfect research topic for your dissertation or thesis. Get the FREE list of 1000+ research ideas plus our proposal template!
Looking for a research title about education? 🎓 Check our list of education research topics! ️ Special education, ️ child development, ️ school issues, & more.
Master the art of crafting 200+ research title ideas with our comprehensive guide. Elevate your scholarly impact today!
Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper Michele McCarthy Department of Health Science and Recreation San José State University Lesson: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper ... Show the title of the lesson plan on PowerPoint slide number one. [2 minutes]
In this post, we will explore some of the most compelling qualitative research topics and provide some tips on how to conduct effective qualitative research. Qualitative Research Titles. Qualitative research titles often reflect the study's focus on understanding the depth and complexity of human behavior, experiences, or social phenomena.
Are you brainstorming for excellent qualitative research titles for your high school curriculum? If yes, then this blog is for you! Academic life throws a lot of thesis and qualitative research papers and essays at you.
Abstract. Schools are an important context for both basic and applied scientific research. Unlike the laboratory, however, the physical and social conditions of schools are not under the exclusive control of scientists. In this article, we liken collecting data in schools to putting on a theatrical production.
Catherine's book is a fantastic resource for anyone who is teaching research methods in the social sciences. Covering all aspects of the research process, it is packed full of innovative ideas, useful tips, and structured activities for use within the classroom.
197 votes, 91 comments. Hi all! Arnold's back with more advice and The Arnold GuideTM that will focus on both how to write your activity section. As…
Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships among variables. This method is widely used in social sciences, psychology, economics, and other fields where researchers aim to understand human behavior and phenomena through statistical analysis.
As an innovative Instructional Specialist in Digital Learning for Kleb Intermediate School, Kim Sharp wanted to find new ways to gain insights into her students' learning and growth. She decided to explore tech solutions that qualified for Title 1 funding. Her research led to Swivl's new interactive reflection station, Mirror.
The Senior Director oversees the fiscal, personnel, operational, and administrative activities of the Office of Research and its units. Examples of responsibilities include, but are not limited to, sound financial management (budget preparation and management); human resource management of managers and staff (including hiring, terminating ...