How to Write a History Essay with Outline, Tips, Examples and More

Before we get into how to write a history essay, let's first understand what makes one good. Different people might have different ideas, but there are some basic rules that can help you do well in your studies. In this guide, we won't get into any fancy theories. Instead, we'll give you straightforward tips to help you with historical writing. So, if you're ready to sharpen your writing skills, let our history essay writing service explore how to craft an exceptional paper.

What is a History Essay?
A history essay is an academic assignment where we explore and analyze historical events from the past. We dig into historical stories, figures, and ideas to understand their importance and how they've shaped our world today. History essay writing involves researching, thinking critically, and presenting arguments based on evidence.
Moreover, history papers foster the development of writing proficiency and the ability to communicate complex ideas effectively. They also encourage students to engage with primary and secondary sources, enhancing their research skills and deepening their understanding of historical methodology.
History Essay Outline
.png)
The outline is there to guide you in organizing your thoughts and arguments in your essay about history. With a clear outline, you can explore and explain historical events better. Here's how to make one:
Introduction
- Hook: Start with an attention-grabbing opening sentence or anecdote related to your topic.
- Background Information: Provide context on the historical period, event, or theme you'll be discussing.
- Thesis Statement: Present your main argument or viewpoint, outlining the scope and purpose of your history essay.
Body paragraph 1: Introduction to the Historical Context
- Provide background information on the historical context of your topic.
- Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay.
Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence
- Each paragraph should focus on a specific argument or aspect of your thesis.
- Present evidence from primary and secondary sources to support each argument.
- Analyze the significance of the evidence and its relevance to your history paper thesis.
Counterarguments (optional)
- Address potential counterarguments or alternative perspectives on your topic.
- Refute opposing viewpoints with evidence and logical reasoning.
- Summary of Main Points: Recap the main arguments presented in the body paragraphs.
- Restate Thesis: Reinforce your thesis statement, emphasizing its significance in light of the evidence presented.
- Reflection: Reflect on the broader implications of your arguments for understanding history.
- Closing Thought: End your history paper with a thought-provoking statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
References/bibliography
- List all sources used in your research, formatted according to the citation style required by your instructor (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
- Include both primary and secondary sources, arranged alphabetically by the author's last name.
Notes (if applicable)
- Include footnotes or endnotes to provide additional explanations, citations, or commentary on specific points within your history essay.
History Essay Format
Adhering to a specific format is crucial for clarity, coherence, and academic integrity. Here are the key components of a typical history essay format:
Font and Size
- Use a legible font such as Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri.
- The recommended font size is usually 12 points. However, check your instructor's guidelines, as they may specify a different size.
- Set 1-inch margins on all sides of the page.
- Double-space the entire essay, including the title, headings, body paragraphs, and references.
- Avoid extra spacing between paragraphs unless specified otherwise.
- Align text to the left margin; avoid justifying the text or using a centered alignment.
Title Page (if required):
- If your instructor requires a title page, include the essay title, your name, the course title, the instructor's name, and the date.
- Center-align this information vertically and horizontally on the page.
- Include a header on each page (excluding the title page if applicable) with your last name and the page number, flush right.
- Some instructors may require a shortened title in the header, usually in all capital letters.
- Center-align the essay title at the top of the first page (if a title page is not required).
- Use standard capitalization (capitalize the first letter of each major word).
- Avoid underlining, italicizing, or bolding the title unless necessary for emphasis.
Paragraph Indentation:
- Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches or use the tab key.
- Do not insert extra spaces between paragraphs unless instructed otherwise.
Citations and References:
- Follow the citation style specified by your instructor (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago).
- Include in-text citations whenever you use information or ideas from external sources.
- Provide a bibliography or list of references at the end of your history essay, formatted according to the citation style guidelines.
- Typically, history essays range from 1000 to 2500 words, but this can vary depending on the assignment.

How to Write a History Essay?
Historical writing can be an exciting journey through time, but it requires careful planning and organization. In this section, we'll break down the process into simple steps to help you craft a compelling and well-structured history paper.
Analyze the Question
Before diving headfirst into writing, take a moment to dissect the essay question. Read it carefully, and then read it again. You want to get to the core of what it's asking. Look out for keywords that indicate what aspects of the topic you need to focus on. If you're unsure about anything, don't hesitate to ask your instructor for clarification. Remember, understanding how to start a history essay is half the battle won!
Now, let's break this step down:
- Read the question carefully and identify keywords or phrases.
- Consider what the question is asking you to do – are you being asked to analyze, compare, contrast, or evaluate?
- Pay attention to any specific instructions or requirements provided in the question.
- Take note of the time period or historical events mentioned in the question – this will give you a clue about the scope of your history essay.
Develop a Strategy
With a clear understanding of the essay question, it's time to map out your approach. Here's how to develop your historical writing strategy:
- Brainstorm ideas : Take a moment to jot down any initial thoughts or ideas that come to mind in response to the history paper question. This can help you generate a list of potential arguments, themes, or points you want to explore in your history essay.
- Create an outline : Once you have a list of ideas, organize them into a logical structure. Start with a clear introduction that introduces your topic and presents your thesis statement – the main argument or point you'll be making in your history essay. Then, outline the key points or arguments you'll be discussing in each paragraph of the body, making sure they relate back to your thesis. Finally, plan a conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces your history paper thesis.
- Research : Before diving into writing, gather evidence to support your arguments. Use reputable sources such as books, academic journals, and primary documents to gather historical evidence and examples. Take notes as you research, making sure to record the source of each piece of information for proper citation later on.
- Consider counterarguments : Anticipate potential counterarguments to your history paper thesis and think about how you'll address them in your essay. Acknowledging opposing viewpoints and refuting them strengthens your argument and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Set realistic goals : Be realistic about the scope of your history essay and the time you have available to complete it. Break down your writing process into manageable tasks, such as researching, drafting, and revising, and set deadlines for each stage to stay on track.

Start Your Research
Now that you've grasped the history essay topic and outlined your approach, it's time to dive into research. Here's how to start:
- Ask questions : What do you need to know? What are the key points to explore further? Write down your inquiries to guide your research.
- Explore diverse sources : Look beyond textbooks. Check academic journals, reliable websites, and primary sources like documents or artifacts.
- Consider perspectives : Think about different viewpoints on your topic. How have historians analyzed it? Are there controversies or differing interpretations?
- Take organized notes : Summarize key points, jot down quotes, and record your thoughts and questions. Stay organized using spreadsheets or note-taking apps.
- Evaluate sources : Consider the credibility and bias of each source. Are they peer-reviewed? Do they represent a particular viewpoint?
Establish a Viewpoint
By establishing a clear viewpoint and supporting arguments, you'll lay the foundation for your compelling historical writing:
- Review your research : Reflect on the information gathered. What patterns or themes emerge? Which perspectives resonate with you?
- Formulate a thesis statement : Based on your research, develop a clear and concise thesis that states your argument or interpretation of the topic.
- Consider counterarguments : Anticipate objections to your history paper thesis. Are there alternative viewpoints or evidence that you need to address?
- Craft supporting arguments : Outline the main points that support your thesis. Use evidence from your research to strengthen your arguments.
- Stay flexible : Be open to adjusting your viewpoint as you continue writing and researching. New information may challenge or refine your initial ideas.
Structure Your Essay
Now that you've delved into the depths of researching historical events and established your viewpoint, it's time to craft the skeleton of your essay: its structure. Think of your history essay outline as constructing a sturdy bridge between your ideas and your reader's understanding. How will you lead them from point A to point Z? Will you follow a chronological path through history or perhaps dissect themes that span across time periods?
And don't forget about the importance of your introduction and conclusion—are they framing your narrative effectively, enticing your audience to read your paper, and leaving them with lingering thoughts long after they've turned the final page? So, as you lay the bricks of your history essay's architecture, ask yourself: How can I best lead my audience through the maze of time and thought, leaving them enlightened and enriched on the other side?
Create an Engaging Introduction
Creating an engaging introduction is crucial for capturing your reader's interest right from the start. But how do you do it? Think about what makes your topic fascinating. Is there a surprising fact or a compelling story you can share? Maybe you could ask a thought-provoking question that gets people thinking. Consider why your topic matters—what lessons can we learn from history?
Also, remember to explain what your history essay will be about and why it's worth reading. What will grab your reader's attention and make them want to learn more? How can you make your essay relevant and intriguing right from the beginning?
Develop Coherent Paragraphs
Once you've established your introduction, the next step is to develop coherent paragraphs that effectively communicate your ideas. Each paragraph should focus on one main point or argument, supported by evidence or examples from your research. Start by introducing the main idea in a topic sentence, then provide supporting details or evidence to reinforce your point.
Make sure to use transition words and phrases to guide your reader smoothly from one idea to the next, creating a logical flow throughout your history essay. Additionally, consider the organization of your paragraphs—is there a clear progression of ideas that builds upon each other? Are your paragraphs unified around a central theme or argument?
Conclude Effectively
Concluding your history essay effectively is just as important as starting it off strong. In your conclusion, you want to wrap up your main points while leaving a lasting impression on your reader. Begin by summarizing the key points you've made throughout your history essay, reminding your reader of the main arguments and insights you've presented.
Then, consider the broader significance of your topic—what implications does it have for our understanding of history or for the world today? You might also want to reflect on any unanswered questions or areas for further exploration. Finally, end with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action that encourages your reader to continue thinking about the topic long after they've finished reading.
Reference Your Sources
Referencing your sources is essential for maintaining the integrity of your history essay and giving credit to the scholars and researchers who have contributed to your understanding of the topic. Depending on the citation style required (such as MLA, APA, or Chicago), you'll need to format your references accordingly. Start by compiling a list of all the sources you've consulted, including books, articles, websites, and any other materials used in your research.
Then, as you write your history essay, make sure to properly cite each source whenever you use information or ideas that are not your own. This includes direct quotations, paraphrases, and summaries. Remember to include all necessary information for each source, such as author names, publication dates, and page numbers, as required by your chosen citation style.
Review and Ask for Advice
As you near the completion of your history essay writing, it's crucial to take a step back and review your work with a critical eye. Reflect on the clarity and coherence of your arguments—are they logically organized and effectively supported by evidence? Consider the strength of your introduction and conclusion—do they effectively capture the reader's attention and leave a lasting impression? Take the time to carefully proofread your history essay for any grammatical errors or typos that may detract from your overall message.
Furthermore, seeking advice from peers, mentors, or instructors can provide valuable insights and help identify areas for improvement. Consider sharing your essay with someone whose feedback you trust and respect, and be open to constructive criticism. Ask specific questions about areas you're unsure about or where you feel your history essay may be lacking.
History Essay Example
In this section, we offer an example of a history essay examining the impact of the Industrial Revolution on society. This essay demonstrates how historical analysis and critical thinking are applied in academic writing. By exploring this specific event, you can observe how historical evidence is used to build a cohesive argument and draw meaningful conclusions.

FAQs about History Essay Writing
How to write a history essay introduction, how to write a conclusion for a history essay, how to write a good history essay.

- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support

How to Write an Introduction For a History Essay Step-by-Step

An introduction of a historical essay acquaints the reader with the topic and how the writer will explain it. It is an important first impression. The introduction is a paragraph long and about five to seven sentences. The parts include the opening sentence, arguments and/or details that will be covered, and a thesis statement (argument of the essay).
What Is A History Essay?
An essay is a short piece of writing that answers a question (“Who are the funniest presidents ”) discusses a subject (“What is Japanese feudalism ”), or addresses a topic (“ Causes and Effects of the Industrial Revolution ”). A historical essay specifically addresses historical matters.
These essays are used to judge a student’s progress in understanding history. They also are used to teach and analyze a student’s ability to write and express their knowledge. A person can know their stuff and still have problems expressing their knowledge.
Skillful communication is an essential tool. When you write your introduction to a historical essay remember that both the information and how you express it are both very important.
Purpose of An Introduction
If a person is formally introduced to you, it is a means of getting acquainted.
An introduction of a historical essay acquaints the reader with the topic and how the writer will explain it. The introduction is a roadmap that lays out the direction you will take in the essay.
This is done by the opening paragraph, which is about five to seven sentences long.
Grab the Reader’s Attention
The introduction of a historical essay should grab the attention of your reader.
It is the first time the reader has to react to your essay. Make sure it is clear, confident, and precise . The introduction should not be generic. It should not be vague.
Do not provide sources in the introduction. You do not want the reader to check them out instead of finishing the introduction. Leave sources to the body of the essay.
When Should You Write The Introduction?
A movie is not filmed straight through. Parts of a movie are filmed separately and later edited together. This is also possible when writing an essay, especially with the ease of computers.
An introduction works off the rest of the essay. If you have already written the whole essay, it can be easier to write an introduction. I often write the blog summary on top last.
Others will find it useful to write the introduction first, perhaps because it provides a helpful outline for the rest of the essay. It is a matter of personal taste and comfort level.
Step-By-Step Instructions
Step one: opening sentence.
The first sentence of your introduction sets the stage and draws the reader in.
The opening sentence should introduce the historical context of the subject matter of your historical essay. Historical context is the political, social, cultural, and economic setting for a particular document, idea, or event. For instance, consider this opening sentence:
The Emancipation Proclamation was an official presidential declaration handed down in the middle of the Civil War declaring slavery was now abolished in areas under Confederate control.
A possible topic of the historical essay is “ The Strengths & Weaknesses of the Emancipation Proclamation .” This opening sentence sets the stage. We are no longer in the current day reading about something in the living room. We are in the middle of the Civil War.
There are various ways to start things off. For instance, you can use a quotation such as President Wilson’s or Winston Churchill’s famous sayings about democracy .
The important thing is to grab the reader’s attention and start the ball rolling. Know your audience. An academic audience expects a more studious approach. And, don’t just start with a catchy sentence that has no value to the rest of the historical essay.
Step Two: Facts/Statistics/Evidence
The next step in writing an introduction is to write a few sentences (three to five) summarizing the argument you will be making. These sentences would provide the facts and arguments that will be expanded upon in the body of the paper. The sentences are basically an outline.
If we continue with the previous subject, the summary section can be like this:
It was a major moral accomplishment to use the abolishment of slavery as a war measure. Meanwhile, it had pragmatic benefits, including as a matter of foreign policy, and harmed the South’s chances to win the war. Nonetheless, the measure was of questionable legality and had the possibility of causing major divisions.
The introduction should be clear and crisp. Try to remove unnecessary content. This is not just about filling a word quota. The introduction should have actual content, not empty calories.
Step Three: Thesis Statement
The finale of the introduction is the thesis statement , the argument being made in the essay. This should be one sentence long. An example would be:
The Emancipation Proclamation was as a whole very successful while having various disadvantages that still made it a risky proposition.
The thesis sentence is very important. It summarizes the core of the essay. The reader is now informed about what you are about to argue. The body of the essay should fill in the details.
In Conclusion About Introductions …
An introduction at a party, date, or in a historical essay is about making a good first impression. The basics are the same. Catch the other person’s attention, provide a snapshot of what you are trying to say, and make the person hungry for more.
The other person often has the obligation to “hear” what you have to say. Take it as an opportunity. And, remember, if you mess up, it will be a lot harder to impress later on.
Teach and Thrive
A Bronx, NY veteran high school social studies teacher who has learned most of what she has learned through trial and error and error and error.... and wants to save others that pain.
RELATED ARTICLES:
How to Write a Conclusion For a History Essay Step-by-Step
A historical essay is a short piece of writing that answers a question or addresses a topic. It shows a student’s historical knowledge and ability to express themselves. The conclusion is a...
The Ultimate Guide to Crafting a Winning Historical Essay Body: Tips and Tricks for Success
A historical essay answers a question or addresses a specific topic. The format is like a sandwich: a body cushioned between the introduction and conclusion paragraphs. Each body paragraph is a...

Introductions & Conclusions
The introduction and conclusion serve important roles in a history paper. They are not simply perfunctory additions in academic writing, but are critical to your task of making a persuasive argument.
A successful introduction will:
- draw your readers in
- culminate in a thesis statement that clearly states your argument
- orient your readers to the key facts they need to know in order to understand your thesis
- lay out a roadmap for the rest of your paper
A successful conclusion will:
- draw your paper together
- reiterate your argument clearly and forcefully
- leave your readers with a lasting impression of why your argument matters or what it brings to light
How to write an effective introduction:
Often students get slowed down in paper-writing because they are not sure how to write the introduction. Do not feel like you have to write your introduction first simply because it is the first section of your paper. You can always come back to it after you write the body of your essay. Whenever you approach your introduction, think of it as having three key parts:
- The opening line
- The middle “stage-setting” section
- The thesis statement
“In a 4-5 page paper, describe the process of nation-building in one Middle Eastern state. What were the particular goals of nation-building? What kinds of strategies did the state employ? What were the results? Be specific in your analysis, and draw on at least one of the scholars of nationalism that we discussed in class.”
Here is an example of a WEAK introduction for this prompt:
“One of the most important tasks the leader of any country faces is how to build a united and strong nation. This has been especially true in the Middle East, where the country of Jordan offers one example of how states in the region approached nation-building. Founded after World War I by the British, Jordan has since been ruled by members of the Hashemite family. To help them face the difficult challenges of founding a new state, they employed various strategies of nation-building.”
Now, here is a REVISED version of that same introduction:
“Since 1921, when the British first created the mandate of Transjordan and installed Abdullah I as its emir, the Hashemite rulers have faced a dual task in nation-building. First, as foreigners to the region, the Hashemites had to establish their legitimacy as Jordan’s rightful leaders. Second, given the arbitrary boundaries of the new nation, the Hashemites had to establish the legitimacy of Jordan itself, binding together the people now called ‘Jordanians.’ To help them address both challenges, the Hashemite leaders crafted a particular narrative of history, what Anthony Smith calls a ‘nationalist mythology.’ By presenting themselves as descendants of the Prophet Muhammad, as leaders of the Arab Revolt, and as the fathers of Jordan’s different tribal groups, they established the authority of their own regime and the authority of the new nation, creating one of the most stable states in the modern Middle East.”
The first draft of the introduction, while a good initial step, is not strong enough to set up a solid, argument-based paper. Here are the key issues:
- This first sentence is too general. From the beginning of your paper, you want to invite your reader into your specific topic, rather than make generalizations that could apply to any nation in any time or place. Students often run into the problem of writing general or vague opening lines, such as, “War has always been one of the greatest tragedies to befall society.” Or, “The Great Depression was one of the most important events in American history.” Avoid statements that are too sweeping or imprecise. Ask yourself if the sentence you have written can apply in any time or place or could apply to any event or person. If the answer is yes, then you need to make your opening line more specific.
- Here is the revised opening line: “Since 1921, when the British first created the mandate of Transjordan and installed Abdullah I as its emir, the Hashemite rulers have faced a dual task in nation-building.”
- This is a stronger opening line because it speaks precisely to the topic at hand. The paper prompt is not asking you to talk about nation-building in general, but nation-building in one specific place.
- This stage-setting section is also too general. Certainly, such background information is critical for the reader to know, but notice that it simply restates much of the information already in the prompt. The question already asks you to pick one example, so your job is not simply to reiterate that information, but to explain what kind of example Jordan presents. You also need to tell your reader why the context you are providing matters.
- Revised stage-setting: “First, as foreigners to the region, the Hashemites had to establish their legitimacy as Jordan’s rightful leaders. Second, given the arbitrary boundaries of the new nation, the Hashemites had to establish the legitimacy of Jordan itself, binding together the people now called ‘Jordanians.’ To help them address both challenges, the Hashemite rulers crafted a particular narrative of history, what Anthony Smith calls a ‘nationalist mythology.’”
- This stage-setting is stronger because it introduces the reader to the problem at hand. Instead of simply saying when and why Jordan was created, the author explains why the manner of Jordan’s creation posed particular challenges to nation-building. It also sets the writer up to address the questions in the prompt, getting at both the purposes of nation-building in Jordan and referencing the scholar of nationalism s/he will be drawing on from class: Anthony Smith.
- This thesis statement restates the prompt rather than answers the question. You need to be specific about what strategies of nation-building Jordan’s leaders used. You also need to assess those strategies, so that you can answer the part of the prompt that asks about the results of nation-building.
- Revised thesis statement: “By presenting themselves as descendants of the Prophet Muhammad, as leaders of the Arab Revolt, and as the fathers of Jordan’s different tribal groups, they established the authority of their regime and the authority of the new nation, creating one of the most stable states in the modern Middle East.”
- It directly answers the question in the prompt. Even though you will be persuading readers of your argument through the evidence you present in the body of your paper, you want to tell them at the outset exactly what you are arguing.
- It discusses the significance of the argument, saying that Jordan created an especially stable state. This helps you answer the question about the results of Jordan’s nation-building project.
- It offers a roadmap for the rest of the paper. The writer knows how to proceed and the reader knows what to expect. The body of the paper will discuss the Hashemite claims “as descendants from the Prophet Muhammad, as leaders of the Arab Revolt, and as the fathers of Jordan’s different tribal groups.”
If you write your introduction first, be sure to revisit it after you have written your entire essay. Because your paper will evolve as you write, you need to go back and make sure that the introduction still sets up your argument and still fits your organizational structure.
How to write an effective conclusion:
Your conclusion serves two main purposes. First, it reiterates your argument in different language than you used in the thesis and body of your paper. Second, it tells your reader why your argument matters. In your conclusion, you want to take a step back and consider briefly the historical implications or significance of your topic. You will not be introducing new information that requires lengthy analysis, but you will be telling your readers what your paper helps bring to light. Perhaps you can connect your paper to a larger theme you have discussed in class, or perhaps you want to pose a new sort of question that your paper elicits. There is no right or wrong “answer” to this part of the conclusion: you are now the “expert” on your topic, and this is your chance to leave your reader with a lasting impression based on what you have learned.
Here is an example of an effective conclusion for the same essay prompt:
“To speak of the nationalist mythology the Hashemites created, however, is not to say that it has gone uncontested. In the 1950s, the Jordanian National Movement unleashed fierce internal opposition to Hashemite rule, crafting an alternative narrative of history in which the Hashemites were mere puppets to Western powers. Various tribes have also reasserted their role in the region’s past, refusing to play the part of “sons” to Hashemite “fathers.” For the Hashemites, maintaining their mythology depends on the same dialectical process that John R. Gillis identified in his investigation of commemorations: a process of both remembering and forgetting. Their myth remembers their descent from the Prophet, their leadership of the Arab Revolt, and the tribes’ shared Arab and Islamic heritage. It forgets, however, the many different histories that Jordanians champion, histories that the Hashemite mythology has never been able to fully reconcile.”
This is an effective conclusion because it moves from the specific argument addressed in the body of the paper to the question of why that argument matters. The writer rephrases the argument by saying, “Their myth remembers their descent from the Prophet, their leadership of the Arab Revolt, and the tribes’ shared Arab and Islamic heritage.” Then, the writer reflects briefly on the larger implications of the argument, showing how Jordan’s nationalist mythology depended on the suppression of other narratives.
Introduction and Conclusion checklist
When revising your introduction and conclusion, check them against the following guidelines:
Does my introduction:
- draw my readers in?
- culminate in a thesis statement that clearly states my argument?
- orient my readers to the key facts they need to know in order to understand my thesis?
- lay out a roadmap for the rest of my paper?
Does my conclusion:
- draw my paper together?
- reiterate my argument clearly and forcefully?
- leave my readers with a lasting impression of why my argument matters or what it brings to light?
Download as PDF

6265 Bunche Hall Box 951473 University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90095-1473 Phone: (310) 825-4601
Other Resources
- UCLA Library
- Faculty Intranet
- Department Forms
- Office 365 Email
- Remote Help
Campus Resources
- Maps, Directions, Parking
- Academic Calendar
- University of California
- Terms of Use
Social Sciences Division Departments
- Aerospace Studies
- African American Studies
- American Indian Studies
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Asian American Studies
- César E. Chávez Department of Chicana & Chicano Studies
- Communication
- Conservation
- Gender Studies
- Military Science
- Naval Science
- Political Science
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a History Essay
Last Updated: December 27, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA . Emily Listmann is a private tutor in San Carlos, California. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 243,395 times.
Writing a history essay requires you to include a lot of details and historical information within a given number of words or required pages. It's important to provide all the needed information, but also to present it in a cohesive, intelligent way. Know how to write a history essay that demonstrates your writing skills and your understanding of the material.
Preparing to Write Your Essay

- The key words will often need to be defined at the start of your essay, and will serve as its boundaries. [2] X Research source
- For example, if the question was "To what extent was the First World War a Total War?", the key terms are "First World War", and "Total War".
- Do this before you begin conducting your research to ensure that your reading is closely focussed to the question and you don't waste time.

- Explain: provide an explanation of why something happened or didn't happen.
- Interpret: analyse information within a larger framework to contextualise it.
- Evaluate: present and support a value-judgement.
- Argue: take a clear position on a debate and justify it. [3] X Research source

- Your thesis statement should clearly address the essay prompt and provide supporting arguments. These supporting arguments will become body paragraphs in your essay, where you’ll elaborate and provide concrete evidence. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Your argument may change or become more nuanced as your write your essay, but having a clear thesis statement which you can refer back to is very helpful.
- For example, your summary could be something like "The First World War was a 'total war' because civilian populations were mobilized both in the battlefield and on the home front".

- Pick out some key quotes that make your argument precisely and persuasively. [5] X Research source
- When writing your plan, you should already be thinking about how your essay will flow, and how each point will connect together.
Doing Your Research

- Primary source material refers to any texts, films, pictures, or any other kind of evidence that was produced in the historical period, or by someone who participated in the events of the period, that you are writing about.
- Secondary material is the work by historians or other writers analysing events in the past. The body of historical work on a period or event is known as the historiography.
- It is not unusual to write a literature review or historiographical essay which does not directly draw on primary material.
- Typically a research essay would need significant primary material.

- Start with the core texts in your reading list or course bibliography. Your teacher will have carefully selected these so you should start there.
- Look in footnotes and bibliographies. When you are reading be sure to pay attention to the footnotes and bibliographies which can guide you to further sources a give you a clear picture of the important texts.
- Use the library. If you have access to a library at your school or college, be sure to make the most of it. Search online catalogues and speak to librarians.
- Access online journal databases. If you are in college it is likely that you will have access to academic journals online. These are an excellent and easy to navigate resources.
- Use online sources with discretion. Try using free scholarly databases, like Google Scholar, which offer quality academic sources, but avoid using the non-trustworthy websites that come up when you simply search your topic online.
- Avoid using crowd-sourced sites like Wikipedia as sources. However, you can look at the sources cited on a Wikipedia page and use them instead, if they seem credible.

- Who is the author? Is it written by an academic with a position at a University? Search for the author online.
- Who is the publisher? Is the book published by an established academic press? Look in the cover to check the publisher, if it is published by a University Press that is a good sign.
- If it's an article, where is published? If you are using an article check that it has been published in an academic journal. [8] X Research source
- If the article is online, what is the URL? Government sources with .gov addresses are good sources, as are .edu sites.

- Ask yourself why the author is making this argument. Evaluate the text by placing it into a broader intellectual context. Is it part of a certain tradition in historiography? Is it a response to a particular idea?
- Consider where there are weaknesses and limitations to the argument. Always keep a critical mindset and try to identify areas where you think the argument is overly stretched or the evidence doesn't match the author's claims. [9] X Research source

- Label all your notes with the page numbers and precise bibliographic information on the source.
- If you have a quote but can't remember where you found it, imagine trying to skip back through everything you have read to find that one line.
- If you use something and don't reference it fully you risk plagiarism. [10] X Research source
Writing the Introduction

- For example you could start by saying "In the First World War new technologies and the mass mobilization of populations meant that the war was not fought solely by standing armies".
- This first sentences introduces the topic of your essay in a broad way which you can start focus to in on more.

- This will lead to an outline of the structure of your essay and your argument.
- Here you will explain the particular approach you have taken to the essay.
- For example, if you are using case studies you should explain this and give a brief overview of which case studies you will be using and why.

Writing the Essay

- Try to include a sentence that concludes each paragraph and links it to the next paragraph.
- When you are organising your essay think of each paragraph as addressing one element of the essay question.
- Keeping a close focus like this will also help you avoid drifting away from the topic of the essay and will encourage you to write in precise and concise prose.
- Don't forget to write in the past tense when referring to something that has already happened.

- Don't drop a quote from a primary source into your prose without introducing it and discussing it, and try to avoid long quotations. Use only the quotes that best illustrate your point.
- If you are referring to a secondary source, you can usually summarise in your own words rather than quoting directly.
- Be sure to fully cite anything you refer to, including if you do not quote it directly.

- Think about the first and last sentence in every paragraph and how they connect to the previous and next paragraph.
- Try to avoid beginning paragraphs with simple phrases that make your essay appear more like a list. For example, limit your use of words like: "Additionally", "Moreover", "Furthermore".
- Give an indication of where your essay is going and how you are building on what you have already said. [15] X Research source

- Briefly outline the implications of your argument and it's significance in relation to the historiography, but avoid grand sweeping statements. [16] X Research source
- A conclusion also provides the opportunity to point to areas beyond the scope of your essay where the research could be developed in the future.
Proofreading and Evaluating Your Essay

- Try to cut down any overly long sentences or run-on sentences. Instead, try to write clear and accurate prose and avoid unnecessary words.
- Concentrate on developing a clear, simple and highly readable prose style first before you think about developing your writing further. [17] X Research source
- Reading your essay out load can help you get a clearer picture of awkward phrasing and overly long sentences. [18] X Research source

- When you read through your essay look at each paragraph and ask yourself, "what point this paragraph is making".
- You might have produced a nice piece of narrative writing, but if you are not directly answering the question it is not going to help your grade.

- A bibliography will typically have primary sources first, followed by secondary sources. [19] X Research source
- Double and triple check that you have included all the necessary references in the text. If you forgot to include a reference you risk being reported for plagiarism.
Sample Essay

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.historytoday.com/robert-pearce/how-write-good-history-essay
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/writing-a-good-history-paper
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/thesis_statement_tips.html
- ↑ http://history.rutgers.edu/component/content/article?id=106:writing-historical-essays-a-guide-for-undergraduates
- ↑ https://guides.lib.uw.edu/c.php?g=344285&p=2580599
- ↑ http://www.hamilton.edu/documents/writing-center/WritingGoodHistoryPaper.pdf
- ↑ http://www.bowdoin.edu/writing-guides/
- ↑ https://www.wgtn.ac.nz/hppi/publications/Writing-History-Essays.pdf
About This Article

To write a history essay, read the essay question carefully and use source materials to research the topic, taking thorough notes as you go. Next, formulate a thesis statement that summarizes your key argument in 1-2 concise sentences and create a structured outline to help you stay on topic. Open with a strong introduction that introduces your thesis, present your argument, and back it up with sourced material. Then, end with a succinct conclusion that restates and summarizes your position! For more tips on creating a thesis statement, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Lea Fernandez
Nov 23, 2017
Did this article help you?

Matthew Sayers
Mar 31, 2019
Millie Jenkerinx
Nov 11, 2017
Oct 18, 2019
Shannon Harper
Mar 9, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
How to Write a History Essay?
04 August, 2020
10 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
There are so many types of essays. It can be hard to know where to start. History papers aren’t just limited to history classes. These tasks can be assigned to examine any important historical event or a person. While they’re more common in history classes, you can find this type of assignment in sociology or political science course syllabus, or just get a history essay task for your scholarship. This is Handmadewriting History Essay Guide - let's start!

Purpose of a History Essay
Wondering how to write a history essay? First of all, it helps to understand its purpose. Secondly, this essay aims to examine the influences that lead to a historical event. Thirdly, it can explore the importance of an individual’s impact on history.
However, the goal isn’t to stay in the past. Specifically, a well-written history essay should discuss the relevance of the event or person to the “now”. After finishing this essay, a reader should have a fuller understanding of the lasting impact of an event or individual.
Need basic essay guidance? Find out what is an essay with this 101 essay guide: What is an Essay?
Elements for Success
Indeed, understanding how to write a history essay is crucial in creating a successful paper. Notably, these essays should never only outline successful historic events or list an individual’s achievements. Instead, they should focus on examining questions beginning with what , how , and why . Here’s a pro tip in how to write a history essay: brainstorm questions. Once you’ve got questions, you have an excellent starting point.
Preparing to Write

Evidently, a typical history essay format requires the writer to provide background on the event or person, examine major influences, and discuss the importance of the forces both then and now. In addition, when preparing to write, it’s helpful to organize the information you need to research into questions. For example:
- Who were the major contributors to this event?
- Who opposed or fought against this event?
- Who gained or lost from this event?
- Who benefits from this event today?
- What factors led up to this event?
- What changes occurred because of this event?
- What lasting impacts occurred locally, nationally, globally due to this event?
- What lessons (if any) were learned?
- Why did this event occur?
- Why did certain populations support it?
- Why did certain populations oppose it?
These questions exist as samples. Therefore, generate questions specific to your topic. Once you have a list of questions, it’s time to evaluate them.
Evaluating the Question

Seasoned writers approach writing history by examining the historic event or individual. Specifically, the goal is to assess the impact then and now. Accordingly, the writer needs to evaluate the importance of the main essay guiding the paper. For example, if the essay’s topic is the rise of American prohibition, a proper question may be “How did societal factors influence the rise of American prohibition during the 1920s? ”
This question is open-ended since it allows for insightful analysis, and limits the research to societal factors. Additionally, work to identify key terms in the question. In the example, key terms would be “societal factors” and “prohibition”.
Summarizing the Argument
The argument should answer the question. Use the thesis statement to clarify the argument and outline how you plan to make your case. In other words. the thesis should be sharp, clear, and multi-faceted. Consider the following tips when summarizing the case:
- The thesis should be a single sentence
- It should include a concise argument and a roadmap
- It’s always okay to revise the thesis as the paper develops
- Conduct a bit of research to ensure you have enough support for the ideas within the paper
Outlining a History Essay Plan

Once you’ve refined your argument, it’s time to outline. Notably, many skip this step to regret it then. Nonetheless, the outline is a map that shows where you need to arrive historically and when. Specifically, taking the time to plan, placing the strongest argument last, and identifying your sources of research is a good use of time. When you’re ready to outline, do the following:
- Consider the necessary background the reader should know in the introduction paragraph
- Define any important terms and vocabulary
- Determine which ideas will need the cited support
- Identify how each idea supports the main argument
- Brainstorm key points to review in the conclusion
Gathering Sources
As a rule, history essays require both primary and secondary sources . Primary resources are those that were created during the historical period being analyzed. Secondary resources are those created by historians and scholars about the topic. It’s a good idea to know if the professor requires a specific number of sources, and what kind he or she prefers. Specifically, most tutors prefer primary over secondary sources.
Where to find sources? Great question! Check out bibliographies included in required class readings. In addition, ask a campus Librarian. Peruse online journal databases; In addition, most colleges provide students with free access. When in doubt, make an appointment and ask the professor for guidance.
Writing the Essay
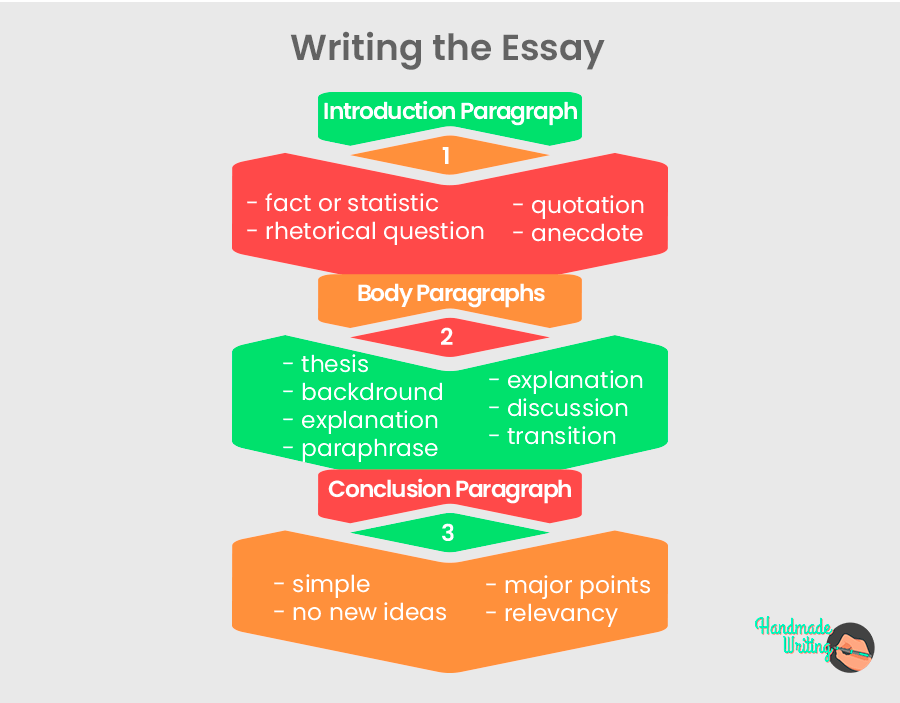
Now that you have prepared your questions, ideas, and arguments; composed the outline ; and gathered sources – it’s time to write your first draft. In particular, each section of your history essay must serve its purpose. Here is what you should include in essay paragraphs.
Introduction Paragraph
Unsure of how to start a history essay? Well, like most essays, the introduction should include an attention-getter (or hook):
- Relevant fact or statistic
- Rhetorical Question
- Interesting quotation
- Application anecdote if appropriate
Once you’ve captured the reader’s interest, introduce the topic. Similarly, present critical historic context. Namely, it is necessary to introduce any key individuals or events that will be discussed later in the essay. At last, end with a strong thesis which acts as a transition to the first argument.
Body Paragraphs
Indeed, each body paragraph should offer a single idea to support the argument. Then, after writing a strong topic sentence, the topic should be supported with correctly cited research. Consequently, a typical body paragraph is arranged as follows:
- Topic sentence linking to the thesis
- Background of the topic
- Research quotation or paraphrase #1
- Explanation and analysis of research
- Research quotation or paraphrase #2
- Transition to the next paragraph
Equally, the point of body paragraphs is to build the argument. Hence, present the weakest support first and end with the strongest. Admittedly, doing so leaves the reader with the best possible evidence.
Conclusion Paragraph
You’re almost there! Eventually, conclusion paragraphs should review the most important points in the paper. In them, you should prove that you’ve supported the argument proposed in the thesis. When writing a conclusion paragraph keep these tips in mind:
- Keep it simple
- Avoid introducing new information
- Review major points
- Discuss the relevance to today
Problems with writing Your History essay ? Try our Essay Writer Service!

Proofreading Your Essay
Once the draft is ready and polished, it’s time to proceed to final editing. What does this process imply? Specifically, it’s about removing impurities and making the essay look just perfect. Here’s what you need to do to improve the quality of your paper:
- Double check the content. In the first place, it’s recommended to get rid of long sentences, correct vague words. Also, make sure that all your paragrahps contain accurate sentences with transparent meaning.
- Pay attention to style. To make the process of digesting your essay easier, focus on crafting a paper with readable style, the one that is known to readers. Above all, the main mission here is to facilitate the perception of your essay. So, don’t forget about style accuracy.
- Practice reading the essay. Of course, the best practice before passing the paper is to read it out loud. Hence, this exercise will help you notice fragments that require rewriting or a complete removal.
History Essay Example
Did you want a history essay example? Take a look at one of our history essay papers.
Make it Shine
An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it’s achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine:
- Write a substantial introduction. Particularly, it’s the first impression the professor will have of the paper.
- State a clear thesis. A strong thesis is easier to support.
- Incorporate evidence critically. If while researching you find opposing arguments, include them and discuss their flaws.
- Cite all the research. Whether direct quotations or paraphrases, citing evidence is crucial to avoiding plagiarism, which can have serious academic consequences.
- Include primary and secondary resources. While primary resources may be harder to find, the professor will expect them—this is, after all, a history essay.
History Essay Sample
Ready to tackle the history essay format? Great! Check out this history essay sample from an upper-level history class. While the essay isn’t perfect, the professor points out its many strengths.
Remember: start early and revise, revise, revise . We can’t revise history, but you can revise your ideas until they’re perfect.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]

- Written Essays
How to write source-based history essays

The biggest assessment task you will be required to complete is a written research essay which develops an argument and uses a range of sources.
All types of assessment tasks will need you to use essay-writing skills in some form, but their fundamental structure and purpose remains the same.
Therefore, learning how to write essays well is central to achieving high marks in History.
What is an 'essay'?
A History essay is a structured argument that provides historical evidence to substantiate its points.
To achieve the correct structure for your argument, it is crucial to understand the separate parts that make up a written essay.
If you understand how each part works and fits into the overall essay, you are well on the way to creating a great assessment piece.
Most essays will require you to write:
- 1 Introduction Paragraph
- 3 Body Paragraphs
- 1 Concluding Paragraph
Explanations for how to structure and write each of these paragraphs can be found below, along with examples of each:
Essay paragraph writing advice

How to write an Introductory Paragraph
This page explains the purpose of an introduction, how to structure one and provides examples for you to read.

How to write Body Paragraphs
This page explains the purpose of body paragraphs, how to structure them and provides examples for you to read.

How to write a Conclusion
This page explains the purpose of conclusions, how to structure them and provides examples for you to read.
More essay resources
What do you need help with, download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
How To Write A History Essay
- Essay Writing Guides

Essay writing is one of the most effortful student assignments. Not everybody can skillfully enunciate their views and ideas, especially when it comes to an essay that requires the presentation of arguments and counterarguments. Simultaneously, it is one of the best tools to improve your critical thinking and research skills.
A history essay is a particular type of creative work that requires brilliant research potential and the ability to analyze and track the consistent picture of historical events. To craft a successful history essay, students should go beyond the regular history classes and demonstrate their significant knowledge in political science, sociology, and even psychology.
If you were lucky to get a creative assignment in history, get ready to experience not the easiest time in your life. To make the overall process more efficient and straightforward, use this history essay writing guide for assistance.
What is a History Essay?
To elaborate an impeccable history paper, it is crucial to answer the ‘what is history essay’ question. The history essay’s essence lies in the successful introduction and confirmation of statements related to some historical events or personalities. To make your work sound professional, you need to:
- elucidate the factors that have led to such consequences;
- build a logical bridge between the past and the present by describing the importance of the phenomenon you are dealing with.
A top-notch history paper never focuses on the past mainly. It rather comes up with the impact the past events have on the present. An ability to fully reveal the given influence is the most significant proof that the author has a good understanding of the topic and can easily share their perspective professionally and to the point.
Having the instructions and practical tips on how to write a history essay is the first key to a successful paper. Many students just start rewriting the historical events in their own words at this stage. Instead, your essay should provide clear answers to three central questions: what, why, and how. These questions may become good starting points for your history essay and help you stay coherent.
Before You Start: Preparing to Write

Having three questions in mind when preparing to write a history essay is already half a work done. Carry out a little brainstorm session and formulate several sub-questions using the mentioned interrogative adverbs. They will contribute much to the creation of an effective structure in your history essay. Here’s a breakdown of the main questions addressed.
- Who are the main characters of the given events?
- Who is against the given events?
- Who won from the given events? Who lost?
- Who is currently in the winning position thanks to the mentioned events?
- What circumstances caused the given events?
- What changes did the given events cause?
- What kind of effect did the events have on the present?
- What conclusions have been made after these events?
- Why did the given events take place?
- Why were they supported/not supported by people?
You may also come up with your suggestions regarding the specific topic to make your essay even more professional.
Nonetheless, it is not enough only to write down the questions. You have to analyze and evaluate them profoundly. You may be very accurate about the described shreds of evidence, proofs, and arguments. However, if your essay doesn’t provide precise answers to the fundamental questions, it is unlikely to be highly scored. To stay coherent and to the point, use an explanation/interpretation scheme that implies the reasons why something has happened, followed by the profound analysis of the events.
When the above-mentioned work is done and questions have been answered, you are ready to form your paper’s thesis statement. If we talk about the history essay, its thesis statement should be strong enough to prove the significance and value of your work. Besides, convincing arguments help create a solid bone to structure your essay around.
Your paper’s thesis statement should accurately elucidate the essay’s essence and be supported with the concise arguments that would become its paragraphs. All you need to do is specify them and then elaborate in more detail.
You can change the arguments throughout the essay, but the thesis statement should remain the same and be rational enough to stay relevant till the end.
Research Stage
Nominally, the sources you will be using for your history essay can be divided into primary and secondary ones. Primary sources refer directly to the description of the events or personalities you base your paper on. Secondary sources represent the works of experienced historians, sociologists, and politicians that contain the profound analysis of the events described within your topic.
The professional history essay cannot exist without trustful primary sources. It can be challenging to find and identify them. Fortunately, the XXIst century provides a decent range of opportunities to complete thorough research work. You can have access to the best scholars’ papers, databases of the world libraries, and blogs of famous experts. Crowd-sourced websites can also be of good service. However, they should be used very selectively after you make sure they are credible.
Secondary sources are as important as the primary ones. You need to be sure of their credibility and choose exclusively scholarly works. Check whether the author of the paper you are going to use in your essay is a professional historian and can be trusted. To make the right choice, ask yourself several questions before referring to any source:
- What do you know about the author?
- Does the author have an academic degree and enough experience to be trusted?
- What can you say about the publishing house? Is it academic? If it is a website, check its nature and audience. The idea to use materials published on Government online platforms in your paper sounds just perfect.
History Essay Outline
Coming to the outline stage means that you have done all the preparatory work and are ready to move forward. The outline is frequently skipped by students, which makes them regret it later. The outline is a so-called roadmap to indicate the direction you need to move in and mark the proper placing of arguments and ideas.
Like all other types of essays, a history paper consists of an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion.
Introduction
Are you wondering how to start a history essay? With the catching introduction, of course. Introduction to your history essay should serve as a so-called hook to immediately grab the readers’ attention. To make it as catching as possible, you may use a few simple yet trusting methods:
- Include some facts or impressive statistics. This will help easily win people’s trust and make your paper more relevant;
- Rhetorical questions always help define the sense of your creative work. Use them in the introduction to indicate the main points your work will be based on;
- Quotations may also be of good service in case you want to make people intrigued.
Provided the hook has worked, don’t hesitate to introduce your paper’s theme: mention the key events or persons your essay is about. Usually, a good introduction ends with a strong thesis statement. Make it short and up to the point. Besides, make sure it provides a smooth transition to the body section of your history essay.
Divide your critical ideas described in the essay and between the paragraphs: one paragraph = one idea. Each idea needs to be supported by concise arguments. There is no standard scheme to build your body paragraphs on. However, you may take the following algorithm for the basis:
- A sentence related to the thesis statement and elucidating the idea;
- Context of your history essay;
- Facts in the form of quotation or rewritten
- Analysis and your point of view
- Description of the controversial points
- Smooth transition to the next paragraph
It is highly recommended to place the arguments of your body section in correct order. Start with the weakest ones and leave the strongest ones for a dessert.
You should put your best effort into making this paragraph as impressive and convincing as possible. The final part of your paper should focus on the main points of the essay and again prove the theory mentioned in the thesis statement. Don’t make the conclusion too complicated – it needs to be simple and straightforward. The conclusion is not a part of the paper where you may introduce some new facts and ideas. Its main goal is in summarizing the critical points previously specified in the essay. If you want to make a conclusion sound professional, don’t forget to mention the historical events’ relevance to today’s reality.
How to Choose a Topic for a History Essay?
In case you were lucky to choose the topic for your history essay by yourself, don’t skip this part. Selecting from a pile of history essay topics may be challenging as you need to know your educational level, interests, and ability to elaborate on the theme. An adequately chosen history essay topic is a basis for a good paper. It affects the overall writing process and the level of your engagement in the subject. Use these tips to choose the best topic for your history paper:
- Focus on the theme that sounds interesting to you. If history is not your cup of tea, try to pick the theme that seems more interesting than others. History is tightly connected with all aspects of human life. So, there should be something that makes your heart beat faster.
- Don’t be guided by interest only when choosing a topic for the history essay. You should know at least something about the given theme. Even the most exciting issues can turn out to be a nightmare to deal with if you know absolutely nothing about them.
- Analyze the broadness of the topic. If it is too broad, you won’t be able to elaborate the theme decently. For example, the topic “Ancient Egypt” is unclear. You won’t be able to elucidate all its aspects and perspectives properly. However, dealing with “Attitudes Towards Women in Ancient Egypt” narrows your research scope and lets you stay clear and precise.
- Make sure the topic you are going to choose has been analyzed before, and you can find a lot of credible materials to base your research on. Even narrow themes can be challenging if they are unexplored.
- If you have a chance to use the theme you have already been dealing with before, don’t hesitate to do it. There is no need to rewrite your old paper – you have an excellent opportunity to analyze things from another perspective. Reusing the topic is hugely advantageous, as you have all the research work done already and may concentrate on your personal opinion.
- In case sitting on the fence while choosing the topic for your history essay becomes unbearable, you can always ask your tutor for a piece of advice. In such a way, you will demonstrate your respect and trust.
- Avoid offbeat themes. They may be interesting, however, totally new. If you are not afraid of being stuck at the research stage – go ahead!
- Make a little brainstorm session before choosing any topic. Provided you can come up with at least five strong arguments related to the theme, don’t hesitate to pick it.
History Essay Examples
Nothing can be more helpful than a brilliant history essay example you can use for your future work. You may take a look at the essay’s purpose, analyze the structure, get an idea about transitions and vocabulary used. Check on these top-notch examples of history paper to get inspired and motivated:
- https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/us-history-slavery-essay/5916771
- https://www.markedbyteachers.com/international-baccalaureate/history/compare-and-contrast-the-causes-of-the-first-world-war-and-the-second-world-war.html
- https://www.markedbyteachers.com/international-baccalaureate/history/how-far-do-trotsky-fa-a-tm-s-own-misjudgments-account-for-his-failure-in-the-power-struggle-which-followed-lenin-fa-a-tm-s-death.html
- https://www.markedbyteachers.com/international-baccalaureate/history/compare-and-contrast-the-policies-of-alexander-ii-and-alexander-iii.html
Writing Tips for a History Essay
Interpretation of the past may be pretty controversial. So are the rules on how to write a perfect history essay. Nevertheless, there are some standard conventions and guidelines for elaborating professional history papers without any special effort from your side. Just follow the below tips to get the highest grade under the toughest history essay rubric.
Use the past tense
The present tense is just inappropriate when dealing with the history essay. Moreover, it can undermine confidence in the qualifications and expertise of the author. The present tense is acceptable only when you draw parallels between past events and the current time.
Avoid generalizations
Specificity and accuracy are the best friends of a highly professional history essay. If you talk about some specific period, introduce exact dates or centuries. In case you mention some personalities, provide their full names. History paper is senseless without these critical details.
Exclude anachronisms
When dealing with some historical events from today’s perspective, it is easy to get lost in chronological order. Such a jumble can confuse the readers and make your work less credible. Mind the vocabulary you use when talking about a specific epoch.
Try not to judge the epoch from a modern perspective
Every generation has its advantages and drawbacks. Your main task as an author is to analyze both and convey them clearly to a reader. Don’t be judgmental.
Paraphrasing is always better than quoting
Stuffing your history essay with the quotes can be more of a hindrance than help. Don’t be afraid to showcase your analytical skills and dive deep into the profound analysis of past events. If paraphrasing is impossible, use the quote indicating its source.
Be responsible for the context
As an author, you assume full responsibility for your personal opinion and ideas. At the same time, you should be sure of the sources you use in your paper. History essays don’t stand uncertainty and double standards.
Choose the proper citation style
As a rule, history papers require Chicago citation style. A poorly arranged citation page can question your reputation as a history expert.

Stick to the proper voice
A formal academic voice is the most appropriate one when we talk about the history essay. Also, avoid passive voice phrases, redundant constructions, and generalizations.
Take care of thorough proofreading
You have made it: your history essay is ready and waits to be polished. The editing stage is crucial as even the brightest ideas can get lost in a sea of mistakes, impurities, and vague phrases. How to proofread your history essay to make it shine? Check the below instructions to learn how to do it:
- Read your history essay aloud several times to make sure it is clear and sounds smooth. Avoid long sentences and inaccurate phrases with unclear meaning.
- Proper style is important when we talk about the academic history essay. Make sure it is formal but readable. Readers should easily percept your message and clearly understand the goal of your research.
- Proofreading may be challenging in case you have spent a lot of time elaborating on the content. If you can ask someone to look at your history paper with a fresh pair of eyes, it would be perfect. Independent readers can identify the weak places in your work faster, and you will get a valuable second opinion on your piece of writing.
Write My History Essay for Me, Please!
History paper is one of the most complicated types of writing. Students dealing with history topics should know more than just a material of a regular history syllabus. Moreover, this paper requires a lot of time and effort to do research, analyze, and establish logical connections and predictions. You have to deal with the vast amount of dates, personalities, and theories that may not always be true. No wonder a lot of students choose to ask someone to write their history assignment for them. This decision appears to be justified as our essay writing service offers help provided by the actual history scholars who, by the way, are excellent in writing.
All you need to do is formulate the task specifying the detailed instructions to your assignment and indicate the deadline. In case you want some specific sources to be used when elaborating on your history paper, you should mention them in your reference list.
In case your history essay is ready and you just need to make it shine, our essay service is always ready to help you with editing and proofreading. In such a way, you pay only for a specific service, not for the whole writing package.
A brilliantly elaborated history essay can serve as a good base for all your future works. You may get a clear idea about the content, research process, vocabulary, structure, and citation style. Just place the order, and our highly professional expert will be there to help you with your history paper.
- Academic Writing Guides
- Citation Guides
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics
- Research Paper Writing Guides
- Study Tips and Tricks
Featured articles

Strategies for Writing a Great Problem Solution Essay
Composing an assignment on a problem and solution essay topic allows you to demonstrate your ability to resolve human challenges. It helps you understand human problems and how to be a part of the solution instead of allocating blame and pointing fingers. So, how do you compose a great problem solutions essay? This post has […]
Author: Marina Kean

Your Complete Guide to Writing a Compelling Leadership Essay
True leadership lies at the heart of human well-being and success. Every positive step humanity ever took required great and responsible leadership. Therefore, people have studied leadership for many edges to unravel its different underlying factors. But how do you write a great essay that demonstrates your grasp of this sacred call? This post shares […]

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- Undergraduate courses
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Postgraduate events
- Fees and funding
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Term dates and calendars
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
- Give to Cambridge
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges & departments
- Email & phone search
- Museums & collections
- Student information
Department of History and Philosophy of Science
- About the Department overview
- How to find the Department
- Annual Report
- Video and audio
- HPS Discussion email list
- Becoming a Visiting Scholar or Visiting Student overview
- Visitor fee payment
- Becoming an Affiliate
- Applying for research grants and post-doctoral fellowships
- Administration overview
- Information for new staff
- Information for examiners and assessors overview
- Operation of the HPS plagiarism policy
- Information for supervisors overview
- Supervising Part IB and Part II students
- Supervising MPhil and Part III students
- Supervising PhD students
- People overview
- Teaching Officers
- Research Fellows and Teaching Associates
- Professional Services Staff
- PhD Students
- Research overview
- Research projects overview
- Natural History in the Age of Revolutions, 1776–1848
- In the Shadow of the Tree: The Diagrammatics of Relatedness as Scientific, Scholarly and Popular Practice
- The Many Births of the Test-Tube Baby
- Culture at the Macro-Scale: Boundaries, Barriers and Endogenous Change
- Making Climate History overview
- Project summary
- Workstreams
- Works cited and project literature
- Research and teaching fellowships
- Histories of Artificial Intelligence: A Genealogy of Power overview
- From Collection to Cultivation: Historical Perspectives on Crop Diversity and Food Security overview
- Call for papers
- How Collections End: Objects, Meaning and Loss in Laboratories and Museums
- Tools in Materials Research
- Epsilon: A Collaborative Digital Framework for Nineteenth-Century Letters of Science
- Contingency in the History and Philosophy of Science
- Industrial Patronage and the Cold War University
- FlyBase: Communicating Drosophila Genetics on Paper and Online, 1970–2000
- The Lost Museums of Cambridge Science, 1865–1936
- From Hansa to Lufthansa: Transportation Technologies and the Mobility of Knowledge in Germanic Lands and Beyond, 1300–2018
- Medical Publishers, Obscenity Law and the Business of Sexual Knowledge in Victorian Britain
- Kinds of Intelligence
- Varieties of Social Knowledge
- The Vesalius Census
- Histories of Biodiversity and Agriculture
- Investigating Fake Scientific Instruments in the Whipple Museum Collection
- Before HIV: Homosex and Venereal Disease, c.1939–1984
- The Casebooks Project
- Generation to Reproduction
- The Darwin Correspondence Project
- History of Medicine overview
- Events overview
- Past events
- Philosophy of Science overview
- Study HPS overview
- Undergraduate study overview
- Introducing History and Philosophy of Science
- Frequently asked questions
- Routes into History and Philosophy of Science
- Part II overview
- Distribution of Part II marks
- BBS options
- Postgraduate study overview
- Why study HPS at Cambridge?
- MPhil in History and Philosophy of Science and Medicine overview
- A typical day for an MPhil student
- MPhil in Health, Medicine and Society
- PhD in History and Philosophy of Science overview
- Part-time PhD
PhD placement record
- Funding for postgraduate students
- Student information overview
- Timetable overview
- Primary source seminars
- Research methods seminars
- Writing support seminars
- Dissertation seminars
- BBS Part II overview
- Early Medicine
- Modern Medicine and Biomedical Sciences
- Philosophy of Science and Medicine
- Ethics of Medicine
- Philosophy and Ethics of Medicine
- Part III and MPhil
- Single-paper options
- Part IB students' guide overview
- About the course
- Supervisions
- Libraries and readings
- Scheme of examination
- Part II students' guide overview
- Primary sources
- Dissertation
- Key dates and deadlines
- Advice overview
- Examination advice
- Learning strategies and exam skills
- Advice from students
- Part III students' guide overview
- Essays and dissertation
- Subject areas
- MPhil students' guide overview
- PhD students' guide overview
- Welcome to new PhDs
- Registration exercise and annual reviews
- Your supervisor and advisor
- Progress log
- Intermission and working away from Cambridge
- The PhD thesis
- Submitting your thesis
- Examination
- News and events overview
- Seminars and reading groups overview
- Departmental Seminars
- Coffee with Scientists
- Cabinet of Natural History overview
- Publications
- History of Medicine Seminars
- The Anthropocene
- Calculating People
- Measurement Reading Group
- Teaching Global HPSTM
- Pragmatism Reading Group
- Foundations of Physics Reading Group
- Atmospheric Humanities Reading Group
- Values in Science Reading Group
- HPS Workshop
- Postgraduate Seminars overview
- Images of Science
- Language Groups overview
- Latin Therapy overview
- Bibliography of Latin language resources
- Fun with Latin
- Archive overview
- Lent Term 2024
- Michaelmas Term 2023
- Easter Term 2023
- Lent Term 2023
- Michaelmas Term 2022
- Easter Term 2022
- Lent Term 2022
- Michaelmas Term 2021
- Easter Term 2021
- Lent Term 2021
- Michaelmas Term 2020
- Easter Term 2020
- Lent Term 2020
- Michaelmas Term 2019
- Easter Term 2019
- Lent Term 2019
- Michaelmas Term 2018
- Easter Term 2018
- Lent Term 2018
- Michaelmas Term 2017
- Easter Term 2017
- Lent Term 2017
- Michaelmas Term 2016
- Easter Term 2016
- Lent Term 2016
- Michaelmas Term 2015
- Postgraduate and postdoc training overview
- Induction sessions
- Academic skills and career development
- Print & Material Sources
- Other events and resources
How to organise a history essay or dissertation
- About the Department
- News and events

Sachiko Kusukawa
There are many ways of writing history and no fixed formula for a 'good' essay or dissertation. Before you start, you may find it helpful to have a look at some sample dissertations and essays from the past: ask at the Whipple Library.
Some people have a clear idea already of what they are going to write about; others find it more difficult to choose or focus on a topic. It may be obvious, but it is worth pointing out that you should choose a topic you find interesting and engaging. Ask a potential supervisor for a list of appropriate readings, chase up any further sources that look interesting or promising from the footnotes, or seek further help. Try to define your topic as specifically as possible as soon as possible. Sometimes, it helps to formulate a question (in the spirit of a Tripos question), which could then be developed, refined, or re-formulated. A good topic should allow you to engage closely with a primary source (text, image, object, etc.) and develop a historiographical point – e.g. adding to, or qualifying historians' current debates or received opinion on the topic. Specific controversies (either historically or historiographically) are often a great place to start looking. Many dissertations and essays turn out to be overambitious in scope, but underambition is a rare defect!
Both essays and dissertations have an introduction and a conclusion . Between the introduction and the conclusion there is an argument or narrative (or mixture of argument and narrative).
An introduction introduces your topic, giving reasons why it is interesting and anticipating (in order) the steps of your argument. Hence many find that it is a good idea to write the introduction last. A conclusion summarises your arguments and claims. This is also the place to draw out the implications of your claims; and remember that it is often appropriate to indicate in your conclusion further profitable lines of research, inquiry, speculation, etc.
An argument or narrative should be coherent and presented in order. Divide your text into paragraphs which make clear points. Paragraphs should be ordered so that they are easy to follow. Always give reasons for your assertions and assessments: simply stating that something or somebody is right or wrong does not constitute an argument. When you describe or narrate an event, spell out why it is important for your overall argument. Put in chapter or section headings whenever you make a major new step in your argument of narrative.
It is a very good idea to include relevant pictures and diagrams . These should be captioned, and their relevance should be fully explained. If images are taken from a source, this should be included in the captions or list of illustrations.
The extent to which it is appropriate to use direct quotations varies according to topic and approach. Always make it clear why each quotation is pertinent to your argument. If you quote from non-English sources say if the translation is your own; if it isn't give the source. At least in the case of primary sources include the original in a note if it is your own translation, or if the precise details of wording are important. Check your quotations for accuracy. If there is archaic spelling make sure it isn't eliminated by a spell-check. Don't use words without knowing what they mean.
An essay or a dissertation has three components: the main text , the notes , and the bibliography .
The main text is where you put in the substance of your argument, and is meant to be longer than the notes. For quotes from elsewhere, up to about thirty words, use quotation marks ("...", or '...'). If you quote anything longer, it is better to indent the whole quotation without quotation marks.
Notes may either be at the bottom of the page (footnotes) or at the end of the main text, but before the bibliography (endnotes). Use notes for references and other supplementary material which does not constitute the substance of your argument. Whenever you quote directly from other works, you must give the exact reference in your notes. A reference means the exact location in a book or article which you have read , so that others can find it also – it should include author, title of the book, place and date of publication, page number. (There are many different ways to refer to scholarly works: see below.) . If you cite a primary source from a secondary source and you yourself have not read or checked the primary source, you must acknowledge the secondary source from which the citation was taken. Whenever you paraphrase material from somebody else's work, you must acknowledge that fact. There is no excuse for plagiarism. It is important to note that generous and full acknowledgement of the work of others does not undermine your originality.
Your bibliography must contain all the books and articles you have referred to (do not include works that you did not use). It lists works alphabetically by the last name of the author. There are different conventions to set out a bibliography, but at the very least a bibliographic entry should include for a book the last name and initials/first name of the author, the title of the book in italics or underlined, and the place, (publisher optional) and date of publication; or, for an article, the last name and initials/first name of the author, the title in inverted commas, and the name of the journal in italics or underlined, followed by volume number, date of publication, and page numbers. Names of editors of volumes of collected articles and names of translators should also be included, whenever applicable.
- M. MacDonald, Mystical Bedlam: Madness, Anxiety, and Healing in Seventeenth-Century England , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1981.
- William Clark, 'Narratology and the History of Science', Studies in History and Philosophy of Science 26 (1995), 1–72.
- M. F. Burnyeat, 'The Sceptic in His Place and Time', in R. Rorty, J. B. Schneewind and Q. Skinner (eds), Philosophy in History , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1984, pp. 225–54.
Alternatively, if you have many works to refer to, it may be easier to use an author-date system in notes, e.g.:
- MacDonald [1981], p. 89; Clark [1995a], p. 65; Clark [1995b], pp. 19–99.
In this case your bibliography should also start with the author-date, e.g.:
- MacDonald, Michael [1981], Mystical Bedlam: Madness, Anxiety, and Healing in Seventeenth-Century England , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Clark, William [1995a], 'Narratology and the History of Science', Studies in History and Philosophy of Science 26, 1–72.
This system has the advantage of making your foot- or endnotes shorter, and many choose it to save words (the bibliography is not included in the word limit). It is the system commonly used in scientific publications. Many feel however that something is historically amiss when you find in a footnote something like 'Plato [1996b]' or 'Locke [1975]'. In some fields of research there are standard systems of reference: you will find that this is the case if, for example, you write an essay/dissertation on classical history or philosophy of science. In such cases it is a good idea to take a standard secondary source as your model (e.g. in the case of classics, see G.E.R. Lloyd's The Revolutions of Wisdom: Studies in the Claims and Practices of Ancient Greek Science , Berkeley 1987).
Whatever system you decide to follow for your footnotes, what matters most is that the end-product is consistent.
Keep accurate records of all the relevant bibliographic information as you do your reading for your essay/dissertation. (If you don't you may waste days trying to trace references when you are close to submission deadlines.)
Consistency of style throughout the essay/dissertation is encouraged. There are many professional guides to thesis writing which give you more information on the style and format of theses – for example the MLS handbook (British) and the Chicago Manual of Style (American), both in the Whipple, and a booklet, H. Teitelbaum, How to Write a Thesis: A Guide to the Research Paper , 3rd ed., 126 pp., New York: Macmillan (& Arco), 1994 (in the UL: 1996.8.2620). But don't try to follow everything they say!
Every now and then you should read through a printout of your whole essay/dissertation, to ensure that your argument flows throughout the piece: otherwise there is a danger that your arguments become compartmentalised to the size of the screen. When reading drafts, ask yourself if it would be comprehensible to an intelligent reader who was not an expert on the specific topic.
It is imperative that you save your work on disk regularly – never be caught out without a back-up.
Before you submit:
- remember to run a spell-check (and remember that a spell check will not notice if you have written, for example, 'pheasant' instead of 'peasant', or, even trickier, 'for' instead of 'from', 'it' instead of 'is', etc.);
- prepare a table of contents, with titles for each chapter of your essay/dissertation, page numbers and all;
- prepare a cover page with the title, your name and college;
- prepare a page with the required statement about length, originality etc.
Email search
Privacy and cookie policies
Study History and Philosophy of Science
Undergraduate study
Postgraduate study
Library and Museum
Whipple Library
Whipple Museum
Museum Collections Portal
Research projects
History of Medicine
Philosophy of Science
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Privacy policy and cookies
- Statement on Modern Slavery
- Terms and conditions
- University A-Z
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Research news
- About research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...

Subscription Offers
Give a Gift

How to Write Your First Undergraduate Essay
Jeremy Black prepares readers for the rigours of university history.
Well done! You have got into university to read history, one of the most interesting subjects on offer. One reason it is very interesting is that there is a clear progression from the challenges at A level to the requirements of a degree. And that is your problem. You have been set your first essay and you are not clear about these requirements.
The first rule is a simple one. The questions may look the same but your answers must be different. One can be set the identical question, say ‘Why did the French Revolution occur?’, at ages 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 or, if you are an academic writing a paper, 50 or 60, but a different type of answer is required.
In what way different? Not primarily in terms of more facts, because university history degrees are not essentially a test of knowledge, not a question of remembering dates or quotes. It is certainly appropriate to support arguments with relevant information, the emphasis being on relevant not information, and, when you deploy facts, do get them right. To get your facts wrong risks undermining the impression you create because it suggests that you do not really know the subject.
Save 35% with a student subscription to History Today
But history is what you remember when you forget the facts. It is a habit of thought, an attitude of critical scrutiny and exposition, a method of enquiry. These should underlie your reading for your essay and should guide your preparation, and it is in their light that facts are to be assessed. They must contribute to the critical argument, and that requires an ability to engage with three elements if the essay is to be a good one:
Conceptualisation
Methodology
- Historiography.
I will go through all three, but do not worry. At this stage, for most students, these are an aspiration and not an achievement; but the aspiration is important as it shows you, first, how your degree course is different from A level and, secondly, what you will be expected to be able to do by the end of your university career. To do well, you should make an effort to begin including each of these elements in your essays.
Many questions relate to key concepts in history. For example, if you are asked ‘What were the causes of the French Revolution?’, the key concepts are causes and revolution. What do you mean by the French Revolution? Is it primarily the violent challenge to royal authority in 1789, the creation of a new political order, a marked ideological discontinuity, the process of socio-economic change, or, if a combination of all of these, which takes precedence and requires most explanation? What do you understand by causes? Are we talking primarily about long-term, ‘structural’ factors that caused problems, or about precipitants that led to a breakdown of the existing situation? These issues need discussing explicitly, out-in-the-open. That is key to a good essay at university level. They should not be left unspoken and unaddressed; and your discussion of them should reflect your awareness that issues are involved in the analysis, and that you are capable of addressing them. You also need to be aware that there will be different answers and this should guide your handling of the concepts. This leads into Methodology.
In this section, you should explicitly address the issue of how scholars, including yourself, can handle the conceptual questions. This follows the previous point closely. What sources should scholars use and how should they use them? Do you put a preference in studying the French Revolution on the declarations made by revolutionaries, on their public debates, or on what happened ‘on the ground’, including the violent opposition they aroused? If you discuss the latter, you underline the fact that the Revolution led to civil war, and that the causes of what you present as the Revolution were not a mass rejection of the existing system. You also point out that in 1789 few people envisaged what they were expected to support in 1792 (a republic and the trial of the king) let alone 1793 (the Reign of Terror). The Revolution is thus presented and studied as a dynamic, changing process, which requires different explanations at particular stages.
Historiography
A key feature of university work is that you need to address explicitly the degree to which historians hold different views, and why, and to show that you understand that these views change, and can locate your own essay in their debates. For the French Revolution, we see a tendency among French scholars to stress socio-economic causes, among American academics to emphasise the conceptual inconsistencies of the French ancien régime , and among British writers to underline short-term political issues.
Ten Key Things To Do
- Read the question and understand what it is asking.
- Work out your approach.
- Write a detailed essay plan, with different points per paragraph.
- Have an introduction in which you reveal your understanding of the current debate in interpretations.
- Remember to handle the concepts in the question and in your answer clearly.
- Remember to introduce the relevant historical methods explicitly.
- Engage with the historiography, the views of different historians.
- In doing so, show how your work is part of the debate.
- Have a clear conclusion that brings out the relevance of the topic and your answer for wider historical issues.
- Include a reading list and a word count.
Sounds difficult? Well, these approaches add interest and understanding, and help make your degree a worthwhile process of education and exposition.
Jeremy Black is Professor of History at the University of Exeter. He is the author, with Donald M. MacRaild, of Studying History (Palgrave, 3rd edition, 2007).
Popular articles

Was Portugal’s Carnation Revolution Inevitable?

Slaying Myths: St George and the Dragon
College of Arts and Sciences
History and American Studies
- What courses will I take as an History major?
- What can I do with my History degree?
- History 485
- History Resources
- What will I learn from my American Studies major?
- What courses will I take as an American Studies major?
- What can I do with my American Studies degree?
- American Studies 485
- For Prospective Students
- Student Research Grants
- Honors and Award Recipients
- Phi Alpha Theta
Alumni Intros
- Internships
Introduction and Conclusion
INTRODUCTIONS The introduction of a paper must introduce its thesis and not just its topic. Readers will lose some—if not much—of what the paper says if the introduction does not prepare them for what is coming (and tell them what to look for and how to evaluate it).
For example, an introduction that says, “The British army fought in the battle of Saratoga” gives the reader virtually no guidance about the paper’s thesis (i.e., what the paper concludes/argues about the British army at Saratoga).
History papers are not mystery novels. Historians WANT and NEED to give away the ending immediately. Their conclusions—presented in the introduction—help the reader better follow/understand their ideas and interpretations.
In other words, an introduction is a MAP that lays out “the trip the author is going to take [readers] on” and thus “lets readers connect any part of the argument with the overall structure. Readers with such a map seldom get confused or lost.”1
Introductions do four things:
attract the ATTENTION of the reader convince the reader that he/she NEEDS TO READ what the author has to say define the paper’s SPECIFIC TOPIC state and explain the paper’s THESIS Writing the introduction: Consider writing the introduction AFTER finishing your paper. By then, you will know what your paper says. You will have thought it through and provided arguments and supporting evidence; therefore, you will know what the reader needs to know—in brief form—in the introduction. (Always think of your initial introduction as “getting started” and as something that “won’t count.” It is for your eyes only; discard it when you know exactly what your paper says.) A common technique is to turn your conclusion into an introduction. It usually reflects what is in the paper—topic, thesis, arguments, evidence—and can be easily adjusted to be a clear and useful introduction.
Some types of introductions:
Quotation Historical overview (provides introduction to topic AND background so that fewer explanations are needed later in paper) Review of literature or a controversy Statistics or startling evidence Anecdote or illustration Question From general to specific OR specific to general Avoid:
“The purpose of this paper is . . .” OR “This paper is about . . . .” First person (e.g., “I will argue that”) Too many questions Dictionary definitions Length: There is no rule other than to be logical. Short papers require short introductions (e.g., a short paragraph); longer ones may require a page or more to provide all that a reader needs. Longer papers require ELABORATION of the thesis; a sentence is not sufficient to prepare the reader for the many pages of arguments and evidence that follow.
CONCLUSIONS Conclusions are the last thing that readers read; they define readers’ final impression of a paper. A flat, boring conclusion means a flat, boring (or, at least, disappointing) paper.
Conclusions should be a climax, not an anti-climax. They do not just restate what has already been said; they interpret, speculate, and provoke thinking.
Some types of conclusions:
Statement of subject’s significance Call for further research Recommendation or speculation Comparison of part to present Anecdote Quotation Questions (with or without answers) Avoid:
“In conclusion”; “finally”; “thus” Additional or new ideas that introduce a new paper First person Length: Again, there is no rule, although too short conclusions should definitely be avoided. Short conclusions leave the reader on the edge of a cliff with no directions on how to get down.
You are the expert – help your reader pull together and appreciate what he/she has read.
____________________________ 1Howard Becker, Writing for Social Scientists (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1986).

How have History & American Studies majors built careers after earning their degrees? Learn more by clicking the image above.
Recent Posts
- History and American Studies Symposium–April 26, 2024
- Fall 2024 Courses
- Fall 2023 Symposium – 12/8 – All Welcome!
- Spring ’24 Course Flyers
- Internship Opportunity – Chesapeake Gateways Ambassador
- Congratulations to our Graduates!
- History and American Studies Symposium–April 21, 2023
- View umwhistory’s profile on Facebook
- View umwhistory’s profile on Twitter
How to Write a Good History Essay. A Sequence of Actions and Useful Tips
/rating_on.png)
Before you start writing your history essay, there is quite a lot of work that has to be done in order to gain success.
You may ask: what is history essay? What is the difference between it and other kinds of essays? Well, the main goal of a history essay is to measure your progress in learning history and test your range of skills (such as analysis, logic, planning, research, and writing), it is necessary to prepare yourself very well.
Your plan of action may look like this. First of all, you will have to explore the topic. If you are going to write about a certain historical event, think of its causes and premises, and analyze what its impact on history was. In case you are writing about a person, find out why and how he or she came to power and how they influenced society and historical situations.
The next step is to make research and collect all the available information about the person or event, and also find evidence.
Finally, you will have to compose a well-organized response.
During the research, make notes and excerpts of the most notable data, write out the important dates and personalities. And of course, write down all your thoughts and findings.
It all may seem complicated at first sight, but in fact, it is not so scary! To complete this task successfully and compose a good history essay, simply follow several easy steps provided below.
Detailed Writing Instruction for Students to Follow
If you want to successfully complete your essay, it would be better to organize the writing process. You will complete the assignment faster and more efficient if you divide the whole work into several sections or steps.
- Introduction
Writing a good and strong introduction part is important because this is the first thing your reader will see. It gives the first impression of your essay and induces people to reading (or not reading) it.
To make the introduction catchy and interesting, express the contention and address the main question of the essay. Be confident and clear as this is the moment when you define the direction your whole essay will take. And remember that introduction is not the right place for rambling! The best of all is, to begin with, a brief context summary, then go to addressing the question and express the content. Finally, mark the direction your essay about history will take.
Its quality depends on how clear you divided the whole essay into sections in the previous part. As long as you have provided a readable and understandable scheme, your readers will know exactly what to expect.
The body of your essay must give a clear vision of what question you are considering. In this section, you can develop your idea and support it with the evidence you have found. Use certain facts and quotations for that. When being judicial and analytical, they will help you to easily support your point of view and argument.
As long as your essay has a limited size, don’t be too precise. It is allowed to summarize the most essential background information, for example, instead of giving a precise list of all the issues that matter.
It is also good to keep in mind that each paragraph of your essay’s body must tell about only one issue. Don’t make a mess out of your paper!
It is not only essential to start your essay well. How you will end it also matters. A properly-written conclusion is the one that restates the whole paper’s content and gives a logical completion of the issue or question discussed above. Your conclusion must leave to chance for further discussion or arguments on the case. It’s time, to sum up, give a verdict.
That is why it is strongly forbidden to provide any new evidence or information here, as well as start a new discussion, etc.
After you finish writing, give yourself some time and put the paper away for a while. When you turn back to it will be easier to take a fresh look at it and find any mistakes or things to improve. Of course, remember to proofread your writing and check it for any grammar, spelling and punctuation errors. All these tips will help you to learn how to write a history essay.


- Peterborough

The Structure of an Essay
Whether they are two pages in length or fifteen, most essays follow a similar structure.
Introduction
- Essays always begin with a clear introduction. The introduction sets up the historical question, presents a clear thesis to the reader, and establishes the scope of the essay--the time period, places, and subjects discussed in the essay.
- In a short paper, the introduction is one paragraph in length. In a longer paper (over ten pages), it could be two or three paragraphs in length. Introductions will be covered in more detail later in this module.
Body Paragraphs
- Following the introduction, the essay contains body paragraphs. These paragraphs systematically, and in a logical order, develop and prove each argument. In the body paragraphs, you present and explain the evidence that supports your thesis.
- There is no set number of body paragraphs for an essay (you are NO LONGER writing only five-paragraph essays). Use as many paragraphs as you need to develop the arguments within your thesis.
- The essay ends with a clear conclusion. The conclusion brings together the points made in the essay and draws out their larger significance.
- In a short paper, the conclusion is one paragraph in length. In a longer paper (over ten pages), it could be two or three paragraphs in length. Conclusions will be covered in more detail later in this module.
How to Write an Introduction to a History Essay
Liza hollis.

The introduction in any essay should grab the attention of your reader while introducing them to the topic of discussion. Introduction paragraphs are generally no more than five to seven sentences in length. In a history essay, your introduction paragraph should serve to give your reader some historical context to your argument, while easily transitioning them to the body of your essay.
Consider your audience. Your history essay should be written with a particular audience in mind, whether it is an instructor, classmates, a journal or any other publication. With that in mind, focus your introduction on piquing the interest of this primary audience.
Write an attention-grabbing lead to draw your readers in. This first sentence should set the tone for your paper and introduce the topic of discussion. You could include a fact or statistic as the first sentence. Or you could introduce a historical quote that relates to your essay. An example of a lead sentence could be, “During World War II, women were called on to step up and fill the roles of men in the workplace.”
Include three to five more sentences that expand on the sentence you posed at the beginning of your introduction. These could include more facts or statistics if your paper is expository, or evidence that support your side of a debate if your paper is argumentative. These sentences should fluidly lead your reader to the thesis, or the main idea of your history essay.
Develop a thesis for your history essay. Your essay will be doomed from the start if it does not express a concise and specific idea that functions as an outline for your paper to follow. This thesis should be conveyed in the final sentence of your introduction, while preparing your reader for the body of the essay. For example, “This paper will address the incidents leading up the Civil War and how the use of the railroad contributed to Union victory.”
About the Author
Liza Hollis has been writing for print and online publications since 2003. Her work has appeared on various digital properties, including USAToday.com. Hollis earned a degree in English Literature from the University of Florida.
Related Articles

How to Write a Page-Long Introduction

What Is a Narrative Response?

How to End an Informative Paper

Tips for High School Students on Creating Introductions...

Steps on Writing a Conclusion to a Rhetorical Response...

Step-by-Step Explanation of How to Write a Research...

How to Write an Excellent Formal Essay

How to Do a Research Paper Outline From Your Note Cards

How to Write a Conclusion for a Critical Essay

How to Write an Introduction for a Descriptive Essay

How to Write the Opening Paragraph of a Research Paper...

How to Write the Intro Paragraph of a Literary Elements...

Steps for Going From Writing a Paragraph to Writing...

How to Write Academic Persuasive Papers

How to Write a Discursive Essay

What Is a Lead-in Statement?

How to Write a Historical Persuasive Essay

Difference Between Topic Sentence Vs. Thesis Statement

Good Ways to Start an Essay

How to Write a Hypothesis to an Analytical Essay
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
How to Write an Introduction for History Essay
Table of Contents
An essay is a sustained piece of writing that responds to a question, topic, or issue.
For example, the skills tested in history essays include historical comprehension, interpretation and analysis, planning, research, and writing.
Students must study the topic, understand its focus and requirements, investigate relevant information, and write a clear, well-organized essay.
Writing a quality history essay could be challenging, even for the most capable students. Essay writing develops and improves with practice and experience, as with other skills.
This article provides straightforward steps and writing aids that will propel you into writing brilliant introductions for your history essays. Read on!

What Is History Essay?
A history essay is an academic essay that responds to a particular historical event. If a paper is about the Battle for Berlin, it would be a history essay. The article would react to the battle’s events, drawing from and analyzing relevant history and drawing conclusions from the fight’s result.
History essays are used to analyze and evaluate student appreciation for history. History essays are generally easier to write than history papers because they provide a format the student already knows.
Step-by-Step Guide: Introduction for History Essay
Here are some basic tips on how to write a successful introduction for history essay .
1. Analyze the Topic
This is an obvious piece of advice that some pupils tragically disregard. Regardless of the subject or topic, the first step to writing a successful essay is to devote considerable attention to the question.
Analyzing the topic may need you to explain the reasons and/or implications of a particular event or circumstance. It may also need to:
- Inquire whether you agree or disagree with a certain assertion.
- Assess the relative importance of a person, organization, or event.
- Describe and/or analyze the reasons and/or implications of a certain action or event.
The first step is to read the essay question numerous times. Underline, highlight, or annotate terms or keywords in the question content.
Consider what it will need of you. Who or what is the target of your attention? Does it specify or imply a specific timeframe? What problem or concern is it requesting you to address?
2. Start With a Plan
Every essay must begin with a detailed outline. You should start formulating a plan as soon as you have received your essay question and given it some attention.
Prepare for research by generating and recording thoughts and ideas. What are your immediate thoughts or reactions to the question? What subjects, events, individuals, or concerns are associated with the question?
Are there any further questions or concerns that arise from the question? What issues or events do you require additional information about? Which historians or resources could be helpful?
If you face a mental “brick wall” or are unsure how to approach the subject, don’t be afraid to share it with another person. Consult your instructor, a qualified classmate, or a reliable individual. Remember that your plan may change after you begin your study as you discover new information.
3. Start Investigating
After analyzing the question and formulating a preliminary plan, you should begin collecting information and proof.
The majority will begin by reading an overview of the topic or issue, typically found in reputable secondary sources. This will refresh or expand your existing knowledge of the problem and offer a foundation for additional questions or research.
From this point on, your research should take shape, directed by the essay question and your planning. Identify unfamiliar terms or concepts and learn their meanings. As you gather information, consider whether it is pertinent or beneficial for answering the question. Be resourceful with your research by looking in several locations.
If you are having trouble accessing information, consult your instructor or a reliable individual for assistance.
4. Develop an Argument
Every good history essay has a clear and convincing thesis statement. A thesis is the central concept or argument of an essay. It acts as both the query response and your paper’s primary focus.
Idealistically, you should be able to articulate your argument in a single sentence.
An essay employing this argument would then clarify and defend these claims in greater depth. Additionally, it will support the claim with argument and facts.
You should begin considering your essay’s thesis at some point during your research. You should be able to summarize it or answer the essay question in a single sentence.
Try to present your argument in a robust, authoritative, and convincing manner. It should sound like the confident response of someone knowledgeable about the topic.
5. Plan an Essay Format
This refers to the history essay structure. Once the majority of your research is complete and you have a solid argument, begin to draft a potential essay structure. This does not need to be elaborate; a few lines or dot points are sufficient.
Every essay must include an introduction, numerous body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Your paragraphs should be well-organized and arranged in a logical order.
Paragraphs can be organized chronologically or thematically (covering events or topics according to their significance or relevance). Each section should have a leading sentence that serves as a clear indicator.
Once you have finalized your essay’s outline, you should begin drafting.
6. Create an Engaging Introduction
Many regard the essay’s start to be its most essential component. It is crucial for multiple reasons.
- It is the initial impression the reader has of your writing.
- Introducing your argument and address the question.
- Outlining the direction of your essay.
Aim for an introduction that is concise, assured, and engaging. Do not squander time with a lengthy story-telling in the beginning; go right to the topic.
Start by providing some context, then address the question, state your argument, and establish the overall direction of your essay.
7. Create Complete Paragraphs
Many students in the field of history fall into the trap of writing brief paragraphs, often consisting of only one or two sentences. A good history essay has paragraphs that are typically 100-200 words in length and function as “mini-essays.”
The focus of a paragraph should be limited to a single topic or issue, which must be thoroughly explored.
A good paragraph will begin with a compelling topic or signposting sentence, also known as an effective introductory sentence.
This phrase introduces the paragraph’s topic and explains its relevance to the issue and your argument. Good paragraphs include comprehensive explanations, some analysis and proof, and a quotation.
8. Conclude With a Powerful Ending
Your essay’s final paragraph is the conclusion. A strong ending should accomplish two goals. First, it should restate or reinforce the thesis statement. Second, you should conclude your essay with a polished conclusion that is neither abrupt nor clunky.
This can be accomplished with a concise summary of “what happened next.” Your conclusion need not be as lengthy or elaborate as your body paragraphs. Avoid providing new evidence or information in conclusion.
9. Cite and Reference Your Sources
A history essay is only likely to be successful if it contains proper citations. Citations or references to credible sources should support your essay’s material, ideas, and arguments.
In addition to acknowledging the work of others, referencing brings legitimacy to your writing. It also provides the instructor or grader with insight into your study.
10. Proofread, Edit, and Solicit Comments
Before being submitted for evaluation, each essay must be checked, amended, and, if required, rewritten. Ideally, essays should be prepared a few days before their due date, then set away for a day or two before being proofread.
While proofreading, check for spelling and grammatical problems, typographical errors, wrong dates, and other factual issues.
Consider how you may improve the essay’s clarity, tone, and organization. Does your writing have a logical structure and flow? Is the navigation in your essay functional and clear? Some sentences may be too long or “rambling.” Repeat yourself often? Do paragraphs require expansion, refinement, or reinforcement with further evidence?
Read your essay out loud, either to yourself or to someone else. Seek assistance and critique from a skilled writer or someone you respect (they need not have expertise in history, only in effective writing).
Writing Tips for Historical Essays
When writing a history essay, the writer must plan out the layout, sequence, and analyze the source material. Here are other tips to follow:
1. Always Use the Third Person When Writing
Never use self-referential language such as “I believe” or “that is my contention.” Good historical writings should adopt the viewpoint of a knowledgeable and impartial third party. They should not sound like an individual giving a perspective, but rather, they should sound rational and factual.
Always use past tense while writing. Using the past tense is an obvious suggestion for a history essay. Always be mindful of your tense usage. When proofreading your writing, watch out for mismatched tenses. One exception to the rule regarding past tense is when discussing the work of contemporary historians.
For example:
“Christian writes…” sounds better than “Christian wrote…” or “Christian has written…”
2. Avoid Generalizations
This is an issue with all writings, but especially with history essays. Generalization is the process of drawing broad conclusions from one or more specific instances.
In history, it occurs most frequently when students examine a particular group and then generalize their experiences to a much wider group. Keep an eye out for them when proofreading.
3. Avoid Rambling
As a general guideline, most of your phrases should be concise and succinct. The longer a sentence develops, the greater the possibility that it may become cumbersome or unclear.
Lengthy sentences easily become disconnected, vague, or ramble. Avoid excessively long sentences and pay particular attention to sentence length when proofreading.
4. Use an Active Voice When Writing
In writing about history, the active voice is preferred above the passive voice. In the active voice, the subject carries out the action. The active voice prevents sentences from being too long, wordy, and unclear.
As with any type of writing, researching, planning, and producing good quality content takes time and effort. With persistence and practice, your historical essay will be as good as it can get.

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Hook Writing Articles
Guide to writing an interesting expository essay introduction.
A good expository essay begins with an introduction that piques the interest of the reader. The expository essay introduction is…
- Hook Writing
Discover the Top Creative Story Introduction Examples
Are you an aspiring author dreaming of becoming the likes of Stephen King or Suzanne Collins? Would you like to…
Creative and Powerful Sentence Starters for Essays
It can’t be said enough, first impressions matter. And it goes the same for essays because your starter sentences will…
Most Important Parts of an Essay Introduction
The introduction is often one of the most important sections in a paper. It creates a sense of what the…
7 Effective Ways to Start a Sentence
There are different ways to start a sentence and convey your message effectively to the readers. Being aware of the…
Six Social Media Hooks to Boost Engagement
To get the most out of your marketing strategy, you should consider using social media hooks to improve your engagement…
History Essay Examples

Top History Essay Examples To Get Inspired By
Published on: May 4, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
History essays are a crucial component of many academic programs, helping students to develop their critical thinking, research, and writing skills.
However, writing a great history essay is not always easy, especially when you are struggling to find the right approach. This is where history essay examples come in handy.
By reading and examining samples of successful history essays, you can gain inspiration, learn new ways to approach your topic. Moreover, you can develop a better understanding of what makes a great history essay.
In this blog, you will find a range of history essay examples that showcase the best practices in history essay writing.
Read on to find useful examples.
On This Page On This Page -->
Sample History Essays
Explore our collection of excellent history paper examples about various topics. Download the pdf examples for free and read to get inspiration for your own essay.
History Essay Samples for Middle School
The Impact of Ancient Civilizations on Modern Society
The Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire
The Causes and Consequences of the American Revolution
History Writing Samples for High School Students
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution on Society
Grade 10 History Essay Example: World War 1 Causes and Effects
Grade 12 History Essay Example: The Impact of Technology on World War II
Ancient History Essay Examples
The Societal and Political Structures of the Maya Civilization
The Role of Phoenicians in the Development of Ancient Mediterranean World
The Contributions of the Indus Civilization
Medieval History Essay Examples
The Crusades Motivations and Consequences
The Beginning of Islamic Golden Age
The Black Death
Modern History Essay Examples
The Suez Crisis and the End of British Dominance
The Rise of China as an Economic Powerhouse
World History Essay Examples
The Role of the Silk Road in Shaping Global Trade and Culture
The Rise and Fall of the Ottoman Empire
The Legacy of Ancient Greek Philosophy and Thought

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
American History Essay Examples
The Civil Rights Movement and its Impact on American Society
The American Civil War and its Aftermath
The Role of Women in American Society Throughout History
African History Essay Examples
The Impact of Colonialism on African Societies
The Rise and Fall of the Mali Empire
European History Essay Examples
The Protestant Reformation and the Rise of Protestantism in Europe
The French Revolution and its Impact on European Politics and Society
The Cold War and the Division of Europe
Argumentative History Essay Examples
Was the US Civil War Primarily About Slavery or States
The Effects of British Colonization on Colonies
Art History Essay Examples
The Influence of Greek and Roman Art on Neoclassicism
The Depiction of Women in Art Throughout History
The Role of Art in the Propaganda of Fascist Regimes
How to Use History Essay Examples
History essay examples are a valuable tool for students looking for inspiration and guidance on how to approach their own essays.
By analyzing successful essays, you can learn effective writing techniques that can be expected in a high-quality history essay.
Here are some tips that will help you take full advantage of the samples above.
Tips for Effectively Using History Essay Examples
- Analyze the Structure:
Pay close attention to how the essay is organized, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Look for how the author transitions between paragraphs and the use of evidence to support their argument.
- Study the Thesis Statement:
The thesis statement is the backbone of any successful history essay. Analyze how the author crafted their thesis statement, and consider how you can apply this to your own writing.
- Take Note of the Evidence:
Effective history essays rely on using strong evidence to support their arguments. Take note of the sources and types of evidence used in the essay. Consider how you can apply similar evidence to support your own arguments.
- Pay Attention to the Formatting and Other Academic Formalities:
The sample essays also demonstrate how you can incorporate academic formalities and standards while keeping the essay engaging. See how these essays fulfill academic standards and try to follow them in your own writing.
- Practice Writing:
While analyzing history essay examples can be helpful, it is important to also practice writing your own essays. Use the examples as inspiration, but try to craft your own unique approach to your topic.
History essays are an essential aspect of learning and understanding the past. By using history essay examples, students can gain inspiration on how to develop their history essays effectively.
Furthermore, following the tips outlined in this blog, students can effectively analyze these essay samples and learn from them.
However, writing a history essay can still be challenging.
Looking for an online essay writing service that specializes in history essays? Look no further!
Our history essay writing service is your go-to source for well-researched and expertly crafted papers.
And for an extra edge in your academic journey, explore our AI essay writing tool . Make history with your grades by choosing our online essay writing service and harnessing the potential of our AI essay writing tool.
Get started today!
Cathy A. (Law, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Background sentences. The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis, your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about. Background sentences explain the important historical ...
Body paragraph 1: Introduction to the Historical Context. Provide background information on the historical context of your topic. Highlight key events, figures, or developments leading up to the main focus of your history essay. Body paragraphs 2-4 (or more): Main Arguments and Supporting Evidence.
sScenario #1: No one has written about my topic. Despite this scholarly neglect, my paper explains the significance of my research topic and offers a provisional interpretation of this new material. sScenario #2: A few scholars have written about my topic, but gaps and deficiencies in the literature still exist.
Step One: Opening Sentence. The first sentence of your introduction sets the stage and draws the reader in. The opening sentence should introduce the historical context of the subject matter of your historical essay. Historical context is the political, social, cultural, and economic setting for a particular document, idea, or event.
Introductions & Conclusions. The introduction and conclusion serve important roles in a history paper. They are not simply perfunctory additions in academic writing, but are critical to your task of making a persuasive argument. A successful introduction will: draw your readers in. culminate in a thesis statement that clearly states your argument.
Download Article. 1. Have a clear structure. When you come to write the body of the essay it is important that you have a clear structure to your argument and to your prose. If your essay drifts, loses focus, or becomes a narrative of events then you will find your grade dropping.
To write an effective essay, students should examine the question, understand its focus and requirements, acquire information and evidence through research, then construct a clear and well-organised response. Writing a good history essay should be rigorous and challenging, even for stronger students. As with other skills, essay writing develops ...
Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine: Write a substantial introduction. Particularly, it's the first impression the professor will have of the paper. State a clear thesis.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Step 1: Understand the History Paper Format. You may be assigned one of several types of history papers. The most common are persuasive essays and research papers. History professors might also ask you to write an analytical paper focused on a particular source or an essay that reviews secondary sources.
If you understand how each part works and fits into the overall essay, you are well on the way to creating a great assessment piece. Most essays will require you to write: 1 Introduction Paragraph. 3 Body Paragraphs. 1 Concluding Paragraph.
Ensure that your introduction is concise and clear so as to capture your reader's curiosity. *Tip: It will be extra impressive to the reader if you outline in a couple of sentences the most prominent schools of thought / historiography on your subject. The introduction is key to making your essay stand out. Mastering a technique for writing ...
Introduction to your history essay should serve as a so-called hook to immediately grab the readers' attention. To make it as catching as possible, you may use a few simple yet trusting methods: Include some facts or impressive statistics. This will help easily win people's trust and make your paper more relevant;
Rather, it requires explication. It requires, as well, that you connect it to your thesis. Remember that you bring evidence in support of your thesis and evidence that's evidence that does not serve that purpose should be excluded. (4) Weave your thesis throughout the body of your essay - Once delineated in your introduction, be sure to weave ...
Dr Nicholas Morton's advice on how to form an essay introduction.
An introduction introduces your topic, giving reasons why it is interesting and anticipating (in order) the steps of your argument. Hence many find that it is a good idea to write the introduction last. ... for example, you write an essay/dissertation on classical history or philosophy of science. In such cases it is a good idea to take a ...
Read the question and understand what it is asking. Work out your approach. Write a detailed essay plan, with different points per paragraph. Have an introduction in which you reveal your understanding of the current debate in interpretations. Remember to handle the concepts in the question and in your answer clearly.
For example, an introduction that says, "The British army fought in the battle of Saratoga" gives the reader virtually no guidance about the paper's thesis (i.e., what the paper concludes/argues about the British army at Saratoga). History papers are not mystery novels. Historians WANT and NEED to give away the ending immediately.
Writing a history essay requires a lot of work and experience. A student needs to show a high level of knowledge and understanding of historical events, as well analytical and research skills. ... To make the introduction catchy and interesting, express the contention and address the main question of the essay. Be confident and clear as this is ...
Introduction. Essays always begin with a clear introduction. The introduction sets up the historical question, presents a clear thesis to the reader, and establishes the scope of the essay--the time period, places, and subjects discussed in the essay. In a short paper, the introduction is one paragraph in length.
The introduction in any essay should grab the attention of your reader while introducing them to the topic of discussion. Introduction paragraphs are generally no more than five to seven sentences in length. In a history essay, your introduction paragraph should serve to give your reader some historical context to ...
Step-by-Step Guide: Introduction for History Essay. Here are some basic tips on how to write a successful introduction for history essay. 1. Analyze the Topic. This is an obvious piece of advice that some pupils tragically disregard. Regardless of the subject or topic, the first step to writing a successful essay is to devote considerable ...
Tips for Effectively Using History Essay Examples. Analyze the Structure: Pay close attention to how the essay is organized, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Look for how the author transitions between paragraphs and the use of evidence to support their argument. Study the Thesis Statement:
research papers on marine fish early life-history and re-lationships would be a good way to do this. With the support of Geoff Moser's family, we sought the partici-pation of larval-fish biologists world-wide to produce re-search papers within Geoff's area of interest. The pres-ent collection of 17 research papers is the result. It is a