
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write a Conclusion for Research Papers (with Examples)

The conclusion of a research paper is a crucial section that plays a significant role in the overall impact and effectiveness of your research paper. However, this is also the section that typically receives less attention compared to the introduction and the body of the paper. The conclusion serves to provide a concise summary of the key findings, their significance, their implications, and a sense of closure to the study. Discussing how can the findings be applied in real-world scenarios or inform policy, practice, or decision-making is especially valuable to practitioners and policymakers. The research paper conclusion also provides researchers with clear insights and valuable information for their own work, which they can then build on and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
The research paper conclusion should explain the significance of your findings within the broader context of your field. It restates how your results contribute to the existing body of knowledge and whether they confirm or challenge existing theories or hypotheses. Also, by identifying unanswered questions or areas requiring further investigation, your awareness of the broader research landscape can be demonstrated.
Remember to tailor the research paper conclusion to the specific needs and interests of your intended audience, which may include researchers, practitioners, policymakers, or a combination of these.
Table of Contents
What is a conclusion in a research paper, summarizing conclusion, editorial conclusion, externalizing conclusion, importance of a good research paper conclusion, how to write a conclusion for your research paper, research paper conclusion examples.
- How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
A conclusion in a research paper is the final section where you summarize and wrap up your research, presenting the key findings and insights derived from your study. The research paper conclusion is not the place to introduce new information or data that was not discussed in the main body of the paper. When working on how to conclude a research paper, remember to stick to summarizing and interpreting existing content. The research paper conclusion serves the following purposes: 1
- Warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend specific course(s) of action.
- Restate key ideas to drive home the ultimate point of your research paper.
- Provide a “take-home” message that you want the readers to remember about your study.

Types of conclusions for research papers
In research papers, the conclusion provides closure to the reader. The type of research paper conclusion you choose depends on the nature of your study, your goals, and your target audience. I provide you with three common types of conclusions:
A summarizing conclusion is the most common type of conclusion in research papers. It involves summarizing the main points, reiterating the research question, and restating the significance of the findings. This common type of research paper conclusion is used across different disciplines.
An editorial conclusion is less common but can be used in research papers that are focused on proposing or advocating for a particular viewpoint or policy. It involves presenting a strong editorial or opinion based on the research findings and offering recommendations or calls to action.
An externalizing conclusion is a type of conclusion that extends the research beyond the scope of the paper by suggesting potential future research directions or discussing the broader implications of the findings. This type of conclusion is often used in more theoretical or exploratory research papers.
Align your conclusion’s tone with the rest of your research paper. Start Writing with Paperpal Now!
The conclusion in a research paper serves several important purposes:
- Offers Implications and Recommendations : Your research paper conclusion is an excellent place to discuss the broader implications of your research and suggest potential areas for further study. It’s also an opportunity to offer practical recommendations based on your findings.
- Provides Closure : A good research paper conclusion provides a sense of closure to your paper. It should leave the reader with a feeling that they have reached the end of a well-structured and thought-provoking research project.
- Leaves a Lasting Impression : Writing a well-crafted research paper conclusion leaves a lasting impression on your readers. It’s your final opportunity to leave them with a new idea, a call to action, or a memorable quote.

Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper is essential to leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here’s a step-by-step process to help you create and know what to put in the conclusion of a research paper: 2
- Research Statement : Begin your research paper conclusion by restating your research statement. This reminds the reader of the main point you’ve been trying to prove throughout your paper. Keep it concise and clear.
- Key Points : Summarize the main arguments and key points you’ve made in your paper. Avoid introducing new information in the research paper conclusion. Instead, provide a concise overview of what you’ve discussed in the body of your paper.
- Address the Research Questions : If your research paper is based on specific research questions or hypotheses, briefly address whether you’ve answered them or achieved your research goals. Discuss the significance of your findings in this context.
- Significance : Highlight the importance of your research and its relevance in the broader context. Explain why your findings matter and how they contribute to the existing knowledge in your field.
- Implications : Explore the practical or theoretical implications of your research. How might your findings impact future research, policy, or real-world applications? Consider the “so what?” question.
- Future Research : Offer suggestions for future research in your area. What questions or aspects remain unanswered or warrant further investigation? This shows that your work opens the door for future exploration.
- Closing Thought : Conclude your research paper conclusion with a thought-provoking or memorable statement. This can leave a lasting impression on your readers and wrap up your paper effectively. Avoid introducing new information or arguments here.
- Proofread and Revise : Carefully proofread your conclusion for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Ensure that your ideas flow smoothly and that your conclusion is coherent and well-structured.
Write your research paper conclusion 2x faster with Paperpal. Try it now!
Remember that a well-crafted research paper conclusion is a reflection of the strength of your research and your ability to communicate its significance effectively. It should leave a lasting impression on your readers and tie together all the threads of your paper. Now you know how to start the conclusion of a research paper and what elements to include to make it impactful, let’s look at a research paper conclusion sample.

How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
A research paper conclusion is not just a summary of your study, but a synthesis of the key findings that ties the research together and places it in a broader context. A research paper conclusion should be concise, typically around one paragraph in length. However, some complex topics may require a longer conclusion to ensure the reader is left with a clear understanding of the study’s significance. Paperpal, an AI writing assistant trusted by over 800,000 academics globally, can help you write a well-structured conclusion for your research paper.
- Sign Up or Log In: Create a new Paperpal account or login with your details.
- Navigate to Features : Once logged in, head over to the features’ side navigation pane. Click on Templates and you’ll find a suite of generative AI features to help you write better, faster.
- Generate an outline: Under Templates, select ‘Outlines’. Choose ‘Research article’ as your document type.
- Select your section: Since you’re focusing on the conclusion, select this section when prompted.
- Choose your field of study: Identifying your field of study allows Paperpal to provide more targeted suggestions, ensuring the relevance of your conclusion to your specific area of research.
- Provide a brief description of your study: Enter details about your research topic and findings. This information helps Paperpal generate a tailored outline that aligns with your paper’s content.
- Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on ‘generate’. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline.
- Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion. The outline serves as a guide, ensuring you cover all critical aspects of a strong conclusion, from summarizing key findings to highlighting the research’s implications.
- Refine and enhance: Paperpal’s ‘Make Academic’ feature can be particularly useful in the final stages. Select any paragraph of your conclusion and use this feature to elevate the academic tone, ensuring your writing is aligned to the academic journal standards.
By following these steps, Paperpal not only simplifies the process of writing a research paper conclusion but also ensures it is impactful, concise, and aligned with academic standards. Sign up with Paperpal today and write your research paper conclusion 2x faster .
The research paper conclusion is a crucial part of your paper as it provides the final opportunity to leave a strong impression on your readers. In the research paper conclusion, summarize the main points of your research paper by restating your research statement, highlighting the most important findings, addressing the research questions or objectives, explaining the broader context of the study, discussing the significance of your findings, providing recommendations if applicable, and emphasizing the takeaway message. The main purpose of the conclusion is to remind the reader of the main point or argument of your paper and to provide a clear and concise summary of the key findings and their implications. All these elements should feature on your list of what to put in the conclusion of a research paper to create a strong final statement for your work.
A strong conclusion is a critical component of a research paper, as it provides an opportunity to wrap up your arguments, reiterate your main points, and leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here are the key elements of a strong research paper conclusion: 1. Conciseness : A research paper conclusion should be concise and to the point. It should not introduce new information or ideas that were not discussed in the body of the paper. 2. Summarization : The research paper conclusion should be comprehensive enough to give the reader a clear understanding of the research’s main contributions. 3 . Relevance : Ensure that the information included in the research paper conclusion is directly relevant to the research paper’s main topic and objectives; avoid unnecessary details. 4 . Connection to the Introduction : A well-structured research paper conclusion often revisits the key points made in the introduction and shows how the research has addressed the initial questions or objectives. 5. Emphasis : Highlight the significance and implications of your research. Why is your study important? What are the broader implications or applications of your findings? 6 . Call to Action : Include a call to action or a recommendation for future research or action based on your findings.
The length of a research paper conclusion can vary depending on several factors, including the overall length of the paper, the complexity of the research, and the specific journal requirements. While there is no strict rule for the length of a conclusion, but it’s generally advisable to keep it relatively short. A typical research paper conclusion might be around 5-10% of the paper’s total length. For example, if your paper is 10 pages long, the conclusion might be roughly half a page to one page in length.
In general, you do not need to include citations in the research paper conclusion. Citations are typically reserved for the body of the paper to support your arguments and provide evidence for your claims. However, there may be some exceptions to this rule: 1. If you are drawing a direct quote or paraphrasing a specific source in your research paper conclusion, you should include a citation to give proper credit to the original author. 2. If your conclusion refers to or discusses specific research, data, or sources that are crucial to the overall argument, citations can be included to reinforce your conclusion’s validity.
The conclusion of a research paper serves several important purposes: 1. Summarize the Key Points 2. Reinforce the Main Argument 3. Provide Closure 4. Offer Insights or Implications 5. Engage the Reader. 6. Reflect on Limitations
Remember that the primary purpose of the research paper conclusion is to leave a lasting impression on the reader, reinforcing the key points and providing closure to your research. It’s often the last part of the paper that the reader will see, so it should be strong and well-crafted.
- Makar, G., Foltz, C., Lendner, M., & Vaccaro, A. R. (2018). How to write effective discussion and conclusion sections. Clinical spine surgery, 31(8), 345-346.
- Bunton, D. (2005). The structure of PhD conclusion chapters. Journal of English for academic purposes , 4 (3), 207-224.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- Paraphrasing in Academic Writing: Answering Top Author Queries
Preflight For Editorial Desk: The Perfect Hybrid (AI + Human) Assistance Against Compromised Manuscripts
You may also like, how to write a high-quality conference paper, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for....
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

3-minute read
- 29th August 2023
If you’re writing a research paper, the conclusion is your opportunity to summarize your findings and leave a lasting impression on your readers. In this post, we’ll take you through how to write an effective conclusion for a research paper and how you can:
· Reword your thesis statement
· Highlight the significance of your research
· Discuss limitations
· Connect to the introduction
· End with a thought-provoking statement
Rewording Your Thesis Statement
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a way that is slightly different from the wording used in the introduction. Avoid presenting new information or evidence in your conclusion. Just summarize the main points and arguments of your essay and keep this part as concise as possible. Remember that you’ve already covered the in-depth analyses and investigations in the main body paragraphs of your essay, so it’s not necessary to restate these details in the conclusion.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Highlighting the Significance of Your Research
The conclusion is a good place to emphasize the implications of your research . Avoid ambiguous or vague language such as “I think” or “maybe,” which could weaken your position. Clearly explain why your research is significant and how it contributes to the broader field of study.
Here’s an example from a (fictional) study on the impact of social media on mental health:
Discussing Limitations
Although it’s important to emphasize the significance of your study, you can also use the conclusion to briefly address any limitations you discovered while conducting your research, such as time constraints or a shortage of resources. Doing this demonstrates a balanced and honest approach to your research.
Connecting to the Introduction
In your conclusion, you can circle back to your introduction , perhaps by referring to a quote or anecdote you discussed earlier. If you end your paper on a similar note to how you began it, you will create a sense of cohesion for the reader and remind them of the meaning and significance of your research.
Ending With a Thought-Provoking Statement
Consider ending your paper with a thought-provoking and memorable statement that relates to the impact of your research questions or hypothesis. This statement can be a call to action, a philosophical question, or a prediction for the future (positive or negative). Here’s an example that uses the same topic as above (social media and mental health):
Expert Proofreading Services
Ensure that your essay ends on a high note by having our experts proofread your research paper. Our team has experience with a wide variety of academic fields and subjects and can help make your paper stand out from the crowd – get started today and see the difference it can make in your work.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research. For most college-level research papers, two or three well-developed paragraphs is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, more paragraphs may be required in describing the key findings and their significance.
Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides you with important opportunities to demonstrate to the reader your understanding of the research problem. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key findings in your analysis that advance new understanding about the research problem, that are unusual or unexpected, or that have important implications applied to practice.
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger significance of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly re-emphasize your answer to the "So What?" question by placing the study within the context of how your research advances past research about the topic.
- Identifying how a gap in the literature has been addressed . The conclusion can be where you describe how a previously identified gap in the literature [first identified in your literature review section] has been addressed by your research and why this contribution is significant.
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers an opportunity to elaborate on the impact and significance of your findings. This is particularly important if your study approached examining the research problem from an unusual or innovative perspective.
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information [which should be avoided], but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing or contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study.
Bunton, David. “The Structure of PhD Conclusion Chapters.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 4 (July 2005): 207–224; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
The general function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of the strengths of your main argument(s) and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Do this by clearly summarizing the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem you investigated in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found in the literature. However, make sure that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings. This reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your paper.
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- Present your conclusions in clear, concise language. Re-state the purpose of your study, then describe how your findings differ or support those of other studies and why [i.e., what were the unique, new, or crucial contributions your study made to the overall research about your topic?].
- Do not simply reiterate your findings or the discussion of your results. Provide a synthesis of arguments presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem and the overall objectives of your study.
- Indicate opportunities for future research if you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper. Highlighting the need for further research provides the reader with evidence that you have an in-depth awareness of the research problem but that further investigations should take place beyond the scope of your investigation.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is presented well:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data [this is opposite of the introduction, which begins with general discussion of the context and ends with a detailed description of the research problem].
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate the research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have conducted will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way. If asked to think introspectively about the topics, do not delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply, not to guess at possible outcomes or make up scenarios not supported by the evidence.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Although an effective conclusion needs to be clear and succinct, it does not need to be written passively or lack a compelling narrative. Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following:
- If your essay deals with a critical, contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem proactively.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action that, if adopted, could address a specific problem in practice or in the development of new knowledge leading to positive change.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion already noted in your paper in order to lend authority and support to the conclusion(s) you have reached [a good source would be from your literature review].
- Explain the consequences of your research in a way that elicits action or demonstrates urgency in seeking change.
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to emphasize the most important finding of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point by drawing from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you presented in your introduction, but add further insight derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results from your study to recast it in new or important ways.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a succinct, declarative statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid
Failure to be concise Your conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too lengthy often have unnecessary information in them. The conclusion is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, and other forms of analysis that you make. Strategies for writing concisely can be found here .
Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from the general [the field of study] to the specific [the research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move from a specific discussion [your research problem] back to a general discussion framed around the implications and significance of your findings [i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In short, the conclusion is where you should place your research within a larger context [visualize your paper as an hourglass--start with a broad introduction and review of the literature, move to the specific analysis and discussion, conclude with a broad summary of the study's implications and significance].
Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. These are problems, deficiencies, or challenges encountered during your study. They should be summarized as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative or unintended results [i.e., findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section and discuss their implications in the discussion section of your paper. In the conclusion, use negative results as an opportunity to explain their possible significance and/or how they may form the basis for future research.
Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to be able to discuss how your research fits within your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize briefly and succinctly how it contributes to new knowledge or a new understanding about the research problem. This element of your conclusion may be only a few sentences long.
Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives in the social and behavioral sciences change while the research is being carried out. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine the original objectives in your introduction. As these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you presumably should know a good deal about it [perhaps even more than your professor!]. Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority as a researcher by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches that...." The overall tone of your conclusion should convey confidence to the reader about the study's validity and realiability.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin Madison; Miquel, Fuster-Marquez and Carmen Gregori-Signes. “Chapter Six: ‘Last but Not Least:’ Writing the Conclusion of Your Paper.” In Writing an Applied Linguistics Thesis or Dissertation: A Guide to Presenting Empirical Research . John Bitchener, editor. (Basingstoke,UK: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), pp. 93-105; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining that they are reaching the end of your paper. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper. This why the conclusion rarely has citations to sources. If you have new information to present, add it to the discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no new information is introduced, the conclusion, along with the discussion section, is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; the conclusion is where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate that you understand the material that you’ve presented, and position your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic, including describing how your research contributes new insights to that scholarship.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: May 25, 2024 4:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Conclusion
Definition:
A research paper conclusion is the final section of a research paper that summarizes the key findings, significance, and implications of the research. It is the writer’s opportunity to synthesize the information presented in the paper, draw conclusions, and make recommendations for future research or actions.
The conclusion should provide a clear and concise summary of the research paper, reiterating the research question or problem, the main results, and the significance of the findings. It should also discuss the limitations of the study and suggest areas for further research.
Parts of Research Paper Conclusion
The parts of a research paper conclusion typically include:
Restatement of the Thesis
The conclusion should begin by restating the thesis statement from the introduction in a different way. This helps to remind the reader of the main argument or purpose of the research.
Summary of Key Findings
The conclusion should summarize the main findings of the research, highlighting the most important results and conclusions. This section should be brief and to the point.
Implications and Significance
In this section, the researcher should explain the implications and significance of the research findings. This may include discussing the potential impact on the field or industry, highlighting new insights or knowledge gained, or pointing out areas for future research.
Limitations and Recommendations
It is important to acknowledge any limitations or weaknesses of the research and to make recommendations for how these could be addressed in future studies. This shows that the researcher is aware of the potential limitations of their work and is committed to improving the quality of research in their field.
Concluding Statement
The conclusion should end with a strong concluding statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. This could be a call to action, a recommendation for further research, or a final thought on the topic.
How to Write Research Paper Conclusion
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion:
- Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study.
- Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results of your research. This can be done by highlighting the most important aspects of your research and the evidence that supports them.
- Discuss the implications: Discuss the implications of your findings for the research area and any potential applications of your research. You should also mention any limitations of your research that may affect the interpretation of your findings.
- Provide a conclusion : Provide a concise conclusion that summarizes the main points of your paper and emphasizes the significance of your research. This should be a strong and clear statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
- Offer suggestions for future research: Lastly, offer suggestions for future research that could build on your findings and contribute to further advancements in the field.
Remember that the conclusion should be brief and to the point, while still effectively summarizing the key findings and implications of your research.
Example of Research Paper Conclusion
Here’s an example of a research paper conclusion:
Conclusion :
In conclusion, our study aimed to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students. Our findings suggest that there is a significant association between social media use and increased levels of anxiety and depression among college students. This highlights the need for increased awareness and education about the potential negative effects of social media use on mental health, particularly among college students.
Despite the limitations of our study, such as the small sample size and self-reported data, our findings have important implications for future research and practice. Future studies should aim to replicate our findings in larger, more diverse samples, and investigate the potential mechanisms underlying the association between social media use and mental health. In addition, interventions should be developed to promote healthy social media use among college students, such as mindfulness-based approaches and social media detox programs.
Overall, our study contributes to the growing body of research on the impact of social media on mental health, and highlights the importance of addressing this issue in the context of higher education. By raising awareness and promoting healthy social media use among college students, we can help to reduce the negative impact of social media on mental health and improve the well-being of young adults.
Purpose of Research Paper Conclusion
The purpose of a research paper conclusion is to provide a summary and synthesis of the key findings, significance, and implications of the research presented in the paper. The conclusion serves as the final opportunity for the writer to convey their message and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
The conclusion should restate the research problem or question, summarize the main results of the research, and explain their significance. It should also acknowledge the limitations of the study and suggest areas for future research or action.
Overall, the purpose of the conclusion is to provide a sense of closure to the research paper and to emphasize the importance of the research and its potential impact. It should leave the reader with a clear understanding of the main findings and why they matter. The conclusion serves as the writer’s opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
When to Write Research Paper Conclusion
The conclusion of a research paper should be written after the body of the paper has been completed. It should not be written until the writer has thoroughly analyzed and interpreted their findings and has written a complete and cohesive discussion of the research.
Before writing the conclusion, the writer should review their research paper and consider the key points that they want to convey to the reader. They should also review the research question, hypotheses, and methodology to ensure that they have addressed all of the necessary components of the research.
Once the writer has a clear understanding of the main findings and their significance, they can begin writing the conclusion. The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, and should reiterate the main points of the research while also providing insights and recommendations for future research or action.
Characteristics of Research Paper Conclusion
The characteristics of a research paper conclusion include:
- Clear and concise: The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, summarizing the key findings and their significance.
- Comprehensive: The conclusion should address all of the main points of the research paper, including the research question or problem, the methodology, the main results, and their implications.
- Future-oriented : The conclusion should provide insights and recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the research.
- Impressive : The conclusion should leave a lasting impression on the reader, emphasizing the importance of the research and its potential impact.
- Objective : The conclusion should be based on the evidence presented in the research paper, and should avoid personal biases or opinions.
- Unique : The conclusion should be unique to the research paper and should not simply repeat information from the introduction or body of the paper.
Advantages of Research Paper Conclusion
The advantages of a research paper conclusion include:
- Summarizing the key findings : The conclusion provides a summary of the main findings of the research, making it easier for the reader to understand the key points of the study.
- Emphasizing the significance of the research: The conclusion emphasizes the importance of the research and its potential impact, making it more likely that readers will take the research seriously and consider its implications.
- Providing recommendations for future research or action : The conclusion suggests practical recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the study.
- Providing closure to the research paper : The conclusion provides a sense of closure to the research paper, tying together the different sections of the paper and leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
- Demonstrating the writer’s contribution to the field : The conclusion provides the writer with an opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
Limitations of Research Paper Conclusion
While the conclusion of a research paper has many advantages, it also has some limitations that should be considered, including:
- I nability to address all aspects of the research: Due to the limited space available in the conclusion, it may not be possible to address all aspects of the research in detail.
- Subjectivity : While the conclusion should be objective, it may be influenced by the writer’s personal biases or opinions.
- Lack of new information: The conclusion should not introduce new information that has not been discussed in the body of the research paper.
- Lack of generalizability: The conclusions drawn from the research may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, limiting the generalizability of the study.
- Misinterpretation by the reader: The reader may misinterpret the conclusions drawn from the research, leading to a misunderstanding of the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Conclusions
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain the functions of conclusions, offer strategies for writing effective ones, help you evaluate conclusions you’ve drafted, and suggest approaches to avoid.
About conclusions
Introductions and conclusions can be difficult to write, but they’re worth investing time in. They can have a significant influence on a reader’s experience of your paper.
Just as your introduction acts as a bridge that transports your readers from their own lives into the “place” of your analysis, your conclusion can provide a bridge to help your readers make the transition back to their daily lives. Such a conclusion will help them see why all your analysis and information should matter to them after they put the paper down.
Your conclusion is your chance to have the last word on the subject. The conclusion allows you to have the final say on the issues you have raised in your paper, to synthesize your thoughts, to demonstrate the importance of your ideas, and to propel your reader to a new view of the subject. It is also your opportunity to make a good final impression and to end on a positive note.
Your conclusion can go beyond the confines of the assignment. The conclusion pushes beyond the boundaries of the prompt and allows you to consider broader issues, make new connections, and elaborate on the significance of your findings.
Your conclusion should make your readers glad they read your paper. Your conclusion gives your reader something to take away that will help them see things differently or appreciate your topic in personally relevant ways. It can suggest broader implications that will not only interest your reader, but also enrich your reader’s life in some way. It is your gift to the reader.
Strategies for writing an effective conclusion
One or more of the following strategies may help you write an effective conclusion:
- Play the “So What” Game. If you’re stuck and feel like your conclusion isn’t saying anything new or interesting, ask a friend to read it with you. Whenever you make a statement from your conclusion, ask the friend to say, “So what?” or “Why should anybody care?” Then ponder that question and answer it. Here’s how it might go: You: Basically, I’m just saying that education was important to Douglass. Friend: So what? You: Well, it was important because it was a key to him feeling like a free and equal citizen. Friend: Why should anybody care? You: That’s important because plantation owners tried to keep slaves from being educated so that they could maintain control. When Douglass obtained an education, he undermined that control personally. You can also use this strategy on your own, asking yourself “So What?” as you develop your ideas or your draft.
- Return to the theme or themes in the introduction. This strategy brings the reader full circle. For example, if you begin by describing a scenario, you can end with the same scenario as proof that your essay is helpful in creating a new understanding. You may also refer to the introductory paragraph by using key words or parallel concepts and images that you also used in the introduction.
- Synthesize, don’t summarize. Include a brief summary of the paper’s main points, but don’t simply repeat things that were in your paper. Instead, show your reader how the points you made and the support and examples you used fit together. Pull it all together.
- Include a provocative insight or quotation from the research or reading you did for your paper.
- Propose a course of action, a solution to an issue, or questions for further study. This can redirect your reader’s thought process and help them to apply your info and ideas to their own life or to see the broader implications.
- Point to broader implications. For example, if your paper examines the Greensboro sit-ins or another event in the Civil Rights Movement, you could point out its impact on the Civil Rights Movement as a whole. A paper about the style of writer Virginia Woolf could point to her influence on other writers or on later feminists.
Strategies to avoid
- Beginning with an unnecessary, overused phrase such as “in conclusion,” “in summary,” or “in closing.” Although these phrases can work in speeches, they come across as wooden and trite in writing.
- Stating the thesis for the very first time in the conclusion.
- Introducing a new idea or subtopic in your conclusion.
- Ending with a rephrased thesis statement without any substantive changes.
- Making sentimental, emotional appeals that are out of character with the rest of an analytical paper.
- Including evidence (quotations, statistics, etc.) that should be in the body of the paper.
Four kinds of ineffective conclusions
- The “That’s My Story and I’m Sticking to It” Conclusion. This conclusion just restates the thesis and is usually painfully short. It does not push the ideas forward. People write this kind of conclusion when they can’t think of anything else to say. Example: In conclusion, Frederick Douglass was, as we have seen, a pioneer in American education, proving that education was a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
- The “Sherlock Holmes” Conclusion. Sometimes writers will state the thesis for the very first time in the conclusion. You might be tempted to use this strategy if you don’t want to give everything away too early in your paper. You may think it would be more dramatic to keep the reader in the dark until the end and then “wow” them with your main idea, as in a Sherlock Holmes mystery. The reader, however, does not expect a mystery, but an analytical discussion of your topic in an academic style, with the main argument (thesis) stated up front. Example: (After a paper that lists numerous incidents from the book but never says what these incidents reveal about Douglass and his views on education): So, as the evidence above demonstrates, Douglass saw education as a way to undermine the slaveholders’ power and also an important step toward freedom.
- The “America the Beautiful”/”I Am Woman”/”We Shall Overcome” Conclusion. This kind of conclusion usually draws on emotion to make its appeal, but while this emotion and even sentimentality may be very heartfelt, it is usually out of character with the rest of an analytical paper. A more sophisticated commentary, rather than emotional praise, would be a more fitting tribute to the topic. Example: Because of the efforts of fine Americans like Frederick Douglass, countless others have seen the shining beacon of light that is education. His example was a torch that lit the way for others. Frederick Douglass was truly an American hero.
- The “Grab Bag” Conclusion. This kind of conclusion includes extra information that the writer found or thought of but couldn’t integrate into the main paper. You may find it hard to leave out details that you discovered after hours of research and thought, but adding random facts and bits of evidence at the end of an otherwise-well-organized essay can just create confusion. Example: In addition to being an educational pioneer, Frederick Douglass provides an interesting case study for masculinity in the American South. He also offers historians an interesting glimpse into slave resistance when he confronts Covey, the overseer. His relationships with female relatives reveal the importance of family in the slave community.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Douglass, Frederick. 1995. Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself. New York: Dover.
Hamilton College. n.d. “Conclusions.” Writing Center. Accessed June 14, 2019. https://www.hamilton.edu//academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/conclusions .
Holewa, Randa. 2004. “Strategies for Writing a Conclusion.” LEO: Literacy Education Online. Last updated February 19, 2004. https://leo.stcloudstate.edu/acadwrite/conclude.html.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
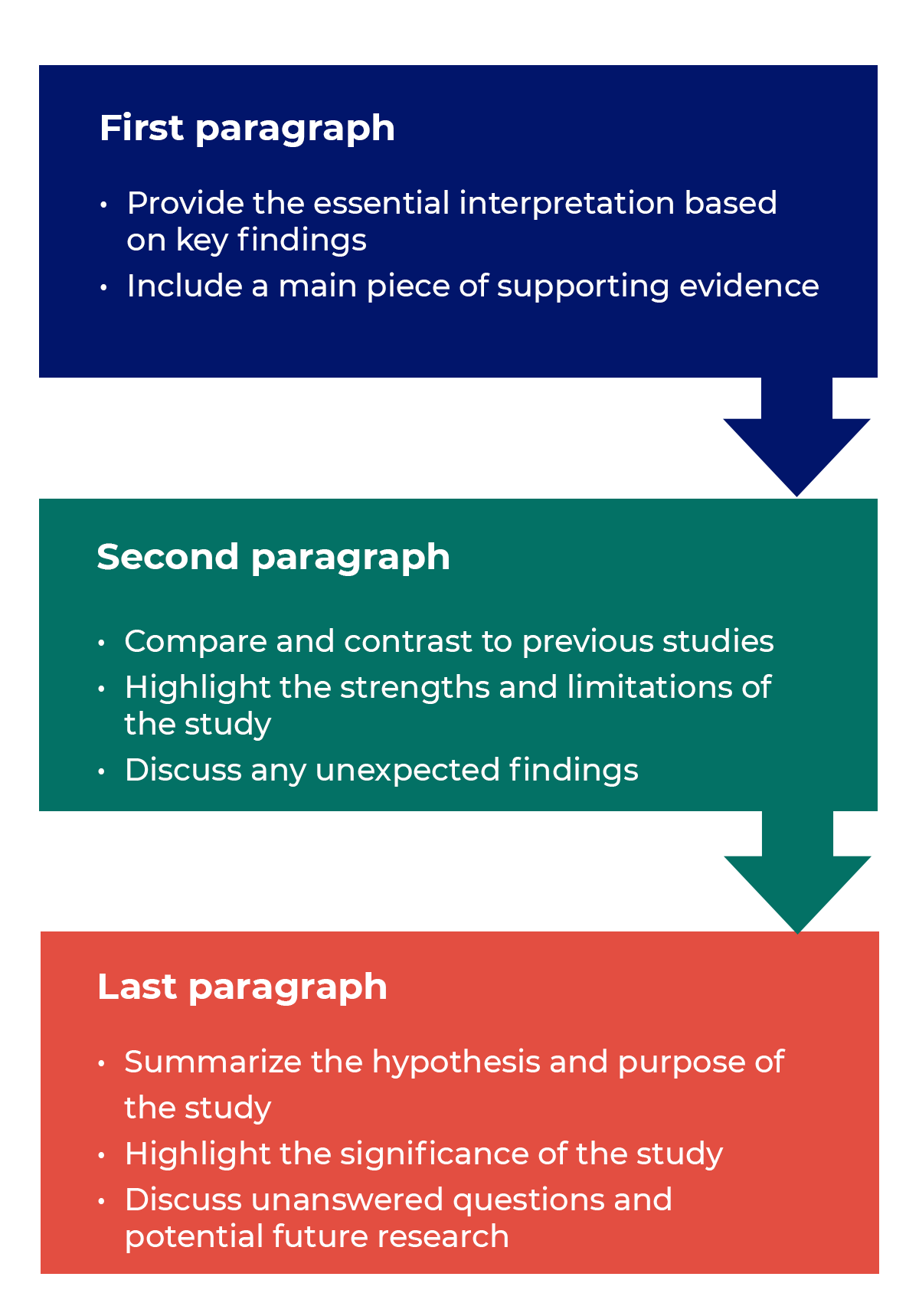
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
Last Updated: May 8, 2024 Approved
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 42 testimonials and 83% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 2,259,999 times.
The conclusion of a research paper needs to summarize the content and purpose of the paper without seeming too wooden or dry. Every basic conclusion must share several key elements, but there are also several tactics you can play around with to craft a more effective conclusion and several you should avoid to prevent yourself from weakening your paper's conclusion. Here are some writing tips to keep in mind when creating a conclusion for your next research paper.
Sample Conclusions
Writing a basic conclusion.

- Do not spend a great amount of time or space restating your topic.
- A good research paper will make the importance of your topic apparent, so you do not need to write an elaborate defense of your topic in the conclusion.
- Usually a single sentence is all you need to restate your topic.
- An example would be if you were writing a paper on the epidemiology of infectious disease, you might say something like "Tuberculosis is a widespread infectious disease that affects millions of people worldwide every year."
- Yet another example from the humanities would be a paper about the Italian Renaissance: "The Italian Renaissance was an explosion of art and ideas centered around artists, writers, and thinkers in Florence."

- A thesis is a narrowed, focused view on the topic at hand.
- This statement should be rephrased from the thesis you included in your introduction. It should not be identical or too similar to the sentence you originally used.
- Try re-wording your thesis statement in a way that complements your summary of the topic of your paper in your first sentence of your conclusion.
- An example of a good thesis statement, going back to the paper on tuberculosis, would be "Tuberculosis is a widespread disease that affects millions of people worldwide every year. Due to the alarming rate of the spread of tuberculosis, particularly in poor countries, medical professionals are implementing new strategies for the diagnosis, treatment, and containment of this disease ."

- A good way to go about this is to re-read the topic sentence of each major paragraph or section in the body of your paper.
- Find a way to briefly restate each point mentioned in each topic sentence in your conclusion. Do not repeat any of the supporting details used within your body paragraphs.
- Under most circumstances, you should avoid writing new information in your conclusion. This is especially true if the information is vital to the argument or research presented in your paper.
- For example, in the TB paper you could summarize the information. "Tuberculosis is a widespread disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Due to the alarming rate of the spread of tuberculosis, particularly in poor countries, medical professionals are implementing new strategies for the diagnosis, treatment, and containment of this disease. In developing countries, such as those in Africa and Southeast Asia, the rate of TB infections is soaring. Crowded conditions, poor sanitation, and lack of access to medical care are all compounding factors in the spread of the disease. Medical experts, such as those from the World Health Organization are now starting campaigns to go into communities in developing countries and provide diagnostic testing and treatments. However, the treatments for TB are very harsh and have many side effects. This leads to patient non-compliance and spread of multi-drug resistant strains of the disease."

- Note that this is not needed for all research papers.
- If you already fully explained what the points in your paper mean or why they are significant, you do not need to go into them in much detail in your conclusion. Simply restating your thesis or the significance of your topic should suffice.
- It is always best practice to address important issues and fully explain your points in the body of your paper. The point of a conclusion to a research paper is to summarize your argument for the reader and, perhaps, to call the reader to action if needed.

- Note that a call for action is not essential to all conclusions. A research paper on literary criticism, for instance, is less likely to need a call for action than a paper on the effect that television has on toddlers and young children.
- A paper that is more likely to call readers to action is one that addresses a public or scientific need. Let's go back to our example of tuberculosis. This is a very serious disease that is spreading quickly and with antibiotic-resistant forms.
- A call to action in this research paper would be a follow-up statement that might be along the lines of "Despite new efforts to diagnose and contain the disease, more research is needed to develop new antibiotics that will treat the most resistant strains of tuberculosis and ease the side effects of current treatments."

- For example, if you are writing a history paper, then you might discuss how the historical topic you discussed matters today. If you are writing about a foreign country, then you might use the conclusion to discuss how the information you shared may help readers understand their own country.
Making Your Conclusion as Effective as Possible

- Since this sort of conclusion is so basic, you must aim to synthesize the information rather than merely summarizing it.
- Instead of merely repeating things you already said, rephrase your thesis and supporting points in a way that ties them all together.
- By doing so, you make your research paper seem like a "complete thought" rather than a collection of random and vaguely related ideas.

- Ask a question in your introduction. In your conclusion, restate the question and provide a direct answer.
- Write an anecdote or story in your introduction but do not share the ending. Instead, write the conclusion to the anecdote in the conclusion of your paper.
- For example, if you wanted to get more creative and put a more humanistic spin on a paper on tuberculosis, you might start your introduction with a story about a person with the disease, and refer to that story in your conclusion. For example, you could say something like this before you re-state your thesis in your conclusion: "Patient X was unable to complete the treatment for tuberculosis due to severe side effects and unfortunately succumbed to the disease."
- Use the same concepts and images introduced in your introduction in your conclusion. The images may or may not appear at other points throughout the research paper.

- Include enough information about your topic to back the statement up but do not get too carried away with excess detail.
- If your research did not provide you with a clear-cut answer to a question posed in your thesis, do not be afraid to indicate as much.
- Restate your initial hypothesis and indicate whether you still believe it or if the research you performed has begun swaying your opinion.
- Indicate that an answer may still exist and that further research could shed more light on the topic at hand.

- This may not be appropriate for all types of research papers. Most research papers, such as one on effective treatment for diseases, will have the information to make the case for a particular argument already in the paper.
- A good example of a paper that might ask a question of the reader in the ending is one about a social issue, such as poverty or government policy.
- Ask a question that will directly get at the heart or purpose of the paper. This question is often the same question, or some version of it, that you may have started with when you began your research.
- Make sure that the question can be answered by the evidence presented in your paper.
- If desired you can briefly summarize the answer after stating the question. You could also leave the question hanging for the reader to answer, though.

- Even without a call to action, you can still make a recommendation to your reader.
- For instance, if you are writing about a topic like third-world poverty, you can various ways for the reader to assist in the problem without necessarily calling for more research.
- Another example would be, in a paper about treatment for drug-resistant tuberculosis, you could suggest donating to the World Health Organization or research foundations that are developing new treatments for the disease.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls

- These sayings usually sound stiff, unnatural, or trite when used in writing.
- Moreover, using a phrase like "in conclusion" to begin your conclusion is a little too straightforward and tends to lead to a weak conclusion. A strong conclusion can stand on its own without being labeled as such.

- Always state the main argument or thesis in the introduction. A research paper is an analytical discussion of an academic topic, not a mystery novel.
- A good, effective research paper will allow your reader to follow your main argument from start to finish.
- This is why it is best practice to start your paper with an introduction that states your main argument and to end the paper with a conclusion that re-states your thesis for re-iteration.

- All significant information should be introduced in the body of the paper.
- Supporting evidence expands the topic of your paper by making it appear more detailed. A conclusion should narrow the topic to a more general point.
- A conclusion should only summarize what you have already stated in the body of your paper.
- You may suggest further research or a call to action, but you should not bring in any new evidence or facts in the conclusion.

- Most often, a shift in tone occurs when a research paper with an academic tone gives an emotional or sentimental conclusion.
- Even if the topic of the paper is of personal significance for you, you should not indicate as much in your paper.
- If you want to give your paper a more humanistic slant, you could start and end your paper with a story or anecdote that would give your topic more personal meaning to the reader.
- This tone should be consistent throughout the paper, however.

- Apologetic statements include phrases like "I may not be an expert" or "This is only my opinion."
- Statements like this can usually be avoided by refraining from writing in the first-person.
- Avoid any statements in the first-person. First-person is generally considered to be informal and does not fit with the formal tone of a research paper.
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/724/04/
- ↑ http://www.crlsresearchguide.org/18_Writing_Conclusion.asp
- ↑ http://writing.wisc.edu/Handbook/PlanResearchPaper.html#conclusion
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/conclusions/
- ↑ http://writing2.richmond.edu/writing/wweb/conclude.html
About This Article

To write a conclusion for a research paper, start by restating your thesis statement to remind your readers what your main topic is and bring everything full circle. Then, briefly summarize all of the main points you made throughout your paper, which will help remind your readers of everything they learned. You might also want to include a call to action if you think more research or work needs to be done on your topic by writing something like, "Despite efforts to contain the disease, more research is needed to develop antibiotics." Finally, end your conclusion by explaining the broader context of your topic and why your readers should care about it, which will help them understand why your topic is relevant and important. For tips from our Academic co-author, like how to avoid common pitfalls when writing your conclusion, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Ummay Aimen
Sep 30, 2016
Did this article help you?

Oct 22, 2017
Sally Larrin
Mar 17, 2018
Maya Loeven
Jun 4, 2017
Sep 26, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
How to write a strong conclusion for your research paper
Last updated
17 February 2024
Reviewed by
Writing a research paper is a chance to share your knowledge and hypothesis. It's an opportunity to demonstrate your many hours of research and prove your ability to write convincingly.
Ideally, by the end of your research paper, you'll have brought your readers on a journey to reach the conclusions you've pre-determined. However, if you don't stick the landing with a good conclusion, you'll risk losing your reader’s trust.
Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper involves a few important steps, including restating the thesis and summing up everything properly.
Find out what to include and what to avoid, so you can effectively demonstrate your understanding of the topic and prove your expertise.
- Why is a good conclusion important?
A good conclusion can cement your paper in the reader’s mind. Making a strong impression in your introduction can draw your readers in, but it's the conclusion that will inspire them.
- What to include in a research paper conclusion
There are a few specifics you should include in your research paper conclusion. Offer your readers some sense of urgency or consequence by pointing out why they should care about the topic you have covered. Discuss any common problems associated with your topic and provide suggestions as to how these problems can be solved or addressed.
The conclusion should include a restatement of your initial thesis. Thesis statements are strengthened after you’ve presented supporting evidence (as you will have done in the paper), so make a point to reintroduce it at the end.
Finally, recap the main points of your research paper, highlighting the key takeaways you want readers to remember. If you've made multiple points throughout the paper, refer to the ones with the strongest supporting evidence.
- Steps for writing a research paper conclusion
Many writers find the conclusion the most challenging part of any research project . By following these three steps, you'll be prepared to write a conclusion that is effective and concise.
- Step 1: Restate the problem
Always begin by restating the research problem in the conclusion of a research paper. This serves to remind the reader of your hypothesis and refresh them on the main point of the paper.
When restating the problem, take care to avoid using exactly the same words you employed earlier in the paper.
- Step 2: Sum up the paper
After you've restated the problem, sum up the paper by revealing your overall findings. The method for this differs slightly, depending on whether you're crafting an argumentative paper or an empirical paper.
Argumentative paper: Restate your thesis and arguments
Argumentative papers involve introducing a thesis statement early on. In crafting the conclusion for an argumentative paper, always restate the thesis, outlining the way you've developed it throughout the entire paper.
It might be appropriate to mention any counterarguments in the conclusion, so you can demonstrate how your thesis is correct or how the data best supports your main points.
Empirical paper: Summarize research findings
Empirical papers break down a series of research questions. In your conclusion, discuss the findings your research revealed, including any information that surprised you.
Be clear about the conclusions you reached, and explain whether or not you expected to arrive at these particular ones.
- Step 3: Discuss the implications of your research
Argumentative papers and empirical papers also differ in this part of a research paper conclusion. Here are some tips on crafting conclusions for argumentative and empirical papers.
Argumentative paper: Powerful closing statement
In an argumentative paper, you'll have spent a great deal of time expressing the opinions you formed after doing a significant amount of research. Make a strong closing statement in your argumentative paper's conclusion to share the significance of your work.
You can outline the next steps through a bold call to action, or restate how powerful your ideas turned out to be.
Empirical paper: Directions for future research
Empirical papers are broader in scope. They usually cover a variety of aspects and can include several points of view.
To write a good conclusion for an empirical paper, suggest the type of research that could be done in the future, including methods for further investigation or outlining ways other researchers might proceed.
If you feel your research had any limitations, even if they were outside your control, you could mention these in your conclusion.
After you finish outlining your conclusion, ask someone to read it and offer feedback. In any research project you're especially close to, it can be hard to identify problem areas. Having a close friend or someone whose opinion you value read the research paper and provide honest feedback can be invaluable. Take note of any suggested edits and consider incorporating them into your paper if they make sense.
- Things to avoid in a research paper conclusion
Keep these aspects to avoid in mind as you're writing your conclusion and refer to them after you've created an outline.
Dry summary
Writing a memorable, succinct conclusion is arguably more important than a strong introduction. Take care to avoid just rephrasing your main points, and don't fall into the trap of repeating dry facts or citations.
You can provide a new perspective for your readers to think about or contextualize your research. Either way, make the conclusion vibrant and interesting, rather than a rote recitation of your research paper’s highlights.
Clichéd or generic phrasing
Your research paper conclusion should feel fresh and inspiring. Avoid generic phrases like "to sum up" or "in conclusion." These phrases tend to be overused, especially in an academic context and might turn your readers off.
The conclusion also isn't the time to introduce colloquial phrases or informal language. Retain a professional, confident tone consistent throughout your paper’s conclusion so it feels exciting and bold.
New data or evidence
While you should present strong data throughout your paper, the conclusion isn't the place to introduce new evidence. This is because readers are engaged in actively learning as they read through the body of your paper.
By the time they reach the conclusion, they will have formed an opinion one way or the other (hopefully in your favor!). Introducing new evidence in the conclusion will only serve to surprise or frustrate your reader.
Ignoring contradictory evidence
If your research reveals contradictory evidence, don't ignore it in the conclusion. This will damage your credibility as an expert and might even serve to highlight the contradictions.
Be as transparent as possible and admit to any shortcomings in your research, but don't dwell on them for too long.
Ambiguous or unclear resolutions
The point of a research paper conclusion is to provide closure and bring all your ideas together. You should wrap up any arguments you introduced in the paper and tie up any loose ends, while demonstrating why your research and data are strong.
Use direct language in your conclusion and avoid ambiguity. Even if some of the data and sources you cite are inconclusive or contradictory, note this in your conclusion to come across as confident and trustworthy.
- Examples of research paper conclusions
Your research paper should provide a compelling close to the paper as a whole, highlighting your research and hard work. While the conclusion should represent your unique style, these examples offer a starting point:
Ultimately, the data we examined all point to the same conclusion: Encouraging a good work-life balance improves employee productivity and benefits the company overall. The research suggests that when employees feel their personal lives are valued and respected by their employers, they are more likely to be productive when at work. In addition, company turnover tends to be reduced when employees have a balance between their personal and professional lives. While additional research is required to establish ways companies can support employees in creating a stronger work-life balance, it's clear the need is there.
Social media is a primary method of communication among young people. As we've seen in the data presented, most young people in high school use a variety of social media applications at least every hour, including Instagram and Facebook. While social media is an avenue for connection with peers, research increasingly suggests that social media use correlates with body image issues. Young girls with lower self-esteem tend to use social media more often than those who don't log onto social media apps every day. As new applications continue to gain popularity, and as more high school students are given smartphones, more research will be required to measure the effects of prolonged social media use.
What are the different kinds of research paper conclusions?
There are no formal types of research paper conclusions. Ultimately, the conclusion depends on the outline of your paper and the type of research you’re presenting. While some experts note that research papers can end with a new perspective or commentary, most papers should conclude with a combination of both. The most important aspect of a good research paper conclusion is that it accurately represents the body of the paper.
Can I present new arguments in my research paper conclusion?
Research paper conclusions are not the place to introduce new data or arguments. The body of your paper is where you should share research and insights, where the reader is actively absorbing the content. By the time a reader reaches the conclusion of the research paper, they should have formed their opinion. Introducing new arguments in the conclusion can take a reader by surprise, and not in a positive way. It might also serve to frustrate readers.
How long should a research paper conclusion be?
There's no set length for a research paper conclusion. However, it's a good idea not to run on too long, since conclusions are supposed to be succinct. A good rule of thumb is to keep your conclusion around 5 to 10 percent of the paper's total length. If your paper is 10 pages, try to keep your conclusion under one page.
What should I include in a research paper conclusion?
A good research paper conclusion should always include a sense of urgency, so the reader can see how and why the topic should matter to them. You can also note some recommended actions to help fix the problem and some obstacles they might encounter. A conclusion should also remind the reader of the thesis statement, along with the main points you covered in the paper. At the end of the conclusion, add a powerful closing statement that helps cement the paper in the mind of the reader.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Conclusions
Writing a conclusion.
A conclusion is an important part of the paper; it provides closure for the reader while reminding the reader of the contents and importance of the paper. It accomplishes this by stepping back from the specifics in order to view the bigger picture of the document. In other words, it is reminding the reader of the main argument. For most course papers, it is usually one paragraph that simply and succinctly restates the main ideas and arguments, pulling everything together to help clarify the thesis of the paper. A conclusion does not introduce new ideas; instead, it should clarify the intent and importance of the paper. It can also suggest possible future research on the topic.
An Easy Checklist for Writing a Conclusion
It is important to remind the reader of the thesis of the paper so he is reminded of the argument and solutions you proposed.
Think of the main points as puzzle pieces, and the conclusion is where they all fit together to create a bigger picture. The reader should walk away with the bigger picture in mind.
Make sure that the paper places its findings in the context of real social change.
Make sure the reader has a distinct sense that the paper has come to an end. It is important to not leave the reader hanging. (You don’t want her to have flip-the-page syndrome, where the reader turns the page, expecting the paper to continue. The paper should naturally come to an end.)
No new ideas should be introduced in the conclusion. It is simply a review of the material that is already present in the paper. The only new idea would be the suggesting of a direction for future research.
Conclusion Example
As addressed in my analysis of recent research, the advantages of a later starting time for high school students significantly outweigh the disadvantages. A later starting time would allow teens more time to sleep--something that is important for their physical and mental health--and ultimately improve their academic performance and behavior. The added transportation costs that result from this change can be absorbed through energy savings. The beneficial effects on the students’ academic performance and behavior validate this decision, but its effect on student motivation is still unknown. I would encourage an in-depth look at the reactions of students to such a change. This sort of study would help determine the actual effects of a later start time on the time management and sleep habits of students.
Related Webinar
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Thesis Statements
- Next Page: Writer's Block
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
So much is at stake in writing a conclusion. This is, after all, your last chance to persuade your readers to your point of view, to impress yourself upon them as a writer and thinker. And the impression you create in your conclusion will shape the impression that stays with your readers after they've finished the essay.
The end of an essay should therefore convey a sense of completeness and closure as well as a sense of the lingering possibilities of the topic, its larger meaning, its implications: the final paragraph should close the discussion without closing it off.
To establish a sense of closure, you might do one or more of the following:
- Conclude by linking the last paragraph to the first, perhaps by reiterating a word or phrase you used at the beginning.
- Conclude with a sentence composed mainly of one-syllable words. Simple language can help create an effect of understated drama.
- Conclude with a sentence that's compound or parallel in structure; such sentences can establish a sense of balance or order that may feel just right at the end of a complex discussion.
To close the discussion without closing it off, you might do one or more of the following:
- Conclude with a quotation from or reference to a primary or secondary source, one that amplifies your main point or puts it in a different perspective. A quotation from, say, the novel or poem you're writing about can add texture and specificity to your discussion; a critic or scholar can help confirm or complicate your final point. For example, you might conclude an essay on the idea of home in James Joyce's short story collection, Dubliners , with information about Joyce's own complex feelings towards Dublin, his home. Or you might end with a biographer's statement about Joyce's attitude toward Dublin, which could illuminate his characters' responses to the city. Just be cautious, especially about using secondary material: make sure that you get the last word.
- Conclude by setting your discussion into a different, perhaps larger, context. For example, you might end an essay on nineteenth-century muckraking journalism by linking it to a current news magazine program like 60 Minutes .
- Conclude by redefining one of the key terms of your argument. For example, an essay on Marx's treatment of the conflict between wage labor and capital might begin with Marx's claim that the "capitalist economy is . . . a gigantic enterprise of dehumanization "; the essay might end by suggesting that Marxist analysis is itself dehumanizing because it construes everything in economic -- rather than moral or ethical-- terms.
- Conclude by considering the implications of your argument (or analysis or discussion). What does your argument imply, or involve, or suggest? For example, an essay on the novel Ambiguous Adventure , by the Senegalese writer Cheikh Hamidou Kane, might open with the idea that the protagonist's development suggests Kane's belief in the need to integrate Western materialism and Sufi spirituality in modern Senegal. The conclusion might make the new but related point that the novel on the whole suggests that such an integration is (or isn't) possible.
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay:
- Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas.
- Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up." These phrases can be useful--even welcome--in oral presentations. But readers can see, by the tell-tale compression of the pages, when an essay is about to end. You'll irritate your audience if you belabor the obvious.
- Resist the urge to apologize. If you've immersed yourself in your subject, you now know a good deal more about it than you can possibly include in a five- or ten- or 20-page essay. As a result, by the time you've finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you've produced. (And if you haven't immersed yourself in your subject, you may be feeling even more doubtful about your essay as you approach the conclusion.) Repress those doubts. Don't undercut your authority by saying things like, "this is just one approach to the subject; there may be other, better approaches. . ."
Copyright 1998, Pat Bellanca, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

When you're wrapping up a research paper, the conclusion is like the grand finale of a fireworks show – it's your chance to leave a lasting impression. In this article, we'll break down the steps to help you write a winning research paper conclusion that not only recaps your main points but also ties everything together. Consider it the "So what?" moment – why should people care about your research? Our professional essay writers will guide you through making your conclusion strong, clear, and something that sticks with your readers long after they've put down your paper. So, let's dive in and ensure your research ends on a high note!
What Is a Conclusion in a Research Paper
In a research paper, the conclusion serves as the final segment, where you summarize the main points and findings of your study. It's not just a repetition of what you've already said but rather a chance to tie everything together and highlight the significance of your research. As you learn how to start a research paper , a good conclusion also often discusses the implications of your findings, suggests potential areas for further research, and leaves the reader with a lasting impression of the importance and relevance of your work in the broader context of the field. Essentially, it's your last opportunity to make a strong impact and leave your readers with a clear understanding of the significance of your research. Here’s a research paper conclusion example:
In conclusion, this research paper has navigated the intricacies of sustainable urban development, shedding light on the pivotal role of community engagement and innovative planning strategies. Through applying qualitative and quantitative research methods, we've uncovered valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities inherent in fostering environmentally friendly urban spaces. The implications of these findings extend beyond the confines of this study, emphasizing the imperative for continued exploration in the realms of urban planning and environmental sustainability. By emphasizing both the practical applications and theoretical contributions, this research underscores the significance of community involvement and forward-thinking strategies in shaping the future of urban landscapes. As cities evolve, incorporating these insights into planning and development practices will create resilient and harmonious urban environments.
Conclusion Outline for Research Paper
This outline for a research paper conclusion provides a structured framework to ensure that your ending effectively summarizes the key elements of your research paper and leaves a lasting impression on your readers. Adjust the content based on the specific requirements and focus of your research.
Restate the Thesis Statement
- Briefly restate the main thesis or research question.
- Emphasize the core objective or purpose of the study.
Summarize Key Findings
- Recap the main points and key findings from each section of the paper.
- Provide a concise overview of the research journey.
Discuss Implications
- Explore the broader implications of the research findings.
- Discuss how the results contribute to the existing body of knowledge in the field.
Address Limitations
- Acknowledge any limitations or constraints encountered during the research process.
- Explain how these limitations may impact the interpretation of the findings.
Suggest Areas for Future Research
- Propose potential directions for future studies related to the topic.
- Identify gaps in the current research that warrant further exploration.
Reaffirm Significance
- Reaffirm the importance and relevance of the research in the broader context.
- Highlight the practical applications or real-world implications of the study.
Concluding Statement
- Craft a strong, memorable closing statement that leaves a lasting impression.
- Sum up the overall impact of the research and its potential contribution to the field.
Study the full guide on how to make a research paper outline here, which will also specify the conclusion writing specifics to improve your general prowess.
Tips on How to Make a Conclusion in Research
Here are key considerations regarding a conclusion for research paper to not only recap the primary ideas in your work but also delve deeper to earn a higher grade:

- Provide a concise recap of your main research outcomes.
- Remind readers of your research goals and their accomplishments.
- Stick to summarizing existing content; refrain from adding new details.
- Emphasize why your research matters and its broader implications.
- Clearly explain the practical or theoretical impact of your findings.
- Prompt readers to reflect on how your research influences their perspective.
- Briefly discuss the robustness of your research methods.
- End with a suggestion for future research or a practical application.
- Transparently address any constraints or biases in your study.
- End on a powerful note, leaving a memorable impression on your readers.
.webp)
For your inspiration, we’ve also prepared this research proposal example APA , which dwells on another important aspect of research writing.
How to Write a Research Paper Conclusion
As you finish your research paper, the conclusion takes center stage. In this section, we've got five practical tips for writing a conclusion for a research paper. We'll guide you through summarizing your key findings, revisiting your research goals, discussing the bigger picture, addressing any limitations, and ending on a powerful note. Think of it as your roadmap to creating a conclusion that not only wraps up your research but also leaves a lasting impact on your readers. Let's dive in and make sure your conclusion stands out for all the right reasons!
.webp)
Synthesize Core Discoveries. Initiate your conclusion by synthesizing the essential discoveries of your research. Offer a succinct recapitulation of the primary points and outcomes you have elucidated in your paper. This aids in reinforcing the gravity of your work and reiterates the pivotal information you have presented.
Revisit Research Objectives. Revisit the research objectives or questions you outlined at the beginning of your paper. Assess whether you have successfully addressed these objectives and if your findings align with the initial goals of your research. This reflection helps tie your conclusion back to the purpose of your study.
Discuss Implications and Contributions. Discuss the broader implications of your research and its potential contributions to the field. Consider how your findings might impact future research, applications, or understanding of the subject matter. This demonstrates the significance of your work and places it within a larger context.
Address Limitations and Future Research. Acknowledge any limitations in your study, such as constraints in data collection or potential biases. Briefly discuss how these limitations might have affected your results. Additionally, suggest areas for future research that could build upon your work, addressing any unanswered questions or unexplored aspects. This demonstrates a thoughtful approach to your research.
End with a Strong Conclusion Statement. Conclude your research paper with a strong and memorable statement that reinforces the key message you want readers to take away. This could be a call to action, a proposal for further investigation, or a reflection on the broader significance of your findings. Leave your readers with a lasting impression that emphasizes the importance of your research. Remember that you can buy a research paper anytime if you lack time or get stuck in writer’s block.
Want to Enjoy the Benefits of Academic Freedom?
With our top-notch writers and 24/7 support, you can relax and focus on what really matters
Stylistic Devices to Use in a Conclusion
Discover distinctive stylistic insights that you can apply when writing a conclusion for a research paper:
- Rhetorical Questions. When using rhetorical questions, strategically place them to engage readers' minds. For instance, you might pose a question that prompts reflection on the broader implications of your findings, leaving your audience with something to ponder.
- Powerful Language. Incorporate strong language to convey a sense of conviction and importance. Choose words that resonate with the overall tone of your research and amplify the significance of your conclusions. This adds weight to your key messages.
- Repetitions. Repetitions can be employed to reinforce essential ideas. Reiterate key phrases or concepts in a way that emphasizes their importance without sounding redundant. This technique serves to drive home your main points.
- Anecdotes. Integrating anecdotes into your conclusion can provide a human touch. Share a brief and relevant story that connects with your research, making the information more relatable and memorable for your audience.
- Vivid Imagery. Lastly, use vivid imagery to paint a picture in the minds of your readers. Appeal to their senses by describing scenarios or outcomes related to your research. This creates a more immersive and lasting impression.
If you have a larger paper to write, for example a thesis, use our custom dissertation writing can help you in no time.
How to Make a Conclusion Logically Appealing
Knowing how to write a conclusion for a research paper that is logically appealing is important for leaving a lasting impression on your readers. Here are some tips to achieve this:
Logical Sequencing
- Present your conclusion in a structured manner, following the natural flow of your paper. Readers should effortlessly follow your thought process, making your conclusion more accessible and persuasive.
Reinforce Main Arguments
- Emphasize the core arguments and findings from your research. By reinforcing key points, you solidify your stance and provide a logical culmination to your paper.
Address Counterarguments
- Acknowledge and address potential counterarguments or limitations in your research. Demonstrate intellectual honesty and strengthen your conclusion by preemptively addressing potential doubts.
Connect with Introduction
- Revisit themes or concepts introduced in your introduction to create a cohesive narrative, allowing readers to trace the logical progression of your research from start to finish.
Propose Actionable Insights
- Suggest practical applications or recommendations based on your findings. This will add a forward-looking dimension, making your conclusion more relevant and compelling.
Highlight Significance
- Clearly articulate the broader implications of your research to convey the importance of your work and its potential impact on the field, making your conclusion logically compelling.
Are you ready to produce an A-grade assignment? If not, opt for a custom research paper from our skilled writers across various disciplines.
Avoid These Things When Writing a Research Paper Conclusion
As you write your conclusion of research paper, there’s a list of things professional writers don’t recommend doing. Consider these issues carefully:

- Repetition of Exact Phrases
- Repetitively using the same phrases or sentences from the main body. Repetition can make your conclusion seem redundant and less engaging.
- Overly Lengthy Summaries
- Providing excessively detailed summaries of each section of your paper. Readers may lose interest if the conclusion becomes too long and detailed.
- Unclear Connection to the Introduction
- Failing to connect the conclusion back to the introduction. A lack of continuity may make the paper feel disjointed.
- Adding New Arguments or Ideas
- Introducing new arguments or ideas that were not addressed in the body. This can confuse the reader and disrupt the coherence of your paper.
- Overuse of Complex Jargon
- Using excessively complex or technical language without clarification. Clear communication is essential in the conclusion, ensuring broad understanding.
- Apologizing or Undermining Confidence
- Apologizing for limitations or expressing doubt about your work. Maintain a confident tone; if limitations exist, present them objectively without undermining your research.
- Sweeping Generalizations
- Making overly broad or unsupported generalizations. Such statements can weaken the credibility of your conclusion.
- Neglecting the Significance
- Failing to emphasize the broader significance of your research. Readers need to understand why your findings matter in a larger context.
- Abrupt Endings
- Concluding abruptly without a strong closing statement. A powerful ending leaves a lasting impression; avoid a sudden or weak conclusion.
Research Paper Conclusion Example
That covers the essential aspects of summarizing a research paper. The only remaining step is to review the conclusion examples for research paper provided by our team.
Like our examples? Order our research proposal writing service to write paper according to your instructions to avoid plagiarizing and to keep your academic integrity strong.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the knowledge of how to write the conclusion of a research paper is pivotal for presenting your findings and leaving a lasting impression on your readers. By summarizing the key points, reiterating the significance of your research, and offering avenues for future exploration, you can create a conclusion that not only reinforces the value of your study but also encourages further academic discourse. Remember to balance brevity and completeness, ensuring your conclusion is concise yet comprehensive. Emphasizing the practical implications of your research and connecting it to the broader academic landscape will help solidify the impact of your work. Pay someone to write a research paper if you are having a hard time finishing your coursework on time.
Tired of Stressing Over Endless Essays and Deadlines?
Let us take the load off your shoulders! Order your custom research paper today and experience the relief of knowing that your assignment is in expert hands
How To Write A Conclusion For A Research Paper?
What should the conclusion of a research paper contain, how to start a conclusion paragraph for a research paper.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Conclusions


Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Conclusions wrap up what you have been discussing in your paper. After moving from general to specific information in the introduction and body paragraphs, your conclusion should begin pulling back into more general information that restates the main points of your argument. Conclusions may also call for action or overview future possible research. The following outline may help you conclude your paper:
In a general way,
- Restate your topic and why it is important,
- Restate your thesis/claim,
- Address opposing viewpoints and explain why readers should align with your position,
- Call for action or overview future research possibilities.
Remember that once you accomplish these tasks, unless otherwise directed by your instructor, you are finished. Done. Complete. Don't try to bring in new points or end with a whiz bang(!) conclusion or try to solve world hunger in the final sentence of your conclusion. Simplicity is best for a clear, convincing message.
The preacher's maxim is one of the most effective formulas to follow for argument papers:
Tell what you're going to tell them (introduction).
Tell them (body).
Tell them what you told them (conclusion).
How to Craft Your Ideal Thesis Research Topic
.webp)
Table of contents

Catherine Miller
Writing your undergraduate thesis is probably one of the most interesting parts of studying, especially because you get to choose your area of study. But as both a student and a teacher who’s helped countless students develop their research topics, I know this freedom can be just as intimidating as it is liberating.
Fortunately, there’a a step-by-step process you can follow that will help make the whole process a lot easier. In this article, I’ll show you how to choose a unique, specific thesis topic that’s true to your passions and interests, while making a contribution to your field.
.webp)
Choose a topic that you’re interested in
First things first: double-check with your teachers or supervisor if there are any constraints on your research topic. Once your parameters are clear, it’s time to identify what lights you up — after all, you’re going to be spending a lot of time thinking about it.
Within your field of study, you probably already have some topics that have grabbed your attention more than others. This can be a great place to start. Additionally, consider using the rest of your academic and extra-curricular interests as a source of ideas. At this stage, you only need a broad topic before you narrow it down to a specific question.
If you’re feeling stuck, here are some things to try:
- Look back through old course notes to remind yourself of topics you previously covered. Do any of these inspire you?
- Talk to potential supervisors about your ideas, as they can point you toward areas you might not have considered.
- Think about the things you enjoy in everyday life — whether that’s cycling, cinema, cooking, or fashion — then consider if there are any overlaps with your field of study.
- Imagine you have been asked to give a presentation or record a podcast in the next three days. What topics would you feel confident discussing?
- Watch a selection of existing lectures or explainer videos, or listen to podcasts by experts in your field. Note which topics you feel curious to explore further.
- Discuss your field of study with teachers friends and family, some with existing knowledge and some without. Which aspects do you enjoy talking about?
By doing all this, you might uncover some unusual and exciting avenues for research. For example, when writing my Master’s dissertation, I decided to combine my field of study (English teaching methodology) with one of my passions outside work (creative writing). In my undergraduate course, a friend drew on her lived experience of disability to look into the literary portrayal of disability in the ancient world.
Do your research
Once you’ve chosen your topic of interest, it’s time to dive into research. This is a really important part of this early process because it allows you to:
- See what other people have written about the topic — you don’t want to cover the same old ground as everyone else.
- Gain perspective on the big questions surrounding the topic.
- Go deeper into the parts that interest you to help you decide where to focus.
- Start building your bibliography and a bank of interesting quotations.
A great way to start is to visit your library for an introductory book. For example, the “A Very Short Introduction” series from the Oxford University Press provides overviews of a range of themes. Similar types of overviews may have the title “ A Companion to [Subject]” or “[Subject] A Student Companion”. Ask your librarian or teacher if you’re not sure where to begin.
Your introductory volume can spark ideas for further research, and the bibliography can give you some pointers about where to go next. You can also use keywords to research online via academic sites like JStor or Google Scholar. Check which subscriptions are available via your institution.
At this stage, you may not wish to read every single paper you come across in full — this could take a very long time and not everything will be relevant. Summarizing software like Wordtune could be very useful here.
Just upload a PDF or link to an online article using Wordtune, and it will produce a summary of the whole paper with a list of key points. This helps you to quickly sift through papers to grasp their central ideas and identify which ones to read in full.

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
You can also use Wordtune for semantic search. In this case, the tool focuses its summary around your chosen search term, making it even easier to get what you need from the paper.

As you go, make sure you keep organized notes of what you’ve read, including the author and publication information and the page number of any citations you want to use.
Some people are happy to do this process with pen and paper, but if you prefer a digital method, there are several software options, including Zotero , EndNote , and Mendeley . Your institution may have an existing subscription so check before you sign up.
Narrowing down your thesis research topic
Now you’ve read around the topic, it’s time to narrow down your ideas so you can craft your final question. For example, when it came to my undergraduate thesis, I knew I wanted to write about Ancient Greek religion and I was interested in the topic of goddesses. So, I:
- Did some wide reading around the topic of goddesses
- Learned that the goddess Hera was not as well researched as others and that there were some fascinating aspects I wanted to explore
- Decided (with my supervisor’s support) to focus on her temples in the Argive region of Greece

As part of this process, it can be helpful to consider the “5 Ws”: why, what, who, when, and where, as you move from the bigger picture to something more precise.
Why did you choose this research topic?
Come back to the reasons you originally chose your theme. What grabbed you? Why is this topic important to you — or to the wider world? In my example, I knew I wanted to write about goddesses because, as a woman, I was interested in how a society in which female lives were often highly controlled dealt with having powerful female deities. My research highlighted Hera as one of the most powerful goddesses, tying into my key interest.
What are some of the big questions about your topic?
During your research, you’ll probably run into the same themes time and time again. Some of the questions that arise may not have been answered yet or might benefit from a fresh look.
Equally, there may be questions that haven’t yet been asked, especially if you are approaching the topic from a modern perspective or combining research that hasn’t been considered before. This might include taking a post-colonial, feminist, or queer approach to older texts or bringing in research using new scientific methods.
In my example, I knew there were still controversies about why so many temples to the goddess Hera were built in a certain region, and was keen to explore these further.
Who is the research topic relevant to?
Considering the “who” might help you open up new avenues. Is there a particular audience you want to reach? What might they be interested in? Is this a new audience for this field? Are there people out there who might be affected by the outcome of this research — for example, people with a particular medical condition — who might be able to use your conclusions?
Which period will you focus on?
Depending on the nature of your field, you might be able to choose a timeframe, which can help narrow the topic down. For example, you might focus on historical events that took place over a handful of years, look at the impact of a work of literature at a certain point after its publication, or review scientific progress over the last five years.
With my thesis, I decided to focus on the time when the temples were built rather than considering the hundreds of years for which they have existed, which would have taken me far too long.
Where does your topic relate to?
Place can be another means of narrowing down the topic. For example, consider the impact of your topic on a particular neighborhood, city, or country, rather than trying to process a global question.
In my example, I chose to focus my research on one area of Greece, where there were lots of temples to Hera. This meant skipping other important locations, but including these would have made the thesis too wide-ranging.
Create an outline and get feedback
Once you have an idea of what you are going to write about, create an outline or summary and get feedback from your teacher(s). It’s okay if you don’t know exactly how you’re going to answer your thesis question yet, but based on your research you should have a rough plan of the key points you want to cover. So, for me, the outline was as follows:
- Context: who was the goddess Hera?
- Overview of her sanctuaries in the Argive region
- Their initial development
- Political and cultural influences
- The importance of the mythical past
In the final thesis, I took a strong view on why the goddess was so important in this region, but it took more research, writing, and discussion with my supervisor to pin down my argument.
To choose a thesis research topic, find something you’re passionate about, research widely to get the big picture, and then move to a more focused view. Bringing a fresh perspective to a popular theme, finding an underserved audience who could benefit from your research, or answering a controversial question can make your thesis stand out from the crowd.
For tips on how to start writing your thesis, don’t miss our advice on writing a great research abstract and a stellar literature review . And don’t forget that Wordtune can also support you with proofreading, making it even easier to submit a polished thesis.
How do you come up with a research topic for a thesis?
To help you find a thesis topic, speak to your professor, look through your old course notes, think about what you already enjoy in everyday life, talk about your field of study with friends and family, and research podcasts and videos to find a topic that is interesting for you. It’s a good idea to refine your topic so that it’s not too general or broad.
Do you choose your own thesis topic?
Yes, you usually choose your own thesis topic. You can get help from your professor(s), friends, and family to figure out which research topic is interesting to you.
Share This Article:

How to Craft an Engaging Elevator Pitch that Gets Results
.webp)
Eight Steps to Craft an Irresistible LinkedIn Profile
.webp)
7 Common Errors in Writing + How to Fix Them (With Examples)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.

How to Write an Explanatory Essay
- Smodin Editorial Team
- Published: May 24, 2024
A study from the English Language Teaching Educational Journal found that students encounter difficulty in organizing thoughts, generating ideas, and understanding writing processes when writing essays [1]. These are all key components of putting together a good explanatory essay. If this sounds like you, then don’t worry.
With the right approach, you can seamlessly combine all these components. This guide will give you a simple step-by-step strategy for writing an explanatory essay. It’ll also give you handy writing tips and tool suggestions, like utilizing artificial intelligence.
With this guide, you’ll be able to write an explanatory essay with confidence.
1. Develop a strong thesis statement
Crafting a strong thesis statement is the cornerstone of any well-written explanatory essay. It sets the stage for what your essay will cover and clarifies the main point you’re going to explain. Here’s how to create a thesis:
- Find the main idea : Start by pinpointing the key concept or question you want to explain. Develop a clear purpose for the essay. This will guide your research and writing process for your explanatory paper. Use other reputable explanatory essay examples to guide your ideas. This may involve exploring other explanatory essay topics within the same field.
- Be specific : A vague thesis can confuse readers. So, make sure your statement is clear. If you’re explaining a complex process, break it down to its key points. After that, break it into a clear, concise statement that’s easy to understand.
- Reflect objectivity : Explanatory essays educate and inform. They do not argue a point. So, your thesis should take an unbiased stance on the topic. It should present the facts as they are, not as you interpret them.
- Use tools like the Smodin Writer : Smodin Writer does all the heavy lifting by leveraging the power of artificial intelligence. With it, you can generate an essay with a thesis statement. How, you ask? Through its dedicated thesis generator . It can create a statement that’s both strong and relevant. Plus, it can pull in all the most interesting information based on your topic to further enrich your thesis statement.
Make your thesis clear, informative, and neutral. This sets a strong foundation for an effective explanatory essay. Next, let’s look at how to gather the information you’ll need to support this thesis effectively.
2. Research and gather information
You need to conduct thorough research that will back your thesis with credible sources and relevant evidence. This will make your explanatory essay both informative and persuasive. Here’s a step-by-step guide to conducting effective research:
- Start with a plan: Put together an explanatory essay outline that includes the information you need to support your thesis. The plan should list the best sources, like academic journals, books, reputable websites, or scholarly articles.
- Use credible sources: They ensure the accuracy of your essay. Libraries, academic databases, and certified websites are excellent places to find trustworthy information.
- Seek detailed information: Look for the most current sources that explain your topic well and provide unique insights related to or opposing your thesis statement. This depth is crucial for explaining complex ideas clearly and thoroughly in your explanatory papers. Pay attention to the explanatory essay structure to guide your topic of choice (more on this later).
- Gather relevant evidence: Collect data, stats, and examples. They should directly support your main points. Make sure this evidence is directly related to your topic and enhances your narrative.
- Employ digital tools: Tools like Smodin’s Research Assistant can accelerate your research process. Smodin’s tools can help you find detailed information quickly, ensuring that the data you use is up-to-date and relevant.
- Document your sources: As you conduct research, keep a meticulous record of where your information comes from. This practice will help you make an accurate bibliography. It can save you time when you need to refer back to details or verify facts. Again, this is something that’s covered thanks to Smodin’s Citation Machine.
- Evaluate your findings: Critically assess the information you collect. Ensure it provides a balanced view and covers the necessary aspects of your topic to give a comprehensive overview of your essay.
By following these steps, you can gather a rich pool of information that provides a strong backbone for your explanatory essay. Now, you can start structuring your findings into well-organized body paragraphs.
3. Structure body paragraphs
Once you’ve gathered relevant evidence through thorough research, it’s time to organize it. You should put it into well-structured body paragraphs that follow a logical flow. Here’s how to structure each body paragraph for a strong explanatory essay:
- Decide how many paragraphs to use : It will depend on your topic’s complexity and the needed detail. Typically, three to five paragraphs are suitable, but longer essays may require more. An explanatory essay example on your topic of choice will be helpful.
- Start with a topic sentence : Each body paragraph should begin with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. This sentence will act as a roadmap for the paragraph, giving the reader a sense of what to expect.
- Provide supporting evidence : After the topic sentence, share the evidence from your research. Ensure the evidence is relevant and directly supports the paragraph’s topic sentence.
- Give a detailed explanation : Follow the evidence with an analysis or explanation that ties it back to the thesis statement. This step is crucial for maintaining logical flow throughout your body paragraphs.
- Use linking words : They connect body paragraphs smoothly, ensuring the reader can follow your argument.
- End each body paragraph with a closing sentence : It should sum up the point and move to the next idea.
Following this structure will help your body paragraphs support your thesis. These paragraphs will also offer a clear, detailed explanation of your essay topic. Strong body paragraphs are essential to maintain objectivity in your writing.
4. Maintain objectivity
An explanatory essay aims to inform and educate, which makes maintaining objectivity crucial. Staying neutral lets readers form their own opinions based on facts. This ensures the writing is both reliable and informative. Here’s how to maintain objectivity:
- Avoid personal opinions: Your goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic. Refrain from injecting your personal opinion or biases. Instead, stick to presenting factual information that supports the thesis.
- Use relevant evidence: As mentioned, ground your arguments with relevant evidence from credible sources. Back up your main points with data and use research findings and verified details. This will make the explanatory article trustworthy.
- Provide a balanced view: In cases with multiple perspectives, offer a balanced view. Cover each side fairly. Even if one view prevails in consensus, acknowledging others gives readers a broader understanding.
- Adopt neutral language: Be careful with word choice and tone. Neutral language implies words that don’t encourage or illustrate bias. This helps avoid emotionally charged phrases and keeps the writing objective.
- Cite sources accurately: Proper citation of sources provides accountability for the evidence presented. This transparency builds credibility and shows you’ve conducted research thoroughly. It’s also worth noting that different intuitions have different citation styles like APA and Chicago, which is important to note before starting your essay.
- Review for biases: After drafting your essay, review it with an eye for biases. Ensure no part leans too much on one viewpoint. And, don’t dismiss an opposing perspective without cause.
Maintaining objectivity enhances the clarity and reliability of explanatory writing. Let’s now focus on crafting an introduction and conclusion that bookend your work effectively.
5. Craft an effective introduction and conclusion
A good introduction and a strong conclusion frame your explanatory essay. They give context at the start and reinforce the main points at the end. Here’s how to craft an effective introduction and conclusion.
In the introduction:
- Hook your reader in the introduction : Use an interesting fact, a compelling quote, or a surprising statistic.
- Provide background information : Be brief and offer only the essential context the reader needs to fully understand the topic. This should give the audience a foundational understanding before diving deeper into your main points.
- Include the thesis statement : Clearly state your thesis near the end of the introduction. This statement will outline the essay’s direction and give readers a preview of the body paragraphs.
In the conclusion:
- Summarize the key points : Start your explanatory essay conclusion with a summary. It should cover the main points from the body paragraphs. This summary should help readers recall and reinforce the information they’ve just read.
- Restate the thesis : Repeat your thesis again but in a new way. Explain how the evidence from the body paragraphs supported or clarified it.
- Provide a conclusion : End the essay with a statement that wraps up the argument. This statement should resonate with the reader. It should leave them with an impression that stresses the topic’s importance.
An effective introduction and conclusion give the essay structure and coherence. They guide readers from start to finish. The next step is revising and editing your entire essay for clarity and precision.
6. Revise and check clarity
Revising and editing are key in writing. They make sure your essay is clear, joined, and polished. Here’s how to refine your writing using an explanatory essay checklist and proven academic writing techniques:
- Take a break: Before diving into revisions, step away from your essay for a few hours or even a day. This break will help you return with fresh eyes, making it easier to spot errors or inconsistencies.
- Follow an essay checklist: Create or use a checklist to ensure your essay has all the needed parts. It needs a strong intro with a clear thesis, well-structured body paragraphs, good sources, and a short conclusion. Check that your arguments follow a logical flow and that all relevant evidence is directly linked to your thesis statement.
- Check for clarity and conciseness: Academic writing needs clarity. So, make sure each paragraph and sentence conveys your point. Don’t use unnecessary jargon or overly complex language. Keep sentences concise while maintaining detailed explanations of your main points.
- Verify facts and citations: Make sure all facts, data, and quotes in the essay are accurate. Also, check that they are cited in the required academic style (e.g. MLA, APA). Improper citations can undermine the credibility of your writing.
- Review the grammar and style: Look for common grammar mistakes, punctuation errors, and awkward phrasing. Reading the essay aloud can help catch odd sentence structures or confusing wording.
- Seek feedback: Share your essay with a peer or use online tools to get constructive criticism. A second perspective can highlight issues you might have missed.
These editing steps will help you produce a polished essay that clearly explains your main points and holds up to academic scrutiny.
Explanatory Essay Format
Understanding the explanatory essay format is key to a well-structured and logical paper. Here’s a basic breakdown of the format for an explanatory essay:
Introduction paragraph
- Begin with an interesting sentence to capture the reader’s attention.
- Give a short intro. It should set the topic and outline the essay’s purpose.
- Present a clear thesis statement summarizing the main idea of the entire essay.
Body paragraphs
- Organize the body paragraphs around logical subtopics related to the essay topic.
- Start each body paragraph with a topic sentence that aligns with the thesis.
- Show evidence from good sources. Also, give key details for each main point.
- Incorporate a robust concluding statement per paragraph that drives home your point and links to the ideas in the next paragraph/section.
- Summarize the key points.
- Provide a final statement that reinforces the main idea without introducing new information.
- Craft a concluding statement that leaves your teacher or professor with a lasting impression.
Following this essay outline ensures that your paper has a clear flow. This makes it easy for readers to understand and follow your argument.
Write Better Explanatory Essays With Smodin
Explanatory essays can be overwhelming. Presenting a solid argument, keeping your professor or teacher interested, and remembering conventions like citations can be a real headache.
But, a strong thesis and thorough research make them easier. Well-structured body paragraphs also help deliver a clear, insightful essay that maintains objectivity. Just remember to revise and check for accuracy!
AI-powered platforms like Smodin simplify and enhance the process of writing explanatory essays.
Smodin’s tools help craft clear and well-structured essays that meet any of your academic standards. With Smodin’s advanced research capabilities, you can gather detailed and relevant information quickly. This will save you time and improve your work.
- Plagiarism Checker : Ensure your essay maintains originality with Smodin’s plagiarism detection tool. This feature helps maintain academic integrity by checking your work against vast databases.
- Auto Citation : Cite your sources accurately without the hassle. Smodin’s auto-citation tool ensures your references are in the right format and meet your academic institution’s rules.
- Text Shortener : If your explanatory essay is too long, use Smodin’s AI writer as an essay shortener. It will help you cut your content without losing key details. This helps keep your essay clear and relevant.
- Text Rewriter : Helps paraphrase existing content, ensuring uniqueness and a fresh perspective.
- Summarizer : The Summarizer boils down long articles into short summaries. They are perfect for making an efficient outline or conclusion.

How to Get a Small Business Loan: A Guide in 10 Steps
S mall business loans are available from a large number of traditional and alternative lenders. Small business loans can help your business grow, fund new research and development, help you expand into new territories, enhance sales and marketing efforts, allow you to hire new people, and much more.
How to get a small business loan
This article explains the 10 key steps you should follow to get a small business loan, with some practical advice and insight on the lending process.
1. Understand the different types of small business loans available
There are multiple types of small business loans available. The options vary depending on your business needs, the length of the loan, and the specific terms of the loan. Here are a number of small business loan choices:
Small business line of credit. Under a small business line of credit, your business can access funds from a lender as needed. There will be a cap on the amount of funds accessible (e.g., $100,000), but a line of credit is useful for managing a company’s cash flow and unexpected expenses. There will typically be a fee for setting up a line of credit, but you don’t get charged interest until you actually draw down the funds. Interest is typically paid monthly, and the principal drawn down on the line is often amortized over years. However, most lines of credit require renewal annually, which may require an additional fee. If the line is not renewed, you will be required to pay it in full at that time.
Accounts receivable financing. An accounts receivable line of credit is a credit facility secured by the company’s accounts receivable (AR). The AR line allows you to get cash immediately, depending on the level of your accounts receivable; the interest rate is variable. The AR line is paid down as the accounts receivable are paid by your customers.
Working capital loans. A working capital loan is a debt-borrowing vehicle used by a company to finance its daily operations. Companies use such loans to manage fluctuations in revenues and expenses due to seasonality or other circumstances in their business. Some working capital loans are unsecured, but companies that have little or no credit history will have to pledge collateral for the loan or provide a personal guarantee. Working capital loans tend to be short-term loans of 30 days to one year. Such loans typically vary from $5,000 to $100,000 for small businesses.
Small business term loans. Term loans are typically for a set dollar amount (e.g., $250,000) and are used for business operations, capital expenditures, or expansion. Interest is paid monthly and the principal is usually repayable within six months to three years (which can be amortized over the term of the loan or have a balloon payment at the end). Term loans can be secured or unsecured, and the interest can be variable or fixed. They are good for small businesses that need capital for growth or for large, onetime expenditures.
SBA small business loans. Some banks offer attractive low-interest-rate loans for small businesses, backed and guaranteed by the SBA. Because of the SBA guarantee, the interest rate and repayment terms are more favorable than most loans. Loan amounts range from $30,000 to as high as $5 million. However, the loan process can be time consuming with strict requirements for eligible small businesses. Visit the SBA website to see a list of the 100 most active SBA lenders .
Equipment loans. Small businesses can buy equipment, vehicles, and software through an equipment loan. This typically requires a down payment of 20% of the purchase price of the equipment, and the loan is secured by the equipment. Interest on the loan is typically paid monthly and the principal is usually amortized over a two- to four-year period. Loan amounts normally range from $5,000 to $500,000, and can accrue interest at either a fixed or variable rate. Equipment loans can also sometimes be structured as equipment leases.
Small business credit cards. While some business owners may be wary of using them, small business credit cards can also act as short-term small business financing. Interest rates will vary depending on the credit card issuer, the amount available on the card, and the creditworthiness of the holder of the card. Many small business credit card issuers require the principal owner to be co-liable with the company. Issuers of small business credit cards include American Express, Brex, Capital One, Bank of America, and many others. Many credit cards offer promotional introductory rates of 0% for a short period of time (six to nine months). Cash-back and rewards programs allow you to earn rewards from purchases on the credit card.
2. Research available lenders
There are more lenders than ever willing to lend to small businesses, and many of the lenders can be found from a simple online search. Here are the main types of lenders:
- Direct online lenders. There are a number of online lenders that make small business loans through a relatively easy online process. Reputable companies such as PayPal can provide very fast small business cash advances, working capital loans , and short-term loans in amounts from $5,000 to $500,000. Sites such as Fundera offer access to multiple lenders, acting as a lead generation service for lenders.
- Large commercial banks. The traditional lenders to the small business market are banks such as Wells Fargo, JP Morgan, and Citibank. The loan approval process tends to be slower due to more rigorous loan underwriting criteria.
- Local community banks. Many community banks have a strong desire to make small business loans to local businesses.
- Peer-to-peer lending sites . There are a number of sites that act as middlemen between individual and institutional lenders and small borrowers, including SMBX , LendingClub , and Funding Circle . These lenders can make decisions relatively quickly.
- Bank lenders backed by SBA guarantees . A number of bank lenders issue loans backed by the SBA, and, as noted above, this backing allows lenders to offer more attractive terms.
3. Anticipate how lenders will view your credit and risk profile
Lenders ultimately make a judgment call on whether or not to make a small business loan based on the borrower’s credit and risk profile. Lenders will look at the following factors, so review them carefully and consider taking any appropriate remedial action:
- Credit score/credit report. Lenders will review your credit report, credit score, and history of making timely payments under credit cards, loans, and vendor contracts. So review your credit report and clean up any blemishes.
- Outstanding loans and cash flow. Lenders will review your outstanding loans and debts to determine that your cash flow will be sufficient to pay existing loans and obligations as well as the new loan contemplated.
- Assets in the business. Lenders will review the assets in the business (particularly current assets such as cash and accounts receivable) to see if there is a good base of assets to go after in the event of a loan default.
- Time in business. Lenders will tend to look more favorably on businesses that have been operating for several years or more.
- Investors in the company. Lenders will view the company more favorably if it has professional venture capital investors, strategic investors, or prominent angel investors.
- Financial statements. Lenders will scrutinize your financials, as set forth in the next section below.
4. Make sure your financial statements are in order
Depending on the size of your loan, your financial statements and accounting records will be reviewed carefully by the lender. So make sure they are complete, correct, and thorough—including balance sheet, income and loss statements, and cash flow statements. The lender will analyze your cash flow, gross margin, debt-to-equity ratio, accounts payable, accounts receivable, EBITDA, and more, so be prepared to answer questions on those topics. Consider having your accountant look over your financial statements to anticipate issues a lender may raise.
Lenders prefer financial statements that have been audited by a certified public accountant (CPA), but many small businesses don’t want to incur the costs of an audit. One alternative is to have the financial statements “reviewed” by a CPA (which is cheaper and faster). However, some lenders may not require either audited or reviewed statements.
5. Gather detailed information for your small business loan application
If you want to be successful getting a small business loan, you have to be prepared to provide detailed information and documents about your business; it is important to be prepared and organized. The following is the type of information that is often required from bank lenders, depending on the type of loan:
- Name of business (including any DBAs)
- Federal Tax ID
- List of executive officers and their background
- Legal structure (such as LLC, S corporation, C corporation)
- Financial statements for the past two to three years and year-to-date financials for the current year (balance sheet, income and loss statements, cash flow statements, shareholder equity)
- Projected financial statements (so that the lender can get a sense of your expected future operations and cash flow)
- State filings for the company, such as a certificate of incorporation, foreign corporation filings, and good standing certificates
- Copies of key man and general liability insurance policies
- Amount of loan requested
- Business credit report (such as from a credit reporting agency like Dun & Bradstreet)
- Potential collateral available for the loan
- Financial statements of the principal shareholder/owner of the business (especially in the case where a personal guarantee will be required)
- Business plan, executive summary, or investor pitch deck of the company (see A Guide to Investor Pitch Decks for Startup Fundraising )
- The tax returns of the company for the past two to three years (signed copies with all attachments and exhibits)
- Business bank statements
6. Be prepared to specify how much you want to borrow and the expected use of proceeds from the loan
The lender will want to know how much funding you are seeking and how the loan proceeds will be used. Will the loan be used for equipment or capital expenditures? Expansion or hiring? Increase in inventory? Enhanced sales and marketing efforts? New research and development of technology? New product development? Expansion into new facilities or territories?
You may want to borrow a little extra in case you run into a cash crunch that lasts a month or two. You have to avoid going into default under the loan.
7. Determine what security or guarantee can be provided
A lender is primarily concerned about the ability of the borrower to repay the loan. To the extent that a security interest can be given to the lender on company assets (company equipment, property, accounts receivable, etc.), the borrower should be able to increase its chances of getting a loan on favorable terms. Some lenders may insist upon the personal guarantee of the principal owner of the business. That is best avoided, if possible, as it puts your personal assets, and not just the business assets, at risk.
8. Analyze the key terms of the proposed business loan
To make sure the proposed business loan makes sense for your business, you will need to analyze the key terms proposed by a lender and compare them with terms available from alternative lenders. Here are the key terms to review:
- What is the interest rate on the loan and how can it vary over time? Many loans vary over time depending on the prevailing “prime rate” or some other benchmark.
- How often is the interest payable?
- When is the principal due or how is it amortized over the life of the loan? You need to be comfortable with the combined interest and principal payments from a cash flow perspective.
- What is the loan origination fee?
- What other costs or fees are imposed (such as underwriting fees, administration fees, loan processing fees, etc.)?
- What operating covenants are imposed on your business (such as a maximum debt-to-equity ratio or a minimum cash threshold held by the company)?
- What are the circumstances when the lender can call a default on the loan?
- Is there any security or collateral required?
- What periodic reports or financial statements are required to be provided to the lender?
- Are there limits on how the loan proceeds can be used?
- Can the loan be prepaid early without a penalty? And if there is a penalty, is the penalty reasonable?
9. Review your online profile and postings
A small business lender will perform due diligence, which can include reviewing the information available online about the business and its principal owner. So do the following review, anticipating such due diligence to see if you should make any changes or deletions to your online presence:
- Review your company’s website. Is it up-to-date and professional-looking?
- Review its presence on LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, and other social media sites.
- Review any Yelp reviews your business may have received.
- Review the principal owner’s postings on LinkedIn and other websites.
10. Get further educated on the small business lending process
The more educated you are about small business lending options and procedures, the more likely you will be successful in obtaining a loan. Here are some additional articles to review:
Small business loans are available from many different lenders, with a myriad of choices tailored to the financial situation of your business. By anticipating what lenders will review and require, you greatly increase your chances of obtaining a beneficial small business loan.
Copyright © by Richard D. Harroch. All Rights Reserved.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
How to Write a Dissertation Conclusion | Checklist and Examples
Published on 9 September 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on 10 October 2022.
The conclusion is the very last part of your thesis or dissertation . It should be concise and engaging, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your main findings, as well as the answer to your research question .
In it, you should:
- Clearly state the answer to your main research question
- Summarise and reflect on your research process
- Make recommendations for future work on your topic
- Show what new knowledge you have contributed to your field
- Wrap up your thesis or dissertation
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Discussion vs. conclusion, how long should your conclusion be, step 1: answer your research question, step 2: summarise and reflect on your research, step 3: make future recommendations, step 4: emphasise your contributions to your field, step 5: wrap up your thesis or dissertation, full conclusion example, conclusion checklist, frequently asked questions about conclusion sections.
While your conclusion contains similar elements to your discussion section , they are not the same thing.
Your conclusion should be shorter and more general than your discussion. Instead of repeating literature from your literature review , discussing specific research results , or interpreting your data in detail, concentrate on making broad statements that sum up the most important insights of your research.
As a rule of thumb, your conclusion should not introduce new data, interpretations, or arguments.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Depending on whether you are writing a thesis or dissertation, your length will vary. Generally, a conclusion should make up around 5–7% of your overall word count.
An empirical scientific study will often have a short conclusion, concisely stating the main findings and recommendations for future research. A humanities topic or systematic review , on the other hand, might require more space to conclude its analysis, tying all the previous sections together in an overall argument.
Your conclusion should begin with the main question that your thesis or dissertation aimed to address. This is your final chance to show that you’ve done what you set out to do, so make sure to formulate a clear, concise answer.
- Don’t repeat a list of all the results that you already discussed
- Do synthesise them into a final takeaway that the reader will remember.
An empirical thesis or dissertation conclusion may begin like this:
A case study –based thesis or dissertation conclusion may begin like this:
In the second example, the research aim is not directly restated, but rather added implicitly to the statement. To avoid repeating yourself, it is helpful to reformulate your aims and questions into an overall statement of what you did and how you did it.
Your conclusion is an opportunity to remind your reader why you took the approach you did, what you expected to find, and how well the results matched your expectations.
To avoid repetition , consider writing more reflectively here, rather than just writing a summary of each preceding section. Consider mentioning the effectiveness of your methodology , or perhaps any new questions or unexpected insights that arose in the process.
You can also mention any limitations of your research, but only if you haven’t already included these in the discussion. Don’t dwell on them at length, though – focus on the positives of your work.
- While x limits the generalisability of the results, this approach provides new insight into y .
- This research clearly illustrates x , but it also raises the question of y .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
You may already have made a few recommendations for future research in your discussion section, but the conclusion is a good place to elaborate and look ahead, considering the implications of your findings in both theoretical and practical terms.
- Based on these conclusions, practitioners should consider …
- To better understand the implications of these results, future studies could address …
- Further research is needed to determine the causes of/effects of/relationship between …
When making recommendations for further research, be sure not to undermine your own work. Relatedly, while future studies might confirm, build on, or enrich your conclusions, they shouldn’t be required for your argument to feel complete. Your work should stand alone on its own merits.
Just as you should avoid too much self-criticism, you should also avoid exaggerating the applicability of your research. If you’re making recommendations for policy, business, or other practical implementations, it’s generally best to frame them as ‘shoulds’ rather than ‘musts’. All in all, the purpose of academic research is to inform, explain, and explore – not to demand.
Make sure your reader is left with a strong impression of what your research has contributed to the state of your field.
Some strategies to achieve this include:
- Returning to your problem statement to explain how your research helps solve the problem
- Referring back to the literature review and showing how you have addressed a gap in knowledge
- Discussing how your findings confirm or challenge an existing theory or assumption
Again, avoid simply repeating what you’ve already covered in the discussion in your conclusion. Instead, pick out the most important points and sum them up succinctly, situating your project in a broader context.
The end is near! Once you’ve finished writing your conclusion, it’s time to wrap up your thesis or dissertation with a few final steps:
- It’s a good idea to write your abstract next, while the research is still fresh in your mind.
- Next, make sure your reference list is complete and correctly formatted. To speed up the process, you can use our free APA citation generator .
- Once you’ve added any appendices , you can create a table of contents and title page .
- Finally, read through the whole document again to make sure your thesis is clearly written and free from language errors. You can proofread it yourself , ask a friend, or consider Scribbr’s proofreading and editing service .
Here is an example of how you can write your conclusion section. Notice how it includes everything mentioned above:
V. Conclusion
The current research aimed to identify acoustic speech characteristics which mark the beginning of an exacerbation in COPD patients.
The central questions for this research were as follows: 1. Which acoustic measures extracted from read speech differ between COPD speakers in stable condition and healthy speakers? 2. In what ways does the speech of COPD patients during an exacerbation differ from speech of COPD patients during stable periods?
All recordings were aligned using a script. Subsequently, they were manually annotated to indicate respiratory actions such as inhaling and exhaling. The recordings of 9 stable COPD patients reading aloud were then compared with the recordings of 5 healthy control subjects reading aloud. The results showed a significant effect of condition on the number of in- and exhalations per syllable, the number of non-linguistic in- and exhalations per syllable, and the ratio of voiced and silence intervals. The number of in- and exhalations per syllable and the number of non-linguistic in- and exhalations per syllable were higher for COPD patients than for healthy controls, which confirmed both hypotheses.
However, the higher ratio of voiced and silence intervals for COPD patients compared to healthy controls was not in line with the hypotheses. This unpredicted result might have been caused by the different reading materials or recording procedures for both groups, or by a difference in reading skills. Moreover, there was a trend regarding the effect of condition on the number of syllables per breath group. The number of syllables per breath group was higher for healthy controls than for COPD patients, which was in line with the hypothesis. There was no effect of condition on pitch, intensity, center of gravity, pitch variability, speaking rate, or articulation rate.
This research has shown that the speech of COPD patients in exacerbation differs from the speech of COPD patients in stable condition. This might have potential for the detection of exacerbations. However, sustained vowels rarely occur in spontaneous speech. Therefore, the last two outcome measures might have greater potential for the detection of beginning exacerbations, but further research on the different outcome measures and their potential for the detection of exacerbations is needed due to the limitations of the current study.
Checklist: Conclusion
I have clearly and concisely answered the main research question .
I have summarized my overall argument or key takeaways.
I have mentioned any important limitations of the research.
I have given relevant recommendations .
I have clearly explained what my research has contributed to my field.
I have not introduced any new data or arguments.
You've written a great conclusion! Use the other checklists to further improve your dissertation.
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
While it may be tempting to present new arguments or evidence in your thesis or disseration conclusion , especially if you have a particularly striking argument you’d like to finish your analysis with, you shouldn’t. Theses and dissertations follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the discussion section and results section .) The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
For a stronger dissertation conclusion , avoid including:
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5-7% of your overall word count.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation should include the following:
- A restatement of your research question
- A summary of your key arguments and/or results
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). How to Write a Dissertation Conclusion | Checklist and Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/conclusion/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write an abstract | steps & examples.
- Get 7 Days Free
There’s No Evidence of a Retirement Crisis
The New York Times stretches too far.
/s3.amazonaws.com/arc-authors/morningstar/1aafbfcc-e9cb-40cc-afaa-43cada43a932.jpg)
Last month, The New York Times printed an article about BlackRock BLK CEO Larry Fink, bearing the headline “He Wants to Address the Retirement Crisis Looming in the U.S.” (The online version carried a different title.)
The argument that the United States faces an impending retirement crisis has been struck many times, over many years. “Unless we as a society do a better job of investing,” said Eli Broad of SunAmerica in a 1994 Associated Press article, “future retirees face a drastically reduced standard of living.” Later in that article, Merrill Lynch’s Daniel Tully fretted that “members of the baby boom generation” could endure lower “living standards” than the retirees of the 1990s.
A decade later, The Coming Retirement Crisis, published in 2004 by Forbes , anticipated a “slow-motion crisis as baby boomers head into retirement.” Ten years after that, in 2014, came the video Broken Eggs: The Looming Retirement Crisis in America. There is no shortage of such examples. Until now, though, I had not seen a major newspaper cross that line.
The Research
In 1994, the nation’s retirement structure was changing rapidly. Over the previous eight years, the number of defined-benefit plans had fallen by more than 50%, from 172,642 to 74,422. Meanwhile, the number of 401(k) accounts was soaring. Baby boomers were the first defined-contribution generation. Unlike their predecessors, they would largely be planning for retirement on their own.
As baby boomers are currently between the ages of 60 and 78, enough time has passed to reveal the early results of this experiment. Fortunately for our purpose, the US Census Bureau publishes a history of median national incomes, sorted by sex and age. (The data used in this column can be found in Table P-8 within this link .)
Unfortunately for our purposes, although the Census Bureau’s research is regarded as the gold standard for US income data, it is nevertheless suspect. For example, the Bureau reports that in 2019, the median real income for female workers from ages 25 through 34 ballooned by 9%. Meanwhile, income for male workers of that age was slightly lower. The next year, it then states, the female workers’ income was flat, while the group’s males increased by 3%.
I’m not buying. Young American working women did not suddenly receive a decade’s worth of real income growth in a single year, even as their male counterparts went nowhere. The Census Bureau’s measurements contain the amount of fluctuation associated with small sample sizes, but for cohorts of 20 million.
The Age Groups’ Results
Thus, I would strongly caution against attempting to decipher the wiggles of the following illustration, which shows the results since 1994 for each of the Census Bureau’s seven age groups. (With these calculations, I combined the female and male results within each age group, to simplify the presentation. Each cohort is indexed, with an initial value of 100 assigned to its 1994 total. Thus, the chart shows changes in relative income, rather than the levels of absolute income—which, for reference, are highest for the 45 to 54 group and by far the lowest for the 15 to 24 group.)
That caveat aside, the overall trend is instructive.
Income Changes Over Time, by Age Group
Over the past 30 years, the median real income for every cohort has improved—for retirees as well as workers. Indeed, retirees have fared somewhat better than the norm. The 65 to 74 group, charted in purple, has enjoyed the second-highest overall gain among the seven cohorts, while the 75-plus crowd places fourth.
One potential concern is the purple line’s recent downturn. Does this indicate that, at long last, retirees’ problems have surfaced? To answer my rhetorical question, I think not. For one thing, as previously written, the data are lumpy, which makes interpretation hazardous. For another, the age group suffered two unusual shocks, just as the research period ended. First, covid-19′s arrival sent many older workers into early retirement and/or cost them their part-time jobs. Second, 2022′s high inflation eroded their purchasing power that year.
However, in 2023—which does not appear in the illustration, as those figures have not yet been released—the Social Security Administration gave retirees an 8.7% cost-of-living raise, while the Consumer Price Index rose by only 3.4%. That makes for a one-year after-inflation raise of 5% for Social Security benefits, which will almost have certainly reversed that near-term trend.
Where’s the Beef?
But I digress. The point isn’t that the evidence has been tried and found lacking. It is instead that it really hasn’t been offered at all. For several decades, people worried about future retirees have argued their case based on broad trends, such as the waning of defined-benefit plans, surveys suggesting that workers don’t own enough investment assets, and the ever-increasing length of retirement as Americans live longer. Those are all worthwhile topics, but they represent questions to be addressed, not answers to be delivered.
To put the matter another way, unless they are accompanied by specific supporting evidence, demographic arguments are insufficient. I should know. I spent much of my investment youth hearing that stock market returns would be strong until about 2010 but would then collapse as baby boomers became more conservative and sold their equity shares. Of course, the opposite occurred. When they were supposed to be declining, stocks instead soared.
None of this should be mistaken for complacency. My feelings about the transition from defined-benefit plans to defined-contribution plans are decidedly mixed . The current system possesses weaknesses as well as strengths . Nor do I discount the demographic concerns. The world is becoming older rather than younger. That shift will have profound implications, including with retirement funding.
But there is a difference between speculation and certainty, particularly when the speculation has existed for several decades. With its headline, The New York Times presented an assertion as a fact. It should not have done so.
The opinions expressed here are the author’s. Morningstar values diversity of thought and publishes a broad range of viewpoints.
The author or authors do not own shares in any securities mentioned in this article. Find out about Morningstar’s editorial policies .
More in Rekenthaler Report
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/morningstar/G3DCA6SF2FAR5PKHPEXOIB6CWQ.jpg)
Is the Stock Market Too Concentrated?
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/morningstar/6ZMXY4RCRNEADPDWYQVTTWALWM.jpg)
Should You Buy and Hold an Artificial Intelligence Portfolio?
Never mind market efficiency: are the markets sensible, about the author, john rekenthaler.
John Rekenthaler is vice president, research for Morningstar Research Services LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Morningstar, Inc.
Rekenthaler joined Morningstar in 1988 and has served in several capacities. He has overseen Morningstar's research methodologies, led thought leadership initiatives such as the Global Investor Experience report that assesses the experiences of mutual fund investors globally, and been involved in a variety of new development efforts. He currently writes regular columns for Morningstar.com and Morningstar magazine.
Rekenthaler previously served as president of Morningstar Associates, LLC, a registered investment advisor and wholly owned subsidiary of Morningstar, Inc. During his tenure, he has also led the company’s retirement advice business, building it from a start-up operation to one of the largest independent advice and guidance providers in the retirement industry.
Before his role at Morningstar Associates, he was the firm's director of research, where he helped to develop Morningstar's quantitative methodologies, such as the Morningstar Rating for funds, the Morningstar Style Box, and industry sector classifications. He also served as editor of Morningstar Mutual Funds and Morningstar FundInvestor.
Rekenthaler holds a bachelor's degree in English from the University of Pennsylvania and a Master of Business Administration from the University of Chicago Booth School of Business, from which he graduated with high honors as a Wallman Scholar.
Bill Gross Warns Investors to Steer Clear of Bond Funds
When low risk means high risk, are you an investment historian or a futurist, tips are on sale, the best bond index funds: part 2, the dangerous myth of ‘the new normal’, sponsor center.
- Open access
- Published: 23 May 2024
Improved pediatric ICU mortality prediction for respiratory diseases: machine learning and data subdivision insights
- Johayra Prithula 1 ,
- Muhammad E. H. Chowdhury 2 ,
- Muhammad Salman Khan 2 ,
- Khalid Al-Ansari 3 ,
- Susu M. Zughaier 4 ,
- Khandaker Reajul Islam 5 &
- Abdulrahman Alqahtani 6 , 7
Respiratory Research volume 25 , Article number: 216 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
24 Accesses
Metrics details
The growing concern of pediatric mortality demands heightened preparedness in clinical settings, especially within intensive care units (ICUs). As respiratory-related admissions account for a substantial portion of pediatric illnesses, there is a pressing need to predict ICU mortality in these cases. This study based on data from 1188 patients, addresses this imperative using machine learning techniques and investigating different class balancing methods for pediatric ICU mortality prediction. This study employs the publicly accessible “Paediatric Intensive Care database” to train, validate, and test a machine learning model for predicting pediatric patient mortality. Features were ranked using three machine learning feature selection techniques, namely Random Forest, Extra Trees, and XGBoost, resulting in the selection of 16 critical features from a total of 105 features. Ten machine learning models and ensemble techniques are used to make accurate mortality predictions. To tackle the inherent class imbalance in the dataset, we applied a unique data partitioning technique to enhance the model's alignment with the data distribution. The CatBoost machine learning model achieved an area under the curve (AUC) of 72.22%, while the stacking ensemble model yielded an AUC of 60.59% for mortality prediction. The proposed subdivision technique, on the other hand, provides a significant improvement in performance metrics, with an AUC of 85.2% and an accuracy of 89.32%. These findings emphasize the potential of machine learning in enhancing pediatric mortality prediction and inform strategies for improved ICU readiness.
Introduction
Pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) mortality for respiratory diseases significantly impacts children’s lives and the healthcare system [ 1 ]. Such pediatric respiratory diseases as severe pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and respiratory failure, contribute to accounted for approximately 40% of PICU admissions, with a mortality rate ranging from 7 to 15% [ 2 , 3 ]. Pediatric mortality is steadily deteriorating on a daily basis, accompanied by an alarming decline in the infant survival rate [ 4 ]. Survivors of severe respiratory diseases in the PICU often experience long-term consequences like neurodevelopmental impairments, physical disabilities, and psychological issues. Approximately 25% of survivors of pediatric ARDS experienced new functional limitations six months after discharge [ 2 ]. PICU care for pediatric respiratory diseases incurs substantial healthcare costs [ 5 ]. The mean hospitalization cost for pediatric ARDS was approximately $67,000 [ 6 ], with an average ICU cost of $25,000 per day [ 7 , 8 , 9 ]. By investing in research, healthcare resources, and preventive measures, we can work towards reducing the impact of these diseases on children’s lives and alleviating the burden on the healthcare system [ 7 , 10 ].
Predicting pediatric mortality is of utmost importance in safeguarding young lives, enabling targeted interventions, and allocating resources to mitigate fatal outcomes [ 11 ]. Managing critically ill children with respiratory diseases demands significant medical resources, including ventilators, specialized medications, and skilled healthcare providers, which may strain the healthcare system, leading to potential shortages and increased costs [ 12 , 13 ]. The loss of a child in the PICU due to respiratory diseases has emotional and psychological impacts on families, caregivers, and healthcare providers, leading to long-term grief and mental health challenges. Early detection, effective management, and technological advancements are essential to mitigate these effects.
EHR data analysis and predictions based on machine learning models have gained popularity in recent years due to their ease of implementation and deployment [ 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 ]. The random forest model with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.72 was used in an analysis at the Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine to predict postoperative mortality [ 19 ]. Another study at the University of Twente employed three classification models achieved an acceptable AUROC score of 0.71, underlining the need for additional study on methods for controlling class imbalance and model enhancement [ 20 ]. For newborns having major non-cardiac surgery, several research have developed postoperative mortality prediction models based on logistic regression [ 3 , 21 ]. Another study offers a simple but effective linear machine learning model with 11 key characteristics from a pediatric ICU dataset producing a predictive model with a ROC-AUC score of 0.7531 that beats current techniques like PRISM III (The Pediatric Risk of Mortality is a third-generation, physiology-based predictor for pediatric ICU patients [ 22 ]). The study highlights the improved efficacy and generalizability of their methods for forecasting pediatric ICU mortality.
Biochemical markers have become crucial in machine learning algorithms for accurate predictions of high-risk scenarios in pediatric patients. For instance, Early Plasma Osmolality Levels using locally weighted-regression scatterplot smoothing (LOWESS) to assess its relationship with hospital mortality, plasma osmolality at 290 mmol/L with in-, while levels below 290 mmol/L showed no significant association with mortality [ 23 ]. Serum magnesium levels were also studied, with an optimal range identified for the lowest mortality risk in critically ill children [ 24 ]. Furthermore, a study including albumin, lactate dehydrogenase, lactate, urea, arterial pH, and glucose develops a new scoring system for predicting in-hospital mortality in children outperforming the Pediatric Critical Illness Score (PCIS) showing higher AUC values in both the training and validation sets (0.81 and 0.80, respectively) [ 25 ].
Despite numerous studies on ICU mortality during COVID-19, research on pediatric populations using machine learning is limited, partly due to the scarcity of publicly available datasets. However, recently the PICU dataset [ 26 ] becomes publicly available which has made the possibility of investigating mortality prediction for different disease group. This paper focuses on enhancing mortality prediction accuracy in pediatric patients with respiratory diseases, integrating specific risk factors, biomarkers, and advanced modeling techniques.
Methodology
In this study, the publicly available PICU dataset [ 26 ] was utilized for data collection and to train, validate, and test different machine learning model. The initial dataset consisted of PICU database records and was filtered and preprocessed to remove outliers and repetitions. Three feature ranking approaches were explored to identify the optimal set of data for mortality prediction. To achieve more accurate outcomes in predicting mortality, various machine learning models, including Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) Classifier, Linear Discriminant Analysis, XGBoost Classifier, Random Forest Classifier, Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machine (SVM), Extra Trees Classifier, AdaBoost Classifier, K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) Classifier, and Gradient Boosting Classifier, along with ensemble models, were applied to the preprocessed data. Given the highly imbalanced dynamics of the dataset (90.49% normal cases to 9.51% mortality cases), a subdivision sampling technique was implemented to obtain the most accurate predictions of mortality in pediatric patients. The prediction models for pediatric respiratory-related mortality were developed using Python software 3.9.13, and the Scikit-learn package was employed for implementing the supervised machine learning algorithms. Figure 1 displays a schematic representation of the methodology:
Step by step flowchart of the methodology
Data description
The PICU database comprises information collected during routine hospital care at The Children’s Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, from 2010 to 2019. This database follows the main schema of the MIMIC-III database but with localization-specific modifications. Standard codes, such as International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) [ 27 ] codes for diagnosis, were used for frequently employed terms, and their English equivalents were derived. To ensure patient privacy, all identifiers required by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of the United States were removed, resulting in completely de-identified patient data. The database contains a total of 13,944 ICU admissions and is structured into 16 tables [ 28 ].
Data preprocessing
The PICU database follows the framework of the MIMIC database, organized into tables for various information groupings. Before inputting this data into our machine learning model, preprocessing steps are necessary to format the database appropriately for training.
Data structuring
The database consists of 17 tables, with three dictionaries helping to interpret certain data fields, and two surgical data tables, which are not relevant to our research. Our dataset is derived from the information in the remaining 12 tables. For each patient admission case, diagnostic information is available, documented using ICD_10 codes. A mapping of ICD_10 codes to diagnose is provided in one of the dictionaries mentioned earlier. The diagnoses are categorized into admission, discharge, and clinical diagnostic categories. Additionally, the dataset includes information about the length of stay (LOS) in the ICU for each admission case, as well as physiological excretion and lab reports, which are mapped using the provided itemid (documentation of lab items mapped from the D_ITEMS table to numeric format) dictionary. The final dataset, constructed using these tables, comprises 13,941 instances and 592 columns.
Missing value removal
Out of the 592 columns used to construct the dataset, not all of them are relevant. Columns with a majority of missing data may introduce bias if imputed, so an iterative process is performed to discard columns lacking more than 70% of data. As a result, the dataset is reduced to 109 columns after discarding 483 columns.
After this reduction, each admission instance is evaluated within these 109 columns to check if the majority of column values are absent. Consequently, the initial 13,941 instances are further reduced to 12,841 instances (Fig. 2 ).
Proposed stacking ensemble technique with base models and meta-model
Filtering and outlier removal
In this study, we focused on respiratory system diseases in the diagnostic column, specifically using ICD-10 index J00-J99. Given the focus on pediatric patients, we also included congenital malformations of the respiratory system (ICD-10 index Q30–Q34). Additionally, four identifier columns were removed in this stage (Additional file 1 : Figure S1). As a result, the filtered dataset comprises a total of 1188 instances and 105 columns [ 29 ].
After filtering the data for our investigation, we conducted a detailed examination of the dataset to identify outliers. Outliers are values that do not align with medical norms as per published laboratory guidelines (Additional file 1 : Figure S2). Through a comprehensive iteration of the 105 columns in the filtered dataset, we removed values that exceeded the thresholds specified in Additional file 1 : Table S1.
Missing data imputation
Ensuring data completeness in the dataset is crucial for the success of this study. The dataset includes multiple demographic and medical biomarker data for each patient admission. However, some parameters may be missing for certain patients. Simply disregarding the available data can lead to the loss of valuable contextual information. To address this issue, data imputation is employed as an alternative to retain and fill in these missing values. Machine learning-based data imputation has been shown to be effective, and for this investigation, we utilized the MICE imputation technique [ 30 ]. Additional file 1 : Figure S3 illustrates the missing values for various characteristics in the dataset, with the spark lines on the figure’s right indicating data completeness.
Data splitting and normalization
To ensure unbiased model performance during training, the training dataset is divided into test sets using cross-validation, a well-established procedure. The entire dataset is split into 5 sets, each containing 80% training data and 20% test data [ 31 ].
For effective training of the machine learning model on the dataset, data normalization is essential to achieve generalized performance [ 32 ]. Normalization ensures that each feature contributes equally to the training process by transforming or scaling the entire dataset to a standardized range. Studies have shown improved performance when using normalized data for training instead of unprocessed data. In our study, we employed standard scalar to normalize the training data, and the scaling parameters were applied to the test set as well [ 32 ].
Data balancing
The dataset poses a fundamental challenge due to the class imbalance. While there are records for 1,075 cases (90.49%) that are alive, only 113 cases (9.51%) are deceased. This imbalance during training can introduce bias, leading the model to primarily recognize healthy cases. To mitigate this issue, a data augmentation method is proposed.
Data augmentation techniques are employed to provide synthetic data for minority classes. One such technique is Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE), a well-known method that generates synthetic data using the nearest kNN data point [ 33 ]. In our study, for both machine learning and ensemble techniques, the minority classes in the training sets are oversampled during augmentation to match the majority class.
Additionally, for the subdivision technique, each division is proportionally oversampled to achieve a balanced dataset. This approach helps address the class imbalance, enhancing the performance of the machine learning models and resulting in more accurate predictions.
Statistical analysis
The Chi-square univariate test and rank-sum test were employed to identify statistically significant characteristics between the two groups. The detailed description of this study is explained in Additional file 1 : S1. This analysis calculates the difference between the observed frequency (O) and the expected frequency (E) for each cell. It then squares the difference, divides it by the expected frequency, and sums the results for all cells in the contingency table [ 34 , 35 ].
Feature ranking
In the preprocessed dataset containing 105 features and a column with target variables, using all features may lead to overfitting and impractical deployment for real-time prediction. To select the most relevant features, three machine learning feature selection models are employed: XGboost, RandomForest and Extratrees. Descriptions of these feature ranking techniques are given in Additional file 1 : S2.
Using these feature selection models, we can identify the most relevant features to enhance prediction accuracy while avoiding overfitting and ensuring practical deployment in real-time scenarios.
Machine learning model development
This study explores several machine learning models from the Sci-kit learn library. We trained our data on MLP Classifier, Linear Discriminant Analysis, XGBoost Classifier, Random Forest Classifier, Logistic Regression, SVM, Extra Trees Classifier, Ada Boost Classifier, KNN Classifier, and Gradient Boosting Classifier [ 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 ]. Notably, Extra Trees, Random Forest and Catboost classifier demonstrated the most promising performance. In the subsequent section, a comprehensive overview of these top-performing models is provided:
Extra trees classifier
Extremely Randomized Trees, or ExtraTrees (ET) Classifier, is a tree-based ensemble technique used in supervised learning. This model introduces extreme randomness in attribute values and tree node cutoff points. It is a subset of the RandomForest classifier, offering computational efficiency through more extensive randomization. The classification score measurement for ExtraTrees is a specific normalization of information gain. For a sample S and a division s, the measure is given by:
where \({H}_{s}(S)\) is the (log) entropy of the classification in S, \({H}_{s}(S)\) is the split entropy (also called split information by Quinlan (1986)), and \({I}_{c}^{s}\left(S\right)\) is the mutual information of the split outcome and the classification [ 42 , 46 , 47 ].
Random forest classifier
The Random Forest (RF) Classifier is a classification-focused machine learning algorithm that uses an ensemble approach by combining multiple decision trees. The term “random forest” comes from the fact that the algorithm creates a forest of decision trees with arbitrary constructions. Important division points in the data, like Gini impurity or information gain, are used to build decision trees based on different criteria. However, in Random Forest, the selection of split points is limited to a random subset of features at each node, rather than considering all features [ 39 , 48 , 49 ]. Additional file 1 : Figure S4 depicts the framework for the RandomForest Classifier.
Catboost classifier
CatBoost (CB) Classifier is a gradient boosting algorithm tailored for efficient handling of categorical features. By constructing decision trees and combining their predictions, it achieves accurate classifications. This specialized algorithm efficiently manages categorical features, feature scaling, and missing values, optimizing training performance. Compared to conventional gradient boosting algorithms, CatBoost offers a more streamlined and automated approach [ 50 , 51 ].
Stacking based machine learning model
Ensemble models are employed when individual models fall short of achieving desired outcomes [ 52 , 53 ]. This method has found extensive application, including in medical applications, where it proves effective in improving the accuracy of predictions by leveraging insights from various models [ 16 , 54 , 55 ]. Stacking ensemble technique is used in this study, combining the predictions of our top three models. Stacking ensemble, also known as stacked generalization, involves training a meta-model to optimally combine base models' predictions, resulting in improved overall performance. By utilizing input x and the predictions of the base-level classifier set M, a probability distribution is created, leading to a final prediction:
where ( \({{\text{c}}}_{1}\) , \({{\text{c}}}_{2}\) … \({{\text{c}}}_{{\text{m}}}\) ) represents the set of potential class values and \({{\text{P}}}^{{\text{M}}}\left({{\text{c}}}_{{\text{i}}}|{\text{x}}\right)\) represents the probability that example x belongs to class \({{\text{c}}}_{{\text{i}}}\) , as calculated (and predicted) by classifier M [ 52 , 53 ]. This investigation employs the classifiers Extra-trees, RandomForest, and CatBoost. The Gradient boosting classifier was used for the meta-model. Our proposed architecture for the stacking ensemble method is depicted in Fig. 2 below:
Data subdivision: an approach for highly imbalances datasets
The main challenge in our study is the significant class disparity, with a distribution of 90.49% to 9.51%, which can lead to biased predictions and an inability to accurately predict the minority class. To address this issue, we explore different techniques to mitigate data imbalance, namely undersampling and oversampling. Undersampling involves reducing the number of samples from the majority class to equalize class distribution. However, this approach results in the loss of valuable information, as a considerable percentage of data is discarded. On the other hand, oversampling aims to increase the number of samples in the minority class by duplicating data points, but applying this method to highly imbalanced datasets can lead to overfitting. The model becomes too reliant on the specific minority data points, leading to inaccuracies in predicting new data.
To overcome these challenges, we propose a subset method for handling imbalanced data in our study. We divide the majority class into three subsets and then create three Subdivisions by combining each subset with an oversampled version of the entire minority class. This division of the dataset into smaller Subdivisions helps reduce class disparity compared to the complete dataset. As a result, when oversampling is applied, it encounters a much lower discrepancy and generates fewer duplications of the minority data points, reducing the risk of overfitting. During the training process, we apply fivefold Cross-Validation for each Subdivision and use SMOTE to achieve class balance in the training set of each fold. The results of each Subdivision are later averaged to obtain the final prediction. This approach ensures that each Subdivision is given equal importance, and the ensemble of results helps improve overall performance. Figure 3 illustrates the data subdivision technique used in our study, depicting how the dataset is divided into Subdivisions, oversampled, and finally combined to achieve more balanced training data.
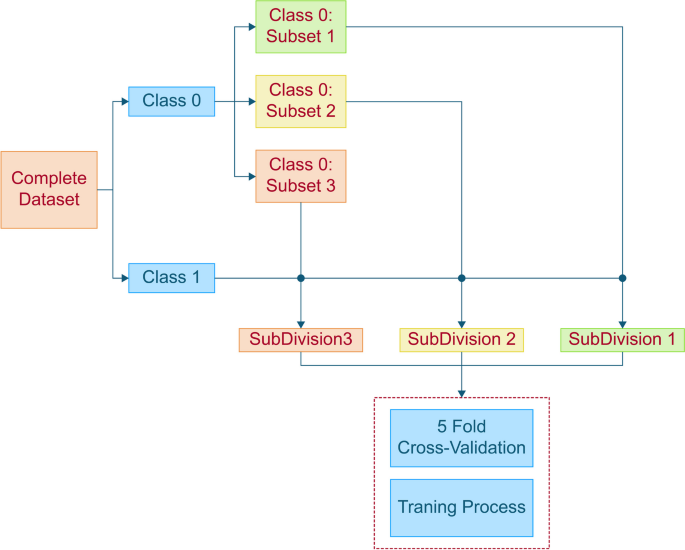
Data subdivision technique
By adopting the data subdivision technique, we aim to enhance the accuracy and reliability of our machine learning models in predicting the minority class while avoiding the pitfalls of traditional undersampling and oversampling methods. This innovative approach contributes to more robust and effective predictions in our study, paving the way for improved results in handling imbalanced data sets in various domains.
To balance the dataset, we divided the majority class into three subsets (359, 359, and 357 cases) and merged them with the minority class (113 instances). SMOTE was then used to achieve class balance.
Performance metrics
The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and area under the curve (AUC), along with Precision, Sensitivity, Specificity, Accuracy, and F1-Score, were used to evaluate the performance of the classifiers. In addition, we utilized five-fold cross-validation, which results in a division of 80% and 20% for the train and test sets, respectively, and according to the fold number, this procedure is repeated five times to validate the entire dataset.
We utilized per-class weighted metrics and overall precision because the number of instances varied between classes. In addition, the AUC value was utilized as an evaluation metric. Five evaluation metrics (weighted sensitivity or recall, specificity, precision, overall accuracy, and F1 score) are represented mathematically in Eqs. 3 through 7 .
here true positive, true negative, false positive, and false negative are represented as TP, TN, FP, and FN, respectively.
Experimental setup
This study was carried out with the sklearn package and Python 3.9.13. All the models were trained with the specifications: Nvidia GForce 1050ti GPU, AMD Ryzen 7 5800X 8-Core Processor and 32 GB High RAM.
The statistical analysis was conducted using the scipy library and the chi-square test on our dataset. Demographic variables were excluded from the analysis, leaving continuous numeric columns. The chi-square rank-sum test was used to assess the statistical significance of individual characteristics for each group, with a significance threshold of P < 0.05. The dataset consisted of 1075 (90.49%) living cases and 113 (9.51%) deceased cases. The mean (SD) value of lactate for deceased cases was 9.99 (7.42), while for living cases, it was 3.63 (2.92). ALB/GLB and Chloride_Whole_Blood had P-values greater than 0.8, indicating no significant difference between the groups. The P-values for Creatine_Kinase (CK), Mean_Platelet_Volume (MPV), thrombin_time, Hematocrit, WBC_Urine, WBC/pus_cell, and Monocyte_Count ranged from 0.79 to 0.50. Additional file 1 : Table S2 presents the class-wise mean, standard deviation, and P-values for all biochemical markers and continuous variables.
In this study, three machine learning feature selection models were employed: XGBoost, RandomForest, and Extra trees. In the initial analysis, RandomForest yielded the most favorable rankings, resulting in higher accuracy scores for predictions compared to the other two methods. Out of the 106 features, the top 16 features were identified as the most effective for achieving optimal results with a minimal number of features. Figure 4 illustrates the F1-Scores for class 1 corresponding to the top features in our three best models.
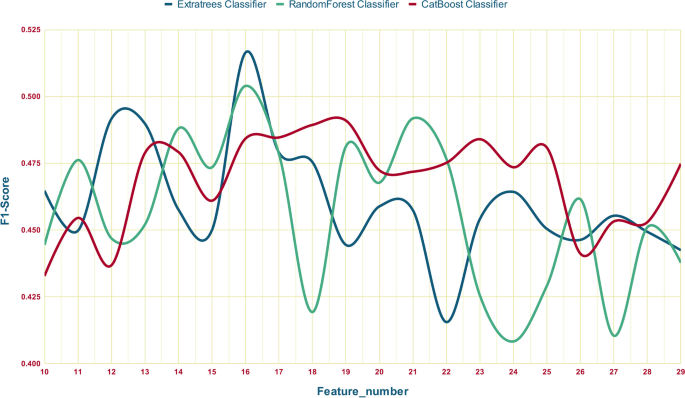
F1-Scores for Class 1 across the top features
In Fig. 5 , the top 20 characteristics assessed by RandomForest are presented, and out of these, 16 were utilized. Among them, lactate was identified as the most significant characteristic.
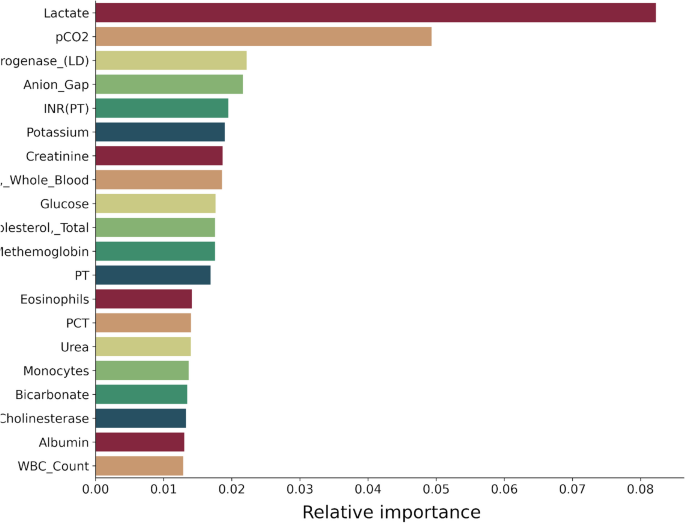
Features ranked according to Random Forest feature selection algorithm
Machine learning model performances
The top 16 features, as ranked by Random Forest's feature importance attribute, along with the ‘HOSPITAL_EXPIRE_FLAG’ as the target variable, were used to train the algorithms. The models were then tested using fivefold cross-validation on the entire dataset. The performance of the top three machine learning models was investigated and evaluated. In the following section, we present and discuss the results of each experiment.
The ET classifier achieved an AUC score of 72.22% and an accuracy of 89.14%. However, its class-wise precision for the deceased class (class 1) was only 43.94%, indicating poor performance in accurately detecting the deceased cases. The RF classifier obtained an AUC score of 70.91% and an accuracy of 88.22%. However, when analyzing individual classes, the precision for class 1 was found to be 40.28%. The CB classifier demonstrates the highest AUC (77.11%) and accuracy (87.96%) among the three classifiers. However, it exhibits lower precision (41%) in predicting the deceased class compared to other classifiers. The stacking technique was employed to create an ensemble model by combining the top three performing models. The layered models were trained using gradient boosting classifier. As a result, the AUC score decreased to 60.59%, while the accuracy increased to 88.89%. Table 1 provides a summary of the results for the ET, RF, CB and stacking ML classifiers.
Figure 6 shows the confusion matrix for Extra Tree, Random Forest, CatBoost and stacking ML model. It is apparent that among these models CatBoost is performing the best in terms of sensitivity and AUC. However, none of the models are showing acceptable performance in this highly imbalance dataset (d). The ROC curves for ET, RF, CB and stacking ML model can be seen in Fig. 7 .
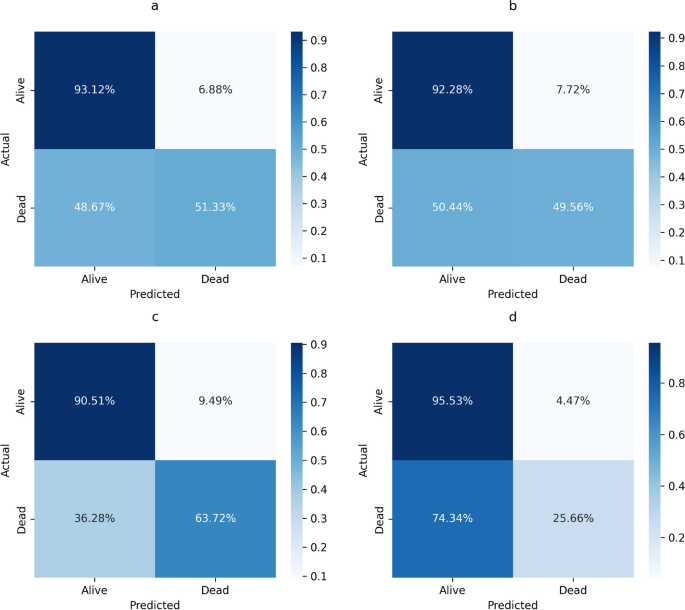
Confusion matrix for Extra Tree ( a ), Random Forest ( b ), CatBoost ( c ) and stacking ensemble method ( d )
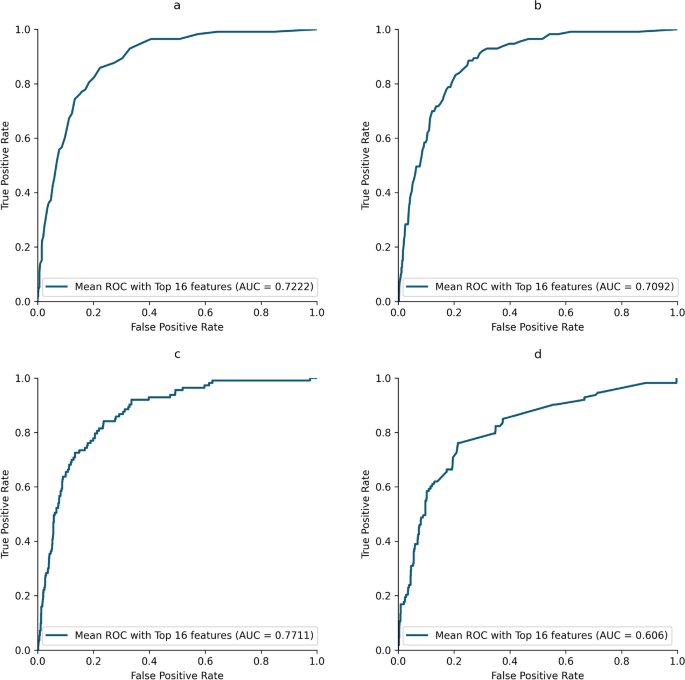
ROC curves for Extra Tree ( a ), Random Forest ( b ), CatBoost ( c ) and stacking ensemble method ( d )
Data subset performances
Utilizing the top 16 features, we employ the CB classifier for the subdivision method. Dividing the dataset into three subdivisions, we independently train each subset on the CB model and then aggregate the results by averaging them. The subdivision method exhibits a noteworthy average subset accuracy of 89.32% with an AUC of 85.20%. The precision and sensitivity for this model are 77.98% and 77.29%, respectively, while the specificity and F1-score stand at 93.11% and 89.30%. For a visual representation of the model’s performance, refer to Fig. 8 , which illustrates the ROC curve for the subdivision method. The summary of the average result of the subdivision method and results for each subdivision is stated in Table 2 and 3 .
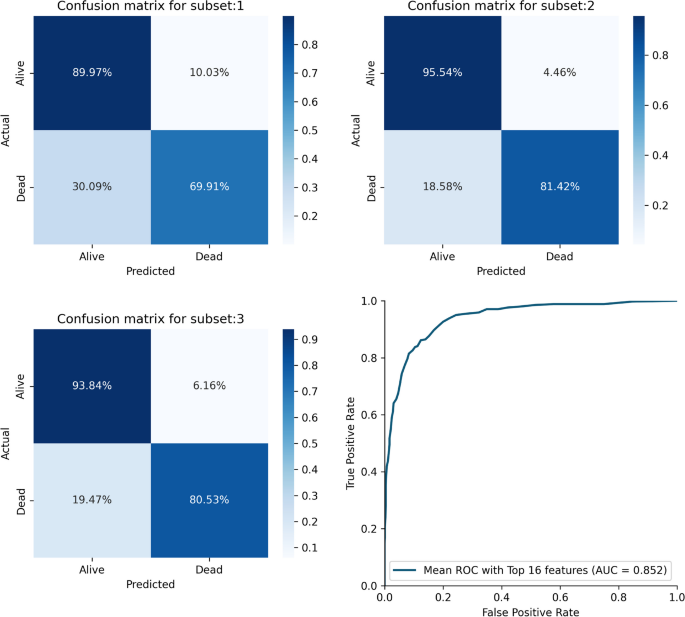
Confusion matrix for the subsets for the best performing model—CB Classifier and average ROC curve for the subdivision technique
The confusion matrix for each subset and average ROC curve are depicted in Fig. 8 .
The findings of this study showcase the significant potential of biomarkers in predicting mortality, offering valuable insights that can aid clinicians in making well-informed decisions. In our exploration of feature selection models for machine learning, namely XGBoost, RandomForest, and Extra tree, we discovered that the top 16 features selected by RandomForest yielded the most optimal results with minimal feature utilization during the initial investigations. This indicated that RandomForest outperformed its competitors in terms of predictive performance.
However, upon conducting further analysis, we unveiled certain limitations of the classifiers, particularly their inability to accurately predict the deceased class. Despite the promising results and efficiency of RandomForest in feature selection, it became evident that more advanced techniques were necessary to tackle the challenge of effectively predicting mortality in the dataset. This highlighted the importance of continually exploring and refining machine learning methodologies to enhance their predictive capabilities and address specific complexities in clinical scenarios. As such, our study not only underscores the significance of biomarkers in mortality prediction but also emphasizes the ongoing need for sophisticated algorithms to achieve more accurate and comprehensive predictions in critical healthcare settings.
We focused on the subdivision technique using the top 16 features for the CB classifier. Dividing the dataset into three distinct subsets, we proceeded to train each of these subsets independently on the CB model. Subsequently, the results were skillfully combined by averaging them, yielding a highly commendable average subset accuracy of 89.32%. Moreover, the AUC for this method achieved an impressive 85.2%, indicative of its robustness in discrimination capability. As a result of this approach, not only did we achieve superior accuracy, but we also observed significant improvements in precision, sensitivity, specificity, and F1-score, all of which are crucial performance metrics in medical predictive modeling. These outcomes underscore the effectiveness of the subdivision technique and its potential to further enhance the reliability and precision of our predictive model.
However, while the CB classifier excelled in predicting the living cases, it exhibited limitations when it came to accurately predicting the deceased class. The model struggled to achieve satisfactory performance in detecting the minority class of deceased cases, resulting in lower sensitivity and F1-score values. This indicates that additional research and further refinement are essential to enhance the model's ability to accurately predict the deceased class. To address these identified limitations, future investigations could focus on improving the handling of imbalanced data and exploring more advanced ensemble techniques or hybrid models that may provide a better balance between the two classes. Moreover, fine-tuning the feature selection process and incorporating domain-specific knowledge may also contribute to enhancing the model's predictive capabilities for the deceased class. A quantitative comparison among relevant studies is provided in Table 4 .
The data size in our study, encompassing 13,944 pediatric ICU cases, is comparable to that in Hong et al.’s study and larger than the datasets used in other referenced studies. This extensive data size provides a robust basis for our analysis and enhances the generalizability of our results. Our approach, focusing on feature engineering and data subdivision, yielded an accuracy of 0.8932 and an AUC of 0.8520. These results are notably higher than those achieved in the studies by Hu et al., Wang et al., and Zhang et al., indicating a strong predictive capability of our model. It is noteworthy that our study’s AUC is comparable to that achieved by Li et al., who employed advanced fusion models.
The variance in approaches and outcomes across these studies underscores the diverse methodologies in mortality prediction research. Our study contributes to this growing body of work by demonstrating the efficacy of feature engineering combined with data subdivision techniques in a pediatric ICU setting. This approach shows promise in enhancing predictive accuracy and could be a valuable addition to the clinician’s toolkit for mortality prediction, emphasizing the need for personalized and data-driven patient care. This comparative analysis not only positions our study within the existing research landscape but also highlights its potential clinical utility and relevance. By benchmarking our findings against these studies, we gain valuable insights into the evolving nature of machine learning applications in healthcare and identify avenues for future research and development in predictive modeling for pediatric respiratory diseases. The findings of this study need to be approached with caution due to the limitations posed by the relatively small dataset size and the class imbalance between deceased and living cases. The restricted sample size may impact the generalizability and robustness of the results. Furthermore, the class imbalance can introduce biases and hinder the accurate prediction of the minority class. To enhance the credibility and efficacy of mortality prediction models for pediatric patients with respiratory diseases, future research endeavors should focus on gathering larger and more balanced datasets. By increasing the sample size, the models can be trained on a more diverse and representative set of instances, leading to improved performance and better generalization to real-world scenarios. In addition to dataset size and class balance, researchers should also explore the incorporation of additional relevant features and biomarkers to refine the predictive models further. Integrating comprehensive and diverse patient data can enable the development of more comprehensive and accurate mortality prediction systems. Moreover, it is essential to conduct external validation of the developed models on independent datasets to verify their reliability and effectiveness in different healthcare settings. This validation process will provide crucial insights into the model’s robustness and its potential to be applied in diverse clinical environments.
Monitoring ICU patients’ parameters (lactate, pCO2, LDH, anion gap, electrolytes, INR, potassium, creatinine, bicarbonate and WBC) provide valuable insights into their pathophysiology i.e. medical progress and severity of critical illness, which help in guiding treatment or decision-making. The following explains the significance of the top parameters: elevated lactate levels indicate tissue hypoxia and anaerobic metabolism, often seen in shock or hypo perfusion states of ICU patients. Monitoring lactate helps assess tissue perfusion and response to treatment. Carbon dioxide (pCO2) is a byproduct of metabolism and is eliminated through respiration. Changes in pCO2 can indicate respiratory status and acid–base balance, especially in patients with respiratory failure or ventilation issues. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) is an enzyme found in various tissues, including the heart, liver, and muscles. Elevated LDH levels can indicate tissue damage or breakdown, as seen in conditions like myocardial infarction, liver disease, or muscle injury. The elevated levels of LDH reflect the severity of critical illness. Whereas the anion gap is a calculated parameter that helps assess metabolic acidosis. An increased anion gap may indicate the presence of unmeasured anions, such as lactate, ketones, or toxins, which can be seen in conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis or lactic acidosis conditions that require extensive monitoring in ICU. Therefore, monitoring electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride helps assess fluid and electrolyte balance, which is crucial in critically ill patients to prevent complications like arrhythmias or neurologic abnormalities. Potassium in particular is essential for proper cardiac and neuromuscular function. Abnormal potassium levels can lead to life-threatening arrhythmias and are often seen in conditions like renal failure or metabolic disorders. Bicarbonate is a buffer that helps maintain acid–base balance in the body. Changes in bicarbonate levels can indicate metabolic acidosis or alkalosis, which can occur in various critical illnesses. Creatinine is a waste product of muscle metabolism and is excreted by the kidneys. Elevated creatinine levels indicate impaired renal function, which is common in critically ill patients and can impact drug dosing and fluid management. Monitoring WBC (White Blood Cell Count helps assess the inflammatory response and immune function in critically ill patients. Elevated WBC counts may indicate infection or inflammatory processes. Similarly, monitoring PCT (procalcitonin) as biomarker of bacterial infections. Additionally, INR (International Normalized Ratio) is a measure of blood coagulation and is used to monitor patients on anticoagulant therapy. Changes in INR can indicate alterations in the coagulation cascade and may require adjustments in medication [ 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 ].
In summary, addressing the limitations of dataset size and class imbalance and incorporating advanced feature selection techniques and external validation can advance the accuracy and dependability of mortality prediction models for pediatric patients with respiratory diseases. These efforts will ultimately contribute to more effective and personalized patient care, leading to improved clinical outcomes for this vulnerable patient population.
In conclusion, this study sheds light on the promising potential of biomarkers in predicting mortality among pediatric patients with respiratory diseases, empowering clinicians to make well-informed admission decisions. Through meticulous evaluation of diverse classifiers, the CatBoost (CB) classifier emerged as the standout performer, exhibiting the highest AUC score and accuracy. However, the challenge lies in improving precision for the deceased class. By employing the stacking ensemble method, we were able to enhance overall accuracy, albeit at the expense of a slightly lower AUC score. Subsequently, the subdivision technique applied to the CB classifier using the top 16 features led to remarkable improvements in precision (89.32%), AUC (85.20%), and other essential predictive metrics. Overall, the CB classifier with the subdivision algorithm proved to be the most effective approach for mortality prediction. Looking ahead, our future objectives for this mortality prediction model in pediatrics encompass its seamless integration into clinical settings, especially in resource-constrained environments, and customization to suit the needs of specific populations. Additionally, we aim to incorporate real-time data streams to ensure up-to-date and accurate predictions. Collaborative efforts to enhance the dataset’s size and diversity are paramount to ensure the model’s robustness and generalizability. By diligently pursuing these avenues, we envision a significant impact on pediatric healthcare, as our model’s enhanced accuracy will bolster preparedness and improve patient outcomes, ultimately saving lives and benefiting young patients and their families.
Availability of data and materials
The preprocessed version of the dataset used in this study is available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Divecha C, Tullu MS, Chaudhary S. Burden of respiratory illnesses in pediatric intensive care unit and predictors of mortality: experience from a low resource country. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2019;54:1234–41.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Ames SG, Davis BS, Marin JR, Fink EL, Olson LM, Gausche-Hill M, et al. Emergency department pediatric readiness and mortality in critically ill children. Pediatrics. 2019;144:e20190568.
Lillehei CW, Gauvreau K, Jenkins KJ. Risk adjustment for neonatal surgery: a method for comparison of in-hospital mortality. Pediatrics. 2012;130:e568–74.
Eisenberg MA, Balamuth F. Pediatric sepsis screening in US hospitals. Pediatr Res. 2022;91:351–8.
Balamuth F, Scott HF, Weiss SL, Webb M, Chamberlain JM, Bajaj L, et al. Validation of the pediatric sequential organ failure assessment score and evaluation of third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock definitions in the pediatric emergency department. JAMA Pediatr. 2022;176:672–8.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Papakyritsi D, Iosifidis E, Kalamitsou S, Chorafa E, Volakli E, Peña-López Y, et al. Epidemiology and outcomes of ventilator-associated events in critically ill children: evaluation of three different definitions. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2023;44:216–21.
Remick K, Smith M, Newgard CD, Lin A, Hewes H, Jensen AR, et al. Impact of individual components of emergency department pediatric readiness on pediatric mortality in US Trauma Centers. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023;94:417–24.
Shamout FE, Zhu T, Sharma P, Watkinson PJ, Clifton DA. Deep interpretable early warning system for the detection of clinical deterioration. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2019;24:437–46.
Marti J, Hall P, Hamilton P, Lamb S, McCabe C, Lall R, et al. One-year resource utilisation, costs and quality of life in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): secondary analysis of a randomised controlled trial. J Intensive Care. 2016;4:1–11.
Article Google Scholar
Lee SW, Loh SW, Ong C, Lee JH. Pertinent clinical outcomes in pediatric survivors of pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome (PARDS): a narrative review. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7:513.
Kortz TB, Kissoon N. Predicting mortality in pediatric sepsis: a laudable but elusive goal. J de Pediatr. 2021;97:260–3.
Mekontso Dessap A, Richard JCM, Baker T, Godard A, Carteaux G. Technical innovation in critical care in a world of constraints: lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023;207:1126–33.
Hughes RG. Tools and strategies for quality improvement and patient safety. In: Patient safety and quality: an evidence-based handbook for nurses. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2008.
Google Scholar
Chowdhury ME, Rahman T, Khandakar A, Al-Madeed S, Zughaier SM, Doi SA, et al. An early warning tool for predicting mortality risk of COVID-19 patients using machine learning. Cogn Comput. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-020-09812-7 .
Rahman T, Al-Ishaq FA, Al-Mohannadi FS, Mubarak RS, Al-Hitmi MH, Islam KR, et al. Mortality prediction utilizing blood biomarkers to predict the severity of COVID-19 using machine learning technique. Diagnostics. 2021;11:1582.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rahman T, Khandakar A, Abir FF, Faisal MAA, Hossain MS, Podder KK, et al. QCovSML: a reliable COVID-19 detection system using CBC biomarkers by a stacking machine learning model. Comput Biol Med. 2022;143: 105284.
Shuzan MNI, Chowdhury MH, Hossain MS, Chowdhury ME, Reaz MBI, Uddin MM, et al. A novel non-invasive estimation of respiration rate from motion corrupted photoplethysmograph signal using machine learning model. IEEE Access. 2021;9:96775–90.
Yang Y, Xu B, Haverstick J, Ibtehaz N, Muszyński A, Chen X, et al. Differentiation and classification of bacterial endotoxins based on surface enhanced Raman scattering and advanced machine learning. Nanoscale. 2022;14:8806–17.
Hu Y, Gong X, Shu L, Zeng X, Duan H, Luo Q, et al. Understanding risk factors for postoperative mortality in neonates based on explainable machine learning technology. J Pediatr Surg. 2021;56:2165–71.
Markova BS. Predicting readmission of neonates to an ICU using data mining. University of Twente; 2021.
Stey AM, Kenney BD, Moss RL, Hall BL, Berman L, Cohen ME, et al. A risk calculator predicting postoperative adverse events in neonates undergoing major abdominal or thoracic surgery. J Pediatr Surg. 2015;50:987–91.
Pollack MM, Patel KM, Ruttimann UE. PRISM III: an updated pediatric risk of mortality score. Crit Care Med. 1996;24:743–52.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Wang H, He Z, Li J, Lin C, Li H, Jin P, et al. Early plasma osmolality levels and clinical outcomes in children admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit: a single-center cohort study. Front Pediatr. 2021;9: 745204.
Hong S, Hou X, Jing J, Ge W, Zhang L. Predicting risk of mortality in pediatric ICU based on ensemble step-wise feature selection. Health Data Sci. 2021. https://doi.org/10.34133/2021/9365125 .
Zhang Y, Shi Q, Zhong G, Lei X, Lin J, Fu Z, et al. Biomarker-based score for predicting in-hospital mortality of children admitted to the intensive care unit. J Investig Med. 2021;69:1458–63.
Zeng X, Yu G, Lu Y, Tan L, Wu X, Shi S, et al. PIC, a paediatric-specific intensive care database. Sci Data. 2020;7:14.
Anker SD, Morley JE, von Haehling S. Welcome to the ICD-10 code for sarcopenia, vol. 7. Wiley; 2016. p. 512–4.
Li H, Zeng X, Yu G. Paediatric intensive care database. PhysioNet; 2019.
October T, Dryden-Palmer K, Copnell B, Meert KL. Caring for parents after the death of a child. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2018;19:S61.
Hegde H, Shimpi N, Panny A, Glurich I, Christie P, Acharya A. MICE vs PPCA: missing data imputation in healthcare. Inf Med Unlocked. 2019;17: 100275.
Mullin MD, Sukthankar R. Complete cross-validation for nearest neighbor classifiers. In: ICML; 2000. p. 639–46.
Singh D, Singh B. Investigating the impact of data normalization on classification performance. Appl Soft Comput. 2020;97: 105524.
Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP. SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Intell earch. 2002;16:321–57.
Tallarida RJ, Murray RB, Tallarida RJ, Murray RB. Chi-square test. In: Manual of pharmacologic calculations: with computer programs. Springer Science & Business Media; 1987. p. 140–2.
Chapter Google Scholar
McHugh ML. The chi-square test of independence. Biochemia medica. 2013;23:143–9.
Taud H, Mas J. Multilayer perceptron (MLP). In: Geomatic approaches for modeling land change scenarios. Springer; 2018. p. 451–5.
Izenman AJ. Linear discriminant analysis. In: Modern multivariate statistical techniques: regression, classification, and manifold learning. Springer; 2013. p. 237–80.
Chen T, He T, Benesty M, Khotilovich V, Tang Y, Cho H et al. Xgboost: extreme gradient boosting. R package version 0.4–2. vol. 1, pp. 1–4; 2015.
Breiman L. Random forests. Mach Learn. 2001;45:5–32.
Wright RE. Logistic regression. American Psychological Association; 1995.
Yue S, Li P, Hao P. SVM classification: its contents and challenges. Appl Math A J Chin Univ. 2003;18:332–42.
Geurts P, Ernst D, Wehenkel L. Extremely randomized trees. Mach Learn. 2006;63:3–42.
Schapire RE. Explaining adaboost. In: Empirical inference: festschrift in honor of Vladimir N. Vapnik. Springer; 2013. p. 37–52.
Peterson LE. K-nearest neighbor. Scholarpedia. 2009;4:1883.
Natekin A, Knoll A. Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial. Front Neurorobot. 2013;7:21.
Wehenkel L, Ernst D, Geurts P. Ensembles of extremely randomized trees and some generic applications. In: Robust methods for power system state estimation and load forecasting; 2006.
Saeed U, Jan SU, Lee Y-D, Koo I. Fault diagnosis based on extremely randomized trees in wireless sensor networks. Reliab Eng Syst Saf. 2021;205: 107284.
Cutler A, Cutler DR, Stevens JR. Random forests. In: Ensemble machine learning: methods and applications. Springer; 2012. p. 157–75.
Biau G. Analysis of a random forests model. J Mach Learn Res. 2012;13:1063–95.
Prokhorenkova L, Gusev G, Vorobev A, Dorogush AV, Gulin A. CatBoost: unbiased boosting with categorical features. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 31; 2018.
Dorogush AV, Ershov V, Gulin A. CatBoost: gradient boosting with categorical features support. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.11363 ; 2018.
Rokach L. Ensemble methods for classifiers. In: Data mining and knowledge discovery handbook. Springer; 2005. p. 957–80.
Opitz D, Maclin R. Popular ensemble methods: an empirical study. J Artif Intell Res. 1999;11:169–98.
Kwon H, Park J, Lee Y. Stacking ensemble technique for classifying breast cancer. Healthcare Inf Res. 2019;25:283–8.
Daza A, Sánchez CFP, Apaza O, Pinto J, Ramos KZ. Stacking ensemble approach to diagnosing the disease of diabetes. Inf Med Unlocked. 2023;44:101427.
Li H, Lu Y, Zeng X, Feng Y, Fu C, Duan H, et al. Risk factors for central venous catheter-associated deep venous thrombosis in pediatric critical care settings identified by fusion model. Thromb J. 2022;20:1–11.
Wang H, Liang R, Liang T, Chen S, Zhang Y, Zhang L, et al. Effectiveness of sodium bicarbonate infusion on mortality in critically ill children with metabolic acidosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 759247.
Caires Silveira E, Mattos Pretti S, Santos BA, Santos Corrêa CF, Madureira Silva L, Freire de Melo F. Prediction of hospital mortality in intensive care unit patients from clinical and laboratory data: a machine learning approach. World J Crit Care Med. 2022;11:317–29.
Vincent JL, Quintairos ESA, Couto L Jr, Taccone FS. The value of blood lactate kinetics in critically ill patients: a systematic review. Crit Care. 2016;20:257.
Jeong S. Scoring systems for the patients of intensive care unit. Acute Crit Care. 2018;33:102–4.
Schmidt GA. Evaluation and management of suspected sepsis and septic shock in adults; 2024. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-and-management-of-suspected-sepsis-and-septic-shock-in-adults?search=ICU%20monitoring%20parameters&topicRef=107337&source=see_link
Download references
This work was made possible by High Impact grant# QUHI-CENG-23/24-216 from Qatar University and is also supported via funding from Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University project number (PSAU/2023/R/1445). The statements made herein are solely the responsibility of the authors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, University of Dhaka, Dhaka, 1000, Bangladesh
Johayra Prithula
Department of Electrical Engineering, Qatar University, 2713, Doha, Qatar
Muhammad E. H. Chowdhury & Muhammad Salman Khan
Emergency Medicine Department, Sidra Medicine, Doha, Qatar
Khalid Al-Ansari
Department of Basic Medical Sciences, College of Medicine, Qatar University, 2713, Doha, Qatar
Susu M. Zughaier
Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University Kebangsaan Malaysia, 56000, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Khandaker Reajul Islam
Department of Biomedical Technology, College of Applied Medical Sciences in Al-Kharj, Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, 11942, Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia
Abdulrahman Alqahtani
Department of Medical Equipment Technology, College of Applied, Medical Science, Majmaah University, 11952, Majmaah, Saudi Arabia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization: JP, MEHC; Data curation: JP, KRI; Formal analysis: JP; Funding acquisition: MEHC, MSK, KA, SMZ, AA; Investigation: JP, MEHC; Project administration: MEHC, MSK, AA; Software: JP, KRI; Supervision: MEHC, MSK, AA; Validation: MEHC, KA, SMZ; Visualization: JP; writing—original draft: JP, MEHC, AA; Writing—review & editing: JP, MEHC, MSK, KA, SMZ, KRI, AA.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Muhammad E. H. Chowdhury .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The authors of this article did not collect the dataset used for this study. It is made publicly available by Zeng et al. [ 26 ].
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this study.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Supplementary materials.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Prithula, J., Chowdhury, M.E.H., Khan, M.S. et al. Improved pediatric ICU mortality prediction for respiratory diseases: machine learning and data subdivision insights. Respir Res 25 , 216 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-024-02753-x
Download citation
Received : 22 September 2023
Accepted : 29 February 2024
Published : 23 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-024-02753-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Pediatric mortality
- Respiratory diseases
- Pediatric ICU
- Mortality prediction
- Early recognition
- Machine learning
Respiratory Research
ISSN: 1465-993X
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Qaleh Kurd Cave (Qazvin, Iran): Oldest Evidence of Middle Pleistocene Hominin Occupations and a Human Deciduous Tooth in the Iranian Central Plateau
- Published: 23 May 2024
- Volume 7 , article number 16 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article

- Hamed Vahdati Nasab 1 , 2 na1 ,
- Gilles Berillon 2 na1 ,
- Seyyed Milad Hashemi 1 , 2 ,
- Jean-Jacques Bahain 15 ,
- Noémie Sévêque 3 ,
- Mozhgan Jayez 4 ,
- Stéphanie Bonilauri 2 ,
- Guillaume Jamet 5 , 6 ,
- Mohammad Akhavan Kharazian 2 , 6 , 12 , 13 ,
- Asghar Nateghi 7 ,
- Alieh Abdollahi 7 ,
- Pierre Antoine 6 ,
- Iraj Beheshti 8 ,
- Nicolas Boulbes 2 , 14 ,
- Cécile Chapon-Sao 2 ,
- Xavier Gallet 2 ,
- Christophe Falguères 2 ,
- Lisa Garbé 2 ,
- Mandan Kazzazi 9 ,
- Ahmad Zavar Mousavi 10 ,
- Sareh Nematollahinia 1 ,
- Jonathan Özçelebi 2 ,
- Emmanuelle Stoetzel 2 ,
- Olivier Tombret 2 &
- Valéry Zeitoun 11
92 Accesses
15 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The Iranian Central Plateau (ICP) with the Alborz and the Zagros Mountains is located at the crossroads between the Levant and the Caucasus to the west and Central Asia and East Asia to the east. These two regions yielded key paleoanthropological and archaeological sites from the Middle Pleistocene period. These discoveries highlight a large human biological and cultural diversity in this area during the Middle Pleistocene and raise questions about the interactions these humans had. Yet, despite decades of field research, no Middle Pleistocene assemblage in a clear chronological and stratigraphic context was known in the ICP, the Zagros, and the Alborz Mountains that could contribute to this debate; so far, the earliest of the area is dated of 80 ka. The Joint Iranian and French Paleoanthropological Project reinvestigated the cave of Qaleh Kurd (Qazvin). The Qaleh Kurd cave is located at 2137 m asl at the very western limit of the ICP, at its boundary with the Zagros Mountains. Here, we report on the discovery of in situ Middle Pleistocene archaeological assemblages, including a human deciduous first upper molar associated with a rich lithic and faunal material, and a first description of the chrono-stratigraphic framework of the deposits. The excavation and the archaeological and geoarchaeological analyses show that humans occupied the site during the Middle Pleistocene, during a period ranging from ca 452 ± 32 and 165 ± 11 ka. This chronology pushes back the earliest dated evidence of human settlement in the ICP by more than 300 ka. The human deciduous first upper molar comes from the upper part of the Middle Pleistocene sequence. The crown of the tooth is widely impacted by wear and carries that limit taxonomic inferences. The study of the three upper archaeological assemblages shows that the cave was recurrently occupied by humans of early Middle Paleolithic cultures. These assemblages recall some traits of sub-contemporary assemblages known in the Caucasus and the Levant but also the later Middle Paleolithic of the Zagros. The faunal assemblage is mainly composed of horse remains. The remains are very fragmented and show numerous anthropogenic stigmata that indicate significant butchery activities on site. From a large regional and chronological perspective, these findings make Qaleh Kurd Cave a key site for the knowledge of early human settlements and dispersals between the Levant and Asia.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Introduction: Azokh Cave and the Transcaucasian Corridor

Porc-Epic Cave, Ethiopia
Hattab ii, morocco, data availability.
No data outside the submitted manuscript file. Data and materials may made available on demand to first authors; archaeological materials being under the care of the cultural heritage service of the Qazvin Province.
The ICP is the large area surrounded by the Zagros Mountains to the west, the Alborz Mountains in the north, the Kopet Dagh Mountains in the east, and the central Iranian block (mainly the Lut Desert) in the south.
Abe, Y. (2005). Hunting and butchering patterns of the Evenki in the Northern Transbaikalia Russia . Ph.D. Dissertation,. Stony Brook University.
Google Scholar
Agam, A., & Zupancich, A. (2020). Interpreting the Quina and demi-Quina scrapers from Acheulo-Yabrudian Qesem Cave, Israel: Results of raw materials and functional analyses. Journal of Human Evolution, 144 , 102798.
Article Google Scholar
AlQahtani, S. J., Hector, M. P., & Liversidge, H. M. (2014). Accuracy of dental age estimation charts: Schour and Massler, Ubelaker and the London Atlas. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 154 , 70–78.
Andrefsky, W. (1994). Raw material availability and the organization of technology. American Antiquity, 59 , 21–35.
Armand, D., & Delagnes, A. (1998). Les retouchoirs en os d’Artenac (couche 6c) : perspectives archéozoologiques, taphonomiques et expérimentales. In J. P. Brugal, L. Meignen, & M. Patou-Mathis (Eds.), Économie Préhistorique : Les Comportements de Subsistance au Paléolithique Moyen. Actes des XVIIIe Rencontres Internationales d’Archéologie et d’Histoire d’Antibes, 23-25 Octobre 1997 (pp. 205–214). Sophia Antipolis: Editions APDCA.
Auguste, P. (1995). Chasse et charognage au Paléolithique moyen: l'apport du gisement de Biache-Saint-Vaast (Pas-de-Calais). Bulletin de la Société Préhistorique Française, 92 , 155–167.
Bahain, J. J., Voinchet, P., Vietti, A., Shao, Q., Tombret, O., Pereira, A., Nomade, S., & Falguères, C. (2021). ESR/U-series and ESR dating of several Middle Pleistocene Italian sites: Comparison with 40Ar/39Ar chronology. Quaternary Geochronology, 63 , 101151.
Bar-Yosef, O. (1994). The lower Paleolithic of the Near East. Journal of World Prehistory, 8 , 211–265.
Bar-Yosef, O. (2008). Asia, West: Paleolithic Cultures. In D. M. Pearsall (Ed.), Encyclopedia of Archaeology (pp. 865–875). Academic Press.
Chapter Google Scholar
Bar-Yosef, O., & Belfer-Cohen, A. (2001). From Africa to Eurasia - Early dispersals. Quaternary international, 75 , 19 –28.
Bar-Yosef, O., & Meignen, L. (2001). The chronology of the Levantine Middle Paleolithic Period in retrospect. Bulletins et mémoires de la Société d’Anthropologie de Paris. BMSAP, 13 , 269–289.
Bazgir, B., Ollé, A., Tumung, L., Becerra-Valdivia, L., Douka, K., Higham, T., van der Made, J., Picin, A., Saladié, P., López-García, J. M., Blain, H.-A., Allué, E., Fernández-García, M., Rey-Rodríguez, I., Arceredillo, D., Bahrololoumi, F., Azimi, M., Otte, M., & Carbonell, E. (2017). Understanding the emergence of modern humans and the disappearance of Neanderthals: Insights from Kaldar Cave (Khorramabad Valley, Western Iran). Nature Scientific Reports, 7 , 43460.
Bazgir, B., Otte, M., Tumung, L., Ollé, A., Deo, S. G., Joglekar, P., López-García, J. M., Picin, A., Davoudi, D., & van der Made, J. (2014). Test excavations and initial results at the Middle and Upper Paleolithic sites of Gilvaran, Kaldar, Ghamari caves and Gar Arjene Rockshelter, Khorramabad Valley, western Iran. Comptes Rendus Palevol, 13 , 511–525.
Becam, G., & Chevalier, T. (2019). Neandertal features of the deciduous and permanent teeth from Portel-Ouest Cave (Ariège, France). American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 168 , 45–69.
Becerra-Valdivia, L., Douka, K., Comeskey, D., Bazgir, B., Conard, N. J., Marean, C. W., Ollé, A., Otte, M., Tumung, L., Zeidi, M., & Higham, T. F. G. (2017). Chronometric investigations of the Middle to Upper Paleolithic transition in the Zagros Mountains using AMS radiocarbon dating and Bayesian age modelling. Journal of Human Evolution, 109 , 57–69.
Beliaeva, E. V., & Lioubine, V. P. (1998). The Caucasus-Levant-Zagros: Possible relations in the Middle Paleolithic. In M. Otte (Ed.), Prehistoire d’Anatolie: Genese des Deux Mondes (Anatolian Prehistory at the crossroads of two worlds) (Vol. 1, pp. 39–55). Liège: ERAUL 85.
Bennett, E. A., Champlot, S., Peters, J., Arbuckle, B., Bălăşescu, A., Bar-David, S., Davis, S., Gautier, M., Germonpré, M., Gündem, C., Hemami, M.-R., Kaczensky, P., Kuehn, R., Mashkour, M., Morales, A., Moullé, P.-E., Pucher, E., Pruvost, M., Tournepiche, J.-F., et al. (2017). Taming the Late Quaternary phylogeography of the Eurasiatic wild ass through ancient and modern DNA. PNAS, 106 , 21754–21759.
Berillon, G., & Asgari Khaneghah, A. (Eds.). (2016). Garm Roud, Hunting place in Iran, Upper Paleolithic (p. 280). Paris: @rchéo-éditions.com/IFRI.
Berillon, G., Asgari Khaneghah, A., Antoine, P., Bahain, J.-J., Chevrier, B., Zeitoun, V., Aminzadeh, N., Beheshti, M., Chanzanagh, H. E., & Nochadi, S. (2007). Discovery of new open-air Paleolithic localities in Central Alborz, Northern Iran. Journal of Human Evolution, 52 , 380–387.
Bewley, R. H. (1984). The Cambridge university archaeological expedition to Iran 1969. Excavations in the Zagros Mountains : Houmian, Mir Malas, and Barde Spid. Iran Journal of the British Institute of Persian Studies, 22 , 1–38.
Biglari, F., & Shidrang, S. (2006). The lower Paleolithic occupation of Iran. Near Eastern Archaeology, 69 (3-4), 160–168.
Biglari, F., Dashtizadeh, A., Zarei, S., Amini, S., & Ghasimi, T. (2023). Dehtal, Evidence of the Large Flake Acheulean at the North of the Persian Gulf. Iran Parseh Journal of Archaeological Studies, 7 , 7–24.
Biglari, F., & Jahani, V. (2011). The Pleistocene human settlement in Gilan, Southwest Caspian Sea: Recent Research. Eurasian Prehistory, 8 , 3–28.
Biglari, F., Jahani, V., Mashkour, M., & Amini, S. (2014). Test excavations at the Lower Paleolithic Site of Darband Cave, Roudbar, Gilan Province. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Symposium on the Iranian Archaeology (pp. 101–104). Iranian Center for Archaeological Research.
Binford, L. R. (1981). Bones: Ancient Men . Academic Press, New York.
Blasco, R., Rosell, J., Cuartero, F., Peris, J. F., Gopher, A., & Barkai, R. (2013). Using bones to shape stones: MIS 9 bone retouchers at both edges of the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS One, 8 , 76780.
Bonilauri, S., Chevrier, B., Khaneghah, A. A., Abolfathi, M., Ejlalipour, R., Nejab, R. S., & Berillon, G. (2019). Garm Roud 2, Iran: Bladelet production and cultural features of a key Upper Paleolithic site south of the Caspian Sea. Comptes Rendus Palevol, 20 , 823–837.
Bordes, F. (1961). Typologie du Paléolithique ancien et moyen . Delmas.
Bordes, F. (1981). Vingt-cinq ans après : le complexe moustérien revisité. Bulletin de la Société Préhistorique Française, 78 (3), 77–87.
Boulbes, N. (2010). Le cheval de Romain-la-Roche, Equus achenheimensis (Mammalia, Perissodactyla), contribution à la biochronologie des équidés caballins au Pléistocène moyen. Rev Paléobiol, 29 , 747–770.
Boulbes, N., & Van Asperen, E. N. (2019). Biostratigraphy and palaeoecology of European Equus. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 7 , 301.
Bourguignon, L. (1997). Le Mousterien de type Quina: nouvelles definitions d'une entite technique . Ph.D. Dissertation,. Universite de Paris X.
Braidwood, R. J., Howe, B., & Reed, C. A. (1961). The Iranian Prehistoric Project: New problems arise as more is learned of the first attempts at food production and settled village life. Science, 133 (3469), 2008–2010.
Brink, J. W. (1997). Fat Content in Leg Bones of Bison bison, and Applications to Archaeology. Journal of Archaeological Science, 24 (3), 259–274.
Brugal, J. P., Argant, A., Boudadi-Maligne, M., Crégut-Bonnoure, E., Croitor, R., Fernandez, P., Fourvel, J. B., Fosse, P., Guadelli, J. L., Labe, B., Magniez, P., & Uzunidis, A. (2020). Pleistocene herbivores and carnivores from France: An updated overview of the litterature, sites and taphonomy. Annales de Paléontologie, 106 (2), 102384 23.
Chen, F., Welker, F., Shen, C.-C., Bailey, S. E., Bergmann, I., Davis, S., Xia, H., Wang, H., Fischer, R., Freidline, S. E., Yu, T.-L., Skinner, M. M., Stelzer, S., Dong, G., Fu, Q., Dong, G., Wang, J., Zhang, D., & Hublin, J.-J. (2019). A late Middle Pleistocene Denisovan mandible from the Tibetan Plateau. Nature, 569 , 409–412.
Chen, X., & Moigne, A. M. (2018). Rhinoceros ( Stephanorhinus hemitoechus ) exploitation in Level F at the Caune de l'Arago (Tautavel, Pyrénées-Orientales, France) during MIS 12. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 28 (6), 669–680.
Chevrier, B., Berillon, G., Zeitoun, V., Khaneghah, A. A., Antoine, P., & Bahain, J.-J. (2006). Moghanak, Otchounak, Garm Roud 2: nouveaux assemblages paléolithiques dans le Nord de l’Iran. Premières caractérisations typo-technologiques et attributions chrono-culturelles. Paléorient, 32 (2), 59–79.
Coon, C. S. (1951). Cave explorations in Iran 1949 . University of Pennsylvania Press.
Copeland, L. (1975). The Middle and Upper Paleolithic in Lebanon and Syria in the Light of Recent Research. In F. Wendorf & A. Close (Eds.), Problems in Prehistory: North Africa and the Levant (pp. 317–350). Southern Methodist University Press.
Copeland, L. (1981). Chronology and distribution of the Middle Paleolithic, as known in 1980. In J. Cauvin & P. Sanlaville (Eds.), Lebanon and Syria, Préhistoire Du Levant Chronologie et Organisation de l’espace Depuis Les Origines Jusqu’au VIe Millénaire, Lyon, CNRS Maison de l’Orient méditerranéen (pp. 239–263)
Copeland, L. (1985). The pointed tools of Hummal Ia (El Kowm, Syria). Cahiers de l’Euphrate, 4 , 177–189.
Costamagno, S., & Rigaud, J.-P. (2014). L’exploitation de la graisse au Paléolithique. In S. Costamagno (Ed.), Histoire de l’alimentation humaine : entre choix et contraintes (pp. 134–152). CTHS.
Courtenay, L. A., Yravedra, J., Herranz-Rodrigo, D., Rodríguez-Alba, J. J., Serrano-Ramos, A., Estaca-Gómez, V., González-Aguilera, D., Solano, J. A., & Jiménez-Arenas, J. M. (2023). Deciphering carnivoran competition for animal resources at the 1.46 Ma early Pleistocene site of Barranco León (Orce, Granada, Spain). Quaternary Science Reviews, 300 , 107912.
Daujeard, C. (2008). Exploitation du milieu animal par les Néanderthaliens dans le Sud-Est de la France . Ph.D. Dissertation,. Université Lumière.
Daujeard, C., Moncel, M. H., Fiore, I., Tagliacozzo, A., Bindon, P., & Raynal, J. P. (2014). Middle Paleolithic bone retouchers in Southeastern France: Variability and functionality. Quaternary International, 326 , 492–518.
Debénath, A., & Dibble, H. L. (1994). Handbook of Paleolithic Typology (Vol. 1). Lower and Middle Paleolithic of Europe. University of Pennsylvania Press.
Delpech, F., & Villa, P. (1993). Activités de chasse et boucherie dans la grotte des Eglises. In J. Desse & F. Audoin-Rouzeau (Eds.), Exploitation des animaux sauvages à travers le Temps (pp. 79–102). IV. Colloque International de l’Homme et l’Animal.
Dennell, R. (2008). The Paleolithic Settlement of Asia . Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Book Google Scholar
Dibble, H., & Holdaway, S. (1993). The Middle Paleolithic of Warwasi Rockshelter. In D. I. Olszewski & H. L. Dibble (Eds.), The Paleolithic Prehistory of the Zagros-Taurus (pp. 75–99). University Museum.
Eisenmann, V. (2022). Old World Fossil Equus (Perissodactyla, Mammalia), Extant Wild Relatives and Incertae Sedis Forms. Quaternary, 5 (3), 38.
Eisenmann, V., & Mashkour, M. (1999). The Small Equids (Perissodactyla, Mammalia) of the Pleistocen of Binagady (Azerbaijan) and Qazvin (Iran): E. hemionus binagadensis nov. subsp. and E. Hydruntinus. Geobios, 32 (1), 105–122.
Farizy, C., David, F., Jaubert, J., & Eisenmann, V. (1994). Hommes et bisons du Paléolithique moyen à Mauran (Haute-Garonne) . CNRS éditions.
Ferring, R., Oms, O., Agustí, J., Berna, F., Nioradze, M., Shelia, T., Tappen, M., Vekua, A., Zhvania, D., & Lordkipanidze, D. (2011). Earliest human occupations at Dmanisi (Georgian Caucasus) dated to 1.85–1.78 Ma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108 , 10432–10436.
Finestone, E. M., Breeze, P. S., Breitenbach, S. F. M., Drake, N., Bergmann, L., Maksudov, F., Muhammadiyev, A., Scott, P., Cai, Y., Khatsenovich, A. M., Rybin, E. P., Nehrke, G., Boivin, N., & Petraglia, M. (2022). Paleolithic occupation of arid Central Asia in the Middle Pleistocene. PLOS ONE, 17 , e0273984.
Fornai, C., Benazzi, S., Svoboda, J., Pap, I., Harvati, K., & Weber, G. W. (2014). Enamel thickness variation of deciduous first and second upper molars in modern humans and Neanderthals. Journal of Human Evolution, 76 , 83–91.
Forsten, A. (1991). Size decrease in Pleistocene-Holocene true or caballoid horses of Europe. Mammalia, 55 (3), 407–420.
Forsten, A., & Moigne, A. M. (1998). The horse from the Middle Pleistocene of Orgnac-3 (Ardèche, France). Quaternaire, 9 , 315–323.
Fortelius, M., Mazza, P., & Sala, B. (1993). Stephanorhinus (Mammalia, Rhinocerotidae) of the western European Pleistocene, with a special revision of Stephanorhinus etruscus (Falconer, 1868). Palaeontographia Italica, 80 , 63–155.
Geneste, J.-M. (1985). Analyse lithique d’industries moustériennes du Périgord: approche technologique du comportement des groupes humaine au Paléolithique moyen . PhD thesis,. Université de Bordeaux.
Ghasidian, E., Bretzke, K., & Conard, N. J. (2017). Excavations at Ghār-e Boof in the Fars Province of Iran and its bearing on models for the evolution of the Upper Paleolithic in the Zagros Mountains. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology, 47 , 33–49.
Ghasidian, E., Heydari-Guran, S., & Mirazón Lahr, M. (2019). Upper Paleolithic cultural diversity in the Iranian Zagros Mountains and the expansion of modern humans into Eurasia. Journal of Human Evolution, 132 , 101–118.
Ghasidian, E., Kafash, A., Kehl, M., Yousefi, M., & Heydari-Guran, S. (2023). Modelling Neanderthals’ dispersal routes from Caucasus towards east. PLOS ONE, 18 , e0281978.
Glantz, M. (2010). The History of Hominin Occupation of Central Asia in Review. In C. Norton & D. R. Braun (Eds.), Asian Paleoanthropology (pp. 101–112). From Africa to China and Beyond.
Glantz, M., Viola, B., Wrinn, P., Chikisheva, T., Derevianko, A., Krivoshapkin, A., Islamov, U., Suleimanov, R., & Ritzman, T. (2008). New hominin remains from Uzbekistan. Journal of Human Evolution, 55 , 223–237.
Golovanova, L. V., & Doronichev, V. R. (2003). The Middle Paleolithic of the Caucasus. Journal of World Prehistory, 17 , 71–140.
Grigolia, G. K. (1963). Paleolit Kvemo-Kartli (Pogrebennaya peshera Tsopi I) . Tbilisi.
Grün, R. (2006). Direct Dating of Human Fossils. Yearbook of Physical Anthropology, 49 , 2–48.
Grün, R., Schwarcz, H. P., & Chadam, J. M. (1988). ESR dating of tooth enamel: Coupled correction for U-uptake and U-series disequilibrium. Nuclear Tracks and Radiation Measurements, 14 , 237–241.
Han, F., Bahain, J.-J., Shao, Q., Sun, X., Voinchet, P., Xiao, P., Huang, M., Li, M., & Yin, G. (2022). The Chronology of Early Human Settlement in Three Gorges Region, China—Contribution of Coupled Electron Spin Resonance and Uranium-Series Dating Method. Frontiers in Earth Science, 10 , 939766.
Hariryan, H., Heydari-Guran, S., Motarjem, A., & Ghasidian, E. (2021). New Evidence of a Late Pleistocene Occupation on the Southern Slopes of the Alborz Mountains. Lithic Technology, 46 (2), 104–110.
Hershkovitz, I., May, H., Sarig, R., Pokhojaev, A., Grimaud-Hervé, D., Bruner, E., Fornai, C., Quam, R., Arsuaga, J. L., Krenn, V. A., Martinón-Torres, M., de Castro, J. M. B., Martín-Francés, L., Slon, V., Albessard-Ball, L., Vialet, A., Schüler, T., Manzi, G., Profico, A., et al. (2021). A Middle Pleistocene Homo from Nesher Ramla. Israel Science, 372 , 1424–1428.
Heydari, M., Guérin, G., Kreutzer, S., Jamet, G., Kharazian, M. A., Hashemi, M., Vahdati Nasab, H. V., & Berillon, G. (2020). Do Bayesian methods lead to more precise chronologies? ‘BayLum’ and a first OSL-based chronology for the Paleolithic open-air site of Mirak (Iran). Quaternary Geochronology, 59 , 101082.
Heydari, M., Guérin, G., Zeidi, M., & Conard, N. J. (2021). Bayesian luminescence dating at Ghār-e Boof, Iran, provides a new chronology for Middle and Upper Paleolithic in the southern Zagros. Journal of Human Evolution, 151 , 102926.
Heydari-Guran, S., Benazzi, S., Talamo, S., Ghasidian, E., Hariri, N., Oxilia, G., Asiabani, S., Azizi, F., Naderi, R., Safaierad, R., Hublin, J.-J., Foley, R. A., & Lahr, M. M. (2021). The discovery of an in situ in situ Neanderthal remain in the Bawa Yawan Rockshelter, West-Central Zagros Mountains Kermanshah. PLOS ONE, 16 , e0253708.
Hillson, S. (2008). The current state of dental decay. Cambridge Studies in Biological and Evolutionary Anthropology, 53 , 111.
Hole, F., & Flannery, K. V. (1967). The prehistory of southwestern Iran: A preliminary report. Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society, Cambridge University Press, 33 , 147–206.
Hutson, J.M., García-Moreno, A., Noack, E.S., Turner, E., Villaluenga, A., Gaudzinski-Windheuser, S., Davidson, I., Mozota, M., Rosell, J., Blasco, R., Martin-Lerma, I., Barkai, R., Gopher, A., Daujeard, C., Valensi, P., Fiore, I., Moigne, A.-M., Tagliacozzo, A., Moncel, M.-H., Santagata, C., Cauche, D., Raynal, J.-P., Sévêque, N., Auguste, P., Costamagno, S., Bourguignon, L., Soulier, M.-C., Meignen, L., Beauval, C., Rendu, W., Mussini, C., Mann, A., Maureille, B., Abrams, G., Neruda, P., Lázničková-Galetová, M., Hohenstein, U.T., Bertolini, M., Channarayapatna, S., Modolo, M., Peretto, C., Toniato, G., Münzel, S.C., Starkovich, B.M., Conard, N.J., Jéquier, C., Livraghi, A., Romandini, M., Peresani, M., Yeshurun, R., Tejero, J.-M., Barzilai, O., Hershkovitz, I., Marder, O., Vitezović, S, 2018. The origins of bone tool technologies: “Retouching the Paleolithic: Becoming Human and the Origins of Bone Tool Technology” Conference at Schloss Herrenhausen in Hannover, Germany, 21.- 23. October 2015, Propylaeum. Propylaeum.
Jacobs, Z., Li, B., Shunkov, M. V., Kozlikin, M. B., Bolikhovskaya, N. S., Agadjanian, A. K., Uliyanov, V. A., Vasiliev, S. K., O’Gorman, K., Derevianko, A. P., & Roberts, R. G. (2019). Timing of archaic hominin occupation of Denisova Cave in southern Siberia. Nature, 565 , 594–599.
Jaubert, J., Biglari, F., Mourre, V., Bruxelles, L., Bordes, J. G., Shidrang, S., Naderi, R., Mashkour, M., Maureille, B., Mallye, J. B., & Quinif, Y. (2009). The Middle Paleolithic occupation of Mar-tarik, a new Zagros Mousterian site in Bisotun massif (kermanshah, Iran). In M. Otte, F. Biglari, & J. Jaubert (Eds.), Iran Paleolithic (pp. 7–27). BAR International Series.
Jelinek, A. J. (1982). The Middle Paleolithic in the southern Levant, with comments on the appearance of modern Homo sapiens. In A. Ronen (Ed.), The transition from Lower to Middle Paleolithic and the origin of modern man, British Archaeological Reports International Series (Vol. 151, pp. 57–101). Oxford: Archaeopress.
Jiangzuo, Q., Wagner, J., Chen, J., Dong, C., Wei, J., Ning, J., & Liu, J. (2018). Presence of the Middle Pleistocene cave bears in China confirmed–Evidence from Zhoukoudian area. Quaternary Science Reviews, 199 , 1–17.
Kamrani, Z., Vahdati Nasab, H., Bonilauri, S., Hashemi Sarvandi, S. M., Jayez, M., Kharrazian, M. A., Beheshti, S. I., & Berillon, G. (2022). Middle Paleolithic Lithic Industry from Qaleh Kurd Cave, Qazvin Province. Iran Iranian Journal of Archaeological Studies, 12 (2), 1–14.
Lacombat, F. (2009). Biochronologie et grands mammifères au Pléistocène moyen et supérieur en Europe occidentale : l’apport des Rhinocerotidae (genre Stephanorhinus ). Quaternaire, 20 (4), 429–435.
Lindly, J. M. (1997). The Mousterian of the Zagros: A regional perspective (Vol. 56 ). Ph.D. Dissertation,). Arizona State University.
Lumley de, M.-A. (Ed.). (2018). Les restes humains fossiles de la grotte du Lazaret (p. 658). CNRS Editions.
Lumley de, M.-A. (Ed.). (2022). Caune de l’Arago (p. 796). Tome IX. Les restes humains du Pléistocène moyen de la Caune de l’Arago. CNRS Editions.
Malinsky-Buller, A. (2016). The Muddle in the Middle Pleistocene: The Lower–Middle Paleolithic Transition from the Levantine Perspective. Journal of World Prehistory, 29 (1), 1–78.
Martínez-Navarro, B., Pérez-Claros, J. A., Palombo, M. R., Rook, L., & Palmqvist, P. (2007). The Olduvai buffalo Pelorovis and the origin of Bos. Quaternary Research, 68 (2), 220–226.
Mashkour, M., Monchot, H., Trinkaus, E., Reyss, J.-L., Biglari, F., Bailon, S., Heydari, S., & Abdi, K. (2009). Carnivores and their prey in the Wezmeh Cave (Kermanshah, Iran): A Late Pleistocene refuge in the Zagros. International Journal of Osteoarchaeology, 19 , 678–694.
McBurney, C. B. M. (1964). Preliminary report on Stone Age reconnaissance in north-eastern Iran. In Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society, Cambridge University Press, 30 , 382–399.
Mehterian, S., Pourmand, A., Sharifi, A., Lahijani, H. A., Naderi, M., & Swart, P. K. (2017). Speleothem records of glacial/interglacial climate from Iran forewarn of future Water Availability in the interior of the Middle East. Quaternary Science Reviews, 164 , 187–198.
Meignen, L. (1998). Hayonim cave lithic assemblages in the context of the Near-Eastern Middle Paleolithic: A preliminary report. In T. Akazawa, K. Aoki, & O. Bar-Yosef (Eds.), Neandertals and Modern Humans in Western Asia (pp. 165–180). Plenum Press.
Meignen, L. (2007). Middle Paleolithic blady assemblages in the Near East: A reassessment. In Caucasus and the initial dispersals in the Old World (pp. 133–148). St. Petersburg.
Meignen, L., & Bar-Yosef, O. (2020). Acheulo-Yabrudian and Early Middle Paleolithic at Hayonim Cave (Western Galilee, Israel): Continuity or break? Journal of Human Evolution, 139 , 102733.
Meignen, L., & Tushabramishvili, N. (2006). Paléolithique moyen laminaire sur les flancs sud du Caucase: productions lithiques et fonctionnement du site de Djruchula (Géorgie). Paléorient, 32 (2), 81–104.
Meignen, L., & Tushabramishvili, N. (2010). Djruchula Cave, on the southern slopes of the Great Caucasus: An extension of the Near Eastern Middle Paleolithic Blady Phenomenon to the North. Journal of The Israel Prehistoric Society, 40 , 35–61.
Mercier, N., & Valladas, H. (2003). Reassessment of TL age estimates of burnt flints from the Paleolithic site of Tabun Cave. Israel Journal of Human Evolution, 45 (5), 401–409.
Mercier, N., Valladas, H., Meignen, L., Joron, J. L., Tushabramishvili, N., Adler, D. S., & Bar-Yosef, O. (2010). Dating the Early Middle Paleolithic laminar industry from Djruchula Cave, Republic of Georgia. Paléorient, 36 (2), 163–173.
Mihailović, D., Kuhn, S. L., Bogićević, K., Dimitrijević, V., Marín-Arroyo, A. B., Marković, J., Mercier, N., Mihailović, B., Morley, M. W., Radović, P., Rink, W. J., Plavšić, S., & Roksandic, M. (2022). Connections between the Levant and the Balkans in the late Middle Pleistocene: Archaeological findings from Velika and Mala Balanica Caves (Serbia). Journal of Human Evolution, 163 , 103138.
Moigne, A. M., Valensi, P., Auguste, P., García-Solano, J., Tuffreau, A., Lamotte, A., Barroso, C., & Moncel, M. H. (2016). Bone retouchers from Lower Paleolithic sites: Terra Amata, Orgnac 3, Cagny-l'Epinette and Cueva del Angel. Quaternary International, 409 , 195–212.
Molnar, S. (1971). Human tooth wear, tooth function and cultural variability. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 34 (2), 175–189.
Moncel, M.-H., Moigne, A.-M., & Combier, J. (2012). Towards the Middle Paleolithic in western Europe: The case of Orgnac 3 (southeastern France). Journal of Human Evolution, 63 , 653–666.
Monchot, H., Mashkour, M., Biglari, F., & Abdi, K. (2020). The Upper Pleistocene brown bear (Carnivora, Ursidae) in the Zagros: Evidence from Wezmeh Cave, Kermanshah. Iran Annales de Paléontologie, 106 , 102381.
Narasimhan, V. M., Patterson, N., Moorjani, P., Rohland, N., Bernardos, R., Mallick, S., Lazaridis, I., Nakatsuka, N., Olalde, I., Lipson, M., Kim, A. M., Olivieri, L. M., Coppa, A., Vidale, M., Mallory, J., Moiseyev, V., Kitov, E., Monge, J., Adamski, N., et al. (2019). The formation of human populations in South and Central Asia. Science, 365 , eaat7487.
Nelson, K. (2010). Environment, cooking strategies and containers. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology, 29 (2), 238–247.
Neuville, R. (1951). Le Paléolithique et le Mésolithique du désert de Judée. In Archives de l’Institut de Paléontologie Humaine, mémoire n°24 . Cie, Paris.
Nikzad, M., Sedighian, H., & Ghasemi, E. (2015). New Evidence of Paleolithic Activity from South Khorasan. Eastern Iran. Antiquity, 89 (347), 1–7.
Nobis, G. (1971). Vom Wildpferd zum Hauspferd: Studien zur Phylogenie pleistozäner Equiden Eurasiens und das Domestikationsproblem unserer Hauspferde (p. 96). Köln: Bõhlau Verlag.
Orlando, L., Mashkour, M., Burke, A., Douady, C. J., Eisenmann, V., & Hanni, C. (2006). Geographic distribution of an extinct equid (Equus hydruntinus: Mammalia, Equidae) revealed by morphological and genetical analyses of fossils. Molecular Ecology, 15 (8), 2083–2093.
Otte, M., Biglari, F., & Jaubert, J. (Eds.). (2009). Iran Paleolithic . BAR International Series.
Otte, M., Shidrang, S., & Flas, D. (2012). L’Aurignacien de la grotte Yafteh et son contexte (fouilles 2005-2008) . Liège: ERAUL 132.
Otte, M., Shidrang, S., Zwyns, N., & Flas, D. (2011). New radiocarbon dates for the Zagros Aurignacian from Yafteh cave. Iran Journal of Human Evolution, 61 , 340–346.
Outram, A. K. (2001). A new approach to identifying bone marrow grease exploitation: Why the indeterminate fragments should not be ignored. Journal of Archaeological Science, 28 , 401–410.
Pan, L., Dumoncel, J., Mazurier, A., & Zanolli, C. (2020). Hominin diversity in East Asia during the Middle Pleistocene: A premolar endostructural perspective. Journal of Human Evolution, 148 , 102888.
Pandolfi, L., Boscato, P., Crezzini, J., Gatta, M., Moroni, A., Rolfo, M., & Tagliacozzo, A. (2017). Late Pleistocene last occurrences of the narrow-nosed rhinoceros Stephanorhinus hemitoechus (Mammalia, Perissodactyla) in Italy. Rivista Italiana Di Paleontologia E Stratigrafia, 123 (2), 177–192.
Pandolfi, L., Bartolini-Lucenti, S., Cirilli, O., Bukhsianidze, M., Lordkipanidze, D., & Rook, L. (2021). Paleoecology, biochronology, and paleobiogeography of Eurasian Rhinocerotidae during the Early Pleistocene: The contribution of the fossil material from Dmanisi (Georgia, Southern Caucasus). Journal of Human Evolution, 156 , 103013.
Peresani, M., Bourguignon, L., Delpiano, D., & Lemorini, C. (2023). Quina on the edge. Insights from a Middle Paleolithic lithic assemblage of Grotta di Fumane, Italy. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 49 , 103998.
Pokines, J. T., Lister, A. M., Ames, C. J. H., Nowell, A., & Cordova, C. E. (2019). Faunal remains from recent excavations at Shishan Marsh 1 (SI1), a Late Lower Paleolithic open-air site in the Azraq Basin. Jordan. Quaternary Research, 91 (2), 768–791.
Pushkina, D., Bocherens, H., & Ziegler, R. (2014). Unexpected palaeoecological features of the Middle and Late Pleistocene large herbivores in southwestern Germany revealed by stable isotopic abundances in tooth enamel. Quaternary International, 339 , 164–178.
Rabinovich, R., & Biton, R. (2011). The Early-Middle Pleistocene faunal assemblages of Gesher Benot Ya'aqov: Inter-site variability. Journal of Human Evolution, 60 (4), 357–374.
Reich, D., Green, R. E., Kircher, M., Krause, J., Patterson, N., Durand, E. Y., Viola, B., Briggs, A. W., Stenzel, U., Johnson, P. L. F., Maricic, T., Good, J. M., Marques-Bonet, T., Alkan, C., Fu, Q., Mallick, S., Li, H., Meyer, M., Eichler, E. E., et al. (2010). Genetic history of an archaic hominin group from Denisova Cave in Siberia. Nature, 468 , 1053–1060.
Rivals, F., Julien, M. A., Kuitems, M., Van Kolfschoten, T., Serangeli, J., Drucker, D., et al. (2015). Investigation of equid paleodiet from Schöningen 13II-4 through dental wear and isotopic analyses: Archaeological implications. Journal of Human Evolution, 89 , 129–137.
Rivals, F., & Lister, A. M. (2016). Dietary flexibility and niche partitioning of large herbivores through the Pleistocene of Britain. Quaternary Science Reviews, 146 , 116–133.
Romandini, M., Nannini, N., Tagliacozzo, A., & Peresani, M. (2014). The ungulate assemblage from layer A9 at Grotta di Fumane, Italy: Azooarchaeological contribution to the reconstruction of Neanderthal ecology. Quaternary International, 337 , 11–27.
Roustaei, K., Vahdati Nasab, H., Biglari, F., Heydari, S., Clark, G. A., & Lindly, M. (2004). Recent Paleolithic surveys in Luristan. Current Anthropology, 45 , 692–707.
Saarinen, J., Eronen, J., Fortelius, M., Seppä, H., & Lister, A. M. (2016). Patterns of diet and body mass of large ungulates from the Pleistocene of Western Europe, and their relation to vegetation. Palaeontologia Electronica, 19 (3), 1–58.
Sadraei, A., Mehneh, M. F., Sheikh, M., Anani, B., & Minaei, Z. H. (2019). Kaftar Kouh of Ferdous, New Evidence of Paleolithic Population in Southern Khorasan. Iran Advances in Anthropology, 9 , 111–123.
Sadraei, A., Shipton, C., Garazhian, O., Azar, M., Zafaranlou, R., & Soroush, M. R. (2023). Tracking Pleistocene occupation on the Eastern Iranian Plateau: Preliminary results. Antiquity, 97 (391), e1.
Sanchez-Gonzalez, E., Pinilla-Cienfuegos, E., Borrero-Lopez, O., Rodríguez-Rojas, F., & Guiberteau, F. (2020). Contact damage of human dental enamel under cyclic axial loading with abrasive particles. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 102 , 103512.
Sarhangzadeh, J., Yavari, A. R., Hemami, M. R., Jafari, H. R., & Shams-Esfandabad, B. (2013). Habitat suitability modeling for wild goat (Capra aegagrus) in a mountainous arid area, central Iran. Caspian Journal of Environmental Sciences, 11 (1), 41–51.
Scott, J. E., & Marean, C. W. (2009). Paleolithic hominin remains from Eshkaft-e Gavi (southern Zagros Mountains, Iran): Description, affinities, and evidence for butchery. Journal of Human Evolution, 57 , 248–259.
Sévêque, N., & Auguste, P. (2018). From West to East: Lower and Middle Paleolithic bone retouchers in Northern France. In J. M. Hutson et al. (Eds.), Retouching the Paleolithic . Becoming Human and the Origins of Bone Tool Technology.
Sévêque, N. (2017). Variabilité des comportements alimentaires au Paléolithique moyen en France septentrionale - Apports des études archéozoologiques (p. 3). Université Lille.
Sheiham, A., & James, W. P. T. (2015). Diet and Dental Caries: The Pivotal Role of Free Sugars Reemphasized. Journal of Dental Research, 94 , 1341–1347.
Shidrang, S., Biglari, F., Bordes, J.G., Jaubert, J., 2016. Continuity and change in the late Pleistocene lithic industries of the central Zagros: A typo-technological analysis of lithic assemblage from Ghar-e Khar cave, Bisotun. Iran. Archaeol. Ethnol. Anthropol. Eurasia 44/1 (2016), 27–38.
Shimelmitz, R., Kuhn, S. L., Ronen, A., & Weinstein-Evron, M. (2014). Predetermined flake production at the Lower/Middle Paleolithic boundary: Yabrudian scraper blank technology. PLoS One, 9 (9), e106293.
Shoaee, M. J., Vahdati Nasab, H., & Petraglia, M. D. (2021). The Paleolithic of the Iranian Plateau: Hominin occupation history and implications for human dispersals across southern Asia. Journal of Anthropological Archaeology, 62 , 101292.
Slimak, L., Zanolli, C., Higham, T., Frouin, M., Schwenninger, J.-L., Arnold, L. J., Demuro, M., Douka, K., Mercier, N., Guérin, G., Valladas, H., Yvorra, P., Giraud, Y., Seguin-Orlando, A., Orlando, L., Lewis, J. E., Muth, X., Camus, H., Vandevelde, S., et al. (2022). Modern human incursion into Neanderthal territories 54,000 years ago at Mandrin, France. Science. Advances, 8 , eabj9496.
Smith, T. M., Toussaint, M., Reid, D. J., Olejniczak, A. J., & Hublin, J.-J. (2007). Rapid Dental Development in a Middle Paleolithic Belgian Neanderthal. PNAS, 104 (51), 20220–20225.
Solecki, R. S. (1959). Three adult neanderthal skeletons from Shanidar cave, Northern Iraq. Annual Report - Smithsonian Institution (pp. 603–635)
Solecki, R. S. (1963). Prehistory in Shanidar Valley, Northern Iraq: Fresh insights into Near Eastern prehistory from the Middle Paleolithic to the Proto-Neolithic are obtained. Science, 139 (3551), 179–193.
Soleymani, S., & Alibaigi, S. (2018). Qaleh Kurd Cave: A Middle Paleolithic site on the western borders of the Iranian Central Plateau. Al-Rāfidān, Journal of Western Asiatic Studies, 39 , 43–54.
Sommer, R. S., Fahlke, J. M., Schmölcke, U., Benecke, N., & Zachos, F. E. (2009). Quaternary history of the European roe deer Capreolus capreolus. Mammal Review, 39 (1), 1–16.
Speth, J. D. (2012). Paleoanthropology and archaeology of big-game hunting . Springer.
Thoma, A. (1963). The dentition of the Subalyuk Neandertal child. Zeitschrift für Morphologie und Anthropologie, 54 , 127–150.
Tillier, A. M. (1979a). La dentition de l’enfant moustérien Chateauneuf 2 découvert à l’Abri de Hauteroche (Charente). L’Anthropologie (Paris), 83 (3), 417–438.
Tillier, A. M. (1979b). Restes crâniens de l'enfant moustérien homo 4 de Qafzeh (Israël), la mandibule et les maxillaires. Paléorient, 5 , 67–85.
Tillier, A. M. (1980). Les dents d’enfant de Ternifine (Pléistocène moyen d’Algérie). L’Anthropologie, 84 , 413–421.
Tillier, A. M. (1995). Paléoanthropologie et pratiques funéraires au Levant méditerranéen durant le Paléolithique moyen: le cas des sujets non-adultes. Paléorient, 21 (2), 63–76.
Tillier, A.-M. (1999). Les enfants moustériens de Qafzeh (p. 239). CNRS Editions.
Tillier, A. M. (2021). Aspects of health status in Pre-Sedentism Populations of Southwestern Asia. Evidence from Qafzeh Site, Lower Galilee. Paléorient, 47 (1), 31–34.
Tillier, A.-M., Arensburg, B., Rak, Y., & Vandermeersch, B. (1995). Middle Paleolithic dental caries: New evidence from Kebara (Mount Carmel, Israel). Journal of Human Evolution, 29 , 189–192.
Tillier, A.-M., Arensburg, B., Vandermeersch, B., & Chech, M. (2003). New human remains from Kebara Cave (Mount Carmel). The place of the Kebara hominids in the Levantine Mousterian fossil record. Paléorient., 29 , 35–62.
Tobias, P. V. (1966). Fossil Hominid Remains from Ubeidiya, Israel. Nature, 211 , 130–133.
Towle, I., Irish, J. D., Groote, I. D., Fernée, C., & Loch, C. (2021). Dental caries in South African fossil hominins. South African Journal of Science, 117 (3-4), 1–8.
Towle, I., Riga, A., Irish, J. D., Dori, I., Menter, C., & Moggi-Cecchi, J. (2019). Root caries on a Paranthropus robustus third molar from Drimolen. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 170 , 319–323.
Trinkaus, E. (1983). The Shanidar Neandertals . Academic Press.
Trinkaus, E., & Biglari, F. (2006). Middle Paleolithic Human Remains from Bisitun Cave. Iran Paléorient, 32 , 105–111.
Trinkaus, E., Biglari, F., Mashkour, M., Monchot, H., Reyss, J. L., Rougier, H., Heydari, S., & Abdi, K. (2008). Late Pleistocene human remains from Wezmeh Cave, western Iran. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 135 , 371–378.
Tsanova, T. (2013). The beginning of the Upper Paleolithic in the Iranian Zagros. A taphonomic approach and techno-economic comparison of Early Baradostian assemblages from Warwasi and Yafteh (Iran). Journal of Human Evolution, 65 (1), 39–64.
Tushabramishvili, D. M. (1963). Pechtchery Dzhrutchulskogo uchtchelia . Pechtchery Gruzii.
Uzunidis, A., Rivals, F., & Brugal, J. P. (2017). Relation between morphology and dietary traits in horse jugal upper teeth during the middle pleistocene in Southern France. Quaternaire. Revue de l'Association française pour l’étude du Quaternaire, 28 (3), 303–312.
Uzunidis-Boutillier, A. (2017). Grands herbivores de la fin du Pléistocène moyen au début du Pléistocène supérieur dans le sud de la France (p. 788). Aix-Marseille université, PhD.
Vahdati Nasab, H., & Hashemi, M. (2016). Playas and Middle Paleolithic settlement of the Iranian Central Desert: The discovery of the Chah-e Jam Middle Paleolithic site. Quaternary International, 408 , 140–152.
Vahdati Nasab, H. (2010). Paleolithic Archaeology of Iran. International Journal of Humanities, 18 (2), 63–87.
Vahdati Nasab, H., Berillon, G., Jamet, G., Hashemi, M., Jayez, M., Khaksar, S., Anvari, Z., Guérin, G., Heydari, M., Kharazian, M. A., & Puaud, S. (2019). The open-air Paleolithic site of Mirak, northern edge of the Iranian Central Desert (Semnan, Iran): Evidence of repeated human occupations during the late Pleistocene. Comptes Rendus Palevol, 18 (4), 465–478.
Vahdati Nasab, H., & Clark, G. (2014). The upper Paleolithic of the Iranian central desert: The delazian site - A case study. Archäologische Mitteilungen aus Iran und Turan, 46 , 1–20.
Vahdati Nasab, H., Clark, G. A., & Torkamandi, S. (2013). Late Pleistocene dispersal corridors across the Iranian Plateau: A case study from Mirak, a Middle Paleolithic site on the northern edge of the Iranian Central desert (Dasht-e Kavir). Quaternary International, 300 , 267–281.
Van der Made, J., Torres, T., Ortiz, J. E., Moreno-Pérez, L., & Fernández-Jalvo, Y. (2016). The new Material of Large Mammals from Azokh and Comments on the Older Collections. In Y. Fernández-Jalvo, T. King, L. Yepiskoposyan, & P. Andrews (Eds.), Azokh Cave and the Transcaucasian Corridor (pp. 117–159). Springer.
Vandermeersch, B. (1981). Les hommes fossiles de Qafzeh (Israël) . CNRS.
Vasilyev, S., & Amirkhanov, H. (2018). Paleolithic Caucasus: Paleoanthropological panorama. Quaternary International, 465 , 105–116.
Vekua, A., Lordkipanidze, D., Rightmire, G. P., Agusti, J., Ferring, C. R., Maisuradze, G., Mouskhelishvili, A., Nioradzé, G., Ponce De León, M. S., Tappen, M., Tvalchrelidze, M., & Zollikofer, C. P. E. (2002). A new skull of early Homo from Dmanisi. Georgia Science, 297 , 85–89.
Vincent, A. (1993). L'outillage osseux au Paléolithique moyen : une nouvelle approche . Ph.D. Dissertation,. Université Paris X.
Wojtczak, D., & Malinsky-Buller, A. (2022). The Levantine Early Middle Paleolithic in retrospect: Reassessing the contribution of Abou-Sif to the understanding of Paleolithic record. Archaeological Research in Asia, 30 , 100366.
Wojtczak, D. B. (2022). More than blades. Early Middle Paleolithic of the Levant. L’Anthropologie, 126 (3), 103046.
Zaidner, Y., Druck, D., & Weinstein-Evron, M. (2006). Acheulo-Yabrudian handaxes from Misliya Cave, Mount Carmel, Israel. In N. Goren-Inbar & G. Sharon (Eds.), Axe Age: Acheulian Toolmaking from Quarry to Discard (pp. 243–266). Equinox Publishers.
Zanolli, C., Biglari, F., Mashkour, M., Abdi, K., Monchot, H., Debue, K., Mazurier, A., Bayle, P., Le Luyer, M., Rougier, H., Trinkaus, E., & Macchiarelli, R. (2019). A Neanderthal from the Central Western Zagros, Iran. Structural reassessment of the Wezmeh 1 maxillary premolar. Journal of Human Evolution, 135 , 102643.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Our work on Qaleh Kurd cave was made possible thanks to the financial support of the Regional Service of Cultural Heritage of the Province of Qazvin, the Iranian Center for Archaeological Research (ICAR), the Ministry of Europe and Foreign Affairs of France (Commission des Fouilles archéologiques à l'étranger), Tarbiat Modares University, the French Embassy in Iran, and the UMR7194 CNRS-MNHN-UPVD. We would like to express our deepest gratitude to them for their support and trust in our team. We would like to thank Dr. Sadjad Alibaigi for his generous allowance to work on this magnificent site. We would also like to express our gratitude to the Iranian Ministry of Cultural Heritage and Tourism, in particular Drs. Rouhollah Shirazi, Kourosh Roustaei, and Leyla Khosravi, directors of the Iranian Center for Archaeological Research (ICAR), at the time of our excavations, for their collaboration in the preparation of our missions and for allowing us to work in the field. We would like to thank Mrs. Solgi and her colleagues at the Tehran University Medical Science Preclinical Core Facility for providing a high-resolution micro-CT scan of the Qaleh Kurd tooth. We also thank Mr. Hazratiha, Director of the Cultural Heritage Office of Qazvin Province at the time of the first mission in 2018; Mr. Khazaeli the current director; and Mrs. Mohammadi, Mr. Asgari, Fanaee, and their Delegate for Archaeology, for their hospitality and logistical support in the field of Qaleh Kurd. We are thankful to Dr. Sébastein Nomade for his assistance in the preparation of 14C samples as well as to Dr. M. Alirezazadeh for his assistance in producing the map used in Fig. 1 . Obviously, the fieldwork was not possible without the tremendous job of the crew, which their names were not included in the author list: in alphabetical order, L. Alinia, M. Alirezazadeh, M. Etminan, T. Izadyari, Z. Kamrani, S. Ganji, A. Khanian, D. Mahmoudi, S. Nazif, S. Shafiee, M.J. Shoaee. We would like to thank Shannon McPherron, editor, as well as Tobias Lauer and other anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments on a previous version of the manuscript.
The Regional Service of Cultural Heritage of the Province of Qazvin for financial support of the field campaigns
The Iranian Center for Archaeological Research (ICAR) for financial support of the field campaigns
A grant from the Ministry of Europe and Foreign Affairs of France (Commission des Fouilles archéologiques à l'étranger) for financial support of the field campaigns and laboratory analyses
Tarbiat Modares University for financial support of the laboratory analyses
UMR7194 CNRS-MNHN-UPVD for financial support of the laboratory analyses. The ESR spectrometer, Q-ICP-mass spectrometer and portable gamma spectrometer of the Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle used for part of the analyses were bought with the financial support of the Région Île-de-France’ (for the two first devices) and Région Centre respectively.
The geoarchaeological analysis has been done in the frame of a doctoral scholarship (M.A. Kharazian) granted by the French Embassy in Iran.
Author information
Hamed Vahdati Nasab and Gilles Berillon are both first co-authors, equally contributing to the research design and the preparation of the manuscript.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Archaeology, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran
Hamed Vahdati Nasab, Seyyed Milad Hashemi & Sareh Nematollahinia
UMR7194 CNRS-MNHN-UPVD/Département Homme et Environnement, Musée de l’Homme—Palais de Chaillot, Paris, France
Hamed Vahdati Nasab, Gilles Berillon, Seyyed Milad Hashemi, Stéphanie Bonilauri, Mohammad Akhavan Kharazian, Nicolas Boulbes, Cécile Chapon-Sao, Xavier Gallet, Christophe Falguères, Lisa Garbé, Jonathan Özçelebi, Emmanuelle Stoetzel & Olivier Tombret
UMR7044 ArcHiMèdE, Strasbourg, France
Noémie Sévêque
Department of Archaeology, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran
Mozhgan Jayez
INRAP, Department Grand Ouest, Paris, France
Guillaume Jamet
UM8591 CNRS/Université Paris 1/UPEC, Laboratoire de Géographie Physique, Environnements Quaternaires et Actuels, Thiais, France
Guillaume Jamet, Mohammad Akhavan Kharazian & Pierre Antoine
Department of Archaeology, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran
Asghar Nateghi & Alieh Abdollahi
Center for Conservation and Restoration Research, Research Institute of Cultural Heritage and Tourism (RICHT), Tehran, Iran
Iraj Beheshti
Sustainable Computing Lab, Vienna University of Economy and Business (Wirtschaftsuniversität Wien WU), Wien, Austria
Mandan Kazzazi
Department of Archaeology, Marlik Institute for Higher Education, Nowshahr, Iran
Ahmad Zavar Mousavi
Centre de Recherche en Paléontologie-Paris CR2P UMR7207 MNHN-SU-CNRS, Paris, France
Valéry Zeitoun
School of Geography, Earth and Atmospheric Sciences, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
Mohammad Akhavan Kharazian
Department of Geography, School of Environment, Education and Development, University of Manchester, Manchester, UK
EPCC, Centre Européen de Recherches Préhistoriques de Tautavel, Tautavel, France
Nicolas Boulbes
UMR7194 CNRS-MNHN-UPVD / Département Homme et Environnement, Institut de Paléontologie Humaine, Paris, France
Jean-Jacques Bahain
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Hamed Vahdati Nasab: head of the mission, data gathering, data analysis, writing the manuscript. Gilles Berillon: head of the mission, data gathering, data analysis, writing the manuscript. Seyyed Milad Hashemi: data gathering, data analysis, writing the manuscript. Jean-Jacques Bahain: data analysis, writing the manuscript. Noémie Sévêque: data gathering, data analysis, writing the manuscript. Mozhgan Jayez: data gathering, data analysis, writing the manuscript. Stéphanie Bonilauri: data gathering, data analysis, writing the manuscript. Guillaume Jamet: data gathering, data analysis, writing the manuscript. Mohammad Akhavan Kharazian: data gathering, data analysis, writing the manuscript. Asghar Nateghi: data gathering. Alieh Abdollahi: data gathering. Pierre Antoine: data analysis. Iraj Beheshti: data analysis. Nicolas Boulbes: data analysis, writing the manuscript. Cécile Chapon-Sao: data analysis. Xavier Gallet: data analysis. Christophe Falguères: data analysis. Lisa Garbé: data analysis. Mandan Kazzazi: data analysis. Ahmad Zavar Mousavi: data gathering. Sareh Nematollahinia: data analysis, data gathering. Jonathan Özçelebi: data analysis. Emmanuelle Stoetzel: data analysis. Olivier Tombret: data analysis. Valéry Zeitoun: data gathering, writing the manuscript
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Hamed Vahdati Nasab or Gilles Berillon .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Vahdati Nasab, H., Berillon, G., Hashemi, S.M. et al. Qaleh Kurd Cave (Qazvin, Iran): Oldest Evidence of Middle Pleistocene Hominin Occupations and a Human Deciduous Tooth in the Iranian Central Plateau. J Paleo Arch 7 , 16 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41982-024-00180-4
Download citation
Accepted : 12 April 2024
Published : 23 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s41982-024-00180-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Iranian Central Plateau
- Middle Pleistocene
- Paleolithic
- Qaleh Kurd Cave
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
NTRS - NASA Technical Reports Server
Available downloads, related records.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: Restate the problem. Step 2: Sum up the paper. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Research paper conclusion examples. Frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
Write your research paper conclusion 2x faster with Paperpal. Try it now! Remember that a well-crafted research paper conclusion is a reflection of the strength of your research and your ability to communicate its significance effectively. It should leave a lasting impression on your readers and tie together all the threads of your paper.
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a way that is slightly different from the wording used in the introduction. Avoid presenting new information or evidence in your conclusion. Just summarize the main points and arguments of your essay and keep this part as concise as possible. Remember that you've already covered the ...
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research.
Highlight the "so what". At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what's at stake—why they should care about the argument you're making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put ...
Step 1: Answer your research question. Step 2: Summarize and reflect on your research. Step 3: Make future recommendations. Step 4: Emphasize your contributions to your field. Step 5: Wrap up your thesis or dissertation. Full conclusion example. Conclusion checklist. Other interesting articles.
Research Paper Conclusion. Definition: A research paper conclusion is the final section of a research paper that summarizes the key findings, significance, and implications of the research. It is the writer's opportunity to synthesize the information presented in the paper, draw conclusions, and make recommendations for future research or ...
The conclusion allows you to have the final say on the issues you have raised in your paper, to synthesize your thoughts, to demonstrate the importance of your ideas, and to propel your reader to a new view of the subject. It is also your opportunity to make a good final impression and to end on a positive note.
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
The conclusion is where you describe the consequences of your arguments by justifying to your readers why your arguments matter (Hamilton College, 2014). Derntl (2014) also describes conclusion as the counterpart of the introduction. Using the Hourglass Model (Swales, 1993) as a visual reference, Derntl describes conclusion as the part of the ...
The point of a conclusion to a research paper is to summarize your argument for the reader and, perhaps, to call the reader to action if needed. 5. Make a call to action when appropriate. If and when needed, you can state to your readers that there is a need for further research on your paper's topic.
A conclusion is the final paragraph of a research paper and serves to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them. The conclusion of a conclusion should: Restate your topic and why it is important. Restate your thesis/claim. Address opposing viewpoints and explain why readers should align with your position.
Step 1: Restate the problem. Always begin by restating the research problem in the conclusion of a research paper. This serves to remind the reader of your hypothesis and refresh them on the main point of the paper. When restating the problem, take care to avoid using exactly the same words you employed earlier in the paper.
Offer a Fresh Perspective: Use the conclusion as an opportunity to provide a fresh perspective or offer insights that go beyond the main body of the paper. This will leave the reader with something new to consider. Leave a Lasting Impression: End your conclusion with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action.
Writing a Conclusion. A conclusion is an important part of the paper; it provides closure for the reader while reminding the reader of the contents and importance of the paper. It accomplishes this by stepping back from the specifics in order to view the bigger picture of the document. In other words, it is reminding the reader of the main ...
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay: Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas. Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up ...
To write a conclusion for a research paper, begin by summarizing the main findings or results of your study. Restate your thesis statement or research question and briefly recap the key points discussed in the paper. Reflect on the significance of your findings and discuss their implications for the broader field of study or real-world ...
Conclusions. Conclusions wrap up what you have been discussing in your paper. After moving from general to specific information in the introduction and body paragraphs, your conclusion should begin pulling back into more general information that restates the main points of your argument. Conclusions may also call for action or overview future ...
Hannah, a writer and editor since 2017, specializes in clear and concise academic and business writing. She has mentored countless scholars and companies in writing authoritative and engaging content. To write an exemplary research paper conclusion, review what you've found and what it means. Summarize like a star with QuillBot.
Conclusion. To choose a thesis research topic, find something you're passionate about, research widely to get the big picture, and then move to a more focused view. Bringing a fresh perspective to a popular theme, finding an underserved audience who could benefit from your research, or answering a controversial question can make your thesis ...
Here's how to create a thesis: Find the main idea: Start by pinpointing the key concept or question you want to explain. Develop a clear purpose for the essay. This will guide your research and writing process for your explanatory paper. Use other reputable explanatory essay examples to guide your ideas.
This article explains the 10 key steps you should follow to get a small business loan, with some practical advice and insight on the lending process. 1. Understand the different types of small ...
Step 3: Make future recommendations. You may already have made a few recommendations for future research in your discussion section, but the conclusion is a good place to elaborate and look ahead, considering the implications of your findings in both theoretical and practical terms. Example: Recommendation sentence.
The Research In 1994, the nation's retirement structure was changing rapidly. Over the previous eight years, the number of defined-benefit plans had fallen by more than 50%, from 172,642 to 74,422.
Introduction Using a duoethnological approach, supported by relational trauma theories, this paper synthesises idiosyncratic formulations and perspectives of working with relational trauma. Aim Initially, focus is centred on reflecting on the authors' research with different and diverse groups. These include in‐reach rehabilitation and recovery services for people with profound and enduring ...
The growing concern of pediatric mortality demands heightened preparedness in clinical settings, especially within intensive care units (ICUs). As respiratory-related admissions account for a substantial portion of pediatric illnesses, there is a pressing need to predict ICU mortality in these cases. This study based on data from 1188 patients, addresses this imperative using machine learning ...
The Iranian Central Plateau (ICP) with the Alborz and the Zagros Mountains is located at the crossroads between the Levant and the Caucasus to the west and Central Asia and East Asia to the east. These two regions yielded key paleoanthropological and archaeological sites from the Middle Pleistocene period. These discoveries highlight a large human biological and cultural diversity in this area ...
The main research contributions of this article are as follows: ... 4 DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION. The current infrared and visible image fusion still has some problems: Existing methods emphasize achieving good fusion effects and preserving image detail features, which often require the use of multiple convolution or Transformer modules. ...
The research dataset, consisting of 20 hours of transcribed planning teleconferences, forms the foundation for fine-tuning and validating the Whisper model. ... In conclusion, this paper presents a comprehensive exploration of the application of automatic speech recognition in Air Traffic Control System Command Center planning teleconferences ...