Our systems are now restored following recent technical disruption, and we’re working hard to catch up on publishing. We apologise for the inconvenience caused. Find out more: https://www.cambridge.org/universitypress/about-us/news-and-blogs/cambridge-university-press-publishing-update-following-technical-disruption
We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites. Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings .

Login Alert
- > Journals
- > Journal of Agricultural and Applied Economics
- > Volume 53 Issue 3
- > US Consumers’ Online Shopping Behaviors and Intentions...

Article contents
- Introduction
- Methodology
- Implications and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Financial support, conflict of interests, data availability, us consumers’ online shopping behaviors and intentions during and after the covid-19 pandemic.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 31 August 2021
A study of 1,558 US households in June 2020 evaluated utilization of online grocery shopping during the COVID-19 pandemic, influences on utilization, and plans for future online grocery shopping. Nearly 55 percent of respondents shopped online in June 2020; 20 percent were first-timers. Cragg model estimates showed influences on online shopping likelihood and frequency included demographics, employment, and prior online shopping. Illness concerns increased likelihood, while food shortage concerns increased frequency of online shopping. A multinomial probit suggested 58 percent respondents planned to continue online grocery shopping regardless of pandemic conditions.
1. Introduction
1.1. the covid-19 pandemic and policy response.
The COVID-19 pandemic has led many American consumers to rapidly and sometimes dramatically change their food shopping behaviors in response to changes in policy, and personal or public health concerns. In March 2020 as the virus started spreading widely in the United States (US), state and local governments began issuing orders to close restaurants to in-person dining to mitigate the spread of the virus. In response to these conditions, many consumers responded by shifting their food expenditures away from food service (e.g. restaurants and eating establishments) to food retailers (Kowitt and Lambert, Reference Kowitt and Lambert 2020 ). In some cases, consumers stockpiled groceries due to concerns about supply chain disruptions and shortages (Acosta, Reference Acosta 2020 ). Part of this stockpiling may also have been due to averting behaviors, as some consumers preferred to shop in-store less frequently, thus reducing the number of their potential exposures. Some of these increased food expenditures were conducted through online purchases, which showed a significant increase in utilization from the early months of the pandemic through the next stage of the pandemic policy response in April when states started issuing stay-at-home or shelter-in-place orders (Redman, Reference Redman 2020 b).
From March 1 to May 31, 2020, 42 states and territories issued stay-at-home orders that covered about 73 percent of US counties (Moreland et al., Reference Moreland, Herlihy, Tynan, Sunshine, McCord, Hilton, Poovey, Werner, Jones, Fulmer, Gundlapalli, Strosnider, Potvien, García, Honeycutt and Baldwin 2020 ). These orders continued the closure of restaurants to in-person dining, while keeping many food retailers open, and asked households to limit their activity outside of their home. The duration of the stay-at-home orders varied from state to state, but they represented a significant disruption to the way households typically acquire food.
As consumers entered into a new phase of pandemic policies marked by the end of stay-at-home orders during the late spring and early summer, questions have arisen as to how consumers will navigate this new environment and which behaviors adopted during the earliest months of the pandemic will endure (Foster and Mundell, Reference Foster and Mundell 2020 ). Even as state policies changed, consumers have continued to encounter some elements of the pandemic including shortages of food at retailers and the concern of contracting the virus while making in-person grocery shopping. Thus, the pandemic likely continued to influence shopper behavior into the summer of 2020. Consumers likely adopted some behaviors, such as online grocery shopping, that they may continue even beyond the end of the pandemic. Therefore, this study not only investigates determinants of online grocery shopping, including delivery and curbside pickup services, in June 2020, but also intentions among online grocery shoppers for future online grocery shopping. The influences on plans for future online shopping are measured, given that the scenarios the pandemic could continue or subside. Hence, the study provides insights into how shoppers may behave with regard to online shopping in the post-pandemic era. The study uses results from an original national US survey administered in July 2020.
This study complements the current literature in two ways. First, we incorporate both previously explored and pandemic-specific variables into our model of current online grocery store use. Prior research has shown that age, income, and the presence of children in the household influence the decision to the utilization of online grocery shopping (Etumnu et al. Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 , Hansen, Reference Hansen 2005 ; Hansen, Reference Hansen 2005 ; Jaller and Pawha, Reference Jaller and Pahwa 2020 ; Melis et al., Reference Melis, Campo, Lamey and Breugelmans 2016 ; Van Droogenbroeck and Hove, Reference Van Droogenbroeck and Van Hove 2017 ). However, it is unclear how the pandemic has influenced the consumer decision-making process. While Ellison et al. ( Reference Ellison, McFadden, Rickard and Wilson 2020 ) documented an increase in online grocery shopping, their primary focus was on changes in purchasing behavior and not the decision to use online grocery shopping. Therefore, we have included pandemic-specific measures to capture how risk perceptions about COVID-19 or food supply chain disruptions influence the choice of online grocery shopping and frequency of online shopping.
Second, we investigate consumers’ anticipated use of online shopping in the future. We consider the possibility that online grocery shopping will persist only during the pandemic, that it will continue regardless of the pandemic, or that it will not be continued in the future. We examine the prevalence of each behavior and then investigate possible determinants of future online grocery shopping using a multinomial logistic regression. Understanding the potential future grocery shopping behavior and its determinants could assist grocers and retailers to reidentify their marketing strategies and enhance online shopping service to better serve online grocery shoppers.
The first section of this paper provides a brief literature overview of studies of online grocery shopping both pre-pandemic and in the pandemic-shaped grocery markets. This literature review helps define hypotheses about how shopper demographics and attitudes may influence online grocery shopping, frequency of online grocery purchases during the pandemic, and plans to continue online grocery shopping. Following the literature review and hypotheses development, the next section presents information about the survey and data collection and model estimations. Results and policy implications are discussed next, along with conclusions.
1.2. Prior Studies of Online Grocery Shopping and Behaviors During the Pandemic
1.2.1. online grocery shopping patterns pre-pandemic.
Several studies have examined the effects of shopper demographics and attitudes on online grocery shopping. Younger shoppers are more likely to use online grocery shopping, perhaps because they are more familiar and comfortable with online shopping in general and related technology (Etumnu et al., Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 ; Farag et al., Reference Farag, Schwanen, Dijst and Faber 2007 b; Hiser, Nayga, and Capps, Reference Hiser, Nayga and Capps 1999 ; Van Droogenbroeck and Hove, Reference Van Droogenbroeck and Van Hove 2017 ). While some studies have found positive influence of female gender on online grocery shopping (Jaller and Pawha, Reference Jaller and Pahwa 2020 ), others have found the opposite (Etumnu et al., Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 ; Farag et al. Reference Farag, Schwanen, Dijst and Faber 2007 b). Prior studies have suggested that presence of younger children has a positive effect on online grocery shopping adoption (Etumnu et al. Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 , Hansen, Reference Hansen 2005 ; Jaller and Pawha, Reference Jaller and Pahwa 2020 , Melis et al., Reference Melis, Campo, Lamey and Breugelmans 2016 ), indicating food shoppers with accompanying children may find in-store trips more time-consuming and challenging than those without children.
Studies have found positive effects of household income (Hansen, Reference Hansen 2005 ) or full-time employment in the household (Van Droogenbroeck and Hove, Reference Van Droogenbroeck and Van Hove 2017 ) on online grocery shopping. Greater likelihood of online grocery shopping has also been associated with higher levels of education (Etumnu et al., Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 ; Hiser, Nayga, and Capps, Reference Hiser, Nayga and Capps 1999 ; Jaller and Pawha, Reference Jaller and Pahwa 2020 ; Van Droogenbroeck and Hove, Reference Van Droogenbroeck and Van Hove 2017 ). Melis et al. ( Reference Melis, Campo, Lamey and Breugelmans 2016 ) found that, if shoppers lived farther from a brick-and-mortar store, they were more likely to spend a larger share of their grocery spending at the online chain. They posited that shoppers would experience relatively higher transportation costs and thus were more inclined to shift more of their purchases to the online store. Findings by Melis et al. ( Reference Melis, Campo, Lamey and Breugelmans 2016 ) might suggest that urban consumers would be less likely to choose online shopping over brick-and-mortar shopping. However, this finding might not hold in more rural areas where there are limited online grocery shopping opportunities. But, with large chains such as WalMart offering online shopping with curbside pickup and Amazon delivery of grocery items even in rural areas, these limitations may be less than in the past (Germain, Reference Germain 2020 ).
Researchers have also investigated the relationship between in-store shopping and online shopping. Farag, Krizek, and Dijst ( Reference Farag, Krizek and Dijst 2007 a) found Dutch online buyers make more shopping trips than non-online buyers and have a shorter duration of shopping trips. Their results were suggestive of a complementary relationship between online buying and in-store shopping. Furthermore, Pozzi ( Reference Pozzi 2013 ) found only limited cannibalization of traditional brick-and-mortar store grocery sales by online sales.
1.2.2. Influences of Attitudes and Pre-Pandemic Lifestyles
Several studies have examined the influence of convenience and perceived risks on online grocery shopping (Campo and Breugelmans Reference Campo and Breugelmans 2015 ; Melis et al. Reference Melis, Campo, Lamey and Breugelmans 2016 ; Ramus and Nielsen, Reference Ramus and Nielsen 2005 ; Rohm and Swaminathan, Reference Rohm and Swaminathan 2004 ; Verhoef and Langerak, Reference Verhoef and Langerak 2001 ). Verhoef and Langerak ( Reference Verhoef and Langerak 2001 ) found that consumers who believed the reduction in the physical efforts of grocery shopping were an important advantage associated with online grocery shopping. Rohm and Swaminathan ( Reference Rohm and Swaminathan 2004 ) found that store-oriented shoppers who derived satisfaction from immediate product possession and contact shopping were much less likely to shop online than were convenience shoppers. Campo and Breugelmans ( Reference Campo and Breugelmans 2015 ) noted that the vast majority of online grocery shoppers were actually multichannel shoppers who visited both online and offline, brick-and-mortar, and grocery stores. Melis et al. ( Reference Melis, Campo, Lamey and Breugelmans 2016 ) found that consumers who had moderate time constraints, indicated by frequency of shopping trips, were more likely to adopt the online channel for grocery retailers. Ramus and Nielsen ( Reference Ramus and Nielsen 2005 ) found that shoppers perceived internet grocery shopping to be convenient, but more likely to result in purchasing poorer quality products that they would either have to accept or return.
A few studies have examined frequency of online grocery shopping. Hansen ( Reference Hansen 2007 ) found that increased utilization of online grocery shopping was associated with the perception of increased physical effort of in-store shopping and decreased perception of the complexity of online shopping, internet grocery risk, and enjoyment of shopping in-store. Hand et al. ( Reference Hand, Dall’Olmo Riley, Rettie, Harris and Singh 2009 ) found that situational factors, for example, birth of a child, health problems, or family circumstances, often were precipitating factors that influenced shoppers to buy groceries online. However, once these precipitating factors were gone, the shoppers tended to return to brick-and-mortar grocery shopping. These results elicit the question of whether those who have initiated or increased their online grocery shopping during the pandemic will plan to continue online shopping or revert to prior brick-and-mortar grocery shopping patterns after the pandemic conditions have eased. Furthermore, some shoppers may plan to continue online grocery shopping only as long as the pandemic conditions prevail. However, this represents an empirical question yet to be answered.
1.2.3. Online and In-Store Shopping During the COVID-19 Pandemic
During the first few months of the pandemic, several changes in food shopping behaviors were found. In a study of Spanish consumers (Laguna et al., Reference Laguna, Fizman, Puerta, Chaya and Tarrega 2020 ), no changes in percentages of where consumers said they mainly purchased their foods (supermarkets, small shops, or online) were found; however, consumers reduced their frequency of shopping trips. While there was not a shift toward online shopping found in their study, the decrease in frequency of shopping suggests averting behaviors. Another study found consumer in the United States and China had changed their food purchase behaviors toward more use of takeout and delivery orders (Dou et al., Reference Dou, Stefanovsi, Galligan, Lindem, Rozin, Chen and Chao 2020 ). In addition, some studies showed that grocery shopping online increased with social distancing measures and concerns about shopping in crowded grocery stores (Ellison et al., Reference Ellison, McFadden, Rickard and Wilson 2020 ; Melo, Reference Melo 2020 ). Melo ( Reference Melo 2020 ) noted during the first few months of the pandemic certain foods were stockpiled by consumers.
Grashius and Skevas ( Reference Grashius and Skevas 2020 ) used a choice experiment to determine how online shopping attributes and COVID-19 conditions might influence preferences for online grocery shopping. They also examined how the spread of COVID-19 may impact consumer preferences. Respondents who were presented with the hypothetical case where COVID-19 was spreading at an increasing rate had the most disutility of shopping in-store. However, where COVID-19 was hypothetically spreading at a decreasing rate, consumer preferences for the home delivery over other methods were not as pronounced. Hence, they postulated that consumer online shopping behavior is motivated at least in part by concerns of shopping inside grocery stores. Their results suggest that when pandemic conditions subside, many online shoppers will choose to return to brick-and-mortar shopping.
The possibility that concerns regarding COVID-19 influence consumer behavior was also investigated by Goolsbee and Syverson ( Reference Goolsbee and Syverson 2020 ) who used cell phone records to track customer visits to 2.25 million businesses across 110 industries during the early months of the pandemic. They found that overall consumer traffic fell by 60 percentage points, but legal restrictions explained only about 7 percentage points of this decline, while individual choices were more explanatory of the decline. They noted, however, that shutdown orders did reallocate consumers from restaurants and bars toward groceries and other food sellers. Hence, during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, a portion of sales gains online may be attributable to both concerns regarding COVID-19 and declines in food-away-from-home purchases.
2. Methodology
2.1. survey and data collection.
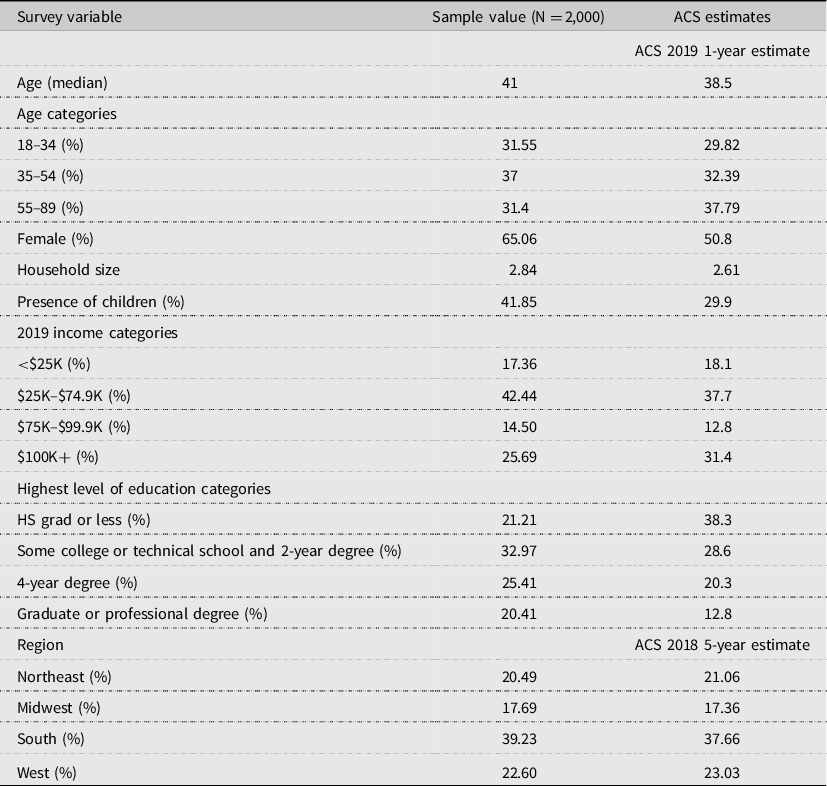
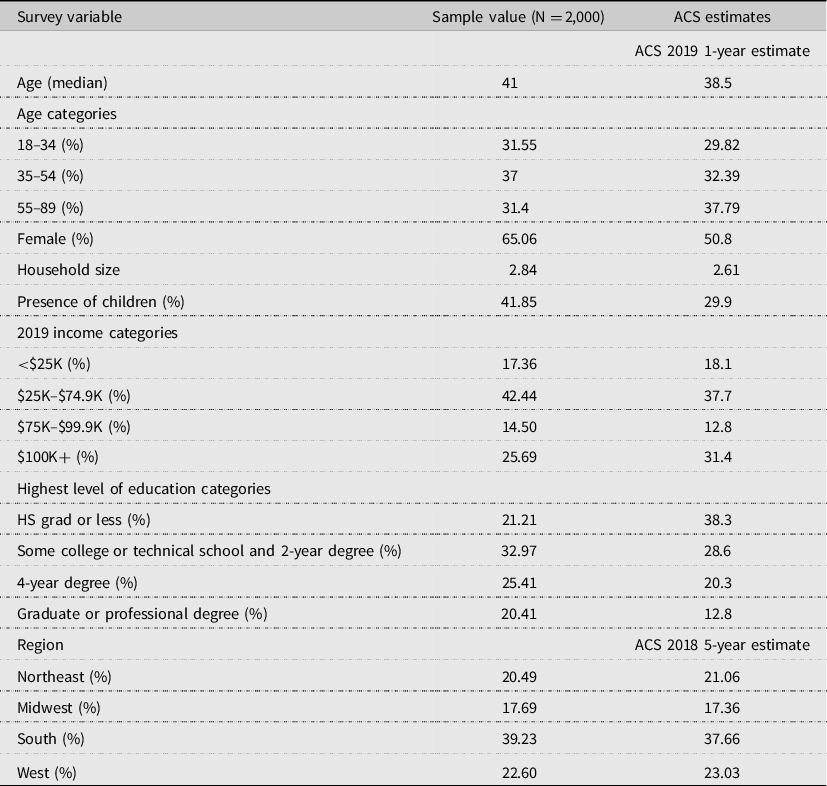
The data for this study were collected via an online survey through the Qualtrics survey platform in July 2020. The survey panel consisted of US primary household food shoppers (person primarily responsible for most of the food shopping in their household) aged 18 years and over, who had lived in the same state since February 1, 2020. Prior to the survey being fielded, a pretest of 50 respondents was conducted and the survey was deemed suitable for broader distribution. The sample panel was drawn by Qualtrics to reflect the distribution of US households according to the American Community Survey (ACS) (U.S. Census Bureau, 2019 ) based on their 2019 income, age, and geographical region (i.e. Northeast, Midwest, West, and South). Qualtrics solicited responses until a total of 2,000 responses were received from respondents who met the qualifications described above while ensuring the age, income, and regional quotas were met. Table 1 displays sample averages for several demographic and household variables compared with ACS estimates for the US population. As can be seen in Table 1 , the sample respondent is more likely to be female than the US average. This may be attributed to the primary shopper inclusion criteria because a higher percentage of primary food shoppers are female (Schaefer, Reference Schaefer 2019 ). Also, our sample has a higher percentage of college graduates than the US average. The sample average household size was larger than the US average and a higher percentage have children under the age of 18 years compared with the US average.
Table 1. Survey sample demographics compared with US American Community Survey (ACS) estimates
The survey instrument consisted of several sections including methods of acquiring food in June 2020 (online or in-person grocery store, in-person or takeaway from restaurants, and other sources), food expenditures, COVID-19 experiences and attitudes, and other demographic and household questions. Appropriate human subjects’ protocols were followed and institutional review board approvals obtained (UTK-IRB-20-05882-XM).
2.2. Modeling of Grocery Purchases Online During the Pandemic and Post-Pandemic Plans
Two consumer decisions regarding the use of online shopping were examined in this study. The first is whether the consumer used online grocery shop during the month of June 2020 and if so, how frequently. The online grocery shopping question respondents asked how many times in June 2020 they purchased groceries online including curbside pickup, and any delivery service (e.g. supermarket delivery, Amazon, and Instacart). The second decision among these online grocery shoppers is whether they planned to continue purchasing groceries online in the future regardless of the pandemic, only under pandemic conditions, or not at all.
Based on the prior studies, we hypothesized that households that are younger, higher income, have children, and more employed individuals in the household will be more likely to utilize online grocery shopping and plan to utilize it in the future regardless of continuation of the pandemic (Hansen, Reference Hansen 2005 ; Etumnu et al., Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 ; Farag et al., Reference Farag, Schwanen, Dijst and Faber 2007 b; Hiser, Nayga, and Capps, Reference Hiser, Nayga and Capps 1999 ; Van Droogenbroeck and Hove, Reference Van Droogenbroeck and Van Hove 2017 ). Due to mixed findings regarding female gender, the direction of influence of female gender was not hypothesized a priori (Etumnu et al., Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 ; Farag et al., Reference Farag, Schwanen, Dijst and Faber 2007 b; Jaller and Pawha, Reference Jaller and Pahwa 2020 ). While several studies have found complementarity between traditional in-store and online grocery shopping, given that the time frame studied here is the span of a month, the influence of greater number of in-store trips is difficult to hypothesize a priori (Farag, Krizek, and Dijst, Reference Farag, Krizek and Dijst 2007 a; Pozzi, Reference Pozzi 2013 ). However, it is more likely that a greater number of in-store trips is more likely to influence the frequency of online shopping, rather than the choice the shop online at all. In addition, it is likely that prior online shopping will strongly influence both online grocery shopping behaviors in June 2020 and plans for online grocery shopping in the future.
Two concerns precipitated by the pandemic that may influence shopping behavior are concern with contracting COVID-19 and concern with food shortages at retailers due to food supply chain disruptions (Ferguson, Reference Ferguson 2020 ). Either has the potential to increase the use of online shopping as consumers seek to avoid stores or plan food expenditures to avoid shortages or stockpile items of which they may experience a shortage at retailers or grocers. To assess consumers’ perceptions of these two pandemic-related risks, we asked respondents to rank their concern with either becoming ill with COVID-19 or that COVID-19 will cause food shortages, both on a scale from 1 to 9, where 1 indicated no concern and 9 indicated extremely concerned. Footnote 1 If the respondent was moderately concerned or greater, the variable was assigned a value of “1” and “0” otherwise.
2.2.1. Cragg Model of Number of Times Purchased Groceries Online
The expected value of the number of times shopper i purchases online groceries conditional on at least one purchase is:
The marginal effect of the jth explanatory variable on the probability of the ith shopper choosing online groceries at least once is
The marginal effect of the jth explanatory variable for the ith individual on the conditional level of Times Online is
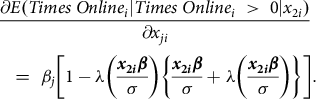
The average marginal effects, which are the average of the individual level effects, are estimated using the Delta method (Greene, Reference Greene 2018 ). The craggit module in STATA 16.0 was used to estimate the Cragg model and the marginal effects of evaluated determinants (Burke, Reference Burke 2009 ).
2.2.2. Multinomial Probit Model of Future Online Grocery Shopping Decisions
The survey question regarding plans for future online shopping for groceries includes three possible outcomes ( M = 3), these are a) 3 = Yes, b) 2 = Yes, but only if COVID-19 is a concern, and c) 1 = No. With three outcomes, a multinomial probit model is used to estimate the probability of each future planned online grocery shopping outcome. The probability that the lth option is chosen among M alternatives by the ith consumer is then (Cameron and Trivedi, Reference Cameron and Trivedi 2005 ):
3.1 Summary Demographics of Respondents Used in the Models
Table 2 contains statistics summary for the variables used in the Cragg and multinomial models. These summary measures are for the 1,558 respondents out of the 2,000 who answered all questions needed for the analysis. Notably, about 54.8 percent of the 1,558 respondents shopped for groceries online in June 2020 and overall 48.3 percent indicated they had not shopped for groceries online before the pandemic. Also, among the June 2020 online grocery shoppers surveyed in this study, about 58.4 percent indicated they planned to continue to shop for groceries online regardless of the pandemic ( Future Online = 3). About 29.5 percent said they would continue to shop online for groceries, but only if COVID-19 remained as a problem ( Future Online = 2). Only 12.1 percent indicated they would not shop online for groceries in the future ( Future Online = 1).
Table 2. Names, definitions, and means for variables used in the Cragg model for online grocery shopping and multinomial model of future online grocery shopping plans
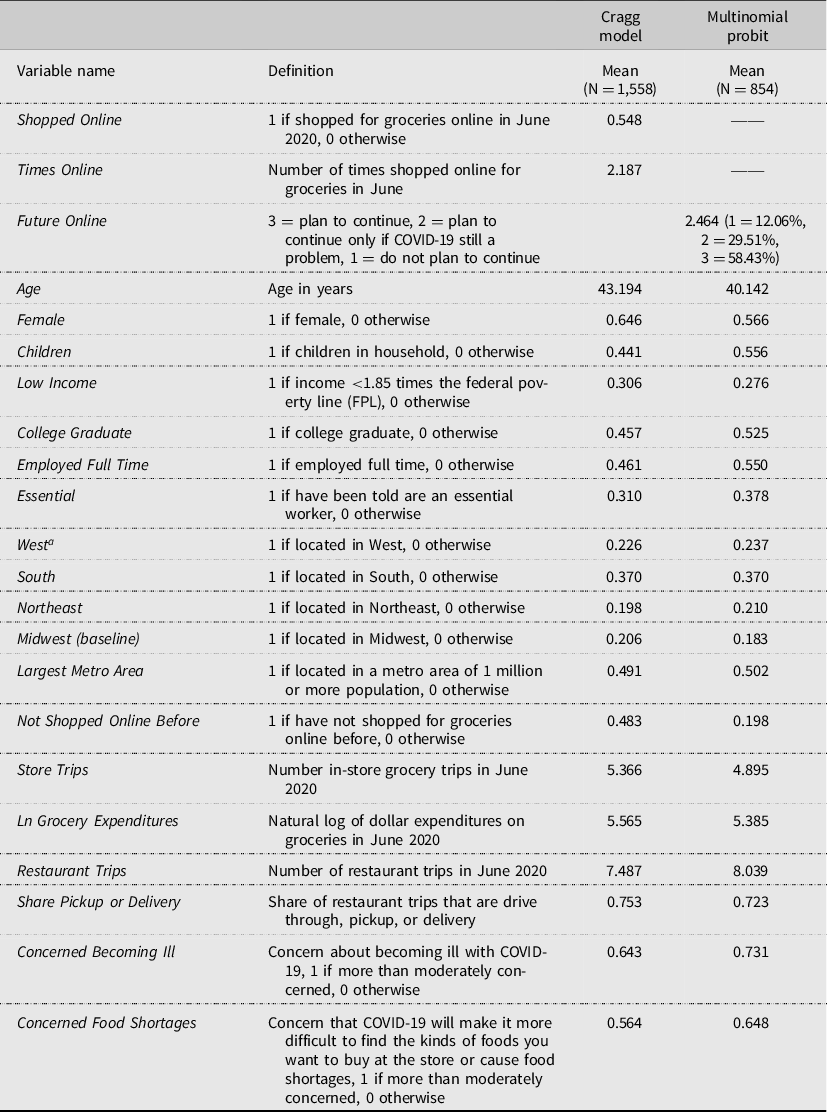
a The baseline region is Midwest. States in the West include AK, AZ, CA, CO, HI, ID, MT, NM, NV, OR, UT, WA, and WY, in the South include AL, AR, DC, FL, GA, KY, LA, MS, NC, OK, SC, TN, TX, VA, and WV, in the Northeast include CT, DE, MA, MD, ME, NH, NJ, NY, PA, RI, and VT, and in the Midwest include IL, IN, IA, KS, MI, MN, MO, ND, NE, OH, SD, and WI.
As shown in Table 2 , similar to the full sample, the responses used in estimating the models were more likely to be female, have children in the household, and be college graduates as compared to the ACS estimates shown in Table 1 . The percentage of respondents residing in each region from Table 2 were similar to ACS regional percentages shown in Table 1 .
3.2. Cragg Model of Number of Times Shopped Online for Groceries in June 2020
Table 3 contains the results from the Cragg model for online grocery shopping in June 2020. The log-likelihood ratio (LLR) test against an intercept-only model (-2*(LL Intercept Only-LL Model)) indicates that the model with the covariates is significant overall. Additionally, the LLR test comparing the Cragg model to the Tobit model, with a test statistic of 188.766 with 17 degrees of freedom from a chi-square distributed LLR test (-2*(LL Tobit-LL Cragg)), indicates that the model fit is improved by using the Cragg specification. The pseudo R 2 for the model is 0.274, while the percent correctly classified for Shopped Online is over 81 percent. The mean variance inflation factor of 1.34 suggests no statistically problematic multicollinearity found within the covariates.
Table 3. Estimated Cragg model of number of times shopped for groceries online and associated marginal effects (ME)
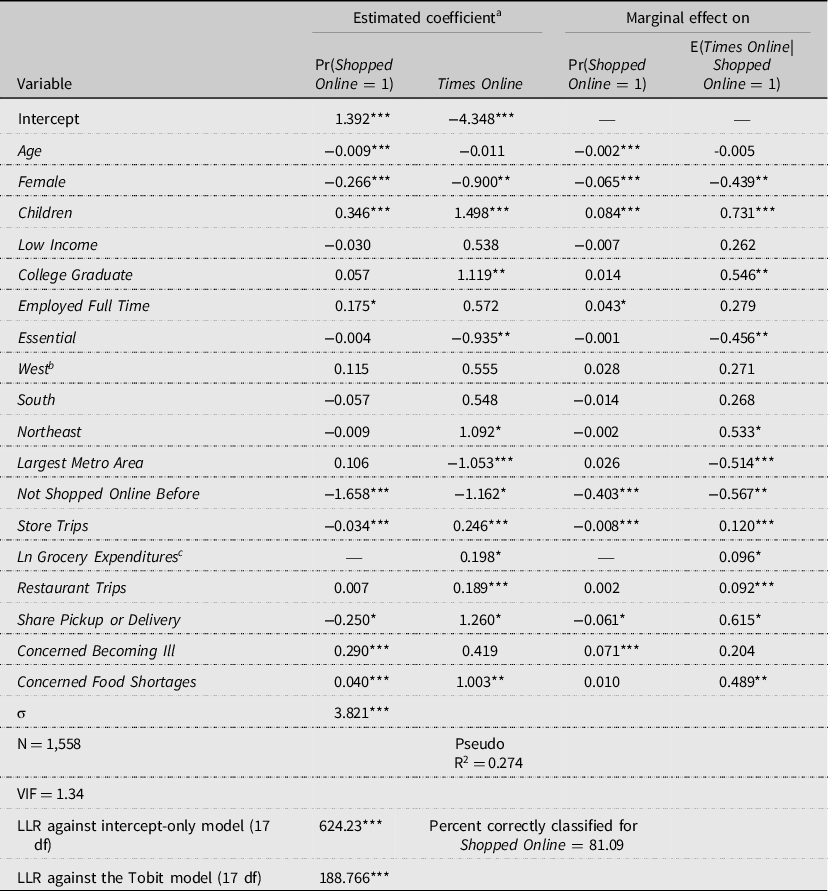
a ***Significance at α = 0.01, **significance at α = 0.05, and *significance at α = 0.1
b The baseline region is Midwest.
c The marginal effect of Grocery Expenditures is calculated as the ME Ln Groc. Expend./Grocery Expenditures.
The second column of Table 3 includes the estimated coefficients for the choice to use online grocery shopping in June 2020 (the probit portion of the Cragg model for Shopped Online = 1) and the third column contains the coefficients for the frequency of online shopping (the truncated portion of the Cragg model for Times Online ). The associated average marginal effects for the explanatory variables on probability of shopping online and the number of times shopped online for groceries were calculated using the estimated coefficients and equations ( 4 ) and ( 5 ), and shown in the third and fourth columns of Table 3 .
As seen in Table 3 , age ( Age ) negatively influences the likelihood of shopping online for groceries by 0.2 percent for each year, which is consistent with prior research findings (Etumnu et al. Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 ; Farag et al., Reference Farag, Schwanen, Dijst and Faber 2007 b; Hiser, Nayga, and Capps, Reference Hiser, Nayga and Capps 1999 ; Van Droogenbroeck and Hove, Reference Van Droogenbroeck and Van Hove 2017 ). However, age does not significantly influence the number of times shopped online. Consistent with Etumnu et al. ( Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 ) and (Farag et al., Reference Farag, Schwanen, Dijst and Faber 2007 b), identifying as female ( Female ) negatively influences the probability of shopping for groceries online by 6.5 percent ( Shopped Online ) and the number of times ( Times Online ) the respondent grocery shopped online by 0.439 times.
Respondents with children in the household ( Children ) are 8.4 percent more likely to have shopped for groceries online in June 2020 and made about 0.731 more trips than households without children. These findings are similar to some previous studies (e.g. Etumnu et al. Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 , Hansen, Reference Hansen 2005 ; Jaller and Pawha, Reference Jaller and Pahwa 2020 , Melis et al., Reference Melis, Campo, Lamey and Breugelmans 2016 ) that suggested that household food shoppers may find it more challenging to shop in-store with accompanying children.
In line with other studies (Etumnu et al., Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 ; Hiser, Nayga, and Capps, Reference Hiser, Nayga and Capps 1999 ; Jaller and Pawha, Reference Jaller and Pahwa 2020 ; Van Droogenbroeck and Hove, Reference Van Droogenbroeck and Van Hove 2017 ), this study found that having a college degree ( College Graduate ) increases the frequency of online grocery shopping 0.546 times among those who used online shopping at least once. However, being a college graduate does not significantly influence the initial decision to shop online.
While full-time employment status ( Employed Full Time ) does not influence the number of times the respondent online grocery shopped, it positively influences the probability that the respondent shopped for groceries online by about 4.4 percent. This finding is consistent with those of Van Droogenbroeck and Hove ( Reference Van Droogenbroeck and Van Hove 2017 ). Identifying as an essential worker ( Essential ) does not significantly influence the probability of online grocery shopping but does decrease the frequency of online shopping by 0.456 trips among those who chose to shop online. For essential workers, the potential convenience of online shopping may not have been outweighed by the convenience and ability to visit their regular store during their commute to or from work. This finding may have implications for retailers as more households return to working in-person in the future and have to re-evaluate the trade-offs of ordering online with the ability to shop at stores along commuting routes.
Poverty status ( Low Income ) does not have the anticipated positive influence on online shopping as suggested by pre-pandemic research (Hansen, Reference Hansen 2005 ). Rather, our study found that Low Income has no significant influence on the choice to shop online, or the frequency of online shopping. Two theories could explain this finding. First, in this study’s definition, both grocery purchases that were delivered or curbside pickup are included. If previous studies did not include curbside pickup, and if lower-income families are more likely to use curbside pickup because it does not incur a delivery fee, then previous studies may have been less likely to detect lower-income households’ use of online grocery shopping. Second, prior to the pandemic lower-income households that participated in the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) could not use their benefits to purchase groceries online. The USDA Food and Nutrition Services (USDA-FNS), which manages the SNAP program, began a limited pilot program pre-pandemic to allow SNAP participants to use their benefits to purchase groceries online, and in March 2020 they began expanding the program into additional states (USDA/FNS, 2020 ). While SNAP benefits could be used for online groceries, they should not be used to pay for delivery fees and could be redeemed at a very limited number of retailers. However, Walmart and Amazon were an option in most states. Reports suggest this policy change may have dramatically increased online purchases by SNAP households since the beginning of the pandemic (Day, Reference Day 2020 ). Additionally, several supermarket chains and Walmart began accepting SNAP as a form of payment for curbside pickup during the pandemic and independent of the FNS pilot program (Berthiaume, Reference Berthiaume 2020 ; Redman, Reference Redman 2020 a; WalMart, 2020 ). Jointly, these may have increased the utilization of online grocery shopping among lower-income households.
Lack of experience with online grocery shopping ( Not Shopped Online Before ) has a large effect both on the use and frequency of online grocery shopping in June 2020. Those who had not shopped online for groceries before are about 40 percent less likely to have shopped online for them in June 2020 and among those who did, they used online shopping 0.567 fewer times than those with previous online shopping experience.
In-store shopping trips ( Store Trips ) have mixed effects on online grocery shopping. Each additional grocery trip decreases the probability of shopping online by 0.8 percent but increases the frequency of online grocery shopping by 0.120 times. This latter finding suggests a complementary, rather than substitution, relationship between online and brick-and-mortar shopping trips which is similar to findings by Farag et al. ( Reference Farag, Krizek and Dijst 2007 a) and Pozzi ( Reference Pozzi 2013 ). However, additional research would be needed to substantiate this hypothesis.
Restaurant trips do not influence probability of shopping online; however, among those who shopped online, each additional restaurant trip increases the frequency they shopped online by 0.092 trips. As the share of restaurant trips for pickup or delivery increases, the probability of shopping online decreases by 6.1 percent hinting at possible substitutability between pickup/delivery restaurant trips and online grocery shopping. Yet, among those who shopped online, increasing the share of restaurant trips that were pickup or delivery by a point increases the number of times the respondent shopped online by 0.615. Since increasing the share of restaurant trips that are pickup/delivery increases the frequency of online grocery shopping, after controlling for the influence of total restaurant trips, this result could reflect averting behaviors during the pandemic among online grocery shoppers. Findings regarding the effects of pandemic risk variables discussed below further support this hypothesis.
As might be expected, overall grocery expenditures, as measured by the natural log of June 2020 grocery expenditures ( Ln Grocery Expenditures ) increases the number of times shopped online ( Times Online ). Footnote 3 Using the untransformed values, for each 100 dollars of grocery expenditures in June 2020, the number of times shopped online increases by 0.160.
Compared with respondents from the Midwest , Northeast respondents who shopped for groceries online did so 0.533 times more often. While large metro area was expected to have a positive influence on online shopping, it does not significantly affect probability of buying groceries online and it negatively affects the frequency for those who used online shopping by 0.533 trips. One possible explanation for the negative effect is that perhaps metro shoppers were less likely to say they were spending more on groceries than normal than the suburban or more rural counterparts. As part of debriefing questions, it was asked whether the respondent thought they spent more or less on groceries than usual in June 2020. However, while 40.42 percent of the metro respondents said they spent more on groceries in June 2020 than normal, only 32.40 percent of the non-metro respondents spent more than usual. Another potential explanation is that metro shoppers may be more experienced with and trusting of online grocery services and hence be willing to purchase more per online shopping trip. Given that they were spending more than usual on groceries in June 2020 than their non-metro counterparts, this seems more plausible. However, additional research would be needed to evaluate metro versus non-metro shopper knowledgeability and trust in online shopping for groceries.
Concerns about becoming ill with COVID-19 or possible pandemic-associated food shortages influenced online grocery shopping but in different ways. Being at least moderately concerned about becoming ill with COVID-19 ( Concern Becoming Ill ) increases the probability of online grocery shopping by 7.1 percent but does not significantly influence the number of times shopped online. However, being at least moderately concerned about food shortages ( Concerned Food Shortages ) positively influence frequency of online grocery shopping by 0.489 times. While the exact reasons for this relationship require further study, they do suggest that COVID-19 concerns related to the food system continued to influence consumer behavior even into the summer of 2020. Some possible explanations may include the increased utilization of online grocery shopping to maintain a continuous supply of items that were previously in short supply, or stockpiling goods. However, these are hypotheses that would require future study.
3.3. Reasons for Not Shopping Online for Groceries in June 2020
The survey also asked respondents the reasons for not online grocery shopping in June 2020 and the results are reported in Figure 1 . Personal preference for shopping in-store is the dominant reason (˜73%), distantly followed by delivery fees being too expensive at 9.64 percent. Only 5 percent indicated that they did not like the previous experiences in online grocery shopping, while less than 5 percent indicated they did not have the services available where they live, that their SNAP benefits were not accepted, or that they had purchased online before, but just did not do so in June 2020.
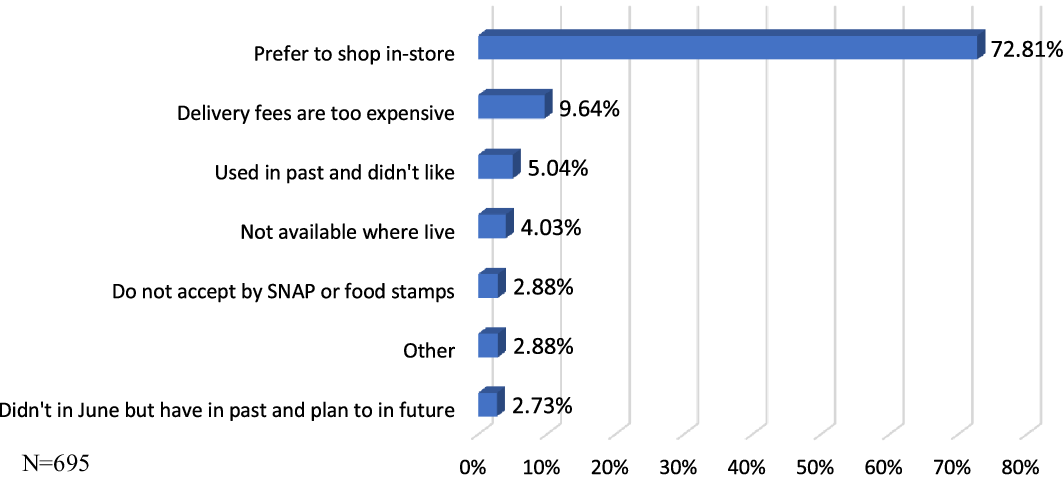
Figure 1. Reasons for not shopping for groceries online in June 2020.
3.4. Multinomial Probit Model of Plans for Future Online Grocery Shopping
The estimated multinomial probit model of future plans for online grocery shopping ( Future Online ) among households that currently use online grocery is reported in Table 4 . The reference category is Future Online = 1, or no plans to grocery shop online in the future. The associated average marginal effects for the explanatory variables on probability of shopping online and the number of times shopped online for groceries are calculated using the estimated coefficients and equation (7) and are shown in the third to fifth columns of Table 4 . The standard errors associated with the marginal effects were calculated using the Delta method. The model was significant overall as indicated by the LLR test against an intercept-only model. The model correctly classified just under 62.3 percent of the observations regarding future online shopping plans.
Table 4. Estimated multinomial probit model of future online grocery shopping plans ( Future Online ) and associated marginal effects (ME) a
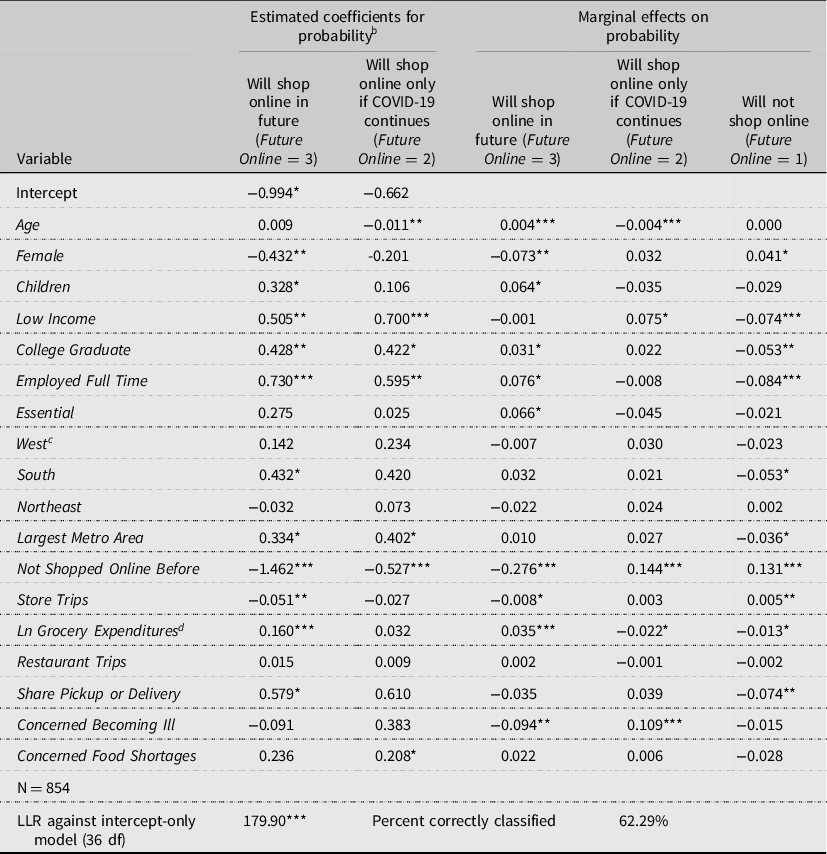
a The baseline category is Future Online = 1 or will not shop online.
b ***Significance at α = 0.01, **significance at α = 0.05, and *significance at α = 0.10.
c The baseline region is Midwest.
d The marginal effect of Grocery Expenditures is calculated as the ME Ln Groc. Expend./Grocery Expenditures .
Several consumer characteristics influenced plans to use online grocery shopping in the futur e, regardless of the pandemic, as indicated by their relationship with the Future Online = 3 outcome in column 3 of Table 4 . The presence of a child ( Children ) increased the probability of respondents stating they would shop online in the future by 6.4 percent, which suggests that respondents with children value the convenience afforded by shopping online that may reduce the number of brick-and-mortar store trips with children even after the pandemic ends (Etumnu et al. Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 ; Hansen, Reference Hansen 2005 ; Jaller and Pawha, Reference Jaller and Pahwa 2020 ; Melis et al., Reference Melis, Campo, Lamey and Breugelmans 2016 ).
College Graduate increased the probability of planning to shop online in the future by 3.1 percent and decreased the probability of not planning to do so by 5.3 percent. This result is similar to findings from prior research about the effects of education on online grocery shopping (Etumnu et al., Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 ; Hiser, Nayga, and Capps, Reference Hiser, Nayga and Capps 1999 ; Jaller and Pawha, Reference Jaller and Pahwa 2020 ; Van Droogenbroeck and Hove, Reference Van Droogenbroeck and Van Hove 2017 ) and suggests that higher educated online grocery shoppers in June 2020 plan to continue to so into the future. In addition, full-time employment increased the probability of planning to use online grocery shopping in the future by 7.6 percent and decreased the probability of saying they would not by 8.4 percent. Full-time workers likely value the convenience afforded by online grocery shopping and plan to continue it into the future which is consistent with prior research findings (Van Droogenbroeck and Hove, Reference Van Droogenbroeck and Van Hove 2017 ).
With each additional year of age ( Age ), the probability of planning to shop online in the future regardless of the pandemic increased by 0.4 percent, while the probability of planning to online shop only if the pandemic persists decreased by 0.4 percent. This finding about the effects of age on future plans is unlike findings from prior research of negative effects of age on online grocery shopping (Etumnu et al. Reference Etumnu, Widmar, Foster and Ortega 2019 ; Farag et al., Reference Farag, Schwanen, Dijst and Faber 2007 b; Hiser, Nayga, and Capps, Reference Hiser, Nayga and Capps 1999 ; Van Droogenbroeck and Hove, Reference Van Droogenbroeck and Van Hove 2017 ). This finding could reflect that older shoppers who have experienced online grocery shopping may now value the convenience it affords so as to plan to continue it into the future.
Compared with higher-income households, lower-income households ( Low Income ) that shopped online in June 2020 are 7.4 percent less likely to continue shopping online in the future and 7.5 percent more likely to choose to shop online only under pandemic conditions. This finding suggests that compared with higher-income households, lower-income households will be more likely to continue online shopping if pandemic conditions persist. This finding could reflect a perceived trade-off in the minds of lower-income online grocery shoppers during the pandemic, weighing any additional grocery costs incurred by online shopping against concerns about becoming ill shopping in-store if the pandemic persists.
Full-time employment status ( Employed Full Time ) positively influences probability of shopping online for groceries in the future (7.6 percent) and negatively influenced probability of not shopping online in the future (−8.4 percent). Furthermore, essential workers ( Essential ) are 6.6 percent more likely to say they would shop online for groceries in the future regardless of the pandemic. These results echo prior research suggesting a link between busy schedules and the convenience of online shopping (Verhoef and Langerak, Reference Verhoef and Langerak 2001 ).
Results also show that regional location and urbanization of residence influence plans for future online grocery shopping. Compared with those in the Midwest , those in the South are 5.3 percent less likely to say they do not plan to shop online for groceries in the future. Also, compared with those outside metro areas, those in the largest metro areas are 3.6 percent less likely to say they do not plan to shop online for groceries in the future.
Lack of previous online grocery purchasing experience ( Not Shopped Online Before ) decreases the probability of plans to shop in the future by 27.6 percent and increases the likelihood of not shopping online in the future by 13.1 percent. However, lack of experience also positively influences shopping online only if the pandemic continues to be a problem (14.4 percent). As this variable gauges experience with shopping online prior to June 2020, it may suggest that households that adopt online shopping during the later period of the pandemic are primarily concerned with minimizing their exposure to COVID-19 and will be unlikely to continue online grocery shopping behaviors after the pandemic ends. This would concur with the finding by Hand et al. ( Reference Hand, Dall’Olmo Riley, Rettie, Harris and Singh 2009 ) that once situational factors that precipitate use of online shopping are removed, shoppers tend to return back to brick-and-mortar shopping.
More frequent in-store grocery store trips positively influence probability of the respondent indicating they do not plan to shop online for groceries in the future (0.5 percent) and negatively influence probability that they plan to shop online for groceries in the future (−0.8 percent). Restaurant trips do not significantly influence future online shopping plans, but as the share of restaurant trips that were pickup or delivery increases, the probability of not shopping online for groceries in the future decreases by 7.4 percent. These findings could reflect planned averting behaviors, with those currently shopping in-store less and using drive through or pickup dining more, being less likely to say they would not shop online in the future.
The natural log of overall grocery expenditures for June 2020 ( Ln Grocery Expenditures ) positively influences respondents’ intentions for future online grocery shopping. For every $100 spent on groceries, the effect on probability of shopping online in the future is 11.0 percent, shopping online only if the pandemic continues is −4.1 percent, and not planning to shop online in the future is −6.9 percent.
The pandemic concern variables primarily influence planned future online shopping behavior related to the pandemic. Moderate concern with becoming ill with COVID-19 ( Concerned Becoming Ill ) decreases the probability of planning to shop online in the future regardless of pandemic conditions (−9.4 percent) but increases the probability of continuing to shop online only while the pandemic continues (10.9 percent). This result suggests that greater concerns about becoming ill will likely only drive online shopping while the pandemic persists. Although concerns about food shortages ( Concerned Food Shortages ) influenced the frequency of online grocery shopping in June 2020, it has no effect on future plans for online grocery shopping. This suggests that grocery shoppers were responding to supply chain disruptions early in the pandemic but do not see this as likely problematic in the future and plan to adjust their shopping plans accordingly. It is possible that those who are most concerned about food shortages may not see online shopping as a preferred means to stockpile as compared to brick-and-mortar shopping. However, additional research would be needed to investigate this possibility further.
4. Implications and Conclusions
While online grocery shopping had been increasing in popularity prior to the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020, the onset of the pandemic accelerated its adoption. With this rapid increase in use of online grocery shopping, developing a better understanding of drivers of its use is of interest not only to the grocery retailing industry but also to policymakers. This study investigated the influence of pandemic-specific drivers, such as concerns about becoming ill and potential food shortages, as well shopper demographics, food shopping behaviors, and grocery expenditure patterns. Furthermore, to understand the potential staying power of online grocery shopping, this study also examined factors influencing online grocery shoppers’ intentions to continue online shopping in the future, under pandemic and non-pandemic conditions.
Many of the household determinants found in pre-pandemic research to increase online grocery shopping were also found in this research to increase online grocery shopping during the pandemic (younger age, full-time employment, college education, and the presence of children). Unexpectedly, low income had no influence on either the use or frequency of using online grocery shopping, whereas in past research it was generally associated with lower utilization of online grocery shopping. While this finding needs to be investigated further in future research, it may suggest that the pandemic has been particularly influential on the choice to grocery shop online among low-income households, who were previously less likely to utilize online grocery shopping. This may be related to the expansion of curbside pickup and the expansion of USDA pilot program allowing SNAP participants to use their benefits to make online grocery purchases (USDA/FNS, 2020 ; Hansen, Reference Hansen 2005 ).
While low income did not influence probability or frequency of online shopping in June 2020, low-income shoppers are more likely to say they would shop online if the pandemic continues, suggesting that lower-income shoppers do not believe the benefits of online shopping will persist beyond the pandemic. These households may be most sensitive to the additional delivery fees or cost associated with online grocery shopping that cannot be paid for with their SNAP benefits (USDA/FNS, 2020 ). This finding is in contrast to the influence of full-time employment and essential worker status which both increase the likelihood of future online shopping regardless of the pandemic. Full-time and essential workers may have less time to shop in-person and value the convenience of online grocery shopping beyond the duration of the pandemic. Given the potential of online grocery shopping to improve access to supermarkets for low-income households, future research should focus on the barriers and benefits of online grocery shopping among lower-income households.
Older populations are another vulnerable population of concern during the pandemic, because they may be more susceptible to serious illness if they contract COVID-19, and thus could benefit from policies and programs to reduce their exposure, such as those encouraging online grocery shopping. However, our results showed that age negatively influenced the probability of shopping for groceries online, perhaps reflecting that older populations are less comfortable with the concept of and technology needed to shop for groceries online. As evidenced by reasons for not shopping online, that majority of those who did not shop online preferred to shop in-store, despite the pandemic. Interestingly, among those who did shop online for groceries, older age had the opposite effects on plans for future grocery shopping. Older age increases the likelihood of continuing to shop online in the future, regardless of the pandemic. These findings suggest that once older shoppers try online shopping, compared with younger shoppers, they are more likely plan to continue it, perhaps due to the convenience, and in some cases, to avoid the physical demands associated with grocery shopping. Thus, developing policies to address barriers to use and increase online grocery shopping among older populations may not only benefit them during the pandemic, but also beyond. For example, some programs might focus on how to access and use online grocery shopping for the more nascent online shopper, while other programs might focus on how to use meal planning with online shopping and online list-making to more efficiently use food budgets and potentially reduce food waste.
Concerns with becoming ill with COVID-19 increased the likelihood of utilizing online grocery shopping in June 2020, while the frequency of online grocery shopping, among those who use online grocery shopping, was driven in part by fears of food shortages. Combined with the finding that increasing total grocery expenditures and in-store trips also increased the frequency of online grocery store shopping, this may suggest stockpiling behaviors among grocery shoppers. However, this behavior was not directly addressed in this study and requires future study for more definitive conclusions. Additional research should likely examine how consumers may be shopping in-store and supplementing with items they cannot find in-store with online purchases and vice versa.
The long-term effects of the pandemic on online grocery shopping will require further analysis, but our research does provide several preliminary insights. Those who had not previously purchased groceries online were 40.3 percent less likely to shop online for groceries in June 2020; however, among online grocery shoppers, new online shoppers were only 27.6 percent less likely to say they would shop online in the future regardless of the pandemic. This latter result suggests that some first-timers will be likely to stay with online shopping regardless of the pandemic. However, among respondents who utilized online grocery shopping in June 2020, about 12 percent indicated they do not plan to continue and 29.5 percent indicated they will continue to shop online only if COVID-19 continues. This foretells that at least some of the increased utilization of online grocery shopping will not persist beyond the pandemic.
Only concerns about becoming ill influence future online shopping intentions, while concerns about food shortages do not. While shoppers may have seen food supply chain disruptions that occurred in the first few months of the pandemic, they may have confidence in the supply chain to resolve disruptions and shortages in the longer term. However, being moderately concerned about becoming ill increased the probability that a respondent would shop online in the future but only if the pandemic persists. This latter finding could suggest that online shoppers who are driven by concerns about becoming ill from COVID-19 may revert to their usual in-store shopping behaviors when the pandemic subsides. Taken together with the finding that those who had not shopped online before were less likely to plan to do so in the future, inexperienced online shoppers who were more driven by pandemic concerns may be less likely to sustain online grocery shopping in the future beyond the pandemic.
This study has several limitations. First, it represents a snapshot of time in June 2020. Hence, some of the variables included in the model of June 2020 online grocery shopping, such as June grocery expenditures, restaurant trips, in-store grocery trips, and share of restaurant trips that were pickup, could represent endogenous decision-making during that month. Additional research including consumer behaviors from multiple time frames could help alleviate this issue. Furthermore, future research should focus on the long-term impacts of the increased utilization of online grocery that began during the pandemic, including how retailers are adapting their online shopping services to meet changing shopper preferences and perhaps improving their services during the pandemic. While out of the scope of this article, future research should examine the availability of online grocery by retailer type to determine if current trends will disproportionately benefit large, chain grocers who may be better able to support online services, while harming smaller, independent grocers. This could have implications for communities that rely on smaller grocers, or for individuals who cannot easily access online services.
Second, we did not ask detailed food shopping questions to investigate how the types of food items purchased may have changed as a result of the pandemic. This could potentially be of importance as some items may be more readily deliverable through online shopping than others. Etumnu and Widmar ( Reference Etumnu and Widmar 2020 ) found certain types of foods were more likely to be ordered online than others among US food shoppers. Additional research should likely examine whether more perishable items, such as fresh fruits and vegetables, are purchased in a brick-and-mortar setting rather than online, particularly in rural areas where delivery services for these types of items may be lacking.
Third, our survey was an online survey, and not an in-person or intercept survey. This could potentially create some sample bias toward those who are more familiar with the internet, and possibly, online shopping. Additional research findings from an in-person or intercept survey in-store could complement the findings from this research.
Conceptualization: K.L.J., J.Y., X.C., and T.Y.; Methodology: K.L.J., J.Y., X.C., and T.Y.; Formal Analysis: K.L.J. and J.Y.; Data Curation: K.L.J. and J.Y.; Writing—Original Draft: K.L.J., J.Y., X.C., and T.Y.; Writing—Review and Editing: K.L.J., J.Y., X.C., and T.Y.
Funding for this study was provided by in part by Ag Research at The University of Tennessee Institute for Agriculture. The findings and views represented in this paper are solely those of the authors and do not necessary represent those of the institution.
Drs. Jensen, Yenerall, Chen, and Yu declare no competing interests.
Data for this study were collected under UTK IRB Approval UTK IRB-20-05882-XM and were done so with respondents being assured of confidentially. Therefore, individual data may not be released.
1 Taherdoost ( Reference Taherdoost 2019 ) provided an overview of use of differing Likert scales, proposing use of a 7-point Likert scale. However, as noted in Taherdoost’s paper, Preston and Colman ( Reference Preston and Colman 2000 ) and Bendig ( Reference Bendig 1954 ) suggested longer scales (7 point to 9 point) are preferable for capturing respondents’ sentiments, with this benefit appearing to decrease with longer scales, such as 12-point scale (McRae, Reference McRae 1970 ).
3 Ln Grocery Expenditures, Store Trips, Restaurant Trips , and ShrPickup are potentially endogenous decisions to probability of choosing to shop online in June and the number of times shopped online in June 2020. Results were validated by estimating the models without these variables and the estimates appeared to be robust. These models are not presented in the interest of parsimony; however, they are available from the authors upon request.
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref .
- Google Scholar
View all Google Scholar citations for this article.
Save article to Kindle
To save this article to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about saving to your Kindle .
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service.
- Volume 53, Issue 3
- Kimberly L. Jensen (a1) , Jackie Yenerall (a1) , Xuqi Chen (a1) and T. Edward Yu (a1)
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/aae.2021.15
Save article to Dropbox
To save this article to your Dropbox account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Dropbox account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox .
Save article to Google Drive
To save this article to your Google Drive account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Google Drive account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive .
Reply to: Submit a response
- No HTML tags allowed - Web page URLs will display as text only - Lines and paragraphs break automatically - Attachments, images or tables are not permitted
Your details
Your email address will be used in order to notify you when your comment has been reviewed by the moderator and in case the author(s) of the article or the moderator need to contact you directly.
You have entered the maximum number of contributors
Conflicting interests.
Please list any fees and grants from, employment by, consultancy for, shared ownership in or any close relationship with, at any time over the preceding 36 months, any organisation whose interests may be affected by the publication of the response. Please also list any non-financial associations or interests (personal, professional, political, institutional, religious or other) that a reasonable reader would want to know about in relation to the submitted work. This pertains to all the authors of the piece, their spouses or partners.
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
A theoretical model of factors influencing online consumer purchasing behavior through electronic word of mouth data mining and analysis
Roles Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation School of Economics and Management, Zhengzhou University of Light Industry, High-tech District, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
Roles Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation School of Politics and Public Administration, Soochow University, Gusu District, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Province, China
Roles Data curation, Funding acquisition, Project administration
Roles Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration
- Qiwei Wang,
- Xiaoya Zhu,
- Manman Wang,
- Fuli Zhou,
- Shuang Cheng

- Published: May 18, 2023
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034
- Peer Review
- Reader Comments
The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic has impacted and changed consumer behavior because of a prolonged quarantine and lockdown. This study proposed a theoretical framework to explore and define the influencing factors of online consumer purchasing behavior (OCPB) based on electronic word-of-mouth (e-WOM) data mining and analysis. Data pertaining to e-WOM were crawled from smartphone product reviews from the two most popular online shopping platforms in China, Jingdong.com and Taobao.com . Data processing aimed to filter noise and translate unstructured data from complex text reviews into structured data. The machine learning based K-means clustering method was utilized to cluster the influencing factors of OCPB. Comparing the clustering results and Kotler’s five products level, the influencing factors of OCPB were clustered around four categories: perceived emergency context, product, innovation, and function attributes. This study contributes to OCPB research by data mining and analysis that can adequately identify the influencing factors based on e-WOM. The definition and explanation of these categories may have important implications for both OCPB and e-commerce.
Citation: Wang Q, Zhu X, Wang M, Zhou F, Cheng S (2023) A theoretical model of factors influencing online consumer purchasing behavior through electronic word of mouth data mining and analysis. PLoS ONE 18(5): e0286034. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034
Editor: Ahmad Samed Al-Adwan, Al-Ahliyya Amman University, JORDAN
Received: April 19, 2023; Accepted: May 5, 2023; Published: May 18, 2023
Copyright: © 2023 Wang et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the manuscript and its Supporting Information files.
Funding: The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: This study was supported by the Henan Province Philosophy and Social Science Planning Project (grant number. 2020CZH012), the Henan Key Research and Development and Promotion Special (Soft Science Research) (grant number. 222400410126), the Jiangsu Province Social Science Foundation Youth Project (grant number. 21GLC012) and the Doctor Fund of Zhengzhou University of Light Industry (grant number. 2020BSJJ022, 2019BSJJ017). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
1. Introduction
A prolonged quarantine and lockdown imposed by the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has changed the human lifestyle worldwide. The COVID-19 pandemic has negatively impacted various sectors such as manufacturing, import and export trade, tourism, catering, transportation, entertainment, especially retail and hence the global economy. Consumer behavior has gradually shifted toward contactless services and e-commerce activities owing to the COVID-19 [ 1 ].
Consumers are relying on e-commerce more than ever to protect their health. Recent advances in information technology, digital transformation, and the Internet helped consumers to encounter the COVID-19 to meet the needs of the daily lives, which led to an increase in the importance of e-commerce and changes in consumers’ online purchasing patterns [ 2 ]. When consumers shop online, their behavior is considered non-traditional, and is illustrated by a new trend and current environment. To analyze the influencing factors of online consumer purchasing behavior (OCPB), it is necessary to consider several factors, such as the price and quality of a product, consumers’ preferences, website design, function, security, search, and electronic word-of-mouth (e-WOM) [ 3 ]. As the current website design and payment security have become a user-friendly and guaranteed system compared with a decade ago, some factors are no longer considered as essential. By contrast, greater diversity and complexity have become the main characteristics of the influencing factors. Furthermore, under the traditional sales model, consumers’ purchase decisions were simple, while online consumers have more options in terms of shopping channels and decision choices. Meanwhile, in recent years, consumers’ preferences have gradually shifted from standardized products to customized and personalized. In line with these changes, information technology and data science, such as big data analytics, data mining from e-WOM, and machine learning (ML), adaptively analyze data regarding online consumers’ needs to obtain more accurate data.
Since the concept of big data was proposed in 2008, it has been applied and developed lasting 14 years, emerging as a valuable tool for global e-commerce recently. However, most enterprises have failed to seize the benefits generated from big data. In the context of big data, a huge number of comments were posted regarding e-malls (Amazon, Taobao, etc.) and online social media (blogs, Bulletin Board System, etc.). For instance, Amazon was the first e-commerce company to establish an e-WOM system in 1995, which provided the company with valuable suggestions from online consumers. E-WOM has greater credibility and persuasiveness, compared with traditional word of mouth (WOM), which is limited by various subjective factors. Moreover, e-WOM has the advantage of containing not only structured data (e.g., ratings) but also unstructured data (e.g., the specific content of consumer reviews). However, e-WOM provides product-related information that cannot be directly transformed to a research objective. Thus, an innovative method of big data analytics needs to be utilized to explore the influencing factors of OCPB, which shows the advantage of interdisciplinary applications.
The research problems are to explore the factors influencing OCPB through e-WOM data mining and analysis and explain the most important influencing factors for online consumers that are likely to exist in the future within the context of the COVID-19. The study fulfills the literature gaps on exploring influencing factors of OCPB from the perspective of e-WOM. The study makes a significant contribution to the consumer study because its findings can adequately identify the influencing factors of OCPB. It also provides the theoretical and managerial implications of its findings including how e-commerce platforms can use such data to adapt their platforms and marketing strategies to diverse situations.
The remainder of this is organized as follows. Section 1 presents the introduction. Section 2 discusses the literature review and hypotheses. Section 3 provides the methodology, including data mining and analysis. Section 4 describes the results, including K-means results, performance metrics, hypotheses results, and a theoretical model. Sections 5 and 6 provide discussion and conclusion, respectively.
2. Literature review and hypotheses
2.1 influencing factors of ocpb.
Online shopping has an increasing sales volume each year, which has become huge challenges for offline retailers. Venkatesh et al. [ 4 ] found that culture, demographics, economics, technology, and personal psychology were the main antecedents of online shopping, and the main drivers of online shopping were congruence, impulse buying behavior, value consciousness, risk, local shopping, shopping enjoyment, and browsing enjoyment by a comprehensive model of consumers online purchasing behavior. Within the context of COVID-19, OCPB is positively impacted by attitude toward online shopping [ 5 ]. Melović et al. [ 6 ] focused on millennials’ online shopping behavior and noted that the demographic characteristics, the affirmative characteristics, risks and barriers of online shopping were the key influencing factors. Based on the stimulus-organism-response (SOR) theory model, consumers’ actual impulsive shopping behavior is impacted by arousal and pleasure [ 7 ]. Furthermore, the influencing factors of consumers’ purchase behavior toward green brands are green perceived quality, green perceived value, green perceived risk, information costs saved, and purchase intentions by perceived risk theory [ 8 ]. The positive and negative effects of corporate social responsibility practices on consumers’ pro-social behavior are moderated by consumer-brand social distance, although it also impacts consumer behavior beyond the consumer-brand dyadic relationship [ 9 ]. Green perceived value, functional value, conditional value, social value, and emotional value may impact green energy consumers’ purchase behavior [ 10 ]. Recipients’ behavior and WOM predict distant consumers’ behavior [ 11 ]. Moreover, consumer behavior is significantly impacted by financial rewards, perceived intrusiveness, attitudes toward e-mail advertising, and intentions toward the senders [ 12 ]. Store brand consumer purchase behavior is positively impacted by store image perceptions, store brand price-image, value consciousness, and store brand attitude [ 13 ]. A meta-analysis summarizes the influencing factors of consumer behavior, household size, store brands, store loyalty, innovativeness, familiarity with store brands, brand loyalty to national brands, price consciousness, value consciousness, perceived quality of store brands, perceived value for money of store brands, and search versus experience positively impact consumer behavior, whereas price–quality consciousness, quality consciousness, price of store brands, and the consequences of making a mistake in a purchase negatively impact consumer behavior [ 14 ].
Based on protection motivation theory and theory of planned behavior (TPB), consumers are more likely to use online shopping channels than offline channels during the COVID-19 pandemic [ 15 ]. The TPB is also adapted to explain the influencing factors of consumers’ behavior in different areas. For instance, the attitude, perceived behavioral control, policy information campaigns, and past-purchase experiences significantly impact consumers’ purchase intention, whereas subjective and moral norms show no significant relationship based on the extended TPB [ 16 ]. Although green purchase behavior has different antecedents, only personal norms and value for money have fully significant relationships with green purchase behavior, environmental concern, materialism, creativity, and green practices. Functional value positively influences purchase satisfaction, physical unavailability, materialism, creativity, and green practices, and negatively influences the frequency of green product purchase by extending the TPB [ 17 ]. Meanwhile, Nimri et al. [ 18 ] utilized the TPB in green hotels and showed that knowledge and attitudes, as well as subjective injunctive norms, positively impacted consumers’ purchase intention. Yi [ 19 ] observed that attitude, social norm, and perceived behavioral control positively impacted consumers’ purchase intention based on the TPB. The factors of supportive behaviors for environmental organizations, subjective norms, consumer attitude toward sustainable purchasing, perceived marketplace influence, consumers’ knowledge regarding sustainability-related issues, and environmental concern are the influencing factors of consumers sustainable purchase behavior [ 20 ]. Consumers’ green purchase behavior is impacted by the intention through support of the TPB [ 21 ].
2.2 Influencing factors of emergency context attribute
Consumers exhibited panic purchase behavior during the COVID-19, which might have been caused by psychological factors such as uncertainty, perceptions of severity, perceptions of scarcity, and anxiety [ 22 ]. In the reacting phase, consumers responded to the perceived unexpected threat of the COVID-19 and intended to regain control of lost freedoms; in the coping phase, they addressed this issue by adopting new behaviors and exerting control in other areas, and in the adapting phase, they became less reactive and accommodated their consumption habits to the new normal [ 23 ]. The positive and negative e-WOMs may have significant influence on online consumers’ psychology. Specifically, e-WOM that conveys positive emotions (pride, surprise) tends to have a greater impact on male readers’ perception of the reviewer’s cognitive effort than female readers, whereas e-WOM that conveys negative emotions (anger, fear) has a greater impact on cognitive effort of female readers than male readers [ 24 ]. When online consumers believe their behavioral effect is feasible and positive, while their behavioral decision is related to the behavioral outcome [ 25 ]. Traditionally, there are five stages of consumer behavior that include demand identification, information search, evaluation of selection, purchase, and post-purchase evaluation. In addition, online purchase behavior involved in the various stages can be categorized into: attitude formation, intention, adoption, and continuation. Most of the important factors that influence online purchasing behavior are attitude, motivation, trust, risk, demographics, website, etc. “Internet Adoption” is widely used as a basic framework for studying “online buying adoption”. Psychological and economic structures associated with the IT adoption model can be used as the online consumer’s behavior models for innovative marketers. The adoption of online purchasing behavior is explained by different classic models of attitude behavior [ 26 ]. Consumer behaviors represented by customer trust and customer satisfaction, influence repurchase and positive WOM intentions [ 27 ]. Return policy leniency, cash on delivery, and social commerce constructs were significant facilitators of customer trust [ 28 ]. Meanwhile, seller uncertainty was negatively influenced by return policy leniency, information quality, number of positive comments, seller reputation, and seller popularity [ 29 ]. Social commerce components were a necessity in complementing the quality dimensions of e-service in the environment of e-commerce [ 30 ]. Perceived security, perceived privacy and perceived information quality were all significant facilitators of online customer trust and satisfaction [ 31 ].
E-service quality, consumer social responsibility, green trust and green perceived value have a significant positive impact on green purchase intention, whereas greenwashing has a significant negative impact on green purchase intention. In addition, consumer social responsibility, green WOM, green trust and green perceived value positively moderated the relationship between e-service quality and green purchase intention, while greenwashing and green participation negatively moderated the relationships [ 32 ]. Large-scale online promotions provide mobile users with a new shopping environment in which contextual variables simultaneously influence consumer behavior. There is ample evidence suggesting that mobile phone users are more impulsive during large-scale online promotion campaigns, which are the important contextual drivers that lead to the occurrence of mobile users’ impulse buying behavior in the “Double 11” promotion. The results show that promotion, impulse buying tendency, social environment, aesthetics, and interactivity of mobile platforms, and available time are the key influencing factors of impulse buying by mobile users [ 33 ]. Environmental responsibility, spirituality, and perceived consumer effectiveness are the key psychological influencing factors of consumers’ sustainable purchase decisions, whereas commercial campaigns encourage young consumers to make sustainable purchases [ 34 ]. The main psychological factors affecting consumers’ green housing purchase intention include the attitude, perceived moral obligation, perceived environmental concern, perceived value, perceived self-identity, and financial risk. Subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, performance risk, and psychological risk are not included. Meanwhile, the purchase intention is an important predictor of consumers’ willingness to buy [ 35 ]. The perceived control of flow and focus will positively affect the utilitarian value of consumers, while focus and cognitive enjoyment will positively impact the hedonic value. Moreover, utilitarian value has a greater impact on satisfaction than hedonic value. Finally, hedonic value positively impacts unplanned purchasing behavior [ 36 ]. Utilitarian and hedonic features achieve high purchase and WOM intentions through social media platforms and also depend on gender and consumption history [ 37 ].
Therefore, we present the following hypothesis:
- Hypothesis 1 (H1): Perceived emergency context attribute is the influencing factor of OCPB.
2.3 Influencing factors of perceived product attribute
Product quality and preferential prices are the major factors considered by online consumers, especially within the context of the COVID-19. Specifically, online shopping offers lower price, more choices for better quality products, and comparison between them [ 1 ]. Under the circumstance of online reviews, an original equipment manufacturer (OEM) selling a new product carefully decides whether to adopt the first phase remanufacturing entry strategy or to adopt the phase 2 remanufacturing entry strategy under certain conditions. Meanwhile, the OEM adopts penetration pricing for new and remanufactured products, when the actual quality of the product is high. Otherwise, it adopts a skimming pricing strategy, which is different from uniform pricing when there are no online reviews. Online reviews significantly impact OEM’s product profits and consumer surplus. Especially when the actual quality of the product is high enough, the OEM and the consumer will be also reciprocal [ 38 ]. Online reviews reduce consumers’ product uncertainty and improve the effect of consumer purchase decisions [ 39 , 40 ]. Uzir et al. [ 41 ] utilized the expectancy disconfirmation theory to prove that product quality positively impacts customer satisfaction, while product quality and customer satisfaction are mediated by customer’s perceived value. Product quality and customer’s perceived value will have greater influence with higher frequency of social media use. Nguyen et al. [ 42 ] studies consumer behavior from a cognitive perspective, and theoretically develops and tests two key moderators that influence the relationship between green consumption intention and behavior, namely the availability of green products and perceived consumer effectiveness.
Both sustainability-related and product-related texts positively influence consumer behavior on social media [ 43 ]. Online environment, price, and quality of the products are significantly impacted by OCPB. Godey et al. [ 44 ] explained the connections between social media marketing efforts and brand preference, price premium, and loyalty. Brand love positively impacts brand loyalty, and both positively impact WOM and purchase intention [ 45 ]. Brand names have a systematic influence on consumer’s product choice, which is moderated by consumer’s cognitive needs, availability of product attribute information, and classification of brand names. In the same choice set, the share of product choices with a higher brand name will increase and be preferred even if it is objectively inferior to other choices. Consumers with low cognitive needs use the heuristic of “higher is better” to select options labeled with brand names and choose brands with higher numerical proportions [ 46 ].
- Hypothesis 2 (H2): Perceived product attribute is the influencing factor of OCPB.
2.4 Influencing factors of perceived innovation attribute
Product innovation increases company’s competitive advantage by attracting consumers, whereas the enhancement of innovative design according to consumer behavior accelerates the development of sustainable product [ 47 , 48 ]. The innovation, WOM intentions and product evaluation can be improved positively by emotional brand attachment and decreased by perceived risk [ 49 ]. Based on the perspective of evolutionary, certain consumer characteristics, such as buyer sophistication, creativity, global identity, and local identity, influence firms’ product innovation performance, which can increase the success rate of product innovation, and enhance firms’ research and development performance [ 50 ]. However, technological innovation faces greater risk as it depends on market acceptance [ 51 ]. Moreover, electronic products rely more on technological innovation compared with other products, which maintain the profit and market [ 52 ]. The technological innovation needs to apply logical plans and profitable marketing strategies to reduce consumer resistance to innovation. Thus, Sun [ 53 ] explains the relationship between consumer resistance to innovation and customer churn based on configurational perspective, whereas the results show that response and functioning effect are significant but cognitive evaluation is not.
Based on the perspective of incremental product innovation, aesthetic and functional dimensions positively impact perceived quality, purchase intention, and WOM, whereas symbolic dimension only positively impacts purchase intention and WOM. By contrast, aesthetic and functional dimensions only positively impact perceived quality, whereas symbolic dimension positively impacts purchase intention and WOM. Furthermore, perceived quality partially mediates the relationship between aesthetic and functional dimensions and purchase intention and WOM by incremental product innovation, whereas perceived quality fully mediates the relationship between aesthetic and functional dimensions and purchase intention and WOM by radical product innovation [ 54 ]. Contextual factors, such as size of organizations and engagement in research and development activity, moderate the relationship between design and product innovation outcomes [ 55 ]. For radical innovations, low level of product innovation leads to more positive reviews and less inference of learning costs. As the functional attribute of radical innovations is not consistent with existing products, it is difficult for consumers to access relevant product category patterns and thus transfer knowledge to new products. The product innovation of aesthetics, functionality, and symbolism positively impact willingness to pay, purchase intention, and WOM through brand attitude [ 56 ]. This poor knowledge transfer results in consumers feeling incapable of effectively utilizing radical innovations, resulting in greater learning costs. In this case, product designs with low design novelty can provide a frame of reference for consumers to understand radical innovations. However, incremental product innovation shows no significant difference between a low and high level of design newness [ 57 ].
- Hypothesis 3 (H3): Perceived innovation attribute is the influencing factor of OCPB.
2.5 Influencing factors of perceived motivation attribute
The research has proven that almost all consumers’ purchases are motivated by emotion. Under this circumstance, an increase in online consumers’ positive emotions increases, their purchase frequency, whereas an increase in online consumers’ negative emotions reduces their purchase frequency. Additionally, user interface quality, product information quality, service information quality, site awareness, safety perception, information satisfaction, relationship benefits and related benefit factors have negative impacts on consumers’ online shopping emotionally. Nevertheless, only product information quality, user interface quality, and safety perception factors have positive effects on online consumer sentiment [ 58 ]. E-WOM carries emotional expressions, which can help consumers express the emotions timely. Pappas et al. [ 59 ] divides consumers’ motivation into four factors, namely entertainment, information, social-psychological, and convenience, while emotions into two factors, namely positive and negative. Specifically, according to complexity and configuration theories, a conceptual model by a fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis examines the relationship between a combination of motivations, emotions, and satisfaction, while results indicate that both positive and negative emotions can lead to high satisfaction when combing motivations.
From the perspective of SOR theory, consumers’ motivation is greatly influenced by self-consciousness, while conscious cognition plays the role of intermediary. First, after being stimulated by the external environment, online consumers will form “cognitive structure” depending on their subjectivity. Instead of taking direct action, they deliberately and actively obtain valid information from the stimulus process, considering whether to choose the product, and then react. Second, the stimulation stage in the retail environment can often attract the attention of consumers and cause the change of their psychological feelings. This stimulation is usually through external environmental factors, including marketing strategies and other objective influences. Third, organism stage is the internal process of an individual. It is a consumers’ cognitive process about themselves, their money, and risks after receiving the information they have seen or heard. Reaction includes psychological response and behavioral response, which is the decision made by the consumer after processing the information [ 60 ]. Based on literature review, 10 utilitarian motivation factors, such as desire for control, autonomy, convenience, assortment, economy, availability of information, adaptability/customization, payment services, absence of social interaction, and anonymity and 11 hedonic motivation factors, such as visual appeal, sensation seeking/entertainment, exploration/curiosity, escape, intrinsic enjoyment, relaxation, pass time, socialize, self-expression, role shopping, and enduring involvement with a product or service, are refined [ 61 ]. Consumers’ incidental moods can improve online shopping decisions impulsivity, while decision making process can be divided into orientation and evaluation [ 62 ]. Sarabia‐Sanchez et al. [ 63 ] combine K-means cluster and ANOVA analyses to explore the 11 motivational types of consumer values, which are achievement, tradition, inner space, universalism, hedonism, ecology, self-direction (reinforcement, creativity, harmony, and independence), and conformity.
- Hypothesis 4 (H4): Perceived motivation attribute is the influencing factor of OCPB.
3. Materials and methods
3.1 research design.
Given the present study’s objective to identify the influencing factors of OCPB, we analyzed e-WOM using big data analysis. To obtain accurate data of the influencing factors on OCPB, smartphones were the main object of data crawling. The rationale behind this choice is as follows. First, the time people spend using their smartphones is gradually increasing. Nowadays, smart phones are not only used for telephone calls or text messages, but also for taking photographs, recording video, surfing the web, online chatting, online shopping, and other such uses [ 64 ]. Second, smartphones have become a symbol of personal identification, as users’ using fingerprint or facial scans are frequently used to unlock devices, conduct online transactions, and make reservations, etc. Finally, smartphones’ software and hardware are updated frequently, so they may be considered high-tech products. Therefore, smartphones were chosen as the research object to determine which influencing factors affect OCPB.
Fig 1 shows the e-WOM data mining process and methods used. A dataset obtained from Taobao.com and Jingdong.com was collected by utilizing a Python crawling code, additional details of which are provided in Section 2.3. Section 2.4 addresses issues regarding language complexity. Moreover, Section 2.5 refers to the clustering of the influencing factors of OCPB through the K-means method of ML.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034.g001
3.2 Data collection
The data were crawled from the e-commerce platforms Jingdong.com and Taobao.com by utilizing Python software. Jingdong and Taobao are the most powerful and popular platforms in China having professional e-WOM and user-friendly review systems. Specifically, the smartphone brands selected for analysis were Apple, Samsung, and Huawei because these three smartphone companies occupy the largest percentage of the smartphone market.
The authors determined that the analysis of the influencing factors of OCPB would be more persuasive and realistic by choosing smartphone models with high usage rate and liquidity. Thus, products reviews were crawled for the purchase of newly launched smartphones from Apple, Samsung, and Huawei in 2022. Specifically, to guarantee high-quality data, reviews from Taobao flagship stores and Jingdong directly operated stores were selected. However, we only collected reviews’ text content instead of images, videos, ratings, or rankings, the rationale was to ensure the reliability of data and meet research objectives. For instance, some e-commerce sellers attempt to increase their sales volume through deceitful methods, such as by faking ratings, rankings, and positive comments. Furthermore, online sellers and e-commerce companies (rather than consumers) often decide which smartphones are highest-rated and highest-selling. Finally, nowadays, the content of online reviews is not limited to text, as they also involve pictures, videos, and ratings, which have limited contribution in analyzing influencing factors of OCPB. Thus, the analyzed data regarding e-WOM in reviews was limited to text content.
In addition, to accurately reflect the real characteristics of OCPB during the COVID-19 pandemic, the study period ranged between February and May, 2022 (4 months). During that 4-month period, consumers exhibited a preference for buying products from e-commerce platforms. Specifically, the number of text reviews for the aforementioned types of smartphones was 51,2613 and 44,3678 in Taobao and Jingdong, respectively, for a total of 956,291 reviews.
3.3 Textual review processing method
As the crawled data exhibited noise, several data cleaning methods were adopted to filter noise and transform unstructured data of complex contextual review into structured data. Fig 1 shows the main procedures of the reviews’ pre-processing and the details are as follows.
First, to identify the range of sentences and for further data processing, sentences were apportioned using Python’s tokenizer package.
Second, this study employed Python’s Jieba package to perform word segmentation. The Jieba package is the Python’s best Chinese word segmentation module, comprising three modes. The exact mode was used to segment the sentences as accurately as possible, so they may be suitable for textual context analysis. The full mode was used to scan and process all words in each sentence, although it had a relatively high speed, it had a low capacity to resolve ambiguity. Additionally, the search engine mode segmented long words a second time, which allowed for the improvement of the recall rate, and was suitable for engine segmentation based on Jieba’s exact mode.
Third, stop words were deleted by referring to a stop words list. These included conjunctions, interjections, determiners, and meaningless words, among others. Finally, Python’s Word-to-vector (Word2vec) package was imported in the next step. Word2vec is an efficient training word vector model proposed by Mikolov [ 65 , 66 ]. The basic starting point was to match pairs of similar words. For instance, when “like” and “satisfy” appeared in a same context, they showed a similar vector, as both words had a similar meaning. Kim et al. [ 67 ] stated that a word could be considered a single vector and real numbers in the Word2vec model. In fact, most supervised ML models could be summarized as f ( x )−> y . Moreover, x could be considered a word in a sentence, while y could be considered this word in the context. Word2vec aimed to decide whether the sample of ( x , y ) could match the laws of natural language. Namely, after the process of Word2vec, the combination of word x and word y could be reasonable and logical or not. Table 1 shows the results of text processing.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034.t001
3.4 Influencing factors analysis by K-means
ML styles are divided into supervised and unsupervised algorithms. This study mainly utilized unsupervised algorithms to analyze the clusters of influencing factors of OCPB. Unsupervised algorithms consist in the clustering of unknown or unmarked objects without a trained sample [ 68 ]. This study utilized K-means to cluster the influencing factors.
For a given sample set, the K-means algorithm divides the sample set into k clusters according to the distance between samples. The main algorithm’s logic is to make the points in the cluster as close as possible, and to make the distance between the clusters as large as possible. Assuming that clusters can be divided into ( C 1 , C 2 ,…, C k ), the Euclidean distance of E is shown in Eq 1 .
The main procedures of K-means were the following.
Step 1 consisted of inputting the samples D = { x 1 , x 2 ,… x m }, K is the number of clusters, and appears as C = { C 1 , C 2 ,… C k }.
In Step 2, K samples were randomly selected from data set D as the initial K centroid vectors: { μ 1 , μ 2 ,… μ k }.
For Step5, it was necessary to repeat Steps 3 and 4, until all the centers μ remained steady. The final clustering result can be shown as C = { C 1 , C 2 ,… C k }.
The main procedures of K-means, according to Jain [ 69 ], are shown in Table 2 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034.t002
4.1 K-means results
Based on the main procedures of K-means ( Table 2 ), the results are presented in Figs 2 – 4 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034.g002
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034.g003
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034.g004
Four clusters of influencing factors of OCPB can be clearly identified in the analyses of the Jingdong dataset, Taobao dataset, and combined Jingdong and Taobao dataset. After checking the context of four clusters, even though small differences were found, their influence was found to be negligible for our analyses. Thus, Fig 4 was chosen as the benchmark of influencing factors of OCPB. In Section 4.3, the explanation and analysis of influencing factors of OCPB will be presented.
4.2 Performance metrics
First, performance metrics of sum of the square errors (SSE) and silhouette coefficient were adapted to verify the clustering results of K-means.
When the number of clusters does not reach the optimal numbers K, SSE decreases rapidly with the increase of the number of clusters, while SSE decreases slowly after reaching the optimal numbers, and the maximum slope is the optimal numbers K.
Where C i is the i th cluster, p is the sample point in C i (the mean value of all samples in C i ), and SSE is the clustering error of all samples, which represents the quality of clustering effect.
Fig 5 indicates that the SSE decreases rapidly when K equals the number of four.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034.g005
The range of sc i is between -1 and 1, the clustering effect is bad when sc i is below zero, whereas the clustering effect is good when sc i is near 1 conversely.
Based on Fig 6 , it is obviously to show that the silhouette coefficient reaches highest when K equals the number of four. Therefore, the results of the SSE and the silhouette coefficient jointly prove the number of K is four.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034.g006
4.3 Hypotheses results
Based on the K-means analysis, this section presents the influencing factors identified in the data from Jingdong and Taobao, which indicate the influencing factors influencing OCPB.
The first cluster comprises the perceived emergency context attribute, such as logistics, expressage, delivery, customer service, promotion, and reputation.
The second cluster comprises the perceived product attribute, such as appearance, brand, hand feeling, color, cost-performance ratio, price, design, and usability.
The third cluster comprises the perceived innovation attribute, such as photograph, quality and effects, screen quality, audio and video quality, pixel density, image resolution, earphone capabilities, and camera specifications.
The fourth cluster comprises the influencing factors, such as processing speed, operation, standby time, battery, system, internal storage, chip, performance, and fingerprint and face recognition, which cannot represent the perceived motivation attribute.
The results match the findings of Zhang et al. [ 70 ] to some extent, who identified 11 smartphone attributes based on online reviews: performance, appearance, battery, system, screen, user experience, photograph, price, quality, audio and video, and after-sale service. In addition, other scholars have explained the relationship between feature preferences and customer satisfaction [ 71 , 72 ], usage behavior and purchase [ 73 , 74 ], importance and costs of smartphones’ features and services [ 75 ], brand effects [ 76 ], and purchase behavior of people of different ages and gender groups [ 77 – 79 ]. Thus, H1, H2 and H3 are supported, while H4 is not supported according to the results of the K-means analysis.
4.4 Theoretical framework and validity of OCPB influencing factors
Kotler’s five product level model states that consumers have five levels of need comprising the core level, generic level, expected level, augmented level, and potential level. First, the core benefit is the fundamental need or want that consumers satisfy by consuming a product or service. Second, the generic level is a basic version of a product made up of only those features necessary for it to function. Third, the expected level includes additional features that the consumer might expect. Fourth, the augmented level refers to any product variations or extra features that might help differentiate a product from its competitors and make the brand a preferred choice amongst its competitors. Finally, a potential product includes all augmentations and improvements that a product might experience in the future [ 80 ].
In contrast with these levels, this study proposed the four influencing factors of OCPB. Based on Table 3 , first, the perceived emergency context H1 is not included in Kotler’s five products level, while the influencing factor expresses the significant characteristics of OCPB compared with Kotler’s model. Second, the perceived product attribute H2 could be considered the core and generic level. Third, the perceived innovation attribute H3 could be considered the potential level. Fourth, the results of H4 mainly reflects additional or special function of product, which meets the definition of the expected and augmented level. To refine the theoretical framework, H4 changes to the perceived functionality attribute by combing the explanation of the expected and augmented level, instead of the perceived motivation attribute. The details are shown in Fig 7 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034.g007
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034.t003
Fig 7 shows the four influencing factors of the theoretical framework of OCPB. Specifically, according to Kotler’s five products level, the perceived product attribute is the necessary influencing factor of OCPB, which meets the core drive and basic requirement. For instance, the core drive of purchasing of a smartphone is the core function of communication, and then the appearance, brand, color, etc. The perceived functionality attribute is the additional influencing factor of OCPB, which meets the expected and augmented requirement. For instance, when smartphones are in the same price range, consumers prefer to choose a smartphone belonging to better quality, smarter design, or better functionality. Moreover, the perceived innovation attribute is the attractive influencing factor of OCPB, which reflects the potential level. For instance, most consumers are the Apple fans mostly because the Apple products offer innovative usage experience and different technology elements yearly. Finally, the perceived emergency context attribute is the adaptive influencing factor of OCPB, which shows the main distinction with Kotler’s five products level. Further, because of the COVID-19, consumers only have online channel to purchase product under a prolonged quarantine and lockdown. Thus, in the emergency context, consumers primarily consider whether the product can be purchased in the e-commerce platform, whether the product can be delivered normally, or whether the packaged has been disinfected fully.
5. Discussion
Traditional consumer behavior is mainly affected by psychological, social, cultural, economic, and personal factors [ 81 , 82 ]. Park and Kim [ 83 ] conducted an empirical study to identify the key influencing factors that impact OCPB, which include service information quality, user interface quality, security perception, information satisfaction, and relational benefit. Further, Sata [ 84 ] conducted an empirical study and found that price, social group, product features, brand name, durability and after-sales services were important to consumers’ buying behavior when choosing a smartphone for purchase. Simultaneously, some studies have utilized big data technology to explore OCPB, exploring online consumers’ attitude toward products in different countries, and identified product features. However, these studies do not identify the influencing factors of OCPB and ignore e-WOM. To better explain OCPB influencing factors, e-WOM should be integrated into the theoretical framework and used in practical applications. Thus, this study contributes to OCPB research by data mining and analysis that can adequately identify the influencing factors based on e-WOM.
5.1 Theoretical implications
First, perceived emergency context attribute is the influencing factor of OCPB. Because of the COVID-19, e-commerce is the priority choice for consumers under circumstances of prolonged quarantine and lockdown, and then considering logistics and delivery. Furthermore, customer service, packaging, promotion, and reputation are critical to online consumers.
Second, perceived product attribute is the influencing factors of OCPB. The basic features of product, such as appearance, brand, hand feeling, price, and design, positively attract online consumers. Elegant appearance, famous brand, better hand feeling, lower price, and better design would be more impactful to OCPB.
Third, perceived innovation attribute is the influencing factor of OCPB. For smartphone, online consumers would show more interest in the innovation of speed, operation, standby time, chip, etc. Scientific and technological innovation for most products could improve the level of OCPB. Thus, the guarantee and improvement of functionality of a product could create more opportunities for online consumers to make purchasing decisions.
Fourth, according to Kotler’s five products level, perceived product attribute satisfies the characteristics of core drive and basic, while the perceived innovation attribute satisfies the characteristics of the potential level. Because hypothesis of perceived motivation attribute is not supported. Based on the analyzing results, the perceived functionality attribute is refined instead of the perceived motivation functionality attribute, which satisfies the expected and augmented. Meanwhile, the perceived emergency context attribute is not included, which shows the main difference with Kotler’s five products level.
5.2 Managerial implications
The influencing factors of OCPB were clustered into four categories: perceived emergency context, product, innovation, and function attributes. The definition and explanation of these categories may have important managerial implications for both OCPB and e-commerce. First, the findings of this study suggest that e-commerce enterprises should pay more attention to improving the quality, user experience, and additional design features of their products to arouse the interest of OCPB. However, this may be difficult for e-commerce enterprises because achieving these goals requires updating the software and hardware constantly, which involves significant investment. For most scientific and technical corporations, making heavy investments is not particularly difficult, however, service-type enterprises and small and medium enterprises may have insufficient funds to afford such heavy investments. This is the main reason that most online consumers buy products from famous brands instead of small and medium enterprises. Therefore, to improve their situation, both types of companies could jointly develop products or services, for instance, small and medium enterprises may purchase patents from large enterprises, jointly researching and developing products, or large enterprises could share their achievements at a price.
Second, the pandemic has accelerated the spread of e-commerce considerably, changing consumers’ shopping style in the process. Accordingly, e-commerce enterprises should adapt their marketing strategies, especially as the COVID-19 pandemic is still ongoing, due to the rapid development of the economy and its dynamic environment. For instance, e-commerce platforms should realize that changes in OCPB will continue to contribute to the growth of the e-commerce market. Moreover, e-commerce enterprises should combine their online presence with brick-and-mortar stores. Even more importantly, e-commerce enterprises should successfully operate their supply chain to adapt to the implementation of lockdown measures and the closing of manufacturing factories. Consumers should exercise caution when facing e-commerce enterprises’ adaptive financial policy, such as interest-free rates, which may cause financial burden.
Third, e-commerce enterprises should offer a simple and smooth shopping experience, clearly display practical information, increase the value of goods (by improving the quality, design, and performance of products or services) and improve their brand image for online consumers. However, e-commerce enterprises sometimes rely on certain fraudulent methods to increase their sales volume, such as falsifying positive e-WOM and deleting negative feedback, as was identified during the data processing stage. Therefore, online consumers should select online stores cautiously to avoid buying products of poor quality or performance.
Fourth, nowadays, technology is constantly evolving at an accelerated rate, particularly in the smartphone industry, as companies launch new products with innovative functions each year. Thus, e-commerce enterprises should strive to innovate to secure their position in the market. In addition, consumers should reconsider the need to experience the state-of-the-art products because these may have high prices.
6. Conclusion and limitations
In conclusion, during the COVID-19 pandemic, consumers highly preferred to buy products online, because most brick-and-mortar stores were closed due to lockdowns and social distancing measures. Additionally, with the rapid development of e-commerce, online shopping has become the most popular shopping style because it allows consumers to not only save time and money, but also review e-WOM before purchasing a product. Moreover, e-WOM is much more reliable compared with traditional WOM. Thus, this study proposed a theoretical framework to explore and define the influencing factors of OCPB based on e-WOM data mining and analyzing. The data were crawled from Jingdong and Taobao, while the data process was also fully demonstrated. Comparing the results, the influencing factors of OCPB were clustered around four categories: perceived emergency context, product, innovation, and function attributes. Moreover, perceived emergency context attribute is the main difference compared with Kotler’s five products level, while perceived product attribute meets the core and generic level, perceived functionality attribute meets the expected and augmented level, and perceived innovation attribute meets the potential level.
However, this study still has certain limitations. First, the data were crawled from Chinese e-commerce websites, hence, they may not be generalized in contexts where the influencing factors and dimensions may vary compared with other countries or regions. Second, this study only explored and defined the antecedents of OCPB. Data should be added from Western e-commerce websites. Moreover, the present study’s results should be compared with Western studies to generate a more comprehensive view of the antecedents of OCPB. Future studies should explore the underlying mechanisms influencing OCPB.
Supporting information
S1 dataset..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286034.s001
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- PubMed/NCBI
- 25. Krishna A, Strack F. Reflection and impulse as determinants of human behavior. Knowledge and Action,Springer, Cham; 2017. p. 145–67.
- 37. Mikalef P, Pappas IO, Giannakos M. Consumer intentions on social media: a fsQCA analysis of motivations. Conference on e-Business, e-Services and e-Society: Springer, Cham; 2016. p. 371–86.
- 58. Cinar D. The effect of consumer emotions on online purchasing behavior. Tools and Techniques for Implementing International E-Trading Tactics for Competitive Advantage. USA: IGI Global; 2020. p. 221–41.
- 61. Martínez-López F. J. P-G, C., Gázquez-Abad JC, Rodríguez-Ardura I. Online consumption motivations: an integrated theoretical delimitation and refinement based on qualitative analyses. Strategic e-Business Management. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2014. p. 347–70.
- 80. Kotler P. Principles of marketing. Boston: Pearson; 2016.
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, online shopping: a systematic review of customers’ perceived benefits and challenges during covid-19 pandemic.
Global Knowledge, Memory and Communication
ISSN : 2514-9342
Article publication date: 30 November 2023
The COVID-19 outbreak has disrupted the habits of customers as well as their shopping behavior. This study aims to critically examine the associated benefits and challenges of online shopping from the perspective of customers in the COVID-19 pandemic.
Design/methodology/approach
A systematic review of the relevant literature published between 2020 and 2022 was conducted via performing comprehensive search query in leading scholarly databases “Scopus and Web of Science” with the restriction of their predefined subject category of “Business.” Overall, 30 research studies were selected for the review and a significant number of studies were published in 2021 ( n = 15).
The research findings revealed that customers are motivated to shop online because of perceived benefits such as time-saving, convenience, 24/7 accessibility, interactive services without physical boundaries, trust, website attractiveness and cost-saving. However, challenging factors such as financial scams, privacy concerns, poor quality of products and services, fake promotions and reduced social interaction have hindered the growth of online shopping. The recommendations regarding designing marketing strategies, secured transaction, multiple payment options, trust building, protection of privacy, promotion via social media, effective mechanism to secure and timely delivery of product are helpful to improve the service quality of online shopping.
Originality/value
The outcomes of this research are valuable to online retailers and policymakers, as it highlights how the benefits can enhance customers’ shopping intentions and minimize the impact of associated challenges. This study also recommends the redesigning of user-friendly interfaces of online shopping websites and ensures their privacy, security and performance on a regular basis.
- Online shopping
- Online retailers
- Systematic review
Acknowledgements
Since submission of this article, the following author has updated their affiliations: Sadaf Rafiq is at the School of Information Management, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China.
Waqas, M. , Rafiq, S. and Wu, J. (2023), "Online shopping: a systematic review of customers’ perceived benefits and challenges during COVID-19 pandemic", Global Knowledge, Memory and Communication , Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/GKMC-04-2023-0129
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2023, Emerald Publishing Limited
Related articles
All feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Online consumer satisfaction during covid-19: perspective of a developing country.

- 1 Antai College of Economics & Management, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
- 2 School of Management, Zhejiang Shuren University, Hangzhou, China
- 3 Faculty of Management Sciences, Riphah International University, Faisalabad Campus, Punjab, Pakistan
- 4 Department of Professional Psychology, Bahria University, Islamabad, Pakistan
A conceptual model based on the antecedents and consequences of online consumer satisfaction has been proposed and empirically proved in this study. Data were collected during Smart Lockdown of COVID-19 from 800 respondents to observe the difference between perceived and actual, and direct and indirect e-stores. Confirmatory factor analysis was used to observe the validity of the data set. The structural equation modeling technique was used to test the hypotheses. The findings indicated that consumers feel more satisfied when they shop through direct e-store than indirect e-store, whereas their perception and actual experience are different. Implications have also been added to the study.
Introduction
Online shopping is the act of buying a product or service through any e-stores with the help of any website or app. Tarhini et al. (2021) stated that shopping through online channels is actively progressing due to the opportunity to save time and effort. Furthermore, online shopping varies from direct e-store and indirect e-store about their perception against the actual experience. Developing countries still face various conflicts and issues while promoting and utilizing e-commerce to the maximum compared with the developed countries ( Rossolov et al., 2021 ). In the developing countries, the difference between the perception and actual experience of the consumers varies when buying from indirect e-store compared to the direct e-store. On the contrary, as the world has been suffering from the COVID-19 pandemic, it has brought drastic changes globally in many sectors, business being one of them. De Vos (2020) stated that a large-scale lockdown was imposed worldwide to prevent the virus from spreading.
To survive, switching traditional shopping or trade toward digital was one factor that captured the attention across the globe on a larger scale. In April 2020, Walmart reported a 74% increase in online sales even though they faced a low customer walk-in at stores ( Nassauer, 2020 ; Redman, 2020 ). This upsurge of swift adoption of online channels has led this research to ask a few questions. First, what will be the difference between the perceived and the actual product purchased online? A recent study has documented that consumers bear actual risk after shopping through online channels ( Yang et al., 2020 ). Research reported that 30% of the products through online channels get returned and are not according to their perception ( Saleh, 2016 ). The same author also showed that the return and complaint rates are getting higher when consumers shop through an online channel.
Second, is there any difference between the perceived and the actual product purchase online from a direct e-store or an indirect e-store? Direct e-store means the online brand store, for example, Walmart, and indirect e-store means third-party stores such as Amazon, Alibaba, Jingdong (JD), and Daraz. The direct e-store strives hard to maintain a clear, potent perception in the mind of its buyer ( Grewal et al., 2009 ). Kumar and Kim (2014) stated that a brand strengthening its relationship with its consumer satisfies its needs through the actual product or services. In the literature ( Olotewo, 2017 ; Rossolov et al., 2021 ), it is stated that the shopping patterns of buyers from direct and indirect e-stores vary greatly, especially in the developing countries. In this way, when shopping through a direct e-store, consumers may easily recognize the difference in buying from a direct and indirect e-stores ( Mendez et al., 2008 ).
Third, a conceptual framework from a consumer perspective, antecedents and consequences of customer satisfaction, has been proposed and empirically proved. The literature ( Alharthey, 2020 ) discussed different risk types in online shopping. Three main types of risk, perceived uncertainty, perceived risk, and price, are addressed in this model. To the best of the knowledge of the authors, no such investigation directed specific circumstances, particularly in the developing countries. Therefore, it is necessary to look for the antecedents and consequences of customer satisfaction to promote online shopping in the developing countries. The degree of consumer satisfaction defines his/her experience and emotions about the product or service purchased through the online channel. Recent studies ( Guzel et al., 2020 ; Mamuaya and Pandowo, 2020 ) stated that the intention of the consumers to repurchase and their electronic-word-of-mouth (e-WOM) depends on their degree of satisfaction. In light of these heavy investments in online shopping, there is an exciting yet unexplored opportunity to comprehend better how the purchasing experiences of consumers through online channels influence their satisfaction level.
The study contributed to the current marketing literature in several ways. First, this study has highlighted that the perceived risk is very high when shopping through online channels, mainly the indirect e-stores. Therefore, the managers should develop strategies that reduce the perceived risk for the online consumer to shop more. Second, the study also disclosed that the perceived uncertainty in shopping through the online channel is high. While shopping online, the website design, graphics, and color scheme make the product more attractive than the actual one. Therefore, the managers must balance the visual appearance of the product on the website with the actual appearance of the product. This would increase the confidence and satisfaction of the consumer. Third, this study has also revealed that people are more satisfied while shopping from direct e-stores than indirect e-stores. Because the focal brands officially sponsor the direct e-stores, they pay more attention to their quality to retain consumers and maintain their brand reputation. Fourth, an indirect e-store works as a third party or a retailer who does not own the reputation of the product. This study exhibited the difference between the perception of the consumer being very high and the actual experience of using that product being quite different when shopping from the indirect channel. Last but not the least, this study is the first to report pre- and post-purchase consumer behavior and confirmed the perceived and the actual quality of a product bought from (i) direct e-store and (ii) indirect e-store.
Literature Review
Theoretical review.
Literature shows that when consumers get influenced to buy a particular product or service, some underlying roots are based on their behavior ( Wai et al., 2019 ). Appraisal theory significantly explains consumer behavior toward shopping and provides an opportunity to analyze the evaluation process (e.g., Roseman, 2013 ; Kähr et al., 2016 ; Moors et al., 2017 ; Ul Haq and Bonn, 2018 ). This research, aligned with the four dimensions of appraisal theory as the first stage, clearly defines the agency stage that either of the factors is responsible for customer satisfaction. The second stage explains that consumer's degree of satisfaction holds great importance and refers to novelty in the literature. The third stage of the model briefly explains the feelings and emotions of the consumers about the incident, aligning with the certainty phase. The last step explains whether the consumers have achieved their goal or are not aligned with the appetitive purpose.
Cognitive appraisal researchers stated that various emotions could be its root cause ( Scherer, 1997 ); it could be the reaction to any stimulus or unconscious response. On the contrary, four dimensions of appraisal theory are discussed in this research ( Ellsworth and Smith, 1988 ; Ma et al., 2013 ). Agency (considering themselves or objects are answerable for the result of the circumstance) ( Smith and Ellswoth, 1985 ; Durmaz et al., 2020 ); novelty (assessing the difference between the perception of an individual and his actual experience) ( Ma et al., 2013 ); certainty (analysis of the apparent probability of a specific outcome and its effect on the emotions of the buyer) ( Roseman, 1984 ), and appetitive goal (judging the degree to what extent the goal has been achieved) ( Hosany, 2012 ).
Hypotheses Development
Perceived risk and consumer satisfaction.
Perceived risk is the perception of shoppers having unpleasant results for buying any product or service ( Gozukara et al., 2014 ). Consumers who buy a specific product or service strongly impact their degree of risk perception toward buying ( Jain, 2021 ). Buyers who tend to indulge in buying through online channels face perceived risk characterized by their perception compared to the actual uncertainty involved in it ( Kim et al., 2008 ). Literature ( Ashoer and Said, 2016 ; Ishfaq et al., 2020 ) showed that as the risk of buying is getting higher, it influences the degree of consumers about information about their buying, either purchasing from the direct or indirect e-shop. Johnson et al. (2008) stated that consumer judgment that appears due to their experience strongly impacts their satisfaction level. Jin et al. (2016) said that as the ratio of risk perception of their consumer decreases, it enhances customer satisfaction. Thus, from the above arguments, it is hypothesized as follows:
H 1 : Perceived risk has a significant negative impact on consumer satisfaction—direct vs. indirect e-store; perceived vs. actual experience .
Perceived Uncertainty and Consumer Satisfaction
Uncertainty is defined as a time that occurs in the future that comprises the predictable situation due to the asymmetry nature of data ( Salancik and Pfeffer, 1978 ). Consumers may not expect the outcome of any type of exchange conducted as far as the retailer and product-oriented elements are concerned ( Pavlou et al., 2007 ). Therefore, uncertainty initiates that retailers may not be completely predictable; on the contrary, consumers tend to analyze and understand their actions about decision making ( Tzeng et al., 2021 ). Thus, the degree of uncertainty involved in buying through online channels influences that degree of customer satisfaction. In addition, when the performance of any particular product or service matches the degree of expectations, he gets satisfied and, hence, repeats his decision of buying ( Taylor and Baker, 1994 ). But if the product quality fails to meet the requirements, it negatively affects the degree of satisfaction ( Cai and Chi, 2018 ).
H 2 : Perceived uncertainty has a significant negative impact on consumer satisfaction—direct vs. indirect e-store; perceived vs. actual experience .
Price Value and Consumer Satisfaction
Oliver and DeSarbo (1988) suggested that the price value is the proportion of the result of the buyer to the input of the retailer. It is defined as an exchange of products/services based on their quality against a price that is to be paid ( Dodds et al., 1991 ). Consumers look for a higher value in return; consumers are willing to pay a higher price ( Pandey et al., 2020 ). Yet, it leads to higher dissatisfaction when they receive a lower degree of profitable products. Besides, the buyers associate such type of product/service they use as less favorable or not according to their needs and desires. Hence, the buyers regret their decision-making degree for choosing that particular product ( Zeelenberg and Pieters, 2007 ). Aslam et al. (2018) indicated that a product/service price influences the satisfaction of a buyer. Afzal et al. (2013) recommended that the price is among those factors that hold great significance for the degree of satisfaction of the consumer. If the price value of any product/service differs from consumer to consumer, consumers tend to switch brands. Hence, it is hypothesized that:
H3 : Price value has a significant positive impact on consumer satisfaction—direct vs. indirect e-store; perceived vs. actual experience .
Consumer Satisfaction With Consumer Delight, Consumer Regret, and Outrage
Satisfaction is defined as how a consumer is pleased with a particular brand or view about a product/service that matches requirements. It is an essential factor that triggers when the product or service performance exceeds the expectation and perception of the customers ( Woodside et al., 1989 ). The decision of the buyer significantly affects their satisfaction toward the product or service ( Park et al., 2010 ). If buyers are satisfied with the product/service they purchased online, this degree of satisfaction significantly affects their repurchase intention and WOM ( Butt et al., 2017 ). Tandon (2021) stated that a consumer satisfied with the product/service would get delighted. Consumer satisfaction, when exceeding the expectations, leads to consumer delight ( Mikulić et al., 2021 ). Mattila and Ro (2008) recommended that the buyer gets disappointed by anger, regret, and outrage. It also defines that negative emotions have a significant effect on the purchasing intention of the consumers. Oliver (1989) stated that unsatisfied buyers or products that do not fulfill the needs of the customers can create negative emotions. Sometimes, their feelings get stronger and result in sadness and outrage. Bechwati and Xia (2003) recommended that the satisfaction of the consumers influences their behavior to repurchase; outraged consumers due to dissatisfaction sometimes want to hurt the company. Besides deciding to purchase, consumers mostly regret their choices compared to other existing choices ( Rizal et al., 2018 ). Hechler and Kessler (2018) investigated that consumers who are outraged in nature actively want to hurt or harm the company or brand from which they got dissatisfied or hurt. Thus, it is proposed that:
H 4 : Consumer satisfaction has a significant negative impact on (a) consumer delight, (b) consumer regret, (c) consumer outrage—direct vs. indirect e-store; perceived vs. actual experience .
Consumer Delight and E-WOM
Oliver et al. (1997) recommended that a degree of delight in a buyer is termed as a positive emotion. Consumers purchase a product/service that raises their degree of expectation and gets them delighted ( Crotts and Magnini, 2011 ). Delighted buyers are involved in sharing their experiences with their friends and family and spreading positive WOM to others ( Parasuraman et al., 2020 ). Happy buyers generally share their opinions while posting positive feedback through social media platforms globally ( Zhang, 2017 ). A positive WOM of the buyer acts as a fundamental factor in spreading awareness about the product/service and strongly impacts other buyers regarding buying it ( Rahmadini and Halim, 2018 ). Thus, it is proposed that:
H5 : Consumer delight has a significant positive impact on E-WOM—direct vs. indirect e-store; perceived vs. actual experience .
Consumer Delight and Repurchase Intention
Delighted consumers tend toward brand loyalty; thus, they increase their buying intention of the service or product ( Ludwig et al., 2017 ; Ahmad et al., 2021 ). Customers can understand the objective of loyalty in purchasing a similar product or a new one from the same company. Delighted consumers tend to indulge in a higher degree of an emotional state that leads them to higher purchase intentions; it eliminates the switching of brands ( Parasuraman et al., 2020 ). Kim et al. (2015) stated that consumers delighted with a product or service of a brand become loyal to it, and the possibility of switching brands gets very low. Research ( Loureiro and Kastenholz, 2011 ; Tandon et al., 2020 ) shows that delighted consumers are more eager to purchase the same product again. Hence, it is proposed that:
H6 : Consumer delight has a significant positive impact on his repurchase intention—direct Vs. indirect e-store; Perceived Vs. actual experience
Consumer Regret and E-WOM
Regret is considered a negative emotion in reaction to an earlier experience or action ( Tsiros and Mittal, 2000 ; Kumar et al., 2020 ). Regret is when individuals frequently feel pity, disgrace, shame, or humiliation after acting in a particular manner and afterward try to amend their possible actions or decisions ( Westbrook and Oliver, 1991 ; Tsiros and Mittal, 2000 ). Regret is that specific negative emotion the buyers feel while making a bad decision that hurts them; their confidence level is badly affected. They blame themselves for choosing or creating a terrible decision ( Lee and Cotte, 2009 ). Li et al. (2010) suggested that buyers quickly start regretting and find their way to express their negative emotions. When they feel betrayed, they tend to spread negative WOM (NWOM) as a response to their anxiety or anger. Jalonen and Jussila (2016) suggested that buyers who get dissatisfied with their selections get involved in negative e-WOM about that particular brand/company. Earlier research says that buyers suffering from failure to buy any product/services tend to participate actively and play a role in spreading NWOM due to the degree of regret after making bad choices. Whelan and Dawar (2014) suggested that consumers sense that business has treated them unreasonably, and many consumers complain about their experience, resulting in e-WOM that may reduce consumer repurchase intention. Thus, it can be stated that:
H7 : Consumer regret has a significant negative impact on e-WOM—direct vs. indirect e-store; perceived vs. actual experience .
Consumer Regret and Repurchase Intention
Regret has a substantial influence on the intentions of the consumers to not entirely be measured by their degree of happiness ( Thibaut and Kelley, 2017 ). Results may not be evaluated by matching the structured degree of expectation but are also linked to alternatives reachable in the market. Therefore, such sort of evaluation and assessments will probably influence repurchase intention. For example, suppose the skipped reserve overtakes the picked alternative. In that case, the customer might change the replacement for the future purchase, regardless of whether the individual is profoundly happy with the picked option ( Liao et al., 2017 ). According to the researchers, there is a negative relationship between regret and consumer repurchase intention ( Liao et al., 2017 ; Durmaz et al., 2020 ). Furthermore, Unal and Aydin (2016) stated that perceived risk negatively impacts regret, influencing the repurchase intention of the consumers. Thus, it can be stated that:
H8 : Customer's regret has a significantly negative influence on his repurchase intention—direct vs. indirect e-store; perceived vs. actual experience .
Consumer Outrage and E-WOM
The disappointment of the consumers is a negative response to a product or a service ( Anderson and Sullivan, 1993 ). Outrage is the negative emotion a consumer experience when he purchases something totally against his requirements ( Lindenmeier et al., 2012 ). Besides, when the perception of the buyer is infringed, such behaviors occur. According to Torres et al. (2019) , enraged consumers get involved in communicating their outrage through e-WOM. Outraged consumers actively hurt the firm or brand from which they got hurt ( Hechler and Kessler, 2018 ). Consumers give e-WOM online reviews to decrease the negative emotions from the experiences of the consumer and re-establish a calm mental state to equilibrium ( Filieri et al., 2021 ). Thus, such consumers tend to give negative comments about the brand or product, which failed to match their expectations. NWOM has been characterized as negative reviews shared among people or a type of interpersonal communication among buyers concerning their experiences with a particular brand or service provider ( Balaji et al., 2016 ). Hence, it is hypothesized that:
H9 : Consumer outrage has a significant negative impact on e-WOM—direct vs. indirect e-store; perceived vs. actual experience .
Consumer Outrage and Repurchase Intentions
Repurchase intentions are characterized as the expressed trust of a buyer that they will or will not purchase a specific product and service again in the future ( Malhotra et al., 2006 ). Establishing relations with buyers should result in the repurchase. Negative disconfirmation ensues dissatisfaction or a higher level of outrage ( Escobar-Sierra et al., 2021 ). When a service/product fails and is not correctly addressed, the negative appraisal is overstated. Hence, “it may be more difficult to recover from feelings of victimization than to recover from irritation or annoyance” typically associated with dissatisfaction ( Schneider and Bowen, 1999 , p. 36). Therefore, consumers get outraged from buying such a product that fails to match their perception. When the experience of a consumer prompts a negative disconfirmation, the purchaser will also have a higher urging level through outrage. Therefore, consumers will probably have negative intentions to repurchase and do not want to indgule in making the same decision repeatedly ( Wang and Mattila, 2011 ; Tarofder et al., 2016 ). Therefore, it is proposed that:
H10 : Consumer outrage has a significant negative impact on repurchase intention—direct vs. indirect e-store; perceived vs. actual experience .
Methodology
This research explores the difference between the perception of the consumers and the actual online shopping experience through direct and indirect e-stores. It was an experimental design in which online shopping was studied in the developing countries. Data were collected from those individuals who shop from online channels; direct e-store and indirect e-store. Taking care of COVID-19 standard operating procedures, only 50 respondents were gathered two times, every time in a university auditorium after obtaining the permission from the administration. The total capacity of the auditorium was 500, as the lockdown restrictions were lifted after the first wave of the coronavirus.
Data Collection Tool
A questionnaire was used for the survey. The questionnaire was adapted in English to guarantee that the respondents quickly understood the questions used. A cross-sectional study technique was used for this research. A cross-sectional study helps in gathering the data immediately and collects data from a large sample size. The total number of distributed questionnaires was 1,250, out of which 800 were received in the usable form: 197 incomplete, 226 incorrect, and dubious responses, and 27 were eliminated. Thus, a 64% response rate was reported. Research showed that a 1:10 ratio is accepted ( Hair et al., 1998 ) as far as the data collection is concerned; for that instance, this study data fell in the acceptable range.
Indirect E-Store
Consumers who prefer to shop through online channels were gathered in an auditorium of an institute. Only those consumers were eligible for this experiment, who themselves buy through e-stores. A few products were brought from an indirect e-store, and later on, those products were shown to the respondents from the website of that indirect e-store. After showing products, we asked the respondents to fill the survey as per their perception of the product. Then we asked them to fill out another questionnaire to ascertain the difference between the perception and actual experience when purchasing from an indirect e-store. Once all the respondents completed the survey, we have shown them the actual products they have selected by seeing the website of the indirect e-store.
Direct E-Store
The second experiment was carried out on those consumers who shop from direct e-stores. For that purpose, a few popular reviewed clothing articles were purchased from the e-store. As in the case of an indirect e-store, respondents were also shown these articles from the websites of these direct e-stores. We then asked the respondents to fill the survey to confirm their perception of the products. Once all the respondents completed the survey, we showed them the actual product and asked them to fill out another questionnaire according to their actual purchasing experience from the direct e-store. The primary purpose of this experiment was to compare buying from direct e-store and indirect e-store.
Construct Instruments
The total number of items was 34, which were added in the earlier section of the questionnaire. These items were evaluated with the help of using a five-point Likert scale that falls from strongly disagree (1) to strongly agree (5). The items used in the study were empirically validated. Table 2 carries the details of the items of the questionnaire. The price value was evaluated using three items used by Venkatesh et al. (2012) . The perceived uncertainty was one of the independent variables that carry four items derived from Pavlou et al. (2007) . Perceived risk was the third independent variable used, held three items; thus, its scale was derived from Shim et al. (2001) . Wang (2011) validated consumer satisfaction carrying three items; consumer delight was measured by a 3-item scale proposed by Finn (2012) ; consumer regret was measured by the scale proposed by Wu and Wang (2017) . It carries a three-item scale. Consumer outrage was measured by Liu et al. (2015 ); it has six items. Repurchase intention was measured through a scale adapted from Zeithaml et al. (1996) , which carries four items. e-WOM was validated by the scale adapted from Goyette et al. (2010) ; it has five items.
Demographics of the Respondents
A total of 800 questionnaires were filled, and the respondents expressed their perception and actual experience from direct e-store and indirect e-store. Respondents belonged to different age groups from 18 to 50 years and above. There were 49% women and 51% men who took part in filling this survey. The income level of the respondents was grouped in different categories from “above 10,000 to above 50,000. The majority (56%) of the respondents were single, and 44% were married (Details can be viewed in Figure 1 ; Table 1 ). Data for both direct and indirect e-store was collected equally; 50% each to compare each category better.
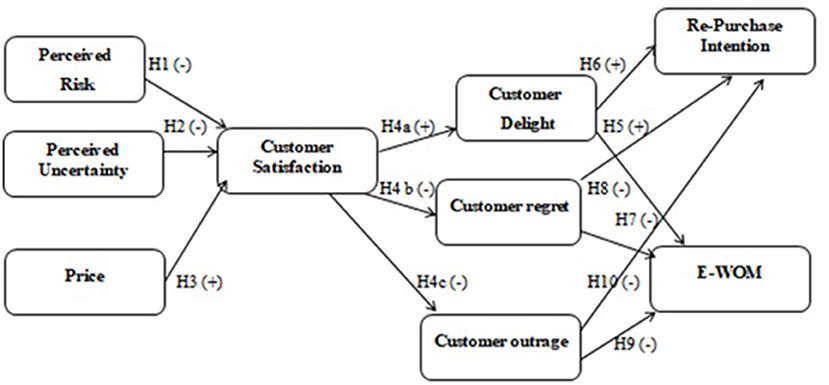
Figure 1 . Proposed conceptual framework.
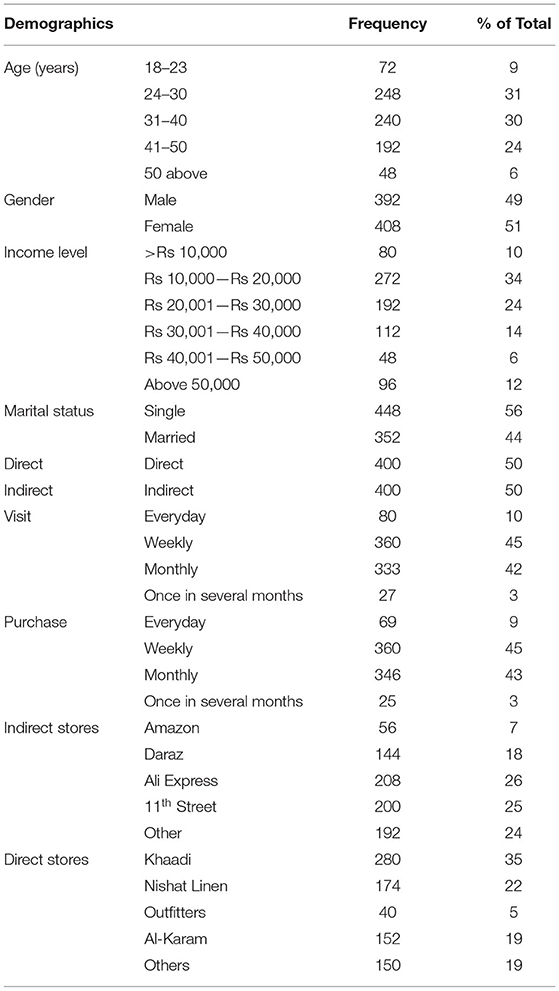
Table 1 . Demographics of the respondents.
Reliability and Validity
Reliability evaluates with the help of composite reliability (CR). All CR values fall into the range of 0.7–0.9, which is acceptable ( Hair et al., 2011 ). Convergent and discriminant validity has been observed through confirmatory factor analysis as recommended by some researchers ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981 ; Hair et al., 2010 ).
Convergent Validity
Convergent validity is evaluated with the help of two standards mentioned in the literature earlier, factor loading and average variance extracted (AVE), both the values should be >0.5 ( Yap and Khong, 2006 ). The values are mentioned in Table 2 .
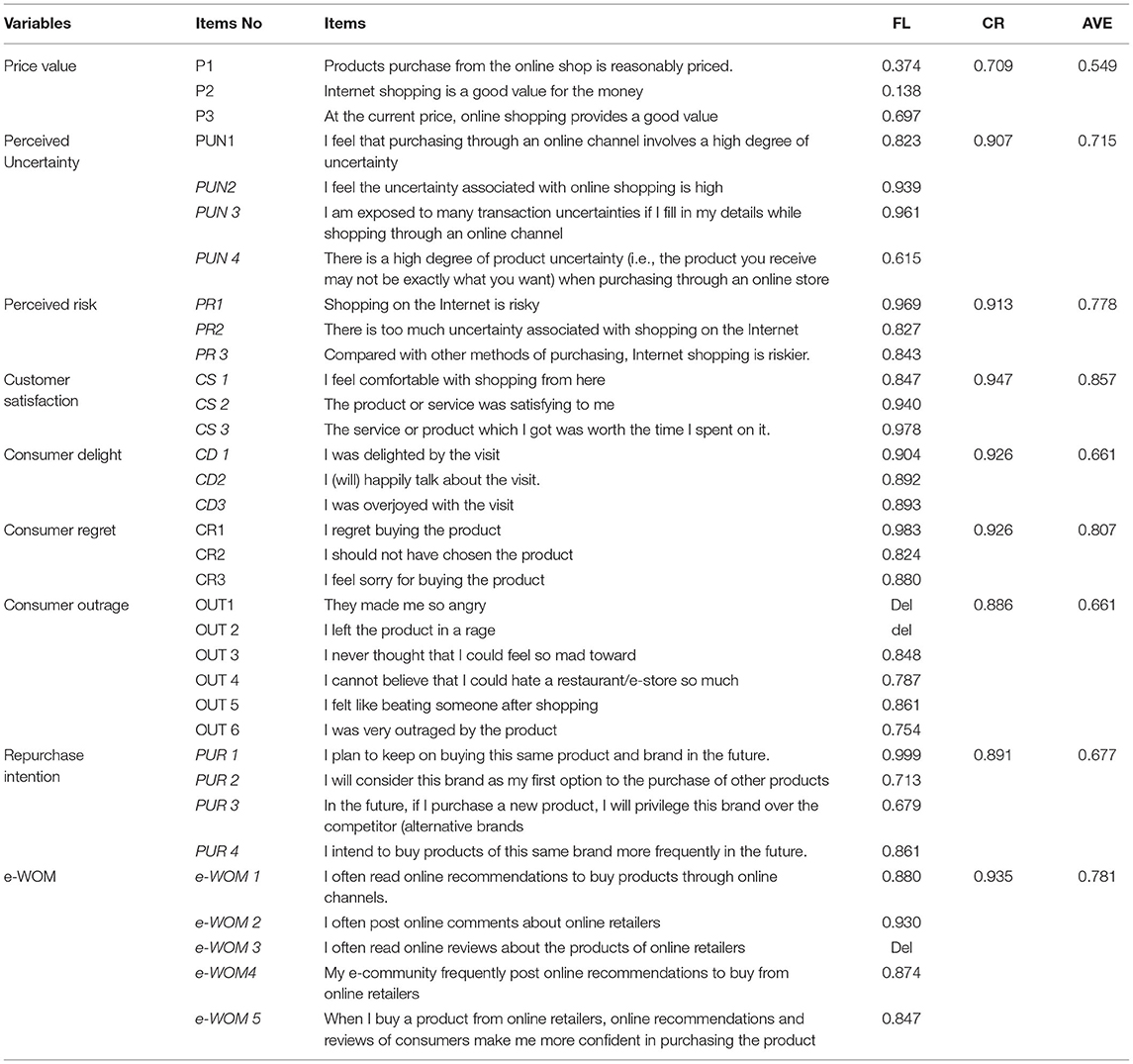
Table 2 . Reliability and convergent validity.
Discriminant Validity
Discriminant validity is evaluated based on two conditions that are required to evaluate it. First, the correlation between the conceptual model variables should be <0.85 ( Kline, 2005 ). Second, the AVE square value must be less than the value of the conceptual model ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981 ). Table 3 depicts the discriminant validity of the construct of the study.

Table 3 . Discriminant validity.
Multi-Group Invariance Tests
Multi-group confirmatory factor analysis was conducted as the pre-requisites for the measurement model. The multi-group analysis was used to investigate a variety of invariance tests. Different invariance tests were performed to guarantee the items working precisely in the same manner in all the groups. In this research, the following are the model fit indexes, that is, CMIN/dF =2.992 CFI = 0.915, TLI = 0.906, and RMSEA = 0.071. Byrne (2010) and Teo et al. (2009) stated that CFI gives more accurate results, especially when comparing variables in different groups.
Hypotheses Testing
Scanning electron microscope technique was used to run and test the proposed hypotheses for the conceptual model. First, all the hypotheses proposed were checked, from which eight were initially accepted. Later, the multi-group test was utilized to test the proposed hypotheses and compare the shopping experience from direct e-store with indirect e-store and consumer perception with actual experience. Table 4 explains this in detail.
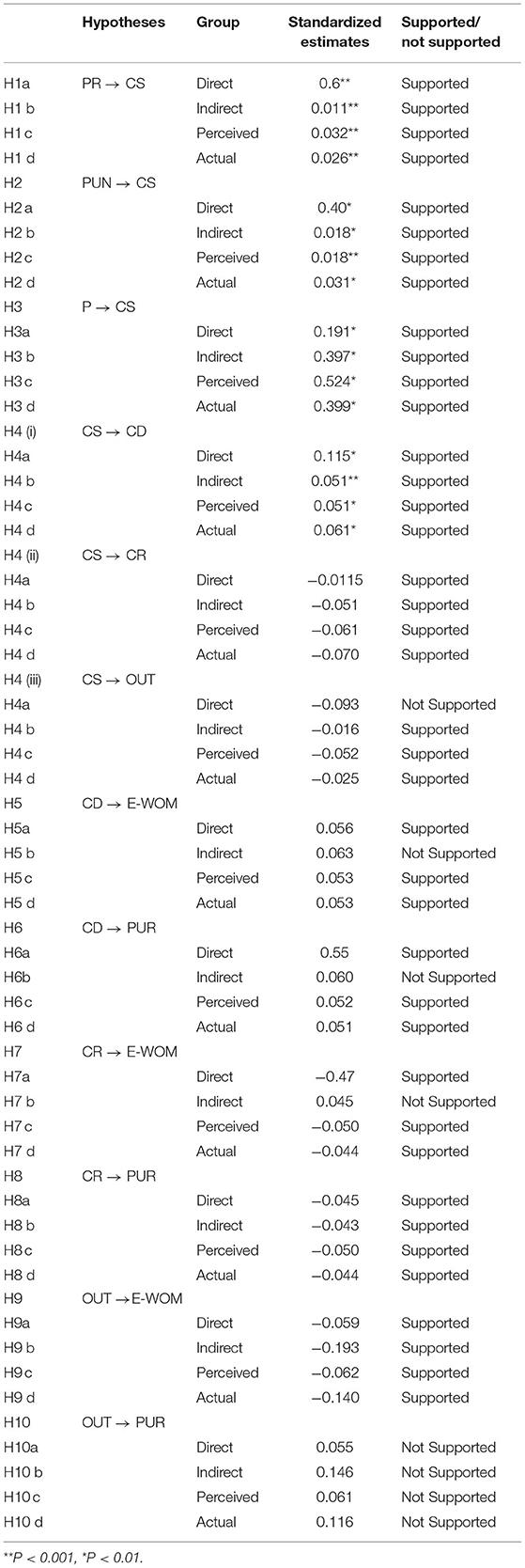
Table 4 . Hypotheses results.
Discussion and Implications
This research offers a remarkable number of facts for practitioners. This study can benefit marketing strategists by reducing the perceived risk, decreasing the intensity of perceived uncertainty, stabilizing the price, enhancing consumer satisfaction, promoting delighting consumers, accepting the negative behavior of the consumers, consumer retention, and establishing a positive e-WOM.
Reducing Risks
Certain factors play a role in antecedents of consumer satisfaction; they are particularly those that resist consumers to shop from any online channel, neither direct e-store nor indirect e-store. Perceived risk, perceived uncertainty, and the price are some of those antecedents that play a significant role in affecting the degree of satisfaction of the consumers, resulting in either to retain a consumer or to outrage a consumer. This study aligns with the existing literature. Tandon et al. (2016) ; Bonnin (2020) and Pandey et al. (2020) showed that consumers seek to shop from an e-store without bearing any risk. Consumers feel more confident about an e-store when the perceived risk is less than shopping from traditional ones as consumers want to feel optimistic about their decision. Second, e-vendors should ensure that the quality of a product is up to the mark and according to the consumer needs. Therefore, vendors should offer complete details about the product/service and its risks to the consumers. Moreover, this study suggests that e-stores must align the visuals of a product with its actual appearance. This would help them to increase customer satisfaction and confidence in the e-store.
Focus on Consumer Satisfaction
Consumer satisfaction is the deal-breaker factor in the online sector. Literature ( Shamsudin et al., 2018 ; Hassan et al., 2019 ) showed that organizations prioritize their consumers by fulfilling their requirements and required assistance. As a result, consumers are more confident and become satisfied consumers in the long run. This study adds to the literature that the degree of satisfaction of the consumers plays an essential role in shopping from an e-store. Consumers feel more confident in shopping from a direct e-store than an indirect e-store as the difference in the perception of consumers and the actual experience varies. Therefore, online vendors should focus on satisfying their consumers as it plays a remarkable role in retaining consumers.
Value Consumer Emotions
Online, retaining, and satisfying consumers are the most vital factor that directly affects the organization. This research aligns with the existing literature ( Jalonen and Jussila, 2016 ; Hechler and Kessler, 2018 ; Coetzee and Coetzee, 2019 ); when the retailer successfully fulfills its requirements, the consumer gets delighted repeating his choice to repurchase. On the other hand, if the online retailer fails to serve the consumer, the consumer regrets and, in extreme cases, becomes outraged about his decision. The negative emotions of the consumers threaten the company from many perspectives, as the company loses its consumer and its reputation in the market is affected. Therefore, first, market practitioners should avoid ignoring the requirements of consumers. Second, online vendors should pay special attention to the feedback of the consumers and assure them that they are valued.
Consumer Retention
The ultimate goal is to retain its consumers, but e-vendors should make proper strategies to satisfy their consumers as far as the online sector is concerned. The earlier studies of Zhang et al. (2015) and Ariffin et al. (2016) contributed to the literature that consumer satisfaction is a significant aspect in retaining a consumer. This research has also suggested that the satisfaction of the consumers plays a vital role in retaining them. Moreover, online shoppers provide the fastest spread of the right WOM about the product/ service. Second, consumers should feel valued and committed to vendors.
Pre- and Post-buying Behavior
This study contributed to a conceptual model that deals with consumer pre- and post-purchase behavior from the direct and indirect e-stores. With the help of experimental design, this study has reported its finding, highlighted how a satisfied customer is delightful and shares e-WOM, and showed repurchase intention. However, if the customer is not satisfied with the flip of a coin, he may feel regretted or outraged and cannot share e-WOM or have a repurchase intention.
Conclusions
This research concludes that online shopping has boomed during this COVID-19 pandemic period, as the lockdown prolonged in both the developed and the developing countries. The study further supports the difference between shopping from a direct e-store and an indirect e-store. The perception of the consumers shopping from direct e-store is more confident, and their degree of satisfaction is much higher, as the actual experience of the consumers aligns with their perceptions. Instead, consumers feel dissatisfied or outraged to choose an indirect e-store for shopping. Indirect e-store makes false promises and guarantees to its buyers, and eventually, when the consumers experience the product, it is against their perception.
This research fills the literature gap about the antecedents that lead to online shopping growth in the developing countries. This study aligns with Hechler and Kessler's (2018) earlier research, which stated that dissatisfied consumers threaten the reputation of the organization. Furthermore, Klaus and Maklan (2013) , Lemon and Verhoef (2016) suggested that handling the experience and satisfaction of the buyers plays a significant role in surviving among its competitors. Grange et al. (2019) recommended that e-commerce develops and attracts consumers by fulfilling their needs and requirements quickly. This study aligned with the existing literature by adding factors influencing the shopping preferences of the consumers from an e-store.
Limitations and Future Research
Despite its significant findings, this research has some limitations and scope for future research. First, this research only examined a few risks involved in online shopping. Future research studies should analyze other risks, for example, quality risk and privacy risk. Second, this study focused on shopping through direct e-stores and indirect e-stores. Future research can implement a conceptual model of a specific brand. Third, this study can be implemented in other sectors, for example, tourism, and hospitality. Fourth, it may be fascinating to look at other fundamentals, such as age, gender, education, relation with the retailer, or the degree of involvement with online shopping to differentiate other factors.
The proposed framework can be utilized in other developing countries, as every country faces different problems according to its growth and development. The model can be examined among specific direct e-stores to compare new customers and loyal customers. Future studies can explore indirect relationships along with adding mediators and moderators in the proposed model.

Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by This study involving human participants was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Department of Management Sciences, Riphah International University, Faisalabad Campus, Faisalabad, Pakistan. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
AS contributed to the conceptualization and writing the first draft of the research. JU contributed to visualizing and supervising the research. All authors who contributed to the manuscript read and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Afzal, S., Chandio, A. K., Shaikh, S., Bhand, M., and Ghumro, B. A. (2013). Factors behind brand switching in cellular networks. Int. J. Asian Soc. Science 3, 299–307.
Google Scholar
Ahmad, W., Kim, W. G., Choi, H. M., and Ul Haq, J. (2021). Modeling behavioral intention to use travel reservation apps: a cross-cultural examination between US and China. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 63:102689. doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2021.102689
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Alharthey, B. (2020). The role of online trust in forming online shopping intentions. Int. J. Online Market. 10, 32–57. doi: 10.4018/IJOM.2020010103
Anderson, E. W., and Sullivan, M. W. (1993). The antecedents and consequences of customer satisfaction for firms. Market. Sci. 12, 125–143. doi: 10.1287/mksc.12.2.125
Ariffin, S., Yusof, J. M., Putit, L., and Shah, M. I. A. (2016). Factors influencing perceived quality and repurchase intention towards green products. Proc. Econ. Finan. 37, 391–396. doi: 10.1016/S2212-5671(16)30142-3
Ashoer, M., and Said, S. (2016). “The impact of perceived risk on consumer purchase intention in Indonesia; a social commerce study,” in Proceeding of the International Conference on Accounting, Management, Economics and Social Sciences . 1–13.
Aslam, W., Arif, I., Farhat, K., and Khursheed, M. (2018). The role of customer trust, service quality and value dimensions in determining satisfaction and loyalty: an Empirical study of mobile telecommunication industry in Pakistan. Market-TrŽište 30, 177–194. doi: 10.22598/mt/2018.30.2.177
Balaji, M. S., Khong, K. W., and Chong, A. Y. L. (2016). Determinants of negative word-of-mouth communication using social networking sites. Inform. Manage. 53, 528–540. doi: 10.1016/j.im.2015.12.002
Bechwati, N. N., and Xia, L. (2003). Do computers sweat? the impact of perceived effort of online decision aids on consumers' satisfaction with the decision process. J. Consum. Psychol. 13, 139–148. doi: 10.1207/S15327663JCP13-1andamp;2_12
Bonnin, G. (2020). The roles of perceived risk, attractiveness of the online store and familiarity with AR in the influence of AR on patronage intention. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 52:101938. doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2019.101938
Butt, M. M., Rose, S., Wilkins, S., and Haq, J. U. (2017). MNCs and religious influences in global markets: drivers of consumer-based halal brand equity. Int. Market. Rev . 12:277. doi: 10.1108/IMR-12-2015-0277
Byrne, B. M. (2010). Structural Equation Modeling With AMOS: Basic Concepts, Applications, and Programming , 2nd Edn. New York, NY: Routledge.
Cai, R., and Chi, C. G. Q. (2018). The impacts of complaint efforts on customer satisfaction and loyalty. Serv. Industr. J. 38, 1095–1115. doi: 10.1080/02642069.2018.1429415
Coetzee, A., and Coetzee, J. (2019). Service quality and attitudinal loyalty: the mediating effect of delight on retail banking relationships. Glob. Bus. Econ. Rev. 21, 120–138. doi: 10.1504/GBER.2019.096856
Crotts, J. C., and Magnini, V. P. (2011). The customer delight construct: is surprise essential? Ann. Tourism Res. 38, 719–722. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2010.03.004
De Vos, J. (2020). The effect of COVID-19 and subsequent social distancing on travel behavior. Transport. Res. Interdisciplin. Perspect. 5:100121. doi: 10.1016/j.trip.2020.100121
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Dodds, W. B., Monroe, K. B., and Grewal, D. (1991). Effects of price, brand, and store information on buyers' product evaluations. J. Market. Res. 28, 307–319. doi: 10.1177/002224379102800305
Durmaz, Y., Demira,g, B., and Çavuşoglu, S. (2020). Influence of regret and regret reversing effort on dissatisfaction and repurchase intention after purchasing fashion products. Preprints. doi: 10.20944/preprints202003.0280.v1
Ellsworth, P. C., and Smith, C. A. (1988). Shades of joy: patterns of appraisal differentiating pleasant emotions. Cogn. Emot. 2, 301–331. doi: 10.1080/02699938808412702
Escobar-Sierra, M., García-Cardona, A., and Vera Acevedo, L. D. (2021). How moral outrage affects consumer's perceived values of socially irresponsible companies. Cogent Bus. Manage. 8:1888668. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2021.1888668
Filieri, R., Galati, F., and Raguseo, E. (2021). The impact of service attributes and category on eWOM helpfulness: an investigation of extremely negative and positive ratings using latent semantic analytics and regression analysis. Comput. Human Behav. 114:106527. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2020.106527
Finn, A. (2012). Customer delight: distinct construct or zone of nonlinear response to customer satisfaction? J. Serv. Res. 15, 99–110. doi: 10.1177/1094670511425698
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Market. Res. 18, 39–50. doi: 10.1177/002224378101800104
Goyette, I., Ricard, L., Bergeron, J., and Marticotte, F. (2010). e-WOM Scale: word-of-mouth measurement scale for e-services context. Can. J. Admin. Sci. 27, 5–23. doi: 10.1002/cjas.129
Gozukara, E., Ozyer, Y., and Kocoglu, I. (2014). The moderating effects of perceived use and perceived risk in online shopping. J. Glob. Strateg. Manage. 16, 67–81. doi: 10.20460/JGSM.2014815643
Grange, C., Benbasat, I., and Burton-Jones, A. (2019). With a little help from my friends: Cultivating serendipity in online shopping environments. Inf. Manage . 56, 225–235.
Grewal, D., Levy, M., and Kumar, V. (2009). Customer experience management in retailing: An organizing framework. J. Retail. 85, 1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jretai.2009.01.001
Guzel, M., Sezen, B., and Alniacik, U. (2020). Drivers and consequences of customer participation into value co-creation: a field experiment. J. Product Brand Manage. doi: 10.1108/JPBM-04-2020-2847
Hair, J. F., Anderson, R. E., Tatham, R. L., and Black, W. C. (1998). Multivariate Data Analysis . 5th ed., Hoboken, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Hair, J. F., Celsi, M., Ortinau, D. J., and Bush, R. P. (2010). Essentials of Marketing Research , Vol. 2. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., and Sarstedt, M. (2011). PLS-SEM: indeed a silver bullet. J. Market. Theor. Pract. 19, 139–152. doi: 10.2753/MTP1069-6679190202
Hassan, S., Shamsudin, M. F., and Mustapha, I. (2019). The effect of service quality and corporate image on student satisfaction and loyalty in TVET higher learning institutes (HLIs). J. Tech. Educ. Train. 11:4.
Hechler, S., and Kessler, T. (2018). On the difference between moral outrage and empathic anger: anger about wrongful deeds or harmful consequences. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 76, 270–282. doi: 10.1016/j.jesp.2018.03.005
Hosany, S. (2012). Appraisal determinants of tourist emotional responses. J. Trav. Res. 51, 303–314. doi: 10.1177/0047287511410320
Ishfaq, M., Nazir, M. S., Qamar, M. A. J., and Usman, M. (2020). Cognitive bias and the Extraversion personality shaping the behavior of investors. Front. Psychol. 11:556506. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.556506
Jain, S. (2021). Examining the moderating role of perceived risk and web atmospherics in online luxury purchase intention. J. Fash. Market. Manage. Int. J. 05:89. doi: 10.1108/JFMM-05-2020-0089
Jalonen, H., and Jussila, J. (2016). “Developing a conceptual model for the relationship between social media behavior, negative consumer emotions and brand disloyalty,” in Conference on e-Business, e-Services and e-Society (Cham: Springer), 134–145. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-45234-0_13
Jin, N., Line, N. D., and Merkebu, J. (2016). The impact of brand prestige on trust, perceived risk, satisfaction, and loyalty in upscale restaurants. J. Hospital. Market. Manage. 25, 523–546. doi: 10.1080/19368623.2015.1063469
Johnson, M. S., Sivadas, E., and Garbarino, E. (2008). Customer satisfaction, perceived risk and affective commitment: an investigation of directions of influence. J. Serv. Market. 5:120. doi: 10.1108/08876040810889120
Kähr, A., Nyffenegger, B., Krohmer, H., and Hoyer, W. D. (2016). When hostile consumers wreak havoc on your brand: the phenomenon of consumer brand sabotage. J. Mark. 80, 25–41. doi: 10.1509/jm.15.0006
Kim, D. J., Ferrin, D. L., and Rao, H. R. (2008). A trust-based consumer decision-making model in electronic commerce: the role of trust, perceived risk, and their antecedents. Decis. Support Syst. 44, 544–564. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2007.07.001
Kim, M., Vogt, C. A., and Knutson, B. J. (2015). Relationships among customer satisfaction, delight, and loyalty in the hospitality industry. J. Hospital. Tourism Res. 39, 170–197. doi: 10.1177/1096348012471376
Klaus, P. P., and Maklan, S. (2013). Towards a better measure of customer experience. Int. J. Market Res. 55, 227–246. doi: 10.2501/IJMR-2013-021
Kline, R. B. (2005). Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling , 2nd Edn. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Kumar, A., Chaudhuri, D., Bhardwaj, D., and Mishra, P. (2020). Impulse buying and post-purchase regret: a study of shopping behaviour for the purchase of grocery products. Int. J. Manage. 11:57. doi: 10.34218/IJM.11.12.2020.057
Kumar, A., and Kim, Y. K. (2014). The store-as-a-brand strategy: the effect of store environment on customer responses. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 21, 685–695. doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2014.04.008
Lee, S. H., and Cotte, J. (2009). Post-purchase Consumer Regret: Conceptualization and Development of the PPCR Scale . ACR North American Advances.
Lemon, K. N., and Verhoef, P. C. (2016). Understanding customer experience throughout the customer journey. J. Market. 80, 69–96. doi: 10.1509/jm.15.0420
Li, S., Zhou, K., Sun, Y., Rao, L. L., Zheng, R., and Liang, Z. Y. (2010). Anticipated regret, risk perception, or both: which is most likely responsible for our intention to gamble? J. Gambl. Stud. 26, 105–116. doi: 10.1007/s10899-009-9149-5
Liao, C., Lin, H. N., Luo, M. M., and Chea, S. (2017). Factors influencing online shoppers' repurchase intentions: the roles of satisfaction and regret. Inform. Manage. 54, 651–668. doi: 10.1016/j.im.2016.12.005
Lindenmeier, J., Schleer, C., and Pricl, D. (2012). Consumer outrage: emotional reactions to unethical corporate behavior. J. Bus. Res. 65, 1364–1373. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2011.09.022
Liu, M. W., and Keh, H. T. (2015). Consumer delight and outrage: scale development and validation. J. Serv. Theory Pract . 25, 680–699. doi: 10.1108/JSTP-08-2014-0178
Loureiro, S. M. C., and Kastenholz, E. (2011). Corporate reputation, satisfaction, delight, and loyalty towards rural lodging units in Portugal. Int. J. Hospital. Manage. 30, 575–583. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2010.10.007
Ludwig, N. L., Heidenreich, S., Kraemer, T., and Gouthier, M. (2017). Customer delight: universal remedy or a double-edged sword? J. Serv. Theory Pract . 8:197. doi: 10.1108/JSTP-08-2015-0197
Ma, J., Gao, J., Scott, N., and Ding, P. (2013). Customer delight from theme park experiences: the antecedents of delight based on cognitive appraisal theory. Ann. Tour. Res. 42, 359–381. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2013.02.018
Malhotra, N., Hall, J., Shaw, M., and Oppenheim, P. (2006). Marketing Research: An Applied Orientation . Melbourne, VC: Pearson Education Australia.
Mamuaya, N. C., and Pandowo, A. (2020). Determinants of customer satisfaction and its implications on word of mouth in e-commerce industry: case study in Indonesia. Asia Pacific J. Manage. Educ. 3, 16–27. doi: 10.32535/apjme.v3i1.740
Mattila, A. S., and Ro, H. (2008). Discrete negative emotions and customer dissatisfaction responses in a casual restaurant setting. J. Hosp. Tour. Res. 32, 89–107. doi: 10.1177/1096348007309570
Mendez, J. L., Oubina, J., and Rubio, N. (2008). Expert quality evaluation and price of store vs. manufacturer brands: an analysis of the Spanish mass market. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 15, 144–155. doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2007.11.003
Mikulić, J., Kreši,ć, D., and Šerić, M. (2021). The factor structure of medical tourist satisfaction: exploring key drivers of choice, delight, and frustration. J. Hospital. Tour. Res. 1177:1096348020987273. doi: 10.1177/1096348020987273
Moors, A., Boddez, Y., and De Houwer, J. (2017). The power of goal-directed processes in the causation of emotional and other actions. Emot. Rev. 9, 310–318. doi: 10.1177/1754073916669595
Nassauer, S. (2020). Walmart sales surge as Coronavirus drives Americans to stockpile. Wall Street J . Availale online at: https://www.wsj.com/articles/walmart-sales-surge-as-coronavirus-drivesamericans-to-stockpile-11589888464?mod=hp_lead_pos5 (accessed on May 18, 2020).
Oliver, R. L. (1989). Processing of the satisfaction response in consumption. J. Consum. Satisfact. Dissatisfact. Complain. Behav. 2, 1–26.
Oliver, R. L., and DeSarbo, W. S. (1988). Response determinants in satisfaction judgments. J. Consum. Res. 14, 495–507. doi: 10.1086/209131
Oliver, R. L., Rust, R. T., and Varki, S. (1997). Customer delight: foundations, findings, and managerial insight. J. Retail. 73:311. doi: 10.1016/S0022-4359(97)90021-X
Olotewo, J. (2017). Examining the antecedents of in-store and online purchasing behavior: a case of Nigeria. J. Market. Res. Case Stud. 15, 1–16. doi: 10.5171/2017.668316
Pandey, N., Tripathi, A., Jain, D., and Roy, S. (2020). Does price tolerance depend upon the type of product in e-retailing? role of customer satisfaction, trust, loyalty, and perceived value. J. Strateg. Market. 28, 522–541. doi: 10.1080/0965254X.2019.1569109
Parasuraman, A., Ball, J., Aksoy, L., Keiningham, T. L., and Zaki, M. (2020). More than a feeling? toward a theory of customer delight. J. Serv. Manage . 3:34. doi: 10.1108/JOSM-03-2019-0094
Park, E. O., Chung, K. H., and Shin, J. I. (2010). The relationship among internal marketing, internal customer satisfaction, organizational commitment and performance. Product. Rev. 24, 199–232. doi: 10.15843/kpapr.24.2.201006.199
CrossRef Full Text
Pavlou, P. A., Liang, H., and Xue, Y. (2007). Understanding and mitigating uncertainty in online exchange relationships: a principal-agent perspective. MIS Q. 105–136. doi: 10.2307/25148783
Rahmadini, Y., and Halim, R. E. (2018). The “Influence of social media towards emotions, brand relationship quality, and word of Mouth (WOM) on Concert's Attendees in Indonesia,” in MATEC Web of Conferences (EDP Sciences) , 05058.
Redman, R. (2020). “Online grocery sales to grow 40% in 2020,” in Supermarket News . Available online at: https://www.supermarketnews.com/onlineretail/online-grocery-sales-grow-40-2020 (accessed on May 21, 2020).
Rizal, H., Yussof, S., Amin, H., and Chen-Jung, K. (2018). EWOM towards homestays lodging: extending the information system success model. J. Hosp. Tour. Technol. doi: 10.1108/JHTT-12-2016-0084
Roseman, I. J. (1984). Cognitive determinants of emotion: a structural theory. Rev. Person. Soc. Psychol. 5, 11–36.
Roseman, I. J. (2013). Author reply: on the frontiers of appraisal theory. Emot. Rev. 5, 187–188. doi: 10.1177/1754073912469592
Rossolov, A., Rossolova, H., and Holguín-Veras, J. (2021). Online and in-store purchase behavior: shopping channel choice in a developing economy. Transportation 20, 1–37. doi: 10.1007/s11116-020-10163-3
Salancik, G. R., and Pfeffer, J. (1978). Uncertainty, secrecy, and the choice of similar others. Soc. Psychol. 23, 246–255. doi: 10.2307/3033561
Saleh, M. A. H. (2016). Website design, technological expertise, demographics, and consumer's e-purchase transactions. Int. J. Market. Stud. 8, 125–138. doi: 10.5539/ijms.v8n1p125
Scherer, K. R. (1997). The role of culture in emotion-antecedent appraisal. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 73:902. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.73.5.902
Schneider, B., and Bowen, D. E. (1999). Understanding customer delight and outrage. Sloan Manage. Rev. 41, 35–45. doi: 10.1016/S0022-4359(01)00035–45
Shamsudin, M. F., Razak, A. A., and Salem, M. A. (2018). The role of customer interactions towards customer satisfaction in theme parks experience. Opcion 34, 546–558.
Shim, S., Eastlick, M. A., Lotz, S. L., and Warrington, P. (2001). An online prepurchase intentions model: the role of intention to search: best overall paper award—the Sixth Triennial AMS/ACRA Retailing Conference, 2000? J. Retail. 77, 397–416. doi: 10.1016/S0022-4359(01)00051-3
Smith, C. A., and Ellsworth, P. C. (1985). Patterns of cognitive appraisal in emotion. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol . 48:813.
Tandon, A., Aakash, A., and Aggarwal, A. G. (2020). Impact of EWOM, website quality, and product satisfaction on customer satisfaction and repurchase intention: moderating role of shipping and handling. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manage. 54, 1–8. doi: 10.1007/s13198-020-00954-3
Tandon, U. (2021). Predictors of online shopping in India: an empirical investigation. J. Market. Anal. 9, 65–79. doi: 10.1057/s41270-020-00084-6
Tandon, U., Kiran, R., and Sah, A. N. (2016). Understanding online shopping adoption in India: unified theory of acceptance and use of technology 2 (UTAUT2) with perceived risk application. Serv. Sci. 8, 420–437. doi: 10.1287/serv.2016.0154
Tarhini, A., Alalwan, A. A., Al-Qirim, N., and Algharabat, R. (2021). “An analysis of the factors influencing the adoption of online shopping,” in Research Anthology on E-Commerce Adoption, Models, and Applications for Modern Business (Pennsylvania: IGI Global), 363–384.
Tarofder, A. K., Nikhashemi, S. R., Azam, S. F., Selvantharan, P., and Haque, A. (2016). The mediating influence of service failure explanation on customer repurchase intention through customers satisfaction. Int. J. Qual. Serv. Sci. 4:44. doi: 10.1108/IJQSS-04-2015-0044
Taylor, S. A., and Baker, T. L. (1994). An assessment of the relationship between service quality and customer satisfaction in the formation of consumers' purchase intentions. J. Retail. 70, 163–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-4359(94)90013-2
Teo, T., Lee, C. B., Chai, C. S., and Wong, S. L. (2009). Assessing the intention to use technology among preservice teachers in Singapore and Malaysia: a multigroup invariance analysis of the technology acceptance model (TAM). Comput. Educ. 53, 1000–1009. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2009.05.017
Thibaut, J. W., and Kelley, H. H. (2017). The Social Psychology of Groups . Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9781315135007
Torres, E. N., Milman, A., and Park, S. (2019). Customer delight and outrage in theme parks: a roller coaster of emotions. Int. J. Hospital. Tour. Administr. 16, 1–23. doi: 10.1080/15256480.2019.1641455
Tsiros, M., and Mittal, V. (2000). Regret: a model of its antecedents and consequences in consumer decision making. J. Consum. Res. 26, 401–417. doi: 10.1086/209571
Tzeng, S. Y., Ertz, M., Jo, M. S., and Sarigöll,ü, E. (2021). Factors affecting customer satisfaction on online shopping holiday. Market. Intell. Plann. 8:346. doi: 10.1108/MIP-08-2020-0346
Ul Haq, J., and Bonn, M. A. (2018). Understanding millennial perceptions of human and nonhuman brands. Int. Hospital. Rev . 9:14. doi: 10.1108/IHR-09-2018-0014
Unal, S., and Aydin, H. (2016). Evaluation of consumer regret in terms of perceived risk and repurchase intention. J. Glob. Strateg. Manage. 2, 31–31. doi: 10.20460/JGSM.20161024354
Venkatesh, V., Thong, J. Y., and Xu, X. (2012). Consumer acceptance and use of information technology: extending the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology. MIS Q. 157–178. doi: 10.2307/41410412
Wai, K., Dastane, O., Johari, Z., and Ismail, N. B. (2019). Perceived risk factors affecting consumers' online shopping behaviour. J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 6, 246–260. doi: 10.13106/jafeb.2019.vol6.no4.249
Wang, C. Y., and Mattila, A. S. (2011). A cross-cultural comparison of perceived informational fairness with service failure explanations. J. Serv. Market . 25, 429–439. doi: 10.1108/08876041111161023
Wang, X. (2011). The effect of unrelated supporting service quality on consumer delight, satisfaction, and repurchase intentions. J. Serv. Res. 14, 149–163. doi: 10.1177/1094670511400722
Westbrook, R. A., and Oliver, R. L. (1991). The dimensionality of consumption emotion patterns and consumer satisfaction. J. Consum. Res. 18, 84–91. doi: 10.1086/209243
Whelan, J., and Dawar, N. (2014). Attributions of blame following a product-harm crisis depend on consumers' attachment styles. Mark. Lett. 27, 285–294. doi: 10.1007/s11002-014-9340-z
Woodside, A. G., Frey, L. L., and Daly, R. T. (1989). Linking service quality, customer satisfaction, and behavio. Mark. Health Serv. 9:5. doi: 10.1016/S0022-4359(01)0009-5
Wu, R., and Wang, C. L. (2017). The asymmetric impact of other-blame regret versus self-blame regret on negative word of mouth: empirical evidence from China. Eur. J. Market. doi: 10.1108/EJM-06-2015-0322
Yang, Y., Gong, Y., Land, L. P. W., and Chesney, T. (2020). Understanding the effects of physical experience and information integration on consumer use of online to offline commerce. Int. J. Inf. Manage. 51:102046. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.102046
Yap, B. W., and Khong, K. W. (2006). Examining the effects of customer service management (CSM) on perceived business performance via structural equation modelling. Appl. Stochast. Models Bus. Indus. 22, 587–605. doi: 10.1002/asmb.648
Zeelenberg, M., and Pieters, R. (2007). A theory of regret regulation 1.0. J. Consum. Psychol. 17, 3–18. doi: 10.1207/s15327663jcp1701_3
Zeithaml, V. A., Berry, L. L., and Parasuraman, A. (1996). The behavioral consequences of service quality. J. Market. 60, 31–46. doi: 10.1177/002224299606000203
Zhang, H. (2017). Understanding the Consumption Experience of Chinese Tourists: Assessing the Effect of Audience Involvement, Flow and Delight on Electronic Word-of-mouth (eWOM) (Doctoral dissertation).
Zhang, Z., Ye, Q., Song, H., and Liu, T. (2015). The structure of customer satisfaction with cruise-line services: an empirical investigation based on online word of mouth. Curr. Issues Tourism . 18, 450–464.
Keywords: consumer perception, online shopping, actual experiences, customer satisfaction, direct shopping, perceived risk, delight, outrage
Citation: Rao YH, Saleem A, Saeed W and Ul Haq J (2021) Online Consumer Satisfaction During COVID-19: Perspective of a Developing Country. Front. Psychol. 12:751854. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.751854
Received: 02 August 2021; Accepted: 30 August 2021; Published: 01 October 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Rao, Saleem, Saeed and Ul Haq. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Junaid Ul Haq, junaid041@yahoo.com
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
A Study of Online Shopping Behaviour by Consumers During COVID-19 Pandemic
- Conference paper
- First Online: 12 April 2022
- Cite this conference paper

- Bhuwandeep 5 &
- Arvind Tripathy 5
Part of the book series: Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics ((SPBE))
908 Accesses
The pandemic has led to an unprecedented change in the way people shop and the mode of shopping. Our paper examines how the pandemic and quarantine precipitates those changes in shopping on e-commerce platforms and use of digital solutions. The literature already talks about the perceived benefits of online shopping such as awareness of utility, awareness of easy to use, awareness of marketing policy, awareness of price and cost. Thus, we have used our research paper to study the triggers of online shopping during COVID19. We administered self-administered Google surveys and as primary and secondary data source to develop the model of perceived benefits of e-shopping during quarantine. The finding of the paper shows that consumer associates e-shopping with value for money, safety, a mode of relaxing, stress release during the quarantine period. The pandemic has changed the global business paradigm irreversibly. It has slowly transformed all business to make them customer centric and digital ready. This paper underlines the how the business can create better value for the customer by working on the perceived benefits to cater them in an effective way.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Factors Affecting the Intention to Buy Online During Covid-19: Electronic Devices in Southern Vietnam

Factors affecting online shopping frequency: lessons from New Zealand

The Moderator Effect of COVID Pandemic on the Relationship Between Online Shopping Services and Online Consumer Purchasing Behavior. A Case of Jordan
Alfonso, Viviana, et al. 2021. E-commerce in the pandemic and beyond. BIS Bulletin 36.
Google Scholar
Andrienko, O. 2020. Ecommerce and Consumer Trends During Coronavirus.
Arora, Nupur, and Aanchal Aggarwal. 2018. The role of perceived benefits in formation of online shopping attitude among women shoppers in India. South Asian Journal of Business Studies 7 (1): 91–110. https://doi.org/10.1108/SAJBS-04-2017-0048 .
Article Google Scholar
Baubonienė, Živilė, and Gintarė Gulevičiūtė. 2015. E-Commerce Factors Influencing Consumers ‘online Shopping Decision .
Busby, Joshua W. 2020. Understanding the Anemic Global Response to COVID-19. Journal of Health Politics, Policy and Law 45 (6): 1013–21 (Duke University Press).
Giallonardo, Vincenzo, et al. 2020. The impact of quarantine and physical distancing following COVID-19 on mental health: Study protocol of a multicentric italian population trial. In Frontiers in Psychiatry , vol. 11. Frontiers Media SA.
Hao, Na, et al. 2020. The impact of online grocery shopping on stockpile behavior in Covid-19. In China Agricultural Economic Review . Emerald Publishing Limited.
Haytko, Diana L., and Julie Baker. 2004. It’s all at the mall: Exploring adolescent girls’ experiences. Journal of Retailing 80 (1): 67–83.
Hobbs, Jill E. 2020. Food supply chains during the COVID-19 pandemic. Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics/Revue Canadienne d’agroeconomie 68(2): 171–76 (Wiley Online Library).
Hori, Masahiro, and Koichiro Iwamoto. 2014. The run on daily foods and goods after the 2011 Tohoku earthquake: A fact finding analysis based on homescan data. The Japanese Political Economy 40(1), 69–113 (Taylor & Francis).
Khusaini, Khusaini, et al. 2019. The influence of shopping and gender differences on online shopping. Jurnal Pendidikan Ekonomi Dan Bisnis (JPEB) 7(1): 22–30.
Lubis, Arlina Nurbaity. 2018. Evaluating the customer preferences of online shopping: Demographic factors and online shop application issue. Academy of Strategic Management Journal 17(2): 1–13 (Jordan Whitney Enterprises, Inc.).
Lufkin, B. 2020. Amid the Coronavirus Outbreak, People Are Flocking to Supermarkets Worldwide—But Are They Simply Preparing, or Irrationally Panicking? BBC .
Nguyen, Hoang Viet, et al. 2020. Online book shopping in Vietnam: The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic situation. Publishing Research Quarterly 36: 437–45 (Springer).
Rollero, Chiara, et al. 2019. Do Men Post and Women View? The Role of Gender, Personality and Emotions in Online Social Activity.
Sans, Pierre, et al. 2008. Value-based labels for fresh beef: An overview of French consumer behaviour in a BSE crises context. International Journal of Consumer Studies 32(5): 407–13 (Wiley Online Library).
Stark, Jerrold, and Robert Meier. 2001. A longitudinal study of usage and satisfaction levels of internet shopping by college students. Journal of Computer Information Systems 41(4): 65–68 (Taylor & Francis).
Theodoridou, Glykeria, et al. 2019. The impact of the economic crisis on Greek consumer behaviour towards food consumption. International Journal on Food System Dynamics 10(3): 298–314.
y Monsuwé, Toñita Perea, et al. 2004. What drives consumers to shop online? A literature review. In International Journal of Service Industry Management (Emerald Group Publishing Limited).
Yang, Kiseol, et al. 2020. Effects of retailers’ service quality and legitimacy on behavioral intention: The role of emotions during COVID-19. The Service Industries Journal 1–23 (Taylor & Francis).
Yet Mee, Lim, et al. 2019. Gender differences in perceptions and attitudes toward online shopping: A study of Malaysian consumers. Lim, Y.M., B.L. Cheng, T.H. Cham, C.K.Y. Ng, and J.X. Tan (2019). Gender Differences in Perceptions and Attitudes Toward Online Shopping: A Study of Malaysian Consumers. Journal of Marketing Advances and Practices , vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 11–24.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
KIIT School of Management, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India
Bhuwandeep & Arvind Tripathy
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Bhuwandeep .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
School of Management, KIIT University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India
Rabi Narayan Subudhi
Sumita Mishra
School of Management, BGL, University of Canberra, Canberra, ACT, Australia
Pennsylvania State University, Harrisburg, PA, USA
Dariush Khezrimotlagh
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Bhuwandeep, Tripathy, A. (2022). A Study of Online Shopping Behaviour by Consumers During COVID-19 Pandemic. In: Subudhi, R.N., Mishra, S., Saleh, A., Khezrimotlagh, D. (eds) Future of Work and Business in Covid-19 Era. Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-0357-1_13
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-0357-1_13
Published : 12 April 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-0356-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-0357-1
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Consumer Economics
- Consumerism
A STUDY ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR TOWARDS ONLINE SHOPPING
- February 2022
- International Journal of Research in Marketing 9(1):864-874

- Kristu Jayanti College
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Emmanuel Obiajulu Ojei
- M.Mallika Madasu Baskara Rao
- Jamila Dani
- K Balakrishna
- S Srinivas Rao
- Ranganathan
- C R Kothari
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
- View PDF
- Download full issue

Procedia Economics and Finance
Factors influencing online shopping behavior: the mediating role of purchase intention ☆.
- Previous article in issue
- Next article in issue
Cited by (0)
- Search Close search
- Find a journal
- Search calls for papers
- Journal Suggester
- Open access publishing
We’re here to help
Find guidance on Author Services
Open access
Consumer buying behavior towards online shopping: An empirical study on Dhaka city, Bangladesh
- Cite this article
- https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2018.1514940
1. Introduction
2. methodology, 3. literature review, 4. findings and discussion, 5. conclusion, additional information.
- Full Article
- Figures & data
- Reprints & Permissions
- View PDF PDF
The World Wide Web has propelled in no small extent of changes in the attitude and behavior of people all over the world. Due to this blessing, online shopping has emerged which influenced the lives of ordinary citizens. Online shopping has also been started in Bangladesh, but consumers are not much habituated yet to go online shopping frequently. This study is undertaken to understand the behavior of online shoppers through a self-constructed questionnaire of 160 respondents from Dhaka city. The survey reveals that consumers shop online to save time, and for available varieties of products and services. Both male and female both have the same type of behavior towards liking and disliking factors; they like home delivery facility and dislike inability to touch and feel the product most. They acquire online shopping information from websites especially from the social network and purchase apparels, accessories mostly through cash on delivery method of payment. The most of the consumers are concern about the security of the payment system, and their overall online shopping satisfaction is mixed.
- online shopping
PUBLIC INTEREST STATEMENT
Online shopping is a buzzword in the modern tech-based business world. In Bangladesh particularly in Dhaka, the capital city of Bangladesh, online shopping is getting popular with the sequence of time. Buyers now consider several factors while they are planning to buy from the online platform. This study revealed the online shoppers’ behavior, i.e., what is the demography, what products or services they like, why they like or dislike online shopping, and which payment method they prefer, etc. We found that consumers are mostly young, who shop online to save time, and for available varieties of products and services and prefers to pay through cash on delivery method. They mostly get the online shopping information from the websites advertisements, especially from social networks. The more experienced they are with online shopping, the more they tend to buy online. However, male and female both have the same type of behavior towards liking and disliking factors.
Online shopping is the easy solution for busy life in today’s world. In the past decade, there had been a massive change in the way of customer’s shopping. Despite consumers’ continuation to buy from a physical store, the users or buyers feel very convenient to online shopping. Online shopping saves crucial time for modern people because they get so busy that they cannot or unwilling to spend much time shopping.
In the twenty-first century, trade and commerce have been so diversified that multichannel has taken place and online shopping has increased significantly throughout the world (Johnson, Gustafsson, Andreassen, Lervik, & Cha, Citation 2001 ). Globally, e-commerce constituted about 2.29 trillion dollar market (John, Citation 2018 ) and expected to reach 4 trillion dollar by 2020 (eMarketer, Citation 2016 ) due to the double-digit worldwide growth in sales (15%) and order (13%) (eMarketer, Citation 2018 ) in all sorts of e-commerce such as business-to-business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C) (Zuroni & Goh, Citation 2012 ).
Asia Pacific region is leading the growth of online shopping as compared to the mature market such as the US, UK, Japan and European Countries. The Asia Pacific recorded massive growth, especially in China. In 2016, Asia Pacific region made about $1 trillion in online sales and majority came from China constituting about $899 billion (eMarketer, Citation 2016 ). With more and more consumers become increasingly familiar with the Internet and its benefit, online shopping is becoming popular and getting preference among a group of consumers seeking better value proposition regarding information, convenience, cost, choice. Like other young Asian citizens, youngsters in Bangladesh are experimenting with new ways of shopping that have led to the popularity and growth of online shopping in Bangladesh.
Unlike a physical store, all the goods in online stores described through text, with photos, and with multimedia files. Many online stores will provide links for much extra information about their product. On the other hand, some online consumers are an adventurous explorer, fun seeker, shopping lover, and some are technology muddler, hate waiting for the product to ship. Consequently, online consumer behavior (user action during searching, buying, using products) became a contemporary research area for an increasing number of researchers to understand this unique nature of online shopping.
The primary goal of a business is to offer product and services that best serve their consumer needs. A business which fulfills the customer needs with satisfaction very well is more successful than its competitors as satisfied buyers tend to make a repetitive purchase. Moreover, in Bangladesh, online shopping has been evolving fast and has the potential to grow exponentially in time to come, as Internet penetration reaches far and wide across the rural areas. However, it is also true that Bangladeshi people are traditionally conservative in their approach to shopping due to modernization and fast-paced life, dependence on online shopping will increase. Thus, the purpose of this study is to understand the consumer behavior towards online shopping, their liking, disliking, and satisfaction level.
To understand the consumer behavior of newly launched online shopping in Bangladesh, we have undertaken a descriptive study through a survey by forming a self-constructed questionnaire considering the research objective. A Likert five-point scale ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree been used to collect a quick response from the respondents.
Convenient non-probability sampling method has been adopted in this study to acquire data from respondents in Dhaka city where about 50% e-commerce customers reside (Jagonews24.com., Citation 2015 ) in Bangladesh. A convenient sampling method is easy to implement and cost-effective and more common in IS research that gets higher response rate (Eze, Manyeki, Yaw, & Har, Citation 2011 ; Ritchie, Lewis, Nicholls, McNaughton, & Ormiston, Citation 2014 ). We have targeted 200 respondents belong to different age-group, student, service holder, business person and the homemaker with various experience in online shopping for a personal interview and 179 participated in the survey resulting in 90% response rate. However, after sorting 160 useful and valid responses were used for further analysis. Accumulated data were analyzed through Microsoft Excel.
Online shopping indicates electronic commerce to buy products or services directly from the seller through the Internet. Internet-based or Click and Order business model has replaced the traditional Brick and Mortar business model. More people than before are using the web to shop for a wide variety of items, from house to shoes to airplane tickets. Now people have multiple options to choose their products and services while they are shopping through an online platform.
Online shopping has unique characteristics. Huseynov and Yıldırım ( Citation 2014 ) emphasized that the lack of physical interaction tends to be the critical impediment in online retail sales followed by the privacy of individual information and security of financial transactions over the Internet. Demangeot and Broderick ( Citation 2010 ) also revealed that perceived ease of use does not affect the behavioral pattern in this case rather influenced by security and privacy issues. No relationship is built between the customer and the online shop in the presence of perceived online risk even if a customer spent hours on the Internet (Zuroni & Goh, Citation 2012 ).
Day-by-day taste, preference and choices are varying regarding different factors such as the Internet emergence. However, this development needs some more understanding related to the consumer’s behavior. Consumer behavior research identifies a general model of buying behavior that depicts the processes used by consumers in making a purchase decision (Vrender, Citation 2016 ). Those designs are paramount to the marketer as they can explain and predict consumer purchase behavior.
Jarvenpaa, Todd, Jarvenpaa, and Todd ( Citation 1997 a) proposed a model of attitude, behavior, and shopping intention towards Internet shopping in general. The design includes several indicators classified into four broad categories like product value, quality services offered through the website, the shopping experience, and the risk perception of the online shopping. Chang, Cheung, and Lai ( Citation 2005 ) studied categories of variables, which drive online shopping activity. In their study, they divided the features into three broad categories. Perceived characteristics of the web sale channel are the first one which includes risk, online shopping experiences, advantage, service quality, trust. The second category is a website and product features which are risk reduction measures, site features, and product characteristics; and the last group is consumer characteristics. Various types of features, demographic variables, consumer shopping orientations, consumer innovativeness and psychological variables, computer, Internet knowledge, and usages drives consumer characteristics.
Consumer attitudes toward online shopping usually been determined by two factors; one is trust, and another is perceived benefits (Hoque, Ali, & Mahfuz, Citation 2015 ). Therefore, trust and perceived benefits seem to be the critical conjectures of consumer behavior toward online shopping (Al-Debei, Akroush, & Ashouri, Citation 2015 ; Hajli, Citation 2014 ). Moreover, information quality, merchandise attribute, website design, transaction capability, payment, security/privacy, delivery, self-consciousness, state of mind, the consumer’s time sense and customer service are strongly predictive of online shopping satisfaction (Katawetawaraks & Wang, Citation 2011 ; Liu, He, Gao, & Xie, Citation 2008 ; Mudambi & Schuff, Citation 2010 ; Novak, Hoffman, & Yung, Citation 2000 ; Shergill & Chen, Citation 2005 ; Sorce, Perotti, & Widrick, Citation 2005 ).
In Malaysia, information quality and purchase quality linked with the post-purchase quality are statistically significant in the case of customer satisfaction (Vegiayan, Ming, & Harun, Citation 2013 ). However, brand image and quality of products, goodwill of country of origin also influence significantly on purchase intention of online products (Haque et al., Citation 2015 ). Moreover, online data extraction about the products, services along with the historical data for individual customers is ingredient element to choose an online store or make re-purchase decision (Liao, Chu, Chen, & Chang, Citation 2012 ).
Koufaris ( Citation 2002 ) identified that both shopping enjoyment and perceived usefulness (website) strongly predict the intention to re-purchase over online. On the contrary, Lee and Lin ( Citation 2005 ) found shopping enjoyment can increase the intent of new customers but does not influence customers to return. In fact, the web store which utilizes value-added mechanisms in the search engine and providing customers a challenging experience may increase customers’ shopping enjoyment. Furthermore, if there are more often customers back to the web store, their shopping enjoyment then be determined by their involvement with the product (Marios Koufaris, Kambil, & LaBarbera, Citation 2001 )
Table 1. Previous study results of consumer behavior of online shopping
Table 2. advantages of online shopping, table 3. disadvantages of online shopping, 3.1. advantages of online shopping, 3.2. disadvantages of online shopping.
Despite the success of buying through online shopping store, there are still some difficulties that most people always complain. Those are giving in the following table:
3.3. Overview of online shopping in Bangladesh
Increasing diffusion of ICTs especially the Internet forcing the global business community to move towards e-business. Online shopping gives consumers the access to the world market, enabling them to compare price across the region and various sites, find out whether price varies by order fragmentation, get awareness about alternative products (Jagonews24.com., Citation 2015 ). Consequently, the sellers ensure that they portrayed themselves in the cyber world through websites and portals. The sellers like consumers also benefit from the increase and more efficient access to the global market through the Internet.
Over the last several years, UNCTAD (United Nation Center for Trade and Development) has emphasized the importance of e-commerce, especially online shopping for developing countries (UNCTAD, Citation 2017 ). To facilitate developing countries to transition into all sectors of e-commerce, UNCTAD has special programs. UNCTAD has also developed rules and guideline for all types of a global e-commerce transaction. The private sector in Bangladesh should be well prepared to meet the requirement and expectation of the customer and also stand out in the competition against rivals from home and abroad because of increasing globalization (Khan, Citation 2014 ).
In such a scenario, businesses need to automate their internal processes with those of ICTs to become increasingly competitive and efficient in a global context. Also, businesses have to have adequate presence and participation in the cyber world. Particularly, these two issues are becoming essential for Bangladeshi corporate sector ( Dhaka Tribune , Citation 2015 ).
3.3.1. Emergences of online shopping in Bangladesh
Although e-Commerce operation first started in late 90s to deliver gifts to Bangladeshi friends and family members by NRBs (Mohiuddin, Citation 2014 ), the first real local e-commerce or m-commerce operation was launched by CellBazaar.com in 2006 through WAP service accessed only by mobile phones (Zainudeen, Samarajiva, & Sivapragasam, Citation 2011 ).
The growth rate of e-commerce was prolonged in Bangladesh from 2000 to 2008. During that period, there were some e-commerce websites, but there was no system for an online transaction (Mahmood, Citation 2015 ). Hardly few people knew about those sites for the high cost of Internet, telephone connections, few credit card holders (Hasan, Citation 2014 ) and lower penetration rate. The opening up of online payment systems, mobile payment systems, inter-banking payment gateways in the 90s by Bangladesh Bank propelled the growth of e-commerce in Bangladesh.
Table 4. Internet usages and population statistics
Table 5. the internet subscribers, table 6. gender of the respondents.
According to BTRC, the total number of Active Internet subscriber has reached 62.004 million at the end of April 2016.
There is an increasing maturity in the way Bangladeshi people use the Internet. It is a standard curve. The online user typically starts by using email, social networking gradually moves on to browsing for news, information, entertainment, and finally, graduate to do shopping and conducting business online (Khan, Citation 2014 ). In the UNCTAD ( Citation 2017 ) B2C e-commerce index report, Bangladesh achieved the rank of 103 among 144 countries studied; however, Bangladesh is also in the biggest annual index ranking changing status (more than 10%).
Today there are more than 7000 e-commerce firms are operating through the website and social media and among these most dominating are chaldal.com, ekhanei.com, bikroy.com, rokomari.com pickaboo.com and daraz.com (Islam, Citation 2017 ). Interestingly, those trends are not limited only to Dhaka, the capital city, but semi-urban and to an extent, rural areas as well ( Dhaka Tribune , Citation 2015 ). There are about 2.55 million online shoppers, who are about 2% of the total population of Bangladesh (UNCTAD, Citation 2017 ). Internet users in Bangladesh spend over Tk 7184.018 crore in online shopping each year. A Google research paper titled “Research Insight: Emerging Trend as Bangladesh goes Digital” found that 22% of the countries total Internet users shop online and spend Tk 7594.10 annually on an average ( Dhaka Tribune , Citation 2015 ).
According to the study of Kaymu.com in 2015 (Jagonews24.com., Citation 2015 ), Dhaka (35%), Chittagong (29%), and Gazipur (15%) are the primary zone for online shopping traffic of Bangladesh. Of the total traffic, new online shopping visitor stands at 49%, while returning visitor is 51%. 71% of online shoppers have used either a desktop or a laptop, followed by mobile phone and tablets. Google and Facebook are primary click-through points for online shoppers. About 69% of the online shoppers use the Windows operating system for online shopping.
Observing the popularity, foreign investors are coming to the Bangladeshi market, for example, recently Chinese giant Alibaba group bought daraz.com and bKash – a mobile payment system to operate in Bangladesh (Ovi, Citation 2018 ). However, analyzing customer behaviors is crucial especially in the case of online shoppers who do not get the touch and feel of the actual product during purchase. The findings of this research may shed light on this issue.
4.1. Demographics of the respondents
The respondents were categorized into several factors, such as gender, age, occupation, income.
4.1.1. Gender
Among the respondents, we found 62.5% were male, and 37.5% were female (see Table 6 ).
Figure 1. Age of the respondents.

4.1.3. Occupation
Figure 2. Occupation of the respondents.

4.1.4. Income
From Figure 3 we can see that nearly 54% interviewees’ average monthly income fall into Tk. 0–10,000 categories, 15.62% respondents’ monthly income was into Tk. 10,001–20,000, 14.38% earn Tk. 20,001–30,000, and 16.88% of the interviewees have more than Tk. 30,000 income per month.
4.1.5. Experiences of online shopping versus online shopping frequencies
About 41.88% of the respondents have less than 0–1 years’ experience of online shopping, 36.25% of them have 1–2 years’ experiences, 14.37% of them have 2–3 years’ experiences and 7.5% of the respondents have experiences in online shopping for more than 3 years. Among those respondents, 57.5% of them occasionally shop online, 28.75% do shop once every month, 10% of the respondents shop online fortnightly, and only 3.75% of them buy online weekly.
Figure 3. Income of the respondents.

Figure 4. Experience in online shopping versus online shopping frequencies.

4.1.6. Sources of online shopping information
Figure 5. Sources of online shopping information.

Additionally, website advertisement, friends and family members are the primary sources of online shopping information for the online consumer. This result confirms the findings of Hajli ( Citation 2014 ) and Alsubagh ( Citation 2015 ). Publicity through various websites (primarily Facebook) will be more beneficial for organizations to promote their online shopping sites and products.
4.1.7. Reasons for choosing online shopping
Both male and female respondents assured that there are specific reasons for choosing online shopping. 38.75% respondents (26.25% male, 12.5% female) mentioned saving time is their primary reason for choosing online shopping and about 29.38% of the interviewees prefer online shopping because of availability of the varieties of products. Nearly, 19% of the respondents prefer online shopping because product comparison is much easier for online shopping and 13.13% choose for a comfortable reason (see Figure 6 ).
Time-saving and available varieties of products are the main grounds for shopping online. All these four factors motivate an online shopper to buy over the Internet. Therefore, companies should design strategies and develop varieties of products to attract and retain online shopper. This findings also confirm the findings of Gong et al. ( Citation 2013 ) and Hoque et al. ( Citation 2015 ), where the respondents found to adopt e-commerce for the usefulness.
4.1.8. Preference for product/service
Figure 6. Reasons for choosing online shopping.

Figure 7. Preference for product/service for online shopping.

Apparels, accessories, and online ticketing are the main three categories that are bringing about online shopping culture among online shoppers. Online shopping tends to grow in the coming years as consumers want to buy more in the future. Merchants should bring out innovative ways so that there is a growth in other categories of goods and services.
4.1.9. Factors for liking online shopping
Figure 8. Factors for liking online shopping.

Both male and female respondents have the same attitude towards liking factor of online shopping. Both like home delivery facility factor most. However, female likes discount offers more than the male does. These findings confirm the study of Rastogi ( Citation 2010 ) and Katawetawaraks and Wang ( Citation 2011 ), where the online shoppers also preferred the online shopping for ease of use and products’ variety.
4.1.10. Factors for disliking online shopping
Figure 9. Factor for disliking online shopping.

Among the female respondents, 45% dislike online shopping for lack of inability to touch and feel factor. 23.33% dislike the high price of the products and services. 16.67% and 15% female respondents hate poor return policy and lack of after sale service factor most respectively.
Inability to touch and feel the product or trust is still the primary disliking factor about online shopping, or we can say the primary barrier to online shopping which confirms the study of Chen and Barnes ( Citation 2007 ), Heijden et al. ( Citation 2003 ) and Huseynov and Yıldırım ( Citation 2014 ). The high price of goods and services is another big issue for the consumers. Marketers need to develop better return policies, improve the products quality and after sale services and charge a reasonable price to encourage online shopping.
4.1.11. Modes of payment preference
Figure 10. Modes of payment in online shopping.

Figure 11. Payment system security.

Figure 12. Online shopping satisfaction.

4.1.12. Payment system security
From the survey it is found that (Figure 11 ) none of the respondents highly agreed to the fact that the payment system for online shopping is highly secured in Bangladesh. 15% of the interviewees agreed to the fact that online payment system is much secured where 27.5% of respondents disagreed. 51.87% of respondents remain neutral about the fact, and 5.63% profoundly disagreed.
Above all, secured payment is a significant concern in Bangladesh. Most of the consumers believe that the payment system for online shopping is not secured. Usually, they do not prefer to use their credit or debit card while shopping from online sites. Companies should introduce new improved technologies to create and gain confidence in the payment system among the consumers.
4.1.13. Online shopping satisfaction
50% of regular online shoppers are satisfied whereas 17.5% are dissatisfied. 28.12% of them are neither satisfied nor dissatisfied. Only 3.75% of regular online shoppers are highly satisfied while 0.63% is highly dissatisfied (see Figure 12 ).
Satisfaction level plays a significant role in online shopping. Satisfied consumers tend to shop more frequently online. After analyzing data, we found that half of the respondents are satisfied with their overall online shopping experience. A note should be taken that only 3.75% of the online shopper is highly satisfied which shows that there are still concerns, which hinder the consumer from using online shopping frequently. Companies should undertake measures so that dissatisfied and neutral category of online shoppers can move towards satisfied or highly satisfied category and shop online more often and it has to be done through better information quality, quality service in during purchase and post-purchase (Vegiayan et al., Citation 2013 ).
Online shopping is more and more driven by the ICT infrastructure development, online payment systems and the Internet penetration rate in Bangladesh. Earlier studies showed that unlike brick and mortar shopping behavior, online shopping behavior is influenced by net connectivity, website esthetics (Constantinides, Citation 2004 ), security, customers’ experience, age and learning curve, etc. Studying these unique characteristics of online shopping and consumer behavior of online shoppers would benefit the tech-entrepreneurs and policymakers to craft their strategies properly for the market. This study empirically reveals the consumer behavior of online shoppers in Bangladesh.
Bangladeshi online shoppers are young (mostly below 40 years) similar to other parts of the world. They do online shopping because it saves time, offers home delivery, provides ease in shopping and offers more variety of products for apparels, accessories, and ticketing than that of brick and mortar stores. They mostly rely on price and their experience as the basis of the quality judgment of items in online shopping and for payment system they prefer cash on delivery option. Most of the shoppers get the information primarily from Facebook advertisements which is pursued by friends and family by following their “word of mouth” communication. However, privacy and inability to touch and feel are the most disliking factors for online shoppers. These findings of our study have both theoretical and practical implications.
5.1. Theoretical implications
This study provides a foundation for the future researchers in studying the consumer behavior of Bangladeshi online shoppers. Further research can be possible by increasing sample size including a rural population that may reflect the entire scenario of consumer behavior of online shopping in Bangladesh. Furthermore, the variables that have been identified in this study may not be sufficient rather more variables are to be considered in future research. Researchers may also look for factors that influence the online shopping behavior, customer satisfaction, and loyalty.
5.2. Managerial implications
The findings of the paper provide managers guideline about the attributes that must be included in their products and service quality, mode of delivery channel, payment gateway, security, trustworthiness, and pricing strategy. Managers should choose the social network for advertisement. As, until now the online payment systems through credit card are not that much available, managers must maintain the cash on a delivery program to gain trust among the customers. To elevate the touch and feel concern, managers can send alternative products to the customer to choose from options and pay after they prefer one. If the managers consider these factors, they might have a competitive advantage in the market.
Notes on contributors
Mohammad anisur rahman.
Mohammad Anisur Rahman is an Associate Professor, Department of MIS, University of Dhaka. He has received his Ph.D. from Donghua University, China, and MBA from University of Akron, USA. His research interest includes, e-business, supply chain management.
Md. Aminul Islam
Md. Aminul Islam is a Lecturer, Department of MIS, Independent University, Bangladesh. He did his BBA and MBA major in MIS, University of Dhaka. His research interest includes digital marketing, mobile banking, and technology transformation.
Bushra Humyra Esha
Bushra Humyra Esha is a Lecturer in MIS, East West University. She is a graduate of University of Dhaka. She achieved Dean’s award in 2013. Her research interest includes e-commerce, mobile banking, ICT policies.
Nahida Sultana
Nahida Sultana is a Lecturer in Business Administration Department, Bangladesh University. She has completed BBA and MBA from Department of MIS, University of Dhaka. She is interested in information system, HRIS, information security.
Sujan Chakravorty
Sujan Chakravorty is an independent researcher. He has completed MBA from Department of MIS, University of Dhaka. His research interest includes e-commerce and e-healthcare system.
Related Research Data
- Al-Debei, M. M., Akroush, M. N., & Ashouri, M. I. (2015). Consumer attitudes towards online shopping. Internet Research , 25 ( 5 ), 707–733. doi:10.1108/IntR-05-2014–0146 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Alsubagh, H. (2015). The impact of social networks on consumers’ behaviors background of the study. International Journal of Business and Social Science , 6 ( 1 ), 2219–6021. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-09450-2_7 Google Scholar
- BTRC. (2018). Internet-subscribers-Bangladesh-April-2018. Retrieved May 30, 2016, from http://www.btrc.gov.bd/content/internet-subscribers-bangladesh-april-2018 Google Scholar
- Chang, M. K., Cheung, W., & Lai, V. S. (2005). Literature-derived reference models for the adoption of online shopping. Information and Management . doi:10.1016/j.im.2004.02.006 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Chen, Y., & Barnes, S. (2007). Initial trust and online buyer behavior. Industrial Management & Data Systems , 107 ( 1 ), 21–36. doi:10.1108/02635570710719034 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Constantinides, E. (2004). Influencing the online consumer’s behavior: The web experience. Internet Research , 14 ( 2 ), 111–126. doi:10.1108/10662240410530835 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Demangeot, C., & Broderick, A. J. (2010). Consumer perceptions of online shopping environments. Psychology & Marketing , 30 ( 6 ), 461–469. doi:10.1002/mar Google Scholar
- Dhaka Tribune. (2015). Online shopping worth Tk7,184cr each year. Retrieved May 8, 2018, from http://www.dhakatribune.com/bangladesh/2015/may/08/online-shopping-worth-tk7184cr-each-year Google Scholar
- eBay. (2013). Advantages-of-online-shopping-and-its-disadvantages . Retrieved May 14, 2018, from https://www.channelreply.com/blog/view/advantages-of-ebay Google Scholar
- eMarketer. (2016). Worldwide retail ecommerce sales will reach $1.915 trillion this year. Retrieved May 14, 2018, from https://www.emarketer.com/Article/Worldwide-Retail-Ecommerce-Sales-Will-Reach-1915-trillion-This-Year/1014369 Google Scholar
- eMarketer. (2018). Retail ecommerce performance metrics. Retrieved May 14, 2018, from https://www.emarketer.com/performance/channel/58fe47a2d2670009840a9ec7/58dd63dd2357af0c900b4d33 Google Scholar
- Eze, U. C., Manyeki, J. K., Yaw, L. H., & Har, L. C. (2011). Factors affecting internet banking adoption among young adults: Evidence from Malaysia. In International Conference on Social Science and Humanity, IPEDR (Vol. 11, pp. 377–381). Singapore: IACSIT Press. Google Scholar
- Gong, W., Stump, R. L., & Maddox, L. M. (2013). Factors influencing consumers’ online shopping in China. Journal of Asia Business Studies , 7 ( 3 ), 214–230. doi:10.1108/JABS-02-2013-0006 Google Scholar
- Hajli, M. N. (2014). A study of the impact of social media on consumers. International Journal of Market Research , 56 ( January ), 387–404. doi:10.2501/IJMR–2014–025 Google Scholar
- Haque, A., Anwar, N., Yasmin, F., Sarwar, A., Ibrahim, Z., & Momen, A. (2015). Purchase intention of foreign products: A study on Bangladeshi consumer perspective. SAGE Open , 5 ( 2 ). doi:10.1177/2158244015592680 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Hasan, S. M. (2014). Advantages and disadvantages of e-Commerce . Retrieved May 11, 2018, from http://www.itseba.com/advantages-and-disadvantages-e-commerce/ Google Scholar
- Hoque, M. R., Ali, M. A., & Mahfuz, M. A. (2015). An Empirical Investigation on the adoption of e-Commerce in Bangladesh. Asia Pacific Journal of Information Systems , 25 ( 1 ). doi:10.14329/apjis.2015.25.1.001 Google Scholar
- Hub pages. (2015). Online shopping tips . Retrieved May 11, 2018, from https://hubpages.com/business/online-shoppingtips Google Scholar
- Huseynov, F., & Yıldırım, S. Ö. (2014). Internet users’ attitudes toward business-to-consumer online shopping: A survey. Information Development , 32 ( 3 ), 452–465. doi:10.1177/0266666914554812 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Internetworldstats.com. (2015). Internet world stats. Retrieved May 18, 2016, from https://www.internetworldstats.com/asia.htm Google Scholar
- Islam, T. (2017). A look into e-commerce trends and companies in Bangladesh. Retrieved May 26, 2018, from https://e27.co/look-e-commerce-trends-companies-bangladesh–20170522/ Google Scholar
- Jagonews24.com. (2015) . Kaymu releases research on online shopping, (30 July). Retrieved from https://www.jagonews24.com/en/business/news/361 Google Scholar
- Jain, A. S. (2016). Top 10 benefits of online shopping that make your life easy. Retrieved May 14, 2017, from https://toughnickel.com/frugal-living/Online-shopping-sites-benefits Google Scholar
- Jarvenpaa, S. L., Todd, P. A., Jarvenpaa, S. L., & Todd, P. A. (1997). Consumer reactions to electronic shopping on the world wide web, Google Scholar
- John, S. (2018). E-commerce trends + facts 2018. Retrieved May 14, 2018, from https://endertech.com/blog/e-commerce-trends-facts Google Scholar
- Johnson, M. D., Gustafsson, A., Andreassen, T. W., Lervik, L., & Cha, J. (2001). The Evolution and future of national customer satisfaction index models. Retrieved from http://scholarship.sha.cornell.edu/articles . Google Scholar
- Jun, G., & Jaafar, N. I. (2011). A study on consumers’ attitude towards online shopping in China. International Journal of Business and Social Science , 2 ( 22 ), 122–132. doi:10.1108/QMR-06-2013–0041 Google Scholar
- Katawetawaraks, C., & Wang, C. L. (2011). Online shopper behavior: Influences of online shopping decision. Asian Journal of Business Research , 1 ( 2 ). doi:10.14707/ajbr.112 Google Scholar
- Khan, M. A. (2014). Financial Express. Retrieved May 18, 2016, from http://print.thefinancialexpress-bd.com/2014/09/30/58964/print Google Scholar
- Kim, C., Zhao, W., & Yang, K. H. (2008). An empirical study on the integrated framework of e-CRM in online shopping. Journal of Electronic Commerce in Organizations , 6 ( 3 ), 1–19. doi:10.4018/JECO Google Scholar
- Koufaris, M. (2002). Applying model the and technology flow theory behavior acceptance to online consumer. Information Systems Research , 13 ( 2 ), 205–223. doi:10.1287/isre.13.2.205.83 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Koufaris, M., Kambil, A., & LaBarbera, P. A. (2001). Consumer behavior in web-based commerce: An empirical study. International Journal of Electronic Commerce , 6 ( 2 ), 115–138. doi:10.1080/10864415.2001.11044233 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Laforet, S., & Li, X. (2005). Consumers’ attitudes towards online and mobile banking in China. International Journal of Bank Marketing , 23 ( 5 ), 362–380. doi:10.1108/02652320510629250 Google Scholar
- Lee, G., & Lin, H. (2005). Customer perceptions of e‐service quality in online shopping. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management , 33 ( 2 ), 161–176. doi:10.1108/09590550510581485 Google Scholar
- Liao, S. H., Chu, P. H., Chen, Y. J., & Chang, C. C. (2012). Mining customer knowledge for exploring online group buying behavior. Expert Systems with Applications , 39 ( 3 ), 3708–3716. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2011.09.066 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Liu, X., He, M., Gao, F., & Xie, P. (2008). An empirical study of online shopping customer satisfaction in China: A holistic perspective, International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management , 36 ( 11 ), 919–940. Retrieved from. doi:10.1108/0959055081091168382 Google Scholar
- Mahmood, Z. (2015). E-commerce in bangladesh-growth of virtual shopping malls. Retrieved May 31, 2017, from http://hifipublic.com/2015/02/19/e-commerce-in-bangladesh-growth-of-virtual-shopping-malls/ Google Scholar
- Mohiuddin, M. (2014). Overview the e-commerce in Bangladesh. Journal of Business and Management , 16(7), 1–6. Retrieved from http://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-jbm/papers/Vol16-issue7/Version-2/A016720106.pdf Google Scholar
- Mudambi, S. M., & Schuff, D. (2010). What makes a helpful online review? A study of customer reviews on Amazon. com. MIS Quarterly , 34 ( 1 ), 185–200. doi:10.2307/20721420 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Novak, T. P., Hoffman, D. L., & Yung, Y.-F. (2000). Measuring the customer experience in online environments: A structural modeling approach. Marketing Science , 19 ( 1 ), 22–42. doi:10.1287/mksc.19.1.22.15184 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Ovi, I. H. (2018, May 8). Alibaba buys out Daraz from rocket Internet. DhakaTribune . Retrieved from https://www.dhakatribune.com/business/2018/05/08/alibaba-buys-daraz-rocket-internet/ Google Scholar
- Park, C., & Kim, Y. (2003). Identifying key factors affecting consumer purchase behavior in an online shopping context. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management , 31 ( 1 ), 16–29. doi:10.1108/09590550310457818 Google Scholar
- Rastogi, A. K. (2010). A Study of Indian online consumers & their. International Research Journal , I(10), 2009–2011. Google Scholar
- Ritchie, J., Lewis, J., Nicholls, C., McNaughton, J., & Ormiston, R. (2014). Qualitative research practice: A guide for social science students and researchers . SAGE Publications. doi:10.4135/9781452230108 Google Scholar
- Sabbir Rahman, M. (2012). Dynamics of consumers’ perception, demographic characteristics and consumers’ behavior towards selection of a restaurant: An exploratory study on Dhaka city consumers. Business Strategy Series , 13 ( 2 ), 75–88. doi:10.1108/17515631211205488 Google Scholar
- Shergill, G. S., & Chen, Z. (2005). Web-based shopping : Consumers ’ attitudes towards online shopping in New Zealand. Journal of Electronic Commerce Research , 6(2), 79–94. Google Scholar
- Sorce, P., Perotti, V., & Widrick, S. (2005). International journal of retail & distribution management, International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management Journal of Consumer Marketing International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management , 33 ( 1 ), 122–132. Retrieved from. doi:10.1108/09590550510581458 Google Scholar
- UNCTAD. (2017). Unctad B2C E-commerce index 2017, 30. Retrieved from http://unctad.org/en/PublicationsLibrary/tn_unctad_ict4d09_en.pdf%0Ahttp://unctad.org/en/PublicationsLibrary/tn_unctad_ict4d07_en.pdf Google Scholar
- Van Der Heijden, H., Verhagen, T., & Creemers, M. (2003). Understanding online purchase intentions: Contributions from technology and trust perspectives. European Journal of Information Systems , 12 ( 1 ), 41–48. doi:10.1057/palgrave.ejis.3000445 Web of Science ® Google Scholar
- Vegiayan, K. D., Ming, C. W., & Harun, M. L. O. (2013). Online shopping and customer satisfaction in Malaysia. International Journal of Marketing Practices , 1(1), 43–51. Google Scholar
- Vrender. (2016). Importance online shopping. Retrieved May 17, 2016, from http://www.sooperarticles.com/shopping-articles/clothing-articles/importance-online-shopping-1495828.html Google Scholar
- Zainudeen, A., Samarajiva, R., & Sivapragasam, N. (2011). CellBazaar : Enabling m-Commerce in Bangladesh. Information Technologies and International Development , 7(3), 61–76. Google Scholar
- Zuroni, M. J., & Goh, H. L. (2012). Factors influencing consumers’ attitude towards e-commerce purchases through online shopping. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science , 2(4), 223–230. Google Scholar
- Back to Top
Related research
People also read lists articles that other readers of this article have read.
Recommended articles lists articles that we recommend and is powered by our AI driven recommendation engine.
Cited by lists all citing articles based on Crossref citations. Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new tab.
- People also read
- Recommended articles
To cite this article:
Download citation, your download is now in progress and you may close this window.
- Choose new content alerts to be informed about new research of interest to you
- Easy remote access to your institution's subscriptions on any device, from any location
- Save your searches and schedule alerts to send you new results
- Export your search results into a .csv file to support your research
Login or register to access this feature
Register now or learn more
Login to your account
If you don't remember your password, you can reset it by entering your email address and clicking the Reset Password button. You will then receive an email that contains a secure link for resetting your password
If the address matches a valid account an email will be sent to __email__ with instructions for resetting your password
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Status | |
| Version | |
| Ad File | |
| Disable Ads Flag | |
| Environment | |
| Moat Init | |
| Moat Ready | |
| Contextual Ready | |
| Contextual URL | |
| Contextual Initial Segments | |
| Contextual Used Segments | |
| AdUnit | |
| SubAdUnit | |
| Custom Targeting | |
| Ad Events | |
| Invalid Ad Sizes |

- Submit Member Login
Access provided by
Comparing Online and In-Store Grocery Purchases
Download started
- Add to Mendeley
Participants
Main outcome measures and analysis, conclusions and implications.
- food preferences
- consumer behavior

Get full text access
Log in, subscribe or purchase for full access.
Article metrics
Related articles.
- Download Hi-res image
- Download .PPT
- Access for Developing Countries
- Articles & Issues
- Articles In Press
- Current Issue
- List of Issues
- Supplements
- For Authors
- Author Guidelines
- Submit Your Manuscript
- Statistical Methods
- Guidelines for Authors of Educational Material Reviews
- Permission to Reuse
- About Open Access
- Researcher Academy
- For Reviewers
- General Guidelines
- Methods Paper Guidelines
- Qualitative Guidelines
- Quantitative Guidelines
- Questionnaire Methods Guidelines
- Statistical Methods Guidelines
- Systematic Review Guidelines
- Perspective Guidelines
- GEM Reviewing Guidelines
- Journal Info
- About the Journal
- Disclosures
- Abstracting/Indexing
- Impact/Metrics
- Contact Information
- Editorial Staff and Board
- Info for Advertisers
- Member Access Instructions
- New Content Alerts
- Sponsored Supplements
- Statistical Reviewers
- Reviewer Appreciation
- New Resources
- New Resources for Nutrition Educators
- Submit New Resources for Review
- Guidelines for Writing Reviews of New Resources for Nutrition Educators
- Podcast/Webinars
- New Resources Podcasts
- Press Release & Other Podcasts
- Collections
- Society News
The content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Accessibility
- Help & Contact

Society Member Access
SNEB Members, full access to the journal is a member benefit. Login via the SNEB Website to access all journal content and features.
- Institutional Access: Log in to ScienceDirect
- Existing Subscriber: Log in
- New Subscriber: Claim access with activation code. New subscribers select Claim to enter your activation code.
Academic & Personal
Corporate r&d professionals.
- Full online access to your subscription and archive of back issues
- Table of Contents alerts
- Access to all multimedia content, e.g. podcasts, videos, slides
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
The PMC website is updating on October 15, 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
The Impact of Online Reviews on Consumers’ Purchasing Decisions: Evidence From an Eye-Tracking Study
1 School of Business, Ningbo University, Ningbo, China
Premaratne Samaranayake
2 School of Business, Western Sydney University, Penrith, NSW, Australia
XiongYing Cen
Yi-chen lan, associated data.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
This study investigated the impact of online product reviews on consumers purchasing decisions by using eye-tracking. The research methodology involved (i) development of a conceptual framework of online product review and purchasing intention through the moderation role of gender and visual attention in comments, and (ii) empirical investigation into the region of interest (ROI) analysis of consumers fixation during the purchase decision process and behavioral analysis. The results showed that consumers’ attention to negative comments was significantly greater than that to positive comments, especially for female consumers. Furthermore, the study identified a significant correlation between the visual browsing behavior of consumers and their purchase intention. It also found that consumers were not able to identify false comments. The current study provides a deep understanding of the underlying mechanism of how online reviews influence shopping behavior, reveals the effect of gender on this effect for the first time and explains it from the perspective of attentional bias, which is essential for the theory of online consumer behavior. Specifically, the different effects of consumers’ attention to negative comments seem to be moderated through gender with female consumers’ attention to negative comments being significantly greater than to positive ones. These findings suggest that practitioners need to pay particular attention to negative comments and resolve them promptly through the customization of product/service information, taking into consideration consumer characteristics, including gender.
Introduction
E-commerce has grown substantially over the past years and has become increasingly important in our daily life, especially under the influence of COVID-19 recently ( Hasanat et al., 2020 ). In terms of online shopping, consumers are increasingly inclined to obtain product information from reviews. Compared with the official product information provided by the sellers, reviews are provided by other consumers who have already purchased the product via online shopping websites ( Baek et al., 2012 ). Meanwhile, there is also an increasing trend for consumers to share their shopping experiences on the network platform ( Floh et al., 2013 ). In response to these trends, a large number of studies ( Floh et al., 2013 ; Lackermair et al., 2013 ; Kang et al., 2020 ; Chen and Ku, 2021 ) have investigated the effects of online reviews on purchasing intention. These studies have yielded strong evidence of the valence intensity of online reviews on purchasing intention. Lackermair et al. (2013) , for example, showed that reviews and ratings are an important source of information for consumers. Similarly, through investigating the effects of review source and product type, Bae and Lee (2011) concluded that a review from an online community is the most credible for consumers seeking information about an established product. Since reviews are comments from consumers’ perspectives and often describe their experience using the product, it is easier for other consumers to accept them, thus assisting their decision-making process ( Mudambi and Schuff, 2010 ).
A survey conducted by Zhong-Gang et al. (2015) reveals that nearly 60% of consumers browse online product reviews at least once a week and 93% of whom believe that these online reviews help them to improve the accuracy of purchase decisions, reduce the risk of loss and affect their shopping options. When it comes to e-consumers in commercial activities on B2B and B2C platforms, 82% of the consumers read product reviews before making shopping choices, and 60% of them refer to comments every week. Research shows that 93% of consumers say online reviews will affect shopping choices, indicating that most consumers have the habit of reading online reviews regularly and rely on the comments for their purchasing decisions ( Vimaladevi and Dhanabhakaym, 2012 ).
Consumer purchasing decision after reading online comments is a psychological process combining vision and information processing. As evident from the literature, much of the research has focused on the outcome and impact of online reviews affecting purchasing decisions but has shed less light on the underlying processes that influence customer perception ( Sen and Lerman, 2007 ; Zhang et al., 2010 ; Racherla and Friske, 2013 ). While some studies have attempted to investigate the underlying processes, including how people are influenced by information around the product/service using online reviews, there is limited research on the psychological process and information processing involved in purchasing decisions. The eye-tracking method has become popular in exploring and interpreting consumer decisions making behavior and cognitive processing ( Wang and Minor, 2008 ). However, there is very limited attention to how the emotional valence and the content of comments, especially those negative comments, influence consumers’ final decisions by adopting the eye-tracking method, including a gender comparison in consumption, and to whether consumers are suspicious of false comments.
Thus, the main purpose of this research is to investigate the impact of online reviews on consumers’ purchasing decisions, from the perspective of information processing by employing the eye-tracking method. A comprehensive literature review on key themes including online reviews, the impact of online reviews on purchasing decisions, and underlying processes including the level and credibility of product review information, and processing speed/effectiveness to drive customer perceptions on online reviews, was used to identify current research gaps and establish the rationale for this research. This study simulated a network shopping scenario and conducted an eye movement experiment to capture how product reviews affect consumers purchasing behavior by collecting eye movement indicators and their behavioral datum, in order to determine whether the value of the fixation dwell time and fixation count for negative comment areas is greater than that for positive comment area and to what extent the consumers are suspicious about false comments. Visual attention by both fixation dwell time and count is considered as part of moderating effect on the relationship between the valence of comment and purchase intention, and as the basis for accommodating underlying processes.
The paper is organized as follows. The next section presents literature reviews of relevant themes, including the role of online reviews and the application of eye movement experiments in online consumer decision research. Then, the hypotheses based on the relevant theories are presented. The research methodology including data collection methods is presented subsequently. This is followed by the presentation of data analysis, results, and discussion of key findings. Finally, the impact of academic practical research and the direction of future research are discussed, respectively.
Literature Review
Online product review.
Several studies have reported on the influence of online reviews, in particular on purchasing decisions in recent times ( Zhang et al., 2014 ; Zhong-Gang et al., 2015 ; Ruiz-Mafe et al., 2018 ; Von Helversen et al., 2018 ; Guo et al., 2020 ; Kang et al., 2020 ; Wu et al., 2021 ). These studies have reported on various aspects of online reviews on consumers’ behavior, including consideration of textual factors ( Ghose and Ipeirotiss, 2010 ), the effect of the level of detail in a product review, and the level of reviewer agreement with it on the credibility of a review, and consumers’ purchase intentions for search and experience products ( Jiménez and Mendoza, 2013 ). For example, by means of text mining, Ghose and Ipeirotiss (2010) concluded that the use of product reviews is influenced by textual features, such as subjectivity, informality, readability, and linguistic accuracy. Likewise, Boardman and Mccormick (2021) found that consumer attention and behavior differ across web pages throughout the shopping journey depending on its content, function, and consumer’s goal. Furthermore, Guo et al. (2020) showed that pleasant online customer reviews lead to a higher purchase likelihood compared to unpleasant ones. They also found that perceived credibility and perceived diagnosticity have a significant influence on purchase decisions, but only in the context of unpleasant online customer reviews. These studies suggest that online product reviews will influence consumer behavior but the overall effect will be influenced by many factors.
In addition, studies have considered broader online product information (OPI), comprising both online reviews and vendor-supplied product information (VSPI), and have reported on different attempts to understand the various ways in which OPI influences consumers. For example, Kang et al. (2020) showed that VSPI adoption affected online review adoption. Lately, Chen and Ku (2021) found a positive relationship between diversified online review websites as accelerators for online impulsive buying. Furthermore, some studies have reported on other aspects of online product reviews, including the impact of online reviews on product satisfaction ( Changchit and Klaus, 2020 ), relative effects of review credibility, and review relevance on overall online product review impact ( Mumuni et al., 2020 ), functions of reviewer’s gender, reputation and emotion on the credibility of negative online product reviews ( Craciun and Moore, 2019 ) and influence of vendor cues like the brand reputation on purchasing intention ( Kaur et al., 2017 ). Recently, an investigation into the impact of online review variance of new products on consumer adoption intentions showed that product newness and review variance interact to impinge on consumers’ adoption intentions ( Wu et al., 2021 ). In particular, indulgent consumers tend to prefer incrementally new products (INPs) with high variance reviews while restrained consumers are more likely to adopt new products (RNPs) with low variance.
Emotion Valence of Online Product Review and Purchase Intention
Although numerous studies have investigated factors that may influence the effects of online review on consumer behavior, few studies have focused on consumers’ perceptions, emotions, and cognition, such as perceived review helpfulness, ease of understanding, and perceived cognitive effort. This is because these studies are mainly based on traditional self-report-based methods, such as questionnaires, interviews, and so on, which are not well equipped to measure implicit emotion and cognitive factors objectively and accurately ( Plassmann et al., 2015 ). However, emotional factors are also recognized as important in purchase intention. For example, a study on the usefulness of online film reviews showed that positive emotional tendencies, longer sentences, the degree of a mix of the greater different emotional tendencies, and distinct expressions in critics had a significant positive effect on online comments ( Yuanyuan et al., 2009 ).
Yu et al. (2010) also demonstrated that the different emotional tendencies expressed in film reviews have a significant impact on the actual box office. This means that consumer reviews contain both positive and negative emotions. Generally, positive comments tend to prompt consumers to generate emotional trust, increase confidence and trust in the product and have a strong persuasive effect. On the contrary, negative comments can reduce the generation of emotional trust and hinder consumers’ buying intentions ( Archak et al., 2010 ). This can be explained by the rational behavior hypothesis, which holds that consumers will avoid risk in shopping as much as possible. Hence, when there is poor comment information presented, consumers tend to choose not to buy the product ( Mayzlin and Chevalier, 2003 ). Furthermore, consumers generally believe that negative information is more valuable than positive information when making a judgment ( Ahluwalia et al., 2000 ). For example, a single-star rating (criticism) tends to have a greater influence on consumers’ buying tendencies than that of a five-star rating (compliment), a phenomenon known as the negative deviation.
Since consumers can access and process information quickly through various means and consumers’ emotions influence product evaluation and purchasing intention, this research set out to investigate to what extent and how the emotional valence of online product review would influence their purchase intention. Therefore, the following hypothesis was proposed:
H1 : For hedonic products, consumer purchase intention after viewing positive emotion reviews is higher than that of negative emotion ones; On the other hand, for utilitarian products, it is believed that negative comments are more useful than positive ones and have a greater impact on consumers purchase intention by and large.
It is important to investigate Hypothesis one (H1) although it seems obvious. Many online merchants pay more attention to products with negative comments and make relevant improvements to them rather than those with positive comments. Goods with positive comments can promote online consumers’ purchase intention more than those with negative comments and will bring more profits to businesses.
Sen and Lerman (2007) found that compared with the utilitarian case, readers of negative hedonic product reviews are more likely to attribute the negative opinions expressed, to the reviewer’s internal (or non-product-related) reasons, and therefore, are less likely to find the negative reviews useful. However, in the utilitarian case, readers are more likely to attribute the reviewer’s negative opinions to external (or product-related) motivations, and therefore, find negative reviews more useful than positive reviews on average. Product type moderates the effect of review valence, Therefore, Hypothesis one is based on hedonic product types, such as fiction books.
Guo et al. (2020) found pleasant online customer reviews to lead to a higher purchase likelihood than unpleasant ones. This confirms hypothesis one from another side. The product selected in our experiment is a mobile phone, which is not only a utilitarian product but also a hedonic one. It can be used to make a phone call or watch videos, depending on the user’s demands.
Eye-Tracking, Online Product Review, and Purchase Intention
The eye-tracking method is commonly used in cognitive psychology research. Many researchers are calling for the use of neurobiological, neurocognitive, and physiological approaches to advance information system research ( Pavlou and Dimoka, 2010 ; Liu et al., 2011 ; Song et al., 2017 ). Several studies have been conducted to explore consumers’ online behavior by using eye-tracking. For example, using the eye-tracking method, Luan et al. (2016) found that when searching for products, customers’ attention to attribute-based evaluation is significantly longer than that of experience-based evaluation, while there is no significant difference for the experiential products. Moreover, their results indicated eye-tracking indexes, for example, fixation dwell time, could intuitively reflect consumers’ search behavior when they attend to the reviews. Also, Hong et al. (2017) confirmed that female consumers pay more attention to picture comments when they buy experience goods; when they buy searched products, they are more focused on the pure text comments. When the price and comment clues are consistent, consumers’ purchase rates significantly improve.
Eye-tracking method to explore and interpret consumers’ decision-making behavior and cognitive processing is primarily based on the eye-mind hypothesis proposed by Just and Carpenter (1992) . Just and Carpenter (1992) stated that when an individual is looking, he or she is currently perceiving, thinking about, or attending to something, and his or her cognitive processing can be identified by tracking eye movement. Several studies on consumers’ decision-making behavior have adopted the eye-tracking approach to quantify consumers’ visual attention, from various perspectives including determining how specific visual features of the shopping website influenced their attitudes and reflected their cognitive processes ( Renshaw et al., 2004 ), exploring gender differences in visual attention and shopping attitudes ( Hwang and Lee, 2018 ), investigating how employing human brands affects consumers decision quality ( Chae and Lee, 2013 ), consumer attention and different behavior depending on website content, functions and consumers goals ( Boardman and McCormick, 2019 ). Measuring the attention to the website and time spent on each purchasing task in different product categories shows that shoppers attend to more areas of the website for purposes of website exploration than for performing purchase tasks. The most complex and time-consuming task for shoppers is the assessment of purchase options ( Cortinas et al., 2019 ). Several studies have investigated fashion retail websites using the eye-tracking method and addressed various research questions, including how consumers interact with product presentation features and how consumers use smartphones for fashion shopping ( Tupikovskaja-Omovie and Tyler, 2021 ). Yet, these studies considered users without consideration of user categories, particularly gender. Since this research is to explore consumers’ decision-making behavior and the effects of gender on visual attention, the eye-tracking approach was employed as part of the overall approach of this research project. Based on existing studies, it could be that consumers may pay more attention to negative evaluations, will experience cognitive conflict when there are contradictory false comments presented, and will be unable to judge good or bad ( Cui et al., 2012 ). Therefore, the following hypothesis was proposed:
H2 : Consumers’ purchasing intention associated with online reviews is moderated/influenced by the level of visual attention.
To test the above hypothesis, the following two hypotheses were derived, taking into consideration positive and negative review comments from H1, and visual attention associated with fixation dwell time and fixation count.
H2a : When consumers intend to purchase a product, fixation dwell time and fixation count for negative comment areas are greater than those for positive comment areas.
Furthermore, when consumers browse fake comments, they are suspicious and actively seek out relevant information to identify the authenticity of the comments, which will result in more visual attention. Therefore, H2b was proposed:
H2b : Fixation dwell time and fixation count for fake comments are greater than those for authentic comments.
When considering the effect of gender on individual information processing, some differences were noted. For example, Meyers-Levy and Sternthal (1993) put forward the selectivity hypothesis, a theory of choice hypothesis, which implies that women gather all information possible, process it in an integrative manner, and make a comprehensive comparison before making a decision, while men tend to select only partial information to process and compare according to their existing knowledge—a heuristic and selective strategy. Furthermore, for an online product review, it was also reported that gender can easily lead consumers to different perceptions of the usefulness of online word-of-mouth. For example, Zhang et al. (2014) confirmed that a mixed comment has a mediating effect on the relationship between effective trust and purchasing decisions, which is stronger in women. This means that men and women may have different ways of processing information in the context of making purchasing decisions using online reviews. To test the above proposition, the following hypothesis was proposed:
H3 : Gender factors have a significant impact on the indicators of fixation dwell time and fixation count on the area of interest (AOI). Male purchasing practices differ from those of female consumers. Male consumers’ attention to positive comments is greater than that of female ones, they are more likely than female consumers to make purchase decisions easily.
Furthermore, according to the eye-mind hypothesis, eye movements can reflect people’s cognitive processes during their decision process ( Just and Carpenter, 1980 ). Moreover, neurocognitive studies have indicated that consumers’ cognitive processing can reflect the strategy of their purchase decision-making ( Rosa, 2015 ; Yang, 2015 ). Hence, the focus on the degree of attention to different polarities and the specific content of comments can lead consumers to make different purchasing decisions. Based on the key aspects outlined and discussed above, the following hypothesis was proposed:
H4 : Attention to consumers’ comments is positively correlated with consumers’ purchasing intentions: Consumers differ in the content of comments to which they gaze according to gender factors.
Thus, the framework of the current study is shown in Figure 1 .

Conceptual framework of the study.
Materials and Methods
The research adopted an experimental approach using simulated lab environmental settings for collecting experimental data from a selected set of participants who have experience with online shopping. The setting of the task was based on guidelines for shopping provided on Taobao.com , which is the most famous and frequently used C2C platform in China. Each experiment was set with the guidelines provided and carried out for a set time. Both behavioral and eye movement data were collected during the experiment.
Participants
A total of 40 healthy participants (20 males and 20 females) with online shopping experiences were selected to participate in the experiment. The participants were screened to ensure normal or correct-to-normal vision, no color blindness or poor color perception, or other eye diseases. All participants provided their written consent before the experiment started. The study was approved by the Internal Review Board of the Academy of Neuroeconomics and Neuromanagement at Ningbo University and by the Declaration of Helsinki ( World Medical Association, 2014 ).
With standardization and small selection differences among individuals, search products can be objectively evaluated and easily compared, to effectively control the influence of individual preferences on the experimental results ( Huang et al., 2009 ). Therefore, this research focused on consumer electronics products, essential products in our life, as the experiment stimulus material. To be specific, as shown in Figure 2 , a simulated shopping scenario was presented to participants, with a product presentation designed in a way that products are shown on Taobao.com . Figure 2 includes two segments: One shows mobile phone information ( Figure 2A ) and the other shows comments ( Figure 2B ). Commodity description information in Figure 2A was collected from product introductions on Taobao.com , mainly presenting some parameter information about the product, such as memory size, pixels, and screen size. There was little difference in these parameters, so quality was basically at the same level across smartphones. Prices and brand information were hidden to ensure that reviews were the sole factor influencing consumer decision-making. Product review areas in Figure 2B are the AOI, presented as a double-column layout. Each panel included 10 (positive or negative) reviews taken from real online shopping evaluations, amounting to a total of 20 reviews for each product. To eliminate the impact of different locations of comments on experimental results, the positions of the positive and negative comment areas were exchanged, namely, 50% of the subjects had positive comments presented on the left and negative comments on the right, with the remaining 50% of the participants receiving the opposite set up.

Commodity information and reviews. (A) Commodity information, (B) Commodity reviews. Screenshots of Alibaba shopfront reproduced with permission of Alibaba and Shenzhen Genuine Mobile Phone Store.
A total of 12,403 product reviews were crawled through and extracted from the two most popular online shopping platforms in China (e.g., Taobao.com and JD.com ) by using GooSeeker (2015) , a web crawler tool. The retrieved reviews were then further processed. At first, brand-related, price-related, transaction-related, and prestige-related contents were removed from comments. Then, the reviews were classified in terms of appearance, memory, running speed, logistics, and so on into two categories: positive reviews and negative reviews. Furthermore, the content of the reviews was refined to retain the original intention but to meet the requirements of the experiment. In short, reviews were modified to ensure brevity, comprehensibility, and equal length, so as to avoid causing cognitive difficulties or ambiguities in semantic understanding. In the end, 80 comments were selected for the experiment: 40 positive and 40 negative reviews (one of the negative comments was a fictitious comment, formulated for the needs of the experiment). To increase the number of experiments and the accuracy of the statistical results, four sets of mobile phone products were set up. There were eight pairs of pictures in total.
Before the experiment started, subjects were asked to read the experimental guide including an overview of the experiment, an introduction of the basic requirements and precautions in the test, and details of two practice trials that were conducted. When participants were cognizant of the experimental scenario, the formal experiment was ready to begin. Participants were required to adjust their bodies to a comfortable sitting position. The 9 points correction program was used for calibration before the experiment. Only those with a deviation angle of less than 1-degree angle could enter the formal eye movement experiment. In our eye-tracking experiment, whether the participant wears glasses or not was identified as a key issue. If the optical power of the participant’s glasses exceeds 200 degrees, due to the reflective effect of the lens, the eye movement instrument will cause great errors in the recording of eye movements. In order to ensure the accuracy of the data recorded by the eye tracker, the experimenter needs to test the power of each participant’s glasses and ensure that the degree of the participant’s glasses does not exceed 200 degrees before the experiment. After drift correction of eye movements, the formal experiment began. The following prompt was presented on the screen: “you will browse four similar mobile phone products; please make your purchase decision for each mobile phone.” Participants then had 8,000 ms to browse the product information. Next, they were allowed to look at the comments image as long as required, after which they were asked to press any key on the keyboard and answer the question “are you willing to buy this cell phone?.”
In this experiment, experimental materials were displayed on a 17-inch monitor with a resolution of 1,024 × 768 pixels. Participants’ eye movements were tracked and recorded by the Eyelink 1,000 desktop eye tracker which is a precise and accurate video-based eye tracker instrument, integrating with SR Research Experiment Builder, Data Viewer, and third-party software tools, with a sampling rate of 1,000 Hz. ( Hwang and Lee, 2018 ). Data processing was conducted by the matching Data Viewer analysis tool.
The experiment flow of each trial is shown in Figure 3 . Every subject was required to complete four trials, with mobile phone style information and comment content different and randomly presented in each trial. After the experiment, a brief interview was conducted to learn about participants’ browsing behavior when they purchased the phone and collected basic information via a matching questionnaire. The whole experiment took about 15 min.

Experimental flow diagram. Screenshots of Alibaba shopfront reproduced with permission of Alibaba and Shenzhen Genuine Mobile Phone Store.
Data Analysis
Key measures of data collected from the eye-tracking experiment included fixation dwell time and fixation count. AOI is a focus area constructed according to experimental purposes and needs, where pertinent eye movement indicators are extracted. It can guarantee the precision of eye movement data, and successfully eliminate interference from other visual factors in the image. Product review areas are our AOIs, with positive comments (IA1) and negative comments (IA2) divided into two equal-sized rectangular areas.
Fixation can indicate the information acquisition process. Tracking eye fixation is the most efficient way to capture individual information from the external environment ( Hwang and Lee, 2018 ). In this study, fixation dwell time and fixation count were used to indicate users’ cognitive activity and visual attention ( Jacob and Karn, 2003 ). It can reflect the degree of digging into information and engaging in a specific situation. Generally, a more frequent fixation frequency indicates that the individual is more interested in the target resulting in the distribution of fixation points. Valuable and interesting comments attract users to pay more attention throughout the browsing process and focus on the AOIs for much longer. Since these two dependent variables (fixation dwell time and fixation count) comprised our measurement of the browsing process, comprehensive analysis can effectively measure consumers’ reactions to different review contents.
The findings are presented in each section including descriptive statistical analysis, analysis from the perspective of gender and review type using ANOVA, correlation analysis of purchasing decisions, and qualitative analysis of observations.
Descriptive Statistical Analysis
Fixation dwell time and fixation count were extracted in this study for each record. In this case, 160 valid data records were recorded from 40 participants. Each participant generated four records which corresponded to four combinations of two conditions (positive and negative) and two eye-tracking indices (fixation dwell time and fixation count). Each record represented a review comment. Table 1 shows pertinent means and standard deviations.
Results of mean and standard deviations.
| Fixation dwell time (ms) | Fixation count | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive review | Negative review | Positive review | Negative review | |||||
| SD | SD | SD | SD | |||||
| Male | 10140.74 | 6048.38 | 11057.59 | 5236.95 | 45.76 | 25.91 | 49.1 | 20.83 |
| Female | 7262.06 | 4543.37 | 12334.06 | 7743.16 | 36.26 | 22.22 | 60.07 | 35.35 |
| Total | 8701.4 | 5524.34 | 11695.82 | 6620.13 | 41.01 | 24.53 | 54.59 | 29.44 |
It can be noted from the descriptive statistics for both fixation dwell time and fixation count that the mean of positive reviews was less than that of negative ones, suggesting that subjects spent more time on and had more interest in negative reviews. This tendency was more obvious in female subjects, indicating a role of gender.
Fixation results can be reported using a heat mapping plot to provide a more intuitive understanding. In a heat mapping plot, fixation data are displayed as different colors, which can manifest the degree of user fixation ( Wang et al., 2014 ). Red represents the highest level of fixation, followed by yellow and then green, and areas without color represent no fixation count. Figure 4 implies that participants spent more time and cognitive effort on negative reviews than positive ones, as evidenced by the wider red areas in the negative reviews. However, in order to determine whether this difference is statistically significant or not, further inferential statistical analyses were required.

Heat map of review picture.
Repeated Measures From Gender and Review Type Perspectives—Analysis of Variance
The two independent variables for this experiment were the emotional tendency of the review and gender. A preliminary ANOVA analysis was performed, respectively, on fixation dwell time and fixation count values, with gender (man vs. woman) and review type (positive vs. negative) being the between-subjects independent variables in both cases.
A significant dominant effect of review type was found for both fixation dwell time ( p 1 < 0.001) and fixation count ( p 2 < 0.001; see Table 2 ). However, no significant dominant effect of gender was identified for either fixation dwell time ( p 1 = 0.234) or fixation count ( p 2 = 0.805). These results indicated that there were significant differences in eye movement indicators between positive and negative commentary areas, which confirms Hypothesis 2a. The interaction effect between gender and comment type was significant for both fixation dwell time ( p 1 = 0.002) and fixation count ( p 2 = 0.001). Therefore, a simple-effect analysis was carried out. The effects of different comment types with fixed gender factors and different gender with fixed comment type factors on those two dependent variables (fixation dwell time and fixation count) were investigated and the results are shown in Table 3 .
Results of ANOVA analysis.
| Fixation dwell time of AOI | Fixation count of AOI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sig. ( ) | Sig. ( ) | |||
| Gender | 1.42 | 0.234 | 0.061 | 0.805 |
| Review type | 19.842 | 0.000 | 20.702 | 0.000 |
| Gender & Review type | 9.552 | 0.002 | 11.774 | 0.001 |
Results of simple-effect analysis.
| Fixed factor | Fixation dwell time of AOI | Fixation count of AOI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean difference (I-J) | Standard error | Sig. ( ) | Mean difference (I-J) | Standard error | Sig. ( ) | |||
| Male | Positive reviews | Negative reviews | −916.85 | 950.68 | 0.336 | −3.34 | 4.22 | 0.430 |
| Female | ||||||||
| −5072.00 | 950.68 | 0.000 | −23.81 | 4.22 | 0.000 | |||
| Positive reviews | Male | Female | 2878.66 | 950.68 | 0.003 | 9.50 | 4.22 | 0.025 |
| Negative reviews | −1276.48 | 950.68 | 0.180 | −10.98 | 4.22 | 0.010 | ||
When the subject was female, comment type had a significant dominant effect for both fixation dwell time ( p 1 < 0.001) and fixation count ( p 2 < 0.001). This indicates that female users’ attention time and cognitive level on negative comments were greater than those on positive comments. However, the dominant effect of comment type was not significant ( p 1 = 0.336 > 0.05, p 2 = 0.43 > 0.05) for men, suggesting no difference in concern about the two types of comments for men.
Similarly, when scanning positive reviews, gender had a significant dominant effect ( p 1 = 0.003 < 0.05, p 2 = 0.025 < 0.05) on both fixation dwell time and fixation count, indicating that men exerted longer focus and deeper cognitive efforts to dig out positive reviews than women. In addition, the results for fixation count showed that gender had significant dominant effects ( p 1 = 0.18 > 0.05, p 2 = 0.01 < 0.05) when browsing negative reviews, suggesting that to some extent men pay significantly less cognitive attention to negative reviews than women, which is consistent with the conclusion that men’s attention to positive comments is greater than women’s. Although the dominant effect of gender was not significant ( p 1 = 0.234 > 0.05, p 2 = 0.805 > 0.05) in repeated measures ANOVA, there was an interaction effect with review type. For a specific type of comment, gender had significant influences, because the eye movement index between men and women was different. Thus, gender plays a moderating role in the impact of comments on consumers purchasing behavior.
Correlation Analysis of Purchase Decision
Integrating eye movement and behavioral data, whether participants’ focus on positive or negative reviews is linked to their final purchasing decisions were explored. Combined with the participants’ purchase decision results, the areas with large fixation dwell time and concerns of consumers in the picture were screened out. The frequency statistics are shown in Table 4 .
Frequency statistics of purchasing decisions.
| Whether to buy | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | |||
| Review type (more attention) | Positive review | 21 | 25 | 46 |
| Negative review | 80 | 34 | 114 | |
| Total | 101 | 59 | 160 | |
The correlation analysis between the type of comment and the decision data shows that users’ attention level on positive and negative comments was significantly correlated with the purchase decision ( p = 0.006 < 0.05). Thus, Hypothesis H4 is supported. As shown in Table 4 above, 114 records paid more attention to negative reviews, and 70% of the participants chose not to buy mobile phones. Also, in the 101 records of not buying, 80% of the subjects paid more attention to negative comments and chose not to buy mobile phones, while more than 50% of the subjects who were more interested in positive reviews chose to buy mobile phones. These experimental results are consistent with Hypothesis H1. They suggest that consumers purchasing decisions were based on the preliminary information they gathered and were concerned about, from which we can deduce customers’ final decision results from their visual behavior. Thus, the eye movement experiment analysis in this paper has practical significance.
Furthermore, a significant correlation ( p = 0.007 < 0.05) was found between the comments area attracting more interest and purchase decisions for women, while no significant correlation was found for men ( p = 0.195 > 0.05). This finding is consistent with the previous conclusion that men’s attention to positive and negative comments is not significantly different. Similarly, this also explains the moderating effect of gender. This result can be explained further by the subsequent interview of each participant after the experiment was completed. It was noted from the interviews that most of the male subjects claimed that they were more concerned about the hardware parameters of the phone provided in the product information picture. Depending on whether it met expectations, their purchasing decisions were formed, and mobile phone reviews were taken as secondary references that could not completely change their minds.
Figure 5 shows an example of the relationship between visual behavior randomly selected from female participants and the correlative decision-making behavior. The English translation of words that appeared in Figure 5 is shown in Figure 4 .

Fixation count distribution.
The subjects’ fixation dwell time and fixation count for negative reviews were significantly greater than those for positive ones. Focusing on the screen and running smoothly, the female participant decided not to purchase this product. This leads to the conclusion that this subject thought a lot about the phone screen quality and running speed while selecting a mobile phone. When other consumers expressed negative criticism about these features, the female participant tended to give up buying them.
Furthermore, combined with the result of each subject’s gaze distribution map and AOI heat map, it was found that different subjects paid attention to different features of mobile phones. Subjects all had clear concerns about some features of the product. The top five mobile phone features that subjects were concerned about are listed in Table 5 . Contrary to expectations, factors, such as appearance and logistics, were no longer a priority. Consequently, the reasons why participants chose to buy or not to buy mobile phones can be inferred from the gazing distribution map recorded in the product review picture. Therefore we can provide suggestions on how to improve the design of mobile phone products for businesses according to the features that users are more concerned about.
Top 5 features of mobile phones.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Running smoothly | Battery life | Fever condition | Pixel | After-sale service |
Fictitious Comments Recognition Analysis
The authenticity of reviews is an important factor affecting the helpfulness of online reviews. To enhance the reputation and ratings of online stores, in the Chinese e-commerce market, more and more sellers are employing a network “water army”—a group of people who praise the shop and add many fake comments without buying any goods from the store. Combined with online comments, eye movement fixation, and information extraction theory, Song et al. (2017) found that fake praise significantly affects consumers’ judgment of the authenticity of reviews, thereby affecting consumers’ purchase intention. These fictitious comments glutted in the purchasers’ real ones are easy to mislead customers. Hence, this experiment was designed to randomly insert a fictitious comment into the remaining 79 real comments without notifying the participants in advance, to test whether potential buyers could identify the false comments and find out their impact on consumers’ purchase decisions.
The analysis of the eye movement data from 40 product review pictures containing this false commentary found that only several subjects’ visual trajectories were back and forth in this comment, and most participants exhibited no differences relative to other comments, indicating that the vast majority of users did not identify the lack of authenticity of this comment. Moreover, when asked whether they had taken note of this hidden false comment in interviews, almost 96% of the participants answered they had not. Thus, Hypothesis H2b is not supported.
This result explains why network “water armies” are so popular in China, as the consumer cannot distinguish false comments. Thus, it is necessary to standardize the e-commerce market, establish an online comment authenticity automatic identification information system, and crack down on illegal acts of employing network troops to disseminate fraudulent information.
Discussion and Conclusion
In the e-commerce market, online comments facilitate online shopping for consumers; in turn, consumers are increasingly dependent on review information to judge the quality of products and make a buying decision. Consequently, studies on the influence of online reviews on consumers’ behavior have important theoretical significance and practical implications. Using traditional empirical methodologies, such as self-report surveys, it is difficult to elucidate the effects of some variables, such as review choosing preference because they are associated with automatic or subconscious cognitive processing. In this paper, the eye-tracking experiment as a methodology was employed to test congruity hypotheses of product reviews and explore consumers’ online review search behavior by incorporating the moderating effect of gender.
Hypotheses testing results indicate that the emotional valence of online reviews has a significant influence on fixation dwell time and fixation count of AOI, suggesting that consumers exert more cognitive attention and effort on negative reviews than on positive ones. This finding is consistent with Ahluwalia et al.’s (2000) observation that negative information is more valuable than positive information when making a judgment. Specifically, consumers use comments from other users to avoid possible risks from information asymmetry ( Hong et al., 2017 ) due to the untouchability of online shopping. These findings provide the information processing evidence that customers are inclined to acquire more information for deeper thinking and to make a comparison when negative comments appear which could more likely result in choosing not to buy the product to reduce their risk. In addition, in real online shopping, consumers are accustomed to giving positive reviews as long as any dissatisfaction in the shopping process is within their tolerance limits. Furthermore, some e-sellers may be forging fake praise ( Wu et al., 2020 ). The above two phenomena exaggerate the word-of-mouth effect of negative comments, resulting in their greater effect in contrast to positive reviews; hence, consumers pay more attention to negative reviews. Thus, Hypothesis H2a is supported. However, when limited fake criticism was mixed in with a large amount of normal commentary, the subject’s eye movements did not change significantly, indicating that little cognitive conflict was produced. Consumers could not identify fake comments. Therefore, H2b is not supported.
Although the dominant effect of gender was not significant on the indicators of the fixation dwell time and fixation count, a significant interaction effect between user gender and review polarity was observed, suggesting that consumers’ gender can regulate their comment-browsing behavior. Therefore, H3 is partly supported. For female consumers, attention to negative comments was significantly greater than positive ones. Men’s attention was more homogeneous, and men paid more attention to positive comments than women. This is attributed to the fact that men and women have different risk perceptions of online shopping ( Garbarino and Strahilevitz, 2004 ). As reported in previous studies, men tend to focus more on specific, concrete information, such as the technical features of mobile phones, as the basis for their purchase decision. They have a weaker perception of the risks of online shopping than women. Women would be worried more about the various shopping risks and be more easily affected by others’ evaluations. Specifically, women considered all aspects of the available information, including the attributes of the product itself and other post-use evaluations. They tended to believe that the more comprehensive the information they considered, the lower the risk they faced of a failed purchase ( Garbarino and Strahilevitz, 2004 ; Kanungo and Jain, 2012 ). Therefore, women hope to reduce the risk of loss by drawing on as much overall information as possible because they are more likely to focus on negative reviews.
The main finding from the fixation count distribution is that consumers’ visual attention is mainly focused on reviews containing the following five mobile phone characteristics: running smoothly, battery life, fever condition of phones, pixels, and after-sales service. Considering the behavior results, when they pay more attention to negative comments, consumers tend to give up buying mobile phones. When they pay more attention to positive comments, consumers often choose to buy. Consequently, there is a significant correlation between visual attention and behavioral decision results. Thus, H4 is supported. Consumers’ decision-making intention can be reflected in the visual browsing process. In brief, the results of the eye movement experiment can be used as a basis for sellers not only to formulate marketing strategies but also to prove the feasibility and strictness of applying the eye movement tracking method to the study of consumer decision-making behavior.
Theoretical Implications
This study has focused on how online reviews affect consumer purchasing decisions by employing eye-tracking. The results contribute to the literature on consumer behavior and provide practical implications for the development of e-business markets. This study has several theoretical contributions. Firstly, it contributes to the literature related to online review valence in online shopping by tracking the visual information acquisition process underlying consumers’ purchase decisions. Although several studies have been conducted to examine the effect of online review valence, very limited research has been conducted to investigate the underlying mechanisms. Our study advances this research area by proposing visual processing models of reviews information. The findings provide useful information and guidelines on the underlying mechanism of how online reviews influence consumers’ online shopping behavior, which is essential for the theory of online consumer behavior.
Secondly, the current study offers a deeper understanding of the relationships between online review valence and gender difference by uncovering the moderating role of gender. Although previous studies have found the effect of review valence on online consumer behavior, the current study first reveals the effect of gender on this effect and explains it from the perspective of attention bias.
Finally, the current study investigated the effect of online reviews on consumer behavior from both eye-tracking and behavioral self-reports, the results are consistent with each other, which increased the credibility of the current results and also provides strong evidence of whether and how online reviews influence consumer behavior.
Implications for Practice
This study also has implications for practice. According to the analysis of experimental results and findings presented above, it is recommended that online merchants should pay particular attention to negative comments and resolve them promptly through careful analysis of negative comments and customization of product information according to consumer characteristics including gender factors. Based on the findings that consumers cannot identify false comments, it is very important to establish an online review screening system that could automatically screen untrue content in product reviews, and create a safer, reliable, and better online shopping environment for consumers.
Limitations and Future Research
Although the research makes some contributions to both theoretical and empirical literature, it still has some limitations. In the case of experiments, the number of positive and negative reviews of each mobile phone was limited to 10 positive and 10 negative reviews (20 in total) due to the size restrictions on the product review picture. The number of comments could be considered relatively small. Efforts should be made in the future to develop a dynamic experimental design where participants can flip the page automatically to increase the number of comments. Also, the research was conducted to study the impact of reviews on consumers’ purchase decisions by hiding the brand of the products. The results would be different if the brand of the products is exposed since consumers might be moderated through brand preferences and brand loyalty, which could be taken into account in future research projects.
Data Availability Statement
Author contributions.
TC conceived and designed this study. TC, PS, and MQ wrote the first draft of the manuscript. TC, XC, and MQ designed and performed related experiments, material preparation, data collection, and analysis. TC, PS, XC, and Y-CL revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Editor-in-Chief, Associate Editor, reviewers and typesetters for their highly constructive comments. The authors would like to thank Jia Jin and Hao Ding for assistance in experimental data collection and Jun Lei for the text-polishing of this paper. The authors thank all the researchers who graciously shared their findings with us which allowed this eye-tracking study to be more comprehensive than it would have been without their help.
- Ahluwalia R., Burnkrant R., Unnava H. (2000). Consumer response to negative publicity: the moderating role of commitment . J. Mark. Res. 37 , 203–214. doi: 10.2307/1558500 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Archak N., Ghose A., Ipeirotis P. (2010). Deriving the pricing power of product features by mining . Con. Rev. Manag. Sci. 57 , 1485–1509. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.1110.1370 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bae S., Lee T. (2011). Product type and consumers’ perception of online consumer reviews . Electron. Mark. 21 , 255–266. doi: 10.1007/s12525-011-0072-0 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baek H., Ahn J., Choi Y. (2012). Helpfulness of online consumer reviews: readers’ objectives and review cues . Int. J. Electron. Commer. 17 , 99–126. doi: 10.2753/jec1086-4415170204 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boardman R., McCormick H. (2019). The impact of product presentation on decision making and purchasing . Qual. Mark. Res. Int. J. 22 , 365–380. doi: 10.1108/QMR-09-2017-0124 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boardman R., Mccormick H. (2021). Attention and behaviour on fashion retail websites: an eye-tracking study . Inf. Technol. People . doi: 10.1108/ITP-08-2020-0580 [Epub ahead of print] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chae S. W., Lee K. (2013). Exploring the effect of the human brand on consumers’ decision quality in online shopping: An eye-tracking approach . Online Inf. Rev. 37 , 83–100. doi: 10.1108/14684521311311649 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Changchit C., Klaus T. (2020). Determinants and impact of online reviews on product satisfaction . J. Internet Commer. 19 , 82–102. doi: 10.1080/15332861.2019.1672135 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen C. D., Ku E. C. (2021). Diversified online review websites as accelerators for online impulsive buying: the moderating effect of price dispersion . J. Internet Commer. 20 , 113–135. doi: 10.1080/15332861.2020.1868227 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cortinas M., Cabeza R., Chocarro R., Villanueva A. (2019). Attention to online channels across the path to purchase: an eye-tracking study . Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 36 :100864. doi: 10.1016/j.elerap.2019.100864 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Craciun G., Moore K. (2019). Credibility of negative online product reviews: reviewer gender, reputation and emotion effects . Comput. Hum. Behav. 97 , 104–115. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2019.03.010 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cui G., Lui H.-K., Guo X. (2012). The effect of online consumer reviews on new product sales. International . J. Elect. Com. 17 , 39–58. doi: 10.2753/jec1086-4415170102 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Floh A., Koller M., Zauner A. (2013). Taking a deeper look at online reviews: The asymmetric effect of valence intensity on shopping behaviour . J. Mark. Manag. 29 :646670, 646–670. doi: 10.1080/0267257X.2013.776620 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Garbarino E., Strahilevitz M. (2004). Gender differences in the perceived risk of buying online and the effects of receiving a site recommendation . J. Bus. Res. 57 , 768–775. doi: 10.1016/S0148-2963(02)00363-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ghose A., Ipeirotiss P. G. (2010). Estimating the helpfulness and economic impact of product reviews: mining text and reviewer characteristics . IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 23 :188. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2010.188 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- GooSeeker (2015), E. coli . Available at: http://www.gooseeker.com/pro/product.html , (Accessed January 20, 2020).
- Guo J., Wang X., Wu Y. (2020). Positive emotion bias: role of emotional content from online customer reviews in purchase decisions . J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 52 :101891. doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2019.101891 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hasanat M., Hoque A., Shikha F., Anwar M., Abdul Hamid A. B., Huam T. (2020). The impact of coronavirus (COVID-19) on E-Business in Malaysia . Asian J. Multidisc. Stud. 3 , 85–90. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hong H., Xu D., Wang G., Fan W. (2017). Understanding the determinants of online review helpfulness: a meta-analytic investigation . Decis. Support. Syst. 102 , 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2017.06.007 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Huang P., Lurie N., Mitra S. (2009). Searching for experience on the web: an empirical examination of consumer behavior for search and experience goods . J. Mark. Am. Mark. Assoc. 73 , 55–69. doi: 10.2307/20619010 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hwang Y. M., Lee K. C. (2018). Using an eye-tracking approach to explore gender differences in visual attention and shopping attitudes in an online shopping environment . Int. J. Human–Comp. Inter. 34 , 15–24. doi: 10.1080/10447318.2017.1314611 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jacob R., Karn K. (2003). “ Eye tracking in human-computer interaction and usability research: ready to deliver the promises, ” in The mind’s eye North-Holland (New York: Elsevier; ), 573–605. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jiménez F. R., Mendoza N. A. (2013). Too popular to ignore: the influence of online reviews on purchase intentions of search and experience products . J. Interact. Mark. 27 , 226–235. doi: 10.1016/j.intmar.2013.04.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Just M., Carpenter P. (1980). A theory of reading: from eye fixations to comprehension . Psychol. Rev. 87 , 329–354. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.87.4.329, PMID: [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Just M., Carpenter P. (1992). A capacity theory of comprehension: individual differences in working memory . Psychol. Rev. 99 , 122–149. doi: 10.1037/0033-295x.99.1.122, PMID: [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kang T. C., Hung S. Y., Huang A. H. (2020). The adoption of online product information: cognitive and affective evaluations . J. Internet Commer. 19 , 373–403. doi: 10.1080/15332861.2020.1816315 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kanungo S., Jain V. (2012). Online shopping behaviour: moderating role of gender and product category . Int. J. Bus. Inform. Syst. 10 , 197–221. doi: 10.1504/ijbis.2012.047147 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kaur S., Lal A. K., Bedi S. S. (2017). Do vendor cues influence purchase intention of online shoppers? An empirical study using SOR framework . J. Internet Commer. 16 , 343–363. doi: 10.1080/15332861.2017.1347861 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lackermair G., Kailer D., Kanmaz K. (2013). Importance of online product reviews from a consumer’s perspective . Adv. Econ. Bus. 1 , 1–5. doi: 10.13189/aeb.2013.010101 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liu H.-C., Lai M.-L., Chuang H.-H. (2011). Using eye-tracking technology to investigate the redundant effect of multimedia web pages on viewers’ cognitive processes . Comput. Hum. Behav. 27 , 2410–2417. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2011.06.012 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Luan J., Yao Z., Zhao F., Liu H. (2016). Search product and experience product online reviews: an eye-tracking study on consumers’ review search behavior . Comput. Hum. Behav. 65 , 420–430. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.08.037 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mayzlin D., Chevalier J. (2003). The effect of word of mouth on sales: online book reviews . J. Mark. Res. 43 :409. doi: 10.2307/30162409 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meyers-Levy J., Sternthal B. (1993). A two-factor explanation of assimilation and contrast effects . J. Mark. Res. 30 , 359–368. doi: 10.1177/002224379303000307 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mudambi S., Schuff D. (2010). What makes a helpful online review? A study of customer reviews on Amazon.com . MIS Q. 34 , 185–200. doi: 10.1007/s10107-008-0244-7 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mumuni A. G., O’Reilly K., MacMillan A., Cowley S., Kelley B. (2020). Online product review impact: the relative effects of review credibility and review relevance . J. Internet Commer. 19 , 153–191. doi: 10.1080/15332861.2019.1700740 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pavlou P., Dimoka A. (2010). NeuroIS: the potential of cognitive neuroscience for information systems research . Inform. Sys. Res. Art. Adv. 19 , 153–191. doi: 10.1080/15332861.2019.1700740 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Plassmann H., Venkatraman V., Huettel S., Yoon C. (2015). Consumer neuroscience: applications, challenges, and possible solutions . J. Mark. Res. 52 , 427–435. doi: 10.1509/jmr.14.0048 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Racherla P., Friske W. (2013). Perceived “usefulness” of online consumer reviews: an exploratory investigation across three services categories . Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 11 , 548–559. doi: 10.1016/j.elerap.2012.06.003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Renshaw J. A., Finlay J. E., Tyfa D., Ward R. D. (2004). Understanding visual influence in graph design through temporal and spatial eye movement characteristics . Interact. Comput. 16 , 557–578. doi: 10.1016/j.intcom.2004.03.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosa P. J. (2015). What do your eyes say? Bridging eye movements to consumer behavior . Int. J. Psychol. Res. 15 , 1250–1256. doi: 10.1116/1.580598 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ruiz-Mafe C., Chatzipanagiotou K., Curras-Perez R. (2018). The role of emotions and conflicting online reviews on consumers’ purchase intentions . J. Bus. Res. 89 , 336–344. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.01.027 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sen S., Lerman D. (2007). Why are you telling me this? An examination into negative consumer reviews on the web . J. Interact. Mark. 21 , 76–94. doi: 10.1002/dir.20090 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Song W., Park S., Ryu D. (2017). Information quality of online reviews in the presence of potentially fake reviews . Korean Eco. Rev. 33 , 5–34. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tupikovskaja-Omovie Z., Tyler D. (2021). Eye tracking technology to audit google analytics: analysing digital consumer shopping journey in fashion m-retail . Int. J. Inf. Manag. 59 :102294. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102294 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vimaladevi K., Dhanabhakaym M. (2012). A study on the effects of online consumer reviews on purchasing decision . Prestige In. J. Manag. 7 , 51–99. doi: 10.1504/IJIMA.2012.044958 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Von Helversen B., Abramczuk K., Kopeć W., Nielek R. (2018). Influence of consumer reviews on online purchasing decisions in older and younger adults . Decis. Support. Syst. 113 , 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2018.05.006 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang Y., Minor M. (2008). Validity, reliability, and applicability of psychophysiological techniques in marketing research . Psychol. Mark. 25 , 197–232. doi: 10.1002/mar.20206 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang Q., Yang S., Cao Z., Liu M., Ma Q. (2014). An eye-tracking study of website complexity from cognitive load perspective . Decis. Support. Syst. 62 , 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2014.02.007 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World Medical Association (2014). World medical association declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects . J. Am. Coll. Dent. 81 , 14–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.2001.tb01222.x, PMID: [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu Y., Liu T., Teng L., Zhang H., Xie C. (2021). The impact of online review variance of new products on consumer adoption intentions . J. Bus. Res. 136 , 209–218. doi: 10.1016/J.JBUSRES.2021.07.014 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wu Y., Ngai E., Pengkun W., Wu C. (2020). Fake online reviews: literature review, synthesis, and directions for future research . Decis. Support. Syst. 132 :113280. doi: 10.1016/j.dss.2020.113280 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yang S. F. (2015). An eye-tracking study of the elaboration likelihood model in online shopping . Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 14 , 233–240. doi: 10.1016/j.elerap.2014.11.007 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yu X., Liu Y., Huang X., An A. (2010). Mining online reviews for predicting sales performance: a case study in the movie domain . IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 24 , 720–734. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2010.269 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yuanyuan H., Peng Z., Yijun L., Qiang Y. J. M. R. (2009). An empirical study on the impact of online reviews sentimental orientation on sale based on movie panel data . Manag. Rev. 21 , 95–103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-00205-2_9 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang K., Cheung C., Lee M. (2014). Examining the moderating effect of inconsistent reviews and its gender differences on consumers’ online shopping decision . Int. J. Inf. Manag. 34 , 89–98. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2013.12.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang J., Craciun G., Shin D. (2010). When does electronic word-of-mouth matter? A study of consumer product reviews . J. Bus. Res. 63 , 1336–1341. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2009.12.011 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhong-Gang Y., Xiao-Ya W., Economics S. O. J. S. E. (2015). Research progress and future prospect on online reviews and consumer behavior . Soft Science. 6 :20. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20200714-02111 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This study confirmed the key role of the moderating effect of e-commerce experience in the online shopping context of the emerging African market, supporting the e-commerce literature (Menidjel et al., Citation 2020; Prashar et al., Citation 2017) that confirms the importance of research studies that measure the Internet usage experience and e ...
This study examines how functional and psychological dimensions of online customers' shopping experience (OCSE) influence online impulsive buying behavior, mediated by attitudinal loyalty and moderated by self-control. The study uses structural equation modeling to analyze data from two leading Chinese e-commerce platforms: Jindong and Taobao.
The rise of e-commerce, busy lifestyles, and the convenience of next- and same-day home deliveries have resulted in exponential growth of online shopping in the U.S., rising from 5% of the total retail in 2011 to 15% in 2020, and it is expected to grow even further in the future (1, 2).Worldwide, spending on e-commerce passed $4.9 trillion in 2021 and it is projected to surge to $7 trillion by ...
A research on the E-shopping behaviours of British and American consumers has also shown that E-shopping is a determinant of online shopping. Likewise, consumer research on E-shopping behaviour accepts that attitude represents a description of the positive or negative self-appraisal of a client's behaviour, values, feelings, and patterns during ...
first stream of research focuses on consumers online shopping behavior at specific online shops. For example, an early study in this domain was Gefen et al. (2003) who explain ed why
The first section of this paper provides a brief literature overview of studies of online grocery shopping both pre-pandemic and in the pandemic-shaped grocery markets. This literature review helps define hypotheses about how shopper demographics and attitudes may influence online grocery shopping, frequency of online grocery purchases during ...
This study proposes a theoretical framework to explore the influencing factors of online consumer purchasing behavior (OCPB) based on electronic word-of-mouth (e-WOM) data mining and analysis. The study uses machine learning to cluster the e-WOM data from two popular online shopping platforms in China and compares the results with Kotler's five product level.
In study by (Baubonienė & Gulevičiūtė, Citation 2015), 183 Lihtuanian consumers who purchase online were surveyed. Within this study, authors determined four factors that influenced the behavior of customers: technical factors (knowledge of IT technologies and IT skills), consumer-related factors (an attitude to online shopping, cultural ...
Overall, 30 research studies were selected for the review and a significant number of studies were published in 2021 (n = 15).,The research findings revealed that customers are motivated to shop online because of perceived benefits such as time-saving, convenience, 24/7 accessibility, interactive services without physical boundaries, trust ...
While studies have primarily considered categories such as apparel and grocery, in terms of methodology experimental and survey-based studies were most common. Additionally, the article suggests some future research directions. The use of combined theories to better understand technology acceptance by consumers of online-shopping is recommended.
According to the theory of multisensory interaction and integration, a good visibility effect can increase the level of virtual touch and enhance the presence of online shopping. Therefore, this study puts forward the following research hypothesis: H2: Vividness has a positive impact on social presence in online shopping.
PDF | In the information era, people's online consumption has been increasingly common. In recent years, since COVID-19 has affected people's shopping... | Find, read and cite all the research ...
First, this research only examined a few risks involved in online shopping. Future research studies should analyze other risks, for example, quality risk and privacy risk. Second, this study focused on shopping through direct e-stores and indirect e-stores. Future research can implement a conceptual model of a specific brand.
This paper explores the criteria that consumers use when buying online from different e-shops. It applies factor analysis to reduce the number of criteria and create seven factors: price, availability, social proof, scarcity, product details, conditions and social media activity.
This article explores the factors that influence online purchase intention and behavior in Colombia and Spain, using social psychology theories and national culture as moderators. It compares the results of a quantitative research with a sample of 584 online consumers in both countries and provides practical implications for e-commerce adoption.
2.1 Online Shopping During COVID-19. World Health Organization (WHO) in early 2020 announced Covid19 as a pandemic. Due to the restrictions imposed by governments across the world, 52% consumers adhered to the social distancing norms by wearing masks to prevent any infection spread by the virus in the communities (Andrienko 2020).Many consumers shifted to e-commerce platforms for purchases ...
First, as demonstrated in Table 1, there is a plethora of mostly anecdotal, non-empirically-based evidence that during the pandemic (and beside the pandemic itself) two major factors, i.e., government restrictions and consumer behavior changes, drove a significant initial surge in online shopping. Second, extant studies failed to offer insights ...
N. Jamila Dani (2017) "A Study on Consumers Attitude Towards Online Shopping" International Journal of Research in Management and Business Studies, Vol,4. Issue. (SPL 2) PP:42-46.
This study examines the relationship between subjective norm, perceived usefulness and purchase intention in online shopping behavior among university students in Malaysia. The study uses structural equation modeling and finds that subjective norm and perceived usefulness positively influence purchase intention, but not online shopping behavior.
Although prior studies have evaluated online shopping (Dayal and Palsapure, 2020; Liu et al., 2020; Sethuraman and Thanigan, 2019), little research has evaluated those factors that will influence consumers to continue their online shopping once the COVID-19 pandemic recedes. Therefore, our research objective is to address this gap in the ...
For more succinct understanding, Table 1 summarizes the previous study results on online shopping followed by advantages of online shopping (Table 2) and disadvantages of online shopping (Table 3). ... Internet users in Bangladesh spend over Tk 7184.018 crore in online shopping each year. A Google research paper titled "Research Insight: ...
The findings that shoppers spent more and purchased more items when shopping online are consistent with the few published studies on online grocery shopping. 18-20 Online shoppers may buy more to meet retailers' minimum spending requirements, which the study retailer did not have, to justify delivery or service fees or reach a threshold ...
This study investigated the impact of online product reviews on consumers purchasing decisions by using eye-tracking. The research methodology involved (i) development of a conceptual framework of online product review and purchasing intention through the moderation role of gender and visual attention in comments, and (ii) empirical investigation into the region of interest (ROI) analysis of ...