Discover the world's scientific knowledge
With 160+ million publication pages, 25+ million researchers and 1+ million questions, this is where everyone can access science.
You can use AND, OR, NOT, "" and () to specify your search.
- Consent preferences
- {{link.text}}

Publications
Google publishes hundreds of research papers each year. Publishing is important to us; it enables us to collaborate and share ideas with, as well as learn from, the broader scientific community. Submissions are often made stronger by the fact that ideas have been tested through real product implementation by the time of publication.
We believe the formal structures of publishing today are changing - in computer science especially, there are multiple ways of disseminating information. We encourage publication both in conventional scientific venues, and through other venues such as industry forums, standards bodies, and open source software and product feature releases.
Open Source
We understand the value of a collaborative ecosystem and love open source software .
Product and Feature Launches
With every launch, we're publishing progress and pushing functionality.
Industry Standards
Our researchers are often helping to define not just today's products but also tomorrow's.
"Resources" doesn't just mean tangible assets but also intellectual. Incredible datasets and a great team of colleagues foster a rich and collaborative research environment.
Couple big challenges with big resources and Google offers unprecedented research opportunities.
22 Research Areas
- Algorithms and Theory 608 Publications
- Data Management 116 Publications
- Data Mining and Modeling 214 Publications
- Distributed Systems and Parallel Computing 208 Publications
- Economics and Electronic Commerce 209 Publications
- Education Innovation 30 Publications
- General Science 158 Publications
- Hardware and Architecture 67 Publications
- Human-Computer Interaction and Visualization 444 Publications
- Information Retrieval and the Web 213 Publications
- Machine Intelligence 1019 Publications
- Machine Perception 454 Publications
- Machine Translation 48 Publications
- Mobile Systems 72 Publications
- Natural Language Processing 395 Publications
- Networking 210 Publications
- Quantum A.I. 30 Publications
- Robotics 37 Publications
- Security, Privacy and Abuse Prevention 289 Publications
- Software Engineering 100 Publications
- Software Systems 250 Publications
- Speech Processing 264 Publications
3 Collections
- Google AI Residency 60 Publications
- Google Brain Team 305 Publications
- Data Infrastructure and Analysis 10 Publications

Research Paper: A step-by-step guide: 1. Getting Started
- 1. Getting Started
- 2. Topic Ideas
- 3. Thesis Statement & Outline
- 4. Appropriate Sources
- 5. Search Techniques
- 6. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
- 7. Evaluating Sources
- 8. Citations & Plagiarism
- 9. Writing Your Research Paper

Let's Get Started
We are here to help.
Writing research papers is an important part of your college learning experience, training you to research and write effectively. However, if you don't know how to start, writing a research paper can be a daunting task. Don't worry! We will guide you through the process. The sections in this step-by-step guide allow you to learn at your own pace. Revisit the information as much as you need. Let's get started!
What Is a Research Paper?
A research paper is an expanded essay that presents your investigation and argument on a focused topic based on the information you gathered. It demonstrates not only your understanding of available information from experts in the area of your research, but also your evaluation and insight on the subject matter through an orderly and logical presentation of your argument.
What Are the Qualities of a Good Research Paper?
Make sure you know the requirements of your specific assignment. But in general, a good research paper will have the following qualities:
- A strong and focused thesis statement
- Logically organized a rguments and main points
- Each main point is supported by persuasive facts and examples
- Opposing viewpoints are included and rebutted, showing why the author's argument is more valid
- The paper shows the author's understanding of the topic and the material being used
- The work is original, not plagiarized
- Every source is correctly documented and credited in a recognized citation style
- The paper is written in clear language in a style suitable for college research
Need help with your research paper? A librarian can help guide you through the process of research.
Here are ways to contact a librarian:
- Email the library at [email protected]
- Find the librarian best suited for your subject area
- Use our 24/7 chat service (use the chat box on the right)
Ebooks on Writing
Looking for a really detailed guide? Try these ebooks:
Research Paper Process
Following the research process will help you with your paper.
Select a Topic
Find Background Information
Formulate a Thesis Statement
Create an Outline
Locate and Retrieve Materials
Evaluate Information
Write the Paper
Review Paper and Citations
- Next: 2. Topic Ideas >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2023 12:12 PM
- URL: https://butte.libguides.com/ResearchPaper
- Skip to main content
- Skip to ChatBot Assistant
- Academic Writing
What is a Research Paper?
- Steps in Writing a Research Paper
- Critical Reading and Writing
- Punctuation
- Writing Exercises
- ELL/ESL Resources
"Research paper." What image comes into mind as you hear those words: working with stacks of articles and books, hunting the "treasure" of others' thoughts? Whatever image you create, it's a sure bet that you're envisioning sources of information--articles, books, people, artworks. Yet a research paper is more than the sum of your sources, more than a collection of different pieces of information about a topic, and more than a review of the literature in a field. A research paper analyzes a perspective argues a point . Regardless of the type of research paper you are writing, your finished research paper should present your own thinking backed up by others' ideas and information.
To draw a parallel, a lawyer researches and reads about many cases and uses them to support his or her own case. A scientist reads many case studies to support an idea about a scientific principle. In the same way, a history student writing about the Vietnam War might read newspaper articles and books and interview veterans to develop and/or confirm a viewpoint and support it with evidence.
A research paper is an expanded essay that presents your own interpretation or evaluation or argument. When you write an essay, you use everything that you personally know and have thought about a subject. When you write a research paper you build upon what you know about the subject and make a deliberate attempt to find out what experts know. A research paper involves surveying a field of knowledge in order to find the best possible information in that field. And that survey can be orderly and focused, if you know how to approach it. Don't worry--you won't get lost in a sea of sources.
In fact, this guide is designed to help you navigate the research voyage, through developing a research question and thesis, doing the research, writing the paper, and correctly documenting your sources.
Need Assistance?
If you would like assistance with any type of writing assignment, learning coaches are available to assist you. Please contact Academic Support by emailing [email protected].
Questions or feedback about SUNY Empire's Writing Support?
Contact us at [email protected] .
Smart Cookies
They're not just in our classes – they help power our website. Cookies and similar tools allow us to better understand the experience of our visitors. By continuing to use this website, you consent to SUNY Empire State University's usage of cookies and similar technologies in accordance with the university's Privacy Notice and Cookies Policy .
How to Write a Research Paper
Angela has taught middle and high school English, Business English and Speech for nine years. She has a bachelor's degree in psychology and has earned her teaching license.
Table of Contents
What is a research paper, the first stages, notes & an outline, the final stages, lesson summary.
The dreaded research paper. Just hearing that phrase sends most students into fits of panic. Where do you begin? How do know if you have a good idea? What if you have no ideas? The good news is, if you have a step-by-step process to follow, these questions will answer themselves. A research paper is just the final product of research, critical thinking, and composition about a specific topic. Usually, a research paper aims to answer a specific question within a more general topic. The rest of this lesson outlines a step-by-step process for creating one.
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account

An error occurred trying to load this video.
Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support.
You must c C reate an account to continue watching
Register to view this lesson.
As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you succeed.
Get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons.
Already registered? Log in here for access
Resources created by teachers for teachers.
I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. It’s like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. I feel like it’s a lifeline.
You're on a roll. Keep up the good work!
Just checking in. are you still watching.
- 0:04 What Is a Research Paper?
- 0:38 The First Stages
- 2:08 Sources
- 3:08 Notes & an Outline
- 4:16 The Final Stages
- 5:53 Lesson Summary
The very first step is to decide on the topic or subject to investigate. Communication, immigration, and terrorism are some examples of general topics you can choose to research. However, keep in mind that in the next step, you'll have to narrow any one of those larger subjects down into a specific research question.
At this point, you also want to determine the purpose , or the reason for writing. Are you informing? Persuading? Offering a unique perspective? Also, who will be reading your paper? Your teacher? Your classmates? Web users? The answers to these questions will influence your writing.
The second step is to create the research question. The research question is the specific focus or controlling idea of the writing project. Again, you can start with a general topic, but before you begin to research, a more precise direction is needed. The research question will give you that direction. Here are some sample research questions for each general topic already mentioned.
- Communication: How does efficient communication affect the success of a business?
- Immigration: What are the influences of varying immigration policies across the globe? Why are there differences?
- Terrorism: How has technology affected the increase in terrorist attacks in the past ten years?
Each of these questions seeks a very specific type of information for each topic. This approach will help narrow down the information you need. Remember, you need to create a specific question before you begin to research.
Once you have a topic and a plan, the third step is to find sources, or search for suppliers of reliable information. Encyclopedias, academic journals, newspapers, and magazines are just some examples of information sources. Nowadays, nearly all of these sources can be found online. The web has amazing information, but you must always remember that anyone can post online. Be very careful about what you decide to include. Check the publisher and author to verify that you are using an official source. Use search engines to discover reliable experts in your topic's field.
Noting this background information about your sources lets you begin the bibliography , which is the list of your sources. As soon as you find a source you deem credible, copy down all the information available about it. The title of the source, its publisher, its author, the credentials of the publisher and author, and the date it was written should all be recorded. Use only the most up-to-date, verifiable sources in your project.
The fourth step involves taking notes and creating an outline. Use notes to single out the useful pieces of information from your sources. Any information that may help answer your research question might be recorded. Remember, it's easier to cut out details than to return to the research stage to find new information.
After taking notes, move onto the outline step. An outline is a general plan for the order of the research paper. We all know a paper should have an introduction, body, and conclusion, but a proper outline goes a step further. It includes a thesis , or a statement of the main focus of the entire paper. Your whole paper needs to relate to this thesis, so be sure to write a detailed and clear statement. Including a general reference to your supporting ideas is a great idea for writing a strong thesis. Place this thesis near the end of your introductory paragraph.
In addition, decide what information will appear in your introduction. What will appear in each body paragraph? What will be the main idea for each paragraph? What will be stated in the conclusion? Answer these questions as you create an outline for your research paper.
The fifth step consists of writing a rough draft. Once you have an outline, you can begin writing your rough draft , which is the first version of your paper. Follow the ideas in your outline, but don't be afraid if your ideas change. Adjust your plan and adapt your research to fit into your final views about the research question.
The sixth step involves revising and editing your rough draft. Once you have a complete rough draft, move onto this step, which may need to be completed along with step five more than once to get everything into focus. To revise means to rework, or alter, the draft, such as rephrasing a sentence or changing an idea. To edit means to correct grammar, spelling, and other mechanical errors, such as using spell check and inserting punctuation, though don't rely exclusively on spellcheck, which may not catch all grammar errors.
The seventh and final step of the research paper is to publish the paper. Publishing simply means to print for or otherwise issue the writing to the public, which in this case, will likely be your teacher and/or fellow classmates. Basically, if you are in school, the published copy is the one you turn in for your final grade. If you're writing for an academic organization, your paper might be published online or in a journal. The final touches and small adjustments to your format are all done in the publishing stage. This is the time to add title pages, visuals, or subtitles. Do a final check on your format, source page, and the presentation notes at this time too.
If you've made it this far, you have one final thing to do: Be proud of what you've accomplished! You've completed a research paper!
Let's review. A research paper involves research, critical thinking, and composition about a specific topic. This long-term assignment can be intimidating, but if you follow these steps, it might be straightforward and successful.
- Decide on the topic.
- Create a research question .
- Find sources and begin a bibliography .
- Take notes and make an outline , including creating a thesis .
- Write a rough draft .
- Revise and edit the rough draft.
- Submit your final paper.
Unlock Your Education
See for yourself why 30 million people use study.com, become a study.com member and start learning now..
Already a member? Log In
Recommended Lessons and Courses for You
Related lessons, related courses, recommended lessons for you.

How to Write a Research Paper Related Study Materials
- Related Topics
Browse by Courses
- Praxis Biology: Content Knowledge (5235) Prep
- ILTS School Counselor (235) Prep
- Praxis Health Education (5551) Prep
- Praxis Earth and Space Sciences: Content Knowledge (5571) Prep
- Praxis Psychology (5391) Prep
- Praxis English Language Arts: Content Knowledge (5038) Prep
- GED Social Studies: Civics & Government, US History, Economics, Geography & World
- Sociology 101: Intro to Sociology
- NY Regents Exam - US History and Government: Test Prep & Practice
- Fundamentals of Counseling
- CAHSEE English Exam: Test Prep & Study Guide
- Political Science 102: American Government
- Praxis Mathematics (5165) Prep
- Praxis Economics (5911) Prep
- Praxis Environmental Education (0831) Prep
Browse by Lessons
- APA Citation | Format, Usage & Examples
- Writing a Works Cited Page | Structure & Formats
- Making In-Text Citations | Definition, Types & Importance
- How to Cite Online Sources
- Formatting Definition, Types & Examples
- How to Read Citations in Texts and Bibliographies
- Journal Article Citations
- Parenthetical Citation | Overview & Examples
- How to Use Parenthetical Citations
- Citation Meaning, Types & Importance
- Article Citation | Definition, Types & Examples
- Works Cited Page | Definition, Formats & Examples
- Citing a Website in APA
- Citing a Source Within a Source
- Citing an Online Newspaper Article
Create an account to start this course today Used by over 30 million students worldwide Create an account
Explore our library of over 88,000 lessons
- Foreign Language
- Social Science
- See All College Courses
- Common Core
- High School
- See All High School Courses
- College & Career Guidance Courses
- College Placement Exams
- Entrance Exams
- General Test Prep
- K-8 Courses
- Skills Courses
- Teacher Certification Exams
- See All Other Courses
- Create a Goal
- Create custom courses
- Get your questions answered

Peer Recognized
Make a name in academia
How to Write a Research Paper: the LEAP approach (+cheat sheet)
In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper .
The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within 9 years since the completion of my PhD. I hope the LEAP approach will help you just as much as it has helped me to make an real, tangible impact with my research.
What is the LEAP research paper writing approach?
I designed the LEAP writing approach not only for merely writing the papers. My goal with the writing system was to show young scientists how to first think about research results and then how to efficiently write each section of the research paper.
In other words, you will see how to write a research paper by first analyzing the results and then building a logical, persuasive arguments. In this way, instead of being afraid of writing research paper, you will be able to rely on the paper writing process to help you with what is the most demanding task in getting published – thinking.
The four research paper writing steps according to the LEAP approach:

I will show each of these steps in detail. And you will be able to download the LEAP cheat sheet for using with every paper you write.
But before I tell you how to efficiently write a research paper, I want to show you what is the problem with the way scientists typically write a research paper and why the LEAP approach is more efficient.
How scientists typically write a research paper (and why it isn’t efficient)
Writing a research paper can be tough, especially for a young scientist. Your reasoning needs to be persuasive and thorough enough to convince readers of your arguments. The description has to be derived from research evidence, from prior art, and from your own judgment. This is a tough feat to accomplish.
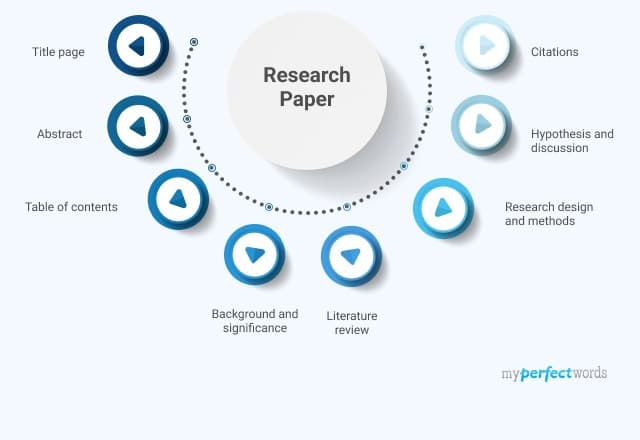
The figure below shows the sequence of the different parts of a typical research paper. Depending on the scientific journal, some sections might be merged or nonexistent, but the general outline of a research paper will remain very similar.

Here is the problem: Most people make the mistake of writing in this same sequence.
While the structure of scientific articles is designed to help the reader follow the research, it does little to help the scientist write the paper. This is because the layout of research articles starts with the broad (introduction) and narrows down to the specifics (results). See in the figure below how the research paper is structured in terms of the breath of information that each section entails.
How to write a research paper according to the LEAP approach
For a scientist, it is much easier to start writing a research paper with laying out the facts in the narrow sections (i.e. results), step back to describe them (i.e. write the discussion), and step back again to explain the broader picture in the introduction.
For example, it might feel intimidating to start writing a research paper by explaining your research’s global significance in the introduction, while it is easy to plot the figures in the results. When plotting the results, there is not much room for wiggle: the results are what they are.
Starting to write a research papers from the results is also more fun because you finally get to see and understand the complete picture of the research that you have worked on.
Most importantly, following the LEAP approach will help you first make sense of the results yourself and then clearly communicate them to the readers. That is because the sequence of writing allows you to slowly understand the meaning of the results and then develop arguments for presenting to your readers.
I have personally been able to write and submit a research article in three short days using this method.
Step 1: Lay Out the Facts

You have worked long hours on a research project that has produced results and are no doubt curious to determine what they exactly mean. There is no better way to do this than by preparing figures, graphics and tables. This is what the first LEAP step is focused on – diving into the results.
How to p repare charts and tables for a research paper
Your first task is to try out different ways of visually demonstrating the research results. In many fields, the central items of a journal paper will be charts that are based on the data generated during research. In other fields, these might be conceptual diagrams, microscopy images, schematics and a number of other types of scientific graphics which should visually communicate the research study and its results to the readers. If you have reasonably small number of data points, data tables might be useful as well.
Tips for preparing charts and tables
- Try multiple chart types but in the finished paper only use the one that best conveys the message you want to present to the readers
- Follow the eight chart design progressions for selecting and refining a data chart for your paper: https://peerrecognized.com/chart-progressions
- Prepare scientific graphics and visualizations for your paper using the scientific graphic design cheat sheet: https://peerrecognized.com/tools-for-creating-scientific-illustrations/
How to describe the results of your research
Now that you have your data charts, graphics and tables laid out in front of you – describe what you see in them. Seek to answer the question: What have I found? Your statements should progress in a logical sequence and be backed by the visual information. Since, at this point, you are simply explaining what everyone should be able to see for themselves, you can use a declarative tone: The figure X demonstrates that…
Tips for describing the research results :
- Answer the question: “ What have I found? “
- Use declarative tone since you are simply describing observations
Step 2: Explain the results

The core aspect of your research paper is not actually the results; it is the explanation of their meaning. In the second LEAP step, you will do some heavy lifting by guiding the readers through the results using logic backed by previous scientific research.
How to define the Message of a research paper
To define the central message of your research paper, imagine how you would explain your research to a colleague in 20 seconds . If you succeed in effectively communicating your paper’s message, a reader should be able to recount your findings in a similarly concise way even a year after reading it. This clarity will increase the chances that someone uses the knowledge you generated, which in turn raises the likelihood of citations to your research paper.
Tips for defining the paper’s central message :
- Write the paper’s core message in a single sentence or two bullet points
- Write the core message in the header of the research paper manuscript
How to write the Discussion section of a research paper
In the discussion section you have to demonstrate why your research paper is worthy of publishing. In other words, you must now answer the all-important So what? question . How well you do so will ultimately define the success of your research paper.
Here are three steps to get started with writing the discussion section:
- Write bullet points of the things that convey the central message of the research article (these may evolve into subheadings later on).
- Make a list with the arguments or observations that support each idea.
- Finally, expand on each point to make full sentences and paragraphs.
Tips for writing the discussion section:
- What is the meaning of the results?
- Was the hypothesis confirmed?
- Write bullet points that support the core message
- List logical arguments for each bullet point, group them into sections
- Instead of repeating research timeline, use a presentation sequence that best supports your logic
- Convert arguments to full paragraphs; be confident but do not overhype
- Refer to both supportive and contradicting research papers for maximum credibility
How to write the Conclusions of a research paper
Since some readers might just skim through your research paper and turn directly to the conclusions, it is a good idea to make conclusion a standalone piece. In the first few sentences of the conclusions, briefly summarize the methodology and try to avoid using abbreviations (if you do, explain what they mean).
After this introduction, summarize the findings from the discussion section. Either paragraph style or bullet-point style conclusions can be used. I prefer the bullet-point style because it clearly separates the different conclusions and provides an easy-to-digest overview for the casual browser. It also forces me to be more succinct.
Tips for writing the conclusion section :
- Summarize the key findings, starting with the most important one
- Make conclusions standalone (short summary, avoid abbreviations)
- Add an optional take-home message and suggest future research in the last paragraph
How to refine the Objective of a research paper
The objective is a short, clear statement defining the paper’s research goals. It can be included either in the final paragraph of the introduction, or as a separate subsection after the introduction. Avoid writing long paragraphs with in-depth reasoning, references, and explanation of methodology since these belong in other sections. The paper’s objective can often be written in a single crisp sentence.
Tips for writing the objective section :
- The objective should ask the question that is answered by the central message of the research paper
- The research objective should be clear long before writing a paper. At this point, you are simply refining it to make sure it is addressed in the body of the paper.
How to write the Methodology section of your research paper
When writing the methodology section, aim for a depth of explanation that will allow readers to reproduce the study . This means that if you are using a novel method, you will have to describe it thoroughly. If, on the other hand, you applied a standardized method, or used an approach from another paper, it will be enough to briefly describe it with reference to the detailed original source.
Remember to also detail the research population, mention how you ensured representative sampling, and elaborate on what statistical methods you used to analyze the results.
Tips for writing the methodology section :
- Include enough detail to allow reproducing the research
- Provide references if the methods are known
- Create a methodology flow chart to add clarity
- Describe the research population, sampling methodology, statistical methods for result analysis
- Describe what methodology, test methods, materials, and sample groups were used in the research.
Step 3: Advertize the research
Step 3 of the LEAP writing approach is designed to entice the casual browser into reading your research paper. This advertising can be done with an informative title, an intriguing abstract, as well as a thorough explanation of the underlying need for doing the research within the introduction.

How to write the Introduction of a research paper
The introduction section should leave no doubt in the mind of the reader that what you are doing is important and that this work could push scientific knowledge forward. To do this convincingly, you will need to have a good knowledge of what is state-of-the-art in your field. You also need be able to see the bigger picture in order to demonstrate the potential impacts of your research work.
Think of the introduction as a funnel, going from wide to narrow, as shown in the figure below:
- Start with a brief context to explain what do we already know,
- Follow with the motivation for the research study and explain why should we care about it,
- Explain the research gap you are going to bridge within this research paper,
- Describe the approach you will take to solve the problem.
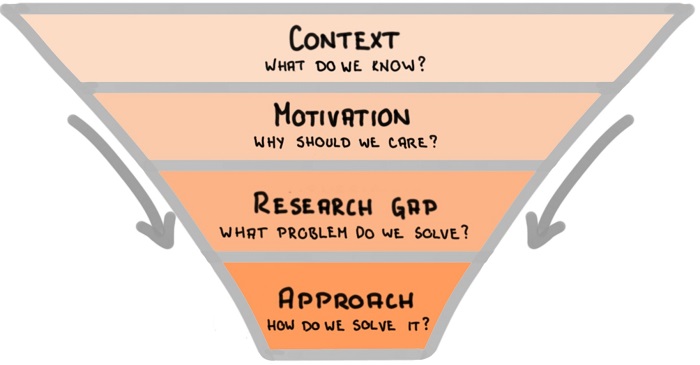
Tips for writing the introduction section :
- Follow the Context – Motivation – Research gap – Approach funnel for writing the introduction
- Explain how others tried and how you plan to solve the research problem
- Do a thorough literature review before writing the introduction
- Start writing the introduction by using your own words, then add references from the literature
How to prepare the Abstract of a research paper
The abstract acts as your paper’s elevator pitch and is therefore best written only after the main text is finished. In this one short paragraph you must convince someone to take on the time-consuming task of reading your whole research article. So, make the paper easy to read, intriguing, and self-explanatory; avoid jargon and abbreviations.
How to structure the abstract of a research paper:
- The abstract is a single paragraph that follows this structure:
- Problem: why did we research this
- Methodology: typically starts with the words “Here we…” that signal the start of own contribution.
- Results: what we found from the research.
- Conclusions: show why are the findings important
How to compose a research paper Title
The title is the ultimate summary of a research paper. It must therefore entice someone looking for information to click on a link to it and continue reading the article. A title is also used for indexing purposes in scientific databases, so a representative and optimized title will play large role in determining if your research paper appears in search results at all.
Tips for coming up with a research paper title:
- Capture curiosity of potential readers using a clear and descriptive title
- Include broad terms that are often searched
- Add details that uniquely identify the researched subject of your research paper
- Avoid jargon and abbreviations
- Use keywords as title extension (instead of duplicating the words) to increase the chance of appearing in search results
How to prepare Highlights and Graphical Abstract
Highlights are three to five short bullet-point style statements that convey the core findings of the research paper. Notice that the focus is on the findings, not on the process of getting there.
A graphical abstract placed next to the textual abstract visually summarizes the entire research paper in a single, easy-to-follow figure. I show how to create a graphical abstract in my book Research Data Visualization and Scientific Graphics.
Tips for preparing highlights and graphical abstract:
- In highlights show core findings of the research paper (instead of what you did in the study).
- In graphical abstract show take-home message or methodology of the research paper. Learn more about creating a graphical abstract in this article.
Step 4: Prepare for submission

Sometimes it seems that nuclear fusion will stop on the star closest to us (read: the sun will stop to shine) before a submitted manuscript is published in a scientific journal. The publication process routinely takes a long time, and after submitting the manuscript you have very little control over what happens. To increase the chances of a quick publication, you must do your homework before submitting the manuscript. In the fourth LEAP step, you make sure that your research paper is published in the most appropriate journal as quickly and painlessly as possible.
How to select a scientific Journal for your research paper
The best way to find a journal for your research paper is it to review which journals you used while preparing your manuscript. This source listing should provide some assurance that your own research paper, once published, will be among similar articles and, thus, among your field’s trusted sources.
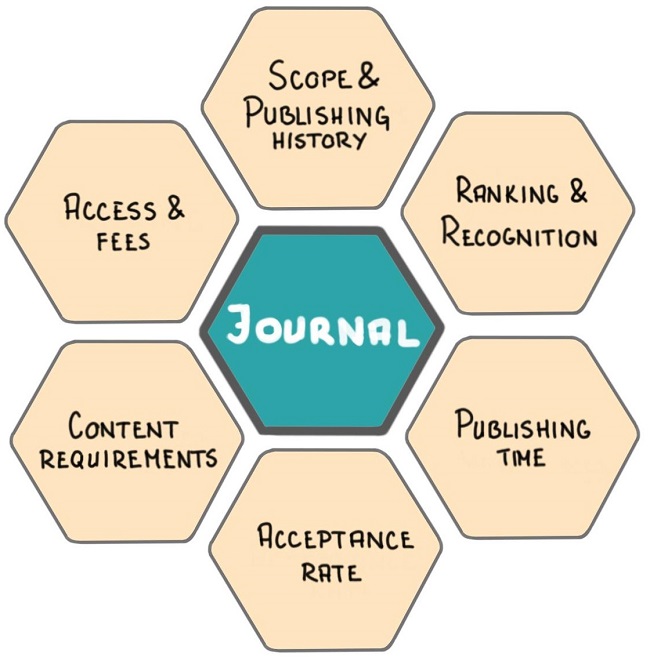
After this initial selection of hand-full of scientific journals, consider the following six parameters for selecting the most appropriate journal for your research paper (read this article to review each step in detail):
- Scope and publishing history
- Ranking and Recognition
- Publishing time
- Acceptance rate
- Content requirements
- Access and Fees
How to select a journal for your research paper:
- Use the six parameters to select the most appropriate scientific journal for your research paper
- Use the following tools for journal selection: https://peerrecognized.com/journals
- Follow the journal’s “Authors guide” formatting requirements
How to Edit you manuscript
No one can write a finished research paper on their first attempt. Before submitting, make sure to take a break from your work for a couple of days, or even weeks. Try not to think about the manuscript during this time. Once it has faded from your memory, it is time to return and edit. The pause will allow you to read the manuscript from a fresh perspective and make edits as necessary.
I have summarized the most useful research paper editing tools in this article.
Tips for editing a research paper:
- Take time away from the research paper to forget about it; then returning to edit,
- Start by editing the content: structure, headings, paragraphs, logic, figures
- Continue by editing the grammar and language; perform a thorough language check using academic writing tools
- Read the entire paper out loud and correct what sounds weird
How to write a compelling Cover Letter for your paper
Begin the cover letter by stating the paper’s title and the type of paper you are submitting (review paper, research paper, short communication). Next, concisely explain why your study was performed, what was done, and what the key findings are. State why the results are important and what impact they might have in the field. Make sure you mention how your approach and findings relate to the scope of the journal in order to show why the article would be of interest to the journal’s readers.
I wrote a separate article that explains what to include in a cover letter here. You can also download a cover letter template from the article.
Tips for writing a cover letter:
- Explain how the findings of your research relate to journal’s scope
- Tell what impact the research results will have
- Show why the research paper will interest the journal’s audience
- Add any legal statements as required in journal’s guide for authors
How to Answer the Reviewers
Reviewers will often ask for new experiments, extended discussion, additional details on the experimental setup, and so forth. In principle, your primary winning tactic will be to agree with the reviewers and follow their suggestions whenever possible. After all, you must earn their blessing in order to get your paper published.
Be sure to answer each review query and stick to the point. In the response to the reviewers document write exactly where in the paper you have made any changes. In the paper itself, highlight the changes using a different color. This way the reviewers are less likely to re-read the entire article and suggest new edits.
In cases when you don’t agree with the reviewers, it makes sense to answer more thoroughly. Reviewers are scientifically minded people and so, with enough logical and supported argument, they will eventually be willing to see things your way.
Tips for answering the reviewers:
- Agree with most review comments, but if you don’t, thoroughly explain why
- Highlight changes in the manuscript
- Do not take the comments personally and cool down before answering
The LEAP research paper writing cheat sheet
Imagine that you are back in grad school and preparing to take an exam on the topic: “How to write a research paper”. As an exemplary student, you would, most naturally, create a cheat sheet summarizing the subject… Well, I did it for you.
This one-page summary of the LEAP research paper writing technique will remind you of the key research paper writing steps. Print it out and stick it to a wall in your office so that you can review it whenever you are writing a new research paper.

Now that we have gone through the four LEAP research paper writing steps, I hope you have a good idea of how to write a research paper. It can be an enjoyable process and once you get the hang of it, the four LEAP writing steps should even help you think about and interpret the research results. This process should enable you to write a well-structured, concise, and compelling research paper.
Have fund with writing your next research paper. I hope it will turn out great!
Learn writing papers that get cited
The LEAP writing approach is a blueprint for writing research papers. But to be efficient and write papers that get cited, you need more than that.
My name is Martins Zaumanis and in my interactive course Research Paper Writing Masterclass I will show you how to visualize your research results, frame a message that convinces your readers, and write each section of the paper. Step-by-step.
And of course – you will learn to respond the infamous Reviewer No.2.

Hey! My name is Martins Zaumanis and I am a materials scientist in Switzerland ( Google Scholar ). As the first person in my family with a PhD, I have first-hand experience of the challenges starting scientists face in academia. With this blog, I want to help young researchers succeed in academia. I call the blog “Peer Recognized”, because peer recognition is what lifts academic careers and pushes science forward.
Besides this blog, I have written the Peer Recognized book series and created the Peer Recognized Academy offering interactive online courses.
Related articles:
One comment
- Pingback: Research Paper Outline with Key Sentence Skeleton (+Paper Template)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I want to join the Peer Recognized newsletter!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Copyright © 2024 Martins Zaumanis
Contacts: [email protected]
Privacy Policy
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Research Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Research Paper
There will come a time in most students' careers when they are assigned a research paper. Such an assignment often creates a great deal of unneeded anxiety in the student, which may result in procrastination and a feeling of confusion and inadequacy. This anxiety frequently stems from the fact that many students are unfamiliar and inexperienced with this genre of writing. Never fear—inexperience and unfamiliarity are situations you can change through practice! Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the reasons this topic is so important.
Becoming an experienced researcher and writer in any field or discipline takes a great deal of practice. There are few individuals for whom this process comes naturally. Remember, even the most seasoned academic veterans have had to learn how to write a research paper at some point in their career. Therefore, with diligence, organization, practice, a willingness to learn (and to make mistakes!), and, perhaps most important of all, patience, students will find that they can achieve great things through their research and writing.
The pages in this section cover the following topic areas related to the process of writing a research paper:
- Genre - This section will provide an overview for understanding the difference between an analytical and argumentative research paper.
- Choosing a Topic - This section will guide the student through the process of choosing topics, whether the topic be one that is assigned or one that the student chooses themselves.
- Identifying an Audience - This section will help the student understand the often times confusing topic of audience by offering some basic guidelines for the process.
- Where Do I Begin - This section concludes the handout by offering several links to resources at Purdue, and also provides an overview of the final stages of writing a research paper.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Research Paper
Last Updated: February 18, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Chris Hadley, PhD . Chris Hadley, PhD is part of the wikiHow team and works on content strategy and data and analytics. Chris Hadley earned his PhD in Cognitive Psychology from UCLA in 2006. Chris' academic research has been published in numerous scientific journals. There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 4,190,187 times.
Whether you’re in a history, literature, or science class, you’ll probably have to write a research paper at some point. It may seem daunting when you’re just starting out, but staying organized and budgeting your time can make the process a breeze. Research your topic, find reliable sources, and come up with a working thesis. Then create an outline and start drafting your paper. Be sure to leave plenty of time to make revisions, as editing is essential if you want to hand in your best work!
Sample Research Papers and Outlines

Researching Your Topic

- For instance, you might start with a general subject, like British decorative arts. Then, as you read, you home in on transferware and pottery. Ultimately, you focus on 1 potter in the 1780s who invented a way to mass-produce patterned tableware.
Tip: If you need to analyze a piece of literature, your task is to pull the work apart into literary elements and explain how the author uses those parts to make their point.

- Authoritative, credible sources include scholarly articles (especially those other authors reference), government websites, scientific studies, and reputable news bureaus. Additionally, check your sources' dates, and make sure the information you gather is up to date.
- Evaluate how other scholars have approached your topic. Identify authoritative sources or works that are accepted as the most important accounts of the subject matter. Additionally, look for debates among scholars, and ask yourself who presents the strongest evidence for their case. [3] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- You’ll most likely need to include a bibliography or works cited page, so keep your sources organized. List your sources, format them according to your assigned style guide (such as MLA or Chicago ), and write 2 or 3 summary sentences below each one. [4] X Research source

- Imagine you’re a lawyer in a trial and are presenting a case to a jury. Think of your readers as the jurors; your opening statement is your thesis and you’ll present evidence to the jury to make your case.
- A thesis should be specific rather than vague, such as: “Josiah Spode’s improved formula for bone china enabled the mass production of transfer-printed wares, which expanded the global market for British pottery.”
Drafting Your Essay

- Your outline is your paper’s skeleton. After making the outline, all you’ll need to do is fill in the details.
- For easy reference, include your sources where they fit into your outline, like this: III. Spode vs. Wedgewood on Mass Production A. Spode: Perfected chemical formula with aims for fast production and distribution (Travis, 2002, 43) B. Wedgewood: Courted high-priced luxury market; lower emphasis on mass production (Himmelweit, 2001, 71) C. Therefore: Wedgewood, unlike Spode, delayed the expansion of the pottery market.

- For instance, your opening line could be, “Overlooked in the present, manufacturers of British pottery in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries played crucial roles in England’s Industrial Revolution.”
- After presenting your thesis, lay out your evidence, like this: “An examination of Spode’s innovative production and distribution techniques will demonstrate the importance of his contributions to the industry and Industrial Revolution at large.”
Tip: Some people prefer to write the introduction first and use it to structure the rest of the paper. However, others like to write the body, then fill in the introduction. Do whichever seems natural to you. If you write the intro first, keep in mind you can tweak it later to reflect your finished paper’s layout.

- After setting the context, you'd include a section on Josiah Spode’s company and what he did to make pottery easier to manufacture and distribute.
- Next, discuss how targeting middle class consumers increased demand and expanded the pottery industry globally.
- Then, you could explain how Spode differed from competitors like Wedgewood, who continued to court aristocratic consumers instead of expanding the market to the middle class.
- The right number of sections or paragraphs depends on your assignment. In general, shoot for 3 to 5, but check your prompt for your assigned length.

- If you bring up a counterargument, make sure it’s a strong claim that’s worth entertaining instead of ones that's weak and easily dismissed.
- Suppose, for instance, you’re arguing for the benefits of adding fluoride to toothpaste and city water. You could bring up a study that suggested fluoride produced harmful health effects, then explain how its testing methods were flawed.

- Sum up your argument, but don’t simply rewrite your introduction using slightly different wording. To make your conclusion more memorable, you could also connect your thesis to a broader topic or theme to make it more relatable to your reader.
- For example, if you’ve discussed the role of nationalism in World War I, you could conclude by mentioning nationalism’s reemergence in contemporary foreign affairs.
Revising Your Paper

- This is also a great opportunity to make sure your paper fulfills the parameters of the assignment and answers the prompt!
- It’s a good idea to put your essay aside for a few hours (or overnight, if you have time). That way, you can start editing it with fresh eyes.
Tip: Try to give yourself at least 2 or 3 days to revise your paper. It may be tempting to simply give your paper a quick read and use the spell-checker to make edits. However, revising your paper properly is more in-depth.

- The passive voice, such as “The door was opened by me,” feels hesitant and wordy. On the other hand, the active voice, or “I opened the door,” feels strong and concise.
- Each word in your paper should do a specific job. Try to avoid including extra words just to fill up blank space on a page or sound fancy.
- For instance, “The author uses pathos to appeal to readers’ emotions” is better than “The author utilizes pathos to make an appeal to the emotional core of those who read the passage.”

- Read your essay out loud to help ensure you catch every error. As you read, check for flow as well and, if necessary, tweak any spots that sound awkward. [13] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- It’s wise to get feedback from one person who’s familiar with your topic and another who’s not. The person who knows about the topic can help ensure you’ve nailed all the details. The person who’s unfamiliar with the topic can help make sure your writing is clear and easy to understand.
Community Q&A
- Remember that your topic and thesis should be as specific as possible. Thanks Helpful 5 Not Helpful 0
- Researching, outlining, drafting, and revising are all important steps, so do your best to budget your time wisely. Try to avoid waiting until the last minute to write your paper. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 2

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/planresearchpaper/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/evaluating-print-sources/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/conducting_research/research_overview/index.html
- ↑ https://poorvucenter.yale.edu/writing/graduate-writing-lab/writing-through-graduate-school/working-sources
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-5-putting-the-pieces-together-with-a-thesis-statement/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/developing_an_outline/index.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/introductions/
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/writingprocess/counterarguments
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/ending-essay-conclusions
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/formandstyle/writing/scholarlyvoice/activepassive
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/reading-aloud/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/index.html
About This Article

To write a research paper, start by researching your topic at the library, online, or using an academic database. As you conduct your research and take notes, zero in on a specific topic that you want to write about and create a 1-2 sentence thesis to state the focus of your paper. Then, create an outline that includes an introduction, 3 to 5 body paragraphs to present your arguments, and a conclusion to sum up your main points. Once you have your paper's structure organized, draft your paragraphs, focusing on 1 argument per paragraph. Use the information you found through your research to back up your claims and prove your thesis statement. Finally, proofread and revise your content until it's polished and ready to submit. For more information on researching and citing sources, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Private And Discrete
Aug 2, 2020
Did this article help you?

Jan 3, 2018
Oct 29, 2016
Maronicha Lyles
Jul 24, 2016
Maxwell Ansah
Nov 22, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Reference management. Clean and simple.
The top list of academic research databases

2. Web of Science
5. ieee xplore, 6. sciencedirect, 7. directory of open access journals (doaj), get the most out of your academic research database, frequently asked questions about academic research databases, related articles.
Whether you are writing a thesis , dissertation, or research paper it is a key task to survey prior literature and research findings. More likely than not, you will be looking for trusted resources, most likely peer-reviewed research articles.
Academic research databases make it easy to locate the literature you are looking for. We have compiled the top list of trusted academic resources to help you get started with your research:
Scopus is one of the two big commercial, bibliographic databases that cover scholarly literature from almost any discipline. Besides searching for research articles, Scopus also provides academic journal rankings, author profiles, and an h-index calculator .
- Coverage: 90.6 million core records
- References: N/A
- Discipline: Multidisciplinary
- Access options: Limited free preview, full access by institutional subscription only
- Provider: Elsevier
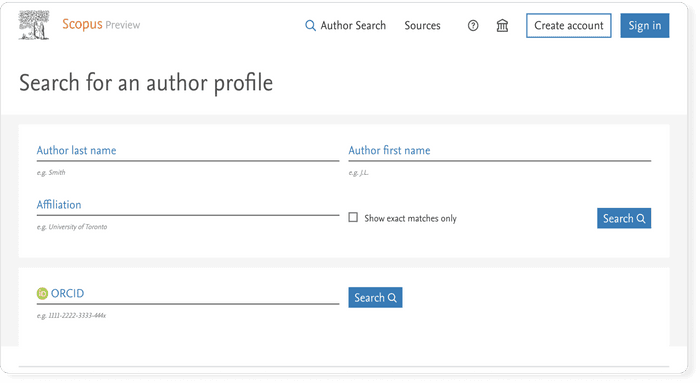
Web of Science also known as Web of Knowledge is the second big bibliographic database. Usually, academic institutions provide either access to Web of Science or Scopus on their campus network for free.
- Coverage: approx. 100 million items
- References: 1.4 billion
- Access options: institutional subscription only
- Provider: Clarivate (formerly Thomson Reuters)
PubMed is the number one resource for anyone looking for literature in medicine or biological sciences. PubMed stores abstracts and bibliographic details of more than 30 million papers and provides full text links to the publisher sites or links to the free PDF on PubMed Central (PMC) .
- Coverage: approx. 35 million items
- Discipline: Medicine and Biological Sciences
- Access options: free
- Provider: NIH
For education sciences, ERIC is the number one destination. ERIC stands for Education Resources Information Center, and is a database that specifically hosts education-related literature.
- Coverage: approx. 1.6 million items
- Discipline: Education
- Provider: U.S. Department of Education
IEEE Xplore is the leading academic database in the field of engineering and computer science. It's not only journal articles, but also conference papers, standards and books that can be search for.
- Coverage: approx. 6 million items
- Discipline: Engineering
- Provider: IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)
ScienceDirect is the gateway to the millions of academic articles published by Elsevier, 1.4 million of which are open access. Journals and books can be searched via a single interface.
- Coverage: approx. 19.5 million items
The DOAJ is an open-access academic database that can be accessed and searched for free.
- Coverage: over 8 million records
- Provider: DOAJ
JSTOR is another great resource to find research papers. Any article published before 1924 in the United States is available for free and JSTOR also offers scholarships for independent researchers.
- Coverage: more than 12 million items
- Provider: ITHAKA
Start using a reference manager like Paperpile to save, organize, and cite your references. Paperpile integrates with PubMed and many popular databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons:
Scopus is one of the two big commercial, bibliographic databases that cover scholarly literature from almost any discipline. Beside searching for research articles, Scopus also provides academic journal rankings, author profiles, and an h-index calculator .
PubMed is the number one resource for anyone looking for literature in medicine or biological sciences. PubMed stores abstracts and bibliographic details of more than 30 million papers and provides full text links to the publisher sites or links to the free PDF on PubMed Central (PMC)
- Our Writers
- How to Order
- Assignment Writing Service
- Report Writing Service
- Buy Coursework
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Research Paper Writing Service
- All Essay Services
- Buy Research Paper
- Buy Term Paper
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Case study
- Buy Presentation
- Buy Personal statement
Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Example
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!

People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper
Crafting a comprehensive research paper can be daunting. Understanding diverse citation styles and various subject areas presents a challenge for many.
Without clear examples, students often feel lost and overwhelmed, unsure of how to start or which style fits their subject.
Explore our collection of expertly written research paper examples. We’ve covered various citation styles and a diverse range of subjects.
So, read on!
- 1. Research Paper Example for Different Formats
- 2. Examples for Different Research Paper Parts
- 3. Research Paper Examples for Different Fields
- 4. Research Paper Example Outline
Research Paper Example for Different Formats
Following a specific formatting style is essential while writing a research paper . Knowing the conventions and guidelines for each format can help you in creating a perfect paper. Here we have gathered examples of research paper for most commonly applied citation styles :
Social Media and Social Media Marketing: A Literature Review
APA Research Paper Example
APA (American Psychological Association) style is commonly used in social sciences, psychology, and education. This format is recognized for its clear and concise writing, emphasis on proper citations, and orderly presentation of ideas.
Here are some research paper examples in APA style:
Research Paper Example APA 7th Edition
Research Paper Example MLA
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is frequently employed in humanities disciplines, including literature, languages, and cultural studies. An MLA research paper might explore literature analysis, linguistic studies, or historical research within the humanities.
Here is an example:
Found Voices: Carl Sagan
Research Paper Example Chicago
Chicago style is utilized in various fields like history, arts, and social sciences. Research papers in Chicago style could delve into historical events, artistic analyses, or social science inquiries.
Here is a research paper formatted in Chicago style:
Chicago Research Paper Sample
Research Paper Example Harvard
Harvard style is widely used in business, management, and some social sciences. Research papers in Harvard style might address business strategies, case studies, or social policies.
View this sample Harvard style paper here:
Harvard Research Paper Sample
Examples for Different Research Paper Parts
A research paper has different parts. Each part is important for the overall success of the paper. Chapters in a research paper must be written correctly, using a certain format and structure.
The following are examples of how different sections of the research paper can be written.
Research Proposal
The research proposal acts as a detailed plan or roadmap for your study, outlining the focus of your research and its significance. It's essential as it not only guides your research but also persuades others about the value of your study.
Example of Research Proposal
An abstract serves as a concise overview of your entire research paper. It provides a quick insight into the main elements of your study. It summarizes your research's purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions in a brief format.
Research Paper Example Abstract
Literature Review
A literature review summarizes the existing research on your study's topic, showcasing what has already been explored. This section adds credibility to your own research by analyzing and summarizing prior studies related to your topic.
Literature Review Research Paper Example
Methodology
The methodology section functions as a detailed explanation of how you conducted your research. This part covers the tools, techniques, and steps used to collect and analyze data for your study.
Methods Section of Research Paper Example
How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper
The conclusion summarizes your findings, their significance and the impact of your research. This section outlines the key takeaways and the broader implications of your study's results.
Research Paper Conclusion Example
Research Paper Examples for Different Fields
Research papers can be about any subject that needs a detailed study. The following examples show research papers for different subjects.
History Research Paper Sample
Preparing a history research paper involves investigating and presenting information about past events. This may include exploring perspectives, analyzing sources, and constructing a narrative that explains the significance of historical events.
View this history research paper sample:
Many Faces of Generalissimo Fransisco Franco
Sociology Research Paper Sample
In sociology research, statistics and data are harnessed to explore societal issues within a particular region or group. These findings are thoroughly analyzed to gain an understanding of the structure and dynamics present within these communities.
Here is a sample:
A Descriptive Statistical Analysis within the State of Virginia
Science Fair Research Paper Sample
A science research paper involves explaining a scientific experiment or project. It includes outlining the purpose, procedures, observations, and results of the experiment in a clear, logical manner.
Here are some examples:
Science Fair Paper Format
What Do I Need To Do For The Science Fair?

Psychology Research Paper Sample
Writing a psychology research paper involves studying human behavior and mental processes. This process includes conducting experiments, gathering data, and analyzing results to understand the human mind, emotions, and behavior.
Here is an example psychology paper:
The Effects of Food Deprivation on Concentration and Perseverance
Art History Research Paper Sample
Studying art history includes examining artworks, understanding their historical context, and learning about the artists. This helps analyze and interpret how art has evolved over various periods and regions.
Check out this sample paper analyzing European art and impacts:
European Art History: A Primer
Research Paper Example Outline
Before you plan on writing a well-researched paper, make a rough draft. An outline can be a great help when it comes to organizing vast amounts of research material for your paper.
Here is an outline of a research paper example:
|
Here is a downloadable sample of a standard research paper outline:
Research Paper Outline
Want to create the perfect outline for your paper? Check out this in-depth guide on creating a research paper outline for a structured paper!
Good Research Paper Examples for Students
Here are some more samples of research paper for students to learn from:
Fiscal Research Center - Action Plan
Qualitative Research Paper Example
Research Paper Example Introduction
How to Write a Research Paper Example
Research Paper Example for High School
Now that you have explored the research paper examples, you can start working on your research project. Hopefully, these examples will help you understand the writing process for a research paper.
If you're facing challenges with your writing requirements, you can hire our essay writing help online.
Our team is experienced in delivering perfectly formatted, 100% original research papers. So, whether you need help with a part of research or an entire paper, our experts are here to deliver.
So, why miss out? Place your ‘ write my research paper ’ request today and get a top-quality research paper!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format / APA Sample Papers
APA Sample Papers
Ever wonder how to format your research paper in APA style? If so, you’re in luck! The team at EasyBib.com has put together an example paper to help guide you through your next assignment. (Actually, looking for MLA? Here’s a page on what is MLA format .)
The featured example is a research paper on the uses of biometrics to inform design decisions in the tech industry, authored by our UX Research Intern Peace Iyiewuare. Like most APA style papers, it includes an APA title page , tables, and several references and APA in-text citations to scholarly journals relevant to its topic. References are an important aspect of scientific research papers, and formatting them correctly is critical to getting a good grade.
This paper follows the formatting rules specified in the 6th edition of The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (the APA is not directly associated with this guide) . We’ve left comments and tips throughout the document, so you’ll know the specific rules around how to format titles, spacing, and font, as well as the citations on the APA reference page .
The reference list needs special care, as it demonstrates to the reader that you have accurately portrayed your outside sources and have given credit to the appropriate parties. Be sure to check our full APA citation guide for more information on paper formatting and citing sources in APA style. There is also a guide on APA footnotes in case that is your preferred form of citation.
Download the APA Visual Guide
When citations are done, don’t forget to finish your paper off with a proofread—EasyBib Plus’s plagiarism and grammar check can help! Got a misspelled adverb ? Missed capitalizing a proper noun ? Struggling with subject-verb agreement ? These are just a few things our checker could help you spot in your paper.
D. Complete Sample APA Paper
We’ve included a full student paper below to give you an idea of what an essay in APA format looks like, complete with a title page, paper, reference list, and index. If you plan to include an APA abstract in your paper, see the Professional Paper for an example.
If you’re looking for an APA format citation generator, we’ve got you covered. Use EasyBib.com! Our APA format machine can help you create every reference for your paper.
Below is an example of a student APA format essay. We also have PDF versions of both a student paper and a professional paper linked below.
See Student Paper See Professional Paper
Using Biometrics to Evaluate Visual Design
Jane Lisa Dekker
Art Department, Northern California Valley State University
UXAD 272: Strategic Web Design
Professor Juan Liu, PhD
January 29, 2020
A vast amount of research has been conducted regarding the importance of visual design, and its role as a mediator of user’s experience when browsing a site or interacting with an interface. In the literature, visual design is one aspect of website quality. Jones and Kim (2010) define website quality as “the perceived quality of a retail website that involves a [user’s] perceptions of the retailer’s website and comprises consumer reactions towards such attributes as information, entertainment/enjoyment, usability, transaction capabilities, and design aesthetics” (p. 632). They further examined the impact web quality and retail brand trust has on purchase intentions. Additional research examining e-commerce sites has shown web quality has an impact on both initial and continued purchase intention (Kuan, Bock, & Vathanophas, 2008), as well as consumer satisfaction (Lin, 2007). Moreso, research on the relationship between visual design and perceived usability (Stojmenovic, Pilgrim, & Lindgaard, 2014) has revealed a positive correlation between the two. As users’ ratings of visual quality increase, their ratings of perceived usability follows a similar trend. Although this research spans various domains, the reliance on self-report measures to gauge concepts like visual design and web quality is prevalent throughout much of the literature.
Although some self-report scales are validated within the literature, there are still issues with the use of self-report questionnaires. One is the reliance on the honesty of the participant. This tends to be more of an issue in studies related to questionnaires that measure characteristics of the participant, rather than objective stimuli. More relevant to this study is the issue of introspection and memory. Surveys are often distributed after a task is completed, and its accuracy is dependent on the ability of the participant to remember their experience during the study. Multiple research studies have shown that human memory is far from static. This can
be dangerous if a researcher chooses to solely rely on self-report methods to test a hypothesis. We believe these self-report methods in tandem with biometric methods can help ensure the validity of the questionnaires, and provide information beyond the scope of self-report scales.
Research Questions
We know from previous research that the quality of websites mediates many aspects of e-commerce, and provides insight as to how consumers view the webpages in general. However, simply knowing a webpage is perceived as lower quality doesn’t give insight as to what aspects of a page are disliked by a user. Additionally, it’s possible that the user is misremembering aspects of the webpage or being dishonest in their assessment. Using eye tracking metrics, galvanic skin response, and facial expression measures in tandem with a scale aimed at measuring visual design quality has a couple of identifiable benefits. Using both can potentially identify patterns amongst the biometric measures and the questionnaire, which would strengthen the validity of the results. More so, the eye tracking data has the potential to identify patterns amongst websites of lower or higher quality.
If found, these patterns can be used to evaluate particular aspects of a page that are impacting the quality of a webpage. Overall, we are interested in answering two questions:
Research Question 1 : Can attitudinal changes regarding substantial website redesigns be captured using biometric measures?
Research Question 2 : How do biometric measures correlate with self-reported measures of visual appeal?
Answering these questions has the potential to provide a method of justification for design changes, ranging from minor tweak to complete rebrands. There is not an easy way for companies to quantitatively analyze visual design decisions. A method for doing so would help companies evaluate visual designs before implementation in order to cost-justify them. To this end, we hope to demonstrate that biometric measurements can be used with questionnaires to verify and validate potential design changes a company or organization might want to implement.
By examining data from test subjects during a brief exposure to several websites, we hoped to explore the relationship between the self-reported evaluation of visual design quality and key biometric measurements of a subject’s emotional valence and arousal. Subjects were exposed to ten pairs of websites before and after a substantial visual design change and asked to evaluate the website based on their initial impressions of the site’s visual design quality using the VisAWI-S scale, as shown in Table 1.
During this assessment we collected GSR, facial expressions (limited by errors in initial study configuration), pupillary response, and fixation data using iMotions software coupled with a Tobii eye tracker, Shimmer GSR device, and Affdex facial expression analysis toolkit. This data was analyzed, in Table 2, to discover relationships between the independent and dependent variables, as well as relationships between certain dependent variables.
Jones, C., & Kim, S. (2010). Influences of retail brand trust, off-line patronage, clothing involvement and website quality on online apparel shopping intention: Online apparel shopping intention. International Journal of Consumer Studies , 34 (6), 627–637. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1470-6431.2010.00871.x
Kuan, H.-H., Bock, G.-W., & Vathanophas, V. (2008). Comparing the effects of website quality on customer initial purchase and continued purchase at e-commerce websites. Behaviour & Information Technology , 27 (1), 3–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/01449290600801959
Lin, H.-F. (2007). The impact of website quality dimensions on customer satisfaction in the B2C e-commerce context. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence , 18 (4), 363–378. https://doi.org/10.1080/14783360701231302
Stojmenovic, M., Pilgrim, C., & Lindgaard, G. (2014). Perceived and objective usability and visual appeal in a website domain with a less developed mental model. Proceedings of the 26 th Australian Computer-Human Interaction Conference on Designing Futures: The Future of Design , 316–323. https://doi.org/10.1145/2686612.2686660
|
| |
| Factor | Item |
| Simplicity | Everything goes together on the site. |
| Diversity | The layout is pleasantly varied. |
| Colorfulness | The color composition is attractive |
| Craftsmanship | The layout appears professionally designed |
| Familiarity* | I am familiar with this website |
| Participants were asked about agreement with the item using a 7-point likert scale. | |
| * question is simply to gauge familiarity for the study, and is not part of the Vis-AWI-S instrument | |
|
| ||||||
| Before | After | |||||
| Website | Mean Difference | |||||
| Joy Kitchen | 3.49 | 1.30 | 5.61 | 0.93 | 2.12 | 0.00 |
| Seacom | 3.27 | 1.59 | 5.35 | 1.20 | 2.08 | 0.00 |
| Food Blog | 3.59 | 1.30 | 5.59 | 0.80 | 2.00 | 0.00 |
| Credit Union | 3.29 | 1.26 | 5.18 | 1.07 | 1.89 | 0.00 |
| Travelers | 3.61 | 1.39 | 5.38 | 1.24 | 1.78 | 0.00 |
| Sporcle | 4.23 | 1.23 | 2.45 | 1.12 | -1.78 | 0.00 |
| Eagle | 3.93 | 1.47 | 5.45 | 0.82 | 1.52 | 0.00 |
| Oberlin | 4.00 | 1.25 | 5.47 | 0.84 | 1.47 | 0.00 |
| Valve | 3.88 | 1.56 | 5.10 | 1.42 | 1.22 | 0.00 |
| Hospital | 4.47 | 1.33 | 5.48 | 0.85 | 1.01 | 0.00 |
| Travel Blog | 4.71 | 1.23 | 5.69 | 1.01 | 0.98 | 0.00 |
| Space | 4.35 | 1.55 | 5.29 | 1.09 | 0.94 | 0.00 |
| School | 5.04 | 1.44 | 5.63 | 0.80 | 0.60 | 0.06 |
| Book Publisher | 5.12 | 1.27 | 5.63 | 1.17 | 0.51 | 0.10 |
| Sneakers | 4.78 | 1.37 | 5.20 | 1.34 | 0.42 | 0.14 |
| Stance | 5.08 | 0.88 | 5.41 | 0.95 | 0.33 | 0.09 |
| City | 4.79 | 1.18 | 5.12 | 0.88 | 0.32 | 0.07 |
| IEEE | 3.95 | 1.30 | 4.26 | 1.40 | 0.31 | 0.24 |
| Rise | 5.08 | 1.00 | 4.89 | 1.27 | -0.18 | 0.30 |
| Audio Technica | 3.94 | 1.52 | 4.05 | 1.37 | 0.11 | 0.71 |
| Bloomberg | 3.63 | 1.35 | 3.52 | 1.26 | -0.11 | 0.73 |
| Stimuli are ranked by largest to smallest absolute mean difference. | ||||||
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Perspective
- Open access
- Published: 03 June 2024
Scientific integrity and U.S. “Billion Dollar Disasters”
- Roger Pielke Jr 1 , 2
npj Natural Hazards volume 1 , Article number: 12 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
2551 Accesses
20 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Attribution
- Climate-change impacts
- Climate sciences
For more than two decades, the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has published a count of weather-related disasters in the United States that it estimates have exceeded one billion dollars (inflation adjusted) in each calendar year starting in 1980. The dataset is widely cited and applied in research, assessment and invoked to justify policy in federal agencies, Congress and by the U.S. President. This paper performs an evaluation of the dataset under criteria of procedure and substance defined under NOAA’s Information Quality and Scientific Integrity policies. The evaluation finds that the “billion dollar disaster” dataset falls short of meeting these criteria. Thus, public claims promoted by NOAA associated with the dataset and its significance are flawed and at times misleading. Specifically, NOAA incorrectly claims that for some types of extreme weather, the dataset demonstrates detection and attribution of changes on climate timescales. Similarly flawed are NOAA’s claims that increasing annual counts of billion dollar disasters are in part a consequence of human caused climate change. NOAA’s claims to have achieved detection and attribution are not supported by any scientific analysis that it has performed. Given the importance and influence of the dataset in science and policy, NOAA should act quickly to address this scientific integrity shortfall.
Similar content being viewed by others
The global historical climate database HCLIM

The evolving landscape of sea-level rise science from 1990 to 2021
No evidence that mandatory open data policies increase error correction
Introduction.
In the late 1990s, the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) began publishing a tally of weather and climate disasters that each resulted in more than $1 billion in damage, noting that the time series had become “one of our more popular web pages” 1 . Originally, the data was reported in current-year U.S. dollars. In 2011, following criticism that the dataset was misleading, NOAA modified its methods to adjusted historical losses to constant-year dollars by accounting for inflation ( https://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/capital-weather-gang/post/2011-billion-dollar-weather-disaster-record-legit-or-bad-economics/2012/01/12/gIQADocztP_blog.html ).
By 2023, the billion dollar disaster time series had become a fixture in NOAA’s public outreach, was highlighted by the U.S. government’s U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP) as a “climate change indicator” ( https://storymaps.arcgis.com/collections/ad628a4d3e7e4460b089d9fe96b2475d?item=1 ), was a cited as evidence in support of a “key message” of the Fifth U.S. National Climate Assessment showing that “extreme events are becoming more frequent and severe” ( https://nca2023.globalchange.gov/chapter/2/ ). The time series is often cited in policy settings as evidence of the effects of human-caused climate change to increase the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events and associated economic damage, including in federal agencies, Congress and by the U.S. President ( https://www.congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/house-bill/598/text ; https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2023/11/14/fact-sheet-biden-harris-administration-releases-fifth-national-climate-assessment-and-announces-more-than-6-billion-to-strengthen-climate-resilience-across-the-country ). In addition to being widely cited in justifications of policy, as of March, 2024, NOAA’s billion dollar dataset has been cited in almost 1000 articles according to Google Scholar ( https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C6&q=%22billion+dollar+disasters%22&btnG= ).
This paper evaluates the billion dollar disaster time series by applying criteria of NOAA’s Information Quality and Scientific Integrity policies. The evaluation finds that billion dollar disaster time series fails to meet NOAA’s criteria for “information quality,” specifically, NOAA’s criteria of traceability, transparency, presentation, and substance.
Thus, the billion dollar disaster dataset is not simply an insufficient basis for claims of the detection and attribution of changes in climate variables (or a consequence of such changes), but the dataset is inappropriate for use in such research. Throughout, I use the terms “detection” and “attribution” as defined by the Intergovernmental panel on Climate Change (IPCC) 2 . Climate data should be the basis for claims of detection and attribution of changes in climate variables, not economic loss data. Because of the shortfalls in scientific integrity documented in this evaluation, policy makers and the public have been misinformed about extreme events and disasters in the United States.
Evaluation of policy or program performance is among the most common and influential practices in applied policy research. Policy evaluation tells us if actions by government programs and agencies are meeting their stated goals and provides insight into reasons for successes and failures. As such, evaluation offers important input that empowers policy makers to correct course and supports efforts by the public to hold governments democratically accountable. A systematic evaluation includes four distinct intellectual tasks 3 , 4 : (a) identification of goals to be achieved, (b) metrics which can be used to assess progress (or lack thereof) with respect to goals, (c) data or evidence related to such metrics, and finally, if possible, (d) judgments of responsibility for observed outcomes.
NOAA’s billion dollar disaster time series is considered a “fundamental research communication” under the Public Communications order of NOAA’s parent agency, the Department of Commerce ( https://www.osec.doc.gov/opog/dmp/daos/dao219_1.html ). NOAA defines a “fundamental research communication” to be “official work regarding the products of basic or applied research in science and engineering, the results of which ordinarily are published and shared broadly within the scientific community” ( https://www.noaa.gov/sites/default/files/legacy/document/2021/Feb/202-735-D.pdf ). NOAA further identifies an important subset of “fundamental research communications” to be “influential information,” which “means information the agency reasonably can determine will have or does have a clear and substantial impact on important public policies or private sector decisions” ( https://www.noaa.gov/organization/information-technology/policy-oversight/information-quality/information-quality-guidelines ). The billion dollar disaster dataset is also what the Office of Management and Budget defines as “Influential Scientific Information” ( https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2005-01-14/pdf/05-769.pdf ).
NOAA’s Information Quality and Scientific Integrity policies set forth the criteria to be used for evaluating “fundamental research communications,” including the subset of “influential information.” Specifically, NOAA’s Information Quality Guidelines identify three criteria of information quality: utility, objectivity, and integrity ( https://www.noaa.gov/organization/information-technology/policy-oversight/information-quality/information-quality-guidelines ).
Utility refers to “the usefulness of research to its intended users, including the public,” with an emphasis on “transparency.” NOAA’s Scientific Integrity Policy provides further guidance: “Transparency, traceability, and integrity at all levels are required” in order for the agency “to achieve” its mission ( https://www.noaa.gov/sites/default/files/legacy/document/2021/Feb/202-735-D.pdf ).
Traceability: “The ability to verify sources, data, information, methodology, results, assessments, research, analysis, conclusions or other evidence to establish the integrity of findings.”
Transparency: “Characterized by visibility or accessibility of information.”
Objectivity refers to presentation and substance:
Presentation: “includes whether disseminated information is presented in an accurate, clear, complete, and unbiased manner and in a proper context.”
Substance: “involves a focus on ensuring accurate, reliable, and unbiased information. In a scientific, financial, or statistical context, the original and supporting data shall be generated, and the analytic results shall be developed, using sound statistical and research methods.”
Integrity refers to “security ‑ the protection of information from unauthorized access or revision, to ensure that the information is not compromised through corruption or falsification.” Integrity will not be further considered as part of this evaluation.
NOAA’s Scientific Integrity Policy also states that it will “ensure that data and research used to support policy decisions undergo independent peer review by qualified experts” ( https://sciencecouncil.noaa.gov/scientific-integrity-commons/sic-integrity-policy/ ). OMB requires that agencies develop “a transparent process for public disclosure of peer review planning, including a Web-accessible description of the peer review plan that the agency has developed for each of its forthcoming influential scientific disseminations” ( https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2005-01-14/pdf/05-769.pdf ). There is no such plan in place for the NOAA “billion dollar” dataset and the methods, which have evolved over time, and results have not been subject to any public or transparent form of peer review.
The evaluation conducted here thus focuses on traceability and transparency (as elements of utility) and presentation and substance (as elements of objectivity).
Traceability and transparency
The NOAA billion dollar disaster dataset is intransparent in many ways, including its sources, input data and methodologies employed to produce results. The intransparency includes elements of event loss estimation, additions to and subtractions of events from the database, and adjustments made to historical loss estimates. There have been an unknown number of versions of the dataset, which have not been documented or made publicly available. Changes are made to the dataset more frequently than annually, suggesting that there have been many dozens of versions of the dataset over the past decades. Replication of the dataset or changes made to it is thus not possible by any independent researcher, as is verification or evaluation of the dataset itself.
Seven examples illustrate the lack of transparency and lack of traceability.
First, NOAA states that it utilizes more than “a dozen sources” to “help capture the total, direct costs (both insured and uninsured) of the weather and climate events” ( https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/billions/faq ). However, NOAA does not specifically identify these sources in relation to specific events, how its estimates are derived from these sources, or the estimates themselves. Almost all data sources that NOAA cites that it relies on for loss estimates are public agencies that produce data released to the public. Insured losses for specific events are aggregated and typically made available to the public, such as by the Florida Office of Insurance Regulation ( https://www.floir.com/home ). Aggregated data provides no information on specific businesses or individuals.
NOAA also states that it includes in it loss estimates various indirect losses such as business interruption, wildfire suppression and others. NOAA does not provide the data or methods for its estimation of such indirect losses. Smith and Matthews 5 (who also have created and maintained the dataset as NOAA employees) also identify livestock feeding costs as a function of national feedstock trends as a variable used in compiling the dataset. Livestock feeding costs are not considered a disaster cost in conventional disaster accounting methods (such as by NOAA Storm Data or SHELDUS), as these are not direct losses due to a local or regional extreme event, but rather an estimate of national market changes in commodity prices which are influenced by many more factors than an extreme event. It is unclear what other measures of indirect costs are included in the NOAA tabulation.
Second, consider the case of Hurricane Idalia, which made landfall in the Big Bend Region of Florida in late September 2023. Initial catastrophe model estimates suggested insured losses of $2.5 to 5 billion ( https://www.insurancejournal.com/news/national/2023/09/05/738970.htm ). The initial NOAA estimate reported on its billion dollar disaster website in the immediate aftermath of the storm was $2.5 billion. However, actual insured losses have been far less than was estimated in the storm’s aftermath, totaling officially about $310 million through mid-November 2023 ( https://www.floir.com/home/idalia ). The historical practice of NOAA’s National Hurricane Center for estimating total direct hurricane damage was to double insured losses to arrive at an estimate of total direct losses 6 . Even accounting for some additional insurance claims to be made, it is unlikely that Idalia would reach $1 billion in total direct losses under the NHC methodology. Yet by December 2023 NOAA had increased its loss estimate for Idalia to $3.6 billion. What is the basis for NOAA’s estimate of Idalia’s total losses being ~12 times insured losses? That is unknown.
Third, similarly unknown is why historical events are periodically added and removed from the dataset. For instance, from a version of the dataset available in December 2022 to an update published in July 2023, 10 new events were added and 3 were deleted (Fig. 1 ). A later comparison with yet another version of the dataset indicates 4 additional historical events were added (not shown in Fig. 1 ). There is no documentation or justification for such changes, I am only aware of them through the happenstance of downloading the currently available dataset at different times.
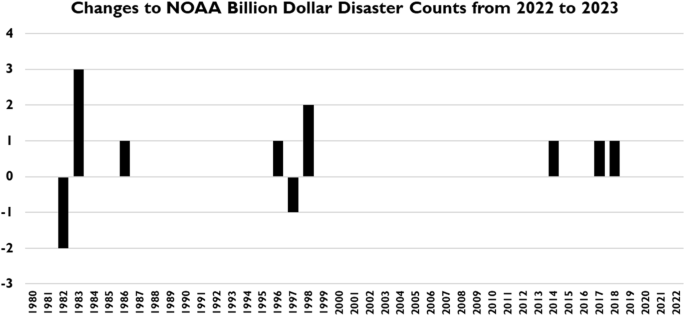
Undocumented changes to disaster counts made by NOAA between two different versions of the billion dollar disaster dataset, one downloaded in 2022 and another in 2023.
Fourth, a comparison of event loss estimates from the 2022 dataset and the 2023 version shows that each individual event has been adjusted by a different amount. According to NOAA, the only annual adjustment acknowledged is for inflation based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI). From 2022 to 2023, most of the adjustments made to individual events are between 4.5% and 6% but nine events are adjusted from 6.6% to 145%, and one is a reduction of about 75%. An annual adjustment for CPI should be constant across all events. No documentation is provided to explain these various adjustments and why they are unique to each event.
Fifth, NOAA states that they perform “key transformations” of loss data estimates by “scaling up insured loss data to account for uninsured and underinsured losses, which differs by peril, geography, and asset class.” NOAA makes no details available on the methodology or basis for such transformations, nor their impact on loss estimates, nor how these transformations may change over time.
Similarly, Smith and Matthews 5 reference an overall bias correction that has been applied to the dataset, as well as an additional correction for crop insurance losses. Smith and Katz 6 reference other adjustments, such as an adjustment to U.S. flood insurance participation rates, but neither the methodologies nor results of these various adjustments are documented, nor has the baseline data to which the adjustments are applied. Table 3 from Smith and Katz 7 suggests an open-ended formulaic approach to loss estimation, but none of the data that would be used in such formulas is available. Nor is it clear that NOAA currently applies the formula to loss estimation. If so, it should be straightforward to provide sources, data and methods for each iteration of the dataset.
Sixth, the number of smaller disasters ranging from $1 to $2 billion was fairly constant from 1980 to 2007 and then sharply increased starting in 2008 (Fig. 2 ). NOAA states that “we introduce events into the time series as they “inflate” their way above $1B in costs in today’s dollars. Every year, this leads to the introduction of several new events added from earlier in the time series” ( https://sciencecouncil.noaa.gov/scientific-integrity-commons/sic-integrity-policy/ ). However, the December 2023 dataset shows a net change of zero events from $1-2 billion for the period of 1980–2000 and a net increase of such 2 events from 2001–2023. NOAA’s statement that it elevates disasters from <1 billion in losses to the billion dollar disaster database also indicates that NOAA has another dataset with sub-billion dollar events that is not publicly available.
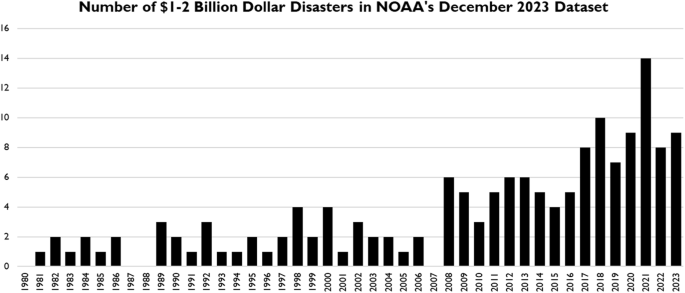
Increasing disaster counts costing $1-2 billion in a version of NOAA’s 2023 dataset.
The sharp discontinuity in the counts of $1-2 billion events starting in 2008 is suggestive of a change in disaster accounting methods, however, the lack of transparency into the creation of the dataset makes it impossible to know the reasons that may underlie this discontinuity.
Seventh, a comparison of 2023 CPI-adjusted official losses of NOAA’s National Hurricane Center (NHC)20 to the loss estimates of the 2023 NOAA billion dollar dataset (BDD), for significant hurricanes shows large differences (Table 1 ).
The NOAA billion dollar disaster estimates are in all cases except Hurricane Andrew substantially higher than the CPI-adjusted estimates based on the official estimates of NHC. There is no obvious pattern to the differences and the lack of methodological and data transparency makes it impossible to understand why there are such large differences and why these differences vary by such a great deal.
These seven examples indicate clearly that the NOAA billion dollar dataset fails with respect to NOAA’s scientific integrity criteria of traceability and transparency. The many issues and questions raised above cannot be answered because it is impossible to verify sources, data or methodology to establish the integrity of findings. These seven examples are just a small subset of issues that I have raised in public forums about the provenance, methods, and publicly communicated results of the application of these methods. The billion dollar dataset thus does not meet NOAA’s requirement that data be transparent and traceable.
Presentation and substance
Even in the absence of the issues documented above, the NOAA billion dollar disaster dataset is potentially misleading, because it has been represented by NOAA and U.S. government officials as evidence of the detection of trends in extreme weather phenomena and the attribution of those trends to human-caused climate change due to the emission of greenhouse gases.
For instance:
The NOAA official responsible for overseeing the dataset claimed that the dataset showed: “Climate change is supercharging many of these extremes that can lead to billion-dollar disasters” ( https://www.cbsnews.com/news/noaa-billion-dollar-weather-disasters-2022-hurricane-ian-drought/ ).
At the press conference where the 2022 dataset was released, the NOAA Administrator claimed that the dataset indicated that, “Climate change is creating more and more intense extreme events that cause significant damage” ( https://www.npr.org/2023/01/12/1148633707/extreme-weather-fueled-by-climate-change-cost-the-u-s-165-billion-in-2022 ).
In 2021 the U.S. Department of Treasury identified increasing billion dollar disasters as evidence of the effects of climate change on financial risks ( https://home.treasury.gov/system/files/261/FSOC-Climate-Report.pdf ).
The Fifth U.S. National Climate Assessment cited the NOAA dataset as evidence that “Climate change is not just a problem for future generations, it’s a problem today,” and claimed that the dataset, in part, demonstrated “the increasing frequency and severity of extreme events” due in part to “human-caused climate change” ( https://nca2023.globalchange.gov/chapter/2/ ).
In 2023, President Biden attributed weather and climate-related disaster costs in the U.S. in 2022 to climate change, citing the NOAA dataset: “[C]limate change related extreme weather events still pose a rapidly intensifying threat – one that costs the U.S. at least $150 billion each year … This year set a record for the number of climate disasters that cost the United States over $1 billion. The United States now experiences a billion-dollar disaster approximately every three weeks on average, compared to once every four months during the 1980s” ( https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2023/11/14/fact-sheet-biden-harris-administration-releases-fifth-national-climate-assessment-and-announces-more-than-6-billion-to-strengthen-climate-resilience-across-the-country/ ).
The point here is not to call into question the reality or importance of human-caused climate change – it is real, and it is important. Rather, the question is whether the NOAA billion dollar disaster time series provides evidence of detection or attribution of changes in the climate of extreme weather events in the United States, as frequently claimed.
Economic loss data is not suitable for detection and attribution of trends in extreme weather events because losses involve more than just climatic factors. It is well understood that a disaster occurs at the intersection of an extreme event and a vulnerable and exposed society (IPCC) 8 . NOAA acknowledges that a combination of risk, vulnerability and exposure is necessary for a disaster to occur ( https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/access/billions/faq ), but it fails to take any of these factors into account in its methodologies prior to making claims of detection and attribution. Of note, NOAA performs such a GDP normalization for disasters at the state level but does not do so for its national billion dollar disaster database. In a June, 2023 insurance industry Webinar, the lead scientist responsible for the NOAA dataset identified the absence of a national GDP-based normalization to be a major challenge for interpreting the database, and suggested that this would be added to the dataset in the future ( https://www.catmanagers.org/event-details/put-past-losses-in-their-proper-context-1 ). Smith and Katz 7 explain that “the billion-dollar dataset is only adjusted for the CPI over time, not currently incorporating any changes in exposure (e.g., as reflected by shifts in wealth or population)”.
Over time, population and wealth have increased dramatically in the United States (and globally), meaning that when an extreme climate or weather event occurs, there is more to be damaged and invariably, more damage occurs even if there is no underlying trend in the frequency or intensity of extreme weather. Consequently, there is a large literature that seeks to “normalize” historical loss data to account for changes in exposure and vulnerability (e.g., a recent literature review identified more than 60 such papers 9 , other relevant studies discuss the importance of the spatial dimensions of land use change 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 ).
A common approach to disaster normalization adjusts historical losses based on GDP, as a proxy for increasing population and wealth 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 . Figure. 3 shows loss per disaster in the NOAA 2023 dataset as a percentage of US GDP ( https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/RGDPNAUSA666NRUG ). According to a simple linear trend, losses per disaster are down by about 80% since 1980, as a proportion of GDP. This is likely due to a combination of actual decreasing losses as a proportion of GDP, as has been documented in many rich countries, as well as the sharp increase in small disasters included in NOAA’s dataset (see Fig. 2 ).
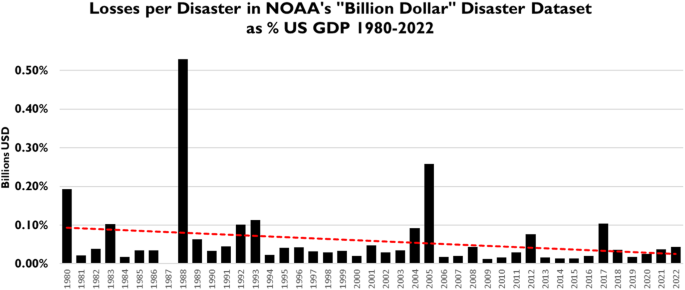
Losses per disaster in NOAA’s billion dollar disaster dataset (the version downloaded in July 2023), 1980 to 2022.
In comparison, weather and climate disasters losses as a percentage of U.S. GDP, show no increase over the period of record, which is 1990–2019 based on these data (Fig. 4 ).
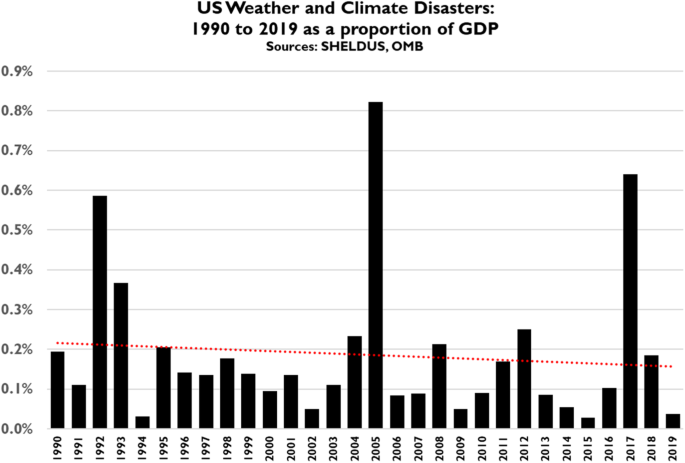
Sources: Spatial Hazard Events and Losses Database for the United States (SHELDUS) at Arizona State University, which has made public aggregate losses from 1990 to 2019. Data on GDP from the U.S. Office of Management and Budget.
Other, more sophisticated and granular approaches to the normalization of U.S. weather and climate related disaster losses robustly confirm the aggregate downward trend in losses, once population growth and wealth are properly accounted 6 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 . Hurricane, flood and tornado losses have all decreased as a proportion of GDP on climate time scales, and as these are responsible for the majority of direct losses, so too have aggregate disaster losses.
NOAA’s failure to consider changes in exposure and vulnerability is significant. Consider for example Hurricane Andrew in 1992. The NOAA 2023 billion dollar disaster loss estimate for Andrew is $58.9 billion, but a 2023 normalized loss estimate is more than twice that at $119.9 billion (based on Weinkle et al.). For comparison, in 2022, Swiss Reinsurance estimated that a recurrence of Hurricane Andrew would result in $120 billion in total damage ( https://www.abcactionnews.com/news/price-of-paradise/experts-say-modern-day-hurricane-andrew-could-cost-florida-120-billion ). Thus, these estimates differ by ~100%.
By adjusting for inflation, but not for changes in exposure or vulnerability, the NOAA billion dollar dataset introduces a bias into the time series, as the upwards trend in losses in the billion dollar disaster time series is a result of growth in population and wealth, and not climate trends. As Smith and Katz 7 acknowledged more than a decade ago of the increase in billion dollar disasters, “the magnitude of such increasing trends is greatly diminished when applied to data normalized for exposure.”
Thus, any claim that the NOAA billion dollar disaster dataset indicates worsening weather or worsening disasters is incomplete at best and misleading at worst. When U.S. disaster losses are considered in the context of exposure changes it becomes clear that as the absolute costs of disasters has increased, the impact relative to the economy has diminished over past decades, which is exactly the opposite of claims made by NOAA, the U.S. National Climate Assessment, the USGCRP, and the president of the United States, among many others.
The most appropriate data for investigating detection and attribution of changes in climate variables will always be climate data, and not economic data. IPCC has assessed research on the detection and attribution of trends in extreme weather events and has only low confidence in the emergence of signals of climate-impact drivers for river floods, heavy precipitation and pluvial flood, landslide, drought, fire weather, tropical cyclones, hail, severe wind storms and heavy snowfall 2 – that is, each of the elements of the billion dollar disaster dataset. The IPCC does express confidence in some regions in the detection and attribution of changes in heat extremes and in extreme precipitation 2 , neither of which is an element of the billion dollar disaster database. The IPCC is explicit in warning against conflating changes in extreme precipitation with changes in pluvial flooding 2 .
NOAA makes strong claims of detection and attribution contrary to the conclusions of the IPCC but provides no analyses in support of these claims. For instance, NOAA states of its time series:
“The increases in population and material wealth over the last several decades are an important factor for higher damage potential. These trends are further complicated by the fact that many population centers and infrastructure exist in vulnerable areas like coasts and river floodplains, while building codes are often insufficient in reducing damage from extreme events. Climate change is also playing a role in the increasing frequency of some types of extreme weather that lead to billion-dollar disasters.”
However, NOAA makes no effort to quantify the roles of increasing population and material wealth, nor does it substantiate its claims that climate change has increased the frequency of some types of extreme weather.
NOAA does not acknowledge a large literature on disaster “normalization” that seeks to quantify the roles of population, material wealth, mitigation, building practices, etc. on increasing losses and also ignores literature on the detection and attribution of trends in various forms of extreme weather 2 , 9 .
Thus, any claim that the NOAA billion dollar disaster dataset indicates the detection trends in climate variables and the attribution of those trends to human-caused climate change is contrary to the most recent assessment of the IPCC. NOAA has provided no evidence or research to support claims that human-caused changes in climate are driving the increase in billion dollar disaster counts. Similarly, the opposite claim, that increasing billion dollar disasters are evidence of changes in the frequency of some extreme events resulting from human-caused climate change is also unsupported. NOAA’s claims are also circular – one claim is that climate change causes increasing billion dollar disasters and the second claim is that increasing billion dollar disasters indicate climate change. The billion dollar dataset fails to meet NOAA’s criteria of presentation and substance.
To summarize: the NOAA billion dollar disaster dataset falls short of NOAA’s guidelines for scientific integrity. The shortfalls documented here are neither small nor subtle. They represent a departure from NOAA’s long-term history of scientific integrity and excellence, which has saved countless lives and supported the nation’s economy.
Identifying the reasons why NOAA’s billion dollar disaster dataset has departed so significantly from the agency’s own standards of scientific integrity goes well beyond the scope of this paper. However, the steps necessary to bring the dataset back into conformance with NOAA’s information quality criteria are straightforward ( https://www.noaa.gov/organization/information-technology/policy-oversight/information-quality/information-quality-guidelines ):
Publish all data, including all versions of the dataset;
Document and publish baseline loss estimates and their provenance;
Clearly describe all methodologies employed to adjust baseline data;
Document every change made to the dataset, give each successive version of the dataset a unique name, and publish all version of the data;
Maintain all historical versions of the dataset in a publicly accessible archive;
Subject the methods and results to annual peer review by experts, including economists and others with subject matter expertise, who are independent of NOAA. Make the peer review reports public;
Align NOAA’s practices with federal government policies for disseminating statistical information that are applied to other agencies ( https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2002/06/04/02-13892/federal-statistical-organizations-guidelines-for-ensuring-and-maximizing-the-quality-objectivity );
Align claims with IPCC methods and standards for any claims of detection and attribution, or justify why the claims are at odds with those of the IPCC.
NOAA is a crucially important agency that sits at the intersection of science, policy and politics. It has a long and distinguished history of providing weather, climate, water, ocean and other data to the nation. These data have saved countless lives, supported the economy and enabled significant scientific research. The agency is far too important to allow the shortfalls in scientific integrity documented in this paper to persist. Fortunately, science and policy are both self-correcting.
Policy evaluation
The analysis in this paper follows the logic of policy evaluation, which compares policy implementation with respect to criteria, with a goal of identifying progress or lack thereof towards goals (sources). Identifying progress requires identification of specific metrics of progress and data relevant to those metrics.
Lott, N. & Ross, T. Tracking and evaluating U.S. billion dollar disasters, 1980-2005, NOAA’s National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, North Carolina, https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/monitoring-content/billions/docs/lott-and-ross-2006.pdf (2005).
IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [eds Masson-Delmotte, V., P et al.]. 2391 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2021) https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009157896 .
Pielke, R. Jr. & Boye, E. Scientific integrity and anti-doping regulation. Int. J. Sport Policy Polit. 11 , 295–313 (2019).
Article Google Scholar
Lasswell, H.D. A pre-view of policy sciences (Elsevier Publishing Company, 1971).
Smith, A. B. & Matthews, J. L. Quantifying uncertainty and variable sensitivity within the US billion-dollar weather and climate disaster cost estimates. Nat. Hazards 77 , 1829–1851 (2015).
Weinkle, J. et al. Normalized hurricane damage in the continental United States 1900–2017. Nat. Sustain. 1 , 808–813 (2018).
Smith, A. B. & Katz, R. W. US billion-dollar weather and climate disasters: data sources, trends, accuracy and biases. Nat. Hazards 67 , 387–410 (2013).
IPCC. Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation. A Special Report of Working Groups I and II of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (eds. Field, C.B. et al.) 582 (Cambridge University Press, 2012).
Pielke, R. Economic ‘normalisation’ of disaster losses 1998–2020: A literature review and assessment. Environ. Hazards 20 , 93–111 (2021).
Ye, M., Wu, J., Liu, W., He, X. & Wang, C. Dependence of tropical cyclone damage on maximum wind speed and socioeconomic factors. Environ. Res. Lett. 15 , 094061 (2020).
Strader, S. M., Ashley, W. S., Pingel, T. J. & Krmenec, A. J. How land use alters the tornado disaster landscape. Appl. Geogr. 94 , 18–29 (2018).
Ferguson, A. P. & Ashley, W. S. Spatiotemporal analysis of residential flood exposure in the Atlanta, Georgia metropolitan area. Nat. Hazards 87 , 989–1016 (2017).
Strader, S. M. & Ashley, W. S. The expanding bull’s-eye effect. Weatherwise 68 , 23–29 (2015).
Nordhaus, W. D. The economics of hurricanes and implications of global warming. Clim. Change Econ. 1 , 1–20 (2010).
Neumayer, E. & Barthel, F. Normalizing economic loss from natural disasters: A global analysis. Global Environ. Change 21 , 13–24 (2011).
Wu, J. et al. Post-disaster recovery and economic impact of catastrophes in China. Earthq. Spectra 30 , 1825–1846 (2014).
Chen, W., Lu, Y., Sun, S., Duan, Y. & Leckebusch, G. C. Hazard footprint-based normalization of economic losses from tropical cyclones in China during 1983–2015. Int. J. Disaster Risk Scie. 9 , 195–206 (2018).
Alstadt, B., Hanson, A. & Nijhuis, A. Developing a Global Method for Normalizing Economic Loss from Natural Disasters. Nat. Hazards Rev. 23 , 04021059 (2022).
Martinez, A. B. Improving normalized hurricane damages. Nat. Sustain. 3 , 517–518 (2020).
Klotzbach, P. J., Bowen, S. G., Pielke, R. & Bell, M. Continental US hurricane landfall frequency and associated damage: Observations and future risks. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 99 , 1359–1376 (2018).
Katz, R. W. Statistical issues in detection of trends in losses from extreme weather and climate events. In Evaluating climate change impact s. 165–186 (Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2020).
Zhang, J., Trück, S., Truong, C., & Pitt, D. Time trends in losses from major tornadoes in the United States. Weather Clim Extremes 41 , 100579 (2023).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Colorado Boulder, Boulder, CO, USA
Roger Pielke Jr
American Enterprise Institute, Washington, DC, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
R.P. did everything.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Roger Pielke Jr .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Pielke, R. Scientific integrity and U.S. “Billion Dollar Disasters”. npj Nat. Hazards 1 , 12 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44304-024-00011-0
Download citation
Received : 05 January 2024
Accepted : 13 April 2024
Published : 03 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s44304-024-00011-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Anthropocene newsletter — what matters in anthropocene research, free to your inbox weekly.
Unfortunately we don't fully support your browser. If you have the option to, please upgrade to a newer version or use Mozilla Firefox , Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Safari 14 or newer. If you are unable to, and need support, please send us your feedback .
We'd appreciate your feedback. Tell us what you think! opens in new tab/window
Sharing and promoting your article
Sharing and promoting your article form an important part of research, in terms of fostering the exchange of scientific information in your field and allowing your paper to contribute to wider scientific progress.
In addition, bringing your research and accomplishments to the attention of a broader audience also makes you more visible in your field. This helps you to get more citations, enabling you to cultivate a stronger reputation, promote your research and move forward in your career. This page describes how you can share your article responsibly and offers advice to help you promote it widely.
Sharing your article
As an author, you benefit from sharing the appropriate version of your article which ensures that:
You always receive credit – you need to be cited accurately, which will ensure that services such as Mendeley will record the impact of your paper correctly. (Don’t have a Mendeley account yet? Please register here opens in new tab/window .)
The integrity of the scientific record is not compromised – you should always direct readers to the most up-to-date version of your article – a link to the published journal article.
Below you will find a number of options for posting and sharing your article. For further information, please see green open access with Elsevier , our sharing policy and our FAQ on posting. Unless otherwise noted, the examples below relate to your published journal article. For information on how you can share preprints and accepted manuscripts, please refer to our sharing policy .
Responsible sharing in line with copyright enables publishers to sustain high quality journals and the services they provide to the research community. Elsevier supports responsible sharing and responsible sharing platforms and we adhere to the voluntary sharing principles opens in new tab/window of the STM Association.
The STM Association has created howcanishareit.com opens in new tab/window which helps to explain how authors and users can share articles published in academic journals. It includes the Can I Share It look-up tool which provides academic researchers with an easy way to check where a journal article can be shared in line with the paper’s access and usage rights.
Sharing options for different contexts
At a conference.
You can always present your research in forms such as a presentation, or poster.
For classroom teaching purposes
You can use your article for your own classroom teaching and internal training at your institution (including use in course packs and courseware programs.
For grant applications
You can include your article for grant funding purposes.
With my colleagues
You can easily share your article with your colleagues (and other individuals) in private communications such as email.
On a preprint server
You can always post your preprint on a preprint server. Additionally, for ArXiv and RePEC you can also immediately update this version with your accepted manuscript . Please note that Cell Press, The Lancet, and some society-owned titles have different preprint policies. Information on these is available on the journal homepage.
On my personal blog or website
We recommend that you list all your publications and link back to the final version on ScienceDirect to make it easier for you to be cited. In addition to this you can also post your preprint or accepted manuscript and any gold open access articles on your non-commercial personal website or blog. Gold open access articles can be posted on your non-commercial personal website or blog. Authors can also share gold OA articles under CC-BY license on commercial websites. See “A word about Gold OA” below.
On my institutional repository
You can post your accepted author manuscript immediately to an institutional repository and make this publicly available after an embargo period has expired. Remember that for gold open access articles, you can post your published journal article and immediately make it publicly available.
On a subject repository (or other non-commercial repository)
You can always post your preprint version and you can also post your accepted author manuscript after the embargo period has expired. Remember for gold open access articles, you can post the published journal article immediately.
On Scholarly Collaboration Network (SCN), such as Mendeley or Scholar Universe
Services such as SCNs enable authors to showcase their work, providing fast and effective ways to collaborate and disseminate research.
A number of SCNs are working together with publishers to help to showcase your work by sharing links to published journal articles on author profiles.
We encourage authors to share their research responsibly on SCNs. You can share your preprint or a link to your article.
Social Media, such as Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter
Elsevier will send you a ' share link ': a personal, customized short link that you will receive after final publication of your article. It provides 50 days free access to your newly-published article on ScienceDirect to anyone clicking on the link. We encourage you to share this link on social media. After 50 days the share link will still work but automatically revert to a link to your full text article.
Open access publishing
You can also share your final published article immediately by publishing it open access .
In the gold open access model, you pay an article publishing charge (APC), making your article immediately, permanently, and freely available for anyone to access, read and build on. In many cases, your institution or research funder will pay the APC on your behalf. All our journals offer a green open access option, meaning you can post a version of your article in a repository after an embargo, so people can access it freely. See our sharing policy for more information.
Gold open access licensing and sharing
If you have chosen to publish your article open access, you can share according to the end user license selected:
CC-BY licensed articles may be shared with anyone, on any platform or via any communication channel.
CC-BY-NC-ND licensed articles may be shared on non-commercial platforms only.
Do you want to make your published paper OA?
If your article has already been published as a subscription article, it may still be possible to make it open access up until 31st January of the following year by paying the Article Publishing Charge (APC) opens in new tab/window associated with your journal. For example, if the article has a formal date of publication of March 2017, authors are able to make their article open access up until the 31st January 2018. This cutoff date is necessary to uphold our no double dipping policy . To request retrospective open access or for further details, please contact us opens in new tab/window .
Promoting your article
Now that your article is published, you can promote it to make a bigger impact with your research. Here's how you can make use of the services we offer.
To help you reach more readers, Elsevier will send you and any co-authors a Share Link when your article is published: A personal, customized short link that provides free access to your article for 50 days. This means you can invite colleagues and peers to access your article ScienceDirect, sharing it by email and social media. Readers who click on the Share Link will be taken directly to your article, with no sign up or registration required.
50 days’ free access to the HTML and PDF versions of your article
Sharing the link via social media accounts and email helps you generate interest in your article
Sharing your article makes it more visible, potentially increasing downloads and citations
The process is simple: just click on the link during the 50-day free access period
You will automatically receive the Share Link at the final citable publication stage of your article. If co-author information is provided at the time of submission, they will also automatically receive a notification with the article's Share Link.
Showcasing yourself and your research
As published author, it's important that you stand out and can be easily found by others.
Mendeley Showcase helps you tell the academic community about yourself as a researcher and the impact of your research. Your Mendeley Profile opens in new tab/window allows you to:
Collate and curate a list of all your outputs in one place.
Track and demonstrate the impact of your research through insights including citations, readers, views, media mentions and h-index. Find out more about measuring an article’s impact here .
Go beyond the metrics and paint your complete research picture by telling others more about yourself and your research interests.
Connect with others and find global collaborators.
Complete your Mendeley Profile and showcase yourself opens in new tab/window
Don’t have a Mendeley Profile? Get one now by creating a Mendeley account opens in new tab/window
Other ways to help you make your article stand out can be found in our free quick guide opens in new tab/window - including tips & tricks on how to promote your article effectively via social media. If you’re interested in a free e-learning course on the topic, visit the"Ensuring Visibility" page on Researcher Academy opens in new tab/window .
Last but not least, don’t forget to monitor your article's impact with article level metrics .
Further reading
Everything you ever wanted to know about open access (but were afraid to ask!)
Questions and answers about Elsevier and open access

Get noticed – Increase the impact of your research
Your path to academic success
Improve your paper with our award-winning Proofreading Services , Plagiarism Checker , Citation Generator , AI Detector & Knowledge Base .
Proofreading & Editing
Get expert help from Scribbr’s academic editors, who will proofread and edit your essay, paper, or dissertation to perfection.
Plagiarism Checker
Detect and resolve unintentional plagiarism with the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker, so you can submit your paper with confidence.
Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr’s free citation generator and save hours of repetitive work.

Happy to help you
You’re not alone. Together with our team and highly qualified editors , we help you answer all your questions about academic writing.
Open 24/7 – 365 days a year. Always available to help you.
Very satisfied students
This is our reason for working. We want to make all students happy, every day.
Having citations copied and pasted…
Having citations copied and pasted pre-formatted is extremely helpful (double-space, Times New Roman, font size 12). Also being up to date with changing standards for different citation styles makes me more trusting of the citations being generated.
Your commitment to excellence and…
Your commitment to excellence and professionalism is truly commendable. The entire process, from submission to receiving the final edits, was seamless and efficient. I am thoroughly impressed with the level of expertise and care that went into editing my essay. Thank you for your outstanding service. I will certainly recommend Scribbr to others and look forward to using your services again in the future.
Love how easy and organised structure…
Love how easy and organised structure of the website!
No ads, I love it!
An honest graduate students review
This is an honest review from a full-time student with a full-time job and 2 kids. I have very little time to try to get my papers right before submitting them to my professor every week. I use Scribbr, seriously, for every single step of writing a paper. I use the APA template that they provide and fill it in with what I need. I use the Citation Generator for every single reference because I have never mastered that art of getting them right. I can honestly say that Scribbr has reduced my school work each week by at least 2 hours by helping me create the things that I need to succeed. I couldn't be more grateful.
Very happy with the editing service for…
Very happy with the editing service for my master thesis. Thank you so much for the help, thorough editing and helpful comments. Amazing!
It's easy to use and makes it simple to…
It's easy to use and makes it simple to find articles when I don't have the full citation
Really useful and easy
I've been using this in college to…
I've been using this in college to store and organize my cite, is really good and amazing
Helpful but...
Helpful tool; however, you still need to double check the information it pulls up, even if you use the DOI information. For APA 7th, there are still quite a few capitalization errors in the titles and journal names. Would get 5 stars if they would fix this and if they wouldn't bug you every time you log in to leave a review!
confident the formatting is correct for…
confident the formatting is correct for my assignments!
The site is intuitively helpful
The site is intuitively helpful, thus easy to navigate, and create and save references by project type. I mostly use it for citation generation, but the other services are noteworthy also. I highly recommend for academic and professional applications.
Great for citing college level papers
Scribbr has helped me many times to cite for college papers. If the article is not in the database, then there is an easy format to enter the information.
I'm currently working on my master's degree in education. This cite has been invaluable.
Easy to Use and Immensely Helpful
I love, love Scribbr. I love how easy it is to use and that all I have to do is copy and paste. I also pleased that I can create an account that saves all my citations. Scribbr also makes it very easy to create manual citations. I highly recommend Scribbr for everyone, especially researchers.
The quality of the work was excellent
The quality of the work was excellent. The turn around was amazing as well.
Exceptionally helpful!
Amazing website!
amazing website.
Love doing references here
Love doing references here. Super organized and helpful especially when its already in Times New Roman font!
Makes APA referencing and citation very…
Makes APA referencing and citation very easy.
Everything you need to write an A-grade paper
Free resources used by 5,000,000 students every month.
Bite-sized videos that guide you through the writing process. Get the popcorn, sit back, and learn!

Lecture slides
Ready-made slides for teachers and professors that want to kickstart their lectures.
- Academic writing
- Citing sources
- Methodology
- Research process
- Dissertation structure
- Language rules
Accessible how-to guides full of examples that help you write a flawless essay, proposal, or dissertation.

Chrome extension
Cite any page or article with a single click right from your browser.
Time-saving templates that you can download and edit in Word or Google Docs.

Help you achieve your academic goals
Whether we’re proofreading and editing , checking for plagiarism or AI content , generating citations, or writing useful Knowledge Base articles , our aim is to support students on their journey to become better academic writers.
We believe that every student should have the right tools for academic success. Free tools like a paraphrasing tool , grammar checker, summarizer and an AI Proofreader . We pave the way to your academic degree.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Frequently asked questions
Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
What is innovation?

When you think of innovation, what springs to mind? Maybe it’s a flashy new gadget—but don’t be mistaken. There’s much more to the world of innovation, which extends far beyond new products and things you’ll find on a store shelf.
Get to know and directly engage with senior McKinsey experts on innovation.
Marc de Jong is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Amsterdam office, Laura Furstenthal is a senior partner in the Bay Area office, and Erik Roth is a senior partner in the Stamford office.
If products alone aren’t the full story, what is innovation? In a business context, innovation is the ability to conceive, develop, deliver, and scale new products, services, processes, and business models for customers.
Successful innovation delivers net new growth that is substantial. As McKinsey senior partner Laura Furstenthal notes in an episode of the Inside the Strategy Room podcast , “However you measure it, innovation has to increase value and drive growth.”
As important as innovation is, getting it right can be challenging. Over 80 percent of executives surveyed say that innovation is among their top three priorities, yet less than 10 percent report being satisfied with their organizations’ innovation performance. Many established companies are better operators than innovators , producing few new and creative game changers. Most succeed by optimizing existing core businesses.
Why is innovation important in business?
Some companies do succeed at innovation. Our research considered how proficient 183 companies were at innovation, and compared that assessment against a proprietary database of economic profit (the total profit minus the cost of capital). We found that companies that harness the essentials of innovation see a substantial performance edge that separates them from others—with evidence that mastering innovation can generate economic profit that is 2.4 times higher than that of other players .
Learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance practice.
How can leaders decide what innovations to prioritize?
Successful innovation has historically occurred at the intersection of several elements, which can guide prioritization efforts. The three most important elements are the who, the what, and the how :
- An unmet customer need (the ‘who’): Who is the customer and what problem do they need to solve? Are macrotrends such as automation driving changes in customer needs?
- A solution (the ‘what’): Is the solution compelling and can it be executed?
- A business model that allows for the solution to be monetized (the ‘how’): How will the solution create value? What is the business model?
Successful innovation requires answers to each of these questions.
An example from inventor and businessman Thomas Edison helps illustrate the concept. “In every case, he did not just invent the what, he also invented a how,” says Furstenthal in a conversation on innovation . “In the case of the light bulb, he created the filament and the vacuum tube that allowed it to turn on and off, and he developed the production process that enabled mass production.”

Introducing McKinsey Explainers : Direct answers to complex questions
How do organizations become better innovators.
McKinsey conducted research into the attributes and behaviors behind superior innovation performance , which were validated in action at hundreds of companies. This research yielded eight critical elements for organizations to master:
- Aspire: Do you regard innovation-led growth as critical, and have you put in place cascaded targets that reflect this?
- Choose: Do you invest in a coherent, time- and risk-balanced portfolio of initiatives, and do you devote sufficient resources to it?
- Discover: Are your business, market, and technology R&D efforts actionable and capable of being translated into winning value propositions?
- Evolve: Do you create new business models that provide defensible, robust, and scalable profit sources?
- Accelerate: Do you develop and launch innovations quickly and effectively?
- Scale: Do you launch innovations at the right scale in the relevant markets and segments?
- Extend: Do you create and capitalize on external networks?
- Mobilize: Are your people motivated, rewarded, and organized to innovate repeatedly?
Of these eight essentials, two merit particular attention : aspire and choose . Without these two elements, efforts may be too scattershot to make a lasting difference. It’s particularly crucial to ensure that leaders are setting bold aspirations and making tough choices when it comes to resource allocation and portfolio moves. To do so successfully, many leaders will need to shift their mindsets or management approaches.
What are examples of successful innovators?
Real-world examples of successful innovation, related to some of the eight essentials listed , can highlight the benefits of pursuing innovation systematically :
- Mercedes-Benz Group invested extensively in digitizing its product development system. That allowed the company to shorten its innovation cycles significantly , and its capabilities for personalizing cars have improved, even as assembly efficiency rose by 25 percent.
- Gavi, a public–private partnership founded to save children’s lives and protect their health by broadening access to immunization, used nonfinancial targets to help drive its innovation efforts —and this helped the organization broaden its aspiration for impact in a way that was bold, specific, measurable, and time bound.
- Lantmännen, a large Nordic agricultural cooperative, faced flat organic growth. Leadership created a vision and strategic plan connected to financial targets cascaded down to business units and product groups. Doing so allowed the organization to move from 4 percent annual growth to 13 percent, on the back of successfully launching several new brands.
- The information services organization RELX Group brought discipline to choosing its innovation portfolio by running ten to 15 experiments in each customer segment in its pipeline every year. It selects one or two of the most successful ideas from the portfolio to continue.
- International insurance company Discovery Group mobilized the organization around innovation by creating incentives for a thousand of the company’s leaders using semiannual divisional scorecards. Innovation isn’t a choice; it’s a requirement and a part of the organization’s culture.
These examples aren’t necessarily what you may think of when you imagine disruptive innovation—which calls to mind moves that shake up an entire industry, and might be more associated with top tech trends such as the Bio Revolution . Yet these examples show how committing to innovation can make a sizable difference.
How can my organization improve the volume and quality of new ideas?
Steps to help aspiring innovators get started include the following:
- Hold collision sessions: Cross-functional groups gather in a structured process to think through the intersection of unmet customer needs, technology trends, and business models, bringing creativity and specificity to the process of idea generation. Then, a venture panel considers these ideas and iterates on them, prioritizing what to do.
- Challenge orthodoxies: Participants gather and describe beliefs that are common but that prevent the organization from innovating for customers. Examples of these orthodoxies include statements such as “budgets are limited” or “we don’t have the digital capabilities to pull it off.” Once the orthodoxies are laid out, teams brainstorm after being prompted to consider if the opposite of the statement were true.
- Make analogies to other industries: A team might create a list of companies with unique value propositions. Then, they systematically apply these value propositions to their ideas to see if the analogy can create new sources of value or fresh opportunities.
- Apply constraints: Rather than searching for blue-sky ideas, tighten the constraints on an idea’s business or operating model and explore potential new solutions. What if you served only one type of customer? What if the only channel you could access was online?
In the words of chemist Linus Pauling, “The way to get to good ideas is to get lots of ideas and throw the bad ones away.”
What is an innovation portfolio?
An innovation portfolio is a thoughtfully curated bundle of potentially innovative initiatives, with clear aspirations and required resources defined for each. Managing the portfolio this way helps find new opportunities and determine the appropriate number and mix of initiatives, including the following:
- confirming the total value of the portfolio needed
- evaluating existing innovation projects based on incremental value delivered, risk, and alignment with strategic priorities
- getting comfortable saying “no” to stop projects that are dilutive, and resisting the siren song of incremental initiatives that are unlikely to pay for themselves
- reallocating resources—including competencies and skills—to new initiatives or to current ones that additional support can accelerate or amplify
- identifying portfolio gaps and defining new initiatives to close them
How to measure innovation?
One way to measure innovation is to look at innovation-driven net new growth, which we call the “green box.” This phrase refers to how you quantify the growth in revenue or earnings that an innovation needs to provide within a defined timeframe. This concept can help clarify aspirations and influence choices on the innovation journey.
While many imagine that innovation is solely about creativity and generating ideas, at its core, innovation is a matter of resource allocation . To put it another way: it’s one thing to frame innovation as a catalyst for growth, and another to act upon it by refocusing people, assets, and management attention on the organization’s best ideas.
The green box can help to solidify a tangible commitment by defining the value that a company creates from breakthrough and incremental innovation, on a defined timeline (say, five years), with quantifiable metrics such as net new revenue or earnings growth. Crucially, the green box looks at growth from innovation alone, setting aside other possible sources such as market momentum, M&A, and so forth. And once defined, the growth aspiration can be cascaded into a set of objectives and metrics that the company’s various operating units can incorporate into its individual innovation portfolios.
It’s useful to note that some organizations may find that measures not solely financial in nature are more appropriate or relevant. For instance, metrics such as the number of subscribers or patients—or customer satisfaction—can resonate. What’s critical is selecting a metric that is a proxy for value creation. A large US healthcare payer , for example, looked to spur innovation that would improve patient satisfaction and the quality of care.
Separate from the concept of the green box, two simple metrics can also offer surprising insight about innovation vis-à-vis the effectiveness of an organization’s R&D spending. Both of these lend themselves to benchmarking, since they can be gauged from the outside in, and they offer insight at the level of a company’s full innovation portfolio. The two R&D conversion metrics are as follows:
- R&D-to-product conversion: This metric is calculated by looking at the ratio of R&D spending (as a portion of sales) to sales from new products. It can show how well your R&D dollars convert to actual sales of new products—and it might reveal that spending more doesn’t necessarily translate into stronger performance.
- New-products-to-margin conversion: This metric considers the ratio of gross margin percentage to sales from new products. It can indicate how new-product sales contribute to lifting margins.
While no metric is perfect, these may offer perspective that keeps the focus squarely on returns from innovation and the value it creates—often more meaningful than looking inward at measures of activity, such as the number of patents secured.
How do you create a high-performing innovation team?
Innovation is a team sport. Experience working with strong innovators and start-ups has helped identify ten traits of successful innovation teams . Those fall into four big categories: vision , or the ability to spot opportunities and inspire others to go after them; collaboration , which relates to fostering effective teamwork and change management (for instance, by telling a good innovation story ); learning or absorbing new ideas; and execution , with traits that facilitate snappy decision making even when uncertainty arises.
Being strategic about the composition of an innovation team can help minimize failures and bring discipline to the process.
What innovation advice can help business leaders?
One broad piece of advice centers on creating a culture that accounts for the human side of innovation . When people worry about failure, criticism, or the career impact of a wrong move, it can keep them from embracing innovation. In a recent poll, 85 percent of executives say fear holds back their organization’s innovation efforts often or always—but there are ways to overcome these barriers .
Additionally, the Committed Innovator podcast and related articles share perspectives from leading experts who have helped their organizations tackle inertia and unlock bold strategic moves. If you are looking for words of wisdom, their insights can help spark inspiration to innovate:
- Naomi Kelman, CEO, Willow . “Creating a safe environment for innovation is really what you need to do to get the greatness out of the people who work with you, which is ultimately what drives growth.”
- Safi Bahcall, author, Loonshots . “Most of the important breakthroughs failed many times before they succeeded. That is where ‘fail fast’ goes wrong. Most companies are too impatient.”
- Amy Brooks, chief innovation officer, National Basketball Association . “You can use data or examples to convince people about what is working in the market or what other industries are doing. We like to share best practices within our own leagues and within sports, but we also pay attention to every other industry that sells to consumers.”
- Tanya Baker, global leader, Goldman Sachs Accelerate . “If someone knowledgeable thinks what you are doing is a bad idea, make sure they have a seat at the table. Put them on your board; make them one of your advisers so you don’t have any blind spots.”
- Neal Gutterson, former chief technology officer, Corteva . “[A] key skill is being able to hold two divergent thoughts and approaches in your brain and in your team at the same time. The great companies will be ambidextrous innovators, able to disrupt themselves in the future while serving the core [business] today.”
- Anjali Sud, CEO, Vimeo . “What keeps me up at night is execution and, within that, focus. Because when you are in a market like ours, at a time like now, the opportunity is huge. We are this nimble, fast-growing, fast-moving company, and everywhere I look I see opportunity. But am I providing enough focus for my teams so that we can truly be great at something? You don’t want to miss a big boat, and it’s hard sometimes to say no to valid, exciting ideas that could be transformative.”
For more in-depth exploration of these topics, see McKinsey’s insights on Strategy & Corporate Finance . Learn more about McKinsey’s Growth & Innovation work—and check out innovation-related job opportunities if you’re interested in working at McKinsey.
Articles referenced include:
- “ Fear factor: Overcoming human barriers to innovation ,” June 3, 2022, Laura Furstenthal , Alex Morris, and Erik Roth
- “ Innovation—the launchpad out of crisis ,” September 15, 2021, Laura Furstenthal and Erik Roth
- “ The innovation commitment ,” October 24, 2019, Daniel Cohen, Brian Quinn, and Erik Roth
- “ Fielding high-performing innovation teams ,” January 17, 2019, Matt Banholzer , Fabian Metzeler, and Erik Roth
- “ Taking the measure of innovation ,” April 20, 2018, Guttorm Aase, Erik Roth , and Sri Swaminathan
- “ The eight essentials of innovation ,” April 1, 2015, Marc de Jong , Nathan Marston, and Erik Roth

Want to know more about innovation?
Related articles.

Fear factor: Overcoming human barriers to innovation

The innovation commitment

The eight essentials of innovation
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Advance Articles
- Editor's Choice
- Braunwald's Corner
- ESC Guidelines
- EHJ Dialogues
- Issue @ a Glance Podcasts
- CardioPulse
- Weekly Journal Scan
- European Heart Journal Supplements
- Year in Cardiovascular Medicine
- Asia in EHJ
- Most Cited Articles
- ESC Content Collections
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Why publish with EHJ?
- Open Access Options
- Submit from medRxiv or bioRxiv
- Author Resources
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Read & Publish
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Advertising
- Reprints and ePrints
- Sponsored Supplements
- Journals Career Network
- About European Heart Journal
- Editorial Board
- About the European Society of Cardiology
- ESC Publications
- War in Ukraine
- ESC Membership
- ESC Journals App
- Developing Countries Initiative
- Dispatch Dates
- Terms and Conditions
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Xylitol is prothrombotic and associated with cardiovascular risk
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Marco Witkowski, Ina Nemet, Xinmin S Li, Jennifer Wilcox, Marc Ferrell, Hassan Alamri, Nilaksh Gupta, Zeneng Wang, Wai Hong Wilson Tang, Stanley L Hazen, Xylitol is prothrombotic and associated with cardiovascular risk, European Heart Journal , 2024;, ehae244, https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehae244
- Permissions Icon Permissions
The pathways and metabolites that contribute to residual cardiovascular disease risks are unclear. Low-calorie sweeteners are widely used sugar substitutes in processed foods with presumed health benefits. Many low-calorie sweeteners are sugar alcohols that also are produced endogenously, albeit at levels over 1000-fold lower than observed following consumption as a sugar substitute.
Untargeted metabolomics studies were performed on overnight fasting plasma samples in a discovery cohort ( n = 1157) of sequential stable subjects undergoing elective diagnostic cardiac evaluations; subsequent stable isotope dilution liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analyses were performed on an independent, non-overlapping validation cohort ( n = 2149). Complementary isolated human platelet, platelet-rich plasma, whole blood, and animal model studies examined the effect of xylitol on platelet responsiveness and thrombus formation in vivo . Finally, an intervention study was performed to assess the effects of xylitol consumption on platelet function in healthy volunteers ( n = 10).
In initial untargeted metabolomics studies (discovery cohort), circulating levels of a polyol tentatively assigned as xylitol were associated with incident (3-year) major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) risk. Subsequent stable isotope dilution LC-MS/MS analyses (validation cohort) specific for xylitol (and not its structural isomers) confirmed its association with incident MACE risk [third vs. first tertile adjusted hazard ratio (95% confidence interval), 1.57 (1.12–2.21), P < .01]. Complementary mechanistic studies showed xylitol-enhanced multiple indices of platelet reactivity and in vivo thrombosis formation at levels observed in fasting plasma. In interventional studies, consumption of a xylitol-sweetened drink markedly raised plasma levels and enhanced multiple functional measures of platelet responsiveness in all subjects.
Xylitol is associated with incident MACE risk. Moreover, xylitol both enhanced platelet reactivity and thrombosis potential in vivo . Further studies examining the cardiovascular safety of xylitol are warranted.

Role of the artificial sweetener xylitol in cardiovascular event risk. In initial untargeted metabolomics studies (discovery cohort) and subsequent stable isotope dilution liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) studies (validation cohort), fasting levels of xylitol are associated with incident major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE). Using human whole blood, platelet-rich plasma, and washed platelets, xylitol enhances multiple indices of platelet reactivity in vitro . Xylitol also was shown to enhance thrombosis formation in a murine arterial injury model in vivo . In human intervention studies, when subjects ingested a typical dietary amount of xylitol in an artificially sweetened food, multiple functional measures of platelet responsiveness were significantly increased. Xylitol is both clinically associated with cardiovascular event risks and mechanistically linked to enhanced platelet responsiveness and thrombosis potential in vivo . ADP, adenosine diphosphate; MI, myocardial infarction.
- cardiovascular diseases
- blood platelets
- sugar alcohols
- sweetening agents
- whole blood
European Society of Cardiology members
Personal account.
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Short-term Access
To purchase short-term access, please sign in to your personal account above.
Don't already have a personal account? Register
| Month: | Total Views: |
|---|---|
| June 2024 | 1,647 |
Email alerts
Companion article.
- Xylitol: bitter cardiovascular data for a successful sweetener
Related articles in PubMed
Citing articles via, looking for your next opportunity, affiliations.
- Online ISSN 1522-9645
- Print ISSN 0195-668X
- Copyright © 2024 European Society of Cardiology
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

COMMENTS
Access 160+ million publications and connect with 25+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research.
Find the research you need | With 160+ million publications, 1+ million questions, and 25+ million researchers, this is where everyone can access science
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
Improved Latin hypercube sampling initialization-based whale optimization algorithm for COVID-19 X-ray multi-threshold image segmentation. Zhen Wang. Dong Zhao. Guoxi Liang. Article Open Access 09 ...
Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Google publishes hundreds of research papers each year. Publishing is important to us; it enables us to collaborate and share ideas with, as well as learn from, the broader scientific community. Submissions are often made stronger by the fact that ideas have been tested through real product implementation by the time of publication.
Formatting a Chicago paper. The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Use 1 inch margins or larger. Apply double line spacing. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch. Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center.
Definition. A research paper is a paper that makes an argument about a topic based on research and analysis. Any paper requiring the writer to research a particular topic is a research paper. Unlike essays, which are often based largely on opinion and are written from the author's point of view, research papers are based in fact.
Read the latest Research articles from Nature. The authors identify naturally occurring senescent glia in aged Drosophila brains and decipher their origin and influence, determining that they can ...
Writing research papers is an important part of your college learning experience, training you to research and write effectively. However, if you don't know how to start, writing a research paper can be a daunting task. Don't worry! We will guide you through the process. The sections in this step-by-step guide allow you to learn at your own pace.
A research paper is an expanded essay that presents your own interpretation or evaluation or argument. When you write an essay, you use everything that you personally know and have thought about a subject. When you write a research paper you build upon what you know about the subject and make a deliberate attempt to find out what experts know.
Unraveling the research process: social bookmarking and collaborative learning. Caroline Sinkinson, Alison Hicks, in The Plugged-In Professor, 2013. Instructional purpose. The research paper is a common rite of passage in the academic world. While students are typically successful at amassing information sources, many grapple with new conventions of academic discourse and the synthesis of ...
A research paper is just the final product of research, critical thinking, and composition about a specific topic. Usually, a research paper aims to answer a specific question within a more ...
Reading Time: 14 minutes In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper.. The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within ...
Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the ...
Get a visual overview of a new academic field. Enter a typical paper and we'll build you a graph of similar papers in the field. Explore and build more graphs for interesting papers that you find - soon you'll have a real, visual understanding of the trends, popular works and dynamics of the field you're interested in.
1. Create an outline to map out your paper's structure. Use Roman numerals (I., II., III., and so on) and letters or bullet points to organize your outline. Start with your introduction, write out your thesis, and jot down your key pieces of evidence that you'll use to defend your argument.
Privacy Policy - Copyright © 2024 First Place Internet, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile. 1. Scopus. Scopus is one of the two big commercial, bibliographic databases that cover scholarly literature from almost any discipline. Besides searching for research articles, Scopus also provides academic journal rankings, author profiles, and an h-index calculator. 2.
In order to write a research paper, you should: 1. Decide on a topic. The person assigning the paper might also assign a topic. If you have a choice, choose a topic that interests you the most. Try choosing a topic with an abundance of research already completed.
Research Paper Example Outline. Before you plan on writing a well-researched paper, make a rough draft. An outline can be a great help when it comes to organizing vast amounts of research material for your paper. Here is an outline of a research paper example: I. Title Page. A. Title of the Research Paper.
4. ( 1078) In this guide, students and researchers can learn the basics of creating a properly formatted research paper according to APA guidelines. It includes information on how to conceptualize, outline, and format the basic structure of your paper, as well as practical tips on spelling, abbreviation, punctuation, and more.
We've included a full student paper below to give you an idea of what an essay in APA format looks like, complete with a title page, paper, reference list, and index. If you plan to include an APA abstract in your paper, see the Professional Paper for an example. If you're looking for an APA format citation generator, we've got you covered.
Abstract. For more than two decades, the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has published a count of weather-related disasters in the United States that it estimates have ...
Showcasing yourself. Sharing and promoting your article form an important part of research, in terms of fostering the exchange of scientific information in your field and allowing your paper to contribute to wider scientific progress. In addition, bringing your research and accomplishments to the attention of a broader audience also makes you ...
Whether we're proofreading and editing, checking for plagiarism or AI content, generating citations, or writing useful Knowledge Base articles, our aim is to support students on their journey to become better academic writers. We believe that every student should have the right tools for academic success.
In a business context, innovation is the ability to conceive, develop, deliver, and scale new products, services, processes, and business models for customers. Successful innovation delivers net new growth that is substantial. As McKinsey senior partner Laura Furstenthal notes in an episode of the Inside the Strategy Room podcast, "However ...
Untargeted metabolomics studies were performed on overnight fasting plasma samples in a discovery cohort (n = 1157) of sequential stable subjects undergoing elective diagnostic cardiac evaluations; subsequent stable isotope dilution liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analyses were performed on an independent, non-overlapping validation cohort (n = 2149).
Free Research Paper Download Websites - 2024. Check the 14 best free websites to download and read research papers listed below: 1. Sci-Hub. Sci-Hub is a website link with over 64.5 million academic papers and articles available for direct download. It bypasses publisher paywalls by allowing access through educational institution proxies.