Essay on Sustainable Development for Class 10, 12 and Mains Exam
Essay on sustainable development for class 10, 12, mains exam (upsc, psc, ssc).
Introduction: The concept of sustainable development was popularized by the World Commission on Environment and Development. Sustainable development refers to the practice of managing production by replacing the already used resources with other resources that has equal value or quality without hampering the environmental systems. It also refers to meet the demands of the present without affecting the capacity of the future generations to meet their demands. This means without wearing the natural resources that would meet the demands of the future generations. Any type of development arises out of a particular need. The more we continue to adopt unsustainable development, the more severe will be the outcomes. Climatic change is one such severe vicissitudes.
Technology – Using eco-friendly, locally suitable, culturally adaptable technologies should be used. Technologies that are indigenous in nature should be used. The technologies should produce minimum waste and minimum resources. Local manpower and resources can be used.
Creating environmental awareness and education: Environmental education shall be introduced as a subject right from the school level. This will help to change the outlook towards environment. Environment awareness campaigns shall be organized to educate the masses about eco friendly use of resources and to make the earth a green planet.
Conclusion: To conclude, it can be said that sustainable development brings out stability in the requirements of the environment. It makes the resources available for use for the future generations. Sustainable development is an amazing way to conserve the resources provided by nature. This can be achieved by using eco- friendly resources and technologies that will have no serious impact on the environment. The resources that are available to us shall be used in a sustainable manner so that they do not become extinct for the usage of future generations.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, up scert solutions class 6 english chapter 16 – the kind price, dav class 6 english literature book solution chapter 3 leisure, dav class 6 english literature book solution chapter 4 my experiment with truth, ncert class 6 extra questions social science – landforms and life.

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Sustainable Development: Samples in 250, 300 and 500 Words

- Updated on
- Nov 18, 2023

On 3rd August 2023, the Indian Government released its Net zero emissions target policy to reduce its carbon footprints. To achieve the sustainable development goals (SDG) , as specified by the UN, India is determined for its long-term low-carbon development strategy. Selfishly pursuing modernization, humans have frequently compromised with the requirements of a more sustainable environment.
As a result, the increased environmental depletion is evident with the prevalence of deforestation, pollution, greenhouse gases, climate change etc. To combat these challenges, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change launched the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) in 2019. The objective was to improve air quality in 131 cities in 24 States/UTs by engaging multiple stakeholders.
‘Development is not real until and unless it is sustainable development.’ – Ban Ki-Moon
Sustainable Development Goals, also known as SGDs, are a list of 17 goals to build a sustained and better tomorrow. These 17 SDGs are known as the ‘World’s Best Plan’ to eradicate property, tackle climate change, and empower people for global welfare.
This Blog Includes:
What is sustainable development, essay on sustainable development in 250 words, 300 words essay on sustainable development, 500 words essay on sustainable development, what are sdgs, introduction, conclusion of sustainable development essay, importance of sustainable development, examples of sustainable development.
As the term simply explains, Sustainable Development aims to bring a balance between meeting the requirements of what the present demands while not overlooking the needs of future generations. It acknowledges nature’s requirements along with the human’s aim to work towards the development of different aspects of the world. It aims to efficiently utilise resources while also meticulously planning the accomplishment of immediate as well as long-term goals for human beings, the planet as well and future generations. In the present time, the need for Sustainable Development is not only for the survival of mankind but also for its future protection.
To give you an idea of the way to deliver a well-written essay, we have curated a sample on sustainable development below, with 250 words:
To give you an idea of the way to deliver a well-written essay, we have curated a sample on sustainable development below, with 300+ words:

We all remember the historical @BTS_twt speech supporting #Youth2030 initiative to empower young people to use their voices for change. Tomorrow, #BTSARMY 💜 will be in NYC🗽again for the #SDGmoment at #UNGA76 Live 8AM EST welcome back #BTSARMY 👏🏾 pic.twitter.com/pUnBni48bq — The Sustainable Development Goals #SDG🫶 (@ConnectSDGs) September 19, 2021
To give you an idea of the way to deliver a well-written essay, we have curated a sample on sustainable development below, with 500 + words:

Sustainable Development Goals or SDGs are a list of 17 goals to build a better world for everyone. These goals are developed by the Department of Economic and Social Affairs of the United Nations. Let’s have a look at these sustainable development goals.
- Eradicate Poverty
- Zero Hunger
- Good Health and Well-being
- Quality Education
- Gender Equality
- Clean Water and Sanitation
- Affordable and Clean Energy
- Decent Work and Economic Growth
- Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- Reduced Inequalities
- Sustainable Cities and Communities
- Responsible Consumption and Production
- Climate Action
- Life Below Water
- Life on Land
- Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions
- Partnership for the Goals
Essay Format
Before drafting an essay on Sustainable Development, students need to get familiarised with the format of essay writing, to know how to structure the essay on a given topic. Take a look at the following pointers which elaborate upon the format of a 300-350 word essay.
Introduction (50-60 words) In the introduction, students must introduce or provide an overview of the given topic, i.e. highlighting and adding recent instances and questions related to sustainable development. Body of Content (100-150 words) The area of the content after the introduction can be explained in detail about why sustainable development is important, its objectives and highlighting the efforts made by the government and various institutions towards it. Conclusion (30-40 words) In the essay on Sustainable Development, you must add a conclusion wrapping up the content in about 2-3 lines, either with an optimistic touch to it or just summarizing what has been talked about above.
How to write the introduction of a sustainable development essay? To begin with your essay on sustainable development, you must mention the following points:
- What is sustainable development?
- What does sustainable development focus on?
- Why is it useful for the environment?
How to write the conclusion of a sustainable development essay? To conclude your essay on sustainable development, mention why it has become the need of the hour. Wrap up all the key points you have mentioned in your essay and provide some important suggestions to implement sustainable development.
The importance of sustainable development is that it meets the needs of the present generations without compromising on the needs of the coming future generations. Sustainable development teaches us to use our resources correctly. Listed below are some points which tell us the importance of sustainable development.
- Focuses on Sustainable Agricultural Methods – Sustainable development is important because it takes care of the needs of future generations and makes sure that the increasing population does not put a burden on Mother Earth. It promotes agricultural techniques such as crop rotation and effective seeding techniques.
- Manages Stabilizing the Climate – We are facing the problem of climate change due to the excessive use of fossil fuels and the killing of the natural habitat of animals. Sustainable development plays a major role in preventing climate change by developing practices that are sustainable. It promotes reducing the use of fossil fuels which release greenhouse gases that destroy the atmosphere.
- Provides Important Human Needs – Sustainable development promotes the idea of saving for future generations and making sure that resources are allocated to everybody. It is based on the principle of developing an infrastructure that is can be sustained for a long period of time.
- Sustain Biodiversity – If the process of sustainable development is followed, the home and habitat of all other living animals will not be depleted. As sustainable development focuses on preserving the ecosystem it automatically helps in sustaining and preserving biodiversity.
- Financial Stability – As sustainable development promises steady development the economies of countries can become stronger by using renewable sources of energy as compared to using fossil fuels, of which there is only a particular amount on our planet.
Mentioned below are some important examples of sustainable development. Have a look:
- Wind Energy – Wind energy is an easily available resource. It is also a free resource. It is a renewable source of energy and the energy which can be produced by harnessing the power of wind will be beneficial for everyone. Windmills can produce energy which can be used to our benefit. It can be a helpful source of reducing the cost of grid power and is a fine example of sustainable development.
- Solar Energy – Solar energy is also a source of energy which is readily available and there is no limit to it. Solar energy is being used to replace and do many things which were first being done by using non-renewable sources of energy. Solar water heaters are a good example. It is cost-effective and sustainable at the same time.
- Crop Rotation – To increase the potential of growth of gardening land, crop rotation is an ideal and sustainable way. It is rid of any chemicals and reduces the chances of disease in the soil. This form of sustainable development is beneficial to both commercial farmers and home gardeners.
- Efficient Water Fixtures – The installation of hand and head showers in our toilets which are efficient and do not waste or leak water is a method of conserving water. Water is essential for us and conserving every drop is important. Spending less time under the shower is also a way of sustainable development and conserving water.
- Sustainable Forestry – This is an amazing way of sustainable development where the timber trees that are cut by factories are replaced by another tree. A new tree is planted in place of the one which was cut down. This way, soil erosion is prevented and we have hope of having a better, greener future.
Related Articles
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global goals established by the United Nations in 2015. These include: No Poverty Zero Hunger Good Health and Well-being Quality Education Gender Equality Clean Water and Sanitation Affordable and Clean Energy Decent Work and Economic Growth Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure Reduced Inequality Sustainable Cities and Communities Responsible Consumption and Production Climate Action Life Below Water Life on Land Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions Partnerships for the Goals
The SDGs are designed to address a wide range of global challenges, such as eradicating extreme poverty globally, achieving food security, focusing on promoting good health and well-being, inclusive and equitable quality education, etc.
India is ranked #111 in the Sustainable Development Goal Index 2023 with a score of 63.45.
Hence, we hope that this blog helped you understand the key features of an essay on sustainable development. If you are interested in Environmental studies and planning to pursue sustainable tourism courses , take the assistance of Leverage Edu ’s AI-based tool to browse through a plethora of programs available in this specialised field across the globe and find the best course and university combination that fits your interests, preferences and aspirations. Call us immediately at 1800 57 2000 for a free 30-minute counselling session
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
Thanks a lot for this important essay.
NICELY AND WRITTEN WITH CLARITY TO CONCEIVE THE CONCEPTS BEHIND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY.
Thankyou so much!

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Essay On Sustainable Development
500 words essay on sustainable development.
Sustainable development is basically an action plan which helps us to achieve sustainability in any activity which makes use of the resource. Moreover, it also demands immediate and intergenerational replication. Through essay on sustainable development, we will help you understand the concept and its advantages.
Through sustainable development, we formulate organising principles which help to sustain the limited resources essential to provide for the needs of our future generations. As a result, they will be able to lead a content life on the planet .

What is Sustainable Development?
The World Commission on Environment and Development popularized this concept in 1987. Their report defines the idea as a “development which meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.”
In other words, they aimed to prevent the stripping the natural world of resources which the future generations will require. As we all know that usually, one particular need drives development. Consequently, the wider future impacts are not considered.
As a result, a lot of damage happens due to this type of approach. Thus, the longer we continue to pursue unsustainable development, the more severe will the consequences be. One of the most common is climate change which is being debated widely worldwide.
In fact, climate change is already wreaking havoc on our surroundings. So, the need of the hour is sustainable development. We must ask ourselves, must we leave a scorched planet with an ailing environment for our future generations?
In order to undo the mess created by us, we must follow sustainable development. This will help us promote a more social, environmental and economical thinking. Most importantly, it is not that difficult to attain this.
We must see that world as a system which connects space, and time. Basically, it helps you understand that water pollution in South Africa will ultimately impact water quality in India. Similarly, it is the case for other things as well.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Measures to Practice Sustainable Development
There are many measures to take up for practising sustainable development. To begin with, it is important to ensure clean and hygienic living and working conditions for the people.
Next, sponsoring research on environmental issues which pertains to regions. Further, ensuring safety against known and proven industrial hazards. It is also important to find economical methods to salvage dangerous industrial wastes.
Most importantly, we must encourage afforestation . Including environmental education as part of the school and college curriculum will also help. Similarly, it is essential to socialize and humanize all environmental issues.
Further, we must encourage uses of non-conventional sources of energy, especially solar energy. Looking for substitutes for proven dangerous materials on the basis of local resources and needs will help. Likewise, we must produce environment-friendly products.
It is also essential to popularize the use of organic fertilizers and other biotechniques. Finally, the key is environmental management which must be monitored and ensure accountability.
Conclusion of Essay on Sustainable Development
To sum it up, sustainable development continuously seeks to achieve social and economic progress in ways which will not exhaust the Earth’s finite natural resources. Thus, we must all develop ways to meet these needs so that our future generations can inherit a healthier and greener planet.
FAQ on Essay on Sustainable Development
Question 1: State two measures we can take for sustainable development.
Answer 1: The first measure we can take is by finding economical methods for salvaging hazardous industrial wastes. Next, we must encourage afforestation.
Question 2: What is the aim of sustainable development?
Answer 2 : The aim of sustainable development is to maximise human well-being or quality of life without having to risk the life support system.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Home — Essay Samples — Business — Community Development — Sustainable Development
Sustainable Development
- Categories: Community Development
About this sample

Words: 889 |
Published: Oct 22, 2018
Words: 889 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read
Works Cited
- United Nations. (2015). Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Retrieved from https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda
- United Nations Development Programme. (2021). Sustainable Development Goals. Retrieved from https://www.undp.org/sustainable-development-goals
- World Commission on Environment and Development. (1987). Our Common Future (Brundtland Report). Retrieved from https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/5987our-common-future.pdf
- Speth, J. G. (2008). The bridge at the edge of the world: Capitalism, the environment, and crossing from crisis to sustainability. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
- Sachs, J. D. (2015). The age of sustainable development. New York, NY: Columbia University Press.
- Steffen, W., et al. (2015). Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science, 347(6223), 1259855.
- Rockström, J., et al. (2009). Planetary boundaries: Exploring the safe operating space for humanity. Ecology and Society, 14(2), 32.
- Greenpeace. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.greenpeace.org/
- Sierra Club. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.sierraclub.org/
- UAE Ministry of Climate Change and Environment. (n.d.). UAE Green Growth Strategy. Retrieved from https://www.moccae.gov.ae/en/our-initiatives/sustainable-development/UAE-Green-Growth-Strategy

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Business

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1111 words
2 pages / 888 words
6 pages / 2734 words
4 pages / 1924 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Whether you're a freshman just starting out or a senior winding down, it's important to take time to build and nurture your community. In this essay, I will explore the benefits of community building, examine the pitfalls of [...]
My passion for helping others has been a driving force in my life for as long as I can remember. From a young age, I have always felt a deep sense of empathy and compassion for those around me. Whether it was volunteering at a [...]
Seedfolks is a novel written by Paul Fleischman that was first published in 1997. The novel is set in Cleveland, Ohio, and tells the story of a diverse group of individuals who come together to create a community garden in an [...]
The Kasanje Case Study is a significant example of the challenges and opportunities faced by developing countries in implementing sustainable development initiatives. The case study focuses on the efforts of the Kasanje [...]
“Today Science is Technology of tomorrow” Technology is the use of scientific knowledge of make easy of daily life. Technology is not an artificial word it is a natural word. We seem technology is nature, how nature is working. [...]
Community development is a process where community members come together to take collective action and generate solutions to common problems. Community wellbeing (economic, social, environmental and cultural) often evolves from [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Sustainable Development Essay
500+ words essay on sustainable development.
Sustainable development is a central concept. It is a way of understanding the world and a method for solving global problems. The world population continues to rise rapidly. This increasing population needs basic essential things for their survival such as food, safe water, health care and shelter. This is where the concept of sustainable development comes into play. Sustainable development means meeting the needs of people without compromising the ability of future generations. In this essay on sustainable development, students will understand what sustainable development means and how we can practise sustainable development. Students can also access the list of CBSE essay topics to practise more essays.
What Does Sustainable Development Means?
The term “Sustainable Development” is defined as the development that meets the needs of the present generation without excessive use or abuse of natural resources so that they can be preserved for the next generation. There are three aims of sustainable development; first, the “Economic” which will help to attain balanced growth, second, the “Environment”, to preserve the ecosystem, and third, “Society” which will guarantee equal access to resources to all human beings. The key principle of sustainable development is the integration of environmental, social, and economic concerns into all aspects of decision-making.
Need for Sustainable Development?
There are several challenges that need attention in the arena of economic development and environmental depletion. Hence the idea of sustainable development is essential to address these issues. The need for sustainable development arises to curb or prevent environmental degradation. It will check the overexploitation and wastage of natural resources. It will help in finding alternative sources to regenerate renewable energy resources. It ensures a safer human life and a safer future for the next generation.
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the need to keep sustainable development at the very core of any development strategy. The pandemic has challenged the health infrastructure, adversely impacted livelihoods and exacerbated the inequality in the food and nutritional availability in the country. The immediate impact of the COVID-19 pandemic enabled the country to focus on sustainable development. In these difficult times, several reform measures have been taken by the Government. The State Governments also responded with several measures to support those affected by the pandemic through various initiatives and reliefs to fight against this pandemic.
How to Practise Sustainable Development?
The concept of sustainable development was born to address the growing and changing environmental challenges that our planet is facing. In order to do this, awareness must be spread among the people with the help of many campaigns and social activities. People can adopt a sustainable lifestyle by taking care of a few things such as switching off the lights when not in use; thus, they save electricity. People must use public transport as it will reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. They should save water and not waste food. They build a habit of using eco-friendly products. They should minimise waste generation by adapting to the principle of the 4 R’s which stands for refuse, reduce, reuse and recycle.
The concept of sustainable development must be included in the education system so that students get aware of it and start practising a sustainable lifestyle. With the help of empowered youth and local communities, many educational institutions should be opened to educate people about sustainable development. Thus, adapting to a sustainable lifestyle will help to save our Earth for future generations. Moreover, the Government of India has taken a number of initiatives on both mitigation and adaptation strategies with an emphasis on clean and efficient energy systems; resilient urban infrastructure; water conservation & preservation; safe, smart & sustainable green transportation networks; planned afforestation etc. The Government has also supported various sectors such as agriculture, forestry, coastal and low-lying systems and disaster management.
Students must have found this essay on sustainable development useful for practising their essay writing skills. They can get the study material and the latest updates on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams, at BYJU’S.
Frequently Asked Questions on Sustainable development Essay
Why is sustainable development a hot topic for discussion.
Environment change and constant usage of renewable energy have become a concern for all of us around the globe. Sustainable development must be inculcated in young adults so that they make the Earth a better place.
What will happen if we do not practise sustainable development?
Landfills with waste products will increase and thereby there will be no space and land for humans and other species/organisms to thrive on.
What are the advantages of sustainable development?
Sustainable development helps secure a proper lifestyle for future generations. It reduces various kinds of pollution on Earth and ensures economic growth and development.
| CBSE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 29 June 2022
The importance of the Sustainable Development Goals to students of environmental and sustainability studies—a global survey in 41 countries
- Matthias Winfried Kleespies ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8413-879X 1 &
- Paul Wilhelm Dierkes ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6046-6406 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 9 , Article number: 218 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
39k Accesses
24 Citations
44 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental studies
To fight the global problems of humanity, the United Nations has adopted 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). To achieve these goals, it is necessary that future decision-makers and stakeholders in society consider these goals to be important. Therefore, in this study, we examined how important students in 41 countries directly related to the environmental sector rated each of the 17 SDGs. Based on the analysis of these ratings, it was possible to categorize the SDGs into three higher-level factors that reflect the three pillars of sustainability (social, economic, environmental). These three pillars are considered to be of varying importance in different countries. We also correlated the ratings of these higher-level factors with country-specific indicators, such as the Human Development Index. The correlations between the indicators and the higher-level factors revealed that in countries with higher indices, the SDGs are rated as less important compared to in countries with lower indices. These results provide stakeholders with important guidance on how the SDGs should be promoted in their country.
Similar content being viewed by others
Measuring museum sustainability in China: a DSR model-driven approach to empower sustainable development goals (SDGs)
Global effects of progress towards Sustainable Development Goals on subjective well-being
Strategies for developing sustainable communities in higher education institutions
Introduction.
Currently, humanity is facing major environmental, social and economic problems worldwide. To address these global issues on an international cross-border level and to create a more sustainable and better future for all, the United Nations adopted the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015 (United Nations, 2015 ). Each of the SDGs has indicators that are used to measure progress towards achieving the goals (United Nations, 2017 ). The individual goals do not stand alone but rather influence each other and are closely linked (Bali Swain and Yang-Wallentin, 2020 ; Nilsson et al., 2016 ; Pham‐Truffert et al., 2020 ; Pradhan et al., 2017 ); each goal addresses environmental, social and economic problems (Elder and Olsen, 2019 ).
It is particularly important how the SDGs are perceived, accepted and evaluated by people worldwide. In this context, there have been several surveys conducted in recent years, some with varying results. While awareness of the SDGs has increased globally compared to their predecessor, i.e., the Millennium Development Goals (GlobeScan, 2016 ), 63% of the respondents in a survey of 28 European countries said they had never heard of the SDGs. Globally, awareness of the SDGs is approximately 50% (Theresa et al., 2020 ); however, only 1% of people say they are very well informed about the SDGs (Lampert and Papadongonas, 2016 ). There are also regional differences in the assessment of the individual goals. Globally, ‘climate action’, ‘good health’ and ‘well-being and quality education’ are considered particularly important (Theresa et al., 2020 ). In another survey, ‘zero hunger’, ‘clean water and sanitation’ and ‘no poverty’ were selected as the most important SDGs (Lampert and Papadongonas, 2016 ). Young people in particular are more likely to have heard of the SDGs, and for them, quality education is particularly important (Youth Speak Survey, 2020 ). In general, people around the world have a high level of acceptance about the content of the SDGs (Ipsos, 2015 ).
The education system has an important role in raising awareness of the SDGs and in teaching skills and values that lead to more sustainable behaviour. Therefore, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) has developed learning objectives for the SDGs to support teachers and learners (UNESCO, 2017 ). Tertiary educational institutions are particularly important in this regard, as they educate the next generation of decision-makers who will have a critical impact on the future of the planet (Yuriev and Sierra‐Barón, 2020 ). Universities, through their education and influence, contribute directly to the achievement of a whole range of SDGs (Kioupi and Voulvoulis, 2020 ). In recent years, there has been a strong increase in sustainability programmes at universities, with a particular focus on student attitudes (Rodríguez-García et al., 2019 ); however, there is wide divergence between programmes (O’Byrne et al., 2015 ). Despite the recent surge of sustainability in higher education, students generally have limited knowledge of the SDGs (Zamora-Polo et al., 2019 ). Higher education institutes, such as universities, have a special responsibility worldwide because they shape future leaders (Alshuwaikhat and Abubakar, 2008 ; Bellou et al., 2017 ), decision-makers (Alshuwaikhat and Abubakar, 2008 ; Lozano et al., 2013 ), professionals (Kioupi and Voulvoulis, 2020 ) and intellectuals in various academic fields (Lozano, 2006 ).
In addition to educating the next generation of decision-makers, which is most likely the most important factor, universities also make an important contribution to achieving the SDGs through research, public engagement or university policy (Kestin et al., 2017 ). They can influence politicians and industry leaders with their clear and unbiased information (Stephens et al., 2008 ) and reach a wide audience in the general population (Kioupi and Voulvoulis, 2020 ).
While elite positions in society can be reached independently of having a university education, universities provide knowledge and technical skills that significantly increase the likelihood that a person will achieve such a socially relevant position (Frank and Meyer, 2007 ; Vicente-Molina et al., 2013 ). Therefore, students, as potential future decision-makers of society, contribute greatly to the achievement of the SDGs and have an impact on the major problems of humanity and thus on the future of the planet. Until now, however, there has been a lack of valid international research that examines the perspective of students in the natural and sustainable sciences on the various SDGs. This study is an attempt to reduce the international research gap and examine the views of environmental students in different countries regarding the SDGs. The aim is to determine how important students in each country consider the SDGs to be. In this context, statistical methods will be used to check whether the individual SDGs can be assigned to higher-order groups on the basis of the students’ evaluation. To identify patterns and differences between the countries, these higher-ranking groups were compared among the individual countries and correlated with country-specific indicators. The results are intended to provide guidance for action for today’s decision-makers in individual countries.
Therefore, in our study, we asked more than 4000 university students in 41 countries whose course of study is directly related to sustainability to rate the 17 SDGs on a scale of 1–5 (important to unimportant). In the first step of the analysis, an exploratory factor analysis was used to investigate the extent to which the SDGs can be categorized into higher-level factors based on the participants’ ratings. In a second step, we examined how these higher ranking factors differed among the 41 countries studied. In the final step, we analysed the relationship between these higher-ranking factors and various country-specific indicators (GDP per capita, the Human Development Index, the Education Index, the Environment Performance Index and the SDG Index).
Data collection procedure
The survey was conducted using an online questionnaire. To guarantee a high level of data protection and the anonymity of the participants, the survey software that is also applied for evaluation at Goethe University in Frankfurt was used. Students were shown the labels and descriptions of each SDG (Table 1 ) and asked to rate them on a scale of 1 to 5 (unimportant to important). The survey was conducted in one of the official languages of the respective countries. The translation of the questionnaires was performed by a native-speaking translator and always checked by an additional person. The translations of the SDGs were taken from the official website of the UN (United Nations, 2016 ). If no translation was available, the SDGs were translated by a translator following the same principle. The English version of the questionnaire can be found in Supplementary Fig. 1 . To collect the data, professors and scientists worldwide were contacted and asked for their help. The scientists were asked to distribute the questionnaire among their students. An English cover letter was provided to participants and described the content and background of the study. In addition, a short introductory text at the beginning of the questionnaire explained the research project to the participants. Only people from natural science courses directly related to sustainability (e.g., biology, environmental sciences, ecology and conservation, natural resources management, etc.) were contacted.
A total of 4305 students (34.3% male, 63.6% female, 0.8% divers, 1.2% no answer) participated in the survey. The participants were on average 22.59 (±0.495) years old and in the 4.29th (±2.744) semester of study. The number of participants broken down by country is shown in Supplementary Table 2 . The survey period was September 2020–July 2021.
The study was reviewed by the ethics committee of the science didactic institutes and departments of the Goethe University Frankfurt am Main under approval number 15-WLSD-2104. If a university required a local ethics vote, that vote was also conducted prior to the survey.
An exploratory factor analysis was conducted to examine the relationship between the individual SDGs and to assign the SDGs to higher ranking factors based on the students’ ratings. This is a structure-simplifying procedure that is used to assign individual variables or items to higher-order factors and thus simplify the interpretation of the data (Yong and Pearce, 2013 ). In simple terms, a factor analysis generates a correlation matrix ( R -matrix) for all items used. Items that correlate particularly well and separate themselves from other item clusters are assigned to a higher ranking factor (Field, 2013 ). The rotation method chosen was varimax, which is considered the most reliable orthogonal rotation method (Fabrigar et al., 1999 ). To check whether the data were at all suitable for this type of analysis, Bartlett’s test of sphericity and the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin measure of sampling adequacy were performed (Dziuban and Shirkey, 1974 ). The number of factors was determined by the Kaiser criterion, which takes into account all factors that have an eigenvalue larger than 1 (Kaiser, 1960 ). To examine whether the values of the three higher-level factors found by the factor analysis differed within countries or whether the factors were perceived to be of similar importance, the (two-tailed) Friedman test was used (Field, 2013 ). For significant results, a pairwise comparison was performed using the (two-tailed) Dunn–Bonferroni test (Dunn, 1964 ). The effect size was calculated using the following formula: r = \(\frac{Z}{{\sqrt N }}\) (Fritz et al., 2012 ).
To investigate whether there is a linear relationship between the factors found through factor analysis and the indices of each country (e.g., the Human Development Index and the Education Index), the Spearman rank correlation was calculated. The Spearman rank correlation was selected because the data were ordinally scaled and not normally distributed (Field, 2013 ; Schober et al., 2018 ).
Selected indices
The following five country-specific indices were selected:
Gross domestic product per capita (GDP per capita, 2021): GDP per capita is a value calculated by organizations such as the international monetary fund (International Monetary Fund, 2021 ). It is often used as an indicator of the standard of living, even though some weaknesses in this interpretation are currently known (Goossens, 2007 ).
Human Development Index (HDI from 2020): The HDI is an indicator of the United Nations (Conceição et al., 2020 ) that consists of life expectancy, the average number of years of schooling, and the standard of living (United Nations Development Programme, 2020b ).
Education Index (EI from 2020): The EI is a United Nations indicator that consists of the number of years of schooling that an adult person has attended on average and the expected years of schooling that a child will attend (United Nations Development Programme, 2020a ).
Environment Performance Index (EPI from 2020): The EPI is an index that assesses environmental health and ecosystem vitality using 32 performance indicators (Wendling et al., 2020 ).
SDG Index (SDGI from 2021): The SDGI is an indicator of the Bertelsmann Foundation that attempts to calculate the progress of the SDGs in percent based on various indicators. For example, if a country has an SDGI of 85.9, then approximately 86% of the SDGs have been achieved by that country (Sachs et al., 2021 ).
Both the Bartlett test ( p < 0.001) and the KMO criterion (KMO = 0.924) confirmed the applicability of an exploratory factor analysis for the 17 SDGs. The analysis revealed three factors with an eigenvalue > 1, indicating that the SDGs can be attributed to three higher-order factors (social, economic, environmental), which together can explain 53.48% of the variance. Overall, there was a clear assignment of items to the factors, and only a few cross-loadings were observed (Table 1 ).
The comparison of the three sustainability factors within the tested countries showed that the countries rated the individual dimensions of the SDGs differently. For example, in some countries, all three sustainability factors were rated as being equally important (Fig. 1a ); thus, there was no significant difference between the factors. In a number of countries, the environmental component was rated higher than the economic component, but no difference was found between the social and environmental components or between the social and economic components (Fig. 1b ). In the third group, the economic factor was rated as slightly less important than the environmental and social factors (Fig. 1c ). In some countries, the environmental factor was rated significantly higher than the other factors (Fig. 1d ). For better clarity, the individual significance levels are not marked in Fig. 1 but can be found along with the effect sizes in Supplementary Table 1 .
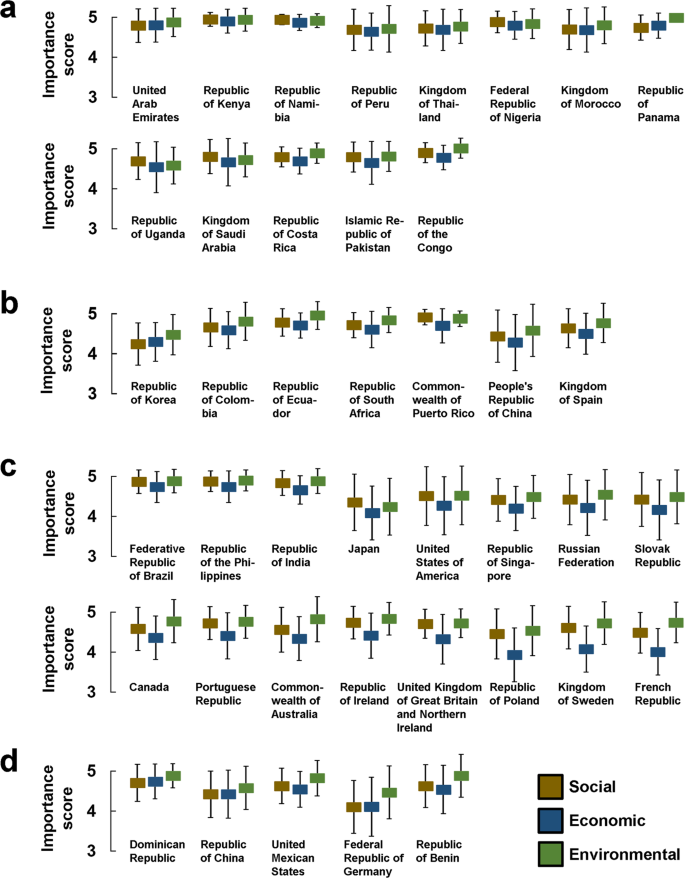
In group ( a ), there are no significant differences between the three factors within the countries. In group ( b ), the environmental factor is rated higher than the economic factor but not higher than the social factor. In group ( c ), the economic factor is rated lower than the other two factors. In group ( d ), the environmental factor is rated significantly higher than both the economic and environmental factors. For clarity, the significance levels are not marked with asterisks in the figure. Exact significance levels and effect sizes can be found in Supplementary Table 1 . The boxes represent the mean of the components; the error bars represent the standard deviation.
The three higher-level sustainability factors show significant correlations with all five selected country-specific global development indices ( p < 0.001). The correlations are shown in Table 2 .
All correlations are in the high range according to the common interpretation (Field, 2013 ). It is noteworthy that there is a negative correlation for all the global development indices examined. It follows that students in countries with higher indices rate the SDGs as less important than do students in countries with lower indices. For all the global development indices tested, a higher score means a higher standard. In other words, students in countries with, for example, a higher standard of education or higher income per person consider the SDGs to be less important compared to their counterparts.
The correlations between the three sustainability factors found and the individual indices are shown in Fig. 2 . The importance score refers to the mean values of the individual sustainability factors for the different countries. The dashed lines represent the linear trend.
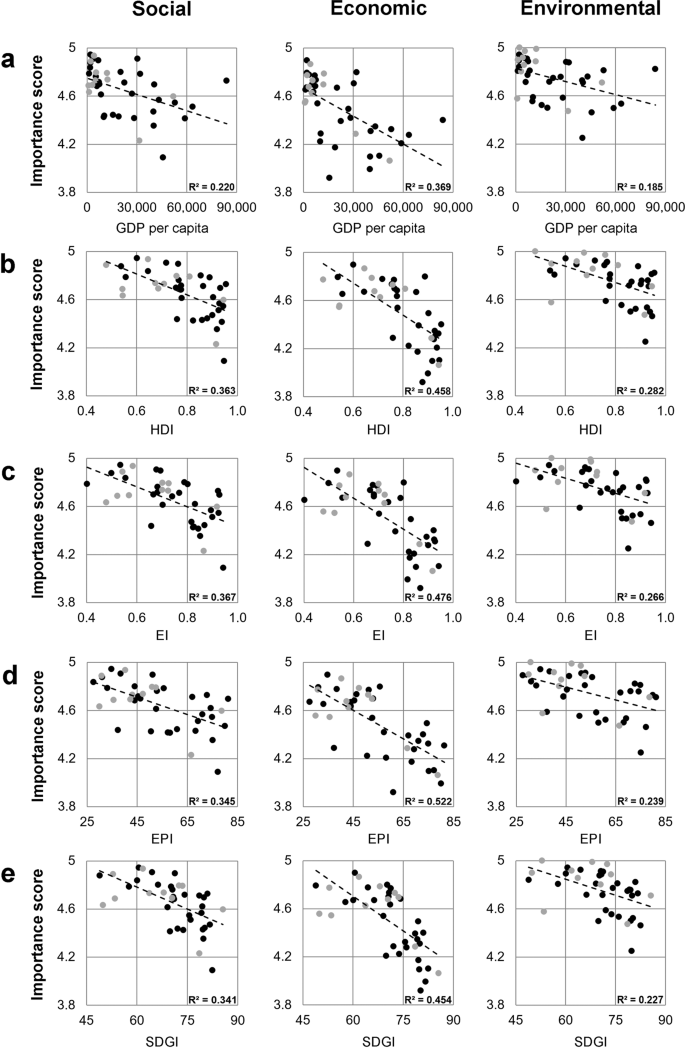
Each point represents one country. Countries with fewer than 50 respondents are shown in grey, and countries with more than 50 respondents are shown in black. a Gross domestic product per capita in US dollars, b Human Development Index, c Education Index, d Environment Performance Index, and e SDG Index.
The results of this study provide important information on how students in the environmental field worldwide perceive and evaluate the 17 SDGs. Based on the rating of the importance of the individual SDGs, it was possible to assign them to three higher-level factors in the factor analysis. Although each of the 17 SDGs contains all three pillars of sustainability (social, economic and environmental (Purvis et al., 2019 )) and the different levels of sustainability build on each other (Sachs, 2012 ; United Nations, 2015 ), it has also been shown in previous studies that people assign the SDGs to individual pillars to varying degrees (Bain et al., 2019 ; Dalampira and Nastis, 2020 ; Elder and Olsen, 2019 ). Reviewing the three higher-level factors, it can be assumed that our data also reflect such a classification. When considering only the labels and short descriptions, Factor 1 includes the SDGs that are primarily considered social, Factor 2 includes the SDGs that are considered economic, and Factor 3 includes the SDGs that are considered environmental (Elder and Olsen, 2019 ). While in previous studies, respondents were often asked directly to assign the SDGs to the three pillars of sustainability, in this study, the classification was solely based on the different ratings of the importance of each SDG.
The clear separation of the SDGs into these three groups and the low cross-loading values suggest that environmental students worldwide make this categorization and assign different importance to the SDGs in the three groups, potentially subconsciously. It can be concluded that the students consider ecological, economic and social challenges to be of varying importance. This finding provides an essential starting point for decision-makers in tertiary education institutions. In addition to the current increasing number of courses with a focus on sustainability (O’Byrne et al., 2015 ; Rodríguez-García et al., 2019 ), more emphasis should be placed on the interconnectedness of the individual layers of the various SDGs. For each SDG, attention should be given to highlighting social, environmental and economic components and to underlining the close relationship between these pillars. In this way, the importance of all three components of each SDG can be taken into account for current issues. Fisheries, for example, have important elements of the social and economic components, in addition to the environmental component, and all of these elements are closely linked (Asche et al., 2018 ). These connections should be addressed and highlighted in environmental education courses.
When comparing these three factors within the countries, different patterns emerge. In approximately two-thirds of the countries, the three factors are not rated as equally important. A noticeable pattern, which is particularly evident in a number of industrialized countries, is that the gap between the economic factor and the other two factors is particularly large. This could well be explained to some extent by the attitudes of people in industrialized countries; i.e., environmental issues, such as fighting climate change, are seen as particularly important aims in North America and Europe (Theresa et al., 2020 ). When considering problems in developing counties, people in Europe often rate issues belonging to the social component (such as peace and security) as particularly important (European Commission. Directorate General for International Cooperation and Development. et al., 2016 ). This potentially leads to the assessment that the environmental and social factors are particularly important, while the economic SDGs are perceived as less important, as they do not fall into either category.
Another pattern that repeatedly emerges is that the environmental component is rated as being more important than one or both of the other components. In no country was the environmental component rated significantly worse than the two other factors. These results are very positive, as environmental problems are currently more relevant than ever before. The boundaries of our planet are being increasingly exhausted, and there is an urgent need for action at the global level (Steffen et al., 2015 ). The high rating of environmental factors also shows a particularly positive trend in all countries. In the past, many governments and experts prioritized economic growth and considered environmental damage as a trade-off (Elder and Olsen, 2019 ). The common approach has been to accept pollution as a consequence of economic growth and to deal with the related environmental problems that arise later (Azadi et al., 2011 ). This view is not reflected in our study of environmental students. In the current study, environmental concerns are considered to be at least as important, and in some countries even more important, than social and economic factors.
The differences identified between countries can serve as a possible guide to action for local decision-makers who can incorporate specific promotion of the importance of different SDGs into the curriculum. In this way, country-specific actions can be implemented that specifically address the economic, ecological or environmental awareness of each of the SDGs. These results can also be seen as a call to those countries in which the gap between the three factors is particularly large. Especially in these countries, political or educational actions, such as emphasizing the global importance of the economic SDGs in the educational context, would be particularly important.
The comparison of the country-specific indicators with the rating of the importance of the higher-level factors shows a similar picture for all indicators. In countries with higher indices (higher GDP per capita, higher health index, etc.), the SDGs are generally rated as being less important than in countries with lower indices. In this context, it does not matter whether the SDGs are perceived as social, economic or environmental. This result is surprising, since in previous international studies, it was often found that people in wealthier countries, i.e., countries with a higher GDP per capita, have a more positive attitude towards, for example, environmental problems, than do people in countries with a lower GDP per capita (Franzen, 2003 ; Franzen and Meyer, 2010 ; Franzen and Vogl, 2013 ). The research of and theory put forth by Inglehart is often used as a basis for explanation. He found that in countries where postmaterialist values dominate, people have a more positive attitude towards environmental protection than they do in countries with more materialist values. Thus, postmaterialist values are more likely to be found in advanced industrial societies (Inglehart, 1995 ). However, postmaterialist values do not necessarily lead to higher support for the SDGs (Guan et al., 2019 ). Our study also supports this assumption. The results show that, on average, people in societies with higher indices (usually industrialized societies) rate the SDGs as being less important than do people in countries with lower indices. This provides important insights for politicians, stakeholders and decision-makers; i.e., in wealthier countries that have already made great progress in implementing the SDGs, the relevance of the SDGs must be communicated at different levels. Particular attention must be paid to higher educational institutions. The fact that the SDGs are rated lower on average in wealthier countries with a higher Education Index outcome shows that it is especially in these countries that there is a need to improve the related knowledge and that the focus of higher education institutions should be placed specifically on content related to the SDGs. In this context, it is not sufficient to teach only basic scientific knowledge (Frick et al., 2004 ); rather, other factors, such as attitudes (Gifford and Sussman, 2012 ) or values (Steg and Groot, 2012 ), should also be a particular focus of education. The importance of the SDGs should be considered not only for specific countries but also in an international and global context. Thus, these topics could be integrated into the curricula of universities and schools to enable students, as future decision-makers in society, to act as multipliers and pass on the relevance and importance of the SDGs in society.
Limitations
Although the study was conducted with great care, some limitations must be addressed. For example, the study surveyed a very select group of students in environmental and sustainability science courses. It can be assumed that people in these courses are more interested in environmental issues than the general population. However, because a similar group of students was surveyed in each country, cross-country comparison is possible. Nevertheless, it must be assumed that the results cannot be generalized to other courses of study or to the general population. Further international studies are necessary to investigate relationships in other groups.
Another limitation of the study is that the survey was conducted by e-mail on a voluntary basis. This could possibly lead to self-selection; i.e., people who were already interested in the topic of the SDGs were more likely to participate in the survey.
It should also be mentioned that the sample size differs in part between the individual countries. While in some countries, several hundred people could be surveyed, in other countries, only a sample size in the two-digit range was possible. This result could potentially have had an influence on the comparison between the countries.
When evaluating the individual SDGs, it cannot be ruled out that the students did not rate each SGD independently but rather related their importance to each other. As a result, some SDGs may have been rated differently than they would have been without such a direct comparison. However, since this effect was equally possible in all countries, the results remain comparable, and the conclusions remain valid.
The current research was able to show that the importance of the SDGs, regardless of the pillar of sustainability (social, economic, environmental), is considered important by students in environmental and sustainability science courses in different countries. However, there are variations between the countries in how important the individual pillars for sustainability are considered to be. This result offers the opportunity to specifically promote individual pillars for sustainability in those countries in which a pillar was perceived as being less important. Another important finding of the study is that especially in countries with high global development indices, the SDGs are rated as less important compared to the ratings in countries with lower global development indices. Therefore, our research is a call to countries with higher indices, where the SDGs have already been implemented to a higher extent, to actively improve the view and acceptance of students regarding the SDGs. This can help to further achieve the SDGs both in individual countries and at the global level.
Data availability
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors to any qualified researcher.
Alshuwaikhat HM, Abubakar I (2008) An integrated approach to achieving campus sustainability: assessment of the current campus environmental management practices. J Cleaner Prod 16(16):1777–1785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2007.12.002
Asche F et al. (2018) Three pillars of sustainability in fisheries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(44):11221–11225. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1807677115
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Azadi H, Verheijke G, Witlox F (2011) Pollute first, clean up later? Global Planet Change 78(3-4):77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2011.05.006
Article ADS Google Scholar
Bain PG et al. (2019) Public views of the Sustainable Development Goals across countries. Nat Sustain 2(9):819–825. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-019-0365-4
Article Google Scholar
Bali Swain R, Yang-Wallentin F (2020) Achieving sustainable development goals: predicaments and strategies. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 27(2):96–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2019.1692316
Bellou C, Petreniti V, Skanavis C (2017) Greening the campus intentions: a study of the University of the Aegean nonacademic staff. Int J Sust Higher Ed 18(4):520–532. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSHE-05-2015-0102
Conceição P et al. (2020) Human development report 2020: the next frontier. Human development and the Anthropocene. United Nations Development Programme, New York
Google Scholar
Dalampira ES, Nastis SA (2020) Back to the future: simplifying Sustainable Development Goals based on three pillars of sustainability. Int J Sustain Agric Manag Inf 6(3):226. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSAMI.2020.10034327
Dunn OJ (1964) Multiple comparisons using rank sums. Technometrics 6(3):241. https://doi.org/10.2307/1266041
Dziuban CD, Shirkey EC (1974) When is a correlation matrix appropriate for factor analysis? Some decision rules. Psychol Bull 81(6):358–361. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0036316
Elder M, Olsen SH (2019) The design of environmental priorities in the SDGs. Glob Policy 10(S1):70–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-5899.12596
European Commission. Directorate General for International Cooperation and Development, TNS Opinion & Social, European Commission. Directorate General for Communication (2016) Special Eurobarometer 441: The European year for development: citizens’s view on development, cooperation and aid. Publications Office
Fabrigar LR, Wegener DT, MacCallum RC, Strahan EJ (1999) Evaluating the use of exploratory factor analysis in psychological research. Psychol Methods 4(3):272–299. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.4.3.272
Field A (2013) Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics: and sex and drugs and rock ‘n’ roll, 4th edn. Sage, Los Angeles, London, New Delhi, Singapore, Washington, DC
Frank DJ, Meyer JW (2007) University expansion and the knowledge society. Theor Soc 36(4):287–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11186-007-9035-z
Franzen A (2003) Environmental attitudes in international comparison: an analysis of the ISSP surveys 1993 and 2000 *. Soc Sci Q 84(2):297–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/1540-6237.8402005
Franzen A, Meyer R (2010) Environmental attitudes in cross-national perspective: A multilevel analysis of the ISSP 1993 and 2000. Eur. Sociol. Rev. 26(2):219–234. https://doi.org/10.1093/esr/jcp018
Franzen A, Vogl D (2013) Two decades of measuring environmental attitudes: a comparative analysis of 33 countries. Global Environ Change 23(5):1001–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2013.03.009
Frick J, Kaiser FG, Wilson M (2004) Environmental knowledge and conservation behavior: exploring prevalence and structure in a representative sample. Personal Individ Differ 37(8):1597–1613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2004.02.015
Fritz CO, Morris PE, Richler JJ (2012) Effect size estimates: current use, calculations, and interpretation. J Exp Psychol Gen 141(1):2–18. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0024338
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Gifford R, Sussman R (2012) Environmental attitudes. In: Clayton SD (ed) The Oxford handbook of environmental and conservation psychology. Oxford library of psychology. Oxford University Press, New York, Oxford, pp 65–80
GlobeScan (2016) Awareness of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) vs. Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). https://globescan.com/awareness-of-sustainable-development-goals-sdgs-vs-millennium-development-goals-mdgs/
Goossens Y (2007) Alternative progress indicators to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) as a means towards sustainable development. European Parliament
Guan T, Meng K, Liu W, Xue L (2019) Public attitudes toward Sustainable Development Goals: evidence from five Chinese cities. Sustainability 11(20):5793. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205793
Inglehart R (1995) Public support for environmental protection: objective problems and subjective values in 43 societies. Political Sci Politics 28(1):57. https://doi.org/10.2307/420583
International Monetary Fund (2021) World Economic Outlook: managing divergent recoveries. https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2021/April
Ipsos (2015) Ipsos public affairs findings from a global poll on the Sustainable Development Goals. https://www.ipsos.com/en-us/17-country-study-foreign-aid-and-sustainable-development-goals
Kaiser HF (1960) The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educ Psychol Meas 20(1):141–151. https://doi.org/10.1177/001316446002000116
Kestin T et al. (2017) Getting started with the SDGs in universities: a guide for universities, higher education institutions, and the academic sector. Sustainable Development Solutions Network, Melbourne
Kioupi V, Voulvoulis N (2020) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): assessing the contribution of higher education programmes. Sustainability 12(17):6701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12176701
Lampert M, Papadongonas P (2016) Towards 2030 Without Poverty: increasing knowledge of progress made and opportunities for engaging frontrunners in the world population with the global goals. https://oxfamsol.be/sites/default/files/documents/towards_2030_without_poverty-glocalities2016-2-new.pdf
Lozano R (2006) Incorporation and institutionalization of SD into universities: breaking through barriers to change. J Cleaner Prod 14(9–11):787–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2005.12.010
Lozano R et al (2013) Declarations for sustainability in higher education: becoming better leaders, through addressing the university system. J Cleaner Prod 48:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.10.006
Nilsson M, Griggs D, Visbeck M (2016) Policy: map the interactions between Sustainable Development Goals. Nature 534(7607):320–322. https://doi.org/10.1038/534320a
Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
O’Byrne D, Dripps W, Nicholas KA (2015) Teaching and learning sustainability: an assessment of the curriculum content and structure of sustainability degree programs in higher education. Sustain Sci 10(1):43–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-014-0251-y
Pham‐Truffert M et al. (2020) Interactions among Sustainable Development Goals: Knowledge for identifying multipliers and virtuous cycles. Sustain Dev 28(5):1236–1250. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2073
Pradhan P et al. (2017) A systematic study of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Interactions. Earth’s Future 5(11):1169–1179. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017EF000632
Purvis B, Mao Y, Robinson D (2019) Three pillars of sustainability: in search of conceptual origins. Sustain Sci 14(3):681–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-018-0627-5
Rodríguez-García A-M, López Belmonte J, Agreda Montoro M, Moreno-Guerrero A-J (2019) Productive, structural and dynamic study of the concept of sustainability in the educational field. Sustainability 11(20):5613. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205613
Sachs JD (2012) From millennium development goals to Sustainable Development Goals. Lancet 379(9832):2206–2211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60685-0
Sachs JD et al. (2021) Sustainable Development Report 2021: the decade of action for the Sustainable Development Goals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Book Google Scholar
Schober P, Boer C, Schwarte LA (2018) Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth Analg 126(5):1763–1768. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000002864
Steffen W et al. (2015) Planetary boundaries: guiding human development on a changing planet. Sustain Sci 347(6223):1259855. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1259855
Article CAS Google Scholar
Steg L, Groot JIMde (2012) Environmental Values. In: Clayton SD (ed.) The Oxford handbook of environmental and conservation psychology. Oxford library of psychology. Oxford University Press, New York, Oxford, pp 81–92
Stephens JC et al. (2008) Higher education as a change agent for sustainability in different cultures and contexts. Int J Sust Higher Ed 9(3):317–338. https://doi.org/10.1108/14676370810885916
Theresa F, Joachim S, Todd C (2020) Report of results global survey on sustainability and the SDGs: awareness, priorities, need for action. Schlange & Co. GmbH, Hamburg
UNESCO (2017) Education for sustainable development goals: learning objectives. UNESCO, Paris
United Nations (2015) Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development: A/RES/71/1. https://undocs.org/A/RES/71/1
United Nations (2016) The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in your language. https://unric.org/en/sdgs-in-your-language/
United Nations (2017) Global indicator framework for the Sustainable Development Goals and targets of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development: A/RES/71/313. https://undocs.org/A/RES/71/313
United Nations Development Programme (2020a) Human development reports: education index. http://hdr.undp.org/en/indicators/103706
United Nations Development Programme (2020b) Technical notes: calculating the human development indices—graphical presentation. http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/hdr2020_technical_notes.pdf
Vicente-Molina MA, Fernández-Sáinz A, Izagirre-Olaizola J (2013) Environmental knowledge and other variables affecting pro-environmental behaviour: comparison of university students from emerging and advanced countries. J Clean Prod 61:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.05.015
Wendling ZA et al. (2020) 2020 Environmental Performance Index. https://epi.yale.edu/
Yong AG, Pearce S (2013) A beginner’s guide to factor analysis: focusing on exploratory factor analysis. Tutor Quant Methods Psychol 9(2):79–94. https://doi.org/10.20982/tqmp.09.2.p079
Youth Speak Survey (2020) Global report 2020. https://www.youthforesight.org/resource-details/Publications/858
Yuriev A, Sierra‐Barón W (2020) Exploring sustainability cross‐culturally: employees’ beliefs on green behaviors. Sustain Dev 28(5):1199–1207. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2069
Zamora-Polo F, Sánchez-Martín J, Corrales-Serrano M, Espejo-Antúnez L (2019) What do university students know about Sustainable Development Goals? A realistic approach to the reception of this UN program amongst the youth population. Sustainability 11(13):3533. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133533
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank all study participants and the more than 300 researchers and universities that shared our questionnaires. This study was partly supported by the Opel-Zoo foundation professorship in zoo biology from the “von Opel Hessische Zoostiftung”.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Bioscience Education and Zoo Biology, Goethe University Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany
Matthias Winfried Kleespies & Paul Wilhelm Dierkes
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization: MWK and PWD; data collection: MWK; methodology: MWK and PWD; validation, formal analysis, investigation: MWK and PWD; figures: PWD and MWK; writing—original: MWK; writing—review and editing: MWK and PWD, funding acquisition: PWD. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Matthias Winfried Kleespies .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of the science didactic institutes and Departments of the Goethe University Frankfurt am Main under approval number 15-WLSD-2104.
Informed consent
Participants were informed in writing before the start of the online survey about the voluntary character of participation, data protection and the aims of the study. After this information, participation in the study was considered informed consent. Participants could withdraw from the study at any time by closing the browser. It is not possible to identify individuals from the anonymously obtained data, and only persons of legal age were surveyed.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplemental file, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kleespies, M.W., Dierkes, P.W. The importance of the Sustainable Development Goals to students of environmental and sustainability studies—a global survey in 41 countries. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 9 , 218 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01242-0
Download citation
Received : 14 December 2021
Accepted : 16 June 2022
Published : 29 June 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01242-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Assessing the unseen consequences: influence of an extreme weather event on environmental perceptions and connection to nature.
- Matthias W. Kleespies
- Thomas Friedrich
- Sabrina Schiwy
Environmental Sciences Europe (2024)
Unlocking the path to environmental sustainability: navigating economic policy uncertainty, ICT, and environmental taxes for a sustainable future
- Xiaomeng Deng
- Mohammad Qamruzzaman
- Salma Karim
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2024)
Understanding the role of green finance and renewable energy consumption for sustainable development in ACI economies
- Muhammad Awais Baloch
- Zubeyde Senturk Ulucak
Climatic Change (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies




























IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay on Sustainable Development for Class 10, 12, Mains Exam (UPSC, PSC, SSC) Introduction: The concept of sustainable development was popularized by the World Commission on Environment and Development.Sustainable development refers to the practice of managing production by replacing the already used resources with other resources that has equal value or quality without hampering the ...
Introduction (50-60 words) In the introduction, students must introduce or provide an overview of the given topic, i.e. highlighting and adding recent instances and questions related to sustainable development. Body of Content (100-150 words)
Conclusion of Essay on Sustainable Development. To sum it up, sustainable development continuously seeks to achieve social and economic progress in ways which will not exhaust the Earth's finite natural resources. Thus, we must all develop ways to meet these needs so that our future generations can inherit a healthier and greener planet.
Published: Oct 22, 2018. In September 2015, 193 countries met at the UN to adopt 17 global goals. These 17 goals provide a roadmap that would help the world achieve sustainable development. You've probably heard the term "sustainability" in some context or another. It is likely that you've used some product or service that was labeled ...
Chapter 6. | Conclusion | 95 CONCLUSION 6 CHAPTER This concluding chapter highlights insights from the report that could contribute to strengthening the science-policy interface for sustainable development. The reader is referred to individual chapters and to the executive summary for a more comprehensive overview.
500+ Words Essay on Sustainable Development. Sustainable development is a central concept. It is a way of understanding the world and a method for solving global problems. The world population continues to rise rapidly. This increasing population needs basic essential things for their survival such as food, safe water, health care and shelter.
The Conclusion chapter discusses the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in relation to human capability and human security analyses. It documents strengths of the SDGs, areas of common ground, disparities and possible future trajectories. The processes leading...
1. Introduction. Sustainable Development (SD) has become a ubiquitous development paradigm—the catchphrase for international aid agencies, the jargon of development planners, the theme of conferences and academic papers, as well as the slogan of development and environmental activists (Ukaga, Maser, & Reichenbach, Citation 2011).The concept seems to have attracted the broad-based attention ...
requirement for sustainable development by reducing damages from non-renewable resources (Destek and Aslan, 2017). Along with trends, the U.S. federal government spent $15.3 billion in 2013 and $6.7 billion in 2016 to enhance renewable energy generation, which are equivalent to 52% and 45% of total energy subsidies (EIA, 2018).
To address these global issues on an international cross-border level and to create a more sustainable and better future for all, the United Nations adopted the 17 Sustainable Development Goals ...
Technical Papers : Supporting Material : Figures and Tables : Glossary : ... 7.7 Conclusions: implications for sustainable development < > Sustainable development is largely about people, their well-being, and equity in their relationships with each other, in a context where nature-society imbalances can threaten economic and social stability. ...
The intellectual underpinnings of sustainable development lie in modern natural resource management, the 20th-century conservation and environmentalism movements, and progressive views of economic development.The first principles of what later became known as sustainable development were laid out at the 1972 United Nations Conference on the Human Environment, also called the Stockholm Conference.
sibility in light of resources they require and the pressures they exert on the environment. The key principle of sustainable development underlying all others is the i. tegration of environmental, social, and economic concerns into all aspects of decision making. All other principles in the SD.
Sustainable development is an approach to growth and human development that aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. [1] [2] The aim is to have a society where living conditions and resources meet human needs without undermining planetary integrity.[3] [4] Sustainable development aims to balance the needs of the ...
The historic agenda lays out 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and targets for dignity, peace, and prosperity for the planet and humankind, to be completed by the year 2030. The agenda targets multiple areas for action, such as poverty and sanitation, and plans to build up local economies while addressing people's social needs.
Note In the outcome document of the Rio+20 Conference, in 2012, entitled "The future we want", and again in "Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development", in 2015, United Nations Member States decided that the High-
Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation. The manufacturing industry's recovery from COVID-19 is incomplete and uneven. Global ...
Disclaimer: This essay is provided as an example of work produced by students studying towards a social policy degree, ... Trade and environment should be reciprocally supportive in the pursuit of sustainable development. Conclusion. In achieving sustainable development, the 3pillars of SD should be integrated. Progress in sustainability will ...
6 Conclusion. It is essential that societies seek ways of becoming environmentally sustainable and adaptable to unknowable environmental changes, particularly in the climate. This must happen in the context of globalisation. The concept of sustainability is coming to prominence at a time when established structures of government are being ...
A whole-school approach to ESD calls for sustainable development to be integrated throughout the formal sector curriculum in a holistic manner, rather than being taught on a stand alone basis. This philosophy supports the notion that ESD is education for sustainable development rather than education about sustainable development. In ...
Abstract. Ongoing environmental innovation is the only way to reduce pressures on environmental qualities while maintaining income growth. However, the views on how to initiate and foster environmental innovations differ. In the essay we discuss three theoretical approaches. From neo-classical economic theory we distill the message that ...
Ans:. Sustainable development refers to a mode of human development in which resource use aims to meet human needs while preserving the environment so that these needs can be met not only in the present, but also for generations to come. The term 'sustainable development ' was used by the Brundtland Commission which coined what has become the ...
Ecotourism has emerged as a significant mechanism for facilitating sustainable development by harmonizing environmental conservation with economic advancement and cultural safeguarding. This scholarly article conducts a thorough review and synthesis of the extant literature concerning the function of ecotourism in sustainable development, with ...
Emmanuel Ndhlovu is a scholar and student of development. His research interests are in peasant and informal sector livelihoods, land reform issues, political economy, digitalisation of industries, and food sovereignty. He holds a PhD in Development Studies from the University of South Africa.
This hesitancy of government intervention in driving sustainable practices within the VC industry poses substantial obstacles to sustainable development. This echoes similar conclusions drawn in the prior study conducted by (Davydova et al., Citation 2020). In light of these challenges, there is a pressing need for the government to establish ...
Conclusion . Building a sustainable talent strategy is not just about hiring the right people. It's about creating a comprehensive approach aligned with your business goals, promoting continuous development, and fostering a diverse and inclusive culture. Watch the Full Webinar and Hear the Q&As
This collection of essays contains eleven contributions from representatives of a wide range of organisations, in which they indicate what they think is needed to make the concept of Safe and Sustainable by Design work in practice. With a recommendation from Jürgen Tiedje of the European Commission.