

83 Qualitative Research Questions & Examples

Free Website Traffic Checker
Discover your competitors' strengths and leverage them to achieve your own success
Qualitative research questions help you understand consumer sentiment. They’re strategically designed to show organizations how and why people feel the way they do about a brand, product, or service. It looks beyond the numbers and is one of the most telling types of market research a company can do.
The UK Data Service describes this perfectly, saying, “The value of qualitative research is that it gives a voice to the lived experience .”
Read on to see seven use cases and 83 qualitative research questions, with the added bonus of examples that show how to get similar insights faster with Similarweb Research Intelligence.

What is a qualitative research question?
A qualitative research question explores a topic in-depth, aiming to better understand the subject through interviews, observations, and other non-numerical data. Qualitative research questions are open-ended, helping to uncover a target audience’s opinions, beliefs, and motivations.
How to choose qualitative research questions?
Choosing the right qualitative research questions can be incremental to the success of your research and the findings you uncover. Here’s my six-step process for choosing the best qualitative research questions.
- Start by understanding the purpose of your research. What do you want to learn? What outcome are you hoping to achieve?
- Consider who you are researching. What are their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs? How can you best capture these in your research questions ?
- Keep your questions open-ended . Qualitative research questions should not be too narrow or too broad. Aim to ask specific questions to provide meaningful answers but broad enough to allow for exploration.
- Balance your research questions. You don’t want all of your questions to be the same type. Aim to mix up your questions to get a variety of answers.
- Ensure your research questions are ethical and free from bias. Always have a second (and third) person check for unconscious bias.
- Consider the language you use. Your questions should be written in a way that is clear and easy to understand. Avoid using jargon , acronyms, or overly technical language.

Types of qualitative research questions
For a question to be considered qualitative, it usually needs to be open-ended. However, as I’ll explain, there can sometimes be a slight cross-over between quantitative and qualitative research questions.
Open-ended questions
These allow for a wide range of responses and can be formatted with multiple-choice answers or a free-text box to collect additional details. The next two types of qualitative questions are considered open questions, but each has its own style and purpose.
- Probing questions are used to delve deeper into a respondent’s thoughts, such as “Can you tell me more about why you feel that way?”
- Comparative questions ask people to compare two or more items, such as “Which product do you prefer and why?” These qualitative questions are highly useful for understanding brand awareness , competitive analysis , and more.
Closed-ended questions
These ask respondents to choose from a predetermined set of responses, such as “On a scale of 1-5, how satisfied are you with the new product?” While they’re traditionally quantitative, adding a free text box that asks for extra comments into why a specific rating was chosen will provide qualitative insights alongside their respective quantitative research question responses.
- Ranking questions get people to rank items in order of preference, such as “Please rank these products in terms of quality.” They’re advantageous in many scenarios, like product development, competitive analysis, and brand awareness.
- Likert scale questions ask people to rate items on a scale, such as “On a scale of 1-5, how satisfied are you with the new product?” Ideal for placement on websites and emails to gather quick, snappy feedback.
Qualitative research question examples
There are many applications of qualitative research and lots of ways you can put your findings to work for the success of your business. Here’s a summary of the most common use cases for qualitative questions and examples to ask.
Qualitative questions for identifying customer needs and motivations
These types of questions help you find out why customers choose products or services and what they are looking for when making a purchase.
- What factors do you consider when deciding to buy a product?
- What would make you choose one product or service over another?
- What are the most important elements of a product that you would buy?
- What features do you look for when purchasing a product?
- What qualities do you look for in a company’s products?
- Do you prefer localized or global brands when making a purchase?
- How do you determine the value of a product?
- What do you think is the most important factor when choosing a product?
- How do you decide if a product or service is worth the money?
- Do you have any specific expectations when purchasing a product?
- Do you prefer to purchase products or services online or in person?
- What kind of customer service do you expect when buying a product?
- How do you decide when it is time to switch to a different product?
- Where do you research products before you decide to buy?
- What do you think is the most important customer value when making a purchase?
Qualitative research questions to enhance customer experience
Use these questions to reveal insights into how customers interact with a company’s products or services and how those experiences can be improved.
- What aspects of our product or service do customers find most valuable?
- How do customers perceive our customer service?
- What factors are most important to customers when purchasing?
- What do customers think of our brand?
- What do customers think of our current marketing efforts?
- How do customers feel about the features and benefits of our product?
- How do customers feel about the price of our product or service?
- How could we improve the customer experience?
- What do customers think of our website or app?
- What do customers think of our customer support?
- What could we do to make our product or service easier to use?
- What do customers think of our competitors?
- What is your preferred way to access our site?
- How do customers feel about our delivery/shipping times?
- What do customers think of our loyalty programs?
Qualitative research question example for customer experience
- ♀️ Question: What is your preferred way to access our site?
- Insight sought: How mobile-dominant are consumers? Should you invest more in mobile optimization or mobile marketing?
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: While using this type of question is ideal if you have a large database to survey when placed on a site or sent to a limited customer list, it only gives you a point-in-time perspective from a limited group of people.
- A new approach: You can get better, broader insights quicker with Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence. To fully inform your research, you need to know preferences at the industry or market level.
- ⏰ Time to insight: 30 seconds
- ✅ How it’s done: Similarweb offers multiple ways to answer this question without going through a lengthy qualitative research process.
First, I’m going to do a website market analysis of the banking credit and lending market in the finance sector to get a clearer picture of industry benchmarks.
Here, I can view device preferences across any industry or market instantly. It shows me the device distribution for any country across any period. This clearly answers the question of how mobile dominate my target audience is , with 59.79% opting to access site via a desktop vs. 40.21% via mobile
I then use the trends section to show me the exact split between mobile and web traffic for each key player in my space. Let’s say I’m about to embark on a competitive campaign that targets customers of Chase and Bank of America ; I can see both their audiences are highly desktop dominant compared with others in their space .
Qualitative question examples for developing new products or services
Research questions like this can help you understand customer pain points and give you insights to develop products that meet those needs.
- What is the primary reason you would choose to purchase a product from our company?
- How do you currently use products or services that are similar to ours?
- Is there anything that could be improved with products currently on the market?
- What features would you like to see added to our products?
- How do you prefer to contact a customer service team?
- What do you think sets our company apart from our competitors?
- What other product or service offerings would like to see us offer?
- What type of information would help you make decisions about buying a product?
- What type of advertising methods are most effective in getting your attention?
- What is the biggest deterrent to purchasing products from us?
Qualitative research question example for service development
- ♀️ Question: What type of advertising methods are most effective in getting your attention?
- Insight sought: The marketing channels and/or content that performs best with a target audience .
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: When using qualitative research surveys to answer questions like this, the sample size is limited, and bias could be at play.
- A better approach: The most authentic insights come from viewing real actions and results that take place in the digital world. No questions or answers are needed to uncover this intel, and the information you seek is readily available in less than a minute.
- ⏰ Time to insight: 5 minutes
- ✅ How it’s done: There are a few ways to approach this. You can either take an industry-wide perspective or hone in on specific competitors to unpack their individual successes. Here, I’ll quickly show a snapshot with a whole market perspective.

Using the market analysis element of Similarweb Digital Intelligence, I select my industry or market, which I’ve kept as banking and credit. A quick click into marketing channels shows me which channels drive the highest traffic in my market. Taking direct traffic out of the equation, for now, I can see that referrals and organic traffic are the two highest-performing channels in this market.
Similarweb allows me to view the specific referral partners and pages across these channels.

Looking closely at referrals in this market, I’ve chosen chase.com and its five closest rivals . I select referrals in the channel traffic element of marketing channels. I see that Capital One is a clear winner, gaining almost 25 million visits due to referral partnerships.

Next, I get to see exactly who is referring traffic to Capital One and the total traffic share for each referrer. I can see the growth as a percentage and how that has changed, along with an engagement score that rates the average engagement level of that audience segment. This is particularly useful when deciding on which new referral partnerships to pursue.
Once I’ve identified the channels and campaigns that yield the best results, I can then use Similarweb to dive into the various ad creatives and content that have the greatest impact.

These ads are just a few of those listed in the creatives section from my competitive website analysis of Capital One. You can filter this list by the specific campaign, publishers, and ad networks to view those that matter to you most. You can also discover video ad creatives in the same place too.
In just five minutes ⏰
- I’ve captured audience loyalty statistics across my market
- Spotted the most competitive players
- Identified the marketing channels my audience is most responsive to
- I know which content and campaigns are driving the highest traffic volume
- I’ve created a target list for new referral partners and have been able to prioritize this based on results and engagement figures from my rivals
- I can see the types of creatives that my target audience is responding to, giving me ideas for ways to generate effective copy for future campaigns
Qualitative questions to determine pricing strategies
Companies need to make sure pricing stays relevant and competitive. Use these questions to determine customer perceptions on pricing and develop pricing strategies to maximize profits and reduce churn.
- How do you feel about our pricing structure?
- How does our pricing compare to other similar products?
- What value do you feel you get from our pricing?
- How could we make our pricing more attractive?
- What would be an ideal price for our product?
- Which features of our product that you would like to see priced differently?
- What discounts or deals would you like to see us offer?
- How do you feel about the amount you have to pay for our product?
Get Faster Answers to Qualitative Research Questions with Similarweb Today
Qualitative research question example for determining pricing strategies
- ♀️ Question: What discounts or deals would you like to see us offer?
- Insight sought: The promotions or campaigns that resonate with your target audience.
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: Consumers don’t always recall the types of ads or campaigns they respond to. Over time, their needs and habits change. Your sample size is limited to those you ask, leaving a huge pool of unknowns at play.
- A better approach: While qualitative insights are good to know, you get the most accurate picture of the highest-performing promotion and campaigns by looking at data collected directly from the web. These analytics are real-world, real-time, and based on the collective actions of many, instead of the limited survey group you approach. By getting a complete picture across an entire market, your decisions are better informed and more aligned with current market trends and behaviors.
- ✅ How it’s done: Similarweb’s Popular Pages feature shows the content, products, campaigns, and pages with the highest growth for any website. So, if you’re trying to unpack the successes of others in your space and find out what content resonates with a target audience, there’s a far quicker way to get answers to these questions with Similarweb.

Here, I’m using Capital One as an example site. I can see trending pages on their site showing the largest increase in page views. Other filters include campaign, best-performing, and new–each of which shows you page URLs, share of traffic, and growth as a percentage. This page is particularly useful for staying on top of trending topics , campaigns, and new content being pushed out in a market by key competitors.
Qualitative research questions for product development teams
It’s vital to stay in touch with changing consumer needs. These questions can also be used for new product or service development, but this time, it’s from the perspective of a product manager or development team.
- What are customers’ primary needs and wants for this product?
- What do customers think of our current product offerings?
- What is the most important feature or benefit of our product?
- How can we improve our product to meet customers’ needs better?
- What do customers like or dislike about our competitors’ products?
- What do customers look for when deciding between our product and a competitor’s?
- How have customer needs and wants for this product changed over time?
- What motivates customers to purchase this product?
- What is the most important thing customers want from this product?
- What features or benefits are most important when selecting a product?
- What do customers perceive to be our product’s pros and cons?
- What would make customers switch from a competitor’s product to ours?
- How do customers perceive our product in comparison to similar products?
- What do customers think of our pricing and value proposition?
- What do customers think of our product’s design, usability, and aesthetics?
Qualitative questions examples to understand customer segments
Market segmentation seeks to create groups of consumers with shared characteristics. Use these questions to learn more about different customer segments and how to target them with tailored messaging.
- What motivates customers to make a purchase?
- How do customers perceive our brand in comparison to our competitors?
- How do customers feel about our product quality?
- How do customers define quality in our products?
- What factors influence customers’ purchasing decisions ?
- What are the most important aspects of customer service?
- What do customers think of our customer service?
- What do customers think of our pricing?
- How do customers rate our product offerings?
- How do customers prefer to make purchases (online, in-store, etc.)?
Qualitative research question example for understanding customer segments
- ♀️ Question: Which social media channels are you most active on?
- Insight sought: Formulate a social media strategy . Specifically, the social media channels most likely to succeed with a target audience.
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: Qualitative research question responses are limited to those you ask, giving you a limited sample size. Questions like this are usually at risk of some bias, and this may not be reflective of real-world actions.
- A better approach: Get a complete picture of social media preferences for an entire market or specific audience belonging to rival firms. Insights are available in real-time, and are based on the actions of many, not a select group of participants. Data is readily available, easy to understand, and expandable at a moment’s notice.
- ✅ How it’s done: Using Similarweb’s website analysis feature, you can get a clear breakdown of social media stats for your audience using the marketing channels element. It shows the percentage of visits from each channel to your site, respective growth, and specific referral pages by each platform. All data is expandable, meaning you can select any platform, period, and region to drill down and get more accurate intel, instantly.

This example shows me Bank of America’s social media distribution, with YouTube , Linkedin , and Facebook taking the top three spots, and accounting for almost 80% of traffic being driven from social media.
When doing any type of market research, it’s important to benchmark performance against industry averages and perform a social media competitive analysis to verify rival performance across the same channels.
Qualitative questions to inform competitive analysis
Organizations must assess market sentiment toward other players to compete and beat rival firms. Whether you want to increase market share , challenge industry leaders , or reduce churn, understanding how people view you vs. the competition is key.
- What is the overall perception of our competitors’ product offerings in the market?
- What attributes do our competitors prioritize in their customer experience?
- What strategies do our competitors use to differentiate their products from ours?
- How do our competitors position their products in relation to ours?
- How do our competitors’ pricing models compare to ours?
- What do consumers think of our competitors’ product quality?
- What do consumers think of our competitors’ customer service?
- What are the key drivers of purchase decisions in our market?
- What is the impact of our competitors’ marketing campaigns on our market share ? 10. How do our competitors leverage social media to promote their products?
Qualitative research question example for competitive analysis
- ♀️ Question: What other companies do you shop with for x?
- Insight sought: W ho are your competitors? Which of your rival’s sites do your customers visit? How loyal are consumers in your market?
- Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: Sample size is limited, and customers could be unwilling to reveal which competitors they shop with, or how often they around. Where finances are involved, people can act with reluctance or bias, and be unwilling to reveal other suppliers they do business with.
- A better approach: Get a complete picture of your audience’s loyalty, see who else they shop with, and how many other sites they visit in your competitive group. Find out the size of the untapped opportunity and which players are doing a better job at attracting unique visitors – without having to ask people to reveal their preferences.
- ✅ How it’s done: Similarweb website analysis shows you the competitive sites your audience visits, giving you access to data that shows cross-visitation habits, audience loyalty, and untapped potential in a matter of minutes.

Using the audience interests element of Similarweb website analysis, you can view the cross-browsing behaviors of a website’s audience instantly. You can see a matrix that shows the percentage of visitors on a target site and any rival site they may have visited.

With the Similarweb audience overlap feature, view the cross-visitation habits of an audience across specific websites. In this example, I chose chase.com and its four closest competitors to review. For each intersection, you see the number of unique visitors and the overall proportion of each site’s audience it represents. It also shows the volume of unreached potential visitors.

Here, you can see a direct comparison of the audience loyalty represented in a bar graph. It shows a breakdown of each site’s audience based on how many other sites they have visited. Those sites with the highest loyalty show fewer additional sites visited.
From the perspective of chase.com, I can see 47% of their visitors do not visit rival sites. 33% of their audience visited 1 or more sites in this group, 14% visited 2 or more sites, 4% visited 3 or more sites, and just 0.8% viewed all sites in this comparison.
How to answer qualitative research questions with Similarweb
Similarweb Research Intelligence drastically improves market research efficiency and time to insight. Both of these can impact the bottom line and the pace at which organizations can adapt and flex when markets shift, and rivals change tactics.
Outdated practices, while still useful, take time . And with a quicker, more efficient way to garner similar insights, opting for the fast lane puts you at a competitive advantage.
With a birds-eye view of the actions and behaviors of companies and consumers across a market , you can answer certain research questions without the need to plan, do, and review extensive qualitative market research .
Wrapping up
Qualitative research methods have been around for centuries. From designing the questions to finding the best distribution channels, collecting and analyzing findings takes time to get the insights you need. Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence drastically improves efficiency and time to insight. Both of which impact the bottom line and the pace at which organizations can adapt and flex when markets shift.
Similarweb’s suite of digital intelligence solutions offers unbiased, accurate, honest insights you can trust for analyzing any industry, market, or audience.
- Methodologies used for data collection are robust, transparent, and trustworthy.
- Clear presentation of data via an easy-to-use, intuitive platform.
- It updates dynamically–giving you the freshest data about an industry or market.
- Data is available via an API – so you can plug into platforms like Tableau or PowerBI to streamline your analyses.
- Filter and refine results according to your needs.
Are quantitative or qualitative research questions best?
Both have their place and purpose in market research. Qualitative research questions seek to provide details, whereas quantitative market research gives you numerical statistics that are easier and quicker to analyze. You get more flexibility with qualitative questions, and they’re non-directional.
What are the advantages of qualitative research?
Qualitative research is advantageous because it allows researchers to better understand their subject matter by exploring people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations in a particular context. It also allows researchers to uncover new insights that may not have been discovered with quantitative research methods.
What are some of the challenges of qualitative research?
Qualitative research can be time-consuming and costly, typically involving in-depth interviews and focus groups. Additionally, there are challenges associated with the reliability and validity of the collected data, as there is no universal standard for interpreting the results.

by Liz March
Digital Research Specialist
Liz March has 15 years of experience in content creation. She enjoys the outdoors, F1, and reading, and is pursuing a BSc in Environmental Science.
Related Posts

What is Market Forecasting? The Art of Predicting Future Trends

How to Measure Mobile App Performance

Market Sizing: Measuring Your TAM, SAM, and SOM

Data-Driven Decision-Making: Unlocking Sustainable Success

Quantitative Market Research: A Guide + Examples

11 Benefits of Market Research + Free Templates
Track your digital metrics and grow market share.
Contact us to set up a call with a market research specialist
Qualitative Research Questions: Gain Powerful Insights + 25 Examples
We review the basics of qualitative research questions, including their key components, how to craft them effectively, & 25 example questions.
Einstein was many things—a physicist, a philosopher, and, undoubtedly, a mastermind. He also had an incredible way with words. His quote, "Everything that can be counted does not necessarily count; everything that counts cannot necessarily be counted," is particularly poignant when it comes to research.
Some inquiries call for a quantitative approach, for counting and measuring data in order to arrive at general conclusions. Other investigations, like qualitative research, rely on deep exploration and understanding of individual cases in order to develop a greater understanding of the whole. That’s what we’re going to focus on today.
Qualitative research questions focus on the "how" and "why" of things, rather than the "what". They ask about people's experiences and perceptions , and can be used to explore a wide range of topics.
The following article will discuss the basics of qualitative research questions, including their key components, and how to craft them effectively. You'll also find 25 examples of effective qualitative research questions you can use as inspiration for your own studies.
Let’s get started!
What are qualitative research questions, and when are they used?
When researchers set out to conduct a study on a certain topic, their research is chiefly directed by an overarching question . This question provides focus for the study and helps determine what kind of data will be collected.
By starting with a question, we gain parameters and objectives for our line of research. What are we studying? For what purpose? How will we know when we’ve achieved our goals?
Of course, some of these questions can be described as quantitative in nature. When a research question is quantitative, it usually seeks to measure or calculate something in a systematic way.
For example:
- How many people in our town use the library?
- What is the average income of families in our city?
- How much does the average person weigh?
Other research questions, however—and the ones we will be focusing on in this article—are qualitative in nature. Qualitative research questions are open-ended and seek to explore a given topic in-depth.
According to the Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry , “Qualitative research aims to address questions concerned with developing an understanding of the meaning and experience dimensions of humans’ lives and social worlds.”
This type of research can be used to gain a better understanding of people’s thoughts, feelings and experiences by “addressing questions beyond ‘what works’, towards ‘what works for whom when, how and why, and focusing on intervention improvement rather than accreditation,” states one paper in Neurological Research and Practice .
Qualitative questions often produce rich data that can help researchers develop hypotheses for further quantitative study.
- What are people’s thoughts on the new library?
- How does it feel to be a first-generation student at our school?
- How do people feel about the changes taking place in our town?
As stated by a paper in Human Reproduction , “...‘qualitative’ methods are used to answer questions about experience, meaning, and perspective, most often from the standpoint of the participant. These data are usually not amenable to counting or measuring.”
Both quantitative and qualitative questions have their uses; in fact, they often complement each other. A well-designed research study will include a mix of both types of questions in order to gain a fuller understanding of the topic at hand.
If you would like to recruit unlimited participants for qualitative research for free and only pay for the interview you conduct, try using Respondent today.
Crafting qualitative research questions for powerful insights
Now that we have a basic understanding of what qualitative research questions are and when they are used, let’s take a look at how you can begin crafting your own.
According to a study in the International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education, there is a certain process researchers should follow when crafting their questions, which we’ll explore in more depth.
1. Beginning the process
Start with a point of interest or curiosity, and pose a draft question or ‘self-question’. What do you want to know about the topic at hand? What is your specific curiosity? You may find it helpful to begin by writing several questions.
For example, if you’re interested in understanding how your customer base feels about a recent change to your product, you might ask:
- What made you decide to try the new product?
- How do you feel about the change?
- What do you think of the new design/functionality?
- What benefits do you see in the change?
2. Create one overarching, guiding question
At this point, narrow down the draft questions into one specific question. “Sometimes, these broader research questions are not stated as questions, but rather as goals for the study.”
As an example of this, you might narrow down these three questions:
into the following question:
- What are our customers’ thoughts on the recent change to our product?
3. Theoretical framing
As you read the relevant literature and apply theory to your research, the question should be altered to achieve better outcomes. Experts agree that pursuing a qualitative line of inquiry should open up the possibility for questioning your original theories and altering the conceptual framework with which the research began.
If we continue with the current example, it’s possible you may uncover new data that informs your research and changes your question. For instance, you may discover that customers’ feelings about the change are not just a reaction to the change itself, but also to how it was implemented. In this case, your question would need to reflect this new information:
- How did customers react to the process of the change, as well as the change itself?
4. Ethical considerations
A study in the International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education stresses that ethics are “a central issue when a researcher proposes to study the lives of others, especially marginalized populations.” Consider how your question or inquiry will affect the people it relates to—their lives and their safety. Shape your question to avoid physical, emotional, or mental upset for the focus group.
In analyzing your question from this perspective, if you feel that it may cause harm, you should consider changing the question or ending your research project. Perhaps you’ve discovered that your question encourages harmful or invasive questioning, in which case you should reformulate it.
5. Writing the question
The actual process of writing the question comes only after considering the above points. The purpose of crafting your research questions is to delve into what your study is specifically about” Remember that qualitative research questions are not trying to find the cause of an effect, but rather to explore the effect itself.
Your questions should be clear, concise, and understandable to those outside of your field. In addition, they should generate rich data. The questions you choose will also depend on the type of research you are conducting:
- If you’re doing a phenomenological study, your questions might be open-ended, in order to allow participants to share their experiences in their own words.
- If you’re doing a grounded-theory study, your questions might be focused on generating a list of categories or themes.
- If you’re doing ethnography, your questions might be about understanding the culture you’re studying.
Whenyou have well-written questions, it is much easier to develop your research design and collect data that accurately reflects your inquiry.
In writing your questions, it may help you to refer to this simple flowchart process for constructing questions:
Download Free E-Book
25 examples of expertly crafted qualitative research questions
It's easy enough to cover the theory of writing a qualitative research question, but sometimes it's best if you can see the process in practice. In this section, we'll list 25 examples of B2B and B2C-related qualitative questions.
Let's begin with five questions. We'll show you the question, explain why it's considered qualitative, and then give you an example of how it can be used in research.
1. What is the customer's perception of our company's brand?
Qualitative research questions are often open-ended and invite respondents to share their thoughts and feelings on a subject. This question is qualitative because it seeks customer feedback on the company's brand.
This question can be used in research to understand how customers feel about the company's branding, what they like and don't like about it, and whether they would recommend it to others.
2. Why do customers buy our product?
This question is also qualitative because it seeks to understand the customer's motivations for purchasing a product. It can be used in research to identify the reasons customers buy a certain product, what needs or desires the product fulfills for them, and how they feel about the purchase after using the product.
3. How do our customers interact with our products?
Again, this question is qualitative because it seeks to understand customer behavior. In this case, it can be used in research to see how customers use the product, how they interact with it, and what emotions or thoughts the product evokes in them.
4. What are our customers' biggest frustrations with our products?
By seeking to understand customer frustrations, this question is qualitative and can provide valuable insights. It can be used in research to help identify areas in which the company needs to make improvements with its products.
5. How do our customers feel about our customer service?
Rather than asking why customers like or dislike something, this question asks how they feel. This qualitative question can provide insights into customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction with a company.
This type of question can be used in research to understand what customers think of the company's customer service and whether they feel it meets their needs.
20 more examples to refer to when writing your question
Now that you’re aware of what makes certain questions qualitative, let's move into 20 more examples of qualitative research questions:
- How do your customers react when updates are made to your app interface?
- How do customers feel when they complete their purchase through your ecommerce site?
- What are your customers' main frustrations with your service?
- How do people feel about the quality of your products compared to those of your competitors?
- What motivates customers to refer their friends and family members to your product or service?
- What are the main benefits your customers receive from using your product or service?
- How do people feel when they finish a purchase on your website?
- What are the main motivations behind customer loyalty to your brand?
- How does your app make people feel emotionally?
- For younger generations using your app, how does it make them feel about themselves?
- What reputation do people associate with your brand?
- How inclusive do people find your app?
- In what ways are your customers' experiences unique to them?
- What are the main areas of improvement your customers would like to see in your product or service?
- How do people feel about their interactions with your tech team?
- What are the top five reasons people use your online marketplace?
- How does using your app make people feel in terms of connectedness?
- What emotions do people experience when they're using your product or service?
- Aside from the features of your product, what else about it attracts customers?
- How does your company culture make people feel?
As you can see, these kinds of questions are completely open-ended. In a way, they allow the research and discoveries made along the way to direct the research. The questions are merely a starting point from which to explore.
This video offers tips on how to write good qualitative research questions, produced by Qualitative Research Expert, Kimberly Baker.
Wrap-up: crafting your own qualitative research questions.
Over the course of this article, we've explored what qualitative research questions are, why they matter, and how they should be written. Hopefully you now have a clear understanding of how to craft your own.
Remember, qualitative research questions should always be designed to explore a certain experience or phenomena in-depth, in order to generate powerful insights. As you write your questions, be sure to keep the following in mind:
- Are you being inclusive of all relevant perspectives?
- Are your questions specific enough to generate clear answers?
- Will your questions allow for an in-depth exploration of the topic at hand?
- Do the questions reflect your research goals and objectives?
If you can answer "yes" to all of the questions above, and you've followed the tips for writing qualitative research questions we shared in this article, then you're well on your way to crafting powerful queries that will yield valuable insights.
Download Free E-Book
.png?width=2500&name=Respondent_100+Questions_Banners_1200x644%20(1).png)
Asking the right questions in the right way is the key to research success. That’s true for not just the discussion guide but for every step of a research project. Following are 100+ questions that will take you from defining your research objective through screening and participant discussions.
Fill out the form below to access free e-book!
Recommend Resources:
- How to Recruit Participants for Qualitative Research
- The Best UX Research Tools of 2022
- 10 Smart Tips for Conducting Better User Interviews
- 50 Powerful Questions You Should Ask In Your Next User Interview
- How To Find Participants For User Research: 13 Ways To Make It Happen
- UX Diary Study: 5 Essential Tips For Conducing Better Studies
- User Testing Recruitment: 10 Smart Tips To Find Participants Fast
- Qualitative Research Questions: Gain Powerful Insights + 25
- How To Successfully Recruit Participants for A Study (2022 Edition)
- How To Properly Recruit Focus Group Participants (2022 Edition)
- The Best Unmoderated Usability Testing Tools of 2022
50 Powerful User Interview Questions You Should Consider Asking
We researched the best user interview questions you can use for your qualitative research studies. Use these 50 sample questions for your next...
A Guide to Usability Testing Questions (Including 100 Examples)
Asking the right questions in the right way is the key to the success of your UX research project. With tips and 100+ question examples, Respondent...
Understanding Why High-Quality Research Needs High-Quality Participants
Why are high-quality participants essential to your research? Read here to find out who they are, why you need them, and how to find them.
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Qualitative Research
- Qualitative Research Questions
Try Qualtrics for free
How to write qualitative research questions.
11 min read Here’s how to write effective qualitative research questions for your projects, and why getting it right matters so much.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a blanket term covering a wide range of research methods and theoretical framing approaches. The unifying factor in all these types of qualitative study is that they deal with data that cannot be counted. Typically this means things like people’s stories, feelings, opinions and emotions , and the meanings they ascribe to their experiences.
Qualitative study is one of two main categories of research, the other being quantitative research. Quantitative research deals with numerical data – that which can be counted and quantified, and which is mostly concerned with trends and patterns in large-scale datasets.
What are research questions?
Research questions are questions you are trying to answer with your research. To put it another way, your research question is the reason for your study, and the beginning point for your research design. There is normally only one research question per study, although if your project is very complex, you may have multiple research questions that are closely linked to one central question.
A good qualitative research question sums up your research objective. It’s a way of expressing the central question of your research, identifying your particular topic and the central issue you are examining.
Research questions are quite different from survey questions, questions used in focus groups or interview questions. A long list of questions is used in these types of study, as opposed to one central question. Additionally, interview or survey questions are asked of participants, whereas research questions are only for the researcher to maintain a clear understanding of the research design.
Research questions are used in both qualitative and quantitative research , although what makes a good research question might vary between the two.
In fact, the type of research questions you are asking can help you decide whether you need to take a quantitative or qualitative approach to your research project.
Discover the fundamentals of qualitative research
Quantitative vs. qualitative research questions
Writing research questions is very important in both qualitative and quantitative research, but the research questions that perform best in the two types of studies are quite different.
Quantitative research questions
Quantitative research questions usually relate to quantities, similarities and differences.
It might reflect the researchers’ interest in determining whether relationships between variables exist, and if so whether they are statistically significant. Or it may focus on establishing differences between things through comparison, and using statistical analysis to determine whether those differences are meaningful or due to chance.
- How much? This kind of research question is one of the simplest. It focuses on quantifying something. For example:
How many Yoruba speakers are there in the state of Maine?
- What is the connection?
This type of quantitative research question examines how one variable affects another.
For example:
How does a low level of sunlight affect the mood scores (1-10) of Antarctic explorers during winter?
- What is the difference? Quantitative research questions in this category identify two categories and measure the difference between them using numerical data.
Do white cats stay cooler than tabby cats in hot weather?
If your research question fits into one of the above categories, you’re probably going to be doing a quantitative study.
Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions focus on exploring phenomena, meanings and experiences.
Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research isn’t about finding causal relationships between variables. So although qualitative research questions might touch on topics that involve one variable influencing another, or looking at the difference between things, finding and quantifying those relationships isn’t the primary objective.
In fact, you as a qualitative researcher might end up studying a very similar topic to your colleague who is doing a quantitative study, but your areas of focus will be quite different. Your research methods will also be different – they might include focus groups, ethnography studies, and other kinds of qualitative study.
A few example qualitative research questions:
- What is it like being an Antarctic explorer during winter?
- What are the experiences of Yoruba speakers in the USA?
- How do white cat owners describe their pets?
Qualitative research question types
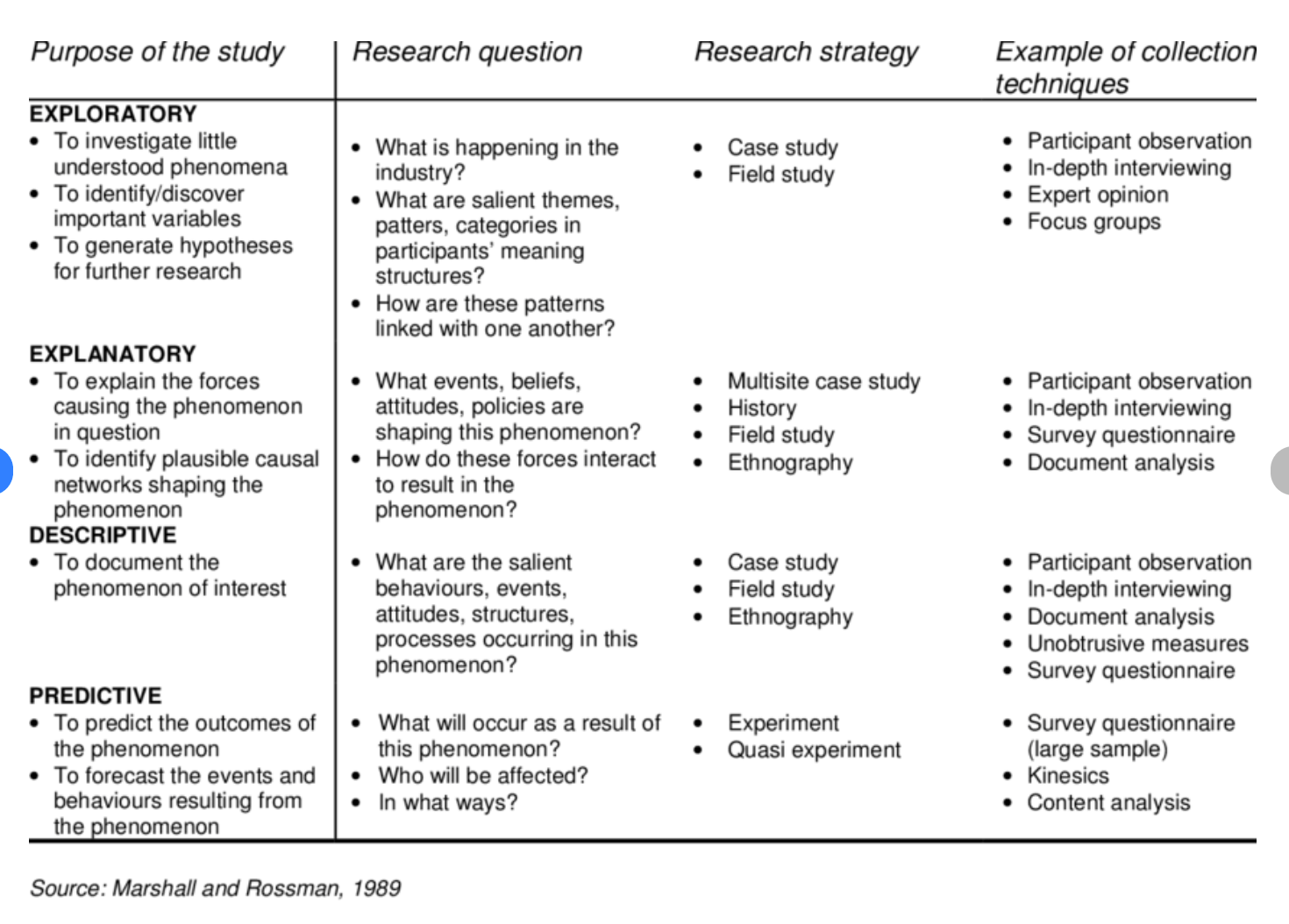
Marshall and Rossman (1989) identified 4 qualitative research question types, each with its own typical research strategy and methods.
- Exploratory questions
Exploratory questions are used when relatively little is known about the research topic. The process researchers follow when pursuing exploratory questions might involve interviewing participants, holding focus groups, or diving deep with a case study.
- Explanatory questions
With explanatory questions, the research topic is approached with a view to understanding the causes that lie behind phenomena. However, unlike a quantitative project, the focus of explanatory questions is on qualitative analysis of multiple interconnected factors that have influenced a particular group or area, rather than a provable causal link between dependent and independent variables.
- Descriptive questions
As the name suggests, descriptive questions aim to document and record what is happening. In answering descriptive questions , researchers might interact directly with participants with surveys or interviews, as well as using observational studies and ethnography studies that collect data on how participants interact with their wider environment.
- Predictive questions
Predictive questions start from the phenomena of interest and investigate what ramifications it might have in the future. Answering predictive questions may involve looking back as well as forward, with content analysis, questionnaires and studies of non-verbal communication (kinesics).
Why are good qualitative research questions important?
We know research questions are very important. But what makes them so essential? (And is that question a qualitative or quantitative one?)
Getting your qualitative research questions right has a number of benefits.
- It defines your qualitative research project Qualitative research questions definitively nail down the research population, the thing you’re examining, and what the nature of your answer will be.This means you can explain your research project to other people both inside and outside your business or organization. That could be critical when it comes to securing funding for your project, recruiting participants and members of your research team, and ultimately for publishing your results. It can also help you assess right the ethical considerations for your population of study.
- It maintains focus Good qualitative research questions help researchers to stick to the area of focus as they carry out their research. Keeping the research question in mind will help them steer away from tangents during their research or while they are carrying out qualitative research interviews. This holds true whatever the qualitative methods are, whether it’s a focus group, survey, thematic analysis or other type of inquiry.That doesn’t mean the research project can’t morph and change during its execution – sometimes this is acceptable and even welcome – but having a research question helps demarcate the starting point for the research. It can be referred back to if the scope and focus of the project does change.
- It helps make sure your outcomes are achievable
Because qualitative research questions help determine the kind of results you’re going to get, it helps make sure those results are achievable. By formulating good qualitative research questions in advance, you can make sure the things you want to know and the way you’re going to investigate them are grounded in practical reality. Otherwise, you may be at risk of taking on a research project that can’t be satisfactorily completed.
Developing good qualitative research questions
All researchers use research questions to define their parameters, keep their study on track and maintain focus on the research topic. This is especially important with qualitative questions, where there may be exploratory or inductive methods in use that introduce researchers to new and interesting areas of inquiry. Here are some tips for writing good qualitative research questions.
1. Keep it specific
Broader research questions are difficult to act on. They may also be open to interpretation, or leave some parameters undefined.
Strong example: How do Baby Boomers in the USA feel about their gender identity?
Weak example: Do people feel different about gender now?
2. Be original
Look for research questions that haven’t been widely addressed by others already.
Strong example: What are the effects of video calling on women’s experiences of work?
Weak example: Are women given less respect than men at work?
3. Make it research-worthy
Don’t ask a question that can be answered with a ‘yes’ or ‘no’, or with a quick Google search.
Strong example: What do people like and dislike about living in a highly multi-lingual country?
Weak example: What languages are spoken in India?
4. Focus your question
Don’t roll multiple topics or questions into one. Qualitative data may involve multiple topics, but your qualitative questions should be focused.
Strong example: What is the experience of disabled children and their families when using social services?
Weak example: How can we improve social services for children affected by poverty and disability?
4. Focus on your own discipline, not someone else’s
Avoid asking questions that are for the politicians, police or others to address.
Strong example: What does it feel like to be the victim of a hate crime?
Weak example: How can hate crimes be prevented?
5. Ask something researchable
Big questions, questions about hypothetical events or questions that would require vastly more resources than you have access to are not useful starting points for qualitative studies. Qualitative words or subjective ideas that lack definition are also not helpful.
Strong example: How do perceptions of physical beauty vary between today’s youth and their parents’ generation?
Weak example: Which country has the most beautiful people in it?
Related resources
Qualitative research design 11 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, business research methods 12 min read, mixed methods research 17 min read, market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- User Experience (UX) Testing User Interface (UI) Testing Ecommerce Testing Remote Usability Testing About the company ' data-html="true"> Why Trymata
- Usability testing
Run remote usability tests on any digital product to deep dive into your key user flows
- Product analytics
Learn how users are behaving on your website in real time and uncover points of frustration
- Research repository
A tool for collaborative analysis of qualitative data and for building your research repository and database.
See an example
- Trymata Blog
How-to articles, expert tips, and the latest news in user testing & user experience
- Knowledge Hub
Detailed explainers of Trymata’s features & plans, and UX research terms & topics
Visit Knowledge Hub
- Plans & Pricing
Get paid to test
- User Experience (UX) testing
- User Interface (UI) testing
- Ecommerce testing
- Remote usability testing
- Plans & Pricing
- Customer Stories
How do you want to use Trymata?
Conduct user testing, desktop usability video.
You’re on a business trip in Oakland, CA. You've been working late in downtown and now you're looking for a place nearby to grab a late dinner. You decided to check Zomato to try and find somewhere to eat. (Don't begin searching yet).
- Look around on the home page. Does anything seem interesting to you?
- How would you go about finding a place to eat near you in Downtown Oakland? You want something kind of quick, open late, not too expensive, and with a good rating.
- What do the reviews say about the restaurant you've chosen?
- What was the most important factor for you in choosing this spot?
- You're currently close to the 19th St Bart station, and it's 9PM. How would you get to this restaurant? Do you think you'll be able to make it before closing time?
- Your friend recommended you to check out a place called Belly while you're in Oakland. Try to find where it is, when it's open, and what kind of food options they have.
- Now go to any restaurant's page and try to leave a review (don't actually submit it).
What was the worst thing about your experience?
It was hard to find the bart station. The collections not being able to be sorted was a bit of a bummer
What other aspects of the experience could be improved?
Feedback from the owners would be nice
What did you like about the website?
The flow was good, lots of bright photos
What other comments do you have for the owner of the website?
I like that you can sort by what you are looking for and i like the idea of collections
You're going on a vacation to Italy next month, and you want to learn some basic Italian for getting around while there. You decided to try Duolingo.
- Please begin by downloading the app to your device.
- Choose Italian and get started with the first lesson (stop once you reach the first question).
- Now go all the way through the rest of the first lesson, describing your thoughts as you go.
- Get your profile set up, then view your account page. What information and options are there? Do you feel that these are useful? Why or why not?
- After a week in Italy, you're going to spend a few days in Austria. How would you take German lessons on Duolingo?
- What other languages does the app offer? Do any of them interest you?
I felt like there could have been a little more of an instructional component to the lesson.
It would be cool if there were some feature that could allow two learners studying the same language to take lessons together. I imagine that their screens would be synced and they could go through lessons together and chat along the way.
Overall, the app was very intuitive to use and visually appealing. I also liked the option to connect with others.
Overall, the app seemed very helpful and easy to use. I feel like it makes learning a new language fun and almost like a game. It would be nice, however, if it contained more of an instructional portion.
All accounts, tests, and data have been migrated to our new & improved system!
Use the same email and password to log in:
Legacy login: Our legacy system is still available in view-only mode, login here >
What’s the new system about? Read more about our transition & what it-->
25 Essential Qualitative Research Questions with Context
- Health and Well-being:
Question: How do individuals with chronic illnesses perceive and manage their overall well-being?
Context: This question aims to explore the subjective experiences of individuals living with chronic illnesses, focusing on their perceptions of well-being and the strategies they employ to manage their health.
Question: What are the experiences of teachers implementing project-based learning in high school science classrooms?
Context: This question delves into the qualitative aspects of teaching practices, seeking to understand the lived experiences of teachers as they implement a specific instructional approach (project-based learning) in a particular academic context (high school science classrooms).
Question: How do marginalized communities perceive and navigate social inclusion in urban environments?
Context: This question addresses the sociological dimensions of social inclusion within urban settings, focusing on the perspectives and strategies of marginalized communities as they navigate societal structures.
- Psychology:
Question: What are the coping mechanisms employed by individuals facing post-traumatic stress disorder?
Context: This question explores the psychological experiences of individuals dealing with post-traumatic stress disorder, aiming to uncover the qualitative aspects of coping strategies and mechanisms.
- Anthropology:
Question: How does a specific cultural group express identity through traditional rituals and ceremonies?
Context: This anthropological question focuses on cultural practices and rituals as expressions of identity within a specific cultural group, aiming to uncover the meanings and functions of these traditions.
- Gender Studies:
Question: What are the lived experiences of transgender individuals in the workplace, particularly regarding inclusion and discrimination?
Context: This question within gender studies explores the qualitative dimensions of transgender individuals’ workplace experiences, emphasizing the nuanced aspects of inclusion and discrimination they may encounter.
- Environmental Studies:
Question: How do local communities perceive and respond to environmental conservation efforts in their region?
Context: This question addresses the intersection of environmental studies and sociology, aiming to understand the qualitative perspectives of local communities toward conservation initiatives, exploring their perceptions and responses.
- Business and Management:
Question: How do employees perceive leadership styles and their impact on workplace culture?
Context: Within the realm of business and management, this question explores the qualitative aspects of organizational culture, focusing on employees’ perceptions of leadership styles and their influence on the workplace environment.
- Technology and Society:
Question: What are the social implications and user experiences of emerging technologies in the context of augmented reality applications?
Context: This question within the field of technology and society investigates the qualitative dimensions of user experiences and social implications related to the adoption of augmented reality applications.
- Communication Studies:
Question: How do individuals from diverse cultural backgrounds interpret and respond to media representations of body image?
Context: This question explores the intersection of communication studies and cultural studies, aiming to understand the qualitative variations in how individuals from diverse cultural backgrounds interpret and respond to media depictions of body image.
- Political Science:
Question: What are the public perceptions and attitudes toward government policies on climate change?
Context: Within political science, this question delves into the qualitative aspects of public opinion, seeking to understand how individuals perceive and respond to government policies related to climate change.
- Cultural Studies:
Question: How do international students experience acculturation and adaptation in a foreign academic environment?
Context: This question within cultural studies explores the qualitative dimensions of acculturation and adaptation, focusing on the experiences of international students within the context of a foreign academic environment.
- Family Studies:
Question: How do families navigate and negotiate roles and responsibilities in the context of remote work?
Context: In the domain of family studies, this question addresses the qualitative aspects of family dynamics, examining how families navigate and negotiate roles and responsibilities in the context of remote work.
- Public Health:
Question: How do community members perceive and engage with public health campaigns aimed at promoting vaccination in underserved urban areas?
Context: This public health question investigates the qualitative aspects of community perceptions and engagement with vaccination campaigns, particularly in urban areas with limited access to healthcare resources.
- Urban Planning:
Question: What are the experiences of residents in gentrifying neighborhoods regarding changes in their community dynamics, affordability, and social cohesion?
Context: Within urban planning, this question explores the qualitative dimensions of gentrification, focusing on residents’ lived experiences and perceptions of neighborhood transformations.
- Literature and Cultural Criticism:
Question: How do contemporary authors use literature to critique and challenge societal norms around gender roles and identity?
Context: In the realm of literature and cultural criticism, this question examines the qualitative dimensions of literary works, exploring how authors use their craft to challenge and critique societal norms related to gender.
- Social Work:
Question: What are the perceptions of social workers regarding the challenges and opportunities in providing mental health support to homeless populations?
Context: This social work question addresses the qualitative aspects of mental health support within homeless populations, exploring social workers’ perspectives on challenges and opportunities in their roles.
- Tourism and Hospitality:
Question: How do tourists from different cultural backgrounds experience and interpret authenticity in local culinary traditions?
Context: Within tourism and hospitality, this question explores the qualitative aspects of cultural experiences, focusing on tourists’ perceptions and interpretations of authenticity in local culinary traditions.
- Media and Entertainment:
Question: How do audiences engage with and interpret representations of diverse identities in streaming platforms’ original content?
Context: In the realm of media and entertainment, this question investigates the qualitative dimensions of audience engagement and interpretation of diverse identities in content produced by streaming platforms.
- Historical Studies:
Question: What are the narratives and memories of individuals who lived through a significant historical event, and how have these narratives evolved over time?
Context: Within historical studies, this question explores the qualitative aspects of personal narratives and memory, investigating how individuals recall and frame their experiences of a significant historical event.
- Linguistics:
Question: How do multilingual individuals navigate language use and identity in diverse linguistic environments?
Context: In the field of linguistics, this question delves into the qualitative dimensions of language use and identity, focusing on how multilingual individuals navigate linguistic diversity in their environments.
- Cybersecurity:
Question: What are the perceptions and behaviors of employees in organizations regarding cybersecurity practices, and how do these perceptions influence organizational security?
Context: Within cybersecurity, this question explores the qualitative aspects of employees’ perceptions and behaviors related to cybersecurity practices, examining their impact on organizational security.
- Human-Computer Interaction:
Question: How do users experience and adapt to voice-controlled virtual assistants in their daily lives, considering factors such as privacy concerns and usability?
Context: In human-computer interaction, this question investigates the qualitative aspects of user experiences with voice-controlled virtual assistants, considering factors such as privacy concerns and usability challenges.
- International Development:
Question: How do local communities perceive and negotiate the impacts of international development projects on their cultural and economic landscapes?
Context: This international development question explores the qualitative dimensions of community perceptions and negotiations regarding the impacts of international development projects, considering cultural and economic factors.
- Sport Psychology:
Question: What are the psychological experiences and coping mechanisms of athletes during periods of extended competition hiatus, such as the postponement of major sporting events?
Context: In sport psychology, this question delves into the qualitative aspects of athletes’ psychological experiences and coping mechanisms during extended competition hiatus, such as the postponement of major sporting events.
These additional detailed examples provide a broader perspective on qualitative research questions, covering diverse fields of study and highlighting the nuanced inquiries within each domain.
Qualitative Research Vs Quantitative Research: Key Comparisons
Conduct End-to-End User Testing & Research
Interested in learning more about the fields of product, research, and design? Search our articles here for helpful information spanning a wide range of topics!
Five Second Test: An Essential Guide for Quick UX Insights
Customer onboarding: using usability tests for success, why empathy gap impact usability testing outcomes, deceptive patterns: what are they, how to identify & avoid them.
- (855) 776-7763
Training Maker
All Products
Qualaroo Insights
ProProfs.com
- Get Started Free
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!
How to Write Qualitative Research Questions: Types & Examples

Market Research Specialist
Emma David, a seasoned market research professional, specializes in employee engagement, survey administration, and data management. Her expertise in leveraging data for informed decisions has positively impacted several brands, enhancing their market position.
Qualitative research questions focus on depth and quality, exploring the “why and how” behind decisions, without relying on statistical tools.
Unlike quantitative research, which aims to collect tangible, measurable data from a broader demographic, qualitative analysis involves smaller, focused datasets, identifying patterns for insights.
The information collected by qualitative surveys can vary from text to images, demanding a deep understanding of the subject, and therefore, crafting precise qualitative research questions is crucial for success.
In this guide, we’ll discuss how to write effective qualitative research questions, explore various types, and highlight characteristics of good qualitative research questions.
Let’s dive in!
What Are Qualitative Research Questions?
Qualitative questions aim to understand the depth and nuances of a phenomenon, focusing on “why” and “how” rather than quantifiable measures.
They explore subjective experiences, perspectives, and behaviors, often using open-ended inquiries to gather rich, descriptive data.
Unlike quantitative questions, which seek numerical data, qualitative questions try to find out meanings, patterns, and underlying processes within a specific context.
These questions are essential for exploring complex issues, generating hypotheses, and gaining deeper insights into human behavior and phenomena.
Here’s an example of a qualitative research question:
“How do you perceive and navigate organizational culture within a tech startup environment?”
This question asks about the respondent’s subjective interpretations and experiences of organizational culture within a specific context, such as a tech startup.
It seeks to uncover insights into the values, norms, and practices that shape workplace dynamics and employee behaviors, providing qualitative data for analysis and understanding.
When Should We Use Qualitative Research Questions?
Qualitative research questions typically aim to open up conversations, encourage detailed narratives, and foster a deep understanding of the subject matter. Here are some scenarios they are best suited for:
- Exploring Complex Phenomena : When the research topic involves understanding complex processes, behaviors, or interactions that cannot be quantified easily, qualitative questions help delve into these intricate details.
- Understanding Contexts and Cultures : To grasp the nuances of different social contexts, cultures, or subcultures, qualitative research questions allow for an in-depth exploration of these environments and how they influence individuals and groups.
- Exploring Perceptions and Experiences : When the aim is to understand people’s perceptions, experiences, or feelings about a particular subject, qualitative questions facilitate capturing the depth and variety of these perspectives.
- Developing Concepts or Theories : In the early stages of research, where concepts or theories are not yet well-developed, qualitative questions can help generate hypotheses, identify variables, and develop theoretical frameworks based on observations and interpretations.
- Investigating Processes : To understand how processes unfold over time and the factors that influence these processes, qualitative questions are useful for capturing the dynamics and complexities involved.
- Seeking to Understand Change : When researching how individuals or groups experience change, adapt to new circumstances, or make decisions, qualitative research questions can provide insights into the motivations, challenges, and strategies involved.
- Studying Phenomena Not Easily Quantified : For phenomena that are not easily captured through quantitative measures, such as emotions, beliefs, or motivations, qualitative questions can probe these abstract concepts more effectively.
- Addressing Sensitive or Taboo Topics : In studies where topics may be sensitive, controversial, or taboo, qualitative research questions allow for a respectful and empathetic exploration of these subjects, providing space for participants to share their experiences in their own words.
How to Write Qualitative Research Questions?
Read this guide to learn how you can craft well-thought-out qualitative research questions:
1. Begin with Your Research Goals
The first step in formulating qualitative research questions is to have a clear understanding of what you aim to discover or understand through your research. There are two types of qualitative questionnaires or research – Ontological and Epistemological.
Finding out the nature of your research influences all aspects of your research design, including the formulation of research questions.
Subsequently:
- Identify your main objective : Consider the broader context of your study. Are you trying to explore a phenomenon, understand a process, or interpret the meanings behind behaviors? Your main objective should guide the formulation of your questions, ensuring they are aligned with what you seek to achieve.
- Focus on the ‘how’ and ‘why’ : Qualitative research is inherently exploratory and aims to understand the nuances of human behavior and experience. Starting your questions with “how” or “why” encourages a deeper investigation into the motivations, processes, and contexts underlying the subject matter. This approach facilitates an open-ended exploration, allowing participants to provide rich, detailed responses that illuminate their perspectives and experiences.
Take a quick look at the following visual for a better understanding:

So, if you are doing Ontological research, ensure that the questions focus on the “what” aspects of reality (the premise of your research) and opt for the nature of the knowledge for Epistemological research.
2. Choose the Right Structure
The structure of your research questions significantly impacts the depth and quality of data you collect. Opting for an open-ended format allows respondents the flexibility to express themselves freely, providing insights that pre-defined answers might miss.
- Open-ended format : These questions do not constrain respondents to a set of predetermined answers, unlike closed-ended questions. By allowing participants to articulate their thoughts in their own words, you can uncover nuances and complexities in their responses that might otherwise be overlooked.
- Avoid yes/no questions : Yes/no questions tend to limit the depth of responses. While they might be useful for gathering straightforward factual information, they are not conducive to exploring the depths and nuances that qualitative research seeks to uncover. Encouraging participants to elaborate on their experiences and perspectives leads to richer, more informative data.
For example, take a look at some qualitative questions examples shown in the following image:

3. Be Clear and Specific
Clarity and specificity in your questions are crucial to ensure that participants understand what is being asked and that their responses are relevant to your research objectives.
- Use clear language : Use straightforward, understandable language in your questions. Avoid jargon, acronyms, or overly technical terms that might confuse participants or lead to misinterpretation. The goal is to make your questions accessible to everyone involved in your study.
- Be specific : While maintaining the open-ended nature of qualitative questions, it’s important to narrow down your focus to specific aspects of the phenomenon you’re studying. This specificity helps guide participants’ responses and ensures that the data you collect directly relates to your research objectives.
4. Ensure Relevance and Feasibility
Each question should be carefully considered for its relevance to your research goals and its feasibility, given the constraints of your study.
- Relevance : Questions should be crafted to address the core objectives of your research directly. They should probe areas that are essential to understanding the phenomenon under investigation and should align with your theoretical framework or literature review findings.
- Feasibility : Consider the practical aspects of your research, including the time available for data collection and analysis, resources, and access to participants. Questions should be designed to elicit meaningful responses within the constraints of your study, ensuring that you can gather and analyze data effectively.
5. Focus on a Single Concept or Theme per Question
To ensure clarity and depth, each question should concentrate on a single idea or theme. However, if your main qualitative research question is tough to understand or has a complex structure, you can create sub-questions in limited numbers and with a “ladder structure”.
This will help your respondents understand the overall research objective in mind, and your research can be executed in a better manner.
For example, suppose your main question is – “What is the current state of illiteracy in your state?”
Then, you can create the following subquestions:
“How does illiteracy block progress in your state?”
“How would you best describe the feelings you have about illiteracy in your state?”
For an even better understanding, you can see the various qualitative research question examples in the following image:
💡 Tips for Refinement:
📊 Pilot your questions : Test them with a small group similar to your study population to ensure they are understood as intended and elicit the kind of responses you are seeking.
📝Be flexible : Be prepared to refine your questions based on pilot feedback or as your understanding of the topic deepens.
Types of Qualitative Research Questions With Examples
Qualitative survey questions primarily focus on a specific group of respondents that are participating in case studies, surveys, ethnography studies, etc., rather than numbers or statistics.
As a result, the questions are mostly open-ended and can be subdivided into the following types as discussed below:
1. Descriptive Questions
Descriptive research questions aim to detail the “what” of a phenomenon, providing a comprehensive overview of the context, individuals, or situations under study. These questions are foundational, helping to establish a baseline understanding of the research topic.
- What are the daily experiences of teachers in urban elementary schools?
- What strategies do small businesses employ to adapt to rapid technological changes?
- How do young adults describe their transition from college to the workforce?
- What are the coping mechanisms of families with members suffering from chronic illnesses?
- How do community leaders perceive the impact of gentrification in their neighborhoods?
2. Interpretive Questions
Interpretive questions seek to understand the “how” and “why” behind a phenomenon, focusing on the meanings people attach to their experiences. These questions delve into the subjective interpretations and perceptions of participants.
- How do survivors of natural disasters interpret their experiences of recovery and rebuilding?
- Why do individuals engage in voluntary work within their communities?
- How do parents interpret and navigate the challenges of remote schooling for their children?
- Why do consumers prefer local products over global brands in certain markets?
- How do artists interpret the influence of digital media on traditional art forms?
3. Comparative Questions
Comparative research questions are designed to explore differences and similarities between groups, settings, or time periods. These questions can help to highlight the impact of specific variables on the phenomenon under study.
- How do the strategies for managing work-life balance compare between remote and office workers?
- What are the differences in consumer behavior towards sustainable products in urban versus rural areas?
- How do parenting styles in single-parent households compare to those in dual-parent households?
- What are the similarities and differences in leadership styles across different cultures?
- How has the perception of online privacy changed among teenagers over the past decade?
4. Process-oriented Questions
These questions focus on understanding the processes or sequences of events over time. They aim to uncover the “how” of a phenomenon, tracing the development, changes, or evolution of specific situations or behaviors.
- How do non-profit organizations develop and implement community outreach programs?
- What is the process of decision-making in high-stakes business environments?
- How do individuals navigate the process of career transition after significant industry changes?
- What are the stages of adaptation for immigrants in a new country?
- How do social movements evolve from inception to national recognition?
5. Evaluative Questions
Evaluative questions aim to assess the effectiveness, value, or impact of a program, policy, or phenomenon. These questions are critical for understanding the outcomes and implications of various initiatives or situations.
- How effective are online therapy sessions compared to in-person sessions in treating anxiety?
- What is the impact of community gardening programs on neighborhood cohesion?
- How do participants evaluate the outcomes of leadership training programs in their professional development?
- What are the perceived benefits and drawbacks of telecommuting for employees and employers?
- How do residents evaluate the effectiveness of local government policies on waste management?
6. One-on-One Questions
The one-on-one questions are asked to a single person and can be thought of as individual interviews that you can conduct online via phone and video chat as well.
The main aim of such questions is to ask your customers or people in the focus group a series of questions about their purchase motivations. These questions might also come with follow-ups, and if your customers respond with some interesting fact or detail, dig deeper and explore the findings as much as you want.
- What makes you happy in regard to [your research topic]?
- If I could make a wish of yours come true, what do you desire the most?
- What do you still find hard to come to terms with?
- Have you bought [your product] before?
- If so, what was your initial motivation behind the purchase?
7. Exploratory Questions
These questions are designed to enhance your understanding of a particular topic. However, while asking exploratory questions, you must ensure that there are no preconceived notions or biases to it. The more transparent and bias-free your questions are, the better and fair results you will get.
- What is the effect of personal smart devices on today’s youth?
- Do you feel that smart devices have positively or negatively impacted you?
- How do your kids spend their weekends?
- What do you do on a typical weekend morning?
8. Predictive Questions
The predictive questions are used for qualitative research that is focused on the future outcomes of an action or a series of actions. So, you will be using past information to predict the reactions of respondents to hypothetical events that might or might not happen in the future.
These questions come in extremely handy for identifying your customers’ current brand expectations, pain points, and purchase motivation.
- Are you more likely to buy a product when a celebrity promotes it?
- Would you ever try a new product because one of your favorite celebs claims that it actually worked for them?
- Would people in your neighborhood enjoy a park with rides and exercise options?
- How often would you go to a park with your kids if it had free rides?
9. Focus Groups
These questions are mostly asked in person to the customer or respondent groups. The in-person nature of these surveys or studies ensures that the group members get a safe and comfortable environment to express their thoughts and feelings about your brand or services.
- How would you describe your ease of using our product?
- How well do you think you were able to do this task before you started using our product?
- What do you like about our promotional campaigns?
- How well do you think our ads convey the meaning?
10. In-Home Videos
Collecting video feedback from customers in their comfortable, natural settings offers a unique perspective. At home, customers are more relaxed and less concerned about their mannerisms, posture, and choice of words when responding.
This approach is partly why Vogue’s 73 Questions Series is highly popular among celebrities and viewers alike. In-home videos provide insights into customers in a relaxed environment, encouraging them to be honest and share genuine experiences.
- What was your first reaction when you used our product for the first time?
- How well do you think our product performed compared to your expectations?
- What was your worst experience with our product?
- What made you switch to our brand?
11. Online Focus Groups
Online focus groups mirror the traditional, in-person format but are conducted virtually, offering a more cost-effective and efficient approach to gathering data. This digital format extends your reach and allows a rapid collection of responses from a broader audience through online platforms.
You can utilize social media and other digital forums to create communities of respondents and initiate meaningful discussions. Once you have them started, you can simply observe the exchange of thoughts and gather massive amounts of interesting insights!
- What do you like best about our product?
- How familiar are you with this particular service or product we offer?
- What are your concerns with our product?
- What changes can we make to make our product better?
Ask the Right Qualitative Research Questions for Meaningful Insights From Your Respondents
Watch: How to Create a Survey Using ProProfs Survey Maker
By now, you might have realized that manually creating a list of qualitative research questions is a daunting task. Keeping numerous considerations in mind, it’s easy to run out of ideas while crafting qualitative survey questions .
However, investing in smart survey tools, like ProProfs Survey Maker, can significantly streamline this process, allowing you to create various types of surveys in minutes.
With this survey tools , you can generate forms, NPS survey , tests, quizzes, and assessments.
It’s also useful for conducting polls, sidebar surveys, and in-app surveys. Offering over 100 templates and more than 1,000,000 ready-to-use examples of phenomenological research questions, this software simplifies the task immensely.
Equipped with the right tools and the professional tips shared here, you’re well-prepared to conduct thorough research studies and obtain valuable insights that drive impactful results.
Frequently Asked Questions on Q ualitative Research Questions
1. how do you choose qualitative research questions.
To choose qualitative research questions, identify your main research goal, focus on exploring ‘how’ and ‘why’ aspects, ensure questions are open-ended, and align them with your theoretical framework and methodology.
2. Why are good qualitative research questions important?
Good qualitative research questions are important because they guide the research focus, enable the exploration of depth and complexity, and facilitate the gathering of rich, detailed insights into human experiences and behaviors.

About the author
Emma David is a seasoned market research professional with 8+ years of experience. Having kick-started her journey in research, she has developed rich expertise in employee engagement, survey creation and administration, and data management. Emma believes in the power of data to shape business performance positively. She continues to help brands and businesses make strategic decisions and improve their market standing through her understanding of research methodologies.
Related Posts

How to Create Rating Scale Surveys: Benefits, Types & Examples

Multiple Choice Questions : With Types and Examples

How to Use Screening Survey Questions Like a Pro

What Are Employee Pulse Surveys: A Detailed Guide with Examples + Tips

What Is Qualitative Research: Methods, Types, Examples & Analysis
75+ Student Survey Questions to Collect Valuable Students Feedback

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
- Introduction
Why are research questions so important?
Research question examples, types of qualitative research questions, writing a good research question, guiding your research through research questions.
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
- Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Case studies
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Research questions
The research question plays a critical role in the research process, as it guides the study design, data collection , analysis , and interpretation of the findings.
A research paper relies on a research question to inform readers of the research topic and the research problem being addressed. Without such a question, your audience may have trouble understanding the rationale for your research project.

People can take for granted the research question as an essential part of a research project. However, explicitly detailing why researchers need a research question can help lend clarity to the research project. Here are some of the key roles that the research question plays in the research process:
Defines the scope and focus of the study
The research question helps to define the scope and focus of the study. It identifies the specific topic or issue that the researcher wants to investigate, and it sets the boundaries for the study. A research question can also help you determine if your study primarily contributes to theory or is more applied in nature. Clinical research and public health research, for example, may be more concerned with research questions that contribute to practice, while a research question focused on cognitive linguistics are aimed at developing theory.
Provides a rationale for the study
The research question provides a rationale for the study by identifying a gap or problem in existing literature or practice that the researcher wants to address. It articulates the purpose and significance of the study, and it explains why the study is important and worth conducting.
Guides the study design
The research question guides the study design by helping the researcher select appropriate research methods , sampling strategies, and data collection tools. It also helps to determine the types of data that need to be collected and the best ways to analyze and interpret the data because the principal aim of the study is to provide an answer to that research question.

Shapes the data analysis and interpretation
The research question shapes the data analysis and interpretation by guiding the selection of appropriate analytical methods and by focusing the interpretation of the findings. It helps to identify which patterns and themes in the data are more relevant and worth digging into, and it guides the development of conclusions and recommendations based on the findings.
Generates new knowledge
The research question is the starting point for generating new knowledge. By answering the research question, the researcher contributes to the body of knowledge in the field and helps to advance the understanding of the topic or issue under investigation.
Overall, the research question is a critical component of the research process, as it guides the study from start to finish and provides a foundation for generating new knowledge.
Supports the thesis statement
The thesis statement or main assertion in any research paper stems from the answers to the research question. As a result, you can think of a focused research question as a preview of what the study aims to present as a new contribution to existing knowledge.
Here area few examples of focused research questions that can help set the stage for explaining different types of research questions in qualitative research . These questions touch upon various fields and subjects, showcasing the versatility and depth of research.
- What factors contribute to the job satisfaction of remote workers in the technology industry?
- How do teachers perceive the implementation of technology in the classroom, and what challenges do they face?
- What coping strategies do refugees use to deal with the challenges of resettlement in a new country?
- How does gentrification impact the sense of community and identity among long-term residents in urban neighborhoods?
- In what ways do social media platforms influence body image and self-esteem among adolescents?
- How do family dynamics and communication patterns affect the management of type 2 diabetes in adult patients?
- What is the role of mentorship in the professional development and career success of early-career academics?
- How do patients with chronic illnesses experience and navigate the healthcare system, and what barriers do they encounter?
- What are the motivations and experiences of volunteers in disaster relief efforts, and how do these experiences impact their future involvement in humanitarian work?
- How do cultural beliefs and values shape the consumer preferences and purchasing behavior of young adults in a globalized market?
- How do individuals whose genetic factors predict a high risk for developing a specific medical condition perceive, cope with, and make lifestyle choices based on this information?
These example research questions highlight the different kinds of inquiries common to qualitative research. They also demonstrate how qualitative research can address a wide range of topics, from understanding the experiences of specific populations to examining the impact of broader social and cultural phenomena.
Also, notice that these types of research questions tend to be geared towards inductive analyses that describe a concept in depth or develop new theory. As such, qualitative research questions tend to ask "what," "why," or "how" types of questions. This contrasts with quantitative research questions that typically aim to verify an existing theory. and tend to ask "when," "how much," and "why" types of questions to nail down causal mechanisms and generalizable findings.
Whatever your research inquiry, turn to ATLAS.ti
Powerful tools to help turn your research question into meaningful analysis, starting with a free trial.
As you can see above, the research questions you ask play a critical role in shaping the direction and depth of your study. These questions are designed to explore, understand, and interpret social phenomena, rather than testing a hypothesis or quantifying data like in quantitative research. In this section, we will discuss the various types of research questions typically found in qualitative research, making it easier for you to craft appropriate questions for your study.
Descriptive questions
Descriptive research questions aim to provide a detailed account of the phenomenon being studied. These questions usually begin with "what" or "how" and seek to understand the nature, characteristics, or functions of a subject. For example, "What are the experiences of first-generation college students?" or "How do small business owners adapt to economic downturns?"
Comparative questions
Comparative questions seek to examine the similarities and differences between two or more groups, cases, or phenomena. These questions often include the words "compare," "contrast," or "differences." For example, "How do parenting practices differ between single-parent and two-parent families?" or "What are the similarities and differences in leadership styles among successful female entrepreneurs?"
Exploratory questions
Exploratory research questions are open-ended and intended to investigate new or understudied areas. These questions aim to identify patterns, relationships, or themes that may warrant further investigation. For example, "How do teenagers use social media to construct their identities?" or "What factors influence the adoption of renewable energy technologies in rural communities?"
Explanatory questions
Explanatory research questions delve deeper into the reasons or explanations behind a particular phenomenon or behavior. They often start with "why" or "how" and aim to uncover underlying motivations, beliefs, or processes. For example, "Why do some employees resist organizational change?" or "How do cultural factors influence decision-making in international business negotiations?"
Evaluative questions
Evaluative questions assess the effectiveness, impact, or outcomes of a particular intervention, program, or policy. They seek to understand the value or significance of an initiative by examining its successes, challenges, or unintended consequences. For example, "How effective is the school's anti-bullying program in reducing incidents of bullying?" or "What are the long-term impacts of a community-based health promotion campaign on residents' well-being?"
Interpretive questions
Interpretive questions focus on understanding how individuals or groups make sense of their experiences, actions, or social contexts. These questions often involve the analysis of language, symbols, or narratives to uncover the meanings and perspectives that shape human behavior. For example, "How do cancer survivors make sense of their illness journey?" or "What meanings do members of a religious community attach to their rituals and practices?"
There are mainly two overarching ways to think about how to devise a research question. Many studies are built on existing research, but others can be founded on personal experiences or pilot research.
Using the literature review
Within scholarly research, the research question is often built from your literature review . An analysis of the relevant literature reporting previous studies should allow you to identify contextual, theoretical, or methodological gaps that can be addressed in future research.

A compelling research question built on a robust literature review ultimately illustrates to your audience what is novel about your study's objectives.
Conducting pilot research
Researchers may conduct preliminary research or pilot research when they are interested in a particular topic but don't yet have a basis for forming a research question on that topic. A pilot study is a small-scale, preliminary study that is conducted in order to test the feasibility of a research design, methods, and procedures. It can help identify unresolved puzzles that merit further investigation, and pilot studies can draw attention to potential issues or problems that may arise in the full study.
One potential benefit of conducting a pilot study in qualitative research is that it can help the researcher to refine their research question. By collecting and analyzing a small amount of data, the researcher can get a better sense of the phenomenon under investigation and can develop a more focused and refined research question for the full study. The pilot study can also help the researcher to identify key themes, concepts, or variables that should be included in the research question.
In addition to helping to refine the research question, a pilot study can also help the researcher to develop a more effective data collection and analysis plan. The researcher can test different methods for collecting and analyzing data, and can make adjustments based on the results of the pilot study. This can help to ensure that the full study is conducted in the most effective and efficient manner possible.
Overall, conducting a pilot study in qualitative research can be a valuable tool for refining the research question and developing a more effective research design, methods, and procedures. It can help to ensure that the full study is conducted in a rigorous and effective manner, and can increase the likelihood of generating meaningful and useful findings.
When you write a research question for your qualitative study, consider which type of question best aligns with your research objectives and the nature of the phenomenon you are investigating. Remember, qualitative research questions should be open-ended, allowing for a range of perspectives and insights to emerge. As you progress in your research, these questions may evolve or be refined based on the data you collect, helping to guide your analysis and deepen your understanding of the topic.

Use ATLAS.ti for every step of your research project
From the research question to the key insights, ATLAS.ti is there for you. See how with a free trial.

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Seminal Authors
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Locating Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks This link opens in a new window
- Quantitative Research Questions
Qualitative Research Questions
- Sampling Methods
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window

What’s in a Qualitative Research Question?
Qualitative research questions are driven by the need for the study. Ideally, research questions are formulated as a result of the problem and purpose, which leads to the identification of the methodology. When a qualitative methodology is chosen, research questions should be exploratory and focused on the actual phenomenon under study.
From the Dissertation Center, Chapter 1: Research Question Overview , there are several considerations when forming a qualitative research question. Qualitative research questions should
Below is an example of a qualitative phenomenological design. Note the use of the term “lived experience” in the central research question. This aligns with phenomenological design.
RQ1: “ What are the lived experiences of followers of mid-level managers in the financial services sector regarding their well-being on the job?”
If the researcher wants to focus on aspects of the theory used to support the study or dive deeper into aspects of the central RQ, sub-questions might be used. The following sub-questions could be formulated to seek further insight:
RQ1a. “How do followers perceive the quality and adequacy of the leader-follower exchanges between themselves and their novice leaders?”
RQ1b. “Under what conditions do leader-member exchanges affect a follower’s own level of well-being?”
Qualitative research questions also display the desire to explore or describe phenomena. Qualitative research seeks the lived experience, the personal experiences, the understandings, the meanings, and the stories associated with the concepts present in our studies.
We want to ensure our research questions are answerable and that we are not making assumptions about our sample. View the questions below:
How do healthcare providers perceive income inequality when providing care to poor patients?
In Example A, we see that there is no specificity of location or geographic areas. This could lead to findings that are varied, and the researcher may not find a clear pattern. Additionally, the question implies the focus is on “income inequality” when the actual focus is on the provision of care. The term “poor patients” can also be offensive, and most providers will not want to seem insensitive and may perceive income inequality as a challenge (of course!).
How do primary care nurses in outreach clinics describe providing quality care to residents of low-income urban neighborhoods?
In Example B, we see that there is greater specificity in the type of care provider. There is also a shift in language so that the focus is on how the individuals describe what they think about, experience, and navigate providing quality care.
Other Qualitative Research Question Examples
Vague : What are the strategies used by healthcare personnel to assist injured patients?
Try this : What is the experience of emergency room personnel in treating patients with a self-inflicted household injury?
The first question is general and vague. While in the same topic area, the second question is more precise and gives the reader a specific target population and a focus on the phenomenon they would have experienced. This question could be in line with a phenomenological study as we are seeking their experience or a case study as the ER personnel are a bounded entity.
Unclear : How do students experience progressing to college?
Try this : How do first-generation community members describe the aspects of their culture that promote aspiration to postsecondary education?
The first question does not have a focus on what progress is or what students are the focus. The second question provides a specific target population and provides the description to be provided by the participants. This question could be in line with a descriptive study.
- << Previous: Quantitative Research Questions
- Next: Sampling Methods >>
- Last Updated: Nov 8, 2024 9:24 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools

25 Qualitative market research questions (and how to write your own)
25 examples of qualitative research questions, how to write your own insightful qualitative market research questions, ask the right qualitative market research questions to the correct audience.
There’s something very satisfying about being asked a great question that really gets you thinking. And in qualitative market research, it’s especially valuable.
If you ask the right person the right question, you’ll be able to uncover next steps — both small ones and big leaps — that will lead you to a better brand.
If you approach qualitative research right, you can get rich and valuable insights into your customers’ behaviors, and how to play into them.
You’ll learn about how customers interact, their motivations, and how to be there when they need you. And, you’ll uncover things about your brand that are difficult to find out from the inside.
We’re about to show you 25 qualitative research questions across six categories, that will allow you to take a deep dive into your target customers’ brain. These research questions are perfect to use in focus groups or with Attest’s Video Responses feature .
Qualitative research questions come in all shapes and sizes. We’ve split them up in several categories to inspire you to mix it up in your next survey or interview and make them work for your choice of qualitative research question types and methods.
Descriptive qualitative research questions
Descriptive questions are effective qualitative research questions that allow participants to describe experiences, opinions and more.
- Describe how this product/service has changed the way you approach [specific task/activity]. This question digs into the tangible impacts of your product on daily life, revealing how it reshapes routines or approaches to tasks.It’s a great way to highlight the practical value and possibly discover unexpected benefits that your product brings to the table.
- If you were to introduce this product/service to a friend, what would you say? Asking this encourages users to put their experience into their words, almost like a personal pitch. It’s a fun and low barrier approach to find out what stands out to them and what they value most about your offering.
- What three words would you use to describe this product/service after your first use? If you’re looking for immediate, instinctive reactions, qualitative research questions like these work best.They allow the user to give a quick snapshot and not have to think long and hard about an answer. Encourage them to respond with the first thing that comes to mind — no wrong answers.
- What aspect of this product/service do you think is underrated? This seeks to uncover hidden gems within your product that may not be getting the spotlight they deserve — even internally.It’s a clever way to find out about features or benefits that might be flying under the radar but have the potential to be major selling points.

Understand the nuance in your audience’s behaviors
Getting that nuance through qual research will help you explain thy why to your quant ‘whats’, and give you much-needed inspiration during ideation
Comparative qualitative research questions
Using comparative qualitative research questions you can invite respondents to talk about your brand, product or services in comparison to others. It can help you understand the differences between you and your competitors, from your consumers’ perspective.
These qualitative research questions are a great addition to numbers, scores and other numerical data derived from quantitative research questions in a quantitative study.
- What differences do you notice between this brand and its competitors in terms of value provided? This question invites customers to think critically about the unique advantages or shortcomings of your product compared to the competition.It’s insightful because it can highlight what customers value most about your brand and whether you are doubling down on the right USPs according to them.
- In what situation would you prefer this competitors’ product/service over ours? Asking this might seem a bit daring, but it’s a golden opportunity to gain honest feedback on where your product may fall short for certain users or use cases.Research questions like this can uncover specific features, price points, or scenarios where competitors have an edge, offering you clear directions for strategic improvements or innovations.
- How does the ease of use of this product/service compare to others you have used in the past? This question zeros in on usability, a crucial aspect of customer satisfaction. It offers direct feedback on how user-friendly your product is compared to others, highlighting areas where you excel or need improvement.
- When choosing between this product/service and others, what factor weighs most heavily on your decision? Understanding the key factors that influence choice can help you fine-tune your offerings and marketing messages to better meet customer needs and preferences.If you look at the answers and compare the marketing efforts of your own brand and main competitors, you’ll be able to spot where you could make improvements.
- Can you identify a feature in a competing product/service that you wish ours had? Sometimes asking what feature they’d love is tricky: it might be hard to dream up. But if you give users the opportunity to shop from your competitors’ features, it might be easier.Qualitative research questions like these are therefore a smart and straightforward way to identify gaps in your product from a user perspective.
Exploratory qualitative research questions
Exploratory qualitative research questions are used in qualitative methods to tap into potential opportunities, and uncover insights that haven’t been previously considered. Add these research questions to your qualitative research studies if you’re on the hunt for new ideas.
- What challenges are you currently facing that this product/service does not address? This question is a gem in qualitative studies because it shines a light on the gaps between what your product offers and what your users actually need.By understanding these challenges, you’re not just guessing; you’re directly addressing the needs that matter most to your users, making every feature more aligned with their real-world problems.
- If you could add any premium features to this product/service, big or small, while the price remains the same, what would it be? Research questions like these open up a playground for users’ imaginations, allowing you to peek into their deepest wishes.It’s a creative way to use qualitative research to uncover independent variables (new features) that could make your product indispensable.
- What would make you stop using this product/service tomorrow? This one might sound a bit scary, but it’s crucial. It helps you pinpoint the deal breakers that could push your users away.Think of it as a preventive measure; by understanding these thresholds, you can steer clear of them in your future updates or service improvements. This question is a cornerstone in crafting a research design that seeks to minimize risks and maximize satisfaction.
- What’s a feature you never knew you needed until you started using this product/service? These insights are gold for marketing and product development, revealing the unexpected delights that can turn casual users into loyal fans.Plus, it’s a great way to highlight the qualitative words or phrases that resonate most with your audience, giving you a direct line to what makes your product stand out.
- If this product/service no longer existed, what would be the biggest gap in your routine or activities? This qualitative question helps to understand the role your product plays in users’ lives, emphasizing its importance and potential areas for highlighting in marketing efforts.Knowing what would replace you also tells you a great deal about the value your product offers.
Experience-based qualitative research questions
These qualitative research questions focus on the personal experiences of your users, and try to understand their journey and interactions with the product or service deeply.
- Describe a situation where this product/service met or exceeded your expectations. The feedback from this research question can reveal the “wow” factors that differentiate your offering in the market. It’s a great way to identify the elements of your product or service that surprise and delight customers.These qualitative questions will also highlight the specific words they use for this will also be great to fine-tune your communications and choice of words. You might be describing the right benefits already, but maybe not in the words they relate to most.
- What’s missing from your experience with this product/service? This research question is a direct line to understanding your customers’ unmet needs and desires. It encourages them to share their thoughts on how your product or service could be more useful, enjoyable, or relevant to their lives.
- What was your initial impression of this product/service, and how has it evolved? A classic, but nonetheless a valuable qualitative research question. If peoples’ experiences with your product change their impression of it over time, it’s crucial you dig into what those experiences are, to better match your marketing to the real world.Especially if impressions tend to take a more negative turn after some experiences, but also when it’s the other way around — don’t undersell your product!
Behavioral qualitative research questions
Behavioral qualitative research questions seek to understand the actions and behaviors of consumers, particularly in relation to your product or service. Adding these to your qualitative study will make it more relevant to daily life applications.
- Have you been using products/services like ours in ways that you didn’t think you would initially? This is a good qualitative research question to learn about unconventional or alternative use cases of your product. Of course, it doesn’t mean you immediately need to pivot, but it can help you map out uncharted or ignored territory and find fans in niche parts of your market.
- Has this product/service replaced something else you used to rely on? If so, what? We’re going there: ask about the ”ex”. Knowing who or what came before you and why things didn’t work out will help you be better in many ways. So, make sure to follow up this question with another one digging into the reasons for the break-up.
- What activity or task do you most frequently pair with this product/service? This might not seem immediately relevant, but it can tell you a great deal about your customer’s behavior. Knowing what place you have in their routine or what products they combine yours with can help you uncover big possibilities for innovations or even partnerships.
- How has this product/service influenced your daily habits or routines? This question doesn’t just focus on the functional benefits of your product, but also how those manifest in someone’s daily life. Do people highlight time they won back, or pleasure gained? Have they made any other changes that are relevant to you? There’s a lot to learn from small habit changes!
Emotional qualitative research questions
These qualitative questions explore the emotional connections and reactions participants have towards a particular topic, product, service, or brand. The qualitative questions examples below specifically bring a human side to quantitative research.
- How does this product/service fit into the moments that matter most to you? This might not be interesting for every product or brand, but if your brand is aiming to significantly impact people’s lives and important moments, this is a must-ask. Are they taking your products along to big moments in their lives? Does it provide them with comfort, confidence or something else when they need it? Research questions like this go way beyond functionality and tap into emotional significance — which is great for brands who really want to integrate with people’s lives.
- How does using this product/service make you feel compared to not using it at all? Are people frustrated when they run out of your product? Sad? Do they miss it at all? This question can reveal some powerful feelings around your product.
- How does this product/service affect your mood? This is a fun question to ask and can give you a great insight into what emotions your product evokes in general. Maybe some people don’t think about how they feel with your product, but others might get a confidence boost out of it, or chuckle every time they read your product copy. This question can reveal teeny tiny details that could matter a lot.

How this team aced their pitch with qual insights
Qual research helped Barrows understand glasses wearers’ pain points and wow a prospective client.
Got a burning question? Here’s how to make it part of a successful qualitative research project.
1. Set clear objectives
Knowing why you’re asking something is what helps you ask it the right way. Ask yourself what your general research objective is and how each of your qualitative research questions helps you get to the main answer.
For every qualitative research question you ask, find out IF it leads you closer to your goals, and make sure you can explain HOW it does so.
2. Ask open-ended questions the right way
There’s an art in asking great open-ended questions. Here’s an example of both seemingly similar open-ended, qualitative research questions, but one’s good, and one’s not:
“Why do you think people say this new smartwatch is better than others on the market?”
“What feedback are you hearing about this smartwatch in comparison to other smartwatches you know?”
The first one already works with the assumption and bias that your product is great. You’re practically putting words into your respondent’s mouth/answer box. The next one lets them come up with their own, unbiased response.
Good qualitative research questions should be:
- Unbiased: avoid qualitative research questions that are leading or show any form of bias whatsoever.
- Clear: only ask one thing at a time, and make it clear what that actually is.
- Relevant: make sure your question makes sense. Not just in the whole qualitative research, but also in the place it has in your survey or interview.
- Truly open: some quantitative research questions are sometimes disguised as qualitative research questions. Make sure yours is truly open and qualitative.
If you tick these boxes, your respondents will feel encouraged to express their opinions and motivations freely, which in turn will add depth and context to your research findings.
3. Balance between structured questions and flexibility
Let’s talk about flow. Imagine the panic that would set in if your first question in a job interview would be ”and how do you tackle problems with coworkers?”
Timing matters. Mixing up the question matters. This will create a great flow and keep respondents engaged and enthusiastic, and will avoid confusion.
Make sure to give respondents space to add comments or feedback where needed, but do so in a structured way, so your data remains easy to analyze.
4. Take measures to avoid survey bias
We’re circling back to bias for a second, but just because there’s more to be said and done. Avoiding bias in your surveys and qualitative research questions isn’t just about avoiding certain words or biased language, it also helps to choose a well-mixed and representative audience. On top of that, make sure your survey churns out high-quality data, not just high-volume. Read more about how we work on keeping your data in great shape.
5. Conduct pilot testing before launching large surveys
Do a mic-check before you send your qualitative research survey out to thousands of people. With pilot testing, you make sure your survey’s research questions are as-to-the-point as you hoped it to be. Send it to a small slice of your total audience, but make sure that the pilot group is just as representative as the total one will be.
When you hit that sweet spot of the right qualitative research questions and a perfectly represented audience , the feedback you receive from qualitative research isn’t just data—it’s a roadmap to deeper understanding and connection with your audience. For those looking to dive into the rich world of conducting qualitative research, Attest offers the market research tools and audience reach you need to make every question count. Check out how Attest can help bring your qualitative research to life.

VP Customer Success
Sam joined Attest in 2019 and leads the Customer Research Team. Sam and her team support brands through their market research journey, helping them carry out effective research and uncover insights to unlock new areas for growth.
Related articles
4 positioning strategies to grow and market your brand, attest sponsors burberry british diversity awards for third year running, product webinar: getting better insights with enhanced segments, subscribe to our newsletter.
Fill in your email and we’ll drop fresh insights and events info into your inbox each week.
* I agree to receive communications from Attest. Privacy Policy .
You're now subscribed to our mailing list to receive exciting news, reports, and other updates!
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Qualitative Research Questions: What it is and how to write it

Qualitative research questions are like a compass that points researchers in the right direction to find rich stories, untangle complicated social relationships, and get a clear picture of how people act in subtle ways. Unlike their quantitative counterparts, these questions go beyond numbers and figures to explore the subjective, contextual, and complex parts of the human experience.
It’s well-established that all forms of research come with their own theories and implementation methods. Qualitative research is much the same. Qualitative research is conducted to understand the thought process of both the respondents as well as researchers. It usually is conducted in a natural setup where respondents will be their true selves and would respond transparently.
Results achieved from this research will not be generalized to the entire population but asked research questions , and their vocabulary gives away the researcher’s motive making it easier for respondents to participate in qualitative market research .
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
Qualitative research survey questions are created to understand a particular topic better or to inspect a new subject to understand the nerve of respondent experiences.
Content Index
What are qualitative research questions?
How to write qualitative research questions, types of qualitative research questions, how to choose qualitative research questions, what should be the process of forming qualitative research questions and questionnaires.
Qualitative research questions are the inquiries that lead to qualitative research studies and investigations. They are meant to help people explore and understand phenomena, experiences, meanings, and views from the participant’s point of view.
Different from quantitative research questions, which often try to measure and quantify variables, qualitative research questions try to understand the richness and complexity of human experiences and social events.
Most qualitative research questions are open-ended and allow for in-depth study. They want more than simple yes/no answers but instead want people to talk about their thoughts, feelings, views, and experiences. These questions try to find deeper meanings, patterns, and connections in a given situation.
Here are some examples of qualitative study questions in different fields:
- In psychology: How do individuals experience and cope with traumatic events?
- In sociology: What factors influence a student’s decision to pursue higher education?
- In anthropology: How do cultural norms and values shape gender roles in a specific community?
- In education: What are the challenges faced by teachers in implementing project-based learning in the classroom?
- In healthcare: What are the experiences and perspectives of patients undergoing long-term treatment for a chronic illness?
Qualitative research questions should be straightforward, specific, and tailored to the research’s goals. They guide the process of gathering data through interviews, observations, or document analysis and give a method for analyzing and interpreting data.
Writing the right qualitative research questions requires careful thought about the research goals, the event being studied, and the wanted level of understanding. Here are some tips to help you write good qualitative research questions:
Begin with a broad research question
Start by posing an all-encompassing question that probes the subject or phenomenon of interest. Exploring and learning from the answer to this open-ended question should be possible.

Specify the research objectives
Clearly state the objectives and purposes of your research. What do you want your qualitative study to accomplish? What facets or dimensions of the subject do you wish to investigate?
Focus on the phenomenon
Decide on whatever specific subject or phenomenon you want to research. Any pertinent topic, including social behavior, cultural customs, personal experiences, and more, may be used.
Use open-ended and exploratory language
In qualitative research, open-ended questions should be used to enable participants to offer thorough and in-depth responses. Avoid yes/no questions and queries with a one-word answer. Use words like “how,” “what,” “why,” or “describe” instead to compel people to express their thoughts and experiences.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Interview
Consider the context and participants
Consider your research’s background as well as the qualities of your subjects. Make sure your qualitative methods are specific to the people you will be studying so that they are pertinent and meaningful to them.
Incorporate theory and literature
Your research questions should be based on pertinent theories and available literature. This gives your investigation a theoretical foundation and places your study within the body of knowledge.
Balance breadth and depth
When formulating your research topics, try to strike a balance between depth and breadth. To fully understand the subject, you should investigate it broadly to get a variety of viewpoints and intensively delve into certain areas.
Avoid leading or biased questions
Ensure your questions are neutral and unbiased. Avoid leading participants towards a particular response. Instead, create questions that allow participants to express their thoughts and experiences freely.
Pilot test your questions
Pilot-test your research questions with a small group of people before finalizing them. This will make it easier to spot any possible problems, ambiguities, or places where clarity may be increased.
Revise and refine
Revise and clarify your research questions based on the comments and understandings received from the pilot testing. Aim for consistency, coherence, and congruence with your research goals.
Remember, qualitative market research questions should be flexible and adaptable throughout the research process. They serve as a guide but may evolve as you delve deeper into the data and discover new insights.
LEARN ABOUT: Steps in Qualitative Research
There are several types of qualitative research questions focus that can be used to guide qualitative studies. Here are some common types:
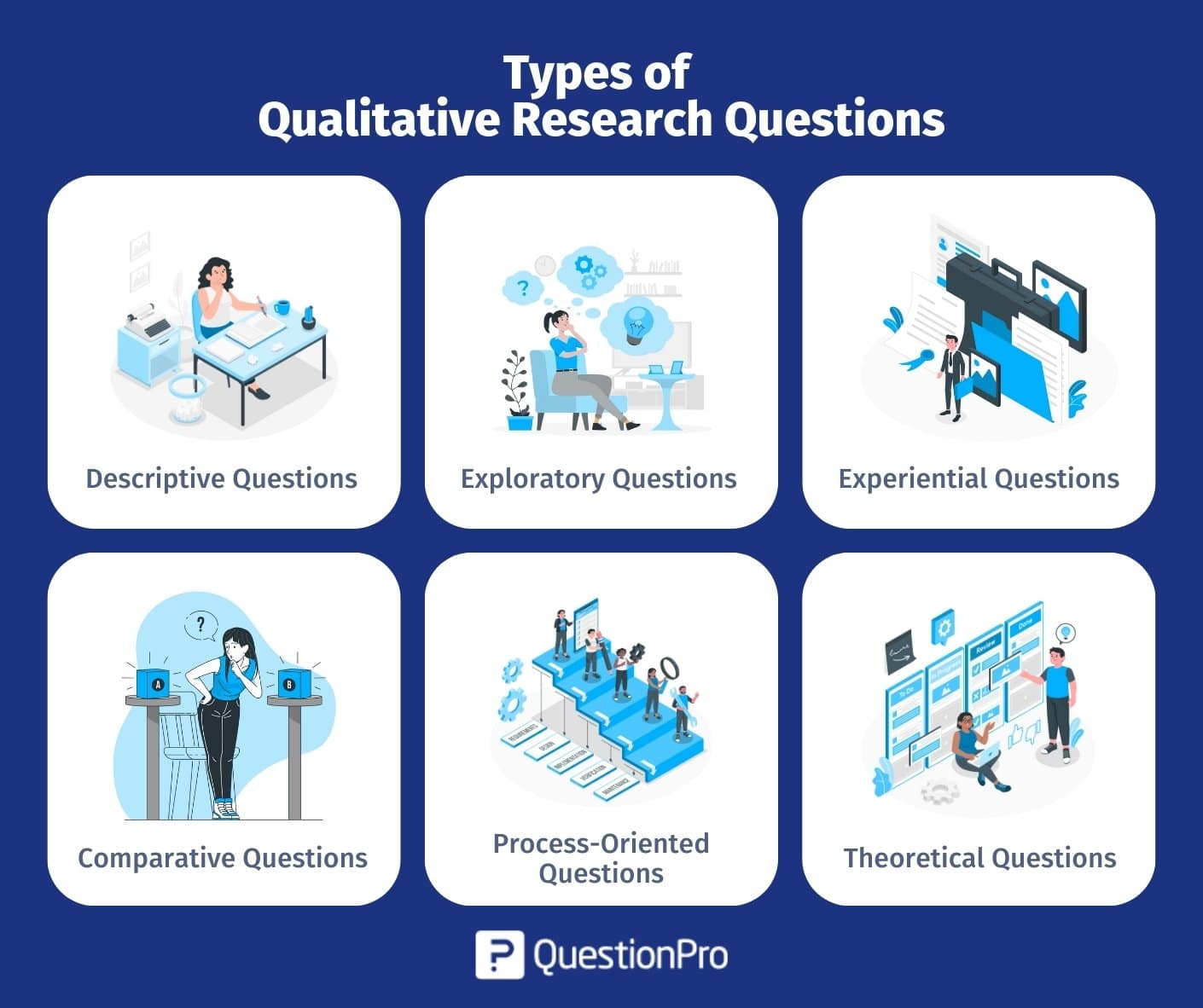
1. Descriptive questions
These questions aim to describe and understand a phenomenon or topic in detail. They focus on providing a comprehensive account of the subject matter. For example:
- What are the experiences of individuals living with chronic pain?
- How do employees perceive the organizational culture in a specific company?
2. Exploratory questions
These questions are used to explore new or under-researched areas. They seek to gain a deeper understanding of a topic or phenomenon. For example:
- What are the factors influencing consumers’ decision-making process when purchasing organic food?
- How do teachers perceive the implementation of project-based learning in the classroom?
3. Experiential questions
These questions focus on understanding individuals’ experiences, perspectives, and subjective meanings related to a particular phenomenon. They aim to capture personal experiences and emotions. For example:
- What are the challenges first-generation college students face during their transition to higher education?
- How do individuals with social anxiety disorder experience social interactions?
4. Comparative questions
These questions involve comparing and contrasting different groups, contexts, or perspectives to identify similarities, differences, or patterns. They explore variations in experiences or phenomena. For example:
- How do parenting practices differ between cultures A and B in terms of child discipline?
- What are the similarities and differences in the coping strategies used by individuals with individuals and depression questionnaire with anxiety disorders?
5. Process-oriented questions
These questions focus on understanding a phenomenon’s processes, mechanisms, or dynamics. They aim to uncover how and why certain outcomes or behaviors occur. For example:
- What are the processes by which teams in a workplace reach a consensus on decision-making?
- How does the negotiation process unfold during conflict resolution in interpersonal relationships?
6. Theoretical questions
These questions seek to generate or refine theory. They explore concepts, relationships, or theoretical frameworks to contribute to the existing body of knowledge. For example:
- How does the concept of “self-efficacy” manifest in the context of entrepreneurship?
- What underlying mechanisms explain the relationship between social support and mental health outcomes?
These are just a few examples of the types of qualitative research questions that can be used. The specific type of question you choose will depend on your research objectives, the phenomenon under investigation, and the depth of understanding you aim to achieve.
Explore Insightfully Contextual Inquiry in Qualitative Research
Choosing a good qualitative research question involves a thoughtful and systematic approach to ensure they align with the objectives of your study and allows for an in-depth exploration of the topic. Here are some steps to help you choose effective qualitative research questions:
Identify your research objectives
Clearly define the purpose of your study. What do you want to explore or understand? What specific insights or knowledge are you seeking to gain through your market research?
Review existing literature
Conduct a thorough review of relevant literature to identify existing research gaps or areas requiring further exploration. This will help you understand the current state of knowledge and inform the development of your research questions.
Brainstorm potential qualitative research question
Generate a list of potential research questions that address your research objectives. Consider different angles, perspectives, and dimensions of your topic. Creating open-ended questions that allow for in-depth exploration rather than simple yes/no answers is important.
Prioritize and refine the questions
Evaluate the generated questions based on their relevance to your research objectives, feasibility, and potential to yield meaningful insights. Prioritize the questions that are most likely to provide rich and valuable data. Refine and rephrase the questions as needed to ensure clarity and focus.
Consider the research design and methodology
Take into account the specific qualitative research design and methodology you plan to use. Different research approaches, such as ethnography, interviews, focus groups, or case studies, may require different types of research questions. Ensure that your questions align with your chosen methodology and will help you gather the desired data.
Pilot test the questions
Before finalizing your research questions, consider conducting a pilot test with a small group of participants. This will allow you to assess your questions’ clarity, appropriateness, and effectiveness. Make necessary revisions based on the feedback received.
Seek feedback
Share your research questions with colleagues, mentors, or experts in your field for feedback and suggestions. They can provide valuable insights and help you refine your questions further.
Finalize your research questions
Based on the steps above, select a set of research questions that are well-aligned with your research objectives, provide scope for exploration, and are feasible within the resources and time available for your study.
1. Mention the purpose of conducting qualitative research. It can be in the form of either of these sentences:
- This study will be on the topic of ….
- The reason for conducting this research is ….
2. Create qualitative statements with a defined objective that can be easily communicated to the target audience .
Keep these pointers in mind while designing this statement:
- Try and form single-sentence statements. Single statements can be much more effective than elaborate ones as they help in communicating important messages in an impactful manner in a short and succinct sentence.
- Clarify the purpose of conducting qualitative research in clear words so that respondents understand their contribution to this research.
- Mention the main topic of research that would prompt respondents to have a clearer idea about what they’re getting into.
- It’s the words that make all the difference. Use qualitative words that demonstrate the quality or feeling behind your purpose, such as understanding, describing, explore.
- Specify details that you would want to communicate to your respondents.
- Mention the name of the research website.
3. Other than the primary qualitative questions, you must create sub-questions so that the purpose is executed in a better manner.
- The main question might be – “What is the state of illiteracy in your state?”
- You can create sub-questions such as: “How does illiteracy hamper progress in your state?” or “How would you best describe your feelings about illiteracy?”
4. Highlight these questions using ‘qualitative’ words:
- Start the questions with “What” or “How” to make sure the respondents provide details about their feelings.
- Communicate what you’re trying to “understand,” “explore,” or “identify” using this Qualitative research online survey questionnaire.
- Questions such as “What happened” can be asked to develop a description of the topic.
- Questions about “how did respondents interpret the what happened question” can be asked to examine the outcome.
- Understand the entire qualitative research process by asking questions about “What happened to you with time?”
5. Develop a skeleton to design the primary questions and also the sub-questions. For example:
- Primary Qualitative research survey question: “How do you think _______ (the main topic of research) means?” or “Describe _____(the main topic of research) as you’ve experienced.”
- Sub-question for qualitative research: “What _________ (characteristic) does __________ (respondents) interest in as a _________ (main topic of research)?”
LEARN ABOUT: Structured Questionnaire
Qualitative research questions are key to giving research studies depth and breadth. These questions go into the details and complexities of human experiences, perceptions, and behaviors. This helps researchers get a full picture of a certain occurrence.
Qualitative research questions are meant to explore, describe, and make sense of subjective truths. Most of the time, they are open-ended, so people can say what they think and feel in their own words.
QuestionPro is an online poll and research platform with several tools and features that can make it easier to make and use qualitative research questions. Its easy-to-use design and variety of question types help researchers collect qualitative data quickly and easily, improving the whole research process.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Maximize Employee Feedback with QuestionPro Workforce’s Slack Integration
Nov 6, 2024

2024 Presidential Election Polls: Harris vs. Trump
Nov 5, 2024

Your First Question Should Be Anything But, “Is The Car Okay?” — Tuesday CX Thoughts

QuestionPro vs. Qualtrics: Who Offers the Best 360-Degree Feedback Platform for Your Needs?
Nov 4, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

6 Main Qualitative Questions Examples
Qualitative vs. quantitative research, the importance of qualitative questions, key elements of effective qualitative research questions, role in the research design, 6 types and examples of qualitative questions, how to choose qualitative research questions, start collecting qualitative data right now, fullsession pricing plans.
- FAQs about Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative research uncovers the details of human behavior, beliefs, and feelings. It gives us insights that numbers can't always tell.
These research questions help us understand the "how" and "why" of things.
In this article, we'll look at six examples of good qualitative questions. We aim to highlight how picking the right questions can improve your study.
It is important to understand the differences between qualitative and quantitative research.
Qualitative research questions aim to explore concepts, experiences, and perspectives. They offer the qualitative research expert an in-depth insight into the subject.
On the other hand, quantitative research questions focus on measurable aspects. They seek statistical comparisons to reach factual conclusions.
Both quantitative and qualitative questions have important roles in research. They serve unique purposes and provide different types of data.
Unlike quantitative research, qualitative questions aren't about numbers and statistical analysis. It's about understanding the reason behind data from a focus group.
Why pick qualitative research? When conducting qualitative research, you want to know why someone does something, not just count how many times they do it.
You ask, and you listen. That's the power of qualitative research. The right question is a key that unlocks valuable knowledge.
Effective qualitative research aims to unveil hidden truths. But how do you achieve it? With thought-provoking questions.
Here are the elements of the qualitative research questions for an in-depth exploration:
Open-ended and Exploratory
Qualitative research questions aim to understand the "how" and "why" of a topic. They invite people to share their views and stories.
Open-ended and exploratory questions help researchers grasp complex issues. These questions allow for diverse and detailed answers to a particular subject.
Clarity and Focus
Qualitative research questions need to be clear, focused, and brief. They help ensure the research meets its goals.
Being specific guides data collection and analysis, leading to valuable findings.
Relationships and Personal Experiences
Qualitative research questions examine how different factors relate to personal experiences and seek to understand why people act in certain ways.
They also explore how people respond to their surroundings, including culture and workplace rules.
Ethical Considerations
When creating qualitative research questions, it's important to think about ethics. Questions need to respect participants' dignity, privacy, and independence.
This makes sure that the research does not cause harm or distress. Ethics also matter when explaining and sharing results, as researchers must present data truthfully and with care.
The right qualitative research questions are crucial in the design of research projects for several reasons:
- Guidance on Research Methods: Directs the choice of qualitative research methods. Options include:
- Focus Groups: Small groups discuss topics with a moderator.
- In-Depth Interviews: Offers detailed insights from individual viewpoints.
- Qualitative Surveys: Gathers open-ended responses from a broad audience.
- Ensuring the Right Tools are Used: Matching objectives with the most suitable research tools. Enables thorough investigation and captures the complexity of experiences.
- Facilitating a Clear Understanding: Aims to uncover not just what is happening but why. Explores thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and the effects of various influences.
- Informing the Research Design: Influences all design aspects, including participant selection and analysis framework. Ensures ethical standards guide the research process.
Here are six types of qualitative questions with examples:
1. Descriptive
These questions are aimed at describing the characteristics or features of a product.
- Example 1: How do users describe their initial impressions when they first interact with our new software interface?
- Example 2: What are the specific colors and design elements that users notice about the new smartphone model when they see it for the first time?
2. Exploratory
Exploratory questions are designed to investigate how things work or how users interact with a product.
- Example 1: What strategies do users employ to navigate through the features of our newly launched app?
- Example 2: How do users attempt to solve problems when they encounter errors using our digital service platform?
3. Experiential
These questions focus on the user's experiences and emotions related to the product.
- Example 1: Can you describe a memorable experience you had while using our product?
- Example 2: What emotions do you feel when using our product under stressful conditions?
4. Comparative
Comparative questions look at differences between products, user groups, or other variables.
- Example 1: How do new users' experiences with our product compare to those of long-term users?
- Example 2: In what ways does our product perform better or worse than our main competitor's product in similar conditions?
5. Process-oriented
These questions delve into the processes or sequences of actions related to using the product.
- Example 1: Can you walk me through the process you typically follow when setting up our product for the first time?
- Example 2: What steps do you take when you troubleshoot an issue with our product?
6. Theoretical
Theoretical questions aim to understand the underlying principles or theories that explain user behavior or product dynamics.
- Example 1: What theories can explain why users prefer our product's design over traditional designs?
- Example 2: Based on your knowledge, what psychological principles might influence how users adapt to our product's innovative features?
When selecting qualitative questions, the aim is to deeply understand user interactions, perceptions, and experiences with the product.
Here are some key considerations for choosing good qualitative research questions:
- Define Your Objectives
Start by clearly defining the research objective of your product testing. What specific aspects of the product are you looking to evaluate? Are you interested in usability, aesthetics, functionality, or user satisfaction? Your objectives will guide the types of questions you need to ask. For example, if user satisfaction is your focus, you might ask about the user's emotional response to the product.
- Consider the Type of Qualitative Research
Different types of qualitative methods—such as ethnographic, narrative, phenomenological, or grounded theory—may influence the style and structure of your questions. For instance, narrative research focuses on stories and experiences, so your questions should encourage storytelling about product use.
- Ensure Questions are Open-Ended
Qualitative questions should be open-ended to allow for detailed responses that can reveal insights not anticipated by the researcher. Instead of asking, "Do you like our product?" which prompts a yes or no answer, ask, "How do you feel about our product?" to encourage a more detailed and nuanced response.
- Be Clear and Concise
While questions should allow for open-ended answers, they must also be clear and concise to avoid confusing the respondent. Ambiguity can lead to unreliable qualitative data , as different participants might interpret the questions differently.
- Sequence the Questions Logically
The order in which you ask questions can impact the flow of conversation and the quality of information gathered. Start with more general questions to make the respondent comfortable before moving to more specific or sensitive topics. This sequence helps build rapport and can lead to more honest and detailed responses later in the discussion.
- Consider the Participant
Tailor your questions to fit the background and experience level of your participants. Questions that are too technical or too basic can frustrate users or fail to elicit useful information. Understanding your audience allows you to frame questions that are appropriately challenging and engaging.
- Pilot Test Your Questions
Before finalizing your set of questions, conduct a pilot test with a small group of participants. This testing can reveal if any questions are confusing or ineffective at eliciting useful responses. Feedback from this phase can be invaluable in refining your questions.
- Be Prepared to Adapt
Finally, while it’s important to prepare your questions carefully, also be flexible during actual interactions. The conversation may reveal new paths of inquiry that are worth exploring. Being adaptive can help you capture deep insights that strictly adhering to a prepared list of questions might miss.
It takes less than 5 minutes to set up your first website or app feedback form, with FullSession , and it’s completely free!
After that, you will be able to collect high-quality feedback and avoid the guesswork.
The FullSession platform offers a 14-day free trial. It provides two paid plans—Basic and Business. Here are more details on each plan.
- The Starter plan costs $39/month or $32/year and allows you to monitor up to 5,000 monthly sessions with up to 6 months of data storage.
- The Business plan costs $75/month or $60/year and helps you to track and analyze up to 100,000 monthly sessions with up to 12 months of data storage.
- The Enterprise plan has custom pricing and offers customizable sessions plus full access to all features.
Book a demo today .
FAQs about Qualitative Research Questions
What is a qualitative research question.
Qualitative research questions focus on ways to gather deep insights into people's experiences, beliefs, and perceptions. Such questions invite detailed narrative responses.
Can qualitative research questions change during the study?
It's not uncommon for qualitative research questions to evolve during the course of a study. As preliminary data is collected and analyzed, new insights may emerge that prompt a qualitative researcher to refine their questions.
How are qualitative questions used in business?
Businesses use qualitative questions to uncover valuable insights. They can explore customer behavior, employee satisfaction, or market trends. One example could be: "What factors drive consumer loyalty to our brand?"
Are there specific words to use in qualitative research questions?
Yes, use words like "describe," "explain," and "how" to frame qualitative questions. These terms promote more detailed and comprehensive answers. They are key to qualitative analysis.

Work With Us
Private Coaching
Done-For-You
Short Courses
Client Reviews
Free Resources
Research Question Examples 🧑🏻🏫

Research Question Examples
- Psychology research questions
- Business research questions
- Education research questions
- Healthcare research questions
- Computer science research questions
Examples: Psychology
Let’s start by looking at some examples of research questions that you might encounter within the discipline of psychology.
How does sleep quality affect academic performance in university students?
This question is specific to a population (university students) and looks at a direct relationship between sleep and academic performance, both of which are quantifiable and measurable variables.
What factors contribute to the onset of anxiety disorders in adolescents?
The question narrows down the age group and focuses on identifying multiple contributing factors. There are various ways in which it could be approached from a methodological standpoint, including both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Do mindfulness techniques improve emotional well-being?
This is a focused research question aiming to evaluate the effectiveness of a specific intervention.
How does early childhood trauma impact adult relationships?
This research question targets a clear cause-and-effect relationship over a long timescale, making it focused but comprehensive.
Is there a correlation between screen time and depression in teenagers?
This research question focuses on an in-demand current issue and a specific demographic, allowing for a focused investigation. The key variables are clearly stated within the question and can be measured and analysed (i.e., high feasibility).

Examples: Business/Management
Next, let’s look at some examples of well-articulated research questions within the business and management realm.
How do leadership styles impact employee retention?
This is an example of a strong research question because it directly looks at the effect of one variable (leadership styles) on another (employee retention), allowing from a strongly aligned methodological approach.
What role does corporate social responsibility play in consumer choice?
Current and precise, this research question can reveal how social concerns are influencing buying behaviour by way of a qualitative exploration.
Does remote work increase or decrease productivity in tech companies?
Focused on a particular industry and a hot topic, this research question could yield timely, actionable insights that would have high practical value in the real world.
How do economic downturns affect small businesses in the homebuilding industry?
Vital for policy-making, this highly specific research question aims to uncover the challenges faced by small businesses within a certain industry.
Which employee benefits have the greatest impact on job satisfaction?
By being straightforward and specific, answering this research question could provide tangible insights to employers.
Examples: Education
Next, let’s look at some potential research questions within the education, training and development domain.
How does class size affect students’ academic performance in primary schools?
This example research question targets two clearly defined variables, which can be measured and analysed relatively easily.
Do online courses result in better retention of material than traditional courses?
Timely, specific and focused, answering this research question can help inform educational policy and personal choices about learning formats.
What impact do US public school lunches have on student health?
Targeting a specific, well-defined context, the research could lead to direct changes in public health policies.
To what degree does parental involvement improve academic outcomes in secondary education in the Midwest?
This research question focuses on a specific context (secondary education in the Midwest) and has clearly defined constructs.
What are the negative effects of standardised tests on student learning within Oklahoma primary schools?
This research question has a clear focus (negative outcomes) and is narrowed into a very specific context.
Need a helping hand?
Examples: Healthcare
Shifting to a different field, let’s look at some examples of research questions within the healthcare space.
What are the most effective treatments for chronic back pain amongst UK senior males?
Specific and solution-oriented, this research question focuses on clear variables and a well-defined context (senior males within the UK).
How do different healthcare policies affect patient satisfaction in public hospitals in South Africa?
This question is has clearly defined variables and is narrowly focused in terms of context.
Which factors contribute to obesity rates in urban areas within California?
This question is focused yet broad, aiming to reveal several contributing factors for targeted interventions.
Does telemedicine provide the same perceived quality of care as in-person visits for diabetes patients?
Ideal for a qualitative study, this research question explores a single construct (perceived quality of care) within a well-defined sample (diabetes patients).
Which lifestyle factors have the greatest affect on the risk of heart disease?
This research question aims to uncover modifiable factors, offering preventive health recommendations.

Examples: Computer Science
Last but certainly not least, let’s look at a few examples of research questions within the computer science world.
What are the perceived risks of cloud-based storage systems?
Highly relevant in our digital age, this research question would align well with a qualitative interview approach to better understand what users feel the key risks of cloud storage are.
Which factors affect the energy efficiency of data centres in Ohio?
With a clear focus, this research question lays a firm foundation for a quantitative study.
How do TikTok algorithms impact user behaviour amongst new graduates?
While this research question is more open-ended, it could form the basis for a qualitative investigation.
What are the perceived risk and benefits of open-source software software within the web design industry?
Practical and straightforward, the results could guide both developers and end-users in their choices.
Remember, these are just examples…
In this post, we’ve tried to provide a wide range of research question examples to help you get a feel for what research questions look like in practice. That said, it’s important to remember that these are just examples and don’t necessarily equate to good research topics . If you’re still trying to find a topic, check out our topic megalist for inspiration.

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
Research ideas on Political Science
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

Qualitative Research Questionnaire – Types & Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 19th, 2024 , Revised On October 24, 2024
Before you start your research, the first thing you need to identify is the research method . Depending on different factors, you will either choose a quantitative or qualitative study.
Qualitative research is a great tool that helps understand the depth and richness of human opinions and experiences. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data , qualitative research allows exploring and interpreting the experiences of the subject. Questionnaires, although mostly associated with quantitative research, can also be a valuable instrument in qualitative studies. Let’s explore what qualitative research questionnaires are and how you can create one.
What Is A Qualitative Research Questionnaire
Qualitative research questionnaires are a structured or semi-structured set of questions designed to gather detailed, open-ended participant responses. It allows you to uncover underlying reasons and opinions and provides insights into a particular phenomenon.
While quantitative questionnaires often have closed-ended questions and numerical responses, a qualitative questionnaire encourages participants to express themselves freely. Before you design your questionnaire, you should know exactly what you need so you can keep your questions specific enough for the participants to understand.
For example:
- Describe your experience using our product.
- How has technology impacted your work-life balance?
Types of Qualitative Research Questions With Examples
Now that you are familiar with what qualitative research questions are, let’s look at the different types of questions you can use in your survey .
Descriptive Questions
These are used to explore and describe a phenomenon in detail. It helps answer the “what” part of the research, and the questions are mostly foundational.
Example: How do students experience online learning?
Comparative Questions
This type allows you to compare and contrast different groups or situations. You can explore the differences and similarities to highlight the impact of specific variables.
Example: How do the study habits of first-year and fourth-year university students differ?
Interpretive Questions
These questions help you understand the meanings people attach to experiences or phenomena by answering the “how” and “why”.
Example: What does “success” mean to entrepreneurs?
Evaluative Questions
You can use these to assess the quality or value of something. These allow you to understand the outcomes of various situations.
Example: How effective is the new customer service training program?
Process-Oriented Questions
To understand how something happens or develops over time, researchers often use process-oriented questions.
Example: How do individuals develop their career goals?
Exploratory Questions
These allow you to discover new perspectives on a topic. However, you have to be careful that there must be no preconceived notions or research biases to it.
Example: What are the emerging trends in the mobile gaming industry?
How To Write Qualitative Research Questions?
For your study to be successful, it is important to consider designing a questionnaire for qualitative research critically, as it will shape your research and data collection. Here is an easy guide to writing your qualitative research questions perfectly.
Tip 1: Understand Your Research Goals
Many students start their research without clear goals, and they have to make substantial changes to their study in the middle of the research. This wastes time and resources.
Before you start crafting your questions, it is important to know your research objectives. You should know what you aim to discover through your research, or what specific knowledge gaps you are going to fill. With the help of a well-defined research focus, you can develop relevant and meaningful information.
Tip 2: Choose The Structure For Research Questions
There are mostly open-ended questionnaires in qualitative research. They begin with words like “how,” “what,” and “why.” However, the structure of your research questions depends on your research design . You have to consider using broad, overarching questions to explore the main research focus, and then add some specific probes to further research the particular aspects of the topic.
Tip 3: Use Clear Language
The more clear and concise your research questions are, the more effective and free from ambiguity they will be. Do not use complex terminology that might confuse participants. Try using simple and direct language that accurately conveys your intended meaning.
Here is a table to explain the wrong and right ways of writing your qualitative research questions.
Tip 4: Check Relevance With Research Goals
Once you have developed some questions, check if they align with your research objectives. You must ensure that each question contributes to your overall research questions. After this, you can eliminate any questions that do not serve a clear purpose in your study.
Tip 5: Concentrate On A Single Theme
While it is tempting to cover multiple aspects of a topic in one question, it is best to focus on a single theme per question. This helps to elicit focused responses from participants. Moreover, you have to avoid combining unrelated concepts into a single question.
If your main research question is complicated, you can create sub-questions with a “ladder structure”. These allow you to understand the attributes, consequences, and core values of your research. For example, let’s say your main broad research question is:
- How do you feel about your overall experience with our company?
The intermediate questions may be:
- What aspects of your experience were positive?
- What aspects of your experience were negative?
- How likely are you to recommend our company to a friend or colleague?
Types Of Survey Questionnaires In Qualitative Research
It is important to consider your research objectives, target population, resources and needed depth of research when selecting a survey method. The main types of qualitative surveys are discussed below.
Face To Face Surveys
Face-to-face surveys involve direct interaction between the researcher and the participant. This method allows observers to capture non-verbal cues, body language, and facial expressions, and helps adapt questions based on participant responses. They also let you clarify any misunderstandings. Moreover, there is a higher response rate because of personal interaction.
Example: A researcher conducting a study on consumer experiences with a new product might visit participants’ homes to conduct a detailed interview.
Telephone Surveys
These type of qualitative research survey questionnaires provide a less intrusive method for collecting qualitative data. The benefits of telephone surveys include, that it allows you to collect data from a wider population. Moreover, it is generally less expensive than face-to-face interviews and interviews can be conducted efficiently.
Example: A market research firm might conduct telephone surveys to understand customer satisfaction with a telecommunication service.
Online Surveys
Online survey questionnaires are a convenient and cost-effective way to gather qualitative data. You can reach a wide audience quickly, and participants may feel more comfortable sharing sensitive information because of anonymity. Additionally, there are no travel or printing expenses.
Example: A university might use online surveys to explore students’ perceptions of online learning experiences.
Strengths & Limitations Of Questionnaires In Qualitative Research
Questionnaires are undoubtedly a great data collection tool. However, it comes with its fair share of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s discuss the benefits of questionnaires in qualitative research and their cons as well.
Qualitative Research Questionnaire Example
Here is a concise qualitative research questionnaire sample for research papers to give you a better idea of its format and how it is presented.
Thank you for participating in our survey. We value your feedback on our new mobile app. Your responses will help us improve the applications and better meet your needs.
Demographic Information
- Occupation:
- How long have you been using smartphones:
- How would you describe your overall experience with the new mobile app?
- What do you like most about the app?
- What do you dislike most about the app?
- Are there any specific features you find particularly useful or helpful? Please explain.
- Are there any features you think are missing or could be improved? Please elaborate.
- How easy is the app to navigate? Please explain any difficulties you encountered.
- How does this app compare to other similar apps you have used?
- What are your expectations for future updates or improvements to the app?
- Is there anything else you would like to share about your experience with the app?
Are questionnaires quantitative or qualitative research?
A survey research questionnaire can have both qualitative and quantitative questions. The qualitative questions are mostly open-ended, and quantitative questions take the form of yes/no, or Likert scale rating.
Can we use questionnaires in qualitative research?
Yes, survey questionnaires can be used in qualitative research for data collection. However, instead of a Likert scale or rating, you can post open-ended questions to your respondents. The participants can provide detailed responses to the questions asked.
Why are questionnaires good for qualitative research?
In qualitative research, questionnaires allow you to collect qualitative data. The open-ended and unstructured questions help respondents present their ideas freely and provide insights.
You May Also Like
A survey includes questions relevant to the research topic. The participants are selected, and the questionnaire is distributed to collect the data.
This post provides the key disadvantages of secondary research so you know the limitations of secondary research before making a decision.
This article provides the key advantages of primary research over secondary research so you can make an informed decision.
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works
18 Qualitative Research Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Qualitative research is an approach to scientific research that involves using observation to gather and analyze non-numerical, in-depth, and well-contextualized datasets.
It serves as an integral part of academic, professional, and even daily decision-making processes (Baxter & Jack, 2008).
Methods of qualitative research encompass a wide range of techniques, from in-depth personal encounters, like ethnographies (studying cultures in-depth) and autoethnographies (examining one’s own cultural experiences), to collection of diverse perspectives on topics through methods like interviewing focus groups (gatherings of individuals to discuss specific topics).
Qualitative Research Examples
1. ethnography.
Definition: Ethnography is a qualitative research design aimed at exploring cultural phenomena. Rooted in the discipline of anthropology , this research approach investigates the social interactions, behaviors, and perceptions within groups, communities, or organizations.
Ethnographic research is characterized by extended observation of the group, often through direct participation, in the participants’ environment. An ethnographer typically lives with the study group for extended periods, intricately observing their everyday lives (Khan, 2014).
It aims to present a complete, detailed and accurate picture of the observed social life, rituals, symbols, and values from the perspective of the study group.
Example of Ethnographic Research
Title: “ The Everyday Lives of Men: An Ethnographic Investigation of Young Adult Male Identity “
Citation: Evans, J. (2010). The Everyday Lives of Men: An Ethnographic Investigation of Young Adult Male Identity. Peter Lang.
Overview: This study by Evans (2010) provides a rich narrative of young adult male identity as experienced in everyday life. The author immersed himself among a group of young men, participating in their activities and cultivating a deep understanding of their lifestyle, values, and motivations. This research exemplified the ethnographic approach, revealing complexities of the subjects’ identities and societal roles, which could hardly be accessed through other qualitative research designs.
Read my Full Guide on Ethnography Here
2. Autoethnography
Definition: Autoethnography is an approach to qualitative research where the researcher uses their own personal experiences to extend the understanding of a certain group, culture, or setting. Essentially, it allows for the exploration of self within the context of social phenomena.
Unlike traditional ethnography, which focuses on the study of others, autoethnography turns the ethnographic gaze inward, allowing the researcher to use their personal experiences within a culture as rich qualitative data (Durham, 2019).
The objective is to critically appraise one’s personal experiences as they navigate and negotiate cultural, political, and social meanings. The researcher becomes both the observer and the participant, intertwining personal and cultural experiences in the research.
Example of Autoethnographic Research
Title: “ A Day In The Life Of An NHS Nurse “
Citation: Osben, J. (2019). A day in the life of a NHS nurse in 21st Century Britain: An auto-ethnography. The Journal of Autoethnography for Health & Social Care. 1(1).
Overview: This study presents an autoethnography of a day in the life of an NHS nurse (who, of course, is also the researcher). The author uses the research to achieve reflexivity, with the researcher concluding: “Scrutinising my practice and situating it within a wider contextual backdrop has compelled me to significantly increase my level of scrutiny into the driving forces that influence my practice.”
Read my Full Guide on Autoethnography Here
3. Semi-Structured Interviews
Definition: Semi-structured interviews stand as one of the most frequently used methods in qualitative research. These interviews are planned and utilize a set of pre-established questions, but also allow for the interviewer to steer the conversation in other directions based on the responses given by the interviewee.
In semi-structured interviews, the interviewer prepares a guide that outlines the focal points of the discussion. However, the interview is flexible, allowing for more in-depth probing if the interviewer deems it necessary (Qu, & Dumay, 2011). This style of interviewing strikes a balance between structured ones which might limit the discussion, and unstructured ones, which could lack focus.
Example of Semi-Structured Interview Research
Title: “ Factors influencing adherence to cancer treatment in older adults with cancer: a systematic review “
Citation: Puts, M., et al. (2014). Factors influencing adherence to cancer treatment in older adults with cancer: a systematic review. Annals of oncology, 25 (3), 564-577.
Overview: Puts et al. (2014) executed an extensive systematic review in which they conducted semi-structured interviews with older adults suffering from cancer to examine the factors influencing their adherence to cancer treatment. The findings suggested that various factors, including side effects, faith in healthcare professionals, and social support have substantial impacts on treatment adherence. This research demonstrates how semi-structured interviews can provide rich and profound insights into the subjective experiences of patients.
4. Focus Groups
Definition: Focus groups are a qualitative research method that involves organized discussion with a selected group of individuals to gain their perspectives on a specific concept, product, or phenomenon. Typically, these discussions are guided by a moderator.
During a focus group session, the moderator has a list of questions or topics to discuss, and participants are encouraged to interact with each other (Morgan, 2010). This interactivity can stimulate more information and provide a broader understanding of the issue under scrutiny. The open format allows participants to ask questions and respond freely, offering invaluable insights into attitudes, experiences, and group norms.
Example of Focus Group Research
Title: “ Perspectives of Older Adults on Aging Well: A Focus Group Study “
Citation: Halaweh, H., Dahlin-Ivanoff, S., Svantesson, U., & Willén, C. (2018). Perspectives of older adults on aging well: a focus group study. Journal of aging research .
Overview: This study aimed to explore what older adults (aged 60 years and older) perceived to be ‘aging well’. The researchers identified three major themes from their focus group interviews: a sense of well-being, having good physical health, and preserving good mental health. The findings highlight the importance of factors such as positive emotions, social engagement, physical activity, healthy eating habits, and maintaining independence in promoting aging well among older adults.
5. Phenomenology
Definition: Phenomenology, a qualitative research method, involves the examination of lived experiences to gain an in-depth understanding of the essence or underlying meanings of a phenomenon.
The focus of phenomenology lies in meticulously describing participants’ conscious experiences related to the chosen phenomenon (Padilla-Díaz, 2015).
In a phenomenological study, the researcher collects detailed, first-hand perspectives of the participants, typically via in-depth interviews, and then uses various strategies to interpret and structure these experiences, ultimately revealing essential themes (Creswell, 2013). This approach focuses on the perspective of individuals experiencing the phenomenon, seeking to explore, clarify, and understand the meanings they attach to those experiences.
Example of Phenomenology Research
Title: “ A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology: current state, promise, and future directions for research ”
Citation: Cilesiz, S. (2011). A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology: Current state, promise, and future directions for research. Educational Technology Research and Development, 59 , 487-510.
Overview: A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology by Sebnem Cilesiz represents a good starting point for formulating a phenomenological study. With its focus on the ‘essence of experience’, this piece presents methodological, reliability, validity, and data analysis techniques that phenomenologists use to explain how people experience technology in their everyday lives.
6. Grounded Theory
Definition: Grounded theory is a systematic methodology in qualitative research that typically applies inductive reasoning . The primary aim is to develop a theoretical explanation or framework for a process, action, or interaction grounded in, and arising from, empirical data (Birks & Mills, 2015).
In grounded theory, data collection and analysis work together in a recursive process. The researcher collects data, analyses it, and then collects more data based on the evolving understanding of the research context. This ongoing process continues until a comprehensive theory that represents the data and the associated phenomenon emerges – a point known as theoretical saturation (Charmaz, 2014).
Example of Grounded Theory Research
Title: “ Student Engagement in High School Classrooms from the Perspective of Flow Theory “
Citation: Shernoff, D. J., Csikszentmihalyi, M., Shneider, B., & Shernoff, E. S. (2003). Student engagement in high school classrooms from the perspective of flow theory. School Psychology Quarterly, 18 (2), 158–176.
Overview: Shernoff and colleagues (2003) used grounded theory to explore student engagement in high school classrooms. The researchers collected data through student self-reports, interviews, and observations. Key findings revealed that academic challenge, student autonomy, and teacher support emerged as the most significant factors influencing students’ engagement, demonstrating how grounded theory can illuminate complex dynamics within real-world contexts.
7. Narrative Research
Definition: Narrative research is a qualitative research method dedicated to storytelling and understanding how individuals experience the world. It focuses on studying an individual’s life and experiences as narrated by that individual (Polkinghorne, 2013).
In narrative research, the researcher collects data through methods such as interviews, observations , and document analysis. The emphasis is on the stories told by participants – narratives that reflect their experiences, thoughts, and feelings.
These stories are then interpreted by the researcher, who attempts to understand the meaning the participant attributes to these experiences (Josselson, 2011).
Example of Narrative Research
Title: “Narrative Structures and the Language of the Self”
Citation: McAdams, D. P., Josselson, R., & Lieblich, A. (2006). Identity and story: Creating self in narrative . American Psychological Association.
Overview: In this innovative study, McAdams et al. (2006) employed narrative research to explore how individuals construct their identities through the stories they tell about themselves. By examining personal narratives, the researchers discerned patterns associated with characters, motivations, conflicts, and resolutions, contributing valuable insights about the relationship between narrative and individual identity.
8. Case Study Research
Definition: Case study research is a qualitative research method that involves an in-depth investigation of a single instance or event: a case. These ‘cases’ can range from individuals, groups, or entities to specific projects, programs, or strategies (Creswell, 2013).
The case study method typically uses multiple sources of information for comprehensive contextual analysis. It aims to explore and understand the complexity and uniqueness of a particular case in a real-world context (Merriam & Tisdell, 2015). This investigation could result in a detailed description of the case, a process for its development, or an exploration of a related issue or problem.
Example of Case Study Research
Title: “ Teacher’s Role in Fostering Preschoolers’ Computational Thinking: An Exploratory Case Study “
Citation: Wang, X. C., Choi, Y., Benson, K., Eggleston, C., & Weber, D. (2021). Teacher’s role in fostering preschoolers’ computational thinking: An exploratory case study. Early Education and Development , 32 (1), 26-48.
Overview: This study investigates the role of teachers in promoting computational thinking skills in preschoolers. The study utilized a qualitative case study methodology to examine the computational thinking scaffolding strategies employed by a teacher interacting with three preschoolers in a small group setting. The findings highlight the importance of teachers’ guidance in fostering computational thinking practices such as problem reformulation/decomposition, systematic testing, and debugging.
Read about some Famous Case Studies in Psychology Here
9. Participant Observation
Definition: Participant observation has the researcher immerse themselves in a group or community setting to observe the behavior of its members. It is similar to ethnography, but generally, the researcher isn’t embedded for a long period of time.
The researcher, being a participant, engages in daily activities, interactions, and events as a way of conducting a detailed study of a particular social phenomenon (Kawulich, 2005).
The method involves long-term engagement in the field, maintaining detailed records of observed events, informal interviews, direct participation, and reflexivity. This approach allows for a holistic view of the participants’ lived experiences, behaviours, and interactions within their everyday environment (Dewalt, 2011).
Example of Participant Observation Research
Title: Conflict in the boardroom: a participant observation study of supervisory board dynamics
Citation: Heemskerk, E. M., Heemskerk, K., & Wats, M. M. (2017). Conflict in the boardroom: a participant observation study of supervisory board dynamics. Journal of Management & Governance , 21 , 233-263.
Overview: This study examined how conflicts within corporate boards affect their performance. The researchers used a participant observation method, where they actively engaged with 11 supervisory boards and observed their dynamics. They found that having a shared understanding of the board’s role called a common framework, improved performance by reducing relationship conflicts, encouraging task conflicts, and minimizing conflicts between the board and CEO.
10. Non-Participant Observation
Definition: Non-participant observation is a qualitative research method in which the researcher observes the phenomena of interest without actively participating in the situation, setting, or community being studied.
This method allows the researcher to maintain a position of distance, as they are solely an observer and not a participant in the activities being observed (Kawulich, 2005).
During non-participant observation, the researcher typically records field notes on the actions, interactions, and behaviors observed , focusing on specific aspects of the situation deemed relevant to the research question.
This could include verbal and nonverbal communication , activities, interactions, and environmental contexts (Angrosino, 2007). They could also use video or audio recordings or other methods to collect data.
Example of Non-Participant Observation Research
Title: Mental Health Nurses’ attitudes towards mental illness and recovery-oriented practice in acute inpatient psychiatric units: A non-participant observation study
Citation: Sreeram, A., Cross, W. M., & Townsin, L. (2023). Mental Health Nurses’ attitudes towards mental illness and recovery‐oriented practice in acute inpatient psychiatric units: A non‐participant observation study. International Journal of Mental Health Nursing .
Overview: This study investigated the attitudes of mental health nurses towards mental illness and recovery-oriented practice in acute inpatient psychiatric units. The researchers used a non-participant observation method, meaning they observed the nurses without directly participating in their activities. The findings shed light on the nurses’ perspectives and behaviors, providing valuable insights into their attitudes toward mental health and recovery-focused care in these settings.
11. Content Analysis
Definition: Content Analysis involves scrutinizing textual, visual, or spoken content to categorize and quantify information. The goal is to identify patterns, themes, biases, or other characteristics (Hsieh & Shannon, 2005).
Content Analysis is widely used in various disciplines for a multitude of purposes. Researchers typically use this method to distill large amounts of unstructured data, like interview transcripts, newspaper articles, or social media posts, into manageable and meaningful chunks.
When wielded appropriately, Content Analysis can illuminate the density and frequency of certain themes within a dataset, provide insights into how specific terms or concepts are applied contextually, and offer inferences about the meanings of their content and use (Duriau, Reger, & Pfarrer, 2007).
Example of Content Analysis
Title: Framing European politics: A content analysis of press and television news .
Citation: Semetko, H. A., & Valkenburg, P. M. (2000). Framing European politics: A content analysis of press and television news. Journal of Communication, 50 (2), 93-109.
Overview: This study analyzed press and television news articles about European politics using a method called content analysis. The researchers examined the prevalence of different “frames” in the news, which are ways of presenting information to shape audience perceptions. They found that the most common frames were attribution of responsibility, conflict, economic consequences, human interest, and morality.
Read my Full Guide on Content Analysis Here
12. Discourse Analysis
Definition: Discourse Analysis, a qualitative research method, interprets the meanings, functions, and coherence of certain languages in context.
Discourse analysis is typically understood through social constructionism, critical theory , and poststructuralism and used for understanding how language constructs social concepts (Cheek, 2004).
Discourse Analysis offers great breadth, providing tools to examine spoken or written language, often beyond the level of the sentence. It enables researchers to scrutinize how text and talk articulate social and political interactions and hierarchies.
Insight can be garnered from different conversations, institutional text, and media coverage to understand how topics are addressed or framed within a specific social context (Jorgensen & Phillips, 2002).
Example of Discourse Analysis
Title: The construction of teacher identities in educational policy documents: A critical discourse analysis
Citation: Thomas, S. (2005). The construction of teacher identities in educational policy documents: A critical discourse analysis. Critical Studies in Education, 46 (2), 25-44.
Overview: The author examines how an education policy in one state of Australia positions teacher professionalism and teacher identities. While there are competing discourses about professional identity, the policy framework privileges a narrative that frames the ‘good’ teacher as one that accepts ever-tightening control and regulation over their professional practice.
Read my Full Guide on Discourse Analysis Here
13. Action Research
Definition: Action Research is a qualitative research technique that is employed to bring about change while simultaneously studying the process and results of that change.
This method involves a cyclical process of fact-finding, action, evaluation, and reflection (Greenwood & Levin, 2016).
Typically, Action Research is used in the fields of education, social sciences , and community development. The process isn’t just about resolving an issue but also developing knowledge that can be used in the future to address similar or related problems.
The researcher plays an active role in the research process, which is normally broken down into four steps:
- developing a plan to improve what is currently being done
- implementing the plan
- observing the effects of the plan, and
- reflecting upon these effects (Smith, 2010).
Example of Action Research
Title: Using Digital Sandbox Gaming to Improve Creativity Within Boys’ Writing
Citation: Ellison, M., & Drew, C. (2020). Using digital sandbox gaming to improve creativity within boys’ writing. Journal of Research in Childhood Education , 34 (2), 277-287.
Overview: This was a research study one of my research students completed in his own classroom under my supervision. He implemented a digital game-based approach to literacy teaching with boys and interviewed his students to see if the use of games as stimuli for storytelling helped draw them into the learning experience.
Read my Full Guide on Action Research Here
14. Semiotic Analysis
Definition: Semiotic Analysis is a qualitative method of research that interprets signs and symbols in communication to understand sociocultural phenomena. It stems from semiotics, the study of signs and symbols and their use or interpretation (Chandler, 2017).
In a Semiotic Analysis, signs (anything that represents something else) are interpreted based on their significance and the role they play in representing ideas.
This type of research often involves the examination of images, sounds, and word choice to uncover the embedded sociocultural meanings. For example, an advertisement for a car might be studied to learn more about societal views on masculinity or success (Berger, 2010).
Example of Semiotic Research
Title: Shielding the learned body: a semiotic analysis of school badges in New South Wales, Australia
Citation: Symes, C. (2023). Shielding the learned body: a semiotic analysis of school badges in New South Wales, Australia. Semiotica , 2023 (250), 167-190.
Overview: This study examines school badges in New South Wales, Australia, and explores their significance through a semiotic analysis. The badges, which are part of the school’s visual identity, are seen as symbolic representations that convey meanings. The analysis reveals that these badges often draw on heraldic models, incorporating elements like colors, names, motifs, and mottoes that reflect local culture and history, thus connecting students to their national identity. Additionally, the study highlights how some schools have shifted from traditional badges to modern logos and slogans, reflecting a more business-oriented approach.
15. Qualitative Longitudinal Studies
Definition: Qualitative Longitudinal Studies are a research method that involves repeated observation of the same items over an extended period of time.
Unlike a snapshot perspective, this method aims to piece together individual histories and examine the influences and impacts of change (Neale, 2019).
Qualitative Longitudinal Studies provide an in-depth understanding of change as it happens, including changes in people’s lives, their perceptions, and their behaviors.
For instance, this method could be used to follow a group of students through their schooling years to understand the evolution of their learning behaviors and attitudes towards education (Saldaña, 2003).
Example of Qualitative Longitudinal Research
Title: Patient and caregiver perspectives on managing pain in advanced cancer: a qualitative longitudinal study
Citation: Hackett, J., Godfrey, M., & Bennett, M. I. (2016). Patient and caregiver perspectives on managing pain in advanced cancer: a qualitative longitudinal study. Palliative medicine , 30 (8), 711-719.
Overview: This article examines how patients and their caregivers manage pain in advanced cancer through a qualitative longitudinal study. The researchers interviewed patients and caregivers at two different time points and collected audio diaries to gain insights into their experiences, making this study longitudinal.
Read my Full Guide on Longitudinal Research Here
16. Open-Ended Surveys
Definition: Open-Ended Surveys are a type of qualitative research method where respondents provide answers in their own words. Unlike closed-ended surveys, which limit responses to predefined options, open-ended surveys allow for expansive and unsolicited explanations (Fink, 2013).
Open-ended surveys are commonly used in a range of fields, from market research to social studies. As they don’t force respondents into predefined response categories, these surveys help to draw out rich, detailed data that might uncover new variables or ideas.
For example, an open-ended survey might be used to understand customer opinions about a new product or service (Lavrakas, 2008).
Contrast this to a quantitative closed-ended survey, like a Likert scale, which could theoretically help us to come up with generalizable data but is restricted by the questions on the questionnaire, meaning new and surprising data and insights can’t emerge from the survey results in the same way.
Example of Open-Ended Survey Research
Title: Advantages and disadvantages of technology in relationships: Findings from an open-ended survey
Citation: Hertlein, K. M., & Ancheta, K. (2014). Advantages and disadvantages of technology in relationships: Findings from an open-ended survey. The Qualitative Report , 19 (11), 1-11.
Overview: This article examines the advantages and disadvantages of technology in couple relationships through an open-ended survey method. Researchers analyzed responses from 410 undergraduate students to understand how technology affects relationships. They found that technology can contribute to relationship development, management, and enhancement, but it can also create challenges such as distancing, lack of clarity, and impaired trust.
17. Naturalistic Observation
Definition: Naturalistic Observation is a type of qualitative research method that involves observing individuals in their natural environments without interference or manipulation by the researcher.
Naturalistic observation is often used when conducting research on behaviors that cannot be controlled or manipulated in a laboratory setting (Kawulich, 2005).
It is frequently used in the fields of psychology, sociology, and anthropology. For instance, to understand the social dynamics in a schoolyard, a researcher could spend time observing the children interact during their recess, noting their behaviors, interactions, and conflicts without imposing their presence on the children’s activities (Forsyth, 2010).
Example of Naturalistic Observation Research
Title: Dispositional mindfulness in daily life: A naturalistic observation study
Citation: Kaplan, D. M., Raison, C. L., Milek, A., Tackman, A. M., Pace, T. W., & Mehl, M. R. (2018). Dispositional mindfulness in daily life: A naturalistic observation study. PloS one , 13 (11), e0206029.
Overview: In this study, researchers conducted two studies: one exploring assumptions about mindfulness and behavior, and the other using naturalistic observation to examine actual behavioral manifestations of mindfulness. They found that trait mindfulness is associated with a heightened perceptual focus in conversations, suggesting that being mindful is expressed primarily through sharpened attention rather than observable behavioral or social differences.
Read my Full Guide on Naturalistic Observation Here
18. Photo-Elicitation
Definition: Photo-elicitation utilizes photographs as a means to trigger discussions and evoke responses during interviews. This strategy aids in bringing out topics of discussion that may not emerge through verbal prompting alone (Harper, 2002).
Traditionally, Photo-Elicitation has been useful in various fields such as education, psychology, and sociology. The method involves the researcher or participants taking photographs, which are then used as prompts for discussion.
For instance, a researcher studying urban environmental issues might invite participants to photograph areas in their neighborhood that they perceive as environmentally detrimental, and then discuss each photo in depth (Clark-Ibáñez, 2004).
Example of Photo-Elicitation Research
Title: Early adolescent food routines: A photo-elicitation study
Citation: Green, E. M., Spivak, C., & Dollahite, J. S. (2021). Early adolescent food routines: A photo-elicitation study. Appetite, 158 .
Overview: This study focused on early adolescents (ages 10-14) and their food routines. Researchers conducted in-depth interviews using a photo-elicitation approach, where participants took photos related to their food choices and experiences. Through analysis, the study identified various routines and three main themes: family, settings, and meals/foods consumed, revealing how early adolescents view and are influenced by their eating routines.
Features of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a research method focused on understanding the meaning individuals or groups attribute to a social or human problem (Creswell, 2013).
Some key features of this method include:
- Naturalistic Inquiry: Qualitative research happens in the natural setting of the phenomena, aiming to understand “real world” situations (Patton, 2015). This immersion in the field or subject allows the researcher to gather a deep understanding of the subject matter.
- Emphasis on Process: It aims to understand how events unfold over time rather than focusing solely on outcomes (Merriam & Tisdell, 2015). The process-oriented nature of qualitative research allows researchers to investigate sequences, timing, and changes.
- Interpretive: It involves interpreting and making sense of phenomena in terms of the meanings people assign to them (Denzin & Lincoln, 2011). This interpretive element allows for rich, nuanced insights into human behavior and experiences.
- Holistic Perspective: Qualitative research seeks to understand the whole phenomenon rather than focusing on individual components (Creswell, 2013). It emphasizes the complex interplay of factors, providing a richer, more nuanced view of the research subject.
- Prioritizes Depth over Breadth: Qualitative research favors depth of understanding over breadth, typically involving a smaller but more focused sample size (Hennink, Hutter, & Bailey, 2020). This enables detailed exploration of the phenomena of interest, often leading to rich and complex data.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research
Qualitative research centers on exploring and understanding the meaning individuals or groups attribute to a social or human problem (Creswell, 2013).
It involves an in-depth approach to the subject matter, aiming to capture the richness and complexity of human experience.
Examples include conducting interviews, observing behaviors, or analyzing text and images.
There are strengths inherent in this approach. In its focus on understanding subjective experiences and interpretations, qualitative research can yield rich and detailed data that quantitative research may overlook (Denzin & Lincoln, 2011).
Additionally, qualitative research is adaptive, allowing the researcher to respond to new directions and insights as they emerge during the research process.
However, there are also limitations. Because of the interpretive nature of this research, findings may not be generalizable to a broader population (Marshall & Rossman, 2014). Well-designed quantitative research, on the other hand, can be generalizable.
Moreover, the reliability and validity of qualitative data can be challenging to establish due to its subjective nature, unlike quantitative research, which is ideally more objective.
Compare Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methodologies in This Guide Here
In conclusion, qualitative research methods provide distinctive ways to explore social phenomena and understand nuances that quantitative approaches might overlook. Each method, from Ethnography to Photo-Elicitation, presents its strengths and weaknesses but they all offer valuable means of investigating complex, real-world situations. The goal for the researcher is not to find a definitive tool, but to employ the method best suited for their research questions and the context at hand (Almalki, 2016). Above all, these methods underscore the richness of human experience and deepen our understanding of the world around us.
Angrosino, M. (2007). Doing ethnographic and observational research. Sage Publications.
Areni, C. S., & Kim, D. (1994). The influence of in-store lighting on consumers’ examination of merchandise in a wine store. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 11 (2), 117-125.
Barker, C., Pistrang, N., & Elliott, R. (2016). Research Methods in Clinical Psychology: An Introduction for Students and Practitioners. John Wiley & Sons.
Baxter, P. & Jack, S. (2008). Qualitative case study methodology: Study design and implementation for novice researchers. The Qualitative Report, 13 (4), 544-559.
Berger, A. A. (2010). The Objects of Affection: Semiotics and Consumer Culture. Palgrave Macmillan.
Bevan, M. T. (2014). A method of phenomenological interviewing. Qualitative health research, 24 (1), 136-144.
Birks, M., & Mills, J. (2015). Grounded theory: A practical guide . Sage Publications.
Bryman, A. (2015) . The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research. Sage Publications.
Chandler, D. (2017). Semiotics: The Basics. Routledge.
Charmaz, K. (2014). Constructing grounded theory. Sage Publications.
Cheek, J. (2004). At the margins? Discourse analysis and qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research, 14(8), 1140-1150.
Clark-Ibáñez, M. (2004). Framing the social world with photo-elicitation interviews. American Behavioral Scientist, 47(12), 1507-1527.
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative and Mixed Methods Approaches. Sage Publications.
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2017). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Sage publications.
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A., Huby, G., Avery, A., & Sheikh, A. (2011). The case study approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 11(100), 1-9.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2011). The Sage Handbook of Qualitative Research. Sage.
Dewalt, K. M., & Dewalt, B. R. (2011). Participant observation: A guide for fieldworkers. Rowman Altamira.
Doody, O., Slevin, E., & Taggart, L. (2013). Focus group interviews in nursing research: part 1. British Journal of Nursing, 22(1), 16-19.
Durham, A. (2019). Autoethnography. In P. Atkinson (Ed.), Qualitative Research Methods. Oxford University Press.
Duriau, V. J., Reger, R. K., & Pfarrer, M. D. (2007). A content analysis of the content analysis literature in organization studies: Research themes, data sources, and methodological refinements. Organizational Research Methods, 10(1), 5-34.
Evans, J. (2010). The Everyday Lives of Men: An Ethnographic Investigation of Young Adult Male Identity. Peter Lang.
Farrall, S. (2006). What is qualitative longitudinal research? Papers in Social Research Methods, Qualitative Series, No.11, London School of Economics, Methodology Institute.
Fielding, J., & Fielding, N. (2008). Synergy and synthesis: integrating qualitative and quantitative data. The SAGE handbook of social research methods, 555-571.
Fink, A. (2013). How to conduct surveys: A step-by-step guide . SAGE.
Forsyth, D. R. (2010). Group Dynamics . Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Fugard, A. J. B., & Potts, H. W. W. (2015). Supporting thinking on sample sizes for thematic analyses: A quantitative tool. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 18 (6), 669–684.
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research. Aldine de Gruyter.
Gray, J. R., Grove, S. K., & Sutherland, S. (2017). Burns and Grove’s the Practice of Nursing Research E-Book: Appraisal, Synthesis, and Generation of Evidence. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Greenwood, D. J., & Levin, M. (2016). Introduction to action research: Social research for social change. SAGE.
Harper, D. (2002). Talking about pictures: A case for photo elicitation. Visual Studies, 17 (1), 13-26.
Heinonen, T. (2012). Making Sense of the Social: Human Sciences and the Narrative Turn. Rozenberg Publishers.
Heisley, D. D., & Levy, S. J. (1991). Autodriving: A photoelicitation technique. Journal of Consumer Research, 18 (3), 257-272.
Hennink, M. M., Hutter, I., & Bailey, A. (2020). Qualitative Research Methods . SAGE Publications Ltd.
Hsieh, H. F., & Shannon, S. E. (2005). Three Approaches to Qualitative Content Analysis. Qualitative Health Research, 15 (9), 1277–1288.
Jorgensen, D. L. (2015). Participant Observation. In Emerging Trends in the Social and Behavioral Sciences: An Interdisciplinary, Searchable, and Linkable Resource. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Jorgensen, M., & Phillips, L. (2002). Discourse Analysis as Theory and Method . SAGE.
Josselson, R. (2011). Narrative research: Constructing, deconstructing, and reconstructing story. In Five ways of doing qualitative analysis . Guilford Press.
Kawulich, B. B. (2005). Participant observation as a data collection method. Forum: Qualitative Social Research, 6 (2).
Khan, S. (2014). Qualitative Research Method: Grounded Theory. Journal of Basic and Clinical Pharmacy, 5 (4), 86-88.
Koshy, E., Koshy, V., & Waterman, H. (2010). Action Research in Healthcare . SAGE.
Krippendorff, K. (2013). Content Analysis: An Introduction to its Methodology. SAGE.
Lannon, J., & Cooper, P. (2012). Humanistic Advertising: A Holistic Cultural Perspective. International Journal of Advertising, 15 (2), 97–111.
Lavrakas, P. J. (2008). Encyclopedia of survey research methods. SAGE Publications.
Lieblich, A., Tuval-Mashiach, R., & Zilber, T. (2008). Narrative research: Reading, analysis and interpretation. Sage Publications.
Mackey, A., & Gass, S. M. (2015). Second language research: Methodology and design. Routledge.
Marshall, C., & Rossman, G. B. (2014). Designing qualitative research. Sage publications.
McAdams, D. P., Josselson, R., & Lieblich, A. (2006). Identity and story: Creating self in narrative. American Psychological Association.
Merriam, S. B., & Tisdell, E. J. (2015). Qualitative Research: A Guide to Design and Implementation. Jossey-Bass.
Mick, D. G. (1986). Consumer Research and Semiotics: Exploring the Morphology of Signs, Symbols, and Significance. Journal of Consumer Research, 13 (2), 196-213.
Morgan, D. L. (2010). Focus groups as qualitative research. Sage Publications.
Mulhall, A. (2003). In the field: notes on observation in qualitative research. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 41 (3), 306-313.
Neale, B. (2019). What is Qualitative Longitudinal Research? Bloomsbury Publishing.
Nolan, L. B., & Renderos, T. B. (2012). A focus group study on the influence of fatalism and religiosity on cancer risk perceptions in rural, eastern North Carolina. Journal of religion and health, 51 (1), 91-104.
Padilla-Díaz, M. (2015). Phenomenology in educational qualitative research: Philosophy as science or philosophical science? International Journal of Educational Excellence, 1 (2), 101-110.
Parker, I. (2014). Discourse dynamics: Critical analysis for social and individual psychology . Routledge.
Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice . Sage Publications.
Polkinghorne, D. E. (2013). Narrative configuration in qualitative analysis. In Life history and narrative. Routledge.
Puts, M. T., Tapscott, B., Fitch, M., Howell, D., Monette, J., Wan-Chow-Wah, D., Krzyzanowska, M., Leighl, N. B., Springall, E., & Alibhai, S. (2014). Factors influencing adherence to cancer treatment in older adults with cancer: a systematic review. Annals of oncology, 25 (3), 564-577.
Qu, S. Q., & Dumay, J. (2011). The qualitative research interview . Qualitative research in accounting & management.
Ali, J., & Bhaskar, S. B. (2016). Basic statistical tools in research and data analysis. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia, 60 (9), 662–669.
Rosenbaum, M. S. (2017). Exploring the social supportive role of third places in consumers’ lives. Journal of Service Research, 20 (1), 26-42.
Saldaña, J. (2003). Longitudinal Qualitative Research: Analyzing Change Through Time . AltaMira Press.
Saldaña, J. (2014). The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers. SAGE.
Shernoff, D. J., Csikszentmihalyi, M., Shneider, B., & Shernoff, E. S. (2003). Student engagement in high school classrooms from the perspective of flow theory. School Psychology Quarterly, 18 (2), 158-176.
Smith, J. A. (2015). Qualitative Psychology: A Practical Guide to Research Methods . Sage Publications.
Smith, M. K. (2010). Action Research. The encyclopedia of informal education.
Sue, V. M., & Ritter, L. A. (2012). Conducting online surveys . SAGE Publications.
Van Auken, P. M., Frisvoll, S. J., & Stewart, S. I. (2010). Visualising community: using participant-driven photo-elicitation for research and application. Local Environment, 15 (4), 373-388.
Van Voorhis, F. L., & Morgan, B. L. (2007). Understanding Power and Rules of Thumb for Determining Sample Sizes. Tutorials in Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 3 (2), 43–50.
Wodak, R., & Meyer, M. (2015). Methods of Critical Discourse Analysis . SAGE.
Zuber-Skerritt, O. (2018). Action research for developing educational theories and practices . Routledge.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
How to write a research proposal?
Devika rani duggappa.
- Author information
- Copyright and License information
Address for correspondence: Dr. Devika Rani Duggappa, 314/2/5, Durganjali Nilaya, 1 st H Cross, 7 th Main, Subbanna Garden, Vijayanagar, Bengaluru - 560 040, Karnataka, India. E-mail: [email protected]
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or ‘blueprint’ for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project should flow smoothly. Even today, many of the proposals at post-graduate evaluation committees and application proposals for funding are substandard. A search was conducted with keywords such as research proposal, writing proposal and qualitative using search engines, namely, PubMed and Google Scholar, and an attempt has been made to provide broad guidelines for writing a scientifically appropriate research proposal.
Key words: Guidelines, proposal, qualitative, research
INTRODUCTION
A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[ 1 ] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under ‘Research methodology II’ section [ Table 1 ] in this issue of IJA) and to request for grants. However, there are very few universally accepted guidelines for preparation of a good quality research proposal. A search was performed with keywords such as research proposal, funding, qualitative and writing proposals using search engines, namely, PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus.
Five ‘C’s while writing a literature review

BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[ 2 ] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the credibility, achievability, practicality and reproducibility (repeatability) of the research design.[ 3 ] Four categories of audience with different expectations may be present in the evaluation committees, namely academic colleagues, policy-makers, practitioners and lay audiences who evaluate the research proposal. Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; ‘be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for crystal clarity and plan before you write’. A researcher must be balanced, with a realistic understanding of what can be achieved. Being persuasive implies that researcher must be able to convince other researchers, research funding agencies, educational institutions and supervisors that the research is worth getting approval. The aim of the researcher should be clearly stated in simple language that describes the research in a way that non-specialists can comprehend, without use of jargons. The proposal must not only demonstrate that it is based on an intelligent understanding of the existing literature but also show that the writer has thought about the time needed to conduct each stage of the research.[ 4 , 5 ]
CONTENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution.
In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators, (iii) institutional affiliation (degree of the investigator and the name of institution where the study will be performed), details of contact such as phone numbers, E-mail id's and lines for signatures of investigators.
The main contents of the proposal may be presented under the following headings: (i) introduction, (ii) review of literature, (iii) aims and objectives, (iv) research design and methods, (v) ethical considerations, (vi) budget, (vii) appendices and (viii) citations.[ 4 ]
Introduction
It is also sometimes termed as ‘need for study’ or ‘abstract’. Introduction is an initial pitch of an idea; it sets the scene and puts the research in context.[ 6 ] The introduction should be designed to create interest in the reader about the topic and proposal. It should convey to the reader, what you want to do, what necessitates the study and your passion for the topic.[ 7 ] Some questions that can be used to assess the significance of the study are: (i) Who has an interest in the domain of inquiry? (ii) What do we already know about the topic? (iii) What has not been answered adequately in previous research and practice? (iv) How will this research add to knowledge, practice and policy in this area? Some of the evaluation committees, expect the last two questions, elaborated under a separate heading of ‘background and significance’.[ 8 ] Introduction should also contain the hypothesis behind the research design. If hypothesis cannot be constructed, the line of inquiry to be used in the research must be indicated.
Review of literature
It refers to all sources of scientific evidence pertaining to the topic in interest. In the present era of digitalisation and easy accessibility, there is an enormous amount of relevant data available, making it a challenge for the researcher to include all of it in his/her review.[ 9 ] It is crucial to structure this section intelligently so that the reader can grasp the argument related to your study in relation to that of other researchers, while still demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. It is preferable to summarise each article in a paragraph, highlighting the details pertinent to the topic of interest. The progression of review can move from the more general to the more focused studies, or a historical progression can be used to develop the story, without making it exhaustive.[ 1 ] Literature should include supporting data, disagreements and controversies. Five ‘C's may be kept in mind while writing a literature review[ 10 ] [ Table 1 ].
Aims and objectives
The research purpose (or goal or aim) gives a broad indication of what the researcher wishes to achieve in the research. The hypothesis to be tested can be the aim of the study. The objectives related to parameters or tools used to achieve the aim are generally categorised as primary and secondary objectives.
Research design and method
The objective here is to convince the reader that the overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem and to impress upon the reader that the methodology/sources chosen are appropriate for the specific topic. It should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
In this section, the methods and sources used to conduct the research must be discussed, including specific references to sites, databases, key texts or authors that will be indispensable to the project. There should be specific mention about the methodological approaches to be undertaken to gather information, about the techniques to be used to analyse it and about the tests of external validity to which researcher is committed.[ 10 , 11 ]
The components of this section include the following:[ 4 ]
Population and sample
Population refers to all the elements (individuals, objects or substances) that meet certain criteria for inclusion in a given universe,[ 12 ] and sample refers to subset of population which meets the inclusion criteria for enrolment into the study. The inclusion and exclusion criteria should be clearly defined. The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article “Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples” published in this issue of IJA.
Data collection
The researcher is expected to give a detailed account of the methodology adopted for collection of data, which include the time frame required for the research. The methodology should be tested for its validity and ensure that, in pursuit of achieving the results, the participant's life is not jeopardised. The author should anticipate and acknowledge any potential barrier and pitfall in carrying out the research design and explain plans to address them, thereby avoiding lacunae due to incomplete data collection. If the researcher is planning to acquire data through interviews or questionnaires, copy of the questions used for the same should be attached as an annexure with the proposal.
Rigor (soundness of the research)
This addresses the strength of the research with respect to its neutrality, consistency and applicability. Rigor must be reflected throughout the proposal.
It refers to the robustness of a research method against bias. The author should convey the measures taken to avoid bias, viz. blinding and randomisation, in an elaborate way, thus ensuring that the result obtained from the adopted method is purely as chance and not influenced by other confounding variables.
Consistency
Consistency considers whether the findings will be consistent if the inquiry was replicated with the same participants and in a similar context. This can be achieved by adopting standard and universally accepted methods and scales.
Applicability
Applicability refers to the degree to which the findings can be applied to different contexts and groups.[ 13 ]
Data analysis
This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated. Author should also mention the names of statistician and suitable software which will be used in due course of data analysis and their contribution to data analysis and sample calculation.[ 9 ]
Ethical considerations
Medical research introduces special moral and ethical problems that are not usually encountered by other researchers during data collection, and hence, the researcher should take special care in ensuring that ethical standards are met. Ethical considerations refer to the protection of the participants' rights (right to self-determination, right to privacy, right to autonomy and confidentiality, right to fair treatment and right to protection from discomfort and harm), obtaining informed consent and the institutional review process (ethical approval). The researcher needs to provide adequate information on each of these aspects.
Informed consent needs to be obtained from the participants (details discussed in further chapters), as well as the research site and the relevant authorities.
When the researcher prepares a research budget, he/she should predict and cost all aspects of the research and then add an additional allowance for unpredictable disasters, delays and rising costs. All items in the budget should be justified.
Appendices are documents that support the proposal and application. The appendices will be specific for each proposal but documents that are usually required include informed consent form, supporting documents, questionnaires, measurement tools and patient information of the study in layman's language.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. Although the words ‘references and bibliography’ are different, they are used interchangeably. It refers to all references cited in the research proposal.
Successful, qualitative research proposals should communicate the researcher's knowledge of the field and method and convey the emergent nature of the qualitative design. The proposal should follow a discernible logic from the introduction to presentation of the appendices.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
- 1. McGranaghan M. Guidelines on Writing a Research Proposal. [Last accessed on 2016 Jun 25]. Available from: https://www.2.hawaii.edu/~matt/proposal.html .
- 2. Nte AR, Awi DD. Research proposal writing: Breaking the myth. Niger J Med. 2006;15:373–81. doi: 10.4314/njm.v15i4.37249. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 3. Saunderlin G. Writing a research proposal: The critical first step for successful clinical research. Gastroenterol Nurs. 1994;17:48–56. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 4. Klopper H. The qualitative research proposal. Curationis. 2008;31:62–72. doi: 10.4102/curationis.v31i4.1062. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 5. Singh MD, Cameron C, Duff D. Writing proposals for research funds. Axone. 2005;26:26–30. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 6. Burns N, Grove SK. The Practice of Nursing Research: Conduct, Critique and Utilization. 5th ed. St. Louis: Elsevier Saunders; 2005. pp. 667–8. [ Google Scholar ]
- 7. Sandelowski M, Barroso J. Writing the proposal for a qualitative research methodology project. Qual Health Res. 2003;13:781–820. doi: 10.1177/1049732303013006003. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 8. Krathwohl DR. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences. Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press; 2005. pp. 45–7. [ Google Scholar ]
- 9. Balakumar P, Inamdar MN, Jagadeesh G. The Critical Steps for Successful Research: The Research Proposal and Scientific Writing: A Report on the Pre-Conference Workshop Held in Conjunction with the 64th Annual Conference of the Indian Pharmaceutical Congress-2012. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2013;4:130–18. doi: 10.4103/0976-500X.110895. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- 10. Labaree RV. Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Writing a Research Proposal. [Last accessed on 2016 Jun 25]. Available from: http://www.libguides.usc.edu/writingguide .
- 11. Research Proposal. [Last accessed on 2016 Jul 04]. Available from: http://www.web.stanford.edu/~steener/gendertech/assignments/ResearchProposal.pdf .
- 12. Burns N, Grove SK. The Practice of Nursing Research: Conduct, Critique and Utilization. 5th ed. St. Louis: Elsevier Saunders; 2005. p. 40. [ Google Scholar ]
- 13. Sliep Y, Poggenpoel M, Gmeiner A. A care counselling model for HIV reactive patients in rural Malawi – Part II. Curationis. 2001;24:66–74. doi: 10.4102/curationis.v24i3.855. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (372.3 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative research questions help you understand consumer sentiment. They're strategically designed to show organizations how and why people feel the way they do about a brand, product, or service.It looks beyond the numbers and is one of the most telling types of market research a company can do.. The UK Data Service describes this perfectly, saying, "The value of qualitative research ...
Learn the basics of qualitative research questions, including their key components, how to craft them effectively, and 25 example questions. Qualitative research questions focus on the "how" and "why" of things, rather than the "what", and can be used to explore a wide range of topics.
Learn how to write effective qualitative research questions for your projects, and why getting it right matters so much. Find out the difference between quantitative and qualitative research questions, and the four types of qualitative research questions with examples.
Learn how to create focused and specific research questions for qualitative studies that guide your data collection and analysis. Find prompts, templates and examples for different types of qualitative questions.
Find examples of qualitative research questions from various disciplines, such as health, education, sociology, psychology, and more. Each question is accompanied by a brief context statement that explains the purpose and scope of the research.
Learn how to write a research question for your project with 10 examples for different types of research, such as qualitative, quantitative, and statistical. Find out what makes a good research question focused, specific, and relevant.
Learn how to write effective qualitative research questions that explore the depth and nuances of a phenomenon, focusing on "why" and "how". See examples of qualitative questions for different scenarios and research goals, and get tips on structure, clarity, and relevance.
Learn how to craft a research question for qualitative research and see examples from various fields and topics. A research question guides the study design, data collection, analysis, and interpretation, and generates new knowledge.
Learn what qualitative research is, how it differs from quantitative research, and what methods and approaches are used to collect and analyze non-numerical data. Find out the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative research and see examples of research questions and data analysis.
When a qualitative methodology is chosen, research questions should be exploratory and focused on the actual phenomenon under study. From the Dissertation Center, Chapter 1: Research Question Overview, there are several considerations when forming a qualitative research question. Qualitative research questions should . Below is an example of a ...
Learn how to write qualitative market research questions to uncover insights into your customers' behaviors, opinions and preferences. See 25 examples of qualitative questions across six categories, and how to use them in focus groups or video responses.
How to Write a Qualitative Research Question. Writing research questions for qualitative research can be tricky. The question needs to prompt the participants to explore more, all the while without straying from the core topic. To create a perfect qualitative research question, you should consider the following. #1. Define Your Objective
Learn how to write qualitative research questions to explore and understand human experiences and social events. Find out the types of qualitative questions, such as descriptive, exploratory, experiential, comparative, and process-oriented, and how to choose them.
We present four parameters for crafting qualitative research questions: a) Number of questions. b) Degree of openness and neutrality. 03_Aurini_et_al_Ch_03.indd 36 3/16/2016 6:22:34 PM. ... Example 2: Assumptions about direction or hierarchical ordering Question: Do cohabitating non-married couples face greater financial troubles than cohabi - ...
Here are six types of qualitative questions with examples: 1. Descriptive. ... Can qualitative research questions change during the study? It's not uncommon for qualitative research questions to evolve during the course of a study. As preliminary data is collected and analyzed, new insights may emerge that prompt a qualitative researcher to ...
Learn how to write a research question with clear examples across various disciplines, such as psychology, business, education, healthcare and computer science. Find out what makes a good research question and get inspired by the ultimate list of 25+ practical examples.
Learn how to create a qualitative research questionnaire with open-ended questions to explore and interpret human opinions and experiences. Find out the different types of qualitative questions, tips for writing them, and examples of survey methods.
Learn about different approaches, methods, and techniques of qualitative research, and how to design and conduct qualitative study visits and data collection. This presentation covers the objectives, strengths, limitations, and tips of qualitative research, as well as examples of qualitative instruments and data analysis.
Learn about different qualitative research methods, such as ethnography, autoethnography, semi-structured interviews, and focus groups, with examples of studies that used them. Find out the strengths, weaknesses, and applications of each method in various fields and contexts.
BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL. A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the ...
Learn what research methodology is, how to choose and justify your methods, and how to write your methodology section. This article covers the basics of quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods, and their applications in different research contexts.