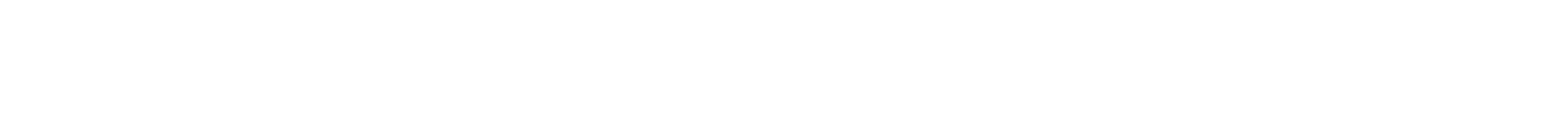

What Works: Ten Education, Training, and Work-Based Pathway Changes That Lead to Good Jobs
Ten education, training, and work-based pathway changes that lead to good jobs, good job definition, explore the data, full report, executive summary.
All along the journey from youth to young adulthood, there are critical junctures at which a change in pathway can have a tremendous impact on a young person’s future. What Works: Ten Education, Training, and Work-Based Pathway Changes That Lead to Good Jobs identifies 10 pathway changes with the greatest potential to improve employment outcomes for young adults. The report uses the Pathways-to-Career policy simulation model, developed by CEW researchers using longitudinal data, to identify promising junctures at which strategic interventions could increase the likelihood of working in a good job.
We define a good job as one that pays a minimum of approximately $38,000 in 2020 dollars for workers younger than age 45 and a minimum of approximately $49,000 for workers ages 45 and older. For the young adults who are the focus of this report—30-year-old workers nationwide—these jobs pay a median of approximately $57,000 annually. Among 30-year-old workers who have a good job, one-quarter earn less than $46,000 annually, while one-quarter earn more than $76,000. Workers with good jobs are more likely than those with low-paying jobs to have access to healthcare and retirement benefits at work.
Many of the most promising pathway changes involve increasing educational attainment, especially progressing toward attainment of a bachelor’s degree, while other promising pathway changes replace or combine classroom learning with on-the-job learning. Importantly, the effectiveness of the 10 pathway changes varies by race, gender, and class. For example, specializing in career and technical education (CTE) in high school increases the likelihood of having a good job at age 30 for white and Black/African American young adults, but reduces the likelihood of having a good job at age 30 for Hispanic/Latino young adults. Nearly every pathway change has the potential to put more men, white youth and young adults, and individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds in good jobs at age 30.

Explore the number of young people who could benefit from each pathway change, overall and by race, gender, and class:
Source: Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce analysis of data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, National Longitudinal Survey of Youth 1997 (NLSY97), 1997–2015.
Note: Good jobs are those paying approximately $38,000 or more in 2020 dollars, adjusted for geographic differences in cost of living. “M” indicates millions; “k” indicates thousands. For details about who is eligible for each scenario, see Appendix A in the full report. Blue-collar occupations include jobs in farming, fishing, and forestry; construction, extraction, maintenance, and repair; and production, transportation, and material moving. Other high-paying occupations include jobs in business, finance, management, law, social science, and skilled healthcare. Low-paying occupations include jobs in the arts, community services, education, food and personal services, and healthcare support. Numbers may not sum due to rounding.
Layered Pathway Changes
Layering certain pathway changes can further boost the number of workers in good jobs at age 30. For example, ensuring college completion after putting the 4.8 million eligible academically prepared young adults on the pathway to a bachelor’s degree could result in 1.2 million more young adults in the current cohort in good jobs at age 30 than are expected at present. That’s 435,000 more young adults in good jobs than would result from increasing enrollment in bachelor’s degree programs alone. Ensuring completion of an associate’s or bachelor’s degree after putting young adults on the pathway to an associate’s degree and ensuring continuous employment from ages 20 to 22 after placing young adults in STEM occupations could also enhance the impact of any one of these pathway changes on its own.
Targeted Interventions
Differences in effectiveness and eligibility mean that narrowing the gaps in good jobs is not as simple as making all 10 pathway changes equally available to youth and young adults regardless of race, class, and gender. That approach would more likely increase the good jobs gaps by race and gender than shrink them, and it would have little effect on the good jobs gap by class. To narrow the gaps in the likelihood of having a good job, effective interventions would need to be targeted to underserved groups as part of a coordinated and comprehensive all-one-system approach that addresses persistent inequalities in society arising outside the classroom and workplace.
What Works: Ten Education, Training, and Work-Based Pathway Changes That Lead to Good Jobs identifies 10 pathway changes with the greatest potential to improve employment outcomes for young adults.
Press Release

Comments are closed.

Home Resource Library Press Room Projects
About CEW Maps & Directions Reprint Permission Privacy Policy EIT accessibility
- Newsletters
- Infographics
- Press Releases
- Media Mentions
- Media Inquiries
- Explore Our ROI Rankings
- COVID-19 Research
- Good Jobs Data
- State Research
10 Education - Luyện thi chứng chỉ tin học quốc tế MOS (Word, Excel, PPT)/ IC3 và tiếng Anh IELTS
- Tin học Văn phòng
- Blog Tin Học
Học chứng chỉ quốc tế cùng 10 Education
10 Education trung tâm đào tạo các chứng chỉ tin học MOS (MOS Word, Excel, PPT,…), IC3 GS5, IC3 GS6.., chứng chỉ tiếng anh IELTS. 10 Education trung tâm đào tạo chứng chỉ MOS hàng đầu, cam kết đầu ra.

MOS PowerPoint 2019
- Giới thiệu về chứng chỉ MOS - Giới thiệu về PowerPoint 2019/365 - Các thao tác cơ bản, các thuật ngữ quan trọng trong một File PowerPoint - Các công cụ thông dụng trong 9 tab - Nội dung bài thi MOS PowerPoint 2019/365 và làm quen giao diện thi Bên cạnh phần lớn nội dung giao thoa với MOS 2016, bài thi MOS 2019 được thực hiện trên Office phiên bản 2019, cùng với sự bổ sung và cập nhật một số câu hỏi liên quan tính năng mới hay thay đổi thao tác để phù hợp với giao diện của phiên bản thi. Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ MOS PPT 2019/365 với điểm số cao (>950) - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ trong PPT, phục vụ cho quá trình học tập và làm việc sau này" data-bs-original-title="ten education"> Nội dung khóa học: - Giới thiệu về chứng chỉ MOS - Giới thiệu về PowerPoint 2019/365 - Các thao tác cơ bản, các thuật ngữ quan trọng trong một File PowerPoint - Các công cụ thông dụng trong 9 tab - Nội dung bài thi MOS PowerPoint 2019/365 và làm quen giao diện thi Bên cạnh phần lớn nội dung giao thoa với MOS 2016, bài thi MOS 2019 được thực hiện trên Office phiên bản 2019, cùng với sự bổ sung và cập nhật một số câu hỏi liên quan tính năng mới hay thay đổi thao tác để phù hợp với giao diện của phiên bản thi. Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ MOS PPT 2019/365 với điểm số cao (>950) - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ trong PPT, phục vụ cho quá trình học tập và làm việc sau này

MOS Word 2019
- Giới thiệu về chứng chỉ MOS - Giới thiệu về Word 2019/365 - Các thao tác cơ bản với Tài liệu Word - Các công cụ thông dụng trong các tab - Nội dung bài thi MOS Word 2019/365 và làm quen giao diện thi Bên cạnh phần lớn nội dung giao thoa với MOS 2016, bài thi MOS 2019 được thực hiện trên Office phiên bản 2019, cùng với sự bổ sung và cập nhật một số câu hỏi liên quan tính năng mới hay thay đổi thao tác để phù hợp với giao diện của phiên bản thi. Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ MOS Word 2019/365 với điểm số cao (>950) - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ trong Word, phục vụ cho quá trình học tập và làm việc sau này" data-bs-original-title="ten education"> Nội dung khóa học: - Giới thiệu về chứng chỉ MOS - Giới thiệu về Word 2019/365 - Các thao tác cơ bản với Tài liệu Word - Các công cụ thông dụng trong các tab - Nội dung bài thi MOS Word 2019/365 và làm quen giao diện thi Bên cạnh phần lớn nội dung giao thoa với MOS 2016, bài thi MOS 2019 được thực hiện trên Office phiên bản 2019, cùng với sự bổ sung và cập nhật một số câu hỏi liên quan tính năng mới hay thay đổi thao tác để phù hợp với giao diện của phiên bản thi. Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ MOS Word 2019/365 với điểm số cao (>950) - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ trong Word, phục vụ cho quá trình học tập và làm việc sau này

MOS Excel 2019
- Giới thiệu về chứng chỉ MOS - Giới thiệu về Excel 2019/365 - Các thao tác cơ bản với Trang tính, Sổ tính - Các công cụ thông dụng trong các tab - Nội dung bài thi MOS Excel 2019/365 và làm quen giao diện thi Bên cạnh phần lớn nội dung giao thoa với MOS 2016, bài thi MOS 2019 được thực hiện trên Office phiên bản 2019, cùng với sự bổ sung và cập nhật một số câu hỏi liên quan tính năng mới hay thay đổi thao tác để phù hợp với giao diện của phiên bản thi. Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ MOS Excel 2019/365 với điểm số cao (>950) - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ trong Excel, phục vụ cho quá trình học tập và làm việc sau này" data-bs-original-title="ten education"> Nội dung khóa học: - Giới thiệu về chứng chỉ MOS - Giới thiệu về Excel 2019/365 - Các thao tác cơ bản với Trang tính, Sổ tính - Các công cụ thông dụng trong các tab - Nội dung bài thi MOS Excel 2019/365 và làm quen giao diện thi Bên cạnh phần lớn nội dung giao thoa với MOS 2016, bài thi MOS 2019 được thực hiện trên Office phiên bản 2019, cùng với sự bổ sung và cập nhật một số câu hỏi liên quan tính năng mới hay thay đổi thao tác để phù hợp với giao diện của phiên bản thi. Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ MOS Excel 2019/365 với điểm số cao (>950) - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ trong Excel, phục vụ cho quá trình học tập và làm việc sau này

- MOS PowerPoint 2016
- Giới thiệu về chứng chỉ MOS - Giới thiệu về PowerPoint 2016 - Các thao tác cơ bản, các thuật ngữ quan trọng trong một File PowerPoint - Các công cụ thông dụng trong 9 tab - Nội dung bài thi MOS PowerPoint 2016 và làm quen giao diện thi Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ MOS PPT 2016 với điểm số cao (>950) - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ trong PPT, phục vụ cho quá trình học tập và làm việc sau này" data-bs-original-title="ten education"> Nội dung khóa học: - Giới thiệu về chứng chỉ MOS - Giới thiệu về PowerPoint 2016 - Các thao tác cơ bản, các thuật ngữ quan trọng trong một File PowerPoint - Các công cụ thông dụng trong 9 tab - Nội dung bài thi MOS PowerPoint 2016 và làm quen giao diện thi Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ MOS PPT 2016 với điểm số cao (>950) - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ trong PPT, phục vụ cho quá trình học tập và làm việc sau này

- Giới thiệu chứng chỉ IC3 - Kiến thức cần có theo cấu trúc bài thi: + Module 1: Máy tính căn bản (Computing Fundamental) + Module 2: Các ứng dụng chính (Key Applications) + Module 3: Cuộc sống trực tuyến (Living Online) - Ứng dụng và làm quen giao diện thi Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ IC3 GS5 với điểm số cao - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ Office, các thao tác với máy tính, các ứng dụng với Internet, phục vụ cho đời sống, học tập và làm việc sau này" data-bs-original-title="ten education"> Nội dung khóa học: - Giới thiệu chứng chỉ IC3 - Kiến thức cần có theo cấu trúc bài thi: + Module 1: Máy tính căn bản (Computing Fundamental) + Module 2: Các ứng dụng chính (Key Applications) + Module 3: Cuộc sống trực tuyến (Living Online) - Ứng dụng và làm quen giao diện thi Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ IC3 GS5 với điểm số cao - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ Office, các thao tác với máy tính, các ứng dụng với Internet, phục vụ cho đời sống, học tập và làm việc sau này

- MOS Word 2016
- Giới thiệu về chứng chỉ MOS - Giới thiệu về Word 2016 - Các thao tác cơ bản với Tài liệu Word - Các công cụ thông dụng trong các tab - Nội dung bài thi MOS Word 2016 và làm quen giao diện thi Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ MOS Word 2016 với điểm số cao (>950) - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ trong Word, phục vụ cho quá trình học tập và làm việc sau này " data-bs-original-title="ten education"> Nội dung khóa học: - Giới thiệu về chứng chỉ MOS - Giới thiệu về Word 2016 - Các thao tác cơ bản với Tài liệu Word - Các công cụ thông dụng trong các tab - Nội dung bài thi MOS Word 2016 và làm quen giao diện thi Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ MOS Word 2016 với điểm số cao (>950) - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ trong Word, phục vụ cho quá trình học tập và làm việc sau này

- MOS Excel 2016
- Giới thiệu về chứng chỉ MOS - Giới thiệu về Excel 2016 - Các thao tác cơ bản với Trang tính, Sổ tính - Các công cụ thông dụng trong các tab - Nội dung bài thi MOS Excel 2016 và làm quen giao diện thi Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ MOS Excel 2016 với điểm số cao (>950) - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ trong Excel, phục vụ cho quá trình học tập và làm việc sau này " data-bs-original-title="ten education"> Nội dung khóa học: - Giới thiệu về chứng chỉ MOS - Giới thiệu về Excel 2016 - Các thao tác cơ bản với Trang tính, Sổ tính - Các công cụ thông dụng trong các tab - Nội dung bài thi MOS Excel 2016 và làm quen giao diện thi Mục tiêu khóa học: - Dễ dàng chinh phục chứng chỉ MOS Excel 2016 với điểm số cao (>950) - Hiểu về bản chất các công cụ trong Excel, phục vụ cho quá trình học tập và làm việc sau này

IELTS FOUNDATION
+ Đầu ra: 3.0 + Mục tiêu: Khóa Foundation dành cho các bạn mất gốc hoặc mới bắt đầu học tiếng anh, chưa tự tin trong phát âm, giao tiếp hàng ngày. Mục tiêu hướng tới của khoá học là nắm chắc được những chủ đề ngữ pháp quan trọng trong Tiếng Anh, có thể hình thành câu đúng ngữ pháp; đồng thời nghe hiểu, phản xạ giao tiếp cơ bản, Speaking Part 1." data-bs-original-title="ten education"> + Đầu vào: Người mất gốc + Đầu ra: 3.0 + Mục tiêu: Khóa Foundation dành cho các bạn mất gốc hoặc mới bắt đầu học tiếng anh, chưa tự tin trong phát âm, giao tiếp hàng ngày. Mục tiêu hướng tới của khoá học là nắm chắc được những chủ đề ngữ pháp quan trọng trong Tiếng Anh, có thể hình thành câu đúng ngữ pháp; đồng thời nghe hiểu, phản xạ giao tiếp cơ bản, Speaking Part 1.

+ Đầu ra: 4.0 + Mục tiêu: Khóa Pre-IELTS sẽ tạo nền tảng vững chắc cho các bạn học viên trước khi bước vào học IELTS. Mục tiêu hướng tới của khoá học là giúp các bạn nắm được cấu trúc và cách làm các dạng bài của cả 4 kỹ năng Nghe, Nói, Đọc, Viết; bỏ túi nhiều từ vựng liên quan." data-bs-original-title="ten education"> + Đầu vào: 3.0 hoặc tương đương + Đầu ra: 4.0 + Mục tiêu: Khóa Pre-IELTS sẽ tạo nền tảng vững chắc cho các bạn học viên trước khi bước vào học IELTS. Mục tiêu hướng tới của khoá học là giúp các bạn nắm được cấu trúc và cách làm các dạng bài của cả 4 kỹ năng Nghe, Nói, Đọc, Viết; bỏ túi nhiều từ vựng liên quan.
IELTS MEDIUM 5.5
+ Đầu ra: 5.5 + Mục tiêu: Khoá IELTS MEDIUM 5.5 cung cấp đầy đủ kiến thức của cả 4 kỹ năng, phù hợp với những bạn có mục tiêu đạt band điểm 5.5+ " data-bs-original-title="ten education"> + Đầu vào: 4.0 hoặc tương đương + Đầu ra: 5.5 + Mục tiêu: Khoá IELTS MEDIUM 5.5 cung cấp đầy đủ kiến thức của cả 4 kỹ năng, phù hợp với những bạn có mục tiêu đạt band điểm 5.5+

IELTS INTENSIVE 6.5+
+ Đầu ra: 6.5+ + Mục tiêu: Khóa IELTS INTENSIVE 6.5+ tập trung củng cố kiến thức, cách làm bài của các kỹ năng, bổ trợ thêm từ vựng sâu rộng giúp các bạn dễ dàng “ăn” điểm và đạt được mục tiêu band điểm 6.5+." data-bs-original-title="ten education"> + Đầu vào: 5.5 hoặc tương đương + Đầu ra: 6.5+ + Mục tiêu: Khóa IELTS INTENSIVE 6.5+ tập trung củng cố kiến thức, cách làm bài của các kỹ năng, bổ trợ thêm từ vựng sâu rộng giúp các bạn dễ dàng “ăn” điểm và đạt được mục tiêu band điểm 6.5+.

IELTS PREMIUM 1-1
+ Đầu ra: Tùy thuộc vào mục tiêu của học viên + Quyền lợi: - Tư vấn lộ trình luyện thi cùng chuyên gia IELTS trước khi bắt đầu khóa học sau bài IELTS Entrance Test đầu khóa - Hướng dẫn 1-1 cùng chuyên gia IELTS trong quá trình học - Sửa lỗi bài IELTS Writing miễn phí đến khi thi (không giới hạn số bài) - Tham gia Câu lạc bộ thực hành tiếng Anh miễn phí hàng tuần - Truy cập miễn phí vào kho tài liệu IELTS trực tuyến của 10 Education - Hỗ trợ đăng kí thi và luyện tập đến ngày bước vào phòng thi" data-bs-original-title="ten education"> + Đầu vào: Dựa vào bài IELTS Entrance Test. + Đầu ra: Tùy thuộc vào mục tiêu của học viên + Quyền lợi: - Tư vấn lộ trình luyện thi cùng chuyên gia IELTS trước khi bắt đầu khóa học sau bài IELTS Entrance Test đầu khóa - Hướng dẫn 1-1 cùng chuyên gia IELTS trong quá trình học - Sửa lỗi bài IELTS Writing miễn phí đến khi thi (không giới hạn số bài) - Tham gia Câu lạc bộ thực hành tiếng Anh miễn phí hàng tuần - Truy cập miễn phí vào kho tài liệu IELTS trực tuyến của 10 Education - Hỗ trợ đăng kí thi và luyện tập đến ngày bước vào phòng thi

IELTS ONLINE
- Đầu vào: Mất gốc - Cam kết đầu ra: 6.5" data-bs-original-title="ten education"> - Hình thức học: ONLINE - Đầu vào: Mất gốc - Cam kết đầu ra: 6.5

EXCEL VĂN PHÒNG ỨNG DỤNG THỰC TIỄN TRONG CÔNG VIỆC
Khoá học Excel văn phòng từ cơ bản đến nâng cao dành cho Sinh viên và Người đi làm để nắm được nền tảng kiến thức vững chắc khi sử dụng phần mềm Excel trong công việc, áp dụng thực tiễn để giải quyết công việc hiệu quả

ỨNG DỤNG WORD CHUYÊN NGHIỆP TRONG VĂN PHÒNG LÀM VIỆC
Khoá học ỨNG DỤNG WORD CHUYÊN NGHIỆP TRONG VĂN PHÒNG LÀM VIỆC hỗ trợ người đi làm nắm được nền tảng kiến thức vững chắc khi sử dụng phần mềm Word trong công việc, áp dụng thực tiễn để tạo lập báo cáo, soạn thảo tài liệu theo đúng chuẩn quy định, chuyên nghiệp và hiệu quả
A journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step

- 🏫 Trụ sở chính phía Bắc: Tầng 6-7, Toà nhà Sacombank số 70 Trần Đại Nghĩa, Hai Bà Trưng, Hà Nội. (Gần Đại học Kinh tế Quốc Dân, học viện Ngân Hàng; Bách Khoa; Xây Dựng).
- 🏫 Trụ sở chính phía Nam: 158-160 Nhật Tảo, Phường 8, Quận 10, TP. Hồ Chí Minh.
- Đội ngũ giảng viên
- Học viên tiêu biểu
- IELTS Medium 5.5
- IELTS Intensive 6.5+
- IELTS Premium 1-1
- IELTS Online
- MOS Word 2019/365
- MOS Excel 2019/365
- MOS PowerPoint 2019/365
- MOS Excel 2013
- MOS Word 2013
- Soạn thảo văn bản chuyên nghiệp với Word
- Excel cơ bản cho sinh viên và người đi làm

- Our Mission

The 10 Most Significant Education Studies of 2021
From reframing our notion of “good” schools to mining the magic of expert teachers, here’s a curated list of must-read research from 2021.
It was a year of unprecedented hardship for teachers and school leaders. We pored through hundreds of studies to see if we could follow the trail of exactly what happened: The research revealed a complex portrait of a grueling year during which persistent issues of burnout and mental and physical health impacted millions of educators. Meanwhile, many of the old debates continued: Does paper beat digital? Is project-based learning as effective as direct instruction? How do you define what a “good” school is?
Other studies grabbed our attention, and in a few cases, made headlines. Researchers from the University of Chicago and Columbia University turned artificial intelligence loose on some 1,130 award-winning children’s books in search of invisible patterns of bias. (Spoiler alert: They found some.) Another study revealed why many parents are reluctant to support social and emotional learning in schools—and provided hints about how educators can flip the script.
1. What Parents Fear About SEL (and How to Change Their Minds)
When researchers at the Fordham Institute asked parents to rank phrases associated with social and emotional learning , nothing seemed to add up. The term “social-emotional learning” was very unpopular; parents wanted to steer their kids clear of it. But when the researchers added a simple clause, forming a new phrase—”social-emotional & academic learning”—the program shot all the way up to No. 2 in the rankings.
What gives?
Parents were picking up subtle cues in the list of SEL-related terms that irked or worried them, the researchers suggest. Phrases like “soft skills” and “growth mindset” felt “nebulous” and devoid of academic content. For some, the language felt suspiciously like “code for liberal indoctrination.”
But the study suggests that parents might need the simplest of reassurances to break through the political noise. Removing the jargon, focusing on productive phrases like “life skills,” and relentlessly connecting SEL to academic progress puts parents at ease—and seems to save social and emotional learning in the process.
2. The Secret Management Techniques of Expert Teachers
In the hands of experienced teachers, classroom management can seem almost invisible: Subtle techniques are quietly at work behind the scenes, with students falling into orderly routines and engaging in rigorous academic tasks almost as if by magic.
That’s no accident, according to new research . While outbursts are inevitable in school settings, expert teachers seed their classrooms with proactive, relationship-building strategies that often prevent misbehavior before it erupts. They also approach discipline more holistically than their less-experienced counterparts, consistently reframing misbehavior in the broader context of how lessons can be more engaging, or how clearly they communicate expectations.
Focusing on the underlying dynamics of classroom behavior—and not on surface-level disruptions—means that expert teachers often look the other way at all the right times, too. Rather than rise to the bait of a minor breach in etiquette, a common mistake of new teachers, they tend to play the long game, asking questions about the origins of misbehavior, deftly navigating the terrain between discipline and student autonomy, and opting to confront misconduct privately when possible.
3. The Surprising Power of Pretesting
Asking students to take a practice test before they’ve even encountered the material may seem like a waste of time—after all, they’d just be guessing.
But new research concludes that the approach, called pretesting, is actually more effective than other typical study strategies. Surprisingly, pretesting even beat out taking practice tests after learning the material, a proven strategy endorsed by cognitive scientists and educators alike. In the study, students who took a practice test before learning the material outperformed their peers who studied more traditionally by 49 percent on a follow-up test, while outperforming students who took practice tests after studying the material by 27 percent.
The researchers hypothesize that the “generation of errors” was a key to the strategy’s success, spurring student curiosity and priming them to “search for the correct answers” when they finally explored the new material—and adding grist to a 2018 study that found that making educated guesses helped students connect background knowledge to new material.
Learning is more durable when students do the hard work of correcting misconceptions, the research suggests, reminding us yet again that being wrong is an important milestone on the road to being right.
4. Confronting an Old Myth About Immigrant Students
Immigrant students are sometimes portrayed as a costly expense to the education system, but new research is systematically dismantling that myth.
In a 2021 study , researchers analyzed over 1.3 million academic and birth records for students in Florida communities, and concluded that the presence of immigrant students actually has “a positive effect on the academic achievement of U.S.-born students,” raising test scores as the size of the immigrant school population increases. The benefits were especially powerful for low-income students.
While immigrants initially “face challenges in assimilation that may require additional school resources,” the researchers concluded, hard work and resilience may allow them to excel and thus “positively affect exposed U.S.-born students’ attitudes and behavior.” But according to teacher Larry Ferlazzo, the improvements might stem from the fact that having English language learners in classes improves pedagogy , pushing teachers to consider “issues like prior knowledge, scaffolding, and maximizing accessibility.”
5. A Fuller Picture of What a ‘Good’ School Is
It’s time to rethink our definition of what a “good school” is, researchers assert in a study published in late 2020. That’s because typical measures of school quality like test scores often provide an incomplete and misleading picture, the researchers found.
The study looked at over 150,000 ninth-grade students who attended Chicago public schools and concluded that emphasizing the social and emotional dimensions of learning—relationship-building, a sense of belonging, and resilience, for example—improves high school graduation and college matriculation rates for both high- and low-income students, beating out schools that focus primarily on improving test scores.
“Schools that promote socio-emotional development actually have a really big positive impact on kids,” said lead researcher C. Kirabo Jackson in an interview with Edutopia . “And these impacts are particularly large for vulnerable student populations who don’t tend to do very well in the education system.”
The findings reinforce the importance of a holistic approach to measuring student progress, and are a reminder that schools—and teachers—can influence students in ways that are difficult to measure, and may only materialize well into the future.
6. Teaching Is Learning
One of the best ways to learn a concept is to teach it to someone else. But do you actually have to step into the shoes of a teacher, or does the mere expectation of teaching do the trick?
In a 2021 study , researchers split students into two groups and gave them each a science passage about the Doppler effect—a phenomenon associated with sound and light waves that explains the gradual change in tone and pitch as a car races off into the distance, for example. One group studied the text as preparation for a test; the other was told that they’d be teaching the material to another student.
The researchers never carried out the second half of the activity—students read the passages but never taught the lesson. All of the participants were then tested on their factual recall of the Doppler effect, and their ability to draw deeper conclusions from the reading.
The upshot? Students who prepared to teach outperformed their counterparts in both duration and depth of learning, scoring 9 percent higher on factual recall a week after the lessons concluded, and 24 percent higher on their ability to make inferences. The research suggests that asking students to prepare to teach something—or encouraging them to think “could I teach this to someone else?”—can significantly alter their learning trajectories.
7. A Disturbing Strain of Bias in Kids’ Books
Some of the most popular and well-regarded children’s books—Caldecott and Newbery honorees among them—persistently depict Black, Asian, and Hispanic characters with lighter skin, according to new research .
Using artificial intelligence, researchers combed through 1,130 children’s books written in the last century, comparing two sets of diverse children’s books—one a collection of popular books that garnered major literary awards, the other favored by identity-based awards. The software analyzed data on skin tone, race, age, and gender.
Among the findings: While more characters with darker skin color begin to appear over time, the most popular books—those most frequently checked out of libraries and lining classroom bookshelves—continue to depict people of color in lighter skin tones. More insidiously, when adult characters are “moral or upstanding,” their skin color tends to appear lighter, the study’s lead author, Anjali Aduki, told The 74 , with some books converting “Martin Luther King Jr.’s chocolate complexion to a light brown or beige.” Female characters, meanwhile, are often seen but not heard.
Cultural representations are a reflection of our values, the researchers conclude: “Inequality in representation, therefore, constitutes an explicit statement of inequality of value.”
8. The Never-Ending ‘Paper Versus Digital’ War
The argument goes like this: Digital screens turn reading into a cold and impersonal task; they’re good for information foraging, and not much more. “Real” books, meanwhile, have a heft and “tactility” that make them intimate, enchanting—and irreplaceable.
But researchers have often found weak or equivocal evidence for the superiority of reading on paper. While a recent study concluded that paper books yielded better comprehension than e-books when many of the digital tools had been removed, the effect sizes were small. A 2021 meta-analysis further muddies the water: When digital and paper books are “mostly similar,” kids comprehend the print version more readily—but when enhancements like motion and sound “target the story content,” e-books generally have the edge.
Nostalgia is a force that every new technology must eventually confront. There’s plenty of evidence that writing with pen and paper encodes learning more deeply than typing. But new digital book formats come preloaded with powerful tools that allow readers to annotate, look up words, answer embedded questions, and share their thinking with other readers.
We may not be ready to admit it, but these are precisely the kinds of activities that drive deeper engagement, enhance comprehension, and leave us with a lasting memory of what we’ve read. The future of e-reading, despite the naysayers, remains promising.
9. New Research Makes a Powerful Case for PBL
Many classrooms today still look like they did 100 years ago, when students were preparing for factory jobs. But the world’s moved on: Modern careers demand a more sophisticated set of skills—collaboration, advanced problem-solving, and creativity, for example—and those can be difficult to teach in classrooms that rarely give students the time and space to develop those competencies.
Project-based learning (PBL) would seem like an ideal solution. But critics say PBL places too much responsibility on novice learners, ignoring the evidence about the effectiveness of direct instruction and ultimately undermining subject fluency. Advocates counter that student-centered learning and direct instruction can and should coexist in classrooms.
Now two new large-scale studies —encompassing over 6,000 students in 114 diverse schools across the nation—provide evidence that a well-structured, project-based approach boosts learning for a wide range of students.
In the studies, which were funded by Lucas Education Research, a sister division of Edutopia , elementary and high school students engaged in challenging projects that had them designing water systems for local farms, or creating toys using simple household objects to learn about gravity, friction, and force. Subsequent testing revealed notable learning gains—well above those experienced by students in traditional classrooms—and those gains seemed to raise all boats, persisting across socioeconomic class, race, and reading levels.
10. Tracking a Tumultuous Year for Teachers
The Covid-19 pandemic cast a long shadow over the lives of educators in 2021, according to a year’s worth of research.
The average teacher’s workload suddenly “spiked last spring,” wrote the Center for Reinventing Public Education in its January 2021 report, and then—in defiance of the laws of motion—simply never let up. By the fall, a RAND study recorded an astonishing shift in work habits: 24 percent of teachers reported that they were working 56 hours or more per week, compared to 5 percent pre-pandemic.
The vaccine was the promised land, but when it arrived nothing seemed to change. In an April 2021 survey conducted four months after the first vaccine was administered in New York City, 92 percent of teachers said their jobs were more stressful than prior to the pandemic, up from 81 percent in an earlier survey.
It wasn’t just the length of the work days; a close look at the research reveals that the school system’s failure to adjust expectations was ruinous. It seemed to start with the obligations of hybrid teaching, which surfaced in Edutopia ’s coverage of overseas school reopenings. In June 2020, well before many U.S. schools reopened, we reported that hybrid teaching was an emerging problem internationally, and warned that if the “model is to work well for any period of time,” schools must “recognize and seek to reduce the workload for teachers.” Almost eight months later, a 2021 RAND study identified hybrid teaching as a primary source of teacher stress in the U.S., easily outpacing factors like the health of a high-risk loved one.
New and ever-increasing demands for tech solutions put teachers on a knife’s edge. In several important 2021 studies, researchers concluded that teachers were being pushed to adopt new technology without the “resources and equipment necessary for its correct didactic use.” Consequently, they were spending more than 20 hours a week adapting lessons for online use, and experiencing an unprecedented erosion of the boundaries between their work and home lives, leading to an unsustainable “always on” mentality. When it seemed like nothing more could be piled on—when all of the lights were blinking red—the federal government restarted standardized testing .
Change will be hard; many of the pathologies that exist in the system now predate the pandemic. But creating strict school policies that separate work from rest, eliminating the adoption of new tech tools without proper supports, distributing surveys regularly to gauge teacher well-being, and above all listening to educators to identify and confront emerging problems might be a good place to start, if the research can be believed.
10 Education Studies You Should Know From 2023

- Share article
The school environment is changing rapidly, as a result of emerging technologies and ongoing problems with student achievement and mental health. This year saw new research insights in critical areas. Here’s a look at some of the findings from some of the studies that were most popular with our readers.
Teenagers need a social media detox
The dangers of adolescents’ social media habits took center stage this year, with the U.S. surgeon general issuing public warnings about the dangers of social media use for developing brains. Federal and state legislatures likewise moved to regulate how minors can use social media, and dozens of districts nationwide are suing major platforms like Facebook, arguing that they damage students’ mental health.
Amid the swirl of activity, a longitudinal and empirical research analysis found that more frequent use of smartphones and social media is associated with higher rates of mental distress, self-harming behaviors, and suicide among teenagers.
The study suggests schools can help counter potential damage from social media by helping students and families engage in open, nonjudgmental, and developmentally appropriate discussions and problem-solving around ways to limit social media.
The wrong problem can make a difference in math
An analysis of more than 100 studies of math interventions in Educational Psychology Review found that students who study already-worked example problems improved in mathematics significantly more than students who used a different approach. Students who had experienced gaps in their math knowledge particularly benefited from studying and discussing incorrectly worked problems in addition to studying correct problems to highlight potential areas of misunderstanding.
However, teachers need to choose their examples carefully: Problems without a clear goal, or with less detail, and those that don’t highlight the steps needed to solve the problem were associated with less student growth in math. A student studying well-chosen worked problems, however, had math growth equal to moving from the 50th percentile to above the 69th percentile.
ChatGPT’s educational uses are still up in the air
Launched a little more than a year ago, the generative artificial intelligence tool ChatGPT has exploded in popularity among teachers and the general public. A meta-analysis of 50 studies in the journal Education Sciences suggests educators use the tool most to generate course materials and sample questions , as well as to provide virtual tutoring for students.
However, the analysis finds mixed evidence so far on ChatGPT’s most effective uses. While the bot provided highly accurate responses in areas like economics and critical-thinking prompts, it was ironically not able to provide highly accurate information in math or software testing. The tool occasionally or often provided out-of-date or incorrect information in various subjects. The study also found ChatGPT often did not provide proper sources for its information and its use led to higher rates of plagiarism with some groups of students who used it.
But artificial intelligence may help to design more equitable school districts
School districts have long struggled to design attendance zones that limit long bus rides while preventing high-poverty students from becoming concentrated in a few schools. One study in the journal Educational Researcher suggests AI might be able to create a more equitable and efficient fit.
Northeastern University and Massachusetts Institute of Technology researchers simulated new attendance zones for nearly 100 of the nation’s largest districts, using algorithms that took into account both parent preferences and district integration goals. The new simulated attendance zones lowered segregation of white students and students of color across district schools by 14 percent on average, while slightly reducing travel times and only requiring a fifth of students to change schools.
Avoiding academic anxiety can worsen and prolong students’ fear
Teachers may be inclined to let students avoid tasks like public presentations that trigger fear and stress, but over time, that can make their anxiety worse. A study in the Journal of Psychologists and Counselors in Schools looked at elementary students with severe anxiety. Teachers reported several common activities that tended to trigger anxiety, such as group work and reading aloud in class. All teachers at least occasionally allowed students to avoid the activities that worried them, but the more avoidance teachers allowed, the higher students’ anxiety around those activities.
The lead researcher, child psychology professor Golda Ginsburg of the University of Connecticut, developed and is now piloting the Teacher Anxiety Program for Elementary Students (TAPES) , in which educators learn and role-play ways to identify students who are experiencing anxiety in class and help them without exacerbating their triggers.
Extra learning days add up
A working paper in the National Bureau of Economic Research found big differences in the amount of time schools are in session. A rising number of schools nationwide have moved to longer school days, weekend school sessions, and longer years or summer sessions.
The study found students who attend schools in the top 10 percent for the amount of time they’re in session receive on average five weeks more instruction every year than do students attending schools in the bottom 10 percent of the spectrum. Over those students’ 12-year academic careers, students in the longest-running schools get nearly two years’ worth of additional instruction.
By contrast, nearly 900 districts nationwide now use four-day weeks . While these districts often have longer school days, the study found this tended to exhaust students and teachers and did not make up for the lost full days.
District leadership has a big gender gap
The names say it all .
A study in the journal Educational Researcher finds it’s just as likely for a district to be led by a man with one of 15 names as it is for one to be led by a woman with any name.
The study finds districts have a 1 in 4 chance of being led by a man named Michael, David, James, Jeff, John, Robert, Steven, Chris, Brian, Scott, Mark, Kevin, Jason, Matthew, or Daniel. While superintendent turnover has risen over time, particularly for men, those open positions are still more likely to be filled by a male candidate than a female one. Meanwhile, more than three-quarters of teachers and 56 percent of principals are women.
Chronic absenteeism isn’t going away
Two out of 3 schools nationwide had high chronic absenteeism in 2022 , up from a quarter before the pandemic, according to an analysis of federal data by the nonprofit Attendance Works.
In 11 states, the study found more than 1 in 4 students were chronically absent—defined as missing 10 percent or more of school days. High-poverty schools have been the hardest hit, with absenteeism nearly tripling since the pandemic.
Want kids in school? Build bridges with families first
While schools have been ramping up efforts to increase student engagement to combat absenteeism, a study by Harvard University researchers and the New Teacher Project suggests keeping parents engaged is equally important.
Schools with higher assessed trust between parents and teachers and higher parent involvement—particularly in schools’ decisionmaking—had 6 percentage points lower chronic-absenteeism rates after remote learning, compared with schools with less parent engagement.
Virtual tutoring can help students, if it follows high-dosage criteria
High-dosage tutoring programs have expanded significantly, with nearly 40 percent of schools now using individual and small-group tutoring with trained teachers or tutors four or five days a week. This approach has been shown to boost student learning, but it can also be expensive. A new study by the National Student Support Accelerator at Stanford University suggests virtual tutoring could be a less-costly option, if it remains as intensive and rigorous as in-person tutoring.
Researchers tracked the reading growth of about 2,000 K-2 students in a dozen Texas charter schools, half of whom participated in intensive remote tutoring for part of the school day, in small-group video chats. Students who received supplemental lessons in phonics and decoding for 20 minutes a day, four times a week, via the remote tutoring performed significantly better on two early-reading tests by the end of the year.
A version of this article appeared in the January 17, 2024 edition of Education Week as 10 Education Studies You Should Know From 2023
Sign Up for The Savvy Principal
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

Committee Of Ten Develops First National Standards
The National Education Association appoints a Committee of Ten to examine high school curriculum issues and make recommendations about methods, standards and programs. The committee’s recommendations, which influence the Committee on College Entrance Requirements founded in 1895, support the teaching of traditional subjects such as Latin, Greek, English, modern languages, mathematics, the physical sciences, the biological sciences, history and geography. The committee also supports an eight-year elementary school followed by a four-year high school and recommends that all subjects be studied for one period each day of a five-day school week.
10 Best U.S. States for Education
These states excel in areas such as preschool enrollment, eighth-grade test scores and college degree completion.

(Getty Images) |
Explore the Best States for Education
From creating statewide curriculum to allocating funding and otherwise regulating schooling, state governments play a fundamental role in the success of their education systems. In turn, how educated a state’s citizens are is linked to key areas like population health and economic success.
But some states stand taller in education than others. As part of the 2023 Best States rankings , U.S. News examined the education environment in each state, considering 10 metrics in two areas: higher education and prekindergarten through 12th grade .
Metrics used in the analysis included preschool enrollment , reading and math scores for eighth-grade students, high school graduation rate , timely completion of a college degree , the level of educational attainment among residents, debt at college graduation and more.
These are the 10 best states for education, according to the Best States analysis. You can learn more about how states are assessed in our methodology .

10. Washington
Pre-K-12 ranking : 31
Higher education ranking : 2
Overall Best States ranking : 2
Learn more about Washington .

(Spencer Platt | Getty Images)
9. New York
Pre-K-12 ranking : 8
Higher education ranking : 17
Overall Best States ranking : 20
Learn more about New York .

8. Connecticut
Pre-K-12 ranking : 3
Higher education ranking : 47
Overall Best States ranking : 16
Learn more about Connecticut .

(Ed Freeman | Getty Images)
7. Nebraska
Pre-K-12 ranking : 11
Higher education ranking : 11
Overall Best States ranking : 4
Learn more about Nebraska .

(Morry Gash | AP)
6. Wisconsin
Pre-K-12 ranking : 10
Higher education ranking : 10
Overall Best States ranking : 8
Learn more about Wisconsin .

(Jason Cameron | Getty Images)
Pre-K-12 ranking : 9
Higher education ranking : 6
Overall Best States ranking : 1
Learn more about Utah .

(Brett Ziegler for USN&WR) |
4. Colorado
Pre-K-12 ranking : 12
Higher education ranking : 4
Overall Best States ranking : 15
Learn more about Colorado .

(John Tlumack | Boston Globe
3. Massachusetts
Pre-K-12 ranking : 2
Higher education ranking : 32
Overall Best States ranking : 11
Learn more about Massachusetts .

(Jewel Samad | AFP
2. New Jersey
Pre-K-12 ranking : 1
Higher education ranking : 29
Overall Best States ranking : 19
Learn more about New Jersey .

(Jim Lo Scalzo for USN&WR) |
Pre-K-12 ranking : 14
Higher education ranking : 1
Overall Best States ranking : 10
Learn more about Florida .
The Are the 10 Best States for Education:
- Massachusetts
- Connecticut

Learn More About Best States
Didn't see your state? Check out the overall rankings , and use the Best States Data Explorer to see how your state stacks up against others in areas like health care , infrastructure , crime and corrections and natural environment .
More From U.S. News

10 Best States for Business

The 10 Best States in America

Best States for Health Care
Related articles, best states.

America 2024

Health News Bulletin
Stay informed daily on the latest news and advice on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
You May Also Like
Why utah is the best state.
Elliott Davis Jr. May 2, 2023

Gene Herrick, AP Photographer Who Covered the Korean War and Civil Rights, Dies at 97
Associated Press April 14, 2024

Wife of Ex-Harvard Morgue Manager Pleads Guilty to Transporting Stolen Human Remains

Divisive? Not for Moviegoers. ‘Civil War’ Declares Victory at Box Office.

Can Homeless People Be Fined for Sleeping Outside? A Rural Oregon City Asks the US Supreme Court

In Politically Riven Pennsylvania, Primary Voters Will Pick Candidates in Presidential Contest Year

A Jury of His Peers: A Look at How Jury Selection Will Work in Donald Trump's First Criminal Trial
Associated Press April 13, 2024

McCormick Gets Trump's Endorsement in Pennsylvania's Senate Race Despite Awkward History

Faith Ringgold, Pioneering Black Quilt Artist and Author, Dies at 93


- Twitter Channel
- Facebook Profile
- YouTube Channel
- Instagram Profile
- Linkedin Profile
- Pinterest Profile

Ten Equity-Centered Proposals for Advancing Educational Justice in 2024

Ten for Tennessee
About the award.
Ten for Tennessee recognizes and celebrates the top ten policy proposals in 2024 that best advance educational equity and justice in the state.
Every legislative session, Tennessee lawmakers offer new ideas or proposed changes to programs and policies that touch the lives of millions of students across the state, from preschool through higher education. The Education Trust–Tennessee is proud to recognize the ideas that have the greatest potential to improve opportunity and access for students of color, students from lower-income communities, students with disabilities, and English Learners. We will continue to monitor and support these bills as they move through the legislature this term.
Learn more about The Education Trust in Tennessee , our Tennessee Alliance for Equity in Education, and our 2024 Policy Agenda .
Creating Early Learning Scholarships for Tennessee’s Youngest Learners
Hb0785/sb0750 | chairman mark white & senator becky massey, what does this bill do.
HB0785 / SB0750 would require the Tennessee Department of Education to create a “Promising Futures” Scholarship Program that would provide scholarships to families and children to enroll in a high-quality early language and literacy skills learning program.
Eligible children include those from six weeks up to kindergarten age with working parents with incomes up to the state median income and/or who live with foster or adoptive parents. Parents may choose to use the scholarships for any learning program that meets Promising Futures’ quality standards, such as Head Start. To create the scholarship fund, sports gambling tax revenue – 80% of which currently goes to the state’s lottery for education account – would be placed into a Promising Futures Account for early learning and literacy.
Why does this bill matter?
Tennessee has a child care crisis. According to The Tennesseans for Quality Early Education (TQEE), the cost of childcare today is more than our average in-state college tuition. Quality childcare is unaffordable and inaccessible for most of our families. The average annual price of center-based childcare is $11,068 for infants and $10,184 for toddlers. For in-home childcare, the price is $7,194 for infants and $6,749 for toddlers. Pre-pandemic, childcare was a growing crisis for our families, especially Black and Latino families, families with low and middle incomes, and families in rural areas. A third of Tennessee children under age 6 live in families with incomes below $40,000 and nearly half with incomes less than $60,000. The COVID-19 crisis not only exacerbated existing inequities in childcare access for families but has also decimated the finances of childcare providers who are predominantly women of color and more likely to be low-income.
According to TQEE’s Report “ Workforce of Today and Tomorrow: The Economics of Tennessee’s Child Care Crisi s ”, our businesses and taxpayers lose $2.6 billion annually in earnings and revenue. TQEE’s study analyzed survey results from 1,297 working parents with children under 6 to determine how childcare challenges adversely affect workforce participation and productivity. Their findings alarmingly showed that more than 80% of working parents reported employment disruptions such as quitting jobs or reducing job hours due to inadequate childcare. 58% of parents cited lack of affordability as a reason. Moreover, 300,000 Tennessee children under the age of 6 have all available parents in the workforce. A study by the Urban Institute also revealed about 41% of these children have parents who work non-traditional hours, yet most childcare programs operate during the week till 5 or 6 PM.
Overall, the childcare crisis continues to increase the growing workforce shortage and threatens families’ financial stability and well-being. Lack of high-quality, accessible, and affordable childcare can significantly impact the development of our children. The first five years of a child’s life is when the brain grows the most, rapidly expanding neural connections and wiring the brain for future learning in K – 12 and beyond. The quality of early care that children receive profoundly impacts their school readiness, development, and our community’s future. Childcare is early education, and when it is successfully implemented, advances early learning and literacy.
Funding Voluntary Pre-Kindergarten Programs
Hb2769 / sb2754 | representative dwayne thompson & senate minority leader raumesh akbari, hb0276 / sb0231 | representative sam mckenzie & senator jeff yarbro.
HB2769/SB2754 would ensure there are 1,200 pre-kindergarten classrooms in the state for the 2024-2025 school year. The Commissioner for the Tennessee Department of Education would be required to approve programs on a competitive basis.
Over 75% of Tennessee school districts have wait lists for pre-kindergarten, according to Tennesseans for Quality Early Education (TQEE). During the 2021-2022 school year, Tennessee preschools enrolled 16,634 children , an increase of 1,033 children from the prior year. The Hechinger Report’s latest study , published in January 2023, shows children who went to preschool are far more likely to go to college within a couple of years of graduating high school. Further, pre-kindergarten has shown relatively large benefits for children who are dual-language learners both in their English-language proficiency and other academic skills.
A voter poll conducted by TQEE in 2021 shows that Tennessee Democrats and Republicans are unified in their support of expanding early education as a fundamental strategy to improve student achievement. Eighty-nine percent said they believe Tennessee Voluntary Pre-Kindergarten (TN-VPK) should be available to all Tennessee 4-year-olds, and 87% support increased state funding to make that possible.
An increase in TN-VPK classrooms yields positive long-term outcomes for students enrolled. Access to early childcare plays a vital role in setting children on the path to increased academic achievement, social competence, and emotional well-being. Investing in high-quality early childhood education benefits not only individual children but also our society as a whole.
Providing TCAP Testing Supports for English Language Learners
Hb2024/sb1892 | house minority caucus chairman john ray clemmons & senator charlane oliver.
HB2024/SB1892 states that the Tennessee Department of Education (TDOE) must have a contract with the testing provider of the Tennessee Comprehensive Assessment Program (TCAP) to ensure that language assistance services are provided to students during the administration of TCAP. Each student who received language assistance services in the previous academic year is eligible to receive services during the TCAP. If passed, this bill will apply to administrations of the TCAP test in the 2024-2025 school year and in each school year thereafter.
This bill impacts English Learners (EL) across Tennessee as it enacts a specific policy measure for ELs to receive language assistance services during TCAP testing. This measure is not currently written in law; as it stands, Local Education Agencies (LEAs) are only required to provide testing accommodations for students with Individual Education Plans (IEPs) or 504 plans.
English Learners receive daily accommodations based on their individual learning plans (ILP). These accommodations must be met throughout the day and with any form of testing, whether it be a pop quiz or formal state assessment. However, Tennessee does not allow language translation of any portions of the TCAP or TCAP-Alt, but assessment accessibility features are available for test administrators to provide for students.
Tennessee’s English Learner population is increasing significantly across the state, nearly doubling in the past five years, increasing from 44,909 ELs in 2018 to 77,388 in 2022 . In 2016-17, 132 Tennessee districts and 1,451 schools served ELs.
Providing language assistance promotes inclusion within educational settings by recognizing and valuing our students’ linguistic diversity . By providing TCAP language assistance, it sends a message that all students, regardless of their language background, are welcome and supported in their academic endeavors.
Establishing a Fund for Educator License Reimbursements
Hb0784/sb0556 | chairman mark white & vice-chairman bill powers.
HB0784/SB0556 requires the Tennessee Department of Education to reimburse educators for licensure assessments as long as the educator: (1) receives a qualifying score and (2) receives a new Tennessee teaching license or – if they are already working as a teacher – an additional teaching endorsement. This bill also includes a requirement for the Tennessee State Board of Education to publish a report by September 1, 2024, with the number of educators reimbursed and the type of license or endorsement earned by each educator.
Across the country, 44% of U.S. public schools reported teacher vacancies in 2022 . The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated existing teacher shortages, which is reflected in our ongoing struggles to attract and retain staff – especially in critical areas such as STEM, early childhood education, special education, and bilingual education. According to the Tennessee Department of Education, in the fall of 2022, a total of 3,897 positions , or 5.5% of total teaching positions in the State, were either vacant or filled with a teacher on an emergency credential. Further, the number of educators graduating from the 43 teacher training programs across the state has dropped by nearly 20% over five years , with much of that decline happening before the COVID-19 pandemic.
By 2028, Tennessee will have a projected 5,090 average annual openings for K-12 teaching positions. Taking the above into consideration, there is a clear and urgent need to support our prospective teachers by making the pathway to become an educator more accessible. Depending on the subject, taking the required licensure exams can cost hundreds of dollars, and some people may need to pay more to retake the tests before passing. Currently, teachers must pay many of these fees out of their own pocket. Studying for and completing various assessments is a burdensome process on top of other training program requirements, and the financial implications could dissuade candidates from wanting to teach.
Reducing the financial burdens of licensure exams is an important step to increasing the pool of highly qualified, effective, and diverse teachers . In 2020, the Tennessee Department of Education identified the importance of recruiting and retaining educators of color in relation to addressing teacher shortages, who remain underrepresented in our current workforce. Overall, there are many ways that Tennessee must continue improving the institutional support and long-term retention of our teaching workforce, and reimbursing educators for licensure and endorsement exams represents a step in the right direction.
Developing a K-12 Conflict Resolution Program
Hb2826/sb1726 | house minority leader karen camper & senate minority caucus chairwoman london lamar.
HB2826/SB1726 requires the Tennessee Department of Education (TDOE) to establish a conflict resolution program using existing resources that Local Education Agencies (LEAs) and public charter schools can adopt and implement. The purpose of this bill is to provide age-appropriate programming for K-12 students to develop skills necessary for nonviolent conflict resolution, including, but not limited to, communication skills, social skills, and relaxation techniques. Additionally, the bill mandates each LEA and public charter school implement an intervention program for students in grades 1-6 that uses conflict resolution to support students in learning and implementing decision-making strategies.
In 2019, about 5% of students ages 12–18 reported being afraid of attack or harm at school during the school year. Tennessee is in the bottom quintile of states for school safety for high school students, and is ranked 44th in the country . Additionally, according to the report, Tennessee is ranked 34th in the nation for incidences of bullying in high schools. In the Tennessee Department of Education and the Department of Safety and Homeland Security Tennessee Safe Schools Report , published in 2024, there has been an increase in student possession of guns, student possession of a weapon other than a firearm, and assaults of both students and teachers. According to the Tennessee Bureau of Investigation, the most commonly reported weapon type used in schools was personal weapons (hands, fists, feet, arms, teeth, etc.).
Students from low-income backgrounds may face additional stressors and challenges in their lives, which can contribute to conflicts both in and out of school. Conflict resolution programs can provide these students with valuable skills to manage these conflicts in a positive and constructive manner. Further, Tennessee is home to a diverse population, with students from various cultural and ethnic backgrounds attending schools across the state. Conflict resolution programs can help students from diverse backgrounds learn to understand and appreciate each other’s perspectives, fostering a more inclusive and respectful school environment.
Limiting Exclusionary Discipline for Pre-Kindergarten to 2nd Grade Students
Hb2493/sb2210 | representative chris hurt and vice-chairman bill powers.
HB2492/SB2216 would prohibit Local Education Agencies (LEA) from suspending or expelling a student enrolled in pre-kindergarten through second grade. If a student’s behavior is endangering the physical safety of school personnel or other students, this bill would allow the LEAs’ director of schools or their designee to determine an appropriate consequence, including suspension.
Banning pre-kindergarten to second-grade suspensions and expulsions would have a foundational impact on students’ social, emotional, and academic development , encouraging our school districts to prioritize trauma-informed and restorative justice practices that help students self-regulate their emotions and behavior, support childhood growth and development, and build healthy learning environments. Research shows that it is not developmentally appropriate to expect students in early childhood education to be able to fully self-regulate, even though many teachers resort to punitive discipline practices. Instead, teachers should provide students with the prerequisite social-emotional skills needed to self-regulate. Further, supporting students’ self-regulation in early childhood supports the effectiveness of early education for all children.
Data shows that suspending students fails to reduce future misbehavior. Instead, it may exacerbate future student misconduct. Suspension also negatively impacts student outcomes. Particularly among young children , suspensions are linked to poor academic outcomes and negative feelings towards school. These outcomes make students significantly more likely to drop out of school or be pushed into the school-to-prison pipeline . Additionally, research shows that suspensions do not improve outcomes for non-suspended students.
Suspension also causes students to miss essential class time and learning opportunities. Cycles of lost class time cause students to fall further behind their peers, which is especially harmful during the pre-kindergarten through second-grade years when students are learning foundational literacy and math skills. Long-term negative impacts of suspension include lower academic achievement and an increased likelihood of future interactions with the criminal legal system. However, students who go to schools with lower suspension rates are more likely to have higher long-term academic success and attend four-year colleges.
Exclusionary discipline practices first emerged as schools were being racially integrated . Overall, exclusionary discipline practices like suspensions result in damage to a student’s development. Exclusionary discipline practices disproportionately punish students of color and students with disabilities, and finding alternatives to suspension is a tool to disrupt the school-to-prison pipeline. Tennessee can further influence district policies and school disciplinary actions by setting clear goals to reduce disparities and overuses in discipline, ensuring a comprehensive set of data is publicly available on an annual basis.
Improving Food Access and Security
Hb0255/sb0208 | vice-chairman kevin raper & senator adam lowe, hb1914/sb1977 | representative michael hale & senator becky massey, hb0255/sb0208 | what does this bill do.
HB0255/SB0208 requires each local school board to establish a free meals program for breakfast and lunch for each student enrolled in a public school in the board’s district. It requires the State to reimburse each Local Education Agency (LEA) for the cost of this program after all available federal funds have been applied.
HB0255/SB0208 | Why does this bill matter?
Hungry kids are in every county in Tennessee, which means 1 in 8 kids can’t get enough food on a regular basis. Some Tennessee students are left to fend for themselves in the cafeteria if they don’t qualify for free or reduced-price meals. Up to 1 in 5 hungry kids don’t qualify for financial help with school meals.
Zooming out, food access and security for children of all stages in their lives are critical to their development. Too many students – especially Black students, Latino students, and students from low-income backgrounds – experience food insecurity . A 2021 child health survey found that 1 in 3 Tennessee families experienced food insecurity. In the survey, roughly 41% of Black families reported food insecurity, compared to 29% of all families. Furthermore, low-income communities, particularly communities of color, are more likely to experience food apartheid (i.e., food deserts), where there is limited access to healthy and affordable food or grocery stores.
Research shows that hunger has direct adverse effects on students’ academic performance. Providing meals in school is important to support students’ cognitive and social, emotional, and academic development . During the pandemic between the end of 2019 and July 2020, child hunger escalated from 4% to 14.4%. COVID-19-related waivers allowed Tennessee schools to serve meals to all kids at no cost to their families. When these waivers expired in June 2022, schools had to charge students if they didn’t qualify for free meals. School lunch debt rose statewide, and participation has dropped in some schools.
Overall, adequate and nutritious food for students and their families is fundamental to education equity. This legislation is an important step in ensuring all students are physically, socially, and academically supported in schools.
HB1914/SB1977 | What does this bill do?
HB1914/SB1977 seeks to address the problem of food insecurity on college campuses. This bill would establish the “Hunger-Free Campus Grant Fund,” funded via the Tennessee General Assembly and other gifts, grants, or donations. This fund would be available to all accredited public and private institutions, with its primary campus domiciled in Tennessee. Institutions that receive a Hunger-Free Campus Grant could utilize these funds to develop a student meal credit donation program, allocate funding for a meal voucher program, or provide financial assistance to a food pantry, in addition to raising awareness of campus resources related to food insecurity.
HB1914/SB1977 | Why does this bill matter?
A report published by the College and University Food Bank Alliance (CUFBA) and the National Student Campaign Against Hunger and Homelessness found that around 48% of surveyed college students experienced food insecurity in the United States . Research shows food insecurity rates are highest at community colleges, Historically Black Colleges and Universities, American Indian/Alaskan Native-serving institutions, and private for-profit colleges. Black or African American students report the highest levels of food insecurity, with more than a third indicating they experience food insecurity. Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander students and American Indian or Alaska Native students followed closely, with reported rates of 32.6% and 29.9%, respectively. 35% of students identifying as genderqueer, gender nonconforming, or another non-binary gender reported food insecurity.
In Tennessee, an estimated 30% of postsecondary students experience food insecurity . Further, 27% of Tennessee higher education administrators responded that their main campus
Permanently Establishing the Completion Grants Program for Tennessee Promise Students
Hb2184/sb1783 | chairman mark white & chairman jon lundberg.
HB2184/SB1783 seeks permanent, recurring funding to support completion grants for Pell-eligible Tennessee Promise students. In 2021, the Tennessee General Assembly approved a four-year pilot program that granted college students who experienced a financial emergency with a coach and up to $1,000 per semester to cover non-tuition expenses. Administered by tnAchieves and the Ayers Foundation , access to these emergency funds help college students address unexpected barriers that otherwise may prevent them from continuing their education.
The Completion Grants program supports Pell-eligible Tennessee Promise students with (1) a coach and (2) up to $1,000/semester to cover non-tuition expenses.
As amended, the bill creates an account in the state treasury called the “Tennessee Promise completion grant special account.” Each year, the Tennessee Higher Education Commission (THEC) may request that up to $5 million of Tennessee Education Lottery Scholarship (TELS) funding be deposited into the special account. The special account will receive an initial deposit in fiscal year 2024, and funds will be made available for use on July 1, 2027. Funds may only be used to award completion grants; unused funds roll over and remain in the special account each fiscal year.
The completion grants program provides targeted resources to students from low-income backgrounds, who are more likely to attend community colleges. Completion grants are a highly effective tool that help students meet unexpected costs while in college, and ensure that students can continue to focus on their academics.
Cost of attendance is the leading reason that students consider stopping out of their degree programs, and this is especially true for students of color . Over half of Tennessee students surveyed by The Education Trust – Tennessee (ET-TN) indicated that they have dropped courses during a semester as a result of financial cost, and Pell-eligible respondents were twice as likely to report that they were working over 20 hours a week than their non-Pell peers. In another survey, 75% of TN Promise students indicated that work-related pressures contribute to their inability to meet program eligibility requirements, like full-time enrollment and maintenance of at least a 2.0 GPA.
In 2021-22, tnAchieves reported that they had distributed all available funding for completion grants within the first 10 weeks of the semester, highlighting significant demand for this program. Disbursing 16,632 grants to over 3,000 students, tnAchieves has reported that students who received coaching and complete grants were 79% more likely to be retained and 183% more likely to graduate than their peers . This outcome demonstrates that coaching, paired with completion grants, are an effective way to support students facing economic hardships as they pursue a post-secondary degree or credential.
Expanding Tennessee Reconnect Eligibility
Hb2132/sb1672 | representative dennis powers & senator becky massey.
HB2132/SB1672 would expand eligibility for the Tennessee Reconnect Grant by lowering the minimum age requirement for the program from 23-years-old to 21-years-old.
The Tennessee Reconnect program traditionally gives adult learners (ages 23+) the opportunity to earn an associate degree, technical degree, or technical diploma tuition free. This bill extends program eligibility to 21- and 22-year olds – who are some of the most likely candidates for re-enrollment and completion. Between 2019-2021, the college-going rate in Tennessee rapidly declined by 9 percentage points, likely due to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic – meaning nearly 7,000 less seniors in the Class of 2021 enrolled in a postsecondary institution. This is particularly true for students of color, with both Black and Latino student college-going dropping over 11 percentage points. Today, many of those pandemic-impacted students are under the age of 23, meaning that they still are unable to access the Tennessee Reconnect Grant.
Accessible and affordable higher education for adult learners is critical to ensure Tennesseans have access to new skills, career advancement, and economic mobility. Further, increased accessibility to higher education has a positive impact on economic growth. Targeted support is required to close this gap and support adult learners to complete high-quality postsecondary programs. Tennessee SCORE points out that since 2010, 65% of new job openings require at least some advanced education. However, today only 48% of Tennesseans have some form of postsecondary credential. Many students, particularly students of color, are deterred by the financial barriers of pursuing postsecondary education. 40% of Tennessee Reconnect graduates earn “ high-needs credentials ,” which underscores this program as a highly effective tool to combat recent declines in college-going while addressing critical workforce shortages.
As a state that leads in postsecondary reforms aimed to improve access and degree completion, this proposal preserves and sustains efforts to increase widespread postsecondary enrollment and attainment. Overall, expanding Tennessee Reconnect eligibility to 21-year-olds can drive Tennessee’s economy forward.
Strengthening the State Longitudinal Data System
Hb0902/sb0461 | representative chris hurt & senator bo watson.
HB0902/SB0461 establishes stronger linkages between data systems and sectors in the Tennessee longitudinal data system . This bill also creates parameters to enhance public access and use, transparency, and data security in Tennessee’s data systems, and includes the creation of publicly facing dashboards that utilize education and workforce data. While Tennessee already collects significant K-12, Higher Education, and workforce data, this bill would make it easier and more accessible for education leaders, agencies, and advocates to make data-informed decisions to drive our state forward.
Connecting data across Tennessee’s education and workforce would tell a more complete story of Tennessee. As Tennessee’s data system currently exists, it primarily supports internal analyses, public reporting, and formal academic research, but is not easily accessible to postsecondary administrators, district leaders, and other organizations across the state. Out of the 40 states with a longitudinal data system in place, Tennessee is one of only three without a public-facing website for its system , making it difficult for leaders to leverage our state’s longitudinal education-to-workforce data system.
Better connected data systems are essential to illuminating which students are being served well by our education system and into the workforce. Local examples, like Nashville State’s “Better Together” partnership, utilize shared data that helps leaders implement targeted support where students are falling out of the education pipeline. Transparent and accessible data is key to ensuring students can make informed decisions about education opportunities, and for leaders to implement innovative practices that respond to student needs. Additionally, a comprehensive data system is key to positively impacting Tennessee’s workforce and economy. Overall, leveraging the robust data that Tennessee already collects has the potential to drive innovation and student success in education.

TEN Collective Impact
Build great schools together, student centered schools.
Students deserve an education that is personalized & right for them – what matters is that every student who graduates from that school is prepared for college, career & real life. Candidates who we support are openly committed to ensuring that every child has access to a great public school in their neighborhood and choices that fit their educational goals.
Measurable Results
Parents have the right to know if their child is making yearly progress. We use assessment as a tool for checking in on whether or not students are on track. Candidates who we support are openly committed to ensuring that every child has access to great schools that are delivering meaningful, measurable results for kids.
Happy, Healthy Kids
& included families.
Great schools are communities where every child can thrive & every family feels like they are included in building their child’s future. Candidates who we support are openly committed to ensuring that families and students drive their policy and decision-making if elected.
TAKE ACTION NOW


Windows 10 end of support updates for education
April 02, 2024.
By Microsoft Education Team

Share this article
Windows 10 will reach end of support (EOS) on October 14, 2025, less than two years from today. While two years may seem like a lot of time, upgrading your school’s devices now will help your organization stay focused on learning outcomes and protect educational data without interruption.
For nearly a decade, you’ve helped shape the learning experiences of countless students and educators with Windows 10. We wish to express our gratitude and appreciation for the ways you’ve used Windows 10 to empower learners, leaders, and intuitions to transform education. Thank you for being an integral part of our mission to enable equitable education for all.
We encourage you to transition to Windows 11 sooner than later, and we’re here to help you plan your move. Learn about the options you have to smoothly transition to Windows 11, including extended protection for Windows 10 devices that may need more time to transition.
What does Windows 10 end of support mean?
End of support means that Microsoft will no longer provide bug fixes for issues, security fixes for vulnerabilities, time zone updates, or technical support for problems that might occur.
As noted on the Windows 10 release information page, version 22H2 is the final version of Windows 10. All editions of Windows 10, version 22H2 will remain in support with monthly security updates through October 14, 2025.
Transition from Windows 10 to Windows 11 to meet your needs
Windows 11 helps every learner do their best work with easy-to-use tools built right in and ready to go from the first day—all in a secure and trusted environment . Windows 11 security features are enabled by default, providing protection for your school’s devices and peace of mind. The accessibility features and AI improvements built into Windows 11 help educators personalize learning and meet the needs of all students.
In addition to upgrading eligible PCs to Windows 11 using Microsoft Intune , your options to adopt Windows 11 include:
- Upgrade eligible PCs to Windows 11.
- Purchase new modern Windows 11 Pro PCs .
- Move to Windows 11 on a Cloud PC with Windows 365.
As we continue to develop Windows 11 for education, along with a wide range of devices from our partners, we remain dedicated to creating products that help all students access the tools and support they need to explore new opportunities and succeed in their learning. Find the perfect learning device at a low cost from Microsoft Education .

Windows 11 helps every learner do their best work with easy-to-use tools built right in and ready to go from the first day.
Take advantage of the Extended Security Update program for Windows 10
We encourage you to switch to Windows 11 , but we recognize that some situations might not allow you to upgrade your Windows 10 devices before the EOS date. For this reason, Microsoft will provide Extended Security Updates (ESU). The ESU for Windows 10 is designed to provide you with peace of mind as you migrate to Windows 11 and identify Windows 10 PCs that need more time to transition.
- Devices enrolled in ESU can receive monthly security updates but no feature or other updates.
- Similar to the Windows 7 ESU program, you will be able to purchase yearly subscriptions to security updates, renewable for up to three years.
- Windows 365 customers, as well as those that run Windows 10 in an Azure Virtual Desktop, will receive ESU at no additional charge.
To help you plan a successful transition, we’re offering special education pricing for the Windows 10 ESU program:
- ESU pricing 1 for Microsoft education customers will be $1 per license for the first year, $2 the following year, and $4 the third year to ensure institutions receive the support they need.
- This offer is extended to all education customers, including K-12 and Higher Education.
We know educators and students have experienced great benefits with Windows 10 and there's even more to love with Windows 11 , including built-in accessibility features on devices that are secure, easy to deploy, and manage. We look forward to helping you plan your transition to Windows 11 and supporting you on your journey.
We’ll continue to share updates about Windows 10 EOS and in the meantime, visit Lifecycle FAQ for Windows for more details. Additionally, more information on the ESU program will be shared later as availability and Windows 10 EOS approach. Read the Tech Community Blog on Windows 10 EOS or our visit the Windows Tech Community for more details on ESU enrollment. Looking for support? Visit Windows on Microsoft Q&A .
Microsoft 365, Windows devices, and comprehensive security combine to help schools and classrooms worldwide accelerate learning, improve efficiency, and enable equitable education. Learn about a suite of products that provide a comprehensive solution for everyone at your school, from educators to students to admins.
1 All prices are in US dollars. Regional prices will vary based on foreign exchange rates at the moment of ordering SKUs.
Related stories
What’s new in edu live: bett day 3.
Introducing seven new affordable Windows 10 devices for education and new tools for simplifying device management to make the most of classroom time. In our last Bett 2019 episode of What’s New in EDU, we recap the week’s exciting news with Anthony Salcito, VP of education, and share some exciting news around more affordable devices and how they work in partnership with tools that simplify device management for IT.

AI and security breakthroughs from Microsoft Ignite 2023 that schools won't want to miss
Each year at Microsoft Ignite—one of our largest and most popular events—we focus on sharing our most innovative updates with the world. The overarching theme for this year’s Microsoft Ignite event was how we are working to empower our customers, partners, and developers so that they can thrive in this exciting era of AI.

Microsoft Ignite: Bringing the innovations of the cloud to your CTE classroom
During November at Microsoft, we focus on innovation, AI, and the cloud at one of our biggest events of the year: the Microsoft Ignite conference. It is free to join online from anywhere November 15 and 16, 2023, so anyone can learn about how Microsoft is innovating in ways that will impact teaching, learning, and the future of work. This year, a large focus of Ignite will be how Microsoft Azure brings your data together securely and privately to analyze your information and leverage other applications to provide enhanced learning, collaboration, and security. With secure access to your data on prem, in the cloud, or in a hybrid implementation, utilizing innovative education solutions with embedded AI and harnessing analytics in your career and technical education (CTE) classroom becomes easier than ever before.
- SCHOOL STORIES
- MICROSOFT EDUCATOR CENTER
- CONTACT SALES
- Service to the State
College of Education - UT Austin
- Academics Overview
- Bachelor’s Programs
- Master’s Programs
- Doctoral Programs
- Post-baccalaureate
- Educator Preparation Programs
- Student Life Overview
- Career Engagement
- For Families
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Tuition, Financial Aid and Scholarships
- Commencement
- Office of Student Affairs
- Departments Overview
- Curriculum and Instruction
- Educational Leadership and Policy
- Kinesiology and Health Education
- Our Programs
- Educational Psychology
- Special Education
- Centers and Institutes
- Find Faculty
- Office of Educational Research
- Alumni and Friends Overview
- Advisory Council
- Meet Our Alumni
- Update Your Information
- About Overview
- College Leadership
- Facts and Rankings
- Reimagine Education
- Visit the college
- Building Renovations
- How to Apply
- How To Apply
- Newly Admitted Students
- Academic Advising
- Student Services
- Office of Educational Research Support
- Communications, Marketing and Media
- Visit the College
UT Austin College of Education Ranks Among Best Graduate Schools in the Nation

The College of Education at The University of Texas at Austin soared eight positions in this year’s U.S. News & World Report Best Graduate School Rankings and now sits at #4 among public schools, #8 overall and among the top 10 best education schools in the country. Four programs moved up as well with nine programs ranked in the top 20 and six ranked in the top 10, including Educational Administration, Education Policy, Educational Psychology and Special Education.
“In the College of Education we take very seriously our commitment to teach innovatively, conduct groundbreaking research and reimagine the education and health landscape,” said Charles R. Martinez, Jr., dean of the College of Education at UT Austin. “The recent rankings reflect our success and commitment to those principles, and to ensuring our students receive the highest quality education to go out and make a positive impact in the world. I am very proud of our entire College of Education community whose hard work and dedication drives our rankings year over year.”
The college’s Kinesiology and Health Education programs also rank highly, with its doctoral program in kinesiology earning the #6 spot from the Academy of Kinesiology and the Master of Education in Sport Management (Online) also ranking #6 by Sports Degrees Online’s Best Sport Management Programs for 2024-25.
College of Education USN&WR specialty rankings:
- No. 5 in Educational Administration and Supervision
- No. 6 in Educational Psychology
- No. 7 in Special Education
- No. 9 in Education Policy
- No. 10 in Elementary Teacher Education (tied)
- No. 10 in Secondary Teacher Education (tied)
- No. 12 in Curriculum & Instruction
- No. 14 in Higher Education Administration
- No. 15 in Student Counseling & Personnel Services
USN&WR ranks colleges and schools across the country on a variety of factors, including peer assessment data, research funding and statistical indicators.
View more of the college’s national rankings and demographics
View all UT Austin 2024-2025 USN&WR rankings
News Categories
- Exclude News
- Graduate Students
- Grant Awards
- In the Media
- Research, Impact and Achievements
- Alumni Stories
- Black History Month
- Donor Stories
- Educator Voices Across Texas
- Women’s History Month
- Undergraduate Students

NOTE: In this website, non 'region10.org' url links open in a new window.
Region 10 Website.
- Announcements
- Online Store
The Texas Education Telecommunications Network, TETN , supports K-12 educators statewide by providing videoconferencing services that save valuable time and money in travel. TETN is funded by the twenty Education Service Centers and the Texas Education Agency and operated by staff in Austin at Education Service Center Region 13.
Examples of videoconferences scheduled on TETN include:
- Administrative Meetings
- Professional Development; Legislative & Policy Updates
- Public Hearings on Commissioner rules
- Peer Collaboration (e.g. special education specialists)
- Special Projects
TETN also supports students through Dual-credit Courses; High School Courses; and Virtual Field Trips.
TETN Services
- Multipoint bridging for, statewide videoconferences among ESCs and school districts they serve
- Point-to-point bridging between school districts for dual-credit and high school courses, electronic field trips and student collaboration
- Special projects such as master degree classes and professional development
- Stream recorded videoconferences/meetings
TETN Scheduling
The TETN system is reserved for educational use only. Public education institutions are eligible, including primary and secondary schools, junior colleges and universities. Educational organizations, such as school boards, and professional education associations may also use TETN.
TETN Requests
Contact Steven Martin (Global Help Desk Manager) at Region 10 Education Service Center for further information or for requesting participation in a TETN videoconference.
A school district videoconference site may be scheduled only up to 24 hours prior to the start of the TETN event.
TETN Digital Recordings
TETN digitally records all statewide videoconferences. You may access recorded events free-of-charge if you are an active member of your local service center’s videoconference network. Recordings are accessed by using a computer and will need a media player such as Window Media Player® or QuickTime®. Event access is protected by an access login so contact your TETN Site Manager or scheduling assistant for instructions.

Advertisement
Supported by
Biden Wipes Out Another $7.4 Billion in Student Loan Debt
President Biden is hoping to shore up support with young voters who are disproportionately affected by soaring education costs. So far, he has canceled $153 billion in debt.
- Share full article

By Zach Montague
Reporting from Washington
President Biden canceled $7.4 billion in student loan debt on Friday as he tries to shore up support with young voters who are disproportionately affected by soaring education costs, but who may be drifting away over his policy on Israel and the war in Gaza.
The latest round of relief is part of a strategy by the White House to take smaller, targeted actions for certain subsets of borrowers after the Supreme Court struck down a far more ambitious plan to wipe out $400 billion in debt last year.
Mr. Biden said this week that he would make another attempt at large-scale debt forgiveness for about 30 million people, despite Republican opposition and legal challenges. But in the meantime, he has been chipping away at student debt by fixing and streamlining existing programs that have been plagued by bureaucratic and other problems for years.
Friday’s announcement was the latest such move, affecting around 277,000 people. White House officials said those borrowers would be notified by email that day.
More than 200,000 of those who qualified had borrowed relatively small amounts originally — $12,000 or less — and have been making payments through the administration’s income-driven repayment plan , known as SAVE.
Others who will see relief include teachers, librarians, academics and public safety workers who have been making student loan payments for 10 years under the Public Service Loan Forgiveness program. Another 65,000 borrowers enrolled in other income-driven repayment plans will see adjustments reducing their debt, Mr. Cardona said.
So far, the Biden administration has forgiven $153 billion in debt for 4.3 million borrowers.
“We’ve approved help for roughly one out of 10 of the 43 million Americans who have federal student loans,” Miguel A. Cardona, the education secretary, told reporters.
Republicans in Congress characterize student debt relief as unfair to borrowers who struggled to pay off their student debt without assistance.
“You’re incentivizing people to not pay back student loans and at the same time penalizing and forcing people who did to subsidize those who didn’t,” Representative John Moolenaar, Republican of Michigan, said during a hearing on Wednesday, in which Mr. Cardona testified about the Education Department’s budget request for next year.
“I don’t see it as unfair. I see it as, we’re fixing something that’s broken,” Mr. Cardona said. “We have better repayment plans now so we don’t have to be in the business of forgiving loans in the future.”
On Monday, Mr. Biden outlined a new attempt to wipe out student loan debt on a larger scale, beyond the scope of the programs he has been relying on so far.
The new plan would reduce the amount that 25 million borrowers still owe on their undergraduate and graduate loans. It would wipe away the entire amount for more than four million Americans. Altogether, White House officials said, 10 million borrowers would see debt relief of $5,000 or more.
That plan must undergo a public comment period that stretches through the summer. It also must survive legal challenges.
The original plan relied on a law called the HEROES Act, which the administration argued allowed the government to waive student debt during a national emergency like the Covid pandemic. The Supreme Court disagreed.
Biden administration officials said because the new approach is based on a different law — the Higher Education Act — it is more likely to survive the expected challenges.
Zach Montague is based in Washington. He covers breaking news and developments around the district. More about Zach Montague
Our Coverage of the 2024 Election
Presidential Race
In his final campaign rally before his criminal trial in Manhattan was set to begin, former President Donald Trump cast himself as a victim of political persecution .
An average of recent surveys, including a new poll by The New York Times and Siena College, shows that President Biden is inching closer to Trump, Nate Cohn writes .
At a rally in Arizona days after the state’s top court upheld a near-total ban on abortion, Vice President Kamala Harris placed the blame directly on Trump .
Vice-Presidential Calculations: As Trump sifts through potential running mates, he has peppered some advisers and associates with a direct question: Which Republican could best help him raise money ?
Embracing the Jan. 6 Rioters: Trump initially disavowed the attack on the Capitol, but he is now making it a centerpiece of his campaign .
Mobilizing the Left: Amid the war in Gaza, the pro-Palestinian movement has grown into a powerful, if disjointed, political force in the United States. Democrats are feeling the pressure .
On a Collision Course: As president, Trump never trusted the intelligence community. His antipathy has only grown since he left office, with potentially serious implications should he return to power .
Texas A&M Dean Named One Of The ‘Most Influential People In Legal Education’

It didn’t take long after moving to Fort Worth for Bobby Ahdieh to realize that blending in wasn’t going to be an option. Within a few minutes of opening his mouth to speak, the New Yorker is inevitably asked where he’s from. So instead, Ahdieh adopted what he calls his “I got here as quick as I could” approach.
That’s how he found himself on the back of a horse in the center of a packed arena within his first year as dean of Texas A&M University’s School of Law. When he got a text message one day asking if he would ride in the Fort Worth Stock Show & Rodeo, Ahdieh’s initial response was to joke that it must be a typo — surely, he thought, he was being asked if he needed a ride to the rodeo. “If you were looking for a case study of someone doing something no one could have predicted just a few years ago, ‘Bobby riding a horse in Texas’ would have been it,” he said.
But then, there are a lot of things Ahdieh has accomplished since joining the law school in 2018 that might seem beyond belief. In the last five years alone, the school has risen 57 places in U.S. News and World Report ’s ranking of top law schools, breaking into the top 30 for the first time last year at No. 29. It jumped another three spots to No. 26 in this year’s recently-released rankings . The school also ranked No. 1 on the Texas Bar Exam last year, and the Class of 2022 had the highest placement in “gold standard” jobs of any law school in the nation.
Ahdieh’s accomplishments were recently acknowledged by The National Jurist , which placed him at No. 5 on its list of the 20 most influential people in legal education.
To Ahdieh, his inclusion on the list is an indication that the law school, which Texas A&M acquired in 2013 from Texas Wesleyan University, is a “player of substance” on the legal education landscape. Over the last few years, the total number of faculty has grown to 146, 67 of whom are full-time. And in addition to 447 juris doctorate students, another 1,218 students are now enrolled in the law school’s graduate programs.
“What it reflects is that Texas A&M is increasingly at the table — in terms of what legal education looks like and should look like,” Ahdieh said. “Our place there is indisputable, when you consider the caliber of our faculty and the work that they’re doing, and when you look at the quality of the students we’re attracting.”

Educating Future Leaders
Ahdieh earned a bachelor’s degree from Princeton University’s School of Public and International Affairs before being trained in the legal profession at Yale Law School. He went on to clerk for Judge James R. Browning of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit, before working in the civil division of the U.S. Department of Justice.
It’s not uncommon for some attorneys to cross over into academia because they don’t enjoy practicing law. But in Ahdieh’s case, he loved his time in the courtroom. He enjoyed the challenge of figuring out how to articulate an argument in an effective fashion, and then respond to the counter-arguments. At the same time, he recognized that the impact he could have through scholarship and policy advocacy, as well as in educating the next generation of lawyers, would be greater as an academic.
In addition to stints teaching at Princeton, Georgetown and Columbia, Ahdieh worked at Atlanta’s Emory University for 18 years, both as a professor and vice dean.
“I still miss legal practice to this day, but educating is what keeps me ticking and gets me up in the morning,” Ahdieh said.
As Texas continues to grow in population and economic activity, the state will need more of the kind of “world-class” lawyers produced by Texas A&M School of Law, Ahdieh said. But he also believes it’s becoming “vitally important” that the law school serve the state beyond just educating future lawyers.
More broadly, Ahdieh said, growing numbers of professionals in heavily regulated industries like healthcare, energy and finance need robust training in law, regulation and compliance, given an increasingly complex business landscape. The School of Law is helping meet this need through its Master of Legal Studies and related certificate programs, which are designed for professionals who don’t intend to practice law, but need a legal education. The program currently enrolls close to 1,100 students.
“In terms of Texas A&M’s land-, sea- and space-grant mission and meeting the needs of Texas as a whole, it’s critical to create a population of professionals able to navigate the complex landscapes their industries are facing,” Ahdieh said.
Despite the 170-mile physical separation from the flagship campus, Ahdieh has also made a concerted effort for the law school to be engaged with and visible in College Station. This is perhaps most tangibly reflected in the joint degree pathways and programs that have been established with several of the university’s colleges and schools — and in the prominent display of the Aggie Core Values, 12th Man imagery and maroon on every wall of the law school.
As part of his 2022 appointment as vice president for professional schools and programs, Ahdieh is also working to identify and establish new practice and coursework-oriented degrees, certificates and programs with growth potential across the length and breadth of the university.

Expanding Presence In Fort Worth
A relocation to Texas wasn’t on Ahdieh’s radar until he interviewed with Texas A&M University System Chancellor John Sharp and other leaders about their vision for the school that had been acquired just five years prior.
“What I saw when I was offered the job was an opportunity to really move the school forward across multiple axes, and that was enough for me to say, ‘OK, I’ll learn how to ride a horse.’”
When Ahdieh reflects on the law school’s trajectory over the last few years, he believes a critical piece of its ascendance was the willingness of university leadership to take on a seemingly impossible challenge — moving an unranked law school into the top tier.
At a gathering of lawyers in Austin about a year and a half ago, Ahdieh was asked to speak on the topic of facilitating change, including with reference to the law school’s dramatically improved rank and reputation. Of the crowd of 400 or so in attendance, most had attended the University of Texas for either their undergraduate or law degree. Ahdieh gave credit to what he described as a “peculiar characteristic of the Aggie mind” — earning some audible sighs and conspicuous eye rolls from the Longhorns in the room.
“I told them to bear with me, and explained that all of us are born and raised with a keen sense of our limitations and what we’re capable of — except for the Aggies,” he said. “I don’t know whether it’s something in the water or something in the air, but this is a group of people who never start with the assumption that something is impossible.”
“Aggies have somehow figured out a way to bottle that mindset and instill it in every one of their current and former students — and that has made for an incredible community to be a part of,” he said. “To join the Aggie family and be charged to move our law school forward and establish a broader presence in Fort Worth, it’s hard to imagine a better place to be.”
Ahdieh added another title to his resume in 2023, when he was appointed chief operating officer of Texas A&M-Fort Worth , the several-hundred-million-dollar research campus envisioned by Texas A&M University System officials and Forth Worth government and business leaders to spur innovation and business development. The Texas A&M System broke ground last summer on the $150 million Law & Education Building, which will be the new eight-story home to both the School of Law and other programs from Texas A&M and Tarleton State University.
“The political will to pull off this massive undertaking can in some significant part be traced to the fact that everyone now looks at the law school and says, ‘If this pretty unbelievable transformation could be accomplished in just 10 years, who knows what amazing things can be accomplished with Texas A&M’s commitment to a broader presence in Fort Worth,’” Ahdieh said.
He hopes the campus, which will sit on four city blocks and change the face of the southeastern part of downtown, will create a larger presence and scope of influence in North Texas for Texas A&M.
For his part in encouraging the creation of the first-of-its-kind campus, Ahdieh was given the “Innovation Trailblazer Award” last year by Downtown Fort Worth, Inc. The city’s convention and visitors bureau has even featured Ahdieh in its series of videos spotlighting local community leaders.
He’s never had a particular taste for attention or visibility, Ahdieh said, but it’s been something he has become more accustomed to as the face of the law school, especially as he’s “embraced the local ways.”
“Nobody expects me to become a professional bull rider, but I go to the rodeo five, six, sometimes seven times over the course of the season and participate in all sorts of activities,” he said. “I think that means a lot in Fort Worth and in Texas. It’s a different world from any I had known previously. But it’s been the honor of my career to be here.”
Media contact: [email protected]

Related Stories

What You Should Know About The Historic Auto Workers Strike Unfolding
A labor law expert from the Texas A&M School of Law breaks down the key points of conflict between the United Auto Workers union and the “Big Three” car manufacturers.

Texas A&M School Of Law Celebrates 10 Years
The law school has climbed more than 120 places in the U.S. News & World Report rankings since its acquisition in 2013.

Will AI Put Lawyers Out Of Work? A Texas A&M Expert Says It’s Unlikely
Artificial intelligence could make legal services more streamlined and accessible — but many aspects of the profession still require a distinctly human touch, says A&M Law Professor Milan Markovic.
Recent Stories

Texas A&M Names Josh Brewton ‘27 As Newest Handler For Reveille X
Cadet from Cedar Park, Texas, will serve as the primary caretaker for the university’s official mascot.

Is Smallpox Still A Threat?
A Texas A&M scientist has collaborated on a new report that warns of its potential return and urges heightened preparedness.

Workplace Law Expert Examines Starbucks Supreme Court Bid
Starbucks is seeking protection from being ordered to rehire baristas who say they were fired for union-promoting activities. Professor Michael Z. Green explains how the case could affect the right to organize unions in the U.S.

Subscribe to the Texas A&M Today newsletter for the latest news and stories every week.
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
6. teachers’ views on the state of public k-12 education.
Overall, teachers have a negative view of the U.S. K-12 education system – both the path it’s been on in recent years and what its future might hold.
The vast majority of teachers (82%) say that the overall state of public K-12 education has gotten worse in the last five years. Only 5% say it’s gotten better, and 11% say it has gotten neither better nor worse.
Looking to the future, 53% of teachers expect the state of public K-12 education to be worse five years from now. One-in-five say it will get better, and 16% expect it to be neither better nor worse.
We asked teachers who say the state of public K-12 education is worse now than it was five years ago how much each of the following has contributed:
- The current political climate (60% of teachers say this is a major reason that the state of K-12 education has gotten worse)
- The lasting effects of the COVID-19 pandemic (57%)
- Changes in the availability of funding and resources (46%)
Elementary school teachers are especially likely to point to resource issues – 54% say changes in the availability of funding and resources is a major reason the K-12 education system is worse now. By comparison, 41% of middle school and 39% of high school teachers say the same.
Differences by party
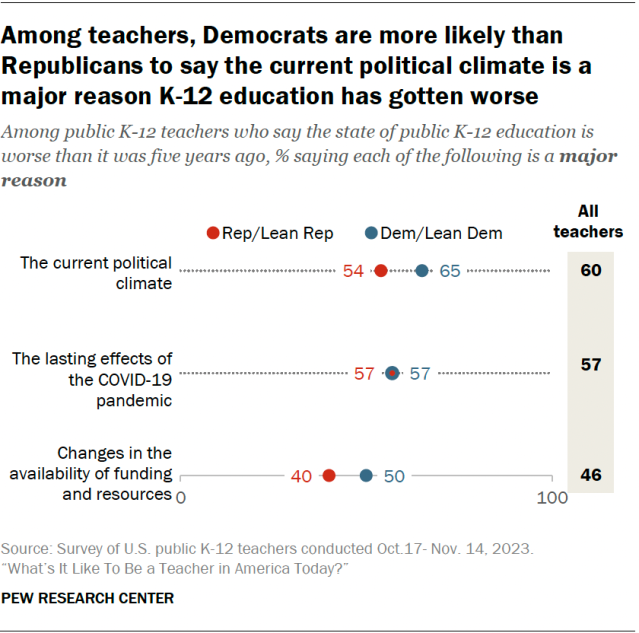
Overall, teachers who are Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents are as likely as Republican and Republican-leaning teachers to say that the state of public K-12 education is worse than it was five years ago.
But Democratic teachers are more likely than Republican teachers to point to the current political climate (65% vs. 54%) and changes in the availability of funding and resources (50% vs. 40%) as major reasons.
Democratic and Republican teachers are equally likely to say that lasting effects of the pandemic are a major reason that the public K-12 education is worse than it was five years ago (57% each).
K-12 education and political parties
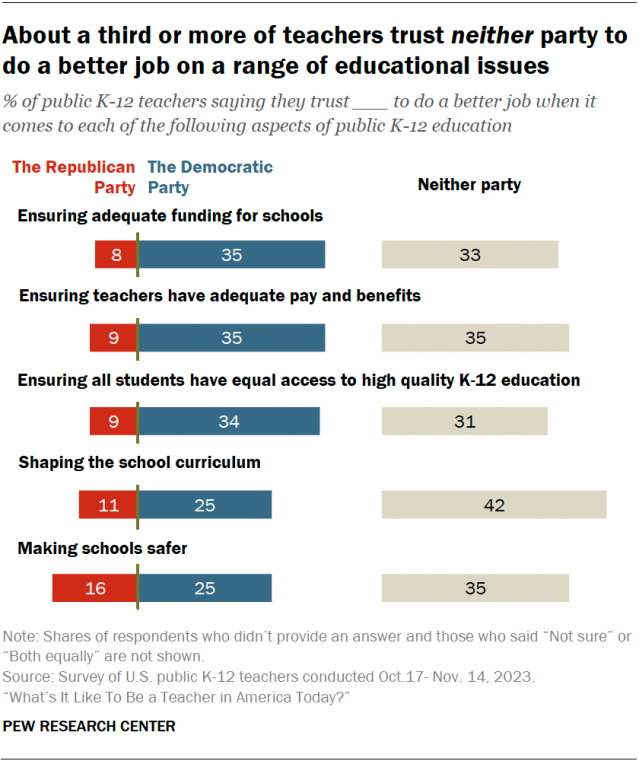
We asked teachers which political party they trust to do a better job on various aspects of public K-12 education.
Across each of the issues we asked about, roughly a third or more of teachers say they don’t trust either party to do a better job. In particular, a sizable share (42%) trust neither party when it comes to shaping the school curriculum.
On balance, more teachers say they trust the Democratic Party to do a better job handling the things we asked about than say they trust the Republican Party.
About a third of teachers say they trust the Democratic Party to do a better job in ensuring adequate funding for schools, adequate pay and benefits for teachers, and equal access to high quality K-12 education for students. Only about one-in-ten teachers say they trust the Republican Party to do a better job in these areas.
A quarter of teachers say they trust the Democratic Party to do a better job in shaping the school curriculum and making schools safer; 11% and 16% of teachers, respectively, say they trust the Republican Party in these areas.
Across all the items we asked about, shares ranging from 15% to 17% say they are not sure which party they trust more, and shares ranging from 4% to 7% say they trust both parties equally.
A majority of public K-12 teachers (58%) identify with or lean toward the Democratic Party. About a third (35%) identify with or lean toward the GOP.
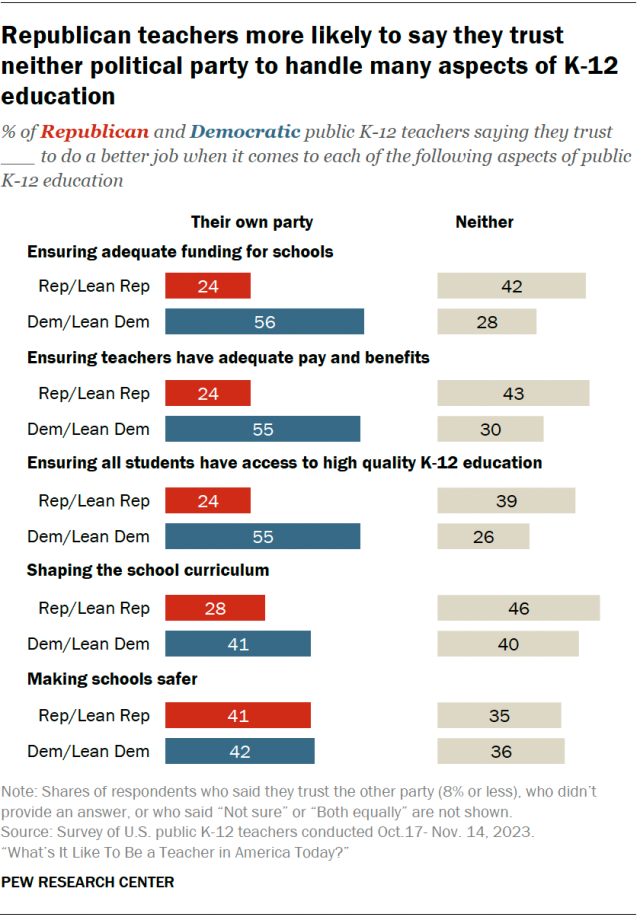
For each aspect of the education system we asked about, both Democratic and Republican teachers are more likely to say they trust their own party to do a better job than to say they trust the other party.
However, across most of these areas, Republican teachers are more likely to say they trust neither party than to say they trust their own party.
For example, about four-in-ten Republican teachers say they trust neither party when it comes to ensuring adequate funding for schools and equal access to high quality K-12 education for students. Only about a quarter of Republican teachers say they trust their own party on these issues.
The noteworthy exception is making schools safer, where similar shares of Republican teachers trust their own party (41%) and neither party (35%) to do a better job.
Social Trends Monthly Newsletter
Sign up to to receive a monthly digest of the Center's latest research on the attitudes and behaviors of Americans in key realms of daily life
Report Materials
Table of contents, ‘back to school’ means anytime from late july to after labor day, depending on where in the u.s. you live, among many u.s. children, reading for fun has become less common, federal data shows, most european students learn english in school, for u.s. teens today, summer means more schooling and less leisure time than in the past, about one-in-six u.s. teachers work second jobs – and not just in the summer, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
- Education News
Jharkhand Board Results 2024: JAC to announce Class 10, 12 results soon; check passing marks here

How to check JAC 10, 12 Results 2024?
Passing marks.
- A minimum of 33% marks in each subject (theory and practical combined, if applicable).
- A minimum of 33% marks in the overall (aggregate of all subjects).
- Minimum of 23 marks out of 70 marks in the theory part of each subject.
- Minimum of 10 marks out of 30 marks in the practical part (if applicable) of each subject.
JAC Matric Result 2023
Jac inter result 2023, visual stories.
- Top 200 Universities in the World
- Top 200 Universities in North America
- Top 200 Universities in Latin America
- Top 200 Universities in Europe
- Top 200 Universities in Africa
- Top 200 Universities in Asia
- Top 50 Universities in Oceania
- Top 200 English-speaking Universities
- Top 200 Spanish-speaking Universities
- Top 200 Arabic-speaking Universities
- Top 200 Universities on Facebook
- Top 200 Universities on Twitter
- Top 200 Universities on Instagram
- Top 200 Universities on YouTube
- Top religiously affiliated Universities
- Universities in North America
- Universities in Latin America
- Universities in Europe
- Universities in Africa
- Universities in Asia
- Universities in Oceania
- A-Z Guide to University Programs, Courses and Degrees
- University Guides and Articles
- Universities on Facebook
- Universities on Twitter
- Universities on Instagram
- Universities on YouTube
- Universities on TikTok
- Universities on LinkedIn
- Free online courses by OEG Universities
- Higher Education-related Organizations
- Directory of University Libraries
- Religiously Affiliated Universities
- Higher Education Glossary
- A-Z list of World Universities
- Top Public Universities
Top Public Universities in Russia
Introduction.
What are the top Public Universities in Russia? uniRank answers this question by publishing a complete list of Public Russian Universities ranked by the 2024 uniRank University Ranking and meeting the following uniRank selection criteria:
- being chartered, licensed or accredited by the appropriate Russian higher education-related organization
- offering at least three-year bachelor's degrees or postgraduate master's or doctoral degrees
- delivering courses predominantly in a traditional, non-distance education format
uniRank aims to provide a non-academic League Table of the top Public Russian Universities based on valid, unbiased and non-influenceable web metrics provided by independent web intelligence sources rather than data submitted by the Universities themselves.
Featured Universities New
Unlock Your University's Global Potential: Spotlight Your Institution on UniRank for International Recognition. Feature your University here. Get in Touch Today . Discover More Information Without Any Obligation!
Share Public Universities
Interesting? Don't forget to share these Public Universities in Russia with your friends now.
Feedback, Errors
We appreciate your feedback and error reports.
Related Russian University resources
- uniRank World Universities Search Engine Search for Russian universities, programs, courses, scholarships and more using our comprehensive search engine.
- Top Russian Universities on Facebook Curious to know which Russian universities are the most popular on Facebook? Check out the uniRank Facebook Ranking.
- Top Russian Universities on Twitter Interested in finding the most popular Russian universities on Twitter? Discover them here.
- Top Russian Universities on Instagram Wondering which Russian universities top the charts on Instagram? Find the answer here.
- Top Russian Universities on YouTube Lastly, explore the Russian universities that are most popular on YouTube. Discover them here.
- Colleges and Universities in Europe by country Looking for other universities and colleges, along with their courses, in the same continent? Find them in our comprehensive list of Colleges and Universities in Europe by country.
Since 2005, with uniRank's World Universities Search Engine and rankings, you can easily find information about Russian Universities and Colleges and explore higher education opportunities in Europe.
© uniRank since 2005
University rankings, universities by country, free online courses, universities on social media, more resources.
About | Methodology | Contact | Advertise | Terms | Privacy | Change privacy settings
©uniRank 2005-2024

Universities in Moscow, Russia - Rankings & Reviews -
For business studies see our separate ranking of business schools in Moscow, Russia
- 27 Sep, 2023: THE World University Rankings updated with Moscow State University M. V. Lomonosov ranked highest among 21 listed universities in Moscow.
- 15 Aug, 2023: ARWU Academic Ranking of World Universities - ShanghaiRanking updated with Moscow State University M. V. Lomonosov ranked highest among 6 listed universities in Moscow.
- 31 Jul, 2023: Webometrics published most recent results of Webometrics Ranking Web of Universities . Includes 42 universities from Moscow.
- 22 Jul, 2023: Latest URAP University Ranking by Academic Performance - By Field (Business) from Urap . 115 universities from Moscow appear in this ranking.
Rankings of universities in Moscow, Russia 2024

Moscow State University M. V. Lomonosov
- University rankings (20)

Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology

National Research University Higher School of Economics

- University rankings (17)

in Business, Computer Science, Medicine, Law, Education, Health... Study at your own pace , conveniently from home .

National Research Nuclear University MEPI
- University rankings (19)

Peoples' Friendship University of Russia

Bauman Moscow State Technical University
- University rankings (16)

National University of Science and Technology "MISIS"

- University rankings (15)

Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University

- University rankings (14)

Plekhanov Russian University of Economics

Finance Academy under the Government of the Russian Federation
- University rankings (10)

MGIMO University
- University rankings (6)

National Research University Moscow Power Engineering Institute
- University rankings (9)

Moscow Aviation Institute (National Research University)

Russian National Research Medical University

- University rankings (7)
Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration
- University rankings (8)

Mendeleev University of Chemical Technology of Russia

Moscow Institute of Electronic Technology

Moscow State University of Civil Engineering

Skolkovo Institute of Science & Technology

Russian State University for the Humanities

Russian Technological University MIREA

- University rankings (12)

Russian State University of Oil and Gas
- University rankings (11)

Russian State Agricultural University

Moscow Polytech

Moscow State Pedagogical University

Moscow State Technological University "Stankin"

Moscow Technical University of Communications and Informatics

- University rankings (5)

Russian State Social University
- University rankings (4)

Moscow City Teachers' Training University

- University rankings (3)

Moscow State University of Food Production

New Economic School

Moscow State University of Psychology and Education
- University rankings (2)

Moscow State Regional University

- University rankings (1)

Moscow State Linguistic University

Russian State Geological Prospecting University

Russian New University

Moscow State University of Railway Engineering

Moscow State University of Technology and Management

Pushkin State Russian Language Institute

Moscow State Technical University of Civil Aviation

Moscow State University of Geodesy and Cartography

Moscow University for the Humanities

Moscow Tchaikovsky Conservatory

Saint Tikhon's Orthodox University

State University of Land Management

Gaidar Institute for Economic Policy

Modern University for the Humanities

Moscow International Higher Business School

Moscow State University of Design and Technology

Moscow Metropolitan Governance University
Highest subject rankings of universities in moscow, moscow key facts for international students.
49 out of 69 Universities in Moscow Ranked in at least one ranking
24 Different Rankings list Universities in Moscow (18 institution and 6 subject rankings)
16 Global Rankings rank Universities in Moscow Among TOP 200
Population: 10382000
Time: GMT +3
District/province: Moscow,
* 100 = prices in London
- Living costs without accommodation 61* (39% cheaper than London)
- All costs including accommodation 57* (43% cheaper than London)
- Meals (grocery & lower cost restaurants) 59* (41% cheaper than London)
- Average Big Mac price 188.65 RUB
- Residential voltage: 230 V
- Frequency: 50 Hz
Map with location of universities in Moscow

Useful related pages

What is the best ranked university in Moscow?
What university in moscow is listed in most university rankings, what university in moscow is best ranked for studying business, what university in moscow is best ranked for studying languages & literature, what university in moscow is best ranked for studying natural sciences, what university in moscow is best ranked for studying mathematics, what university in moscow is best ranked for studying education, what university in moscow is best ranked for studying social studies & humanities, what university in moscow is best ranked for studying engineering, what university in moscow is best ranked for studying law, what university in moscow is best ranked for studying computer science, what university in moscow is best ranked for studying medicine & health, what university in moscow is best ranked for studying agriculture, ranking publishers, british quacquarelli symonds, uk, qs world university rankings (published: 27 june, 2023).
Academic Reputation 40% Employer Reputation 10% Faculty/Student Ratio 20% Citations per faculty 20% International Faculty Ratio 5% International Student Ratio 5%
view methodology
QS Employability Rankings (Published: 23 September, 2021)
Employer reputation 30% Alumni outcomes 25% Partnerships with Employers per Faculty 25% Employer/Student Connections 10% Graduate employment rate 10%
QS 50 under 50 (Published: 24 June, 2020)
Based on the QS World University rankings methodology, the top 50 universities that are under 50 years old.
QS University Rankings: EECA Emerging Europe & Central Asia (Published: 15 December, 2021)
Academic reputation 30% Employer reputation 20% Faculty/student ratio 10% Papers per faculty 10% International research network 10%
QS University Rankings BRICS (Published: 06 May, 2019)
Academic reputation 30% Employer reputation 20% Faculty/student ratio 20% Staff with a PhD 10% Papers per faculty 10%
QS World University Rankings: Sustainability (Published: 26 October, 2022)
Cwur center for world university rankings, cwur center for world university rankings (published: 25 april, 2022).
Research Performance: 40%
- Research Output: 10%
- High-Quality Publications: 10%
- Influence: 10%
- Citations: 10%
Quality of Education: 25%
Alumni Employment: 25%
Quality of Faculty: 10%
Centre for Science and Technology Studies, Leiden University, Netherlands
Cwts leiden ranking (published: 22 june, 2022).
Scientific Impact Number of Publications Collaboration Open Access Gender Diversity
NTU ranking
Ntu performance ranking of scientific papers (published: 11 july, 2023).
Research Productivity: 25%
- # Articles last 11 years: 10%
- # Articles current year: 15%
Research Impact: 35%
- # Citations last 11 years: 15%
- # Citations last 2 years: 10%
- Average # citations last 11 years: 10%
Research Excellence: 40%
- H-index last 2 years: 10%
- # Highly cited papers last 11 years: 15%
- # Articles current year in high-impact journals: 15%
Nature Index
Nature index - young universities (published: 08 december, 2021), rur ranking agency (moscow, russia), rur world university rankings (published: 25 may, 2023).
Teaching: 40%
- Ratio Faculty/Student: 8%
- Ratio Faculty/Bachelor Degrees Awarded: 8%
- Ratio Faculty/Doctoral Degrees Awarded: 8%
- Ratio Doctoral Degrees Awarded/Bachelor Degrees Awarded: 8%
- World Teaching Reputation: 8%
Research: 40%
- Citations per Academic/Research Staff: 8%
- Doctoral Degrees per Accepted PhD: 8%
- Normalized Citation Impact: 8%
- Papers per Academic/Research Staff: 8%
- World Research Reputation: 8%
International Diversity: 10%
- International Faculty: 2%
- International Students: 2%
- International Co-Authored Papers: 2%
- Reputation Outside Geographical Region: 2%
- International Level: 2%
Financial Sustainability: 10%
- Institutional Income per Faculty: 2%
- Institutional Income per Student: 2%
- Papers per Research Income: 2%
- Research Income per Academic/Research Staff: 2%
- Research Income per Institutional Income: 2%
RUR Academic Rankings (Published: 25 May, 2023)
Normalized citation impact (Citations of research publications from all university authors compared with world averages) 20% Citation per papers 20% Papers per academic and research staff 20% International research reputation 20% Share of research publications written in international co-authorship 20%
RUR Reputation Ranking (Published: 25 May, 2023)
Teaching Reputation 50% Research Reputation 50%
Scimago Institutions
Scimago institutions rankings (published: 06 march, 2023).
Research 50% Innovation 30% Societal 20%
ShanghaiRanking Consultancy
Arwu academic ranking of world universities - shanghairanking (published: 15 august, 2023).
Quality of Education 10%
- Alumni winning Nobel Prizes/Field Medals 10%
Quality of Faculty 40%
- Staff winning Nobel Prizes/Field Medals 20%
- Highly Cited Researchers 20%
Research Output 40%
- Papers published in Nature and Science 20%
- Papers indexed in Science Citation Index-Expanded & Social Science Citation Index 20%
Per Capita Performance 10%
THE Times Higher Education, UK
The world university rankings (published: 27 september, 2023).
30% Teaching (the Learning Environment)
- Reputation survey: 15%
- Staff-to-student ratio: 4.5%
- Doctorate-to-bachelor’s ratio: 2.25%
- Doctorates-awarded-to-academic-staff ratio: 6%
- Institutional income: 2.25%
30% Research (Volume, Income and Reputation)
- Reputation survey: 18%
- Research income: 6%
- Research productivity: 6%
30% Citations (Research Influence)
7.5% International Outlook (Staff, Students and Research)
- Proportion of international students: 2.5%
- Proportion of international staff: 2.5%
- International collaboration: 2.5%
2.5% Industry Income (Knowledge Transfer)"
THE World Reputation Rankings (Published: 16 November, 2022)
Research Reputation 66,6% Teaching Reputation 33,3%
THE Emerging Economies University Ranking - Times Higher Education (Published: 19 October, 2021)
Teaching 30% Research (volume, income and reputation) 30% Citations 20% International outlook (staff, students, research) 10% Industry income (knowledge transfer) 10%
THE Young University Rankings (Published: 03 July, 2023)
Teaching 30% Research (volume, income and reputation) 30% Citations 30% International outlook (staff, students, research) 7.5% Industry income (knowledge transfer) 2.5%
THE World University Impact Rankings - Overall (Published: 01 June, 2023)
The china subject ratings overall (published: 11 may, 2022), urap world ranking - university ranking by academic performance (published: 28 november, 2022), us news: best global universities (published: 24 october, 2022), webometrics, webometrics ranking web of universities (published: 31 july, 2023).
Visibility 50% Excellence 35% Transparency 10% Presence 5%


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Welcome to Ten Education - Your Gateway to Learning Excellence! 📚 At Ten Education, we believe in making education accessible and enjoyable for everyone. Join us as we unravel complex ...
What Works: Ten Education, Training, and Work-Based Pathway Changes That Lead to Good Jobs identifies 10 pathway changes with the greatest potential to improve employment outcomes for young adults. The report uses the Pathways-to-Career policy simulation model, developed by CEW researchers using longitudinal data, to identify promising ...
Wednesday, April 10, 2024 | 01:00pm. Nashville, TN— This month, the Tennessee Department of Education is promoting the annual Tennessee Comprehensive Assessment Program (TCAP), which will be administered to students in grades 3-8 from April 15 - May 3. Read full story. News.
Tweet your comments with #K12BigIdeas. No. 1: Kids are right. School is boring. Out-of-school learning is often more meaningful than anything that happens in a classroom, writes Kevin Bushweller ...
10 Education, Hanoi, Vietnam. 42,074 likes · 674 talking about this · 295 were here. Tin học MOS & IC3
Building education and professional development opportunities for Lawyers, Accounting, Corporate and Government staff to ensure they are kept up to date with an ever-changing legal environment.
Học chứng chỉ quốc tế cùng 10 Education. 10 Education trung tâm đào tạo các chứng chỉ tin học MOS (MOS Word, Excel, PPT,…), IC3 GS5, IC3 GS6.., chứng chỉ tiếng anh IELTS. 10 Education trung tâm đào tạo chứng chỉ MOS hàng đầu, cam kết đầu ra. Nhận Tư Vấn
The 10 Most Significant Education Studies of 2023. Following our annual tussle with hundreds of studies of merit, we've pared them down to 10 you shouldn't miss—from what AI can (and can't) do to the neuroscience of brain synchrony. By Youki Terada, Stephen Merrill. December 7, 2023. For those of us hoping for a quiet, back-to-normal ...
The 10 Most Significant Education Studies of 2021. From reframing our notion of "good" schools to mining the magic of expert teachers, here's a curated list of must-read research from 2021. By Youki Terada, Stephen Merrill, Sarah Gonser. December 9, 2021. It was a year of unprecedented hardship for teachers and school leaders.
Sarah D. Sparks covers education research, data, and the science of learning for Education Week. A version of this article appeared in the January 17, 2024 edition of Education Week as 10 ...
Stay in touch TEN EDUCATION S.R.L. https://ecm.teneducation.it/ [email protected], [email protected]
The National Education Association of the United States Committee on Secondary School Studies known as the NEA Committee of Ten was a working group of educators that convened in 1892. They were charged with taking stock of current practices in American high schools and making recommendations for future practice. They collected data via surveys and interviews with educators across the United ...
About Ten Education. For rehabilitation, fitness and exercise professionals who understand the importance of quality of movement, a TenEducation Dynamic Reformer certification is a powerful addition to their repertoire of treatment and teaching tools. Established in 2007, Ten has trained hundreds of health and fitness professionals to use the ...
The National Education Association appoints a Committee of Ten to examine high school curriculum issues and make recommendations about methods, standards and programs. The committee's recommendations, which influence the Committee on College Entrance Requirements founded in 1895, support the teaching of traditional subjects such as Latin, Greek, English, modern languages, mathematics, the ...
These are the 10 best states for education, according to the Best States analysis. You can learn more about how states are assessed in our methodology. Next: 10. Washington. Next: 9. New York ...
Ten for Tennessee recognizes and celebrates the top ten policy proposals in 2024 that best advance educational equity and justice in the state. ... The Education Trust-Tennessee is proud to recognize the ideas that have the greatest potential to improve opportunity and access for students of color, students from lower-income communities ...
The Biden-Harris Administration announced today the approval of $7.4 billion in additional student loan debt relief for 277,000 borrowers. These discharges are for borrowers who signed up for President Biden's Saving on a Valuable Education (SAVE) Plan and are eligible for its shortened time-to-forgiveness benefit and as a result of fixes made by the Administration to income-driven repayment ...
The DPS Board of Education has 4 seats up in November, commit to voting for lead . COMMIT TO VOTE. English; Español; About TEN Collective Impact. TEN Collective Impact is a grassroots collective of community members, parents and policy experts focused on ensuring that we have strong leaders, strong policies and a strong understanding of impact ...
Windows 10 will reach end of support (EOS) on October 14, 2025, less than two years from today. While two years may seem like a lot of time, upgrading your school's devices now will help your organization stay focused on learning outcomes and protect educational data without interruption. For nearly a decade, you've helped shape the ...
The College of Education at The University of Texas at Austin soared eight positions in this year's U.S. News & World Report Best Graduate School Rankings and now sits at #4 among public schools, #8 overall and among the top 10 best education schools in the country. Four programs moved up as well with nine programs ranked in the top 20 and six ranked in the top 10, including Educational ...
Overview. The Texas Education Telecommunications Network, TETN, supports K-12 educators statewide by providing videoconferencing services that save valuable time and money in travel. TETN is funded by the twenty Education Service Centers and the Texas Education Agency and operated by staff in Austin at Education Service Center Region 13.
President Biden is hoping to shore up support with young voters who are disproportionately affected by soaring education costs. So far, he has canceled $153 billion in debt.
Bobby Ahdieh, who has led the Fort Worth-based law school since 2018, was recently ranked the fifth-most influential individual in legal education by The National Jurist. By Caitlin Clark, Texas A&M University Division of Marketing & Communications April 11, 2024. Dean Bobby Ahdieh outside the law school's building in downtown Fort Worth.
About Ten Education. The professional training arm of Ten Health & Fitness, London's leading Pilates Studio, TenEducation offers courses to Pilates instructors, Physiotherapists, fitness, exercise and rehab professionals. For rehabilitation, fitness and exercise professionals who understand the importance of quality of movement, a TenEducation qualification is a powerful addition to their ...
Overall, teachers have a negative view of the U.S. K-12 education system - both the path it's been on in recent years and what its future might hold. The vast majority of teachers (82%) say that the overall state of public K-12 education has gotten worse in the last five years. Only 5% say it's gotten better, and 11% say it has gotten ...
The Jharkhand Academic Council (JAC) is soon expected to announce the JAC Class 10, 12 Results 2024. As per the media reports, the Matric and Inter results are likely to be declared in the month ...
Punished for daring to seek an education, the Chibok girls endured forced marriages, religious coercion, and physical violence. On the 10th anniversary of their kidnapping, CNN shares these ...
Moscow (Russian: Москва́, romanized: Moskva, IPA:) is the capital of Russia and the country's economic, financial, educational, and transportation center. It is located on the Moskva River in the Central Federal District, in the European part of Russia. The most populous city in Europe, metropolitan Moscow has a population of close to 12 million, which constitutes about 7 percent of the ...
What are the top Public Universities in Russia? uniRank answers this question by publishing a complete list of Public Russian Universities ranked by the 2024 uniRank University Ranking and meeting the following uniRank selection criteria:. being chartered, licensed or accredited by the appropriate Russian higher education-related organization; offering at least three-year bachelor's degrees or ...
QS World University Rankings. [Published 27 June, 2023] #1. #312. Scimago Institutions Rankings. [Published 06 March, 2023] Show 17 more rankings of Moscow State University M. V. Lomonosov and subject specific rankings for 10 subjects. #2.