

Quantitative Market Research: A Guide + Examples

Quantitative market research is a numbers game.
It’s one of the four types of traditional market research; and a tried, trusted, and proven way to get answers to strategically important questions.
Whether you’re already familiar with quantitative research, looking for practical examples, or considering using it in your business, I will cover everything you need to know.

What is quantitative market research?
Quantitative market research collects numerical data to help answer a research question or objective. Popular forms of quantitative research include surveys, polls, questionnaires, and demographical data from primary and secondary sources. The data can be easily quantified, compared, and analyzed to establish patterns, trends, and insights that disprove or prove a research question. It’s used by large and small organizations, thanks to modern market research tools like Similarweb.

What questions can quantitative market research answer?
Quantitative data can help a company find answers to strategic questions. It can help organizations find patterns, spot trends, make predictions, and establish averages. Most questions that can be answered by quantitative research help determine the: how, when, what, and where. Some of these include:
- What is the market size ?
- How have the needs of a market changed?
- What is the number of people that make up your target audience?
- How many people are interested in buying your product?
- Is there a market for your products?
- Where does my target audience spend most of their time online?
- The frequency that people buy your product or service?
- How many people are aware of your brand, product, or service?
- What type of people are your best customers?
- How long do people spend on your website?
- What percentage of customers are happy with your product or service?
Read More: 98 Quantitative Market Research Questions & Examples
Types of quantitative market research design
Quantitative market research deals with secondary and primary data–as long as it’s presented in numerical form. There are five key techniques of quantitative research design to know.
Experimental research
Experimental research (AKA true experimental research) is a research technique that analyzes to prove a theory. In most cases, it will involve several theories yet to be proved or disproved.
This type of design creates a controlled environment where multiple variables are examined and observed to establish the cause and effect they each have. Various data types of manipulated in the process and each impact is assessed. The study aims to determine the precise conditions in which the different variables affect each other.
A few examples of experimental quantitative research design include
- The effect of Black Friday Marketing on the success of a business.
- Impact of service delivery issues on the perceived reliability of a brand.
- The effect of a gift with purchase on customer satisfaction levels.
Choosing a suitable quantitative research method is vital, as data collection can be utilized for different effects. For instance, statistics can be correlational (which helps infer conclusions about differences) or descriptive (which help to summarize data).
Descriptive research

This type of quantitative research is used to learn more about a specific topic, for instance:
Through observation, it measures different variables and investigates each in detail. It aims to describe characteristics– and is focused more on the ‘what’ of a research problem than the ‘why’ behind it. Aptly named, it describes a research subject without investigating why it happens.
A few examples of descriptive research include:
- A company’s Black Friday marketing campaign description.
- The description of service delivery issues a company or its customers face.
- An outline of what companies offer a gift with online purchases.
Quasi-experimental research

This is similar to experimental research (aka casual comparative research), which seeks to evaluate cause-and-effect relations among variables. However, in the case of quasi-experimental research, the key difference is that it’s an independent and dependent variable that is used.
This type of quantitative research design takes at least two types of data, analyzing each together to examine the differences–using a typical cause-and-effect methodology. Research is usually undertaken in a near-natural setting, with information being gathered from two groups.
- A naturally occurring group that’s closely matched with the original environment.
- A group that is not naturally present.
In doing this, causal links can be made. However, not all casual links will be correct due to other variables impacting results.
Examples of descriptive quantitative design include:
- The effect of the Black Friday campaign’s success on employee productivity.
- Service delivery issues effect on the public perception of a brand.
- The effect of free gifts on customer loyalty.
Stop Guessing, Start Analyzing
Get actionable insights for market research here
Correlational research

Correlational research is usually conducted to determine the relationship between two closely related entities. It looks at how each impacts the other and details the changes that occur.
This type of quantitative research design examines relationships between multiple data types. It will examine the extent to which they align with one another or where they differ. It will not delve into casual links any deeper than this.
Examples of quantitative correlational design include:
- The relationship between Black Friday campaign success and annual revenues.
- Correlations between delivery issues and brand reputation.
- The relationship between free gifts and their perceived loyalty.
Quantitative market research data collection methods
You have a few options when considering which type of quantitative research is best. The first thing you’ll need to do is choose the data collection method. Below, I’ve summarized three of the most common quantitative research data collection methods.
This applies to telephone, video conference, or face-to-face interviews. While it’s an ideal way to connect with individuals to collect data, it’s a method that utilizes resources due to the time it takes to set up and conduct them.
A market research survey is a cost-effective way to collect quantitative data. Information can be obtained from large groups of people quickly, and the survey itself is relatively easy to set up. Your survey questions must be carefully considered for the results to provide meaningful data . When creating any form of survey for this type of market research , the questions should remain close-ended, giving participants a yes/no answer or one that requests a numerical result.
A few examples of quantitative market research survey questions include:
- Would you recommend Similarweb to a colleague?
2. On a scale of 1-10, with one being the lowest and ten being the highest, how would you rate your experience with the Similarweb customer support team today?
3. Could you find the information you were looking for on our site today?
4. On a scale of 1-10, with one being the lowest and ten being the highest, how easy could you find the information you were looking for on our site today?
5. Was your query resolved in full by our support representative?
While similar, a poll is a shorter survey version. It’s often used to give researchers a point-in-time perspective of a large group of people. Data can be collected in person, over the phone, or online. The costs for polls can vary, depending on whether you buy questions on an existing poll, such as YouGov, or if you opt for a more bespoke survey that you create from scratch.
Fun fact: The origins of polls date back to the 19th century. They were first used in America to predict the outcome of the presidential elections.
Quantitative market research advantages and disadvantages
As with all market research, there are pros and cons to consider. While there are many benefits of using quantitative market research, it’s important to weigh these up with the drawbacks to ensure you make the best choice for your project.
Benefits of quantitative market research
The information you obtain directly results from the questions asked and the audience you choose. Get these two factors right, and you’ll reap the rewards in your research. Here’s a quick summary of the advantages doing quantitative research offers.
- Collect a vast volume of data efficiently with a larger sample pool.
- Get a generalized view of a target audience and demographic.
- Results can be processed quickly as they are highly structured.
- Easy comparison of results from different groups of participants.
- Its objective–relying on solid numbers with fewer variables.
- Number-based research is ideal for analysis.
Disadvantages of quantitative market research
While all quantitative market research collection methods can generate insightful data showing a wider opinion, there are limitations to consider.
- If respondents are not representative of your target audience, this could potentially impact the accuracy of results–it’s also known as a sampling error.
- The wording of questions can impact the findings–consider this carefully when designing interviews, polls, or surveys.
- Quantitative research is close-ended, with no ability to receive data about the ‘why’ or ‘how’ behind the numbers. Findings can only provide a small part of the story without two-way dialogue.
- You’ll need a hypothesis and an appropriate model to avoid invalid results or bias to collect and analyze the data.
What strategies are used to ensure the accuracy of quantitative market research?
Researchers employ several strategies to ensure the accuracy of their quantitative market research. This includes using various data sources to ensure that no single source is unduly influencing the results. Additionally, researchers may use advanced statistical techniques such as regression analysis and factor analysis to ensure that their results are accurate and valid. Lastly, researchers may employ survey design principles such as random and stratified sampling to ensure that the results represent the studied population.
Using Similarweb for quantitative market research
For all the advantages that quantitative market research offers, it’s hard to ignore the limitations. Things like timeliness, bias, and the close-ended nature of this method all matter when you need to make important decisions and don’t have time to take on a lengthy research project.
That’s where we come in.
Depending on your market research questions, there’s usually a faster way to achieve your goals with insights gained from digital research intelligence software like Similarweb. Whether you want to learn more about a target audience, market, industry, or competitors, you can get up-to-date intel that’s on point, easy to understand, and accurate.
Consider your research question, and see what insights and information are available to you right now. With a world of data at your fingertips, you can harness Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence to uncover telling facts, that inform research and strengthen your position. Use it for:
Market Research
Benchmarking
Audience Insights
Company Research
Consumer Journey Tracking
Use it to uncover the insights you need to make decisions and develop strategies that help you win.
Wrapping up
With all types of market research, it’s important to take a balanced approach. Organizations that use quantitative market research to get numerical data must balance this with qualitative data to understand the sentiment behind the numbers. So, while quantitative research has its advantages, it must be done in tandem with other research types to provide a complete picture that tells you what, when, how, and why.
Similarweb’s suite of digital intelligence solutions offers unbiased, accurate, honest insights you can trust. Take it for a trial run today, and see how it can power up your research and save you time.
What are the four types of market research?
The four main types of market research include primary, secondary, quantitative, and qualitative. While there are subcategories, most research falls into one of these four key categories.
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative market research?
Quantitative market research is focused on numbers. It collects numerical data to inform a research question or develop a theory. On the other hand, qualitative research is more about consumer sentiment, looking at how and why people feel a certain way about a product, service, or brand.
What are the benefits of quantitative market research?
As it deals with numerical data, quantitative research data can be analyzed quickly and consistently. Future replication is an easy and effective way to conduct a broad study across a large sample size. There are also fewer variables as data is close-ended. Both collection and analysis can be automated and costs less than qualitative research.
What types of questions can quantitative market research answer?
Quantitative research can help answer questions that explain what, how much, when, and where. It seeks to quantify attitudes, behaviors, and opinions but can also be used for establishing averages, making future predictions, and trendspotting.
Who is quantitative market research for?
Quantitative research data delivers information that can help shed light on a market or business. This makes it valuable to both established firms and start-ups of any size. Practically, it can help with market sizing, forecasting, market validation , and more.
What advancements have been made in quantitative market research?
In the past decade, technological advances have enabled quantitative market research to become even more precise and comprehensive. AI and machine learning have allowed researchers to collect and analyze large amounts of data faster and more accurately.
Related Posts

What is a Niche Market? And How to Find the Right One

The Future of UK Finance: Top Trends to Watch in 2024

From AI to Buy: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Retail
How to Conduct a Social Media Competitor Analysis: 5 Quick Steps

Industry Research: The Data-Backed Approach
How to Do a Competitive Analysis: A Complete Guide
Wondering what similarweb can do for you.
Here are two ways you can get started with Similarweb today!


- Pollfish School
- Market Research
- Survey Guides
- Get started
The Complete Guide to Quantitative Market Research

Quantitative research is a chief category in the research sphere, along with qualitative research. An encompassing aspect of market research , it can include both primary and secondary methods of extracting data.
Although used interchangeably with qualitative research, quantitative research is a distinct process that should not be confused with its counterpart. In fact, it is the opposite of qualitative research.
Let’s navigate through the waters of quantitative research in this complete guide.
What Defines & Makes Up Quantitative Research?
As its name suggests, quantitative research is the process of aggregating quantitative, or numerical data for research purposes. This data is used for a number of applications. These include:
- Quantifying opinions, behaviors, attitudes and problems
- Making generalizations
- Forming predictions
- Discovering patterns
- Determining averages
- Testing relationships
Quantitative research generally relies on a larger sample size in order to quantify any issue or variable. In order to achieve this, this research method involves using mathematical and statistical means.
This type of research answers the “what” and the “how much” of a subject within a research endeavor. As it forms generalizations, this type of method involves surveying a larger population, using measurable data and processing all the data first and then analyzing it from a statistical standpoint.
The Four Main Types of Quantitative Research
There are four main ways to perform quantitative research. Aside from their methodology, these sub-categories also seek different types of answers and conclusions.

1. Descriptive Research
This is used to determine the state of variables. It describes the situation and environment surrounding a variable or topic. As such, it is used for arranging comparisons, outlining sample characteristics, overlooking emerging trends and confirming existing phenomena.
The data is collected by way of observation. Descriptive Research is used to form a hypothesis, but only after having aggregated all the necessary data.
2. Correlational Research
This research method is used to examine the relationships between different subjects and variables. Analyzing relationships is necessary to either test a hypothesis or a prediction. Because this research focuses on relationships between fixed variables, other outlying variables are not part of the investigation.
Correlational research is in direct opposition to experimental research, as none of the studied variables are manipulated. Correlations can be either positive or negative, with different degrees of the relationship’s strength.
3. Experimental Research
This method is used for finding whether there is a cause and effect relationship among variables. This kind of research relies on the scientific method. Unlike correlational research, experimental research involves manipulating variables.
Researchers would manipulate a variable to uncover its effect on another one. This method is frequently referred to as true experimentation, as no experimental undertaking leaves all variables unchanged; at least one must be influenced in some way.
This includes manipulating, randomizing or reverting back a variable. The variables are then measured, calculated and compared.
4. Survey Research
The final research method is crucial to understanding behavior. In market research, it is often used to acclimate a brand with its target market’s desires, needs, points of contention and behaviors.
Surveys allow researchers to ask pointed questions to either discover their target audience or get a granular sense of their opinions. As such, they can be conducted within one group or many, for the sake of comparison.
Instead of turning to survey panels , which are likely to have skewed or biased results, researchers should use a random sample of people. A non-panel-based survey will garner more respondents that aren’t motivated by professional compensation.
Surveys can be administered by mail, in-person, on the phone, or digitally. The latter has even more options: online surveys, third-party surveys, emails and in-app.
Examples of Questions for Quantitative Research
Survey research has a far larger scope of questions than do the other three types, as researchers can ask practically anything to conduct their studies. However, there are some best practices in survey questionnaires, such as focusing on your industry, your product and the desires of customers.
Learn more about asking insightful market research questions . Here are a few examples of quantitative research questions in the three other categories.
- Is working from home the best option to improve productivity for employees with long commutes? Variable: Working from home and in-office Demographic: Employees with long commutes Quantitative Research Type : Experimental
- How has the coronavirus changed employment for white-collar workers? Variable: Employment types and statuses Demographic: White-collar workers Quantitative Research Type : Experimental
- How often do working people travel for a holiday? Variable: Amount of times respondents travel during a holiday Demographic: working people Quantitative Research Type : Descriptive
- How much would you pay for a subscription to an entertainment magazine? Variable: payments for a magazine subscription Demographic: women aged 14-44, those interested in celebrities Quantitative Research Type : Descriptive
- What is the difference in smartphone usage between Millennials and senior citizens? Variable: Time spent on using a smartphone Demographic: Millennials and seniors Quantitative Research Type: Correlational
- Does the leadership style of car shop owners predict the job satisfaction of car salespeople? Variable: Leadership style and job satisfaction Demographic: Car shop employers and salespeople Quantitative Research Type: Correlational
When to Use Quantitative Research and How to Analyze It

The quantitative research method has specific use cases. You ought to consider which is best for your particular business, which includes your strategy, your marketing and other facets.
The core of quantitative research is to quantify a phenomenon (a problem, an inadequacy, and a slew of other occurrences) and understand its prevalence. Researchers do this by observing large portions of a population.
You should use this form of research whenever you need to be presented with the state of things at a higher level, or from a bird’s eye view. This Is because this type of research can identify links between various factors, look for correlations and discover cause and effect relationships.
Researchers can then use the results of their findings to form predictions. This is useful in market research when launching a new product, brainstorming product ideas or innovations or growing a customer base.
To analyze this research, it should first be made quantifiable and objective. Researchers should pin down the scales and units of measurements in their various studies. Then, they should organize them into easily interpretable formats.
For example, once you gather the numerical data, you can enter it into a spreadsheet. Thereafter, you can organize it by desegregating it into graphs, charts and tables. Finally, you should draw data-based conclusions from your study. You can also do further sleuthing via advanced analytics.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research has a bevy of benefits; it also has some hindrances. You should peruse both the positive and negative qualities of this research type before setting out on any major research project. The following may help you choose one form of research over the other, or use aspects of both.
- Larger sample pools: the larger the group of respondents, the more accurate are the results.
- Highly structured: Surveys, questionnaires, and other tools for recording numerical data
- Focused: The design of the study is determined before it begins
- Theory-based: Research tests a theory to provide support/proof
- Designed to Be Analyzed: Numbers/statistics exist as tables, charts, figures and other non-textual forms for easy analysis.
- Objective: Steering clear of bias as the research is separated from the data & only objective responses are sought.
- Direct comparisons of results: The study can be set in different cultural environments, times or different groups of participants with a statistical comparison of results.
- Focuses solely on numbers: This can be limiting as researchers may overlook other data and larger themes.
- Superficial Representations: It cannot adequately describe complex concepts (ex: feelings, opinions) it only shows the numbers behind them.
- Several factors can invalidate results: A hypothesis and a model for collecting/ analyzing data.is required; any mistake can lead to bias and inaccurate illustrations.
- Erred Structure: If any data is missing or if measurements are not clear, biases easily take precedence.
The Final Word on Quantitative Research
Market research is far too encompassing to fully complete, especially in a limited amount of time. To tackle market research, begin with a research method. Quantitative research is often a good starting point, as it shows you the existence of a problem by way of quantifying it.
Aside from confirming the existence, it can help confirm a hypothesis, find correlations and prove cause and effect relationships. A hard set of data can also help you make educated predictions.
While the three types of quantitative research methods are useful, they do have several disadvantages. The fourth one, ie, survey research helps fill in the gaps and inadequacies of numerical limitations. Interestingly enough, they too can be a source of hard data and numbers.
Either way, market research is sure to benefit from incorporating surveys as part of the processes.
Frequently asked questions
What is quantitative market research.
Quantitative market research utilizes the techniques of quantitative research in order to better understand the target market. In quantitative research, the information gathered from surveys and questionnaires is converted into numerical values so it can be easily analyzed.
What types of questions do quantitative research answer?
Quantitative research seeks to define “what” and “how much.” It is used for identifying patterns, making predictions, establishing averages, and quantifying opinions, attitudes or behaviors.
What are the four main types of quantitative research?
The four main types of quantitative research are survey research, correlational research, descriptive research, and experimental research.
What type of surveys are used for quantitative research?
Quantitative surveys are best suited for quantitative research. In this type of survey, there are no open-ended questions, and all responses can be assigned a numerical value. In most cases, a quantitative survey is distributed to a large and random sample of individuals.
Why are large sample sizes important when conducting quantitative research?
A small sample size can lead to inaccurate results. The larger the sample size (i.e. the group of individuals who receive the survey), the more likely it is that the results will be statistically significant and accurate.
Do you want to distribute your survey? Pollfish offers you access to millions of targeted consumers to get survey responses from $0.95 per complete. Launch your survey today.
Privacy Preference Center
Privacy preferences.
Quantitative market research questions to ask for actionable insights
Types of quantitative market research questions, 36 quantitative research questions and examples, how to write your own quantitative market research questions, how to collect insightful data from your quantitative surveys, receive quantitative insights in weeks, not months.
There’s a big difference between asking “Why do you like our product?” and “On a scale of 1-10, how much do you like our product?” But both ways of asking are valuable in their own way.
Knowing your audience is not about guesswork or intuition, it is about concrete data. And while it’s valuable to learn the ‘why’ behind the ‘what’ with qualitative research, quantitative research is just as necessary — to spot trends, patterns and more.
Unlike qualitative research, which explores attitudes, opinions, and motivations through open-ended questions, quantitative research zeroes in on the numbers (see what we did there?). It’s the difference between gathering general opinions and collecting measurable, specific data.
But when is this approach the way to go? For starters, whenever you need to track factors over time, such as customer satisfaction. Or when assessing the popularity of a potential product feature, understanding demographic preferences, or analyzing consumer purchasing behavior in different locations.
Quantitative research reveals the impact and scale of sentiments for better decision-making. It’s also valuable when you’re looking to quantify the extent of a trend, measure the impact of a marketing campaign, or pin down the specifics of consumer behavior.
But how do you ask quantitative market research questions that don’t just scratch the surface? We’re here to give you some great examples of quantitative survey questions.
In the US? Check out these research platforms
Here are the top market research platforms in the US for reliable insights – check them out and start getting your insights today!
When thinking of quantitative market research questions, people often think ‘ ah, numbers ‘. But there’s more than meets the eye. Here’s how you can categorize the different types of quantitative research questions:
Descriptive quantitative research questions
These are your what , when , and how many types of questions. They help you sketch out the basic landscape of your market. For example, “How often do you shop online in a month?” or “What is your preferred method of payment while shopping online?” When you give answers people can select, it is quantifiable data. That’s different from asking: ”describe what a day out shopping looks like for you”, which is a qualitative question.
Comparative quantitative survey questions
These questions measure differences or changes over time or between groups. For instance, “How has your spending on online shopping changed since last year?” Comparative questions help you understand the dynamics and shifts in your market. Remember that you’re not just trying to find overlap: it’s just as important to know what differences there are.
Relationship-based quantitative survey questions
These questions aim to uncover correlations or relationships between two or more variables. They can reveal insights like, “Is there a link between age and the likelihood of using mobile payments?” These questions help you understand the deeper connections within your market, as well as test assumptions, as long as you dare to ask questions that challenge what you’re hoping to find.
Now, a quick note on reducing bias in quantitative survey questions . Here are some key points to remember:
- The key is in how you frame your questions.
- Always aim for neutrality.
- Avoid leading questions that suggest a particular answer.
- Be specific and clear to avoid confusion.
- Consider the order of your questions, as earlier questions can influence responses to later ones.
And finally, test your survey with a small group before a full rollout, to catch and correct any unintentional bias. This way, you ensure the data you collect is as accurate and reliable as possible, giving you the best insights to make those crucial business decisions.
If you want to make a quantitative survey that hits the spot, don’t just ask generic questions. We’re here with some examples that you can adapt to make your research a success.
Descriptive market research questions
With a descriptive quantitative research question, you can quickly get the most important info for your respondents on anything ranging from buying frequency to satisfaction levels.
- Insight : this question reveals the frequency of use, indicating customer dependency on your product or service.
- Benefit : understanding usage patterns can guide inventory management and marketing strategies.
- Insight : reveals the communication channels most favored by your audience.
- Benefit : tailor your customer service and marketing outreach to your customers’ preferred channels.
- Insight : provides an average spending figure for budget allocation in that category.
- Benefit : helps in pricing strategies and identifying the most lucrative customer segments.
- Insight : uncovers patterns in online shopping behavior.
- Benefit : optimizes the timing of online marketing campaigns and promotions.
- Insight : identifies the most effective channels for brand discovery.
- Benefit : informs where to allocate advertising spend for maximum impact.
- Insight : measures the likelihood (not effectiveness!) of word-of-mouth referrals.
- Benefit : assesses customer satisfaction and the potential for organic growth.
- Insight : highlights your unique selling points from the customer’s perspective.
- Benefit : guides messaging to emphasize what customers value most about your brand.
- Insight : offers a quantifiable measure of customer service satisfaction.
- Benefit : identifies areas for improvement in customer support.
- Insight : sheds light on the most popular aspects of your product.
- Benefit : informs product development and feature enhancement.
- Insight : uncovers the key motivators behind purchasing decisions.
- Benefit : helps create targeted marketing campaigns to focus on these driving factors.
Comparative market research questions
If you want to analyze and compare different variables, these questions can help.
- Insight : highlights changes in consumer spending habits over time.
- Benefit : useful for identifying trends and shifts in consumer behavior, aiding in long-term planning. Especially valuable if you add qualitative insights to this quantitative data.
- Insight : compares consumer preferences between different shopping channels.
- Benefit : guides omnichannel marketing strategies and resource allocation.
- Insight : tracks changing consumer values and preferences over time.
- Benefit : useful for aligning product development and marketing with evolving consumer values.
- Insight : compares the weight of price versus brand in purchasing decisions.
- Benefit : informs pricing strategies and brand positioning efforts.
- Insight : evaluates customer perception of marketing efforts in product packaging.
- Benefit : assesses the impact of packaging on brand image and customer approval.
What are the top research platforms in the UK?
Here’s our list of the pros and cons of key market research platforms for UK brands
Relationship-based questions for quantitative research
In quantitative research, especially when exploring relationship-based aspects, the key is not to cram multiple inquiries into one question but to ask them sequentially.
This approach allows for a clearer and more focused response to each individual question. Later, during the analysis phase, you can then correlate the responses to uncover relationships between different variables.
For instance, instead of asking, “How often do you use our product and how satisfied are you with it?”, split this into two separate questions:
- “How often do you use our product (daily, weekly, monthly)?”
- “On a scale of 1-10, how satisfied are you with our product?”
By asking these questions separately, you ensure that respondents clearly focus on each aspect without being overwhelmed or confused by a dual-focused question. This approach yields more accurate and reliable data.
After the survey, you can analyze the results to see if there’s a correlation between usage frequency and satisfaction levels.
Here are some examples of combinations that can work well:
- What is your age group?
- Insight : correlates age with shopping preferences.
- Benefit : you can tailor marketing and sales strategies to different age demographics based on their preferred shopping channels.
- How long have you been using our products/services?
- Insight : links customer tenure with brand loyalty.
- Benefit : assesses the impact of long-term use on loyalty, informing customer retention initiatives.
- What is your approximate annual income?
- Insight : examines the relationship between income levels and purchasing behavior for premium products.
- Benefit : guides product and pricing strategies targeting different income segments.
- How often do you use social media for product discovery?
- Insight : assesses if frequent social media use for product discovery actually influences online shopping behavior.
- Benefit : informs the effectiveness of social media marketing in driving online sales in your target market.
- How would you rate your satisfaction with our post-purchase customer service (scale of 0-10)?
- Insight : links the level of service post-purchase with the likelihood of repeat purchases.
- Benefit : identifies if customer service is negatively or positively affecting repeat custom rates.
Brand tracking questions for quantitative insights
One thing you should definitely gather numerical data on, is your brand’s health. Just like your own health, stats, and numbers matter and can show you where to further investigate to ask qualitative research questions about. Learn if your brand stands strong through market trends and gain insights on whether your brand is growing in terms of awareness — and in which segments.
- Insight : measures brand awareness among the target audience.
- Benefit : helps assess the effectiveness of your marketing and branding efforts.
- Insight : evaluates brand loyalty and the potential for organic growth through word-of-mouth.
- Benefit : indicates customer satisfaction and the potential for brand advocacy.
- Insight: Identifies the most effective channels for brand discovery.
- Benefit: Informs where to focus marketing efforts for increased brand exposure.
- Insight: Measures brand visibility and frequency of encounters with the brand.
- Benefit: Helps evaluate the reach and frequency of marketing campaigns.
- Insight: Determines which brand values resonate most with the audience.
- Benefit: Aids in refining brand messaging and aligning it with customer values.
Quantitative consumer segmentation questions
Quantitative questions about customer segments can go beyond age group and gender. King Charles III is the same age as Ozzy Osbourne – would you say they’re very similar?

It is vital that you look at more variables so you can really tell the difference between your respondents, and make informed decisions based on the whole truth. Putting these consumer profiling questions and answers in specific ranges helps you create segments to tailor your marketing and customer experience for, rather than just aiming at the entire population.
- Insight : helps understand the economic demographics of your customers.
- Benefit : assists in pricing strategies and identifying which income groups are most engaged with your brand.
- Insight : reveals geographical spread and regional preferences.
- Benefit : guides regional marketing efforts and product distribution strategies.
- Insight : helps categorize customers by education level.
- Benefit : useful for tailoring communication and content complexity to different education backgrounds.
- Insight : provides insights into the professional background of your customers.
- Benefit : helps in creating industry-specific marketing campaigns and products.
- Insight : gives an idea of household size and composition.
- Benefit : useful for targeting products and services aimed at families or individuals.
- Insight : identifies customers who are parents of minors (which is different from parents of young adults, or even grown adults).
- Benefit : informs product and marketing strategies aimed at families with children.
Okay, so now you got the gist of it and have seen what quantitative questions can look like — as they come in all shapes and sizes. But they might feel too generic for your research, or you’re looking for something specific.
Here’s how you can whip up your own quantitative questions that deliver the insights you need for data-driven decisions.
Identify the key variables you need to measure
Start by pinpointing exactly what you want to know. Is it customer satisfaction, buying behavior, or brand awareness? Determining the specific variables you need to measure sets the foundation for your entire survey.
Choose the right survey distribution method
Think about how your questions will reach your audience. Will it be online through email or social media, over the phone, or in person? Your method should align with where your target audience is most active and responsive.
Make sure your questions are crystal-clear and unequivocally unbiased
We’ve mentioned it earlier, and we’ll do it again if we have to. The way you phrase your questions can make or break your survey. Aim for clarity and simplicity – questions should be easy to understand and answer. Avoid leading or loaded questions that might sway a respondent’s answer. Remember: it’s a survey, not a sales pitch.
Know where to ask for more detailed information and qualitative data
Quantitative market research questions only tell part of the story. If you see interesting trends in say purchase behavior or price sensitivity, or a particular product gets a bad rating, dig a little deeper. Follow up important questions with qualitative research questions to analyze what’s going on behind the numbers.
If you don’t want to end up with a pile of quantitative data that doesn’t do much for you or breaks the bank unnecessarily, it’s vital you choose a form of distributing the survey that makes sense. You can work with UK market research companies to outsource it all, or do it yourself. Here’s a brief look at the pros and cons of popular methods:
Telephone surveys:
- Pros : good for less tech-savvy demographics.
- Cons : time-consuming, potentially costly, and declining response rates. They might be better for qualitative research.
In-person surveys:
- Pros : also avoids any confusion with tech.
- Cons : logistically demanding and expensive, not suited for quick data collection.
Online survey software:
- Pros : cost-effective, broad reach, real-time data analysis, and versatile formats.
- Cons : it’s extra important to pay close attention to survey design, so people don’t get the urge to give false answers just to get to the end.
The choice is yours, but generally, quantitative research thrives when done with online surveys and it’s the go-to method for most international market research . And here at Attest, we help you get even more out of it by giving you a chock-full toolkit. From various types of questions to robust analytical tools (and a dedicated research expert for when you need a little extra help) — we set you up for measurable success.
Speed and accuracy in market research matter — but we don’t want you to sacrifice quality. With Attest, you get fast, actionable and high-quality insights.
Which market analysis tool is right for you?
Check our rundown of the top platforms for market analysis – and start making better decisions with reliable insights in no time!

VP Customer Success
Sam joined Attest in 2019 and leads the Customer Research Team. Sam and her team support brands through their market research journey, helping them carry out effective research and uncover insights to unlock new areas for growth.
Related articles
A guide to brand tracking: what it is & how to boost your brand roi, brand tracking, how to gather consumer insights (and use them to improve your business), 12 brand management software, platforms and tools to understand customer perception in 2024, subscribe to our newsletter.
Fill in your email and we’ll drop fresh insights and events info into your inbox each week.
* I agree to receive communications from Attest. Privacy Policy .
You're now subscribed to our mailing list to receive exciting news, reports, and other updates!

Quantitative Market Research: The Complete Guide
Quantitative market research is an essential tool for businesses looking to gain insights into their target market and make data-driven decisions. In this guide, we’ll provide an overview of quantitative market research and the steps involved in conducting it.
What is Quantitative Market Research? Quantitative market research involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to understand the preferences, behavior, and opinions of a target audience. The goal is to provide statistically significant data that can be used to make informed business decisions.

Step 1 : Define the Research Problem The first step in conducting quantitative market research is to clearly define the research problem. What are the key questions that you want to answer? What specific information are you trying to obtain? Defining the research problem is essential as it will guide the entire research process.
Step 2: Develop the Research Plan Once the research problem is defined, the next step is to develop a research plan. This includes determining the target audience, selecting the research methodology, and designing the research instrument. The research plan should be comprehensive and clearly outline the research objectives, sample size, data collection method, and analysis plan.
Step 3: Collect Data The next step is to collect the data. There are several methods of data collection including surveys, polls, online questionnaires, and phone interviews. It’s essential to ensure that the sample size is representative of the target audience and that the data is collected using a standardized approach.
Step 4: Analyze Data Once the data is collected, the next step is to analyze it. The data should be organized and summarized using statistical analysis techniques such as mean, mode, and standard deviation. The objective is to identify patterns and trends in the data that can be used to make informed business decisions.
Step 5: Draw Conclusions The final step is to draw conclusions based on the data analysis. The conclusions should be based on the data and provide insights into the target audience. It’s essential to ensure that the conclusions are supported by statistical evidence and that they can be used to make informed business decisions.

Quantitative market research is a research method that involves collecting numerical data that can be analyzed statistically. This method is widely used in market research to gather information about customer behavior, opinions, and preferences. Here are some of the benefits of quantitative market research:
1. Large Sample Size: One of the significant benefits of quantitative research is the ability to collect data from a large sample size. This provides a more accurate representation of the population and reduces the margin of error.
2. Objective Results: Quantitative research provides objective results, as the data collected is numerical and can be analyzed statistically. This minimizes the impact of personal bias and ensures that the results are reliable and valid.
3. Easy Data Analysis: The data collected through quantitative research can be analyzed using statistical software, making it easy to identify trends, patterns, and correlations. This allows researchers to draw conclusions and make data-driven decisions.
4. Cost-effective: Compared to other research methods, quantitative research is cost-effective. It requires fewer resources and can be conducted quickly and efficiently, making it an ideal method for businesses with limited budgets.
5. Easy to Replicate: Quantitative research is easy to replicate as it involves standard methods of data collection and analysis. This allows businesses to conduct similar research in different locations or with different groups of people, ensuring consistency in the results.
6. Measurable Results: The numerical data collected through quantitative research provides measurable results, making it easy to track progress over time. This is particularly useful in tracking customer satisfaction or changes in customer behavior.
In summary, quantitative market research is a reliable and cost-effective method for gathering data, providing objective results that can be easily analyzed and replicated. These benefits make it an essential tool for businesses looking to make data-driven decisions and stay competitive in the market.
Quantitative market research is a powerful tool for businesses looking to gain insights into their target audience. It’s essential to define the research problem, develop a research plan, collect and analyze the data, and draw conclusions based on the data analysis. By following these steps, businesses can make data-driven decisions that can help them succeed in the market. To know more about quantitative research reach us at www.philomathresearch.com
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
- Power of Qualitative Research in Primary Market Analysis
- Power of Quantitative Market Research: Unravelling its Key Advantages
- Crafting Effective Strategies through B2B Market Research & Analysis
- Exploring Effective Sampling Techniques in Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Researchers
- Unlocking Growth: A Comprehensive Market Analysis in Healthcare
Recent Comments
Blog , Marketing
All you need to know about quantitative marketing
- By Mayank Sharma

Have you heard of the term ‘Quantitative Marketing’?
Yes? No? Maybe?
Whether you’re someone who has never heard of quantitative marketing or someone who has little knowledge about the same, this article will be beneficial for you.
When discussing marketing research, we usually have two options, or rather two types of research: Qualitative and Quantitative . Qualitative research relies on descriptive and holistic responses and analysis , whereas quantitative research focuses on numbers, statistics, and specific data .
Let’s begin the article by discussing quantitative marketing in detail.
What is quantitative marketing?
Characteristics of quantitative marketing research, pros and cons of quantitative marketing, quantitative marketing research process roadmap, quantitative marketing data collection techniques, types of quantitative research questions, statistical analysis techniques used in quantitative research, errors in quantitative marketing research, market research in the app industry, frequently asked questions.
Quantitative marketing is the science of understanding markets and making better decisions using empirical facts collected via research . It is a complicated but necessary component of any marketing activity and requires the application of quantitative research methods to the field of marketing research.
This method involves asking questions to a target group through surveys, polls, and questionnaires . Marketers use this information to gather and comprehend the demands of consumers in the marketplace and develop strategies and marketing plans.
Marketing is an interactive process in which both buyers and sellers should agree on the four Ps of marketing: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion . Market research helps to achieve this agreement.
We live in a digital era where data is the new fuel. Companies’ fate depends on how well they can collect and analyze data to draw meaningful conclusions. Firms rely on quantitative methods to draw these conclusions because these methods provide systematic, detailed information about the problem or the target group.
The following are the key characteristics of quantitative marketing research:
- Large sample size: Quantitative research uses a large sample size to gather the data. This sample size is representative of the entire target population.
- Hypothesis: Quantitative research depends upon a hypothesis, and the goal is to prove or disprove the same.
- Dependent on quantitative data: As the name suggests, this research methodology relies on numbers, statistics, or other quantifiable data to draw conclusions.
- Structured: This method follows a structured approach to data collection and analysis.
- Close-ended: The questions are close-ended to facilitate better data analysis and avoid ambiguity.
- Reusable outcome: Researchers can use the results obtained for the prior study of the subsequent research problem.
- Generalization: The outcome can be generalized to the whole population because of the large sample size.
The below tables summarize the key advantages and disadvantages of quantitative research.

The quantitative research process follows a five-step process, which is as follows:
1. problem definition.
The first stage is defining the problem statement. It requires answering a few questions like:
- What is the point of conflict?
- What do we aim to find a solution to?
- Which information is needed?
Here, you must also create a hypothesis based on which you will assess your final result.
For example, suppose the problem statement is ‘Consumer perception of travel apps among teenagers in the USA.’ The hypothesis can be ‘Teenagers in the USA do not prefer using travel apps.’ The final result of the research will either prove or disprove the hypothesis.
You need to note that both the problem statement and the hypothesis must be specific regarding the idea, the target population, age group, the region, etc.
2. Research design
The next stage requires you to create the research design . Here, you need to specify what methodologies you will use to conduct the research. Research design establishes an outline for the study and guides how the research will be conducted.
The critical elements of research design are:
- Specific purpose statement
- Research techniques and methods
- Type of Research
- Possible objections to the research
- Settings for the study
- Timeline of the research
- Assumptions and limitations of the study
3. Data collection
Once you define the problem statement and the research design, you must begin with the actual research by collecting relevant data from various sources. The data collection technique will differ based on the type of research: primary or secondary . Ideal research involves elements of both primary and secondary research.
4. Data analysis and interpretation
Collected data is of no use by itself, and you need to analyze and interpret the data to generate meaningful conclusions. You can create charts, tables, graphs, and other diagrams to quickly present and analyze the information.
However, you must note that data analysis and interpretation are two different processes. Data analysis is the process of structuring, organizing, transforming, and modeling the data to observe trends and patterns. On the other hand, data interpretation assigns meaning to the analyzed data . It involves determining the relationship between different variables, how the information is significant to us, and so on.
5. Report writing
The final stage in the research process is writing a report. A report is usually very detailed and contains all the findings and conclusions of the research.
It includes headings such as:
- Executive summary
- Introduction
- Research objective
- Research Methodology
- Primary and secondary research findings
- Charts and diagrams for data analysis
- Data interpretation
Marketers can use this report to understand the market trends, draft marketing strategies, present the findings to the clients, and for future marketing purposes.
As discussed earlier, data collection is of two types: primary and secondary data collection . The techniques for both these methods are as follows:
Primary data collection techniques

This technique typically requires the respondents to answer a list of questions related to the research problem. Quantitative research surveys have close-ended questions easing the respondent’s work and making the results specific and accurate. Traditionally, researchers relied on pen and paper to conduct surveys by individually contacting the sample. But now, we have tools like Google Forms and Microsoft Forms , making reaching a wider group of people easier.
2. Interviews
Interviews involve a detailed interaction between the researcher and the interviewee. Quantitative interview questions are structured to gather extensive information from the participants. The researcher can conduct the interview face-to-face, over the telephone, or via video conference .
3. Observations
This technique does not require asking any questions to people. It involves the recording of factual information through observation. The researcher observes instances and notes down the key highlights. This type of data collection is objective as it does not depend on a person’s memory or personal bias.
Secondary data collection techniques
The secondary research does not require the researcher to personally collect the data by contacting a group of people. It depends on the data already available or what someone else has recorded. Based on this information, the researcher draws insights and inferences. Secondary data sources can include research papers, blogs, books, videos, etc.
The questions that researchers ask while conducting quantitative research are specific compared to open-ended qualitative questions, which are harder to analyze.
The major types of quantitative market research questions are:
1. net promoter score.
You can ask this question to determine customer satisfaction and brand shareability. Based on the responses, you can divide the respondents into three categories: promoters, passives, and detractors . This question usually has a 0-10 scale providing an efficient perspective about brand recommendation.
For example,
Considering your experience with us, how likely would you recommend our services to a friend?
2. Likert scale
This question evaluates a respondent’s opinion toward a particular situation. It has two extreme opinions at each end of the scale. This type of question is usually asked to know the agreement level of the respondent to a particular statement or situation. It typically has 5, 7, or 9 options to choose from.
Do you agree with the statement, “App marketing is as crucial as the other app development stages”?
3. Semantic scale
A semantic differential rating scale is used to generate quantitative data about ideologies, products, or events with drastically opposing answers at the polar points of the scale to quantify their implicative meaning.
How satisfied are you with our customer service?
4. Multiple-choice
These questions are crucial as they help in getting the best responses. The reason is that the marketer gives the respondent the exact options to choose from, and the analysis thus becomes more straightforward and quantifiable. The question can be designed in a way that the respondent can choose either only one option or multiple options.
Which video streaming platform do you prefer using?
- Amazon Prime Video
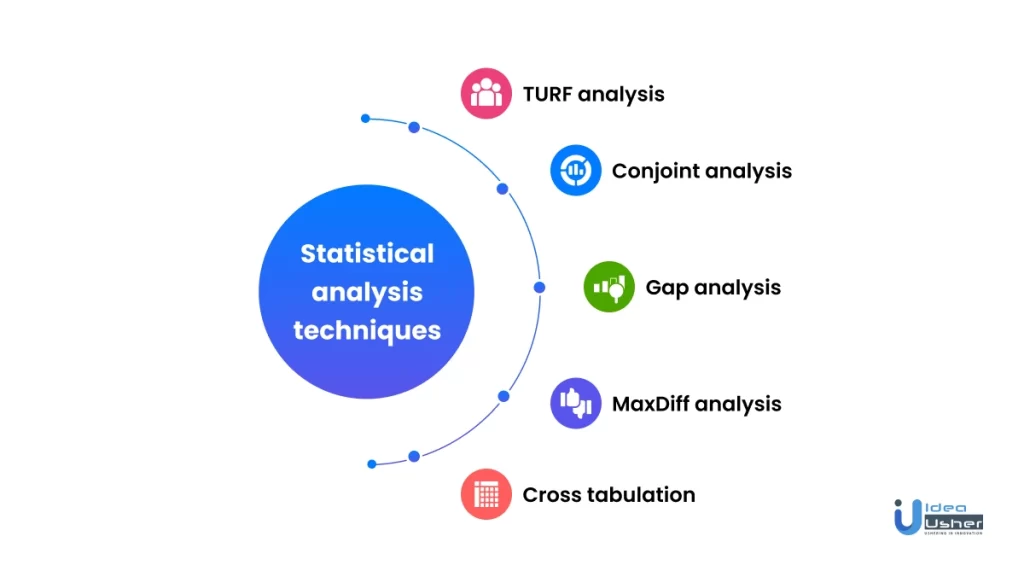
Various statistical analysis techniques can be used to analyze quantitative research data. Some of them are listed below:
1. turf analysis.
Total Unduplicated Reach and Frequency (TURF) analysis is a statistical approach to assess the potential of market research for a combination of products and services. With firms launching products and services regularly and new markets being explored daily, it becomes inevitable to leave no stone unturned in ensuring the products are well-received in new areas.
For example, if an app company wishes to launch a new feature, TURF analysis can help answer the following questions:
- What market share will we receive if we introduce Feature X in our app?
- Where should we promote this feature to get maximum reach in the app industry?
2. Conjoint analysis
Conjoint analysis is a way of determining the worth of numerous aspects for customers, such as pricing, features, and benefits that lead to purchasing a specific product or service. With the increasing technology integration in devices and gadgets, this analysis method has become common for product pricing, market positioning, and product introduction.
3. Gap analysis
Gap analysis is a technique for assessing the difference between the desired and the actual performance of a product or service. By measuring this, a firm can make efforts to close the gap and make its features more enticing.
Businesses use gap analysis to answer the following questions:
- What is the current position of the company?
- Where do we wish to reach?
- What can we do to close the gap?
4. MaxDiff analysis
MaxDiff analysis, also known as best-worst scaling , is used to gauge survey respondents’ preference scores for multiple attributes such as product features, brand image, activities around branding, etc. This technique is similar to conjoint analysis; however, MaxDiff analysis is easier and more comprehensive in analyzing critical situations.
5. Cross tabulation
As the name suggests, cross-tabulation allows you to compare two or more categories in a tabular format for quicker analysis. Researchers utilize cross-tabulation to look for hidden relationships in data. It’s great for market research and surveys as a cross-tab report depicts the relationship between two or more study questions.
The following table summarizes the different types of errors that might arise while conducting quantitative marketing research:
Apart from the above errors, the study can also have hypothesis errors , which are of two types:
- Alpha error , in which the study outcomes lead to the rejection of the hypothesis even though it is true.
- Beta error , in which the study outcomes lead to the acceptance of the hypothesis even though it is false.
App development is a sector that requires intensive research about the market. It includes the analysis of the target audience, the competitors, and the various other associated factors . A business starting in this sector might find it overwhelming to conduct thorough market research without proper guidance. As a result, it is better to consult app development experts for this task .
Idea Usher is a technology company providing various digital services like app development , blockchain development, AI and IoT-related services, etc. In addition to qualified app developers, we also have experts who assist clients in understanding the feasibility of their app idea by conducting a thorough analysis of the target market. Once the feasibility is confirmed, we help turn the app idea into reality through our development services.
Contact us to get a clear vision of your app idea and take off your app business.
E-mail: [email protected]
Phone Numbers : (+91) 946 340 7140 , (+91) 859 140 7140 , and (+1) 732 962 4560
Build Better Solutions With Idea Usher
Professionals
Quantitative marketing research is an excellent way for marketers to understand the market situation and plan their marketing strategies accordingly. The results obtained through the research can be used to derive insightful conclusions because of their precise nature.
Expert tip: Always aim to keep your research objective, specific, and bias-free to ensure better outcomes and marketing decisions.
Here are a few exciting FAQs about quantitative marketing.
Q 1. What is an example of quantitative research in marketing?
A great example of quantitative research in marketing is conducting surveys to determine the potential demand for a particular product, service, or feature.
Q 2. Why is quantitative research important in marketing?
Quantitative research is necessary because it provides marketers with objective, reliable data to identify trends and patterns for better marketing decisions.
Q 3. Which is better: quantitative or qualitative marketing research?
Both these methods of market research have their pros and cons. You should do quantitative analysis if you need quick, specific, and quantifiable data. However, you should consider qualitative research if you need descriptive, theoretical information.
Related posts:
- Top 10 Mobile App Christmas Marketing Tips
- Marketing Strategies for Small Business 2021
- 5 Fool-proof Digital Marketing Tips for Startups
- Enter the next profitable market by building influencer marketing software
- Influencer Marketing and top 8 influencer marketing tools
- How email marketing can bring your business back to life?
Powered by YARPP .

Mayank Sharma
A writer turning ideas into reality using words. With an eye for detail and a creative bent of mind, I aim to engage readers with content that is fun to read and easy to understand. Apart from writing, I love to spend my time using social media and creating videos.
Hire the best developers
100% developer skill guarantee or your money back. Trusted by 500+ brands

Quick Links
- Become a Partner
- Get in Touch
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Web Development
- App Development
- Game Development
- Blockchain Development
- Non Fungible Token
- Internet of Things
- Artificial Intelligence
- Project Management
- Digital Marketing
- SCF 98, Phase 11, Sector-67 Mohali, 160062
- 651 B Broad St, Middletown, 19709, county New Castle Delaware, USA
- [email protected]
- (+1) 628 432 4305
HR contact details
- +91-8930090960
- +91-93900 89678
Follow us on

Idea Usher is a pioneering IT company with a definite set of services and solutions. We aim at providing impeccable services to our clients and establishing a reliable relationship.
Our Partners
- (+1) 628-432-4305

Enter Your Info, And We Will Get In Touch

Congratulations on taking the first step towards taking your business to new heights!
We are ready to take you there. We will soon contact you for more details.

You're closer to success than you think!
Get the MASTER KEY to grow your website sales from scratch.
Are you ready to grow your business?
Hi 👋 Can I help you?

- Agile & Development
- Prioritization
- Product Management
- Product Marketing & Growth
- Product Metrics
- Product Strategy
Home » Quantitative Research: Definition, Methods, and Examples
Quantitative Research: Definition, Methods, and Examples
June 13, 2023 max 8min read.

This article covers:
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research methods .
- Data Collection and Analysis
Types of Quantitative Research
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
Examples of Quantitative Research
Picture this: you’re a product or project manager and must make a crucial decision. You need data-driven insights to guide your choices, understand customer preferences, and predict market trends. That’s where quantitative research comes into play. It’s like having a secret weapon that empowers you to make informed decisions confidently.
Quantitative research is all about numbers, statistics, and measurable data. It’s a systematic approach that allows you to gather and analyze numerical information to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations.
Quantitative research provides concrete, objective data to drive your strategies, whether conducting surveys, analyzing large datasets, or crunching numbers.
In this article, we’ll dive and learn all about quantitative research; get ready to uncover the power of numbers.
Quantitative Research Definition:
Quantitative research is a systematic and objective approach to collecting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data. It measures and quantifies variables, employing statistical methods to uncover patterns, relationships, and trends.
Quantitative research gets utilized across a wide range of fields, including market research, social sciences, psychology, economics, and healthcare. It follows a structured methodology that uses standardized instruments, such as surveys, experiments, or polls, to collect data. This data is then analyzed using statistical techniques to uncover patterns and relationships.
The purpose of quantitative research is to measure and quantify variables, assess the connections between variables, and draw objective and generalizable conclusions. Its benefits are numerous:
- Rigorous and scientific approach : Quantitative research provides a comprehensive and scientific approach to studying phenomena. It enables researchers to gather empirical evidence and draw reliable conclusions based on solid data.
- Evidence-based decision-making : By utilizing quantitative research, researchers can make evidence-based decisions. It helps in developing informed strategies and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions or policies by relying on data-driven insights.
- Advancement of knowledge : Quantitative research contributes to the advancement of knowledge by building upon existing theories. It expands understanding in various fields and informs future research directions, allowing for continued growth and development.
Here are various quantitative research methods:
Survey research : This method involves collecting data from a sample of individuals through questionnaires, interviews, or online surveys. Surveys gather information about people’s attitudes, opinions, behaviors, and characteristics.
Experimentation: It is a research method that allows researchers to determine cause-and-effect relationships. In an experiment, participants randomly get assigned to different groups. While the other group does not receive treatment or intervention, one group does. The outcomes of the two groups then get measured to analyze the effects of the treatment or intervention.
Here are the steps involved in an experiment:
- Define the research question. What do you want to learn about?
- Develop a hypothesis. What do you think the answer to your research question is?
- Design the experiment. How will you manipulate the variables and measure the outcomes?
- Recruit participants. Who will you study?
- Randomly assign participants to groups. This ensures that the groups are as similar as possible.
- Apply the treatments or interventions. This is what the researcher is attempting to test the effects of.
- Measure the outcomes. This is how the researcher will determine whether the treatments or interventions had any effect.
- Analyze the data. This is how the researcher will determine whether the results support the hypothesis.
- Draw conclusions. What do the results mean?
- Content analysis : Content analysis is a systematic approach to analyzing written, verbal, or visual communication. Researchers identify and categorize specific content, themes, or patterns in various forms of media, such as books, articles, speeches, or social media posts.
- Secondary data analysis : It is a research method that involves analyzing data already collected by someone else. This data can be from various sources, such as government reports, previous research studies, or large datasets like surveys or medical records.
Researchers use secondary data analysis to answer new research questions or gain additional insights into a topic.
Data Collection and Analysis for Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is research that uses numbers and statistics to answer questions. It often measures things like attitudes, behaviors, and opinions.
There are three main methods for collecting quantitative data:
- Surveys and questionnaires: These are structured instruments used to gather data from a sample of people.
- Experiments and controlled observations: These are conducted in a controlled setting to measure variables and determine cause-and-effect relationships.
- Existing data sources (secondary data): This data gets collected from databases, archives, or previous studies.
Data preprocessing and cleaning is the first step in data analysis. It involves identifying and correcting errors, removing outliers, and ensuring the data is consistent.
Descriptive statistics is a branch of statistics that deals with the description of the data. It summarizes and describes the data using central tendency, variability, and shape measures.
Inferential statistics again comes under statistics which deals with the inference of properties of a population from a sample. It tests hypotheses, estimates parameters, and makes predictions.
Here are some of the most common inferential statistical techniques:
- Hypothesis testing : This assesses the significance of relationships or differences between variables.
- Confidence intervals : This estimates the range within which population parameters likely fall.
- Correlation and regression analysis : This examines relationships and predicts outcomes based on variables.
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA) : This compare means across multiple groups or conditions.
Statistical software and tools for data analysis can perform complex statistical analyses efficiently. Some of the most popular statistical software packages include SPSS, SAS, and R.
Here are some of the main types of quantitative research methodology:
- Descriptive research describes a particular population’s characteristics, trends, or behaviors. For example, a descriptive study might look at the average height of students in a school, the number of people who voted in an election, or the types of food people eat.
- Correlational research checks the relationship between two or more variables. For example, a correlational study might examine the relationship between income and happiness or stress and weight gain. Correlational research can show that two variables are related but cannot show that one variable causes the other.
- Experimental research is a type of research that investigates cause-and-effect relationships. In an experiment, researchers manipulate one variable (the independent variable) and measure the impact on another variable (the dependent variable). This allows researchers to make inferences about the relationship between the two variables.
- Quasi-experimental research is similar to experimental research. However, it does not involve random assignment of participants to groups. This can be due to practical or ethical considerations, such as when assigning people to receive a new medication randomly is impossible. In quasi-experimental research, researchers try to control for other factors affecting the results, such as the participant’s age, gender, or health status.
- Longitudinal research studies change patterns over an extended time. For example, a longitudinal study might examine how children’s reading skills develop over a few years or how people’s attitudes change as they age. But longitudinal research can be expensive and time-consuming. Still, it can offer valuable insights into how people and things change over time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
Here are the advantages and downsides of quantitative research:
Advantages of Quantitative Research:
- Objectivity: Quantitative research aims to be objective and unbiased. This is because it relies on numbers and statistical methods, which reduce the potential for researcher bias and subjective interpretation.
- Generalizability: Quantitative research often involves large sample sizes, which increases the likelihood of obtaining representative data. The study findings are more likely to apply to a wider population.
- Replicability: Using standardized procedures and measurement instruments in quantitative research enhances replicability. This means that other researchers can repeat the study using the same methods to test the reliability of the findings.
- Statistical analysis: Quantitative research employs various statistical techniques for data analysis. This allows researchers to identify data patterns, relationships, and associations. Additionally, statistical analysis can provide precision and help draw objective conclusions.
- Numerical precision: Quantitative research produces numerical data that can be analyzed using mathematical calculations. This numeric precision allows for clear comparisons and quantitative interpretations.
Disadvantages of Quantitative Research :
- Lack of Contextual Understanding : Quantitative research often focuses on measurable variables, which may limit the exploration of complex phenomena. It may overlook the social, cultural, and contextual factors that could influence the research findings.
- Limited Insight : While quantitative research can identify correlations and associations, it may not uncover underlying causes or explanations of these relationships. It may provide answers to “what” and “how much,” but not necessarily “why.”
- Potential for Simplification : The quantification of data can lead to oversimplification, as it may reduce complex phenomena into numerical values. This simplification may overlook nuances and intricacies important to understanding the research topic fully.
- Cost and Time-Intensive : Quantitative research requires significant resources. It includes time, funding, and specialized expertise. Researchers must collect and analyze large amounts of numerical data, which can be lengthy and expensive.
- Limited Flexibility : A systematic and planned strategy typically gets employed in quantitative research. It signifies the researcher’s use of a predetermined data collection and analysis approach. As a result, you may be more confident that your study gets conducted consistently and equitably. But it may also make it more difficult for the researcher to change the research plan or pose additional inquiries while gathering data. This could lead to missing valuable insights.
Here are some real-life examples of quantitative research:
- Market Research : Quantitative market research is a type of market research that uses numerical data to understand consumer preferences, buying behavior, and market trends. This data typically gets gathered through surveys and questionnaires, which are then analyzed to make informed business decisions.
- Health Studies : Quantitative research, such as clinical trials and epidemiological research, is vital in health studies. Researchers collect numerical data on treatment effectiveness, disease prevalence, risk factors, and patient outcomes. This data is then analyzed statistically to draw conclusions and make evidence-based recommendations for healthcare practices.
- Educational Research : Quantitative research is used extensively in educational studies to examine various aspects of learning, teaching methods, and academic achievement. Researchers collect data through standardized tests, surveys, or observations. The reason for this approach is to analyze factors influencing student performance, educational interventions, and educational policy effectiveness.
- Social Science Surveys : Social science researchers often employ quantitative research methods. The aim here is to study social phenomena and gather data on individuals’ or groups’ attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors. Large-scale surveys collect numerical data, then statistically analyze to identify patterns, trends, and associations within the population.
- Opinion Polls : Opinion polls and public opinion research rely heavily on quantitative research techniques. Polling organizations conduct surveys with representative samples of the population. The companies do this intending to gather numerical data on public opinions, political preferences, and social attitudes. The data then gets analyzed to gauge public sentiment and predict election outcomes or public opinion on specific issues.
- Economic Research : Quantitative research is widely used in economic studies to analyze economic indicators, trends, and patterns. Economists collect numerical data on GDP, inflation, employment, and consumer spending. Statistical analysis of this data helps understand economic phenomena, forecast future trends, and inform economic policy decisions.
More To Read :-
- Daily Active Users: Calculate + Tips to Increase DAU
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Definition and Examples
- What Is Operations Management? Definition and Overview
Qualitative research is about understanding and exploring something in depth. It uses non-numerical data, like interviews, observations, and open-ended survey responses, to gather rich, descriptive insights. Quantitative research is about measuring and analyzing relationships between variables using numerical data.
Quantitative research gets characterized by the following:
- The collection of numerical information
- The use of statistical analysis
- The goal of measuring and quantifying phenomena
- The purpose of examining relationships between variables
- The purpose of generalizing findings to a larger population
- The use of large sample sizes
- The use of structured surveys or experiments
- The usage of statistical techniques to analyze data objectively
The primary goal of quantitative research is to gather numerical data and analyze it statistically to uncover patterns, relationships, and trends. It aims to provide objective and generalizable insights using systematic data collection methods, standardized instruments, and statistical analysis techniques. Quantitative research seeks to test hypotheses, make predictions, and inform decision-making in various fields.
Crafting great product requires great tools. Try Chisel today, it's free forever.

Quantitative Marketing Research Examples
Are you curious about how businesses harness the power of data to make informed marketing decisions? In the dynamic world of marketing, quantitative research is a cornerstone of data-driven strategies. By leveraging statistical methods, it enables businesses to gain deep insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and market trends. In this article, we’ll explore some captivating examples of how quantitative marketing research empowers companies to make data-backed choices that propel their success. From customer surveys to data analytics, get ready to dive into the realm of quantitative research and discover its impact on modern marketing.
Importance of Quantitative Marketing Research
Quantitative marketing research plays a crucial role in providing businesses with valuable data and insights that help inform strategic decision-making and drive growth. Here are the key reasons why quantitative marketing research is important:
Discover Fresh Marketing Insights!
Join other smart marketers to uncover amazing marketing strategies.
We will never give away, trade or sell your email address. You can unsubscribe at any time.
I. Understanding Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior lies at the core of any successful marketing strategy. Quantitative marketing research allows businesses to gain deep insights into their target audience’s preferences, needs, and buying habits. By conducting surveys, businesses can collect numerical data on customer demographics, purchasing patterns, and brand preferences. These quantitative insights provide a solid foundation for tailoring products and services to meet customers’ demands effectively.
II. Identifying Market Trends
Market trends are constantly evolving, and staying attuned to these changes is crucial for businesses to maintain their competitive edge. Quantitative marketing research enables businesses to track and analyze market trends through data-driven approaches. By using statistical tools and techniques, marketers can identify emerging opportunities and potential threats in the market. This information empowers businesses to adapt their strategies and offerings in response to changing market dynamics.
III. Evaluating Marketing Campaigns
Investing in marketing campaigns is a significant undertaking for any business. Therefore, it becomes essential to evaluate the success and impact of these campaigns accurately. Quantitative marketing research provides a systematic and objective way to measure the effectiveness of marketing initiatives. By collecting and analyzing data on key performance indicators (KPIs), such as brand awareness, customer engagement, and conversion rates, businesses can assess their return on investment (ROI) and make data-backed decisions for future campaigns.
Overview of the Article
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the various facets of quantitative marketing research and its practical applications in the business world. From understanding the fundamentals of surveys and data analysis to diving deep into customer segmentation and market analysis, we will cover a wide range of topics that highlight the significance of quantitative research methods in marketing.
Through insightful subchapters and keyword-rich titles, readers will gain a clear understanding of the MECE (Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive) framework used to structure the article. Each section will provide actionable insights and practical examples that illustrate how businesses can leverage quantitative marketing research to optimize their decision-making processes and achieve sustainable growth in today’s competitive landscape. So, let’s embark on this data-driven journey and unlock the power of quantitative marketing research together.
7 Examples of Quantitative Marketing Research
Quantitative marketing research involves gathering numerical data to quantify customer behaviors, preferences, and market trends. Here are seven examples of quantitative marketing research:

Surveys are a fundamental tool in quantitative marketing research, allowing businesses to gather valuable data from their target audience. By utilizing various survey types and well-designed questions, researchers can obtain insights that are crucial for understanding customer behavior, preferences, and opinions.
Types of Surveys
I. online surveys.
- Conducted through web-based platforms, online surveys offer cost-effectiveness and efficiency in reaching a large audience.
- Ideal for collecting data from geographically dispersed respondents and obtaining real-time results.
- Commonly used in customer satisfaction surveys, market research, and product feedback.
II. Phone Surveys
- Involving direct interaction with respondents, phone surveys allow for personalized communication.
- Particularly useful when in-depth answers and clarifications are needed from participants.
- Suitable for conducting surveys with complex questions or exploring emotional responses.
III. In-Person Surveys
- Face-to-face surveys offer the unique advantage of observing non-verbal cues and body language.
- Effective for capturing detailed feedback on emotionally charged topics or products.
- Often utilized in focus groups or contextual inquiries to gain deeper insights.
Survey Question Design
I. open-ended questions.
- Encourage respondents to provide unrestricted, qualitative responses.
- Useful for capturing unique perspectives, uncovering new insights, and understanding complex issues.
- Allow researchers to gain a deeper understanding and discover unexpected trends.
II. Closed-ended Questions
- Offer predefined response options for participants to choose from.
- Provide quantitative data that is easy to analyze and compare across respondents.
- Commonly used for demographic data and measuring customer preferences.
III. Likert Scale Questions
- Present a statement and ask participants to rate their agreement or disagreement on a scale.
- Provide a standardized way to measure attitudes, opinions, or satisfaction levels.
- Useful for conducting customer feedback surveys and gauging sentiment towards products or services.
Sampling Techniques
I. random sampling.
- Involves selecting a random subset of the population to participate in the survey.
- Reduces bias and ensures each member of the population has an equal chance of being included.
- Commonly used when surveying a large population and seeking representative results.
II. Stratified Sampling
- Divides the population into subgroups or strata based on specific characteristics (e.g., age, gender, location).
- Enables researchers to obtain more precise data from each subgroup.
- Suitable for ensuring adequate representation of diverse segments within the population.
III. Cluster Sampling
- Divides the population into clusters or groups based on certain criteria.
- Randomly selects clusters and surveys all individuals within the chosen clusters.
- Particularly useful when dealing with geographically dispersed populations.
In this chapter, we have explored the various types of surveys, their question designs, and sampling techniques used in quantitative marketing research. Surveys serve as a powerful tool to gather numerical data, understand customer behavior, and make data-driven decisions that drive business growth and success.
2: Experiments
Experiments are a powerful tool in quantitative marketing research that allows businesses to test hypotheses, evaluate causation, and make data-driven decisions. In this chapter, we will explore different types of experiments and their applications in the marketing domain.
A/B Testing
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a common experimental method used to compare two versions (A and B) of a marketing element to determine which one performs better. It is widely employed in digital marketing to optimize website design, content, and advertising campaigns.
I. Designing A/B Tests
- Identify the Variable: Determine the specific element to be tested, such as the headline, call-to-action button, or email subject line.
- Define Metrics: Establish measurable metrics, such as click-through rates, conversion rates, or bounce rates, to evaluate the performance of each variation.
- Randomize Samples: Randomly divide the target audience into two groups, ensuring that each group is comparable in terms of demographics and characteristics.
- Run Simultaneously: Implement both versions simultaneously to minimize external factors’ influence on the results.
- Analyze Results: Compare the performance of A and B variations using the defined metrics to identify the winning version.
II. Interpreting Results
- Statistical Significance: Use statistical analysis to determine if the observed differences between A and B are statistically significant or due to chance.
- Implement Changes: Implement the winning variation and monitor its performance to ensure sustained improvements.
- Continuous Optimization: Continue conducting A/B tests to refine marketing elements and enhance overall campaign performance.
Field Experiments
Field experiments involve testing marketing strategies in real-world settings to understand their impact on consumer behavior and business outcomes. These experiments provide valuable insights into the practical implications of marketing initiatives.
I. Selecting Test Markets
- Choose Representative Markets: Select markets that accurately represent the target audience and demographics of interest.
- Control and Experimental Groups: Establish control groups that do not receive the marketing intervention and experimental groups that are exposed to the marketing strategy.
- Monitor Data: Collect data on relevant variables, such as sales, customer response, and brand perception, during the experimental period.
II. Controlling External Factors
- Minimize External Interference: Control for external factors that could influence the results, such as seasonality, competitor activities, or economic conditions.
- Randomization: Randomly assign participants to control and experimental groups to ensure unbiased results.
Quasi-Experiments
Quasi-experiments are conducted when true randomization is challenging or impossible, but researchers still seek to understand the causal relationship between variables.
I. Non-Equivalent Control Group
- Use Non-Equivalent Control Group: Instead of randomly assigning participants, researchers select a control group that is similar to the experimental group in relevant characteristics.
- Statistical Techniques: Utilize statistical techniques to account for differences between the groups and identify the causal impact of the marketing intervention.
II. Regression Discontinuity Design
- Apply Regression Discontinuity Design: This method involves identifying a cutoff point and analyzing the impact of the marketing intervention on outcomes near the cutoff.
- Causal Inference: Use statistical analysis to determine the causal relationship between the marketing intervention and the observed outcomes.
By understanding and implementing various experimental methods, businesses can gain valuable insights into consumer behavior, optimize marketing strategies, and drive success in a competitive market landscape. The combination of A/B testing, field experiments, and quasi-experiments empowers marketers to make informed decisions based on solid data and evidence.
3: Data Analysis

In marketing research, data analysis is a critical step that involves processing and interpreting the collected data to draw meaningful insights and make informed decisions. This chapter explores various data analysis techniques commonly used in both qualitative and quantitative research.
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics provide a summary of the main features of a dataset, offering an overview of the data’s characteristics.
I. Mean, Median, Mode
- Mean: The arithmetic average of a set of data, calculated by summing all values and dividing by the number of data points. It represents the central tendency of the data.
- Median: The middle value in an ordered dataset. It is less sensitive to outliers and extreme values than the mean.
- Mode: The most frequently occurring value in a dataset. It represents the most common observation.
II. Frequency Distribution
Frequency distribution is a table or graph that displays the number of times each value occurs in a dataset, showing the distribution pattern of the data.
Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics involves using sample data to make inferences or predictions about a larger population.
I. Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is used to assess whether there is a significant difference between groups or variables in a dataset. It helps researchers determine if the observed differences are due to chance or represent meaningful effects.
II. Confidence Intervals
A confidence interval is a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie with a certain level of confidence. It provides a measure of the uncertainty associated with sample estimates.
III. T-tests and ANOVA
- T-tests: T-tests are used to compare the means of two groups and determine if there is a significant difference between them. It is commonly used when comparing the effectiveness of two marketing strategies or measuring the impact of a treatment.
- ANOVA (Analysis of Variance): ANOVA is used to compare means among three or more groups. It helps identify significant differences between multiple groups, such as different customer segments’ responses to a marketing campaign.
Correlation and Regression Analysis
I. pearson correlation.
Pearson correlation is a measure of the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two continuous variables. It ranges from -1 to 1, where -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation, 0 indicates no correlation, and 1 indicates a perfect positive correlation.
II. Multiple Regression
Multiple regression analysis assesses the relationship between a dependent variable and two or more independent variables. It helps identify which independent variables have a significant impact on the dependent variable and predict outcomes based on the model.
III. Interpreting Regression Output
Interpreting regression output involves understanding the coefficients of independent variables and their significance, the overall model fit, and making predictions based on the regression equation.
By employing these data analysis techniques, marketing researchers can gain deeper insights into their data, identify patterns, relationships, and trends, and make data-driven decisions that lead to more effective marketing strategies and successful business outcomes.
4: Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation is a crucial marketing strategy that involves dividing a larger market into distinct groups of consumers with similar characteristics and preferences. This chapter explores the importance of customer segmentation, its benefits, and the different criteria and methods used for segmentation.
Importance of Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation is a critical strategy for businesses seeking to better understand and cater to the diverse needs of their target market. It involves dividing the larger market into distinct groups based on shared characteristics, behaviors, and preferences.
I. Benefits of Segmentation
- Targeted Marketing : Segmentation allows businesses to tailor their marketing efforts to specific customer groups, increasing the relevance and effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Better Customer Understanding : By understanding the unique needs and preferences of different segments, companies can improve their products and services to meet customer expectations.
- Resource Allocation : Segmentation helps allocate marketing resources efficiently by focusing on high-potential customer segments and avoiding wasteful spending on irrelevant audiences.
- Competitive Advantage : A well-defined segmentation strategy can lead to a competitive edge by offering personalized experiences that competitors may not be providing.
II. Criteria for Segmentation
- Measurable : Segments should be identifiable and measurable using specific criteria, such as demographics, behaviors, or purchase patterns.
- Substantial : Segments should be large enough to warrant separate marketing efforts and profitability.
- Accessible : Companies should be able to reach and engage the identified segments through their marketing channels.
- Differentiable : Segments should be distinct from each other in terms of their needs and preferences to justify separate marketing approaches.
- Actionable : Marketing strategies should be effective in influencing the behavior of the identified segments.
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation is a common and widely used approach to customer segmentation, dividing a market based on various demographic factors. These factors include age, gender, income, education, occupation, marital status, ethnicity, family size, and more. Demographic segmentation is essential in marketing as it provides valuable insights into the characteristics and behaviors of different customer groups. Here are the key aspects and advantages of demographic segmentation:
I. Age, Gender, and Income
- Age : Dividing customers based on age groups allows companies to target products and messages to specific life stages and generational preferences.
- Gender : Gender-based segmentation can be useful in industries where preferences and needs vary significantly between males and females.
- Income : Income segmentation helps in offering products and services that align with the spending power of different customer groups.
II. Education and Occupation
- Education : Education level can indicate the knowledge and sophistication of customers, influencing their purchasing decisions.
- Occupation : Occupation-based segmentation can help in targeting products and services relevant to specific professional needs.
Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation is a marketing technique that categorizes consumers based on their psychological characteristics, lifestyle, interests, values, opinions, and behavior. Unlike demographic segmentation, which groups customers based on objective traits like age or income, psychographic segmentation delves into the subjective aspects of consumer behavior. This approach provides businesses with a deeper understanding of their target audience, allowing them to create more personalized and relevant marketing strategies. Here are the key aspects and advantages of psychographic segmentation:
I. Personality Traits
- Personality Traits : Psychographic segmentation based on personality traits helps understand consumer behavior and preferences influenced by individual characteristics.
II. Values and Lifestyles
- Values : Segmenting customers based on their values and beliefs enables businesses to align their brand messaging with customers’ core principles.
- Lifestyles : Lifestyles segmentation focuses on customers’ habits, interests, and activities to create targeted marketing campaigns.
Customer segmentation is a powerful tool in understanding and engaging with diverse customer groups. By employing appropriate criteria and methods for segmentation, businesses can effectively cater to the unique needs of different customer segments, leading to improved customer satisfaction, loyalty, and overall business success.
5: Market Analysis

Market analysis is a critical aspect of marketing research that involves understanding the size and potential of a market, assessing brand awareness and perception, and conducting pricing research. This chapter delves into various methods and approaches used for market analysis.
Market Sizing and Forecasting
Market sizing and forecasting are essential activities in business and marketing that provide valuable insights into the potential size and growth of a target market. These analyses help businesses understand the market’s opportunities and challenges, make informed decisions, and develop effective strategies. Here’s an overview of market sizing and forecasting:
I. Top-Down Approach
The top-down approach to market sizing involves starting with the total market size and then breaking it down into segments. This approach relies on existing data and industry reports to estimate the market size and potential.
II. Bottom-Up Approach
In contrast, the bottom-up approach begins by estimating the potential market size of individual segments and then aggregating them to determine the total market size. This approach is more granular and relies on data from primary research, surveys, and customer feedback.
III. Data Sources for Market Sizing
- Industry Reports : Existing industry reports and market studies provide valuable data and insights for market sizing.
- Government Data : Government sources often publish data related to specific industries, which can be useful for market analysis.
- Customer Surveys : Conducting surveys with potential customers helps gather data on market preferences and behaviors.
- Competitor Analysis : Analyzing competitors’ market share and performance can provide insights into the overall market size.
Brand Awareness and Perception
Brand awareness and perception are two critical aspects of branding that significantly influence a company’s success. They are closely related but represent different dimensions of how consumers perceive and interact with a brand. Let’s delve into each of these concepts:
I. Surveys for Brand Awareness
Brand awareness surveys assess the level of awareness and recognition that consumers have of a particular brand. These surveys often include questions about brand recall, brand recognition, and brand associations.
II. Measuring Brand Perception
Brand perception surveys delve deeper into consumers’ perceptions and attitudes toward a brand. This research helps understand how a brand is perceived in terms of attributes, values, and emotional connections.
Pricing Research
Pricing research is a market research technique that focuses on understanding consumers’ price sensitivity, preferences, and willingness to pay for a product or service. It is a crucial component of the pricing strategy and helps businesses determine optimal pricing levels that balance profitability and customer demand. Pricing research provides valuable insights to make informed pricing decisions, whether introducing a new product, adjusting prices, or assessing the competitive landscape. Here are the key aspects of pricing research:
I. Price Sensitivity Analysis
Price sensitivity analysis evaluates how sensitive consumers are to changes in pricing. This research helps determine the optimal price point for a product or service that maximizes revenue while satisfying customer demand.
II. Conjoint Analysis
Conjoint analysis is a powerful pricing research method that involves presenting consumers with various product configurations and prices. By analyzing their choices, businesses can identify the most preferred product features and price combinations.
Market analysis plays a crucial role in guiding marketing strategies, product development, and pricing decisions. By employing various market sizing techniques, assessing brand awareness and perception, and conducting pricing research, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of their target market, competitors, and consumer preferences, leading to more effective marketing and business outcomes.
6: Product Development
Product development is a crucial phase in the lifecycle of a product, where ideas and concepts are tested and refined to meet customer needs and market demands. This chapter explores various methods and techniques used in product development.
Concept Testing
Concept testing is a market research technique used to evaluate the viability and appeal of a new product, service, or marketing concept before its full development or launch. It involves presenting a new idea or concept to a representative sample of the target audience and gathering their feedback and opinions. Concept testing helps businesses assess consumer reactions, identify potential issues, and make data-driven decisions to refine or enhance the concept before investing significant resources in its implementation.
I. Gathering Feedback on Concepts
Concept testing involves presenting potential product ideas or concepts to a sample of target customers to gather feedback. This feedback helps businesses understand how appealing and relevant the concepts are to the target audience and whether they align with customer needs.
II. Iterative Concept Testing
Iterative concept testing involves refining and iterating on product concepts based on the feedback received from customers. Multiple rounds of testing and refinement can lead to a more polished and market-ready product.
Product Usage and Satisfaction
Product usage and satisfaction are crucial aspects of understanding how customers interact with a product or service and how satisfied they are with their overall experience. Monitoring product usage and measuring customer satisfaction provide businesses with valuable insights to improve product offerings, enhance customer experiences, and build long-term customer loyalty.
I. Analyzing Product Usage Data
Analyzing product usage data provides insights into how customers are interacting with the product after its launch. This data can include information on product adoption, usage patterns, and user behavior. Understanding how customers use the product can highlight areas for improvement and feature enhancements.
II. Customer Satisfaction Surveys
Customer satisfaction surveys assess how satisfied customers are with the product and their overall experience. These surveys help identify strengths and weaknesses in the product and provide valuable feedback for future improvements.
Market Demand Estimation
Market demand estimation is a critical process in marketing and business strategy that involves assessing the potential level of demand for a product or service within a specific market or target audience. By understanding market demand, businesses can make informed decisions regarding production, pricing, marketing, and resource allocation. Estimating market demand involves analyzing various factors that influence consumers’ willingness and ability to purchase a product or service.
I. Estimating Product Demand
Estimating product demand involves predicting the level of interest and demand for the product in the market. This estimation is crucial for production planning, inventory management, and overall business strategy.
II. Projecting Sales Volume
Projecting sales volume goes hand-in-hand with market demand estimation. By understanding the expected demand for the product, businesses can project the likely sales volume over a specific period, helping with resource allocation and financial planning.
Product development is a dynamic process that requires continuous evaluation and adjustment. By conducting concept testing, gathering usage data, assessing customer satisfaction, and estimating market demand, businesses can make informed decisions and enhance their products to meet customer expectations and market demands effectively. This iterative approach to product development ensures that the final product aligns with customer needs and preferences, ultimately leading to greater success in the market.

7: Marketing ROI Measurement

Marketing Return on Investment (ROI) measurement is essential for businesses to understand the effectiveness and profitability of their marketing efforts. This chapter delves into various methods and models used to calculate and analyze marketing ROI.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Return on Investment (ROI) is a financial metric used to evaluate the profitability and efficiency of an investment or business initiative. It measures the ratio between the gain or benefit generated from the investment and the cost of the investment itself. ROI is a critical tool for businesses to assess the success of various projects, marketing campaigns, or overall business performance. It enables decision-makers to determine whether an investment is worthwhile and provides valuable insights for resource allocation and strategic planning.
I. Calculating ROI
ROI is a financial metric that evaluates the profitability of an investment relative to its cost. In marketing, ROI helps determine the revenue generated from marketing activities compared to the investment made in those activities. The formula for calculating ROI is:
ROI = (Revenue from Marketing – Cost of Marketing) / Cost of Marketing
II. Factors Affecting Marketing ROI
Several factors can influence marketing ROI, including the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, the efficiency of marketing spending, market conditions, competition, and overall business strategy. Understanding these factors can help businesses make data-driven decisions to optimize marketing ROI.
Marketing Mix Modeling
Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM), also known as Marketing Mix Analysis or Business Mix Modeling, is a statistical technique used by businesses to measure the impact of various marketing activities on sales and other key performance indicators (KPIs). MMM helps marketing teams and decision-makers optimize their marketing strategies by understanding which marketing elements contribute the most to overall success and return on investment (ROI). It is a valuable tool for assessing the effectiveness of marketing efforts, allocating resources, and making data-driven decisions.
Using Regression Analysis for ROI
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used in marketing mix modeling to identify relationships between marketing variables and sales performance. By using regression analysis, businesses can quantify the impact of each marketing element on ROI.
Attribution Modeling
Attribution modeling is a marketing analytics technique used to determine the contribution of different marketing channels and touchpoints in the customer journey toward conversion or desired outcomes. It aims to understand the various interactions a customer has with different marketing efforts before making a purchase or taking a specific action. Attribution modeling helps businesses allocate credit to the most influential marketing channels accurately, providing valuable insights for optimizing marketing strategies and budget allocation.
Types of Attribution Models
Attribution modeling aims to attribute credit to different marketing touchpoints that contribute to a conversion or sale. Various attribution models exist, including first-touch, last-touch, linear, time decay, and more. Each model offers a different perspective on how marketing efforts influence customer behavior.
Multi-Touch Attribution
Multi-touch attribution takes into account all the touchpoints a customer interacts with during their journey with a brand. This approach provides a more comprehensive view of how marketing activities collectively contribute to conversions and ROI.
Accurate measurement of marketing ROI is crucial for optimizing marketing strategies, allocating resources wisely, and demonstrating the value of marketing efforts to stakeholders. By understanding the calculations and methodologies behind ROI measurement, businesses can make informed decisions to improve their marketing effectiveness and drive better business outcomes.
Embracing both qualitative and quantitative research methods is key to unlocking valuable insights into consumers and their preferences. By combining statistical data with a deeper understanding of individual perspectives, businesses can make informed decisions that lead to marketing success. The future of quantitative marketing holds even more promise as technology advances, providing sophisticated tools for data-driven decision making. Integrating these approaches will pave the way for better customer experiences and increased marketing impact, driving success in the dynamic business landscape.
Q1. What are the advantages of quantitative marketing research over qualitative research?
A: Quantitative marketing research offers several advantages over qualitative research. Some of the key advantages include:
- Statistical significance: Quantitative research provides numerical data, allowing researchers to analyze results statistically and draw reliable conclusions.
- Generalizability: Large sample sizes in quantitative research enable findings to be applied to a broader population, making it useful for market trends and general consumer behavior.
- Objectivity: Quantitative research reduces the influence of researcher subjectivity, as it focuses on numerical data rather than interpretations of individual responses.
- Ease of analysis: The use of software tools facilitates the analysis of large datasets, making it efficient to process and interpret the findings.
Q2. How can businesses ensure the accuracy of survey data?
A: To ensure the accuracy of survey data, businesses can follow these best practices:
- Clearly define objectives: Clearly outline the purpose of the survey and the specific information you want to gather.
- Design unbiased questions: Craft questions that are neutral and free from leading or biased language to avoid influencing respondents’ answers.
- Pretest the survey: Conduct a pilot test with a small group to identify any issues with question clarity or survey flow before launching the full-scale survey.
- Random sampling: Use random sampling techniques to select participants, ensuring that each member of the target population has an equal chance of being included.
- Data validation: Implement checks to verify the accuracy and consistency of responses, removing any outliers or inconsistent data.
- Anonymity and confidentiality: Assure respondents that their answers will be kept confidential, encouraging honest and candid responses.
Q3. What sample size is considered statistically significant in marketing research?
A: The appropriate sample size for statistical significance in marketing research depends on various factors, such as the population size, confidence level, and desired margin of error. Generally, larger sample sizes provide more accurate results. Researchers often use formulas such as the Sample Size Formula for Proportions or the Sample Size Formula for Means to calculate the required sample size based on specific parameters.
Q4. How does market segmentation help in targeted marketing campaigns?
A: Market segmentation involves dividing a larger market into distinct groups based on common characteristics, preferences, or behavior. It helps in targeted marketing campaigns by allowing businesses to:
- Understand customer needs: Segmentation enables businesses to identify specific customer groups and tailor products and messages to meet their unique needs and preferences.
- Optimize marketing efforts: Targeted marketing ensures that marketing resources are focused on the most relevant audience, increasing the efficiency of campaigns.
- Improve customer engagement: Personalized marketing resonates better with consumers, leading to higher engagement and brand loyalty.
- Increase conversion rates: Targeted campaigns are more likely to convert prospects into customers, as they address specific pain points and motivations.
Q5. What are some common challenges in conducting A/B tests?
A: A/B testing, also known as split testing, involves comparing two versions (A and B) of a webpage, email, or advertisement to determine which one performs better. Common challenges in conducting A/B tests include:
- Sample size: Ensuring that the sample size is large enough to detect significant differences between the variations.
- Test duration: Running the test for an appropriate length of time to capture sufficient data without being influenced by external factors.
- Validity of results: Ensuring that the test setup is reliable and free from biases that could impact the accuracy of the results.
- Multiple variations: Handling tests with more than two variations (A/B/C or more) can become complex and may require more data to draw meaningful conclusions.
Q6. Which statistical software is best for data analysis in marketing research?
A: Several statistical software tools are commonly used for data analysis in marketing research, each with its strengths and applications. Some popular choices include:
- SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences): Widely used in social sciences and marketing research, SPSS is known for its user-friendly interface and versatile statistical analysis capabilities.
- R: A free and open-source software environment for statistical computing and graphics, R is highly customizable and offers a wide range of statistical techniques.
- Excel: While not dedicated solely to statistical analysis, Excel is accessible and familiar to many researchers, making it a popular choice for basic data analysis tasks.
- Python: Python’s data analysis libraries, such as Pandas and NumPy, provide powerful tools for statistical analysis and data manipulation.
The choice of software depends on the complexity of the analysis, the researcher’s familiarity with the tool, and the specific requirements of the marketing research project.
Similar Posts
Creative website content ideas, importance of sales and marketing department.
The synergy between the Sales and Marketing departments stands as a linchpin of success in the world of marketing. Research indicates that companies with well-aligned Sales and Marketing teams achieve 208% higher marketing revenue than those with misaligned teams, underscoring the pivotal role this collaboration plays in driving growth. In this article, we delve into…

7 Steps to a Successful Marketing Public Relations Plan
Welcome to our blog post, “7 Steps to a Successful Marketing Public Relations Plan.” In today’s fast-paced and interconnected world, a well-crafted marketing public relations (PR) plan is essential for businesses to effectively communicate their message, build brand credibility, and connect with their target audience. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through seven…
Gardy Dahl’s “Pet Rock”
In the 1970s, amidst a cultural landscape filled with hippies, disco balls, and lava lamps, one man’s unconventional idea took the world by storm: Pet Rock. Created by an advertising executive named Gary Dahl, this seemingly absurd concept turned into a cultural phenomenon, capturing the imaginations of millions and becoming a symbol of the era….
Market Analysis Business Plan Pdf
Example of a marketing plan pdf, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Please enter an answer in digits: thirteen + two =
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Quantitative Research: What It Is, Practices & Methods
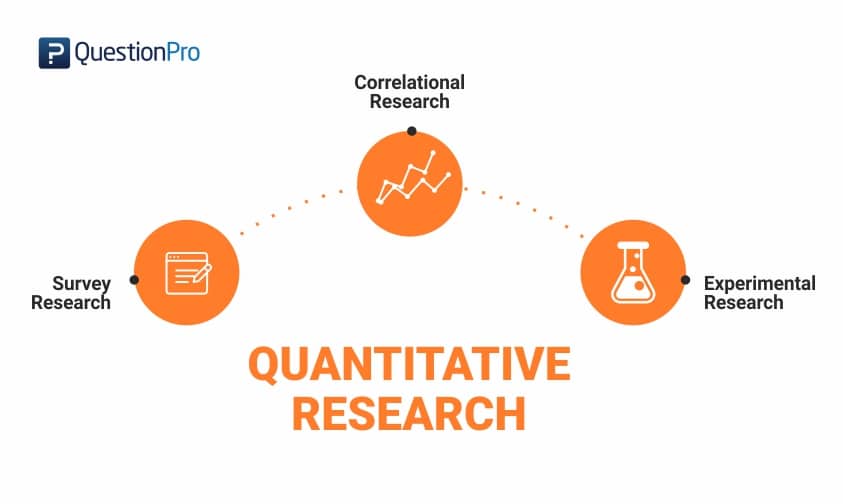
Quantitative research involves analyzing and gathering numerical data to uncover trends, calculate averages, evaluate relationships, and derive overarching insights. It’s used in various fields, including the natural and social sciences. Quantitative data analysis employs statistical techniques for processing and interpreting numeric data.
Research designs in the quantitative realm outline how data will be collected and analyzed with methods like experiments and surveys. Qualitative methods complement quantitative research by focusing on non-numerical data, adding depth to understanding. Data collection methods can be qualitative or quantitative, depending on research goals. Researchers often use a combination of both approaches to gain a comprehensive understanding of phenomena.
What is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is a systematic investigation of phenomena by gathering quantifiable data and performing statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. Quantitative research collects statistically significant information from existing and potential customers using sampling methods and sending out online surveys , online polls , and questionnaires , for example.
One of the main characteristics of this type of research is that the results can be depicted in numerical form. After carefully collecting structured observations and understanding these numbers, it’s possible to predict the future of a product or service, establish causal relationships or Causal Research , and make changes accordingly. Quantitative research primarily centers on the analysis of numerical data and utilizes inferential statistics to derive conclusions that can be extrapolated to the broader population.
An example of a quantitative research study is the survey conducted to understand how long a doctor takes to tend to a patient when the patient walks into the hospital. A patient satisfaction survey can be administered to ask questions like how long a doctor takes to see a patient, how often a patient walks into a hospital, and other such questions, which are dependent variables in the research. This kind of research method is often employed in the social sciences, and it involves using mathematical frameworks and theories to effectively present data, ensuring that the results are logical, statistically sound, and unbiased.
Data collection in quantitative research uses a structured method and is typically conducted on larger samples representing the entire population. Researchers use quantitative methods to collect numerical data, which is then subjected to statistical analysis to determine statistically significant findings. This approach is valuable in both experimental research and social research, as it helps in making informed decisions and drawing reliable conclusions based on quantitative data.
Quantitative Research Characteristics
Quantitative research has several unique characteristics that make it well-suited for specific projects. Let’s explore the most crucial of these characteristics so that you can consider them when planning your next research project:

- Structured tools: Quantitative research relies on structured tools such as surveys, polls, or questionnaires to gather quantitative data . Using such structured methods helps collect in-depth and actionable numerical data from the survey respondents, making it easier to perform data analysis.
- Sample size: Quantitative research is conducted on a significant sample size representing the target market . Appropriate Survey Sampling methods, a fundamental aspect of quantitative research methods, must be employed when deriving the sample to fortify the research objective and ensure the reliability of the results.
- Close-ended questions: Closed-ended questions , specifically designed to align with the research objectives, are a cornerstone of quantitative research. These questions facilitate the collection of quantitative data and are extensively used in data collection processes.
- Prior studies: Before collecting feedback from respondents, researchers often delve into previous studies related to the research topic. This preliminary research helps frame the study effectively and ensures the data collection process is well-informed.
- Quantitative data: Typically, quantitative data is represented using tables, charts, graphs, or other numerical forms. This visual representation aids in understanding the collected data and is essential for rigorous data analysis, a key component of quantitative research methods.
- Generalization of results: One of the strengths of quantitative research is its ability to generalize results to the entire population. It means that the findings derived from a sample can be extrapolated to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions for improvement based on numerical data analysis.
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods are systematic approaches used to gather and analyze numerical data to understand and draw conclusions about a phenomenon or population. Here are the quantitative research methods:
- Primary quantitative research methods
- Secondary quantitative research methods
Primary Quantitative Research Methods
Primary quantitative research is the most widely used method of conducting market research. The distinct feature of primary research is that the researcher focuses on collecting data directly rather than depending on data collected from previously done research. Primary quantitative research design can be broken down into three further distinctive tracks and the process flow. They are:
A. Techniques and Types of Studies
There are multiple types of primary quantitative research. They can be distinguished into the four following distinctive methods, which are:
01. Survey Research
Survey Research is fundamental for all quantitative outcome research methodologies and studies. Surveys are used to ask questions to a sample of respondents, using various types such as online polls, online surveys, paper questionnaires, web-intercept surveys , etc. Every small and big organization intends to understand what their customers think about their products and services, how well new features are faring in the market, and other such details.
By conducting survey research, an organization can ask multiple survey questions , collect data from a pool of customers, and analyze this collected data to produce numerical results. It is the first step towards collecting data for any research. You can use single ease questions . A single-ease question is a straightforward query that elicits a concise and uncomplicated response.
This type of research can be conducted with a specific target audience group and also can be conducted across multiple groups along with comparative analysis . A prerequisite for this type of research is that the sample of respondents must have randomly selected members. This way, a researcher can easily maintain the accuracy of the obtained results as a huge variety of respondents will be addressed using random selection.
Traditionally, survey research was conducted face-to-face or via phone calls. Still, with the progress made by online mediums such as email or social media, survey research has also spread to online mediums.There are two types of surveys , either of which can be chosen based on the time in hand and the kind of data required:
Cross-sectional surveys: Cross-sectional surveys are observational surveys conducted in situations where the researcher intends to collect data from a sample of the target population at a given point in time. Researchers can evaluate various variables at a particular time. Data gathered using this type of survey is from people who depict similarity in all variables except the variables which are considered for research . Throughout the survey, this one variable will stay constant.
- Cross-sectional surveys are popular with retail, SMEs, and healthcare industries. Information is garnered without modifying any parameters in the variable ecosystem.
- Multiple samples can be analyzed and compared using a cross-sectional survey research method.
- Multiple variables can be evaluated using this type of survey research.
- The only disadvantage of cross-sectional surveys is that the cause-effect relationship of variables cannot be established as it usually evaluates variables at a particular time and not across a continuous time frame.
Longitudinal surveys: Longitudinal surveys are also observational surveys , but unlike cross-sectional surveys, longitudinal surveys are conducted across various time durations to observe a change in respondent behavior and thought processes. This time can be days, months, years, or even decades. For instance, a researcher planning to analyze the change in buying habits of teenagers over 5 years will conduct longitudinal surveys.
- In cross-sectional surveys, the same variables were evaluated at a given time, and in longitudinal surveys, different variables can be analyzed at different intervals.
- Longitudinal surveys are extensively used in the field of medicine and applied sciences. Apart from these two fields, they are also used to observe a change in the market trend analysis , analyze customer satisfaction, or gain feedback on products/services.
- In situations where the sequence of events is highly essential, longitudinal surveys are used.
- Researchers say that when research subjects need to be thoroughly inspected before concluding, they rely on longitudinal surveys.
02. Correlational Research
A comparison between two entities is invariable. Correlation research is conducted to establish a relationship between two closely-knit entities and how one impacts the other, and what changes are eventually observed. This research method is carried out to give value to naturally occurring relationships, and a minimum of two different groups are required to conduct this quantitative research method successfully. Without assuming various aspects, a relationship between two groups or entities must be established.
Researchers use this quantitative research design to correlate two or more variables using mathematical analysis methods. Patterns, relationships, and trends between variables are concluded as they exist in their original setup. The impact of one of these variables on the other is observed, along with how it changes the relationship between the two variables. Researchers tend to manipulate one of the variables to attain the desired results.
Ideally, it is advised not to make conclusions merely based on correlational research. This is because it is not mandatory that if two variables are in sync that they are interrelated.
Example of Correlational Research Questions :
- The relationship between stress and depression.
- The equation between fame and money.
- The relation between activities in a third-grade class and its students.
03. Causal-comparative Research
This research method mainly depends on the factor of comparison. Also called quasi-experimental research , this quantitative research method is used by researchers to conclude the cause-effect equation between two or more variables, where one variable is dependent on the other independent variable. The independent variable is established but not manipulated, and its impact on the dependent variable is observed. These variables or groups must be formed as they exist in the natural setup. As the dependent and independent variables will always exist in a group, it is advised that the conclusions are carefully established by keeping all the factors in mind.
Causal-comparative research is not restricted to the statistical analysis of two variables but extends to analyzing how various variables or groups change under the influence of the same changes. This research is conducted irrespective of the type of relationship that exists between two or more variables. Statistical analysis plan is used to present the outcome using this quantitative research method.
Example of Causal-Comparative Research Questions:
- The impact of drugs on a teenager. The effect of good education on a freshman. The effect of substantial food provision in the villages of Africa.
04. Experimental Research
Also known as true experimentation, this research method relies on a theory. As the name suggests, experimental research is usually based on one or more theories. This theory has yet to be proven before and is merely a supposition. In experimental research, an analysis is done around proving or disproving the statement. This research method is used in natural sciences. Traditional research methods are more effective than modern techniques.
There can be multiple theories in experimental research. A theory is a statement that can be verified or refuted.
After establishing the statement, efforts are made to understand whether it is valid or invalid. This quantitative research method is mainly used in natural or social sciences as various statements must be proved right or wrong.
- Traditional research methods are more effective than modern techniques.
- Systematic teaching schedules help children who struggle to cope with the course.
- It is a boon to have responsible nursing staff for ailing parents.
B. Data Collection Methodologies
The second major step in primary quantitative research is data collection. Data collection can be divided into sampling methods and data collection using surveys and polls.
01. Data Collection Methodologies: Sampling Methods
There are two main sampling methods for quantitative research: Probability and Non-probability sampling .
Probability sampling: A theory of probability is used to filter individuals from a population and create samples in probability sampling . Participants of a sample are chosen by random selection processes. Each target audience member has an equal opportunity to be selected in the sample.
There are four main types of probability sampling:
- Simple random sampling: As the name indicates, simple random sampling is nothing but a random selection of elements for a sample. This sampling technique is implemented where the target population is considerably large.
- Stratified random sampling: In the stratified random sampling method , a large population is divided into groups (strata), and members of a sample are chosen randomly from these strata. The various segregated strata should ideally not overlap one another.
- Cluster sampling: Cluster sampling is a probability sampling method using which the main segment is divided into clusters, usually using geographic segmentation and demographic segmentation parameters.
- Systematic sampling: Systematic sampling is a technique where the starting point of the sample is chosen randomly, and all the other elements are chosen using a fixed interval. This interval is calculated by dividing the population size by the target sample size.
Non-probability sampling: Non-probability sampling is where the researcher’s knowledge and experience are used to create samples. Because of the researcher’s involvement, not all the target population members have an equal probability of being selected to be a part of a sample.
There are five non-probability sampling models:
- Convenience sampling: In convenience sampling , elements of a sample are chosen only due to one prime reason: their proximity to the researcher. These samples are quick and easy to implement as there is no other parameter of selection involved.
- Consecutive sampling: Consecutive sampling is quite similar to convenience sampling, except for the fact that researchers can choose a single element or a group of samples and conduct research consecutively over a significant period and then perform the same process with other samples.
- Quota sampling: Using quota sampling , researchers can select elements using their knowledge of target traits and personalities to form strata. Members of various strata can then be chosen to be a part of the sample as per the researcher’s understanding.
- Snowball sampling: Snowball sampling is conducted with target audiences who are difficult to contact and get information. It is popular in cases where the target audience for analysis research is rare to put together.
- Judgmental sampling: Judgmental sampling is a non-probability sampling method where samples are created only based on the researcher’s experience and research skill .
02. Data collection methodologies: Using surveys & polls
Once the sample is determined, then either surveys or polls can be distributed to collect the data for quantitative research.
Using surveys for primary quantitative research
A survey is defined as a research method used for collecting data from a pre-defined group of respondents to gain information and insights on various topics of interest. The ease of survey distribution and the wide number of people it can reach depending on the research time and objective makes it one of the most important aspects of conducting quantitative research.
Fundamental levels of measurement – nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales
Four measurement scales are fundamental to creating a multiple-choice question in a survey. They are nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio measurement scales without the fundamentals of which no multiple-choice questions can be created. Hence, it is crucial to understand these measurement levels to develop a robust survey.
Use of different question types
To conduct quantitative research, close-ended questions must be used in a survey. They can be a mix of multiple question types, including multiple-choice questions like semantic differential scale questions , rating scale questions , etc.
Survey Distribution and Survey Data Collection
In the above, we have seen the process of building a survey along with the research design to conduct primary quantitative research. Survey distribution to collect data is the other important aspect of the survey process. There are different ways of survey distribution. Some of the most commonly used methods are:
- Email: Sending a survey via email is the most widely used and effective survey distribution method. This method’s response rate is high because the respondents know your brand. You can use the QuestionPro email management feature to send out and collect survey responses.
- Buy respondents: Another effective way to distribute a survey and conduct primary quantitative research is to use a sample. Since the respondents are knowledgeable and are on the panel by their own will, responses are much higher.
- Embed survey on a website: Embedding a survey on a website increases a high number of responses as the respondent is already in close proximity to the brand when the survey pops up.
- Social distribution: Using social media to distribute the survey aids in collecting a higher number of responses from the people that are aware of the brand.
- QR code: QuestionPro QR codes store the URL for the survey. You can print/publish this code in magazines, signs, business cards, or on just about any object/medium.
- SMS survey: The SMS survey is a quick and time-effective way to collect a high number of responses.
- Offline Survey App: The QuestionPro App allows users to circulate surveys quickly, and the responses can be collected both online and offline.
Survey example
An example of a survey is a short customer satisfaction (CSAT) survey that can quickly be built and deployed to collect feedback about what the customer thinks about a brand and how satisfied and referenceable the brand is.
Using polls for primary quantitative research
Polls are a method to collect feedback using close-ended questions from a sample. The most commonly used types of polls are election polls and exit polls . Both of these are used to collect data from a large sample size but using basic question types like multiple-choice questions.
C. Data Analysis Techniques
The third aspect of primary quantitative research design is data analysis . After collecting raw data, there must be an analysis of this data to derive statistical inferences from this research. It is important to relate the results to the research objective and establish the statistical relevance of the results.
Remember to consider aspects of research that were not considered for the data collection process and report the difference between what was planned vs. what was actually executed.
It is then required to select precise Statistical Analysis Methods , such as SWOT, Conjoint, Cross-tabulation, etc., to analyze the quantitative data.
- SWOT analysis: SWOT Analysis stands for the acronym of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threat analysis. Organizations use this statistical analysis technique to evaluate their performance internally and externally to develop effective strategies for improvement.
- Conjoint Analysis: Conjoint Analysis is a market analysis method to learn how individuals make complicated purchasing decisions. Trade-offs are involved in an individual’s daily activities, and these reflect their ability to decide from a complex list of product/service options.
- Cross-tabulation: Cross-tabulation is one of the preliminary statistical market analysis methods which establishes relationships, patterns, and trends within the various parameters of the research study.
- TURF Analysis: TURF Analysis , an acronym for Totally Unduplicated Reach and Frequency Analysis, is executed in situations where the reach of a favorable communication source is to be analyzed along with the frequency of this communication. It is used for understanding the potential of a target market.
Inferential statistics methods such as confidence interval, the margin of error, etc., can then be used to provide results.
Secondary Quantitative Research Methods
Secondary quantitative research or desk research is a research method that involves using already existing data or secondary data. Existing data is summarized and collated to increase the overall effectiveness of the research.
This research method involves collecting quantitative data from existing data sources like the internet, government resources, libraries, research reports, etc. Secondary quantitative research helps to validate the data collected from primary quantitative research and aid in strengthening or proving, or disproving previously collected data.
The following are five popularly used secondary quantitative research methods:
- Data available on the internet: With the high penetration of the internet and mobile devices, it has become increasingly easy to conduct quantitative research using the internet. Information about most research topics is available online, and this aids in boosting the validity of primary quantitative data.
- Government and non-government sources: Secondary quantitative research can also be conducted with the help of government and non-government sources that deal with market research reports. This data is highly reliable and in-depth and hence, can be used to increase the validity of quantitative research design.
- Public libraries: Now a sparingly used method of conducting quantitative research, it is still a reliable source of information, though. Public libraries have copies of important research that was conducted earlier. They are a storehouse of valuable information and documents from which information can be extracted.
- Educational institutions: Educational institutions conduct in-depth research on multiple topics, and hence, the reports that they publish are an important source of validation in quantitative research.
- Commercial information sources: Local newspapers, journals, magazines, radio, and TV stations are great sources to obtain data for secondary quantitative research. These commercial information sources have in-depth, first-hand information on market research, demographic segmentation, and similar subjects.
Quantitative Research Examples
Some examples of quantitative research are:
- A customer satisfaction template can be used if any organization would like to conduct a customer satisfaction (CSAT) survey . Through this kind of survey, an organization can collect quantitative data and metrics on the goodwill of the brand or organization in the customer’s mind based on multiple parameters such as product quality, pricing, customer experience, etc. This data can be collected by asking a net promoter score (NPS) question , matrix table questions, etc. that provide data in the form of numbers that can be analyzed and worked upon.
- Another example of quantitative research is an organization that conducts an event, collecting feedback from attendees about the value they see from the event. By using an event survey , the organization can collect actionable feedback about the satisfaction levels of customers during various phases of the event such as the sales, pre and post-event, the likelihood of recommending the organization to their friends and colleagues, hotel preferences for the future events and other such questions.
What are the Advantages of Quantitative Research?
There are many advantages to quantitative research. Some of the major advantages of why researchers use this method in market research are:
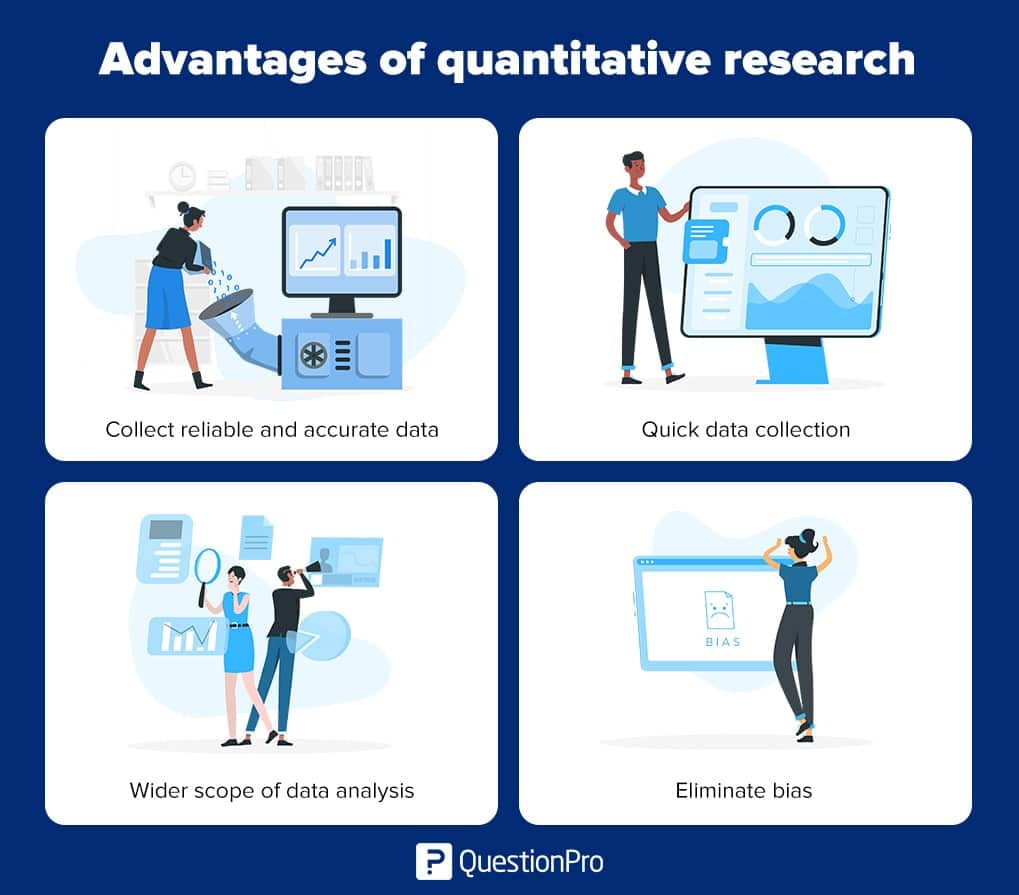
Collect Reliable and Accurate Data:
Quantitative research is a powerful method for collecting reliable and accurate quantitative data. Since data is collected, analyzed, and presented in numbers, the results obtained are incredibly reliable and objective. Numbers do not lie and offer an honest and precise picture of the conducted research without discrepancies. In situations where a researcher aims to eliminate bias and predict potential conflicts, quantitative research is the method of choice.
Quick Data Collection:
Quantitative research involves studying a group of people representing a larger population. Researchers use a survey or another quantitative research method to efficiently gather information from these participants, making the process of analyzing the data and identifying patterns faster and more manageable through the use of statistical analysis. This advantage makes quantitative research an attractive option for projects with time constraints.
Wider Scope of Data Analysis:
Quantitative research, thanks to its utilization of statistical methods, offers an extensive range of data collection and analysis. Researchers can delve into a broader spectrum of variables and relationships within the data, enabling a more thorough comprehension of the subject under investigation. This expanded scope is precious when dealing with complex research questions that require in-depth numerical analysis.
Eliminate Bias:
One of the significant advantages of quantitative research is its ability to eliminate bias. This research method leaves no room for personal comments or the biasing of results, as the findings are presented in numerical form. This objectivity makes the results fair and reliable in most cases, reducing the potential for researcher bias or subjectivity.
In summary, quantitative research involves collecting, analyzing, and presenting quantitative data using statistical analysis. It offers numerous advantages, including the collection of reliable and accurate data, quick data collection, a broader scope of data analysis, and the elimination of bias, making it a valuable approach in the field of research. When considering the benefits of quantitative research, it’s essential to recognize its strengths in contrast to qualitative methods and its role in collecting and analyzing numerical data for a more comprehensive understanding of research topics.
Best Practices to Conduct Quantitative Research
Here are some best practices for conducting quantitative research:

- Differentiate between quantitative and qualitative: Understand the difference between the two methodologies and apply the one that suits your needs best.
- Choose a suitable sample size: Ensure that you have a sample representative of your population and large enough to be statistically weighty.
- Keep your research goals clear and concise: Know your research goals before you begin data collection to ensure you collect the right amount and the right quantity of data.
- Keep the questions simple: Remember that you will be reaching out to a demographically wide audience. Pose simple questions for your respondents to understand easily.
Quantitative Research vs Qualitative Research
Quantitative research and qualitative research are two distinct approaches to conducting research, each with its own set of methods and objectives. Here’s a comparison of the two:

Quantitative Research
- Objective: The primary goal of quantitative research is to quantify and measure phenomena by collecting numerical data. It aims to test hypotheses, establish patterns, and generalize findings to a larger population.
- Data Collection: Quantitative research employs systematic and standardized approaches for data collection, including techniques like surveys, experiments, and observations that involve predefined variables. It is often collected from a large and representative sample.
- Data Analysis: Data is analyzed using statistical techniques, such as descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and mathematical modeling. Researchers use statistical tests to draw conclusions and make generalizations based on numerical data.
- Sample Size: Quantitative research often involves larger sample sizes to ensure statistical significance and generalizability.
- Results: The results are typically presented in tables, charts, and statistical summaries, making them highly structured and objective.
- Generalizability: Researchers intentionally structure quantitative research to generate outcomes that can be helpful to a larger population, and they frequently seek to establish causative connections.
- Emphasis on Objectivity: Researchers aim to minimize bias and subjectivity, focusing on replicable and objective findings.
Qualitative Research
- Objective: Qualitative research seeks to gain a deeper understanding of the underlying motivations, behaviors, and experiences of individuals or groups. It explores the context and meaning of phenomena.
- Data Collection: Qualitative research employs adaptable and open-ended techniques for data collection, including methods like interviews, focus groups, observations, and content analysis. It allows participants to express their perspectives in their own words.
- Data Analysis: Data is analyzed through thematic analysis, content analysis, or grounded theory. Researchers focus on identifying patterns, themes, and insights in the data.
- Sample Size: Qualitative research typically involves smaller sample sizes due to the in-depth nature of data collection and analysis.
- Results: Findings are presented in narrative form, often in the participants’ own words. Results are subjective, context-dependent, and provide rich, detailed descriptions.
- Generalizability: Qualitative research does not aim for broad generalizability but focuses on in-depth exploration within a specific context. It provides a detailed understanding of a particular group or situation.
- Emphasis on Subjectivity: Researchers acknowledge the role of subjectivity and the researcher’s influence on the Research Process . Participant perspectives and experiences are central to the findings.
Researchers choose between quantitative and qualitative research methods based on their research objectives and the nature of the research question. Each approach has its advantages and drawbacks, and the decision between them hinges on the particular research objectives and the data needed to address research inquiries effectively.
Quantitative research is a structured way of collecting and analyzing data from various sources. Its purpose is to quantify the problem and understand its extent, seeking results that someone can project to a larger population.
Companies that use quantitative rather than qualitative research typically aim to measure magnitudes and seek objectively interpreted statistical results. So if you want to obtain quantitative data that helps you define the structured cause-and-effect relationship between the research problem and the factors, you should opt for this type of research.
At QuestionPro , we have various Best Data Collection Tools and features to conduct investigations of this type. You can create questionnaires and distribute them through our various methods. We also have sample services or various questions to guarantee the success of your study and the quality of the collected data.
Quantitative research is a systematic and structured approach to studying phenomena that involves the collection of measurable data and the application of statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques for analysis.
Quantitative research is characterized by structured tools like surveys, substantial sample sizes, closed-ended questions, reliance on prior studies, data presented numerically, and the ability to generalize findings to the broader population.
The two main methods of quantitative research are Primary quantitative research methods, involving data collection directly from sources, and Secondary quantitative research methods, which utilize existing data for analysis.
1.Surveying to measure employee engagement with numerical rating scales. 2.Analyzing sales data to identify trends in product demand and market share. 4.Examining test scores to assess the impact of a new teaching method on student performance. 4.Using website analytics to track user behavior and conversion rates for an online store.
1.Differentiate between quantitative and qualitative approaches. 2.Choose a representative sample size. 3.Define clear research goals before data collection. 4.Use simple and easily understandable survey questions.
MORE LIKE THIS

NPS Survey Platform: Types, Tips, 11 Best Platforms & Tools
Apr 26, 2024
User Journey vs User Flow: Differences and Similarities

Best 7 Gap Analysis Tools to Empower Your Business
Apr 25, 2024

12 Best Employee Survey Tools for Organizational Excellence
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Marketing91
Quantitative Market Research
June 12, 2023 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Marketing
Quantitative research involves gathering numerical data, which is further analyzed via mathematical and statistical methods to measure variables. This type of research often requires a larger sample size due to the techniques used.
It involves conducting surveys on a large group of people to gather tangible data related to the “what” and “how much” aspects of the topic. Statistical techniques are then used to analyze the acquired information and make broad conclusions.
This data can be utilized for various applications such as –
- Understanding the size and scope of a market
- Analyzing customer opinion
- Making generalizations
- Predicting future trends
- Discovering patterns, etc
Table of Contents
What is Quantitative Market Research?
Quantitative market research is a method of collecting numerical data about various aspects of the market, including customers, competitors, products, and markets. It involves using techniques like surveys, questionnaires , interviews, polls, and focus groups to gather data that can be analyzed statistically.
For instance, a market research firm may conduct an online survey to gather quantitative data such as customer preferences, buying habits, or the potential size of a new market. The analysis of such data can provide valuable insights into customer behavior, market trends, and the potential success of new products.
For example – the Net Promoter Score question, “How likely are you to recommend us to a friend or colleague based on your overall experience with us?” has revolutionized the way businesses worldwide measure customer loyalty .
By asking a single question, companies can gather real data from actual customers to determine the impact of organic word-of-mouth referrals on their business growth, as well as identify areas where they may need to allocate more or fewer resources to paid advertising and promotions or improve product /service quality.
Why conduct Quantitative Market Research?
Quantitative Market Research provides organizations with valuable insights such as identifying target market segments , understanding customer needs and preferences, measuring brand recognition and loyalty, evaluating pricing sensitivity, and making overall decisions.
- To achieve a successful marketing campaign, the initial step involves research, whether it’s for launching a new product, positioning a sales pitch , or performing statistical analysis based on data.
- Online quantitative market research can provide insights into marketing activities such as website updates, social media management , and newsletters.
- Quantitative Market Research can answer important questions such as “Who is currently purchasing my products/services?”, “Why are others not buying my product?”, and “How can I reach my potential customers ?”
- To gather desired insights, the process of quantitative research begins with creating and designing surveys, followed by distributing them to the appropriate individuals. Once the surveys are completed, data collection and analysis can take place.
Four Main Types of Quantitative Research

1. Descriptive Research
This is a tool for evaluating the status of variables. It provides information on the circumstances and context that surround a variable or topic. It is commonly used for conducting comparisons, detailing sample characteristics, monitoring emerging trends, and verifying existing phenomena. Descriptive research involves collecting all the required data before forming a hypothesis.
Example –
For example, a descriptive research study can be used to identify the age and gender of customers purchasing a particular product.
2. Correlational Research
This method of research examines the connections between various subjects and variables to test a hypothesis or prediction. It only focuses on the relationships between set variables and does not include any unrelated variables in the investigation.
Correlational research and experimental research differ as variables are not manipulated in correlational research. A correlation can be positive or negative, and the strength of the relationship varies.
A correlational research study can be used to identify the relationship between customer spending and age.
3. Experimental Research
This type of research is quantitative and aims to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between variables. The method involves changing one or more independent variables, and then observing how it affects one or more dependent variables. Experimental research can be classified into two types: controlled experiments and quasi-experiments. Controlled experiments involve manual manipulation of all variables and monitoring their effects, while quasi-experiments test variables without manipulation.
Experimental research can be used to compare two different methods of delivery and measure their effectiveness
4. Survey Research
Understanding behavior often requires the use of survey research methods. This method is commonly employed in market research to familiarize a brand with the desires, needs, points of contention, and behaviors of its target market .
Researchers conduct surveys to ask specific questions to understand their target audience or get a detailed understanding of their opinions. Surveys can be performed in a single group or across multiple groups to facilitate comparison.
A survey research study can be used to understand the preferences of customers when it comes to new product features.
Common Techniques to Conduct a Quantitative Market Research
1) primary quantitative market research techniques.
Quantitative market research typically involves primary techniques, which refer to the most commonly used and widely recognized methods. Examples of these techniques include –
1.1) Surveys
Surveys are a commonly used method to gather data from consumers . They can be done through various channels like online, mail, or in-person. The surveys mostly consist of closed-ended questions that yield quantitative data efficiently. The survey creators provide predefined answer choices they consider suitable for each question. Surveys are important for gathering feedback from a larger audience beyond conventional means.
- Cross-sectional research survey – It is a way of studying a group of people at one specific time to collect data on certain variables. The research looks at a population or subset of people who are similar in all ways except for the variable being studied. This method is quantitative and aims to analyze the data collected.
- Longitudinal research survey s – It is a quantitative approach that involves collecting statistical data over years or decades on a particular target demographic or individuals.
1.2) One-on-one Interviews
In the past, interviews for collecting quantitative data were typically carried out in person, but now they can be conducted over the phone or through online means. Interviews provide marketers with a great chance to collect in-depth data from the participants.
Online quantitative interviews are highly structured and serve as a crucial tool for gathering information. These interviews typically consist of two major sections –
- Face-to-Face Interviews – To gather comprehensive information, an interviewer can create a set of significant questions in addition to those already included in the survey. This will encourage interviewees to provide in-depth insights on the discussed topic.
- Online/Telephonic Interviews – Online interviews have become a common practice for conducting quantitative interviews, just like telephone-based interviews. Platforms such as Skype or Zoom enable communication between interviewers and interviewees regardless of their location or time zone, making it a more accessible option.
1.3) Computer-Assisted Personal Interview
This technique involves the interviewer inputting collected data directly into a laptop or similar device during a one-on-one interview. This reduces processing time and eliminates the need for physical questionnaires as answers can be entered directly into the device.
2) Secondary Quantitative Market Research Techniques
Using secondary techniques in conducting quantitative market research can help to confirm a hypothesis or make deductions from both primary and empirical data.
It utilizes historical data to support the statistical observations made from primary data and is categorized as an observational form of market research.
Secondary research methods typically involve gathering data from sources such as the Internet, archives, libraries, schools & organizational reports, etc. It is important to note that online data specifically refers to data collected from the internet.
What are the Characteristics of Quantitative Market Research
- Quantitative market research aims to confirm hypotheses related to numerical aspects of phenomena.
- The data that has been gathered consists only of numerical values, allowing statistical formulas to be applied to derive quantified and actionable insights.
- The data has been collected in a structured manner using various methods like questionnaires and surveys.
- The study has predetermined questions with structured options for responses. The structure is planned beforehand.
- The questions are not asking for open-ended responses, which limits the possibility of ambiguity.
When to Use Quantitative Research and How to Analyze It?
When answering “what” questions about customers’ most important features, preferred products, or services, using quantitative research is useful. It’s important to consider which quantitative research method is best for your business, taking into account factors such as your strategy , marketing, and other facets.
Quantitative research aims to measure and understand the prevalence of a phenomenon such as a problem or inadequacy by observing a significant portion of a population. Use this type of research when you require a higher-level overview or a broader perspective. It is capable of uncovering connections between different factors, identifying correlations, and establishing cause-and-effect relationships.
The findings of researchers can be used to make predictions, which is especially helpful in market research endeavors such as launching new products, brainstorming innovative ideas , or expanding your customer base .
Before analyzing this research, it is important to make it measurable and unbiased. Researchers should establish specific scales and units of measurement for their studies, and present their findings in a clear and easy-to-understand way. After collecting the numerical data, input it into a spreadsheet. Then, arrange the data by creating graphs, charts, and tables. Lastly, conclude the study based on the data. You can also utilize advanced analytics for further investigation.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Quantitative Research
Some of the upsides and downsides of using quantitative research data are –
- Larger sample pools – The results are more accurate when there are more respondents in the group.
- Highly structured – The methods used to gather numerical data such as surveys, questionnaires, and other data recording tools ensure effective structuring of data.
- Focused – The study’s design is established before its commencement.
- Theory -based – Conducting research is a way to test a theory and get evidence to support or prove it.
- Designed to Be Analyzed – Non-textual forms such as tables, charts, and figures are used to present numbers and statistics for easier analysis.
- Objective – The research aims to eliminate bias by keeping the data separate and only collecting objective responses.
Disadvantages
- Focuses solely on numbers – Researchers may overlook other data and larger themes if they solely rely on this approach, which can be limiting.
- Superficial Representations – The tool only displays numerical data and is not capable of explaining intricate ideas like emotions and perspectives.
- Several factors can invalidate results – To collect and analyze data, you must create a hypothesis and a model. It’s important to be careful to avoid mistakes that can cause bias and inaccurate results.
- Erred Structure – Biases can easily become dominant if there is missing data or unclear measurements.
Different between Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Businesses use quantitative and qualitative market research methods to collect data for market research. Qualitative research data is collected through interviews, focus groups , observations, and surveys, and it gives insight into a specific issue or problem by examining the experiences, opinions, and behaviors of a sample of target customers.
On the contrary, quantitative market research data is utilized to gauge trends and events including web traffic or sales figures. This sort of research is more organized and greatly depends on numerical figures. It supports companies in comprehending customer behavior, inclinations, and expenditure habits by analyzing vast amounts of data.
What is a quantitative research question?
Quantitative market research questions can help you understand the specifics of a subject, such as what, how, when, and where. By analyzing quantitative data, you can identify trends and patterns, and establish averages to effectively tackle business problems.
What are the Quantitative Market Research Questions?
Quantitative research seeks the answers of following questions
- What is the size of the target market?
- How have the requirements of a particular market evolved?
- What is the size of your target audience in terms of the number of people?
- What is the level of interest in purchasing your product?
- Does a market exist for your products?
- On which online platforms does the target audience spend the majority of their time?
- How often do people purchase your product or service?
- What is the awareness level of your brand, product, or service among the public?
- Who are the customers that most frequently use your services?
- What is the average duration of time that people spend on your website?
- What is the percentage of satisfied customers with your product or service?
Statistical Analysis Techniques Used in Quantitative Market Research

Statistical analysis is used in quantitative market research to process response data and gather clear insights. These insights help researchers conclude the research findings. Quantitative market research offers the following statistical analysis techniques –
Conjoint Analysis
The purpose of conjoint analysis is to determine the worth of different factors, like price, characteristics, and advantages, in influencing customers to buy a specific product or service.
TURF Analysis
TURF (Total Unduplicated Reach and Frequency) analysis helps organizations understand which combination of products or services will appeal to the highest number of customers.
GAP Analysis
The purpose of GAP analysis is to determine the gap between the expected and actual performance of a product or service. By analyzing the GAP, companies can identify areas for improvement and enhance their features to minimize the gap.
MaxDiff Analysis
MaxDiff is a choice model that is sometimes referred to as “best-worst” scaling. It is used to determine customer preferences for various features, such as product features, brand images , activities associated with branding , and so on.
Cross Tabulation
Cross-tabulation is a method of statistical analysis that presents a concise table format to compare two or more categories for easy data analysis .
Frequently Asked Questions
What is quantitative market research.
Quantitative market research uses surveys and questionnaires to gather information about the target market. The data collected is then converted into numerical values for easier analysis.
What types of questions do quantitative research answer?
Quantitative research is used to measure and identify patterns, averages, and predictions and quantify opinions, attitudes , or behaviors. Its main focus is on defining “what” and “how much.”
What are the four main types of quantitative research?
Quantitative research can be categorized into four main types: survey research, correlational research, descriptive research, and experimental research.
What using a large sample is the important size in quantitative research?
Having a small sample size may result in unreliable outcomes. On the other hand, if the sample size (referring to the number of individuals participating in the study) is bigger, then there is a higher chance of obtaining statistical significance and accurate findings.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Market research
Related posts:
- 11 Types Of Quantitative Research options that exist for Market Researchers
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research: What is the Difference?
- Importance of Quantitative Research
- What are the Characteristics of Quantitative Research?
- What is Research Design? Type of Research Designs
- How to Write Research Proposal? Research Proposal Format
- 7 Key Differences between Research Method and Research Methodology
- Qualitative Research: Meaning, and Features of Qualitative Research
- Research Ethics – Importance and Principles of Ethics in Research
- What are the Types of Market Research?
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors
- Privacy Policy

Home » Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Table of Contents

Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a type of research that collects and analyzes numerical data to test hypotheses and answer research questions . This research typically involves a large sample size and uses statistical analysis to make inferences about a population based on the data collected. It often involves the use of surveys, experiments, or other structured data collection methods to gather quantitative data.
Quantitative Research Methods

Quantitative Research Methods are as follows:
Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design is used to describe the characteristics of a population or phenomenon being studied. This research method is used to answer the questions of what, where, when, and how. Descriptive research designs use a variety of methods such as observation, case studies, and surveys to collect data. The data is then analyzed using statistical tools to identify patterns and relationships.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to investigate the relationship between two or more variables. Researchers use correlational research to determine whether a relationship exists between variables and to what extent they are related. This research method involves collecting data from a sample and analyzing it using statistical tools such as correlation coefficients.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This research method is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks full control over the independent variable. Researchers use quasi-experimental research designs when it is not feasible or ethical to manipulate the independent variable.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This research method involves manipulating the independent variable and observing the effects on the dependent variable. Researchers use experimental research designs to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships.
Survey Research
Survey research involves collecting data from a sample of individuals using a standardized questionnaire. This research method is used to gather information on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors of individuals. Researchers use survey research to collect data quickly and efficiently from a large sample size. Survey research can be conducted through various methods such as online, phone, mail, or in-person interviews.
Quantitative Research Analysis Methods
Here are some commonly used quantitative research analysis methods:
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis is the most common quantitative research analysis method. It involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis can be used to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze the relationship between one dependent variable and one or more independent variables. Researchers use regression analysis to identify and quantify the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is a statistical technique used to identify underlying factors that explain the correlations among a set of variables. Researchers use factor analysis to reduce a large number of variables to a smaller set of factors that capture the most important information.
Structural Equation Modeling
Structural equation modeling is a statistical technique used to test complex relationships between variables. It involves specifying a model that includes both observed and unobserved variables, and then using statistical methods to test the fit of the model to the data.
Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze data that is collected over time. It involves identifying patterns and trends in the data, as well as any seasonal or cyclical variations.
Multilevel Modeling
Multilevel modeling is a statistical technique used to analyze data that is nested within multiple levels. For example, researchers might use multilevel modeling to analyze data that is collected from individuals who are nested within groups, such as students nested within schools.
Applications of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research has many applications across a wide range of fields. Here are some common examples:
- Market Research : Quantitative research is used extensively in market research to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform marketing strategies, product development, and pricing decisions.
- Health Research: Quantitative research is used in health research to study the effectiveness of medical treatments, identify risk factors for diseases, and track health outcomes over time. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze data from clinical trials, surveys, and other sources to inform medical practice and policy.
- Social Science Research: Quantitative research is used in social science research to study human behavior, attitudes, and social structures. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform social policies, educational programs, and community interventions.
- Education Research: Quantitative research is used in education research to study the effectiveness of teaching methods, assess student learning outcomes, and identify factors that influence student success. Researchers use experimental and quasi-experimental designs, as well as surveys and other quantitative methods, to collect and analyze data.
- Environmental Research: Quantitative research is used in environmental research to study the impact of human activities on the environment, assess the effectiveness of conservation strategies, and identify ways to reduce environmental risks. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze data from field studies, experiments, and other sources.
Characteristics of Quantitative Research
Here are some key characteristics of quantitative research:
- Numerical data : Quantitative research involves collecting numerical data through standardized methods such as surveys, experiments, and observational studies. This data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns and relationships.
- Large sample size: Quantitative research often involves collecting data from a large sample of individuals or groups in order to increase the reliability and generalizability of the findings.
- Objective approach: Quantitative research aims to be objective and impartial in its approach, focusing on the collection and analysis of data rather than personal beliefs, opinions, or experiences.
- Control over variables: Quantitative research often involves manipulating variables to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships. Researchers aim to control for extraneous variables that may impact the results.
- Replicable : Quantitative research aims to be replicable, meaning that other researchers should be able to conduct similar studies and obtain similar results using the same methods.
- Statistical analysis: Quantitative research involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis allows researchers to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories.
- Generalizability: Quantitative research aims to produce findings that can be generalized to larger populations beyond the specific sample studied. This is achieved through the use of random sampling methods and statistical inference.
Examples of Quantitative Research
Here are some examples of quantitative research in different fields:
- Market Research: A company conducts a survey of 1000 consumers to determine their brand awareness and preferences. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify trends and patterns that can inform marketing strategies.
- Health Research : A researcher conducts a randomized controlled trial to test the effectiveness of a new drug for treating a particular medical condition. The study involves collecting data from a large sample of patients and analyzing the results using statistical methods.
- Social Science Research : A sociologist conducts a survey of 500 people to study attitudes toward immigration in a particular country. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify factors that influence these attitudes.
- Education Research: A researcher conducts an experiment to compare the effectiveness of two different teaching methods for improving student learning outcomes. The study involves randomly assigning students to different groups and collecting data on their performance on standardized tests.
- Environmental Research : A team of researchers conduct a study to investigate the impact of climate change on the distribution and abundance of a particular species of plant or animal. The study involves collecting data on environmental factors and population sizes over time and analyzing the results using statistical methods.
- Psychology : A researcher conducts a survey of 500 college students to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify correlations and potential causal relationships.
- Political Science: A team of researchers conducts a study to investigate voter behavior during an election. They use survey methods to collect data on voting patterns, demographics, and political attitudes, and analyze the results using statistical methods.
How to Conduct Quantitative Research
Here is a general overview of how to conduct quantitative research:
- Develop a research question: The first step in conducting quantitative research is to develop a clear and specific research question. This question should be based on a gap in existing knowledge, and should be answerable using quantitative methods.
- Develop a research design: Once you have a research question, you will need to develop a research design. This involves deciding on the appropriate methods to collect data, such as surveys, experiments, or observational studies. You will also need to determine the appropriate sample size, data collection instruments, and data analysis techniques.
- Collect data: The next step is to collect data. This may involve administering surveys or questionnaires, conducting experiments, or gathering data from existing sources. It is important to use standardized methods to ensure that the data is reliable and valid.
- Analyze data : Once the data has been collected, it is time to analyze it. This involves using statistical methods to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables. Common statistical techniques include correlation analysis, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing.
- Interpret results: After analyzing the data, you will need to interpret the results. This involves identifying the key findings, determining their significance, and drawing conclusions based on the data.
- Communicate findings: Finally, you will need to communicate your findings. This may involve writing a research report, presenting at a conference, or publishing in a peer-reviewed journal. It is important to clearly communicate the research question, methods, results, and conclusions to ensure that others can understand and replicate your research.
When to use Quantitative Research
Here are some situations when quantitative research can be appropriate:
- To test a hypothesis: Quantitative research is often used to test a hypothesis or a theory. It involves collecting numerical data and using statistical analysis to determine if the data supports or refutes the hypothesis.
- To generalize findings: If you want to generalize the findings of your study to a larger population, quantitative research can be useful. This is because it allows you to collect numerical data from a representative sample of the population and use statistical analysis to make inferences about the population as a whole.
- To measure relationships between variables: If you want to measure the relationship between two or more variables, such as the relationship between age and income, or between education level and job satisfaction, quantitative research can be useful. It allows you to collect numerical data on both variables and use statistical analysis to determine the strength and direction of the relationship.
- To identify patterns or trends: Quantitative research can be useful for identifying patterns or trends in data. For example, you can use quantitative research to identify trends in consumer behavior or to identify patterns in stock market data.
- To quantify attitudes or opinions : If you want to measure attitudes or opinions on a particular topic, quantitative research can be useful. It allows you to collect numerical data using surveys or questionnaires and analyze the data using statistical methods to determine the prevalence of certain attitudes or opinions.
Purpose of Quantitative Research
The purpose of quantitative research is to systematically investigate and measure the relationships between variables or phenomena using numerical data and statistical analysis. The main objectives of quantitative research include:
- Description : To provide a detailed and accurate description of a particular phenomenon or population.
- Explanation : To explain the reasons for the occurrence of a particular phenomenon, such as identifying the factors that influence a behavior or attitude.
- Prediction : To predict future trends or behaviors based on past patterns and relationships between variables.
- Control : To identify the best strategies for controlling or influencing a particular outcome or behavior.
Quantitative research is used in many different fields, including social sciences, business, engineering, and health sciences. It can be used to investigate a wide range of phenomena, from human behavior and attitudes to physical and biological processes. The purpose of quantitative research is to provide reliable and valid data that can be used to inform decision-making and improve understanding of the world around us.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
There are several advantages of quantitative research, including:
- Objectivity : Quantitative research is based on objective data and statistical analysis, which reduces the potential for bias or subjectivity in the research process.
- Reproducibility : Because quantitative research involves standardized methods and measurements, it is more likely to be reproducible and reliable.
- Generalizability : Quantitative research allows for generalizations to be made about a population based on a representative sample, which can inform decision-making and policy development.
- Precision : Quantitative research allows for precise measurement and analysis of data, which can provide a more accurate understanding of phenomena and relationships between variables.
- Efficiency : Quantitative research can be conducted relatively quickly and efficiently, especially when compared to qualitative research, which may involve lengthy data collection and analysis.
- Large sample sizes : Quantitative research can accommodate large sample sizes, which can increase the representativeness and generalizability of the results.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
There are several limitations of quantitative research, including:
- Limited understanding of context: Quantitative research typically focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, which may not provide a comprehensive understanding of the context or underlying factors that influence a phenomenon.
- Simplification of complex phenomena: Quantitative research often involves simplifying complex phenomena into measurable variables, which may not capture the full complexity of the phenomenon being studied.
- Potential for researcher bias: Although quantitative research aims to be objective, there is still the potential for researcher bias in areas such as sampling, data collection, and data analysis.
- Limited ability to explore new ideas: Quantitative research is often based on pre-determined research questions and hypotheses, which may limit the ability to explore new ideas or unexpected findings.
- Limited ability to capture subjective experiences : Quantitative research is typically focused on objective data and may not capture the subjective experiences of individuals or groups being studied.
- Ethical concerns : Quantitative research may raise ethical concerns, such as invasion of privacy or the potential for harm to participants.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
What is Marketing Research? Examples and Best Practices
12 min read

Marketing research is essentially a method utilized by companies to collect valuable information regarding their target market. Through the common practice of conducting market research, companies gather essential information that enables them to make informed decisions and develop products that resonate with consumers. It encompasses the gathering, analysis, and interpretation of data, which aids in identifying consumer demands, anticipating market trends, and staying ahead of the competition.
Exploratory research is one of the initial steps in the marketing research process. It helps businesses gain broad insights when specific information is unknown. If you are seeking insight into how marketing research can influence the trajectory of your SaaS, then you have come to the right place!
- Market research is a systematic and objective process crucial for understanding target markets, refining business strategies, and informing decisions, which includes collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data on customers, competitors, and the industry.
- Primary market research gathers specific data directly from the target audience using tools like surveys and focus groups, while secondary market research utilizes existing data from various sources to provide broader market insights.
- Effective market research combines both qualitative methods, which explore consumer motivations, and quantitative methods, which provide measurable statistics, to create comprehensive insights that guide business strategy and decision-making.
Try Userpilot and Take Your Product Marketing to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

Defining marketing research

Launching a product without knowing what your target audience wants is like walking in the dark. Market research lights the way, helping you collect, analyze, and understand information about your target market. This allows you to refine your business strategies and make decisions based on solid evidence.
Gone are the days when just intuition or subjective judgment was enough. Objective insights from market research help avoid costly mistakes and meet consumer needs by identifying trends and changes in the market. This is crucial for assessing a product’s potential success, optimizing marketing strategies, and preparing for market shifts.
Market research is a systematic approach that provides essential information, helping businesses navigate the complexities of the commercial world. Partnering with market research companies can offer additional benefits, leveraging their expertise in understanding market demands, trends, market size, economic indicators, location, market saturation, and pricing. Whether starting a new business, developing products, or updating marketing plans, understanding how to conduct effective market research is key to success.
To conduct market research effectively, businesses must determine study goals, identify target consumers, collect and analyze data, and use the findings to make informed decisions. This process is vital for evaluating past performance, measuring changes over time, and addressing specific business needs. It guides businesses in product development, marketing strategies, and overall decision-making, ensuring a better ROI and providing an eye-opening view of the market through various research methods, whether conducted in-house or outsourced.
The purpose of marketing research
Conducting marketing research is more than just gathering data; it’s about turning that data into actionable insights to refine your business strategies. This process helps you understand what motivates your customers, enabling you to tailor your products and services to minimize risks from the start. Importantly, market research plays a pivotal role in measuring and enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are critical for understanding key demographics, improving user experience, designing better products, and driving customer retention. Customer satisfaction is measured as a key outcome, directly linked to the success of marketing strategies and business activities.
For SaaS product managers, market research, including competitive analysis, is crucial. It evaluates past strategies and gauges the potential success of new offerings. This research provides essential insights into brand strength, consumer behavior, and market position, which are vital for teams focused on sales, marketing, and product development.
A key aspect of market research is analyzing customer attitudes and usage. This analysis offers detailed insights into what customers want, the choices they make, and the challenges they face. It helps identify opportunities in the market and aids in formulating effective strategies for market entry.
Overall, market research equips SaaS entrepreneurs with the knowledge to meet their target audience’s needs effectively, guiding product adjustments and innovations based on informed decisions.
Key components of market research
Conducting market research is analogous to preparing a cake, requiring precise ingredients in specific quantities to achieve the intended outcome. Within this realm, necessary components consist of primary and secondary data gathering, thorough analysis, and insightful interpretation.
Primary research techniques such as exploratory studies, product evolution inquiries, estimations of market dimensions and shares, and consumer behavior examinations play a crucial role in collecting targeted information that can be directly applied. These methods afford a deeper understanding of your target demographic, allowing for customized strategy development.
In contrast, secondary research enriches the specificity of primary findings by adding wider context. It taps into external resources encompassing works from other investigators, sector-specific reports, and demographics data, which provide an expansive yet less particularized landscape view of the marketplace.
The subsequent phase involves meticulous analysis of collated data offering unbiased perspectives critical for identifying deficiencies while recognizing emerging patterns. Technological progress now facilitates examination efforts on both structured and unstructured datasets effectively addressing large-scale analytical complexities.
Ultimately, it’s through expert-led interpretation that value transcends raw figures, yielding strategies grounded in deep comprehension. Akin to decoding recipes using selected ingredients—this interpretative step enables crafting optimal business maneuvers just as one would bake their ideal confectionery creation utilizing proper culinary guidance.
Types of market research: primary and secondary
Now that you know the importance of clear research objectives, let’s explore the different types of market research and the techniques available to achieve these goals. Market research methods can be divided into two main categories: primary research and secondary research . The choice between these depends on factors like your budget, time constraints, and whether you need exploratory data or definitive answers.
Primary research involves collecting new data directly from sources. This process is like mining for precious metals, as it requires using various methods to gather fresh insights.
- Surveys (here – in-app survey templates from Userpilot ).
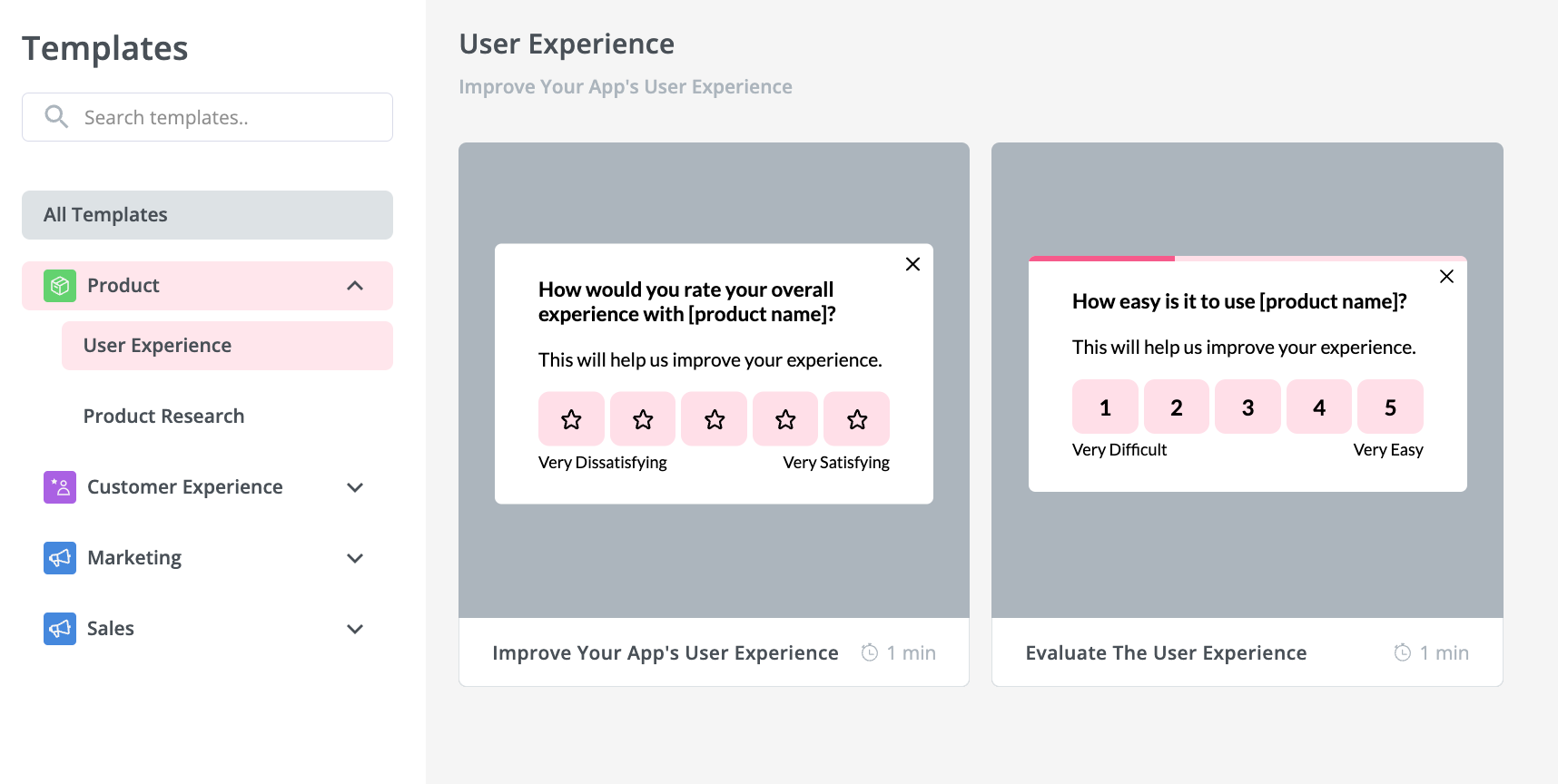
- Interviews.
- Focus groups.
- Product trials.
This approach gives you first-hand insight into your target audience.
Conversely, secondary research uses already established datasets of primary data – which can add depth and reinforcement to your firsthand findings.
Conducting your own market research using primary research tools can be a cost-effective strategy, allowing businesses to gather valuable insights directly and tailor their research to specific needs.
Let’s look a bit deeper into them now.
What is primary market research?
Market research uses primary market research as an essential tool. This involves collecting new data directly from your target audience using various methods, such as surveys , focus groups, and interviews.
Each method has its benefits. For example, observational studies allow you to see how consumers interact with your product.
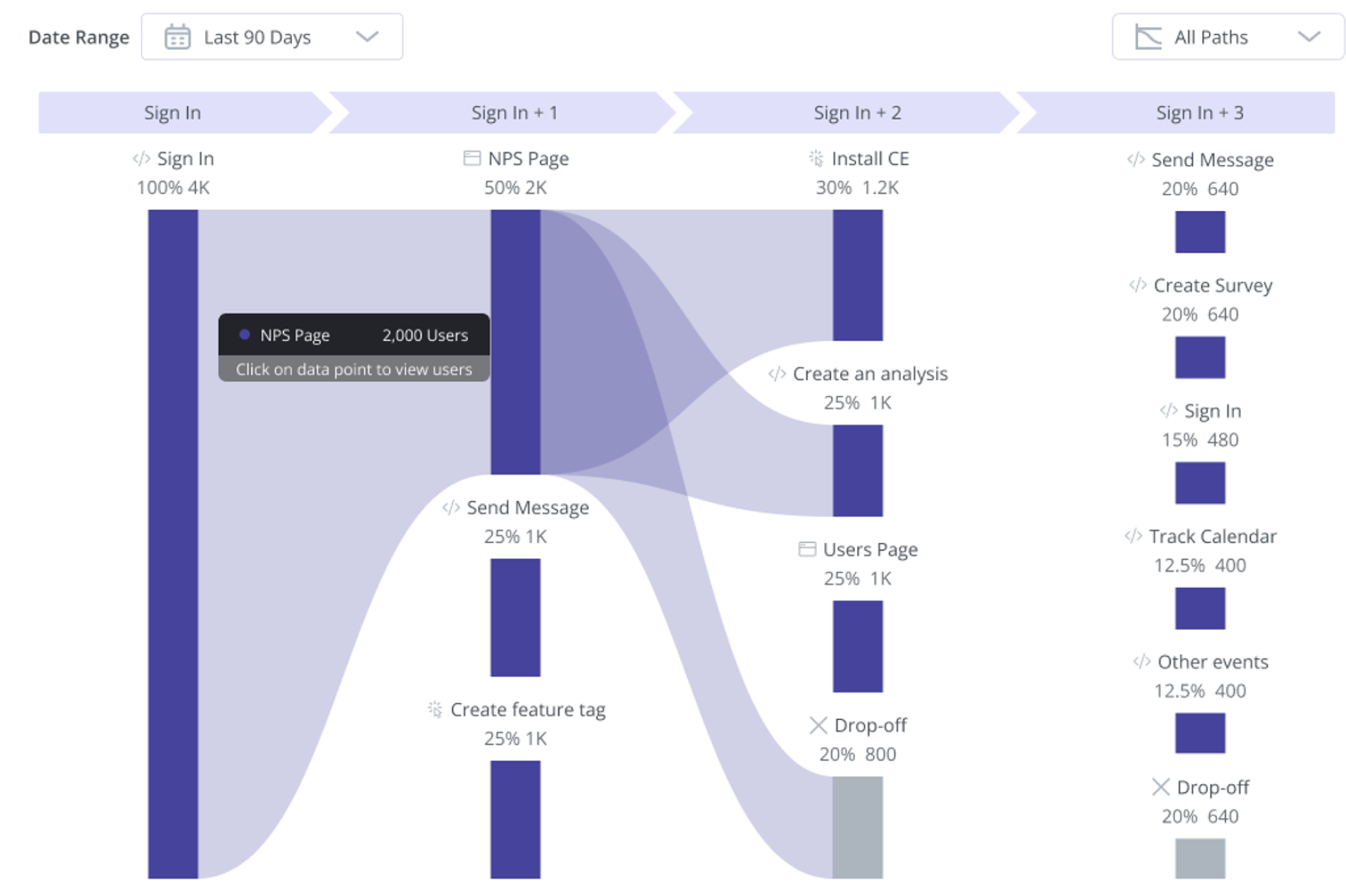
There are many ways to conduct primary research.
Focus Groups : Hold discussions with small groups of 5 to 10 people from your target audience. These discussions can provide valuable feedback on products, perceptions of your company’s brand name, or opinions on competitors. Additionally, these discussions can help understand the characteristics, challenges, and buying habits of target customers, optimizing brand strategy.
Interviews : Have one-on-one conversations to gather detailed information from individuals in your target audience.
Surveys : These are a common tool in primary market research and can be used instead of focus groups to understand consumer attitudes. Surveys use structured questions and can reach a broad audience efficiently.
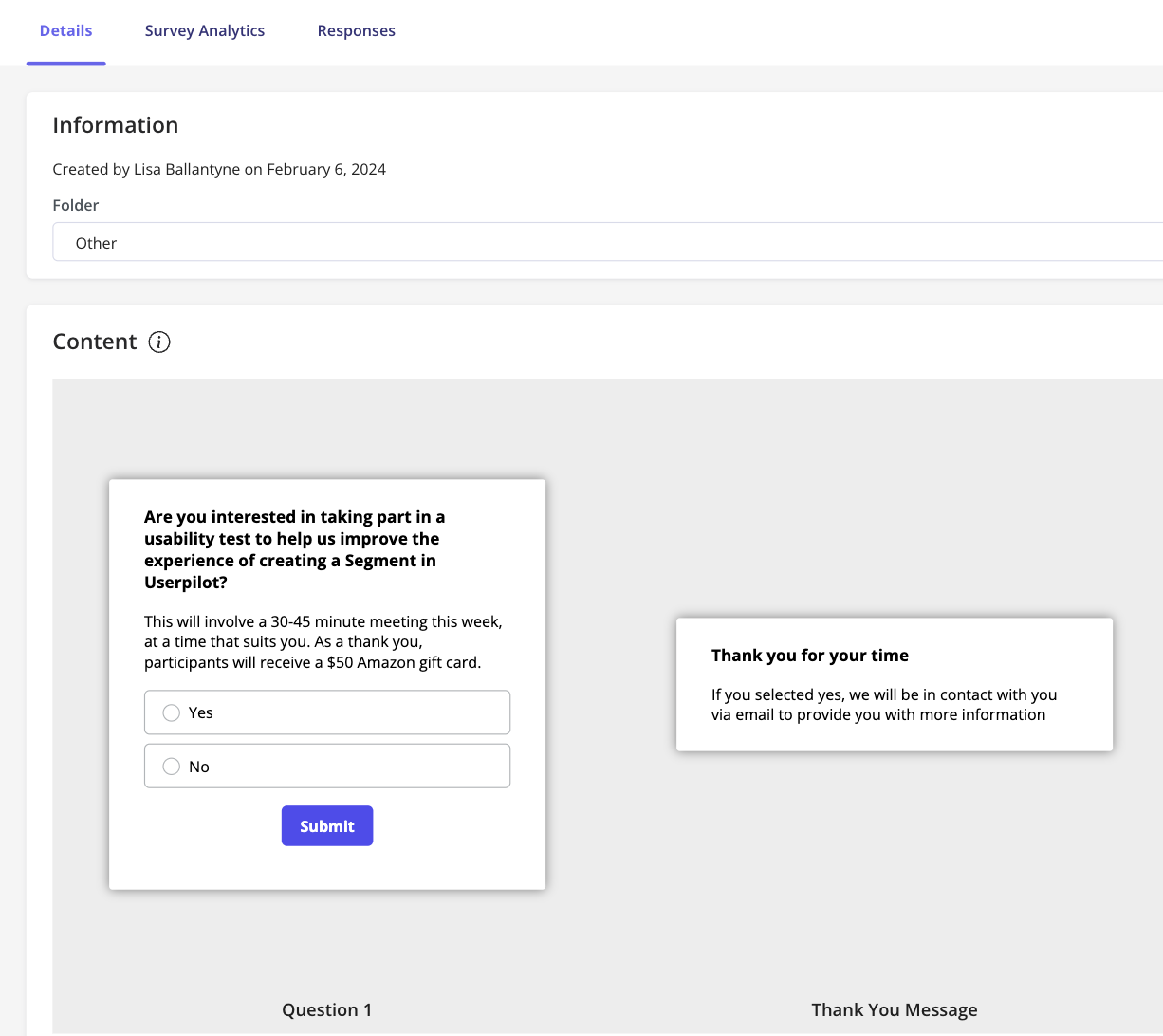
Navigating secondary market research
While marketing research using primary methods is like discovering precious metals, secondary market research technique is like using a treasure map. This approach uses data collected by others from various sources, providing a broad industry view. These sources include market analyses from agencies like Statista, historical data such as census records, and academic studies.
Secondary research provides the basic knowledge necessary for conducting primary market research goals but may lack detail on specific business questions and could also be accessible to competitors.
To make the most of secondary market research, it’s important to analyze summarized data to identify trends, rely on reputable sources for accurate data, and remain unbiased in data collection methods.
The effectiveness of secondary research depends significantly on how well the data is interpreted, ensuring that this information complements the insights from primary research.
Qualitative vs quantitative research
Market research employs both qualitative and quantitative methods, offering distinct insights that complement each other. Qualitative research aims to understand consumer behaviors and motivations through detailed analysis, while quantitative research collects measurable data for statistical analysis.
The selection of qualitative or quantitative methods should align with your research goals. If you need to uncover initial insights or explore deep consumer motivations, qualitative techniques like surveys or interviews are ideal.
On the other hand, if you need data that can be measured and analyzed for reliability, quantitative methods are more suitable.
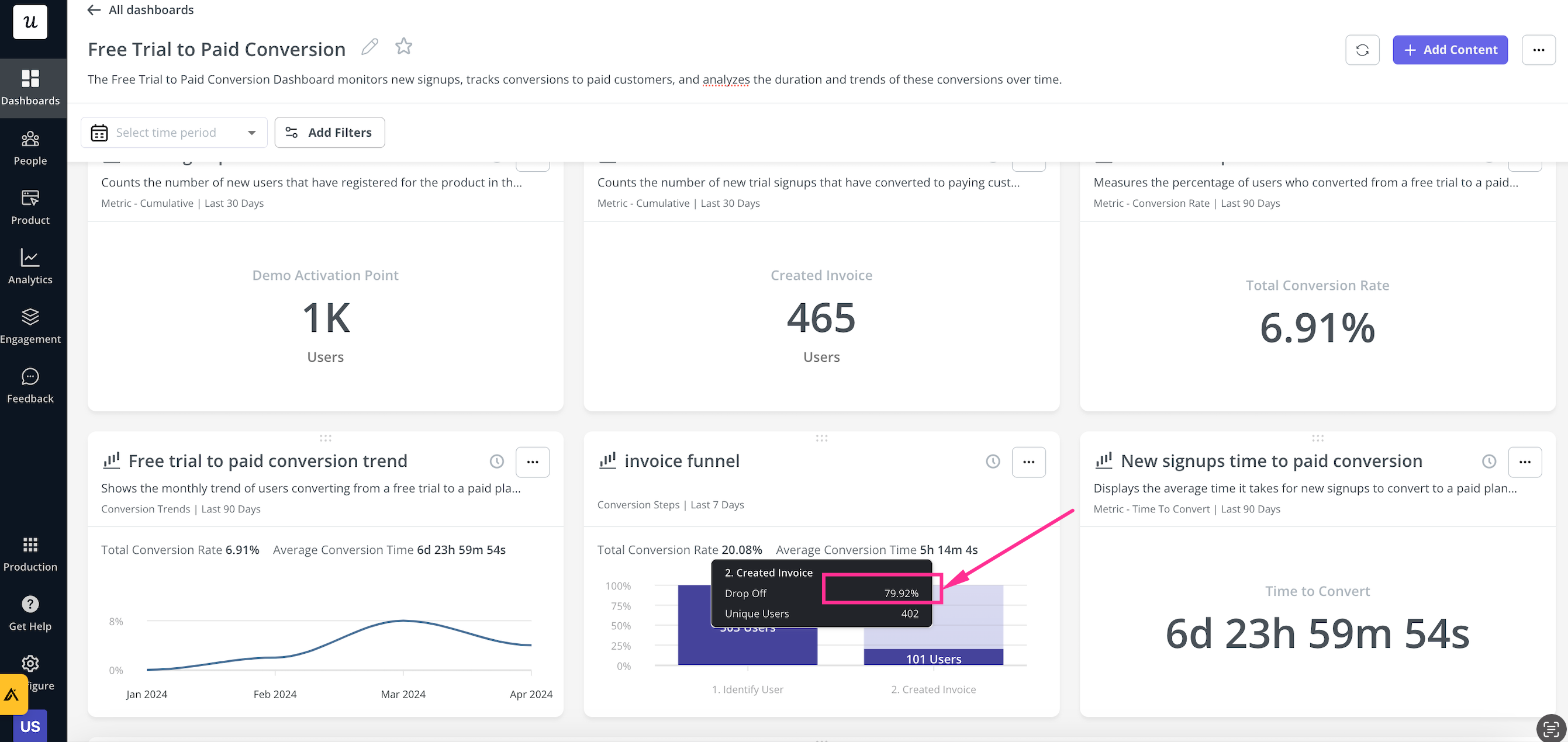
However, these approaches don’t have to be used separately. Combining qualitative and quantitative methods in mixed-method studies allows you to capture both detailed exploratory responses and concrete numerical data. This integration offers a comprehensive view of the market, leveraging the strengths of both approaches to provide a fuller understanding of market conditions.
Implementing market research tools: Userpilot’s role
Similar to how a compass is essential for navigation at sea, businesses need appropriate instruments to carry out effective market research. Userpilot’s suite of product analytics and in-app engagement tools are critical components for this purpose.
Acting as a Buyer Persona Research instrument, Userpilot’s product analytics provide key quantitative research capabilities. This helps clearly define and comprehend the attributes and behaviors of potential customers, providing you with insights into your ICP (Ideal Customer Persona), user preferences, and product-market fit.
Beyond product analytics, Userpilot offers robust in-app engagement features such as modals and surveys that support real time collection of market research information. These interactive features work synergistically with the analytical tools to enable companies to gather detailed data and feedback crucial for informed business decision-making.
Marketing research process: Step-by-step guide
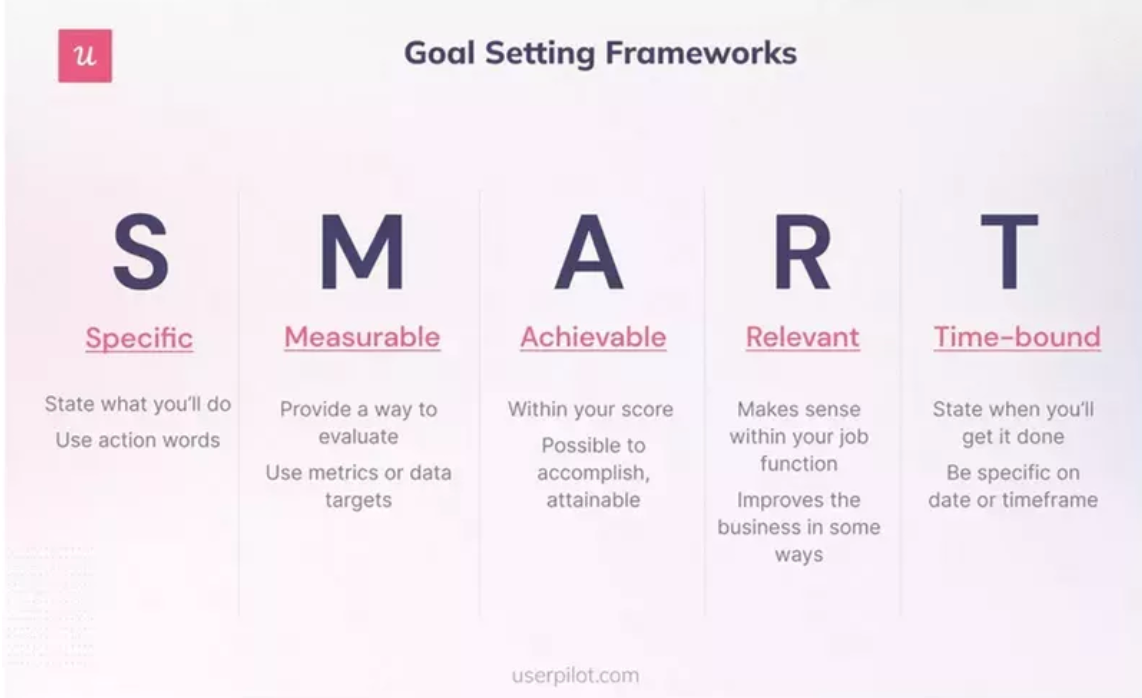
Marketing research conists of several critical stages:
- Defining precise goals.
- Delving into the knowledge of your target demographic.
- Collecting and scrutinizing data.
- Revealing insights that can be translated into tangible actions.
Following these steps allows you to gather critical information that guides business decisions.
An effective research strategy is crucial and involves:
- Properly allocating funds.
- Formulating testable hypotheses.
- Choosing appropriate methods for the study.
- Determining the number of study participants.
- Considering external variables.
A well-planned strategy ensures that your market research is focused, efficient, and produces useful outcomes.
After collecting data, the next step is to analyze it. This involves comparing the data to your initial questions to draw conclusions relevant to your business strategies.
Userpilot makes your data analysis easier by providing handy analytics dashboards for key user metrics such as activation, engagement, core feature adoption, and retention out of the box:
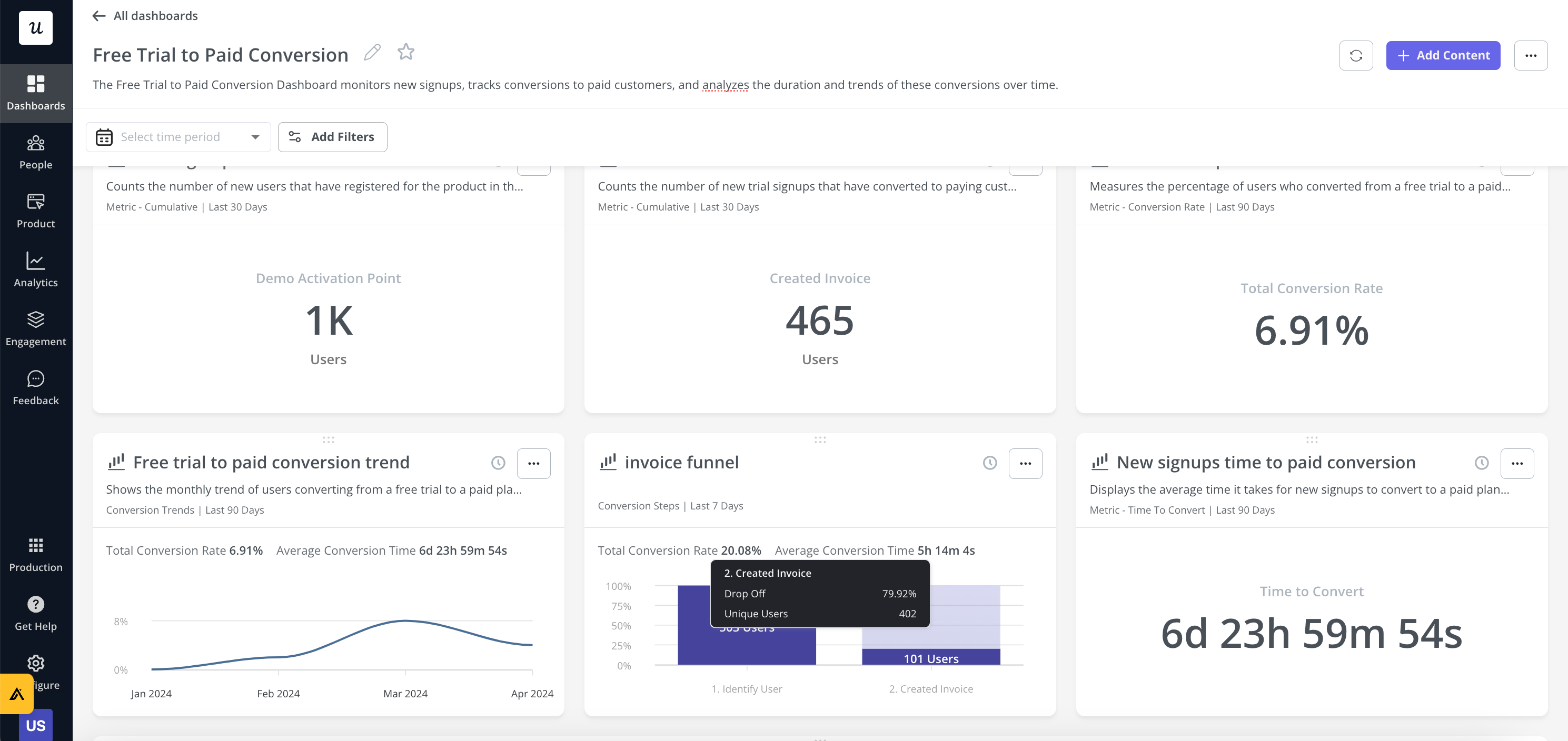
Finally, you report the findings and the process, providing recommendations based on the evidence. This is like solving a puzzle: each piece helps to complete the overall picture.
Challenges and best practices in market research
Delving into market research comes with its own set of hurdles. Those conducting the research must deliver more profound insights within increasingly shorter timespans, and they need to cultivate strategic, continuous research methods to stay abreast of an ever-changing business landscape.
Ensuring high-quality data can be demanding due to issues such as disjointed tools or insufficient analytical expertise. New solutions like Userpilot are surfacing that make these obstacles less daunting by offering accessible and user-friendly options. Maintaining clear lines of communication with your market research team is crucial for achieving both punctuality and quality in outcomes.
The advantages of engaging in marketing research cannot be overstated.
Real-life examples of successful market research
Real-life examples of market research in the SaaS industry often showcase innovative approaches to understanding customer needs and product-market fit.
For instance, Slack, the communication platform, utilized extensive market research to identify gaps in communication tools and understand the workflows of teams. This led to the development of features that seamlessly integrated with other tools and catered to the needs of various team sizes and structures.
Another example is HubSpot, which conducted market research to understand the pain points of small to medium-sized businesses in managing customer relationships. The insights gained helped shape their all-in-one inbound marketing, sales, and service platform, which has become integral to their users’ daily operations. These examples demonstrate how SaaS companies can employ market research to inform product development, improve user experience, and strategically position themselves in a competitive market.
Choosing the right market research tools
For B2B SaaS product managers aiming to do market research, having the right set of tools can make a significant difference. Here’s a list of valuable SaaS tools that can be leveraged for effective market research:
- Userpilot : A comprehensive Product Growth Platform offering in-depth product analytics, a code-free in-app experience builder, bespoke in-app survey capabilities, and robust integration options with platforms like Salesforce and Hubspot. This tool is particularly useful for understanding user behavior, enhancing user engagement, and gathering targeted feedback.
- Qualtrics : Known for its powerful survey tools, Qualtrics helps businesses gather and analyze customer feedback effectively. Its advanced analytics features are ideal for testing market hypotheses and understanding customer sentiments.
- SurveyMonkey : A versatile tool that enables product managers to create, send, and analyze surveys quickly and easily. SurveyMonkey is suitable for gauging customer satisfaction and collecting feedback on potential new features.
- Mixpanel : Specializes in user behavior analytics, offering detailed insights into how users interact with your product. This is essential for identifying patterns and optimizing product features.
- Hotjar : Combines analytics and feedback tools to give teams insights into user behavior and preferences. Hotjar’s heatmaps and session recordings are invaluable for understanding the user experience on a deeper level.
- Tableau : A leading platform for business intelligence and data visualization, Tableau allows product managers to create comprehensive visual reports that can inform strategic decisions based on user data analysis.
Each of these tools provides unique functionalities that can assist SaaS product managers in conducting thorough market research, thereby ensuring that their products are perfectly aligned with user needs and market demands.
Measuring the impact of market research
The pivotal challenge for market research lies in demonstrating its return on investment (ROI) and overall influence on corporate success sufficiently enough to justify regular financial commitment from company leaders. The worth attributed to a market research firm hinges not only on their ability to deliver relevant and high-caliber information, but also on their pricing structures and their contribution towards propelling organizational growth.
To gauge how effectively business choices made based on market research findings succeed, various metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are utilized. These numerical tools act as navigational aids directing enterprises toward achieving objectives while simultaneously verifying that efforts invested in conducting market analysis are yielding fruitful guidance.
Throughout our look at market research, we’ve seen its importance and impact. Our discussion covered the basics of market research, its key components, and different types, including both qualitative and quantitative methods, and the role of Userpilot’s tools. We’ve examined the details of the market research process, tackled challenges, identified best practices, and shared success stories. We also provided advice on choosing the right market research partner and how to measure the effectiveness of your market research.
In today’s data-driven world, comprehensive market research is crucial for companies that want to succeed. It acts like a guide, helping businesses navigate the complex market landscape. Start your own detailed research today, supported by insightful analytics to help you succeed.
Frequently asked questions
What is market research and why is it important.
Understanding your target market, honing business strategies, and making informed decisions are all essential components that depend heavily on effective market research. It offers objective insights to help avoid expensive errors and foresees the needs of customers .
What is the difference between primary and secondary market research?
Primary market research is characterized by the direct gathering of data, in contrast to secondary market research which leverages existing information from alternative sources for addressing research inquiries.
Such a distinction can guide you in selecting an approach that aligns with your precise needs for conducting specific research.
What are some examples of successful market research?
Examples of successful market research are evident in the operations of well-known companies such as Starbucks, Apple, and McDonald’s. They have harnessed this tool to fine-tune their business strategies and make decisions based on solid information.
By employing market research, these businesses have managed to gain insight into their customers’ desires and needs, which has contributed significantly to their success.
How can I choose the right market research partner?
Selecting an ideal market research ally involves identifying a firm that resonates with your project requirements, financial plan, and corporate goals while also verifying their track record of dependability and consistency via reviews from previous clients.
Best wishes on your endeavor!
How is the impact of market research measured?
The effectiveness of market research hinges on the precision, representativeness, and pertinence of its data, along with how successful business decisions are when they’re based on the findings from this research. These elements define the impact of the research conducted.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
Funnel marketing: definition and strategies that work for saas, how to do market research: a step-by-step guide.
- Mobile Forms
- INTEGRATIONS
- See 100+ integrations
- FEATURED INTEGRATIONS
- See more Integrations
- See more CRM Integrations

- See more Storage Integrations
- See more Payment Integrations

- See more Email Integrations
- Jotform Teams
- Enterprise Mobile
- Prefill Forms
- HIPAA Forms
- Secure Forms
- Assign Forms
- Online Payments
- See more features
- Multiple Users
- Admin Console
- White Labeling
- See more Enterprise Features
- Contact Sales
- Contact Support
- Help Center
- Jotform Books
- Jotform Academy
Get a dedicated support team with Jotform Enterprise.
Apply to Jotform Enterprise for a dedicated support team.
- Sign Up for Free

- Market Research
Quantitative research question examples

One of the best ways to determine how your target audience feels about your company or organization is through quantitative research. Once you understand user opinions, attitudes, behaviors, preferences, and market trends, you can make informed decisions that help you improve your products, services, and every aspect of the customer experience.
In this post, we’ll review what a quantitative research question is, cover the types of quantitative research questions, share examples of quantitative research questions across various fields, and highlight tips for creating a quantitative research survey.
Some background on quantitative research questions
Quantitative research questions collect objective, measurable, numerical data through
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Controlled observations
- Reviewing existing research to produce sound statistical analysis
The data includes ratings, counts, measurements, and percentages. Because this data is objective, it’s considered more reliable than qualitative research data.
Quantitative data helps researchers identify trends and patterns. They can use these insights to make informed decisions about company or organizational goals, targets, and strategic improvements to undertake.
Quantitative research questions are useful for measuring many things, but businesses commonly use them to determine overall customer satisfaction , gather feedback on existing products and services, gauge the demand for new products and services, and decide on business improvements to roll out.
Some examples of quantitative research questions include
- How many times per week do you use social media?
- How often do you visit our website?
- How many mobile shopping apps do you use?
Types of quantitative research questions
The three main types of quantitative research questions are descriptive, comparative, and relationship-based. Which type or types you use will depend on the kind of data you want to collect and your research objective.
Descriptive research questions are usually closed-ended, and they elicit participants’ opinions about a specific variable. With these questions, you may ask how often someone uses your product, when they use your product, or how much they’d be willing to pay for a specific product.
Comparative research questions consider differences between groups based on dependable variables. With these questions, you may want to compare brand preferences among men versus women, compare how often individuals use similar products, or assess how your products stack up against competitors’ offerings.
Relationship-based research questions are helpful for gauging trends, causal relationships, or connections between variables. You may develop questions that help you explore how color influences buying decisions for a product or assess the relationship between employee turnover and workplace environment.
Examples of quantitative research questions
Now let’s take a look at some examples of quantitative research questions in the fields of education, health, marketing, and social sciences.
Examples of quantitative research questions in education
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how much does parental participation in education impact student academic achievement?
- What impact does classroom size have on academic performance? Choose from the following: no impact, limited impact, high impact.
- How many times were you (the student) absent last semester?
- Is the relationship between extracurricular activities and student performance positive, negative, or neutral?
- On a scale of 1 to 5, how much do study habits impact student grades and test scores?
Examples of quantitative research questions in the mental and physical health fields
- On a scale of 1–10, how often do you feel stressed?
- How many times per week do you engage in activities to improve your mental well-being?
- How frequently do you exercise?
- Do you have a health insurance plan?
- How would you rate the care you received on your last visit with a primary care provider?
- What is the relationship between stress levels and physical health in retirees?
- On average, how many times per year do you visit a healthcare provider or facility?
Examples of quantitative research questions in marketing
- How often do you make buying decisions based on advertising or marketing campaigns?
- How often do you use products in this category?
- On a scale of 1–10, how satisfied are you with the quality of this product?
- On a scale of 1–10, how likely are you to recommend this product to others?
- How much are you willing to pay for this product?
- Which product features are the most important to you when making buying decisions in this category?
- How much do customer reviews impact your buying decisions?
- What is your preferred way to purchase products in this category (online or in the store)?
Examples of quantitative research questions in social sciences
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how much does income inequality impact academic performance?
- To what extent is there still a gender imbalance in pay/wages? Rate your answer on a scale of 1 to 5.
- To what degree does race impact rates of mental health diagnosis in adults? Rate your answer on a scale of 1 to 5.
- Does gender affect an individual’s contribution to household tasks?
Tips for creating quantitative research questions
Now that we’ve seen some examples, let’s review a few tips for creating your own quantitative research questions.
Since you’re looking for concrete data, ask questions such as
- What percentage?
- What proportion?
Let’s look at some concrete examples:
- How much is your weekly grocery budget?
- How many times per month do you visit a brick-and-mortar store?
- What percentage of your monthly income is spent on housing?
To increase the quality of your questions and ensure the best results
- Use different question types (i.e., descriptive, comparative, relationship-based).
- Keep the survey or questionnaire as short as you can without sacrificing data collection.
- Don’t use leading or biased questions.
- Use clear language and avoid jargon.
- Address one topic per question, starting with easier questions first to build momentum.
- Be sure to get approvals and informed consent before proceeding.
How to create a quantitative research survey
- Select the type of quantitative research question or questions from among the three discussed above — descriptive, comparative, or relationship-based — based on your research objective.
- Identify the type of variable you’re trying to measure — either independent (the variable being manipulated) or dependent (the outcome variable) — and the target audience. Measurement variables include nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio.
- Decide on the structure of your research questions based on the type of questions you’ll be presenting. Structure pertains to variables, groups, and the order of the variables and groups in the questions.
- Draft your research questions and finalize your survey.
If you’re interested in learning more, we offer a more in-depth look at quantitative market research best practices . Also, check out our detailed, step-by-step guide on how to do market research .
You can build beautiful, easy-to-use, fully customizable surveys using Jotform’s premade survey templates or create them from scratch — no coding required. Tailor your surveys to match your business and your specific goals, and even share, collect, and analyze your survey results with our free online survey maker .
If you want to gather invaluable insights into user behavior, opinions, attitudes, and preferences, quantitative research is a great way to go about it. Jotform’s robust survey and questionnaire tools make it easy to get started.
Photo by ODISSEI on Unsplash
Thank you for helping improve the Jotform Blog. 🎉
RECOMMENDED ARTICLES

How to Do Market Research

5 quantitative market research best practices

9 customer-focused market research survey questions

4 expert tips for conducting qualitative market research

What is the population of interest?

7 common types of market research

4 ways to conduct online market research

How to do customer research

How to conduct data collection in market research

7 market research tools you should start using today

6 insights for running effective marketing research surveys
Send Comment :

The Importance of Quantitative Research in Marketing Decision Making
- January 30, 2024

In the dynamic realm of marketing, where every trend is a shifting landscape and consumer preferences resemble a kaleidoscope of ever-changing patterns, the role of quantitative research emerges as the compass guiding decision-makers through this vibrant maze.
Picture this: a symphony of data, a dance of numbers, and a canvas painted with statistical insights. Welcome to the world where the alchemy of numbers not only deciphers market trends but also unveils the secrets hidden within the labyrinth of consumer behavior.
As we embark on this journey into the heart of data-driven decision-making , the spotlight falls on the unsung hero – quantitative research. In this exploration, we unravel the significance, the power, and the transformative impact that harnessing the quantitative can have on steering the ship of marketing strategies toward success.
So, buckle up as we delve into the captivating narrative of why, in the grand tapestry of marketing, numbers aren't just digits; they are the pulsating heartbeat of informed choices and strategic triumphs.
Overview of Decision-Making Process
Let's take a quick pit stop to understand the decision-making process. Picture this: you're at a crossroads, faced with choices that could make or break your marketing strategy. How do you navigate through this maze of possibilities? Data-driven insights are the compass that guides you.
Role of Data in Decision-Making
Data is the backbone of decision-making. Whether you're deciding on your next data-driven marketing campaign or fine-tuning your target audience, having solid data at your fingertips is like having a secret weapon. It minimizes the risk of guesswork and transforms your decisions from shots in the dark to well-calculated moves.
How to use quantitative research to make better marketing decisions?
Now, let's shine a spotlight on the star of our show – quantitative research. What is it, you ask? In simple terms, it's the method of collecting and analyzing numerical data to understand patterns, trends, and correlations.
Quantitative research plays a vital role in market research, utilizing concrete facts and numerical data to achieve an objective understanding of people's opinions. Think surveys, experiments, and statistical analyses – the kind of stuff that turns raw numbers into actionable insights.
What are the benefits of Quantitative Research in Marketing?
Quantitative research isn't just a fancy term; it's a marketing superhero.
Here are some of its key benefits:
- Precision in Decision-Making: Numbers don't lie. With quantitative research, you get precise data that forms a solid foundation for your marketing decisions.
- Measurable Results: Ever heard the phrase "what gets measured gets managed"? Quantitative research allows you to measure the impact of your marketing efforts with tangible metrics.
- Risk Mitigation: In the dynamic world of marketing, risks are inevitable. However, with quantitative data, you can identify potential pitfalls early on and navigate your strategy accordingly.
Applications of Quantitative Research
Now that we're singing the praises of quantitative research, let's see it in action. From market segmentation to product testing, this method wears many hats.
- Market Segmentation: Want to tailor your message to a specific audience? Quantitative research helps you understand the demographics, behaviors, and preferences of your target market.
- Product Development: Before launching a new product, test the waters with quantitative research. Get insights on potential demand, pricing strategies, and consumer preferences.
- Campaign Effectiveness: Ever wondered if your latest marketing campaign actually resonated with your audience? Quantitative research can measure its success through metrics like conversion rates and customer feedback.
Challenges in Quantitative Decision-Making
Of course, no superhero is without its challenges. Quantitative research, too, faces a few hurdles, such as:
- Limited Context : Numbers tell a story, but sometimes the context is lost. Quantitative research may only capture part of the picture, especially when it comes to understanding the 'why' behind certain trends.
- Inflexibility: Unlike qualitative research, which allows for flexibility and exploration, quantitative methods can be rigid. This can be a limitation when dealing with complex, multifaceted issues.
Considerations in Quantitative Decision-Making
Now, before you go all-in on quantitative research, there are a few considerations to keep in mind:
- Sample Size : Ensure your sample size is representative of your target audience. Small samples may lead to skewed results.
- Data Quality : Garbage in, garbage out. The accuracy of your findings depends on the quality of your data. Ensure it's reliable and relevant.
- Ethical Considerations: Respect privacy and ethical standards when collecting and using data. It's not just about numbers; it's about people.
Steps to Conduct Quantitative Research
Alright, you're convinced and ready to embark on your market research journey. Here's a roadmap to guide you:
- Define Your Objective: Clearly outline what you want to achieve through your research.
- Design Your Study: Choose the right methodology – surveys, experiments, or statistical analyses – based on your objectives.
- Collect Data: Implement your study and gather the numerical data needed for analysis .
- Analysis and Interpretation: Crunch the numbers and derive meaningful insights.
- Draw Conclusions : Use your findings to make informed decisions for your marketing strategy.
The Final Thoughts
In a nutshell, quantitative research isn't just a tool; it's a mindset. It transforms the way we approach decision-making in the dynamic landscape of marketing. By embracing the power of numbers, you're not just making decisions – you're making informed, strategic moves that can propel your brand to new heights.
Summary of Key Points
- Data is the compass in decision-making.
- Quantitative research offers precision and measurable results.
- Applications include market segmentation, product development, and campaign effectiveness.
- Challenges include limited context and inflexibility.
- Considerations involve sample size, data quality, and ethical standards.
- Steps include defining objectives, designing studies, collecting data, analyzing, and drawing conclusions.
NextGen Business Leadership Program: Nurturing Executives for Strategic Success
Imarticus Learning's NextGen Business Leadership Program is tailored for high-potential executives with proven managerial track records who aspire to become business leaders. This program helps you develop the leadership abilities and strategic thinking skills you need to navigate organizations effectively and make informed decisions.
The program uses an experiential approach with case studies and simulations from Wharton Interactive, StratX, and Imarticus Game Studio. This hands-on approach allows you to apply what you learn to real-world business scenarios and help you become a chief business officer .
The NextGen Business Leadership Program focuses on developing a high degree of sales and marketing acumen, strategic thinking, people leadership, and execution skills. These are the essential skills that business leaders need to succeed in today's competitive landscape.
Key Benefits of the NextGen Business Leadership Program:
- Develop the leadership abilities and strategic thinking skills you need to navigate organizations effectively and make informed decisions.
- Gain hands-on experience in overcoming modern-day challenges faced by business leaders with effective strategies.
- Learn from industry experts and connect with a network of peers.
- Earn a certificate of completion from Imarticus Learning.
Ready to supercharge your marketing decisions with quantitative research? Dive into the numbers, explore the possibilities, and watch your strategies soar. If you want to learn more insights, join our sales and marketing management program and take your skills to the next level. Let's not just make decisions; let's make data-driven, game-changing decisions together. Are you in?
Remember, in the world of marketing, numbers aren't just numbers – they're the keys to unlocking success.
Happy researching!
Share This Post
Subscribe to our newsletter, get updates and learn from the best, more to explore.

Your Ultimate Guide to Becoming a Chartered Financial Analyst

Your Startup Can Grow With Tax Planning Training
Our programs.

Keep In Touch

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Quantitative market research is defined as a type of research that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to understand market trends, consumer behavior, and other business-related variables. Learn more about quantitative market research methods, examples and best practices.
A powerful example of quantitative research in play is when it's used to inform a competitive analysis. A process that's used to analyze and understand how industry leaders and companies of interest are performing. Pro Tip: Collect data systematically, and use a competitive analysis framework to record your findings.
Quantitative market research is conducted under two broad buckets of the frequency they are administered at: Cross-sectional research survey: Cross-sectional market research is a quantitative market research method that analyzes data of variables collected at one given point of time across a sample population. population or a pre-defined subset ...
Quantitative market research is a numbers game. It's one of the four types of traditional market research; and a tried, trusted, and proven way to get answers to strategically important questions.. Whether you're already familiar with quantitative research, looking for practical examples, or considering using it in your business, I will cover everything you need to know.
Quantitative research generally relies on a larger sample size in order to quantify any issue or variable. In order to achieve this, this research method involves using mathematical and statistical means. This type of research answers the "what" and the "how much" of a subject within a research endeavor.
Quantitative market research questions to ask for actionable insights. February 16, 2024. 14 min read. In this article. There's a big difference between asking "Why do you like our product?" and "On a scale of 1-10, how much do you like our product?". But both ways of asking are valuable in their own way. Knowing your audience is not ...
Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio). Quantitative research is widely used in the natural and social sciences: biology, chemistry, psychology, economics, sociology, marketing, etc. Quantitative research question examples
Advantages: Disadvantages: Larger sample sizes: Since quantitative research surveys are smaller and easier to fill, you can distribute them to a larger audience in a given time.: Lack of specific data: Since the focus is on numbers, you could end up with inconclusive results.For example, the number of unsatisfied customers but no clue why. Easy analysis: Since the data is numerical, it's ...
This method is widely used in market research to gather information about customer behavior, opinions, and preferences. Here are some of the benefits of quantitative market research: 1. Large Sample Size: One of the significant benefits of quantitative research is the ability to collect data from a large sample size. This provides a more ...
Quantitative marketing research is the application of quantitative research techniques to the field of marketing research.It has roots in both the positivist view of the world, and the modern marketing viewpoint that marketing is an interactive process in which both the buyer and seller reach a satisfying agreement on the "four Ps" of marketing: Product, Price, Place (location) and Promotion.
A great example of quantitative research in marketing is conducting surveys to determine the potential demand for a particular product, service, or feature. Q2. Why is quantitative research important in marketing? Quantitative research is necessary because it provides marketers with objective, reliable data to identify trends and patterns for ...
Examples of Quantitative Research. Here are some real-life examples of quantitative research: Market Research: Quantitative market research is a type of market research that uses numerical data to understand consumer preferences, buying behavior, and market trends. This data typically gets gathered through surveys and questionnaires, which are ...
Here are seven examples of quantitative marketing research: 1: Surveys source: questionpro. Surveys are a fundamental tool in quantitative marketing research, allowing businesses to gather valuable data from their target audience. By utilizing various survey types and well-designed questions, researchers can obtain insights that are crucial for ...
Quantitative Research Questions and Examples. Quantitative research questions should be closed-ended, which means they ask respondents to choose from a pre-populated list. Because much of the work is done for the participant, quantitative research can typically include more questions. Some common questions include: Net promoter score. This ...
Sample size: Quantitative research is conducted on a significant sample size representing the target market. Appropriate Survey Sampling methods, a fundamental aspect of quantitative research methods, must be employed when deriving the sample to fortify the research objective and ensure the reliability of the results.
Quantitative research involves gathering numerical data that can be statistically analyzed. This method is often used to measure the frequency of behaviors, attitudes, or opinions within a ...
Businesses use quantitative and qualitative market research methods to collect data for market research. Qualitative research data is collected through interviews, focus groups , observations, and surveys, and it gives insight into a specific issue or problem by examining the experiences, opinions, and behaviors of a sample of target customers.
Examples of Quantitative Research. Here are some examples of quantitative research in different fields: Market Research: A company conducts a survey of 1000 consumers to determine their brand awareness and preferences. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify trends and patterns that can inform marketing strategies.
Qualitative vs quantitative research. Market research employs both qualitative and quantitative methods, offering distinct insights that complement each other. ... Real-life examples of market research in the SaaS industry often showcase innovative approaches to understanding customer needs and product-market fit. For instance, Slack, the ...
Quantitative research questions collect objective, measurable, numerical data through. Surveys and questionnaires. Polls. Interviews. Controlled observations. Reviewing existing research to produce sound statistical analysis. The data includes ratings, counts, measurements, and percentages. Because this data is objective, it's considered more ...
Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest. This type of research helps in testing the causal relationships between variables, making predictions, and generalizing results to wider populations. The purpose of quantitative research is to test a predefined ...
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge. Quantitative research. Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions.
Data is the compass in decision-making. Quantitative research offers precision and measurable results. Applications include market segmentation, product development, and campaign effectiveness. Challenges include limited context and inflexibility. Considerations involve sample size, data quality, and ethical standards.
Journal of marketing research, 43(3), 355-365. ... the effect of personalization on long-term relationships with service customers and to test it empirically on the example of high personal ...