Literary Devices
Literary devices, terms, and elements, definition of thesis.
A thesis is a statement or central idea that a writer puts forward at the beginning of an argument, and will support throughout the following text. The thesis is a premise that the author believes to be true, and will give evidence for by way of facts or situations that reinforce this central idea. Thesis statements are most often found in academic writing, and have a subtler yet analogous role in fiction.
The word “thesis” comes from Greek, in which it means “something put forth.” The definition of thesis developed from this reference to an proposition for which the author wants to argue the validity.

Common Examples of Thesis
We generally do not use formal thesis examples in ordinary life. It is possible, however, to state a main idea and back this idea up with evidence. Someone could say, for example, “We’re destined to be together,” and give reasons why this is the case. The lyrics of the popular song “Ho Hey” by the Lumineers illustrates this concept:
1, 2, 3 I belong with you, you belong with me, you’re my sweetheart I belong with you, you belong with me, you’re my sweet (Ho!) So show me family (Hey!) All the blood that I would bleed (Ho!) I don’t know where I belong (Hey!) I don’t know where I went wrong (Ho!) But I can write a song (Hey!)
Bob Dylan’s song “The Hurricane” also puts forward a thesis statement—Rubin Carter “The Hurricane was innocent of a crime he was charged with—and supports it with evidence of the story:
Pistols shots ring out in the barroom night Enter Patty Valentine from the upper hall She sees the bartender in a pool of blood Cries out “My God they killed them all” Here comes the story of the Hurricane The man the authorities came to blame For something that he never done Put him in a prison cell but one time he could-a been The champion of the world.
There are also countless examples of theses in academia; everyone who attains a Ph.D. must first present a thesis paper, sometimes called a dissertation, that is the product of many years of research and investigation. Examples of thesis papers are often found in other undergraduate and graduate studies as well.
Significance of Thesis in Literature
While the thesis of a work of literature can be harder to extract from the body of the text than in academic writing, it can be just as important. Writers have a certain point of view from which they are writing, and may construct entire poems and novels to prove certain ideas true. While an academic writer can base his or her argument off of fact and data, the literary writer often uses situations and the emotions they provoke to help prove certain ideas. This process can take longer to develop than in academic thesis examples, and yet the result can often be stronger. When authors of poetry and prose appeal to emotion as well as logic (both pathos and logos), the reader is more likely to be convinced of a certain message, as well as remember the message for a longer period of time.
Examples of Thesis in Literature
JAQUES: All the world’s a stage, And all the men and women merely players; They have their exits and their entrances, And one man in his time plays many parts, His acts being seven ages.
( As You Like It by William Shakespeare)
This famous example of thesis from the character of Jaques is a beautiful metaphor for the similarities between life and the stage. It is often quoted because it seems to reflect a world-view that Shakespeare probably held; everything that happens in the world can be read as a type of performance with everyone just trying to play their part.
You never really understand a person until you consider things from his point of view . . . until you climb into his skin and walk around in it.
( To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee)
The above excerpt from Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird is famous because it is an important central idea to the novel. Atticus Finch believes in empathy and understanding other people’s life stories and points of view. Therefore, he strongly believes that we must try to understand where other people are coming from. This one statement is a thesis that the rest of the book supports.
TOM: Yes, I have tricks in my pocket, I have things up my sleeve. But I am the opposite of a stage magician. He gives you illusion that has the appearance of truth. I give you truth in the pleasant disguise of illusion.
( The Glass Menagerie by Tennessee Williams) Thesis examples can often be found at the beginning of a work of poetry, prose, or drama, as is the case with Tennessee Williams’s The Glass Menagerie . The character of Tom narrates the play, and often breaks the fourth wall to address the audience directly. In this quote, which opens the play, Tom presents the idea that the drama that is about to unfold is entertaining yet tells the truth. Similar to Shakespeare, this could be understood as Tennessee William’s thesis about the power of drama.
And this I believe: that the free, exploring mind of the individual human is the most valuable thing in the world. And this I would fight for: the freedom of the mind to take any direction it wishes, undirected. And this I must fight against: any idea, religion, or government which limits or destroys the individual.
( East of Eden by John Steinbeck)
In his novel East of Eden , John Steinbeck often makes authorial interjections. These passages seem to highlight Steinbeck’s own views on different matters, rather than any particular character’s views. The short excerpt above is one of the strongest examples of a thesis statement in all of literature; Steinbeck firmly believe in free will, and vows to fight against anything that would limit free will. He presents more than one example of thesis in his novel, and creates characters and situations that support his beliefs.
so much depends upon a red wheel barrow glazed with rain water beside the white chickens.
(“The Red Wheelbarrow” by William Carlos Williams)
Poetry can have examples of thesis statements just as easily as prose or drama. William Carlos Williams’s poem “The Red Wheelbarrow” is famously enigmatic, while also being quite direct. He makes the straightforward argument that “so much depends” on a certain intangible object. In this case, “a red wheel / barrow.” Many readers and scholars have interpreted this short thesis statement in countless different ways. Thus, it is an interesting thesis example because Williams states it so unswervingly, yet does not support it with other evidence. Readers are left to interpret and prove this thesis example themselves.
Test Your Knowledge of Thesis
1. Which of the following statements is the best thesis definition? A. A minor claim to support the main proposition that author has put forth. B. A central idea which the author intends to support via evidence. C. A piece of evidence or a fact. [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #1″] Answer: B is the correct answer.[/spoiler]
2. What thesis could be extracted from the following quote from John Steinbeck’s East of Eden?
Monsters are variations from the accepted normal to a greater or a less degree. As a child may be born without an arm, so one may be born without kindness or the potential of conscience.
A. All people with physical deformities are monsters. B. All monsters are evil. C. Some people can be born without kindness, making them monstrous. [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #2″] Answer: C is the correct answer.[/spoiler]
3. What is the thesis in William Shakespeare’s “Sonnet 116”?
Let me not to the marriage of true minds Admit impediments. Love is not love Which alters when it alteration finds, Or bends with the remover to remove: O no; it is an ever-fixed mark, That looks on tempests, and is never shaken; It is the star to every wandering bark, Whose worth’s unknown, although his height be taken. Love’s not Time’s fool, though rosy lips and cheeks Within his bending sickle’s compass come; Love alters not with his brief hours and weeks, But bears it out even to the edge of doom. If this be error and upon me proved, I never writ, nor no man ever loved.
A. True love does not change when problems arise. B. Love is a game for fools. C. Only married people understand true love. [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #3″] Answer: A is the correct answer.[/spoiler]


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

12.6: Literary Thesis Statements
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 43636

- Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
The Literary Thesis Statement
Literary essays are argumentative or persuasive essays. Their purpose is primarily analysis, but analysis for the purposes of showing readers your interpretation of a literary text. So the thesis statement is a one to two sentence summary of your essay's main argument, or interpretation.
Just like in other argumentative essays, the thesis statement should be a kind of opinion based on observable fact about the literary work.
Thesis Statements Should Be
- This thesis takes a position. There are clearly those who could argue against this idea.
- Look at the text in bold. See the strong emphasis on how form (literary devices like symbolism and character) acts as a foundation for the interpretation (perceived danger of female sexuality).
- Through this specific yet concise sentence, readers can anticipate the text to be examined ( Huckleberry Finn) , the author (Mark Twain), the literary device that will be focused upon (river and shore scenes) and what these scenes will show (true expression of American ideals can be found in nature).
Thesis Statements Should NOT Be
- While we know what text and author will be the focus of the essay, we know nothing about what aspect of the essay the author will be focusing upon, nor is there an argument here.
- This may be well and true, but this thesis does not appear to be about a work of literature. This could be turned into a thesis statement if the writer is able to show how this is the theme of a literary work (like "Girl" by Jamaica Kincaid) and root that interpretation in observable data from the story in the form of literary devices.
- Yes, this is true. But it is not debatable. You would be hard-pressed to find someone who could argue with this statement. Yawn, boring.
- This may very well be true. But the purpose of a literary critic is not to judge the quality of a literary work, but to make analyses and interpretations of the work based on observable structural aspects of that work.
- Again, this might be true, and might make an interesting essay topic, but unless it is rooted in textual analysis, it is not within the scope of a literary analysis essay. Be careful not to conflate author and speaker! Author, speaker, and narrator are all different entities! See: intentional fallacy.
Thesis Statement Formula
One way I find helpful to explain literary thesis statements is through a "formula":
Thesis statement = Observation + Analysis + Significance
- Observation: usually regarding the form or structure of the literature. This can be a pattern, like recurring literary devices. For example, "I noticed the poems of Rumi, Hafiz, and Kabir all use symbols such as the lover's longing and Tavern of Ruin "
- Analysis: You could also call this an opinion. This explains what you think your observations show or mean. "I think these recurring symbols all represent the human soul's desire." This is where your debatable argument appears.
- Significance: this explains what the significance or relevance of the interpretation might be. Human soul's desire to do what? Why should readers care that they represent the human soul's desire? "I think these recurring symbols all show the human soul's desire to connect with God. " This is where your argument gets more specific.
Thesis statement: The works of ecstatic love poets Rumi, Hafiz, and Kabir use symbols such as a lover’s longing and the Tavern of Ruin to illustrate the human soul’s desire to connect with God .
Thesis Examples
SAMPLE THESIS STATEMENTS
These sample thesis statements are provided as guides, not as required forms or prescriptions.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________
The Literary Device Thesis Statement
The thesis may focus on an analysis of one of the elements of fiction, drama, poetry or nonfiction as expressed in the work: character, plot, structure, idea, theme, symbol, style, imagery, tone, etc.
In “A Worn Path,” Eudora Welty creates a fictional character in Phoenix Jackson whose determination, faith, and cunning illustrate the indomitable human spirit.
Note that the work, author, and character to be analyzed are identified in this thesis statement. The thesis relies on a strong verb (creates). It also identifies the element of fiction that the writer will explore (character) and the characteristics the writer will analyze and discuss (determination, faith, cunning).
The character of the Nurse in Romeo and Juliet serves as a foil to young Juliet, delights us with her warmth and earthy wit, and helps realize the tragic catastrophe.
The Genre / Theory Thesis Statement
The thesis may focus on illustrating how a work reflects the particular genre’s forms, the characteristics of a philosophy of literature, or the ideas of a particular school of thought.
“The Third and Final Continent” exhibits characteristics recurrent in writings by immigrants: tradition, adaptation, and identity.
Note how the thesis statement classifies the form of the work (writings by immigrants) and identifies the characteristics of that form of writing (tradition, adaptation, and identity) that the essay will discuss.
Samuel Beckett’s Endgame reflects characteristics of Theatre of the Absurd in its minimalist stage setting, its seemingly meaningless dialogue, and its apocalyptic or nihilist vision.
A close look at many details in “The Story of an Hour” reveals how language, institutions, and expected demeanor suppress the natural desires and aspirations of women.
Generative Questions
One way to come up with a riveting thesis statement is to start with a generative question. The question should be open-ended and, hopefully, prompt some kind of debate.
- What is the effect of [choose a literary device that features prominently in the chosen text] in this work of literature?
- How does this work of literature conform or resist its genre, and to what effect?
- How does this work of literature portray the environment, and to what effect?
- How does this work of literature portray race, and to what effect?
- How does this work of literature portray gender, and to what effect?
- What historical context is this work of literature engaging with, and how might it function as a commentary on this context?
These are just a few common of the common kinds of questions literary scholars engage with. As you write, you will want to refine your question to be even more specific. Eventually, you can turn your generative question into a statement. This then becomes your thesis statement. For example,
- How do environment and race intersect in the character of Frankenstein's monster, and what can we deduce from this intersection?
Expert Examples
While nobody expects you to write professional-quality thesis statements in an undergraduate literature class, it can be helpful to examine some examples. As you view these examples, consider the structure of the thesis statement. You might also think about what questions the scholar wondered that led to this statement!
- "Heart of Darkness projects the image of Africa as 'the other world,' the antithesis of Europe and therefore civilization, a place where man's vaunted intelligence and refinement are finally mocked by triumphant bestiality" (Achebe 3).
- "...I argue that the approach to time and causality in Boethius' sixth-century Consolation of Philosophy can support abolitionist objectives to dismantle modern American policing and carceral systems" (Chaganti 144).
- "I seek to expand our sense of the musico-poetic compositional practices available to Shakespeare and his contemporaries, focusing on the metapoetric dimensions of Much Ado About Nothing. In so doing, I work against the tendency to isolate writing as an independent or autonomous feature the work of early modern poets and dramatists who integrated bibliographic texts with other, complementary media" (Trudell 371).
Works Cited
Achebe, Chinua. "An Image of Africa" Research in African Literatures 9.1 , Indiana UP, 1978. 1-15.
Chaganti, Seeta. "Boethian Abolition" PMLA 137.1 Modern Language Association, January 2022. 144-154.
"Thesis Statements in Literary Analysis Papers" Author unknown. https://resources.finalsite.net/imag...handout__1.pdf
Trudell, Scott A. "Shakespeare's Notation: Writing Sound in Much Ado about Nothing " PMLA 135.2, Modern Language Association, March 2020. 370-377.
Contributors and Attributions
Thesis Examples. Authored by: University of Arlington Texas. License: CC BY-NC

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Thesis Statements for a Literature Assignment
A thesis prepares the reader for what you are about to say. As such, your paper needs to be interesting in order for your thesis to be interesting. Your thesis needs to be interesting because it needs to capture a reader's attention. If a reader looks at your thesis and says "so what?", your thesis has failed to do its job, and chances are your paper has as well. Thus, make your thesis provocative and open to reasonable disagreement, but then write persuasively enough to sway those who might be disagree.
Keep in mind the following when formulating a thesis:
- A Thesis Should Not State the Obvious
- Use Literary Terms in Thesis With Care
- A Thesis Should be Balanced
- A Thesis Can be a Blueprint
Avoid the Obvious
Bland: Dorothy Parker's "Résumé" uses images of suicide to make her point about living.
This is bland because it's obvious and incontestable. A reader looks at it and says, "so what?"
However, consider this alternative:
Dorothy Parker's "Résumé" doesn't celebrate life, but rather scorns those who would fake or attempt suicide just to get attention.
The first thesis merely describes something about the poem; the second tells the reader what the writer thinks the poem is about--it offers a reading or interpretation. The paper would need to support that reading and would very likely examine the way Parker uses images of suicide to make the point the writer claims.
Use Literary Terms in Thesis Only to Make Larger Points
Poems and novels generally use rhyme, meter, imagery, simile, metaphor, stanzas, characters, themes, settings and so on. While these terms are important for you to use in your analysis and your arguments, that they exist in the work you are writing about should not be the main point of your thesis. Unless the poet or novelist uses these elements in some unexpected way to shape the work's meaning, it's generally a good idea not to draw attention to the use of literary devices in thesis statements because an intelligent reader expects a poem or novel to use literary of these elements. Therefore, a thesis that only says a work uses literary devices isn't a good thesis because all it is doing is stating the obvious, leading the reader to say, "so what?"
However, you can use literary terms in a thesis if the purpose is to explain how the terms contribute to the work's meaning or understanding. Here's an example of thesis statement that does call attention to literary devices because they are central to the paper's argument. Literary terms are placed in italics.
Don Marquis introduced Archy and Mehitabel in his Sun Dial column by combining the conventions of free verse poetry with newspaper prose so intimately that in "the coming of Archy," the entire column represents a complete poem and not a free verse poem preceded by a prose introduction .
Note the difference between this thesis and the first bland thesis on the Parker poem. This thesis does more than say certain literary devices exist in the poem; it argues that they exist in a specific relationship to one another and makes a fairly startling claim, one that many would disagree with and one that the writer will need to persuade her readers on.
Keep Your Thesis Balanced
Keep the thesis balanced. If it's too general, it becomes vague; if it's too specific, it cannot be developed. If it's merely descriptive (like the bland example above), it gives the reader no compelling reason to go on. The thesis should be dramatic, have some tension in it, and should need to be proved (another reason for avoiding the obvious).
Too general: Edna St. Vincent Millay wrote many poems with love as the theme. Too specific: Edna St. Vincent Millay wrote "Love is not all: it is not meat nor drink" in <insert date> after <insert event from her life>. Too descriptive: Edna St. Vincent Millay's "Love is not all: it is not meat nor drink" is a sonnet with two parts; the first six lines propose a view of love and the next eight complicate that view. With tension and which will need proving: Despite her avowal on the importance of love, and despite her belief that she would not sell her love, the speaker in Edna St. Vincent Millay's "Love is not all: it is not meat nor drink" remains unconvinced and bitter, as if she is trying to trick herself into believing that love really does matter for more than the one night she is in some lover's arms.
Your Thesis Can Be A Blueprint
A thesis can be used as roadmap or blueprint for your paper:
In "Résumé," Dorothy Parker subverts the idea of what a résumé is--accomplishments and experiences--with an ironic tone, silly images of suicide, and witty rhymes to point out the banality of life for those who remain too disengaged from it.
Note that while this thesis refers to particular poetic devices, it does so in a way that gets beyond merely saying there are poetic devices in the poem and then merely describing them. It makes a claim as to how and why the poet uses tone, imagery and rhyme.
Readers would expect you to argue that Parker subverts the idea of the résumé to critique bored (and boring) people; they would expect your argument to do so by analyzing her use of tone, imagery and rhyme in that order.
Citation Information
Nick Carbone. (1994-2024). Thesis Statements for a Literature Assignment. The WAC Clearinghouse. Colorado State University. Available at https://wac.colostate.edu/repository/writing/guides/.
Copyright Information
Copyright © 1994-2024 Colorado State University and/or this site's authors, developers, and contributors . Some material displayed on this site is used with permission.
Thesis Statement
Definition of thesis statement.
A thesis statement is a statement that occurs at the end of the introduction , after the background information on the topic. The thesis statement is connected with the background information through a transition , which could be a full sentence , or a simple transition word, such as therefore, because, but etc.
The thesis statement is called the “heart of the essay .” The idea of an essay without a thesis statement is akin to a body without its heart. It also is called the “central point” or the “core” of an essay. It is comprised of evidences that the writer uses to elaborate on his topic further. Each of these evidences is then elaborated and discussed in the body paragraphs .
If there are three body paragraphs, the thesis statement must have three evidences, and should it have more than three body paragraphs, may be additional evidences. In argumentative essays, three evidences support the topic, while the fourth evidence is against it. The same is the case of persuasive essays. This applies to five-paragraph essays, but in case of a longer essay, the thesis statement could make use of more than one sentence.
There is a slight controversy over the placement of a thesis statement. Some writers and professors argue that it could be placed in the first paragraph at the end, while others feel that, in longer essays, it is not possible to give background information in just one paragraph. As background information takes two or three paragraphs, the thesis statement is kept slightly larger, having two or three sentences, and is placed at the end of the second or third paragraph. However, in a five-paragraph essay, the thesis statement is always placed at the end of the introduction, after the background information.
Qualities of a Good Thesis Statement
- It must have evidences.
- It should be interesting.
- It should be limited.
- It should be manageable.
- It should be researchable.
Difference Between a Thesis Statement and Topic
Sometimes students confuse a thesis statement with a topic, mistaking the thesis statement as the very topic of the essay they are going to read. However, it must be kept in mind that a thesis statement is not a topic, but a brief explanation of the topic in a way that sets the direction of the essay. It predicts the path the essay will take, and tells readers how the essay is going to be organized, and what each part contains.
The topic, however, is a general idea of the essay. It is a specific topic, which has been organized by the thesis statement. The thesis statement in turn elaborates evidences to support to the topic.
Examples of Good and Bad Thesis Statements
- Bad Thesis Statement – “Social media is proving a good marketing tool.”
- Good Thesis Statement – “Social media is proving to be, not only a better marketing tool, but also a source of advertisement for short and medium enterprises intending to expand their consumer base.”
Examples of Thesis Statements in Literature
Example #1: dream on (by mark krikorian in national review online ).
“The core principal behind this amnesty proposal is that it is amid at those who have grown up here and are, psychologically and emotionally, Americans.”
This is the first sentence of the second paragraph. The second sentence further elaborates this thesis. It is placed in the second paragraph because the first paragraph introduces the controversial DREAM Act. As the writer is going to argue against the bill, he has stated his argument as to why he is going to oppose it. This is a very compact thesis statement with various implicit counter arguments.
Example #2: Editorial (by The Washington Post)
“There is no doubt that the attacks profoundly affected our country’s policy, politics, economics, society and even collective psychology. Moreover, in addition to sharing the immediate experience of September 9/11, Americans have dealt with its consequences in the years since.”
This is the best thesis statement with clear evidences in it. It is not as complicated as other thesis statements usually are.
Example #3: I Have a Dream (by Martin Luther King)
“In a sense we’ve come to our nation’s capital to cash a check. When the architects of our republic wrote the magnificent words of the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence, they were signing a promissory note to which every American was to fall heir. This note was a promise that all men, yes, black men as well as white men, would be guaranteed the ‘unalienable Rights’ of ‘Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness.’ It is obvious today that America has defaulted on this promissory note, insofar as her citizens of color are concerned. Instead of honoring this sacred obligation, America has given the Negro people a bad check, a check which has come back marked ‘insufficient funds’.”
This is one of the best examples of long thesis statements. It highlights what Martin Luther King is going to speak about. It comes after three paragraphs of background information.
Function of Thesis Statement
A good thesis statement is the heart of an essay. It gives a gist of the thoughts a writer expresses in his essay. It determines the shape of the essay, predicts its content, and foreshadows its events. It narrates the whole story in just one sentence, provided the essay is a short one. Without a thesis statement, an essay is just a written piece, not an organized and well-connected essay
Related posts:
Post navigation.

What is a Thesis in Literature? Definition, Examples of Literary Thesis
Thesis is the major claim or point made by an author in a work of writing. A thesis statement is the sentence in a composition that introduces the main argument or main point of view. It introduces the main idea of the following writing.
What is a Thesis?
Thesis statements can be found in all types of writing and are used by the author to introduce what is the intended topic of focus. A thesis gives a work of writing direction and indicates to the reader what is about to be discussed, supported, or developed.
Since thesis statements help to give context to the following writing, they are found in the beginning of a composition— usually in the first paragraph.
For example, in an essay about a literary work, a thesis statement would look something like this:
- In Ovid’s Metamorphoses , stories of transformation are told in order to support Ovid’s personal belief that art and art alone allows humans to transcend suffering.
The Importance of a Thesis Statement
Without a thesis statement to guide it, an essay, narrative story, or any other kind of writing, may lack direction. Without a clearly defined thesis, readers can have trouble comprehending and following what the writer plans to explain and develop.
In an essay, a thesis statement will introduce the writer’s main point or argument so that the reader understands what is about to be discussed. A structure and source of direction is developed in a successful thesis statement when it is introduced in the first paragraph. The rest of the essay then follows what the thesis has clearly outlined.
In narrative, or story-telling writing, a narrative thesis also provides a jumping-off point for the story by giving the reader information which helps set context. Narrative theses can be apparent or implied, or hidden. In either case, thesis guides the story towards development and its overall purpose.
The Importance of Thesis in Literature
In literature, a thesis acts as an early source of information about what kind of story is about to be told. Authors can state the thesis outright in a literary work, or they can hide the thesis so that it blends in with the beginning of the story.
The main purpose of a thesis in any type of literature, whether narrative or essay/academic, is to concisely outline the writing that will follow. The function of this is to provide readers with a clear concept of what kinds of material they are about to read.
For example, in an argumentative essay, the thesis will clearly state the argument and how it will be supported. In a narrative thesis statement, some context will be given to the story. This can include hints about setting, characters, and tone or style.
How Theses are Used in Literature
The following examples show how thesis has been used in various ways in classic literary works:
In One Hundred Years of Solitude by Gabriel García Márquez , the thesis serves to frame the overall context for the story that is about to follow:
- Many years later, as he faced the firing squad, Colonel Aureliana Buendía was to remember that distant afternoon when his father took him to discover ice.
Anna Karenina by Leo Tolstoy does a similar thing by informing the reader that they are about to read a story about one unhappy family’s trials and tribulations:
- Happy families are all alike; every unhappy family is unhappy in its own way.
The wildly popular contemporary memoir, Wild by Cheryl Strayed uses thesis to provide a framework and also set the plot in motion:
- My solo three-month hike on the Pacific Crest Trail had many beginnings. There was the first, flip decision to do it, followed by the second, more serious decision to actually do it, and then the long third beginning, composed of weeks of shopping and packing and preparing to do it.
Recap: What is a Thesis in Literature?
Thesis is a tool used to provide context in the beginning of a work of writing that will help the reader to gain an idea of what is about to be argued, revealed, or developed. Thesis statements are necessary to providing structure and direction for the reader and good writing upholds the thesis statement throughout the entirety of the piece.
Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects

Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing a Thesis

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Once you've read the story or novel closely, look back over your notes for patterns of questions or ideas that interest you. Have most of your questions been about the characters, how they develop or change?
For example: If you are reading Conrad's The Secret Agent , do you seem to be most interested in what the author has to say about society? Choose a pattern of ideas and express it in the form of a question and an answer such as the following: Question: What does Conrad seem to be suggesting about early twentieth-century London society in his novel The Secret Agent ? Answer: Conrad suggests that all classes of society are corrupt. Pitfalls: Choosing too many ideas. Choosing an idea without any support.
Once you have some general points to focus on, write your possible ideas and answer the questions that they suggest.
For example: Question: How does Conrad develop the idea that all classes of society are corrupt? Answer: He uses images of beasts and cannibalism whether he's describing socialites, policemen or secret agents.
To write your thesis statement, all you have to do is turn the question and answer around. You've already given the answer, now just put it in a sentence (or a couple of sentences) so that the thesis of your paper is clear.
For example: In his novel, The Secret Agent , Conrad uses beast and cannibal imagery to describe the characters and their relationships to each other. This pattern of images suggests that Conrad saw corruption in every level of early twentieth-century London society.
Now that you're familiar with the story or novel and have developed a thesis statement, you're ready to choose the evidence you'll use to support your thesis. There are a lot of good ways to do this, but all of them depend on a strong thesis for their direction.
For example: Here's a student's thesis about Joseph Conrad's The Secret Agent . In his novel, The Secret Agent , Conrad uses beast and cannibal imagery to describe the characters and their relationships to each other. This pattern of images suggests that Conrad saw corruption in every level of early twentieth-century London society. This thesis focuses on the idea of social corruption and the device of imagery. To support this thesis, you would need to find images of beasts and cannibalism within the text.

What is a Thesis? Definition, Examples of Theses in Literature
Home » The Writer’s Dictionary » What is a Thesis? Definition, Examples of Theses in Literature
Thesis definition: A thesis is a statement in which the writer conveys his position regarding a topic.
What is a Thesis?
A thesis statement refers to part of an essay where the writer establishes his position regarding a topic. This is the position that the writer will further explore throughout his paper.
Example of Thesis
- Topic : religious freedom.
- Thesis : All citizens of the United States should be allowed to exercise the religion of their choice freely without interference from government.
- Explanation : In this thesis statement, the writer has taken the position that all citizens should be free to worship and practice their religion as they see fit. The government should not pressure citizens into any religion, and it should not persecute members of any faith community.
The Importance of a Thesis Statement
Thesis statements are important in order to establish the writer’s position regarding a topic or idea. They help to introduce the essay and set a focus for the reader.
Narrative thesis statements are found in narrative essays or in literature. They set the scene for the lesson that will be explored or taught through the piece.
Famous opening lines that exemplify a narrative thesis:
- The following narrative thesis is found in A Tale of Two Cities by Charles Dickens:
“It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair.”
The Function of Thesis in Literature
Narrative thesis statements are important in literature in order to establish the purpose for the work or introduce the lesson that the novel will attempt to teach. This allows the reader to have a focus when beginning the novel in order to effectively engage them into the story.
Examples of Theses in Literature
In the memoir, I am Malala by Malala Yousafzai, a thesis statement can be found in the beginning pages of her story.
- “One year ago I left my home for school and never returned. I was shot by a Taliban bullet and was flown out of Pakistan unconscious. Some people say I will never return home, but I believe firmly in my heart that I will. To be torn from the country that you love is not something to wish on anyone.”
In this thesis statement, Yousafzai establishes the basis of her memoir, which is to tell the story of how she was forced to leave her home.
In Vladmir Nabokov’s Lolita , a thesis can be seen in the line, “Lolita, light of my life, the fire of my loins”.
Here the narrator establishes the identity of the young nymph that he is unhealthily obsessed with in the story. Lolita is a young child while he is a grown man; therefore, this statement creates the uneasy feeling about him that continues throughout the novel.
Summary: What Are Theses?
Define thesis in literature: In summation, a thesis statement establishes a purpose in the piece of writing. It may establish the lesson or story to be told, or in an essay it may establish the position the writer assumes when exploring a topic.
Either way, it is important for the thesis to be clear in order to effectively convey the writer’s message.
Final Example:
In Edgar Allan Poe’s “The Cask of Amontillado,” the thesis statement can be found in the first line of the short story. Montresor immediately states his purpose, “the thousand injuries of Fortunato I had borne as best I could, but when he ventured upon insult I vowed revenge.”
In this statement, Montresor states that he will be seeking revenge after being treated wrongly by Fortunato. By beginning the story with the narrative thesis establishes the purpose for the remainder of the piece.
Thesis Definition
A thesis is a statement in a non- fiction or a fiction work that a writer intends to support and prove. One can find examples of thesis statement at the beginning of literary pieces. These thesis statements are of utmost importance, as they provide clear indicators as to which direction the writer will follow in their work.
A thesis statement is carefully crafted by a writer, and is marked by vigilant selection of words that will never miss its target. Generally, such a statement shows up in the first paragraph, or what is called an introduction. Despite writers’ efforts to prove their thesis statements, not all of these statements can be verified for their exactness. Nevertheless, they do develop an argument .
Importance of a Thesis Statement
In writing an essay , a thesis statement determines the worth of the essay by its capacity to stay focused on its thesis statement. For instance, if a writer fails to clearly mention or define a solid thesis statement in his or her essay , it will be difficult for readers to track the issue the writer plans to discuss and explain. Suppose a writer wants to write an essay on how to make a perfect fruit salad, the quality of his or her writing will exceedingly improve if he or she lets the readers know the subject matter at the start of the essay , for example:
“In this essay , I will tell you how to make the perfect fruit salad. Not only will it be tasty, but also healthy for your body.”
Narrative Thesis
In a narrative essay , or narrative section of a piece of literature, a thesis statement is called a “ narrative thesis.” A narrative thesis can be an apparent one or a hidden or implied one. In both cases, such a statement is a powerful, propelling force behind an entire work, that guides it toward its ultimate purpose and the lesson it intends to instruct.
Narrative Thesis Examples
Below is a list of a few narrative thesis examples – opening lines that determine the entire course of the narratives.
Example #1: Pride and Prejudice (By Jane Austen)
“It is a truth universally acknowledged that a single man in possession of a good fortune, must be in want of a wife.”
Example #2: One Hundred Years of Solitude (By Gabriel García Márquez)
“Many years later, as he faced the firing squad, Colonel Aureliano Buendía was to remember that distant afternoon when his father took him to discover ice.”
Example #3: Lolita (By Vladimir Nabokov)
“Lolita, light of my life, fire of my loins.”
Example #4: Anna Karenina (By Leo Tolstoy)
“Happy families are all alike; every unhappy family is unhappy in its own way.”
Example #5: 1984 (By George Orwell)
“It was a bright cold day in April, and the clocks were striking thirteen.”
Example #6: A Tale of Two Cities (By Charles Dickens)
“It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair.”
Example #7: The Catcher in the Rye (By J. D. Salinger)
“If you really want to hear about it, the first thing you’ll probably want to know is where I was born, and what my lousy childhood was like, and how my parents were occupied and all before they had me, and all that David Copperfield kind of crap, but I don’t feel like going into it, if you want to know the truth.”
Example #8: A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man (By James Joyce)
“Once upon a time and a very good time it was there was a moocow coming down along the road and this moocow that was coming down along the road met a nicens little boy named baby tuckoo.”
Function of Thesis
The above arguments clearly reveal the function of a thesis statements or a narrative thesis as a driving force behind a literary composition. It guides the narrative toward its ultimate purpose, which is the moral lesson it aims to inculcate.
beginner's guide to literary analysis
Understanding literature & how to write literary analysis.
Literary analysis is the foundation of every college and high school English class. Once you can comprehend written work and respond to it, the next step is to learn how to think critically and complexly about a work of literature in order to analyze its elements and establish ideas about its meaning.
If that sounds daunting, it shouldn’t. Literary analysis is really just a way of thinking creatively about what you read. The practice takes you beyond the storyline and into the motives behind it.
While an author might have had a specific intention when they wrote their book, there’s still no right or wrong way to analyze a literary text—just your way. You can use literary theories, which act as “lenses” through which you can view a text. Or you can use your own creativity and critical thinking to identify a literary device or pattern in a text and weave that insight into your own argument about the text’s underlying meaning.
Now, if that sounds fun, it should , because it is. Here, we’ll lay the groundwork for performing literary analysis, including when writing analytical essays, to help you read books like a critic.
What Is Literary Analysis?
As the name suggests, literary analysis is an analysis of a work, whether that’s a novel, play, short story, or poem. Any analysis requires breaking the content into its component parts and then examining how those parts operate independently and as a whole. In literary analysis, those parts can be different devices and elements—such as plot, setting, themes, symbols, etcetera—as well as elements of style, like point of view or tone.
When performing analysis, you consider some of these different elements of the text and then form an argument for why the author chose to use them. You can do so while reading and during class discussion, but it’s particularly important when writing essays.
Literary analysis is notably distinct from summary. When you write a summary , you efficiently describe the work’s main ideas or plot points in order to establish an overview of the work. While you might use elements of summary when writing analysis, you should do so minimally. You can reference a plot line to make a point, but it should be done so quickly so you can focus on why that plot line matters . In summary (see what we did there?), a summary focuses on the “ what ” of a text, while analysis turns attention to the “ how ” and “ why .”
While literary analysis can be broad, covering themes across an entire work, it can also be very specific, and sometimes the best analysis is just that. Literary critics have written thousands of words about the meaning of an author’s single word choice; while you might not want to be quite that particular, there’s a lot to be said for digging deep in literary analysis, rather than wide.
Although you’re forming your own argument about the work, it’s not your opinion . You should avoid passing judgment on the piece and instead objectively consider what the author intended, how they went about executing it, and whether or not they were successful in doing so. Literary criticism is similar to literary analysis, but it is different in that it does pass judgement on the work. Criticism can also consider literature more broadly, without focusing on a singular work.
Once you understand what constitutes (and doesn’t constitute) literary analysis, it’s easy to identify it. Here are some examples of literary analysis and its oft-confused counterparts:
Summary: In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” the narrator visits his friend Roderick Usher and witnesses his sister escape a horrible fate.
Opinion: In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” Poe uses his great Gothic writing to establish a sense of spookiness that is enjoyable to read.
Literary Analysis: “Throughout ‘The Fall of the House of Usher,’ Poe foreshadows the fate of Madeline by creating a sense of claustrophobia for the reader through symbols, such as in the narrator’s inability to leave and the labyrinthine nature of the house.
In summary, literary analysis is:
- Breaking a work into its components
- Identifying what those components are and how they work in the text
- Developing an understanding of how they work together to achieve a goal
- Not an opinion, but subjective
- Not a summary, though summary can be used in passing
- Best when it deeply, rather than broadly, analyzes a literary element
Literary Analysis and Other Works
As discussed above, literary analysis is often performed upon a single work—but it doesn’t have to be. It can also be performed across works to consider the interplay of two or more texts. Regardless of whether or not the works were written about the same thing, or even within the same time period, they can have an influence on one another or a connection that’s worth exploring. And reading two or more texts side by side can help you to develop insights through comparison and contrast.
For example, Paradise Lost is an epic poem written in the 17th century, based largely on biblical narratives written some 700 years before and which later influenced 19th century poet John Keats. The interplay of works can be obvious, as here, or entirely the inspiration of the analyst. As an example of the latter, you could compare and contrast the writing styles of Ralph Waldo Emerson and Edgar Allan Poe who, while contemporaries in terms of time, were vastly different in their content.
Additionally, literary analysis can be performed between a work and its context. Authors are often speaking to the larger context of their times, be that social, political, religious, economic, or artistic. A valid and interesting form is to compare the author’s context to the work, which is done by identifying and analyzing elements that are used to make an argument about the writer’s time or experience.
For example, you could write an essay about how Hemingway’s struggles with mental health and paranoia influenced his later work, or how his involvement in the Spanish Civil War influenced his early work. One approach focuses more on his personal experience, while the other turns to the context of his times—both are valid.
Why Does Literary Analysis Matter?
Sometimes an author wrote a work of literature strictly for entertainment’s sake, but more often than not, they meant something more. Whether that was a missive on world peace, commentary about femininity, or an allusion to their experience as an only child, the author probably wrote their work for a reason, and understanding that reason—or the many reasons—can actually make reading a lot more meaningful.
Performing literary analysis as a form of study unquestionably makes you a better reader. It’s also likely that it will improve other skills, too, like critical thinking, creativity, debate, and reasoning.
At its grandest and most idealistic, literary analysis even has the ability to make the world a better place. By reading and analyzing works of literature, you are able to more fully comprehend the perspectives of others. Cumulatively, you’ll broaden your own perspectives and contribute more effectively to the things that matter to you.
Literary Terms to Know for Literary Analysis
There are hundreds of literary devices you could consider during your literary analysis, but there are some key tools most writers utilize to achieve their purpose—and therefore you need to know in order to understand that purpose. These common devices include:
- Characters: The people (or entities) who play roles in the work. The protagonist is the main character in the work.
- Conflict: The conflict is the driving force behind the plot, the event that causes action in the narrative, usually on the part of the protagonist
- Context : The broader circumstances surrounding the work political and social climate in which it was written or the experience of the author. It can also refer to internal context, and the details presented by the narrator
- Diction : The word choice used by the narrator or characters
- Genre: A category of literature characterized by agreed upon similarities in the works, such as subject matter and tone
- Imagery : The descriptive or figurative language used to paint a picture in the reader’s mind so they can picture the story’s plot, characters, and setting
- Metaphor: A figure of speech that uses comparison between two unlike objects for dramatic or poetic effect
- Narrator: The person who tells the story. Sometimes they are a character within the story, but sometimes they are omniscient and removed from the plot.
- Plot : The storyline of the work
- Point of view: The perspective taken by the narrator, which skews the perspective of the reader
- Setting : The time and place in which the story takes place. This can include elements like the time period, weather, time of year or day, and social or economic conditions
- Symbol : An object, person, or place that represents an abstract idea that is greater than its literal meaning
- Syntax : The structure of a sentence, either narration or dialogue, and the tone it implies
- Theme : A recurring subject or message within the work, often commentary on larger societal or cultural ideas
- Tone : The feeling, attitude, or mood the text presents
How to Perform Literary Analysis
Step 1: read the text thoroughly.
Literary analysis begins with the literature itself, which means performing a close reading of the text. As you read, you should focus on the work. That means putting away distractions (sorry, smartphone) and dedicating a period of time to the task at hand.
It’s also important that you don’t skim or speed read. While those are helpful skills, they don’t apply to literary analysis—or at least not this stage.
Step 2: Take Notes as You Read
As you read the work, take notes about different literary elements and devices that stand out to you. Whether you highlight or underline in text, use sticky note tabs to mark pages and passages, or handwrite your thoughts in a notebook, you should capture your thoughts and the parts of the text to which they correspond. This—the act of noticing things about a literary work—is literary analysis.
Step 3: Notice Patterns
As you read the work, you’ll begin to notice patterns in the way the author deploys language, themes, and symbols to build their plot and characters. As you read and these patterns take shape, begin to consider what they could mean and how they might fit together.
As you identify these patterns, as well as other elements that catch your interest, be sure to record them in your notes or text. Some examples include:
- Circle or underline words or terms that you notice the author uses frequently, whether those are nouns (like “eyes” or “road”) or adjectives (like “yellow” or “lush”).
- Highlight phrases that give you the same kind of feeling. For example, if the narrator describes an “overcast sky,” a “dreary morning,” and a “dark, quiet room,” the words aren’t the same, but the feeling they impart and setting they develop are similar.
- Underline quotes or prose that define a character’s personality or their role in the text.
- Use sticky tabs to color code different elements of the text, such as specific settings or a shift in the point of view.
By noting these patterns, comprehensive symbols, metaphors, and ideas will begin to come into focus.
Step 4: Consider the Work as a Whole, and Ask Questions
This is a step that you can do either as you read, or after you finish the text. The point is to begin to identify the aspects of the work that most interest you, and you could therefore analyze in writing or discussion.
Questions you could ask yourself include:
- What aspects of the text do I not understand?
- What parts of the narrative or writing struck me most?
- What patterns did I notice?
- What did the author accomplish really well?
- What did I find lacking?
- Did I notice any contradictions or anything that felt out of place?
- What was the purpose of the minor characters?
- What tone did the author choose, and why?
The answers to these and more questions will lead you to your arguments about the text.
Step 5: Return to Your Notes and the Text for Evidence
As you identify the argument you want to make (especially if you’re preparing for an essay), return to your notes to see if you already have supporting evidence for your argument. That’s why it’s so important to take notes or mark passages as you read—you’ll thank yourself later!
If you’re preparing to write an essay, you’ll use these passages and ideas to bolster your argument—aka, your thesis. There will likely be multiple different passages you can use to strengthen multiple different aspects of your argument. Just be sure to cite the text correctly!
If you’re preparing for class, your notes will also be invaluable. When your teacher or professor leads the conversation in the direction of your ideas or arguments, you’ll be able to not only proffer that idea but back it up with textual evidence. That’s an A+ in class participation.
Step 6: Connect These Ideas Across the Narrative
Whether you’re in class or writing an essay, literary analysis isn’t complete until you’ve considered the way these ideas interact and contribute to the work as a whole. You can find and present evidence, but you still have to explain how those elements work together and make up your argument.
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay
When conducting literary analysis while reading a text or discussing it in class, you can pivot easily from one argument to another (or even switch sides if a classmate or teacher makes a compelling enough argument).
But when writing literary analysis, your objective is to propose a specific, arguable thesis and convincingly defend it. In order to do so, you need to fortify your argument with evidence from the text (and perhaps secondary sources) and an authoritative tone.
A successful literary analysis essay depends equally on a thoughtful thesis, supportive analysis, and presenting these elements masterfully. We’ll review how to accomplish these objectives below.
Step 1: Read the Text. Maybe Read It Again.
Constructing an astute analytical essay requires a thorough knowledge of the text. As you read, be sure to note any passages, quotes, or ideas that stand out. These could serve as the future foundation of your thesis statement. Noting these sections now will help you when you need to gather evidence.
The more familiar you become with the text, the better (and easier!) your essay will be. Familiarity with the text allows you to speak (or in this case, write) to it confidently. If you only skim the book, your lack of rich understanding will be evident in your essay. Alternatively, if you read the text closely—especially if you read it more than once, or at least carefully revisit important passages—your own writing will be filled with insight that goes beyond a basic understanding of the storyline.
Step 2: Brainstorm Potential Topics
Because you took detailed notes while reading the text, you should have a list of potential topics at the ready. Take time to review your notes, highlighting any ideas or questions you had that feel interesting. You should also return to the text and look for any passages that stand out to you.
When considering potential topics, you should prioritize ideas that you find interesting. It won’t only make the whole process of writing an essay more fun, your enthusiasm for the topic will probably improve the quality of your argument, and maybe even your writing. Just like it’s obvious when a topic interests you in a conversation, it’s obvious when a topic interests the writer of an essay (and even more obvious when it doesn’t).
Your topic ideas should also be specific, unique, and arguable. A good way to think of topics is that they’re the answer to fairly specific questions. As you begin to brainstorm, first think of questions you have about the text. Questions might focus on the plot, such as: Why did the author choose to deviate from the projected storyline? Or why did a character’s role in the narrative shift? Questions might also consider the use of a literary device, such as: Why does the narrator frequently repeat a phrase or comment on a symbol? Or why did the author choose to switch points of view each chapter?
Once you have a thesis question , you can begin brainstorming answers—aka, potential thesis statements . At this point, your answers can be fairly broad. Once you land on a question-statement combination that feels right, you’ll then look for evidence in the text that supports your answer (and helps you define and narrow your thesis statement).
For example, after reading “ The Fall of the House of Usher ,” you might be wondering, Why are Roderick and Madeline twins?, Or even: Why does their relationship feel so creepy?” Maybe you noticed (and noted) that the narrator was surprised to find out they were twins, or perhaps you found that the narrator’s tone tended to shift and become more anxious when discussing the interactions of the twins.
Once you come up with your thesis question, you can identify a broad answer, which will become the basis for your thesis statement. In response to the questions above, your answer might be, “Poe emphasizes the close relationship of Roderick and Madeline to foreshadow that their deaths will be close, too.”
Step 3: Gather Evidence
Once you have your topic (or you’ve narrowed it down to two or three), return to the text (yes, again) to see what evidence you can find to support it. If you’re thinking of writing about the relationship between Roderick and Madeline in “The Fall of the House of Usher,” look for instances where they engaged in the text.
This is when your knowledge of literary devices comes in clutch. Carefully study the language around each event in the text that might be relevant to your topic. How does Poe’s diction or syntax change during the interactions of the siblings? How does the setting reflect or contribute to their relationship? What imagery or symbols appear when Roderick and Madeline are together?
By finding and studying evidence within the text, you’ll strengthen your topic argument—or, just as valuably, discount the topics that aren’t strong enough for analysis.
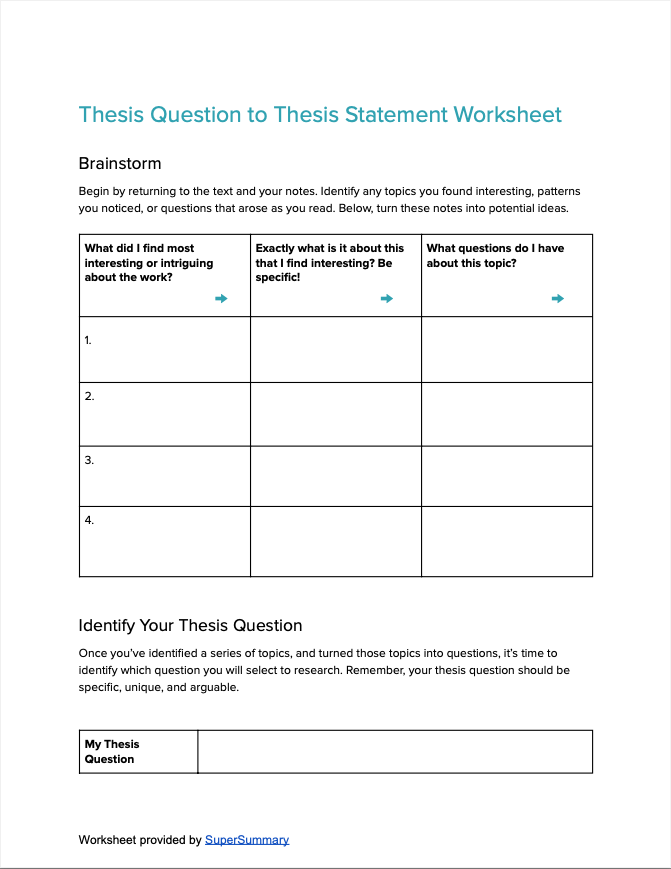
Step 4: Consider Secondary Sources
In addition to returning to the literary work you’re studying for evidence, you can also consider secondary sources that reference or speak to the work. These can be articles from journals you find on JSTOR, books that consider the work or its context, or articles your teacher shared in class.
While you can use these secondary sources to further support your idea, you should not overuse them. Make sure your topic remains entirely differentiated from that presented in the source.
Step 5: Write a Working Thesis Statement
Once you’ve gathered evidence and narrowed down your topic, you’re ready to refine that topic into a thesis statement. As you continue to outline and write your paper, this thesis statement will likely change slightly, but this initial draft will serve as the foundation of your essay. It’s like your north star: Everything you write in your essay is leading you back to your thesis.
Writing a great thesis statement requires some real finesse. A successful thesis statement is:
- Debatable : You shouldn’t simply summarize or make an obvious statement about the work. Instead, your thesis statement should take a stand on an issue or make a claim that is open to argument. You’ll spend your essay debating—and proving—your argument.
- Demonstrable : You need to be able to prove, through evidence, that your thesis statement is true. That means you have to have passages from the text and correlative analysis ready to convince the reader that you’re right.
- Specific : In most cases, successfully addressing a theme that encompasses a work in its entirety would require a book-length essay. Instead, identify a thesis statement that addresses specific elements of the work, such as a relationship between characters, a repeating symbol, a key setting, or even something really specific like the speaking style of a character.
Example: By depicting the relationship between Roderick and Madeline to be stifling and almost otherworldly in its closeness, Poe foreshadows both Madeline’s fate and Roderick’s inability to choose a different fate for himself.
Step 6: Write an Outline
You have your thesis, you have your evidence—but how do you put them together? A great thesis statement (and therefore a great essay) will have multiple arguments supporting it, presenting different kinds of evidence that all contribute to the singular, main idea presented in your thesis.
Review your evidence and identify these different arguments, then organize the evidence into categories based on the argument they support. These ideas and evidence will become the body paragraphs of your essay.
For example, if you were writing about Roderick and Madeline as in the example above, you would pull evidence from the text, such as the narrator’s realization of their relationship as twins; examples where the narrator’s tone of voice shifts when discussing their relationship; imagery, like the sounds Roderick hears as Madeline tries to escape; and Poe’s tendency to use doubles and twins in his other writings to create the same spooky effect. All of these are separate strains of the same argument, and can be clearly organized into sections of an outline.
Step 7: Write Your Introduction
Your introduction serves a few very important purposes that essentially set the scene for the reader:
- Establish context. Sure, your reader has probably read the work. But you still want to remind them of the scene, characters, or elements you’ll be discussing.
- Present your thesis statement. Your thesis statement is the backbone of your analytical paper. You need to present it clearly at the outset so that the reader understands what every argument you make is aimed at.
- Offer a mini-outline. While you don’t want to show all your cards just yet, you do want to preview some of the evidence you’ll be using to support your thesis so that the reader has a roadmap of where they’re going.
Step 8: Write Your Body Paragraphs
Thanks to steps one through seven, you’ve already set yourself up for success. You have clearly outlined arguments and evidence to support them. Now it’s time to translate those into authoritative and confident prose.
When presenting each idea, begin with a topic sentence that encapsulates the argument you’re about to make (sort of like a mini-thesis statement). Then present your evidence and explanations of that evidence that contribute to that argument. Present enough material to prove your point, but don’t feel like you necessarily have to point out every single instance in the text where this element takes place. For example, if you’re highlighting a symbol that repeats throughout the narrative, choose two or three passages where it is used most effectively, rather than trying to squeeze in all ten times it appears.
While you should have clearly defined arguments, the essay should still move logically and fluidly from one argument to the next. Try to avoid choppy paragraphs that feel disjointed; every idea and argument should feel connected to the last, and, as a group, connected to your thesis. A great way to connect the ideas from one paragraph to the next is with transition words and phrases, such as:
- Furthermore
- In addition
- On the other hand
- Conversely
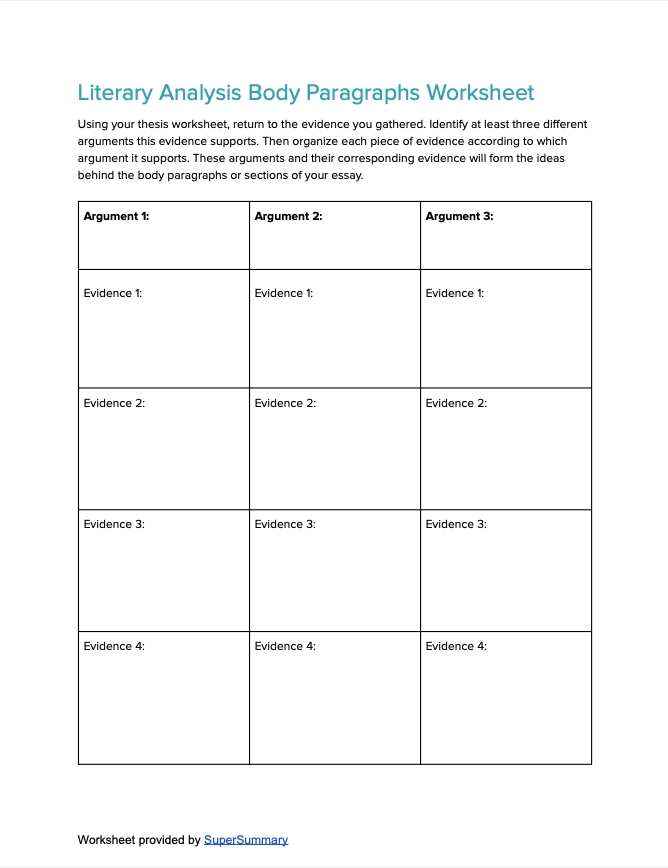
Step 9: Write Your Conclusion
Your conclusion is more than a summary of your essay's parts, but it’s also not a place to present brand new ideas not already discussed in your essay. Instead, your conclusion should return to your thesis (without repeating it verbatim) and point to why this all matters. If writing about the siblings in “The Fall of the House of Usher,” for example, you could point out that the utilization of twins and doubles is a common literary element of Poe’s work that contributes to the definitive eeriness of Gothic literature.
While you might speak to larger ideas in your conclusion, be wary of getting too macro. Your conclusion should still be supported by all of the ideas that preceded it.
Step 10: Revise, Revise, Revise
Of course you should proofread your literary analysis essay before you turn it in. But you should also edit the content to make sure every piece of evidence and every explanation directly supports your thesis as effectively and efficiently as possible.
Sometimes, this might mean actually adapting your thesis a bit to the rest of your essay. At other times, it means removing redundant examples or paraphrasing quotations. Make sure every sentence is valuable, and remove those that aren’t.
Other Resources for Literary Analysis
With these skills and suggestions, you’re well on your way to practicing and writing literary analysis. But if you don’t have a firm grasp on the concepts discussed above—such as literary devices or even the content of the text you’re analyzing—it will still feel difficult to produce insightful analysis.
If you’d like to sharpen the tools in your literature toolbox, there are plenty of other resources to help you do so:
- Check out our expansive library of Literary Devices . These could provide you with a deeper understanding of the basic devices discussed above or introduce you to new concepts sure to impress your professors ( anagnorisis , anyone?).
- This Academic Citation Resource Guide ensures you properly cite any work you reference in your analytical essay.
- Our English Homework Help Guide will point you to dozens of resources that can help you perform analysis, from critical reading strategies to poetry helpers.
- This Grammar Education Resource Guide will direct you to plenty of resources to refine your grammar and writing (definitely important for getting an A+ on that paper).
Of course, you should know the text inside and out before you begin writing your analysis. In order to develop a true understanding of the work, read through its corresponding SuperSummary study guide . Doing so will help you truly comprehend the plot, as well as provide some inspirational ideas for your analysis.
- Literary Terms
Literary terms refer to the technique, style, and formatting used by writers and speakers to masterfully emphasize, embellish, or strengthen their compositions. Literary terms can refer to playful techniques employed by comedians to make us laugh or witty tricks wordsmiths use to coin new words or phrases. They can also include the tools of persuasion that writers use to convince and drive audiences to action. With their carefully crafted speeches geared towards both logical and emotional thinking, they challenge our everyday modes of thinking.
Literary terms also include powerful figurative language that writers use to summon emotion ranging from guilt to anger to bliss, and to allow us to see the world in new and magical ways. Words can be arranged to give poems, songs, and prose alike, rhythm and musicality. They can animate a story with such wealth of detail, character development, and action that as readers, we are taken by a story, and feel as if the people on the page are real. Literary terms have a wide range of application, from the poet’s beauty, to the speaker’s persuasion, to the novelist’s story development.
The importance of Literary Terms
Literary terms are important in a wide variety of ways. They allow writers and speakers to make comments on society, politics, and trends. Rhetorical devices can be used to strengthen arguments which persuade and convince audiences. Poetic figurative language can summon emotions and visions of nature and the world in unique and compelling ways. Literary terms have the power to create serious, comedic, or whimsical moods via tools of persuasion, poeticism, and wordplay.
When to use Literary Terms
This depends. The variety of uses for literary terms spans across genres and is remarkably wide-ranging based on the goals or needs of the writer. Below we have categorized this vast subject.
1. Persuasion
One of the most difficult tasks in the world is making people change their minds. Most of us are stubborn in our thinking and stick to our guns when it comes to views on morality, politics, and our own personal lives. For a rhetorician or speechwriter, writing and speaking in a convincing and persuasive manner is a profession, one which utilizes numerous tools of the trade to appeal to an audience. The power of persuasion can gain voters for a politician, convince people to take action for a cause, or get you a raise at your job. With appeals to both pure logic and powerful emotion, persuasion is an art that has been employed for centuries.
The importance of Persuasion
Persuasion is an extremely powerful tool, as gaining the hearts and minds of an audience means gaining their support and action. Persuasion empowers the writer to change the mind of the audience and to compel the audience to take action in a certain way.
When to use Persuasion
Persuasive tools are utilized by politicians, professional speakers, speechwriters, journalists, and poetry and prose writers. Persuasion should be used when convincing others is the goal in mind. In a piece which is supposed to be objective or unbiased such as a journalistic report, tools of persuasion should be avoided.
Common Terms
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); satire.
Satire refers to a play, novel, poem, film or other composition which uses comedy, irony, mockery, and exaggeration to criticize the absurdity or weaknesses of a certain person, institution, or situation. Often, satire utilizes comedy for more serious means, such as political and social commentary.
For an example of satire, see Jon Stewart’s The Daily Show which regularly satirizes news media:

Rhetorical Questions
A rhetorical question is a question asked in a form which does not in reality seek an answer but rather emphasizes a certain point. We often use rhetorical questions in everyday conversation as well as in speeches. Here are a few examples of rhetorical questions:
- Why would anyone do such a thing?
- How much longer will we allow such injustices to exist?
- Are you kidding me?
2. Figurative Language
For centuries, poets and laypeople alike have used beautiful language to celebrate nature, compliment lovers, and launch the mundane into the mystical. Figurative language is writing which appeals to the senses. Rather than operating on logic or literalness, figurative language makes unique connections based on connotation, sound, and construction of words and phrases.
The importance of Figurative Language
Figurative language creates connections between unlike things which have never been considered before. It encourages complicated, creative, and poetic thought processes which give rise to beautiful, strange, and unique conceptions. Figurative language allows writers to transcend logical and typical bounds of thinking in order to present things in a new and meaningful way.
When to use Figurative Language
Figurative language is a chief component of poetic language as used in prose, poetry, speeches, and songs. Because figurative language is not literal, it should not be used in compositions which are meant to be taken literally, such as scientific and mathematic manuals or textbooks.
A metaphor is a direct and vivid comparison between two things usually considered distinct or unrelated. Metaphors discover the connections between unique things and emphasize their similarities poetically without being taken literally. Here are a few examples of metaphor:
- Her smile is the sun.
- He’s a black sheep.
- All the world’s a stage.
Hyperbole is a remarkably exaggerated statement or idea meant to be taken figuratively rather than literally. Hyperbole exaggerates certain elements of ideas or things for comedic or dramatic effects. Here are a few examples of hyperbole:
- I’m so hungry I could eat a horse!
- That was the best performance I’ve ever seen in my entire life.
- I’d kill for a glass of Coca-Cola.
3. Plot and Character Devices
A story is not a story without a plot and characters . Things must happen, and they must happen to interesting people who are flawed, capable of change, and active in their world. Plots are not always simple or linear, though, and characters are elements of a story which may be built, developed, and complicated. Novelists, poets, journalists, filmmakers, and others use numerous elements in making a compelling, interesting, and believable story.
The importance of Plot and Character Devices
Plot and character devices reveal how complicated compositions can be with a variety of necessary elements that piece the story together. Stories in any form require a variety of plot and character devices to shape their development and supply their meaning.
When to use Plot and Character Devices
Plot and character devices are elements of the story which could be told in many forms including poetry, prose, playwriting, song, television, film, and others. Devices used in Greek tragedies and in Shakespeare’s classics are still in use by novelists, story writers, poets, and playwrights today.
A flashback is a moment in which the linear story is interrupted and launched to an event that occurred in the past. Flashbacks are used to provide more information about the present and to further develop plots and characters in a way that is more interesting and complicated than a simple chronological plot. Here is an example of flashback:
A man is shopping when he sees a woman at the end of the aisle. The story flashes back, showing that he previously had a relationship with her, a relationship that ended badly. He swiftly turns around and enters a different aisle, avoiding her sight.
This flashback shows us that the woman in the store is important to the man, as she was an important person in his past.
Climax is one of the most important and necessary elements of a story’s plot, as all drama that has been developing over the course of the story reaches a breaking point when something or someone must change. This is the most dramatic, meaningful, and suspenseful moment in the story. Here is an example of the climax in a story:
A boy has been shipwrecked and has struggled to survive on a desert island. When a plane flies over him, he is prepared with a large fire burning. The plane circles back and lands on the island, where he is at last rescued.
The climax of this story occurs when the boy’s suffering and struggling end with his rescue.
4. Sound and Rhythm
The way we word things can create rhythm, musicality, and poetry for the reader or listener. Poetry in particular operates on syllable counts, arrangement of lines, usage of certain hard or soft sounds, and pattern-making with rhyme and other devices. Soft s sounds can create calm and smoothness, whereas hard k sounds create chaos and harshness. A variety of sound and rhythm devices take advantage of connotative noises and the feelings they evoke in the audience. Sound and rhythm create powerful poetry, prose, speeches, and songs.
The importance of Sound and Rhythm
Sound and rhythm appeal to us just as naturally as heartbeats, rain on the roof, and the shuffle of feet on the sidewalk do. Rhythm provides soothing and meaningful repetition and emphasis in prose and poetry. Sound, on the other hand, is connotative of numerous feelings from anger to sadness based on arrangement of vowel and consonant sounds.
When to use Sound and Rhythm
Sound and rhythm can be used in all compositions from poetry and song to prose and speechmaking to film and television dialogue. Poetic emphasis on sound and rhythm is typically artistic, so it should not be emphasized in more serious and logical compositions such as formal essays or textbooks.
- Alliteration
Alliteration is the repetition of a certain sound at the beginning of successive words or phrases. Alliteration is used to create rhythm through repetition and to evoke emotion through connotations attached to certain sounds. Here are a few examples of alliteration:
- Sarah swam smoothly and silently across the sound.
- Kathy creates crazy and chaotic chants.
- Bret brought bundles of bread to the bakery.
- Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia refers to words which sound like that which they describe. Onomatopoeia creates a vivid reading experience, as words are automatic forms of sound imagery. Here are a few examples of onomatopoeia:
- The explosion erupted with a boom !
- The horses clip-clopped across the street.
- Fall leaves rustled in the whistling
5. Wordplay
Have you ever heard someone describe a phrase as “punny”? Punny is a blend word, or portmanteau, which combines “pun” and “funny” to describe a funny pun. This is an act of wordplay: rearranging a word in a creative way to change, emphasize, or mock its meaning. Wordplay is a creative act which allows writers and readers to flex their thinking muscles. Wordplay has been employed by greats like Shakespeare to create entirely new words, modern poets to hide interesting messages, and quirky comedians to show off witty thinking.
The importance of Wordplay
Much of poetry and comedy makes use of wordplay to emphasize beauty, intelligence, and wit. It is also a way for wordsmiths to sharpen their creative-thinking in crafting words in new and unique ways. Wordplay serves as proof that literature is evolving, as new words are invented each year. Readers and writers alike value wit and comedy in poetry, prose, and other forms.
When to use Wordplay
Wordplay is primarily a playful and creative technique which is used by poets, playwrights, novels, short story writers, and children’s writers in lighthearted and imaginative compositions. Wordplay can also be used in creating new words serious and silly alike. Because wordplay is creative and new, it should not be used in formal essays or manuals with a pre-designated lexicon.
Neologisms are literally new words, or words recently created in order to describe something which has never been described.
For example, a recent neologism is “spork,” meaning a combined spoon and fork.
Anagrams are a type of wordplay in which the letters of a word or phrase are rearranged to create a new word or phrase containing the exact same letters.
For example, an anagram of the word “anagram” would be “nag a ram!”
6. Errors to Avoid
Although it is important to be aware of useful devices at your disposal, it is also important to be aware of potential mistakes you may be making. Just as there are terms for correct usage of literary devices , there are terms for incorrect usage as well. These are the errors you should work to avoid in your writing.
- Malapropism
Malapropism is when a word is used incorrectly, often in place of one that sounds similar to the correct one. Here are a few common examples of malapropisms:
- “Supposively” instead of “supposedly”
- “For all intensive purposes” instead of “for all intents and purposes”
- “Fortuitously” instead of “fortunately”
A cliché is an overused saying or idea which has lost its original meaning or power. Clichés are to be avoided because they are trite and shallow. Here are a few common examples of clichés:
- Time heals all wounds
- What goes around comes around
- Every cloud has a silver lining
List of Terms
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The thesis (pronounced thee -seez), also known as a thesis statement, is the sentence that introduces the main argument or point of view of a composition (formal essay, nonfiction piece, or narrative). It is the main claim that the author is making about that topic and serves to summarize and introduce that writing that will be discussed ...
Definition of Thesis. A thesis is a statement or central idea that a writer puts forward at the beginning of an argument, and will support throughout the following text. The thesis is a premise that the author believes to be true, and will give evidence for by way of facts or situations that reinforce this central idea.
Thesis Definition. A thesis is a statement in a non-fiction or a fiction work that a writer intends to support and prove.One can find examples of thesis statement at the beginning of literary pieces. These thesis statements are of utmost importance, as they provide clear indicators as to which direction the writer will follow in their work.
Thesis Statement Formula. One way I find helpful to explain literary thesis statements is through a "formula": Thesis statement = Observation + Analysis + Significance. Observation: usually regarding the form or structure of the literature. This can be a pattern, like recurring literary devices.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Use Literary Terms in Thesis With Care; A Thesis Should be Balanced; A Thesis Can be a Blueprint; Avoid the Obvious. A thesis prepares the reader for what you are about to say. As such, your paper needs to be interesting in order for your thesis to be interesting. Your thesis needs to be interesting because it needs to capture a reader's attention.
A good thesis statement is the heart of an essay. It gives a gist of the thoughts a writer expresses in his essay. It determines the shape of the essay, predicts its content, and foreshadows its events. It narrates the whole story in just one sentence, provided the essay is a short one. Without a thesis statement, an essay is just a written ...
In literature, a thesis acts as an early source of information about what kind of story is about to be told. Authors can state the thesis outright in a literary work, or they can hide the thesis so that it blends in with the beginning of the story. The main purpose of a thesis in any type of literature, whether narrative or essay/academic, is ...
Use Literary Terms in Thesis With Care; A Thesis Should be Balanced; A Thesis Can be a Blueprint; Avoid the Obvious. A thesis prepares the reader for what you are about to say. As such, your paper needs to be interesting in order for your thesis to be interesting. Your thesis needs to be interesting because it needs to capture a reader's attention.
A thesis novel or play (a problem novel or play) is a literary work that advances, demonstrates, or defends a particular thesis. A thesis can also refer to the unstressed syllable in a metrical foot.
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
This thesis focuses on the idea of social corruption and the device of imagery. To support this thesis, you would need to find images of beasts and cannibalism within the text. This handout covers major topics relating to writing about fiction. This covers prewriting, close reading, thesis development, drafting, and common pitfalls to avoid.
A thesis statement is the main argument of a piece of writing. It can be found in academic/formal writing novel writing. A thesis statement is a position the author holds and that which they're going to prove through the text. It summarizes the writing that's going to follow and is usually found in the first paragraph of the introduction.
Thesis statements are important in order to establish the writer's position regarding a topic or idea. They help to introduce the essay and set a focus for the reader. Narrative thesis statements are found in narrative essays or in literature. They set the scene for the lesson that will be explored or taught through the piece.
Thesis Definition. A thesis is a statement in a non- fiction or a fiction work that a writer intends to support and prove. One can find examples of thesis statement at the beginning of literary pieces. These thesis statements are of utmost importance, as they provide clear indicators as to which direction the writer will follow in their work.
However, you can use literary terms in a thesis if the purpose is to explain how the terms contribute to the work's meaning or understanding. Here's an example of thesis statement that does call attention to literary devices because they are central to the paper's argument. Literary terms are placed in italics.
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
Literary Terms to Know for Literary Analysis . There are hundreds of literary devices you could consider during your literary analysis, but there are some key tools most writers utilize to achieve their purpose—and therefore you need to know in order to understand that purpose. These common devices include: Characters: The people (or entities) who play roles in the work.
A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay, and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay. A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to ...
Literary terms refer to the technique, style, and formatting used by writers and speakers to masterfully emphasize, embellish, or strengthen their compositions. Literary terms can refer to playful techniques employed by comedians to make us laugh or witty tricks wordsmiths use to coin new words or phrases. They can also include the tools of ...