My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics

170 Good Policy Speech Topics

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

A policy speech will essentially be a persuasive speech on some area of public policy . The subject can be an existing public policy, along with the speaker’s statements either supporting or opposing the policy. It may also be a proposed policy that the speaker believes is ineffective. Finally, the speech may concern a public problem and the speaker’s own ideas on how it could best be solved. This could be the speaker’s own ideas, or any combination of ideas already proposed by experts.
The speaker’s first challenge is to clearly describe the problem, and to persuade the audience to care about seeking a resolution . If the audience does not understand why the issue is important to society, and how it affects them personally, the rest of the speech is unlikely to be successful. The chosen problem may be a well-known controversial issue, or it may be a new concern that is unfamiliar to the audience. Regardless, the key to a successful speech is getting the audience to understand the problem, and to instill in them a desire to solve it.
The second part of the speech will present the policy in question . The speaker will share their opinion on the procedure, specifically whether or not they believe it will be effective. It is important to remember that this should be an educated opinion, not simply an emotional viewpoint. For example, a speaker should not argue an abortion topic from an emotional perspective, but rather with scientific facts and reliable researched data.
The speech’s topic should concern a problematic subject area that will elicit audience participation in solving it. It should also be a topic in which the speaker can become highly proficient, and there should be adequate research and data to back up any argument for or against the subject. At the end of the speech, the speaker’s goal may be to ask for passive agreement, or to call for the audience to take immediate action.
Please also see other topic ideas: list of persuasive topics , list of informative topics , and list of argumentative speech topics .
Writing research paper? See our list of 667 research paper topics .
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
List of policy persuasive speech topics
- Adoptees Right-to-Know Law
- Affirmative Action
- Aggregate productivity
- Agricultural Policy
- Agricultural subsidies damage African nations
- Art Censorship
- Attendance Policies (School, Work, etc.)
- Ban car racing in mass pollution areas
- Break Periods
- Censorship of Music
- Change K- School Start Times
- Client Complaints Procedures
- Climate Change Policy
- Company policy on computer usage
- Controlling the transportation fairs
- Corruption and bribery run today’s economy
- Crime Prevention
- Defense budget priorities
- Defense budget reduction
- Do you think immigration laws need to be revised
- Domestic Violence Drug Policy
- Downsizing Schools/Classrooms
- Drug Testing In The Workplace
- Election reform
- Emergency Procedures
- Eminent Domain
- Environmental sciences
- Equal Employment Opportunities
- Expanding Oil and Gas Drilling
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Feminists should be terminated
- Financial Assistance for Students
- Flood victims’ reforms
- Foreign Policy
- Freedom of Expression / Freedom of Speech
- Gambling Age should be Lowered
- Global Warming Laws
- Harassment Precautions
- Health Care Policy
- Hygiene Standards
- Identification Protocols
- Immigration Policies
- Job Discrimination based on Hair Color/Style
- Language Policy
- Legalizing prostitution could avoid campus date rape incidents
- Legalizing the sale of human organs could help reduce the lack of organ donors
- Maintaining Discipline in the Campus
- Medical Examination
- Merit Pay for Teachers
- National Tobacco Settlement
- Obstruction of Justice Laws
- Our constitution should protect hate speech
- Our foreign agenda for the United Nations
- Parents should be held responsible for their children’s actions
- Parliamentary terms should be limited
- Pension reform
- Police Brutality
- Policy to avoid betting in sporting events
- Political organizations should be forbidden at campuses
- Pornography on the Internet
- Prisoners’ Reforms
- Privacy Codes
- Racism and Racial Slurs (1st Amendment)
- Recycling Rules
- Regulations on applying safety devices
- School physical education should be required
- School Uniforms
- Sensor policy on the use of internet
- Sex education should stay the responsibility of the parents
- Sexist images of women should be banned
- Should our prison system change
- should teacher be graded
- Skateboarding Policies
- Smokers should be treated as drug addicts
- Social Security Reform
- State and church should be combined
- Sticking to the scheduled work hours and no two hour lunches
- Taxes (i.e. “sin” taxes, car taxes, taxation of the super rich)
- Teachers and Tenure
- Technical Loopholes in Law
- Teen Dating Violence Laws Strengthened
- The morning-after pill should be freely prescribed in drugstores and pharmacies
- The Patriot Act
- There is nothing wrong with the contents of Ten Commandments
- Trying Children as Adults
- U.S. policy toward Cuba
- VA Demerit Point System (driving)
- Videotaping In The Workplace
- Visitation Rules at your University/College
- Voter registration and absentee ballot
- Voting System (electoral college)
- Welfare mothers should be treated as working mothers
- Welfare reform
- What should be the minimum age for the voter?
- Whistleblower Procedure
- Why meals in school should be free
- Why restaurants who fail the health inspection the first time should be closed down
- Women in the Military
- Work Hours Plans
- Good governance means openness, transparency and accountability.
- Involvement of animals in research should be minimized, there are alternatives.
- Warrantless search and seizure must be allowed in the war on drugs and narcotics.
- We must ensure greater protection for marine environment biodiversity trough international protocols.
- There is nothing wrong with Double Dipping in collecting retirement pensions and company paycheck at the same time.
- We should spend 0.7 % of our gross national income on projects of international development.
- Guarantee free personal care for people with highest needs and serious diseases.
- Why invading North Korea is a no go plan.
- Tax exemptions on church property should be used for charitable and community work only.
- Terrorists should be tried in military tribunals and not in the regular criminal justice system.
- Why cities should insist on having their own local economic development policy.
- It is an illusion that green jobs are contributing to the economy and environment.
- Regulations to encourage healthy weight conditions among our youth.
- Stop clothing and textiles sweatshops.
- Support scholarship programs for street kids and at-risk kids.
- Eliminate weapons-usable materials from stores and shops.
- Administrative divisions ought to provide meaningful opportunities for disabled persons to access.
- The Kyoto Protocol does not effectively address carbon emission.
- Sanctions on Myanmar are largely ineffective.
- Western politicians should do more for the people on the African continent.
- Provide everywhere in our town access for people with disabilities. Parking, sanitary and access to a building.
- All voters should be required to show a photo identification or a fingerprint.
- Limit the President’s power to impose political sanctions on foreign nations. Using the blocking of assets method and trade restrictions often are effective.
- Everyone should have free access to some health care services.
- Urban shelters could help the homeless survive.
- We should spend more money to improve highways and railroads.
- We should not allow that the poor sell their organs for money.
- Housing, hiring and education must be equal for all.
- The government should spend more money to explore space solar systems.
- Corporation should have an accountability policy.
- It should be more difficult to get a divorce.
- Garbage recycling should be required.
- Sex-segregating classes improve achievements.
- Media producers should not prosecute students for downloading music education.
- K-12 students should learn a foreign language.
- Improving the economic infrastructure is the key to Middle East stability.
- Why smokers deserve rights.
- Stop child slave labor.
- Prohibit airliners to charge extra carry-on luggage fees.
- Offer appropriate and affordable housing to all citizens, just like companies do with expat housing for their overseas workers.
- Initiate a self-regulatory policy for the media.
- Nationalize oil spilling companies and seize all oil resources.
- Form a military alliance with East Asian countries.
- Enact laws to fight corruption in Africa to ensure economic growth and prosperity.
- Abolish diplomatic immunity for criminal activities.
- Guarantee fundamental rights for victims of cybercrime.
- Discontinue medically drugs that are unnecessary.
- Shut down all domestic internet traffic for state security reasons.
- Punish severely pupils taking drugs.
- Promote world literacy by adopting a school in development nations.
- Implement bullying policies.
- Ensure that the foods served are nutritionally balanced.
- Enact harsh penalties against public offensive behavior.
- Provide safe alternatives to regular vehicular travel.
- No-fly lists of airliners do have a lack of accuracy.
- We need an international forestry agency.
- Water is a hot issue in the Middle East.
- An international certification system for diamond exploration prevents conflict-diamonds trade.
- Russia is a growing threat.
- Cut import taxes for tourists in towns that need more income revenues.
- Impose a second home ownership tax.
- The government should cooperate with China.
- Police and community should join efforts to prevent crime.
- Employers should have the right to know a co-worker has HIV.
- Why China’s one-child policy violated basic human rights.
- The European Union have a federal president.
- The use of drugs in sport should be legalized.
- Parents should have to obtain a license for having children.
- Recycling should be the cornerstone of the environment policy course of action.
- Should we outlaw modifying genes or should we allow biotech interventions?
- Every nation should accommodate asylum seekers who are entering the country with a legal visa?
Famous Persuasive Speeches
Top 5 Extraordinary Motivational Speakers
2 thoughts on “170 Good Policy Speech Topics”
Issues of housing
should teachers get graded
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
📕 Studying HQ
Persuasive policy speech topics | example & outline, rachel r.n..
- September 8, 2022
- Essay Topics and Ideas
In a policy speech, the speaker sets out to persuade the audience on a particular issue. This could be something like convincing them to vote for a certain candidate or changing their opinion on current law. No matter what the topic is, the key to giving a successful policy speech is to be persuasive. In this article, we’ll give you some tips on how to choose persuasive policy speech topics that will help you get your message across loud and clear!
As you continue, thestudycorp.com has the top and most qualified writers to help with any of your assignments. All you need to do is place an order
What You'll Learn
List of Thirty Persuasive Policy Speech Topics
1. E-cigarettes should be banned in public places. 2. The drinking age should be lowered to 18. 3. Marijuana should be legalized nationwide. 4. School uniforms should be mandatory in all schools. 5. All students should be required to take a foreign language in high school. 6. The voting age should be lowered to 16. 7. The use of cell phones should be banned while driving. 8. The death penalty should be abolished. 9. Gun control laws should be stricter. 10. Animal testing should be banned. 11. Plastic bags should be banned from grocery stores. 12. The use of fossil fuels should be phased out. 13. Fracking should be banned. 14. GMOs should be labeled. 15. Factory farming should be banned. 16. Palm oil should be boycotted. 17. The use of single-use plastics should be reduced. 18. Recycling should be mandatory. 19. Public transportation should be free or heavily subsidized. 20. Car emissions standards should be stricter. 21. Nuclear power plants should be shut down. 22. Solar and wind energy should be incentivized and subsidized. 23.. Coal-fired power plants should be phased out.. 24.. Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) should be banned.. 25.. lead pipesShould be replaced in all homes and public buildings.. 26.. All schoolsShould have gardens and teach students about gardening and healthy eating.. 27.. ThereShould be a nationwide ban on the use of pesticides.. 28.. The militaryShould focus on renewable energy sources.. 29ThereShould be a tax on carbon emissions.. 30The governmentShould invest in clean energy research and development

List of Thirty Persuasive Policy Speech Ideas
If you’re looking for some good persuasive policy speech ideas, then you’ve come to the right place. Below is a list of thirty persuasive policy speech topics that you can use as inspiration for your next presentation.
1. The need for stricter gun control laws in the United States 2. The benefits of free trade agreements 3. The importance of investing in renewable energy 4. The dangers of climate change and what we can do to prevent it 5. The merits of universal healthcare 6. The negative effects of tax cuts for the wealthy 7. The positives of implementing a nationwide minimum wage 8. Why we need to invest more in infrastructure projects 9. How to reduce the number of people living in poverty 10. Why immigration reform is necessary 11. What can be done to reduce crime rates 12. How to improve educational outcomes in underperforming schools 13. The benefits of early childhood education 14. Why environmental protection is important 15. What can be done to combat homelessness 16. How to reduce the number of teen pregnancies 17. Why drug legalization is a good idea 18. How to decrease the number of traffic fatalities 19. What measures can be taken to improveroad safety 20. Why public transportation is important 21. How to reduce air pollution 22. What can be done to conserve water 23. Why recycling is important 24. How to reduce the amount of waste produced 25. Why energy efficiency is important 26. What can be done to combat climate change 27. How to preserve endangered species 28. The importance of environmental education 29. What can be done to reduce littering and improve waste management 30. Why it is important to protect our natural resources
You can also check out :
How Many Sentences Are in a Paragraph
Creative Narrative Essay Topics
Creative Synthesis Essay Topics
1 Step on how to write an introduction for an argumentative essay
Find out more Capstone Project Ideas for Nursing Leadership [50 Topics]
check out 130+ Good nursing capstone project ideas to Write About )
As you continue, thestudycorp.com has the top and most qualified writers to help with any of your assignments. All you need to do is place an order
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, popular topics.
Business StudyingHq Essay Topics and Ideas How to Guides Samples
- Nursing Solutions
- Study Guides
- Free College Essay Examples
- Privacy Policy
- Writing Service
- Discounts / Offers
Study Hub:
- Studying Blog
- Topic Ideas
- How to Guides
- Business Studying
- Nursing Studying
- Literature and English Studying
Writing Tools
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Maker
- Research Title Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Summarizing Tool
- Terms and Conditions
- Confidentiality Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Refund and Revision Policy
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Contact Us:
📞 +15512677917
2012-2024 © studyinghq.com. All rights reserved

Learning Objectives
- Define persuasive speaking
- Explore organizational patterns for persuasive speeches
Explain the barriers to persuading an audience
- Identify common logical fallacies
On the first day of class, your instructor provided you a “lay of the land.” They introduced you to course documents, the syllabus, and reading materials.
“It’s important that you read your textbook,” they likely shared. “The material will allow you to dive deeper into the course material and, even if you don’t initially realize its importance, the reading material will build throughout the semester. The time spent reading will be worth it because without that knowledge, it will be difficult to complete assignments and receive full credit. The time spent reading will benefit you after you leave for the semester, too, and you’ll have critical thinking skills that will permeate your life out of the classroom.” Sound familiar?
This is persuasion. Your instructor is persuading you that reading the textbook is a good idea—that it’s an action that you should take throughout the semester. As an audience member, you get to weigh the potential benefits of reading the textbook in relation to the consequences. But if your instructor has succeeded in their persuasive attempt, you will read the book because they have done a good job of helping you to conclude in favor of their perspective.
Persuasion is everywhere. We are constantly inundated with ideas, perspectives, politics, and products that are requesting our attention. Persuasion is often positively paired with ideas of encouragement, influence, urging, or logic. Your instructors, for example, are passionate about the subject position and want you to succeed in the class. Sadly, persuasion can also be experienced as manipulation, force, lack of choice, or inducement. You might get suspicious if you think someone is trying to persuade you. You might not appreciate someone telling you to change your viewpoints.
In this chapter, we explore persuasive speaking and work through best practices in persuasion. Because persuasion is everywhere, being critical and aware of persuasive techniques will allow you to both ethically persuade audiences and evaluate arguments when others attempt to persuade you. We’ll start with the basics by answering the question, “what is persuasion?”
Introducing Persuasive Speaking
Persuasion is “the process of creating, reinforcing, or changing people’s beliefs or actions” (Lucas, 2015, p. 306). Persuasion is important in all communication processes and contexts—interpersonal, professional, digital—and it’s something that you do every day. Convincing a friend to go see the latest movie instead of staying in to watch TV; giving your instructor a reason to give you an extension on an assignment; writing a cover letter and resume and going through an interview for a job—all of these and so many more are examples of persuasion. In fact, it is hard to think of life without the everyday give-and-take of persuasion. In each example listed, Lucas’s definition of persuasion is being implemented: you are asking a person or group to agree with your main idea.
When using persuasion in a public speech, the goal is to create, change, or reinforce a belief or action by addressing community problems or controversies. Remember that public speaking is a long-standing type of civic engagement; when we publicly speak, we are participating in democratic deliberation. Deliberatio n , or the process of discussing feasible choices that address community problems, is important in resolving community concerns because it allows all perspectives to be considered. Persuasive speaking means addressing a public controversy and advocating for a perspective that the speaker hopes the audience will adopt. If the issue isn’t publicly controversial – if everyone agrees or if there are not multiple perspectives – you are not persuading. You’re informing.
So, what’s a public controversy? Public controversies are community disputes that affect a large number of people. Because they involve a large number of people, public controversies often have multiple perspectives, leading to public deliberation and debate to resolve each dispute.
We experience public controversies daily. Through our social media feeds, we continuously scroll past shared articles, comments, or posts that provide different perspectives on community problems and potential solutions. You might, for example, join your local neighborhood (or dorm) Facebook group where neighbors share information and collaborate on solutions to specific problems facing the community. Each problem has consequences for different neighbors, and Facebook allows a space to deliberate and organize to address community priorities. They are controversial, however, because not all neighbors agree what which problems should be solved first or what those solutions are.
Sadly, there is no shortage of public controversies, and advocating for solutions to key community problems can feel overwhelming.
“How do I figure out one controversy to speak out about?” you may wonder.
Identify public controversies by listening and engaging with your community. What issues are affecting them? What are priorities? Once you’re able to locate a key community dispute, ask yourself:
- What is it? What is the problem? Are there more than 1? Is this the key problem or are there other hidden issues?
- What is the impact? What will happen if the problem is not resolved?
- Who’s affected? Who’s being affected or implicated by this problem? Who are the audiences or stakeholders affected? Are the stakeholders a part of my formal audience?
- What can solve it? Are there suggested solutions?
Controversies arise when a community experiences a problem, so your job is to decipher the breadth and depth of that problem. It’s impossible to address all issues in one speech, so researching and prioritizing are key to identifying what advocacy you find most urgent. For any controversy that you can address in a persuasive speech, keep context and power in mind.
Your public speaking context always informs what’s possible to accomplish during a speech. Like we outlined in Chapter 1, the public speaking context refers to both the physical space and cultural context.
The physical context will influence how much information you can provide to your audience. In other words, “Do I have time to talk about this issue?” “What is the most essential information to cover in a limited timeframe?” The broader cultural context can help you in situating your advocacy alongside other community conversations. What else is happening? Have other communities experienced this problem?
As persuasive speakers, you are attempting to influence an audience. What you select and how you present that information will alter how audiences understand the world, and that’s a pretty powerful thought. When you select an advocacy that addresses a public controversy, you are asking the audience to trust your perspective. To uphold that trust, it’s key to examine who is empowered or disempowered by our perspective.
When you’re considering a position toward a public controversy, you might ask, who’s empowered or disempowered by this problem? Who’s left out of the research? How are communities being represented? What am I assuming about those communities? Who is affected by my advocacy?
We can be well-meaning in our advocacies, especially when we select a persuasive insight based on our own experience. We become passionate about issues that we have seen, and that’s OK! Such passion can also, however, mean that we represent information in ways that are stereotypical or lead to the disempowerment of others.
If your city, for example, is deciding where to place a landfill, you may advocate against the plant being placed in your neighborhood. That advocacy, on face, makes sense!
“This will reduce our property values and just be plain stinky,” you might argue.
When we think about the issue reflexively and with power in mind, however, we may find that landfills are much more likely to be placed in neighborhoods that are predominant people of color (Massey, 2004). Advocating against placing the plant in your home may inadvertently mean the plant is placed in more vulnerable neighborhoods. Those neighbors become disempowered in your attempt to empower your own community.
In this example, practicing reflexivity might include asking: What are the potential solutions? What options do I have to avoid disempowering groups? Using sound research skills, considering other alternatives or perspectives, and listening can be mechanisms to answer these inquiries
There are no easy answers, but we are confident that you can select advocacies that are meaningful and worthwhile.
Formulating Persuasive Propositions
Once you feel comfortable and confident about a controversial issue that is ethical, timely and contextually relevant, you will need to identify what type of persuasive proposition that you’ll use in your speech. There are three types of persuasive propositions: propositions of fact, value, or policy. Each type will require different approaches and may have different persuasive outcomes for your audience.
Propositions of Fact
Propositions of fact answer the question, “is this true?” Speeches with this type of proposition attempt to establish the truth of a statement. There is not a sense of what is morally right and wrong or what should be done about the issue, only that a statement is supported by evidence or not.
These propositions are not facts like “the chemical symbol for water is H20” or “Barack Obama won the presidency in 2008.” Propositions or claims of fact are advocacies with evidence on different sides and/or spark disagreement. Some examples of propositions of fact are:
- Converting to solar energy can save homeowners money.
- John F. Kennedy was assassinated by Lee Harvey Oswald working alone.
- Coal exacerbates global warming.
- Climate change has been caused by human activity.
- Granting tuition tax credits to the parents of children who attend private schools will perpetuate educational inequity.
- Watching violence on television causes violent behavior in children.
- William Shakespeare did not write most of the plays attributed to him.
- John Doe committed the crime of which he is accused.
Notice that no values—good or bad—are explicitly mentioned. The point of these propositions is to prove with evidence the truth of a statement, not its inherent value. Your goal is to persuade the audience to update their understanding or belief about the topic in question. Because you are likely not asking the audience to overtly act, it’s necessary to embed arguments that highlight how or why this factual information is meaningful for them or how the factual statement resolves a public controversy.
Propositions of fact are meaningful persuasive claims when new evidence or scientific observations arise that your audience may not know. Facts, statistics, definitions, or expert testimony are common evidence types for these propositions.
Propositions of Value
Propositions of value argue that something is good/bad or right/wrong. When the proposition has a word such as good, bad, best, worst, just, unjust, ethical, unethical, moral, immoral, advantageous or disadvantageous, it is a proposition of value. Some examples include:
- Hybrid cars are the best form of automobile transportation available today.
- Homeschooling is more beneficial for children than traditional schooling.
- The War in Iraq was not justified.
- The United States is not the greatest country on earth.
- Capital punishment is morally wrong.
- White supremacy is wrong.
- Mascots that involve Native American names, characters, and symbols are demeaning.
- A vegan diet is the healthiest one for adults.
Communication is a key vehicle in understanding values because communication is how communities collectively determine what is right or wrong. Because values are culturally-situated and not universal, as a speaker, you must ground and describe what value or moral judgement you’re utilizing. If a war is unjustified, what makes a war “just” or “justified” in the first place? What makes a form of transportation “best” or “better” than another? Isn’t that a matter of personal approach? For different people, “best” might mean “safest,” “least expensive,” “most environmentally responsible,” “most stylish,” “powerful,” or “prestigious.”
Effective propositions of value rely on shared beliefs held by your audience. Developing confidence about your audience will allow you to determine what value systems they rely on and how your proposition relies on similar belief systems. We’ll talk more about appealing to your audience below.
Propositions of Policy
Policy propositions identify a solution to correct the problem. These propositions call for a change in policy (including those in a government, community, or school) or call for the audience to adopt a certain behavior.
Speeches with propositions of policy try to instigate the audience to act immediately, in the long-term, or alter their perspective on an issue. A few examples include:
- Our state should require mandatory recertification of lawyers every ten years.
- The federal government should act to ensure clean water standards for all citizens.
- The state of Georgia should require drivers over the age of 75 to take a vision test and present a certificate of good health from a doctor before renewing their licenses.
- Wyeth Daniels should be the next governor of the state.
- The Supreme Court should rule that migrant detention centers are unconstitutional.
These propositions are easy to identify because they almost always have the word “should” in them.
Many policy propositions advocate for a solution through a specific organization or government agency. In the examples above, the federal government, the state, and the Supreme Court are all listed as relevant actors to resolve the problem.
Alternatively, you could advocate for your audience to make specific behavioral changes that lead to solutions. If you’re addressing the consequences of climate change in your local community, do solutions require government or non-profit action? Could your audience make in-roads to reducing the negative effects of climate change alone? Thorough research will assist you in determining what actors – organizations or your audience—are best suited to implement your policy solution.
Policy propositions commonly embed a specific call-to-action. What should the audience do if they are persuading by your perspective? What actions can and should they take that can support your policy proposition? This can include “call your senator” (though more specificity is often helpful), but your call-to-action should be crafted with audience adaptation and information in mind.
Organizing Persuasive Propositions
Organization plays a key role in comprehending an argument. Chapter 6 on organizing provides you a nice starting place to decide which organizational pattern is best suited for different speech types. In this section, we discuss organizing persuasive speeches with a focus on propositions of policy.
Once you’ve identified your main argument, ask, “what organizational pattern best suits my argument?”
For propositions of fact or value, you might select a categorical organization. Essentially that means that you will have two to four discrete, separate arguments in support of the proposition. For example:
Proposition of Fact: Converting to solar energy can save homeowners money.
- Solar energy reduces power bills.
- Solar energy requires less money for maintenance.
- Solar energy works when the power grid goes down.
For propositions of policy, the problem-solution organization pattern is commonly used. We do not typically feel any motivation to change unless we are convinced that some harm, problem, need, or deficiency exists, and even more, that it affects us personally. As the saying goes, “If it ain’t broke, why fix it?” In a problem-solution pattern, you can spend ample and organized time outlining the consequences to inaction, i.e. the problem.
Although a simple problem-solution organization is permissible for a speech of actuation, you will probably do well to utilize the more detailed format called Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
This format, designed by Alan Monroe (1951), is based on John Dewey’s reflective thinking process to consider audience listening patterns. Monroe’s Motivated Sequence involves five steps, which should not be confused with the main points of the outline. Some steps in Monroe’s Motivated Sequence may take two points. Each step is described below:
- Attention . This is the introduction, where the speaker brings attention to the importance of the topic as well as their own credibility and connection to the topic.
- Need. Here the problem is defined and defended. It is important to make the audience see the severity of the problem, and how it affects them, their family, or their community. The harm or need can be physical, financial, emotional, educational, or social. It will have to be supported by evidence.
- Satisfaction. A need calls for satisfaction in the same way a problem requires a solution. Not only does the speaker present the solution and describe it, but they must defend that it works and will address the causes of the problem as well as the symptoms.
- Visualization. This step looks to the future either positively or negatively. If positive, the benefits from enacting or choosing the solution are shown. If negative, the disadvantages of not doing any-thing to solve the problem are shown.
- Action . In the action step, the goal is to give specific steps for the audience to take as soon as possible to move toward solving the problem. Whereas the satisfaction step explains the solution overall, the action step gives concrete ways to begin making the solution happen.
The more concrete you can make the action step, the better. Research shows that people are more likely to act if they know how accessible the action can be. For example, if you want students to be vaccinated against the chicken pox virus (after establishing that it is a key public controversy), you can give them directions to and hours for a clinic or health center where vaccinations at a free or discounted price can be obtained.
With any organizational pattern selected, it’s imperative to group your main points around clear claims that are supported with evidence and explained with a warrant. As you develop your persuasive arguments, stay appraised of who your audience is and best practices for persuasion.
Developing the Persuasive Speech: Appealing to an Audience
Persuasion only occurs with an audience, so your main goal is to answer the question, “how do I persuade the audience to believe my proposition of fact, value, or policy?”
To accomplish this goal, identify your target audience —individuals who are willing to listen to your argument despite disagreeing, having limited knowledge, or lacking experience with your advocacy. Because persuasion involves change, you are targeting individuals who have not yet changed their beliefs in favor of your argument.
The persuasive continuum (Figure 13.1) is a tool that allows you to visualize your audience’s relationship with your topic.

Figure 13.1
The persuasive continuum views persuasion as a line going both directions. Your audience members, either as a group or individually, are sitting somewhere on that line in reference to your thesis statement, claim, or proposition.
For example, your proposition might be, “The main cause of climate change is human activity.” In this case, you are not denying that natural forces, such as volcanoes, can affect the climate, but you are claiming that human pollution is the central force behind global warming. To be an effective persuasive speaker, one of your first jobs is determining where your audience “sits” on the continuum.
+3 means strongly agree to the point of making lifestyle choices to lessen climate change (such as riding a bike instead of driving a car, recycling, eating certain kinds of foods). +2 means agree but not to the point of acting upon it. +1 as mildly in favor of your proposition; that is, they think it’s probably true but the issue doesn’t affect them personally. 0 means neutral, no opinion, or feeling uninformed enough to make a decision. -1 means mildly opposed to the proposition but willing to listen to those with whom they disagree. -2 means disagreement to the point of dismissing the idea pretty quickly. -3 means strong opposition to the point that the concept of climate change itself is not even listened to or acknowledged as a valid subject.
Since everyone in the audience is somewhere on this line or continuum, persuasion means moving them to the right, somewhere closer to +3.
Your topic will inform which strategy you use to move your audience along the continuum. If you are introducing an argument that the audience lacks knowledge in, you are moving an audience from 0 to +1, +2, or +3. The audience’s attitude will be a 0 because they have no former opinion or experience.
Thinking about persuasion as a continuum has three benefits:
- You can visualize and quantify where your audience lands on the continuum
- You can accept the fact that any movement toward +3 or to the right is a win.
- You can see that trying to change an audience from -3 to +3 in one speech is just about impossible. Therefore, you will need to take a reasonable approach. In this case, if you knew most of the audience was at -2 or -3, your speech would be about the science behind climate change in order to open their minds to its possible existence. However, that audience is not ready to hear about its being caused mainly by humans or what action should be taken to reverse it.
As you identify where your target audience sits on the continuum, you can dig deeper to determine what values, attitude, or beliefs would prohibit individuals from supporting the proposition or values, attitudes, or beliefs that support your proposition. At the same time, avoid language that assumes stereotypical beliefs about the audience.
For example, your audience may value higher education and believe that education is useful for critical thinking skills. Alternatively, you may have an audience that values work experience and believes that college is frivolous and expensive. Being aware of these differing values will deepen your persuasive content by informing what evidence or insights to draw on and upon for each audience type.
Once you’re confident about where your audience is on the continuum and what values they hold, you can select the appropriate rhetorical appeals – ethos, pathos, and logos—to motivate your audience toward action. Yes, we’ve discussed these rhetorical appeals before, but they are particularly useful in persuasive speaking, so let’s re-cap.
Ethos is the influence of speaker credentials and character in a speech. Ethos is achieved through citing reliable, authoritative sources, strong arguments, showing awareness of the audience, and effective delivery.
Pathos means using the emotions such as love, anger, joy, hate, desire for community to persuade the audience of the rightness of a proposition.
Finally, logos refers to the organized and logical arguments that are used to support a claim.
So, what do these mean in practice? Suppose that your speech is trying to motivate the audience to support expanding bus routes on your campus. Use Table 13.2 to track the use of rhetorical appeals.
In sum, the audience plays a central role in persuasion, so staying tuned-in to audience beliefs and expectations is key.
Barriers to Effective Persuasi ve Speaking
Persuasive speaking can provide opportunities to advocate for important community solutions. But persuasion is really difficult, and there are often barriers to effectively persuading our audience to change their beliefs or act in a new way.
Persuasion is hard because we have a bias against change. As much as we hear statements like “The only constant is change” or “Variety is the spice of life,” the evidence from research and from our personal experience shows that, in reality, we do not like change. Recent risk aversion research, for example, found that humans are concerned more with what we lose than what we gain. Change is often seen as a loss of something rather than a gain of something else, and that’s stressful. We do not generally embrace things that bring us stress.
Given our aversion to change, audiences often go out of their way to protect their beliefs, attitudes, and values. We (as audience members) selectively expose ourselves to messages that we already agree with, rather than those that confront or challenge us. This selective exposure is especially seen in choices of mass media that individuals listen to, watch, and read. Not only do we selectively expose ourselves to information, we selectively attend to, perceive, and recall information that supports our existing viewpoints (referred to a s elective recall ).
This principle led Leon Festinger (1957) to form the theory of cognitive dissonance , which states, among other ideas, that when we are confronted with conflicting information or viewpoints, we reach a state of dissonance, or tension between ideas and beliefs. It often occurs when we’re presented information that’s out of line with our values or experiences. This state can be very uncomfortable, and we will do things to get rid of the dissonance and maintain “consonance.” We don’t want to accept that our beliefs may be wrong or inconsistent; we want to remain harmonious.
In a sense, not changing can outweigh very logical reasons to change. For example, you probably know a friend who will not wear a seatbelt in a car. You can say to your friend, “Don’t you know that the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (2009) says, and I quote, ‘1,652 lives could be saved and 22,372 serious injuries avoided each year on America’s roadways if seat belt use rates rose to 90 percent in every state’?” What will your friend probably say, even though you have cited a credible source?
They will come up with some reason for not wearing it, even something as dramatic as “I knew a guy who had a cousin who was in an accident and the cop said he died because he was wearing his seatbelt.” They may even say, “Well I am a good driver, so you only need seat belts if you’re driving poorly.” You may have had this conversation, or one like it. Their argument may be less dramatic, such as “I don’t like how it feels” or “I don’t like the government telling me what to do in my car.” For your friend, the argument for wearing a seat belt is not as strong as the argument against it, at least at this moment. Ideally, at least for a public speaker, the dissonance is relieved or resolved by being persuaded (changed) to a new belief, attitude, or behavior.
So, what is a speaker to do to overcome these barriers? We suggest making reasonable requests, articulating the benefits or consequences, and answering oppositional arguments.
Make Reasonable Requests
Setting reasonable persuasive goals is the first way to meet audience resistance. Look back to the persuasive continuum scale in Figure 13.1. Trying to move an audience from -3 to +2 or +3 is too big a move. Since change is resisted, we do not make many large or major changes in our lives. We do, however, make smaller, concrete, step-by-step or incremental changes every day. Even moving someone from -3 to -2 is progress, and over time these small shifts can eventually result in a significant amount of persuasion. Aim small, especially within a time constraint, and work to find future room to build.
Focus on Benefits and Consequences
When problems aren’t resolved, there are consequences. When problems are resolved, there are positive benefits for the community. Because you are asking the audience to change something, they must view the benefits of acting as worth the stress of the change. A speaker should be able to engage the audience at the level of needs, wants, and values as well as logic and evidence.
Identify the benefits, advantages, or improvements that would happen for the audience members who enacted your advocacy. If you do good audience analysis, you know that audiences are asking, “What’s in it for me?” “Why do I need this?”
Alternatively, you could outline the short and long-term consequences of inaction and detail how the problem would negatively affect the audience and/or their community. In other words, you’re identifying what would occur if the audience does nothing; if they choose not to act. Using Monroe’s Motivated Sequences can assist in organizing these arguments.
Answer Oppositional Arguments
During a persuasive speech, audience members are holding a mental dialogue, and they are thinking through rebuttals or oppositional arguments to your advocacy. These mental dialogues could be called the “yeah-buts”—the audience members are saying in their minds, “Yeah, I see what you are arguing, but—”. Reservations can be very strong, since, again, our human bias is to be loss averse and not to change our actions or beliefs.
If you’re advocating a claim that humans are the primary cause of climate change, your audience may think, “yeah, but these consequences won’t happen for a long time,” or “yeah, but we have time to resolve these problems.”
As a speaker, address these! Refute the arguments that may prohibit your audience from changing.
It’s common to call oppositional arguments “misconceptions,” “myths,” or “mistaken ideas” that are widely held about the proposition. You may answer oppositional arguments around climate change by saying, “One common misconception about climate change is that we won’t see the negative impacts for decades. A recent study determined that consequences are already upon us.”
After acknowledging oppositional arguments and seeking to refute or rebut the reservations, you must also provide evidence for your refutation. Ultimately, this will show your audience that you are aware of both sides of the issue you are presenting and make you a more credible speaker.
Understanding and Avoiding Fallacies
So far, we’ve discussed persuasive speaking and strategies to move your audience along the persuasive continuum. Motivating your audience to change, however, must be done ethically while using good reasons.
In Chapter 5, we began discussing best practices in constructing arguments. In this section, we dive deeper into reasoning by highlighting a common pitfall: the use of fallacies — erroneous conclusions or statements made from poor analyses. There are actually dozens upon dozens of fallacies, and we identify 9 common fallacies below.
False Cause
False cause is a fallacy that assumes that one thing causes another, but there is no logical connection between the two. In a false cause fallacy, the alleged cause might not be strong or direct enough. For example, there has been much debate over the causes of the recession in 2008. If someone said, “The exorbitant salaries paid to professional athletes contributed to the recession” that would be the fallacy of false cause. Why? For one thing, the salaries, though large, are an infinitesimal part of the whole economy. Second, those salaries only affect a small number of people. A cause must be direct and strong, not just something that occurred before a problem arose.
Slippery Slope
A slippery slope fallacy is a type of false cause which assumes that taking a first step will lead to subsequent events that cannot be prevented. The children’s book, If You Give a Moose a Muffin , is a good example of slippery slope; it tells all the terrible things (from a child’s point of view) that will happen, one after another, if a moose is given a muffin. If A happens, then B will happen, then C, then D, then E, F, G and it will get worse and worse and before you know it, we will all be in some sort of ruin. So, don’t do A or let A happen because it will inevitably lead to Z, and of course, Z is terrible.
This type of reasoning fails to look at alternate causes or factors that could keep the worst from happening, and often is somewhat silly when A is linked directly to Z. Slippery slope arguments are often used in discussions over emotional and hot button topics that are linked with strong values and beliefs. One might argue that “If guns are outlawed, only outlaws will have guns,” a bumper sticker you may have seen. This is an example of a slippery slope argument because it is saying that any gun control laws will inevitably lead to no guns being allowed at all in the U.S. and then the inevitable result that only criminals will have guns because they don’t obey gun control laws anyway.
In any instance where you’re identifying potential consequences if action is or is not taken, credible evidence and ethical warrants are good checks against our tendency to slippery-slope to the audience.
Hasty Generalization
Making a hasty generalization means making a generalization with too few examples. It is so common that we might wonder if there are any legitimate generalizations. Consider this hastily generalized argument:
A college degree is unnecessary. For example, Mark Zuckerberg dropped out of college, invented Fac e book, and made billions of dollars. As this example demonstrates, dropping out of college leads to great financial success , so a complete degree is pointless.
The key to generalizations is how the conclusions are “framed” or put into language. The conclusions should be specific about the limited nature of the sample.
Straw Person
A straw person fallacy is a fallacy that shows only the weaker side of an opponent’s argument in order to more easily tear it down. The term “straw person” brings up the image of a scarecrow, and that is the idea behind the expression. Even a child can beat up a scarecrow; anyone can.
A straw person fallacy happens when an opponent in a debate misinterprets or takes a small part of their opponent’s position in a debate and makes it a major part of the opponent’s position. This is often done by ridicule, taking statements out of context, or misquoting.
Politicians, unfortunately, commit the straw person fallacy quite frequently. If someone states, “College A is not as good as College B because the cafeteria food at College A is not as good” is a pretty weak argument—and making too big of a deal over of a minor thing—for attending one college over another.
False Dilemma
False Dilemma is often referred to as the “either-or” fallacy. When you are given only two options, and more than two options exist, that is false dilemma. Usually in false dilemma, one of the options is undesirable and the other is the one the persuader wants you to take. False dilemma is common. “America: Love it or Leave It.” “If you don’t buy this furniture today, you’ll never get another chance.” “Vote for Candidate Y or see our nation destroyed.”
Appeal to Tradition
Appeals to tradition is the argument that “We’ve always done it this way.” This fallacy happens when traditional practice is the only reason for continuing a policy. Tradition is a great thing. We do many wonderful things for the sake of tradition, and it makes us feel good. But doing something only because it’s always been done a certain way is not an argument.
You’ve likely experienced this through politicians. For example, if a politician says that we should support coal mining because “it’s a great American tradition and we’ve coal mined for decades,” it certainly highlights values inherent within the speaker, but it’s a fallacy.
This fallacy, the bandwagon , is also referred to as “appeal to majority” and “appeal to popularity,” using the old expression of “get on the bandwagon” to support an idea. Bandwagon is a fallacy that asserts that because something is popular (or seems to be), it is therefore good, correct, or desirable.
You’ve probably heard that “Everybody is doing it” or “more than 50% of the population supports this idea.” Just because 50% of the population is engaging in an activity does not make that a wise choice based on sound reasoning. Historically, 50% of the population believed or did something that was not good or right. In a democracy we make public policy to some extent based on majority rule, but we also have protections for the minority or other vulnerable populations. This is a wonderful part of our system. It is sometimes foolish to say that a policy is morally right or wrong or wise just because it is supported by 50% of the people.
Red Herring
A herring is a fish, and it was once used to throw off or distract foxhounds from a particular scent. A red herring , then, is creating a diversion or introducing an irrelevant point to distract someone or get someone off the subject of the argument. When a politician in a debate is asked about their stance on immigration, and the candidate responds, “I think we need to focus on reducing the debt. That’s the real problem!.” they are introducing a red herring to distract from the original topic under discussion.
This is a fallacy that attacks the person rather than dealing with the real issue in dispute. A person using ad hominem connects a real or perceived flaw in a person’s character or behavior to an issue he or she supports, asserting that the flaw in character makes the position on the issue wrong. Obviously, there is no connection. In a sense, ad hominem is a type of red herring because it distracts from the real argument. In some cases, the “hidden agenda” is to say that because someone of bad character supports an issue or argument, therefore the issue or argument is not worthy or logical.
A person using ad hominem might say, “Climate change is not true. It is supported by advocates such as Congressperson Jones, and we all know that Congressperson Jones was convicted of fraud last year.” This is not to say that Congressperson Jones should be re-elected, only that climate change’s being true or false is irrelevant to their fraud conviction. Do not confuse ad hominem with poor credibility or ethos. A speaker’s ethos, based on character or past behavior, does matter. It just doesn’t mean that the issues they support are logically or factually wrong.
Section Summary
Fallacies reduce good reasoning and they weaken your argument. To avoid fallacies, think critically about what evidence is being used, and if your claim and warrant are reasonable explanations and articulations of that evidence. A key way to avoid fallacies is to double and triple check your evidence to make sure that a) the evidence is credible, b) there is enough evidence to support your claim, and c) you have explained the evidence using good reasons.
Persuasive speaking is an opportunity to share a passion or cause that you believe will matter to society and help the audience live a better life. Even if you are initially uncomfortable with the idea of persuasion, we use it all the time in different ways. Choose your topic based on your own commitment and experience, look for quality evidence, craft your proposition so that it will be clear and audience appropriate, and put the finishing touches on it with an eye toward enhancing your logos, ethos, and pathos.
Speak Out, Call In: Public Speaking as Advocacy Copyright © 2019 by Meggie Mapes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
9 Speaking to Persuade/Advocacy
Gillian, Bonanno, M.A.
Learning Objectives
- Define persuasion and advocacy.
- Ethos , Pathos , and Logos
- Choose a topic.
- Conduct research.
- Structuring an outline.
- Use visual aids.
- Prepare for feedback.
Defining Persuasion and Advocacy
Persuasion is “the act of influencing someone to do something or to change their mind” (“Persuasion”). In a persuasive presentation, the goal is to provide the audience with information that will convince them to see your side on an issue. According to Cialdini and Goldstein, “the six basic principles that govern how one person might influence another are: liking , reciprocation , consistency , scarcity , social validation , and authority ” (41). First, an individual may be more likely to be persuaded by someone that they “ like ” which ranges from knowing someone personally to having an “instant bond” with a stranger (Cialdini and Goldstein, 41). Reciprocation refers to the notion that there is an exchange of some kind, such as in business negotiations (Cialdini and Goldstein, 45). Consistency encourages individuals to persuade others by recognizing “a fundamental human tendency to be and to appear consistent with one’s actions, statements, and beliefs” (Cialdini and Goldstein, 45). Scarcity principle focuses on the idea that “items and opportunities that are in short supply or unavailable tend to be more desirable than those… that are plentiful and more accessible” (Cialdini and Goldstein, 46). For example, think about a product that you may be interested in purchasing. If the product is limited in production or availability, it might persuade you to be more interested in purchasing the item. Social validation refers to the idea that individuals “look to others for cues,” and this will influence their decisions (Cialdini and Goldstein, 48). Finally, authority suggests that individuals are persuaded by those they consider to have an expertise in a particular area (Cialdini and Goldstein, 49).
These six principles provide some examples of how an individual (or an audience) can be persuaded. There are certainly other methods and note that not all these principles need to be included in a persuasive presentation for it to be effective.
In addition to the principles listed above, you may consider choosing a basis, or claim, for formulating an argument. This chapter will address three types of persuasive speech claims: questions of fact, value, and policy. In general:
- “ Claims of fact are quantifiable statements that focus on the accuracy, correctness or validity of such statements and can be verified using some objective evidence.
- Claims of value are qualitative statements that focus on judgments made about the environment and invite comparisons.
- Claims of policy are statements that focus on actions that should be taken to change the status quo” ( Types of Claims ).
Let’s explore each claim above in more detail, starting with a discussion of statements of fact. A claim of fact is “something quantifiable has existed, does exist, or will exist” (Types of Claims). This type of claim focuses on data that may not necessarily be refutable based on quantitative data used to present your side of an issue. There are many examples of speeches that use statements of fact as a basis for an argument. The claim may stem from something that you do every day (such as brushing your teeth or taking a walk), but you may want to persuade the audience that they should also do these things if they are not already doing so. In these examples, you may state something specific and able to be verified such as, ‘Brushing your teeth teeth twice a day can decrease tooth decay’ or ‘Walking every day decreases risk of cardiovascular disease’ and then support these claims with clear statistics, charts, or data that will help them to embrace your claim. (Please note that the claims above are simply examples, and data is not included to support or refute these claims in this chapter.)
You may also wish to consider a speech that addresses a question of value. A claim of value “asserts qualitative judgments along a good-to-bad continuum relating to persons, events, and things in one’s environment” (Types of Claims). This type of speech may include more qualitative data, such as open ended responses. The claim of value may include words such as good, bad, better, best, or worse. These are often considered to be subjective terms (one person may have a different idea of good/bad/better/best/worst) and it is the responsibility of the presenter to define these subjective terms and also provide evidence to support the claims. Some examples might include ‘Car X is better than Car Y’ or ‘Coffee is the best morning beverage.’ (Note that these are simply examples, and support for these claims are not provided in this chapter.)
In a claim of policy , the word “should” helps to formulate your argument. Using the word “should” is important as it “implies that some action ought to be taken, but not that it must or will be taken” ( Types of Claims ).
You may use this type of claim to address issues of politics, policies, health, environment, safety, or other larger global concerns . Your speech will describe the reason why you feel that a policy or issue should (or should not) be addressed in a specific way based on your research. In this type of speech, you are asking your audience to support your solution to an issue that you have presented to them. Examples may include “Policy A should be changed to include (mention what should be included)” or “College students should have access to (mention what students should have access to).” Presenters for this type of speech should clearly explain the policy and then share with the audience why it should be changed (or upheld) by using their research to support the position.
Advocacy , on the other hand, is “the act or process of supporting a cause or proposal” (“Advocacy”). An advocate feels strongly about an issue and will work diligently to encourage others to support their cause. An advocate should be able to speak about an issue in a concise, professional, and persuasive manner. Enthusiasm for a cause will shine through if the advocate thoroughly embraces the role. This can be accomplished by conducting research, exploring opposing views on the issue at hand, preparing effective visual aids, and practicing the delivery of the content before a presentation or event. An advocate takes on many forms. A lawyer advocates for clients. A patient may advocate for rights to care. A student may advocate for a higher grade from a professor.
An advocate can be described as:
1) One who pleads the cause of another, specifically one who pleads the cause of another before a tribunal or judicial court.
2) One who defends or maintains a cause or proposal.
3) One who supports or promotes the interest of a cause or group (“Advocate”)
Types of Advocacy
There are many types of advocacy. This chapter will address self- advocacy, peer advocacy, and citizen advocacy.
Self- advocacy addresses the need for an individual to advocate for oneself. Examples might include negotiating with a boss for a raise, or perhaps used when applying for college or health insurance. According to an advocacy website, Advocacy: inclusion, empowerment and human rights, “The goal of self-advocacy is for people to decide what they want and to carry out plans to help them get it …. the individual self-assesses a situation or problem and then speaks for his or her own needs.”
Individuals who share experiences, values, or positions will join together in a group advocacy setting. This type of advocacy includes sharing ideas with one another and speaking collectively about issues. The groups “aim to influence public opinion, policy and service provision” and are often part of committees with varying “size, influence, and motive.” (Advocacy: inclusion, empowerment and human rights.) Examples might include groups interested in protecting the environment, rights to adequate health care, addressing issues of diversity, equity, and/or inclusion, or working together to save an endangered species.
A citizen advocate involves local community members who work together to have a platform to address issues that affect their lives. An example might include community school boards or participation in town hall meetings. (Advocacy: inclusion, empowerment and human rights)
As you can see, persuasion and advocacy have been defined in different ways. As the presenter, you have the opportunity to persuade your audience, and can use these definitions to help you decide what type of advocate or persuasive presentation that you would like to develop.
Before we begin developing our speeches, let us take a moment to address Aristotle’s appeals for persuasion: ethos, logos, and pathos.
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos
What is ethos ?
Ethos relates to the credibility of the speaker (Ethos). An audience member should feel as if they can trust the information provided by the speaker. When listening to a presenter, ask yourself:
- Does the speaker seem to have knowledge about the topic?
- Do you feel that this person is qualified to share information with you?
Using ethos as a tool for persuasion
As a presenter, you can let your audience experience your credibility in a few different ways. Using more than one of the methods below can certainly increase your credibility.
- Tell the audience directly. For example, you may wish to convince your audience to drink tea for breakfast. You can share something like, “My experience stems from a lifelong enjoyment of tea. I drink one cup each day and have tried a variety of types, so I feel that I can share with you some of my favorite types to try based on my personal experience.”
- Share quality research. For example, you may have visited the BMCC databases to gather information about types of tea, benefits of drinking tea, and information about individuals who drink tea. You may have also done some individual research (surveying classmates about their morning beverage preferences). These types of data will help to support your claim and help the audience to agree with your perspective.
- Acknowledge the perspective(s) of others. Perhaps your audience is full of individuals who prefer coffee, water, or nothing to drink in the morning, Acknowledging these different perspectives lets the audience know that while you may be knowledgeable about your chosen topic, you also understand that others may have a different (and also valued) opinion that differs from your own.
What is pathos ?
Pathos relates to the emotional appeal given to the audience by the presenter. This includes the language and presentation style of the presenter. It ties to your organizational style, your choice of words, and your overall stage presence. Some examples are: using vivid language to paint images in the minds of audience members, providing testimony (personal stories or stories relayed to you by others), and/or using figurative language such as metaphor, similes, and personification. A presenter can also use various vocal tools such as vocal variety and repetition to appeal to the audience on an emotional level. (Pathos. 2020)
Using pathos as a tool for persuasion
When you are describing drinking tea to your classmates, you can use words or phrases to encourage them to try it. You can tell them about its delicious aroma. You can also tell a story – perhaps having the audience members picture themselves getting up in the morning, making a nice cup of tea, holding it in their hands, and taking a moment enjoying the tea as they get ready to embrace the day!
An emotional appeal can also be used to gain sympathy from your audience. Think about commercials or advertisements that you may have seen, perhaps ones that encourage you to donate to an organization or to adopt an animal. These types of advertisements appeal to your emotions through their use of images, music, and/or detailed stories.
What is logos ?
Logos ties to both reasoning and logic of an argument. Speakers appeal to logos “by presenting factual, objective information that serves as reasons to support the argument; presenting a sufficient amount of relevant examples to support a proposition; deriving conclusions from known information; and using credible supporting material like expert testimony, definitions, statistics, and literal or historical analogies.” (Logos, 2020)
Using logos as a tool for persuasion
Logos relates to using the data collected to form a reasonable argument for why your audience members should agree with the speaker. After you have collected your data, you must now create an argument that will potentially persuade your audience. If we continue with our persuasive speech directed at drinking tea in the morning, you might find an article that relates to college students who drink tea. Using valid reasoning is key! Take some time to ensure that your argument is logical and well-organized. A logical, well-structured argument will help to persuade your audience.
Now that we have learned some foundational concepts related to persuasion, let us move to a discussion of choosing a topic for a persuasive speech.
Choosing a Persuasive Speech Topic
Now that we have explored some definitions of persuasion and advocacy, let us move on to choosing the topic that you will be presenting to your audience. When picking a topic, you may consider choosing something that you are passionate about and/or something that you want to know more about. Take a moment to consider topics that we would like to share with your audience. Individuals have different experiences and perspectives on varying issues. Sharing your perspective on a topic is what can make your presentation unique and exciting to the audience.
When looking for a topic, cause, or issue to discuss, consider asking yourself the following questions (also located in worksheets):
- What is important to me?
- What excites me?
- What makes me happy?
- What makes me angry?
- Do I have a good idea that others might embrace?
- Is there an issue that ‘speaks’ to me?
- Can I make a change?
- Have I experienced something inspiring or life-changing that I can share with others?
Here are some additional ideas to consider when choosing a topic:
- Choose a topic that is (relatively) new to you! You may consider taking some time to explore a topic that you do not yet know about and/or one that you want to learn more about. Perhaps you recently read, saw, or experienced something that you would like to research and share with your audience. Maybe you began your process with not knowing which side you support on an issue, and you take some time to research both sides of an issue and determine which you support. You can use this presentation as an opportunity to learn more about that topic and can then talk about this process in your presentation. Using the research that you have gathered will help you as you explain to the audience why they should share your perspective on the item at hand.
- Choose a topic that you already know about and feel strongly that your audience should share your views on this topic. For this type of presentation, you will be taking your knowledge and expanding it. You can search for items that support your side and also take some time to review the data provided by those that support the opposite side of the issue.
Conducting Research
Research can be fun! In an earlier chapter you read about how to conduct research using the college library. Please reread that chapter again closely to help you conduct research to get data to build your persuasive speech. If you are able to accumulate data from a variety of sources, this will help you to persuade your audience members to share your passion about the topic at hand.
Some things may be easier than others to convince your audience to agree upon and others may be more challenging. If, for example, you want to encourage your classmates to exercise, it is important to consider the current exercise levels of your classmates. Ultimately, you would like each audience member to feel involved in your presentation, so you may wish to provide various suggestions.
For example, some members of the class may not currently exercise for a variety of reasons, so you may suggest that they try to incorporate 5-10 minutes of light activity 1-3 times a week. For classmates who are exercising once a week or more, you may encourage them to increase their exercise by one extra day per week. Finally, a group that may be currently exercising daily, you may wish to suggest adding a new type of exercise to their routine.
Structuring an Outline
There are many ways to structure a speech, and this chapter will offer one suggestion that may work well as you work to advocate for a cause or attempt to persuade your audience. A blank sample outline is located in the worksheet section of this chapter/book that can be used when you are preparing your speech. The length/time allotted for delivery of your presentation will be provided to you by your instructor, but let’s consider the speech in three general parts: Introduction, Body, and Conclusion. Between each section of the presentation, one should consider including a transition to let the audience member know that the speaker is moving on to the next segment of the presentation. Transitional devices are “words or phrases that help carry a thought from one sentence to another, from one idea to another, or from one paragraph to another…. transitional devices link sentences and paragraphs together smoothly so that there are no abrupt jumps or breaks between ideas” (Purdue Writing Lab Transitional Devices // Purdue Writing Lab).
If the speech requirement is 4-6 minutes long, below is one way to consider timing the different sections of the presentation: One minute for the introduction, one minute for each main point, and one minute for the conclusion. This will be a roughly 5 minute speech, with a minute to spare for transitions. Here is a diagram to provide a visual guide to the elements of your outline. Start at the introduction and make your way clockwise around the image:
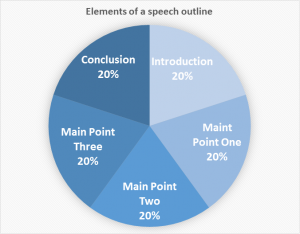
In the body of your presentation, you will formulate your argument in WHAT, WHY and HOW. Each area is equally important, so let’s take a moment to discuss the details of each part.
Let’s start with WHAT.
What does the listener need to know about your topic? If you are passionate about a topic or cause, remember that your audience may have a range of knowledge about the topic. Setting a strong foundation in the beginning of your speech will help the audience members to understand your speech. Remember, the amount of information that you include here will depend on the amount of time allotted by the instructor. You may wish to clarify by letting your audience members know that there are many things that you can tell them about the topic, but your presentation is going to focus on (insert your focus here).
Now, WHY does your audience need to feel the same way you do about this topic?
The first section of your presentation has provided the foundation for your listeners. The second section will be your opportunity to tell your audience why they should share your perspective on the issue. Provide them with details, including facts, images, stories, and/or statistics that will help them embrace your side of the issue.
Finally, HOW can the audience members act upon what you have told them?
Overall, for an individual to make a change, the person will need information and a way to use the information. If the audience is provided with the tools needed to make a change, they may be more likely to make the change. Sounds simple, right? It certainly can be, if you have conducted sound research and organized it in a way to reach your listeners. Refer to the sample speech outlines in the appendices of this book.
Visual Aids
Think about something that you saw recently that caught your eye. It may have been an advertisement on the subway, something you saw on a social media page, or anything else that you remember. Visual aids can certainly assist in connecting with your audience.
When you are designing your presentation, you may wish to consider including images, video clips, charts, and other visual media types to capture the attention of your audience. Think about what you want the audience to gather from your image. Where will you include the image? What will you say about this image? You may wish to discuss these images with your classmates and/or your professor to gain some feedback on the chosen visual aid(s). This will help you in selecting items that work most effectively in your presentation.
Here are two of the prototypes:
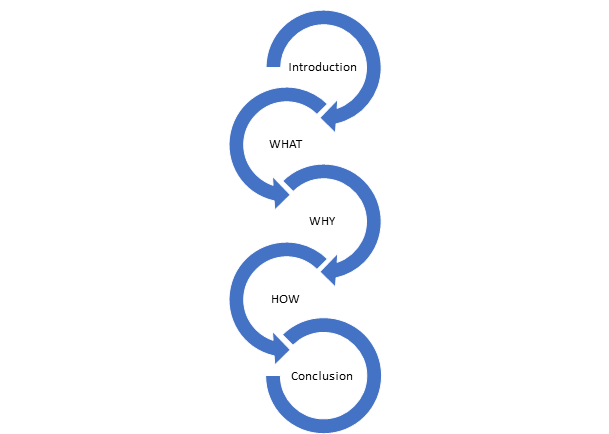
Above, the author thought it might be visually appealing to put the pieces of the speech outline in this arrowed path format. The feedback received was not positive, mostly “what is that?” “I don’t get it” and the like.
The point is: while all of your ideas and images may not be the final versions that you choose, it can be fun to experiment, and asking for feedback may help you to fine tune your work, or even spark an idea or image that you had not previously considered. The author truly enjoyed designing these graphs, and at the end of the day chose the one that the author felt would be best suited for the chapter based on the feedback received.
Preparing for Feedback
Turning to feedback, now that you have completed your speech, it will now be time to interact with your audience. Some audience members may respond to your presentation with questions. If you have inspired your audience, they may want additional information, or may even want to talk further about your presentation. Others may disagree with your speech and respond to your presentation with hostility or frustration. Remember, you are in charge of addressing the audience members, and, as such, you must formulate a strategy for handling feedback. Your instructor may also set some guidelines for expectations for question and answer segment(s) for your presentation.
Here are some questions that you may wish to ask yourself as you prepare to address feedback:
- Have I addressed the other side of the issue discussed in my speech?
- What will I do if someone gets angry with me?
- What questions might my audience have for me?
- Have I used quality sources to prove my points?
- Can I explain any charts or graphs that I have presented?
- If the audience members want to know more about my cause, what information will I provide to them?
Ready to Begin: Inspiration
Now it is your turn to persuade your audience. Be the advocate! Share your knowledge and passion with your classmates. Use this chapter, the worksheets, and your own talents to help you with the process of writing, researching, outlining, and presenting. Take your time with each step and enjoy the process. Below are some voices of advocates discussing what they do and why they do it. Perhaps these stories will inspire you as you work! Survey data collected via surveymonkey.com, and some names have been changed.
Melissa S., Cystic Fibrosis Advocate
What does the term “advocate” mean to you?
Sharing your story to educate and inspire in order to further your cause.
How did you become an advocate?
I was asked to formally advocate for an organization, but in truth, I advocate for myself or my family or issues I believe in.
What do you advocate for?
I advocate for the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation on behalf of families who endure life with Cystic Fibrosis (CF). I advocate for policy change that betters the lives of CF families with issues surrounding disability and bettering research methods, as well as funding (from various agencies) so that research can be conducted in the most efficient, expedited, and safe fashion.
Why is it so important to advocate for your cause?
It is important because I have Cystic Fibrosis and have also lost a brother to Cystic Fibrosis. I wasn’t to ensure that my family doesn’t suffer another loss that no family should suffer.
What advice can you give others who are looking to become an advocate?
It can seem intimidating to stand in front of a group of people to advocate for your cause, but the truth is that your story, and why you’re advocating is THE most important part of it. Don’t get bogged down or scared about memorizing facts and figures – the best thing someone can take away from talking with you is the visceral reaction they get from hearing how your issue affects you and your family.
In a few sentences, describe yourself.
I am (a) decidedly optimistic person who lives with a debilitating progressive disease (Cystic Fibrosis). While having CF occupies a lot of time in my daily life, I try not to let it define me and live my life with joy and purpose. I love my family and friends and will do anything in my power to protect them. I also love standing up for things I believe in. Becoming an advocate for CF has lifted my voice and given me the confidence to speak out. Now, I can’t stop! (updated 7/2021).
D. D., Registered Nurse
Advocate means to support or fight for a cause.
I became an advocate since working within the medical field and because I am a mother.
I am an advocate for my son. He is an alcoholic and drug addict. I am involved with helping addicts and families that are in need of support and guidance. I am a volunteer for (a) local YMCA to help bring a face to the disease of addiction. I am also an advocate for people with Cystic Fibrosis. I am a Registered Nurse who has been caring for patients and families affected by this disease. I am there for medical, emotional and fundraising support.
It is important for me to put a face to the families that are suffering from these diseases. To make it more personal.
Be strong and vigilant. Really believe in what you are supporting. Passion goes a long way.
I am a mom and an RN. I am a recent widow with 2 children who have had their struggles but are now doing well. I work full time as a Nurse Manager at NY hospital.
Is there anything else that you would like to share? A story, perhaps, about a time that you felt very strongly about something, and what you did to advocate for that person or cause?
Every day I feel like I advocate for addiction. Many people do not realize addiction affects everyone. I constantly have to remind people that I meet of this. It is difficult at times because most people have the most horrible things to say about addicts. I try to educate people about addiction as much as I can.
C. B., Breast Cancer Survivor
Supporter of something you are passionate about and believe in.
I became an advocate of breast cancer through my own experience.
I am an advocate for breast cancer! This disease generally affects women but in some cases men are also affected! It is a silent beast that can creep up on you at any time in your life… it has no discrimination and age is not a factor.
It is simple… it is the difference between life and death! So many women are so afraid they choose to ignore the signs. It is so important to find your strength, face your fears and deal with this head on!!!
Speak your truth! Tell your story! You have no idea how much it can help someone else who is facing the very same fears!
I have always believed where there is a will, there is a way! I never take no for an answer when it is something really important that matters! It is one of my earliest mottos I have followed through life. I have always been determined to find my strength and face my fears even on my darkest day!!!
I feel it is so important to help women face their fears when it comes to breast cancer. It is for this reason so many do not examine themselves and/or go for mammograms. I can tell you first hand every moment counts!!!! I did one whole year of chemotherapy, lost my beautiful hair but fared through! Again I was LUCKY!! I can only hope that this will help others facing breast cancer!
Review Questions
- Define Ethos, Pathos and Logos.
- What are three types of persuasive claims listed in this chapter?
- What are the three types of advocacy listed in this chapter?
Works Cited
“Advocacy.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/advocacy . Accessed 2 Jul. 2021.
“Advocacy: Inclusion, Empowerment and Human Rights.” Social Care Institute for Excellence (SCIE), Updated Oct. 2020, www.scie.org.uk/care-act-2014/advocacy-services/commissioning-independent-advocacy/inclusion-empowerment-human-rights/types.asp .
“Advocate.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/advocate .
Bonanno, G. “What does it mean to be an advocate?” Survey . November 2016.
Cialdini, Robert B., and Noah J. Goldstein. “The Science and Practice of Persuasion.” The Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly , vol. 43, no. 2, Elsevier Inc, 2002.
“Persuasion – Dictionary Definition.” Vocabulary.com , www.vocabulary.com/dictionary/persuasion .
Purdue Writing Lab. “Transitional Devices // Purdue Writing Lab.” Purdue Writing Lab , 2018, owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/mechanics/transitions_and_transitional_devices/transitional_devices.html#:~:text=Transitional%20devices%20are%20words%20or,jumps%20or%20breaks%20between%20ideas .
Marteni, Jim. “Types of Claims.” Social Science LibreTexts . Los Angeles Valley College, 3 Dec. 2020, https://socialsci.libretexts.org/@go/page/67166.
Start Here, Speak Anywhere! Copyright © by Gillian, Bonanno, M.A. is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
112 Persuasive Speech Topics That Are Actually Engaging
What’s covered:, how to pick an awesome persuasive speech topic, 112 engaging persuasive speech topics, tips for preparing your persuasive speech.
Writing a stellar persuasive speech requires a carefully crafted argument that will resonate with your audience to sway them to your side. This feat can be challenging to accomplish, but an engaging, thought-provoking speech topic is an excellent place to start.
When it comes time to select a topic for your persuasive speech, you may feel overwhelmed by all the options to choose from—or your brain may be drawing a completely blank slate. If you’re having trouble thinking of the perfect topic, don’t worry. We’re here to help!
In this post, we’re sharing how to choose the perfect persuasive speech topic and tips to prepare for your speech. Plus, you’ll find 112 persuasive speech topics that you can take directly from us or use as creative inspiration for your own ideas!
Choose Something You’re Passionate About
It’s much easier to write, research, and deliver a speech about a cause you care about. Even if it’s challenging to find a topic that completely sparks your interest, try to choose a topic that aligns with your passions.
However, keep in mind that not everyone has the same interests as you. Try to choose a general topic to grab the attention of the majority of your audience, but one that’s specific enough to keep them engaged.
For example, suppose you’re giving a persuasive speech about book censorship. In that case, it’s probably too niche to talk about why “To Kill a Mockingbird” shouldn’t be censored (even if it’s your favorite book), and it’s too broad to talk about media censorship in general.
Steer Clear of Cliches
Have you already heard a persuasive speech topic presented dozens of times? If so, it’s probably not an excellent choice for your speech—even if it’s an issue you’re incredibly passionate about.
Although polarizing topics like abortion and climate control are important to discuss, they aren’t great persuasive speech topics. Most people have already formed an opinion on these topics, which will either cause them to tune out or have a negative impression of your speech.
Instead, choose topics that are fresh, unique, and new. If your audience has never heard your idea presented before, they will be more open to your argument and engaged in your speech.
Have a Clear Side of Opposition
For a persuasive speech to be engaging, there must be a clear side of opposition. To help determine the arguability of your topic, ask yourself: “If I presented my viewpoint on this topic to a group of peers, would someone disagree with me?” If the answer is yes, then you’ve chosen a great topic!
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork for what it takes to choose a great persuasive speech topic, here are over one hundred options for you to choose from.
- Should high school athletes get tested for steroids?
- Should schools be required to have physical education courses?
- Should sports grades in school depend on things like athletic ability?
- What sport should be added to or removed from the Olympics?
- Should college athletes be able to make money off of their merchandise?
- Should sports teams be able to recruit young athletes without a college degree?
- Should we consider video gamers as professional athletes?
- Is cheerleading considered a sport?
- Should parents allow their kids to play contact sports?
- Should professional female athletes be paid the same as professional male athletes?
- Should college be free at the undergraduate level?
- Is the traditional college experience obsolete?
- Should you choose a major based on your interests or your potential salary?
- Should high school students have to meet a required number of service hours before graduating?
- Should teachers earn more or less based on how their students perform on standardized tests?
- Are private high schools more effective than public high schools?
- Should there be a minimum number of attendance days required to graduate?
- Are GPAs harmful or helpful?
- Should schools be required to teach about standardized testing?
- Should Greek Life be banned in the United States?
- Should schools offer science classes explicitly about mental health?
- Should students be able to bring their cell phones to school?
- Should all public restrooms be all-gender?
- Should undocumented immigrants have the same employment and education opportunities as citizens?
- Should everyone be paid a living wage regardless of their employment status?
- Should supremacist groups be able to hold public events?
- Should guns be allowed in public places?
- Should the national drinking age be lowered?
- Should prisoners be allowed to vote?
- Should the government raise or lower the retirement age?
- Should the government be able to control the population?
- Is the death penalty ethical?
Environment
- Should stores charge customers for plastic bags?
- Should breeding animals (dogs, cats, etc.) be illegal?
- Is it okay to have exotic animals as pets?
- Should people be fined for not recycling?
- Should compost bins become mandatory for restaurants?
- Should electric vehicles have their own transportation infrastructure?
- Would heavier fining policies reduce corporations’ emissions?
- Should hunting be encouraged or illegal?
- Should reusable diapers replace disposable diapers?
Science & Technology
- Is paper media more reliable than digital news sources?
- Should automated/self-driving cars be legalized?
- Should schools be required to provide laptops to all students?
- Should software companies be able to have pre-downloaded programs and applications on devices?
- Should drones be allowed in military warfare?
- Should scientists invest more or less money into cancer research?
- Should cloning be illegal?
- Should societies colonize other planets?
- Should there be legal oversight over the development of technology?
Social Media
- Should there be an age limit on social media?
- Should cyberbullying have the same repercussions as in-person bullying?
- Are online relationships as valuable as in-person relationships?
- Does “cancel culture” have a positive or negative impact on societies?
- Are social media platforms reliable information or news sources?
- Should social media be censored?
- Does social media create an unrealistic standard of beauty?
- Is regular social media usage damaging to real-life interactions?
- Is social media distorting democracy?
- How many branches of government should there be?
- Who is the best/worst president of all time?
- How long should judges serve in the U.S. Supreme Court?
- Should a more significant portion of the U.S. budget be contributed towards education?
- Should the government invest in rapid transcontinental transportation infrastructure?
- Should airport screening be more or less stringent?
- Should the electoral college be dismantled?
- Should the U.S. have open borders?
- Should the government spend more or less money on space exploration?
- Should students sing Christmas carols, say the pledge of allegiance, or perform other tangentially religious activities?
- Should nuns and priests become genderless roles?
- Should schools and other public buildings have prayer rooms?
- Should animal sacrifice be legal if it occurs in a religious context?
- Should countries be allowed to impose a national religion on their citizens?
- Should the church be separated from the state?
- Does freedom of religion positively or negatively affect societies?
Parenting & Family
- Is it better to have children at a younger or older age?
- Is it better for children to go to daycare or stay home with their parents?
- Does birth order affect personality?
- Should parents or the school system teach their kids about sex?
- Are family traditions important?
- Should parents smoke or drink around young children?
- Should “spanking” children be illegal?
- Should parents use swear words in front of their children?
- Should parents allow their children to play violent video games?
Entertainment
- Should all actors be paid the same regardless of gender or ethnicity?
- Should all award shows be based on popular vote?
- Who should be responsible for paying taxes on prize money, the game show staff or the contestants?
- Should movies and television shows have ethnicity and gender quotas?
- Should newspapers and magazines move to a completely online format?
- Should streaming services like Netflix and Hulu be free for students?
- Is the movie rating system still effective?
- Should celebrities have more privacy rights?
Arts & Humanities
- Are libraries becoming obsolete?
- Should all schools have mandatory art or music courses in their curriculum?
- Should offensive language be censored from classic literary works?
- Is it ethical for museums to keep indigenous artifacts?
- Should digital designs be considered an art form?
- Should abstract art be considered an art form?
- Is music therapy effective?
- Should tattoos be regarded as “professional dress” for work?
- Should schools place greater emphasis on the arts programs?
- Should euthanasia be allowed in hospitals and other clinical settings?
- Should the government support and implement universal healthcare?
- Would obesity rates lower if the government intervened to make healthy foods more affordable?
- Should teenagers be given access to birth control pills without parental consent?
- Should food allergies be considered a disease?
- Should health insurance cover homeopathic medicine?
- Is using painkillers healthy?
- Should genetically modified foods be banned?
- Should there be a tax on unhealthy foods?
- Should tobacco products be banned from the country?
- Should the birth control pill be free for everyone?
If you need more help brainstorming topics, especially those that are personalized to your interests, you can use CollegeVine’s free AI tutor, Ivy . Ivy can help you come up with original persuasive speech ideas, and she can also help with the rest of your homework, from math to languages.
Do Your Research
A great persuasive speech is supported with plenty of well-researched facts and evidence. So before you begin the writing process, research both sides of the topic you’re presenting in-depth to gain a well-rounded perspective of the topic.
Understand Your Audience
It’s critical to understand your audience to deliver a great persuasive speech. After all, you are trying to convince them that your viewpoint is correct. Before writing your speech, consider the facts and information that your audience may already know, and think about the beliefs and concerns they may have about your topic. Then, address these concerns in your speech, and be mindful to include fresh, new information.
Have Someone Read Your Speech
Once you have finished writing your speech, have someone read it to check for areas of strength and improvement. You can use CollegeVine’s free essay review tool to get feedback on your speech from a peer!
Practice Makes Perfect
After completing your final draft, the key to success is to practice. Present your speech out loud in front of a mirror, your family, friends, and basically, anyone who will listen. Not only will the feedback of others help you to make your speech better, but you’ll become more confident in your presentation skills and may even be able to commit your speech to memory.
Hopefully, these ideas have inspired you to write a powerful, unique persuasive speech. With the perfect topic, plenty of practice, and a boost of self-confidence, we know you’ll impress your audience with a remarkable speech!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
17.3 Organizing Persuasive Speeches
Learning objectives.
- Understand three common organizational patterns for persuasive speeches.
- Explain the steps utilized in Monroe’s motivated sequence.
- Explain the parts of a problem-cause-solution speech.
- Explain the process utilized in a comparative advantage persuasive speech.

Steven Lilley – Engaged – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Previously in this text we discussed general guidelines for organizing speeches. In this section, we are going to look at three organizational patterns ideally suited for persuasive speeches: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantages.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
One of the most commonly cited and discussed organizational patterns for persuasive speeches is Alan H. Monroe’s motivated sequence. The purpose of Monroe’s motivated sequence is to help speakers “sequence supporting materials and motivational appeals to form a useful organizational pattern for speeches as a whole” (German et al., 2010).
While Monroe’s motivated sequence is commonly discussed in most public speaking textbooks, we do want to provide one minor caution. Thus far, almost no research has been conducted that has demonstrated that Monroe’s motivated sequence is any more persuasive than other structural patterns. In the only study conducted experimentally examining Monroe’s motivated sequence, the researchers did not find the method more persuasive, but did note that audience members found the pattern more organized than other methods (Micciche, Pryor, & Butler, 2000). We wanted to add this sidenote because we don’t want you to think that Monroe’s motivated sequence is a kind of magic persuasive bullet; the research simply doesn’t support this notion. At the same time, research does support that organized messages are perceived as more persuasive as a whole, so using Monroe’s motivated sequence to think through one’s persuasive argument could still be very beneficial.
Table 17.1 “Monroe’s Motivated Sequence” lists the basic steps of Monroe’s motivated sequence and the subsequent reaction a speaker desires from his or her audience.
Table 17.1 Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
The first step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the attention step , in which a speaker attempts to get the audience’s attention. To gain an audience’s attention, we recommend that you think through three specific parts of the attention step. First, you need to have a strong attention-getting device. As previously discussed in Chapter 9 “Introductions Matter: How to Begin a Speech Effectively” , a strong attention getter at the beginning of your speech is very important. Second, you need to make sure you introduce your topic clearly. If your audience doesn’t know what your topic is quickly, they are more likely to stop listening. Lastly, you need to explain to your audience why they should care about your topic.
In the need step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the speaker establishes that there is a specific need or problem. In Monroe’s conceptualization of need, he talks about four specific parts of the need: statement, illustration, ramification, and pointing. First, a speaker needs to give a clear and concise statement of the problem. This part of a speech should be crystal clear for an audience. Second, the speaker needs to provide one or more examples to illustrate the need. The illustration is an attempt to make the problem concrete for the audience. Next, a speaker needs to provide some kind of evidence (e.g., statistics, examples, testimony) that shows the ramifications or consequences of the problem. Lastly, a speaker needs to point to the audience and show exactly how the problem relates to them personally.
Satisfaction
In the third step of Monroe’s motivated sequence, the satisfaction step , the speaker sets out to satisfy the need or solve the problem. Within this step, Monroe (1935) proposed a five-step plan for satisfying a need:
- Explanation
- Theoretical demonstration
- Reference to practical experience
- Meeting objections
First, you need to clearly state the attitude, value, belief, or action you want your audience to accept. The purpose of this statement is to clearly tell your audience what your ultimate goal is.
Second, you want to make sure that you clearly explain to your audience why they should accept the attitude, value, belief, or action you proposed. Just telling your audience they should do something isn’t strong enough to actually get them to change. Instead, you really need to provide a solid argument for why they should accept your proposed solution.
Third, you need to show how the solution you have proposed meets the need or problem. Monroe calls this link between your solution and the need a theoretical demonstration because you cannot prove that your solution will work. Instead, you theorize based on research and good judgment that your solution will meet the need or solve the problem.
Fourth, to help with this theoretical demonstration, you need to reference practical experience, which should include examples demonstrating that your proposal has worked elsewhere. Research, statistics, and expert testimony are all great ways of referencing practical experience.
Lastly, Monroe recommends that a speaker respond to possible objections. As a persuasive speaker, one of your jobs is to think through your speech and see what counterarguments could be made against your speech and then rebut those arguments within your speech. When you offer rebuttals for arguments against your speech, it shows your audience that you’ve done your homework and educated yourself about multiple sides of the issue.
Visualization
The next step of Monroe’s motivated sequence is the visualization step , in which you ask the audience to visualize a future where the need has been met or the problem solved. In essence, the visualization stage is where a speaker can show the audience why accepting a specific attitude, value, belief, or behavior can positively affect the future. When helping people to picture the future, the more concrete your visualization is, the easier it will be for your audience to see the possible future and be persuaded by it. You also need to make sure that you clearly show how accepting your solution will directly benefit your audience.
According to Monroe, visualization can be conducted in one of three ways: positive, negative, or contrast (Monroe, 1935). The positive method of visualization is where a speaker shows how adopting a proposal leads to a better future (e.g., recycle, and we’ll have a cleaner and safer planet). Conversely, the negative method of visualization is where a speaker shows how not adopting the proposal will lead to a worse future (e.g., don’t recycle, and our world will become polluted and uninhabitable). Monroe also acknowledged that visualization can include a combination of both positive and negative visualization. In essence, you show your audience both possible outcomes and have them decide which one they would rather have.
The final step in Monroe’s motivated sequence is the action step , in which a speaker asks an audience to approve the speaker’s proposal. For understanding purposes, we break action into two distinct parts: audience action and approval. Audience action refers to direct physical behaviors a speaker wants from an audience (e.g., flossing their teeth twice a day, signing a petition, wearing seat belts). Approval, on the other hand, involves an audience’s consent or agreement with a speaker’s proposed attitude, value, or belief.
When preparing an action step, it is important to make sure that the action, whether audience action or approval, is realistic for your audience. Asking your peers in a college classroom to donate one thousand dollars to charity isn’t realistic. Asking your peers to donate one dollar is considerably more realistic. In a persuasive speech based on Monroe’s motivated sequence, the action step will end with the speech’s concluding device. As discussed elsewhere in this text, you need to make sure that you conclude in a vivid way so that the speech ends on a high point and the audience has a sense of energy as well as a sense of closure.
Now that we’ve walked through Monroe’s motivated sequence, let’s look at how you could use Monroe’s motivated sequence to outline a persuasive speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that the United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments.
Main Points:
- Attention: Want to make nine thousand dollars for just three weeks of work lying around and not doing much? Then be a human guinea pig. Admittedly, you’ll have to have a tube down your throat most of those three weeks, but you’ll earn three thousand dollars a week.
- Need: Every day many uneducated and lower socioeconomic-status citizens are preyed on by medical and pharmaceutical companies for use in for-profit medical and drug experiments. Do you want one of your family members to fall prey to this evil scheme?
- Satisfaction: The United States should have stronger laws governing the use of for-profit medical experiments to ensure that uneducated and lower-socioeconomic-status citizens are protected.
- Visualization: If we enact tougher experiment oversight, we can ensure that medical and pharmaceutical research is conducted in a way that adheres to basic values of American decency. If we do not enact tougher experiment oversight, we could find ourselves in a world where the lines between research subject, guinea pig, and patient become increasingly blurred.
- Action: In order to prevent the atrocities associated with for-profit medical and pharmaceutical experiments, please sign this petition asking the US Department of Health and Human Services to pass stricter regulations on this preying industry that is out of control.
This example shows how you can take a basic speech topic and use Monroe’s motivated sequence to clearly and easily outline your speech efficiently and effectively.
Table 17.2 “Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Checklist” also contains a simple checklist to help you make sure you hit all the important components of Monroe’s motivated sequence.
Table 17.2 Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Checklist
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing a persuasive speech is the problem-cause-solution format. In this specific format, you discuss what a problem is, what you believe is causing the problem, and then what the solution should be to correct the problem.
Specific Purpose: To persuade my classroom peers that our campus should adopt a zero-tolerance policy for hate speech.
- Demonstrate that there is distrust among different groups on campus that has led to unnecessary confrontations and violence.
- Show that the confrontations and violence are a result of hate speech that occurred prior to the events.
- Explain how instituting a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy against hate speech could stop the unnecessary confrontations and violence.
In this speech, you want to persuade people to support a new campus-wide policy calling for zero-tolerance of hate speech. Once you have shown the problem, you then explain to your audience that the cause of the unnecessary confrontations and violence is prior incidents of hate speech. Lastly, you argue that a campus-wide zero-tolerance policy could help prevent future unnecessary confrontations and violence. Again, this method of organizing a speech is as simple as its name: problem-cause-solution.
Comparative Advantages
The final method for organizing a persuasive speech is called the comparative advantages speech format. The goal of this speech is to compare items side-by-side and show why one of them is more advantageous than the other. For example, let’s say that you’re giving a speech on which e-book reader is better: Amazon.com’s Kindle or Barnes and Nobles’ Nook. Here’s how you could organize this speech:
Specific Purpose: To persuade my audience that the Nook is more advantageous than the Kindle.
- The Nook allows owners to trade and loan books to other owners or people who have downloaded the Nook software, while the Kindle does not.
- The Nook has a color-touch screen, while the Kindle’s screen is black and grey and noninteractive.
- The Nook’s memory can be expanded through microSD, while the Kindle’s memory cannot be upgraded.
As you can see from this speech’s organization, the simple goal of this speech is to show why one thing has more positives than something else. Obviously, when you are demonstrating comparative advantages, the items you are comparing need to be functional equivalents—or, as the saying goes, you cannot compare apples to oranges.

Key Takeaways
- There are three common patterns that persuaders can utilize to help organize their speeches effectively: Monroe’s motivated sequence, problem-cause-solution, and comparative advantage. Each of these patterns can effectively help a speaker think through his or her thoughts and organize them in a manner that will be more likely to persuade an audience.
- Alan H. Monroe’s (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience’s attention. In the second stage, the speaker shows an audience that a need exists. In the third stage, the speaker shows how his or her persuasive proposal could satisfy the need. The fourth stage shows how the future could be if the persuasive proposal is or is not adopted. Lastly, the speaker urges the audience to take some kind of action to help enact the speaker’s persuasive proposal.
- The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem. Lastly, the speaker proposes a solution to the problem that corrects the underlying causes.
- The comparative advantages speech format is utilized when a speaker is comparing two or more things or ideas and shows why one of the things or ideas has more advantages than the other(s).
- Create a speech using Monroe’s motivated sequence to persuade people to recycle.
- Create a speech using the problem-cause-solution method for a problem you see on your college or university campus.
- Create a comparative advantages speech comparing two brands of toothpaste.
German, K. M., Gronbeck, B. E., Ehninger, D., & Monroe, A. H. (2010). Principles of public speaking (17th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon, p. 236.
Micciche, T., Pryor, B., & Butler, J. (2000). A test of Monroe’s motivated sequence for its effects on ratings of message organization and attitude change. Psychological Reports, 86 , 1135–1138.
Monroe, A. H. (1935). Principles and types of speech . Chicago, IL: Scott Foresman.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10 Chapter 10: Persuasive Speaking
Amy Fara Edwards and Marcia Fulkerson, Oxnard College
Victoria Leonard, Lauren Rome, and Tammera Stokes Rice, College of the Canyons
Adapted by Jamie C. Votraw, Professor of Communication Studies, Florida SouthWestern State College

Figure 10.1: Abubaccar Tambadou 1
Introduction
The American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA) was founded on April 10, 1866. You may be familiar with their television commercials. They start with images of neglected and lonely-looking cats and dogs while the screen text says: “Every hour… an animal is beaten or abused. They suffer… alone and terrified…” Cue the sad song and the request for donations on the screen. This commercial causes audiences to run for the television remote because they can’t bear to see those images! Yet it is a very persuasive commercial and has proven to be very successful for this organization. According to the ASPCA website, they have raised $30 million since 2006, and their membership has grown to over 1.2 million people. The audience’s reaction to this commercial showcases how persuasion works! In this chapter, we will define persuasive speaking and examine the strategies used to create powerful persuasive speeches.

Figure 10.2: Caged Dogs 2
Defining Persuasive Speaking
Persuasion is the process of creating, reinforcing, or changing people’s beliefs or actions. It is not manipulation, however! The speaker’s intention should be clear to the audience in an ethical way and accomplished through the ethical use of methods of persuasion. When speaking to persuade, the speaker works as an advocate. In contrast to informative speaking, persuasive speakers argue in support of a position and work to convince the audience to support or do something.
As you learned in chapter five on audience analysis, you must continue to consider the psychological characteristics of the audience. You will discover in this chapter the attitudes, beliefs, and values of the audience become particularly relevant in the persuasive speechmaking process. A key element of persuasion is the speaker’s intent. You must intend to create, reinforce, and/or change people’s beliefs or actions in an ethical way.
Types of Persuasive Speeches
There are three types of persuasive speech propositions. A proposition , or speech claim , is a statement you want your audience to support. To gain the support of our audience, we use evidence and reasoning to support our claims. Persuasive speech propositions fall into one of three categories, including questions of fact, questions of value, and questions of policy. Determining the type of persuasive propositions your speech deals with will help you determine what forms of argument and reasoning are necessary to effectively advocate for your position.
Questions of Fact
A question of fact determines whether something is true or untrue, does or does not exist, or did or did not happen. Questions of fact are based on research, and you may find research that supports competing sides of an argument! You may even find that you change your mind about a subject when researching. Ultimately, you will take a stance and rely on credible evidence to support your position, ethically.
Today there are many hotly contested propositions of fact: humans have walked on the moon, the Earth is flat, Earth’s climate is changing due to human action, we have encountered sentient alien life forms, life exists on Mars, and so on.
Here is an example of a question of fact:
Recreational marijuana does not lead to hard drug use.
Recreational marijuana does lead to hard drug use.
Questions of Value
A question of value determines whether something is good or bad, moral or immoral, just or unjust, fair or unfair. You will have to take a definitive stance on which side you’re arguing. For this proposition, your opinion alone is not enough; you must have evidence and reasoning. An ethical speaker will acknowledge all sides of the argument, and to better argue their point, the speaker will convince the audience why their position is the “best” position.
Here is an example of a question of value:
Recreational marijuana use is immoral .
Recreational marijuana use is moral .
Questions of Policy
A question of policy advances a specific course of action based on facts and values. You are telling the audience what you believe should be done and/or you are asking your audience to act in a particular way to make a change. Whether it is stated or implied, all policy speeches focus on values. To be the most persuasive and get your audience to act, you must determine their beliefs, which will help you organize and argue your proposition.
Persuasive speeches on questions of policy must address three elements: need, plan, and practicality . First, the speaker must demonstrate there is a need for change (i.e., there is a problem). Next, the speaker offers the audience a plan (i.e., the policy solution) to address the problem. Lastly, the speaker shows the audience that the solution is practical . This requires that the speaker demonstrate how their proposed plan will address the identified problem without creating new problems.
Consider the topic of car accidents. A persuasive speech on a question of policy might focus on reducing the number of car accidents on a Florida highway. First, the speaker could use evidence from their research to demonstrate there is a need for change (e.g., statistics showing a higher-than-average rate of accidents). Then, the speaker would offer their plan to address the problem. Imagine their proposed plan was to permanently shut down all Florida highways. Would this plan solve the problem and reduce the number of accidents on Florida highways? Well, yes. But is it practical? No. Will it create new problems? Yes – side roads will be congested, people will miss work, kids will miss school, emergency response teams will be slowed, and tourism will decrease. The speaker could not offer such a plan and demonstrate that it is practical. Alternatively, maybe the speaker advocates for a speed reduction in a particularly problematic stretch of highway or convinces the audience to support increasing the number of highway patrol cars.
Here is an example of a question of policy:
Recreational marijuana use should be legal in all 50 states.
Recreational marijuana use should not be legal in all 50 states.
Persuasive Speech Organizational Patterns
There are several methods of organizing persuasive speeches. Remember, you must use an organizational pattern to outline your speech (think back to chapter eight). Some professors will specify a specific pattern to use for your assignment. Otherwise, the organizational pattern you select should be based on your speech content. What pattern is most logical based on your main points and the goal of your speech? This section will explain five common formats of persuasive outlines: Problem-Solution, Problem-Cause-Solution, Comparative Advantages, Monroe’s Motivated Sequence, and Claim to Proof.
Problem-Solution Pattern
Sometimes it is necessary to share a problem and a solution with an audience. In cases like these, the problem-solution organizational pattern is an appropriate way to arrange the main points of a speech. It’s important to reflect on what is of interest to you, but also what is critical to engage your audience. This pattern is used intentionally because, for most problems in society, the audience is unaware of their severity. Problems can exist at a local, state, national, or global level.
For example, the nation has recently become much more aware of the problem of human sex trafficking. Although the US has been aware of this global issue for some time, many communities are finally learning this problem is occurring in their own backyards. Colleges and universities have become engaged in the fight. Student clubs and organizations are getting involved and bringing awareness to this problem. Everyday citizens are using social media to warn friends and followers of sex-trafficking tricks to look out for.
Let’s look at how you might organize a problem-solution speech centered on this topic. In the body of this speech, there would be two main points; a problem and a solution. This pattern is used for speeches on questions of policy.
Topic: Human Sex Trafficking
General Purpose: To persuade
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to support increased legal penalties for sex traffickers.
Thesis (Central Idea): Human sex trafficking is a global challenge with local implications, but it can be addressed through multi-pronged efforts from governments and non-profits.
Preview of Main Points: First, I will define and explain the extent of the problem of sex trafficking within our community while examining the effects this has on the victims. Then, I will offer possible solutions to take the predators off the streets and allow the victims to reclaim their lives and autonomy.
- The problem of human sex trafficking is best understood by looking at the severity of the problem, the methods by which traffickers kidnap or lure their victims, and its impact on the victim.
- The problem of human sex trafficking can be solved by working with local law enforcement, changing the laws currently in place for prosecuting the traffickers and pimps, and raising funds to help agencies rescue and restore victims.
Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
To review the problem-solution pattern, recall that the main points do not explain the cause of the problem, and in some cases, the cause is not necessary to explain. For example, in discussing the problem of teenage pregnancy, most audiences will not need to be informed about what causes someone to get pregnant. However, there are topics where discussing the cause is imperative to understanding the solution. The Problem-Cause-Solution organizational pattern adds a main point between the problem and solution by discussing the cause of the problem. In the body of the speech, there will be three main points: the problem, the cause, and finally, the solution. This pattern is also used for speeches dealing with questions of policy. One of the reasons you might consider this pattern is when an audience is not familiar with the cause. For example, if gang activity is on the rise in the community you live in, you might need to explain what causes an individual to join a gang in the first place. By explaining the causes of a problem, an audience might be more likely to accept the solution(s) you’ve proposed. Let’s look at an example of a speech on gangs.
Topic: The Rise of Gangs in Miami-Dade County
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to urge their school boards to include gang education in the curriculum.
Thesis (Central Idea): The uptick in gang affiliation and gang violence in Miami-Dade County is problematic, but if we explore the causes of the problem, we can make headway toward solutions.
Preview of Main Points: First, I will explain the growing problem of gang affiliation and violence in Miami-Dade County. Then, I will discuss what causes an individual to join a gang. Finally, I will offer possible solutions to curtail this problem and get gangs off the streets of our community.
- The problem of gang affiliation and violence is growing rapidly, leading to tragic consequences for both gang members and their families.
- The causes of the proliferation of gangs can be best explained by feeling disconnected from others, a need to fit in, and a lack of supervision after school hours.
- The problem of the rise in gangs can be solved, or minimized, by offering after-school programs for youth, education about the consequences of joining a gang, and parent education programs offered at all secondary education levels.
Let’s revisit the human sex trafficking topic from above. Instead of using only a problem-solution pattern, the example that follows adds “cause” to their main points.
Preview of Main Points: First, I will define and explain the extent of the problem of sex trafficking within our community while examining the effects this has on the victims. Second, I will discuss the main causes of the problem. Finally, I will offer possible solutions to take the predators off the streets and allow the victims to reclaim their lives.
- The cause of the problem can be recognized by the monetary value of sex slavery.
- The problem of human sex trafficking can be solved by working with local law enforcement, changing the current laws for prosecuting traffickers, and raising funds to help agencies rescue and restore victims.
Comparative Advantages
Sometimes your speech will showcase a problem, but there are multiple potential solutions for the audience to consider. In cases like these, the comparative advantages organizational pattern is an appropriate way to structure the speech. This pattern is commonly used when there is a problem, but the audience (or the public) cannot agree on the best solution. When your goal is to convince the audience that your solution is the best among the options, this organizational pattern should be used.
Consider the hot topic of student loan debt cancellation. There is a rather large divide among the public about whether or not student loans should be canceled or forgiven by the federal government. Once again, audience factors come into play as attitudes and values on the topic vary greatly across various political ideologies, age demographics, socioeconomic statuses, educational levels, and more.
Let’s look at how you might organize a speech on this topic. In the body of this speech, one main point is the problem, and the other main points will depend on the number of possible solutions.
Topic: Federal Student Loan Debt Cancellation
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to support the government cancellation of $10,000 in federal student loan debt.
Thesis (Central Idea): Student loans are the largest financial hurdle faced by multiple generations, and debt cancellation could provide needed relief to struggling individuals and families.
Preview of Main Points: First, I will define and explain the extent of the student loan debt problem in the United States. Then, I will offer possible solutions and convince you that the best solution is a debt cancellation of $10,000.
- Student loan debt is the second greatest source of financial debt in the United States and several solutions have been proposed to address the problem created by unusually high levels of educational debt.
- The first proposed solution is no debt cancellation. This policy solution would not address the problem.
- The second proposed solution is $10,000 of debt cancellation. This is a moderate cancellation that would alleviate some of the financial burden faced by low-income and middle-class citizens without creating vast government setbacks.
- The third proposed solution is full debt cancellation. While this would help many individuals, the financial setback for the nation would be too grave.
- As you can see, there are many options for addressing the student loan debt problem. However, the best solution is the cancellation of $10,000.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Format
Alan H. Monroe, a Purdue University professor, used the psychology of persuasion to develop an outline for making speeches that will deliver results and wrote about it in his book Monroe’s Principles of Speech (1951). It is now known as Monroe’s Motivated Sequence . This is a well-used and time-proven method to organize persuasive speeches for maximum impact. It is most often used for speeches dealing with questions of policy. You can use it for various situations to create and arrange the components of any persuasive message. The five steps are explained below and should be followed explicitly and in order to have the greatest impact on the audience.
Step One: Attention
In this step, you must get the attention of the audience. The speaker brings attention to the importance of the topic as well as their own credibility and connection to the topic. This step of the sequence should be completed in your introduction like in other speeches you have delivered in class. Review chapter 9 for some commonly used attention-grabber strategies.
Step Two: Need
In this step, you will establish the need; you must define the problem and build a case for its importance. Later in this chapter, you will find that audiences seek logic in their arguments, so the speaker should address the underlying causes and the external effects of a problem. It is important to make the audience see the severity of the problem, and how it affects them, their families, and/or their community. The harm , or problem that needs changing, can be physical, financial, psychological, legal, emotional, educational, social, or a combination thereof. It must be supported by evidence. Ultimately, in this step, you outline and showcase that there is a true problem that needs the audience’s immediate attention. For example, it is not enough to say “pollution is a problem in Florida,” you must demonstrate it with evidence that showcases that pollution is a problem. For example, agricultural runoff is said to cause dangerous algal blooms on Florida’s beaches. You could show this to your audience with research reports, pictures, expert testimony, etc.
Step Three: Satisfaction
In this step, the need must be “satisfied” with a solution. As the speaker, this is when you present the solution and describe it, but you must also defend that it works and will address the causes and symptoms of the problem. Do you recall “need, plan, and practicality”? This step involves the plan and practicality elements. This is not the section where you provide specific steps for the audience to follow. Rather, this is the section where you describe “the business” of the solution. For example, you might want to change the voting age in the United States. You would not explain how to do it here; you would explain the plan – what the new law would be – and its practicality – how that new law satisfies the problem of people not voting. Satisfy the need!
Step Four: Visualization
In this step, your arguments must look to the future either positively or negatively, or both. If positive, the benefits of enacting or choosing your proposed solution are explained. If negative, the disadvantages of not doing anything to solve the problem are explained. The purpose of visualization is to motivate the audience by revealing future benefits or using possible fear appeals by showing future harms if no changes are enacted. Ultimately, the audience must visualize a world where your solution solves the problem. What does this new world look like? If you can help the audience picture their role in this new world, you should be able to get them to act. Describe a future where they fail to act, and the problem persists or is exacerbated. Or, help them visualize a world where their adherence to the steps you outlined in your speech remediates the problem.
Step Five: Action
In the final step of Monroe’s Motivated Sequence, we tell the audience exactly what needs to be done by them . Not a general “we should lower the voting age” statement, but rather, the exact steps for the people sitting in front of you to take. If you really want to move the audience to action, this step should be a full main point within the body of the speech and should outline exactly what you need them to do. It isn’t enough to say “now, go vote!” You need to tell them where to click, who to write, how much to donate, and how to share the information with others in their orbit. In the action step, the goal is to give specific steps for the audience to take, as soon as possible, to move toward solving the problem. So, while the satisfaction step explains the solution overall, the action section gives concrete ways to begin making the solution happen. The more straightforward and concrete you can make the action step, the better. People are more likely to act if they know how accessible the action can be. For example, if you want your audience to be vaccinated against the hepatitis B virus (HBV), you can give them directions to a clinic where vaccinations are offered and the hours of that location. Do not leave anything to chance. Tell them what to do. If you have effectively convinced them of the need/problem, you will get them to act, which is your overall goal.
Claim-to-Proof Pattern
A claim-to-proof pattern provides the audience with reasons to accept your speech proposition (Mudd & Sillars, 1962). State your claim (your thesis) and then prove your point with reasons (main points). The proposition is presented at the beginning of the speech, and in the preview, tells the audience how many reasons will be provided for the claim. Do not reveal too much information until you get to that point in your speech. We all hear stories on the news about someone killed by a handgun, but it is not every day that it affects us directly, or that we know someone who is affected by it. One student told a story of a cousin who was killed in a drive-by shooting, and he was not even a member of a gang.
Here is how the setup for this speech would look:
Thesis and Policy Claim: Handgun ownership in America continues to be a controversial subject, and I believe that private ownership of handguns should have limitations.
Preview: I will provide three reasons why handgun ownership should be limited.
When presenting the reasons for accepting the claim, it is important to consider the use of primacy-recency . If the audience is against your claim, put your most important argument first. For this example, the audience believes in no background checks for gun ownership. As a result, this is how the main points may be written to try and capture the audience who disagrees with your position. We want to get their attention quickly and hold it throughout the speech. You will also need to support these main points. Here is an example:
- The first reason background checks should be mandatory is that when firearms are too easily accessed by criminals, more gun violence occurs.
- A second reason why background checks should be mandatory is that they would lower firearm trafficking.
Moving forward, the speaker would select one or two other reasons to bring into the speech and support them with evidence. The decision on how many main points to have will depend on how much time you have for this speech, and how much research you can find on the topic. If this is a pattern your instructor allows, speak with them about sample outlines. This pattern can be used for fact, value, or policy speeches.
Methods of Persuasion
The three methods of persuasion were first identified by Aristotle, a Greek philosopher in the time of Ancient Greece. In his teachings and book, Rhetoric, he advised that a speaker could persuade their audience using three different methods: Ethos (persuasion through credibility), Pathos (persuasion through emotion), and Logos (persuasion through logic). In fact, he said these are the three methods of persuasion a speaker must rely on.

Figure 10.3: Aristotle 3
By definition, ethos is the influence of a speaker’s credibility, which includes character, competence, and charisma. Remember in earlier chapters when we learned about credibility? Well, it plays a role here, too. The more credible or believable you are, the stronger your ethos. If you can make an audience see you believe in what you say and have knowledge about what you say, they are more likely to believe you and, therefore, be more persuaded by you. If your arguments are made based on credibility and expertise, then you may be able to change someone’s mind or move them to action. Let’s look at some examples.
If you are considering joining the U.S. Air Force, do you think someone in a military uniform would be more persuasive than someone who was not in uniform? Do you think a firefighter in uniform could get you to make your house more fire-safe than someone who was not in uniform? Their uniform contributes to their ethos. Remember, credibility comes from audience perceptions – how they perceive you as the speaker. You may automatically know they understand fire safety without even opening their mouths to speak. If their arguments are as strong as the uniform, you may have already started putting your fire emergency kit together! Ultimately, we tend to believe in people in powerful positions. We often obey authority figures because that’s what we have been taught to do. In this case, it works to help us persuade an audience.
Advertising campaigns also use ethos well. Think about how many celebrities sell you products. Whose faces do you regularly see? Taylor Swift, Kerry Washington, Kylie Jenner, Jennifer Aniston? Do they pick better cosmetics than the average woman, or are they using their celebrity influence to persuade you to buy? If you walk into a store to purchase makeup and remember which ones are Kylie Jenner’s favorite makeup, are you more likely to purchase it? Pop culture has power, which is why you see so many celebrities selling products on social media. Now, Kylie may not want to join you in class for your speech (sorry!), so you will have to be creative with ethos and incorporate experts through your research and evidence. For example, you need to cite sources if you want people to get a flu shot, using a doctor’s opinion or a nurse’s opinion is critical to get people to make an appointment to get the shot. You might notice that even your doctor shares data from research when discussing your healthcare. Similarly, y ou have to be credible. You need to become an authority on your topic, show them the evidence, and persuade them using your character and charisma.
Finally, ethos also relates to ethics. The audience needs to trust you and your speech needs to be truthful. Most importantly, this means ethical persuasion occurs through ethical methods – you should not trick your audience into agreeing with you. It also means your own personal involvement is important and the topic should be something you are either personally connected to or passionate about. For example, if you ask the audience to adopt a puppy from a rescue, will your ethos be strong if you bought your puppy from a pet store or breeder? How about asking your audience to donate to a charity; have you supported them yourself? Will the audience want to donate if you haven’t ever donated? How will you prove your support? Think about your own role in the speech while you are also thinking about the evidence you provide.
The second appeal you should include in your speech is pathos , an emotional appeal . By definition, pathos appeals evoke strong feelings or emotions like anger, joy, desire, and love. The goal of pathos is to get people to feel something and, therefore, be moved to change their minds or to act. You want your arguments to arouse empathy, sympathy, and/or compassion. So, for persuasive speeches, you can use emotional visual aids or thoughtful stories to get the audience’s attention and hook them in. If you want someone to donate to a local women’s shelter organization to help the women further their education at the local community college, you might share a real story of a woman you met who stayed at the local shelter before earning her degree with the help of the organization. We see a lot of advertisement campaigns rely on this. They show injured military veterans to get you to donate to the Wounded Warriors Project , or they show you injured animals to get you to donate to animal shelters. Are you thinking about how your own topic is emotional yet? We hope so!
In addition, we all know that emotions are complex. So, you can’t just tell a sad story or yell out a bad word to shock them and think they will be persuaded. You must ensure the emotions you engage relate directly to the speech and the audience. Be aware that negative emotions can backfire, so make sure you understand the audience, so you will know what will work best. Don’t just yell at people that they need to brush their teeth for two minutes or show a picture of gross teeth; make them see the benefits of brushing for two minutes by showing beautiful teeth too.
Emotional appeals also need to be ethical and incorporated responsibly. Consider a persuasive speech on distracted driving. If your audience is high school or college students, they may be mature enough to see an emotional video or photo depicting the devastating consequences of distracted driving. If you’re teaching an elementary school class about car safety (e.g., keeping your seatbelt on, not throwing toys, etc.), it would be highly inappropriate to scare them into compliance by showing a devastating video of a car accident. As an ethical public speaker, it is your job to use emotional appeals responsibly.
One way to do this is to connect to the theory by Abraham Maslow, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, which states that our actions are motivated by basic (physiological and safety), psychological (belongingness, love, and esteem), and self-fulfillment needs (self-actualization). To persuade, we have to connect what we say to the audience’s real lives. Here is a visual of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Pyramid:
Figure 10.4: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 4
Notice the pyramid is largest at the base because our basic needs are the first that must be met. Ever been so hungry you can’t think of anything except when and what you will eat? (Hangry anyone?) Well, you can’t easily persuade people if they are only thinking about food. It doesn’t mean you need to bring snacks to your speech class on the day of your speech (albeit, this might be relevant to a food demonstration speech). Can you think about other ways pathos connects to this pyramid? How about safety and security needs, the second level on the hierarchy? Maybe your speech is about persuading people to purchase more car insurance. You might argue they need more insurance so they can feel safer on the road. Or maybe your family should put in a camera doorbell to make sure the home is safe. Are you seeing how we can use arguments that connect to emotions and needs simultaneously?
The third level in Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, love and belongingness, is about the need to feel connected to others. This need level is related to the groups of people we spend time with like friends and family. This also relates to the feeling of being “left out” or isolated from others. If we can use arguments that connect us to other humans, emotionally or physically, we will appeal to more of the audience. If your topic is about becoming more involved in the church or temple, you might highlight the social groups one may join if they connect to the church or temple. If your topic is on trying to persuade people to do a walk for charity, you might showcase how doing the event with your friends and family becomes a way of raising money for the charity and carving out time with, or supporting, the people you love. For this need, your pathos will be focused on connection. You want your audience to feel like they belong in order for them to be persuaded. People are more likely to follow through on their commitments if their friends and family do it. We know that if our friends go to the party, we are more likely to go, so we don’t have FOMO (fear of missing out). The same is true for donating money; if your friends have donated to a charity, you might want to be “in” the group, so you would donate also.
Finally, we will end this pathos section with an example that connects Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs to pathos. Maybe your speech is to convince people to remove the Instagram app from their phones, so they are less distracted from their life. You could argue staying away from social media means you won’t be threatened online (safety), you will spend more real-time with your friends (belongingness), and you will devote more time to writing your speech outlines (esteem and achievement). Therefore, you can use Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs as a roadmap for finding key needs that relate to your proposition which helps you incorporate emotional appeals.
The third and final appeal Aristotle described is logos , which, by definition, is the use of logical and organized arguments that stem from credible evidence supporting your proposition. When the arguments in your speech are based on logic, you are utilizing logos. You need experts in your corner to persuade; you need to provide true, raw evidence for someone to be convinced. You can’t just tell them something is good or bad for them, you have to show it through logic. You might like to buy that product, but how much does it cost? When you provide the dollar amount, you provide some logos for someone to decide if they can and want to purchase that product. How much should I donate to that charity? Provide a dollar amount reasonable for the given audience, and you will more likely persuade them. If you asked a room full of students to donate $500.00 to a charity, it isn’t logical. If you asked them to donate $10.00 instead of buying lattes for two days, you might actually persuade them.
So, it is obvious that sources are a part of logos, but so is your own honest involvement with the topics. If you want people to vote, you need to prove voting matters and make logical appeals to vote. We all know many people say, “my vote doesn’t count.” Your speech needs to logically prove that all votes count, and you need to showcase that you always vote in the local and national elections. In this example, we bring together your ethos and your pathos to sell us on the logos. All three appeals together help you make your case. Audiences are not only persuaded by experts, or by emotions, they want it all to make sense! Don’t make up a story to “make it fit”. Instead, find a real story that is truthful, emotional, and one your audience can relate to make your speech logical from beginning to end and, therefore, persuasive.
Reasoning and Fallacies in Your Speech
In this chapter, we have provided you with several important concepts in the persuasive speech process, including patterns of organization and methods of persuasion. Now, we want to make sure your speech content is clear and includes strong and appropriate arguments. You have done extensive research to support the claims you will make in your speech, but we want to help you ensure that your arguments aren’t flawed. Thus, we will now look at different forms of reasoning and fallacies (or errors) to avoid in your logic.
Thus far, you have read how Aristotle’s proofs can and should be used in a persuasive speech. But, you might wonder how that influences the approach you take in writing your speech outline. You already know your research needs to be credible, and one way to do this is through research. Let’s now put this all together by explaining how reasoning is used in a speech, as well as the fallacies, or errors in reasoning, that often occur when speechwriting.
You may have seen graduation requirements include the category of critical thinking, which is the ability to think about what information you are given and make sense of it to draw conclusions. Today, colleges, universities, and employers are seeking individuals who have these critical thinking skills. Critical thinking can include abilities like problem-solving or decision-making. How did you decide on which college to start your higher educational journey? Was it a decision based on finances, being close to home, or work? This decision involved critical thinking. Even if you had an emotional investment in this decision (pathos), you still needed to use logic, or logos, in your thought process. Reasoning is the process of constructing arguments in a logical way. The use of evidence, also known as data , is what we use to prove our claims. We have two basic and important approaches for how we come to believe something is true. These are known as induction and deduction. Let us explain.
Inductive Reasoning
You have probably used inductive reasoning in your life without even knowing it! Inductive reasoning is a type of reasoning in which examples or specific instances are used to provide strong evidence for (though not absolute proof of) the truth of the conclusion (Garcia, 2022). In other words, you are led to a conclusion through your “proof”. With inductive reasoning, we are exposed to several different examples of a situation, and from those examples, we conclude a general truth because there is no theory to test. Think of it this way: you first make an observation, then, observe a pattern, and finally, develop a theory or general conclusion.
For instance, you visit your local grocery store daily to pick up necessary items. You notice that on Sunday, two weeks ago, all the clerks in the store were wearing football jerseys. Again, last Sunday, the clerks wore their football jerseys. Today, also a Sunday, they’re wearing them again. From just these three observations, you may conclude that on Sundays, these supermarket employees wear football jerseys to support their favorite teams. Can you conclude that this pattern holds indefinitely? Perhaps not; the phenomenon may only take place during football season. Hypotheses typically need much testing before confirmation. However, it seems likely that if you return next Sunday wearing a football jersey, you will fit right in.
In another example, imagine you ate an avocado, and soon afterward, the inside of your mouth swelled. Now imagine a few weeks later you ate another avocado and again the inside of your mouth swelled. The following month, you ate yet another avocado, and you had the same reaction as the last two times. You are aware that swelling on the inside of your mouth can be a sign of an allergy to avocados. Using induction, you conclude, more likely than not, you are allergic to avocados.
Data (evidence): After I ate an avocado, the inside of my mouth was swollen (1st time).
Data (evidence): After I ate an avocado, the inside of my mouth was swollen (2nd time).
Data (evidence): I ate an avocado, and the inside of my mouth was swollen (3rd time).
Additional Information: Swollen lips can be a sign of a food allergy.
Conclusion: Likely, I am allergic to avocados.
Inductive reasoning can never lead to absolute certainty. Instead, induction allows you to say, given the examples provided for support, the conclusion is most likely true. Because of the limitations of inductive reasoning, a conclusion will be more credible if multiple lines of reasoning are presented in its support. This is how inductive reasoning works. Now, let’s examine four common methods of inductive reasoning to help you think critically about your persuasive speech.
An analogy allows you to draw conclusions about an object or phenomenon based on similarities to something else (Garcia, 2022). Sometimes the easiest way to understand reasoning is to start with a simple analogy. An avid DIY enthusiast may love to paint -walls, furniture, and objects. To paint well, you need to think about what materials you will need, a knowledge of the specific steps to paint, and the knowledge of how to use an approach to painting so that your paint doesn’t run and your project comes out perfectly! Let’s examine how this example works as an analogy.
Analogies can be figurative or literal. A figurative analogy compares two things that share a common feature, but are still different in many ways. For example, we could say that painting is like baking; they both involve making sure that you have the correct supplies and follow a specific procedure. There are similarities in these features, but there are profound differences. However, a literal analogy is where the two things under comparison have sufficient or significant similarities to be compared fairly (Garcia, 2022). A literal analogy might compare different modalities at the school where your authors teach. If we claim that you should choose Florida SouthWestern State College’s face-to-face courses rather than enrolling in online courses , we could make literal comparisons of the courses offered, available student services, or the classroom atmosphere, for instance.
If we use the more literal analogy of where you choose to go to college, we are using an analogy of two similar “things,” and hopefully, this makes your analogy carry more weight. What this form of reasoning does is lead your audience to a conclusion. When we address fallacies later in this chapter, you will see that comparing two things that are not similar enough could lead you might make an error, or what we call a false analogy fallacy.
Generalization
Another effective form of reasoning is through the use of generalizations. Generalization is a form of inductive reasoning that draws conclusions based on recurring patterns or repeated observations (Garcia, 2022), observing multiple examples and looking for commonalities in those examples to make a broad statement about them. For example, if I tried four different types of keto bread (the new craze), and found that each of them tasted like Styrofoam , I could generalize and say all keto bread is NOT tasty! Or, if in your college experience, you had two professors that you perceived as “bad professors,” you might take a big leap and say that all professors at your campus are “bad.” As you will see later in the discussion on fallacies, this type of reasoning can get us into trouble if we draw a conclusion without sufficient evidence, also known as a hasty generalization. Have you ever drawn a conclusion about a person or group of people after only one or two experiences with them? Have you ever decided you disliked a pizza place because you didn’t like the pizza the first time you tried it? Sometimes, we even do this in our real lives.
Causal Reasoning
Causal reasoning is a form of inductive reasoning that seeks to make cause-effect connections (Garcia, 2022). We don’t typically give this a lot of thought. In the city where one of your authors lives, there are periodic street closures with cones up or signs to redirect drivers. The past several times this has happened, it has been because there was a community 5K run. It is easy to understand why each time I see cones I assume there is a 5K event. However, there could be a completely different cause that I didn’t even think about. The cones could be there due to a major accident or road work.
Reasoning from Sign
Reasoning from sign is a form of inductive reasoning in which conclusions are drawn about phenomena based on events that precede or co-exist with (but do not cause) a subsequent event (Garcia, 2022). In Southern California, a part of the country with some of the worst droughts, one may successfully predict when summer is coming. The lawn begins to die, and the beautiful gardens go limp. All of this occurs before the temperature reaches 113 degrees and before the calendar changes from spring to summer. Based on this observation, there are signs that summer has arrived.
Like many forms of reasoning, it is easy to confuse “reasoning from sign” with “causal reasoning.” Remember, that for this form of reasoning, we looked at an event that preceded another, or co-existed, not an event that occurred later. IF the weather turned to 113 degrees, and then the grass and flowers began to die, then it could be causal.
Deductive Reasoning
The second type of reasoning is known as deductive reasoning , or deduction, which is a conclusion based on the combination of multiple premises that are generally assumed to be true (Garcia, 2022). Whereas with inductive reasoning, we were led to a conclusion, deductive reasoning starts with the overall statement and then identifies examples that support it to reach the conclusion.
Deductive reasoning is built on two statements whose logical relationship should lead to a third statement that is an unquestionably correct conclusion, as in the following example:
Grocery store employees wear football jerseys on Sundays.
Today is Sunday.
Grocery store employees will be wearing football jerseys today.
Suppose the first statement is true (Grocery store employees wear football jerseys on Sundays) and the second statement is true (Today is Sunday). In that case, the conclusion (Grocery store employees will be wearing football jerseys today) is reasonably expected. If a group must have a certain quality, and an individual is a member of that group, then the individual must have that quality.
Unlike inductive reasoning, deductive reasoning allows for certainty as long as certain rules are followed.
Fallacies in Reasoning
As you might recall from our discussion, we alluded to several fallacies. Fallacies are errors in reasoning logic or making a mistake when constructing an inductive or deductive argument. There are dozens of fallacies we could discuss here, but we will highlight those we find to be the most common. Our goal is to help you think through the process of writing your persuasive speech so that it is based on sound reasoning with no fallacies in your arguments.
Table 10.1 describes fifteen fallacies that can be avoided once you understand how to identify them.
Table 10.1: Fallacies
In this chapter, you can feel confident that you have learned what you need to know to complete an effective persuasive speech. We have defined persuasion, explained speech propositions and patterns, and offered strategies to persuade, including ways to use logic. We also helped you learn more about inductive and deductive reasoning, and all of the various ways these methods help you construct your speeches. Finally, we provided you with the most common fallacies that could trip you up if you aren’t careful. The goal is to be clear, logical, and persuasive! Motivate your audience. Hey, have you been persuaded to start your speech outline yet? We hope so!
Reflection Questions
- What is the difference between propositions of fact, value, and policy?
- How will you determine which pattern of organization to use for your persuasive speech?
- How might you use ethos, pathos, and logos effectively in your speech? How can you write these three proofs into your content?
- What form(s) of reasoning will you use in your speech? How can you ensure you are not using any fallacies?
Appeal to Novelty
Appeal to Tradition
Circular Reasoning
Claim-to-Proof
Critical Thinking
Emotional Appeal
False Analogy
False Cause
Figurative Analogy
Hasty Generalization
Literal Analogy
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
Non-Sequitur
Primacy-recency
Problem-Cause-Solution
Problem-Solution
Proposition
Question of Fact
Question of Policy
Question of Value
Red Herring
Slippery Slope
Sweeping Generalization
Two Wrongs Make a Right
Garcia, A. R. (2022). Inductive and Deductive Reasoning. Retrieved May 5, 2022, from https://englishcomposition.org/advanced-writing/inductive-and-deductive-reasoning/.
Monroe, A. H. (1949). Principles and types of speech . Glenview, IL: Scott, Foresman and Company.
Mudd, C. S. & Sillars, M.O. (1962), Speech; content and communication. San Francisco, CA: Chandler Publishing Company.
Introduction to Public Speaking Copyright © by Jamie C. Votraw, M.A.; Katharine O'Connor, Ph.D.; and William F. Kelvin, Ph.D.. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
75 Persuasive Speech Topics and Ideas
October 4, 2018 - Gini Beqiri
To write a captivating and persuasive speech you must first decide on a topic that will engage, inform and also persuade the audience. We have discussed how to choose a topic and we have provided a list of speech ideas covering a wide range of categories.
What is persuasive speech?
The aim of a persuasive speech is to inform, educate and convince or motivate an audience to do something. You are essentially trying to sway the audience to adopt your own viewpoint.
The best persuasive speech topics are thought-provoking, daring and have a clear opinion. You should speak about something you are knowledgeable about and can argue your opinion for, as well as objectively discuss counter-arguments.
How to choose a topic for your speech
It’s not easy picking a topic for your speech as there are many options so consider the following factors when deciding.
Familiarity
Topics that you’re familiar with will make it easier to prepare for the speech.
It’s best if you decide on a topic in which you have a genuine interest in because you’ll be doing lots of research on it and if it’s something you enjoy the process will be significantly easier and more enjoyable. The audience will also see this enthusiasm when you’re presenting which will make the speech more persuasive.
The audience’s interest
The audience must care about the topic. You don’t want to lose their attention so choose something you think they’ll be interested in hearing about.
Consider choosing a topic that allows you to be more descriptive because this allows the audience to visualize which consequently helps persuade them.
Not overdone
When people have heard about a topic repeatedly they’re less likely to listen to you as it doesn’t interest them anymore. Avoid cliché or overdone topics as it’s difficult to maintain your audience’s attention because they feel like they’ve heard it all before.
An exception to this would be if you had new viewpoints or new facts to share. If this is the case then ensure you clarify early in your speech that you have unique views or information on the topic.
Emotional topics
Emotions are motivators so the audience is more likely to be persuaded and act on your requests if you present an emotional topic.
People like hearing about issues that affect them or their community, country etc. They find these topics more relatable which means they find them more interesting. Look at local issues and news to discover these topics.
Desired outcome
What do you want your audience to do as a result of your speech? Use this as a guide to choosing your topic, for example, maybe you want people to recycle more so you present a speech on the effect of microplastics in the ocean.

Persuasive speech topics
Lots of timely persuasive topics can be found using social media, the radio, TV and newspapers. We have compiled a list of 75 persuasive speech topic ideas covering a wide range of categories.
Some of the topics also fall into other categories and we have posed the topics as questions so they can be easily adapted into statements to suit your own viewpoint.
- Should pets be adopted rather than bought from a breeder?
- Should wild animals be tamed?
- Should people be allowed to own exotic animals like monkeys?
- Should all zoos and aquariums be closed?
Arts/Culture
- Should art and music therapy be covered by health insurance?
- Should graffiti be considered art?
- Should all students be required to learn an instrument in school?
- Should automobile drivers be required to take a test every three years?
- Are sports cars dangerous?
- Should bicycles share the roads with cars?
- Should bicycle riders be required by law to always wear helmets?
Business and economy
- Do introverts make great leaders?
- Does owning a business leave you feeling isolated?
- What is to blame for the rise in energy prices?
- Does hiring cheaper foreign employees hurt the economy?
- Should interns be paid for their work?
- Should employees receive bonuses for walking or biking to work?
- Should tipping in restaurants be mandatory?
- Should boys and girls should be taught in separate classrooms?
- Should schools include meditation breaks during the day?
- Should students be allowed to have their mobile phones with them during school?
- Should teachers have to pass a test every decade to renew their certifications?
- Should online teaching be given equal importance as the regular form of teaching?
- Is higher education over-rated?
- What are the best ways to stop bullying?
- Should people with more than one DUI lose their drivers’ licenses?
- Should prostitution be legalised?
- Should guns be illegal in the US?
- Should cannabis be legalised for medical reasons?
- Is equality a myth?
- Does what is “right” and “wrong” change from generation to generation?
- Is there never a good enough reason to declare war?
- Should governments tax sugary drinks and use the revenue for public health?
- Has cosmetic surgery risen to a level that exceeds good sense?
- Is the fast-food industry legally accountable for obesity?
- Should school cafeterias only offer healthy food options?
- Is acupuncture a valid medical technique?
- Should assisted suicide be legal?
- Does consuming meat affect health?
- Is dieting a good way to lose weight?
Law and politics
- Should voting be made compulsory?
- Should the President (or similar position) be allowed to serve more than two terms?
- Would poverty reduce by fixing housing?
- Should drug addicts be sent for treatment in hospitals instead of prisons?
- Would it be fair for the government to detain suspected terrorists without proper trial?
- Is torture acceptable when used for national security?
- Should celebrities who break the law receive stiffer penalties?
- Should the government completely ban all cigarettes and tobacco products
- Is it wrong for the media to promote a certain beauty standard?
- Is the media responsible for the moral degradation of teenagers?
- Should advertising be aimed at children?
- Has freedom of press gone too far?
- Should prayer be allowed in public schools?
- Does religion have a place in government?
- How do cults differ from religion?
Science and the environment
- Should recycling be mandatory?
- Should genetically modified foods be sold in supermarkets?
- Should parents be allowed to choose the sex of their unborn children?
- Should selling plastic bags be completely banned in shops?
- Should smoking in public places be banned?
- Should professional female athletes be paid the same as male athletes in the same sport?
- Should doping be allowed in professional sports?
- Should schools be required to teach all students how to swim?
- How does parental pressure affect young athletes?
- Will technology reduce or increase human employment opportunities?
- What age should children be allowed to have mobile phones?
- Should libraries be replaced with unlimited access to e-books?
- Should we recognize Bitcoin as a legal currency?
- Should bloggers and vloggers be treated as journalists and punished for indiscretions?
- Has technology helped connect people or isolate them?
- Should mobile phone use in public places be regulated?
- Do violent video games make people more violent?
World peace
- What is the safest country in the world?
- Is planetary nuclear disarmament possible?
- Is the idea of peace on earth naive?
These topics are just suggestions so you need to assess whether they would be suitable for your particular audience. You can easily adapt the topics to suit your interests and audience, for example, you could substitute “meat” in the topic “Does consuming meat affect health?” for many possibilities, such as “processed foods”, “mainly vegan food”, “dairy” and so on.
After choosing your topic
After you’ve chosen your topic it’s important to do the following:
- Research thoroughly
- Think about all of the different viewpoints
- Tailor to your audience – discussing your topic with others is a helpful way to gain an understanding of your audience.
- How involved are you with this topic – are you a key character?
- Have you contributed to this area, perhaps through blogs, books, papers and products.
- How qualified are you to speak on this topic?
- Do you have personal experience in it? How many years?
- How long have you been interested in the area?
While it may be difficult to choose from such a variety of persuasive speech topics, think about which of the above you have the most knowledge of and can argue your opinion on.
For advice about how to deliver your persuasive speech, check out our blog Persuasive Speech Outline and Ideas .
Module 10: Persuasive Speaking
Structure of a persuasive speech, learning objectives.
Identify characteristic structures of a persuasive speech.
In many ways, a persuasive speech is structured like an informative speech. It has an introduction with an attention-getter and a clear thesis statement. It also has a body where the speaker presents their main points and it ends with a conclusion that sums up the main point of the speech.
The biggest difference is that the primary purpose of an informative speech is to explain whereas the primary purpose of a persuasive speech is to advocate the audience adopt a point of view or take a course of action. A persuasive speech, in other words, is an argument supported by well-thought-out reasons and relevant, appropriate, and credible supporting evidence.
We can classify persuasive speeches into three broad categories:
- The widely used pesticide Atrazine is extremely harmful to amphibians.
- All house-cats should be kept indoors to protect the songbird population.
- Offshore tax havens, while legal, are immoral and unpatriotic .
The organizational pattern we select and the type of supporting material we use should support the overall argument we are making.
The informative speech organizational patterns we covered earlier can work for a persuasive speech as well. In addition, the following organization patterns are especially suited to persuasive speeches (these are covered in more detail in Module 6: Organizing and Outlining Your Speech):
- Causal : Also known as cause-effect, the causal pattern describes some cause and then identifies what effects resulted from the cause. This can be a useful pattern to use when you are speaking about the positive or negative consequences of taking a particular action.
- Problem-solution : With this organizational pattern, you provide two main points. The first main point focuses on a problem that exists and the second details your proposed solution to the problem. This is an especially good organization pattern for speeches arguing for policy changes.
- Problem-cause-solution: This is a variation of the problem-solution organizational pattern. A three-step organizational pattern where the speaker starts by explaining the problem, then explains the causes of the problem, and lastly proposes a solution to the problem.
- Comparative advantage : A speaker compares two or more things or ideas and explains why one of the things or ideas has more advantages or is better than the other.
- Monroe’s motivated sequence : An organizational pattern that is a more elaborate variation of the problem-cause-solution pattern. We’ll go into more depth on Monroe’s motivated sequence on the next page.
- Structure of a Persuasive Speech. Authored by : Mike Randolph with Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution

How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you.
You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular problem is important to them, and then you must convince them that you have the solution to make things better.
Note: You don't have to address a real problem. Any need can work as the problem. For example, you could consider the lack of a pet, the need to wash one's hands, or the need to pick a particular sport to play as the "problem."
As an example, let's imagine that you have chosen "Getting Up Early" as your persuasion topic. Your goal will be to persuade classmates to get themselves out of bed an hour earlier every morning. In this instance, the problem could be summed up as "morning chaos."
A standard speech format has an introduction with a great hook statement, three main points, and a summary. Your persuasive speech will be a tailored version of this format.
Before you write the text of your speech, you should sketch an outline that includes your hook statement and three main points.
Writing the Text
The introduction of your speech must be compelling because your audience will make up their minds within a few minutes whether or not they are interested in your topic.
Before you write the full body you should come up with a greeting. Your greeting can be as simple as "Good morning everyone. My name is Frank."
After your greeting, you will offer a hook to capture attention. A hook sentence for the "morning chaos" speech could be a question:
- How many times have you been late for school?
- Does your day begin with shouts and arguments?
- Have you ever missed the bus?
Or your hook could be a statistic or surprising statement:
- More than 50 percent of high school students skip breakfast because they just don't have time to eat.
- Tardy kids drop out of school more often than punctual kids.
Once you have the attention of your audience, follow through to define the topic/problem and introduce your solution. Here's an example of what you might have so far:
Good afternoon, class. Some of you know me, but some of you may not. My name is Frank Godfrey, and I have a question for you. Does your day begin with shouts and arguments? Do you go to school in a bad mood because you've been yelled at, or because you argued with your parent? The chaos you experience in the morning can bring you down and affect your performance at school.
Add the solution:
You can improve your mood and your school performance by adding more time to your morning schedule. You can accomplish this by setting your alarm clock to go off one hour earlier.
Your next task will be to write the body, which will contain the three main points you've come up with to argue your position. Each point will be followed by supporting evidence or anecdotes, and each body paragraph will need to end with a transition statement that leads to the next segment. Here is a sample of three main statements:
- Bad moods caused by morning chaos will affect your workday performance.
- If you skip breakfast to buy time, you're making a harmful health decision.
- (Ending on a cheerful note) You'll enjoy a boost to your self-esteem when you reduce the morning chaos.
After you write three body paragraphs with strong transition statements that make your speech flow, you are ready to work on your summary.
Your summary will re-emphasize your argument and restate your points in slightly different language. This can be a little tricky. You don't want to sound repetitive but will need to repeat what you have said. Find a way to reword the same main points.
Finally, you must make sure to write a clear final sentence or passage to keep yourself from stammering at the end or fading off in an awkward moment. A few examples of graceful exits:
- We all like to sleep. It's hard to get up some mornings, but rest assured that the reward is well worth the effort.
- If you follow these guidelines and make the effort to get up a little bit earlier every day, you'll reap rewards in your home life and on your report card.
Tips for Writing Your Speech
- Don't be confrontational in your argument. You don't need to put down the other side; just convince your audience that your position is correct by using positive assertions.
- Use simple statistics. Don't overwhelm your audience with confusing numbers.
- Don't complicate your speech by going outside the standard "three points" format. While it might seem simplistic, it is a tried and true method for presenting to an audience who is listening as opposed to reading.
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- 5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- How to Structure an Essay
- Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Audience Analysis in Speech and Composition
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 9: Persuasive Speaking
Proposition of Policy
- Fact claim: Smoking marijuana is less harmful to one’s health than smoking cigarettes.
- Value claim: The prejudices about the social conditions that led to current marijuana legislation are outdated.
- Policy claim: Because the social conditions that gave rise to current marijuana legislation no longer exist and because of the potential medical and financial benefits of its decriminalization, lawmakers should reconsider the legal status of cannabis.
Examples from the right might include:
- Fact claim: Public school performance in the United States has plummeted over the past twenty years.
- Value claim: It is unfair to force taxpayers to contribute to a school system that does not serve them.
- Policy claim: Following the Canadian system, Congress should form a system for public funding of religious schools for families that opt out of the public school system.
Fundamentals of Public Speaking Copyright © by Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

10 Tips for a Persuasive Presentation
Powerful presentation is persuasion. here's how to elevate your impact..
Posted May 11, 2024 | Reviewed by Ray Parker
- Presentations aim to effect change. It's essential to be clear about what change you want to see.
- Powerful presenters embrace and extend empathy to seek first to understand their audience.
- Substance and style both matter to create an audience-informed communication experience.
- Persuasive presentations are relevant, reasoned, real, and resonant.

How many of us realize that giving a presentation or making a speech is all about persuasion , influence, and emotional intelligence ? Impactful presenters understand the power of empathy to understand and engage their audience, the efficiency and kindness of having a clear objective and message, and the importance of substance and style—all as a way to connect in a way that engages and inspires.
Much has been written on the power and behavioral science of persuasion, not least by expert Robert Cialdini. His bestselling book Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion explains seven research-based universal principles of influence .
From my experience as a leadership coach working with thousands of people worldwide, I have compiled a list of ten essentials to elevate our presentation.
1. Maintain an "other" focus. What do you know about your audience and how can you find out more? Ask yourself what kind of a speaker will appeal to your audience, what arguments are likely to resonate with them, and what feelings you want to inspire so the audience will positively respond to your ask.
If your audience is predominantly data-driven, you may want to use more evidence-based arguments. If the audience is mixed, a combination of data, authority, and storytelling may be more appropriate. Extend Daniel Goleman’s three types of empathy to gather intelligence , understand your audience, and tailor your intervention to connect more profoundly.
2. Determine a specific objective. Presentations aim to effect change in some way. What change do you want to see in your audience?
For instance, gaining their approval for a certain investment, soliciting their buy-in for a change, or creating a sense of enthusiasm for an idea or initiative. The purpose of a presentation is to bring about change so make sure you are clear on what kind of change you want to bring about.
3. Design a grabber. Our attention spans have shrunk as we have more and more competing demands on our attention . If you want to get someone’s attention, you need to grab it at the outset and try and hold on.
You can do this in several different ways. Throw out a question that demands a response from the audience. Give a surprising fact or statistic, or quote from a well-known figure. Tell a story or an anecdote. A good grabber captures the attention of everyone there and makes them focus on what you have to say.
4. Crystalize your message and construct your arguments. Your message is the heart of your speech. Craft a brief phrase that clearly defines your proposal in 10-12 words—for example, “This post is about crafting presentations that inspire and engage others to elevate their presentations.”
Make it memorable by choosing inspiring words, symbols, catchy expressions, something that will remain in the audience's mind. As Brené Brown says: “Clear is kind,” and a clear message provides a path to develop your ideas.
When you have a clear and concise message, it helps you formulate your arguments. Think of developing your arguments using the rule of three —three compelling arguments to convince but not overwhelm your audience.
5. Prepare a call to action. Remember, we want to change our audience in some way, so we need to make our ask clearly and concretely. Consider your call to action in terms of what you want your audience to think/feel/do:
- Think: “I want you to think about how you can improve your presentations.”
- Feel: “I want you to feel enthusiastic and motivated so that you can elevate your power to persuade.”
- Do: “I want you to try out some of these tips and tools for yourself.”
6. Craft a memorable closing. Close the speech in an elegant and memorable way. We need people to remember what we've told them, so prepare it well.

This is not the time to improvise. Try to connect your closing to your opening grabber, which makes the presentation more memorable. Good preparation means preparing everything to the very end—finish well.
7. Plan your delivery. A dynamic speaker draws listeners in by using vocal variety (tone, intonation, speed, volume, pace, pauses, silence) and body language (posture, gestures, expression, and movement) to highlight important points and hold the audience’s attention. Be intentional: How will you use your voice and your body to emphasize a thought or idea? Think about it: If you increased the time you spent on style or delivery by 20 percent, what would it mean for the impact you make?
8. Think about how you will engage your audience. You want the audience to feel considered throughout. Include pauses so they can process what’s being said; connect with individuals throughout the room and make deliberate eye contact while speaking, especially when delivering key points. Read and respond to the audience by changing how you deliver as you go based on the audience’s nonverbal communication .
9. Rehearse and practice. Practice is one of the most crucial elements of presenting—and probably the most neglected one. If this is new to you, start by reading your presentation in front of a mirror to get comfortable speaking your presentation.
Next, video yourself and watch out for nervous or distracting habits to eliminate them and identify any areas where you can improve your delivery. If you are feeling brave, practice in front of an audience and ask for feedback.
10. Prepare your success rituals and mantra. Public speaking and/or stage fright can feel debilitating for some. Have your calm-down ritual prepared and ready to go before you start your presentation. This might be a certain gesture, a power pose, breathwork, or a mantra.
Try this tip: Identify three adjectives to describe how you would like to show up during this presentation. This sets an intention and helps focus our cognitive and emotional resources on success.
Powerful presenters embrace and extend empathy to seek first to understand their audience. They use this intelligence to carefully make choices about substance and style to create an audience-informed communication experience that feels relevant, reasoned, real, and resonant and creates a pathway for change.

Palena Neale, Ph.D. , is a women’s leadership coach, lecturer, and founder of unabridged, a boutique leadership development practice.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

Here are the policy ideas Trump talks about the most
D ata: Axios analysis of 49 public Trump speeches from a database maintained by Rev ; Note: OpenAI's ChatGPT 4 was used to help sort the phrases, which were confirmed by journalists; Chart: Erin Davis/Axios
In public remarks about plans for a second term, former President Trump often talks about banning mask and vaccine mandates, and deporting undocumented immigrants — while spending only about 11% of his time on policy plans, an Axios analysis found.
Why it matters: The analysis reveals the extent to which Trump's talking points reflect MAGA conservatives' lingering anger about COVID restrictions, their focus on tying immigrants to the nation's problems, and their push to regulate education.
- He says relatively little about his plans for the economy, according to the analysis of his comments in 49 speeches, interviews and public appearances over the past 16 months.
Zoom in: The graphic above represents the most common phrases Axios found in a review of 697 instances Trump spoke publicly about policy from January 2023 through mid-April 2024.
- Trump most frequently promised to "defund any school with a vaccine or mask mandate" and to conduct "the largest domestic deportation operation in American history."
- He also frequently vowed to "defund any school pushing critical race theory," "rebuild our cities," "indemnify all police officers," and "keep men out of women's sports."
The big picture: Trump still spends nearly 90% of his speeches talking about everything but his policy plans: railing on President Biden , denouncing Democratic policies, telling stories and complaining that prosecutors are out to get him.
- Trump's team has laid out a detailed policy platform on his campaign's website . He has proposed dramatically increasing presidential powers and gutting protections for federal employees in order to stack the government with loyalists.
- But very few of those specifics make it into his speeches.
- Trump's campaign did not comment on this story.
Between the lines: For this project, Axios defined Trump's policy references as specific, actionable statements about legislative policies that Trump intends to implement, change, repeal or keep.
- Our analysis examined 190,573 words Trump said and found 20,821 of them (10.9%) related to policy plans.
Many of Trump's most common phrases reflect how he's made restricting immigration the cornerstone of his 2024 campaign.
- His most common pitches to voters on the issue: "stop the invasion," "terminate every single open border policy," reinstate the "Trump travel ban," and implement "ideological screening on all immigrants."
Democrats have said Trump's language is racist, encourages hate and ignores the economic and cultural benefits immigrants bring to the U.S.
- But Trump's attacks on immigrants haven't seemed to hurt him in recent polls , which have indicated that more Americans trust or approve of him than Biden to handle issues such as immigration and the economy.
Such polls have indicated that voters prefer Biden over Trump when it comes to dealing with abortion rights.
- Trump has bragged about appointing the three conservative Supreme Court justices who helped overturn Roe v. Wade. "Protecting innocent life" is one of his frequently used policy phrases — but it isn't among his top 10.
The intrigue: Trump often mentions that he'd stop "Joe Biden's inflation nightmare."
- But noticeably absent from his most frequent policy references are phrases about how he plans to improve the economy, aside from his "drill baby, drill" calls to increase oil production.
Methodology: Axios used OpenAI's ChatGPT 4.0 to research a Rev database of Trump's public statements from Jan. 1, 2023 , through April 16, 2024 , to determine phrase-usage frequency. Generative AI was not used to create the story content.
First, our journalists sorted transcripts from Rev to identify the political rallies, press conferences or interviews where Trump spoke more than 100 words. Our final dataset contained 49 speeches.
Then, we used traditional natural-language processing to identify paragraphs that might contain forward-looking policies: statements that had at least one or more first-person "will" statements, "going to" statements, or other words indicating potential future action.
Next, we used ChatGPT to review each paragraph and extract potential forward-looking policies.We then manually reviewed every output, confirming nearly 700 items. Frequency of speech about policy was determined by counting the number of words pertaining to legislative policies that Trump intends to implement, change, repeal, or keep.
Finally, we used an algorithm to group similar policy-related phrases, which were reviewed by our journalists to confirm relevance.
Get the rundown of the biggest stories of the day with Axios Daily Essentials.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

16.5: Constructing a Persuasive Speech
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 107434

- Lisa Coleman, Thomas King, & William Turner
- Southwest Tennessee Community College
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
In a sense, constructing your persuasive speech is the culmination of the skills you have learned already. In another sense, you are challenged to think somewhat differently. While the steps of analyzing your audience, formulating your purpose and central idea, applying evidence, considering ethics, framing the ideas in appropriate language, and then practicing delivery will of course apply, you will need to consider some expanded options about each of these steps.
Formulating a Proposition
As mentioned before, when thinking about a central idea statement in a persuasive speech, we use the terms “proposition”. Persuasive speeches have one of three types of propositions, which determine your overall approach. Before you move on, you need to determine what type of proposition you should have (based on the audience, context, issues involved in the topic, and assignment for the class).
Proposition of Fact
Speeches with this type of proposition attempt to establish the truth of a statement. The core of the proposition is not whether something is morally right and wrong or what should be done about the topic, only that a statement is supported by evidence or not. These propositions are not facts such as “the chemical symbol for water is H20” or “Barack Obama won the presidency in 2008 with 53% of the vote.” Propositions or claims of fact are statements over which persons disagree and there is evidence on both sides, although probably more on one than the other. Some examples of propositions of fact are:
- Converting to solar energy can save homeowners money.
- John F. Kennedy was assassinated by Lee Harvey Oswald working alone.
- Experiments using animals are essential to the development of many life-saving medical procedures.
- Climate change has been caused by human activity.
- Granting tuition tax credits to the parents of children who attend private schools will perpetuate educational inequality.
- Watching violence on television causes violent behavior in children.
- William Shakespeare did not write most of the plays attributed to him.
- John Doe committed the crime of which he is accused.
Notice that in none of these are any values—good or bad—mentioned. Perpetuating segregation is not portrayed as good or bad, only as an effect of a policy. Of course, most people view educational inequality negatively, just as they view life-saving medical procedures positively. But the point of these propositions is to prove with evidence the truth of a statement, not its inherent value or what the audience should do about it. In fact, in some propositions of fact, no action response would even be possible, such as the proposition listed above that Lee Harvey Oswald acted alone in the assassination of President Kennedy.
Propositions of Value
It is likely that you or some of your classmates will give speeches with propositions of value. When the proposition has a word such as “good,” “bad,” “best,” “worst,” “just,” “unjust,” “ethical,” “unethical,” “moral,” “immoral,” “beneficial,” “harmful,” “advantageous,” or “disadvantageous,” it is a proposition of value. Some examples include:
- Hybrid cars are the best form of automobile transportation available today.
- Homeschooling is more beneficial for children than traditional schooling.
- The War in Iraq was not justified.
- Capital punishment is morally wrong.
- Mascots that involve Native American names, characters, and symbols are demeaning.
- A vegan diet is the healthiest one for adults.
Propositions of value require a first step: defining the “value” word. If a war is unjustified, what makes a war “just” or “justified” in the first place? That is a fairly philosophical question. What makes a form of transportation “best” or “better” than another? Isn’t that a matter of personal approach? For different people, “best” might mean “safest,” “least expensive,” “most environmentally responsible,” “stylish,” “powerful,” or “prestigious.” Obviously, in the case of the first proposition above, it means “environmentally responsible.” It would be the first job of the speaker, after introducing the speech and stating the proposition, to explain what “best form of automobile transportation” means. Then the proposition would be defended with separate arguments.
Propositions of Policy
These propositions are easy to identify because they almost always have the word “should” in them. These propositions call for a change in policy or practice (including those in a government, community, or school), or they can call for the audience to adopt a certain behavior. Speeches with propositions of policy can be those that call for passive acceptance and agreement from the audience and those that try to instigate the audience to action, to actually do something immediately or in the long-term.
- Our state should require mandatory recertification of lawyers every ten years.
- The federal government should act to ensure clean water standards for all citizens.
- The federal government should not allow the use of technology to choose the sex of an unborn child.
- The state of Georgia should require drivers over the age of 75 to take a vision test and present a certificate of good health from a doctor before renewing their licenses.
- Wyeth Daniels should be the next governor of the state.
- Young people should monitor their blood pressure regularly to avoid health problems later in life.
As mentioned before, the proposition determines the approach to the speech, especially the organization. Also as mentioned earlier in this chapter, the exact phrasing of the proposition should be carefully done to be reasonable, positive, and appropriate for the context and audience. In this next section, we will examine organizational factors for speeches with propositions of fact, value, and policy.
Organization Based on Type of Proposition
Organization for a proposition of fact.
If your proposition is one of fact, you will do best to use a topical organization. Essentially that means that you will have two to four discrete, separate arguments in support of the proposition. For example:
Proposition: Converting to solar energy can save homeowners money.
I. Solar energy can be economical to install.
A. The government awards grants.
B. The government gives tax credits.
II. Solar energy reduces power bills.
III. Solar energy requires less money for maintenance.
IV. Solar energy works when the power grid goes down.
Here is a first draft of another outline for a proposition of fact:
Proposition: Experiments using animals are essential to the development of many life-saving medical procedures.
I. Research of the past shows many successes from animal experimentation.
II. Research on humans is limited for ethical and legal reasons.
III. Computer models for research have limitations.
However, these outlines are just preliminary drafts because preparing a speech of fact requires a great deal of research and understanding of the issues. A speech with a proposition of fact will almost always need an argument or section related to the “reservations,” refuting the arguments that the audience may be preparing in their minds, their mental dialogue. So the second example needs revision, such as:
I. The first argument in favor of animal experimentation is the record of successful discoveries from animal research.
II. A second reason to support animal experimentation is that research on humans is limited for ethical and legal reasons.
III. Animal experimentation is needed because computer models for research have limitations.
IV. Many people today have concerns about animal experimentation.
A. Some believe that all experimentation is equal.
1. There is experimentation for legitimate medical research.
2. There is experimentation for cosmetics or shampoos.
B. Others argue that the animals are mistreated.
1. There are protocols for the treatment of animals in experimentation.
2. Legitimate medical experimentation follows the protocols.
C. Some believe the persuasion of certain advocacy groups like PETA.
1. Many of the groups that protest animal experimentation have extreme views.
2. Some give untrue representations.
To complete this outline, along with the introduction and conclusion, there would need to be quotations, statistics, and facts with sources provided to support both the pro-arguments in Main Points I-III and the refutation to the misconceptions about animal experimentation in Sub-points A-C under Point IV.
Organization for a proposition of value
A persuasive speech that incorporates a proposition of value will have a slightly different structure. As mentioned earlier, a proposition of value must first define the “value” word for clarity and provide a basis for the other arguments of the speech. The second or middle section would present the defense or “pro” arguments for the proposition based on the definition. The third section would include a refutation of the counterarguments or “reservations.” The following outline draft shows a student trying to structure a speech with a value proposition. Keep in mind it is abbreviated for illustrative purposes, and thus incomplete as an example of what you would submit to your instructor, who will expect more detailed outlines for your speeches.
Proposition: Hybrid cars are the best form of automotive transportation available today.
I. Automotive transportation that is best meets three standards. (Definition)
A. It is reliable and durable.
B. It is fuel-efficient and thus cost-efficient.
C. It is therefore environmentally responsible.
II. Studies show that hybrid cars are durable and reliable. (Pro-Argument 1)
A. Hybrid cars have 99 problems per 100 cars versus 133 problems per 100 conventional cars, according to TrueDelta, a car analysis website much like Consumer Reports.
B. J.D. Powers reports hybrids also experience 11 fewer engine and transmission issues than gas-powered vehicles, per 100 vehicles.
III. Hybrid cars are fuel-efficient. (Pro-Argument 2)
A. The Toyota Prius gets 48 mpg on the highway and 51 mpg in the city.
B. The Ford Fusion hybrid gets 47 mpg in the city and in the country.
IV. Hybrid cars are environmentally responsible. (Pro-Argument 3)
A. They only emit 51.6 gallons of carbon dioxide every 100 miles.
B. Conventional cars emit 74.9 gallons of carbon dioxide every 100 miles.
C. The hybrid produces 69% of the harmful gas exhaust that a conventional car does.
V. Of course, hybrid cars are relatively new to the market and some have questions about them. (Reservations)
A. Don’t the batteries wear out and aren’t they expensive to replace?
1. Evidence to address this misconception.
2. Evidence to address this misconception.
B. Aren’t hybrid cars only good for certain types of driving and drivers?
C. Aren’t electric cars better?
Organization for a proposition of policy
The most common types of outline organization for speeches with propositions of policy are problem-solution or problem-cause-solution. Typically we do not feel any motivation to change unless we are convinced that some harm, problem, need, or deficiency exists, and even more, that it affects us personally. As the saying goes, “If it ain’t broke, why fix it?”As mentioned before, some policy speeches look for passive agreement or acceptance of the proposition. Some instructors call this type of policy speech a “think” speech since the persuasion is just about changing the way your audience thinks about a policy.
On the other hand, other policy speeches seek to move the audience to do something to change a situation or to get involved in a cause, and these are sometimes called a “do” speech since the audience is asked to do something. This second type of policy speech (the “do” speech) is sometimes called a “speech to actuate.” Although a simple problem-solution organization with only two main points is permissible for a speech of actuation, you will probably do well to utilize the more detailed format called Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
This format, designed by Alan Monroe (1951), who wrote a popular speaking textbook for many years, is based on John Dewey’s reflective thinking process. It seeks to go in-depth with the many questions an audience would have in the process of listening to a persuasive speech. Monroe’s Motivated Sequence involves five steps, which should not be confused with the main points of the outline. Some steps in Monroe’s Motivated Sequence may take two points.
- Attention . This is the introduction, where the speaker brings attention to the importance of the topic as well as his or her own credibility and connection to the topic. This step will include the central idea and preview.
- Need . Here the problem is defined and defended. This step may be divided into two main points, such as the problem and the causes of it, since logically a solution should address the underlying causes as well as the external effects of a problem. It is important to make the audience see the severity of the problem, and how it affects them, their family, or their community. The harm or need can be physical, financial, psychological, legal, emotional, educational, social, or a combination. It will have to be supported by evidence.
- Satisfaction . A need calls for satisfaction in the same way a problem requires a solution. This step could also, in some cases, take up two main points. Not only does the speaker present the solution and describe it, but they must also defend that it works and will address the causes of the problem as well as the symptoms.
- Visualization . This step looks to the future either positively or negatively. If positive, the benefits from enacting or choosing the solution are shown. If negative, the disadvantages of not doing anything to solve the problem are shown. There may be times when it is acceptable to skip this step, especially if time is limited. The purpose of visualization is to motivate the audience by revealing future benefits or through fear appeals by showing future harms.
- Action . This can be the conclusion, although if the speaker really wants to spend time on moving the audience to action, the action step should be a full main point and the conclusion saved for summary and a dramatic ending. In the action step, the goal is to give specific steps for the audience to take as soon as possible to move toward solving the problem. Whereas the satisfaction step explains the solution overall, the action step gives concrete ways to begin making the solution happen.
The more concrete you can make the action step, the better. Research shows that people are more likely to act if they know how accessible the action can be. For example, if you want students to be vaccinated against the chickenpox virus (which can cause a serious disease called shingles in adults), you can give them directions to and hours for a clinic or health center where vaccinations at a free or discounted price can be obtained.
In some cases for speeches of policy, no huge problem needs solving. Or, there is a problem, but the audience already knows about it and is convinced that the problem exists and is important. In those cases, a format called “comparative advantages” is used, which focuses on how one possible solution is better than other possible ones. The organizational pattern for this kind of proposition might be topical:
I. This policy is better because…
II. This policy is better because…
III. This policy is better because…
If this sounds a little like a commercial that is because advertisements often use comparative advantages to show that one product is better than another. Here is an example:
Proposition: Owning the Barnes and Noble Nook is more advantageous than owning the Amazon Kindle.
I. The Nook allows owners to trade and loan books to other owners or people who have downloaded the Nook software, while the Kindle does not.
II. The Nook has a color-touch screen, while the Kindle’s screen is black and grey and non-interactive.
III. The Nook’s memory can be expanded through microSD, while the Kindle’s memory cannot be upgraded.
Building Upon Your Persuasive Speech’s Arguments
Once you have constructed the key arguments and order of points (remembering that if you use topical order, to put your strongest or most persuasive point last), it is time to be sure your points are well supported. In a persuasive speech, there are some things to consider about evidence.
First, your evidence should be from sources that the audience will find credible. If you can find the same essential information from two sources but know that the audience will find the information more credible from one source than another, use and cite the information from the more credible one. For example, if you find the same statistical data on Wikipedia and the U.S. Department of Labor’s website, cite the U.S. Department of Labor (your instructor will probably not accept the Wikipedia site anyway). Audiences also accept information from sources they consider unbiased or indifferent. Gallup polls, for example, have been considered reliable sources of survey data because, unlike some organizations, Gallup does not have a cause (political or otherwise) it is supporting.
Secondly, your evidence should be new to the audience. In other words, the best evidence is that which is from credible sources and the audience has not heard before (Reinard, 1988; McCroskey, 1969). If they have heard it before and discounted it, they will not consider your argument well supported. An example is telling people who smoke that smoking will cause lung cancer. Everyone in the U.S. has heard that thousands of times, but 14% of the population still smokes, which is about one in seven (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2017)). Many of those who smoke have not heard the information that really motivates them to quit yet, and of course, quitting is very difficult. Additionally, new evidence is more attention-getting, and you will appear more credible if you tell the audience something new (as long as you cite it well) than if you use the “same old, same old” evidence they have heard before.
Third, in order to be effective and ethical, your supporting evidence should be relevant and not used out of context, and fourth, it should be timely and not out of date.
After choosing the evidence and apportioning it to the correct parts of the speech, you will want to consider the use of metaphors, quotations, rhetorical devices, and narratives that will enhance the language and “listenability” of your speech. Narratives are especially good for introduction and conclusions, to get attention, and to leave the audience with something dramatic. You might refer to the narrative in the introduction again in the conclusion to give the speech a sense of finality.
Next, you will want to decide if you should use any type of presentation aid for the speech. The decision to use visuals such as PowerPoint slides or a video clip in a persuasive speech should take into consideration the effect of the visuals on the audience and the time allotted for the speech (as well as your instructor’s specifications). The charts, graphs, or photographs you use should be focused and credibly done.
One of your authors remembers a speech by a student about using seat belts (which is, by the way, an overdone topic). What made the speech effective in this case were photographs of two totaled cars, both of which the student had been driving when they crashed. The devastation of the wrecks and his ability to stand before us and give the speech because he had worn his seat belt were effective (although it didn’t say much for his driving ability). If you wanted an audience to donate to disaster relief after an earthquake in a foreign country, a few photographs of the destruction would be effective, and perhaps a map of the area would be helpful. But in this case, less is more. Too many visual aids will likely distract from your overall speech claim.
Finally, since you’ve already had experience in class giving at least one major speech prior to this one, your delivery for the persuasive speech should be especially strong. Since delivery does affect credibility (Burgoon, Birk, & Pfau, 1990), you want to be able to connect visually as you make your appeals. You want to be physically involved and have vocal variety when you tell dramatic narratives that emphasize the human angle on your topic. If you do use presentation slides, you want them to work seamlessly, using black screens when the visuals are not necessary.
Your persuasive speech in class, as well as in real life, is an opportunity to share a passion or cause that you believe will matter to society and help the audience live a better life. Even if you are initially uncomfortable with the idea of persuasion, we use it all the time in different ways. Choose your topic based on your own commitment and experience, look for quality evidence, craft your proposition so that it will be clear and audience appropriate, and put the finishing touches on it with an eye toward enhancing your logos, ethos, and pathos.
Something to Think About
Go to YouTube and look for “Persuasive Speeches by College Students.” There are quite a few. Here’s one example: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SNr7Fx-SM1Y . Do you find this speech persuasive? Why or why not? Based on the content of this chapter, what did the speaker do correctly or perhaps not so correctly that affected his or her persuasiveness?
Hate Speech: Crisis & Conversation
- College of Liberal Arts and Social Sciences
- Modern and Classical Languages
- Hate Speech Regulation and Reactionary Power after October 7, 2023
Hate speech regulation and reactionary power after October 7, 2023
April 11, 2024
By Gregory P. Magarian Washington University School of Law
In December 2023, the U.S. public watched a powerful congressional committee try to browbeat four university presidents into punishing their students for expressing pro-Palestinian political views. The premise for this legislative ambush was that the slogans “Intifada” (Arabic for “uprising”) and “Palestine will be free from the river to the sea” constitute anti-Semitic hate speech.
Members of the congressional committee, and many commentators, loudly condemned the university presidents for asserting that the U.S. Constitution’s First Amendment (which private universities need not obey as a legal matter but to which they nearly all choose to adhere) bars official reprisals against political speech even if the speech is hateful. The university presidents were right. The First Amendment does let the government punish threats, harassment, and “fighting words” when a speaker directs any of those sorts of invective at a particular person or small group of people. Hate speech has proven more likely than other speech to take one of those proscribable forms. Absent such a convergence, however, the government may not punish hateful rhetoric about an identity group. For example, the First Amendment does not protect shouting “Armenian scum!” in an Armenian person’s face or sending several Armenians an email that says “I’m going to kill you because you’re Armenian,” but it does protect a social media post that states “All Armenians deserve to die.”
The E.U., Canada, and many other liberal democracies take a divergent view of hate speech. Their rights charters leave substantial latitude for legal restriction of speech that denies the dignity and humanity of identity groups, even if the speech does not directly assault any individual or discrete gathering. Debates about the relative merits of different legal approaches toward constitutional speech protection often focus on hate speech. U.S. civil libertarians claim that liberal democracy requires constitutional protection for hate speech. European communitarians counter that hate speech restrictions improve the social circumstances of identity minorities. This normative disagreement about hate speech regulation eludes any simple, broadly persuasive resolution.
However, even if we conclude that hate speech regulation is normatively appealing, the spectacle of the U.S. congressional hearing foregrounds one strong reason to favor the U.S. resistance to regulation: the danger that putative government speech regulators will, counterintuitively, use concerns about hate speech to promote powerful interests and suppress vulnerable dissidents’ political advocacy.
Representative Elise Stefanik, the far-right U.S. legislator who led the congressional inquisition of the university presidents, commanded the presidents to confess the hateful character of slogans like “Intifada” and “from the river to the sea.” Ironically, while Israel was pressing a bombing campaign against Gazans that South Africa has challenged as genocidal in the International Court of Justice, Rep. Stefanik insisted that virtually any full-throated call for Palestinian liberation amounted to genocidal rhetoric against Israeli Jews.
Rep. Stefanik’s broad rhetorical brush obscured a complicated and contentious semiotic reality. The Arabic word “Intifada,” meaning “uprising,” entered the western media lexicon during two Palestinian rebellions, one in the late 1980s and the second in the early 2000s, against Israel’s occupation of the West Bank and Gaza. No prominent commentary during those conflicts equated “Intifada” with genocide.
The phrase “Palestine will be free from the river to the sea” has a more fraught and fractured dossier. [1] Terrorist groups, notably Hamas, have indeed used that slogan to call for wiping out Israeli Jews. At the same time, other Palestinians and their supporters use the phrase to demand full equality for Palestinians alongside Jews in the whole of Israel / Palestine. Such equality would entail a right for Palestinian refugees to return to Israel, a political nonstarter for Israeli Jews who fear any compromise of political control over the country. Power sharing, however, is not genocide. Israel’s hard-right Likud party has itself adapted the slogan, declaring in its original 1977 platform that “between the Sea and the Jordan there will only be Israeli sovereignty.” [2]
In the context of the present Gaza War, condemning “Intifada” and “from the river to the sea” as hate speech serves a political strategy. Israel has long enjoyed the steadfast patronage of the U.S. government, leaders in both major national political parties, and most of American civil society. Some of those patrons, amid growing public disapproval of Israel’s actions, want to silence criticism of Israel and discredit advocacy of Palestinian interests. Coding potent pro-Palestinian political appeals as hateful and genocidal advances that effort. The First Amendment protects expression of dissenting political viewpoints. Accordingly, censorious stalwarts of the pro-Israel majority, such as Rep. Stefanik, seek to marginalize the First Amendment.
Hate speech does its harm when powerful speakers use hateful attacks to subordinate identity groups with less power. Powerful actors control government institutions. Why, then, should we expect governments to effectively, even honestly, protect underpowered communities from hate speech? Optimists about benign hate speech regulation try, sensibly, to leverage institutions that tend to resist concentrated power. Thus, U.S. proponents of hate speech regulation have focused their advocacy on colleges and universities. Those institutions’ limited power, however, ends up enabling official coercion. Too often, colleges and universities have failed to protect vulnerable minorities from hate speech, and now Rep. Stefanik is turning the hate speech tables to intimidate those institutions into suppressing political dissidents’ advocacy of a vulnerable minority’s interests.
Some expressions and symbols pass from public respectability into disfavor. Not long ago, many people viewed the battle flag of the Confederate States of America as a vague symbol of generalized rebellion against unjust authority. No longer. Most (though not all) people today recognize the Confederate flag as a willful emblem of violent racism. [3] In contrast, efforts to tar the slogan “Black Lives Matter” as insurrectionary and anti-white have failed to gain traction. [4]
Social mechanisms of political contestation are hardly immune from powerful influences. Even so, those mechanisms offer a more fluid, broadly accessible medium than government coercion for struggles over political meaning. Let diverse factions make their claims about “Intifada” and “from the river to the sea,” as factions have done over the Confederate flag and “Black Lives Matter.” Let political communities filter those claims through their many and varied prisms of understanding. Perhaps “Intifada” and “from the river to the sea” will someday meet the same rhetorical fate in our society as the Confederate flag. But any such outcome should result from public discourse, not government force.
[1] See Ellen Ioanes, The Controversial Phrase “From the River to the Sea,” Explained, Vox (Nov. 24, 2023), https://www.vox.com/world-politics/23972967/river-to-sea-palestine-israel-hamas .
[2] Likud Party: Original Party Platform (1977), American-Israeli Cooperative Enterprise, Jewish Virtual Library, https://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/original-party-platform-of-the-likud-party .
[3] See Clark Merrefield & John Wihbey, Research on the Confederate Flag, Divisive Politics and Enduring Meanings, The Journalist’s Resource (Jan. 15, 2021) (compiling studies), https://journalistsresource.org/home/confederate-flag-divisive-politics-and-enduring-meanings-2/ .
[4] See Jenn Hatfield, 8 Facts About Black Lives Matter, Pew Research Center (July 12, 2023), https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2023/07/12/8-facts-about-black-lives-matter/ .
Gregory P. Magarian is the Thomas and Karole Green Professor of Law at the Washington University School of Law in St. Louis. He teaches and writes about U.S. constitutional law, focusing on expressive freedom. His first book, Managed Speech: The Roberts Court’s First Amendment , was published in 2017 by Oxford University Press. His writing also examines church and state, gun regulation, and regulations of the media and the political process. He received his B.A. from Yale and his law degree from the University of Michigan. He previously served as a law clerk for U.S. Supreme Court Justice John Paul Stevens.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Constructing a policy speech may appear to be very similar to creating a persuasive speech.Although it is true that a policy speech is a type of persuasive speech, and many of the rules for persuasive speeches will indeed apply, a policy speech is a very particular type of persuasive presentation, and the speaker needs to be aware of some important guidelines before choosing their topic.
Below is a list of thirty persuasive policy speech topics that you can use as inspiration for your next presentation. 1. The need for stricter gun control laws in the United States. 2. The benefits of free trade agreements. 3. The importance of investing in renewable energy. 4.
Policy Claims. The third common claim that is seen in persuasive speeches is the policy claim —a statement about the nature of a problem and the solution that should be implemented. Policy claims are probably the most common form of persuasive speaking because we live in a society surrounded by problems and people who have ideas about how to fix these problems.
Identify strategies for choosing a persuasive speech topic. Identify strategies for adapting a persuasive speech based on an audience's orientation to the proposition. Distinguish among propositions of fact, value, and policy. Choose an organizational pattern that is fitting for a persuasive speech topic.
Conclusion. Your persuasive speech in class, as well as in real life, is an opportunity to share a passion or cause that you believe will matter to society and help the audience live a better life. Even if you are initially uncomfortable with the idea of persuasion, we use it all the time in different ways.
Organizing Persuasive Propositions . Organization plays a key role in comprehending an argument. Chapter 6 on organizing provides you a nice starting place to decide which organizational pattern is best suited for different speech types. In this section, we discuss organizing persuasive speeches with a focus on propositions of policy.
The three main types of persuasive speeches are factual, value, and policy. A factual persuasive speech focuses solely on factual information to prove the existence or absence of something through substantial proof. This is the only type of persuasive speech that exclusively uses objective information rather than subjective.
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples. A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything - voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on. A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing ...
Presenters for this type of speech should clearly explain the policy and then share with the audience why it should be changed (or upheld) by using their research to support the position. ... Choosing a Persuasive Speech Topic. Now that we have explored some definitions of persuasion and advocacy, let us move on to choosing the topic that you ...
We've compiled a list of 110 persuasive speech topics—broken down by category—for you to choose from or use as inspiration. Use the set of three questions we shared above to determine which of these interesting persuasive speech topics is right for you. Art, Media, and Culture.
Problem-Cause-Solution. One format for organizing a persuasive speech is the Problem-Cause-Solution format. In this organizational pattern, you would provide evidence to show that a problem exists, explain what is causing the problem to persist, and then propose a solution with additional evidence or reasoning to justify the course of action.
112 Engaging Persuasive Speech Topics. Tips for Preparing Your Persuasive Speech. Writing a stellar persuasive speech requires a carefully crafted argument that will resonate with your audience to sway them to your side. This feat can be challenging to accomplish, but an engaging, thought-provoking speech topic is an excellent place to start.
Types of Persuasive Speeches. Persuasive speeches revolve around propositions that can be defended through the use of data and reasoning. Persuasive propositions respond to one of three types of questions: questions of fact, questions of value, and questions of policy. These questions can help the speaker determine what forms of argument and ...
Alan H. Monroe's (1935) motivated sequence is a commonly used speech format that is used by many people to effectively organize persuasive messages. The pattern consists of five basic stages: attention, need, satisfaction, visualization, and action. In the first stage, a speaker gets an audience's attention.
Consider the topic of car accidents. A persuasive speech on a question of policy might focus on reducing the number of car accidents on a Florida highway. First, the speaker could use evidence from their research to demonstrate there is a need for change (e.g., statistics showing a higher-than-average rate of accidents). ...
Persuasive speeches on propositions of value imply that audience member should take certain actions, but they are not explicitly calls to action. Persuasive Speeches of Policy Persuasive speeches of policy advocate for a change from the status quo, or the way things currently are. Propositions of policy include a "should," or at the very ...
75 Persuasive Speech Topics and Ideas. To write a captivating and persuasive speech you must first decide on a topic that will engage, inform and also persuade the audience. We have discussed how to choose a topic and we have provided a list of speech ideas covering a wide range of categories.
A persuasive speech will fall primarily into one of three categories: propositions of fact, value, or policy (Mackay, 2012). A speech may have elements of any of the three propositions, but you can usually determine the overall proposition of a speech from the specific purpose and thesis statements.
In many ways, a persuasive speech is structured like an informative speech. It has an introduction with an attention-getter and a clear thesis statement. It also has a body where the speaker presents their main points and it ends with a conclusion that sums up the main point of the speech. ... Those that deal with propositions of policy. When ...
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you. You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your ...
Proposition of Policy. A proposition of policy is one that includes a statement calling for an action. The action is examined to determine whether such an action would be desirable or undesirable. For example, proposing that students should spend more time on homework is a proposition of policy calling for a specific action.
Few of us naturally excel at writing speeches. Imagine being asked to speak in front of a group, even a small one. Chances are, you'd be at a loss for words. Nonetheless, your academic requirements don't consider this, and completing all assignments is essential for graduation. One such task might involve crafting a speech on controversial topics.
In this section, we are going to look at another organizational pattern that is ideally suited for persuasive speeches: Monroe's motivated sequence. 11.1: Organizing Policy Speeches 11: Organizing Policy Speeches is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.
1 Reinforcing Ideas. Repetition in persuasive speeches serves as a reinforcement tool, hammering home the core message to ensure it sticks. By repeating key phrases or concepts, you emphasize ...
5. Prepare a call to action. Remember, we want to change our audience in some way, so we need to make our ask clearly and concretely. Consider your call to action in terms of what you want your ...
The big picture: Trump still spends nearly 90% of his speeches talking about everything but his policy plans: railing on President Biden, denouncing Democratic policies, telling stories and ...
Poet Simon Armitage explores key features of some of the most memorable speeches from the last hundred years. This short film includes extracts of speeches from influential figures such as Martin ...
A persuasive speech that incorporates a proposition of value will have a slightly different structure. As mentioned earlier, a proposition of value must first define the "value" word for clarity and provide a basis for the other arguments of the speech. The second or middle section would present the defense or "pro" arguments for the ...
Washington University School of Law. April 11, 2024. In December 2023, the U.S. public watched a powerful congressional committee try to browbeat four university presidents into punishing their students for expressing pro-Palestinian political views. The premise for this legislative ambush was that the slogans "Intifada" (Arabic for ...
In public remarks about plans for a second term, former President Trump often talks about banning mask and vaccine mandates, and deporting undocumented immigrants — while spending only about 11% of his time on policy plans, an Axios analysis found. Why it matters: The analysis reveals the extent to which Trump's talking points reflect MAGA conservatives' lingering anger about COVID ...