Nokia Change Management Case Study
Nokia is a company that has undergone significant change over the years, transforming itself from a mobile phone manufacturer to a leading player in the telecommunications infrastructure market.
This transformation was driven by a range of factors, including changes in market conditions, advancements in technology, and shifting customer needs and preferences.
However, perhaps the most important factor in Nokia’s successful transformation was its approach to change management.
In this blog post of Nokia’s change management case study, we’ll examine key strategies and tactics that the company employed to drive its successful transformation.
By examining the lessons learned from Nokia’s experience, we can gain valuable insights into effective change management and the critical factors that are required for a successful organizational transformation.
Let’s start reading.
Brief History of Nokia Journey of Change
Nokia was a Finnish company that produced a wide range of products, including paper, rubber, and cables. It was not until the 1980s that Nokia started focusing on telecommunications equipment, but even then, it was still a relatively small player in the industry.
In the late 1990s, Nokia made a strategic decision to focus solely on mobile phones, which at the time were rapidly growing in popularity. Nokia recognized the potential of the mobile phone market early on and invested heavily in research and development to create innovative and user-friendly devices.
Nokia’s decision to focus on mobile phones paid off, and by the early 2000s, the company had become the world’s largest mobile phone manufacturer, with a dominant market share. Nokia’s success was due to its ability to offer a wide range of phones at different price points and to develop cutting-edge technology such as the first mobile phones with built-in cameras and internet connectivity.
However, Nokia’s dominance in the mobile phone market was short-lived. The company struggled to keep up with the rapid pace of technological innovation and the rise of new competitors, such as Apple and Samsung. As a result, Nokia’s market share declined sharply in the late 2000s and early 2010s, and the company eventually sold its mobile phone business to Microsoft in 2014.
Nokia refocused on telecommunications infrastructure and services. It was a again a success story. In 2015 Nokia acquires French telecommunications equipment company Alcatel-Lucent.
What are those external and internal factors that caused change?
There were several external and internal factors that led to Nokia’s change management and transformation from a mobile phone producer to a telecommunication infrastructure service provider. Here are some of the key factors:
External factors:
- Increased competition: The rise of new competitors such as Apple and Samsung in the mobile phone market put pressure on Nokia’s mobile phone business, leading to declining market share and profits.
- Rapid technological change: The rapid pace of technological innovation in the mobile phone industry made it difficult for Nokia to keep up and remain competitive.
- Shift towards smartphones: The shift towards smartphones and the decline of feature phones also contributed to Nokia’s decline in the mobile phone market.
- Opportunities in telecommunication infrastructure: The growing demand for 5G networks and other telecommunications infrastructure services presented an opportunity for Nokia to diversify and expand its business.
Internal factors:
- Strategic decision-making : Nokia’s leadership recognized the need to adapt to changing market conditions and made the strategic decision to shift its focus towards telecommunications infrastructure services.
- Strengths in telecommunications: Nokia had a strong history and expertise in the telecommunications industry, which gave it a foundation to build on in expanding its business.
- Investment in research and development: Nokia continued to invest in research and development, allowing it to develop new products and services in the telecommunications infrastructure market.
- Acquisitions and partnerships: Nokia made strategic acquisitions and partnerships to expand its capabilities in telecommunications infrastructure services, such as the acquisition of Alcatel-Lucent and the partnership with Xiaomi.

07 Key Drivers of successful change management of Nokia
The successful change management of Nokia from a mobile phone manufacturer to a telecommunications infrastructure provider was driven by several key factors. Here are some of the most important drivers:
1. Clear Strategic Direction
Nokia’s clear strategic direction helped guide decision-making at all levels of the organization, ensuring that all stakeholders were aligned towards common goals and objectives. This helped Nokia to allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that investments were directed towards initiatives that supported the company’s long-term goals.
The leadership and employees focused its efforts on key priorities, such as developing new products and services in the telecommunications infrastructure market, and helped to minimize distractions from other activities that were not aligned with the company’s strategic objectives.
2. Agility and Adaptability
Agility and adaptability are important characteristics for organizations looking to succeed in a rapidly changing market environment. Nokia’s ability to demonstrate both agility and adaptability was key to its successful transformation from a mobile phone manufacturer to a telecommunications infrastructure provider. Nokia was able to quickly recognize and respond to changing market conditions and pivot its business towards new opportunities, such as the growing demand for telecommunications infrastructure services.
3. Research and Development
Nokia’s continued investment in R&D played a critical role in its successful transformation from a mobile phone manufacturer to a telecommunications infrastructure provider. By investing in R&D, Nokia was able to develop new products and services in the telecommunications infrastructure market and stay ahead of its competitors. This allowed the company to offer innovative and cutting-edge solutions that met the evolving needs of its customers. Additionally, Nokia’s investment in R&D helped the company to build a strong intellectual property portfolio, which further strengthened its competitive advantage in the market.
4. Operational Excellence
Nokia’s focus on operational efficiency and continuous improvement was a critical factor in its successful transformation from a mobile phone manufacturer to a telecommunications infrastructure provider. By streamlining its operations and reducing costs, Nokia was able to improve its competitiveness and profitability in the highly competitive telecommunications infrastructure market. This focus on operational excellence helped the company to optimize its production processes, reduce waste, and improve product quality, which in turn helped it to deliver products and services to its customers more efficiently and at a lower cost.
5. Strong Leadership
Nokia’s success in transforming itself from a mobile phone manufacturer to a telecommunications infrastructure provider was due in part to the strong and experienced leadership of CEO Rajeev Suri, who played a key role in leading the company through the transformation process. Suri’s leadership was critical in rallying employees around the new strategic direction and ensuring that all stakeholders were aligned towards common goals and objectives. Suri also provided clear direction and guidance to the organization, helping to steer the company through the challenges and uncertainties of the transformation process.
6. Cultural Change
Nokia’s success in transformation is also due to cultural change. Nokia encouraged employees to be more innovative and agile in their work, fostering a culture of experimentation and continuous improvement. The company also emphasized the importance of collaboration and teamwork, encouraging employees to work together to solve complex problems and achieve common goals. Nokia invested in employee development and training, helping to foster a culture of continuous learning and development. This cultural shift helped to create a more flexible, innovative, and agile organization that was better able to adapt to changing market conditions and drive the company’s successful transformation.
7. Acquisition and Partnerships
Acquisitions and partnerships are critical tools that Nokia used to expand its capabilities and build a competitive advantage. By acquiring companies with complementary products and services, Nokia was able to expand its capabilities in telecommunications infrastructure services, giving the company a competitive advantage and helping it to build a comprehensive portfolio of products and services. Additionally, by partnering with other companies in the industry, Nokia was able to leverage the strengths of its partners to deliver innovative solutions that met the evolving needs of its customers.
Final Words
Nokia’s successful transformation from a mobile phone manufacturer to a leading player in the telecommunications infrastructure market is a powerful case study in effective change management. By adopting a clear strategic direction, investing in research and development, focusing on operational excellence, fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration, and pursuing strategic acquisitions and partnerships, Nokia was able to adapt to changing market conditions and pivot its business towards new opportunities. Ultimately, Nokia’s transformation serves as a powerful example of how organizations can successfully adapt and evolve in response to changing market conditions, leveraging their strengths and capabilities to drive growth and success in new markets and industries.
About The Author
Tahir Abbas
Related posts.

The Promising Potential of Nudge Theory in Healthcare

How to Write a Business Case for Change Management?

ITIL Change Management Roles and Responsibilities
Case Study 4: The Collapse of Nokia’s Mobile Phone Business
- First Online: 30 July 2018
Cite this chapter

- Tuomo Peltonen 2
2124 Accesses
2 Citations
14 Altmetric
This chapter provides a wisdom-oriented reading of one of the most spectacular business failures of recent times: the collapse of Nokia mobile phones between 2007 and 2015. Using executive biographies and other published accounts of Nokia’s organisational patterns, the chapter attempts to offer a more balanced explanation of the processes behind Nokia’s inability to respond to the changing industry circumstances. The following analysis pays attention to the shaping of Nokia’s organisational culture. Company and its new leadership adopted a professional, no-nonsense approach in the aftermath of the problems of the late 1980s and early 1990s. The new generation of managers believed in a rational mindset supported by a bureaucratic organisational form. Leaning on a superior technological competence within the mobile phone sector, Nokia was capable of ultimately becoming the market leader. However, in 2007, with two major players, Apple and Google, joining the business, the established rules of competitive dynamics were irrevocably changed. Focus shifted to software and applications. Nokia’s risk-aversive and closed organisational culture could not respond in a situation where an open search for new innovations and a cooperative internal working mode were needed. An analysis of the development of Nokia’s organisational psyche following the emergence of a new generation of managers and executives highlights the role of local beliefs in using philosophical wisdom in critical circumstances. Nokia and its leadership were not able to abandon the outmoded habits and structures, as these had become integrated with the very identity of the company.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bibliography
Agarwal, R., & Helfat, C. E. (2009). Strategic renewal of organizations. Organization Science, 20 (2), 281–293. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.1090.0423 .
Article Google Scholar
Alahuhta, M. (2015). Johtajuus [Leadership]. Helsinki: Bookwell.
Google Scholar
Borden, M. (2009, January 9). Nokia rocks the world: The phone King’s plan to redefine its business. Fast Company . https://www.fastcompany.com/1325729/nokia-rocks-world-phone-kings-plan-redefine-its-business . (read 1.4.2018).
Brannen, M. Y., & Doz, Y. L. (2012). Corporate languages and strategic agility: Trapped in your jargon or lost in translation? California Management Review, 54 (3), 77–97. https://doi.org/10.1525/cmr.2012.54.3.77 .
Bryman, A. (2015). Social research methods . Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781849209939 .
Cooper, R. (1986). Organization/Disorganization. Social Science Information, 25 (2), 299–335.
Cooper, R. (1997). The visibility of social systems. In K. Hetherington & R. Mundo (Eds.), Ideas of difference (pp. 32–41). Oxford: Blackwell.
Cord, D. J. (2014). The decline and fall of Nokia . Helsingfors: Schildt & Söderström.
Donaldson, L. (2001). The contingency theory of organizations . Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Book Google Scholar
Häikiö, M. (2009). Nokia – matka maailman huipulle [Nokia – the journey to the top of the world] (in Finnish). Helsinki: Edita.
Heikkinen, M.-P. (2010). Mokia. Helsingin Sanomat , April 27, 2011. http://www.hs.fi/kuukausiliite/a1305875065676 (read 1.4.2018).
Insead. (2014). The decline of Nokia: Interview with former CEO Olli-Pekka Kallasvuo. Insead Knowledge , April 12, 2013. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jR5a_DBYSmI
Isaacson, W. (2011). Steve Jobs . Helsinki: Otava.
Kärppä, H. (2016). Tässä ovat 2000-luvun suurimmat irtisanomiset – kärkisijoilla Nokia ja Microsoft [The biggest layoffs during the 2000’s] (in Finnish). Helsingin Sanomat. http://www.hs.fi/talous/a1459916372158 (read 1.4.2018).
Kortteinen, M. (1992). Kunnian kenttä: suomalainen palkkatyö kulttuurisena muotona [Field of honor: Finnish work as a cultural form] (in Finnish). Hämeenlinna: Karisto.
Laamanen, T., Lamberg, J. A., & Vaara, E. (2016). Explanations of success and failure in management learning: What can we learn from Nokia’s rise and fall? Academy of Management Learning & Education, 15 (1), 2–25.
Linden, C.-G. (2015). Nokia och Finland [Nokia and Finland] (in Swedish). Helsinki: Schildt & Söderström.
March, J. G., & Sutton, R. I. (1997). Organizational performance as a dependent variable. Organization Science, 8 (6), 698–706 http://doi.org/Article .
Milne, R. (2009, March 23). Jorma Ollila: Champion of Nordic capitalism. Financial Times . http://royaldutchshellplc.com/2009/03/23/jorma-ollila-champion-of-nordic-capitalism/ (read 1.4.2018).
Nykänen, M., & Salminen, M. (2014). Operaatio Elop [Operation Elop] (in Finnish). Helsinki: Teos.
Ollila, J. (2016, Augest 29). Tervetuliaispuhe Etlan 70-vuotisjuhlaseminaarissa [Welcome speech in the 70th anniversary of Etla] (in Finnish). https://www.etla.fi/wp-content/uploads/Jorma-Ollila-Etla70.pdf (read 1.4.2018).
Ollila, J., & Saukkomaa, H. (2013). Mahdoton menestys: kasvun paikkana Nokia [Impossible success: Nokia as a place for growth] (in Finnish). Helsinki: Otava.
Ollila, J., & Saukkomaa, H. (2016). Against all odds: Leading nokia from near catastrophe to global success . Palmyra, VA: Maven House.
Palmu-Joroinen, A.-L. (2009). Nokia-vuodet [Nokia years]. Helsinki: Atena.
Ristimäki, M. (2006, October 13). Nokian ex-pomo: nykyjohtajilta puuttuu yleissivistys [Ex-Nokia boss: Current leaders are lacking general education]. Taloussanomat . http://www.iltasanomat.fi/taloussanomat/art-2000001477674.html (read 1.4.2018).
Taleb, N. N. (2007). The black swan: The impact of the highly improbable . New York: Random house.
The Editorial Staff of Ylioppilaslehti. (2004, April 9). Tuhannen ja yhden yön taistolaisuus [The Stalinism of thousand and one nights]. Ylioppilaslehti . http://ylioppilaslehti.fi/2004/04/274/ (read 1.4.2018).
Virtanen, J. (2013). Näin Nokia on irtisanonut Suomessa [This is the way Nokia has laid off employees in Finland]. Yle Uutiset . http://yle.fi/uutiset/3-6455026 (read 1.4.2018).
Vuori, T. O., & Huy, Q. N. (2016). Distributed attention and shared emotions in the innovation process: How Nokia lost the smartphone battle. Administrative Science Quarterly, 61 (1), 9–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/0001839215606951 .
Weber, M. (1976). Protestant ethic and the spirit of capitalism (4th ed., T. Parsons, Trans.). London: Allen & Unwin (Original work published 1930).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Business, Aalto University, Helsinki, Finland
Tuomo Peltonen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Peltonen, T. (2019). Case Study 4: The Collapse of Nokia’s Mobile Phone Business. In: Towards Wise Management. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91719-1_6
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-91719-1_6
Published : 30 July 2018
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-91718-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-91719-1
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
About Stanford GSB
- The Leadership
- Dean’s Updates
- School News & History
- Commencement
- Business, Government & Society
- Centers & Institutes
- Center for Entrepreneurial Studies
- Center for Social Innovation
- Stanford Seed
About the Experience
- Learning at Stanford GSB
- Experiential Learning
- Guest Speakers
- Entrepreneurship
- Social Innovation
- Communication
- Life at Stanford GSB
- Collaborative Environment
- Activities & Organizations
- Student Services
- Housing Options
- International Students
Full-Time Degree Programs
- Why Stanford MBA
- Academic Experience
- Financial Aid
- Why Stanford MSx
- Research Fellows Program
- See All Programs
Non-Degree & Certificate Programs
- Executive Education
- Stanford Executive Program
- Programs for Organizations
- The Difference
- Online Programs
- Stanford LEAD
- Seed Transformation Program
- Aspire Program
- Seed Spark Program
- Faculty Profiles
- Academic Areas
- Awards & Honors
- Conferences
Faculty Research
- Publications
- Working Papers
- Case Studies
Research Hub
- Research Labs & Initiatives
- Business Library
- Data, Analytics & Research Computing
- Behavioral Lab
Research Labs
- Cities, Housing & Society Lab
- Golub Capital Social Impact Lab
Research Initiatives
- Corporate Governance Research Initiative
- Corporations and Society Initiative
- Policy and Innovation Initiative
- Rapid Decarbonization Initiative
- Stanford Latino Entrepreneurship Initiative
- Value Chain Innovation Initiative
- Venture Capital Initiative
- Career & Success
- Climate & Sustainability
- Corporate Governance
- Culture & Society
- Finance & Investing
- Government & Politics
- Leadership & Management
- Markets & Trade
- Operations & Logistics
- Opportunity & Access
- Organizational Behavior
- Political Economy
- Social Impact
- Technology & AI
- Opinion & Analysis
- Email Newsletter
Welcome, Alumni
- Communities
- Digital Communities & Tools
- Regional Chapters
- Women’s Programs
- Identity Chapters
- Find Your Reunion
- Career Resources
- Job Search Resources
- Career & Life Transitions
- Programs & Services
- Career Video Library
- Alumni Education
- Research Resources
- Volunteering
- Alumni News
- Class Notes
- Alumni Voices
- Contact Alumni Relations
- Upcoming Events
Admission Events & Information Sessions
- MBA Program
- MSx Program
- PhD Program
- Alumni Events
- All Other Events
- Operations, Information & Technology
- Classical Liberalism
- The Eddie Lunch
- Accounting Summer Camp
- Videos, Code & Data
- California Econometrics Conference
- California Quantitative Marketing PhD Conference
- California School Conference
- China India Insights Conference
- Homo economicus, Evolving
- Political Economics (2023–24)
- Scaling Geologic Storage of CO2 (2023–24)
- A Resilient Pacific: Building Connections, Envisioning Solutions
- Adaptation and Innovation
- Changing Climate
- Civil Society
- Climate Impact Summit
- Climate Science
- Corporate Carbon Disclosures
- Earth’s Seafloor
- Environmental Justice
- Operations and Information Technology
- Organizations
- Sustainability Reporting and Control
- Taking the Pulse of the Planet
- Urban Infrastructure
- Watershed Restoration
- Junior Faculty Workshop on Financial Regulation and Banking
- Ken Singleton Celebration
- Marketing Camp
- Quantitative Marketing PhD Alumni Conference
- Presentations
- Theory and Inference in Accounting Research
- Stanford Closer Look Series
- Quick Guides
- Core Concepts
- Journal Articles
- Glossary of Terms
- Faculty & Staff
- Researchers & Students
- Research Approach
- Charitable Giving
- Financial Health
- Government Services
- Workers & Careers
- Short Course
- Adaptive & Iterative Experimentation
- Incentive Design
- Social Sciences & Behavioral Nudges
- Bandit Experiment Application
- Conferences & Events
- Get Involved
- Reading Materials
- Teaching & Curriculum
- Energy Entrepreneurship
- Faculty & Affiliates
- SOLE Report
- Responsible Supply Chains
- Current Study Usage
- Pre-Registration Information
- Participate in a Study
Nokia Corporation, Innovation and Efficiency in a High-Growth Global Firm

- Priorities for the GSB's Future
- See the Current DEI Report
- Supporting Data
- Research & Insights
- Share Your Thoughts
- Search Fund Primer
- Affiliated Faculty
- Faculty Advisors
- Louis W. Foster Resource Center
- Defining Social Innovation
- Impact Compass
- Global Health Innovation Insights
- Faculty Affiliates
- Student Awards & Certificates
- Changemakers
- Dean Jonathan Levin
- Dean Garth Saloner
- Dean Robert Joss
- Dean Michael Spence
- Dean Robert Jaedicke
- Dean Rene McPherson
- Dean Arjay Miller
- Dean Ernest Arbuckle
- Dean Jacob Hugh Jackson
- Dean Willard Hotchkiss
- Faculty in Memoriam
- Stanford GSB Firsts
- Certificate & Award Recipients
- Teaching Approach
- Analysis and Measurement of Impact
- The Corporate Entrepreneur: Startup in a Grown-Up Enterprise
- Data-Driven Impact
- Designing Experiments for Impact
- Digital Business Transformation
- The Founder’s Right Hand
- Marketing for Measurable Change
- Product Management
- Public Policy Lab: Financial Challenges Facing US Cities
- Public Policy Lab: Homelessness in California
- Lab Features
- Curricular Integration
- View From The Top
- Formation of New Ventures
- Managing Growing Enterprises
- Startup Garage
- Explore Beyond the Classroom
- Stanford Venture Studio
- Summer Program
- Workshops & Events
- The Five Lenses of Entrepreneurship
- Leadership Labs
- Executive Challenge
- Arbuckle Leadership Fellows Program
- Selection Process
- Training Schedule
- Time Commitment
- Learning Expectations
- Post-Training Opportunities
- Who Should Apply
- Introductory T-Groups
- Leadership for Society Program
- Certificate
- 2023 Awardees
- 2022 Awardees
- 2021 Awardees
- 2020 Awardees
- 2019 Awardees
- 2018 Awardees
- Social Management Immersion Fund
- Stanford Impact Founder Fellowships and Prizes
- Stanford Impact Leader Prizes
- Social Entrepreneurship
- Stanford GSB Impact Fund
- Economic Development
- Energy & Environment
- Stanford GSB Residences
- Environmental Leadership
- Stanford GSB Artwork
- A Closer Look
- California & the Bay Area
- Voices of Stanford GSB
- Business & Beneficial Technology
- Business & Sustainability
- Business & Free Markets
- Business, Government, and Society Forum
- Second Year
- Global Experiences
- JD/MBA Joint Degree
- MA Education/MBA Joint Degree
- MD/MBA Dual Degree
- MPP/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Computer Science/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Electrical Engineering/MBA Joint Degree
- MS Environment and Resources (E-IPER)/MBA Joint Degree
- Academic Calendar
- Clubs & Activities
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Military Veterans
- Minorities & People of Color
- Partners & Families
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Support
- Residential Life
- Student Voices
- MBA Alumni Voices
- A Week in the Life
- Career Support
- Employment Outcomes
- Cost of Attendance
- Knight-Hennessy Scholars Program
- Yellow Ribbon Program
- BOLD Fellows Fund
- Application Process
- Loan Forgiveness
- Contact the Financial Aid Office
- Evaluation Criteria
- GMAT & GRE
- English Language Proficiency
- Personal Information, Activities & Awards
- Professional Experience
- Letters of Recommendation
- Optional Short Answer Questions
- Application Fee
- Reapplication
- Deferred Enrollment
- Joint & Dual Degrees
- Entering Class Profile
- Event Schedule
- Ambassadors
- New & Noteworthy
- Ask a Question
- See Why Stanford MSx
- Is MSx Right for You?
- MSx Stories
- Leadership Development
- Career Advancement
- Career Change
- How You Will Learn
- Admission Events
- Personal Information
- Information for Recommenders
- GMAT, GRE & EA
- English Proficiency Tests
- After You’re Admitted
- Daycare, Schools & Camps
- U.S. Citizens and Permanent Residents
- Requirements
- Requirements: Behavioral
- Requirements: Quantitative
- Requirements: Macro
- Requirements: Micro
- Annual Evaluations
- Field Examination
- Research Activities
- Research Papers
- Dissertation
- Oral Examination
- Current Students
- Education & CV
- International Applicants
- Statement of Purpose
- Reapplicants
- Application Fee Waiver
- Deadline & Decisions
- Job Market Candidates
- Academic Placements
- Stay in Touch
- Faculty Mentors
- Current Fellows
- Standard Track
- Fellowship & Benefits
- Group Enrollment
- Program Formats
- Developing a Program
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Transformation
- Program Experience
- Contact Client Services
- Campus Experience
- Live Online Experience
- Silicon Valley & Bay Area
- Digital Credentials
- Faculty Spotlights
- Participant Spotlights
- Eligibility
- International Participants
- Stanford Ignite
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Founding Donors
- Location Information
- Participant Profile
- Network Membership
- Program Impact
- Collaborators
- Entrepreneur Profiles
- Company Spotlights
- Seed Transformation Network
- Responsibilities
- Current Coaches
- How to Apply
- Meet the Consultants
- Meet the Interns
- Intern Profiles
- Collaborate
- Research Library
- News & Insights
- Program Contacts
- Databases & Datasets
- Research Guides
- Consultations
- Research Workshops
- Career Research
- Research Data Services
- Course Reserves
- Course Research Guides
- Material Loan Periods
- Fines & Other Charges
- Document Delivery
- Interlibrary Loan
- Equipment Checkout
- Print & Scan
- MBA & MSx Students
- PhD Students
- Other Stanford Students
- Faculty Assistants
- Research Assistants
- Stanford GSB Alumni
- Telling Our Story
- Staff Directory
- Site Registration
- Alumni Directory
- Alumni Email
- Privacy Settings & My Profile
- Success Stories
- The Story of Circles
- Support Women’s Circles
- Stanford Women on Boards Initiative
- Alumnae Spotlights
- Insights & Research
- Industry & Professional
- Entrepreneurial Commitment Group
- Recent Alumni
- Half-Century Club
- Fall Reunions
- Spring Reunions
- MBA 25th Reunion
- Half-Century Club Reunion
- Faculty Lectures
- Ernest C. Arbuckle Award
- Alison Elliott Exceptional Achievement Award
- ENCORE Award
- Excellence in Leadership Award
- John W. Gardner Volunteer Leadership Award
- Robert K. Jaedicke Faculty Award
- Jack McDonald Military Service Appreciation Award
- Jerry I. Porras Latino Leadership Award
- Tapestry Award
- Student & Alumni Events
- Executive Recruiters
- Interviewing
- Land the Perfect Job with LinkedIn
- Negotiating
- Elevator Pitch
- Email Best Practices
- Resumes & Cover Letters
- Self-Assessment
- Whitney Birdwell Ball
- Margaret Brooks
- Bryn Panee Burkhart
- Margaret Chan
- Ricki Frankel
- Peter Gandolfo
- Cindy W. Greig
- Natalie Guillen
- Carly Janson
- Sloan Klein
- Sherri Appel Lassila
- Stuart Meyer
- Tanisha Parrish
- Virginia Roberson
- Philippe Taieb
- Michael Takagawa
- Terra Winston
- Johanna Wise
- Debbie Wolter
- Rebecca Zucker
- Complimentary Coaching
- Changing Careers
- Work-Life Integration
- Career Breaks
- Flexible Work
- Encore Careers
- Join a Board
- D&B Hoovers
- Data Axle (ReferenceUSA)
- EBSCO Business Source
- Global Newsstream
- Market Share Reporter
- ProQuest One Business
- Student Clubs
- Entrepreneurial Students
- Stanford GSB Trust
- Alumni Community
- How to Volunteer
- Springboard Sessions
- Consulting Projects
- 2020 – 2029
- 2010 – 2019
- 2000 – 2009
- 1990 – 1999
- 1980 – 1989
- 1970 – 1979
- 1960 – 1969
- 1950 – 1959
- 1940 – 1949
- Service Areas
- ACT History
- ACT Awards Celebration
- ACT Governance Structure
- Building Leadership for ACT
- Individual Leadership Positions
- Leadership Role Overview
- Purpose of the ACT Management Board
- Contact ACT
- Business & Nonprofit Communities
- Reunion Volunteers
- Ways to Give
- Fiscal Year Report
- Business School Fund Leadership Council
- Planned Giving Options
- Planned Giving Benefits
- Planned Gifts and Reunions
- Legacy Partners
- Giving News & Stories
- Giving Deadlines
- Development Staff
- Submit Class Notes
- Class Secretaries
- Board of Directors
- Health Care
- Sustainability
- Class Takeaways
- All Else Equal: Making Better Decisions
- If/Then: Business, Leadership, Society
- Grit & Growth
- Think Fast, Talk Smart
- Spring 2022
- Spring 2021
- Autumn 2020
- Summer 2020
- Winter 2020
- In the Media
- For Journalists
- DCI Fellows
- Other Auditors
- Academic Calendar & Deadlines
- Course Materials
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Campus Drive Grove
- Campus Drive Lawn
- CEMEX Auditorium
- King Community Court
- Seawell Family Boardroom
- Stanford GSB Bowl
- Stanford Investors Common
- Town Square
- Vidalakis Courtyard
- Vidalakis Dining Hall
- Catering Services
- Policies & Guidelines
- Reservations
- Contact Faculty Recruiting
- Lecturer Positions
- Postdoctoral Positions
- Accommodations
- CMC-Managed Interviews
- Recruiter-Managed Interviews
- Virtual Interviews
- Campus & Virtual
- Search for Candidates
- Think Globally
- Recruiting Calendar
- Recruiting Policies
- Full-Time Employment
- Summer Employment
- Entrepreneurial Summer Program
- Global Management Immersion Experience
- Social-Purpose Summer Internships
- Process Overview
- Project Types
- Client Eligibility Criteria
- Client Screening
- ACT Leadership
- Social Innovation & Nonprofit Management Resources
- Develop Your Organization’s Talent
- Centers & Initiatives
- Student Fellowships
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- January 2014 (Revised June 2020)
- HBS Case Collection
The Rise and Fall of Nokia
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 26
About The Authors
Juan Alcacer
Tarun Khanna
Related work.
- Faculty Research
- November 2020
The Rise and Fall of Nokia (Abridged)
- The Rise and Fall of Nokia By: Juan Alcácer
- The Rise and Fall of Nokia By: Juan Alcacer, Tarun Khanna and Christine Snively
- The Rise and Fall of Nokia (Abridged) By: Juan Alcácer and Tarun Khanna
Brought to you by:

Nokia: The Inside Story of the Rise and Fall of a Technology Giant
By: Quy Huy, Timo O. Vuori, Lisa Duke
The case examines the downward spiral of Nokia, the mobile technology giant that once conquered the world, seen from the perspective of 'insiders' - based on interviews with Nokia executives at top…
- Length: 15 page(s)
- Publication Date: Sep 26, 2016
- Discipline: General Management
- Product #: IN1289-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Teaching Note
- Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
The case examines the downward spiral of Nokia, the mobile technology giant that once conquered the world, seen from the perspective of 'insiders' - based on interviews with Nokia executives at top and middle management level. They describe the emotional undercurrents of the innovation process that caused temporal myopia - an excessive focus on short-term innovation at the expense of longer-term more beneficial activities. Nokia's once-stellar performance was undermined by misaligned collective fear: top managers were afraid of competition from rival products, while middle managers were afraid of their bosses and even their peers. It was their reluctance to share negative information with top managers - who thus remained overly optimistic about the organisation's capabilities - that generated inaccurate feedback and poorly adapted organizational responses that led to the company's downfall. The case covers the period from the early 2000s to 2010, with a focus on 2007 (the introduction of the iPhone) to 2010, when the CEO left.
Learning Objectives
After reading and analysing the case, students will understand (i) how emotional dynamics influence hard technological and strategic decisions in organizations as they translate into challenges for innovation, (ii) how emotional dynamics can undermine innovation and performance.
Sep 26, 2016 (Revised: Dec 12, 2022)
Discipline:
General Management
IN1289-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Management and Leadership: Nokia Corporation Case Study
Introduction.
Organizations need qualitative management to optimally utilize their resources. Management is the art of organizing and coordinating activities in accordance to certain principles or policies to attain forethought objectives. Management has the role of utilizing physical, human, financial, and environmental resources effectively for the good of their firms.
Managerial functions include formulation of corporate functions, organizing, planning, controlling, monitoring, and directing activities to achieve corporate goals and objectives. In contemporary organizational management styles, there has been emphasis on leadership-management approach to managerial-management approach, thought the difference is minimal the net effect is improved competitiveness and efficiency.
This paper differentiates leaders and managers; it will also discuss how leadership shapes organizational culture; to discuss the issues, the paper will use Nokia Corporation as a sample company.
The Difference between Leaders and Managers
The difference between leaders and managers is minimal, however, in contemporary management styles, the difference appears on how they handle situations and the attitude they hold for their works and subordinates. According to Ketchen & Hult, 2006, managers manage, control, monitor tasks through instructions and orders; managers assume the position of authority over subordinates.
The driving force behind managers is to see the attainment of organisational goals. When dealing with subordinates, managers are seen as people who issue instructions and controls the procedure to follow a certain way already predetermined, participation of subordinates in decision-making is minimal.
On the other hand, leaders are defined as the change agents focusing on attaining corporate goals through collective responsibilities and involvement of subordinates in decision making; leaders manage people while managers instruct subordinates (Ketchen & Hult, 2006).
Other than focusing on attainment of corporate goals, leader are highly empowering, supportive and nurturing to their subordinates and uses management policies like delegation to boost confidence among staffs. Managers’ attitude is that tasks must be accomplished irrespective of the way; but leaders have the attitude that the goals should be attained after the people are well managed and guided.
At Nokia, there has been much emphasis to have leaders as the industry is highly competitive, the quality of the leaders called for are expected to match and outdo those of competitor companies like Apple, Ericson, and Samsung who seem to be driving the market through their innovations.
Currently the company’s management can be termed as managers as they are more concerned on maintaining the company’s competitiveness without much of innovation.
Nokia Corporation Historical Background
The international phone industry is advancing fast with both multinational and domestic companies in the market. Nokia is an international phone company listed in New York Stock Exchange and Frankfurt Stock exchange, with its headquarters in Finland; according to the company’s website, the company in 2010 enjoyed a market share of about 37% and aims at increasing the market share to over 40% by the end of 2011.
It has a strong brand all over the world, the companies positioning statement is “technology connecting people”. The company’s headquarters are located in Keilaniemi, Espoo. Currently it has over 123,000 employees distributed in various countries; it has full operational branch in over 120 countries.
In 2009, the company was able to make a profit of €1.2 billion this was over 10% than what it had recorded the previous year.
In 2010, the company’s operations increased to record a revenue of €42 billion and operating profit of €2 billion; the main driver of this profits are sales of phones, which in 2010, the segment enjoyed an average of 32% of worlds phone market. The idea of the company was started in 1865 however; it became a telecommunication company in 1960’s.
Nokia is an international company that has a simple and straightforward mission statement as “Connecting People”. Its vision statement is “Our strategic intent is to build great mobile products” (Nokia Official website, 2011), this vision statement has more focus on the phone section of the company as the main business segment that the company has.
The main purpose of the company is “Our job is to enable billions of people everywhere to get more of life’s opportunities through mobile” (Nokia Official website, 2011).
To ensure that the company fulfils its vision, mission and purpose, it operates under marketing values and principles; they include innovation, products development, respect for the people and respect for research and development projects (Nokia Official website, 2011).
The current electronic market is fiancé and competitive, there are number of players in the industry that calls for Nokia to keep changing its operating policies and strategies. It has to keep changing its approach to ensure that it remains competitive.
The main competitors of the company include Samsung, Apple, and Sony-Ericson. To fight the competition, Nokia has engaged in a number of collaborations with other likeminded companies to ensure that it remains competitive. One of the recent strategic alliances that the company has made is strategic partnership with Microsoft to offer the company with the right software to compete effectively.
The drive to remain competitive and offer high returns to the company has made the management to develop new strategies that will see it succeed.
Organizational Managers and Leaders in Creating and Maintaining Healthy Organizational Culture
Nokia management has the role of building, maintaining, and enforcing positive organisational culture within its business; it has embarked on effective communication channels where staffs can share their views, inputs and standpoints with the management when making decisions.
The human resources have enacted policies that have enabled staffs to establish, develop, tap, and explore their talents, skills and intellectualism. The approach of the company is to have an innovative and outstanding teamwork; though the company has a departmental approach, the company ensures that it has teams in all sections that are mandated and empowered to conduct a certain task within the firm.
Change is inevitable at Nokia’s processes and products; the organizational culture adopted ensures that the human resources understands the need to continuous change and supports it accordingly. The structure of the company has some operational values, virtues and management operating ethics, the values are embedded in the company’s philosophy.
Nokia is divided into four main departments where every department, also called business group, is given some mandate to undertake, the departments are Mobile Phones; Multimedia; Enterprise Solutions and Networks; other than the departments, the company has two horizontal departments as Technology Platforms and Customer and Market Operations.
Neither the business group nor the horizontal department work independent, however, they are interdependent towards each other, the following chart shows the companies organizational culture:
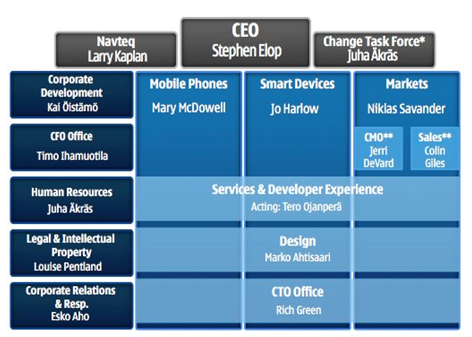
Each manager or departmental head is responsible for his area and is expected to work for the good of the entire firm. As strategic tool, Nokia have realized the need to have an effectively managed human capital; human resources are the greatest asset of an organization.
A number of issues that hinder maximum performance of Nokia are evident in the company’s organizational culture, they include; the company does not have a clear division of power in the management, there is not sure way of saying who is supposed to do what (note this is not in all places), this leads to crisis-crossing of management powers.
For example, the marketing department has a marketing research within its frameworks, while the company has a marketing research department.
Strong informal groups operating in the company affect the company’s organizational culture; these groups shape the company’s direction sometimes negatively; for example, they have made protests against some issues in the company in a way that is not ethical or not in line with Nokia conflict resolution structure.
Sometimes the company faces some poor employee relations and work ethic issues, the issues affect the performance of the company.
The Effect of Globalization on Contemporary Management Strategies
In contemporary business environment, there is need to consider the international community when making decisions; since Nokia has an international operation, it has to consider international business environment and its effects on the business.
When managing human resources, a company has to consider human resources diversity issues like multicultural, international human resources legal administration, and employees’ relations.
Globalization has led to improvement of trade among countries, when trade is enhanced, customers are diverse and have varying needs. The management must understand the needs of the diverse customers and make policies that not only address local customer issues but the entire international community.
When making products and choosing the marketing strategy to adopt, the strategy should be internationally accepted, policies that seem to address or sell the products to certain region should not be used. When coming up with products, the company has to consider the divers income among different nations and regions; this creates a wide variety of products that costs differently.
Recommendations to Improve Organizational Culture
When an organization has positive organizational culture, it easily adopts to change, nurture invention and innovation; although Nokia organizational behavior can be applauded, the following strategies can improve the culture, they include:
Team building activities
Occasionally, the company should be having team building exercises; the activities should be organized from section, departments, and eventually the entire organization. When undertaking teambuilding activities, the management should ensure they interact with subordinates at an informal level; this will facilitate communication and sharing of ideas.
Adopt effective communication strategy
Nokia management should enact policies that continually improve communication among staffs and their leaders. With the fast growing technological development, there are new communication policies and channels that the company should adopt and boost its efficiency. In the event that there is some opinion leaders established, the management should address them directly to change their attitude (Bateman & Snell, 2011).
The success of Nokia Corporation in the competitive electronics industry can be attributed to its robust, innovative, and motivated workforce. The company’s management has cultivated a positive organisational culture that nurtures talents, invention and innovation.
Globalisation, international trade and human resources diversity have changed contemporary management strategies where polices are formulated to address issues at the international level. Nokia management appreciates the benefits and challenges brought about by a globalizing world and enact policies that enables it gaining from opportunities mitigate related risks.
Bateman, T. S., & Snell, S. A. (2011). Management: Leading & collaborating in a competitive world . New York: McGraw-Hill Irwin.
Ketchen Jr., G., & Hult, T.M. (2006). Bridging organization theory and supply chain management: The case of best value supply chains. Journal of Operations Management, 25(2) , 573-580.
Nokia Official Website . (2011). Nokia: Connecting People . Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, May 13). Management and Leadership: Nokia Corporation. https://ivypanda.com/essays/management-and-leadership-the-case-study-of-nokia-corporation-essay/
"Management and Leadership: Nokia Corporation." IvyPanda , 13 May 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/management-and-leadership-the-case-study-of-nokia-corporation-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Management and Leadership: Nokia Corporation'. 13 May.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Management and Leadership: Nokia Corporation." May 13, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/management-and-leadership-the-case-study-of-nokia-corporation-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "Management and Leadership: Nokia Corporation." May 13, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/management-and-leadership-the-case-study-of-nokia-corporation-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Management and Leadership: Nokia Corporation." May 13, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/management-and-leadership-the-case-study-of-nokia-corporation-essay/.
- Nokia Corporation Marketing
- Nokia Corporation: Financial Statement Analysis
- Nokia Change Management
- Apple Human Resources and Knowledge Management Strategies
- HR Management at British Airways: The Hardest Times of the History of Airlines Industry
- The Ecological Effect of the Victorian’s Desalination Project
- Companies competing in the wireless devise and apps products
- CarMax: Sales Revolution Through Innovation
For a better experience, please use a modern browser like Chrome, Firefox, Safari or Edge.
London Business School Publishing
- Create a profile

- Browse cases
- How to order
Preview case
Click Preview case to review the first page of this case
The Rise and Fall of Nokia
By julian birkinshaw , lisa duke.
The case describes Nokia’s spectacular rise and fall, shedding light on the combination of external factors and internal decisions that resulted in the company’s handset business being sold to Microsoft in 2010.During the successful period of growth (roughly 1990 through to 2006), Nokia’s focus on design and functionality gained it a worldwide reputation. It was acknowledged as the first smartphone manufacturer. Through the early-mid 2000s it was the undisputed leader in the global mobile phone business. The case traces the first signs of trouble and the company’s subsequent decline over the period 2005 to 2010. Pressure in the early 2000s from low-end competitors led to early signs of problems. Then of course the game changed in 2007 with Apple’s iPhone and a year later with phones powered by Google’s Android operating system from HTC, Samsung and others. Nokia was initially dismissive of these new offerings but its proprietary OS, Symbian, was ageing badly and its App store (Ovi) was no match for Apple’s. In September 2010 it was announced that American Stephen Elop, formerly of Microsoft, would become CEO. Not long afterwards a partnership with Microsoft was signed which subsequently led to Nokia’s handset business being sold to Microsoft.
Learning objectives
- Understand why good companies go bad; in other words, see how the assets that enable companies to succeed can also be liabilities when the market turns against them.
- Provide insight into the nature of disruption in an established industry and why incumbent firms struggle to adapt.
- Examine the different paths companies should take to respond to disruptive forces.
- Understand the leadership challenge for executives when their performance starts to decline2. To understand the dynamics of change in a fast-changing industry.
- Identify strategies companies can use to adapt quickly to disruptive changes.
Other cases in Strategy

- Entrepreneurship
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship
- Management Science and Operations
- Organisational Behaviour
- Organizational Behaviour and Strategy’
- Sustainability
Privacy Overview
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The Real Cause of Nokia’s Crisis
- Michael Schrage
Nokia’s technology isn’t a root cause of its current crisis. Don’t blame its engineers and designers either. The company still knows how to innovate. There’s a simpler and more strategic explanation for why this once-perennial market leader became second-rate. Nokia ignored America. The company simply refused to compete energetically, ingeniously and respectfully in the U.S. […]
Nokia’s technology isn’t a root cause of its current crisis. Don’t blame its engineers and designers either. The company still knows how to innovate . There’s a simpler and more strategic explanation for why this once-perennial market leader became second-rate.
- MS Michael Schrage , a research fellow at MIT Sloan School’s Center for Digital Business, is the author of the books Serious Play (HBR Press), Who Do You Want Your Customers to Become? (HBR Press) and The Innovator’s Hypothesis (MIT Press).
Partner Center
- Solutions for industry
- Manufacturing and logistics
- Public sector
- Transportation
- Patent licensing
- Technology licensing
- SEP licensing principles
- Standardization
- Go to market
- Virtual events
- Video series
- Sustainability
- Security and privacy
Choose your language
- English (International)
- Chinese, Simplified
- Core networks
- Data center
- Fixed networks
- Internet of Things
- IP networks
- Mobile networks
- Optical networks
- Private networks
- Fixed networks services
- Services for mobile networks
- Cable operators
- Neutral hosts
- Rural broadband
- Subsea terrestrial networks
- Webscale network providers
- Training and certifications
- Financial services
- Manufacturing
- Research and education
- Stadiums, arenas and entertainment venues
- Transportation and logistics
- Services for industry
- Solutions for industry and the public sector
- Go to market partners
- Nokia Bell Labs
- Network solutions
Case studies

Find out more about how our solutions are solving your business challenges

20 Nov 2023
stc improves RAN energy efficiency with Artificial Intelligence powered energy savings management
This case study describes how the AI/ML-powered Energy Savings Management module of MantaRay SON helped stc reduce radio network energy consumption without compromising any…

10 Nov 2023
Airtel uses Nokia security product
Nokia NetGuard Identity and Access Manager to address security threats

Indosat conducts the world’s fastest large-scale multi-operator network integration
Find out how Nokia's digital planning and digital orchestration services helped Indosat consolidate over 40,000 radio sites in just 12 months.

SRT and Nokia – Working together to connect North Dakotans to their broadband future
SRT communications provides broadband service to rural North Dakota. Their all fiber network, powered by Nokia, passes every home and business in their service area

25 Jul 2023

MobiFone reduces radio network energy consumption by close to 14% with digital design
This case study illustrates how Nokia helped MobiFone tackle the raising energy consumption and costs with the Digital Design for Energy Efficiency service

18 Jul 2023
BT partners with Nokia to deliver superior customer experience and improve operational efficiency
Elevated customer expectations and growing data consumption drive AIOps demand

27 Jun 2023
SK Telecom boosts 5G downlink data rates in metropolitan city centers with SRS-based Beamforming
This case study illustrates how Sounding Reference Signal (SRS) based Beamforming was key to increasing the average downlink throughput for SK Telecom’s 5G users in…

stc reinvents customer experience on its fixed network
As the largest service provider in Saudi Arabia, Saudi Telecommunications Company (stc) was keen to ensure its leading position and achieve its ‘dare’ strategy to digitize,…

18 May 2023
Saudi Arabian operator provides outstanding Hajj experience by trusting in automation
This case study illustrates how Nokia SON helped a Saudi Arabian operator optimize its radio network for high performance during Hajj when the traffic volume increased by 40%.…

du extends high-capacity microwave backhaul over long distance to Dubai World Islands
This case study describes how Nokia helped du trial and subsequently deploy a multiband microwave backhaul solution combining high-capacity E-band radios with the extended…

du exceeds 2.4 Gbps data rates with 5G Carrier Aggregation on mid-band in commercial network
This case study describes how Nokia’s 5G Carrier Aggregation solution, and AirScale radio access products helped du achieve Multi-Gigabit data rates on mid-band spectrum in…

21 Feb 2023
TPG Telecom pioneers Carrier Aggregation in 5G Standalone
This case study provides aThis case study describes how 5G Carrier Aggregation was a key element for the launch of 5G Standalone, enabling enhanced user experience and…

12 Feb 2023
North American operator trials near real-time Advanced Traffic Steering for cell load balancing

Bharti Airtel disaster recovery case study
In this case study with Bharti Airtel, Nokia Core Networks Global Services implemented the largest VoLTE geo-redundancy disaster recovery solution.

Chorus network operations transformation case study
Chorus and Nokia have implemented dozens of transformation initiatives to bring greater automation into areas such as customer care and field maintenance

KDDI energy efficiency case study
Find out why KDDI partnered with Nokia to trial Japan’s first AI-controlled radio access network using Nokia AVA for Energy Efficiency.

China Mobile landslide monitoring and alarm system with IMPACT IoT platform
Nokia partnered with China Mobile to develop a landslide monitoring and alarm system (LMAS) built on Nokia’s IMPACT IoT platform.

PTCL customer service transformation case study
Read how PTCL was able to get greater visibility into all aspects of its network by using Nokia Network Analyzer.

23 Dec 2022
Safaricom accelerates incident resolution with automation and AI/ML based analytics
Safaricom was one of the first operators in the world to adopt Nokia’s Digital Care Services model leveraging Nokia Unified Troubleshooting Framework and the AI-driven…

28 Nov 2022
Elisa lays the foundation for superior 5G Standalone experience with Carrier Aggregation
This case study provides a closer look at how 5G Carrier Aggregation helps meet the high expectations of 5G subscribers for enhanced data rates on the path to reaching…

T-Mobile boosts 5G mid-band coverage by 30% with Carrier Aggregation
The case study illustrates how aggregating low-band and mid-band spectrum assets can significantly extend the availability of mid-band bandwidth, providing enhanced quality of…

Telecom Argentina boosts service quality and radio network performance with automation
This case study describes how EdenNet SON helped Telecom Argentina optimize network performance and service quality in its 3G and 4G networks.

17 Oct 2022
Nokia demonstrates 800GE routing
800GE routing is here, to help you meet the growing demand for IP network capacity in a more sustainable manner by simultaneously decreasing the space and power required.

26 Sep 2022
Improve RAN performance and quality with Nokia SON
This Mobile Networks case study focuses on how Nokia EdenNet Self-Organizing Networks (SON) helps boost end user experience without compromising network performance.

How KDDI used AI to cut RAN energy consumption in half
KDDI partnered with Nokia to trial Japan’s first AI-controlled radio access network. Using the capabilities of Nokia AVA for Energy Efficiency, the trial validated to adapt…

PTCL is transforming its customer service
Nokia Customer Care Applications and Network Insights

18 Aug 2022
Nokia Core Talk: How did they do it? DISH, Nokia and the world’s first 5G on AWS’s cloud
Explore how DISH Wireless USA and Nokia achieved the world’s first deployment of 5G Standalone Core on AWS’s cloud. You’ll learn how, by deploying 5G on either a public or…

27 Jul 2022
Chorus is transforming its network operations
Through a highly collaborative Service Improvement Program, Chorus and Nokia have implemented dozens of transformation initiatives since 2016 to bring greater automation into…

Best practices in fiber broadband operations
Fiber rollouts are accelerating and broadband access networks have become mission critical. Coping with this growth and complexity requires network operations that can scale…

10 Jun 2022
Analysys Mason study on SPTel
This case study provides an outline of SPTel's strategy and an overview of the business drivers behind the project.

26 May 2022
The home of best-in-class network interconnection
DE-CIX’s Internet Exchange in Frankfurt is the world’s leading interconnection platform with the highest peak traffic in the world. Founded in 1995, today it manages more than…

28 Mar 2022
Real Action solving smart agriculture challenges
In our Real Action influencer series we build better futures

18 Feb 2022
Spectral Performance Analysis for better customer experience
Hutchinson 3 Indonesia using spectral performance analysis to ensure extraordinary customer experience.

17 Feb 2022
Nokia Vodafone Germany aims to boost network quality with intelligent alarm correlation
Find out how Nokia and Vodafone Germany created an intelligent alarm correlation system to ensure consistent network quality.

Disaster recovery in large VoLTE deployments - Bharti AirTel
Read this case study from India to learn how Nokia Core Networks Global Services team was able to implement the largest VoLTE geo-redundancy disaster recovery solution rapidly…

21 Jan 2022
DISH Wireless 5G Standalone Deployed in the Cloud
In this case study, TBR Inc examines why AWS's cloud is a compelling path for DISH Wireless to deploy Nokia 5G Standalone Core. DISH Wireless is a pioneering CSP that is…

16 Dec 2021
LG U+ talks 5G monetization
In this interview with Son Minseon, Vice President and Head of XaaS Business at LG U+, hear about what makes LG U+ customers unique and how that is shaping their 5G services…

13 Dec 2021
PTCL Fixed Network Insights
Learn how Pakistan Telecommunication Company Limited (PTCL) has deployed Nokia automation, analytics and machine learning software to enhance the customer experience and…

Telenet Belgium selected Google Anthos & Nokia to deploy their cloud-native 5G Standalone Core
Service Providers need a fast, efficient method to launch and grow 5G services. Telenet Belgium selected Google Anthos and Nokia for the deployment of their cloud-native 5G…

23 Sep 2021
Vodafone is partnering with Nokia to build an anomaly detection application on GCP

21 Jul 2021
Anyhaul network fabric gives maximum flexibility
A North American Tier 1 MNO implements a common IP anyhaul network fabric to support diverse 5G implementations

19 Jul 2021
How China Mobile is using Nokia AI for energy-efficient 5G
China Mobile case study

Telenor & 5G-VINNI: Proving the potential of 5G innovation
Through the 5G Verticals Innovation Infrastructure (5G-VINNI) consortium, Nokia and Norwegian CSP Telenor are proving it’s possible to simplify slicing with zero-touch digital…

10 Jun 2021
Ooredoo Algeria: Leading the way to digital enablement - cloud-native core solution
Digital transformation is the key to realizing the potential and promise of 5G, but only if Communication Service Providers (CSPs) overcome the challenge of network complexity…

11 Feb 2021
Automating IP services delivery over a multivendor network
Tier1 CSP in Brazil with Nokia NSP

17 Nov 2020
INEA test the 25G PON technology with Nokia
Karol Kowalik, technical development manager at Polish network operator INEA, talks about the company's next gen fiber network strategy with 25G PON.

Automated, customer-centric network management with NSP
Automate your networks for maximum performance

23 Sep 2020
Global Industry Scan: How CSPs are adapting to the new normal
With pandemic-related traffic volumes and subscriber behaviors becoming the “new normal” for the foreseeable future, what comes next?

19 Aug 2020
SDN Communications and NSP
Automation of IP transport network for 5G services

20 Mar 2020
LG U+ and Nokia NSP

23 Jan 2020
POST Luxemburg
POST Luxembourg utilizes AI insights to improve the home broadband experience

19 Nov 2019
AVA - US CSP using predictive analytics to deliver extraordinary video experiences
US CSP using predictive analytics to deliver extraordinary video experiences

16 Apr 2019
Nokia Customer Care success stories: Redefining the customer experience
Nokia offers a portfolio of Customer eXperience Solutions (CXS) to help communications service providers (CSPs) around the world adopt care processes that deliver the highest…

29 Nov 2018
Ensuring public safety with a TETRA radio communication system
Learn how we helped Austria’s Federal Ministry of the Interior deploy and manage a digital radio network for first responders

15 Nov 2018
Tele2 4G upgrade: 41 percent lower emissions than conventional roll outs
The 4G upgrade with 41% lower carbon emissions than a conventional network
Advertisement

Voice of the Engineer
Supply chain agility: Nokia’s supply chain management success

Nokia did not start manufacturing phones until 1982. The company's interests and businesses were diverse: Telecommunications, consumer electronics, rubber, and cable kept it busy until 1992, when it gave its telecom business all its attention and focus and closed down the others. By making this strategic decision, Nokia became a global leader in telecommunications by 1998.
A history of adaptation in supply chain management
Industry experts have been fascinated by Nokia's ability to manage and adapt its supply chain over almost 150 years. According to the experts, the secret is its supply chain management and its long-term relationships with its suppliers, which make the company ideal for case studies.
The Harvard Business Review published such a case study in 2012 (subscription required). Throughout the study, we learn how Nokia's effective chain of command, its well-placed crisis plan, and an aggressive, multi-pronged strategy helped it avoid production losses for its new cellphone when a March 2000 fire damaged its entire supply of semiconductor chips at the Royal Philips Electronics plant.
Having a strategic risk management plan in place can help you avoid, or at least alleviate, financial difficulty. In a world where supply chain disruptions are simply inevitable, handling them successfully can lead to a happy. The Harvard Business Review case study contrasts Nokia's supply chain management success with the not-so-successful ending the Swedish company Ericsson experienced (with serious financial consequences) when losing its semiconductor chip supply in the same fire delayed production of its new mobile phone.
Lessons from Nokia on supply chain agility
A research paper published in the International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management in 2006 points to the ways that Nokia Networks' demand planning can make supply chain networks more agile. The authors take lessons from Nokia's integrated project management program, which is based on the implementation of a “truly customer-focused delivery process.”
The researchers found, “Supply chain agility does not just happen but requires continuous planning,” something Nokia Networks has mastered.
According to the paper, there are several ways companies can implement agility into operations:
- Promoting the flow of information with suppliers and customers
- Developing collaborative relationships with suppliers
- Designing for postponement
- Building inventory buffers by maintaining a stockpile of inexpensive but key components
- Having a dependable logistics system or partnership
- Drawing up contingency plans and developing crisis management teams
Building Nokia's global supply chain management success
Since 1995, Nokia's SCM approach has been to create the most efficient supplier network in order to offer the best solutions and meet customer expectations. The pillars for the company's success include:
- Creating value-based partnerships with suppliers backed by factual information
- Flexibility
“Making the impossible possible through collaboration” is one of the company’s well-known and often-used mottos. Following this approach, it has made its supplier network a central element of efforts to reach its corporate objectives:
- Great products
- Operational excellence
- Customer satisfaction
Nokia's leadership philosophy responds to four elements: head, heart, hands, and sisu (a Finnish word that may be roughly translated into English as “guts”). That last one plays an important role in making the impossible possible at Nokia.
Below, Max Sjöström from Nokia Oyj talks about gaining a competitive advantage with supply chain.
- Smart watches: a healthy opportunity for OEMs
- The changing face of distribution
- Top 25 global electronics distributors
div-gpt-ad-inread
2 comments on “ Supply chain agility: Nokia’s supply chain management success ”
“how to create a nokia care suite to use user id or password”
“how to use a nokia care suite to user id or passwordn”
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must Sign in or Register to post a comment.
[ninja_form id=2]
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

How fear of change, lack of innovation led to Nokia’s failure?

International Journal of Business Ecosystem & Strategy (2687-2293)
The aim of the paper to investigates the reason for business failure using Nokia as a case study. The paper applies the explanatory conclusive research design since there are cause and effect relations that seek to provide a better understanding of the reasons for the market failure. The mobile manufacturing sector is the most interesting and innovative of all in the “Information & Communications Technology” sector (ICT). Nokia was once known as the market’s dominant company, leader, and pacesetter until it underwent a tremendous market failure. The aim of this research is to shed light on Nokia’s failure in the market due to its complacency & fear of change, lack of innovation moving too slowly in terms of being too late in making decisions & inventing of the iPhone. Paper elaborately discusses and analyses the failure reasons supported by a literature review in addition to the characteristics of this industry and its market structure. Finally provide advice for business makers
Related Papers
ramanajaneyulu pokathota
Nokia was a synonym for the mobile phone industry for a long time; however, when it came into the era of smart phones, the former leader was under an awkward situation. Nokia sold its mobile phone business to Microsoft on September 3, 2013. A company following Kodak with the legendary color failed in the impact of the new technology revolution. This was a typical case of the subversion of an industry; therefore, the author believed that it was necessary to analyze the process. This paper studied Nokia's decline mainly from the three parts. First of all, looking back Nokia's development process from the glory to the decline, it can be divided into three stages: the transition period, the peak period and the decline period, followed by analyzing the reasons of its decline from three parts: Nokia executives' grasp for the market, the company's business strategy and business cooperation, and finally analyzing its inspiration for modern enterprises from the marketing perspective.
Business History
Towards Wise Management
Tuomo Peltonen
From: Peltonen, Tuomo (2018). Towards Wise Management: Wisdom and Stupidity in Strategic Decision-making. Springer.
Raluca Leustean
Microsoft will take over Nokia's Devices and Services business, which includes both Smart Devices and Mobile Devices. In other words: The Lumia, Asha and X series are now all under Microsoft's umbrella. Design teams, supply chain, accessories, employees, developer relations and most of Nokia's manufacturing plants and testing facilities are also on Microsoft's side, as are most of the company's services like MixRadio, Store and more. Here, Nokia's mapping entity, is considered a separate business and isn't included as part of the deal, but Microsoft has agreed to a 10-year licensing agreement. On the one hand, Nokia's decision to sell its mobile phone business to Microsoft is a Finnish tragedy. At Nokia's best times, this giant contributed a quarter of Finland's economic growth for past 10 years: it paid 23% of Finland's corporate taxes. On the other hand, getting out of the mobile phone business sector is a probable blessing for Nokia. Life is tough nowadays for second-tier smartphone companies. Nokia's global market share in the mobile phone market has dropped to 14 percent (from 19.9 percent a year ago, according to Gartner). The revenue of the company brings in from its devices and services division is down by more than half since 2008.This paper is aimed to show why Nokia had to be saved by someone external, both from the technological and financial point of view.
Mateus B O L D R I N E Abrita
The mobile phone devices industry, whose structure is an oligopolistic technological frontier, suffered a structural change in the 2000s, with firms once leaders giving way to emerging ones. This study's hypothesis is that this chance happened due to different innovation strategies adopted by the firms. The objective is to analyze innovation strategies' influence on business performance of the industry's firms in general, with Apple, Nokia and Samsung cases in particular-considered representative firms of the industry for the period. The methodology used was the game theory, comparatively analyzing two games with Nash-Bayesian equilibrium. The results show that, in the face of an aggressive strategy of innovation by products of the first firm (Apple), there is a worse outcome for the company that competes by innovations by product (Nokia) than by markets (Samsung). It is concluded that companies should pay attention to their innovative strategies to remain operative in dynamic markets. Resumo: A indústria de dispositivos de telefonia móvel, cuja estrutura é de fronteira tecnológica oligopolista, sofreu uma mudança estrutural na década de 2000, com firmas antes líderes perdendo espaço para firmas emergentes. A hipótese do trabalho é que as diferentes estratégias de inovação adotadas pelas firmas foram responsáveis por essa mudança estrutural. O objetivo do trabalho é analisar a influência dos tipos de inovação no desempenho das empresas da indústria em geral, e da Apple, Nokia e Samsung em particular, firmas tidas como representativas. Para tanto, utiliza-se como metodologia um modelo com base na teoria de jogos, analisando dois casos. Os resultados, sob equilíbrio Nash-Bayesiano, evidenciam que, em face a uma estratégia agressiva em inovações via produtos por parte da Apple, há um pior resultado para a empresa competidora que decide competir com inovações via produtos (caso da Nokia) do que a que compete em inovações via mercados (caso da Samsung).
Dr. Netra Pal Singh
Ramzi Dziri
Technology and Investment
Kshitiz Soni
RELATED PAPERS
Mario Lafuente Gómez
Paradeigmata 78, Baden-Baden
Matthias Steinhart
Ralf Vandam
The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering
shahzad barghi
Edith Garcia
Metodicki Ogledi Methodical Review
Ivana Zagorac
Cultura de los Cuidados. Revista de Enfermería y Humanidades
Genival Fernandes de Freitas
… Seminar Nasional Aplikasi Teknologi Informasi (SNATI …
tri fajar yurmama
Luis Hernández Ibáñez
Payavard Salamat
ali ahangar
Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health
Margaret Broom
European Journal of Psychotraumatology
Journal of biomedical materials research. Part A
Mariana Cruz
Journal of Wildlife Management
Lowell Suring
Molecular cell
Jefferson Vinco
Glycobiology
Diamond and Related Materials
Elena Salernitano
Zarządzanie w Kulturze
Małgorzata Budzowska
加急办理skku学位证书 韩国成均馆大学毕业证硕士文凭证书在读证明原版一模一样
Journal of Microbiological Methods
Richard van Leeuwen
B P International
Abdo Abou Jaoude
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Nokia Change Management Case Study. Tahir Abbas March 3, 2023. Nokia is a company that has undergone significant change over the years, transforming itself from a mobile phone manufacturer to a leading player in the telecommunications infrastructure market. This transformation was driven by a range of factors, including changes in market ...
Case Study 4: The Collapse of Nokia's Mobile Phone Business: Wisdom and Stupidity in Strategic Decision-making
A key finding of the case study of Nokia Telecommunications is that the performance of different types of expatriates in varying situations is, and should be, managed dissimilarly. Reflecting this ...
Until today, however, there has existed little understanding about how these companies manage the performance of their critical personnel group, the expatriate employees. A key finding of the case study of Nokia Telecommunications is that the performance of different types of expatriates in varying situations is, and should be, managed ...
In response to this need, I present several key findings from a case study on performance management practices at Nokia Telecommu- nications (NTC). The study addresses previ- ously neglected areas of expatriate PM in an attempt to increase our understanding of this increasingly key international HRM topic.
In business history, we can think of very few other cases in which new competitors so quickly and forcefully dethroned an overwhelmingly dominant market leader (cf. Langlois, Citation 1992; Finkelstein, Citation 2006, Van Rooij, Citation 2015) as the case of the Nokia Corporation between 2007 and 2013.Nokia was by no means a passive follower of the novel competitive landscape dominated by the ...
Abstract. This chapter provides a wisdom-oriented reading of one of the most spectacular business failures of recent times: the collapse of Nokia mobile phones between 2007 and 2015. Using executive biographies and other published accounts of Nokia's organisational patterns, the chapter attempts to offer a more balanced explanation of the ...
Expatriate Performance Appraisal Management: The Use Of A 360-Degree Feedback At Nokia Telecommunications June 2011 Journal of Business Case Studies (JBCS) 5(1):45
By spring 2000, Nokia had the highest margins in the mobile phone industry, a negative debt-equity ratio, the most valuable non-U.S. brand in the world, Europe's highest market capitalization, a presence in 140 countries, and unique corporate structures, processes and culture that gave it the feel of "a small company soul in a big corporate ...
The case describes Nokia's spectacular rise and fall, shedding light on the combination of external factors and internal decisions that resulted in the company's handset business being sold to Microsoft in 2010. During the successful period of growth (roughly 1990 through to 2006), Nokia's focus on design and functionality gained it a worldwide reputation. It was acknowledged as the first ...
Abstract. In 2013, Nokia sold its Device and Services business to Microsoft for €5.4 billion. For decades Nokia had led the telecommunications (telecom) industry in handsets and networking. By the late 2000s, however, Nokia's position as market leader in mobile devices was threatened by competition from new lower-cost Asian manufacturers.
The case examines the downward spiral of Nokia, the mobile technology giant that once conquered the world, seen from the perspective of 'insiders' - based on interviews with Nokia executives at top and middle management level. They describe the emotional undercurrents of the innovation process that caused temporal myopia - an excessive focus on short-term innovation at the expense of longer ...
I found this article on the strategic decisions behind Nokia's failure incredibly insightful! 📉 As someone interested in business strategy and management, understanding the factors that led to Nokia's downfall provides valuable lessons for avoiding similar pitfalls in the future. 💡 The analysis of Nokia's missteps, from failing to adapt to changing market trends to underestimating the ...
Nevertheless, Nokia's performance started declining as the new competitors' offerings were perceived as superior to Nokia's. In particular, Nokia's Symbian-based touch-screen devices, 5800, N97, and N8, underperformed.
Introduction. Organizations need qualitative management to optimally utilize their resources. Management is the art of organizing and coordinating activities in accordance to certain principles or policies to attain forethought objectives. Management has the role of utilizing physical, human, financial, and environmental resources effectively ...
The case describes Nokia's spectacular rise and fall, shedding light on the combination of external factors and internal decisions that resulted in the company's handset business being sold to Microsoft in 2010.During the successful period of growth (roughly 1990 through to 2006), Nokia's focus on design and functionality gained it a worldwide reputation.
1. Activity-based costing—Case studies. 2. Managerial accounting—Case studies. 3. Cost accounting—Case studies. 4. Performance—Management—Case studies. 5. Industrial management—Cost effectiveness—Case studies. I. Adkins, Tony (Tony C.) HF5686.C8C295 2006 658.4′013—dc22 2005029726 Printed in the United States of America 10987654321
The Real Cause of Nokia's Crisis. by. Michael Schrage. February 15, 2011. Nokia's technology isn't a root cause of its current crisis. Don't blame its engineers and designers either. The ...
This case study illustrates how Nokia SON helped a Saudi Arabian operator optimize its radio network for high performance during Hajj when the traffic volume increased by 40%.… 3 Apr 2023 du extends high-capacity microwave backhaul over long distance to Dubai World Islands
The study is executed to assess the efficacy of performance management practices as well as company size over innovation which then affect organizational performance. Findings of the Study:
The Harvard Business Review published such a case study in 2012 (subscription required). Throughout the study, we learn how Nokia's effective chain of command, its well-placed crisis plan, and an aggressive, multi-pronged strategy helped it avoid production losses for its new cellphone when a March 2000 fire damaged its entire supply of semiconductor chips at the Royal Philips Electronics plant.
3.1.1. Strategy Diagnosis I. Product differentiation and positive network effects:The reason behind Nokia's new strategy in the smart phone market was given by Nokia's CEO and is based on the belief thatthe battle of devices has now become a war of ecosystems.
The aim of the paper to investigates the reason for business failure using Nokia as a case study. The paper applies the explanatory conclusive research design since there are cause and effect relations that seek to provide a better understanding of ... Towards Wise Management. Case Study 4: The Collapse of Nokia's Mobile Phone Business. 2018 ...