

PhD Program
Year after year, our top-ranked PhD program sets the standard for graduate economics training across the country. Graduate students work closely with our world-class faculty to develop their own research and prepare to make impactful contributions to the field.
Our doctoral program enrolls 20-24 full-time students each year and students complete their degree in five to six years. Students undertake core coursework in microeconomic theory, macroeconomics, and econometrics, and are expected to complete two major and two minor fields in economics. Beyond the classroom, doctoral students work in close collaboration with faculty to develop their research capabilities, gaining hands-on experience in both theoretical and empirical projects.
How to apply
Students are admitted to the program once per year for entry in the fall. The online application opens on September 15 and closes on December 15.
Meet our students
Our PhD graduates go on to teach in leading economics departments, business schools, and schools of public policy, or pursue influential careers with organizations and businesses around the world.
- The Inventory
Support Quartz
Fund next-gen business journalism with $10 a month
Free Newsletters
The complete guide to getting into an economics PhD program
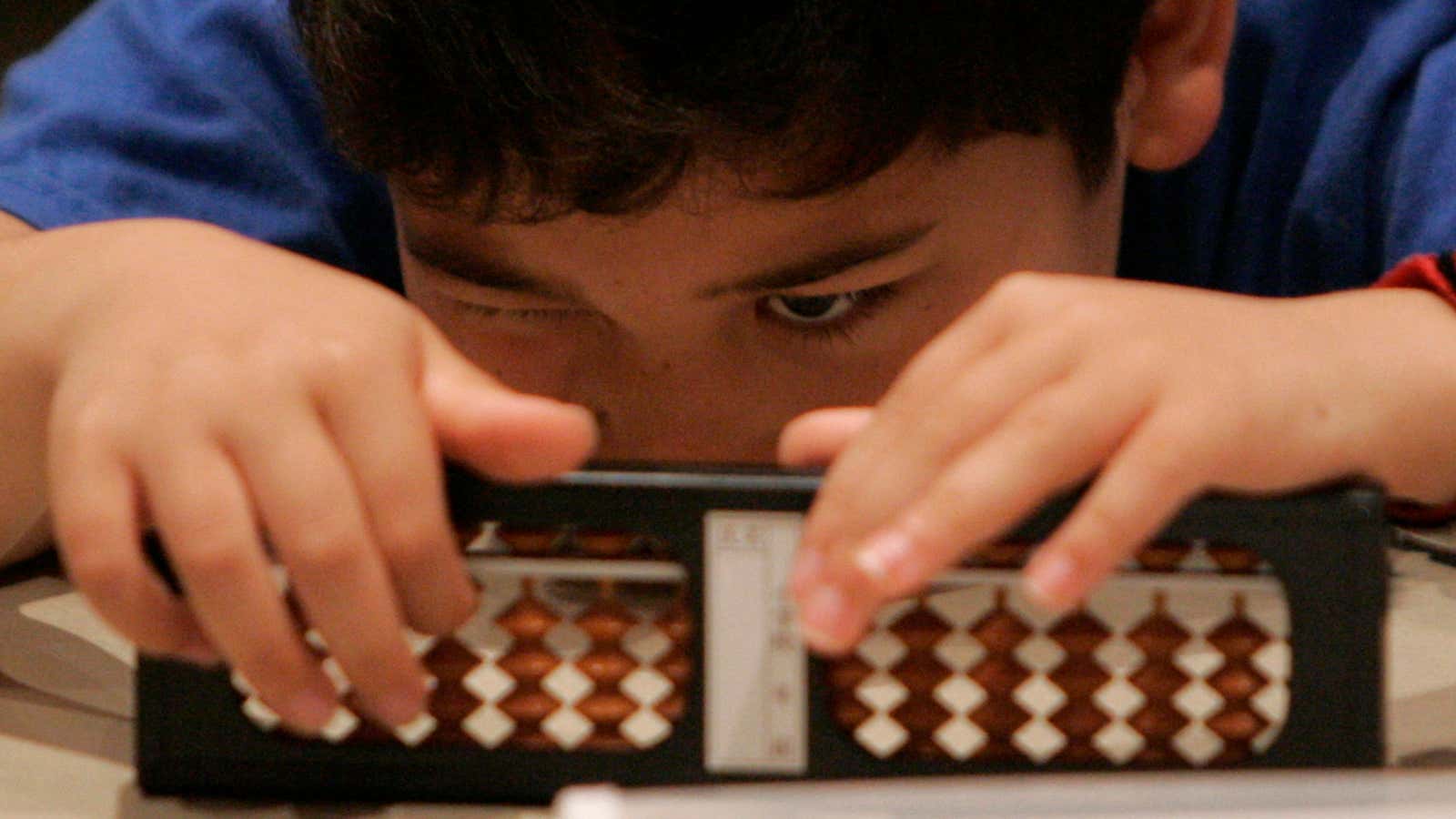

Back in May, Noah wrote about the amazingly good deal that is the PhD in economics. Why? Because:
- You get a job.
- You get autonomy.
- You get intellectual fulfillment.
- The risk is low.
- Unlike an MBA, law, or medical degree, you don’t have to worry about paying the sticker price for an econ PhD: After the first year, most schools will give you teaching assistant positions that will pay for the next several years of graduate study, and some schools will take care of your tuition and expenses even in the first year. (See Miles’s companion post for more about costs of graduate study and how econ PhD’s future earnings makes it worthwhile, even if you can’t get a full ride.)
Of course, such a good deal won’t last long now that the story is out, so you need to act fast! Since he wrote his post , Noah has received a large number of emails asking the obvious follow-up question: “How do I get into an econ PhD program?” And Miles has been asked the same thing many times by undergraduates and other students at the University of Michigan. So here, we present together our guide for how to break into the academic Elysium called Econ PhD Land:
(Note: This guide is mainly directed toward native English speakers, or those from countries whose graduate students are typically fluent in English, such as India and most European countries. Almost all highly-ranked graduate programs teach economics in English, and we find that students learn the subtle non-mathematical skills in economics better if English is second nature. If your nationality will make admissions committees wonder about your English skills, you can either get your bachelor’s degree at a—possibly foreign—college or university where almost all classes are taught in English, or you will have to compensate by being better on other dimensions. On the bright side, if you are a native English speaker, or from a country whose graduate students are typically fluent in English, you are already ahead in your quest to get into an economics PhD.)
Here is the not-very-surprising list of things that will help you get into a good econ PhD program:
- good grades, especially in whatever math and economics classes you take,
- a good score on the math GRE,
- some math classes and a statistics class on your transcript,
- research experience, and definitely at least one letter of recommendation from a researcher,
- a demonstrable interest in the field of economics.
Chances are, if you’re asking for advice, you probably feel unprepared in one of two ways. Either you don’t have a sterling math background, or you have quantitative skills but are new to the field of econ. Fortunately, we have advice for both types of applicant.
If you’re weak in math…
Fortunately, if you’re weak in math, we have good news: Math is something you can learn . That may sound like a crazy claim to most Americans, who are raised to believe that math ability is in the genes. It may even sound like arrogance coming from two people who have never had to struggle with math. But we’ve both taught people math for many years, and we really believe that it’s true. Genes help a bit, but math is like a foreign language or a sport: effort will result in skill.
Here are the math classes you absolutely should take to get into a good econ program:
- Linear algebra
- Multivariable calculus
Here are the classes you should take, but can probably get away with studying on your own:
- Ordinary differential equations
- Real analysis
Linear algebra (matrices, vectors, and all that) is something that you’ll use all the time in econ, especially when doing work on a computer. Multivariable calculus also will be used a lot. And stats of course is absolutely key to almost everything economists do. Differential equations are something you will use once in a while. And real analysis—by far the hardest subject of the five—is something that you will probably never use in real econ research, but which the economics field has decided to use as a sort of general intelligence signaling device.
If you took some math classes but didn’t do very well, don’t worry. Retake the classes . If you are worried about how that will look on your transcript, take the class the first time “off the books” at a different college (many community colleges have calculus classes) or online. Or if you have already gotten a bad grade, take it a second time off the books and then a third time for your transcript. If you work hard, every time you take the class you’ll do better. You will learn the math and be able to prove it by the grade you get. Not only will this help you get into an econ PhD program, once you get in, you’ll breeze through parts of grad school that would otherwise be agony.
Here’s another useful tip: Get a book and study math on your own before taking the corresponding class for a grade. Reading math on your own is something you’re going to have to get used to doing in grad school anyway (especially during your dissertation!), so it’s good to get used to it now. Beyond course-related books, you can either pick up a subject-specific book (Miles learned much of his math from studying books in the Schaum’s outline series ), or get a “math for economists” book; regarding the latter, Miles recommends Mathematics for Economists by Simon and Blume, while Noah swears by Mathematical Methods and Models for Economists by de la Fuente. When you study on your own, the most important thing is to work through a bunch of problems . That will give you practice for test-taking, and will be more interesting than just reading through derivations.
This will take some time, of course. That’s OK. That’s what summer is for (right?). If you’re late in your college career, you can always take a fifth year, do a gap year, etc.
When you get to grad school, you will have to take an intensive math course called “math camp” that will take up a good part of your summer. For how to get through math camp itself, see this guide by Jérémie Cohen-Setton .
One more piece of advice for the math-challenged: Be a research assistant on something non-mathy . There are lots of economists doing relatively simple empirical work that requires only some basic statistics knowledge and the ability to use software like Stata. There are more and more experimental economists around, who are always looking for research assistants. Go find a prof and get involved! (If you are still in high school or otherwise haven’t yet chosen a college, you might want to choose one where some of the professors do experiments and so need research assistants—something that is easy to figure out by studying professors’ websites carefully, or by asking about it when you visit the college.)
If you’re new to econ…
If you’re a disillusioned physicist, a bored biostatistician, or a neuroscientist looking to escape that evil Principal Investigator, don’t worry: An econ background is not necessary . A lot of the best economists started out in other fields, while a lot of undergrad econ majors are headed for MBAs or jobs in banks. Econ PhD programs know this. They will probably not mind if you have never taken an econ class.
That said, you may still want to take an econ class , just to verify that you actually like the subject, to start thinking about econ, and to prepare yourself for the concepts you’ll encounter. If you feel like doing this, you can probably skip Econ 101 and 102, and head straight for an Intermediate Micro or Intermediate Macro class.
Another good thing is to read through an econ textbook . Although economics at the PhD level is mostly about the math and statistics and computer modeling (hopefully getting back to the real world somewhere along the way when you do your own research), you may also want to get the flavor of the less mathy parts of economics from one of the well-written lower-level textbooks (either one by Paul Krugman and Robin Wells , Greg Mankiw , or Tyler Cowen and Alex Tabarrok ) and maybe one at a bit higher level as well, such as David Weil’s excellent book on economic growth ) or Varian’s Intermediate Microeconomics .
Remember to take a statistics class , if you haven’t already. Some technical fields don’t require statistics, so you may have missed this one. But to econ PhD programs, this will be a gaping hole in your resume. Go take stats!
One more thing you can do is research with an economist . Fortunately, economists are generally extremely welcoming to undergrad RAs from outside econ, who often bring extra skills. You’ll get great experience working with data if you don’t have it already. It’ll help you come up with some research ideas to put in your application essays. And of course you’ll get another all-important letter of recommendation.
And now for…
General tips for everyone
Here is the most important tip for everyone: Don’t just apply to “top” schools . For some degrees—an MBA for example—people question whether it’s worthwhile to go to a non-top school. But for econ departments, there’s no question. Both Miles and Noah have marveled at the number of smart people working at non-top schools. That includes some well-known bloggers, by the way—Tyler Cowen teaches at George Mason University (ranked 64th ), Mark Thoma teaches at the University of Oregon (ranked 56th ), and Scott Sumner teaches at Bentley, for example. Additionally, a flood of new international students is expanding the supply of quality students. That means that the number of high-quality schools is increasing; tomorrow’s top 20 will be like today’s top 10, and tomorrow’s top 100 will be like today’s top 50.
Apply to schools outside of the top 20—any school in the top 100 is worth considering, especially if it is strong in areas you are interested in. If your classmates aren’t as elite as you would like, that just means that you will get more attention from the professors, who almost all came out of top programs themselves. When Noah said in his earlier post that econ PhD students are virtually guaranteed to get jobs in an econ-related field, that applied to schools far down in the ranking. Everyone participates in the legendary centrally managed econ job market . Very few people ever fall through the cracks.
Next—and this should go without saying— don’t be afraid to retake the GRE . If you want to get into a top 10 school, you probably need a perfect or near-perfect score on the math portion of the GRE. For schools lower down the rankings, a good GRE math score is still important. Fortunately, the GRE math section is relatively simple to study for—there are only a finite number of topics covered, and with a little work you can “overlearn” all of them, so you can do them even under time pressure and when you are nervous. In any case, you can keep retaking the test until you get a good score (especially if the early tries are practice tests from the GRE prep books and prep software), and then you’re OK!
Here’s one thing that may surprise you: Getting an econ master’s degree alone won’t help . Although master’s degrees in economics are common among international students who apply to econ PhD programs, American applicants do just fine without a master’s degree on their record. If you want that extra diploma, realize that once you are in a PhD program, you will get a master’s degree automatically after two years. And if you end up dropping out of the PhD program, that master’s degree will be worth more than a stand-alone master’s would. The one reason to get a master’s degree is if it can help you remedy a big deficiency in your record, say not having taken enough math or stats classes, not having taken any econ classes, or not having been able to get anyone whose name admissions committees would recognize to write you a letter of recommendation.
For getting into grad school, much more valuable than a master’s is a stint as a research assistant in the Federal Reserve System or at a think tank —though these days, such positions can often be as hard to get into as a PhD program!
Finally—and if you’re reading this, chances are you’re already doing this— read some econ blogs . (See Miles’s speculations about the future of the econ blogosphere here .) Econ blogs are no substitute for econ classes, but they’re a great complement. Blogs are good for picking up the lingo of academic economists, and learning to think like an economist. Don’t be afraid to write a blog either, even if no one ever reads it (you don’t have to be writing at the same level as Evan Soltas or Yichuan Wang ); you can still put it on your CV, or just practice writing down your thoughts. And when you write your dissertation, and do research later on in your career, you are going to have to think for yourself outside the context of a class . One way to practice thinking critically is by critiquing others’ blog posts, at least in your head.
Anyway, if you want to have intellectual stimulation and good work-life balance, and a near-guarantee of a well-paying job in your field of interest, an econ PhD could be just the thing for you. Don’t be scared of the math and the jargon. We’d love to have you.
Update: Miles’s colleague Jeff Smith at the University of Michigan amplifies many of the things we say on his blog. For a complete guide, be sure to see what Jeff has to say, too.
📬 Sign up for the Daily Brief
Our free, fast, and fun briefing on the global economy, delivered every weekday morning.
- Utility Menu
44d3fa3df9f06a3117ed3d2ad6c71ecc
- Administration
- PhD Program
The Ph.D. Program in the Department of Economics at Harvard is addressed to students of high promise who wish to prepare themselves in teaching and research in academia or for responsible positions in government, research organizations, or business enterprises. Students are expected to devote themselves full-time to their programs of study.
The program prepares students for productive and stimulating careers as economists. Courses and seminars offered by the department foster an intellectually active and stimulating environment. Each week, the department sponsors more than 15 different seminars on such topics as environmental economics, economic growth and development, monetary and fiscal policy, international economics, industrial organization, law and economics, behavioral economics, labor economics, and economic history. Top scholars from both domestic and international communities are often invited speakers at the seminars. The Harvard community outside of the department functions as a strong and diverse resource. Students in the department are free to pursue research interests with scholars throughout the University. Faculty of the Harvard Law School, Kennedy School of Government, and Harvard Business School, for example, are available to students for consultation, instruction, and research guidance. As a member of the Harvard community, students in the department can register for courses in the various schools and have access to the enormous library resources available through the University. There are over 90 separate library units at Harvard, with the total collections of books and pamphlets numbering over 13 million. Both the department and the wider University draw some of the brightest students from around the world, which makes for a student body that is culturally diverse and likely unequaled in the range of intellectual interests of its members. These factors combine to add an important dimension to the educational process. Students are able to learn from one another, collaborate on research projects and publications, and form bonds that are not broken by distance once the degree is completed and professional responsibilities lead them in different directions.
- Program Requirements
- Job Placement
- Financial Support

About the Ph.D. Program
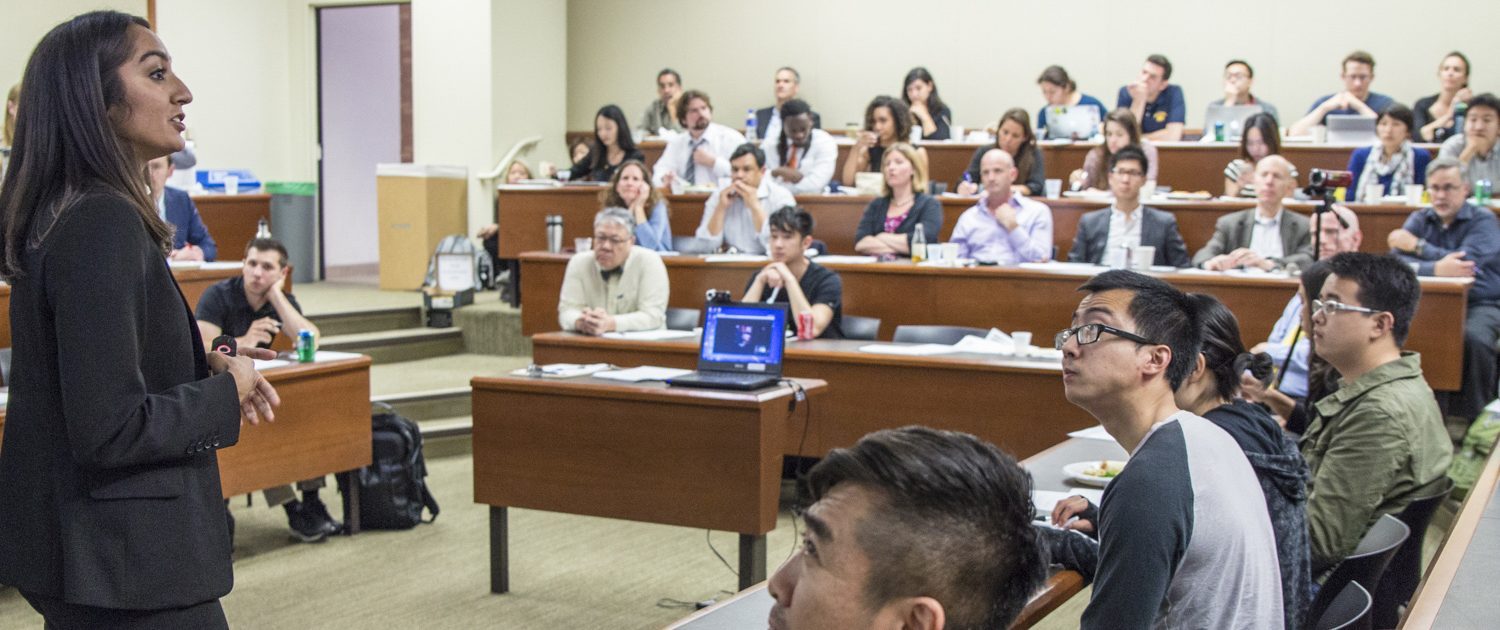

The Ph.D. Program in Economics at UCLA prepares students for careers as economists in academia, business and government. The program combines rigorous work in economic theory and careful study of real-world problems and institutions. Graduates from this program work at major universities around the world, national and international government agencies, banks, research centers and in private businesses. Some of our graduates have achieved great prominence, such as William Sharpe , who earned both his B.A. and Ph.D. degrees at UCLA, and was co-recipient of the 1990 Nobel Prize in Economics for his work on the capital asset pricing model.
The department includes internationally recognized scholars in economic theory, econometrics, and all the major applied fields. These outstanding scholars form one of the foremost departments of economics in the world.
The Economics Department is situated within one of the world’s most youthful and vibrant universities. Founded in 1919, UCLA first developed into a major university in the 1950’s. After so short a history, the university was ranked second in the United States among public research universities by the Conference Board of Associated Research Councils in 1982. Thirty-one of its Ph.D. programs are currently ranked in the top 20 in their field–third best in the nation.
The Ph.D. is the degree objective of the graduate program. This degree is awarded to students who demonstrate professional competence by passing written qualifying exams and by completing a major piece of individual research (the Ph.D. dissertation).
Preparation for the qualifying exams through coursework and independent study occupies most student time for the first two years. Thereafter the focus shifts to independent research and finally to the writing of a Ph.D. dissertation. Research in progress by our graduate students as well as our faculty is presented at workshops that meet weekly throughout the academic year. Currently, the Dept. has workshops in Theory and Mathematical Economics, International and Development Economics, Labor and Population Economics, Business Organization and Regulation Economics, Economic History, Econometrics, and Monetary Theory. In addition, many graduate students work as research or teaching assistants for faculty members. The normal time to degree is six years.
This degree program classifies as STEM (CIP Code 45.0603: Econometrics and Quantitative Economics).

UCLA Department of Economics
8283 Bunche Hall Mail Stop: 147703 Los Angeles, CA 90095
Campus Resources
- Academic Calendar
- Maps, Directions, Parking
- University of California
- Terms of Use
- Injury & Illness Prevention Program
Internal Resources Manager’s Manual Admin Login Webmail (O365 Server) Contact Webmaster
- About the Department
- Administration
- Board of Visitors
- Department Newsletters
- Ladder Faculty
- Courtesy Faculty
- In Memoriam
- Recent Publications
- Research Spotlight
- Economics Major
- Business Economics Major
- Declare our Majors
- Degree Planning
- Benjamin Graham Value Investing Program
- Enrollment Procedures
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Student Wellness & Community
- Department of Economics Commencement 2024
- Course Descriptions
- Economics Class Schedule
- Learning Objectives
- Common Syllabus
- Non-UCLA Course Credit
- Econ Summer Courses for 2024
- Departmental Honors
- Departmental Scholar
- Departmental Scholarships
- Career Pathways
- Fellowships
- Career Center
- Internships
- Research Opportunities
- Preparing for a Ph.D. in Economics
- EDI Courses in Economics
- EDI Research
- EDI Resources for Students
- Incoming Undergraduates
- Why Study Economics?
- Freshmen Information
- Transfers Information
- Economics Courses
- Graduate Handbook
- Graduate Student Awards
- Standards and Procedures
- Second Year
- Thesis Writing
- TA Resources
- Job Market Prep
- Grad Econ Association
- Computing Resources
- Placement History
- Job Market Candidates
- Graduate Counseling Office
- Commencement videos
- Alumni Career Engagement
- UCLA Alumni Affairs
- Update Your Information
- Alumni Interviews
- Women in Business
- Proseminars
Doctoral Program
The Ph.D. program is a full time program leading to a Doctoral Degree in Economics. Students specialize in various fields within Economics by enrolling in field courses and attending field specific lunches and seminars. Students gain economic breadth by taking additional distribution courses outside of their selected fields of interest.
General requirements
Students are required to complete 1 quarter of teaching experience. Teaching experience includes teaching assistantships within the Economics department or another department .
University's residency requirement
135 units of full-tuition residency are required for PhD students. After that, a student should have completed all course work and must request Terminal Graduate Registration (TGR) status.
Department degree requirements and student checklist
1. core course requirement.
Required: Core Microeconomics (202-203-204) Core Macroeconomics (210-211-212) Econometrics (270-271-272). The Business School graduate microeconomics class series may be substituted for the Econ Micro Core. Students wishing to waive out of any of the first year core, based on previous coverage of at least 90% of the material, must submit a waiver request to the DGS at least two weeks prior to the start of the quarter. A separate waiver request must be submitted for each course you are requesting to waive. The waiver request must include a transcript and a syllabus from the prior course(s) taken.
2. Field Requirements
Required: Two of the Following Fields Chosen as Major Fields (click on link for specific field requirements). Field sequences must be passed with an overall grade average of B or better. Individual courses require a letter grade of B- or better to pass unless otherwise noted.
Research fields and field requirements :
- Behavioral & Experimental
- Development Economics
- Econometric Methods with Causal Inference
- Econometrics
- Economic History
- Environmental, Resource and Energy Economics
- Industrial Organization
- International Trade & Finance
- Labor Economics
- Market Design
- Microeconomic Theory
- Macroeconomics
- Political Economy
- Public Economics
3. Distribution
Required: Four other graduate-level courses must be completed. One of these must be from the area of economic history (unless that field has already been selected above). These courses must be distributed in such a way that at least two fields not selected above are represented. Distribution courses must be passed with a grade of B or better.
4. Field Seminars/Workshops
Required: Three quarters of two different field seminars or six quarters of the same field seminar from the list below.
PhD in Economics

PhD students take 16 courses, roughly half of which are spent acquiring the core analytic tools of the profession (microeconomics, macroeconomics, and quantitative methods), with the balance spent applying those tools in particular fields of specialization. All PhD students must complete a doctoral dissertation (thesis).
The PhD in Economics is a STEM designated degree program.
View the complete PhD Rules here
Program Requirements
Doctoral students must complete a minimum of 16 semester courses (64 credits). They are required to successfully complete the core courses by the end of the first year.
Theory and Quantitative Core Requirements
These core courses must be passed by the end of the first year with a grade of at least B- in each course.
- EC 701 Advanced Microeconomics I (4 credits)
- EC 702 Advanced Macroeconomics I (4 credits)
- EC 703 Advanced Microeconomics II (4 credits)
- EC 704 Advanced Macroeconomics II (4 credits)
- EC 707 Advanced Statistics for Economists (4 credits)
- EC 708 Advanced Econometrics I (4 credits)
Students must also take EC 705 Mathematical Economics in the first semester, unless a waiver is granted, and EC 709 Advanced Econometrics II (4 credits) in the third semester.
In addition, students must pass a qualifying examination in both microeconomics and macroeconomics. Students have at most three opportunities to take the qualifying examinations; failing may result in termination from the PhD program.
Field Requirements
All students must pass 2 2-course fields, each with a minimum grade average of B.
In addition, students must take at least 2 other courses. The following fields are generally offered each year:
- Development
- Econometrics
- Economic Theory
- Empirical Finance
- Financial Econometrics
- Industrial Organization
- International Economics
- Labor Economics
- Money/Macroeconomics
- Public Economics
GPA Requirements
All courses must be passed with a grade of B– or higher. An overall grade point average (GPA) of 3.0 must be attained in all courses taken after enrollment in the Graduate School of Arts & Sciences.
Time Requirement
The PhD program is designed so that a typical student can complete all requirements within 5 to 6 years. International students may be subject to additional restrictions imposed by the terms of their visas, as governed by the International Students & Scholars Office (ISSO).
Students are expected to meet the following milestones each year:
By the end of the 1st year:
- Finish and pass all core first-year courses, as well as EC 705 (unless exempted through placement exam).
- Sit for the first attempt at the micro and macro qualifying exams in June. The second attempt, if necessary, is in August.
By the end of the 2nd year:
- Pass EC 709, a required course in Advanced Econometrics.
- Continue and, if possible, complete remaining coursework, including a two-course sequence in each of two fields. A B average (3.0) is required in each of the field course sequence.
- Achieve an overall GPA of at least 3.0.
- If both qualifiers are not passed, the third and final attempt is in June of the second year.
- Each student must prepare a research paper during the second year and the following summer. By April 1 of the second year, the student must ask a faculty member to serve as an advisor on this paper; have this faculty member agree to serve in this manner; and inform the DGS of the topic of the paper and the advisor’s name. The paper is due in the third year as described below.
By the end of the 3rd year:
- Submit the second-year paper by October 1. By October 15, the faculty advisor must provide (i) a grade for the paper; and (ii) a brief written evaluation the paper. These documents will be sent to the DGS and the student. A student must receive a passing grade on the research paper.
- Complete all coursework with GPA of at least 3.0.
- Continue work on research for the dissertation.
- Attend and present at least annually in one of the research workshops until completion of all degree requirements.
Years 4, 5, and (if necessary) 6:
- Student carries out thesis research, defending the thesis no later than the end of the sixth year.
Dissertation
Under the supervision of two faculty advisers, a student prepares a dissertation proposal for presentation at a proposal seminar. If the proposal is approved, the student proceeds to research and write the dissertation. When the dissertation is completed, the student must defend it at a final oral examination. The Graduate School of Arts & Sciences requires that the dissertation be completed within seven years of initial enrollment in the program.
For more details, view the complete PhD Rules here and check out our past PhD Placements here .
This website uses cookies.
By clicking the "Accept" button or continuing to browse our site, you agree to first-party and session-only cookies being stored on your device to enhance site navigation and analyze site performance and traffic. For more information on our use of cookies, please see our Privacy Policy .
- Resources for Students
- Careers in economics
The economics profession
Becoming a professor, researcher, or educator.
The Doctor of Philosophy degree (PhD) in economics is necessary for a faculty position in economics at most four-year colleges in the US. A masters degree is the typical credential for faculty at two-year colleges. Although some students complete masters programs before entering PhD programs, many go directly from BA programs into PhD programs. Completion of a PhD requires about six years of full-time study. Holders of the PhD often also choose research careers outside of academics, including roles at the Federal Reserve, international agencies, and government policy and evaluation departments as well as in private banks, investment houses, and other for-profit ventures.
The AEA's Universal Academic Questionnaire Summary Statistics reports that average starting salaries for assistant professors at PhD granting institutions was $149,378 in 2023–2024. The table below reports the average salary of economists at each academic rank by type of institution.
Average Academic Salaries for Tenured or Tenure-Track Economists by Rank and Type of Institution, 2023–2024
Source: American Economic Association 2023–2024 Universal Academic Questionnaire Summary Statistics , AEA Papers and Proceedings 2024, 114: 712–716.
Academic economists at PhD granting institutions play leading roles in the development of new ideas in economics and publish their work in journals like those published by the AEA . As teachers, economists play an important role in supporting the undergraduate major in economics and the various graduate programs.
A number of PhD economists hold faculty positions in MBA programs, law and medical schools, public policy programs, and in a number of other fields. Economists on the faculty of leading professional schools often earn premium salaries.
A number of for-profit and not-for-profit enterprises hire research economists as do many government and international agencies. The National Association of Business Economics provides information about business careers for economists. The career sites for government and not-for-profits mentioned above also point to opportunities for researchers.
Current job openings for economists in academia and with some other employers appears in the American Economic Association's network for job seekers called Job Openings in Economics (JOE) .
Preparing for graduate school
Funding opportunities for graduate school, universal academic questionnaire (uaq).

Current Degree Requirements for the Ph.D.
- Basic Courses
You must take the following courses in your first year:
- GR6211 Microeconomic analysis I
- GR6212 Microeconomic analysis II
- GR6215 Macroeconomic analysis I
- GR6216 Macroeconomic analysis II
- GR6411 Econometrics I
- GR6412 Econometrics II
- GR6410 Mathematical methods for economists
- GR6930 Perspectives
You must receive a grade of B- or better in each of these courses. If you do not receive a grade of B- or better in any one of these courses, you must retake it the following year. If you still do not receive a grade of B- or better, you are not permitted to continue in the program.
You may petition the Director of Graduate Studies (DGS) to take another course in lieu of Mathematical Methods for Economists. The DGS may ask you to prove your math competency in a manner of his/her choosing. If the DGS grants your petition, and your alternate course is a 2nd year elective course in the economics department, then you may count this towards your 2nd year field requirement and your 2nd year 6 course requirement. In both cases, the relevant rules will apply- -in particular, you will have to get a grade of B or better in that course, and questions from this course will be part of any field exam you may be required to take in that field.
- Certifying Exams
You must pass the certifying examinations in microeconomics, macroeconomics, and econometrics. These examinations are taken in the summer after your first year. They are graded pass or fail. If you fail any of these examinations, you are not permitted to continue in the program. You will not be permitted to continue in the program unless you have passed all certification examinations by the end of your second year.
If you receive a grade of B+ or better in both of the one-semester courses that make up the first-year sequence in microeconomics, macroeconomics, or econometrics, you are exempted from the requirement to pass the certification exam in that field.
You must select two fields during your second year. A list of fields and the required courses for each field will be available in the summer before your second year. Recent second-year fields can be found here . You may not use the same course to satisfy more than one requirement.
Individually-designed field : In lieu of one of the fields designated by the department, you may petition to take an individually-designed field. An individually-designed field consists of 3 courses, not all of which need to be offered by the Department. In order to take an individually-designed field, you must petition the DGS no later than two weeks before the semester starts, and receive DGS approval.
A petition should set out the courses in the field, and explain how these courses will further your education and how they fit together. Approval is solely at the discretion of the DGS. The DGS may approve an individually-designed field in which some (but not all) courses are taken during your third year. Generally, this will occur when a faculty member is on leave and no one else is teaching the material you will need. For more information about individually-designed fields, please see the following FAQ page . Generally, an individually-designed field should be an intellectually coherent set of courses that will provide you with a set of research skills to tackle some important problems. These skills should not be available in any of the regular fields being offered that year.
Course Requirements : You must take at least 6 courses for credit in your second year. The DGS may waive this requirement if you are taking an individually-designed field with courses in your third year. If you wish to count a course from outside the Department of Economics towards your required 6 courses in your second year, you must get approval from the DGS.
Successful completion of any field requires a grade of B or better in all required courses in the field. If you do not receive this grade or better in any required field course, you must retake that course in the following year, and receive a grade of B or better. If that course is not offered in the following year, you must take a substitute course designated by the DGS, and receive a grade of B or better.
Field Exams : In addition to courses, you must pass a field exam in each field you have selected. Field exams are given in the summer after your second year. You will not be permitted to continue in the program unless you have fulfilled all field requirements by the end of your third year.
If you receive a grade of B+ or better in all of the courses that you have taken to satisfy the requirements of a second-year field, you are exempted from the requirement to pass the field exam in that field.
- Colloquium Requirements
You must enroll in and attend a colloquium in your second year, and must make at least one presentation in that colloquium.
You must enroll in and participate in a colloquium each semester after your second year. You must make an appropriate presentation in each semester. With the permission of colloquium faculty, you may substitute a presentation in a regular department workshop, lunch, or breakfast for presentation in a colloquium. You may also substitute a job talk at a different university for presentation in a colloquium. During the year that you are on the job market, a Spring semester colloquium presentation is optional; with the agreement of your main advisor, you can also not enroll in a colloquium that semester.
You should invite your main advisor to all of your colloquium presentations.
You are strongly encouraged to attend department workshops as well as colloquia.
- Paper Requirements, Proposal Requirements, and Advising
Second-year papers : You must write a research paper in your second year. This paper will be due during the summer after your second year. In the spring of your second year, you must find a faculty advisor for your second year paper. This faculty advisor will judge whether your second year paper is of satisfactory quality to fulfill the second year paper requirement. You need approval from the DGS to choose a faculty advisor outside the Economics Department for your second year paper. The DGS sets deadlines and rules regarding advisor selection, interim reports, and final submission of the second year paper.
Third-year papers : You must write a research paper in your third year. This paper will be due during the spring semester of your third year. In the fall of your third year, you must find a faculty advisor for your third year paper. This faculty advisor will judge whether your third year paper is of satisfactory quality to fulfill the third year paper requirement. You need approval from the DGS to choose a faculty advisor outside the Economics Department for your third year paper. The DGS sets deadlines and rules regarding advisor selection, interim reports, and final submission of the third year paper.
Co-authorship of second-year papers : You are allowed to coauthor your second-year paper with another graduate student, either at Columbia or elsewhere, or a faculty member at Columbia. If you are would like a faculty coauthor outside Columbia, or if you wish to coauthor with more than person, please run that by your second-year paper advisor and the DGS well in advance. A paper co-authored by two second-year students may serve as the second-year paper for both students. A single paper cannot win more than one paper prize.
Co-authorship of third-year papers : You are allowed to coauthor your third-year paper with another graduate student, either at Columbia or elsewhere, or a faculty member at Columbia. Third-year papers may not be co-authored with faculty. A paper co-authored by two third-year students may serve as the third-year paper for both students. A single paper cannot win more than one paper prize.
Annual research proposal : In each year after your third year, you must write a one-page progress report and get a faculty member to endorse this report. The faculty member who endorses this report will serve as your advisor on record (main advisor). This progress report will be due in December. The DGS sets the deadline for these reports.
If your advisor on record is not a member of the Economics Department, you must receive prior approval from the DGS and the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences. You must also designate a faculty member within the department as co-advisor, and that faculty member must agree in writing to be co-advisor. If you change your advisor on record, you must inform the DGS within two weeks of the change.
Dissertation Prospectus Defense : You must defend a dissertation prospectus before a committee of at least three faculty members, and at least two of them must be members of the Economics Department. ( Exactly three faculty—no more, no less—must sign your prospectus report .) Your main advisor (and co-advisor if you have a co-advisor) must be a member of this committee. The other members should be faculty that you expect to become members of your dissertation committee. For more information about departmental guidelines, please consult the following document .
This dissertation prospectus will be graded pass or fail. You must pass your dissertation prospectus defense by May 31st of your fourth year in order to continue in the program. If your first defense is unsuccessful, you may request authorization from the DGS to undertake a second defense prior to the May 31st deadline. If you do not pass the dissertation prospectus defense, you will not be allowed to continue in the program. The successful defense of the dissertation proposal is a prerequisite for making use of your Dissertation Fellowship. For more information about these requirements, please consult the following link .
Advisors of Ph.D. students must be assistant professors, associate professors, or professors.
- Dissertation Requirements
You must complete a dissertation, and defend it before a committee of five faculty members. At least three members of this committee must be faculty of the Department, and either one or two must come from outside the Department. Your main advisor will serve as the sponsor at your dissertation defense. If you have two co-advisors, they will serve as co-sponsors.
Co-authoring : At least a third of your dissertation must be your sole-authored work. For instance, if your dissertation consists of three papers, at most two of them may be co-authored. Co-authored work may be part of more than one dissertation. For instance, a paper written by two students, may appear in each of their dissertations. In any co-authored paper, your contribution must be at least as great as that of any other co-author. No more than a third of your dissertation may be co-authored work with a Columbia University faculty member. Co-authors should agree in advance how their research output may be used because they share copyright jointly.
Additional rules about dissertations may be found online.
You must complete the dissertation within seven years from the date you enter the program. You are strongly encouraged to complete the dissertation within six years.
- Teaching Requirements
Students are expected to participate in the Department’s instructional activities during their second, third, and fourth years. You may be excused from this requirement for particular semesters because you have other responsibilities either to the department or to outside funders. However, you must participate in the instructional activities of the Department for at least two semesters during your first four years. You will gain exposure to teaching as assistants to faculty, as section leaders in lecture courses, or as instructors. Before participating in any of these capacities, you must attend the training sessions sponsored by the Director of Undergraduate Studies.
When you are a teaching assistant, you are expected to live in the New York consolidated metropolitan area for the entire semester. You cannot be a teaching assistant in absentia.
- Miscellaneous Requirements
You must register for at least six consecutive Residence Units.
If you hold a Columbia fellowship, you cannot work more than 20 hours a week during the academic year. Being a teaching fellow or a research fellow counts as 15 hours a week. If you are a fifth year or sixth year student with a dissertation fellowship, you cannot hold any other appointment.
- Master Degrees
Masters of Arts (M.A.) degree : To receive the M.A. degree en route to the Ph.D., you must complete 30 points of graduate credit. Generally, the required courses carry 4 credits and other courses carry 3 credits. You must achieve a grade of B or better in at least 6 courses. You must complete at least two residence units. Generally, the M.A. degree can be completed in two years. You must have an M.A. degree to be eligible for the Ph.D. degree.
Masters of Philosophy (M.Phil.) degree : To receive the MPhil degree, you must complete the certifying exams, the basic courses, and the field requirements. You must also have fulfilled the colloquium requirements for second and third year students, except for completing a third-year paper (see the subsection on third-year papers under section 5 above). You must also have registered for at least six residence units. Generally, the MPhil degree can be completed in three years. You must have an MPhil degree to be eligible for the Ph.D. degree.
- Rules of the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
You must comply with the rules of the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences.
Graduate students are expected to exhibit the high level of personal and academic integrity and honesty required of all members of an academic community as they engage in scholarly discourse and research.
Scholars draw inspiration from the work done by other scholars; they argue their claims with reference to others’ work; they extract evidence from the world or from earlier scholarly works. When a student engages in these activities, it is vital to credit properly the source of his or her claims or evidence. Failing to do so violates one’s scholarly responsibility.
In practical terms, students must not cheat on examinations, and deliberate plagiarism is of course prohibited. Plagiarism includes buying, stealing, borrowing, or otherwise obtaining all or part of a paper (including obtaining or posting a paper online); hiring someone to write a paper; copying from or paraphrasing another source without proper citation or falsification of citations; and building on the ideas of another without citation. Students also should not submit the same paper to more than one class. This information is adapted from the material published by Purdue University’s Online Writing Lab .
Graduate students are responsible for proper citation and paraphrasing, and must also take special care to avoid even accidental plagiarism. The best strategy is to use great caution in the handling of ideas and prose passages: take notes carefully and clearly mark words and ideas not one’s own. When in doubt, consult your professor. Failure to observe these rules of conduct will result in serious academic consequences, which can include dismissal from the university.
All incoming doctoral and master’s students in the Arts and Sciences at Columbia are required to complete an academic integrity tutorial prior to arrival on campus.
Students engaging in research must be aware of and follow university policies regarding intellectual and financial conflicts of interest, integrity and security in data collection and management, intellectual property rights, and data ownership, and necessary institutional approval for research with human subjects and animals .
Academic integrity concerns honest research practices as much as avoiding plagiarism. Research misconduct falls into three categories: plagiarism, falsification, and fabrication. Falsification includes purposeful manipulation, modification, or omission of data or results. Fabrication is the making up of data or results and the recording or reporting thereof. The university does not tolerate any form of research misconduct , and violation of this policy may result in serious sanctions, including termination.
Beyond the academic integrity tutorial sent to incoming students each year, students should consult the following resources for further information:
- Indiana University Plagiarism site
- Duke University Plagiarism Tutorial
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Institutional Review Regarding Human Subjects Research
Columbia’s Office of Research Compliance and Training offers a variety of useful training materials and information.
Columbia University also offers Responsible Conduct of Research training developed by the Collaborative Institutional Training Initiative , or CITI Program, at the University of Miami. Students who are or will be supported by funding from the NIH or NSF are required to complete this training. All GSAS students, however, stand to benefit from the training, which explores graduate students’ rights and responsibilities across a variety of disciplines, and addresses how to identify and prevent accidental misconduct as well as mistreatment and abuse from others.
The training is specific to one of four divisions (biomedical sciences, humanities, physical sciences, and social and behavioral sciences) and includes modules on the following topics:
- Intellectual property rights, attribution, and criteria for claiming authorship of publications
- Ownership of data produced at the university and how is it managed
- The process of peer review and potential obstacles to publication
- Regulations and requirements for research involving human subjects
- Conflicts of interest, financial relationships with industry partners, and entrepreneurship
- The advantages and possible challenges of collaborative research
- Research misconduct, including plagiarism, falsification, and fabrication
- Mentoring and career development
To complete the training, you will need to register with the CITI Program website. From the CITI Program homepage , click “Register,” then search for “Columbia University” as the Affiliate Organization. Continue through the registration process and provide your UNI when prompted. Once you have registered and logged in, click on “Main Menu,” then “Add a Course.” Choose “Responsible Conduct of Research Training,” followed by your field (Biomedical, Social and Behavioral Sciences, Humanities, or Physical Sciences). You will then be able to begin the course.
1022 International Affairs Building (IAB)
Mail Code 3308
420 West 118th Street
New York, NY 10027
- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Chair's Message
- Commitment to Diversity
- Department History
- Press Contact
- Economics Roundtable
- Conferences
- Career Workshops
- Faculty Profiles
- Research Groups
- Research Centers
- Faculty Recruitment
- Faculty Resources
- Faculty Recognition
- In Memoriam
- Graduate Advising
- Current Students
- Prospective Students
- Resources for Current Students
- Majors & Minors
- About the Undergraduate Program
- Prospective Student Info
- Hire A Triton
- Stay Connected
- Undergraduate Program
- How to Prepare for a Ph.D. in Economics
First Steps
- How to prepare for a PhD in Economics
- The key thing you need to know is that PhD programs in economics are highly mathematical and the mathematics required by both our Economics and Management Science degrees is not enough to get you into a top PhD program. To be a competitive applicant, you will need to take some upper division mathematics classes such as how to write proofs (Math 109), linear algebra (Math 102), real analysis (Math 140A or 142AB), probability (Math 180A) and statistics (Math 181AB). See more below.
- Graduate schools care a lot about the difficulty and content of the classes you’ve taken. Getting a high GPA won’t necessarily get you into a good program unless they are the right classes.
- If you want to get into a top PhD program, it is especially important to take real analysis (Math 142AB or Math 140ABC—likely Math 140A is enough) and do well in the class. Real analysis teaches you how to write and understand proofs. These skills will be important to your success in first-year graduate courses as well as in your research career. Since real analysis tends to be a difficult course everywhere, your grade in this course is often taken as a key signal of your ability to succeed in a PhD program by admissions committees. If possible, try to take this course when you don’t have a lot of other commitments so that you can devote a significant amount of time to this course, learn the material well and get a good grade.
- Other upper division mathematics and statistics courses are also helpful. In particular, understanding linear algebra is important in graduate-level econometrics courses. Therefore, taking Math 18 and Math 102 (lower and upper division linear algebra courses) can give you a strong foundation in these topics.
- It is also important to have a strong foundation in statistics and probability theory. You will learn a lot of this in the econometrics sequence (if you are interested in pursuing graduate school, you should consider taking the honors classes 120AH-BH-CH). Another class to add to your statistics foundation would be a course in probability (Math 180A).
- In general, if you are interested in going to graduate school in Economics, you should seriously consider majoring in Joint Mathematics-Economics. This major will undoubtedly increase your workload, but it will both make you a more attractive applicant for graduate school and give you the mathematical foundation needed to succeed in graduate school. Students who took many math classes in while in high school should consider double majoring in math and economics.
- If you have exhausted your undergraduate opportunities to take classes in math and economics, consider taking a graduate class. Taking graduate courses in economics or mathematics can send a strong signal to admissions committees. This can be slightly risky, however. Undergraduates may be at a disadvantage as graduate students tend to form study groups for first year courses. If you decide to take a graduate course, you should plan on devoting A LOT of time to the course. Again, it is extremely important that you to do well in a graduate class.
- Coding is an essential skill to have in graduate school. Therefore, taking courses with a data analysis and coding component (for example, Econ5/Poli5D: Introduction to Social Data Analytics, Econ 112: Macro Data Analysis and Econ 121: Applied Econometrics) can help develop your coding skills. The most popular statistical packages in economics are STATA, R, and MATLAB. If you have the time, it may also be a good idea to take an introduction to programming course from the computer science department.
- Courses that have a research component (Econ 191A-B and Econ 199) will also be invaluable preparation for graduate school. By developing your own research topic, you can learn about each step of the research process: from topic selection, background research, data management all the way to analysis and writing. Selecting an empirical topic is especially encouraged as it will give you valuable experience cleaning and analyzing data and getting more comfortable with various data analysis software. This might also be a good indication of whether a career in research is a good fit for you personally. Finally, the Professor teaching Econ 191AB will get to know you and how you tackle problems very well and so be able to write the kind of informed letter of recommendation that graduate schools like to see.
To summarize, in order to prepare for graduate school, it is extremely important to take the right courses and do well in them. To be competitive, you will need to have a record of performing well in difficult mathematics and economics courses.
- Why earn a PhD in Economics?
- Talking to a UCSD grad: ECONnected
What You Should Know Before Applying to an Economics PhD Program
Here's One Student's Experience Applying to an Economics PhD Program
- U.S. Economy
- Supply & Demand
- Archaeology
- Ph.D., Business Administration, Richard Ivey School of Business
- M.A., Economics, University of Rochester
- B.A., Economics and Political Science, University of Western Ontario
I recently wrote an article about the types of people who shouldn't pursue a Ph.D. in economics . Don't get me wrong, I love economics. I've spent a majority of my adult life in the pursuit of knowledge in the field studying around the world and even teaching it at the university level. You may love studying economics, too, but a Ph.D. program is an entirely different beast that requires a very specific type of person and student. After my article was published, I received an email from a reader, who just happened to be a potential Ph.D. student.
This reader's experience and insights into the economics Ph.D. program application process were so on point that I felt the need to share the insights. For those considering applying to a Ph.D. program in Economics, give this email a read.
One Student's Experience Applying to an Economics Ph.D. Program
"Thanks for the graduate school focus in your recent articles. Three of the challenges you mentioned [in your recent article ] really hit home:
- American students have a comparative disadvantage for selection compared to foreign students.
- The importance of math cannot be overstated.
- Reputation is a huge factor, especially that of your undergraduate program.
I applied unsuccessfully to Ph.D. programs for two years before conceding that I might not be ready for them. Only one, Vanderbilt , gave me even a wait-list consideration.
I was a little embarrassed at being shunned. My mathematics GRE was 780. I had graduated at the top of my class with a 4.0 GPA in my economics major and completed a statistics minor . I had two internships: one in research, one in public policy. And accomplished this all while working 30 hours a week to support me . It was a brutally hard couple of years.
The Ph.D. departments I applied to and my undergraduate adviser all pointed out:
- I attended a small, regional public university, and our professors spent significant time with students to the detriment of their own publishing.
- Though I took a heavy load of statistics coursework, I only had two terms of calculus.
- I had never been published; not even in an undergraduate journal.
- I aimed for highly-ranked schools in the Midwest like Illinois, Indiana, Vanderbilt, Michigan, Wisconsin, Washington University in St. Louis, but neglected schools on the coasts, which might have seen me as a more 'diverse' candidate.
I also made what many considered a tactical error: I went to talk with the graduate programs before I applied. I was later told that this is a taboo and seen as schmoozing. I even talked at length with the director of one program. We ended up talking shop for two hours and he invited me to attend presentations and brown bags whenever I was in town. But soon I would learn that he would be ending his tenure to take a position at another college, and would no longer be involved in the approval process for that program.
After going through these obstacles, some suggested I prove myself with a Master's Degree in Economics first. I had originally been told that many schools pick top candidates immediately after undergraduate, but this new advice made sense because departments commit considerable resources to their Ph.D. candidates and want to make sure their investment will survive first-year exams.
With that path in mind, I found it interesting that so few departments offer a terminal Masters in Economic. I'd say about half as many as those that offer only the terminal Ph.D. Fewer still offer an academic Master's - most of these are professional programs. Still, I'm glad it gives me a chance to dig deeper into research and see if I'm ready for Ph.D. research."
My Response
This was such a great letter for many reasons. First, it was genuine. It wasn't a "why didn't I get into a Ph.D. program" rant, but a personal story told with thoughtful insights. In fact, my experience has been nearly identical, and I would encourage any undergraduate student considering pursuing a Ph.D. in economics to take this reader's insights to heart. I, myself, was in a Master's program (at Queen's University in Kingston, Ontario, Canada) before I entered my Ph.D. program. Today, I must admit that I wouldn't have survived three months as a Ph.D. student had I not attempted an MA in Economics first.
- Why Get an Economics Ph.D?
- Books to Study Before Going to Graduate School in Economics
- How to Decide Between a Ph.D. or Psy.D. in Psychology
- Why You Should Get a PhD in Chemistry
- Applying to Graduate Programs in Clinical or Counseling Psychology
- Should I Earn a PhD in Business Administration?
- What It's Like Being a Chemist
- The Meaning and Significance of a PsyD
- A Doctor of Philosophy or Doctorate
- How to Request a Reference Letter from a Professor Years After Graduating
- Model Essay on Identity
- Pros and Cons of Earning a Master's Degree Before a PhD
- Medical School Personal Statement Examples and Analysis
- Find the Best School for Architecture
- Choosing an Ivy League Business School
- Top 25 U.S. Colleges for a Geology Ph.D.
Jump to navigation

Search form

- History of Women Faculty in Economics
- Chairs & Managers
- Research Centers
- Publications
- Year-end letter: Berkeley Economics
- Faculty Profiles
- In Memoriam
- Graduate Program
- Current Students
- Graduate Profiles
- 2023-2024 Job Market Candidates
- 2023-2024 Ph.D. Job Market Infopage
Undergraduate Program
- Course Enrollment
- Prospective Majors
- Current Majors
- Student Organizations
- Commencement
- Course List
- This Week's Seminars
- Next Week's Seminars
- Spring 2024 Economics Classes
- Summer 2024 Economics Classes
- Charter Hill Society for Economics
- Submit a note
- Alumni Notes

Preparing for a PhD in Economics
The minimum requirements of the Economics undergraduate major are not designed to be training for doctoral economics programs. Students who plan to continue their education should take more quantitative courses than the minimum required for the major. Preparation should start early in your undergraduate education. In addition to the information below, we recommend visiting the Career Center and the Career Library for additional graduate school planning resources.
Students who plan on going on to graduate school should participate in research as an undergraduate, and plan on writing an honors thesis during their senior year. NOTE: For students who completed P/NP courses in 2020-2021, we recommend reviewing this statement from the Council of Deans which reaffirms UC Berkeley's Graduate Division committment to a holistic review.
Course recommendations
- Math 53 and Math 54 (multivariable calculus and linear algebra)
- Economics 101A-B, the quantitative theory sequence
- Economics 141, the more quantitative econometrics course
- Additional math and statistics courses (linear algebra, real analysis, probability, etc.)
- Additional economics courses that emphasize theory and quantitative methods, such as Economics 103, 104, and 142.
Upper-division math and statistics courses for those who are adequately prepared (in order of importance)
- Math 110, Linear Algebra
- Math 104, Introduction to Analysis
- Stat 134, Concepts of Probability
- Stat 150, Stochastic Processes
- Math 105, Second Course of Analysis
- Math 170, Mathematical Methods of Optimization
- Stat 102/Stat 135, Linear modeling Theory and Applications
- Stat 151A, Statistical Inference
- Math 185, Introduction to Complex Analysis
Graduate math and statistics courses for those who are adequately prepared (in order of importance)
- Math 202A/202B, Introduction to Topology
- Stat 200A/200B,Introduciton to Probability and Statistics at an Advanced Level; graduate version of 101/102 sequence, not much more difficult, but harder than 134/135
- Stat 205A/205B,Probability Theory; graduate probability, much higher level than 200A/200B
Please note: This is just a recommendation; not all courses are required. Admissions requirements vary by university and by program. Students interested in pursuing graduate school should begin gathering information from prospective programs as early as possible.
Post-Baccalaureate Research Opportunities
Pursuing research after completing an undegraduate degree is a great option for students who would like to gain more experience prior to graduate school. Post-baccalaureate research opportunities can be found through the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) and PREDOC: Pathways to Research and Doctoral Careers . For research opportunities outside of the NBER, click here and follow @econ_ra on Twitter.
Graduate School Preparation Additional Resources
http://www.aeaweb.org/resources/students/grad-prep/considerations/ (Considerations for prospective graduate students in Economics)
https://www.aeaweb.org/resources/students/schools/ (Alphabetical list of U.S Graduate Programs in Economics)
https://www.aeaweb.org/about-aea/committees/cswep/programs/resources/events2 (Conferences, events and fellowships through the American Economic Association)
https://www.aeaweb.org/about-aea/committees/aeasp (American Economic Association Summer Training Program, AEASP)
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

- Future Students
- Current Students
- Apply to UWI
- Programme Search
- Campus Life
- Research & Innovation
- Faculties/Academics
Online Systems
- Student Administration System
- Student Portal
- Bursary Online Student System (BOSS)
- Online Tuition Payment
- Online Transcript Request
- ASKMONA: Library Virtual Reference Service
Student Services
- Office of Student Financing
- Mona Information Technology Services
- Campus Registrar
- Campus Security
- Guild of Students
- Graduate Studies & Research Information Portal
- Health Services
- The Office of Student Services
Registration & Fees
- Undergraduate Fees
- Graduate Fees
- Financial Aid
Online Support
- Password Self Service
- Five Islands
- Global Campus
- St. Augustine
- Business with UWI

The University of the West Indies, Mona
- HOD Message
- Administrative
- Honorary Professors
- Quick guide
- Undergraduate
- Summer School
- Publications
Ph.D Economics
The subject of Economics is concerned with the allocation of resources, not as an end in itself but to enhance people's quality of life. This task is often much more complex than it first appears. In many instances, full information is not available to the persons seeking to allocate these resources, either directly (for example, managers in the private sector), or indirectly (as would be the case of policymakers in the public sector). The Ph.D. Economics programme is a research degree which will provide the requisite tools and skills for advanced economics research in academia, and the public and private sectors. Also, the degree will increase domestic and regional capacity to produce advanced economic research of high quality, which is necessary for the sustained growth and development of open economies.
- Provide students with strong foundations in microeconomics, macroeconomics and econometric theory.
- Provide opportunities for students to strengthen their research skills.
- Provide students with the skills necessary to fill high-level positions domestically, regionally and internationally.
Admission Requirements
Applicants must have an MSc in Economics, or a related major, from a reputable institution. In exceptional circumstances, applicants who have completed their first year of a two year Masters programme will be considered if they maintain at least a B+ average.
Programme Structure
Year 1 and 2 will be comprised of a core and elective courses. N.B. All students are required to complete an intensive orientation of advanced mathematics (Mathematics Camp) in the summer prior to the start of the programme.
Core Requirements
- Advanced Microeconomics I
- Advanced Microeconomics II
- Advanced Macroeconomics I
- Advanced Macroeconomics II
- Advanced Econometrics I
- Advanced Econometrics II
- Mathematics for Economists
- Applied Economic Research & Analysis
***Four Electives of which two must constitute a field. Available fields can change from over time and will be posted each year starting in 2020/2021
Course Descriptions
Follow us on social media.
Department of Economics
Emergency Contacts | Campus Contacts | MITS Helpdesk
The University of the West Indies Mona, Jamaica
Tel: (876) 927-1660-9 Fax: (876) 927-2765

- Undergraduate Students
- Graduate Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Mona Business Hub
- Support UWI
- Media Centre
Our 7 faculties and 12 professional schools offer more than 200 programmes to some 18,000 graduate, undergraduate and continuing studies students.
The UWI, Mona ranks first in Jamaica among accredited tertiary-level programmes. In 2012, the University was again one of Jamaica’s Top 100 Employers.
Disclaimer | Privacy Statement
Who earned PhDs in economics in 2020?
Subscribe to the hutchins roundup and newsletter, david wessel david wessel director - the hutchins center on fiscal and monetary policy , senior fellow - economic studies @davidmwessel.
December 28, 2021
The latest data from the National Science Foundation’s Survey of Earned Doctorates for the 1216 PhDs in economics awarded in 2020 find that men outnumbered women by nearly 2-to-1, 60% of the doctorates went to foreigners with temporary visas, and 24 of the 493 recipients (about 5%) who were U.S. citizens or permanent residents were Black.
A few gleanings from the data:
Of 1216 PhDs awarded in economics in 2020, 797 (66%) went to men and 419 (34%) to women. For comparison, in physics, 21% of the doctorates were awarded to women; in computer and information sciences, also 21%; in math and statistics, 29%; in political science, 39%; in chemistry, also 39%; in business management and administration, 42%; in sociology, 59%; in psychology, 72%.
Data on the race/ethnicity of PhDs are available only for those who are U.S. citizens or permanent residents. Here’s the breakdown for 2020 and 2019:
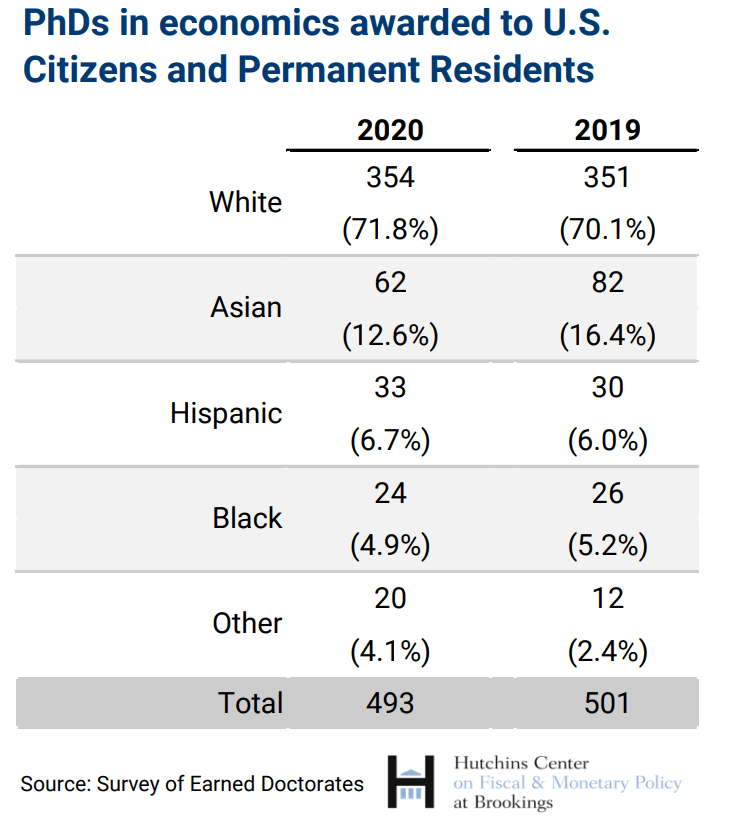
The number of PhDs awarded to Black U.S. citizens or permanent residents has risen slightly in the past few years, from an average of 16 in 2013 through 2017 to an average of 25 in the following three years.
Among the 1216 recipients of PhDs in economics in 2020:
- About half were married when they got their degree. Men and women were equally likely to be married.
- The median age at completion was 31, the same for women and men.
- About 12% took five years or less from graduate school entry to completion, 68% took more than five years and up to 10 years, and 20% took more than 10 years. The median was 7.5 years; the median for men was a few months shorter than the median for women.
- Almost 80% had no debt from graduate school; half of the remainder owed less than $20,000. About 85% had no debt from undergrad. (These data don’t distinguish between those who did their undergraduate work abroad and those who did it in the U.S.)
To read the Hutchins Center report on gender and racial diversity among PhD economists employed by the federal government in 2020, visit this page .
The data in this post are from the Restricted-Use Data Analysis System of the Survey of Earned Doctorates, a survey of 55,000 individuals who earned doctorates in the prior year. The Hutchins Center report uses data from the American Economic Association’s Committee on the Status of Minority Groups in the Economics Profession, which are drawn from the Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System, and differ slightly from the data in the Survey of Earned Doctorates.
The Brookings Institution is financed through the support of a diverse array of foundations, corporations, governments, individuals, as well as an endowment. A list of donors can be found in our annual reports published online here . The findings, interpretations, and conclusions in this report are solely those of its author(s) and are not influenced by any donation.
Related Content
David Wessel, Lorena Hernandez Barcena, Nasiha Salwati
December 9, 2021
Walter G. Ecton, Shaun M. Dougherty
October 18, 2021
Dominique J. Baker, Stephanie Riegg Cellini, Judith Scott-Clayton, Lesley J. Turner
December 14, 2021
Economic Studies
The Hutchins Center on Fiscal and Monetary Policy
Phillip Levine
April 12, 2024
Harry J. Holzer
December 21, 2023
Anne Case, Janice C. Eberly, Carol Graham, Jón Steinsson
October 12, 2023
The Complete Guide to Getting Into an Economics Ph.D. Program
Math challenged? Never taken an econ class? Don't worry about it. There's hope for you yet.
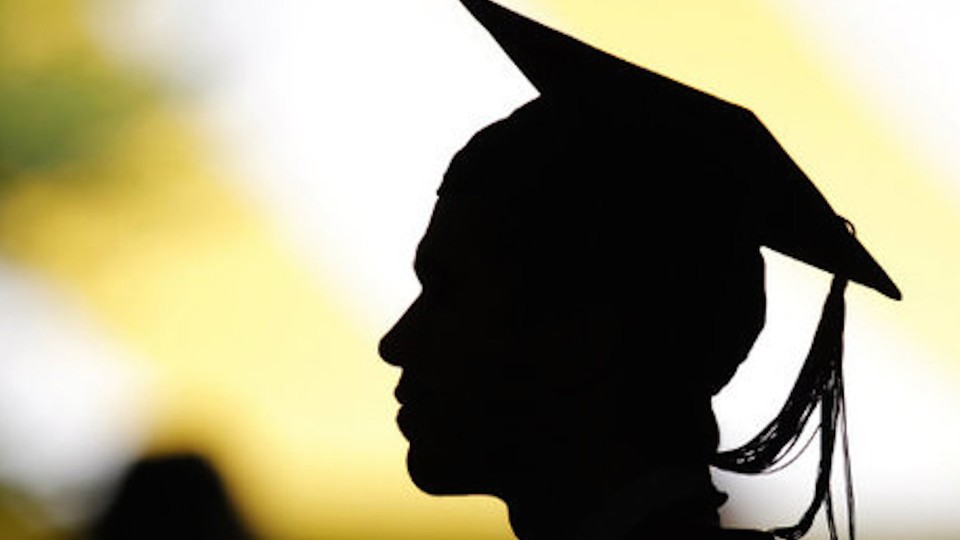

Back in May, Noah wrote about the amazingly good deal that is the PhD in economics. Why? Because:
- You get a job.
- You get autonomy.
- You get intellectual fulfillment.
- The risk is low.
- Unlike an MBA, law, or medical degree, you don't have to worry about paying the sticker price for an econ PhD: After the first year, most schools will give you teaching assistant positions that will pay for the next several years of graduate study, and some schools will take care of your tuition and expenses even in the first year.
Of course, such a good deal won't last long now that the story is out, so you need to act fast! Since he wrote his post , Noah has received a large number of emails asking the obvious follow-up question: "How do I get into an econ PhD program?" And Miles has been asked the same thing many times by undergraduates and other students at the University of Michigan. So here, we present together our guide for how to break into the academic Elysium called Econ Ph.D. Land:
(Note: This guide is mainly directed toward native English speakers, or those from countries whose graduate students are typically fluent in English, such as India and most European countries. Almost all highly ranked graduate programs teach economics in English, and we find that students learn the subtle non-mathematical skills in economics better if English is second nature. If your nationality will make admissions committees wonder about your English skills, you can either get your bachelor's degree at a -- possibly foreign -- college or university where almost all classes are taught in English, or you will have to compensate by being better on other dimensions. On the bright side, if you are a native English speaker, or from a country whose graduate students are typically fluent in English, you are already ahead in your quest to get into an economics Ph.D. program.)
Here is the not-very-surprising list of things that will help you get into a good econ Ph.D. program:
- good grades, especially in whatever math and economics classes you take,
- a good score on the math GRE,
- some math classes and a statistics class on your transcript,
- research experience, and definitely at least one letter of recommendation from a researcher,
- a demonstrable interest in the field of economics.
Chances are, if you're asking for advice, you probably feel unprepared in one of two ways. Either you don't have a sterling math background, or you have quantitative skills but are new to the field of econ. Fortunately, we have advice for both types of applicant.
If You're Weak in Math... Fortunately, if you're weak in math, we have good news: Math is something you can learn . That may sound like a crazy claim to most Americans, who are raised to believe that math ability is in the genes. It may even sound like arrogance coming from two people who have never had to struggle with math. But we've both taught people math for many years, and we really believe that it's true. Genes help a bit, but math is like a foreign language or a sport: effort will result in skill.
Here are the math classes you absolutely should take to get into a good econ program:
- Linear algebra
- Multivariable calculus
Here are the classes you should take, but can probably get away with studying on your own:
- Ordinary differential equations
- Real analysis
Linear algebra (matrices, vectors, and all that) is something that you'll use all the time in econ, especially when doing work on a computer. Multivariable calculus also will be used a lot. And stats of course is absolutely key to almost everything economists do. Differential equations are something you will use once in a while. And real analysis -- by far the hardest subject of the five -- is something that you will probably never use in real econ research, but which the economics field has decided to use as a sort of general intelligence signaling device.
If you took some math classes but didn't do very well, don't worry. Retake the classes. If you are worried about how that will look on your transcript, take the class the first time "off the books" at a different college (many community colleges have calculus classes) or online. Or if you have already gotten a bad grade, take it a second time off the books and then a third time for your transcript. If you work hard, every time you take the class you'll do better. You will learn the math and be able to prove it by the grade you get. Not only will this help you get into an econ Ph.D. program, once you get in, you'll breeze through parts of grad school that would otherwise be agony.
Here's another useful tip: Get a book and study math on your own before taking the corresponding class for a grade. Reading math on your own is something you're going to have to get used to doing in grad school anyway (especially during your dissertation!), so it's good to get used to it now. Beyond course-related books, you can either pick up a subject-specific book (Miles learned much of his math from studying books in the Schaum's outline series ), or get a "math for economists" book; regarding the latter, Miles recommends Mathematics for Economists by Simon and Blume, while Noah swears by Mathematical Methods and Models for Economists by de la Fuente. When you study on your own, the most important thing is to work through a bunch of problems . That will give you practice for test-taking, and will be more interesting than just reading through derivations.
This will take some time, of course. That's OK. That's what summer is for (right?). If you're late in your college career, you can always take a fifth year, do a gap year, etc.
When you get to grad school, you will have to take an intensive math course called "math camp" that will take up a good part of your summer. For how to get through math camp itself, see this guide by Jérémie Cohen-Setton .
One more piece of advice for the math-challenged: Be a research assistant on something non-mathy. There are lots of economists doing relatively simple empirical work that requires only some basic statistics knowledge and the ability to use software like Stata. There are more and more experimental economists around, who are always looking for research assistants. Go find a prof and get involved! (If you are still in high school or otherwise haven't yet chosen a college, you might want to choose one where some of the professors do experiments and so need research assistants -- something that is easy to figure out by studying professors' websites carefully, or by asking about it when you visit the college.)
If You're New to Econ... If you're a disillusioned physicist, a bored biostatistician, or a neuroscientist looking to escape that evil Principal Investigator, don't worry: An econ background is not necessary . A lot of the best economists started out in other fields, while a lot of undergrad econ majors are headed for MBAs or jobs in banks. Econ Ph.D. programs know this. They will probably not mind if you have never taken an econ class.
That said, you may still want to take an econ class, just to verify that you actually like the subject, to start thinking about econ, and to prepare yourself for the concepts you'll encounter. If you feel like doing this, you can probably skip Econ 101 and 102, and head straight for an Intermediate Micro or Intermediate Macro class.
Another good thing is to read through an econ textbook. Although economics at the Ph.D. level is mostly about the math and statistics and computer modeling (hopefully getting back to the real world somewhere along the way when you do your own research), you may also want to get the flavor of the less mathy parts of economics from one of the well-written lower-level textbooks (either one by Paul Krugman and Robin Wells , Greg Mankiw , or Tyler Cowen and Alex Tabarrok ) and maybe one at a bit higher level as well, such as David Weil's excellent book on economic growth ) or Varian's Intermediate Microeconomics .
Remember to take a statistics class, if you haven't already. Some technical fields don't require statistics, so you may have missed this one. But to econ Ph.D. programs, this will be a gaping hole in your resume. Go take stats!
One more thing you can do is research with an economist. Fortunately, economists are generally extremely welcoming to undergrad research assistants from outside econ, who often bring extra skills. You'll get great experience working with data if you don't have it already. It'll help you come up with some research ideas to put in your application essays. And of course, you'll get another all-important letter of recommendation.
And now for...
General Tips for Everyone Here is the most important tip for everyone: Don't just apply to "top" schools . For some degrees -- an MBA for example -- people question whether it's worthwhile to go to a non-top school. But for econ departments, there's no question. Both Miles and Noah have marveled at the number of smart people working at non-top schools. That includes some well-known bloggers, by the way--Tyler Cowen teaches at George Mason University (ranked 64th ), Mark Thoma teaches at the University of Oregon (ranked 56th ), and Scott Sumner teaches at Bentley, for example. Additionally, a flood of new international students is expanding the supply of quality students. That means that the number of high-quality schools is increasing; tomorrow's top 20 will be like today's top 10, and tomorrow's top 100 will be like today's top 50.
Apply to schools outside of the top 20 -- any school in the top 100 is worth considering, especially if it is strong in areas you are interested in. If your classmates aren't as elite as you would like, that just means that you will get more attention from the professors, who almost all came out of top programs themselves. When Noah said in his earlier post that econ Ph.D. students are virtually guaranteed to get jobs in an econ-related field, that applied to schools far down in the ranking. Everyone participates in the legendary centrally managed econ job market . Very few people ever fall through the cracks.
Next -- and this should go without saying -- don't be afraid to retake the GRE. If you want to get into a top 10 school, you probably need a perfect or near-perfect score on the math portion of the GRE. For schools lower down the rankings, a good GRE math score is still important. Fortunately, the GRE math section is relatively simple to study for -- there are only a finite number of topics covered, and with a little work you can "overlearn" all of them, so you can do them even under time pressure and when you are nervous. In any case, you can keep retaking the test until you get a good score (especially if the early tries are practice tests from the GRE prep books and prep software), and then you're OK!
Here's one thing that may surprise you: Getting an econ master's degree alone won't help. Although master's degrees in economics are common among international students who apply to econ PhD programs, American applicants do just fine without a master's degree on their record. If you want that extra diploma, realize that once you are in a PhD program, you will get a master's degree automatically after two years. And if you end up dropping out of the PhD program, that master's degree will be worth more than a stand-alone master's would.
For getting into grad school, much more valuable than a master's is a stint as a research assistant in the Federal Reserve System or at a think tank -- though these days, such positions can often be as hard to get into as a Ph.D. program!
Finally -- and if you're reading this, chances are you're already doing this -- read some econ blogs. (See Miles's speculations about the future of the econ blogosphere here .) Econ blogs are no substitute for econ classes, but they're a great complement. Blogs are good for picking up the lingo of academic economists, and learning to think like an economist. Don't be afraid to write a blog either, even if no one ever reads it (you don't have to be writing at the same level as Evan Soltas or Yichuan Wang ); you can still put it on your CV, or just practice writing down your thoughts. And when you write your dissertation, and do research later on in your career, you are going to have to think for yourself outside the context of a class. One way to practice thinking critically is by critiquing others' blog posts, at least in your head.
Anyway, if you want to have intellectual stimulation and good work-life balance, and a near-guarantee of a well-paying job in your field of interest, an econ PhD could be just the thing for you. Don't be scared of the math and the jargon. We'd love to have you.
Congratulations to the Economics PhD Class of 2024!

The Department of Economics would like to give a heartfelt congratulations to the Class of 2024! At this week’s Commencement ceremony, the Department awarded 20 new PhDs. Welcome to the Yale alumni community and we wish you the best in what comes next!
“We are celebrating the graduation of our remarkable class of 2024. Their impressive achievements, showcased by their cutting edge theses, resulted in fantastic job placements. As they embark on their new endeavors, the Economics Department congratulates them on a job well done. Class of 2024 we are very proud of you!” — Yuichi Kitamura, Director of Graduate Studies
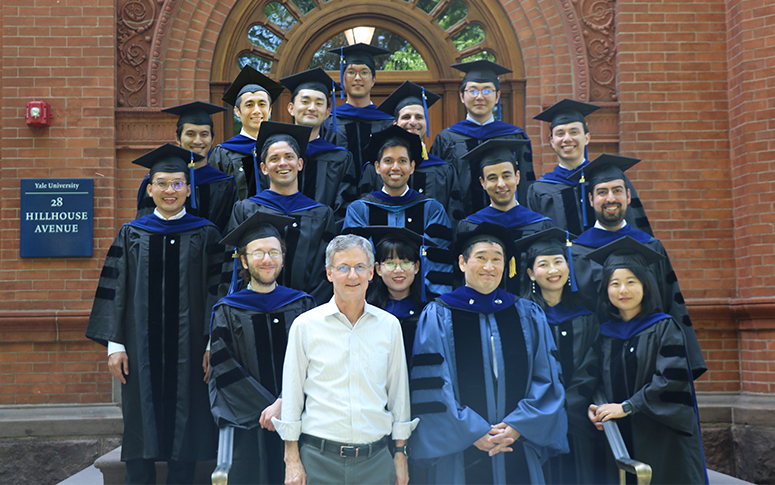

The Class of 2024 with Department Chair Tony Smith and Director of Graduate Studies Yuichi Kitamura
Below we highlight the achievements and next steps of this diverse group of graduates. See here for the Economic Growth Center's article celebrating the Class of 2024, their achievements, and future plans. A full list of placement outcomes can be viewed here .

Pedro Casavilca Silva
Pedro is an economist with a policy-driven research agenda in Labor Economics and Macroeconomics. His current research seeks to enhance understanding of how labor market frictions and credit supply shocks affect informal employment prevalence, wage disparities, and firms' performance. His job market paper (Job Ladder Consequences of Employment Protection: Theory and Evidence from Peru) examines how employment protection shapes the incentives for both workers and firms to demand and supply informal employment and different types of formal labor. In addition to his policy-driven research agenda, he is passionate about teaching and mentoring, and was awarded a Teaching Fellowship Prize in 2021-22 for contributing to courses taught by Professors William Nordhaus and Kaivan Munshi. In the Summer of 2024, he will join Davidson College as an Assistant Professor in the Economics Department.
Personal website Linkedin Profile

Fernando Cordeiro
Fernando's primary field of research is industrial organization, and much of his work has focused on higher education markets and productivity differences between public and private utilities. His job market paper, “College Quality and Tuition Subsidies in Equilibrium,” uses administrative data to gauge the quality of undergraduate programs in Brazil and studies how demand-side subsidies interact with the equilibrium level of price and quality in the Brazilian higher education sector. After graduation, Fernando will join Charles River Associates as a Senior Associate in its antitrust and competition practice.
Alvaro's research interests include economic growth and development. He focuses on the role of human capital in inducing firm growth and the aggregate implications of education policies aimed at reducing the cost of access to higher education. Alvaro’s job market paper, titled “ From Classroom to Prosperity: Fostering Development Through Higher Education ,” assesses the contribution to Brazilian economic growth of the reduction in access costs to higher education with a particular focus on the implications for firms' growth as a mechanism. After Yale, Alvaro will join the University of Oslo as a Full-Time Researcher for the academic year 2024-2025; later, he will join Universidad Carlos III de Madrid as an Assistant Professor.
Personal website @Alv_Cox

Hanxiao Cui
Hanxiao’s research interests include matching and sorting in the labor market and the marriage market, particularly matching and production in teams. Her job market paper studies the complementarity of multidimensional skills in innovation and the skill composition of inventor teams, using novel data linking social security data and patent records. Her dissertation also examines how childcare policies affect marital sorting and household allocation in the long run, as well as gender disparities among investors in terms of life-cycle productivity and teamwork dynamics. She will join Capital One as a principal quantitative analyst this summer.
Linkedin Profile

Mirco Dinelli
Mirco's research interests include macroeconomics, environmental economics, and political economy. His job market paper, titled “ The Political Economy of Climate Bonds ,” investigates the interplay between government debt and climate change policy in a setting where voters from different generations have different interests. The paper finds conditions under which debt instruments can help stimulate climate change policy as well as circumstances in which debt is a hindrance to climate policy. In the 2024-2025 academic year, Mirco will be joining the economics department at St. John Fisher University as an Assistant Professor.
Personal website

Tan Gan is a microeconomic theorist with broad interests in both theoretical and applied topics. Methodologically, he is interested in principal-agent frameworks, including mechanism design, information design, and contract theory, especially with robust objectives. Topicwise, he is interested in exploring the implication of digitalization on economic behaviors. Tan's job market paper, titled “ From Doubt to Devotion Trials and Learning-Based Pricing ,” studies the dynamic mechanism design problem of an informed seller of experience goods. In the fall of 2024, Tan will join LSE as an Assistant Professor in the Management Department.
Personal website @TanGan96

Daniel Giraldo Paez
Daniel's research is in labor and public economics. His work explores the evolution in the last fifty years of labor supply among major demographic groups, with particular focus on the elderly and women. Daniel's job market paper, “ The Changing Nature of Work, Old-Age Labor Supply, and Social Security ,” evaluates the extent to which the increase in older Americans' employment rate can be attributed to changes in the nature of work and this phenomenon's implications for Social Security reforms. Daniel is joining the U.S. Department of Treasury's Office of Microeconomic Analysis as an Economist.
Personal website @WDanielGiraldoP Linkedin Profile

Rodrigo Guerrero
Rodrigo's research focuses on household behavior and education in low-income countries. In his job market paper, titled “ Parental Death and Schooling: Gendered Spheres of Production and Parental Preferences ,” he exploits variation in the timing of parental loss to estimate a structural model of household consumption and time allocation in India. He finds stark differences in the impact of parental death based on the gender of the child and the gender of the deceased parent. The strict gender division of labor in Indian households and the differences in preferences for education of mothers and fathers play a crucial role in explaining the observed effects. After graduation, Rodrigo will join Analysis Group as an Associate.

Nghiem Huynh
Nghiem's research interests lie at the intersection of development economics, international trade, and spatial economics. His job market paper, “ Place-based Policy, Migration Barriers, and Spatial Inequality ,” uses a dynamic model and data from Vietnam to analyze how place-based tax incentives and reducing migration barriers affect regional inequality. After graduation, Nghiem will join the Department of Economics at the University of Oklahoma as an Assistant Professor in July 2024.
Personal website @nghiemqhuynh Linkedin Profile

Sid Kankanala
Sid's primary field of research is Econometrics. His job market paper develops a quasi-Bayesian approach to estimate a large class of models in which observed economic behavior depends on several latent unobservables. Sid will join University of Chicago's Booth School of Business as an Assistant Professor in Econometrics and Statistics.
“This was an impressive cohort. Following Yale’s intellectual tradition of rigorous economic research, the graduating class produced rigorous and groundbreaking work across many economics topics. We look forward to seeing what they do next. Congratulations, class of 2024!” — Fabrizio Zilibotti, Tuntex Professor of International and Development Economics — John Eric Humphries, Assistant Professor of Economics

Jaewon’s research interests include Industrial Organization and Applied Econometrics. His current research focuses on proper inference in the context of demand estimation. His job market paper, titled “Computationally feasible identification-robust inference on discrete choice demand,” explores how to adapt a recent econometric method that is robust to weak identification to BLP-style demand models, in a computationally feasible way. After completing his studies at Yale, Jaewon will join Compass Lexecon as a Senior Economist.

Ryungha's research interests include macroeconomics, spatial economics, and labor economics. Her research investigates why economic activities are concentrated across space and the policy implications of this concentration. Her job market paper, titled “ Spatial Sorting of Workers and Firms ,” develops a new theory of two-sided sorting where heterogeneous workers and firms sort across space and shows that cities can become excessively congested. Ryungha will join Northwestern and Becker Friedman Institute as a post-doctoral fellow before joining the University of Chicago Booth School of Business as an Assistant Professor.

Bernardo Ribeiro
Bernardo’s research interests include economic growth and innovation. He currently focuses on the innovation life cycle of technologies and how society allocates research efforts across technologies of different maturities. In his Job Market paper, “ Embracing the Future or Building on the Past? Growth with New and Old Technologies ,” Bernardo shows that only a small fraction of innovative investment goes into new, cutting-edge technologies, compared to technologies that emerged half a century ago. He then explores the determinants of this pattern and whether policymakers should try to change it. In the academic year 2024-2025, Bernardo will join Princeton University as a Postdoctoral Associate in the Economics Department. In 2025, he will join the Einaudi Institute for Economics and Finance (EIEF) as an Assistant Professor of Economics.
Personal website @bernardo_scrib

Hiroki Saruya
Hiroki’s research interests include health economics and industrial organization, and his current research projects focus on the demand and supply of medical care and long-term care under capacity constraints. His job market paper “Congestion-Quality Tradeoff: Evidence from Japanese Long-Term Care Facilities” explores the tradeoff between nursing facilities' congestion and quality for producing desirable care outcomes, estimates users' preferences for these and other facility characteristics, and then discusses impacts of policies on outcomes and user welfare. After Yale, Hiroki will join the Economic and Social Research Institute of the Cabinet Office, Government of Japan, as a 3-year postdoc researcher.

Jihoon Sung
Jihoon’s research interests include macroeconomics, economic growth, data analysis, corporate structure, and international trade. His dissertation, titled “Business Conglomerates and Misallocation: Theory and Evidence from Chaebols” explores the role of business groups—collections of firms owned by a single family—in determining factor misallocation and aggregate productivity. After graduation, he will join Konektis Capital Management.

Anthony Tokman
Anthony uses tools from industrial organization to study the economics of cities and housing supply. His dissertation research quantifies the neighborhood-level stringency of housing density restrictions in over thirty U.S. metro areas and investigates the disparate effects of these restrictions on housing affordability and spatial mobility across the income distribution. After Yale, Anthony will join Charles River Associates as a senior associate in the antitrust and competition economics practice.

Allen’s research interests lie in economic theory, particularly game theory and its applications. His current research focuses on dynamic games and communication. His job market paper, “ Mediated Repeated Moral Hazard ,” shows how a manager uses dynamic communication with a worker, hidden from the clients, to improve this worker’s productivity in serving the clients. Allen will join the National University of Singapore as an Assistant Professor.

Siu Yuat Wong
Siu Yuat’s research interests in development economics focus on migration, both temporary and permanent, and its intersection with child development and climate change. Siu Yuat’s job market paper, titled “ Maternal and Paternal Migration and Children’s Human Capital ,” explores how maternal and paternal migration will impact a child’s human capital development, which in turn will affect future parental migration decisions. After graduating, Siu Yuat will begin a postdoctoral research position at Stanford University.

Wei’s research interests include trade, growth, and the environment. His current research investigates how globalization affects growth and the environment through technology diffusion and innovation. His job market paper, titled “ Clean Growth and Environmental Policies in the Global Economy ,” provides a dynamic framework to evaluate environmental policies in the global economy. Wei will join the Department of Economics at University of Michigan as an Assistant Professor.

Qianyao's research interests include Labor Economics and Applied Microeconomics. Her current research focuses on human capital development, particularly the determinants of the development process. Qianyao's job market paper, titled “ Child Development, Parental Investments, and Social Capital ,” explores the impacts of social capital and parental investments on child skill development. After Yale, Qianyao will join Xiamen University as an Assistant Professor.
Aarhus University logo
Graduate School of Technical Sciences
3-year phd student position in environmental economics with focus on a nature positive economy in the eu.
Applicants are invited for a PhD fellowship/scholarship at Graduate School of Technical Sciences, Aarhus University, Denmark, within the Environmental Science programme. The position is available from 1 September 2024 or later. You can submit your application via the link under 'how to apply'.
Title: 3-year PhD student position in Environmental Economics with focus on a Nature Positive Economy in the EU.
Research area and project description: The multiple values of nature to planetary and human health are not fully recognized by our current economic systems. Mainstream economic drivers negatively affect the natural world both directly and indirectly, yet substantive solutions remain elusive. These economic drivers need to change, providing incentives for a Nature-Positive Economy (NPE).
There is a growing call for a NPE, but the conceptualisation and pathways towards realizing it remain poorly understood. To date, only few companies assess the impacts of their operations on nature and biodiversity and their dependency on nature and ecosystem services.
This PhD project will investigate i) the concept of NPE and ii) to what extent Europe’s economy is nature-positive and the prospects for alignment to NPE. Empirically, the project focuses on the sector of Nature Based Enterprises (NBEs) and five pre-selected mainstream business sectors: agri-food, forestry, tourism, blue economy and built environment. The PhD is primarily funded through GoNaturePositive!, a Horizon Europe project, which involves 13 research partners from across Europe and 7 industry partners representing the aforementioned five business sectors.
The PhD student will review the concept of NPE; critically investigate various sources of data, approaches and indicators metrics and benchmarks to measure and compare green/nature positive jobs and activities at European and national levels, and across sectors; employ annual market surveys and approximate the market size of nature-positive economic activities at European and national levels.
The PhD-position is based at the Department of Environmental Science, an interdisciplinary department under the Faculty of Science & Technology at Aarhus University. The expertise ranges from social science, geography, economics and policy analysis to mathematical modelling, physics, chemistry, and microbiology. Both pure and applied research is conducted on some of the major societal challenges. Currently, about 150 staff and PhD-students are working at the department. Further information may be found at www.envs.au.dk .
The selected PhD candidate will be affiliated with the Section for Environmental Social Science and Geography at the Roskilde campus. The section employs 25 staff and focuses on analyses of the interlinkages between the environment and society, involving the disciplines of economics, geography, political science, and sociology. The strategic foci of the section include policy analysis, spatial modelling, and economics of ecosystem services, with applications to water quality management, climate policy, and biodiversity. Results are published in international scientific journals and disseminated to policy makers, stakeholders, and the wider society through popular publications, conferences, and seminars. For further information: envs.au.dk/en/research-areas/society-environment-and-resources
Project description The applicant is required to submit a brief description (max. 2 pages) of research ideas that would potentially be pursued within the boundaries of this specific project. It should include research questions, theoretical framework, and planned methodologies. If you wish to, you can indicate an URL where further information can be found.
Qualifications and specific competences: Applicants to the PhD position must have a Master’s degree (120 ECTS) in Economics, Business Economics, Environmental Economics or Economics and Business Administration or equivalent.
Proficiency and fluency in English, both written and spoken, are a requirement along with strong skills in quantitative methods, data curation and processing, and demonstrated skills in academic writing. We expect the applicants to have strong skills in working independently, but also in collaborations with other consortium partners and colleagues.
As we are based in an interdisciplinary and very international academic environment, we expect the applicant to be an active part of the research environment and that the applicant will contribute positively to the social working environment.
If graduation is expected in the near future, documentation for final thesis and date of examination must be enclosed in the application.
Applicants demonstrating a good understanding of integrated, problem-oriented analysis are highly preferred.
Project description: The applicant is required to submit a brief description (max 2 pages) of research ideas that would potentially be pursued within the boundaries of the project described above. It should include research questions, theoretical framework, and planned methodologies.
Place of employment and place of work: The place of employment is Aarhus University, and the place of work is Department of Environmental Science, Frederiksborgvej 399, DK-4000 Roskilde
Contacts: Applicants seeking further information are invited to contact:
- Marianne Zandersen, [email protected] (main supervisor)
- Doan Nainggolan, [email protected] (co-supervisor)
How to apply: Please follow this link to submit your application.
Application deadline is 23 June 2024 at 23:59 CEST.
Preferred starting date is 1 September 2024.
For information about application requirements and mandatory attachments, please see our application guide .
Please note:
- Only documents received prior to the application deadline will be evaluated. Thus, documents sent after deadline will not be taken into account.
- The programme committee may request further information or invite the applicant to attend an interview.
- Shortlisting will be used, which means that the evaluation committee only will evaluate the most relevant applications.
Aarhus University’s ambition is to be an attractive and inspiring workplace for all and to foster a culture in which each individual has opportunities to thrive, achieve and develop. We view equality and diversity as assets, and we welcome all applicants. All interested candidates are encouraged to apply, regardless of their personal background. Salary and terms of employment are in accordance with applicable collective agreement.

Marianne Zandersen

Doan Nainggolan

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Year after year, our top-ranked PhD program sets the standard for graduate economics training across the country. Graduate students work closely with our world-class faculty to develop their own research and prepare to make impactful contributions to the field. Our doctoral program enrolls 20-24 full-time students each year and students ...
Test scores are valid for five years (scores must be from no earlier than January 5, 2019 for Fall 2024 admission). ... Many students in these programs have considerable overlap in their coursework with courses offered to PhD students in economics. Many also have dissertation committees that include faculty members of the economics department. ...
Here is the not-very-surprising list of things that will help you get into a good econ PhD program: good grades, especially in whatever math and economics classes you take, a good score on the ...
The Ph.D. Program in the Department of Economics at Harvard is addressed to students of high promise who wish to prepare themselves in teaching and research in academia or for responsible positions in government, research organizations, or business enterprises. Students are expected to devote themselves full-time to their programs of study.
The Ph.D. Program in Economics at UCLA prepares students for careers as economists in academia, business and government. The program combines rigorous work in economic theory and careful study of real-world problems and institutions. Graduates from this program work at major universities around the world, national and international government ...
A PhD in economics is a research degree. Students should pursue this degree if they are interested in a career answering questions on issues from health to monetary policy to development using economic models and/or data. ... As many as 20% of PhDs awarded to minorities in economics over the past 20 years are graduates of the program. All ...
The Ph.D. program is a full time program leading to a Doctoral Degree in Economics. Students specialize in various fields within Economics by enrolling in field courses and attending field specific lunches and seminars. Students gain economic breadth by taking additional distribution courses outside of their selected fields of interest.
Department of Economics. 530 Evans Hall #3880. Berkeley, CA 94720-3880. Fax: (510) 642-6615. Email: [email protected]. The Ph.D. program at Berkeley is designed for students interested in pursuing advanced study and conducting original research in Economics. The Ph.D. degree is awarded in recognition of the recipient's qualifications as ...
All PhD students must complete a doctoral dissertation (thesis). The PhD in Economics is a STEM designated degree program. View the complete PhD Rules here. Program Requirements. Doctoral students must complete a minimum of 16 semester courses (64 credits). They are required to successfully complete the core courses by the end of the first year.
The coursework for the PhD program is divided into 7 core courses and 7 field courses. The. 8 core courses cover the areas of Microeconomics (ECON 611, 612), Macroeconomics (ECON 613, 614), and Econometrics (ECON 615, 616, 617). The purpose of the core courses is to provide the basic framework for an understanding of academic economic analyses ...
The Doctor of Philosophy degree (PhD) in economics is necessary for a faculty position in economics at most four-year colleges in the US. A masters degree is the typical credential for faculty at two-year colleges. Although some students complete masters programs before entering PhD programs, many go directly from BA programs into PhD programs.
Generally, the required courses carry 4 credits and other courses carry 3 credits. You must achieve a grade of B or better in at least 6 courses. You must complete at least two residence units. Generally, the M.A. degree can be completed in two years. You must have an M.A. degree to be eligible for the Ph.D. degree.
If you want to get into a top PhD program, it is especially important to take real analysis (Math 142AB or Math 140ABC—likely Math 140A is enough) and do well in the class. Real analysis teaches you how to write and understand proofs. These skills will be important to your success in first-year graduate courses as well as in your research career.
First, it was genuine. It wasn't a "why didn't I get into a Ph.D. program" rant, but a personal story told with thoughtful insights. In fact, my experience has been nearly identical, and I would encourage any undergraduate student considering pursuing a Ph.D. in economics to take this reader's insights to heart.
Commonly given advice is that you should only do an economics PhD if you: Are good at math and enjoy formal models in economics. Are willing to study 50-80 hours per week (hours are particularly long in the first year) Love intellectual pursuits and have a strong drive to do self-directed research. 11.
Ph.D. in Economics. UF Economics offers the top-ranked Ph.D. in Economics program in the state of Florida. Doctoral students are an integral part of our vibrant research community, and their success is central to our mission. Our program is defined by a highly collegial environment that fosters individual student's development as economists ...
Preparing for a PhD in Economics. The minimum requirements of the Economics undergraduate major are not designed to be training for doctoral economics programs. Students who plan to continue their education should take more quantitative courses than the minimum required for the major. Preparation should start early in your undergraduate education.
Applicants must have an MSc in Economics, or a related major, from a reputable institution. In exceptional circumstances, applicants who have completed their first year of a two year Masters programme will be considered if they maintain at least a B+ average. Programme Structure. Year 1 and 2 will be comprised of a core and elective courses. N.B.
Of 1216 PhDs awarded in economics in 2020, 797 (66%) went to men and 419 (34%) to women. ... residents has risen slightly in the past few years, from an average of 16 in 2013 through 2017 to an ...
But to econ Ph.D. programs, this will be a gaping hole in your resume. Go take stats! One more thing you can do is research with an economist. Fortunately, economists are generally extremely ...
In the second year of a typical PhD in economics program, students focus on specialized areas of economics and complete a research project, either with faculty supervision or as a research assistant. ... Choosing a specialization is a key component of a PhD in economics, with many programs requiring students to select one or two areas of focus ...
A PhD isn't for everyone. It requires alot of self motivation and a desire to research. It will help open up some private sector jobs. I know a few consulting firms hire PhDs and they start out at with more responsibilities and higher salaries. 7.
He then explores the determinants of this pattern and whether policymakers should try to change it. In the academic year 2024-2025, Bernardo will join Princeton University as a Postdoctoral Associate in the Economics Department. In 2025, he will join the Einaudi Institute for Economics and Finance (EIEF) as an Assistant Professor of Economics.
Applicants to the PhD position must have a Master's degree (120 ECTS) in Economics, Business Economics, Environmental Economics or Economics and Business Administration or equivalent. Proficiency and fluency in English, both written and spoken, are a requirement along with strong skills in quantitative methods, data curation and processing ...