- IELTS Scores
- Life Skills Test
- Find a Test Centre
- Alternatives to IELTS
- General Training
- Academic Word List
- Topic Vocabulary
- Collocation
- Phrasal Verbs
- Writing eBooks
- Reading eBook
- All eBooks & Courses
- Sample Essays

Vegetarianism Essay
This is a model vegetarianism essay .
As I always stress, you should read the question very carefully before you answer it to make sure you are writing about the right thing.
Take a look at the question:
Every one of us should become a vegetarian because eating meat can cause serious health problems.
To what extent do you agree or disagree?
Staying on topic
If you rush to start writing and don't analyse the question and brainstorm some ideas you may include the wrong information.
There are religious or moral arguments for not eating meat, but if you discuss those you will be going off topic .
This question is specifically about the health problems connected to eating meat.
So you must discuss in your answer what some of these problems are and if you think there are real health risks or not.
Knowing about the topic

And don't get worried that you do not know much about diet and health.
As part of your IELTS study it will help if you know the basics of most topics such as some health vocabulary in this case, but you are not expected to be an expert on nutrition.
Remember, you are being judged on your English ability and your ability to construct an argument in a coherent way, not to be an expert in the subject matter. So relax and work with
Organisation
In this vegetarianism essay, the candidate disagrees with the statement, and is thus arguing that everyone does not need to be a vegetarian.
The essay has been organised in the following way:
Body 1: Health issues connected with eating meat (i.e. arguments in support of being a vegetarian Body 2: Advantages of eating meat
Now take a look at the model answer.
Model Essay
You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.
Write about the following topic:
Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own experience or knowledge.
Write at least 250 words.
IELTS Vegetarianism Essay - Sample Answer
Vegetarianism is becoming more and more popular for many people, particularly because of the harm that some people believe meat can cause to the body. However, I strongly believe that it is not necessary for everybody to be a vegetarian.
Vegetarians believe that meat is unhealthy because of the diseases it has been connected with. There has been much research to suggest that red meat is particularly bad, for example, and that consumption should be limited to eating it just a few times a week to avoid such things as cancer. Meats can also be high in saturated fats so they have been linked to health problems such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
However, there are strong arguments for eating meat. The first reason is that as humans we are designed to eat meat, which suggests it is not unhealthy, and we have been eating meat for thousands of years. For example, cavemen made hunting implements so that they could kill animals and eat their meat. Secondly, meat is a rich source of protein which helps to build muscles and bones. Vegetarians often have to take supplements to get all the essential vitamins and minerals. Finally, it may be the case that too much meat is harmful, but we can easily limit the amount we have without having to cut it out of our diet completely.
To sum up, I do not agree that everyone should turn to a vegetarian diet. Although the overconsumption of meat could possibly be unhealthy, a balanced diet of meat and vegetables should result in a healthy body.
(264 words)
You should begin by intoducing the topi c. The introduction in this vegetarianism essay begins by mentioning vegetarians and the possible harm of eating meat .
It then goes on to the thesis statement , which makes it clear what the candidate's opinion is.
The first body paragraph has a topic sentence which makes it clear that the paragraph is going to address the possible health issues of eating meat.
Some reasons and examples are then given to support this.
The second body paragraph then has a topic sentence which makes it clear that the main idea is now about the arguments for eating meat .
The conclusion in this vegetarianism essay then repeats the opinion and gives the candidates final thoughts.
<<< Back
Next >>>
More Agree / Disagree Essays:

Dying Languages Essay: Is a world with fewer languages a good thing?
Dying languages essays have appeared in IELTS on several occasions, an issue related to the spread of globalisation. Check out a sample question and model answer.

Employing Older People Essay: Is the modern workplace suitable?
Employing Older People Essay. Examine model essays for IELTS Task 2 to improve your score. This essay tackles the issue of whether it it better for employers to hire younger staff rather than those who are older.

Ban Smoking in Public Places Essay: Should the government ban it?
Ban smoking in public places essay: The sample answer shows you how you can present the opposing argument first, that is not your opinion, and then present your opinion in the following paragraph.

Essay for IELTS: Are some advertising methods unethical?
This is an agree / disagree type question. Your options are: 1. Agree 100% 2. Disagree 100% 3. Partly agree. In the answer below, the writer agrees 100% with the opinion. There is an analysis of the answer.
Technology Development Essay: Are earlier developments the best?
This technology development essay shows you a complex IELTS essay question that is easily misunderstood. There are tips on how to approach IELTS essay questions

Return of Historical Objects and Artefacts Essay
This essay discusses the topic of returning historical objects and artefacts to their country of origin. It's an agree/disagree type IELTS question.

Airline Tax Essay: Would taxing air travel reduce pollution?
Airline Tax Essay for IELTS. Practice an agree and disagree essay on the topic of taxing airlines to reduce low-cost air traffic. You are asked to decide if you agree or disagree with taxing airlines in order to reduce the problems caused.

Free University Education Essay: Should it be paid for or free?
Free university education Model IELTS essay. Learn how to write high-scoring IELTS essays. The issue of free university education is an essay topic that comes up in the IELTS test. This essay therefore provides you with some of the key arguments about this topic.

Internet vs Newspaper Essay: Which will be the best source of news?
A recent topic to write about in the IELTS exam was an Internet vs Newspaper Essay. The question was: Although more and more people read news on the internet, newspapers will remain the most important source of news. To what extent do you agree or disagree?

Examinations Essay: Formal Examinations or Continual Assessment?
Examinations Essay: This IELTS model essay deals with the issue of whether it is better to have formal examinations to assess student’s performance or continual assessment during term time such as course work and projects.

Scientific Research Essay: Who should be responsible for its funding?
Scientific research essay model answer for Task 2 of the test. For this essay, you need to discuss whether the funding and controlling of scientific research should be the responsibility of the government or private organizations.
IELTS Sample Essay: Is alternative medicine ineffective & dangerous?
IELTS sample essay about alternative and conventional medicine - this shows you how to present a well-balanced argument. When you are asked whether you agree (or disagree), you can look at both sides of the argument if you want.
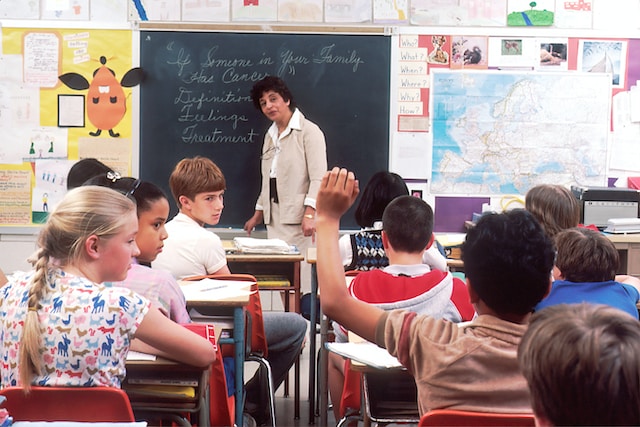

Role of Schools Essay: How should schools help children develop?
This role of schools essay for IELTS is an agree disagree type essay where you have to discuss how schools should help children to develop.

Extinction of Animals Essay: Should we prevent this from happening?
In this extinction of animals essay for IELTS you have to decide whether you think humans should do what they can to prevent the extinction of animal species.

Paying Taxes Essay: Should people keep all the money they earn?
Paying Taxes Essay: Read model essays to help you improve your IELTS Writing Score for Task 2. In this essay you have to decide whether you agree or disagree with the opinion that everyone should be able to keep their money rather than paying money to the government.

Human Cloning Essay: Should we be scared of cloning humans?
Human cloning essay - this is on the topic of cloning humans to use their body parts. You are asked if you agree with human cloning to use their body parts, and what reservations (concerns) you have.

Multinational Organisations and Culture Essay
Multinational Organisations and Culture Essay: Improve you score for IELTS Essay writing by studying model essays. This Essay is about the extent to which working for a multinational organisation help you to understand other cultures.

Sample IELTS Writing: Is spending on the Arts a waste of money?
Sample IELTS Writing: A common topic in IELTS is whether you think it is a good idea for government money to be spent on the arts. i.e. the visual arts, literary and the performing arts, or whether it should be spent elsewhere, usually on other public services.

Truthfulness in Relationships Essay: How important is it?
This truthfulness in relationships essay for IELTS is an agree / disagree type essay. You need to decide if it's the most important factor.
IELTS Internet Essay: Is the internet damaging social interaction?
Internet Essay for IELTS on the topic of the Internet and social interaction. Included is a model answer. The IELTS test usually focuses on topical issues. You have to discuss if you think that the Internet is damaging social interaction.
Any comments or questions about this page or about IELTS? Post them here. Your email will not be published or shared.
Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
Band 7+ eBooks
"I think these eBooks are FANTASTIC!!! I know that's not academic language, but it's the truth!"
Linda, from Italy, Scored Band 7.5

IELTS Modules:
Other resources:.
- All Lessons
- Band Score Calculator
- Writing Feedback
- Speaking Feedback
- Teacher Resources
- Free Downloads
- Recent Essay Exam Questions
- Books for IELTS Prep
- Useful Links

Recent Articles
IELTS Bundle Writing eBooks: 30% Off
Jun 01, 24 09:55 AM

House Sitting
May 31, 24 03:59 AM
Key Phrases for IELTS Speaking: Fluency and Coherence
May 26, 24 06:52 AM
Important pages
IELTS Writing IELTS Speaking IELTS Listening IELTS Reading All Lessons Vocabulary Academic Task 1 Academic Task 2 Practice Tests
Connect with us
Before you go...
Check out the ielts buddy band 7+ ebooks & courses.

Copyright © 2022- IELTSbuddy All Rights Reserved
IELTS is a registered trademark of University of Cambridge, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia.

- Chef Services
Physical Health Benefits of Vegetarianism: A Review of the Scientific Evidence

A healthy, nutritious diet is essential for your physical and mental well-being .
Increasing evidence is showing the detrimental impact of a diet high in red meat, saturated fat, and refined foods on health and longevity, with increased risk of cardiovascular disease, cancers, diabetes, obesity, and mortality.
Recently, increasing interest is being shown in the adoption of a plant-based diet and the benefits this diet can have on your health, and the health of the planet.
In this article, we explain (in plain English!) the conclusions of scientific studies that have looked at the physical health benefits of vegetarianism.
Vegetarian diets consist of plant-based foods rich in whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables, while avoiding red meat, processed meat products, refined foods, and sweets.
There are several variations of a vegetarian diet:
- Lacto-vegetarians allow the consumption of low-fat dairy products
- Ovo-vegetarians allow the consumption of eggs
- Pescatarians allow the consumption of fish
- Pollotarians allow lean white meat such as chicken to be consumed.
Drawbacks of Vegetarianism
Restrictive, unbalanced vegetarian diets could lead to nutrient deficiencies such as vitamin B 12 , iron, zinc, calcium, and vitamin D.
Physical Benefits of Vegetarianism
Despite the drawbacks of vegetarianism covered in the previous section, numerous studies have reported the many health benefits of vegetarianism.
In the sections that follow we highlight studies that have linked vegetarianism with physical health benefits such as:
- Weight loss
- Lowered blood pressure
- Reduced risk of diabetes
- Reduced risk of cardiovascular disease
- Cancer prevention
- Improved skin health
- Improved gut health
- Improved memory and cognition
- Reduced risk of all-cause mortality
According to the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics “An appropriately planned vegetarian, including vegan, diets are healthful, nutritionally adequate, and may provide health benefits for the prevention and treatment of certain diseases. These diets are appropriate for all stages of the life cycle, including pregnancy, lactation, infancy, childhood, adolescence, older adulthood, and for athletes” (Melina et al., 2016).
Weight Loss
Vegetarianism may aid in weight-loss and assist in maintaining a healthy body weight.
Scientists from the University of Bergen, investigated the influence of a plant-based diet on weight-loss “The results in this review propose that a shift to a plant-based diet may have beneficial health effects on body weight and BMI in individuals with overweight” (Tran et al., 2020).
According to a study performed by Huang et al. (2016), who investigating the link between vegetarian diets and weight loss “Vegetarian diets appeared to have significant benefits on weight reduction compared to non-vegetarian diets”.
A study published in the journal, Nutrition, investigated the effect of a plant-based diet on weight loss. Adherence to a vegan diet resulted in significantly higher weight loss “Vegan diets may result in greater weight loss than more modest recommendations” (Turner-McGrievy et al., 2015).
Lowered Blood Pressure
Vegetarianism may be effective against high blood pressure.
A study published in the journal, JAMA Internal Medicine, evaluated the effectiveness of a vegetarian diet on reducing blood pressure (BP), compared to an omnivorous diet. A vegetarian diet proved effective in reducing blood pressure “consumption of vegetarian diets was associated with a reduction in mean systolic BP and diastolic BP compared with the consumption of omnivorous diets” (Yokoyama et al., 2014).
Reduced Risk of Diabetes
A vegetarian diet may reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
A study published in the journal, JAMA Internal Medicine, assessed the link between a plant-based diet and the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. A reduction in diabetes risk was observed with increased consumption of healthful plant-based foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole-grains, and nuts “Plant-based dietary patterns, especially when they are enriched with healthful plant-based foods, may be beneficial for the primary prevention of type 2 diabetes” (Qian et al., 2019).
A review published in the journal, Current Diabetes Reports, investigated the association between vegetarian diet and risk of diabetes. Adherence to a vegetarian diet was associated with a reduced risk of diabetes “A vegetarian diet characterized by whole plant foods is most beneficial for diabetes prevention and management” (Olfert & Wattick, 2018).
Skin Health: Anti-Aging and Treatment of Psoriasis
Vegetarianism may improve skin health and prevent skin aging.
A study published in The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, evaluated the effectiveness of a whole-food, plant-based diet (WFPB) on preventing and reversing skin aging . They found that the abundance of antioxidants in a WFPB diet prevented inflammation and oxidative stress which are both factors that promote skin aging “A WFPB diet maximizes the antioxidant potential within our cells by providing essential vitamins, including vitamins A, C, and E. It also helps to eliminate harmful carcinogens and gerontotoxins within our bloodstream and has been shown to lengthen telomeres, which prevents cellular damage” (Solway et al., 2020).
A vegetarian diet may treat the symptoms of psoriasis, a skin condition that leads to red, itchy scaly patches.
A study published in the journal, Alternative Medicine Review, analysed the effectiveness of a plant-based diet consisting of fresh fruit and vegetables, olive oil, small quantities of fish and poultry, while avoiding red meat, and refined carbohydrates to treat mild to severe psoriasis . They found that all cases improved over the 6-month period “These results suggest a dietary regimen based on Edgar Cayce’s readings may be an effective medical nutrition therapy for the complementary treatment of psoriasis” (Brown et al., 2004).
Cancer Prevention
Vegetarianism may reduce your risk of developing cancer and other chronic diseases.
A study published in the journal, Nutrition Research and Practice, investigated the link between diet and cancer risk. They found that plant-based diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts are able to reduce inflammation and prevent disease “chronic inflammation contributes to the development of cancer, cardiovascular disease and diabetes, consumption of a varied plant-based diet, as recommended by multiple public health agencies, could effectively reduce the incidence of cancer and other chronic diseases ” (Hardman, 2014).
A study published in the journal, Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Prevention, investigated the relationship between diet and overall cancer incidence among 69 000 participants. Cancer incidence was lowest in participants who followed vegetarian diets “Vegetarian diets seem to confer protection against cancer ” (Tantamango-Bartley et al., 2013).
Vegetarianism may even assist with disease management and slow cancer progression.
A study published in the journal, Integrative Cancer Therapies, evaluated the effectiveness of a plant-based diet and stress management on progression of prostate cancer. A plant-based diet slowed the progression of prostate cancer “adoption of a plant-based diet, in combination with stress reduction, may attenuate disease progression and have therapeutic potential for clinical management of recurrent prostate cancer” (Saxe et al., 2006).
Heart Health
Vegetarianism may provide a protective benefit to your heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
A study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, investigated the association between plant-based diets and the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD), CVD mortality, and all-cause mortality. Participants who followed a healthful plant-based diet had a 19% reduced risk of CVD mortality “Diets higher in plant foods and lower in animal foods were associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in a general population” (Kim et al., 2019).
A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, evaluated the effectiveness of a plant-based diet and incidence of coronary heart disease (CHD). A positive relationship was observed between the consumption of healthful plant-based foods and a reduced risk of CHD “Higher intake of a plant-based diet index rich in healthier plant foods is associated with substantially lower coronary heart disease risk ” (Satija et al., 2017).
According to research conducted by Hu (2003) “plant-based diets including whole grains as the main form of carbohydrate, unsaturated fats as the predominate form of dietary fat, an abundance of fruit and vegetables, and adequate n−3 fatty acids can play an important role in preventing CVD ”.
Reduced Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Vegetarianism may reduce the symptoms of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis is one of the most common types of arthritis, and is characterised by degradation of cartilage and bone in joints.
A study conducted by scientists from the Department of Internal Medicine at Michigan University, investigated the effectiveness of a 6-week whole-food, plant-based diet (WFPB) on alleviating symptoms of osteoarthritis “WFPB diet was associated with a significant reduction in pain compared to an ordinary omnivorous diet, with statistically significant pain reduction seen as early as two weeks after initiation of the dietary modification” (Clinton et al., 2015).
Improved Gut Health
Vegetarianism may positively impact your gut health, by providing your gut fuel to stimulate the growth of “good” gut microbes that produce health promoting compounds.
A review published in the journal, Frontiers in Nutrition, investigated the effects of a vegetarian and vegan diet on the gut microbiota. A vegetarian diet conferred a positive impact on gut microbiota , with an increase in microbial diversity and production of beneficial compounds that support a healthy gut “diet is the essential factor for human gut microbiota composition; a plant-based diet may be an effective way to promote a diverse ecosystem of beneficial microbes that support overall health” (Tomova et al., 2019).
Memory and Cognition
Vegetarianism may improve cognitive function.
Scientists from the University of California, investigated the relationship between a plant-based diet and cognitive function. Participants who followed a plant-based diet had improved results on all cognitive tasks “Greater adherence to a dietary pattern consistent with a plant-based diet was related to better performance on all cognitive tasks ” (Ramey et al., 2020).
Vegetarianism may protect your eye health and reduce the risk of developing cataracts.
A study published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, investigated the link between a vegetarian diet and the risk of cataracts. A 20% reduction in cataract risk was observed for participants who followed a vegetarian diet “A vegetarian diet was associated with a lower risk of cataracts ” (Chiu et al., 2021).
Reduced Risk of All-Cause Mortality
Vegetarianism may lead to a reduced risk of all-cause mortality.
A review published in the journal, Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, evaluated the relationship between adherence to a plant-based diet and the risk of mortality. Adherence to a healthful vegetarian diet was linked to a reduced risk of mortality for chronic disease “Our findings show the potential protective role of plant-based diets against chronic disease mortality ” (Jafari et al., 2021).
A study published in The Journal of Nutrition, analysed the link between a plant-based diet and all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality risk. They found that adoption of a healthful plant-based foods was associated with a reduced risk of all-cause mortality “Healthy plant-based diet scores above the median were associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality in US adults” (Kim et al., 2018).
Scientists from Wageningen University, investigated the influence of a Mediterranean diet on all-cause mortality in an elderly European population. They found that adherence to a Mediterranean diet was linked to an incredible 50% reduction in all-cause mortality risk “Among individuals aged 70 to 90 years, adherence to a Mediterranean diet and healthful lifestyle is associated with a more than 50% lower rate of all-causes and cause-specific mortality ” (Knoops et al., 2004).
Wrapping Up
Substantial evidence suggests that a well-planned, balanced and varied vegetarian diet abundant in healthful plant-based foods such as whole-grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, and nuts, while monitoring for deficiencies is able to provide you with an abundance of health benefits, including:
- Healthy heart
- Healthy skin and eyes
Adopting a healthful rich plant-based diet, is beneficial for your physical and mental health, and may lead to a longer life-span with fewer visits to the doctor.
- Brown, A. C., Hairfield, M., Richards, D. G., McMillin, D. L., Mein, E. A., & Nelson, C. D. (2004). Medical nutrition therapy as a potential complementary treatment for psoriasis-five case reports. Alternative Medicine Review , 9 (3), 297-307.
- Chiu, T. H., Chang, C. C., Lin, C. L., & Lin, M. N. (2021). A Vegetarian Diet Is Associated with a Lower Risk of Cataract, Particularly Among Individuals with Overweight: A Prospective Study. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics , 121 (4), 669-677.
- Clinton, C. M., O’Brien, S., Law, J., Renier, C. M., & Wendt, M. R. (2015). Whole-foods, plant-based diet alleviates the symptoms of osteoarthritis. Arthritis , 2015 .
- Hardman, W. E. (2014). Diet components can suppress inflammation and reduce cancer risk. Nutrition research and practice , 8 (3), 233-240.
- Hu, F. B. (2003). Plant-based foods and prevention of cardiovascular disease: an overview. The American journal of clinical nutrition , 78 (3), 544S-551S.
- Huang, R. Y., Huang, C. C., Hu, F. B., & Chavarro, J. E. (2016). Vegetarian diets and weight reduction: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of general internal medicine , 31 (1), 109-116.
- Jafari, S., Hezaveh, E., Jalilpiran, Y., Jayedi, A., Wong, A., Safaiyan, A., & Barzegar, A. (2021). Plant-based diets and risk of disease mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition , 1-13.
- Kim, H., Caulfield, L. E., Garcia‐Larsen, V., Steffen, L. M., Coresh, J., & Rebholz, C. M. (2019). Plant‐based diets are associated with a lower risk of incident cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular disease mortality, and all‐cause mortality in a general population of middle‐aged adults. Journal of the American Heart Association , 8 (16), e012865.
- Kim, H., Caulfield, L. E., & Rebholz, C. M. (2018). Healthy plant-based diets are associated with lower risk of all-cause mortality in US adults. The Journal of nutrition , 148 (4), 624-631.
- Knoops, K. T., de Groot, L. C., Kromhout, D., Perrin, A. E., Moreiras-Varela, O., Menotti, A., & Van Staveren, W. A. (2004). Mediterranean diet, lifestyle factors, and 10-year mortality in elderly European men and women: the HALE project. Jama , 292 (12), 1433-1439.
- Olfert, M. D., & Wattick, R. A. (2018). Vegetarian diets and the risk of diabetes. Current diabetes reports , 18 (11), 1-6.
- Qian, F., Liu, G., Hu, F. B., Bhupathiraju, S. N., & Sun, Q. (2019). Association between plant-based dietary patterns and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA internal medicine , 179 (10), 1335-1344.
- Ramey, M. M., Shields, G. S., & Yonelinas, A. P. (2020). Markers of a plant-based diet relate to memory and executive function in older adults. Nutritional neuroscience , 1-10.
- Satija, A., Bhupathiraju, S. N., Spiegelman, D., Chiuve, S. E., Manson, J. E., Willett, W., … & Hu, F. B. (2017). Healthful and unhealthful plant-based diets and the risk of coronary heart disease in US adults. Journal of the American College of Cardiology , 70 (4), 411-422.
- Saxe, G. A., Major, J. M., Nguyen, J. Y., Freeman, K. M., Downs, T. M., & Salem, C. E. (2006). Potential attenuation of disease progression in recurrent prostate cancer with plant-based diet and stress reduction. Integrative cancer therapies , 5 (3), 206-213.
- Solway, J., McBride, M., Haq, F., Abdul, W., & Miller, R. (2020). Diet and dermatology: the role of a whole-food, plant-based diet in preventing and reversing skin aging—a review. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology , 13 (5), 38.
- Tantamango-Bartley, Y., Jaceldo-Siegl, K., Fan, J., & Fraser, G. (2013). Vegetarian diets and the incidence of cancer in a low-risk population. Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention Biomarkers , 22 (2), 286-294.
- Tran, E., Dale, H. F., Jensen, C., & Lied, G. A. (2020). Effects of plant-based diets on weight status: a systematic review. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy , 13 , 3433.
- Turner-McGrievy, G. M., Davidson, C. R., Wingard, E. E., Wilcox, S., & Frongillo, E. A. (2015). Comparative effectiveness of plant-based diets for weight loss: a randomized controlled trial of five different diets. Nutrition , 31 (2), 350-358.
- Yokoyama, Y., Nishimura, K., Barnard, N. D., Takegami, M., Watanabe, M., Sekikawa, A., … & Miyamoto, Y. (2014). Vegetarian diets and blood pressure: a meta-analysis. JAMA internal medicine , 174 (4), 577-587.
Physical Health Benefits Studies
Physical health benefits of vegetarianism (including impact on weight loss and the skin)
About the Author Lillian
Share your thoughts.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked
Name * * * * * * * * * * *
Email * * * * * * * * * * *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Search Please fill out this field.
- Newsletters
- Sweepstakes
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Sustainability
Why a Vegetarian Diet Is Good for Your Health and the Health of the Planet
One woman's foray into a meatless approach to cooking.
Rachael Moeller Gorman is an award-winning food and science writer with almost 20 years of experience. Her work has appeared in The Scientist, EatingWell, Good Housekeeping, Scientific American, Shape, Fitness, Men's Health and many other publications.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/rachael-moeller-gorman-751cd840d7a74df39e53dac2af0718b3.jpg)
As a journalist, I've been following news on the health benefits of meatless eating for years. Recently I started toying with the idea of shifting toward a meatless diet myself. Some people skip meat for spiritual reasons. Many go vegetarian to help the environment (the United Nations determined recently that livestock is one of the top contributors to the world's most serious environmental problems, for example). But today, there's something else driving people-including me-to move toward a plant-based diet: health.
Science is showing that cutting back on meat is healthier for just about everyone, and more and more people are doing just that: today, 3 percent of American adults-over 7 million people-never eat meat, fish or poultry, up from less than 1 percent in 1994. The Meatless Monday campaign-a successful voluntary reduction effort in the U.S. during both World War I and World War II that was relaunched in 2003 at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health to help Americans cut down on saturated fat-has become a full-blown movement. Cities like San Francisco have made official Meatless Monday proclamations; public school systems and college dining halls have adopted the philosophy; celebrity chefs like Mario Batali are leading the charge in restaurants. Meatless Monday programs are thriving in countries such as Korea, Brazil, Croatia and Canada. You probably know several people who've given up meat-maybe dairy and eggs too-every day of the week. Maybe you're one of them.
The more I learned about meatless eating, the more comfortable I became with the idea of changing my diet. The American Dietetic Association maintains that vegetarian diets are safe and healthful for everyone, from pregnant mothers to children to athletes, so long as they are planned with care. Research has shown that cutting meat usually means getting more dietary fiber, folic acid, vitamins C and E, potassium, magnesium and unsaturated fat, and less saturated fat and cholesterol. Studies have shown that eating less meat reduces the risk of heart disease and perhaps even type 2 diabetes and some cancers. "Vegetarians have lower blood pressure, lower cholesterol levels and tend to be a little bit thinner, so vegetarians are automatically going to be at lower risk of certain chronic diseases," says Virginia Messina, M.P.H., R.D., who has written extensively about vegetarian diets.
Inspired by these facts, my husband and I decided that our family of four (which also includes our 3-year-old son and 1-year-old daughter) would shift to more vegetarian meals.
A Case Study for Plant-Based Diets
We have, in many ways, a good model for a meatless society, and it's one I looked at closely as we made our choice to change our diet. In southern California's Inland Empire, a suburban valley spread some 60 miles east of Los Angeles, is a city called Loma Linda, home to several thousand people who are part of a religious group called the Seventh-Day Adventists. The Seventh-Day Adventist (SDA) church believes the human body is the temple of the Holy Spirit, and, as such, shouldn't be polluted with alcohol or tobacco-and, some members believe, meat. Some 30 percent of Adventists are vegetarian. In 1958, researchers from Loma Linda University, an SDA medical center, published an observational study showing that Adventists were significantly less likely to die from cancer, heart disease and other lifestyle-related diseases. In 1974, the researchers began looking at whether their diets might help to explain their better health. They found that eating less beef was in fact associated with lower risk of coronary heart disease.
Studies in other vegetarian populations have come to similar conclusions. For example, a 1999 compilation of several studies found that, compared to meat-eaters, people who were vegetarian for more than five years were 24 percent less likely to die of ischemic heart disease/coronary heart disease. (People who ate meat occasionally were still 20 percent less likely to die of these diseases.)
At first, I was heartened by these findings. As a family, we've always eaten mostly whole foods-including healthy staples like fruits and veggies, brown rice and whole-wheat pastas-and tend to stay away from highly processed foods. But the more I peered at our diet, the more I realized that meat-not vegetables or grains-defined our meals.
So I vowed that, for a month, I not only would cut back on meat and make healthy recipes from EatingWell's new book, EatingWell Fast & Flavorful Meatless Meals, I would also buy a bigger variety of fruits and vegetables, especially greens and colorful peppers and carrots. I would eat more beans. I would also make sure we were all getting enough of the nutrients that vegetarians need to pay closer attention to: vitamin B12 (only found naturally in animal products); iron (more easily absorbed from meat); DHA and EPA, omega-3 fatty acids (mainly in fish); zinc and iodine. To be safe, I bought everyone in my family multivitamins.
Meeting Our Meatless Month
At the beginning of the week, I headed to the supermarket to buy ingredients for our new dishes. That night, I cooked Sesame-Crusted Tofu over Vegetables. It was amazing. I actually craved it the next day and reheated the leftovers for lunch.
The rest of the week was just as tasty. The Bean & Hominy Potpie-total comfort food-was a particular hit. Cooking meatlessly started feeling like an adventure, and I began packing more "good stuff" into breakfast and lunch, too: I made smoothies with silken tofu, kale, blueberries, bananas and orange juice. They were so good my 3-year-old began asking for one every day. I boiled edamame and sprinkled it with sea salt and when my son successfully popped the soybean out of the pod into his mouth, he said, "I did it, Mommy! Mmmmm! I love soybeans!" Since soy has been linked to cholesterol reduction, and my family has a history of cholesterol issues, I was thrilled.
Lower LDL (bad) and total cholesterol levels may be a major reason for vegetarians' reduced risk for heart disease, say scientists. High cholesterol can contribute to plaque in our arteries, which can lead to heart attacks or strokes. Meat contains high levels of saturated fat, which raises cholesterol levels, while vegetables contain lots of fiber and plant sterols, which can keep cholesterol levels in a healthy range. Our new diet was, most likely, already improving our cholesterol levels, and helping our hearts.
Of course, "vegetarian" doesn't always mean heart-healthy. "Because vegetarian diets are defined, basically, as just eliminating meat, the word ‘vegetarian' labels a huge diversity of eating styles," says Winston Craig, Ph.D., M.P.H., R.D., of Andrews University in Berrien Springs, Michigan, and the lead author of the American Dietetic Association's position paper on vegetarian diets. Case in point: A diet consisting of tons of white bread and loads of cheese is "vegetarian."
Using EatingWell's formula for healthy vegetarian meals (lots of veggies and whole grains, little high-fat dairy and moderate amounts of healthy fats, like oils and nuts), we started making simple changes to the rest of our diet. We limited cheeses and ice cream. I spread peanut butter, instead of regular butter, on toast. Many experts believe that a high intake of nuts, which contain cholesterol-lowering unsaturated fats, contribute to vegetarians' superior heart health. (Studies have shown that people who eat nuts more than four times a week suffer half as many heart attacks as people who eat nuts less than once a week.)
The minor dietary shifts felt so effortless that I began to believe this new way of eating could stick. A successful vegetarian dinner with guests underscored that notion: I served Tomato & Spinach Dinner Strata and no one noticed the lack of meat. My dad, a hardcore carnivore, went back for seconds.
An Evolved Eating Approach
After a few weeks, I had a realization: food is way more than just fuel. Eating can be a thoughtful, yet almost automatic way to live out one's beliefs (e.g., good health, humane treatment of animals, better environment). I'd become much more mindful of the food entering my body, and I was forced to make small decisions every time I encountered it. This made it much more difficult to mindlessly consume coconut-coated chocolate Sno Balls or dozens of chocolate chip cookies. "I think I have been practicing self control by eating more vegetarian meals; it gives me the muscles to control my junk food eating," I wrote in my journal.
Plus, I had doubled my consumption of fruits and vegetables and just felt great about the food I was putting into my body-and great generally. "Typically a person who goes on a vegetarian diet tells me they feel better all around," says Craig. I agree. Perhaps because being healthy was always on my mind and my taste buds were satisfied by the interesting flavors I was feeding them, I had fewer cravings. I didn't feel restricted. I felt liberated. And it tasted good.
Rachael Moeller Gorman is a contributing editor to EatingWell and an award-winning science writer.
Related Articles
Vegan diet can benefit both health and the environment
There is strong evidence that a plant-based diet is the optimal diet for living a long and healthy life, according to Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health nutrition expert Walter Willett .
In a January 7, 2019 interview on the NPR show “1A,” Willett, professor of epidemiology and nutrition, said that it’s not necessary to be 100% vegan in order to reap the benefits of a plant-based diet, which has been linked with lower risk of type 2 diabetes , heart disease , and overall mortality. Diets with modest amounts of dairy and fish, and even some poultry and meat, can also be healthy, as long as people steer clear of refined starches and sugar and focus on vegetables , fruits , nuts , seeds, and whole grains.
Willett also said that veganism is good for the planet. That’s because cattle grazing generates massive amounts of methane and carbon dioxide, both of which are potent greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change .
“I think if we really care about the world our children and grandchildren will inherit, we do need to shift toward [a vegan diet],” said Willett. “And the good news is that it’s not just our planet that will be more healthy, but we will be more healthy as well.”
Listen to the 1A interview: Planting A Seed: The Vegan Diet in 2019
Healthy plant-based diet linked with substantially lower type 2 diabetes risk ( Harvard Chan School release )
Vegetarian Recipes for a Healthy Eating Plate ( The Nutrition Source )
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.9(5); 2023 May
- PMC10200863

Forty-five years of research on vegetarianism and veganism: A systematic and comprehensive literature review of quantitative studies
Gelareh salehi.
a Faculty of Economics and Business Administration, Universidad Pontificia Comillas. ICADE, Spain
b Business Management Department, Spain
Estela Díaz
Raquel redondo.
c Quantitative and Statistical Analysis Department, Spain
Associated Data
Data will be made available on request.
Meat production and consumption are sources of animal cruelty, responsible for several environmental problems and human health diseases, and contribute to social inequality. Vegetarianism and veganism (VEG) are two alternatives that align with calls for a transition to more ethical, sustainable, and healthier lifestyles. Following the PRISMA guidelines, we conducted a systematic literature review of 307 quantitative studies on VEG (from 1978 to 2023), collected from the Web of Science in the categories of psychology, behavioral science, social science, and consumer behavior. For a holistic view of the literature and to capture its multiple angles, we articulated our objectives by responding to the variables of “WHEN,” “WHERE,” “WHO,” “WHAT,” “WHY,” “WHICH,” and “HOW” (6W1H) regarding the VEG research. Our review highlighted that quantitative research on VEG has experienced exponential growth with an unbalanced geographical focus, accompanied by an increasing richness but also great complexity in the understating of the VEG phenomenon. The systematic literature review found different approaches from which the authors studied VEG while identifying methodological limitations. Additionally, our research provided a systematic view of factors studied on VEG and the variables associated with VEG-related behavior change. Accordingly, this study contributes to the literature in the field of VEG by mapping the most recent trends and gaps in research, clarifying existing findings, and suggesting directions for future research.
Non-standard Abbreviations
- • Vgt: Vegetarianism; Vgn: Veganism, M: Meat consumption; AHR: Animal-Human relationship; C: Cultured meat consumption; D: Diet; F : Food; P : Philosophy of life.
- • HL: Health; EN: Environment; AN: Animals; CL: Cultural & Social; SN: Sensory; FT: Faith; FN: Financial & economic; PL: Political; JS: Justice & world hunger.
- • A: Attitudes; M: Motivations; V: Values, T: Personality; E: Emotions; K: Knowledge; B: Behavior; I: Intentions; S: Self-efficacy or Perceived Behavioral Control; N: Networks; O: Norms; D: Identity; P: Product Attributes; F: Information.
- • CR: Correlational: M-CR: Mixed method study including Correlational section; EX: Experimental; EXC: Choice Experiment.
1. Introduction
Meat production contributes to animal suffering [ 1 ], environmental problems (loss of biodiversity, climate change, or water pollution) [ 2 ], and public health problems (zoonotic diseases such as COVID-19 and chronic non-communicable diseases such as type II diabetes) [ 3 ]. Consequently, there is an increasing interest in a dietary transition to reduce or exclude animal products [ [4] , [5] , [6] , [7] ]. Such dietary transitions would directly support goal 12 of the Agenda for Sustainable Development of the United Nations (2019), which is to “ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns” [ 8 ]. Adopting and maintaining vegetarian and vegan lifestyles are two of the most promising ways to achieve this goal [ 9 , 10 ].
VEG has a long history, dating back to ancient Greek philosophers, and can encompass various underlying approaches, including dietary behaviors, food and other product choices, social justice movements, and political activism [ 11 ]. Vegetarianism, as a philosophy of life, generally relates to the protection of non-human animals (hereafter referred to as “animals”), which, in practice, translates to a lifestyle that abstains from the consumption of all types of animal flesh, including meat (i.e., beef, pork), poultry (i.e., chicken, turkey), and fish and seafood [ 12 ]. Vegetarianism comprises several modalities: ovo-vegetarianism (accepts the consumption of eggs but not dairy products), lacto-vegetarianism (accepts the consumption of dairy products but not eggs), or lacto-ovo-vegetarianism (accepts the consumption of both eggs and dairy products) [ 13 , 14 ]. By contrast, veganism can be understood as a philosophy of life rooted in anti-speciesism, which, in practice, translates to rejecting the consumption of any product (or service) which involves the exploitation of an animal either in the context of food (meat, eggs, dairy, honey, gelatin), clothing (leather, silk), or any other form (entertainment and experimentation) as far as possible and practicable [ 15 , 16 ]. Veganism also promotes the production and consumption of alternatives free of animal use. To address vegetarianism and veganism (VEG), both of which avoid animal flesh products, many authors use the term “ veg*an-ism ” [ 8 , 17 ].
Over the last 50 years, the interest of consumers, entrepreneurs, and public institutions in the VEG phenomenon has grown [ 18 , 19 ]. VEG has increasingly spread worldwide [ 7 , 18 , 20 , 21 ]; for example, the number of individuals following some kind of VEG lifestyles is considered to have doubled from 2009 to 2016 [ 21 ], with 2019 being labelled “the year of the vegan” by The Economist [ 8 ]. The growing realization of the importance of these phenomena has also been reflected in academia, where studies on VEG have flourished in the last decade [ 7 ]. In this regard, VEG has rapidly expanded from philosophical and medical disciplines to other areas related to psychology, consumer behavior, and behavioral science [ 22 ]. One of the reasons for the increase in this research is related to the fact that, although VEG is seen as a promising avenue that brings a more ethical, sustainable, and healthier society, such a lifestyle transition is also seen as a challenge [ 23 , 24 ].
This extraordinary progression of scientific knowledge makes it advisable to know the current trends to map and have an overview of VEG research. Previous narrative literature reviews [ 11 , 22 , 25 ] have been of great relevance for this and have illuminated the way for researchers, practitioners, and public actors. However, owing to the increasing number of studies published in the last decade, it is highly recommended to update the knowledge and have a holistic view of the VEG literature. To achieve this, the most appropriate methodology is a systematic literature review [ 26 , 27 ]. This logic has been recently used to analyze the aspect of identity in veganism [ 28 ].
In this study, we conducted a systematic literature review in the VEG field to extend, complete, and update previous literature reviews. Specifically, our work principally focused on reviewing the quantitative studies in psychology, behavioral science, social science, and consumer behavior literature published in scientific journals from 1978 up to December 31, 2022, on VEG. A successful systematic literature review relies on straightforward research questions provided at the beginning of the process [ 27 ]; therefore, we articulated our objectives using the 5W1H [ 29 ], which explores a phenomenon from multiple perspectives based on the following questions: (1 W) “WHEN” refers to the period of the analysis and possible trends in VEG research; (2 W) “WHERE” focuses on the countries in which VEG studies have been conducted; (3 W) “WHO” refers to the journals in which VEG studies have been published; (4 W) “WHAT” refers to the different research streams and frames included in the VEG body of research; (5 W) “WHY” includes the reasons (environmental, health, or animals) that made VEG an essential topic for scholars to study; and (1H) “HOW” focuses on reviewing the different research methodologies and statistical analyses employed in the literature on VEG. Additionally, we added another question, “WHICH,” comprising the variables measured in the studies. Thus, we followed a 6W1H approach ( Fig. 1 ).

6 W & 1H approach applied to VEG literature.
This study contributes to the existing literature on VEG by mapping the state of the art, identifying trends and gaps in research, clarifying existing findings, and suggesting directions for future research. Our systematic literature review also highlighted the factors examined in VEG and the variables associated with VEG-related behavior change, thus playing an important role in advancing research on VEG. For practitioners, our study will help elucidate possible interventions and design more effective (marketing) campaigns to improve and promote the transition to VEG. Additionally, these interventions may be beneficial for private organizations and public authorities seeking to design policies to encourage fairer and more sustainable consumption and healthier lifestyles.
This article is organized as follows: In Section 2 , we outline the methodology. Next, we present the results of our analysis, which was performed using the 6W1H approach. In Section 4 , we discuss the main findings and future avenues of research. Finally, in Section 5 , we highlight the main contributions and managerial implications of the study.
The systematic search included articles up to December 31, 2022. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines were used for reporting the methods of this systematic literature review [ 30 ]. The systematic literature review protocol included the following steps: (1) search strategy; (2) inclusion, exclusion, and selection criteria; and (3) data extraction.
2.1. Search strategy
The first step of conducting the systematic literature review was keyword design. Following the backward and forward search methods [ 27 ], we created a pool of terms related to VEG literature that represented the main objectives of the review and were included in the previous reviews [ 11 , 22 ]. Additionally, we screened through the preliminary keyword results in several non-medical articles that focused on VEG. The resulting keyword syntax designed was: title, abstract, and keywords = [(vegan* OR vegetarian* OR plant-based*)] AND [(diet* OR food* OR lifestyle* OR movement* OR activism*) OR (eat* OR choos* OR choice* OR behavio* OR chang* OR purchas* OR buy* OR pay* OR cosnum* OR substitut* OR lik* OR familiar* OR reject* OR avoid* OR accept* OR restrict* OR disgust* OR information*) OR (motiv* OR reason* OR attitude* OR intention* OR willing* OR belief* OR perception* OR value* OR identity* OR emotion* OR empathy* OR norm* OR social* OR knowledge* OR familiarity* OR gender*)].
We used Web of Science (WoS) for our search. WoS was preferred to other databases because it is the world's leading scientific citation search engine and the most widely used research database [ 31 , 32 ]. WoS has guaranteed scientific content, strict filtering, and anti-manipulation policies, and offers many resources for searching and collecting metadata [ [33] , [34] , [35] , [36] ]. In addition, WoS focuses on Social Sciences and Humanities (and less on Health Sciences) [ 37 ], which is more in line with the objectives of our study and covered all major journals relevant to our topic. However, it is worth mentioning that the final number of articles included in our systematic literature review resulted from reviewing the reference list of studies retrieved through WoS.
2.2. Inclusion, exclusion, and selection criteria
2.2.1. inclusion criteria.
The systematic search included articles up to December 31, 2022. During the initial search, 25,73 9 articles were identified through their titles, abstracts, and keywords ( Fig. 2 ). Once the articles were identified, we filtered the results following the inclusion criteria based on the following: (1) discipline: we included articles related to behavioral science, psychology, sociology, and business economics; (2) document type : we included only peer-reviewed articles; and (3) language: we only included articles written in English to ensure consistency and comparability of terms across the included studies. This was especially important as VEG is a recently emerging multi-disciplinary area.

PRISMA Flow diagram of the systematic literature review of quantitative VEG studies [ 30 ].
2.2.2. Exclusion criteria
Initially selected articles were removed based on the following: (1) research area : if their key focus was not on behavioral and psychological aspects of VEG. Thus, articles concerning medical issues (e.g., nutritional status or diseases), specific environmental problems (e.g., gas emissions or water), and technological challenges of food science (e.g., the chemical process of producing vegan products) were not included; (2) unit of analysis: studies with units of analysis different from individuals or households were excluded; and (3) methodology : we excluded qualitative studies. This decision was made because qualitative and quantitative approaches differ not only in their research techniques but, more importantly, in the ontological and epistemological perspectives they adopt [ 38 ]. Thus, we considered that separating quantitative from qualitative studies was advisable to gain a deeper knowledge on the issue. We focused on quantitative studies because there has been a more pronounced growth of quantitative studies and a greater interest in statistically measuring the factors that explain the adoption (or rejection) of VEG lifestyles. The selection protocol had no restrictions on sample characteristics (country and sex) and study setting (laboratory or restaurant).
This step left 203 articles for a full manuscript review. Finally, the reference list of articles was also reviewed, and 48 qualifying articles were added to the sample for data extraction. A total of 251 articles (307 studies, given that some articles included several studies) were recognized for data extraction. Initial screening for eligibility was performed by the three authors, each of whom reviewed one-third of the articles through the abstracts. To ensure consistency in the selection process, 5% of the articles were randomly assigned to a different author to perform an inter-reviewer reliability test [ 39 , 40 ]. The results indicated excellent agreement in this first step, as 96.5% of the articles were equally identified by the reviewers, and Cohen's kappa was 0.91.
2.3. Data extraction
A coding template was designed in Excel to extract specific data to answer the 6W1H questions. Information on WHEN (year of publication), WHERE (country of the sample), and WHO (journals) was coded directly. The coding of WHAT was more complicated; therefore, we designed a coding protocol to perform a preliminary content analysis of the data following the recommendations of Welch and Bjorkman [ 41 ]. We initially started pilot coding 30 articles, considering two main research streams : veganism (Vgn) and vegetarianism (Vgt). The coding of these research streams was based on the provided definitions of VEG and explained earlier. In this understanding, some scholars addressed their objective on vegetarianism (Vgt) and considered veganism (Vgn) as a sub-category of vegetarianism (Vgt). In these studies, we coded the stream as Vgt-Vgn. It should be noted that some studies also used the term “plant-based” in their studies; however, when reviewing the work, we observed that the authors used that term as a synonym for vegetarianism, veganism, or both. Therefore, following the same approach for vegetarianism, we coded these studies in the corresponding group of currents. In the second round of coding, we identified that veganism and vegetarianism were also studied simultaneously (Vgt-Vgn) as well as with other phenomena: meat consumption, animal-human relationship, and cultured meat consumption; we called these three new streams secondary streams . In total, coding was performed with seven streams.
To provide more nuanced information concerning WHAT, a further coding step was conducted to reclassify the studies not only concerning the streams but also the following three frames: (1) food, referring to specific products; (2) diet, referring to dietary practices; and (3) philosophy of life, referring to a social movement and lifestyle, focusing on the characteristics of the person consuming VEG products or following a VEG diet or philosophy of life. As mentioned previously, sometimes, these three frames were analyzed in combination (e.g., food and diet). Overall, five research frames were identified. To ensure the decision in coding, each article was scanned for keywords using an agreed a priori system. The manuscripts were also re-checked, ensuring accuracy and agreement, and differences were discussed with the third researcher to reach inter-coding agreement, which provided a measure of consistency.
For WHY, we were interested in coding the reasons that scholars considered VEG as an important subject to be studied. Reasons from existing literature were classified into two broad categories: central and peripheral reasons. Central reasons included health issues, concern for animals, and environmental sustainability. Peripheral reasons comprised justice and world hunger; faith, religion, and spirituality concerns; sensory factors; cultural and social aspects; financial and economic aspects; and political concerns.
WHICH aimed to explore the variables measured in the VEG studies (attitudes or values). Finally, for HOW, we collected information contained in the methodology section of the articles regarding the type of study, sample, and statistical techniques. Thus, we collected information regarding the unit of analysis (individuals vs. objects), type of data (longitudinal vs. cross-sectional), data sources (secondary vs. primary), number of data sources, data collection methods (archival data, or surveys), and the year of data collection. Information on the sample comprised the size, country, mean age, percentage of female participants, racial or ethnic origin of respondents, and VEG orientation of respondents (vegetarian or vegan). Additionally, we checked whether the sample was representative of the corresponding general population. Subsequently, the studies were classified into non-experimental or correlational or experimental (choice experiment, or within-subject and between-subjects).
We also collected information regarding the dependent and independent variables, number of constructs, and the theoretical frameworks and scales used to measure them (especially if the scale used was designed ad ho c to study the VEG phenomenon). Finally, regarding the statistical techniques, we compiled information about the analyses and techniques used (e.g., t-tests, correlation tests, ANOVA, MANOVA, regressions, SEM, and latent class analysis). We also checked for the use of normality tests (if required), scale validation, moderation, and mediation tests, as well as whether the study was aware of the possible threat of common method effects (if required), social desirability, or other potential biases. The criteria for coding HOW included the guidelines of the Effective Public Health Practice Project.
3.1. WHEN were the VEG studies conducted?
The final 307 studies covered a period from 1978 to December 31, 2022. The characteristics of the studies are summarized in Table 8 in Annex. Eighty-four percent of the studies included in this review were published in the last ten years (see Fig. 3 ). The findings provide reasonable evidence that academic interest in VEG research has grown exponentially. Exploring the evolution in more detail, we observed three peaks in the number of publications. First, in 1999 the number of publications per year increased from one to four; second, in 2015, the number of publications increased again to approximately more than ten articles per year. Finally, the most significant evolution occurred in 2019, when the number of publications doubled (from 14 to 35). The trend also grew steadily until 2021; in 2022, this number increased to 61 studies. Most of the publications in 2021 were related to the special issue of Appetite journal, titled “The psychology of meat-eating and vegetarianism.”

Count of VEG topic studies published from 1978 up to December 31, 2022.
3.2. WHERE were the VEG studies conducted?
In terms of regional concentration, research was focused on developed countries, mainly in the US (33%), the UK (10%), Germany (6.5%), Australia (3.5%), Canada (3.3%), and Spain (3.3%). It should be noted that many studies (12%) included data from more than one country, but these international samples were mainly from the US and the UK. A simultaneous analysis of WHEN (publication year) and WHERE (country) also showed that the pioneer countries were the US, UK, Australia, and Canada. Other countries’ quantitative inquiries on VEG started in 2000 by studies in New Zealand, Finland, and the Netherlands. Geographical orientations became more widespread from 2015 onward ( Table 1 ).
Simultaneous analysis of WHERE and WHEN.
3.3. WHO published the VEG studies?
The reviewed articles were published in 92 different journals ( Table 2 ). Regarding the number of articles published in each journal, the relevance of Appetite was evident, with 21.8% of all articles reviewed published in this journal. This was followed by Food Quality and Preference (6.8%), Sustainability (4%), and British Food Journal (3%).
Journals and their research areas.

3.4. WHAT has been studied in VEG research?
3.4.1. streams of veg.
As it is shown in Table 3 , we discerned the following seven streams: vegetarianism and veganism (Vgt-Vgn); vegetarianism (Vgt); veganism (Vgn); vegetarianism, veganism, and meat consumption (Vgt-Vgn-M); vegetarianism and meat consumption (Vgt-M); vegetarianism, veganism, meat consumption, and cultured meat consumption (Vgt-Vgn- M -C); and vegetarianism, veganism, animal-human relationship (Vgt-Vgn-AHR) . The research mainly focused on Vgt-Vgn (30%), Vgt-Vgn-M (17.6%), Vgt (13%), and Vgt-M (12%).
WHAT streams have emerged in the VEG quantitative studies? a .
Vgt: Vegetarianism; Vgn: Veganism; M: Meat consumption; AHR: Animal-Human relationship; C: Cultured meat consumption.
By simultaneously analyzing WHAT (streams) and WHEN (publication years), we noticed that the first quantitative study on the Vgn stream was conducted in 2010 ( Fig. 4 ). Academic interest in Vgn research grew steadily, except for a decline in 2018. However, Vgt studies started decades earlier, in 1981. The Vgt stream was the pioneer in the quantitative approach of VEG, but this trend was not continuous; we observed a gap from 2010 to 2016 in the Vgt stream. Interestingly, in 2020 there was a peak in research focused on Vgn and Vgt streams. Finally, we observed an evolutionary increase of studies in the Vgt-Vgn- M -C stream.

When and what (streams).
3.4.2. Frames of VEG
By analyzing the different conceptualizations of VEG in research, we observed that 56% of studies framed it as diet, 24% as consumption of VEG food products, and 6% as the philosophy of life. Some studies also considered VEG as a combination of two frames: diet and consumption of VEG food products (6.5%) and diet and philosophy of life (6%). To get a more accurate picture of the focus of researchers, we crossed the streams with the frames of VEG. As shown in Table 4 , framing the VEG phenomenon as diet was more present in Vgt stream (70.7%), followed by Vgt-Vgn-M (68.5%) and Vgt-M (67%) streams. Expectedly, framing VEG as food was more prevalent in Vgt-Vgn- M -C (79%). Through the simultaneous evaluation of seven streams and five frames, we found a total of 35 distinct research categories on VEG. This analysis showed that 19.5% of studies focused on Vgt-Vgn. D stream, followed by Vgt-Vgn-M. D (12%), Vgt- D (9%), and Vgt-M. D (8%). It is noteworthy to mention that in four research categories (Vgt-Vgn-M. P , Vgt-Vgn-M. DP , Vgt-Vgn- M -C. P , and Vgt-Vgn-AHR. DF ) , we did not find any published articles.
VEG has been studied in WHAT frames through the streams?
Vgt: Vegetarianism; Vgn: Veganism; M: Meat consumption; AHR: Animal-Human relationship; C: Cultured meat consumption; D : Diet; F : Food; P : Philosophy of life.
The publication of five VEG research frames over the years is shown in Fig. 5 . Studying VEG through the diet frame increased over the years, with peaks in 2021 (28 studies) and 2015 (11 studies). However, this interest decreased to 15 studies in 2022. By contrast, there was a relatively high number of studies analyzing VEG in the food consumption frame, with two peaks in 2022 (35 studies) and 2020 (10 studies). It is worth noting that the number of studies in other frames was relatively small and did not seem to follow any temporal pattern.

When and what (frames).
3.5. WHY have researchers found it relevant to study VEG?
In Section 2.3 , we undertook a classification of the relevance of studying the VEG phenomenon as cited in the reviewed articles. Our analysis yielded two distinct groups: central and peripheral reasons. The former comprised concerns related to health, environmental issues, and animal welfare. The latter encompassed a diverse range of additional factors, including cultural and social considerations, sensory preferences, faith, financial and economic implications, political concerns, and world hunger. For clarity, we will discuss these nine motives below according to the order of importance in which they appear in the reviewed studies (see Fig. 6 ).

WHY it is important to study VEG.
3.5.1. Central motives
Among the reasons identified in the studies to justify the importance of studying VEG, health concerns (83%) had the highest presence. Exploring this further, we found that many articles referred to the health aspect of VEG as the respondents’ motivation [ 42 , 143 ]. Some authors explained the positive effect of VEG on the human body by mentioning specific benefits, such as reducing cholesterol, blood pressure, or risk of diabetes, as well as reducing the incidence of cancers, heart disease, and hypertension [ 2 , 3 , 63 , 144 ]. More recently, a body of research interested in a more holistic view of health considered VEG options as an essential contributor to well-being and quality of life [ 8 , 53 , 115 ]. However, a minority referred to the potential adverse physical health effects, such as nutritional deficiencies (vitamin B12, zinc, or iron) if a well-planned VEG diet is not followed [ 53 ], or mental health risks, such as risks of stigmatization, discrimination, or feelings of embitterment [ 48 , 91 , 168 ]. Simultaneous analysis of WHY and WHAT showed that health considerations were the most frequently cited concern across all streams. Notably, more articles focused on Vgn (93%) and Vgt-Vgn (89%). Table 5 summarizes the convergence of these motives in each stream.
WHY did scholars considered VEG important to be studied?
HL: Health; EN: Environment; AN: Animals; CL: Cultural & Social; SN: Sensory factors; FT: Fait; FN: Financial & economic; PL: Political; JS: Justice & world hunger.
In the reviewed literature, there was a significant presence of referring to the environmental benefits of VEG (75%). Diversity in arguments and approaches was also observed when analyzing the environmentalist discourse. Some authors emphasized specific impacts; for example, they discussed how replacing animal-based diets with VEG diets could help reduce greenhouse gas emissions [ 9 , 60 , 67 ] and soil degradation [ 19 , 62 , 66 ], and tackle current problems related to air, soil, and water pollution [ 214 ], biodiversity loss [ 62 ], as well as climate change [ 61 ]. Nevertheless, most studies addressed the environmental benefits of VEG quite loosely, using terms such as a “sustainable” strategy [ 183 ] or alternatives to lessen the impacts of the current animal agriculture. Similarly, some authors mentioned that VEG alternatives comply with the United Nations 2030 Sustainable Development Goals. However, the terms “vegan” or “vegetarian” are absent in these goals [ 8 ]. Analyzing the frequency of environmental concerns among different streams indicated that environmental issues were the most frequently cited concern in the Vgt-Vgn- M -C stream with a prevalence of 89.6%, followed by 87% in the Vgt-Vgn-M stream and 83% in the Vgt-M stream. This suggests that environmental issues may have a significant role in encouraging studies transitioning from meat consumption to cultured meat consumption.
Approximately two-thirds of the reviewed studies (67%) included varied arguments on animal-related concerns. In some instances, animal-related concerns were considered a central aspect of VEG discourse, while in others, they were only tangentially referenced. References to animal concerns appeared implicit and subsumed under the general term of “ethical” [ 64 , 170 ] or “moral” reasons [ 117 , 212 ]. Conversely, in other instances, the phenomenon of VEG appeared firmly rooted in the animal rights or animal protection movement [ 255 ]. Another example of these differences was found when researchers discussed the drivers of following, adopting, or consuming VEG options. For example, some researchers emphasized the positive aspects of VEG for animals; we found references to “compassion toward animals” [ 54 ], “animal advocacy” [ 258 ], “affection toward animals” [ 255 ], or “animal welfare” [243,263 ] . In contrast, other researchers highlighted the detrimental effects of the current animal agriculture on animals and how VEG alleviates this negative impact. These studies often used expressions such as “animal suffering” [ 117 ], “animal exploitation” [ 260 ], or “animal slaughter” [ 81 ].
Notably, we also found diverse philosophical approaches adopted in the studies to defend VEG. Some research aligned strongly with welfarist positions [ 114 , 145 , 215 ], while others aligned with abolitionist or animal rights perspectives [ 60 , 116 , 256 ]; to a lesser extent, anti-speciesism discourses were also incorporated [ 15 ]. The presence of animal concerns significantly depended on the stream. Expectedly, in the Vgt-Vgn-AHR stream, animal considerations were found in all of the studies, followed by 86% in the Vgn stream.
3.5.2. Peripheral motives
In this category, distinguished three sub-groups according to the relevance with which they appeared in the reviewed research. In the first sub-group, we found cultural and social, and sensory motives, each present in 33% of the studies. Cultural and social factors included the influence exerted by certain people or groups on an individual's decisions about their VEG choices. Specifically, studies focused on analyzing the impact of people's close networks, mainly families or peers [ 21 ], and online vegan discussion groups [ 19 ]. Cultural and social factors were mainly observed in the Vgt stream (41%).
For sensory reasons we referred to consumer or producer concerns about the sensory aspects of VEG alternatives, which are typically related to VEG foods (i.e., taste, texture, odor, or appearance) [ 99 , 117 , 143 ]. Sensory reasons were primarily observed in the Vgt-Vgn-AHR (50%) and Vgn (46%) streams.
In the second place, we found references to financial and economic, and faith reasons, present in 25% and 22% of the articles, respectively. VEG studies citing financial and economic reasons were relatively scarce. These typically covered cost savings from the consumer's perspective [ 174 ]. These concerns were primarily mentioned in the studies on the Vgt-Vgn- M -C stream (72%), which was expected owing to the growing market of VEG products. Faith motives included both religious [ 109 , 231 ] and spiritual beliefs [ 45 ]. Generally, these reasons were typically studied as drivers of VEG choices [ 68 , 100 ]; however, these concepts require further exploration. Faith reasons appeared mainly in the Vgt-Vgn-AHR stream (37%).
Finally, we found that political, and justice and world hunger arguments [ 130 , 153 ] had a much lower presence in the studies; specifically, they were each mentioned in only 12% of the articles. Political aspect of the VEG referred to connections to other social movements and other political issues beyond animal protection; in this sense, we found references to claims for women's or LGBTQ rights [ 258 ]. In most cases, these political issues were neither defined nor explained in depth. Political motives were primarily observed in the Vgn (20%) and Vgt-Vgn-AHR (16%) streams. Justice and world hunger concerns referred to the world hunger problem [ 13 , 205 ] and various arguments on how VEG can improve food availability or exacerbate social inequality and injustices [ 161 , 164 ]. However, these arguments require more specificity and detail. They were mainly explored in Vgn studies (36%). In general, we observed that 50% of studies were commonly mentioned in HL-EN-AN ( Table 8 in Annex).
3.6. WHICH variables were analyzed in VEG studies?
Before proceeding to a detailed study of the variables examined in the literature, it should be noted that only 29.6% of the studies used theoretical frameworks to measure the variables under examination. In this group of studies, we found that 33.7% used the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) [ 270 ]; 8.6% of the studies used the Unified Model of Vegetarian Identity [ 271 ]; 7.6% applied human values theory [ 272 ]; 7.6% employed the Transtheoretical Model [ 273 ], and 4% used Social Dominance Orientation [ 274 ]. The usage of these theories across the seven streams of studies is summarized in Table 6 . It is worth noting that approximately 11% of the reviewed studies applied other theoretical frameworks than the five most prevalent ones.
Most extensively researched theories in each stream of VEG studies.
For the specific variables analyzed in the literature, we grouped them into five categories: psychological dispositions, cognitive-affective variables, behavioral constructs, social determinants, and situational variables. Table 7 summarizes the convergence of these variables and constructs in each stream; as illustrated, the prevalence of the variables depended on the stream in question, and in many of them, some variables were overlooked. For clarity, we analyzed each construct group according to the order of frequency in which the variables appeared in the studies.
WHICH variables has been measured in each stream of VEG quantitative studies?
A: Attitudes; M: Motivations; V: Values, T: Personality; E: Emotions; K: Knowledge; B: Behavior; I: Intentions; S: Self-efficacy or Perceived Behavioral Control; N: Networks; O: Norms; D: Identity; P: Product Attributes; F: Information.
3.6.1. Psychological dispositions
Psychological dispositions included variables related to attitudes, motivations, values, and personality traits. Attitudes , understood as perceptions, and opinions on VEG-related issues, applied to different aspects and 67% of the studies measured attitudes. This variable was mainly constructed as attitudes toward animals [ 15 , 136 , 167 ], meat [ 137 , 141 ], and VEG lifestyles [ 54 , 108 ]. In addition, some studies measured attitudes in the context of justification strategies for non-VEG lifestyle choices [ 258 ]. Some authors differentiated between positive, negative, and neutral attitudes [ 23 , 49 ], but most studies did not make such distinctions and referred to attitudes as a uniform construct. Similarly, they did not differentiate between cognitive, affective, and conative aspects recognized in the consumer behavior literature [ 275 ]. Attitudes were primarily found in studies on Vgt-Vgn-AHR (87%), followed by those focusing on Vgt-Vgn- M -C (79%).
Regarding motivations , 39% of the reviewed studies were interested in studying the reasons that encouraged consumers to practice VEG (i.e., becoming a VEG, following a VEG diet, consuming VEG products). Particularly, studies focused on analyzing three types of motivations. First, studies with a strong hedonistic character, which were related to personal health, sensory appeals, and economic considerations [ 43 ]. Second, studies with a strong altruistic, ethical [ 8 , 151 ], or even spiritual character (e.g., Buddhism) on the adoption of VEG choices [ 68 , 261 ]. Here, authors differentiated between interest in animal protection (protecting animals from unnecessary suffering), environmental conservation (climate change and global warming), and human rights (the relationship between world hunger and the dedication of resources to livestock production rather than agriculture) [ 2 , 19 , 113 , 208 ]. Third, studies with a strong social character, in which we detected an interest in studying the effect of following VEG diets due to living with VEG family members or friends [ 53 , 114 ]. It is worth mentioning that some studies took a broader approach to motivations and studied them abstractly as a general concern to pursue their choice of VEG, but without delving into the type of motivation that affected the decision-making [ 13 ]. The interest in measuring motivations was observed, especially in studies on Vgn (53%), Vgt (46%), and Vgt-M (51%).
Values , understood guiding principles [ 42 ], were present in 21% of the studies. They were typically measured with extensively validated instruments, such as the Social Dominance Orientation scale [ 274 ], [e.g., 74 , 104 , 136 , 213 ], the Theory of Basic Human Values of Schwartz [ 271 ], [e.g., 114 ], or Altemeyer's Authoritarianism scale [ 276 ], [e.g., 67,74]. These studies concluded that the likelihood of practicing VEG was associated with greater endorsements of liberalism, universalism, and left-wing ideology [ 54 , 164 , 165 ]. As more specific values related to the VEG, we found speciesism measurement, understood as the belief in the supremacy of humans over animals [ 19 , 94 , 136 , 213 ]; in these cases, the use of the Dhont et al.‘s [ 277 ] speciesism scale stood out. Similarly, we found the measurement of carnism, namely, the belief system that supports the consumption of certain animals as food [ 132 ]; in this case, the variable was measured using Monteiro et al.‘s [ 278 ] scale. It should be mentioned that many scholars considered values as motivations (i.e., referring to religious reasons as religious values) [ 64 ]. Values were observed the most in the Vgt-Vgn-M stream (25%).
Our data also showed that 12% of studies focused on measuring personality traits [ 3 , 109 ]. These studies employed the Eysenck Personality Questionnaire [ 45 , 113 ], the Big Five test [ 69 , 84 , 87 ], and the Food Neophobia (reluctant to try or eat novel food) scale [ 52 , 172 ]. Personality traits were observed in the Vgt-Vgn stream (19.5%), followed by the Vgt stream (12%).
3.6.2. Cognitive-affective variables
Cognitive-affective variables referred to variables associated with the emotional responses to and knowledge regarding VEG. Regarding emotions , many scholars acknowledged that VEG lifestyles and choices were affectively charged [ 279 , 280 ]. Despite this recognition, emotions were only present in 23% of the studies in this field. The emotions associated with VEG lifestyle and choices included disgust (toward meat) [ 96 ], sensory (dis)liking VEG foods [ 96 , 143 ], guilt related to diet consistency or pet food choice [ 96 , 268 ], anger [ 144 ], shame [ 213 ], fear [ 74 ], and affect or empathy responses (the capacity to feel what others are experiencing) [ 3 , 15 , 47 , 136 , 194 ]. Most previous studies did not use validated instruments to measure these emotions. Notable exceptions were found in the assessment of meat disgust and meat enjoyment, which was mainly measured using the disgust scale [ 3 ] and the meat attachment questionnaire [ 84 , 213 ], respectively. Emotional concerns were more prevalent in the Vgt-Vgn-AHR (41%) and Vgt-M (32%) streams.
Knowledge was measured in 17% of studies and referred to the familiarity with VEG products [ 143 , 227 ], VEG diet [ 13 , 171 ], and the understanding of the relevance and impacts of VEG on health [ 103 ] and environment [ 202 ]. Knowledge was explored primarily in studies focused on Vgt-Vgn-M (24%).
3.6.3. Behavioral constructs
In the behavioral constructs, we observed behaviors, intentions, and self-efficacy. The measurement of behaviors was present in 72% of the reviewed studies, primarily involving self-reported food consumption habits [ 2 , 3 , 167 ]. In many cases, the inclusion of this construct was intended to complement and compare the self-reported status as vegan, vegetarian, or neither [ 2 , 167 ]. Most of these scales measured general food consumption behaviors. The Food Frequency Questionnaire [ 4 , 90 ], the Food Choice Questionnaire [ 131 ], and purchase frequency [ 8 , 183 , 251 ] were the most commonly used instruments to measure this variable. Notably, two articles advanced the measurement of behaviors using observational measurement via experimental designs [ 126 , 136 ]. Another pattern we observed in our review was the interest in the temporal aspect in which behaviors are performed. In this regard, although most studies focused on current consumption behaviors, some highlighted the relevance of past behaviors [ 110 ] and the duration for which individuals practiced VEG lifestyles [ 2 , 18 , 64 , 141 , 165 , 260 ]. Additionally, a few studies measured more than one behavior; as sometimes, all behaviors were directly related to food consumption. For example, Crimarco et al. [ 145 ] measured participants’ overall food consumption frequency, adherence to the vegan diet, and restaurant-related behaviors. In other studies, measured behaviors were related more to health, such as alcohol consumption [ 113 ] or adequate nutritional intake [ 192 ], and more rarely, to animal-related behaviors [ 128 , 256 , 268 ]. This variable appeared most frequently in the Vgt-Vgn-M (85%) and Vgn (76%) studies.
Intentions were included in 25% of the studies. In the reviewed articles, they were measured as the willingness to cut down on meat [ 205 ], try VEG foods [ 143 ], adopt a VEG lifestyle [ 190 , 226 ], being VEG [ 255 ], or continue practicing a VEG lifestyle in the future [ 2 ]. Some studies specified a time frame (e.g., next month, next two years) in their questions [ 49 , 255 ]. For example, in Wyker and Davison's [ 108 ] study, intention was measured by asking for agreement to the statement, “ I intend to follow a plant-based diet in the next year .” To assess intentions, some studies applied the Transtheoretical Model [ 13 , 108 ], but primarily drew on TPB [ 13 , 15 ]. Among the different streams, measuring intention was predominant in the Vgt-Vgn- M -C (65%), Vgn (33%), and Vgt-Vgn-M (27%).
Self-efficacy was only present in 8% of the studies, and referred to personal control, perceived ability, and perceived level of ease or difficulty in following the VEG lifestyle [ 2 , 108 , 200 ]. Self-efficacy was predominantly based on TPB, referred to under the term Perceived Behavioral Control. This construct was adapted to the VEG context by several scholars [ 15 , 60 , 190 ]. This variable was most prevalent in studies on Vgt-Vgn-M (13%). Interestingly self-efficacy was not observed in Vgn and Vgt-M streams.
3.6.4. Social determinants
The social determinants included variables related to the influence of social ties or networks , as well as identity and social norms to act (or not) in accordance with VEG. Social network was present in 20% of the studies and measured through a variety of constructs, such as group membership [ 136 ], having VEG friends and family [ 8 ], or participation in a social movement [ 165 ]. An analysis of its presence in the different streams showed that it was most prevalent in research on Vgn (43%) and Vgt-M (29%). None of the reviewed studies measured social networks in the Vgt-Vgn- M -C stream.
Our analysis showed that identity was present in 11% of the studies and was analyzed using different approaches, such as political [ 165 ], social [ 18 , 127 , 131 ], or self [ 142 , 190 ] identities. A notable recent construct was that of “dietarian identity” [ 14 , 18 , 132 , 179 ], as measured by the Dietary Identity Questionnaire [ 271 ]. Dietarian identity refers to individuals' self-image with regard to consuming or avoiding animal-based products, regardless of their actual food choices [ 2 , 166 , 168 ]. This latter qualifier is important to consider in VEG studies, because people's actual diets and their self-reported dietary identity may appear inconsistent. For example, people who self-identify as a “vegan” might still consume animal products occasionally, while other people may strictly avoid animal products but not consider themselves to be “vegan.” [ 166 ]. This variable stood out in studies on the Vgt-Vgn-M stream (20%), followed by Vgt (19%).
Finally, another way in which social determinants appeared in the literature was through the social norms , which referred to the social pressure received from society and significant others to adopt (or reject) VEG alternatives [ 60 ]. Specifically, we found this variable in 8% of the studies. In some cases, it referred to imperative (perceived social pressure) and descriptive norms (the number of VEG people in the participant's circle) [ 141 , 205 ]. However, it was more commonly understood as subjective norms, close to the operationalization in TPB (as the extent to which participants consider that significant people in their lives think they should follow or avoid a VEG lifestyle) [ 2 , 15 ]. Social norms were mainly analyzed in the Vgt-Vgn-AHR (16%) and Vgt-Vgn-M (14%) streams.
3.6.5. Situational variables
This group included product attributes and informational signals regarding VEG. Present in 22% of the studies, research on product attributes focused on two types of attributes: (1) extrinsic attributes, such as labeling, nutrition information, functional claim, visibility, affordability, accessibility, promotion, or availability [ 21 , 86 , 242 ]; and (2) intrinsic attributes, such as texture, taste, smell, visual appearance, color, or size [ 143 , 231 ]. Product attributes were observed dominantly in studies on Vgt-Vgn- M -C (55%), followed by Vgt-Vgn-M (27%), and Vgt-Vgn (21%).
Our analysis identified that 19% of the studies focus on analyzing the effect of different informational signals on raising awareness of VEG [ 144 ], promoting VEG products [ 52 ], and eliciting cognitive or emotional responses to VEG information [ 52 ]. For example, some studies focused on measuring the effect of exposure to specific ethical or environmental messages [ 170 , 182 , 258 ], documentaries [ 165 ], or campaigns [ 174 ] on the perception of VEG alternatives. Another group of studies measured the impact that different VEG food images had on consumers [ 5 , 52 , 188 ]. It is worth noting that these studies were often experimental and were conducted online or in laboratory settings [ 3 , 170 ]. Informational signals were mainly explored in studies in Vgn (33%), followed by Vgt-Vgn- M -C (31%) and Vgt-Vgn-AHR (29%) streams.
As discussed above, research has focused on examining a wide range of variables to understand the VEG phenomenon. To summarize, Fig. 7 depicts a conceptual map of the relationships explored in the reviewed studies. It is important to note that the aim of this map was not to provide a conclusive explanatory model, but rather to show how the relationship between the variables has been conceptualized in the literature and illuminate future avenues of research. The map schematically proposes that situational variables elicit certain emotional responses, which in turn can affect knowledge and attitudes toward VEG. Likewise, attitudes, a variable closely related to individuals’ values and beliefs, have a direct impact on intention, which may originate from different motivations. Intentions are assumed to be directly affected by social networks, social norms and self-efficacy, and indirectly affected by identity and personality traits. Finally, the direct and indirect effect of all these variables translates into actual behavior. All these variables translate into actual behavior.

Conceptual map of measured variables in quantitative VEG studies.
3.7. HOW the VEG studies were conducted?
All 307 studies in this review were quantitative, as per the inclusion criteria; however, we found that the studies included different research designs. Sixty-eight percent of the studies were conducted based on correlational or non-experimental design (collecting data based on surveys). Among the non-experimental studies, eight were mix-method designs and included both qualitative and quantitative data, for which we coded the quantitative part ( Table 8 in Annex). Thirty-two percent of the studies were experimental. Among these, 17 were choice experiments. In addition to varied research designs, we observed different types of information regarding the data collection, sample characteristics, and statistical analysis. We discuss these three aspects below.
3.7.1. Data collection
Regarding the type of studies conducted, 87% were based on cross-sectional data (vs. 13% longitudinal data) [ 138 , 162 , 204 ]. It is worth mentioning that only 47.5% of the studies reported the year of data collection. Among the experimental studies, 31% dealt with between-participant and 9% with within-participant designs. Furthermore, the settings of these experiments were mainly online [ 156 , 159 , 269 ], in research laboratories [ 135 , 209 ], or in restaurants or cafeterias [ 186 ]. Manipulations varied depending on the research objective, but many involved the use of exposures to different stimuli, such as informational text messages [ 110 , 114 , 187 ], images of food [ 5 , 86 , 111 , 167 ], or manipulated menu design [ 110 , 125 , 186 ].
Analyzing the data sources utilized in the reviewed studies revealed that 92% of the studies relied on primary sources, 7% employed secondary data, and only a limited number used both primary and secondary data [ 2 , 21 , 231 ]. The secondary data sources were mainly obtained from national panels, such as the US National Health Survey [ 53 ], the Swiss Food Panel [ 4 , 176 ], the UK Integrated Household Survey [ 204 ], and the German Socioeconomic Panel [ 87 ]. An examination of the methodologies used for collecting primary data revealed that a large number of studies relied on a single source (89.5%). Relatedly, the most commonly used method was self-reported data. Only 13% of the studies supplemented the self-reported method with additional information such as body measurements [ 101 , 113 , 164 ], brain responses [ 135 , 167 ], or implicit attitudes [ 3 , 43 , 111 , 209 ].
Of the studies that used primary data, most employed surveys to collect data; among these, the use of Likert scales (ranging from 1 to 5) and yes-or-no questions was prominent. Although the reliability of the scales was addressed in general terms (mainly through Cronbach's alpha), the validity of the scales was often not considered. In this sense, factor analyses (exploratory and confirmatory) were only used in 14% of studies as the most appropriate techniques to test the validity of the scales. It should be mentioned that although many complex concepts related to VEG were investigated, 65% of the studies did not use constructs but single variables. Moreover, most variables did not result from the operationalization of the constructs from a specific theoretical framework.
3.7.2. Sample
The unit of analysis in 98% of the studies was the individual respondents; the rest focused on other units, such as households [ 183 , 204 ]. Additionally, we found that sample sizes ranged from 10 [ 101 ] to 143,362 [ 204 ] and that 11% of the studies used 100% student samples. The measurement of some socio-demographic variables was present in all the studies as necessary information to describe the sample; however, not all studies presented all or the same type of information. Regarding sex, the sample consisted of both male and female participants, except for six studies conducted exclusively with females [ 112 , 122 , 172 , 185 , 197 ]. The data also showed that female participation was generally higher than male participation, with an average of 64% of the total sample. Among those that provided this data, the percentage of female participants was higher than 50% of the total number of cases in 72% of the cases. Concerning the ethnic composition of the sample, we found that only 8% of the studies provided information on ethnicity, 74% of the respondents from the samples (on average) were Caucasian and that one study was conducted entirely on African-Americans [ 230 ]. In terms of age, 40% of the studies did not report the mean age of respondents and 98% used adults as a sample, meaning that only a few studies focused on children [ 12 , 44 , 140 , 141 , 215 ]. Regarding the VEG status of the respondents, 54% of the studies were conducted on VEG and non-VEG participants [ 42 , 205 , 230 ], 25% on only VEG participants [ 18 , 45 , 177 ], and 20.84% on only non-VEG participants [ 13 , 110 , 143 ].
3.7.3. Statistical techniques
The most used statistical techniques in order of relevance were ANOVA (or ANCOVA and MANCOVA; 44%), chi-square test (21%), t-tests (17%), and Mann-Whitney test (3%). A few studies adopted a more predictive approach by running a model with the corresponding dependent and independent variables. In these cases, the most used techniques were OLS regression (16%) [e.g., 41], logistic regression (15%) [ 110 ], or SEM/PLS models (9.7%) [ 15 , 23 , 255 ]. Very few studies performed additional analyses, such as mediation (8%) [ 144 ], and moderation (2%) [ 15 ]. Some other studies tried to classify individuals according to different characteristics and primarily used statistical techniques, such as cluster (2%), [e.g., 84, 90, 151,193] or latent class (1%) [ 202 , 231 ] analyses.
However, normality was assumed in most cases; only 14% of all studies (experimental and non-experimental) reported (non)compliance with the normality assumption [ 15 , 42 , 144 ]. Additionally, very few studies (20%) warned of the risk of certain or potential bias, especially the risk associated with Common Method Effects, such as selection or social desirability biases. Of these few studies, only some performed any statistical technique to ensure that bias did not threaten the results; they mainly mentioned this it in the limitations.
4. Discussion
This systematic literature review shed light on the development of quantitative peer-review studies on VEG published up to December 31, 2022, within psychology, behavioral science, social science, and consumer behavior domains. The 6W1H analytical approach was chosen as a guide for analysis to have a holistic view of the literature and capture its multiple angles. This approach aimed to answer the questions of WHEN, WHERE, WHO, WHAT, WHICH, WHY, and HOW the research on VEG was published. To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first systematic literature review conducted on VEG. In this section, we highlight and discuss the most relevant findings and gaps we drew from the study.
In line with the increasing worldwide attention to VEG alternatives and with other authors' observations [ 7 , 11 , 22 ], our study confirmed that researchers’ interest in studying VEG has grown, especially in the last ten years. The results of our review showed exponential growth of publications in recent years; specifically, the average number of publications, which increased from one in the 1980s and 1990s to 61 in 2022.
The present study also showed that such interest is particularly robust within English-speaking Western countries; in this regard, we identified a geographical gap in the literature, as the studies reviewed were mainly concentrated in the US, [e.g., 2,13,143] and the UK [e.g. Refs. [ 14 , 21 , 49 ]]. This geographical dominance, which could be due to multiple causes beyond the scope of this article (e.g., greater number of researchers, potential for research funding, availability of technology, and trajectory of veganism), is a major constraint to advancing knowledge on VEG, given that both human-animal relationships and food consumption are strongly influenced by cultural factors [ 281 , 282 ]. Accordingly, several criticisms have emerged, claiming that research on VEG is racially biased and strongly appropriated by Western culture [ 165 ].
As for the journals in which research on VEG was published, we observed an interesting change of focus. The study on this phenomenon was born with a strong link to journals focused on animal rights and activism as VEG was clearly presented as a manifestation of a philosophical, ethical, and political stance that questions the anthropocentric position of human beings with respect to the rest of the animals. However, our review clearly showed the preference of authors in recent years to publish their research in journals highly focused on analyzing the relationship between behavioral change and nutritional or dietary choices. In this sense, we found that Appetite was the journal chosen most frequently to publish quantitative studies on VEG. This evolution indicates that the rationale for healthy and sustainable eating in VEG research has become more prominent than ever, while the implications these alternatives have for animals have been diluted. In line with this, we found that the Vgt-Vgn. D approach of research dominated the literature, while the most prominent gap in the literature was of VEG as a life philosophy or social movement. This was illustrated by the arguments expressed by researchers to defend the relevance of studying VEG, the main driver being health, followed by animal protection, environmental concerns, and other considerations (religion or spirituality, world hunger, social factors, and sensory appeal). Taken together, our results add evidence to a recent concern in the literature about the depoliticization of VEG in society (especially in veganism) that is fading from its antagonistic origins [ 283 ]. The spread of VEG in academic endeavors, as well as in business and personal practices, seems more often motivated by personal health reasons (understood in terms of physiological health) than by ethical considerations.
Focusing on the objectives and methodological approach of the studies reviewed, we highlighted five main gaps. First, through the overview obtained on the topic, we realized a notable lack of research on consumer behavior change or the process of transitioning to VEG. We identified only a few studies that analyzed self-reported lifestyle changes [e.g. Ref. [ 177 ]], especially measuring actual behavior change over time [e.g. Ref. [ 174 ]].
Second, among the variables used, we noted a preference for studying rational and conscious content over emotions, feelings, and the unconscious mind in human behavior, [e.g. Refs. [ [284] , [285] , [286] ]]. To illustrate, although there was a strong interest in studying attitudes toward meat substitutes [ 231 ], VEG individuals [ 75 ], or VEG diet [ 144 ], it was very rarely accompanied by an adequate definition and measurement of the cognitive, affective, and conative dimensions widely recognized in the literature [ 287 , 288 ]. Despite plenty of measures developed to examine the psychology of meat-eating [ 22 , 289 ], such as carnism inventory [ 278 ], meat attachment [ 60 ], or moral disengagement to meat [ 213 ], we found gaps in the tools used to measure the variables examined in VEG studies. Although some well-known scales were incorporated, such as the disgust scale [ 290 ], or personality traits [ 291 ], in general, the instruments used to measure the constructs were often not validated in the literature but constructed ad hoc for the specific research being conducted. Very little progress has been made in the development of constructs and scales tailored to VEG. The exceptions to this are the Dietary Identity Questionnaire [ 271 ], Vegetarian Eating Motives Inventory [ 116 ], and Vegetarianism Treat Scale [ 277 ].
Third, we observed that in the field of VEG, data-driven research was more prominent than theory-driven research. This is an important shortcoming, given that data-driven methods are less likely to offer clear theoretical perspectives to help analyze results [ 292 ]. We agree with Schoenfeld [ 293 ] that “theory is, or should be, the soul of the empirical scientist” [p [ 105 ]]. Theory-driven approach is especially important in quantitative research owing to its deductive logic based on “a priori theories.” [ [ 294 ] p312]. Thus, the lack of anchoring research on VEG in theoretical frameworks is another of the gaps detected in our review.
Fourth, the rapid growth and innovation of software, together with the increased availability of diverse data sources, have expanded analytical capabilities and methodological options adapted to each topic. However, our research showed that such advances had very little impact on the field of VEG studies (at least in the non-medical VEG literature), as the richness of the data was not large (mainly self-reported and cross-sectional studies); descriptive and correlational statistical techniques remained the most used analytical approaches, highlighting another gap in VEG literature. However, one innovation that was recently incorporated in VEG research and is worth mentioning is brain response measurements. These types of measurement methods were rarely used [ 167 ] as the field is still dominated by self-reported surveys, as mentioned above. Nevertheless, the contrasting results of self-reported versus physiological responses in Anderson et al.‘s [ 167 ] study highlighted the importance of using multiple data sources when attempting to analyze people's responses and to inform the dietary patterns required in dietary scales, as they provide a richer and better picture of consumer behavior.
Fifth, with respect to the samples used in the VEG studies, it is pertinent to address two important matters. On the one hand, vegans and vegetarians were often merged and studied as a unified group. However, a growing body of research demonstrated that vegans and vegetarians not only present differences in terms of behavioral and attitudinal characteristics (such as identity profiles [ 93 ], value orientations [ 42 ], and cognitive ability [ 113 ]), but that the motivations driving the adoption of their lifestyles (animal protection, environment, and health) also influence how the person experiences the VEG alternative. On the other hand, studies were expected to clearly indicate the composition of their sample according to socio-demographic variables; however, our review showed that this practice was not always met, especially regarding ethnicity, sex, and age, variables highly relevant to food, ethical consumption, and animal protection [ 15 , 144 ]. Analyzing the studies that provide such information would reveal that research involving minors and culturally diverse groups [ 54 ] is notably scarce. However, considering that the adoption of VEG has traditionally had a philosophical foundation [ 1 , 16 , [295] , [296] , [297] ] and that certain responses to it are learned by social contagion [ 298 ], different mechanisms depending on the age of the participants and their cultural setting are expected. In addition, we detected a very narrow and traditional approach to the concept of “gender” in that most studies used the dichotomous categories of male and female. This approach does not align with the existing discourse on diversity and gender fluidity [ 299 ] and could hinder progress in deepening our understanding of the relationship between VEG, gender issues, and animal advocacy [ 300 , 301 ].
5. Conclusion
5.1. contribution.
Our systematic literature review contributes to the literature by providing an overview and mapping the growing body of research on VEG, which allowed us to clarify existing findings as well as identify trends and gaps in existing research. Using the 6W1H approach, we offered a novel lens for examining the topic and a systematized mapping of the variables examined by researchers when studying VEG, and more specifically, the new and emerging factors that influence VEG-related behavior change.
Three main conclusions can be drawn from our research. First, our study highlighted the growing body of research on VEG. However, Anglophone countries dominate the research in this field, which may lead to a certain bias in the analysis of the phenomenon. In this regard, some scholars and practitioners have raised some criticisms, claiming that VEG is racially biased and strongly appropriated by Western thought.
Second, reflecting holistically on the evolution of VEG research, it appears to be shifting from a political-philosophical positioning to an individual consumption choice or dietary option. This shift in framing is relevant because it may have important implications for its progress in the sense that the approach we adopt as researchers, when investigating any phenomenon or idea, influences its conceptualization and development in society [ 302 ]. After all, “meanings do not naturally or automatically attach to the objects, events, or experiences we encounter, but arise through culturally mediated interpretive processes” [303 p. 144].
Third, we observed that the field of VEG is still dominated by data-driven research; however, to gain a richer and deeper understanding of the VEG phenomenon and advance the discipline, studies should be grounded in theory. In addition, it is advisable to increase the richness of the data, quality of the measurements, and sophistication of the statistical techniques applied by broadening the variables examined, extending the populations under investigation, and improving the methods of analysis.
5.2. Academic and managerial implications
Our comprehensive overview and mapping of VEG research can benefit scholars in different ways. On the one hand, by highlighting and identifying the latest gaps, this study can be useful in leading and guiding researchers toward topics, the unit of analysis, and methods to advance VEG research and, thus, move the discipline forward. In this sense, our study aimed to show “the path” so that by understanding our current status, we can plan the future of our research. On the other hand, as academics, we need to select the journal that we consider most appropriate for disseminating our work. To this end, we usually apply two central criteria [ 39 , 304 ]: (1) the suitability of the topic studied that is of interest to an audience of academics and practitioners; and (2) the prestige of the journal, a variable that contributes to the credibility and diffusion of our findings. In some cases, this decision may be a simple task; however, it is more complicated in novel fields studied from multiple disciplines and approaches, as is the case of VEG. Therefore, we expect that this study will assist researchers in this regard.
The systematized mapping of measured variables can also help practitioners and public policymakers design innovative and more effective interventions aimed at fostering more just, healthy, and environmentally sustainable societies. Considering that the lack of awareness and confusion about the different VEG options acts as barriers to their adoption, this study can help clarify the different perspectives on the phenomena. This, in turn, can help public and private institutions involved in animal rights, environmental sustainability, and public health in designing educational programs tailored to the idiosyncrasies of the target group. In this sense, future policies could develop educational activities targeting adults and younger generations. In addition, interventions have focused on VEG food choices or reducing meat consumption as stand-alone strategies so far, but future interventions could be more effective if designed through nudging strategies.
From the perspective of understanding consumer behavior, marketers of VEG foods could benefit from our study by having a deeper understanding of consumers' motivations, goals, and objectives toward VEG products, which, in turn, will serve to better segment markets and offer products more tailored to their needs and desires. Marketers can also encourage the consumption of VEG products; for example, by promoting the adoption of short-term actions, such as the “Lundi-Vert” campaign in France or “Veganuary” in the UK, aimed at increasing people's familiarity with these products and improving their perception of them. In addition, the studies reviewed showed the role of monetary incentives on VEG products, which could be used in future policies to increase the willingness to buy them.
5.3. Limitations
Systematic literature reviews present potential shortcomings, especially in the selection process of the publications that constitute the corpus, which could exclude some relevant information. In this sense, although WoS is a very comprehensive and reputable database, we cannot exclude the possibility that some articles may have been excluded from our selection and analysis. Additionally, to provide greater homogeneity and consistency to the study, we focused on articles published in English and in peer-reviewed academic literature. Future research could complement our study with those published in other languages (e.g., Spanish, French, German, or Chinese) as well as in books, conferences, or “gray literature” [ 305 , 306 ].
Another difficulty inherent to the systematic literature review is related to the process of coding the content of the studies that constitute the corpus to be analyzed. As mentioned in the Methodology, in our study the coding was agreed upon and performed by the three researchers. However, it cannot be ruled out that the position of the three investigators may sometimes differ from that of the readers or authors of the studies reviewed.
5.4. Recommendations and future research avenue
In accordance with the research gaps identified, we propose some avenues for future research to contribute to the advancement of VEG research. First, to address geographical gap, we consider it important to broaden the scope of studies to other countries (e.g., Eastern regions or Spanish-speaking countries), and to conduct more cross-cultural research [e.g. Ref. [ 224 ]]. We also recommend that future research focus on the analysis of the less examined VEG frames (e.g., as a philosophy of life or social movement), and explore the sociological and political aspects or dimensions of the phenomenon to have a more comprehensive understanding of it, especially in the case of veganism, which goes far beyond eating habits. However, we also believe that research attempts on VEG will be more fruitful if they incorporate separate (or comparative) analyses of the different streams, as well as the study of attitudes and behaviors toward animals.
To overcome the lack of research on VEG, we encourage scholars to adopt a more dynamic perspective on the phenomenon by incorporating the temporal factor into the design of their studies. This can be achieved, for example, by conducting longitudinal and experimental studies, and by using the so-called “stage theories” in their research. This approach will make it possible to observe how different constructs develop over time and how they influence the process of rejecting or adopting VEG. It may be of great interest for future literature reviews could focus on other topics related to VEG that were only tangentially explored in our work (e.g., cultured meat, pescatarianism, flexitarianism). Additionally, it would be interesting to synthesize the manifold advantages and disadvantages from multiple angles (ethical, environmental, social, and health) of adopting the different VEG options.
In addition, to advance research knowledge, theoretically underpinning future research attempts on VEG will provide a richer and deeper understanding not only on the topic under analysis but also the theoretical framework used in the research. In this regard, it would also be desirable to be more innovative (e.g., including gender diversity and fluidity) [ 299 ] and to show greater diversity (e.g., in terms of age and race) with respect to the population analyzed. This recommendation is more than timely, considering the current overrepresentation of some groups of participants.
In terms of methodology, our research showed that there is much room for improvement in terms of data collection, the variables studied, the tools used to measure these variables, and the statistical techniques used for subsequent analysis. Broadly speaking, future research should consider the following recommendations: (1) use diverse sources to collect information so that studies can combine observed, self-reported, and behavioral data, for which digital technologies can be implemented; (2) examine new variables and use scales and instruments previously validated in the literature to obtain good reliability and validity of the measures to capture the proposed concepts and avoid biases; and (3) conduct complementary analyses to delve deeper into the topic under investigation, using powerful statistical techniques to go beyond simple descriptive and correlational analyses and pave the way for deeper causal analyses.
As stated on multiple occasions, the present article aimed to review the existing quantitative literature to date on VEG. The large number of studies selected and the great heterogeneity observed among them (related to objectives, data, and streams) highlighted the complexity of performing a meta-analysis. Nevertheless, in future research, we will consider the possibility of performing a meta-analysis to deepen the effect of the relationships between some of the variables revealed in our study. Additionally, future reviews can focus on qualitative studies to examine whether their results are similar to ours.
The general conclusion we reach is that, despite the boom in research on VEG in recent years and the great and laudable efforts made to date by researchers, the study of the phenomenon is still in its early stages. This conclusion offers good news: the path of VEG research is still ahead of us and there is sufficient scope for innovation.
Author contribution statement
All authors listed have significantly contributed to the development and the writing of this article.
Funding statement
This study has been funded by Universidad Pontificia Comillas, reference number PP2021_10.
Data availability statement
Declaration of competing interest.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank four anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful feedback. The authors also thank Dr. Ben De Groeve and Dr. Jeffrey Soar for their helpful comments on an earlier draft of this manuscript.
6W1H of VEG quantitative studies in psychology, behavioral science, social science and consumer behavior domains of WoS (1978–2022)
Vgt: Vegetarianism; Vgn: Veganism; M: Meat consumption; AHR: Animal-Human relationship; C: Cultured meat consumption; D: Diet; F: Food; P:Philosophy of life.
HL: Health; EN: Environment; AN: Animals; CL: Cultural & Social; SN: Sensory; FT: Faith; FN: Financial & economic; PL: Political; JS: Justice & world hunger.
A: Attitudes; M: Motivations; V: Values, T: Personality; E: Emotions; K: Knowledge; B: Behavior; I: Intentions; S: Self-efficacy or Perceived Behavioral Control; N: Networks; O: Norms; D: Identity; F: Information; P: Product Attributes.
CR: Correlational or non-experimental: M-CR: Mixed method study including Correlational section; EX: Experimental; EXC: Choice Experiment.
Shifting to a plant-based diet has the potential to lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduce environmental degradation, and promote a healthy diet.
However, policy makers should explore the range of impacts this shift can have on various populations.
By understanding these impacts, policy makers can create a truly sustainable agriculture system.
By Nathanial Konrad, Amy Shearer, Jake Schwartz, Ulrich Monthe
Vegetarianism is often touted as a way to achieve better health outcomes and decrease humanity’s ecological footprint, yet it has not translated into significant policy action.[1] A vegetarian diet is associated with a reduction in risk of type II diabetes, cancer, coronary mortality, and overall mortality compared to the typical meat-centric omnivorous diet common in developed countries.[2] It also is projected to contribute to a significant reduction in environmental degradation from lowered greenhouse gas emissions and land usage.[3]
Although the benefits of vegetarian diets are clear and widely accepted, policymakers must consider other factors to translate these benefits into effective policy action and a smooth transition.[4] The considerations include loss of income for certain farmers and pastoralists, reliance on global markets for food imports, and specific cases in which meat may be beneficial. By understanding the diverse impacts caused by a shift to a vegetarian diet, especially on the poor, policymakers can create a truly sustainable agriculture system.
Pressure on the agriculture industry due to climate change is making the ability to earn a livelihood producing food increasingly difficult. A global shift to a plant-focused diet could introduce further concerns due to price fluctuations in the agriculture industry. A transition to lower meat consumption would reduce the amount of crops produced for livestock feed.[5] In turn, the price of these inputs would drop in tandem with a reduction in the price of meat in the long term.[6] While these changing prices would seem beneficial for the consumer, the producer’s needs must be considered as well. The reduced cost would lead to lower revenues for the producers, whether they are growing animal feed or raising livestock.[7]
Another issue to consider when transitioning to a plant-based diet is crop seasonality. Because fruits and vegetables are only in season for part of the year, many countries rely on imports once their growing season has ended.[8] This trading pattern causes greenhouse gas emissions through air, land, and sea transport. For instance, asparagus imported to England from Peru produces 5.3 kg of carbon dioxide for every 1 kg of asparagus [9]. Further, transportation emissions are not the only downside to consider. Popular foods like avocados, mangoes, and nuts have massive water inputs and are often grown in areas that are becoming increasingly water insecure.[10] While a vegetarian diet is associated with lower emissions, it does not mean that all plant-based foods are off the hook for considering their environmental footprint. To address these potential environmental impacts, many researchers suggest that people should eat seasonal and locally produced foods, irrespective of being vegetarian.[11]
It is widely agreed that the global rise in meat consumption, specifically in highly developed countries, has resulted in an increase in cardiovascular-related deaths.[12] However this is not to say that meat cannot be a beneficial source of vitamins and nutrients if eaten in moderation. More specifically, meat consumption can provide a high concentration of protein for children and undernourished people in developing countries.[13] An additional benefit of meat consumption is that livestock can graze on lands that are unsuitable for crops. Grazing on marginal lands increases the efficiency of food systems and production, providing another valuable food source to populations and increasing income for producers.[14] Managed livestock grazing can also improve ecosystem health; intensive managed grazing can improve soil nutrition, increase carbon sequestration, and promote biodiversity on grazed lands.[15]
Adopting a vegetarian diet is not a one-size-fits-all solution for addressing the environmental impacts of food production. It presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities for governments and development practitioners around the world. Shifting to a plant-based diet has the potential to lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduce environmental degradation, and promote a healthy diet. However, the reduction of meat consumption has implications for farmers’ livelihoods, among other considerations that decision makers should address.
When considering the transition to a vegetarian diet, policy makers should explore the range of impacts this shift can have on various populations. It is necessary to approach these problems on a case-by-case basis and provide localized solutions. Incentivizing localized plant and meat-based food chains can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from food transport. Furthermore, the adoption of integrated crop-livestock systems and managed grazing can help restore soils and promote biodiversity.[16] Policies like these emphasize agro-ecological solutions within our current food systems rather than a complete shift to a new food system. Ultimately, it is important to recognize that plant-based diets also have ecological and socioeconomic impacts, which must be kept in mind by policy makers moving forward.
This article was authored by Nathanial Konrad, Amy Shearer, Jake Schwartz, Ulrich Monthe. Konrad is an International Relations and Affairs M.A. candidate at The George Washington University. Shearer and Schwartz are Environmental Resource Policy M.A. candidates at The George Washington University. Monthe is an International Development Studies M.A. candidate at The George Washington University.
[1] Fresán, U., & Sabaté, J. 2019. “Vegetarian Diets: Planetary Health and Its Alignment with Human Health.” Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 10(Suppl_4), S380–S388. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmz019
[2] Tilman, David, and Michael Clark. 2014. “Global Diets Link Environmental Sustainability and Human Health.” Nature 515 (7528). Nature Publishing Group: 518–22. doi:10.1038/nature13959.
[4] Tirado-von der Pahlen, Cristina. 2017. “Sustainable Diets for Healthy People and a Healthy Planet.” United Nations System Standing Committee on Nutrition. Retrieved from: https://www.unscn.org/uploads/web/news/document/Climate-Nutrition-Paper-EN-WEB.pdf
[5] Lusk, L. Jayson, and Norwood, Bailey. 2009. “Some Economic Benefits and Costs of Vegetarianism.” Agricultural and Resource Economics Review, 38(2), 109-124. Cambridge University Press. doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1068280500003142
[8] Karp, David. 2018. “Most of America’s Fruit Is Now Imported. Is That a Bad Thing?” Retrieved November 30, 2020, from https://www.nytimes.com/2018/03/13/dining/fruit-vegetables-imports.html
[9] Gray, Richard. 2020. “Why the vegan diet is not always green.” British Broadcasting Company. Retrieved from: https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20200211-why-the-vegan-diet-is-not-always-green
[10] Ibid.
[12] Eating red meat daily triples heart disease-related chemical. 2019. Retrieved November 30, 2020, from https://www.nih.gov/news-events/nih-research-matters/eating-red-meat-daily-triples-heart-disease-related-chemical
[13] Friel, Sharon, et al. 2009. “Public health benefits of strategies to reduce greenhouse-gas emissions: food and agriculture.” The Lancet, Health and Climate Change, Volume 374, Issue 9706, P2016-2025. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61753-0
[15] Nargi, Lela. 2018. “Can Cows Help Mitigate Climate Change? Yes, They Can!” JSTOR Daily. Retrieved from: https://daily.jstor.org/can-cows-help-mitigate-climate-change-yes-they-can/
related posts
Adaptation finance update: global commission catalyzes financial resources for action 8 october 2019 0 then 4 else u.id end as user_id , u.user_email as user_email , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' when left(u.user_login,2) = 'z_' or u.id=64 then 'guest-authors' else 'thematic-experts' end as user_link_role , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' else u.user_nicename end as user_link_slug , p.pid, p.uid from wp_2_posts_authors p join wp_users u on u.id=case when find_in_set(p.post_author,'228,8,9,22,421,373')>0 then 4 else p.post_author end where p.id in (394953) ) pu join wp_usermeta fn on pu.user_id = fn.user_id join wp_usermeta ln on pu.user_id = ln.user_id join wp_usermeta dl on pu.user_id = dl.user_id join wp_usermeta ur on pu.user_id = ur.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'description_short') ds on pu.user_id = ds.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_prefix') px on pu.user_id = px.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_suffix') sx on pu.user_id = sx.user_id where fn.meta_key = 'first_name' and ln.meta_key = 'last_name' and dl.meta_key = 'description' and ur.meta_key = 'wp_capabilities' order by pu.pid desc, pu.uid asc;--> |, adaptation finance update: global commission catal... 8 october 2019 0 then 4 else u.id end as user_id , u.user_email as user_email , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' when left(u.user_login,2) = 'z_' or u.id=64 then 'guest-authors' else 'thematic-experts' end as user_link_role , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' else u.user_nicename end as user_link_slug , p.pid, p.uid from wp_2_posts_authors p join wp_users u on u.id=case when find_in_set(p.post_author,'228,8,9,22,421,373')>0 then 4 else p.post_author end where p.id in (394953) ) pu join wp_usermeta fn on pu.user_id = fn.user_id join wp_usermeta ln on pu.user_id = ln.user_id join wp_usermeta dl on pu.user_id = dl.user_id join wp_usermeta ur on pu.user_id = ur.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'description_short') ds on pu.user_id = ds.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_prefix') px on pu.user_id = px.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_suffix') sx on pu.user_id = sx.user_id where fn.meta_key = 'first_name' and ln.meta_key = 'last_name' and dl.meta_key = 'description' and ur.meta_key = 'wp_capabilities' order by pu.pid desc, pu.uid asc;--> |, iges report discusses pathways to reverse “unsustainable land transformations” in asia pacific 23 may 2019 0 then 4 else u.id end as user_id , u.user_email as user_email , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' when left(u.user_login,2) = 'z_' or u.id=64 then 'guest-authors' else 'thematic-experts' end as user_link_role , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' else u.user_nicename end as user_link_slug , p.pid, p.uid from wp_2_posts_authors p join wp_users u on u.id=case when find_in_set(p.post_author,'228,8,9,22,421,373')>0 then 4 else p.post_author end where p.id in (388828) ) pu join wp_usermeta fn on pu.user_id = fn.user_id join wp_usermeta ln on pu.user_id = ln.user_id join wp_usermeta dl on pu.user_id = dl.user_id join wp_usermeta ur on pu.user_id = ur.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'description_short') ds on pu.user_id = ds.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_prefix') px on pu.user_id = px.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_suffix') sx on pu.user_id = sx.user_id where fn.meta_key = 'first_name' and ln.meta_key = 'last_name' and dl.meta_key = 'description' and ur.meta_key = 'wp_capabilities' order by pu.pid desc, pu.uid asc;--> |, iges report discusses pathways to reverse “unsus... 23 may 2019 0 then 4 else u.id end as user_id , u.user_email as user_email , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' when left(u.user_login,2) = 'z_' or u.id=64 then 'guest-authors' else 'thematic-experts' end as user_link_role , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' else u.user_nicename end as user_link_slug , p.pid, p.uid from wp_2_posts_authors p join wp_users u on u.id=case when find_in_set(p.post_author,'228,8,9,22,421,373')>0 then 4 else p.post_author end where p.id in (388828) ) pu join wp_usermeta fn on pu.user_id = fn.user_id join wp_usermeta ln on pu.user_id = ln.user_id join wp_usermeta dl on pu.user_id = dl.user_id join wp_usermeta ur on pu.user_id = ur.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'description_short') ds on pu.user_id = ds.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_prefix') px on pu.user_id = px.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_suffix') sx on pu.user_id = sx.user_id where fn.meta_key = 'first_name' and ln.meta_key = 'last_name' and dl.meta_key = 'description' and ur.meta_key = 'wp_capabilities' order by pu.pid desc, pu.uid asc;--> |, ngos call for action on sdgs under review at 2019 hlpf 16 april 2019 0 then 4 else u.id end as user_id , u.user_email as user_email , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' when left(u.user_login,2) = 'z_' or u.id=64 then 'guest-authors' else 'thematic-experts' end as user_link_role , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' else u.user_nicename end as user_link_slug , p.pid, p.uid from wp_2_posts_authors p join wp_users u on u.id=case when find_in_set(p.post_author,'228,8,9,22,421,373')>0 then 4 else p.post_author end where p.id in (386651) ) pu join wp_usermeta fn on pu.user_id = fn.user_id join wp_usermeta ln on pu.user_id = ln.user_id join wp_usermeta dl on pu.user_id = dl.user_id join wp_usermeta ur on pu.user_id = ur.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'description_short') ds on pu.user_id = ds.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_prefix') px on pu.user_id = px.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_suffix') sx on pu.user_id = sx.user_id where fn.meta_key = 'first_name' and ln.meta_key = 'last_name' and dl.meta_key = 'description' and ur.meta_key = 'wp_capabilities' order by pu.pid desc, pu.uid asc;--> |, ngos call for action on sdgs under review at 2019 ... 16 april 2019 0 then 4 else u.id end as user_id , u.user_email as user_email , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' when left(u.user_login,2) = 'z_' or u.id=64 then 'guest-authors' else 'thematic-experts' end as user_link_role , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' else u.user_nicename end as user_link_slug , p.pid, p.uid from wp_2_posts_authors p join wp_users u on u.id=case when find_in_set(p.post_author,'228,8,9,22,421,373')>0 then 4 else p.post_author end where p.id in (386651) ) pu join wp_usermeta fn on pu.user_id = fn.user_id join wp_usermeta ln on pu.user_id = ln.user_id join wp_usermeta dl on pu.user_id = dl.user_id join wp_usermeta ur on pu.user_id = ur.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'description_short') ds on pu.user_id = ds.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_prefix') px on pu.user_id = px.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_suffix') sx on pu.user_id = sx.user_id where fn.meta_key = 'first_name' and ln.meta_key = 'last_name' and dl.meta_key = 'description' and ur.meta_key = 'wp_capabilities' order by pu.pid desc, pu.uid asc;--> |, non-party stakeholders provide inputs to the talanoa dialogue 12 april 2018 0 then 4 else u.id end as user_id , u.user_email as user_email , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' when left(u.user_login,2) = 'z_' or u.id=64 then 'guest-authors' else 'thematic-experts' end as user_link_role , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' else u.user_nicename end as user_link_slug , p.pid, p.uid from wp_2_posts_authors p join wp_users u on u.id=case when find_in_set(p.post_author,'228,8,9,22,421,373')>0 then 4 else p.post_author end where p.id in (365671) ) pu join wp_usermeta fn on pu.user_id = fn.user_id join wp_usermeta ln on pu.user_id = ln.user_id join wp_usermeta dl on pu.user_id = dl.user_id join wp_usermeta ur on pu.user_id = ur.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'description_short') ds on pu.user_id = ds.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_prefix') px on pu.user_id = px.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_suffix') sx on pu.user_id = sx.user_id where fn.meta_key = 'first_name' and ln.meta_key = 'last_name' and dl.meta_key = 'description' and ur.meta_key = 'wp_capabilities' order by pu.pid desc, pu.uid asc;--> |, non-party stakeholders provide inputs to the talan... 12 april 2018 0 then 4 else u.id end as user_id , u.user_email as user_email , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' when left(u.user_login,2) = 'z_' or u.id=64 then 'guest-authors' else 'thematic-experts' end as user_link_role , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' else u.user_nicename end as user_link_slug , p.pid, p.uid from wp_2_posts_authors p join wp_users u on u.id=case when find_in_set(p.post_author,'228,8,9,22,421,373')>0 then 4 else p.post_author end where p.id in (365671) ) pu join wp_usermeta fn on pu.user_id = fn.user_id join wp_usermeta ln on pu.user_id = ln.user_id join wp_usermeta dl on pu.user_id = dl.user_id join wp_usermeta ur on pu.user_id = ur.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'description_short') ds on pu.user_id = ds.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_prefix') px on pu.user_id = px.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_suffix') sx on pu.user_id = sx.user_id where fn.meta_key = 'first_name' and ln.meta_key = 'last_name' and dl.meta_key = 'description' and ur.meta_key = 'wp_capabilities' order by pu.pid desc, pu.uid asc;--> |, arctic circle assembly, amap report promote adaptation, sdgs in the arctic 19 october 2017 0 then 4 else u.id end as user_id , u.user_email as user_email , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' when left(u.user_login,2) = 'z_' or u.id=64 then 'guest-authors' else 'thematic-experts' end as user_link_role , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' else u.user_nicename end as user_link_slug , p.pid, p.uid from wp_2_posts_authors p join wp_users u on u.id=case when find_in_set(p.post_author,'228,8,9,22,421,373')>0 then 4 else p.post_author end where p.id in (354980) ) pu join wp_usermeta fn on pu.user_id = fn.user_id join wp_usermeta ln on pu.user_id = ln.user_id join wp_usermeta dl on pu.user_id = dl.user_id join wp_usermeta ur on pu.user_id = ur.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'description_short') ds on pu.user_id = ds.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_prefix') px on pu.user_id = px.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_suffix') sx on pu.user_id = sx.user_id where fn.meta_key = 'first_name' and ln.meta_key = 'last_name' and dl.meta_key = 'description' and ur.meta_key = 'wp_capabilities' order by pu.pid desc, pu.uid asc;--> |, arctic circle assembly, amap report promote adapta... 19 october 2017 0 then 4 else u.id end as user_id , u.user_email as user_email , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' when left(u.user_login,2) = 'z_' or u.id=64 then 'guest-authors' else 'thematic-experts' end as user_link_role , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' else u.user_nicename end as user_link_slug , p.pid, p.uid from wp_2_posts_authors p join wp_users u on u.id=case when find_in_set(p.post_author,'228,8,9,22,421,373')>0 then 4 else p.post_author end where p.id in (354980) ) pu join wp_usermeta fn on pu.user_id = fn.user_id join wp_usermeta ln on pu.user_id = ln.user_id join wp_usermeta dl on pu.user_id = dl.user_id join wp_usermeta ur on pu.user_id = ur.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'description_short') ds on pu.user_id = ds.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_prefix') px on pu.user_id = px.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_suffix') sx on pu.user_id = sx.user_id where fn.meta_key = 'first_name' and ln.meta_key = 'last_name' and dl.meta_key = 'description' and ur.meta_key = 'wp_capabilities' order by pu.pid desc, pu.uid asc;--> |, un biodiversity conference advances discussions on resource mobilization, ebsas, synthetic biology 7 december 2016 0 then 4 else u.id end as user_id , u.user_email as user_email , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' when left(u.user_login,2) = 'z_' or u.id=64 then 'guest-authors' else 'thematic-experts' end as user_link_role , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' else u.user_nicename end as user_link_slug , p.pid, p.uid from wp_2_posts_authors p join wp_users u on u.id=case when find_in_set(p.post_author,'228,8,9,22,421,373')>0 then 4 else p.post_author end where p.id in (338966) ) pu join wp_usermeta fn on pu.user_id = fn.user_id join wp_usermeta ln on pu.user_id = ln.user_id join wp_usermeta dl on pu.user_id = dl.user_id join wp_usermeta ur on pu.user_id = ur.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'description_short') ds on pu.user_id = ds.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_prefix') px on pu.user_id = px.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_suffix') sx on pu.user_id = sx.user_id where fn.meta_key = 'first_name' and ln.meta_key = 'last_name' and dl.meta_key = 'description' and ur.meta_key = 'wp_capabilities' order by pu.pid desc, pu.uid asc;--> |, un biodiversity conference advances discussions on... 7 december 2016 0 then 4 else u.id end as user_id , u.user_email as user_email , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' when left(u.user_login,2) = 'z_' or u.id=64 then 'guest-authors' else 'thematic-experts' end as user_link_role , case when u.user_nicename like '%-account' then '' else u.user_nicename end as user_link_slug , p.pid, p.uid from wp_2_posts_authors p join wp_users u on u.id=case when find_in_set(p.post_author,'228,8,9,22,421,373')>0 then 4 else p.post_author end where p.id in (338966) ) pu join wp_usermeta fn on pu.user_id = fn.user_id join wp_usermeta ln on pu.user_id = ln.user_id join wp_usermeta dl on pu.user_id = dl.user_id join wp_usermeta ur on pu.user_id = ur.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'description_short') ds on pu.user_id = ds.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_prefix') px on pu.user_id = px.user_id left join (select * from wp_usermeta where meta_key = 'user_suffix') sx on pu.user_id = sx.user_id where fn.meta_key = 'first_name' and ln.meta_key = 'last_name' and dl.meta_key = 'description' and ur.meta_key = 'wp_capabilities' order by pu.pid desc, pu.uid asc;--> |.
The SDG Update compiles the news, commentary and upcoming events that are published on the SDG Knowledge Hub each day, delivering information on the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development to your inbox.
Welcome to IISD's SDG Knowledge Hub
- Weight Management
- Nutrition Facts
- Nutrition Basics
- Meal Delivery Services
- Fitness Gear
- Apparel & Accessories
- Recipe Nutrition Calculator
- Weight Loss Calorie Goal
- BMI Calculator
- Body Fat Percentage Calculator
- Calories Burned by Activity
- Daily Calories Burned
- Pace Calculator
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
Pros and Cons of a Vegan Diet
Shereen Lehman, MS, is a former writer for Verywell Fit and Reuters Health. She's a healthcare journalist who writes about healthy eating and offers evidence-based advice for regular people.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/shereen-1f60ac63296d45eb89b4c7a7d782067e-5608c06027ba4ebeb5c54ccdc47f9d42-124899b94c76488b9fb1896447b45474.jpg)
Verywell / Alexandra Shytsman
A vegan diet is a vegetarian eating style, but it's completely devoid of animal products, including eggs , honey, and dairy products. Some vegans choose the diet for health reasons, but others prefer it for ethical reasons, such as avoiding animal cruelty and consuming more sustainable foods.
While there are documented health benefits of a vegan diet, some find the lifestyle challenging to maintain. Consider each of the pros and cons of a vegan diet before you decide if it is the right program for you.
Evidence-based health benefits
Encourages mindful eating
Wider variety of foods
May lead to weight loss
Reduced food costs
Healthier for the environment
No animal impact
Limited food choices
Possible nutrient deficiencies
Requires diligence
Difficulty dining out
Unrealistic expectations
Social isolation
The reason (or reasons) that you choose a vegan eating plan will determine the benefits that are most relevant for you. But advantages to this lifestyle are substantial, regardless of whether you are choosing it for health, environmental, or ethical reasons.
Health Benefits
Since a vegan diet is plant-based , it's easier to load up on healthy whole grains , legumes, fruits, and vegetables that many people on regular diets lack. Studies comparing different types of diets have found that vegan eating ranks highest for nutritional quality. A vegan diet is generally high in fiber, vitamin C , magnesium, iron, and folate and lower in calories and saturated fats.
The nutritional quality of a vegan diet leads to more significant health benefits. Eating a diet rich in plant-based foods has been associated with a decreased risk of many chronic diseases. A large cohort study evaluated vegetarian and vegan diets. Researchers found that both groups experienced a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases, cardiometabolic risk factors, some cancers, and total mortality. Those who were vegan enjoyed those benefits along with a reduced risk of obesity, hypertension, type-2 diabetes, and cardiovascular mortality.
Other studies have confirmed those findings and have also found that plant-based eating may be helpful in the treatment and management of high blood pressure, diverticular disease, and eye cataracts.
Mindful Eating
Mindful eating is a practice that involves paying more attention to our food and increasing sensual awareness and experience of a meal. It requires the eater to be focused intentionally on eating behavior to enjoy the process of eating rather than any specific nutritional outcome ( calories , protein, fat, carbohydrates). Mindful eating practices are associated with a healthier relationship with food and have been used in some weight-loss interventions.
Vegan eating and mindful eating are different. But because vegan eaters—unlike omnivores—choose to eliminate certain categories of food from their diet, they need to be more selective and conscious about their food choices. In many cases, certain mindful eating practices are built into their meal planning .
For example, if you consume a traditional American diet, it is easy to grab a meal on the go at a fast-food restaurant, convenience mart, or coffee shop. It is easy to consume the meal without being fully aware of the eating process (i.e.chewing, tasting, and feeling a sense of fullness). But on a vegan diet, you may have to plan meals in advance to find foods that you enjoy and that are compliant on the eating plan. Or you may have to make careful selections in the moment. The choosing and planning process requires consideration, focus, and thoughtfulness about your food choices—critical components of mindful eating.
Wider Food Variety
An omnivore diet eliminates no foods. The standard American diet is an omnivore diet. But most people who consume a traditional diet eat a relatively limited number of foods or types of food. For instance, many traditional American dinners include meat, starch (potato or rice), and maybe a vegetable. Dairy products are often used as ingredients, side dishes, or toppings.
On a vegan diet, however, many traditional foods are not compliant. Therefore, when you begin this diet, you may have to get creative and experiment with foods that are not familiar.
But there is a caveat to this benefit. Many food manufacturers are creating plant-based versions of traditional favorites. For instance, most grocery stores carry vegan-friendly meatless burgers, processed chicken or turkey alternatives, and dairy substitutes that are made from soy or other ingredients. Sometimes, these products are no healthier than their meat/dairy alternative, and relying on them can lead to the same limited food palate like a traditional American diet.
Possible Weight Loss
Studies have shown that you may lose weight on a vegan diet. Of course, just choosing to go vegan does not cause weight loss to occur. But when you adopt this lifestyle, you eliminate many foods that are high in fat and calories.
Plant-based eating is often associated with losing weight. In 2018, a limited 16-week clinical trial found that a vegan diet proved to be superior to a control diet (that included animal protein) in improving body weight and fat mass. And a broad evidence review published in 2017 found that plant-based diets are an effective tool in the management and prevention of overweight and obesity.
Even if you have problems staying on a weight loss plan, a vegan lifestyle might be the best choice. Studies have also shown that a vegan eating plan may be more effective for weight loss , even if you don't completely stick to the program.
Reduced Food Costs
Choosing a vegan diet may help you to reduce your food costs. But whether or not you gain this benefit depends on what you eat before adopting this eating style and what you choose to eat after.
There is no doubt that meat, seafood, and dairy products are expensive. Some convenience foods can also be pricey. When you remove these foods from your diet, you eliminate the substantial food costs that are associated with them.
Vegan-friendly-grains and legumes are usually budget-friendly. And even though fresh produce and vegan-friendly convenience foods can be expensive, they are likely to cost less overall than a diet rich in animal-based products.
Better for the Environment
Some people choose a vegan diet because they feel it is better for the planet. There is increased concern in the environmental community about the impact of livestock and livestock farming practices on the earth.
By comparison, the farming of vegan-friendly plants requires fewer resources (land and water) than the production of typical western foods such as meat, poultry, and dairy. And cows produce more greenhouses gasses (methane) than plants do, which leads some to believe that eating vegan helps to reduce the risk of global warming.
Several research studies have even suggested that a vegan diet is better for the planet than other diets, including the popular Mediterranean diet .
No Animal Impact
Because no animals are harmed or killed to produce vegan-friendly foods, many choose this diet because of concerns about animal cruelty.
One study showed that the most popular reason for choosing a vegan diet is to support the more humane treatment of animals. These vegans may also avoid clothing or other products that are made from animals, poultry, fish, or bees.
Interestingly, another research study published in the journal Appetite found that people who chose a vegan diet for ethical reasons were likely to stick to the diet longer than those who follow the program for other reasons.
Even though a vegan diet may be healthier for you and the planet, this program doesn't work for everyone. Consider these drawbacks.
Limited Food Choices
The vegan diet is often referred to as the most restrictive version of a plant-based diet. Certainly, if you adopt this eating plan, and you currently eat a standard American diet, you can expect to eliminate most foods from your typical weekly menu. For some people, that level of restriction is too severe.
To get a greater sense of the scope of the restriction, remember that not only are animal products eliminated, but any food or product that contains an animal by-product is eliminated. Many traditional home recipes, groceries, and restaurant foods contain at least one animal by-product.
Of course, many vegans will tell you that there is a wealth of food variety in this diet. But because it varies substantially from what you might be used to eating, you may find it to be limiting at first.
Possible Nutritional Deficiencies
A vegan diet can be healthy, but there are a few potential nutritional deficiencies that need to be addressed. Researchers have found that vegan diets are generally lacking in calcium , required for bone formation, muscle contraction, and other essential functions. Vegans can increase their intake by eating calcium-rich foods such as green leafy vegetables, pulses, sesame seeds, some dried fruits, and calcium-fortified foods such as plant milks, non-milk yogurt, or cereal with calcium added. Similarly, they can supplement their diet with multivitamins .
Vitamin B-12 , or cobalamin, is another nutrient that may be lacking because it's found primarily in foods of animal origin. Vitamin B-12 is needed for healthy nerve function and blood cell production. A deficiency can lead to a condition called pernicious anemia . Although some seaweed, mushrooms, and fermented foods can be a useful source of this essential B-complex vitamin, researchers have found that vitamin B-12 supplementation may be needed for people who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet.
Protein can be another issue, but it's one that is easily solved. Proteins are made up of building blocks called amino acids that your body needs to maintain organs and muscles and important functions. Essential amino acids are those that your body does not make so you need to get them from the foods you eat. Many vegans also take creatine supplements .
While animal proteins contain all of the essential amino acids, plant proteins are usually missing one or more of those amino acids. So, it's crucial to eat a variety of protein sources to ensure you get all those amino acids you need.
Vegan diets can also be low in vitamin D , though to be fair, so are other diets since most of your vitamin D comes from exposure to sunlight. Two potentially good vegan sources of vitamin D include maitake mushrooms and portobello mushrooms that have been exposed to UV light. Fortified nut milks can also help you get vitamin D during the winter months. In some cases, however, a vitamin D supplement may be needed.
A vegan diet is also deficient in two omega-3 fatty acids called eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid that your body needs for a healthy heart and eyes and brain function. Eating foods such as walnuts, soy, pumpkin, flax, or chia seeds , will help increase your intake of an omega-3 fatty acid called alpha-linolenic acid, which your body converts to the other two forms. Still, supplementing with a product such as a micro algae supplement may be needed. Also, if you're pregnant, however, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider to make sure you get enough omega-3s during your pregnancy.
Lastly, iron is a nutrient of concern in vegan diets. According to the Vegan Society, good plant sources of iron include lentils, chickpeas, beans, tofu, cashew nuts, chia seeds, ground linseed, hemp seeds, pumpkin seeds, kale, dried apricots and figs, raisins, quinoa and fortified breakfast cereal.
Requires Diligence
Those who follow a vegan diet will need to become accustomed to carefully reading nutrition labels and ingredient lists, especially if they choose to consume processed foods . Foods that you might assume to be free from animal by-products may contain gelatin, whey, casein, honey, or other foods that are non-compliant on a vegan diet.
You'll also need to carefully read nutrition labels to stay healthy on a vegan diet. It is important to choose foods that contain important vitamins and minerals to avoid nutritional deficiencies.
Difficulty Dining Out
When shopping for vegan-friendly food, consumers can read product information. But if you eat at someone's home or in a restaurant, you don't have access to an ingredient list. For this reason, dining out can be a challenge for those who choose a vegan diet.
A few restaurants make a note of vegan or vegetarian foods on their menus, but not many. You may be able to create a vegan meal from the salads or side dishes that they already serve. However, you'll need to ask to be sure that no animal products are used in the preparation.
And sometimes, even asking about food isn't helpful. It is not uncommon for well-meaning restaurant staff (or well-intentioned friends and family) to assume that plant-based foods are vegan if they don't contain dairy. But that isn't always the case. Vegetable soup, for example, might be made with broth that used an animal bone for flavoring.
Many vegan experts recommend that when dining at someone's home, bring a recipe that you can enjoy and that you can share with others. And choose restaurants that you know to be vegan-savvy.
Unrealistic Expectations
While consuming a vegan diet is likely to produce health benefits and a healthier weight, it is not a guarantee. For example, if you are trying to slim down, you still need to be mindful of the foods you choose and the amount you eat.
There is an increasing number of heavily processed vegan foods. Many times, these foods are just as unhealthy—containing more fat and calories—as their traditional counterparts.
And health benefits are not a slam dunk either. A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology compared a large number of women who ate a healthy vegan diet (including whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, oils, tea and coffee) to those who ate a less healthy vegan food (including juices, sweetened beverages, refined grains, potatoes, fries, and sweets). Researchers concluded that the healthier vegan diet resulted in a substantially lower risk for heart disease, whereas the less healthy vegan diet was associated with a higher risk.
Social Isolation
People's food choices can come under scrutiny from friends, family, coworkers, and other acquaintances. While veganism is more normalized these days and plant-based foods are more widely available, you might still find that you are questioned and challenged about your reasons for choosing this lifestyle. Additionally, those who don't know how to accommodate your diet may exclude you from social gatherings. Or worse, they may invite you and encourage you to eat foods that are not vegan-friendly.
Some vegan blogs address these issues and provide guidance for those adapting to the eating style. Experts advise that you reach out to other vegans in your community and build a network, while also being patient with those who don't understand your choices.
Clarys P, Deliens T, Huybrechts I, et al. Comparison of nutritional quality of the vegan, vegetarian, semi-vegetarian, pesco-vegetarian and omnivorous diet. Nutrients . 2014;6(3):1318–1332. doi:10.3390/nu6031318
Le, L., & Sabaté, J. (2014). Beyond Meatless, the Health Effects of Vegan Diets: Findings from the Adventist Cohorts . Nutrients, 6(6), 2131–2147. doi:10.3390/nu6062131
Mantzios M. Editorial: Mindfulness and Eating Behavior . Front Psychol . 2018;9:1986. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01986
Turner-McGrievy G, Mandes T, Crimarco A. A plant-based diet for overweight and obesity prevention and treatment. J Geriatr Cardiol . 2017;14(5):369–374. doi:10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2017.05.002
Moore W, McGrievy M, Turner-McGrievy G. Dietary adherence and acceptability of five different diets, including vegan and vegetarian diets, for weight loss : The New DIETs study. Eating Behaviors . 2015;19:33-38.
Castañé, S., & Antón, A. (2017). Assessment of the nutritional quality and environmental impact of two food diets: A Mediterranean and a vegan diet . Journal of Cleaner Production, 167, 929–937. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.04.121
Janssen, M., Busch, C., Rödiger, M., & Hamm, U. (2016). Motives of consumers following a vegan diet and their attitudes towards animal agriculture . Appetite, 105, 643–651. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2016.06.039
Radnitz, C., Beezhold, B., & DiMatteo, J. (2015). Investigation of lifestyle choices of individuals following a vegan diet for health and ethical reasons . Appetite, 90, 31–36. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2015.02.026
Rizzo G, Laganà AS, Rapisarda AM, et al. Vitamin B12 among Vegetarians: Status, Assessment and Supplementation . Nutrients . 2016;8(12):767. doi:10.3390/nu8120767
Sakkas H, Bozidis P, Touzios C, et al. Nutritional status and the influence of the vegan diet on the gut microbiota and human mealth . Medicina (Kaunas) . 2020;56(2):88. doi:10.3390/medicina56020088
Iron . The Vegan Society.
Satija A, Bhupathiraju S. et al. Healthful and Unhealthful Plant-Based Diets and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in U.S. Adults . Journal of the American College of Cardiology . 2017;70(4):411-422. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.05.047
Alexander S, Ostfeld RJ, Allen K, Williams KA. A plant-based diet and hypertension . J Geriatr Cardiol . 2017;14(5):327–330. doi:10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2017.05.014
Clarys P, Deliens T, Huybrechts I, et al. Comparison of nutritional quality of the vegan, vegetarian, semi-vegetarian, pesco-vegetarian and omnivorous diet. Nutrients . 2014;6(3):1318–1332. Published 2014 Mar 24. doi:10.3390/nu6031318
Harvard Women's Health Watch. " Becoming a Vegetarian ."
Kahleova H, Fleeman R, Hlozkova A, Holubkov R, Barnard ND. A plant-based diet in overweight individuals in a 16-week randomized clinical trial: metabolic benefits of plant protein. Nutr Diabetes . 2018;8(1):58. Published 2018 Nov 2. doi:10.1038/s41387-018-0067-4
Mantzios M. Editorial: Mindfulness and Eating Behavior . Front Psychol . 2018;9:1986. Published 2018 Oct 12. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01986
Moore W, McGrievy M, Turner-McGrievy G. Dietary adherence and acceptability of five different diets, including vegan and vegetarian diets, for weight loss : The New DIETs study. Eating Behaviors . 2015;19:33-38.
Satija A, Bhupathiraju S. et al. Healthful and Unhealthful Plant-Based Diets and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in U.S. Adults . Journal of the American College of Cardiology . 2017;70(4):411-422. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.05.047
- Craig WJ. " Health Effects of Vegan Diets ." Am J Clin Nutr . 2009 May;89(5):1627S-1633S.
By Shereen Lehman, MS Shereen Lehman, MS, is a former writer for Verywell Fit and Reuters Health. She's a healthcare journalist who writes about healthy eating and offers evidence-based advice for regular people.
IELTS Blog & IELTS Mock Test
Ielts exam preparation for a higher band score., ielts essay: everyone should adopt a vegetarian diet.
You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.
Write about the following topic:
Everyone should adopt a vegetarian diet because eating meat can cause serious health problems.
Do you agree or disagree?
Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own experience or knowledge.
Write at least 250 words.
Model Answer 1:
People should consume more vegetables and fruits and as little meat as possible because intake high amount of meat can cause serious health issues. In my opinion, the consumption of a vegetarian diet is a better way to live a healthy life and I agree with the notion.
Firstly, vegetarian diets are cheaper and more healthy. If the majority of people become vegetarians, a nation needs to struggle less to become self-sufficient on food production. Moreover, such diets are easily accessible both for the poor and rich citizens. Most importantly, plant-based food provides necessary vitamins and food values, especially fibre, which protect us from many dangerous diseases. Not to mention, producing vegetarian food is more ecologically sustainable, and it reduces damage to the environment.
On the contrary, a certain portion of meat is necessary for a balanced diet because it contains protein, calcium and other vitamins. Nevertheless, these can be also gained from alternative sources like beans, mushrooms and nuts. Most meats are cholesterol-rich, which is detrimental to the human body and cause diseases. On top of that, deadly illnesses like cardiovascular diseases, obesity and brain haemorrhage are increasing gradually all around the world due to a high intake of red meat in different countries and I believe a vegetarian diet is a perfect solution to all these problems.
In conclusion, a healthy diet determines our wellbeing and life expectancy. Since a vegetarian diet is far beneficial than meats, we should choose wisely and decrease our meat intake as little as possible.
[By – Amraiz Ali Shahzad ]
Model Answer 2:
When it is perfectly possible to lead a healthy life by eating plant-based food, I see no justification for killing birds or animals for our food. Therefore, I completely agree with the argument that everyone should adopt a vegetarian diet.
There are several benefits to following a vegetarian diet. To start with, plant-based food is rich in vitamins, minerals, anti-oxidants and other nutrients required for good health. What’s more, most fruits and vegetables contain little or no cholesterol or calories. Research has shown that vegetarians are less likely to develop health-related problems like obesity, cancer or heart diseases. Health benefits are not the only reason to follow a vegetarian diet. When we obtain our food from plants, we can also stop cruelty to animals.
By contrast, non-vegetarian foods such as fish and meat are high in cholesterol, fat and calories. Regular consumption of red meat is known to increase a person’s risk of cancer and heart disease. In addition, unlike fruits or vegetables, fish and meat cannot be eaten raw. The slaughtered animal may have some illness. If half-cooked meat is eaten, it can cause deadly infections in human beings. In fact, many cases of food poisoning are caused by the consumption of contaminated meat.
The quality of non-vegetarian food has also deteriorated over the years. Seafood has become contaminated due to the pollution in ocean water. It is a well-known fact that farm animals are given steroids to grow rapidly. When we eat their meat, the steroid also enters into our body. This leads to several problems like precocious puberty in children.
To conclude, vegetarian diets are healthy and do not constitute cruelty to animals. Therefore, I believe that everyone should adopt vegetarianism.
[Written by – Manoj ]
3 thoughts on “ IELTS Essay: Everyone should adopt a vegetarian diet ”
Excellent examples to prove to be vegetarian in IELTS essay. I need help in IELTS reading & listening in table chart completion.
Thanks for essay. My question is what is the best way to end an IELTS essay?
Wow! Read magazine to read more and learn for IELTS.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
CAPTCHA eighteen + = 19

Home / IELTS, CAE, FCE Writing Samples / IELTS Writing Task 2: Vegetarianism
IELTS Writing Task 2: Vegetarianism
Everyone should become vegetarian because they do not need to eat meat to have a healthy diet. Do you agree or disagree?
As veganism trending is becoming extremely common, many people hold the view that people can maintain a healthy lifestyle without the need of meat. I agree that being a vegetarian means being healthier. However, I would argue that remove meat from daily diet can lead to variously-detrimental consequences which directly associates to our health (1) . To begin with, there are many undeniable positive aspects of having a vegetarian diet. The most significant benefit is that this diet helps reverse several chronic illnesses such as heart disease, cancer or obesity. This is mainly because plant-based foods consume less cholesterol so consequently, there will be a lower level of blood pressure and cholesterol (2) . Another advantage is that vegetarians are less likely to be overweight as the amount of fat in vegetables is extremely lower than that in meat (3) . However, meat can nourish our body more than plant-based foods can. Firstly, vegetables are deficient in protein whereas a large amount of this is found in meat (4) . The main reason why human’s body needs to consume a balanced diet of protein is to build and repair tissue as well as maintain a healthy body, which is vital when doing anything energetic (5) . Secondly, besides promoting mental health, meat also improve physical health as meat is extremely rich in various vitamins and minerals such as vitamin A, B, D (6) . It has been proven that these vitamins play an important role in promoting good vision, stronger teeth and bones system (7) . In conclusion, it is true that following vegetarian diets results in many benefits such as lowering risks of getting chronic illnesses. However, I believe that meat is highly required while maintaining healthy diets (8) . 283 words
The commentaries are marked in brackets with number (*). The numbered commentaries are found below. The part in italics is taken from the text, the word underlined is the suggested correction. Words in (brackets) are the suggested addition to the original phrase or sentence.
- However, I would argue that removing meat from daily diet can lead to variously detrimental consequences for our health . — a gerund form is needed instead of ‘remove’. You don’t need a hyphen between ‘variously’ and ‘detrimental’. I have shortened your construction because the extra words do not add anything to the text. In that case the syntax was wrong too. Using more words that do not add any meaning is bad for your final score.
- This is mainly because plant-based foods contain less cholesterol so consequently, blood pressure will be lower. — ‘Cholesterol’ is pretty difficult to paraphrase, avoid using it twice in the same sentence.
- Another advantage is that vegetarians are less likely to be overweight as the amount of fat in vegetables is much lower than that in meat. — don’t forget that you are making a comparison here, a comparative adjective should be used.
- Firstly, vegetables are deficient in protein whereas a large amount of it is found in meat. — ‘it’ should be used to refer to something mentioned just now.
- The main reason why human’s body needs (to have ) a balanced diet of protein is to build and repair tissue (what tissue?) as well as maintain a healthy body, which is vital when doing anything energetic. — ‘to have a diet’ is a better collocation . Alternatively (and preferably) it could be omitted (the text in the brackets is optional).The second part of the sentence is a bit vague — it lacks specific information and hardly adds anything new to the essay. It states the obvious like ‘you need a healthy body to do something that requires energy’. Use your essay to conduct more interesting thoughts and less trite ideas e.g. ‘A healthy, energetic lifestyle is rare nowadays as most people spend their time in front of their computers. To maintain an active life like this one has to have a balanced diet’. This is just an example of how you can use the precious writing space to convey a message.
- Secondly, besides promoting mental health, meat also improves physical health as it is extremely rich in various vitamins and minerals such as vitamin A, B, D. — ‘meat’ is singular. Also avoid using this word twice — I have replaced it with with a pronoun.
- It has been proven that these vitamins play an important role in ensuring good vision, stronger teeth and bones — ‘Promote’ is not the best verb for this context. I have also dropped ‘system’ as it is redundant here.
- However, I believe that meat is highly recommended while maintaining healthy diets — ‘highly required’ is rarely used, and almost of all the uses are by foreign speakers (or so my google research indicates). Use ‘highly recommended’ or simply ‘required’.
The essay has adequate structure — both positive and negative aspects of the approach are given equal attention. The reader would be well-informed on the issue of vegetarianism. The language is fairly varied with a good range of health-related vocabulary. Occasional mistakes and inaccuracies do not stand in the way of understanding the message. The author occasionally repeats the same word — proof-reading the essay would have helped eliminating this.
Harmfulness of Vegetarianism: The False Health Claim Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Background of the Vegetarianism and Unproved Reasons Why it is Bad for Health
It is possible to notice that Vegetarianism, as a trend, is widespread today and has thousands of supporters. However, despite its popularity, there is no common opinion in society regarding it, which leads to the rise of various contradictory statements about the phenomenon. False health claims that “Vegetarianism is bad for health” are supported with numerous declarations, which do not have scientific evidence of their credibility. It is possible to find many Internet resources that mistakenly display Vegetarianism as a lifestyle, which influences adversely.
One of the unproven claims is that the brain is being deteriorated through vegetarian diets. Reinagel (2019) claims that “creatine is important for brain functioning and vegetarians have lower creatine levels,” which implies the existence of direct dependency between degradation of cognitive abilities and the absence of meat protein intake (Is a vegetarian diet bad for your brain? section, para 1.). The other unsupported, with references on studies argument, is that “Vegetarians had a 20% higher rate of stroke than meat-eaters’ ‘ (Doheny, 2019, Downsides to Eating Vegetarian/Vegan? Section, para. 1). The third unsupported statement, which is common throughout web resources, is that plants do not contain saturated fat in sufficient quantities. According to the article “How vegetarianism is bad for you and the environment” (n.d.), “Plant-based sources tend to be low in saturated fat, a component of the brain and a macronutrient vital for human health.” (Eating meat is unhealthy section, para. 2). This source also claims that plants contain much insoluble fiber that cannot be digested and can lead to abdominal discomforts, malabsorption, and toxic accumulation (“How vegetarianism is bad for you and the environment,” n.d.).
The fourth argument is related to the necessary micro-elements, the absence of which can trigger various diseases. Some resources claim, without evidence, that vitamin D3 can only be taken with meat, while a vegetarian diet is deprived of it and can cause brittle bones (Schreiber, 2016, Low Vitamin D section, para 1). Simultaneously, Vegetarianism provokes the lack of calcium, micro-element zinc, which is responsible for immune function, and iron, which is vital for blood cells producing (Schreiber, 2016, Not Enough Zinc section, para 1). Finally, it is possible to find resources that provide readers with subjective, unproved claims based on personal experience. Several negative consequences of being vegetarian, such as leading to the impossibility for women to become pregnant because of hormone levels deterioration, are claimed in the article by Campbell (2019). (The return of bacon section). In addition, the author provides another negative influence she experienced, which is reduced bone density (Campbell, 2019, More long-lasting adverse effects section, para 3). Therefore, websites, social media, and posts usually provide readers with unverified information, the irrelevancy of which is discussed further.
Scientifically Supported Arguments that Vegetarianism may has a Positive Influence on Health
On the other hand, credible sources support the usefulness of a vegetarian diet with scientifically proved evidence. According to Amit (2010), one of the arguments that Vegetarianism does not cause effects of deterioration on health is that “a variety of plant foods can provide all of the essential amino acids required for healthy adults (p. 304). This claim, which is opposite to the one mentioned in the previous paragraph, one, reveals the usefulness of the diet from the perspective of micro-elements containing, based on studies, appropriately cited. The second source shows that a Vegetarian diet can be prescribed for high blood pressure. Based on studies conducted, Garbett et al. (2016) claim that “a significant decrease in the prevalence of hypertension was associated with a vegetarian diet when compared with a non-vegetarian diet” (p. 455). Moreover, the other article dispels the myth that Vegetarianism negatively influences subjective well-being (SWB). According to Pfeiler & Egloff (2020), “The findings provided evidence that vegetarianism has, overall, no relationship to SWB” (p. 17). The myths associated with a potentially negative effect Vegetarianism may cause on the immune system and gut microbiota are also revealed in other credible studies. For instance, Zhang et al. (2018) claim that “vegetarian diets might provide certain benefits to our health through modulation of the immune system and the gut microbiota” (p. 11). Finally, the study conducted by McDougal et al. (1995) shows positive influences of vegetarian diets, such as total cholesterol reduction, regardless of the age of gender, weight loss for all of the experiment participants, and fall in systolic and diastolic blood pressure (p. 493). It is possible to notice that multiply credible sources prove the usefulness of Vegetarianism and refute all the unvalidated statements provided by web resources.
Why it is Important to Check the Sources of Information
The sources of information are vital for any research conducting, as they form an insight into a specific topic. It is especially significant for healthcare professionals to know how to distinguish credible sources, as this form of information can be crucial for treatment. Simultaneously, data is being constantly changed and improved, which complicates its correct utilization and obligates validating it during the research (“Evaluating Health Information,” n.d.). Sources such as magazines, TV stories, and advertisements may not be accurate. Only resources, which provide links to studies they are based on and correspond to criteria of credibility, can be considered reliable ones (“Finding reliable health information,” n.d.). It is necessary to evaluate sources per five benchmarks: authority, accuracy, objectivity, currency, and coverage, to ensure their reliability that directly influences the quality of care (Evaluating Information Resources, 2018). Therefore, the checking of sources of information is the primary ability health care professional should possess and utilize for the compliance of their knowledge with recent, significant findings, which is vital for patients’ well-being.
Reinagel, M. (2019). Is a Vegetarian diet bad for your brain? Scientificamerican. Web.
Doheny, K. (2019). Are there health downsides to Vegetarian diets? Nourish. Web.
How Vegetarianism is bad for you and the environment? (n.d.). PaleoLeap. Web.
Campbell, L. (2019). I Was a Vegetarian for 13 Years… and Now I Totally Regret It. Healthline. Web.
Schreiber, K. (2016). 6 Ways Being a Vegetarian Could Seriously Mess You Up. Cosmopolitan. Web.
Amit, M. (2010). Vegetarian diets in children and adolescents. Canadian Paediatric Society, 15 (5), 303-314. Web.
Garbett, T. M., Garbett, D. L., & Wendorf, A. (2016). Vegetarian Diet: A Prescription for High Blood Pressure? A Systematic Review of the Literature. The Journal for Nurse Practitioners, 12 (7), 452–458. Web.
Pfeiler, T. M., & Egloff, B. (2020). Do Vegetarians Feel Bad? Examining the Association Between Eating Vegetarian and Subjective Well-Being in Two Representative Samples. Food Quality and Preference, 104018. Web.
Zhang, C., Björkman, A., Cai, K., Liu, G., Wang, C., Li, Y., Pan-Hammarström, Q. (2018). Impact of a 3-Months Vegetarian Diet on the Gut Microbiota and Immune Repertoire. Frontiers in Immunology, 9. Web.
McDougall, J., Litzau, K., Haver, E., Saunders, V., & Spiller, G. A. (1995). Rapid reduction of serum cholesterol and blood pressure by a twelve-day, very low fat, strictly vegetarian diet. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 14 (5), 491–496. Web.
Evaluating Health Information (n.d.). UCSFHealth. Web.
Finding reliable health information (n.d.). BetterHealth. Web.
Evaluating Information Resources (2018). Elmer E. Rasmuson Library. Web.
- Weight and Muscle Gain: Different Ways Comparison
- Why You Should Not Be a Vegetarian
- Vegetarian Diet as a Health-Conscious Lifestyle
- Insulin Access and Affordability Working Group
- Benefits of Milk: The False Health Claim
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Role in Influenza Preparedness
- Native Americans' Health and Discriminatory Practices
- Discussion of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, October 22). Harmfulness of Vegetarianism: The False Health Claim. https://ivypanda.com/essays/harmfulness-of-vegetarianism-the-false-health-claim/
"Harmfulness of Vegetarianism: The False Health Claim." IvyPanda , 22 Oct. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/harmfulness-of-vegetarianism-the-false-health-claim/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Harmfulness of Vegetarianism: The False Health Claim'. 22 October.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Harmfulness of Vegetarianism: The False Health Claim." October 22, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/harmfulness-of-vegetarianism-the-false-health-claim/.
1. IvyPanda . "Harmfulness of Vegetarianism: The False Health Claim." October 22, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/harmfulness-of-vegetarianism-the-false-health-claim/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Harmfulness of Vegetarianism: The False Health Claim." October 22, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/harmfulness-of-vegetarianism-the-false-health-claim/.

What’s the difference between vegan and vegetarian?
NHMRC Emerging Leadership Fellow and Senior Research Fellow at the Institute for Physical Activity and Nutrition, Deakin University
Disclosure statement
Katherine Livingstone receives funding from the National Health and Medical Research Council (APP117380) and the National Heart Foundation (ID106800).
Deakin University provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
What’s the difference? is a new editorial product that explains the similarities and differences between commonly confused health and medical terms, and why they matter.
Vegan and vegetarian diets are plant-based diets . Both include plant foods, such as fruits, vegetables, legumes and whole grains.
But there are important differences, and knowing what you can and can’t eat when it comes to a vegan and vegetarian diet can be confusing.
So, what’s the main difference?
What’s a vegan diet?
A vegan diet is an entirely plant-based diet. It doesn’t include any meat and animal products. So, no meat, poultry, fish, seafood, eggs, dairy or honey.
What’s a vegetarian diet?
A vegetarian diet is a plant-based diet that generally excludes meat, poultry, fish and seafood, but can include animal products. So, unlike a vegan diet, a vegetarian diet can include eggs, dairy and honey.
But you may be wondering why you’ve heard of vegetarians who eat fish, vegetarians who don’t eat eggs, vegetarians who don’t eat dairy, and even vegetarians who eat some meat. Well, it’s because there are variations on a vegetarian diet:
a lacto-ovo vegetarian diet excludes meat, poultry, fish and seafood, but includes eggs, dairy and honey
an ovo-vegetarian diet excludes meat, poultry, fish, seafood and dairy, but includes eggs and honey
a lacto-vegetarian diet excludes meat, poultry, fish, seafood and eggs, but includes dairy and honey
a pescatarian diet excludes meat and poultry, but includes eggs, dairy, honey, fish and seafood
a flexitarian , or semi-vegetarian diet, includes eggs, dairy and honey and may include small amounts of meat, poultry, fish and seafood.
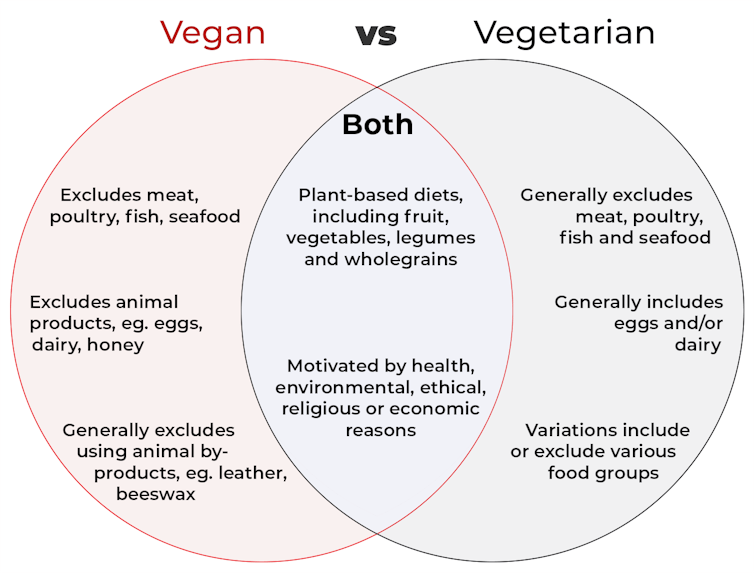
Are these diets healthy?
A 2023 review looked at the health effects of vegetarian and vegan diets from two types of study.
Observational studies followed people over the years to see how their diets were linked to their health. In these studies, eating a vegetarian diet was associated with a lower risk of developing cardiovascular disease (such as heart disease or a stroke), diabetes, hypertension (high blood pressure), dementia and cancer.
For example, in a study of 44,561 participants, the risk of heart disease was 32% lower in vegetarians than non-vegetarians after an average follow-up of nearly 12 years.
Further evidence came from randomised controlled trials. These instruct study participants to eat a specific diet for a specific period of time and monitor their health throughout. These studies showed eating a vegetarian or vegan diet led to reductions in weight, blood pressure, and levels of unhealthy cholesterol.
For example, one analysis combined data from seven randomised controlled trials. This so-called meta-analysis included data from 311 participants. It showed eating a vegetarian diet was associated with a systolic blood pressure (the first number in your blood pressure reading) an average 5 mmHg lower compared with non-vegetarian diets.
It seems vegetarian diets are more likely to be healthier, across a number of measures.
For example, a 2022 meta-analysis combined the results of several observational studies. It concluded a vegetarian diet, rather than vegan diet, was recommended to prevent heart disease.
There is also evidence vegans are more likely to have bone fractures than vegetarians. This could be partly due to a lower body-mass index and a lower intake of nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D and protein.
But it can be about more than just food
Many vegans, where possible, do not use products that directly or indirectly involve using animals.
So vegans would not wear leather, wool or silk clothing, for example. And they would not use soaps or candles made from beeswax, or use products tested on animals.
The motivation for following a vegan or vegetarian diet can vary from person to person. Common motivations include health, environmental, ethical, religious or economic reasons.
And for many people who follow a vegan or vegetarian diet, this forms a central part of their identity .

So, should I adopt a vegan or vegetarian diet?
If you are thinking about a vegan or vegetarian diet, here are some things to consider:
eating more plant foods does not automatically mean you are eating a healthier diet. Hot chips, biscuits and soft drinks can all be vegan or vegetarian foods. And many plant-based alternatives , such as plant-based sausages, can be high in added salt
meeting the nutrient intake targets for vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and iodine requires more careful planning while on a vegan or vegetarian diet. This is because meat, seafood and animal products are good sources of these vitamins and minerals
eating a plant-based diet doesn’t necessarily mean excluding all meat and animal products. A healthy flexitarian diet prioritises eating more whole plant-foods, such as vegetables and beans, and less processed meat, such as bacon and sausages
the Australian Dietary Guidelines recommend eating a wide variety of foods from the five food groups (fruit, vegetables, cereals, lean meat and/or their alternatives and reduced-fat dairy products and/or their alternatives). So if you are eating animal products, choose lean, reduced-fat meats and dairy products and limit processed meats.
- Consumer health
- Plant-based diet
- Vegetarian diet
- What's the difference?

Chief Operating Officer (COO)

Technical Assistant - Metabolomics

Data Manager

Director, Social Policy

Head, School of Psychology
Essays About Veganism: Top 5 Examples and 10 Prompts
Veganism is on the rise. See below for our great examples of essays about veganism and helpful writing prompts to get started.
Veganism is the practice of abstaining from animal-based foods and products. The movement originated from the philosophies against using animals as commodities and for capitalist gains. Now a booming industry, veganism promises better health benefits, a more humane world for animals, and an effective solution to global warming.
Here is our round-up of essays examples about veganism:
1. A Brief History of Veganism by Claire Suddath
2. animal testing on plant-based ingredients divides vegan community by jill ettinger, 3. as vegan activism grows, politicians aim to protect agri-business, restaurateurs by alexia renard, 4. bezos, gates back fake meat and dairy made from fungus as next big alt-protein by bob woods, 5. going vegan: can switching to a plant-based diet really save the planet by sarah marsh, 1. health pros and cons of veganism, 2. veganism vs. vegetarianism, 3. the vegan society, 4. making a vegan diet plan, 5. profitability of vegan restaurants, 6. public personalities who are vegan, 7. the rise of different vegan products, 8. is vegan better for athletes, 9. vegans in your community, 10. most popular vegan activists.
“Veganism is an extreme form of vegetarianism, and though the term was coined in 1944, the concept of flesh-avoidance can be traced back to ancient Indian and eastern Mediterranean societies.”
Suddath maps out the historical roots of veganism and the global routes of its influences. She also laid down its evolution in various countries where vegan food choices became more flexible in considering animal-derived products critical to health.
“Along with eschewing animal products at mealtime, vegans don’t support other practices that harm animals, including animal testing. But it’s a process rampant in both the food and drug industries.”
Ettinger follows the case of two vegan-founded startups that ironically conducts animal testing to evaluate the safety of their vegan ingredients for human consumption. The essay brings to light the conflicts between the need to launch more vegan products and ensuring the safety of consumers through FDA-required animal tests.
“Indeed, at a time when the supply of vegan products is increasing, activists sometimes fear the reduction of veganism to a depoliticized way of life that has been taken over by the food industry.”
The author reflects on a series of recent vegan and animal rights activist movements and implies disappointment over the government’s response to protect public safety rather than support the protests’ cause. The essay differentiates the many ways one promotes and fights for veganism and animal rights but emphasizes the effectiveness of collective action in shaping better societies.
“Beyond fungus, Nature’s Fynd also is representative of the food sustainability movement, whose mission is to reduce the carbon footprint of global food systems, which generate 34% of greenhouse emissions linked to climate change.”
The essay features a company that produces alternative meat products and has the backing of Jeff Bezos, Bill Gates, and Al Gore. The essay divulges the company’s investments and plans to expand in the vegan market while providing a picture of the burgeoning alternative foods sector.
“Experts say changing the way we eat is necessary for the future of the planet but that government policy is needed alongside this. If politicians are serious about wanting dietary changes, they also need to incentivise it, scientists and writers add.”
The article conveys the insights and recommendations of environmental and agriculture experts on how to turn more individuals into vegans. The experts emphasize the need for a whole-of-society approach in shifting more diets to vegan instead of putting the onus for change on an individual.
10 Writing Prompts on Essays About Veganism
Here is our round-up of the best prompts to create interesting essays about veganism:
While veganism has been a top choice for those desiring to lose weight and have a healthier lifestyle, some studies have also shown its detrimental effects on health due to deficiencies in specific vitamins. First, find out what existing research and experts say about this. Then, lay down the advantages and disadvantages of going vegan, explain each, and wrap up your essay with your insights.
Differentiate veganism from vegetarianism. Tackle the foods vegans and vegetarians consume and do not consume and cite the different effects they have on your health and the environment. You may also expand this prompt to discuss the other dietary choices that spawned from veganism.
The Vegan Society is a UK-based non-profit organization aimed at educating the public on the ways of veganism and promoting this as a way of life to as many people. Expound on its history, key organizational pillars, and recent and future campaigns. You may also broaden this prompt by listing down vegan organizations around the world. Then discuss each one’s objectives and campaigns.
Write down the healthiest foods you recommend your readers to include in a vegan diet plan. Contrary to myths, vegan foods can be very flavorful depending on how they are cooked and prepared. You may expand this prompt to add recommendations for the most flavorful spices and sauces to take any vegan recipe a notch higher.
Vegan restaurants were originally a niche market. But with the rise of vegan food products and several multinational firms’ foray into the market, the momentum for vegan restaurants was launched into an upward trajectory—research on how profitable vegan restaurants are against restos offering meat on the menu. You may also recommend innovative business strategies for a starting vegan restaurant to thrive and stay competitive in the market.

From J.Lo to Bill Gates, there is an increasing number of famous personalities who are riding the vegan trend with good reason. So first, list a few celebrities, influencers, and public figures who are known advocates of veganism. Then, research and write about stories that compelled them to change their dietary preference.
The market for vegan-based non-food products is rising, from makeup to leather bags and clothes. First, create a list of vegan brands that are growing in popularity. Then, research the materials they use and the processes they employ to preserve the vegan principles. This may prompt may also turn into a list of the best gift ideas for vegans.
Many believe that a high-protein diet is a must for athletes. However, several athletes have dispelled the myth that vegan diets lack the protein levels for rigorous training and demanding competition. First, delve deeper into the vegan foods that serve as meat alternatives regarding protein intake. Then, cite other health benefits a vegan diet can offer to athletes. You may also add research on what vegan athletes say about how a vegan diet gives them energy.
Interview people in your community who are vegan. Write about how they made the decision and how they transitioned to this lifestyle. What were the initial challenges in their journey, and how did they overcome these? Also, ask them for tips they would recommend to those who are struggling to uphold their veganism.
Make a list of the most popular vegan activists. You may narrow your list to personalities in digital media who are speaking loud and proud about their lifestyle choice and trying to inspire others to convert. Narrate the ways they have made and are making an impact in their communities.
To enhance your essay, read our guide explaining what is persuasive writing .
If you’d like to learn more, check out our guide on how to write an argumentative essay .

Yna Lim is a communications specialist currently focused on policy advocacy. In her eight years of writing, she has been exposed to a variety of topics, including cryptocurrency, web hosting, agriculture, marketing, intellectual property, data privacy and international trade. A former journalist in one of the top business papers in the Philippines, Yna is currently pursuing her master's degree in economics and business.
View all posts
- Share full article

The Interview
Richard linklater sees the killer inside us all.
Credit... Devin Oktar Yalkin for The New York Times
Supported by

By David Marchese
- June 1, 2024
Richard Linklater’s latest movie, “ Hit Man ,” is a bit of a departure for the director, who has made some of the most acclaimed and influential indie films of the last 30-plus years. The movie, which stars the ascendant Glen Powell, is about a mild-mannered college professor who has a side gig with the New Orleans Police Department, setting up stings by posing as different hit men. It’s a tight, stylish and sexy thriller, with some twisted romance added in, from a filmmaker better known for the ambling rhythms and gently existential tone of beloved classics like “Dazed and Confused,” “Boyhood” and “Before Sunrise” (not to mention his great comedy “School of Rock,” which exists in a category of its own).
Listen to the Conversation With Richard Linklater
But alongside its pop charms, “Hit Man” still manages to sneak in a provocative exploration of one of Linklater’s pet themes: the nature and malleability of personal identity. It’s also, as so many of the 63-year-old’s films are, a movie that understands the pure cinematic pleasure of watching smart, inquisitive people converse — exploring ideas and philosophies, making one another laugh, testing one another.
It’s the talking that made me fall in love with Linklater’s films, which he almost always writes or co-writes. (He co-wrote “Hit Man” with Powell.) The way his vivid, relatable characters discuss the big questions, with so much soul and hang-looseness, free from any highfalutin airs, has long been something of a north star for me as a movie lover and as a talker. The searching, openhearted discussions in Linklater films are the kind of conversations most meaningful to me in my own life and work. I don’t want to make too big a deal of it, but I can see a pretty clear line from adolescent me sitting around watching all the chatty oddballs in “Waking Life” and “Slacker” to middle-aged me, here and now, speaking with Richard Linklater — who, surprise surprise, sounds a lot like a character from one of his movies.
I’m curious how you think about your identity at 63 years old. Do you feel as if it’s fixed? Do you still have formative experiences? It’s the kind of thing I’ve thought a lot about my entire life: What could transform me? I was probably more in the camp of we’re fixed, give or take whatever little percentage around the edges. So I was interested in this notion lately that, oh, you can change, the personality isn’t fixed. That seems current: this notion of self and identity, gender. I sort of like that it’s all on the table, that everybody’s thinking you kind of are who you say you are. To me, that’s interesting.
Do you have a lot of different identities? Probably as many as anybody else.
What are the different ones? Well, if you get me on a Ping-Pong table — my third rail is athletics. I feel this little rush of competitiveness, which I really don’t have in the world of art at all — or my life even. I’m the guy looking at the world through glass. I was always the guy in the corner thinking about everything. I’m an introvert who gets put in extroverted situations occasionally, and I can play that role. But roles I currently play? I don’t know. It’s nice to care less about it as you get older.

About what? Consistency maybe? But my purest self is on the set making a movie. That’s the pure me, but it’s manufactured me. Catch me at dinner later, and you get the guy who’s processing the [expletive] of the day and having his lectures about whatever lunatic political ideas that are flowing through my system in real time like everybody else. But I process the world through art, in particular cinema, and that’s the space that I’ve been lucky enough to live in.
What’s a lunatic political idea that’s in your system right now? If you’re unfortunate enough to be sitting next to me at dinner, I will spout off what I’m putting together superficially in my head to have the world make sense, but I don’t have a need to share that publicly. I could share my brain snot with the whole world the way everybody else does, but I don’t see any value in it for me, because I’ve been privileged to make the greatest, most expressive storytelling art form ever invented. So why would I put any effort into these transitory, weird, reactive areas?
I read t he New Yorker profile of you from around the time of “Boyhood.” It said that there was some point in your life as a young man when you were watching 600 movies a year. I think a lot of us can relate to that feeling, especially in early adulthood or late adolescence, of falling in love with an art form. I’m curious about the feeling you get from movies now and how it’s different from what it used to be. I don’t think you can ever replace that initial passion and fury when you’ve discovered your art form and you take it in with your entire being. A lot of it, looking back, it’s like, Oh, that’s what you had to do, transitioning from the real world to your world, and in my case, it was cinema. It was the world of film. It’s this wonderful parallel universe. The arts are this other world you want to live in. But it’s different now. I don’t have the need to see that many movies. I still love movies, still dedicated to it, but you feed yourself in different ways.
What’s a recent movie that blew the top of your head off? That’s a good question. I can’t get the same jolt. I can get a jolt, but it’s a different kind of jolt. I know too much. I’m behind the camera. I know what they’re doing. But what got my cinematic blood circulating? I kind of put “The Zone of Interest” in that category. I was looking at that going: bold . You know, boom, that’s a movie.
You’re working currently on an adaptation of the Sondheim musical “Merrily We Roll Along.” The musical takes place over the course of 20 years, and you’re filming your adaptation over 20 years. So when you finish this movie — I guess with the caveat if you finish this movie — [Laughs.] Yeah, throw that in there, please.
You’re going to be over 80 years old. I’ll be about 80.
The film is going to be kind of a life and career capstone. So tell me: Why that project? You want to hear something that’s technically insane, and I admit it?
Yes. You said capstone to a career at age 80. I’ve never thought that, because I see myself making a film when I’m like 94. I really do. I’ll go along, try to stay in shape, try to be healthy, hope to get lucky. But we’re telling a story that takes place over 20 years, and it’s really important, for this story to work, that you feel those years go by. That was “Boyhood.” You had to feel life going by. And this movie is about long-term friendship and the way life treats people and how that shifts around over 20 years. Everybody involved is clearly doing it because they care, so we just have to assume they’ll keep caring and they’ll care 10 years, 15, 16, 17 more years. You judge people on that. Before I cast someone, I go, You’re a lifer. I did that on “Boyhood.” I asked Patricia Arquette, “What are you going to be doing 12 years from now?” She’s like, “I’m going to probably be looking for a part to play.” I said, “Yeah and I’m going to be trying to make a film, so let’s just start now and we’ll be who we are now and in the future.” That’s all it was. It’s not some huge leap of faith.
It’s blowing my mind that you could say this movie that I’m going to spend 20 years making, that I’m going to finish when I’m 83 — 80. I’ll be 80.
If anybody spent 20 years working on something, you’d say, Well, that says something about who they are and what’s important to them. Telling a well-told story the right way is what means the most to me. Finding the form that meets the content. That’s what a director does: not just the story but how to tell it, what it should look and feel like. I love that Jay DeFeo painting “ The Rose .” Have you ever seen it?
It’s huge, right? It’s huge. It’s like a foot thick because she spent so many years painting layers of paint on it. I find it so moving. It’s a stunning work, but how’d it get so thick? I mean, most artists, we have found the right therapy for our conditions. If you ask any actor, what do film directors have in common, they would probably say stuff like obsession, perfection. We’re just — everyone’s wired a little different. I admit that about myself and just go with it.
Do you have some contingency plan if, I don’t know, your vision starts to go 10 years from now? What happens to “Merrily We Roll Along”? Oh, good thought. Hmm. If I had everything else and the vision went, I would probably get — I don’t know! That’s a good question.
I can make you a list. I would adapt somehow. Or just turn the whole thing over to someone else. I’ll deal with that when it happens. I mean, what’s the alternative? I think of death regularly. But then I have this other side that just expects to play it out, I guess.
You think of death regularly? Sure. Not in a bad way. Just, I see life as kind of fleeting. Is that bad?
That sounds like a question that could be posed by a character in one of your films. [Laughs.] Well, it comes from somewhere. It’s kind of poetic to know I’m not going to be here forever. No one is. I walk through graveyards, and I read obits. I’m not morbid about it. I just acknowledge life passing and all of us being here for a little while, and it’s kind of beautiful that we’re all here, crossing paths at the same moment. I saw that as a kid.
Saw what as a kid? I knew it from the earliest of ages. I liked astronomy and I liked science and knowing how old everything was and, like, oh, we really are insignificant. That scares some people, but I love that feeling. I love that feeling of how random and small we are in the universe. It doesn’t bother me at all. I always thought that was kind of beautiful. Like, instead of being nothing, we’re kind of special. This is kind of a miracle, actually.
I was reading about the poet Delmore Schwartz. He has this poem called “Seurat’s Sunday Afternoon Along the Seine,” and it’s all about the artist as someone who observes life but doesn’t fully participate in it. I read that and was then thinking about you. Because I think of your films as having all these very intimately observed moments of what on the surface just seem like normal life; throughout “Boyhood,” there are countless scenes of just normal life. That’s all it is.
Are you always sitting back and observing life from a distance? Always. That’s the curse. I’m in the moment, I’m out of the moment. But then there’s also kind of a mentality, I think not uncommon to writers and film people, like, this will only be real when I process it through my art form. Something terrible is happening right in front of you: Your loved one is dying or relationship is ending, and you’re processing it not in the moment but, like, I’m going to have a character in a movie someday experience this, and I’m going to try to capture this. But you’re robbing yourself and the person you’re with of that moment. You can’t say you’re not heightened — you have a very heightened awareness of it. You’re bringing a lot of depth to it, but maybe it’s a self-preservation way of taking something and storing it away or processing it — like nothing’s real until I make it work in a movie .
Linklater and I spoke again five days later.
There was something on the tip of my tongue the whole time we spoke before, and I didn’t know if it was OK to bring up: the ending of “Hit Man,” which threw me for a loop. Oh, I’m not a spoiler person. I don’t care.
One idea of the film — and this is something we talked about earlier — is that we all have the power to create our own identity. The film then suggests that this includes the identity of someone capable of murder and living happily after having committed murder. That’s pretty dark! Yes, but, I mean, everybody wants someone dead, probably. I’ve been in the film business over 30 years. Of course I could murder somebody.
Whom do you want dead? No, I don’t want anyone dead. I’ll spread that out: I don’t want any thing dead. But I think there’s a surprising number of people in the world who, to whatever degree voluntary or involuntary, have done something that has ended a life and can compartmentalize it away. A lot of killers among us. Not just soldiers and people who did it for love of country and all. I don’t know if you saw my documentary —
I was going to say! What you’re talking about reminds me of the doc you did for “God Save Texas,” the HBO series. Do you want to tell people what that documentary was about? Well, it’s an exploration of my hometown and the world I grew up in. But it does circle around the death penalty, mainly from the people who are involved in the killing machine of it, the state-sanctioned-murder part of it. I want people to have empathy for the people whose job it was to participate on behalf of the state.
You grew up in Huntsville, which is the town where Texas carries out its state executions? Yeah, it’s where the prison system is based, and they do the executions there.
The questions posed by your documentary about how people find a way to coexist with a moral abomination, which is the death penalty, also reminded me of how you mentioned “The Zone of Interest.” That film, in an even more extreme way, asks similar questions about how people go about their lives right beside something awful. And I wondered, do you feel as if you have an understanding of how people are able to compartmentalize? I don’t know. I’ve always been fascinated by that, how we can compartmentalize. Just think of the way we treat animals. If you eat meat, you are supporting a supercruel, horrible industry that creates incredible pain and suffering.
You’ve been a vegetarian for a long time, right? Yeah. You can’t make it through the modern world without pushing out the horror show that is a lot of life. We all do that. It’s happening all the time. We’re all doing this little psychic dance to let ourselves think we’re not horrible people. You know, we’re suing the state of Texas right now.
I didn’t know that. What are you suing Texas for? My friend, Bernie Tiede —
Oh, the real life inspiration for your movie “Bernie”! Yeah, he’s the lead plaintiff. They have just an unbelievably cruel system where they don’t have to air-condition prison cells. They do federal, they do local jails, they do for animal facilities, but somehow you don’t have to for state, and it’s just horrible. So there’s this big lawsuit that we really think will change a lot of people’s lives. You could dedicate your entire life to trying to make the world a better place. But I pick my spots. Can I bring up something?
Yeah. When you were asking — and it’s a poignant, important question — What’s your relationship now to the work back then? Are you as passionate? I really had to think about that. My analysis of that is, you’re a different person with different needs. A lot of that is based on confidence. When you’re starting out in an art form or anything in life, you can’t have confidence because you don’t have experience, and you can only get confidence through experience. But you have to be pretty confident to make a film. So the only way you counterbalance that lack of experience and confidence is absolute passion, fanatical spirit. And I’ve had this conversation over the years with filmmaker friends: Am I as passionate as I was in my 20s? Would I risk my whole life? If it was my best friend or my negative drowning, which do I save? The 20-something self goes, I’m saving my film! Now it’s not that answer. I’m not ashamed to say that, because all that passion doesn’t go away. It disperses a little healthfully. I’m passionate about more things in the world. I care about more things, and that serves me. The most fascinating relationship we all have is to ourselves at different times in our lives. You look back, and it’s like, I’m not as passionate as I was at 25. Thank God. That person was very insecure, very unkind. You’re better than that now. Hopefully.
Director of photography (video): Aaron Katter
This interview has been edited and condensed from two conversations. Listen to and follow “The Interview” on Apple Podcasts , Spotify , YouTube , Amazon Music or the New York Times Audio app .
David Marchese is a writer and co-host of The Interview , a regular series featuring influential people across culture, politics, business, sports and beyond. More about David Marchese
Conversations with the world’s most fascinating people.
Ted Sarandos : The Netflix chief has a plan to get you to binge even more film and television on the streaming platform.
Dr. Ayana Elizabeth Johnson : The scientist believes she has an antidote to our delusions over climate change .
Charlamagne Tha God : The radio host has become a political force. Here’s how he plans to wield his influence .
Marlon Wayans : The comedian talks about working through loss — including the death of his parents — by finding humor in everything .
Yair Lapid : The Israeli opposition leader is a fierce critic of Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, but defends his country’s conduct in the Gaza war .
Anne Hathaway : The seasoned actress says she’s been learning to let go of other people’s opinions and expectations .
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Organisation. In this vegetarianism essay, the candidate disagrees with the statement, and is thus arguing that everyone does not need to be a vegetarian. The essay has been organised in the following way: Body 1: Health issues connected with eating meat (i.e. arguments in support of being a vegetarian. Body 2: Advantages of eating meat.
Quality of life relates to a subjective perception of well-being and functionality, and encompasses four main life domains: physical, psychological, social, and environmental. The adoption of a vegetarian diet, despite being a dietary pattern, could potentially influence and be influenced by all of these domains, either positively or negatively ...
Their motivation for making the transition ranges from extreme dissatisfaction with killing and eating animals to beliefs that meat is an unhealthy product that is detrimental to their health. The relationship between the vegetarian diet and person's health- conscious lifestyle has been established. We will write a custom essay on your topic.
Vegetarianism may aid in weight-loss and assist in maintaining a healthy body weight. Scientists from the University of Bergen, investigated the influence of a plant-based diet on weight-loss "The results in this review propose that a shift to a plant-based diet may have beneficial health effects on body weight and BMI in individuals with overweight" (Tran et al., 2020).
Meat contains high levels of saturated fat, which raises cholesterol levels, while vegetables contain lots of fiber and plant sterols, which can keep cholesterol levels in a healthy range. Our new diet was, most likely, already improving our cholesterol levels, and helping our hearts. Of course, "vegetarian" doesn't always mean heart-healthy.
Longtime vegetarians already know: To be a vegetarian is to eat really well. But if you're looking to make the switch to vegetarianism or just a more plant-forward diet, you may have questions ...
There is strong evidence that a plant-based diet is the optimal diet for living a long and healthy life, according to Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health nutrition expert Walter Willett.. In a January 7, 2019 interview on the NPR show "1A," Willett, professor of epidemiology and nutrition, said that it's not necessary to be 100% vegan in order to reap the benefits of a plant-based ...
Researchers said their review of 49 studies published between 2000 and 2023 found that plant-based diets are associated with significant health benefits. "Overall, vegetarian and vegan diets are ...
It is going to be argued that; Being a vegetarian is good for health since it leads to the prevention of obesity and overweight, developing strong bones, prevention of heart disease, having cancer protection, having diabetes prevention and also enables one to have more energy in the body.
Vegetarianism, the theory or practice of living solely upon vegetables, fruits, grains, legumes, and nuts—with or without the addition of milk products and eggs—generally for ethical, ascetic, environmental, or nutritional reasons.All forms of flesh (meat, fowl, and seafood) are excluded from all vegetarian diets, but many vegetarians use milk and milk products; those in the West usually ...
Adopting and maintaining vegetarian and vegan lifestyles are two of the most promising ways to achieve this goal [9,10]. VEG has a long history, dating back to ancient Greek philosophers, and can encompass various underlying approaches, including dietary behaviors, food and other product choices, social justice movements, and political activism ...
Vegan diets tend to include plenty of fruits, vegetables, beans, nuts, and seeds. Eating a variety of these foods will provide a wide range of important vitamins, minerals, healthful fats, and ...
Vegetarianism is often touted as a way to achieve better health outcomes and decrease humanity's ecological footprint, yet it has not translated into significant policy action.[1] A vegetarian diet is associated with a reduction in risk of type II diabetes, cancer, coronary mortality, and overall mortality compared to the typical meat-centric ...
Previous studies have identified health, the environment and animal welfare as key motivations for becoming and remaining vegetarian/vegan. However, the idea of vegetarianism/veganism appears to have interesting facets that go beyond those drivers. This paper describes and examines this attraction. Twenty-six in depth interviews and two group discussions were conducted using the Morphological ...
Hello, sir . I will be grateful if you could evaluate this essay. In past few years, vegetarianism has entered the mainstream of many societies. It is often argued that individuals can maintain a healthy lifestyle without the need of meat. I agree that being a vegetarian means being healthier.
A vegan diet is generally high in fiber, vitamin C, magnesium, iron, and folate and lower in calories and saturated fats. The nutritional quality of a vegan diet leads to more significant health benefits. Eating a diet rich in plant-based foods has been associated with a decreased risk of many chronic diseases.
Model Answer 1: People should consume more vegetables and fruits and as little meat as possible because intake high amount of meat can cause serious health issues. In my opinion, the consumption of a vegetarian diet is a better way to live a healthy life and I agree with the notion. Firstly, vegetarian diets are cheaper and more healthy.
The essay has adequate structure — both positive and negative aspects of the approach are given equal attention. The reader would be well-informed on the issue of vegetarianism. The language is fairly varied with a good range of health-related vocabulary. Occasional mistakes and inaccuracies do not stand in the way of understanding the message.
We will write a custom essay on your topic. First, the health problem in vegetarians often starts with an inability to substitute animal resources for the appropriate nutrients. Consequently, an organism lacks such valuable sources of vitamin D, calcium, and protein (Myers par. 3). Second, vegetarian diets are low in fat and do not provide a ...
What's a vegan diet? A vegan diet is an entirely plant-based diet. It doesn't include any meat and animal products. So, no meat, poultry, fish, seafood, eggs, dairy or honey. What's a ...
3. The Vegan Society. The Vegan Society is a UK-based non-profit organization aimed at educating the public on the ways of veganism and promoting this as a way of life to as many people. Expound on its history, key organizational pillars, and recent and future campaigns.
The way his vivid, relatable characters discuss the big questions, with so much soul and hang-looseness, free from any highfalutin airs, has long been something of a north star for me as a movie ...