Explore Our Affordable Courses
- UPSC Offline
- UPSC Online
- UPSC (Live From Classroom)
- UPSC Optional
- UPPSC Offline
- BPSC Offline
- UPPCS Online
- BPSC Online
- MPSC Online
- MPPSC Online
- WBPSC Online
- OPSC Online
- BPSC (Live from Classroom)
- UPPSC (Live From Classroom)
- UPSC Test Series
- State PSC Test Series
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS
- SUBJECT WISE CURRENT AFFAIRS
- DAILY EDITORIAL ANALYSIS
- DAILY CURRENT AFFAIRS QUIZ
- Daily Prelims(MCQs) Practice
- Daily Mains Answer Writing
- Prahaar (Mains Wallah) 2024
- Prahaar Summary 2024
- Mains Marks Booster 2024
- Mains Wallah (Q&A)
- Monthly Current Wallah
- Daily Editorial Summary
- NCERT Wallah
- Prelims PYQs
- Optionals PYQs
- NCERT Notes
- Udaan Notes
- UPSC Prelims Answer Key
- UPSC Syllabus
- Topper's Copies
- Delhi – Mukherjee Nagar Centre
- Delhi – Old Rajinder Nagar Centre
- UP – Lucknow Centre
- UP – Prayagraj Centre
- Bihar – Patna Centre
- Galgotia University Centre

- Offline Centres
- UDAAN Notes
- UPSC Prelims PYQs
- UPSC Mains PYQs


Q. [Weekly Essay] Universal health care is a basic requirement of Indian society. (1200 Words)
How to approach the Essay?
❖ Introduction:
➢ Start with an example that shows the necessity of UHC.
➢ Explain thesis and topic
➢ Answer the following questions in body part:
➢ Why did we require UHC?
➢ What are the benefits of UHC?
➢ Why is India behind providing UHC?
➢ Sustainable strategies required to Achieve UHC.
❖ Conclusion
➢ Write way forward in conclusion.
It is the story of Kamla, one widow of Marathwada region, who migrated to Mumbai after suicide by her husband. In Mumbai she was living in Dharavi slum with a 5 year old girl. In 2020 sudden arrival of COVID 19, and infection to her small girl hampered her livelihood. She doesn’t have any savings and any financial support. Only option remaining with her was to sell everything in the house. Because she didn’t have any financial cover . How will she survive? Does a poor child not have the right to life? Why do poor people suffer a lot while purchasing health services? When will we achieve universal health coverage and affordable health to all?
The concept of universal health coverage is associated with the right to life provided by the Indian constitution and DPSP that secure good living conditions to all. Universal health coverage (UHC) refers to a healthcare system that ensures all individuals, regardless of their socio-economic status, have access to essential healthcare services without suffering financial hardship. Here the concept comes with three ‘As’ . Those are affordability, availability and accessibility. Health coverage should be affordable and cost friendly,
health services should be available at decentralised level and easy to access all and health services available to all with inclusiveness . That brings universal health coverage. Providing UHC has emerged as a critical requirement for societies, states and all over the country.
In this essay, we will delve into the significance of universal health coverage, its benefits, challenges of acquiring universal health coverage and possible strategies for achieving this ambitious goal and role of government to achieve this.
Universal Health Coverage: A Platform for healthy India
First and most significant is that it improves health outcomes . By providing access to timely and affordable healthcare services, nations can significantly reduce mortality rates, enhance life expectancy, and ensure better quality of life for their citizens. As per the data published by NITI aayog , timely available hospitalised delivery reduces CMR (Child mortality Rate) by 75%. That is a huge number. Also it is similar for some chronic diseases, where in rural areas the rate of TB death significantly reduced in Gujarat after having an effective health care system.
Next important thing is that the UHC reduces the financial burden on families. As per Bill Gates foundation report, one single hospital admit in the rural areas pushes the family into poverty trap. That has been seen during the COVID-19. That extra burden has cascading effects on other life functions. For example, in Jharkhand, extra burden of health expenditure forced a tribal man to sell his daughter for prostitution. Such an awakening and disastrous situation! As per study conducted by Pune urban police department after COVID 19, there has been a fifty percent drop in slum area school enrollment. That shows these children working as a child labour.
Increased health costs created problems with hunger and nutritional security. Poor people are not able to purchase quality nutrients and fall into hidden hunger traps. As per ICMR, 27% children in India are facing issues of hunger. And that’s why there is the essentiality of Universal health coverage. This frees up resources that can be utilised for other essential needs, leading to poverty reduction and socio-economic development.
Next dimension and it is the social dimension of health security is associated with equality and Social Justice . Martin Luther King says that Of all the forms of inequality, injustice in health care is the most shocking and inhuman. As per World Bank, Increased health cost has different effects on purchasing parity of different income groups. For example poor people suffer more and an extra percentage of daily earnings goes towards fulfilling the health costs. That not only affects the finance but also creates inequality in terms of exclusion. Universal health coverage aims to ensure equitable access to healthcare for all citizens, promoting social justice by eliminating disparities in healthcare outcomes based on socio-economic status, gender, and region. That brings real regional equality and reduces imbalance.
Now we will discuss disease level benefits and advantages of universal health coverage. First and foremost is that it will improve Disease Prevention and Early Diagnosis capacity of the country. UHC facilitates preventive measures, vaccinations, and regular screenings, which can identify health concerns early on, leading to effective treatment and cost savings. Take the example of Kerala, where good health conditions and established health facilities show low disease burden on society. As per national health mission, 92% Public Health Centre (government owned) working effectively that yielded in to very low Infant mortality(6) and Maternal mortality rate(19).
Another important advantage is Financial Protection of poor people . UHC safeguards individuals and families from catastrophic healthcare expenses, eliminating the risk of being pushed into poverty due to unforeseen medical costs. As per Dr. Arole NGO, if universal health coverage is provided it will directly impact on increase in saving in Marathwada region.
UHC has a Patient-Centred Approach , Universal health coverage prioritises patient-centred care, emphasising individual needs and preferences, resulting in higher patient satisfaction and better health outcomes. As per NITI aayog India has very low Doctor to bed ratio, low ambulance ratio. So universal health coverage will challenge such challenges. It will promote the available accessible and affordable health to all.
Next dimension is universal health coverage to increase Productivity of the population as well as the health system itself. Access to healthcare services through UHC enables individuals to maintain good health, increasing their productivity and contributing positively to the nation’s economy.
Challenges to Achieving Universal Health Coverage: speed breakers to highway of healthy india campaign
Important constraint while considering UHC in India is funding. Implementing UHC requires substantial financial support. National Health Policy also discussed this challenge. India requires at least 2.5% spending as per national Health Policy. Governments must allocate sufficient funds to healthcare, which can be challenging, particularly in low-income countries with limited budgets.
Second is human resource management and availability of Health Infrastructure. Expanding access to healthcare demands a robust health infrastructure and an adequate number of trained healthcare professionals. Decentralised health infrastructure has many challenges . First is poor building and unavailable electricity creating issues of functionality. Second is doctors are not available and ready to work at rural and suburban level. And third important is competition from private hospitals.As per PIB there is a huge skew in the distribution of doctors working in the Urban and Rural areas with the urban to rural doctor density ratio being 3.8:1. With these another issue is Very few areas have good colleges of medicine. That’s why the island of colleges creates the issue of balanced availability of resources.
Also take the example of Ambulance availability.According to the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM), 6,226 ambulances are available with the government to cater to the country’s rural areas. This is half the required number of ambulances (see graph on p28). As per the, WHOstandards, there should be at least one ambulance per 100,000 population in the plains, and one for every 70,000 population in hilly terrain or tribal areas where population is scattered.
After the human resource problem next is the problem of Indian bureaucracy, administration and governance. Corruption in health care costs more than money. The price of corruption in health care is paid in human lives. Corruption at the functioning level of PHC and infrastructure building creates issues. Implementing UHC involves dealing with administrative complexities, effective governance, and strong political will. Very high corruption in the medicine field, data complexity and issue of red tapism creates concern. Decentralisation, capacity building, and efficient public-private partnerships are vital for successful implementation.
With above mentioned problems, another important is Behavioural and Cultural Factors of Indian society. Changing behaviour patterns and cultural norms in healthcare-seeking practices often prove challenging, requiring concerted efforts towards education, awareness, and community engagement. India has many superstitions and beliefs on traditional approaches. As per NITI aayog aspirational district programme, in
Osmanabad distric t even having available infrastructure, people don’t go to hospital for deliveries and that resulted in high CMR and MMR.
Strategies for Achieving Universal Health Coverage: Healthy india – Happy India ‘Health care should be a human right and not a commodity for sale .’
Although we have challenges, without challenges we don’t know our potential. Our civilization always grows by accepting challenges and improving on it And that is the basis of a brave, innovative and successful society.
First strategy is investment from the Government side. Governments need to increase public spending on healthcare, allocating a significant portion of the budget for UHC. This may necessitate improvement in taxation systems, prioritising health care financing, and reducing out-of-pocket expenditures. National health policy focuses on targeted funding rather than single funding . For example separate allocation for doctors training, separate fund for village level administration etc.
India can check for some Innovative Financing Mechanisms. Exploring innovative financing models such as social health insurance, public-private partnerships, and international aid can provide an additional funding source for UHC implementation. In Kerala community owned financing is prevalent. Or cess for health is also a good idea.
After that we need to work on Strengthening Health Systems. Here we can take the help of some civil society organisations like Magsaysay Prize winner Dr. Arole and his NGO is doing an excellent work in providing universal health in some areas like Marathwada region of Maharashtra. Also we are required to Invest in health infrastructure, expanding health facilities in underserved areas, and improving the availability of essential medicines and technologies are crucial for UHC. Strengthening Gramin Arogya Kendra is the need of the hour. And the most important work to do is effective and quality health workforce development. Governments must prioritise training, recruitment, and retention of healthcare professionals to ensure adequate human resources for delivering quality healthcare services. For this purpose we have already started the Public Health Cadre Management System. Also AYUSHMAN BHARAT is doing excellent, and needs to work on continuous success. Under this scheme, 83.74 lakh beneficiary families get benefits of availing cashless medical facilities of upto Rs. 5 lakh per family per year for treatments in nearly more than 1000 procedures in 30 specialities. These include treatments like hip replacement surgery, knee replacement surgery, renal transplant, etc. That shows we are placing one step close to UHC.
And last part of this whole discussion is community involvement and awareness creation. Promoting community involvement and educating individuals about the benefits of UHC can help overcome cultural barriers and increase healthcare. College and school students are the best source to educate society. NGO Snehalaya is doing exemplary work. Recent drive of anaemia awareness and drive of HIV protection in urban areas by Snehalaya shows decent success.
Going ahead.
Universal health coverage is a fundamental requirement of any society aiming to ensure the well-being of its citizens. By providing equitable access to healthcare services, UHC can enhance health outcomes, reduce financial burden, and contribute to societal development. Although challenges exist, through concerted efforts, commitment, and sound policies, nations can work towards realising the goal of UHC and create a healthier future for all.
Health care must be recognized as a right, not a privilege. Every man, woman and child in our country should be able to access the health care they need regardless of their income.
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.

- Recent Questions
- Related Post
- Most Viewed Questions
Latest Comments
Recent editorial.
Solar energy, a game changer in women’s empo...
The under-representation of women in the judiciary
Indian Agriculture on the Cusp of a Tech Revolutio...
Tackling Learning Disabilities Head-On
Dedication to Public Service
Beyond intoxication: On alcohol regulation, judici...
Popular Current Affairs
Data-Based Policymaking in India: Challenges and R...
Brazil Opts Out of China’s Belt and Road Initiat...
Chhattisgarh Doubles Quota in Panchayat, Urban Bod...
Report of The Lancet Countdown on Health and Clima...
India’s TB Burden and Progress Towards Elimi...
Electoral College in US Presidential Elections
Our Courses

Need help preparing for UPSC or State PSCs?
Connect with our experts to get free counselling & start preparing
THE MOST LEARNING PLATFORM
Learn From India's Best Faculty
Our Initiatives
Beginner’s roadmap, quick links.

PW-Only IAS came together specifically to carry their individual visions in a mission mode. Infusing affordability with quality and building a team where maximum members represent their experiences of Mains and Interview Stage and hence, their reliability to better understand and solve student issues.
Subscribe our Newsletter
Sign up now for our exclusive newsletter and be the first to know about our latest Initiatives, Quality Content, and much more.
Contact Details
G-Floor,4-B Pusa Road, New Delhi, 110060
- +91 9920613613
- [email protected]
Download Our App
Biginner's roadmap, suscribe now form, fill the required details to get early access of quality content..
Join Us Now
(Promise! We Will Not Spam You.)
CURRENT AF.
<div class="new-fform">
Select centre Online Mode Hybrid Mode PWonlyIAS Delhi (ORN) PWonlyIAS Delhi (MN) PWonlyIAS Lucknow PWonlyIAS Patna Other
Select course UPSC Online PSC ONline UPSC + PSC ONLINE UPSC Offline PSC Offline UPSC+PSC Offline UPSC Hybrid PSC Hybrid UPSC+PSC Hybrid Other
</div>

Health Sector of India
COVID-19 exposed several weaknesses in India’s underfunded health system. Rural primary care is underfunded and has shortages of staff, equipment, drugs and infrastructure in many parts of the country. Urban primary healthcare has still not emerged as an active programme in many States. District and medical college hospitals suffer shortages of specialist doctors and support staff.

Issues and Challenges for health sector
India’s healthcare system has been battling various issues, including the low number of institutions and less-than-adequate human resources for quite a while now.
- Lack of Infrastructure: India has been struggling with deficient infrastructure in the form of lack of well-equipped medical institutes for quite a while now.
- For a considerable time, the government regulation mandated that private medical colleges must be built on at least five acres of land.
- As a result, quite a few private colleges were built in rural areas, where it became quite difficult to recruit adequately qualified, full-time doctors due to lack of proper living conditions, besides low pay scales.
- National Medical Commission (NMC) has put forward the idea to do away with the requirement of minimum five acres of land for setting up a medical college.
- Further, the commission has proposed to curtail the minimum number of beds required as a proportion of the number of seats in the college.
- Shortage of trained manpower: this includes doctors, nurses, paramedics and primary healthcare workers.
- The situation remains worrisome in rural areas, where almost 66 per cent of India’s population resides.
- The doctor-to-patient ratio remains abysmally low, which is merely 0.7 doctors per 1,000 people. This is compared to the World Health Organisation (WHO) average of 2.5 doctors per 1,000 people.
- Unmanageable load of Patients: Healthcare facilities had been feeling the strain due to unmanageable patient-load.
- In addition, there is the challenge to think beyond the obvious and promote virtual care protocols, and telehealth services, which can be leveraged to reduce the patient-load burden to a large extent.
- Public health policy and proactive healthcare: The latest National Health Policy (NHP) 2017 highlights the ‘Health for All’ approach to provide assured healthcare for all at an affordable cost.
- Ideally, the public health policy needs to be focussed towards proactive healthcare, not reactive healthcare.
- High out-of-pocket expenditure remains a stress factor: While public hospitals offer free health services, these facilities are understaffed, poorly equipped, and located mainly in urban areas.
- Most health services are, therefore, provided by private facilities, and 65 per cent of medical expenses in India are paid out of pocket by patients.
- Unregulated private sector: NITI Aayog has recently published the document, ‘Investment Opportunities in India’s Healthcare Sector’. This promotes further privatisation of health care in a country which already has one of the most privatised health systems in the world .
- The report fails to acknowledge the negative aspects of unregulated private health care; neither is there any mention of the need for regulation of private hospitals.

Government Initiatives
- Anganwadi System: The Anganwadi system was established as part of the Integrated as Child Development Service (ICDS) programme , which has since been renamed Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0.
- Under the MoWCD, the Anganwadi Services Scheme is a centrally sponsored programme.
- It stands for one of the biggest and most distinctive early childhood care and development projects in the entire globe.
- Objectives: The program's objectives are to enhance the nutritional and physical health of young children (0–6 years), expectant mothers, and nursing mothers, as well as to lower the occurrences of mortality, morbidity, and malnutrition.
- System Depth: Through Anganwadi Centres (AWCs), Anganwadi Workers (AWWs), and Anganwadi Helpers (AWHs), the system provides services to 906.17 lakh beneficiaries.
- NATIONAL FAMILY HEALTH SURVEY-5 (NFHS) REPORT: NFHS-5 was released by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
- Objective: To deliver accurate and comparable data on various topics, such as family welfare and health.
- The NFHS-5's scope is broadened by the inclusion of new dimensions like death registration, pre-school instruction, enlarged child immunisation areas, menstrual hygiene, etc.
RIGHT TO HEALTH IN INDIA
- Provisions in Constitution:
- Article 21: This article of the Constitution guarantees the right to life and personal liberty, which has been interpreted by the courts to include the Right to Health .
- DPSP: Part IV of the Constitution under the Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP) (Articles 38, 39, 42, 43, & 47) ensures social and economic justice to its citizens directly or indirectly relating to public policy in terms of health putting the obligation on the state to ensure the effective realization of the Right to Health.
- Judicial Activism:
- Supreme Court in Paschim Banga Khet Mazdoor Samity case (1996) held that the primary duty of the government is to secure the welfare of the people being an obligation of the government to provide adequate medical facilities for its people in a welfare state.
- Supreme Court had ruled that every doctor whether at a government hospital or otherwise has the professional obligation to extend his services with due expertise for protecting life in Parmanand Katara Vs Union of India (1989) .
- Human Dignity: The right to health is an essential component of human dignity and should be protected and promoted for all individuals, regardless of their gender, race, ethnicity, religion, or socioeconomic status.
- International Conventions: India is a signatory of the Article 25 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948) by the United Nations that grants the right to a standard of living adequate for the health and well-being to humans including food, clothing, housing and medical care and necessary social services.
Need of RTH in India
- Privilege to few: The right to equality guaranteed under Article 15 upholds non-discrimination on the basis religion, race, caste, gender, place of birth, etc. still the dismal investment in public health for decades has made healthcare a privilege available to a few.
- Break Discriminatory Structure: Right to health is critical to breaking discriminatory structures that will otherwise continue to perpetuate inequality in all spheres of life, including education, opportunity, wealth, and social mobility.
- Article 21’s Interpretation: The judicial interpretation of the right to life and liberty under Article 21 in several judgments as inclusive of health was crucial.
- As the universal access to healthcare is now as achievable as it is indispensable.
- Progressive Rights of the people: The rights of people are not stagnant, and must evolve as the country evolves.
- Service-Delivery Model: Ayushman Bharat is an ambitious scheme with great potential, but there is a difference between a right and a service-delivery model of development.
- Lack of Efficiency in healthcare: Healthcare facilities across the country lacks different levels of efficiency and sufficiency which can be outdone RTH.
- Dismal Primary Health Sector: RTH will help in developing the root of the healthcare sector i.e., the primary healthcare sector that lacks proper guidance and implementation of policies which makes people disbelieve in healthcare sector in India.
Arguments against RTH
- Due to the lack of clarity over who will be responsible for paying for the required free emergency treatment, private healthcare providers have been the most vocal opponents of the RTH.
- Critics claim that it is an attempt to surrender the State's duty to provide health protection and increases the burden of patients on the private sector.
- Many believe that the RTH will be unnecessary and highly restrictive.
- Without development or improvisation of the present structure of the healthcare facilities, implementing RTH will be devastating for already stressed medical field in India.
Challenges Related to Right to Health in India
- Inadequate Healthcare Infrastructure: India's healthcare infrastructure remains inadequate, particularly in rural areas where the 73% of the Indian population lack even basic medical facilities.
- Burden of schemes : Doctors are protesting against the RTH because they question the need for it when there are already schemes like Chiranjeevi that cover most of the population.
- Specialization concerns : They are also objecting to certain clauses, such as defining “emergency” and being compelled to treat patients outside their specialty as part of an emergency.
- High Disease Burden: India has a high burden of communicable and non-communicable diseases which requires significant investment in healthcare infrastructure and resources.
- Frontiers in Public Health Report: More than 33% of the individuals are still suffering from infectious diseases out of the total ailing population in India.
- Gender Inequalities: Women in India face significant health disparities.
- World Economic Forum 2021: India consistently ranks among the five worst countries in the world for the health and survival of females.
- Health Financing: Low levels of public spending on healthcare limits the government's ability to invest in healthcare infrastructure and resources, leading to inadequate healthcare services for individuals.
- Government of India spent 2.1% of GDP on healthcare in FY23 which is lower than the average health spending share of the GDP — at around 5.2% — of the Lower- and Middle-Income Countries (LMIC).
- No detailing of the process : To the charge that there is no detailing of the process, health rights activists have pointed out that it would be a function of the Rules, not the law itself.
- Concerns pertaining to compensation: Healthcare providers have a problem with reimbursement delays. Additionally, there are complaints that the predetermined package rates for various medical procedures and treatments are not sufficiently profitable or do not cover the actual cost.
Government Initiative in tackling the Challenges
- Implementing Universal Health Coverage: As a critical indicator for human equity, security and dignity UHC makes sure that all people have access to the health services they need without the risk of financial hardship when paying for them.
- Health accessibility and affordability : A crucial healthcare problem even in the 21st century prompted World Health Organization to choose “Universal Health Coverage” as the theme for World Health Day 2019.
- India started working towards the universal problem of affordability and accessibility with the introduction of Ayushman Bharat.
Significance of UHC:
- Universal health coverage has a direct impact on a population’s health and welfare.
- Access and use of health services enables people to be more productive and active contributors to their families and communities.
- Financial risk protection prevents people from being pushed into poverty when they have to pay for health services out of their own pockets.
- Universal health coverage is a critical component of sustainable development and poverty reduction, and a key element of any effort to reduce social inequities.
- Universal coverage is the hallmark of a government’s commitment to improve the wellbeing of all its citizens.
Issues and Challenges related to UHC
- Lack of Funds: Public sector is severely underfunded.
- Unaffordable Healthcare: Private sector is witnessing a high-cost healthcare service which is problematic.
- Regulation: Ineffective regulation is a concerned area.
- Poor Health Education: Lack of education and awareness regarding healthy lifestyles and preventive health measures can lead to an increase in preventable illnesses and conditions.
Government Steps for implementing UHC in Healthcare sector
- National Health Policy (NHP) 2017 : Allocating resources of up to two-thirds or more to primary care for achieving “the highest possible level of good health and well-being, through a preventive and promotive healthcare orientation”.
- A 167% increase in allocation for the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) — the insurance programme which aims to cover 10 crore poor families for hospitalisation expenses of up to ?5 lakh per family per annum.
- The government’s steps to incentivise the private sector to open hospitals in Tier II and Tier III cities.
- Individual states are adopting technology to support health-insurance schemes. Example: Remedinet Technology (India’s first completely electronic cashless health insurance claims processing network) has been signed on as the technology partner for the Karnataka Government’s recently announced cashless health insurance schemes.
National Health Policy
National Health Policy: National Health Policy is an initiative by the Central Government to strengthen the health system in India covering various dimensions of health sectors like disease prevention, promotion of good health via cross-sectoral actions, health investment, strengthening human resources, technological advancements and more.
Launched in 2017 by the Central Government, has introduced four significant goals:
- Changing health priorities : Aims to tackle the increasing non- communicable and infectious diseases in India.
- Growth of the health care industry : Strengthen the health care industry by introducing technological advancement.
- Lower the expenditure : Aims to reduce medical expenses and provide superior services to poor and backward communities.
- Economic growth : Aims to enhance fiscal capacity by boosting economic growth.
Objectives of National Health Policy
- Basic Structure: National Health Policy commits to integrity, highest professional standards and ethics integrating these functions in health care delivery services by maintaining transparency and a sustainable environment.
- Doing away Disparities: Aims to offer superior health services to every age group and gender.
- Universal Healthcare Services: Focuses on providing universal access to excellent quality health care services at an affordable price preventing regional disparities.
- Reducing Mortality Rate: Aims to reduce premature mortality from cancer, cardiovascular diseases, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes by 25% within 2025.
- Recognises the importance of sustainable development and time-bound quantitative goals.
- Developing Overall Health Structure: Aims to improve overall health structure through promotive, palliative, and rehabilitative services.
Drawbacks of the policy
- Repetition of Ideas: The new policy repeats several old ideas, and fails to fulfil 2015 promise of a Right to Health.
- It fails to make health a justiciable right in the way the Right to Education 2005 did for school education.
- Assurance-based Approach: The policies reference to an “assurance-based approach” abandons a radical change proposed in the draft policy of 2015 where National Health Rights Act aimed at making health a right.
- Disagreement with States: Health Ministry officials said the idea was dropped because state governments felt that health infrastructure was not yet at levels at which health could be made an entitlement, and the citizen could theoretically take a government to court for its denial.
- Diagnostics, drugs and essential health care services are already free in many states.
- Longevity in Implementation: The policy says that 2.5% GDP spend target for Health would be met by 2025 but the HLEG report of 2011, quoted by the 12th Plan document, had set the same target for the Plan that ends at the end of this march 2017.
- Health Cess: A health cess was a pathbreaking idea in the Health Ministry’s draft policy but now it has been rejected, with health officials maintaining that there is no dearth of funds.
WAY FORWARD:
- Increase Public Investment in Healthcare : The government should increase the budgetary spending on healthcare and allocate more resources to build a strong healthcare infrastructure.
- Enhancement of Health Expenditure: Health Expenditure which currently stands lower than most of the developing nations needs to be enhanced as a percentage of GDP .
- Prioritize Primary Sector: Strengthening the primary healthcare sector should be the priority.
- Expand Health Insurance Coverage: Expanding the health insurance coverage to all citizens would help reducing out-of-pocket expenses and make healthcare more affordable.
- Improve Healthcare Quality: The government should invest in improving the quality of care by developing quality standards, ensuring adherence to these standards, and providing training to healthcare providers.
- Invest in Health Information Systems: Priority should to given to develop robust health information systems that can provide timely and accurate data.
- Promote Preventive Healthcare: Focusing on preventive healthcare can reduce the burden of disease and the cost of healthcare.
Drug regulation in India:
India, has been mulling the creation of a mandatory recall law for substandard drugs since 1976, and yet no law exists that mandates such medicine be removed from the market to this day.
- In 1976, the Drugs Consultative Committee (DCC), which consists of all the state drug controllers along with senior bureaucrats from the Ministry of Health and the national drug regulator, the Central Drug Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), discussed the issue of drug recalls.
- The issue of recalls came up again in meetings of the DCC in 1989, 1996, 1998, 2004, 2007, and 2011 but none of them resulted in amendments to the Drugs & Cosmetics Act to create a mandatory recall mechanism.
- Why has this issue been pending for so long in India with no redress?
- the Drug Regulation Section of the Union health ministry is simply not up to the task of tackling complex drug regulatory issues
- combination of different factors including apathy, lack of expertise in the area, and a greater interest in enabling the growth of the pharmaceutical industry than protecting public health.
- India’s highly fragmented regulatory structure , with each state having its own drug regulator.
- India’s drug regulators are aware of the fact that a mandatory drug recall system, which necessarily has to be centred on a system of wide publicity, will bring to public attention to the rotten state of affairs in India’s pharmaceutical industry.
- Dozens of drugs fail random-testing in government laboratories . Ideally, these drugs will be mandatorily recalled in a transparent manner, with the people being informed of the failures.
- Liberal punishments: Guidelines were first published by the Drugs Consultative Committee in 1993 and again in 2010. According to these recommendations, harassing medication makers would result from prosecuting every instance of inferior drugs. Therefore, the committee was established to carefully punish the producers.

- The Union Health Ministry recently published a new draft Bi ll to replace the antiquated Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- To create an effective recall mechanism, the responsibility of recalling drugs has to be centralised, with one authority that has the legal power to hold companies liable for failures to recall drugs from across the country.
- If India is a single market for drugs, it follows that it should have one regulator.
- The Drug and Cosmetics Act, 1940 : imposes regulatory restrictions on the in-country production, distribution, and sale of medicines and cosmetics. The Act designates the sale of subpar medications as a serious violation since these medications have the potential to cause patients harm. A jail sentence or fine may be issued in accordance with this Act.
- Amend the Drugs and Cosmetics Act: The medications and Cosmetics Act's main objective is to prevent inferior medications from entering the market in the first place rather than to react to them after the fact. Therefore, the DCA must be changed to stop the production of inferior pharmaceuticals in the first place.
- Good Manufacturing Practices: Manufacturers ought to implement a rigorous system of quality control. Simple checks and balances must be followed, such as checking raw materials before incorporating them into drugs, purchasing raw materials from authorised producers, keeping equipment clean, etc. Any time there is a quality issue, a root cause analysis should be carried out right away.
Zero Tolerance to Drugs
The Centre has adopted a zero-tolerance policy towards narcotics
- According to the 2019 National Survey on Extent and Pattern of Substance Use in India, 2.26 crore people, or roughly 2.1% of the population, use opioids.
- Additionally, same poll revealed that 31 million Indians, or 2.8% of the population, used cannabis for bhang, ganja and charas.
- Drug abuse has increased as a result of the breakdown of the united family system, a reduction in religious and moral values, and other factors, such as the desire to escape the harsh reality of life.
- Peer pressure: Many young people begin using drugs as a result of peer pressure from friends, teachers, or other members of their informal social networks.
- Easy Accessibility — India is positioned in such a way that the "Golden Triangle" and the "Golden Crescent" are to its east and west, respectively.
Initiatives:
- The MHA established the Narcos Coordination Centre (NCORD) system in 2016 to ensure efficient drug law enforcement.
- The portal serves as an efficient method for exchanging information amongst various institutions and authorities.
- The minister added that the Supreme Court is discussing the creation of fast-track courts and exclusive courts for the expeditious trial of drug cases.
Way Forward:
India could reduce the treatment gap for mental disorders, increase the number of personnel in the mental health sector, work towards reducing discriminatory attitudes, and devise an integrated approach for detecting, treating, and managing patient needs.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) should be encouraged in the field of mental health.
Mental Health
Mental health issues are a major health challenge in the world today. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there is a 10-25-year life expectancy reduction in patients with severe mental disorders. About 72% of member states had a standalone policy or plan for mental health in 2017.
- India introduced the National Mental Health Policy (NMHP) in 2014, and a rights-based Mental Healthcare Act in 2017, which replaced the Mental Healthcare Act of 1987.
- The NMHP, National Health Mission, National Adolescent Health Programme, and Ayushman Bharat have the necessary components to address the mental health issues of all sections of the population.
Issues and Challenges
- The share of mental hospitals per 1,00,000 population is as low as 0.01 in line with developing countries, according to the WHO.
- India was at the 99th position in the distribution of mental health outpatient facilities (per 1,00,000 population), with 0.18 units per 1,00,000 population.
- India was also at the 64th position in the distribution of mental health day treatment facilities
- The distribution of community residential facilities globally for the median year 2016 showed India at the 58th position, with 0.017 units per 1,00,000 population among the WHO member countries.
- Mental Illness: Mental illnesses include anxiety disorders, psychotic disorders, mood disorders, substance use disorders, personality disorders and eating disorders.
- The suicide rate was 10.6 per 1,00,000 population whereas in India, it was 16.3 per 1,00,000 in 2016.
- The suicide rate was higher among males compared to females.
- Mental health facilities: There are also challenges regarding funding, delivery of mental health packages, lack of trained staff, etc.

- Mental Healthcare Act, 2017
- The Act ensures healthcare for people suffering from mental illness through health services funded by the Government. It decriminalises suicide, disallows sterilisation.
- As part of Section 19, the government was made responsible for creating opportunities to access less restrictive options for community living — such as halfway homes, sheltered accommodations, rehab homes, and supported accommodation.
- Under the MHCA, all States are required to establish a State Mental Health Authority and Mental Health Review Boards (MHRBs) – bodies.
- While Ayushman Bharat allows for insurance for medical treatment of the mentally unwell, financial protection in the form of allowances should be initiated.
- National suicide Prevention Strategy: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare’s recently published National Suicide Prevention Strategy fits right there.
- The most common reasons include family problems and illnesses, while other causes include marital conflicts, love affairs, bankruptcy, substance abuse and dependence .
- In India, more than one lakh lives are lost every year to suicide. In the past three years, the suicide rate has increased from 10.2 to 11.3 per 1,00,000 population.
- The Strategy also intends to write in mental health in the curriculum in educational institutions within the next eight years.
- It also lists interventions that have reduced the suicide rate in various sections in the country, including among students and rural groups, by limiting the availability of pesticides.
Answer our survey to get FREE CONTENT

Feel free to get in touch! We will get back to you shortly
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
- Quality Enrichment Program (QEP)
- Intensive News Analysis (INA)
- Topper's UPSC PYQ Answer
- Essay Enrichment Program
- NEEV GS + CSAT Foundation
- News-CRUX-10
- Daily Headlines
- Geo. Optional Monthly Editorials
- Past Papers
- © Copyright 2024 - theIAShub
Talk To Our Counsellor
- Our Centers Delhi Bhubaneswar Lucknow
CURRENT AFFAIRS FOR UPSC IAS

Indian Health Sector: Opportunities and Challenges
Published: 10th Apr, 2021
In Budget 2021 health sector is focused on by Government, which was severely hit by the unprecedented pandemic. The focus has been laid on healthcare and infrastructure with an eye on achieving the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- The unprecedented COVID-19 pandemic has completely changed the situation no one could ever imagine. Almost all aspects of society have witnessed disruptions.
- However, every challenge comes with various opportunities, so does this pandemic.
- It has opened a wide window of opportunities to restructure and reform the Indian health industry which has been in a bad state of repair.
- Underscoring the significant importance of health and wellbeing for the growth and development of the country, the Budget allocation for the same was increased to ?2,23,846 crore in 2021-22 as against this year's ?94,452 crores, according to an official release.
- This manifests into an increase of 137%.
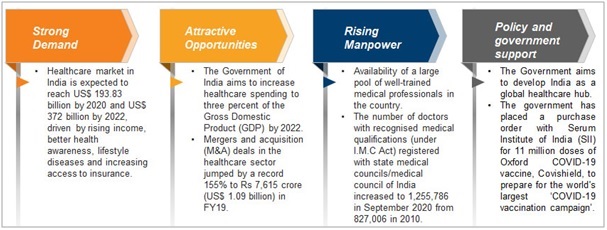
Assessing Indian Healthcare Industry
- In India, the Health care sector is one of the largest sectors in terms of both revenue and employment.
- Public health care hospitals comprise secondary and tertiary care institutions in urban areas while primary basic facilities are focused in rural areas.
- Private health care sectors provide secondary, tertiary, and quaternary services in metro cities.
Healthcare Industry in India
What are the issues and concerns of the Sector?
India’s health care sector has achieved some positive achievements on the health indicators but suffers some serious shortcomings in care delivery.
- Inadequate reach: The inadequate reach of basic healthcare services, shortage of medical personnel, quality assurance, the inadequate outlay for health, and most importantly insufficient impetus to research.
- Inadequate Fund: The inadequate fund allocation by the administrations is one of the grave concerns.
- Optimal Insurance: The concept of health insurance is still not clear in India and the market is still virgin.
- No focus on Preventive Care : In India, there is a very low emphasis on preventive care, which can be proved very effective in solving a lot of problems for the patient in terms of misery or financial losses.
- Less emphasis on Medical Research: In India, there is no much impetus is being given to R&D and cutting-edge technology-led new initiatives. Such technologies could be useful in an unprecedented situation like Covid-19.
- Issue of Policymaking: For providing effective and efficient healthcare services policymaking is certainly an important aspect. In India, the problem is fundamental of supply than demand, where policymaking can be effective.
- Shortage of Medical Workforce: In India, there is a shortage of doctors, nurses, and other staff in the health sector. As per a report laid down by a minister in Parliament, there is a shortage of 600,000 doctors in India.
- Inadequate outlay for health: As per National Health Policy 2002, India contributes only 0.9 percent of its GDP to the Health care sector.
- Lack of structure: Private hospitals are expensive and public hospitals are either not enough for the Indian Population or lack the basic facilities.
Opportunities in Health Care Sector
- Indian health care sector is expected to increase to Rs. 8.6 trillion (US$ 133.44 billion) by 2022. It is almost three times which is what it’s now in present.
- Data Analytics: With the arrival of the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM), the digital Health ID will come which will store the data of patients. It would help in effective policymaking and private players can get an edge in introducing the new technologies in the market.
- Employment opportunity: As we know Indian health care sector lacks a workforce, there is a space for thousands of employees.
- Start-ups: With the help of Government and private players an environment of start-ups and entrepreneurship can be created in this field.
- Medical Tourism: India is already one of the favorite medical Tourism Destinations in the world and in the upcoming years this sector can be harnessed efficiently.
What measures are required in the sector?
- Improving infrastructure: There is a need of improvising the infrastructure of public hospitals which have a lot of burden due to the high population in India.
- Focus on private hospitals: Private hospitals must be encouraged by the government because their contribution is important. Private sector also needs to participate because the challenges are significant and these cannot be resolved only by the government alone.
- Efficiency enhancement: More medical personnel must be recruited to enhance the capabilities and efficiency of the sector.
- Technology utilisation: Technologies must be used to connect the dots in the health system. Medical devices in hospitals/ clinics, mobile care applications, wearables, and sensors are some forms of technology that should be added in this sector.
- Awareness: People should be made aware of early detection and preventive care. It would help them in saving pocket expenditure also.
The year 2021 could be the year when India consolidates and expands on its social determinants of health (SDH) approach. India now needs to sustain its current interest in strategic health policy as a key pillar of the economy.
More Articles

Verifying, please be patient.
Our Centers
DELHI (Karol Bagh)
GS SCORE, 1B, Second Floor, Pusa Road, Karol Bagh, New Delhi - 110005 (Beside Karol Bagh Metro Station Gate No. 8)
Get directions on Google Maps
BHUBANESWAR (Jaydev Vihar)
GS SCORE, Plot No.2298, Jaydev Vihar Square, Near HCG Day Care, BBSR - 751013
LUCKNOW (Aliganj)
GS SCORE, 2nd Floor, B-33, Sangam Chauraha, Sector H, Aliganj, Lucknow, UP - 226024
Delhi (Karol Bagh) Centre
GS SCORE, Second Floor, Metro Tower, 1B, Pusa Road, Karol Bagh, New Delhi - 110005 (Beside Karol Bagh Metro Station Gate No. 8)
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +91 8448496262
Classroom / online / Live programs
- Mains Classes
- Mains Advance Classes
- Ethics & Essay Classes
- IAS Foundation
- Aadhar:NCERT Foundation
- Target PT:Prelims Classes
- Current Affairs Mentorship Program
- Optional Classes
- Optional Q&A (TEST SERIES & Mentorship)
- Mains Previous Year Questions
- Offline Test Centers
- All Courses
TOPPER'S CORNER
- Topper's copy
- Topper's profile
- Reports & Magazines
- UPSC Previous Year Papers
- Meet the Mentor
- Privacy Policy
Still Have Questions?
- © 2024 - IAS SCORE
All Rights Reserved.
Welcome to our secure login portal. Access your account with ease.

- Using Password
Not registered yet? register here!
Welcome to our secure register portal. For a brighter future, register now and unlock endless learning opportunities.
User Register
Already have an account? Login
Oops, forgot your password? Don't worry, we've got you covered. Reset it here
Lost your login details? No problem! forgot your password in just a few clicks
Forgot Password
Verify your mobile number, you have successfully logged in.
Join Us on WhatsApp
Online Learning Portal
Forgot password
If you haven’t created your account yet, please SIGN UP HERE
Quick Links Testimonials FAQ
Hybrid Classes
We provide offline, online and recorded lectures in the same amount.
Personalised Mentoring
Every aspirant is unique and the mentoring is customised according to the strengths and weaknesses of the aspirant
Topicwise Mindmaps
In every Lecture. Director Sir will provide conceptual understanding with around 800 Mindmaps.
Quality Content
We provide you the best and Comprehensive content which comes directly or indirectly in UPSC Exam.
If you haven’t created your account yet, please SIGNUP HERE
UPSC Courses
IAS Foundation 2024
- C2U-NCERT 2024
- Newspaper Analysis Program
- Basic Daily Answer Writing
Optional Classes
- Geography Crash Course
Current Affairs
- Daily Newspaper Analysis - DNA
- UPSC Facts & Data
- GS Prelims PT Pointers
- Press Information Bureau - PIB
- Good Morning Times - Subject Wise
- EASY TO PICK MONTHLY CURRENT
- GS Paper Wise Current Affairs
- Daily Question Practice (PT-Mains)
Test Series
- RAW Live MCQ
- Oral Test Session By Director Sir
Others Links
- Testimonials
UPSC Prelims Classes 2024
Crash Course
- Sanjeevani @ 60Days
- Morden History
- Science & Technology
Regular Modules 2024
- Mapping & Geography
- Environment
- Economics Basic To Advance
- Polity & History
- News Paper Analysis Programme
- Prelims Test Series
- About Civil Services
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus & Strategy
- UPSC Previous Years Paper
- Prelims Modular Batches
- UPSC Prelims - PT Pointers
- Exclusive Test Series - Mock
- CSAT Classes
- Prelims Sanjeevani 2024 Crash Course
Mains Classes 2024
- RAW GS Crash Course
- Target 50 Program
- Ethics & Case Studies
- Editorial & Current Affairs – QIP
- Writing Skill Development Program
Mains & Interview
- Mains Syllabus & Strategy
- Daily UPSC Answer Writing
- Target 50 For Mains Batch
- Personality Test
- Mains Crash Course
- MAINS Previous Papers
- Optionals Previous Papers
Mains Material
- Mains Kunji
- Prelims (Live-MCQ)
- Prelims PT Tricks-2024
- Daily Answer Writing
Free Study Material
- Important Video Lectures
- Previous Years Papers
- Newspaper Analysis & ENY Notes
- UPSC GS Mains Notes
- 2 nd ARC Report Summary
- Aspire IAS Notes
- Free Download - UPSC Content
- Paid Material(SLP)
- UPSC Optional Notes
Major Topics
- International Relation
- International Organization
- Government Policies And Interventions
Issues relating to development and management of Health

- 07 Jul,2023
The " Right to Life " is considered essential by the Constitution, and the government is required to protect everyone's " right to health ." The federal system of India, as well as the responsibilities and funding splits between the Centre and the states, have affected the health sector to a large extent. The states are in charge of planning and delivering health care to their citizens. Healthcare has become more focused on innovation and technology over the past two years and 80% of healthcare systems are aiming to increase their investment in digital healthcare tools in the coming five years .
According to some estimations, the Indian healthcare sector will be worth $774 billion by 2030. Hospitals, medical tourism, health insurance, medical equipment, telemedicine, outsourcing, clinical trials, and medical gadgets are all part of India's healthcare industry.
Problems pertaining to the Healthcare sector
Insufficient Medical personnel :
- There is a massive shortage of medical staff, infrastructure and last-mile connectivity in rural areas. Ex. Doctor: Population 1:1800 and 78% of doctors cater to urban India (population of 30%).
- Massive shortages in the supply of services (human resources, hospitals and diagnostic centres in the private/public sector) are made worse by grossly inequitable availability between and within States.
- For example, even a well-placed State such as Tamil Nadu has an over 30% shortage of medical and non-medical professionals in government facilities.
- 61% of PHCs have just one doctor, while nearly 7% are functioning without any
- 33% of PHCs do not have a lab technician, and 20% don’t have a pharmacist.
- In states like Odisha, more than 3,000 government posts for doctors or about 50% of all government medical doctor posts are lying vacant.
Health budget :
- India’s expenditure on the health sector has risen meagerly from 1.2 per cent of the GDP in 2013-14 to 4 per cent in 2017-18 . The National Health Policy 2017 had aimed for this to be 2.5% of GDP .
- The health budget has neither increased in real terms nor is there any policy to strengthen the public/private sector in deficit areas. While the Ayushmaan Bharat provides portability , one must not forget that it will take time for hospitals to be established in deficit areas.
- This in turn could cause patients to gravitate toward the southern States that have a comparatively better health infrastructure than the rest of India.
Infrastructure constraints :
- There are doubts about the capacity of India’s infrastructure to take on the additional load of patients during pandemics like Covid-19 as seen recently.
- There is a growing medical tourism (foreign tourists/patients) as a policy being promoted by the government, and also domestic patients, both insured and uninsured.
Crumbling public health infrastructure :
- Given the country’s crumbling public healthcare infrastructure, most patients are forced to go to private clinics and hospitals.
- There is a shortage of PHCs (22%) and sub-health centres (20%) , while only 7% of sub-health centres and 12% of primary health centres meet Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS) norms .
- In the northern States, there are hardly any sub-centres and primary health centres are practically non-existent. First-mile connectivity to a primary healthcare centre is broken. For eg, in Uttar Pradesh, there is one PHC for every 28 villages .
The strong role of Private players :
- Approximately 70 per cent of the healthcare services in India are provided by private players. If private healthcare crumbles due to economic constraints or other factors, India’s entire healthcare system can crumble.
- Over 70 per cent of the total healthcare expenditure is accounted for by the private sector.
- However, Private hospitals don’t have adequate presence in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities and there is a trend towards super specialisation in Tier-1 cities.
- lack of transparency and unethical practices in the private sector.
- The lack of a level playing field between the public and private hospitals has been a major concern as public hospitals would continue receiving budgetary support. This would dissuade the private players from actively participating in the Governmental scheme .
High Out of pocket expenditure :
- According to the latest National Health Accounts (NHA) estimates released in March 2021, patients bear a big chunk of health expenses, as high as 61 per cent of the total health expenditure, by themselves.
- Even the poor are forced to opt for private healthcare, and, hence, pay from their own pockets. As a result, an estimated 63 million people fall into poverty due to health expenditures, annually.
- Inequities in the health sector exist due to many factors like geography, socio-economic status and income groups among others. Compared with countries like Sri Lanka, Thailand and China, which started at almost similar levels, India lags behind its peers on healthcare outcomes.
Poor insurance penetration :
- India has one of the lowest per capita healthcare expenditures in the world. Government contribution to insurance stands at roughly 32 per cent, as opposed to 83.5 per cent in the UK.
- The high out-of-pocket expenses in India stem from the fact that 76 per cent of Indians do not have health insurance.
Fake doctors :
- Rural medical practitioners (RMPs) , who provide 80% of outpatient care, have no formal qualifications for it .
- People fall prey to quacks , often leading to grave disabilities and loss of life.
Numerous Schemes and their limitations :
- The Government has launched many policies and health programmes but success has been partial at best.
- The National Health Policy(NHP) 2002 proposed to increase Government spending on health by two to three per cent of the gross domestic product (GDP) by 2010 which has not happened yet.
- Now, the National Health Policy 2017 , has proposed to take it to 2.5 per cent of the GDP by 2025.
- The overall situation with the National Health Mission , India’s flagship programme in primary health care, continues to be dismal.
- The NHM’s share in the health budget fell from 73% in 2006 to 50% in 2019 in the absence of uniform and substantial increases in health spending by States.
Healthcare without a holistic approach :
- There are a lot of determinants for better health like improved drinking water supply and sanitation; better nutritional outcomes, health and education for women and girls; improved air quality and safer roads which are outside the purview of the Health Ministry .
Issues in particular with Urban healthcare
- Rural-urban disparity : Until recently , Union government mostly focused on rural healthcare. Ex: expenditure on urban areas was ₹ 850 crore in 2019-20, compared to nearly ₹30,000 crore for rural.
- Lack of government primary and preventive health infrastructure : Against a norm-based target of 9,072 urban primary health centres (UPHCs), only 5,190 are operational.
- Most states do not have urban sub-centres (SCs ) , people’s first point of access to healthcare services. There are only 3,000 urban SCs compared to over 150,000 in rural areas.
- Urban areas also suffer from ‘ over-hospitalization ’ of basic care, ideally done in clinics.
- Lack of devolution of functions by state government and inadequate role clarity among various health-related agencies
- The poor financial condition of ULBs and low priority accorded to health.

Issues in particular with Rural healthcare
- Only 11% of sub-centres, 13% of Primary Health Centres (PHCs) and 16% of Community Health Centres (CHCs) in rural India meet the Indian Public Health Standards (IPHS) .
- Only one allopathic doctor is available for every 10,000 people and one state-run hospital is available for 90,000 people.
- Innocent and illiterate patients or their relatives are exploited, and they are allowed to know their rights.
- Most of the centres are run by unskilled or semi-skilled paramedics and doctor in the rural setup is rarely available.
- Patients when in emergency sent to the tertiary care hospital where they get more confused and get easily cheated by a group of health workers and middlemen.
- Non-availability of basic drugs is a persistent problem in India’s rural healthcare.
- In many rural hospitals, the number of nurses is much less than required.
Central Government Schemes for Healthcare Sector in India
Health is a state subject , the Central Government supplements the efforts of the State Governments in the delivery of health services through various schemes for primary, secondary, and tertiary care.
- By 2025, the Government of India is planning to increase the expenditure on Health care to 2.5% of the GDP.
- In the Union Budget 2020-21, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare was allocated a budget of more than Rs 65,000 crores.
- In Budget 2020-21, the Government of India has approved the extension of the National Health Mission with an allocated budget of around Rs 34,000 crores.
- Under the National Health Mission (NHM) , financial support is provided in the following areas: ASHAs workers, ambulances, mobile medical units (MMUs), drugs and equipment, support for Reproductive, Maternal, New-born, Child & Adolescent Health (RMNCH+A).
- The National Nutrition Mission has set an objective of reducing undernutrition, and problems of stunting by 2%
- The Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) – This is the largest healthcare program funded by the Government.
- In the Union Budget 2020-21, PMJAY was allocated a budget of more than Rs 6400 crores.
- As of Nov 2019, more than 63 lakh people have received free treatment under Ayushman Bharat – PMJAY.
- In the Union Budget 2020-21, the Government of India allocated Rs 3,000 crores for Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY) .
The potential of the Indian Health Sector?
- India's competitive advantage lies in its large pool of well-trained medical professionals . India is also cost-competitive compared to its peers in Asia and Western countries. The cost of surgery in India is about one-tenth of that in the US or Western Europe.
- India has all the essential ingredients for the exponential growth in this sector, including a large population, a robust pharma and medical supply chain, 750 million plus smartphone users, 3 rd largest start-up pool globally with easy access to VC (Venture Capital Fund) funding and innovative tech entrepreneurs looking to solve global healthcare problems.
- India will have about 50 clusters for faster clinical testing of medical devices to boost product development and innovation .
- The sector will be driven by life expectancy, shift in disease burden, changes in preferences, growing middle class, increase in health insurance, medical support, infrastructure development and policy support and incentives.
- As of 2021, the Indian healthcare sector is one of India’s largest employers as it employs a total of 4.7 million people . The sector has generated 2.7 million additional jobs in India between 2017-22 -- over 500,000 new jobs per year
Opportunities in Health Care Sector
- By 2030, the Indian healthcare sector is estimated to reach US$ 744 billion according to a report by Aspire Circle.
- Data Analytics : The National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) will bring with it the digital Health ID , which will save patient data. It would aid in effective policymaking, and private firms would gain an advantage in the market introduction of innovative technology.
- Investing privately : It would be simple for private players to spend strategically with the arrival of information technology and big data . As we all know, the Indian healthcare sector is in urgent need of workers, and there is room for thousands of people.
- Start-ups : A climate conducive to start-ups and entrepreneurship can be formed in this field with the support of the government and private stakeholders.
- Medical Tourism : India is already one of the most popular medical tourism destinations in the world, and this industry can be effectively tapped in the next years.
Measures Required in the Health Sector
- Improving infrastructure : There is an urgent need to improve the infrastructure of public hospitals, which are overburdened as a result of India's large population.
- Focus on private hospitals : The government should encourage private hospitals because they make a significant contribution. Because the difficulties are severe and cannot be tackled just by the government, the private sector must also engage.
- Increased efficiency : To improve the sector's capabilities and efficiency, more medical personnel must be hired.
- Utilization of technology : In order to connect the dots in the health system, technology must be used. Medical gadgets in hospitals and clinics, mobile health apps, wearables, and sensors are only a few examples of technology that should be included in this area.
- Awareness : People should be made aware of the importance of early detection and prevention. It would also assist them in reducing their out-of-pocket expenses .
There is an urgent need to improve the infrastructure of public hospitals , which are overburdened as a result of India's large population. The government should encourage private hospitals because they make a significant contribution. Because the difficulties are severe and cannot be tackled just by the government, the private sector must also engage . To improve the sector's capabilities and efficiency, more medical personnel must be inducted . In order to connect the dots in the health system, technology must be used. Medical gadgets in hospitals and clinics, mobile health apps, wearables, and sensors are only a few examples of technology that should be included in this area.
Newsletter Subscription
Important links.
- Economic Issues
- International Relations
- Miscellaneous
- Human Geography
- Modern History
- Indian Society
- Art and Culture
- Government policies and interventions
- Biodiversity & Environment
- Bilateral Relations
- Important Bills
- Internal security
- Important reports
- Social issues
- Various acts
- International organisation
- International treaties and conventions
- Disaster and Disaster management
- Indian Polity
- World History
- Indian Geography
- Physical Geography
- Developmental Issues
- Indian Economy
- Government Policies & Reports
- Tolerance and Intolerance
- Ancient History

Challenge UPSC 2024 - PT Tricks
Update Info
- Prelims Sanjeevani 2021 Crash Course
Mains & Interview
- Mains Sanjeevani 7Days Batch (coming soon)
- MAINS Test Series By Toppers
- RAW Prelims Live MCQ 2021
UPSC Resource
- General Studies Notes
- SLP - Paid Notes
General Studies
All Programmes
Study Material
Shaping India’s Path to Inclusive Health Care
Why in news.
- World Health Day, observed annually on April 7 , serves as a reminder of the importance of health equity, a fundamental human right as declared by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Therefore, it is important to examine the theme of "My Health, My Right," exploring the challenges and solutions to achieving health equity in India , a nation grappling with diverse socioeconomic disparities in healthcare access and outcomes.
Health Equity and Its Significance
- Health equity, as defined by the WHO, is the principle that every individual should have the opportunity to achieve their highest level of health , regardless of their social, economic, or environmental circumstances.
- This concept goes beyond mere access to healthcare services; it encompasses addressing the underlying determinants of health disparities , such as poverty, discrimination, and unequal distribution of resources.
- One of the fundamental aspects of health equity is the recognition that health outcomes are shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including social, economic, and environmental determinants.
- Individuals from disadvantaged socioeconomic backgrounds often face barriers to accessing healthcare services , including financial constraints, lack of transportation, and limited availability of healthcare facilities in their communities.
- Health equity is essential not only from a moral and ethical standpoint but also from a public health perspective.
- Research has consistently shown that populations with greater levels of health equity tend to experience better overall health outcomes , including lower rates of morbidity and mortality, reduced healthcare costs, and increased life expectancy.
- On the other hand, persistent health inequities can lead to societal instability, economic burden, and diminished human potential.
Health Equity Challenges in India
- India grapples with significant disparities in healthcare access and outcomes between urban and rural areas.
- While urban centres often have better healthcare infrastructure and services, rural communities face numerous barriers , including limited access to healthcare facilities, shortage of healthcare professionals, and inadequate healthcare infrastructure.
- As a result, residents of rural areas often have poorer health outcomes compared to their urban counterparts.
- Urban slums in India represent pockets of extreme poverty and deprivation , characterised by overcrowding, poor sanitation, and limited access to clean water.
- These conditions create fertile grounds for the spread of infectious diseases , leading to higher morbidity and mortality rates among slum dwellers.
- Moreover, the lack of adequate healthcare facilities in slum areas further exacerbates health inequities , as residents struggle to access essential healthcare services.
- Marginalised groups, including S cheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and economically disadvantaged populations, experience higher rates of morbidity and mortality due to limited access to healthcare services, lower health literacy, and social discrimination.
- These disparities intersect with other social determinants of health, such as education, employment, and housing , further widening the gap in health outcomes.
- Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer, pose a growing challenge to health equity in India.
- While infectious diseases have traditionally been a major focus of public health efforts, NCDs now account for a significant proportion of the disease burden in the country.
- However, access to preventive services and treatment for NCDs remains limited, particularly among marginalised populations, leading to disparities in health outcomes and exacerbating existing social and economic inequalities.
- A critical shortage of doctors exacerbates these issues, with WHO data indicating only 0.8 doctors per 1,000 people, which is below the advised ratio.
- Even though over 75% of health-care professionals work in metropolitan regions, which only account for 27% of the population, the shortage is particularly severe in rural areas.
- As a result, residents of rural areas often lack access to primary healthcare services, leading to delayed diagnosis, inadequate treatment, and poorer health outcomes.
- Inadequate healthcare infrastructure, limited funding, and resource constraints pose significant challenges to health equity in India.
- Many public healthcare facilities lack essential equipment , medicines, and trained staff, hindering their ability to deliver quality healthcare services.
- Moreover, the unequal distribution of healthcare resources between urban and rural areas further exacerbates disparities in access to healthcare.
Way Forward: Solutions and Initiatives to Address Health Equity in India
- One of the key strategies to address health equity in India is strengthening primary healthcare services, particularly in rural and underserved areas.
- This includes improving the availability and accessibility of primary care facilities, enhancing the skills and capacity of frontline healthcare workers , and ensuring the provision of essential health services, including preventive care, maternal and child health services, and management of chronic diseases.
- Initiatives such as the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) and the National Urban Health Mission (NUHM) aim to expand access to primary healthcare services and reduce disparities in healthcare access between urban and rural areas.
- Universal health coverage (UHC) is critical for ensuring that all individuals have access to essential healthcare services without financial hardship.
- Initiatives such as Ayushman Bharat, India's flagship health insurance scheme, aim to provide financial protection to vulnerable populations by offering cashless coverage for hospitalisation expenses.
- By expanding access to quality healthcare services and reducing out-of-pocket expenses, UHC can help address disparities in healthcare access and improve health outcomes for all citizens.
- Health equity cannot be achieved solely through healthcare interventions; it also requires addressing the underlying social determinants of health, such as poverty, education, housing, and employment.
- Initiatives aimed at poverty alleviation, improving access to education and sanitation, and creating livelihood opportunities can have a significant impact on health outcomes and help reduce disparities in health status.
- For example, programs like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) provide employment opportunities to rural households, contributing to improved socioeconomic conditions and better health outcomes.
- Raising health literacy is essential for empowering individuals to make informed health decisions and seek equitable care.
- Integrating health education into existing healthcare programs can enhance public awareness and promote preventive healthcare practices.
- Effective collaboration among governments, civil society, healthcare providers, and international organisations is crucial for addressing health inequities.
- By leveraging their respective strengths and resources, these stakeholders can develop culturally sensitive health initiatives tailored to the unique needs of communities.
- Promoting health equity in India requires concerted efforts across multiple sectors and stakeholders.
- By addressing the socioeconomic determinants of health , strengthening healthcare infrastructure, and fostering collaborative partnerships, India can move towards a future where access to high-quality healthcare is a shared reality for all its citizens.
Achieving health equity is not merely a moral imperative but also a prerequisite for sustainable development and social progress.
Q) What is Aushman Bharat Yojna?
Aushman Bharat Yojna, also known as the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojna (PMJAY), is a flagship healthcare scheme launched by the Government of India in 2018. It aims to provide health insurance coverage to over 500 million economically vulnerable individuals and families in India.
Q) What are the key benefits of Aushman Bharat Yojna?
Aushman Bharat Yojna offers several benefits, including cashless access to healthcare services, coverage of up to ₹5 lakh per family per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalisation, provision for treatment of pre-existing diseases, and coverage of hospitalisation expenses such as room charges, medical tests, and surgical procedures. Additionally, the scheme promotes the use of technology for effective implementation and monitoring, ensuring transparency and accountability in healthcare delivery.
Source: The Hindu
Download PDF
Share this article.
© 2024 Vajiram & Ravi. All rights reserved

- Insights IAS Brochure |
- OUR CENTERS Bangalore Delhi Lucknow Mysuru --> Srinagar Dharwad Hyderabad
Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2025
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude
- Insights IAS Brochure

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGE
Following are the topics on which our followers have written (and writing essays) every Sunday to hone their essay writing skills. The topics are chosen based on UPSC previous year topics. Writing one essay on each Sunday will help you get better marks in this paper.
ESSAY STRATEGY by Topper – Rank 1 CSE 2017
ESSAY STRATEGY by Topper – Rank 25 CSE 2015
ESSAY STRATEGY by Topper – Rank 40 CSE 2015
- [VIDEO] How to Improve Marks in Essay and Ethics Papers?
- [VIDEO] How to Write Philosophical Essays
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2024
- 27 October 2024 : The doubter is a true man of science.
- 20 October 2024 : There is no path to happiness; Happiness is the path.
- 13 October 2024 : The empires of the future will be the empires of mind.
- 06 October 2024 : Forests precede Civilization and deserts follow them.
- 29 September 2024 : How you do anything is how you do everything
- 22 September 2024 : “Wonder is the beginning of wisdom.”
- 15 September 2024 : “The moral arc of the universe bends at the elbow of justice.”
- 8 September 2024 : “The unexamined life is not worth living.”
- 1 September 2024 : The worst form of injustice is pretended justice
- 25 August, 2024 : Science is the poetry of reality.
- 18 August, 2024 : A Budget Tells Us What We Cannot Afford, But It Doesn’t Keep Us from buying it
- 11 August, 2024 : The world is not magic and that is the most magical thing about it.
- 4 August, 2024 : Art is I; Science is We.
- 28 July, 2024 : History, in general, only informs us what bad government is
- 21 July, 2024 : Sarcasam : the last refuge of the chaste-souled individuals when their privacy is coarsely invaded.
- 14 July, 2024 : Wound is the place where light enters you
- 7 July, 2024 : What is Religion to One is Superstition To Another
- June 30, 2024 : Gender Is Spectrum
- June 23, 2024 : Those who were seen dancing were thought to be insane by those who could not hear the music.
- June 16, 2024 : Saint Has A Past. Sinner Has A Future
- June 9, 2024 : The worst disease in the world today is corruption and the cure for it is transparency.
- June 2, 2024 : Escape Competition Through Authenticity.
- May 26, 2024 : Creativity Is Allowing Yourself to Make Mistakes. Art Is Knowing Which Ones to Keep.
- May 19 2024 : In No Man’s Land, the only way to survive is to adapt.
- May 12, 2024 : Economics is concerned with what emerges, not what anyone intended.
- May 5, 2024 : A right is not what someone gives you; it’s what no one can take from you.
- April 28, 2024 : We come nearest to the great when we are great in humility.
- April 21, 2024 : Well done is better than well said.
- April 14, 2024 : Consistency is the last refuge of the unimaginative.
- April 07, 2024 : Came from plant, use it; made in plant, don’t.
- March 30, 2024 : A Business That Makes Nothing More Than Money Is Poor Business
- March 24, 2024 : If Voting Really Made Difference, They Would Not Let Us Do It
- March 17, 2024 : Cinema Is Not A Slice Of Life, But A Piece Of Cake.
- March 10, 2024 : Education Can give skill, but a liberal education can give dignity
- March 3, 2024 : Sometimes when you lose your way you find yourself
- February 25, 2024 : Who Looks Inside Awakes, Who Looks Outside Dream
- February 18, 2024 : Never Let School Interfere With Your Education
- February 11, 2024 : Whoever Controls the Media Controls the Mind
- February 04, 2024 : A certain darkness is needed to see the stars
- January 28, 2024 : Those who cannot remember the past are condemned to repeat it
- January 21, 2024 : Subtle Is powerful
- January 14, 2024 : The power of community to create health is far greater than any physician, clinic or hospital.
- January 07, 2024 : Give them Quality. That’s The Best Kind of Advertising
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2023
- December 31, 2023 : The only antidote to mental suffering is physical pain
- December 24, 2023 : All Great Changes Are Preceded By Chaos
- December 17, 2023 : We are drowning in information, but starved for Knowledge
- December 10, 2023 : Violence Is the last resort of the incompetent
- December 03, 2023 : Be a Voice, Not an Echo
- November 26, 2023 : A Society that has more justice is the society that needs less charity
- November 19, 2023 : Sell Your Cleverness and Buy Bewilderment
- November 12, 2023 : love takes off the masks that we fear we cannot live without and know we cannot live within
- November 5, 2023 : Clothes Make The Man
- October 29, 2023 : Education is what remains after one has forgotten what one has learned in school.
- October 22, 2023 : Mathematics is the music of reason
- October 15, 2023 : Girls are weighed down by restrictions, boys with demands – two equally harmful disciplines
- October 08, 2023 : Inspiration for creativity springs from the effort to look for the magical in the mundane.
- October 01, 2023 : Not All Who Wander Are Lost
- September 24, 2023 : Visionary Decision-Making happens at the intersection of intuition and logic
- September 17, 2023 : Thinking Is Like A game. It does not begin unless there is an opposition team.
- September 10, 2023 : Unless we have well-educated people, we are vulnerable on National Security
- September 03, 2023 : Harsh Laws are, at times, better than No laws
- August 27, 2023 : Nations Do Not Die From Invasion. They Die From Internal Rottenness
- August 20, 2023 : In Individuals, insanity is rare; In groups, parties and nations, it is the rule.
- August 13, 2023 : Economics Is Too Important To Leave To The Economists.
- August 06, 2023 : A self without a book-shelf is naked.
- July 30, 2023 : Wrong Choices Lead To Right Places
- July 23, 2023 : Credit where credit is due.
- July 16, 2023 : A right is not what someone gives you; it’s what no one can take away from you.
- July 9, 2023 : The measure of intelligence is the ability to change
- July 2, 2023 : Do what you can, with what you have, where you are.
- June 25, 2023 : In the long run , the sword will always be conquered by the spirit
- June 18, 2023 : The company you keep determines your Success
- June 11, 2023 : A disciplined mind brings happiness.
- June 4, 2023 : Our moral responsibility is not to stop the future but to shape it
- May 28, 2023 : Action breeds confidence and courage
- May 21, 2023 : A library is a hospital for the mind
- May 14, 2023 : Self-Education is Life-Long Curiosity
- May 7, 2023 : Silence is Spurious Golden
- April 30, 2023 : The price of greatness is responsibility
- April 23, 2023 : Progress is impossible without change
- April 16, 2023 : The Impact of Artificial Intelligence.
- April 9, 2023 : People would rather believe than know.
- April 2, 2023 : Prioritizing education technology for global growth
- March 26, 2023 : Technology is a weapon against poverty
- March 19, 2023 : Every choice you make makes you
- March 12, 2023 : Patience is a virture ; virtue is a grace
- March 5, 2023 : Before any fight, it is the fight of mind
- February 26, 2023 : The Measure of a man is what he does with Power.
- February 19, 2023 : When you kill time, you kill life.
- February 12, 2023 : Delayed success mostly stays forever.
- February 05, 2023 : The wound is the place where the Light enters you.
- January 29, 2023 : Doubt is an uncomfortable condition, but certainty is a ridiculous one.
- January 22, 2023 : I am what I am, so take me as I am
- January 15, 2023 : Real learning comes about when the competitive spirit has ceased
- January 08, 2023 : Time hurts but it also heals. It punishes but it rewards too- it is the greatest teacher ever for a human.
- January 01, 2023 : The Beginning is the End and the End is The Beginning.
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2022
- December 25, 2022 : To tolerate is purely an act of mind
- December 18, 2022 : The arc of moral universe is long, but it bends towards justice
- December 11, 2022 : Religion is a culture of faith; Science is a culture of doubt.
- December 04, 2022 : My best friend is a person who will give me a book I have not read
- November 27, 2022 : Everything comes to him who hustles while he waits
- November 20, 2022 : We are always blind as we want to be
- November 13, 2022 : By your stumbling, the world is perfected.
- November 6, 2022 : You cannot step twice in the same river
- October 30, 2022 : Just because you have a choice, it does not mean that any of them has to be right.
- October 23, 2022 : A smile is the chosen vehicle for all ambiguities
- October 16, 2022 : The time to repair the roof is when the sun is shining
- October 9, 2022 : A ship in harbour is safe, but that is not what ship is for
- October 2, 2022 : History is a series of victories won by the scientific man over the romantic man
- September 25, 2022 : Poets are the unacknowledged legislators of the world
- September 18, 2022 : Forests are the best case studies for economic excellence
- September 11, 2022 : Culture changes with economic development.
- September 4 2022 : We don’t see things as they are, we see them as we are.
- August 28 2022 : The obstacle is the path.
- August 21 2022 : What is to give light must endure burning.
- August 14 2022 : “He who has never learned to obey cannot be a good commander.” Aristotle.
- August 7 2022 : Any fool can know. The point is to understand.” Albert Einstein
- July 31, 2022 : A bad conscience is easier to cope with than a bad reputation. Friedrich Nietzsche.
- July 24, 2022 : Time is all we have and don’t
- July 17, 2022 : Life fritters away when distractions become your lifestyle
- July 10, 2022 : After every darkness comes the dawn July 10, 2022 : After every darkness comes the dawn
- July 3, 2022 : Mind – a beautiful servant? Or a dangerous master?
- June 26, 2022 : Education Breeds Peace
- June 19, 2022 : A great leader is never angry
- June 12, 2022 : That which hurts, instructs; That which instructs, creates; Creates Wonders!
- June 05, 2022 : Don’t let what you cannot do interfere with what you can do
- May 29, 2022 : The journey is a reward as well as destination
- May 22, 2022 : Imagination creates reality
- May 15, 2022 : The curious paradox is, only if we accept things as they are, things can change
- May 08, 2022: The whole problem with the world is that fools and fanatics are so certain of themselves, while wiser people are so full of doubts
- May 01, 2022: Loyalty To Country Always. Loyalty To Government Only When It Deserves
- April 24, 2022: Successful Investing Is Anticipating The Anticipations of Others
- April 17, 2022: Courage is resistance to fear, mastery of fear, not absence of fear
- April 10, 2022 : Tell me and I forget. Teach me and I remember. Involve me and I learn
- April 03, 2022 : Forgiveness is the final form of love
- March 27, 2022 : The world of reality has its limits; the world of imagination is boundless
- March 20, 2022 : Reason has always existed, but not always in a reasonable form.
- March 13, 2022 : Everything we hear is an opinion; not a fact
- March 5, 2022 : There are better practices to “best practices”
- February 27, 2022 : History repeats itself first as a tragedy second as a farce.
- February 20, 2022 : What is research, but a blind date with knowledge!
- February 13, 2022 : Hand that rocks the cradle rules the world
- February 6, 2022 : The real is rational and the rational is real.
- January 30, 2022 : Philosophy of Wantlessness Is Utopian, while the philosophy of materialism is chimera.
- January 23, 2022 : Your perception of me is a reflection of you; my reaction to you is an awareness of me.
- January 16, 2022 : The process of self-discovery has now been technologically outsourced.
- January 09, 2022 : Knowing oneself is the beginning of all wisdom
- January 02, 2022 : Biased Media Is A Real Threat To Indian Democracy
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2021
- December 26, 2021 : What Gets Measured Gets Managed
- December 19, 2021 : The enemy of stability is complacency
- December 12, 2021 : A clear conscience fears no accusation
- December 05, 2021 : Power of vested interests is vastly exaggerated compared with the gradual encroachment of ideas
- November 28, 2021 : The whole is more than a sum of its parts
- November 21, 2021 : Scientific and technological progress cannot be equated with the progress of humanity
- November 14, 2021 : The price of our vitality is the sum of all our fears
- November 7, 2021 : Lawlessness is the result of failure to cultivate a sense of self-evaluation
- October 30, 2021 : What you do makes a difference, and you have to decide what kind of difference you want to make
- October 24, 2021 : Science for the economic freedom of humanity
- October 17, 2021 : An interdependent world cannot be an inequitable world
- October 03, 2021 : Strength comes from an indomitable Will
- SEPTEMBER 26, 2021 : Ethnocracy and concentration of power can derail even an affluent nation
- SEPTEMBER 19, 2021 : Conservation is a state of harmony between men and land.
- SEPTEMBER 12, 2021 : Culture of entitlement comes with unreasonable expectations and insecurities
- SEPTEMBER 5, 2021 : Literacy is a vital skill that enhances dignity, improves health outcomes, empowers people to access their rights and bolsters opportunities
- AUGUST 29, 2021 : A parliamentary system of government rests on a functioning opposition as ‘no democracy can do without it’.
- AUGUST 22, 2021 : Development must lead to dismantle all kinds of human unfreedom
- AUGUST 15, 2021 : Sport is a reflection of larger social phenomena
- AUGUST 8, 2021 : Every social stratum has its own Common Sense and its own good sense
- AUGUST 1, 2021 : Capitalism without competition is not Capitalism. It is Exploitation.
- JULY 25, 2021 : We don’t have to sacrifice a Strong Economy for a Healthy Environment
- JULY 18,2021 : We Need not a social conscience, but a social consciousness.
- JULY 11, 2021 : The cure for evils of democracy is more democracy.
- JULY 04, 2021 : No Constitution by itself achieves perfect justice
- JUNE 27, 2021 : Our world has achieved brilliance without conscience.
- JUNE 20, 2021 : Our common humanity demands that we make the impossible possible.
- JUNE 13, 2021 : Without courage we cannot practice any other virtue with consistency. We can’t be kind, true, merciful, generous, or honest.
- JUNE 06, 2021 : The political problem of mankind is to combine three things: economic efficiency, social justice and individual liberty.
- MAY 30, 2021 : Economics without ethics is a caricature & ethics without economics is a fairy tale.
- MAY 23 , 2021 : Indecisiveness is the rival of Progression
- MAY 16 , 2021 : Time changes everything except something within us which is always surprised by change.
- May 09, 2021 : The possession of arbitrary power has always, the world over, tended irresistibly to destroy humane sensibility, magnanimity, and truth
- May 02, 2021 : The truth of character is expressed through choice of act ions
- April 25, 2021 : It is not our differences that divide us; It is our inability to recognise, accept, and celebrate those differences.
- April 18, 2021 : Nothing in the world is more dangerous than sincere ignorance and conscientious stupidity.
- April 11, 2021 : Solutions emerge if situations are not forced
- April 04, 2021 : Morality is subservient to materialistic values in present times
- March 28, 2021 : Prejudice is a burden that confuses the past, threatens the future and renders the present inaccessible
- March 21, 2021 : Our major social problems are not the cause of our decadence but are a reflection of it
- March 14, 2021 : The Future of Multilateralism : Towards a responsible Globalization
- March 07, 2021 : Subtlety may deceive you; Integrity never will
- February 28, 2021 :Technology as the silent factor in international relations
- February 21, 2021 :Patriarchy is the least noticed yet the most significant structure of social inequality
- February 14, 2021:There can be no social justice without economic prosperity but economic prosperity without social justice is meaningless
- February 07, 2021: Culture is what we are civilization is what we have
- January 31, 2021: Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication
- January 24, 2021: Ships do not sink because of water around them , ships sink because of water that gets into them
- January 17, 2021: Mindful manifesto is the catalyst to a tranquil self
- January 10, 2021: Life is long journey between human being and being humane
- January 03, 2021: The Covid pandemic has revealed the urgent need for effective governance everywhere”
- December 27, 2020: Challenges of 21st Century – insurmountable?
- December 20, 2020: Too much Democracy is Detrimental to Development
- December 13, 2020: Happiness is not an ideal of reason, but of imagination.
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2020
- December 06, 2020 : As you Start to walk on the way, the Way appears
- November 29, 2020: Need of the Hour is to Maximise Possibilities of Agriculture in India
- November 22, 2020: The survival of democracy depends on its ability to lower social uncertainty
- November 15, 2020: There is no greatness where there is no simplicity
- November 08, 2020: Inequality can be Reduced by the Power of the Market rather than the Government
- November 01, 2020: Civil liberties are fundamental to the functioning of modern democracies
- October 25, 2020: Artificial Intelligence is Not All Evil – It can Promote Social Good Too
- October 18, 2020: Wherever law ends, tyranny begins
- October 11, 2020:Hyper-globalism is threat to human prosperity
- September 27, 2020: Our World is in a Surplus of Multilateral Challenges and a Deficit of Solutions
- September 20, 2020: In India Agriculture and the Farmer are both the Victims of Narrow Political Vision
- September 13, 2020: India Needs Aggressive and Pragmatic Neighbourhood Policy
- September 6, 2020: “The greatest discovery of all time is that a person can change his future by merely changing his attitude .
- August 30, 2020: The worst form of inequality is to try to make unequal things equal
- August 23, 2020: Justice will not be served until those who are unaffected are as outraged as those who are.
- August 16, 2020: Life without liberty is like a body without spirit.
- August 09, 2020: Strive not to be a success, but rather to be of value
- August 02, 2020: New Education Policy 2020: A Progressive Policy with Diverse Challenges
- July 26, 2020: In a democracy, the individual enjoys not only the ultimate power but carries the ultimate responsibility
- July 19, 2020: Education is a progressive discovery of our own ignorance
- July 12, 2020: The human spirit must prevail over technology
- July 05, 2020: When the power of love overcomes the love of power the world will know peace.
- June 28, 2020: Today India Needs ‘Harmony in Diversity’, Not Unity in Diversity.
- June 21, 2020: A people without the knowledge of their past history, origin and culture is like a tree without roots.
- June 14, 2020: Post Independence, the Issue of Land is at the Core of India’s Non-Achievement of Its Development Aspirations
- June 7, 2020: Never Let a Good Crisis Go to Waste
- May 31, 2020: Despite Challenges, To be a Healthy and Successful Nation, India must Ensure Universal Health Coverage
- May 24, 2020: Nearly all men can stand adversity, but if you want to test a man’s character, give him power.
- May 17, 2020:The test of our progress is not whether we add more to the abundance of those who have much it is whether we provide enough for those who have too little
- May 10, 2020: Urban Exclusion of Migrant Workers in India is a Reality and Needs Urgent Robust Policy Measures
- May 03, 2020: Uncertainty should ignite creativity, not depravity
- April 26, 2020: The fool doth think he is wise but the wise man knows himself to be a fool
- April 19, 2020: Social Harmony, not Social Distancing, is the final solution to all our problems
- April 12, 2020: It is our choices, that show what we truly are, far more than our abilities
- April 05, 2020: Education must also train one for quick, resolute and effective thinking
- March 29, 2020: “Problems cannot be solved at the same level of awareness that created them”
- March 22, 2020: In order to understand the world one has to turn away from it on occasion
- March 15, 2020: Pandemics such as COVID-19, though Catastrophic, are in the end Meant to Reset Humanity and its Priorities
- March 08, 2020: Those who have wisdom have all: Fools with all have nothing
- March 01, 2020: Indifferentism is the worst kind of disease that can affect people.
- [VIDEO] Perspectives on Essay Topic of Feb 23
- February 23, 2020: To ease another’s heartache is to forget one’s own.
- February 16, 2020 : When civil services does its job, people will not need social service
- February 09, 2020 : The greatest threat to our planet is the belief that someone else will save it.
- February 02, 2020: Ability will get you success, Character will keep you successful.
- January 26, 2020: Media’s duty is to inform public, not manufacture opinion.
- January 19, 2020: Freedom is not worth having if it does not include the freedom to make mistakes
- January 12, 2020 : Women who seek to be equal with men lack ambition
- J anuary 5, 2020 : All war is a symptom of man’s failure as a thinking animal
- December 29, 2019 : There cannot be daily democracy without daily citizenship
- December 22, 2019: War is the ultimate Price we pay for lasting Peace
- December 15, 2019 : Inclusivity and Plurality are the hallmarks of a peaceful society
- December 08, 2019: Justice Loses Character if it becomes Revenge
- December 01. 2019: Economic Growth and Development are Shaped by the Societies in which they Operate
- November 24, 2019: Social Media is the Fourth Pillar of Democracy
- November 17, 2019: Media is No More a Fourth Pillar of Democracy
- November 10, 2019: Rise of Artificial Intelligence: the threat of jobless future or better job opportunities through reskilling and upskilling
- November 03, 2019:Biased media is a real threat to Indian democracy
- October 27, 2019: Neglect of primary health care and education in India are reasons for its backwardness
- October 20, 2019: South Asian societies are woven not around the state, but around their plural cultures and plural identities
- October 13, 2019: Courage to accept and dedication to improve are two keys to success
- October 06, 2019: Best for an individual is not necessarily best for the society
- September 29, 2019: Values are not what humanity is, but what humanity ought to be
- September 22, 2019: Wisdom finds truth
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2019
- September 15, 2019: Kashmir Problem – Historical Injustice or Misguided Geopolitics?
- September 08, 2019: India’s Space Ambitions – Are they Welfarist?
- September 01, 2019: India – $5 Trillion Economy: Dream or Reality?
- August 25, 2019 Knowledge will give you power, but character respect.
- August 18, 2019 The mind is everything. What you think you become.
- August 11, 2019: Virtue is Knowledge
- August 04, 2019: Inclusive governance begets Inclusive growth
- July 28, 2019: India’s headache: Unemployment or Underemployment?
- July 21, 2019: The road to science and spirituality are opposite, but we should tread both
- July 14, 2019: India is a leading power, rather than just a balancing power
- July 07, 2019: Should the world embrace democratic socialism or progressive capitalism?
- June 30, 2019: Impact of Digital Revolution on Human Wellbeing
- June 23, 20 19: Contentment is natural wealth, luxury is artificial poverty
- June 16, 2019: The definition of happiness is the full use of your powers, along the lines of excellence.
- June 09, 2019: Not Corruption, Communalism is the Greatest Threat India is facing Today
- May 19, 2019: First they ignore you, then they laugh at you, then they fight you, then you win.
- May 12, 2019: Never interrupt your enemy when he is making a mistake
- May 05, 2019: Happiness equals reality minus expectations
- April 28, 2019: Political correctness is tyranny with manners
- April 21, 2019: The only thing necessary for the triumph of evil is for good men to do nothing.
- April 07, 2019: Dogma is the sacrifice of wisdom to consistency
- March 31, 2019: The true measure of a man is how he treats someone who can do him absolutely no good.
- March 24, 2019: Terrorism has No Religion
- March 17, 2019: Money and Religion – Great Unifiers of Humankind?
- March 10, 2019: Tradition becomes our security, and when the mind is secure it is in decay
- March 03, 2019: Innovation distinguishes between a leader and a follower
- February 24,2019: Knowledge speaks, but wisdom listens
- February 17, 2019: Problems worthy of attack prove their worth by fighting back
- February 10, 2019: Nothing in the world is more dangerous than sincere ignorance and conscientious stupidity.
- February 03, 2019: You can avoid reality, but you cannot avoid the consequences of avoiding reality
- January 27, 2019: Glory is fleeting, but obscurity is forever
- January 20, 2019: All that we are is the result of what we have thought.
- January 12, 2019: All differences in this world are of degree, and not of kind, because oneness is the secret of everything.
- January 06, 2019: National security is Irreversibly linked to good economic growth
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2018
- December 28, 2018: To plan for smart development, governments and business must recognize nature’s role in supporting economic activity
- December 23, 2018: Government Surveillance – Good or Bad?
- December 16, 2018: Trade Wars – Economic or Geopolitical?
- December 02, 2018: Immigration is Not a Threat, but Fundamentally it’s an Economic Issue
- November 25, 2018: A people that values its privileges above its principles loses both
- November 18, 2018: “The past’ is a permanent dimension of human consciousness and values
- November 11, 2018: A good life is one inspired by love and guided by knowledge
- November 04, 2018: Management of Indian border disputes – a complex task
- October 28, 2018: Alternative technologies for a climate change resilient India
- October 21, 2018: Poverty anywhere is a threat to prosperity everywhere
- October 14, 2018: Reality does not conform to the ideal, but confirms it
- October 07, 2018: Customary morality cannot be a guide to modern life
- September 30, 2018: Commercialization of Space : Importance and the need for regulation
- September 23, 2018: E-commerce as a new form of trade and its challenges to India.
- September 16, 2018: Ability is nothing without opportunity
- September 09, 2018: Death Penalty eliminates Criminals, not Crime.
- September 02, 2018: Dissent is the foundation of democracy.
- August 26, 2018: Mars Mission and Mob lynchings are two obverse faces of India
- August 19, 2018: Strengthening Land Rights Strengthens Development
- August 12, 2018: Age of Big Data: Data is the New Oil, History is its oldest bank
- August 05, 2018: Strong Institutions and fair procedures, not personalities constitute the fundamentals of good governance
- July 29, 2018: Social reform is a myth if places of worship are open only to all castes and not to all genders.
- July 22, 2018: Section 377, not the carnal acts banned under it is ‘against the order of nature ‘
- July 15, 2018: Schooling Is Not Education
- July 08, 2018: Sometimes it takes a natural disaster to reveal a social disaster.
- July 01, 2018: Normal human activity is worse for nature than the greatest nuclear accident in history
- June 24, 2018: Gender Sensitive Indian Society is Prerequisite for Women and Child Empowerment
- June 17, 2018: Where Should India Invest More – Human Capital or Human Development?
- June 10, 2018: Has Democracy Taken Backseat Due to the Rise of Populists and Demagogues?
- June 03, 2018: We won’t have a society ,if we destroy the environment
- May 27, 2018: Can Development and Environment Protection Go Together?
- May 20, 2018: Governor is the Choke Point of Federal Circuit of India
- May 13, 2018: Anonymity is the Best and the Worst Feature of Urbanism
- May 06, 2018: A man is but the product of his thoughts; what he thinks, he becomes
- April 29, 2018: Guaranteeing Right to Vote may Establish a Democracy, But Ensuring it’s Right Use Only Will Bring a True Democracy
- April 22, 2018: Stereotyping is an Ideological Force Which Hinders and Endangers Consolidation of India
- April 15, 2018: Can Education and legislation Address Violence Against Women and Children in India?
- April 8, 2018: Banking Crisis in India – Failure of Governance and Regulation?
- April 1, 2018: Privacy is the fountainhead of all other rights
- March 25, 2018: Impact of Technology on Human Relations and Human Productivity
- March 18, 2018: India’s Focus should be on Ease of Living, not on Easy of Doing Business
- March 11, 2018: A friend to everybody is a friend to nobody
- March 04, 2018: Capitalism can not Bring Inclusive Growth
- February 25, 2018: The unprecedented advance of technologies facilitate individual empowerment but at the cost of Institutions and Democratic societies
- February 18, 2018: Threats being Faced by Liberal Democratic Systems are both Dangerous and Permanent
- February 11, 2018: For India, Stigmatised Capitalism is Better than Crony Socialism
- February 04, 2018: Art, freedom and creativity will change society faster than politics.
- January 28, 2018: Politics of Identity is the Politics of the Weak
- January 21, 2018: Poverty is the parent of revolution and crime
- January 14, 2018: Peace cannot be kept by force; it can only be achieved by understanding
- January 07, 2018: The Root Cause of Agrarian Distress in India – Failure of Policies or Failure of Governance?
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2017
- December 31, 2017: Impact of the new economic measures on fiscal ties between the union and states in India
- December 24, 2017: Fulfilment of ‘new woman’ in India is a myth
- December 17, 2017: Joy is the simplest form of gratitude.
- December 10, 2017: Farming has lost the ability to be a source of subsistence for majority of farmers in India
- December 03, 2017: Destiny of a nation is shaped in its classrooms
- November 19, 2017: Has the Non- Alignment Movement(NAM) lost its relevance in a multipolar world
- November 12, 2017: Social media is inherently a selfish medium.
- November 04, 2017: We may brave human laws but cannot resist natural laws
- October 29, 2017: Gratitude is not only the greatest of virtues, but the parent of all the others.
- October 22, 2017: Harith Diwali, Swasth Diwali : What measures are needed to deal with Festivity and Air Pollution?
- October 15, 2017: Biggest Threat to Humanity – Moral Crisis or Climate Change?
- October 08, 2017: The monsoon is a defining aspect of India’s nationhood
- October 01, 2017: India’s Infrastructure Story – Why is India not able to Build like China?
- September 24, 2017: Impact of Digital Technologies on Globalisation
- September 17, 2017: Urbanisation and Solid Waste Management in India – Challenges and Opportunities
- September 10,2017: Gender Equality and Peace: Are They Connected?
- September 03, 2017: Recent Natural Disasters – What do they Reveal about Humanity?
- August 27, 2017: Godmen – A Threat to Indian Society and Culture
- August 20, 2017: Corruption in India: Neither Systemic Reforms nor Surgical Strikes would End it
- August 13,2017: Interrelationship between Gender Equality and Sustainable Development
- August 06, 2017: Utility and relevance of Parliament in our polity
- July 30, 2017: Caste System – Source of India’s Eternal Inequality?
- July 23, 2017: Indian Democracy, Media and Public Opinion – Does Public Opinion Matter in Policymaking?
- July 16, 2017: Poverty and Environment – Their Interrelationship is the Key to Sustainable World
- July 09, 2017: Soft Power is India’s Strength, not its Weakness
- July 02, 2017: Technology and Jobs – Is Technology a Curse?
- June 25, 2017: Democracy’s Relevance in the Face of New Global Threats
- June 18, 2017: Federalism in India – Competitive or Cooperative?
- June 11, 2017: Peace, Environment and Development: Are these Interrelated?
- June 04, 2017: Role of Technology in Development – Is Technology Helping or Hindering Development?
- May 28, 2017: Poverty is a State of Mind
- May 21, 2017: Does India Need Superpower Status?
- May 14, 2017: India’s Achilles Heel – Lack of Ambition or Lack of Leadership in Achieving Greatness?
- May 07, 2017: Don’t limit a child to your own learning, for he was born in another time.
- April 29, 2017: The greatest happiness of the greatest number is the foundation of morals and legislation
- April 23, 2017: To conquer fear is the beginning of wisdom
- April 16, 2017: One-Party-Dominant System – Is it Good for India?
- April 09, 2017: Should Youth in India Consider Politics as Career?
- April 02, 2017: Can World Save Succeeding Generations from the Scourge of War?
- March 26, 2017: Low, stagnating female labour-force participation in India: An anomaly or an outcome of economic reforms?
- March 19, 2017: When a man is denied the right to live the life he believes in, he has no choice but to become an outlaw
- March 12, 2017: The marks humans leave are too often scars
- March 05, 2017: Environmental Challenges and Geopolitics: How to save our Environment?
- February 27, 2017: Radical Solutions are Needed to Address Today’s Radical Problems
- February 19, 2017: India’s Importance in the Post-truth World
- February 12, 2017: The Role of Politics in Development
- February 05, 2017: Facts do not cease to exist because they are ignored
- January 29, 2017: Building Walls and Banning Refugees – Does this Help Humanity?
- January 22, 2017: Digital economy: A leveller or a source of economic inequality
- January 15, 2017: Cyberspace and internet: Blessing or curse to the human civilization in the long run
- January 08, 2017: Water disputes between states in federal India
- January 01, 2017: Need brings greed, if greed increases it spoils breed
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2016
- (December 25, 2016) – Cooperative federalism: Myth or reality
- (December 18, 2016) – Innovation is the key determinant of economic growth and social welfare
- (December 11, 2016) – Near jobless growth in India: An anomaly or an outcome of economic reforms
- (December 04, 2016) – If development is not engendered, it is endangered
- (November 27, 2016) – Social media is better at breaking things than at making things
- (November 20, 2016) – Deglobalization is good for the world
- (November 12, 2016) – Democracy is the worst form of government, except for all the others
- (November 06, 2016) – It is not inequality which is the real misfortune, it is dependence
- (October 30, 2016) – Reducing Poverty while also Conserving Nature is an Impossible Task
- (October 23, 2016) – Poverty can be eliminated by putting science at the heart of development
- (October 16, 2016) – People shouldn’t be afraid of their government. Governments should be afraid of their people
- (October 09, 2016) – Better Access is Key to Inclusive Cities
- (October 02, 2016) – The weaker sections of Indian society – Are their Rights and Access to Justice Getting Better?
- (September 25, 2016) – Imagination is more important than intelligence
- (September 18, 2016) – Science is organized knowledge. Wisdom is organized life
- (September 11, 2016) – Not what we have But what we enjoy, constitutes our abundance
- (September 04, 2016) – It is the mark of an educated mind to be able to entertain a thought without accepting it
- (August 28, 2016) – If one can Address Moral Crisis, many of World’s Problems can be Solved
- (August 21, 2016) – Overdependence on Technology will Advance Human Development
- (August 14, 2016) – Geography may remain the same ; history need not
- (August 07, 2016) – Knowing yourself is the beginning of all wisdom
- (July 31, 2016) – To live is the rarest thing in the world. Most people exist, that is all
- (July 24, 2016) – True knowledge exists in knowing that you know nothing
- (July 17, 2016) – We Can Not Fight Terrorism – We have to Live With it
- (July 10, 2016) – A house divided against itself cannot stand
- (July 02, 2016) – When the going gets tough, the tough get going
- (June 26, 2016) – India a Reluctant Participant in the New Global Order?
- (June 19, 2016) – Inclusiveness in India – Still a Dream?
- (June 12, 2016) – No one can make you feel inferior without your consent
- (June 05, 2016) – Not everything that can be counted counts, and not everything that counts can be counted
- (May 29, 2016) – It is hard to free fools from the chains they revere
- (May 22, 2016) – Honest disagreement is often a good sign of progress
- (May 15, 2016) – Fire is a good servant but a bad master
- (May 08, 2016) – The grass is always greener on the other side of the fence
- (May 01, 2016) – Labour Reforms in India and its Role in Economic Development
- (April 24, 2016) – It takes a whole village to raise a child
- (April 17, 2016) – Trust take years to Build, Seconds to Break
- (April 10, 2016) – Cleanliness is next to Godliness
- (April 03, 2016) – Honesty is the Best Policy
- (March 27, 2016) – Before criticizing a man, walk a mile in his shoes
- (March 20, 2016) – Caste System – India’s Enduring Curse
- (March 13, 2016) – Fortune favors the bold
- (March 06, 2016) – Quick but steady wins the race
- (February 28, 2016) – Dreams which should not let India sleep
- (February 21, 2016) – Lending hands to someone is better than giving a dole
- (February 14, 2016) – Technology cannot replace manpower
- (February 7, 2016) – Character of an institution is reflected in its leader
- (January 31, 2016) – Can Capitalism bring Inclusive Growth?
- (January 24, 2016) – Crisis Faced in India – Moral or Economic?
- (January 17, 2016) – Too many cooks spoil the broth
- (January 10, 2016) – The Best Things in Life are Free
- (January 3, 2016) – Don’t count your chickens before they hatch.
WEEKLY ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2015
- 27 December 2015
- 20 December 2015
- 13 December 2015
- 06 December 2015
- 28 November 2015
- 21 November 2015
- 15 November 2015
- 08 November 2015
- 01 November 2015
- 25 October 2015
- 18 October 2015
- 11 October 2015
- 04 October 2015
- 27 September 2015
- 20 September 2015
- 13 September 2015
- 06 September 2015
- 31 August 2015
- 30 August 2015
- 23 August 2015
- 16 August 2015
- 09 August 2015
- 01 August 2015
- 26 July 2015
- 19 July 2015
- 12 July 2015
- 05 July 2015
- 28 June 2015
- 21 June 2015
- 14 June 2015
- 07 June 2015
- 31 May 2015
- 24 May 2015
- 17 May 2015
- 10 May 2015
- 03 May 2015
- 26 April 2015
- 19 April 2015
- 12 April 2015
- 05 April 2015
- 29 March 2015
- 22 March 2015
- 15 March 2015
- 01 March 2015
- 22 February 2015
- 15 February 2015
- 08 February 2015
- 01 February 2015
- 25 January 2015
- 18 January 2015
- 11 January 2015
- 04 January 2015

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Addressing the neglect of primary health care and education in India requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing policy reforms, increased investment, and community …
In this essay, we will delve into the significance of universal health coverage, its benefits, challenges of acquiring universal health coverage and possible strategies for …
Health is not just a state of being disease-free but it features multiple dimensions like nutrition, clean environment, sanitation, a healthy lifestyle etc. Further, achieving Zero …
Health Sector of India. Mains Marks Booster 1st August 2023. Download PDF (English) COVID-19 exposed several weaknesses in India’s underfunded health system. Rural primary care is underfunded and has shortages of staff, …
India will have about 50 clusters for faster clinical testing of medical devices to boost product development and innovation. As of 2021, the Indian healthcare sector is one of India’s largest …
CURRENT AFFAIRS FOR UPSC IAS. Indian Health Sector: Opportunities and Challenges. Published: 10th Apr, 2021. In Budget 2021 health sector is focused on by …
There are a lot of determinants for better health like improved drinking water supply and sanitation; better nutritional outcomes, health and education for women and girls; …
Raising health literacy is essential for empowering individuals to make informed health decisions and seek equitable care. Integrating health education into existing healthcare programs can …
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2023. December 31, 2023 : The only antidote to mental suffering is physical pain. December 24, 2023 : All Great …