- Get Started

How to start a solar business — the basics
Want to learn more about the solar industry? Join us for Empower 2024 on June 5-6! You’ll hear from industry experts on everything from how to run a successful solar business, to how AI is affecting the industry, and more.
Register Now

Note: This blog was originally published in February 2021. It was updated October 25, 2023 to reflect recent information. If you have any questions, please contact us .
The solar industry is growing, and its sun is still just starting to rise. Solar power continues to lead the way when it comes to renewable energy — and arguably energy in general. According to SEIA data, in the first half of 2023, 45% of all new electric capacity added to the US grid was from solar.
Likewise, solar installation professionals is among the fastest growing professions in the United States. The trade is projected to enjoy a 22 percent growth rate between 2022-2032, and the 2022 median income was $45,230 per year.
This data represents a promising prospect for contractors looking to cut their teeth in this exciting business. If you’re wondering what it takes to start your own solar business, this post is for you.
How to start a solar business — beginnings
Of course, there’s much more to solar installation than slapping up panels: there’s general contracting, roofing, metal fabrication, sales, repair and maintenance, consultation, landscape design, and so much more.
The best place to start a new solar business is between the cracks of large, over-saturated markets. Find out what solar professionals are doing in your area by checking in with local SEIA chapters and chambers of commerce, and conducting internet searches. It’s highly likely that even if your market is saturated with traditional solar businesses, you can find a niche that only you can fill.
Solar incentives
Becoming an expert means more than knowing your product. It requires having your finger on the pulse of the various rebates and incentives available, an important differentiator for companies looking to get ahead of the pack. Businesses that do the research to save their customers time and money have a leg up when it comes to getting the contracts.
Solar sales
Starting a solar business doesn’t necessarily mean you’ll need a crew up on roofs installing panels. If sales is your thing, there are many businesses that focus on just that.
These companies do all the work of selling solar systems : getting leads, qualifying them, doing in-home or virtual consultations, and getting the customer to sign. Once a customer has signed on, these organizations then work with a contractor that takes care of the rest of the installation process.
With the recent improvements in solar sales software, it’s easier than ever to stand out from the crowd. Click through this Tourial to see how Aurora’s reimagined Sales Mode can help you sell with confidence and close more sales.
Solar installers
Solar installers are usually the most saturated business in the market. If you’re wondering how to start a solar installation business , you might want to start at the basics: Roofing. If you’re a roofer, solar installation could be a great option to add to your business. The solar and roofing industries are starting to converge, and for good reason. Solar panels and roofs have about the same lifespan (approximately 25 years), and savvy roofers are realizing the one-two punch of installing a new roof and solar system simultaneously. Whether you’re a roofing contractor or solar installer, there’s a lot of overlap between the two, and plenty of untapped market opportunities for incorporating roofing and solar into your business plan.
What is a PV system?
Before we move on, let’s take a quick look at how a PV system works to get a better idea of how you can make money building one.
How does a solar photovoltaic system work?
Solar panels convert the energy of the sun into electricity through a process called the photovoltaic effect. When a photon hits a photovoltaic (PV) device, its energy knocks electrons in the material. These electrons begin to flow, producing an electric current.
At a high level, the process of how solar panels works involves three primary steps:
- Solar cells within solar panels absorb light from the sun, which causes electric current to begin flowing.
- An inverter converts DC electricity to AC electricity .
- This electricity is used to supply current energy demands in the customer’s building and excess electricity beyond what the customer can use is exported to the grid (or used to charge a battery).
The photovoltaic process occurs at the solar cell level. Solar panels are composed of multiple cells, and PV systems are a series of solar panels wired together (called “ stringing ”) to provide appropriate voltage to the system’s inverter.
After a PV system is installed , there’s nothing standing between a customer and cheap, green energy.

Solar company licensing & certifications
Solar licensing.
Not every state requires solar licensing, but some do. Keep in mind that if you’re planning on working outside of your home state, you’ll need licenses for any state you want to work in. For states requiring licenses, you’ll often need a plumbing or electrician license, or both. Some states require a specialized solar contractor license.
Check here to check on what type of licensing you may need in your state, region, or municipality.
Solar certifications
Even if you don’t need a license to operate in your area, earning a solar certification is a great idea. Solar certifications are an important way to promote customer confidence, putting you ahead of the average uncertified business.
Certification can also lead to more income, with certified solar professionals earning an average of $11,000 more annually. Getting certified may also allow you to operate in more than one municipality or state, increasing your competitiveness.
The North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP) voluntary certifications provide national standards for PV professionals, certifying they have the skills, experience, and competency to set themselves apart. NABCEP’s certifications include :
- PV Installation Professional (PVIP)
- PV Design Specialist (PVDS)
- PV Technical Sales Professional (PVTS)
- PV Installer Specialist (PVIS)
- PV Commissioning & Maintenance Specialist (PVCMS)
- PV System Inspector (PVSI)
Set up your solar business
You’ve nailed down your niche, identified solar certifications and licenses, and are ready to make the jump. Let’s take a dive into how to start a solar business from the ground up, starting with the legal stuff first.
Establish an LLC
An LLC, or limited liability company, is a business structure set up by state statute. LLCs provide several benefits, including liability protection, flexible structure, and tax advantages. They provide the same limited liability as a corporation but are much cheaper and easier to form and operate.
In most states, getting an LLC entails choosing a name, selecting members (which can include just you), creating articles of organization and operating agreements, and getting an EIN (employer identification number). You’ll then need to obtain any seller’s permits and licensing required by your state. Check your state’s LLC requirements for more information.
Business insurance
The right insurance coverage is essential to mitigate potential risks and liabilities. Every contracting business must meet general insurance requirements, but there are a few considerations specific to the solar industry. Here’s your solar business insurance checklist:
- General liability insurance
- Workers’ compensation
- Automobile liability insurance
- Excess/umbrella liability insurance
Most contractor general liability insurances provide a minimum of $500,000 coverage. Keep track of your inventory, equipment, and properties, and get the right insurance that would cover the worst-case scenario. Do yourself a favor and get the right insurance before you even land your first contract. Click here for an in-depth look into the right solar business insurance .
Establishing a solar team
1. how to find salespeople.
Salespeople are the backbone of most solar businesses. Regardless of your niche, chances are that someone on your team is making at least part of their paycheck knocking on doors and making phone calls.
When seeking out a salesperson, here are three elements to consider when vetting your candidate pool:
- Knowledge about your niche
- Passion and persistence
- Familiarity with questions and concerns that customers have about solar
It’s crucial that you foster a culture of customer satisfaction in all of your employees, but salespeople in particular. They are usually the folks leading your conversion process and are often the face of your business.
If an in-house sales team isn’t feasible, there are several options available for sales outsourcing. Many businesses exist that specialize in outsourcing solar sales for installers, consultants, and retailers.
2. Ramping up a team
Start out with nothing but the best right from the gate. Find team members that are NABCEP certified (see above). If your team isn’t certified, give them the time and resources to do so.
Make sure your salespeople, installers, marketing team, and others know the ins and outs of your product. Give everybody on your team the time and resources to learn about your product and services.
Your dream team doesn’t have to be all employees. Network with other solar experts outside of your niche. They will become invaluable sources of help and referrals if you keep at it.
3. Setting up compensation structures
Solar salespeople are usually paid by commission. Commission payouts are usually paid as a percentage of the total contract price or as a cut of the base contract price.
Commissions have various pros and cons. On one hand, they can motivate your teams to work hard. On the other hand, commissions may encourage your salespeople to sell more than a customer needs, take on cost-prohibitive projects, and inflate project costs above market rates.
Read more on common commission structures in the solar sales industry today.
Pro tips: Avoid these solar sales barriers
There are many barriers when it comes to getting a solar business off the ground. Here are three common ones that can be easily solved with the right solar software.
Incorrect or inefficient designs
It’s all too easy to under- or over-engineer a solar system. Incorrect or inefficient designs are a surefire way to sink your business. Aurora Solar’s sophisticated solar design software uses technology like LIDAR-based shade analysis and AI-assisted 3D modeling to give you a pixel perfect design almost instantly — without a truck roll.

Electric quotes from customers
Customers are often wary of providing their electricity bills. Just a few days can mean the difference between landing a new customer and losing them, so make this process as seamless as possible for your customers.
Most electric customers receive a bill in the mail every month. If they don’t, they can likely access it online from their utility. Either way, Aurora can provide a forecast of year-round energy usage from just one month’s bill — taking into account factors like weather, HVAC, and more.
Take this opportunity to remind your customer that making efficiency upgrades in the home could drastically improve energy efficiency.
And don’t forget to study up on the net metering rules for your state. Being able to sell excess power back to the grid can be a huge selling point for solar installations.
Permitting problems
Flawed designs can lead you straight back to the drawing board. If a solar design isn’t compliant with state or local regulations, your plans will be rejected. Collecting and reporting permit-related project data constitutes up to 8% of soft costs associated with solar, owed largely to mistakes and regulatory bottlenecks.
Aurora’s Plan Sets Service expedites your post-sales permitting process. It’s also a great tool for new businesses looking to scale without the growing pains and backlogs of permitting — Aurora can handle any growing volume of plan sets you need.
See how it works in the Tourial below.
Starting a solar business takes research, investment, time, and leadership. But, it can be worth the effort, providing a great career in a growing and fulfilling industry.
When you do start your business, make sure you have a software solution that sets you up for success. Schedule a free demo today to see how Aurora can help you get started in the solar industry.
Ready to learn more?

How to Sell Solar in 2023 Despite NEM 3.0

Sales Mode: Proposals You Can Build Your Reputation ...

PV Education 101: A Guide for Solar Installation Pro...
- Solar Panels Contracts
Solar Farm Business Plan
Used 4,872 times
Give your solar farm business the best start by creating a professional business plan to keep your company on the right track.
e-Sign with PandaDoc

Created by:
[Sender.FirstName] [Sender.LastName]
[Sender.Company]
Prepared for:
[Founder.FirstName] [Founder.LastName]
[Founder.Company]
1. Executive Summary
Our mission is
to provide professional solar panel installation,maintenance and repair services that will assist businesses, individuals, households, and non-profit organizations in ensuring that their solar panels always produce sustainable power.
Our vision is
to establish a standard and world-class solar farm and solar panel installation, maintenance, and repair company whose services and brand will not only be accepted in (Enter State) but also in other cities in the United States of America.
2. Business Description
[Founder.Company] was founded by [Founder.FirstName] [Founder.LastName] in (Add year). [Founder.FirstName] [Founder.LastName] (Add the founder’s background) and his friend and business partner for many years (Add your business partner’s name and background if relevant). They have a combined experience that can help them build [Founder.Company] to favorably compete with other solar farm businesses.
[Founder.Company] , is a solar farm and solar panel installation, maintenance, and repair company that intends to start small in [Founder.State] , but hope to grow big in order to compete favorably with leading solar energy companies and solar panel installation, maintenance, and repair companies in the industry both in the United States and on a global stage.
3. Mission Statement
[Founder.FirstName] [Founder.LastName] , the brains behind this company, has a vision to make Photovoltaic Panels be the main source of energy for (Enter State).
The rising concern for the environment can be lessened by using renewable sources of energy, this is where [Founder.State] comes in the picture. Our company has a team of experts in the solar farms industry that will provide the best and the most reliable services to all our clients.
Goal 1: Energy Supply
Supply solar energy to domestic, commercial and industrial enterprises in need of clean, efficient and reliable solar energy.
Goal 2: Plant Constructions
Construction of CSP power plants, CSP tower power plants and CSP through power plants using the latest environmentally friendly technologies.
Goal 3: Panel Installations
Installation of solar panels, repair and maintenance services thanks to a qualified and reputable installation and quality assurance team.
Goal 4: Consultation
Consultation, energy analysis studies and designing of integrated solar system plans. This involves holding discussions with potential customers to determine their solar needs and recommend an appropriate solution.
[Founder.Company] is uniquely qualified to succeed due to the following reasons:
[Founder.Company] provides customized residential and business energy solutions. In addition, we have surveyed the local population and received extremely positive feedback saying that they explicitly want to make use of our services when launched.
Our location is in a high-wealth area and is environment friendly; customers here are interested in renewable and sustainable energy.
The management team has a track record of success in the solar energy industry.
In order to ensure business goals are met, [Founder.Company] intends to offer a wide range of services in order to cater to different types of customers. The focus will be placed on offering quality services and deployment of the latest infrastructure and technologies to ensure this solar energy farm business plan realizes its intended purpose.
[Founder.Company] will primarily serve the residents and businesses within a 10 mile radius of our location. The demographics of these customers are as follows:
50,336 residents
1,876 businesses
6 utility companies
Annual utility spend/household=$3200
If you are keeping tabs on happenings in the Solar Farm Developers industry, you will agree that the demand for construction of utility-scale solar power projects has skyrocketed many thanks to substantial government support. So also, technological advancements in solar panel construction will definitely lead to a greater supply of low-cost panels, making solar power more affordable and sustainable.
Over the next five years, revenue within the Solar Farm industry is expected to grow tremendously. In general, the capital costs associated with developing and constructing a new solar farm are expected to fall substantially over the next five years due to an excess supply of solar panels as well as general improvements and advancements in solar power technology, which will reduce the per kilowatt-hour (kilowatt of electricity generated in one hour) cost of solar power.
The key industry drivers include:
Tax credits for energy efficiency-Tax credits generally encourage private investment into solar technologies by making development of solar energy projects cheaper. Demand for solar farm development will increase while the tax credit is in effect.
Electric power consumption-Demand for solar power hinges primarily on the level of electric power consumption throughout the United States. Increased demand typically translates into growth in renewable energy implementation.
World price of steaming coal- The price of steaming coal generally reflects demand for coal to produce electricity. An increase in the price of steaming coal leads to higher demand for alternative sources, including solar energy, to the benefit of solar farm developers.
Aside from the fact that we have a vast acre of land in a strategic location in the outskirts of [Founder.State] for our solar farm, our core strength lies in the power of our team and our workforce.
We have a team of certified and highly trained and experienced solar panel installation, maintenance, and repair engineers and technicians, a team with excellent qualifications and experience in various niche areas in The Solar Farm Developers industry.
Aside from the synergy that exists in our carefully selected workforce, our services will be guided by best practices in the industry.
Status of Ownership
[Founder.FirstName] [Founder.LastName] the founder of [Founder.Company] will be mostly in charge of managing the solar farm business and approving projects and product developments. His business partner, (Name), will be in charge of handling the company’s finances.
The team is composed of a Projects Manager, Head Engineers, Design and Construction Head, Marketing Head and Administrative Head. These people are the company’s spine and they all work together to take the company to the next level.
4. Products and Services
[Founder.Company] has designated (Size of the land) on which it will install (Type of solar panels, along with any relevant details). It will begin as a (Production size of the solar farm) farm, with ample land for capacity growth. The company will keep abreast of solar technology innovations as it grows to ensure optimal returns on investment.
5. Marketing Plan
The [founder.company] brand.
The [Founder.Company] brand will focus on the Company’s unique value proposition:
Offering high quality renewable source of energy
Giving high quality services and products to all of its clients
In Depth industry knowledge and expertise
Promotions Strategy
[Founder.Company] ’s target market are residents and businesses in [Founder.State] . The Company’s promotions strategy to reach these individuals includes:
Local Publications
[Founder.Company] will create brand awareness through features in multiple local newspapers and publications. Regular advertisements will run to maintain exposure and build brand awareness to relevant markets.
Direct and Digital Marketing
[Founder.Company] will blanket neighborhoods surrounding its locations with direct mail pieces. These pieces will provide general information on [Founder.Company] , offer discounts and/or provide other enticements for people to avail our services.
Additionally, [Founder.Company] will also use digital marketing to reach a wider audience. Based on demographic analysis, the company will create a social media presence on (List all relevant social media platforms). Along with these channels, [Founder.Company] will also set aside part of the marketing budget specifically for digital/online ads.
Public Relations
We will contact all local and area newspapers and television stations and send them a press release describing the benefits of renewable energy and solar farms and the unique value proposition of [Founder.Company] .
Community Events/Organizations
[Founder.Company] will conduct informative community discussions and seminars regarding the advantages of using sustainable energy. This seeks to educate people on the negative effects of nonrenewable resources on the environment, while simultaneously promoting our solar farm.
6. Operations Plan
Functional roles.
In order to execute on [Founder.Company] ’s business model, the Company needs to perform many functions including the following:
Service Functions:
Operations Management
Construction and Installation
Research and Development
Administrative Functions
General administrative function
Marketing and advertising
[Founder.Company] ’s long term goal is to become the dominant solar farmer and renewable energy provider in (Enter State). We seek to the standard by which other providers are judged.
The following are a series of steps that lead to our vision of long-term success. [Founder.Company] expects to achieve the following milestones in the following (Enter Number) months:
7. Management Organization
8. financial plan, profit/loss statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, funding requirements, 9. confidentiality statement.
The confidential information and trade secrets described above shall remain the exclusive property of the Company and shall not be shared or removed from the premises of the Company under any circumstances whatsoever without the express prior written consent of the Company.
10. Addendums
[Founder.FirstName] [Founder.LastName]
Care to rate this template?
Your rating will help others.
Thanks for your rate!
Useful resources
- Featured Templates
- Sales Proposals
- NDA Agreements
- Operating Agreements
- Service Agreements
- Sales Documents
- Marketing Proposals
- Rental and Lease Agreements
- Quote Templates
- Business Proposals
- Agreement Templates
- Purchase Agreements
- Contract Templates
- Sample Business Plans
- Manufacturing & Wholesale
Solar Panel Business Plan
With an extensive market chunk, the solar panel business is easy to enter and provides the most promising rewards in terms of growth and financial scalability.
Want to secure funds for your clean energy business? Want to get large-scale utility and federal government projects? You definitely need a comprehensive business plan to grow an idea into a terrific business opportunity.
Need help writing a business plan for your solar panel business? You’re at the right place. Our solar panel business plan template will help you get started.

Free Business Plan Template
Download our free solar panel business plan template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
How to Write A Solar Panel Business Plan?
Writing a solar panel business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan:
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready and summarizes each section of your plan.
Here are a few key components to include in your executive summary:
- Introduce your Business: Start your executive summary by briefly introducing your business to your readers.This section may include the name of your solar panel business, its location, when it was founded, the type of solar panel business (E.g., solar panel manufacturing, solar panel retailer, solar panel installation company, solar project developers), etc.
- Market Opportunity: Summarize your market research, including market size, growth potential, and marketing trends. Highlight the opportunities in the market and how your business will fit in to fill the gap.
- Products and Services: Highlight the solar panel services you offer your clients. The USPs and differentiators you offer are always a plus.For instance, you may include installation, repair and maintenance, consultation and site assessment as services and mention custom system designing and lifetime support as some of your USPs.
- Marketing & Sales Strategies: Outline your sales and marketing strategies—what marketing platforms you use, how you plan on acquiring customers, etc.
- Financial Highlights: Briefly summarize your financial projections for the initial years of business operations. Include any capital or investment requirements, associated startup costs, projected revenues, and profit forecasts.
- Call to Action: Summarize your executive summary section with a clear CTA, for example, inviting angel investors to discuss the potential business investment.
Ensure your executive summary is clear, concise, easy to understand, and jargon-free.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Business Overview
The business overview section of your business plan offers detailed information about your company. The details you add will depend on how important they are to your business. Yet, business name, location, business history, and future goals are some of the foundational elements you must consider adding to this section:
- Solar Panel Manufacturing
- Solar project development
- Solar panel installation
- Solar Panel retailing
- Describe the legal structure of your solar panel company, whether it is a sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, or others.
- Explain where your business is located and why you selected the place.
- Owners: List the names of your solar panel company’s founders or owners. Describe what shares they own and their responsibilities for efficiently managing the business.
- Mission Statement: Summarize your business’ objective, core principles, and values in your mission statement. This statement needs to be memorable, clear, and brief.
This section should provide a thorough understanding of your business, its history, and its future plans. Keep this section engaging, precise, and to the point.
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should offer a thorough understanding of the industry with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. You should include the following components in this section.
- Target market: Start this section by describing your target market. Define your ideal customer and explain what types of services they prefer. Creating a buyer persona will help you easily define your target market to your readers.For instance, residential and commercial sectors would be an ideal target audience for solar panel installation companies.
- Market size and growth potential: Describe your market size and growth potential and whether you will target a niche or a much broader market.For instance, the solar panel installation industry is 14.7 Billion dollars large and is booming at an unprecedented rate. It shows a promise of growth in residential and commercial projects.
- Competitive Analysis: Identify and analyze your direct and indirect competitors. Identify their strengths and weaknesses, and describe what differentiates your solar panel services from them. Point out how you have a competitive edge in the market.
- Market Trends: Analyze emerging trends in the industry, such as technology disruptions like virtual site assessments, smart energy management, Integrated photovoltaics, etc. Explain how your business will cope with all the trends.For instance, residential solar panel installation has a booming market; explain how you plan on dealing with this potential growth opportunity.
- Regulatory Environment: List regulations and licensing requirements that may affect your solar panel company, such as business registration, electrical contracting licenses, installation and inspection permits, solar-specific certifications, environmental regulations, state and federal regulations, etc.
Here are a few tips for writing the market analysis section of your solar panel business plan::
- Conduct market research, industry reports, and surveys to gather data.
- Provide specific and detailed information whenever possible.
- Illustrate your points with charts and graphs.
- Write your business plan keeping your target audience in mind.
4. Products And Services
The product and services section should describe the specific services and products that will be offered to customers. To write this section should include the following:
- Monocrystalline solar panels
- Polycrystalline solar panels
- Thin film solar panels
- Bifacial solar panels
- Installation
- Consultation and site assessment
- System design
- Repair and Mantainence
- Quality measures: This section should explain how you maintain quality standards and consistently provide the highest quality service.This may include compliance with quality and safety standards, product testing and certifications, monitoring and maintenance practices, etc.
- Additional Services: Mention if your solar panel company offers any additional services. You may include services like solar panel financing, lifetime support, smart home energy-efficient services, etc.
In short, this section of your solar panel plan must be informative, precise, and client-focused. By providing a clear and compelling description of your offerings, you can help potential investors and readers understand the value of your business.
5. Sales And Marketing Strategies
Writing the sales and marketing strategies section means a list of strategies you will use to attract and retain your clients. Here are some key elements to include in your sales & marketing plan:
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Define your business’s USPs depending on the market you serve, the equipment you use, and the unique services you provide. Identifying USPs will help you plan your marketing strategies.For example, custom designing, smart energy management, and virtual site assessment could be some of the great USPs for a solar panel installation company.
- Pricing Strategy: Describe your pricing strategy—how you plan to price your solar panel services and stay competitive in the local market. You can mention pricing strategies like leasing power purchase agreements to attract corporate and institutional buyers.
- Marketing Strategies: Discuss your marketing strategies to market your services. You may include some of these marketing strategies in your business plan—social media marketing, Google ads, brochures, email marketing, content marketing, print marketing in trade magazines, networking events, etc.
- Sales Strategies: Outline the strategies you’ll implement to maximize your sales. Your sales strategies may include direct sales calls, consultative selling, partnering with home builders, real estate agencies and relevant businesses, offering referral programs, etc.
- Customer Retention: Describe your customer retention strategies and how you plan to execute them. For instance, offering lifetime support, annual maintenance services, referral bonuses, etc.
Overall, this section of your solar panel installation business plan should focus on customer acquisition and retention.
Have a specific, realistic, and data-driven approach while planning sales and marketing strategies for your solar panel business, and be prepared to adapt or make strategic changes in your strategies based on feedback and results.
6. Operations Plan
The operations plan section of your business plan should outline the processes and procedures involved in your business operations, such as staffing requirements and operational processes. Here are a few components to add to your operations plan:
- Staffing & Training: Mention your solar panel business’s staffing requirements, including the number of employees needed. Include their qualifications, the training required, and the duties they will perform.A solar panel company usually requires engineers, installers, sales and CSR representatives, and support executives for smooth business operations.
- Operational Process: Outline the processes and procedures you will use to run your solar panel business. Your operational processes may include performing installation, maintaining solar panels, processing paperwork, site assessments, and writing grants.
- Equipment & Machinery: Include the list of equipment and machinery required for the solar panel business, such as manufacturing and installation equipment, testing and maintenance machinery, transport vehicles, office equipment, etc.Explain how these technologies help you maintain quality standards and improve the efficiency of your business operations.
Adding these components to your operations plan will help you lay out your business operations, which will eventually help you manage your business effectively.
7. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of your solar panel business’s management team. This section should provide a detailed description of each manager’s experience and qualifications, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
- Founders/CEO: Mention the founders and CEO of your solar panel company, and describe their roles and responsibilities in successfully running the business.
- Key managers: Introduce your management and key members of your team, and explain their roles and responsibilities.It should include, key executives(e.g. COO, CMO.), senior management, and other department managers (e.g. operations manager, sales manager, finance manager.) involved in the solar panel business operations, including their education, professional background, and any relevant experience in the solar panel industry.
- Organizational structure: Explain the organizational structure of your management team. Include the reporting line and decision-making hierarchy.
- Compensation Plan: Describe your compensation plan for the management and staff. Include their salaries, incentives, and other benefits.
- Advisors/Consultants: Mentioning advisors or consultants in your business plans adds credibility to your business idea.So, if you have any advisors or consultants, include them with their names and brief information consisting of roles and years of experience.
This section should describe the key personnel for your solar panel services, highlighting how you have the perfect team to succeed.
8. Financial Plan
Your financial plan section should provide a summary of your business’s financial projections for the first few years. Here are some key elements to include in your financial plan:
- Profit & loss statement: Describe details such as projected revenue, operational costs, and service costs in your projected profit and loss statement . Make sure to include your business’s expected net profit or loss.
- Cash flow statement: The cash flow for the first few years of your operation should be estimated and described in this section. This may include billing invoices, payment receipts, loan payments, and any other cash flow statements.
- Balance Sheet: Create a projected balance sheet documenting your solar panel business’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Break-even point: Determine and mention your business’s break-even point—the point at which your business costs and revenue will be equal.This exercise will help you understand how much revenue you need to generate to sustain or be profitable.
- Financing Needs: Calculate costs associated with starting a solar panel business, and estimate your financing needs and how much capital you need to raise to operate your business. Be specific about your short-term and long-term financing requirements, such as investment capital or loans.
Be realistic with your financial projections, and make sure you offer relevant information and evidence to support your estimates.
9. Appendix
The appendix section of your plan should include any additional information supporting your business plan’s main content, such as market research, legal documentation, financial statements, and other relevant information.
- Add a table of contents for the appendix section to help readers easily find specific information or sections.
- In addition to your financial statements, provide additional financial documents like tax returns, a list of assets within the business, credit history, and more. These statements must be the latest and offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
- Provide data derived from market research, including stats about the solar panel industry, user demographics, and industry trends.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Include any additional documentation related to your business plan, such as product brochures, marketing materials, operational procedures, etc.
Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the necessary information.
Remember, the appendix section of your solar panel business plan should only include relevant and important information supporting your plan’s main content.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
This sample solar panel business plan will provide an idea for writing a successful solar panel plan, including all the essential components of your business.
After this, if you still need clarification about writing an investment-ready business plan to impress your audience, download our solar panel business plan pdf .
Related Posts
Welding Business Plan
Machine Shop Business Plan
Free Sample Business Plans
Writing Table of Contents in Business Plan
Writing a Business Plan from Scratch
Best Business Planning Tools
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do you need a solar panel business plan.
A business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful solar panel business. It helps to get clarity in your business, secures funding, and identifies potential challenges while starting and growing your business.
Overall, a well-written plan can help you make informed decisions, which can contribute to the long-term success of your solar panel company.
How to get funding for your solar panel business?
There are several ways to get funding for your solar panel business, but self-funding is one of the most efficient and speedy funding options. Other options for funding are:
- Bank loan – You may apply for a loan in government or private banks.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loan – SBA loans and schemes are available at affordable interest rates, so check the eligibility criteria before applying for it.
- Crowdfunding – The process of supporting a project or business by getting a lot of people to invest in your business, usually online.
- Angel investors – Getting funds from angel investors is one of the most sought startup options.
Apart from all these options, there are small business grants available, check for the same in your location and you can apply for it.
What is the easiest way to write your solar panel business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of any solar farm business plan example and edit it as per your need. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software .

How detailed should the financial projections be in my solar panel business plan?
The level of detail of the financial projections of your solar panel business may vary considering various business aspects like direct and indirect competition, pricing, and operational efficiency. However, your financial projections must be comprehensive enough to demonstrate a comprehensive view of your financial performance.
Generally, the statements included in a business plan offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
Can a good solar panel business plan help me secure funding?
Indeed. A well-crafted solar panel business will help your investors better understand your business domain, market trends, strategies, business financials, and growth potential—helping them make better financial decisions.
So, if you have a profitable and investable business, a comprehensive business plan can certainly help you secure your business funding.
What's the importance of a marketing strategy in a solar panel business plan?
Marketing strategy is a key component of your solar panel business plan. Whether it is about achieving certain business goals or helping your investors understand your plan to maximize their return on investment—an impactful marketing strategy is the way to do it!
Here are a few pointers to help you understand the importance of having an impactful marketing strategy:
- It provides your business an edge over your competitors.
- It helps investors better understand your business and growth potential.
- It helps you develop products with the best profit potential.
- It helps you set accurate pricing for your products or services.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more

Turn your business idea into a solid business plan
Explore Plan Builder
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

Solar Farm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Solar Farm Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Solar Farm business plan.
We have helped over 10,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their solar farms.
Solar Farm Business Plan Example
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Solar Farm business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Helios Solar is a startup Solar Farm company located in northern New Mexico. The company was founded by husband and wife team Derek and Meri Smith. Derek has deep experience in the construction industry, and Meri has a background in accounting. The combination of these skills positions the couple to succeed in building and maintaining a solar farm. What’s more, Derek and Meri already own a 250-acre tract of land in sunny New Mexico.
Product Offering
Helios Solar has designated 50 acres on which it will install crystalline silicon solar panels with sun tracking technology. It will begin as a 5MW farm, with ample land for capacity growth. The company will keep abreast of solar technology innovations as it grows.
Customer Focus
Helios Solar will offer wholesale electricity to established utility companies in New Mexico and surrounding states.
Management Team
Helios Solar will be owned and operated by Derek and Meri. Derek will oversee the physical operation of the farm, while Meri will oversee the administrative side.
Derek Smith has a background in construction, and is a graduate of Solar Energy International, and subsequently earned a North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP) certification as a PV Commissioning & Maintenance Specialist.
Meri Smith is a graduate of the University of New Mexico with a Bachelor’s degree in Accounting. She has been working at a local accounting firm for over a decade as a CPA. Meri’s experience in accounting has given her the skills to manage the company’s finances, and the knowledge to steer the company to financial stability and success.
Success Factors
Helios Solar will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Friendly, knowledgeable, and highly qualified PV experts
- An ideal location in New Mexico, with ample room for expansion
Financial Highlights
Helios Solar is seeking $2 million in debt financing to launch its solar farm. The funding will be dedicated towards installing solar panels and payroll of the staff until the farm reaches break even. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Hardware (modules, inverters, mounts, etc.): $1.7 million
- Office equipment, supplies, and materials: $10,000
- Overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $200,000
- Marketing costs: $10,000
- Working capital: $10,000
To supplement its funding requirements, Helios Solar intends to apply for government grants and take advantage of incentive programs for the installation of solar equipment.
Company Overview
Who is helios solar.
Helios Solar aims to deliver utility-scale solar power, starting with a 5MW capacity. The husband and wife team is highly qualified and experienced in PV maintenance, accounting, and financial reporting.
Helios Solar History
Helios Solar is owned and operated by Derek and Meri Smith, a former construction manager and certified PV Commissioning & Maintenance Specialist (Derek), and CPA (Meri). Derek has worked for a large construction company and oversaw a variety of construction projects in the Albuquerque metro area. Derek’s tenure with the construction company, as well as his education in PV maintenance, combined with Meri’s financial acumen has given them the skills and knowledge required to venture out and start their own company. Derek and Meri have been awarded contracts with two large utility companies, which guarantees Helios Solar stability while they work to increase capacity.
Since incorporation, Helios Solar has achieved the following milestones:
- Registered Helios Solar, LLC to transact business in the state of New Mexico.
- Has cleared and prepared a 5-acre parcel of land for PV installation, and constructed an office building nearby.
- Reached out to numerous utilities in order to start getting wholesale contracts.
- Began recruiting PV maintenance workers, and office personnel to work at Helios Solar.
Helios Solar Services
Industry analysis.
The Solar Power industry is expected to grow over the next five years to over $18.3 billion.
The growth will be driven by the large expansion of government spending is set to support the solar industry as the push toward renewables accelerates. Electric power consumption is expected to increase slightly, but is expected to continue its shift toward renewable sources and away from fossil fuels.
The Solar Power industry in the United States is growing rapidly, underpinned by a combination of favorable government incentives and consistent technological advancements. Furthermore, solar power falls into the emergent green energy sector and benefits from rising public and private support.
Costs will likely be reduced as PV panels continue to gain efficiency and manufacturers compete to drive down the price of producing the panels. Solar Farms have also benefited from attractive tax credits and requirements for downstream utilities to diversify energy holdings and integrate renewable energy into their portfolio.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Helios Solar will target utility companies in New Mexico, Colorado, Utah, and Arizona.
The precise data for these target states are:
Customer Segmentation
Helios Solar will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Non-profit utility companies
- Corporate utility companies
- Government administered utilities
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Helios Solar will face competition from other companies with similar business models. A description of each competitor company is below.
Sunrise Solar Power Plant
Sunrise Solar is a 794 MWp (614 MWAC) photovoltaic power station in California, near the Mexican border. The facility was developed and constructed in three phases.
The first phase was commissioned in 2014, and supplies 266 MW under a 25-year agreement. The third phase was commissioned in 2018, and provides 328 MW using 2.8 million thin film panels. Phase two was commissioned in early 2020, and provides 200 MW.
The plant users more than 3 million thin-film CdTe photovoltaic modules and 138 skids which rotate on a north-south axis tracking the path of the Sun, and produces enough energy to power 72,000 homes.
Sun Mountain Solar Facility
The Sun Mountain Solar Facility is an 802 megawatt solar photovoltaic power plant. The plant entered service on December 1, 2010. It is co-located with three other solar projects in the region, thus forming a more than 1 gigawatt (GW) solar generating complex.
100 GW·h/year from phase 1 has been sold under a 20-year power purchase agreement (PPA). Power generated from phase 2 has been sold under a 25-year power purchase agreement (PPA).
This solar complex creates enough electricity to power 200,000 homes. It sits on 4,000 acres of land and has about 4.3 million solar panels. The facility has been built in phases and the first one came on line in 2010, with the rest following in 2012, 2015, 2016, and 2021.
Badlands Solar Park
Badlands Solar Park is one of the largest solar parks in the US. The park is spread over a total area of 7,000 acres, and has a total capacity of 2,000 MW. It is expected to eventually have a total capacity of 3,000 MW. The project is a joint effort between state-owned energy companies, which provide electricity across the country. Construction on the Badlands Solar Park began in 2016.
It was built in four phases:
- Phase I – 420 MW of capacity
- Phase II – 250 MW of capacity
- Phase III – 500 MW of capacity
- Phase IV – 250 MW of capacity
Competitive Advantage
Helios Solar will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
- Local, family-owned operation, with highly-qualified PV experts
- Helios Solar stays abreast of all technology developments, takes care of all maintenance and property improvements, and delivers an accurate and complete set of financials each month.
- Helios Solar offers the best pricing in town. Their pricing structure is the most cost effective compared to the competition.
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Helios Solar will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Highly-qualified team of PV experts that provide a comprehensive set of solar services (financial, accounting, marketing, maintenance, and improvements).
- Unbeatable pricing to its clients – Helios Solar does not mark up its services at a large percentage. They will offer the lowest pricing in the region.
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Helios Solar is as follows:
Professional Associations and Networking
Helios Solar will become a member of solar associations such as Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), American Council on Renewable Energy (ACRE), and Solar Energy International (SEI). They will focus their networking efforts on expanding their brand recognition and relevance.
Print Advertising
Helios Solar will invest in professionally designed print ads to display in programs or flyers at solar industry networking events.
Website/SEO Marketing
Helios Solar will maintain a well-organized and informative website, which will list all their services. The website will also list their contact information. The company will also hire a digital marketer to enhance their website presence with SEO marketing tactics so that Helios Solar’s website will be well-positioned at the top of internet search results.
Helios Solar’s pricing will be moderate and on par with competitors, so clients feel they receive value when purchasing their services.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Helios Solar.
Operation Functions:
- Meri Smith will be President of the company. She will oversee the office and manage client relations.
- Derek Smith will be CEO of the company. He will oversee field operations: performing installation, maintenance, and upgrades to the solar array.
Milestones:
Helios Solar will have the following milestones complete in the next eight months.
5/1/202X – Finalize construction of office space
615/202X – Finalize property preparation and solar array planning
8/1/202X – Installation of racks and mounts
12/1/202X – Installation of solar array
12/15/202X – Begin networking at industry events
1/1/202X – Helios Solar opens its office for business
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for Helios Solar are the electricity fees they will charge to utility companies for their services. Most other solar energy wholesale companies charge $83 per MWh; Helios Solar will initially charge $80 per MWh.
The cost drivers will be the overhead costs required to maintain and upgrade solar arrays. The major expenses will be payroll, and hardware purchases.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and to pay off the startup business loan.
- Number of MWh Per Year: 1,750
- Average Fees: $27/MWh
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, solar farm business plan faqs, what is a solar farm business plan.
A solar farm business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your solar farm business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your solar farm business plan using our Solar Farm Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Solar Farms?
There are a number of different kinds of solar farms , some examples include: Crystalline Silicon Power Plant, Thin-Film Solar Power Plant, solar panel farms, renewable energy and alternative energy providers.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Solar Farm Business Plan?
Solar farm businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
A well crafted solar farm business plan is essential to attract any type of potential investor. This is true for a new solar farm, a solar energy business plan and a solar panel business plan.
What are the Steps To Start a Solar Farm Business?
Starting a solar farm business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Write A Solar Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed solar farm business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include market research on the solar farm industry and potential target market size, information on the services and/or products you will offer, your mission statement, marketing strategy, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your solar farm business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your solar farm business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Solar Farm Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your solar farming business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your solar farm business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Solar Farm Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your solar farm business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your solar farming business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising to attract potential customers.
Learn more about how to start a successful solar farm business:
- How to Start a Solar Farm Business

Solar Farm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Solar Farm Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 10,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their solar farm business. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a solar farm business plan step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Solar Farm Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your solar farm business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Solar Farm
If you’re looking to start a solar farm, or grow your existing solar farms, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your solar farms in order to improve your chances of success. Your solar farm business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Solar Farms
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a solar farm are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a solar energy farm business.
The second most common form of funding for a solar farm is angel investors. Angel investors are wealthy individuals who will write you a check. They will either take equity in return for their funding, or, like a bank, they will give you a loan.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to Write a Business Plan for a Solar Farm
Your business plan should include 10 sections as follows:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your solar farm business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of solar farms you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have an existing solar farms that you would like to grow, or are you operating a network of solar farms?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the solar farm industry. Discuss the type of solar farms you are running. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target market. Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of solar panel farms you are running.
For example, you might operate one of the following types:
- Crystalline Silicon Power Plant: this type of solar farm uses Crystalline Silicon PV technology.
- Thin-Film Solar Power Plant: this type of solar farm uses cadmium telluride (CdTe) solar panels.
In addition to explaining the type of solar farm businesses you operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the solar farm business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the solar farm business?
- What is your mission statement?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include sales goals you’ve reached, number of new attractions, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the solar power industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the solar energy industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy particularly if your research identifies industry trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the market analysis section:
- How big is the solar farms industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your solar farms service. You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your solar energy business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
These are the main customers for the industry: Solar Power Utilities, and Federal Government.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of solar farms you operate. Clearly, commercial utilities would want different products and services, and would respond to different marketing tactics than government entities.
Try to break out your target market in terms of their location, and their wants and needs. With regards to location, include a discussion of the demand for solar energy for utilities’ renewable power portfolio standards. Because most solar farms primarily serve customers living in their same region, such information is usually available on local or county government websites.
Finish Your Solar Farm Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your solar farm business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other solar energy projects.
Indirect competitors are other options customers may use that aren’t direct competitors. This includes traditional energy suppliers, other alternative energy providers, and other power plant contractors, such as fossil fuel and other renewable energy power plant contractors. You need to mention such competition to show you understand that not all energy needs will be met by a solar farms.
With regards to direct competition, you want to detail the other solar farms with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be solar farms located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What types of renewable energy technology do they use?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you use cutting-edge solar technologies?
- Will you provide options or automations that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you make it easier or faster for customers to engage your services?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a solar farm business, your marketing plan should include the following:
Product: in the product section you should reiterate the type of solar farms that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific services you will be offering.
Price: Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the services you offer and their prices.
Place: Place refers to the location of your solar farms. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your solar farms located in a high-sunlight exposure area, or in a desert, etc. Discuss how your location might allow you to serve a greater volume of customers.
Promotions: the final part of your solar farms marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in trade magazines
- Attending trade shows
- Attending networking events
- Joining local organizations
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your solar energy business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your solar farms, such as researching and writing grants, maintaining solar panels, staying abreast of new technology developments, processing paperwork, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to sign your 100 th contract, or when you hope to reach $X in sales. It could also be when you expect to purchase additional solar panels, or when you expect to launch a new solar farm location.
Management Team
To demonstrate your solar farm’s ability to succeed as a business, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in renewable energy or in power generation. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in renewable energy and/or successfully running small businesses.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Projected Balance Sheets : Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $1,000,000 on building out your solar farms, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $1,000,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a solar farms business:
- Location build-out including design fees, construction, etc.
- Cost of solar equipment
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business and liability insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your solar farm design blueprint or location lease.
Putting together a business plan for your solar farms company is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will really understand the solar industry, your competition and your potential customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful solar farms.
Finish Your Solar Farms Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your solar farm business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. See how Growthink’s professional business plan consultants can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


How to Start a Solar Business. A-Z Guide
The solar industry is one of the fastest-growing industries globally, so it’s no surprise that new entrepreneurs consider getting involved in this boom every day. If you’re reading this right now, you’re likely thinking about riding this solar wave yourself, but you’re not sure where or how to start.
While starting any business can be a large endeavor for anyone, this article will serve as an introduction and guide on starting a solar company, from the very beginning to how to generate leads and scale your company up from a one-man operation to a fully staffed and operational business.
Whether you’re brand new to the solar industry and just earned the required PV licenses to work in your state, or you’re a solar installer or salesperson looking to branch out and start something new, there’s something in this guide for you.
How to start a successful solar company
Congratulations! Choosing the solar energy industry as the path for your business is a wise and responsible choice. Not only is it a growing industry with tons of room for success, but it also contributes to a cleaner, more sustainable environment.
Before you jump right into it, though, let’s talk about one thing: goal setting. Without proper goal setting, your solar company will be like everyone else’s – with no direction and nowhere to go. You can’t just say what you want to do; you need to set deadlines and create action plans that will help you sustain the business. Can your actions meet your expectations?
Examine past projects or events that were successful in this field and see if you can follow their pattern of success in creating your own goals. Also, keep an eye on other companies in this field who are doing well with their goals. If one of them has set up five branches around the globe in six months, don’t try to match them if you’re still new to this industry, as the chances are high that you won’t be able to meet their standards yet.
Instead, aim for more realistic goals like hiring your first wave of staff within the first year; whatever works for you and helps build your confidence and reputation among clients and competitors over time.
How to Get Started/First Steps
Once you’ve set some realistic goals for yourself, it’s time to plan and get started. Here’s a quick list of every step you should consider before starting your business.
- Settle on a business structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation).
- Write a detailed business plan. This is important as it will guide all your decisions and help you secure funding.
- Educate yourself further on the solar industry and learn to analyze the market. This will help you understand how your business fits in and determine its prospects for success. Learn what your competition is doing and identify how to stand out from them; that is, offer something different or better than they do.
- Design a solar marketing plan . This should be based on a SWOT analysis; that is, an analysis of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats concerning other businesses in the same industry. If this sounds complicated, don’t worry too much, as there are plenty of online resources detailing exactly how to go about this step-by-step.
- Apply for funding if required. You can apply for grants or loans from various government agencies. If successful, you’ll then have to figure out what equipment/inventory you need to buy and build so you can have everything ready when the funds arrive. You may also need some initial investment capital which can come from personal savings or friends/family members willing to invest their money into your venture (be sure they’re aware of any potential risks, though!). Consider using crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter, too – it could give your company exposure while raising money simultaneously!
Writing A Solar Business Plan
Writing a business plan is one of the first steps in starting a solar business . For many, this means creating a comprehensive, 30-plus page document covering all aspects of your proposed company, from market research to financing and marketing.
However, there’s no need to panic – it’s possible to create an effective business plan without spending weeks at it. Below are the six most important things you need to understand when writing one:
- Know your market
- Know your competition
- Know what makes you unique
- Know how you’re going to finance your business
- Know what equipment and tools you’ll need
- Know how you’re going to find clients
When writing your business plan, you must answer a few questions about what makes your solar installation business unique. What sets you apart from the competition? What expertise do you bring to the market? Why would people want to buy from you rather than someone else?
The truth is that most of your competitors will have roughly the same level of experience as you. So, when thinking about what makes your business unique, think about why it’s in a good position to succeed.
Perhaps you are passionate about sustainable energy and believe that our society should be powering itself with renewable energy sources like solar power. If so, make sure this passion comes through in your marketing materials and customer interactions because it might be what sets you apart from other installers who just see this as a way to make money. Make sure that potential customers know how passionate you are about what they are buying rather than being sold on price or naivety alone.
Understand what tools and equipment you’ll need to invest in to get your business up and running. This includes what kind of stock of PV panels, inverters, wires, etc. you’ll want to have on hand to start with, as well as any common or specialized tools and safety/construction equipment you’ll need to provide yourself and your team with.
Your business plan should also include some plans about staffing your company for the upcoming year. How many salespeople do you think you’ll need? Do you want to build multiple small teams of installers to cover more ground, or do you just need one or two to start with? Will you hire an in-house marketer or rely on agencies and freelancers? How much are you willing to pay people to provide the level of quality you want your business to offer, and how much do you want to spend on advertising to get your name out there?
Ready to launch your solar business? Unlock success with our solar software solutions now!
Funding Your Solar Business Startup
There are many ways to go about funding your solar business. You can use your own cash (a home equity line of credit is a popular option), take out a small business loan, get an SBA loan, or even use crowdfunding or credit cards. If you’re unsure of how much money you’ll need to start up, it’s best to consult with a nonprofit organization that offers advice and guidance on the process (like SCORE).
If you don’t have enough money to start an entire business right now, consider starting off as a subcontractor for another company until you’re able to stand on your own. This will give you some time to save up and gather the funds you need, but it will also keep you in the loop of what’s going on in the solar industry and help you build and maintain your own solar skills and knowledge.
Learn about your local solar market
You can have all the skills and certifications in the world, but if you don’t understand what your own, local solar market looks like, you’ll probably have some trouble starting a business that fits in with what your potential clients need. Market research can take many forms. Here are a few things to learn about when discovering your local solar market.
- Size: How big is your solar market? How many solar companies already operate in your area?
- Customers: Who are the people in your service area? What do they want? Where do they find their information and spend their time? How much do they like to spend?
- Competitors: What do your competitors offer? Why do your potential solar customers choose your competitors for their solar projects?
- Potential Gaps: Are there any gaps in the market that your competitors are neglecting? How can you fill them?
Now that you know about the major solar markets in your area, what are some of the factors that make them more attractive to do business in than others? Each business has different needs and goals, and yours might differ from others. This is why your next step is to take a deep dive into your local market’s trends and big players.
What are the trends in your local solar market?
Understanding trends is important for any solar business. Solar is a growing industry, but how fast it grows and why depends on many factors.
Solar market trends can be tracked using the following sources:
- The Database of State Incentives for Renewables and Efficiency (DSIRE) tracks incentives in real-time. DSIRE has one of the most comprehensive and up-to-date lists of state, local, utility, and federal incentive programs that promote renewable energy. Explore their website to search for financial incentives related to solar applications where your company will operate.
- Access the U.S Department of Energy’s SunShot Initiative website regularly to stay up to date on market data, reports, and current news in the solar industry.
- It is also important to learn about which companies are active at both the national level and within your local area by reading trade journals like PV Magazine or subscribing to newsletters such as those published by SEIA, SEPA, and Canary Media. This will also help you stay updated on new programs, incentives, and new equipment.
Learn about your competitors
No business should be run without some competitor research. This is essential to the success of your solar business. You need to know who you will be competing with within your market, what they do, and how they do it. This will help you create a plan to beat them.
Identify their strengths and weaknesses. While your competition should be taken very seriously, do not forget that for a new business, it is also essential that you identify your own strengths and weaknesses to fill any gaps in the market left open by other companies.
Find out how they reach customers. What channels do they use? How effective are these channels? Which channels could you potentially use as well? Do they have a blog with content that helps them to generate leads? What are they missing on their blog, and how can you put together content to draw traffic to your own website?
Generating Leads, Clients
There are many proven ways of generating leads and potential clients, but the one that we have found to be most successful and cost-effective is online marketing. With online marketing, you can target your customers based on location, income range, age range, interests, titles, etc. These targeting options allow you to find your ideal customer easily and provide your services right when they need them.
To generate leads with this method requires a few things: A website and landing page created for conversions, a blog where you offer useful information about solar energy, and some form of lead magnet that offers people something valuable in exchange for their contact information (like an eBook or report). An email marketing campaign designed to nurture leads over time until they are ready to make a purchase should also be set up to build trust with people who provide you with their information.
You should also consider setting up a presence on social media since most people have accounts nowadays and visit these places often. Here, you can build a community, educate people, and display what services you offer, all for free. You can also run paid ads on these platforms to supplement your search engine marketing efforts and link back to your website as many times as you’d like in an effort to gather emails and phone numbers for your salespeople.
How to Scale
Scaling a solar business is no easy feat, but it’s not impossible either. Once you have a small team of passionate employees and a few processes in place, building up from below shouldn’t be too complicated or challenging. Here are the three main things you need to build at your solar company if you’re looking to scale.
- Documentation: Keeping a record of everything is essential to growing a business. Document everything from sales processes, important information, and logins, instructions on how to complete certain tasks, manage inboxes and communicate with other teams in the company. All this documentation should be kept in a secure location, and everyone who needs to be in the know should have access. This prevents employees from leaving with essential information that no one else knows and helps new hires get onboarded effectively.
- Structure: Even if you don’t have the employees to fill certain roles yet, build up a company structure that you aspire to have in the future. For example, if you only have one salesperson right now, plan for that person to get promoted to team lead and hire below them. When people start telling you that their workload is increasing, make plans to hire people to cover the added workload.
- Trust: Your first employees should be people you believe can do a great job and people you trust to make decisions for you. As your company grows, you won’t be able to be as hands-on as you might have been when you started the business. Trust that the people you hired are competent enough to handle their departments, and let them build them up as necessary.
Every company starts from nothing. The difference between those that make it, and those that don’t lie in how well they are able to handle growth and scale up.
Difficulties of running a solar company
The solar sales industry is not for everyone. Not everyone has the work ethic, personality and attitude to succeed in this type of business. So if you are looking for your get-rich-quick scheme or something to do on the weekends, this isn’t it.
The solar sales industry requires an extremely high level of commitment from your employees and incredible discipline, patience, and self-motivation. Every day, you will face rejection, challenges, and obstacles you never even thought about before venturing into business ownership. If you cannot handle adversity or have a low threshold for stress, then maybe running a solar company isn’t for you.
On the solar industry side of things, supply issues might cause problems for the solar jobs you have in the pipeline, state and federal incentives or programs might be canceled or dry up, and there’s always the risk that some newer, better renewable energy technology pops up and leapfrogs right over everyone in the solar industry.
On the business side, employees will quit, customers will occasionally be unhappy with your work, and money might be lost along the way. The difference between a successful business and an unsuccessful one is how the owners and CEO can effectively adapt and handle these issues.
In Closing
Starting a solar business requires a lot of planning, consideration, money, and effort, and it isn’t for everyone. The good news is that if you follow this guide, you’ll have a great foundation to start off with. While we can’t help everyone build their own solar companies, the tips we’ve laid out here are definitely a great starting point for anyone looking to grow and be successful in the solar industry.
Looking to scope, sell and complete more solar projects than ever? Solargraf is the most user-friendly, robust, and fully integrated solution on the market. Book your free demo today to learn more about growing your business with Solargraf.
- API Documentation
- Solargraf Help Center
- Training Package
- [email protected]
- 1-888-997-1101
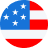
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Accessibility statement
- Do not Sell or Share my Personal Information
© Solargraf
- Residential
- Proposal services
- Permit services
- NEM 3.0 in Solargraf
- Help Center
- Schedule a demo

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The best place to start a new solar business is between the cracks of large, over-saturated markets. Find out what solar professionals are doing in your area by checking in with local SEIA chapters and chambers of commerce, and conducting internet searches.
Plan your solar farm venture with confidence using our customizable Business Plan template. Navigate the path to sustainable energy success.
Discover the key elements to include in your solar panel business plan. Our guide offers practical advice, templates, and examples to help you write your own.
We have helped over 10,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their solar farms. Below is a template to help you create each section of your Solar Farm business plan. Helios Solar is a startup Solar Farm company located in northern New Mexico.
Download Growthink’s solar farm business plan template & step-by-step instructions to quickly and easily create your business plan today.
Whether you’re brand new to the solar industry and just earned the required PV licenses to work in your state, or you’re a solar installer or salesperson looking to branch out and start something new, there’s something in this guide for you.