Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals

Clinical microbiology articles from across Nature Portfolio
Latest research and reviews.
Bidirectional Mendelian randomization links gut microbiota to primary biliary cholangitis
- Zhijia Zhou
Natal factors influencing newborn’s oral microbiome diversity
- Yoon-Hee Kim
- Tae yang Lee
- Chung-Min Kang
The role of antibiotic-derived mycobacterial vesicles in tuberculosis pathogenesis
- C. J. Davids
- K. Umashankar-Rao
- Gabriela Godaly
Polymicrobial infection in cystic fibrosis and future perspectives for improving Mycobacterium abscessus drug discovery
- Emily, J. Baker
- Gemma Allcott
- Jonathan A. G. Cox
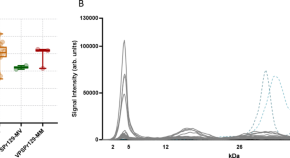
Characterization of variably protease-sensitive prionopathy by capillary electrophoresis
- Jennifer Myskiw
- Ben A. Bailey-Elkin
- Stephanie A Booth
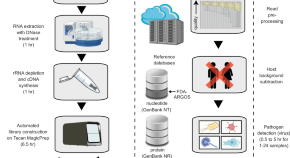
Laboratory validation of a clinical metagenomic next-generation sequencing assay for respiratory virus detection and discovery
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing has the potential to support diagnosis of unknown infections as it can identify all potential pathogens without requiring a prior suspected cause. Here, the authors develop and clinically validate a metagenomics-based assay for common and novel respiratory viral pathogens.
- Jessica Karielle Tan
- Venice Servellita
- Charles Y. Chiu
News and Comment
Uncovering the hpv types causing cervical cancer.
- Fernando Dias Gonçalves Lima
- Mariano A. Molina
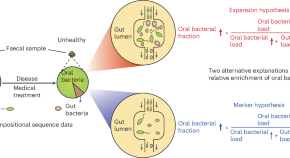
The meaning of oral bacteria in faeces
Our study investigated microbial dynamics involved in the relative enrichment of oral bacteria in faeces. Results in mice and from human patients indicated that high percentages of oral bacteria reflect a depleted gut microbiota, with oral bacteria simply passing through rather than expanding in the gut, which has implications for gastrointestinal disease treatment.
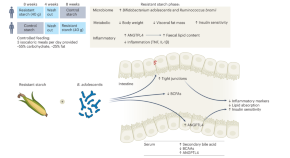
Resisting weight gain with prebiotic fibre
Resistant starch is a prebiotic fibre that is fermented by the gut microbiota and leads to benefits for host physiology. A clinical trial in Nature Metabolism demonstrates weight loss when resistant starch was given to individuals with excess weight.
- Matthew M. Carter
- Sean P. Spencer
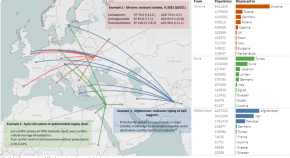
The contribution of human conflict to the development of antimicrobial resistance
Pallett et al. discuss the impact of human conflict on development of antimicrobial resistance. They overview approaches to limit the spread of antimicrobial resistance, using the ongoing conflict in Ukraine as an example of the challenges and opportunities.
- Scott J. C. Pallett
- Sara E. Boyd
- Emma J. Hutley
In vitro activity of cefiderocol in combination with new β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations (βL-βLICs) against multidrug resistant KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Paolo Gaibani
- Tiziana Lazzarotto
- Simone Ambretti
Doxycycline-PEP — novel and promising but needs monitoring
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) remain public health concerns. Doxycycline post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent STIs is a novel promising intervention, which in a new study caused an ∼65% reduction in incident STIs. However, long-term effects on STI prevalence, microbiomes and antimicrobial resistance among STI pathogens, non-STI pathogens and commensals need to be monitored.
- Magnus Unemo
- Fabian Yuh Shiong Kong
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Microbiology News
Top headlines, latest headlines.
- Soy Protein: Slowing Heart Failure Progression
- How Ants Create Trails to Multiple Food Sources
- How Salmonella Causes Infection
- Need for New Malaria Treatments
- Zinc Deficiency: Acinetobacter Lung Infection
- Genetic 'Switch' Behind Parrot Color Diversity
- Gut Microbiota: Immunostimulatory Members
- Living Microbes in Earth's Driest Desert
- Gene Therapy for Muscular Dystrophies, More
- AI Method: Spotting Potential Disease Faster
Earlier Headlines
Thursday, november 14, 2024.
- Revolutionizing Biology Education: Scientists Film 'giant' Mimivirus in Action
Wednesday, November 13, 2024
- Researchers Reveal Why a Key Tuberculosis Drug Works Against Resistant Strains
- How Studying Fruit Flies Can Help Us Understand Congenital Defects
- Children's Gut Bacteria May Hold the Key to Diarrhea Treatment
- On the Origin of Life: How the First Cell Membranes Came to Exist
- Key Influenza-Severity Risk Factor Found Hiding in Plain Sight on Our Antibodies
- We May Be Overestimating the Association Between Gut Bacteria and Disease, Machine Learning Study Finds
Tuesday, November 12, 2024
- From Pets to Pests: Researchers Explore New Tool to Fight Disease-Carrying Insects
- Synthetic Cells Emulate Natural Cellular Communication
- In Unity Towards Complex Structures
- One Genomic Test Can Diagnose Nearly Any Infection
- Using CRISPR to Decipher Whether Gene Variants Lead to Cancer
- Bulges Calculated in the Supercomputer: How Cells Digest Their Internal Canal System
- DNA Packaging Directly Affects How Fast DNA Is Copied in Cells
Monday, November 11, 2024
- A New Wrinkle in Turtles: Their Genomes Fold in a Unique Way, Researchers Find
- Research Team Successfully Produces Microbial Plastic to Replace PET Bottles
- The Mystery of 'selfish' B Chromosomes in Rye Solved
- International Canine Gene Research Database Accelerates Biomedical Research
- Secret Behind the Corpse Flower's Famous Stench
- A New Paradigm in High-Speed Photoacoustic Small Animal Whole-Body Imaging
- Super Microscope Shows Nanoscale Biological Process for the First Time

Friday, November 8, 2024
- Heartier Heinz? How Scientists Are Learning to Help Tomatoes Beat the Heat
- Greener and Cleaner: Yeast-Green Algae Mix Improves Water Treatment
- Deep-Sea Corals Are Home to Previously Unknown Bacteria With Extremely Small Genomes
- Signals from the Gut Could Transform Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Thursday, November 7, 2024
- Insect-Killing Fungi Find Unexpected Harmony in War
- Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Could Pose Major Health Threat Across Asia
- GPS System for Microorganisms Could Revolutionize Police Work
- New Fungal Spore Calendar Helps Allergy and Asthma Sufferers Plan for Better Health
- Finding Function for Noncoding RNAs Using a New Kind of CRISPR
Wednesday, November 6, 2024
- How Gophers Brought Mount St. Helens Back to Life in One Day
- Pathogens Which Cling to Microplastics May Survive Wastewater Treatment
- How Plants Evolved Multiple Ways to Override Genetic Instructions
- Use of 'genetic Scissors' Carries Risks
- Study Expands Understanding of How Fecal Microbiota Transplants May Work to Restore Gut Health
- The Egg or the Chicken? An Ancient Unicellular Says Egg
Tuesday, November 5, 2024
- Microbes in Mouth Reflect Lifestyle Choices
- Testing Thousands of RNA Enzymes Helps Find First 'twister Ribozyme' In Mammals
- Gut Microbes Play a Key Role in Regulating Stress Responsiveness Throughout the Day, Research Finds
- Researchers Develop Artificial Plants That Purify Indoor Air, Generate Electricity
- A Molecular Switch Reshapes a Dividing Cell in Minutes
Monday, November 4, 2024
- Bacteria Breakthrough Could Accelerate Mosquito Control Schemes
Friday, November 1, 2024
- Increased Rates of Severe Human Infections Caused by Streptococcus Subspecies
- AI Tackles Huge Problem of Antimicrobial Resistance in Intensive Care
- Researchers Challenge Longstanding Theories in Cellular Reprogramming
Thursday, October 31, 2024
- MRSA's Double Defense Against Antibiotics
- Immune System Review Provides Insight Into More Effective Biotechnology
- New Findings on Animal Viruses With Potential to Infect Humans
- A Newly Developed Algorithm Shows How a Gene Is Expressed at Microscopic Resolution
Wednesday, October 30, 2024
- Nanoplastics Can Reduce the Effectiveness of Antibiotics
- Scientists Develop Cellulose Recycling Method With Applications Ranging from Textiles to Medical Devices
- Algae Research Provides Insight on Immune Health
- Ancient DNA Brings to Life History of the Iconic Aurochs, Whose Tale Is Intertwined With Climate Change and Human Culture
- Discovery Illuminates How Sleeping Sickness Parasite Outsmarts Immune Response
Tuesday, October 29, 2024
- Newly Discovered Cyanobacteria Could Help Sequester Carbon from Oceans and Factories
Monday, October 28, 2024
- What Animal Societies Can Teach Us About Aging
- Invasive Plants Drive Homogenization of Soil Microbial Communities Across U.S.
- Understanding How Mutations Affect Diseases
- Co-Culture System for Sustainable Cultured Meat Production
- Thin Skin Significantly Blunts Injury from Puncture
- Lab-Grown Pork Gets Support from Sorghum Grain
- Researchers Discover Underlying Mechanisms That Make CRISPR an Effective Gene Editing Tool
- H5N1 Virus Isolated from Infected Dairy Worker Is 100% Lethal in Ferrets, but Does Not Appear to Be Circulating in Nature Anymore
Friday, October 25, 2024
- Scientific Discovery Scratching Beneath the Surface of Itchiness
- Invisible Anatomy in the Fruit Fly Uterus
- A Lung Pathogen's Dilemma: Infect or Resist Antibiotics?
Thursday, October 24, 2024
- Beneficial Gut Microbe Has Surprising Metabolic Capabilities
- Plastic Chemical Causes Causes DNA Breakage and Chromosome Defects in Sex Cells, Study Finds
- Gut Bacteria Transfer Genes to Disable Weapons of Their Competitors
- Microbes Feed on Iron: New Study Reveals How They Do It
- Plant Diversity Enhances Soil Carbon Retention
- Harnessing Plant Odors to Revolutionize Sustainable Agriculture
- Tiny Medicine Combats Infections and Drug Resistance
- Scientists May Have Discovered Important Step in the Fight Against Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
- The Cellular Superhero That Protects Us Against RNA Viruses
- Bacterial Pathogen Shows Alarming Resistance to Common Cleaners, Chemists Discover
- Unnoticeable Electric Currents Could Reduce Skin Infections
- Researchers Use Cryo-EM to Identify What Makes Bacteria Strong
- Maternal Antibodies Interfere With Malaria Vaccine Responses
Wednesday, October 23, 2024
- Breathing Deep: A Metabolic Secret of Ethane-Consuming Archaea Unraveled
- Antibiotics and Antifungals May Slightly Affect Parkinson's Risk, Study Finds
- Polar Bears' Exposure to Pathogens Is Increasing as Their Environment Changes
- Scientists Discover How Excessive Red Meat Consumption Increases Colorectal Cancer Risk
- Lyme Borreliosis: New Approach for Developing Targeted Therapy
- New Parasite Discovered Amid Decline of California's Unique Channel Island Fox
- New Tool Enables a More Complete and Rapid Decoding of the Language of Algal Gene Expression
- Saving the Bats: Researchers Find Bacteria, Fungi on Bat Wings That Could Help Fight Deadly White-Nose Syndrome
- With 'electro-Agriculture,' Plants Can Produce Food in the Dark and With 94% Less Land, Bioengineers Say
Tuesday, October 22, 2024
- Structural Biology Analysis of a Pseudomonas Bacterial Virus Reveals a Genome Ejection Motor
- How Our Gut Cells Detect Harmful Invaders
- How the Coronavirus Defeats the Innate Immune Response
- Scientists Discover How Fungi Interact With Soil Actinomycetes
Monday, October 21, 2024
- Unexpected Beauty, Major Antimicrobial Power Boost as Phages Form Into Surprising Flower Shapes
- Turtle Genome Provides New Clues on the Evolution of Vertebrates
Friday, October 18, 2024
- Finding Could Help Turn Trees Into Affordable, Greener Industrial Chemicals
- Butterfly Brains Reveal the Tweaks Required for Cognitive Innovation
Thursday, October 17, 2024
- Gut Instincts: Intestinal Nutrient Sensors
- Marine Bacterium: Catching Prey With Grappling Hooks and Cannons
- Providencia Rustigianii Has Virulence Gene Akin to Salmonella's
- A Mushroom for Colorectal Cancer Therapy
- LATEST NEWS
- Top Science
- Top Physical/Tech
- Top Environment
- Top Society/Education
- Health & Medicine
- Mind & Brain
- Living Well
- Space & Time
- Matter & Energy
- Computers & Math
- Plants & Animals
- Agriculture & Food
- Beer and Wine
- Bird Flu Research
- Genetically Modified
- Pests and Parasites
- Cows, Sheep, Pigs
- Dolphins and Whales
- Frogs and Reptiles
- Insects (including Butterflies)
- New Species
- Spiders and Ticks
- Veterinary Medicine
- Business & Industry
- Biotechnology and Bioengineering
- CRISPR Gene Editing
- Food and Agriculture
- Endangered Animals
- Endangered Plants
- Extreme Survival
- Invasive Species
- Wild Animals
- Education & Learning
- Animal Learning and Intelligence
- Life Sciences
- Behavioral Science
- Biochemistry Research
- Biotechnology
- Cell Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Epigenetics Research
- Evolutionary Biology
- Marine Biology
- Mating and Breeding
- Molecular Biology
- Microbes and More
- Microbiology
- Zika Virus Research
- Earth & Climate
- Fossils & Ruins
- Science & Society
Strange & Offbeat
- Effortless Robot Movements
- Mouse Created from Gene Older Than Animal Life
- Optogenetics: Treating Epilepsy Seizures
- Advancing the Search for Life On Mars
- Precambrian Worm: Big Evolutionary Discovery
- Dieting: Cause of the Yo-Yo Effect
- Global Warming and Net Zero
- Enigma of the Crab Nebula's 'Zebra' Pattern
- Big Benefits to Online Gaming
- Abrupt Drop in Global Freshwater Levels
Trending Topics
