- Data Science
- Data Analysis
- Data Visualization
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
- Computer Vision
- Artificial Intelligence
- AI ML DS Interview Series
- AI ML DS Projects series
- Data Engineering
- Web Scrapping

Charts and Graphs for Data Visualization
As companies and groups deal with more and more data, it’s crucial to present it visually. Data is everywhere these days, and it can be overwhelming.
This article is your guide to Data Visualization , which is turning all that data into pictures and charts that are easy to understand. Whether you work in business, marketing, or anything else, these charts can help you explain ideas, track how things are going, and make smart choices.
What is Data Visualization?
Data visualization is taking a bunch of numbers and information and turning it into pictures or any kind of charts that are easier to understand. It takes a big pile of information and sorts it into pictures (like bar charts, line graphs, or pie charts) that make it easier to understand or see patterns and trends. Here are some of the things data visualization can help you see:
- How things are changing over time
- How things compare to each other
- Relationships between things
Different Types of Graphs for Data Visualization
Data can be a jumble of numbers and facts. Charts and graphs turn that jumble into pictures that make sense. 10 prime super useful chart types are:
Bar graphs are one of the most commonly used types of graphs for data visualization. They represent data using rectangular bars where the length of each bar corresponds to the value it represents. Bar graphs are effective for comparing data across different categories or groups.
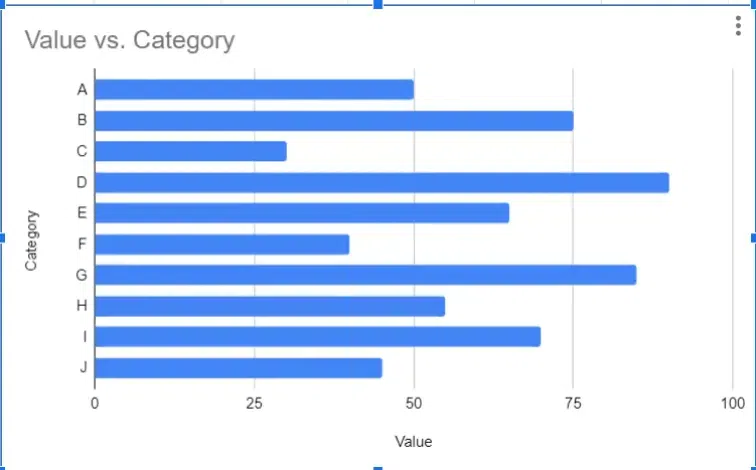
Advantages of Bar Graphs
- Highlighting Trends : Bar graphs are effective at highlighting trends and patterns in data, making it easy for viewers to identify relationships and comparisons between different categories or groups.
- Customizations : Bar graphs can be easily customized to suit specific visualization needs, such as adjusting colors, labels, and styles to enhance clarity and aesthetics.
- Space Efficiency : Bar graphs can efficiently represent large datasets in a compact space, allowing for the visualization of multiple variables or categories without overwhelming the viewer.
Disadvantages of Bar Graphs
- Limited Details : Bar graphs may not provide detailed information about individual data points within each category, limiting the depth of analysis compared to other visualization methods.
- Misleading Scaling : If the scale of the y-axis is manipulated or misrepresented, bar graphs can potentially distort the perception of data and lead to misinterpretation.
- Overcrowding : When too many categories or variables are included in a single bar graph, it can become overcrowded and difficult to read, reducing its effectiveness in conveying clear insights.
Line Graphs
Line graphs are used to display data over time or continuous intervals. They consist of points connected by lines, with each point representing a specific value at a particular time or interval. Line graphs are useful for showing trends and patterns in data. Perfect for showing trends over time, like tracking website traffic or how something changes.
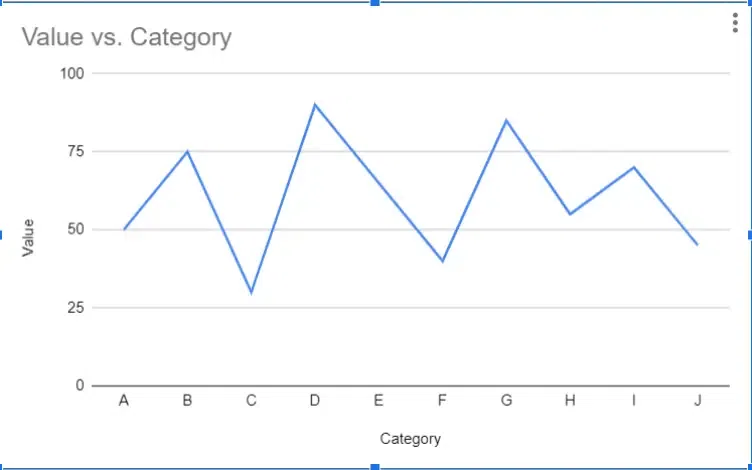
Advantages of Line Graphs
- Clarity : Line graphs provide a clear representation of trends and patterns over time or across continuous intervals.
- Visual Appeal : The simplicity and elegance of line graphs make them visually appealing and easy to interpret.
- Comparison : Line graphs allow for easy comparison of multiple data series on the same graph, enabling quick insights into relationships and trends.
Disadvantages of Line Graphs
- Data Simplification: Line graphs may oversimplify complex data sets, potentially obscuring nuances or outliers.
- Limited Representation : Line graphs are most effective for representing continuous data over time or intervals and may not be suitable for all types of data, such as categorical or discrete data.
Different Types of Charts for Data Visualization
Pie charts are circular graphs divided into sectors, where each sector represents a proportion of the whole. The size of each sector corresponds to the percentage or proportion of the total data it represents. Pie charts are effective for showing the composition of a whole and comparing different categories as parts of a whole.
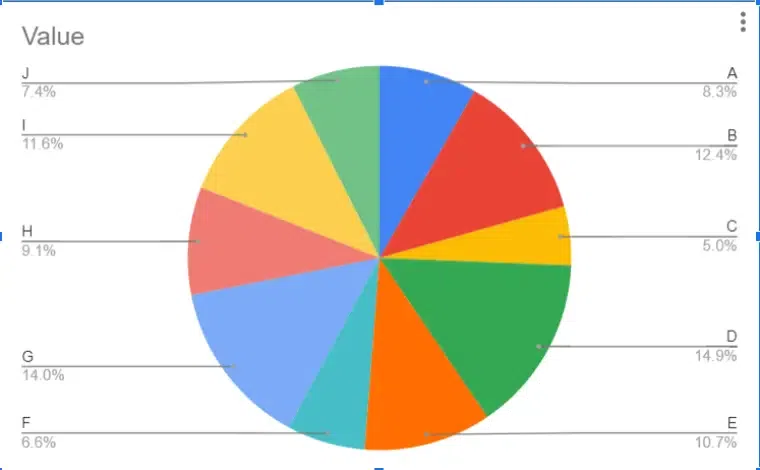
Advantages of Pie Charts
- Easy to create: Pie charts can be quickly generated using various software tools or even by hand, making them accessible for visualizing data without specialized knowledge or skills.
- Visually appealing: The circular shape and vibrant colors of pie charts make them visually appealing, attracting the viewer's attention and making the data more engaging.
- Simple and easy to understand: Pie charts present data in a straightforward manner, making it easy for viewers to grasp the relative proportions of different categories at a glance.
Disadvantages of Using a Pie Chart
- Limited trend analysis: Pie charts are not ideal for showing trends or changes over time since they represent static snapshots of data at a single point in time.
- Limited data slice: Pie charts become less effective when too many categories are included, as smaller slices can be difficult to distinguish and interpret accurately. They are best suited for representing a few categories with distinct differences in proportions.
Scatter Plots
Scatter plots are used to visualize the relationship between two variables. Each data point in a scatter plot represents a value for both variables, and the position of the point on the graph indicates the values of the variables. Scatter plots are useful for identifying patterns and relationships between variables, such as correlation or trends.
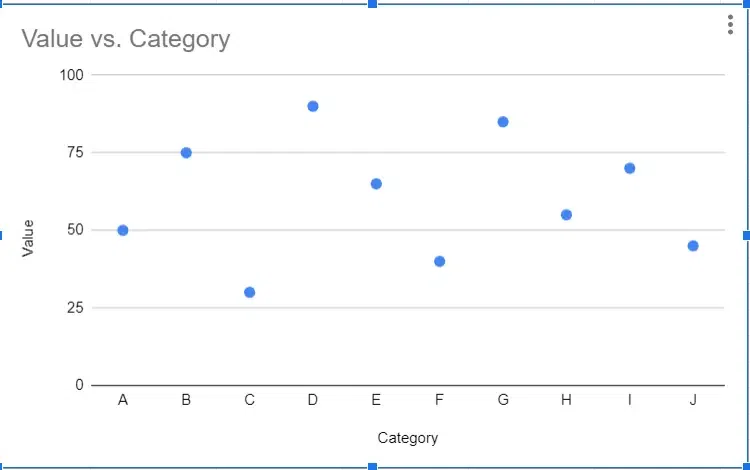
Advantages of Using Scatter Plots
- Revealing Trends and Relationships: Scatter plots are excellent for visually identifying patterns, trends, and relationships between two variables. They allow for the exploration of correlations and dependencies within the data.
- Easy to Understand: Scatter plots provide a straightforward visual representation of data points, making them easy for viewers to interpret and understand without requiring complex statistical knowledge.
- Highlight Outliers: Scatter plots make it easy to identify outliers or anomalous data points that deviate significantly from the overall pattern. This can be crucial for detecting unusual behavior or data errors within the dataset.
Disadvantages of Using Scatter Plot Charts
- Limited to Two Variables: Scatter plots are limited to visualizing relationships between two variables. While this simplicity can be advantageous for focused analysis, it also means they cannot represent interactions between more than two variables simultaneously.
- Not Ideal for Precise Comparisons: While scatter plots are excellent for identifying trends and relationships, they may not be ideal for making precise comparisons between data points. Other types of graphs, such as bar charts or box plots, may be better suited for comparing specific values or distributions within the data.
Area Charts
Area charts are similar to line graphs but with the area below the line filled in with color. They are used to represent cumulative totals or stacked data over time. Area charts are effective for showing changes in composition over time and comparing the contributions of different categories to the total.
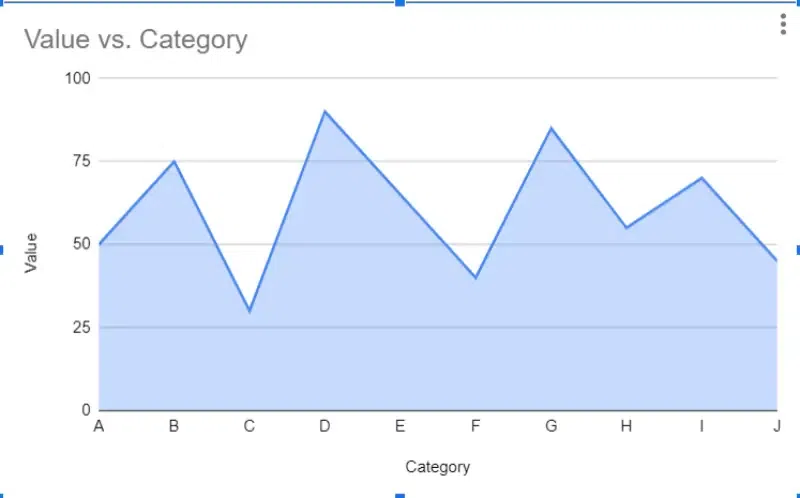
Advantages of Using Area Charts
- Visually Appealing: Area charts are aesthetically pleasing and can effectively capture the audience's attention due to their colorful and filled-in nature.
- Great for Trends: They are excellent for visualizing trends over time, as the filled area under the line emphasizes the magnitude of change, making it easy to identify patterns and fluctuations.
- Compares Well: Area charts allow for easy comparison between different categories or datasets, especially when multiple areas are displayed on the same chart. This comparative aspect aids in highlighting relative changes and proportions.
Disadvantages of Using Area Charts
- Limited Data Sets: Area charts may not be suitable for displaying large or complex datasets, as the filled areas can overlap and obscure details, making it challenging to interpret the data accurately.
- Not for Precise Values: Area charts are less effective for conveying precise numerical values, as the emphasis is on trends and proportions rather than exact measurements. This can be a limitation when precise data accuracy is crucial for analysis or decision-making.
Radar Charts
A radar chart , also known as a spider chart or a web chart, is a graphical method of displaying multivariate data in the form of a two-dimensional chart. It is particularly useful for visualizing the relative values of multiple quantitative variables across several categories. Radar charts compare things across many aspects, like how different employees perform in various skills.
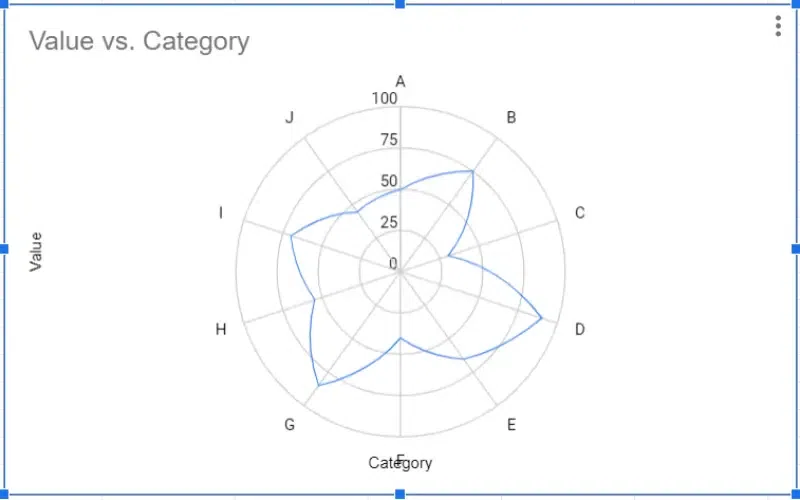
Advantages of Using Radar Chart
- Highlighting Strengths and Weaknesses: Radar charts allow for the clear visualization of strengths and weaknesses across multiple variables, making it easy to identify areas of excellence and areas for improvement.
- Easy Comparisons: The radial nature of radar charts facilitates easy comparison of different variables or categories, as each axis represents a different dimension of the data, enabling quick visual assessment.
- Handling Many Variables: Radar charts are particularly useful for handling datasets with many variables, as each variable can be represented by a separate axis, allowing for comprehensive visualization of multidimensional data.
Disadvantages of Using Radar Chart
- Scaling Issues: Radar charts can present scaling issues, especially when variables have different units or scales. Inaccurate scaling can distort the representation of data, leading to misinterpretation or misunderstanding.
- Misleading Comparisons: Due to the circular nature of radar charts, the area enclosed by each shape can be misleading when comparing variables. Small differences in values can result in disproportionately large visual differences, potentially leading to misinterpretation of data.
Histograms are similar to bar graphs but are used specifically to represent the distribution of continuous data. In histograms, the data is divided into intervals, or bins, and the height of each bar represents the frequency or count of data points within that interval.
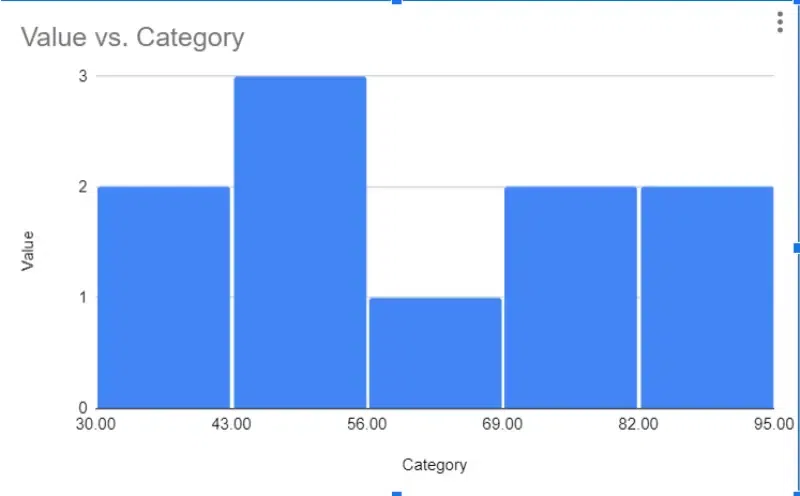
Advantages of using Histogram
- Easy to understand: Histograms provide a visual representation of the distribution of data, making it easy for viewers to grasp the overall pattern.
- Identify Patterns: Histograms allow for the identification of patterns and trends within the data, such as skewness, peaks, or gaps.
- Compare Data Sets: Histograms enable comparisons between different datasets, helping to identify similarities or differences in their distributions.
Disadvantages of using Histogram
- Not for small datasets: Histograms may not be suitable for very small datasets as they require a sufficient amount of data to accurately represent the distribution.
- Limited details: Histograms provide a summary of the data distribution but may lack detailed information about individual data points, such as specific values or outliers.
Treemap Charts
Treemap charts are a type of data visualization that represent hierarchical data as a set of nested rectangles. Each rectangle, or "tile," in the treemap represents a category or subcategory of the data, and the size of the rectangle corresponds to a quantitative value, such as the proportion or absolute value of that category within the dataset.
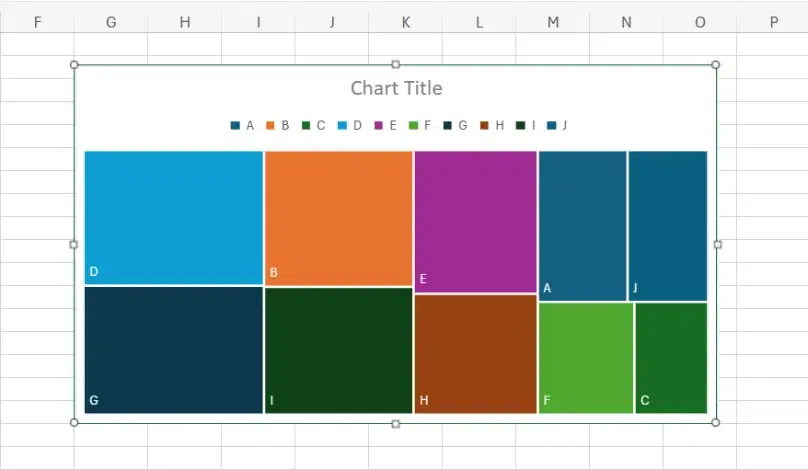
Advantages of using a Treemap Chart
- Identifying patterns and trends: Treemap charts help in visually identifying patterns and trends within hierarchical data structures by representing data in nested rectangles, making it easier to see how smaller components contribute to the whole.
- Highlighting Proportions: Treemaps effectively highlight proportions by using varying sizes and colors of rectangles to represent different values or categories, making it easy to understand the relative significance of each component.
- Efficient use of space: Treemap charts efficiently utilize space by packing rectangles within larger rectangles, allowing for the visualization of large datasets in a compact and organized manner.
Disadvantages of using a Treemap Chart
- Difficulty comparing exact values: Due to the varying sizes and shapes of the rectangles in a treemap, it can be challenging to accurately compare exact values between different categories or components, especially when the differences are subtle.
- Order dependence: The arrangement of rectangles within a treemap can significantly impact perception. Small changes in sorting or hierarchical structure can lead to different visual interpretations, making it important to carefully consider the ordering of data elements.
Pareto Charts
A Pareto chart is a specific type of chart that combines both bar and line graphs. It's named after Vilfredo Pareto, an Italian economist who first noted the 80/20 principle, which states that roughly 80% of effects come from 20% of causes. Pareto charts are used to highlight the most significant factors among a set of many factors.
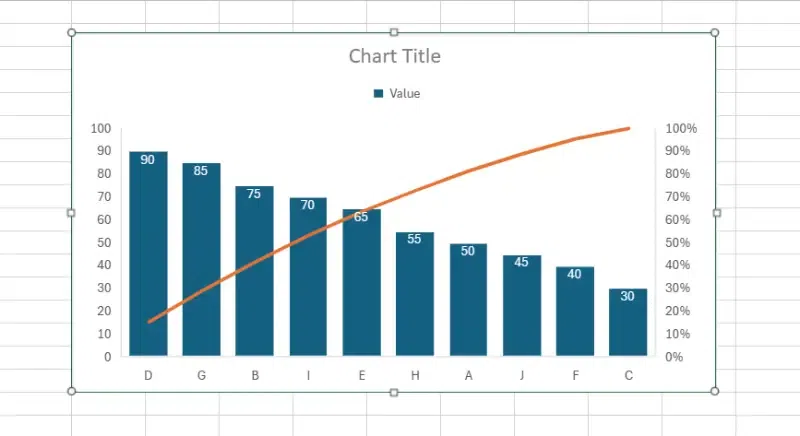
Advantages of using a Pareto Chart
- Simple to understand: Pareto charts present data in a straightforward manner, making it easy for viewers to grasp the most significant factors at a glance.
- Visually identify key factors: By arranging data in descending order of importance, Pareto charts allow users to quickly identify the most critical factors contributing to a problem or outcome.
- Focus resources effectively: With the ability to prioritize factors based on their impact, Pareto charts help organizations allocate resources efficiently by addressing the most significant issues first.
Disadvantages of Using a Pareto Chart
- Limited Data Exploration: Pareto charts primarily focus on identifying the most critical factors, which may lead to overlooking nuances or subtle trends present in the data.
- Assumes 80/20 rule applies: The Pareto principle, which suggests that roughly 80% of effects come from 20% of causes, is a foundational concept behind Pareto charts. However, this assumption may not always hold true in every situation, potentially leading to misinterpretation or oversimplification of complex data relationships.
Waterfall Charts
Waterfall charts are a type of data visualization tool that display the cumulative effect of sequentially introduced positive or negative values. They are particularly useful for understanding the cumulative impact of different factors contributing to a total or final value.
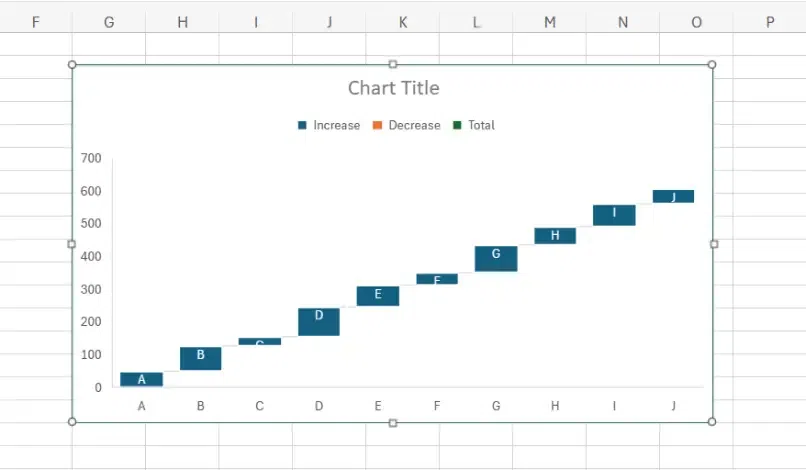
Advantages of Using a Waterfall Chart
- Clear Breakdown of Changes: Waterfall charts provide a clear and visual breakdown of changes in data over a series of categories or stages, making it easy to understand the cumulative effect of each change.
- Easy to Identify the Impact: By displaying the incremental additions or subtractions of values, waterfall charts make it easy to identify the impact of each component on the overall total.
- Focus on the Journey: Waterfall charts emphasize the journey of data transformation, showing how values evolve from one stage to another, which can help in understanding the flow of data changes.
Disadvantages of Using a Waterfall Chart
- Complexity with Too Many Categories: Waterfall charts can become complex and cluttered when there are too many categories or stages involved, potentially leading to confusion and difficulty in interpreting the data.
- Not Ideal for Comparisons: While waterfall charts are effective for illustrating changes over a sequence of categories, they may not be suitable for direct comparisons between different datasets or groups, as they primarily focus on showing the cumulative effect of changes rather than individual values.

How to Choose Right Charts or Graphs for Data Visualization?
Choosing the right chart for your data visualization depends on what you want to communicate with your data. Here are some questions provided below to ask yourself before doing Data Visualization,
- How much Data do you have?
- What type of Data are you working with?
- What is the goal of your Visualization?
Also, you can check the general guidelines below to help you pick the right chart type for your reference,
- Distribution of Data
- Relationship between variables
- Comparisons between groups
- Trends over time
- Audience familiarity with different types of Charts and Graphs
The right choice of chart or graph depends on your specific data and the information you want to convey to others. Whether you’re motivating your team, impressing stakeholders, or showcasing your business values, thoughtful data visualization builds trust and drives informed decision-making.
Remember, the key to impactful data visualization lies in choosing the right tool to transform complex data into clear, understanding actionable insights for your audience.
FAQs- Best Types of Charts and Graphs For Data Visualization
Which type of graph is best for data visualization.
The best type of graph depends on the nature of the data. Line graphs are ideal for showing trends over time, bar graphs for comparisons, scatter plots for correlations, and pie charts for proportions.
What type of chart would be best for this visualization?
If you're comparing categories or groups, a bar chart is often best. It offers a clear visual representation of comparisons between discrete data points.
What are the 4 types of graphs and charts?
Bar Graph Line Graph Pie Chart, and Area Chart
What are the 4 main visualization types?
Spatial, Temporal, Hierarchical, and Network are the 4 main types of visualizations.

Similar Reads
- Charts and Graphs for Data Visualization As companies and groups deal with more and more data, it’s crucial to present it visually. Data is everywhere these days, and it can be overwhelming. This article is your guide to Data Visualization, which is turning all that data into pictures and charts that are easy to understand. Whether you wor 13 min read
- 10 Types of Tableau Charts For Data Visualization Suppose you have data and you need to demonstrate the different trends in that data to other people. What's the best method of doing so? A data visualization of course! You can use various types of charts depending on your data and the conclusions you want to convey. In fact, charts are a very impor 8 min read
- Top Datasets for data visualization Data Visualization is a graphical structure representing the data to share its insight information. Whether you're a data scientist, analyst, or enthusiast, working with high-quality datasets is essential for creating compelling visualizations that tell a story and provide valuable insights. To help 7 min read
- The Art and Science of Data Visualization Data visualization is both an art and a science, blending creativity and technical skill to transform raw data into meaningful insights. It bridges the gap between complex information and human understanding, enabling us to see patterns, trends, and relationships that might otherwise remain hidden. 6 min read
- How To Use AI for Data Visualizations and Dashboards Data visualizations and dashboards have become essential tools for businesses to analyze and interpret data. With the advent of artificial intelligence (AI), these tools have evolved, offering more sophisticated insights and interactivity. This article explores how AI can be leveraged to enhance dat 9 min read
- Types of Data Visualization Charts: From Basic to Advanced Data Visualization Charts is a method of presenting information and data in a visual way using graphical representation elements like charts, graphs and maps. These visual elements help users easily understand complex datasets quickly and efficiently. There are many different types of visualization 15+ min read
- Techniques for Data Visualization and Reporting Data Visualization and reporting are ways to present a bunch of information provocatively, that is interactive and engaging for the viewer and the audience in mass amounts. In this article, we examine the main tools for data visualization and identify the important variables that affect the selectio 8 min read
- Data Visualization for Business It is the portrayal of any data in the form of chart, graphs, images, examples etc. It is used not only in one sector but in many sectors. Due to an increase in statistical data, visual representation of that data is appreciated rather than going through spreadsheets. It is easy to understand as wel 4 min read
- Best Data Visualization Tools for 2024 Choosing the right Data Visualization Tool is critical for turning complex data into actionable insights. With many options available, businesses and analysts are looking for tools that create clear, visually appealing charts and dashboards while easily fitting into their current workflows. In this 11 min read
- How Good is R for Data Visualization? R is highly regarded for data visualization due to its robust set of libraries and packages designed specifically for this purpose due to the following reasons: Comprehensive Visualization Packages:ggplot2: Based on the grammar of graphics, ggplot2 allows users to build complex and multi-layered vis 2 min read
- 5 Best Practices for Effective and Good Data Visualizations The ability to effectively visualize information is more crucial than ever. Data visualization not only simplifies complex statistics but also enables individuals to identify patterns, trends, and insights that might otherwise remain hidden within vast datasets. As we navigate the digital era, where 8 min read
- What is a Data Visualization Dashboard? Businesses and organizations are continuously looking for ways to make sense of the enormous volumes of data they generate and gather in this era of information overload. Organizations gain crucial insights and patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed by converting data into visual representations 15+ min read
- Top 10 BI Tools for Data Visualization & Analysis In today's world is lot of information is available, and businesses are using it to their advantage. They're analyzing and making sense of this data to make smart decisions and stay competitive. Companies need to realize that there's a story behind all the numbers and to understand this story, they 12 min read
- Power BI - Data Visualization With Multiple Charts Sometimes while dealing with hierarchical data we need to combine two or more various chart types into a single chart for better visualization and analysis. These are known as “Combination charts”. In this article, we are going to see how to combine a stacked column chart and a line chart in Power B 9 min read
- Top 15 Data Visualization Frameworks Data Visualization Frameworks are known as tools and libraries that can assist analysts, data scientists, and decision-makers in transforming raw data into meaningful visuals. Such frameworks provide all sorts of things, starting with a basic chart and graphical representation of data and going up t 11 min read
- 12 Popular Data Visualization Books In today's data-driven world, the ability to effectively communicate insights through visualization is a skill that is highly required across various industries. Whether you're a data scientist, analyst, business professional, or simply someone understanding the power of visual storytelling, masteri 9 min read
- Data Visualisation with Chartify Chartify is an open-source data visualization library from Spotify that makes it easy for data analysts to create charts and graphs. Chartify is built on top of Bokeh, which is a very popular data visualization library. This article gives a brief introduction to this technology. Modules Needed Insta 4 min read
- Top 10 Libraries for Data Visualization in 2024 Data is becoming the backbone of our current society. Companies can use data to predict their customer reactions, the success of their products and services, and the areas they need to work on. Data can also be used to understand many social and natural phenomena in the world such as social media tr 8 min read
- Why Data Visualization Matters in Data Analytics? What if you wanted to know the number of movies produced in the world per year in different countries? You could always read this data in the form of a black and white text written on multiple pages. Or you could have a colorful bar chart that would immediately tell you which countries are producing 7 min read
- 15 Tools for Visualizing Neo4j Graph Database Graph Databases have revolutionized the way we handle and analyze complex, interconnected data. Neo4j, a leading graph database, is renowned for its efficiency in representing and querying relationships. However, to fully leverage the power of Neo4j, effective visualization tools are essential. Thes 5 min read
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
21 Best Data Visualization Types: Examples of Graphs and Charts Uses
Those who master different data visualization types and techniques (such as graphs, charts, diagrams, and maps) are gaining the most value from data.
Why? Because they can analyze data and make the best-informed decisions.
Whether you work in business, marketing, sales, statistics, or anything else, you need data visualization techniques and skills.
Graphs and charts make data much more understandable for the human brain.
On this page:
- What are data visualization techniques? Definition, benefits, and importance.
- 21 top data visualization types. Examples of graphs and charts with an explanation.
- When to use different data visualization graphs, charts, diagrams, and maps?
- How to create effective data visualization?
- 10 best data visualization tools for creating compelling graphs and charts.
What Are Data V isualization T echniques? Definition And Benefits.
Data visualization techniques are visual elements (like a line graph, bar chart, pie chart, etc.) that are used to represent information and data.
Big data hides a story (like a trend and pattern).
By using different types of graphs and charts, you can easily see and understand trends, outliers, and patterns in data.
They allow you to get the meaning behind figures and numbers and make important decisions or conclusions.
Data visualization techniques can benefit you in several ways to improve decision making.
Key benefits:
- Data is processed faster Visualized data is processed faster than text and table reports. Our brains can easily recognize images and make sense of them.
- Better analysis Help you analyze better reports in sales, marketing, product management, etc. Thus, you can focus on the areas that require attention such as areas for improvement, errors or high-performing spots.
- Faster decision making Businesses who can understand and quickly act on their data will gain more competitive advantages because they can make informed decisions sooner than the competitors.
- You can easily identify relationships, trends, patterns Visuals are especially helpful when you’re trying to find trends, patterns or relationships among hundreds or thousands of variables. Data is presented in ways that are easy to consume while allowing exploration. Therefore, people across all levels in your company can dive deeper into data and use the insights for faster and smarter decisions.
- No need for coding or data science skills There are many advanced tools that allow you to create beautiful charts and graphs without the need for data scientist skills . Thereby, a broad range of business users can create, visually explore, and discover important insights into data.
How Do Data Visualization Techniques work?
Data visualization techniques convert tons of data into meaningful visuals using software tools.
The tools can operate various types of data and present them in visual elements like charts, diagrams, and maps.
They allow you to easily analyze massive amounts of information, discover trends and patterns in data and then make data-driven decisions .
Why data visualization is very important for any job?
Each professional industry benefits from making data easier to understand. Government, marketing, finance, sales, science, consumer goods, education, sports, and so on.
As all types of organizations become more and more data-driven, the ability to work with data isn’t a good plus, it’s essential.
Whether you’re in sales and need to present your products to prospects or a manager trying to optimize employee performance – everything is measurable and needs to be scored against different KPI s.
We need to constantly analyze and share data with our team or customers.
Having data visualization skills will allow you to understand what is happening in your company and to make the right decisions for the good of the organization.
Before start using visuals, you must know…
Data visualization is one of the most important skills for the modern-day worker.
However, it’s not enough to see your data in easily digestible visuals to get real insights and make the right decisions.
- First : to define the information you need to present
- Second: to find the best possible visual to show that information
Don’t start with “I need a bar chart/pie chart/map here. Let’s make one that looks cool” . This is how you can end up with misleading visualizations that, while beautiful, don’t help for smart decision making.
Regardless of the type of data visualization, its purpose is to help you see a pattern or trend in the data being analyzed.
The goal is not to come up with complex descriptions such as: “ A’s sales were more than B by 5.8% in 2018, and despite a sales growth of 30% in 2019, A’s sales became less than B by 6.2% in 2019. ”
A good data visualization summarizes and presents information in a way that enables you to focus on the most important points.
Let’s go through 21 data visualization types with examples, outline their features, and explain how and when to use them for the best results.
21 Best Types Of Data Visualization With Examples And Uses
1. Line Graph
The line graph is the most popular type of graph with many business applications because they show an overall trend clearly and concisely.
What is a line graph?
A line graph (also known as a line chart) is a graph used to visualize the values of something over a specified period of time.
For example, your sales department may plot the change in the number of sales your company has on hand over time.
Data points that display the values are connected by straight lines.
When to use line graphs?
- When you want to display trends.
- When you want to represent trends for different categories over the same period of time and thus to show comparison.
For example, the above line graph shows the total units of a company sales of Product A, Product B, and Product C from 2012 to 2019.
Here, you can see at a glance that the top-performing product over the years is product C, followed by Product B.
2. Bar Chart
At some point or another, you’ve interacted with a bar chart before. Bar charts are very popular data visualization types as they allow you to easily scan them for valuable insights.
And they are great for comparing several different categories of data.
What is a bar chart?
A bar chart (also called bar graph) is a chart that represents data using bars of different heights.
The bars can be two types – vertical or horizontal. It doesn’t matter which type you use.
The bar chart can easily compare the data for each variable at each moment in time.
For example, a bar chart could compare your company’s sales from this year to last year.
When to use a bar chart?
- When you need to compare several different categories.
- When you need to show how large data changes over time.
The above bar graph visualizes revenue by age group for three different product lines – A, B, and C.
You can see more granular differences between revenue for each product within each age group.
As different product lines are groups by age group, you can easily see that the group of 34-45-year-old buyers are the most valuable to your business as they are your biggest customers.
3. Column Chart
If you want to make side-by-side comparisons of different values, the column chart is your answer.
What is a column chart?
A column chart is a type of bar chart that uses vertical bars to show a comparison between categories.
If something can be counted, it can be displayed in a column chart.
Column charts work best for showing the situation at a point in time (for example, the number of products sold on a website).
Their main purpose is to draw attention to total numbers rather than the trend (trends are more suitable for a line chart).
When to use a column chart?
- When you need to show a side-by-side comparison of different values.
- When you want to emphasize the difference between values.
- When you want to highlight the total figures rather than the trends.
For example, the column chart above shows the traffic sources of a website. It illustrates direct traffic vs search traffic vs social media traffic on a series of dates.
The numbers don’t change much from day to day, so a line graph isn’t appropriate as it wouldn’t reveal anything important in terms of trends.
The important information here is the concrete number of visitors coming from different sources to the website each day.
4. Pie Chart
Pie charts are attractive data visualization types. At a high-level, they’re easy to read and used for representing relative sizes.
What is a pie chart?
A Pie Chart is a circular graph that uses “pie slices” to display relative sizes of data.
A pie chart is a perfect choice for visualizing percentages because it shows each element as part of a whole.
The entire pie represents 100 percent of a whole. The pie slices represent portions of the whole.
When to use a pie chart?
- When you want to represent the share each value has of the whole.
- When you want to show how a group is broken down into smaller pieces.
The above pie chart shows which traffic sources bring in the biggest share of total visitors.
You see that Searches is the most effective source, followed by Social Media, and then Links.
At a glance, your marketing team can spot what’s working best, helping them to concentrate their efforts to maximize the number of visitors.
5. Area Chart
If you need to present data that depicts a time-series relationship, an area chart is a great option.
What is an area chart?
An area chart is a type of chart that represents the change in one or more quantities over time. It is similar to a line graph.
In both area charts and line graphs, data points are connected by a line to show the value of a quantity at different times. They are both good for showing trends.
However, the area chart is different from the line graph, because the area between the x-axis and the line is filled in with color. Thus, area charts give a sense of the overall volume.
Area charts emphasize a trend over time. They aren’t so focused on showing exact values.
Also, area charts are perfect for indicating the change among different data groups.
When to use an area chart?
- When you want to use multiple lines to make a comparison between groups (aka series).
- When you want to track not only the whole value but also want to understand the breakdown of that total by groups.
In the area chart above, you can see how much revenue is overlapped by cost.
Moreover, you see at once where the pink sliver of profit is at its thinnest.
Thus, you can spot where cash flow really is tightest, rather than where in the year your company simply has the most cash.
Area charts can help you with things like resource planning, financial management, defining appropriate storage space, and more.
6. Scatter Plot
The scatter plot is also among the popular data visualization types and has other names such as a scatter diagram, scatter graph, and correlation chart.
Scatter plot helps in many areas of today’s world – business, biology, social statistics, data science and etc.
What is a Scatter plot?
Scatter plot is a graph that represents a relationship between two variables . The purpose is to show how much one variable affects another.
Usually, when there is a relationship between 2 variables, the first one is called independent. The second variable is called dependent because its values depend on the first variable.
But it is also possible to have no relationship between 2 variables at all.
When to use a Scatter plot?
- When you need to observe and show relationships between two numeric variables.
- When just want to visualize the correlation between 2 large datasets without regard to time.
The above scatter plot illustrates the relationship between monthly e-commerce sales and online advertising costs of a company.
At a glance, you can see that online advertising costs affect monthly e-commerce sales.
When online advertising costs increase, e-commerce sales also increase.
Scatter plots also show if there are unexpected gaps in the data or if there are any outlier points.
7. Bubble chart
If you want to display 3 related dimensions of data in one elegant visualization, a bubble chart will help you.
What is a bubble chart?
A bubble chart is like an extension of the scatter plot used to display relationships between three variables.
The variables’ values for each point are shown by horizontal position, vertical position, and dot size.
In a bubble chart, we can make three different pairwise comparisons (X vs. Y, Y vs. Z, X vs. Z).
When to use a bubble chart?
- When you want to depict and show relationships between three variables.
The bubble chart above illustrates the relationship between 3 dimensions of data:
- Cost (X-Axis)
- Profit (Y-Axis)
- Probability of Success (%) (Bubble Size).
Bubbles are proportional to the third dimension – the probability of success. The larger the bubble, the greater the probability of success.
It is obvious that Product A has the highest probability of success.
8. Pyramid Graph
Pyramid graphs are very interesting and visually appealing graphs. Moreover, they are one of the most easy-to-read data visualization types and techniques.
What is a pyramid graph?
It is a graph in the shape of a triangle or pyramid. It is best used when you want to show some kind of hierarchy. The pyramid levels display some kind of progressive order, such as:
- More important to least important. For example, CEOs at the top and temporary employees on the bottom level.
- Specific to least specific. For example, expert fields at the top, general fields at the bottom.
- Older to newer.
When to use a pyramid graph?
- When you need to illustrate some kind of hierarchy or progressive order
Image Source: Conceptdraw
The above is a 5 Level Pyramid of information system types that is based on the hierarchy in an organization.
It shows progressive order from tacit knowledge to more basic knowledge. Executive information system at the top and transaction processing system on the bottom level.
The levels are displayed in different colors. It’s very easy to read and understand.
9. Treemaps
Treemaps also show a hierarchical structure like the pyramid graph, however in a completely different way.
What is a treemap?
Treemap is a type of data visualization technique that is used to display a hierarchical structure using nested rectangles.
Data is organized as branches and sub-branches. Treemaps display quantities for each category and sub-category via a rectangle area size.
Treemaps are a compact and space-efficient option for showing hierarchies.
They are also great at comparing the proportions between categories via their area size. Thus, they provide an instant sense of which data categories are the most important overall.
When to use a treemap?
- When you want to illustrate hierarchies and comparative value between categories and subcategories.
Image source: Power BI
For example, let’s say you work in a company that sells clothing categories: Urban, Rural, Youth, and Mix.
The above treemap depicts the sales of different clothing categories, which are then broken down by clothing manufacturers.
You see at a glance that Urban is your most successful clothing category, but that the Quibus is your most valuable clothing manufacturer, across all categories.
10. Funnel chart
Funnel charts are used to illustrate optimizations, specifically to see which stages most impact drop-off.
Illustrating the drop-offs helps to show the importance of each stage.
What is a funnel chart?
A funnel chart is a popular data visualization type that shows the flow of users through a sales or other business process.
It looks like a funnel that starts from a large head and ends in a smaller neck. The number of users at each step of the process is visualized from the funnel width as it narrows.
A funnel chart is very useful for identifying potential problem areas in the sales process.
When to use a funnel chart?
- When you need to represent stages in a sales or other business process and show the amount of revenue for each stage.
Image Source: DevExpress
This funnel chart shows the conversion rate of a website.
The conversion rate shows what percentage of all visitors completed a specific desired action (such as subscription or purchase).
The chart starts with the people that visited the website and goes through every touchpoint until the final desired action – renewal of the subscription.
You can see easily where visitors are dropping out of the process.
11. Venn Diagram
Venn diagrams are great data visualization types for representing relationships between items and highlighting how the items are similar and different.
What is a Venn diagram?
A Venn Diagram is an illustration that shows logical relationships between two or more data groups. Typically, the Venn diagram uses circles (both overlapping and nonoverlapping).
Venn diagrams can clearly show how given items are similar and different.
Venn diagram with 2 and 3 circles are the most common types. Diagrams with a larger number of circles (5,6,7,8,10…) become extremely complicated.
When to use a Venn diagram?
- When you want to compare two or more options and see what they have in common.
- When you need to show how given items are similar or different.
- To display logical relationships from various datasets.
The above Venn chart clearly shows the core customers of a product – the people who like eating fast foods but don’t want to gain weight.
The Venn chart gives you an instant understanding of who you will need to sell.
Then, you can plan how to attract the target segment with advertising and promotions.
12. Decision Tree
As graphical representations of complex or simple problems and questions, decision trees have an important role in business, finance, marketing, and in any other areas.
What is a decision tree?
A decision tree is a diagram that shows possible solutions to a decision.
It displays different outcomes from a set of decisions. The diagram is a widely used decision-making tool for analysis and planning.
The diagram starts with a box (or root), which branches off into several solutions. That’s why it is called a decision tree.
Decision trees are helpful for a variety of reasons. Not only they are easy-to-understand diagrams that support you ‘see’ your thoughts, but also because they provide a framework for estimating all possible alternatives.
When to use a decision tree?
- When you need help in making decisions and want to display several possible solutions.
Imagine you are an IT project manager and you need to decide whether to start a particular project or not.
You need to take into account important possible outcomes and consequences.
The decision tree, in this case, might look like the diagram above.
13. Fishbone Diagram
Fishbone diagram is a key tool for root cause analysis that has important uses in almost any business area.
It is recognized as one of the best graphical methods to understand and solve problems because it takes into consideration all the possible causes.
What is a fishbone diagram?
A fishbone diagram (also known as a cause and effect diagram, Ishikawa diagram or herringbone diagram) is a data visualization technique for categorizing the potential causes of a problem.
The main purpose is to find the root cause.
It combines brainstorming with a kind of mind mapping and makes you think about all potential causes of a given problem, rather than just the one or two.
It also helps you see the relationships between the causes in an easy to understand way.
When to use a fishbone diagram?
- When you want to display all the possible causes of a problem in a simple, easy to read graphical way.
Let’s say you are an online marketing specialist working for a company witch experience low website traffic.
You have the task to find the main reasons. Above is a fishbone diagram example that displays the possible reasons and can help you resolve the situation.
14. Process Flow Diagram
If you need to visualize a specific process, the process flow diagram will help you a lot.
What is the process flow diagram?
As the name suggests, it is a graphical way of describing a process, its elements (steps), and their sequence.
Process flow diagrams show how a large complex process is broken down into smaller steps or tasks and how these go together.
As a data visualization technique, it can help your team see the bigger picture while illustrating the stages of a process.
When to use a process flow diagram?
- When you need to display steps in a process and want to show their sequences clearly.
The above process flow diagram shows clearly the relationship between tasks in a customer ordering process.
The large ordering process is broken down into smaller functions and steps.
15. Spider/Radar Chart
Imagine, you need to rank your favorite beer on 8 aspects (Bitterness, Sweetness, Sourness, Saltiness, Hop, Malt, Yeast, and Special Grain) and then show them graphically. You can use a radar chart.
What is a radar chart?
Radar chart (also called spider, web, and polar bar) is a popular data visualization technique that displays multivariate data.
In can compare several items with many metrics of characteristics.
To be effective and clear, the radar chart should have more than 2 but no more than 6 items that are judged.
When to use a radar chart?
- When you need to compare several items with more than 5 metrics of characteristics.
The above radar chart compares employee’s performance with a scale of 1-5 on skills such as Communications, Problem-solving, Meeting deadlines, Technical knowledge, Teamwork.
A point that is closer to the center on an axis shows a lower value and a worse performance.
It is obvious that Mary has a better performance than Linda.
16. Mind Map
Mind maps are beautiful data visuals that represent complex relationships in a very digestible way.
What is a mind map?
A mind map is a popular diagram that represents ideas and concepts.
It can help you structure your information and analyze, recall, and generate new ideas.
It is called a mind map because it is structured in a way that resembles how the human brain works.
And, best of all, it is a fun and artistic data visualization technique that engages your brain in a much richer way.
When to use a mind map?
- When you want to visualize and connect ideas in an easy to digest way.
- When you want to capture your thoughts/ideas and bring them to life in visual form.
Image source: Lucidchart
The above example of a mind map illustrates the key elements for running a successful digital marketing campaign.
It can help you prepare and organize your marketing efforts more effectively.
17. Gantt Chart
A well-structured Gantt chart aids you to manage your project successfully against time.
What is a Gantt chart?
Gantt charts are data visualization types used to schedule projects by splitting them into tasks and subtasks and putting them on a timeline.
Each task is listed on one side of the chart. This task also has a horizontal line opposite it representing the length of the task.
By displaying tasks with the Gantt chart, you can see how long each task will take and which tasks will overlap.
Gantt charts are super useful for scheduling and planning projects.
They help you estimate how long a project should take and determine the resources needed.
They also help you plan the order in which you’ll complete tasks and manage the dependencies between tasks.
When to use a Gantt chart?
- When you need to plan and track the tasks in project schedules.
Image Source: Aha.io
The above example is a portfolio planning Gantt Chart Template that illustrates very well how Gantt Charts work.
It visualizes the release timeline for multiple products for an entire year.
It shows also dependencies between releases.
You can use it to help team members understand the release schedule for the upcoming year, the duration of each release, and the time for delivering.
This helps you in resource planning and allows teams to coordinate implementation plans.
18. Organizational Charts
Organizational charts are data visualization types widely used for management and planning.
What is an organizational chart?
An organizational chart (also called an org chart) is a diagram that illustrates a relationship hierarchy.
The most common application of an org chart is to display the structure of a business or other organization.
Org charts are very useful for showing work responsibilities and reporting relationships.
They help leaders effectively manage growth or change.
Moreover, they show employees how their work fits into the company’s overall structure.
When to use the org chart?
- When you want to display a hierarchical structure of a department, company or other types of organization.
Image Source: Organimi
The above hierarchical org chart illustrates the chain of command that goes from the top (e.g., the CEOs) down (e.g., entry-level and low-level employees) and each person has a supervisor.
It clearly shows levels of authority and responsibility and who each person reports to.
It also shows employees the career paths and chances for promotion.
19. Area Map
Most business data has a location. Revenue, sales, customers, or population are often displayed with a dimensional variable on a map.
What is an area map?
It is a map that visualizes location data.
They allow you to see immediately which geographical locations are most important to your brand and business.
Image Source: Infogram
The map above depicts sales by location and the color indicates the level of sales (the darker the blue, the higher the sales).
These data visualization types are very useful as they show where in the world most of your sales are from and where your most valuable sales are from.
Insights like these illustrate weaknesses in a sales and marketing strategy in seconds.
20. Infographics
In recent years, the use of infographics has exploded in almost every industry.
From sales and marketing to science and healthcare, infographics are applied everywhere to present information in a visually appealing way.
What is an infographic?
Infographics are specific data visualization types that combine images, charts, graphs, and text. The purpose is to represent an easy-to-understand overview of a topic.
However, the main goal of an infographic is not only to provide information but also to make the viewing experience fun and engaging for readers.
It makes data beautiful—and easy to digest.
When you want to represent and share information, there are many data visualization types to do that – spreadsheets, graphs, charts, emails, etc.
But when you need to show data in a visually impactful way, the infographic is the most effective choice.
When to use infographics?
- When you need to present complex data in a concise, highly visually-pleasing way.
Image Source: Venngage
The above statistical infographic represents an overview of Social Buzz’s biggest social platforms by age and geography.
For example, we see that 75% of active Facebook users are 18-29 years old and 48% of active users live in North America.
21. T-Chart
If you want to compare and contrast items in a table form, T-Chart can be your solution.
What is a T-Chart?
A T-Chart is a type of graphic organizer in the shape of the English letter “T”. It is used for comparison by separating information into two or more columns.
You can use T-Chart to compare ideas, concepts or solutions clearly and effectively.
T-Charts are often used for comparison of pros and cons, facts and opinions.
By using T-Chart, you can list points side by side, achieve a quick, at-a-glance overview of the facts, and arrive at conclusions quickly and easily.
When to use a T-Chart?
- When you need to compare and contrast two or more items.
- When you want to evaluate the pros and cons of a decision.
The above T-Chart example clearly outlines the cons and pros of hiring a social media manager in a company.
10 Best Data Visualization Tools
There is a broad range of data visualization tools that allow you to make fascinating graphs, charts, diagrams, maps, and dashboards in no time.
They vary from BI (Business Intelligence) tools with robust features and comprehensive dashboards to more simple software for just creating graphs and charts.
Here we’ve collected some of the most popular solutions. They can help you present your data in a way that facilitates understanding and decision making.
1. Visme is a data presentation and visualization tool that allows you to create stunning data reports. It provides a great variety of presentation tools and templates for a unique design.
2. Infogram is a chart software tool that provides robust diagram-making capabilities. It comes with an intuitive drag-and-drop editor and ready-made templates for reports. You can also add images for your reports, icons, GIFs, photos, etc.
3. Venngage is an infographic maker. But it also is a great chart software for small businesses because of its ease of use, intuitive design, and great templates.
4. SmartDraw is best for those that have someone graphic design skills. It has a slightly more advanced design and complexity than Venngage, Visme, and Infogram, … so having some design skills is an advantage. It’s a drawing tool with a wide range of charts, diagrams, maps, and well-designed templates.
5. Creately is a dynamic diagramming tool that offers the best free version. It can be deployed from the cloud or on the desktop and allows you to create your graphs, charts, diagrams, and maps without any tech skills.
6. Edraw Max is an all-in-one diagramming software tool that allows you to create different data visualization types at a high speed. These include process flow charts, line graphs, org charts, mind maps, infographics, floor plans, network diagrams, and many others. Edraw Max has a wide selection of templates and symbols, letting you to rapidly produce the visuals you need for any purpose.
7. Chartio is an efficient business intelligence tool that can help you make sense of your company data. Chartio is simple to use and allows you to explore all sorts of information in real-time.
8. Sisense – a business intelligence platform with a full range of data visualizations. You can create dashboards and graphical representations with a drag and drop user interface.
9. Tableau – a business intelligence system that lets you quickly create, connect, visualize, and share data seamlessly.
10. Domo is a cloud business intelligence platform that helps you examine data using graphs and charts. You can conduct advanced analysis and create great interactive visualization.
Data visualization techniques are vital components of data analysis, as they can summarize large amounts of data effectively in an easy to understand graphical form.
There are countless data visualization types, each with different pros, cons, and use cases.
The trickiest part is to choose the right visual to represent your data.
Your choice depends on several factors – the kind of conclusion you want to draw, your audience, the key metrics, etc.
I hope the above article helps you understand better the basic graphs and their uses.
When you create your graph or diagram, always remember this:
A good graph is the one reduced to its simplest and most elegant form without sacrificing what matters most – the purpose of the visual.
About The Author
Silvia Valcheva
Silvia Valcheva is a digital marketer with over a decade of experience creating content for the tech industry. She has a strong passion for writing about emerging software and technologies such as big data, AI (Artificial Intelligence), IoT (Internet of Things), process automation, etc.
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Graphical Representation of Data
Graphical representation of data is an attractive method of showcasing numerical data that help in analyzing and representing quantitative data visually. A graph is a kind of a chart where data are plotted as variables across the coordinate. It became easy to analyze the extent of change of one variable based on the change of other variables. Graphical representation of data is done through different mediums such as lines, plots, diagrams, etc. Let us learn more about this interesting concept of graphical representation of data, the different types, and solve a few examples.
Definition of Graphical Representation of Data
A graphical representation is a visual representation of data statistics-based results using graphs, plots, and charts. This kind of representation is more effective in understanding and comparing data than seen in a tabular form. Graphical representation helps to qualify, sort, and present data in a method that is simple to understand for a larger audience. Graphs enable in studying the cause and effect relationship between two variables through both time series and frequency distribution. The data that is obtained from different surveying is infused into a graphical representation by the use of some symbols, such as lines on a line graph, bars on a bar chart, or slices of a pie chart. This visual representation helps in clarity, comparison, and understanding of numerical data.
Representation of Data
The word data is from the Latin word Datum, which means something given. The numerical figures collected through a survey are called data and can be represented in two forms - tabular form and visual form through graphs. Once the data is collected through constant observations, it is arranged, summarized, and classified to finally represented in the form of a graph. There are two kinds of data - quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative data is more structured, continuous, and discrete with statistical data whereas qualitative is unstructured where the data cannot be analyzed.
Principles of Graphical Representation of Data
The principles of graphical representation are algebraic. In a graph, there are two lines known as Axis or Coordinate axis. These are the X-axis and Y-axis. The horizontal axis is the X-axis and the vertical axis is the Y-axis. They are perpendicular to each other and intersect at O or point of Origin. On the right side of the Origin, the Xaxis has a positive value and on the left side, it has a negative value. In the same way, the upper side of the Origin Y-axis has a positive value where the down one is with a negative value. When -axis and y-axis intersect each other at the origin it divides the plane into four parts which are called Quadrant I, Quadrant II, Quadrant III, Quadrant IV. This form of representation is seen in a frequency distribution that is represented in four methods, namely Histogram, Smoothed frequency graph, Pie diagram or Pie chart, Cumulative or ogive frequency graph, and Frequency Polygon.
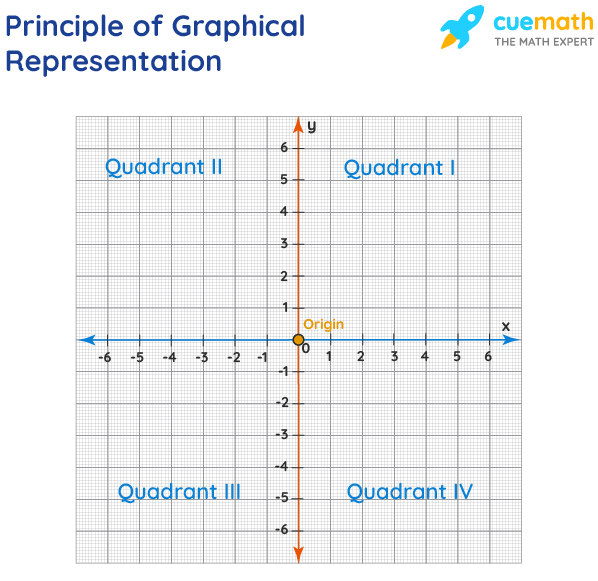
Advantages and Disadvantages of Graphical Representation of Data
Listed below are some advantages and disadvantages of using a graphical representation of data:
- It improves the way of analyzing and learning as the graphical representation makes the data easy to understand.
- It can be used in almost all fields from mathematics to physics to psychology and so on.
- It is easy to understand for its visual impacts.
- It shows the whole and huge data in an instance.
- It is mainly used in statistics to determine the mean, median, and mode for different data
The main disadvantage of graphical representation of data is that it takes a lot of effort as well as resources to find the most appropriate data and then represent it graphically.
Rules of Graphical Representation of Data
While presenting data graphically, there are certain rules that need to be followed. They are listed below:
- Suitable Title: The title of the graph should be appropriate that indicate the subject of the presentation.
- Measurement Unit: The measurement unit in the graph should be mentioned.
- Proper Scale: A proper scale needs to be chosen to represent the data accurately.
- Index: For better understanding, index the appropriate colors, shades, lines, designs in the graphs.
- Data Sources: Data should be included wherever it is necessary at the bottom of the graph.
- Simple: The construction of a graph should be easily understood.
- Neat: The graph should be visually neat in terms of size and font to read the data accurately.
Uses of Graphical Representation of Data
The main use of a graphical representation of data is understanding and identifying the trends and patterns of the data. It helps in analyzing large quantities, comparing two or more data, making predictions, and building a firm decision. The visual display of data also helps in avoiding confusion and overlapping of any information. Graphs like line graphs and bar graphs, display two or more data clearly for easy comparison. This is important in communicating our findings to others and our understanding and analysis of the data.
Types of Graphical Representation of Data
Data is represented in different types of graphs such as plots, pies, diagrams, etc. They are as follows,
Related Topics
Listed below are a few interesting topics that are related to the graphical representation of data, take a look.
- x and y graph
- Frequency Polygon
- Cumulative Frequency
Examples on Graphical Representation of Data
Example 1 : A pie chart is divided into 3 parts with the angles measuring as 2x, 8x, and 10x respectively. Find the value of x in degrees.
We know, the sum of all angles in a pie chart would give 360º as result. ⇒ 2x + 8x + 10x = 360º ⇒ 20 x = 360º ⇒ x = 360º/20 ⇒ x = 18º Therefore, the value of x is 18º.
Example 2: Ben is trying to read the plot given below. His teacher has given him stem and leaf plot worksheets. Can you help him answer the questions? i) What is the mode of the plot? ii) What is the mean of the plot? iii) Find the range.
Solution: i) Mode is the number that appears often in the data. Leaf 4 occurs twice on the plot against stem 5.
Hence, mode = 54
ii) The sum of all data values is 12 + 14 + 21 + 25 + 28 + 32 + 34 + 36 + 50 + 53 + 54 + 54 + 62 + 65 + 67 + 83 + 88 + 89 + 91 = 958
To find the mean, we have to divide the sum by the total number of values.
Mean = Sum of all data values ÷ 19 = 958 ÷ 19 = 50.42
iii) Range = the highest value - the lowest value = 91 - 12 = 79
go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Graphical Representation of Data
Faqs on graphical representation of data, what is graphical representation.
Graphical representation is a form of visually displaying data through various methods like graphs, diagrams, charts, and plots. It helps in sorting, visualizing, and presenting data in a clear manner through different types of graphs. Statistics mainly use graphical representation to show data.
What are the Different Types of Graphical Representation?
The different types of graphical representation of data are:
- Stem and leaf plot
- Scatter diagrams
- Frequency Distribution
Is the Graphical Representation of Numerical Data?
Yes, these graphical representations are numerical data that has been accumulated through various surveys and observations. The method of presenting these numerical data is called a chart. There are different kinds of charts such as a pie chart, bar graph, line graph, etc, that help in clearly showcasing the data.
What is the Use of Graphical Representation of Data?
Graphical representation of data is useful in clarifying, interpreting, and analyzing data plotting points and drawing line segments , surfaces, and other geometric forms or symbols.
What are the Ways to Represent Data?
Tables, charts, and graphs are all ways of representing data, and they can be used for two broad purposes. The first is to support the collection, organization, and analysis of data as part of the process of a scientific study.
What is the Objective of Graphical Representation of Data?
The main objective of representing data graphically is to display information visually that helps in understanding the information efficiently, clearly, and accurately. This is important to communicate the findings as well as analyze the data.
tableau.com is not available in your region.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Graphical Representation of Data: Graphical Representation of Data," where numbers and facts become lively pictures and colorful diagrams.Instead of staring at boring lists of numbers, we use fun charts, cool graphs, and interesting visuals to understand information better. In this exciting concept of data visualization, we'll learn about different kinds of graphs, charts, and pictures ...
A Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of vertices and edges. The vertices are sometimes also referred to as nodes and the edges are lines or arcs that connect any two nodes in the graph. More formally a Graph is composed of a set of vertices( V) and a set of edges( E).The graph is denoted by G(V, E).. Representations of Graph
Disadvantages of Line Graphs. Data Simplification: Line graphs may oversimplify complex data sets, potentially obscuring nuances or outliers. Limited Representation: Line graphs are most effective for representing continuous data over time or intervals and may not be suitable for all types of data, such as categorical or discrete data.
As graphical representations of complex or simple problems and questions, decision trees have an important role in business, finance, marketing, and in any other areas. ... Domo is a cloud business intelligence platform that helps you examine data using graphs and charts. You can conduct advanced analysis and create great interactive visualization.
What is data visualization? Data visualization is the graphical representation of information and data. By using visual elements like charts, graphs, and maps, data visualization tools provide an accessible way to see and understand trends, outliers, and patterns in data.Additionally, it provides an excellent way for employees or business owners to present data to non-technical audiences ...
The data that is obtained from different surveying is infused into a graphical representation by the use of some symbols, such as lines on a line graph, bars on a bar chart, or slices of a pie chart. This visual representation helps in clarity, comparison, and understanding of numerical data.
Data visualization involves the use of graphical representations of data, such as graphs, charts, and maps. Compared to descriptive statistics or tables, visuals provide a more effective way to analyze data, including identifying patterns, distributions, and correlations and spotting outliers in complex datasets.
A chart is a representation of data in the form of a graph, diagram, map, or tabular format. This could make the other two families, Geospatial and Tables, subfamilies of it. We distinguish between them to help you identify when one works better for your data. Consider the most common Charts: Scatterplots, Bar Charts, Line Graphs, and Pie ...
Data visualization is the graphical representation of different pieces of information or data, using visual elements such as charts, graphs, or maps. Data visualization tools provide the ability to see and understand data trends, outliers, and patterns in an easy, intuitive way. Learn more about data visualization.
An area chart is a graphical representation of quantitative data, emphasizing the magnitude of change over time. Unlike a line chart, it fills the area beneath the line, making it more visually striking and useful for illustrating cumulative values.