Quantitative Market Research: Fundamentals, Methods, and Applications
- by Alice Ananian
- August 16, 2024

Did you know that 99% of successful businesses use data to drive their decisions? In our increasingly digital world, quantitative market research has become an essential tool. It doesn’t just provide random facts; it offers precise insights into consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive landscapes, giving businesses the edge they need to storm ahead.
This article explores the fundamentals, methods, and applications of quantitative market research, helping business owners, marketing professionals, and entrepreneurs improve their decision-making and drive their businesses forward.

What is Quantitative Market Research?
Quantitative market research is a methodical approach to gather and analyze numerical data, offering businesses a practical understanding of customer behavior and market trends.
This can be part of both primary and secondary market research. Quantitative market research predominantly relies on structured tools like surveys, polls, and questionnaires to collect quantifiable pieces of information such as percentages, frequencies, and ratings. This research is carried out on a large, representative sample of the target audience to ensure accurate reflection of widespread attitudes and behaviors.
Following the data collection, statistical techniques are applied to reveal patterns, track trends, and identify relationships, effectively converting raw data into actionable insights to guide marketing strategies.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research
To fully appreciate quantitative research, it’s essential to understand how it differs from qualitative market research:
| Data Type | Numerical | Textual, visual |
| Sample Size | Large | Small |
| Data Collection | Structured surveys, experiments | Interviews, focus groups, observations |
| Analysis | Statistical | Interpretive |
| Outcome | Generalizable findings | In-depth insights |
| Question Types | Closed-ended | Open-ended |
| Flexibility | Low (standardized approach) | High (adaptable to responses) |
While quantitative research provides broad, generalizable insights, qualitative research offers deeper, context-rich understanding. Many successful market research strategies combine both approaches to gain a comprehensive view of the market.
Applications of Quantitative Market Research
Quantitative market research finds applications across various business functions and industries. Here are some key areas where this research method proves invaluable:
Product Development
- Measuring consumer preferences for product features: This involves surveying potential customers to rank or rate different product features, helping companies prioritize which features to include or improve.
- Assessing market demand for new products: Researchers can use quantitative methods to estimate the potential market size and gauge consumer interest in a new product concept before investing in development .
- Evaluating pricing strategies: Through techniques like conjoint analysis or price sensitivity meters, companies can determine optimal price points that maximize both sales and profitability.
Brand Management
- Tracking brand awareness and perception: Regular surveys can measure how many consumers recognize a brand and what associations they have with it, allowing companies to monitor their brand’s health over time.
- Measuring brand loyalty and customer satisfaction: Quantitative research can assess how likely customers are to repurchase or recommend a brand, providing insights into customer retention strategies.
- Comparing brand performance against competitors: Competitive benchmarking surveys can reveal a brand’s strengths and weaknesses relative to competitors in various attributes.
Customer Segmentation
- Identifying distinct customer groups: By analyzing survey data on demographics, behaviors, and preferences, researchers can use cluster analysis to group customers with similar characteristics.
- Determining the size and value of different market segments: Once segments are identified, quantitative research can estimate the size of each segment and its potential value to the business.
Advertising Effectiveness
- Measuring ad recall and recognition: Surveys conducted after ad campaigns can quantify how many people remember seeing an ad and can correctly identify the brand associated with it.
- Assessing the impact of advertising on purchase intent: Researchers can measure how exposure to ads influences consumers’ likelihood to buy a product, helping to justify advertising spend.
- Evaluating return on investment for marketing campaigns: By linking advertising exposure data with sales data, companies can calculate the ROI of their marketing efforts.
Market Sizing and Forecasting
- Estimating market size and growth potential: Using survey data and secondary sources, researchers can quantify the current market size and project future growth based on trends and economic factors.
- Projecting future sales and market share: Time series analysis and regression models can be used to forecast a company’s sales and market share based on historical data and market conditions.
Customer Experience
- Measuring customer satisfaction and loyalty: Regular surveys can track customer satisfaction scores and Net Promoter Scores (NPS) to gauge overall customer sentiment and loyalty.
- Identifying pain points in the customer journey: Quantitative analysis of customer feedback can highlight common issues or areas of dissatisfaction in the customer experience.
- Quantifying the impact of service improvements: By measuring customer satisfaction before and after implementing changes, companies can assess the effectiveness of their improvement initiatives.
Competitive Analysis
- Benchmarking product or service performance: Surveys can compare how a company’s offerings stack up against competitors on various attributes, helping identify areas for improvement.
- Assessing market share and competitive positioning: Regular tracking studies can monitor changes in market share and brand positioning relative to competitors, informing strategic decisions.
Collect Insights From Your True Customers
Benefits and Challenges of Quantitative Market Research
Quantitative market research offers a range of advantages that make it a valuable tool for businesses seeking data-driven insights. Understanding these benefits can help organizations leverage this research method effectively to inform their strategies and decision-making processes.
Objectivity: Quantitative research provides unbiased, numerical data that can be statistically analyzed. This objectivity ensures that the findings are not influenced by the researcher’s personal biases or perspectives.
Generalizability: Results derived from large sample sizes can be extrapolated to represent the broader population. This means that the findings are more likely to be valid for all individuals within the target group, enhancing the reliability of the study.
Comparability: Standardized data collection methods allow for easy comparison across different time periods or market segments. This comparability is crucial for tracking changes and trends over time, as well as for identifying differences between various subgroups.
Scalability: Quantitative research methods can efficiently gather data from large sample sizes. This scalability makes it possible to conduct studies on a much larger scale, providing more comprehensive insights into the research question.
Hypothesis testing: Quantitative research enables researchers to test specific theories or assumptions about market behavior. By confirming or disproving these hypotheses, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the factors driving market trends and consumer behaviors.
Decision support: The concrete data obtained from quantitative research provides a solid foundation to support strategic decision-making. This evidence-based approach facilitates more informed and effective decisions, reducing the risk of error and improving outcomes.
While quantitative market research provides numerous advantages, it’s important to recognize that this approach also comes with its own set of limitations and potential pitfalls. Being aware of these challenges can help researchers and businesses plan more effectively and interpret results with appropriate caution.
Limited depth: Quantitative research methods may not capture the nuanced reasons behind consumer behavior or attitudes, often resulting in a superficial understanding of complex issues.
Inflexibility: Structured surveys and experiments may miss unexpected insights that could emerge in more open-ended research methods, limiting the scope of discovery.
Response bias: Respondents may not always provide honest or accurate answers, particularly on sensitive or personal topics, leading to skewed data and unreliable conclusions.
Cost: Conducting large-scale surveys or experiments can be expensive, often requiring significant financial resources for data collection, participant incentives, and analysis.
Time-consuming: The proper design, implementation, and analysis of quantitative research can be time-intensive, potentially delaying the results and impacting project timelines.
Expertise required: Quantitative research requires extensive knowledge of statistical analysis and research methodologies, necessitating skilled professionals to ensure accurate and reliable outcomes.
Examples of Quantitative Market Research
To illustrate the practical applications of quantitative market research, let’s explore some real-world examples:
Netflix A/B Testing Titles
Ever noticed how Netflix displays different titles or artwork for the same movie or show depending on your profile? This is A/B testing, a form of quantitative research. Netflix uses surveys and click-through rates to determine which title or artwork generates the most clicks and engagement.
Spotify Optimizing Playlists
How does Spotify create those eerily perfect playlists that seem to know exactly what you’re in the mood for? Quantitative research plays a role! Spotify analyzes user listening habits, including skip rates, play time, and song popularity, to curate playlists that resonate with different user preferences.
Coca-Cola Testing New Flavors
Developing a new beverage flavor requires understanding consumer preferences. Coca-Cola uses surveys and taste tests to gather quantitative data on sweetness levels, flavor combinations, and overall appeal. This data helps them refine new flavors before a full-scale launch.
Apple gauging iPhone Screen Size Preferences
Before increasing iPhone screen sizes, Apple likely conducted quantitative research. Online surveys and focus groups could have gathered data on user preferences for screen size, one-handed usability, and content viewing experience. This data likely helped Apple determine the optimal screen size for future iPhones.
Dominos Revamping its Pizza Recipe
In 2009, Domino ‘s faced declining sales. Quantitative research came to the rescue. Domino’s conducted customer surveys and taste tests to understand customer dissatisfaction with its pizza crust and sauce. Based on the findings, they revamped the recipe, leading to a significant turnaround in customer satisfaction and sales.
These are just a few examples, but they showcase the power of quantitative research in helping businesses make data-driven decisions that resonate with their target audiences.
Tools and Resources for Quantitative Research
To conduct effective quantitative market research, consider utilizing these tools and resources :
Survey Platforms
Qualtrics : Comprehensive survey software with advanced analytics
Prelaunch : Lets you gather data via a landing page that concisely presents your product
SurveyMonkey : User-friendly platform for creating and distributing surveys
Google Forms : Free tool for basic surveys and data collection
Statistical Analysis Software
SPSS : Powerful software for complex statistical analysis
R : Open-source programming language for statistical computing
Prelaunch : The platform is a comprehensive concept-validating tool that complies and presents the data you gather via your product’s landing page into insightful section that make it easier to make data-driven decisions.
Excel : Suitable for basic data analysis and visualization
Online Panel Providers
Dynata : Large global panel for diverse respondent recruitment
Amazon Mechanical Turk : Platform for crowdsourcing survey participants
Data Visualization Tools
Tableau : Creates interactive data visualizations and dashboards
Power BI : Microsoft’s business analytics tool for data visualization
Datawrapper : User-friendly tool for creating charts and maps
Market Research Associations
ESOMAR : Global voice of the data, research, and insights community
Insights Association : Leading voice, resource, and network of the marketing research and data analytics community
Academic Resources
Journal of Marketing Research : Scholarly journal featuring cutting-edge research methodologies
Market Research Society (MRS) : Provides training, qualifications, and resources for market researchers
Remember to choose tools that align with your research objectives, budget, and level of expertise. Many of these platforms offer free trials or basic versions, allowing you to experiment before committing to a paid solution.
Quantitative market research is a powerful tool for making data-driven decisions. By providing objective, measurable insights into consumer behavior and market trends, it helps businesses develop targeted strategies and stay ahead of the competition.
While it has its limitations, combining quantitative methods with qualitative approaches can offer a comprehensive market understanding. Careful planning, rigorous methodology, and thoughtful interpretation of results are key to successful quantitative research.
Embrace the power of numbers and let data guide your business success.

Alice Ananian
Alice has over 8 years experience as a strong communicator and creative thinker. She enjoys helping companies refine their branding, deepen their values, and reach their intended audiences through language.
Related Articles

How to Use Google Trends for Market Research in 2024
- July 17, 2024

Top 19 Future Business Ideas That Will Trend in 2040
- by Dikran Seferian
- April 8, 2024

What is Quantitative Data? Your Guide to Data-Driven Success

Free Website Traffic Checker
Discover your competitors' strengths and leverage them to achieve your own success
In the world of market research , quantitative data is the lifeblood that fuels strategic decision-making, product innovation and competitive analysis .
This type of numerical data is a vital part of any market research professional’s toolkit because it provides measurable and objective evidence for the effectiveness of market and consumer behavioral insights.
Here, we’ll dive into the different types of quantitative data and provide a step-by-step guide on how to analyze quantitative data for the biggest impact on business strategy, optimization of campaigns, product placement and market entry decisions. All with a little help from Similarweb.
Let’s dive right in!
What is quantitative data?
Simply put, quantitative data is strictly numerical in nature. It’s any metric that can be counted, measured or quantified, like length in inches, distance in miles or time in seconds, minutes, hours or days.
Basically, it’s the type of data that answers questions like ‘how many?’, ‘how much?’ or ‘how big or small?’.
If you’re a market research professional, we’re talking statistics like market share percentage, web traffic visits , product views and ROI – all the crucial data you need to accurately gauge market potential .
Quantitative vs. qualitative data: what’s the difference?
If quantitative data is concerned with numbers, qualitative data deals with more descriptive or categorical information that can’t be as easily measured.
Quantitative answers ‘ how much ’ but qualitative explains ‘why’ or ‘how’ . This can be simple information like gender, eye color, types of cars or a description of the weather, i.e. very cold or rainy.
In business, qualitative data is information collected from things like research, open-ended surveys or questionnaires, interviews, focus groups, panels and case studies . Anything that delves into the underlying reasons, motivations and opinions that lie behind quantitative data.
Together, quantitative and qualitative data paint a reliable and robust picture. Quantitative data offers the assurance of fact and evidence, while qualitative data gives essential context and depth, and is able to capture more complex insight.
This match made in ‘data heaven’ leads to the best possible foundation for informed, data-driven decision making across the entire business.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of quantitative data?

Advantages of quantitative data:
✅ Accuracy and precision
Quantitative data is numerical, which allows for precise measurements and accuracy in the results. This precision is crucial for statistical analysis and making data-driven decisions where exact figures are key
✅ Simplicity
Numerical data can often be easier to handle and interpret compared to more complex qualitative data. Graphs, charts and tables can be used to represent quantitative data simply and effectively, making it accessible to a wider audience
✅ Reliability and credibility
Quantitative data can be collected and analyzed using standardized methods which increase the reliability of the data. This standardization helps in replicating studies, ensuring that results are consistent over time and across different researchers or studies
✅ Ease of comparability
Since quantitative data is numerical, it can be easily compared across different groups, time periods or other variables. This comparability is essential for trend analysis, forecasting, and competitive benchmarking/analysis
✅ Scalability
Quantitative research methods are generally scalable, meaning they can handle large sample sizes. This is particularly advantageous in studies where large data sets are required for generalizability of the findings
Disadvantages of quantitative data:
❌ Lack of context
What quantitative data has in precision, it lacks in broader context – or the “why” behind the data. While it shows the numbers and trends, it may not explain the underlying motives, emotions or experiences which are better captured by qualitative data
❌ Inflexibility
Once a quantitative data collection has begun, altering the process can be difficult or even impossible. This inflexibility can be a disadvantage if initial assumptions change or if unexpected factors arise
❌ Oversimplification
While the simplicity of quantitative data is certainly an advantage, it can also lead to oversimplification of complex issues. Reducing complex human behaviors or social phenomena to mere numbers can sometimes lead to the wrong conclusions or missed nuances
❌ Resource heavy
Quantitative research often requires significant resources in terms of time, money and expertise. Large-scale surveys and experiments necessitate comprehensive planning, robust data collection tools and sometimes sophisticated statistical analysis, making them very resource-intensive
❌ Surface-level insight
Quantitative data can provide broad overviews and identify trends but might not delve deep enough to extract truly useful insight. It tends to offer surface-level insights, which might be insufficient when detailed understanding or deep explorations of issues are required
Quantitative data examples
Quantitative data is an integral part of our day-to-day life, as well as being critical in a business sense. To get a clearer picture of what sort of information qualifies, let’s start with some more everyday examples of quantitative data before moving on to a few quantitative market research examples:
🌡️ Temperature: Most of us check the weather every day to decide what to wear and how to plan our activities; it’s also a critical metric for cooking and heating your home.
⚖️ Height and weight: Regular measurements can monitor growth in children or manage health and fitness in adults.
🕐 Time: We use time data to manage almost every part of our lives, from timing a morning commute or setting alarms for appointments, to making future plans.
⚡️ Speed: This helps in gauging how fast a vehicle travels, influencing travel time estimates and safety considerations.
📚 Test scores: Teachers and students use these to assess academic performance and areas of improvement.
❤️ Heart rate: Monitored during exercise or for health management, indicating physical exertion levels or potential medical conditions.
🥗 Calorie intake : Counting calories is a common method for managing diet and health
🚶 Number of steps: With fitness trackers, counting steps has become a popular way to gauge daily physical activity.
Ready for some market research-specific examples of quantitative data?
This type of data is absolutely indispensable in market research as it provides a foundation to analyze the market, consumer behavior and business performance. Here’s how market research professionals often leverage quantitative data:
- Sales volume and revenue: These metrics help businesses understand market demand and the financial success of their products and services
- Market share: This is a good example for quantitative data that helps companies gauge their competitive edge and market presence
- Conversion rates: Useful for evaluating the effectiveness of promotional activities and customer service initiatives
- Advertising spend and ROI: Businesses assess the profitability and effectiveness of their marketing campaigns
- Engagement rates: These metrics show how engaging online content is and how effectively it converts viewers into customers
- Web traffic: Analyzed to determine the effectiveness of online presence and digital marketing strategies
- Marketing channel performance : Evaluating direct , organic search , email, social media, paid search and referral traffic are vital for understanding the most lucrative marketing channels to invest in
What are the different types of quantitative data?
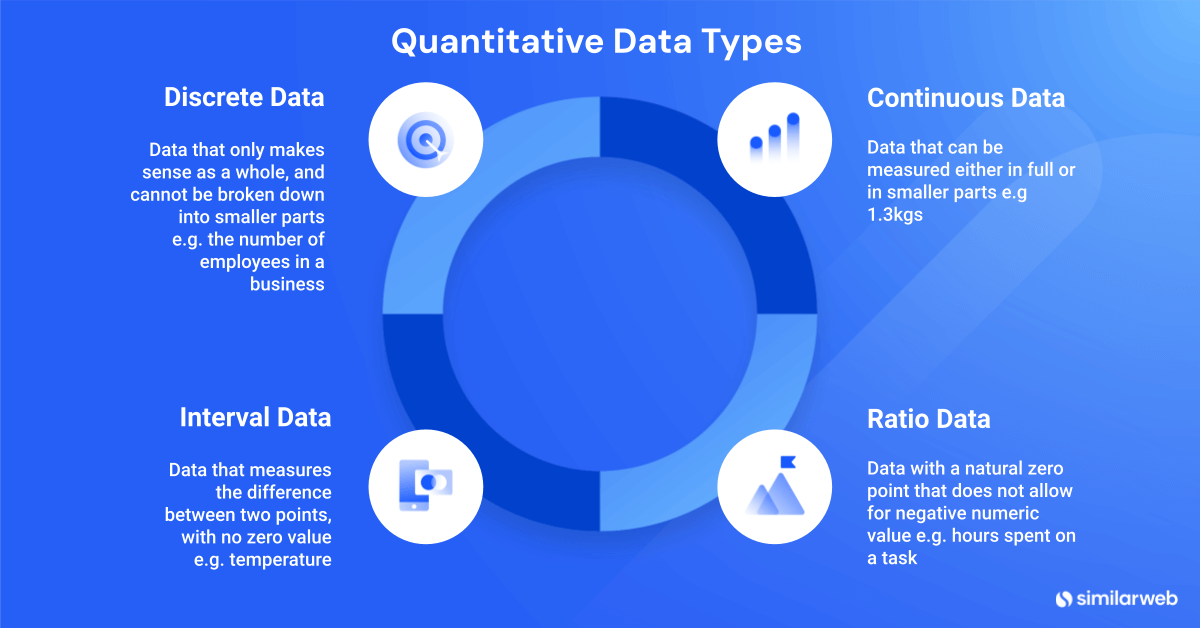
1) Discrete data
These are numbers that can’t be broken down into smaller parts and only make sense as a whole when you list them. This could be the number of employees in a business or sales volume, as you can’t have 1.3 of a person or half a unit sold.
2) Continuous data
This is the type of data that can be measured both in full or broken down into smaller parts, making it continuous. Examples of continuous data include height or weight metrics as it is possible to have 0.5 kilograms of flour. In business sense, something like revenue or advertising spend is continuous as it can be any value, including decimals.
3) Interval data
This type of quantitative data measures the difference between points and doesn’t have a real starting point or value of zero. For example, temperature always exists, even at zero degrees – which is merely a point on the temperature scale. But it’s still useful to be able to discuss the difference between 30 and 40 degrees.
4) Ratio data
Unlike interval data, ratio data has a natural zero point, which means that zero means nothing is there. This allows for the calculation of ratios. Examples of ratio data could be time spent doing a task (where 0 hours means no time was spent at all) or conversion or engagement rates (where 0% engagement means no interaction.)
5) Ordinal data
Though this type of data is technically qualitative, ordinal data can often be seen as quantitative, especially when used in statistical models. For example, in categories such as a customer satisfaction scale from 1 to 10, where higher numbers indicate higher satisfaction.
What are the main collection methods of quantitative data?
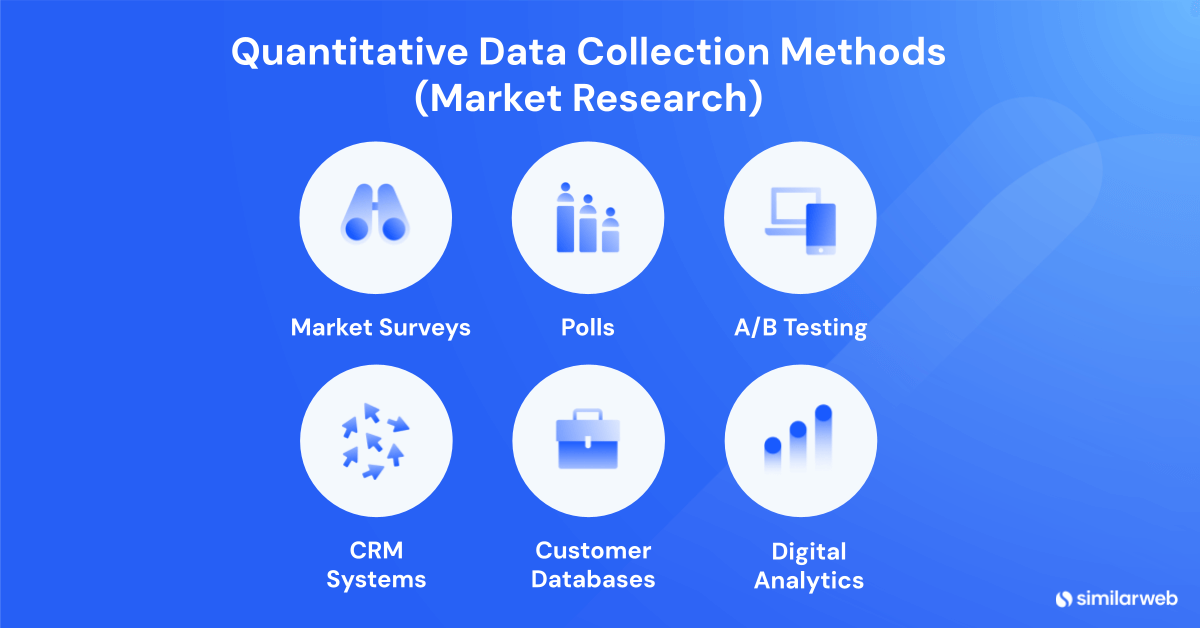
Most types of research simply would not be possible without quantitative data, and there are many different ways of collecting this type of information, depending on the context. To start, here are some broad ways of collecting quantitative data:
- Experiments
- Observations
- Document and record analysis
In the realm of market research, quantitative data will often be gathered to shed light on market dynamics, trends or consumer behavior. Here are some specific examples of how market research professionals may collect quantitative data:
Market surveys and polls – Surveys and polls are designed to gauge consumer opinions and preferences, and can gather large volumes of data from targeted demographics that can be used to enhance product development and marketing strategies.
Digital analytics – With tools like Google Analytics and Similarweb, market researchers can analyze online behavior and track website interactions, marketing channel engagement and online purchasing patterns.
Customer databases and CRM systems – Transactional data gathered by customer relationship management (CRM) systems can be used to better understand things like purchase behaviors, customer lifecycle and audience loyalty trends.
A/B testing – This is an experimental approach used extensively in digital marketing to compare two versions of something, such as a landing page or email subject line, to determine which performs better in terms of user engagement and conversion rates.
Why is quantitative data so important in market research?
It’s hard to imagine a world without quantitative data. It would likely be very tricky to do your job, depending on what industry you work in.
Indeed, quantitative data is often indispensable to businesses across a wide range of industries as it provides a solid foundation for analyzing trends, measuring the effectiveness of different strategies and predicting future outcomes. But that’s just the tip of the iceberg. Here’s why quantitative data is so critical, particularly within the realm of market research:
Data-driven decision making
Quantitative data takes away a lot of the guesswork and subjectivity when it comes to making important decisions. With numbers and statistics, businesses can move beyond conjecture and personal bias to make more objective, data-backed decisions. In market research, this is particularly important when deciding whether to enter a particular market or expand within an existing one.
This is where Similarweb steps in 👋
Similarweb’s platform offers powerful market research tools that streamline the gathering and analyzing of quantitative research , particularly useful when evaluating a potential new market or expanding within a current one.
Market research professionals need look no further than Similarweb’s Market Analysis feature, which provides detailed insights into how challenging it may be to penetrate a particular market.
It does this by analyzing quantitative data surrounding competitor density, market saturation, and customer loyalty to get a robust picture of the competitive landscape .
As an example, here’s a snapshot of the market difficulty for the Consumer Electronics industry, using Market Analysis:
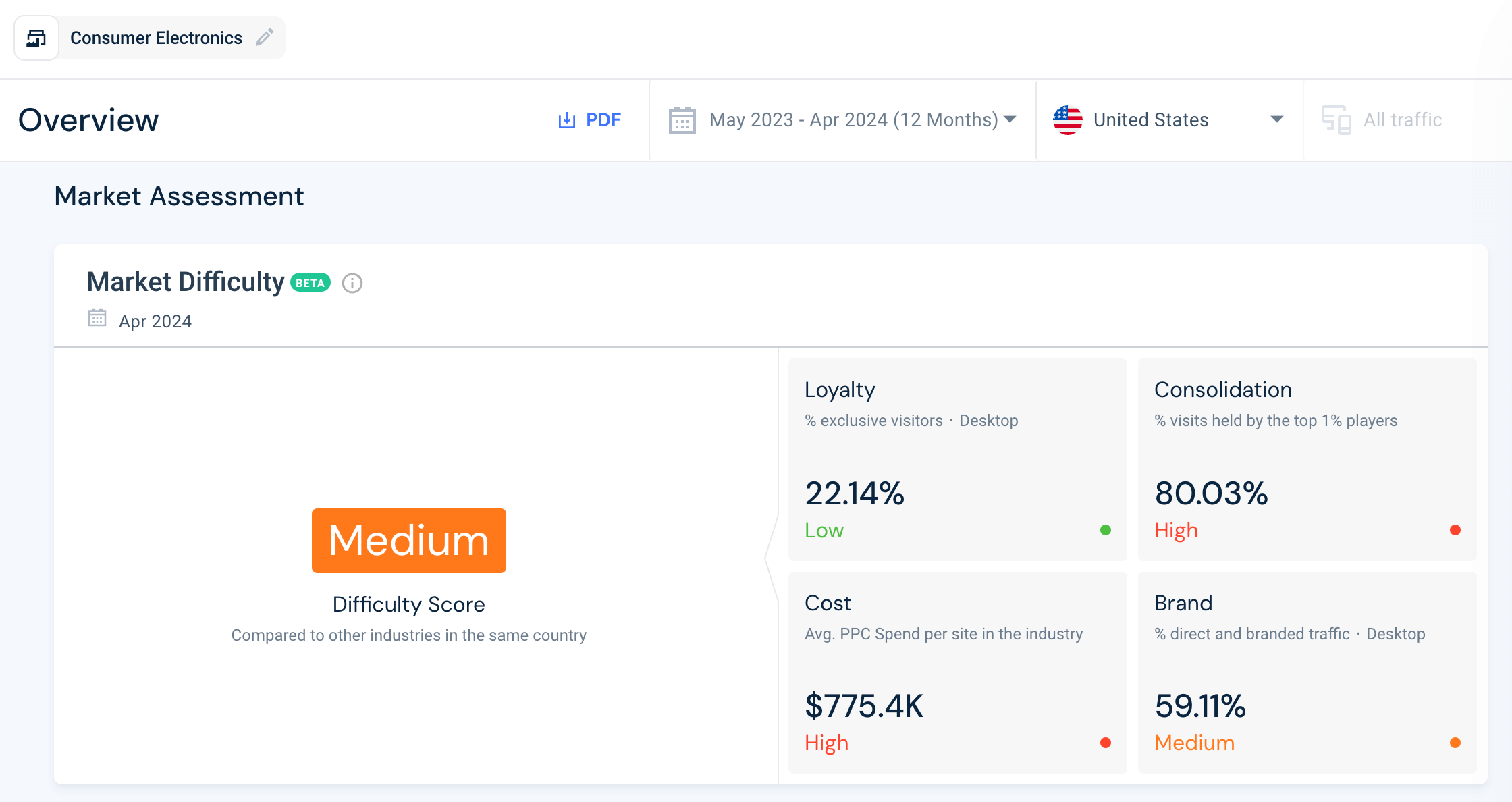
Here, we can see that based on a variety of analyzed quantitative data, market difficulty is ‘medium’, meaning it would be moderately challenging for new entrants to gain a foothold or existing players to increase market share , and would require time and investment.
You may think this means that an electronics company can simply choose whether on not to launch a new product or grow their market share based on this medium difficulty.
However, the devil is often in the details. When you break down the metrics on display and investigate further, more nuanced insights emerge about how a company can succeed in the market:
Audience loyalty in the Electronics and Technology industry – measured by the percentage of exclusive website visits (meaning the customers did not look at more than one brand) – is fairly low at 22.14%. Here’s a further breakdown, highlighting the top players:

This suggests that customers that are interested in Consumer Electronics sites are not particularly loyal to a single brand and will switch easily, indicating a price-driven market.
Therefore, a new market entrant should focus on developing unique value propositions, loyalty programs, or more competitive pricing models in order to gain traction in this otherwise difficult market.
Consolidation
This engagement metric is concerned with the percentage of players that hold the most market share (measured in website visits). In this industry, the consolidation rate is high, with the top 1% of players getting a whopping 80.03% on website visits.
While this means the competitive landscape is dominated by a few large players (Apple, Samsung etc.,) smaller players may be able to edge their way in:
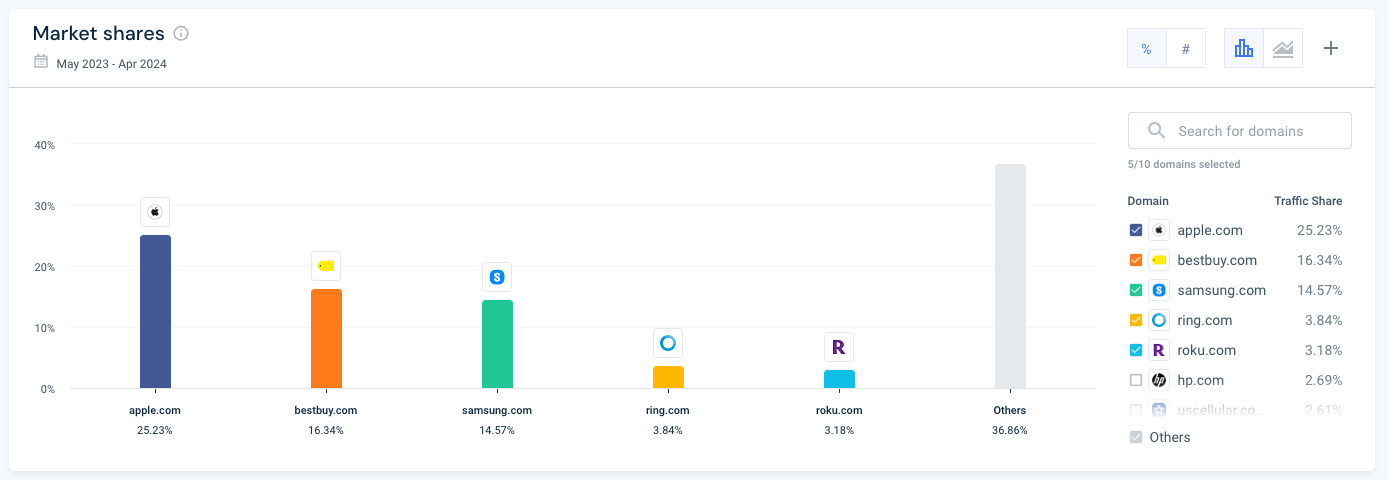
Indeed, with this information, new entrants can strategically focus on targeting niche segments within the wider industry or creating innovative strategies to set themselves apart from the usual suspects.
Average PPC Spend
The data suggests that, at a glance, there is a high average PPC spend within the Consumer Electronics industry, likely due to strong competition over high-value keywords and ad placements. This can outprice companies with a smaller budget or lead to wasted ad spend with little to no results.
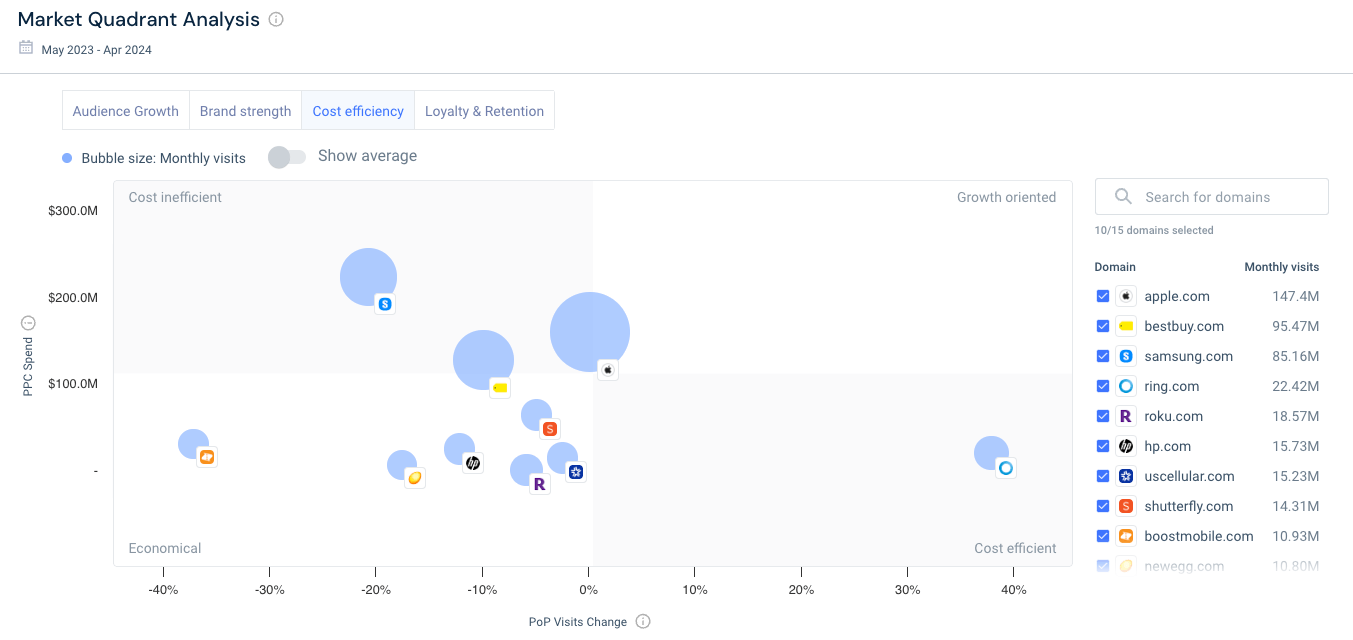
Understanding the investment needed to compete on paid channels can encourage smaller companies to either target more cost-effective options, like more niche or long-tail keywords , or redirect spend to more lucrative marketing channels that will yield better results.
Brand strength
Interestingly, brand strength is measured as ‘medium’ at 59.11% for the Consumer Electronics industry, despite featuring household names like Apple and Samsung. Brand strength is calculated by the percentage of direct and branded traffic to the top websites in the industry:
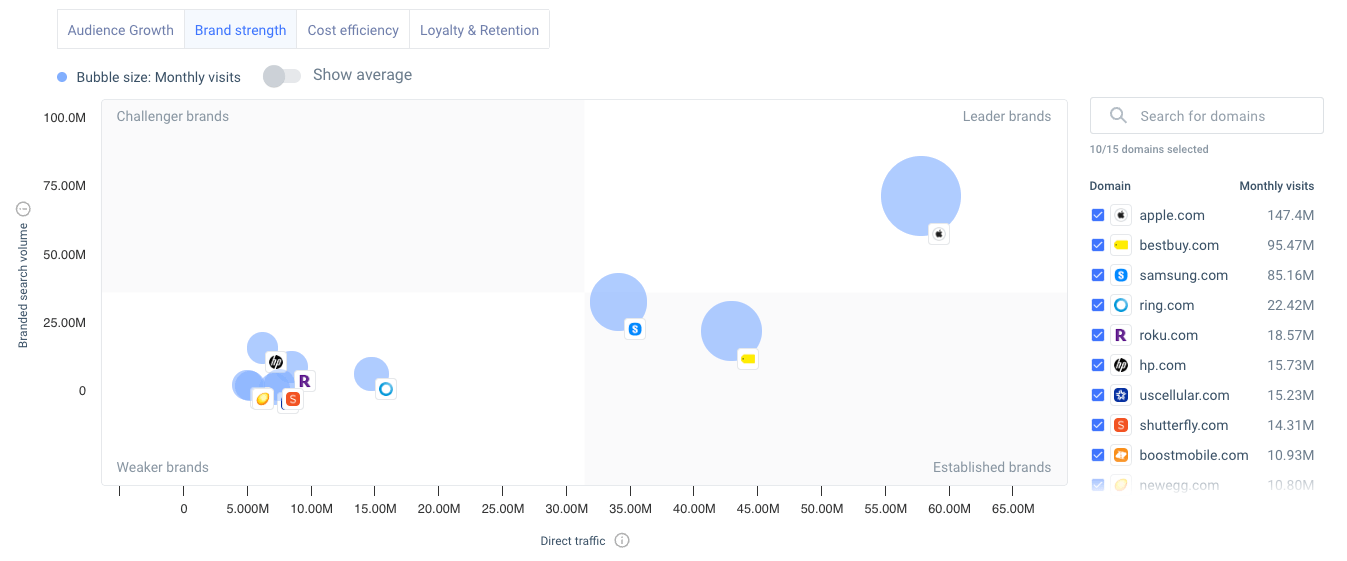
This means it could be relatively tricky – but certainly not impossible – for new market entrants to build brand awareness .
With the understanding that strong brand recognition and marketing is effective in this industry, potential market entrants can focus significant effort on building a strong, yet unique, brand identity and decide on strategies that will help them cut through the noise, like influencer marketing and PR campaigns.
Understanding consumer behavior
Data analysis for quantitative data is like a compass for understanding what your customers are doing and what they want. Metrics like click-through rate , conversion rate , page visit duration , and bounce rate all tell a story about how engaged your customers are with your website and content. This is instrumental in refining marketing campaigns, improving product or service offerings and elevating the customer experience.
Want another shortcut to understanding consumer behavior and preferences? Similarweb delivers this (and more) with our Demand Analysis feature.
Demand Analysis offers a direct look into what consumers are searching for, the trends shaping their behaviors, and how they respond to various market stimuli.
By leveraging real-time and historical data on consumer search behavior, you can gain a detailed understanding of demand patterns and shifts in consumer interests.
Demand Analysis reveals trends through customized keyword lists. By leveraging these personalized insights, you can forecast demand within your category and track how it evolves over time. This enables you to identify—and potentially forecast—both significant macro trends and nuanced micro trends that are likely to influence your business.
Here’s how demand forecasting works using Similarweb:
Let’s find out how popular the topic ‘dresses’ is based on real-time consumer searches and clicks. Based on a customized keyword list, we can see that demand for this topic has grown by 9.09% over the last three months:
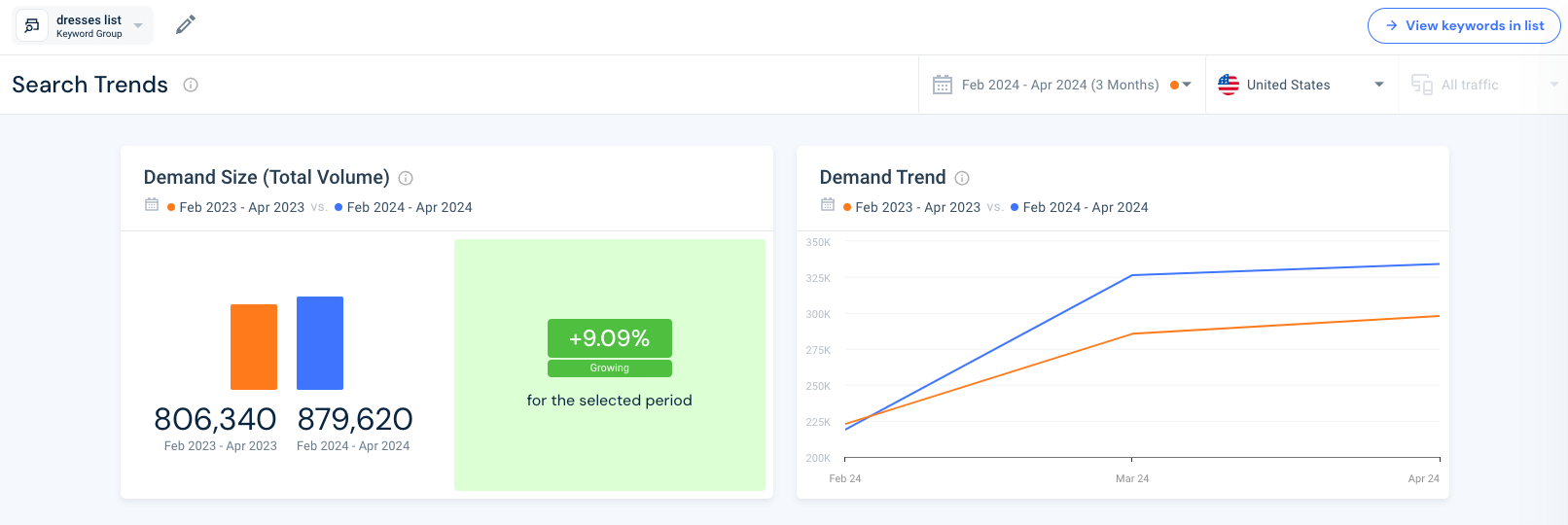
With total searches for dress-related keywords rising by almost 10% in the last 3 months, we can clearly see the demand trend is steadily rising – to be expected as we enter the warmer months. Here, there is also the option to change the time period of comparison, for example to see how demand has changed Year over Year.
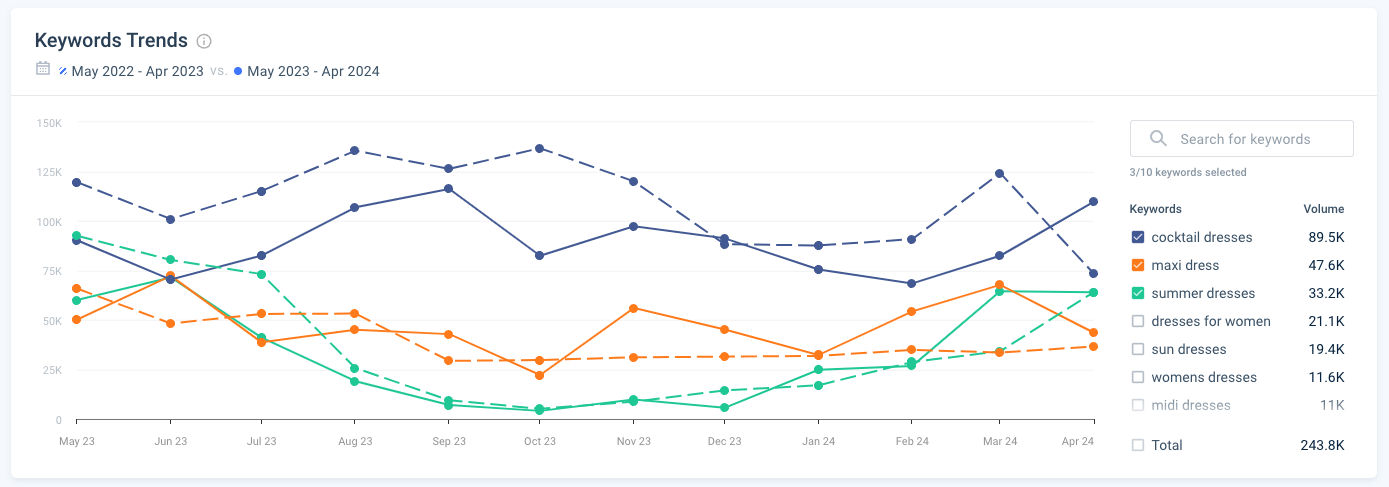
Looking at a YoY view of keyword trends, this graph reveals further key consumer insights surrounding demand for dresses, such as:
- The lowest search volumes are seen in more generic keyword s like “dresses for women” and “women’s dresses,” which indicates that consumers are searching more specifically when looking online
- ‘Cocktail dresses’ has the highest search volume among the dress types, peaking at around 116K searches in Sept 2023 and then again in April 2024. However, there is a decrease of 8-30% during these peaks when compared with data from 2022
- The consistently high volume for dresses suggests strong, steady demand throughout the year , however the peak in September for ‘cocktail dresses’ and in November for ‘maxi dresses’ is not quite consistent with the expected seasonal trend, which could point to event-driven consumer demand or targeted marketing campaigns
Benchmarking performance/competitive analysis
Quantitative data analysis is also vital for comparing business performance against competitors, particularly industry leaders . By analyzing competitors’ data alongside their own, like product sales or views, marketing channel performance and engagement metrics , businesses and brands can benchmark their success and better gauge their position in the market. This also helps identify opportunities or areas of improvement.
When it comes to this kind of comparative quantitative data, Similarweb’s platform has it all.
Let’s compare the website performance of two leading click-and-mortar retailers – walmart.com and target.com – using our Website Analysis feature.
Before diving into the nitty gritty, Similarweb offers an overview or snapshot of each company’s key performance metrics, displayed side-by-side for easier comparison:
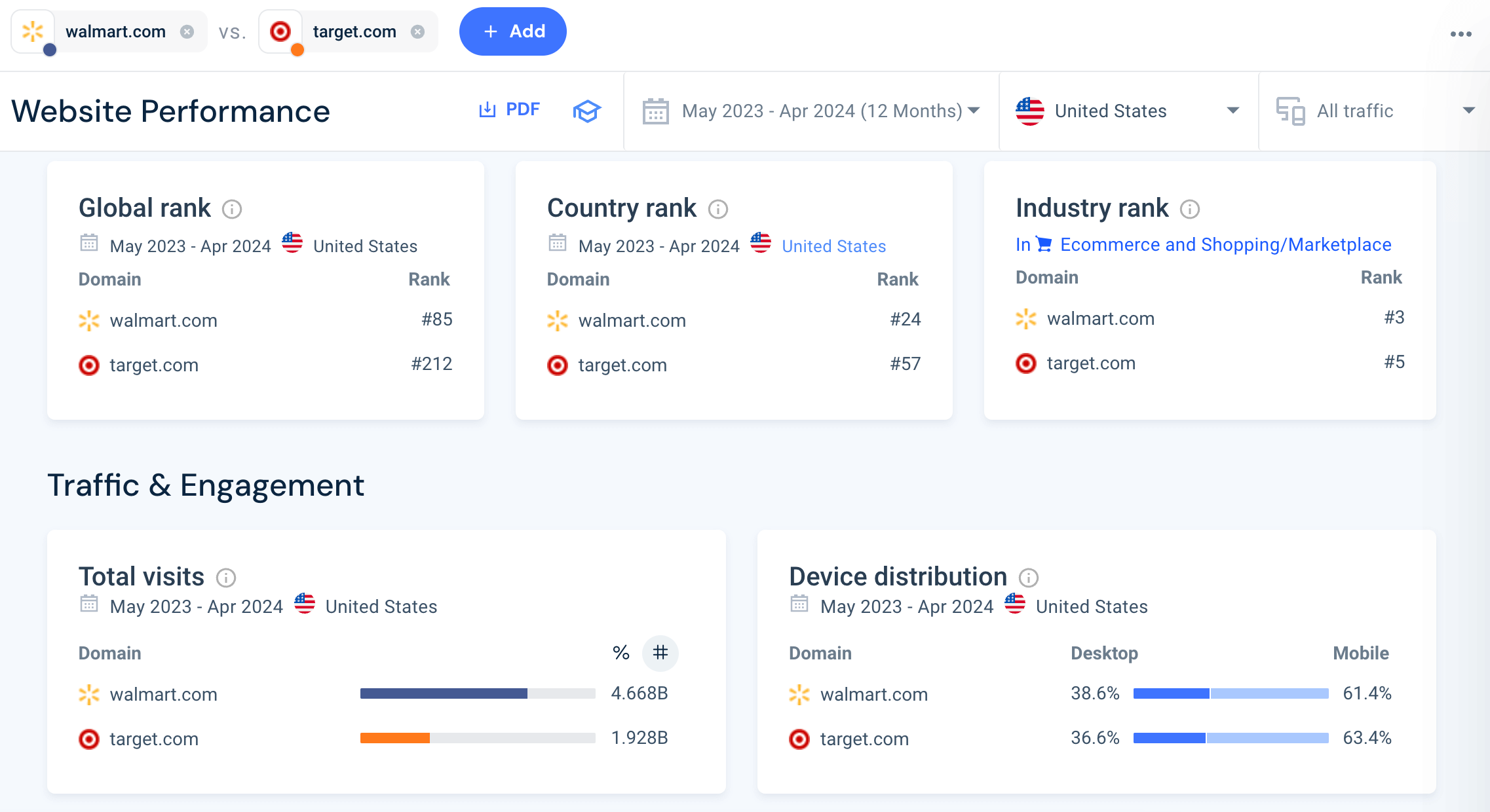
With this initial overview, market research professionals can quickly gauge where they stand against their competitors in terms of market share, total website visits, desktop/mobile device distribution and how they compare in the global, country and industry arena.
Diving into the data further, Website Analysis offers a look into high-level traffic and engagement metrics:
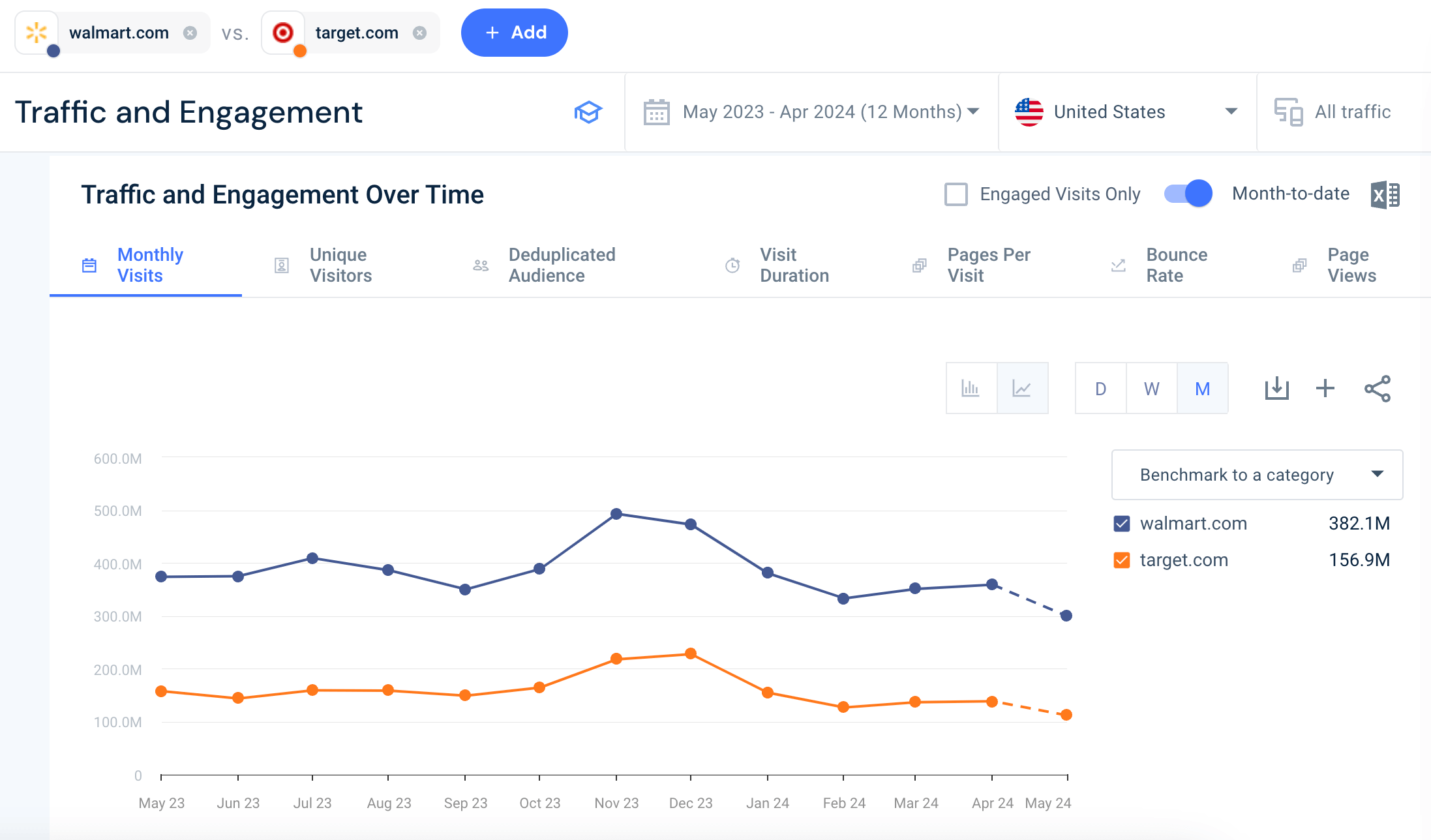
Here, there is the option to compare the website traffic trend of each competitor analyzed over a specific period. Then, they can view other engagement trends concerning visit duration, pages per visit , page views , and bounce rate.
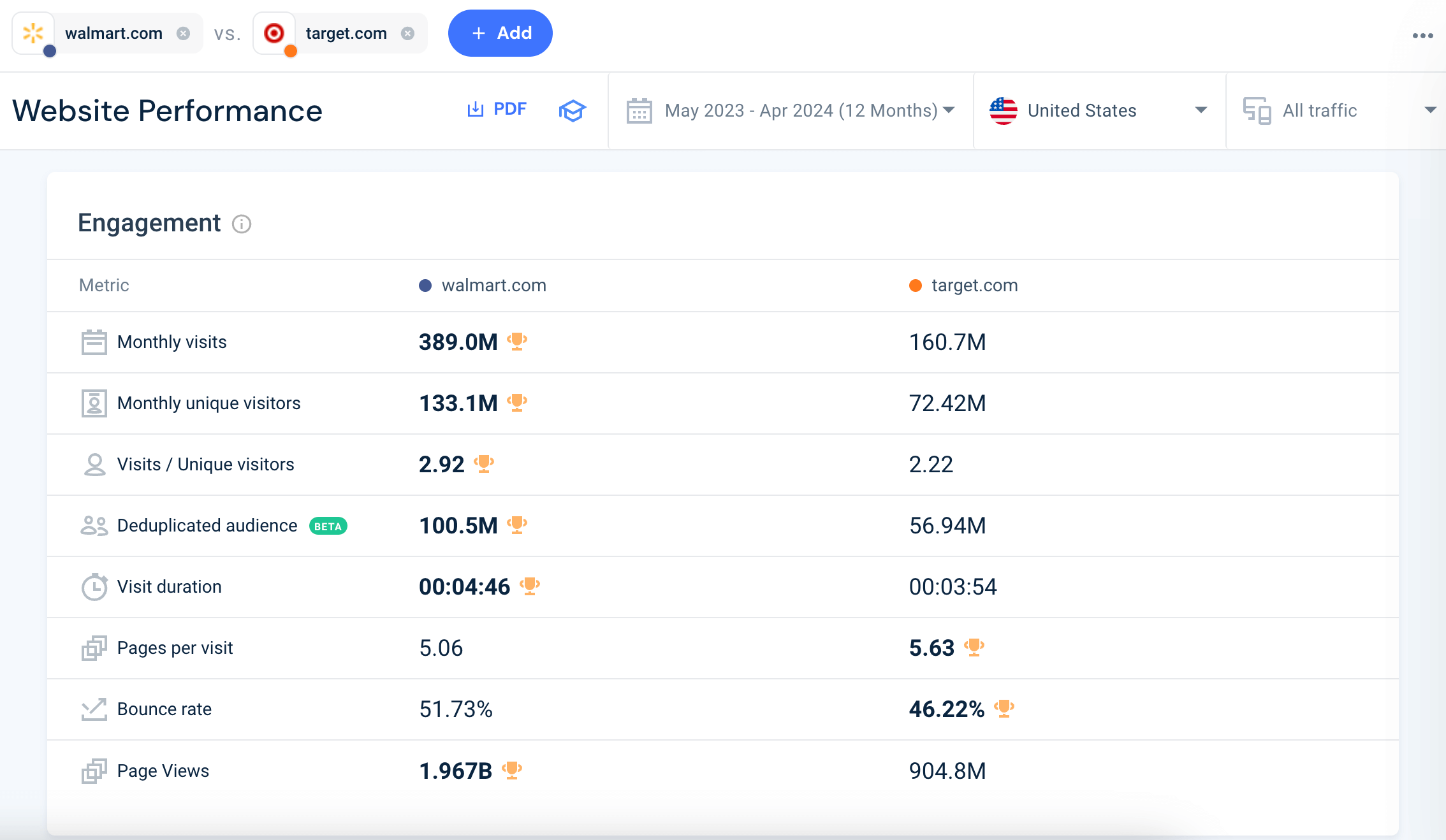
Alternatively, this data can be seen even more clearly under our specific Engagement segment:
Next up, the Marketing Channels overview gives a snapshot into the performance of each competitors’ marketing channels, so businesses can compare their most successful traffic sources:
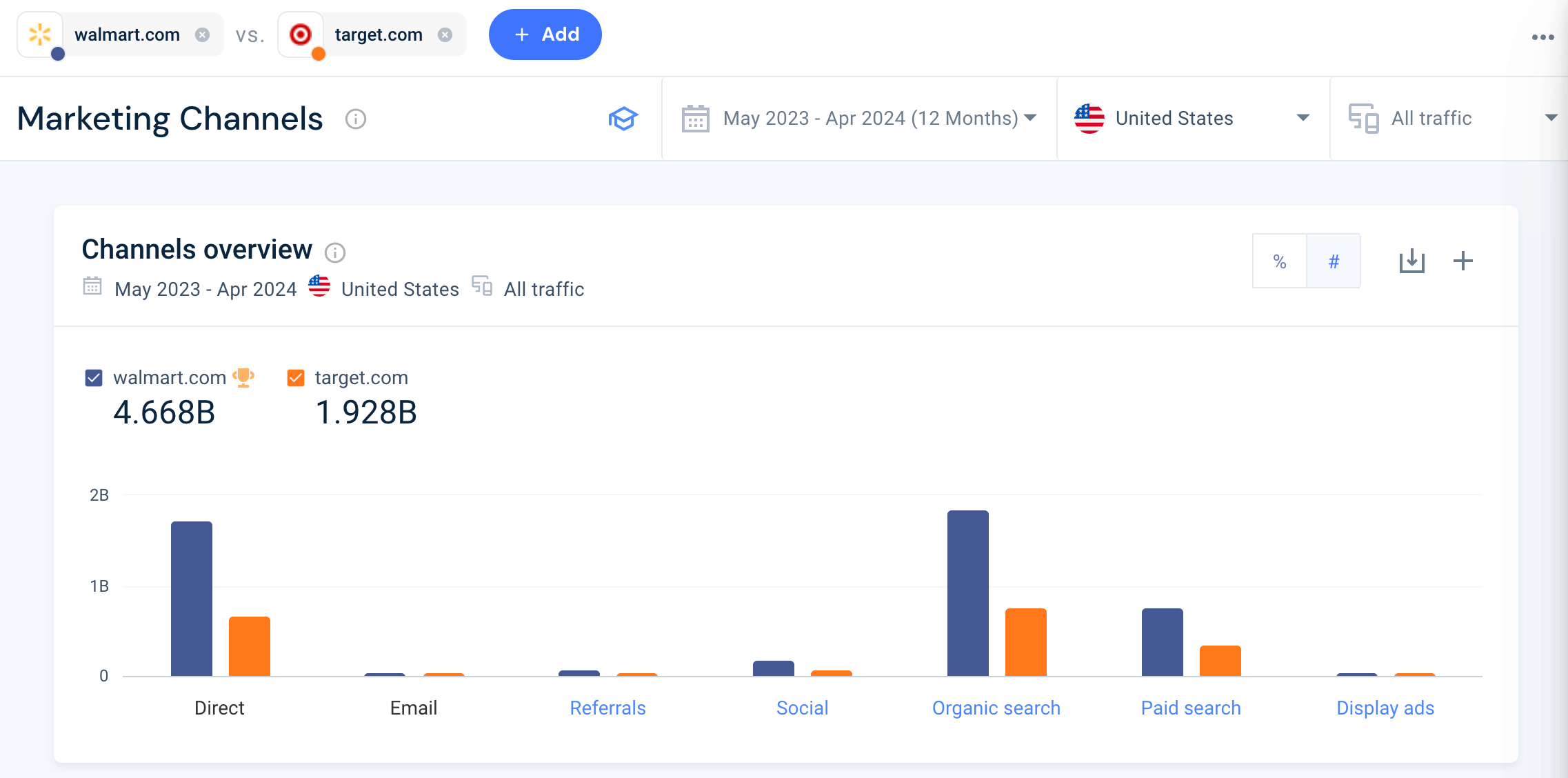
Walmart is the clear winner in this example, taking the lead across every channel. Target may use this information to understand the most lucrative channels to invest in based on their competitors’ success.
And finally, get one last snapshot of quantitative data in the form of some juicy audience demographics for more targeted strategies:
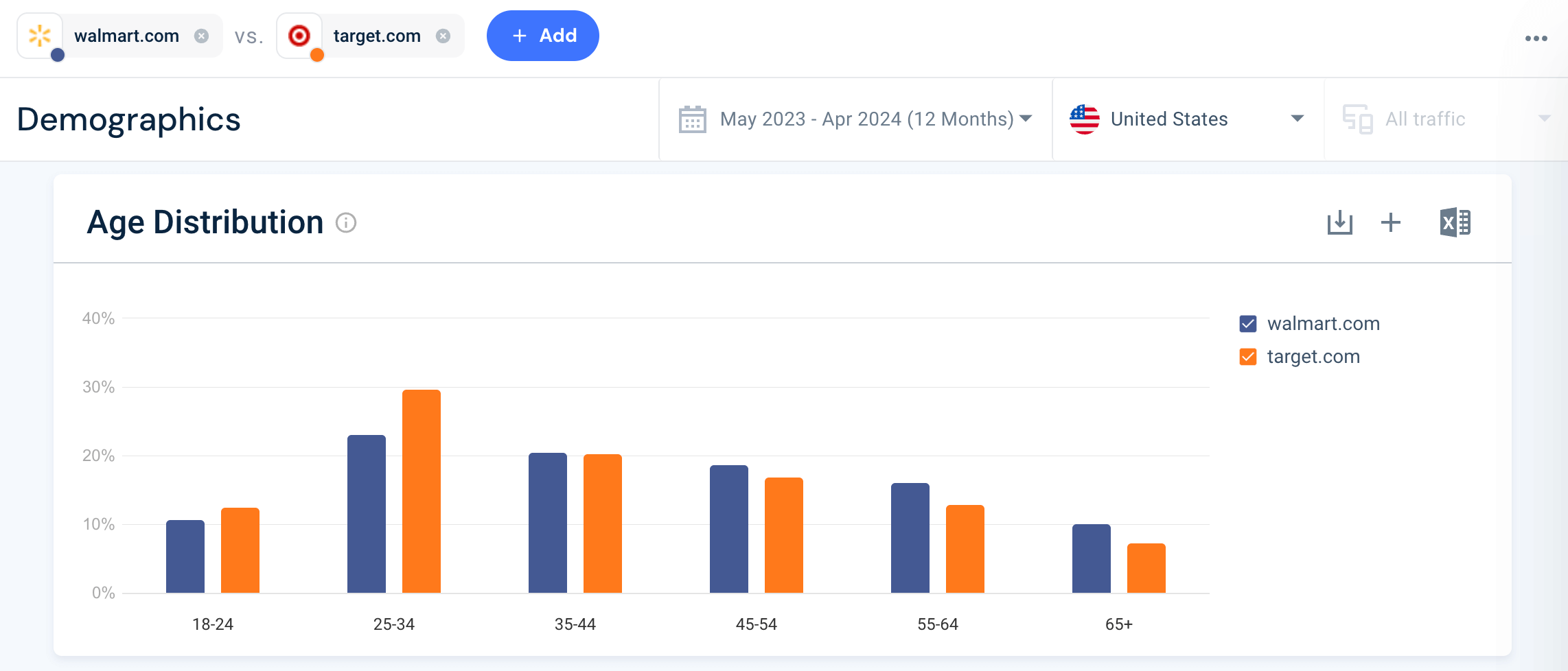
Tracking market trends
Understanding (and anticipating) market trends is one of the most important parts of market research. Trendspotting is possible by tracking certain quantitative data, such as sales numbers, market share, customer demographics, and purchase patterns over time. These data points can help provide clear insight into how a market is evolving, and what might be on the horizon. This is especially useful when forecasting future trends or demand for products and services.
Elevating the customer experience
Last but certainly not least, quantitative data is very useful in getting an idea of how satisfied customers are with a product or service. Gathering feedback via market research surveys can be used to fine-tune product features, elevate customer service and enhance the user experience – sending customer satisfaction, loyalty, and sales through the roof.
That’s a wrap on quantitative data…
In market research, quantitative data is indispensable, fueling data-driven decisions, product innovation and competitive analysis. This type of data provides measurable, objective evidence crucial for assessing strategies, understanding consumer behaviors and predicting future trends.
Similarweb is a goldmine of quantitative data, showcasing the power of these metrics with its advanced analytical tools.
The platform’s Market Analysis feature, in particular, offers deep insights into market dynamics, empowering market research professionals to make data-driven decisions with more precision.
Whether exploring new markets or expanding existing ones, Similarweb provides the essential quantitative data needed to turn data into actionable insights and navigate the complexities of today’s dynamic landscape – with confidence.
Dive into a treasure trove of quantitative data
With the best analytics platform in the world.
Quantitative data refers to any data that can be quantified and expressed numerically. This includes measurements, counts or other data that can be represented by numbers.
Why is quantitative data important in market research?
Quantitative data is crucial in market research as it provides a solid foundation for making objective decisions. It helps in analyzing trends, measuring the effectiveness of different strategies and predicting future outcomes. With quantitative data, businesses can take out the guesswork, allowing for more precise planning and assessment.
What’s the difference between quantitative and qualitative data?
Quantitative data involves numerical measurements and provides insights in terms of numbers and stats, allowing for statistical analysis and more concrete conclusions. Qualitative data is more descriptive and observational, providing deeper insights into thoughts, opinions, and motivations.
Quantitative data is categorized into four main types. Discrete data consists of counts that cannot be meaningfully divided into smaller parts, such as the number of children in a family. Continuous data includes measurements that can be infinitely divided into finer increments, like weight.
Interval data involves measurements where the difference between values is meaningful but lacks a true zero point, such as temperature in Celsius. Lastly, ratio data is similar to interval data but includes a meaningful zero point, allowing for ratio calculations, examples include height, weight, and distance.
How can I find and analyze quantitative data using Similarweb?
Similarweb offers a variety of tools that help in discovering and analyzing quantitative data. Features like Market Analysis provide insights into market dynamics, including competitor density, market saturation and customer loyalty. To track consumer behavior, the Demand Analysis tool offers real-time data on search trends and keyword volumes, making it easier to gauge market demand and interest.

by Monique Ellis
Content Marketing Manager
Monique, with 7 years in data storytelling, enjoys crafting content and exploring new places. She’s also a fan of historical fiction.
Related Posts

Geographic Segmentation: Definition, Pros & Cons, Examples, and More

Demographic Segmentation: The Key To Transforming Your Marketing Strategy

Unlocking Consumer Behavior: What Makes Your Customers Tick?
Customer Segmentation: Expert Tips on Understanding Your Audience

Market Demand 101: How to Gauge Demand for Your Products

Data Quality and Its Importance: Examples, Benefits, and Best Practices
Wondering what similarweb can do for your business.
Give it a try or talk to our insights team — don’t worry, it’s free!
Accounting , Administrative assistants , Blog , Data Entry , Ecommerce , Outsourcing , Research , Small Business Owners , Virtual Assistants
Quantitative market research- everything you need to know, table of contents, introduction.
Did you ever wonder how companies like Amazon or Google seem to predict your preferences with uncanny accuracy? The answer often lies in the realm of quantitative market research. But what precisely does this entail, and how does it enable businesses to comprehend consumer behavior with such finesse?
According to recent studies, over 75% of businesses worldwide rely on market research to guide their decision-making processes, highlighting its pivotal role in today’s competitive landscape. By quantifying consumer opinions and behaviors, companies can make informed strategic choices, tailor products and services to meet specific needs, and stay ahead of market trends.
What is Quantitative Market Research?
Quantitative market research is a systematic approach to gathering and analyzing data from a target market. It relies on numerical data and statistical analysis to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. This method involves collecting data through structured surveys, questionnaires, and experiments conducted with a large sample size representative of the target population. The objective is to obtain measurable insights into consumer opinions, attitudes, and purchasing habits.
One of the key advantages of quantitative marketing research is its ability to provide precise and quantifiable data. By using statistical techniques such as regression analysis, correlation, and hypothesis testing, researchers can identify patterns and relationships within the data, allowing for informed decision-making. This data-driven approach enables businesses to make strategic decisions regarding product development, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns.
Furthermore, quantitative research allows for generalization of findings to a larger population. With a sizable and diverse sample, researchers can draw conclusions that are applicable beyond the study group. This scalability enhances the reliability and validity of the research findings, providing businesses with confidence in their market strategies. Overall, quantitative market research serves as a powerful tool for businesses seeking to understand market dynamics and make data-driven decisions in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Common Types Of Quantitative Market Research
Quantitative market research encompasses various methods tailored to gather numerical data for analysis. Some common types include surveys, experiments, and observational studies.
Surveys are one of the most widely used methods in quantitative market research. They involve structured questionnaires administered to a representative sample of the target population. Surveys can be conducted through various channels such as online platforms, telephone interviews, or in-person interactions. By asking specific questions and collecting responses in a standardized format, researchers can quantify consumer opinions, preferences, and behaviors.
2. Experiments
Experiments are another essential type of quantitative marketing research. In experiments, researchers manipulate one or more variables to observe their effect on consumer behavior. This method allows for causal inference, helping businesses understand the impact of changes in product features, pricing strategies, or marketing tactics. Through controlled experiments, researchers can measure and analyze quantitative data to identify trends and patterns.
3. Observational studies
Observational studies involve systematically observing and recording consumer behavior in real-life settings. Researchers may use techniques such as tracking consumer purchases, monitoring website traffic, or analyzing social media interactions. By quantifying observational data, businesses can gain insights into consumer habits, trends, and preferences without direct intervention. Observational studies provide valuable quantitative data that complement findings from surveys and experiments, offering a comprehensive understanding of the market landscape.
Overall, these common types of quantitative market research enable businesses to gather, analyze, and interpret numerical data to make informed decisions and drive success in the marketplace. Each method offers unique advantages and insights, contributing to a robust understanding of consumer behavior and market dynamics.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Market Research
Quantitative market research and qualitative market research are two distinct approaches used to gather and analyze data about consumer behavior and preferences. Here’s a breakdown of their key differences:
Data Collection Methods
- Quantitative Research: Utilizes structured methods such as surveys, experiments, and observational studies to gather numerical data from a large sample size. The focus is on quantifiable information, allowing for statistical analysis and measurement of trends and patterns.
- Qualitative Research: Relies on unstructured or semi-structured techniques like interviews, focus groups, and observations to gather in-depth insights into consumer attitudes, motivations, and perceptions. It emphasizes open-ended questions and discussions to explore nuances and uncover underlying reasons behind behaviors. In addition to these traditional methods, leveraging web data from Coresignal on companies can provide valuable real-time information about market dynamics and competitor activities. By analyzing web data on companies, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of industry trends, customer preferences, and emerging opportunities.
Data Analysis Techniques
- Quantitative Research: Involves the use of statistical tools and techniques to analyze numerical data systematically. Researchers employ methods such as regression analysis, correlation, and hypothesis testing to identify relationships, trends, and statistical significance.
- Qualitative Research: Focuses on interpreting non-numerical data through thematic analysis, content analysis, or grounded theory. Researchers analyze textual or visual data to identify themes, patterns, and emerging concepts, providing rich, descriptive insights into consumer experiences and perspectives.
3. Scope and Generalizability
- Quantitative Research: Offers the advantage of scalability and generalizability, allowing findings to be applied to a broader population. With a large and representative sample size, researchers can draw statistically valid conclusions and make predictions about market trends and consumer behavior.
- Qualitative Research: Emphasizes depth over breadth, providing detailed insights into specific contexts or segments of the target market. While findings may not be statistically generalizable, qualitative research offers rich, contextual understanding that can inform product development, marketing strategies, and decision-making.
4. Objective and Purpose
- Quantitative Research: Often used to quantify phenomena, measure market trends, evaluate product performance, or assess customer satisfaction through numerical metrics. It aims to provide precise, quantifiable data to support strategic decision-making and hypothesis testing.
- Qualitative Research: Focuses on exploring perceptions, attitudes, and motivations behind consumer behavior, uncovering underlying emotions and motivations. It is valuable for generating hypotheses, uncovering emerging trends, and gaining deeper insights into consumer needs and preferences.
In summary, quantitative market research focuses on numerical data collection and statistical analysis to quantify market phenomena and trends, while qualitative market research delves into the subjective experiences and perceptions of consumers through in-depth exploration and interpretation of non-numerical data. Both approaches offer valuable insights and have unique strengths, often complementing each other in comprehensive market research strategies.
Top Advantages of Quantitative Market Research
Quantitative market research offers numerous advantages for businesses seeking to understand their target market, make informed decisions, and stay ahead of the competition. Here are some of the top advantages:
1. Statistical Validity
Quantitative research allows for the collection of numerical data that can be analyzed statistically. This statistical analysis provides a level of validity and reliability to the findings, enabling businesses to make confident decisions based on concrete evidence rather than intuition or anecdotal evidence.
2. Large Sample Sizes
One of the key strengths of quantitative research is its ability to gather data from large sample sizes. This ensures that the findings are representative of the broader population, providing a comprehensive understanding of market trends, preferences, and behaviors.
3. Generalizability
With its focus on numerical data and large sample sizes, Quantitative market research results are often generalizable to a larger population. This means that insights drawn from the research can be applied to a wider audience, helping businesses make strategic decisions that resonate with their target market.
4. Measurable Insights
Quantitative research allows businesses to measure various aspects of consumer behavior, such as purchasing habits, brand loyalty, and product preferences. These measurable insights provide actionable data points that can inform marketing strategies, product development, and overall business planning.
5. Comparative Analysis
Quantitative market research enables businesses to conduct comparative analysis across different demographic groups, geographic regions, or time periods. By comparing data sets, businesses can identify trends, patterns, and correlations, helping them understand how various factors impact consumer behavior and market dynamics.
6. Predictive Modeling
Quantitative research often involves the use of advanced statistical techniques and predictive modeling. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, businesses can forecast future market trends, anticipate consumer demands, and proactively adjust their strategies to stay ahead of the competition.
7. Cost-Effective Data Collection
While quantitative research may require initial investment in survey development and data analysis tools, it is generally more cost-effective than qualitative research methods such as focus groups or in-depth interviews. Online surveys and data collection platforms make it easier and more affordable to gather large volumes of data from diverse respondents.
8. Data-driven Decision Making
In today’s data-driven business landscape, Quantitative market research plays a crucial role in informed decision-making. By leveraging data analytics and empirical evidence, businesses can make strategic decisions based on real-world data rather than gut feelings or assumptions, leading to more successful outcomes and sustainable growth.
Disadvantages of Quantitative Marketing Research
While quantitative market research offers numerous advantages, it’s also important to recognize its limitations and potential drawbacks. Here are some disadvantages of quantitative marketing research:
1. Limited Depth of Understanding
Quantitative research often focuses on numerical data and standardized survey instruments, which may limit the depth of understanding compared to qualitative research methods such as interviews or focus groups. It may not capture the richness of consumer experiences, emotions, or underlying motivations behind their behavior.
Quantitative research often involves surveying a large number of respondents, which provides a representative sample of the target population. The large sample size enhances the reliability and generalizability of the findings, allowing businesses to make informed decisions with confidence.
3. Inability to Explore Complex Issues
Quantitative market research research is well-suited for exploring straightforward questions and measuring predefined variables. However, it may struggle to address complex or nuanced issues that require in-depth exploration and qualitative insights. Complex phenomena often cannot be fully captured or understood through quantitative measures alone.
4. Lack of Contextual Understanding
Quantitative market research provides numerical data without always providing context or meaning behind the numbers. Without a deeper understanding of the context in which data was collected, businesses may misinterpret findings or overlook important insights. Contextual understanding is essential for making informed decisions based on quantitative research findings.
5. Difficulty in Capturing Unforeseen Variables
Quantitative research relies on predetermined survey questions and predefined variables, which may overlook unforeseen variables or emerging trends that could influence consumer behavior. This limitation can result in incomplete or outdated insights, particularly in fast-changing industries or markets.
Key Steps for Quantitative Marketing Research
Conducting quantitative market research involves several key steps to ensure the collection of reliable data and the generation of actionable insights. Here are the steps for conducting quantitative marketing research:
Define Research Objectives
Clearly define the research objectives and goals. Determine what specific information you want to gather, what questions you need to answer, and how you plan to use the research findings to inform business decisions.
Identify Target Population
Identify the target population or the group of individuals you want to survey. Define the characteristics of your target audience, such as demographics (age, gender, income), geographic location, behavior patterns, or other relevant criteria.
Develop Research Instrument
Design the survey instrument or questionnaire to collect quantitative data. Craft clear, concise, and unbiased questions that address your research objectives. Consider using a mix of closed-ended (e.g., multiple-choice, rating scales) and open-ended questions to gather both quantitative and qualitative insights.
Select Sampling Method
Choose an appropriate sampling method to select participants from the target population. Common sampling methods include random sampling, stratified sampling, cluster sampling, or convenience sampling. Ensure that your sample size is sufficient to achieve statistical significance and representativeness.
Data Collection
Administer the survey to the selected participants using appropriate data collection methods. This may include online surveys, telephone interviews, face-to-face interviews, or mail surveys, depending on the characteristics of your target population and the research objectives.
Ensure Data Quality
Implement measures to ensure the quality and validity of the collected data. This includes pretesting the survey instrument to identify any issues or ambiguities, monitoring data collection procedures to minimize errors, and verifying the accuracy of responses through data validation techniques.
Data Analysis
Analyze the collected data using statistical analysis techniques. This may involve descriptive statistics to summarize the data (e.g., mean, median, mode), inferential statistics to test hypotheses and make predictions (e.g., t-tests, regression analysis), and data visualization techniques to present findings effectively (e.g., charts, graphs, tables).
Interpret Findings
Interpret the findings of the data analysis in relation to the research objectives. Identify key trends, patterns, correlations, and insights that emerge from the data. Consider how the findings align with the research objectives and what implications they have for decision-making.
Draw Conclusions
Draw conclusions based on the interpreted findings and assess their implications for the business. Determine whether the research objectives have been met and what actionable insights can be derived from the findings. Consider any limitations or caveats associated with the research findings.
Report and Present Findings
Prepare a comprehensive research report that summarizes the methodology, findings, conclusions, and recommendations of the quantitative market research. Present the findings to relevant stakeholders in a clear and engaging manner, using visual aids and storytelling techniques to enhance understanding and facilitate decision-making.
By following these steps, businesses can conduct effective quantitative marketing research to gain valuable insights into their target market, make informed decisions, and achieve strategic objectives.
10 Best Practices for Quantitative Market Research
Quantitative research finds wide-ranging applications across various domains and industries due to its ability to provide systematic, numerical insights into market dynamics, consumer behavior, and business performance. Some key applications of quantitative research include:
1. Clearly Define Objectives
Start by clearly defining the research objectives and goals. Understand what specific information you need to gather and how you plan to use the research findings to inform decision-making.
2. Use Validated Measures
Utilize validated measurement tools and standardized survey instruments to ensure the reliability and validity of your data. Choose established scales and question formats that have been tested and proven to produce accurate results.
3. Pretest Survey Instrument
Before launching the survey, pretest the survey instrument with a small sample of respondents to identify any issues or ambiguities. This allows you to refine the questionnaire, improve question clarity, and ensure that respondents interpret questions as intended.
4. Ensure Representative Sampling
For quantitative market research, use appropriate sampling methods to ensure that your sample is representative of the target population. Consider factors such as demographics, geographic location, and behavior patterns when selecting participants to minimize sampling bias.
5. Maximize Response Rate
Implement strategies to maximize the response rate and minimize non-response bias. This may include personalized invitations, clear instructions, incentives for participation, and multiple reminders to encourage survey completion.
6. Maintain Data Quality
Implement measures to maintain data quality throughout the research process. This includes monitoring data collection procedures, verifying the accuracy of responses, and conducting data validation checks to identify and address errors.
7. Analyze Data Rigorously
Conduct rigorous data analysis using appropriate statistical techniques. Ensure that the analysis is conducted accurately and transparently, and interpret the findings in relation to the research objectives.
8. Consider Contextual Factors
Consider contextual factors that may influence the interpretation of research findings, such as market trends, competitive landscape, and consumer preferences. Contextual understanding helps provide a deeper understanding of the data and its implications.
9. Provide Actionable Insights
Focus on providing actionable insights that can inform decision-making and drive business outcomes. Present the findings in a clear, concise manner, and highlight key trends, patterns, and recommendations that stakeholders can act upon.
10. Continuously Improve
Continuously evaluate and improve your quantitative research processes based on feedback and learnings from each study. Incorporate lessons learned into future research initiatives to enhance the effectiveness and reliability of your market research efforts.
Quantitative Data Collection Methods for Marketing Research
Quantitative market research relies on various data collection methods to gather numerical data and statistical insights about consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. Here are some commonly used quantitative data collection methods for marketing research:
Online Surveys
Online surveys are one of the most popular methods for quantitative data collection in marketing research. Surveys are distributed electronically via email, websites, or social media platforms, allowing respondents to provide feedback on their preferences, purchasing habits, brand perceptions, and more. Online surveys offer the advantages of cost-effectiveness, wide reach, and the ability to collect large volumes of data quickly.
Telephone Surveys
Telephone surveys involve conducting interviews with respondents over the phone to gather quantitative data. Trained interviewers follow a standardized script and ask respondents a series of structured questions. Telephone surveys are useful for reaching diverse populations, including those without internet access, and can provide immediate feedback from respondents.
Face-to-Face Interviews
Face-to-face interviews involve direct interaction between interviewers and respondents in person. Interviewers use structured questionnaires to collect quantitative data on topics such as product preferences, satisfaction levels, and brand perceptions. Face-to-face interviews allow for deeper probing and clarification of responses but can be more time-consuming and expensive compared to other methods.
Mail Surveys
Mail surveys involve sending questionnaires to respondents via postal mail and asking them to complete and return the surveys by mail. While less common in the digital age, mail surveys can still be effective for reaching certain demographic groups, particularly older or rural populations. However, they tend to have lower response rates and longer turnaround times compared to online or telephone surveys.
Mobile Surveys
With the widespread use of smartphones and mobile devices, mobile surveys have become increasingly popular for quantitative data collection. Mobile surveys are designed to be mobile-friendly, allowing respondents to complete surveys on their smartphones or tablets at their convenience. Mobile surveys offer the advantages of accessibility, real-time data collection, and the ability to capture location-based information.
Point-of-Sale (POS) Data Collection
POS data collection involves capturing transactional data from point-of-sale systems used in retail stores, e-commerce platforms, and other sales channels. POS data provides quantitative insights into consumer purchasing behavior, including sales volumes, product preferences, pricing strategies, and seasonal trends. POS data collection is valuable for analyzing market trends, monitoring sales performance, and optimizing marketing strategies.
Website Analytics
Website analytics tools track and analyze quantitative data about website visitors’ behavior, interactions, and engagement metrics. These tools provide insights into website traffic, user demographics, conversion rates, bounce rates, and other key performance indicators (KPIs). Website analytics help marketers understand how visitors navigate their websites, identify areas for improvement, and optimize digital marketing efforts.
Social Media Monitoring
Social media monitoring tools collect quantitative data from social media platforms, such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn. These tools track metrics such as follower counts, likes, shares, comments, and sentiment analysis to gauge brand awareness, customer engagement, and social media ROI. Social media monitoring provides valuable insights into consumer conversations, trends, and competitive intelligence in real-time.
In conclusion, quantitative market research is like a reliable guidebook for understanding how consumers behave and what’s happening in the market. It uses numbers and straightforward analysis to uncover insights that help businesses make smart decisions and plan for the future. By carefully collecting and studying data, companies can get a clear picture of who their customers are and what they want, which guides everything from product development to marketing strategies. Essentially, quantitative research helps businesses stay on track and ahead of the competition by giving them the knowledge they need to navigate the twists and turns of the market.
In today’s fast-paced business world, quantitative marketing research is essential for companies looking to understand what’s going on with their customers and in their industry. It’s like having a map that shows you where to go and how to get there. By using simple tools and techniques to analyze data, businesses can spot trends, predict what’s coming next, and make decisions with confidence.
Read more –
The 10 Best Keyword Research Services in 2024
B2B Market Research Services: A Comprehensive Overview
1. What is quantitative markeing research?
Quantitative marketing research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to understand market trends, consumer behavior, and preferences. It employs structured surveys, polls, and statistical methods to quantify insights, providing measurable data for making informed business decisions and assessing market opportunities.
2. Is market research qualitative or quantitative?
Market research can be both qualitative and quantitative, depending on the type of data collected and analyzed. Quantitative research uses numerical data and statistical methods, while qualitative research uses non-numerical data and interpretive methods.
3.What are examples of the most common quantitative marketing research
Examples of common quantitative marketing research include surveys, experiments, observational studies, and data analysis techniques such as regression analysis and factor analysis.
4. How qualitative research can be useful in marketing?
Qualitative research can be useful in marketing for various purposes, such as exploring new product ideas, testing concepts, understanding customer satisfaction and loyalty, identifying market segments and personas, developing brand positioning and messaging, and generating creative solutions.
5. How to analyze quanitative data for marketing research?
To analyze qualitative data for marketing research, start by transcribing or summarizing the data. Then, use thematic analysis or coding techniques to identify recurring themes, patterns, and insights. Interpret these findings within the context of the research objectives to inform marketing strategies effectively.
6. How to conduct qualitative market research?
Qualitative market research can be conducted by using different methods and techniques, such as focus groups, in-depth interviews, observation, ethnography, case studies, and online communities. The choice of method depends on the research objectives, questions, budget, and time constraints.
7. What are some common quantitative market research techniques?
Common techniques include online surveys, telephone interviews, face-to-face interviews, mail surveys, and statistical analysis using software. These methods help gather numerical data and analyze consumer behavior and market trends.
8. How can businesses benefit from quantitative market research services?
Businesses gain expertise in designing robust methodologies, collecting high-quality data, and gaining insights into consumer preferences and market trends. This enables data-driven decision-making and staying competitive.
Case Studies
Building brands online- a case study of ossisto’s e-commerce website development for patissiers, healthcare efficiency – a case study with ossisto’s administrative support , enhancing healthcare efficiency with ossisto administrative support – a case study, lokation real estate’s journey to success with ossisto – case study, real estate success – a case study of kings homes & associates with ossisto’s virtual…, kaizen karate success story – a case study of kaizen karate with ossisto’s virtual assistance, empowering cornerstone engineering llc’s growth with ossisto’s integrated virtual assistance solutions, from job seeker to trailblazer- a success story with ossisto’s strategic job search support, how ossisto’s business support transformed a cybersecurity firm’s operations: a success story, ossisto’s job search assistance journey- a case study in achievement, start your free trial now, featured posts, optimizing your virtual assistant workflow for increased client satisfaction, top benefits of outsourcing python development for your business, explore the benefits of hubspot white label services, top 20 – best cloud migration service providers in usa 2024, outsource php development in 2024 – a step-by-step guide, 10 best offshore development companies to elevate your business, 10 best criteria of online business startup cpa, why your business needs offshore it outsourcing, top 15 devops consulting companies in 2024, top cloud migration consulting companies of 2024, best practices to hire frontend developers, offshore wordpress development – top 10 benefits explained, top 15 companies providing monthly bookkeeping services, how virtual assistants can simplify student’s lives, content moderation services – top companies, benefits and tools, what are website management services a complete overview, cold calling virtual assistant – generate leads with benefits, 10 best remote bookkeeping companies for startups in 2024, how outsourcing your controller services can boost your business , corporate travel planner – why your business needs one, sign up for two hours free trial.

- Pollfish School
- Market Research
- Survey Guides
- Get started
The Complete Guide to Quantitative Market Research

Quantitative research is a chief category in the research sphere, along with qualitative research. An encompassing aspect of market research , it can include both primary and secondary methods of extracting data.
Although used interchangeably with qualitative research, quantitative research is a distinct process that should not be confused with its counterpart. In fact, it is the opposite of qualitative research.
Let’s navigate through the waters of quantitative research in this complete guide.
What Defines & Makes Up Quantitative Research?
As its name suggests, quantitative research is the process of aggregating quantitative, or numerical data for research purposes. This data is used for a number of applications. These include:
- Quantifying opinions, behaviors, attitudes and problems
- Making generalizations
- Forming predictions
- Discovering patterns
- Determining averages
- Testing relationships
Quantitative research generally relies on a larger sample size in order to quantify any issue or variable. In order to achieve this, this research method involves using mathematical and statistical means.
This type of research answers the “what” and the “how much” of a subject within a research endeavor. As it forms generalizations, this type of method involves surveying a larger population, using measurable data and processing all the data first and then analyzing it from a statistical standpoint.
The Four Main Types of Quantitative Research
There are four main ways to perform quantitative research. Aside from their methodology, these sub-categories also seek different types of answers and conclusions.

1. Descriptive Research
This is used to determine the state of variables. It describes the situation and environment surrounding a variable or topic. As such, it is used for arranging comparisons, outlining sample characteristics, overlooking emerging trends and confirming existing phenomena.
The data is collected by way of observation. Descriptive Research is used to form a hypothesis, but only after having aggregated all the necessary data.
2. Correlational Research
This research method is used to examine the relationships between different subjects and variables. Analyzing relationships is necessary to either test a hypothesis or a prediction. Because this research focuses on relationships between fixed variables, other outlying variables are not part of the investigation.
Correlational research is in direct opposition to experimental research, as none of the studied variables are manipulated. Correlations can be either positive or negative, with different degrees of the relationship’s strength.
3. Experimental Research
This method is used for finding whether there is a cause and effect relationship among variables. This kind of research relies on the scientific method. Unlike correlational research, experimental research involves manipulating variables.
Researchers would manipulate a variable to uncover its effect on another one. This method is frequently referred to as true experimentation, as no experimental undertaking leaves all variables unchanged; at least one must be influenced in some way.
This includes manipulating, randomizing or reverting back a variable. The variables are then measured, calculated and compared.
4. Survey Research
The final research method is crucial to understanding behavior. In market research, it is often used to acclimate a brand with its target market’s desires, needs, points of contention and behaviors.
Surveys allow researchers to ask pointed questions to either discover their target audience or get a granular sense of their opinions. As such, they can be conducted within one group or many, for the sake of comparison.
Instead of turning to survey panels , which are likely to have skewed or biased results, researchers should use a random sample of people. A non-panel-based survey will garner more respondents that aren’t motivated by professional compensation.
Surveys can be administered by mail, in-person, on the phone, or digitally. The latter has even more options: online surveys, third-party surveys, emails and in-app.
Examples of Questions for Quantitative Research
Survey research has a far larger scope of questions than do the other three types, as researchers can ask practically anything to conduct their studies. However, there are some best practices in survey questionnaires, such as focusing on your industry, your product and the desires of customers.
Learn more about asking insightful market research questions . Here are a few examples of quantitative research questions in the three other categories.
- Is working from home the best option to improve productivity for employees with long commutes? Variable: Working from home and in-office Demographic: Employees with long commutes Quantitative Research Type : Experimental
- How has the coronavirus changed employment for white-collar workers? Variable: Employment types and statuses Demographic: White-collar workers Quantitative Research Type : Experimental
- How often do working people travel for a holiday? Variable: Amount of times respondents travel during a holiday Demographic: working people Quantitative Research Type : Descriptive
- How much would you pay for a subscription to an entertainment magazine? Variable: payments for a magazine subscription Demographic: women aged 14-44, those interested in celebrities Quantitative Research Type : Descriptive
- What is the difference in smartphone usage between Millennials and senior citizens? Variable: Time spent on using a smartphone Demographic: Millennials and seniors Quantitative Research Type: Correlational
- Does the leadership style of car shop owners predict the job satisfaction of car salespeople? Variable: Leadership style and job satisfaction Demographic: Car shop employers and salespeople Quantitative Research Type: Correlational
When to Use Quantitative Research and How to Analyze It

The quantitative research method has specific use cases. You ought to consider which is best for your particular business, which includes your strategy, your marketing and other facets.
The core of quantitative research is to quantify a phenomenon (a problem, an inadequacy, and a slew of other occurrences) and understand its prevalence. Researchers do this by observing large portions of a population.
You should use this form of research whenever you need to be presented with the state of things at a higher level, or from a bird’s eye view. This Is because this type of research can identify links between various factors, look for correlations and discover cause and effect relationships.
Researchers can then use the results of their findings to form predictions. This is useful in market research when launching a new product, brainstorming product ideas or innovations or growing a customer base.
To analyze this research, it should first be made quantifiable and objective. Researchers should pin down the scales and units of measurements in their various studies. Then, they should organize them into easily interpretable formats.
For example, once you gather the numerical data, you can enter it into a spreadsheet. Thereafter, you can organize it by desegregating it into graphs, charts and tables. Finally, you should draw data-based conclusions from your study. You can also do further sleuthing via advanced analytics.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research has a bevy of benefits; it also has some hindrances. You should peruse both the positive and negative qualities of this research type before setting out on any major research project. The following may help you choose one form of research over the other, or use aspects of both.
- Larger sample pools: the larger the group of respondents, the more accurate are the results.
- Highly structured: Surveys, questionnaires, and other tools for recording numerical data
- Focused: The design of the study is determined before it begins
- Theory-based: Research tests a theory to provide support/proof
- Designed to Be Analyzed: Numbers/statistics exist as tables, charts, figures and other non-textual forms for easy analysis.
- Objective: Steering clear of bias as the research is separated from the data & only objective responses are sought.
- Direct comparisons of results: The study can be set in different cultural environments, times or different groups of participants with a statistical comparison of results.
- Focuses solely on numbers: This can be limiting as researchers may overlook other data and larger themes.
- Superficial Representations: It cannot adequately describe complex concepts (ex: feelings, opinions) it only shows the numbers behind them.
- Several factors can invalidate results: A hypothesis and a model for collecting/ analyzing data.is required; any mistake can lead to bias and inaccurate illustrations.
- Erred Structure: If any data is missing or if measurements are not clear, biases easily take precedence.
The Final Word on Quantitative Research
Market research is far too encompassing to fully complete, especially in a limited amount of time. To tackle market research, begin with a research method. Quantitative research is often a good starting point, as it shows you the existence of a problem by way of quantifying it.
Aside from confirming the existence, it can help confirm a hypothesis, find correlations and prove cause and effect relationships. A hard set of data can also help you make educated predictions.
While the three types of quantitative research methods are useful, they do have several disadvantages. The fourth one, ie, survey research helps fill in the gaps and inadequacies of numerical limitations. Interestingly enough, they too can be a source of hard data and numbers.
Either way, market research is sure to benefit from incorporating surveys as part of the processes.
Frequently asked questions
What is quantitative market research.
Quantitative market research utilizes the techniques of quantitative research in order to better understand the target market. In quantitative research, the information gathered from surveys and questionnaires is converted into numerical values so it can be easily analyzed.
What types of questions do quantitative research answer?
Quantitative research seeks to define “what” and “how much.” It is used for identifying patterns, making predictions, establishing averages, and quantifying opinions, attitudes or behaviors.
What are the four main types of quantitative research?
The four main types of quantitative research are survey research, correlational research, descriptive research, and experimental research.
What type of surveys are used for quantitative research?
Quantitative surveys are best suited for quantitative research. In this type of survey, there are no open-ended questions, and all responses can be assigned a numerical value. In most cases, a quantitative survey is distributed to a large and random sample of individuals.
Why are large sample sizes important when conducting quantitative research?
A small sample size can lead to inaccurate results. The larger the sample size (i.e. the group of individuals who receive the survey), the more likely it is that the results will be statistically significant and accurate.
Do you want to distribute your survey? Pollfish offers you access to millions of targeted consumers to get survey responses from $0.95 per complete. Launch your survey today.
Privacy Preference Center
Privacy preferences.
How to Do Market Research: The Complete Guide
Learn how to do market research with this step-by-step guide, complete with templates, tools and real-world examples.
Access best-in-class company data
Get trusted first-party funding data, revenue data and firmographics
Market research is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing and interpreting information about a specific market or industry.
What are your customers’ needs? How does your product compare to the competition? What are the emerging trends and opportunities in your industry? If these questions keep you up at night, it’s time to conduct market research.
Market research plays a pivotal role in your ability to stay competitive and relevant, helping you anticipate shifts in consumer behavior and industry dynamics. It involves gathering these insights using a wide range of techniques, from surveys and interviews to data analysis and observational studies.
In this guide, we’ll explore why market research is crucial, the various types of market research, the methods used in data collection, and how to effectively conduct market research to drive informed decision-making and success.
What is market research?
The purpose of market research is to offer valuable insight into the preferences and behaviors of your target audience, and anticipate shifts in market trends and the competitive landscape. This information helps you make data-driven decisions, develop effective strategies for your business, and maximize your chances of long-term growth.

Why is market research important?
By understanding the significance of market research, you can make sure you’re asking the right questions and using the process to your advantage. Some of the benefits of market research include:
- Informed decision-making: Market research provides you with the data and insights you need to make smart decisions for your business. It helps you identify opportunities, assess risks and tailor your strategies to meet the demands of the market. Without market research, decisions are often based on assumptions or guesswork, leading to costly mistakes.
- Customer-centric approach: A cornerstone of market research involves developing a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences. This gives you valuable insights into your target audience, helping you develop products, services and marketing campaigns that resonate with your customers.
- Competitive advantage: By conducting market research, you’ll gain a competitive edge. You’ll be able to identify gaps in the market, analyze competitor strengths and weaknesses, and position your business strategically. This enables you to create unique value propositions, differentiate yourself from competitors, and seize opportunities that others may overlook.
- Risk mitigation: Market research helps you anticipate market shifts and potential challenges. By identifying threats early, you can proactively adjust their strategies to mitigate risks and respond effectively to changing circumstances. This proactive approach is particularly valuable in volatile industries.
- Resource optimization: Conducting market research allows organizations to allocate their time, money and resources more efficiently. It ensures that investments are made in areas with the highest potential return on investment, reducing wasted resources and improving overall business performance.
- Adaptation to market trends: Markets evolve rapidly, driven by technological advancements, cultural shifts and changing consumer attitudes. Market research ensures that you stay ahead of these trends and adapt your offerings accordingly so you can avoid becoming obsolete.
As you can see, market research empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions, cater to customer needs, outperform competitors, mitigate risks, optimize resources and stay agile in a dynamic marketplace. These benefits make it a huge industry; the global market research services market is expected to grow from $76.37 billion in 2021 to $108.57 billion in 2026 . Now, let’s dig into the different types of market research that can help you achieve these benefits.
Types of market research
- Qualitative research
- Quantitative research
- Exploratory research
- Descriptive research
- Causal research
- Cross-sectional research
- Longitudinal research
Despite its advantages, 23% of organizations don’t have a clear market research strategy. Part of developing a strategy involves choosing the right type of market research for your business goals. The most commonly used approaches include:
1. Qualitative research
Qualitative research focuses on understanding the underlying motivations, attitudes and perceptions of individuals or groups. It is typically conducted through techniques like in-depth interviews, focus groups and content analysis — methods we’ll discuss further in the sections below. Qualitative research provides rich, nuanced insights that can inform product development, marketing strategies and brand positioning.
2. Quantitative research
Quantitative research, in contrast to qualitative research, involves the collection and analysis of numerical data, often through surveys, experiments and structured questionnaires. This approach allows for statistical analysis and the measurement of trends, making it suitable for large-scale market studies and hypothesis testing. While it’s worthwhile using a mix of qualitative and quantitative research, most businesses prioritize the latter because it is scientific, measurable and easily replicated across different experiments.
3. Exploratory research
Whether you’re conducting qualitative or quantitative research or a mix of both, exploratory research is often the first step. Its primary goal is to help you understand a market or problem so you can gain insights and identify potential issues or opportunities. This type of market research is less structured and is typically conducted through open-ended interviews, focus groups or secondary data analysis. Exploratory research is valuable when entering new markets or exploring new product ideas.
4. Descriptive research
As its name implies, descriptive research seeks to describe a market, population or phenomenon in detail. It involves collecting and summarizing data to answer questions about audience demographics and behaviors, market size, and current trends. Surveys, observational studies and content analysis are common methods used in descriptive research.
5. Causal research
Causal research aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It investigates whether changes in one variable result in changes in another. Experimental designs, A/B testing and regression analysis are common causal research methods. This sheds light on how specific marketing strategies or product changes impact consumer behavior.
6. Cross-sectional research
Cross-sectional market research involves collecting data from a sample of the population at a single point in time. It is used to analyze differences, relationships or trends among various groups within a population. Cross-sectional studies are helpful for market segmentation, identifying target audiences and assessing market trends at a specific moment.
7. Longitudinal research
Longitudinal research, in contrast to cross-sectional research, collects data from the same subjects over an extended period. This allows for the analysis of trends, changes and developments over time. Longitudinal studies are useful for tracking long-term developments in consumer preferences, brand loyalty and market dynamics.
Each type of market research has its strengths and weaknesses, and the method you choose depends on your specific research goals and the depth of understanding you’re aiming to achieve. In the following sections, we’ll delve into primary and secondary research approaches and specific research methods.
Primary vs. secondary market research
Market research of all types can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: primary research and secondary research. By understanding the differences between these approaches, you can better determine the most appropriate research method for your specific goals.
Primary market research
Primary research involves the collection of original data straight from the source. Typically, this involves communicating directly with your target audience — through surveys, interviews, focus groups and more — to gather information. Here are some key attributes of primary market research:
- Customized data: Primary research provides data that is tailored to your research needs. You design a custom research study and gather information specific to your goals.
- Up-to-date insights: Because primary research involves communicating with customers, the data you collect reflects the most current market conditions and consumer behaviors.
- Time-consuming and resource-intensive: Despite its advantages, primary research can be labor-intensive and costly, especially when dealing with large sample sizes or complex study designs. Whether you hire a market research consultant, agency or use an in-house team, primary research studies consume a large amount of resources and time.
Secondary market research
Secondary research, on the other hand, involves analyzing data that has already been compiled by third-party sources, such as online research tools, databases, news sites, industry reports and academic studies.

Here are the main characteristics of secondary market research:
- Cost-effective: Secondary research is generally more cost-effective than primary research since it doesn’t require building a research plan from scratch. You and your team can look at databases, websites and publications on an ongoing basis, without needing to design a custom experiment or hire a consultant.
- Leverages multiple sources: Data tools and software extract data from multiple places across the web, and then consolidate that information within a single platform. This means you’ll get a greater amount of data and a wider scope from secondary research.
- Quick to access: You can access a wide range of information rapidly — often in seconds — if you’re using online research tools and databases. Because of this, you can act on insights sooner, rather than taking the time to develop an experiment.
So, when should you use primary vs. secondary research? In practice, many market research projects incorporate both primary and secondary research to take advantage of the strengths of each approach.
One rule of thumb is to focus on secondary research to obtain background information, market trends or industry benchmarks. It is especially valuable for conducting preliminary research, competitor analysis, or when time and budget constraints are tight. Then, if you still have knowledge gaps or need to answer specific questions unique to your business model, use primary research to create a custom experiment.
Market research methods
- Surveys and questionnaires
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Online research tools
- Experiments
- Content analysis
- Ethnographic research
How do primary and secondary research approaches translate into specific research methods? Let’s take a look at the different ways you can gather data:
1. Surveys and questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are popular methods for collecting structured data from a large number of respondents. They involve a set of predetermined questions that participants answer. Surveys can be conducted through various channels, including online tools, telephone interviews and in-person or online questionnaires. They are useful for gathering quantitative data and assessing customer demographics, opinions, preferences and needs. On average, customer surveys have a 33% response rate , so keep that in mind as you consider your sample size.
2. Interviews
Interviews are in-depth conversations with individuals or groups to gather qualitative insights. They can be structured (with predefined questions) or unstructured (with open-ended discussions). Interviews are valuable for exploring complex topics, uncovering motivations and obtaining detailed feedback.
3. Focus groups
The most common primary research methods are in-depth webcam interviews and focus groups. Focus groups are a small gathering of participants who discuss a specific topic or product under the guidance of a moderator. These discussions are valuable for primary market research because they reveal insights into consumer attitudes, perceptions and emotions. Focus groups are especially useful for idea generation, concept testing and understanding group dynamics within your target audience.
4. Observational research
Observational research involves observing and recording participant behavior in a natural setting. This method is particularly valuable when studying consumer behavior in physical spaces, such as retail stores or public places. In some types of observational research, participants are aware you’re watching them; in other cases, you discreetly watch consumers without their knowledge, as they use your product. Either way, observational research provides firsthand insights into how people interact with products or environments.
5. Online research tools
You and your team can do your own secondary market research using online tools. These tools include data prospecting platforms and databases, as well as online surveys, social media listening, web analytics and sentiment analysis platforms. They help you gather data from online sources, monitor industry trends, track competitors, understand consumer preferences and keep tabs on online behavior. We’ll talk more about choosing the right market research tools in the sections that follow.
6. Experiments
Market research experiments are controlled tests of variables to determine causal relationships. While experiments are often associated with scientific research, they are also used in market research to assess the impact of specific marketing strategies, product features, or pricing and packaging changes.
7. Content analysis
Content analysis involves the systematic examination of textual, visual or audio content to identify patterns, themes and trends. It’s commonly applied to customer reviews, social media posts and other forms of online content to analyze consumer opinions and sentiments.
8. Ethnographic research
Ethnographic research immerses researchers into the daily lives of consumers to understand their behavior and culture. This method is particularly valuable when studying niche markets or exploring the cultural context of consumer choices.
How to do market research
- Set clear objectives
- Identify your target audience
- Choose your research methods
- Use the right market research tools
- Collect data
- Analyze data
- Interpret your findings
- Identify opportunities and challenges
- Make informed business decisions
- Monitor and adapt
Now that you have gained insights into the various market research methods at your disposal, let’s delve into the practical aspects of how to conduct market research effectively. Here’s a quick step-by-step overview, from defining objectives to monitoring market shifts.
1. Set clear objectives
When you set clear and specific goals, you’re essentially creating a compass to guide your research questions and methodology. Start by precisely defining what you want to achieve. Are you launching a new product and want to understand its viability in the market? Are you evaluating customer satisfaction with a product redesign?
Start by creating SMART goals — objectives that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. Not only will this clarify your research focus from the outset, but it will also help you track progress and benchmark your success throughout the process.
You should also consult with key stakeholders and team members to ensure alignment on your research objectives before diving into data collecting. This will help you gain diverse perspectives and insights that will shape your research approach.
2. Identify your target audience
Next, you’ll need to pinpoint your target audience to determine who should be included in your research. Begin by creating detailed buyer personas or stakeholder profiles. Consider demographic factors like age, gender, income and location, but also delve into psychographics, such as interests, values and pain points.
The more specific your target audience, the more accurate and actionable your research will be. Additionally, segment your audience if your research objectives involve studying different groups, such as current customers and potential leads.
If you already have existing customers, you can also hold conversations with them to better understand your target market. From there, you can refine your buyer personas and tailor your research methods accordingly.
3. Choose your research methods
Selecting the right research methods is crucial for gathering high-quality data. Start by considering the nature of your research objectives. If you’re exploring consumer preferences, surveys and interviews can provide valuable insights. For in-depth understanding, focus groups or observational research might be suitable. Consider using a mix of quantitative and qualitative methods to gain a well-rounded perspective.
You’ll also need to consider your budget. Think about what you can realistically achieve using the time and resources available to you. If you have a fairly generous budget, you may want to try a mix of primary and secondary research approaches. If you’re doing market research for a startup , on the other hand, chances are your budget is somewhat limited. If that’s the case, try addressing your goals with secondary research tools before investing time and effort in a primary research study.
4. Use the right market research tools
Whether you’re conducting primary or secondary research, you’ll need to choose the right tools. These can help you do anything from sending surveys to customers to monitoring trends and analyzing data. Here are some examples of popular market research tools:
- Market research software: Crunchbase is a platform that provides best-in-class company data, making it valuable for market research on growing companies and industries. You can use Crunchbase to access trusted, first-party funding data, revenue data, news and firmographics, enabling you to monitor industry trends and understand customer needs.
- Survey and questionnaire tools: SurveyMonkey is a widely used online survey platform that allows you to create, distribute and analyze surveys. Google Forms is a free tool that lets you create surveys and collect responses through Google Drive.
- Data analysis software: Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets are useful for conducting statistical analyses. SPSS is a powerful statistical analysis software used for data processing, analysis and reporting.
- Social listening tools: Brandwatch is a social listening and analytics platform that helps you monitor social media conversations, track sentiment and analyze trends. Mention is a media monitoring tool that allows you to track mentions of your brand, competitors and keywords across various online sources.
- Data visualization platforms: Tableau is a data visualization tool that helps you create interactive and shareable dashboards and reports. Power BI by Microsoft is a business analytics tool for creating interactive visualizations and reports.
5. Collect data
There’s an infinite amount of data you could be collecting using these tools, so you’ll need to be intentional about going after the data that aligns with your research goals. Implement your chosen research methods, whether it’s distributing surveys, conducting interviews or pulling from secondary research platforms. Pay close attention to data quality and accuracy, and stick to a standardized process to streamline data capture and reduce errors.
6. Analyze data
Once data is collected, you’ll need to analyze it systematically. Use statistical software or analysis tools to identify patterns, trends and correlations. For qualitative data, employ thematic analysis to extract common themes and insights. Visualize your findings with charts, graphs and tables to make complex data more understandable.
If you’re not proficient in data analysis, consider outsourcing or collaborating with a data analyst who can assist in processing and interpreting your data accurately.

7. Interpret your findings
Interpreting your market research findings involves understanding what the data means in the context of your objectives. Are there significant trends that uncover the answers to your initial research questions? Consider the implications of your findings on your business strategy. It’s essential to move beyond raw data and extract actionable insights that inform decision-making.
Hold a cross-functional meeting or workshop with relevant team members to collectively interpret the findings. Different perspectives can lead to more comprehensive insights and innovative solutions.
8. Identify opportunities and challenges
Use your research findings to identify potential growth opportunities and challenges within your market. What segments of your audience are underserved or overlooked? Are there emerging trends you can capitalize on? Conversely, what obstacles or competitors could hinder your progress?
Lay out this information in a clear and organized way by conducting a SWOT analysis, which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Jot down notes for each of these areas to provide a structured overview of gaps and hurdles in the market.
9. Make informed business decisions
Market research is only valuable if it leads to informed decisions for your company. Based on your insights, devise actionable strategies and initiatives that align with your research objectives. Whether it’s refining your product, targeting new customer segments or adjusting pricing, ensure your decisions are rooted in the data.
At this point, it’s also crucial to keep your team aligned and accountable. Create an action plan that outlines specific steps, responsibilities and timelines for implementing the recommendations derived from your research.
10. Monitor and adapt
Market research isn’t a one-time activity; it’s an ongoing process. Continuously monitor market conditions, customer behaviors and industry trends. Set up mechanisms to collect real-time data and feedback. As you gather new information, be prepared to adapt your strategies and tactics accordingly. Regularly revisiting your research ensures your business remains agile and reflects changing market dynamics and consumer preferences.
Online market research sources
As you go through the steps above, you’ll want to turn to trusted, reputable sources to gather your data. Here’s a list to get you started:
- Crunchbase: As mentioned above, Crunchbase is an online platform with an extensive dataset, allowing you to access in-depth insights on market trends, consumer behavior and competitive analysis. You can also customize your search options to tailor your research to specific industries, geographic regions or customer personas.
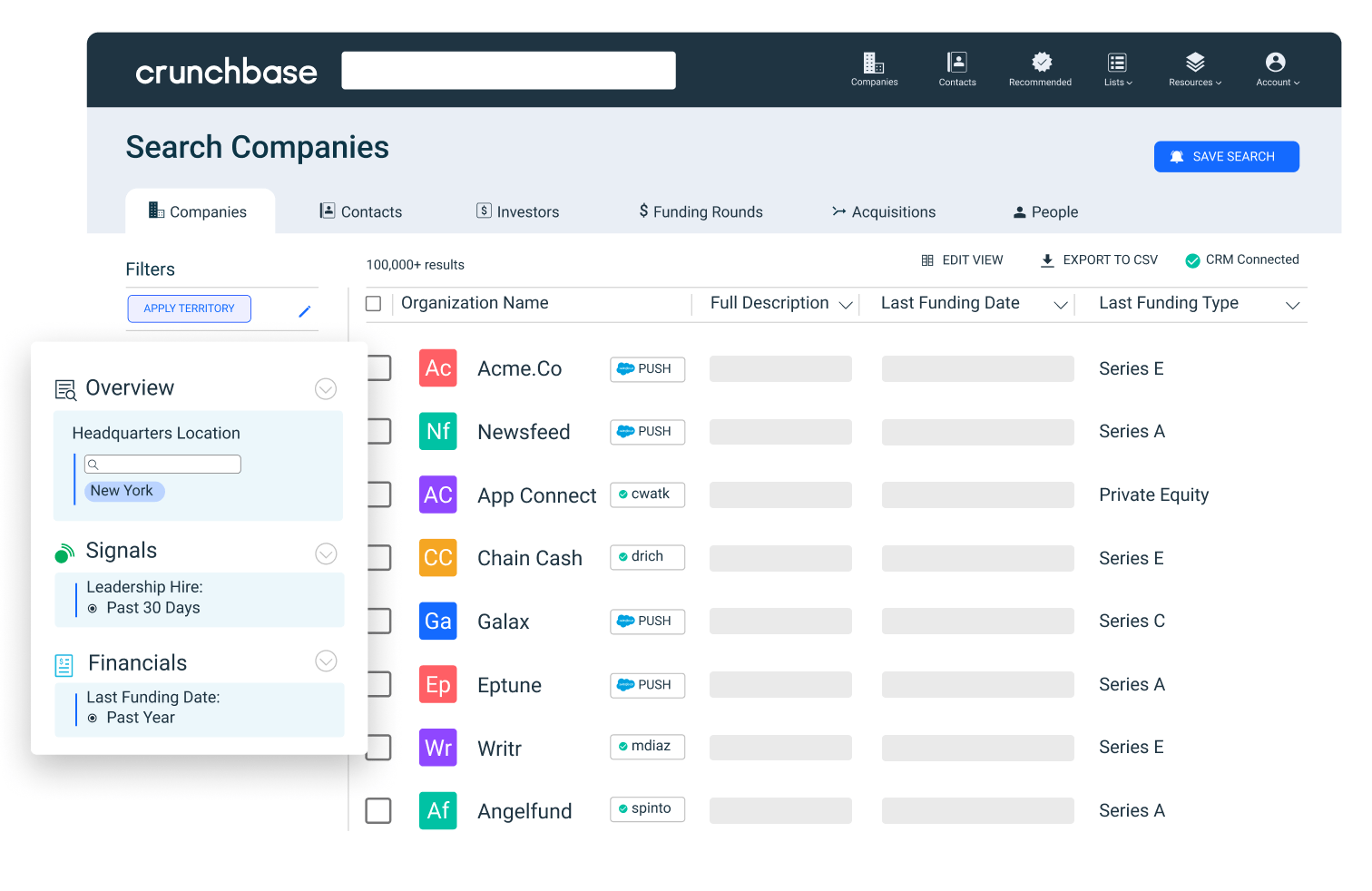
- Academic databases: Academic databases, such as ProQuest and JSTOR , are treasure troves of scholarly research papers, studies and academic journals. They offer in-depth analyses of various subjects, including market trends, consumer preferences and industry-specific insights. Researchers can access a wealth of peer-reviewed publications to gain a deeper understanding of their research topics.
- Government and NGO databases: Government agencies, nongovernmental organizations and other institutions frequently maintain databases containing valuable economic, demographic and industry-related data. These sources offer credible statistics and reports on a wide range of topics, making them essential for market researchers. Examples include the U.S. Census Bureau , the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the Pew Research Center .
- Industry reports: Industry reports and market studies are comprehensive documents prepared by research firms, industry associations and consulting companies. They provide in-depth insights into specific markets, including market size, trends, competitive analysis and consumer behavior. You can find this information by looking at relevant industry association databases; examples include the American Marketing Association and the National Retail Federation .
- Social media and online communities: Social media platforms like LinkedIn or Twitter (X) , forums such as Reddit and Quora , and review platforms such as G2 can provide real-time insights into consumer sentiment, opinions and trends.
Market research examples
At this point, you have market research tools and data sources — but how do you act on the data you gather? Let’s go over some real-world examples that illustrate the practical application of market research across various industries. These examples showcase how market research can lead to smart decision-making and successful business decisions.
Example 1: Apple’s iPhone launch
Apple ’s iconic iPhone launch in 2007 serves as a prime example of market research driving product innovation in tech. Before the iPhone’s release, Apple conducted extensive market research to understand consumer preferences, pain points and unmet needs in the mobile phone industry. This research led to the development of a touchscreen smartphone with a user-friendly interface, addressing consumer demands for a more intuitive and versatile device. The result was a revolutionary product that disrupted the market and redefined the smartphone industry.
Example 2: McDonald’s global expansion
McDonald’s successful global expansion strategy demonstrates the importance of market research when expanding into new territories. Before entering a new market, McDonald’s conducts thorough research to understand local tastes, preferences and cultural nuances. This research informs menu customization, marketing strategies and store design. For instance, in India, McDonald’s offers a menu tailored to local preferences, including vegetarian options. This market-specific approach has enabled McDonald’s to adapt and thrive in diverse global markets.
Example 3: Organic and sustainable farming
The shift toward organic and sustainable farming practices in the food industry is driven by market research that indicates increased consumer demand for healthier and environmentally friendly food options. As a result, food producers and retailers invest in sustainable sourcing and organic product lines — such as with these sustainable seafood startups — to align with this shift in consumer values.
The bottom line? Market research has multiple use cases and is a critical practice for any industry. Whether it’s launching groundbreaking products, entering new markets or responding to changing consumer preferences, you can use market research to shape successful strategies and outcomes.
Market research templates
You finally have a strong understanding of how to do market research and apply it in the real world. Before we wrap up, here are some market research templates that you can use as a starting point for your projects:
- Smartsheet competitive analysis templates : These spreadsheets can serve as a framework for gathering information about the competitive landscape and obtaining valuable lessons to apply to your business strategy.
- SurveyMonkey product survey template : Customize the questions on this survey based on what you want to learn from your target customers.
- HubSpot templates : HubSpot offers a wide range of free templates you can use for market research, business planning and more.
- SCORE templates : SCORE is a nonprofit organization that provides templates for business plans, market analysis and financial projections.
- SBA.gov : The U.S. Small Business Administration offers templates for every aspect of your business, including market research, and is particularly valuable for new startups.
Strengthen your business with market research
When conducted effectively, market research is like a guiding star. Equipped with the right tools and techniques, you can uncover valuable insights, stay competitive, foster innovation and navigate the complexities of your industry.
Throughout this guide, we’ve discussed the definition of market research, different research methods, and how to conduct it effectively. We’ve also explored various types of market research and shared practical insights and templates for getting started.
Now, it’s time to start the research process. Trust in data, listen to the market and make informed decisions that guide your company toward lasting success.
Related Articles

- Entrepreneurs
- 15 min read
What Is Competitive Analysis and How to Do It Effectively
Rebecca Strehlow, Copywriter at Crunchbase
17 Best Sales Intelligence Tools for 2024

- Market research
- 10 min read
How to Do Market Research for a Startup: Tips for Success
Jaclyn Robinson, Senior Manager of Content Marketing at Crunchbase
Search less. Close more.
Grow your revenue with Crunchbase, the all-in-one prospecting solution. Start your free trial.
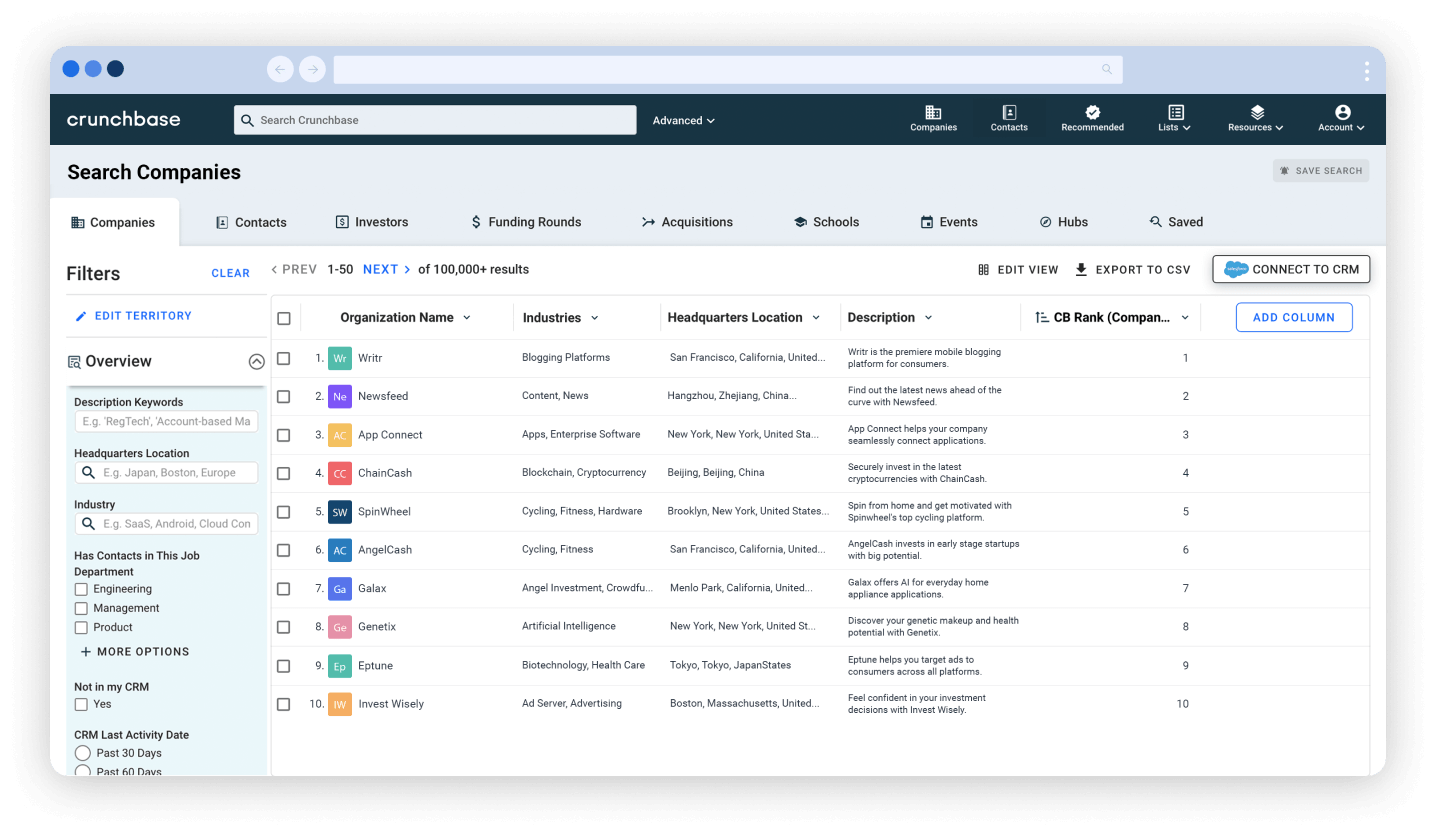
Quantitative market research questions to ask for actionable insights
Types of quantitative market research questions, 36 quantitative research questions and examples, how to write your own quantitative market research questions, how to collect insightful data from your quantitative surveys, receive quantitative insights in weeks, not months.
There’s a big difference between asking “Why do you like our product?” and “On a scale of 1-10, how much do you like our product?” But both ways of asking are valuable in their own way.
Knowing your audience is not about guesswork or intuition, it is about concrete data. And while it’s valuable to learn the ‘why’ behind the ‘what’ with qualitative research, quantitative research is just as necessary — to spot trends, patterns and more.
Unlike qualitative research, which explores attitudes, opinions, and motivations through open-ended questions, quantitative research zeroes in on the numbers (see what we did there?). It’s the difference between gathering general opinions and collecting measurable, specific data.
But when is this approach the way to go? For starters, whenever you need to track factors over time, such as customer satisfaction. Or when assessing the popularity of a potential product feature, understanding demographic preferences, or analyzing consumer purchasing behavior in different locations.
Quantitative research reveals the impact and scale of sentiments for better decision-making. It’s also valuable when you’re looking to quantify the extent of a trend, measure the impact of a marketing campaign, or pin down the specifics of consumer behavior.
But how do you ask quantitative market research questions that don’t just scratch the surface? We’re here to give you some great examples of quantitative survey questions.
In the US? Check out these research platforms
Here are the top market research platforms in the US for reliable insights – check them out and start getting your insights today!
When thinking of quantitative market research questions, people often think ‘ ah, numbers ‘. But there’s more than meets the eye. Here’s how you can categorize the different types of quantitative research questions:
Descriptive quantitative research questions
These are your what , when , and how many types of questions. They help you sketch out the basic landscape of your market. For example, “How often do you shop online in a month?” or “What is your preferred method of payment while shopping online?” When you give answers people can select, it is quantifiable data. That’s different from asking: ”describe what a day out shopping looks like for you”, which is a qualitative question.
Comparative quantitative survey questions
These questions measure differences or changes over time or between groups. For instance, “How has your spending on online shopping changed since last year?” Comparative questions help you understand the dynamics and shifts in your market. Remember that you’re not just trying to find overlap: it’s just as important to know what differences there are.
Relationship-based quantitative survey questions
These questions aim to uncover correlations or relationships between two or more variables. They can reveal insights like, “Is there a link between age and the likelihood of using mobile payments?” These questions help you understand the deeper connections within your market, as well as test assumptions, as long as you dare to ask questions that challenge what you’re hoping to find.
Now, a quick note on reducing bias in quantitative survey questions . Here are some key points to remember:
- The key is in how you frame your questions.
- Always aim for neutrality.
- Avoid leading questions that suggest a particular answer.
- Be specific and clear to avoid confusion.
- Consider the order of your questions, as earlier questions can influence responses to later ones.
And finally, test your survey with a small group before a full rollout, to catch and correct any unintentional bias. This way, you ensure the data you collect is as accurate and reliable as possible, giving you the best insights to make those crucial business decisions.
If you want to make a quantitative survey that hits the spot, don’t just ask generic questions. We’re here with some examples that you can adapt to make your research a success.
Descriptive market research questions
With a descriptive quantitative research question, you can quickly get the most important info for your respondents on anything ranging from buying frequency to satisfaction levels.
- Insight : this question reveals the frequency of use, indicating customer dependency on your product or service.
- Benefit : understanding usage patterns can guide inventory management and marketing strategies.
- Insight : reveals the communication channels most favored by your audience.
- Benefit : tailor your customer service and marketing outreach to your customers’ preferred channels.
- Insight : provides an average spending figure for budget allocation in that category.
- Benefit : helps in pricing strategies and identifying the most lucrative customer segments.
- Insight : uncovers patterns in online shopping behavior.
- Benefit : optimizes the timing of online marketing campaigns and promotions.
- Insight : identifies the most effective channels for brand discovery.
- Benefit : informs where to allocate advertising spend for maximum impact.
- Insight : measures the likelihood (not effectiveness!) of word-of-mouth referrals.
- Benefit : assesses customer satisfaction and the potential for organic growth.
- Insight : highlights your unique selling points from the customer’s perspective.
- Benefit : guides messaging to emphasize what customers value most about your brand.
- Insight : offers a quantifiable measure of customer service satisfaction.
- Benefit : identifies areas for improvement in customer support.
- Insight : sheds light on the most popular aspects of your product.
- Benefit : informs product development and feature enhancement.
- Insight : uncovers the key motivators behind purchasing decisions.
- Benefit : helps create targeted marketing campaigns to focus on these driving factors.
Comparative market research questions
If you want to analyze and compare different variables, these questions can help.
- Insight : highlights changes in consumer spending habits over time.
- Benefit : useful for identifying trends and shifts in consumer behavior, aiding in long-term planning. Especially valuable if you add qualitative insights to this quantitative data.
- Insight : compares consumer preferences between different shopping channels.
- Benefit : guides omnichannel marketing strategies and resource allocation.
- Insight : tracks changing consumer values and preferences over time.
- Benefit : useful for aligning product development and marketing with evolving consumer values.
- Insight : compares the weight of price versus brand in purchasing decisions.
- Benefit : informs pricing strategies and brand positioning efforts.
- Insight : evaluates customer perception of marketing efforts in product packaging.
- Benefit : assesses the impact of packaging on brand image and customer approval.
What are the top research platforms in the UK?
Here’s our list of the pros and cons of key market research platforms for UK brands

Relationship-based questions for quantitative research
In quantitative research, especially when exploring relationship-based aspects, the key is not to cram multiple inquiries into one question but to ask them sequentially.
This approach allows for a clearer and more focused response to each individual question. Later, during the analysis phase, you can then correlate the responses to uncover relationships between different variables.
For instance, instead of asking, “How often do you use our product and how satisfied are you with it?”, split this into two separate questions:
- “How often do you use our product (daily, weekly, monthly)?”
- “On a scale of 1-10, how satisfied are you with our product?”
By asking these questions separately, you ensure that respondents clearly focus on each aspect without being overwhelmed or confused by a dual-focused question. This approach yields more accurate and reliable data.
After the survey, you can analyze the results to see if there’s a correlation between usage frequency and satisfaction levels.
Here are some examples of combinations that can work well:
- What is your age group?
- Insight : correlates age with shopping preferences.
- Benefit : you can tailor marketing and sales strategies to different age demographics based on their preferred shopping channels.
- How long have you been using our products/services?
- Insight : links customer tenure with brand loyalty.
- Benefit : assesses the impact of long-term use on loyalty, informing customer retention initiatives.
- What is your approximate annual income?
- Insight : examines the relationship between income levels and purchasing behavior for premium products.
- Benefit : guides product and pricing strategies targeting different income segments.
- How often do you use social media for product discovery?
- Insight : assesses if frequent social media use for product discovery actually influences online shopping behavior.
- Benefit : informs the effectiveness of social media marketing in driving online sales in your target market.
- How would you rate your satisfaction with our post-purchase customer service (scale of 0-10)?
- Insight : links the level of service post-purchase with the likelihood of repeat purchases.
- Benefit : identifies if customer service is negatively or positively affecting repeat custom rates.
Brand tracking questions for quantitative insights
One thing you should definitely gather numerical data on, is your brand’s health. Just like your own health, stats, and numbers matter and can show you where to further investigate to ask qualitative research questions about. Learn if your brand stands strong through market trends and gain insights on whether your brand is growing in terms of awareness — and in which segments.
- Insight : measures brand awareness among the target audience.
- Benefit : helps assess the effectiveness of your marketing and branding efforts.
- Insight : evaluates brand loyalty and the potential for organic growth through word-of-mouth.
- Benefit : indicates customer satisfaction and the potential for brand advocacy.
- Insight: Identifies the most effective channels for brand discovery.
- Benefit: Informs where to focus marketing efforts for increased brand exposure.
- Insight: Measures brand visibility and frequency of encounters with the brand.
- Benefit: Helps evaluate the reach and frequency of marketing campaigns.
- Insight: Determines which brand values resonate most with the audience.
- Benefit: Aids in refining brand messaging and aligning it with customer values.
Quantitative consumer segmentation questions
Quantitative questions about customer segments can go beyond age group and gender. King Charles III is the same age as Ozzy Osbourne – would you say they’re very similar?

It is vital that you look at more variables so you can really tell the difference between your respondents, and make informed decisions based on the whole truth. Putting these consumer profiling questions and answers in specific ranges helps you create segments to tailor your marketing and customer experience for, rather than just aiming at the entire population.
- Insight : helps understand the economic demographics of your customers.
- Benefit : assists in pricing strategies and identifying which income groups are most engaged with your brand.
- Insight : reveals geographical spread and regional preferences.
- Benefit : guides regional marketing efforts and product distribution strategies.
- Insight : helps categorize customers by education level.
- Benefit : useful for tailoring communication and content complexity to different education backgrounds.
- Insight : provides insights into the professional background of your customers.
- Benefit : helps in creating industry-specific marketing campaigns and products.
- Insight : gives an idea of household size and composition.
- Benefit : useful for targeting products and services aimed at families or individuals.
- Insight : identifies customers who are parents of minors (which is different from parents of young adults, or even grown adults).
- Benefit : informs product and marketing strategies aimed at families with children.
Okay, so now you got the gist of it and have seen what quantitative questions can look like — as they come in all shapes and sizes. But they might feel too generic for your research, or you’re looking for something specific.
Here’s how you can whip up your own quantitative questions that deliver the insights you need for data-driven decisions.
Identify the key variables you need to measure
Start by pinpointing exactly what you want to know. Is it customer satisfaction, buying behavior, or brand awareness? Determining the specific variables you need to measure sets the foundation for your entire survey.
Choose the right survey distribution method
Think about how your questions will reach your audience. Will it be online through email or social media, over the phone, or in person? Your method should align with where your target audience is most active and responsive.
Make sure your questions are crystal-clear and unequivocally unbiased
We’ve mentioned it earlier, and we’ll do it again if we have to. The way you phrase your questions can make or break your survey. Aim for clarity and simplicity – questions should be easy to understand and answer. Avoid leading or loaded questions that might sway a respondent’s answer. Remember: it’s a survey, not a sales pitch.
Know where to ask for more detailed information and qualitative data
Quantitative market research questions only tell part of the story. If you see interesting trends in say purchase behavior or price sensitivity, or a particular product gets a bad rating, dig a little deeper. Follow up important questions with qualitative research questions to analyze what’s going on behind the numbers.
If you don’t want to end up with a pile of quantitative data that doesn’t do much for you or breaks the bank unnecessarily, it’s vital you choose a form of distributing the survey that makes sense. You can work with UK market research companies to outsource it all, or do it yourself. Here’s a brief look at the pros and cons of popular methods:
Telephone surveys:
- Pros : good for less tech-savvy demographics.
- Cons : time-consuming, potentially costly, and declining response rates. They might be better for qualitative research.
In-person surveys:
- Pros : also avoids any confusion with tech.
- Cons : logistically demanding and expensive, not suited for quick data collection.
Online survey software:
- Pros : cost-effective, broad reach, real-time data analysis, and versatile formats.
- Cons : it’s extra important to pay close attention to survey design, so people don’t get the urge to give false answers just to get to the end.
The choice is yours, but generally, quantitative research thrives when done with online surveys and it’s the go-to method for most international market research . And here at Attest, we help you get even more out of it by giving you a chock-full toolkit. From various types of questions to robust analytical tools (and a dedicated research expert for when you need a little extra help) — we set you up for measurable success.
Speed and accuracy in market research matter — but we don’t want you to sacrifice quality. With Attest, you get fast, actionable and high-quality insights.
Which market analysis tool is right for you?
Check our rundown of the top platforms for market analysis – and start making better decisions with reliable insights in no time!

VP Customer Success
Sam joined Attest in 2019 and leads the Customer Research Team. Sam and her team support brands through their market research journey, helping them carry out effective research and uncover insights to unlock new areas for growth.
Related articles
A guide to brand tracking: what it is & how to boost your brand roi, brand tracking, how to gather consumer insights (and use them to improve your business), 12 brand management software, platforms and tools to understand customer perception in 2024, subscribe to our newsletter.
Fill in your email and we’ll drop fresh insights and events info into your inbox each week.
* I agree to receive communications from Attest. Privacy Policy .
You're now subscribed to our mailing list to receive exciting news, reports, and other updates!
Types of market research: Methods and examples

- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn

Here at GWI we publish a steady stream of blogs, reports, and other resources that dig deep into specific market research topics.
But what about the folks who’d appreciate a more general overview of market research that explains the big picture? Don’t they deserve some love too?
Of course they do. That’s why we’ve created this overview guide focusing on types of market research and examples. With so many market research companies to choose from, having a solid general understanding of how this sector works is essential for any brand or business that wants to pick the right market research partner.
So with that in mind, let’s start at the very beginning and get clear on…
Market research definition
At the risk of stating the slightly obvious, market research is the gathering and analyzing of data on consumers, competitors, distributors, and markets. As such it’s not quite the same as consumer research , but there’s significant overlap.
Market research matters because it can help you take the guesswork out of getting through to audiences. By studying consumers and gathering information on their likes, dislikes, and so on, brands can make evidence-based decisions instead of relying on instinct or experience.
What is market research?
Market research is the organized gathering of information about target markets and consumers’ needs and preferences. It’s an important component of business strategy and a major factor in maintaining competitiveness.
If a business wants to know – really know – what sort of products or services consumers want to buy, along with where, when, and how those products and services should be marketed, it just makes sense to ask the prospective audience.
Without the certainty that market research brings, a business is basically hoping for the best. And while we salute their optimism, that’s not exactly a reliable strategy for success.
What are the types of market research?
Primary research .
Primary research is a type of market research you either conduct yourself or hire someone to do on your behalf.
A classic example of primary research involves going directly to a source – typically customers or prospective customers in your target market – to ask questions and gather information about a product or service. Interviewing methods include in-person, online surveys, phone calls, and focus groups.
The big advantage of primary research is that it’s directly focused on your objectives, so the outcome will be conclusive, detailed insights – particularly into customer views – making it the gold standard.
The disadvantages are it can be time-consuming and potentially costly, plus there’s a risk of survey bias creeping in, in the sense that research samples may not be representative of the wider group.
Secondary research
Primary market research means you collect the data your business needs, whereas the types of market research known as secondary market research use information that’s already been gathered for other purposes but can still be valuable. Examples include published market studies, white papers, analyst reports, customer emails, and customer surveys/feedback.
For many small businesses with limited budgets, secondary market research is their first choice because it’s easier to acquire and far more affordable than primary research.
Secondary research can still answer specific business questions, but with limitations. The data collected from that audience may not match your targeted audience exactly, resulting in skewed outcomes.
A big benefit of secondary market research is helping lay the groundwork and get you ready to carry out primary market research by making sure you’re focused on what matters most.

Qualitative research
Qualitative research is one of the two fundamental types of market research. Qualitative research is about people and their opinions. Typically conducted by asking questions either one-on-one or in groups, qualitative research can help you define problems and learn about customers’ opinions, values, and beliefs.
Classic examples of qualitative research are long-answer questions like “Why do you think this product is better than competitive products? Why do you think it’s not?”, or “How would you improve this new service to make it more appealing?”
Because qualitative research generally involves smaller sample sizes than its close cousin quantitative research, it gives you an anecdotal overview of your subject, rather than highly detailed information that can help predict future performance.
Qualitative research is particularly useful if you’re developing a new product, service, website or ad campaign and want to get some feedback before you commit a large budget to it.
Quantitative research
If qualitative research is all about opinions, quantitative research is all about numbers, using math to uncover insights about your audience.
Typical quantitative research questions are things like, “What’s the market size for this product?” or “How long are visitors staying on this website?”. Clearly the answers to both will be numerical.
Quantitative research usually involves questionnaires. Respondents are asked to complete the survey, which marketers use to understand consumer needs, and create strategies and marketing plans.
Importantly, because quantitative research is math-based, it’s statistically valid, which means you’re in a good position to use it to predict the future direction of your business.
Consumer research
As its name implies, consumer research gathers information about consumers’ lifestyles, behaviors, needs and preferences, usually in relation to a particular product or service. It can include both quantitative and qualitative studies.
Examples of consumer research in action include finding ways to improve consumer perception of a product, or creating buyer personas and market segments, which help you successfully market your product to different types of customers.
Understanding consumer trends , driven by consumer research, helps businesses understand customer psychology and create detailed purchasing behavior profiles. The result helps brands improve their products and services by making them more customer-centric, increasing customer satisfaction, and boosting bottom line in the process.
Product research
Product research gives a new product (or indeed service, we don’t judge) its best chance of success, or helps an existing product improve or increase market share.
It’s common sense: by finding out what consumers want and adjusting your offering accordingly, you gain a competitive edge. It can be the difference between a product being a roaring success or an abject failure.
Examples of product research include finding ways to develop goods with a higher value, or identifying exactly where innovation effort should be focused.
Product research goes hand-in-hand with other strands of market research, helping you make informed decisions about what consumers want, and what you can offer them.
Brand research
Brand research is the process of gathering feedback from your current, prospective, and even past customers to understand how your brand is perceived by the market.
It covers things like brand awareness, brand perceptions, customer advocacy, advertising effectiveness, purchase channels, audience profiling, and whether or not the brand is a top consideration for consumers.
The result helps take the guesswork out of your messaging and brand strategy. Like all types of market research, it gives marketing leaders the data they need to make better choices based on fact rather than opinion or intuition.
Market research methods
So far we’ve reviewed various different types of market research, now let’s look at market research methods, in other words the practical ways you can uncover those all-important insights.
Consumer research platform
A consumer research platform like GWI is a smart way to find on-demand market research insights in seconds.
In a world of fluid markets and changing attitudes, a detailed understanding of your consumers, developed using the right research platform, enables you to stop guessing and start knowing.
As well as providing certainty, consumer research platforms massively accelerate speed to insight. Got a question? Just jump on your consumer research platform and find the answer – job done.
The ability to mine data for answers like this is empowering – suddenly you’re in the driving seat with a world of possibilities ahead of you. Compared to the most obvious alternative – commissioning third party research that could take weeks to arrive – the right consumer research platform is basically a magic wand.
Admittedly we’re biased, but GWI delivers all this and more. Take our platform for a quick spin and see for yourself.
And the downside of using a consumer research platform? Well, no data set, however fresh or thorough, can answer every question. If you need really niche insights then your best bet is custom market research , where you can ask any question you like, tailored to your exact needs.
Face-to-face interviews
Despite the rise in popularity of online surveys , face-to-face survey interviewing – using mobile devices or even the classic paper survey – is still a popular data collection method.
In terms of advantages, face-to-face interviews help with accurate screening, in the sense the interviewee can’t easily give misleading answers about, say, their age. The interviewer can also make a note of emotions and non-verbal cues.
On the other hand, face-to-face interviews can be costly, while the quality of data you get back often depends on the ability of the interviewer. Also, the size of the sample is limited to the size of your interviewing staff, the area in which the interviews are conducted, and the number of qualified respondents within that area.
Social listening
Social listening is a powerful solution for brands who want to keep an ear to the ground, gathering unfiltered thoughts and opinions from consumers who are posting on social media.
Many social listening tools store data for up to a couple of years, great for trend analysis that needs to compare current and past conversations.
Social listening isn’t limited to text. Images, videos, and emojis often help us better understand what consumers are thinking, saying, and doing better than more traditional research methods.
Perhaps the biggest downside is there are no guarantees with social listening, and you never know what you will (or won’t) find. It can also be tricky to gauge sentiment accurately if the language used is open to misinterpretation, for example if a social media user describes something as “sick”.
There’s also a potential problem around what people say vs. what they actually do. Tweeting about the gym is a good deal easier than actually going. The wider problem – and this may shock you – is that not every single thing people write on social media is necessarily true, which means social listening can easily deliver unreliable results.
Public domain data
Public domain data comes from think tanks and government statistics or research centers like the UK’s National Office for Statistics or the United States Census Bureau and the National Institute of Statistical Sciences. Other sources are things like research journals, news media, and academic material.
Its advantages for market research are it’s cheap (or even free), quick to access, and easily available. Public domain datasets can be huge, so potentially very rich.
On the flip side, the data can be out of date, it certainly isn’t exclusive to you, and the collection methodology can leave much to be desired. But used carefully, public domain data can be a useful source of secondary market research.
Telephone interviews
You know the drill – you get a call from a researcher who asks you questions about a particular topic and wants to hear your opinions. Some even pay or offer other rewards for your time.
Telephone surveys are great for reaching niche groups of consumers within a specific geographic area or connected to a particular brand, or who aren’t very active in online channels. They’re not well-suited for gathering data from broad population groups, simply because of the time and labor involved.
How to use market research
Data isn’t an end in itself; instead it’s a springboard to make other stuff happen. So once you’ve drawn conclusions from your research, it’s time to think of what you’ll actually do based on your findings.
While it’s impossible for us to give a definitive list (every use case is different), here are some suggestions to get you started.
Leverage it . Think about ways to expand the use – and value – of research data and insights, for example by using research to support business goals and functions, like sales, market share or product design.
Integrate it . Expand the value of your research data by integrating it with other data sources, internal and external. Integrating data like this can broaden your perspective and help you draw deeper insights for more confident decision-making.
Justify it . Enlist colleagues from areas that’ll benefit from the insights that research provides – that could be product management, product development, customer service, marketing, sales or many others – and build a business case for using research.
How to choose the right type of market research
Broadly speaking, choosing the right research method depends on knowing the type of data you need to collect. To dig into ideas and opinions, choose qualitative; to do some testing, it’s quantitative you want.
There are also a bunch of practical considerations, not least cost. If a particular approach sounds great but costs the earth then clearly it’s not ideal for any brand on a budget.
Then there’s how you intend to use the actual research, your level of expertise with research data, whether you need access to historical data or just a snapshot of today, and so on.
The point is, different methods suit different situations. When choosing, you’ll want to consider what you want to achieve, what data you’ll need, the pros and cons of each method, the costs of conducting the research, and the cost of analyzing the results.
Market research examples
Independent agency Bright/Shift used GWI consumer insights to shape a high-impact go-to-market strategy for their sustainable furniture client, generating £41K in revenue in the first month. Here’s how they made the magic happen .
Never miss a post
By subscribing you confirm you’re happy for us to send you our latest articles.
You’ve read our blog, now see our platform
Every business has questions about its audiences, GWI has answers. Powered by consistent, global research, our platform is an on-demand window into their world.
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Quantitative Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Your ultimate guide to quantitative research.
12 min read You may be already using quantitative research and want to check your understanding, or you may be starting from the beginning. Here’s an exploration of this research method and how you can best use it for maximum effect for your business.
You may be already using quantitative research and want to check your understanding, or you may be starting from the beginning. Here’s an exploration of this research method and how you can best use it for maximum effect for your business.
What is quantitative research?
Quantitative is the research method of collecting quantitative data – this is data that can be converted into numbers or numerical data, which can be easily quantified, compared, and analyzed.
Quantitative research deals with primary and secondary sources where data is represented in numerical form. This can include closed-question poll results, statistics, and census information or demographic data .
Quantitative data tends to be used when researchers are interested in understanding a particular moment in time and examining data sets over time to find trends and patterns.
To collect numerical data, surveys are often employed as one of the main research methods to source first-hand information in primary research . Quantitative research can also come from third-party research studies .
Quantitative research is widely used in the realms of social sciences, such as biology, chemistry, psychology, economics, sociology, and marketing .
Research teams collect data that is significant to proving or disproving a hypothesis research question – known as the research objective. When they collect quantitative data, researchers will aim to use a sample size that is representative of the total population of the target market they’re interested in.
Then the data collected will be manually or automatically stored and compared for insights.
Free eBook: The ultimate guide to conducting market research
Quantitative vs qualitative research
While the quantitative research definition focuses on numerical data, qualitative research is defined as data that supplies non-numerical information.
Quantitative research focuses on the thoughts, feelings, and values of a participant , to understand why people act in the way they do . They result in data types like quotes, symbols, images, and written testimonials.
These data types tell researchers subjective information, which can help us assign people into categories, such as a participant’s religion, gender , social class, political alignment, likely favored products to buy, or their preferred training learning style.
For this reason, qualitative research is often used in social research, as this gives a window into the behavior and actions of people.
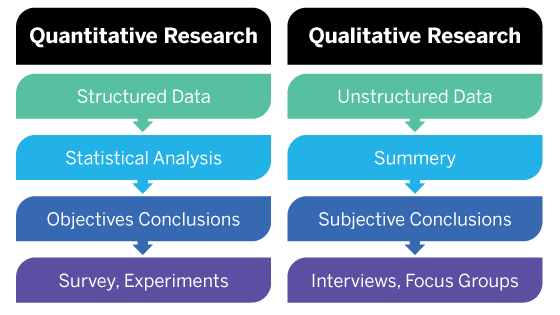
In general, if you’re interested in measuring something or testing a hypothesis, use quantitative methods. If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods.
However, quantitative and qualitative research methods are both recommended when you’re looking to understand a point in time, while also finding out the reason behind the facts.
Quantitative research data collection methods
Quantitative research methods can use structured research instruments like:
- Surveys : A survey is a simple-to-create and easy-to-distribute research method , which helps gather information from large groups of participants quickly. Traditionally, paper-based surveys can now be made online, so costs can stay quite low.
Quantitative questions tend to be closed questions that ask for a numerical result, based on a range of options, or a yes/no answer that can be tallied quickly.
- Face-to-face or phone interviews: Interviews are a great way to connect with participants , though they require time from the research team to set up and conduct.
Researchers may also have issues connecting with participants in different geographical regions . The researcher uses a set of predefined close-ended questions, which ask for yes/no or numerical values.
- Polls: Polls can be a shorter version of surveys , used to get a ‘flavor’ of what the current situation is with participants. Online polls can be shared easily, though polls are best used with simple questions that request a range or a yes/no answer.
Quantitative data is the opposite of qualitative research, another dominant framework for research in the social sciences, explored further below.
Quantitative data types
Quantitative research methods often deliver the following data types:
- Test Scores
- Percent of training course completed
- Performance score out of 100
- Number of support calls active
- Customer Net Promoter Score (NPS)
When gathering numerical data, the emphasis is on how specific the data is, and whether they can provide an indication of what ‘is’ at the time of collection. Pre-existing statistical data can tell us what ‘was’ for the date and time range that it represented
Quantitative research design methods (with examples)
Quantitative research has a number of quantitative research designs you can choose from:
Descriptive
This design type describes the state of a data type is telling researchers, in its native environment. There won’t normally be a clearly defined research question to start with. Instead, data analysis will suggest a conclusion , which can become the hypothesis to investigate further.
Examples of descriptive quantitative design include:
- A description of child’s Christmas gifts they received that year
- A description of what businesses sell the most of during Black Friday
- A description of a product issue being experienced by a customer
Correlational
This design type looks at two or more data types, the relationship between them, and the extent that they differ or align. This does not look at the causal links deeper – instead statistical analysis looks at the variables in a natural environment.
Examples of correlational quantitative design include:
- The relationship between a child’s Christmas gifts and their perceived happiness level
- The relationship between a business’ sales during Black Friday and the total revenue generated over the year
- The relationship between a customer’s product issue and the reputation of the product
Causal-Comparative/Quasi-Experimental
This design type looks at two or more data types and tries to explain any relationship and differences between them, using a cause-effect analysis. The research is carried out in a near-natural environment, where information is gathered from two groups – a naturally occurring group that matches the original natural environment, and one that is not naturally present.
This allows for causal links to be made, though they might not be correct, as other variables may have an impact on results.
Examples of causal-comparative/quasi-experimental quantitative design include:
- The effect of children’s Christmas gifts on happiness
- The effect of Black Friday sales figures on the productivity of company yearly sales
- The effect of product issues on the public perception of a product
Experimental Research
This design type looks to make a controlled environment in which two or more variables are observed to understand the exact cause and effect they have. This becomes a quantitative research study, where data types are manipulated to assess the effect they have. The participants are not naturally occurring groups, as the setting is no longer natural. A quantitative research study can help pinpoint the exact conditions in which variables impact one another.
Examples of experimental quantitative design include:
- The effect of children’s Christmas gifts on a child’s dopamine (happiness) levels
- The effect of Black Friday sales on the success of the company
- The effect of product issues on the perceived reliability of the product
Quantitative research methods need to be carefully considered, as your data collection of a data type can be used to different effects. For example, statistics can be descriptive or correlational (or inferential). Descriptive statistics help us to summarize our data, while inferential statistics help infer conclusions about significant differences.
Advantages of quantitative research
- Easy to do : Doing quantitative research is more straightforward, as the results come in numerical format, which can be more easily interpreted.
- Less interpretation : Due to the factual nature of the results, you will be able to accept or reject your hypothesis based on the numerical data collected.
- Less bias : There are higher levels of control that can be applied to the research, so bias can be reduced , making your data more reliable and precise.
Disadvantages of quantitative research
- Can’t understand reasons: Quantitative research doesn’t always tell you the full story, meaning you won’t understand the context – or the why, of the data you see, why do you see the results you have uncovered?
- Useful for simpler situations: Quantitative research on its own is not great when dealing with complex issues. In these cases, quantitative research may not be enough.
How to use quantitative research to your business’s advantage
Quantitative research methods may help in areas such as:
- Identifying which advert or landing page performs better
- Identifying how satisfied your customers are
- How many customers are likely to recommend you
- Tracking how your brand ranks in awareness and customer purchase intent
- Learn what consumers are likely to buy from your brand.
6 steps to conducting good quantitative research
Businesses can benefit from quantitative research by using it to evaluate the impact of data types. There are several steps to this:
- Define your problem or interest area : What do you observe is happening and is it frequent? Identify the data type/s you’re observing.
- Create a hypothesis : Ask yourself what could be the causes for the situation with those data types.
- Plan your quantitative research : Use structured research instruments like surveys or polls to ask questions that test your hypothesis.
- Data Collection : Collect quantitative data and understand what your data types are telling you. Using data collected on different types over long time periods can give you information on patterns.
- Data analysis : Does your information support your hypothesis? (You may need to redo the research with other variables to see if the results improve)
- Effectively present data : Communicate the results in a clear and concise way to help other people understand the findings.
How Qualtrics products can enhance & simplify the quantitative research process
The Qualtrics XM system gives you an all-in-one, integrated solution to help you all the way through conducting quantitative research. From survey creation and data collection to statistical analysis and data reporting, it can help all your internal teams gain insights from your numerical data.
Quantitative methods are catered to your business through templates or advanced survey designs. While you can manually collect data and conduct data analysis in a spreadsheet program, this solution helps you automate the process of quantitative research, saving you time and administration work.
Using computational techniques helps you to avoid human errors, and participant results come in are already incorporated into the analysis in real-time.
Our key tools, Stats IQ™ and Driver IQ™ make analyzing numerical data easy and simple. Choose to highlight key findings based on variables or highlight statistically insignificant findings. The choice is yours.
Some examples of your workspace in action, using drag and drop to create fast data visualizations quickly:
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Quantitative Research: What It Is, Practices & Methods
Quantitative research involves analyzing and gathering numerical data to uncover trends, calculate averages, evaluate relationships, and derive overarching insights. It’s used in various fields, including the natural and social sciences. Quantitative data analysis employs statistical techniques for processing and interpreting numeric data.
Research designs in the quantitative realm outline how data will be collected and analyzed with methods like experiments and surveys. Qualitative methods complement quantitative research by focusing on non-numerical data, adding depth to understanding. Data collection methods can be qualitative or quantitative, depending on research goals. Researchers often use a combination of both approaches to gain a comprehensive understanding of phenomena.
What is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is a systematic investigation of phenomena by gathering quantifiable data and performing statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. Quantitative research collects statistically significant information from existing and potential customers using sampling methods and sending out online surveys , online polls , and questionnaires , for example.
One of the main characteristics of this type of research is that the results can be depicted in numerical form. After carefully collecting structured observations and understanding these numbers, it’s possible to predict the future of a product or service, establish causal relationships or Causal Research , and make changes accordingly. Quantitative research primarily centers on the analysis of numerical data and utilizes inferential statistics to derive conclusions that can be extrapolated to the broader population.
An example of a quantitative research study is the survey conducted to understand how long a doctor takes to tend to a patient when the patient walks into the hospital. A patient satisfaction survey can be administered to ask questions like how long a doctor takes to see a patient, how often a patient walks into a hospital, and other such questions, which are dependent variables in the research. This kind of research method is often employed in the social sciences, and it involves using mathematical frameworks and theories to effectively present data, ensuring that the results are logical, statistically sound, and unbiased.
Data collection in quantitative research uses a structured method and is typically conducted on larger samples representing the entire population. Researchers use quantitative methods to collect numerical data, which is then subjected to statistical analysis to determine statistically significant findings. This approach is valuable in both experimental research and social research, as it helps in making informed decisions and drawing reliable conclusions based on quantitative data.
Quantitative Research Characteristics
Quantitative research has several unique characteristics that make it well-suited for specific projects. Let’s explore the most crucial of these characteristics so that you can consider them when planning your next research project:

- Structured tools: Quantitative research relies on structured tools such as surveys, polls, or questionnaires to gather quantitative data . Using such structured methods helps collect in-depth and actionable numerical data from the survey respondents, making it easier to perform data analysis.
- Sample size: Quantitative research is conducted on a significant sample size representing the target market . Appropriate Survey Sampling methods, a fundamental aspect of quantitative research methods, must be employed when deriving the sample to fortify the research objective and ensure the reliability of the results.
- Close-ended questions: Closed-ended questions , specifically designed to align with the research objectives, are a cornerstone of quantitative research. These questions facilitate the collection of quantitative data and are extensively used in data collection processes.
- Prior studies: Before collecting feedback from respondents, researchers often delve into previous studies related to the research topic. This preliminary research helps frame the study effectively and ensures the data collection process is well-informed.
- Quantitative data: Typically, quantitative data is represented using tables, charts, graphs, or other numerical forms. This visual representation aids in understanding the collected data and is essential for rigorous data analysis, a key component of quantitative research methods.
- Generalization of results: One of the strengths of quantitative research is its ability to generalize results to the entire population. It means that the findings derived from a sample can be extrapolated to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions for improvement based on numerical data analysis.
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods are systematic approaches used to gather and analyze numerical data to understand and draw conclusions about a phenomenon or population. Here are the quantitative research methods:
- Primary quantitative research methods
- Secondary quantitative research methods
Primary Quantitative Research Methods
Primary quantitative research is the most widely used method of conducting market research. The distinct feature of primary research is that the researcher focuses on collecting data directly rather than depending on data collected from previously done research. Primary quantitative research design can be broken down into three further distinctive tracks and the process flow. They are:
A. Techniques and Types of Studies
There are multiple types of primary quantitative research. They can be distinguished into the four following distinctive methods, which are:
01. Survey Research
Survey Research is fundamental for all quantitative outcome research methodologies and studies. Surveys are used to ask questions to a sample of respondents, using various types such as online polls, online surveys, paper questionnaires, web-intercept surveys , etc. Every small and big organization intends to understand what their customers think about their products and services, how well new features are faring in the market, and other such details.
By conducting survey research, an organization can ask multiple survey questions , collect data from a pool of customers, and analyze this collected data to produce numerical results. It is the first step towards collecting data for any research. You can use single ease questions . A single-ease question is a straightforward query that elicits a concise and uncomplicated response.
This type of research can be conducted with a specific target audience group and also can be conducted across multiple groups along with comparative analysis . A prerequisite for this type of research is that the sample of respondents must have randomly selected members. This way, a researcher can easily maintain the accuracy of the obtained results as a huge variety of respondents will be addressed using random selection.
Traditionally, survey research was conducted face-to-face or via phone calls. Still, with the progress made by online mediums such as email or social media, survey research has also spread to online mediums.There are two types of surveys , either of which can be chosen based on the time in hand and the kind of data required:
Cross-sectional surveys: Cross-sectional surveys are observational surveys conducted in situations where the researcher intends to collect data from a sample of the target population at a given point in time. Researchers can evaluate various variables at a particular time. Data gathered using this type of survey is from people who depict similarity in all variables except the variables which are considered for research . Throughout the survey, this one variable will stay constant.
- Cross-sectional surveys are popular with retail, SMEs, and healthcare industries. Information is garnered without modifying any parameters in the variable ecosystem.
- Multiple samples can be analyzed and compared using a cross-sectional survey research method.
- Multiple variables can be evaluated using this type of survey research.
- The only disadvantage of cross-sectional surveys is that the cause-effect relationship of variables cannot be established as it usually evaluates variables at a particular time and not across a continuous time frame.
Longitudinal surveys: Longitudinal surveys are also observational surveys , but unlike cross-sectional surveys, longitudinal surveys are conducted across various time durations to observe a change in respondent behavior and thought processes. This time can be days, months, years, or even decades. For instance, a researcher planning to analyze the change in buying habits of teenagers over 5 years will conduct longitudinal surveys.
- In cross-sectional surveys, the same variables were evaluated at a given time, and in longitudinal surveys, different variables can be analyzed at different intervals.
- Longitudinal surveys are extensively used in the field of medicine and applied sciences. Apart from these two fields, they are also used to observe a change in the market trend analysis , analyze customer satisfaction, or gain feedback on products/services.
- In situations where the sequence of events is highly essential, longitudinal surveys are used.
- Researchers say that when research subjects need to be thoroughly inspected before concluding, they rely on longitudinal surveys.
02. Correlational Research
A comparison between two entities is invariable. Correlation research is conducted to establish a relationship between two closely-knit entities and how one impacts the other, and what changes are eventually observed. This research method is carried out to give value to naturally occurring relationships, and a minimum of two different groups are required to conduct this quantitative research method successfully. Without assuming various aspects, a relationship between two groups or entities must be established.
Researchers use this quantitative research design to correlate two or more variables using mathematical analysis methods. Patterns, relationships, and trends between variables are concluded as they exist in their original setup. The impact of one of these variables on the other is observed, along with how it changes the relationship between the two variables. Researchers tend to manipulate one of the variables to attain the desired results.
Ideally, it is advised not to make conclusions merely based on correlational research. This is because it is not mandatory that if two variables are in sync that they are interrelated.
Example of Correlational Research Questions :
- The relationship between stress and depression.
- The equation between fame and money.
- The relation between activities in a third-grade class and its students.
03. Causal-comparative Research
This research method mainly depends on the factor of comparison. Also called quasi-experimental research , this quantitative research method is used by researchers to conclude the cause-effect equation between two or more variables, where one variable is dependent on the other independent variable. The independent variable is established but not manipulated, and its impact on the dependent variable is observed. These variables or groups must be formed as they exist in the natural setup. As the dependent and independent variables will always exist in a group, it is advised that the conclusions are carefully established by keeping all the factors in mind.
Causal-comparative research is not restricted to the statistical analysis of two variables but extends to analyzing how various variables or groups change under the influence of the same changes. This research is conducted irrespective of the type of relationship that exists between two or more variables. Statistical analysis plan is used to present the outcome using this quantitative research method.
Example of Causal-Comparative Research Questions:
- The impact of drugs on a teenager. The effect of good education on a freshman. The effect of substantial food provision in the villages of Africa.
04. Experimental Research
Also known as true experimentation, this research method relies on a theory. As the name suggests, experimental research is usually based on one or more theories. This theory has yet to be proven before and is merely a supposition. In experimental research, an analysis is done around proving or disproving the statement. This research method is used in natural sciences. Traditional research methods are more effective than modern techniques.
There can be multiple theories in experimental research. A theory is a statement that can be verified or refuted.
After establishing the statement, efforts are made to understand whether it is valid or invalid. This quantitative research method is mainly used in natural or social sciences as various statements must be proved right or wrong.
- Traditional research methods are more effective than modern techniques.
- Systematic teaching schedules help children who struggle to cope with the course.
- It is a boon to have responsible nursing staff for ailing parents.
B. Data Collection Methodologies
The second major step in primary quantitative research is data collection. Data collection can be divided into sampling methods and data collection using surveys and polls.
01. Data Collection Methodologies: Sampling Methods
There are two main sampling methods for quantitative research: Probability and Non-probability sampling .
Probability sampling: A theory of probability is used to filter individuals from a population and create samples in probability sampling . Participants of a sample are chosen by random selection processes. Each target audience member has an equal opportunity to be selected in the sample.
There are four main types of probability sampling:
- Simple random sampling: As the name indicates, simple random sampling is nothing but a random selection of elements for a sample. This sampling technique is implemented where the target population is considerably large.
- Stratified random sampling: In the stratified random sampling method , a large population is divided into groups (strata), and members of a sample are chosen randomly from these strata. The various segregated strata should ideally not overlap one another.
- Cluster sampling: Cluster sampling is a probability sampling method using which the main segment is divided into clusters, usually using geographic segmentation and demographic segmentation parameters.
- Systematic sampling: Systematic sampling is a technique where the starting point of the sample is chosen randomly, and all the other elements are chosen using a fixed interval. This interval is calculated by dividing the population size by the target sample size.
Non-probability sampling: Non-probability sampling is where the researcher’s knowledge and experience are used to create samples. Because of the researcher’s involvement, not all the target population members have an equal probability of being selected to be a part of a sample.
There are five non-probability sampling models:
- Convenience sampling: In convenience sampling , elements of a sample are chosen only due to one prime reason: their proximity to the researcher. These samples are quick and easy to implement as there is no other parameter of selection involved.
- Consecutive sampling: Consecutive sampling is quite similar to convenience sampling, except for the fact that researchers can choose a single element or a group of samples and conduct research consecutively over a significant period and then perform the same process with other samples.
- Quota sampling: Using quota sampling , researchers can select elements using their knowledge of target traits and personalities to form strata. Members of various strata can then be chosen to be a part of the sample as per the researcher’s understanding.
- Snowball sampling: Snowball sampling is conducted with target audiences who are difficult to contact and get information. It is popular in cases where the target audience for analysis research is rare to put together.
- Judgmental sampling: Judgmental sampling is a non-probability sampling method where samples are created only based on the researcher’s experience and research skill .
02. Data collection methodologies: Using surveys & polls
Once the sample is determined, then either surveys or polls can be distributed to collect the data for quantitative research.
Using surveys for primary quantitative research
A survey is defined as a research method used for collecting data from a pre-defined group of respondents to gain information and insights on various topics of interest. The ease of survey distribution and the wide number of people it can reach depending on the research time and objective makes it one of the most important aspects of conducting quantitative research.
Fundamental levels of measurement – nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales
Four measurement scales are fundamental to creating a multiple-choice question in a survey. They are nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio measurement scales without the fundamentals of which no multiple-choice questions can be created. Hence, it is crucial to understand these measurement levels to develop a robust survey.
Use of different question types
To conduct quantitative research, close-ended questions must be used in a survey. They can be a mix of multiple question types, including multiple-choice questions like semantic differential scale questions , rating scale questions , etc.
Survey Distribution and Survey Data Collection
In the above, we have seen the process of building a survey along with the research design to conduct primary quantitative research. Survey distribution to collect data is the other important aspect of the survey process. There are different ways of survey distribution. Some of the most commonly used methods are:
- Email: Sending a survey via email is the most widely used and effective survey distribution method. This method’s response rate is high because the respondents know your brand. You can use the QuestionPro email management feature to send out and collect survey responses.
- Buy respondents: Another effective way to distribute a survey and conduct primary quantitative research is to use a sample. Since the respondents are knowledgeable and are on the panel by their own will, responses are much higher.
- Embed survey on a website: Embedding a survey on a website increases a high number of responses as the respondent is already in close proximity to the brand when the survey pops up.
- Social distribution: Using social media to distribute the survey aids in collecting a higher number of responses from the people that are aware of the brand.
- QR code: QuestionPro QR codes store the URL for the survey. You can print/publish this code in magazines, signs, business cards, or on just about any object/medium.
- SMS survey: The SMS survey is a quick and time-effective way to collect a high number of responses.
- Offline Survey App: The QuestionPro App allows users to circulate surveys quickly, and the responses can be collected both online and offline.
Survey example
An example of a survey is a short customer satisfaction (CSAT) survey that can quickly be built and deployed to collect feedback about what the customer thinks about a brand and how satisfied and referenceable the brand is.
Using polls for primary quantitative research
Polls are a method to collect feedback using close-ended questions from a sample. The most commonly used types of polls are election polls and exit polls . Both of these are used to collect data from a large sample size but using basic question types like multiple-choice questions.
C. Data Analysis Techniques
The third aspect of primary quantitative research design is data analysis . After collecting raw data, there must be an analysis of this data to derive statistical inferences from this research. It is important to relate the results to the research objective and establish the statistical relevance of the results.
Remember to consider aspects of research that were not considered for the data collection process and report the difference between what was planned vs. what was actually executed.
It is then required to select precise Statistical Analysis Methods , such as SWOT, Conjoint, Cross-tabulation, etc., to analyze the quantitative data.
- SWOT analysis: SWOT Analysis stands for the acronym of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threat analysis. Organizations use this statistical analysis technique to evaluate their performance internally and externally to develop effective strategies for improvement.
- Conjoint Analysis: Conjoint Analysis is a market analysis method to learn how individuals make complicated purchasing decisions. Trade-offs are involved in an individual’s daily activities, and these reflect their ability to decide from a complex list of product/service options.
- Cross-tabulation: Cross-tabulation is one of the preliminary statistical market analysis methods which establishes relationships, patterns, and trends within the various parameters of the research study.
- TURF Analysis: TURF Analysis , an acronym for Totally Unduplicated Reach and Frequency Analysis, is executed in situations where the reach of a favorable communication source is to be analyzed along with the frequency of this communication. It is used for understanding the potential of a target market.
Inferential statistics methods such as confidence interval, the margin of error, etc., can then be used to provide results.
Secondary Quantitative Research Methods
Secondary quantitative research or desk research is a research method that involves using already existing data or secondary data. Existing data is summarized and collated to increase the overall effectiveness of the research.
This research method involves collecting quantitative data from existing data sources like the internet, government resources, libraries, research reports, etc. Secondary quantitative research helps to validate the data collected from primary quantitative research and aid in strengthening or proving, or disproving previously collected data.
The following are five popularly used secondary quantitative research methods:
- Data available on the internet: With the high penetration of the internet and mobile devices, it has become increasingly easy to conduct quantitative research using the internet. Information about most research topics is available online, and this aids in boosting the validity of primary quantitative data.
- Government and non-government sources: Secondary quantitative research can also be conducted with the help of government and non-government sources that deal with market research reports. This data is highly reliable and in-depth and hence, can be used to increase the validity of quantitative research design.
- Public libraries: Now a sparingly used method of conducting quantitative research, it is still a reliable source of information, though. Public libraries have copies of important research that was conducted earlier. They are a storehouse of valuable information and documents from which information can be extracted.
- Educational institutions: Educational institutions conduct in-depth research on multiple topics, and hence, the reports that they publish are an important source of validation in quantitative research.
- Commercial information sources: Local newspapers, journals, magazines, radio, and TV stations are great sources to obtain data for secondary quantitative research. These commercial information sources have in-depth, first-hand information on market research, demographic segmentation, and similar subjects.
Quantitative Research Examples
Some examples of quantitative research are:
- A customer satisfaction template can be used if any organization would like to conduct a customer satisfaction (CSAT) survey . Through this kind of survey, an organization can collect quantitative data and metrics on the goodwill of the brand or organization in the customer’s mind based on multiple parameters such as product quality, pricing, customer experience, etc. This data can be collected by asking a net promoter score (NPS) question , matrix table questions, etc. that provide data in the form of numbers that can be analyzed and worked upon.
- Another example of quantitative research is an organization that conducts an event, collecting feedback from attendees about the value they see from the event. By using an event survey , the organization can collect actionable feedback about the satisfaction levels of customers during various phases of the event such as the sales, pre and post-event, the likelihood of recommending the organization to their friends and colleagues, hotel preferences for the future events and other such questions.
What are the Advantages of Quantitative Research?
There are many advantages to quantitative research. Some of the major advantages of why researchers use this method in market research are:
Collect Reliable and Accurate Data:
Quantitative research is a powerful method for collecting reliable and accurate quantitative data. Since data is collected, analyzed, and presented in numbers, the results obtained are incredibly reliable and objective. Numbers do not lie and offer an honest and precise picture of the conducted research without discrepancies. In situations where a researcher aims to eliminate bias and predict potential conflicts, quantitative research is the method of choice.
Quick Data Collection:
Quantitative research involves studying a group of people representing a larger population. Researchers use a survey or another quantitative research method to efficiently gather information from these participants, making the process of analyzing the data and identifying patterns faster and more manageable through the use of statistical analysis. This advantage makes quantitative research an attractive option for projects with time constraints.
Wider Scope of Data Analysis:
Quantitative research, thanks to its utilization of statistical methods, offers an extensive range of data collection and analysis. Researchers can delve into a broader spectrum of variables and relationships within the data, enabling a more thorough comprehension of the subject under investigation. This expanded scope is precious when dealing with complex research questions that require in-depth numerical analysis.
Eliminate Bias:
One of the significant advantages of quantitative research is its ability to eliminate bias. This research method leaves no room for personal comments or the biasing of results, as the findings are presented in numerical form. This objectivity makes the results fair and reliable in most cases, reducing the potential for researcher bias or subjectivity.
In summary, quantitative research involves collecting, analyzing, and presenting quantitative data using statistical analysis. It offers numerous advantages, including the collection of reliable and accurate data, quick data collection, a broader scope of data analysis, and the elimination of bias, making it a valuable approach in the field of research. When considering the benefits of quantitative research, it’s essential to recognize its strengths in contrast to qualitative methods and its role in collecting and analyzing numerical data for a more comprehensive understanding of research topics.
Best Practices to Conduct Quantitative Research
Here are some best practices for conducting quantitative research:

- Differentiate between quantitative and qualitative: Understand the difference between the two methodologies and apply the one that suits your needs best.
- Choose a suitable sample size: Ensure that you have a sample representative of your population and large enough to be statistically weighty.
- Keep your research goals clear and concise: Know your research goals before you begin data collection to ensure you collect the right amount and the right quantity of data.
- Keep the questions simple: Remember that you will be reaching out to a demographically wide audience. Pose simple questions for your respondents to understand easily.
Quantitative Research vs Qualitative Research
Quantitative research and qualitative research are two distinct approaches to conducting research, each with its own set of methods and objectives. Here’s a comparison of the two:

Quantitative Research
- Objective: The primary goal of quantitative research is to quantify and measure phenomena by collecting numerical data. It aims to test hypotheses, establish patterns, and generalize findings to a larger population.
- Data Collection: Quantitative research employs systematic and standardized approaches for data collection, including techniques like surveys, experiments, and observations that involve predefined variables. It is often collected from a large and representative sample.
- Data Analysis: Data is analyzed using statistical techniques, such as descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and mathematical modeling. Researchers use statistical tests to draw conclusions and make generalizations based on numerical data.
- Sample Size: Quantitative research often involves larger sample sizes to ensure statistical significance and generalizability.
- Results: The results are typically presented in tables, charts, and statistical summaries, making them highly structured and objective.
- Generalizability: Researchers intentionally structure quantitative research to generate outcomes that can be helpful to a larger population, and they frequently seek to establish causative connections.
- Emphasis on Objectivity: Researchers aim to minimize bias and subjectivity, focusing on replicable and objective findings.
Qualitative Research
- Objective: Qualitative research seeks to gain a deeper understanding of the underlying motivations, behaviors, and experiences of individuals or groups. It explores the context and meaning of phenomena.
- Data Collection: Qualitative research employs adaptable and open-ended techniques for data collection, including methods like interviews, focus groups, observations, and content analysis. It allows participants to express their perspectives in their own words.
- Data Analysis: Data is analyzed through thematic analysis, content analysis, or grounded theory. Researchers focus on identifying patterns, themes, and insights in the data.
- Sample Size: Qualitative research typically involves smaller sample sizes due to the in-depth nature of data collection and analysis.
- Results: Findings are presented in narrative form, often in the participants’ own words. Results are subjective, context-dependent, and provide rich, detailed descriptions.
- Generalizability: Qualitative research does not aim for broad generalizability but focuses on in-depth exploration within a specific context. It provides a detailed understanding of a particular group or situation.
- Emphasis on Subjectivity: Researchers acknowledge the role of subjectivity and the researcher’s influence on the Research Process . Participant perspectives and experiences are central to the findings.
Researchers choose between quantitative and qualitative research methods based on their research objectives and the nature of the research question. Each approach has its advantages and drawbacks, and the decision between them hinges on the particular research objectives and the data needed to address research inquiries effectively.
Quantitative research is a structured way of collecting and analyzing data from various sources. Its purpose is to quantify the problem and understand its extent, seeking results that someone can project to a larger population.
Companies that use quantitative rather than qualitative research typically aim to measure magnitudes and seek objectively interpreted statistical results. So if you want to obtain quantitative data that helps you define the structured cause-and-effect relationship between the research problem and the factors, you should opt for this type of research.
At QuestionPro , we have various Best Data Collection Tools and features to conduct investigations of this type. You can create questionnaires and distribute them through our various methods. We also have sample services or various questions to guarantee the success of your study and the quality of the collected data.
Quantitative research is a systematic and structured approach to studying phenomena that involves the collection of measurable data and the application of statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques for analysis.
Quantitative research is characterized by structured tools like surveys, substantial sample sizes, closed-ended questions, reliance on prior studies, data presented numerically, and the ability to generalize findings to the broader population.
The two main methods of quantitative research are Primary quantitative research methods, involving data collection directly from sources, and Secondary quantitative research methods, which utilize existing data for analysis.
1.Surveying to measure employee engagement with numerical rating scales. 2.Analyzing sales data to identify trends in product demand and market share. 4.Examining test scores to assess the impact of a new teaching method on student performance. 4.Using website analytics to track user behavior and conversion rates for an online store.
1.Differentiate between quantitative and qualitative approaches. 2.Choose a representative sample size. 3.Define clear research goals before data collection. 4.Use simple and easily understandable survey questions.
MORE LIKE THIS

Age Gating: Effective Strategies for Online Content Control
Aug 23, 2024

Customer Experience Lessons from 13,000 Feet — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Aug 20, 2024

Insight: Definition & meaning, types and examples
Aug 19, 2024

Employee Loyalty: Strategies for Long-Term Business Success
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- Privacy Policy

Home » Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Table of Contents

Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a type of research that collects and analyzes numerical data to test hypotheses and answer research questions . This research typically involves a large sample size and uses statistical analysis to make inferences about a population based on the data collected. It often involves the use of surveys, experiments, or other structured data collection methods to gather quantitative data.
Quantitative Research Methods

Quantitative Research Methods are as follows:
Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design is used to describe the characteristics of a population or phenomenon being studied. This research method is used to answer the questions of what, where, when, and how. Descriptive research designs use a variety of methods such as observation, case studies, and surveys to collect data. The data is then analyzed using statistical tools to identify patterns and relationships.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to investigate the relationship between two or more variables. Researchers use correlational research to determine whether a relationship exists between variables and to what extent they are related. This research method involves collecting data from a sample and analyzing it using statistical tools such as correlation coefficients.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This research method is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks full control over the independent variable. Researchers use quasi-experimental research designs when it is not feasible or ethical to manipulate the independent variable.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This research method involves manipulating the independent variable and observing the effects on the dependent variable. Researchers use experimental research designs to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships.
Survey Research
Survey research involves collecting data from a sample of individuals using a standardized questionnaire. This research method is used to gather information on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors of individuals. Researchers use survey research to collect data quickly and efficiently from a large sample size. Survey research can be conducted through various methods such as online, phone, mail, or in-person interviews.
Quantitative Research Analysis Methods
Here are some commonly used quantitative research analysis methods:
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis is the most common quantitative research analysis method. It involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis can be used to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze the relationship between one dependent variable and one or more independent variables. Researchers use regression analysis to identify and quantify the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is a statistical technique used to identify underlying factors that explain the correlations among a set of variables. Researchers use factor analysis to reduce a large number of variables to a smaller set of factors that capture the most important information.
Structural Equation Modeling
Structural equation modeling is a statistical technique used to test complex relationships between variables. It involves specifying a model that includes both observed and unobserved variables, and then using statistical methods to test the fit of the model to the data.
Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze data that is collected over time. It involves identifying patterns and trends in the data, as well as any seasonal or cyclical variations.
Multilevel Modeling
Multilevel modeling is a statistical technique used to analyze data that is nested within multiple levels. For example, researchers might use multilevel modeling to analyze data that is collected from individuals who are nested within groups, such as students nested within schools.
Applications of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research has many applications across a wide range of fields. Here are some common examples:
- Market Research : Quantitative research is used extensively in market research to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform marketing strategies, product development, and pricing decisions.
- Health Research: Quantitative research is used in health research to study the effectiveness of medical treatments, identify risk factors for diseases, and track health outcomes over time. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze data from clinical trials, surveys, and other sources to inform medical practice and policy.
- Social Science Research: Quantitative research is used in social science research to study human behavior, attitudes, and social structures. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform social policies, educational programs, and community interventions.
- Education Research: Quantitative research is used in education research to study the effectiveness of teaching methods, assess student learning outcomes, and identify factors that influence student success. Researchers use experimental and quasi-experimental designs, as well as surveys and other quantitative methods, to collect and analyze data.
- Environmental Research: Quantitative research is used in environmental research to study the impact of human activities on the environment, assess the effectiveness of conservation strategies, and identify ways to reduce environmental risks. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze data from field studies, experiments, and other sources.
Characteristics of Quantitative Research
Here are some key characteristics of quantitative research:
- Numerical data : Quantitative research involves collecting numerical data through standardized methods such as surveys, experiments, and observational studies. This data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns and relationships.
- Large sample size: Quantitative research often involves collecting data from a large sample of individuals or groups in order to increase the reliability and generalizability of the findings.
- Objective approach: Quantitative research aims to be objective and impartial in its approach, focusing on the collection and analysis of data rather than personal beliefs, opinions, or experiences.
- Control over variables: Quantitative research often involves manipulating variables to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships. Researchers aim to control for extraneous variables that may impact the results.
- Replicable : Quantitative research aims to be replicable, meaning that other researchers should be able to conduct similar studies and obtain similar results using the same methods.
- Statistical analysis: Quantitative research involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis allows researchers to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories.
- Generalizability: Quantitative research aims to produce findings that can be generalized to larger populations beyond the specific sample studied. This is achieved through the use of random sampling methods and statistical inference.
Examples of Quantitative Research
Here are some examples of quantitative research in different fields:
- Market Research: A company conducts a survey of 1000 consumers to determine their brand awareness and preferences. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify trends and patterns that can inform marketing strategies.
- Health Research : A researcher conducts a randomized controlled trial to test the effectiveness of a new drug for treating a particular medical condition. The study involves collecting data from a large sample of patients and analyzing the results using statistical methods.
- Social Science Research : A sociologist conducts a survey of 500 people to study attitudes toward immigration in a particular country. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify factors that influence these attitudes.
- Education Research: A researcher conducts an experiment to compare the effectiveness of two different teaching methods for improving student learning outcomes. The study involves randomly assigning students to different groups and collecting data on their performance on standardized tests.
- Environmental Research : A team of researchers conduct a study to investigate the impact of climate change on the distribution and abundance of a particular species of plant or animal. The study involves collecting data on environmental factors and population sizes over time and analyzing the results using statistical methods.
- Psychology : A researcher conducts a survey of 500 college students to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify correlations and potential causal relationships.
- Political Science: A team of researchers conducts a study to investigate voter behavior during an election. They use survey methods to collect data on voting patterns, demographics, and political attitudes, and analyze the results using statistical methods.
How to Conduct Quantitative Research
Here is a general overview of how to conduct quantitative research:
- Develop a research question: The first step in conducting quantitative research is to develop a clear and specific research question. This question should be based on a gap in existing knowledge, and should be answerable using quantitative methods.
- Develop a research design: Once you have a research question, you will need to develop a research design. This involves deciding on the appropriate methods to collect data, such as surveys, experiments, or observational studies. You will also need to determine the appropriate sample size, data collection instruments, and data analysis techniques.
- Collect data: The next step is to collect data. This may involve administering surveys or questionnaires, conducting experiments, or gathering data from existing sources. It is important to use standardized methods to ensure that the data is reliable and valid.
- Analyze data : Once the data has been collected, it is time to analyze it. This involves using statistical methods to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables. Common statistical techniques include correlation analysis, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing.
- Interpret results: After analyzing the data, you will need to interpret the results. This involves identifying the key findings, determining their significance, and drawing conclusions based on the data.
- Communicate findings: Finally, you will need to communicate your findings. This may involve writing a research report, presenting at a conference, or publishing in a peer-reviewed journal. It is important to clearly communicate the research question, methods, results, and conclusions to ensure that others can understand and replicate your research.
When to use Quantitative Research
Here are some situations when quantitative research can be appropriate:
- To test a hypothesis: Quantitative research is often used to test a hypothesis or a theory. It involves collecting numerical data and using statistical analysis to determine if the data supports or refutes the hypothesis.
- To generalize findings: If you want to generalize the findings of your study to a larger population, quantitative research can be useful. This is because it allows you to collect numerical data from a representative sample of the population and use statistical analysis to make inferences about the population as a whole.
- To measure relationships between variables: If you want to measure the relationship between two or more variables, such as the relationship between age and income, or between education level and job satisfaction, quantitative research can be useful. It allows you to collect numerical data on both variables and use statistical analysis to determine the strength and direction of the relationship.
- To identify patterns or trends: Quantitative research can be useful for identifying patterns or trends in data. For example, you can use quantitative research to identify trends in consumer behavior or to identify patterns in stock market data.
- To quantify attitudes or opinions : If you want to measure attitudes or opinions on a particular topic, quantitative research can be useful. It allows you to collect numerical data using surveys or questionnaires and analyze the data using statistical methods to determine the prevalence of certain attitudes or opinions.
Purpose of Quantitative Research
The purpose of quantitative research is to systematically investigate and measure the relationships between variables or phenomena using numerical data and statistical analysis. The main objectives of quantitative research include:
- Description : To provide a detailed and accurate description of a particular phenomenon or population.
- Explanation : To explain the reasons for the occurrence of a particular phenomenon, such as identifying the factors that influence a behavior or attitude.
- Prediction : To predict future trends or behaviors based on past patterns and relationships between variables.
- Control : To identify the best strategies for controlling or influencing a particular outcome or behavior.
Quantitative research is used in many different fields, including social sciences, business, engineering, and health sciences. It can be used to investigate a wide range of phenomena, from human behavior and attitudes to physical and biological processes. The purpose of quantitative research is to provide reliable and valid data that can be used to inform decision-making and improve understanding of the world around us.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
There are several advantages of quantitative research, including:
- Objectivity : Quantitative research is based on objective data and statistical analysis, which reduces the potential for bias or subjectivity in the research process.
- Reproducibility : Because quantitative research involves standardized methods and measurements, it is more likely to be reproducible and reliable.
- Generalizability : Quantitative research allows for generalizations to be made about a population based on a representative sample, which can inform decision-making and policy development.
- Precision : Quantitative research allows for precise measurement and analysis of data, which can provide a more accurate understanding of phenomena and relationships between variables.
- Efficiency : Quantitative research can be conducted relatively quickly and efficiently, especially when compared to qualitative research, which may involve lengthy data collection and analysis.
- Large sample sizes : Quantitative research can accommodate large sample sizes, which can increase the representativeness and generalizability of the results.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
There are several limitations of quantitative research, including:
- Limited understanding of context: Quantitative research typically focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, which may not provide a comprehensive understanding of the context or underlying factors that influence a phenomenon.
- Simplification of complex phenomena: Quantitative research often involves simplifying complex phenomena into measurable variables, which may not capture the full complexity of the phenomenon being studied.
- Potential for researcher bias: Although quantitative research aims to be objective, there is still the potential for researcher bias in areas such as sampling, data collection, and data analysis.
- Limited ability to explore new ideas: Quantitative research is often based on pre-determined research questions and hypotheses, which may limit the ability to explore new ideas or unexpected findings.
- Limited ability to capture subjective experiences : Quantitative research is typically focused on objective data and may not capture the subjective experiences of individuals or groups being studied.
- Ethical concerns : Quantitative research may raise ethical concerns, such as invasion of privacy or the potential for harm to participants.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Quasi-Experimental Research Design – Types...

Experimental Design – Types, Methods, Guide

Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples

9 Quantitative Research Methods With Real Client Examples
- June 21, 2021
- Tallwave Team
Share Article
Quantitative research is essential to developing a clear understanding of consumer engagement and how to increase satisfaction.
Primary Quantitative Research Methods
When it comes to quantitative research, many people often confuse this type of research with the methodology. The research type refers to style of research while the data collection method can be different.
Research types
These are the primary types of quantitative research used by businesses today.
- Survey research: Ideally when conducting survey research businesses will use a statistically relevant sample to understand the sentiments and actions of a large group of people. This could be their current customers or consumers who fit into their ideal demographic.
- Correlational research: Correlational research compares two variables to come to a conclusion about whether there is a relationship between the two. Keep in mind that correlation does not always imply causation, which is to say you need to account for external variables that could cause an apparent relationship.
- Experimental research: This form of research takes a scientific approach, testing a hypothesis by manipulating certain variables to understand what changes this could cause. In these experiments, there is a control group and a manipulated group.
Also read: 6 Factors Influencing Customer Behaviors in 2021
Data collection methods
Launching the above research requires creating a plan to collect data. After all, quantitative research relies on data. Here are the common primary data collection methods for quantitative research.
- Surveys: A common approach to collecting data is using a survey. This is ideal especially if the business can obtain a statistically relevant sample from their responses. Surveys are often conducted through web or email questionnaires.
- Interviews: Yes, interviews can be used to obtain quantitative data. While this form of data collection is typically associated with qualitative research, interviewers can ask a standard set of questions to collate formal, quantitative data.
- Documentation review: With an increasing amount of business occurring digitally, there is more documentation now than ever before to help inform quantitative conclusions. Businesses can assess website metrics such as return visits, time on page or even use a pixel to track customer movement across websites. They can also view how many times their app has been opened and actions users have taken on their platform to determine customer engagement.
Secondary research can be helpful when formulating a plan for obtaining primary quantitative data. It can help narrow areas of focus or illuminate key challenges.
Secondary Quantitative Research Methods
Secondary data is information that is already collected and not necessarily exclusive to the company but still relevant when understanding overall industry and marketplace trends. Here are a few examples of secondary data:
- Government reports: Government research can indicate potential regulatory roadblocks, customer pain points and future opportunities. For example, a fitness company might use government data that shows an increase in use of outdoor running trials to develop a new product used to meet that specific use case.
- Survey-based secondary data: Polls or surveys that have been conducted for a primary use could be reused for secondary purposes. This could include survey data obtained by other companies or governments.
- Academic research: Research that has been previously conducted and published in peer-reviewed journals can help inform trends and consumer behavior, even if it doesn’t apply to a company’s specific customers.
Secondary research can be helpful when formulating a plan for obtaining primary quantitative data. It can help narrow areas of focus or illuminate key challenges. It can also help when it comes to interpreting primary data, especially when trying to understand the relationship between two variables of correlated data.
Also read: The What, Why, & How of Customer Behavior Analysis
Real Examples of Quantitative Research
We regularly use quantitative research to help our clients understand where they can best add value to increase customer engagement. Here are three examples of quantitative research in motion.
Example 1: Leading food distribution company
We helped a leading food distribution company identify changes in the needs and values of their restaurant clients as a result of COVID-19. This helped inform opportunities to become more valuable partners.
The research plan involved creating a survey that was emailed to clients. The questions were specific and numeric. For example, respondents were asked what percentage of their weekly spend was used with the food distribution company. They were also asked to assign a percentage to the way their food ordering had changed during COVID-19 and to rate their satisfaction with the food distribution company.
The results showed changes that had occurred for clients of the food distribution company as a result of the unique stressors of the pandemic. We were able to determine changes in weekly food supply and customer count as well as menu adaptations and purchase behavior.
Example 2: Leading credit card company
Our work with a leading credit card company required us to understand what current travel card members valued about the rewards program and their preferred communication method for booking travel in order to create an omnichannel servicing strategy and ideal customer journey.
Through an online survey of younger cardholders, the target demographic for this project, we asked questions such as length of card membership, total spend and the number of annual leisure trips in addition to more specific questions that showed how members get inspiration for trip planning and where they research.
The results highlighted ways to overcome resistance to pricing by proving more value. It also illuminated ways to make the benefits of membership more tangible to card holders and how to influence travelers in the early stages of planning their journey.
Example 3: Internal research report
We’re in the business of drinking our own champagne, so to speak, which is why we conducted our own quantitative research aimed at understanding the consumer trends that were spurred by the pandemic and how these will transform behaviors in the future.
There’s no question that new customer experiences emerged from the pandemic. Think of offerings such as “buy online, pickup in store (BOPIS),” or blended restaurant meals that are cooked at home. We wanted to understand how consumers truly felt about these new experiences and which they were likely to continue using even after restrictions were lifted. We also wanted to know more about the changing expectations for branded communication and how all of these pieces of the puzzle fit together to create consumer engagement. Our method of data collection was a survey.
Our research led us to develop insights we could use to inform our customers in their decision making. For example, we found convenience is paramount for consumers who are seeking out hybrid experiences such as BOPIS to take the best of both worlds. We also found many of these changes are permanent as consumers embraced new experiences that made their lives easier.
We regularly use quantitative research to help our clients understand where they can best add value to increase customer engagement.
The Bottom Line
Quantitative research is essential to developing a clear understanding of consumer engagement and how to increase satisfaction. Though online surveys are one of the most common methods for obtaining data, research isn’t limited to this strategy. It’s important to use whatever strategies are within your scope to constantly evaluate new trends and consumer behaviors that could significantly impact your offerings. The results can show you how to re-engage customers and drive loyalty.
Interested in partnering with us to learn more about your customers needs, wants, and behaviors to inform future experience design? Contact us today !
Tallwave Headquarters
6720 N. Scottsdale Road, Suite 140 Scottsdale, Arizona 85253 (602) 840-0400
For business inquiries, contact Ed Borromeo, Tallwave Partner at [email protected]

©2024 Tallwave LLC. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use

Bunger Steel
Doing some things and making some impacts

21 Types of Market Research and Examples
Last updated August 21, 2024
If you are involved in market research and are interested in qualitative research methods, you might be interested in the different types of market research that you can choose from. There are various types of market research but here are 21 of the main types.

Page Contents
Types of Market Research
1. focus groups.
Using focus groups can be a fairly simple yet highly effective method for learning about a product or service that you plan to push into the marketplace.
Inviting a small number of people as a group to come and try out your product and discuss their thoughts can be invaluable. You can observe the discussion, questions, ideas, complaints, etc about your product or service.
This is a fairly inexpensive but powerful way to get feedback on your product that you might otherwise miss.
The focus group generally will be made up of a wide range of people who reflect your typical audience or customer and are people whose opinions you can normally trust , because you have chosen them specifically for this task.
2. Observation
Observation can be used in focus groups (as discussed above) and it is an incredibly powerful way to begin to understand how people react, interact, and use products and services in real-world everyday situations.
You can also use observation to watch users in a real-world environment interact with your product or service.
If you want to understand why people never seem to enter your store even though it is on the main route to other stores, for, example, observation might provide you with the answer.
- Is there something that distracts them as they approach your storefront?
- Do they think about entering and then seem to choose not to enter?
- Is there perhaps a person selling something directly outside that people seem to try and avoid and affects your business?
Observation alone can sometimes provide you with a lot of the information you need and is sometimes the only type of research needed.
Using pricing is another great way to gather data and do market research.
You might, for example, want to do A and B pricing, meaning two different prices presented under similar market conditions, and then compare the results.
Does lowering the price point result in far higher sales? Or vice versa?
Also, recording and documenting all of your main competitors’ prices and then analyzing these against your prices can provide insight into the market conditions and expectations.
Your prices might be higher as you try and provide a higher quality offering. This is something you can factor in as you undertake pricing market research.
4. Brand Sentiment
Brand Sentiment is something that we can more easily study and do market research on these days, given that so many companies are on social media.
Brand sentiment is about the impression, feeling, and general thoughts a person (and people in general) have about a brand.
What words, emotions, and feelings do people associate with a given brand? With your brand?
One way to analyze brand sentiment is by doing market research on a company’s social media sites.
What terms, words, and tags do customers and anyone who comments on the brand use in hashtags, in any social media comments, and in discussions?

>> Qualitative Market Research Teaching Materials
5. Analyse Sales Data
Perhaps one of the more obvious and easiest (easiest in that you will already have access to the data) research tools is to analyze the historical sales data.
What is the most popular product in terms of sales and are there extra products you can attach to this to boost further sales, i.e. are there any follow-up products you can release?
Are you spending too much on marketing products that simply never sell? Could that budget be refocused on the better-selling items?
How do the products/services sell in relation to the marketing budget each receives, as a percentage?
There are numerous questions and ways to analyze sales data and it certainly is a key option in terms of market research.
6. Interviews
Market research interviews can come in a variety of ways including through:
- Interviews as part of a focus group
- Semi-structured of structured one-on-one interviews
If you want to try and get as much information as possible about a new product, for example, then a small focus group can work well.
With the focus group, you might leave them in the room for an hour to discuss your product and they talk about whatever they want in relation to the product and get to try it (as mentioned earlier).
You might want to find out specific information, so you might use more structured interviews where you ask more specific questions to the group or to individuals one-on-one.
Interviews can also come in the form of general questionnaires that you have trained interviewers/market researchers use to approach the general public to ask about a given product or service.
7. Mystery Shopper
Some people are hired in market research to act as mystery shoppers, whereby they act as a customer in order to experience the full customer journey, be it in person or online, to provide feedback on the whole experience.
This is a common approach for in-person market research and can work really well for services related to retail and similar service-related businesses.
You can have the mystery shopper also though, not only shop in your own business but also act to research your competitors and to then provide information on:
- Prices differences
- Customer service experience comparison
- Anything else at all they noted about the overall customer experience (i.e. perhaps the wayfinding experience was easier in a certain store)
8. Competitor Analysis
When we look at the different types of market research, in addition to the mystery shopper idea above, in terms of competitor analysis, we can also do a far more in-depth piece of research and ask ourselves:
- What direction are our competitors taking in terms of new products and services?
- What size are they in terms of employees, budgets and how can we compete (and win)?
- What is the brand sentiment for our competitors’ products?
- What are they doing well that we are failing to do well?
- What do we do better and what do we need to continue improving on?
The Internet, of course, can provide many of the answers through market research online.
Polls are relatively easy to run and they can provide some quick and handy information.
There are numerous ways to run a poll and one easy way is through your social media site, i.e. you can run a poll on Facebook if you have a company Facebook page. Likewise, you can also use a service such as ‘ Polls Everywhere ‘.
A poll can be useful for trying to understand one issue at a time such as:
- How much are people willing to pay for a product?
- What is the key reason for buying a product?
10. Secondary Research
As the term suggests, secondary research is about taking and using data from secondary resources.
So, for example, statistics that you take from a government website or from the media. Or the data might be from statistics companies such as Gartner or Statista.
Secondary data can be extremely useful because it tends to be data that we otherwise could never realistically have the money or time to collect ourselves.
11. Feasibility Studies
Feasibility studies are another type of market research and are an option that many large companies often undertake when the intended project involves a large amount of money.
A feasibility study will normally be about trying to evaluate, percentage-wise, the chance of a project succeeding or not succeeding in the future.
The idea is to invest early on in the market research to work out if it is worth the costs involved with proceeding further with the project.
12. Field Trials
A field trial is an interesting form of market research in that it is a testing stage where the product becomes available only to a small number of people so that it can be tested before fully being launched.
So, it might be available for your very best customers to have a peak preview of an upcoming product such as a new game you are releasing.
In return for their feedback, they get to see the game first and perhaps get a sizable discount when the final product is released market-wide.
13. Advertising Testing
There are a few types of market research related to direct advertising and one such method is advertising testing.
The concept is fairly straightforward in that this is about organizing small advertising campaigns as premises for doing much larger campaigns later on.
The test will help you evaluate the market so that you can better understand how best to run a larger campaign most effectively.
The options for online advertising are endless and herein lies the reason for testing as it is incredibly easy these days to spend on advertising budgets, and it’s getting harder to get a ROI (Return On Investment) for the advertising spend.
14. Customer Research
Before even building a product or service, you might want to consider customer research as a form of market research to really drill down to who your ideal customer is.
What you might want to do is plan a customer avatar.
This means working out who your ideal customer would be. This will be a fictional character and you will research and then detail what age they would be, their types of interests and hobbies, and as much information as you can about their character, background, and skills.
This is your ideal target customer and this can greatly help you in understanding then how to market your product to the intended customer avatar.
15. Descriptive Research
Descriptive research is a little more complex than some of the other methods discussed in this list, but it is important to also mention.
Typically, this type of research answers questions that start with “What…” and it often combines both qualitative and quantitative data to answer the research question.
16. Primary Research
We have already mentioned secondary research so it might be no surprise to you that there is also primary research.
There are different types of primary market research and these include some of the items we have already mentioned, but they come under this umbrella as ‘Primary Research’ and can include:
- Questionnaires
- Focus groups
Primary research as the term perhaps suggests, is research where you directly gather the data yourself in-house, rather than, for example, using secondary data that someone else has collected.
17. Concept Testing
Concept testing can be used in connection to product development and might incorporate focus groups that we talked about earlier.
As you develop a product and prepare it for release, it can be extremely useful to better understand:
- What features people might want included
- What price people are likely to be willing to pay
It can be worth providing a focus group or focus individuals with a prototype at a few different stages as it can be extremely useful to get key feedback and ideas early on and at every stage possible.
Concept testing can literally save you thousands in income when a focus group member points out an obvious design flaw or obvious error, but one that those closely aligned with the design have overlooked.
18. Online Surveys
You might also choose to do an online survey (different from polls) to gather more information about the needs, wants, and thoughts of your target customers.
An online survey is different from an online poll in that a poll tends to ask one specific question and typically there will be 4 or 5 options to choose from.
Surveys tend to be much more open and allow for open questions to be included so that participants are not limited in the feedback that they can give you.
Just be aware though that the survey design is a skill unto itself in that you need to ensure that you:
- Ask the right questions
- Ask open-ended questions
- and that the questions do not guide the participants to answer in a specific way
19. Quantitative Data
When talking about market research, even though many of the options already discussed include quantitative data or qualitative data, it is worth explaining the two as unique entities.
Quantitative data is about taking what is considered a scientific approach based on numbers.
For sales figures, for example, this is quantitative data as the data is based on exact sales.
In market research though, we can only learn a certain amount through analyzing quantitative data, hence why qualitative data can be so useful.
20. Qualitative data
Qualitative data is data that does not rely on numbers but instead more so on feelings, thoughts, perceptions, etc.
This type of data is extremely useful in market research because we are looking at the unknowns and things that cannot yet be measured.
21. Social Media
In addition to being able to analyze brand sentiment through companies’ social media sites, we can also use social media for researching the overall market conditions including:
- Competitors
- Opportunities
- Gaps in the market
Given the options for market research through social media, I have placed this as its own point in the types of market research, as social media is a great opportunity to learn about the marketplace, before making key decisions .
Market Research Further Resources
I hope you have found this post on all types of market research useful. There are a few other resources though that might also be of interest below:
- Market research training activities
- How to write research questions
- Market research design activity
- Also, make sure to take a look at the teaching materials for qualitative research and market research.

- Recent Posts
- 21 Types of Market Research and Examples - August 20, 2024
- 5 Free Qualitative Teaching Activities for Market Research Training - August 19, 2024
- 21 Effective and Essential Coaching Skills for Managers - August 15, 2024

Training Materials Catalogue & Prices

Payment Options

Bulk Discounts

What Is Included in Our Training Packages?


Salesforce is closed for new business in your area.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods
Published on April 12, 2019 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on June 22, 2023.
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge.
Common quantitative methods include experiments, observations recorded as numbers, and surveys with closed-ended questions.
Quantitative research is at risk for research biases including information bias , omitted variable bias , sampling bias , or selection bias . Qualitative research Qualitative research is expressed in words . It is used to understand concepts, thoughts or experiences. This type of research enables you to gather in-depth insights on topics that are not well understood.
Common qualitative methods include interviews with open-ended questions, observations described in words, and literature reviews that explore concepts and theories.
Table of contents
The differences between quantitative and qualitative research, data collection methods, when to use qualitative vs. quantitative research, how to analyze qualitative and quantitative data, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about qualitative and quantitative research.
Quantitative and qualitative research use different research methods to collect and analyze data, and they allow you to answer different kinds of research questions.
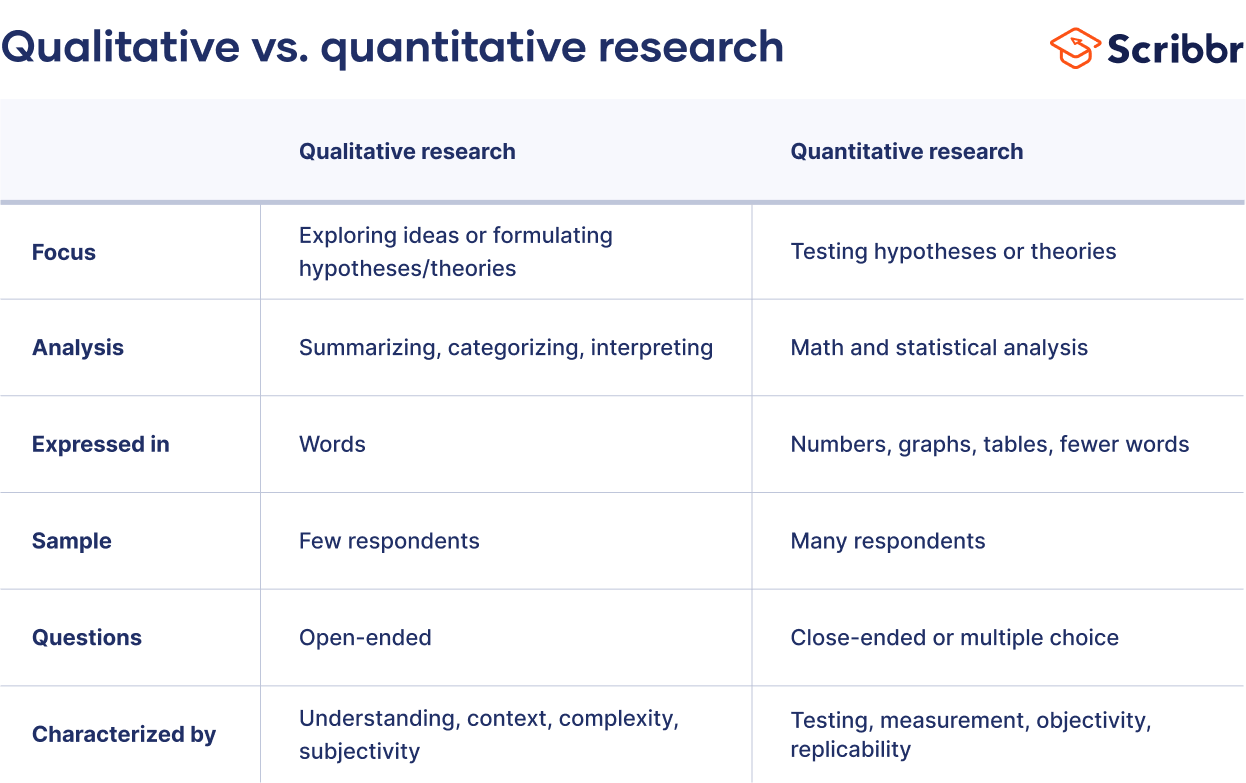
Quantitative and qualitative data can be collected using various methods. It is important to use a data collection method that will help answer your research question(s).
Many data collection methods can be either qualitative or quantitative. For example, in surveys, observational studies or case studies , your data can be represented as numbers (e.g., using rating scales or counting frequencies) or as words (e.g., with open-ended questions or descriptions of what you observe).
However, some methods are more commonly used in one type or the other.
Quantitative data collection methods
- Surveys : List of closed or multiple choice questions that is distributed to a sample (online, in person, or over the phone).
- Experiments : Situation in which different types of variables are controlled and manipulated to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Observations : Observing subjects in a natural environment where variables can’t be controlled.
Qualitative data collection methods
- Interviews : Asking open-ended questions verbally to respondents.
- Focus groups : Discussion among a group of people about a topic to gather opinions that can be used for further research.
- Ethnography : Participating in a community or organization for an extended period of time to closely observe culture and behavior.
- Literature review : Survey of published works by other authors.
A rule of thumb for deciding whether to use qualitative or quantitative data is:
- Use quantitative research if you want to confirm or test something (a theory or hypothesis )
- Use qualitative research if you want to understand something (concepts, thoughts, experiences)
For most research topics you can choose a qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods approach . Which type you choose depends on, among other things, whether you’re taking an inductive vs. deductive research approach ; your research question(s) ; whether you’re doing experimental , correlational , or descriptive research ; and practical considerations such as time, money, availability of data, and access to respondents.
Quantitative research approach
You survey 300 students at your university and ask them questions such as: “on a scale from 1-5, how satisfied are your with your professors?”
You can perform statistical analysis on the data and draw conclusions such as: “on average students rated their professors 4.4”.
Qualitative research approach
You conduct in-depth interviews with 15 students and ask them open-ended questions such as: “How satisfied are you with your studies?”, “What is the most positive aspect of your study program?” and “What can be done to improve the study program?”
Based on the answers you get you can ask follow-up questions to clarify things. You transcribe all interviews using transcription software and try to find commonalities and patterns.
Mixed methods approach
You conduct interviews to find out how satisfied students are with their studies. Through open-ended questions you learn things you never thought about before and gain new insights. Later, you use a survey to test these insights on a larger scale.
It’s also possible to start with a survey to find out the overall trends, followed by interviews to better understand the reasons behind the trends.
Qualitative or quantitative data by itself can’t prove or demonstrate anything, but has to be analyzed to show its meaning in relation to the research questions. The method of analysis differs for each type of data.
Analyzing quantitative data
Quantitative data is based on numbers. Simple math or more advanced statistical analysis is used to discover commonalities or patterns in the data. The results are often reported in graphs and tables.
Applications such as Excel, SPSS, or R can be used to calculate things like:
- Average scores ( means )
- The number of times a particular answer was given
- The correlation or causation between two or more variables
- The reliability and validity of the results
Analyzing qualitative data
Qualitative data is more difficult to analyze than quantitative data. It consists of text, images or videos instead of numbers.
Some common approaches to analyzing qualitative data include:
- Qualitative content analysis : Tracking the occurrence, position and meaning of words or phrases
- Thematic analysis : Closely examining the data to identify the main themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying how communication works in social contexts
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how it is generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2023, June 22). Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved August 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-quantitative-research/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, what is quantitative research | definition, uses & methods, what is qualitative research | methods & examples, mixed methods research | definition, guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- How it works

Quantitative Research Questionnaire – Types & Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 20th, 2024 , Revised On August 21, 2024
Research is usually done to provide solutions to an ongoing problem. Wherever the researchers see a gap, they tend to launch research to enhance their knowledge and to provide solutions to the needs of others. If they want to research from a subjective point of view, they consider qualitative research. On the other hand, when they research from an objective point of view, they tend to consider quantitative research.
There’s a fine line between subjectivity and objectivity. Qualitative research, related to subjectivity, assesses individuals’ personal opinions and experiences, while quantitative research, associated with objectivity, collects numerical data to derive results. However, the best medium to collect data in quantitative research is a questionnaire.
Let’s discuss what a quantitative research questionnaire is, its types, methods of writing questions, and types of survey questions. By thoroughly understanding these key essential terms, you can efficiently create a professional and well-organised quantitative research questionnaire.
What is a Quantitative Research Questionnaire?
Quantitative research questionnaires are preferably used during quantitative research. They are a well-structured set of questions designed specifically to gather specific, close-ended participant responses. This allows the researchers to gather numerical data and obtain a deep understanding of a particular event or problem.
As you know, qualitative research questionnaires contain open-ended questions that allow the participants to express themselves freely, while quantitative research questionnaires contain close-ended and specific questions, such as multiple-choice and Likert scales, to assess individuals’ behaviour.
Quantitative research questionnaires are usually used in research in various fields, such as psychology, medicine, chemistry, and economics.
Let’s see how you can write quantitative research questions by going through some examples:
- How much do British people consume fast food per week?
- What is the percentage of students living in hostels in London?
Types of Quantitative Research Questions With Examples
After learning what a quantitative research questionnaire is and what quantitative research questions look like, it’s time to thoroughly discuss the different types of quantitative research questions to explore this topic more.
Dichotomous Questions
Dichotomous questions are those with a margin for only two possible answers. They are usually used when the answers are “Yes/No” or “True/False.” These questions significantly simplify the research process and help collect simple responses.
Example: Have you ever visited Istanbul?
Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple-choice questions have a list of possible answers for the participants to choose from. They help assess people’s general knowledge, and the data gathered by multiple-choice questions can be easily analysed.
Example: Which of the following is the capital of France?
Multiple Answer Questions
Multiple-answer questions are similar to multiple-choice questions. However, there are multiple answers for participants to choose from. They are used when the questions can’t have a single, specific answer.
Example: Which of the following movie genres are your favourite?
Likert Scale Questions
Likert scale questions are used when the preferences and emotions of the participants are measured from one extreme to another. The scales are usually applied to measure likelihood, frequency, satisfaction, and agreement. The Likert scale has only five options to choose from.
Example: How satisfied are you with your job?
Semantic Differential Questions
Similar to Likert scales, semantic differential questions are also used to measure the emotions and attitudes of participants. The only difference is that instead of using extreme options such as strongly agree and strongly disagree, opposites of a particular choice are given to reduce bias.
Example: Please rate the services of our company.
Rank Order Questions
Rank-order questions are usually used to measure the preferences and choices of the participants efficiently. In this, multiple choices are given, and participants are asked to rank them according to their perspective. This helps to create a good participant profile.
Example: Rank the given books according to your interest.
Matrix Questions
Matrix questions are similar to Likert scales. In Likert scales, participants’ responses are measured through separate questions, while in matrix questions, multiple questions are compiled in a single row to simplify the data collection method efficiently.
Example: Rate the following activities that you do in daily life.
How To Write Quantitative Research Questions?
Quantitative research questions allow researchers to gather empirical data to answer their research problems. As we have discussed the different types of quantitative research questions above, it’s time to learn how to write the perfect quantitative research questions for a questionnaire and streamline your research process.
Here are the steps to follow to write quantitative research questions efficiently.
Step 1: Determine the Research Goals
The first step in writing quantitative research questions is to determine your research goals. Determining and confirming your research goals significantly helps you understand what kind of questions you need to create and for what grade. Efficiently determining the research goals also reduces the need for further modifications in the questionnaire.
Step 2: Be Mindful About the Variables
There are two variables in the questions: independent and dependent. It is essential to decide what would be the dependent variable in your questions and what would be the independent. It significantly helps to understand where to emphasise and where not. It also reduces the probability of additional and vague questions.
Step 3: Choose the Right Type of Question
It is also important to determine the right type of questions to add to your questionnaire. Whether you want Likert scales, rank-order questions, or multiple-answer questions, choosing the right type of questions will help you measure individuals’ responses efficiently and accurately.
Step 4: Use Easy and Clear Language
Another thing to keep in mind while writing questions for a quantitative research questionnaire is to use easy and clear language. As you know, quantitative research is done to measure specific and simple responses in empirical form, and using easy and understandable language in questions makes a huge difference.
Step 5: Be Specific About The Topic
Always be mindful and specific about your topic. Avoid writing questions that divert from your topic because they can cause participants to lose interest. Use the basic terms of your selected topic and gradually go deep. Also, remember to align your topic and questions with your research objectives and goals.
Step 6: Appropriately Write Your Questions
When you have considered all the above-discussed things, it’s time to write your questions appropriately. Don’t just haste in writing. Think twice about the result of a question and then consider writing it in the questionnaire. Remember to be precise while writing. Avoid overwriting.
Step 7: Gather Feedback From Peers
When you have finished writing questions, gather feedback from your researcher peers. Write down all the suggestions and feedback given by your peers. Don’t panic over the criticism of your questions. Remember that it’s still time to make necessary changes to the questionnaire before launching your campaign.
Step 8: Refine and Finalise the Questions
After gathering peer feedback, make necessary and appropriate changes to your questions. Be mindful of your research goals and topic. Try to modify your questions according to them. Also, be mindful of the theme and colour scheme of the questionnaire that you decided on. After refining the questions, finalise your questionnaire.
Types of Survey Questionnaires in Quantitative Research
Quantitative research questionnaires have close-ended questions that allow the researchers to measure accurate and specific responses from the participants. They don’t contain open-ended questions like qualitative research, where the response is measured by interviews and focus groups. Good combinations of questions are used in the quantitative research survey .
However, here are the types of surveys in quantitative research:
Descriptive Survey
The descriptive survey is used to obtain information about a particular variable. It is used to associate a quantity and quantify research variables. The questions associated with descriptive surveys mostly start with “What is” and “How much”.
Example: A descriptive survey to measure how much money children spend to buy toys.
Comparative Survey
A comparative survey is used to establish a comparison between one or more dependable variables and two or more comparison groups. This survey aims to form a comparative relation between the variables under study. The structure of the question in a comparative survey is, “What is the difference in [dependable variable] between [two or more groups]?”.
Example: A comparative survey on the difference in political awareness between Eastern and Western citizens.
Relationship-Based Survey
Relationship-based survey is used to understand the relationship or association between two or more independent and dependent variables. Cause and effect between two or more variables is measured in the relationship-based survey. The structure of questions in a relationship-based survey is, “What is the relation [between or among] [independent variable] and [dependable variable]?”.
Example: What is the relationship between education and lifestyle in America?
Advantages & Disadvantages of Questionnaires in Quantitative Research
Quantitative research questionnaires are an excellent tool to collect data and information about the responses of individuals. Quantitative research comes with various advantages, but along with advantages, it also has its disadvantages. Check the table below to learn about the advantages and disadvantages of a quantitative research questionnaire.
| It is an efficient source for quickly collecting data. | It restricts the depth of the topic during collection. |
| There is less risk of subjectivity and research bias. | There is a high risk of artificial and unreal expectations of research questions. |
| It significantly helps to collect extensive insights into the population. | It overemphasises empirical data, avoiding personal opinions. |
| It focuses on simplicity and particularity. | There is a risk of over-simplicity. |
| There are clear and achievable research objectives. | There is a risk of additional amendments and modifications. |
Quantitative Research Questionnaire Example
Here is an example of a quantitative research questionnaire to help you get the idea and create an efficient and well-developed questionnaire for your research:


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Examples of Quantitative Market Research. To illustrate the practical applications of quantitative market research, let's explore some real-world examples: Netflix A/B Testing Titles. Ever noticed how Netflix displays different titles or artwork for the same movie or show depending on your profile? This is A/B testing, a form of quantitative ...
Here, I've detailed 23 use cases and curated 98 quantitative market research questions with examples - making this a post you should add to your bookmark list , so you can quickly refer back. I've formatted this post to show you 10-15 questions for each use case. At the end of each section, I also share a quicker way to get similar ...
Quantitative market research is defined as a type of research that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to understand market trends, consumer behavior, and other business-related variables. Learn more about quantitative market research methods, examples and best practices.
Quantitative market research is conducted under two broad buckets of the frequency they are administered at: Cross-sectional research survey: Cross-sectional market research is a quantitative market research method that analyzes data of variables collected at one given point of time across a sample population. population or a pre-defined subset ...
Quantitative market research is a numbers game. It's one of the four types of traditional market research; and a tried, trusted, and proven way to get answers to strategically important questions.. Whether you're already familiar with quantitative research, looking for practical examples, or considering using it in your business, I will cover everything you need to know.
In the world of market research, quantitative data is the lifeblood that fuels strategic decision-making, product innovation and competitive analysis.. This type of numerical data is a vital part of any market research professional's toolkit because it provides measurable and objective evidence for the effectiveness of market and consumer behavioral insights.
Quantitative market research is a systematic approach to gathering and analyzing data from a target market. It relies on numerical data and statistical analysis to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. This method involves collecting data through structured surveys, questionnaires, and experiments conducted with a large sample ...
Advantages: Disadvantages: Larger sample sizes: Since quantitative research surveys are smaller and easier to fill, you can distribute them to a larger audience in a given time.: Lack of specific data: Since the focus is on numbers, you could end up with inconclusive results.For example, the number of unsatisfied customers but no clue why. Easy analysis: Since the data is numerical, it's ...
Quantitative research generally relies on a larger sample size in order to quantify any issue or variable. In order to achieve this, this research method involves using mathematical and statistical means. This type of research answers the "what" and the "how much" of a subject within a research endeavor.
This method is widely used in market research to gather information about customer behavior, opinions, and preferences. Here are some of the benefits of quantitative market research: 1. Large Sample Size: One of the significant benefits of quantitative research is the ability to collect data from a large sample size. This provides a more ...
Quantitative research. Quantitative research, in contrast to qualitative research, involves the collection and analysis of numerical data, often through surveys, experiments and structured questionnaires. ... Apple's iconic iPhone launch in 2007 serves as a prime example of market research driving product innovation in tech. Before the iPhone ...
36 Quantitative research questions and examples. If you want to make a quantitative survey that hits the spot, don't just ask generic questions. We're here with some examples that you can adapt to make your research a success. Descriptive market research questions
For example, focus groups, one-on-one interviews, case studies, etc are popular qualitative methods of market research. Quantitative Market Research Methods; Quantitative market research focuses on data-intensive methods that return solid data that can be quantitatively analyzed in bulk. These methods often rely on a large sample of respondents ...
Examples include published market studies, white papers, analyst reports, customer emails, and customer surveys/feedback. For many small businesses with limited budgets, secondary market research is their first choice because it's easier to acquire and far more affordable than primary research. Secondary research can still answer specific ...
Quantitative research is a type of research that focuses on collecting and analyzing numerical data to answer research questions. There are two main methods used to conduct quantitative research: 1. Primary Method. There are several methods of primary quantitative research, each with its own strengths and limitations.
Quantitative vs qualitative research. While the quantitative research definition focuses on numerical data, qualitative research is defined as data that supplies non-numerical information. Quantitative research focuses on the thoughts, feelings, and values of a participant, to understand why people act in the way they do.
Sample size: Quantitative research is conducted on a significant sample size representing the target market. Appropriate Survey Sampling methods, a fundamental aspect of quantitative research methods, must be employed when deriving the sample to fortify the research objective and ensure the reliability of the results.
Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio). Quantitative research is widely used in the natural and social sciences: biology, chemistry, psychology, economics, sociology, marketing, etc. Quantitative research question examples
Quantitative research has many applications across a wide range of fields. Here are some common examples: Market Research: Quantitative research is used extensively in market research to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform ...
Here are three examples of quantitative research in motion. Example 1: Leading food distribution company. We helped a leading food distribution company identify changes in the needs and values of their restaurant clients as a result of COVID-19. This helped inform opportunities to become more valuable partners.
There are numerous questions and ways to analyze sales data and it certainly is a key option in terms of market research. 6. Interviews. Market research interviews can come in a variety of ways including through: Interviews as part of a focus group; Semi-structured of structured one-on-one interviews
Here are a few examples of how market research has recognized and taken advantage of these opportunities: The rise of plant-based diets: ... Quantitative research. Quantitative research, on the other hand, involves collecting numerical data and analyzing it statistically. This can be done through surveys, experiments, or data analysis.
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge. Quantitative research. Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions.
Types of Survey Questionnaires in Quantitative Research. Quantitative research questionnaires have close-ended questions that allow the researchers to measure accurate and specific responses from the participants. They don't contain open-ended questions like qualitative research, where the response is measured by interviews and focus groups.