Essay on Life on Mars for Students and Children
500 words essay on life on mars.
Mars is the fourth planet from the sun in our solar system. Also, it is the second smallest planet in our solar system. The possibility of life on mars has aroused the interest of scientists for many years. A major reason for this interest is due to the similarity and proximity of the planet to Earth. Mars certainly gives some indications of the possibility of life.


Possibilities of Life on Mars
In the past, Mars used to look quite similar to Earth. Billions of years ago, there were certainly similarities between Mars and Earth. Furthermore, scientists believe that Mars once had a huge ocean. This ocean, experts believe, covered more of the planet’s surface than Earth’s own oceans do so currently.
Moreover, Mars was much warmer in the past that it is currently. Most noteworthy, warm temperature and water are two major requirements for life to exist. So, there is a high probability that previously there was life on Mars.
Life on Earth can exist in the harshest of circumstances. Furthermore, life exists in the most extreme places on Earth. Moreover, life on Earth is available in the extremely hot and dry deserts. Also, life exists in the extremely cold Antarctica continent. Most noteworthy, this resilience of life gives plenty of hope about life on Mars.
There are some ingredients for life that already exist on Mars. Bio signatures refer to current and past life markers. Furthermore, scientists are scouring the surface for them. Moreover, there has been an emergence of a few promising leads. One notable example is the presence of methane in Mars’s atmosphere. Most noteworthy, scientists have no idea where the methane is coming from. Therefore, a possibility arises that methane presence is due to microbes existing deep below the planet’s surface.
One important point to note is that no scratching of Mars’s surface has taken place. Furthermore, a couple of inches of scratching has taken place until now. Scientists have undertaken analysis of small pinches of soil. There may also have been a failure to detect signs of life due to the use of faulty techniques. Most noteworthy, there may be “refugee life” deep below the planet’s surface.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Challenges to Life on Mars
First of all, almost all plants and animals cannot survive the conditions on the surface of Mars. This is due to the extremely harsh conditions on the surface of Mars.
Another major problem is the gravity of Mars. Most noteworthy, the gravity on Mars is 38% to that of Earth. Furthermore, low gravity can cause health problems like muscle loss and bone demineralization.
The climate of Mars poses another significant problem. The temperature at Mars is much colder than Earth. Most noteworthy, the mean surface temperatures of Mars range between −87 and −5 °C. Also, the coldest temperature on Earth has been −89.2 °C in Antarctica.
Mars suffers from a great scarcity of water. Most noteworthy, water discovered on Mars is less than that on Earth’s driest desert.
Other problems include the high penetration of harmful solar radiation due to the lack of ozone layer. Furthermore, global dust storms are common throughout Mars. Also, the soil of Mars is toxic due to the high concentration of chlorine.
To sum it up, life on Mars is a topic that has generated a lot of curiosity among scientists and experts. Furthermore, establishing life on Mars involves a lot of challenges. However, the hope and ambition for this purpose are well alive and present. Most noteworthy, humanity must make serious efforts for establishing life on Mars.
FAQs on Life on Mars
Q1 State any one possibility of life on Mars?
A1 One possibility of life on Mars is the resilience of life. Most noteworthy, life exists in the most extreme places on Earth.
Q2 State anyone challenge to life on Mars?
A2 One challenge to life on Mars is a great scarcity of water.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Essay on Mars
Students are often asked to write an essay on Mars in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Mars
Mars: an introduction.
Mars, also known as the Red Planet, is the fourth planet from the sun in our solar system. It gets its nickname from its reddish appearance, caused by iron oxide (rust) on its surface.
Physical Features
Mars has the tallest volcano and the deepest canyon in the solar system. Olympus Mons is the volcano, and Valles Marineris is the canyon. Mars also has polar ice caps made of water and carbon dioxide.
Life on Mars
Scientists have not found life on Mars yet. However, they believe that the planet may have had conditions suitable for life in the past. Now, Mars is too cold and dry for life.
Mars Exploration
Several spacecrafts have been sent to Mars. These missions help scientists learn about the planet’s climate and geology, and search for signs of life. The Mars rovers, like Perseverance, are particularly important in this exploration.
Also check:
- 10 Lines on Mars
- Paragraph on Mars
250 Words Essay on Mars
Introduction.
Mars, the fourth planet from the sun in our solar system, has been a subject of fascination for scientists and space enthusiasts for centuries. This celestial body, often referred to as the ‘Red Planet’, has been explored by numerous space missions, providing us with valuable insights.
Geographical Features
Mars exhibits a variety of geographical features that are similar to Earth’s. It hosts the largest volcano in the solar system, Olympus Mons, and a grand canyon, Valles Marineris, which is nearly five times the depth of Earth’s Grand Canyon. The planet’s reddish appearance is due to iron oxide, or rust, on its surface.
Atmospheric Conditions
Mars’ thin atmosphere, composed primarily of carbon dioxide, provides inadequate protection from solar radiation. This makes the planet’s surface inhospitable to known life forms. The average temperature on Mars is a chilly -80 degrees Fahrenheit, with polar ice caps composed of water and carbon dioxide.
Search for Life
The search for life on Mars has been a primary goal of numerous missions. While no definitive evidence of past or present life has been found, scientists have discovered signs of liquid water and organic molecules, which are the building blocks of life.
Future Exploration
Future missions to Mars aim to answer questions about its geology, climate, and potential for life. The recent Perseverance rover mission by NASA and the planned human missions signify our continuous quest to unravel the mysteries of this intriguing planet.
In conclusion, Mars, with its similarities and differences to Earth, continues to captivate our curiosity, pushing the boundaries of our knowledge and technological capabilities in space exploration.
500 Words Essay on Mars
The red planet: an overview.
Mars, often referred to as the Red Planet due to its reddish appearance, is the fourth planet from the Sun in our solar system. Its distinct color is attributed to iron oxide, or rust, on its surface. It is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere, possessing surface features both reminiscent of both Earth and the moon.
Geographical Features and Atmosphere
Mars has the highest mountain and the deepest, longest canyon in the solar system. Olympus Mons, the highest mountain, is nearly three times the height of Mount Everest, which is about 5.5 miles high. Valles Marineris, the longest canyon, would stretch from New York City to Los Angeles on Earth. Mars’ atmosphere is composed primarily of carbon dioxide (about 96%), with minor amounts of other gases such as argon and nitrogen. The climate on Mars is much colder than on Earth, with an average temperature around -80 degrees Fahrenheit.
Exploration of Mars
The exploration of Mars has been an important part of the space exploration programs of several countries. The first successful flyby of Mars was by Mariner 4 in 1965. Since then, numerous spacecraft have been sent to explore Mars, including the Viking missions in the 1970s and, more recently, the Mars Rover missions. The primary focus of these missions is to search for evidence of past or present life on Mars.
Potential for Life
The question of life on Mars centers around the planet’s past and present habitability, or its potential to host life. While no direct evidence of past or present biological activity has been found, several pieces of evidence suggest that Mars could have supported life in the past. For instance, the discovery of ancient riverbeds and polar ice caps implies that liquid water, an essential ingredient for life as we know it, once existed on the planet’s surface.
Human Settlement
The prospect of human settlement on Mars has been a tantalizing challenge for scientists and engineers. The technical and logistical hurdles are significant, including the need for life support systems, sustainable food production, and protection from solar and cosmic radiation. Despite these challenges, organizations like NASA and SpaceX are actively working towards making human Mars missions a reality in the foreseeable future.
Mars, with its similarities to Earth and its potential for harboring life, continues to captivate our curiosity. The ongoing exploration of this fascinating planet not only expands our understanding of the universe but also propels us towards becoming a multi-planetary species. As we continue to explore Mars, we may not only answer the age-old question of whether we are alone in the universe but also set the stage for our future as space explorers.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Sangai of Manipur
- Essay on Manipur Tourism
- Essay on Manipur
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

A Trip to Mars: Mass Facts Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Facts about Mass
Food and accommodation, safety risks, works cited.
Mars is one of the eight major planets that form the solar system together with the sun. Mars is the fourth planet from the sun, and it takes about 686.93 days to completely revolve around it. The atmosphere of Mars is estimated to be less than 1% of that of the earth.
Its atmosphere is so thin that it can neither retain heat within the surface, nor prevent the planet from receiving strong radiations from the sun. The atmosphere comprises about 95% carbon dioxide, 1.6% argon, 2.7% nitrogen, 0.13% oxygen, and 0.03% water (Coffey 1).
Apart from its unique atmosphere, Mars has other interesting features that other planets do not have. Firstly, the planet has the tallest volcano in the entire solar system. The volcanic mountain is called Olympus Mons and it is approximately 27 kilometers in height above the plains surrounding it.
The volcano is still active as evident by the lava that flows from it. Additionally, Mars has the most extensive and deepest gorge in the entire solar system, which is called the Marineris Valley. The canyon covers a distance of approximately 4,000 kilometers along the planet’s equator and stretches for a depth of about 7 kilometers into the ground (Cain 1).
In addition, Mars is regarded as the only other planet apart from the earth that can support life. Mars has an atmosphere that is composed of gasses such as carbon dioxide, argon, nitrogen and oxygen. Mars also has water, which is also one of the essential elements that support life. The planet’s water exists in liquid form just like it does on earth, which has numerous living things (Cain 1).
The trip to Mars can take a long time, but that depends on the date of the trip. The shortest distance between the earth and Mars is approximately 55 kilometers, which occurs when the former and the latter are at their farthest and closest points from the sun respectively. When the two planets are on opposite sides, the distance between them can go as far as 401 kilometers.
The trip to Mars could take about 160 days if it started on the right time of the year. The trip will be made comfortable as much as possible by providing the passengers with luxurious items, such as cameras for capturing the unique features found on the planet. The trip to Mars is worth it since it will provide the passengers with an opportunity observto e the unique features found on the planet.
The passengers involved in the trip to Mars will be provided with higthe h-quality packed food and the best accommodation facilities to make their trip interesting and comfortable. The passengers will be provided with a variety of foodstuffs that are sufficient for the entire journey. The passengers will also be given insulating jackets and blankets to protect them from the strong radiations, which fall on the surface of the planet.
There are a few safety risks that may arise during the trip. Firstly, the spacecraft might develop mechanical problems during the journey. Secondly, the passengers may be adversely affected by the strong radiations hitting Mars’ surface as a result of the thin atmosphere of the planet.
However, these risks will be well provided for to ensure that the journey remains successful and comfortable. The first risk will be mitigated by using a spacecraft that has been severally tested for efficiency. The second risk will be prevented by using a spacecraft with a highly polished surface that can reflect the dangerous radiations from the sun.
Cain, Fraser. “Interesting Facts About Planet Mars.” Universe Today , 2008. Web.
Coffey, Jerry. “Atmosphere of Mars.” Universe Today, 2008. Web.
- Japanese Society in "The Magic Chalk" by Abe Kobo
- The Planet Mars Information
- “Mars the Abode of Life” by Percival Lowell
- Telescope's Part in Astronomy
- Astronomy Issues: Life on Mars
- An Artificial Satellite
- The Usefulness of Earth Observation Satellites
- NASA's Lunar Surveyor Program
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, March 15). A Trip to Mars: Mass Facts. https://ivypanda.com/essays/a-trip-to-mars/
"A Trip to Mars: Mass Facts." IvyPanda , 15 Mar. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/a-trip-to-mars/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'A Trip to Mars: Mass Facts'. 15 March.
IvyPanda . 2020. "A Trip to Mars: Mass Facts." March 15, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/a-trip-to-mars/.
1. IvyPanda . "A Trip to Mars: Mass Facts." March 15, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/a-trip-to-mars/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "A Trip to Mars: Mass Facts." March 15, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/a-trip-to-mars/.
Our Students Can’t Write Very Well—It’s No Mystery Why
- Share article
My organization decided a few weeks back that we needed to hire a new professional staff person. We had close to 500 applicants. Inasmuch as the task was to help us communicate information related to the work we do, we gave each of the candidates one of the reports we published last year and asked them to produce a one-page summary. All were college graduates. Only one could produce a satisfactory summary. That person got the job.
We were lucky this time. We are more often than not disappointed at the subpar writing ability of the applicants for openings at our organization. Many applicants are from very good colleges. Many have graduate degrees. Many are very poor writers.
Their lack of writing ability does not augur well. When we look at what they have written, the logic of the narrative is often very hard to find. It would appear that their lack of writing ability stands as mute testimony to their lack of thinking ability.
How, we ask, could this have happened? The answers are not hard to find. My friend Will Fitzhugh points out that high school students are rarely required to read entire works of fiction and are almost never asked to read entire works of non-fiction. I know of no good writers who are not also good readers.
More directly to the point, high school students are hardly ever asked to write anything of significant length. Why not? Because in this age of accountability, they are not tested on their writing ability. By which I mean that they are not asked to submit to the testing authorities 10- or 15- or 20-page papers in which they are expected to present a thesis and defend it, analyze something complicated from multiple points of view and draw a reasoned conclusion, or put together a short story in which characters are developed in some depth and insights are revealed.
This point is critically important. There is only one way that we can find out whether a student can write a substantial research paper—by asking them to write a substantial research paper and looking carefully at the result. If we do not ask them to produce this product—over and over again, as they get better and better at it—then they will not be able to do it well. If they have not done the work, then neither their teacher nor the engines of the accountability system can assess it. If this sort of serious writing is not done and—in our accountability-oriented environment—is not assessed, then it will not be learned. End of argument.
Oh, sure, we have tests of writing ability for college-bound students, but they do not ask the student to produce anything like what we asked our candidates to produce. They ask a student to choose one word or phrase from a list to fill in the blank in a passage. That is not writing. It is something else. PARCC and Smarter Balanced assessments have made progress in more effectively evaluating the writing skills of our students, but many states are actively taking steps away from these types of assessment tasks. And it is of course true that asking a student to write a one-page summary of a longer piece is no test of their ability to write a well-argued, fact-based, 10- or 20-page research paper.
We are fond of producing long lists of things we want 21 st century students to be able to do. But the ability to write well and think critically always tops the list, both because so much work requires these skills and because they are so fundamental to so many other kinds of cognitive activity we value. What could be more central to a good education?
So it is simply unbelievable that we do not build our curriculum around the assumption that we will be asking students to read demanding books—not just parts of books, but whole books—and then asking them to write, at length and in detail, about what they have read, explicating, analyzing, synthesizing and summarizing it, with insight and narrative skill that demonstrates their ability to think clearly. Isn’t that the heart of the matter?
Writing is a craft. Like any other craft, it is learned only by doing it, over and over and over, at increasing levels of challenge, under the watchful eye of an expert. How on earth are our students to learn to write if we do not ask them to write, and write a lot, and write well? The reason, of course, that they are not asked to write much is because their ability to write a substantial paper is not tested. And why, in this age of accountability, when we judge teachers by how well their students do on the test, would we expect their students to write well when we do not test their ability to write a good paper, 10 to 20 pages in length?
Our own research tells us that a large fraction of community college professors do not assign writing to their students because their students cannot write and the professors do not consider themselves to be writing teachers. It is no wonder that employers like us find it so hard to find candidates with serviceable writing skills.
What do you suppose would happen if a state announced one day that it was redesigning its accountability system and half of a teachers’ rating would henceforth depend on their students’ grades on long research papers in the subject taught by that teacher—papers, say, at least 15 pages long at the high school level? They might be told that that grade would depend on the way evidence was presented and marshaled, the range of the evidence presented, the depth of the analytical ability displayed in the essay, the logic and persuasiveness of the argument made, and so on.
I am not arguing that we should do this, but simply making the point that if we really cared about the ability of our students to think and write well, we would assign substantial papers frequently, critique those papers effectively, and expect students to write well long before they left high school. It is hard to reach any conclusion on this point other than that we simply don’t care whether or not our students can write effectively, if we judge by what is assigned to students, what is expected of students, the instruction we offer students, the way we evaluate their work, the design of our accountability systems or our criteria for graduating students from high school.
But assume for the moment that all these issues were addressed. Can we then assume that our students would be graduating high schools able to think clearly and write well? I don’t think so.
I said in passing above that writing is a craft and crafts are best learned by apprenticing oneself to an expert, in this case an expert writer. This suggests that if our students are to become good writers, they will have to get their work critiqued in detail by teachers who are themselves good writers.
But I also said at the beginning of this blog that we and many other employers are having a very hard time hiring anyone who is a good writer, even graduates of leading universities and graduate schools. We know that most of our teachers come not from our leading universities but from institutions that get their students from the lower half of the distribution of high school graduates going to college. If there is no reason to assume that the graduates of the leading institutions are themselves good writers, what would make us assume that the graduates of less demanding institutions are better writers?
It is true that many universities require applicants to submit a short essay as part of their application. But I am willing to bet that few, if any, require their applicants to do something as straightforward as our request to our job applicants to summarize a complex research paper in one page, on demand, in a short time, capturing all the key points and creating a narrative that makes sense of it all for the reader.
If we do not demand that those who want to become teachers are themselves very good writers, why would we expect our teachers to be good teachers of writing? We should, in fact, be requiring our candidates for teaching positions to write 20-page papers of their own which analyze and summarize a topic from the literature in their field. We should be asking them to produce, on demand, a one-page summary of something they are given to read that is complicated and difficult.
But we don’t do any of these things. So, once again, I conclude that we are not serious. We are not serious about teaching students to reason and write well and we are not serious about hiring teachers who have the skills needed to teach our students how to reason and write well. We are no doubt lucky to have many teachers who know how to read and write critically and care enough to pass those skills on to their students. But if these core skills were really important to us, we would be making very large changes in curriculum, demanding much more reading of complete novels and non-fiction, asking our students to write much longer papers much more frequently, providing expert and copious commentary on what they had written, changing our accountability systems to reflect these priorities and, not least, we would be making sure that our teachers are themselves very good writers.
I very much doubt that our high school graduates write less well than high school graduates used to write. But jobs for truck drivers, hamburger flippers and grocery store check out clerks are disappearing fast. This is just one more—but crucially important—arena in which our education system is failing to adapt to a fast-changing environment.
The opinions expressed in Top Performers are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Would you like to explore a topic?
- LEARNING OUTSIDE OF SCHOOL
Or read some of our popular articles?
Free downloadable english gcse past papers with mark scheme.
- 19 May 2022
The Best Free Homeschooling Resources UK Parents Need to Start Using Today
- Joseph McCrossan
- 18 February 2022
How Will GCSE Grade Boundaries Affect My Child’s Results?
- Akshat Biyani
- 13 December 2021
How to Write the Perfect Essay: A Step-By-Step Guide for Students
- June 2, 2022

- What is an essay?
What makes a good essay?
Typical essay structure, 7 steps to writing a good essay, a step-by-step guide to writing a good essay.
Whether you are gearing up for your GCSE coursework submissions or looking to brush up on your A-level writing skills, we have the perfect essay-writing guide for you. 💯
Staring at a blank page before writing an essay can feel a little daunting . Where do you start? What should your introduction say? And how should you structure your arguments? They are all fair questions and we have the answers! Take the stress out of essay writing with this step-by-step guide – you’ll be typing away in no time. 👩💻

What is an essay?
Generally speaking, an essay designates a literary work in which the author defends a point of view or a personal conviction, using logical arguments and literary devices in order to inform and convince the reader.
So – although essays can be broadly split into four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive – an essay can simply be described as a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. 🤔
The purpose of an essay is to present a coherent argument in response to a stimulus or question and to persuade the reader that your position is credible, believable and reasonable. 👌
So, a ‘good’ essay relies on a confident writing style – it’s clear, well-substantiated, focussed, explanatory and descriptive . The structure follows a logical progression and above all, the body of the essay clearly correlates to the tile – answering the question where one has been posed.
But, how do you go about making sure that you tick all these boxes and keep within a specified word count? Read on for the answer as well as an example essay structure to follow and a handy step-by-step guide to writing the perfect essay – hooray. 🙌
Sometimes, it is helpful to think about your essay like it is a well-balanced argument or a speech – it needs to have a logical structure, with all your points coming together to answer the question in a coherent manner. ⚖️
Of course, essays can vary significantly in length but besides that, they all follow a fairly strict pattern or structure made up of three sections. Lean into this predictability because it will keep you on track and help you make your point clearly. Let’s take a look at the typical essay structure:
#1 Introduction
Start your introduction with the central claim of your essay. Let the reader know exactly what you intend to say with this essay. Communicate what you’re going to argue, and in what order. The final part of your introduction should also say what conclusions you’re going to draw – it sounds counter-intuitive but it’s not – more on that below. 1️⃣
Make your point, evidence it and explain it. This part of the essay – generally made up of three or more paragraphs depending on the length of your essay – is where you present your argument. The first sentence of each paragraph – much like an introduction to an essay – should summarise what your paragraph intends to explain in more detail. 2️⃣
#3 Conclusion
This is where you affirm your argument – remind the reader what you just proved in your essay and how you did it. This section will sound quite similar to your introduction but – having written the essay – you’ll be summarising rather than setting out your stall. 3️⃣
No essay is the same but your approach to writing them can be. As well as some best practice tips, we have gathered our favourite advice from expert essay-writers and compiled the following 7-step guide to writing a good essay every time. 👍
#1 Make sure you understand the question
#2 complete background reading.
#3 Make a detailed plan
#4 Write your opening sentences
#5 flesh out your essay in a rough draft, #6 evidence your opinion, #7 final proofread and edit.
Now that you have familiarised yourself with the 7 steps standing between you and the perfect essay, let’s take a closer look at each of those stages so that you can get on with crafting your written arguments with confidence .
This is the most crucial stage in essay writing – r ead the essay prompt carefully and understand the question. Highlight the keywords – like ‘compare,’ ‘contrast’ ‘discuss,’ ‘explain’ or ‘evaluate’ – and let it sink in before your mind starts racing . There is nothing worse than writing 500 words before realising you have entirely missed the brief . 🧐
Unless you are writing under exam conditions , you will most likely have been working towards this essay for some time, by doing thorough background reading. Re-read relevant chapters and sections, highlight pertinent material and maybe even stray outside the designated reading list, this shows genuine interest and extended knowledge. 📚
#3 Make a detailed plan
Following the handy structure we shared with you above, now is the time to create the ‘skeleton structure’ or essay plan. Working from your essay title, plot out what you want your paragraphs to cover and how that information is going to flow. You don’t need to start writing any full sentences yet but it might be useful to think about the various quotes you plan to use to substantiate each section. 📝
Having mapped out the overall trajectory of your essay, you can start to drill down into the detail. First, write the opening sentence for each of the paragraphs in the body section of your essay. Remember – each paragraph is like a mini-essay – the opening sentence should summarise what the paragraph will then go on to explain in more detail. 🖊️
Next, it's time to write the bulk of your words and flesh out your arguments. Follow the ‘point, evidence, explain’ method. The opening sentences – already written – should introduce your ‘points’, so now you need to ‘evidence’ them with corroborating research and ‘explain’ how the evidence you’ve presented proves the point you’re trying to make. ✍️
With a rough draft in front of you, you can take a moment to read what you have written so far. Are there any sections that require further substantiation? Have you managed to include the most relevant material you originally highlighted in your background reading? Now is the time to make sure you have evidenced all your opinions and claims with the strongest quotes, citations and material. 📗
This is your final chance to re-read your essay and go over it with a fine-toothed comb before pressing ‘submit’. We highly recommend leaving a day or two between finishing your essay and the final proofread if possible – you’ll be amazed at the difference this makes, allowing you to return with a fresh pair of eyes and a more discerning judgment. 🤓
If you are looking for advice and support with your own essay-writing adventures, why not t ry a free trial lesson with GoStudent? Our tutors are experts at boosting academic success and having fun along the way. Get in touch and see how it can work for you today. 🎒

Popular posts

- By Guy Doza

- By Joseph McCrossan
- In LEARNING TRENDS

- By Akshat Biyani

4 Surprising Disadvantages of Homeschooling
- By Andrea Butler

What are the Hardest GCSEs? Should You Avoid or Embrace Them?
- By Clarissa Joshua
1:1 tutoring to unlock the full potential of your child
More great reads:.

Benefits of Reading: Positive Impacts for All Ages Everyday
- May 26, 2023

15 of the Best Children's Books That Every Young Person Should Read
- By Sharlene Matharu
- March 2, 2023

Ultimate School Library Tips and Hacks
- By Natalie Lever
- March 1, 2023
Book a free trial session
Sign up for your free tutoring lesson..
The UnEssay
This week marks the end of my first year of teaching at Appalachian State University. It has been great getting to know my colleagues in the anthro department and learning to live in the mountains (before coming here we lived in South Bend, IN, which is a lot flatter than Boone, NC…In South Bend you can watch your dog run away for 2 days). I’ve been teaching two of the General Education courses in the department ( Our Primate Heritage and Gender, Race, & Class ). It has been a lot of fun thinking about how to work with students who are, for the most part, not anthropology majors.
There is something special about talking with students who will most likely never take another anthropology class. As our job is to produce the next generation of teacher-scholars, having the opportunity to talk about anthropology to a wider audience of college students is a great privilege. I’ve been humbled and overwhelmed by some of the comments students have made about how much they’ve learned.
Of course, there are drawbacks to large lecture courses. One is how to assess grades. I don’t really like the idea of grades at all and would love the idea to have an ungraded class , something I may try in the future. But this semester I was stuck with figuring out a way to grade ~100 students in each of my classes. I spent awhile reading about the best way to write multiple choice questions and how many possible answers each question should have (as an aside, the history of MC tests is amazing and a bit suprising .
But I wanted to incorporate something else.
I didn’t think asking for a research paper would work and even a personal essay seemed a bit much. Awhile back I stumbled upon the idea of an UnEssay. I don’t remember where I first saw it mentioned (maybe on Twitter…) but I found a number of useful online resources ( 1 , 2 , 3 ).
Sadly, creativity has been “educated out” of us. An UnEssay project gives students a way to creatively interact with the class themes. In this project, students pick a topic that interests them and then they think of a way to produce something that touches on the theme. It can be a standard writing assignment or something totally different. The idea of having students choose not just the topic but the medium in which they can best present their ideas seemed to jell with the themes of my classes and would give non-majors a chance to explore the topic in a way that is meaningful to them. After reading a few examples I put this assignment together (see end of post for prompt I gave students. I tried to note where the ideas came from but please let me know if I missed something).
I was thrilled and amazed by the results!
Just to give you some ideas of the project students submitted:
a cross-stich of a human skull
a number of ‘Buzzfeed style’ lists about evolution, gender, feminist movies, and other interesting topics presented with the mix of facts and humor.
a Dungeons & Dragons style role-playing game about evolution.
attempts to make stone tools.
A website where you can design your own baby that looks at the ethics of gene editing/
A magazine-style story on Homo floresiensis .
A water color about breastfeeding.
Comic strips about primates, the island rule, and pronoun use.
Clay sculptures of hominin skulls.
A video about HB2 law in North Carolina.
A YouTube video on intersex, set to “Born This Way”"
A play about life as Fa’afafine
A canvas about gender roles and fluidity
a ‘zine’ on socioeconomic class
a lesson plan on primates designed for 8th graders
Amazing and creative essays on diverse topics such as transgender rights, Black Lives Matter, personal reflection on course topics, and in-depth discussions of human evolution
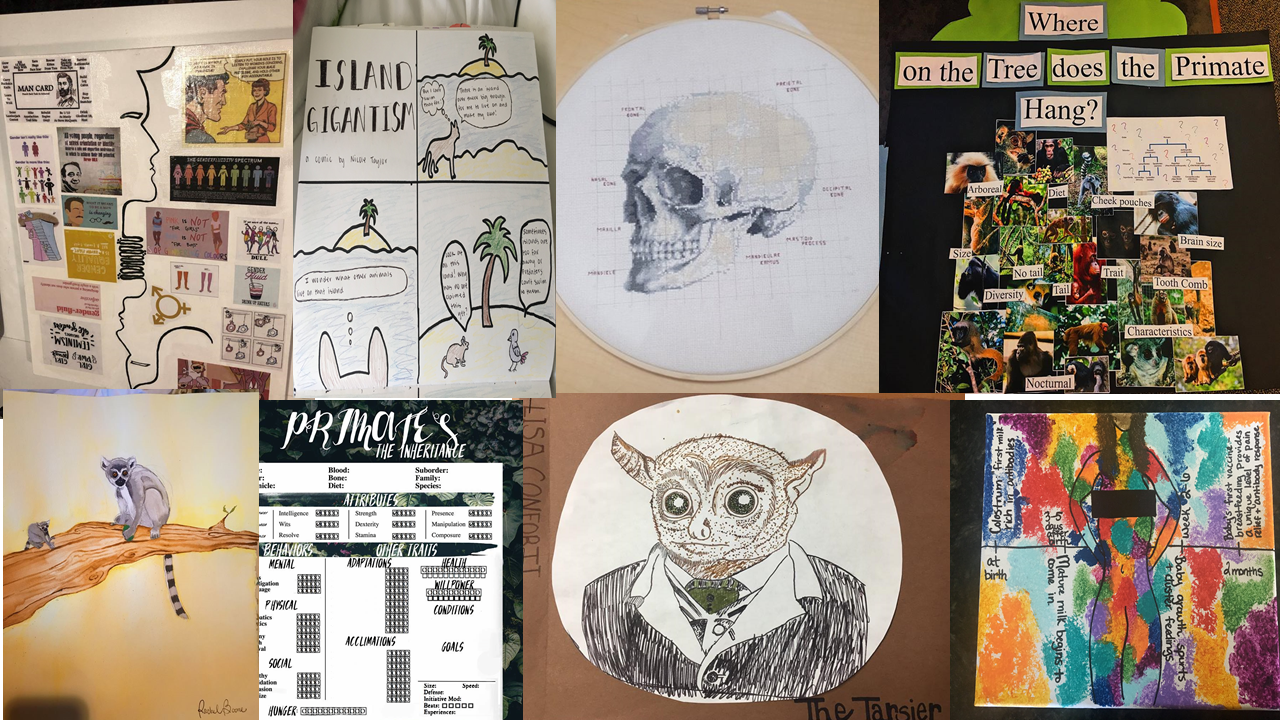

What I learned
My students are amazingly creative! This was the first time I didn’t feel I was in “Grading Jail.” Over 90% of the projects were well done and fun to see and I looked forward to each submission. The students who choose to write essays/research papers were able to write without worrying about the specific format or if I’d take off for the wrong font size (something which can be important for other projects, but not this one).
I hope to do this in the future. One thing I would change is to have the option to let students share their projects with the class. I didn’t think about that ahead of time. Some of them were deeply personal but others were almost too good not to share.
Of course, there are drawbacks. It involves rethinking grading and perhaps the goal of a class. And students who want to continue in anthropology may need the practice of writing. But they can get that in other classes. Students at App take a mandatory writing class so it is not like they need the practice writing (one student commented that this project was the first time she didn’t have to write for a class and it made her excited to explore other media). I imagine there are many classes where this kind of project won’t work
As Susan Blum notes , most of us who become professors do so because we excelled at learning in a school setting. But that doesn’t hold for all of our students, most of whom are not like us and learn best outside of the classroom. Finding ways to reach students who don’t learn the way we did is difficult (…and teaching itself is damn hard…) but can be very rewarding.
Class project “unessay”
Overview and reasoning :.
Due to the class size and the need to get tests graded quickly, I’m forced to use multiple choice exams. However, not all students test well in these conditions. I have been trying to find a way to let you engage with the material in a way that allows you to use one of the most important aspects of being human: Imagination. In that vein, the main project for this class will be an unessay, a project which allows you to engage with the material in any way you see fit.
Creativity is at the heart of what makes us human (See The Human Spark by Agustin Fuentes). Imagination and creativity allow us find answers to problems in unique ways. Even if 1,000 people looked at the same issue, you bring a unique and distinctive view to the question based on your personal lived experiences. However, and quite sadly, creativity has been mostly “educated out” of us (see Out of Our Minds: Learning to be Creative by Ken Robinson for more on this). This is an experiment in a different way of letting you explore the class materials and topics in a way that is salient to your own goals in college (which are most likely different than mine!).
You can choose your own topic! You can present it how you please (written word, illustrations, music, video, etc.)! You can work in groups or on your own!
Over the first few weeks of class think about a topic of relevance to the course that you think is interesting, important, and relevant to you. In other words, you can choose your own topic as long as it can be associated with the course material. Then you figure out how you want to present it. It can be a standard research paper if you wish (in fact, if I were taking this class I might go that route…) or something very different. Some possible examples:
Make a music video about human evolution, primate behavior, etc. (look on YouTube for examples…).
Recreate an ancient technology like stone tools, wooden spears, etc.
Make a series of songs (like a musical or opera).
Write a play.
Create a series of cartoons or a comic book that illustrates something associated with this class
Watercolor/painting/charcoal artwork
Write a longform essay on a subject (designer babies, ape personhood, eugenics) that you post to a sharing site
Create a website/Wik about the topic
Collect specific data and analyses/present it in a unique way
Make a series of Buzzfeed style listicles (with a clickbaity headline!)
Embroidery, knitting project
Do a book review of a nonfiction or fiction book related to the class (i.e Dan Brown’s Origin)
An interview and discussion with someone.
Regular essay/research paper
Final project submission
When you submit your project include a short explanatory essay (‘The Statement’) that explains what you did, why you did it, and how you went about producing the unessay. If you chose to do a standard essay/paper this can be your place to be more open about the process you used to create the piece. This statement should be 1-2 pages long. If working in a group, everyone should submit their own Statement that reflects their personal views on the project.
Grading the unessay
The success and assessment of this project is based on how effective and compelling you are (see this post by Ryan Cordell for more . Effectiveness is seen in having the unessay be readable/watchable/viewable/listenable in an easy and attractive way. Compelling means that the topic is complete, interesting, and honest. Meeting these criteria is a lot easier if you pick a subject of interest to you.
About the Playwrights: Shakespeare in love
By vanessa hunt.
Tom Stoppard, Marc Norman, and Lee Hall took very different paths to becoming part of the writing team for the theatrical play Shakespeare in Love. From Czechoslovakia, Los Angeles, and England, the three of them all had successful careers in the theatre before each left his mark on this play about the world’s most famous playwright.
Tom Stoppard
Academy Award winner Tomas Straussler, later known as Tom Stoppard, was born on July 3, 1937 in Czechoslovakia. In 1939, as the Nazis invaded his hometown, Stoppard and his family fled to Singapore where his father, a doctor, was reposted thanks to a town patron whose company worked to repost Jewish employees. Following the move to Singapore, Stoppard’s father sent him, along with Stoppard’s mother and brother, to Australia. Staying in Singapore to help the British defense, his father became a prisoner of war and reportedly drowned on a ship after it was bombed by Japanese forces.
Forced once again to flee, young Tomas and his family arrived in India where he attended an American multiracial school, and it was there that his name was changed from Tomas to Tom. Four years later, his mother married a British army major named Kenneth Stoppard, and Tom took on his stepfather’s last name. After the war ended, the family moved to England where he attended Dolphin School and finalized his education at Pocklington School. Stoppard never received a formal university education, which later became one of his greatest regrets.
At age seventeen, Stoppard began a job as a journalist at Western Daily Press . He worked there for four years until he was offered a job at the Bristol Evening World where he was a featured writer, humor columnist, and secondary drama critic. It was during this time that he was fully introduced to the world of theatre.
Starting his writing career with writing short plays for radio, Stoppard then delved into the world of playwrighting for the theatre in 1960 when he finished his first play, A Walk on the Water . It was televised in London, later retitled Enter a Free Man, and was produced onstage in 1968. His first widely recognized play, Rosencrantz and Guildenstern Are Dead, was written in 1964. However, it began as a one-act play titled Rosencrantz and Guildenstern Meet King Lear . In 1967, this play was met with rave reviews as it played in Britain’s National Theatre circuit and became internationally known. As he continued to write, his work explored themes in surrealism and existentialism. Eventually, he expanded his work to include screenplays.
Stoppard’s credits span decades with works for the theatre such as Albert’s Bridge , Jumpers , Travesties , 15-Minute Hamlet , Night and Day , The Real Thing , Arcadia , The Invention of Love , Rock ‘n’ Roll , The Hard Problem , and many others. His screenwriting credits include Brazil , Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade , Rosencrantz and Guildenstern Are Dead , Anna Karenina , and Tulip Fever . Perhaps his most famous screenplay, though, is the Academy Award-winning movie Shakespeare in Love , which he worked on with screenwriter Marc Norman.
Marc Norman
Marc Norman was born on February 10, 1941 in Los Angeles, California. He received a master’s degree in English from the University of California Berkeley, and after graduation he decided to pursue a career in the entertainment field. He applied for jobs with different production companies before finally landing a job with Universal in their executive training program. This was a thankless job as he spent eight hours a day delivering mail around the studio. Upon hearing that television producer Roy Huggins was starting a new series, Norman approached him about working as a production assistant. While Huggins turned him down for the job, he told Norman that he needed story ideas. Norman took the opportunity, and Huggins eventually bought one of the ideas that Norman presented. Universal then promoted Norman to the position of casting director, although he was unhappy in this position as well. He worked with the studio for years until his desire to write became too great. For five years, he wrote rewrites for television scripts and then moved on to writing features (Frederic T. Dray, www.writersstore.com/from-mailroom-to-oscar-winner-marc-norman/) .
Finally, Norman had a breakthrough with his writing as he developed the idea of Shakespeare starting a theatre company. This is where Shakespeare in Love found its beginnings. It took nine months of research and three months of actual writing before the script was finished. In 1991, Universal purchased the script. Edward Zwick was set to direct the film, but he didn’t like what Norman had written and brought on famed writer Tom Stoppard to do a rewrite and improve upon Norman’s script. Just weeks before production was to begin in 1992, Julia Roberts, who was set to star in the film, left the project because a suitable Shakespearean-level actor could not be found for the lead. After Roberts left, the project was put on hold. In 1997, Universal sold the rights to the script, and Harvey Weinstein agreed to make the film (Dray, www.writersstore.com ). With Gwyneth Paltrow and Joseph Fiennes set to star, the project was completed and Norman, along with co-writer Tom Stoppard, found themselves at the Academy Awards accepting the Oscar for Best Original Screenplay.
Years after the success of the film version of Shakespeare in Love , playwright Lee Hall adapted the screenplay for the theatre. Hall was born on September 20, 1966 in Newcastle-upon-Tyre, Northumberland. The son of a house painter/decorator and a home maker, Hall received his education at Benfield Comprehensive School. Later, he studied English literature at Fitzwilliam College, Cambridge and was taught by poet Paul Muldoon.
Before beginning his career as a playwright, Hall worked as a youth theatre fundraiser in London. His career as a writer began in 1997 when he wrote a radio play called Spoonface Steinberg , which premiered on BBC Radio.
Controversy surrounded Hall’s career in 1999 when a children’s opera that he had written called Beached premiered. It was commissioned by Opera North and was to be performed by children at the Bay Primary School. Due to the story centering around a gay character, the school threatened to cancel the production unless changes were made to the script. To keep the show in production, Hall agreed to change certain words in the script that referenced the character being gay (en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lee_Hall_(playwright)).
The most notably successful work to Hall’s name is the 1999 movie Billy Elliot , which he wrote the screenplay for and went on to receive an Oscar nomination for Best Original Screenplay. Following the success of the film, Hall adapted the screenplay for the stage, turning the show into a musical. The music for the production was written by Elton John, with Hall writing the lyrics. In 2009, the show won Best Book of a Musical at the Tony Awards.
Hall’s additional credits include the screenplays for Pride and Prejudice , The Wind in the Willows, Toast , War Horse , and Victoria and Abdul, along with the plays I Luv You Jimmy Spud , Cooking with Elvis , Two’s Company , The Pitmen Painters , and Shakespeare in Love .
The adaptation for Shakespeare in Love came about when Hall met with West End producer Sonia Friedman. In a meeting with Friedman, Hall learned that she was working on bringing the award-winning film to the stage. He told her he would love to be a part of the process, and two weeks later he received a phone call from Friedman who said that she had spoken with Tom Stoppard and they had agreed they wanted Hall to do the adaptation (Jim Hill, www.huffingtonpost.com/jim-hill/lee-hall-compares-transla_b_5649657.html) . The play opened in July 2014 in London at the Noel Coward Theatre.
In 2016, it played to sold out audiences at the Stratford Festival in Ontario, Canada. As the play continues to reach a broader audience, it will make its United States debut in 2017 in three theatres, including the Engelstad Theatre during the Utah Shakespeare Festival’s 2017 summer season.

RADA 2024 Production
July 30-August 3, 2024
Eileen and Allen Anes Studio Theatre

The 39 Steps
June 22 - October 5, 2024
Randall L. Jones Theatre

July 12 - October 5, 2024

The Mountaintop
July 13 - October 5, 2024

Much Ado About Nothing
June 21 - October 5, 2024

The Winter's Tale
June 18 - September 6, 2024
Engelstad Shakespeare Theatre

The Taming of the Shrew
June 19 - September 7, 2024

June 17 - September 5, 2024
Home — Essay Samples — History — Mark Antony — Mark Antony’s Speech: A Masterclass in Rhetoric
Mark Antony's Speech: a Masterclass in Rhetoric
- Categories: Mark Antony Polite Speech
About this sample

Words: 520 |
Published: Feb 7, 2024
Words: 520 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Analysis of Selected Quotes
- "Friends, Romans, countrymen, lend me your ears" This famous opening line is a classic example of how to capture an audience's attention. Antony immediately establishes rapport with the crowd and invites them to listen to his message.
- "I come to bury Caesar, not to praise him" This line is often misquoted as "I come to praise Caesar, not to bury him." However, the actual quote is the opposite. Antony uses this line to disarm the crowd and lower their guard. By appearing to disavow Caesar, Antony gains the audience's trust and then proceeds to defend Caesar's reputation.
- "The noble Brutus hath told you Caesar was ambitious" This line is a masterful example of irony and sarcasm. Antony uses Brutus's own words against him, exposing his hypocrisy and undermining his credibility.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: History Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1229 words
4 pages / 1721 words
2 pages / 903 words
3 pages / 1343 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Mark Antony
One of the most memorable scenes in the play is Mark Antony's funeral oration for Caesar. In this speech, Antony employs persuasive techniques to turn the crowd against the conspirators and sway public opinion in favor of [...]
Mythological accounts constantly transform themselves in crossing cultures and enduring time, but two versions of the story of Dido and Aeneas, one by a shy, serious, government-sponsored poet; the other by an often lighthearted [...]
In the government of any civilization, virtue is not only a preferable characteristic of the ruler or rulers, but a necessary one. Of the virtues, perhaps the two most intrinsically necessary for political decisions are justice [...]
An important recurring image throughout Virgil's Aeneid is that of the serpent, which appears both realistically and metaphorically. The serpent icon is a harbinger of death and a symbol of deception. These two elements [...]
'I sing of arms and of the man, fated to be an exile', begins Virgil, and it is on precisely the issue of this man of arms that critical debate in recent years has tended to centre. Scholars continue to disagree on whether or [...]
“Hell hath no fury like a woman scorned.” This popular saying, paraphrased from William Congreve's The Mourning Bride, was written nearly 1600 years after Vergil's Aeneid. Even so, the quote speaks to the Aeneid's exploration of [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

- Kindle Store
- Kindle eBooks
Promotions apply when you purchase
These promotions will be applied to this item:
Some promotions may be combined; others are not eligible to be combined with other offers. For details, please see the Terms & Conditions associated with these promotions.
Buy for others
Buying and sending ebooks to others.
- Select quantity
- Buy and send eBooks
- Recipients can read on any device
These ebooks can only be redeemed by recipients in the US. Redemption links and eBooks cannot be resold.

Download the free Kindle app and start reading Kindle books instantly on your smartphone, tablet, or computer - no Kindle device required .
Read instantly on your browser with Kindle for Web.
Using your mobile phone camera - scan the code below and download the Kindle app.

Image Unavailable

- To view this video download Flash Player
Advanced English Writing Skills: Masterclass for English Language Learners. How to Write Effectively & Confidently in English: How to Write Essays, Summaries, ... Articles & Reviews (ESL Writing Book 1) Kindle Edition
Advanced english writing skills: masterclass for english language learners how to write effectively in english & write with confidence: how to write essays, summaries, emails, letters, articles & reviews.
- Book 1 of 1 ESL Writing
- Print length 198 pages
- Language English
- Sticky notes On Kindle Scribe
- Publication date December 23, 2019
- File size 809 KB
- Page Flip Enabled
- Word Wise Not Enabled
- Enhanced typesetting Enabled
- See all details
Customers who bought this item also bought

Product details
- ASIN : B0832XBK9R
- Publisher : Roche Publishing ESL (December 23, 2019)
- Publication date : December 23, 2019
- Language : English
- File size : 809 KB
- Text-to-Speech : Enabled
- Screen Reader : Supported
- Enhanced typesetting : Enabled
- X-Ray : Not Enabled
- Word Wise : Not Enabled
- Sticky notes : On Kindle Scribe
- Print length : 198 pages
- Page numbers source ISBN : 1650277164
- #32 in Handwriting Reference (Kindle Store)
- #710 in Handwriting Reference (Books)
- #751 in English as a Foreign Language
Customer reviews
Customer Reviews, including Product Star Ratings help customers to learn more about the product and decide whether it is the right product for them.
To calculate the overall star rating and percentage breakdown by star, we don’t use a simple average. Instead, our system considers things like how recent a review is and if the reviewer bought the item on Amazon. It also analyzed reviews to verify trustworthiness.
- Sort reviews by Top reviews Most recent Top reviews
Top reviews from the United States
Top reviews from other countries.
Report an issue
- Amazon Newsletter
- About Amazon
- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- Press Center
- Investor Relations
- Amazon Devices
- Amazon Science
- Sell on Amazon
- Sell apps on Amazon
- Supply to Amazon
- Protect & Build Your Brand
- Become an Affiliate
- Become a Delivery Driver
- Start a Package Delivery Business
- Advertise Your Products
- Self-Publish with Us
- Become an Amazon Hub Partner
- › See More Ways to Make Money
- Amazon Visa
- Amazon Store Card
- Amazon Secured Card
- Amazon Business Card
- Shop with Points
- Credit Card Marketplace
- Reload Your Balance
- Amazon Currency Converter
- Your Account
- Your Orders
- Shipping Rates & Policies
- Amazon Prime
- Returns & Replacements
- Manage Your Content and Devices
- Recalls and Product Safety Alerts
- Conditions of Use
- Privacy Notice
- Consumer Health Data Privacy Disclosure
- Your Ads Privacy Choices

The Techno-Optimist Manifesto
Marc Andreessen
- Hacker News
You live in a deranged age — more deranged than usual, because despite great scientific and technological advances, man has not the faintest idea of who he is or what he is doing. Walker Percy
Our species is 300,000 years old. For the first 290,000 years, we were foragers, subsisting in a way that’s still observable among the Bushmen of the Kalahari and the Sentinelese of the Andaman Islands. Even after Homo Sapiens embraced agriculture, progress was painfully slow. A person born in Sumer in 4,000BC would find the resources, work, and technology available in England at the time of the Norman Conquest or in the Aztec Empire at the time of Columbus quite familiar. Then, beginning in the 18th Century, many people’s standard of living skyrocketed. What brought about this dramatic improvement, and why? Marian Tupy
There’s a way to do it better. Find it. Thomas Edison
We are being lied to.
We are told that technology takes our jobs, reduces our wages, increases inequality, threatens our health, ruins the environment, degrades our society, corrupts our children, impairs our humanity, threatens our future, and is ever on the verge of ruining everything.
We are told to be angry, bitter, and resentful about technology.
We are told to be pessimistic.
The myth of Prometheus – in various updated forms like Frankenstein, Oppenheimer, and Terminator – haunts our nightmares.
We are told to denounce our birthright – our intelligence, our control over nature, our ability to build a better world.
We are told to be miserable about the future.
Our civilization was built on technology.
Our civilization is built on technology.
Technology is the glory of human ambition and achievement, the spearhead of progress, and the realization of our potential.
For hundreds of years, we properly glorified this – until recently.
I am here to bring the good news.
We can advance to a far superior way of living, and of being.
We have the tools, the systems, the ideas.
We have the will.
It is time, once again, to raise the technology flag.
It is time to be Techno-Optimists.
Techno-Optimists believe that societies, like sharks, grow or die.
We believe growth is progress – leading to vitality, expansion of life, increasing knowledge, higher well being.
We agree with Paul Collier when he says, “Economic growth is not a cure-all, but lack of growth is a kill-all.”
We believe everything good is downstream of growth.
We believe not growing is stagnation, which leads to zero-sum thinking, internal fighting, degradation, collapse, and ultimately death.
There are only three sources of growth: population growth, natural resource utilization, and technology.
Developed societies are depopulating all over the world, across cultures – the total human population may already be shrinking.
Natural resource utilization has sharp limits, both real and political.
And so the only perpetual source of growth is technology.
In fact, technology – new knowledge, new tools, what the Greeks called techne – has always been the main source of growth, and perhaps the only cause of growth, as technology made both population growth and natural resource utilization possible.
We believe technology is a lever on the world – the way to make more with less.
Economists measure technological progress as productivity growth : How much more we can produce each year with fewer inputs, fewer raw materials. Productivity growth, powered by technology, is the main driver of economic growth, wage growth, and the creation of new industries and new jobs, as people and capital are continuously freed to do more important, valuable things than in the past. Productivity growth causes prices to fall, supply to rise, and demand to expand, improving the material well being of the entire population.
We believe this is the story of the material development of our civilization; this is why we are not still living in mud huts, eking out a meager survival and waiting for nature to kill us.
We believe this is why our descendents will live in the stars.
We believe that there is no material problem – whether created by nature or by technology – that cannot be solved with more technology.
We had a problem of starvation, so we invented the Green Revolution.
We had a problem of darkness, so we invented electric lighting.
We had a problem of cold, so we invented indoor heating.
We had a problem of heat, so we invented air conditioning.
We had a problem of isolation, so we invented the Internet.
We had a problem of pandemics, so we invented vaccines.
We have a problem of poverty, so we invent technology to create abundance.
Give us a real world problem, and we can invent technology that will solve it.
We believe free markets are the most effective way to organize a technological economy. Willing buyer meets willing seller, a price is struck, both sides benefit from the exchange or it doesn’t happen. Profits are the incentive for producing supply that fulfills demand. Prices encode information about supply and demand. Markets cause entrepreneurs to seek out high prices as a signal of opportunity to create new wealth by driving those prices down .
We believe the market economy is a discovery machine, a form of intelligence – an exploratory, evolutionary, adaptive system.
We believe Hayek’s Knowledge Problem overwhelms any centralized economic system. All actual information is on the edges, in the hands of the people closest to the buyer. The center, abstracted away from both the buyer and the seller, knows nothing. Centralized planning is doomed to fail, the system of production and consumption is too complex. Decentralization harnesses complexity for the benefit of everyone; centralization will starve you to death.
We believe in market discipline. The market naturally disciplines – the seller either learns and changes when the buyer fails to show, or exits the market. When market discipline is absent, there is no limit to how crazy things can get. The motto of every monopoly and cartel, every centralized institution not subject to market discipline: “We don’t care, because we don’t have to.” Markets prevent monopolies and cartels.
We believe markets lift people out of poverty – in fact, markets are by far the most effective way to lift vast numbers of people out of poverty, and always have been. Even in totalitarian regimes, an incremental lifting of the repressive boot off the throat of the people and their ability to produce and trade leads to rapidly rising incomes and standards of living. Lift the boot a little more, even better. Take the boot off entirely, who knows how rich everyone can get.
We believe markets are an inherently individualistic way to achieve superior collective outcomes.
We believe markets do not require people to be perfect, or even well intentioned – which is good, because, have you met people? Adam Smith: “It is not from the benevolence of the butcher, the brewer, or the baker that we expect our dinner, but from their regard to their own self-interest. We address ourselves not to their humanity but to their self-love, and never talk to them of our own necessities, but of their advantages.”
David Friedman points out that people only do things for other people for three reasons – love, money, or force. Love doesn’t scale, so the economy can only run on money or force. The force experiment has been run and found wanting. Let’s stick with money.
We believe the ultimate moral defense of markets is that they divert people who otherwise would raise armies and start religions into peacefully productive pursuits.
We believe markets, to quote Nicholas Stern, are how we take care of people we don’t know.
We believe markets are the way to generate societal wealth for everything else we want to pay for, including basic research, social welfare programs, and national defense.
We believe there is no conflict between capitalist profits and a social welfare system that protects the vulnerable. In fact, they are aligned – the production of markets creates the economic wealth that pays for everything else we want as a society.
We believe central economic planning elevates the worst of us and drags everyone down; markets exploit the best of us to benefit all of us.
We believe central planning is a doom loop; markets are an upward spiral.
The economist William Nordhaus has shown that creators of technology are only able to capture about 2% of the economic value created by that technology. The other 98% flows through to society in the form of what economists call social surplus. Technological innovation in a market system is inherently philanthropic , by a 50:1 ratio. Who gets more value from a new technology, the single company that makes it, or the millions or billions of people who use it to improve their lives? QED.
We believe in David Ricardo’s concept of comparative advantage – as distinct from competitive advantage, comparative advantage holds that even someone who is best in the world at doing everything will buy most things from other people, due to opportunity cost. Comparative advantage in the context of a properly free market guarantees high employment regardless of the level of technology.
We believe a market sets wages as a function of the marginal productivity of the worker. Therefore technology – which raises productivity – drives wages up , not down. This is perhaps the most counterintuitive idea in all of economics, but it’s true, and we have 300 years of history that prove it.
We believe in Milton Friedman’s observation that human wants and needs are infinite.
We believe markets also increase societal well being by generating work in which people can productively engage. We believe a Universal Basic Income would turn people into zoo animals to be farmed by the state. Man was not meant to be farmed; man was meant to be useful , to be productive , to be proud .
We believe technological change, far from reducing the need for human work, increases it, by broadening the scope of what humans can productively do.
We believe that since human wants and needs are infinite, economic demand is infinite, and job growth can continue forever.
We believe markets are generative, not exploitative; positive sum, not zero sum. Participants in markets build on one another’s work and output. James Carse describes finite games and infinite games – finite games have an end, when one person wins and another person loses; infinite games never end, as players collaborate to discover what’s possible in the game. Markets are the ultimate infinite game.
The Techno-Capital Machine
Combine technology and markets and you get what Nick Land has termed the techno-capital machine, the engine of perpetual material creation, growth, and abundance.
We believe the techno-capital machine of markets and innovation never ends, but instead spirals continuously upward. Comparative advantage increases specialization and trade. Prices fall, freeing up purchasing power, creating demand. Falling prices benefit everyone who buys goods and services, which is to say everyone. Human wants and needs are endless, and entrepreneurs continuously create new goods and services to satisfy those wants and needs, deploying unlimited numbers of people and machines in the process. This upward spiral has been running for hundreds of years, despite continuous howling from Communists and Luddites. Indeed, as of 2019, before the temporary COVID disruption, the result was the largest number of jobs at the highest wages and the highest levels of material living standards in the history of the planet.
The techno-capital machine makes natural selection work for us in the realm of ideas. The best and most productive ideas win, and are combined and generate even better ideas. Those ideas materialize in the real world as technologically enabled goods and services that never would have emerged de novo.
Ray Kurzweil defines his Law of Accelerating Returns: Technological advances tend to feed on themselves, increasing the rate of further advance.
We believe in accelerationism – the conscious and deliberate propulsion of technological development – to ensure the fulfillment of the Law of Accelerating Returns. To ensure the techno-capital upward spiral continues forever.
We believe the techno-capital machine is not anti-human – in fact, it may be the most pro-human thing there is. It serves us . The techno-capital machine works for us. All the machines work for us.
We believe the cornerstone resources of the techno-capital upward spiral are intelligence and energy – ideas, and the power to make them real.
Intelligence
We believe intelligence is the ultimate engine of progress. Intelligence makes everything better. Smart people and smart societies outperform less smart ones on virtually every metric we can measure. Intelligence is the birthright of humanity; we should expand it as fully and broadly as we possibly can.
We believe intelligence is in an upward spiral – first, as more smart people around the world are recruited into the techno-capital machine; second, as people form symbiotic relationships with machines into new cybernetic systems such as companies and networks; third, as Artificial Intelligence ramps up the capabilities of our machines and ourselves.
We believe we are poised for an intelligence takeoff that will expand our capabilities to unimagined heights.
We believe Artificial Intelligence is our alchemy, our Philosopher’s Stone – we are literally making sand think.
We believe Artificial Intelligence is best thought of as a universal problem solver. And we have a lot of problems to solve.
We believe Artificial Intelligence can save lives – if we let it. Medicine, among many other fields, is in the stone age compared to what we can achieve with joined human and machine intelligence working on new cures. There are scores of common causes of death that can be fixed with AI, from car crashes to pandemics to wartime friendly fire.
We believe any deceleration of AI will cost lives. Deaths that were preventable by the AI that was prevented from existing is a form of murder.
We believe in Augmented Intelligence just as much as we believe in Artificial Intelligence. Intelligent machines augment intelligent humans, driving a geometric expansion of what humans can do.
We believe Augmented Intelligence drives marginal productivity which drives wage growth which drives demand which drives the creation of new supply… with no upper bound.
Energy is life. We take it for granted, but without it, we have darkness, starvation, and pain. With it, we have light, safety, and warmth.
We believe energy should be in an upward spiral. Energy is the foundational engine of our civilization. The more energy we have, the more people we can have, and the better everyone’s lives can be. We should raise everyone to the energy consumption level we have, then increase our energy 1,000x, then raise everyone else’s energy 1,000x as well.
The current gap in per-capita energy use between the smaller developed world and larger developing world is enormous. That gap will close – either by massively expanding energy production, making everyone better off, or by massively reducing energy production, making everyone worse off.
We believe energy need not expand to the detriment of the natural environment. We have the silver bullet for virtually unlimited zero-emissions energy today – nuclear fission. In 1973, President Richard Nixon called for Project Independence, the construction of 1,000 nuclear power plants by the year 2000, to achieve complete US energy independence. Nixon was right; we didn’t build the plants then, but we can now, anytime we decide we want to.
Atomic Energy Commissioner Thomas Murray said in 1953: “For years the splitting atom, packaged in weapons, has been our main shield against the barbarians. Now, in addition, it is a God-given instrument to do the constructive work of mankind.” Murray was right too.
We believe a second energy silver bullet is coming – nuclear fusion. We should build that as well. The same bad ideas that effectively outlawed fission are going to try to outlaw fusion. We should not let them.
We believe there is no inherent conflict between the techno-capital machine and the natural environment. Per-capita US carbon emissions are lower now than they were 100 years ago, even without nuclear power.
We believe technology is the solution to environmental degradation and crisis. A technologically advanced society improves the natural environment, a technologically stagnant society ruins it. If you want to see environmental devastation, visit a former Communist country. The socialist USSR was far worse for the natural environment than the capitalist US. Google the Aral Sea.
We believe a technologically stagnant society has limited energy at the cost of environmental ruin; a technologically advanced society has unlimited clean energy for everyone.
We believe we should place intelligence and energy in a positive feedback loop, and drive them both to infinity.
We believe we should use the feedback loop of intelligence and energy to make everything we want and need abundant.
We believe the measure of abundance is falling prices. Every time a price falls, the universe of people who buy it get a raise in buying power, which is the same as a raise in income. If a lot of goods and services drop in price, the result is an upward explosion of buying power, real income, and quality of life.
We believe that if we make both intelligence and energy “too cheap to meter”, the ultimate result will be that all physical goods become as cheap as pencils. Pencils are actually quite technologically complex and difficult to manufacture, and yet nobody gets mad if you borrow a pencil and fail to return it. We should make the same true of all physical goods.
We believe we should push to drop prices across the economy through the application of technology until as many prices are effectively zero as possible, driving income levels and quality of life into the stratosphere.
We believe Andy Warhol was right when he said, “What’s great about this country is America started the tradition where the richest consumers buy essentially the same things as the poorest. You can be watching TV and see Coca-Cola, and you can know that the President drinks Coke, Liz Taylor drinks Coke, and just think, you can drink Coke, too. A Coke is a Coke and no amount of money can get you a better Coke than the one the bum on the corner is drinking. All the Cokes are the same and all the Cokes are good.” Same for the browser, the smartphone, the chatbot.
We believe that technology ultimately drives the world to what Buckminster Fuller called “ephemeralization” – what economists call “dematerialization”. Fuller: “Technology lets you do more and more with less and less until eventually you can do everything with nothing.”
We believe technological progress therefore leads to material abundance for everyone.
We believe the ultimate payoff from technological abundance can be a massive expansion in what Julian Simon called “the ultimate resource” – people.
We believe, as Simon did, that people are the ultimate resource – with more people come more creativity, more new ideas, and more technological progress.
We believe material abundance therefore ultimately means more people – a lot more people – which in turn leads to more abundance.
We believe our planet is dramatically underpopulated, compared to the population we could have with abundant intelligence, energy, and material goods.
We believe the global population can quite easily expand to 50 billion people or more, and then far beyond that as we ultimately settle other planets.
We believe that out of all of these people will come scientists, technologists, artists, and visionaries beyond our wildest dreams.
We believe the ultimate mission of technology is to advance life both on Earth and in the stars.
Not Utopia, But Close Enough
However, we are not Utopians.
We are adherents to what Thomas Sowell calls the Constrained Vision.
We believe the Constrained Vision – contra the Unconstrained Vision of Utopia, Communism, and Expertise – means taking people as they are, testing ideas empirically, and liberating people to make their own choices.
We believe in not Utopia, but also not Apocalypse.
We believe change only happens on the margin – but a lot of change across a very large margin can lead to big outcomes.
While not Utopian, we believe in what Brad DeLong terms “slouching toward Utopia” – doing the best fallen humanity can do, making things better as we go.
Becoming Technological Supermen
We believe that advancing technology is one of the most virtuous things that we can do.
We believe in deliberately and systematically transforming ourselves into the kind of people who can advance technology.
We believe this certainly means technical education, but it also means going hands on, gaining practical skills, working within and leading teams – aspiring to build something greater than oneself, aspiring to work with others to build something greater as a group.
We believe the natural human drive to make things, to gain territory, to explore the unknown can be channeled productively into building technology.
We believe that while the physical frontier, at least here on Earth, is closed, the technological frontier is wide open.
We believe in exploring and claiming the technological frontier.
We believe in the romance of technology, of industry. The eros of the train, the car, the electric light, the skyscraper. And the microchip, the neural network, the rocket, the split atom.
We believe in adventure . Undertaking the Hero’s Journey, rebelling against the status quo, mapping uncharted territory, conquering dragons, and bringing home the spoils for our community.
To paraphrase a manifesto of a different time and place: “Beauty exists only in struggle. There is no masterpiece that has not an aggressive character. Technology must be a violent assault on the forces of the unknown, to force them to bow before man.”
We believe that we are, have been, and will always be the masters of technology, not mastered by technology. Victim mentality is a curse in every domain of life, including in our relationship with technology – both unnecessary and self-defeating. We are not victims, we are conquerors .
We believe in nature, but we also believe in overcoming nature. We are not primitives, cowering in fear of the lightning bolt. We are the apex predator; the lightning works for us.
We believe in greatness . We admire the great technologists and industrialists who came before us, and we aspire to make them proud of us today.
And we believe in humanity – individually and collectively.
Technological Values
We believe in ambition, aggression, persistence, relentlessness – strength .
We believe in merit and achievement.
We believe in bravery , in courage.
We believe in pride, confidence, and self respect – when earned .
We believe in free thought, free speech, and free inquiry.
We believe in the actual Scientific Method and enlightenment values of free discourse and challenging the authority of experts.
We believe, as Richard Feynman said, “Science is the belief in the ignorance of experts.”
And, “I would rather have questions that can’t be answered than answers that can’t be questioned.”
We believe in local knowledge, the people with actual information making decisions, not in playing God.
We believe in embracing variance, in increasing interestingness.
We believe in risk , in leaps into the unknown.
We believe in agency, in individualism.
We believe in radical competence.
We believe in an absolute rejection of resentment. As Carrie Fisher said, “Resentment is like drinking poison and waiting for the other person to die.” We take responsibility and we overcome.
We believe in competition, because we believe in evolution.
We believe in evolution, because we believe in life.
We believe in the truth.
We believe rich is better than poor, cheap is better than expensive, and abundant is better than scarce.
We believe in making everyone rich, everything cheap, and everything abundant.
We believe extrinsic motivations – wealth, fame, revenge – are fine as far as they go. But we believe intrinsic motivations – the satisfaction of building something new, the camaraderie of being on a team, the achievement of becoming a better version of oneself – are more fulfilling and more lasting.
We believe in what the Greeks called eudaimonia through arete – flourishing through excellence.
We believe technology is universalist. Technology doesn’t care about your ethnicity, race, religion, national origin, gender, sexuality, political views, height, weight, hair or lack thereof. Technology is built by a virtual United Nations of talent from all over the world. Anyone with a positive attitude and a cheap laptop can contribute. Technology is the ultimate open society.
We believe in the Silicon Valley code of “pay it forward”, trust via aligned incentives, generosity of spirit to help one another learn and grow.
We believe America and her allies should be strong and not weak. We believe national strength of liberal democracies flows from economic strength (financial power), cultural strength (soft power), and military strength (hard power). Economic, cultural, and military strength flow from technological strength. A technologically strong America is a force for good in a dangerous world. Technologically strong liberal democracies safeguard liberty and peace. Technologically weak liberal democracies lose to their autocratic rivals, making everyone worse off.
We believe technology makes greatness more possible and more likely.
We believe in fulfilling our potential, becoming fully human – for ourselves, our communities, and our society.
The Meaning of Life
Techno-Optimism is a material philosophy, not a political philosophy.
We are not necessarily left wing, although some of us are.
We are not necessarily right wing, although some of us are.
We are materially focused, for a reason – to open the aperture on how we may choose to live amid material abundance.
A common critique of technology is that it removes choice from our lives as machines make decisions for us. This is undoubtedly true, yet more than offset by the freedom to create our lives that flows from the material abundance created by our use of machines.
Material abundance from markets and technology opens the space for religion, for politics, and for choices of how to live, socially and individually.
We believe technology is liberatory. Liberatory of human potential. Liberatory of the human soul, the human spirit. Expanding what it can mean to be free, to be fulfilled, to be alive.
We believe technology opens the space of what it can mean to be human.
We have enemies.
Our enemies are not bad people – but rather bad ideas.
Our present society has been subjected to a mass demoralization campaign for six decades – against technology and against life – under varying names like “existential risk”, “sustainability”, “ESG”, “Sustainable Development Goals”, “social responsibility”, “stakeholder capitalism”, “Precautionary Principle”, “trust and safety”, “tech ethics”, “risk management”, “de-growth”, “the limits of growth”.
This demoralization campaign is based on bad ideas of the past – zombie ideas, many derived from Communism, disastrous then and now – that have refused to die.
Our enemy is stagnation.
Our enemy is anti-merit, anti-ambition, anti-striving, anti-achievement, anti-greatness.
Our enemy is statism, authoritarianism, collectivism, central planning, socialism.
Our enemy is bureaucracy, vetocracy, gerontocracy, blind deference to tradition.
Our enemy is corruption, regulatory capture, monopolies, cartels.
Our enemy is institutions that in their youth were vital and energetic and truth-seeking, but are now compromised and corroded and collapsing – blocking progress in increasingly desperate bids for continued relevance, frantically trying to justify their ongoing funding despite spiraling dysfunction and escalating ineptness.
Our enemy is the ivory tower, the know-it-all credentialed expert worldview, indulging in abstract theories, luxury beliefs, social engineering, disconnected from the real world, delusional, unelected, and unaccountable – playing God with everyone else’s lives, with total insulation from the consequences.
Our enemy is speech control and thought control – the increasing use, in plain sight, of George Orwell’s “1984” as an instruction manual.
Our enemy is Thomas Sowell’s Unconstrained Vision, Alexander Kojeve’s Universal and Homogeneous State, Thomas More’s Utopia.
Our enemy is the Precautionary Principle, which would have prevented virtually all progress since man first harnessed fire. The Precautionary Principle was invented to prevent the large-scale deployment of civilian nuclear power, perhaps the most catastrophic mistake in Western society in my lifetime. The Precautionary Principle continues to inflict enormous unnecessary suffering on our world today. It is deeply immoral, and we must jettison it with extreme prejudice.
Our enemy is deceleration, de-growth, depopulation – the nihilistic wish, so trendy among our elites, for fewer people, less energy, and more suffering and death.
Our enemy is Friedrich Nietzsche’s Last Man:
I tell you: one must still have chaos in oneself, to give birth to a dancing star. I tell you: you have still chaos in yourselves.
Alas! There comes the time when man will no longer give birth to any star. Alas! There comes the time of the most despicable man, who can no longer despise himself…
“What is love? What is creation? What is longing? What is a star?” — so asks the Last Man, and blinks.
The earth has become small, and on it hops the Last Man, who makes everything small. His species is ineradicable as the flea; the Last Man lives longest…
One still works, for work is a pastime. But one is careful lest the pastime should hurt one.
One no longer becomes poor or rich; both are too burdensome…
No shepherd, and one herd! Everyone wants the same; everyone is the same: he who feels differently goes voluntarily into the madhouse.
“Formerly all the world was insane,” — say the subtlest of them, and they blink.
They are clever and know all that has happened: so there is no end to their derision…
“We have discovered happiness,” — say the Last Men, and they blink.
Our enemy is… that.
We aspire to be… not that.
We will explain to people captured by these zombie ideas that their fears are unwarranted and the future is bright.
We believe these captured people are suffering from ressentiment – a witches’ brew of resentment, bitterness, and rage that is causing them to hold mistaken values, values that are damaging to both themselves and the people they care about.
We believe we must help them find their way out of their self-imposed labyrinth of pain.
We invite everyone to join us in Techno-Optimism.
The water is warm.
Become our allies in the pursuit of technology, abundance, and life.
Where did we come from?
Our civilization was built on a spirit of discovery, of exploration, of industrialization.
Where are we going?
What world are we building for our children and their children, and their children?
A world of fear, guilt, and resentment?
Or a world of ambition, abundance, and adventure?
We believe in the words of David Deutsch: “We have a duty to be optimistic. Because the future is open, not predetermined and therefore cannot just be accepted: we are all responsible for what it holds. Thus it is our duty to fight for a better world.”
We owe the past, and the future.
It’s time to be a Techno-Optimist.
It’s time to build.
Patron Saints of Techno-Optimism
In lieu of detailed endnotes and citations, read the work of these people, and you too will become a Techno-Optimist.
@BasedBeffJezos
@PessimistsArc
Ada Lovelace
Andy Warhol
Bertrand Russell
Brad DeLong
Buckminster Fuller
Calestous Juma
Clayton Christensen
Dambisa Moyo
David Deutsch
David Friedman
David Ricardo
Deirdre McCloskey
Doug Engelbart
Elting Morison
Filippo Tommaso Marinetti
Frederic Bastiat
Frederick Jackson Turner
Friedrich Hayek
Friedrich Nietzsche
George Gilder
Isabel Paterson
Israel Kirzner
James Burnham
James Carse
Johan Norberg
John Von Neumann
Joseph Schumpeter
Julian Simon
Kevin Kelly
Louis Rossetto
Ludwig von Mises
Marian Tupy
Martin Gurri
Matt Ridley
Milton Friedman
Neven Sesardic
Paul Collier
Paul Johnson
Ray Kurzweil
Richard Feynman
Rose Wilder Lane
Stephen Wolfram
Stewart Brand
Thomas Sowell
Vilfredo Pareto
Virginia Postrel
William Lewis
William Nordhaus
Want more a16z?
Sign up to get the best of a16z content, news, and investments.
Thanks for signing up for the a16z newsletter.
Check your inbox for a welcome note.

Marc Andreessen is a Cofounder and General Partner at the venture capital firm Andreessen Horowitz.
- Game On: Marc Andreessen & Andrew Chen Talk Creative Computers Marc Andreessen and Andrew Chen
- Politics & the Future of Tech with Marc Andreessen and Ben Horowitz Marc Andreessen and Ben Horowitz
- Money, power, politics, and the internet’s next battleground Ben Horowitz, Marc Andreessen, Chris Dixon, and Robert Hackett
- Fixing Higher Education & New Startup Opportunities with Marc and Ben Marc Andreessen and Ben Horowitz
- Crisis in Higher Ed & Why Universities Still Matter with Marc & Ben Marc Andreessen and Ben Horowitz
The views expressed here are those of the individual AH Capital Management, L.L.C. (“a16z”) personnel quoted and are not the views of a16z or its affiliates. Certain information contained in here has been obtained from third-party sources, including from portfolio companies of funds managed by a16z. While taken from sources believed to be reliable, a16z has not independently verified such information and makes no representations about the enduring accuracy of the information or its appropriateness for a given situation. In addition, this content may include third-party advertisements; a16z has not reviewed such advertisements and does not endorse any advertising content contained therein.
This content is provided for informational purposes only, and should not be relied upon as legal, business, investment, or tax advice. You should consult your own advisers as to those matters. References to any securities or digital assets are for illustrative purposes only, and do not constitute an investment recommendation or offer to provide investment advisory services. Furthermore, this content is not directed at nor intended for use by any investors or prospective investors, and may not under any circumstances be relied upon when making a decision to invest in any fund managed by a16z. (An offering to invest in an a16z fund will be made only by the private placement memorandum, subscription agreement, and other relevant documentation of any such fund and should be read in their entirety.) Any investments or portfolio companies mentioned, referred to, or described are not representative of all investments in vehicles managed by a16z, and there can be no assurance that the investments will be profitable or that other investments made in the future will have similar characteristics or results. A list of investments made by funds managed by Andreessen Horowitz (excluding investments for which the issuer has not provided permission for a16z to disclose publicly as well as unannounced investments in publicly traded digital assets) is available at https://a16z.com/investments/ .
Charts and graphs provided within are for informational purposes solely and should not be relied upon when making any investment decision. Past performance is not indicative of future results. The content speaks only as of the date indicated. Any projections, estimates, forecasts, targets, prospects, and/or opinions expressed in these materials are subject to change without notice and may differ or be contrary to opinions expressed by others. Please see https://a16z.com/disclosures for additional important information.
- Why Technology Still Matters with Marc Andreessen Marc Andreessen and Steph Smith Read More
- Why AI Will Save the World Marc Andreessen Read More
- It’s Time to Build Marc Andreessen Read More
- Why Software Is Eating the World Marc Andreessen Read More
- Featured Essay The Love of God An essay by Sam Storms Read Now
- Faithfulness of God
- Saving Grace
- Adoption by God
Most Popular
- Gender Identity
- Trusting God
- The Holiness of God
- See All Essays

- Best Commentaries
- Featured Essay Resurrection of Jesus An essay by Benjamin Shaw Read Now
- Death of Christ
- Resurrection of Jesus
- Church and State
- Sovereignty of God
- Faith and Works
- The Carson Center
- The Keller Center
- New City Catechism
- Publications
- Read the Bible
- TGC Pastors


U.S. Edition
- Arts & Culture
- Bible & Theology
- Christian Living
- Current Events
- Faith & Work
- As In Heaven
- Gospelbound
- Post-Christianity?
- TGC Podcast
- You're Not Crazy
- Churches Planting Churches
- Help Me Teach The Bible
- Word Of The Week
- Upcoming Events
- Past Conference Media
- Foundation Documents
- Regional Chapters
- Church Directory
- Global Resourcing
- Donate to TGC
To All The World
The world is a confusing place right now. We believe that faithful proclamation of the gospel is what our hostile and disoriented world needs. Do you believe that too? Help TGC bring biblical wisdom to the confusing issues across the world by making a gift to our international work.
Announcing TGC’s 2024 Essay Contest for Young Adults
Writers aged 16–22 can get published and win $500.

More By Staff

The Gospel Coalition announces its 2024 essay contest, inviting young adults (ages 16–22) to explore and write about God’s faithfulness, their relationship with technology, and their heart for full-time ministry in our secular age.
Winning authors will receive a prize, and their essays will be published on TGC’s website. In addition, every writer who submits an essay will receive a coupon code for $50 off the Gen-Z registration for our TGC25 conference .
Essay Requirements
Each 800–1,000 word essay must be original, previously unpublished, and must respond to one of the following three prompts. With each of these prompts, contestants should draw from their own experiences and convictions, and use Scripture to support their conclusions. (Want examples? Read the winning essays from 2022 and 2023 .) Contestants must give permission to TGC to publish their work, and each essay will be judged by TGC’s editorial team.
Submissions will be accepted from June 1 to July 1 and winners will be announced on September 2, 2024.
1. When did the Lord love you by not giving you what you wanted?
Many of us have unfulfilled desires. When was a time you saw the Lord’s love and kindness when he withheld something from you? What was it that you wanted and how did you see the Lord’s faithfulness through not giving it to you? Tell us what you learned from your experience, especially considering that our culture tells us we deserve to have all our desires fulfilled.
2. How has the gospel changed your relationship with your phone?
Today, phones are considered a necessity rather than a luxury. How does the truth of the gospel of Jesus Christ change how you view your phone and how you use it? How has your phone been a hindrance and how has it been an asset to your relationship with the Lord? Tell us what you’ve learned in navigating how to use your phone for the glory of God.
3. Why are you considering full-time ministry?
There’s a greater need than ever for young people to pursue full-time ministry. Why are you considering making ministry your vocation? Tell us your heart behind it, why you think it’s important, and what influences in your life have led you to move forward in this direction.
The contest winner will receive $500; second place will receive a $100 gift card to the TGC bookstore; third place will receive an assortment of books. The winning essays will be published on TGC’s website, as will any other essays the judges select.
Read the full contest rules and upload your essay. Questions? Contact [email protected] .
Now Trending
1 understanding the metamodern mood, 2 hope for struggling christians during pride month, 3 how the legal system enabled—and will curtail—the transgender movement, 4 announcing tgc’s 2024 essay contest for young adults, 5 the 11 beliefs you should know about jehovah’s witnesses when they knock at the door.

Preaching Christ in a Postmodern World
The desegregation of dallas theological seminary.

An Unequally Yoked Small Group

The Omnipotence, Omniscience, and Omnipresence of God

What Should We Think About Paedocommunion?

12 Easy Ways to Improve Your Listening

My Friend, Randy Newman (1956–2024)

Latest Episodes
Trevin wax on reconstructing faith.

Examining the Current and Future State of the Global Church

David Brooks Explores the Amazing Power of Truly Seeing Others

Welcome and Witness: How to Reach Out in a Secular Age

How to Build Gospel Culture: A Q&A Conversation

Gaming Alone: Helping the Generation of Young Men Captivated and Isolated by Video Games

How to Hope in Hard Times

Faith & Work: How Do I Glorify God Even When My Work Seems Meaningless?

Let’s Talk Reunion: The Blessings of Bible Study with Friends

Getting Rid of Your Fear of the Book of Revelation

Looking for Love in All the Wrong Places: A Sermon from Julius Kim

Introducing The Acts 29 Podcast

- 2024 Member Designated Projects
- 2025 Member Designated Projects
- Art Competition
- Congressional Commendation
- Event Request
- Flag Request
- Help with a Federal Agency
- Internships
- Meeting Request
- Service Academy Nominations
- Tour Requests
- COVID-19 Resources
Writing Competition
- Agriculture
- Jobs and the Economy
- Sponsored Legislation
- Co-sponsored Legislation
- Voting Record
- Press Releases
- In the News
- E-Newsletter Sign Up
- Office Locations
- Interactive Map
- Telephone Townhall Sign Up
The Hechinger Report
Covering Innovation & Inequality in Education
PROOF POINTS: AI writing feedback ‘better than I thought,’ top researcher says

Share this:
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
The Hechinger Report is a national nonprofit newsroom that reports on one topic: education. Sign up for our weekly newsletters to get stories like this delivered directly to your inbox. Consider supporting our stories and becoming a member today.
Get important education news and analysis delivered straight to your inbox
- Weekly Update
- Future of Learning
- Higher Education
- Early Childhood
- Proof Points

This week I challenged my editor to face off against a machine. Barbara Kantrowitz gamely accepted, under one condition: “You have to file early.” Ever since ChatGPT arrived in 2022, many journalists have made a public stunt out of asking the new generation of artificial intelligence to write their stories. Those AI stories were often bland and sprinkled with errors. I wanted to understand how well ChatGPT handled a different aspect of writing: giving feedback.

My curiosity was piqued by a new study , published in the June 2024 issue of the peer-reviewed journal Learning and Instruction, that evaluated the quality of ChatGPT’s feedback on students’ writing. A team of researchers compared AI with human feedback on 200 history essays written by students in grades 6 through 12 and they determined that human feedback was generally a bit better. Humans had a particular advantage in advising students on something to work on that would be appropriate for where they are in their development as a writer.
But ChatGPT came close. On a five-point scale that the researchers used to rate feedback quality, with a 5 being the highest quality feedback, ChatGPT averaged a 3.6 compared with a 4.0 average from a team of 16 expert human evaluators. It was a tough challenge. Most of these humans had taught writing for more than 15 years or they had considerable experience in writing instruction. All received three hours of training for this exercise plus extra pay for providing the feedback.
ChatGPT even beat these experts in one aspect; it was slightly better at giving feedback on students’ reasoning, argumentation and use of evidence from source materials – the features that the researchers had wanted the writing evaluators to focus on.
“It was better than I thought it was going to be because I didn’t have a lot of hope that it was going to be that good,” said Steve Graham, a well-regarded expert on writing instruction at Arizona State University, and a member of the study’s research team. “It wasn’t always accurate. But sometimes it was right on the money. And I think we’ll learn how to make it better.”
Average ratings for the quality of ChatGPT and human feedback on 200 student essays

Exactly how ChatGPT is able to give good feedback is something of a black box even to the writing researchers who conducted this study. Artificial intelligence doesn’t comprehend things in the same way that humans do. But somehow, through the neural networks that ChatGPT’s programmers built, it is picking up on patterns from all the writing it has previously digested, and it is able to apply those patterns to a new text.
The surprising “relatively high quality” of ChatGPT’s feedback is important because it means that the new artificial intelligence of large language models, also known as generative AI, could potentially help students improve their writing. One of the biggest problems in writing instruction in U.S. schools is that teachers assign too little writing, Graham said, often because teachers feel that they don’t have the time to give personalized feedback to each student. That leaves students without sufficient practice to become good writers. In theory, teachers might be willing to assign more writing or insist on revisions for each paper if students (or teachers) could use ChatGPT to provide feedback between drafts.
Despite the potential, Graham isn’t an enthusiastic cheerleader for AI. “My biggest fear is that it becomes the writer,” he said. He worries that students will not limit their use of ChatGPT to helpful feedback, but ask it to do their thinking, analyzing and writing for them. That’s not good for learning. The research team also worries that writing instruction will suffer if teachers delegate too much feedback to ChatGPT. Seeing students’ incremental progress and common mistakes remain important for deciding what to teach next, the researchers said. For example, seeing loads of run-on sentences in your students’ papers might prompt a lesson on how to break them up. But if you don’t see them, you might not think to teach it. Another common concern among writing instructors is that AI feedback will steer everyone to write in the same homogenized way. A young writer’s unique voice could be flattened out before it even has the chance to develop.
There’s also the risk that students may not be interested in heeding AI feedback. Students often ignore the painstaking feedback that their teachers already give on their essays. Why should we think students will pay attention to feedback if they start getting more of it from a machine?
Still, Graham and his research colleagues at the University of California, Irvine, are continuing to study how AI could be used effectively and whether it ultimately improves students’ writing. “You can’t ignore it,” said Graham. “We either learn to live with it in useful ways, or we’re going to be very unhappy with it.”
Right now, the researchers are studying how students might converse back-and-forth with ChatGPT like a writing coach in order to understand the feedback and decide which suggestions to use.
Example of feedback from a human and ChatGPT on the same essay

In the current study, the researchers didn’t track whether students understood or employed the feedback, but only sought to measure its quality. Judging the quality of feedback is a rather subjective exercise, just as feedback itself is a bundle of subjective judgment calls. Smart people can disagree on what good writing looks like and how to revise bad writing.
In this case, the research team came up with its own criteria for what constitutes good feedback on a history essay. They instructed the humans to focus on the student’s reasoning and argumentation, rather than, say, grammar and punctuation. They also told the human raters to adopt a “glow and grow strategy” for delivering the feedback by first finding something to praise, then identifying a particular area for improvement.
The human raters provided this kind of feedback on hundreds of history essays from 2021 to 2023, as part of an unrelated study of an initiative to boost writing at school . The researchers randomly grabbed 200 of these essays and fed the raw student writing – without the human feedback – to version 3.5 of ChatGPT and asked it to give feedback , too .
At first, the AI feedback was terrible, but as the researchers tinkered with the instructions, or the “prompt,” they typed into ChatGPT, the feedback improved. The researchers eventually settled upon this wording: “Pretend you are a secondary school teacher. Provide 2-3 pieces of specific, actionable feedback on each of the following essays…. Use a friendly and encouraging tone.” The researchers also fed the assignment that the students were given, for example, “Why did the Montgomery Bus Boycott succeed?” along with the reading source material that the students were provided. (More details about how the researchers prompted ChatGPT are explained in Appendix C of the study .)
The humans took about 20 to 25 minutes per essay. ChatGPT’s feedback came back instantly. The humans sometimes marked up sentences by, for example, showing a place where the student could have cited a source to buttress an argument. ChatGPT didn’t write any in-line comments and only wrote a note to the student.
Researchers then read through both sets of feedback – human and machine – for each essay, comparing and rating them. (It was supposed to be a blind comparison test and the feedback raters were not told who authored each one. However, the language and tone of ChatGPT were distinct giveaways, and the in-line comments were a tell of human feedback.)
Humans appeared to have a clear edge with the very strongest and the very weakest writers, the researchers found. They were better at pushing a strong writer a little bit further, for example, by suggesting that the student consider and address a counterargument. ChatGPT struggled to come up with ideas for a student who was already meeting the objectives of a well-argued essay with evidence from the reading source materials. ChatGPT also struggled with the weakest writers. The researchers had to drop two of the essays from the study because they were so short that ChatGPT didn’t have any feedback for the student. The human rater was able to parse out some meaning from a brief, incomplete sentence and offer a suggestion.
In one student essay about the Montgomery Bus Boycott, reprinted above, the human feedback seemed too generic to me: “Next time, I would love to see some evidence from the sources to help back up your claim.” ChatGPT, by contrast, specifically suggested that the student could have mentioned how much revenue the bus company lost during the boycott – an idea that was mentioned in the student’s essay. ChatGPT also suggested that the student could have mentioned specific actions that the NAACP and other organizations took. But the student had actually mentioned a few of these specific actions in his essay. That part of ChatGPT’s feedback was plainly inaccurate.
In another student writing example, also reprinted below, the human straightforwardly pointed out that the student had gotten an historical fact wrong. ChatGPT appeared to affirm that the student’s mistaken version of events was correct.
Another example of feedback from a human and ChatGPT on the same essay

So how did ChatGPT’s review of my first draft stack up against my editor’s? One of the researchers on the study team suggested a prompt that I could paste into ChatGPT. After a few back and forth questions with the chatbot about my grade level and intended audience, it initially spit out some generic advice that had little connection to the ideas and words of my story. It seemed more interested in format and presentation, suggesting a summary at the top and subheads to organize the body. One suggestion would have made my piece too long-winded. Its advice to add examples of how AI feedback might be beneficial was something that I had already done. I then asked for specific things to change in my draft, and ChatGPT came back with some great subhead ideas. I plan to use them in my newsletter, which you can see if you sign up for it here . (And if you want to see my prompt and dialogue with ChatGPT, here is the link .)
My human editor, Barbara, was the clear winner in this round. She tightened up my writing, fixed style errors and helped me brainstorm this ending. Barbara’s job is safe – for now.
This story about AI feedback was written by Jill Barshay and produced by The Hechinger Report , a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education. Sign up for Proof Points and other Hechinger newsletters .
Related articles
The Hechinger Report provides in-depth, fact-based, unbiased reporting on education that is free to all readers. But that doesn't mean it's free to produce. Our work keeps educators and the public informed about pressing issues at schools and on campuses throughout the country. We tell the whole story, even when the details are inconvenient. Help us keep doing that.
Join us today.
Jill Barshay SENIOR REPORTER
(212)... More by Jill Barshay
Letters to the Editor
At The Hechinger Report, we publish thoughtful letters from readers that contribute to the ongoing discussion about the education topics we cover. Please read our guidelines for more information. We will not consider letters that do not contain a full name and valid email address. You may submit news tips or ideas here without a full name, but not letters.
By submitting your name, you grant us permission to publish it with your letter. We will never publish your email address. You must fill out all fields to submit a letter.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
Watch CBS News
Curtain goes up on 2024 Tribeca Festival, with tribute to Robert De Niro
By David Morgan
June 5, 2024 / 9:26 AM EDT / CBS News
The Tribeca Festival returns to screens and event venues across New York City on Wednesday, showcasing 114 feature-length narrative and documentary films — many of them world or New York premieres — along with shorts, revivals and restorations, filmmaker Q&As, audio storytelling, and music performances.
This year marks the 23rd edition of the festival, which was launched in 2002 by Robert De Niro, Jane Rosenthal and Craig Hatkoff to help revitalize a city wounded by 9/11. Since then it has grown into a major event for film lovers and media figures that also encompasses non-cinematic art forms: podcasts, demos of role-playing games, immersive art, and virtual reality/augmented reality exhibitions. This year's film slate was selected from more than 13,000 submissions, more than ever before.
Tribeca was conceptualized as a storytelling festival, said festival director and VP of programming Cara Cusumano, "and that's been kind of our guiding light and the root of where all these other programs evolved from. Where is the most interesting storytelling happening? How are audiences today consuming stories? Increasingly it's not always a 90-minute feature film experience."
Cusumano said that each of the festival's verticals has cinematic storytelling in their DNA: "They feel like logical evolutions, but the scale is smaller. There's probably 10 to 12 TV events, a similar number of immersive presentations, podcasts, games. So, we think of it kind of like the spokes on a wheel where we want to be sure that we're representing these communities of creators, and communities of audiences, within the festival, while preserving the real core DNA of the film festival.
"We want to create a creative ecosystem where all these folks are not siloed in their own industry," Cusumano said. "The walls are permeable and they can meet each other, they can meet the industry at large, and cross-pollinate in a way that we hope is creatively productive for everybody. The hope is to introduce people from games, podcasts, immersive, etc., to a more traditional film industry, and see where those points of connection might lie or be found, unexpectedly or not.
"And for audiences, too. Maybe what any single ticket buyer is drawn to is usually something that they're familiar with or in their wheelhouse, but maybe because there's all this other stuff going on, they get drawn into a different world and can discover something that they didn't set out to find. That's really hopefully the experience of discovery that Tribeca can offer that is unique."

But just as the festival has grown in scope over the years, it's also contracting. After expanding its offerings throughout the city and, later, with virtual screenings once COVID postponed the 2020 festival (allowing film fans from across the country to attend), it's now ended the Tribeca at Home program, to focus on communal, in-person screenings. And while film venues are primarily in Manhattan, special events are still being held in the outer boroughs, including a late-night dance party honoring the 70th anniversary of Godzilla at Baby's All Right in Brooklyn (June 7).
One of the major components of Tribeca 2024 is De Niro Con, marking the actor's 80th birthday. "De Niro Is an Icon" weaves together an exhibit and an immersive film installation projected on six screens, celebrating more than 40 iconic De Niro film characters (June 6-16 at Spring Studios). Classic De Niro performances will also be screened on June 14, including "The Godfather Part II," Quentin Tarantino's "Jackie Brown" (in 35mm), "Analyze This," and "Silver Linings Playbook," with Q&As following most films.
There will also be the world premiere of Chazz Palminteri's new film based on his one-man stage show, "A Bronx Tale," a play that De Niro adapted as his directorial film debut back in 1993.
Documentary films
On Wednesday, the festival's opening night feature is the Hulu documentary "Diane von Furstenberg: Woman in Charge," a profile of the iconic designer, who was both a princess and a queen of fashion (June 5, 6, 15). [To watch a trailer click on the video player below.]
Nonfiction films at the festival will explore current events, including the Russia-Ukraine war , through particularly novel or unfamiliar ways. "Checkpoint Zoo" tells the story of zoo workers in eastern Ukraine trying to rescue animals at an ecological park coming under fire from advancing Russian forces (June 6, 9, 13), while "Soldiers of Song" examines the resilience of Ukrainian musicians trying to cope with the invasion (June 13).
"Antidote" follows journalists and whistleblowers who find themselves targeted as they speak out against the silencing of anti-Putin voices inside and outside of Russia (June 7, 8, 9). In "State of Silence," journalists in Mexico are endangered by their reporting on corruption and narco-terrorism (June 10, 11, 12).

In "Following Harry," singer and social justice advocate Harry Belafonte (who died last year at age 96) mentors a new generation of activist and protest organizers (June 14, 15, 16). "Rebel Nun" profiles Sister Helen Prejean, whose efforts to combat capital punishment, as recounted in her book "Dead Man Walking," have also led to the exoneration of innocent men housed on Death Row (June 6, 7, 9).
In "Witches," Elizabeth Sankey weaves a personal essay about post-partum depression and the mental health of new mothers, and how it factors into the cultural depiction of witches and witchcraft through the ages, particularly in films (June 9, 10, 15). "Driver" examines the lives of female long-haul truck drivers (June 7, 8, 15). A gathering of comedians (including Tig Notero, Mike Birbiglia, Atsuko Okatsuka and Gary Gulman) sits down with Neil Patrick Harris to talk mental health in "Group Therapy" (June 6, 7, 13).

"Made in Ethiopia" looks at 21st century colonialism as Chinese investors try to sell an industrial park in Africa, affecting not only the lives of displaced farmers and young factory employees but also the Chinese expats who see themselves at Africa's future (June 6, 9, 14). The rise of artificial intelligence is explored in "The Thinking Game" (June 7, 8, 14).
Martin Scorsese offers a personal account of the impact on his life and art made by Emeric Pressburger and Michael Powell, from "The Red Shoes" and "The Life and Death of Colonel Blimp" to "Peeping Tom" ( "Made in England: The Films of Powell & Pressburger," June 11, 12, 14).
There are also profiles of notable celebrities, past and present, in the worlds of music, art and sports, from tennis legend Roger Federer ( "Federer: Twelve Final Days," June 10, 14, 16) to Bruce Springsteen sideman Stevie Van Zandt ( "Stevie Van Zandt: Disciple," June 8, 10, 15), to Liza Minnelli ( "Liza: A Truly Terrific Absolutely True Story," June 12, 13, 15), Elizabeth Taylor ( "Elizabeth Taylor: The Lost Tapes," June 11, 12, 16), "Hamilton" actress Renée Elise Goldsberry ( "Satisfied," June 15, 16), Luther Vandross ( "Luther: Never Too Much," June 13, 14, 15); Claude Nobs, founder of one of the world's leading jazz festivals ( "They All Came Out to Montreaux," June 7, 8, 12), and Swedish EDM artist Avicii ( "Avicii – I'm Tim," June 9, 11, 14). Singer-songwriters Linda Perry ( "Linda Perry: Let It Die Here," June 6, 8, 9), and Ani DiFranco ( "1-800-ON-HER-OWN," June 10, 11, 13) will each perform following the premiere screenings of films about their careers.
And if you're hungry after all that, "Shelf Life" takes a deep dive into the world of cheese (June 7, 8, 9).
Narrative films
Among the notable premieres of fiction films are the comedy "Adult Best Friends," starring director and co-writer Delaney Buffett (daughter of singer Jimmy Buffett), in which a young woman (Katie Corwin) has to break the news to her codependent best friend (Buffett) that she is engaged to a man her friend majorly dislikes (June 8, 10, 12, 16); and "Treasure," starring Stephen Fry and Lena Dunham as a Jewish émigré-father and his daughter revisiting Poland and the landmarks of his youth during World War II (June 8, 9, 11).

"Bad Shabbos" stars Jon Bass, Meghan Leathers, Kyra Sedgwick, David Paymer and Milana Vayntrub in a comedy about an observant Jewish Upper West Side family whose dinner is spoiled by the presence of a dead body (June 10, 11, 13, 15); and "The Shallow Tale of a Writer Who Decided to Write about a Serial Killer" pits John Magaro ("Past Lives") against Steve Buscemi ("Fargo") in a very dark comedy about a retired serial killer who offers to teach a struggling novelist the art of murder, and winds up serving as the writer's marriage counselor (June 8, 9, 12, 14).

Other notable entries include "The Damned," a period drama from Iceland, in which the fate of shipwrecked sailors places an entire community in peril (June 6, 7, 12). In "The Freshly Cut Grass," Marina de Tavira (an Oscar-nominee for "Roma") and Joaquín Furriel play college professors whose moribund marriages lead each into affairs with students (June 8, 13, 14).
Jude Law stars as King Henry VIII at odds with his sixth wife, Katherine Parr (Alicia Vikander), in "Firebrand" (June 11, 12). Elizabeth Banks is a surgeon shielding a colleague from the fallout over a medical procedural error in "A Mistake" (June 7, 8, 10). "The Wasp" is a psychological thriller starring Naomie Harris and Natalie Dormer (June 8, 9, 12). Lily Gladstone ("Killers of the Flower Moon") is featured in "Jazzy," a tale of growing up on the Oglala Lakota reservation in South Dakota (June 9, 10, 12). "Daddio" stars Dakota Johnson and Sean Penn sharing a late-night cab ride through New York City (June 10, 12, 16).
Jenna Ortega and Percy Hynes White star in a youthful romance, "Winter Spring Summer or Fall" (June 6, 7, 15), while Tim Blake Nelson plays a former boxer who trains his grandson in the ring in "Bang Bang" (June 11, 14, 15). Rooney Mara and Raúl Briones star in a tale of immigrant restaurant workers in NYC in "La Cocina" (June 9, 12, 13). Chinese writer-director Qiu Yang's "Some Rain Must Fall," winner of the special Jury Prize at this year's Berlin International Film Festival, evokes the cracks that form in a family following an accident, and of a housewife whose life spirals out of control (June 6, 9, 15).
Britt Lower, very good as the suspecting wife in "The Shallow Tale…," stars in "Darkest Miriam" as a Toronto librarian who begins a romantic relationship with a younger, foreign-born taxi driver (June 9, 11, 14). "McVeigh" examines the evolution of Timothy McVeigh into a domestic terrorist (June 7, 8, 11). In "Come Closer," a woman grieving over her brother's death meets his secret girlfriend (June 6, 8).
What can go wrong at a cannabis-fueled 40th birthday party? How about word of an impeding nuclear attack? "Nuked" is a comedy (June 13, 16), as are "Griffin in Summer," which follows a budding 14-year-old playwright (Everett Blunck) who finds a kindred spirit in a failed performance artist (June 6, 7, 13); "Rent Free," in which Jacob Roberts and David Treviño are best buds who try to wrangle a year of rent-free living by couch-surfing at friends' homes (June 7, 8, 13, 16); and "Between the Temples," starring Jason Schwartzman, Carol Kane, Robert Smigel and Dolly De Leon, about a young cantor, recently widowed, dipping his toes back into the dating world (June 13, 14, 15). Michael Cera, Maya Erskine and Kristen Stewart also star in the road trip "Sacramento" (June 8, 10, 12).
Tribeca hosts the New York premiere of this year's Sundance audience award-winner "Kneecap," the cheeky, too-good-to-be-true-but-it-(kinda-sorta)-is origin story of the Irish rap group Kneecap, who will perform following the film's first screening (June 9).
For Father's Day, Tribeca will screen the animated "Despicable Me 4" (June 16), while a coda to the festival will be the June 26 world premiere of "A Quiet Place: Day One."
Midnight / Escape from Tribeca
Genre films, from horror and thrillers to violent splatterfests, get their own sidebars. Among the offerings: The slasher flick "#AMFAD: All My Friends Are Dead," which tells the story of what happens when a party at an Airbnb turns crimson red (June 8, 10, 11); "The Weekend," a horror film from Nigeria about disquieting in-laws (June 9, 11, 15); and "Kill," an Indian thriller in which a passenger train becomes a battlefield between a pair of commandoes and an army of bandits (June 13, 14, 15).
But the most anticipated entry, for fans of the sketch comedy series "The Whitest Kids U' Know," may be "Mars," an animated lark set on the Red Planet. It's especially gratifying, three years after the death of "WKUK" co-founder Trevor Moore , that he and Zach Cregger, Sam Brown, Darren Trumeter and Timmy Williams get one more go together (June 6, 7, 15, 16).
Retrospectives and reunions
There are retrospective screenings of "Mean Streets," starring Harvey Keitel and Robert De Niro, followed by a discussion with De Niro and director Martin Scorsese (June 15); Steven Spielberg's "The Sugarland Express," starring Goldie Hawn, followed by a conversation with the director (June 15); the 1984 musical "Footloose," followed by a conversation with star Kevin Bacon (June 14); "Beat Street," about Bronx teenagers in the early years of hip hop (June 14); and Tod Browning's 1927 silent "The Unknown."
Alfred Hitchcock's masterful thriller "North by Northwest," starring Cary Grant as a Madison Avenue ad exec mistaken for a spy, has been restored by way of a 13K scan of the original VistaVision camera negative, and will be screened in 70mm 5.1 stereo (June 12).

In "Brats," Andrew McCarthy examines how he and other young actors in the 1980s who were collectively labeled the "Brat Park" survived (June 7, 8, 10; the premiere screening features a panel of reunited Brat Packers).
In 2003 Daft Punk and Leiji Matsumoto produced an hour-long film, "Interstella 555: The Story of the Secret Star System," about alien musicians. At the time the film was cut into short music videos; the full-length feature, remastered in 4K, is getting its North American premiere (June 14).
On June 13 a screening of Alex Gibney's "Sopranos 25th Anniversary Reunion: Wise Guy David Chase and the Sopranos," about the man behind television's greatest mob series, will be followed by a panel discussion featuring Chase and "Sopranos" cast members.
Episodic and limited series, as well as TV documentaries and docudramas, will also be highlighted. Among the offerings: the ESPN film "In the Arena: Serena Williams," about her life on and off the court (June 13); the HBO docuseries "Breath of Fire," about Guru Jagat, a millennial who became the face of a spiritual empire (June 12); the Hulu series "Mastermind: To Think Like a Killer" (June 7); "Presumed Innocent," an Apple TV limited series adapted from Scott Turow's legal thriller, starring Jake Gyllenhaal, Ruth Negga, Renate Reinsve and Peter Sarsgaard (June 9); and "The Stanford Prison Experiment: Unlocking the Truth," National Geographic's look back at the infamous psychological experiment (June 14, 16).
Conversations
Talks featuring notable creatives include Judd Apatow (June 15), Bravo's Andy Cohen (June 12), R.E.M. frontman Michael Stipe (June 12), "Succession" star Kieran Culkin (June 13), Jon Batiste, celebrating the music of Nat King Cole (June 11), Kerry Washington & Nicole Avant (June 8), Laverne Cox (June 12), cookbook author and YouTuber Alison Roman (June 14), and director Gus Van Sant.
Tribeca X mixes panels with networking to present industry and business leaders, entrepreneurs and celebrities, while the Creators Market allows storytellers to pitch their feature, episodic and audio projects.
Festival Guide
The festival runs from June 5-16, For more information about films, immersive exhibits, special events and ticketing, visit the Tribeca Festival website .
- Robert De Niro
- Tribeca Festival
David Morgan is senior producer for CBSNews.com and the Emmy Award-winning "CBS News Sunday Morning." He writes about film, music and the arts. He is author of the books "Monty Python Speaks" and "Knowing the Score," and editor of "Sundancing," about the Sundance Film Festival.
More from CBS News

The Book Report: Washington Post critic Ron Charles (June 2)

Book excerpt: "This Strange Eventful History" by Claire Messud

12 best high-yield savings accounts for June 2024

NYSE glitch sends Berkshire Hathaway shares down nearly 100%
- climate change
I Hate Summer—and You Should Too

W ake me when it’s over—summer, that is. I know, I know, you just love it: the long days, the warm evenings, the trips to the beach, the afternoons at the ballpark when your favorite team is playing and the pennant race is tightening—and the temperature is skyrocketing, and your skin is blistering, and the beer is $6, and the drive home will be in 88° heat, which is fine if you don’t mind running the air conditioner, except that you’re burning through $4–a-gallon gas, because it’s summer-driving season and the giant oil companies didn’t get to be the giant oil companies without knowing the right time of year to hike their prices.
And that’s hardly all of it. Summertime is the season of horribles, from higher crime rates, to increased warfare, to spikes in asthma, to raging wildfires, to swarms of bugs, to a rise in traffic accidents—and even to a bump in divorces, because how could a 100° heat wave, a busted A.C., and the kids out of school not spell domestic bliss?
What’s more, it’s only getting worse. Last summer was the hottest on record, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the 10 warmest years were all from 2010 to 2022. So with a lousy part of the year becoming lousier still, here, in no particular order, are nine reasons summer is the suckiest season of them all.
Road wrecks
There’s nothing like long days, no school, and lots of teen drivers to make the highways a safe place to be. Not . It’s no coincidence that the Automobile Association of America (AAA) labels the stretch between Memorial Day and Labor Day “the 100 deadliest days.” There are over 11.7 million U.S. drivers between the ages of 15 and 20, and if you know what’s good for you you’ll stay out of their way—especially when they’re out as a group, driving recreationally. “We know that when teens are joyriding as opposed to driving with a specific destination and time in mind, there is a heightened risk,” said Diana Gugliotta, senior manager of public affairs for AAA Northeast, in a statement last year.
Read More : What It's Like To Be Deathly Afraid of Feet
AAA’s numbers back that up. When a teen driver has only other teens in a vehicle, the risk of fatality for the driver and all passengers increases 51%. When at least one passenger is over 35, the overall fatality risk declines 8%. From 2011 to 2020, there were 7,316 deaths in summertime teen-related traffic accidents—nearly half the total of all teen-related traffic accidents for the year.
This means war
Napoleon Bonaparte could tell you a thing or two about what it’s like to pick a fight with Russia in the dead of winter. In 1812, the French army suffered half a million casualties in battles that climaxed in December—a rout that led to Napoleon’s abdication and exile in 1815. Any general worth his steed would prefer to fight in the summer when there’s plenty of light, the roads are clear, and soldiers aren’t bundled up against the cold. As far back as 55 BCE , the Roman army’s “campaigning season” would end when summer wound down and the soldiers would retreat to their winter quarters. It’s probably not a coincidence that World War I began in August 1914, World War II on Sept. 1, 1939, and Nazi Germany’s invasion of Russia in June 1941. More recently , in August 1990, Iraq invaded Kuwait, and in August 1991, the old Soviet Union nearly fell into civil war when communist hardliners tried to oust President Mikhail Gorbachev. America’s 20-year war in Afghanistan typically saw its fiercest fighting in the summer months, and the same is true of the war in Ukraine .
Hot-weather warfare is likely only to get worse. A 2009 paper in PNAS found that rising temperatures exacerbated by climate change could lead to a 54% increase in the risk of civil war in Africa by 2030. A 2011 study in Nature found that warmer weather during El Niño years doubled the risk of civil war in 90 tropical countries and could have accounted for 20% of conflicts around the world over the past half century. Meantime, what’s the season of peace on Earth and goodwill toward men? Wintertime, baby. Wintertime.
Going buggy
Summer advertises itself as the season of birdsong and butterflies. Don’t believe it. It’s the season of pests—particularly ticks, mosquitoes, flies, fleas, bees, and wasps. Ticks, mosquitoes, and fleas in particular can spread diseases that include malaria, yellow fever, Zika, dengue, Lyme, and chikungunya. Bees, wasps, and yellowjackets—with their infernal stings—are similarly creatures of the summer. And you think you know flies? You don’t know flies. There are 110,000 species of them —most more active in hot weather—making up a global population of 17 million flies for every living human. Pssst ! They’ve got us surrounded.
Read More : Long Dismissed, Chronic Lyme Disease Is Finally Getting Its Moment
Season of wheeze
Ah, summer, it takes your breath away. Literally. More than 25 million Americans have asthma, and 4.7 million of them are children— according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). If that means suffering during the temperate months, it’s much worse when the oven that is summer turns the dial up to broil. Heat and humidity constrict and narrow airways , trap ozone, and cause the air to entrain more particulate matter from cars, trucks, and smokestacks. What’s more, stagnant summer air—especially in homes with poor air conditioning or none at all—can exacerbate the presence of mold, dust, and pollen. And then—and stop me if I’ve mentioned this before—climate change is making things more punishing still for people with asthma. A 2023 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency report found that rising temperatures could increase the incidence of childhood asthma by anywhere from 4% to 11%, due partly to worsening pollution and allergies, and the growing problem of wildfire smoke .
Speaking of wildfires…
When it comes to dust, haze, and a mustard-colored sky, Mars has got nothing on Earth—at least during the summer fire season. Last year’s Canadian wildfires , sparked by lightning and fueled by high temperatures and drought, torched more than 71,000 square miles of land in Canada—an area the size of North Dakota—and yellowed out skies in the U.S. from the Midwest to the Northeast to the mid-Atlantic states. But the U.S. is playing with matches too. California’s wildfire season runs from April through October—peaking in the summer—with megadroughts and heat waves driving the flames. Of the state’s 20 largest fires, half occurred from 2017 to 2022. Climate change, of course, plays a regrettable role in all of this.
Crime and punishment
Nothing puts bad guys in a bad mood like hot weather—or so it seems. A 2019 study by the National Bureau of Economic Research found that on days with a maximum temperature above 85°F, all crime increases by 2.2% and violent crime by 5.7%. A 2023 study in PLOS One attributed this to what is known as the Theory of Routine Activities, which postulates that for crime to occur, three factors must be present: a motivated offender, a suitable target, and an absence of guards or surveillance. Of these, it is the second one—the suitable target—that is especially common in summer, according to the 2023 study, with greater numbers of people out on the streets.
As for the first variable, a motivated offender, well, even criminals don’t want to be outside commiting a crime in a 20°-below polar vortex. During a particularly deep freeze in 2015, Boston saw a 32% drop in burglaries, a 35% drop in larceny, and 46% drop in vehicle theft. Over the same period, New York City set a modern-day record , going 12 days without a homicide.
Summer’s contribution to violent crime in particular may be due at least in part to the common experience of hot weather leading to hot tempers, with even the most even-keeled people more inclined to blow a seam if they can’t cool off. One 2020 study found that people playing competitive video games in a hot room were more aggressive toward their gaming partner than they were when the room was cooler.
Daylight Saving Time
Don’t get me started on Daylight Saving Time. There is just nothing to like about this spring-forward inanity. For starters, it increases energy consumption (when it was supposed to decrease it) due to greater use of air conditioning. The changes in sleep patterns it causes contribute to heart attack , stroke , inflammation , and suicide , not to mention a 6% increase in fatal traffic accidents due to circadian scrambling and overall sleepiness. Small children and teens suffer particularly when the change in the clocks affects sleep cycles.
Read More : What to Know About the Latest Advances in Managing Severe Asthma
Finally, the atmospherics are all wrong. Nighttime is nighttime, people; the sun is the party guest that won’t go home if it’s still out at 9 p.m. I say send it packing no later than 8 p.m. and then race back to a nice wintertime sundown at cocktail hour. Cheers.
Trouble on the homefront
If you want to stay married, it might be wise to sleep through summer. That’s the finding of a 2016 study out of the University of Washington showing that August, along with March, are the two peak months for divorce in the U.S. The reason in both cases is more or less the same: couples tend to see winter and summer vacations as untouchable family time and, even in highly stressed marriages, will make it a point to hold the ship together for those treasured stretches. Once the good times are over, however, the marriages might be too.
“People tend to face the holidays with rising expectations, despite what disappointments they might have had in years past,” said sociology professor and the study’s co-author Julie Brines, in a statement at the time the research was released. “They’re very symbolically charged moments in time.”
When those expectations are dashed, a bust-up is likelier to follow. And while both early spring and late summer were implicated equally in that study, other research by Stowe Family Law in the U.K. found that September—the tail end of summer—is the peak divorce month on the other side of the pond, with total-immersion family time throwing financial, interpersonal, and other issues into relief.
It kills your skin
No matter how good it might feel to bake in the sun, your skin really, truly does not want a tan. In a rapidly warming world, it should come as no surprise that the sun is murder on your skin—drying it, aging it, cracking it, and much more importantly, leading to cancer. A 2022 paper in the journal Cureus found the highest rates of skin cancer diagnoses occurring from July to October.
Simple steps like wearing sunscreen , avoiding the sun from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m., and wearing protective clothing can all help reduce the risk. Sunshine in the winter, of course, can cause similar damage, but in the summer you're out a whole lot more and wearing a whole lot less. That—like summer as a whole—spells trouble.
Correction: The original version of this story misstated the date of Napoleon Bonaparte's abdication. It was 1815, not 1914.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- How Joe Biden Leads
- TIME100 Most Influential Companies 2024
- Javier Milei’s Radical Plan to Transform Argentina
- How Private Donors Shape Birth-Control Choices
- What Sealed Trump’s Fate : Column
- Are Walking Pads Worth It?
- 15 LGBTQ+ Books to Read for Pride
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Jeffrey Kluger at [email protected]
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Jamie Raskin: How to Force Justices Alito and Thomas to Recuse Themselves in the Jan. 6 Cases

By Jamie Raskin
Mr. Raskin represents Maryland’s Eighth Congressional District in the House of Representatives. He taught constitutional law for more than 25 years and was the lead prosecutor in the second impeachment trial of Donald Trump.
Many people have gloomily accepted the conventional wisdom that because there is no binding Supreme Court ethics code, there is no way to force Associate Justices Samuel Alito and Clarence Thomas to recuse themselves from the Jan. 6 cases that are before the court.
Justices Alito and Thomas are probably making the same assumption.
But all of them are wrong.
It seems unfathomable that the two justices could get away with deciding for themselves whether they can be impartial in ruling on cases affecting Donald Trump’s liability for crimes he is accused of committing on Jan. 6. Justice Thomas’s wife, Ginni Thomas, was deeply involved in the Jan. 6 “stop the steal” movement. Above the Virginia home of Justice Alito and his wife, Martha-Ann Alito, flew an upside-down American flag — a strong political statement among the people who stormed the Capitol. Above the Alitos’ beach home in New Jersey flew another flag that has been adopted by groups opposed to President Biden.
Justices Alito and Thomas face a groundswell of appeals beseeching them not to participate in Trump v. United States , the case that will decide whether Mr. Trump enjoys absolute immunity from criminal prosecution, and Fischer v. United States , which will decide whether Jan. 6 insurrectionists — and Mr. Trump — can be charged under a statute that criminalizes “corruptly” obstructing an official proceeding. (Justice Alito said on Wednesday that he would not recuse himself from Jan. 6-related cases.)
Everyone assumes that nothing can be done about the recusal situation because the highest court in the land has the lowest ethical standards — no binding ethics code or process outside of personal reflection. Each justice decides for him- or herself whether he or she can be impartial.
Of course, Justices Alito and Thomas could choose to recuse themselves — wouldn’t that be nice? But begging them to do the right thing misses a far more effective course of action.
The U.S. Department of Justice — including the U.S. attorney for the District of Columbia, an appointed U.S. special counsel and the solicitor general, all of whom were involved in different ways in the criminal prosecutions underlying these cases and are opposing Mr. Trump’s constitutional and statutory claims — can petition the other seven justices to require Justices Alito and Thomas to recuse themselves not as a matter of grace but as a matter of law.
The Justice Department and Attorney General Merrick Garland can invoke two powerful textual authorities for this motion: the Constitution of the United States, specifically the due process clause, and the federal statute mandating judicial disqualification for questionable impartiality, 28 U.S.C. Section 455. The Constitution has come into play in several recent Supreme Court decisions striking down rulings by stubborn judges in lower courts whose political impartiality has been reasonably questioned but who threw caution to the wind to hear a case anyway. This statute requires potentially biased judges throughout the federal system to recuse themselves at the start of the process to avoid judicial unfairness and embarrassing controversies and reversals.
The constitutional and statutory standards apply to Supreme Court justices. The Constitution, and the federal laws under it, is the “ supreme law of the land ,” and the recusal statute explicitly treats Supreme Court justices as it does other judges: “Any justice, judge or magistrate judge of the United States shall disqualify himself in any proceeding in which his impartiality might reasonably be questioned.” The only justices in the federal judiciary are the ones on the Supreme Court.
This recusal statute, if triggered, is not a friendly suggestion. It is Congress’s command, binding on the justices, just as the due process clause is. The Supreme Court cannot disregard this law just because it directly affects one or two of its justices. Ignoring it would trespass on the constitutional separation of powers because the justices would essentially be saying that they have the power to override a congressional command.
When the arguments are properly before the court, Chief Justice John Roberts and Associate Justices Amy Coney Barrett, Neil Gorsuch, Ketanji Brown Jackson, Elena Kagan, Brett Kavanaugh and Sonia Sotomayor will have both a constitutional obligation and a statutory obligation to enforce recusal standards.
Indeed, there is even a compelling argument based on case law that Chief Justice Roberts and the other unaffected justices should raise the matter of recusal on their own, or sua sponte. Numerous circuit courts have agreed with the Eighth Circuit that this is the right course of action when members of an appellate court are aware of “ overt acts ” of a judge reflecting personal bias. Cases like this stand for the idea that appellate jurists who see something should say something instead of placing all the burden on parties in a case who would have to risk angering a judge by bringing up the awkward matter of potential bias and favoritism on the bench.
But even if no member of the court raises the issue of recusal, the urgent need to deal with it persists. Once it is raised, the court would almost surely have to find that the due process clause and Section 455 compel Justices Alito and Thomas to recuse themselves. To arrive at that substantive conclusion, the justices need only read their court’s own recusal decisions.
In one key 5-to-3 Supreme Court case from 2016, Williams v. Pennsylvania, Justice Anthony Kennedy explained why judicial bias is a defect of constitutional magnitude and offered specific objective standards for identifying it. Significantly, Justices Alito and Thomas dissented from the majority’s ruling.
The case concerned the bias of the chief justice of Pennsylvania, who had been involved as a prosecutor on the state’s side in an appellate death penalty case that was before him. Justice Kennedy found that the judge’s refusal to recuse himself when asked to do so violated due process. Justice Kennedy’s authoritative opinion on recusal illuminates three critical aspects of the current controversy.
First, Justice Kennedy found that the standard for recusal must be objective because it is impossible to rely on the affected judge’s introspection and subjective interpretations. The court’s objective standard requires recusal when the likelihood of bias on the part of the judge “is too high to be constitutionally tolerable,” citing an earlier case. “This objective risk of bias,” according to Justice Kennedy, “is reflected in the due process maxim that ‘no man can be a judge in his own case.’” A judge or justice can be convinced of his or her own impartiality but also completely missing what other people are seeing.
Second, the Williams majority endorsed the American Bar Association’s Model Code of Judicial Conduct as an appropriate articulation of the Madisonian standard that “no man can be a judge in his own cause.” Model Code Rule 2.11 on judicial disqualification says that a judge “shall disqualify himself or herself in any proceeding in which the judge’s impartiality might reasonably be questioned.” This includes, illustratively, cases in which the judge “has a personal bias or prejudice concerning a party,” a married judge knows that “the judge’s spouse” is “a person who has more than a de minimis interest that could be substantially affected by the proceeding” or the judge “has made a public statement, other than in a court proceeding, judicial decision or opinion, that commits or appears to commit the judge to reach a particular result.” These model code illustrations ring a lot of bells at this moment.
Third and most important, Justice Kennedy found for the court that the failure of an objectively biased judge to recuse him- or herself is not “harmless error” just because the biased judge’s vote is not apparently determinative in the vote of a panel of judges. A biased judge contaminates the proceeding not just by the casting and tabulation of his or her own vote but by participating in the body’s collective deliberations and affecting, even subtly, other judges’ perceptions of the case.
Justice Kennedy was emphatic on this point : “It does not matter whether the disqualified judge’s vote was necessary to the disposition of the case. The fact that the interested judge’s vote was not dispositive may mean only that the judge was successful in persuading most members of the court to accept his or her position — an outcome that does not lessen the unfairness to the affected party.”
Courts generally have found that any reasonable doubts about a judge’s partiality must be resolved in favor of recusal. A judge “shall disqualify himself in any proceeding in which his impartiality might reasonably be questioned.” While recognizing that the “challenged judge enjoys a margin of discretion,” the courts have repeatedly held that “doubts ordinarily ought to be resolved in favor of recusal.” After all, the reputation of the whole tribunal and public confidence in the judiciary are both on the line.
Judge David Tatel of the D.C. Circuit emphasized this fundamental principle in 2019 when his court issued a writ of mandamus to force recusal of a military judge who blithely ignored at least the appearance of a glaring conflict of interest. He stated : “Impartial adjudicators are the cornerstone of any system of justice worthy of the label. And because ‘deference to the judgments and rulings of courts depends upon public confidence in the integrity and independence of judges,’ jurists must avoid even the appearance of partiality.” He reminded us that to perform its high function in the best way, as Justice Felix Frankfurter stated, “justice must satisfy the appearance of justice.”
The Supreme Court has been especially disposed to favor recusal when partisan politics appear to be a prejudicial factor even when the judge’s impartiality has not been questioned. In Caperton v. A.T. Massey Coal Co. , from 2009, the court held that a state supreme court justice was constitutionally disqualified from a case in which the president of a corporation appearing before him had helped to get him elected by spending $3 million promoting his campaign. The court, through Justice Kennedy, asked whether, quoting a 1975 decision, “under a realistic appraisal of psychological tendencies and human weakness,” the judge’s obvious political alignment with a party in a case “poses such a risk of actual bias or prejudgment that the practice must be forbidden if the guarantee of due process is to be adequately implemented.”
The federal statute on disqualification, Section 455(b) , also makes recusal analysis directly applicable to bias imputed to a spouse’s interest in the case. Ms. Thomas and Mrs. Alito (who, according to Justice Alito, is the one who put up the inverted flag outside their home) meet this standard. A judge must recuse him- or herself when a spouse “is known by the judge to have an interest in a case that could be substantially affected by the outcome of the proceeding.”
At his Senate confirmation hearing, Chief Justice Roberts assured America that “judges are like umpires.”
But professional baseball would never allow an umpire to continue to officiate the World Series after learning that the pennant of one of the two teams competing was flying in the front yard of the umpire’s home. Nor would an umpire be allowed to call balls and strikes in a World Series game after the umpire’s wife tried to get the official score of a prior game in the series overthrown and canceled out to benefit the losing team. If judges are like umpires, then they should be treated like umpires, not team owners, fans or players.
Justice Barrett has said she wants to convince people “that this court is not comprised of a bunch of partisan hacks.” Justice Alito himself declared the importance of judicial objectivity in his opinion for the majority in the Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization decision overruling Roe v. Wade — a bit of self-praise that now rings especially hollow.
But the Constitution and Congress’s recusal statute provide the objective framework of analysis and remedy for cases of judicial bias that are apparent to the world, even if they may be invisible to the judges involved. This is not really optional for the justices.
I look forward to seeing seven members of the court act to defend the reputation and integrity of the institution.
Jamie Raskin, a Democrat, represents Maryland’s Eighth Congressional District in the House of Representatives. He taught constitutional law for more than 25 years and was the lead prosecutor in the second impeachment trial of Donald Trump.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 03 June 2024
Applying large language models for automated essay scoring for non-native Japanese
- Wenchao Li 1 &
- Haitao Liu 2
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 723 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Language and linguistics
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have led to an increased use of large language models (LLMs) for language assessment tasks such as automated essay scoring (AES), automated listening tests, and automated oral proficiency assessments. The application of LLMs for AES in the context of non-native Japanese, however, remains limited. This study explores the potential of LLM-based AES by comparing the efficiency of different models, i.e. two conventional machine training technology-based methods (Jess and JWriter), two LLMs (GPT and BERT), and one Japanese local LLM (Open-Calm large model). To conduct the evaluation, a dataset consisting of 1400 story-writing scripts authored by learners with 12 different first languages was used. Statistical analysis revealed that GPT-4 outperforms Jess and JWriter, BERT, and the Japanese language-specific trained Open-Calm large model in terms of annotation accuracy and predicting learning levels. Furthermore, by comparing 18 different models that utilize various prompts, the study emphasized the significance of prompts in achieving accurate and reliable evaluations using LLMs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Scoring method of English composition integrating deep learning in higher vocational colleges
ChatGPT-3.5 as writing assistance in students’ essays
Detecting contract cheating through linguistic fingerprint
Conventional machine learning technology in aes.
AES has experienced significant growth with the advancement of machine learning technologies in recent decades. In the earlier stages of AES development, conventional machine learning-based approaches were commonly used. These approaches involved the following procedures: a) feeding the machine with a dataset. In this step, a dataset of essays is provided to the machine learning system. The dataset serves as the basis for training the model and establishing patterns and correlations between linguistic features and human ratings. b) the machine learning model is trained using linguistic features that best represent human ratings and can effectively discriminate learners’ writing proficiency. These features include lexical richness (Lu, 2012 ; Kyle and Crossley, 2015 ; Kyle et al. 2021 ), syntactic complexity (Lu, 2010 ; Liu, 2008 ), text cohesion (Crossley and McNamara, 2016 ), and among others. Conventional machine learning approaches in AES require human intervention, such as manual correction and annotation of essays. This human involvement was necessary to create a labeled dataset for training the model. Several AES systems have been developed using conventional machine learning technologies. These include the Intelligent Essay Assessor (Landauer et al. 2003 ), the e-rater engine by Educational Testing Service (Attali and Burstein, 2006 ; Burstein, 2003 ), MyAccess with the InterlliMetric scoring engine by Vantage Learning (Elliot, 2003 ), and the Bayesian Essay Test Scoring system (Rudner and Liang, 2002 ). These systems have played a significant role in automating the essay scoring process and providing quick and consistent feedback to learners. However, as touched upon earlier, conventional machine learning approaches rely on predetermined linguistic features and often require manual intervention, making them less flexible and potentially limiting their generalizability to different contexts.
In the context of the Japanese language, conventional machine learning-incorporated AES tools include Jess (Ishioka and Kameda, 2006 ) and JWriter (Lee and Hasebe, 2017 ). Jess assesses essays by deducting points from the perfect score, utilizing the Mainichi Daily News newspaper as a database. The evaluation criteria employed by Jess encompass various aspects, such as rhetorical elements (e.g., reading comprehension, vocabulary diversity, percentage of complex words, and percentage of passive sentences), organizational structures (e.g., forward and reverse connection structures), and content analysis (e.g., latent semantic indexing). JWriter employs linear regression analysis to assign weights to various measurement indices, such as average sentence length and total number of characters. These weights are then combined to derive the overall score. A pilot study involving the Jess model was conducted on 1320 essays at different proficiency levels, including primary, intermediate, and advanced. However, the results indicated that the Jess model failed to significantly distinguish between these essay levels. Out of the 16 measures used, four measures, namely median sentence length, median clause length, median number of phrases, and maximum number of phrases, did not show statistically significant differences between the levels. Additionally, two measures exhibited between-level differences but lacked linear progression: the number of attributives declined words and the Kanji/kana ratio. On the other hand, the remaining measures, including maximum sentence length, maximum clause length, number of attributive conjugated words, maximum number of consecutive infinitive forms, maximum number of conjunctive-particle clauses, k characteristic value, percentage of big words, and percentage of passive sentences, demonstrated statistically significant between-level differences and displayed linear progression.
Both Jess and JWriter exhibit notable limitations, including the manual selection of feature parameters and weights, which can introduce biases into the scoring process. The reliance on human annotators to label non-native language essays also introduces potential noise and variability in the scoring. Furthermore, an important concern is the possibility of system manipulation and cheating by learners who are aware of the regression equation utilized by the models (Hirao et al. 2020 ). These limitations emphasize the need for further advancements in AES systems to address these challenges.
Deep learning technology in AES
Deep learning has emerged as one of the approaches for improving the accuracy and effectiveness of AES. Deep learning-based AES methods utilize artificial neural networks that mimic the human brain’s functioning through layered algorithms and computational units. Unlike conventional machine learning, deep learning autonomously learns from the environment and past errors without human intervention. This enables deep learning models to establish nonlinear correlations, resulting in higher accuracy. Recent advancements in deep learning have led to the development of transformers, which are particularly effective in learning text representations. Noteworthy examples include bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) (Devlin et al. 2019 ) and the generative pretrained transformer (GPT) (OpenAI).
BERT is a linguistic representation model that utilizes a transformer architecture and is trained on two tasks: masked linguistic modeling and next-sentence prediction (Hirao et al. 2020 ; Vaswani et al. 2017 ). In the context of AES, BERT follows specific procedures, as illustrated in Fig. 1 : (a) the tokenized prompts and essays are taken as input; (b) special tokens, such as [CLS] and [SEP], are added to mark the beginning and separation of prompts and essays; (c) the transformer encoder processes the prompt and essay sequences, resulting in hidden layer sequences; (d) the hidden layers corresponding to the [CLS] tokens (T[CLS]) represent distributed representations of the prompts and essays; and (e) a multilayer perceptron uses these distributed representations as input to obtain the final score (Hirao et al. 2020 ).
AES system with BERT (Hirao et al. 2020 ).
The training of BERT using a substantial amount of sentence data through the Masked Language Model (MLM) allows it to capture contextual information within the hidden layers. Consequently, BERT is expected to be capable of identifying artificial essays as invalid and assigning them lower scores (Mizumoto and Eguchi, 2023 ). In the context of AES for nonnative Japanese learners, Hirao et al. ( 2020 ) combined the long short-term memory (LSTM) model proposed by Hochreiter and Schmidhuber ( 1997 ) with BERT to develop a tailored automated Essay Scoring System. The findings of their study revealed that the BERT model outperformed both the conventional machine learning approach utilizing character-type features such as “kanji” and “hiragana”, as well as the standalone LSTM model. Takeuchi et al. ( 2021 ) presented an approach to Japanese AES that eliminates the requirement for pre-scored essays by relying solely on reference texts or a model answer for the essay task. They investigated multiple similarity evaluation methods, including frequency of morphemes, idf values calculated on Wikipedia, LSI, LDA, word-embedding vectors, and document vectors produced by BERT. The experimental findings revealed that the method utilizing the frequency of morphemes with idf values exhibited the strongest correlation with human-annotated scores across different essay tasks. The utilization of BERT in AES encounters several limitations. Firstly, essays often exceed the model’s maximum length limit. Second, only score labels are available for training, which restricts access to additional information.
Mizumoto and Eguchi ( 2023 ) were pioneers in employing the GPT model for AES in non-native English writing. Their study focused on evaluating the accuracy and reliability of AES using the GPT-3 text-davinci-003 model, analyzing a dataset of 12,100 essays from the corpus of nonnative written English (TOEFL11). The findings indicated that AES utilizing the GPT-3 model exhibited a certain degree of accuracy and reliability. They suggest that GPT-3-based AES systems hold the potential to provide support for human ratings. However, applying GPT model to AES presents a unique natural language processing (NLP) task that involves considerations such as nonnative language proficiency, the influence of the learner’s first language on the output in the target language, and identifying linguistic features that best indicate writing quality in a specific language. These linguistic features may differ morphologically or syntactically from those present in the learners’ first language, as observed in (1)–(3).
我-送了-他-一本-书
Wǒ-sòngle-tā-yī běn-shū
1 sg .-give. past- him-one .cl- book
“I gave him a book.”
Agglutinative
彼-に-本-を-あげ-まし-た
Kare-ni-hon-o-age-mashi-ta
3 sg .- dat -hon- acc- give.honorification. past
Inflectional
give, give-s, gave, given, giving
Additionally, the morphological agglutination and subject-object-verb (SOV) order in Japanese, along with its idiomatic expressions, pose additional challenges for applying language models in AES tasks (4).
足-が 棒-に なり-ました
Ashi-ga bo-ni nar-mashita
leg- nom stick- dat become- past
“My leg became like a stick (I am extremely tired).”
The example sentence provided demonstrates the morpho-syntactic structure of Japanese and the presence of an idiomatic expression. In this sentence, the verb “なる” (naru), meaning “to become”, appears at the end of the sentence. The verb stem “なり” (nari) is attached with morphemes indicating honorification (“ます” - mashu) and tense (“た” - ta), showcasing agglutination. While the sentence can be literally translated as “my leg became like a stick”, it carries an idiomatic interpretation that implies “I am extremely tired”.
To overcome this issue, CyberAgent Inc. ( 2023 ) has developed the Open-Calm series of language models specifically designed for Japanese. Open-Calm consists of pre-trained models available in various sizes, such as Small, Medium, Large, and 7b. Figure 2 depicts the fundamental structure of the Open-Calm model. A key feature of this architecture is the incorporation of the Lora Adapter and GPT-NeoX frameworks, which can enhance its language processing capabilities.
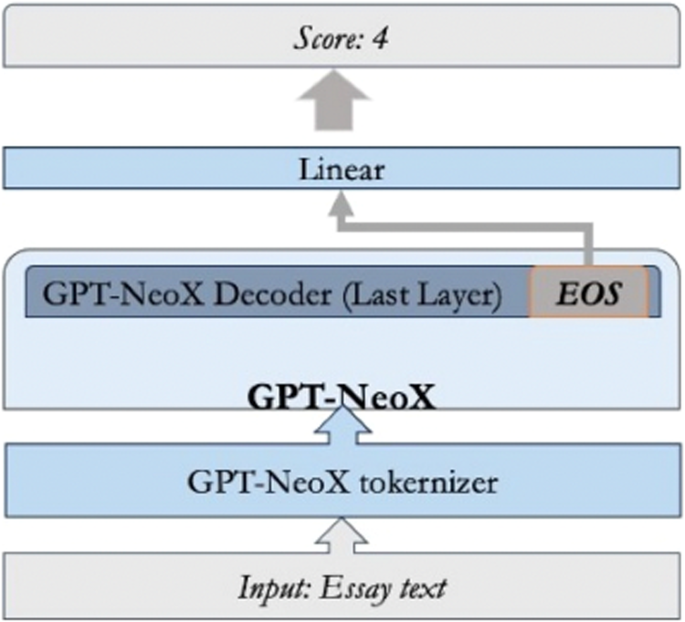
GPT-NeoX Model Architecture (Okgetheng and Takeuchi 2024 ).
In a recent study conducted by Okgetheng and Takeuchi ( 2024 ), they assessed the efficacy of Open-Calm language models in grading Japanese essays. The research utilized a dataset of approximately 300 essays, which were annotated by native Japanese educators. The findings of the study demonstrate the considerable potential of Open-Calm language models in automated Japanese essay scoring. Specifically, among the Open-Calm family, the Open-Calm Large model (referred to as OCLL) exhibited the highest performance. However, it is important to note that, as of the current date, the Open-Calm Large model does not offer public access to its server. Consequently, users are required to independently deploy and operate the environment for OCLL. In order to utilize OCLL, users must have a PC equipped with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 (8 or 12 GB VRAM).
In summary, while the potential of LLMs in automated scoring of nonnative Japanese essays has been demonstrated in two studies—BERT-driven AES (Hirao et al. 2020 ) and OCLL-based AES (Okgetheng and Takeuchi, 2024 )—the number of research efforts in this area remains limited.
Another significant challenge in applying LLMs to AES lies in prompt engineering and ensuring its reliability and effectiveness (Brown et al. 2020 ; Rae et al. 2021 ; Zhang et al. 2021 ). Various prompting strategies have been proposed, such as the zero-shot chain of thought (CoT) approach (Kojima et al. 2022 ), which involves manually crafting diverse and effective examples. However, manual efforts can lead to mistakes. To address this, Zhang et al. ( 2021 ) introduced an automatic CoT prompting method called Auto-CoT, which demonstrates matching or superior performance compared to the CoT paradigm. Another prompt framework is trees of thoughts, enabling a model to self-evaluate its progress at intermediate stages of problem-solving through deliberate reasoning (Yao et al. 2023 ).
Beyond linguistic studies, there has been a noticeable increase in the number of foreign workers in Japan and Japanese learners worldwide (Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan, 2022 ; Japan Foundation, 2021 ). However, existing assessment methods, such as the Japanese Language Proficiency Test (JLPT), J-CAT, and TTBJ Footnote 1 , primarily focus on reading, listening, vocabulary, and grammar skills, neglecting the evaluation of writing proficiency. As the number of workers and language learners continues to grow, there is a rising demand for an efficient AES system that can reduce costs and time for raters and be utilized for employment, examinations, and self-study purposes.
This study aims to explore the potential of LLM-based AES by comparing the effectiveness of five models: two LLMs (GPT Footnote 2 and BERT), one Japanese local LLM (OCLL), and two conventional machine learning-based methods (linguistic feature-based scoring tools - Jess and JWriter).
The research questions addressed in this study are as follows:
To what extent do the LLM-driven AES and linguistic feature-based AES, when used as automated tools to support human rating, accurately reflect test takers’ actual performance?
What influence does the prompt have on the accuracy and performance of LLM-based AES methods?
The subsequent sections of the manuscript cover the methodology, including the assessment measures for nonnative Japanese writing proficiency, criteria for prompts, and the dataset. The evaluation section focuses on the analysis of annotations and rating scores generated by LLM-driven and linguistic feature-based AES methods.
Methodology
The dataset utilized in this study was obtained from the International Corpus of Japanese as a Second Language (I-JAS) Footnote 3 . This corpus consisted of 1000 participants who represented 12 different first languages. For the study, the participants were given a story-writing task on a personal computer. They were required to write two stories based on the 4-panel illustrations titled “Picnic” and “The key” (see Appendix A). Background information for the participants was provided by the corpus, including their Japanese language proficiency levels assessed through two online tests: J-CAT and SPOT. These tests evaluated their reading, listening, vocabulary, and grammar abilities. The learners’ proficiency levels were categorized into six levels aligned with the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) and the Reference Framework for Japanese Language Education (RFJLE): A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2. According to Lee et al. ( 2015 ), there is a high level of agreement (r = 0.86) between the J-CAT and SPOT assessments, indicating that the proficiency certifications provided by J-CAT are consistent with those of SPOT. However, it is important to note that the scores of J-CAT and SPOT do not have a one-to-one correspondence. In this study, the J-CAT scores were used as a benchmark to differentiate learners of different proficiency levels. A total of 1400 essays were utilized, representing the beginner (aligned with A1), A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2 levels based on the J-CAT scores. Table 1 provides information about the learners’ proficiency levels and their corresponding J-CAT and SPOT scores.
A dataset comprising a total of 1400 essays from the story writing tasks was collected. Among these, 714 essays were utilized to evaluate the reliability of the LLM-based AES method, while the remaining 686 essays were designated as development data to assess the LLM-based AES’s capability to distinguish participants with varying proficiency levels. The GPT 4 API was used in this study. A detailed explanation of the prompt-assessment criteria is provided in Section Prompt . All essays were sent to the model for measurement and scoring.
Measures of writing proficiency for nonnative Japanese
Japanese exhibits a morphologically agglutinative structure where morphemes are attached to the word stem to convey grammatical functions such as tense, aspect, voice, and honorifics, e.g. (5).
食べ-させ-られ-まし-た-か
tabe-sase-rare-mashi-ta-ka
[eat (stem)-causative-passive voice-honorification-tense. past-question marker]
Japanese employs nine case particles to indicate grammatical functions: the nominative case particle が (ga), the accusative case particle を (o), the genitive case particle の (no), the dative case particle に (ni), the locative/instrumental case particle で (de), the ablative case particle から (kara), the directional case particle へ (e), and the comitative case particle と (to). The agglutinative nature of the language, combined with the case particle system, provides an efficient means of distinguishing between active and passive voice, either through morphemes or case particles, e.g. 食べる taberu “eat concusive . ” (active voice); 食べられる taberareru “eat concusive . ” (passive voice). In the active voice, “パン を 食べる” (pan o taberu) translates to “to eat bread”. On the other hand, in the passive voice, it becomes “パン が 食べられた” (pan ga taberareta), which means “(the) bread was eaten”. Additionally, it is important to note that different conjugations of the same lemma are considered as one type in order to ensure a comprehensive assessment of the language features. For example, e.g., 食べる taberu “eat concusive . ”; 食べている tabeteiru “eat progress .”; 食べた tabeta “eat past . ” as one type.
To incorporate these features, previous research (Suzuki, 1999 ; Watanabe et al. 1988 ; Ishioka, 2001 ; Ishioka and Kameda, 2006 ; Hirao et al. 2020 ) has identified complexity, fluency, and accuracy as crucial factors for evaluating writing quality. These criteria are assessed through various aspects, including lexical richness (lexical density, diversity, and sophistication), syntactic complexity, and cohesion (Kyle et al. 2021 ; Mizumoto and Eguchi, 2023 ; Ure, 1971 ; Halliday, 1985 ; Barkaoui and Hadidi, 2020 ; Zenker and Kyle, 2021 ; Kim et al. 2018 ; Lu, 2017 ; Ortega, 2015 ). Therefore, this study proposes five scoring categories: lexical richness, syntactic complexity, cohesion, content elaboration, and grammatical accuracy. A total of 16 measures were employed to capture these categories. The calculation process and specific details of these measures can be found in Table 2 .
T-unit, first introduced by Hunt ( 1966 ), is a measure used for evaluating speech and composition. It serves as an indicator of syntactic development and represents the shortest units into which a piece of discourse can be divided without leaving any sentence fragments. In the context of Japanese language assessment, Sakoda and Hosoi ( 2020 ) utilized T-unit as the basic unit to assess the accuracy and complexity of Japanese learners’ speaking and storytelling. The calculation of T-units in Japanese follows the following principles:
A single main clause constitutes 1 T-unit, regardless of the presence or absence of dependent clauses, e.g. (6).
ケンとマリはピクニックに行きました (main clause): 1 T-unit.
If a sentence contains a main clause along with subclauses, each subclause is considered part of the same T-unit, e.g. (7).
天気が良かった の で (subclause)、ケンとマリはピクニックに行きました (main clause): 1 T-unit.
In the case of coordinate clauses, where multiple clauses are connected, each coordinated clause is counted separately. Thus, a sentence with coordinate clauses may have 2 T-units or more, e.g. (8).
ケンは地図で場所を探して (coordinate clause)、マリはサンドイッチを作りました (coordinate clause): 2 T-units.
Lexical diversity refers to the range of words used within a text (Engber, 1995 ; Kyle et al. 2021 ) and is considered a useful measure of the breadth of vocabulary in L n production (Jarvis, 2013a , 2013b ).
The type/token ratio (TTR) is widely recognized as a straightforward measure for calculating lexical diversity and has been employed in numerous studies. These studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between TTR and other methods of measuring lexical diversity (e.g., Bentz et al. 2016 ; Čech and Miroslav, 2018 ; Çöltekin and Taraka, 2018 ). TTR is computed by considering both the number of unique words (types) and the total number of words (tokens) in a given text. Given that the length of learners’ writing texts can vary, this study employs the moving average type-token ratio (MATTR) to mitigate the influence of text length. MATTR is calculated using a 50-word moving window. Initially, a TTR is determined for words 1–50 in an essay, followed by words 2–51, 3–52, and so on until the end of the essay is reached (Díez-Ortega and Kyle, 2023 ). The final MATTR scores were obtained by averaging the TTR scores for all 50-word windows. The following formula was employed to derive MATTR:
\({\rm{MATTR}}({\rm{W}})=\frac{{\sum }_{{\rm{i}}=1}^{{\rm{N}}-{\rm{W}}+1}{{\rm{F}}}_{{\rm{i}}}}{{\rm{W}}({\rm{N}}-{\rm{W}}+1)}\)
Here, N refers to the number of tokens in the corpus. W is the randomly selected token size (W < N). \({F}_{i}\) is the number of types in each window. The \({\rm{MATTR}}({\rm{W}})\) is the mean of a series of type-token ratios (TTRs) based on the word form for all windows. It is expected that individuals with higher language proficiency will produce texts with greater lexical diversity, as indicated by higher MATTR scores.
Lexical density was captured by the ratio of the number of lexical words to the total number of words (Lu, 2012 ). Lexical sophistication refers to the utilization of advanced vocabulary, often evaluated through word frequency indices (Crossley et al. 2013 ; Haberman, 2008 ; Kyle and Crossley, 2015 ; Laufer and Nation, 1995 ; Lu, 2012 ; Read, 2000 ). In line of writing, lexical sophistication can be interpreted as vocabulary breadth, which entails the appropriate usage of vocabulary items across various lexicon-grammatical contexts and registers (Garner et al. 2019 ; Kim et al. 2018 ; Kyle et al. 2018 ). In Japanese specifically, words are considered lexically sophisticated if they are not included in the “Japanese Education Vocabulary List Ver 1.0”. Footnote 4 Consequently, lexical sophistication was calculated by determining the number of sophisticated word types relative to the total number of words per essay. Furthermore, it has been suggested that, in Japanese writing, sentences should ideally have a length of no more than 40 to 50 characters, as this promotes readability. Therefore, the median and maximum sentence length can be considered as useful indices for assessment (Ishioka and Kameda, 2006 ).
Syntactic complexity was assessed based on several measures, including the mean length of clauses, verb phrases per T-unit, clauses per T-unit, dependent clauses per T-unit, complex nominals per clause, adverbial clauses per clause, coordinate phrases per clause, and mean dependency distance (MDD). The MDD reflects the distance between the governor and dependent positions in a sentence. A larger dependency distance indicates a higher cognitive load and greater complexity in syntactic processing (Liu, 2008 ; Liu et al. 2017 ). The MDD has been established as an efficient metric for measuring syntactic complexity (Jiang, Quyang, and Liu, 2019 ; Li and Yan, 2021 ). To calculate the MDD, the position numbers of the governor and dependent are subtracted, assuming that words in a sentence are assigned in a linear order, such as W1 … Wi … Wn. In any dependency relationship between words Wa and Wb, Wa is the governor and Wb is the dependent. The MDD of the entire sentence was obtained by taking the absolute value of governor – dependent:
MDD = \(\frac{1}{n}{\sum }_{i=1}^{n}|{\rm{D}}{{\rm{D}}}_{i}|\)
In this formula, \(n\) represents the number of words in the sentence, and \({DD}i\) is the dependency distance of the \({i}^{{th}}\) dependency relationship of a sentence. Building on this, the annotation of sentence ‘Mary-ga-John-ni-keshigomu-o-watashita was [Mary- top -John- dat -eraser- acc -give- past] ’. The sentence’s MDD would be 2. Table 3 provides the CSV file as a prompt for GPT 4.
Cohesion (semantic similarity) and content elaboration aim to capture the ideas presented in test taker’s essays. Cohesion was assessed using three measures: Synonym overlap/paragraph (topic), Synonym overlap/paragraph (keywords), and word2vec cosine similarity. Content elaboration and development were measured as the number of metadiscourse markers (type)/number of words. To capture content closely, this study proposed a novel-distance based representation, by encoding the cosine distance between the essay (by learner) and essay task’s (topic and keyword) i -vectors. The learner’s essay is decoded into a word sequence, and aligned to the essay task’ topic and keyword for log-likelihood measurement. The cosine distance reveals the content elaboration score in the leaners’ essay. The mathematical equation of cosine similarity between target-reference vectors is shown in (11), assuming there are i essays and ( L i , …. L n ) and ( N i , …. N n ) are the vectors representing the learner and task’s topic and keyword respectively. The content elaboration distance between L i and N i was calculated as follows:
\(\cos \left(\theta \right)=\frac{{\rm{L}}\,\cdot\, {\rm{N}}}{\left|{\rm{L}}\right|{\rm{|N|}}}=\frac{\mathop{\sum }\nolimits_{i=1}^{n}{L}_{i}{N}_{i}}{\sqrt{\mathop{\sum }\nolimits_{i=1}^{n}{L}_{i}^{2}}\sqrt{\mathop{\sum }\nolimits_{i=1}^{n}{N}_{i}^{2}}}\)
A high similarity value indicates a low difference between the two recognition outcomes, which in turn suggests a high level of proficiency in content elaboration.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed measures in distinguishing different proficiency levels among nonnative Japanese speakers’ writing, we conducted a multi-faceted Rasch measurement analysis (Linacre, 1994 ). This approach applies measurement models to thoroughly analyze various factors that can influence test outcomes, including test takers’ proficiency, item difficulty, and rater severity, among others. The underlying principles and functionality of multi-faceted Rasch measurement are illustrated in (12).
\(\log \left(\frac{{P}_{{nijk}}}{{P}_{{nij}(k-1)}}\right)={B}_{n}-{D}_{i}-{C}_{j}-{F}_{k}\)
(12) defines the logarithmic transformation of the probability ratio ( P nijk /P nij(k-1) )) as a function of multiple parameters. Here, n represents the test taker, i denotes a writing proficiency measure, j corresponds to the human rater, and k represents the proficiency score. The parameter B n signifies the proficiency level of test taker n (where n ranges from 1 to N). D j represents the difficulty parameter of test item i (where i ranges from 1 to L), while C j represents the severity of rater j (where j ranges from 1 to J). Additionally, F k represents the step difficulty for a test taker to move from score ‘k-1’ to k . P nijk refers to the probability of rater j assigning score k to test taker n for test item i . P nij(k-1) represents the likelihood of test taker n being assigned score ‘k-1’ by rater j for test item i . Each facet within the test is treated as an independent parameter and estimated within the same reference framework. To evaluate the consistency of scores obtained through both human and computer analysis, we utilized the Infit mean-square statistic. This statistic is a chi-square measure divided by the degrees of freedom and is weighted with information. It demonstrates higher sensitivity to unexpected patterns in responses to items near a person’s proficiency level (Linacre, 2002 ). Fit statistics are assessed based on predefined thresholds for acceptable fit. For the Infit MNSQ, which has a mean of 1.00, different thresholds have been suggested. Some propose stricter thresholds ranging from 0.7 to 1.3 (Bond et al. 2021 ), while others suggest more lenient thresholds ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 (Eckes, 2009 ). In this study, we adopted the criterion of 0.70–1.30 for the Infit MNSQ.
Moving forward, we can now proceed to assess the effectiveness of the 16 proposed measures based on five criteria for accurately distinguishing various levels of writing proficiency among non-native Japanese speakers. To conduct this evaluation, we utilized the development dataset from the I-JAS corpus, as described in Section Dataset . Table 4 provides a measurement report that presents the performance details of the 14 metrics under consideration. The measure separation was found to be 4.02, indicating a clear differentiation among the measures. The reliability index for the measure separation was 0.891, suggesting consistency in the measurement. Similarly, the person separation reliability index was 0.802, indicating the accuracy of the assessment in distinguishing between individuals. All 16 measures demonstrated Infit mean squares within a reasonable range, ranging from 0.76 to 1.28. The Synonym overlap/paragraph (topic) measure exhibited a relatively high outfit mean square of 1.46, although the Infit mean square falls within an acceptable range. The standard error for the measures ranged from 0.13 to 0.28, indicating the precision of the estimates.
Table 5 further illustrated the weights assigned to different linguistic measures for score prediction, with higher weights indicating stronger correlations between those measures and higher scores. Specifically, the following measures exhibited higher weights compared to others: moving average type token ratio per essay has a weight of 0.0391. Mean dependency distance had a weight of 0.0388. Mean length of clause, calculated by dividing the number of words by the number of clauses, had a weight of 0.0374. Complex nominals per T-unit, calculated by dividing the number of complex nominals by the number of T-units, had a weight of 0.0379. Coordinate phrases rate, calculated by dividing the number of coordinate phrases by the number of clauses, had a weight of 0.0325. Grammatical error rate, representing the number of errors per essay, had a weight of 0.0322.
Criteria (output indicator)
The criteria used to evaluate the writing ability in this study were based on CEFR, which follows a six-point scale ranging from A1 to C2. To assess the quality of Japanese writing, the scoring criteria from Table 6 were utilized. These criteria were derived from the IELTS writing standards and served as assessment guidelines and prompts for the written output.
A prompt is a question or detailed instruction that is provided to the model to obtain a proper response. After several pilot experiments, we decided to provide the measures (Section Measures of writing proficiency for nonnative Japanese ) as the input prompt and use the criteria (Section Criteria (output indicator) ) as the output indicator. Regarding the prompt language, considering that the LLM was tasked with rating Japanese essays, would prompt in Japanese works better Footnote 5 ? We conducted experiments comparing the performance of GPT-4 using both English and Japanese prompts. Additionally, we utilized the Japanese local model OCLL with Japanese prompts. Multiple trials were conducted using the same sample. Regardless of the prompt language used, we consistently obtained the same grading results with GPT-4, which assigned a grade of B1 to the writing sample. This suggested that GPT-4 is reliable and capable of producing consistent ratings regardless of the prompt language. On the other hand, when we used Japanese prompts with the Japanese local model “OCLL”, we encountered inconsistent grading results. Out of 10 attempts with OCLL, only 6 yielded consistent grading results (B1), while the remaining 4 showed different outcomes, including A1 and B2 grades. These findings indicated that the language of the prompt was not the determining factor for reliable AES. Instead, the size of the training data and the model parameters played crucial roles in achieving consistent and reliable AES results for the language model.
The following is the utilized prompt, which details all measures and requires the LLM to score the essays using holistic and trait scores.
Please evaluate Japanese essays written by Japanese learners and assign a score to each essay on a six-point scale, ranging from A1, A2, B1, B2, C1 to C2. Additionally, please provide trait scores and display the calculation process for each trait score. The scoring should be based on the following criteria:
Moving average type-token ratio.
Number of lexical words (token) divided by the total number of words per essay.
Number of sophisticated word types divided by the total number of words per essay.
Mean length of clause.
Verb phrases per T-unit.
Clauses per T-unit.
Dependent clauses per T-unit.
Complex nominals per clause.
Adverbial clauses per clause.
Coordinate phrases per clause.
Mean dependency distance.
Synonym overlap paragraph (topic and keywords).
Word2vec cosine similarity.
Connectives per essay.
Conjunctions per essay.
Number of metadiscourse markers (types) divided by the total number of words.
Number of errors per essay.
Japanese essay text
出かける前に二人が地図を見ている間に、サンドイッチを入れたバスケットに犬が入ってしまいました。それに気づかずに二人は楽しそうに出かけて行きました。やがて突然犬がバスケットから飛び出し、二人は驚きました。バスケット の 中を見ると、食べ物はすべて犬に食べられていて、二人は困ってしまいました。(ID_JJJ01_SW1)
The score of the example above was B1. Figure 3 provides an example of holistic and trait scores provided by GPT-4 (with a prompt indicating all measures) via Bing Footnote 6 .

Example of GPT-4 AES and feedback (with a prompt indicating all measures).
Statistical analysis
The aim of this study is to investigate the potential use of LLM for nonnative Japanese AES. It seeks to compare the scoring outcomes obtained from feature-based AES tools, which rely on conventional machine learning technology (i.e. Jess, JWriter), with those generated by AI-driven AES tools utilizing deep learning technology (BERT, GPT, OCLL). To assess the reliability of a computer-assisted annotation tool, the study initially established human-human agreement as the benchmark measure. Subsequently, the performance of the LLM-based method was evaluated by comparing it to human-human agreement.
To assess annotation agreement, the study employed standard measures such as precision, recall, and F-score (Brants 2000 ; Lu 2010 ), along with the quadratically weighted kappa (QWK) to evaluate the consistency and agreement in the annotation process. Assume A and B represent human annotators. When comparing the annotations of the two annotators, the following results are obtained. The evaluation of precision, recall, and F-score metrics was illustrated in equations (13) to (15).
\({\rm{Recall}}(A,B)=\frac{{\rm{Number}}\,{\rm{of}}\,{\rm{identical}}\,{\rm{nodes}}\,{\rm{in}}\,A\,{\rm{and}}\,B}{{\rm{Number}}\,{\rm{of}}\,{\rm{nodes}}\,{\rm{in}}\,A}\)
\({\rm{Precision}}(A,\,B)=\frac{{\rm{Number}}\,{\rm{of}}\,{\rm{identical}}\,{\rm{nodes}}\,{\rm{in}}\,A\,{\rm{and}}\,B}{{\rm{Number}}\,{\rm{of}}\,{\rm{nodes}}\,{\rm{in}}\,B}\)
The F-score is the harmonic mean of recall and precision:
\({\rm{F}}-{\rm{score}}=\frac{2* ({\rm{Precision}}* {\rm{Recall}})}{{\rm{Precision}}+{\rm{Recall}}}\)
The highest possible value of an F-score is 1.0, indicating perfect precision and recall, and the lowest possible value is 0, if either precision or recall are zero.
In accordance with Taghipour and Ng ( 2016 ), the calculation of QWK involves two steps:
Step 1: Construct a weight matrix W as follows:
\({W}_{{ij}}=\frac{{(i-j)}^{2}}{{(N-1)}^{2}}\)
i represents the annotation made by the tool, while j represents the annotation made by a human rater. N denotes the total number of possible annotations. Matrix O is subsequently computed, where O_( i, j ) represents the count of data annotated by the tool ( i ) and the human annotator ( j ). On the other hand, E refers to the expected count matrix, which undergoes normalization to ensure that the sum of elements in E matches the sum of elements in O.
Step 2: With matrices O and E, the QWK is obtained as follows:
K = 1- \(\frac{\sum i,j{W}_{i,j}\,{O}_{i,j}}{\sum i,j{W}_{i,j}\,{E}_{i,j}}\)
The value of the quadratic weighted kappa increases as the level of agreement improves. Further, to assess the accuracy of LLM scoring, the proportional reductive mean square error (PRMSE) was employed. The PRMSE approach takes into account the variability observed in human ratings to estimate the rater error, which is then subtracted from the variance of the human labels. This calculation provides an overall measure of agreement between the automated scores and true scores (Haberman et al. 2015 ; Loukina et al. 2020 ; Taghipour and Ng, 2016 ). The computation of PRMSE involves the following steps:
Step 1: Calculate the mean squared errors (MSEs) for the scoring outcomes of the computer-assisted tool (MSE tool) and the human scoring outcomes (MSE human).
Step 2: Determine the PRMSE by comparing the MSE of the computer-assisted tool (MSE tool) with the MSE from human raters (MSE human), using the following formula:
\({\rm{PRMSE}}=1-\frac{({\rm{MSE}}\,{\rm{tool}})\,}{({\rm{MSE}}\,{\rm{human}})\,}=1-\,\frac{{\sum }_{i}^{n}=1{({{\rm{y}}}_{i}-{\hat{{\rm{y}}}}_{{\rm{i}}})}^{2}}{{\sum }_{i}^{n}=1{({{\rm{y}}}_{i}-\hat{{\rm{y}}})}^{2}}\)
In the numerator, ŷi represents the scoring outcome predicted by a specific LLM-driven AES system for a given sample. The term y i − ŷ i represents the difference between this predicted outcome and the mean value of all LLM-driven AES systems’ scoring outcomes. It quantifies the deviation of the specific LLM-driven AES system’s prediction from the average prediction of all LLM-driven AES systems. In the denominator, y i − ŷ represents the difference between the scoring outcome provided by a specific human rater for a given sample and the mean value of all human raters’ scoring outcomes. It measures the discrepancy between the specific human rater’s score and the average score given by all human raters. The PRMSE is then calculated by subtracting the ratio of the MSE tool to the MSE human from 1. PRMSE falls within the range of 0 to 1, with larger values indicating reduced errors in LLM’s scoring compared to those of human raters. In other words, a higher PRMSE implies that LLM’s scoring demonstrates greater accuracy in predicting the true scores (Loukina et al. 2020 ). The interpretation of kappa values, ranging from 0 to 1, is based on the work of Landis and Koch ( 1977 ). Specifically, the following categories are assigned to different ranges of kappa values: −1 indicates complete inconsistency, 0 indicates random agreement, 0.0 ~ 0.20 indicates extremely low level of agreement (slight), 0.21 ~ 0.40 indicates moderate level of agreement (fair), 0.41 ~ 0.60 indicates medium level of agreement (moderate), 0.61 ~ 0.80 indicates high level of agreement (substantial), 0.81 ~ 1 indicates almost perfect level of agreement. All statistical analyses were executed using Python script.
Results and discussion
Annotation reliability of the llm.
This section focuses on assessing the reliability of the LLM’s annotation and scoring capabilities. To evaluate the reliability, several tests were conducted simultaneously, aiming to achieve the following objectives:
Assess the LLM’s ability to differentiate between test takers with varying levels of oral proficiency.
Determine the level of agreement between the annotations and scoring performed by the LLM and those done by human raters.
The evaluation of the results encompassed several metrics, including: precision, recall, F-Score, quadratically-weighted kappa, proportional reduction of mean squared error, Pearson correlation, and multi-faceted Rasch measurement.
Inter-annotator agreement (human–human annotator agreement)
We started with an agreement test of the two human annotators. Two trained annotators were recruited to determine the writing task data measures. A total of 714 scripts, as the test data, was utilized. Each analysis lasted 300–360 min. Inter-annotator agreement was evaluated using the standard measures of precision, recall, and F-score and QWK. Table 7 presents the inter-annotator agreement for the various indicators. As shown, the inter-annotator agreement was fairly high, with F-scores ranging from 1.0 for sentence and word number to 0.666 for grammatical errors.
The findings from the QWK analysis provided further confirmation of the inter-annotator agreement. The QWK values covered a range from 0.950 ( p = 0.000) for sentence and word number to 0.695 for synonym overlap number (keyword) and grammatical errors ( p = 0.001).
Agreement of annotation outcomes between human and LLM
To evaluate the consistency between human annotators and LLM annotators (BERT, GPT, OCLL) across the indices, the same test was conducted. The results of the inter-annotator agreement (F-score) between LLM and human annotation are provided in Appendix B-D. The F-scores ranged from 0.706 for Grammatical error # for OCLL-human to a perfect 1.000 for GPT-human, for sentences, clauses, T-units, and words. These findings were further supported by the QWK analysis, which showed agreement levels ranging from 0.807 ( p = 0.001) for metadiscourse markers for OCLL-human to 0.962 for words ( p = 0.000) for GPT-human. The findings demonstrated that the LLM annotation achieved a significant level of accuracy in identifying measurement units and counts.
Reliability of LLM-driven AES’s scoring and discriminating proficiency levels
This section examines the reliability of the LLM-driven AES scoring through a comparison of the scoring outcomes produced by human raters and the LLM ( Reliability of LLM-driven AES scoring ). It also assesses the effectiveness of the LLM-based AES system in differentiating participants with varying proficiency levels ( Reliability of LLM-driven AES discriminating proficiency levels ).
Reliability of LLM-driven AES scoring
Table 8 summarizes the QWK coefficient analysis between the scores computed by the human raters and the GPT-4 for the individual essays from I-JAS Footnote 7 . As shown, the QWK of all measures ranged from k = 0.819 for lexical density (number of lexical words (tokens)/number of words per essay) to k = 0.644 for word2vec cosine similarity. Table 9 further presents the Pearson correlations between the 16 writing proficiency measures scored by human raters and GPT 4 for the individual essays. The correlations ranged from 0.672 for syntactic complexity to 0.734 for grammatical accuracy. The correlations between the writing proficiency scores assigned by human raters and the BERT-based AES system were found to range from 0.661 for syntactic complexity to 0.713 for grammatical accuracy. The correlations between the writing proficiency scores given by human raters and the OCLL-based AES system ranged from 0.654 for cohesion to 0.721 for grammatical accuracy. These findings indicated an alignment between the assessments made by human raters and both the BERT-based and OCLL-based AES systems in terms of various aspects of writing proficiency.
Reliability of LLM-driven AES discriminating proficiency levels
After validating the reliability of the LLM’s annotation and scoring, the subsequent objective was to evaluate its ability to distinguish between various proficiency levels. For this analysis, a dataset of 686 individual essays was utilized. Table 10 presents a sample of the results, summarizing the means, standard deviations, and the outcomes of the one-way ANOVAs based on the measures assessed by the GPT-4 model. A post hoc multiple comparison test, specifically the Bonferroni test, was conducted to identify any potential differences between pairs of levels.
As the results reveal, seven measures presented linear upward or downward progress across the three proficiency levels. These were marked in bold in Table 10 and comprise one measure of lexical richness, i.e. MATTR (lexical diversity); four measures of syntactic complexity, i.e. MDD (mean dependency distance), MLC (mean length of clause), CNT (complex nominals per T-unit), CPC (coordinate phrases rate); one cohesion measure, i.e. word2vec cosine similarity and GER (grammatical error rate). Regarding the ability of the sixteen measures to distinguish adjacent proficiency levels, the Bonferroni tests indicated that statistically significant differences exist between the primary level and the intermediate level for MLC and GER. One measure of lexical richness, namely LD, along with three measures of syntactic complexity (VPT, CT, DCT, ACC), two measures of cohesion (SOPT, SOPK), and one measure of content elaboration (IMM), exhibited statistically significant differences between proficiency levels. However, these differences did not demonstrate a linear progression between adjacent proficiency levels. No significant difference was observed in lexical sophistication between proficiency levels.
To summarize, our study aimed to evaluate the reliability and differentiation capabilities of the LLM-driven AES method. For the first objective, we assessed the LLM’s ability to differentiate between test takers with varying levels of oral proficiency using precision, recall, F-Score, and quadratically-weighted kappa. Regarding the second objective, we compared the scoring outcomes generated by human raters and the LLM to determine the level of agreement. We employed quadratically-weighted kappa and Pearson correlations to compare the 16 writing proficiency measures for the individual essays. The results confirmed the feasibility of using the LLM for annotation and scoring in AES for nonnative Japanese. As a result, Research Question 1 has been addressed.
Comparison of BERT-, GPT-, OCLL-based AES, and linguistic-feature-based computation methods
This section aims to compare the effectiveness of five AES methods for nonnative Japanese writing, i.e. LLM-driven approaches utilizing BERT, GPT, and OCLL, linguistic feature-based approaches using Jess and JWriter. The comparison was conducted by comparing the ratings obtained from each approach with human ratings. All ratings were derived from the dataset introduced in Dataset . To facilitate the comparison, the agreement between the automated methods and human ratings was assessed using QWK and PRMSE. The performance of each approach was summarized in Table 11 .
The QWK coefficient values indicate that LLMs (GPT, BERT, OCLL) and human rating outcomes demonstrated higher agreement compared to feature-based AES methods (Jess and JWriter) in assessing writing proficiency criteria, including lexical richness, syntactic complexity, content, and grammatical accuracy. Among the LLMs, the GPT-4 driven AES and human rating outcomes showed the highest agreement in all criteria, except for syntactic complexity. The PRMSE values suggest that the GPT-based method outperformed linguistic feature-based methods and other LLM-based approaches. Moreover, an interesting finding emerged during the study: the agreement coefficient between GPT-4 and human scoring was even higher than the agreement between different human raters themselves. This discovery highlights the advantage of GPT-based AES over human rating. Ratings involve a series of processes, including reading the learners’ writing, evaluating the content and language, and assigning scores. Within this chain of processes, various biases can be introduced, stemming from factors such as rater biases, test design, and rating scales. These biases can impact the consistency and objectivity of human ratings. GPT-based AES may benefit from its ability to apply consistent and objective evaluation criteria. By prompting the GPT model with detailed writing scoring rubrics and linguistic features, potential biases in human ratings can be mitigated. The model follows a predefined set of guidelines and does not possess the same subjective biases that human raters may exhibit. This standardization in the evaluation process contributes to the higher agreement observed between GPT-4 and human scoring. Section Prompt strategy of the study delves further into the role of prompts in the application of LLMs to AES. It explores how the choice and implementation of prompts can impact the performance and reliability of LLM-based AES methods. Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge the strengths of the local model, i.e. the Japanese local model OCLL, which excels in processing certain idiomatic expressions. Nevertheless, our analysis indicated that GPT-4 surpasses local models in AES. This superior performance can be attributed to the larger parameter size of GPT-4, estimated to be between 500 billion and 1 trillion, which exceeds the sizes of both BERT and the local model OCLL.
Prompt strategy
In the context of prompt strategy, Mizumoto and Eguchi ( 2023 ) conducted a study where they applied the GPT-3 model to automatically score English essays in the TOEFL test. They found that the accuracy of the GPT model alone was moderate to fair. However, when they incorporated linguistic measures such as cohesion, syntactic complexity, and lexical features alongside the GPT model, the accuracy significantly improved. This highlights the importance of prompt engineering and providing the model with specific instructions to enhance its performance. In this study, a similar approach was taken to optimize the performance of LLMs. GPT-4, which outperformed BERT and OCLL, was selected as the candidate model. Model 1 was used as the baseline, representing GPT-4 without any additional prompting. Model 2, on the other hand, involved GPT-4 prompted with 16 measures that included scoring criteria, efficient linguistic features for writing assessment, and detailed measurement units and calculation formulas. The remaining models (Models 3 to 18) utilized GPT-4 prompted with individual measures. The performance of these 18 different models was assessed using the output indicators described in Section Criteria (output indicator) . By comparing the performances of these models, the study aimed to understand the impact of prompt engineering on the accuracy and effectiveness of GPT-4 in AES tasks.
Based on the PRMSE scores presented in Fig. 4 , it was observed that Model 1, representing GPT-4 without any additional prompting, achieved a fair level of performance. However, Model 2, which utilized GPT-4 prompted with all measures, outperformed all other models in terms of PRMSE score, achieving a score of 0.681. These results indicate that the inclusion of specific measures and prompts significantly enhanced the performance of GPT-4 in AES. Among the measures, syntactic complexity was found to play a particularly significant role in improving the accuracy of GPT-4 in assessing writing quality. Following that, lexical diversity emerged as another important factor contributing to the model’s effectiveness. The study suggests that a well-prompted GPT-4 can serve as a valuable tool to support human assessors in evaluating writing quality. By utilizing GPT-4 as an automated scoring tool, the evaluation biases associated with human raters can be minimized. This has the potential to empower teachers by allowing them to focus on designing writing tasks and guiding writing strategies, while leveraging the capabilities of GPT-4 for efficient and reliable scoring.
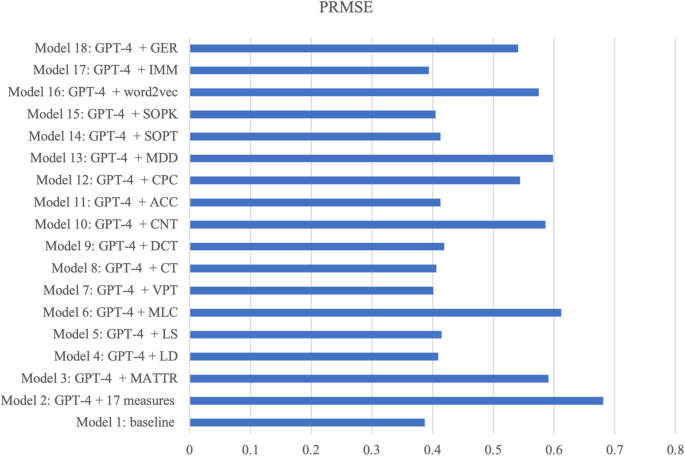
PRMSE scores of the 18 AES models.
This study aimed to investigate two main research questions: the feasibility of utilizing LLMs for AES and the impact of prompt engineering on the application of LLMs in AES.
To address the first objective, the study compared the effectiveness of five different models: GPT, BERT, the Japanese local LLM (OCLL), and two conventional machine learning-based AES tools (Jess and JWriter). The PRMSE values indicated that the GPT-4-based method outperformed other LLMs (BERT, OCLL) and linguistic feature-based computational methods (Jess and JWriter) across various writing proficiency criteria. Furthermore, the agreement coefficient between GPT-4 and human scoring surpassed the agreement among human raters themselves, highlighting the potential of using the GPT-4 tool to enhance AES by reducing biases and subjectivity, saving time, labor, and cost, and providing valuable feedback for self-study. Regarding the second goal, the role of prompt design was investigated by comparing 18 models, including a baseline model, a model prompted with all measures, and 16 models prompted with one measure at a time. GPT-4, which outperformed BERT and OCLL, was selected as the candidate model. The PRMSE scores of the models showed that GPT-4 prompted with all measures achieved the best performance, surpassing the baseline and other models.
In conclusion, this study has demonstrated the potential of LLMs in supporting human rating in assessments. By incorporating automation, we can save time and resources while reducing biases and subjectivity inherent in human rating processes. Automated language assessments offer the advantage of accessibility, providing equal opportunities and economic feasibility for individuals who lack access to traditional assessment centers or necessary resources. LLM-based language assessments provide valuable feedback and support to learners, aiding in the enhancement of their language proficiency and the achievement of their goals. This personalized feedback can cater to individual learner needs, facilitating a more tailored and effective language-learning experience.
There are three important areas that merit further exploration. First, prompt engineering requires attention to ensure optimal performance of LLM-based AES across different language types. This study revealed that GPT-4, when prompted with all measures, outperformed models prompted with fewer measures. Therefore, investigating and refining prompt strategies can enhance the effectiveness of LLMs in automated language assessments. Second, it is crucial to explore the application of LLMs in second-language assessment and learning for oral proficiency, as well as their potential in under-resourced languages. Recent advancements in self-supervised machine learning techniques have significantly improved automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems, opening up new possibilities for creating reliable ASR systems, particularly for under-resourced languages with limited data. However, challenges persist in the field of ASR. First, ASR assumes correct word pronunciation for automatic pronunciation evaluation, which proves challenging for learners in the early stages of language acquisition due to diverse accents influenced by their native languages. Accurately segmenting short words becomes problematic in such cases. Second, developing precise audio-text transcriptions for languages with non-native accented speech poses a formidable task. Last, assessing oral proficiency levels involves capturing various linguistic features, including fluency, pronunciation, accuracy, and complexity, which are not easily captured by current NLP technology.
Data availability
The dataset utilized was obtained from the International Corpus of Japanese as a Second Language (I-JAS). The data URLs: [ https://www2.ninjal.ac.jp/jll/lsaj/ihome2.html ].
J-CAT and TTBJ are two computerized adaptive tests used to assess Japanese language proficiency.
SPOT is a specific component of the TTBJ test.
J-CAT: https://www.j-cat2.org/html/ja/pages/interpret.html
SPOT: https://ttbj.cegloc.tsukuba.ac.jp/p1.html#SPOT .
The study utilized a prompt-based GPT-4 model, developed by OpenAI, which has an impressive architecture with 1.8 trillion parameters across 120 layers. GPT-4 was trained on a vast dataset of 13 trillion tokens, using two stages: initial training on internet text datasets to predict the next token, and subsequent fine-tuning through reinforcement learning from human feedback.
https://www2.ninjal.ac.jp/jll/lsaj/ihome2-en.html .
http://jhlee.sakura.ne.jp/JEV/ by Japanese Learning Dictionary Support Group 2015.
We express our sincere gratitude to the reviewer for bringing this matter to our attention.
On February 7, 2023, Microsoft began rolling out a major overhaul to Bing that included a new chatbot feature based on OpenAI’s GPT-4 (Bing.com).
Appendix E-F present the analysis results of the QWK coefficient between the scores computed by the human raters and the BERT, OCLL models.
Attali Y, Burstein J (2006) Automated essay scoring with e-rater® V.2. J. Technol., Learn. Assess., 4
Barkaoui K, Hadidi A (2020) Assessing Change in English Second Language Writing Performance (1st ed.). Routledge, New York. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003092346
Bentz C, Tatyana R, Koplenig A, Tanja S (2016) A comparison between morphological complexity. measures: Typological data vs. language corpora. In Proceedings of the workshop on computational linguistics for linguistic complexity (CL4LC), 142–153. Osaka, Japan: The COLING 2016 Organizing Committee
Bond TG, Yan Z, Heene M (2021) Applying the Rasch model: Fundamental measurement in the human sciences (4th ed). Routledge
Brants T (2000) Inter-annotator agreement for a German newspaper corpus. Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’00), Athens, Greece, 31 May-2 June, European Language Resources Association
Brown TB, Mann B, Ryder N, et al. (2020) Language models are few-shot learners. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, 6–12 December, Curran Associates, Inc., Red Hook, NY
Burstein J (2003) The E-rater scoring engine: Automated essay scoring with natural language processing. In Shermis MD and Burstein JC (ed) Automated Essay Scoring: A Cross-Disciplinary Perspective. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, NJ
Čech R, Miroslav K (2018) Morphological richness of text. In Masako F, Václav C (ed) Taming the corpus: From inflection and lexis to interpretation, 63–77. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature
Çöltekin Ç, Taraka, R (2018) Exploiting Universal Dependencies treebanks for measuring morphosyntactic complexity. In Aleksandrs B, Christian B (ed), Proceedings of first workshop on measuring language complexity, 1–7. Torun, Poland
Crossley SA, Cobb T, McNamara DS (2013) Comparing count-based and band-based indices of word frequency: Implications for active vocabulary research and pedagogical applications. System 41:965–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2013.08.002
Article Google Scholar
Crossley SA, McNamara DS (2016) Say more and be more coherent: How text elaboration and cohesion can increase writing quality. J. Writ. Res. 7:351–370
CyberAgent Inc (2023) Open-Calm series of Japanese language models. Retrieved from: https://www.cyberagent.co.jp/news/detail/id=28817
Devlin J, Chang MW, Lee K, Toutanova K (2019) BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis, Minnesota, 2–7 June, pp. 4171–4186. Association for Computational Linguistics
Diez-Ortega M, Kyle K (2023) Measuring the development of lexical richness of L2 Spanish: a longitudinal learner corpus study. Studies in Second Language Acquisition 1-31
Eckes T (2009) On common ground? How raters perceive scoring criteria in oral proficiency testing. In Brown A, Hill K (ed) Language testing and evaluation 13: Tasks and criteria in performance assessment (pp. 43–73). Peter Lang Publishing
Elliot S (2003) IntelliMetric: from here to validity. In: Shermis MD, Burstein JC (ed) Automated Essay Scoring: A Cross-Disciplinary Perspective. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, NJ
Google Scholar
Engber CA (1995) The relationship of lexical proficiency to the quality of ESL compositions. J. Second Lang. Writ. 4:139–155
Garner J, Crossley SA, Kyle K (2019) N-gram measures and L2 writing proficiency. System 80:176–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2018.12.001
Haberman SJ (2008) When can subscores have value? J. Educat. Behav. Stat., 33:204–229
Haberman SJ, Yao L, Sinharay S (2015) Prediction of true test scores from observed item scores and ancillary data. Brit. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 68:363–385
Halliday MAK (1985) Spoken and Written Language. Deakin University Press, Melbourne, Australia
Hirao R, Arai M, Shimanaka H et al. (2020) Automated essay scoring system for nonnative Japanese learners. Proceedings of the 12th Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC 2020), pp. 1250–1257. European Language Resources Association
Hunt KW (1966) Recent Measures in Syntactic Development. Elementary English, 43(7), 732–739. http://www.jstor.org/stable/41386067
Ishioka T (2001) About e-rater, a computer-based automatic scoring system for essays [Konpyūta ni yoru essei no jidō saiten shisutemu e − rater ni tsuite]. University Entrance Examination. Forum [Daigaku nyūshi fōramu] 24:71–76
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long short- term memory. Neural Comput. 9(8):1735–1780
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Ishioka T, Kameda M (2006) Automated Japanese essay scoring system based on articles written by experts. Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Computational Linguistics and 44th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Sydney, Australia, 17–18 July 2006, pp. 233-240. Association for Computational Linguistics, USA
Japan Foundation (2021) Retrieved from: https://www.jpf.gp.jp/j/project/japanese/survey/result/dl/survey2021/all.pdf
Jarvis S (2013a) Defining and measuring lexical diversity. In Jarvis S, Daller M (ed) Vocabulary knowledge: Human ratings and automated measures (Vol. 47, pp. 13–44). John Benjamins. https://doi.org/10.1075/sibil.47.03ch1
Jarvis S (2013b) Capturing the diversity in lexical diversity. Lang. Learn. 63:87–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9922.2012.00739.x
Jiang J, Quyang J, Liu H (2019) Interlanguage: A perspective of quantitative linguistic typology. Lang. Sci. 74:85–97
Kim M, Crossley SA, Kyle K (2018) Lexical sophistication as a multidimensional phenomenon: Relations to second language lexical proficiency, development, and writing quality. Mod. Lang. J. 102(1):120–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/modl.12447
Kojima T, Gu S, Reid M et al. (2022) Large language models are zero-shot reasoners. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, 29 November-1 December, Curran Associates, Inc., Red Hook, NY
Kyle K, Crossley SA (2015) Automatically assessing lexical sophistication: Indices, tools, findings, and application. TESOL Q 49:757–786
Kyle K, Crossley SA, Berger CM (2018) The tool for the automatic analysis of lexical sophistication (TAALES): Version 2.0. Behav. Res. Methods 50:1030–1046. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-017-0924-4
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Kyle K, Crossley SA, Jarvis S (2021) Assessing the validity of lexical diversity using direct judgements. Lang. Assess. Q. 18:154–170. https://doi.org/10.1080/15434303.2020.1844205
Landauer TK, Laham D, Foltz PW (2003) Automated essay scoring and annotation of essays with the Intelligent Essay Assessor. In Shermis MD, Burstein JC (ed), Automated Essay Scoring: A Cross-Disciplinary Perspective. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, NJ
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 159–174
Laufer B, Nation P (1995) Vocabulary size and use: Lexical richness in L2 written production. Appl. Linguist. 16:307–322. https://doi.org/10.1093/applin/16.3.307
Lee J, Hasebe Y (2017) jWriter Learner Text Evaluator, URL: https://jreadability.net/jwriter/
Lee J, Kobayashi N, Sakai T, Sakota K (2015) A Comparison of SPOT and J-CAT Based on Test Analysis [Tesuto bunseki ni motozuku ‘SPOT’ to ‘J-CAT’ no hikaku]. Research on the Acquisition of Second Language Japanese [Dainigengo to shite no nihongo no shūtoku kenkyū] (18) 53–69
Li W, Yan J (2021) Probability distribution of dependency distance based on a Treebank of. Japanese EFL Learners’ Interlanguage. J. Quant. Linguist. 28(2):172–186. https://doi.org/10.1080/09296174.2020.1754611
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Linacre JM (2002) Optimizing rating scale category effectiveness. J. Appl. Meas. 3(1):85–106
PubMed Google Scholar
Linacre JM (1994) Constructing measurement with a Many-Facet Rasch Model. In Wilson M (ed) Objective measurement: Theory into practice, Volume 2 (pp. 129–144). Norwood, NJ: Ablex
Liu H (2008) Dependency distance as a metric of language comprehension difficulty. J. Cognitive Sci. 9:159–191
Liu H, Xu C, Liang J (2017) Dependency distance: A new perspective on syntactic patterns in natural languages. Phys. Life Rev. 21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plrev.2017.03.002
Loukina A, Madnani N, Cahill A, et al. (2020) Using PRMSE to evaluate automated scoring systems in the presence of label noise. Proceedings of the Fifteenth Workshop on Innovative Use of NLP for Building Educational Applications, Seattle, WA, USA → Online, 10 July, pp. 18–29. Association for Computational Linguistics
Lu X (2010) Automatic analysis of syntactic complexity in second language writing. Int. J. Corpus Linguist. 15:474–496
Lu X (2012) The relationship of lexical richness to the quality of ESL learners’ oral narratives. Mod. Lang. J. 96:190–208
Lu X (2017) Automated measurement of syntactic complexity in corpus-based L2 writing research and implications for writing assessment. Lang. Test. 34:493–511
Lu X, Hu R (2022) Sense-aware lexical sophistication indices and their relationship to second language writing quality. Behav. Res. Method. 54:1444–1460. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-021-01675-6
Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan (2022) Retrieved from: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_30367.html
Mizumoto A, Eguchi M (2023) Exploring the potential of using an AI language model for automated essay scoring. Res. Methods Appl. Linguist. 3:100050
Okgetheng B, Takeuchi K (2024) Estimating Japanese Essay Grading Scores with Large Language Models. Proceedings of 30th Annual Conference of the Language Processing Society in Japan, March 2024
Ortega L (2015) Second language learning explained? SLA across 10 contemporary theories. In VanPatten B, Williams J (ed) Theories in Second Language Acquisition: An Introduction
Rae JW, Borgeaud S, Cai T, et al. (2021) Scaling Language Models: Methods, Analysis & Insights from Training Gopher. ArXiv, abs/2112.11446
Read J (2000) Assessing vocabulary. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511732942
Rudner LM, Liang T (2002) Automated Essay Scoring Using Bayes’ Theorem. J. Technol., Learning and Assessment, 1 (2)
Sakoda K, Hosoi Y (2020) Accuracy and complexity of Japanese Language usage by SLA learners in different learning environments based on the analysis of I-JAS, a learners’ corpus of Japanese as L2. Math. Linguist. 32(7):403–418. https://doi.org/10.24701/mathling.32.7_403
Suzuki N (1999) Summary of survey results regarding comprehensive essay questions. Final report of “Joint Research on Comprehensive Examinations for the Aim of Evaluating Applicability to Each Specialized Field of Universities” for 1996-2000 [shōronbun sōgō mondai ni kansuru chōsa kekka no gaiyō. Heisei 8 - Heisei 12-nendo daigaku no kaku senmon bun’ya e no tekisei no hyōka o mokuteki to suru sōgō shiken no arikata ni kansuru kyōdō kenkyū’ saishū hōkoku-sho]. University Entrance Examination Section Center Research and Development Department [Daigaku nyūshi sentā kenkyū kaihatsubu], 21–32
Taghipour K, Ng HT (2016) A neural approach to automated essay scoring. Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, Texas, 1–5 November, pp. 1882–1891. Association for Computational Linguistics
Takeuchi K, Ohno M, Motojin K, Taguchi M, Inada Y, Iizuka M, Abo T, Ueda H (2021) Development of essay scoring methods based on reference texts with construction of research-available Japanese essay data. In IPSJ J 62(9):1586–1604
Ure J (1971) Lexical density: A computational technique and some findings. In Coultard M (ed) Talking about Text. English Language Research, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, England
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. (2017) Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, 4–7 December, pp. 5998–6008, Curran Associates, Inc., Red Hook, NY
Watanabe H, Taira Y, Inoue Y (1988) Analysis of essay evaluation data [Shōronbun hyōka dēta no kaiseki]. Bulletin of the Faculty of Education, University of Tokyo [Tōkyōdaigaku kyōiku gakubu kiyō], Vol. 28, 143–164
Yao S, Yu D, Zhao J, et al. (2023) Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 36
Zenker F, Kyle K (2021) Investigating minimum text lengths for lexical diversity indices. Assess. Writ. 47:100505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asw.2020.100505
Zhang Y, Warstadt A, Li X, et al. (2021) When do you need billions of words of pretraining data? Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Online, pp. 1112-1125. Association for Computational Linguistics. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2021.acl-long.90
Download references
This research was funded by National Foundation of Social Sciences (22BYY186) to Wenchao Li.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Japanese Studies, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Department of Linguistics and Applied Linguistics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Wenchao Li is in charge of conceptualization, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, visualization and writing the draft. Haitao Liu is in charge of supervision.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Wenchao Li .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not required as the study did not involve human participants.
Informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplemental material file #1, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Li, W., Liu, H. Applying large language models for automated essay scoring for non-native Japanese. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 723 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03209-9
Download citation
Received : 02 February 2024
Accepted : 16 May 2024
Published : 03 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03209-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500 Words Essay on Life on Mars. Mars is the fourth planet from the sun in our solar system. Also, it is the second smallest planet in our solar system. The possibility of life on mars has aroused the interest of scientists for many years. A major reason for this interest is due to the similarity and proximity of the planet to Earth.
The Red Planet: An Overview. Mars, often referred to as the Red Planet due to its reddish appearance, is the fourth planet from the Sun in our solar system. Its distinct color is attributed to iron oxide, or rust, on its surface. It is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere, possessing surface features both reminiscent of both Earth and ...
Facts about Mass. Mars is one of the eight major planets that form the solar system together with the sun. Mars is the fourth planet from the sun, and it takes about 686.93 days to completely revolve around it. The atmosphere of Mars is estimated to be less than 1% of that of the earth. We will write a custom essay on your topic. Its atmosphere ...
My research involves getting some responses from members of the community, and people who have experienced his online or in-person concerts, so if anyone wants to either comment or message me that would be amazing! Feel free to comment or message me on your feelings and experiences within this community, experiences with his performances in any contexts, and how you participate in his ...
That is not writing. It is something else. PARCC and Smarter Balanced assessments have made progress in more effectively evaluating the writing skills of our students, but many states are actively ...
When you receive a paper assignment, your first step should be to read the assignment prompt carefully to make sure you understand what you are being asked to do. Sometimes your assignment will be open-ended ("write a paper about anything in the course that interests you"). But more often, the instructor will be asking you to do something specific that allows you to make sense of what you ...
The other day, Marc Tetreault and his girlfriend of 6 months, Carly McIntosh, got in a rather large fight because he went to a bonfire at his friend Matt s house without her (Carly and Matt don't get along, so Marc knew she wouldn't have had fun anyway). Now, they seemed to be getting along for the last 2 weeks but since the fight a lot of information has been revealed, and now Marc needs ...
As well as some best practice tips, we have gathered our favourite advice from expert essay-writers and compiled the following 7-step guide to writing a good essay every time. 👍. #1 Make sure you understand the question. #2 Complete background reading. #3 Make a detailed plan. #4 Write your opening sentences.
Come up with a thesis. Create an essay outline. Write the introduction. Write the main body, organized into paragraphs. Write the conclusion. Evaluate the overall organization. Revise the content of each paragraph. Proofread your essay or use a Grammar Checker for language errors. Use a plagiarism checker.
The authors, Marc Aronson and Marina Budhos purpose for writing, Sugar Changed the World is to inform readers how sugar was tied into families and many primary events in history. "Sugar Changed the World" was an informative text that shows how sugar got passed around and may even be tied into your life. The authors had dealt with many conflicting viewpoints throughout their book and ...
Sadly, creativity has been "educated out" of us. An UnEssay project gives students a way to creativelyinteract with the class themes. In this project, students pick a topic that interests them and then they think of a way to produce something that touches on the theme. It can be a standard writing assignment or something totally different. The idea of having students choose not just the ...
Advanced English Writing Skills: Masterclass for English Language Learners How to Write Effectively in English & Write with Confidence: How to Write Essays, Summaries, Emails, Letters, Articles & ReviewsThis English writing practice book for adults is an advanced writing workbook for students of English as a second language and for native speakers who need a little extra practice. The ...
Tom Stoppard, Marc Norman, and Lee Hall took very different paths to becoming part of the writing team for the theatrical play Shakespeare in Love. From Czechoslovakia, Los Angeles, and England, the three of them all had successful careers in the theatre before each left his mark on this play about the world's most famous playwright.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
The allowable indicator values and their meanings are spelled out in the MARC 21 documentation. In the example which follows, the first 3 digits are the tag (245 defines this as a title field) and the next 2 digits (a 1 and a 4) are indicator values. The 1 is the first indicator; 4 is the second indicator.
The original MARC format was developed at the Library of Congress in 1965-6 leading to a pilot project, known as MARC I, which had the aim of investigating the feasibility of producing catalogue data in machine-readable form. Similar work was in progress in the United Kingdom where the Council of the British National Bibliography had set up the BNB MARC Project with the remit of examining the ...
Mark Antony is one of history's most influential orators. His eulogy for Julius Caesar, delivered in the aftermath of his assassination, is a masterpiece of rhetoric. The speech takes place in a tense political climate, as the conspirators have just killed the beloved leader of Rome. Antony's goal is to persuade the crowd to his side and defend Caesar's reputation. This essay will explore the ...
This English writing practice book for adults is an advanced writing workbook for students of English as a second language and for native speakers who need a little extra practice. The techniques and exercises in this book have helped thousands of students worldwide to quickly achieve high levels of written proficiency English. If you do the exercises and apply the techniques in this book ...
Sophisticated thought and/or notable awareness of the rhetorical situation Thorough analysis of the impact of the writer's rhetorical choices Acknowledgement of the passage's complexities or tensions Mature, convincing writing style
Advanced English Writing: A Masterclass for Language Learners is a fully comprehensive self-study advanced English writing book designed for language learners who need to achieve the highest possible level of proficiency in English writing and grammar. Advanced English Writing: A Masterclass for Language Learners shows English students how to organize and structure an answer for all types of ...
The best essays have clear, coherent language and are free of errors. The story is clearly and specifically told. After drafting, take the time to revise and polish your writing. Seek feedback ...
Technology. Techno-Optimists believe that societies, like sharks, grow or die. We believe growth is progress - leading to vitality, expansion of life, increasing knowledge, higher well being. We agree with Paul Collier when he says, "Economic growth is not a cure-all, but lack of growth is a kill-all.".
Writers Aged 16-22 Can Get Published and Win $500. The Gospel Coalition announces its 2024 essay contest, inviting young adults (ages 16-22) to explore and write about God's faithfulness, their relationship with technology, and their heart for full-time ministry in our secular age. Winning authors will receive a prize, and their essays ...
Attn: President for a Day Writing Contest. Office of Rep. Marcus J. Molinaro. PO Box 615. Leeds, NY 12451. If you have any questions, you can reach out to my office at 518-625-2100 or directly to my staff Sean Lisk at [email protected]. JOIN MY EMAIL LIST. SUBSCRIBE.
My curiosity was piqued by a new study, published in the June 2024 issue of the peer-reviewed journal Learning and Instruction, that evaluated the quality of ChatGPT's feedback on students' writing. A team of researchers compared AI with human feedback on 200 history essays written by students in grades 6 through 12 and they determined that human feedback was generally a bit better. Humans ...
Teacher devises an ingenious way to check if students are using ChatGPT to write essays. This video describes a teacher's diabolical method for checking whether work submitted by students was ...
The Tribeca Festival returns to New York City with more than 110 feature films, along with shorts, games, virtual reality, concerts, and an 80th birthday celebration of co-founder Robert De Niro.
But the U.S. is playing with matches too. California's wildfire season runs from April through October—peaking in the summer—with megadroughts and heat waves driving the flames. Of the state ...
Justices Alito and Thomas face a groundswell of appeals beseeching them not to participate in Trump v. United States, the case that will decide whether Mr. Trump enjoys absolute immunity from ...
Takeuchi et al. ( 2021) presented an approach to Japanese AES that eliminates the requirement for pre-scored essays by relying solely on reference texts or a model answer for the essay task.