
Press Enter to search

How to List Research Experience on Your Resume
Applying for a role that requires research skills? Here’s how to list your research experience on a resume, with examples you can follow.
3 years ago • 7 min read
Research experience isn’t just for science and academia. Research is a valuable skill that’s required for a number of roles and industries, which means it almost certainly has a place on your resume. And no — that doesn’t mean writing “research” in your skills section and moving on.
Why you should list research experience on your resume
If you’re applying for a job that involves research, listing research experience is a no-brainer. Research-specific positions, scientific jobs like Research Assistants , Lab Assistants or Technicians, graduate school applications, and most jobs in academia all require evidence of research skills. Even outside these positions, research experience demonstrates valuable transferable skills, like critical thinking and attention to detail . Which is not to say that you need to include research experience on every resume — if it makes you a stronger candidate, include it, but if it isn’t relevant and doesn’t add anything else to your candidacy, leave it off.
Research experience resume example
Before we dive right in, here's a sample resume that emphasizes research skills. You can use this as a template or as inspiration to write your own resume from scratch.
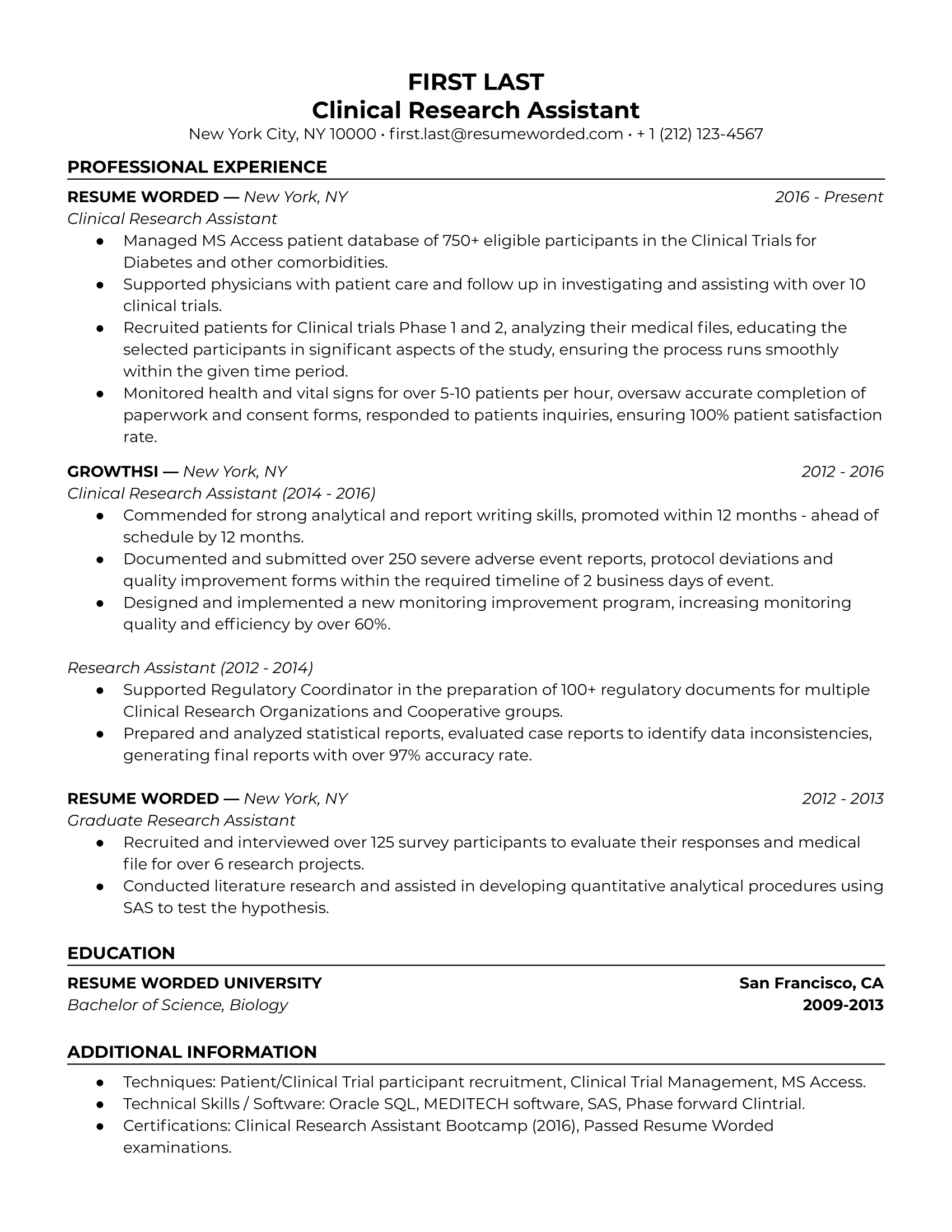
Download: PDF | Google Docs
How to list research experience in your resume
Like a lot of desirable skills, research is a soft skill , meaning it’s not something you can claim as an objective fact on your resume without backing it up. What you can do instead is prove it — what previous role involved a lot of research? What resume accomplishments do you have that highlight your research experience? Showing how you used research skills in action is the best way to demonstrate the value you could bring to the company and role you’re applying for.
There are a number of ways you can highlight research experience on your resume:
In a dedicated section
In your work experience, in your education section, listing research publications, in a projects section, in your skills section, in your resume summary.
Let's take a look at each of these options in a little more depth. But first, let's look at an annotated example to help set the context.

If you come from a research background, you might want to title your work experience ‘Research.’ Alternatively, you could create two experience sections — one titled ‘Work Experience’ and one titled ‘Research Experience’ — if you also have a lot of non-research experience but want to highlight your most relevant experience first. You can go into more detail when applying for a research-focused role by describing the project and specifying the nature of the research and your role in it.
More information: How to title different sections of your resume
Including research experience in your main work experience section is appropriate if it was paid work or if it was your most recent and relevant experience. List the employer — for example, the university or research department — job title, dates, and accomplishments, just like you would any other work experience.
More information: How to list your work experience on your resume
If you’re a current student or recent graduate, you can list your education section at the top of your resume. You can also make this section a little more comprehensive if you don’t have a lot of work experience, by including things like awards, coursework, and academic research.
If you undertook research as part of your studies and it demonstrates skills relevant to the job you’re applying for, list your research accomplishments in bullet points under the education section of your resume.
More information: The must-haves when writing your education on your resume
If you have a lot of publications that came out of your research, and you want to draw attention to them — and if they’re relevant to the job you’re applying for — consider creating a separate publications section . Formal publications like these are an excellent way to add credibility to your research experience.
List each publication in a new bullet point with the title, year, and name of the magazine, website, or journal. Academic publications can be listed more formally if it’s relevant, like if you’re applying for graduate school or a role in academia.
When it comes to listing research on your resume, like other soft skills, you need to show you’ve used this skill in your previous roles by showcasing your research related accomplishments. Upload your resume to the tool below to find out if your resume highlights your most relevant research experience and achievements.
If your research experience is less extensive or wasn’t quite relevant enough to include alongside your work experience or education, you can still highlight it in a projects section. Keep this brief and include 1-2 bullet points showcasing your key research accomplishments.
More information: How to list projects on a resume
Research skills can go in your skills section — as long as they’re hard skills. Steer clear of listing generic skills like “Research” — instead, use our keyword finder to look for relevant skills and keywords and include specific hard skills like data analysis, project management, software proficiency, and certifications.
You can also use the skills search tool below to get a list of hard skills relevant to the research-focused role you’re applying for.
More information: How to write a resume skills section
If you’re applying for a position where research experience is essential, consider emphasizing your experience by including a short resume summary at the top of your resume. This should include the title of the job you’re applying for and a brief overview of your background and key skills.
More information: Generate a summary for your resume
Examples of listing research experience on your resume
No matter where you choose to include it, always list research experience in concise, accomplishment-focused bullet points . These should follow the structure of action verb + what you did + what the result was. Here are some examples of resume bullet points you can use or modify to suit your own research experiences.
Highlight research projects
- Assisted with cell development research projects as part of the Leukemia Research team — identifying cell changes, determining cell counts and coulter counters with 98% accuracy.
If you have significant research experience, describe it! The more relevant it is to the position you’re applying for, the more detail you can go into. Make sure to specify exactly what stages of research you worked on and what your contribution was.
Mention awards for your research
- Awarded “Total Quality Award” in recognition of consistent high standards of quality work for research excellence (only 3 awarded in class of 500).
If the high quality of your work has been acknowledged by an award, early promotion , or similar outside recognition, include it! In addition to the name of the award or accolade, don’t forget to specify context (e.g. 'out of class of 500 people' to increase its credibility.
Demonstrate technical expertise
- Created over 75 3D models with CAD tools such as Solidworks and ANSYS.
If you have experience with specific software or tools that you’ll be using in the position you’re applying for, include a bullet point accomplishment specifying how you’ve used them. While this isn't direct 'research' experience, it uses tools that are relevant to research projects — this is a good way of showing that you have research skill sets without having formal research experience.
Use 'research-focused' action verbs
- Researched and edited two articles and one book chapter on prenatal substance abuse, policy implication of Human Genome Project.
Use action verbs like "Researched" or "Scoured" which clearly emphasize research skills. In some cases (like in this example), you can list publications in your bullet points itself. If you’ve authored academic papers, books, or articles, this is a great way to show the validity and importance of your research.
Include accomplishments related to research studies
- Oversaw screening and recruitment of over 100 participants to study, liaised with laboratory personnel and site coordinators to ensure study is completed on time with 100% success.
Not all research positions involve pure research. Make sure you highlight appropriate related accomplishments, like managing research study participant data and enrolments or managing a team of research assistants.
Include accomplishments relating to research in your field
- Conducted legal research; organized and analyzed data and evidence for over 50 cases annually.
If research is part of the job description, make sure you include at least one bullet point highlighting how you’ve used those skills in the past. Including metrics, like the number of cases you’ve researched, contextualizes your accomplishments and helps them stand out.
- Conducted marketing research for both buy-side and sell-side resulting in 15 strong leads.
Research isn’t just limited to science and academia. Demonstrate your skills in action by the context and end results of your research, like the number of leads it generated or the increase in sales figures.
Spread the word
Hiring manager’s guide: how to list work experience on your resume, you lied on your resume and got the job. what now, keep reading, how to show bilingualism on your resume (with examples), oops what to do if there’s a mistake on your resume, getting the basics right: resume line spacing, subscribe to our newsletter.
Stay updated with Resume Worded by signing up for our newsletter.
🎉 Awesome! Now check your inbox and click the link to confirm your subscription.
Please enter a valid email address
Oops! There was an error sending the email, please try later

Thank you for the checklist! I realized I was making so many mistakes on my resume that I've now fixed. I'm much more confident in my resume now.


Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
Tips for Writing about Your Research Experience (Even if You Don’t Think You Have Any)
If you’re someone who hasn’t yet done formal research in a university setting, one of the most intimidating parts of the process can be simply getting your foot in the door. Just like the way your options can seem very limited when applying for your first job, asking for a research position when you have no “experience” can seem discouraging — maybe even to the point of causing you to question whether you should apply in the first place. With that being said, there are some simple tips you can employ when applying for research positions to highlight the link between your existing interests and the work of the position for which you are applying.

First things first: tailor not just your cover letter (for applications that ask for it) but your resume to the position for which you are applying. Even if you’re just sending a casual email to a professor to ask about the research that they’re doing, as a rule, it never hurts to attach your resume. I also like to think that submitting a resume even without being asked to shows that you’re serious about doing research, and have taken the time to put together a thoughtful inquiry into a position. If you’ve never written a cover letter or resume before, don’t fret. The Center for Career Development has some great online resources to help you create one from scratch. If you are looking for more individualized help, you can also schedule an appointment to get one-on-one feedback on your application at any stage in the writing process.
One of the things that I’ve found, however, is that the single-page format of a resume often isn’t enough space to include all of the information about every single thing you’ve ever done. Rather than trying to jam as many impressive accomplishments as you can onto a page, your goal should be to create a resume that gives a cumulative sense of your interests and experiences as they relate to the position for which you are applying. One of my favorite ways to do this is to create a “Research” section. “But Kate, what if I don’t have any research experience?,” you ask. Remember that paper you wrote about a painting by Monet in your favorite class last semester? Write the title down, or even a sentence or two that summarizes your main argument. The art museum you’re hoping to do research at will love knowing that your interest in their current exhibition on Impressionism is rooted in classes you’ve taken and the projects you’ve done in them, no matter how new you may be to a topic. Your interest in a specific research position has to come from somewhere, and your resume is an important part of demonstrating this to others.
What I would like to reassure you of is that it’s normal to be an undergraduate with very little research experience. The people reading your application —whether it be for an official program or even if it’s just a friendly email with a few questions— know that you are a student and will probably be excited to offer you guidance on how to get involved with more specific research projects even if all you have to offer at this point is enthusiasm for the topic. Working in a lab or with a professor on a research project is an opportunity designed to help you learn above all else, so it’s ok if you don’t know what you’re doing! It goes without saying that having little experience will make the final result of your research experience all the more worthwhile because of the potential to gain knowledge in ways you haven’t even imagined.
— Kate Weseley-Jones, Humanities Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Explore Jobs
- Jobs Near Me
- Remote Jobs
- Full Time Jobs
- Part Time Jobs
- Entry Level Jobs
- Work From Home Jobs
Find Specific Jobs
- $15 Per Hour Jobs
- $20 Per Hour Jobs
- Hiring Immediately Jobs
- High School Jobs
- H1b Visa Jobs
Explore Careers
- Business And Financial
- Architecture And Engineering
- Computer And Mathematical
Explore Professions
- What They Do
- Certifications
- Demographics
Best Companies
- Health Care
- Fortune 500
Explore Companies
- CEO And Executies
- Resume Builder
- Career Advice
- Explore Majors
- Questions And Answers
- Interview Questions
How To Put Research On Your Resume (With Examples)
- How To Write A Resume
- How To Build A Resume
- Specific Resume Words
- Action Verbs On A resume
- Words To Describe Yourself
- Resume Outline
- How To Make A Resume
- How To Make A Resume On Word
- How To Write A Resume Profile
- General Resume Examples
- Resume With No Experience
- Student Resume
- College Resume
- Entry Level Resume
- Military Resume
- Internship Resume
- First Resume
- College Application Resume
- 2 Page Resume
- Blank Resume Template
- College Freshman Resume
- Work History
- Resume Templates
- Resume Tips
- Best Resume Writing Services
- Things To Avoid On A Resume
- Resume Paper To Use
- What To Include In A Resume
- How To Write A Bio
- How To Write A Personal Statement
- Lied on Your Resume?
- Avoid Age Discrimination
- Words and Phrases You Shouldn't Include in Your Resume
- How Many Skills Should You List On A Resume
- Send A Resume As A Pdf
- Resume Critique
- Make A Resume Stand Out
- Resume Spelling
- Resume Past Or Present Tense
- How To List Projects On A resume
- Best Resume Action Words
- How To Quantify Your Resume
- Resume Bullet Points
- Are Resume Writers Worth It
- How Many Jobs To List On Resume
- Please Find Attached My Resume
- How To List Contract Work On Your Resume
- How To Put Research On Your Resume
- What Is A CV?
- CV Vs Resume
- CV Templates
- CV Examples
Find a Job You Really Want In
Research experiences and skills are an incredibly important aspect of many job applications, so it’s important to know how to put them on your resume correctly. Hiring managers and recruiters want employees who can help drive innovation by being able to apply research skills to problem solve and come up with creative growth solutions.
If you’re a job seeker looking to include your research skills on a resume , we’ll go over how to list research on resume, where you can include it on a resume, and give you some examples.
Key Takeaways:
If you don’t have traditional research experience, highlight the skills used for research that you’ve used in past jobs.
Consider creating a separate research section in your resume if you have a lot of research experience or merge sections, depending on which section you want to bolster with research.
Research experience is one of the best assets to include on a resume so be on the lookout for more opportunities.

What are research skills?
Where to put research experience on your resume
How to include research on your resume, examples of research on a resume, how to put research on your resume faq.
- Sign Up For More Advice and Jobs
Research skills are any skills related to your ability to locate, extract, organize, and evaluate data relevant to a particular subject. It also involves investigation, critical thinking , and presenting or using the findings in a meaningful way.
Depending on what job you’re applying for, research skills could make or break your ability to land the job. Almost every job requires some research skills and you probably already have some of those skills mastered by now.
For most careers, research is a vital process to be able to answer questions. “Research skills” are not a single skill, but multiple ones put together.
Some skills that are necessary for research are organization, problem-solving, critical thinking, communication, and specific technical skills, like coding, Excel, and copywriting.
Including research experience and skills on a resume can be incredibly flexible. When thinking about how to add it to your resume, you want to consider how the research experience adds to your resume.
Your research experience can be included in a few different sections of your resume. Some of those sections include:
Academic accomplishments
Research experience
Work experience/history
College activities
Volunteer work
Presentations and publications
Skills section
If you’ve had smaller research roles but no “official” research experience, you can highlight the skills associated with the types of research mentioned above in your job description under the work history section in your resume.
If your job history is a research position, then naturally, you would include research under the work history section. You can also merge your sections depending on what type of position you are applying for.
For example, you could create a “Research and Education” section or a “Research and Publications” section. If your research is not related to your education and you don’t have any publications, you can also detail it in a separate “Research” section in your resume.
To include your research on your resume, you should gather all the necessary information and then quantify your accomplishments to fit into specific sections. Here is a more detailed list of how to write about research experience in resume:
Gather all the necessary information. The first step is to collect all of the important details like the title of the research project, the location of the research project, the principal investigator of the project (if applicable), and the dates of the project. You will list these details much like you would list a company you have worked for in the past.
Read the job description carefully. Every resume and cover letter you write should be tailored to the job you’re applying for. When a hiring manager puts a necessary qualification in their job posting, you must be sure to include it in your resume.
Make sure that you highlight the right types of research skills on your job applications and resumes.
Quantify your accomplishments. When describing your role on the project, you will want to summarize your accomplishments and deliverables. Hiring managers and recruiters love seeing numbers. When you write out the deliverables from your project, make sure you quantify them.
Incorporate into your work history section. If there were times when you used your research skills in your past employment opportunities, include them in your work experience section. You can also include publications, conferences you may have presented at, and any awards or recognition your research had received.
If you have completed research in an academic setting, then presentations (oral and poster) are an important part of the research process. You should include those details along with the titles of your publications.
Add to your research section. Other aspects of research that you can detail to make your application more competitive are adding skills specific to your project to the skills section of your resume.
These skills will vary depending on the subject matter, but some examples include coding languages, interviewing skills, any software you used and are proficient in using, managerial skills , and public speaking if you have presented your research at conferences.
Add research to your skills section. If the specific research you did is less important than the skills you used to perform it, highlight that in your skills section. That way, you don’t have to take up a lot of work or education history with slightly irrelevant information, but hiring managers can still see you have research skills.
Just be sure you’re more specific about a research methodology you’re an expert in because the skills section doesn’t give you as much room to explain how you leveraged these abilities.
Sprinkle research throughout your resume. If you have a lot of experience performing research in professional, volunteer, and educational settings, pepper it in a few different sections. The more hands-on experience you have with research, the better (for jobs that require research).
Let’s look at some examples of how research can be included on a resume:
University research example
EDUCATION Undergraduate Thesis, University of Connecticut, Dec. 2017-May 2018 Worked alongside UCONN English Department head Penelope Victeri to research the poetry of New England writers of the 20th century. Explored common themes across the works of Elizabeth Bishop, Wallace Stevens, and Robert Lowell. Performed online and in-person research on historical documents relating to each author , including information on the political, religious, and economic landscape of the US at the time. Analyzed poetic works of each author and drew on similar contemporary regional authors’ works. Prepared 20,000 words thesis entitled “Place, Allegory, and Religion: Three 20th Century New England Poets” and defended my written arguments to a panel of English professors.
Customer service research example
WORK EXPERIENCE Conducted interviews with 20 customers each week to gain insight into the user experience with company products Used Google analytics to determine which pages were driving most web traffic, and increased traffic by 11% Reviewed thousands of customer surveys and compiled findings into monthly reports with graphic findings Presented at weekly marketing meeting to inform marketing team of trends in customer experience with our products
Laboratory research example
RESEARCH Conducted experiments on rat brains by introducing various novel chemical compounds and levels of oxygen Ran electricity through brain slices to view interaction of different chemical compounds on active brain cells Prepared sterile samples for daily check and maintained 89% percent yield over the course of a 3-month study Presented findings in a final 15 -page research report and presentation to the Research and Development team
Examples of common research skills to list on your resume
Here are examples of research skills in action that you may have overlooked:
Searching for local business competition
Sending out customer satisfaction surveys
Summarizing current policies and laws in effect for a particular topic
Creating lesson plans based on current education standards
Reading literature reviews and implementing changes in clinical practice
Attention to detail
Problem-solving skills
Critical thinking
Project management skills
Communication skills
Why are research skills important?
Research skills are important because they can help you identify a problem, gather information, and evaluate that information for relevancy. Including your research skills on a resume will show hiring managers that you have the ability to suggest new ideas and help their organization adapt and change as the industry changes.
Some common research skills include:
critical thinking
Computer skills
Can I list research as a skill?
Yes, you can list research as a skill on your resume. Including your research skills in your resume can help show a potential employer that you have the ability to suggest new ideas and use critical thinking to find solutions to problems. Most research skills will use attention to detail, problem-solving, and project management skills.
California State University San Bernardino – Incorporating Research Project Experience on Your Resume
University of Missouri – How to Put Research on Your Resume
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Heidi Cope is a former writer for the Zippia Career Advice blog. Her writing focused primarily on Zippia's suite of rankings and general career advice. After leaving Zippia, Heidi joined The Mighty as a writer and editor, among other positions. She received her BS from UNC Charlotte in German Studies.
Recent Job Searches
- Registered Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Truck Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Call Center Representative Jobs Resume Location
- Customer Service Representative Jobs Resume
- Delivery Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Warehouse Worker Jobs Resume Location
- Account Executive Jobs Resume Location
- Sales Associate Jobs Resume Location
- Licensed Practical Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Company Driver Jobs Resume
Related posts

20 Things Only People Who Work From Home Will Understand
Nurse Vs. Nurse Practitioner
How To Make A Resume (With Examples)

30 Resume Tips To Help You Get Hired
- Career Advice >
- Get The Job >
- How To Put Research On Resume Research Experience
Want To Add Research Experience in a Resume? Learn How! (+10 Examples)

3 key takeaways
- Why you should include research experience in a resume
- How to write your research experience using the Teal AI Resume Builder
- 10 examples of resume research experience
Research penetrates virtually every profession, from healthcare to finance and tech to the arts.
In fields like biotechnology, the value is clear. Still, even in areas like market analysis, design, and humanities, research experience can highlight your capacity to dig deep, discern patterns, and contribute original insights. It's also a testament to your in-depth knowledge in your chosen domain.
Research experience in your resume is a powerful way to demonstrate your analytical insight and unique expertise. So where should it go? And what's the best approach to describe, quantify, and showcase these accomplishments?
Why you should include research experience in your resume
Research experience showcases your dedication to and in-depth understanding of your field.
Whether you're after a research assistant position, a job in molecular biology, a position as a marketing generalist, or a prominent spot on the leukemia research team, including research on a resume highlights technical skills (like data interpretation and statistical analysis), soft skills (such as collaboration, critical thinking, and teamwork), and their corresponding impact.
Especially when these research skills are listed in a job description, it’s crucial to incorporate them into your resume. This helps align your qualifications with what the hiring manager, recruiter, or prospective employer is looking for.
Also, every role you apply to will likely have a variety of skills you’ve gained through your research experience. So before you submit an application, be sure to tailor your resume to that specific role—focusing on the unique skills and keywords for each position.
Pro Tip: Teal+ offers insight into unlimited hard skills, soft skills, and other important language from any job description. The free Teal AI Resume Builder and Job Application Tracker pull the top five hard skills—helping you align your resume with every role you apply to.
How research experience on a resume differentiates you
As a job seeker, skills gained through traditional research experience set you apart as a candidate who not only has theoretical knowledge but also has the hands-on experience to apply this knowledge, tackle complex challenges, conduct research, and contribute meaningful insights in real-world scenarios.
For example, if you conducted research in data analytics, you know how to collect, process, and interpret large data sets, whereas those who haven’t engaged in real-world research experience may only be able to interpret large sets of data.
What fields value research experience?
So, what are some fields where adding research experience to a resume can help differentiate you from other candidates?
- Engineering & Technology: Emphasizing your ability to tackle technical challenges and innovate using cutting-edge technologies.
- Social Sciences & Humanities: Emphasizing your analytical skills in understanding human behaviors, societal trends, and cultural nuances.
- Business & Economics: Showcasing your skill for dissecting market trends, predicting economic shifts, and strategizing based on concrete data.
- Life Sciences & Medicine: Demonstrating your expertise in laboratory techniques and understanding of complex biological systems.
Other fields where research might be less prominent but still relevant are marketing, event management, web development, and hospitality.
How to write about your research experience
The power of your research experience lies in quantifying your impact and success.
Rather than just listing your research experience, by emphasizing the measurable impact you've made, you offer undeniable proof of concept—turning abstract research skills into concrete accomplishments.
In the same way you would create resume work experience achievements, research experience should follow this structure (or something similar) to emphasize your research skills, how you used them, and the outcome.
Success Verb + Noun + Metric + Context (Research Experience) + Outcome = 1 bulleted achievement
You can also incorporate research experience on a resume using a similar structure into your “Professional Summary,” “Education,” and “Projects” sections.
If you’re feeling stuck, the Achievement Assistant in the free Teal AI Resume Builder can help you write impactful resume achievements for all of your research experience.

How to list research experience on your resume with Teal
Step 1: Log in to your Teal account. (If you don’t have one, sign up for free!)
Step 2: Click “Resume Builder” in the navigation panel on the far left. From here, you can click “Add New Resume” or select a resume you’re already working on.

Teal note: Start with steps one and two. Then, proceed with the directions for each of the following sections.
To list research experience in your professional summary
To add research experience to your professional resume summary, scroll to Professional Summaries, click the drop-down button, then click "Add Professional Summary." Create one from scratch, or click the "Generate With AI" Button. Then, edit as needed to incorporate your relevant research experience.
To list research experience in your work experience
To add research experience to your work experience achievements, from the Resume Builder, scroll to Work Experience. Then, click the drop-down button. Click "Add Work Experience" to create a new section or "Add an Achievement" in an existing work history.

To list research experience in education
To add research experience to your education, from the Resume Builder, scroll to Education. Then, click the drop-down button. Click "Add Education" to create a new section or the “Edit Education Item” icon to add research experience to existing education.

To list research experience in your projects
To include research on a resume in your projects, from the Resume Builder, scroll to Projects. Then, click the drop-down button. Click "Add Project " to create a new section or the "Edit Project" icon to add research experience to an existing project.

How to include undergraduate research experience on your resume
Undergraduate academic research experience is more than just academic work; it's a testament to your commitment, curiosity, and capability.
By actively engaging in research at an early stage, undergraduates like you demonstrate a proactive approach to learning and a desire to dig deeper into your field.
Not only is this research experience valuable for students pursuing, say, a career in academia, but also for students of all fields of study entering the professional world.
In real-world scenarios, prospective employers view undergraduate research as an indicator of problem-solving project management skills, technical knowledge, and the ability to collaborate.
5 tips for including undergraduate research experience on a resume
If you’re looking to learn how to put undergraduate research experience on a resume, the best placements are within your “Education” section or as projects in a resume .
Here are five tips to help you get started.
1. Use a clear title
2. Include the duration of the research
3. Be specific about your role and contributions
4. Highlight achievements and outcome
5. Incorporate relevant hard and soft skills
Resume research experience examples
Let’s take a look at some research experience examples on a resume across different levels of experience and professions to get an idea of what this can look like.
High school student
Collaborated and utilized botanical techniques in an 'Effects of Light on Photosynthesis' study, examining 40+ seedlings during a semester-long biology research project, revealing blue light's heightened influence on photosynthesis.
Undergraduate student
Surveying 500+ meals over six months in the 'Dietary Habits of University Students' research projects, using Excel's advanced statistical functions and critical thinking, revealed a 58% decline in protein-rich food choices.
Recent College graduate
As an Environmental Science graduate, I'm skilled in the hands-on application of advanced chromatography techniques, with a focus on the 'Efficiency of Modern Water Purification Methods' research. I've successfully analyzed and improved purification methods for over 300 water samples, achieving a 90% reduction in contaminants.
Masters student in Psychology
Led the data analysis of 100+ patient evaluations during the 'Efficiency of Cognitive Therapies on Stress' study, resulting in a 20% improvement in therapeutic outcomes.
Human resources intern
Used the Qualtrics survey tool to capture insights from 250+ employee responses as part of the 'Employee Satisfaction Metrics' evaluation. This collaboration and data-driven analysis highlighted key opportunities for organizational enhancements, leading to a 10% increase in overall employee satisfaction scores within Q2.
Junior-level data engineer
Developed an ETL pipeline capable of processing 2TB+ of data daily as part of the 'Real-time Data Integration' research project, significantly reducing data latency by 80%
Financial analyst
Leveraged Excel's advanced financial functions to dissect 3 years' worth of company financials in the 'Company Health Audit' study, identifying potential savings of $1.2M
Product manager
As a seasoned Product Manager with 7 years of experience, I've spearheaded research-centric product developments, aligning technical capabilities with market demands. My most notable accomplishment was the 'User Experience Revamp' research project, where I employed data analytics tools and cross-functional teamwork to gather feedback from 10,000+ users. This feedback-centric approach led to a 20% increase in user retention and positioned our product as a market leader in its segment.
Lead mechanical engineer
Project: Efficiency Enhancement of HVAC Systems Research - Innovated novel airflow designs tested on 100+ HVAC units as part of the 'Airflow Optimization Research,' achieving an efficiency boost of 15%. - Collaborated with electrical engineers to integrate smart sensors in 50 existing HVAC systems during the 'Smart HVAC Retrofit' initiative, leading to a 10% reduction in energy consumption.
Senior machine learning engineer
Optimized neural network architectures, improving over 2,500 lines of Python code, during a collaborative research initiative on image recognition, resulting in a 15% boost in model accuracy.
Add your research experience to your resume with Teal
Highlighting research experience in your resume is more than just filling space.
It's about showcasing a depth of understanding, commitment to a field, and practical skills that can differentiate you from other job seekers.
Research proves you have the hard and soft skills employers want and demonstrates your proactive approach to leveraging those skills for tangible outcomes.
The Teal AI Resume Builder makes adding this research-focused experience to your resume seamless. Whether it's capturing intricate details of an independent research project, translating theoretical skills into actionable results, or giving context to your hands-on experience, Teal provides the tools and guidance to do it with precision. And by tailoring your research for each application, you make a compelling case that you're the best fit for a role.
Sign up for Teal today and let your research experience take the spotlight it deserves.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can i effectively quantify my research experience on a resume, should i include all my research projects on my resume or only the most relevant ones, how can i describe undergraduate research on my resume if i don't have any publications or presentations.

Kayte Grady
Related articles.
.png)
How Ashleigh Went From Zero to 11 Job Interviews With Teal

How to List Publications on Your Resume (+ Examples)

How to Email a Resume to an Employer [Template + Examples]

How to Ask for a Letter of Recommendation (Templates + Examples)
.jpeg)
We help you find the career dream.
- • Directed a multi-sector research project evaluating the impact of digital resources in academic environments, benefiting over 30 institutions.
- • Implemented innovative qualitative research methods that increased project efficiency by 25%.
- • Authored impactful research reports presented at national conferences, influencing educational policy directions.
- • Supervised and mentored a team of 3 junior analysts, improving team productivity and research output quality.
- • Managed project timelines and deliverables for complex studies, resulting in 95% on-time completion rate.
- • Developed strong professional relationships with stakeholders and collaborators, which led to securing 2 significant research grants.
- • Conducted in-depth analysis on STEM education trends, influencing curriculum development for 100+ educational institutions.
- • Played a critical role in a team that delivered 4 major research projects yearly, exceeding stakeholder expectations.
- • Managed cross-functional teams, increasing overall project efficiency by 15%.
- • Presented research findings at 10+ industry conferences, enhancing the company's professional reputation.
- • Leveraged advanced data collection tools to gather and analyze information from over 500 interview subjects.
- • Assisted in the preparation of grant proposals that secured funding of over $500,000 for environmental research.
- • Organized and managed data collection for a large-scale research study on conservation best practices.
- • Played a key role in publishing 3 research papers that contributed to new sustainability guidelines.
- • Supported senior researchers in conducting fieldwork and data analysis for interdisciplinary research projects.
13 Researcher Resume Examples & Guide for 2024
Your researcher resume must demonstrate your expertise in your field. Clearly highlight publications, presentations, or projects you've contributed to. Showcase your analytical and data collection skills. Elaborate on the methodologies you're proficient with to prove your technical capabilities.
All resume examples in this guide

UX Researcher

User Researcher

Student Researcher
Quantitative Researcher

Qualitative Researcher

Market Researcher
Undergraduate Researcher

Product Researcher

Psychology Researcher
Design Researcher

Lab Researcher

Machine Learning Researcher
Resume guide.
Resume Format Tips
Resume Experience
Skills on Resume
Education & Certifications
Resume Summary Tips
Additional Resume Sections
Key Takeaways

As a researcher, you may struggle with translating your extensive project experience into a concise format that appeals to a broad range of employers. Our guide will provide you with tailored strategies to effectively distill your research accomplishments into an impactful resume that resonates across industries.
- Utilize real-life examples to refine your researcher resume;
- Effectively write the experience section of your researcher resume, even if you have minimal or no professional experience;
- Incorporate the industry's top 10 essential skills throughout your resume;
- Include your education and certifications to highlight your specific expertise.
If the researcher resume isn't the right one for you, take a look at other related guides we have:
- Lab Manager Resume Example
- Lab Technician Resume Example
- Scientist Resume Example
- Chemist Resume Example
- Research Assistant Resume Example
- Lab Assistant Resume Example
- Research Director Resume Example
- Radiologic Technologist Resume Example
- Research Manager Resume Example
- Research Associate Resume Example
Simple guide to your researcher resume format and layout
- professional experience - use the reverse-chronological resume format;
- skills and achievements - via the functional skill-based resume format;
- both experience and skills - with a hybrid resume format .
What is more, keep in mind that your resume may be initially assessed by the ATS (Applicant Tracker System) (or the software used by companies in the hiring process). The researcher resumes that suit the ATS:
- have a header that includes either a role keyword or the job you're applying for;
- should be no longer than two pages;
- be submitted as PDF, unless specified otherwise.
Upload & Check Your Resume
Drop your resume here or choose a file . PDF & DOCX only. Max 2MB file size.
If you happen to have some basic certificates, don't invest too much of your researcher resume real estate in them. Instead, list them within the skills section or as part of your relevant experience. This way you'd ensure you meet all job requirements while dedicating your certificates to only the most in-demand certification across the industry.
The five (plus) definite sections your resume for a researcher job should include are:
- Header with your headline, contact details, and/or a preview of your work
- Summary (or objective) to pinpoint how your success aligns with the role
- Experience with bullets of your most relevant achievements in the field
- Skills to integrate vital job requirements (both technical and personal)
- Your further dedication to the field, showcased via relevant higher education and/or certifications
What recruiters want to see on your resume:
- Publishing Record: Evidence of publications in reputable journals or conferences relevant to the field.
- Research Experience: Detailed description of past research projects, roles, and contributions.
- Grant Writing Skills: Demonstrated success in securing research funding from grants, fellowships, or scholarships.
- Technical Expertise: Proficiency with tools and methodologies specific to the research area, like statistical analysis software, lab techniques, or data analysis programs.
- Collaboration and Communication: Examples of working effectively within interdisciplinary research teams and communicating complex research findings to diverse audiences.
Creating your researcher resume experience to catch recruiters' attention
Remember that for the researcher role, hiring managers are looking to see how your expertise aligns with their requirements. Here's where your resume experience section can help out. Make sure you:
- Include mainly roles that are relevant to the researcher job you're applying for;
- Don't go too far back in your experience - recruiters will only care what you did a decade ago if it's really important for the researcher role;
- Each bullet you include should say what you did, followed by the skills you used and the actual end result of your efforts;
- Quantify each of your achievements with numbers and possibly the overall effect it had on the organization;
- Highlight transferrable skills - or personal skills you've attained thanks to past jobs - that could be applicable within your potential workplace. This would showcase your unique value as a professional.
Formatting the experience section of your resume doesn't have to be an over-the-top deep dive into your whole career. Follow the researcher resume examples below to see how industry-leading professionals are presenting their experience:
- Designed and executed a comprehensive experimental study on the effects of new agricultural chemicals, increasing crop yields by 20% over a two-year period.
- Authored and co-authored 6 peer-reviewed journal articles in the field of synthetic biology, enhancing the company's academic presence and fostering collaborative opportunities.
- Mentored a team of junior researchers and interns, improving team productivity by 30% and helping to establish a robust research pipeline.
- Implemented new data collection protocols for patient trials, which improved data accuracy by 25% and ensured regulatory compliance.
- Coordinated with cross-functional teams to manage over 15 multi-center clinical trials, ensuring that deadlines were met and budgets were maintained.
- Presented findings at 3 international conferences, significantly raising the profile of the research programs and attracting future funding.
- Led the research and prototype development for a new medical device, which subsequently received FDA approval and led to a 150% increase in departmental revenue.
- Coordinated with a team of scientists to integrate artificial intelligence in the device's diagnostic process, improving prediction accuracy by 35%.
- Managed the intellectual property process for developed technologies, resulting in the granting of 5 patents and protecting the company's assets.
- Analyzed consumer behavior data and trends to inform the company's marketing strategies, contributing to a 40% increase in market share.
- Developed and administered over 200 surveys and focus groups to gather actionable customer insights, directly influencing product development.
- Worked directly with the sales team to refine target demographics, which led to more effective ad spend and a 25% increase in conversion rates.
- Directed a groundbreaking research initiative on renewable energy that secured $2M in grants from government and private sectors.
- Managed collaborations with industry partners to test and refine prototype solar panels, achieving a 50% increase in efficiency over existing models.
- Organized and chaired a successful international symposium on sustainable energy, fostering partnerships that led to further R&D investments.
- Led the development of a novel gene-editing platform, which resulted in a 200% increase in experiment throughput and reduced costs by 40%.
- Collaborated with pharmaceutical companies to leverage the platform for drug development, accelerating the timeline from discovery to preclinical trials.
- Managed the submission of regulatory documents for new research protocols, ensuring full compliance with all federal and state regulations.
- Processed and analyzed big data sets using advanced analytics tools, uncovering patterns that led to a 20% improvement in operational efficiency.
- Developed custom scripts and algorithms to automate data collection processes, saving the company an average of 250 man-hours per month.
- Designed an interactive dashboard that provided real-time insights into market trends, which became a key decision-making tool for the executive team.
- Monitored patient enrollment and data integrity for over 10 international clinical trials, ensuring adherence to study protocols and Good Clinical Practice guidelines.
- Provided key contributions to the successful launch of a Phase III trial, which saw a 95% retention rate of study participants due to enhanced engagement strategies.
- Developed training materials and conducted workshops for new clinical research coordinators, greatly improving the effectiveness and compliance of the research team.
Quantifying impact on your resume
- Include the number of publications you've authored to demonstrate the depth and breadth of your research experience.
- List the amount of research funds you've secured, as it shows your capability to attract significant financial resources for your work.
- State the number of experiments or studies you've conducted to quantify your hands-on experience in your field.
- Mention the number of citations your work has received to reflect its influence and acceptance in the research community.
- Highlight the size of the research teams you've led or participated in to show your collaborative and leadership skills.
- Detail the number of conferences you've presented at to exhibit your ability to communicate your findings to a professional audience.
- Provide the percentage by which your findings have improved a process or technique within your field to illustrate the practical impact of your research.
- Specify the number of patents you hold, if applicable, to demonstrate innovation and potential for commercial application of your work.
Action verbs for your researcher resume
Four quick steps for candidates with no resume experience
Those with less or no relevant experience could also make a good impression on recruiters by:
- Taking the time to actually understand what matters most to the role and featuring this within key sections of their resume
- Investing resume space into defining what makes them a valuable candidate with transferrable skills and personality
- Using the resume objective to showcase their personal vision for growth within the company
- Heavily featuring their technical alignment with relevant certifications, education, and skills.
Remember that your resume is about aligning your profile to that of the ideal candidate.
The more prominently you can demonstrate how you answer job requirements, the more likely you'd be called in for an interview.
Recommended reads:
- How To Include Your Relevant Coursework On A Resume
- How to List Continuing Education on Your Resume
The more trusted the organization you've attained your certificate (or degree) from, the more credible your skill set would be.
Balancing hard and soft skills in your researcher resume
Recruiters indeed pay close attention to the specific hard and soft skills candidates possess. Hard skills refer to technical abilities or your proficiency in technologies, while soft skills are the personal attributes and qualities developed over your lifetime.
If you're unsure about effectively quantifying these skills on your resume, follow our step-by-step guide. It's crucial to first understand the key job requirements for the role. Doing so enables you to accurately list your:
- Hard skills in sections like skills, education, and certifications. Your technical expertise is straightforward to quantify. Most organizations find it sufficient to mention the certificates you've earned, along with your proficiency level.
- Soft skills within your experience, achievements, strengths, etc. Defining interpersonal communication traits in your resume can be challenging. Focus on showcasing the accomplishments you've achieved through these skills.
Remember, when tailoring your researcher resume, ensure that the skills you list match exactly with those in the job requirements. For instance, if the job listing specifies "Microsoft Word," include this exact term rather than just "Word" or "MSO."
Top skills for your researcher resume:
Data Analysis
Statistical Analysis
Qualitative Research
Quantitative Research
Research Design
Literature Review
Data Collection
Data Interpretation
Academic Writing
Scientific Publication
Critical Thinking
Problem Solving
Attention to Detail
Time Management
Communication
Adaptability
Project Management
Ethical Judgment
List your educational qualifications and certifications in reverse chronological order.
The importance of your certifications and education on your researcher resume
Pay attention to the resume education section . It can offer clues about your skills and experiences that align with the job.
- List only tertiary education details, including the institution and dates.
- Mention your expected graduation date if you're currently studying.
- Exclude degrees unrelated to the job or field.
- Describe your education if it allows you to highlight your achievements further.
Your professional qualifications: certificates and education play a crucial role in your researcher application. They showcase your dedication to gaining the best expertise and know-how in the field. Include any diplomas and certificates that are:
- Listed within the job requirements or could make your application stand out
- Niche to your industry and require plenty of effort to obtain
- Helping you prepare for professional growth with forward-facing know-how
- Relevant to the researcher job - make sure to include the name of the certificate, institution you've obtained it at, and dates
Both your certificates and education section need to add further value to your application. That's why we've dedicated this next list just for you - check out some of the most popular researcher certificates to include on your resume:
The top 5 certifications for your researcher resume:
- Project Management Professional (PMP) - Project Management Institute
- Certified Research Administrator (CRA) - Research Administrators Certification Council
- Institutional Review Board Professional (CIP) - Public Responsibility in Medicine and Research
- Certified Clinical Research Professional (CCRP) - Society of Clinical Research Associates
- Data Analysis & Statistics Certificate (DASC) - Various Institutions
Highlight any significant extracurricular activities that demonstrate valuable skills or leadership.
- When Should You Include Your High School on Your Resume?
- How To List Certifications On A Resume (Examples Included)
Researcher resume summary or objective? The best choice is based on your experience
If you're wondering about the relevancy of the resume summary or the resume objective to your Researcher application - here's the truth.
The summary and objective provide recruiters with your expertise and accomplishments at a glance, within an up-to-five-sentence structure.
The difference is that the:
- Resume objective is also more focused on emphasizing your career goals. The objective is the perfect fit for (potentially more junior) candidates who'd like to balance their relevant experience with their career goals.
- Resume summary can provide you with space to also detail the unique value of what it's like to work with you. Researcher candidates who have many noteworthy accomplishments start from the get-go with their summary.
Ensure that either type of resume introduction presents your Researcher expertise in the best light and aligns it with the job advert.
The more details you can provide with numbers, the more compelling your resume summary or objective will be.
Real-world Researcher candidates follow these frameworks in writing their resume summaries and objectives.
The end results are usually as such:
Resume summaries for a researcher job
- With a decade of profound experience in molecular biology, an extensive publication record, and a Ph.D. from MIT, the candidate is adept in genomics, proteomics, and bioinformatics. Awarded with the Young Scientist Award, they have led teams in groundbreaking cancer research, yielding patents and significant advancements in targeted therapy.
- A seasoned chemist with 15 years at GlaxoSmithKline specializing in pharmaceutical development, pivoting into biotechnology research with a strong desire to apply synthetic chemistry skills towards developing novel biologics. Recognized for innovation in small molecule synthesis, keen to contribute to interdisciplinary approaches in disease treatment.
- Former aerospace engineer with 12 years' tenure at NASA seeking to transition into climate research. Armed with robust analytical skills, a deep understanding of complex systems, and a master’s degree in environmental engineering, aiming to utilize simulation modeling to address pressing environmental challenges and climate change.
- After years of developing market forecasts and data models for economic research at a leading think tank, the candidate is eager to transfer their refined quantitative analysis skills into computational neuroscience research. With a strong grasp of machine learning and predictive analytics, they are ready to contribute to elucidating neural network functionalities.
- Graduating magna cum laude with a B.S. in biology, the applicant is enthusiastic about beginning a research career in immunology. Committed to lifelong learning and making impactful contributions, they are determined to leverage their strong foundation in cell biology and genetics to aid in developing innovative immunotherapies.
- As an ambitious recent graduate with a Master's in Computer Science and a passion for algorithm design, I am eager to delve into the world of bioinformatics research. With a zest for problem-solving and a commitment to advancing healthcare through technology, I aim to contribute to projects focused on genetic data analysis and personalized medicine.
Showcasing your personality with these four researcher resume sections
Enhance your researcher expertise with additional resume sections that spotlight both your professional skills and personal traits. Choose options that not only present you in a professional light but also reveal why colleagues enjoy working with you:
- My time - a pie chart infographic detailing your daily personal and professional priorities, showcasing a blend of hard and soft skills;
- Hobbies and interests - share your engagement in sports, fandoms, or other interests, whether in your local community or during personal time;
- Quotes - what motivates and inspires you as a professional;
- Books - indicating your reading and comprehension skills, a definite plus for employers, particularly when your reading interests align with your professional field.
Key takeaways
At the end of our guide, we'd like to remind you to:
- Invest in a simple, modern resume design that is ATS friendly and keeps your experience organized and legible;
- Avoid just listing your responsibilities in your experience section, but rather focus on quantifiable achievements;
- Always select resume sections that are relevant to the role and can answer job requirements. Sometimes your volunteering experience could bring more value than irrelevant work experience;
- Balance your technical background with your personality traits across various sections of your resume to hint at how much time employers would have to invest in training you and if your profile would be a good cultural fit to the organization;
- Include your academic background (in the form of your relevant higher education degrees and certifications) to show recruiters that you have the technical basics of the industry covered.
Researcher resume examples
Explore additional researcher resume samples and guides and see what works for your level of experience or role.
Looking to build your own Researcher resume?

- Resume Examples
How To Spot Toxic Work Culture At The Interview: 17 Signs To Watch Out For
Resume for a 16-year-old, microsoft word resume templates, what to write in email when sending resume to a friend, what to write instead of "to whom it may concern", a breakdown of a successful one page resume – and how to write yours.
- Create Resume
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Preferences
- Resume Templates
- AI Resume Builder
- Resume Summary Generator
- Resume Formats
- Resume Checker
- Resume Skills
- How to Write a Resume
- Modern Resume Templates
- Simple Resume Templates
- Cover Letter Builder
- Cover Letter Examples
- Cover Letter Templates
- Cover Letter Formats
- How to Write a Cover Letter
- Resume Guides
- Cover Letter Guides
- Job Interview Guides
- Job Interview Questions
- Career Resources
- Meet our customers
- Career resources
- English (UK)
- French (FR)
- German (DE)
- Spanish (ES)
- Swedish (SE)
© 2024 . All rights reserved.
Made with love by people who care.
University of Missouri
- Bias Hotline: Report bias incidents
Undergraduate Research
How to put research on your resumé.
Resumés are important documents for all kinds of application packages — jobs, scholarships, grad school, etc. Your resumé should fit within the total package highlighting your achievements in a concise manner that can be further expounded upon in your personal statement, cover letter, or your letters of reference. It is important to custom tailor your resumé to any particular position, or program you are applying for. Some information needs to be emphasized more than other depending on what the reviewers may be looking for.
Using Your Space Wisely
In general, a resumé should be no more than two pages long — unless you have a large number of presentations or publications that need to be listed. Avoid the tendency to add more “stuff” to your resumé to try to look impressive. Use the relevant experience you have and determine what was impressive about it (for example, demonstrated independence, innovation, grit, or tenacity; helped improve ways of doing things in the lab; were given additional responsibilities as time went on; etc.)
- A reviewer would rather read about the two positions you had that are relevant, than try to sift through seven or eight clubs or fast-food job descriptions.
- Transcript?
- Recommendation Letters?
- Personal Statement?
Typically, resumes are formatted so that your most recent position is listed first. However, don’t put working at Dairy Queen first, if you are applying for a research position. Instead, consider using some of the following sections:
- Academic Accomplishments
- Research Experience
- Work Experience/Employment
- College Activities
- Volunteer Work
- Presentations and Publications
You do not need all of these categories, especially if you do not have relevant, interesting, or recent experience with them. Do not feel forced to try to fit your resume into someone else’s template. Make a list of what you want to include then design categories that fit your experience and story. Keep in mind that these categories will change over time (for example: five years after college, you will no longer need to include a section on “college activities”).
Research Mentor
- Area of research
- Not only does it show that you worked directly with a faculty member in your position, but reviewers might be familiar with your mentor’s work which could put you at an advantage.
- Consider listing projects and accomplishments the group achieved first before breaking things out on a year to year basis.
- If you were funded by different sources at different times, put a list of these sources at the bottom of the experience in this position.
Job Titles, Time Periods
- Use something that makes sense (sometimes HR titles do not)
- Instead of “MUURS Scholar” say “Student Researcher funded by the MU Undergraduate Research Scholars Program”
- Summer 2017 (9 weeks, full time internship)
- Academic Year 2018-2019 (15 hrs/week)
- What does that award mean?
- Will anyone outside of campus know what that is?
- Was the program selective?
- What was the award amount?
- What was the duration of the award?
- You can list various funding sources at the end of the relevant section
- External funding (from a government entity such as NIH, for example) is impressive. Be sure to list it.
You need to take the time to seriously consider your experience and how that allowed you to grow and mature as a researcher. Ask yourself these questions when brainstorming about your experience:
- What are areas you excelled in?
- What are lessons you learned?
- What are things you improved upon from the person before you?
- How did you spend your time?
- What skills did you gain?
- What research outcomes were reached?
- How long were you in the lab?
Use specific numbers or other qualifiers when applicable to show just how much work, effort, independence, or tenacity you had.
If your publication and presentation experience is limited, it is recommended that you include it with your relevant experience. However, if you have extensive or otherwise impressive experience (won a presentation award at a conference, or presented your work to state legislators at the Undergraduate Research Day at the the State Capitol, for example) then include a new category specifically for Presentations and/or Publications.
Presentations
- Include full list of authors
- Include full and official title
- Include if it was poster or oral presentation (ie, 15 minute presentation)
- Include location, event
- Include date (at least month and year)
- Include any award
- Check in with your mentor, to find out if a poster you co-authored was presented elsewhere.
Publications
- Full citation when published
- In Press – journal, date?
- Submitted for review – journal/date
- In preparation
- Check with your mentor as many projects are not completed by the time as student graduates.
Final Reminders
- Know your audience
- Explain (or spell out)
- Organize to fit your own situation
- Make it easy to follow – esp. if you have ‘time away’
- But have on comprehensive and cohesive running resumé.
- Have a system in place to update/organize your resumés.
- Use professional language, as most files are submitted electronically — the reviewer will see if you named a file “Better Resumé”
- ex: Jane Doe Resumé – Biochemistry REU, UT Austin
- This will ensure that the reviewer knows who you are and what you are applying for without even opening the file.
We encourage students to visit the MU Career Center in the Student Success Center for help on their specific application needs.
- Resume Tips
How to Include Research On A Resume (Examples and Tips)

Research skills are highly prized across a wide spectrum of industries. The fact is that researchers are invaluable for many employers. After all, new ideas often come only after exhaustive analysis of existing practices. Is it any surprise then that many of the most innovative companies in the world look for employees who possess these skills?
The good news is that most of us possess at least some skill in researching. Unfortunately, too many of us don’t recognize those skills or why they matter to employers. In this post, we’ll help you identify your research skills and show you how to include them on a resume.
What Are Research Skills?
Research skills are all those skills needed to investigate and analyze a subject and then communicate your findings to others. In short, there is no simple easily-defined skill that encompasses all these talents. Instead, your ability to research involves the effective use of a range of other skills.
Most of these skills relate to critical thinking in some way. They involve accumulating information and using it to draw reasoned conclusions. Naturally, those conclusions need to be conveyed to others with effective communication skills.
Research skills are among the most highly-prized transferable skills employers are looking for in today's competitive job market.
Employers value these skills because they are essential to progress. Innovation only comes from research and inspired insight. As a result, companies that rely on innovation to remain competitive tend to rely on employees who are talented researchers. Obviously, there are entire fields of industry that use researchers only for that purpose. In a more general sense, however, research skills are widely used by many different types of employees. And they use them in almost every industry in the marketplace.
How to List Research on a Resume
Including research on your resume:.
For research, summarize your accomplishments in a brief section. You should include a description of your role in the research, the topic that you were exploring, and some information about your findings. For example,
_ Research Project , Economics Department, Dynamic University, Dec 2017 – Apr 20_20
Key participant in research project examining blockchain technology’s potential impact on financial intermediation. Explored use case studies for cross-border payment systems, intrabank transactions, and microtransactions for e-commerce.
Designed model simulation to study blockchain-based payment system
Worked in tandem with Alpha and Delta Finance to create simulated intrabank transfers using digitalized tokens
Studied e-commerce script integration for cryptocurrency payments
Member of 3-person team tasked with presenting findings to 2018 National Banking Technology Conference
Example of Research Listed On a Resume:

View 200+ more professional resume samples for all industries, along with a guide to writing resumes from our career experts.
You can also combine your research with other sections:
Research and Publications
Research and Professional Development
Educations and Research
We wrote a good post here on how to include publications on a resume.

Join more than 1 million people who have already received our complimentary resume review.
In 48 hours, you will know how your resume compares. We’ll show you what’s working--and what you should fix.
Some Important Research Skills You May Already Possess
When listing research skills on your resume, it’s important to remember that most of them won’t be core skills for the job you’re seeking. Unless you’re applying for a job as a researcher, these skills will basically be transferable skills. That means that they might not be essential for the position but will certainly enhance your value as a potential employee.
To better understand your own research skills, it’s important to be able to identify them.
Here are some common and valuable research skills that many employees possess. Chances are that you have used at least some of these skills in your career. For example:
Attention to detail. This seemingly simple skill is one that employers truly appreciate. People who possess an ability to note even the smallest details can be invaluable for identifying problems and creating solutions.
Planning and scheduling skills. Every research project starts with a plan and a schedule. This is also one of those transferable skills that has application throughout nearly every industry.
Data collection skills. Good research depends upon good data. If you’re a skilled data collector, that talent will be useful for any company’s research needs.
Problem-solving skills. At some level, all research is about solving problems. Whether it’s a graduate thesis or a corporate study, there’s always a question that needs to be answered.
Technical skills . Proficiency with computers and other technology is an essential skill for modern research.
Critical thinking skills. Data collection is useless if no one ever considers what that data means. That analysis requires critical thinking and the ability to analyze and draw conclusions.
Project management skills. Can you manage projects in an orderly and effective way? Every research project requires effective management.
Communication skills . Whether it’s an oral presentation or a written report, research findings always need to be communicated to others.
Make Your Research Skills Work for You
Finally, do more than just list your research skills in your resume. Put them to use. Research the company you’re trying to join, and mention things you’ve learned in your cover letter and interview. That can not only showcase your research abilities but will demonstrate your real desire to join their team. In the end, that can be the best way to improve your odds of landing that great job you need.
Related posts:
Writing Your Education Section: Samples & How to Guide
How To Find A Job Fast
ZipJob Team
The ZipJob team is made up of professional writers and career experts located across the USA and Canada with backgrounds in HR, recruiting, career coaching, job placement, and professional writing.

Is your resume working?
Find out with a free review from ZipJob.
Get a free resume review today
Our experts will review your resume’s grammar, layout, and ability to pass ATS — all free and delivered straight to your inbox.
PROTECT YOUR DATA
This site uses cookies and related technologies for site operation, and analytics as described in our Privacy Policy. You may choose to consent to our use of these technologies, reject non-essential technologies, or further manage your preferences.

- Self & Career Exploration
- Blue Chip Leadership Experience
- Experiential Learning
- Research Experiences
- Transferable Skills
- Functional Skills
- Resume, CV & Cover Letter
- Online Profiles
- Networking & Relationship Building
- Internships
- Interviewing
- Offer Evaluation & Negotiation
- Career Core by Kaplan
- Arts & Media
- Commerce & Management
- Data & Technology
- Education & Social Services
- Engineering & Infrastructure
- Environment & Resources
- Global Impact & Public Service
- Health & Biosciences
- Law & Justice
- Research & Academia
- Recent Alumni
- Other Alumni Interest Areas
- People of Color
- First Generation
- International
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Families
Tips for Adding Research to Your Resume
- Share This: Share Tips for Adding Research to Your Resume on Facebook Share Tips for Adding Research to Your Resume on LinkedIn Share Tips for Adding Research to Your Resume on X
Getting involved in research is a unique experience that can help you build important skill for school and beyond! Once you get started, it’s important to think about adding it to your resume. When applying to future research positions, jobs, internships, and/or graduate school, it’s important to show off your experience. You will want to show that you have this kind of experience and also show off the skills that you have used/developed in your research position.
What You Need to Include
Its important to summarize the basic details of each position on your resume so that whoever reads it understands what each position was before they even read your bullet points.
Your research experience should have; • Your Role/Title Example: Research Assistant, Student Lab Member, etc.
• Lab and University Name Example: Wildcat Lab, University of Arizona
• City/State, not the full address! Example: Tucson, AZ
• Start Month/Year – End Month/Year. Examples: February 2023 – Present | January 2022 – May 2022
Putting it all together! Research Assistant | Tucson, AZ Wildcat Lab, University of Arizona | February 2023 – Present
Next – Writing About Your Experience s
Writing about your experience is important because this is the part that shows off what you did in your research experience! It’s important to write in a way that shows off the skills you used in the role. This is why we recommend writing in a style called APR format.
APR stands for Action – Project/Problem – Results. This format gives the employer, or whoever is reading your resume, enough information to see what you did, which skills you used, and why or how the task was completed. You can review more about APR format on the Resume Section on our website.
When preparing to write this section, think about what you did in your research position. What did you do? Why were you doing it? What skills did you use? Why or How was it completed? These are some questions to think about why writing about your experience. Then, use bullet points to list specific roles, tasks, or accomplishments.
Example Bullet Points: • Code participants answers in Excel to ensure data is HIPAA compliance • Analyze data using IBM SPSS to create correlation models and to find significant numbers • Present at weekly meetings to share findings with research team members
In these examples, you can see each bullet point includes skills such as coding, analyzing, programming (IBM SPSS), and communication.
Putting It On The Page
Once you have finished your bullet points, you can add them to your resume! Students typically put their research experience in a section that allows these activities to stand out. If you feel like your research is something that you want to highlight, you can create a specific section for it!
Give it a unique header such as Lab Experience , Research Experience, etc. and you’re ready to go!
Example Resumes with Research

Adding Your Research Skills
Remember, you can also add your research skills to your skills section, if you have one! This is a good place to directly state the skills you used in your research experience. It’s important to state your technical skills, such as programming, equipment, etc. and transferrable skills such as communication, data analysis, etc.
Example Skills Sections

Resume Help
Get more resume information, templates, and more on our website or make an appointment with a Career Peer Coach , who can help you create a new resume or review your current one!
We respectfully acknowledge the University of Arizona is on the land and territories of Indigenous peoples. Today, Arizona is home to 22 federally recognized tribes, with Tucson being home to the O'odham and the Yaqui. Committed to diversity and inclusion, the University strives to build sustainable relationships with sovereign Native Nations and Indigenous communities through education offerings, partnerships, and community service.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Graduate School Applications: Writing a Research Statement


Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is a Research Statement?
A research statement is a short document that provides a brief history of your past research experience, the current state of your research, and the future work you intend to complete.
The research statement is a common component of a potential candidate’s application for post-undergraduate study. This may include applications for graduate programs, post-doctoral fellowships, or faculty positions. The research statement is often the primary way that a committee determines if a candidate’s interests and past experience make them a good fit for their program/institution.
What Should It Look Like?
Research statements are generally one to two single-spaced pages. You should be sure to thoroughly read and follow the length and content requirements for each individual application.
Your research statement should situate your work within the larger context of your field and show how your works contributes to, complicates, or counters other work being done. It should be written for an audience of other professionals in your field.
What Should It Include?
Your statement should start by articulating the broader field that you are working within and the larger question or questions that you are interested in answering. It should then move to articulate your specific interest.
The body of your statement should include a brief history of your past research . What questions did you initially set out to answer in your research project? What did you find? How did it contribute to your field? (i.e. did it lead to academic publications, conferences, or collaborations?). How did your past research propel you forward?
It should also address your present research . What questions are you actively trying to solve? What have you found so far? How are you connecting your research to the larger academic conversation? (i.e. do you have any publications under review, upcoming conferences, or other professional engagements?) What are the larger implications of your work?
Finally, it should describe the future trajectory on which you intend to take your research. What further questions do you want to solve? How do you intend to find answers to these questions? How can the institution to which you are applying help you in that process? What are the broader implications of your potential results?
Note: Make sure that the research project that you propose can be completed at the institution to which you are applying.
Other Considerations:
- What is the primary question that you have tried to address over the course of your academic career? Why is this question important to the field? How has each stage of your work related to that question?
- Include a few specific examples that show your success. What tangible solutions have you found to the question that you were trying to answer? How have your solutions impacted the larger field? Examples can include references to published findings, conference presentations, or other professional involvement.
- Be confident about your skills and abilities. The research statement is your opportunity to sell yourself to an institution. Show that you are self-motivated and passionate about your project.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
Academic CV (Curriculum Vitae) for Research: CV Examples
What is an academic CV (or research CV)?
An academic CV or “curriculum vitae” is a full synopsis (usually around two to three pages) of your educational and academic background. In addition to college and university transcripts, the personal statement or statement of purpose , and the cover letter, postgraduate candidates need to submit an academic CV when applying for research, teaching, and other faculty positions at universities and research institutions.
Writing an academic CV (also referred to as a “research CV” or “academic resume”) is a bit different than writing a professional resume. It focuses on your academic experience and qualifications for the position—although relevant work experience can still be included if the position calls for it.
What’s the difference between a CV and a resume?
While both CVs and resumes summarize your major activities and achievements, a resume is more heavily focused on professional achievements and work history. An academic CV, on the other hand, highlights academic accomplishments and summarizes your educational experience, academic background and related information.
Think of a CV as basically a longer and more academic version of a resume. It details your academic history, research interests, relevant work experience, publications, honors/awards, accomplishments, etc. For grad schools, the CV is a quick indicator of how extensive your background is in the field and how much academic potential you have. Ultimately, grad schools use your academic resume to gauge how successful you’re likely to be as a grad student.
Do I need an academic CV for graduate school?
Like personal statements, CVs are a common grad school application document (though not all programs require them). An academic CV serves the same basic purpose as a regular CV: to secure you the job you want—in this case, the position of “grad student.” Essentially, the CV is a sales pitch to grad schools, and you’re selling yourself !
In addition to your college transcripts, GRE scores, and personal statement or statement of purpose , graduate schools often require applicants submit an academic CV. The rules for composing a CV for a Master’s or doctoral application are slightly different than those for a standard job application. Let’s take a closer look.
Academic CV Format Guidelines
No matter how compelling the content of your CV might be, it must still be clear and easy for graduate admissions committee members to understand. Keep these formatting and organization tips in mind when composing and revising your CV:
- Whatever formatting choices you make (e.g., indentation, font and text size, spacing, grammar), keep it consistent throughout the document.
- Use bolding, italics, underlining, and capitalized words to highlight key information.
- Use reverse chronological order to list your experiences within the sections.
- Include the most important information to the top and left of each entry and place associated dates to the right.
- Include page numbers on each page followed by your last name as a header or footer.
- Use academic verbs and terms in bulleted lists; vary your language and do not repeat the same terms. (See our list of best verbs for CVs and resumes )
How long should a CV be?
While resumes should be concise and are usually limited to one or two pages, an academic CV isn’t restricted by word count or number of pages. Because academic CVs are submitted for careers in research and academia, they have all of the sections and content of a professional CV, but they also require additional information about publications, grants, teaching positions, research, conferences, etc.
It is difficult to shorten the length without shortening the number of CV sections you include. Because the scope and depth of candidates’ academic careers vary greatly, academic CVs that are as short as two pages or as long as five pages will likely not surprise graduate admissions faculty.
How to Write an Academic CV
Before we look at academic CV examples, let’s discuss the main sections of the CV and how you can go about writing your CV from scratch. Take a look at the sections of the academic CV and read about which information to include and where to put each CV section. For academic CV examples, see the section that follows this one.
Academic CV Sections to Include (with Examples)
A strong academic CV should include the following sections, starting from the top of the list and moving through the bottom. This is the basic Academic CV structure, but some of the subsections (such as research publications and academic awards) can be rearranged to highlight your specific strengths and achievements.
- Contact Information
- Research Objective or Personal Profile
- Education Section
- Professional Appointments
- Research Publications
- Awards and Honors
- Grants and Fellowships
- Conferences Attended
- Teaching Experience
- Research Experience
- Additional Activities
- Languages and Skills
Now let’s go through each section of your academic CV to see what information to include in detail.
1. Contact Information
Your academic curriculum vitae must include your full contact information, including the following:
- Professional title and affiliation (if applicable)
- Institutional address (if you are currently registered as a student)
- Your home address
- Your email address
- Your telephone number
- LinkedIn profile or other professional profile links (if applicable)
In more business-related fields or industries, adding your LinkedIn profile in your contact information section is recommended to give reviewers a more holistic understanding of your academic and professional profile.
Check out our article on how to use your LinkedIn profile to attract employers .
2. Research Objective or Personal Profile
A research objective for an academic CV is a concise paragraph (or long sentence) detailing your specific research plans and goals.
A personal profile gives summarizes your academic background and crowning achievements.
Should you choose a research objective or a personal profile?
If you are writing a research CV, include a research objective. For example, indicate that you are applying to graduate research programs or seeking research grants for your project or study
A research objective will catch the graduate admission committee’s attention and make them want to take a closer look at you as a candidate.
Academic CV research objective example for PhD application
MA student in Sociology and Gender Studies at North American University who made the President’s List for for six consecutive semesters seeking to use a semester-long research internship to enter into postgraduate research on the Impetus for Religious In-groups in Eastern Europe in the Twentieth Century.
Note that the candidate includes details about their academic field, their specific scholastic achievements (including an internship), and a specific topic of study. This level of detail shows graduate committees that you are a candidate who is fully prepared for the rigors of grad school life.
While an academic CV research objective encapsulates your research objective, a CV personal profile should summarize your personal statement or grad school statement of purpose .
Academic CV personal profile example for a post-doctoral university position
Proven excellence in the development of a strong rapport with undergraduate students, colleagues, and administrators as a lecturer at a major research university. Exhibits expertise in the creation and implementation of lifelong learning programs and the personalized development of strategies and activities to propel learning in Higher Education, specifically in the field of Education. Experienced lecturer, inspirational tutor, and focused researcher with a knack for recognizing and encouraging growth in individuals. Has completed a Master’s and PhD in Sociology and Education with a BA in Educational Administration.
What makes this CV personal profile example so compelling? Again, the details included about the applicant’s academic history and achievements make the reader take note and provide concrete examples of success, proving the candidate’s academic acumen and verifiable achievements.
3. Education Section
If you are applying to an academic position, the Education section is the most essential part of your academic CV.
List your postsecondary degrees in reverse chronological order . Begin with your most recent education (whether or not you have received a degree at the time of application), follow it with your previous education/degree, and then list the ones before these.
Include the following educational details:
- Year of completion or expected completion (do not include starting dates)
- Type of Degree
- Any minor degrees (if applicable)
- Your department and institution
- Your honors and awards
- Dissertation/Thesis Title and Advisor (if applicable)
Because this is arguably the most important academic CV section, make sure that all of the information is completely accurate and that you have not left out any details that highlight your skills as a student.
4. Professional Appointments
Following the education section, list your employment/professional positions on your academic CV. These should be positions related to academia rather than previous jobs or positions you held in the private section (whether it be a chef or a CEO). These appointments are typically tenure-track positions, not ad hoc and adjunct professor gigs, nor TA (teacher assistant) experience. You should instead label this kind of experience under “Teaching Experience,” which we discuss further down the list.
List the following information for each entry in your “Professional Appointments” section:
- Institution (university/college name)
- Department
- Your professional title
- Dates employed (include beginning and end dates)
- Duties in this position
5. Research Publications
Divide your publications into two distinct sections: peer-reviewed publications and other publications. List peer-reviewed publications first, as these tend to carry more weight in academia. Use a subheading to distinguish these sections for the reader and make your CV details easier to understand.
Within each subsection, further divide your publications in the following order:
- Book chapters
- Peer-reviewed journal articles
- Contributions to edited volumes equivalent to peer-reviewed journals
All of your other research publications should be put into a subcategory titled “Other Publications.” This includes all documents published by a third party that did not receive peer review, whether it is an academic journal, a science magazine, a website, or any other publishing platform.
Tip: When listing your publications, choose one academic formatting style ( MLA style , Chicago style , APA style , etc.) and apply it throughout your academic CV. Unsure which formatting style to use? Check the website of the school you are applying to and see what citation style they use.
6. Awards and Honors
This section allows you to show off how your skills and achievements were officially acknowledged. List all academic honors and awards you have received in reverse chronological order, just like the education and professional appointments sections. Include the name of the award, which year you received it, and the institution that awarded it to you.
Should you include how much money you were awarded? While this is not recommended for most academic fields (including humanities and social sciences), it is more common for business or STEM fields.
7. Fellowships and Grants
It is important to include fellowships and grants you received because it evidences that your research has been novel and valuable enough to attract funding from institutions or third parties.
Just like with awards and honors, list your grants and fellowships in reverse chronological order. Enter the years your fellowship or grant spanned and the name of the institution or entity providing the funding. Whether you disclose the specific dollar amount of funding you received depends on your field of study, just as with awards and honors.
8. Conferences Attended
Involvement in academic conferences shows admissions committees that you are already an active member of the research community. List the academic conferences in which you took part and divide this section into three subsections:
- Invited talks —conferences you presented at other institutions to which you received an invitation
- Campus talks —lectures you gave on your own institution’s campus
- Conference participation —conferences you participated in (attended) but gave no lecture
9. Teaching Experience
The “Teaching Experience” section is distinct from the “Professional Appointments” section discussed above. In the Teaching Experience CV section, list any courses you taught as a TA (teacher’s assistant) you have taught. If you taught fewer than ten courses, list all of them out. Included the name of the institution, your department, your specific teaching role, and the dates you taught in this position.
If you have a long tenure as an academic scholar and your academic CV Appointments section strongly highlights your strengths and achievements, in the Teaching Experience sections you could list only the institutions at which you were a TA. Since it is likely that you will be teaching, lecturing, or mentoring undergraduates and other research students in your postgraduate role, this section is helpful in making you stand out from other graduate, doctoral, or postdoctoral candidates.
10. Research Experience
In the “Research Experience” section of your CV, list all of the academic research posts at which you served. As with the other CV sections, enter these positions in reverse chronological order.
If you have significant experience (and your academic CV is filling up), you might want to limit research and lab positions to only the most pertinent to the research position to which you are applying. Include the following research positions:
- Full-time Researcher
- Research Associate
- Research Assistant
For an academic or research CV, if you do not have much research experience, include all research projects in which you participated–even the research projects with the smallest roles, budget, length, or scope.
11. Additional Activities
If you have any other activities, distinctions, positions, etc. that do not fit into the above academic CV sections, include them here.
The following items might fit in the “Additional Activities” section:
- Extracurriculars (clubs, societies, sports teams, etc.)
- Jobs unrelated to your academic career
- Service to profession
- Media coverage
- Volunteer work
12. Languages and Skills
Many non-academic professional job positions require unique skillsets to succeed. The same can be true with academic and research positions at universities, especially when you speak a language that might come in handy with the specific area of study or with the other researchers you are likely to be working alongside.
Include all the languages in which you are proficient enough to read and understand academic texts. Qualify your proficiency level with the following terms and phrases:
- IntermediateNative/bilingual in Language
- Can read Language with a dictionary
- Advanced use of Language
- Fully proficient in Language
- Native fluency in Language
- Native/Bilingual Language speaker
If you only have a basic comprehension of a language (or if you simply minored in it a decade ago but never really used it), omit these from this section.
Including skills on an academic CV is optional and MIGHT appear somewhat amateur if it is not a skill that is difficult and would likely contribute to your competency in your research position. In general, include a skill only if you are in a scientific or technical field (STEM fields) and if they realistically make you a better candidate.
13. References
The final section of your academic CV is the “References” section. Only include references from individuals who know you well and have first-hand experience working with you, either in the capacity of a manager, instructor, or professor, or as a colleague who can attest to your character and how well you worked in that position. Avoid using personal references and never use family members or acquaintances–unless they can somehow attest to your strength as an academic.
List your references in the order of their importance or ability to back up your candidacy. In other words, list the referrers you would want the admissions faculty to contact first and who would give you a shining review.
Include the following in this order:
- Full name and academic title
- Physical mailing address
- Telephone number
- Email address
Academic CV Examples by Section
Now that you have a template for what to include in your academic CV sections, let’s look at some examples of academic CV sections with actual applicant information included. Remember that the best CVs are those that clearly state the applicant’s qualifications, skills, and achievements. Let’s go through the CV section-by-section to see how best to highlight these elements of your academic profile. Note that although this example CV does not include EVERY section detailed above, this doesn’t mean that YOU shouldn’t include any of those sections if you have the experiences to fill them in.
CV Example: Personal Details (Basic)
Write your full name, home address, phone number, and email address. Include this information at the top of the first page, either in the center of the page or aligned left.
- Tip: Use a larger font size and put the text in bold to make this info stand out.
CV Example: Profile Summary (Optional)
This applicant uses an academic research profile summary that outlines their personal details and describes core qualifications and interests in a specific research topic. Remember that the aim of this section is to entice admissions officials into reading through your entire CV.
- Tip: Include only skills, experience, and what most drives you in your academic and career goals.
CV Example: Education Section (Basic)
This applicant’s academic degrees are listed in reverse chronological order, starting with those that are currently in progress and recently completed and moving backward in time to their undergraduate degrees and institutions.
- Include the name of the institution; city, state, and country (if different from the institution to which you are applying); degree type and major; and month/year the degree was or will be awarded.
- Provide details such as the title of your thesis/dissertation and your advisor, if applicable.
- Tip: Provide more details about more recent degrees and fewer details for older degrees.
CV Example: Relevant Experience (Basic)
List professional positions that highlight your skills and qualifications. When including details about non-academic jobs you have held, be sure that they relate to your academic career in some way. Group experiences into relevant categories if you have multiple elements to include in one category (e.g., “Research,” “Teaching,” and “Managerial”). For each position, be sure to:
- Include position title; the name of organization or company; city, state, and country (if different from the institution to which you are applying); and dates you held the position
- Use bullet points for each relevant duty/activity and accomplishment
- Tip: For bulleted content, use strong CV words , vary your vocabulary, and write in the active voice; lead with the verbs and write in phrases rather than in complete sentences.
CV Example: Special Qualifications or Skills (Optional)
Summarize skills and strengths relevant to the position and/or area of study if they are relevant and important to your academic discipline. Remember that you should not include any skills that are not central to the competencies of the position, as these can make you appear unprofessional.
CV Example: Publications (Basic)
Include a chronological (not alphabetical) list of any books, journal articles, chapters, research reports, pamphlets, or any other publication you have authored or co-authored. This sample CV does not segment the publications by “peer-reviewed” and “non-peer-reviewed,” but this could simply be because they do not have many publications to list. Keep in mind that your CV format and overall design and readability are also important factors in creating a strong curriculum vitae, so you might opt for a more streamlined layout if needed.
- Use bibliographic citations for each work in the format appropriate for your particular field of study.
- Tip: If you have not officially authored or co-authored any text publications, include studies you assisted in or any online articles you have written or contributed to that are related to your discipline or that are academic in nature. Including any relevant work in this section shows the faculty members that you are interested in your field of study, even if you haven’t had an opportunity to publish work yet.
CV Example: Conferences Attended (Basic)
Include any presentations you have been involved in, whether you were the presenter or contributed to the visual work (such as posters and slides), or simply attended as an invitee. See the CV template guide in the first section of this article for how to list conference participation for more seasoned researchers.
- Give the title of the presentation, the name of the conference or event, and the location and date.
- Briefly describe the content of your presentation.
- Tip: Use style formatting appropriate to your field of study to cite the conference (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.)
CV Example: Honors and Awards (Basic)
Honors and awards can include anything from university scholarships and grants, to teaching assistantships and fellowships, to inclusion on the Dean’s list for having a stellar GPA. As with other sections, use your discretion and choose the achievements that best highlight you as a candidate for the academic position.
- Include the names of the honors and official recognition and the date that you received them.
- Tip: Place these in order of importance, not necessarily in chronological order.
CV Example: Professional/Institutional Service (Optional)
List the professional and institutional offices you have held, student groups you have led or managed, committees you have been involved with, or extra academic projects you have participated in.
- Tip: Showing your involvement in campus life, however minor, can greatly strengthen your CV. It shows the graduate faculty that you not only contribute to the academic integrity of the institution but that you also enrich the life of the campus and community.
CV Example: Certifications and Professional Associations (Optional)
Include any membership in professional organizations (national, state, or local). This can include nominal participation as a student, not only as a professional member.
CV Example: Community Involvement and Volunteer Work (Optional)
Include any volunteer work or outreach to community organizations, including work with churches, schools, shelters, non-profits, and other service organizations. As with institutional service, showing community involvement demonstrates your integrity and willingness to go the extra mile—a very important quality in a postgraduate student or faculty member.
While the CV template guide above suggests including these activities in a section titled “Additional Activities,” if you have several instances of volunteer work or other community involvement, creating a separate heading will help catch the eye of the admissions reviewer.
CV Example: References Section (Basic)
References are usually listed in the final section of an academic CV. Include 3-5 professional or academic references who can vouch for your ability and qualifications and provide evidence of these characteristics.
- Write the name of the reference, professional title, affiliation, and contact information (phone and email are sufficient). You do not need to write these in alphabetical order. Consider listing your references in order of relevance and impact.
CV Editing for Research Positions
After you finish drafting and revising your academic CV, you still need to ensure that your language is clear, compelling, and accurate and that it doesn’t have any errors in grammar, spelling, or punctuation.
A good academic CV typically goes through at least three or four rounds of revision before it is ready to send out to university department faculty. Be sure to have a peer or CV editing service check your CV or academic resume, and get cover letter editing and application essay editing for your longer admissions documents to ensure that there are no glaring errors or major room for improvement.
For professional editing services that are among the highest quality in the industry, send your CV and other application documents to Wordvice’s admissions editing services . Our professional proofreaders and editors will ensure that your hard work is reflected in your CV and help make your postgrad goals a reality.
Check out our full suite of professional proofreading and English editing services on the Wordvice homepage.
Which program are you applying to?
Accepted Admissions Blog
Everything you need to know to get Accepted
December 8, 2023
How to Write About Your Research Interests
The most common challenge that my master’s and PhD applicant clients face when writing a statement of research interests or a statement of purpose (SOP) is how to describe in concrete terms what their research interests and goals are. This is understandable. Their ideas are still evolving, and some worry that they’ll later be held to the ideas they stated in their applications, as though they were chiseled in stone. Others simply haven’t yet thought those ideas through very much.
Take a deep breath! By the time you begin writing your thesis, I promise that no one will pop up and wave your SOP or research interests statement around, saying, “But that’s not what you said here!” Everyone knows that your knowledge and ideas will develop throughout your grad program.
Here are the two things that a great statement of research interests or SOP will do:
- It will clearly illustrate to the admissions committee that you possess a depth of interest and comprehension in your field and that you understand what goes into research. You will sound naïve if you talk about ideas that are too vague or nebulous, or ones that cannot be addressed adequately through your discipline.
- It will explain any relevant background you have in this field, why you find it compelling, and why you are well suited for this career track .
Four questions to help you find your statement focus
To narrow your interests into something that is concrete enough for you to be able to write about convincingly, without being overly general, ask yourself these questions:
- What are the broad research questions/issues that interest you? Create a summary of your interests that you can work with, and describe your interests in a sentence – or a paragraph, at most.
- Within those broad areas of interest, can you begin to focus on more specific questions? If you’re not sure what the current questions/problems are in your field, now is the time to start catching up. Read recent journal publications, and go to conferences if you can. Reading the literature in your field will also give you a sense of how to frame your ideas in the language of your field.
- Have you done any research in this field already? If so, do you intend to build on your previous work in grad school or go in a new direction?
- How will your research contribute to the field?
Understanding how to present your goals
Some projects described in SOPs are achievable in the short term, while others are big enough to last a career. If your interests/goals fall into this latter category, acknowledge your ambitions, and try to identify some element of your interests that you can pursue as a first step.
Once you have demonstrated your skills (and past experience) in your field, you will be better equipped to define your next steps.
Focusing your interests will also involve doing more detailed research about the programs to which you plan to apply. For example, consider the following questions:
- Who might be your research supervisor?
- How do your interests relate to the work this scholar or these scholars are doing now?
- How would you contribute to the department and to the discipline?
Your SOP will also address your post-degree, longer-term goals. Consider this: do you envision yourself pursuing a career in research/academia? (For many PhD programs, this remains the department’s formal expectation, even though many PhDs find employment outside the academy.) If you’re applying for a master’s degree, be prepared to discuss what your future plans are and how the degree will help you.
Working on your SOP or statement of research interests?
Your SOP needs to be direct, informative, and… well… purposeful! When you choose Accepted, we match you with a dedicated advisor who will help you create an SOP that best reflects your experiences, goals, and intense desire to attend your target graduate school program. And did you know that Accepted’s clients have received millions of dollars in scholarship offers? Don’t delay – get started now by checking out our Graduate School Application Services .
For 25 years, Accepted has helped applicants gain acceptance to top undergraduate and graduate programs. Our expert team of admissions consultants features former admissions directors, PhDs, and professional writers who have advised clients to acceptance at top programs worldwide, including Harvard, Stanford, Yale, Princeton, Penn, Columbia, Oxford, Cambridge, INSEAD, MIT, Caltech, UC Berkeley, and Northwestern. Want an admissions expert to help you get Accepted? Click here to get in touch!
Related Resources:
- STEM Applicants: Why Your Statement of Purpose is So Important
- Three Must-Have Elements of a Good Statement of Purpose
- Writing Your Career Goals Essay
About Us Press Room Contact Us Podcast Accepted Blog Privacy Policy Website Terms of Use Disclaimer Client Terms of Service
Accepted 1171 S. Robertson Blvd. #140 Los Angeles CA 90035 +1 (310) 815-9553 © 2022 Accepted

The Significant Research Experience Essay
- First Online: 23 September 2020
Cite this chapter

- Jonathan Sussman 4 ,
- Jordan Setayesh 5 &
- Amitej Venapally 6
2283 Accesses
One of the most unique and substantial parts of the MD/PhD application is the significant research experience essay, which is a part of the primary AMCAS application. In this essay, applicants describe their research positions, projects, and accomplishments in detail. This chapter explains how to structure and write this essay in terms of the scientific method. It is important for applicants to demonstrate involvement in every step of the scientific process, from designing the experiments to communicating the results. However, this essay serves as an excellent medium through which applicants can explain how their research interests have evolved over time and the most important lessons they learned through research. In effect, this essay can be viewed as a technical-based personal statement.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
2020 AMCAS Applicant Guide. American Association of Medical Colleges. 2020. https://aamc-orange.global.ssl.fastly.net/production/media/filer_public/14/6f/146f366e-d54a-4792-9870-ffe451b2e473/aamc-2020-amcas-applicant-guide041119.pdf . Accessed 11 June 2020.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA
Jonathan Sussman
University of Michigan Medical School, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
Jordan Setayesh
Emory School of Medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, USA
Amitej Venapally
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Sussman, J., Setayesh, J., Venapally, A. (2021). The Significant Research Experience Essay. In: The Complete MD/PhD Applicant Guide. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-55625-9_8
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-55625-9_8
Published : 23 September 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-55624-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-55625-9
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Graduate School
Research Resume: Format, Structure and Samples

A research resume is crucial for presenting your research knowledge, skills, and suitability for a research position you are applying to. This is similar to how your law school resume presents your background with respect to the needs of an academic law program. Or, how your medical school resume presents information relevant to your medical background for med school applications. In this blog, we will look at what constitutes a good research resume and how you can create one. We will also look at some research resume examples so you can get some ideas for your own!
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 8 min read
What is a research resume.
A research resume presents your background specifically tailored to a research position. It is useful for you whether you are an undergrad or a grad student looking to apply for positions in research. It will help with med school applications , grad school applications, premed research opportunities , and other future academic endeavors you might undertake, regardless of your field. Also, research is not always lab work. It can include investigative studies in fields like liberal arts and physical sciences.
You have to create a strong resume to stand out among the other candidates. For this, highlight your relevant experience to show your potential. A good resume will complement other elements of your application. Think of your resume as the first point of interaction for your profile. A recruiter or an admission committee member doesn't know you personally but gets your information from your resume. A well-structured resume will serve its purpose of informing them about your qualifications and background clearly to help them determine whether you are suitable for the position or not.
Want to skip to a summary of our top 3 tips? Take a look at this infographic:
Your research resume has a significant part in helping a recruiter in understand your skills with respect to the position you have applied for. Thus, to illustrate your skills properly, you should include the following sections in your research resume:
If you have bagged an award at one of your previous jobs or academic positions, you should mention that in your resume. Your awards can include scholarships and grants, research awards, honorary recognition from the university, and more. These convey that your performance at your job has been exceptional. Similarly, if you have completed any particular certification such as a clinical research certification, you should mention that in your resume. ","label":"Achievements and Certifications","title":"Achievements and Certifications"}]" code="tab1" template="BlogArticle">
There might be a huge amount of information that you might wish to include in your research resume. However, present only your most recent and relevant details. Evaluate whether what you are mentioning in your research resume is related to the position or not Also, avoid including additional details with respect to your research interests, since you would be including other documents with your application that can outline these details, such as a research interest statement .
How to Format Your Research Resume
Complex resumes usually end up in the rejected pile, and this is something that you must be looking to avoid. The aim is to structure your research resume neatly and draw attention to skills and achievements to make an unforgettable impression on any recruiter. Usually, there are three main types of resume formats:
As evident from the name, a combination resume mixes both reverse-chronological and functional resume formats for providing information about both experiences and skills "}]" code="timeline1">
Despite the existence of other formats, the most used format for a research resume is a reverse-chronological resume.
Your work experience constitutes a major part of your resume, and it gives you the scope to highlight your past activities in such a way that your skills are aligned to the position that you are applying for. Here are the best ways to make your work experience stand out from other candidates:
Use appropriate keywords and phrases to highlight your accomplishments and qualifications. Find these my carefully going through the job ad. Use these keywords in your sentences to add to the relevance of your previous experience and skill set. Many institutions use an Applicant Tracking Systems to filter out resumes, based on the keywords related to the job. "}]">
Let’s take a look at an example to get a better idea:
XYZ State University Department
Research Assistant| Month 20XX - Month 20XX
- Managed a team of 6 research scholars for successful completion of ABC research project.
- Ensured all research databases and libraries are easily accessible to the research team.
- Isolated, purified, and analyzed RNA to assist senior researchers in lab work.
Since your research resume isn’t the only step in your recruitment, you should be clear about your past and avoid lying because you will be asked for further information post the initial resume screening. For instance, if you are applying for positions like a research assistant, you will be describing your experience in your research assistant interview questions . Thus, do not mention something that you didn’t do because you will not be able to talk about it later.
How to Create a Research Resume with Little or No Experience
If you are looking to enter the field of research for the first time, you might not have a lot of research experience. In this case, you must remember that the quality of the experience is more important than its quantity. Even if you completed one project, you can demonstrate what you learned and achieved in your research resume.
If you have no experience at all, start by volunteering now! A resume is still necessary for volunteering positions, but you can include transferable skills. For instance, talk about attention to detail, communication skills, people management, and more, by illustrating the experiences where you used them such as your part-time job at McDonald's, class projects, and extracurricular activities.
Tips to Write a Strong Research Resume
For perfecting your research resume, some of the tips that you can follow are:
Highlight Skills Separately
It is advisable to create a separate section for research skills. Highlight research and analysis skills to grab the attention of recruiter easily.
Use Bullet Points, Be Concise, and Format Clearly
Another key to an organized structure is to stick to bullet points or short paragraphs. Avoid smalls fonts and too many colors. Do not remove all your margins and use the white space as breathing space.
Use Clear Language
Writing in plain language is necessary for creating a comprehensible resume. But you can use technical terms which were related to your research to demonstrate that you understand your past research thoroughly. Avoid repetition and omit irrelevant information.
Sample 1 - Clinical Research
Jemma Thompson
[email protected] •Pasadena, CA• 666-000-7766•linkedin.com/thompsonj • https://jemma.com
Research Assistant with 5+ years of hands-on experience in the field of molecular biology and immunogenetics. Seeking to join the Research Team at XXXXX to leverage my scientific skills and statistical analysis for contributing to clinical studies.
Whitfield Health Sciences / Clinical Research Assistant
Month 20XX - Present | San Marino, CA
- Prepared libraries for whole-genome sequencing using Illumina MiSeq and HiSeq NGS platforms which improved the success rate of NGS by 54%.
- Used Sequencher for SNP genotyping with 90% accuracy and evaluated data for minimizing errors by 70%.
- Led a team of 5 members in performing genomic DNA and RNA extractions.
- Quantitative PCR reaction analysis for determining gene expression levels and gene copy number for 35 models.
Elixir Health/ Research Associate
Month 20XX - Month 20XX | Altadena, CA
- Analyzed and authenticated various molecular techniques over 2 years.
- Developed 5 new protocols in bacterial genomics and molecular microbiology for the team that increased the workflow efficiency by 3 times.
- Independently headed a team of 6 colleagues in conducting assays and provided initial analysis.
- Created training modules for new junior assistants and reduced training time by 50%.
- University of Southern California / MSc in Molecular Biology
Month 20XX - Month 20XX | Los Angeles, CA
- University of Southern California / BSc in Biotechnology
- Cell Culture
- Quality Control
- Molecular Biology
- Data Analysis
- Data Maintenance
- Research Technical Staff Recognition Award, Whitfield Health, 20XX
Publications
- The Evolution of Biochemical Connection Among Promoter- and Primer-Dependent Polymerases
Journal of Biotechnology, 20XX
- Primer extension reactions for the PCR-based lacZα complementation fidelity assay
The FASEB Journal, 20XX
Trying to understand how undergrad and grad school differ? Check out this video:
Sample 2 - Laboratory Research Assistant
Sam Westcott
Louise Street, Chicago, IL
[email protected]
XXX-000-0000
Linkedin.com/samwestcott
https://www.samwestcott.com
Skilled laboratory research assistant with 3 years of experience in working with molecular cloning and CRISPR. Looking for the laboratory assistant position at XXXXX for assisting in day-to-day lab operations.
CRISPR based techniques, Molecular cloning, Literature review, RNA isolation, Flow cytometry, Literature Review
Work Experience
Laboratory Research Assistant, Pick Labs, Chicago
Month 20XX- Present
- Led a project involving the application of protocols to produce induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to study the contribution of actin and myosin in the changes in 3D genome organization for 2 months and collected data with 90% accuracy.
- Discovered CRP augments for intestinal ischemia damage with increased complement 3 activations, decay-accelerating factor (CD55) attenuates gut insults via suppression of complement activity.
- Headed company-wide strain and maintenance of Qiagen QIAcube and AATI Fragment Analyzer for 5 months.
- Managed a team of 3 junior assistants and improved the workflow by 30% through the use of XYZ software.
Research Assistant, So-bio, Chicago
Month 20XX- Month 20XX
- Implemented data analysis techniques in R to increase the speed of demonstrating the efficacy of new techniques by over 50% Perform Rapid Plasma Reagin (RPR).
- Used Beckman Coulter Act dif. 2 to perform CBC, and performed Becton Dickinson Facs to optimize flow cytometry CD4 (T-CELL) by 2 times.
- Planned, developed, and executed 4 assays to monitor structural changes in protein conformations in collaboration with the team.
- Biotechnology (Master of Science)
Month 20XX - Month 20XX | University of Chicago, IL
- Chemistry (Bachelor of Science)
- Research Staff Support Recognition Award, So-bio
Andrew Pelton Brooklyn, NY
333-888-5444
[email protected]
https://hiitsandrew.com
Communications researcher with 3 years of experience in conducting studies related to modes and methods of communication to share ideas and forecast trends.
Academic Projects
Modern rhetorical theory of communication: Effective communication in corporate environment
Brooklyn College, 20XX
- Analyzed modern communication theories in 4 different corporate setups and suggested 2 new methods of improvement for the communication flow in each setting.
- Interview 2 CEOs, 5 regional managers, and 8 associates for evaluating the accuracy of communication.
- Optimized the existing process of communication to improve productivity by 40%.
An analysis of the impact of social media in peer-to-peer communication among Teenagers
- Conducted interviews with 150 teenagers from 4 high schools in Brooklyn to analyze social media related trends.
- Introduced the online mode of interview and optimized the data collection process by 80%.
- Transcribed 60+ interviews through the use of ABC software and improved the project speed by two times.
- Created 25+ recommendations for optimization of social media usage among teenagers which were officially recognized in all 4 schools.
International Experience
Insights into communication practices in the Spanish culture
Study Abroad Participant, Universidad de Costa Rica, 20XX
- Analyzed local means of communication by interacting with over 100 citizens.
- Led 2 public awareness campaigns for the endangered “Boruca” language of Costa Rica.
Retail Sales Associate (Part-time)
Macy’s, 422 Fultron St., Brooklyn, NY
- Exceeded the quarterly sales target by 40% for the last quarter.
- Assisted in training of 20 new part-time sales associates.
- Assisted in new floor arrangement that reduced time wastage for customers by half.
- Awarded the “Sales Superstar of the Year: Part-time” award for 2 consequent years.
Bachelor of Arts in Communication
Brooklyn College, 20XX-Present
- Fluency in English and Spanish
- Data collection
- Data management through MS Office
A strong research resume will show your potential to work in a research environment in collaboration with a team. If you are applying for an entry-level position and have no prior work experience, you should mention your volunteering or part-time positions. If this is not possible, try highlighting your skills through a past project to demonstrate that you are suitable for a research position. Always consider providing additional documents such as a research assistant cover letter to improve your chances of selection. With a good research resume and other documents, you will surely succeed in getting selected for a research position.
A research resume is a document that shows your skills related to positions in research. You should be able to demonstrate working knowledge of collecting and analyzing data in a research resume.
Mention your previous experience in research-related positions. Demonstrate expertise in research by describing your skills. Use action verbs to make your research resume more impactful.
Demonstrate your research skills by mention what was the objective of your previous research, how you contributed to it, and what you learned from the research.
Analytical and problem-solving skills are essential for a research resume. You should be able to show that you are comfortable working with collecting data and working on it to arrive at results.
The duties in research vary as per the positions that you are selected for. However, the basic set of activities is identifying sources for data collection and implementation of the research strategy, analysis of data, and finding a conclusion.
Research experience consists of the projects that you have worked in analyzing data with a particular objective.
A research resume should be one page long. Keep it to the point and mention only the relevant information.
For writing a research resume with no experience, consider mentioning your lab projects in your undergrad. If you assisted with some responsibilities in the lab, mention those. If you have no prior research experience, try to include transferable skills that are valued everywhere, such as attention to detail, problem-solving, communication skills, and so on.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into grad school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
Research Experience for Prospective PhD Candidates
New section.
Most graduate schools will expect applicants to have practical experience in a lab. A strong application portfolio will most likely include participation in research throughout the undergraduate years, both during the academic year and the summers.
It's important that you pursue research opportunities during the academic year and summers (which provide full-time experience) to immerse yourself in a laboratory/project and to show your commitment and motivation for research. The letters of recommendation from your research mentors are a very important part of your graduate school application.
Making the most of your summer experiences
- Participate in research summer programs throughout the undergraduate years. These can be at your home institution or at other institutions.
- Identify and apply to several summer programs. This will give you a preview of the application process for graduate school.
- Apply to summer programs that take place at schools where you may be interested in pursuing your graduate degree.
- Complete and submit the application materials during the prior winter/spring.
- Become fully immersed in the research projects that you work on.
- Talk with advanced students and faculty advisors about graduate school and their experiences.
- Take advantage of other skill-building activities that the summer program offers.
Finding opportunities
- Summer Undergraduate Research Programs.
- NIH Summer Internship Program in Biomedical Research.
- NIH Undergraduate Scholarship Program.
Baylor College of Medicine/National Science Foundation brochure on the importance of summer research experience.
Helpful tools and information regarding medical MD-PhD programs.
Helpful tools for those applying to medical PhD programs
- Search UNH.edu
- Search Hamel Center for Undergraduate Research
Commonly Searched Items:
- How to Begin
- Present and Publish
- Researchers
- Student Ambassadors
- Benefactors
- Research Experience and Apprenticeship Program (REAP)
- INCO 590 & INCO 790
- Undergraduate Research Awards (URA)
- Summer Undergraduate Research Fellowships (SURF)
- SURF for Interdisciplinary Teams (SURF IT)
- International Research Opportunities Program (IROP)
- Research Presentation Grants
- Application Deadlines
- Writing an Effective Research Proposal
- Student FAQs
- Responsible Conduct of Research
- Other Research Opportunities
- Faculty Mentor Eligibility
- Faculty Memos and Recommendation Forms
- Department Liaisons
- Faculty FAQs
- Grant Recipients
- Publications
- About the URC
- URC for Students
- URC for Faculty
- Attending the URC
A Survival Guide to Summer Research

Let’s face it. The idea of conducting research for the first time can be simultaneously one of the most terrifying and exciting prospects in one’s college career. Whether you plan to pursue a career in research and development, industry, or something completely different, the skills gained through undergraduate research are invaluable. But where do you start?
This is exactly what I was asking myself after my Research Experience and Apprenticeship Program (REAP) proposal was accepted last year. My project involved the conversion of carbon dioxide into methane through catalysis. My job was to synthesize different catalysts containing varying nickel, titanium dioxide, and varying weight percentages of heteropoly acids to determine its effect on increasing the amount of carbon dioxide converted. Despite having done hours of research to understand the topic enough to write a proposal essay, I still had some doubts about whether I was truly qualified. After completing my project, I can safely say that any similar thoughts you may be experiencing are unfounded. There were several things that made the learning curve much smoother for me. . While not required, these steps may be beneficial to keep in mind as you begin to embark on your own summer research experience.
Prior to research:
If commuting to campus, get a summer parking permit. It can provide peace of mind to not worry about getting a parking permit at the last second. There are also options for summer on-campus housing if that is preferred.
Clearly outline what your goals are. Depending on the type of research project, this could include minimum amounts of data collected, a certain number of experiments run, the hours you plan to work, etc. Ask your mentor what their expectations are to ensure your goals are aligned.
Create an organizational system. For me, this was one of the first times I had to juggle multiple projects simultaneously outside of school. This can quickly become overwhelming. It is important to organize your time and materials in a way that makes sense to you. For me, this involved a research folder for physical documents and a research computer file with Word documents and Excel sheets. Create backups of any files if possible.
Continue learning. Before your project begins, continue to educate yourself as much as possible on your topic of choice. The UNH library has countless databases filled with scholarly articles that likely align with your research topic. They may provide useful insight on how other professionals explore these ideas or what questions are pertinent.
During your research:
Now for the exciting part. Here are the practices I found most useful for efficient research.
Plan each week. This is a 10-week process. It can be very difficult to utilize your time effectively if you are figuring it out as you go. Once you have a solid understanding of the tasks you do, write down what you hope to accomplish before beginning each week.

This is an example from one of my own weekly plans. Even writing a simple plan made me more motivated to complete tasks. I also used a weekly planner to mark important dates, created folders on my computer to make files easy to retrieve, and backed up my files as much as possible. If you ever need to revisit your work months or years later, it is extremely helpful for it to have its own reliable spot.
Document everything. This goes along with planning to some degree, but write down everything you do, even if it seems inconsequential. There are several reasons for this. First, it will greatly help diagnosing errors if results do not make sense or do not meet expectations. When I was having a problem getting my catalyst to form properly, being able to review every step of the process was invaluable to determine the issue, which was slightly too much deionized water being added. Second, if your results are statistically significant, or if you publish your results, understanding exactly what you did to achieve certain results is crucial. Finally, it will assist with writing your project summary once your summer is complete.
Communication is key. If ever you feel stuck or have concerns about anything related to your project, express them to your mentor. No one expects you to solve every problem alone, and whether it be by email, zoom, or in person, mentors are usually happy to assist in any way they can.
Once your research experience is over:
Congratulations! Hopefully you found the process to be as valuable and rewarding as I did. Besides wrapping up final details, many opportunities can be built off your project if want to continue your work.
Tie up loose ends. While you write your research summary and polish any results, I recommend backing up files, organizing and digitalizing documents, and most importantly, thanking everyone who helped you along the process and expressing appreciation for the opportunity.
Consider publishing your research. Did you know the University of New Hampshire has a research journal? Inquiry is an excellent spot to complete the final step of research, which is publication. If written well, the research summary in your final report can be converted to a research brief with minimal work, or you may choose to undergo a longer writing and revision process to publish a full-length research article.
Update your resume and share your experience on LinkedIn. This project likely taught you countless invaluable skills that employers would love to see from prospective employees.
Hopefully these tips help you feel more confident throughout your summer and prove to be as useful as I found them. Anyone can conduct research and there are countless resources available to those ready to utilize them. Good luck and happy researching!
Hamel Center for Undergraduate Research
- URC Archives
- All Colleges Undergraduate Research Symposium
- COLSA Undergraduate Research Conference
- Interdisciplinary Science & Engineering Symposium (ISE)
- Naked Arts - Creativity Exposed!
- Paul College Undergraduate Research Conference
- UNH Manchester Undergraduate Research Conference
- Poster Printing Information & Pricing
- Faculty Mentoring 101

- Sustainability
- Embrace New Hampshire
- University News
- The Future of UNH
- Campus Locations
- Calendars & Events
- Directories
- Facts & Figures
- Academic Advising
- Colleges & Schools
- Degrees & Programs
- Undeclared Students
- Course Search
- Academic Calendar
- Study Abroad
- Career Services
- How to Apply
- Visit Campus
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Net Price Calculator
- Graduate Admissions
- UNH Franklin Pierce School of Law
- Housing & Residential Life
- Clubs & Organizations
- New Student Programs
- Student Support
- Fitness & Recreation
- Student Union
- Health & Wellness
- Student Life Leadership
- Sport Clubs
- UNH Wildcats
- Intramural Sports
- Campus Recreation
- Centers & Institutes
- Undergraduate Research
- Research Office
- Graduate Research
- FindScholars@UNH
- Business Partnerships with UNH
- Professional Development & Continuing Education
- Research and Technology at UNH
- Request Information
- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Alumni & Friends

How to Get Started on Your First Psychology Experiment
Acquiring even a little expertise in advance makes science research easier..
Updated May 16, 2024 | Reviewed by Ray Parker
- Why Education Is Important
- Find a Child Therapist
- Students often struggle at the beginning of research projects—knowing how to begin.
- Research projects can sometimes be inspired by everyday life or personal concerns.
- Becoming something of an "expert" on a topic in advance makes designing a study go more smoothly.

One of the most rewarding and frustrating parts of my long career as a psychology professor at a small liberal arts college has been guiding students through the senior capstone research experience required near the end of their college years. Each psychology major must conduct an independent experiment in which they collect data to test a hypothesis, analyze the data, write a research paper, and present their results at a college poster session or at a professional conference.
The rewarding part of the process is clear: The students' pride at seeing their poster on display and maybe even getting their name on an article in a professional journal allows us professors to get a glimpse of students being happy and excited—for a change. I also derive great satisfaction from watching a student discover that he or she has an aptitude for research and perhaps start shifting their career plans accordingly.
The frustrating part comes at the beginning of the research process when students are attempting to find a topic to work on. There is a lot of floundering around as students get stuck by doing something that seems to make sense: They begin by trying to “think up a study.”
The problem is that even if the student's research interest is driven by some very personal topic that is deeply relevant to their own life, they simply do not yet know enough to know where to begin. They do not know what has already been done by others, nor do they know how researchers typically attack that topic.
Students also tend to think in terms of mission statements (I want to cure eating disorders) rather than in terms of research questions (Why are people of some ages or genders more susceptible to eating disorders than others?).
Needless to say, attempting to solve a serious, long-standing societal problem in a few weeks while conducting one’s first psychology experiment can be a showstopper.
Even a Little Bit of Expertise Can Go a Long Way
My usual approach to helping students get past this floundering stage is to tell them to try to avoid thinking up a study altogether. Instead, I tell them to conceive of their mission as becoming an “expert” on some topic that they find interesting. They begin by reading journal articles, writing summaries of these articles, and talking to me about them. As the student learns more about the topic, our conversations become more sophisticated and interesting. Researchable questions begin to emerge, and soon, the student is ready to start writing a literature review that will sharpen the focus of their research question.
In short, even a little bit of expertise on a subject makes it infinitely easier to craft an experiment on that topic because the research done by others provides a framework into which the student can fit his or her own work.
This was a lesson I learned early in my career when I was working on my own undergraduate capstone experience. Faced with the necessity of coming up with a research topic and lacking any urgent personal issues that I was trying to resolve, I fell back on what little psychological expertise I had already accumulated.
In a previous psychology course, I had written a literature review on why some information fails to move from short-term memory into long-term memory. The journal articles that I had read for this paper relied primarily on laboratory studies with mice, and the debate that was going on between researchers who had produced different results in their labs revolved around subtle differences in the way that mice were released into the experimental apparatus in the studies.
Because I already had done some homework on this, I had a ready-made research question available: What if the experimental task was set up so that the researcher had no influence on how the mouse entered the apparatus at all? I was able to design a simple animal memory experiment that fit very nicely into the psychological literature that was already out there, and this prevented a lot of angst.
Please note that my undergraduate research project was guided by the “expertise” that I had already acquired rather than by a burning desire to solve some sort of personal or social problem. I guarantee that I had not been walking around as an undergraduate student worrying about why mice forget things, but I was nonetheless able to complete a fun and interesting study.

My first experiment may not have changed the world, but it successfully launched my research career, and I fondly remember it as I work with my students 50 years later.

Frank McAndrew, Ph.D., is the Cornelia H. Dudley Professor of Psychology at Knox College.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
What is an Annotated Bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is a summary and evaluation of a resource. According to Merriam-Webster, a bibliography is “the works or a list of the works referred to in a text or consulted by the author in its production.” Your references (APA) or Works Cited (MLA) can be considered a bibliography. A bibliography follows a documentation style and usually includes bibliographic information (i.e., the author(s), title, publication date, place of publication, publisher, etc.). An annotation refers to explanatory notes or comments on a source.
An annotated bibliography, therefore, typically consists of:
Documentation for each source you have used, following the required documentation style.
For each entry, one to three paragraphs that:
Begins with a summary ,
Evaluates the reliability of the information,
Demonstrates how the information relates to previous and future research.
Entries in an annotated bibliography should be in alphabetical order.
** Please note: This may vary depending on your professor’s requirements.
Why Write an Annotated Bibliography?
Why Write an Annotated Bibliography
Writing an annotated bibliography will help you understand your topics in-depth.
An annotated bibliography is useful for organizing and cataloging resources when developing an argument.
Formatting an Annotated Bibliography
Formatting Annotated Bibliographies
- Use 1-inch margins all around
- Indent annotations ½ inch from the left margin.
- Use double spacing.
- Entries should be in alphabetical order.
Structure of an Annotated Bibliography
This table provides a high-level outline of the structure of a research article and how each section relates to important information for developing an annotated bibliography.
Annotated Bibliography Sample Outline
Author, S. A. (date of publication). Title of the article. Title of Periodical, vol. (issue), page-page. https://doi.org/XXXXXX
Write one or two paragraphs that focus on the study and its findings.
- Two or more sentences that outline the thesis, hypothesis, and population of the study.
- Two or more sentences that discuss the methodology.
- Two or more sentences that discuss the study findings.
- One or more sentences evaluating the study and its relationship to other studies.
Sample Annotated Bibliographies

Student Experience Feedback Buttons
Was this resource helpful.
- << Previous: Step 5: Illustrate
- Next: Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: May 16, 2024 8:25 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools


- Teacher Education
- Nursing Education
- Behavioral Sciences
- Sign & Foreign Languages
- Performing Arts
- Communication
- Any Skill You Teach
WATCH FOR FREE
ReAction On-Demand!
Dive into our on-demand library from the skills based conference.

SEE GOREACT IN ACTION
Try for Free
See how GoReact can help empower confident skills
CONTENT TYPE
- Case Studies
- Product Demos

ReAction On-Demand
Dive into our on-demand library from ReAction, the skills based conference. Whether you missed a session or want to rewatch, it's all here (and free)!
- CONTACT SALES EXPLORE GOREACT TRY FOR FREE CONTACT SALES
Higher Education
Session Recap: AI in Teaching Writing and Literature

In the realm of education, particularly in writing and literature, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) presents both innovative opportunities and notable challenges. Valerie Guyant, Associate Professor at Montana State University Northern, presented on this topic at ReAction Virtual . Her session focused on how educators are increasingly using AI in teaching methods to enhance learning and foster skill development.
The Role of AI as a Research & Writing Tool
AI tools, such as ChatGPT , have surged in popularity and utility, with applications spanning various academic fields. In writing courses, AI can serve as an ally. For instance, students can use these tools to research a topic, breaking down questions into manageable components.
Guyant gave an example of students asked to research “Does participation in youth sports reduce recidivism rates?” ChatGPT provided different angles for the students to explore, such as demographic factors, countries, types of sports involved, and the nature of the offenses. This breakdown helped students see the question from multiple perspectives, enabling them to narrow their focus and research more effectively before tackling the writing. They also used AI to identify relevant keywords to use for deeper research. Guyant noted that the students were using AI as a tool to gather information rather than writing the paper for them.
The utility of AI extends beyond simple research. In creative writing classes, AI can kickstart the writing process for students unfamiliar with certain genres. For example, AI-generated scripts or stories can provide a basic structure on which students can build, refine, and infuse with personal insights, ensuring their final submissions are less dependent on AI-generated content.
Ethical Considerations and Academic Integrity
Despite its benefits, the use of AI in academic settings raises significant ethical and integrity concerns. One primary worry is that students might become overly reliant on AI, potentially stunting their learning and engagement. There is also the risk of inadvertent plagiarism or the misuse of AI-generated content, which can lead to serious academic misconduct charges.
To address these issues, educators are encouraged to teach students about the ethical use of AI, including the importance of citing AI contributions accurately. Recent updates from academic institutions and organizations like MLA and APA have begun to provide guidelines on how to cite AI-generated content, reflecting its growing influence in academic writing.
Another example Guyant shared was professors who provide guidelines in their syllabus on using and citing AI-generated work, from what prompts were used, what results AI produced and highlighting any AI-generated content within their final papers or presentations. This clearly spells out what AI use is allowable and what is not, so students are aware of permissible AI use within a class.

Navigating Challenges: Accuracy and Personalization
Another challenge with using AI in teaching is the accuracy of the information it provides. AI systems can sometimes produce false or misleading information. Additionally, because AI often lacks a deep understanding of context, the materials it generates can sometimes be superficial or biased. Educators must teach students how to discern reliable information from AI-generated errors and biases, a crucial skill in the digital age. Discussing plagiarism policy, and how AI tools fit within that policy is helpful for students to understand how and when they can use the tools. To help students better understand allowable AI use, Guyant compares using AI in school to other practices that qualify as misconduct when it comes to turning in work created by someone else. Having AI write an entire essay and simply turning it in is just like paying someone to write a paper for you, she said.
Practical Classroom Applications
In practical terms, educators are finding innovative ways to integrate AI in teaching strategies effectively. For example, after an AI tool summarizes a text, students can be tasked with analyzing and critiquing the summary to identify what’s missing or misrepresented. This exercise not only improves their analytical skills but also helps them understand the limitations of AI.
Furthermore, AI can be used to generate discussion points or essay outlines, which students can then expand upon, ensuring that their engagement with the topic is active and personal.
AI as a Tool, Not a Replacement
No matter what classes AI is being used in, AI should be viewed as a tool that augments the educational process, not as a substitute for genuine learning and engagement. By carefully integrating AI into the curriculum, educators can help students harness its potential while also teaching them the skills necessary to use it responsibly and effectively.
As AI continues to evolve, so will its role in education. It’s up to educators and students alike to navigate this landscape thoughtfully, ensuring that AI serves as a bridge to greater understanding and not as a barrier to genuine intellectual engagement.

Personalize Your GoReact Experience
More From Forbes
Positive market breadth is a bullish setup.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Positive Market Breadth is a Bullish Setup
It’s no secret that the US stock market has become increasingly concentrated in recent years, with the largest, most dominant technology companies representing a disproportionate amount of the S&P 500 Index’s market capitalization. The top 10 largest S&P 500 companies account for 1/3 of the index’s total market capitalization and therefore the overall direction of the market can easily be swayed by a minority of stocks. With the growth of the “Magnificent Seven” mega-cap names to multi-trillion-dollar valuations, even a single name can drive the S&P 500 on any given day.
Consider April 25, a day when the S&P 500 was up 0.95%, a solid single day return. One would think that a considerable majority of the index would be green on such a day, yet the underlying data shows that 240 stocks, nearly half the index, were flat or negative. The overall index performance was skewed by a 6.2% daily return from Nvidia (NVDA) and a 10% return on Alphabet (GOOG). This example demonstrates how a single-day pop due to earnings or positive news on even one mega-cap name can create a misleading narrative of overall market direction if we only pay attention to the headline index performance. For this reason, it is important that we keep an eye on what is taking place under the surface.
One of the ways we assess the overall “health” of the market is by looking at measures of market breadth (see prior commentaries here , and here ). When the market is in an uptrend, we want to see most of the stocks within the index advancing to give us confidence that the rally is sustainable. We can measure market participation, or breadth, by looking at indicators such as the Advance-Decline (A/D) Line, which simply plots the number of advancing vs. declining stocks, or the McClellan Oscillator, which smooths out A/D fluctuations and puts more emphasis on recent data via the application of an exponential moving average.
The below chart shows how the McClellan Oscillator (the green and red bars below the chart) can give additional insight to the daily price action of the index (shown in the main, larger chart). At the onset of November 2023, the market bottomed out and reversed higher after a dovish Fed meeting. The market rally was broad, as reflected by the strong, persistent green McClellan Oscillator readings. The rally continued to start 2024, but as the McClellan chart reveals, breadth was relatively poor because big tech was moving higher while the rest of the market stalled out. In the second half of February through the beginning of April, the market kept appreciating but breadth was choppy. Breadth quickly deteriorated in April as inflation data led investors to de-risk and initiate broad selling. This brings us to our present situation roughly 1/3 of the way through May, as breadth looks healthier thanks to strong Q1 earnings and positive 2024 guidance.
Exhibit 1. S&P 500 and McClellan Oscillator
‘Fallout’ Dethroned In Amazon Prime Video’s Top 10 List By A New Offering
Google chrome gets second emergency update in a week as new exploit confirmed, trump accepts biden s challenge to debate twice starting next month.
As the consecutive green bars on the McClellan Oscillator show, the recent breadth expansion is the strongest thus far in 2024 and indicative of a market that could gain breakout momentum as we retest the prior highs. While it is a small sample size, looking at the five-day run from May 3 through May 9th shows all sectors moving higher in unison.
Exhibit 2. S&P 500 SPDR Sector ETF Performance 5/3/2024-5/9/2024
Year-to-date, all sectors aside from Real Estate are positive, which is encouraging considering that investors were expecting as many as six rate cuts coming into 2024 and now have repriced those expectations to a baseline of just one or two cuts at most. Stronger-than-expected corporate earnings have offset the negative impact of disappointing inflation readings and the good news is that those strong earnings have come from more than just the technology sector. In addition, CEOs are striking an upbeat tone, with fewer and fewer mentioning recession. The dreaded R-word came up just 100 times in Q1 earnings calls, compared to triple that amount a year ago.
Exhibit 3. “Recession” Mentions during Q1 Earnings Calls
We may need a better-than-expected inflation reading to spark a major rally, but the setup appears to be in place. The great corporate earnings, positive guidance, and willingness to engage in capex are all reflected in the strong GDP growth we have seen in recent quarters and expect to see yet again in Q2. The fact that participation is broad among US equity sectors gives us some confidence here that if we do see a rally commence from present levels, it could be one with staying power.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
There are a number of ways you can highlight research experience on your resume: In a dedicated section. In your work experience. In your education section. Listing research publications. In a projects section. In your skills section. In your resume summary.
Just like the way your options can seem very limited when applying for your first job, asking for a research position when you have no "experience" can seem discouraging — maybe even to the point of causing you to question whether you should apply in the first place.
Here is a more detailed list of how to write about research experience in resume: Gather all the necessary information. The first step is to collect all of the important details like the title of the research project, the location of the research project, the principal investigator of the project (if applicable), and the dates of the project.
Follow these steps to add research skills to your resume: 1. Review the job description. Start by reviewing the job description closely and identifying whether the employer is looking for specific types of research skills. Make a list of all of the research-related skills they're looking for in a candidate. 2.
How to list research experience on your resume with Teal. Step 1: Log in to your Teal account. (If you don't have one, sign up for free!) Step 2: Click "Resume Builder" in the navigation panel on the far left. From here, you can click "Add New Resume" or select a resume you're already working on.
1. Write a resume summary. One way to introduce your research abilities is to share them as part of your professional summary at the top of your document. If research is an important part of your background experience, you can feature it by giving an overview of your research topic or role such as lab assistant.
The five (plus) definite sections your resume for a researcher job should include are: Header with your headline, contact details, and/or a preview of your work. Summary (or objective) to pinpoint how your success aligns with the role. Experience with bullets of your most relevant achievements in the field.
Use professional language, as most files are submitted electronically — the reviewer will see if you named a file "Better Resumé". Include your first and last name and the title of the position in the file name. ex: Jane Doe Resumé - Biochemistry REU, UT Austin. This will ensure that the reviewer knows who you are and what you are ...
There are several steps you can take when writing a research CV: 1. Determine the role you want. Before creating your research CV, try to determine the research role you want. Researchers apply for positions closely related to the field they study or hope to extend their education through research opportunities.
For research, summarize your accomplishments in a brief section. You should include a description of your role in the research, the topic that you were exploring, and some information about your findings. For example, _ Research Project, Economics Department, Dynamic University, Dec 2017 - Apr 20_20.
Next - Writing About Your Experiences. Writing about your experience is important because this is the part that shows off what you did in your research experience! It's important to write in a way that shows off the skills you used in the role. ... Research Experience, etc. and you're ready to go! Example Resumes with Research. Adding ...
Consider this list of steps when creating your own researcher resume summary: 1. Review the job listing. Before writing your summary, review the job listing to identify any keywords and qualification requirements. Consider writing some of these keywords down and referencing them later when creating your resume summary.
The research statement is a common component of a potential candidate's application for post-undergraduate study. This may include applications for graduate programs, post-doctoral fellowships, or faculty positions. The research statement is often the primary way that a committee determines if a candidate's interests and past experience make them a good fit for their program/institution.
Writing an academic CV (also referred to as a "research CV" or "academic resume") is a bit different than writing a professional resume. It focuses on your academic experience and qualifications for the position—although relevant work experience can still be included if the position calls for it.
Here are the two things that a great statement of research interests or SOP will do: It will clearly illustrate to the admissions committee that you possess a depth of interest and comprehension in your field and that you understand what goes into research. You will sound naïve if you talk about ideas that are too vague or nebulous, or ones ...
Psychology alumni who gain research experience during college rate themselves higher on the skills needed to succeed in the job market, perceive their psychology training to be more useful to them in their current job, and report more satisfaction with their undergraduate education than those without research experience, regardless of the ...
Abstract. One of the most unique and substantial parts of the MD/PhD application is the significant research experience essay, which is a part of the primary AMCAS application. In this essay, applicants describe their research positions, projects, and accomplishments in detail. This chapter explains how to structure and write this essay in ...
Next, choose a structure for your CV. Start with the main headings and sub-headings you will use. In general, you should start by providing some brief personal details, then a brief career summary. The first section of your CV should focus on your education, publications and research.
A research resume is a document that shows your skills related to positions in research. You should be able to demonstrate working knowledge of collecting and analyzing data in a research resume. 2. How to write a research resume? Mention your previous experience in research-related positions. Demonstrate expertise in research by describing ...
SHARE: Most graduate schools will expect applicants to have practical experience in a lab. A strong application portfolio will most likely include participation in research throughout the undergraduate years, both during the academic year and the summers. It's important that you pursue research opportunities during the academic year and summers ...
I'm confused by what the term "research experience" actually means in a PhD application. The following examples come into my mind: ... those will be worth more. If you actually contributed to the writing of papers or presentation at conferences, even better. As a rule of thumb, the more that what you did was something other people could not ...
2. Include personal information and a professional summary. Add your name and contact information, including your phone number and email address. A professional summary is a brief paragraph of two or three sentences outlining your experience and education and showing why you qualify for the role. As it aims to demonstrate that you possess ...
Once your research experience is over: Congratulations! Hopefully you found the process to be as valuable and rewarding as I did. Besides wrapping up final details, many opportunities can be built off your project if want to continue your work. ... While you write your research summary and polish any results, I recommend backing up files ...
When applying to a research and development position, follow these steps to create your research and development resume: 1. Write your contact information. Including your contact information in an easy-to-identify format makes the job of the hiring professional reading your resume easier. Place your name at the top of your resume in the largest ...
The frustrating part comes at the beginning of the research process when students are attempting to find a topic to work on. There is a lot of floundering around as students get stuck doing ...
Abstract: Reviewing this section allows the reader to develop a quick understanding of the "why" the study was conducted, the methodology that was used, the most important findings, and why the findings are important. Reviewing this section is important as it helps you quickly evaluate if the study is applicable to your specific topic or needs. ...
The Role of AI as a Research & Writing Tool. AI tools, such as ChatGPT, have surged in popularity and utility, with applications spanning various academic fields. In writing courses, AI can serve as an ally. For instance, students can use these tools to research a topic, breaking down questions into manageable components.
Whilst the University of York announced its divestment from arms companies last month, students and staff are demanding that the institution fully cuts ties with weapon manufacturers in the form ...
One of the ways we assess the overall "health" of the market is by looking at measures of market breadth (see prior commentaries here, and here).When the market is in an uptrend, we want to ...
View our Fast Facts dashboard. 6. Study Abroad Programs - Exploring the World Maricopa Community Colleges incorporates learning and cultural experiences with summer study abroad programs. During the affordable study abroad programs, students can earn up to six academic credit hours while exploring different countries and cultures.