Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples

Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on October 26, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
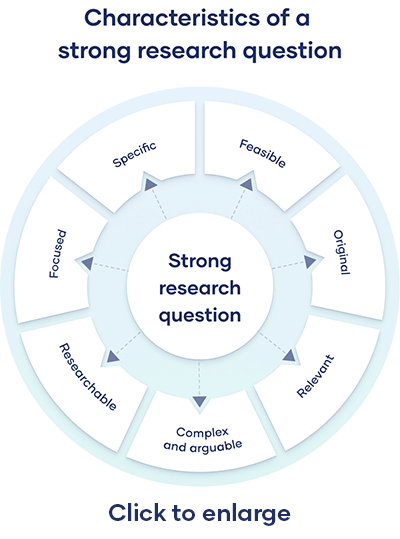
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, using sub-questions to strengthen your main research question, research questions quiz, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
| Research question formulations | |
|---|---|
| Describing and exploring | |
| Explaining and testing | |
| Evaluating and acting | is X |
Using your research problem to develop your research question
| Example research problem | Example research question(s) |
|---|---|
| Teachers at the school do not have the skills to recognize or properly guide gifted children in the classroom. | What practical techniques can teachers use to better identify and guide gifted children? |
| Young people increasingly engage in the “gig economy,” rather than traditional full-time employment. However, it is unclear why they choose to do so. | What are the main factors influencing young people’s decisions to engage in the gig economy? |
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Focused on a single topic | Your central research question should work together with your research problem to keep your work focused. If you have multiple questions, they should all clearly tie back to your central aim. |
| Answerable using | Your question must be answerable using and/or , or by reading scholarly sources on the to develop your argument. If such data is impossible to access, you likely need to rethink your question. |
| Not based on value judgements | Avoid subjective words like , , and . These do not give clear criteria for answering the question. |
Feasible and specific
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Answerable within practical constraints | Make sure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific. |
| Uses specific, well-defined concepts | All the terms you use in the research question should have clear meanings. Avoid vague language, jargon, and too-broad ideas. |
| Does not demand a conclusive solution, policy, or course of action | Research is about informing, not instructing. Even if your project is focused on a practical problem, it should aim to improve understanding rather than demand a ready-made solution. If ready-made solutions are necessary, consider conducting instead. Action research is a research method that aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as it is solved. In other words, as its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time. |
Complex and arguable
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Cannot be answered with or | Closed-ended, / questions are too simple to work as good research questions—they don’t provide enough for robust investigation and discussion. |
| Cannot be answered with easily-found facts | If you can answer the question through a single Google search, book, or article, it is probably not complex enough. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation prior to providing an answer. |
Relevant and original
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Addresses a relevant problem | Your research question should be developed based on initial reading around your . It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline. |
| Contributes to a timely social or academic debate | The question should aim to contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on. |
| Has not already been answered | You don’t have to ask something that nobody has ever thought of before, but your question should have some aspect of originality. For example, you can focus on a specific location, or explore a new angle. |
Chances are that your main research question likely can’t be answered all at once. That’s why sub-questions are important: they allow you to answer your main question in a step-by-step manner.
Good sub-questions should be:
- Less complex than the main question
- Focused only on 1 type of research
- Presented in a logical order
Here are a few examples of descriptive and framing questions:
- Descriptive: According to current government arguments, how should a European bank tax be implemented?
- Descriptive: Which countries have a bank tax/levy on financial transactions?
- Framing: How should a bank tax/levy on financial transactions look at a European level?
Keep in mind that sub-questions are by no means mandatory. They should only be asked if you need the findings to answer your main question. If your main question is simple enough to stand on its own, it’s okay to skip the sub-question part. As a rule of thumb, the more complex your subject, the more sub-questions you’ll need.
Try to limit yourself to 4 or 5 sub-questions, maximum. If you feel you need more than this, it may be indication that your main research question is not sufficiently specific. In this case, it’s is better to revisit your problem statement and try to tighten your main question up.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.

Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-questions/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, what is your plagiarism score.

How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
| Descriptive research questions | These measure the responses of a study’s population toward a particular question or variable. Common descriptive research questions will begin with “How much?”, “How regularly?”, “What percentage?”, “What time?”, “What is?” Research question example: How often do you buy mobile apps for learning purposes? |
| Comparative research questions | These investigate differences between two or more groups for an outcome variable. For instance, the researcher may compare groups with and without a certain variable. Research question example: What are the differences in attitudes towards online learning between visual and Kinaesthetic learners? |
| Relationship research questions | These explore and define trends and interactions between two or more variables. These investigate relationships between dependent and independent variables and use words such as “association” or “trends. Research question example: What is the relationship between disposable income and job satisfaction amongst US residents? |
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
| Exploratory Questions | These question looks to understand something without influencing the results. The aim is to learn more about a topic without attributing bias or preconceived notions. Research question example: What are people’s thoughts on the new government? |
| Experiential questions | These questions focus on understanding individuals’ experiences, perspectives, and subjective meanings related to a particular phenomenon. They aim to capture personal experiences and emotions. Research question example: What are the challenges students face during their transition from school to college? |
| Interpretive Questions | These questions investigate people in their natural settings to help understand how a group makes sense of shared experiences of a phenomenon. Research question example: How do you feel about ChatGPT assisting student learning? |
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
| Topic selection | Choose a broad topic, such as “learner support” or “social media influence” for your study. Select topics of interest to make research more enjoyable and stay motivated. |
| Preliminary research | The goal is to refine and focus your research question. The following strategies can help: Skim various scholarly articles. List subtopics under the main topic. List possible research questions for each subtopic. Consider the scope of research for each of the research questions. Select research questions that are answerable within a specific time and with available resources. If the scope is too large, repeat looking for sub-subtopics. |
| Audience | When choosing what to base your research on, consider your readers. For college papers, the audience is academic. Ask yourself if your audience may be interested in the topic you are thinking about pursuing. Determining your audience can also help refine the importance of your research question and focus on items related to your defined group. |
| Generate potential questions | Ask open-ended “how?” and “why?” questions to find a more specific research question. Gap-spotting to identify research limitations, problematization to challenge assumptions made by others, or using personal experiences to draw on issues in your industry can be used to generate questions. |
| Review brainstormed questions | Evaluate each question to check their effectiveness. Use the FINER model to see if the question meets all the research question criteria. |
| Construct the research question | Multiple frameworks, such as PICOT and PEA, are available to help structure your research question. The frameworks listed below can help you with the necessary information for generating your research question. |
| Framework | Attributes of each framework |
| FINER | Feasible Interesting Novel Ethical Relevant |
| PICOT | Population or problem Intervention or indicator being studied Comparison group Outcome of interest Time frame of the study |
| PEO | Population being studied Exposure to preexisting conditions Outcome of interest |
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
| Unclear: How does social media affect student growth? |
| Clear: What effect does the daily use of Twitter and Facebook have on the career development goals of students? |
| Explanation: The first research question is unclear because of the vagueness of “social media” as a concept and the lack of specificity. The second question is specific and focused, and its answer can be discovered through data collection and analysis. |
- Example 2
| Simple: Has there been an increase in the number of gifted children identified? |
| Complex: What practical techniques can teachers use to identify and guide gifted children better? |
| Explanation: A simple “yes” or “no” statement easily answers the first research question. The second research question is more complicated and requires the researcher to collect data, perform in-depth data analysis, and form an argument that leads to further discussion. |
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, how to cite in apa format (7th edition):..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence.
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How to Craft a Strong Research Question (With Research Question Examples)
A sound and effective research question is a key element that must be identified and pinned down before researchers can even begin their research study or work. A strong research question lays the foundation for your entire study, guiding your investigation and shaping your findings. Hence, it is critical that researchers spend considerable time assessing and refining the research question based on in-depth reading and comprehensive literature review. In this article, we will discuss how to write a strong research question and provide you with some good examples of research questions across various disciplines.
Table of Contents
The importance of a research question
A research question plays a crucial role in driving scientific inquiry, setting the direction and purpose of your study, and guiding your entire research process. By formulating a clear and focused research question, you lay the foundation for your investigation, ensuring that your research remains on track and aligned with your objectives so you can make meaningful contribution to the existing body of knowledge. A well-crafted research question also helps you define the scope of your study and identify the appropriate methodologies and data collection techniques to employ.
Key components of a strong research question
A good research question possesses several key components that contribute to the quality and impact of your study. Apart from providing a clear framework to generate meaningful results, a well-defined research question allows other researchers to understand the purpose and significance of your work. So, when working on your research question, incorporate the following elements:
- Specificity : A strong research question should be specific about the main focus of your study, enabling you to gather precise data and draw accurate conclusions. It clearly defines the variables, participants, and context involved, leaving no room for ambiguity.
- Clarity : A good research question is clear and easily understood, so articulate the purpose and intent of your study concisely without being generic or vague. Ensuring clarity in your research question helps both you and your readers grasp the research objective.
- Feasibility : While crafting a research question, consider the practicality of conducting the research and availability of necessary data or access to participants. Think whether your study is realistic and achievable within the constraints of time, resources, and ethical considerations.
How to craft a well-defined research question
A first step that will help save time and effort is knowing what your aims are and thinking about a few problem statements on the area or aspect one wants to study or do research on. Contemplating these statements as one undertakes more progressive reading can help the researcher in reassessing and fine-tuning the research question. This can be done over time as they read and learn more about the research topic, along with a broad literature review and parallel discussions with peer researchers and supervisors. In some cases, a researcher can have more than one research question if the research being undertaken is a PhD thesis or dissertation, but try not to cover multiple concerns on a topic.
A strong research question must be researchable, original, complex, and relevant. Here are five simple steps that can make the entire process easier.
- Identify a broad topic from your areas of interest, something that is relevant, and you are passionate about since you’ll be spending a lot of time conducting your research.
- Do a thorough literature review to weed out potential gaps in research and stay updated on what’s currently being done in your chosen topic and subject area.
- Shortlist possible research questions based on the research gaps or see how you can build on or refute previously published ideas and concepts.
- Assess your chosen research question using the FINER criteria that helps you evaluate whether the research is Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant. 1
- Formulate the final research question, while ensuring it is clear, well-written, and addresses all the key elements of a strong research question.
Examples of research questions
Remember to adapt your research question to suit your purpose, whether it’s exploratory, descriptive, comparative, experimental, qualitative, or quantitative. Embrace the iterative nature of the research process, continually evaluating and refining your question as you progress. Here are some good examples of research questions across various disciplines.
Exploratory research question examples
- How does social media impact interpersonal relationships among teenagers?
- What are the potential benefits of incorporating mindfulness practices in the workplace?
Descriptive research question examples
- What factors influence customer loyalty in the e-commerce industry?
- Is there a relationship between socioeconomic status and academic performance among elementary school students?
Comparative research question examples
- How does the effectiveness of traditional teaching methods compare to online learning platforms in mathematics education?
- What is the impact of different healthcare policies on patient outcomes in various countries?
Experimental research question examples
- What are the effects of a new drug on reducing symptoms of a specific medical condition?
- Does a dietary intervention have an impact on weight loss among individuals with obesity?
Qualitative research question examples
- What are the lived experiences of immigrants adapting to a new culture?
- What factors influence job satisfaction among healthcare professionals?
Quantitative research question examples
- Is there a relationship between sleep duration and academic performance among college students?
- How effective is a specific intervention in reducing anxiety levels among individuals with phobias?
With these simple guidelines and inspiring examples of research questions, you are equipped to embark on your research journey with confidence and purpose. Here’s wishing you all the best for your future endeavors!
References:
- How to write a research question: Steps and examples. Indeed Career Guide. Available online at https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-research-questions
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

What is Convenience Sampling: Definition, Method, and Examples

What are Experimental Groups in Research
- Our Mission
- Code of Conduct
- The Consultants
- Hours and Locations
- Apply to Become a Consultant
- Make an Appointment
- Face-to-Face Appointments
- Zoom Appointments
- Written Feedback Appointments
- Support for Writers with Disabilities
- Policies and Restrictions
- Upcoming Workshops
- Class Workshops
- Meet the Consultants
- Writing Center Quick Guides
- Citation Resources
- Helpful Links
- Video Resources
- Login or Register
- Graduate Writing Consultations
- Thesis and Dissertation Consultations
- Weekly Write-Ins
- ESOL Graduate Peer Feedback Groups
- Setting Up Your Own Writing Group
- Writing Resources for Graduate Students
- Support for Multilingual Students
- ESOL Opt-In Program
- About Our Consulting Services
- Promote Us to Your Students
- Recommend Consultants
How to Write a Research Question
What is a research question? A research question is the question around which you center your research. It should be:
- clear : it provides enough specifics that one’s audience can easily understand its purpose without needing additional explanation.
- focused : it is narrow enough that it can be answered thoroughly in the space the writing task allows.
- concise : it is expressed in the fewest possible words.
- complex : it is not answerable with a simple “yes” or “no,” but rather requires synthesis and analysis of ideas and sources prior to composition of an answer.
- arguable : its potential answers are open to debate rather than accepted facts.
You should ask a question about an issue that you are genuinely curious and/or passionate about.
The question you ask should be developed for the discipline you are studying. A question appropriate for Biology, for instance, is different from an appropriate one in Political Science or Sociology. If you are developing your question for a course other than first-year composition, you may want to discuss your ideas for a research question with your professor.
Why is a research question essential to the research process? Research questions help writers focus their research by providing a path through the research and writing process. The specificity of a well-developed research question helps writers avoid the “all-about” paper and work toward supporting a specific, arguable thesis.
Steps to developing a research question:
- Choose an interesting general topic. Most professional researchers focus on topics they are genuinely interested in studying. Writers should choose a broad topic about which they genuinely would like to know more. An example of a general topic might be “Slavery in the American South” or “Films of the 1930s.”
- Do some preliminary research on your general topic. Do a few quick searches in current periodicals and journals on your topic to see what’s already been done and to help you narrow your focus. What issues are scholars and researchers discussing, when it comes to your topic? What questions occur to you as you read these articles?
- Consider your audience. For most college papers, your audience will be academic, but always keep your audience in mind when narrowing your topic and developing your question. Would that particular audience be interested in the question you are developing?
- Start asking questions. Taking into consideration all of the above, start asking yourself open-ended “how” and “why” questions about your general topic. For example, “Why were slave narratives effective tools in working toward the abolishment of slavery?” or “How did the films of the 1930s reflect or respond to the conditions of the Great Depression?”
- Is your research question clear? With so much research available on any given topic, research questions must be as clear as possible in order to be effective in helping the writer direct his or her research.
- Is your research question focused? Research questions must be specific enough to be well covered in the space available.
- Is your research question complex? Research questions should not be answerable with a simple “yes” or “no” or by easily-found facts. They should, instead, require both research and analysis on the part of the writer. They often begin with “How” or “Why.”
- Begin your research . After you’ve come up with a question, think about the possible paths your research could take. What sources should you consult as you seek answers to your question? What research process will ensure that you find a variety of perspectives and responses to your question?
Sample Research Questions
Unclear: How should social networking sites address the harm they cause? Clear: What action should social networking sites like MySpace and Facebook take to protect users’ personal information and privacy? The unclear version of this question doesn’t specify which social networking sites or suggest what kind of harm the sites might be causing. It also assumes that this “harm” is proven and/or accepted. The clearer version specifies sites (MySpace and Facebook), the type of potential harm (privacy issues), and who may be experiencing that harm (users). A strong research question should never leave room for ambiguity or interpretation. Unfocused: What is the effect on the environment from global warming? Focused: What is the most significant effect of glacial melting on the lives of penguins in Antarctica?
The unfocused research question is so broad that it couldn’t be adequately answered in a book-length piece, let alone a standard college-level paper. The focused version narrows down to a specific effect of global warming (glacial melting), a specific place (Antarctica), and a specific animal that is affected (penguins). It also requires the writer to take a stance on which effect has the greatest impact on the affected animal. When in doubt, make a research question as narrow and focused as possible.
Too simple: How are doctors addressing diabetes in the U.S.? Appropriately Complex: What main environmental, behavioral, and genetic factors predict whether Americans will develop diabetes, and how can these commonalities be used to aid the medical community in prevention of the disease?
The simple version of this question can be looked up online and answered in a few factual sentences; it leaves no room for analysis. The more complex version is written in two parts; it is thought provoking and requires both significant investigation and evaluation from the writer. As a general rule of thumb, if a quick Google search can answer a research question, it’s likely not very effective.
Last updated 8/8/2018

The Writing Center
4400 University Drive, 2G8 Fairfax, VA 22030
- Johnson Center, Room 227E
- +1-703-993-1200
- [email protected]
Quick Links
- Register with us
© Copyright 2024 George Mason University . All Rights Reserved. Privacy Statement | Accessibility

Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
The “Golden Thread” Explained Simply (+ Examples)
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022
The research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
41 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
This is a well researched and superbly written article for learners of research methods at all levels in the research topic from conceptualization to research findings and conclusions. I highly recommend this material to university graduate students. As an instructor of advanced research methods for PhD students, I have confirmed that I was giving the right guidelines for the degree they are undertaking.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Examples of good research questions
Last updated
Reviewed by
Tanya Williams
However, developing a good research question is often challenging. But, doing appropriate data analysis or drawing meaningful conclusions from your investigation with a well-defined question make it easier.
So, to get you on the right track, let’s start by defining a research question, what types of research questions are common, and the steps to drafting an excellent research question.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is a research question?
The definition of a research question might seem fairly obvious.
At its simplest, a research question is a question you research to find the answer.
Researchers typically start with a problem or an issue and seek to understand why it has occurred, how it can be solved, or other aspects of its nature.
As you'll see, researchers typically start with a broad question that becomes narrower and more specific as the research stages are completed.
In some cases, a study may tackle more than one research question.
- Research question types
Research questions are typically divided into three broad categories: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-method.
These categories reflect the research type necessary to answer the research question.
Qualitative research
When you conduct qualitative research, you're broadly exploring a subject to analyze its inherent qualities.
There are many types of qualitative research questions, which include:
Descriptive: describing and illuminating little-known or overlooked aspects of a subject
Emancipatory: uncovering data that can serve to emancipate a particular group of people, such as disadvantaged or marginalized communities
Evaluative: assessing how well a particular research approach or method works
Explanatory: answering “how” or “why” a given phenomenon occurs
Exploratory: identifying reasons behind certain behaviors and exploring motivations (also known as generative research because it can generate solutions to problems)
Ideological: researching ideologies or beliefs, such as political affiliation
Interpretive: understanding group perceptions, decision-making, and behavior in a natural setting
Predictive: forecasting a likely outcome or scenario by examining past events
While it's helpful to understand the differences between these qualitative research question types, writing a good question doesn't start with determining the precise type of research question you'll be asking.
It starts with determining what answers you're seeking.
Quantitative research
Unlike broad, flexible qualitative research questions, quantitative research questions are precise. They also directly link the research question and the proposed methodology.
So, in a quantitative research question, you'll usually find
The study method
An independent variable (or variables)
A dependent variable
The study population
Quantitative research questions can also fall into multiple categories, including:
Comparative research questions compare two or more groups according to specific criteria and analyze their similarities and differences.
Descriptive questions measure a population's response to one or more variables.
Relationship (or relationship-based) questions examine how two or more variables interact.
Mixed-methods research
As its name suggests, mixed-methods research questions involve qualitative and quantitative components.
These questions are ideal when the answers require an evaluation of a specific aspect of a phenomenon that you can quantify and a broader understanding of aspects that can't.
- How to write a research question
Writing a good research question can be challenging, even if you're passionate about the subject matter.
A good research question aims to solve a problem that still needs to be answered and can be solved empirically.
The approach might involve quantitative or qualitative methodology, or a mixture of both. To write a well-developed research question, follow the four steps below:
1. Select a general topic
Start with a broad topic. You may already have one in mind or get one assigned to you. If you don't, think about one you're curious about.
You can also use common brainstorming techniques , draw on discussions you've had with family and friends, take topics from the news, or use other similar sources of inspiration.
Also, consider a subject that has yet to be studied or addressed. If you're looking to tackle a topic that has already been thoroughly studied, you'll want to examine it from a new angle.
Still, the closer your question, approach, and outcomes are to existing literature, the less value your work will offer. It will also be less publishing-worthy (if that’s your goal).
2. Conduct preliminary research
Next, you'll want to conduct some initial research about your topic. You'll read coverage about your topic in academic journals, the news, and other credible sources at this stage.
You'll familiarize yourself with the terminology commonly used to describe your topic and the current take from subject matter experts and the general public.
This preliminary review helps you in a few ways. First, you'll find many researchers will discuss challenges they found conducting their research in their "Limitations," "Results," and "Discussion" sections of research papers.
Assessing these sections also helps you avoid choosing the wrong methodological approach to answering your question. Initial research also enables you to avoid focusing on a topic that has already been covered.
You can generate valuable research questions by tracking topics that have yet to be covered.
3. Consider your audience
Next, you'll want to give some thought to your audience. For example, what kinds of research material are they looking for, and what might they find valuable?
Reflect on why you’re conducting the research.
What is your team looking to learn if your research is for a work assignment?
How does what they’re asking for from you connect to business goals?
Understanding what your audience is seeking can help you shape the direction of your research so that the final draft connects with your audience.
If you're writing for an academic journal, what types of research do they publish? What kinds of research approaches have they published? And what criteria do they expect submitted manuscripts to meet?
4. Generate potential questions
Take the insights you've gained from your preliminary research and your audience assessment to narrow your topic into a research question.
Your question should be one that you can answer using the appropriate research methods. Unfortunately, some researchers start with questions they need more resources to answer and then produce studies whose outcomes are limited, limiting the study's value to the broader community.
Make sure your question is one you can realistically answer.
- Examples of poor research questions
"How do electronics distract teen drivers?"
This question could be better from a researcher's perspective because it is overly broad. For instance, what is “electronics” in this context? Some electronics, like eye-monitoring systems in semi-autonomous vehicles, are designed to keep drivers focused on the road.
Also, how does the question define “teens”? Some states allow you to get a learner's permit as young as 14, while others require you to be 18 to drive. Therefore, conducting a study without further defining the participants' ages is not scientifically sound.
Here's another example of an ineffective research question:
"Why is the sky blue?"
This question has been researched thoroughly and answered.
A simple online search will turn up hundreds, if not thousands, of pages of resources devoted to this very topic.
Suppose you spend time conducting original research on a long-answered question; your research won’t be interesting, relevant, or valuable to your audience.
Alternatively, here's an example of a good research question:
"How does using a vehicle’s infotainment touch screen by drivers aged 16 to 18 in the U.S. affect driving habits?"
This question is far more specific than the first bad example. It notes the population of the study, as well as the independent and dependent variables.
And if you're still interested in the sky's color, a better example of a research question might be:
"What color is the sky on Proxima Centauri b, based on existing observations?"
A qualitative research study based on this question could extrapolate what visitors on Proxima Centauri b (a planet in the closest solar system to ours) might see as they look at the sky.
You could approach this by contextualizing our understanding of how the light scatters off the molecules of air resulting in a blue sky, and the likely composition of Proxima Centauri b's atmosphere from data NASA and others have gathered.
- Why the right research question is critical
As you can see from the examples, starting with a poorly-framed research question can make your study difficult or impossible to complete.
Or it can lead you to duplicate research findings.
Ultimately, developing the right research question sets you up for success. It helps you define a realistic scope for your study, informs the best approach to answer the central question, and conveys its value to your audience.
That's why you must take the time to get your research question right before you embark on any other part of your project.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Questions
Definition:
Research questions are the specific questions that guide a research study or inquiry. These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective.
Types of Research Questions
Types of Research Questions are as follows:
Descriptive Research Questions
These aim to describe a particular phenomenon, group, or situation. For example:
- What are the characteristics of the target population?
- What is the prevalence of a particular disease in a specific region?
Exploratory Research Questions
These aim to explore a new area of research or generate new ideas or hypotheses. For example:
- What are the potential causes of a particular phenomenon?
- What are the possible outcomes of a specific intervention?
Explanatory Research Questions
These aim to understand the relationship between two or more variables or to explain why a particular phenomenon occurs. For example:
- What is the effect of a specific drug on the symptoms of a particular disease?
- What are the factors that contribute to employee turnover in a particular industry?
Predictive Research Questions
These aim to predict a future outcome or trend based on existing data or trends. For example :
- What will be the future demand for a particular product or service?
- What will be the future prevalence of a particular disease?
Evaluative Research Questions
These aim to evaluate the effectiveness of a particular intervention or program. For example:
- What is the impact of a specific educational program on student learning outcomes?
- What is the effectiveness of a particular policy or program in achieving its intended goals?
How to Choose Research Questions
Choosing research questions is an essential part of the research process and involves careful consideration of the research problem, objectives, and design. Here are some steps to consider when choosing research questions:
- Identify the research problem: Start by identifying the problem or issue that you want to study. This could be a gap in the literature, a social or economic issue, or a practical problem that needs to be addressed.
- Conduct a literature review: Conducting a literature review can help you identify existing research in your area of interest and can help you formulate research questions that address gaps or limitations in the existing literature.
- Define the research objectives : Clearly define the objectives of your research. What do you want to achieve with your study? What specific questions do you want to answer?
- Consider the research design : Consider the research design that you plan to use. This will help you determine the appropriate types of research questions to ask. For example, if you plan to use a qualitative approach, you may want to focus on exploratory or descriptive research questions.
- Ensure that the research questions are clear and answerable: Your research questions should be clear and specific, and should be answerable with the data that you plan to collect. Avoid asking questions that are too broad or vague.
- Get feedback : Get feedback from your supervisor, colleagues, or peers to ensure that your research questions are relevant, feasible, and meaningful.
How to Write Research Questions
Guide for Writing Research Questions:
- Start with a clear statement of the research problem: Begin by stating the problem or issue that your research aims to address. This will help you to formulate focused research questions.
- Use clear language : Write your research questions in clear and concise language that is easy to understand. Avoid using jargon or technical terms that may be unfamiliar to your readers.
- Be specific: Your research questions should be specific and focused. Avoid broad questions that are difficult to answer. For example, instead of asking “What is the impact of climate change on the environment?” ask “What are the effects of rising sea levels on coastal ecosystems?”
- Use appropriate question types: Choose the appropriate question types based on the research design and objectives. For example, if you are conducting a qualitative study, you may want to use open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed responses.
- Consider the feasibility of your questions : Ensure that your research questions are feasible and can be answered with the resources available. Consider the data sources and methods of data collection when writing your questions.
- Seek feedback: Get feedback from your supervisor, colleagues, or peers to ensure that your research questions are relevant, appropriate, and meaningful.
Examples of Research Questions
Some Examples of Research Questions with Research Titles:
Research Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
- Research Question : What is the relationship between social media use and mental health, and how does this impact individuals’ well-being?
Research Title: Factors Influencing Academic Success in High School
- Research Question: What are the primary factors that influence academic success in high school, and how do they contribute to student achievement?
Research Title: The Effects of Exercise on Physical and Mental Health
- Research Question: What is the relationship between exercise and physical and mental health, and how can exercise be used as a tool to improve overall well-being?
Research Title: Understanding the Factors that Influence Consumer Purchasing Decisions
- Research Question : What are the key factors that influence consumer purchasing decisions, and how do these factors vary across different demographics and products?
Research Title: The Impact of Technology on Communication
- Research Question : How has technology impacted communication patterns, and what are the effects of these changes on interpersonal relationships and society as a whole?
Research Title: Investigating the Relationship between Parenting Styles and Child Development
- Research Question: What is the relationship between different parenting styles and child development outcomes, and how do these outcomes vary across different ages and developmental stages?
Research Title: The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy in Treating Anxiety Disorders
- Research Question: How effective is cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating anxiety disorders, and what factors contribute to its success or failure in different patients?
Research Title: The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity
- Research Question : How is climate change affecting global biodiversity, and what can be done to mitigate the negative effects on natural ecosystems?
Research Title: Exploring the Relationship between Cultural Diversity and Workplace Productivity
- Research Question : How does cultural diversity impact workplace productivity, and what strategies can be employed to maximize the benefits of a diverse workforce?
Research Title: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- Research Question: How can artificial intelligence be leveraged to improve healthcare outcomes, and what are the potential risks and ethical concerns associated with its use?
Applications of Research Questions
Here are some of the key applications of research questions:
- Defining the scope of the study : Research questions help researchers to narrow down the scope of their study and identify the specific issues they want to investigate.
- Developing hypotheses: Research questions often lead to the development of hypotheses, which are testable predictions about the relationship between variables. Hypotheses provide a clear and focused direction for the study.
- Designing the study : Research questions guide the design of the study, including the selection of participants, the collection of data, and the analysis of results.
- Collecting data : Research questions inform the selection of appropriate methods for collecting data, such as surveys, interviews, or experiments.
- Analyzing data : Research questions guide the analysis of data, including the selection of appropriate statistical tests and the interpretation of results.
- Communicating results : Research questions help researchers to communicate the results of their study in a clear and concise manner. The research questions provide a framework for discussing the findings and drawing conclusions.
Characteristics of Research Questions
Characteristics of Research Questions are as follows:
- Clear and Specific : A good research question should be clear and specific. It should clearly state what the research is trying to investigate and what kind of data is required.
- Relevant : The research question should be relevant to the study and should address a current issue or problem in the field of research.
- Testable : The research question should be testable through empirical evidence. It should be possible to collect data to answer the research question.
- Concise : The research question should be concise and focused. It should not be too broad or too narrow.
- Feasible : The research question should be feasible to answer within the constraints of the research design, time frame, and available resources.
- Original : The research question should be original and should contribute to the existing knowledge in the field of research.
- Significant : The research question should have significance and importance to the field of research. It should have the potential to provide new insights and knowledge to the field.
- Ethical : The research question should be ethical and should not cause harm to any individuals or groups involved in the study.
Purpose of Research Questions
Research questions are the foundation of any research study as they guide the research process and provide a clear direction to the researcher. The purpose of research questions is to identify the scope and boundaries of the study, and to establish the goals and objectives of the research.
The main purpose of research questions is to help the researcher to focus on the specific area or problem that needs to be investigated. They enable the researcher to develop a research design, select the appropriate methods and tools for data collection and analysis, and to organize the results in a meaningful way.
Research questions also help to establish the relevance and significance of the study. They define the research problem, and determine the research methodology that will be used to address the problem. Research questions also help to determine the type of data that will be collected, and how it will be analyzed and interpreted.
Finally, research questions provide a framework for evaluating the results of the research. They help to establish the validity and reliability of the data, and provide a basis for drawing conclusions and making recommendations based on the findings of the study.
Advantages of Research Questions
There are several advantages of research questions in the research process, including:
- Focus : Research questions help to focus the research by providing a clear direction for the study. They define the specific area of investigation and provide a framework for the research design.
- Clarity : Research questions help to clarify the purpose and objectives of the study, which can make it easier for the researcher to communicate the research aims to others.
- Relevance : Research questions help to ensure that the study is relevant and meaningful. By asking relevant and important questions, the researcher can ensure that the study will contribute to the existing body of knowledge and address important issues.
- Consistency : Research questions help to ensure consistency in the research process by providing a framework for the development of the research design, data collection, and analysis.
- Measurability : Research questions help to ensure that the study is measurable by defining the specific variables and outcomes that will be measured.
- Replication : Research questions help to ensure that the study can be replicated by providing a clear and detailed description of the research aims, methods, and outcomes. This makes it easier for other researchers to replicate the study and verify the results.
Limitations of Research Questions
Limitations of Research Questions are as follows:
- Subjectivity : Research questions are often subjective and can be influenced by personal biases and perspectives of the researcher. This can lead to a limited understanding of the research problem and may affect the validity and reliability of the study.
- Inadequate scope : Research questions that are too narrow in scope may limit the breadth of the study, while questions that are too broad may make it difficult to focus on specific research objectives.
- Unanswerable questions : Some research questions may not be answerable due to the lack of available data or limitations in research methods. In such cases, the research question may need to be rephrased or modified to make it more answerable.
- Lack of clarity : Research questions that are poorly worded or ambiguous can lead to confusion and misinterpretation. This can result in incomplete or inaccurate data, which may compromise the validity of the study.
- Difficulty in measuring variables : Some research questions may involve variables that are difficult to measure or quantify, making it challenging to draw meaningful conclusions from the data.
- Lack of generalizability: Research questions that are too specific or limited in scope may not be generalizable to other contexts or populations. This can limit the applicability of the study’s findings and restrict its broader implications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

APA Table of Contents – Format and Example

Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Research Methodology – Types, Examples and...

Research Objectives – Types, Examples and...
Writing Studio
Formulating your research question (rq).
In an effort to make our handouts more accessible, we have begun converting our PDF handouts to web pages. Download this page as a PDF: Formulating Your Research Question Return to Writing Studio Handouts
In a research paper, the emphasis is on generating a unique question and then synthesizing diverse sources into a coherent essay that supports your argument about the topic. In other words, you integrate information from publications with your own thoughts in order to formulate an argument. Your topic is your starting place: from here, you will develop an engaging research question. Merely presenting a topic in the form of a question does not transform it into a good research question.
Research Topic Versus Research Question Examples
1. broad topic versus narrow question, 1a. broad topic.
“What forces affect race relations in America?”
1b. NARROWER QUESTION
“How do corporate hiring practices affect race relations in Nashville?”
The question “What is the percentage of racial minorities holding management positions in corporate offices in Nashville?” is much too specific and would yield, at best, a statistic that could become part of a larger argument.
2. Neutral Topic Versus Argumentative Question
2a. neutral topic.
“How does KFC market its low-fat food offerings?”
2b. Argumentative question
“Does KFC put more money into marketing its high-fat food offerings than its lower-fat ones?”
The latter question is somewhat better, since it may lead you to take a stance or formulate an argument about consumer awareness or benefit.
3. Objective Topic Versus Subjective Question
Objective subjects are factual and do not have sides to be argued. Subjective subjects are those about which you can take a side.
3a. Objective topic
“How much time do youth between the ages of 10 and 15 spend playing video games?”
3b. Subjective Question
“What are the effects of video-gaming on the attention spans of youth between the ages of 10 and 15?”
The first question is likely to lead to some data, though not necessarily to an argument or issue. The second question is somewhat better, since it might lead you to formulate an argument for or against time spent playing video games.
4. Open-Ended Topic Versus Direct Question
4a. open-ended topic.
“Does the author of this text use allusion?”
4b. Direct question (gives direction to research)
“Does the ironic use of allusion in this text reveal anything about the author’s unwillingness to divulge his political commitments?”
The second question gives focus by putting the use of allusion into the specific context of a question about the author’s political commitments and perhaps also about the circumstances under which the text was produced.
Research Question (RQ) Checklist
- Is my RQ something that I am curious about and that others might care about? Does it present an issue on which I can take a stand?
- Does my RQ put a new spin on an old issue, or does it try to solve a problem?
- Is my RQ too broad, too narrow, or OK?
- within the time frame of the assignment?
- given the resources available at my location?
- Is my RQ measurable? What type of information do I need? Can I find actual data to support or contradict a position?
- What sources will have the type of information that I need to answer my RQ (journals, books, internet resources, government documents, interviews with people)?
Final Thoughts
The answer to a good research question will often be the THESIS of your research paper! And the results of your research may not always be what you expected them to be. Not only is this ok, it can be an indication that you are doing careful work!
Adapted from an online tutorial at Empire State College: http://www.esc.edu/htmlpages/writerold/menus.htm#develop (broken link)
Last revised: November 2022 | Adapted for web delivery: November 2022
In order to access certain content on this page, you may need to download Adobe Acrobat Reader or an equivalent PDF viewer software.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Good Research Question (w/ Examples)
What is a Research Question?
A research question is the main question that your study sought or is seeking to answer. A clear research question guides your research paper or thesis and states exactly what you want to find out, giving your work a focus and objective. Learning how to write a hypothesis or research question is the start to composing any thesis, dissertation, or research paper. It is also one of the most important sections of a research proposal .
A good research question not only clarifies the writing in your study; it provides your readers with a clear focus and facilitates their understanding of your research topic, as well as outlining your study’s objectives. Before drafting the paper and receiving research paper editing (and usually before performing your study), you should write a concise statement of what this study intends to accomplish or reveal.
Research Question Writing Tips
Listed below are the important characteristics of a good research question:
A good research question should:
- Be clear and provide specific information so readers can easily understand the purpose.
- Be focused in its scope and narrow enough to be addressed in the space allowed by your paper
- Be relevant and concise and express your main ideas in as few words as possible, like a hypothesis.
- Be precise and complex enough that it does not simply answer a closed “yes or no” question, but requires an analysis of arguments and literature prior to its being considered acceptable.
- Be arguable or testable so that answers to the research question are open to scrutiny and specific questions and counterarguments.
Some of these characteristics might be difficult to understand in the form of a list. Let’s go into more detail about what a research question must do and look at some examples of research questions.
The research question should be specific and focused
Research questions that are too broad are not suitable to be addressed in a single study. One reason for this can be if there are many factors or variables to consider. In addition, a sample data set that is too large or an experimental timeline that is too long may suggest that the research question is not focused enough.
A specific research question means that the collective data and observations come together to either confirm or deny the chosen hypothesis in a clear manner. If a research question is too vague, then the data might end up creating an alternate research problem or hypothesis that you haven’t addressed in your Introduction section .
| What is the importance of genetic research in the medical field? | |
| How might the discovery of a genetic basis for alcoholism impact triage processes in medical facilities? |
The research question should be based on the literature
An effective research question should be answerable and verifiable based on prior research because an effective scientific study must be placed in the context of a wider academic consensus. This means that conspiracy or fringe theories are not good research paper topics.
Instead, a good research question must extend, examine, and verify the context of your research field. It should fit naturally within the literature and be searchable by other research authors.
References to the literature can be in different citation styles and must be properly formatted according to the guidelines set forth by the publishing journal, university, or academic institution. This includes in-text citations as well as the Reference section .
The research question should be realistic in time, scope, and budget
There are two main constraints to the research process: timeframe and budget.
A proper research question will include study or experimental procedures that can be executed within a feasible time frame, typically by a graduate doctoral or master’s student or lab technician. Research that requires future technology, expensive resources, or follow-up procedures is problematic.
A researcher’s budget is also a major constraint to performing timely research. Research at many large universities or institutions is publicly funded and is thus accountable to funding restrictions.
The research question should be in-depth
Research papers, dissertations and theses , and academic journal articles are usually dozens if not hundreds of pages in length.
A good research question or thesis statement must be sufficiently complex to warrant such a length, as it must stand up to the scrutiny of peer review and be reproducible by other scientists and researchers.
Research Question Types
Qualitative and quantitative research are the two major types of research, and it is essential to develop research questions for each type of study.
Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research questions are specific. A typical research question involves the population to be studied, dependent and independent variables, and the research design.
In addition, quantitative research questions connect the research question and the research design. In addition, it is not possible to answer these questions definitively with a “yes” or “no” response. For example, scientific fields such as biology, physics, and chemistry often deal with “states,” in which different quantities, amounts, or velocities drastically alter the relevance of the research.
As a consequence, quantitative research questions do not contain qualitative, categorical, or ordinal qualifiers such as “is,” “are,” “does,” or “does not.”
Categories of quantitative research questions
| Attempt to describe the behavior of a population in regard to one or more variables or describe characteristics of those variables that will be measured. These are usually “What?” questions. | Seek to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable. These questions can be causal as well. Researchers may compare groups in which certain variables are present with groups in which they are not. | Designed to elucidate and describe trends and interactions among variables. These questions include the dependent and independent variables and use words such as “association” or “trends.” |
Qualitative Research Questions
In quantitative research, research questions have the potential to relate to broad research areas as well as more specific areas of study. Qualitative research questions are less directional, more flexible, and adaptable compared with their quantitative counterparts. Thus, studies based on these questions tend to focus on “discovering,” “explaining,” “elucidating,” and “exploring.”
Categories of qualitative research questions
| Attempt to identify and describe existing conditions. | Attempt to describe a phenomenon. | Assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures. |
| Examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena. | Focus on the unknown aspects of a particular topic. |
Quantitative and Qualitative Research Question Examples
| Descriptive research question | |
| Comparative research question | |
| Correlational research question | |
| Exploratory research question | |
| Explanatory research question | |
| Evaluation research question |

Good and Bad Research Question Examples
Below are some good (and not-so-good) examples of research questions that researchers can use to guide them in crafting their own research questions.
Research Question Example 1
The first research question is too vague in both its independent and dependent variables. There is no specific information on what “exposure” means. Does this refer to comments, likes, engagement, or just how much time is spent on the social media platform?
Second, there is no useful information on what exactly “affected” means. Does the subject’s behavior change in some measurable way? Or does this term refer to another factor such as the user’s emotions?
Research Question Example 2
In this research question, the first example is too simple and not sufficiently complex, making it difficult to assess whether the study answered the question. The author could really only answer this question with a simple “yes” or “no.” Further, the presence of data would not help answer this question more deeply, which is a sure sign of a poorly constructed research topic.
The second research question is specific, complex, and empirically verifiable. One can measure program effectiveness based on metrics such as attendance or grades. Further, “bullying” is made into an empirical, quantitative measurement in the form of recorded disciplinary actions.
Steps for Writing a Research Question
Good research questions are relevant, focused, and meaningful. It can be difficult to come up with a good research question, but there are a few steps you can follow to make it a bit easier.
1. Start with an interesting and relevant topic
Choose a research topic that is interesting but also relevant and aligned with your own country’s culture or your university’s capabilities. Popular academic topics include healthcare and medical-related research. However, if you are attending an engineering school or humanities program, you should obviously choose a research question that pertains to your specific study and major.
Below is an embedded graph of the most popular research fields of study based on publication output according to region. As you can see, healthcare and the basic sciences receive the most funding and earn the highest number of publications.
2. Do preliminary research
You can begin doing preliminary research once you have chosen a research topic. Two objectives should be accomplished during this first phase of research. First, you should undertake a preliminary review of related literature to discover issues that scholars and peers are currently discussing. With this method, you show that you are informed about the latest developments in the field.
Secondly, identify knowledge gaps or limitations in your topic by conducting a preliminary literature review . It is possible to later use these gaps to focus your research question after a certain amount of fine-tuning.
3. Narrow your research to determine specific research questions
You can focus on a more specific area of study once you have a good handle on the topic you want to explore. Focusing on recent literature or knowledge gaps is one good option.
By identifying study limitations in the literature and overlooked areas of study, an author can carve out a good research question. The same is true for choosing research questions that extend or complement existing literature.
4. Evaluate your research question
Make sure you evaluate the research question by asking the following questions:
Is my research question clear?
The resulting data and observations that your study produces should be clear. For quantitative studies, data must be empirical and measurable. For qualitative, the observations should be clearly delineable across categories.
Is my research question focused and specific?
A strong research question should be specific enough that your methodology or testing procedure produces an objective result, not one left to subjective interpretation. Open-ended research questions or those relating to general topics can create ambiguous connections between the results and the aims of the study.
Is my research question sufficiently complex?
The result of your research should be consequential and substantial (and fall sufficiently within the context of your field) to warrant an academic study. Simply reinforcing or supporting a scientific consensus is superfluous and will likely not be well received by most journal editors.

Editing Your Research Question
Your research question should be fully formulated well before you begin drafting your research paper. However, you can receive English paper editing and proofreading services at any point in the drafting process. Language editors with expertise in your academic field can assist you with the content and language in your Introduction section or other manuscript sections. And if you need further assistance or information regarding paper compositions, in the meantime, check out our academic resources , which provide dozens of articles and videos on a variety of academic writing and publication topics.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 12 December 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
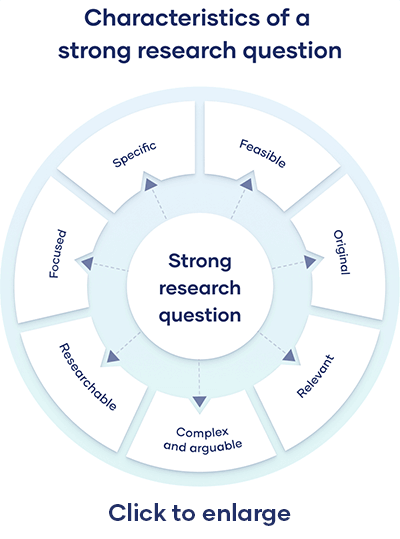
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, research questions quiz, frequently asked questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
| Research question formulations | |
|---|---|
| Describing and exploring | |
| Explaining and testing | |
| Evaluating and acting |
Using your research problem to develop your research question
| Example research problem | Example research question(s) |
|---|---|
| Teachers at the school do not have the skills to recognize or properly guide gifted children in the classroom. | What practical techniques can teachers use to better identify and guide gifted children? |
| Young people increasingly engage in the ‘gig economy’, rather than traditional full-time employment. However, it is unclear why they choose to do so. | What are the main factors influencing young people’s decisions to engage in the gig economy? |
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Focused on a single topic | Your central research question should work together with your research problem to keep your work focused. If you have multiple questions, they should all clearly tie back to your central aim. |
| Answerable using | Your question must be answerable using and/or , or by reading scholarly sources on the topic to develop your argument. If such data is impossible to access, you likely need to rethink your question. |
| Not based on value judgements | Avoid subjective words like , , and . These do not give clear criteria for answering the question. |
Feasible and specific
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Answerable within practical constraints | Make sure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific. |
| Uses specific, well-defined concepts | All the terms you use in the research question should have clear meanings. Avoid vague language, jargon, and too-broad ideas. |
| Does not demand a conclusive solution, policy, or course of action | Research is about informing, not instructing. Even if your project is focused on a practical problem, it should aim to improve understanding rather than demand a ready-made solution. |
Complex and arguable
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Cannot be answered with or | Closed-ended, / questions are too simple to work as good research questions—they don’t provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. |
| Cannot be answered with easily-found facts | If you can answer the question through a single Google search, book, or article, it is probably not complex enough. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation prior to providing an answer. |
Relevant and original
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Addresses a relevant problem | Your research question should be developed based on initial reading around your . It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline. |
| Contributes to a timely social or academic debate | The question should aim to contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on. |
| Has not already been answered | You don’t have to ask something that nobody has ever thought of before, but your question should have some aspect of originality. For example, you can focus on a specific location, or explore a new angle. |
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarised in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, December 12). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 26 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-question/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, how to write a results section | tips & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Qualitative Research Questions
Try Qualtrics for free
How to write qualitative research questions.
11 min read Here’s how to write effective qualitative research questions for your projects, and why getting it right matters so much.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a blanket term covering a wide range of research methods and theoretical framing approaches. The unifying factor in all these types of qualitative study is that they deal with data that cannot be counted. Typically this means things like people’s stories, feelings, opinions and emotions , and the meanings they ascribe to their experiences.
Qualitative study is one of two main categories of research, the other being quantitative research. Quantitative research deals with numerical data – that which can be counted and quantified, and which is mostly concerned with trends and patterns in large-scale datasets.
What are research questions?
Research questions are questions you are trying to answer with your research. To put it another way, your research question is the reason for your study, and the beginning point for your research design. There is normally only one research question per study, although if your project is very complex, you may have multiple research questions that are closely linked to one central question.
A good qualitative research question sums up your research objective. It’s a way of expressing the central question of your research, identifying your particular topic and the central issue you are examining.
Research questions are quite different from survey questions, questions used in focus groups or interview questions. A long list of questions is used in these types of study, as opposed to one central question. Additionally, interview or survey questions are asked of participants, whereas research questions are only for the researcher to maintain a clear understanding of the research design.
Research questions are used in both qualitative and quantitative research , although what makes a good research question might vary between the two.
In fact, the type of research questions you are asking can help you decide whether you need to take a quantitative or qualitative approach to your research project.
Discover the fundamentals of qualitative research
Quantitative vs. qualitative research questions
Writing research questions is very important in both qualitative and quantitative research, but the research questions that perform best in the two types of studies are quite different.
Quantitative research questions
Quantitative research questions usually relate to quantities, similarities and differences.
It might reflect the researchers’ interest in determining whether relationships between variables exist, and if so whether they are statistically significant. Or it may focus on establishing differences between things through comparison, and using statistical analysis to determine whether those differences are meaningful or due to chance.
- How much? This kind of research question is one of the simplest. It focuses on quantifying something. For example:
How many Yoruba speakers are there in the state of Maine?
- What is the connection?
This type of quantitative research question examines how one variable affects another.
For example:
How does a low level of sunlight affect the mood scores (1-10) of Antarctic explorers during winter?
- What is the difference? Quantitative research questions in this category identify two categories and measure the difference between them using numerical data.
Do white cats stay cooler than tabby cats in hot weather?
If your research question fits into one of the above categories, you’re probably going to be doing a quantitative study.
Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions focus on exploring phenomena, meanings and experiences.
Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research isn’t about finding causal relationships between variables. So although qualitative research questions might touch on topics that involve one variable influencing another, or looking at the difference between things, finding and quantifying those relationships isn’t the primary objective.
In fact, you as a qualitative researcher might end up studying a very similar topic to your colleague who is doing a quantitative study, but your areas of focus will be quite different. Your research methods will also be different – they might include focus groups, ethnography studies, and other kinds of qualitative study.
A few example qualitative research questions:
- What is it like being an Antarctic explorer during winter?
- What are the experiences of Yoruba speakers in the USA?
- How do white cat owners describe their pets?
Qualitative research question types
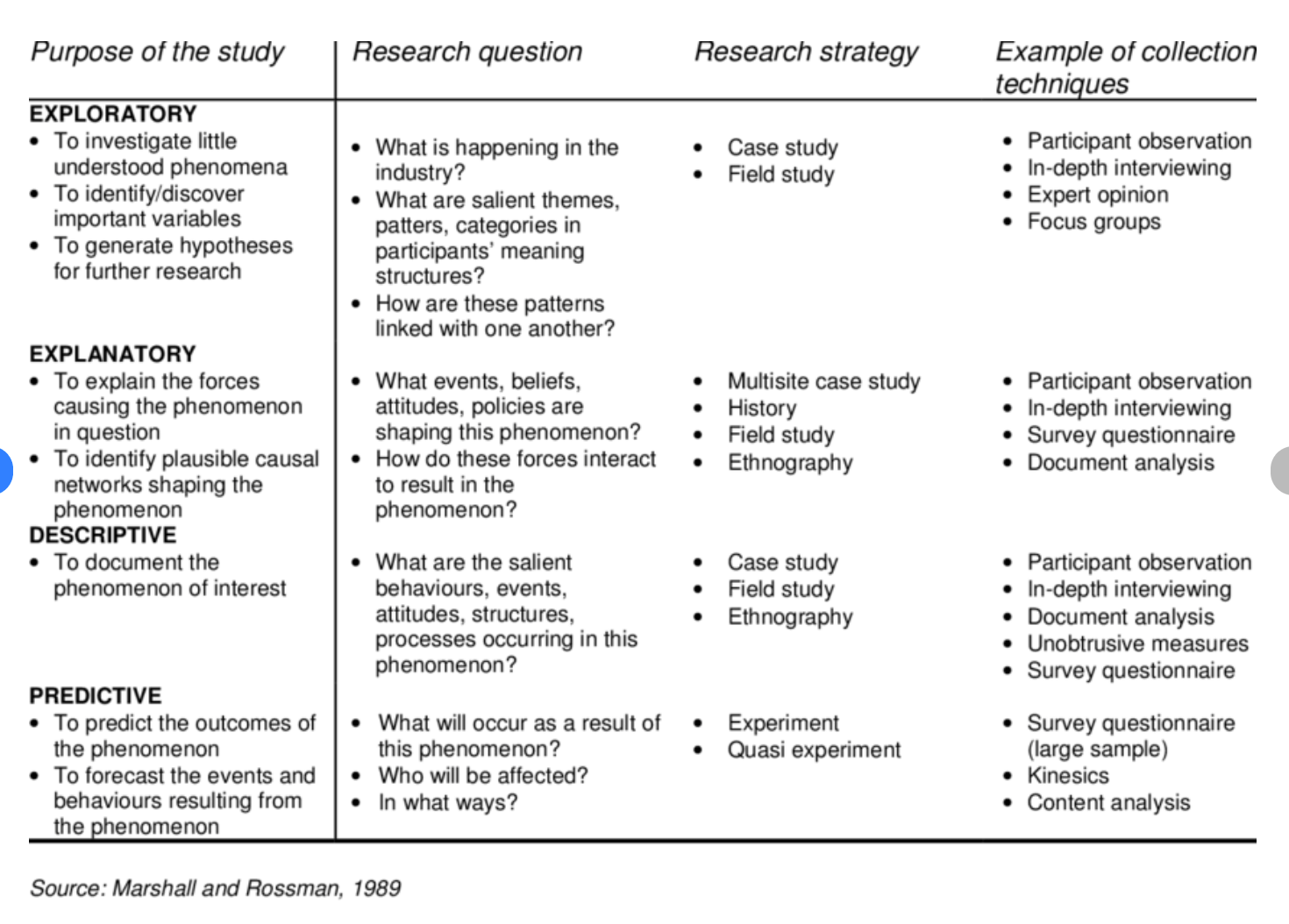
Marshall and Rossman (1989) identified 4 qualitative research question types, each with its own typical research strategy and methods.
- Exploratory questions
Exploratory questions are used when relatively little is known about the research topic. The process researchers follow when pursuing exploratory questions might involve interviewing participants, holding focus groups, or diving deep with a case study.
- Explanatory questions
With explanatory questions, the research topic is approached with a view to understanding the causes that lie behind phenomena. However, unlike a quantitative project, the focus of explanatory questions is on qualitative analysis of multiple interconnected factors that have influenced a particular group or area, rather than a provable causal link between dependent and independent variables.
- Descriptive questions
As the name suggests, descriptive questions aim to document and record what is happening. In answering descriptive questions , researchers might interact directly with participants with surveys or interviews, as well as using observational studies and ethnography studies that collect data on how participants interact with their wider environment.
- Predictive questions
Predictive questions start from the phenomena of interest and investigate what ramifications it might have in the future. Answering predictive questions may involve looking back as well as forward, with content analysis, questionnaires and studies of non-verbal communication (kinesics).
Why are good qualitative research questions important?
We know research questions are very important. But what makes them so essential? (And is that question a qualitative or quantitative one?)
Getting your qualitative research questions right has a number of benefits.
- It defines your qualitative research project Qualitative research questions definitively nail down the research population, the thing you’re examining, and what the nature of your answer will be.This means you can explain your research project to other people both inside and outside your business or organization. That could be critical when it comes to securing funding for your project, recruiting participants and members of your research team, and ultimately for publishing your results. It can also help you assess right the ethical considerations for your population of study.
- It maintains focus Good qualitative research questions help researchers to stick to the area of focus as they carry out their research. Keeping the research question in mind will help them steer away from tangents during their research or while they are carrying out qualitative research interviews. This holds true whatever the qualitative methods are, whether it’s a focus group, survey, thematic analysis or other type of inquiry.That doesn’t mean the research project can’t morph and change during its execution – sometimes this is acceptable and even welcome – but having a research question helps demarcate the starting point for the research. It can be referred back to if the scope and focus of the project does change.
- It helps make sure your outcomes are achievable
Because qualitative research questions help determine the kind of results you’re going to get, it helps make sure those results are achievable. By formulating good qualitative research questions in advance, you can make sure the things you want to know and the way you’re going to investigate them are grounded in practical reality. Otherwise, you may be at risk of taking on a research project that can’t be satisfactorily completed.
Developing good qualitative research questions
All researchers use research questions to define their parameters, keep their study on track and maintain focus on the research topic. This is especially important with qualitative questions, where there may be exploratory or inductive methods in use that introduce researchers to new and interesting areas of inquiry. Here are some tips for writing good qualitative research questions.
1. Keep it specific
Broader research questions are difficult to act on. They may also be open to interpretation, or leave some parameters undefined.
Strong example: How do Baby Boomers in the USA feel about their gender identity?
Weak example: Do people feel different about gender now?
2. Be original
Look for research questions that haven’t been widely addressed by others already.
Strong example: What are the effects of video calling on women’s experiences of work?
Weak example: Are women given less respect than men at work?
3. Make it research-worthy
Don’t ask a question that can be answered with a ‘yes’ or ‘no’, or with a quick Google search.
Strong example: What do people like and dislike about living in a highly multi-lingual country?
Weak example: What languages are spoken in India?
4. Focus your question
Don’t roll multiple topics or questions into one. Qualitative data may involve multiple topics, but your qualitative questions should be focused.
Strong example: What is the experience of disabled children and their families when using social services?
Weak example: How can we improve social services for children affected by poverty and disability?
4. Focus on your own discipline, not someone else’s
Avoid asking questions that are for the politicians, police or others to address.
Strong example: What does it feel like to be the victim of a hate crime?
Weak example: How can hate crimes be prevented?
5. Ask something researchable
Big questions, questions about hypothetical events or questions that would require vastly more resources than you have access to are not useful starting points for qualitative studies. Qualitative words or subjective ideas that lack definition are also not helpful.
Strong example: How do perceptions of physical beauty vary between today’s youth and their parents’ generation?
Weak example: Which country has the most beautiful people in it?
Related resources
Qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, business research methods 12 min read, qualitative research interviews 11 min read, market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
We track anonymous visitor behavior on our website to ensure you have a great experience. Learn more about our Privacy Policy .
- The Learning Accelerator
- Resources & Guidance
- Parabola Project
- What can teaching and learning practice look like?
- What are the conditions needed for success?
- How can blended learning help?
- How can I support quality remote and hybrid learning?
- Lovett Elementary School
- Trailblazer Elementary School
- The Forest School Online
- Valor Collegiate Academies
- ASU Prep Digital
- Lindsay High School
- Laurel Springs School
- Pleasant View Elementary School
- My Tech High
- CICS West Belden
- Bronx Arena High School
- Map Academy
- ReNEW DTA Academy
- Virtual Learning Academy Charter School (VLACS)
- Cisco Junior High School
- Locust Grove Middle School
- Crossroads FLEX High School
- Roots Elementary
- Gem Prep Online
- LPS Richmond
- Texas Tech University K-12
- Montana Digital Academy
- Cajon Valley Home School Program
- Valor Preparatory Academy of Arizona
- Teaching & Learning Practices
- Conditions for Success & Scale
- Train Your People
- Research & Measurement
- Learning Commons
- Problems of Practice
How to Write a Research Question: Types, Steps, and Examples
This website provides strategies for writing different types of research questions, the steps to creating research questions, and concrete examples.
Explore More

Driving EdTech Systems: Build Research and Measurement Capacity
Beginning with developing research questions and then describing methodologies to capture data and share findings, this strategy supports...

Using Data to Advocate for Changes in Virtual and Hybrid Learning Models
Districts that establish new virtual and/or hybrid schools should regularly collect data and engage stakeholders to evaluate the strength...


Using Data to Advocate for Students with Learning Differences
To foster the right learning environment for students with learning differences, educators must understand the data around how their...
- Research Paper Guides
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- How to Write a Research Question: Types & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write a Research Question: Types & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A research question is the main query that researchers seek to answer in their study. It serves as the basis for a scholarly project such as research paper, thesis or dissertation. A good research question should be clear, relevant and specific enough to guide the research process. It should also be open-ended, meaning that it allows for multiple possible answers or interpretations.
If you have located your general subject and main sources but still aren’t quite sure about the exact research questions for your paper, this guide will help you out. First, we will explore the concept of it together, so you could answer it in your work. Then some simple steps on composing your inquiry will be suggested. In the end, we will draw your attention to some specific details which can make your work good or bad. Sometimes it’s just easier to delegate all challenging tasks to a reliable research paper service . StudyCrumb is a trustable network of qualified writers ready to efficiently solve students’ challenges.
What Is a Good Research Question: Full Definition
Good research questions provide a concise definition of a problem. As a scholar, your main goal at the beginning is to select the main focus. It should be narrow enough so you could examine it within your deadline. Your work should be focused on something specific. Otherwise, it will require too much work and might not produce clear answers. At the same time your answer should be arguable and supported by data you’ve collected. Take a look at this example:

How to Write a Research Question: Step-By-Step Guide
In this section we will examine the process of developing a research question. We will guide you through it, step by step. Keep in mind that your subject should be important for your audience. So it requires some preliminary study and brainstorming. Let’s take a closer look at the main steps.
Step 1. Choose a Broad Topic for Your Research Paper Question
First, you need to decide on your general direction. When trying to identify your research paper questions, it is better to choose an area you are really interested in. You should be able to obtain enough data to write something about this topic. Therefore, do not choose something out of your reach. At the same time, your broad topic should not be too simple. Research paper questions that can be answered without any study would hardly make any sense for your project.
Step 2. Do Preliminary Reading Before Starting Your Research Question
Next, it is time we explore the context of the selected topic. You wouldn’t want to choose research questions that have already been examined and answered in detail. On the other hand, choosing a topic that is a complete ‘terra incognita’ might be a bridge too far for your project. Browse through available sources that are related to this topic. You should try and find out what has been discovered about it before. Do you see a gap that you can fill with your study? You can proceed with developing your exact inquiry! Have no time for in-depth topic exploration? Leave this task to professionals. Entrust your “ write my research paper ” order to StudyCrumb and get a top-notch work.
Step 3. Consider an Audience for Your Research Question
It is good to know your reader well to be able to convey your ideas and results to them in the best possible way. Before writing research questions for your projects, you might need to perform a brief analysis of your audience. That's how you'll be able to understand what is interesting for them and what is not. This will allow you to make better decisions when narrowing your broad topic down. Select a topic that is interesting for your reader! This would contribute much to the success for writing a research paper .
Step 4. Start Asking a Good Research Question
After you have considered your options, go ahead and compose the primary subject of your paper. What makes a good research question? It should highlight some problematic and relevant aspects of the general topic. So, after it is answered, you should have obtained some new valuable knowledge about the subject. Typically scholars start narrowing down their general topic by asking ‘how’, ‘why’ or ‘what’s next’ questions. This approach might help you come up with a great idea quickly.
Step 5. Evaluate Your Research Question
Finally, after you have composed a research paper question, you should take a second look at it and see if it is good enough for your paper. It would be useful to analyze it from the following sides:
- Is it clear for your audience?
- Is it complex enough to require significant study?
- Is it focused on a certain aspect of your general topic?
You might use the help of your peers or your friends at this step. You can also show it to your tutor and ask for their opinion.
Types of Research Questions: Which to Choose
A number of research questions types are available for use in a paper. They are divided into two main groups:
Qualitative questions:
- Explanatory
- Ethnographic
Quantitative questions:
- Descriptive
- Comparative
- Relationship based.
Selecting a certain type would impact the course of your study. We suggest you think about it carefully. Below you can find a few words about each type. Also, you can seek proficient help from academic experts. Buy a research paper from real pros and forget about stress once and for all.
Qualitative Research Questions: Definition With Example
When doing qualitative research, you are expected to aim to understand the different aspects and qualities of your target problem. Therefore, your thesis should focus on analyzing people’s experience, ideas and reflections rather than on obtaining some statistical data and calculating trends. Thus, this inquiry typically requires observing people’s behavior, interacting with them and learning how they interpret your target problem. Let’s illustrate this with an example:

What Is Contextual Research Questions
Contextual research revolves around examining your subject in its natural, everyday environment. It may be watching animals living in their usual habitats or people doing their normal activities in their familiar surroundings (at home, at school or at office). This academic approach helps to understand the role of the context. You'll be able to better explain connections between your problem, its environment and outcomes. This type of inquiry ought to be narrow enough. You shouldn’t have to examine each and every aspect of the selected problem in your paper. Consider this example:

Definition and Sample of Evaluative Research Questions
Evaluative research is performed in order to carefully assess the qualities of a selected object, individual, group, system or concept. It typically serves the purpose of collecting evidence that supports or contradicts solutions for a problem. This type of inquiry should focus on how useful a certain quality is for solving the problem. To conduct such study, you need to examine selected qualities in detail. Then, you should assume whether they match necessary criteria. It might include some quantitative methods such as collecting statistics. Although, the most important part is analyzing the qualities. If you need some examples, here’s one for you:

Explanatory Research Questions: Definition With Example
Your paper can be dedicated to explaining a certain phenomenon, finding its reasons and important relationships between it and other important things. Your explanatory research question should aim to highlight issues, uncertainties and problematic aspects of your subject. So, your study should bring clarity about these qualities. It should show how and why they have developed this way. An explanation may include showing causes and effects of issues in question, comparing the selected phenomenon to other similar types and showing whether the selected qualities match some predefined criteria. If you need some examples, check this one:

Generative Research Questions
This type of research is conducted in order to better understand the subject. With its help, you can find some new solutions or opportunities for improvement. Therefore, its main purpose is to develop a theoretical basis for further actions. You need to compose your generative research questions in a way that facilitates obtaining new ideas. It would help to begin with asking ‘why’, ‘what is the relationship between the subject and the problems X, Y, and Z’, ‘what can be improved here’, ‘how we can prevent it’ and so on. Need relevant examples? We’ve got one for you:

Ethnographic Research Question
Ethnography research is focused on a particular group of people. The aim is to study their behavior, typical reactions to certain events or information, needs, preferences or habits. Important parameters of this group which are most relevant to your general subject are taken into consideration. These are age, sex, language, religion, ethnicity, social status and so on. Main method in this case is first-hand observation of people from the selected group during an extended period of time. If you need strong examples, here’s one:

Quantitative Research Questions: Full Definition With Examples
Quantitative research deals with data – first of all, it is numeric data. It involves mathematical calculations and statistical analysis. It helps to obtain knowledge which is mostly expressed in numbers, graphs and tables. Unlike the qualitative type, the purpose of quantitative research is finding patterns, calculating probabilities, testing causal relationships and making predictions. It is focused on testing theories and hypotheses. (We have the whole blog on what is a hypothesis .) It is mostly used in natural and social sciences. These are: chemistry, biology, psychology, economics, sociology, marketing, etc. Here are a couple of examples:

Descriptive Research Questions: Definition With Example
This is probably the most widespread type of quantitative research question. Such inquiries seek to explain when, where, why, or how something occurred. They describe it accurately and systematically. These inquiries typically start with ‘what’. You are expected to use various methods to investigate one or more variables and determine their dependencies. Note, however, that you cannot control or manipulate any of these variables. You can only observe and measure them. Looking for some interesting examples? Here is one:

Definition of Comparative Research Questions
Comparative research question is used to highlight different variables and provide numerical evidence. This type is based on comparing one object, parameter or issue with another one of a similar kind. It can help to discover the differences between two or more groups by examining their outcome variables. Take a look at these two examples:

Relationship Research Questions
We conduct this type of research when we need to make it clear whether one parameter of a selected object causes another one. A relationship based quantitative research question should help us to explore and define trends and interactions between two or more variables. Are these two things mutually dependent? What kind of dependence is it? How has it developed? And what are possible outcomes of this connection? Here is an example of relationship-based quantitative research questions:

Research Questions Examples: Free
This section contains a number of helpful examples of research questions. Feel free to use them as inspiration to create your own questions and conduct productive study. Let’s start with two simple ones:

Are you interested in well written and inspiring questions? Do you want to learn what to avoid in your study? Just stay with us – there will be more of them below.
Examples of Good and Bad Research Questions
Everyone is interested in getting the best possible appraisal for their study. Choosing a topic which doesn't suit your specific situation may be discouraging. Thus, the quality of your paper might get affected by a poor choice. We have put together some good and bad examples so that you could avoid such mistakes.
Good Research Questions Examples
It is important to include clear terms into your questions. Otherwise, it would be difficult for you to plan your investigation properly. Also, they must be focused on a certain subject, not multiple ones. And finally, it should be possible to answer them. Let’s review several good examples:

Examples of Bad Research Questions
It is difficult to evaluate qualities of objects, individuals or groups if your purpose is not clear. This is why you shouldn’t create unclear research questions or try to focus on many problems at once. Some preliminary study might help to understand what you should focus on. Here are several bad examples:

In case you may need some information about the discussion section of a research paper example , find it in our blog.
Final Thoughts on Research Questions
In this article we have made a detailed review of the most popular types of research questions. We described peculiarities. We also provided some tips on conducting various kinds of study. Besides, a number of useful examples have been given for each category of questions.
Feel free to check out essay writing services. We have experienced writers who can help you compose your paper in time. They will absolutely ensure the high quality of your text.
Frequently Asked Questions About Research Questions
1. what is an example of a weak research question.
Here is an example of the weakest research question:
What kinds of animals live in the USA? |
An answer would be simply making a list of species that inhabit the country. This subject does not require any actual study to be conducted. There is nothing to calculate or analyze here.
2. What is the most effective type of research question?
Most effective type of research question is the one that doesn't have a single correct answer. However, you should also pay close attention to your audience. If you need to create a strong effect, better choose a topic which is relevant for them.
3. What is a good nursing research question?
If you need an idea for a nursing research question, here are a few helpful examples you could use as a reference:
How do you analyze the development of telehealth? |
How to evaluate critical care nursing? |
What are some cardiovascular issues? |
4. What are some sociological research questions?
Sociological questions are the ones that examine the social patterns or a meaning of a social phenomenon. They could be qualitative or quantitative. They should target groups of people with certain parameters, such as age or income level. Keep in mind that type of study usually requires collecting numerous data about your target groups.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

Training videos | Faqs

Formulating Strong Research Questions: Examples and Writing Tips
Abstract | Introduction | Literature Review | Research question | Materials & Methods | Results | Discussion | Conclusion
In this blog, we will see how to construct and present the research question in your research paper. We will also look at other components that make up the final paragraph of the introduction section of your paper.
1. What is a research question in a research paper?

The research questions are normally the aims and objectives of your work. The research question pinpoints exactly what it is you want to find out in your work. You can have a single research question or multiple research questions in your paper depending on the complexity of your research. Generally, it is a good idea to keep the number of research questions to less than four.
2. Research question examples
Let’s look at some examples of research questions. The research question is normally one of the major components of the final paragraph of the introduction section. We will look at the examples of the entire final paragraph of the introduction along with the research questions to put things into perspective.
2.1. Example #1 (Health sciences research paper)
Here is an example from a health sciences research paper. The passage starts with the research gap. The authors are saying that there is a need for a better understanding of the relationship between social media and mental health. Then, the authors explain the aims of their research and elaborate on what methodology they will be using to achieve their aims. The authors say that they will be using online surveys and face-to-face interviews to collect data to answer their research question. The passage flows very well and the author nicely lays out the research gap, the study aims, and the plan of action.
The effects of social media usage on mental health are poorly documented in the literature as research papers on the topic give contradictory conclusions. The present study aims to improve our understanding of the effects of social media usage on mental health. The data were collected from a variety of age-group over a period of two years in a structured manner. The methods of data collection involved online surveys and face-to-face interviews. _ Research gap _ Research question _ _ Method summary
2.2. Example #2 (Hypothesis-driven research paper)
Here is a slightly different variant of the previous example. Here, the authors have formulated the research question in the form of a hypothesis. Same as before, the authors are establishing the research gap in the first statement. In the next couple of statements, they are defining a specific hypothesis that they will be testing in the paper. In this case, they are testing the link between social media and mental health. And in the final statement, they are explaining the research methodology they will be employing to either prove or disprove the hypothesis. This is a pretty good example to follow if your research work is hypothesis-driven.
Past research suggests that while social media use is correlated with levels of anxiety and depression, the evidence so far is limited [1-2]. Therefore, building on previous discussion, Hypothesis 1 proposes: The levels of anxiety and depression will be lower among those who use social media platforms less frequently compared to those who use social media more frequently. This hypothesis (H1) is tested in this study through surveys and face-to-face interviews. _ Research gap _ Research question (Hypothesis) _ Method summary
2.3. Example #3 (Computer sciences research paper)
Here is an example from a computer sciences research paper. The authors establish the research gap by saying that there aren’t many papers on the topic of stock price prediction. Then, they explain what they are proposing. They are proposing a new method called the ‘Hybrid prediction model’. Then, they are providing a brief breakdown of their method by explaining how their method functions. They are saying that in their approach they are combining multiple methods in a structured way to improve the overall prediction accuracy of stock prices.
Only a few papers have addressed the problem of accurately predicting stock prices. In this paper, we propose a method, called the Hybrid Prediction Method that combines a selection of existing methods in a structured way to improve on the results obtained by using any single method alone. This paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, we introduce the Hybrid Analysis. Section 3 presents a number of experiments and results, and these results are discussed in Section 6. Section 7 concludes the paper. _ Research gap _ Research question _ Paper outline
Finally, they finish off the section by providing the outline of the paper. Please note, providing the paper outline is optional. It depends on your personal preference and journal requirements. This passage is a typical format you will see in engineering research papers that propose a new method to solve a particular problem.
2.4. Example #4 (Psychology research paper)
Here is an example from a psychology research paper. In the first line, the authors clearly state the research question, and the methodology they will be using to address it. The authors aim to test the impact of background music on the listener’s ability to remember words. They will be addressing this by performing a series of experiments in which observers will be shown words on the computer screen while playing different types of background music. Then, they are finishing off the section with a very brief summary of the results. This is a good idea because it will provide readers with a rough idea of what to expect from the rest of the paper.
In two experiments, we tested whether the presence of background music had an effect on memory recall. More precisely, we examined whether the type of music, either classical or pop, had an impact on the ability of people to remember a list of words. Observers viewed a list of words on a computer screen and listened to either classical or pop music in the background. The results of this study indicate significant differences between classical and pop music in terms of their effects on memory recall and cognition. _ _ Research questions _ Methods summary _ Results summary
3. Frequently Asked Questions
Your research question should align with your research gap and the problem statement. The research question should logically follow the problem statement and research gap you established in the previous sections of your paper. If your research objectives are misaligned with your problem statement and research gap, then reviewers will reject your paper. So make sure they are all tightly aligned with each other.
Look at the first example. We are saying that we are going to study the impact of social media on young people. The research question is too broad. As you can see there is no clear direction, and the study attempts to take on too much.
The research aims to find out the impact of social media on young people. Bad research question (Too broad)
Now, look at the second example. It is much more focused. We are very specific about our research questions. We are saying that we are attempting to measure the average time spent by teenagers on social media. And, we are also trying to understand the exact nature of their interactions on social media. We will be using an online questionnaire to answer the questions and we will be choosing participants from England and Scotland. This is a good research question, because it clearly defines what you have set out to do and how you plan to achieve it.
The research aims to estimate the average time spent by 18-24 year-olds on social media, and investigate the nature of interactions and conversations they have on social media. We attempt to answer these questions by conducting an online questionnaire survey in England and Scotland. Good research question (Very specific and focussed)
Similar Posts

How to Write a Research Paper? A Beginners Guide with Useful Academic Phrases
This blog explains how to write a research paper and provides writing ideas in the form of academic phrases.

How to Make Your Study Limitations Sound Positive?
In this blog, we will look at some clever techniques to present the study limitations without reducing the impact of your work.

Abstract Section Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through many abstract examples and understand how to construct a good abstract for your research paper.
Conclusion Section Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through many conclusion examples and learn how to present a powerful final take-home message to your readers.

Critical Literature Review : How to Critique a Research Article?
In this blog, we will look at how to use constructive language when critiquing other’s work in your research paper.

Examples of Good and Bad Research Questions
In this blog, we will look at some examples of good and bad research questions and learn how to formulate a strong research question.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 2 Share Facebook
- 1 Share Twitter
- 0 Share LinkedIn
- 1 Share Email
- How it works

Quantitative Research Questionnaire – Types & Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 20th, 2024 , Revised On August 21, 2024
Research is usually done to provide solutions to an ongoing problem. Wherever the researchers see a gap, they tend to launch research to enhance their knowledge and to provide solutions to the needs of others. If they want to research from a subjective point of view, they consider qualitative research. On the other hand, when they research from an objective point of view, they tend to consider quantitative research.
There’s a fine line between subjectivity and objectivity. Qualitative research, related to subjectivity, assesses individuals’ personal opinions and experiences, while quantitative research, associated with objectivity, collects numerical data to derive results. However, the best medium to collect data in quantitative research is a questionnaire.
Let’s discuss what a quantitative research questionnaire is, its types, methods of writing questions, and types of survey questions. By thoroughly understanding these key essential terms, you can efficiently create a professional and well-organised quantitative research questionnaire.
What is a Quantitative Research Questionnaire?
Quantitative research questionnaires are preferably used during quantitative research. They are a well-structured set of questions designed specifically to gather specific, close-ended participant responses. This allows the researchers to gather numerical data and obtain a deep understanding of a particular event or problem.
As you know, qualitative research questionnaires contain open-ended questions that allow the participants to express themselves freely, while quantitative research questionnaires contain close-ended and specific questions, such as multiple-choice and Likert scales, to assess individuals’ behaviour.
Quantitative research questionnaires are usually used in research in various fields, such as psychology, medicine, chemistry, and economics.
Let’s see how you can write quantitative research questions by going through some examples:
- How much do British people consume fast food per week?
- What is the percentage of students living in hostels in London?
Types of Quantitative Research Questions With Examples
After learning what a quantitative research questionnaire is and what quantitative research questions look like, it’s time to thoroughly discuss the different types of quantitative research questions to explore this topic more.
Dichotomous Questions
Dichotomous questions are those with a margin for only two possible answers. They are usually used when the answers are “Yes/No” or “True/False.” These questions significantly simplify the research process and help collect simple responses.
Example: Have you ever visited Istanbul?
Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple-choice questions have a list of possible answers for the participants to choose from. They help assess people’s general knowledge, and the data gathered by multiple-choice questions can be easily analysed.
Example: Which of the following is the capital of France?
Multiple Answer Questions
Multiple-answer questions are similar to multiple-choice questions. However, there are multiple answers for participants to choose from. They are used when the questions can’t have a single, specific answer.
Example: Which of the following movie genres are your favourite?
Likert Scale Questions
Likert scale questions are used when the preferences and emotions of the participants are measured from one extreme to another. The scales are usually applied to measure likelihood, frequency, satisfaction, and agreement. The Likert scale has only five options to choose from.
Example: How satisfied are you with your job?
Semantic Differential Questions
Similar to Likert scales, semantic differential questions are also used to measure the emotions and attitudes of participants. The only difference is that instead of using extreme options such as strongly agree and strongly disagree, opposites of a particular choice are given to reduce bias.
Example: Please rate the services of our company.
Rank Order Questions
Rank-order questions are usually used to measure the preferences and choices of the participants efficiently. In this, multiple choices are given, and participants are asked to rank them according to their perspective. This helps to create a good participant profile.
Example: Rank the given books according to your interest.
Matrix Questions
Matrix questions are similar to Likert scales. In Likert scales, participants’ responses are measured through separate questions, while in matrix questions, multiple questions are compiled in a single row to simplify the data collection method efficiently.
Example: Rate the following activities that you do in daily life.
How To Write Quantitative Research Questions?
Quantitative research questions allow researchers to gather empirical data to answer their research problems. As we have discussed the different types of quantitative research questions above, it’s time to learn how to write the perfect quantitative research questions for a questionnaire and streamline your research process.
Here are the steps to follow to write quantitative research questions efficiently.
Step 1: Determine the Research Goals
The first step in writing quantitative research questions is to determine your research goals. Determining and confirming your research goals significantly helps you understand what kind of questions you need to create and for what grade. Efficiently determining the research goals also reduces the need for further modifications in the questionnaire.
Step 2: Be Mindful About the Variables
There are two variables in the questions: independent and dependent. It is essential to decide what would be the dependent variable in your questions and what would be the independent. It significantly helps to understand where to emphasise and where not. It also reduces the probability of additional and vague questions.
Step 3: Choose the Right Type of Question
It is also important to determine the right type of questions to add to your questionnaire. Whether you want Likert scales, rank-order questions, or multiple-answer questions, choosing the right type of questions will help you measure individuals’ responses efficiently and accurately.
Step 4: Use Easy and Clear Language
Another thing to keep in mind while writing questions for a quantitative research questionnaire is to use easy and clear language. As you know, quantitative research is done to measure specific and simple responses in empirical form, and using easy and understandable language in questions makes a huge difference.
Step 5: Be Specific About The Topic
Always be mindful and specific about your topic. Avoid writing questions that divert from your topic because they can cause participants to lose interest. Use the basic terms of your selected topic and gradually go deep. Also, remember to align your topic and questions with your research objectives and goals.
Step 6: Appropriately Write Your Questions
When you have considered all the above-discussed things, it’s time to write your questions appropriately. Don’t just haste in writing. Think twice about the result of a question and then consider writing it in the questionnaire. Remember to be precise while writing. Avoid overwriting.
Step 7: Gather Feedback From Peers
When you have finished writing questions, gather feedback from your researcher peers. Write down all the suggestions and feedback given by your peers. Don’t panic over the criticism of your questions. Remember that it’s still time to make necessary changes to the questionnaire before launching your campaign.
Step 8: Refine and Finalise the Questions
After gathering peer feedback, make necessary and appropriate changes to your questions. Be mindful of your research goals and topic. Try to modify your questions according to them. Also, be mindful of the theme and colour scheme of the questionnaire that you decided on. After refining the questions, finalise your questionnaire.
Types of Survey Questionnaires in Quantitative Research
Quantitative research questionnaires have close-ended questions that allow the researchers to measure accurate and specific responses from the participants. They don’t contain open-ended questions like qualitative research, where the response is measured by interviews and focus groups. Good combinations of questions are used in the quantitative research survey .
However, here are the types of surveys in quantitative research:
Descriptive Survey
The descriptive survey is used to obtain information about a particular variable. It is used to associate a quantity and quantify research variables. The questions associated with descriptive surveys mostly start with “What is” and “How much”.
Example: A descriptive survey to measure how much money children spend to buy toys.
Comparative Survey
A comparative survey is used to establish a comparison between one or more dependable variables and two or more comparison groups. This survey aims to form a comparative relation between the variables under study. The structure of the question in a comparative survey is, “What is the difference in [dependable variable] between [two or more groups]?”.
Example: A comparative survey on the difference in political awareness between Eastern and Western citizens.
Relationship-Based Survey
Relationship-based survey is used to understand the relationship or association between two or more independent and dependent variables. Cause and effect between two or more variables is measured in the relationship-based survey. The structure of questions in a relationship-based survey is, “What is the relation [between or among] [independent variable] and [dependable variable]?”.
Example: What is the relationship between education and lifestyle in America?
Advantages & Disadvantages of Questionnaires in Quantitative Research
Quantitative research questionnaires are an excellent tool to collect data and information about the responses of individuals. Quantitative research comes with various advantages, but along with advantages, it also has its disadvantages. Check the table below to learn about the advantages and disadvantages of a quantitative research questionnaire.
| It is an efficient source for quickly collecting data. | It restricts the depth of the topic during collection. |
| There is less risk of subjectivity and research bias. | There is a high risk of artificial and unreal expectations of research questions. |
| It significantly helps to collect extensive insights into the population. | It overemphasises empirical data, avoiding personal opinions. |
| It focuses on simplicity and particularity. | There is a risk of over-simplicity. |
| There are clear and achievable research objectives. | There is a risk of additional amendments and modifications. |
Quantitative Research Questionnaire Example
Here is an example of a quantitative research questionnaire to help you get the idea and create an efficient and well-developed questionnaire for your research:















.webp)


.webp)
IMAGES
COMMENTS
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
3. Narrow down your topic and determine potential research questions. Once you have gathered enough knowledge on the topic you want to pursue, you can start focusing on a more specific area of study and narrowing down a research question. One option is to focus on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature.
A well-crafted research question (or set of questions) sets the stage for a robust study and meaningful insights. But, if you're new to research, it's not always clear what exactly constitutes a good research question. In this post, we'll provide you with clear examples of quality research questions across various disciplines, so that you can approach your research project with confidence!
Choose a broad topic, such as "learner support" or "social media influence" for your study. Select topics of interest to make research more enjoyable and stay motivated. Preliminary research. The goal is to refine and focus your research question. The following strategies can help: Skim various scholarly articles.
As the name suggests, these types of research questions seek to explore the relationships between variables. Here, an example could be something like "What is the relationship between X and Y" or "Does A have an impact on B". As you can see, these types of research questions are interested in understanding how constructs or variables ...
There are two types of research: Qualitative research and Quantitative research. There must be research questions for every type of research. Your research question will be based on the type of research you want to conduct and the type of data collection. The first step in designing research involves identifying a gap and creating a focused ...
Assess your chosen research question using the FINER criteria that helps you evaluate whether the research is Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant. 1. Formulate the final research question, while ensuring it is clear, well-written, and addresses all the key elements of a strong research question.
Most professional researchers focus on topics they are genuinely interested in studying. Writers should choose a broad topic about which they genuinely would like to know more. An example of a general topic might be "Slavery in the American South" or "Films of the 1930s.". Do some preliminary research on your general topic.
Here is our step-by-step guide: 1. Choose a topic. The first step is to select a broad research topic for your study. Pick something within your expertise and field that interests you. After all, the research itself will stem from the initial research question. 2.
Learn how to craft the perfect research question for your research project, be it a dissertation, a thesis, or any other sort of research paper. Derek Jansen...
Research Aims: Examples. True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording "this research aims to…", "this research seeks to…", and so on. For example: "This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.". "This study sets out to assess the interaction between student ...
A good research question aims to solve a problem that still needs to be answered and can be solved empirically. The approach might involve quantitative or qualitative methodology, or a mixture of both. To write a well-developed research question, follow the four steps below: 1. Select a general topic. Start with a broad topic.
Definition: Research questions are the specific questions that guide a research study or inquiry. These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective.
In a research paper, the emphasis is on generating a unique question and then synthesizing diverse sources into a coherent essay that supports your argument about the topic. In other words, you integrate information from publications with your own thoughts in order to formulate an argument. Your topic is your starting place: from here, you will ...
It can be difficult to come up with a good research question, but there are a few steps you can follow to make it a bit easier. 1. Start with an interesting and relevant topic. Choose a research topic that is interesting but also relevant and aligned with your own country's culture or your university's capabilities.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
5. Ask something researchable. Big questions, questions about hypothetical events or questions that would require vastly more resources than you have access to are not useful starting points for qualitative studies. Qualitative words or subjective ideas that lack definition are also not helpful.
This website provides strategies for writing different types of research questions, the steps to creating research questions, and concrete examples. We track anonymous visitor behavior on our website to ensure you have a great experience.
Example Research Question (s) Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem. Example Research Problem. Example Research Question (s) A small-scale company, 'A' in the UK, cannot allocate a marketing budget for next year due to their poor ...
Step 1. Choose a Broad Topic for Your Research Paper Question. Step 3. Consider an Audience for Your Research Question. Step 4. Start Asking a Good Research Question. Step 5. Evaluate Your Research Question. Types of Research Questions: Which to Choose.
Follow these steps when writing a research question: 1. Select a general topic. The first step to writing a research question is to choose a broad topic for your question. This can be something like "1920s novels" or "effects of technology." It's helpful to select something you are interested in and want to know more about, which can make ...
The research question is normally one of the major components of the final paragraph of the introduction section. We will look at the examples of the entire final paragraph of the introduction along with the research questions to put things into perspective. 2.1. Example #1 (Health sciences research paper)
Here are the steps to follow to write quantitative research questions efficiently. Step 1: Determine the Research Goals. The first step in writing quantitative research questions is to determine your research goals. Determining and confirming your research goals significantly helps you understand what kind of questions you need to create and ...
Research Question. Your research question is the catalyst that drives your search. In an assignment a research question can be given to you by a professor, which can be distinct or vague, or you might have to come up with your own question(s). All of these have their own difficulties. Your research question is bound to change overtime.
Finally, allocate your resources effectively. This includes budgeting for any costs, such as software, travel, or materials, and ensuring you have access to necessary resources like libraries or labs. Proper resource allocation can make a significant difference in the quality and feasibility of your research. Writing the Research Proposal
To Sum Up. Writing a research proposal can be straightforward if you break it down into manageable steps: Pick a strong research proposal topic that interests you and has enough material to explore.; Craft an engaging introduction that clearly states your research question and objectives.; Do a thorough literature review to see how your work fits into the existing research landscape.