- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
By: History.com Editors
Updated: June 16, 2023 | Original: January 4, 2018

The Great Sphinx of Giza is a giant 4,500-year-old limestone statue situated near the Great Pyramid in Giza, Egypt. Measuring 240 feet (73 meters) long and 66 feet (20 meters) high, the Great Sphinx is one of the world’s largest monuments. It is also one of the most recognizable relics of the ancient Egyptians, though the origins and history of the colossal structure are still debated.

What Is a Sphinx?
A sphinx (or sphynx) is a creature with the body of a lion and the head of a human, with some variations. It is a prominent mythological figure in Egyptian, Asian, and Greek mythology.
In ancient Egypt , the sphinx was a spiritual guardian and most often depicted as a male with a pharaoh headdress—as is the Great Sphinx—and figures of the creatures were often included in tomb and temple complexes. For instance, the so-called Sphinx Alley in Upper Egypt is a two-mile avenue that connects the temples of Luxor and Karnak and is lined with sphinx statues.
Sphinxes with the likeness of the female pharaoh Hatshepsut also exist, such as the granite sphinx statue at the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York and the large alabaster sphinx at the Ramessid temple in Memphis, Egypt.
From Egypt, the sphinx imported to both Asia and Greece around 15th to 16th century B.C. Compared with the Egyptian model, the Asian sphinx had eagle wings, was frequently female, and often sat on its haunches with one paw raised in depictions.
In Greek traditions, the sphinx also had wings, as well as the tail of a serpent—in legends, it devours all travelers unable to answer its riddle.
How Old Is the Sphinx?
The most common and widely accepted theory about the Great Sphinx suggests the statue was erected for the Pharaoh Khafre (about 2603-2578 B.C.).
Hieroglyphic texts suggest Khafre’s father, Pharaoh Khufu, built the Great Pyramid, the oldest and largest of the three pyramids in Giza. When he became Pharaoh, Khafre constructed his own pyramid next to his father’s; though Khafre’s pyramid is 10 feet shorter than the Great Pyramid, it is surrounded by a more elaborate complex that includes the Great Sphinx and other statues.
Residues of red pigments on the face of the Sphinx suggest the statue may have been painted.
Given the organization of the pyramids and the Sphinx, some scholars believe there may have been a celestial purpose to the Great Sphinx and temple complex, that is, to resurrect the soul of the pharaoh (Khafre) by channeling the power of the sun and other gods.
Several lines of evidence exist that tie the Great Sphinx to Pharaoh Khafre and his temple complex.
For one thing, the head and face of the Sphinx are strikingly similar to a life-size statue of Khafre that French archaeologist Auguste Mariette found in the Valley Temple—the ruins of a building situated adjacent to the Great Sphinx—in the mid-1800s.
Additionally, Mariette discovered remnants of a causeway (processional road) that connect the Valley Temple to a mortuary temple next to Khafre’s pyramid. In the early 1900s, French archaeologist Emile Baraize dug up another building (the Sphinx Temple) directly in front of the Sphinx that’s similar in design to the Valley Temple.
In the 1980s, researchers uncovered evidence that the limestone blocks used in the walls of the Sphinx Temple came from the ditch surrounding the great statue, suggesting workmen hauled away quarry blocks for the Sphinx Temple as they were being chipped off the Great Sphinx during its construction.
Researchers estimate that it would have taken 100 people 3 years to carve the Great Sphinx out of a single mass of limestone. But there’s some evidence that these workers may have suddenly quit before fully finishing the sphinx and temple complex, such as partially quarried bedrock and remnants of a workman’s lunch and tool kit.
Other Theories
Over the years, researchers have put forth many other theories for the Great Sphinx’s origins, though most are refuted by mainstream Egyptologists.
Some theories suggest the face of the sphinx actually resembles Khufu and, therefore, Khufu built the structure. Alternatively, Pharaoh Djedefre—Khafre’s older half-brother and Khufu’s other son—built the Great Sphinx in commemoration of his father.
Other theories hold that the statue depicts Amenemhat II (around 1929 to 1895 B.C.) based on the style of the stripes on the sphinx’s head cloth.
Some scientists also contend that the Great Sphinx is far older than is widely believed, based on the potential age of the causeway or various patterns of erosion of the statue.
Riddle of the Sphinx
What Egyptians called the Great Sphinx during its prime remains a riddle, because the word sphinx originates from Greek mythology some 2,000 years after the statue was built.
It’s also unclear in what regard Egyptians held the Great Sphinx during the Old Kingdom (c. 2613-2181 B.C.), as there are few texts that discuss the statue. However, Khafre associated himself with the god Horus and the Great Sphinx may have been known as Harmakhet (“Horus on the Horizon”), as it was during the New Kingdom (1570-1069 B.C.).
Whatever the case, the statue began to fade into the desert background at the end of the Old Kingdom, at which point it was ignored for centuries.
Inscriptions on a pink granite slab between the Great Sphinx’s paws tell the story of how the statue was saved from the sands of time. Prince Thutmose, son of Amenhotep II, fell asleep near the Sphinx, the story goes. In Thutmose’s dream, the statue, calling itself Harmakhet, complained about its state of disarray and made a deal with the young prince: It would help him become pharaoh if he cleared away the sand from the statue and restored it.
Whether or not the dream actually occurred is unknown, but when the prince did, in fact, become Pharaoh Thutmose IV, he introduced a Sphinx-worshipping cult to his people. Statues, paintings, and reliefs of the figure popped up across the country and the sphinx became a symbol of royalty and the power of the sun.
Great Sphinx Restoration
The Great Sphinx was eventually forgotten again. Its body suffered from erosion and its face became damaged by time as well.
Though some stories claim Napoleon ‘s troops shot off the statue’s nose with a cannon when they arrived in Egypt in 1798, 18th-century drawings suggest the nose went missing long before then. More likely, the nose was purposely destroyed by a Sufi Muslim in the 15th century to protest idolatry. Part of the Sphinx’s royal cobra emblem from its headdress and sacred beard have also broken off, the latter of which is now displayed in the British Museum .
The Sphinx was actually buried in sand up to its shoulders until the early 1800s, when a Genoese adventurer named Capt. Giovanni Battista Caviglia attempted (and ultimately failed) to dig out the statue with a team of 160 men.
Mariette managed to clear some of the sand from around the sculpture and Baraize made another large excavation push in the 19th and 20th centuries. But it wasn’t until the late 1930s that Egyptian archaeologist Selim Hassan was able to finally free the creature from its sandy tomb.
Today, the Sphinx is continuing to deteriorate thanks to wind, humidity, and pollution. Restoration efforts have been ongoing since the mid-1900s, some of which failed and ultimately caused more damage to the Sphinx.
In 2007, authorities learned that the local water table under the statue was rising due to sewage being dumped in a nearby canal. The moisture ultimately spread through the porous limestone of the structure, causing the rock to crumble and break away in large flakes in some cases. Authorities installed pumps close to the Great Sphinx, diverting the groundwater and saving the relic from further destruction.
Sphinx-lined road unearthed in Egypt; PhysOrg .
The Great Sphinx of Giza; Ancient History Encyclopedia .
The Mystery of the Great Sphinx; Ancient History Encyclopedia .
Old Kingdom of Egypt; Ancient History Encyclopedia .
What happened to the Sphinx’s nose?; Smithsonian .
Saving the Sphinx; PBS/NOVA .

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
National Geographic content straight to your inbox—sign up for our popular newsletters here
- INTELLIGENT TRAVEL
The Icon: Egypt’s Great Sphinx
In Arabic, it’s called “the father of terror.” To us, it’s a riddle.
Who built the Great Sphinx of Giza ? No one can say for sure (though several of the more crazy theories point fingers at space aliens). The huge limestone statue, as tall as the White House in Washington, D.C., with paws bigger than city buses, was erected in the time of the Old Kingdom , probably during the reign of the Pharaoh Khafre, between the years 2558 and 2532 B.C.
The crouching lion with a man’s head was ancient when Cleopatra gazed upon it in 47 B.C. It retains its allure to the powerful, as world leaders from Napoleon to Barack Obama have trekked to Giza to contemplate the same view that captivated the queen of the Nile.
Name game: The Sphinx is an alias, created by the ancient Greeks when the statue was already centuries old. The early name was Hor-em-akhet, meaning “Horus in the horizon.” Horus is the Egyptian god of the sky.
Test of time: Out of the seven wonders of the ancient world, only the Giza Pyramids and the Sphinx are still standing.
Color me mysterious: The Sphinx was originally painted in garish comic-book colors like red. Traces of the pigment can be seen by its ear.
Copycat: In Las Vegas, the Egyptian-themed Luxor Hotel ‘s foam and plaster version is 35 feet taller than the original Sphinx, which rises 66 feet.
Close shave: The Sphinx originally sported a beard, which eventually crumbled. A piece of its “stubble” is displayed in the British Museum in London.
Secrets and lies: Legend says the library of the sunken island of Atlantis is stowed beneath the Sphinx, with an entrance near its right paw. Nothing has been found, according to bemused archaeologists.
- Nat Geo Expeditions
Nose job: Contrary to popular history, Napoleon’s cannonballs did not shoot off the Sphinx’s nose. The evidence suggests the nose was intentionally cleaved off at least 300 years before the Little Corporal invaded Egypt in 1798.
Pyramid scheme: If you don’t like the Saharan sun, try booking a seat for the sound-and-light show at night when desert temperatures are cooler. The program bathes the Sphinx and pyramids in vivid colors as a narrator relays their history.
Andrew Nelson is an editor at large at National Geographic Traveler magazine. Follow him on Twitter @AndrewNelson .
For Hungry Minds
Related topics, you may also like.

Inside this ‘Andean Easter Island,’ these volcanic statues are the rock stars

Where to travel in May

To see the real Los Angeles, visit its historic movie theaters

The world’s largest flattop mountain is an adventurer’s paradise

Walk across the sky in the U.S.’s highest-elevation city
- Environment
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Gory Details
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Paid Content
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved

- Ancient History
The Great Sphinx: exploring the enigma of its creation and purpose

The Great Sphinx of Egypt has long been a source of fascination and speculation for historians and archaeologists. Its massive size, intricate details, and enigmatic expression have sparked countless theories about its creation and purpose.
While there is still much debate about these topics, recent archaeological discoveries have shed new light on the history of the Great Sphinx.
What is the Sphinx?
The Great Sphinx is believed to have been constructed during the reign of the Pharaoh Khafre, who ruled Egypt from approximately 2558 to 2532 BCE.
The statue stands approximately 66 feet tall and 240 feet long, making it one of the largest monolithic statues in the world. It is carved from a single piece of limestone and depicts a lion's body with a human head, believed to be that of Khafre himself.
A sphinx is a mythological creature that typically has the body of a lion and the head of a human, although some variations depict the creature with the head of a falcon, ram, or other animal.
In ancient Egypt, sphinxes were typically depicted as having the head of a human and the body of a lion, and were associated with guardianship and protection. The Great Sphinx of Giza in Egypt is one of the most famous examples of a sphinx.
Why was it built?
While the Great Sphinx has long been associated with the Pharaoh Khafre, there is still much debate about its purpose. Some believe that it was constructed as a guardian of the Giza Necropolis, where the pharaohs were buried.
Others suggest that it was a symbol of the pharaoh's power and authority, while still others believe that it had a religious significance.
One theory that has gained traction in recent years is that the Great Sphinx was part of a larger complex of temples and monuments. Excavations in the area have uncovered evidence of a massive temple dedicated to the worship of the sun god Ra, as well as a series of smaller temples and tombs.
This suggests that the Great Sphinx may have been part of a larger architectural plan designed to celebrate the power and glory of the pharaohs.
What don't we know?
Despite these discoveries, much about the Great Sphinx remains shrouded in mystery. For example, it is still not clear how the statue was originally painted, or what color it may have been. Some scholars have suggested that it was painted in bright colors, while others believe that it was left unpainted.
One surprising point of contention is about the statue's face. It is often described as having a mysterious and enigmatic expression, but it is not clear what this expression might have meant to the ancient Egyptians.
What about the mysterious tablet found with the Sphinx?
An ancient table, known as the Dream Stele, has fascinated people for a long time. The Dream Stele is an ancient Egyptian monument that is located between the paws of the Great Sphinx in Giza, Egypt.
Also known as the Sphinx Stele, it was erected by the Pharaoh Thutmose IV in the 14th century BCE, during the 18th dynasty of Egypt.
The Dream Stele is a large slab of pink granite that is inscribed with hieroglyphs that describe a dream that Thutmose IV had while he was still a prince.
According to the inscription, Thutmose was out hunting when he fell asleep in the shadow of the Great Sphinx. In his dream, the Sphinx spoke to him and promised to make him king of Egypt if he cleared away the sand that was covering its body.
After waking up, Thutmose did as the Sphinx had instructed, and was eventually crowned as pharaoh. As a result, he believed that the Sphinx had granted him divine favor and protection, and he erected the Dream Stele as a testament to his connection with the powerful statue.
The Dream Stele is significant not only for its depiction of Thutmose IV's dream, but also for the information it provides about the history of the Sphinx. The inscription suggests that the Sphinx was already an ancient and revered monument by the time of Thutmose's reign, and that it was already surrounded by sand that had accumulated over the centuries.
The mystery lives on
Regardless of its original purpose and appearance, the Great Sphinx remains a powerful symbol of the ancient world. Its massive size and intricate details are a testament to the skill and creativity of the ancient Egyptians, while its enduring presence is a reminder of the enduring power of human civilization.
As archaeologists continue to explore the mysteries of the Great Sphinx, we can only hope that it will reveal more of its secrets in the years to come.
What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
The Art Form: The Great Sphinx Essay
Creation of the sphinx, the art form: algebra, the art form: the migrant mother, reference list.
It is quite interesting to note that unlike its counterpart within Greek mythology who mercilessly killed travelers who could not answer its riddle the Egyptian Sphinx was actually thought of as a benevolent guardian with a special relationship with the Sun (World Wonders, 2009).
This startling contrast between two cultures that existed at almost the same time throughout antiquity yet were separated by thousands of miles is indicative of a form of cultural “sharing” that is actually quite common throughout history and is indicative of some form of contact between Egypt and Greece, possibly through maritime trade (World Wonders, 2009).
An examination of the burial customs of ancient Egypt reveals a prominent usage of the Sphinx (for royalty and important officials at least).
It was often the case that the body of the Sphinx had the head of the person who was actually within the tomb (World Wonders, 2009). It can be hypothesized that by including an image of an individual on top of the guardian “beast” this was to indicate a special relationship between that person and the deity of the sun.
In fact Sphinx statues were also thought of as immobile guardians of tombs who were to protect the sanctity of a pharaoh’s resting place (World Wonders, 2009).
Thus the size of the Great Sphinx at Giza can be thought of as a greater display of an already accepted burial tradition within the ancient Egyptian world.
While the specifics regarding the precise history of the construction of the Sphinx is to this day generally unknown it is assumed by various local residents that the Great Sphinx at Giza was commissioned by Pharaoh Khafra in 2500 BC and was possibly created along the same time as the second pyramid of Giza.
As for how the giant statue itself was made various accounts by local residents have indicated that the mystery of its construction can actually be solved by looking at the very pyramids behind it.
Due to the interlocking nature of the limestone blocks found in the pyramids and the fact that the Sphinx itself is almost similarly made of limestone it can assumed that several of the limestone blocks from the same quarry as the pyramids were used in the statues construction with the same method of erecting different blocks utilized as a means do creating the height of the piece with the more intricate details added in later by stone carvers (Hadingham, 2010).
Aspects of Civilization and Cultural Development
Just by viewing the Sphinx itself it becomes obvious that the Sphinx represents not only the advanced nature of the fields of architecture and engineering during this particular time period within ancient Egyptian civilization but it also represents how important religious iconography was to the ancient Egyptian people and how the concept of death was thought of more highly than it is today (World Wonders, 2009).
Influence of Previous Civilizations
It must be noted that the Great Sphinx at Giza is not unique in the sense that it is the only example of its kind, such an assumption is fallacious given that it has already been mentioned within this paper that the iconography of the Sphinx was featured prominently in the burial customs of ancient Egyptian Pharaohs hundreds of years before the creation of the Great Sphinx.
Rather, a far more accurate statement would be that the Sphinx at Giza is the largest and most well known example of its kind and is a representation of hundreds of years of ancient Egyptian tradition in which it was known as a guardian of tombs and a representation of an aspect of their Sun deity.
Related to Artwork within the Same Civilization
It is quite interesting to note that the Great Sphinx at Giza has several stylistic elements which were quite prominent within this particular period of ancient Egyptian civilization.
For instance, the same headdress theme often utilized on a variety of pharaoh statues is utilized in the case of the Sphinx as well as the overall shape of the body is consistent with the way in which Sphinx statues at the time were created (Hadingham, 2010).
In fact it can even be said that the Great Sphinx at Giza is nothing more than a larger version of its smaller counterparts seen in a variety of ancient Egyptian tombs.
Value for Modern day Civilization
The value the Sphinx holds for modern day civilization is how it has come to represent the lack of knowledge we at the present still have on how ancient civilizations actually worked and functioned.
There are still numerous areas underneath the Sphinx that have yet to be explored, facets of how it was created that are still to be uncovered as well as mysteries regarding ancient Egypt that are still buried beneath the sands waiting to be found.
The art form in this particular case is Algebra which is well known method of calculating various concepts related to equations, variables and other similar mathematical concepts.
The purpose of the piece
When looking around at the present it is quite interesting to note that one of the greatest traditions of the Islamic civilization is mercantile behavior with various local merchants stating that the tradition of entrepreneurship and taking over businesses within Islamic civilization goes back hundreds if not thousands of years (Oliver, 2007).
As such, the original purpose of algebra in this particular case is one related to assisting merchants in their calculations for business.
Where did it originate from?
It is interesting to note that while basic calculations of algebra as we know it today originated from the Islamic civilization its roots actually stretch as far back as the ancient Babylonians who utilized it to great effect for accountancy, mercantile practices, and even calculations involving crop cycles and other such beneficial practices (Healey, 2006).
How the piece was made
Algebra was actually made as direct result of the combination of ancient mercantile practices involving calculation until it was further improved by Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī in 780 to 850 in the book “The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing” (Healey, 2006).
The meaning of the work
The work itself represents the importance numerical calculation within the Islamic culture and is actually indicative of the fact that mercantilism and accountancy were important facets of their cultural traditions.

Aspects of the civilization and the cultural development
This piece represents great advancements in analytical thought and mathematical understanding within the Islamic civilization at the time.
Influences from Previous Civilizations
The ancient Babylonian civilization greatly influenced the various precepts and rules utilized in algebra by the Islamic civilization.
Related to artwork within the same civilization
Unfortunately, aside from its use in business there is little similarity between algebra and what can be defined as the Islamic art form
Meaning and value in modern-day cultures
Algebra is widely utilized in a variety of everyday circumstances and is considered one of the fundamental building blocks of knowledge in modern day society.
The Migrant Mother is a black and white photograph taken in the midst of the Great Depression in 1936 (Hayes et al., 2012). The principal subject of the photo is a mother surrounded by two of her kids who are shielding their eyes from what is apparently the harsh glare of the afternoon sun.
When the photo was published it became symbolic of the hardships encountered by the families all across America and can even be considered a rallying point from which the wealthy and well to do within society became more inclined towards helping those in need (Hayes et al., 2012).
Overall, this photo became a symbol of the great depression and is one of the lasting and most poignant legacies of this dark period in America’s history.
Purpose of the Piece
The purpose of this piece was to encapsulate the economic hardship experienced by people during this particular period of time.
It is a representation of the suffering of the American people who have lost their jobs, their savings and even their hope for a better tomorrow (Hayes et al., 2012).
When looking at the mother who is the main subject of the picture one cannot help but feel the depression that is coming off of her in waves and how it reflects the way in which people at the time viewed their lives as a direct result of a collapsed economy.
It must be noted though that the subject of the photo Florence Owens Thompson was quoted by the photographer as stating that the she had little if nothing to eat and actually had to sell the tires of her car in order to support her family (Hayes et al., 2012).
In reality this did not actually occur with the photographer obviously embellishing some aspects of the photo in order to create a greater degree of hype. As such, in the end the main purpose of the photo in eyes of the photographer was nothing more than a way to gain a bit of fame through the misrepresentation of facts.
The individual Responsible for Creating the Piece
It is interesting to note that this particular photo was created almost by accident and was not intentional in the least.
Dorothea Lange, the photographer, was working for the Resettlement Administration at the time and by happenstance encountered the subject, Florence Owens Thompson by chance on Highway 101.
It must be noted that when it comes to aspects of civilization and cultural development this photo is actually a representation of a step back from the development of a society.
It was taken during a time of economic hardship for the U.S. and as such can be considered a way of seeing one of the lowest points a modern day industrialized civilization can fall.
When examining “the Migrant Mother” it becomes immediately obvious that it is neither a painting nor a sculpture but rather is a black and white photo of a family in a desperate period of time during their life.
The influence of previous civilizations in this particular case comes from the way in which photographs increasingly were acknowledged as a way of capturing both the poignant and depressing aspects of the world that we live in today (Hayes et al., 2012).
Earliest known examples of this can be seen in the heliographic process popularized in 1825 which was used to capture images that seemed that more like they were stenciled rather than photographed.
Overall, previous civilizations helped to popularize the concept of photography and how an ordinary photo can be considered a window into how the world is like during a particular period of time.
When examining the artwork at the time of the Great Depression it can be seen that an ongoing theme is one of capturing the despair and helplessness that pervaded society at the time.
What you have to understand is that the Great Depression is not just a period of low economic performance but it is also a time when a vast percentage of American society could barely feed itself.
People here on the streets have a hollowed, depressed and hopeless look in their eyes and this reflects on the various pictures, paintings and news articles which describe such an adverse situation (Hayes et al., 2012).
As such, the Migrant Mother can be considered an apt way of encapsulating the suffering, despair and utter helplessness that people during this particular time feel.
Value of the Piece in Modern Day Society
At the present the U.S. economy is far from sound, emerging from a period that can be considered just as bad as the great depression, millions of Americans at the present are still feeling the aftermath of the foolish financial decisions that resulted in proliferation of toxic subprime debt that devastated the savings of millions and made just as many lose their jobs.
The value of the Migrant Mother at the present is one that helps to remind us that people in times such as these are more than mere numbers on a statistic sheet; there are people all across the country that are suffering with little money, almost no food and eke out a living day by day.
As such, all of us should do our part in helping such individuals live decent lives, to give them dignity, honor and above all hope for the future rather than the black emptiness of despair that surrounds their lives on a daily basis.
Hadingham, E. (2010). Uncovering secrets of the sphinx. (cover story). Smithsonian , 40 (11), 32.
Hayes, D., Hertsgaard, M., Ryan, F., Walen Jr, R. C., Holton, T., & Grace, T. M. (2012). Letters. Nation, 294 (24), 2-26.
Healey, C. (2006). Al-Khwarizmi. Al-Khwarizmi , 1.
Oliver, J. (2007). How our methods of writing algebra have evolved: A thread through history. Australian Senior Mathematics Journal, 21 (2), 12.
World Wonders. (2009). Weekly Reader – Edition 2, 78 1.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, November 30). The Art Form: The Great Sphinx. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-art-form-the-great-sphinx/
"The Art Form: The Great Sphinx." IvyPanda , 30 Nov. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/the-art-form-the-great-sphinx/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'The Art Form: The Great Sphinx'. 30 November.
IvyPanda . 2023. "The Art Form: The Great Sphinx." November 30, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-art-form-the-great-sphinx/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Art Form: The Great Sphinx." November 30, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-art-form-the-great-sphinx/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Art Form: The Great Sphinx." November 30, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-art-form-the-great-sphinx/.
- Jocasta - Victim or Villainess: Mythological Discussion
- "Oedipus the King" by Sophocles
- Allegory in "The Second Coming" by William Yeats
- High Court of Australia
- Does a strong axial plan always create ritual space?
- Comparison between Romanesque and Gothic Architectures
- Nanna Ziggurats and Pyramids of Khafre Comparison
- Queen Victoria Building
Heather on History
Making history matter.

Ancient Egyptian Art: The Great Sphinx
The Great Sphinx is one of the most recognizable monuments in Egypt. Built during the Old Kingdom, an amazing period for Egyptian art, it is thought to represent the pharaoh Khaefre (c. 2555-2532 B.C.). The Great Sphinx guards the entrance to Khaefre’s mortuary temple and the second largest pyramid on the Giza plateau.
With the head of a human and the body of a lion, the Sphinx was the perfect symbol of Egyptian kingship. Lions were associated with the very first pharaohs. At Abydos, site of early Egyptian burials, lions were found buried with pharaohs. The Great Sphinx represented a combination of animal strength and royal power. It wore the pleated nemes head cloth often used by pharaohs, which provided a substitute for a lion’s mane.

The Great Sphinx. Photo by Manek Kocjan May 30, 2006 http://www.kocjan.pl
Building the Great Sphinx was a massive undertaking, especially during an era when only stone and copper tools were available. The base of the sphinx was carved from hard limestone that stuck out of the surface of the Giza plateau. The middle section of the Sphinx was made of softer limestone, and the head was made of very firm limestone. When the workers finished, the Great Sphinx was approximately 240 feet long (about the length of a football field) and almost 70 feet tall. Though other pharaohs built colossal statues, Khaefre’s Sphinx remained the largest.
Though the Great Sphinx was impressive, by the New Kingdom (c. 1539 B.C.), it needed some major repairs. Since the Sphinx was built on a seabed, salt eroded parts of it, including the paws. In addition, its body was covered in sand. According to the legend carved on a stela between the Sphinx’s paws, a young prince named Tuthmosis IV came to the Sphinx’s rescue. One day while Tuthmosis hunted in the desert, he needed a place to rest. He fell asleep in the shadow of the Sphinx. By the New Kingdom a god named Horemakhet, whose name meant Horus on the Horizon, was associated with the Sphinx. The god appeared in the prince’s dream and promised him that if Tuthmosis helped to restore the Sphinx, Horemakhet would make him pharaoh.
Tuthmosis set about restoring the Great Sphinx. He had tons of sand removed from it and had its broken paw repaired. To top off the restoration, the prince had the Sphinx repainted in bright colors, including blue, yellow, and red. The god must have been satisfied with Tuthmosis’ project, since he became king despite not being first in line for the throne.
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
Great Sphinx of Giza in Ancient Egypt’s Culture
The Sphinx is a colossal structure, the mystery of which still is not completely revealed. Located near the Great Pyramid in Giza, Egypt, this monument is considered as one of the most recognizable relics, whose origin, despite the number of researches, remains unclear (History.com Editors). Professor of Philosophy at Marist College, New York, Joshua claims that the contemporary world does not have the definite answer to questions: who built it, when, and why? However, the one statement about the Sphinx is indisputable, it is a significant part of ancient Egypt’s culture and represents the certain convictions of the nation that created it. This essay will examine the premises for building this monument and how it represents the value system of the Egyptians, complementing the discussion with descriptions of the Sphinx.
The ancient Egyptians were highly spiritual people, as their culture and religion were closely associated. The rationale for this phenomenon is the divine reign of pharaohs, based on the conviction that this power is the gift of gods. Therefore, the reason for building the Sphinx is cultural and religious at the same time, as these two definitions are indivisible. This monument is located in the area known as the Giza necropolis or Al Harram , which means “the Sacred Place” (Schoch and Bauval). At the same time, the Great Sphinx was originally named shesepankh , which implies “living image.” Both facts together evidence that the Giza was the “gateway” to the afterlife, while the colossal structure represented the one of the high significance in this belief, which is a spiritual guardian (History.com Editors). Therefore, the Great Sphinx played a vital role in Egyptians’ value system, as it was a sacred protector of dead souls and the remainder of the pharaohs’ reign splendor and the existence of the afterlife.
To obtain an understanding of the rationale to create the Sphinx, it is necessary to be familiar with the description of its physical characteristics and historical background. This monument is 4,500-year-old, 73 meters long, and 20 meters high (History.com. Editors). The Great Sphinx represents a creature with the body of a lion and the head of a human (the Figure 1), particularly a male with a pharaoh headdress (Barrett, 1994). According to Professor Joshua, the statue was built by the pharaoh Khufu’s order. The evidence that supports this opinion is the fact that by this period, Egyptians had enough knowledge in monument construction, which enabled them to create the Sphinx. The other evidence is that the statue is part of the king’s Khufu pyramid complex, built next to his father’s one. Mass of unutilized rock was used to carve the statue with the face of Khufu on it (Joshua). The mentioned statements imply that the reason to build the Sphinx of Giza is to honor the pharaoh Khufu, and it can be considered as cultural rationale.

The other way, in which the Great Sphinx contributes to the Egyptians’ value system is the religious one. According to Professor Joshua, “During the time of the New Kingdom of Egypt (1570-1069 BCE), the Sphinx was known by the Egyptians as Horemakhet (“Horus of the Horizon”). This statue was associated with the god of the sky by the solar cult. As Khufu was representative of Horus on Earth, his monument was honored with a temple by the pharaoh Amenhotep II, who patronized the solar cult. Later, his son, prince Thutmose had a dream that he would become the next pharaoh if he would agree to restore the Sphinx. “The deal” was accepted and completed, and after Thutmose’s reign, the solar cult grew up. This phenomenon made Egyptian society believe that the Great Sphinx is a living deity that can predict and influence the future (Joshua). Eventually, the statue, which was built to honor the Khufu, became the religious sanctuary respected by people. The mysterious image of Sphinx is the spiritual contribution to Egyptian society’s value system.
President of Research Autism LLC (FL) Antonio Cassella claims that the premises for building the Sphinx and the union of Pyramids were the intention to display all three attentions (10). Those mean an individual’s view of their daily life, inner perception of it, and the level of awareness about the world. This phenomenon also implies the existence of an imaginable circle, which determines people’s understanding about all matters and this circle can be expanded by new experience and knowledge obtaining. Ancient Egyptian civilization is known for its tendency to develop and invent, which is the result of considering the three attentions’ provisions, as they make individuals look deeper into opportunities.
The Sphinx’s symbolic head belongs to the pharaoh Khufu, which is the reference to the first attention, which considers problems of surviving, on the cognitive function basis. The Head is the part of the body, primarily responsible for thinking and deciding, and the statue’s one represents part of the mentioned circle of awareness. The creativity of the Sphinx’s leonine body is the reference to the second attention. Its function is spiritual, fulfilled through the inner action of witnessing and perceiving the events that are beyond the imagination and understanding. According to Cassella, the Sphinx and the Great Pyramid united together point directly on the Third Attention, which is the glow of awareness inside an individual (10). Therefore, the perfect composure, which includes the Great Sphinx and Pyramid, serves the purpose of symbolizing natural systems, dreams, and social progress.
Ancient Egyptian architecture was built on symbolic shape and forms basis, in accordance with the primary provisions of Astronomy. Egyptians had connected religion with this science and it affected their view. Therefore, it was a significant contribution to their value system, culture, and religion. According to Cassella, the Sphinx of Giza is part of four united structures, the monument itself, and three pyramids (3). This conglomerate is intended to repeat the move of Sirius. It is possible to notice in the Figure 2 that this star’s trajectory creates a circle around the Sphinx and the pyramids (3). From this perspective, the monument is directly under the Leo constellation. The Great Sphinx of Giza is the part of the uniting, which represents Sirius’s trajectory in the sky. Moreover, it is possible to notice the symbolism in the monument’s location, as it is located under the Leo constellation, while part of the structure is the body of a lion in stone.

The ancient Egyptians had a unique vision, the manifestations of which is a mystery for contemporary researchers. It is possible to notice that The Great Sphinx of Giza is a significant part of their value system. The rationale for the statue being created was religious and cultural monument representing both the mortal pharaoh, Khufu, and the god, Horus. Three attentions, considered in the Sphinx’s appearance and location indicate the Egyptians level of awareness and development. In addition, the appropriate place between other pyramids reveals ancient people’s substantial knowledge of astronomy. All reasons for the Great Sphinx of Giza creating show the place this statue has in the value system of Egyptians.
Barrett, Terry. Criticizing Art: Understanding the Contemporary . Mayfield Publishing Company, 1994.
Cassella, Antonio. “Exploring the Sphinx and the Great Pyramid Through the Logos Heuristics”. Redfame Publishing , Publications, vol. 6, no. 9, 2018, pp. 10-30.
History.com Editors. “The Sphinx.” History , 2018. Web.
Joshua, Mark J. “The Great Sphinx of Giza.” Ancient History Encyclopedia , 2016. Web.
Schoch, Robert M, and Bauval Robert. “The Great Paradox.” Origins of the Sphinx: Celestial Guardian of Pre-Pharaonic Civilization , Inner Traditions, 2017.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2023, January 21). Great Sphinx of Giza in Ancient Egypt’s Culture. https://studycorgi.com/great-sphinx-of-giza-in-ancient-egypts-culture/
"Great Sphinx of Giza in Ancient Egypt’s Culture." StudyCorgi , 21 Jan. 2023, studycorgi.com/great-sphinx-of-giza-in-ancient-egypts-culture/.
StudyCorgi . (2023) 'Great Sphinx of Giza in Ancient Egypt’s Culture'. 21 January.
1. StudyCorgi . "Great Sphinx of Giza in Ancient Egypt’s Culture." January 21, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/great-sphinx-of-giza-in-ancient-egypts-culture/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Great Sphinx of Giza in Ancient Egypt’s Culture." January 21, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/great-sphinx-of-giza-in-ancient-egypts-culture/.
StudyCorgi . 2023. "Great Sphinx of Giza in Ancient Egypt’s Culture." January 21, 2023. https://studycorgi.com/great-sphinx-of-giza-in-ancient-egypts-culture/.
This paper, “Great Sphinx of Giza in Ancient Egypt’s Culture”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: January 21, 2023 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Study Like a Boss
The Great Sphinx of Giza
A reaserch team has discovered evidence that the Great Sphinx of Giza, Egypt, may date from 5000 and 7000 BCE and possibly earlier. In response , archeoligist have thrown mud at geologist, historians caught in the middle, and the Sphinx , having revealed one secret, challenges us to unravel even greater The dicovery originated half a century ago in the work of R. A. Schwaller de Lubicz, between 1937 and 1952. Schwaller conducted a survey on the pyrimds and surrounding monuments. Schwaller observed a physical anomaly in the pyrimid complex at Giza.
The erosoin on the Sphinx was quite different from the erosion on the other structures. Schwaller sugested that the cause of erosion on the Sphynx was water rather than wind-borne sand. Since no one understood the implacations this study went unnoticed until the 1970’s, when an indepent Egyptologist John West took up the question. Archaeologists atrribute the Sphinx to the Old Kingdom fourth dynasty ruler chepron, though others belive that the Sphinx dates as far back as 10000 BCE. This is the side that I’m defending because of ll of the convincing evidence that has been found.
On the Sphinx the edges were rounded and deep fissures were prominent. On the other structures the surfaces showed only the sharper abrasion of wind and sand. Egypt experianced periods of heavy rainfalls in the millennia the marked the post-glacial northward shift of the tempeture zone. This period lasted from about 10000 to 5000 BCE and by its end the Sahara had turned from green savanna into a desert. A shorter but more intense period of rainfall lasted from about 4000 to 3000 BCE.
Westy thought that flooding from the post-glacial transition caused the distinctive weatering on the Sphinx which meant that the Sphinx must have been carved during or before the transition. Robert Schoch, a geologist, joined West in his investigation on the dating of the Sphinx. Archeologist agreed that the lower half of the Sphinx may have been eroded by the flood waters, but Schoch observed that the upper level and the encloser walls, of the Sphinx was the most heavily eroded, not the bottom half. The degree of the subsurface weathering could be measured by bouncing sound waves off of eeper layeers of rocks. Schoch discovered that the encloser floor in front and alongside of the Sphinx had a weathered depth of six to eight feet. Also that the back of the encloser had weathered only half as far.
Behind the Sphinx had been excavated during the Old Kingdom but he concluded that the sides and front of the monument were twice as old. Schoch estimated the date of the Sphinx and most of its encloser between 5000 and 7000BCE, far earlier than the date assumed by archeologist. Schoch noted that the weathering ould have been non-linear, slowing as it got deeper because of the increasing mass of rock overhead. On this assumption, the Sphinx could have been signifigantly older than 7000 BCE. West disaproved one piece of supposed evidence. With the help of a New York City police artist , Detective Sgt. Frank Domingo. WEst compared the head of the Sphinx with a known head of chepron. Sergent Domingo generated profiles of the two heads by computer and by hand and found a very different facial structure in the profile of the Sphinx compared to the profile of chepron.
The difference is easily seen To the problem of the archeological context for an earlier Sphinx, Schoch replied that urban centers had to existed in the eastern Mediterranean at Catal Huyuk from the seventh millenium and at Jericho from the ninth millennium BCE. At Jericho there were large stone walls and a thirty foot tower. No such ssettlement had been found in Egypt itself but clearly there was civiazation in the region. More evidence could be under milennia of the Nile river silt. An advanced civilazation may not have been necessary.
A Neolithic culture was able to erect Stonehenge in Britain. Astronomist soon joined the debate over the Sphinx and brought more evidence of a possible earlier civilazation. In 1993 Graham Hancock had a hunch that the curios harking back to the epoch of 10,500 BCEBy the pyrimd builders was an invitation to them to consider the actual age of the Sphinx. If this hypothesis is true, then the Sphinx must be an “original” time-markerof that remote epoch using a celestial tag. Hancock pointed out that the First Time date of 10500 BCE also denoted the begining or First Time of the Age of the Leo.
This is the time when the lion constellation would have risen at dawn before the sun on the day of spring equinox. This event brought the celestial lion to rest due east, thus in perfect elinment with the Sphinx. The Sphinx , in other words was made to look at his own image in the horizon- – and consequently at his own “time”. Hancock pointed out that 10500 BCE was no random date. A ” luck turn of the spade” form one of the laborers unearthed part of ananceint complex of underground galleries and pathways. It looked as if part of the area had already been excavated some years go but the, for reasons unknown, it was covered up again.
This was evident by the blotches of moder mortar and iron bars that were left embedded in the ceiling of the ancient pathways, probably in an attempt to reinforce the relics. But why the vestiges were covered up again , and why and how they came to be West has suggested that an ice age date for the Sphinx raises anew the question of a lost ice age civilazation, posibaly the Atlantis of ancient legend. The evidence dating the Sphinx to an earlier time peroid doesn’t prove such legends.
But if the hypothesis of rainfall erosoin is true, it does call the known chronology of African and indeed world civilazation into question. The evidence for an earlier Sphinx raises additional questions: If the Sphinx complex is so much older who built it and why? Should we be more tenative in what we assume about the first half of the last ten thousand years? If so, how should that affect what we know about the second half ? Some answers may come in the next few years as the new findings are examined and tested. Until then, the Sphinx challenges us to rethink our history and keep an open mind.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Related posts:
- The Great Pyramid Of Giza Was Not Constructed As A Burial Chamber
- The Great Gatsby, a really good book
- The Great Gatsby, a novel that is about the rich people of the roaring twenties
- The Great Gatsby – American dream
- The Great Gatsby – Chapter 7 Summary
- Great Gatsby – Comparison
- F. Scott Fitzgeralds novel “The Great Gatsby”
- Egyptian Pyramids Research Paper
- The novel The Great Gatsby
- Symbolism in The Great Gatsby
- The Great Gatsby: Morality and Gatsby
- Great Gatsby And Jazz Times
- The Great Gatsby Essay
- Bipolar Disorder: Cause of Great Madness or Great Genius
- The novels Great Expectations and The Great Gatsby
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

The Great Pyramids of Giza

The Great Pyramids at Giza, Egypt (photo: KennyOMG , CC BY-SA 4.0)
One of the Seven Wonders of the ancient world
The last remaining of the Seven Wonders of the ancient world, the great pyramids of Giza, are perhaps the most famous and discussed structures in history. These massive monuments were unsurpassed in height for thousands of years after their construction and continue to amaze and enthrall us with their overwhelming mass and seemingly impossible perfection. Their exacting orientation and mind-boggling construction has elicited many theories about their origins, including unsupported suggestions that they had extra-terrestrial impetus. However, by examining the several hundred years prior to their emergence on the Giza plateau, it becomes clear that these incredible structures were the result of many experiments, some more successful than others, and represent an apogee in line with the development of the royal mortuary complex.
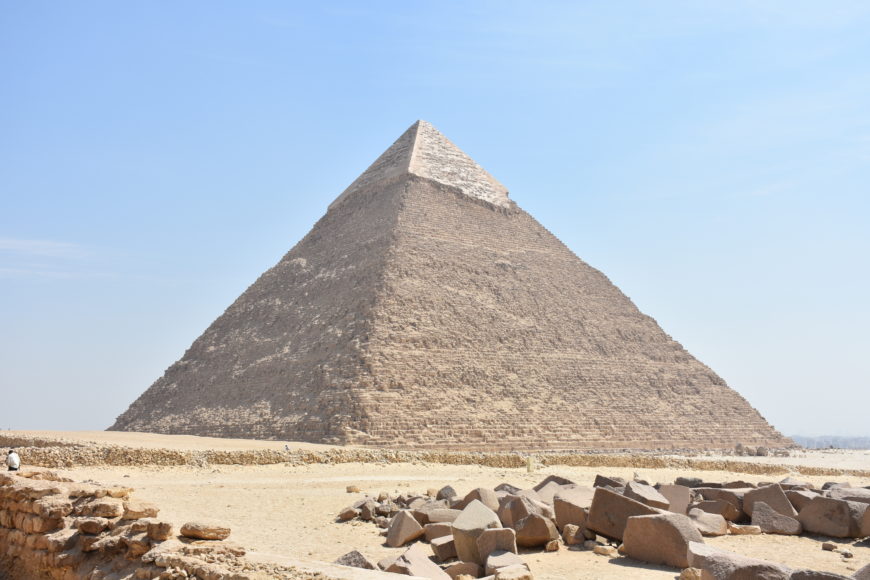

Pyramid of Khafre (photo: MusikAnimal , CC BY-SA 3.0)

The causeway of the Khafre (Chephren) pyramid complex, taken from the entrance of the Khafre Valley Temple (photo: Hannah Pethen , CC BY-NC-ND 2.0)
Three pyramids, three rulers
The three primary pyramids on the Giza plateau were built over the span of three generations by the rulers Khufu , Khafre , and Menkaure . Each pyramid was part of a royal mortuary complex that also included a temple at its base and a long stone causeway (some nearly 1 kilometer in length) leading east from the plateau to a valley temple on the edge of the floodplain.
Other (smaller) pyramids, and small tombs
In addition to these major structures, several smaller pyramids belonging to queens are arranged as satellites. A large cemetery of smaller tombs, known as mastabas (Arabic for ‘bench’ in reference to their shape—flat-roofed, rectangular, with sloping sides), fills the area to the east and west of the pyramid of Khufu . These were arranged in a grid-like pattern and constructed for prominent members of the court. Being buried near the pharaoh was a great honor and helped ensure a prized place in the Afterlife.
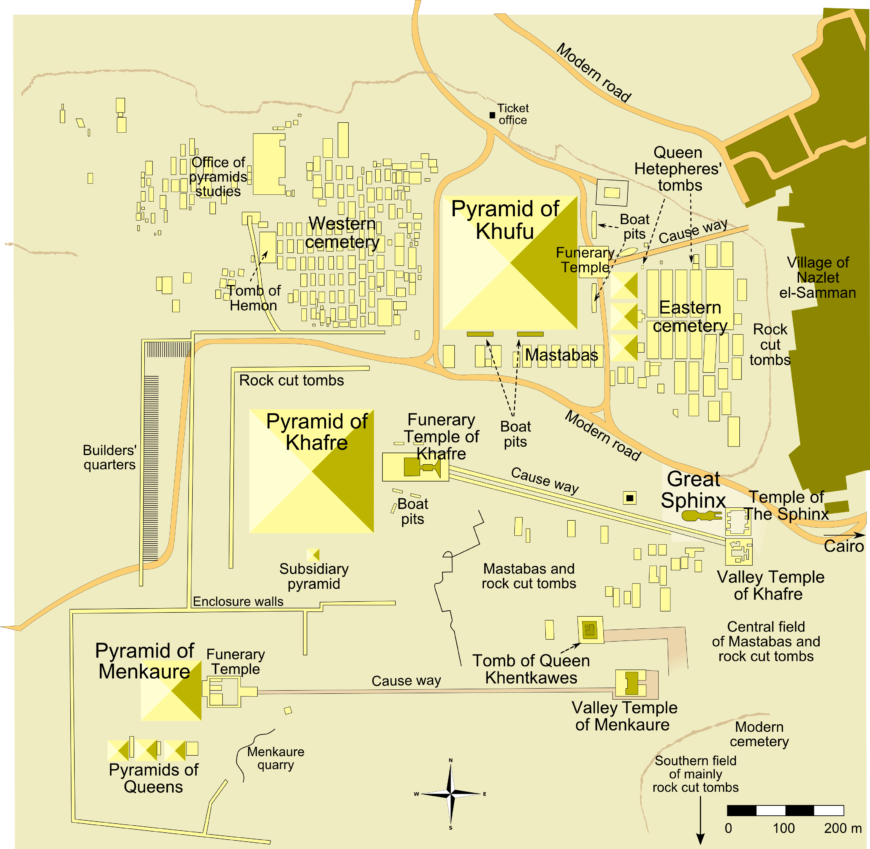
Map of Giza pyramid complex (map by: MesserWoland , CC BY-SA 3.0)
A reference to the sun
The shape of the pyramid was a solar reference, perhaps intended as a solidified version of the rays of the sun. Texts talk about the sun’s rays as a ramp the pharaoh mounts to climb to the sky—the earliest pyramids, such as the Step Pyramid of Djoser at Saqqara —were actually designed as a staircase. The pyramid was also clearly connected to the sacred ben-ben stone, an icon of the primeval mound that was considered the place of initial creation. The pyramid was viewed as a place of regeneration for the deceased ruler.

View up the side of Khufu’s pyramid showing scale of the core blocks (Photo: Dr. Amy Calvert)
Construction
Many questions remain about the construction of these massive monuments, and theories abound as to the actual methods used. The workforce needed to build these structures is also still much discussed. Discovery of a town for workers to the south of the plateau has offered some answers. It is likely that there was a permanent group of skilled craftsmen and builders who were supplemented by seasonal crews of approximately 2000 conscripted peasants. These crews were divided into gangs of 200 men, with each group further divided into teams of 20. Experiments indicate that these groups of 20 men could haul the 2.5 ton blocks from quarry to pyramid in about 20 minutes, their path eased by a lubricated surface of wet silt. An estimated 340 stones could be moved daily from quarry to construction site, particularly when one considers that many of the blocks (such as those in the upper courses) were considerably smaller.
We are used to seeing the pyramids at Giza in alluring photographs, where they appear as massive and remote monuments rising up from an open, barren desert. Visitors might be surprised to find, then, that there is a golf course and resort only a few hundred feet from the Great Pyramid , and that the burgeoning suburbs of Giza (part of the greater metropolitan area of Cairo) have expanded right up to the foot of the Sphinx . This urban encroachment and the problems that come with it—such as pollution, waste, illegal activities, and auto traffic—are now the biggest threats to these invaluable examples of global cultural heritage.
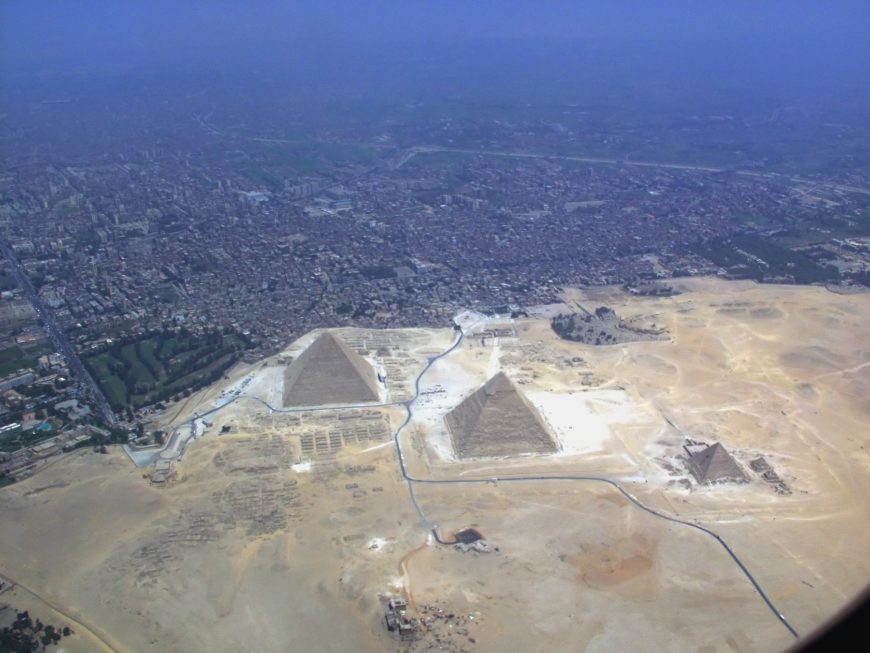

Aerial view of the Giza pyramid complex and development nearby (photo: © Raimond Spekking , CC BY-SA 4.0)
The pyramids were inscribed into the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1979, and since 1990, the organization has sponsored over a dozen missions to evaluate their status. It has supported the restoration of the Sphinx, as well as measures to curb the impact of tourism and manage the growth of the neighboring village. Still, threats to the site continue: air pollution from waste incineration contributes to the degradation of the stones , and the massive illegal quarrying of sand on the neighboring plateau has created holes large enough to be seen on Google Earth. Egypt’s 2011 uprisings and their chaotic political and economic aftermath also negatively impacted tourism, one of the country’s most important industries, and the number of visitors is only now beginning to rise once more .
UNESCO has continually monitored these issues, but its biggest task with regard to Giza has been to advocate for the rerouting of a highway that was originally slated to cut through the desert between the pyramids and the necropolis of Saqqara to the south. The government eventually agreed to build the highway north of the pyramids. However, as the Cairo metropolitan area (the largest in Africa, with a population of over 20 million) continues to expand, planners are now proposing a multilane tunnel to be constructed underneath the Giza Plateau. UNESCO and ICOMOS are calling for in-depth studies of the project’s potential impact, as well as an overall site management plan for the Giza pyramids that would include ways to halt the continued impact of illegal dumping and quarrying.
As massive as they are, the pyramids at Giza are not immutable. With the rapid growth of Cairo, they will need sufficient attention and protection if they are to remain intact as key touchstones of ancient history.
Backstory by Dr. Naraelle Hohensee
Bibliography
Egyptian Art in the Age of the Pyramids, The Metropolitan Museum of Art
UNESCO webpage for Memphis and its Necropolis – the Pyramid Fields from Giza to Dahshur
Digital Giza
Giza archives, Museum of Fine Arts, Boston
Building the Great Pyramid, BBC
Mark Lehner, The Complete Pyramids , Thames and Hudson, 2008.
Cite this page
Your donations help make art history free and accessible to everyone!
Great Sphinx of Giza in Egypt: A Photographic Essay
The Great Sphinx of Giza — also known simply as the Sphinx, although there are many other sphinxes in Egypt — is the largest monolith statue in the world created out of limestone.
As the oldest known monumental sculpture, it sits, seemingly guarding the famous Pyramids of Giza behind it.
There are still many questions to be answered pertaining to this mysterious work of the ancient Egyptians. Why was it erected? By whom exactly was it built?
We may never know the answer to the myriad questions which surround what is arguably one of the most famous and recognized historic landmarks in the world; but we can certainly admire it — as well as all of the work which went into it.
The following photograph shows the walkway from the entrance to the Great Sphinx of Giza from the parking lot.
I have read by numerous accounts posted in various places on the Internet that the Great Sphinx of Giza is staring at a Pizza Hut.
Actually, the Great Sphinx of Giza is staring at a restaurant which combines a Pizza Hut and a Kentucky Fried Chicken.
I cannot imagine that the Great Sphinx of Giza is happy to be viewing the urban sprawl inching towards her over the years.
I could swear I saw the tracks of stone tears coming out of its eyes as a result of that sad site — especially as its nose was already broken at some point over the millennia.
The following photograph shows a close view of its right rear “foot” or “paw”…
…and the structure — similar to a “penalty box” of some sort in hockey — immediately behind its front “foot” or “paw” on its right side.
Hide the children — here is a close-up view of its rear end. Salacious!
…and here it is from afar.
I hope that you enjoy the rest of the photographs.
You can stay as long as you like to admire the Great Sphinx of Giza — even into the night to view a sound and light show — along with the pyramids in the background. I left long before sunset to navigate the rental car through the living nightmare known as the outer Ring Road and I did not want to experience that at night. Additionally, I was departing for the long drive to Hurghada — a resort city by the Red Sea — the next morning.
Consider Lynn Canyon Instead of Capilano Park When in North Vancouver
The cost of admission to see both the Pyramids of Giza and the Great Sphinx of Giza is 80 Egyptian pounds per person — or approximately $10.35. If you are a student, you are eligible to pay 40 Egyptian pounds — or approximately $5.18.
I intend to post an article of photographs of the Pyramids of Giza in a future article; but let me just say this: do not miss viewing both the Great Sphinx of Giza and the pyramids — they are both included as part of the same admission fee — if you find yourself in the Cairo metropolitan area.
All photographs ©2015 by Brian Cohen.
Share this:
Subscribe to the gate with brian cohen.
View previous campaigns.
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from our team.
You have Successfully Subscribed!

The Great Sphinx Essay Example
- Pages: 2 (338 words)
- Published: April 11, 2017
- Type: Essay
The Great Sphinx, standing on the edge of the Giza plateau was an amazing monument created by the Egyptians. The Great sphinx is the largest Surviving Egyptian Monument ever to be found by man. The Sphinx was carved out of natural bedrock and the sized was increased with blocks of limestone which explains the small head of the sphinx and the massive body with dimensions 20m high, 57m long and 6m wide. That’s taller than a 6 story high building!
The massive statue resembles a lion’s body with a human head of the pharaoh Kafre wearing the pharaohs head garment on its head. The age of the sphinx is not known, guesses of its age vary between six thousand and thirteen thousand years old. A common belief is that the sphinx was built during the 2700s BC. Many people also belie
ve that the sphinx was made at King Khafras demand because the sphinx sits in front of his pyramid.
The Great sphinx is located near the Nile and is positioned facing east, away from Khafra’s pyramid and facing towards the rising sun. all the years the sphinx stood, it suffered a considerable amount of damage, losing its ceremonial beard and nose. However many believe that the sphinx’s damage was far too great for just natural erosion. There is a story about the Sphinx saying that napoleon and his army used the sphinx for target practice but people found drawings on the sphinx that say the statue has had no nose for hundreds of years before napoleon came.
Although the head has been badly damaged, near one of the ears, there are slight traces of original paint. It i
believed that the Sphinx was originally colourful. The actual purpose of the sphinx is not known to man, and the Egyptian government refuses to let people explore the tunnels of the sphinx. Could there be a long lost secrets and treasures in there, tombs? No one is quite sure, thus we have the “Riddle of the Sphinx. ”
- Sumerian Ziggurats Essay Example
- The Narmer palette Essay Example
- Who Built the Pyramids Essay Example
- Hoda Shaarawi Essay Example
- Who built the pyramids Narrative Essay Example
- The palette of King Narmer: Formal Analysis Essay Example
- Ancient Egypt vs Modern Egypt Essay Example
- Kamwese and Princess Mayet Essay Example
- The King, Tomb and Treasures Essay Example
- Ancient Civilizations Example Essay Example
- In Search Of The Ancient Anasazi Essay Example
- Cats in Ancient Egypt Essay Example
- “Farmhand” by James K. Baxter Essay Example
- Creating a Scene Essay Example
- The Hobbit Example Essay Example
- Ranch essays
- Culture essays
- Social Control essays
- Citizenship essays
- Social Justice essays
- Caste System essays
- Social Responsibility essays
- Socialization essays
- Deviance essays
- Modern Society essays
- Popularity essays
- Civil Society essays
- Community essays
- Female essays
- Filipino People essays
- Igbo People essays
- Indigenous Australians essays
- Indigenous Peoples essays
- Minority Group essays
- Social Institution essays
- The nation essays
- Middle Class essays
- Social Norms essays
- Discourse Community essays
- Popular Culture essays
- Car Culture essays
- American Culture essays
- Mormon essays
- Indian Culture essays
- Mexican Culture essays
- Pop Culture essays
- Cultural Differences essays
- Culture Shock essays
- Different Cultures essays
- Abolitionism essays
- Adam Smith essays
- American History essays
- American Revolution essays
- Ancient Egypt essays
- Articles Of Confederation essays
- Atlantic Slave Trade essays
- Aztec essays
- Benjamin Franklin essays
- Civil Rights Act of 1964 essays
- Civil Rights Movement essays
- Civil war essays
- Cleopatra essays
- French And Indian War essays
- Gettysburg essays
Haven't found what you were looking for?
Search for samples, answers to your questions and flashcards.
- Enter your topic/question
- Receive an explanation
- Ask one question at a time
- Enter a specific assignment topic
- Aim at least 500 characters
- a topic sentence that states the main or controlling idea
- supporting sentences to explain and develop the point you’re making
- evidence from your reading or an example from the subject area that supports your point
- analysis of the implication/significance/impact of the evidence finished off with a critical conclusion you have drawn from the evidence.
Unfortunately copying the content is not possible
Tell us your email address and we’ll send this sample there..
By continuing, you agree to our Terms and Conditions .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Great Sphinx, near Giza, Egypt. Great Sphinx of Giza, colossal limestone statue of a recumbent sphinx located in Giza, Egypt, that likely dates from the reign of King Khafre ( c. 2575- c. 2465 bce) and depicts his face. It is one of Egypt's most famous landmarks and is arguably the best-known example of sphinx art.
The Great Sphinx of Giza is a giant 4,500-year-old limestone statue situated near the Great Pyramid in Giza, Egypt. Measuring 240 feet (73 meters) long and 66 feet (20 meters) high, the Great ...
The Great Sphinx. Right next to the causeway leading from Khafre's valley temple to the mortuary temple sits the first truly colossal sculpture in Egyptian history: the Great Sphinx. This close physical association (along with other evidence) indicates that this massive depiction of a recumbent lion with the head of a king was carved for Khafre.
The Great Sphinx of Giza is a limestone statue of a reclining sphinx, a mythical creature with the head of a human and the body of a lion. Facing directly from west to east, it stands on the Giza Plateau on the west bank of the Nile in Giza, Egypt.The face of the Sphinx appears to represent the pharaoh Khafre. The original shape of the Sphinx was cut from the bedrock, and has since been ...
Name game: The Sphinx is an alias, created by the ancient Greeks when the statue was already centuries old. The early name was Hor-em-akhet, meaning "Horus in the horizon.". Horus is the ...
The Great Sphinx is believed to have been constructed during the reign of the Pharaoh Khafre, who ruled Egypt from approximately 2558 to 2532 BCE. The statue stands approximately 66 feet tall and 240 feet long, making it one of the largest monolithic statues in the world. It is carved from a single piece of limestone and depicts a lion's body ...
Abbie Dennett. Over 4, 500 years ago, a creature was carved out of limestone on the Giza Plateau, Egypt. This large animal is called the Great Sphinx, complete with a lion's body and a human's head. After being buried in the sand for many years, it was uncovered, and its grandiose height and width were revealed (Dunn 2, 3).
The Greek sphinx typically had lion haunches, great bird wings, and the face of a woman. But, unlike the Greek sphinx, the Egyptian sphinx was typically shown as a man (an androsphinx) and may omit bird features. The Great Sphinx of Giza, for example, is a lion body with what is believed to be Pharaoh Khafra's head.
Purpose. An examination of the burial customs of ancient Egypt reveals a prominent usage of the Sphinx (for royalty and important officials at least). It was often the case that the body of the Sphinx had the head of the person who was actually within the tomb (World Wonders, 2009). It can be hypothesized that by including an image of an ...
The Great Sphinx of Giza is one of the most iconic monuments of ancient Egypt, standing at the edge of the Giza plateau and guarding the pyramids of Khafre and Khufu. It is a mysterious and enigmatic statue, with a lion's body and a human face that has been the subject of much speculation and research. This essay will delve into the history, construction, and symbolism of the Great Sphinx, as ...
The Great Sphinx is one of the most recognizable monuments in Egypt. Built during the Old Kingdom, an amazing period for Egyptian art, it is thought to represent the pharaoh Khaefre (c. 2555-2532 B.C.). The Great Sphinx guards the entrance to Khaefre's mortuary temple and the second largest pyramid on the Giza plateau. With the head….
This essay will examine the premises for building this monument and how it represents the value system of the Egyptians, complementing the discussion with descriptions of the Sphinx. ... Mark J. "The Great Sphinx of Giza." Ancient History Encyclopedia, 26 October 2016, Definition. On-time delivery! Get your 100% customized paper done in as ...
A reaserch team has discovered evidence that the Great Sphinx of Giza, Egypt, may date from 5000 and 7000 BCE and possibly earlier. In response , archeoligist have thrown mud at geologist, historians caught in the middle, and the Sphinx , having revealed one secret, challenges us to unravel even greater The dicovery originated half a century ago in the work of R. A. Schwaller de Lubicz ...
1637 Words7 Pages. The Great Sphinx of Giza is one of the world's most iconic monuments. It was carved from a massive block of limestone, making it the biggest single stone statue in existence. The measurements of the sculpture are 60 feet in height, or as tall as a six-story building, and 240 feet in length.
Sphinx King Taharqo. 291 Words | 2 Pages. The sphinx of Taharqo was build around 100BC- 600 BC. This sphinx was located in Kawa, Sudan Africa. The Sphinx of Taharqo is made of sand stone. It has a height of 40.6cm and a width of 73cm. In African cultures, figures made with a human head and the body of a lion symbolizes Egyptian royalty and power.
The three primary pyramids on the Giza plateau were built over the span of three generations by the rulers Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure . Each pyramid was part of a royal mortuary complex that also included a temple at its base and a long stone causeway (some nearly 1 kilometer in length) leading east from the plateau to a valley temple on the ...
In 2001, Zive and his crew found a mummified lion in the tomb of a woman understood to be the wet nurse of Pharaoh Tutankhamen dated to 1430. The wear of the lion's teeth indicate it lived to old age and was in captivity. One theorist, Robert Temple, declares the Sphinx is not a lion at all, because of the flat back, lack of mane, and the ...
The three primary pyramids on the Giza plateau were built over the span of three generations by the rulers Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure . Each pyramid was part of a royal mortuary complex that also included a temple at its base and a long stone causeway (some nearly 1 kilometer in length) leading east from the plateau to a valley temple on the ...
Essay On Sphinx. 1631 Words7 Pages. The Great Sphinx Of Giza Name : Abdullah Ahmed Jillani Introduction : The Limestone Statue of Loin's Body And Human Face (Head) is called "The Great Sphinx of Giza". The Great Sphinx lies on the Giza Plateau on the West Bank of Nile River in Giza,Egypt. It Include in the 7 Wonder of World.
Great Sphinx of Giza in Egypt: A Photographic Essay It looks like she is a lady in waiting — waiting, that is, in the same spot for greater than 4,500 years. The Great Sphinx of Giza — also known simply as the Sphinx, although there are many other sphinxes in Egypt — is the largest monolith statue in the world created out of limestone.
The sphinx was inscribed with the names of the pharaohs Ammenemes II (12th Dynasty, 1929-1895 BC), Merneptah (19th Dynasty, 1212-02 BC) and Shoshenq I (22nd Dynasty, 945-24 BC). According to archaeologists, certain details suggest that this sphinx dates to an earlier period - the Old Kingdom (c. 2600 BC). This is one of the largest sphinxes outside of Egypt, currently housed in the Louvre, Paris.
Filter Results. The Great Sphinx, standing on the edge of the Giza plateau was an amazing monument created by the Egyptians. The Great sphinx is the largest Surviving Egyptian Monument ever to be found by man. The Sphinx was carved out of natural bedrock and the sized was increased with blocks of limestone which explains the small head of the ...
The Great Sphinx Essay Example 🎓 Get access to high-quality and unique 50 000 college essay examples and more than 100 000 flashcards and test answers from around the world! Paper Samples; ... The Great sphinx is located near the Nile and is positioned facing east, away from Khafra's pyramid and facing towards the rising sun. all the years ...