
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

6.3 Types of Consumer Decisions
As you read through the stages of the decision making process, did you think “Wait a minute. I do this sometimes but not all the time”? That is indicative of the different levels of involvement within the decision making process. In this section, we will examine this difference in more detail and how it may impact the marketing strategy.
Levels of Involvement in Decision Making
As you have seen, many factors influence a consumer’s behavior. Depending on a consumer’s experience and knowledge, some consumers may be able to make quick purchase decisions and other consumers may need to get information and be more involved in the decision process before making a purchase. The level of involvement reflects how personally important or interested you are in consuming a product and how much information you need to make a decision. The level of involvement in buying decisions may be considered a continuum from decisions that are fairly routine (consumers are not very involved) to decisions that require extensive thought and a high level of involvement. Whether a decision is low, high, or limited, involvement varies by consumer, not by product, although some products such as purchasing a house typically require a high-involvement for all consumers. Consumers with no experience purchasing a product may have more involvement than someone who is replacing a product.
You have probably thought about many products you want or need but never did much more than that. At other times, you’ve probably looked at dozens of products, compared them, and then decided not to purchase any one of them. When you run out of products such as milk or bread that you buy on a regular basis, you may buy the product as soon as you recognize the need because you do not need to search for information or evaluate alternatives. As Nike would put it, you “just do it.” Low-involvement decisions are, however, typically products that are relatively inexpensive and pose a low risk to the buyer if they makes a mistake by purchasing them.
Consumers often engage in routine, or habitual, behavior when they make low-involvement decisions—that is, they make automatic purchase decisions based on limited information or information they have gathered in the past. For example, if you always order a Diet Coke at lunch, you’re engaging in routine response behavior. You may not even think about other drink options at lunch because your routine is to order a Diet Coke, and you simply do it. Similarly, if you run out of Diet Coke at home, you may buy more without any information search.
Some low-involvement purchases are made with no planning or previous thought. These buying decisions are called impulse buying. While you’re waiting to check out at the grocery store, perhaps you see a magazine with the latest celebrity or influencer on the cover and buy it on the spot simply because you want it. You might see a roll of tape at a check-out stand and remember you need one or you might see a bag of chips and realize you’re hungry or just want them.
By contrast, high-involvement decisions carry a higher risk to buyers if they fail, are complex, and/or have high price tags. A car, a house, and an insurance policy are examples. These items are not purchased often but are relevant and important to the buyer. Buyers don’t engage in routine response behavior when purchasing high-involvement products. Instead, consumers engage in what’s called extended problem solving where they spend a lot of time comparing different aspects such as the features of the products, prices, and warranties.
High-involvement decisions can cause buyers a great deal of cognitive (postpurchase) dissonance (anxiety) if they are unsure about their purchases or if they had a difficult time deciding between two alternatives. Companies that sell high-involvement products are aware that dissonance can be a problem. Frequently, they try to offer consumers a lot of information about their products, including why they are superior to competing brands and how they won’t let the consumer down. Salespeople may be utilized to answer questions and do a lot of customer “hand-holding.”

Allstate’s “You’re in Good Hands” advertisements are designed to convince consumers that the insurance company won’t let them down.
Mike Mozart – Allstate, – CC BY 2.0.
Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip. While you are familiar with backpacks, you know that new features and materials are available since you purchased your last backpack. You’re going to spend some time looking for one that’s decent because you don’t want it to fall apart while you’re traveling and dump everything you’ve packed on a hiking trail. You might do a little research online and come to a decision relatively quickly. You might consider the choices available at your favorite retail outlet but not look at every backpack at every outlet before making a decision. Or you might rely on the advice of a person you know who’s knowledgeable about backpacks. In some way you shorten or limit your involvement and the decision-making process.
Products, such as chewing gum, which may be low-involvement for many consumers, often use advertising such as commercials and sales promotions such as coupons to reach many consumers at once. Companies also try to sell products such as gum in as many locations as possible. Many products that are typically high-involvement such as automobiles may use more personal selling to answer consumers’ questions. Brand names can also be very important regardless of the consumer’s level of purchasing involvement. Consider a low- versus high-involvement decision—say, purchasing a tube of toothpaste versus a new car. You might routinely buy your favorite brand of toothpaste, not thinking much about the purchase (engage in routine response behavior), but not be willing to switch to another brand either. Having a brand you like saves you “search time” and eliminates the evaluation period because you know what you’re getting.
When it comes to the car, you might engage in extensive problem solving but, again, only be willing to consider a certain brand or brands. For example, in the 1970s, American-made cars had such a poor reputation for quality that buyers joked that a car that’s “not Jap [Japanese made] is crap.” The quality of American cars is very good today, but you get the picture. If it’s a high-involvement product you’re purchasing, a good brand name is probably going to be very important to you. That’s why the manufacturers of products that are typically high-involvement decisions can’t become complacent about the value of their brands.
You Try It!
Marketing Copyright © by Kim Donahue is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Individual Consumer Decision Making
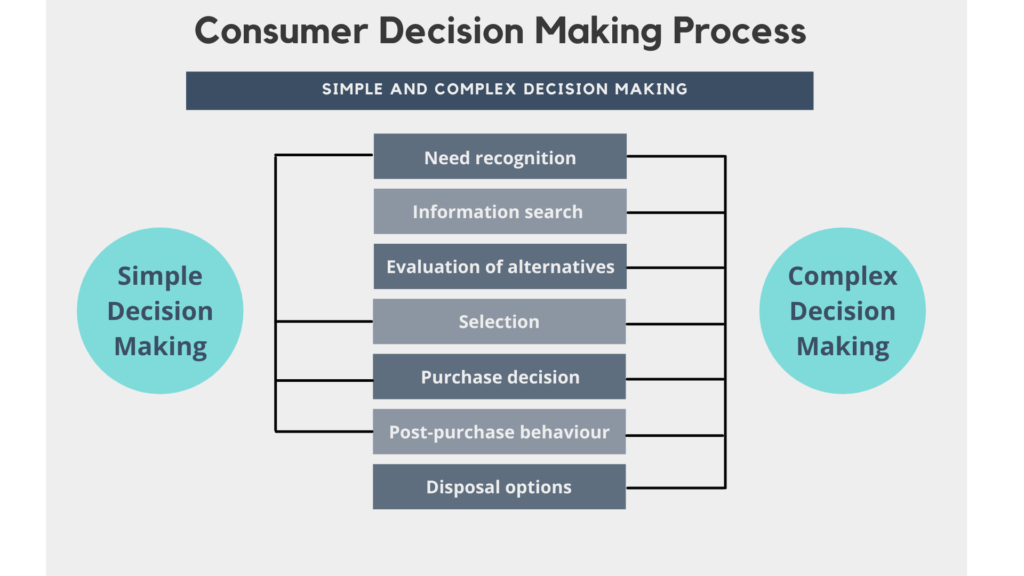
29 Consumer Decision Making Process
An organization that wants to be successful must consider buyer behavior when developing the marketing mix. Buyer behavior is the actions people take with regard to buying and using products. Marketers must understand buyer behavior, such as how raising or lowering a price will affect the buyer’s perception of the product and therefore create a fluctuation in sales, or how a specific review on social media can create an entirely new direction for the marketing mix based on the comments (buyer behavior/input) of the target market.
The Consumer Decision Making Process
Once the process is started, a potential buyer can withdraw at any stage of making the actual purchase. The tendency for a person to go through all six stages is likely only in certain buying situations—a first time purchase of a product, for instance, or when buying high priced, long-lasting, infrequently purchased articles. This is referred to as complex decision making .
For many products, the purchasing behavior is a routine affair in which the aroused need is satisfied in a habitual manner by repurchasing the same brand. That is, past reinforcement in learning experiences leads directly to buying, and thus the second and third stages are bypassed. This is called simple decision making .
However, if something changes appreciably (price, product, availability, services), the buyer may re-enter the full decision process and consider alternative brands. Whether complex or simple, the first step is need identification (Assael, 1987).
When Inertia Takes Over
Need Recognition
Whether we act to resolve a particular problem depends upon two factors: (1) the magnitude of the discrepancy between what we have and what we need, and (2) the importance of the problem. A consumer may desire a new Cadillac and own a five-year-old Chevrolet. The discrepancy may be fairly large but relatively unimportant compared to the other problems they face. Conversely, an individual may own a car that is two years old and running very well. Yet, for various reasons, they may consider it extremely important to purchase a car this year. People must resolve these types of conflicts before they can proceed. Otherwise, the buying process for a given product stops at this point, probably in frustration.
Once the problem is recognized it must be defined in such a way that the consumer can actually initiate the action that will bring about a relevant problem solution. Note that, in many cases, problem recognition and problem definition occur simultaneously, such as a consumer running out of toothpaste. Consider the more complicated problem involved with status and image–how we want others to see us. For example, you may know that you are not satisfied with your appearance, but you may not be able to define it any more precisely than that. Consumers will not know where to begin solving their problem until the problem is adequately defined.
Marketers can become involved in the need recognition stage in three ways. First they need to know what problems consumers are facing in order to develop a marketing mix to help solve these problems. This requires that they measure problem recognition. Second, on occasion, marketers want to activate problem recognition. Public service announcements espousing the dangers of cigarette smoking is an example. Weekend and night shop hours are a response of retailers to the consumer problem of limited weekday shopping opportunities. This problem has become particularly important to families with two working adults. Finally, marketers can also shape the definition of the need or problem. If a consumer needs a new coat, do they define the problem as a need for inexpensive covering, a way to stay warm on the coldest days, a garment that will last several years, warm cover that will not attract odd looks from their peers, or an article of clothing that will express their personal sense of style? A salesperson or an ad may shape their answers

Information Search
After a need is recognized, the prospective consumer may seek information to help identify and evaluate alternative products, services, and outlets that will meet that need. Such information can come from family, friends, personal observation, or other sources, such as Consumer Reports, salespeople, or mass media. The promotional component of the marketers offering is aimed at providing information to assist the consumer in their problem solving process. In some cases, the consumer already has the needed information based on past purchasing and consumption experience. Bad experiences and lack of satisfaction can destroy repeat purchases. The consumer with a need for tires may look for information in the local newspaper or ask friends for recommendation. If they have bought tires before and was satisfied, they may go to the same dealer and buy the same brand.
Information search can also identify new needs. As a tire shopper looks for information, they may decide that the tires are not the real problem, that the need is for a new car. At this point, the perceived need may change triggering a new informational search. Information search involves mental as well as the physical activities that consumers must perform in order to make decisions and accomplish desired goals in the marketplace. It takes time, energy, money, and can often involve foregoing more desirable activities. The benefits of information search, however, can outweigh the costs. For example, engaging in a thorough information search may save money, improve quality of selection, or reduce risks. The Internet is a valuable information source.
Evaluation of Alternatives
After information is secured and processed, alternative products, services, and outlets are identified as viable options. The consumer evaluates these alternatives , and, if financially and psychologically able, makes a choice. The criteria used in evaluation varies from consumer to consumer just as the needs and information sources vary. One consumer may consider price most important while another puts more weight (importance) upon quality or convenience.
Using the ‘Rule of Thumb’
Consumers don’t have the time or desire to ponder endlessly about every purchase! Fortunately for us, heuristics , also described as shortcuts or mental “rules of thumb”, help us make decisions quickly and painlessly. Heuristics are especially important to draw on when we are faced with choosing among products in a category where we don’t see huge differences or if the outcome isn’t ‘do or die’.
Heuristics are helpful sets of rules that simplify the decision-making process by making it quick and easy for consumers.
Common Heuristics in Consumer Decision Making
- Save the most money: Many people follow a rule like, “I’ll buy the lowest-priced choice so that I spend the least money right now.” Using this heuristic means you don’t need to look beyond the price tag to make a decision. Wal-Mart built a retailing empire by pleasing consumers who follow this rule.
- You get what you pay for: Some consumers might use the opposite heuristic of saving the most money and instead follow a rule such as: “I’ll buy the more expensive product because higher price means better quality.” These consumers are influenced by advertisements alluding to exclusivity, quality, and uncompromising performance.
- Stich to the tried and true: Brand loyalty also simplifies the decision-making process because we buy the brand that we’ve always bought before. therefore, we don’t need to spend more time and effort on the decision. Advertising plays a critical role in creating brand loyalty. In a study of the market leaders in thirty product categories, 27 of the brands that were #1 in 1930 were still at the top over 50 years later (Stevesnson, 1988)! A well known brand name is a powerful heuristic .
- National pride: Consumers who select brands because they represent their own culture and country of origin are making decision based on ethnocentrism . Ethnocentric consumers are said to perceive their own culture or country’s goods as being superior to others’. Ethnocentrism can behave as both a stereotype and a type of heuristic for consumers who are quick to generalize and judge brands based on their country of origin.
- Visual cues: Consumers may also rely on visual cues represented in product and packaging design. Visual cues may include the colour of the brand or product or deeper beliefs that they have developed about the brand. For example, if brands claim to support sustainability and climate activism, consumers want to believe these to be true. Visual cues such as green design and neutral-coloured packaging that appears to be made of recycled materials play into consumers’ heuristics .
The search for alternatives and the methods used in the search are influenced by such factors as: (a) time and money costs; (b) how much information the consumer already has; (c) the amount of the perceived risk if a wrong selection is made; and (d) the consumer’s predisposition toward particular choices as influenced by the attitude of the individual toward choice behaviour. That is, there are individuals who find the selection process to be difficult and disturbing. For these people there is a tendency to keep the number of alternatives to a minimum, even if they have not gone through an extensive information search to find that their alternatives appear to be the very best. On the other hand, there are individuals who feel it necessary to collect a long list of alternatives. This tendency can appreciably slow down the decision-making function.
Consumer Evaluations Made Easier
The evaluation of alternatives often involves consumers drawing on their evoke, inept, and insert sets to help them in the decision making process.
The brands and products that consumers compare—their evoked set – represent the alternatives being considered by consumers during the problem-solving process. Sometimes known as a “consideration” set, the evoked set tends to be small relative to the total number of options available. When a consumer commits significant time to the comparative process and reviews price, warranties, terms and condition of sale and other features it is said that they are involved in extended problem solving. Unlike routine problem solving, extended or extensive problem solving comprises external research and the evaluation of alternatives. Whereas, routine problem solving is low-involvement, inexpensive, and has limited risk if purchased, extended problem solving justifies the additional effort with a high-priced or scarce product, service, or benefit (e.g., the purchase of a car). Likewise, consumers use extensive problem solving for infrequently purchased, expensive, high-risk, or new goods or services.
As opposed to the evoked set, a consumer’s inept set represent those brands that they would not given any consideration too. For a consumer who is shopping around for an electric vehicle, for example, they would not even remotely consider gas-guzzling vehicles like large SUVs.
The inert set represents those brands or products a consumer is aware of, but is indifferent to and doesn’t consider them either desirable or relevant enough to be among the evoke set. Marketers have an opportunity here to position their brands appropriately so consumers move these items from their insert to evoke set when evaluation alternatives.
The selection of an alternative, in many cases, will require additional evaluation. For example, a consumer may select a favorite brand and go to a convenient outlet to make a purchase. Upon arrival at the dealer, the consumer finds that the desired brand is out-of-stock. At this point, additional evaluation is needed to decide whether to wait until the product comes in, accept a substitute, or go to another outlet. The selection and evaluation phases of consumer problem solving are closely related and often run sequentially, with outlet selection influencing product evaluation, or product selection influencing outlet evaluation.
While many consumers would agree that choice is a good thing, there is such a thing as “too much choice” that inhibits the consumer decision making process. Consumer hyperchoice is a term used to describe purchasing situations that involve an excess of choice thus making selection for difficult for consumers. Dr. Sheena Iyengar studies consumer choice and collects data that supports the concept of consumer hyperchoice. In one of her studies, she put out jars of jam in a grocery store for shoppers to sample, with the intention to influence purchases. Dr. Iyengar discovered that when a fewer number of jam samples were provided to shoppers, more purchases were made. But when a large number of jam samples were set out, fewer purchases were made (Green, 2010). As it turns out, “more is less” when it comes to the selection process.
The Purchase Decision
After much searching and evaluating, or perhaps very little, consumers at some point have to decide whether they are going to buy.
Anything marketers can do to simplify purchasing will be attractive to buyers. This may include minimal clicks to online checkout; short wait times in line; and simplified payment options. When it comes to advertising marketers could also suggest the best size for a particular use, or the right wine to drink with a particular food. Sometimes several decision situations can be combined and marketed as one package. For example, travel agents often package travel tours with flight and hotel reservations.
To do a better marketing job at this stage of the buying process, a seller needs to know answers to many questions about consumers’ shopping behaviour. For instance, how much effort is the consumer willing to spend in shopping for the product? What factors influence when the consumer will actually purchase? Are there any conditions that would prohibit or delay purchase? Providing basic product, price, and location information through labels, advertising, personal selling, and public relations is an obvious starting point. Product sampling, coupons, and rebates may also provide an extra incentive to buy.
Actually determining how a consumer goes through the decision-making process is a difficult research task.
Post-Purchase Behaviour
All the behaviour determinants and the steps of the buying process up to this point are operative before or during the time a purchase is made. However, a consumer’s feelings and evaluations after the sale are also significant to a marketer, because they can influence repeat sales and also influence what the customer tells others about the product or brand.
Keeping the customer happy is what marketing is all about. Nevertheless, consumers typically experience some post-purchase anxiety after all but the most routine and inexpensive purchases. This anxiety reflects a phenomenon called cognitive dissonance . According to this theory, people strive for consistency among their cognitions (knowledge, attitudes, beliefs, values). When there are inconsistencies, dissonance exists, which people will try to eliminate. In some cases, the consumer makes the decision to buy a particular brand already aware of dissonant elements. In other instances, dissonance is aroused by disturbing information that is received after the purchase. The marketer may take specific steps to reduce post-purchase dissonance. Advertising that stresses the many positive attributes or confirms the popularity of the product can be helpful. Providing personal reinforcement has proven effective with big-ticket items such as automobiles and major appliances. Salespeople in these areas may send cards or may even make personal calls in order to reassure customers about their purchase.
Media Attributions
- The graphic of the “Consumer Decision Making Process” by Niosi, A. (2021) is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA and is adapted from Introduction to Business by Rice University.
Text Attributions
- The sections under the “Consumer Decision Making Process,” “Need Recognition” (edited), “Information Search,” “Evaluation of Alternatives”; the first paragraph under the section “Selection”; the section under “Purchase Decision”; and, the section under “Post-Purchase Behaviour” are adapted from Introducing Marketing [PDF] by John Burnett which is licensed under CC BY 3.0 .
- The opening paragraph and the image of the Consumer Decision Making Process is adapted from Introduction to Business by Rice University which is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
- The section under “Using the ‘Rule of Thumb'” is adapted (and edited) from Launch! Advertising and Promotion in Real Time [PDF] by Saylor Academy which is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 .
Assael, H. (1987). Consumer Behavior and Marketing Action (3rd ed.), 84. Boston: Kent Publishing.
Green, P. (2010, March 17). An Expert on Choice Chooses. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2010/03/18/garden/18choice.html.
Consumer purchases made when a (new) need is identified and a consumer engages in a more rigorous evaluation, research, and alternative assessment process before satisfying the unmet need.
Consumer purchases made when a need is identified and a habitual ("routine") purchase is made to satisfy that need.
Purchasing decisions made out of habit.
The first stage of the Consumer Decision Making Process, need recognition takes place when a consumer identifies an unmet need.
The second stage of the Consumer Decision Making Process, information search takes place when a consumer seeks relative information that will help them identify and evaluate alternatives before deciding on the final purchase decision.
The third stage of the Consumer Decision Making Process, the evaluation of alternatives takes place when a consumer establishes criteria to evaluate the most viable purchasing option.
Also known as "mental shortcuts" or "rules of thumb", heuristics help consumers by simplifying the decision-making process.
A small set of "go-to" brands that consumers will consider as they evaluate the alternatives available to them before making a purchasing decision.
The brands a consumer would not pay any attention to during the evaluation of alternatives process.
The brands a consumer is aware of but indifferent to, when evaluating alternatives in the consumer decision making process. The consumer may deem these brands irrelevant and will therefore exclude them from any extensive evaluation or consideration.
A term that describes a purchasing situation in which a consumer is faced with an excess of choice that makes decision making difficult or nearly impossible.
A type of cognitive inconsistency, this term describes the discomfort consumers may feel when their beliefs, values, attitudes, or perceptions are inconsistent or contradictory to their original belief or understanding. Consumers with cognitive dissonance related to a purchasing decision will often seek to resolve this internal turmoil they are experiencing by returning the product or finding a way to justify it and minimizing their sense of buyer's remorse.
Introduction to Consumer Behaviour Copyright © 2021 by Andrea Niosi is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

IMAGES
VIDEO