Study Design 101: Case Report
- Case Report
- Case Control Study
- Cohort Study
- Randomized Controlled Trial
- Practice Guideline
- Systematic Review
- Meta-Analysis
- Helpful Formulas
- Finding Specific Study Types
- Case Reports
An article that describes and interprets an individual case, often written in the form of a detailed story. Case reports often describe:
- Unique cases that cannot be explained by known diseases or syndromes
- Cases that show an important variation of a disease or condition
- Cases that show unexpected events that may yield new or useful information
- Cases in which one patient has two or more unexpected diseases or disorders
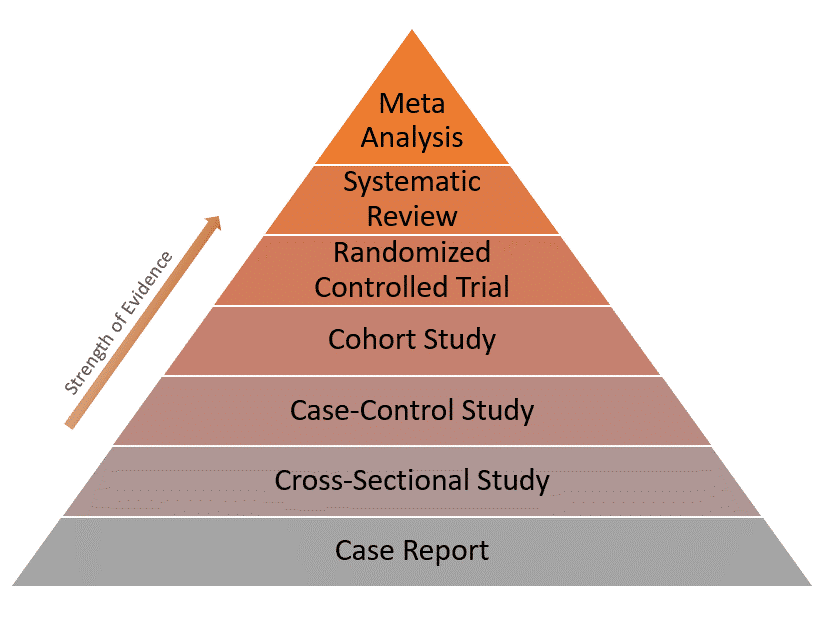
Case reports are considered the lowest level of evidence, but they are also the first line of evidence, because they are where new issues and ideas emerge. This is why they form the base of our pyramid. A good case report will be clear about the importance of the observation being reported.
If multiple case reports show something similar, the next step might be a case-control study to determine if there is a relationship between the relevant variables.
- Can help in the identification of new trends or diseases
- Can help detect new drug side effects and potential uses (adverse or beneficial)
- Educational - a way of sharing lessons learned
- Identifies rare manifestations of a disease

Disadvantages
- Cases may not be generalizable
- Not based on systematic studies
- Causes or associations may have other explanations
- Can be seen as emphasizing the bizarre or focusing on misleading elements
Design pitfalls to look out for
The patient should be described in detail, allowing others to identify patients with similar characteristics.
Does the case report provide information about the patient's age, sex, ethnicity, race, employment status, social situation, medical history, diagnosis, prognosis, previous treatments, past and current diagnostic test results, medications, psychological tests, clinical and functional assessments, and current intervention?
Case reports should include carefully recorded, unbiased observations.
Does the case report include measurements and/or recorded observations of the case? Does it show a bias?
Case reports should explore and infer, not confirm, deduce, or prove. They cannot demonstrate causality or argue for the adoption of a new treatment approach.
Does the case report present a hypothesis that can be confirmed by another type of study?
Fictitious Example
A physician treated a young and otherwise healthy patient who came to her office reporting numbness all over her body. The physician could not determine any reason for this numbness and had never seen anything like it. After taking an extensive history the physician discovered that the patient had recently been to the beach for a vacation and had used a very new type of spray sunscreen. The patient had stored the sunscreen in her cooler at the beach because she liked the feel of the cool spray in the hot sun. The physician suspected that the spray sunscreen had undergone a chemical reaction from the coldness which caused the numbness. She also suspected that because this is a new type of sunscreen other physicians may soon be seeing patients with this numbness.
The physician wrote up a case report describing how the numbness presented, how and why she concluded it was the spray sunscreen, and how she treated the patient. Later, when other doctors began seeing patients with this numbness, they found this case report helpful as a starting point in treating their patients.
Real-life Examples
Hymes KB. Cheung T. Greene JB. Prose NS. Marcus A. Ballard H. William DC. Laubenstein LJ. (1981). Kaposi's sarcoma in homosexual men-a report of eight cases. Lancet. 2 (8247),598-600.
This case report was published by eight physicians in New York city who had unexpectedly seen eight male patients with Kaposi's sarcoma (KS). Prior to this, KS was very rare in the U.S. and occurred primarily in the lower extremities of older patients. These cases were decades younger, had generalized KS, and a much lower rate of survival. This was before the discovery of HIV or the use of the term AIDS and this case report was one of the first published items about AIDS patients.
Wu, E. B., & Sung, J. J. Y. (2003). Haemorrhagic-fever-like changes and normal chest radiograph in a doctor with SARS. Lancet, 361 (9368), 1520-1521.
This case report is written by the patient, a physician who contracted SARS, and his colleague who treated him, during the 2003 outbreak of SARS in Hong Kong. They describe how the disease progressed in Dr. Wu and based on Dr. Wu's case, advised that a chest CT showed hidden pneumonic changes and facilitate a rapid diagnosis.
Related Terms
Case Series
A report about a small group of similar cases.
Preplanned Case-Observation
A case in which symptoms are elicited to study disease mechanisms. (Ex. Having a patient sleep in a lab to do brain imaging for a sleep disorder).
Now test yourself!
1. Case studies are not considered evidence-based even though the authors have studied the case in great depth.
2. When are Case reports most useful?
When you encounter common cases and need more information When new symptoms or outcomes are unidentified When developing practice guidelines When the population being studied is very large
Evidence Pyramid - Navigation
- Meta- Analysis
- << Previous: Welcome to Study Design 101
- Next: Case Control Study >>

- Last Updated: Sep 25, 2023 10:59 AM
- URL: https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/studydesign101

- Himmelfarb Intranet
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- GW is committed to digital accessibility. If you experience a barrier that affects your ability to access content on this page, let us know via the Accessibility Feedback Form .
- Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library
- 2300 Eye St., NW, Washington, DC 20037
- Phone: (202) 994-2962
- [email protected]
- https://himmelfarb.gwu.edu
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved September 4, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Chester Fritz Library
- Library of the Health Sciences
- Thormodsgard Law Library
- University of North Dakota
- Research Guides
- SMHS Library Resources
Case Reports -- Writing & Publishing
- What is a case report?
- How do I write a case report?
- Where can I publish a case report?
Other Useful Guides
- Citations / Bibliographies / Style Manual
- Internal Medicine
- Scholarly Publishing
"The basic definition of a case report is the detailed report of an individual including aspects like exposure, symptoms, signs, intervention, and outcome. . . . A case report may describe an unusual etiology, an unusual or unknown disorder, a challenging differential diagnosis, an unusual setting for care, information that can not be reproduced due to ethical reasons, unusual or puzzling clinical features, improved or unique technical procedures, unusual interactions, rare or novel adverse reactions to care, or new insight into the pathogenesis of disease."
Source: Garg R, Lakhan SE, Dhanasekaran AK. How to review a case report. J Med Case Rep . 2016 Apr 6;10:88. doi: 10.1186/s13256-016-0853-3
Contact Your Campus Librarian
In Grand Forks: 701.293.4173 Sara Westall , MLIS Southeast/Northeast Clinical Campus Library
In Fargo : 701.293.4173 Sara Westall , MLIS Southeast/Northeast Clinical Campus Library
In Bismarck : 701.751.6767 Sandi L. Bates , MLIS Southwest Clinical Campus Library
In Minot : 701.418.7710 Janet Anderson , MLIS Northwest Clinical Campus Library
Ask a Librarian
- Next: How do I write a case report? >>

- Last Updated: Apr 26, 2024 2:32 PM
- URL: https://libguides.und.edu/case-reports
- Open access
- Published: 06 April 2016
How to review a case report
- Rakesh Garg 1 ,
- Shaheen E. Lakhan 2 &
- Ananda K. Dhanasekaran 3
Journal of Medical Case Reports volume 10 , Article number: 88 ( 2016 ) Cite this article
73k Accesses
19 Citations
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Sharing individual patient experiences with clinical colleagues is an essential component of learning from each other. This sharing of information may be made global by reporting in a scientific journal. In medicine, patient management decisions are generally based on the evidence available for use of a particular investigation or technology [ 1 ]. The hierarchical rank of the evidence signifies the probability of bias. The higher up the hierarchy, the better its reliability and thus its clinical acceptance (Table 1 ). Though case reports remain lowest in the hierarchy of evidence, with meta-analysis representing the highest level, they nevertheless constitute important information with regard to rare events and may be considered as anecdotal evidence [ 2 ] (Table 1 ). Case reports may stimulate the generation of new hypotheses, and thus may support the emergence of new research.
The definition of a case report or a case series is not well defined in the literature and has been defined variously by different journals and authors. However, the basic definition of a case report is the detailed report of an individual including aspects like exposure, symptoms, signs, intervention, and outcome. It has been suggested that a report with more than four cases be called a case series and those with fewer than four a case report [ 3 ]. A case series is descriptive in design. Other authors describe “a collection of patients” as a case series and “a few patients” as a case report [ 4 ]. We suggest that should more than one case be reported, it may be defined as a case series—a concept proposed by other authors [ 5 ].
The importance of case reports
A case report may describe an unusual etiology, an unusual or unknown disorder, a challenging differential diagnosis, an unusual setting for care, information that can not be reproduced due to ethical reasons, unusual or puzzling clinical features, improved or unique technical procedures, unusual interactions, rare or novel adverse reactions to care, or new insight into the pathogenesis of disease [ 6 , 7 ]. In recent years, the publication of case reports has been given low priority by many high impact factor journals. However, the need for reporting such events remains. There are some journals dedicated purely to case reports, such as the Journal of Medical Case Reports , emphasizing their importance in modern literature. In the past, isolated case reports have led to significant advancements in patient care. For example, case reports concerning pulmonary hypertension and anorexic agents led to further trials and the identification of the mechanism and risk factors associated with these agents [ 2 , 8 ].
Reporting and publishing requirements
The reporting of cases varies for different journals. The authors need to follow the instructions for the intended publication. Owing to significant variability, it would be difficult to have uniform publication guidelines for case reports. A checklist called the CARE guidelines is useful for authors writing case reports [ 9 , 10 ]. However, it would be universally prudent to include a title, keywords, abstract, introduction, patient information, clinical findings, timeline, diagnostic assessment, therapeutic interventions, follow-up and outcomes, discussion, patient perspective, and informed consent.
Peer review process
The peer review process is an essential part of ethical and scientific writing. Peer review ultimately helps improve articles by providing valuable feedback to the author and helps editors make a decision regarding publication. The peer reviewer should provide unbiased, constructive feedback regarding the manuscript. They may also highlight the strengths and weaknesses of the report. When reviewing an article, it is prudent to read the entire manuscript first to understand the overall content and message. The reviewer than may read section-wise and provide comments to the authors and editorial team accordingly. The reviewer needs to consider the following important points when reviewing a case for possible publication [ 8 , 9 ] (summarized in Table 2 ).
Novelty remains the foremost important aspect of a case. The case report should introduce novel aspects of patient evaluation, investigation, treatment, or any other aspect related to patient care. The relevant information becomes a hypothesis generator for further study. The novelty may at times be balanced with some important information like severe adverse effects, even if they have been reported earlier. Reporting adverse events remains important so that information on cumulative adverse effects can be gathered globally, which helps in preparing a policy or guideline or a warning note for its use in patients. The data related to adverse effects include not only the impact but also the number of patients affected. This becomes more important for serious adverse effects. In the absence of an international registry for adverse effects, published case reports are important pieces of information. Owing to ethical concerns, formal evaluation may not be feasible in the format of prospective study.
Essential description
The case needs to have all essential details to allow a useful conclusion to emerge. For example, if a case is being reported for hemodynamic variability due to a drug, then the drug dose and timing along with timed vital signs need to be described.
Authenticity and genuineness
Honesty remains the most important basic principle of all publications. This remains a primary responsibility of the authors. However, if there is any doubt, reviewers may seek clarification. This doubt may result from some discordance in the case description. At times, a lack of correlation between the figures and description may act as “red flags.” For instance, authors may discuss a technique for dealing with a difficult airway, but the figure is of a normal-appearing airway. Another example would be where the data and figure do not correlate in a hemodynamic response related to a drug or a technique, with the graphical picture or screenshot of hemodynamics acting as an alert sign. Such cause for concern may be communicated in confidence to the editor.
Ethical or competing interests
Ethical issues need to be cautiously interpreted and communicated. The unethical use of a drug or device is not desirable and often unworthy of publication. This may relate to the route or dose of the drug administered. The off-label use of drugs where known side effects are greater than potential benefit needs to be discouraged and remains an example of unethical use. This use may be related to the drug dose, particularly when the drug dose exceeds the routine recommended dose, or to the route of administration. As an example, the maximal dose of acetaminophen (paracetamol) is 4g/day, and if an author reports exceeding this dose, it should be noted why a greater than recommended dose was used. Ultimately, the use of a drug or its route of administration needs to be justified in the manuscript. The reviewers need to serve as content experts regarding the drugs and other technologies used in the case. A literature search by the reviewer provides the data to comment on this aspect.
Competing interests (or conflicts of interest) are concerns that interfere or potentially interfere with presentation, review, or publication. They must be declared by the authors. Conflicts can relate to patient-related professional attributes (like the use of a particular procedure, drug, or instrument) being affected by some secondary gains (financial, non-financial, professional, personal). Financial conflict may be related to ownership, paid consultancy, patents, grants, honoraria, and gifts. Non-financial conflicts may be related to memberships, relationships, appearance as an expert witness, or personal convictions. At times, the conflict may be related to the author’s relationship with an organization or another person. A conflict may influence the interpretation of the outcome in an inappropriate and unscientific manner. Although conflicts may not be totally abolished, they must be disclosed when they reasonably exist. This disclosure should include information such as funding sources, present membership, and patents pending. Reviewers should cautiously interpret any potential bias regarding the outcome of the case based on the reported conflicts. This is essential for transparent reporting of research. At times, competing interests may be discovered by a reviewer and should be included in comments to the editorial team. Such conflicts may again be ascertained when the reviewer reviews the literature during the peer review process. The reviewer should also disclose their own conflicts related to the manuscript review when sending their report to the editorial team.
Impact on clinical practice
This is an important aspect for the final decision of whether to publish a case report. The main thrust or carry-home message needs to be emphasized clearly. It needs to be elaborated upon in concluding remarks.
Patient anonymity, consent, and ethical approval
When reviewing the manuscript of a case report, reviewers should ensure that the patient’s anonymity and confidentiality is protected. The reviewers should check that patient identifiers have been removed or masked from all aspects of the manuscript, whether in writing or within photograph. Identifiers can include things like the name of the patient, geographical location, date of birth, phone numbers, email of the patient, medical record numbers, or biometric identifiers. Utmost care needs to be taken to provide full anonymity for the patient.
Consent is required to participate in research, receive a certain treatment, and publish identifiable details. These consents are for different purposes and need to be explained separately to the patient. A patient’s consent to participate in the research or for use of the drug may not extend to consent for publication. All these aspects of consent must be explained to the patient, written explicitly in the patient’s own language, understood by the patient, and signed by the patient. For the purpose of the case, the patient must understand and consent for any new technique or drug (its dose, route, and timing) being used. In the case of a drug being used for a non-standard indication or route, consent for use must also be described. Patient consent is essential for the publication of a case if patient body parts are displayed in the article. This also includes any identifiers that can reveal the identity of the patient, such as the patient’s hospital identification number, address, and any other unique identifier. In situations where revealing the patient’s identity cannot be fully avoided, for example if the report requires an image of an identifiable body part like the face, then this should be explained to the patient, the image shown to them, and consent taken. Should the patient die, then consent must be obtained from next of kin or legal representative.
With case series, securing individual patient consent is advised and preferable. The authors may also need institutional review board (IRB) approval to publish a case series. IRBs can waive the need for consent if a study is conducted retrospectively and data are collected from patient notes for the purpose of research, usually in an anonymized way. However, wherever possible, individual patient consent is preferable, even for a retrospective study. Consent is mandatory for any prospective data collection for the purpose of publication as a case series. Consent and/or IRB approval must be disclosed in the case report and reasons for not obtaining individual consent may be described, if applicable.
There may be situations in which publishing patient details without their consent is justified, but this is a decision that should be made by the journal editor, who may decide to discuss the case with the Committee on Publication Ethics. Reviewers need to emphasize the issue to the editor when submitting their comments.
Manuscript writing
The CARE guidelines provide a framework that supports transparency and accuracy in the publication of case reports and the reporting of information from patient encounters. The acronym CARE was created from CA (the first two letters in “case”) and RE (the first two letters in “reports”). The initial CARE tools are the CARE checklist and the Case Report Writing Templates. These tools support the writing of case reports and provide data that inform clinical practice guidelines and provide early signals of effectiveness, harms, and cost [ 10 ].
The presentation of the case and its interpretation should be comprehensive and related. The various components of the manuscript should have sufficient information for understanding the key message of the case. The reviewer needs to comment on the relevant components of the manuscript. The reviewer should ascertain that the title of the case manuscript is relevant and includes keywords related to the case. The title should be short, descriptive, and interesting. The abstract should be brief, without any abbreviations, and include keywords. It is preferable to use Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) keywords. Reviewers must ensure that the introduction emphasizes the context of the case and describes the relevance and its importance in a concise and comprehensive manner. The case description should be complete and should follow basic rules of medical communication. The details regarding patient history, physical examination, investigations, differential diagnosis, management, and outcome should be described in chronological order. If repeated observations are present, then they may be tabulated. The use of graphs and figures helps the readers to better understand the case. Interpretation or inferences based on the outcomes should be avoided in this section and should be considered a part of the discussion. The discussion should highlight important aspects of the case, with its interpretation within the context of the available literature. References should be formatted as per the journal style. They should be complete and preferably of recent publications.
Reviewer responsibility
The reviewer’s remarks are essential not only for the editorial team but also for authors. A good peer review requires honesty, sincerity, and punctuality. Even if a manuscript is rejected, the authors should receive learning points from peer review commentary. The best way to review a manuscript is to read the manuscript in full for a gross overview and develop general comments. Thereafter, the reviewer should address each section of the manuscript separately and precisely. This may be done after a literature search if the reviewer needs to substantiate his/her commentary.
Constructive criticism
The reviewer’s remarks should be constructive to help the authors improve the manuscript for further consideration. If the manuscript is rejected, the authors should have a clear indication for the rejection. The remarks may be grouped as major and minor comments. Major comments likely suggest changes to the whole presentation, changing the primary aim of the case report, or adding images. Minor comments may include grammatical errors or getting references for a statement. The editorial team must be able to justify their decision on whether or not to accept an article for publication, often by citing peer review feedback. It is also good style to tabulate a list of the strengths and weaknesses of the manuscript.
Fixed time for review
Reviewer remarks should be submitted within a specified timeframe. If any delay is expected, it should be communicated to the editorial team. Reviewers should not rush to submit feedback without sufficient time to adequately review the paper and perform any necessary literature searches. Should a reviewer be unable to submit the review within the specified timeframe, they should reply to the review invitation to decline at their earliest convenience. If, after accepting a review invitation, the reviewer realizes they do not have time to perform the review, this must be communicated to the editorial team.
Conflict of interest
The reviewer’s conflicts of interest should be included along with the review. The conflicts may be related to the contents of the case, drugs, or devices pertaining to the case; the author(s); or the affiliated institution(s) of the author(s).
Lack of expertise
The reviewer may decline to review the manuscript if they think the topic is out of their area of expertise. If, after accepting an invitation to review, the reviewer realizes they are unable to review the manuscript owing to a lack of expertise in that particular field, they should disclose the fact to the editorial team.
Confidentiality
The reviewer should keep the manuscript confidential and should not use the contents of the unpublished manuscript in any form. Discussing the manuscript among colleagues or any scientific forum or meetings is inappropriate.
Review of revised manuscript
At times, a manuscript is sent for re-review to the reviewer. The reviewer should read the revised manuscript, the author’s response to the previous round of peer review, and the editorial comments. Sometimes, the authors may disagree with the reviewer’s remarks. This issue needs to be elaborated on and communicated with the editor. The reviewer should support their views with appropriate literature references. If the authors justify their reason for disagreeing with the viewer, then their argument should be considered evidence-based. However, if the reviewer still requests the revision, this may be politely communicated to the author and editor with justification for the same. In response to reviewers remarks, authors may not agree fully and provide certain suggestion in the form of clarification related to reviewers remarks. The reviewers should take these clarifications judiciously and comment accordingly with the intent of improving the manuscript further.
Peer reviewers have a significant role in the dissemination of scientific literature. They act as gatekeepers for science before it is released to society. Their sincerity and dedication is paramount to the success of any journal. The reviewers should follow a scientific and justifiable methodology for reviewing a case report for possible publication. Their comments should be constructive for the overall improvement of the manuscript and aid the editorial team in making a decision on publication. We hope this article will help reviewers to perform their important role in the best way possible. We send our best wishes to the reviewer community and, for those who are inspired to become reviewers after reading this article, our warm welcome to the reviewers’ club.
Burns PB, Rohrich RJ, Chung KC. The levels of evidence and their role in evidence-based medicine. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011;128:305–10.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Green BN, Johnson CD. How to write a case report for publication. J Chiropr Med. 2006;5:72–82.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Abu-Zidan FM, Abbas AK, Hefny AF. Clinical “case series”: a concept analysis. Afr Health Sci. 2012;12:557–62.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Porta M, editor. A dictionary of epidemiology/edited for the International Epidemiological Association. 5th ed. UK: Oxford University Press; 2008. p. 33.
Medical Research Council of South Africa. Evidence-based medicine. 2016. http://www.mrc.ac.za/healthsystems/sai.htm . Accessed on 1 Nov 2015.
Cohen H. How to write a patient case report. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 2006;63:1888–92.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Roberts LW, Coverdale J, Edenharder K, Louie A. How to review a manuscript: a “down-to-earth” approach. Acad Psychiatry. 2004;28:81–7.
Rutowski JL, Cairone JV. How to review scientific manuscripts and clinical case reports for Journal of Oral Implantology. J Oral Implantol. 2009;35:310–4.
Article Google Scholar
Jabs DA. Improving the reporting of clinical case series. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;139:900–5.
Gagnier JJ, Kienle G, Altman DG, Moher D, Sox H, Riley D; CARE Group. The CARE guidelines: consensus-based clinical case reporting guideline development. BMJ Case Reports. 2013; doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-201554 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Anaesthesiology, Pain and Palliative Care, DR BRAIRCH, AIIMS, Ansari Nagar, New Delhi, 110029, India
Rakesh Garg
Neurology and Medical Education, California University of Science and Medicine - School of Medicine, Colton, CA, USA
Shaheen E. Lakhan
Sandwell & West Birmingham Hospitals, NHS Trust, Birmingham, UK
Ananda K. Dhanasekaran
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rakesh Garg .
Additional information
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Garg, R., Lakhan, S.E. & Dhanasekaran, A.K. How to review a case report. J Med Case Reports 10 , 88 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-016-0853-3
Download citation
Received : 27 August 2015
Accepted : 25 February 2016
Published : 06 April 2016
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-016-0853-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Journal of Medical Case Reports
ISSN: 1752-1947
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Quantitative study designs: Case Studies/ Case Report/ Case Series
Quantitative study designs.
- Introduction
- Cohort Studies
- Randomised Controlled Trial
- Case Control
- Cross-Sectional Studies
- Study Designs Home
Case Study / Case Report / Case Series
Some famous examples of case studies are John Martin Marlow’s case study on Phineas Gage (the man who had a railway spike through his head) and Sigmund Freud’s case studies, Little Hans and The Rat Man. Case studies are widely used in psychology to provide insight into unusual conditions.
A case study, also known as a case report, is an in depth or intensive study of a single individual or specific group, while a case series is a grouping of similar case studies / case reports together.
A case study / case report can be used in the following instances:
- where there is atypical or abnormal behaviour or development
- an unexplained outcome to treatment
- an emerging disease or condition
The stages of a Case Study / Case Report / Case Series
Which clinical questions does Case Study / Case Report / Case Series best answer?
Emerging conditions, adverse reactions to treatments, atypical / abnormal behaviour, new programs or methods of treatment – all of these can be answered with case studies /case reports / case series. They are generally descriptive studies based on qualitative data e.g. observations, interviews, questionnaires, diaries, personal notes or clinical notes.
What are the advantages and disadvantages to consider when using Case Studies/ Case Reports and Case Series ?
What are the pitfalls to look for?
One pitfall that has occurred in some case studies is where two common conditions/treatments have been linked together with no comprehensive data backing up the conclusion. A hypothetical example could be where high rates of the common cold were associated with suicide when the cohort also suffered from depression.
Critical appraisal tools
To assist with critically appraising Case studies / Case reports / Case series there are some tools / checklists you can use.
JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Case Series
JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Case Reports
Real World Examples
Some Psychology case study / case report / case series examples
Capp, G. (2015). Our community, our schools : A case study of program design for school-based mental health services. Children & Schools, 37(4), 241–248. A pilot program to improve school based mental health services was instigated in one elementary school and one middle / high school. The case study followed the program from development through to implementation, documenting each step of the process.
Cowdrey, F. A. & Walz, L. (2015). Exposure therapy for fear of spiders in an adult with learning disabilities: A case report. British Journal of Learning Disabilities, 43(1), 75–82. One person was studied who had completed a pre- intervention and post- intervention questionnaire. From the results of this data the exposure therapy intervention was found to be effective in reducing the phobia. This case report highlighted a therapy that could be used to assist people with learning disabilities who also suffered from phobias.
Li, H. X., He, L., Zhang, C. C., Eisinger, R., Pan, Y. X., Wang, T., . . . Li, D. Y. (2019). Deep brain stimulation in post‐traumatic dystonia: A case series study. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics. 1-8. Five patients were included in the case series, all with the same condition. They all received deep brain stimulation but not in the same area of the brain. Baseline and last follow up visit were assessed with the same rating scale.
References and Further Reading
Greenhalgh, T. (2014). How to read a paper: the basics of evidence-based medicine. (5th ed.). New York: Wiley.
Heale, R. & Twycross, A. (2018). What is a case study? Evidence Based Nursing, 21(1), 7-8.
Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library. (2019). Study design 101: case report. Retrieved from https://himmelfarb.gwu.edu/tutorials/studydesign101/casereports.cfm
Hoffmann T., Bennett S., Mar C. D. (2017). Evidence-based practice across the health professions. Chatswood, NSW: Elsevier.
Robinson, O. C., & McAdams, D. P. (2015). Four functional roles for case studies in emerging adulthood research. Emerging Adulthood, 3(6), 413-420.
- << Previous: Cross-Sectional Studies
- Next: Study Designs Home >>
- Last Updated: Jul 30, 2024 9:12 AM
- URL: https://deakin.libguides.com/quantitative-study-designs
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Guideline on writing a case report
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Surgery, King Abdulaziz Medical City, Ministry of National Guard, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- 2 Department of Research Unit, College of Medicine, King Saud Bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- 3 Department of Pediatric, Rabigh Branch, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- 4 Department of Medicine, King Abdulaziz Medical City, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
- PMID: 31040594
- PMCID: PMC6476221
- DOI: 10.4103/UA.UA_177_18
Research is an important competency that should be mastered by medical professionals. It provides an opportunity for physicians to develop numerous skills including communication, collaboration, time management, and teamwork. Case report, as a research design, describes important scientific observations that are encountered in a clinical setting to expand our knowledge base. Preparing a case report is far easier than conducting any other elaborative research design. Case report, with its main components, should be focused and delivers a clear message. In this article, the key components of a case report were described with the aim of providing guidance to novice authors to improve the quality of their reporting.
Keywords: Case report; education; guideline; publication; research; writing.
PubMed Disclaimer
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Hierarchy of evidence base medicine
Similar articles
- The Single-Case Reporting Guideline In BEhavioural Interventions (SCRIBE) 2016 Statement. Tate RL, Perdices M, Rosenkoetter U, Shadish W, Vohra S, Barlow DH, Horner R, Kazdin A, Kratochwill T, McDonald S, Sampson M, Shamseer L, Togher L, Albin R, Backman C, Douglas J, Evans JJ, Gast D, Manolov R, Mitchell G, Nickels L, Nikles J, Ownsworth T, Rose M, Schmid CH, Wilson B. Tate RL, et al. Phys Ther. 2016 Jul;96(7):e1-e10. doi: 10.2522/ptj.2016.96.7.e1. Phys Ther. 2016. PMID: 27371692
- The Single-Case Reporting Guideline In BEhavioural Interventions (SCRIBE) 2016 Statement. Tate RL, Perdices M, Rosenkoetter U, Shadish W, Vohra S, Barlow DH, Horner R, Kazdin A, Kratochwill T, McDonald S, Sampson M, Shamseer L, Togher L, Albin R, Backman C, Douglas J, Evans JJ, Gast D, Manolov R, Mitchell G, Nickels L, Nikles J, Ownsworth T, Rose M, Schmid CH, Wilson B. Tate RL, et al. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016 May;73:142-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2016.04.006. Epub 2016 Apr 19. J Clin Epidemiol. 2016. PMID: 27101888
- The Single-Case Reporting guideline In BEhavioural interventions (SCRIBE) 2016 statement. Tate RL, Perdices M, Rosenkoetter U, Shadish W, Vohra S, Barlow DH, Horner R, Kazdin A, Kratochwill T, McDonald S, Sampson M, Shamseer L, Togher L, Albin R, Backman C, Douglas J, Evans JJ, Gast D, Manolov R, Mitchell G, Nickels L, Nikles J, Ownsworth T, Rose M, Schmid CH, Wilson B. Tate RL, et al. J Sch Psychol. 2016 Jun;56:133-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jsp.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 May 19. J Sch Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27268573
- The Single-Case Reporting Guideline In Behavioural Interventions (SCRIBE) 2016 statement. Tate RL, Perdices M, Rosenkoetter U, Shadish W, Vohra S, Barlow DH, Horner R, Kazdin A, Kratochwill T, McDonald S, Sampson M, Shamseer L, Togher L, Albin R, Backman C, Douglas J, Evans JJ, Gast D, Manolov R, Mitchell G, Nickels L, Nikles J, Ownsworth T, Rose M, Schmid CH, Wilson B. Tate RL, et al. Can J Occup Ther. 2016 Jun;83(3):184-95. doi: 10.1177/0008417416648124. Can J Occup Ther. 2016. PMID: 27231387
- Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature. Eddy K, Jordan Z, Stephenson M. Eddy K, et al. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314 Review.
- Journals accepting case reports. Gotschall T, Spencer A, Hoogland MA, Cortez E, Irish E. Gotschall T, et al. J Med Libr Assoc. 2023 Oct 2;111(4):819-822. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2023.1747. J Med Libr Assoc. 2023. PMID: 37928130 Free PMC article.
- Editorial: Case reports in pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition 2022. Rakotoambinina B, Vagedes J. Rakotoambinina B, et al. Front Pediatr. 2023 May 25;11:1206993. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1206993. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37303749 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
- Fulminant myocarditis with adult-onset Still's disease: case-based review. Ono R, Iwahana T, Toriumi S, Aoki K, Kato H, Kato K, Yasui M, Nakagawa Y, Furuta S, Nakajima H, Kobayashi Y. Ono R, et al. Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Sep;42(9):2507-2514. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06648-y. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37261655 Review.
- Writing a Case Report in Pediatric Surgery: A Comprehensive Guideline. Feng X, Wagner R, Rogers S, Lacher M, Aubert O. Feng X, et al. European J Pediatr Surg Rep. 2022 Feb 10;10(1):e13-e19. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1740935. eCollection 2022 Jan. European J Pediatr Surg Rep. 2022. PMID: 35155079 Free PMC article.
- How to Write a Case Report? Das A, Singh I. Das A, et al. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2021 Sep 12;12(5):683-686. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.325856. eCollection 2021 Sep-Oct. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2021. PMID: 34667753 Free PMC article.
- Jenicek M. Clinical case Reporting in Evidence-Based Medcine. Hamilton (ontario) and Montreal (quebec): Canada Butterworth Heinemann. 1999
- Barr JE. Research & writing basics: Elements of the case study. Ostomy Wound Manage. 1995;41:18, 20–1. - PubMed
- Rison RA. A guide to writing case reports for the journal of medical case reports and bioMed central research notes. J Med Case Rep. 2013;7:239. - PMC - PubMed
- DeBakey L, DeBakey S. The case report. I. Guidelines for preparation. Int J Cardiol. 1983;4:357–64. - PubMed
- Nissen T, Wynn R. The history of the case report: A selective review. JRSM Open. 2014;5:1–5. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- Search in MeSH
Related information
Linkout - more resources, full text sources.
- Europe PubMed Central
- Medknow Publications and Media Pvt Ltd
- Ovid Technologies, Inc.
- PubMed Central
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
Case Report: A Beginner’s Guide with Examples
A case report is a descriptive study that documents an unusual clinical phenomenon in a single patient. It describes in details the patient’s history, signs, symptoms, test results, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment. It also contains a short literature review, discusses the importance of the case and how it improves the existing knowledge on the subject.
A similar design involving a group of patients (with the similar problem) is referred to as case series.

Advantages of case reports
Case reports offer, in general a fast, easy and cheap way to report an unusual observation or a rare event in a clinical setting, as these have very small probability of being detected in an experimental study because of limitations on the number of patients that can be included.
These events deserve to be reported since they might provide insights on some exceptions to general rules and theories in the field.
Case reports are great to get first impressions that can generate new hypotheses (e.g. detecting a potential side effect of a drug) or challenge existing ones (e.g. shedding the light on the possibility of a different biological mechanism of a disease).
In many of these cases, additional investigation is needed such as designing large observational studies or randomized experiments or even going back and mining data from previous research looking for evidence for theses hypotheses.
Limitations of case reports
Observing a relationship between an exposure and a disease in a case report does not mean that it is causal in nature.
This is because of:
- The absence of a control group that provides a benchmark or a point of reference against which we compare our results. A control group is important to eliminate the role of external factors which can interfere with the relationship between exposure and disease
- Unmeasured Confounding caused by variables that influence both the exposure and the disease
A case report can have a powerful emotional effect (see examples of case reports below). This can lead to overrate the importance of the evidence provided by such case. In his book Against Empathy: The Case for Rational Compassion , Paul Bloom explains how a powerful story affects our emotions, can distort our judgement and even lead us to make bad moral choices.
When a case report describes a rare event it is important to remember that what we’re reading about is exceptional and most importantly resist generalizations especially because a case report is, by definition, a study where the sample is only 1 patient.
Selection bias is another issue as the cases in case reports are not chosen at random, therefore some members of the population may have a higher probability of being included in the study than others.
So, results from a case report cannot be representative of the entire population.
Because of these limitations, case reports have the lowest level of evidence compared to other study designs as represented in the evidence pyramid below:
Real-world examples of case reports
Example 1: normal plasma cholesterol in an 88-year-old man who eats 25 eggs a day.
This is the case of an old man with Alzheimer’s disease who has been eating 20-30 eggs every day for almost 15 years. [ Source ]
The man had an LDL-cholesterol level of only 142 mg/dL (3.68 mmol/L) and no significant clinical atherosclerosis (deposition of cholesterol in arterial walls)!
His body adapted by reducing the intestinal absorption of cholesterol, lowering the rate of its synthesis and increasing the rate of its conversion into bile acid.
This is indeed an unusual case of biological adaptation to a major change in dietary intake.
Example 2: Recovery from the passage of an iron bar through the head
This is an interesting case of a construction foreman named Phineas Gage. [ Source ]
In 1848, due to an explosion at work, an iron bar passed through his head destroying a large portion of his brain’s frontal lobe. He survived the event and the injury only affected 1 thing: His personality!
After the accident, Gage became profane, rough and disrespectful to the extent that he was no longer tolerable to people around him. So he lost his job and his family.
His case inspired further research that focused on the relationship between specific parts of the brain and personality.
- Sayre JW, Toklu HZ, Ye F, Mazza J, Yale S. Case Reports, Case Series – From Clinical Practice to Evidence-Based Medicine in Graduate Medical Education . Cureus . 2017;9(8):e1546. Published 2017 Aug 7. doi:10.7759/cureus.1546.
- Nissen T, Wynn R. The clinical case report: a review of its merits and limitations . BMC Res Notes . 2014;7:264. Published 2014 Apr 23. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-7-264.
Further reading
- Case Report vs Cross-Sectional Study
- Cohort vs Cross-Sectional Study
- How to Identify Different Types of Cohort Studies?
- Matched Pairs Design
- Randomized Block Design
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide

Correlational Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types...

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Triangulation in Research – Types, Methods and...

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
- Remote Access
- Save figures into PowerPoint
- Download tables as PDFs

Chapter 7: Case Reports and Case Series
Jane R. Mort; Olayinka O. Shiyanbola
- Download Chapter PDF
Disclaimer: These citations have been automatically generated based on the information we have and it may not be 100% accurate. Please consult the latest official manual style if you have any questions regarding the format accuracy.
Download citation file:
- Search Book
Jump to a Section
Chapter objectives, key terminology, introduction, case reports.
- CASE SERIES
- SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
- REVIEW QUESTIONS
- ONLINE RESOURCES
- Full Chapter
- Supplementary Content
Discuss the objectives of case series and case reports
Outline the necessary components of case reports
Describe design and methodology of case series studies
Evaluate strengths and weaknesses of case reports and case series
Evaluate the results reported in case reports and case series
Case report
Case series
Publication bias
Reliability
Case reports and case series are descriptive studies that recount a patient scenario complete with pertinent medical information such as laboratory values, medications, and diagnoses. 1 , 2 A case report includes a detailed discussion of a unique medical scenario of a single case or event in light of the currently available literature and provides an evaluation of the findings. 3 Case series describe “a group of patients with similar diagnoses or undergoing the same procedure followed over time.” 4 Although case reports and case series are at the lower end in the hierarchy of evidence, they provide valuable information to practitioners and policy makers. 1 In fact, five of the “51 Landmark Articles in Medicine” identified over a 150-year period were case reports. 5–7
With increasing emphasis on randomized studies for evidence-based medicine, some have come to question the need and utility of case reports and case series. 8 , 9 Over the last several years, the number of published case reports has declined due to the perception that they are anecdotal and limited in their ability to be generalized. 5 In addition, publication costs, limitations in print space, need for peer reviewers, journal competition, and emphasis on the impact factor have brought about a decrease in number of case reports published. 5 , 10 However, journals exclusively publishing case reports have been developed and include the Journal of Medical Case Reports and Clinical Case Reports. These journals recognize the importance and need for case report literature. 11 Despite the need for well-designed studies, case reports have provided significant information that has helped to advance medical treatment. 5–7 Case reports have been found to be a viable source for identifying unexpected or uncommon occurrences, previously unknown conditions, new adverse drug reactions (ADRs), and innovative indications for medications. 9 This chapter will provide a description of case reports and case series including, for each, a definition, characteristics, study design features, writing guidelines, strengths/limitations, and points for critical evaluation.
Case Report Definition
Get free access through your institution, pop-up div successfully displayed.
This div only appears when the trigger link is hovered over. Otherwise it is hidden from view.
Please Wait
A case report is a detailed report of the diagnosis, treatment, response to treatment, and follow-up after treatment of an individual patient. A case series is group of case reports involving patients who were given similar treatment. Case reports and case series usually contain demographic information about the patient(s), for example, age, gender, ethnic origin.
When information on more than three patients is included, the case series is considered to be a systematic investigation designed to contribute to generalizable knowledge (i.e., research ), and therefore submission is required to the IRB.
For all case reports and case series, a signed HIPAA authorization should be obtained from the patients or their legally authorized representatives for the use and disclosure of their Protected Health Information. The only exception to the requirement for obtaining authorization is if the author of a case report or case series believes that the information is not identifiable; in this case, the author must consult with the Privacy Officer at Boston Medical Center ( [email protected] ) or the HIPAA Privacy Officer of Boston University ( [email protected] ) to seek an expert opinion about the magnitude of the risk of identifying an individual.
For case reports or case series containing more than three patients, the HIPAA authorization should be part of the consent form that is reviewed by the IRB.
For case reports or case series containing three or fewer patients, authors should prepare an authorization form using the following templates and arrange for review as indicated below. The red text in the template should be customized for the specific case report or case series. Please note that for deceased patients, authorization must be obtained from the personal representative, who is the administrator or executor of the patient’s estate.
- Boston Medical Center ( BMC Case Report HIPAA Authorization Template ) – review by the Privacy Officer at Boston Medical Center ( [email protected] ); a copy of the authorization must be filed in each patient’s medical record.
- Goldman School of Dental Medicine ( GSDM Case Report HIPAA Authorization Template ) – review by the HIPAA Privacy Officer of Boston University ( [email protected] )

- HRP Staff Directory
- Office Hours
- Quality Improvement Project vs. Research
- Self Exempt & UROP
Case Reports
- UCI as the Relying IRB
- UCI as the Reviewing IRB
- Submitting the Application
- Lead Researcher Eligibility
- Training & Education
- Ethical Guidelines, Regulations and Statutes
- Other Institutional Requirements
- Department of Defense Research Requirements
- Levels of Review
- Artificial Intelligence and Human Subject Research
- Required Elements of Informed Consent
- Drafting the Informed Consent Form
- Consent and Non-English or Disabled Subjects
- Use Of Surrogate Consent In Research
- Vulnerable Populations
- Data Security
- Protected Health Information (HIPAA)
- European Union General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR)
- China’s Personal Information Protection Law
- Data and Safety Monitoring for Clinical Research
- Placebo-Controlled Studies
- Expanded Access to Unapproved Drugs or Biologics
- Right to Try: Unapproved Drugs or Biologics
- Use of Controlled Substances
- Expanded Access to Unapproved Medical Devices
- Humanitarian Use Devices
- Human Gene Transfer Research
- ClinicalTrials.gov
- Post-Review Responsibilities
Case Reports typically involve retrospective medical record reviews (of three or less patients ) and the only interaction with the patient has been for purposes of treating the patient, and not for the purpose of gathering research data. Case reports or case series of three or less individuals are not considered Human Subject's Research therefore UCI IRB review is not required. However an Administrative Self-Determination of Non-Human Subject's Research is required to be submitted via Kuali Research (KR) Protocols . The UCI IRB will not review or approve the submission . Activities may begin once the self-determination form is completed and submitted.
Per UCI HRP Policy #2 , a case series involving access to more than three patient medical records or case reports requires submission for IRB review
Defining a case report.
Often, Case Report activity involves sharing medical knowledge, improving quality, and providing education, and therefore will fall under the HIPAA definition of health care operations (45 CFR 164.501) , which includes:
- "Conducting quality assessment and improvement activities, including outcomes evaluation and development of clinical guidelines, provided that the obtaining of generalizable knowledge is not the primary purpose of any studies resulting from such activities; population-based activities relating to improving health or reducing health care costs, [and] protocol development.... and
- Reviewing the competence or qualifications of health care professionals, evaluating practitioner and provider performance, health plan performance, conducting training programs in which students, trainees, or practitioners in areas of health care learn under supervision to practice or improve their skills as health care providers, training of non-health care professionals, accreditation, certification, licensing, or credentialing activities."
PHI may be used within the covered entity for the purpose of preparing a case report without obtaining a HIPAA Authorization. Often, a case report will be presented or published outside of the covered entity. If the case report does not contain any of the 18 identifiers that cause medical information to be considered PHI under HIPAA, the case report is considered de-identified, and its presentation or publication does not require a HIPAA authorization. If the case report contains PHI, then a HIPAA authorization would be required in order for it to be presented or published outisde of the covered entity.
- Health Care Privacy Compliance Handbook, published by Health Care Compliance Association, 2011, Chapter 4, pages 49-50.
- Institutional Review Board Management and Function, 2nd edition, 2006, Chapter 4-3, pages 103-104.
Conducting a Case Report
If an activity meets the definition of a Case Report, UCI faculty/resident should complete a request for non human subject research determination in via Kuali Research (KR) Protocols .
- Journals and science conference venues will generally inquire if an IRB review occurred for the Case Report activity
- UCI faculty/resident should retain the IRB-signed Request for Determination of Non-Human Subjects Research form (indefinitely) in the event that a journal (or, a Public Request Act/PRA, or external audit) request occurs
A HIPAA Authorization from the subject(s) of the Case Report is NOT required if there is access to PHI however there is no disclosure of PHI (outside of the covered/hybrid entity) in the Case Report publication.
A HIPAA Authorization from the subject(s) of the Case Report is required if there is disclosure of PHI outside of the covered/hybrid entity in the Case Report publication. ( Disclosure of photos, even if de-identified, would require an Authorization Form. )
Use this HIPAA Authorization Form :
- Section “Release Records To”: indicate the UCI faculty/resident name , and include the caveat “to be further disclosed in a Case Report publication
- Section “Purpose”: indicate “Case Report publication”
The signed HIPAA Authorization Form should be uploaded and maintained in the patient's record. At the time of signing the Authorization Form, the patient has the right to ask for a copy of the signed Authorization Form.
HIPAA Authorization Forms are located here (under "HIPAA Forms"): https://research.uci.edu/human-research-protections/research-subjects/privacy-and-confidentiality/protected-health-information-hipaa/
Translated HIPAA Authorization Forms are located here (under "Foreign Language Translations"): https://research.uci.edu/human-research-protections/irb-forms/
A list of PHI data elements: https://research.uci.edu/human-research-protections/research-subjects/privacy-and-confidentiality/protected-health-information-hipaa/#phi-ids
Death Data and Records
If the Case Report involves access, use, and disclosure of data from death records, the above described process would be similar (i.e., Request for Determination of Non-Human Subjects Research, Authorization Form ).
For death data/records accessed through the UCI Medical Center:
- If there is no disclosure of PHI in the Case Report publication, a HIPAA Authorization is not required .
- A HIPAA Authorization Form from the legally authorized representative of the deceased patient is required if there is disclosure of PHI outside the covered/hybrid entity in the Case Report publication. (Follow the above "PROCESS")
For death data/records accessed publicly through CDPH:
- Reach out to the CDPH IRB to inquire if an IRB review would be required (when there is no disclosure of PHI, and when there is disclosure of PHI): https://www.cdph.ca.gov/Programs/CHSI/Pages/Committee-for-the-Protection-of-Human-Subjects.aspx
- 2005 UCOP Fact Sheet on SB 13
- California State CPHS: https://www.chhs.ca.gov/cphs/https://oshpd.ca.gov/data-and-reports/data-resources/cphs/
You need to enable JavaScript to run this app.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Res Methodol

The case study approach
Sarah crowe.
1 Division of Primary Care, The University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
Kathrin Cresswell
2 Centre for Population Health Sciences, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Ann Robertson
3 School of Health in Social Science, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Anthony Avery
Aziz sheikh.
The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in their real-life settings. The value of the case study approach is well recognised in the fields of business, law and policy, but somewhat less so in health services research. Based on our experiences of conducting several health-related case studies, we reflect on the different types of case study design, the specific research questions this approach can help answer, the data sources that tend to be used, and the particular advantages and disadvantages of employing this methodological approach. The paper concludes with key pointers to aid those designing and appraising proposals for conducting case study research, and a checklist to help readers assess the quality of case study reports.
Introduction
The case study approach is particularly useful to employ when there is a need to obtain an in-depth appreciation of an issue, event or phenomenon of interest, in its natural real-life context. Our aim in writing this piece is to provide insights into when to consider employing this approach and an overview of key methodological considerations in relation to the design, planning, analysis, interpretation and reporting of case studies.
The illustrative 'grand round', 'case report' and 'case series' have a long tradition in clinical practice and research. Presenting detailed critiques, typically of one or more patients, aims to provide insights into aspects of the clinical case and, in doing so, illustrate broader lessons that may be learnt. In research, the conceptually-related case study approach can be used, for example, to describe in detail a patient's episode of care, explore professional attitudes to and experiences of a new policy initiative or service development or more generally to 'investigate contemporary phenomena within its real-life context' [ 1 ]. Based on our experiences of conducting a range of case studies, we reflect on when to consider using this approach, discuss the key steps involved and illustrate, with examples, some of the practical challenges of attaining an in-depth understanding of a 'case' as an integrated whole. In keeping with previously published work, we acknowledge the importance of theory to underpin the design, selection, conduct and interpretation of case studies[ 2 ]. In so doing, we make passing reference to the different epistemological approaches used in case study research by key theoreticians and methodologists in this field of enquiry.
This paper is structured around the following main questions: What is a case study? What are case studies used for? How are case studies conducted? What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided? We draw in particular on four of our own recently published examples of case studies (see Tables Tables1, 1 , ,2, 2 , ,3 3 and and4) 4 ) and those of others to illustrate our discussion[ 3 - 7 ].
Example of a case study investigating the reasons for differences in recruitment rates of minority ethnic people in asthma research[ 3 ]
| Minority ethnic people experience considerably greater morbidity from asthma than the White majority population. Research has shown however that these minority ethnic populations are likely to be under-represented in research undertaken in the UK; there is comparatively less marginalisation in the US. |
| To investigate approaches to bolster recruitment of South Asians into UK asthma studies through qualitative research with US and UK researchers, and UK community leaders. |
| Single intrinsic case study |
| Centred on the issue of recruitment of South Asian people with asthma. |
| In-depth interviews were conducted with asthma researchers from the UK and US. A supplementary questionnaire was also provided to researchers. |
| Framework approach. |
| Barriers to ethnic minority recruitment were found to centre around: |
| 1. The attitudes of the researchers' towards inclusion: The majority of UK researchers interviewed were generally supportive of the idea of recruiting ethnically diverse participants but expressed major concerns about the practicalities of achieving this; in contrast, the US researchers appeared much more committed to the policy of inclusion. |
| 2. Stereotypes and prejudices: We found that some of the UK researchers' perceptions of ethnic minorities may have influenced their decisions on whether to approach individuals from particular ethnic groups. These stereotypes centred on issues to do with, amongst others, language barriers and lack of altruism. |
| 3. Demographic, political and socioeconomic contexts of the two countries: Researchers suggested that the demographic profile of ethnic minorities, their political engagement and the different configuration of the health services in the UK and the US may have contributed to differential rates. |
| 4. Above all, however, it appeared that the overriding importance of the US National Institute of Health's policy to mandate the inclusion of minority ethnic people (and women) had a major impact on shaping the attitudes and in turn the experiences of US researchers'; the absence of any similar mandate in the UK meant that UK-based researchers had not been forced to challenge their existing practices and they were hence unable to overcome any stereotypical/prejudicial attitudes through experiential learning. |
Example of a case study investigating the process of planning and implementing a service in Primary Care Organisations[ 4 ]
| Health work forces globally are needing to reorganise and reconfigure in order to meet the challenges posed by the increased numbers of people living with long-term conditions in an efficient and sustainable manner. Through studying the introduction of General Practitioners with a Special Interest in respiratory disorders, this study aimed to provide insights into this important issue by focusing on community respiratory service development. |
| To understand and compare the process of workforce change in respiratory services and the impact on patient experience (specifically in relation to the role of general practitioners with special interests) in a theoretically selected sample of Primary Care Organisations (PCOs), in order to derive models of good practice in planning and the implementation of a broad range of workforce issues. |
| Multiple-case design of respiratory services in health regions in England and Wales. |
| Four PCOs. |
| Face-to-face and telephone interviews, e-mail discussions, local documents, patient diaries, news items identified from local and national websites, national workshop. |
| Reading, coding and comparison progressed iteratively. |
| 1. In the screening phase of this study (which involved semi-structured telephone interviews with the person responsible for driving the reconfiguration of respiratory services in 30 PCOs), the barriers of financial deficit, organisational uncertainty, disengaged clinicians and contradictory policies proved insurmountable for many PCOs to developing sustainable services. A key rationale for PCO re-organisation in 2006 was to strengthen their commissioning function and those of clinicians through Practice-Based Commissioning. However, the turbulence, which surrounded reorganisation was found to have the opposite desired effect. |
| 2. Implementing workforce reconfiguration was strongly influenced by the negotiation and contest among local clinicians and managers about "ownership" of work and income. |
| 3. Despite the intention to make the commissioning system more transparent, personal relationships based on common professional interests, past work history, friendships and collegiality, remained as key drivers for sustainable innovation in service development. |
| It was only possible to undertake in-depth work in a selective number of PCOs and, even within these selected PCOs, it was not possible to interview all informants of potential interest and/or obtain all relevant documents. This work was conducted in the early stages of a major NHS reorganisation in England and Wales and thus, events are likely to have continued to evolve beyond the study period; we therefore cannot claim to have seen any of the stories through to their conclusion. |
Example of a case study investigating the introduction of the electronic health records[ 5 ]
| Healthcare systems globally are moving from paper-based record systems to electronic health record systems. In 2002, the NHS in England embarked on the most ambitious and expensive IT-based transformation in healthcare in history seeking to introduce electronic health records into all hospitals in England by 2010. |
| To describe and evaluate the implementation and adoption of detailed electronic health records in secondary care in England and thereby provide formative feedback for local and national rollout of the NHS Care Records Service. |
| A mixed methods, longitudinal, multi-site, socio-technical collective case study. |
| Five NHS acute hospital and mental health Trusts that have been the focus of early implementation efforts. |
| Semi-structured interviews, documentary data and field notes, observations and quantitative data. |
| Qualitative data were analysed thematically using a socio-technical coding matrix, combined with additional themes that emerged from the data. |
| 1. Hospital electronic health record systems have developed and been implemented far more slowly than was originally envisioned. |
| 2. The top-down, government-led standardised approach needed to evolve to admit more variation and greater local choice for hospitals in order to support local service delivery. |
| 3. A range of adverse consequences were associated with the centrally negotiated contracts, which excluded the hospitals in question. |
| 4. The unrealistic, politically driven, timeline (implementation over 10 years) was found to be a major source of frustration for developers, implementers and healthcare managers and professionals alike. |
| We were unable to access details of the contracts between government departments and the Local Service Providers responsible for delivering and implementing the software systems. This, in turn, made it difficult to develop a holistic understanding of some key issues impacting on the overall slow roll-out of the NHS Care Record Service. Early adopters may also have differed in important ways from NHS hospitals that planned to join the National Programme for Information Technology and implement the NHS Care Records Service at a later point in time. |
Example of a case study investigating the formal and informal ways students learn about patient safety[ 6 ]
| There is a need to reduce the disease burden associated with iatrogenic harm and considering that healthcare education represents perhaps the most sustained patient safety initiative ever undertaken, it is important to develop a better appreciation of the ways in which undergraduate and newly qualified professionals receive and make sense of the education they receive. | |
|---|---|
| To investigate the formal and informal ways pre-registration students from a range of healthcare professions (medicine, nursing, physiotherapy and pharmacy) learn about patient safety in order to become safe practitioners. | |
| Multi-site, mixed method collective case study. | |
| : Eight case studies (two for each professional group) were carried out in educational provider sites considering different programmes, practice environments and models of teaching and learning. | |
| Structured in phases relevant to the three knowledge contexts: | |
| Documentary evidence (including undergraduate curricula, handbooks and module outlines), complemented with a range of views (from course leads, tutors and students) and observations in a range of academic settings. | |
| Policy and management views of patient safety and influences on patient safety education and practice. NHS policies included, for example, implementation of the National Patient Safety Agency's , which encourages organisations to develop an organisational safety culture in which staff members feel comfortable identifying dangers and reporting hazards. | |
| The cultures to which students are exposed i.e. patient safety in relation to day-to-day working. NHS initiatives included, for example, a hand washing initiative or introduction of infection control measures. | |
| 1. Practical, informal, learning opportunities were valued by students. On the whole, however, students were not exposed to nor engaged with important NHS initiatives such as risk management activities and incident reporting schemes. | |
| 2. NHS policy appeared to have been taken seriously by course leaders. Patient safety materials were incorporated into both formal and informal curricula, albeit largely implicit rather than explicit. | |
| 3. Resource issues and peer pressure were found to influence safe practice. Variations were also found to exist in students' experiences and the quality of the supervision available. | |
| The curriculum and organisational documents collected differed between sites, which possibly reflected gatekeeper influences at each site. The recruitment of participants for focus group discussions proved difficult, so interviews or paired discussions were used as a substitute. | |
What is a case study?
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table (Table5), 5 ), the central tenet being the need to explore an event or phenomenon in depth and in its natural context. It is for this reason sometimes referred to as a "naturalistic" design; this is in contrast to an "experimental" design (such as a randomised controlled trial) in which the investigator seeks to exert control over and manipulate the variable(s) of interest.
Definitions of a case study
| Author | Definition |
|---|---|
| Stake[ ] | (p.237) |
| Yin[ , , ] | (Yin 1999 p. 1211, Yin 1994 p. 13) |
| • | |
| • (Yin 2009 p18) | |
| Miles and Huberman[ ] | (p. 25) |
| Green and Thorogood[ ] | (p. 284) |
| George and Bennett[ ] | (p. 17)" |
Stake's work has been particularly influential in defining the case study approach to scientific enquiry. He has helpfully characterised three main types of case study: intrinsic , instrumental and collective [ 8 ]. An intrinsic case study is typically undertaken to learn about a unique phenomenon. The researcher should define the uniqueness of the phenomenon, which distinguishes it from all others. In contrast, the instrumental case study uses a particular case (some of which may be better than others) to gain a broader appreciation of an issue or phenomenon. The collective case study involves studying multiple cases simultaneously or sequentially in an attempt to generate a still broader appreciation of a particular issue.
These are however not necessarily mutually exclusive categories. In the first of our examples (Table (Table1), 1 ), we undertook an intrinsic case study to investigate the issue of recruitment of minority ethnic people into the specific context of asthma research studies, but it developed into a instrumental case study through seeking to understand the issue of recruitment of these marginalised populations more generally, generating a number of the findings that are potentially transferable to other disease contexts[ 3 ]. In contrast, the other three examples (see Tables Tables2, 2 , ,3 3 and and4) 4 ) employed collective case study designs to study the introduction of workforce reconfiguration in primary care, the implementation of electronic health records into hospitals, and to understand the ways in which healthcare students learn about patient safety considerations[ 4 - 6 ]. Although our study focusing on the introduction of General Practitioners with Specialist Interests (Table (Table2) 2 ) was explicitly collective in design (four contrasting primary care organisations were studied), is was also instrumental in that this particular professional group was studied as an exemplar of the more general phenomenon of workforce redesign[ 4 ].
What are case studies used for?
According to Yin, case studies can be used to explain, describe or explore events or phenomena in the everyday contexts in which they occur[ 1 ]. These can, for example, help to understand and explain causal links and pathways resulting from a new policy initiative or service development (see Tables Tables2 2 and and3, 3 , for example)[ 1 ]. In contrast to experimental designs, which seek to test a specific hypothesis through deliberately manipulating the environment (like, for example, in a randomised controlled trial giving a new drug to randomly selected individuals and then comparing outcomes with controls),[ 9 ] the case study approach lends itself well to capturing information on more explanatory ' how ', 'what' and ' why ' questions, such as ' how is the intervention being implemented and received on the ground?'. The case study approach can offer additional insights into what gaps exist in its delivery or why one implementation strategy might be chosen over another. This in turn can help develop or refine theory, as shown in our study of the teaching of patient safety in undergraduate curricula (Table (Table4 4 )[ 6 , 10 ]. Key questions to consider when selecting the most appropriate study design are whether it is desirable or indeed possible to undertake a formal experimental investigation in which individuals and/or organisations are allocated to an intervention or control arm? Or whether the wish is to obtain a more naturalistic understanding of an issue? The former is ideally studied using a controlled experimental design, whereas the latter is more appropriately studied using a case study design.
Case studies may be approached in different ways depending on the epistemological standpoint of the researcher, that is, whether they take a critical (questioning one's own and others' assumptions), interpretivist (trying to understand individual and shared social meanings) or positivist approach (orientating towards the criteria of natural sciences, such as focusing on generalisability considerations) (Table (Table6). 6 ). Whilst such a schema can be conceptually helpful, it may be appropriate to draw on more than one approach in any case study, particularly in the context of conducting health services research. Doolin has, for example, noted that in the context of undertaking interpretative case studies, researchers can usefully draw on a critical, reflective perspective which seeks to take into account the wider social and political environment that has shaped the case[ 11 ].
Example of epistemological approaches that may be used in case study research
| Approach | Characteristics | Criticisms | Key references |
|---|---|---|---|
| Involves questioning one's own assumptions taking into account the wider political and social environment. | It can possibly neglect other factors by focussing only on power relationships and may give the researcher a position that is too privileged. | Howcroft and Trauth[ ] Blakie[ ] Doolin[ , ] | |
| Interprets the limiting conditions in relation to power and control that are thought to influence behaviour. | Bloomfield and Best[ ] | ||
| Involves understanding meanings/contexts and processes as perceived from different perspectives, trying to understand individual and shared social meanings. Focus is on theory building. | Often difficult to explain unintended consequences and for neglecting surrounding historical contexts | Stake[ ] Doolin[ ] | |
| Involves establishing which variables one wishes to study in advance and seeing whether they fit in with the findings. Focus is often on testing and refining theory on the basis of case study findings. | It does not take into account the role of the researcher in influencing findings. | Yin[ , , ] Shanks and Parr[ ] |
How are case studies conducted?
Here, we focus on the main stages of research activity when planning and undertaking a case study; the crucial stages are: defining the case; selecting the case(s); collecting and analysing the data; interpreting data; and reporting the findings.
Defining the case
Carefully formulated research question(s), informed by the existing literature and a prior appreciation of the theoretical issues and setting(s), are all important in appropriately and succinctly defining the case[ 8 , 12 ]. Crucially, each case should have a pre-defined boundary which clarifies the nature and time period covered by the case study (i.e. its scope, beginning and end), the relevant social group, organisation or geographical area of interest to the investigator, the types of evidence to be collected, and the priorities for data collection and analysis (see Table Table7 7 )[ 1 ]. A theory driven approach to defining the case may help generate knowledge that is potentially transferable to a range of clinical contexts and behaviours; using theory is also likely to result in a more informed appreciation of, for example, how and why interventions have succeeded or failed[ 13 ].
Example of a checklist for rating a case study proposal[ 8 ]
| Clarity: Does the proposal read well? | |
| Integrity: Do its pieces fit together? | |
| Attractiveness: Does it pique the reader's interest? | |
| The case: Is the case adequately defined? | |
| The issues: Are major research questions identified? | |
| Data Resource: Are sufficient data sources identified? | |
| Case Selection: Is the selection plan reasonable? | |
| Data Gathering: Are data-gathering activities outlined? | |
| Validation: Is the need and opportunity for triangulation indicated? | |
| Access: Are arrangements for start-up anticipated? | |
| Confidentiality: Is there sensitivity to the protection of people? | |
| Cost: Are time and resource estimates reasonable? |
For example, in our evaluation of the introduction of electronic health records in English hospitals (Table (Table3), 3 ), we defined our cases as the NHS Trusts that were receiving the new technology[ 5 ]. Our focus was on how the technology was being implemented. However, if the primary research interest had been on the social and organisational dimensions of implementation, we might have defined our case differently as a grouping of healthcare professionals (e.g. doctors and/or nurses). The precise beginning and end of the case may however prove difficult to define. Pursuing this same example, when does the process of implementation and adoption of an electronic health record system really begin or end? Such judgements will inevitably be influenced by a range of factors, including the research question, theory of interest, the scope and richness of the gathered data and the resources available to the research team.
Selecting the case(s)
The decision on how to select the case(s) to study is a very important one that merits some reflection. In an intrinsic case study, the case is selected on its own merits[ 8 ]. The case is selected not because it is representative of other cases, but because of its uniqueness, which is of genuine interest to the researchers. This was, for example, the case in our study of the recruitment of minority ethnic participants into asthma research (Table (Table1) 1 ) as our earlier work had demonstrated the marginalisation of minority ethnic people with asthma, despite evidence of disproportionate asthma morbidity[ 14 , 15 ]. In another example of an intrinsic case study, Hellstrom et al.[ 16 ] studied an elderly married couple living with dementia to explore how dementia had impacted on their understanding of home, their everyday life and their relationships.
For an instrumental case study, selecting a "typical" case can work well[ 8 ]. In contrast to the intrinsic case study, the particular case which is chosen is of less importance than selecting a case that allows the researcher to investigate an issue or phenomenon. For example, in order to gain an understanding of doctors' responses to health policy initiatives, Som undertook an instrumental case study interviewing clinicians who had a range of responsibilities for clinical governance in one NHS acute hospital trust[ 17 ]. Sampling a "deviant" or "atypical" case may however prove even more informative, potentially enabling the researcher to identify causal processes, generate hypotheses and develop theory.
In collective or multiple case studies, a number of cases are carefully selected. This offers the advantage of allowing comparisons to be made across several cases and/or replication. Choosing a "typical" case may enable the findings to be generalised to theory (i.e. analytical generalisation) or to test theory by replicating the findings in a second or even a third case (i.e. replication logic)[ 1 ]. Yin suggests two or three literal replications (i.e. predicting similar results) if the theory is straightforward and five or more if the theory is more subtle. However, critics might argue that selecting 'cases' in this way is insufficiently reflexive and ill-suited to the complexities of contemporary healthcare organisations.
The selected case study site(s) should allow the research team access to the group of individuals, the organisation, the processes or whatever else constitutes the chosen unit of analysis for the study. Access is therefore a central consideration; the researcher needs to come to know the case study site(s) well and to work cooperatively with them. Selected cases need to be not only interesting but also hospitable to the inquiry [ 8 ] if they are to be informative and answer the research question(s). Case study sites may also be pre-selected for the researcher, with decisions being influenced by key stakeholders. For example, our selection of case study sites in the evaluation of the implementation and adoption of electronic health record systems (see Table Table3) 3 ) was heavily influenced by NHS Connecting for Health, the government agency that was responsible for overseeing the National Programme for Information Technology (NPfIT)[ 5 ]. This prominent stakeholder had already selected the NHS sites (through a competitive bidding process) to be early adopters of the electronic health record systems and had negotiated contracts that detailed the deployment timelines.
It is also important to consider in advance the likely burden and risks associated with participation for those who (or the site(s) which) comprise the case study. Of particular importance is the obligation for the researcher to think through the ethical implications of the study (e.g. the risk of inadvertently breaching anonymity or confidentiality) and to ensure that potential participants/participating sites are provided with sufficient information to make an informed choice about joining the study. The outcome of providing this information might be that the emotive burden associated with participation, or the organisational disruption associated with supporting the fieldwork, is considered so high that the individuals or sites decide against participation.
In our example of evaluating implementations of electronic health record systems, given the restricted number of early adopter sites available to us, we sought purposively to select a diverse range of implementation cases among those that were available[ 5 ]. We chose a mixture of teaching, non-teaching and Foundation Trust hospitals, and examples of each of the three electronic health record systems procured centrally by the NPfIT. At one recruited site, it quickly became apparent that access was problematic because of competing demands on that organisation. Recognising the importance of full access and co-operative working for generating rich data, the research team decided not to pursue work at that site and instead to focus on other recruited sites.
Collecting the data
In order to develop a thorough understanding of the case, the case study approach usually involves the collection of multiple sources of evidence, using a range of quantitative (e.g. questionnaires, audits and analysis of routinely collected healthcare data) and more commonly qualitative techniques (e.g. interviews, focus groups and observations). The use of multiple sources of data (data triangulation) has been advocated as a way of increasing the internal validity of a study (i.e. the extent to which the method is appropriate to answer the research question)[ 8 , 18 - 21 ]. An underlying assumption is that data collected in different ways should lead to similar conclusions, and approaching the same issue from different angles can help develop a holistic picture of the phenomenon (Table (Table2 2 )[ 4 ].
Brazier and colleagues used a mixed-methods case study approach to investigate the impact of a cancer care programme[ 22 ]. Here, quantitative measures were collected with questionnaires before, and five months after, the start of the intervention which did not yield any statistically significant results. Qualitative interviews with patients however helped provide an insight into potentially beneficial process-related aspects of the programme, such as greater, perceived patient involvement in care. The authors reported how this case study approach provided a number of contextual factors likely to influence the effectiveness of the intervention and which were not likely to have been obtained from quantitative methods alone.
In collective or multiple case studies, data collection needs to be flexible enough to allow a detailed description of each individual case to be developed (e.g. the nature of different cancer care programmes), before considering the emerging similarities and differences in cross-case comparisons (e.g. to explore why one programme is more effective than another). It is important that data sources from different cases are, where possible, broadly comparable for this purpose even though they may vary in nature and depth.
Analysing, interpreting and reporting case studies
Making sense and offering a coherent interpretation of the typically disparate sources of data (whether qualitative alone or together with quantitative) is far from straightforward. Repeated reviewing and sorting of the voluminous and detail-rich data are integral to the process of analysis. In collective case studies, it is helpful to analyse data relating to the individual component cases first, before making comparisons across cases. Attention needs to be paid to variations within each case and, where relevant, the relationship between different causes, effects and outcomes[ 23 ]. Data will need to be organised and coded to allow the key issues, both derived from the literature and emerging from the dataset, to be easily retrieved at a later stage. An initial coding frame can help capture these issues and can be applied systematically to the whole dataset with the aid of a qualitative data analysis software package.
The Framework approach is a practical approach, comprising of five stages (familiarisation; identifying a thematic framework; indexing; charting; mapping and interpretation) , to managing and analysing large datasets particularly if time is limited, as was the case in our study of recruitment of South Asians into asthma research (Table (Table1 1 )[ 3 , 24 ]. Theoretical frameworks may also play an important role in integrating different sources of data and examining emerging themes. For example, we drew on a socio-technical framework to help explain the connections between different elements - technology; people; and the organisational settings within which they worked - in our study of the introduction of electronic health record systems (Table (Table3 3 )[ 5 ]. Our study of patient safety in undergraduate curricula drew on an evaluation-based approach to design and analysis, which emphasised the importance of the academic, organisational and practice contexts through which students learn (Table (Table4 4 )[ 6 ].
Case study findings can have implications both for theory development and theory testing. They may establish, strengthen or weaken historical explanations of a case and, in certain circumstances, allow theoretical (as opposed to statistical) generalisation beyond the particular cases studied[ 12 ]. These theoretical lenses should not, however, constitute a strait-jacket and the cases should not be "forced to fit" the particular theoretical framework that is being employed.
When reporting findings, it is important to provide the reader with enough contextual information to understand the processes that were followed and how the conclusions were reached. In a collective case study, researchers may choose to present the findings from individual cases separately before amalgamating across cases. Care must be taken to ensure the anonymity of both case sites and individual participants (if agreed in advance) by allocating appropriate codes or withholding descriptors. In the example given in Table Table3, 3 , we decided against providing detailed information on the NHS sites and individual participants in order to avoid the risk of inadvertent disclosure of identities[ 5 , 25 ].
What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided?
The case study approach is, as with all research, not without its limitations. When investigating the formal and informal ways undergraduate students learn about patient safety (Table (Table4), 4 ), for example, we rapidly accumulated a large quantity of data. The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted on the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources. This highlights a more general point of the importance of avoiding the temptation to collect as much data as possible; adequate time also needs to be set aside for data analysis and interpretation of what are often highly complex datasets.
Case study research has sometimes been criticised for lacking scientific rigour and providing little basis for generalisation (i.e. producing findings that may be transferable to other settings)[ 1 ]. There are several ways to address these concerns, including: the use of theoretical sampling (i.e. drawing on a particular conceptual framework); respondent validation (i.e. participants checking emerging findings and the researcher's interpretation, and providing an opinion as to whether they feel these are accurate); and transparency throughout the research process (see Table Table8 8 )[ 8 , 18 - 21 , 23 , 26 ]. Transparency can be achieved by describing in detail the steps involved in case selection, data collection, the reasons for the particular methods chosen, and the researcher's background and level of involvement (i.e. being explicit about how the researcher has influenced data collection and interpretation). Seeking potential, alternative explanations, and being explicit about how interpretations and conclusions were reached, help readers to judge the trustworthiness of the case study report. Stake provides a critique checklist for a case study report (Table (Table9 9 )[ 8 ].
Potential pitfalls and mitigating actions when undertaking case study research
| Potential pitfall | Mitigating action |
|---|---|
| Selecting/conceptualising the wrong case(s) resulting in lack of theoretical generalisations | Developing in-depth knowledge of theoretical and empirical literature, justifying choices made |
| Collecting large volumes of data that are not relevant to the case or too little to be of any value | Focus data collection in line with research questions, whilst being flexible and allowing different paths to be explored |
| Defining/bounding the case | Focus on related components (either by time and/or space), be clear what is outside the scope of the case |
| Lack of rigour | Triangulation, respondent validation, the use of theoretical sampling, transparency throughout the research process |
| Ethical issues | Anonymise appropriately as cases are often easily identifiable to insiders, informed consent of participants |
| Integration with theoretical framework | Allow for unexpected issues to emerge and do not force fit, test out preliminary explanations, be clear about epistemological positions in advance |
Stake's checklist for assessing the quality of a case study report[ 8 ]
| 1. Is this report easy to read? |
| 2. Does it fit together, each sentence contributing to the whole? |
| 3. Does this report have a conceptual structure (i.e. themes or issues)? |
| 4. Are its issues developed in a series and scholarly way? |
| 5. Is the case adequately defined? |
| 6. Is there a sense of story to the presentation? |
| 7. Is the reader provided some vicarious experience? |
| 8. Have quotations been used effectively? |
| 9. Are headings, figures, artefacts, appendices, indexes effectively used? |
| 10. Was it edited well, then again with a last minute polish? |
| 11. Has the writer made sound assertions, neither over- or under-interpreting? |
| 12. Has adequate attention been paid to various contexts? |
| 13. Were sufficient raw data presented? |
| 14. Were data sources well chosen and in sufficient number? |
| 15. Do observations and interpretations appear to have been triangulated? |
| 16. Is the role and point of view of the researcher nicely apparent? |
| 17. Is the nature of the intended audience apparent? |
| 18. Is empathy shown for all sides? |
| 19. Are personal intentions examined? |
| 20. Does it appear individuals were put at risk? |
Conclusions
The case study approach allows, amongst other things, critical events, interventions, policy developments and programme-based service reforms to be studied in detail in a real-life context. It should therefore be considered when an experimental design is either inappropriate to answer the research questions posed or impossible to undertake. Considering the frequency with which implementations of innovations are now taking place in healthcare settings and how well the case study approach lends itself to in-depth, complex health service research, we believe this approach should be more widely considered by researchers. Though inherently challenging, the research case study can, if carefully conceptualised and thoughtfully undertaken and reported, yield powerful insights into many important aspects of health and healthcare delivery.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AS conceived this article. SC, KC and AR wrote this paper with GH, AA and AS all commenting on various drafts. SC and AS are guarantors.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/11/100/prepub
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participants and colleagues who contributed to the individual case studies that we have drawn on. This work received no direct funding, but it has been informed by projects funded by Asthma UK, the NHS Service Delivery Organisation, NHS Connecting for Health Evaluation Programme, and Patient Safety Research Portfolio. We would also like to thank the expert reviewers for their insightful and constructive feedback. Our thanks are also due to Dr. Allison Worth who commented on an earlier draft of this manuscript.
- Yin RK. Case study research, design and method. 4. London: Sage Publications Ltd.; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Keen J, Packwood T. Qualitative research; case study evaluation. BMJ. 1995; 311 :444–446. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Halani L, Bhopal R, Netuveli G, Partridge M, Car J. et al. Facilitating the Recruitment of Minority Ethnic People into Research: Qualitative Case Study of South Asians and Asthma. PLoS Med. 2009; 6 (10):1–11. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pinnock H, Huby G, Powell A, Kielmann T, Price D, Williams S, The process of planning, development and implementation of a General Practitioner with a Special Interest service in Primary Care Organisations in England and Wales: a comparative prospective case study. Report for the National Co-ordinating Centre for NHS Service Delivery and Organisation R&D (NCCSDO) 2008. http://www.sdo.nihr.ac.uk/files/project/99-final-report.pdf
- Robertson A, Cresswell K, Takian A, Petrakaki D, Crowe S, Cornford T. et al. Prospective evaluation of the implementation and adoption of NHS Connecting for Health's national electronic health record in secondary care in England: interim findings. BMJ. 2010; 41 :c4564. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pearson P, Steven A, Howe A, Sheikh A, Ashcroft D, Smith P. the Patient Safety Education Study Group. Learning about patient safety: organisational context and culture in the education of healthcare professionals. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2010; 15 :4–10. doi: 10.1258/jhsrp.2009.009052. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Harten WH, Casparie TF, Fisscher OA. The evaluation of the introduction of a quality management system: a process-oriented case study in a large rehabilitation hospital. Health Policy. 2002; 60 (1):17–37. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8510(01)00187-7. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE. The art of case study research. London: Sage Publications Ltd.; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Smeeth L, Ashcroft R. Randomised controlled trials in primary care: scope and application. Br J Gen Pract. 2002; 52 (482):746–51. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King G, Keohane R, Verba S. Designing Social Inquiry. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doolin B. Information technology as disciplinary technology: being critical in interpretative research on information systems. Journal of Information Technology. 1998; 13 :301–311. doi: 10.1057/jit.1998.8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- George AL, Bennett A. Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Eccles M. the Improved Clinical Effectiveness through Behavioural Research Group (ICEBeRG) Designing theoretically-informed implementation interventions. Implementation Science. 2006; 1 :1–8. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-1-1. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Netuveli G, Hurwitz B, Levy M, Fletcher M, Barnes G, Durham SR, Sheikh A. Ethnic variations in UK asthma frequency, morbidity, and health-service use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2005; 365 (9456):312–7. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Panesar SS, Lasserson T, Netuveli G. Recruitment of ethnic minorities to asthma studies. Thorax. 2004; 59 (7):634. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hellström I, Nolan M, Lundh U. 'We do things together': A case study of 'couplehood' in dementia. Dementia. 2005; 4 :7–22. doi: 10.1177/1471301205049188. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Som CV. Nothing seems to have changed, nothing seems to be changing and perhaps nothing will change in the NHS: doctors' response to clinical governance. International Journal of Public Sector Management. 2005; 18 :463–477. doi: 10.1108/09513550510608903. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lincoln Y, Guba E. Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park: Sage Publications; 1985. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barbour RS. Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog? BMJ. 2001; 322 :1115–1117. doi: 10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1115. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mays N, Pope C. Qualitative research in health care: Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ. 2000; 320 :50–52. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7226.50. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mason J. Qualitative researching. London: Sage; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brazier A, Cooke K, Moravan V. Using Mixed Methods for Evaluating an Integrative Approach to Cancer Care: A Case Study. Integr Cancer Ther. 2008; 7 :5–17. doi: 10.1177/1534735407313395. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles MB, Huberman M. Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook. 2. CA: Sage Publications Inc.; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N. Analysing qualitative data. Qualitative research in health care. BMJ. 2000; 320 :114–116. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7227.114. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cresswell KM, Worth A, Sheikh A. Actor-Network Theory and its role in understanding the implementation of information technology developments in healthcare. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2010; 10 (1):67. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-10-67. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Malterud K. Qualitative research: standards, challenges, and guidelines. Lancet. 2001; 358 :483–488. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05627-6. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. Case study research: design and methods. 2. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. Enhancing the quality of case studies in health services research. Health Serv Res. 1999; 34 :1209–1224. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Green J, Thorogood N. Qualitative methods for health research. 2. Los Angeles: Sage; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Howcroft D, Trauth E. Handbook of Critical Information Systems Research, Theory and Application. Cheltenham, UK: Northampton, MA, USA: Edward Elgar; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blakie N. Approaches to Social Enquiry. Cambridge: Polity Press; 1993. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doolin B. Power and resistance in the implementation of a medical management information system. Info Systems J. 2004; 14 :343–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2575.2004.00176.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bloomfield BP, Best A. Management consultants: systems development, power and the translation of problems. Sociological Review. 1992; 40 :533–560. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shanks G, Parr A. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems. Naples; 2003. Positivist, single case study research in information systems: A critical analysis. [ Google Scholar ]
- Introduction
- Conclusions
- Article Information
Distributions for sex (A), decedents (B), race and ethnicity (C), and dual-eligibility (D). Beneficiary race and ethnicity was determined using the Research Triangle Institute race code; Other and unknown race and ethnicity category includes Asian and Pacific Islander, American Indian or Alaska Native, and any race or ethnicity not otherwise specified. ASR indicates age-standardized rate.
eAppendix. Literature Review Protocol
eTable 1. ICD-10-CM Codes and Prescription Drugs Used in the CCW and 21 Unique Researcher-Developed Claims-Based Dementia Identification Algorithms
eTable 2. Characteristics of Beneficiaries Categorized Into Each Tier of ICD-10-CM Codes (as Defined by Frequency of Use Across the CCW and Researcher-Developed Algorithms) and NDCs
eTable 3 . Raw and Age-Adjusted Characteristics of Beneficiaries Identified as Having Highly Likely ADRD, Likely ADRD, Possible ADRD, and No Evidence of ADRD
eTable 4. Beneficiary Age Distribution in the Full Sample, Within LTC Users and Non-Users, and Within Decedents and Non-Decedents
eTable 5. New Subcodes Associated With F01, F02, and F03 That Went Into Effect in October 2022
eReferences
Data Sharing Statement
See More About
Sign up for emails based on your interests, select your interests.
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
Get the latest research based on your areas of interest.
Others also liked.
- Download PDF
- X Facebook More LinkedIn
Gianattasio KZ , Wachsmuth J , Murphy R, et al. Case Definition for Diagnosed Alzheimer Disease and Related Dementias in Medicare. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(9):e2427610. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.27610
Manage citations:
© 2024
- Permissions
Case Definition for Diagnosed Alzheimer Disease and Related Dementias in Medicare
- 1 NORC at the University of Chicago, Bethesda, Maryland
- 2 Department of Epidemiology, George Washington University School of Public Health, Washington, DC
Question How many Medicare beneficiaries have diagnostic codes or drug prescriptions indicating Alzheimer disease and related dementias (ADRD) using a refined case definition, and what are the characteristics of these beneficiaries?
Findings This cross-sectional study of more than 60 million Medicare beneficiaries identified 7.2% with evidence of highly likely ADRD, 1.9% with likely ADRD, and 4.3% with possible ADRD. Beneficiaries with evidence of ADRD were older, more frail, more likely to use long-term care, and more likely to die than those without evidence of ADRD; these differences persisted after age-standardization.
Meaning In this cross-sectional study, more than 5.4 million Medicare beneficiaries (9.1%) had evidence of likely or highly likely ADRD in 2019; pending validation, this case definition can be adopted provisionally for national surveillance of persons with diagnosed dementia in the Medicare system.
Importance Lack of a US dementia surveillance system hinders efforts to support and address disparities among persons living with Alzheimer disease and related dementias (ADRD).
Objective To review diagnosis and prescription drug code ADRD identification algorithms to develop and implement case definitions for national surveillance.
Design, Setting, and Participants In this cross-sectional study, a systematic literature review was conducted to identify unique International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) and prescription drug codes used by researchers to identify ADRD in administrative records. Code frequency of use, characteristics of beneficiaries identified by codes, and expert and author consensus around code definitions informed code placement into categories indicating highly likely, likely, and possible ADRD. These definitions were applied cross-sectionally to 2017 to 2019 Medicare fee-for-service (FFS) claims and Medicare Advantage (MA) encounter data to classify January 2019 Medicare enrollees. Data analysis was conducted from September 2022 to March 2024.
Exposures ICD-10-CM and national drug codes in FFS claims or MA encounters.
Main Outcomes and Measures The primary outcome was counts and rates of beneficiaries meeting each case definition. Category-specific age, sex, race and ethnicity, MA enrollment, dual-eligibility, long-term care utilization, mortality, and rural residence distributions, as well as frailty scores and FFS monthly expenditures were also analyzed. Beneficiary characteristics were compared across categories, and age-standardized to minimize confounding by age.
Results Of the 60 000 869 beneficiaries included (50 853 806 aged 65 years or older [84.8%]; 32 567 891 female [54.3%]; 5 555 571 Hispanic [9.3%]; 6 318 194 non-Hispanic Black [10.5%]; 44 384 980 non-Hispanic White [74.0%]), there were 4 312 496 (7.2%) with highly likely ADRD, 1 124 080 (1.9%) with likely ADRD, and 2 572 176 (4.3%) with possible ADRD, totaling more than 8.0 million with diagnostic evidence of at least possible ADRD. These beneficiaries were older, more frail, more likely to be female, more likely to be dual-eligible, more likely to use long-term care, and more likely to die in 2019 compared with beneficiaries with no evidence of ADRD. These differences became larger when moving from the possible ADRD group to the highly likely ADRD group. Mean (SD) FFS monthly spending was $2966 ($4921) among beneficiaries with highly likely ADRD compared with $936 ($2952) for beneficiaries with no evidence of ADRD. Differences persisted after age standardization.
Conclusions and Relevance This cross-sectional study of 2019 Medicare beneficiaries identified more than 5.4 million Medicare beneficiaries with evidence of at least likely ADRD in 2019 using the diagnostic case definition. Pending validation against clinical and other methods of ascertainment, this approach can be adopted provisionally for national surveillance.
Surveillance is a fundamental public health activity. Lack of a US dementia surveillance system hinders public health efforts to support persons living with Alzheimer disease and related dementias (ADRD), address health disparities, and plan ADRD care resources.
Medicare administrative data are an attractive source upon which to build a dementia surveillance system and are commonly used to identify persons living with ADRD, but a consensus diagnostic code case definition does not exist. Perhaps the most widely used definition (the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services [CMS] Chronic Conditions Warehouse [CCW] algorithm) uses 22 International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) codes, from the commonly accepted G30.X (Alzheimer disease) and F01.XX (vascular dementia), to less specific codes such as R54 (age-related physical debility). 1 In contrast, most researcher-developed ICD-10 - CM –based algorithms exclude R54, but may include codes such as G31.0 (frontotemporal dementia) that are not in the CCW algorithm. 2 - 4 Moreover, while some algorithms use Medicare Part D data to identify prescriptions for Alzheimer disease–related drugs, 5 - 8 most do not.
The impact of using different ICD-10-CM or prescription codes on the number of people identified or their characteristics is unknown. Because ICD-10-CM codes are used for billing (rather than diagnostic) purposes, specific codes may not be sensitive nor specific to dementia, and coding practices may differ systematically by health care practice, patient characteristics, and geography.
We examined how choices of ICD-10-CM and prescription drug codes used to identify persons with clinically recognized ADRD in Medicare fee-for-service (FFS) claims and Medicare Advantage (MA) encounter data affect dementia prevalence estimates and characteristics of the people identified. We synthesized this information to develop a new case definition using diagnostic and prescription drug codes that can be applied to administrative data to support surveillance of persons with diagnosed dementia in the Medicare system.
This cross-sectional study was deemed exempt from review and the requirement of informed consent by the NORC Institutional Review Board. The reporting of this research follows the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology ( STROBE ) reporting guideline.
We searched PubMed for articles published from 2012 to 2022, with all-cause dementia or ADRD as a primary exposure or primary outcome, or where the research population of interest was persons living with all-cause dementia or ADRD (eAppendix in Supplement 1 ). We found 28 studies utilizing 20 distinct researcher-developed ICD-10-CM or prescription drug code algorithms in addition to the CCW algorithm (eTable 1 in Supplement 1 ). 2 - 21
We extracted 43 ICD-10-CM codes and 5 prescription drugs across algorithms ( Table 1 and eTable 1 in Supplement 1 ). We shared the codes with 3 clinicians (2 neurology clinicians and 1 geriatrics clinician) who provide care to persons living with dementia, who recommended excluding 8 codes deemed to not indicate dementia ( Table 1 ). We grouped the remaining codes into tiers by use frequency (tier 1, ≥15 algorithms; tier 2, 10-14 algorithms; tier 3, 5-9 algorithms; and tier 4, 1-4 algorithms). We designated prescriptions for ADRD-targeting drugs as indicated by National Drug Codes (NDC) without presence of an ADRD ICD-10-CM code as tier 5.
We used 100% of the 2017 to 2019 Medicare FFS inpatient, outpatient, carrier, skilled nursing facility, home health agency, and hospice claims; MA inpatient, outpatient, carrier, skilled nursing facility, and home health agency encounter data; and Medicare Part D prescription drug event (PDE) data. We used the minimum dataset (MDS 3.0) to identify long-term care (LTC) utilization. We limited analysis to Medicare beneficiaries with at least Part A (the premium-free Medicare benefit) enrollment in January 2019, nonmissing sex, and a valid US state or territory code based on the Medicare beneficiary summary files. We did not exclude beneficiaries based on age or lack of Part B enrollment because our aim was to identify all people in the Medicare system with evidence of ADRD.
To categorize beneficiaries with or without evidence of dementia as of 2019, we conducted a cross-sectional analysis of January 2017 to December 2019 FFS and MA data to identify all claims and encounters with a relevant ICD-10-CM code listed in any position, and all PDE claims for a relevant NDC. We classified beneficiaries hierarchically, first with a tier 1 ICD-10-CM code, then with a tier 2 code among remaining beneficiaries, and so on, identifying only the incremental beneficiaries in each tier if they had not been classified earlier. We compared distributions of age, sex, race and ethnicity (as indicated by the Research Triangle Institute race code 22 ), MA enrollment, LTC use, and 2019 mortality across tiers. Race and ethnicity categories included American Indian or Alaska Native, Asian or Pacific Islander, Hispanic, non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic White, unknown, and other (defined as any race or ethnicity not otherwise specified); race and ethnicity were included because existing evidence shows that there are disparities in dementia prevalence across race and ethnicity groups. We compared cross-tier beneficiary frailty using a claims-based frailty index (CFI), 23 an adapted CFI that excludes ADRD codes in tiers 1 to 4, and per-member-per-month (PMPM) spending, averaged across all months of 2019 FFS coverage.
Using these data (eTable 2 in Supplement 1 ), we found that beneficiaries in tiers 1 and 2 were older, more frail, more likely to be female, in LTC, and die than those in tiers 3 to 5. There were minimal differences in race and ethnicity across tiers, with exception of a higher-than-expected representation of Hispanic and Asian and Pacific Islander beneficiaries in tier 5; however, the overall size of the sample categorized as tier 5 was very small, at just 0.1% (52 338 of 60 000 869 beneficiaries). Based on the findings from the cross-tier comparison and author consensus, we further aggregated codes into 3 categories with decreasing confidence of having a true ADRD diagnosis: a highly likely ADRD category requiring at least 2 claims or encounters on different dates with ICD-10-CM codes from tiers 1 or 2; a likely ADRD category requiring 1 claim or encounter with an ICD-10-10-CM code from tiers 1 or 2; and a possible ADRD category requiring at least 1 claim or encounter with an ICD-10-CM or NDC code from tiers 3, 4, or 5 over a 3-year lookback period. We categorized beneficiaries and reevaluated group demographics, health insurance type, frailty and mortality, and rural residency. We then computed prevalence of highly likely, likely, and possible ADRD within population subgroups defined by these characteristics. We age-standardized to the full analytical population to evaluate differences unconfounded by age.
All analyses were conducted in SAS Enterprise Guide 7.1 and SAS Studio version 3.81 (SAS Institute). Data analysis was conducted from September 2022 to March 2024.
Of 64 430 729 2019 Medicare beneficiaries, we excluded 3 940 831 due to lack of Part A enrollment in January, 8 due to missing sex, and 489 021 due to a nonvalid US state or territory code, resulting in a total of 60 000 869 beneficiaries (50 853 806 aged 65 years or older [84.8%]; 32 567 891 female [54.3%]; 5 555 571 Hispanic [9.3%]; 6 318 194 non-Hispanic Black [10.5%]; 44 384 980 non-Hispanic White [74.0%]) included in the study sample. Of all beneficiaries, 11 502 479 (19.2%) had Medicaid dual-eligibility, while 23 607 426 (39.3%) had MA. Mean (SD) FFS PMPM spending in 2019 was $1220 ($3426) ( Table 2 ).
We identified 4 312 496 beneficiaries (7.2%) as having highly likely ADRD, and 1 124 080 (1.9%) as having likely ADRD ( Table 3 ). The proportion of beneficiaries with highly likely ADRD increased to 8.1% (4 125 639 beneficiaries) after limiting age to 65 years or older, and to 8.8% (4 093 008 beneficiaries) when further limiting to those with both Parts A and B enrollment. The proportion of beneficiaries with likely ADRD increased to 2.1% (996 379 beneficiaries) after these restrictions. Compared with those with likely ADRD, those with highly likely ADRD were older and more frail, more likely to be female and dual-eligible, had over 3 times the rate of LTC utilization (681 923 of 4 312 496 beneficiaries [15.8%] vs 51 332 of 1 124 080 beneficiaries [4.6%]), and almost double the rate of death (828 366 of 4 312 496 beneficiaries [19.2%] vs 129 705 of 1 124 080 beneficiaries [11.5%]). We identified an additional 2 572 176 beneficiaries (4.3%) as having possible ADRD; this percentage increased to 4.8% (2 231 673 beneficiaries) after restricting to beneficiaries aged 65 years or older with Parts A and B enrollment. The possible ADRD group was younger and healthier (lower CFI, mortality, and LTC utilization) than those with highly likely or likely ADRD but was older and less healthy than those with no evidence of ADRD (51 992 117 beneficiaries). Mean (SD) PMPM spending was approximately 3 times as high in the ADRD groups (ranging from $2559 [$2952] among those with possible ADRD to $2966 [$4921] among those with highly likely ADRD) as that of the no ADRD group ($936 [$2952]). Age standardization narrowed differences in sex distribution and death rates, widened differences in race and ethnicity distribution and dual-eligible rates, and had minimal impact on differences in MA enrollment, LTC utilization, and frailty ( Figure and eTable 3 in Supplement 1 ). FFS spending increased slightly for all categories after age standardization.
The proportion of beneficiaries with any evidence of ADRD increased with age, from 6.5% (1 931 517 of 29 878 739 beneficiaries) among beneficiaries aged 65 to 74 years to 42.5% (2 544 205 of 5 983 967) among those aged 85 years or older, with the largest increase seen in the percentage of those with highly likely ADRD (2.6% [770 296 of 29 878 739 beneficiaries] to 29.1% [1 739 705 of 5 983 967 beneficiaries]) ( Table 4 ). Prevalence of any ADRD was higher in females than in males but was similar between non-Hispanic White (5 950 598 beneficiaries [13.4%]), non-Hispanic Black (892 541 beneficiaries [14.1%]), and Hispanic (792 948 beneficiaries [14.3%]) beneficiaries. Those with LTC use were substantially more likely to have ADRD than those with no LTC (681 923 of 937 248 beneficiaries [72.8%] vs 3 630 573 of 59 063 621 beneficiaries [6.1%] categorized as highly likely). Similarly, prevalence of highly likely or likely ADRD was much higher in decedents (958 071 of 2 285 257 beneficiaries [41.9%]) than nondecedents (4 478 505 of 57 715 612 beneficiaries [7.7%]) and in those who were dual-eligible (1 917 434 of 11 502 479 beneficiaries [16.7%]) than among those who were not (3 519 142 of 48 498 390 beneficiaries [7.2%]). MA beneficiaries had a higher prevalence of highly likely or likely ADRD (2 296 154 of 23 607 426 beneficiaries [9.7%]) than FFS beneficiaries (3 140 422 of 36 393 443 beneficiaries [8.6%]), and any evidence of ADRD (4 595 211 of 23 607 426 beneficiaries [14.5%] for MA vs 4 593 211 of 36 393 443 beneficiaries [12.6%] for FFS).
Age-standardizing subgroups to the age distribution of the Medicare population resulted in changes in ADRD prevalence estimates in some groups ( Table 4 ). Relative differences in ADRD prevalence narrowed across sex but widened across race and ethnicity groups. Most notably, non-Hispanic White beneficiaries became less likely to have any evidence of ADRD (12.9% across categories), while racial and ethnic minority groups became more likely to have evidence of ADRD (non-Hispanic Black beneficiaries, 16.5%; Hispanic beneficiaries, 15.3%). Among non-Hispanic Black beneficiaries, age standardization resulted in a substantial increase in the proportion of those with highly likely or likely ADRD (9.9% to 12.0%). Age standardization also reduced ADRD prevalence among LTC users (from 72.8% to 62.8% with highly likely ADRD) and decedents (from 36.2% to 23.8% with highly likely ADRD) but had minimal impact in ADRD prevalence among non–LTC users and nondecedents; this is because LTC-users and decedent groups were heavily skewed toward older ages, while the age distribution of the non–LTC users and nondecedent groups mimicked that of the general Medicare population (eTable 4 in Supplement 1 ).
Among 2019 Medicare beneficiaries in this cross-sectional study, we identified approximately 4.3 million (7.2%) with highly likely ADRD, 1.1 million (1.9%) with likely ADRD, and 2.6 million (4.3%) with possible ADRD, for a total of more than 8.0 million (13.4%) in any category. Specifically, we developed new diagnosis and NDC code ADRD case definitions informed by a systematic review of previous algorithms, author and expert input, and analyses of Medicare data. The review identified 43 ICD-10-CM codes and 5 prescription drugs used by the CCW and 20 researcher-developed algorithms to identify ADRD in Medicare data. We divided codes into categories that were likely to indicate ADRD vs those that were possibly ADRD based on past frequency of use by other researchers, characteristics of beneficiaries identified by codes, and author and expert consensus around code definitions. We then added a highly likely category to describe beneficiaries who received 2 or more likely codes on different dates of service. We posit that these categories are superior to previous definitions for provisional use in surveillance systems, but caution that validation is necessary. To our knowledge, this is the first application of claims identification algorithms to all-age FFS and MA beneficiaries. We have used this case definition to compute provisional national-, state-, and county-level estimates of ADRD prevalence and incidence in 2020 Medicare and published them on our dementia surveillance website. 24 Estimates will be refined pending validation and updated with additional years of data as they become available.
Our 3-level case definition is novel in that it was driven by researcher-consensus as well as data analysis and identifies dementia with varying degrees of certainty. Of note, ICD-10-CM codes used to identify possible ADRD have lower researcher consensus and less specific code descriptions (ie, do not contain dementia or Alzheimer ). Use of the possible ADRD codes may reflect physician uncertainty about a dementia diagnosis or medical events involving ADRD-like symptoms in patients without underlying dementia. 25 - 27 Our definition also excludes several previously used codes that were determined to not indicate ADRD by expert clinicians. Compared with the commonly used CCW algorithm, which similarly uses a 3-year look-back period, our case definition is more specific when limited to the highly likely and likely categories, but broader when also including the possible ADRD category. The CCW algorithm estimated prevalence of 10.7% in 2019 Medicare FFS beneficiaries 28 falls between our estimates for FFS beneficiaries of 8.6% for highly likely or likely ADRD and 12.6% for all 3 categories.
Importantly, we saw expected and meaningful differences between beneficiaries identified in each ADRD category. Moving from the no evidence of ADRD to the highly likely ADRD groups, beneficiaries became progressively older and more frail and had greater rates of dual-eligibility, LTC use, and death, which is consistent with prior research. 29 - 35 Notably, prevalence of highly likely ADRD was 29.1% in beneficiaries aged 85 years or older, 72.8% in LTC users, and 36.2% in decedents, compared with 7.2% in the general Medicare population. Higher rates of dual-eligibility in ADRD groups may be driven by ADRD beneficiaries spending down assets to qualify for Medicaid and obtain LTC coverage. These differences persisted after age standardization and lend confidence to our case definitions.
Application of our case definitions also showed disparities in diagnosis rates by race in the expected direction—higher dementia risk among non-Hispanic Black beneficiaries relative to non-Hispanic White beneficiaries 36 , 37 —after age standardization to account for lower life expectancy among non-Hispanic Black individuals. 38 However, because non-Hispanic Black individuals also have a greater risk of under-diagnosis of ADRD than non-Hispanic White individuals, 39 disparities in true underlying rates may be higher than observed. Additionally, we found higher-than-expected representation of Hispanic and Asian and Pacific Islander beneficiaries among those that had an ADRD-targeting drug without diagnostic ( ICD-10-CM ) evidence. We hypothesize that differences in cultural perceptions around dementia and cognitive decline (eg, memory loss as a normal aging process) 40 , 41 may result in lower utilization of diagnosis codes when providers suspect dementia. Using PDE claims may result in higher and more accurate rates of ADRD among Hispanic and Asian and Pacific Islander individuals despite the overall small number of beneficiaries identified by PDE claims alone.
Finally, also consistent with past research, 29 , 35 , 42 PMPM FFS spending was substantially higher for beneficiaries with evidence of ADRD compared with those with no evidence of ADRD. Medicare FFS PMPM spending was relatively similar across the highly likely, likely, and possible ADRD groups despite differences in frailty and mortality. Medicare FFS spending may not be generalizable to those with MA (for whom costs cannot be computed) and is only part of the economic story. Medicaid is the primary US payer of LTC; higher rates of dual-eligibility and LTC use among the highly likely ADRD group indicate that differences in total federal and state spending between the highly likely ADRD and other groups are likely larger. We also did not capture patient and family health–related out-of-pocket expenses and informal care costs ($203 117 in families caring for a patient living with dementia vs $102 955 in families caring for a patient without dementia over the last 7 years of the patient’s life 42 ), forgone wages, or other impacts on informal caregivers, and payments made by other assistance programs. Finally, we caution that our spending measure represents total Medicare FFS spending, rather than the incremental ADRD costs.
This study is limited by at least the following. First, our ADRD case definition was driven by researcher-consensus, and validation against other dementia ascertainment methods (including ascertainment based on in-person clinical and neuropsychological assessments) is necessary. Both over- and under-diagnosis of ADRD have been documented in Medicare claims, 35 , 39 and the 8.0 million beneficiaries identified as having some evidence of ADRD by our case definition will include some without ADRD, especially those in the possible category. Similarly, this method only captures documented cases of dementia in Medicare administrative records and cannot capture beneficiaries with unrecognized and/or undocumented ADRD. If we assume a 60% rate of undetected dementia in the US 43 our estimates would suggest an additional 12 million beneficiaries may be living with ADRD. Additionally, our data show a marginally higher rate of ADRD in MA than in FFS enrollees (14.5% vs 12.6% across the 3 categories), which may reflect beneficiary selection in MA plans, MA vs FFS differences in clinical ADRD assessment and diagnosis rates, differences in claims or encounter documentation, or a combination thereof. Given the rapid rise in MA participation (from 33% in 2017 to 51% in 2023) and variation in MA penetration across counties, 44 , 45 it is also important to understand potential differences in performance of this case definition between MA and FFS beneficiaries. As such, validation of this case definition against in-person clinical and other ascertainment methods to assess performance (including sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value), separately for Medicare FFS and MA, is critical for refining and calibrating estimates to accurately capture the diagnosed prevalence and incidence of dementia. Pending validation, our case definitions should be considered provisional. Notably, we expect the possible ADRD category to identify a higher proportion of individuals who do not have ADRD. Thus, it is important to report the possible ADRD category separately from the likely and highly likely ADRD categories in research and surveillance efforts using these case definitions.
Second, evidence for ADRD documented in electronic health or insurance records outside the Medicare system is not captured by our method; this is particularly problematic for beneficiaries without Medicare Parts B or D (7.5% and 25.6% of Medicare enrollees, respectively 43 , 46 ). Third, we deliberately used data from 2017 to 2019 to avoid the COVID-19 pandemic years, which resulted in secular shocks, including excess senior deaths, forgone or deferred care, and increased telehealth, which may have impacted dementia diagnosis. Research is necessary to understand these effects but will necessarily be delayed pending new data. Fourth, Namzaric, a memantine and donepezil combination drug approved in 2014, was not included by any prescription-drug based identification strategy; while the impact of including this drug necessitates further investigation, we anticipate a negligible effect given that just 0.1% of the sample had an ADRD-targeting prescription drug without ICD-10-CM evidence. Similarly, ICD-10 -CM code updates from October 2022 added 29 highly specific codes each under code roots F01 (vascular dementia) F02 (dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere), and F03 (unspecified dementia) (eTable 5 in Supplement 1 ). 47 We recommend that applications of our approach to Medicare records beginning in October 2022 include these for identifying highly likely and likely ADRD. Fifth, in developing our case definitions, we only considered use of ICD-10-CM codes and prescription drugs but did not consider other criteria of existing ADRD-identification algorithms, including look-back period, types of claims or encounter data considered, number of claims or encounters with relevant ICD-10-CM codes required, and time elapsed between claims and encounters; sensitivity analyses around these different criteria are beyond the scope of this paper.
In this cross-sectional study, our novel case definition for ADRD identified approximately 5.4 million Medicare beneficiaries with evidence of at least likely ADRD in 2019. Pending validation against in-person clinical and other ascertainment methods, this definition can be adopted for provisional use in national surveillance efforts.
Accepted for Publication: June 17, 2024.
Published: September 3, 2024. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.27610
Open Access: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the CC-BY License . © 2024 Gianattasio KZ et al. JAMA Network Open .
Corresponding Author: Kan Z. Gianattasio, PhD, NORC at the University of Chicago, 4350 East-West Hwy 8th Floor, Bethesda, MD 20814 ( [email protected] ).
Author Contributions: Mr Wachsmuth and Mr Murphy had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Concept and design: Gianattasio, Hartzman, Wittenborn, Power, Rein.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: All authors.
Drafting of the manuscript: Gianattasio, Wachsmuth, Hartzman, Cutroneo, Wittenborn, Rein.
Critical review of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Gianattasio, Murphy, Hartzman, Montazer, Power, Rein.
Statistical analysis: Gianattasio, Wachsmuth, Murphy.
Obtained funding: Wittenborn, Rein.
Administrative, technical, or material support: Hartzman, Montazer, Cutroneo.
Supervision: Hartzman, Rein.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: None reported.
Funding/Support: Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health (Award No. R01AG075730).
Role of the Funder/Sponsor: The funder had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Disclaimer: The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Data Sharing Statement: See Supplement 2 .
Additional Contributions: We would like to thank Christina Prather, MD (George Washington University); Tania Alchalabi, MD (George Washington University); and Raymond Scott Turner, MD, PhD (Georgetown University), for providing critical review of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) codes from a clinical perspective. Drs Prather, Alchalabi, and Turner did not receive compensation for their contributions to this work. We also wish to acknowledge the critical input into data processing and analysis decisions made by Qian Gu, PhD (KPMG); Carrie Bao, BS (KPMG); and Samuel Knisely, BA, (KPMG). Dr Gu, Ms Bao, and Mr Knisely received funding from the same National Institute on Aging grant (R01AG075730) that funded this study for their input.
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An article that describes and interprets an individual case, often written in the form of a detailed story. Case reports often describe: Unique cases that cannot be explained by known diseases or syndromes. Cases that show an important variation of a disease or condition. Cases that show unexpected events that may yield new or useful information.
This part describes the existing theories and research findings on the key issue in the patient's condition. The review should narrow down to the source of confusion or the main challenge in the case. Finally, the case report should be connected to the existing literature, mentioning the message that the case conveys.
Case report. In medicine, a case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports may contain a demographic profile of the patient, but usually describe an unusual or novel occurrence. Some case reports also contain a literature review of other reported cases.
Preparing a case report is far easier than conducting any other elaborative research design. Case report, with its main components, should be focused and delivers a clear message. In this article, the key components of a case report were described with the aim of providing guidance to novice authors to improve the quality of their reporting.
The case report is a specific type of research. design that reports on an aspect of the. management of one or two patients. It is the first. piece of research writing in the health field and ...
A case report form (CRF) is designed to collect the patient data in a clinical trial; its development represents a significant part of the clinical trial and can affect study success. [1] Site personnel capture the subject's data on the CRF, which is collected during their participation in a clinical trial.
Case studies are good for describing, comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem. Table of contents. When to do a case study. Step 1: Select a case. Step 2: Build a theoretical framework. Step 3: Collect your data. Step 4: Describe and analyze the case.
"The basic definition of a case report is the detailed report of an individual including aspects like exposure, symptoms, signs, intervention, and outcome. . . . A case report may describe an unusual etiology, an unusual or unknown disorder, a challenging differential diagnosis, an unusual setting for care, information that can not be ...
Case reports may stimulate the generation of new hypotheses, and thus may support the emergence of new research. Table 1 Levels of evidence. Full size table. The definition of a case report or a case series is not well defined in the literature and has been defined variously by different journals and authors. However, the basic definition of a ...
A case study, also known as a case report, is an in depth or intensive study of a single individual or specific group, while a case series is a grouping of similar case studies / case reports together. A case study / case report can be used in the following instances: where there is atypical or abnormal behaviour or development.
Preparing a case report is far easier than conducting any other elaborative research design. Case report, with its main components, should be focused and delivers a clear message. In this article, the key components of a case report were described with the aim of providing guidance to novice authors to improve the quality of their reporting ...
A case report is a descriptive study that documents an unusual clinical phenomenon in a single patient. It describes in details the patient's history, signs, symptoms, test results, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment. It also contains a short literature review, discusses the importance of the case and how it improves the existing knowledge on the subject.
Introduction. The case report or case series report is defined as a detailed narration about medical or scientific experiences, characterized by being innovative and informative and because it generally describes contents on clinical manifestations of rare diseases, epidemics, new diagnostic methods, drug effectiveness and safety, among other topics of medical practice.
Defnition: A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
Editorial. Introduction. Case reports and case series or case study research are descriptive studies to present patients in their natural clinical setting. Case reports, which generally consist of three or fewer patients, are prepared to illustrate features in the practice of medicine and potentially create new research questions that may contribute to the acquisition of additional knowledge ...
Case reports are a time-honored, important, integral, and accepted part of the medical literature. Both the Journal of Medical Case Reports and the Case Report section of BioMed Central Research Notes are committed to case report publication, and each have different criteria.Journal of Medical Case Reports was the world's first international, PubMed-listed medical journal devoted to ...
Case reports and case series are descriptive studies that recount a patient scenario complete with pertinent medical information such as laboratory values, medications, and diagnoses. 1,2 A case report includes a detailed discussion of a unique medical scenario of a single case or event in light of the currently available literature and provides an evaluation of the findings. 3 Case series ...
2.3. DIFFERENT STUDY TYPES USED IN MEDICAL AND EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RESEARCH Case Report. The Case Report describes the occurrence of a health condition in one or two patients usually in terms of patient symptoms, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome. E.g. Description of a case of trachoma with unusual manifestations and evolution.
A case report is a detailed report of the diagnosis, treatment, response to treatment, and follow-up after treatment of an individual patient. A case series is group of case reports involving patients who were given similar treatment. Case reports and case series usually contain demographic information about the patient (s), for example, age ...
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Defining a Case Report. Often, Case Report activity involves sharing medical knowledge, improving quality, and providing education, and therefore will fall under the HIPAA definition of health care operations (45 CFR 164.501), which includes: "Conducting quality assessment and improvement activities, including outcomes evaluation and development of clinical guidelines, provided that the ...
An article that describes and interprets an individual case, often written in the form of a detailed story. Case reports often describe: Unique cases that cannot be explained by known diseases or syndromes. Cases that show an important variation of a disease or condition. Cases that show unexpected events that may yield new or useful information.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute USA.gov. A detailed report of the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports also contain some demographic information about the patient (for example, age, gender, ethnic origin).
A case report form (or CRF) is a paper or electronic questionnaire specifically used in clinical trial research. [1] The case report form is the tool used by the sponsor of the clinical trial to collect data from each participating patient. All data on each patient participating in a clinical trial are held and/or documented in the CRF ...
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table 5), the ...
Key Points. Question How many Medicare beneficiaries have diagnostic codes or drug prescriptions indicating Alzheimer disease and related dementias (ADRD) using a refined case definition, and what are the characteristics of these beneficiaries?. Findings This cross-sectional study of more than 60 million Medicare beneficiaries identified 7.2% with evidence of highly likely ADRD, 1.9% with ...