- +1.8337753787

- Our Process
- Privacy Policy
- Contact Form
- Instant Quote
- LED Products
- LED Posters
- Universities
- Trade Show LED
- Conference Room LED
- Control Room LED
- Theatre LED
- Virtual Studios
- Tampa, Florida
- Las Vegas, Nevada
- Finance Options
- Customer Reviews
- Download Buyers Guide
- Motion Graphics
- LED Screen Installation
- Stage Design Ideas
- From Projector to LED
- Join Backstage Pass

Refresh LED Blog

How to Start a Successful AV Company
User Rating: 5 / 5

Be part of creating memorable experiences with your own audio-visual (AV) company. Delving into the AV industry is a promising venture, especially in today's flourishing digital landscape. Just like any other business pursuit, there are things you need to know — the overall process, relevant tips and more.
What Is an AV Company?
An audio-visual business is the pillar of event production . AV companies handle the technical aspects, from digital displays to audio sources. The two key elements of an AV business are audio and visual.
Audio equipment covers a wide range of devices that capture, reproduce and process sound. These include microphones, headphones, mixing consoles, amplifiers, speakers and CD players. Visual equipment refers to devices that offer clear and polished visual content , including images and video presentations. Common visual equipment includes video cameras, video players, LED walls and projectors.
How to Start an AV Company
Now that you know what an audio-visual company is, it's time to learn how to establish an AV business. Here are some key steps on how to start an AV production company:
1. Kick-Off With Market Research
Start your business venture by identifying your market. Who is your target audience? What are their specific needs? Determine economic trends and customer behavior to understand the competition in the market. At this point, you should know what makes your business unique.
2. Create a Business Plan
Whether you're a start-up or an established company, you need a business plan. This written document lays out the company's main purpose, objectives and direction. It creates a structured framework for your financial, operational and marketing plans, helping you achieve your goals. Just like any business, your AV company needs a strategic business plan to succeed.
3. Prepare the Legal Documentation
Legal compliance is essential when running a business. Ensure you meet local business requirements by applying for the appropriate licenses and permits. Guidelines and documents may vary depending on your location. Make sure to adhere to national or local regulations to protect your business assets and enhance customer trust.
4. Invest in the Right Equipment
Keep operations organized and effective with the right equipment. Invest in high-quality equipment for your AV company to fulfill customer needs and expectations. When sourcing materials, it's highly recommended to choose newer equipment with the latest technologies to be more agile. Trends change, and customer habits shift easily,
5. Establish Your Pricing and Packages
When setting your price, you need to consider many factors, including the equipment cost and the event duration. Determine a competitive pricing strategy that caters to various needs and budgets. Offering different packages and rental options enables your company to accommodate a wide range of customers.
6. Market Your Company
Knowing how to market an AV company can be a challenge, especially if you're new to the industry. Use social media to your advantage. Create a solid online presence with your own professional website. You can also increase visibility through digital marketing strategies, like search engine optimization and email marketing.
How to Make Your AV Company Successful
Deliver better and richer experiences to your customers with the right partnership. Forming partnerships with trusted names in the industry widens your customer base and fosters overall growth. Aside from collaborative strategies, providing superior customer service helps build your reputation. Train your team to handle any event scenario and satisfy customer demands professionally and efficiently.
Trust Refresh LED for Your LED Walls
If you're looking for a credible source of LED walls , you can count on us to provide you with the highest-quality and user-friendly equipment for your business. At Refresh LED, we recognize our clients' needs and go above and beyond to meet them. From scheduling a consultation to our free design mock-ups and installing the equipment , we help make your business venture worthwhile.
Request a quote today , and let us help you make your AV company a success.

Sort Articles
- LED screen 2
- LED Tips 33

+1 833-775-0633
Mechanicsburg, pa, las vegas, nv.

Who We Are & Who We Serve
- For Churches
Request Our Free LED Wall Buyers Guide


Recording Studio Business Plan [Free Downloadable Template]
- Recent Posts
- How Our Client Boost Organic Traffic by 800% and 3x Sales in Just One Year - September 6, 2024
- 11 Proven Ways to Monetize Your Blog (Practical Guide) - February 16, 2024
- Making Money Blogging: How to Build a Passive Income Stream? - February 16, 2024
Last Updated on February 28, 2024 by Arif Chowdhury
So, you’ve got dreams of running your own recording studio, huh? Well, my friend, you’re in for a wild ride! Starting a recording studio business is like diving headfirst into the world of music and sound with a splash of entrepreneurial spirit. It’s not just about setting up some fancy equipment and hitting the record button. Oh no, there’s so much more to it!
The recording studio industry is booming louder than ever before. With artists craving that perfect sound and music lovers hungry for high-quality tunes, there’s a world of potential waiting for you. But let me warn you – it’s not all glitz and glamour. Running a recording studio comes with its fair share of challenges, too.
Before you jump into this crazy adventure, take a moment to consider the key factors involved. From understanding the basics to navigating the complex landscape of music production, we’ve got you covered.
Here is the free, downloadable , readymade template PDF for your recording studio business plan, as we promised.
So? Get ready to unlock the secrets behind building your very own recording studio brand.
Market Analysis and Research for Recording Studios
To ensure the success of your recording studio business, it’s essential to conduct thorough market analysis and research .
This step will help you understand your target customers, analyze competitors in the local recording studio market, determine the demand for recording studios in your area, and identify trends and opportunities in the music industry that can impact your business.
1. Conduct Thorough Market Research
Before diving headfirst into starting a recording studio, it’s crucial to gather as much information as possible about your target market. Conducting thorough market research will provide valuable insights into the preferences, needs, and behaviors of potential customers.
It will help you identify their demographics, such as age groups, musical genres they prefer, and their willingness to pay for professional recording services.
Some key aspects to consider during market research include:
- Demographic analysis: Understand the characteristics of your target audience by considering factors like age, gender, location, income level, and musical interests.
- Market size estimation: Determine how many potential customers exist within your geographical area.
- Customer preferences: Identify what specific services or features potential customers are looking for in a recording studio.
- Pricing analysis: Research pricing strategies used by other studios in your area to determine competitive pricing for your services.
2. Analyze Competitors in the Local Recording Studio Market
Analyzing the competition is vital to gaining a competitive edge in the local recording studio market. By studying existing studios’ strengths and weaknesses, you can position yourself strategically and differentiate your business from others.
Here are some steps to conduct a comprehensive competitor analysis:
- Identify competitors : Make a list of all the recording studios operating within your vicinity.
- Research their offerings : Study their service packages, equipment quality, pricing structures, additional amenities offered (such as mixing/mastering services), and customer reviews.
- Assess strengths and weaknesses : Identify what sets your competitors apart and determine areas where they may be lacking.
- Differentiate your business : Use the information gathered to develop unique selling points that will attract customers to your studio.
3. Determine the Demand for Recording Studios in Your Area
Understanding the demand for recording studios in your area is crucial for gauging potential success. Conducting market research will help you assess whether there is enough demand to sustain a profitable business.
Consider these factors when determining demand:
- Local Music Scene: Analyze your area’s music industry. Count the number of local artists, bands, and music events. A vibrant music scene suggests a need for recording studios, as musicians often require professional facilities.
- Existing Studios: Assess the utilization of current studios. If they’re consistently booked or if musicians must travel long distances for recording, it may indicate an unmet demand. Conversely, if studios are largely underutilized, you must consider market saturation.
- Industry Trends: Study music industry growth trends . Changes in technology and music distribution methods can impact studio demand. Observe streaming services’ influence and emerging music genres.
- Market Surveys: Conduct surveys and interviews with local musicians, producers, and engineers to understand their needs and preferences.
- Competitor Analysis: Study your potential competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, pricing, and customer reviews to identify opportunities.
Recommended Reading: Small Business Flight Plan: 25 Steps to Boost Success
Essential Equipment and Supplies for a Recording Studio
To set up a professional recording studio, you’ll need some essential equipment. Let’s dive in and explore the key components of a recording studio business plan that will help you create good music and produce high-quality audio .
1. Microphones, Headphones, and Audio Interfaces
Having the right microphones is crucial. Different types of microphones serve various purposes in a recording studio. Dynamic microphones are durable and versatile, making them suitable for live performances or recording loud instruments like drums. Condenser microphones are more sensitive and accurate, ideal for capturing vocals or acoustic instruments with precision.
Headphones are another vital piece of equipment for monitoring audio during recording and mixing sessions. Look for closed-back headphones that provide isolation from external noise while delivering accurate sound reproduction.
Audio interfaces act as the bridge between your computer and other devices in the studio setup. They convert analog signals into digital data that can be processed by your computer’s software. Ensure your audio interface offers high-quality preamps, low latency performance, and sufficient inputs/outputs to accommodate multiple instruments or microphones.
2. Software Options for Audio Editing
To edit, mix, and master your recordings effectively, you’ll need reliable software tools. Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs) are powerful software programs used for recording, editing, arranging, and producing music or audio content.
Popular DAWs include Pro Tools, Logic Pro X (for Mac users), Ableton Live (great for electronic music production), FL Studio (ideal for beginners), and Reaper (an affordable option with robust features). Each DAW has its own unique interface and workflow, so it’s worth exploring different options to find one that suits your needs.
3. Acoustic Treatment Materials
Creating a well-balanced acoustic environment is essential in a recording studio to ensure accurate monitoring of sound. Acoustic treatment materials help control reflections within the room by reducing echoes or unwanted resonances.
Consider using bass traps to tame low-frequency buildup, diffusers to scatter sound waves and minimize flutter echoes, and acoustic panels to absorb mid-range and high-frequency reflections. These materials can be strategically placed on walls, ceilings, and corners to optimize the sound quality in your studio.
4. Additional Equipment and Supplies
In addition to the essentials mentioned above, there are a few more items that can enhance your recording studio setup:
- Studio monitors: These specialized speakers provide accurate and detailed audio reproduction, allowing you to hear the nuances in your recordings.
- Cables: Invest in high-quality cables for connecting microphones, instruments, and other devices. Balanced XLR cables are commonly used for professional audio connections.
Recommended Reading: LinkedIn Sales Navigator vs. ZoomInfo Unveiling the Best B2B Tool
Sales and Marketing Strategy for Recording Studios
To run a successful recording studio business, it’s crucial to have an effective sales and marketing strategy in place. This will help you attract clients, promote your services, and ultimately grow your business within the competitive music industry.
Let’s explore some key strategies that can help you achieve these goals.
1. Develop effective sales strategies
It’s essential to showcase what sets you apart from other studio companies in the industry. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Offer competitive pricing packages tailored to different client needs: Providing flexible pricing options can appeal to a wide range of music artists and bands. Consider offering hourly rates, project-based packages, or subscription plans.
- Provide exceptional customer service: Building strong relationships with your clients is crucial for repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals. Ensure that you prioritize customer satisfaction by delivering high-quality services and addressing any concerns promptly.
- Showcase your portfolio: Displaying a portfolio of successful projects can demonstrate your expertise and credibility as a recording studio. Create an online presence where potential clients can listen to samples of your work or view testimonials from satisfied artists.
2. Implement online marketing techniques
In today’s digital age, online marketing plays a vital role in promoting any business, including recording studios. Here are some effective techniques:
- Leverage search engine optimization (SEO): Optimize your website by using relevant keywords related to music production and recording studios. This will help improve your visibility on search engines when potential clients are looking for recording services in their area.
- Utilize social media platforms: Establish a strong presence on popular social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube. Regularly share engaging content such as behind-the-scenes footage, artist spotlights, or tips for aspiring musicians.
- Launch email marketing campaigns: Build an email list of potential clients and music industry professionals. Send out regular newsletters or promotions to keep them informed about your services, special offers, and upcoming events.
3. Utilize networking opportunities
Networking is a powerful tool for growth in the music industry. Here are some ways you can leverage networking opportunities:
- Attend industry events and conferences: Participate in music-related events, conferences, and workshops where you can meet artists, producers, managers, and other industry professionals. Networking at these events can lead to collaborations or referrals.
- Collaborate with local musicians: Partnering with local musicians or bands can help expand your reach within the community. Offer recording discounts or promotional packages for artists who refer other clients to your studio.
Recommended Reading: How to Boost Sales with LinkedIn Sales Navigator Chrome Extension?
Creating a Comprehensive Recording Studio Business Plan
Having a well-defined business plan is crucial for the success of your recording studio. It serves as a roadmap, guiding you through the various aspects of your business and helping you make informed decisions.
Let’s delve into the key components that should be included in your recording studio business plan.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is a concise overview of your recording studio business plan. It highlights the key points and provides readers with an understanding of what your business is all about.
2. Market Analysis
Conducting thorough market research is essential to understand the industry landscape and identify potential opportunities for growth. Analyze the demand for recording studios in your area, assess the competition, and identify your target audience. This will help you tailor your services to meet their needs effectively.
3. Financial Projections
Financial projections are an integral part of any business plan. They provide insights into the expected revenue streams, expenses, and profitability of your recording studio. Include details on start-up costs, equipment purchases, operational expenses, marketing budget, and projected revenue streams from services like music production or audio engineering.
4. Goals and Objectives
Setting realistic goals and objectives based on market research findings will guide your actions toward achieving success. Determine what you want to accomplish with your recording studio in terms of revenue targets, client base expansion, or service diversification. Break down these goals into smaller milestones that can be measured over time.
5. Actionable Timeline
Creating an actionable timeline with measurable milestones is crucial for tracking progress and ensuring accountability. Divide larger goals into smaller tasks with specific deadlines attached to them. For example:
- Establish legal entity: 1 month
- Secure funding: 2 months
- Set up physical space: 3 months
- Acquire necessary equipment: 4 months
By breaking down tasks in this way, you can stay organized and motivated to achieve each milestone.
6. Business Structure
Deciding on the right business structure is essential for legal and financial reasons. Consider whether you want to operate as a sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), or corporation. Each structure has its pros and cons, so weigh them carefully before making a decision.
You can download a free, readymade business plan template (PDF) for your recording studio business.
Recommended Reading: How to Use a LinkedIn Ad Budget Calculator for Your Campaigns?
Staffing and Equipment Needs for Success
To run a successful recording studio, it’s crucial to have the right staff and equipment in place. Let’s dive into the key aspects you need to consider.
1. Skilled audio engineers or sound technicians
One of the first things you’ll need is a talented management team with experience in operating professional equipment. Hiring skilled audio engineers or sound technicians who are familiar with industry-standard tools and techniques is essential.
These individuals will be responsible for capturing high-quality recordings and ensuring that your clients’ artistic vision is realized.
2. High-quality equipment
Investing in top-notch equipment that meets industry standards is vital for delivering exceptional results. From microphones to mixing consoles, speakers to software, every piece of gear should be carefully chosen to ensure optimal performance.
High-quality equipment not only enhances the overall sound quality but also reflects positively on your studio’s professionalism and credibility.
3. Evaluate staffing requirements
Determining your staffing requirements is crucial for maintaining a smooth workflow and meeting client demands. Assess your projected workload based on factors such as the number of potential customers, revenue forecasts, and services offered.
This evaluation will help you determine how many employees you need to hire, whether full-time or part-time, to handle various tasks efficiently.
4. Ongoing training opportunities
In an ever-evolving industry like music production, staying up-to-date with the latest technologies and techniques is essential. Provide ongoing training opportunities for your staff to ensure they are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to deliver excellent results consistently.
This can include workshops, seminars, online courses, or even inviting industry experts for guest lectures.
Recommended Reading: Google Ads vs. LinkedIn Ads for B2B & B2C Companies
Publicity, Advertising, Pricing, Sustainability, and Expansion Strategies
To ensure the success of your recording studio business, it’s crucial to have effective strategies in place for publicity, advertising, pricing, sustainability , and expansion.
Let’s dive into each of these areas and explore how they can contribute to the growth and sustainability of your business.
Promote your recording studio through online platforms, local media, and industry events.
Marketing plays a vital role in attracting customers to your recording studio. A well-planned marketing strategy will help you reach your target market effectively. Here are some ways to promote your studio:
- Utilize online platforms: Create a professional website that showcases your services and portfolio. Engage with potential clients through social media channels like Instagram or Facebook.
- Collaborate with local media: Build relationships with local radio stations or newspapers to feature stories about your studio or offer special promotions.
- Participate in industry events: Attend music festivals or conferences where you can network with artists and industry professionals.
Set competitive pricing based on market analysis and value proposition
Pricing is an essential aspect of running a successful recording studio business. It’s crucial to strike a balance between profitability and offering competitive rates that attract clients. Consider the following factors when determining your pricing:
- Market analysis: Research what other studios in your area are charging for similar services. This will give you an idea of the prevailing rates.
- Value proposition: Highlight any unique features or advantages that set your studio apart from competitors. This could be state-of-the-art equipment or experienced engineers.
Implement sustainable practices to reduce environmental impact
In today’s world, sustainability is becoming increasingly important for businesses across all industries. By adopting eco-friendly practices within your recording studio, you not only contribute to environmental conservation but also enhance your reputation among environmentally conscious clients.
Here are some steps you can take:
- Energy-efficient equipment: Invest in energy-saving devices like LED lights and low-power consumption equipment.
- Recycling and waste management: Implement recycling programs for paper, plastic, and other materials. Properly dispose of hazardous waste such as batteries or electronics.
- Green partnerships: Collaborate with eco-friendly suppliers or vendors who share your commitment to sustainability.
Develop expansion strategies such as offering additional services or opening new locations.
As your recording studio business grows, you may consider expanding your offerings or opening new locations. This can help you attract a wider range of clients and increase your profits. Here are some expansion strategies to consider:
- Mixing and Mastering Services: Offer professional mixing and mastering services to musicians and bands who may not have access to high-quality equipment or expertise. This can generate additional revenue and attract clients looking for a one-stop solution.
- Music Production Courses: Consider providing music production courses for aspiring artists and producers. These can range from beginner to advanced levels, helping you tap into the educational aspect of the music industry and establish your studio as an educational hub.
- Instrument Rental: If your recording studio has the space, consider renting out musical instruments and equipment. This can be especially lucrative if you’re in an area with a thriving music scene.
- Live Recording and Streaming: Offer live recording and streaming services for concerts, events, and performances. This can attract both local bands and touring artists who want to capture their live shows professionally.
- Collaborative Workshops: Organize collaborative workshops, songwriting sessions, or jamming events within your studio space. This fosters a sense of community among musicians and keeps your studio buzzing with creative energy.
Recommended Reading: 5 Steps to Promote Your Content in Search Engines to Get Organic Traffic
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the essential steps to start a recording studio.
Starting a recording studio can be an exciting venture, but it requires careful planning and execution. Here are the essential steps you need to take:
- Research and Planning : Begin by conducting thorough research about the recording industry, understanding the market demand, and identifying your target audience. Create a detailed business plan that outlines your goals, services offered, marketing strategies, and financial projections.
- Acquire Equipment : Invest in high-quality audio equipment such as microphones, headphones, speakers, mixers, and recording software. Ensure that you have all the necessary tools to provide professional-grade sound quality.
- Choose a Suitable Location : Find a location that is easily accessible for your clients and has enough space to accommodate your equipment and recording booths. Consider factors like soundproofing and acoustic treatment to ensure optimal sound quality.
- Set Up Recording Booths : Design soundproof recording booths within your studio space to eliminate external noise interference during recordings. Install proper acoustic panels or foam to achieve balanced sound absorption.
- Hire Skilled Staff : Employ experienced engineers, producers, and technicians who can handle the technical aspects of running a recording studio effectively. Having knowledgeable professionals on board will enhance the overall quality of your services.
- Develop Pricing Structure : Determine competitive rates for various services offered by your studio based on factors like studio time, mixing/mastering fees, and additional equipment rental charges, if applicable.
- Create Marketing Strategies : Develop effective marketing strategies to attract clients to your recording studio. Utilize social media platforms to create a website with samples of previous work or testimonials from satisfied clients.
- Network with Industry Professionals : Attend music industry events or join local music communities where you can meet artists, bands, and producers who might require recording services in the future.
- Provide Exceptional Customer Service : Focus on providing excellent customer service to ensure client satisfaction. Maintain open communication, be responsive to their needs, and go the extra mile to exceed their expectations.
Is owning a recording studio profitable?
Running a recording studio has the potential for profitability when you maintain a consistent flow of clients, establish a strong reputation, and gain a competitive advantage in the industry. Nevertheless, the degree of profitability hinges on various factors. These include the studio’s location, the caliber of clients you can attract, and your adeptness at managing both expenses and revenues.
According to certain resources, a recording studio could potentially yield annual profits surpassing $100,000 after accounting for wages, operating costs, and taxes. However, it’s essential to note that this accomplishment often demands a substantial upfront investment in equipment, studio facilities, and marketing efforts.
What are the expenses of a recording studio?
The expenses associated with operating a recording studio can fluctuate considerably, contingent upon the studio’s size, quality, and overall scale. Among the common expenditures encountered are:
- Rental or mortgage payments for the studio space
- Utilities like electricity, water, internet, and phone services
- Maintenance and repair costs for equipment
- Expenses linked to insurance and taxes
- Costs attributed to marketing and advertising initiatives
- Salaries and wages designated for staff and contracted workers
- Licenses and subscriptions for software
- Procurement of supplies such as cables, tapes, CDs, and more
Building a recording studio can carry a price tag ranging from $500 to $20,000 or even more, depending on the level of technological sophistication and quality you aspire to attain.
Furthermore, the cost of renting a music studio can exhibit substantial variation, with budget studios typically priced at around $30 per hour and more upscale studios demanding rates of $100 per hour or higher.
What makes a successful recording studio?
A thriving recording studio is characterized by its ability to deliver top-notch audio services to clients while maintaining a dedicated customer base and a stellar reputation. Several key factors contribute to the success of a recording studio, including:
- Expertise and Professionalism: The proficiency and professionalism of the producer or engineer play a pivotal role in ensuring high-quality output.
- Equipment and Facilities: Availability and reliability of top-notch equipment and facilities are crucial for consistent results.
- Customer Service and Communication: Exceptional customer service and effective communication skills among staff members foster client satisfaction and loyalty.
- Niche and Genre Focus: Specializing in particular niches or genres can attract clients looking for specific expertise.
- Marketing and Networking: Strategic marketing and networking efforts help in expanding clientele and building brand recognition.
- Pricing and Value: Competitive pricing with a clear value proposition can make the studio more appealing to potential clients.
As for acquiring clients, recording studios employ various marketing methods, such as:
- Online Presence: Creating a professional website and active social media profiles, regularly updating them with relevant content to engage and attract potential clients.
- Networking: Attending local music events, conferences, and industry gatherings to connect with musicians and professionals in the field.
- Promotions: Offering promotions, discounts, referral incentives, or free samples to entice new customers and encourage referrals.
- Client Feedback: Requesting reviews, testimonials, and referrals from satisfied clients to build trust and credibility.
- Collaborations: Collaborating with other studios, artists, or media outlets to cross-promote services and tap into wider networks.
- Showcases and Contests: Hosting showcases, contests, or giveaways to showcase the studio’s work, create buzz, and attract attention.
What type of business is a recording studio?
A recording studio falls within the category of service businesses that offer a range of audio-related services. These services encompass audio recording, mixing, mastering, editing, production, and other related offerings. Recording studios cater to a diverse clientele, including musicians, singers, songwriters, composers, podcasters, voice actors, and various audio professionals.
In terms of legal structure, a recording studio can take on several forms, each with its own set of legal and tax considerations. These options include:
- Sole Proprietorship: In this structure, a single individual owns and operates the recording studio. It’s the simplest form, but the owner is personally liable for business debts and obligations.
- Partnership: When two or more individuals collaborate to run the studio, they can form a partnership. Partners share profits, losses, and responsibilities, but personal liability is a concern in general partnerships.
- Corporation: Establishing a corporation for the studio provides legal separation between the business and its owners (shareholders). This separation can protect personal assets but comes with additional administrative and tax requirements.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): An LLC combines elements of both partnerships and corporations. It offers limited liability protection to its members (owners) while allowing for more flexibility in management and taxation.
The choice of legal structure depends on factors like liability protection, tax implications, and management preferences. Studio owners should consult with legal and financial professionals to determine the most suitable structure for their specific needs and circumstances.
Are there any legal requirements or permits needed to operate a recording studio?
Yes, it is important to research and comply with the legal requirements and permits necessary to operate a recording studio in your specific location. This may include obtaining licenses for music production, copyright laws, noise regulations, and business operation permits.
Consult with local authorities or seek legal advice to ensure you are compliant with all necessary regulations.
How long does it typically take for a new recording studio to become profitable?
The timeframe for profitability varies depending on various factors such as location demographics, competition level, marketing efforts employed by the owner(s), reputation within the industry, etc.
Generally speaking, though, it may take anywhere from six months up to two years before a new recording studio starts generating consistent profits.
Congratulations! You have now completed all the essential sections of your recording studio business plan. By conducting thorough market research, identifying the necessary equipment and supplies, formulating a sales and marketing strategy, creating a comprehensive business plan, addressing staffing and equipment needs, exploring publicity and advertising strategies, and utilizing our sample business plan template and resources, you are well on your way to setting up a successful recording studio.
Now that you have all the information you need, it’s time to take action. Start by implementing your carefully crafted business plan. Remember, success in this industry requires dedication, perseverance, and continuous learning.
Stay updated with the latest trends in music production and adapt your strategies accordingly. Network with other professionals in the field to expand your reach and gain valuable insights.
Good luck on your journey to establishing a thriving recording studio business!

- Development
How to Create a Production Company Business Plan [FREE Template]
H ighly successful video companies start with a strong production company business plan. Whether your company has been around for a while, or you’re a freelancer ready to take your services to the next level, this post will provide you with actionable strategies for success to compete more effectively right now.
It all beings with formulating the business plan that will get you where you want to go. If you don’t have a business plan, don’t worry. We provide a free business plan template below and will walk you through it.
Step by step.
- Production Company Business Plan
- The Executive Summary
- Perform a Video Company Self Assessment
- How to Get Started
- Financing a Video Production Company
- Marketing Plan
- Day to Day Operations
Freebie: Business Plan Template for Video Production

Download your FREE printable business plan template for your video production. Just enter your email address and we'll instantly send it to you!
business plan template
1. what is a production company business plan.
Essentially it's a tool for raising funds, creating a roadmap, or altering course and plotting out the next steps.
One purpose of any business plan to so convey to investors, or a bank, why they should put money into this business.

Think of creating a business plan you could bring to them
What does that mean?
It means you need this business plan for a production company to prove that you will make money. To prove it to you, but also to any investors.
After all, nobody invests to lose money. Or break even. So with that in mind, let's forge ahead into the actual writing of the business plan.
how to make a business plan
2. what is an executive summary.
Every business plan starts from the top down, with an executive summary.
What is that, exactly?
An executive summary is a short part of a larger proposal or report that summarizes the main points so the reader can become quickly educated on the whole document without having to read it all.
So it’s a detailed overview.
Of course, "executive summary" has a nice ring to it...
Your job here is to lay out the big picture of your plan. Some questions to ask yourself: Why do you want this business in the first place?
Similarly, what inspired you to start it? What's going to make it work?
Next, start to answer the questions your investors might have. Try getting into their head-space.
"Why would YOU invest in this business?"
You might want to write about the competition. The targeted demographic. Be specific here.
What need does your business fill? Which kinds of customers and clients are you targeting?
Think about your target market
Furthermore, what else sets you and your business apart?
Especially relevant is using concrete examples and not only ideas. Can you cite previous work you've done?
This brings us to...
Your production companies competition
What does the rest of the field looks like. Your investor will want to know if they don't already.
What sets this company and this production company business plan apart from others?
Knowing the entire field of competitors you have is a good idea, even if it's a very long list.
Your production company business plan must factor in what else is being offered. That way you can adjust, and target a more specific niche.
Or, you can figure out what you can do better.
For example: what can you identify in your competitor's list of services that you know you can nail?
This is what your video company plan needs to convey.
Finally, remember to think of it from the investor's standpoint. How is this an opportunity for them?
how to create a business plan
3. why a video company self-assessment.
This step is easy to do, but hard to do well.
Can you take a good long look at your video production studio? With the intent to circle problems? Areas that need improvement?
The second part of this step might be easier. Find the areas where your video production studio can really shine.
In contrast, you don't want to elaborate on weaknesses in your video production company business plan. Rather, you want to identify them so you can find ways to address them.
You need to have answers to the questions these flaws might bring to the mind of your investors.

You are not required to sing “Man in the Mirror”
Then go beyond looking in the mirror.
Look back at the field before you.
This is a business plan for a production company. What opportunities exist for that?
Most of all, try and tailor this production house business plan to specific needs.
Here are a few methods of company self-analysis:
This is a way to identify changes in your industry, to target potential growth opportunities. The acronym stands for:
P olitical Factors
E conomic Factors
S ocial Factors
T echnological Factors
P roduction company business plan would include a PEST
We've mentioned elements of SWOT:
W eaknesses
O pportunities
The one to focus in on here is threats. Don't assume everything will work out for the plan just the why you'd like it to.
Because it won't. Investors will know that. You should not only know it, you should expect it.
Most important of all: prove that you're prepared for whatever may happen.
Here's a cool way to approach your SWOT analysis. Try applying your strengths to your opportunities and see what kind of leverage you can create.
Then theoretically expose your weaknesses to your threats. Are you in trouble? Do you need to address something to better protect your company?
Think of this as planning for a battle. Therefore, you don't want to ignore cracks in the wall if your enemy is bringing a battering ram.
Business plan can benefit from SWOT
Strategy, structure, systems, style, shared values, staff, and skills. The 7S model was developed by business consultants Robert H. Waterman Jr. and Tom Peters . It's also known as the McKinsey 7S framework.
The idea here is that your business needs these elements to be aligned and "mutually reinforcing". Let's go over each "S".
Strategy: How does this business plan to gain an advantage.
Structure: How do you divide the various operations of the company.
Systems: Procedure for measurement, reward and resource allocation.
Skills: the companies core and distinctive capabilities.
Staff: Human resources.
Style: Behavior patterns of the key groups like managers.
Shared values are in the middle of them all on the diagram. It's somewhat self-explanatory.
In theory, using these methods of self-analysis will help you a great deal. Due to them you'll know, and decide, all sorts of things about your production company.
The 7 S model of analysis
Start putting these ideas onto paper now! If you haven’t already…
Gentlemen, start your engines
4. how to get started.
A business plan for a production company must lay out how you will get started. This is also referred to as a "roll out plan".
How you engineer your beginning is critical to your cash flow. What do you need to get started?
And can you start at a sustainable level?
Will you open a physical office space right off the bat?
Overhead is a major cost. If this is more of a production house business plan then you’ll want to factor that in.
Do you have existing clients?
Equipment or gear already in place?
A video production business plan suggests that your focus will be on video production. Things like equipment will be critical.
In addition to considering this an entertainment production company business plan you may also want to focus on creative development.
How you want to focus effects how you want to phrase things. And it matters almost immediately.
START FEES YOU CAN AVOID
It's a good idea to propose that you start small.
There are two reasons for this.
The first is that you will scare away investors if you ask for too much up front, almost without fail they can tell if you are asking for more than it seems like you need.
It also throws into question how serious you are about sustaining success.
Which leads to the second reason.
It'll be much harder for you to sustain success if you ask for big upfront funding that you aren't sure you can earn back plus profit.
Let's say because you know of a few jobs you'll have early on, that you ask for less up front.
You'll be able to get rolling right away, earning back the initial investments and then some.
Above all you want to start off with easy wins.
Or as close to easy wins as you can get when launching or re-launching a video production business plan.
Seems like it would somewhat obvious not to ask for more than you can earn back...
Rather, it's a mistake people make all the time.
Speaking of which...
do have the capital?
5. financing a company.
Any business needs capital. As a result, you need a section where you lay out the cash flow for the production house business plan.
What kind of money do you expect to have coming in, and how much do you expect to be spending?
Make the budget, while also estimating how you'll be earning.
If you can't demonstrate this, then you need to go back to the drawing board.

Just pose like this and you’ll reassure any investor
You will want to get involved with an accountant at some point soon.
But remember, this is a business plan for a production company. So you may have a lot of costs coming at you early just to get started.
What is a marketing plan?
Your video production business plan is almost complete. Another section worth including would be one on marketing.
Here is a good additional resource on small business accounting .
You want to prove that business will be coming in, and not assume it will on faith alone.
Building a strong portfolio is a must. Consider again what niche you may be able to serve best. Find a solid "bread and butter" to start with.
Remember, good businesses expand when they need to. They don't bite off more than they can chew right out of the gate.
INVEST IN A GOOD WEBSITE
Do some research on how you’ll be building the best website for your product.
Get your production company a few social media accounts, and start trying to create a presence there. You'll need to find many ways to attract clients, and show your work.
Do some additional research on how to market a production company.
All this needs to find its way into the marketing section of your production company business plan.
what's your daily workflow?
7. day to day operations.
The day to day operations are a critical part of the plan. Have you visualized what the daily workflow will be?
Now is the time to do that. Who is going to be on your team, and how will it grow and change over time?
Determine what tasks will take priority each day, and how to best utilize your resources and finances.
This will be a key step in determining if your production company business plan is sustainable.
Ask yourself a few of the following questions:
How much time per day will you spend building your client base? What elements of each job will you tackle in-house? Which tasks might you outsource?
What equipment and gear do you own?
When will it need to be replaced and/or upgraded?
Are you going to hire anyone to start? Will they be full-time employees?
Will you hire independent contractors per project? How many, roughly?
As mentioned in the finance section, you need to know how you'll plan your reporting for taxes and your bookkeeping process.
These questions will help you start to determine what each "day at the office" will look like.
The clearer a picture you can paint here, the better.
Write a Business Plan
Get as specific as possible in each section of your entertainment company business plan. The more you know... right?
Now, let's get a little more advanced. In our next post we'll dive into writing a 4 part business plan.
Up Next: Write a 4-Part Business Plan →
Project management for video creatives. tasks, file sharing, calendars and more..
Manage video production timelines, tasks, storyboards, shot lists, breakdowns, call sheets. Made for video creatives, new media and film.
Learn More ➜
1.1 CHAPTER TITLE HERE...
Short, actionable h3 phrase....
Marshmallow pie sweet roll gummies candy icing. I love candy canes soufflé I love jelly beans biscuit. Marshmallow pie sweet roll gummies candy icing.
- Pricing & Plans
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- What is a Biopic — Definition & Best Examples Explained
- How Many Rocky Movies Are There — All Rocky Movies in Order
- Storyboard Ideas, Examples, and Techniques Explained
- What is a Femme Fatale — Definition, Characteristics, Examples
- Screenplay Example for Formatting, Genres & PDF Downloads
- 1.2K Facebook
- 44 Pinterest
- 20 LinkedIn

If you want to grow your audio visual business, you have to invest in it. That’s a fact. There are two issues with that. No. 1, most company owners and executives are slow to acknowledge that they have enough cash flow to start investing.
No. 2, it’s extremely difficult to come up with a smart game plan for investing in your company’s growth.
Tackling No. 1 is easy. Whether you think you have a lot of extra capital or not, chances are the economy may force you to invest in your audio visual business sooner than later.
Our State of the Industry Report shows a 9.5 percent growth rate for the average integrator in 2019…but the problem is that — despite high demand for integration work — gross profits for integrators aren’t particularly high compared to overhead costs.

In other words: you’re probably making less per job, and you need to combat that in case of an economic downturn.
We’re not intentionally trying to scare you with that last line, but if you read our State of the Industry, you’ll notice that one of our sources says 2020 may not be a great economic year.
Regardless of the economy, you shouldn’t let your firm’s ability to turn a profit fall prey to higher overhead. If you have extra money that you can safely and responsibly invest in your business, it may now be time to do so.Now, let’s tackle No. 2.
How to Invest in Your Audio Visual Business
Here’s an important disclaimer: The point of this article is to get you thinking about what’s right for YOUR business. We can’t do that for you, but we can offer what other professionals say works for them. Your job after reading this is to think critically about if it will work for you, too.
That said, we’d love to be able to say “large firms seeking to expand should spend their money here; ” or “small firms seeking to grow should do this. ”
But the problem is that each AV business reaches success in its own particular way under very particular circumstances. We can’t therefore make broad claims about what firms in these distinct positions can do, but we can provide a different kind of framework.
“Four Circles” of AV Businesses
Chuck Wilson — our friend at the National Systems Contractor’s Association and regular CI resource — says that firms seeking to improve themselves should start with a day-to-day framework revolving around “four circles.”
Chuck says you should envision yourself walking into the office each day and seeing these circles on a chart near your desk… So we took it upon ourselves to make the mock-up you see below. Go ahead, print it out, learn it, and live it.
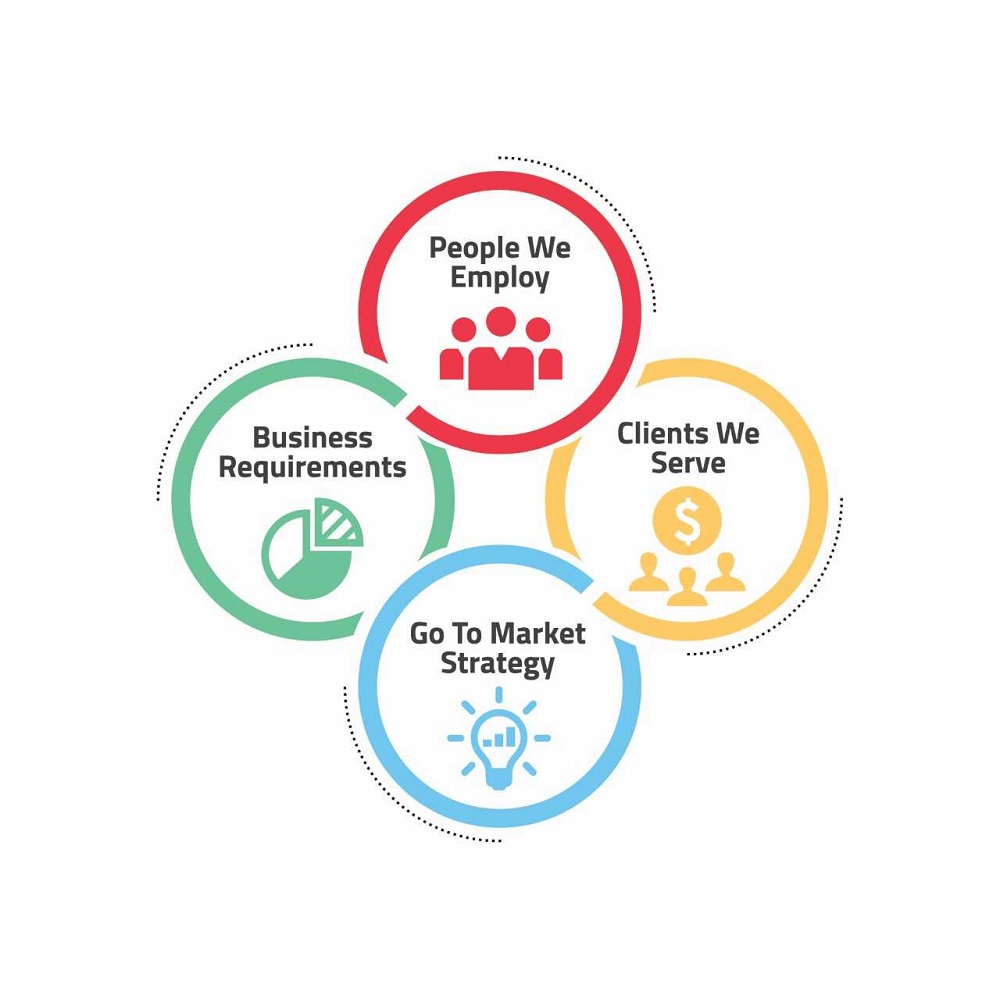
Click for full size
People We Employ
One of the most strategic parts of your company is the people who operate it. So it is incredibly important to think about employees’ skill sets today, but more importantly, what they should be three years from now.
If you or your company hires someone today, are they going to be relevant and will their employment be sustainable in three years?
Asking this question regularly will help you monitor your organizational structure and make better hiring decisions in-the-moment.
Clients We Serve
So much audio visual business is based on clients predisposed to hire you if you have the lowest bid.
But you need customers who truly value you for what you do for them; clients who want an ongoing business relationship.
Some firms have to remove clients from their lists because of continually driven-down margins and wasted time — so if that’s happening to you, don’t be afraid to politely refrain from those small, fruitless jobs.
Go To Market Strategy
Again, this circle isn’t so much about what’s happening today as much as what’s happening in the future. What trends are truly impacting the markets you serve? How are you reacting to those, if at all?
Your strategy should always include a section that focuses solely on what you can do to respond to future market needs — which, coincidentally often coincides with the “People We Hire” circle. If potential employees can’t see future innovation at your firm before their first day begins, where will your customers see innovation?
Business Requirements
This is perhaps the most important part of any business’s plan to invest because it runs counter to the idea of spending to grow: simply put, what could be cut from the company?
Think “lean,” and be honest with yourself. Where are your inefficiencies? Do you have any form of KPI measurement? Every company has bottlenecks. What are yours?
The important thing under this circle is that you don’t immediately start to build extra costs into your budget once you start seeing successful outcomes. Investments, like every other part of your audio visual business, should be measured.
Hopefully, you’ll start to think about how each of these four circles interconnect and affect each other.
What To Avoid
Look, there are many ways to drop money on your business ( which, I promise, we will cover below!) , but it is more important to caution you against the approaches many have taken, and failed.
Opening offices in new places too soon
Medium AV firms who want to expand tend to underestimate just how challenging that is. Chuck Wilson says it is foolhardy to open up an office in a new region without fully understanding the regulations, licensing, and legislation that will impact your business there.
“When we go into a location and underestimate the local nature of the trade jurisdiction climate or the licensure arena… That’s been a huge problem even more so in this last year, where we’re seeing licensing changes and jurisdiction issues galore. It’s never been as bad as it is right now,” Wilson says.
Poaching from other companies
Chuck says integrators also often underestimate the loyalty of the people they employ.
“If we’re a company trying to grow rapidly and we use a recruitment technique known as ‘poaching,’ we see a growing longevity issue happening where they will come to work for a shorter time,” he says.
That’s not great if you’ve invested time and money into training them. So you’ve really got to focus on hiring people whose vision seems complementary to company goals. If it feels like you’re “poaching” someone, that may be a bad sign. Here are some hiring resources for audio visual businesses.
A “my-way-or-the-highway” approach to acquisition
There’s nothing more socially excruciating and inefficient than trying to simply insert your work methods into other peoples’ lives. You’re not going to win over new employees gained from acquisitions if you simply assume that they’ll bend to your will.
Do everything you possibly can to make your employees know you’re going above and beyond to help make the transition smooth.
Parlay with the other side — the sellers — to make sure they’re treating their handed-over employees with respect. If the “new boss” shows they care right off the bat, new employees will be more likely to be excited, rather than concerned with, their new station.
[eh_quiz id=”54214″]
Thinking Global? What to Do
You may very likely be focused on tackling global markets if you’ve already established a solid presence in one or more regions. This could be a good idea for your firm — but, again, only if you thoroughly comprehend the different legal & regulatory considerations impacting a given area.
We’re not about to go on about the many steps involved in a global expansion process — we’ll save that for another day. But what if you’re just getting your feet wet in another market?
If you’re seriously considering global expansion but haven’t done anything about it yet, start by going to Integrated Systems Europe .
The industry’s largest trade show is also a great place to make contacts in other markets and study up on which ones could be right for you.
If You’re Smaller & Want to Change That
So your audio visual business isn’t big enough to even have the global market on your radar? Congrats, most firms are like you…But, also, yikes! Most firms are like you! How are you standing out?!
You’ll stand out if you invest in your employees
By putting your technicians through extra training, you’re investing in your firm’s ability to change with the ever-evolving technological landscape. You’re also providing them valuable tip-off opportunities when they network at these events. Here’s everything you need to know about AV training.
You’ll stand out if your company culture inspires employees
Right about here is where you’d expect to see corporate, mind-numbing phrases like “self-directed leadership” … and, ok, we admit to using these words before. But they all mean something, and your challenge now is to figure out if they mean something positive to you.
Here are some different audio visual business approaches to company culture:
Buying Out the Competition
It is very, very difficult to take one company with one set of standards and workflows and insert it into another, different company. Whenever an acquisition is considered, its impact on company culture must be at the top of the list.
That isn’t to say that acquisitions are something your audio visual business should avoid, however.
Look for under-performing companies that don’t seem motivated to take the next step towards growth.
If your company culture and business practices are solid enough to put you in a position to acquire, it can be beneficial to both sides if you consider seeking out companies who could really use your help. Become their opportunity , especially if they are in a strategic position for you.
Again, this only works if you already have time-tested on-boarding processes, company culture, and training standards.
Posted in: Insights , News
Tagged with: Managed Service , Managed Services , Recurring Monthly Revenue , Recurring Revenue , RMR
Related Posts
Strategies for effective remote and hybrid collaboration, making your business future ready: how integrators can optimize their businesses for enduring success, the here, now and science of quantum computing, the importance of virtual-meeting attendance.

Multimedia Business Plan Template & Guidebook
Are you interested in starting your own multimedia company but unsure of where to start? We can assist you with our multimedia business plan template and manual. You can simply construct a business plan that details every facet of your enterprise, from market analysis and financial predictions to marketing plans and operational tactics, with the help of our comprehensive template and professional advice. You may easily start your profitable multimedia business using our step-by-step method, allowing you to realize your ambition. With the help of our tried-and-true template and direction, you can confidently start the process of creating a successful multimedia company. Join the ranks of prosperous multi-media entrepreneurs by getting started right away!
Get worry-free services and support to launch your business starting at $0 plus state fees.
- How to Start a Profitable Multimedia Business [11 Steps]
- 25 Catchy Multimedia Business Names:
- List of the Best Marketing Ideas For Your Multimedia Business:
How to Write a Multimedia Business Plan in 7 Steps:
1. describe the purpose of your multimedia business..
The first step to writing your business plan is to describe the purpose of your multimedia business. This includes describing why you are starting this type of business, and what problems it will solve for customers. This is a quick way to get your mind thinking about the customers’ problems. It also helps you identify what makes your business different from others in its industry.
It also helps to include a vision statement so that readers can understand what type of company you want to build.
Here is an example of a purpose mission statement for a multimedia business:
Our mission at Multimedia is to provide high-quality audio and visual solutions for businesses, events, and organizations. We are dedicated to using the latest technology and techniques to create engaging and effective multimedia experiences. We strive to make the process seamless and stress-free for our clients, and to provide exceptional customer service at every step of the way. We are committed to innovation and to pushing the boundaries of what is possible in multimedia. By delivering unmatched quality and value, we aim to be the go-to provider of multimedia solutions in our region.

2. Products & Services Offered by Your Multimedia Business.
The next step is to outline your products and services for your multimedia business.
When you think about the products and services that you offer, it's helpful to ask yourself the following questions:
- What is my business?
- What are the products and/or services that I offer?
- Why am I offering these particular products and/or services?
- How do I differentiate myself from competitors with similar offerings?
- How will I market my products and services?
You may want to do a comparison of your business plan against those of other competitors in the area, or even with online reviews. This way, you can find out what people like about them and what they don’t like, so that you can either improve upon their offerings or avoid doing so altogether.

3. Build a Creative Marketing Stratgey.
If you don't have a marketing plan for your multimedia business, it's time to write one. Your marketing plan should be part of your business plan and be a roadmap to your goals.
A good marketing plan for your multimedia business includes the following elements:
Target market
- Who is your target market?
- What do these customers have in common?
- How many of them are there?
- How can you best reach them with your message or product?
Customer base
- Who are your current customers?
- Where did they come from (i.e., referrals)?
- How can their experience with your multimedia business help make them repeat customers, consumers, visitors, subscribers, or advocates for other people in their network or industry who might also benefit from using this service, product, or brand?
Product or service description
- How does it work, what features does it have, and what are its benefits?
- Can anyone use this product or service regardless of age or gender?
- Can anyone visually see themselves using this product or service?
- How will they feel when they do so? If so, how long will the feeling last after purchasing (or trying) the product/service for the first time?
Competitive analysis
- Which companies are competing with yours today (and why)?
- Which ones may enter into competition with yours tomorrow if they find out about it now through word-of-mouth advertising; social media networks; friends' recommendations; etc.)
- What specific advantages does each competitor offer over yours currently?
Marketing channels
- Which marketing channel do you intend to leverage to attract new customers?
- What is your estimated marketing budget needed?
- What is the projected cost to acquire a new customer?
- How many of your customers do you instead will return?
Form an LLC in your state!

4. Write Your Operational Plan.
Next, you'll need to build your operational plan. This section describes the type of business you'll be running, and includes the steps involved in your operations.
In it, you should list:
- The equipment and facilities needed
- Who will be involved in the business (employees, contractors)
- Financial requirements for each step
- Milestones & KPIs
- Location of your business
- Zoning & permits required for the business
What equipment, supplies, or permits are needed to run a multimedia business?
Multimedia businesses provide a variety of services related to the creation, management, and distribution of audio, video, and other types of digital media. The equipment and supplies needed to run a multimedia business can vary depending on the specific services offered, but may include:
- Audio and video recording equipment, such as microphones, cameras, and lighting, to capture high-quality media
- Editing software and hardware, such as computers and specialized software, to create and manipulate digital media
- Storage and backup equipment, such as hard drives and cloud storage, to securely store media files
- Distribution equipment, such as servers and CD/DVD burners, to share media with clients and audiences
- Marketing and advertising materials, such as business cards and websites, to promote the business and its services
In addition to the equipment and supplies needed to run a multimedia business, it is important to obtain any necessary permits and licenses that may be required by local regulations. These permits and licenses may vary depending on the location of the business and the specific services offered.
In summary, the equipment, supplies, and permits needed to run a multimedia business can include audio and video recording equipment, editing software and hardware, storage and backup equipment, distribution equipment, and marketing materials, as well as any necessary licenses and permits.
5. Management & Organization of Your Multimedia Business.
The second part of your multimedia business plan is to develop a management and organization section.
This section will cover all of the following:
- How many employees you need in order to run your multimedia business. This should include the roles they will play (for example, one person may be responsible for managing administrative duties while another might be in charge of customer service).
- The structure of your management team. The higher-ups like yourself should be able to delegate tasks through lower-level managers who are directly responsible for their given department (inventory and sales, etc.).
- How you’re going to make sure that everyone on board is doing their job well. You’ll want check-ins with employees regularly so they have time to ask questions or voice concerns if needed; this also gives you time to offer support where necessary while staying informed on how things are going within individual departments too!
6. Multimedia Business Startup Expenses & Captial Needed.
This section should be broken down by month and year. If you are still in the planning stage of your business, it may be helpful to estimate how much money will be needed each month until you reach profitability.
Typically, expenses for your business can be broken into a few basic categories:
Startup Costs
Startup costs are typically the first expenses you will incur when beginning an enterprise. These include legal fees, accounting expenses, and other costs associated with getting your business off the ground. The amount of money needed to start a multimedia business varies based on many different variables, but below are a few different types of startup costs for a multimedia business.
Running & Operating Costs
Running costs refer to ongoing expenses related directly with operating your business over time like electricity bills or salaries paid out each month. These types of expenses will vary greatly depending on multiple variables such as location, team size, utility costs, etc.
Marketing & Sales Expenses
You should include any costs associated with marketing and sales, such as advertising and promotions, website design or maintenance. Also, consider any additional expenses that may be incurred if you decide to launch a new product or service line. For example, if your multimedia business has an existing website that needs an upgrade in order to sell more products or services, then this should be listed here.
7. Financial Plan & Projections
A financial plan is an important part of any business plan, as it outlines how the business will generate revenue and profit, and how it will use that profit to grow and sustain itself. To devise a financial plan for your multimedia business, you will need to consider a number of factors, including your start-up costs, operating costs, projected revenue, and expenses.
Here are some steps you can follow to devise a financial plan for your multimedia business plan:
- Determine your start-up costs: This will include the cost of purchasing or leasing the space where you will operate your business, as well as the cost of buying or leasing any equipment or supplies that you need to start the business.
- Estimate your operating costs: Operating costs will include utilities, such as electricity, gas, and water, as well as labor costs for employees, if any, and the cost of purchasing any materials or supplies that you will need to run your business.
- Project your revenue: To project your revenue, you will need to consider the number of customers you expect to have and the average amount they will spend on each visit. You can use this information to estimate how much money you will make from selling your products or services.
- Estimate your expenses: In addition to your operating costs, you will need to consider other expenses, such as insurance, marketing, and maintenance. You will also need to set aside money for taxes and other fees.
- Create a budget: Once you have estimated your start-up costs, operating costs, revenue, and expenses, you can use this information to create a budget for your business. This will help you to see how much money you will need to start the business, and how much profit you can expect to make.
- Develop a plan for using your profit: Finally, you will need to decide how you will use your profit to grow and sustain your business. This might include investing in new equipment, expanding the business, or saving for a rainy day.
Frequently Asked Questions About Multimedia Business Plans:
Why do you need a business plan for a multimedia business.
A business plan is a document that outlines the goals and objectives of a business, as well as the strategies and tactics that will be used to achieve those goals. It is important to have a business plan for your multimedia business because it helps to focus the efforts of the company, communicate the business's goals and objectives to potential investors, and provide a roadmap for the business to follow. Additionally, a business plan can be used to help secure funding from investors or lenders, who will want to see that the business has a solid plan in place before they provide funding.
How to write a business plan for your multimedia business?)
To build a business plan for your multimedia business, start by researching your industry, competitors, and target market. Use this information to define your business's goals and objectives, as well as the strategies and tactics that you will use to achieve those goals. Next, create a financial plan that outlines your projected income, expenses, and profit. This should include a projected income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet. Once you have all of this information, you can use it to create a comprehensive business plan that outlines the goals and objectives of your business, as well as the strategies and tactics that you will use to achieve those goals. A well-written multimedia business plan contains the following sections: Purpose, Products & Services, Marketing Plan (including Marketing Strategy), Operations/Management Plan (including Operations/Management Strategy), Financial Plan (including Financial Forecasts), and Appendixes.
Can you write a multimedia business plan yourself?
Yes, you can write a multimedia business plan yourself. Writing a business plan is a valuable exercise that can help you clarify your business idea, identify potential challenges and opportunities, and develop a roadmap for success. While there are many resources and templates available to help you write a business plan, the process of creating one is ultimately up to you.
Related Business Plans

Home Inventory Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Home Inspection Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Home Decor Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Health And Wellness Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hauling Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hardware Business Plan Template & Guidebook


Handyman Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hair Extension Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Handbag Business Plan Template & Guidebook
We're newfoundr.com, dedicated to helping aspiring entrepreneurs succeed. As a small business owner with over five years of experience, I have garnered valuable knowledge and insights across a diverse range of industries. My passion for entrepreneurship drives me to share my expertise with aspiring entrepreneurs, empowering them to turn their business dreams into reality.
Through meticulous research and firsthand experience, I uncover the essential steps, software, tools, and costs associated with launching and maintaining a successful business. By demystifying the complexities of entrepreneurship, I provide the guidance and support needed for others to embark on their journey with confidence.
From assessing market viability and formulating business plans to selecting the right technology and navigating the financial landscape, I am dedicated to helping fellow entrepreneurs overcome challenges and unlock their full potential. As a steadfast advocate for small business success, my mission is to pave the way for a new generation of innovative and driven entrepreneurs who are ready to make their mark on the world.
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Video Production Business Plan
Start your own video production business plan
Michael's Video Service
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
Michael’s Video Service uses the latest technology to provide video production services. This means that the services provided achieve a level of quality previously reserved for only the most expensive video production companies.
Michael’s Video Service is a new company and as such, we will need to meet market acceptance. To that end, the company is working to determine trends in the industry, the needs of the customer, and how best to address the needs of the customer.
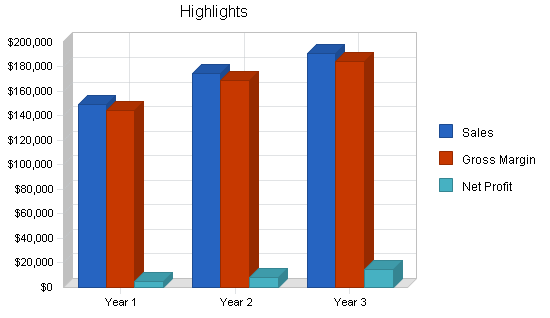
Our services are geared for several markets, including television stations, companies, high schools, and families. We will initially target high schools with whom we can establish strategic alliances that will enable us to establish long term relationships with them. In our first year of operation, we believe we can capture 15 to 25% of the market, which translates into $100,000 – $130,000 in sales.
We believe that we can earn $149,000 in our first year, rising to $175,000 and $191,000 in our second and third years, respectively. Our market strategy will be to advertise and capitalize on the services that our competitors do not offer.
There are several companies with whom we will be competing. We have a competitive advantage, however, because our equipment is more aligned with the video production industry trends requiring digital technology, as opposed to analog devices.
The company is seeking a loan in the amount of $300,000 which will be used to purchase the equipment and start-up expenses. The company’s revenue projections for the first three years are $149,000, $175,000, and $191,000, respectively. Michael’s Video Service expects to achieve profitability early on.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
Legal Business Description
Michael’s Video Service was founded in May 1996 by Mr. Michael Morrison. Michael’s Video Service is a Limited Liability Company (LLC) with principal offices located in Denton, Ohio.
| Start-up Funding | |
| Start-up Expenses to Fund | $15,000 |
| Start-up Assets to Fund | $302,000 |
| Total Funding Required | $317,000 |
| Assets | |
| Non-cash Assets from Start-up | $242,000 |
| Cash Requirements from Start-up | $60,000 |
| Additional Cash Raised | $0 |
| Cash Balance on Starting Date | $60,000 |
| Total Assets | $302,000 |
| Liabilities and Capital | |
| Liabilities | |
| Current Borrowing | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $300,000 |
| Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills) | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $300,000 |
| Capital | |
| Planned Investment | |
| Michael Morisson | $17,000 |
| Other | $0 |
| Additional Investment Requirement | $0 |
| Total Planned Investment | $17,000 |
| Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses) | ($15,000) |
| Total Capital | $2,000 |
| Total Capital and Liabilities | $302,000 |
| Total Funding | $317,000 |
2.1 Mission
Our mission is to become the leading freelance and video production company in state, utilizing the latest technology to shift market share from competitors to Michael’s Video Service.
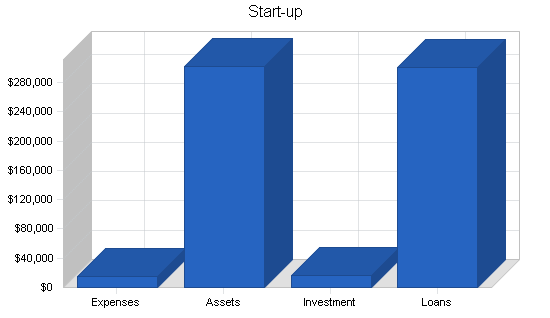
| Start-up | |
| Requirements | |
| Start-up Expenses | |
| Legal | $500 |
| Stationery etc. | $200 |
| Brochures | $300 |
| Consultants | $1,000 |
| Insurance | $1,200 |
| Rent | $600 |
| Expensed equipment | $10,000 |
| Other | $1,200 |
| Total Start-up Expenses | $15,000 |
| Start-up Assets | |
| Cash Required | $60,000 |
| Start-up Inventory | $2,000 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 |
| Long-term Assets | $240,000 |
| Total Assets | $302,000 |
| Total Requirements | $317,000 |
Michael’s Video Service is in business to cover events and special occasions on a freelance basis. What we will be providing is an alternative solution for video companies or out of town television stations. Instead of them sending a crew or taking time out of their busy schedules, they can hire us to do the filming for them. This gives them the opportunity to focus on their core competencies.
We will attend any and every event that we will have to cover for our customer. Using our experience, we will find a strategic location from which we will film. Once the filming is complete, we will then deliver the tape to the customer.
Michael’s Video Service will contract video services to its target markets. Services are not only limited to the Denton, we are able to travel around the country. Our main goal is to contract our services to anyone who may need an event video taped.
3.1 Service Description
The operation begins with the customer contacting Michael’s Video Service with the intent of using our services. All the details of the event are gathered and all the relevant information pertaining the specific requirements, as well as the delivery of the tape. Thereafter, we attend the event and proceed to do the filming. Once the filming is completed, the next step is to deliver the tape to the customer.
3.2 Technology
Analog is the old technology and digital is the new. Analog communication systems involve the amplitude modulation of a radio signal. In other words, they transmit and receive information through a continuous flow of electromagnetic signals. An inherent weakness of the technology is that analog signals weaken over distances and require additional equipment to boost them as they travel.
Digital cameras are the future of television broadcasting as well as the future of consumer camcorders. The FCC has mandated that all television stations must transmit a digital signal to the homes of its viewers by 2002.
In keeping up with the trends in the industry, we plan to purchase the latest digital equipment on the market. We plan to use the following equipment:
- DLC Qualcomm 500
- Sanyo 2000 video equipment
- Sanyo 2000 wireless equipment
Strategy and Implementation Summary
We plan to initially market our products and services as an alternative solution for television networks and video companies. These markets were selected because of their size, trends in technology, our experience with video production, our industry contacts, and an overall belief that they are most appropriate to initially target.
We aim to rapidly develop alliances with the major high schools to enable us to gain credibility as the best video production company. Our market strategy will be to advertise and capitalize on the products and services that our competitors do not have.
4.1 Market Analysis Summary
We expect to compete as a freelance video production company in the broadcasting industry. Companies in the industry are involved in the creation and delivery of various types of programming to consumers. Much of that programming is recorded on film, tape, or disk, so that it can be seen or heard repeatedly by both new audiences and those that are familiar with it. Many of the events that are broadcast live are likely to be recorded, with some or all of such events to be rebroadcast at future times.
Within this national market, Michael’s Video Service will initially focus on supplying its services to the high school market market. We intend to be the only freelance video company in the city and state to offer our services to companies of any size. Our goal is to be on the freelance list for all the major television networks for news and sports coverage in the southeast region of the United States.
4.1.1 Market Segmentation
Our customer is defined as any individual or organization that has need for one of the services we provide. Our target customers are as follows.
| Market Analysis | |||||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | |||
| Potential Customers | Growth | CAGR | |||||
| TV stations | 5% | 600 | 630 | 662 | 695 | 730 | 5.03% |
| Video production companies | 10% | 150 | 165 | 182 | 200 | 220 | 10.05% |
| Movie directors and producers | 10% | 500 | 550 | 605 | 666 | 733 | 10.04% |
| High schools | 5% | 160 | 168 | 176 | 185 | 194 | 4.94% |
| Future brides and grooms | 20% | 900 | 1,080 | 1,296 | 1,555 | 1,866 | 20.00% |
| Families | 15% | 260 | 299 | 344 | 396 | 455 | 15.02% |
| Total | 13.05% | 2,570 | 2,892 | 3,265 | 3,697 | 4,198 | 13.05% |
4.1.2 Competition and Buying Patterns
Customers are expected to use our services based on traditional factors:
- Performance
- Flexibility
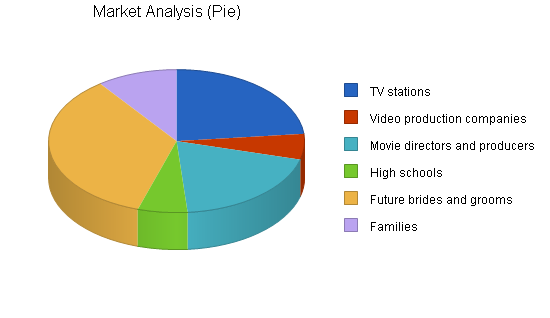
4.1.3 Distribution Strategy

4.1.4 Service Business Analysis
The major companies that compete in the market are:
- Synergy Productions
- Local Television Stations
- Video Production, Inc.
- Gene’s Video Productions
- Denton Video Service
- VIP Productions
All of our competitors specialize in one aspect of video production. We are a diversified company and we believe that there will be no down period for us. We are not seasonal based, our services are offered throughout the year. With our diversity, we will be able to attract the larger organizations that like to entrust one company to handle all of their affairs.
4.1.4.1 Possible Barriers to Entry
Michael’s Video Service will benefit from several significant barriers to entry which include:
- Strategic Alliances
- Experience in the field
4.1.5 Strategic Alliances
The company plans to form strategic alliances with clients who require a freelancer to cover various events for them. Michael’s Video Service will also develop strategic alliances with video production companies and work with them as a sub-contractor.
4.1.6 Value Proposition
By using Michael’s Video Service to cover various events for them, companies will be able to save time. They can then use this time saved to focus on their core competencies and the things that they do best. We are in business to provide a service that is second to none. As such, we guarantee that our customers will receive first class service and a final product that is well worth the money invested. To that end, we guarantee a full refund in the event that a customer is not satisfied. At Michael’s Video Service, we take pride in our work and it is our aim to be the best at what we do. We will conduct our business in a professional manner from our methods and character to our standards and ethics.
4.2 Sales Forecast
The following table and chart show our planned sales.
| Sales Forecast | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | |||
| Video services | $149,000 | $175,000 | $191,000 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Sales | $149,000 | $175,000 | $191,000 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Video services | $4,800 | $5,700 | $6,600 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $4,800 | $5,700 | $6,600 |
4.2.1 Channels
Sales, Distribution, and Marketing Channels
In marketing our products and services, we will rely on a combination of the following channels:
- Direct approach
- Yellow pages
- Radio and television
- Word of mouth
- Trade shows
Alliances with video companies that have industry credibility, presence, and distribution are key to our strategy. In monitoring our services and market position, we will rely on feedback from customers with whom we have relationships. This will be done through direct sales. The message associated with our products and services is high quality for less money. Our promotional plan is diverse and will include a range of marketing communications.
4.2.2 Pricing Strategy
We plan to set our pricing based on market value. Our actual price will be based on whether our services are required on a daily or an hourly basis. It is anticipated that we will charge $300 per hour and $1,000 per day. For out of town travel, additional charges will be added for expenses.
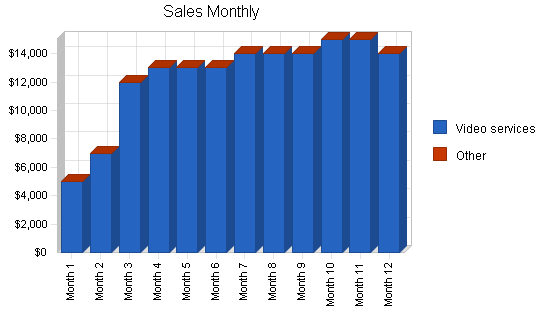
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
The company’s management philosophy will be based on responsibility and mutual respect. Michael Video Services will maintain an environment and structure that will encourage productivity and respect for customers and fellow employees. Additionally, the environment will encourage employees to have fun by allowing creative independence and providing challenges that are realistic and rewarding.
Michael’s Video Service’s management team is highly experienced and qualified. The management team is lead by Mr. Michael Morisson.
| Personnel Plan | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Michael Morisson | $30,000 | $32,000 | $34,000 |
| Other | $18,000 | $30,000 | $32,000 |
| Total People | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| Total Payroll | $48,000 | $62,000 | $66,000 |
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
We are requesting a loan of $300,000. The funds will be used to purchase video equipment and to cover initial operating expenses.
Payback Strategy
Our repayment for this loan will come from cash in excess of profits, paid monthly. The increase in profits generated by business from television stations will provide funds to repay the loan in 10 years.
6.1 Important Assumptions
The table below highlights some assumptions that are key to the success of the company.
| General Assumptions | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Current Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% |
| Tax Rate | 25.42% | 25.00% | 25.42% |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 |
6.2 Break-even Analysis
For our Break-even Analysis, we assume running costs of approximately $9,000 per month, which includes gas, phone, and an estimation of other running costs. Variable costs mostly include video tapes. The chart and table below show our break-even point.

| Break-even Analysis | |
| Monthly Revenue Break-even | $9,351 |
| Assumptions: | |
| Average Percent Variable Cost | 3% |
| Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost | $9,050 |
6.3 Projected Profit and Loss
The table below provides the projected income statements for Michael’s Video Service. The company is basing its revenue projections on anticipated sales of services, initially to the television networks and video companies, then to other markets such as high school events and weddings.

| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | $149,000 | $175,000 | $191,000 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $4,800 | $5,700 | $6,600 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Cost of Sales | $4,800 | $5,700 | $6,600 |
| Gross Margin | $144,200 | $169,300 | $184,400 |
| Gross Margin % | 96.78% | 96.74% | 96.54% |
| Expenses | |||
| Payroll | $48,000 | $62,000 | $66,000 |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $18,600 | $21,400 | $24,600 |
| Depreciation | $24,000 | $24,000 | $24,000 |
| Gas | $4,800 | $5,700 | $6,600 |
| Utilities & phone | $2,400 | $3,000 | $3,600 |
| Rent | $3,600 | $3,600 | $3,600 |
| Payroll Taxes | $7,200 | $9,300 | $9,900 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $108,600 | $129,000 | $138,300 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | $35,600 | $40,300 | $46,100 |
| EBITDA | $59,600 | $64,300 | $70,100 |
| Interest Expense | $30,000 | $28,984 | $26,844 |
| Taxes Incurred | $1,065 | $2,829 | $4,894 |
| Net Profit | $4,535 | $8,487 | $14,362 |
| Net Profit/Sales | 3.04% | 4.85% | 7.52% |
6.4 Financial Risks and Contingencies
The company recognizes that it is subject to both market and industry risks. We believe our risks are as follows, and we are addressing each as indicated. We face all the risks associated with being a start-up company. We feel that we can overcome these with our experience in the industry and by quickly establishing desired relationships. The economy in south Ohio is based on the oil and gas industry, which is very unstable. Having seen the oil bust in the 1980’s and its effects on the economy, we have diversified our efforts and will be going after markets that will not be affected by fluctuations in the oil and gas industry.
6.5 Projected Cash Flow
The following chart and table present the cash flow assumptions for the company.

| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash Received | |||
| Cash from Operations | |||
| Cash Sales | $37,250 | $43,750 | $47,750 |
| Cash from Receivables | $90,375 | $127,520 | $140,955 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $127,625 | $171,270 | $188,705 |
| Additional Cash Received | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $127,625 | $171,270 | $188,705 |
| Expenditures | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||
| Cash Spending | $48,000 | $62,000 | $66,000 |
| Bill Payments | $64,802 | $80,965 | $86,360 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $112,802 | $142,965 | $152,360 |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $20,330 | $22,458 |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $112,802 | $163,295 | $174,818 |
| Net Cash Flow | $14,823 | $7,975 | $13,887 |
| Cash Balance | $74,823 | $82,798 | $96,685 |
6.6 Projected Balance Sheet
Projected balance sheets are provided below.
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $74,823 | $82,798 | $96,685 |
| Accounts Receivable | $21,375 | $25,105 | $27,400 |
| Inventory | $1,200 | $1,425 | $1,650 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $97,398 | $109,328 | $125,736 |
| Long-term Assets | |||
| Long-term Assets | $240,000 | $240,000 | $240,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $24,000 | $48,000 | $72,000 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $216,000 | $192,000 | $168,000 |
| Total Assets | $313,398 | $301,328 | $293,736 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $6,863 | $6,636 | $7,139 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $6,863 | $6,636 | $7,139 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $300,000 | $279,670 | $257,212 |
| Total Liabilities | $306,863 | $286,306 | $264,351 |
| Paid-in Capital | $17,000 | $17,000 | $17,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($15,000) | ($10,465) | ($1,978) |
| Earnings | $4,535 | $8,487 | $14,362 |
| Total Capital | $6,535 | $15,022 | $29,384 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $313,398 | $301,328 | $293,736 |
| Net Worth | $6,535 | $15,022 | $29,384 |
6.7 Business Ratios
The following table presents important business ratios from the motion picture production industry, as determined by the Standard Industry Classification (SIC) Index code 7812, Motion Picture and Video Production.
| Ratio Analysis | ||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 0.00% | 17.45% | 9.14% | 0.00% |
| Percent of Total Assets | ||||
| Accounts Receivable | 6.82% | 8.33% | 9.33% | 0.00% |
| Inventory | 0.38% | 0.47% | 0.56% | 0.00% |
| Other Current Assets | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 100.00% |
| Total Current Assets | 31.08% | 36.28% | 42.81% | 100.00% |
| Long-term Assets | 68.92% | 63.72% | 57.19% | 0.00% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | 2.19% | 2.20% | 2.43% | 0.00% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 95.72% | 92.81% | 87.57% | 0.00% |
| Total Liabilities | 97.91% | 95.01% | 90.00% | 0.00% |
| Net Worth | 2.09% | 4.99% | 10.00% | 100.00% |
| Percent of Sales | ||||
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 96.78% | 96.74% | 96.54% | 0.00% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 93.96% | 91.89% | 88.98% | 0.00% |
| Advertising Expenses | 4.03% | 4.00% | 4.19% | 0.00% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | 23.89% | 23.03% | 24.14% | 0.00% |
| Main Ratios | ||||
| Current | 14.19 | 16.48 | 17.61 | 0.00 |
| Quick | 14.02 | 16.26 | 17.38 | 0.00 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 97.91% | 95.01% | 90.00% | 0.00% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | 85.69% | 75.33% | 65.53% | 0.00% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | 1.79% | 3.76% | 6.56% | 0.00% |
| Additional Ratios | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Net Profit Margin | 3.04% | 4.85% | 7.52% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | 69.40% | 56.50% | 48.88% | n.a |
| Activity Ratios | ||||
| Accounts Receivable Turnover | 5.23 | 5.23 | 5.23 | n.a |
| Collection Days | 57 | 65 | 67 | n.a |
| Inventory Turnover | 4.50 | 4.34 | 4.29 | n.a |
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 10.44 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 27 | 31 | 29 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 0.48 | 0.58 | 0.65 | n.a |
| Debt Ratios | ||||
| Debt to Net Worth | 46.96 | 19.06 | 9.00 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | n.a |
| Liquidity Ratios | ||||
| Net Working Capital | $90,535 | $102,692 | $118,596 | n.a |
| Interest Coverage | 1.19 | 1.39 | 1.72 | n.a |
| Additional Ratios | ||||
| Assets to Sales | 2.10 | 1.72 | 1.54 | n.a |
| Current Debt/Total Assets | 2% | 2% | 2% | n.a |
| Acid Test | 10.90 | 12.48 | 13.54 | n.a |
| Sales/Net Worth | 22.80 | 11.65 | 6.50 | n.a |
| Dividend Payout | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Sales Forecast | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | |||||||||||||
| Video services | 0% | $5,000 | $7,000 | $12,000 | $13,000 | $13,000 | $13,000 | $14,000 | $14,000 | $14,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $14,000 |
| Other | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Sales | $5,000 | $7,000 | $12,000 | $13,000 | $13,000 | $13,000 | $14,000 | $14,000 | $14,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $14,000 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Video services | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | |
| Personnel Plan | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Michael Morisson | 0% | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 |
| Other | 0% | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 |
| Total People | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Total Payroll | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | |
| General Assumptions | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Current Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | |
| Tax Rate | 30.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | $5,000 | $7,000 | $12,000 | $13,000 | $13,000 | $13,000 | $14,000 | $14,000 | $14,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $14,000 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Cost of Sales | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | |
| Gross Margin | $4,600 | $6,600 | $11,600 | $12,600 | $12,600 | $12,600 | $13,600 | $13,600 | $13,600 | $14,600 | $14,600 | $13,600 | |
| Gross Margin % | 92.00% | 94.29% | 96.67% | 96.92% | 96.92% | 96.92% | 97.14% | 97.14% | 97.14% | 97.33% | 97.33% | 97.14% | |
| Expenses | |||||||||||||
| Payroll | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $1,300 | $1,300 | $1,600 | $1,600 | $1,600 | $1,600 | $1,600 | $1,600 | $1,600 | $1,600 | $1,600 | $1,600 | |
| Depreciation | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | |
| Gas | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | $400 | |
| Utilities & phone | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | |
| Rent | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | $300 | |
| Payroll Taxes | 15% | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 | $600 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | $8,800 | $8,800 | $9,100 | $9,100 | $9,100 | $9,100 | $9,100 | $9,100 | $9,100 | $9,100 | $9,100 | $9,100 | |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | ($4,200) | ($2,200) | $2,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $4,500 | $4,500 | $4,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 | $4,500 | |
| EBITDA | ($2,200) | ($200) | $4,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 | $6,500 | $6,500 | $6,500 | $7,500 | $7,500 | $6,500 | |
| Interest Expense | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | $2,500 | |
| Taxes Incurred | ($2,010) | ($1,175) | $0 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $500 | $500 | $500 | $750 | $750 | $500 | |
| Net Profit | ($4,690) | ($3,525) | $0 | $750 | $750 | $750 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 | $2,250 | $2,250 | $1,500 | |
| Net Profit/Sales | -93.80% | -50.36% | 0.00% | 5.77% | 5.77% | 5.77% | 10.71% | 10.71% | 10.71% | 15.00% | 15.00% | 10.71% | |
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Cash from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Sales | $1,250 | $1,750 | $3,000 | $3,250 | $3,250 | $3,250 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,500 | $3,750 | $3,750 | $3,500 | |
| Cash from Receivables | $0 | $125 | $3,800 | $5,375 | $9,025 | $9,750 | $9,750 | $9,775 | $10,500 | $10,500 | $10,525 | $11,250 | |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $1,250 | $1,875 | $6,800 | $8,625 | $12,275 | $13,000 | $13,250 | $13,275 | $14,000 | $14,250 | $14,275 | $14,750 | |
| Additional Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | 0.00% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $1,250 | $1,875 | $6,800 | $8,625 | $12,275 | $13,000 | $13,250 | $13,275 | $14,000 | $14,250 | $14,275 | $14,750 | |
| Expenditures | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Spending | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | $4,000 | |
| Bill Payments | $110 | $3,318 | $4,174 | $5,642 | $6,817 | $5,850 | $5,892 | $7,067 | $6,133 | $7,075 | $6,350 | $6,375 | |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $4,110 | $7,318 | $8,174 | $9,642 | $10,817 | $9,850 | $9,892 | $11,067 | $10,133 | $11,075 | $10,350 | $10,375 | |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $4,110 | $7,318 | $8,174 | $9,642 | $10,817 | $9,850 | $9,892 | $11,067 | $10,133 | $11,075 | $10,350 | $10,375 | |
| Net Cash Flow | ($2,860) | ($5,443) | ($1,374) | ($1,017) | $1,458 | $3,150 | $3,358 | $2,208 | $3,867 | $3,175 | $3,925 | $4,375 | |
| Cash Balance | $57,140 | $51,698 | $50,323 | $49,307 | $50,765 | $53,915 | $57,273 | $59,482 | $63,348 | $66,523 | $70,448 | $74,823 | |
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $60,000 | $57,140 | $51,698 | $50,323 | $49,307 | $50,765 | $53,915 | $57,273 | $59,482 | $63,348 | $66,523 | $70,448 | $74,823 |
| Accounts Receivable | $0 | $3,750 | $8,875 | $14,075 | $18,450 | $19,175 | $19,175 | $19,925 | $20,650 | $20,650 | $21,400 | $22,125 | $21,375 |
| Inventory | $2,000 | $1,600 | $1,200 | $800 | $1,400 | $1,000 | $600 | $1,200 | $800 | $1,400 | $1,000 | $600 | $1,200 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $62,000 | $62,490 | $61,773 | $65,198 | $69,157 | $70,940 | $73,690 | $78,398 | $80,932 | $85,398 | $88,923 | $93,173 | $97,398 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $240,000 | $240,000 | $240,000 | $240,000 | $240,000 | $240,000 | $240,000 | $240,000 | $240,000 | $240,000 | $240,000 | $240,000 | $240,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $2,000 | $4,000 | $6,000 | $8,000 | $10,000 | $12,000 | $14,000 | $16,000 | $18,000 | $20,000 | $22,000 | $24,000 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $240,000 | $238,000 | $236,000 | $234,000 | $232,000 | $230,000 | $228,000 | $226,000 | $224,000 | $222,000 | $220,000 | $218,000 | $216,000 |
| Total Assets | $302,000 | $300,490 | $297,773 | $299,198 | $301,157 | $300,940 | $301,690 | $304,398 | $304,932 | $307,398 | $308,923 | $311,173 | $313,398 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $0 | $3,180 | $3,988 | $5,413 | $6,622 | $5,655 | $5,655 | $6,863 | $5,897 | $6,863 | $6,138 | $6,138 | $6,863 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $0 | $3,180 | $3,988 | $5,413 | $6,622 | $5,655 | $5,655 | $6,863 | $5,897 | $6,863 | $6,138 | $6,138 | $6,863 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 |
| Total Liabilities | $300,000 | $303,180 | $303,988 | $305,413 | $306,622 | $305,655 | $305,655 | $306,863 | $305,897 | $306,863 | $306,138 | $306,138 | $306,863 |
| Paid-in Capital | $17,000 | $17,000 | $17,000 | $17,000 | $17,000 | $17,000 | $17,000 | $17,000 | $17,000 | $17,000 | $17,000 | $17,000 | $17,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($15,000) | ($15,000) | ($15,000) | ($15,000) | ($15,000) | ($15,000) | ($15,000) | ($15,000) | ($15,000) | ($15,000) | ($15,000) | ($15,000) | ($15,000) |
| Earnings | $0 | ($4,690) | ($8,215) | ($8,215) | ($7,465) | ($6,715) | ($5,965) | ($4,465) | ($2,965) | ($1,465) | $785 | $3,035 | $4,535 |
| Total Capital | $2,000 | ($2,690) | ($6,215) | ($6,215) | ($5,465) | ($4,715) | ($3,965) | ($2,465) | ($965) | $535 | $2,785 | $5,035 | $6,535 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $302,000 | $300,490 | $297,773 | $299,198 | $301,157 | $300,940 | $301,690 | $304,398 | $304,932 | $307,398 | $308,923 | $311,173 | $313,398 |
| Net Worth | $2,000 | ($2,690) | ($6,215) | ($6,215) | ($5,465) | ($4,715) | ($3,965) | ($2,465) | ($965) | $535 | $2,785 | $5,035 | $6,535 |

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Business Plan Template for Audio Engineers
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Creating a successful audio engineering business requires careful planning and strategic decision-making. That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Audio Engineers comes in handy!
With this template, audio engineers can:
- Outline their company's goals and objectives with clarity and precision
- Identify target markets and develop effective marketing strategies to reach potential clients
- Allocate resources efficiently, ensuring optimal use of time, money, and equipment
- Establish realistic financial projections to maintain profitability and growth
Whether you're starting a new audio production business or fine-tuning your existing one, ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Audio Engineers provides the roadmap you need for long-term success. Start planning your way to a thriving audio engineering business today!
Business Plan Template for Audio Engineers Benefits
A business plan template for audio engineers can provide numerous benefits for your audio production business, including:
- Streamlining the process of outlining your company's goals and objectives
- Helping you define your target markets and identify potential clients
- Assisting in the development of effective marketing strategies to attract new customers
- Guiding you in allocating resources efficiently to maximize productivity and profitability
- Enabling you to establish realistic financial projections and monitor your business's financial health
- Providing a comprehensive roadmap for success and a clear direction for growth in the audio engineering industry.
Main Elements of Audio Engineers Business Plan Template
To help audio engineers in the audio production business, ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Audio Engineers provides the following key elements:
- Custom Statuses: Keep track of the progress of each section of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Use custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to add additional details and categorize different aspects of your business plan.
- Custom Views: Utilize different views such as Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and the Getting Started Guide to visualize and organize your business plan in the way that works best for you.
- Project Management: Enhance your business plan with ClickUp's project management features, including task dependencies, time tracking, document collaboration with Docs, and integrations with other tools to streamline your audio engineering business.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Audio Engineers
If you're an audio engineer looking to create a solid business plan, follow these four steps using the Business Plan Template in ClickUp:
1. Define your business goals
Start by clearly defining your business goals as an audio engineer. Are you looking to start your own recording studio, provide live sound services, or offer mixing and mastering services? Identifying your specific objectives will help you create a targeted plan.
Use the Goals feature in ClickUp to set and track your business goals for each quarter or year.
2. Conduct market research
Before diving into your business plan, conduct thorough market research to understand your target audience, competition, and industry trends. Identify your ideal clients, assess their needs, and determine how you can differentiate yourself from competitors.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to organize your market research findings and track important data points.
3. Outline your services and pricing
Next, outline the services you plan to offer as an audio engineer. This could include recording, mixing, mastering, sound design, or equipment rental. Determine your pricing structure based on factors like experience, location, and market demand.
Create custom fields in ClickUp to track your services and pricing options, making it easy to adjust and update as needed.
4. Develop a marketing and sales strategy
To attract clients and grow your business, you'll need a solid marketing and sales strategy. Identify the most effective marketing channels for reaching your target audience, such as social media, networking events, or partnerships. Develop a sales strategy that outlines how you'll convert leads into paying clients.
Use the Automations feature in ClickUp to streamline your marketing and sales processes, such as sending automated follow-up emails or tracking leads.
By following these steps and utilizing ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you'll be well on your way to creating a comprehensive and effective business plan for your audio engineering business.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Audio Engineers
Audio engineers can use the Business Plan Template for Audio Engineers in ClickUp to create a comprehensive plan for their audio production businesses.
First, hit “Add Template” to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a solid business plan:
- Use the Topics View to outline and organize different sections of your business plan, such as goals, target markets, marketing strategies, and financial projections.
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section of your business plan, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- The Timeline View will give you a visual representation of the deadlines and milestones for your business plan.
- The Business Plan View will provide a comprehensive overview of your entire business plan, allowing you to easily navigate and review different sections.
- Use the Getting Started Guide View to create a step-by-step guide on how to execute your business plan.
- Utilize custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to add additional information and categorize different aspects of your business plan.
- Collaborate with team members and stakeholders to gather input and feedback on your business plan.
- Monitor and analyze the progress of your business plan to ensure you're on track to meet your goals and objectives.
- Business Plan Template for Wholesale Suppliers
- Business Plan Template for Insurance Agents
- Business Plan Template for Architects
- Business Plan Template for Hair Salon
- Business Plan Template for Culinary Professionals
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
- Resources for Entrepreneurs > Opening a Business > Starting a Business
How to Start an Audio Equipment & Supplies Rental Business

Starting a Business
Launching an audio equipment and supplies rental business is your ticket to owning a good, stable business if you do it right. Here are nuts-and-bolts information to give you a jump-start on planning for your business.
Interested in learning how to start an audio equipment and supplies rental business? Here, you'll find world-class guidance on a few key aspects of small business success.
Business Plan Mechanics for Audio Equipment & Supplies Rental Businesses
If you're putting off writing a business plan because you're intimidated by the process, here are the words you've been dying to hear: Business plans for audio equipment and supplies rental businesses don't have to be complicated.
At Gaebler, we advise new business owners to keep your business plan simple . Ultimately, your business plan is intended to be a resource for you, the business owner.
As your company matures, you can circle back to your business plan to make revisions and adjustments.
Assess Competitors
Before you open an audio equipment and supplies rental business in your town, it's a good idea to determine how strong the competition is. Try our link below to find competitors near you. After following the link, enter your city, state and zip code to get a list of audio equipment and supplies rental businesses in your area.
- Get a List of Nearby Audio Equipment & Supplies Rental Businesses
How tough is the competition in the market you are considering? If the competition is too tough, you may need to think about starting the business in a different area or even start a completely different business instead.
Studying the Market
As part of your due diligence on opening an audio equipment and supplies rental business, be sure to talk to somebody who is already in the business. If you think your local competitors will give you advice, you're being overoptimistic. The last thing they want to do is help you to be a better competitor.
However, an entrepreneur who owns an audio equipment and supplies rental business in a location that is not competitive to you may be more than happy to give you a few tips, provided that you won't be directly competing with them. Indeed, many experienced entrepreneurs enjoy offering advice to startup entrepreneurs. If you are persistent, you can find a business mentor who is willing to help you out.
How do you find an owner of an audio equipment and supplies rental business in another city who you can speak with?
No problem! Just use the link below and try a random city/state or zipcode. Then start dialing for advice until you are successful.
- Find an Experienced Audio Equipment & Supplies Rental Business Entrepreneur
Why You Should Buy (Instead of Start) an Audio Equipment & Supplies Rental Business
Spurred on by dreams of a future big money buyout and an undeniable entrepreneurial impulse, many would-be audio equipment and supplies rental business owners are driven to pursue startup strategies.
Yet a healthier and safer strategy may be to purchase an existing audio equipment and supplies rental business.
Existing audio equipment and supplies rental businesses are proven operations with dependable revenue streams. As an added bonus, you'll also gain the ability to headaches and hassles of startup trial-and-error .
The four-year survival rate for business startups is less than fifty-percent. Survival rates improve when entrepreneurs launch an audio equipment and supplies rental business franchise. Unlike traditional business models, franchise startups launch with many of the resources and learnings that other startups acquire over time.
At a minimum, click the link below to explore the possibility of pursuing a franchised approach to your audio equipment and supplies rental business startup.
- Rental Franchises
Related Articles on Starting a Company
These additional resources regarding starting a business may be of interest to you.
LLC Advantages
Buying vs. Starting a Business
Share this article
Additional Resources for Entrepreneurs
Lists of Venture Capital and Private Equity Firms Franchise Opportunities Contributors Business Glossary
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Franchise Directory
- Entrepreneurial Resources
- Small Business News
- Gaebler France
- Gaebler Mexico
- Gaebler Philippines
- Gaebler Czech Republic
- Gaebler Germany
- Gaebler China
Copyright © 2001-2024. Gaebler Ventures. All rights reserved.
- Business Plans Handbook
- Business Plans - Volume 04
- Audio Production Service Business Plan
Audio Production Service
BUSINESS PLAN
JACK CORNWALL PRODUCTIONS
58305 South 20th St. Kellogg, ID 83837
March 31, 1995
Jack Cornwall Productions is a business founded and run using the latest high-tech sound and recording equipment. By taking advantage of the latest equipment, Cornwall can maximize quality and profits, while decreasing the amount of time spent per project. Cornwall's business plan describes how the business will take advantage of the latest and greatest in technology to grow the business and become a leader, both regionally and nationally.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Product & service descriptions, marketing plan, operations plan, competitors, competitive advantages, financial data, effects of loan, targeting new markets.
Jack Cornwall has been doing freelance audio production in the Northwest since the mid-1970s, usually while involved with specific broadcast stations. Jack has also had a high interest in consumer and professional electronics since the early '60s. The two areas have interwoven well over the years…and now it's time to take that interaction to a higher level.
Area One: Productions & Narrations
- Radio & television commercial audio
- Sales, training & industrial narrations
Area Two: Business Holding Message Services
- Custom production of message-on-hold messages, with possible expansion into message system hardware
Area Three: Audio Archiving
- Transfer of irreplaceable audio from analog media (cassette and open-reel) to compact disc (CD).
Jack Cornwall Productions is an audio production service business, providing audio for radio and television commercials with both industrial and sales narrations, audio and/or video training tapes and telephone holding message services.
Jack Cornwall Productions operated as an in-home, part-time venture for just under a year. Beginning with a minimum investment in selected new and used studio equipment (financed through personal credit), the operation recouped start-up costs within 9 months. Since February, 1995, Jack Cornwall Productions has become more formal, with the filing of an Assumed Business Name, acquisition of a Federal Employer Identification Number, a business banking account and Merchant Services Agreement with Bank of America to accept VISA and MasterCard for telephone/mail orders. Jack Cornwall Productions has also been granted a Home Occupation Certificate by the city of Kellogg. The business is operated as a sole proprietorship.
There are three basic areas Jack Cornwall Productions intends to expand upon and/or venture into:
Productions and Narrations
Although radio & television stations, advertising agencies, video production houses and individual businesses have contacted Jack Cornwall Productions to provide voice-overs and narrations, so far Jack Cornwall Productions has never committed time or funds to promote these services to others. If word-of-mouth is good ($3000-$4000 per year in gross income), an active promotional effort, targeted to specific users in underserved markets, should be great ($15,000-$18,000 per year).
Growth opportunities exist in providing quality voice-over services to small and medium market producers. This is simply an expansion of present operations, combined with identifying and contacting new users of produced audio and selling them on the idea of major-market quality with fast turnaround and efficient delivery.
Prior experience indicates atypical radio or television voice-over production job requires about two hours work and bills $75.00 in total charges at present rates.
Normal radio-television production experiences some seasonal swings. They are mostly oriented toward holidays and are not a major factor here.
A sample of the Jack Cornwall Productions brochure and demo cassette are available upon request.
Holding Message Service
Study shows there is very little organized marketing to the small businesses around the country that have the capability of using Holding Messages. Jack Cornwall Productions has already begun reaching into that market.
A reader of Message or Techno-Speak magazines can order the Holding Messages Kit for $7.95. The kit is shipped Priority Mail, and includes an audio cassette with music and voice samples, a self-help page detailing How to Develop a Message Script, a sample script and an order form. The $7.95 is refundable on the first order and the charge for the message is $50.00, plus shipping. VISA and MasterCard are accepted.
A typical Holding Message order will total $65.00 and require about an hour to complete. The Holding Message kit offers the customer a choice of three other voices. Message announcers are paid talent fees as needed.
It is expected that most Holding Message customers will want to seasonalize their messages. Because of this, after-sale marketing will focus on the April-May and October-November time frames. The Fall promotions will push new year images, while the Summer copy changes will remind customers about upcoming Fall holidays.
If sufficient demand is realized, Jack Cornwall Productions may offer Holding Message hardware. Distributorships are available. Samples of the Holding Message Kit are also available upon request.
Audio Archiving
Thousands of people have made family history recordings. In the '50s they were recorded on bulky tube-type open-reel tape recorders. In the '60s, many people switched to the smaller machines with the 3-inch reels. We sent tapes to loved ones in Vietnam, Korea and Europe, and they sent back their living letters. In the 70s and into the '90s, people are still recording their family history on audio cassette. While the cassette player is everywhere, most of those old open reel decks, if they still exist in the back corner of the basement, probably don't work anymore.
Today's emphasis is on digital and permanent recordings. The technology is available to transfer from the orphan format of analog open-reel and cassette tape to compact disc (CD).
Jack Cornwall Productions has access to machines that will still play many of the old orphan tape formats, as well as, the technical expertise to keep them running. Through using modern equalization software and a compact disc recorder Jack Cornwall Productions can transfer these recordings from tape to CD, and clean up the background hiss in the process.
Jack Cornwall Productions Audio Archive Service would:
- Market using 800 number advertisements in selected magazines.
- Charge a per-hour fee plus media costs.
- Return originals and new discs Mailspeed Next Day Service.
It's anticipated that there will be very little seasonally to this endeavor, except for the desire for holiday gifts. That, coupled with the natural seasonality of radio & TV production and Holding Message will make November and December very busy months at Jack Cornwall Productions.
Since this is a new endeavor, there is no definition of a "typical" job, but it is anticipated that an order for 4 hours of audio transfer, plus target media and shipping, should be approximately $ 100.00 and would take about 5 hours.
To accomplish these three goals, Jack Cornwall Productions needs $ 15,000.00, which will be used to finance working capital, equipment purchases, and the time and effort to fully market all three areas.
- Keep up-to-date on advances in audio and video production techniques in order to provide the best service to existing customers.
- Discover new uses for new and existing technologies.
- Expand facilities and staff as volume dictates.
- Update studio tools to streamline production and decrease turnaround.
- Expand services offered - Real Estate/Travelers' Radio systems, etc.
- Expand marketing area.
- Use CD recorder for telephone Holding Messages to eliminate expensive hardware at end-user location.
Productions & Narrations
Jack Cornwall's ability to create straightforward audio production is well known to just a handful of advertising agencies, broadcast and cable operators, and businesses in the inland Northwest. Active marketing of Cornwall's capabilities and services throughout the region has been hampered by the need to work full time elsewhere.
A cursory check of the Phone Pages for Sand Point, Priest River, Wallace, St. Maries and Kellogg shows:
- 42 advertising agencies
- 49 video and cable production facilities
- 32 telephone system resellers
Dozens more in other small to medium Northwest markets.
An infusion of capital would allow Jack Cornwall Productions to:
- Actively contact these facilities to determine their audio needs.
- Produce and ship demo tapes to the decision-makers for presentation to their clients.
Holding Message Services
The marketing of this service has already begun. Depending on the results achieved with Phone Center and Connect, other areas may be explored. These may include other magazines, direct mail, participation in a card deck mailing, or other areas. Serious re-marketing to Holding Message customers for seasonal repeats is also planned.
This a brand new service. Sharing the concept with others has brought a favorable reaction. It's expected the first few months' jobs would be turned locally. Increasing to a regional or possibly national customer base would be accomplished by:
Placing classified ads in publications like Parks in the NW, Outdoor Today, Modern Mankind and Trailer Expo.
Evaluating the demographic and sociographic background of those leads and targeting the advertising appropriately.
Modern high-quality, high-tech systems give Jack Cornwall Productions the capabilities to:
- receive a script by fax
- consult on the script by telephone if necessary
- record the job
- preview the job with the customer by telephone
- deliver the finished product (tape) by courier (local, regional or national) the next business day.
Technology exists today to deliver finished audio productions on computer disk or by modem. However, many stations, agencies and production facilities are not yet equipped to support this type of transfer. Modem delivery would shift delivery costs from supplier to customer.
Holding Message marketing is targeted at the small-to-medium independent business.
- Potential customer responds to marketing with check or money order for $7.95 and is shipped the Holding Messages kit.
- Customer information is entered in database for follow-up marketing.
- Customer sends script and order information.
- Script is produced as written and return-shipped ASAP by method chosen (Jack Cornwall Productions brochure is included in package)
A prospect responds to classified ad by calling for details. Determination is made as to whether transfer is possible:
- Source format
- Age and quality of source material
- Length of source material
- Non-binding estimate is given, based on above criteria. Charges include new media, hourly transfer charge and return shipment. Customer ships source materials (prepaid & insured) via U. S. Postal, Mailspeed, Quick D, etc.
- Material is transferred, with one-pass equalization to remove baseband hiss, to media chosen (CD, DAT, analog cassette)
- Call to customer to advise of outcome (play before/after sample if available)
- Return shipment by customer chosen method
There are several audio production facilities in the inland Northwest. They are all part of a video service and do not employ full-time announcers.
The only competition at this time comes from radio announcers working as free-lance, using either their employers studio or working with one of the above independent production facilities.
This service is provided by one or two national telephone equipment manufacturers and by a few local telephone equipment resellers. Most businesses that want such service contact their local disk-jockey.
Recent issues of Dial It showed only two classified ads for this service, none mentioned price and only one offered a demo tape.
There are no known organizations actively marketing such a service in this region.
The distinctive competitive advantages which Jack Cornwall Productions brings to these enterprises are:
- Experience in this market. Jack Cornwall has over 20 years of hands-on experience in writing and producing radio and television voiceovers and narrations.
- Sophistication in distribution. Using today's (and tomorrow's) technologies to receive, produce and deliver finished product is a major advantage. This results in being the quick turnaround supplier in many time sensitive yet somewhat isolated markets.
- High quality, low price - Jack Cornwall Productions' rates are below others in the market, while the quality and service exceeds expectations.
By keeping overhead low, Jack Cornwall Productions will be able to funnel profits back into operations thus avoiding high debt or lost sales opportunities.
Three Year Cash Flow Projection Assumptions
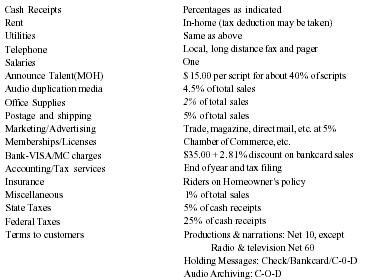
| Cash Receipts | Percentages as indicated |
| Rent | In-home (tax deduction may be taken) |
| Utilities | Same as above |
| Telephone | Local, long distance fax and pager |
| Salaries | One |
| Announce Talent (MOH) | $ 15.00 per script for about 40% of scripts |
| Audio duplication media | 4.5% of total sales |
| Office Supplies | 2% of total sales |
| Postage and shipping | 5% of total sales |
| Marketing/Advertising | Trade, magazine, direct mail, etc. at 5% |
| Memberships/Licenses | Chamber of Commerce, etc. |
| Bank-VISA/MC charges | $35.00 + 2.81% discount on bankcard sales |
| Accounting/Tax services | End of year and tax filing |
| Insurance | Riders on Homeowner's policy |
| Miscellaneous | 1% of total sales |
| State Taxes | 5% of cash receipts |
| Federal Taxes | 25% of cash receipts |
| Terms to customers | Productions & narrations: Net 10, except Radio & television Net 60 |
| Holding Messages: Check/Bankcard/C-0-D | |
| Audio Archiving: C-O-D |
Our projections are for industries that have never been reached. Therefore they are based upon present real buying conditions and our own experience. Should sales not be up to projections, adjustments will be made in marketing, and long term commitments decreased or postponed.
The money loaned to Jack Cornwall Productions will be used for the following purposes:
- Purchase of Simmons TX7D Portable DAT recorder for remote recording - ($700.00)
- Working capital and initial marketing costs - ($6,000)
- Purchase of Hollowitz Compact Disc Recorder - (est. $4,500.00)
- Purchase of PC-Based audio editing and equalization workstation - ($2,800)
- Misc. Startup costs - Accountant, technical consultant, misc. furnishings-($1,000)
These outlays will enable Jack Cornwall Productions to function as a full-time productions & narrations facility, continue marketing of Holding Messages and expand into Audio Archiving, and meet our conservative sales goals for the first year. This will also allow us to purchase these items rather than finance or lease them.
The world of audio and video is changing constantly. The spoken word alone, and spoken words with pictures will always be apart of life. Five years ago, few people were thinking of narrations on multimedia CD-ROM. Today, major companies are using pre-programmed "live" talent for on-hold system advisories. Tomorrow's audio applications might include interactive television or real-time audio transfer by internet. Jack Cornwall Productions wants to be poised for these coming technologies.
User Contributions:
Comment about this article, ask questions, or add new information about this topic:.

What is Audio Visual Production?
If you ask most people what audio visual production is, they can probably give you a reasonably accurate answer- it’s in the name, right? The work that’s done to create and execute a plan for the audio, visual, and lighting components of an event may seem basic, but it’s actually typically the single factor most affecting the success of an event. If people can’t see and hear what’s going on, they can’t stay engaged and they won’t value their experience. That’s why hiring the right production company is so essential. We are able to work with clients throughout the planning process to provide specialized solutions and professional support, ensuring that events are produced smoothly and at the highest standard.

Understanding audio visual production
The basic production requirements for any event typically include many of the same elements. There is a need for a quality, dependable sound system including speakers, microphones, a sound board, and other components. A projector, screens, and other types of displays are often required, as are stage, lobby, and venue lighting. Of course none of this is helpful if it doesn’t come with an experienced, efficient production team that makes sure everything is set up and runs as it’s meant to.
Equipment for A/V production
Event planners sometimes have the option of using a venue’s “in-house” AV setup. This can work, but there are significant limitations, see our article with more details here. The equipment options are narrow and often dated or unreliable, and there may not be adequate production staff to handle any issues beyond basic setup. Despite this, the per-equipment costs can be higher than what production companies charge. A production company’s job is not to make easy additional money for the venue, but to serve the client directly with a customized audio visual plan.
Applications of A/V production
In addition to the typical AV services, avad3 offers a wide range of other options to make events effective and memorable. We can work with clients from the first day of planning, assisting with concept and set design, graphics, and creative services. We produce hybrid and virtual events and have streaming and video production capabilities. Our extensive experience allows us to present our clients with innovative and varied ways to enhance their events, always with the confidence that the production will be flawless.
A/V production as a business
Our process with clients is one way we ensure success. We begin as soon as we’re brought on board, meeting with planners to understand the vision and goals for an event. We are then able to customize a plan for the event based on achieving those goals while maximizing the budget. We communicate regularly, run rehearsals as needed, and create a detailed plan. Our setup is a thing to behold- we prioritize a load in process that is astonishing in its efficiency. Our production staff is one step ahead of every moment so there are no disasters. Dependability is essential and we provide it every time. We have a post-event meeting with our clients to discuss the outcome and make notes for next time. Our clients’ event success is our success.
We’ve been creating A/V production, and loving what we do, for years. Take a look at some recent examples of our work:
Walmart Seller’s Summit Asa Hutchinson Campaign America Strong and Free
Get in touch to see how we can help you with your next event!
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- Company/Organization *

Proposal Templates > Audio Visual Proposal Template
Audio Visual Proposal Template
There’s a lot that goes into running an AV company. Managing your technicians, keeping all of your equipment in shape, managing client expectations, and dealing with the liability that comes from your employees having to work in risky environments. We’ve made it easy to impress prospective clients with our free and fillable audio visual proposal template. Customize it to your needs in minutes then send off for approval with our built in eSigning capabilities.

Best proposal software ever!
I’ve tried soooo many proposal softwares and I’ll never try another one after Proposable. It’s so easy to use and it looks good, which all the others don’t.
Account Executive , Grow.com
Smart, reliable, and constantly improving.
Proposable just works. I can make visually interesting sales presentations, dynamically insert content, and execute agreements. Proposable powers our entire sales process.
CEO , Periodic

Proposal writing is not so different from script writing. Script writing is the process of drafting a script for a video proposal. Because the video itself serves as the proposal, you would essentially be writing an audio visual proposal in script form.
Becoming a better script writer takes some practice and an understanding of how the spoken word may be accepted differently than written words. A template can also make writing a script much easier and more of an organized process.
Proposable has some excellent script templates and blank script templates to choose from. Whether you need a script template pdf file or an audio visual script template that is highly detailed, we’ve got you covered.

15 Audio-Visual Solutions That Will Transform Your Business
- December 8, 2023
Let us be your collaborative partner during your next Audio Visual Project
Audio-visual solutions provide businesses with a means to communicate efficiently and effectively. By effectively, I mean memorable and immersive experiences that inspire the mood to drive the results in question.
In this article, we dive straight into how Century AV’s cutting-edge AV solutions are changing the game for enterprises like yours. Gone are the days of mediocre conference calls and unimpressive presentations. We’re going to reveal a world where every meeting is a powerhouse of clarity and engagement, where digital signage turns into a strategic tool, and where interactive technology isn’t just for show; instead, it’s a catalyst for business growth.
5 Key AV Technologies and Their Successful Applications For Business

Boardroom Technology
Advanced audio-visual systems enhance teleconferencing and decision-making in boardrooms across the world. As our technology has grown, so has our ability to communicate with shareholders, team members, clients, and the general public. A significant reflection of this change is apparent in today’s boardroom technologies that enhance communication in small, medium, and enterprise-scale organizations.
Digital Signage and Marketing
Digital Signage has exploded into multiple industries, from restaurants changing signboards to airport terminals showing flight status. Digital signage has made an enormous impact on many sectors, not just advertising or retail.
One of the great benefits of digital signage is how it can relay information and entice potential clients at the same time. The impact of digital signage is apparent. Studies (1) show that people can and often do retain upwards of 65% of information provided via digital signage for up to three days after viewing.
Interactive Digital Maps
Interactive digital maps and displays have been in use for some time in retail and other establishments. These forms of audio-visual technology encourage a high degree of engagement and work very well at delivering information quickly to the desired audience.
Security and Surveillance Systems
Security and surveillance are nothing new, but they are both growing at a surprising rate. In fact, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, from 2015 to 2018, the number of surveillance cameras in operation grew from 47 to 70 million (2) .
As businesses don’t generally like theft, as technology has become available, companies have increased their security. The cost of CCTV systems has dramatically dropped since its inception, and with easily accessible equipment, it’s no stretch of the imagination to understand why organizations have opted for higher security standards.
Public Address Systems
When an organization has grown to a specific size, it is often advantageous to utilize a public address system. Just think of large department stores that have used this technology for some time to page customers for missing children or a clean-up in aisle twelve.
Public address systems are highly effective for essential communications in large premises. Although these sorts of systems lack privacy, with the intent of reaching as many people on-site as possible, it’s an aspect of communication that is still highly useful and used in many facilities today.
Okay, we’ve gone over the current AV technologies operating in various verticals, but do you know what technology is coming? Next, I’ll look at ten technology trends you should keep your eye on and consider adopting into your operations.
10 Technology Trends To Keep Your Eye On

Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in Meeting Spaces
Keep your eyes open for augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) systems. The AR/VR market is projected to grow at an average annual rate of 12.6%, leading to a market volume of $58.1bn by 2028 (3) .
These technologies are transforming how interactive meetings and presentations are conducted. They offer immersive experiences, making remote collaborations more engaging and memorable.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in AV Systems
AI can be used for various purposes, such as optimizing sound quality in different environments, automating camera angles for video conferences based on speaker detection, and predictive maintenance of AV equipment.
AI is anticipated to take a much more significant role in future software systems, making AV solutions better than ever. Furthermore, with generative AI around the corner, we may see AI change technologies more than anyone ever thought possible.
Wireless Presentation Systems
Wireless Presentation Systems allow for seamless, cable-free presentations and collaborations. These presentation systems are growing in popularity due to their ease of use and the ability to connect multiple devices simultaneously.
4K Ultra HD and 8K Displays
The rise of ultra-high-definition displays provides unparalleled clarity and detail for digital signage and presentations, making them more impactful and engaging.
If you’re wondering why high resolution and more screens matter, studies have shown that the most productive is more than one screen and both with high resolution, which enables one to put more into the workspace (4) .
Voice-Activated Systems and IoT Integration
Voice control and Internet of Things (IoT) integration offer hands-free operation of AV equipment, which can be particularly useful in large conference settings or when managing multiple AV systems simultaneously.
Statistics show that as of 2023, there were over eight bn voice-activated systems in operation (5) . Keep that number in mind and then consider that at the time of writing, there were 8.1bn people on Earth (6) . Do you see the trend here?
Holographic Displays
While still emerging, holographic technology for presentations and meetings can offer a futuristic and highly interactive experience.
Sound Masking Technology

Sound masking is becoming increasingly essential in open-plan offices and in environments where privacy and noise control are crucial. In fact, studies show that distractions at work are not only a morale killer (7) , but they are also costing businesses much money. The money lost is due to the lack of productivity that occurs due to distractions throughout the workday.
The top two distractions at work, according to the same study, include chatty coworkers and two office noises. Using the latest soundproofing and masking can help eliminate unwanted noise in your workplace.
Interactive Video Walls
Interactive Video Walls offer dynamic and customizable ways to display content, which can be particularly effective in retail and public spaces.
Cloud-Based AV Management
New software integrates our connected world with equipment. This feature provides you with the ability to control and monitor AV systems remotely through cloud services for greater flexibility and efficiency.
Century AV’s Unique Approach to AV Solutions
At Century AV, we don’t just install systems; we build partnerships. Our philosophy is simple yet profound: enduring support long after the initial sale. It’s a commitment that sets us apart in a market often fixated on the short-term.
Beyond the Sale: A Partnership for Success
Imagine having an AV partner who’s as invested in your success as you are. That’s what we offer at Century AV. Our approach goes beyond just selling you a system. We’re here to ensure your AV solutions continue to drive your business forward, year after year.
Customized Solutions, Tailored Support
Every business is unique, and so are your AV needs. We don’t believe in one-size-fits-all solutions. Instead, we tailor our systems and support to fit your specific requirements, ensuring maximum efficiency and effectiveness.
Reliability and Trust
No matter the industry, downtime can mean lost opportunities. Reliability is non-negotiable. That’s why our commitment to quality and excellence ensures your AV systems are reliable and efficient, fostering trust and peace of mind.
With Century AV, you’re not just investing in technology; you’re investing in a relationship built on reliability and trust.
Case Studies: Transforming Businesses with AV Solutions
Below, you’ll find links to our case studies. We interviewed clients after job completion and wanted to share what they had to say.
The Long-Term Value of Quality AV Support
Whether you’re upgrading an outdated system, finally getting the system you need, or looking for help with designing the perfect audio-visual experience for your clients or team members, Century AV helps deliver long-term value.
Between our client-use-focused training, we provide post-installation, and our unwavering support, you can trust that partnering with us as your audio-visual technology provider will deliver long-term value. That’s something that many AV professionals don’t seem to offer, so talk to us first. We provide value in the long run.
The Verdict
In the landscape of modern enterprise communication, standing still is not an option. As we’ve explored, the integration of advanced audio-visual solutions is not just a step but a leap toward transforming your business. Century AV is at the forefront of this transformation, offering not just technology but also a partnership that grows with your enterprise.
From boardroom technology that enhances global connectivity to digital signage that captures and retains customer attention, every AV solution we discussed is a building block toward a more dynamic, efficient, and engaging business environment.
As we look to the future, technologies like AR, VR, AI, and cloud-based management are not just trends but essential tools in your arsenal to stay ahead in a competitive market.
Choosing Century AV means opting for a future where your business communication is not just practical but exemplary. Our commitment to long-term support and tailor-made solutions ensures that your investment today continues to yield returns well into the future.
Additional Resources
- Stay Ahead with the Latest Trends and Stats in Audio-visual Technology
- A Corporate Guide to Designing, Installing, and Maintaining Microsoft Teams and Zoom Rooms
- How to Troubleshoot Common Audio-Visual Issues in Commercial Settings
- Customizing Your Audio-Visual Setup: Tips and Tricks for Ontario Businesses
Article Sources
- “100 Proven ROI-Driven Digital Signage Statistics 2022.” 2023. Www.digitalsignagetoday.com. 2023. https://www.digitalsignagetoday.com/blogs/100-proven-roi-driven-digital-signage-statistics-2022/#:~:text=After%20three%20days%2C%20people%20retain,47.7%25%20effectiveness%20on%20brand%20awareness. .
- Stanislava Ilic-Godfrey. 2021. “Artificial Intelligence: Taking on a Bigger Role in Our Future Security : Beyond the Numbers: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.” Bls.gov. May 3, 2021. https://www.bls.gov/opub/btn/volume-10/investigation-and-security-services.htm#:~:text=From%202015%20to%202018%2C%20the,million%2C%20in%20the%20United%20States.&text=Surveillance%20camera%20installations%20are%20expected,increase%20of%20about%2021%20percent. .
- “AR & vr – Worldwide | Statista Market Forecast.” 2023. Statista. Statista. 2023. https://www.statista.com/outlook/amo/ar-vr/worldwide#:~:text=User%20penetration%20will%20be%2026.4,B2C%20%26%20B2B)%20is%20covered. .
- “Productivity, Screens, and Aspect Ratios | Electronic University Archive.” 2023. Utah.edu. 2023. https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=214166 .
- “Topic: Voice Technology.” 2023. Statista. Statista. 2023. https://www.statista.com/topics/6760/voice-technology/#topicOverview .
- “World Population Clock: 8.1 Billion People (LIVE, 2023) – Worldometer.” 2023. Worldometers.info. 2023. https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/#:~:text=8.1%20Billion%20(current),currently%20living)%20of%20the%20world. .
- Feldman, Sarah. 2019. “Infographic: What People Find Distracting at Work.” Statista Daily Data. Statista. March 13, 2019. https://www.statista.com/chart/17356/work-distractions/ .
Table of Contents
You might also enjoy.

The Ultimate Guide To The Sound Masking System
Transform your workspace with a sound masking system—enhance privacy, boost productivity, and integrate seamlessly into your AV environment. Discover how in this comprehensive guide.

Your #1 Guide to Audio Visual Equipment Suppliers in Ontario
Choosing the right AV equipment supplier can transform your business. Explore top suppliers in Ontario, compare their services, and find the perfect match for your needs.

The Only LED Video Wall Guide You Need for Your Business
Unlock your business’s potential with cutting-edge LED video walls. From enhanced brand visibility to improved communication, this guide has everything you need to know.

Retail AV Systems: Enhancing the Customer Shopping Experience
Discover the transformative power of retail AV systems in enhancing the customer shopping experience. Learn how digital signage, interactive displays, and reliable AV support can drive sales and customer satisfaction.

The Importance of AV Support for Institutions and Organizations in 2024
Explore the critical role of AV support for institutions, organizations, and businesses in today’s fast-paced world. Learn why ongoing AV maintenance and professional support are essential to seamless communication and operational success.

Choosing Your Video Wall: Guide for Enterprise
Discover how to choose the perfect video wall for your enterprise! From display technology to maintenance, our guide covers everything you need to know to make an informed decision and elevate your business environment.
Work Showcase

- Audio Visual System Design
- Audio Visual System Installation
- Audio Visual System Repair/Upgrade
- Other (Please specify)
Creating your workspace, together.
We would be thrilled to be a part of your new exciting project. Contact us to find out how we can help.
Let us know how we can help you.
Trusted & Professional Staff, AV/IT Expertise, Innovative & Adaptable Solutions, 24 Hour Support, Service & Repair to all AV Equipment.
Privacy Policy ~ Website Terms and Conditions of Use
Contact Us Today
- Century Audio Visual Ltd. 1773 Mattawa Ave. Mississauga, ON L4X 1K5
- (905) 275-6010
- [email protected]
- Mon - Fri: 8:30 AM - 5:00 PM EST
- Sat - Sun: Closed
Popular Solutions
© 2022 Century Audio Visual Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Site managed by Farm 6 Media .
- General Discussion

- Remember me Not recommended on shared computers
Forgot your password?
audio visual company business plan
By RonaldCype , March 26 in General Discussion
- Reply to this topic
- Start new topic
Recommended Posts

Link to comment
Share on other sites, join the conversation.
You can post now and register later. If you have an account, sign in now to post with your account.

× Pasted as rich text. Paste as plain text instead
Only 75 emoji are allowed.
× Your link has been automatically embedded. Display as a link instead
× Your previous content has been restored. Clear editor
× You cannot paste images directly. Upload or insert images from URL.
- Insert image from URL
- Submit Reply
- Existing user? Sign In
- Online Users
- Leaderboard
- All Activity
- Create New...

COMMENTS
Just like any business, your AV company needs a strategic business plan to succeed. 3. Prepare the Legal Documentation. Legal compliance is essential when running a business. Ensure you meet local business requirements by applying for the appropriate licenses and permits.
Let's dive in and explore the key components of a recording studio business plan that will help you create good music and produce high-quality audio. 1. Microphones, Headphones, and Audio Interfaces. Having the right microphones is crucial. Different types of microphones serve various purposes in a recording studio.
We provide a free business plan template below and will walk you through it. Step by step. Production Company Business Plan. The Executive Summary. Perform a Video Company Self Assessment. How to Get Started. Financing a Video Production Company. Marketing Plan. Day to Day Operations.
Tackling No. 1 is easy. Whether you think you have a lot of extra capital or not, chances are the economy may force you to invest in your audio visual business sooner than later. Our State of the Industry Report shows a 9.5 percent growth rate for the average integrator in 2019…but the problem is that — despite high demand for integration ...
Learn how to write a business plan for your multimedia business in just 7 steps. Also, download your business plan guides & templates needed. ... Our mission at Multimedia is to provide high-quality audio and visual solutions for businesses, events, and organizations. ... newfounderz is a modern day business media company that helps ...
The best business plans are practical documents that reflect actual business realities. Fudging the numbers is the equivalent of sabotaging your audiovisual production services business's strategic interests. Instead, commit to creating the most precise business plan possible. For more information about audiovisual production services company ...
Explore a real-world video production business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan. ... The company is seeking a loan in the amount of $300,000 which will be used to purchase the equipment and start-up expenses. The company's revenue projections for the first three years are ...
With HitSend Audio professionals get a set of comprehensive project approval and payment tools that streamline the entire process to keep clients happy and get invoices paid fast. HitSend has been developed over the last 3 years with the collaboration of some of the top names in the professional audio production world.
A business plan has 2 main parts: a financial forecast outlining the funding requirements of your video production company and the expected growth, profits and cash flows for the next 3 to 5 years; and a written part which gives the reader the information needed to decide if they believe the forecast is achievable.
Lastly, address any funding needs in the "ask" section of your executive summary. 2. The presentation of the company. As you build your broadcast production company business plan, the second section deserves attention as it delves into the structure and ownership, location, and management team of your company.
That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Audio Engineers comes in handy! With this template, audio engineers can: Outline their company's goals and objectives with clarity and precision. Identify target markets and develop effective marketing strategies to reach potential clients. Allocate resources efficiently, ensuring optimal use of ...
First, you should brainstorm with your project team. The best way to do this is by using questions to stimulate discussion. These questions will prompt the team to dig deep into how your users function and how the business works day-to-day. It will also uncover other problems you might be able to solve with your AV solution.
At Gaebler, we advise new business owners to keep your business plan simple. Ultimately, your business plan is intended to be a resource for you, the business owner. As your company matures, you can circle back to your business plan to make revisions and adjustments. Assess Competitors. Before you open an audio equipment and supplies rental ...
Jack Cornwall Productions is an audio production service business, providing audio for radio and television commercials with both industrial and sales narrations, audio and/or video training tapes and telephone holding message services. Jack Cornwall Productions operated as an in-home, part-time venture for just under a year.
A production company's job is not to make easy additional money for the venue, but to serve the client directly with a customized audio visual plan. Applications of A/V production In addition to the typical AV services, avad3 offers a wide range of other options to make events effective and memorable.
An audio visual company may also be hired for live events such as business conferences and concerts. Most audio visual companies use audio visual proposals. Such a proposal covers a wide range of things, such as the exact details of the job the company will provide, how long they will provide it, the kind of equipment they will be leasing or ...
The written part of an audiovisual equipment rental store business plan. The written part of an audiovisual equipment rental store business plan plays a key role: it lays out the plan of action you intend to execute to seize the commercial opportunity you've identified on the market and provides the context needed for the reader to decide if they believe your plan to be achievable and your ...
Installations and AV production can be very different beasts. Installs usually require a contractor's license, so start with that. Then a lot of your money is made on gear, so you'll have to pick companies and push to become a dealer. The heaviest cost usually go to insurance / Workman comp (if you have employees).
The AR/VR market is projected to grow at an average annual rate of 12.6%, leading to a market volume of $58.1bn by 2028 (3). These technologies are transforming how interactive meetings and presentations are conducted. They offer immersive experiences, making remote collaborations more engaging and memorable.
audio visual company business plan Followers 1. audio visual company business plan. By RonaldCype, March 26 in General Discussion. Reply to this topic; Start new topic; Recommended Posts. RonaldCype. Posted March 26. RonaldCype.
A business plan has 2 main parts: a financial forecast outlining the funding requirements of your visual effects studio and the expected growth, profits and cash flows for the next 3 to 5 years; and a written part which gives the reader the information needed to decide if they believe the forecast is achievable.
The equipment you need will depend on the type of business you run and its size. Here are some of the most common AV components you might want to consider: Interactive Whiteboards. Video Projector and Screen. Control Systems. Amplifiers & Speakers. Video Cables and Connectors. Lighting System. Digital Signage Monitors.