
Fish Farm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Fish Farm Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Fish Farm business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Fish Farms.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Fish Farm business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm is an aquaculture business located 30 miles north of Madison, Wisconsin. The farm is owned by Jason Newcomb, a fish farm manager for over ten years, who had responsibility for all operations and customer supply in his former position. Now that Jason has garnered a sizable reputation as an experienced fish farmer, several former clients of his last employer are asking Jason if they can begin using his services to supply the fish they need. Jason plans on recruiting a team of professionals to help manage and operate the day-to-day activities found at the AcquaHarvest Fish Farm.
The AquaHarvest Fish Farm will provide high-quality, locally sourced fish to meet the growing demand for fresh and sustainable seafood in the region. By utilizing advanced aquaculture techniques and maintaining a focus on environmental stewardship, AquaHarvest Fish Farm aims to become a leading provider of farm-raised fish in Wisconsin.
Product Offering
The following are the products that AquaHarvest Fish Farm will provide:
- Fresh, locally-sourced, farm-raised trout and tilapia
- Fish products, such as smoked trout, fish jerky, fish for stocking ponds
- Sustainably produced farmed fish in a low-impact environment
Customer Focus
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will target a wide range of customers, including individual consumers, restaurants, grocery stores, and seafood distributors. Additionally, we will focus on promoting our fish as an alternative to wild-caught fish, emphasizing the traceability and sustainability of our farming practices.
Management Team
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be owned and operated by Jason Newcomb. He recruited his former marketing and sales manager, Tim Olsen, to be the new marketing and sales director for AcquaHarvest Fish Farm.
Jason Newcomb holds a certification from the National Institute of Fish Farming in Sustainable and Environmental Protections. He has been working at a well-known fish farm outside Madison for the past decade. Recently, he determined that he could take the best attributes of his former employer, apply them to his new business, and add several improvements to the fish farming process that would appeal to consumers and lower the environmental toll on the land he purchased.
Tim Olsen, who will be the new Marketing and Sales Director, has been working in his former position for over thirteen years and has won the “Outstanding Sales & Marketing Promotions” award multiple times within the fish farming community groups in Madison, Wisconsin. Tim is known for his ability to strategically market and sell long-term contracts from fish buyers on both a national and international level.
Success Factors
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Friendly, knowledgeable, and highly-qualified team of AquaHarvest Fish Farm
- A selection of farmed fresh fish, sustainably raised and locally-sourced
- Fish products; including fish for stocking ponds, fish jerky, and smoked trout
- AquaHarvest Fish Farm will offer the best pricing in town. The pricing structure is the most cost-effective when compared to the competition.
Financial Highlights
AquaHarvest Fish Farm is seeking $200,000 in debt financing to launch its AquaHarvest Fish Farm. The funding will be dedicated toward securing the office building and purchasing office equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated toward three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the print ads and marketing costs. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Office space build-out: $20,000
- Office equipment, supplies, and materials: $10,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $10,000
- Working capital: $10,000
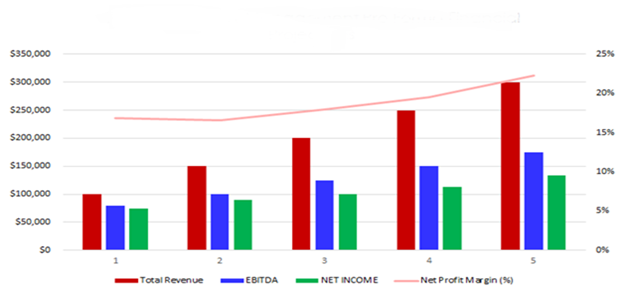
The following graph outlines the financial projections for AquaHarvest Fish Farm.
Company Overview
Who is aquaharvest fish farm.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm is a newly established, full-service fish farm 30 miles from Madison, Wisconsin. AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be the most reliable, cost-effective, and efficient choice for customers in Madison and the surrounding communities. AquaHarvest Fish Farm will provide a comprehensive menu of fish and fish products for multiple customer segments to utilize. Their full-service approach includes a comprehensive array of locally-sourced, sustainable fresh fish, smoked fish, fish jerky and other fish products.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be able to effectively provide 300 fresh fish each week, with fish products numbering 200-300 pounds per week. The team of professionals are highly qualified and experienced in the fish farming industry and the management and operations of a fish farm. AquaHarvest Fish Farm provides the perfect one-stop shop for all the fresh, locally-sourced fish customers may need, including filets, steaks, whole fish, fish for sushi, and other expanded customer uses. AquaHarvest will meet every customer expectation or offer refunds, if ever needed.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm History
Since incorporation, AquaHarvest Fish Farm has achieved the following milestones:
- Registered AquaHarvest Fish Farm, LLC to transact business in the state of Wisconsin.
- Has a contract in place at one of the office buildings, where the operations and management teams will set up office space within the 10,000 square foot area.
- Reached out to numerous former clients to include fish handlers, maintenance workers and other staff members for the new fish farm company.
- Began recruiting a staff of ten associates and office personnel to work at AquaHarvest Fish Farm.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm Services
The following will be the products AquaHarvest Fish Farm will provide:
Industry Analysis
- The fish farm industry is expected to grow over the next five years to over $202 billion.
- The growth will be driven by the increased need for regulated raising and harvesting of fresh fish and crustaceans.
- The growth will also be driven by the consumer demand for sustainable fish-farmed sources of fish.
- The growth will be driven by the increased interest by consumers in healthful eating practices, including fresh fish.
- Costs will likely be reduced as more fish farms are established and can provide fresh, locally-produced fish.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will target customers within the Madison, Wisconsin region. They will target individual consumers, restaurants, grocery stores and seafood distributors.They will also target consumer groups focused on traceability and sustainability of food, including fish.
| Total | Percent | |
|---|---|---|
| Total population | 1,680,988 | 100% |
| Male | 838,675 | 49.9% |
| Female | 842,313 | 50.1% |
| 20 to 24 years | 114,872 | 6.8% |
| 25 to 34 years | 273,588 | 16.3% |
| 35 to 44 years | 235,946 | 14.0% |
| 45 to 54 years | 210,256 | 12.5% |
| 55 to 59 years | 105,057 | 6.2% |
| 60 to 64 years | 87,484 | 5.2% |
| 65 to 74 years | 116,878 | 7.0% |
| 75 to 84 years | 52,524 | 3.1% |
Customer Segmentation
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Restaurants
- Grocery stores
- Seafood distributors
- Individual customers
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Fresh SeaPack Fish
The Fresh SeaPack Fish Company is located in Chicago, Illinois. The company is owned by Jerome Packson, a former restaurateur who now oversees the supply of fish and seafood into the finest Chicago restaurants. The company sources locally-raised fish, vacuum-packs and seals each filet, and ships the fish to regional and city-wide restaurants. With one-day service, the fish is as fresh as when it was shipped, which offers excellent flavors for consumers.
Jerome Packson established Fresh SeaPack Fish in 2000, when it became apparent the fish supplies coming in from Alaska were being depleted by wild-caught fishermen. This created in him a drive to change the process, so his company could guarantee a “fresh fish” result in restaurants, while processing and packing up to 24 hours in advance of shipment.
Sea & Land Distributors
Sea & Land Distributors are co-owned by brothers, Dean and Dave Lancaster, who have located their distribution company in Suamico, Wisconsin. From this location, vacuum packed fish can be flown to customers within a multi-state area, typically within 4 hours. The distribution company was formed in 2004 by Dean Lancaster, a former sales manager for a fish industry networking company, and Dave Lancaster, a former seafood salesman for the large, well-known fish and fish product provider.
In addition to fish and fish products, Sea & Land Distributors began distributing fresh beef to restaurants and grocery stores. Using the same processes and techniques, the beef filets, steaks, ribs and other choice cuts are sent to regional clients within 4-hours of processing. This addition to the company has resulted in a significant increase in revenue and the addition of staff to cover the beef portion of the business.
Harris Seafood Company
The Harris Seafood Company is a certified “organic and sustainable” seafood distributor, focusing on the Madison region of Wisconsin. Trent Harris is the owner and president of the company, while six employees process and pack seafood for delivery to Madison restaurants. The company was formed in 2021 and has an estimated 100 customers or clients, who are served weekly or monthly with vacuum-packed seafood.
The Harris Seafood Company has plans to open another processing center in Chicago within three years in order to grow the highly successful seafood sales industry into high-end Chicago restaurants. With demand rising, the Harris Seafood Company plans to meet that demand and exceed current company expectations.
Competitive Advantage
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Highly-qualified team of skilled employees that is able to provide an array of fish and fish products, including smoked trout and fish jerky.
- Fresh locally-sourced fish farmed include: trout and tilapia. These two fish are the most sought-after and easily raised fish in the species, leading AquaHarvest to recognize their prominence in the restaurant industry and provide these two fish for all customers.
- Fish that is sustainably-raised and locally-sourced. Unlike other fish farms, AquaHarvest depends on aqua hydroponic techniques to successfully bring the oxygen and nutrients needed by the fish. These are not harmful to the environment; in fact, these elements enhance our environment over all.
- Unbeatable pricing for clients; AcquaHarvest will offer the lowest pricing in the region.
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for AquaHarvest Fish Farm is as follows:
Word of Mouth/Referrals
AquaHarvest Fish Farm has built up an extensive list of contacts over the years by providing exceptional service and products to former clients. AquaHarvest Fish Farm will garner the former clients before they begin advertising and marketing to new clients. The former clients have already committed to referring associates to AquaHarvest Fish Farm, as well.
Professional Associations and Networking
Both Jason Newcomb and Tim Olsen are well-known in the fish farm industry and have extensive networking contacts. As such, they will work to secure long term contracts with their core target audience to raise the awareness of the new company as soon as possible.
Print Advertising
Two weeks prior to launch, a direct mail piece will be sent to every restaurant, grocery store, seafood distributor and related fishmonger to announce the opening of the company. A discount for clients to sign contracts in the first month will be announced and special packages of service and products will be offered at that time, as well.
Website/SEO Marketing
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will fully utilize their website. The website will be well-organized, informative, and list all the products and services that AquaHarvest Fish Farm provides. The website will also list their contact information and available fish and fish products each day. The sales and marketing director, Tim Olsen, will also manage AquaHarvest Fish Farm’s website presence with SEO marketing tactics. When someone searches in the Google or Bing search engine “fish farm” or “fresh fish near me”, AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be listed at the top of the search results.
The pricing of AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be moderate and on par with competitors so customers feel they receive excellent value when purchasing their services.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for AquaHarvest Fish Farm. Operation Functions:
- Jason Newcomb – will be the Owner and President of the company. He will oversee all staff and manage client relations. Jason has spent the past year recruiting the following staff:
- Nancy Dyce – will be the Office Manager, who will manage the office administration, client files, and accounts payable.
- Tina Stevens – whose role will be the Staff Accountant, providing all accounting, tax payments, and monthly financial reporting.
- Tim Olsen – Sales and Marketing Manager, who will provide all marketing for AquaHarvest Fish Farm and each product offered.
- John Quinten – Farm Manager, who will operate all fish tanks and facilities and provide all maintenance at the properties.
Milestones:
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
- 5/1/202X – Finalize contract to lease office space
- 5/15/202X – Finalize personnel and staff employment contracts for the AquaHarvest Fish Farm
- 6/1/202X – Finalize contracts for AquaHarvest Fish Farm clients
- 6/15/202X – Begin networking at industry events
- 6/22/202X – Begin moving into AquaHarvest Fish Farm office
- 7/1/202X – AquaHarvest Fish Farm opens its office for business
Tina Stevens will be the Staff Accountant, providing all accounting, tax payments, and monthly financial reporting to Jason Newcomb.
Nancy Dyce will be the Office Manager, who will be responsible for the office administration, client files, and act as an executive assistant, upon request.
John Quinten, will take on the role of Farm Manager, in charge of the tank operations, cleaning, facilities oversight and all maintenance at the property buildings.
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for AquaHarvest Fish Farm are the customer fees they will charge to the target audience for their services.
The cost drivers will be the overhead costs required in order to staff AquaHarvest Fish Farm. The expenses will be the payroll cost, rent, utilities, office supplies, and marketing materials.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
AquaHarvest Fish Farm is seeking $200,000 in debt financing to launch its fish farm. The funding will be dedicated towards securing the office space and purchasing office equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated towards three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the print ads and association memberships. The breakout of the funding is below:
Key Assumptions
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and in order to pay off the startup business loan.
- Number of Customers Per Month: 185
- Average Revenue per Month: $44,500
- Office Lease per Year: $100,000
Financial Projections
Income statement.
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Total Revenues | $360,000 | $793,728 | $875,006 | $964,606 | $1,063,382 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $64,800 | $142,871 | $157,501 | $173,629 | $191,409 | |
| Lease | $50,000 | $51,250 | $52,531 | $53,845 | $55,191 | |
| Marketing | $10,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Salaries | $157,015 | $214,030 | $235,968 | $247,766 | $260,155 | |
| Initial expenditure | $10,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $291,815 | $416,151 | $454,000 | $483,240 | $514,754 | |
| EBITDA | $68,185 | $377,577 | $421,005 | $481,366 | $548,628 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| EBIT | $41,025 | $350,417 | $393,845 | $454,206 | $521,468 | |
| Interest | $23,462 | $20,529 | $17,596 | $14,664 | $11,731 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $6,147 | $115,461 | $131,687 | $153,840 | $178,408 | |
| NET INCOME | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 |
Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $30,000 | $33,072 | $36,459 | $40,192 | $44,308 | |
| Total Current Assets | $184,257 | $381,832 | $609,654 | $878,742 | $1,193,594 | |
| Fixed assets | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $54,320 | $81,480 | $108,640 | $135,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $153,790 | $126,630 | $99,470 | $72,310 | $45,150 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $315,831 | $270,713 | $225,594 | $180,475 | $135,356 | |
| Accounts payable | $10,800 | $11,906 | $13,125 | $14,469 | $15,951 | |
| Total Liability | $326,631 | $282,618 | $238,719 | $194,944 | $151,307 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| Total Equity | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 |
Cash Flow Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | ||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 | |
| Change in working capital | ($19,200) | ($1,966) | ($2,167) | ($2,389) | ($2,634) | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $19,376 | $239,621 | $269,554 | $310,473 | $355,855 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | ||||||
| Investment | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | ||||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from debt | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow | $154,257 | $194,502 | $224,436 | $265,355 | $310,736 | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | |
| Cash at End of Period | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 |
Fish Farm Business Plan FAQs
What is a fish farm business plan.
A fish farm business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your fish farm business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Fish Farm business plan using our Fish Farm Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Fish Farm Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of fish farm businesses , some examples include: Inland pond fish farm, Open-net pen and cage system fish farm, and Mariculture fish farms.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Fish Farm Business Plan?
Fish Farm businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Fish Farm Business?
Starting a fish farm business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Fish Farm Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed fish farm business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your fish farm business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your fish farm business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Fish Farm Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your fish farm business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your fish farm business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Fish Farm Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your fish farm business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your fish farm business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.

Fish Farm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their fish farms. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a fish farm business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Fish Farm Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your fish farm as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Fish Farm
If you’re looking to start a fish farm, or grow your existing fish farm, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your fish farm in order to improve your chances of success. Your fish farm business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Fish Farms
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a fish farm are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for fish farms.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
If you want to start a fish farming business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. Below are links to each section of your fish farm business plan template:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of fish farm you are operating and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a fish farm that you would like to grow, or are you operating fish farms in multiple markets?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the fish farm industry. Discuss the type of fish farm you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of fish farm you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types of fish farms:
- Inland pond fish farm : this type of fish farm specializes in inland artificial ponds around 20 acres in size and has an aeration system to add oxygen to the ponds.
- Open-net pen and cage system fish farm: this type of fish farm is usually located offshore and in freshwater lakes. Mesh cages are installed with the fish in it.
- Mariculture fish farms: this type of fish farm involves the use of seawater and can be done next to an ocean or in ponds that contain seawater.
In addition to explaining the type of fish farm you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of customers served, number of positive reviews, reaching X amount of clients served, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the fish farm industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the fish farm industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your fish farm business plan:
- How big is the fish farm industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your fish farm? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your fish farm business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: restaurants, grocery retailers, and the local public.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of fish farm you operate. Clearly, grocery retailers would respond to different marketing promotions than the average citizen, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Fish Farm Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other fish farms.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes grocery stores and restaurants. You need to mention such competition as well.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other fish farms with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be fish farms located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of fish do they farm?
- What type of fish farm are they?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Are your fish more responsibly farmed than the competition?
- Will you provide fish products that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a fish farm business plan, your marketing plan should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of fish farm company that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to a fish farm, will you provide delivery, shipping, gutting and/or preparation, and any other services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your fish farm company. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your fish farm located near an ocean, a river, a large pond, etc. Discuss how your location might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your fish farm marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Reaching out to grocers and local restaurants
- Social media marketing
- Local radio advertising
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your fish farm, including prepping the nets, pulling in the fish, cleaning the fish,weighing and pricing the daily catch, and updating inventory and pricing.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to catch your XXth fish, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your fish farm to a new location.
Management Team
To demonstrate your fish farm’s ability to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing fish farms. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing a fish farm or is an experienced aquaculturist .
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you take on one new grocer or restaurant at a time or multiple new grocers or restaurants ? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your fish farm, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a fish farm:
- Cost of boats and nets.
- Cost of equipment and supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your boat and equipment lease or the list of the different types of fish you will be farming.
Putting together a business plan for your fish farm is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will really understand the fish farm industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful fish farm.
Fish Farm Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my fish farm business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily complete your Fish Farming Business Plan.
What is the Goal of a Business Plan's Executive Summary?
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of fish farm you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have a fish farm that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of fish farms?
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Fish Farm business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Small Business Trends
How to start a fish farming business.
Getting started raising farmed fish does require a significant financial outlay. You can make good profits, depending on the type of fish farming you do and the fish species you choose.
How To Start Fish Farms: 14 Key Steps
1. decide on the fish species you will farm.
Freshwater – Tilapia and catfish are the most common species grown in the US. Both are fast growers. Tilapia are often the chosen species for indoor fish farming because of their need for a constant warm water temperature between 82 and 86 F. Worldwide, carp (Common, grass, silver and Rohu)are the most commonly grown species. Rainbow trout are the most common trout species grown.
British Columbia and Vancouver Island lead the world in salmon farming. Asian markets lead the world in demand, with South America showing strong growth.
2. Choose Your Fish Farming Method
3. site selection, 4. name your business, 5. create an amazing business plan.
Check into government-backed loans. Fish farming as part of aquaculture systems is considered to be an “alternative” agriculture organization. As an alternative agriculture organization, it may qualify for special financing.
6. Handle the Legal Stuff
7. decide on a location.
What’s the perfect location to build a series of ponds? The best soil type for ponds has a lot of clay.
8. Water Quality Management
9. acquire all the equipment needed.
Hydroponic beds – Not a “must have” but an attractive system. Here’s how it works. Fish are being raised indoors in tanks or vats. Nearby, hydroponic beds are positioned for growing plants. The waste water from the fish tanks fertilizes the plants in the hydroponic beds. The most common pairing for this set up is tilapia and herbs.
10. Design Your Pond
How many gallons of water are in a pond? If you wanted a pond with a million gallons, it would be 267 feet long, 50 feet wide and 10 feet deep.
11. Fish Health Management
12. create your pond, 13. hire staff, 14. market your fish farm, running fish farms: a complete guide, optimum conditions for raising farmed fish, feeding the fish.
To achieve a favorable feed conversion ratio, you will need approximately 1.5 to 2 pounds of feed for each pound of fish produced. These feeding ratios are crucial in aquaculture to optimize efficiency and sustainability. With the current cost of feed, it typically takes about 60 cents to produce one pound of fish, making it a cost-effective venture. Generally, fish are fed two times a day to maintain their health and accelerate growth. This frequency can be adjusted depending on the species of fish and their life stage.
Harvesting the Fish
What is a fish farm, why you should start a large-scale fish farming business.
It can be expensive to start large-scale fish farms and much of the work involves physical labor. So why start large-scale fish farming?
Indoor Fish Farming Vs Outdoor: Which is the Best Business Model?
| Indoor Fish Farming | Outdoor Fish Farming | |
|---|---|---|
| Land Requirements | Can be set up anywhere with enough indoor space. Existing infrastructure like buildings can be used. | Requires land with suitable water bodies or the ability to construct them. Already owned land with existing ponds can be used, but these might not always be suitable. |
| Depth of System | Depth can be regulated according to the species of fish and farming requirements. | Ponds shouldn't be more than 4 to 6 feet deep to facilitate netting of fish. Depth control can be challenging. |
| Water Supply | Requires a reliable source of fresh water, likely pumped from a well. About 15-20 gallons per minute per surface acre of water is needed. | Same as indoor farming, a reliable source of fresh water is required. It should provide 15-20 gallons per minute per surface acre of water. |
| Impact of Environmental Factors | Indoors, it's easier to control water quality and temperature, providing a more stable environment. This can be especially beneficial for fish like Tilapia that prefer warm water (82-86 F degrees). | Outdoor farming is subject to environmental fluctuations, such as temperature changes, storms, and seasonal variations. These factors can impact water quality and temperature, potentially making maintenance more challenging. |
| Risks | Predation and escape of fish are significantly reduced due to the controlled indoor environment. | Outdoor farming has an increased risk of fish escaping and becoming invasive. Predation from birds, mammals, and other fish is also a significant risk. |
| Maintenance | Generally, indoor systems require more technical knowledge and can be more labor-intensive due to the need to closely monitor and adjust environmental parameters. | Outdoor systems, while still needing regular maintenance and monitoring, can be less labor-intensive as some parameters are naturally regulated. |
Indoor systems eliminate potential problems such as escaped fish and predation. With indoor it is easier to maintain optimal water quality, because you’re not subject to outdoor elements. It is also easier to control the temperature.
How Much Does it Cost to Start Fish Farming?
Costs can also vary depending on the species of fish farmed. Some species require more specialized equipment or feed, impacting the overall startup costs. Additionally, consider the ongoing costs of utilities, labor, feed, and maintenance when budgeting for your fish farm.
Things to Consider Before Starting
Just as with traditional “land” farm crops, conditions in fish farming must be consistently monitored and adjusted as needed throughout the process. This involves checking and regulating water quality parameters like pH, temperature, and oxygen levels. Moreover, keeping an eye on feed quality and quantity is necessary to ensure healthy growth. In addition, regular health check-ups help identify any potential diseases and provide early treatment. Also, note that potential external threats, such as predators or invasive species, need to be managed.
Inflow and Outflow
Disease control, predator control, water pollution.
Poor water quality, often resulting from stormwater runoff, can occur, especially during periods of heavy rains. Runoff can wash contaminants into outdoor fish ponds, deteriorating the water quality and threatening the fish’s health. Maintaining good water quality is thus crucial to the success of fish farming. If the water quality deteriorates significantly, it can become unsuitable for fish, leading to mass mortality. To prevent this, regular water testing and monitoring are needed, and preventive measures should be in place.
Space Between Ponds
Environmental concerns, faqs: fish farming, how do i start fish farming.
Starting a fish farm involves several key steps. Begin by conducting thorough market research to understand the demand for different fish species in your area. This will help you decide which species to farm.
What is aquaculture?
It can be practiced in various water bodies, ranging from freshwater ponds and rivers to marine environments like the ocean. The goal of aquaculture is to produce seafood for consumption, restock wild populations, and build aquarium collections.
Is fish farming easy?
How much does a fish farmer make per year.
The income of a fish farmer can vary widely based on factors such as the scale of the operation, the types of fish farmed, and the efficiency of the farming practices. On average, fish farmers in the United States earned between $44,000 and $54,000 annually as of 2021.
What is the most profitable fish to farm?
Can fish farming be green.
This includes efficient feed management to reduce waste, maintaining water quality to prevent pollution, and ensuring that farmed fish do not escape into the wild, which could disrupt local ecosystems.

Fish Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
By: Author Tony Martins Ajaero
Home » Business ideas » Agriculture Industry » Livestock Farming » Fish Farming

Are you about starting a fish farming business ? If YES, here is a complete sample fish farming business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE .
Fish farming is a very lucrative business. It has been in existence for a very long time and more and more people have found it a very good means of livelihood. One of the unique things about the fish farming trade is that you have the opportunity to rear fishes and watch them grow from tiny to big enough to be traded with.
This business isn’t so capital intensive, however it requires that one garners a good skill in the trade so that one can apply expertise in the business and not lose money at a slightest mistake. Much more than the skills to be garnered there is the business plan that needs to be written.
Business plans help you to decipher how a business is really being run. Here below is a sample fish farming business plan;
A Sample Fish Farming Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
The agricultural industry of which Fish and Seafood Aquaculture business is a subset of is no doubt among the leading industry in most countries of the world; it is the industry that produces fish and seafood for the populace.
Because of the significant role the agriculture sector plays, the government of most countries ensures that they go all the way to subsidize seedlings, fertilizers, and farming implements and machinery for farmers and also encourage entrepreneurs to go into commercial farming (fish farming inclusive).
The Fish and Seafood Aquaculture industry comprises of businesses that farm aquatic animals or plants in controlled aquatic environments. Businesses in this industry make use of some form of intervention in the rearing process to enhance production, such as holding in captivity and protecting from predators, pests and disease.
It is important to state that this industry does not including the fishing and harvesting of wild fish and shellfish especially on the high sea. A study conducted by IBISWORLD shows that the Fish and Seafood Aquaculture industry has indeed experienced slow growth over the last five years.
Given that the vast majority of the revenue generated in the industry is derived from sales of fish, mollusks and crustaceans that will be processed into food products, this industry’s success is tied to levels of seafood consumption. Per capita seafood consumption in the united states has declined over the last five years, putting strain on businesses in this industry.
Nonetheless, increases in the price of seafood, combined with a healthy export market, have boosted the revenue growth in this industry. The revenue generation from The Fish and Seafood Aquaculture industry is projected to grow at an annualized rate of 0.3 percent to $1.5 billion over the five-year period.
The Fish and Seafood Aquaculture industry is indeed a very large industry and pretty much thriving in all parts of the world especially in developed countries such as United States of America, Canada, United Kingdom, Portugal Germany, Australia and the Caribbean et al.
Statistics has it that in the United States of America alone, there are about 2,087 licensed and registered Fish and Seafood Aquaculture company directly responsible for employing about 10,440 employees and indirectly responsible for employing roughly 1,339,900.
The industry rakes in a whooping sum of $1billion annually with an annual growth rate projected at 0.3 percent. It is important to state that there are no establishments with a lion share of the available market in this industry. If you are looking towards leveraging on the agriculture industry to generate huge income, then one of your best bet is to start a fish and seafood aquaculture business.
One thing is certain about starting fish and seafood aquaculture business, if you are able to conduct your market research and feasibility studies , you are more likely not going to struggle to sell your fish and seafood because there are always food processing companies and consumers out there who are ready to buy from you.
2. Executive Summary
St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC is a world – class and licensed Fish and Seafood Aquaculture Company that will be based in a riverine area in Columbia, South Carolina – United States. We have done our detailed market research and feasibility studies and we were able to secure a hundred hectares of land to start our fish and seafood aquaculture business.
Our fish and seafood farm is going to be standard fish and seafood farm hence will be involved in raising and harvesting finfish (e.g. catfish, trout, tilapia and minnows), raising and harvesting shellfish (e.g. clams, oysters, crustaceans, mollusks and shrimp), raising and harvesting ornamental fish (e.g. goldfish and tropical fish), raising and harvesting aquaculture species to augment or replenish wild habitats, and raising and harvesting other aquaculture (e.g. seaweed, alligators, frogs and turtles) et al.
We are in the Fish and Seafood Aquaculture industry because we want to leverage on the vast opportunities available in the agriculture industry, to contribute our quota in growing the U.S. economy, in national food production, and also to fish and seafood from the United States to other countries and over and above to make profit.
St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC is well positioned to become one of the leading fish and seafood farming business in the United States of America, which is why we have been able to source for the best hands and machines to run the company with.
We have put process and strategies in place that will help us employ best practices when it comes to fish and seafood farming processes as required by the regulating bodies in the United States of America. At St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC, our customer’s best interest will always come first, and everything we do will be guided by our values and professional ethics.
We will ensure that we hold ourselves accountable to the highest standards by meeting our client’s needs precisely and completely. We will cultivate a working environment that provides a human, sustainable approach to earning a living, and living in our world, for our partners, employees and for our clients.
St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC is a private registered fish and seafood farming company that is owned by Vincent Denis and his immediate family members.
The fish and seafood farm will be fully and single handedly financed by the owner – Vincent Denis and his immediate family members at least for a period of time. Vincent Denis studied Fishery and he has well over 10 years of hands on experience in the fish and seafood aquaculture industry.
3. Our Products and Services
St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC is a standard fish and seafood farming company that is committed to raising fish and seafood for both the United States’ market and the global market. We are in the fish and seafood to make profits and we are going to do all we can to achieve our business goals, aim and objectives.
These are the areas we will concentrate on in our fish and seafood farming business;
- Raising and harvesting finfish (e.g. catfish, trout, tilapia and minnows)
- Raising and harvesting shellfish (e.g. clams, oysters, crustaceans, mollusks and shrimp)
- Raising and harvesting ornamental fish (e.g. goldfish and tropical fish)
- Raising and harvesting aquaculture species to augment or replenish wild habitats
- Raising and harvesting other aquaculture (e.g. seaweed, alligators, frogs and turtles)
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our Vision is to become one of the leading fish and seafood farm brands not just in the United States of America but also on the global stage.
- St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC is a world class and registered fish and seafood farming company that is committed to raising fish and seafood for both the United States’ market and the global market. We want our fish and seafood to flood the nooks and crannies of the United States and other countries of the world.
Our Business Structure
St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC is a privately owned and managed fish and seafood business that intend starting small in fishing community in Columbia – South Carolina, but hope to grow big in order to compete favorably with leading fish and seafood farming companies in the industry both in the United States and on a global stage.
We are aware of the importance of building a solid business structure that can support the picture of the kind of world class business we want to own. This is why we are committed to only hire the best hands within our area of operations.
At St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC, we will ensure that we hire people that are qualified, hardworking, and creative, result driven, customer centric and are ready to work to help us build a prosperous business that will benefit all the stakeholders (the owners, workforce, and customers).
As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our senior management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of five years or more as agreed by the board of trustees of the company. In view of the above, we have decided to hire qualified and competent hands to occupy the following positions;
- Chief Operating Officer
General Fish and Seafood Farm Manager
Human Resources and Admin Manager
- Accountant / Cashier
- Sales and Marketing Executive
- Field Employees
- Front Desk Officer
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Chief Executive Officer – CEO:
- Increases management’s effectiveness by recruiting, selecting, orienting, training, coaching, counseling, and disciplining managers; communicating values, strategies, and objectives; assigning accountabilities; planning, monitoring, and appraising job results; developing incentives; developing a climate for offering information and opinions; providing educational opportunities.
- Responsible for providing direction for the business
- Creates, communicates, and implements the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy.
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization
- Responsible for the planning, management and coordinating all farm activities across the various sections on behalf of the organization
- Supervises other section manager
- Ensures compliance during project executions
- Provides advice on the management of farming activities across all section
- Responsible for carrying out risk assessment
- Using IT systems and software to keep track of people and progress of the growth of fish and seafood in our ponds
- Responsible for overseeing the accounting, costing and sale of fish and seafood farm produce
- Represents the organization’s interest at various stakeholders meetings
- Ensures that farming goals desired result are achieved, the most efficient resources (manpower, equipment, tools and chemicals et al) are utilized and different interests involved are satisfied.
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Updates job knowledge by participating in educational opportunities; reading professional publications; maintaining personal networks; participating in professional organizations.
- Enhances department and organization reputation by accepting ownership for accomplishing new and different requests; exploring opportunities to add value to job accomplishments.
- Defines job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carries out staff induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Oversees the smooth running of the daily office.
Accountant / Cashier:
- Provides managements with financial analyses, development budgets, and accounting reports; analyzes financial feasibility for the most complex proposed projects; conducts market research to forecast trends and business conditions.
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis.
- Performs cash management, general ledger accounting, and financial reporting for one or more properties.
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensures compliance with taxation legislation
- Handles all financial transactions for St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC
- Serves as internal auditor for St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC.
Sales and Marketing Manager
- Manage external research and coordinate all the internal sources of information to retain the organizations’ best customers and attract new ones
- Model demographic information and analyze the volumes of transactional data generated by customer
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts; participates in the structuring and financing of projects; assures the completion of development projects.
- Writing winning proposal documents, negotiate fees and rates in line with organizations’ policy
- Responsible for handling business research, market surveys and feasibility studies for clients
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with clients
- Develops, executes and evaluates new plans for expanding increase sales
- Creates new markets cum businesses for the organization
- Empowers and motivates the sales team to meet and surpass agreed targets
Field Workers / Contract Staff
- Responsible for feeding fish and seafood as instructed by the supervisor
- Responsible for cleaning the ponds and the entire fish farm environment
- Changes the water in the pond as instructed by the supervisor on a regular basis
- Handles fish and seafood farm implements and machines (hatchery) as instructed by the section manager / supervisor
- Responsible for raising and harvesting finfish (e.g. catfish, trout, tilapia and minnows)
- Responsible for raising and harvesting shellfish (e.g. clams, oysters, crustaceans, mollusks and shrimp)
- Responsible for raising and harvesting ornamental fish (e.g. goldfish and tropical fish)
- Responsible for raising and harvesting aquaculture species to augment or replenish wild habitats
- Responsible for raising and harvesting other aquaculture (e.g. seaweed, alligators, frogs and turtles)
- Carries out task in line with the stated job description
- Assists in transport working tools and equipment from the fish and seafood farm and back to the designated store room
- Handles any other duties as assigned my the line manager
Front Desk / Customer’s Service Officer
- Welcomes clients and potential clients by greeting them in person, online or on the telephone; answering or directing inquiries.
- Ensures that all contacts with clients (e-mail, walk-In center, SMS or phone) provides the client with a personalized customer service experience of the highest level
- Through interaction with clients on the phone, uses every opportunity to build client’s interest in the company’s products and services
- Manages administrative duties assigned by the creative director in an effective and timely manner
- Consistently stays abreast of any new information on the organizations’ products, promotional campaigns etc. to ensure accurate and helpful information is supplied to clients when they make enquiries
6. SWOT Analysis
St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC do not intend to launch out with trial and error hence the need to conduct a proper SWOT analysis.
We know that if we get it right from the onset, we would have succeeded in creating the foundation that will help us build a standard fish and seafood farming company that will favorably compete with leading players in the Fish and Seafood Aquaculture industry in the United States of America and in the rest part of the world.
We engaged the services of a core professional in the area of business consulting and structuring to assist our organization in building a well – structured fish and seafood farming company that can favorably compete in the highly competitive fish and seafood aquaculture industry in the United States and the world at large.
Part of what the team of business consultant did was to work with the management of our organization in conducting a SWOT analysis for St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC. Here is a summary from the result of the SWOT analysis that was conducted on behalf of St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC;
Our strength as a fish and seafood farming company is the fact that we have healthy relationships with loads of major players (agriculture merchants) in the industry; both suppliers of fish and seafood feeds and medications and buyers of fish and seafood within and outside of the United States of America.
We have some of the latest fish farming hatchery, tools and equipment that will help us raise and produce fish and seafood in commercial quantities with less stress. Aside from our relationship (network) and equipment, we can confidently boast that we have some the most experienced hands in Columbia – South Carolina in our payroll.
Our weakness could be that we are a new fish and seafood farming company in the United States, and perhaps it might take us sometime to attract big time customers in the industry. We are aware of this and from our projection will overcome this weakness with time and turn it to a major advantage for the business.
- Opportunities:
The opportunities that are available to us as a standard and world – class fish and seafood farming company cannot be quantified, we know that there are loads of households, and businesses such as hotels and fast food restaurants that can’t do without daily supply of fresh water fish and seafood. We are well positioned to take advantage of this opportunity
Some of the threats and challenges that we are likely going to face when we start our own fish and seafood farming company are global economic downturn that can impact negatively on household spending, bad weather cum natural disasters (draughts, epidemics), unfavorable government policies and the arrival of a competitor within same location.
There is hardly anything you can do as regards this threats and challenges other than to be optimistic that things will continue to work for your good.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
The Fish and Seafood Aquaculture industry has greatly benefited from campaigns advertising the health benefits of fish and seafood as a good source of protein. The vast majority of the revenue generated in the industry is derived from sales of fish, mollusks and crustaceans that will be processed into food products; this industry’s success is tied to levels of seafood consumption.
Per capita seafood consumption in the united states has declined over the last five years, putting strain on businesses in this industry.
As a matter of fact, one of the new trends is that with the recent advancement in technology, fish and seafood farmers can now comfortably predict and produce the quantities of fish and seafood they want to produce per time from their hatchery.
8. Our Target Market
Naturally, the target market of those who are the end consumer of fish and seafood and also those who benefits from the business value chain of the fish and seafood aquaculture industry is all encompassing; it is far – reaching.
Every household consumes produce from fish and seafood farms be it finfish (e.g. catfish, trout, tilapia and minnows), shellfish (e.g. clams, oysters, crustaceans, mollusks and shrimp), ornamental fish (e.g. goldfish and tropical fish), and other aquaculture (e.g. seaweed, alligators, frogs and turtles). So also almost all hotels and fast restaurants sell fish and seafood.
In essence a fish and seafood farmer should be able to sell his or her farm produce to as many people as possible. In view of that, we have positioned our business to attract consumers of fish and seafood not just in the United States of America alone but also other parts of the world.
We have conducted our market research and survey and we will ensure that we meet and surpass the expectations we set for the business. Below is a list of the people and business that we will market our fish and seafood to;
- Individuals
- Restaurants
- Fast food eateries
- Agriculture merchants
Our Competitive Advantage
It is easier to find entrepreneur flocking towards an industry that is known to generate consistent income which is why there are increase number of fish and seafood farmers in the United States of America and of course in most parts of the world.
For example, Statistics has it that there are 2.2 million farms in the United States of America, covering an area of 922 million acres. These goes to show that there are appreciable numbers of farmers in the United States of America but that does not mean that there is stiffer competition in the industry.
As a matter of fact, entrepreneurs are encouraged by the government to embrace commercial farming cum fish and seafood farming business. This is so because part of the success of any nation is her ability to cultivate her own food and also export food to other nations of the world.
St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC is fully aware that there are competitions when it comes to selling fish and seafood all over the globe, which is why we decided to carry out thorough market research so as to know how to take advantage of the available market in the United States and in other parts of the world.
We have done our homework and we have been able to highlight some factors that will give us competitive advantage in the marketplace; some of the factors are effective and reliable fish and seafood farming processes that can help us sell our produce at competitive prices, good network and excellent relationship management.
Another competitive advantage that we are bringing to the industry is the fact that we have healthy relationships with loads of major players (agriculture merchants) in the industry; both suppliers of fish and seafood feeds and medications and buyers of fish and seafood within and outside of the United States of America.
We have some of the latest fish and seafood farming hatchery, tools and equipment that will help us raise fish and seafood in commercial quantities with less stress. Aside from our relationship (network) and equipment, we can confidently boast that we have some the most experienced hands in Columbia – South Carolina in our payroll.
Lastly, all our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category (startups fish and seafood farming companies in the United States) in the industry. It will enable them to be more than willing to build the business with us and help deliver our set goals and achieve all our business aims and objectives.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
- Sources of Income
St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC is in the fish and seafood aquaculture industry for the purpose of maximizing profits hence we have decided to explore all the available opportunities within the industry to achieve our corporate goals and objectives. Below are the sources we intend exploring to generate income for St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC;
10. Sales Forecast
From the studies and the survey conducted, we were are able to discover that the sales generated by a fish and seafood farming business depends on the size of the fish and seafood farm, the types of fishes and seafood available in the fish and seafood farm and of course the size of their marketing network.
We have been able to critically examine the fish and seafood aquaculture industry and we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast. The sales projection is based on information gathered on the field and some workable assumptions as well with respect to the nature of fish and seafood farming business that we run.
Below are the projections that we were able to come up with for the first three years of running St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC;
- First Fiscal Year-: $250,000
- Second Fiscal Year-: $600,000
- Third Fiscal Year-: $900,000
N.B : This projection is done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown that can impact negatively on household spending, bad weather cum natural disasters (draughts, epidemics), and unfavorable government policies
- Marketing Strategy and Sales Strategy
We are quite aware that the reason why some fish and seafood farming companies hardly make good profits is their inability to sell off their fish and seafood as at when due.
Our sales and marketing team will be recruited based on their vast experience in the fish and seafood aquaculture industry and they will be trained on a regular basis so as to be well equipped to meet their targets and the overall business goal of St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC.
Over and above, we have perfected our sale and marketing strategies first by networking with agriculture merchants and businesses that rely on daily supply of fish and seafood that are likely to become our customers. In summary, St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC will adopt the following strategies in marketing our fish and seafood;
- Introduce our business by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to stake holders in the agriculture industry, households, hotels and restaurants and agriculture produce merchant et al.
- Advertise our business in agriculture and food related magazines and websites
- List our business on yellow pages ads
- Attend related agriculture and food expos, seminars, and business fairs et al
- Leverage on the internet to promote our business
- Engage in direct marketing
- Encourage the use of Word of mouth marketing (referrals)
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
Any business that wants to grow beyond the corner of the street or the city they are operating from must be ready and willing to utilize every available means (both conventional and non – conventional means) to advertise and promote the business. We intend growing our business which is why we have perfected plans to build our brand via every available means.
We know that it is important to create strategies that will help us boost our brand awareness and to create a corporate identity for our fish and seafood farming business. Below are the platforms we will leverage on to boost our fish and seafood farming brand and to promote and advertise our business;
- Place adverts on community based newspapers, radio stations and TV stations.
- Encourage the use of word of mouth publicity from our loyal customers
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like; YouTube, Instagram, Facebook ,Twitter, LinkedIn, Snapchat, Badoo, Google+ and other platforms to promote our business.
- Ensure that our we position our banners and billboards in strategic positions all around Columbia – South Carolina
- Distribute our fliers and handbills in target areas in and around our neighborhood
- Contact corporate organizations, households, landlord associations and schools by calling them up and informing them of St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC and the fish and seafood we sell
- Advertise our business in our official website and employ strategies that will help us pull traffic to the site
- Brand all our official cars and trucks and ensure that all our staff members and management staff wears our branded shirt or cap at regular intervals.
12. Our Pricing Strategy
Some of the factors that will help you sell your farm produce at the right price that will guarantee that you make profits is dependent on your strategy while some of the factors are beyond your control. For example, if the climatic condition is unfavorable and if there is natural disaster in the location where you have your fish and seafood farm, then it will directly affect the prices of your fish and seafood.
Over and above, if you want to get the right pricing for your fish and seafood, then you should ensure that you choose a good location for the fish and seafood farm, choose a good breed that will guarantee bountiful harvest, cut the cost of running your fish and seafood farm to the barest minimum and of course try as much as possible to attract buyers to your fish and seafood farm as against taking your fish and seafood to the market to source for buyers; with this, you would have successfully eliminate the cost of transporting the goods to the market and other logistics.
We are quite aware that one of the easiest means of penetrating the market and acquiring loads of customers for all our fishes and seafood is to sell them at competitive prices hence we will do all we can to ensure that the prices of our fish and seafood are going to be what other fish and seafood farmers would look towards beating.
One thing is certain; the nature of fish and seafood farming business makes it possible for fish and seafood farmers to place prices for their fish and seafood based on their discretion without following the benchmark in the industry. The truth is that it is one of the means of avoiding running into loss.
- Payment Options
The payment policy adopted by St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC is all inclusive because we are quite aware that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them but at the same time, we will ensure that we abide by the financial rules and regulation of the United States of America.
Here are the payment options that St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC will make available to her clients;
- Payment via bank transfer
- Payment with cash
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via mobile money
- Payment via bank draft
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will enable our client make payment for farm produces purchase without any stress on their part. Our bank account numbers will be made available on our website and promotional materials to clients who may want to deposit cash or make online transfer for fishes and seafood.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
When it comes to calculating the cost of starting a fish and seafood farm, there are some key factors that should serve as a guide. The different types of fishes and seafood to be raised in the fish and seafood farms determine the total cost of setting up the business.
Besides, in setting up any business, the amount or cost will depend on the approach and scale you want to undertake. If you intend to go big by renting / leasing a big facility, then you would need a good amount of capital as you would need to ensure that your employees are well taken care of, and that your facility is conducive enough for workers to be creative and productive.
This means that the start-up can either be low or high depending on your goals, vision and aspirations for your business. The tools and equipment that will be used are nearly the same cost everywhere, and any difference in prices would be minimal and can be overlooked.
As for the detailed cost analysis for starting a fish and seafood farming business; it might differ in other countries due to the value of their money. Below are some of the basic areas we will spend our start – up capital in setting up our fish and seafood farm;
- The Total Fee for incorporating the Business (commercial farm) in United States of America – $750.
- The amount needed to acquire / lease a fish farm land – $50,000
- The amount required for preparing the farm land (fish ponds and fresh water supply et al) – $30,000
- Legal expenses for obtaining licenses and permits as well as the accounting services (software, P.O.S machines and other software) – $3,300.
- Marketing promotion expenses for the grand opening of St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC in the amount of $3,500 and as well as flyer printing (2,000 flyers at $0.04 per copy) for the total amount of $3,580.
- The total cost for hiring Business Consultant – $2,500.
- The total cost for payment of insurance policy covers (general liability, workers’ compensation and property casualty) coverage at a total premium – $9,400
- The amount required for the purchase of the first set of fishes and seafood (fingerlings) – $10,000
- The cost for acquiring the required working tools and equipment / machines / hatchery et al– $50,000
- Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) – $60,000
- The Cost of Launching an official Website – $600
- Additional Expenditure (Business cards, Signage, Adverts and Promotions et al) – $2,000
Going by the report from detailed research and feasibility studies conducted, we will need an average of $500,000 to start a standard fish and seafood farming business in the United States of America.
Generating Funding / Startup Capital for St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC
No matter how fantastic your business idea might be, if you don’t have the required money to finance the business, the business might not become a reality.
No doubt raising start – up capital for a business might not come cheap, but it is a task that an entrepreneur must go through. St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC is a family business that is solely owned and financed by Vincent Denis and his immediate family members.
They do not intend to welcome any external business partners, which is why he has decided to restrict the sourcing of the start – up capital to 3 major sources. These are the areas we intend generating our start – up capital;
- Generate part of the start – up capital from personal savings
- Source for soft loans from family members and friends
- Apply for loan from my Bank
N.B: We have been able to generate about $150,000 (Personal savings $100,000 and soft loan from family members $50,000) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $350,000 from our bank. All the papers and document have been signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited with the amount.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
The future of a business lies in the numbers of loyal customers that they have the capacity and competence of the employees, their investment strategy and the business structure. If all of these factors are missing from a business (company), then it won’t be too long before the business close shop.
One of our major goals of starting St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC is to build a business that will survive off its own cash flow without the need for injecting finance from external sources once the business is officially running.
We know that one of the ways of gaining approval and winning customers over is to retail our fishes and seafood a little bit cheaper than what is obtainable in the market and we are well prepared to survive on lower profit margin for a while.
St. Vincent Fish and Seafood Aquaculture, LLC will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our company’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and retraining of our workforce is at the top burner.
As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of six years or more. We know that if that is put in place, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry; they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.
Check List / Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check: Completed
- Business Registration: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts: Completed
- Securing Point of Sales (POS) Machines: Completed
- Opening Mobile Money Accounts: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Leasing of farm land and building of standard fish ponds: In Progress
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Generating capital from family members: Completed
- Applications for Loan from the bank: In Progress
- Writing of Business Plan: Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Drafting of Contract Documents and other relevant Legal Documents: In Progress
- Design of The Company’s Logo: Completed
- Graphic Designs and Printing of Packaging Marketing / Promotional Materials: In Progress
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Purchase of the Needed furniture, racks, shelves, computers, electronic appliances, office appliances and CCTV: In progress
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business both online and around the community: In Progress
- Health and Safety and Fire Safety Arrangement (License): Secured
- Opening party / launching party planning: In Progress
- Compilation of our list of products that will be available in our store: Completed
- Establishing business relationship with vendors – key players in the industry: In Progress
Related Posts:
- Tilapia Fish Farm Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Dairy Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Abalone Farming Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Quail Egg Production Business Plan [Sample Template]
- How to Start a Catfish Farm – Sample Business Plan Template

LIKE WHAT YOU’VE READ? WHY NOT SHARE

Diving into Success with a Fish Farming Business Plan in 2023
Fish farming, also known as aquaculture, is a rapidly growing industry that offers promising opportunities for entrepreneurs and individuals interested in the agricultural sector. With the increasing demand for seafood and the depletion of wild fish populations, fish farming provides a sustainable solution while offering profitable returns. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of a successful fish farming business plan and guide you through the process of starting your own fish farm.
What is a Fish Farming Business Plan?
Market analysis, startup costs and capital investment, revenue projections, operational expenses, financial forecasting, funding options, risk management, marketing and sales strategy, monitoring and evaluation, legal and regulatory considerations, expansion and growth plans, fish species selection, feeding and nutrition, disease prevention and management, tips for running a profitable fish farming business, can fish farming be profitable, what are the best fish species for beginners in fish farming, how long does it take for fish to reach market size, are there any government regulations or permits required for fish farming, can fish farming be environmentally sustainable.
A fish farming business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the key aspects of starting and running a successful fish farming venture. It serves as a roadmap and strategic guide for entrepreneurs, providing a clear understanding of the business goals, strategies, and operations involved in fish farming.
Essential Components of a Fish Farming Business Plan
To establish a successful fish farming venture, it is essential to develop a comprehensive business plan. The following components should be considered when creating your best business plan for fish farming:
Before diving into the financial aspects, it is crucial to conduct a thorough market analysis. Understanding the fish farming market helps you identify potential customers, assess the competition, and determine the market demand for your products. Researching the preferences of consumers, their purchasing power, and the prevailing market prices will assist you in making informed decisions.
Starting a fish farming business involves various initial expenses. These may include the cost of land, construction or renovation of ponds or tanks, purchase of fish fingerlings, equipment, and other necessary infrastructure. Additionally, you need to account for administrative costs, licenses, and permits. By accurately estimating these startup costs, you can calculate the required capital investment.
To ensure a successful fish farming business, you need to develop revenue projections. Consider factors such as the species of fish you plan to farm, their growth rate, and the market demand. Estimate the potential sales volume and price per unit to project your income. Additionally, explore additional revenue streams, such as selling fish by-products or offering fish-related services.
Operating a fish farming business involves ongoing expenses that must be accounted for in your financial plan. These expenses may include the cost of fish feed, labor, utilities, transportation, maintenance, and administrative overheads. By identifying and analyzing these operational expenses, you can determine the profitability of your venture.
Creating a comprehensive financial model is crucial for the success of your fish farming business. Use the revenue projections and operational expenses to project your income and expenses over a specific period, usually three to five years. A financial forecast will help you identify potential cash flow issues, plan for growth, and make informed financial decisions.
Once you have determined the financial requirements of your fish farming business, it is essential to explore funding options. While self-funding is an option, you may also consider loans from financial institutions, grants from government agencies, or attracting investors interested in the aquaculture industry. Thoroughly research and compare different funding sources to make the best choice for your business.
As with any business, fish farming comes with its own set of risks and challenges. These can include disease outbreaks, changes in market conditions, natural disasters, or regulatory changes. It is crucial to assess these risks and develop strategies for risk mitigation. This may involve implementing biosecurity measures, diversifying your fish stock, or having contingency plans in place.
To ensure the success of your fish farming business, you need to develop an effective marketing and sales strategy. Identify your target markets and understand their preferences and needs. Implement promotional activities such as advertising, online marketing, and participation in trade shows. Build relationships with retailers, restaurants, and wholesalers to secure sales channels for your fish products.
Regular monitoring and evaluation of your fish farming business’s financial performance are vital for its long-term success. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) such as revenue, profitability, and customer satisfaction. Regularly review your financial statements, compare them against your projections, and identify areas for improvement. Adjust your strategies based on the insights gained from this analysis.
Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is critical for any business, including fish farming. Research and understand the permits, licenses, and certifications necessary to operate your fish farm legally. Ensure that you adhere to local, state, and national regulations related to water quality, waste management, and fish health. Non-compliance can result in penalties or the closure of your business.
As your fish farming plan for business grows and matures, you may consider expansion and diversification. Identify opportunities to scale your operations, such as increasing the number of ponds or tanks or introducing new fish species. Explore options for value-added products or fish-related services to expand your revenue streams. Plan for growth while ensuring the financial sustainability of your business.
Choose fish species that are suitable for your local climate and market demand. Consider factors such as growth rate, disease resistance, and market value when selecting the species for your fish farm.
Develop a feeding program that ensures the optimal growth and health of your fish. Determine the appropriate feed types, feeding frequency, and feeding protocols based on the nutritional requirements of the chosen fish species.
Implement measures to prevent and control diseases in your fish farm. Establish biosecurity protocols, maintain proper water quality, and monitor the health of your fish regularly. Seek guidance from aquatic health professionals to ensure the well-being of your fish population.
Get the Funding Your Business Needs! Partner with Easy Capraise Today!
Are you struggling to find the right investors for your business? Look no further! Easy Capraise , your trusted capital-raising partner, is here to help you secure the funding you need to take your business to new heights.
With our expertise in capital raising and pitch deck creation , we have a proven track record of connecting businesses with the right investors who believe in their potential. Our team of experienced professionals understands the intricacies of the investment landscape and knows what it takes to capture the attention of investors.
To ensure the profitability and success of your fish farming venture, consider the following tips:
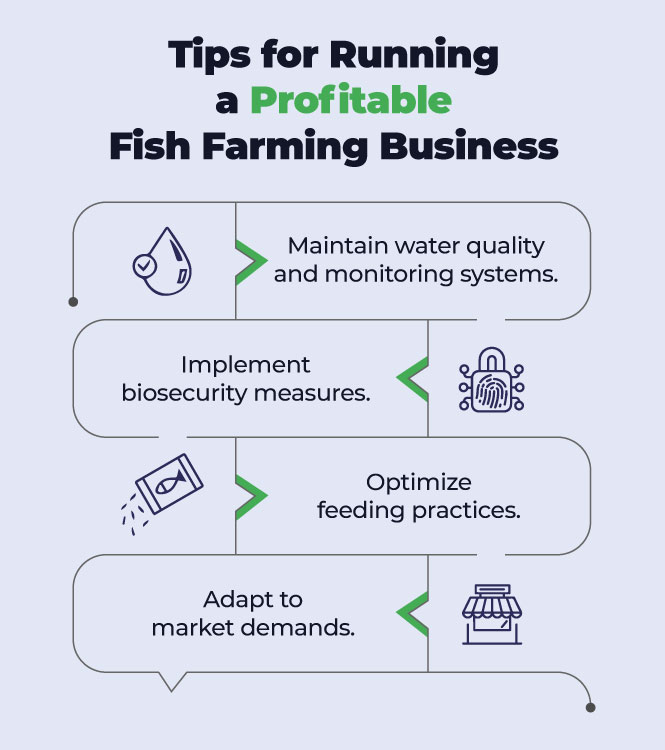
Maintain water quality and monitoring systems : Regularly test and monitor water parameters such as temperature, pH, and oxygen levels. Implement filtration systems and proper water circulation to ensure optimal conditions for fish growth.
Implement biosecurity measures : Prevent disease outbreaks by practicing strict biosecurity measures. Limit the introduction of potential pathogens, quarantine new fish arrivals, and maintain proper hygiene and disinfection protocols.
Optimize feeding practices : Develop feeding protocols based on the nutritional needs of your fish species. Use high-quality feed and ensure proper feeding frequency and portion sizes to optimize growth and minimize waste.
Adapt to market demands : Stay updated on market trends and consumer preferences. Consider diversifying your product offerings, exploring niche markets, or producing value-added fish products to cater to specific customer demands.
Yes, fish farming can be profitable if properly planned and executed. Factors such as market demand, efficient operations, and effective marketing strategies contribute to the profitability of a fish farming business.
Tilapia, catfish, and trout are some fish species that are considered suitable for beginners in fish farming. These species are known for their hardiness, fast growth, and market demand.
The time it takes for fish to reach market size depends on the species and environmental conditions. Generally, it can range from several months to a couple of years.
The regulations and permits required for fish farming vary by country and region. It is essential to research and comply with the legal requirements, including permits, licenses, and environmental regulations specific to your area.
Yes, fish farming can be environmentally sustainable. By implementing proper waste management, water-quality monitoring, and responsible farming practices, fish farming can minimize its ecological impact and contribute to the conservation of natural resources.
A fish farming business plan is crucial for setting up and running a successful fish farm. By conducting thorough market research, selecting suitable fish species, establishing feeding and disease management protocols, and implementing effective marketing strategies, you can maximize the profitability of your fish farming venture. Overcoming challenges through water quality management, disease prevention, and adapting to market demands will ensure the long-term success of your fish farming business.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post Comment
Related Articles

Hire a Business Planner Consultant for Success

Partnering with Top Startup Consulting Firms in 2024

Crafting a Winning Consulting Business Plan in 2024
Good to have you here! If you have any queries, please leave your message. Our team will reach out soon:)
Subscribe to Easy Capraise newsletter: Stay up to date with the latest capital raising trends from Easy Capraise!
[quform id=”6″ name=”sub222″]
- Sample Business Plans
- Food, Beverage & Restaurant
Fishing Farming Business Plan
A fishing farming business can be profitable through various revenue streams and cost management strategies. But to grow a business seriously you will need a business plan in place to guide you as a roadmap.
Need help writing a business plan for your fishing farming business? You’re at the right place. Our fishing farming business plan template will help you get started.

Free Business Plan Template
Download our free fishing business plan template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
How to Write A Fishing Farming Business Plan?
Writing a fishing farming business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan:
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready and summarizes each section of your plan.
Here are a few key components to include in your executive summary:
- Market Opportunity: Summarize your market research, including market size, growth potential, and marketing trends. Highlight the opportunities in the market and how your business will fit in to fill the gap.
- Marketing & Sales Strategies: Outline your sales and marketing strategies—what marketing platforms you use, how you plan on acquiring customers, etc.
- Financial Highlights: Briefly summarize your financial projections for the initial years of business operations. Include any capital or investment requirements, associated startup costs, projected revenues, and profit forecasts.
- Call to Action: Summarize your executive summary section with a clear CTA, for example, inviting angel investors to discuss the potential business investment.
Ensure your executive summary is clear, concise, easy to understand, and jargon-free.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Business Overview
The business overview section of your business plan offers detailed information about your company. The details you add will depend on how important they are to your business. Yet, business name, location, business history, and future goals are some of the foundational elements you must consider adding to this section:
- Finfish farming
- Shellfish farming
- Integrated fish farming
- Inland pond fish farm
- Describe the legal structure of your fishing farming company, whether it is a sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, or others.
- Explain where your business is located and why you selected the place.
- Owners: List the names of your fishing farming company’s founders or owners. Describe what shares they own and their responsibilities for efficiently managing the business.
- Mission Statement: Summarize your business’ objective, core principles, and values in your mission statement. This statement needs to be memorable, clear, and brief.
- Future Goals: It’s crucial to convey your aspirations and vision. Mention your short-term and long-term goals; they can be specific targets for revenue, market share, or expanding your services.
This section should provide a thorough understanding of your business, its history, and its future plans. Keep this section engaging, precise, and to the point.
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should offer a thorough understanding of the industry with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. You should include the following components in this section.
- Competitive Analysis: Identify and analyze your direct and indirect competitors. Identify their strengths and weaknesses, and describe what differentiates your fishing farming business from them. Point out how you have a competitive edge in the market.
- Regulatory Environment: List regulations and licensing requirements that may affect your fishing farming company, such as permits & licenses, environmental regulations, food safety & inspection, etc.
Here are a few tips for writing the market analysis section of your fish farm business plan:
- Conduct market research, industry reports, and surveys to gather data.
- Provide specific and detailed information whenever possible.
- Illustrate your points with charts and graphs.
- Write your business plan keeping your target audience in mind.
4. Products And Services
The product and services section should describe the specific services and products that will be offered to customers. To write this section should include the following:
- Fingerlings
- Grow-out fish
- Mention the species of the fish too
- Environmental service: Describe any environmental services you provide, such as restoring ponds or other water bodies or using eco-friendly aquaculture techniques.
- Additional Services: Mention if your fishing farming company offers any additional services. You may include services like farm management, equipment sales or rental, supply of fish feed, farming supplies, consultancy, etc.
In short, this section of your fishing farming plan must be informative, precise, and client-focused. By providing a clear and compelling description of your offerings, you can help potential investors and readers understand the value of your business.
5. Sales And Marketing Strategies
Writing the sales and marketing strategies section means a list of strategies you will use to attract and retain your clients. Here are some key elements to include in your sales & marketing plan:
- Pricing Strategy: Describe your pricing strategy—how you plan to price your products & services and stay competitive in the local market. You can mention any discounts you plan on offering to attract new customers.
- Marketing Strategies: Discuss your marketing strategies to market your services. You may include some of these marketing strategies in your business plan—social media marketing, brochures, email marketing, content marketing, and print marketing.
- Sales Strategies: Outline the strategies you’ll implement to maximize your sales. Your sales strategies may include partnering with other businesses, collaborations, offering referral programs, etc.
- Customer Retention: Describe your customer retention strategies and how you plan to execute them. For instance, introducing loyalty programs, discounts on bulk orders, personalized service, etc.
Overall, this section of your fishing farming business plan should focus on customer acquisition and retention.
Have a specific, realistic, and data-driven approach while planning sales and marketing strategies for your fishing farming business, and be prepared to adapt or make strategic changes in your strategies based on feedback and results.
6. Operations Plan
The operations plan section of your business plan should outline the processes and procedures involved in your business operations, such as staffing requirements and operational processes. Here are a few components to add to your operations plan:
- Staffing & Training: Mention your business’s staffing requirements, including the number of employees, fish husbandry technicians, or other employees needed. Include their qualifications, the training required, and the duties they will perform.
- Operational Process: Outline the processes and procedures you will use to run your fishing farming business. Your operational processes may include site selection & preparation, farm design & infrastructure, fish stocking, feeding & nutrition, etc.
Adding these components to your operations plan will help you lay out your business operations, which will eventually help you manage your business effectively.
7. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of your fishing farming business’s management team. This section should provide a detailed description of each manager’s experience and qualifications, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
- Founders/CEO: Mention the founders and CEO of your fishing farming company, and describe their roles and responsibilities in successfully running the business.
- Organizational structure: Explain the organizational structure of your management team. Include the reporting line and decision-making hierarchy.
- Compensation Plan: Describe your compensation plan for the management and staff. Include their salaries, incentives, and other benefits.
This section should describe the key personnel for your fishing farming services, highlighting how you have the perfect team to succeed.
8. Financial Plan
Your financial plan section should summarize your business’s financial projections for the first few years. Here are some key elements to include in your financial plan:
- Profit & loss statement: Describe details such as projected revenue, operational costs, and service costs in your projected profit and loss statement . Make sure to include your business’s expected net profit or loss.
- Cash flow statement: The cash flow for the first few years of your operation should be estimated and described in this section. This may include billing invoices, payment receipts, loan payments, and any other cash flow statements.
- Balance Sheet: Create a projected balance sheet documenting your fishing farming business’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Financing Needs: Calculate costs associated with starting a fishing farming business, and estimate your financing needs and how much capital you need to raise to operate your business. Be specific about your short-term and long-term financing requirements, such as investment capital or loans.
Be realistic with your financial projections, and make sure you offer relevant information and evidence to support your estimates.
9. Appendix
The appendix section of your plan should include any additional information supporting your business plan’s main content, such as market research, legal documentation, financial statements, and other relevant information.
- Add a table of contents for the appendix section to help readers easily find specific information or sections.
- In addition to your financial statements, provide additional financial documents like tax returns, a list of assets within the business, credit history, and more. These statements must be the latest and offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
- Provide data derived from market research, including stats about the industry, user demographics, and industry trends.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Include any additional documentation related to your business plan, such as product brochures, marketing materials, operational procedures, etc.
Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the necessary information.
Remember, the appendix section of your fishing farming business plan should only include relevant and important information supporting your plan’s main content.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
This sample fishing farming business plan will provide an idea for writing a successful fishing farming plan, including all the essential components of your business.
After this, if you still need clarification about writing an investment-ready business plan to impress your audience, download our fishing farming business plan pdf .
Related Posts
Farmers Market Business Plan
Food Processing Business Plan
How To Write a Business Plan Cover Page
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
Free Sample Business Plan Template
Automated Business Plan Generators
Frequently asked questions, why do you need a fishing farming business plan.
A business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful fishing farming business. It helps to get clarity in your business, secures funding, and identifies potential challenges while starting and growing your business.
Overall, a well-written plan can help you make informed decisions, which can contribute to the long-term success of your fishing farming company.
How to get funding for your fishing farming business?
There are several ways to get funding for your fishing farming business, but self-funding is one of the most efficient and speedy funding options. Other options for funding are:
- Bank loan – You may apply for a loan in government or private banks.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loan – SBA loans and schemes are available at affordable interest rates, so check the eligibility criteria before applying for it.
- Crowdfunding – The process of supporting a project or business by getting a lot of people to invest in your business, usually online.
- Angel investors – Getting funds from angel investors is one of the most sought startup options.
Apart from all these options, there are small business grants available, check for the same in your location and you can apply for it.
Where to find business plan writers for your fishing farming business?
There are many business plan writers available, but no one knows your business and ideas better than you, so we recommend you write your fishing farming business plan and outline your vision as you have in your mind.
What is the easiest way to write your fishing farming business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of any fishing farming business plan example and edit it as per your need. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software .
How do I write a good market analysis in a fishing farming business plan?
Market analysis is one of the key components of your business plan that requires deep research and a thorough understanding of your industry. We can categorize the process of writing a good market analysis section into the following steps:
- Stating the objective of your market analysis—e.g., investor funding.
- Industry study—market size, growth potential, market trends, etc.
- Identifying target market—based on user behavior and demographics.
- Analyzing direct and indirect competitors.
- Calculating market share—understanding TAM, SAM, and SOM.
- Knowing regulations and restrictions
- Organizing data and writing the first draft.
Writing a marketing analysis section can be overwhelming, but using ChatGPT for market research can make things easier.
How detailed should the financial projections be in my fishing farming business plan?
The level of detail of the financial projections of your fishing farming business may vary considering various business aspects like direct and indirect competition, pricing, and operational efficiency. However, your financial projections must be comprehensive enough to demonstrate a complete view of your financial performance.
Generally, the statements included in a business plan offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

Business Plan Template for Fish Farmers
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Are you a fish farmer looking to dive into the world of aquaculture? Whether you're starting from scratch or expanding your existing business, having a solid business plan is essential to making waves in the industry. That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Fish Farmers comes in!
This comprehensive template is designed specifically for fish farmers, helping you outline your goals, strategies, and financial projections. With this template, you can:
- Secure funding and attract investors by showcasing your growth potential
- Create a roadmap for your operations, ensuring every aspect of your business is well-structured
- Make informed decisions based on accurate financial projections
Don't let your dreams of success swim away. Get started with ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Fish Farmers today and make a splash in the aquaculture industry!
Business Plan Template for Fish Farmers Benefits
Starting or expanding a fish farming business can be a complex endeavor, but with a business plan template for fish farmers, you can enjoy a range of benefits, including:
- Clear roadmap: Create a comprehensive plan that outlines your goals, strategies, and financial projections, providing a clear roadmap for success.
- Funding opportunities: Increase your chances of securing funding by presenting a well-structured and professional business plan to potential investors and lenders.
- Operational guidance: Use the template to guide your day-to-day operations, ensuring that you stay on track and make informed decisions.
- Industry insights: Gain a deeper understanding of the aquaculture industry and its market trends, allowing you to position your business for long-term success.
- Risk management: Identify potential risks and challenges in advance, enabling you to develop contingency plans and minimize potential setbacks.
Main Elements of Fish Farmers Business Plan Template
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Fish Farmers provides all the necessary elements to help fish farmers create a comprehensive and effective business plan for their aquaculture operations.
Key features of this template include:
- Custom Statuses: Track the progress of different sections of your business plan using statuses such as Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Add important details to your plan, such as a Reference number, Approval status, and Section categorization, to ensure a well-organized and easily accessible document.
- Custom Views: Utilize a variety of views, including Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide, to navigate your plan and stay organized throughout the planning process.
- Collaboration Tools: Collaborate with team members, stakeholders, and investors by sharing your business plan directly within ClickUp, allowing for real-time feedback, comments, and suggestions.
- Goal Tracking: Set and track goals within ClickUp's Goals feature to align your business plan with your long-term objectives and monitor progress towards achieving them.
- Financial Projections: Use ClickUp's Table view to create and manage financial projections, including revenue forecasts, expense tracking, and cash flow analysis.
- Document Integration: Seamlessly integrate external documents, such as spreadsheets, market research reports, and financial statements, directly into your business plan for easy reference and analysis.
- Task Management: Break down your business plan into actionable tasks using ClickUp's task feature, assigning responsibilities, setting due dates, and tracking progress to ensure timely completion of each section.
With ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Fish Farmers, you can streamline your planning process, enhance collaboration, and create a comprehensive business plan to drive the success of your aquaculture business.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Fish Farmers
If you're a fish farmer looking to create a solid business plan, ClickUp has a template that can help you get started. Follow these steps to make the most of the Business Plan Template for Fish Farmers:
1. Define your business goals and objectives
Start by clearly defining what you want to achieve with your fish farming business. Are you looking to increase production, expand your customer base, or explore new markets? Knowing your goals and objectives will help you structure your business plan effectively.
Use Goals in ClickUp to set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for your fish farming business.
2. Conduct market research
Before diving into your business plan, it's crucial to gather information about the fish farming industry and your target market. Research market trends, competition, customer preferences, and potential challenges. This information will help you make informed decisions and develop strategies to stay ahead in the market.
Create a Board view in ClickUp to organize your market research findings and track key insights.
3. Develop a production plan
Your fish farming business plan should outline your production process, including the types of fish you will farm, the size and capacity of your farm, and the production techniques you will employ. Consider factors like water quality, feeding strategies, growth rates, and disease prevention measures.
Use recurring tasks in ClickUp to schedule and track important production activities such as feeding, water quality testing, and fish health monitoring.
4. Create a financial forecast
A comprehensive financial forecast is essential for any business plan. Project your revenue, expenses, and cash flow for the next few years. Include costs for fish feed, equipment, labor, marketing, and any other relevant expenses. This will give you a clear picture of the financial viability and sustainability of your fish farming venture.
Use Dashboards in ClickUp to analyze and visualize your financial forecast, comparing actual performance against projected numbers.
5. Outline your marketing and sales strategy
To succeed in the fish farming industry, you need to have a solid marketing and sales strategy. Identify your target customers, determine your pricing strategy, and outline your promotional activities. Consider online and offline marketing channels, partnerships, and distribution channels to reach your target market effectively.
Use the Calendar view in ClickUp to plan and schedule your marketing and sales activities, ensuring that you stay on track and meet your goals.
By following these steps and using the Business Plan Template for Fish Farmers in ClickUp, you can create a comprehensive and actionable plan for your fish farming business.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Fish Farmers
Fish farmers can use the Business Plan Template for Fish Farmers in ClickUp to create a comprehensive plan for their aquaculture business.
First, hit "Add Template" to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you'd like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a successful business plan:
- Use the Topics View to organize your plan into different sections, such as Executive Summary, Market Analysis, Operations, and Financial Projections.
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Use the Timeline View to set deadlines for each section and ensure you stay on track.
- The Business Plan View will give you an overview of your entire plan, allowing you to easily navigate between sections.
- Create a Getting Started Guide View to provide step-by-step instructions for completing the business plan.
- Customize the Reference, Approved, and Section custom fields to add additional information and track important details.
- Update statuses and custom fields as you work on each section to keep team members informed of progress.
- Monitor and analyze your business plan to ensure it aligns with your goals and attracts potential investors.
- Business Plan Template for Fitness Trainers
- Business Plan Template for Vodacom
- Business Plan Template for Telecom Operators
- Business Plan Template for KMart
- Business Plan Template for Photojournalists
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
[Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Fish Farming Docx
In recent years, fish farming has gained significant popularity as a lucrative business opportunity. This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with a well-structured fish farming business plan in PDF format. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or a beginner in the industry, this article will equip you with the essential knowledge and insights to start and run a successful fish farming venture.
[Pdf Sample] Fish Farming Business Plan Proposal Docx
Table of Contents
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Sunflower Farming Docx
Executive Summary
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Onion Farming Docx
Market Analysis
Conducting a thorough market analysis is essential for understanding the current trends, demand, and competition in the fish farming industry. This section explores market size, consumer preferences, and potential opportunities for growth.
Choosing the Right Fish Species
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Tomatoes Plantation Docx
Site Selection and Pond Construction
Water management and quality.
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Potato Farming Docx
Fish Feeding and Nutrition
Disease prevention and management, harvesting and processing.
When it’s time to harvest your fish, proper techniques and handling are essential to maintain product quality. We discuss various harvesting methods, post-harvest handling practices, and processing options to ensure you deliver the best possible products to the market.
Marketing and Sales Strategies
Financial projections and budgeting.
Accurate financial projections and budgeting are essential for assessing the financial viability of your fish farming venture. This section guides you through the process of estimating costs, revenue projections, profit margins, and return on investment (ROI) analysis.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Sustainability practices.
Embracing sustainable practices in fish farming is not only environmentally responsible but also beneficial for long-term profitability. We highlight eco-friendly approaches, water conservation methods, waste management strategies, and the importance of social responsibility in the industry.
Risks and Challenges
Here Is The Download Link To Business Plan Proposal For Fish Farming By Agrolearner
Business Model for Agrolearner.com’s Fish Farming Business
Value Proposition: Agrolearner.com Farm aims to provide the local market with high-quality, sustainable, and locally-produced fish products. Our value proposition includes:
Traceability and Transparency: We provide full transparency regarding our farming methods , allowing customers to trace the origin and production process of our fish products.
Health-conscious individuals: Customers who prioritize nutritious and sustainably sourced food.
Channels: We utilize multiple channels to reach our target customers and distribute our fish products:
Online Presence: Leveraging our website and social media platforms to engage with customers, share information, and promote our products.
Communication: Engaging with customers through social media, newsletters, and educational content.
Wholesale and Retail Sales: Selling fish directly to customers through various channels, including online and on-site.
Fish Farming: Cultivating fish species, such as tilapia and catfish, through proper management and nutrition.
Sustainability Practices: Implementing environmentally responsible practices, including water and energy conservation, waste management , and community engagement.
Fish Stock and Feed: Sourcing high-quality fish stock and formulating nutritious feed for optimal growth.
Key Partnerships: Agrolearner.com Farm establishes strategic partnerships to support its operations and enhance market reach:
Restaurants and Chefs: Building relationships with local restaurants and chefs to secure long-term partnerships for the supply of fresh fish.
Infrastructure Costs: Investments in land, pond construction, processing facilities, and equipment.
Key Metrics: Agrolearner.com Farm tracks the following key metrics to assess the performance and success of the business:
Production Efficiency: Assessing fish growth rates, feed conversion ratios, and other operational metrics to optimize production processes.
Required Capital to Start a Fish Farming Business
The required capital to start a fish farming business can vary depending on several factors, such as the scale of operation, the type of fish species being farmed, and the infrastructure needed. Generally, the capital required includes expenses for land or pond lease, construction or renovation of ponds, purchase of fingerlings (young fish), feed, equipment, water management systems , and other operational costs.
Time to Start Generating Profits from a Fish Farm
Some fast-growing fish species may allow for quicker returns on investment, while others with longer growth cycles may require more patience. Effective management practices, such as proper feeding, water quality management, and disease prevention, can help expedite the growth process and shorten the time to profitability.
Feasibility of Fish Farming in Landlocked Areas
Key factors affecting fish growth.
Genetics and the specific breed or strain of fish being farmed can also affect growth rates. Environmental factors like stocking density, availability of space, and light exposure can influence fish growth and overall health. Disease management and prevention, including timely vaccinations and biosecurity measures, are also critical for ensuring optimal fish growth.
Government Subsidies and Funding Options for Fish Farming Startups
Engaging with relevant industry associations and networking with experienced fish farmers can also provide valuable insights into available funding sources and support programs.
Share this:
Author: adewebs, you may also like:, [pdf sample] business plan for pig farming docx, starting a poultry farm with limited resources in ghana: a comprehensive guide for new farmers, how to register agribusiness company in kenya (see full guide), starting a poultry farm with limited resources in nigeria: guide for new farmers, leave a reply cancel reply.

How to Start a Fish Farming Business
Main Sections In This Post Steps To Starting A Fish Farming Business Points to Consider Knowledge Is Power Featured Video
This post offers a step-by-step guide to launch a fish farming business, along with samples and examples. It links to our “Knowledge Is Power” section for current and popular insights.
These resources are useful for both startup and established businesses.
If you find this post helpful, consider sharing and bookmarking for future reference due to the comprehensive coverage of valuable information.
Let’s get started with the steps.
The Steps to Take To Start Your Fish Farming Business
Below are the steps to starting a fish farming business.
Each step is linked to a specific section, allowing you to jump to your desired section or scroll to follow the steps in order.
- An Overview of What You’re Getting Into
- Fish Farming Business Overview
- Researching Your Fish Farming Business
- Looking at Financials
- Choosing A Business Location
- Creating Your Mission Statement
- Creating A Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
- Choose a Fish Farming Business Name
- Register Your Company
- Create Your Corporate Identity
- Writing a Business Plan
- Banking Considerations
- Getting the Funds for Your Operation
- Software Setup
- Business Insurance Considerations
- Supplier and Service Provider Considerations
- Physical Setup
- Creating a Website
- Create an External Support Team
- Hiring Employees
1. An Overview of What You’re Getting Into
An Overview of What You’re Getting Into: Is Starting a Fish Farming Business the Right Step for You?
At the heart of business success lies a key factor—you! Before embarking on a fish farming venture, it’s vital to gauge your feelings about owning and operating such a business.
Passion: The Driving Force for Success
Passion isn’t just a desirable trait; it’s a critical component of business success. Your level of passion determines your response to challenges. With passion, you seek solutions; without it, you seek an escape.
Assessing Your Passion
Consider this exercise: Imagine you’ve achieved every dream—wealth, travel, philanthropy, and more. You own every possession you have ever wanted. You possess substantial wealth and income.
Now, would you still choose to start a fish farming business?
- Answering ‘Yes’ : Your passion for the business is evident, and you’re headed in the right direction.
- Answering ‘No’ : Reflect on what you’d prefer to do instead. Perhaps an alternative path is more aligned with your passions.
Passion Over Profit
Your business choice should be driven by passion, not just financial goals. Solely pursuing money can undermine success compared to investing in a business that genuinely excites you.
In summary, the foundation of a successful fish farming business is your fervor for the venture. Passion fuels determination, innovation, and adaptability—the bedrock of a thriving enterprise.
For More, See How Passion Affects Your Business . Also, see Considerations Before You Start Your Business to identify key points for a new business owner.
2. Gaining an Overview of Owning a Fish Farming Business
Next, let’s spend some time on key issues to give you an overview of what to expect from owning and running your business.
a.) A Quick Overview of Owning a Fish Farming Business
Fish Farming Business: An Overview
A fish farming business, also known as aquaculture, involves cultivating fish for commercial purposes in controlled environments like ponds, tanks, or recirculating systems.
This industry addresses the demand for seafood while mitigating overfishing concerns and supporting sustainability.
Fish farming encompasses various species, from freshwater to marine, and provides a reliable source of fish for markets and consumers.
Day-to-Day Tasks in Fish Farming Business Management
Running and managing a fish farming business entails a range of day-to-day responsibilities:
- Feeding and Nutrition: Ensuring the fish receive proper nutrition through regular feeding, adjusting diets as they grow.
- Water Quality Maintenance: Monitoring and maintaining optimal water parameters such as temperature, oxygen levels, and pH for fish health.
- Health Monitoring: Regularly checking fish for signs of diseases or stress, and promptly addressing any issues that arise.
- Harvesting and Processing: Planning and executing the harvest of mature fish, followed by processing, cleaning, and packaging for market.
- Equipment Maintenance: Regularly inspecting and maintaining equipment like pumps, filters, and aeration systems to ensure proper functioning.
- Record Keeping: Keeping meticulous records of feeding schedules, water quality data, stock levels, and financial transactions.
- Marketing and Sales: Promoting and selling fish to customers, which involves managing orders, deliveries, and customer interactions.
- Staff Management: If applicable, supervising employees involved in feeding, maintenance, and other aspects of the operation.
- Environmental Stewardship: Adhering to sustainable practices to minimize environmental impact and ensure the long-term health of fish stocks.
- Business Planning: Continuously strategizing for growth, expansion, and adapting to changes in market demand and industry trends.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to local, state, and federal regulations regarding water usage, environmental impact, and food safety.
- Emergency Response: Being prepared to handle emergencies such as disease outbreaks, equipment failures, or adverse weather conditions.
In essence, running a fish farming business demands a multi-faceted approach that integrates biological understanding, operational expertise, and business acumen.
It’s a dynamic endeavor that requires adaptability and a commitment to providing quality fish sustainably.
b.) Fish Farming Business Models
Types of Fish Farming Business Setups and Their Business Models
Fish farming offers diverse setups and business models catering to various market demands and resources:
- Ponds or tanks are used to raise freshwater fish like tilapia, catfish, or carp.
- Business Model: Bulk production for local markets or wholesalers, supplying restaurants and retailers.
- Operating in coastal areas, marine fish farms cultivate species like salmon, sea bass, or trout.
- Business Model: Typically focused on supplying high-end markets due to the premium value of marine fish.
- Closed-loop systems that recirculate water through filters, enabling controlled environment farming.
- Business Model: High-value fish like ornamental species or premium seafood, often targeting niche markets.
- Combining different species, such as fish, mollusks, and seaweed, to create a balanced ecosystem.
- Business Model: Diverse revenue streams from multiple species and products, enhancing sustainability.
- Focusing on breeding and producing fish fry or fingerlings for sale to other fish farms.
- Business Model: Supplying hatchlings to other farms, ensuring a consistent source of new stock.
- Integrating fish farming with hydroponics, where fish waste fertilizes plant growth.
- Business Model: Selling both fish and produce, targeting environmentally-conscious consumers.
Choosing the Right Business Model
Selecting an appropriate business model is critical from the outset, as changing it later can be complex.
Evaluate available resources, market demand, and your expertise when making this decision.
Identifying a profitable and high-demand niche is paramount. Research consumer preferences, assess competition, and consider sustainability trends.
A well-defined niche allows you to tailor your business to meet specific customer needs and maximize profitability. With the right model and niche, your fish farming venture can thrive in a competitive market.
c.) Pros and Cons of Owning a Fish Farming Business
Pros and cons are inherent in any business venture. While owning and operating a business offers remarkable benefits, overlooking challenges can be detrimental.
Many entrepreneurs fixate on rewards without acknowledging potential difficulties.
It’s crucial to assess both sides to gain a comprehensive understanding. By anticipating challenges, you’re well-prepared and avoid unwelcome surprises, ensuring a proactive approach to business management.
For more, see Pros and Cons of Starting a Small Business.
d.) Challenges You Could Face When Starting and Operating a Fish Farming Business
Challenges When Starting a Fish Farming Business:
Launching a fish farming business entails several challenges:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex regulations related to water usage, environmental impact, and food safety can be daunting.
- Site Selection: Identifying an optimal location with suitable water sources, accessibility, and infrastructure is crucial.
- Capital Investment: Securing funds for equipment, infrastructure, fish stock, and operational expenses poses a significant challenge.
- Technical Knowledge: Acquiring expertise in fish biology, water quality management, disease prevention, and aquaculture techniques is essential.
- Market Research: Conducting thorough market research to identify demand, competition, and pricing is critical for success.
- Sustainable Practices: Implementing eco-friendly and ethical practices to ensure long-term environmental and financial sustainability.
Challenges in Full Operation:
Once your fish farming business is operational, new challenges emerge:
- Scale Management: Maintaining consistent quality and health standards as the business grows requires effective scaling strategies.
- Disease Management: Preventing and managing diseases becomes more complex with increased fish stock and higher density.
- Market Competition: As your business gains traction, staying competitive in a saturated market demands continuous innovation and differentiation.
- Supply Chain Management: Ensuring a consistent supply of feed, equipment, and other essentials becomes pivotal to avoid disruptions.
- Customer Satisfaction: Sustaining high levels of customer satisfaction while managing increased orders and demand.
- Staff Training: Training and managing employees to uphold quality standards and follow best practices becomes vital.
- Cash Flow Management: With growing expenses and revenue fluctuations, effectively managing cash flow becomes more challenging.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ongoing adherence to changing regulations and compliance standards becomes an ongoing task.
- Technology Integration: Incorporating technological advancements to streamline operations and stay competitive.
- Sustainability: Balancing growth with sustainable practices, ensuring minimal environmental impact.
Navigating these challenges requires adaptability, resilience, and continuous learning.
Being prepared for these obstacles and having a well-defined strategy can help you overcome them and achieve success in the fish farming industry.
e.) Questions You Need to Consider for Your Fish Farming Business
Questions to Consider for Your Fish Farming Business:
By addressing these questions, you’ll better prepare for potential challenges in your fish farming venture:
Before Starting:
- What fish farming model do you plan to adopt?
- Do you possess the necessary skills for managing and operating a fish farming business?
- Will you manage the business alone or hire employees?
- Are you considering personal management or hiring a manager?
- How will you attract and retain customers?
- What strategies will ensure customer loyalty?
- Are partnerships or investors something you’re interested in?
- How will you finance your startup expenses?
- Have you estimated the time required to achieve profitability?
Early Stage Considerations:
- How will you support yourself during the financially demanding initial phase?
- What products and services will your business offer?
- How can you verify the demand for your offerings?
- What unique value will differentiate you from competitors?
Anticipating these queries will equip you to navigate the complexities of a fish farming business, ensuring strategic planning and a higher likelihood of success.
3. Research
Inside information fish farming business research.
Conducting comprehensive research before launching your business is paramount. Quality information equips you to make informed decisions and prevents unexpected pitfalls.
Engaging with experienced individuals in the fish farming industry is invaluable. Their insights, derived from years of practical expertise, offer essential guidance.
Spending time with seasoned professionals offers insights that extend beyond this post’s scope. An article provides detailed strategies for identifying and approaching knowledgeable mentors.
This approach assures you’re connecting with the right people in a respectful manner. For in-depth insights, read the article “An Inside Look Into the Business You Want To Start” via the provided link.
It’s a crucial step to grasp the intricacies of your intended endeavor and set yourself up for success.
See An Inside Look Into the Business You Want To Start for all the details.
Target Audience
Understanding Your Target Audience:
Comprehending your target audience brings significant advantages. With a deep understanding, you can tailor products, services, and offers precisely to their preferences.
This focused approach allows you to provide what genuinely resonates with your customers, rather than attempting to cater to a wide spectrum of needs.
Target Market Ideas:
- Health Enthusiasts: Individuals seeking nutritious and sustainable protein sources.
- Restaurants and Chefs: Culinary professionals looking for fresh, locally sourced seafood.
- Aquarium Enthusiasts: Hobbyists interested in ornamental fish for home aquariums.
- Eco-conscious Consumers: Those who prioritize sustainable and ethical food sources.
- Local Markets and Grocers: Retailers looking to provide fresh, locally produced fish.
- Pet Supply Stores: Offering fish for pet owners who maintain aquariums.
- Food Trucks and Caterers: Mobile food services seeking quality seafood options.
- Farm-to-Table Advocates: Supporters of locally sourced and transparent food supply chains.
- Gourmet Food Stores: Outlets catering to high-quality, specialty food items.
- Educational Institutions: Schools and colleges interested in promoting aquaculture education.
Identifying and targeting these segments can lead to a more effective and strategic marketing approach for your fish farming business.
For more, see How To Understand Your Target Market.
Product & Service Demand
Assessing Market Demand Before Starting:
Understanding the demand for your products and services before launching is pivotal.
High quality and competitive pricing alone won’t suffice if there’s inadequate demand. Overlooking this crucial aspect can lead to a business destined for failure.
Commencing a fish farming business without gauging demand risks early closure and overwhelming debt. Quality and affordability won’t matter if the market isn’t interested.
Strategies to Assess Market Demand:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Distribute surveys to potential customers, asking about their interest in locally sourced fish and their preferred types.
- Competitor Analysis: Research existing fish farms in the area to evaluate their customer base and popularity.
- Local Events and Farmers Markets: Attend community events or farmers markets to gauge interest and gather feedback from attendees.
- Online Engagement: Create social media profiles or a simple website to showcase your fish farming concept and gather responses.
- Focus Groups: Organize focus groups to discuss your business idea with potential customers and collect insights.
- Talk to Restaurants and Retailers: Approach local restaurants, markets, and retailers to understand if they’d be interested in sourcing fish from you.
- Community Engagement: Engage with local community groups or forums to introduce your business idea and gather opinions.
- Pilot Programs: Consider a small-scale trial run to gauge interest and gather direct feedback.
- Local Government and Agencies: Consult local authorities and economic development agencies for insights into potential demand.
- Networking: Attend industry events, workshops, and conferences to connect with professionals and gain insights into market trends.
These straightforward strategies provide valuable insights into the demand for your fish farming business in your chosen location, guiding your decision-making and setting you up for a successful venture.
For more, see the Demand for Your Products and Services.
4. Looking at Financials:
Overview of Startup Costs, Revenues, and Profits for Your Fish Farming Business:
In this section, we delve into key considerations regarding startup costs, monthly expenses, revenues, and profits for your fish farming venture.
Startup Costs:
Accurate estimation of startup costs is vital for a smooth launch and ongoing success.
Underestimating might lead to financial shortages, while overestimation can deter potential investors.
Costs depend on factors like operation size, location, equipment choice (new/used), staffing, and leasing/renting.
To estimate costs, list required items and gather prices, allowing for unexpected expenses as you research.
For more detailed information, refer to my article on Estimating Startup Costs.
Sales and Profit:
Sales success hinges on customer service, product/service popularity, demand, and effective marketing to your target audience.
Simplifying profit illustration:
- Low-Volume Scenario: Earning $300 profit per sale with one monthly sale might not cover expenses.
- High-Volume Scenario: Generating 5,000 sales monthly with $0.05 profit per sale could still yield inadequate funds for expenses.
Understanding Profitability:
To gauge your fish farming business’s profitability, analyze profit per sale, potential sales volume, and overhead (monthly expenses). This overview helps anticipate revenue generation against costs and supports strategic financial planning.
For More, See Estimating Profitability and Revenue.
Understanding these financial aspects equips you to make informed decisions and ensure a sustainable and profitable fish farming business.
Simple Sample: Financial Lists to Consider As a Starting Point
Note: Focus on the list items more than the numbers. The numbers are samples. Your estimates will differ due to how you set up your business, location, expenses, and revenues.
Sample Estimated Startup Costs for a Fish Farming Business in the USA:
- Site Selection and Preparation: $20,000 – $50,000
- Infrastructure and Construction: $50,000 – $100,000
- Equipment (Tanks, Pumps, Filters): $30,000 – $70,000
- Fish Stock Initial Purchase: $10,000 – $20,000
- Licensing and Permits: $5,000 – $10,000
- Marketing and Branding: $3,000 – $8,000
- Utilities and Initial Supplies: $5,000 – $10,000
- Legal and Professional Fees: $2,000 – $5,000
- Insurance: $1,000 – $3,000
- Miscellaneous (Contingency): $5,000 – $10,000
Total Estimated Startup Costs (Low – High Range): $131,000 – $286,000
Sample Estimated Monthly Expenses for a Fish Farming Business in the USA:
- Labor (Salary and Wages): $5,000 – $10,000
- Feed and Supplements: $3,000 – $6,000
- Utilities (Water, Electricity): $1,000 – $2,500
- Maintenance and Repairs: $1,000 – $3,000
- Insurance Premiums: $500 – $1,000
- Marketing and Advertising: $500 – $1,500
- Administrative Expenses: $500 – $1,000
- Loan Payments: $2,000 – $4,000
Total Estimated Monthly Expenses (Low – High Range): $13,500 – $28,000
Please note that these are sample figures for illustrative purposes only.
Actual costs, expenses, and profits can vary based on location, market conditions, operational efficiency, and other factors.
Always conduct thorough research and financial planning tailored to your specific circumstances before starting a business.
Consider revisiting Step 3. Researching Your Fish farming business , where there is a technique to get inside information, will benefit you in this step.
5. Choosing The Right Business Location
The prosperity or downfall of your conventional brick-and-mortar business, catering to locals, hinges on location.
Establishing your venture in an area without of demand guarantees failure.
Conversely, launching in a competitive zone can impede market entry. Striking a balance between demand and competition is ideal.
Affordability is also key. While a populous locale can boost exposure, you must gauge if heightened costs outweigh profits.
Opting for a budget-friendly site must ensure sufficient footfall to sustain sales. In essence, location significantly influences business success.
Thoroughly researching and analyzing potential locales is vital. This informed decision-making process ensures your business finds the right space to flourish.
For more about business locations, see Choosing The Best Location for Your Business.
6. Create Your Mission Statement
The Significance of a Mission Statement for Your Business:
A mission statement serves as a compass, guiding your business by articulating its purpose.
It keeps you focused and reminds you of the core value you offer to customers and the community.
Examples of Fish Farming Business Mission Statements:
- “Our mission is to provide sustainably raised, premium-quality seafood to our local community, fostering health and environmental responsibility.”
- “At XYZ Aquafarms, our purpose is to offer fresh and nutritious fish while championing ethical aquaculture practices that preserve marine ecosystems.”
- “We are committed to delivering a diverse range of locally sourced, farm-to-table seafood that promotes both culinary excellence and ecological harmony.”
- “Driven by a passion for responsible aquaculture, our mission is to supply our region with delicious, ethically produced fish, supporting health and sustainability.”
- “Our business is dedicated to enriching lives through access to wholesome, homegrown fish, contributing to the region’s culinary landscape and food security.”
These mission statements exemplify the commitment of fish farming businesses to quality, sustainability, community well-being, and culinary enhancement.
For more, see How To Create a Mission Statement.
7. Creating A Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Harnessing the Power of a Unique Selling Proposition (USP):
A Unique Selling Proposition (USP) helps your business stand out by pinpointing and crafting a distinctive quality.
It aids in identifying what sets your business apart, inspiring innovation that makes it truly special.
Examples of USPs for a Fish Farming Business:
- “Unmatched Freshness”: Offering fish harvested daily, ensuring unparalleled freshness that sets us apart from competitors.
- “Eco-Friendly Aquaculture”: Our commitment to sustainable practices minimizes environmental impact, setting a new standard in responsible fish farming.
- “Tailored Culinary Partnerships”: Collaborating with local chefs, we provide exclusive fish varieties and sizes tailored to culinary needs.
- “Transparency and Traceability”: Empowering customers with the ability to trace the journey of their fish from farm to plate, ensuring trust and authenticity.
- “Nutritional Prowess”: Our fish are raised with specialized feed for optimal nutrition, offering a healthier choice that stands out in the market.
These USPs carve a distinct niche for fish farming businesses, offering advantages that resonate with customers and make them choose your products over competitors’.
8. Choose a Business Name
Choosing a Memorable Business Name:
Selecting a business name is a pivotal decision. It should align with your industry, be catchy, and easy to remember. Since names rarely change, it’s crucial not to rush the process.
Additionally, securing a matching domain name is vital for your online presence.
Before finalizing, ensure your desired name isn’t already registered by another business.
Here Is a List of Sample Fish Farming Business Names:
- AquaticHarvest Farms
- FinestCatch Aquafarms
- SeaBounty Fisheries
- AquaGlow Aquaculture
- FreshWave Fishery
- OceanicFlavor Farms
- SustainableSplash
- AquaNourish Fish Farms
- CrystalStream Aquatics
- Neptune’s Plate Fisheries
- MarineHarbor Farms
- AquaGem Fishery
- PearlScale Aquafarms
- CoastalCuisine Fisheries
- CoralCrest Aquatics
- Streamline Seafoods
- AquaNurture Harvests
- AquaFusion Fish Farms
- SeaZen Aquaculture
- BlueHarvest Fisheries
- TerraMarine Farms
- AquaAroma Fishery
- TideCrest Aquafarms
- CoralTide Fisheries
- MarineElegance Aquatics
- AquaVita Harvests
- OceanicOrigins Fish Farms
- AquaFlare Aquaculture
- SeaSymphony Fisheries
- AquaEssence Farms
Use this list as a springboard to ignite your creativity, helping you devise an original and satisfying name that resonates with your fish farming businesses essence.
For more, see the following articles:
- How To Register a Business Name
- Registering a Domain Name For Your Business
9. Register Your Company
Ensuring Legal Compliance for Your Business:
It’s imperative to ensure your fish farming business operates within the bounds of the law.
Consulting a professional can aid in establishing a suitable legal structure for tax benefits and liability mitigation.
Common Types of Registrations for a Fish Farming Business:
- Sole Proprietorship: A simple structure where you’re the sole owner.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): Offers liability protection with flexible management.
- Partnership: Shared ownership with one or more partners.
- Corporation: A separate legal entity with shareholders.
Permits and Licenses to Consider:
- Aquaculture Permit: Regulated by state agencies, allowing fish farming.
- Environmental Permit: Ensuring adherence to environmental regulations.
- Business License: Required for operating legally within your locality.
- Zoning Permits: Compliance with land use and zoning regulations.
- Health Department Clearance: Ensuring food safety and handling standards.
- Water Use Permit: Permission to utilize water resources for aquaculture.
- Fish Import/Export License: If dealing with foreign markets.
- Sales Tax Permit: Necessary for selling fish and related products.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN): Required for tax purposes if you have employees.
Ensuring legal compliance from registrations to permits guarantees your fish farming business operates ethically, transparently, and within regulatory boundaries.
Registration:
- How to Register Your Business
- How To Register a DBA
- How to Register a Trademark
- How to Get a Business License
Business Structures:
- How to Choose a Business Structure
- Pros & Cons of a Sole Proprietorship
- How To Form an LLC
- How To Register a Business Partnership
- How To Form a Corporation
- How To Choose a Business Registration Service
10. Create Your Corporate Identity
Crafting a Strong Corporate Identity:
A Corporate Identity (ID) is the visual representation of your business, creating a lasting impression.
It encompasses essential components like your logo, business cards, website, signage, stationery, and promotional materials.
Key Elements of Corporate Identity:
- Logo: The cornerstone of your brand’s visual identity, conveying your business essence.
- Business Cards: A tangible introduction that reinforces your brand.
- Website: An online presence reflecting your business’s values and offerings.
- Business Sign: An inviting beacon that represents your brand physically.
- Stationery: Consistent design across letterheads, envelopes, and more.
- Promotional Items: Tangible giveaways that promote brand recall.
Maintaining a Consistent Professional Design:
Consistency in design is vital to leave a lasting impact on both new and existing customers.
A strong corporate identity ensures recognition, trust, and a sense of professionalism.
Every touchpoint, from digital to physical, should exude the same design language, reflecting your business’s values and goals.
A well-crafted corporate identity can set your fish farming business apart and foster customer loyalty.
You can see our page for an overview of your logo , business cards , website , and business sign , or see A Complete Introduction to Corporate Identity Packages.
11. Writing a Business Plan
A Business Plan Is Essential:
A business plan is an essential document. It’s used when applying for financing or when looking for investors.
A business plan is a guide to keep you on track during the startup phase and when your business is fully operational.
It Takes Time and Effort to Create an Effective Business Plan:
Writing a business plan takes time and effort because you are creating a vision of what your business will be like when it is fully operational.
It takes time and consideration to plan and express the details.
It will be worth it because once it’s completed, you will understand what you need to get started and have a clear vision of how to operate it.
Options Are Available:
When creating your business plan, it’s important to remember that you have various options available.
You can write it from scratch, hire a professional, use a template, or use business plan software.
Regardless of the approach you take to create your business plan.
It’s crucial to actively participate in the process, especially if you decide to hire a professional, because you want to effectively communicate the nature of your business and how you will manage it.
There Is a Good Chance That Your Business Plan and or Operations Will Change:
Your business plan can change and be optimized as you gain experience or changes to operations or the market.
Reviewing the document periodically and making necessary changes to your business plan or operation is advisable.
Business Plan Template for a Fish Farming Business
Business Plan for [Your Fish Farming Business Name]
Table of Contents:
- Executive Summary
- Company Overview
- Market Analysis
- Products and Services
- Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organization
- Financial Plan
1. Executive Summary:
- Briefly introduce your fish farming business.
- Highlight key points about your business’s mission, products, target market, and competitive advantage.
- Summarize your financial projections and funding needs.
2. Company Overview:
- Describe your fish farming business, its history, location, and legal structure.
- Explain your mission, vision, and values.
- Highlight the uniqueness of your business and your competitive edge.
3. Market Analysis:
- Define your target market, including demographics and preferences.
- Analyze industry trends, market size, growth potential, and competition.
- Outline your market entry strategy and potential challenges.
4. Products and Services:
- Detail the types of fish you will farm and any related products.
- Explain your farming methods, sustainability practices, and quality standards.
- Highlight any value-added services, such as processing or delivery.
5. Marketing and Sales Strategy:
- Describe your branding, logo, and corporate identity.
- Explain your pricing strategy and value proposition.
- Outline your promotional and advertising efforts.
- Describe your distribution channels and sales tactics.
6. Operational Plan:
- Detail your fish farming process, including water source, tanks, feed, and breeding.
- Explain your production capacity, growth cycles, and harvesting methods.
- Describe maintenance, disease control, and waste management.
- Outline safety protocols and compliance with regulations.
7. Management and Organization:
- Introduce key team members and their roles.
- Describe your organizational structure and reporting hierarchy.
- Explain the qualifications and expertise of your team.
8. Financial Plan:
- Provide detailed financial projections for the first 3-5 years.
- Include income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Outline your startup costs, operating expenses, and capital requirements.
- Describe your funding sources and repayment plans.
9. Appendices:
- Include any additional information, such as market research, permits, licenses, and legal documents.
- Attach relevant resumes of key team members.
- Provide supporting documents for financial projections.
Please note that this template is a guideline and can be customized according to your specific fish farming business’s needs and circumstances.
Make sure to conduct thorough research and seek professional advice when creating your business plan.
See How to Write a Business Plan for information on creating your business plan.
12. Banking Considerations
Choosing a Business-Friendly Bank:
Consider choosing a nearby bank that has a strong focus on small businesses.
A business account allows you to separate your business and personal transactions.
As a result, it’s easier to track expenses and create accurate reports while having everything accounted for when you file your taxes.
Developing a Strong Banker Relationship:
Developing a professional relationship with your banker is also a good idea.
Your banker can assist you with advice and financial services and streamline applications.
Merchant Account for Payment Processing:
It is essential to have a merchant account or an online service to accept credit and debit cards from your customers, increasing sales and making it more convenient for your customers.
For more, see How to Open a Business Bank Account. You may also want to look at What Is a Merchant Account and How to Get One.
13. Getting the Funds for Your Operation
Securing Financing for Your Fish Farming Business:
Use the tips in this section if you need a loan to start your fish farming business.
There are options to fund your fish farming business, such as traditional lenders, private loans, investors, and selling your assets.
Meeting with a Loan Officer:
A list of documents needed to apply for a business loan.
- Research: Understand the types of loans and interest rates available.
- Prepare: Have a solid business plan outlining your needs and projections.
- Credit Score: Ensure your credit score is in good standing.
- Collateral: Determine what assets you can use as collateral.
- Financial Records: Have accurate financial records and tax returns ready.
- Loan Amount: Determine the exact amount you need and how it will be used.
- Repayment Plan: Outline how you plan to repay the loan.
- Questions: Prepare questions to ask the loan officer.
Sample List of Documents Needed:
- Business plan with financial projections
- Personal and business tax returns
- Financial statements (balance sheet, income statement, cash flow)
- Proof of collateral
- Legal documents (business licenses, permits)
- Personal identification (driver’s license, passport)
- Bank statements
- Resumes of key team members
- Credit history report
Remember that the specific requirements may vary depending on the lender and loan type, so it’s crucial to inquire with your chosen financial institution.
See Getting a Small Business Loan for more.
14. Software Setup
Efficient Software Selection for Your Fish Farming Business:
- Research the software because it’s easier to implement a program from scratch than switch to a new system after your data is in another program.
- You want a company with a history so you can depend on support in the future.
- When demos are available, you have the option to try before you buy.
- Software reviews and forums offer insight into what others have experienced.
- You will also want to research software for tracking expenses and preparing financial documents to file taxes.
Speaking with your bookkeeper or accountant can help you make the right choice for your accounting software.
Types of Software for Fish Farming Business:
- Farm Management Software: For tracking fish growth, feeding schedules, and water quality.
- Inventory Management Software: To monitor feed, equipment, and other supplies.
- Accounting Software: For financial record-keeping and tax preparation.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software: To manage customer data and interactions.
- Sales and Invoicing Software: For processing sales and generating invoices.
- Marketing Automation Software: To manage marketing campaigns and customer communication.
- Project Management Software: For planning and managing operational tasks.
- Aquaculture Software: Specialized software for aquaculture business needs.
Choosing the right software can enhance your operational efficiency, data management, and decision-making processes.
Check out Google’s latest search results for software packages for a fish farming business.
15. Get The Right Business Insurance
Ensuring Comprehensive Insurance Coverage for Your Fish Farming Business:
Incidents can happen anytime, so you must have the right insurance before any activity occurs at your business.
Consider insurance to protect customers, employees, yourself, anyone on the premises, your property, etc.
Consider professional liability insurance to protect you against lawsuits.
Another consideration is Interruption Insurance which can be a lifeline to your operation in case of an incident That causes an involuntary shutdown.
Use a competent insurance broker to guide you and ensure you have sufficient coverage.
For more, see What to Know About Business Insurance . You can also browse the latest Google search results for fish farming business insurance .
16. Suppliers and Service Providers
Building Strong Supplier Relationships for Your Fish Farming Business:
Selecting Suppliers:
Include: a list of items and services a fish farming business might need from suppliers.
A strong relationship with your suppliers and service providers is crucial for your business.
Having a reliable and trustworthy supplier is a key factor in your success.
Suppliers can offer competitive prices, allowing you to pass on savings to your customers and increase your profit margin.
Additionally, they can ensure that you always have the necessary supplies to run your business smoothly.
Treating your suppliers and service providers respectfully and ensuring they also benefit financially is important, as this will improve your working relationship with them.
For More, See How To Choose a Supplier.
17. Physical Setup
A fish farming business requires careful planning of its layout and setup to ensure efficient operations.
The business setup generally consists of both on-site farm facilities and an organized office space.
Farm Layout:
- Ponds/Tanks: The heart of the operation, these are where fish are bred and raised. Ponds or tanks should be designed to provide appropriate water depth, temperature, and oxygen levels for the specific fish species.
- Water Supply System: A well-designed water supply system is crucial for maintaining water quality. It involves pumps, pipes, and filtration systems to ensure a consistent flow of clean water.
- Feeding Area: A designated spot for feeding the fish with appropriate feed. Automated feeders can also be installed to regulate feeding schedules.
- Harvesting Zone: An area where fish are harvested. It should be equipped with tools for safe and efficient fish collection.
- Quarantine Area: A separate section to isolate new fish arrivals, preventing the spread of diseases to the existing stock.
- Processing Facility: If the business involves processing fish for sale, a processing facility with proper equipment for cleaning, gutting, and packaging is necessary.
Office Setup: Managing a fish farming business can be time-consuming, involving administrative tasks, record-keeping, and communication with suppliers and customers. An organized office setup is crucial to enhance productivity and streamline operations.
- Workspace: Designate a comfortable and dedicated workspace for administrative tasks. A desk, chair, computer, and telephone are essentials.
- Storage: Shelves, cabinets, or drawers are important for storing documents, records, and office supplies. Use labeling for easy access.
- Communication Tools: Equip the office with communication tools like a phone, email access, and perhaps video conferencing capabilities.
- Computer Systems: A computer with necessary software for record-keeping, financial management, and communication is indispensable.
- Filing System: Establish a systematic filing system for documents related to inventory, sales, expenses, permits, and legal documentation.
- Calendar/Planner: Maintain a calendar or planner to schedule tasks, appointments, meetings, and reminders.
- Internet Connectivity: A stable and high-speed internet connection is vital for online research, communication, and managing online sales.
- Printer/Scanner: Having a printer and scanner can facilitate document printing, scanning, and archiving.
- Stationery: Stock up on basic office supplies such as pens, notepads, paper, envelopes, and labels.
Maintaining an organized and fully equipped office enhances the efficiency of your fish farming business.
It ensures that administrative tasks are handled promptly, records are accurately maintained, and communication with stakeholders is smooth.
See Here are Considerations for The Setup of Your Office for tips and ideas to make your office work for you.
18. Creating a Website
A website is essential for your fish farming business. It acts as the main point of contact, providing vital business information.
Unlike social media, a website is entirely yours when you register a domain and host it.
It also functions as a potent marketing tool.
Blogging about your industry and offering tailored tips build customer trust and establish your expertise.
For more, see How to Build a Website for Your Business .
19. Create an External Support Team
An external support team for your fish farming business offers:
- Dependable Expertise: Professionals who provide advice and services.
- Payroll Independence: Not on your payroll, reducing fixed costs.
- Flexible Engagement: Services for projects, tasks, contracts, hourly work, or on retainer.
While you might already collaborate with certain individuals, recognizing them as your team enhances your understanding of their importance and allows for potential expansion.
It’s not necessary to have all team members from the start, as building reliable relationships takes time. However, continuous effort is essential. A strong team, which may include:
- An Accountant: Managing finances and ensuring compliance.
- A Lawyer: Offering legal guidance and risk mitigation.
- A Financial Advisor: Providing insights for fiscal decisions.
- A Marketing Specialist: Developing strategies to promote your business.
- Technical Advisors: Offering expertise on farming practices.
Developing and maintaining this team is an ongoing process that contributes to your business’s success.
When assistance is needed, your dependable team can provide valuable support and insights.
For more, see Building a Team of Professional Advisors for Your Business.
20. Hiring Employees
Running a fish farming business solo in the early stages can minimize costs, a prudent move due to the substantial expense of payroll, especially during the startup phase.
As the business expands, the dual roles of managing and operating may become overwhelming, necessitating employee recruitment.
Ensuring new hires are qualified and possess strong work ethics is pivotal for seamless growth.
The following are job positions or outsourced services you may want to consider as your fish farming business grows:
- Farm Manager or Operator
- Fish Health Specialist
- Operations Assistant
- Marketing and Sales Personnel
- Administrative Staff
- Aquaculture Technician
- Feed and Nutrition Expert
- Maintenance Technician
- Water Quality Analyst
- Harvesting and Processing Crew
- Customer Service Representative
- Logistics Coordinator
- Accountant or Financial Consultant
- Legal Advisor
- Human Resources Manager
Outsourced Services:
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance Services
- Marketing and Advertising Agencies
- Accounting and Financial Management Services
- Veterinary and Fish Health Consulting
- Equipment Maintenance and Repair Services
Adding these roles or services can contribute to a well-organized and successful fish farming venture as it grows.
For more, see How and When to Hire a New Employee.
Points To Consider
Hours of Operation:
Consider regular operational hours, typically 8-10 hours per day. Prior to customer interaction, tasks include feeding, water quality checks, and maintenance, requiring 1-2 hours.
After dealing with customers, tasks like cleaning, inventory, and record-keeping take about 1-2 hours.
Additional hours, around 1-3 per day, may be necessary during peak seasons or emergencies, such as disease outbreaks or equipment failures.
A List of Equipment and Supplies to Consider for a Fish Farming Business:
- Fish Ponds/Tanks
- Pond Liners
- Aerator or Diffuser System
- Water Circulation System
- Water Testing Kits
- Netting or Covers
- Fish Feeding System (Automatic or Manual)
- Fish Feeders
- Feed Storage Bins
- Feeding Platforms
- Water Filtration Systems
- Water Pumps
- UV Sterilizers
- Oxygenation Devices
- Fish Nets or Seines
- Harvesting Bins or Tubs
- Fish Grading Tools
- Fish Transport Tanks
- Water Quality Monitors (pH, Oxygen, Temperature)
- Fish Health Management Tools
- Quarantine Tanks
- Workstations and Sheds
- Storage Facilities
- Tools (Pliers, Cutters, Wrenches, etc.)
- Cleaning Equipment
- Electrical Wiring and Lighting
- Power Distribution Units
- Plumbing Fixtures and Pipes
- First Aid Kits
- Safety Signage
- Fire Extinguishers
- Security Cameras
- Utility Vehicles
- Fish Transport Vehicles
- Farm Management Software
- Logbooks and Records
- Heating or Cooling Systems (if required)
- Shade Structures
- Educational Materials
- Training Resources
- Packaging Materials
- Marketing Displays
- Phones or Communication Systems
- Miscellaneous Tools and Supplies
Remember that the specific equipment needed can vary based on the scale of your fish farming operation, the type of fish you’re cultivating, and the local conditions.
It’s advisable to consult with aquaculture experts and conduct a thorough assessment of your requirements before purchasing equipment.
Key Points To Succeeding in a Fish Farming Business
To excel in operating a fish farming business, several key points are essential:
- Niche Focus: Concentrate on a specific segment within the aquaculture industry to establish expertise and target a defined customer base.
- Customer Base Building: During the startup phase, building a customer base can be challenging, but persistence and effective marketing strategies are crucial.
- Relationship Building: Foster strong relationships with customers, suppliers, and employees to create a network that supports business growth.
- Relevant Offerings: Provide products and services that align with customer preferences and demands.
- Customer Feedback: Act on credible customer feedback to enhance your operation and address issues that benefit the majority.
- Exceptional Customer Service: Prioritize exceptional customer service as satisfied customers drive business success.
- Continuous Value: Focus on consistently delivering value to customers to retain their loyalty and attract new ones.
- Talented Team: Hire skilled individuals for each role to form a capable team, a critical factor in achieving success.
- Effective Management: Treat staff with respect, manage them effectively, and create a positive work environment to improve retention.
- Cash Flow Management: Monitor cash flow meticulously to ensure the financial stability of the business.
- Cost Efficiency: Strive to keep costs low while maintaining product quality and customer service.
- Adaptation to Change: Stay updated with industry shifts, evolving technology, and changing business processes to remain competitive.
- Revenue Fluctuations: Prepare for revenue fluctuations by maintaining financial reserves and diversifying income streams.
- Competition Management: Address both new and existing competition by emphasizing unique selling points and differentiating factors.
- Effective Marketing: Implement effective marketing strategies, whether through personal efforts or professional assistance, to raise awareness about your fish farming business.
Adhering to these principles can guide your fish farming business towards sustained growth and success in a dynamic market.
Making Your Fish Farming Business stand out
Ideas to Make Your Fish Farming Business Stand Out:
- Sustainability Showcase: Emphasize your commitment to eco-friendly practices like responsible water usage and minimal environmental impact. Consumers appreciate businesses that prioritize sustainability.
- Transparency Talks: Share your farming process openly. Highlight the care and attention given to the fish, showcasing a transparent supply chain that builds trust.
- Educational Workshops: Host workshops on aquaculture, sustainable fishing, and seafood cooking. Position your business as a knowledge hub, attracting those interested in learning more.
- Unique Varieties: Offer exotic or lesser-known fish varieties that are not easily found in traditional markets, catering to adventurous foodies.
- Custom Orders: Allow customers to request specific cuts or sizes of fish, providing personalized service that larger suppliers might not offer.
- Recipe Sharing: Share creative and easy-to-follow fish recipes on your website and social media, encouraging customers to experiment with your products.
- Collaborations: Partner with local chefs to create signature dishes featuring your fish, showcasing its quality and versatility.
- Direct-to-Consumer Sales: Provide an online platform for customers to order directly from your farm, ensuring freshness and traceability.
- Visual Storytelling: Use engaging visuals like videos and photos to showcase your farm’s journey, from hatching to harvesting.
- Customer Loyalty Program: Reward frequent customers with discounts, exclusive offers, or early access to new products.
Add on Ideas for a Fish Farming Business
- Aquaponics System Sales: Offer aquaponics systems that allow customers to grow their own fish and plants in a symbiotic environment.
- Fish Farm Tours: Organize guided tours of your fish farm, educating visitors about aquaculture practices and sustainability.
- Seafood Cooking Classes: Host classes teaching customers how to prepare and cook different types of seafood, enhancing their culinary skills.
- Fish Feed Products: Sell high-quality fish feed that customers can use for their home aquariums or ponds.
- Fishing Equipment: Provide basic fishing gear, appealing to customers who enjoy catching their fish before preparing them.
- Seafood Spices and Sauces: Offer a range of specially crafted spices, sauces, and marinades that pair perfectly with your fish.
- Seafood Subscription Boxes: Curate subscription boxes that include a variety of your fresh fish along with recipe cards and cooking tips.
- Frozen Seafood Selection: Expand your offerings by providing frozen fish products that customers can keep on hand for convenience.
- Fish-Related Merchandise: Create branded merchandise like aprons, utensils, or cutting boards, allowing customers to showcase their support for your business.
- Environmental Workshops: Host workshops on topics like ocean conservation, sustainable fishing practices, and marine ecosystem health.
- Aquatic Plants: Offer a selection of aquatic plants for customers interested in creating their own fish habitats.
- Fish-Related Events: Organize fishing tournaments, seafood festivals, or ocean cleanup events to engage the community and raise awareness.
- Seafood Tastings: Arrange tasting events where customers can sample various fish varieties and learn about their unique flavors.
- Fish Oil and Supplements: Develop fish oil supplements rich in omega-3 fatty acids, capitalizing on the health benefits of fish consumption.
- Corporate Gifts: Create gift packages with premium fish selections, perfect for corporate gifts or special occasions.
Adding value through these ideas can elevate your fish farming business, attract diverse customer segments, and enhance your revenue streams.
Marketing Considerations
A fish farming business’s viability hinges on its customer base. Attracting suitable customers is crucial for success.
Initial challenges arise due to novelty, but as reputation grows, marketing becomes smoother and more effective. Ongoing marketing efforts are vital.
Investing in marketing yields revenue growth. While not always necessary, employing a marketing agency or expert can be advantageous when aligned with your needs.
To simplify marketing, consider it as creating awareness. Seize opportunities to spread the word about your business. Here are a few straightforward methods:
- Social Media: Utilize platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn to showcase your products, share insights, and engage with potential customers.
- Local Events: Participate in community fairs, farmers’ markets, or food festivals to introduce your fish to a broader audience.
- Collaborations: Partner with local restaurants or food businesses to feature your products on their menus, increasing exposure.
- Educational Content: Share articles, videos, or blog posts about sustainable fish farming to educate and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
- Networking: Attend industry gatherings, workshops, and meetings to connect with other professionals and potential customers.
- Direct Outreach: Reach out to local businesses, chefs, and food enthusiasts to introduce your products and establish relationships.
- Online Presence: Maintain an informative website with product details, contact information, and customer testimonials.
- Word of Mouth: Encourage satisfied customers to spread the word about your exceptional fish.
Remember, consistent efforts to raise awareness about your fish farming business contribute to long-term growth and success.
See How To Get Customers Through the Door and our marketing section to provide ideas to help you bring awareness to your business.
Sample Ad Ideas:
Ad 1: Fresh Catch Delivered to You!
Indulge in the finest, sustainably farmed fish from our waters. Order now for doorstep delivery. Taste the difference of premium quality seafood!
Ad 2: Your Aquatic Adventure Starts Here!
Dive into a thriving underwater world with our locally sourced fish. From farm to table, experience flavor and health like never before.
Ad 3: Reel in Freshness at Your Doorstep!
Experience oceanic flavors at home. Our farm-fresh fish guarantee an unforgettable culinary journey. Order today for a taste of the sea.
Ad 4: Unleash Your Inner Chef with Our Fish!
Create gourmet masterpieces with our premium fish.
Elevate your recipes with the finest ingredients straight from our farm.
Ad 5: Savor Purity with Every Bite!
Discover seafood excellence with our sustainably cultivated fish. Delight in the freshest flavors while supporting local aquaculture.
(Note: Each ad contains a headline and a body text of approximately 20-25 words to fit within the specified display ad length of around 100 words.)
Consider collaborating with these businesses to establish a mutually beneficial referral network:
- Local Restaurants: Partner with restaurants to supply them with fresh fish. In return, they can refer their patrons to your fish farming business.
- Pet Stores: Pet stores often sell fish as pets. They can refer customers seeking live fish to your business.
- Aquarium Shops: Similar to pet stores, aquarium shops have customers interested in aquatic life. They can refer hobbyists to you.
- Fishing Tackle Shops: These shops serve fishing enthusiasts. You can refer customers in need of fishing supplies to them.
- Grocery Stores: Local markets can refer customers looking for fresh, locally sourced fish.
- Tourist Attractions: If your area attracts tourists, partner with attractions that could recommend your business to visitors.
- Catering Companies: Collaborate with caterers who might require a bulk supply of fish for events.
- Health Food Stores: Health-conscious customers might seek out locally produced, sustainable fish.
- Cooking Schools: Culinary schools could recommend your products to students learning about seafood preparation.
- Online Food Delivery Platforms: If you sell directly to consumers, partnering with delivery platforms can expand your reach.
Remember, your referral system should offer value to the other businesses.
This might include referral fees, reciprocal referrals, or joint marketing efforts. Such partnerships can help you tap into a wider customer base and foster symbiotic growth.
Importance of Evaluating Your Skill Set:
Focusing on your skill set and evaluating its suitability for a fish farming business is essential.
Your skills shape your ability to manage operations effectively and make informed decisions.
Learning or Delegating Essential Skills:
If a crucial skill is lacking, you have options. You can learn it through training or courses.
Alternatively, you can hire someone with expertise in that area to fill the gap.
Essential Skills for a Fish Farming Business Owner:
- Aquaculture Knowledge: Understanding fish rearing techniques, breeding, and health maintenance is fundamental.
- Financial Literacy: Proficiency in budgeting, financial analysis, and pricing strategies is vital.
- Marketing and Sales: Skills to promote products and attract customers are essential for growth.
- Operational Management: Ensuring equipment maintenance, resource allocation, and efficiency in day-to-day activities.
- Business Leadership: Planning, organization, and team management drive long-term success.
- Problem-Solving: Addressing challenges that arise in production, logistics, or market shifts.
- Regulatory Compliance: Understanding industry regulations and environmental standards.
- Communication Abilities: Effective interaction with customers, suppliers, and employees fosters collaboration and growth.
Knowledge Is Power if You Use It!
Leverage knowledge for action. Industry insights abound, aiding startups and established businesses.
Valuable links provide information for both launch and ongoing operations.
Trends and Statistics
Analyzing industry trends and statistics for a fish farming business provides insights into market demand, growth potential, and informed decision-making for sustainable success.
See the latest search results for trends and statistics related to the fish farming industry.
Fish Farming Associations
Trade associations provide benefits like industry updates and networking chances, aiding professionals in staying informed and connected within their field.
See the search results related to fish farming associations and the benefits of Joining the Chamber of Commerce.
The Top Fish Farming Businesses
Studying an established fish farming business can spark innovation, reveal industry gaps for competitive edges, and uncover overlooked offerings from other enterprises.
See the latest search results for the top fish farming businesses.
The Future of the Fish Farming
Researching the industry’s future aids potential fish farming business owners in anticipating trends, adapting strategies, and making informed decisions for long-term success.
See the search results for the future of the fish farming industry.
Researching pricing for a fish farming business helps determine competitive rates, optimize profitability, and attract customers effectively.
See the latest bulk fish prices.
Find a Fish Farming Business For Sale
Benefits of buying an established fish farming business:
- Immediate revenue from day one.
- Bypassing the challenging startup phase.
- Confidence in a proven and functional business model.
- Knowledge of existing revenue, profits, and expenses.
- Access to an established customer base.
- Benefit from the business’s built reputation.
- Higher cost due to purchasing goodwill and customer base.
- Risk of losing customers if operational changes are made.
- Inheriting both positive and negative aspects of the business’s reputation.
The latest search results for a fish farming business for sale and others in the same category.
Franchise Opportunities Related Fish Farming
Owning a fish farming franchise presents merits and drawbacks, warranting thorough consideration. Uncover unexplored possibilities within this field.
- Proven business model; guided by corporate plan.
- Leverage existing reputation and marketing.
- Preceding knowledge of business operations.
- Corporate support provides stability.
- High initial costs.
- Limited autonomy; major changes need corporate approval.
- Restricted to approved products/services.
- Bound by agreement terms.
- Ongoing franchise fees.
Explore related industry franchises if an exact fish farming match is absent. Investigate opportunities using provided link.
See the latest search results for franchise opportunities related to this industry.
Expert Tips
Expert tips enhance skills for novices and experts alike.
Experts gain efficiency and new perspectives; novices access knowledge for skill enhancement.
See the latest search results for fish farming to gain tips and insights.
Fish Farming Business Insights
Examining tips and insights yields innovative ideas, prevents pitfalls in fish farming, and enhances industry expertise effectively.
See the latest search results about insights into running a fish farming business.
Fish Farming Publications
Engage in fish farming forums to connect with industry peers and customers.
Discussions provide insights for understanding customer perspectives and improving business relationships.
See the search results for fish farming publications.
Fish Farming Forums
See the latest search results related to fish farming forums.
Online or local courses enhance fish farming skills and knowledge, benefiting your business significantly.
See the latest courses that could benefit a fish farming business owner . Also, see our management articles for tips and insights for managing your business.
Fish Farming Blogs
Subscribing to diverse fish farming blogs provides industry insights. Filter for active, valuable ones to create a dependable information source.
Look at the latest search results for fish farming blogs to follow.
Fish Farming News
Utilize news sources to stay updated on fish farming-related media coverage and news stories for relevant information.
See the latest results for fish farming news.
Millions of monthly YouTube uploads include valuable videos. Browse to gather fish-related tips and insights amid this vast collection.
YouTube videos related to fish.
Privacy Overview

Swimming to Success! Guide for the Fish Farming Business

Have you ever considered starting a fish farming business? Imagine a world where you’re not just swimming with the fishes, but you’re swimming straight to success! Fish farming, also known as aquaculture, is a fantastic opportunity to dive into a thriving industry.
In this guide, we’ll explore the basics of fish farming in a way that’s easy to understand, even if you’re new to the world of aquaculture. Whether you dream of raising your own fish, contributing to sustainable food production, or simply want to learn more about this fascinating industry, we’ve got you covered.
Choosing the Right Fish Species
Picking the perfect location, budgeting for success, exploring aquaculture systems, key aspects of design and construction, environmental considerations and regulations, getting your fishy babies – fry and fingerlings, feeding and nutrition, water quality control and disease prevention, finding your fish fans, promoting your fish farm, building relationships with distributors and buyers, getting your papers in order – registration and permits, following food safety standards, exploring government support – subsidies and incentives, facing the common challenges, strategies for efficiency and risk reduction, ensuring ongoing success, practicing sustainable aquaculture, learning from successful fish farmers, initial planning🐟.
In the exciting world of fish farming business , success begins with a solid plan. Just like building a sandcastle, every great venture needs a strong foundation. So, let’s put on our thinking caps and explore the crucial initial steps to make your fish farming dreams come true.

Making your fish farm a reality requires some cash, just like buying your favorite video game or going to the movies. It’s time to figure out the costs. Start by assessing your initial investment. How much will you need for tanks, fish feed, and other equipment? Then, create a budget to manage your expenses. This budget acts like a roadmap for your fish farming business plan , ensuring you don’t run out of money before your fish are ready for the market.
Design and Construction of Your Fish Farm🐟

There are various ways to raise fish, and it’s a bit like choosing the right house for you. Fish can live in ponds, sea cages, or special recirculating systems. Each has its own pros and cons. Ponds are like a fishy neighborhood where they have more space, while sea cages are like fishy condos where they live closer to nature. Recirculating systems are like high-tech fishy homes with controlled environments. Depending on your location and budget, you’ll pick the system that suits you best.
Just like building a treehouse, constructing a fish farm needs careful planning. It’s essential to design and build the facilities in a way that keeps your fish happy and healthy. You’ll need proper tanks, filtration systems, and oxygen supplies. Think of it as setting up the perfect playground for your fish friends. Keep in mind the importance of good water circulation and a safe environment to prevent escapes and predators.
Now, picture your fish farm as a part of the whole underwater ecosystem. It’s like being a good neighbor in your community. You must consider how your farm affects the environment. It’s crucial to follow local living standards and regulations to ensure you’re not harming the environment or other marine life. This is a key aspect of responsible fish farming.
Managing and Caring for Your Fish🐟
In the world of fish farming business , your underwater buddies rely on you for everything, from a cozy home to delicious meals. Let’s dive in and explore how to be the best fish parent ever.

Imagine you’re a chef for your fishy friends. Providing them with the right food is vital. Different fish need different diets. Some may prefer fish flakes, while others might like pellets or live food. It’s important to follow a feeding schedule and not overfeed, just like you don’t want to eat too many sweets. Fish need a balanced diet to grow strong and healthy.
Maintaining the right water quality is similar to keeping your room clean. You don’t want dirty water, right? Regularly check the water’s temperature, pH levels, and oxygen content. It’s like creating a perfect swimming pool for your fish. If you notice any signs of illness, such as strange behavior or unusual spots, you’ll need to act fast, just like taking care of a sick friend. Consult with a fish veterinarian or an expert to keep your underwater buddies healthy.
Marketing and Sales for Your Fish Farm🐟
In the fascinating world of fish farming business , it’s not just about raising fish; it’s also about letting the world know about your amazing underwater friends and making sure they end up on dinner plates. Let’s explore how to make your fish farm shine in the market.

Just like superheroes have their emblems, your fish farm needs a brand. Create a catchy name and logo for your farm to stand out. You can also use social media, like Facebook and Instagram, to share pictures of your fish. It’s like showing off your amazing artwork or cool video game achievements. The more people see your fish, the more they’ll want to buy them.
Getting your fish into the hands of eager buyers is like sharing your favorite things with your friends. Look for local seafood distributors and restaurants. Offer them samples of your fish to try. Once they taste the quality of your fish, they’ll keep coming back for more. Building these connections is like making lifelong friends who share your interests.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects for Your Fish Farm🐟
In the extraordinary world of fish farming business , it’s not all about fish and water. There are rules and regulations, just like in any game or sport. Let’s explore the legal side of making your fish farm a smooth and successful operation.
Think of starting a fish farm like driving a car. You need a license, right? In the world of fish farming, you’ll need to register your farm and obtain necessary permits. This is like having the right papers for your fishy adventure. It ensures that you’re following the law and that your fish are raised in a safe and controlled environment.
When you cook or eat, you follow certain hygiene rules, don’t you? Similarly, in your fish farm, you must adhere to food safety regulations. It’s like ensuring your fish are prepared and delivered to customers in a clean and healthy way. This guarantees that your fish are safe to eat and that you’re maintaining high-quality standards.
Imagine you’re playing a game, and you receive a bonus or a special power-up. The government can offer something similar for your fish farm! In some places, there might be subsidies or incentives available to support your fish farming business . These can help reduce your costs and make your venture more profitable. It’s like getting a boost in your game that helps you win.
Challenges and Solutions in Fish Farming🐟
In the exciting world of fish farming business , just like in your favorite video game, there are levels of challenges to conquer. But don’t worry, with the right strategies and a bit of creativity, you can overcome any hurdle and swim toward success. Let’s explore the common challenges fish farmers face and how to tackle them.

In your favorite game, you plan your moves, right? Similarly, in the fish farming world, it’s essential to have a strategy. You can maximize efficiency by optimizing feed, managing water quality, and investing in better technology. This is like upgrading your gear in a game to perform better. It reduces risks and makes your fish farming business more profitable.
For example, if diseases are a common challenge, you can implement a health management plan. This plan may include regular check-ups for your fish and quick response to any signs of illness. Think of it as having a medic on your team in a game to heal your characters.
Success and Sustainability in Fish Farming🐟
In the amazing world of the fish farming business , success isn’t just about making money, but also about ensuring that our underwater friends thrive and the environment remains healthy. Let’s dive into what it takes to have a successful and sustainable fish farm.
Picture your fish farm as a garden you tend to every day. Success here means keeping your fish healthy and your business profitable. To achieve this, you must continually learn and adapt. Regularly update your knowledge about fish farming techniques, stay informed about the latest industry trends, and implement the best practices. Think of it like leveling up your skills in your favorite video game.

Imagine if you could learn from the best players in your favorite sport or game. In the world of fish farming, you can do just that by studying the stories of successful fish farmers. Their experiences and wisdom are like cheat codes to success. You can find inspiration and learn valuable lessons from their journey.
Previous Post
Ocean Conservation in Namibia: Challenges and Solutions
Exploring the fascinating world of color phenomena in the oceans..
seafoodpeddler.com is a participant in the Amazon Associate program and will earn from qualifying purchases.
Fish Farm Business Plan Template & Guidebook
How to write a fish farm business plan in 7 steps:, 1. describe the purpose of your fish farm business..
It also helps to include a vision statement so that readers can understand what type of company you want to build.
2. Products & Services Offered by Your Fish Farm Business.
When you think about the products and services that you offer, it's helpful to ask yourself the following questions:
3. Build a Creative Marketing Stratgey.
If you don't have a marketing plan for your fish farm business, it's time to write one. Your marketing plan should be part of your business plan and be a roadmap to your goals.
Target market
Customer base , product or service description, competitive analysis, marketing channels, form an llc in your state, 4. write your operational plan., what equipment, supplies, or permits are needed to run a fish farm business, 5. management & organization of your fish farm business..
The second part of your fish farm business plan is to develop a management and organization section.
6. Fish Farm Business Startup Expenses & Captial Needed.
Startup costs are typically the first expenses you will incur when beginning an enterprise. These include legal fees, accounting expenses, and other costs associated with getting your business off the ground. The amount of money needed to start a fish farm business varies based on many different variables, but below are a few different types of startup costs for a fish farm business.
You should include any costs associated with marketing and sales, such as advertising and promotions, website design or maintenance. Also, consider any additional expenses that may be incurred if you decide to launch a new product or service line. For example, if your fish farm business has an existing website that needs an upgrade in order to sell more products or services, then this should be listed here.
7. Financial Plan & Projections
Here are some steps you can follow to devise a financial plan for your fish farm business plan:
Frequently Asked Questions About Fish Farm Business Plans:
Why do you need a business plan for a fish farm business, who should you ask for help with your fish farm business plan.
It is a good idea to consult with experts when creating a business plan for a fish farm. Consider reaching out to local fisheries and fish farming associations, or to fish farm management consultants. You may also find online resources such as guides and tutorials that provide guidance on creating a business plan for a fish farm.
Can you write a fish farm business plan yourself?
Related business plans, home inventory business plan template & guidebook, home inspection business plan template & guidebook, home decor business plan template & guidebook, health and wellness business plan template & guidebook, hauling business plan template & guidebook, hardware business plan template & guidebook, handyman business plan template & guidebook, hair extension business plan template & guidebook, handbag business plan template & guidebook.
I'm Nick, co-founder of newfoundr.com, dedicated to helping aspiring entrepreneurs succeed. As a small business owner with over five years of experience, I have garnered valuable knowledge and insights across a diverse range of industries. My passion for entrepreneurship drives me to share my expertise with aspiring entrepreneurs, empowering them to turn their business dreams into reality.

Fish Farming Business Plan Template [Updated 2024]
VI. Marketing Plan
This Section's Contents
The [Company Name] Brand
Promotions strategy, pricing strategy.
The [Company Name] brand will focus on the Company’s unique value proposition:
- Fresh, healthy, organic salmon
- Contains no GMOs, antibiotics, or growth hormones
- Farmed sustainably using the latest technology and best practices
- Service built on long-term relationships
- Transparency of operations to achieve customer assurance of organic quality
[Company Name] expects its target market to be food processors and local restaurant and grocery store owners within a 50-mile radius of its location. The Company’s promotion strategy to reach these customers includes:
Targeted Cold Calls [Company Name] will initially invest significant time and energy into contacting potential customers via telephone and then by visiting their facilities. In order to improve the effectiveness of this phase of the marketing strategy, a highly-focused call list will be used; targeting food processors, local restaurant owners, and independent grocery stores with an expressed interest in organic salmon. As this is a very time-consuming process, it will primarily be used during the startup phase to build an initial customer base.
Industry Events By attending regional fish farming and aquaculture conferences, association meetings, and other events, [Company Name] will network with industry leaders and seek referrals to potential customers. [Founder’s Name] will often attend with the company sales manager, but both may attend separately in the future as they gain experience in this type of networking.
Networking Networking is one of the most effective methods for improving brand awareness in the fish farming market. The Company will attend seminars, trade shows, conferences, and other gatherings of the aquaculture community.
Local Directory Marketing [Company Name] will announce details about its products in local directories to keep readers informed about the Company’s offerings.
Social Media [Company Name] will invest in a social media advertising campaign. The marketing manager will create the Company’s social media accounts and invest in ads on all social media platforms. It will use targeted social media marketing tactics to appeal to the target demographics.
Local Publications The Company will also invest in advertising in selected local publications until it has achieved significant brand awareness. Publications such as local newspapers, magazines, and advertisements will be used to introduce the community to the company.
Website [Company Name] will invest heavily in developing a professional website that displays all of the benefits of its fish farm and the quality of the salmon it offers. It will also invest heavily in SEO so that the brand’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Special Offers Offers and incentives are an excellent approach to assisting businesses in replenishing the churn in their customer base that they lose each year. The Company will introduce special offers to attract new consumers and encourage repeat purchases, which will be quite advantageous in the long run.
[Company Name]’s pricing will be premium and higher than competitors due to the products being better quality. Consumers will feel they are getting the best value when purchasing salmon from the Company’s fish farm.
Comments are closed.
Fish Farming Business Plan Home I. Executive Summary II. Company Overview III. Industry Analysis IV. Customer Analysis V. Competitive Analysis VI. Marketing Plan VII. Operations Plan VIII. Management Team IX. Financial Plan

Financial modeling spreadsheets and templates in Excel & Google Sheets
- Your cart is empty.

Start Your Aquaculture Venture: Fish Farming Business Plan Pdf

Starting an aquaculture venture requires a comprehensive fish farming business plan. This plan is crucial for outlining operational strategies and financial projections.
Embarking on an aquaculture business journey involves meticulous planning and a clear understanding of the industry’s nuances. Your path to a successful fish farming enterprise begins with the creation of a detailed business plan PDF, which serves as a roadmap to navigate the complexities of aquaculture.
It ensures that all aspects, from selecting the right species and securing equipment to understanding market demand and establishing sales channels, are carefully considered. Facilitating strategy development and financial management , a well-crafted business plan can attract investors, secure loans, and guide the venture through its critical first steps. It’s essential for aspiring fish farmers to prioritize this document to set the stage for a thriving business in an industry that requires both scientific and entrepreneurial acumen.

Diving Into Aquaculture
Aquaculture, or fish farming, presents a thriving frontier for entrepreneurs and investors. With the global demand for seafood on the rise, delving into aquaculture offers a chance to tap into a continuously expanding market. A comprehensive fish farming business plan is essential for success and sustainability in this sector.
The Lure Of The Blue Economy
The ‘blue economy’ refers to the sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and jobs. Fish farming plays a significant role here. It offers a lucrative opportunity for business growth while contributing to food security.
- Meets rising seafood demand : As global populations grow, so does appetite for seafood.
- Promotes economic development : Aquaculture generates income and employment.
- Supports rural communities : Fish farms can uplift local economies.
Sustainability And Fish Farming
Fish farming’s future hinges on sustainability. It’s vital to balance economic output with environmental responsibility. A business plan for fish farming should encompass sustainable practices.
| Aspect | Action for Sustainability |
|---|---|
| Use resource-efficient, sustainable feedstock | |
| Implement systems to minimize and recycle waste | |
| Choose species with lower environmental impacts |
A balanced ecosystem approach ensures long-term viability. Plus, ethical considerations and regulatory compliance should guide every step.
Aquaculture Ventures Demystified
Imagine a world where your favorite seafood is homegrown. That is aquaculture for you. Dive into the world of fish farming. Learn everything from setting up to harvest. A clear business plan is your roadmap. It leads to success in aquaculture.
Types Of Aquaculture Systems
Fish farming employs various systems. Each system fits different needs. Know your options before diving in.
- Open-net pens – These float in oceans or freshwater. Fish live in a natural habitat but are confined.
- Closed-containment systems – Tanks on land ensure no interaction with wild species. It gives farmers full control.
- Raceways – Stream of fresh water allows fish to swim. Raceways are often used for trout.
- Aquaponics – Plant cultivation combines with fish farming. Waste from fish feeds plants.
Pros And Cons Of Fish Farming
Fish farming has its ups and downs. Let’s weigh them.
| Year-round production | Costly startup investments |
| Control over fish health | Environmental concerns |
| Local supply of seafood | Disease management |
| High market demand | Water usage issues |
Success in fish farming comes from knowing your system and its impact. A solid business plan helps turn challenges into waves of opportunity.
Crafting Your Business Blueprint
The journey to establishing a thriving aquaculture venture begins with a solid foundation — your business blueprint. Think of this blueprint as your roadmap to success, outlining every critical aspect of your fish farming business. Careful planning now can save countless hours and resources later.
Key Components Of A Business Plan
A well-structured business plan serves as a guiding star for your aquaculture venture. It must include several imperative elements:
- Executive Summary: This snapshot highlights your business goals and vision.
- Business Description: Detail what your fish farm will do and its unique strengths.
- Market Analysis : Provide data on your target market, customer needs, and competitors.
- Organization and Management: Describe the structure of your business and the team.
- Products/Services: List the types of fish you plan to farm and any additional offerings.
- Marketing Plan: Outline strategies to attract and retain customers.
- Operational Plan: Explain day-to-day operations, from feeding regimes to harvest.
- Financial Plan: Include projections, budgeting, and funding requirements.
Setting Smart Objectives
Setting objectives steers your business in the right direction. Ensure your goals follow the SMART criteria:
| pecific | Clearly define what you want to achieve with your fish farm. |
|---|---|
| easurable | Set precise amounts, dates, and deadlines to measure progress. |
| chievable | Your goals should challenge you, but remain attainable. |
| elevant | Ensure your objectives align with the overall vision of your aquaculture venture. |
| imely | Define a timeline for when each objective should be met. |
Market Research And Analysis
Before diving into the fish farming business, it’s vital to comprehend the market terrain. “Market Research and Analysis” is a cornerstone of your aquaculture venture. This phase is crucial. It helps predict potential profits, understand buyer preferences, and recognize competition. Data gathered will guide your business plan and strategy.
Understanding Consumer Demand
Understanding what your future customers want is the key. Consumer demand drives sales . It’s about knowing:
- The types of fish in-demand
- Preferred sizes and cuts
- Organic and sustainable aquaculture trends
Research methods include:
- Surveys with local residents
- Interviews with seafood vendors
- Analyzing online search trends
These methods will unveil what consumers buy frequently. This information helps you decide which fish species to raise and how to market them.
Competitive Landscape
Know your competitors. Recognizing their strengths and weaknesses gives you an advantage. Consider:
| Factor | Importance |
|---|---|
| Range of Products | Offers insight into market variety. |
| Pricing Strategies | Helps in setting competitive prices. |
| Marketing Tactics | Guides how to promote your business. |
| Customer Reviews | Highlights areas for improvement. |
Analyzing these aspects will identify where you can excel. The goal is to differentiate your fish farm and capture market share.
Site Selection And Design
Are you ready to dive into the world of aquaculture? Your journey begins with an essential step: selecting the right spot and crafting the perfect design. A well-chosen site fused with a carefully planned design lays the bedrock for a thriving fish farm. Let’s explore how you can ace this stage in your aquaculture venture.
Criteria For Site Selection
Choosing the right site is crucial for your fish farming success . There are several factors you need to consider:
- Water supply: Look for a reliable and clean source.
- Soil quality: Check that the soil can hold water well.
- Topography: Seek level land to minimize construction costs.
- Climate: Make sure the weather supports your chosen fish species.
- Accessibility: Ensure easy access for feed delivery and fish distribution.
- Regulations: Comply with local zoning and environmental laws.
Taking the time to evaluate these criteria will save you from setbacks.
System Design And Construction
Once you’ve found the perfect site, it’s time to focus on system design and construction .
- Design for species: Tailor your design to fit the needs of the fish you are farming.
- Water management: Plan for efficient water flow and quality maintenance.
- Energy efficiency: Incorporate sustainable energy sources when possible.
- Space utilization: Optimize space for breeding, growing, and harvesting.
- Ongoing maintenance: Design for ease of maintenance to save time and money.
Involving experts in aquaculture system design and construction can ensure you create a space that supports your fish farming business for years to come.
Financial Planning
Embarking on a fish farming venture requires thorough financial planning. It is a key pillar that supports the structure of your business . Knowing the costs, projecting profits, and understanding the risks ensures that your business stands on firm financial ground from the start.
Cost Estimation And Management
Smart cost estimation and management are vital for a thriving aquaculture business .
- Include start-up costs: tanks, feed, fingerlings, and permits.
- Factor in operational expenses: labor, maintenance, and utilities.
- Expect unexpected costs: Keep a reserve for emergencies.
| Cost Type | Estimation | Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | $XX,XXX | Research suppliers, bulk discounts |
| Running Costs | $X,XXX/month | Regular review, optimize operations |
| Emergency Fund | $X,XXX | Set aside monthly, no-touch policy |
Life throws unexpected challenges ; be ready with solid financial buffers .
Profitability And Risk Assessment
Assessing profitability and risk keeps a fish farm business healthy.
- Analyze market demand for selected fish species.
- Calculate break-even point and return on investment.
- Identify potential risks: disease, market fluctuations.
Profitability relies on careful market research and pricing strategy . Risks can decrease with diligent planning and insurance coverage.
Use financial tools like SWOT analysis for clearer insight.
A detailed financial plan in your fish farming business plan PDF is not just a requirement—it’s a roadmap to success.
Regulatory Compliance And Best Practices
Starting a fish farming business requires knowledge of rules and eco-friendly methods. Detailed planning is essential for success.
Navigating Legal Requirements
Understanding the laws is key in fish farming. Each country, state, and locality may have specific regulations. A business plan must align with these standards to operate legally. To start, research the permits needed for your aquaculture venture. Also, check for inspections and reporting obligations. Compliance with legalities ensures smooth operation.
- Water use permits : Required for sourcing water.
- Discharge permits : Needed for waste management.
- Stocking permits : Necessary for aquaculture species.
Collaborating with legal advisors can streamline this process.
Adopting Eco-friendly Practices
Sustainable methods benefit businesses and the environment. Implementing them can optimize resource use and minimize negative impacts. Best practices in aquaculture include:
- Recirculating systems : This saves water and controls waste.
- Feeding management : Keep feed inputs precise to reduce waste.
- Habitat conservation : Protect local ecosystems during operation.
Eco-certifications can improve market position and customer trust.
Marketing And Sales Strategies
Marketing and Sales Strategies are the engines that drive your aquaculture venture towards success. Establishing a solid plan to attract customers and generate sales is key. Understand the market, define your brand, engage with customers, and leverage sales channels to outpace competition. Let’s dive into the specifics of branding and outreach, followed by sales channel optimization.
Branding And Customer Outreach
Creating a powerful brand identity is crucial for connecting with your target market. Your brand communicates your business values, mission, and the quality of your fish products. A strong brand can lead to customer loyalty and more sales.
- Develop a unique logo and color scheme that embodies your farm’s spirit.
- Design eye-catching packaging that stands out in the market.
- Use social media platforms to tell your story and showcase your farms and fish.
- Attend industry events to network and build relationships.
- Offer promotions and discounts to new customers.
Effective outreach can turn the curious into loyal customers.
Sales Channels And Partnerships
Choosing the right sales channels can make your fish farming business soar. A diverse mix can reach different customer segments. Partnerships can broaden your market reach.
| Channel | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Direct customer feedback, community presence. | |
| Wide reach, convenience for customers. | |
| Larger volume sales, stable revenue. | |
| High-quality clientele, consistent orders. |
Strengthening sales channels and forming strategic partnerships can drive significant business growth.
Operation And Management Plans
Embarking on an aquaculture venture requires meticulous planning. Success hinges on a comprehensive Operation and Management Plan . This plan ensures smooth daily activities and outlines the needs for skilled staff. Together, they form the backbone of a thriving fish farming business.
Daily Operations Workflow
The daily grind in fish farming encompasses a myriad of tasks. A clear workflow keeps operations ticking like clockwork. Here’s a glimpse:
- Feeding: Fish require timely, balanced meals for healthy growth.
- Water Quality Checks: Good water means healthy fish.
- Health Monitoring: Spotting sickness early keeps all fish safe.
- Harvesting: Efficient methods bring fish quickly to market.
- Record Keeping: Tracking data informs future decisions.
Staffing And Training Needs
Skilled staff are vital in a fish farming operation. Specific roles must be filled:
| Aquaculture Technician | Care for fish, monitor water quality | Attention to detail, problem-solving |
| Feed Manager | Manage diet, feeding schedules | Nutrition knowledge, organizational skills |
| Harvesting Crew | Collect and prepare fish for sale | Efficiency, teamwork |
High-quality training turns newcomers into experts. It covers areas such as:
- Safety Procedures: Keeping everyone safe around water and equipment.
- Operational Protocols: Steps for feeding, harvesting, and maintenance.
- Best Practices: Sustainable methods for long-term success.
Launching Your Aquaculture Venture
Are you ready to dive into the world of aquaculture? Launching your aquaculture venture takes more than just a vision—it requires a detailed plan. Follow these steps to set your fish farming business on a path to success.
Milestones And Timeline
Setting clear milestones and a timeline is crucial for your venture’s progress. Here’s what you should consider:
- Research Phase: Understand the market, species, and site selection.
- Plan Drafting: Create a detailed business plan, which includes financial forecasting .
- Permit Acquisition: Secure all necessary permits and licenses.
- System Setup: Construct ponds or tanks with proper equipment.
- Stocking: Introduce fish to their new habitat carefully.
- Marketing: Develop relationships with potential customers and suppliers.
- First Harvest: Plan and execute the first fish harvest.
- Review and Scale: Analyze data, make improvements, and scale operations as needed.
Remember to align these milestones with a specific timeline.
Preparing For The Grand Opening
Your grand opening is a big deal. It sets the stage for your business’s future. Prepare with these steps:
- Final Checks: Ensure all systems are fully operational.
- Team Readiness: Train your staff for top-notch service and knowledge.
- Marketing Push: Use social media, flyers, and local media to spread the word.
- Local Engagement: Invite the community for support and awareness.
- Soft Launch: Consider opening to a small group before the official date.
With these steps, the launch of your fish farming business will make a splash!
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does it cost to start an aquaculture farm.
Starting an aquaculture farm can cost between $10,000 to over $500,000, depending on scale, species, and technology used.
How To Start An Aquaculture Business?
Research local regulations and acquire permits for aquaculture operations. Develop a business plan covering species selection, system design, and market analysis. Secure a suitable location and invest in necessary equipment. Focus on sustainable practices to ensure long-term success. Implement effective marketing strategies to reach your target audience.
Is Aquaculture A Profitable Business?
Aquaculture can be profitable, with proper management, market analysis, and sustainable practices. Startup costs and species choice greatly impact overall returns.
What Is The Most Profitable Fish Farming Business?
The most profitable fish farming business often involves cultivating salmon, shrimp, or tilapia due to their high demand and market value.
Embarking on an aquaculture venture demands careful planning and a strategic approach. Our comprehensive guide in PDF format paves the path for your success in fish farming. Arm yourself with knowledge, streamline your operations, and bring your aquaculture dream to life.
Let’s dive into a flourishing future together.

Fish Farm Financial Model Excel Template
Get the Best Fish Farm Pro Forma Projection. This well-tested, robust, and powerful template is your solid foundation to plan a success. Highly ... read more
- Excel - Multi-User – $129.00
- Excel - Single-User – $99.00
- Free Demo – $0.00

Agriculture Financial Model Templates Bundle
This is a collection of financial model templates for businesses in the Agriculture Industry and its related sectors.

Fish Farm Valuation Model
This valuation model in Excel assists fish farmers and investors to value a fish farm based on the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Method. The model is ful... read more
- Full Excel Version – $49.95 Version 2.1
- PDF Demo Version – $0.00 Version 2.1
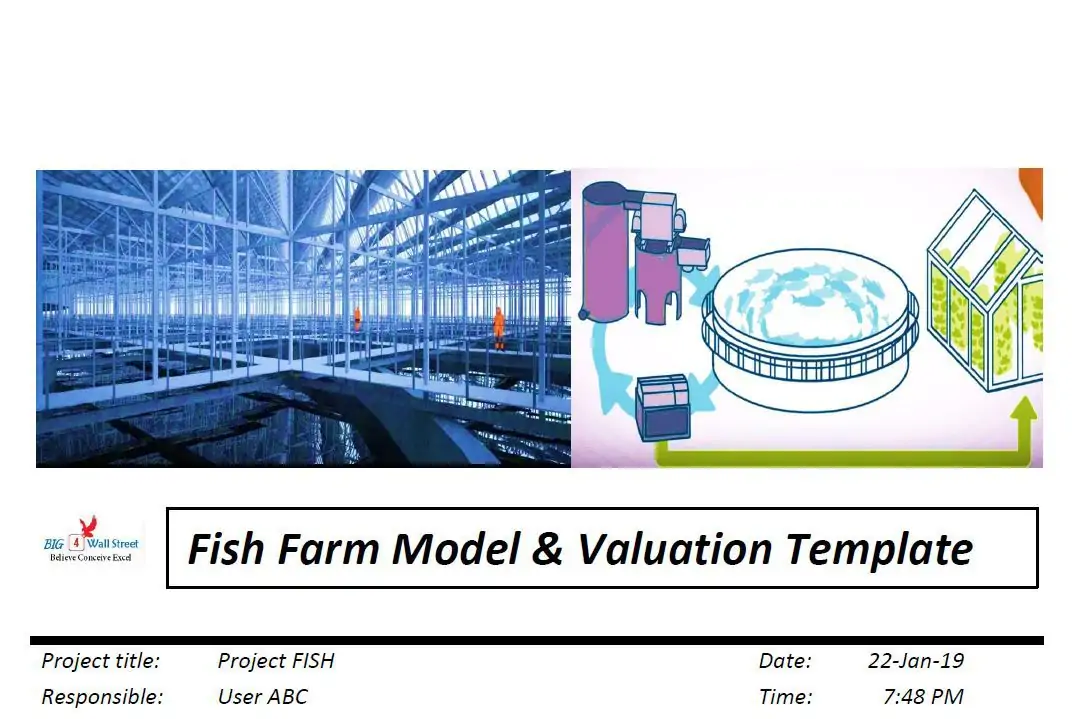
Fish Farm Financial and Valuation Model
Financial Model Templates that generates a three statement financial model and a valuation for a fish farm start up and / or an up and running company... read more
- Free PDF Land Based Metric System – $0.00
- Free PDF Land Based Imperial System – $0.00
- Free PDF Offshore Metric System – $0.00
- Paid Excel Model Land Based Metric System – $65.00
- Paid Excel Model Land Based Imperial System – $65.00
- Paid Excel Model Offshore Metric System – $59.00

Agricultural Financial Model Bundle
This is a collection of financial model templates related to the Agriculture Industry.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Fish Farming
- Pinterest 11
Fish farming (also known as aquaculture) means ‘raising fish commercially in tanks, ponds or other enclosures for the purpose of producing food’.
Commercial fish farming has already established as a profitable business venture throughout the world. Fish is a great source of food and protein.
The demand and price of fish and fish related products are also increasing rapidly, in accordance with rapid population growth. This is the main reason of increasing this business around the world.
Almost all countries around the world are somehow suitable for fish farming business. But the countries with coastal areas are very suitable for this business.
There are many areas, where fish farming business is the only way of livings for the people.
However, here we are describing more about the advantages of fish farming and the steps for starting this business commercially.
Table of Contents
How to Start Fish Farming Business
For maintaining a profitable fish farming business, you have to go through some step by step process.
The steps for starting a fish rearing business includes selecting suitable farm land or area, fish farm type (cage, tank or pond), cage or pond construction, selecting fish species, feeding, care & management, harvesting and marketing.

We are shortly describing all the steps below. For running a successful fish farming business, follow every steps very carefully.
Complete a Fish Farming Training
Fish farming is an important industry that is rapidly growing worldwide. It is a sustainable practice that produces high-quality protein and supports the local economy.
Fish farming training is crucial for those who want to enter the industry, as it equips them with the knowledge and skills needed to establish and operate a successful fish farm.
Fish farming training is a critical component of the industry and plays an important role in promoting sustainable practices and improving production and profitability.
By providing the knowledge and skills needed to start and operate a successful fish farm, training programs can help farmers achieve their goals and contribute to the local community.
Whether through on-site training, online courses, or workshops and conferences, fish farming training offers many benefits and opportunities for growth and success.
Here, we will explore the importance of fish farming training and the benefits of this practice.
Why is Fish Farming Training Important?
Fish farming training is important for several reasons.
First, it provides the knowledge and skills needed to start and operate a successful fish farm. Fish farming involves several critical aspects, including water quality management, fish nutrition, disease prevention, and marketing. Without proper training, farmers may struggle to establish and maintain a profitable fish farm.
Second, fish farming training promotes sustainable practices that protect the environment and support the local community. Fish farming has the potential to generate employment opportunities, stimulate the local economy, and reduce the pressure on wild fish populations.
However, without proper training, fish farming can also harm the environment, such as through overuse of antibiotics, improper waste disposal, and damage to natural habitats. Fish farming training promotes sustainable practices that ensure the long-term viability of the industry.
Benefits of Fish Farming Training
There are some benefits of completing a fish farming training. Here are the top benefits of completing a fish farming training:
Improved Production and Profitability
Fish farming training can help farmers improve their production and profitability by teaching them best practices for fish rearing, feeding, and disease management. By optimizing these aspects of their operation, farmers can produce high-quality fish that meet the market demand, and generate higher profits.
Enhanced Sustainability
Fish farming training can promote sustainable practices that protect the environment, reduce the impact on wild fish populations, and support the local community. This includes proper waste management, disease prevention, and water quality management, among other practices.
Networking Opportunities
Fish farming training provides opportunities to connect with other farmers, researchers, and industry experts. This can lead to collaborations, new ideas, and opportunities for growth.
Access to Funding and Resources
Fish farming training can help farmers access funding and resources to establish and expand their operations. Many training programs offer information on funding opportunities, grants, and other resources that can help farmers get started and grow their business.
Fish Farming Training Programs
There are several fish farming training programs available that cater to different levels of experience and interests. These include:
On-Site Training
On-site training involves attending training sessions at a fish farm or aquaculture facility. These training sessions provide hands-on experience in fish rearing, feeding, and disease management.
Online Training
Online training programs are increasingly popular and offer flexible schedules and access to a wide range of resources. Online courses cover a range of topics, including fish nutrition, water quality management, and disease prevention.
Workshops and Conferences
Workshops and conferences provide opportunities to network with other fish farmers and industry experts. These events cover a range of topics and offer a platform to exchange ideas and learn about new trends and practices.
Make an Effective Fish Farming Business Plan
With the increasing demand for fish as a source of protein and the decline of wild fish populations due to overfishing and environmental factors, fish farming has become an important industry worldwide.
If you are interested in starting a fish farming business, it is important to have a well-thought-out fish farming business plan.
A well-designed fish farming business plan is essential for the success of your business. Conduct a thorough market analysis, choose the right location, select the appropriate fish species, and decide on the farming system that works best for your farm.
Develop a comprehensive business plan that outlines your goals, operational plan, financial projections, and risk management plan.
Finally, create a strong marketing strategy to promote your fish farm and increase your sales. With careful planning and hard work, your fish farming business can be a profitable and rewarding venture.
Market Analysis
Before starting a fish farming business, it is important to understand the market demand for fish in your region. Conduct a thorough market analysis to identify the types of fish that are in high demand and the potential customers who are interested in buying fish.

You can do this by visiting local fish markets, conducting surveys, and researching online.
Site Selection
Choosing the right location for your fish farm is crucial for the success of your business. Consider factors such as the availability of water, proximity to markets, accessibility, and the availability of land.
Ensure that the site is free from pollutants and contaminants that may affect the health of your fish.
Fish Species Selection
The next step is to choose the fish species that you want to raise in your farm. Consider factors such as the market demand for the fish, the availability of fingerlings, the feeding requirements, and the growth rate of the fish. Popular fish species for aquaculture include tilapia, catfish, trout, and salmon.
Farming System
There are several fish farming systems to choose from, including pond culture, cage culture, and recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS).
Each system has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it is important to choose the system that is best suited for your farm based on factors such as the available resources, the fish species, and the market demand.
Business Plan
A fish farming business plan should outline your business goals, target market, marketing strategy, operational plan, financial projections, and risk management plan.
Your business plan should also include details on the cost of setting up and running the fish farm, such as the cost of land, equipment, feed, and labor.
Starting a fish farming business can be capital-intensive, and it is important to have a solid financing plan in place. Consider options such as bank loans, grants, and investment from venture capitalists or angel investors.
Ensure that you have a realistic financial plan that takes into account the initial investment and the ongoing operating costs of the farm.
Marketing Strategy
To succeed in the fish farming business, you need to have a strong marketing strategy in place. Identify your target market, develop a brand identity for your farm, and create a marketing plan that includes advertising, promotions, and sales tactics. Consider partnering with local restaurants, supermarkets, and fish markets to increase your sales.
Select A Suitable Farm Land/Area
Selecting a suitable land or area is very important for starting commercial fish rearing business. All the areas are not suitable for profitable business.
And some areas have plenty of natural resources, which are very effective for fish farming business.
Especially coastal areas and the areas near big rivers or stream are very suitable for establishing fish farming business. Consider the followings while selecting land or areas for your business.
- Select relatively level land and avoid steeply sloped lands.
- Consider your future business plan, while selecting the land. It will be better if you can select a large piece of land, where you can perform all types of necessary farm activities.
- Avoid flooding and polluted areas, because flooding area can harm your business seriously.
- Don’t select fish farming land near the crop fields. Farmers usually use a lots of fertilizers and pesticides in their field for better production. These chemicals get mixed with water and the polluted water can affect your fish farm.
- It will be better,if your selected land become slightly lower than the main water source. It also help to reduce the cost of filling your farm land with water. Natural gravity will fill the land without any cost.
- Ensure good transportation system is available in your selected area. Good transportation system will be very effective for marketing your products and purchasing necessary commodities from the market.
Type of Your Farm
There are numerous specific type of fish farms in both intensive and extensive fish farming system. You can start fish farming business by choosing any type.
You can choose cage system, tank system or pond system. In cage system, make a suitable cage and place it in lakes, ponds, bayous or oceans and start feeding the fish until they reach marketing age.
In case of raising fish in tanks, make a or a few tanks and stock fish there. Here we are describing more about fish rearing in pond system.
Pond Design & Construction
Construct a suitable pond, after selecting your farm area. Before constructing, make a good design and make the pond according to your desired design.
While designing the pond, ensure the availability of all types of necessary facilities for maintaining a profitable fish farming business.
Although the design of a pond depends on the fish species you intend to raise and your location.
You can consult with your nearest fisheries institute to learn more about specific pond design for specific fish species.
Always try to maintain a good environment in the pond. Good environment helps to live and grow the fish well, and it directly involved with better production and maximum profits. See pond management .
Suitable Fish Species
Selecting suitable fish species is very important for maximizing profits form fish farming business. Select those breeds, which have a huge demand and high price in your local market.
The most important fish species used in fish farming throughout the world are carp, salmon, tilapia and catfish .

All of these fish species have many varieties and suitable for farming in all types of agro-climatic conditions. Select the fish species for farming, depending on your local facilities, demand and price.
Feeding is the most important part of commercial fish farming business. Always try to provide your fish high quality and nutritious food.
High quality food not only ensures maximum production but also help to keep the fish healthy. So provide your fish supplementary fish feed along with natural food.
There are various types of prepared commercial fish feed available in the market for specific fish species. You can purchase those commercial feed from the market or prepare it by your own.
Learn more about preparing supplementary fish feed, if you want to prepare it by your own. Don’t forget to add all types of necessary nutrient elements, such as vitamins, minerals, salt etc. Feed your fish several times a day, depending on the fish species.
Fish breeding is the practice of controlling the reproduction of fish for commercial or recreational purposes. It is a critical component of the aquaculture industry, which is becoming increasingly important as wild fish populations decline due to overfishing and environmental factors.
Most of the fish species are naturally very good breeders. But some species require artificial environment for breeding. If you want to avoid breeding, then you have to purchase fingerlings from the hatcheries.
Here, we will explore the different aspects of fish breeding and the benefits of this practice.
Why is Fish Breeding Important?
Fish breeding is essential for sustaining the global demand for fish as a source of protein. With the growing population and increased awareness of the health benefits of fish consumption, the demand for fish is expected to increase in the coming years.
Fish breeding enables farmers to produce a steady supply of fish that meet the market demand, while also reducing the pressure on wild fish populations.
Benefits of Fish Breeding
Here are some top benefits of fish breeding:
Quality Control
Fish breeding enables farmers to control the quality of the fish they produce. By selectively breeding fish with desirable traits, such as rapid growth, disease resistance, and high meat yield, farmers can ensure that their fish meet the market demand for high-quality fish.
Improved Genetics
Through selective breeding, farmers can improve the genetics of their fish stock over time. This results in fish that are better adapted to the farming environment, have higher survival rates, and are more resistant to diseases.
Increased Productivity
Fish breeding can increase the productivity of fish farms by producing faster-growing fish that are ready for market sooner. This enables farmers to produce more fish in a shorter period of time, increasing their profits.
Sustainable Practice
Fish breeding is a sustainable practice that reduces the pressure on wild fish populations. By producing fish in a controlled environment, farmers can reduce the impact of overfishing and habitat destruction on wild fish populations.
Fish Breeding Techniques
There are several fish breeding techniques that farmers can use to control the reproduction of their fish. These include:
Spawning involves inducing fish to reproduce by simulating the natural conditions that trigger reproduction. This can be done by manipulating water temperature, light, and feeding patterns. Once the fish have laid their eggs, they are collected and incubated until they hatch.
Crossbreeding
Crossbreeding involves mating two different fish species to produce offspring with desirable traits. This technique is commonly used to produce hybrid fish, which are often faster-growing and more disease-resistant than their parent species.
Artificial Insemination
Artificial insemination involves manually fertilizing fish eggs with sperm collected from male fish. This technique is commonly used in fish species that are difficult to spawn naturally, or when a farmer wants to breed specific fish with desirable traits.
Care & Management
Always try to provide your fish fresh and nutritious foods. It will be better, if you can change water from the pond occasionally. If not possible, then you can use some chemicals according to the suggestion of an expert.
Monitor the health of your fish on a regular basis. Do all your necessary farm tasks timely. Keep the pond environment clean and suitable for proper growth.
Test the water and soil quality of your pond on a regular basis. Always stock some necessary drugs on your farm. Prevent all types of predators, including frogs, snakes etc.
After a certain period, the fish become suitable for harvesting. Although this time depends on the fish species. Start harvesting, when a major numbers of fish reach marketing age.
You can use net for harvesting fish or by removing water from the pond. Try to harvest during morning or afternoon, when temperature is low. After harvesting, send the fish to the market as soon as possible.
Marketing is the easiest step of fish farm business. There are numerous markets available where you can sell your products. And all types of fish have a huge demand in the market.
After harvesting, you can easily sell the fish at any of your nearest local market. Even there are many companies available who export fish to the foreign countries. So don’t worry about marketing the products, just focus on the other steps.
In a word, commercial fish farming business is really very profitable and a good source of earning livings. If you intend to join this venture, then visit some fish farms in your area and try to have some practical knowledge. God bless you!
Interesting Facts About Fish Farming Business
Fish farming, also known as aquaculture, is the practice of cultivating fish in tanks, ponds or other water bodies. It has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its ability to provide a sustainable source of protein for a growing population. Here are some interesting facts about fish farming business that you may not have known.
- Fish farming dates back over 4,000 years, with evidence of the practice found in ancient China and Egypt.
- Over half of the world’s seafood supply now comes from fish farming operations.
- The top three countries producing farmed fish are China, India, and Vietnam.
- Tilapia is one of the most commonly farmed fish species in the world, due to its hardiness and ability to adapt to different environments.
- Salmon is also a popular species for farming, with much of the global supply of farmed salmon coming from Norway, Chile and Scotland.
- Fish farming can be done using either freshwater, saltwater or brackish water.
- In some cases, fish farming can actually help to improve water quality by reducing pollution and nutrient levels.
- Fish farming can also reduce pressure on wild fish populations by providing an alternative source of seafood.
- Some species of fish can be grown entirely on vegetarian diets, which can help to reduce the reliance on fishmeal made from wild-caught fish.
- Fish farming can be done on a small scale, such as in backyard ponds, or on a large scale in commercial operations.
- Recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) are a type of fish farming that uses closed-loop tanks to recycle water and nutrients, resulting in less waste and lower environmental impact.
- Fish farming can be a source of income for rural communities in developing countries, helping to alleviate poverty and improve food security.
- Fish farming can also provide employment opportunities in areas where traditional fishing has declined.
- Fish farming can be done in indoor or outdoor settings, depending on the species being raised and the climate.
- In some cases, fish farming can be used to restore and enhance natural habitats, such as wetlands and estuaries.
- Fish farming can be a more sustainable alternative to wild-caught seafood, which can be subject to overfishing and habitat destruction.
- Fish farming can also reduce the risk of disease transmission between wild and farmed fish populations.
- Some species of fish can be raised in tanks on land, eliminating the need for open-water pens that can have negative impacts on wild fish populations.
- Fish farming can also help to reduce carbon emissions by providing a local source of seafood, reducing the need for long-distance transportation.
- In some cases, fish farming can be used to control invasive species by cultivating native fish that can outcompete the invaders.
- Fish farming can also be used to produce other products besides food, such as fish oil and fertilizer.
- Fish farming has its challenges, including environmental impacts from waste and escaped fish, disease outbreaks, and the use of antibiotics and other chemicals. However, with careful management and innovation, these challenges can be overcome.
Best Fish Farming Tips for Beginners
Fish farming is a sustainable practice that provides high-quality protein and supports the local economy. If you are new to fish farming, it can be overwhelming to know where to start. Here, we are going to provide you with some essential tips to help you get started on your fish farming journey.
1. Choose the Right Fish Species
The first step in starting a fish farm is to choose the right fish species. Different fish species have different requirements in terms of water temperature, pH level, oxygen content, and feeding habits.
It is essential to select a fish species that is well suited to the climate and water conditions in your area.
Some of the most popular fish species for farming include tilapia, catfish, trout, and salmon. These fish species are hardy, fast-growing, and adaptable to different water conditions.
2. Select a Suitable Site
The next step is to select a suitable site for your fish farm. The ideal site should have access to a reliable source of clean water, adequate space for tanks or ponds, and a suitable climate.
The site should also be free from contaminants such as pesticides and chemicals that can harm the fish.
When selecting a site, it is important to consider factors such as water quality, temperature, and pH levels. You may need to conduct a water test to determine the quality of the water source and assess whether it is suitable for fish farming.
3. Plan Your Farm
Before starting your fish farm, you need to develop a comprehensive farm plan that includes details such as the number of fish you plan to raise, the type of feed you will use, and the expected market demand for your fish.
Your farm plan should also include a budget that outlines the cost of building tanks or ponds, purchasing equipment, and buying fish feed. It is important to have a clear understanding of the costs involved in running a fish farm and to ensure that your business is financially viable.
4. Build Your Farm Infrastructure
Once you have selected a suitable site and developed your farm plan, the next step is to build your farm infrastructure. This includes constructing tanks or ponds, installing a water supply system, and purchasing equipment such as aerators, filters, and pumps.
When building your infrastructure, it is important to ensure that it is designed to meet the needs of your chosen fish species. For example, tilapia requires a shallow pond with a temperature range of 26 to 30°C, while catfish can be raised in deeper tanks with a temperature range of 22 to 28°C.
5. Manage Water Quality
Water quality is critical to the success of your fish farm. Poor water quality can lead to stress, disease, and even death in fish. It is essential to maintain the correct pH levels, temperature, and oxygen content in the water.
To ensure good water quality, you may need to install a water treatment system or use natural methods such as aquatic plants to absorb excess nutrients and maintain oxygen levels. Regular water testing is also necessary to monitor water quality and make any necessary adjustments.
6. Feed Your Fish
Feeding your fish is an essential aspect of fish farming. Fish require a balanced diet that contains the right amount of protein, fat, and nutrients. It is important to select a high-quality fish feed that is appropriate for the species and age of your fish.
Overfeeding can lead to excess waste, which can harm water quality and increase the risk of disease. It is important to feed your fish the correct amount of food at the right time of day to ensure optimal growth and health.
7. Monitor Fish Health
Monitoring fish health is critical to the success of your fish farm. Fish can be vulnerable to diseases and parasites that can quickly spread throughout the population.
It is important to observe your fish daily and look for any signs of illness such as lethargy, loss of appetite, or abnormal behavior.
Regular health checks should also be conducted to monitor fish growth and detect any potential health issues. If you suspect that your fish are sick, it is important to seek the advice of a veterinarian or fish health expert.
8. Market Your Fish
Marketing is an essential aspect of fish farming. You need to have a clear understanding of your target market and develop a marketing strategy to reach your customers. Some of the most common marketing channels for fish farmers include local markets, restaurants, and fishmongers.
It is important to promote your fish as a high-quality and sustainable product that supports the local economy. You can also consider offering value-added products such as smoked or filleted fish to increase the value of your product.
9. Join a Fish Farming Association
Joining a fish farming association is a great way to connect with other farmers, learn about the latest trends and techniques, and stay informed about industry developments. You can also benefit from training and education programs, marketing support, and advocacy efforts.
There are many fish farming associations and organizations that cater to different regions and fish species. Some of the most well-known organizations include the World Aquaculture Society, the Aquaculture Association of Canada, and the National Aquaculture Association.
10. Continuously Learn and Improve
Fish farming is a dynamic and constantly evolving industry. It is important to stay up-to-date with the latest trends, techniques, and best practices to ensure the success of your business. This can involve attending training programs, reading industry publications, and attending conferences and workshops.
Continuous learning and improvement are key to staying ahead of the competition and maintaining a profitable fish farm. By implementing these tips and continuously improving your skills and knowledge, you can build a successful and sustainable fish farming business.
11. Stay Up-to-Date with Regulations
Fish farming is a highly regulated industry and it is important to stay up-to-date with local, state, and federal regulations. This includes obtaining necessary permits and licenses, adhering to environmental standards, and following health and safety guidelines.
Make sure you are familiar with all regulations pertaining to your fish farm and stay informed about any changes or updates. Failure to comply with regulations can result in fines, legal action, or even the shutdown of your business.
12. Consider Diversifying Your Farm
Diversifying your fish farm can help you reduce risk and increase profitability. This can involve raising different species of fish or adding other types of aquaculture products such as shellfish or seaweed.
By diversifying your farm, you can also tap into new markets and expand your customer base. However, it is important to carefully research and plan any diversification efforts to ensure they are feasible and profitable.
13. Invest in Quality Equipment
Investing in high-quality equipment and infrastructure is essential for the success of your fish farm. This includes tanks, pumps, filters, and other equipment needed to maintain water quality and regulate temperature.
Low-quality equipment can result in poor fish growth, disease outbreaks, and reduced profitability. While high-quality equipment can be expensive, it is worth the investment in the long run.
14. Develop a Business Plan
Developing a comprehensive business plan is crucial for the success of any fish farming operation. A business plan should include a detailed overview of your business, marketing strategy, financial projections, and operational plan.
A well-written business plan can help you secure financing, attract investors, and guide your decision-making. It is also a useful tool for measuring progress and making adjustments to your strategy as needed.
15. Consider Environmental Sustainability
Fish farming can have a significant impact on the environment if not managed properly. It is important to implement environmentally sustainable practices to minimize your impact on the surrounding ecosystem.
This can include using renewable energy sources, minimizing water use, and avoiding the use of harmful chemicals and antibiotics. By implementing environmentally sustainable practices, you can help protect the environment and build a more sustainable business.
16. Consider Financial Sustainability
Financial sustainability is crucial for the long-term success of your fish farming business. This involves carefully managing your finances, including expenses, income, and cash flow.
Make sure you have a clear understanding of your costs and revenues, and develop a realistic budget to guide your financial decisions. It is also important to keep accurate records and regularly monitor your financial performance.
17. Seek Professional Advice
Starting a fish farming business can be challenging, and it is important to seek professional advice when needed. This can include consulting with experts in fish health, aquaculture engineering, and business management.
You can also consider hiring a business consultant or working with a mentor who has experience in the industry. Seeking professional advice can help you avoid costly mistakes and ensure the success of your business.
18. Practice Good Record-Keeping
Good record-keeping is essential for the success of your fish farming business. This involves keeping detailed records of fish health, water quality, expenses, and revenue.
By maintaining accurate records, you can track your progress, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions about the future of your business.
19. Stay Passionate and Motivated
It is important to stay passionate and motivated about your fish farming business. This can involve setting goals, celebrating successes, and staying connected with your community and customers.
By staying passionate and motivated, you can overcome challenges and stay focused on the long-term success of your business.
20. Be Patient and Persistent
Finally, it is important to be patient and persistent when starting a fish farming business. Like any agricultural endeavor, fish farming takes time and hard work to become successful. Don’t expect to see immediate profits or results, and be prepared to make mistakes and learn from them.
By being patient and persistent, and implementing these tips for success, you can build a profitable and sustainable fish farming business.
Fish farming can be a rewarding and profitable business venture. By following these tips for success, you can build a sustainable and thriving fish farming operation. Remember to stay patient, persistent, and committed to the success of your business.
Related Queries & FAQ
There are lots of questions and queries related to fish farming business. Here we are trying to list the common questions and queries about this profitable business and trying to answer them. Hope you will find answers of your questions or queries. Don’t hesitate to ask us if you have more questions.
What is fish farming?
Fish farming, also known as aquaculture, is the practice of breeding, raising, and harvesting fish in tanks or ponds for commercial purposes.
Why is fish farming important?
Fish farming is important because it can provide a sustainable source of seafood and help meet the growing demand for fish products. It can also create jobs and promote economic development in rural areas.
What types of fish can be farmed?
Many types of fish can be farmed, including tilapia, salmon, catfish, trout, and carp.
What is the process for starting a fish farming business?
The process for starting a fish farming business typically involves selecting a suitable site, obtaining necessary permits and licenses, selecting fish species, building infrastructure and purchasing equipment, and developing a marketing plan.
How do you ensure the health of the fish?
Ensuring the health of the fish involves maintaining proper water quality, monitoring for disease, providing adequate nutrition, and implementing appropriate management practices.
What are some common challenges associated with fish farming?
Common challenges associated with fish farming include disease outbreaks, water quality issues, regulatory compliance, and fluctuating market demand.
Can fish farming be environmentally sustainable?
Yes, fish farming can be environmentally sustainable if it is managed properly. This can involve using renewable energy sources, minimizing water use, and avoiding the use of harmful chemicals and antibiotics.
How long does it take for fish to reach harvest size?
The time it takes for fish to reach harvest size depends on the species, but typically ranges from several months to several years.
How can you market your fish products?
Marketing fish products can involve selling directly to consumers at farmers markets or through online platforms, as well as selling to restaurants, grocery stores, and other retailers.
Is fish farming profitable?
Fish farming can be profitable, but it depends on a variety of factors including the species of fish, market demand, and management practices. Proper planning, management, and marketing can help increase profitability.
What equipment is needed for fish farming?
Equipment needed for fish farming can include tanks or ponds, water pumps and filters, aerators, heaters, feeders, and harvesting equipment.
What kind of water is best for fish farming?
The best water for fish farming is clean, fresh water that is free from pollutants and disease. The specific water requirements will vary depending on the species of fish being farmed.
How much space is needed for fish farming?
The amount of space needed for fish farming depends on the species of fish and the production goals. Generally, fish require at least 1-2 square meters of water per kilogram of fish.
How do you manage the waste generated by fish farming?
Managing waste generated by fish farming involves implementing appropriate management practices, such as reducing feed waste, using water efficiently, and properly disposing of waste.
How can you ensure the safety of fish products?
Ensuring the safety of fish products involves implementing appropriate food safety and quality assurance measures, such as good manufacturing practices, HACCP, and regular testing for contaminants.
What are the benefits of fish farming compared to wild fish harvesting?
Fish farming can provide a sustainable source of seafood that is not dependent on wild fish populations. It can also reduce pressure on wild fish populations and support rural development.
How can you stay up-to-date on the latest developments in fish farming?
Staying up-to-date on the latest developments in fish farming can involve attending conferences, reading industry publications, and networking with other industry professionals.
What are some resources for learning more about fish farming?
Resources for learning more about fish farming include government agencies, universities, trade organizations, and industry publications.
How can you ensure the long-term success of a fish farming business?
Ensuring the long-term success of a fish farming business involves implementing appropriate management practices, staying informed about market trends, and continually adapting to changing conditions.
What are some potential risks associated with fish farming?
Potential risks associated with fish farming include disease outbreaks, water quality issues, and regulatory compliance. It is important to implement appropriate management practices to mitigate these risks.
What are some key factors to consider when selecting a fish species for farming?
Some key factors to consider when selecting a fish species for farming include the market demand for that species, its growth rate, its tolerance to environmental conditions, and its feed conversion ratio.
Can fish farming be done in urban areas?
Yes, fish farming can be done in urban areas using indoor aquaponics systems, rooftop ponds, or other innovative techniques.
What is the difference between extensive and intensive fish farming?
Extensive fish farming involves raising fish in natural bodies of water, such as ponds or lakes, with minimal intervention. Intensive fish farming, on the other hand, involves raising fish in tanks or ponds with a high level of management and input.
How can you ensure the ethical treatment of fish in aquaculture?
Ensuring the ethical treatment of fish in aquaculture involves implementing humane handling practices, providing appropriate living conditions, and minimizing stress and suffering.
What are some common misconceptions about fish farming?
Some common misconceptions about fish farming include that it is environmentally damaging, that farmed fish are less nutritious than wild fish, and that it is an easy and low-cost business to start.
How can you find financing for a fish farming business?
Financing for a fish farming business can come from a variety of sources, including loans, grants, and crowdfunding. It is important to have a solid business plan and financial projections to attract potential investors.
Can fish farming be done sustainably in developing countries?
Yes, fish farming can be done sustainably in developing countries, and can provide an important source of food and income for rural communities.
How can you reduce the environmental impact of fish farming?
Reducing the environmental impact of fish farming can involve using sustainable feed sources, implementing best management practices, and minimizing water use and waste.
What are some potential health benefits of consuming farmed fish?
Farmed fish can be a good source of protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and other essential nutrients. They can also be lower in contaminants than some wild fish species.
What is the future of fish farming?
The future of fish farming is likely to involve continued innovation and technological advancements to improve efficiency, sustainability, and profitability. It is also likely to play an increasingly important role in meeting global demand for seafood.
How can you ensure the quality of fish feed?
Ensuring the quality of fish feed involves selecting high-quality ingredients, following proper manufacturing and storage practices, and regularly testing for contaminants.
Can fish farming be done organically?
Yes, fish farming can be done organically by using organic feed, avoiding the use of synthetic chemicals, and adhering to organic certification standards.
How can you prevent disease outbreaks in fish farming?
Preventing disease outbreaks in fish farming involves implementing appropriate biosecurity measures, maintaining good water quality, and using disease-resistant fish strains.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in fish farming?
Common mistakes to avoid in fish farming include overstocking, overfeeding, neglecting water quality, and failing to monitor for disease.
What are some alternative forms of fish farming?
Alternative forms of fish farming include integrated multi-trophic aquaculture, where different species are grown together to reduce waste, and recirculating aquaculture systems, which use advanced technology to conserve water and reduce environmental impact.
Can fish farming contribute to food security?
Yes, fish farming can contribute to food security by providing a reliable source of protein and other essential nutrients, particularly in developing countries where traditional fishing methods may be limited.
How can you market and sell farmed fish?
Marketing and selling farmed fish involves identifying potential markets, developing a strong brand, and building relationships with buyers such as wholesalers, retailers, and restaurants.
How can you ensure the safety of farm workers in fish farming?
Ensuring the safety of farm workers in fish farming involves providing appropriate safety equipment and training, implementing safety protocols, and complying with relevant regulations.
What are some challenges facing the fish farming industry?
Challenges facing the fish farming industry include regulatory compliance, disease outbreaks, environmental impact, and market fluctuations.
Can fish farming be profitable?
Yes, fish farming can be profitable, but it requires careful planning, management, and investment. The profitability will depend on factors such as the species of fish, the size of the operation, and the market demand.
Is fish farming a sustainable practice?
Fish farming can be a sustainable practice if it is done responsibly, with consideration for the environmental impact, animal welfare, and social and economic implications. However, if done irresponsibly, it can have negative impacts on the environment and local communities.
Potential risks associated with fish farming include disease outbreaks, escapes of farmed fish into the wild, environmental degradation, and competition with wild fish populations for resources.
How can you ensure the quality of the fish produced through aquaculture?
Ensuring the quality of fish produced through aquaculture involves implementing good management practices, monitoring water quality, and regular testing for contaminants.
How can fish farming contribute to rural development?
Fish farming can contribute to rural development by providing employment opportunities, generating income, and contributing to food security in rural communities.
What is the role of government in regulating fish farming?
Government plays a role in regulating fish farming by setting standards for environmental and animal welfare, monitoring compliance, and providing support for research and development.
What are some best practices for fish farming?
Best practices for fish farming include selecting appropriate species, maintaining good water quality, monitoring for disease, using sustainable feed sources, and practicing responsible management.
Can fish farming help to conserve wild fish populations?
Fish farming can help to conserve wild fish populations by reducing fishing pressure on wild stocks, but it must be done in a responsible and sustainable manner.
How can you ensure the traceability of farmed fish?
Ensuring the traceability of farmed fish involves maintaining accurate records of production and processing, labeling products appropriately, and complying with relevant regulations.
What are some common challenges faced by fish farmers?
Common challenges faced by fish farmers include disease outbreaks, fluctuating market prices, and access to financing and technical support.
Can fish farming be a solution to overfishing?
Fish farming can be a solution to overfishing by reducing pressure on wild fish populations, but it must be done responsibly and sustainably to avoid creating new environmental problems.
Fish farming techniques
Fish farming techniques refer to the various methods used to breed, rear, and harvest fish in a controlled environment. These techniques may include pond culture, cage culture, raceway culture, and recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS).
Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique depends on the type of fish being cultured, the size of the operation, and the available resources.
Fish farming equipment
Fish farming equipment includes a variety of tools and devices used to manage the fish farming operation. This may include nets, pumps, aerators, water quality monitoring equipment, feeding systems, and harvesting equipment.
The type of equipment needed depends on the size and type of fish farming operation, as well as the specific needs of the fish being raised.
Fish farming business plan
A fish farming business plan is a written document that outlines the goals, strategies, and financial projections for a fish farming operation.
The plan typically includes information on the market demand for the fish being raised, the production process, the equipment and resources needed, and the expected revenue and expenses. A well-crafted business plan can help secure funding, attract investors, and guide the development of a successful fish farming operation.
Fish farming training
Fish farming training refers to programs and courses that provide education and hands-on experience for individuals interested in starting or expanding a fish farming operation.
Training may cover topics such as fish biology, water quality management, feeding and nutrition, disease prevention and control, and business planning. Training can be found through universities, government agencies, and private organizations.
Fish farming in India
Fish farming in India is a growing industry, with both freshwater and marine aquaculture operations. India is the second largest producer of fish in the world, with the majority of production coming from inland freshwater aquaculture. Carp, catfish, and tilapia are among the most commonly raised species in India.
Fish farming in Africa
Fish farming in Africa is an important source of food and income for many people on the continent. Both freshwater and marine aquaculture operations are found in various African countries, with tilapia, catfish, and carp being among the most commonly raised species.
Fish farming in Africa faces challenges such as poor infrastructure, limited access to markets, and disease outbreaks.
Fish farming vs traditional fishing
Fish farming and traditional fishing are two different methods of obtaining fish for human consumption. Traditional fishing involves catching fish in the wild, whereas fish farming involves raising fish in a controlled environment.
Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on factors such as sustainability, environmental impact, and economic viability.
Fish farming for beginners
Fish farming for beginners is an introductory guide to the basics of starting and managing a fish farming operation. Topics covered may include choosing the right fish species, selecting a location, understanding water quality, and managing feeding and nutrition. Resources for beginners may include training courses, online tutorials, and guidebooks.
Fish farming in the USA
Fish farming in the USA is a diverse industry, with freshwater and marine aquaculture operations found in various regions of the country. Salmon, tilapia, and catfish are among the most commonly raised species in the US. The industry faces challenges such as regulation, environmental impact, and market competition from imported fish.
Fish farming sustainability
Fish farming sustainability refers to the ability of a fish farming operation to maintain ecological, social, and economic viability over the long term. Sustainable fish farming practices may include using renewable energy sources, minimizing water and resource use, and avoiding the use of harmful chemicals and antibiotics.
Fish farming in Nigeria
Fish farming in Nigeria is a growing industry, with both freshwater and marine aquaculture operations. Nigeria is the largest producer of catfish in Africa and tilapia is also commonly raised. The industry faces challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, lack of access to finance, and high production costs.
Fish farming in Bangladesh
Fish farming in Bangladesh is a significant industry, with a large number of small-scale operations. The industry produces a variety of fish species, including tilapia, carp, and catfish. Fish farming in Bangladesh faces challenges such as limited access to finance, water pollution, and low fish prices.
Fish farming techniques in India
Fish farming techniques in India vary depending on the type of fish being raised and the resources available. Common techniques include pond culture, cage culture, and recirculating aquaculture systems. In India, carp, catfish, and tilapia are among the most commonly raised species.
Fish farming business opportunities
Fish farming can offer a variety of business opportunities, including producing fish for human consumption, selling fish fingerlings or fry to other fish farmers, or supplying fish feed and equipment.
Opportunities may also exist for fish processing and value-added products. The availability of business opportunities depends on factors such as market demand, production costs, and regulatory environment.
Fish farming in Kenya
Fish farming in Kenya is a significant industry, with both freshwater and marine aquaculture operations. Tilapia, catfish, and carp are among the most commonly raised species in Kenya. The industry faces challenges such as limited access to finance, disease outbreaks, and market competition from imported fish.
Fish farming in the Philippines
Fish farming in the Philippines is a significant industry, with both freshwater and marine aquaculture operations. Tilapia, milkfish, and catfish are among the most commonly raised species. The industry faces challenges such as typhoons and other natural disasters, disease outbreaks, and market competition from imported fish.
Fish farming in Uganda
Fish farming in Uganda is a growing industry, with both freshwater and marine aquaculture operations. Tilapia, catfish, and carp are among the most commonly raised species in Uganda. The industry faces challenges such as limited access to finance, high production costs, and low market prices.
Fish farming in Indonesia
Fish farming in Indonesia is a significant industry, with both freshwater and marine aquaculture operations. Tilapia, catfish, and milkfish are among the most commonly raised species. The industry faces challenges such as limited access to finance, water pollution, and market competition from imported fish.
Fish farming economics
Fish farming economics refer to the financial aspects of running a fish farming operation. Key factors that affect the economics of fish farming include production costs, market demand, and pricing of fish. Economies of scale, government policies, and access to finance are also important considerations.
Fish farming certification
Fish farming certification refers to a system of standards and protocols that ensure sustainable and responsible practices in the fish farming industry.
Certification may be provided by third-party organizations such as the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) or Global Aquaculture Alliance (GAA). Certification can help improve market access, consumer trust, and environmental sustainability.
Fish farming in Vietnam
Fish farming in Vietnam is a significant industry, with both freshwater and marine aquaculture operations. Tilapia, catfish, and shrimp are among the most commonly raised species. The industry faces challenges such as disease outbreaks, environmental pollution, and market competition from imported fish.
Fish farming grants
Fish farming grants are financial resources provided to fish farmers to support their operations. Grants may be provided by government agencies, non-profit organizations, or private foundations.
Grants may be used for various purposes such as building or improving fish farming infrastructure, purchasing equipment, or expanding production. Availability of grants and eligibility criteria vary by location and organization.
Fish farming technology
Fish farming technology refers to the use of advanced tools and techniques to improve the efficiency and sustainability of fish farming operations.
Examples of fish farming technology include recirculating aquaculture systems, genetic breeding, and automated feeding systems. Technology can help reduce production costs, improve fish health and welfare, and reduce environmental impact.
Fish farming regulations
Fish farming regulations refer to laws and policies that govern the operation of fish farming businesses. Regulations may cover various aspects such as water quality standards, fish health management, and marketing and labeling requirements. Compliance with regulations is important to ensure food safety, environmental sustainability, and consumer trust.
Fish farming courses
Fish farming courses refer to educational programs that provide training and knowledge about fish farming. Courses may be offered by universities, vocational schools, or training centers.
Course topics may include fish biology and behavior, production systems, disease management, and marketing. Fish farming courses can help individuals interested in starting or improving their fish farming operations.
Fish farming research
Fish farming research refers to scientific studies and investigations related to the fish farming industry. Research topics may include genetics, nutrition, disease management, and environmental impact. Research can help improve the efficiency and sustainability of fish farming operations, as well as advance scientific knowledge in the field.
Fish farming jobs
Fish farming can offer various job opportunities, including fish farm managers, technicians, feeders, and harvesters. Other job opportunities may include fish processing and marketing, equipment and feed sales, and research and development.
Availability of jobs depends on factors such as the size and location of the fish farming operation, as well as market demand and competition.
Fish farming profitability
Fish farming profitability refers to the ability of a fish farming operation to generate income and profits. Profitability depends on various factors such as production efficiency, market demand and price, and production costs. Fish farmers can improve profitability by implementing efficient production systems, reducing production costs, and identifying and targeting profitable markets.
Fish farming in Nigeria pdf
Fish farming in Nigeria pdf refers to various documents and publications related to the fish farming industry in Nigeria. These may include research reports, policy documents, business plans, and training materials.
Pdf documents can provide valuable information and insights into various aspects of fish farming in Nigeria, including production systems, market opportunities, and regulatory requirements.
Fish farming in Kenya pdf
Fish farming in Kenya pdf refers to various documents and publications related to the fish farming industry in Kenya. These may include research reports, policy documents, business plans, and training materials.
Pdf documents can provide valuable information and insights into various aspects of fish farming in Kenya, including production systems, market opportunities, and regulatory requirements.
Health Benefits of Fish
Fish is very nutritious and it is among the healthiest foods on the planet. It is rich in nutrients such as protein, vitamins and minerals. It is also a great source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are incredibly important for your body and brain.
Here we are trying to describe more about the top advantages of consuming fish.
- Fish is high in many important nutrients. It is rich in high-quality protein, iodine, and various vitamins and minerals.
- Some fish also pack omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D.
- Consuming fish regularly is safe for heart patients.
- Omega-3 fatty acids is essential for brain and eye development. And some fish is great source of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Regular consumption of fish is very important for controlling memory and emotion. People who eat fish on a regular basis have more grey matter in their brain centers that control memory and emotion.
- Omega-3 fatty acids in fish may also combat depression.
- Consuming regularly is also beneficial for reducing the risk of type 1 diabetes and several other autoimmune conditions.
- Some studies show that children who eat more fish have a lower risk of asthma.
- People who eat more fish have a much lower risk of AMD, a leading cause of vision impairment and blindness.
- Currently, sleep disorders have become incredibly common throughout the world. Some evidence indicates that eating fatty fish (such as salmon) may improve sleep.[ 1 ]
- Fish is no doubt delicious and very easy to prepare. You can prepare fish in a number of ways, including baked and fried.
Advantages of Fish Farming Business
There are many advantages of starting commercial fish farming business. Here we are describing the main advantages of fish farming business.
- According to the demand, commercial fish farming business allows for large supplies of fish. Catching fish from the wild can’t always fulfill the consumer’s demand. In such cases commercial fish farming can meet up this demand.
- Fish can be raised in tanks until they are ready for marketing, and they don’t require the extensive capture of wild fish. Thus commercial fish farming helps to preserve natural ecosystems.
- Compared to the wild brethren, some farm raised fish species are more nutritious. Fish are usually fed a wide variety of protein and nutrient enriched foods or pellets on commercial fish farms. So farm fish become more healthier than the wild fish.
- Various types of fish species are available throughout the world. So you can choose your desired species for your fish farming business.
- Fish are very popular as food around the world. So there is an established fish market, and you don’t have to worry about marketing your products.
- You can start fish farming business in both large or small scale production purpose.
- If you don’t have enough capital for starting this business, then you can apply for bank loans. Many banks will allow loans for starting this business commercially.
- Fish farming business is a great source of employment. More than 1 billion people around the world depend on fish as their primary protein source. And most of this people are directly or indirectly involved with fish products or fish farming business. As a result, fish farming creates a great income and employment source for the people. Global fish exportation business is now earning more money every year, than any other food commodity.
- Even you can meet up your daily family nutritional demands through small scale fish farming in tanks or ponds.
Disadvantages of Fish Farming Business
It’s important to note that while there are disadvantages to fish farming, there are also many potential benefits when it is done responsibly and sustainably.
By addressing these challenges and mitigating negative impacts, fish farming can help meet the growing demand for seafood while supporting economic development and conservation efforts.
Here are some of the disadvantages of fish farming:
- Water pollution: Fish farms can generate a significant amount of waste and excess feed, which can pollute surrounding water sources and harm natural ecosystems.
- Disease and parasites: Fish farms are often overcrowded, making it easier for diseases and parasites to spread among the fish population. This can lead to the use of antibiotics and other chemicals to treat and prevent illness, which can have negative impacts on both the fish and the environment.
- Escape and invasion: Farmed fish that escape from their pens can pose a threat to wild fish populations by competing with them for resources and spreading diseases or parasites.
- High initial costs: Setting up a fish farm can be expensive, requiring significant investment in infrastructure such as tanks, pumps, filters, and other equipment.
- Dependence on feed: Farmed fish rely on a steady supply of feed, which can be costly and may contribute to overfishing of wild fish populations.
- Environmental impacts: The use of land and water resources for fish farming can have negative impacts on the surrounding environment, including the destruction of habitats and the displacement of local wildlife.
- Social impacts: Fish farming can have negative social impacts on local communities, including displacement, loss of traditional livelihoods, and conflicts over resource use.
Fish farming profits
Fish farming can be a profitable business, but the profitability can vary depending on a number of factors such as the type of fish being farmed, the market demand for the fish, the cost of feed, and the operational expenses.
Generally, fish farming profits can be maximized by carefully managing costs and optimizing production efficiency, while also ensuring high quality and consistent product output.
It’s important for fish farmers to carefully research market demand and pricing trends, and to work with suppliers and buyers to negotiate favorable pricing and distribution arrangements.
With careful planning and management, fish farming can be a sustainable and lucrative business opportunity for entrepreneurs and investors alike.
Fish farming at home
Fish farming at home, also known as aquaponics, is a growing trend among hobbyists and small-scale farmers who want to produce their own food in a sustainable and self-sufficient way.
This involves raising fish in a closed system that also includes plants, which use the waste generated by the fish as fertilizer. The plants, in turn, help filter and clean the water, creating a mutually beneficial environment.
Fish farming at home can be done using small tanks or even outdoor ponds, and can be a great way to grow fresh, healthy fish and vegetables for personal consumption or to sell to local markets.
However, it’s important to note that successful fish farming at home requires careful attention to water quality, temperature, and other environmental factors, and may require additional equipment and knowledge compared to traditional home gardening.
Fish farming project report
A fish farming project report is a comprehensive document that outlines the key aspects of a proposed or existing fish farming venture.
A fish farming project report typically includes details such as the project scope and objectives, market analysis and demand projections, financial projections and budgeting, production plans and methods, risk assessment and mitigation strategies, and environmental and social impact assessments.
The purpose of a fish farming project report is to provide a detailed and transparent overview of the project to potential investors, lenders, or other stakeholders, and to serve as a roadmap for the implementation and management of the project.
A well-crafted fish farming project report can help ensure that the project is viable, financially sustainable, and environmentally and socially responsible.
Final Words
Fish farming, also known as aquaculture, is the practice of raising fish in controlled environments such as tanks, ponds, or floating cages in rivers, lakes or oceans. This is a rapidly growing industry that provides an important source of food and income for millions of people worldwide.
Fish farming can be done on a small scale by individuals or on a large scale by commercial enterprises, and it can involve a wide range of fish species such as salmon, tilapia, trout, and catfish, among others. The advantages of fish farming include increased food production, reduced pressure on wild fish stocks, and improved livelihoods for fish farmers and communities.
However, it also presents environmental and social challenges such as habitat degradation, disease outbreaks, and the use of antibiotics and other chemicals. Sustainable fish farming practices aim to minimize these negative impacts while maximizing the benefits of fish farming.
Recommended for You

Fish Feeding Guide

Pangasius Fish

Shrimp Farming

Yellowhead Catfish

Largehead Hairtail Fish
13 thoughts on “fish farming”.
Very interesting.hope to start this year.
May God bless you!
This is valuable information. Can you provide more reference material on making own fish feed.
please assist with more information [email protected]
Educating introduction to fish farming, thumbs up
Thanks for your guide lines. I’m newly in the business, I stocked just 2 wks ago. Please, I’d like to learn how to make own fish feed
I am in Durban and have intention to start fish farming (pond) using my swimming pool at home. Who can guide me on this one? Thanks. Email [email protected]
Hi how are you I have a place I need someone to hire it and raise fishes
Please keep your contact details here so that interested people can contact you. Good luck!
I have learned alot from your site and thank you
Have no experience whatsoever and would like to start as small as subsistence farming would permit so I can grow organically into a more commercial entity. Any assistance or pointed pointers would be appreciated.
Hi sir, i have made a 7000 square feet mud pond in our house back. I don’t know if it is small for fish farming. Can i stock some tilapia fish in it. is this pond good for raising tilapia. how many fish can this pond tilapia?
Yes, sure! You can definitely stock tilapia fish your pond. Your pond is enough for stocking around or up to 5000 tilapia fish if you provide them supplementary fish feeds. The number will be far less if you provide them with no food. Good luck!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
How To Start A Fish Farming Business – Complete Guide
Do you want to start a fish farming business? Find here a stepwise fish farming business plan guide for beginners along with selected fish farming business ideas.
Is the Fish Farming Business Profitable?
Fish farming is a lucrative business for several reasons. Some of them are the following:
Here are the 7 Steps to Start Fish Farming Business
1. choose the type of fish for farming, a) tilapia fish farming.
Tilapia has become the third most important and popular fish after carp and salmon. High protein content, large size, rapid growth (6 to 7 months to grow to harvest size), and palatability; are the major reasons that make tilapia fish farming highly profitable and popular.
b) Shrimp Farming
C) ornamental fish farming, d) cat fish farming.
Commercial catfish farming is very profitable. Aquaculture farmers can initiate catfish farming alone or combined with other species. Catfish farming can be initiated at a comparatively low cost and on a small-scale basis.
e) Crab Farming
Intensive commercial crab farming can be performed in smaller areas and at greater densities, minimizing land and labor, but the environmental impacts of these techniques can be significant. The mud crab ( Scylla Serrata ) is a promising aquaculture species due to its fast growth and good market acceptability and price.
f) Prawn Farming
G) fish hatchery.
A fish hatchery is an artificial place for breeding, hatching, and rearing through the early life stages of animals, finfish, and shellfish. The selection of the right species is important in starting a fish hatchery business. Some species that are commonly raised in hatcheries include Pacific oysters, shrimp, Indian prawns, Carp fishes, salmon, tilapia, and scallops.
h) Carp Fish Farming
I) salmon fish farming, j) indoor fish farming.
An entrepreneur can initiate indoor fish-related farming from the home location with moderate capital investment. You can also integrate an aquaponic system to grow plants with your indoor fish containers and raise fish, vegetables, and herbs at the same time.
Choosing the right species of fish plays a major role in getting success in the fish farming business. The decision should be based on market demand, maintenance point of view, availability of resources, etc.
2. Understand the Market
Feasibility analysis and business planning are a must before starting a fish farming business. Do intensive market research before getting into fish farming. Understand the local market demand. If you are going to start fish farming for export, then talk to fish processing units prior. Prepare an alternative marketing strategy to rely on.
3. Learn the Skills of Fish Farming
4. create a fish farming business plan, 5. calculate the cost of starting a fish farming business.
Operating costs include purchasing eggs or fingerlings, fish feed, electricity, fuel, labor, chemical, medicine, tax, insurance, telephone, transportation, and other maintenance cost involved.
6. Choose the Right Location
7. what equipment is needed for fish farming.
Another important aspect is the procurement of certain types of equipment. Some of the basic tools and equipment needed in fish farming are the following:
- Thu. Jun 27th, 2024
NG Business
NGBusiness Gives You Access To Over 100 Business Plan Samples As Well As Other Important Business Related Information...
Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria (2024 DOC)

Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria 2024 Sample
Starting a Fish Farming Business today requires you get a professional help or buy a well written business Plan which can serve as a guide through the set up period. The truth is that there are several business challenge
CHAT WITH US ON WHATSAPP FOR YOUR
Business plans and feasibility studies to get a discount.
facing the average businessman/ woman In Nigeria today, especially when it has to do with fish farming as well as the stiff competition that comes with this type of investment, the question now is how to start fish farming in a country like Nigeria? And the get the required return on the investment made in the business.
Overcoming these challenges places you at the pinnacle for your business career. And also the business you get to understand how to start up a business venture in country like Nigeria and being able to running it successfully irrespective of the challenges’ that comes your way.
The Commercial fish farming business plan In Nigeria feasibility study PDF file offers a detailing information on how to start up a fish farming business. For a fact, these are over a thousand species of edible fishes one can actual farm, the most common among them is the catfish, you can see Catfish Farming business plan in Nigeria.
In the business of farming fishes , there are categories of fishes to be farmed, and these fishes has procedures which must be adopted; they are subdivided into two categories, they include;
- Grow-out pond operation
Nursery – The nursery subdivision is a kind of feeder operation which forms the basis for the grow-out pond subdivision. The thing is that the later won’t operate maximally without a functioning nursery. The primary function of the nursery entails the ability of the fish farmer to induce the female fish which makes them to be able to lay eggs. After laying on of eggs, these eggs are either fertilized, incubated or are hatched, these are also known as the fries. In their tiny state, these fries are nurtured for a short period of time, approximately 3 to 4 weeks. At this stage they become what is called fingerlings, the fingerlings can now be transferred to the fish grow-out operation.
Grow-Out Pond operation – This subdivision talks about the fingerlings gotten from the nursery subdivision which will be nurtured until they are matured enough to be sold. This is also applicable to the Catfish farming business.
This feasibility study on commercial catfish business plan centers on the processes involved in growing a fish from the nursery to the grow-out pond operation level. The stages include;
- Pre fingerlings
- Fingerlings
- mini juveniles and then
These stages can take place within a period of say 4 to 5 months. At that final stage when is has matured into a table size fish , you can then offer them for sale.
Factors Involved In Setting Up A Fish Farming Business
One thing the Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria PDF feasibility study will help you in achieving is effective planning and the proper implementation of detailed information that will be useful, below are some of the factors to consider;
Location To Site The Fish Farm – You need to secure a site where the fish farm will be located, getting a suitable land earns you a huge step in the right direction as regards your fish farming business plan In Nigeria. In setting up this farm, things like an accessible road to the farm, nearness to the market etc should be considered. Then after securing your land, carefully map out how every department will operate, from (i) Ponds to the (ii) Farm house (iii) Water supply (iv) Drainage facility etc.
Note – Effective water draining helps your business not to constitute public nuisance in your area of establishment.
Map Out A Workable Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria – Your plan is the blood stream of the business. What you have in your plans tells the size of the fish farm you want, either large scale or small-scale. Your plans will also tell of the pond system you will adopt. We have different pond system, they include;
- Re-circulatory system
- Earthen pond system
- concrete/plastic pond system, you can go for both.
Where To Source For Water supply – For your Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria to be successful, you need constant water supply, you can use the following sources,
- Bore hole water source, this source has been considered as the best water for fish farming.
- Installing Overhead tanks, this system will help you to retain water and then pumping it into the pond. You can hold water in the tanks for a period as it can also maintain a certain temperature.
Pond Construction – This has to be included in your Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria. There are professional pond constructors you can employ to help you construct a quality pond.
Aquaculture Production In Nigeria
The aquaculture production in Nigeria has in recent time attracted considerable attention. With a well written feasibility studies like the commercial fish farming business plan pdf that has created an avenue for private individuals to participate in the venture as a business.
The procedure and technology adapted for growing these fish in the farm method are well detailed in this business plan. Also information contained therein was written with respect to principles of sustainable aquaculture, as well as aquaculture production technology system where the ecological as well as the economic viability persists indefinitely’.
Fish like other living creatures are affected the happening of their environment (water), these happenings can either help their growth or hinder their growth. Fish has an ecosystem that is dynamic in nature, a fact that is contributed by nutrient, weather or season. It is important to know that the dynamic nature of the ecosystem is even more visible in the fish farm system. Hence, ensure that your water supply is constant and then also know when to change the water.
Fish farmers can be successful if they can be pretty much observant and then adapt their farming schedule, this alone can help to boost their fish productivity as well as profitability. By getting this Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria , you have a well detailed feasibility study that has all you need to have your commercial production of catfish set up in Nigeria.
TO GET YOUR FISH FARMING BUSINESS PLAN IN NIGERIA. Simply order yours by paying N10,000 to
GTBank (Guaranty Trust Bank)
Account Name – Okite Joseph ikenna
Account No – 0044083736
Once payment is made for the FISH FARMING BUSINESS PLAN IN NIGERIA / FEASIBILITY STUDY PDF, send the following info (i) a valid email address and (ii) your payment details to any of these numbers – 07039768549.
NOTE – It is important to note that the Business Plan for Fish Farming PDF will immediately be sent to the email address after your payment has been confirmed.(Soft copy only)
What will the Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria Look Like?
INTRODUCTION
- Current Situation of aquaculture in Nigeria
- Aquaculture Production in Nigeria
- Aquaculture Policy Environment at National and State Levels
- Success potential
- Skills and abilities for success
- Production feasibility
MARKET ANALYSIS & TECHNICAL ANALYSIS for Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria
- Product description
- Financial projections
- Competitors marketing analysis
- Proposed Marketing Strategy
- Operational Details and Structure
- Machinery/Equipment Requirements, housing, drugs and feeding
- Raw materials and sources
Labour Force, Admin Requirements, And Organisation for Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria
- Personnel requirement
- Organization structure
Capital (Investment Analysis) Involved
This covers for;
- Cost production of 50,000 fingerlings and their expected returns (ROI). Investment in feed, fingerlings etc
- Cost production of 50,000 Grow-out pond and their expected returns (ROI)
- Cost production of 50,000 smoked fish and their expected returns (ROI).
Additional Information
- A MANUAL, FIND BELOW THE CONTENT
- TOPICS COVERED IN THE FISH FARMING BUSINESS MANUAL
HOW TO IMPLEMENT THE BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES for Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria
- Introduction
- Commercial Fish Production
- Sustainable aquaculture production
- Why some fish farmers fail
- Sitting the farm
POND REQUIREMENTS, DESIGNS, CONSTRUCTION AND POND TYPES for Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria
- Earthen pond
- Flow through system (Concrete tank, plastic tanks or vat)
REPRODUCTION IN CATFISH for Fish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria
- Choosing Your Male & Female Brood Stock
- Injecting the Female Fish
- Getting the Male Sperm
- Stripping the Female Fish
- Mixing Sperm with Eggs & Spreading Inside the Vat
- Feeding the Fries
- Daily schedules of works in trough rearing of fries
- Sorting: A Necessary Factor
- Operational cost for fingerlings production
- Diseases of fingerlings
- Transportation of fish
How To Start Fish Farming Business In Nigeria
Fish farming business in Nigeria can be regarded as one of the most profitable businesses out there, this is easy to know due to the high level of patronage the very few fish farms around us get, not only that, fish has been described by nutritionist as an alternative source of protein, so instead of buying the red meat you so much dread, you simply buy either iced fish from a cold room or buy from the fish farm around your area.
Without a doubt Catfish farming is a profitable business ventures and the good thing about starting one is that beginning your fish farm with a catfish, will yield returns earlier since catfishes are easy to get as well as cultivate, with easy accessibility to all types of fish feeds. In a very short and very brief review, we are going to look at how to start a fish farm, things you need to rung a standard fishery in Nigeria, and then a list of equipment required to kick start your business venture.
Entrepreneurship and extensive innovation has made it possible for business enthusiast to run a fish farm business without necessarily going to the river to fish or constant visit to a nearby pond. Today, with enough money at hand, you can easily build a fish pond, supply enough water constantly and your fish will grow and becomes some of the biggest in the market, in order words a commercial fish farm is possible if the capital is available.
Why Fish Farming Is Lucrative With High Profit Margin
A lot could be could be attributed to the reason why fish farm business in Nigeria comes with loads of advantages for the business owner, below are three reasons you should consider going into fish farming;
Affordability but highly Lucrative – In comparison with other meats, fish is cheaper than birds such as chicken and Turkey and then goat mean or beef. Fishery products are popular, with different types, from dried fish to smoked fish and many more, the Nigerian market is filled with different types, hence the possibility of selling faster than meat.
Alternative Source of Protein – As stated earlier, fish offers another protein source, the good thing about it is that it comes with a lot of zero fat. Fish according to nutritionists are of the opinion that fish contains vitamins such as the Riboflavin as well as the ever important vitamin D, also present is the omega-3 fatty acids, in essence, the nutrients in fish could help in situations such as when an individual needs a heart or brain surgery. Other nutrients found in fish includes but not limited to the following;
- Omega-3 fatty acids
Rapid Growth – Another reason why fish farming is assumed to be lucrative is because of the rapid growth cycle in fishes, this means you could make profit within a very time from constant reselling of your farm produce.
Hurry now, TO GET YOUR FISH FARMING BUSINESS PLAN IN NIGERIA. Simply order yours by paying N10,000 to
NOTE – It is important to note that the Business Plan for Fish Farming PDF will immediately be sent to the email address after your payment has been confirmed.(Soft copy only),
Other Business Plans
Supermarket Business Plan In Nigeria
Catfish Farming Business Plan In Nigeria
Solar Energy Installation Business Plan
Haulage & Trucking/Logistics Business Plan
Cooking Gas (LPG) Plant Business In Nigeria
Bread Bakery Business Plan in Nigeria
Cosmetics Business Plan in Nigeria
Fashion Design Business Plan In Nigeria
Related Post
Cashew nuts production business plan (2024 doc), coconut chips processing business (2024 doc), hotel business plan in nigeria (2024 doc), leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
NIRSAL MFB Loan Application Portal Login
Cbn naira intervention | currency intervention, cbn low interest intervention loans 2024/2025, artificial intelligence and small business in nigeria.
We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
Fish Farming Business Name Ideas
242 Fish Farming Business Name Ideas
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Published on June 24, 2024 Updated on June 24, 2024

If you’re starting a fish farming business , we congratulate you! In front of you is an exciting journey filled with success but also many decisions — like picking a perfect business name.
Since the name will be the first impression people will have of your fish farm, you should carefully consider your options to come up with the best one.
Choosing a winning name is not always easy, but luckily, you’ll find valuable tips and suggestions in this handy guide.
- Fish Farming Business Name Generator
Register domain
We’ve done some work and come up with business name suggestions for your fish farming business. The names are divided into categories so that you can choose one that fits your brand’s personality.
- Location-Based
- BayBounty
- RiverRise Fish Farms
- CoastalCatch
- DeltaDwell Fisheries
- LakeView Aqua Harvest
- IslandHarvest Fishery
- AquaValley Farms
- OceanTide Fisheries
- Pond Aquaculture
- Hillside Fishery
- EstuaryEdge Aqua Farms
- SoundShore Aquatics
- FjordFlow Fisheries
- Marshland Marine Farms
- Riverview Aqua Harvest
- LagoonLand Aquaculture
- BrookBank Aquafarms
- Inlet Isle Fisheries
- ChannelCoast Aqua Farms
- BayouBloom Aquatics
- DeltaDive Fisheries
- CoralCanvas
- Gilded Gills
- Prismatic Ponds
- FinFiesta Exotics
- ColorCrest Farms
- Finorama
- RainbowReef
- AquaticAura
- Shimmer Shoals
- KaleidoFish
- Aqua Aria Exotics
- Fintasia
- LuminaPiscis
- BrillianceBay
- Luminous Lagoon
- Aqua Glow Gardens
- Spectrumarium
- Lush Lagoon Finery
- Scale Symphony
- Finaria
- FinFlare Fisheries
- TideTrail Farms
- Aqua Harvest
- ScaleScape Aquatics
- Finfinity Fisheries
- AquaCrest Aquafarms
- NeptuneNest Aquafarms
- Splash Sphere
- BluHorizon Harvests
- DeepBlue Dynamics
- Oceanic Origins Farms
- Finestra
- Fin Haven Aquaculture
- Oceanique Orchards
- Aqua Harbor
- ScaleSavvy Aquaculture
- AquaAcre Aquafarms
- AquaThrive Enterprises
- Streamside Solutions
- Finestream Fisheries
- FinClarity Cultivators
- WaveCrest Farms
- StreamSide Aquatics
- AquaGrowth Gardens
- Splash Hatch
- SplashHaven Fisheries
- Aquatic Apex Farms
- Finny Haven
- AquaGrove Oasis
- Splashy Stream Farms
- Fishy Frolic Haven
- FinWhisper Farms
- SwimScape Farms
- FinFelicity Fisheries
- AquaTranquil Haven
- ScaleBliss Farms
- FinGrove Haven
- AquaJoy Farmscape
- FinnyBloom Farms
- SplashFusion Farms
- Aqua Ripple
- Ripple Vibe
- Poseidon’s Pantry
- FinCraft Farms
- AquaCrest Fisheries
- FinSplash Farms
- FinestFlows Fisheries
- Neptune’s Nurtures
- FinSpectrum
- AquaVita Ranch
- Tidal Thrives
- BrineBloom Aquatics
- FishHaven Acres
- BlueRibbon Fisheries
- EternalTide Farms
- FinSail Farms
- WaterWealth Farm
- SilverStream
- Marine Majesty
- FinWells Farms
- MarineMeadows
- RoyalReef Fisheries
- Emerald Waters
- TidePool Farms
- ClearCurrent Aquafarm
- Oceanic Grove
- Fish FinNest
- FinFluent Fisheries
- Fin-tastic Farms
- The Codfather
- Ray of Laughs
- Bass-ically Bliss Farms
- SalmoNirvana
- The Koi Club
- Splashdance
- Cod’s Gift
- Scale Mail Delights
- Gill-ty Pleasures Farm
- Fin Flappers Haven
- Aquaholics Anonymous
- Flap-tacular
- Sole Mates Farms
- Mariner’s Bounty
- TideTurn Fishery
- Finest Catch
- AquaVista Gardens
- StreamStar Aquafarms
- DeepSea Delights
- Gills’n’Thrills
- Fin Fishin’
- Marine Crown
- ScaleMagic Fisheries
- AquaWave Gardens
- BlueWave Aquatics
- Fish Finesse
- OceanGem Farms
- FinFlex Fisheries
- Nautical Nurtures
- TideFlow Aquatics
- AquaSpectra Aquafarms
- Scale Craft
- Finity Farms
- SplashBurst
- AquaFalls Fisheries
- ReefCraft Farms
- Ripple Quest
- Marlin Meadows
- SeaHarvest Haven
- Coastal Current Farms
- SeaSpectrum
- AquaSprout Aquaculture
- AquaWonders Ranch
- Splashorama
- FinnedFriends Farm
- FinFab Farmstead
- Gills & Grins
- FinWonder Waters
- Splashopolis
- Aquatic Eden Fields
- ScaleSong Sanctuary
- AquaCraze Gardens
- Splash Harmony
- FinFable Farms
- ScaleQuest Quarters
Find a Domain
Powered by GoDaddy.com
- How to Choose a Name for Your Fish Farming Business
Here are some key factors to consider when choosing your fish farming business name.
1. Check Name Availability
When you come up with name options, you must make sure they’re available and don’t sound similar to other fish farms’ names.
You’ll need to do a business name search on your state’s Secretary of State’s website to check if the name is available. The search will also show similar names, so you can ensure your name is unique in your state.
Also, go to the United States Patent and Trademark Office’s website to see if the name is trademarked.
2. Check Your State’s Business Name Regulations
Each state has rules regarding business names, often restricting words such as “bank” or “university.” Some states have stricter rules than others; for example, Michigan has quite a list of prohibited words. You should be able to find your state’s rules on the Secretary of State’s website.
Upon creating an LLC , it’s mandatory to have either ‘LLC’, ‘limited liability company’, or ‘limited liability’ as part of its official name . This ensures clarity and compliance with naming conventions for such entities.
3. Choose a Name with Relevance
Your name should be relevant to your fish farm services and products, reflecting your business mission. Often, if you write down a description of your brand identity, you’ll come up with words that have the potential to be used in your business name.
4. Keep It Simple
Your name should be easy to say so that it’s more memorable. It should also be easy to spell so people can search for your fish farming business online.
5. Short and Unique
Short, unique, and catchy names stand out. Think Google, which is so catchy and memorable that it’s become a verb!
6. Get Feedback
Family and friends can give you an outside perspective on your fish farm name. They can offer suggestions and give you feedback on the names you have in mind.
7. Allow for Expansion
If you plan to expand your business and go into new products or service lines, you should aim for a name that’s not too narrow. For example, “Pete’s Perch Farm” is much more restrictive than “Pete’s Fish Farm.”
The name should also have timeless appeal. Don’t try to capture a trend — trends continuously change, and you don’t want a name that could become outdated.
8. .com is Best
Generally, domain names ending in .com reflect more credibility than alternatives, so you should reserve this domain for your business name, if possible. Use our Domain Name Search Tool to find an available website name and get the perfect domain name for your fish farming business.
9. Use Keywords to Boost SEO
You’ll want your name to be SEO-friendly to boost your organic search engine rankings. Think of what potential customers might search for when looking for a fish farming business on Google (e.g., “Fish,” “Aquaculture,” and “Fishery”) and include those keywords in your business name and on your website.
10. How Does it Sound?
Say the name out loud to see how it rolls off the tongue. Is it pleasant? Does it evoke positivity? You’d be surprised how different a name sounds when you say it compared to when you think it.
11. Appeal to Emotions
Names that evoke positive emotions can create a connection with your target customers. You want them to feel good about your fish farm.
It can be advantageous as it provides clarity and communicates your specialization. However, if you plan to diversify or expand in the future, a broader name might be more suitable.
In an environmentally conscious market, reflecting sustainability can be a powerful branding strategy. A name that hints at eco-friendly practices or responsible aquaculture can appeal to conscientious consumers.
Including a geographical reference can help establish a local connection. However, be cautious, as it might limit your business if you plan to expand beyond the initial location.
Using your name can add a personal touch to the business, especially if you have a strong reputation in the field. However, ensure that it resonates with the audience and fits the industry.
While it’s possible, it’s best to choose a name you can commit to for the long term. Changing a business name can be challenging and may involve rebranding efforts. Consider your choice carefully from the start.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.

How Shira Yevin Is Empowering Women in Music with Gritty In Pink
Carolyn Young
Published on June 21, 2024
In this interview, we delve into the inspiring journey of Shira Yevin, Founder and CEO of Gritty In Pink and the INPINK marketplace, and frontwomano ...

How a Traditional German Bakery Thrives in Arlington, VA
Esther Strauss
Published on June 20, 2024
Welcome to an interview with Wolfgang Büchler, the visionary behind Heidelberg Pastry Shoppe, a celebrated German bakery in Arlington, VA. Since197 ...

Building a Top NYC Recording Studio with Michael Kevin Walsh
Michael Kevin Walsh is the owner of The Smooth Spot, a premier recording studio located in midtown Manhattan. Known for its high-quality vocalrecord ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The fish farm industry is expected to grow over the next five years to over $202 billion. The growth will be driven by the increased need for regulated raising and harvesting of fresh fish and crustaceans. The growth will also be driven by the consumer demand for sustainable fish-farmed sources of fish.
Fish Farm Business Plan Template. Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their fish farms. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a fish farm business plan ...
In other words, the species have different needs for food and habitat. 3. Site Selection. Choose a site that has access to clean water and is suitable for the type of fish farming you plan to do. Consider factors like water source, soil quality, and proximity to markets. 4. Name Your Business.
The Total Fee for incorporating the Business (commercial farm) in United States of America - $750. The amount needed to acquire / lease a fish farm land - $50,000. The amount required for preparing the farm land (fish ponds and fresh water supply et al) - $30,000.
2. Draft a fish farm business plan. 3. Develop a fish farm brand. 4. Formalize your business registration. 5. Acquire necessary licenses and permits for fish farm. 6. Open a business bank account and secure funding as needed. 7. Set pricing for fish farm services. 8. Acquire fish farm equipment and supplies. 9.
The financial plan. Below, we go over each section in more detail. 1. The executive summary. The executive summary of a fish farm business plan should provide an overview of the business, market, and key financials. When writing an executive summary, start by introducing the company and its mission. Give a brief overview of the market for fish ...
fish farming business plan. Maintain water quality and monitoring systems: Regularly test and monitor water parameters such as temperature, pH, and oxygen levels. Implement filtration systems and proper water circulation to ensure optimal conditions for fish growth. Implement biosecurity measures: Prevent disease outbreaks by practicing strict ...
Market size and growth potential: Describe your market size and growth potential and whether you will target a niche or a much broader market. For instance, the global fishing-farming market size is to be $378,005.5 million by 2027, so it is crucial to define the segment of your target market and its growth potential.
Crafting a compelling fish farming business plan requires careful research and strategic thinking. Here's a step-by-step guide to writing a fish farming business plan: Executive Summary: Provide ...
This comprehensive template is designed specifically for fish farmers, helping you outline your goals, strategies, and financial projections. With this template, you can: Secure funding and attract investors by showcasing your growth potential. Create a roadmap for your operations, ensuring every aspect of your business is well-structured.
Sample Business Plan For Fish Farm Businesses. Below are links to each of the key sections of your Fish Farming business plan. It can be used for a seafood farming business, catfish farming business, wild fish or any other type of fish farms. I. Executive Summary II. Company Overview III. Industry Analysis IV. Customer Analysis V. Competitive ...
Cost Structure: The main costs involved in Agrolearner.com Farm's fish farming business include: Operational Costs: Expenses related to farm operations, including labor, utilities, feed, and maintenance. Infrastructure Costs: Investments in land, pond construction, processing facilities, and equipment.
Business Model: Supplying hatchlings to other farms, ensuring a consistent source of new stock. Aquaponics: Integrating fish farming with hydroponics, where fish waste fertilizes plant growth. Business Model: Selling both fish and produce, targeting environmentally-conscious consumers.
This budget acts like a roadmap for your fish farming business plan, ensuring you don't run out of money before your fish are ready for the market. ... Let's dive in and explore how to be the best fish parent ever. Getting Your Fishy Babies - Fry and Fingerlings. Think of acquiring fish fry and fingerlings like getting a new puppy. It's ...
Step 4: Create a Fish Farm Business Plan. Here are the key components of a business plan: Executive Summary: A brief overview outlining the essential details of the fish farming business, ... Catfish are the most popular farm fish. They usually provide the best return on investment. Tilapia, trout, and yellow perch are also popular.
Get the best start with this essential business plan template & guidebook. Learn expert tips and tricks to create the ultimate business plan & ensure your success in finding success in the eyelash extension industry. ... The #1 Fish Farm Business Plan Template & Guidebook is a comprehensive tool to help you create a solid business plan, prepare ...
Use this free fish farming business plan template to quickly & easily create a great business plan to start or grow your fish farm business. ... seeks to position itself as a high-quality premium source of fresh salmon in the fish farming market. Consumers can expect the best tasting salmon on the market grown and harvested by skilled fish ...
This plan is crucial for outlining operational strategies and financial projections. Embarking on an aquaculture business journey involves meticulous planning and a clear understanding of the industry's nuances. Your path to a successful fish farming enterprise begins with the creation of a detailed business plan PDF, which serves as a ...
A fish farming business plan is a written document that outlines the goals, strategies, and financial projections for a fish farming operation. The plan typically includes information on the market demand for the fish being raised, the production process, the equipment and resources needed, and the expected revenue and expenses.
Here are the 7 Steps to Start Fish Farming Business. 1. Choose the Type of Fish for Farming. The first thing you must consider while starting fish farming is the type of fish you are going to produce. Below find the most popular types of fish farming business ideas that are presently fetching good returns.
This document provides a comprehensive business plan for starting a fish farming business in 2018. It outlines the necessary requirements and start-up capital needed, including purchasing land, hiring staff, obtaining permits and licenses. A detailed projected income statement and cash flow analysis is included to evaluate the profitability of the business over three years. The plan also ...
GTBank (Guaranty Trust Bank) Account Name - Okite Joseph ikenna. Account No - 0044083736. Once payment is made for the FISH FARMING BUSINESS PLAN IN NIGERIA / FEASIBILITY STUDY PDF, send the following info (i) a valid email address and (ii) your payment details to any of these numbers - 07039768549.
8. .com is Best. Generally, domain names ending in .com reflect more credibility than alternatives, so you should reserve this domain for your business name, if possible. Use our Domain Name Search Tool to find an available website name and get the perfect domain name for your fish farming business. 9.
The risk of the business is mainly getting a market and we have already identified our. target market. The cost benefit analysis of this plan shows that in the startup year, with. 12,000 ...