Technology and Digital Media in the Classroom: A Guide for Educators
By andy minshew.
- January 23, 2020
Technology has done more to change school curriculum and practices than nearly anything else—and in such a short amount of time! While it can be hard to keep up with every trend in educational technology, the mindset you have when it comes to classroom tech matters just as much as which ones you use. By learning to view it as a means of enhancing your lessons and resources, you can provide your students with tools and opportunities they may not otherwise access.
So, why and how should you use technology in your classroom? Read on to discover the impact of technology in education and how to get the most from its unique benefits.

What Is the Proper Role of Technology in the Classroom?
If you struggle to use technology in your classroom, you’re not alone. Many educators aren’t motivated to use digital resources in class, often because they’re unsure how to use them effectively or are unaware of the benefits.[1] In such cases, it’s easy to question not only how to make technology useful, but also whether technology should be used in schools at all.
Even with the latest and best digital technology, classrooms will not benefit unless the students and faculty understand how to use it.[15] In fact, educational technology should never be viewed as a perfect resource to teach your students everything they need to know to succeed. Instead, view it as a tool that can inform and supplement lessons, and even then, only if teachers and administrators are well trained in its use.
While technology can be an excellent resource in a classroom, it’s important to set limitations. Technology—no matter how good—should never be a substitute for face-to-face interaction with a teacher or classmates.[4] Technology is best used to augment non-digital lessons rather than the other way around. The goal when using technology should be to enhance your teaching rather than replace it.[6]
Benefits of Using Tech and Digital Media in Education
With the help of technology, you can introduce your classroom to opportunities and resources they may not otherwise be able to access.[5] In fact, this is one of the greatest ways technology has changed education. You may not be able to take your students to one of NASA’s space centers to witness a rocket launch, for example, but you can teach them all about rockets using resources on NASA’s website . Video clips, educational games, and virtual simulations are just a few examples of technology resources you can use to engage and educate in the classroom.
Plus, the vast majority of today’s careers require at least some digital skills (which include anything from complex skills like coding to simpler ones like composing and sending emails). Using tech in class can prepare students to successfully enter the workforce after graduation.[4] Even though the technology is likely to change from their early school years to the time they start their first career, teaching digital literacy in elementary school is a great way to get students started.
Why else is understanding how to use technology in the classroom important? Using technology alongside non-digital lessons can have many academic and behavioral benefits for your students, including:[2,7,11,12]
- Longer attention span
- Increased intrinsic motivation to learn
- Higher classroom participation and student engagement
- Greater academic achievement
- Stronger digital literacy
And finally, the benefits of classroom technology can expand far beyond the classroom and right into your students’ homes.[4] Rather than handing out paper worksheets, you can send your students online lessons or activities to complete at their own convenience. This practice provides better flexibility, plus the opportunity for you to provide audio or video clips alongside homework assignments. Additionally, if you have under-resourced students in your classroom, you may be able to supplement the resources available to their families by providing take-home technology.
How to Get the Most from Technology in Schools
One of the major concerns parents and educators have with classroom technology is how to limit excessive screen time. The American Association of Pediatrics suggests the following screen time recommendations by age. Keep these guidelines in mind when you teach lessons that involve screen time in your classroom:[17]
- 2–5 years old : No more than one hour of high-quality digital activities or programming
- 6 or older : Consistent limits to prevent screen time getting in the way of sleep, physical activity, or other healthy behaviors

Whenever possible, prioritize active digital screen time over passive.[16] Active screen time, like playing an educational game or learning a new digital skill, engages a student’s mind or body in a way that involves more than observation. Passive screen time—think watching a video or listening to an online lecture—involves limited interaction or engagement with the technology. Active digital activities are more likely to help your students experience new concepts, and they encourage your class to work together during the lesson.
Although teachers at under-resourced and rural schools are less likely to use technology, any tech you have available can greatly add to the opportunities you provide your students.[13, 18] Technology can remove some of the physical or financial barriers to educational resources and experiences.[17] If you’re unable to go on a field trip, for example, you can access plenty of virtual field trips at no cost.[16] Use the technology you do have to supplement your lessons and provide students with information you may not otherwise be able to access.
And finally, use school technology to teach your students digital citizenship .[14] Broadly defined, digital citizenship is the safe, ethical, informed, and responsible use of technology.[16] It encompasses skills like internet safety, setting healthy screen time habits, and communicating with others online. Lessons that involve digital citizenship can help a student use technology responsibly well beyond their elementary school years.
6 Quick Tips for Using Technology in the Classroom
The benefits of technology in education can revolutionize your classroom, but only when used intentionally. All it takes is a little time and personal training to help you understand the ins and outs of useful classroom tech.
Keep these six strategies and ideas in mind to help you get the most out of your classroom technology:
- Always use technology or learning programs yourself before trying it with your students so you can troubleshoot any issues in advance.[9]
- Most of today’s students are digital natives and have grown up around technology for their entire life. Listen to what your students know about technology and ask them for tip. They may just teach you something new![8]
- Use digital resources (like apps, texts, or social media groups) to keep parents informed about class activities and upcoming assignments.[5]
- Prioritize active digital activities, like online learning games or interactive lessons, over passive activities (like watching a video).
- If you’re an administrator, schedule a faculty training session on how to use your school’s technology and answer any questions.[10]
- Focus your technology-based lessons on teaching your students digital citizenship , or skills that will help them thoughtfully and effectively navigate digital media.[14]
- Groff, J., and Mouza, C. A Framework for Addressing Challenges to Classroom Technology Use. AACE Journal, January 2008, 16(1), pp. 21-46.
- Levy, L.A. 7 Reasons Why Digital Literacy is Important for Teachers. Retrieved from usc.edu: https://www.rossieronline.usc.edu/blog/teacher-digital-literacy/.
- Van Dusen, L.M., and Worthen, B.R. Can Integrated Instructional Technology Transform the Classroom? Educational Leadership, October 1995, 53(2), pp. 28-33.
- Rosenberg, J. Technology in the classroom: Friend or Foe? Retrieved from huffpost.com: hhttps://www.huffpost.com/entry/technology-in-the-classro_2_b_2018558..
- Venezky, R.L. Technology in the classroom: steps toward a new vision. Education, Communication & Information, 2004, 4(1), pp. 3-21.
- Buckenmeyer, J.A. Beyond Computers In The Classroom: Factors Related To Technology Adoption To Enhance Teaching And Learning. Contemporary Issues in Education Research. April 2010, 3(4), pp. 27-36.
- Bester, G., and Brand, L. The effect of technology on learner attention and achievement in the classroom. South African Journal of Education, 2013, 33(2), pp. 1-15.
- Reissman, H. 7 smart ways to use technology in classrooms. Retrieved from ted.com: https://ideas.ted.com/7-smart-ways-to-use-technology-in-classrooms/.
- Edutopia Staff. How to Integrate Technology. Retrieved from edutopia.org: https://www.edutopia.org/technology-integration-guide-implementation. Winters-Robinson, E. How Tech Can Engage Students, Simplify the School Day and Save Time for Teachers. Retrieved from edsurge.com: https://www.edsurge.com/news/2019-10-15-how-tech-can-engage-students-simplify-the-school-day-and-save-time-for-teachers.
- Couse, L.J., and Chen, D.W. A Tablet Computer for Young Children? Exploring its Viability for Early Childhood Education. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 2010, 43(1), pp. 75-96.
- Filer, D. Everyone’s Answering: Using Technology to Increase Classroom Participation. Nursing Education Perspectives, 2010, 31(4), pp. 247-250.
- Friedman, S. How Teachers Use Technology in the Classroom. Retrieved from thejournal.com: https://thejournal.com/articles/2019/04/15/how-teachers-use-technology-in-the-classroom.aspx.
- Mace, N. 8 Strategies to Manage the 21st Century Classroom . Retrieved from education.cu-portland.edu: https://education.cu-portland.edu/blog/classroom-resources/using-classroom-technology/.
- Keswani, B., Patni, P., and Banerjee, D. Role Of Technology In Education: A 21st Century Approach. Journal of Commerce and Instructional Technology, 2008, 8, pp.54-59.
- The Office of Educational Technology. Reimagining the Role of Technology in Education: 2017 National Education Technology Plan Update . Retrieved from tech.ed.gov: tech.ed.gov/files/2017/01/NETP17.pdf.
- Courville, K. Technology and its use in Education: Present Roles and Future Prospects. 2011 Recovery School District Technology Summit, 2011, pp. 1-19.
- Klopfer, E., Osterweil, S., Groff, J., and Haas, J. Using the technology of today, in the classroom today: the instructional power of digital games, social networking, simulations, and how teachers can leverage them . The Education Arcade, 2009, pp. 1-20.
- American Academy of Pediatrics. American Academy of Pediatrics Announces New Recommendations for Children’s Media Use. Retrieved from aap.org: https://www.aap.org/en-us/about-the-aap/aap-press-room/Pages/American-Academy-of-Pediatrics-Announces-New-Recommendations-for-Childrens-Media-Use.aspx.
More education articles

Celebrating Juneteenth 2024: Children’s Books and Activities for Families and Educators
Happy Juneteenth! This American holiday is celebrated annually on June 19th and marks a significant historical moment in Black American heritage. Originating as a Texas

Supporting LGBTQ+ Families in the Classroom
The Waterford.org vision is for every child to reach their full potential through accessible and effective early learning experiences that put them on a meaningful

10 of the Best Elementary Activities for the Last Days of School
The end of the school year can evoke a bittersweet feeling. It marks a moment for celebration as educators contemplate the growth and achievements of

Mental Health Awareness Month 2024: 7 Ways to Nurture Your Child’s Mental Health

MacKenzie Scott’s Yield Giving Awards Waterford.org a $10 Million Grant
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
Image credit: Claire Scully
New advances in technology are upending education, from the recent debut of new artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots like ChatGPT to the growing accessibility of virtual-reality tools that expand the boundaries of the classroom. For educators, at the heart of it all is the hope that every learner gets an equal chance to develop the skills they need to succeed. But that promise is not without its pitfalls.
“Technology is a game-changer for education – it offers the prospect of universal access to high-quality learning experiences, and it creates fundamentally new ways of teaching,” said Dan Schwartz, dean of Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE), who is also a professor of educational technology at the GSE and faculty director of the Stanford Accelerator for Learning . “But there are a lot of ways we teach that aren’t great, and a big fear with AI in particular is that we just get more efficient at teaching badly. This is a moment to pay attention, to do things differently.”
For K-12 schools, this year also marks the end of the Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) funding program, which has provided pandemic recovery funds that many districts used to invest in educational software and systems. With these funds running out in September 2024, schools are trying to determine their best use of technology as they face the prospect of diminishing resources.
Here, Schwartz and other Stanford education scholars weigh in on some of the technology trends taking center stage in the classroom this year.
AI in the classroom
In 2023, the big story in technology and education was generative AI, following the introduction of ChatGPT and other chatbots that produce text seemingly written by a human in response to a question or prompt. Educators immediately worried that students would use the chatbot to cheat by trying to pass its writing off as their own. As schools move to adopt policies around students’ use of the tool, many are also beginning to explore potential opportunities – for example, to generate reading assignments or coach students during the writing process.
AI can also help automate tasks like grading and lesson planning, freeing teachers to do the human work that drew them into the profession in the first place, said Victor Lee, an associate professor at the GSE and faculty lead for the AI + Education initiative at the Stanford Accelerator for Learning. “I’m heartened to see some movement toward creating AI tools that make teachers’ lives better – not to replace them, but to give them the time to do the work that only teachers are able to do,” he said. “I hope to see more on that front.”
He also emphasized the need to teach students now to begin questioning and critiquing the development and use of AI. “AI is not going away,” said Lee, who is also director of CRAFT (Classroom-Ready Resources about AI for Teaching), which provides free resources to help teach AI literacy to high school students across subject areas. “We need to teach students how to understand and think critically about this technology.”
Immersive environments
The use of immersive technologies like augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality is also expected to surge in the classroom, especially as new high-profile devices integrating these realities hit the marketplace in 2024.
The educational possibilities now go beyond putting on a headset and experiencing life in a distant location. With new technologies, students can create their own local interactive 360-degree scenarios, using just a cell phone or inexpensive camera and simple online tools.
“This is an area that’s really going to explode over the next couple of years,” said Kristen Pilner Blair, director of research for the Digital Learning initiative at the Stanford Accelerator for Learning, which runs a program exploring the use of virtual field trips to promote learning. “Students can learn about the effects of climate change, say, by virtually experiencing the impact on a particular environment. But they can also become creators, documenting and sharing immersive media that shows the effects where they live.”
Integrating AI into virtual simulations could also soon take the experience to another level, Schwartz said. “If your VR experience brings me to a redwood tree, you could have a window pop up that allows me to ask questions about the tree, and AI can deliver the answers.”
Gamification
Another trend expected to intensify this year is the gamification of learning activities, often featuring dynamic videos with interactive elements to engage and hold students’ attention.
“Gamification is a good motivator, because one key aspect is reward, which is very powerful,” said Schwartz. The downside? Rewards are specific to the activity at hand, which may not extend to learning more generally. “If I get rewarded for doing math in a space-age video game, it doesn’t mean I’m going to be motivated to do math anywhere else.”
Gamification sometimes tries to make “chocolate-covered broccoli,” Schwartz said, by adding art and rewards to make speeded response tasks involving single-answer, factual questions more fun. He hopes to see more creative play patterns that give students points for rethinking an approach or adapting their strategy, rather than only rewarding them for quickly producing a correct response.
Data-gathering and analysis
The growing use of technology in schools is producing massive amounts of data on students’ activities in the classroom and online. “We’re now able to capture moment-to-moment data, every keystroke a kid makes,” said Schwartz – data that can reveal areas of struggle and different learning opportunities, from solving a math problem to approaching a writing assignment.
But outside of research settings, he said, that type of granular data – now owned by tech companies – is more likely used to refine the design of the software than to provide teachers with actionable information.
The promise of personalized learning is being able to generate content aligned with students’ interests and skill levels, and making lessons more accessible for multilingual learners and students with disabilities. Realizing that promise requires that educators can make sense of the data that’s being collected, said Schwartz – and while advances in AI are making it easier to identify patterns and findings, the data also needs to be in a system and form educators can access and analyze for decision-making. Developing a usable infrastructure for that data, Schwartz said, is an important next step.
With the accumulation of student data comes privacy concerns: How is the data being collected? Are there regulations or guidelines around its use in decision-making? What steps are being taken to prevent unauthorized access? In 2023 K-12 schools experienced a rise in cyberattacks, underscoring the need to implement strong systems to safeguard student data.
Technology is “requiring people to check their assumptions about education,” said Schwartz, noting that AI in particular is very efficient at replicating biases and automating the way things have been done in the past, including poor models of instruction. “But it’s also opening up new possibilities for students producing material, and for being able to identify children who are not average so we can customize toward them. It’s an opportunity to think of entirely new ways of teaching – this is the path I hope to see.”
Global Education Monitoring Report
Technology in education
As recognised in the Incheon Declaration, the achievement of SDG 4 is dependent on opportunities and challenges posed by technology, a relationship that was strengthened by the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Technology appears in six out of the ten targets in the fourth Sustainable Development goal on education. These references recognize that technology affects education through five distinct channels, as input, means of delivery, skill, tool for planning, and providing a social and cultural context.
There are often bitter divisions in how the role of technology is viewed, however. These divisions are widening as the technology is evolving at breakneck speed. The 2023 GEM Report on technology and education explores these debates, examining education challenges to which appropriate use of technology can offer solutions (access, equity and inclusion; quality; technology advancement; system management), while recognizing that many solutions proposed may also be detrimental.
The report also explores three system-wide conditions (access to technology, governance regulation, and teacher preparation) that need to be met for any technology in education to reach its full potential. It provides the mid-term assessment of progress towards SDG 4 , which was summarized in a brochure and promoted at the 2023 SDG Summit.
The 2023 GEM Report and 200 PEER country profiles on technology and education were launched on 26 July. A recording of the global launch event can be watched here and a south-south dialogue between Ministers of education in Latin America and Africa here .

Background material

Watch the launch event
Consultations

The GEM Report is partnering with Restless Development to mobilize youth globally to inform the development of the 2023 Youth Report, exploring how technology can address various education challenges.

The GEM Report ran a consultation process to collect feedback and evidence on the proposed lines of research of the 2023 concept note.

Related resources
on technology and education
in quality and school infrastructure

Related content
Monitoring SDG 4: Quality
- Our Mission
- How to Integrate Technology
Successful technology integration is more than just getting the tools into the classroom; here are some ideas on how to engage students and enliven your lessons with those tools.
When technology integration in the classroom is seamless and thoughtful, students not only become more engaged, they begin to take more control over their own learning, too. Effective tech integration changes classroom dynamics, encouraging student-centered project-based learning.
Think about how you are using technology with your students. Are they employing technology daily in the classroom, using a variety of tools to complete assignments and create projects that show a deep understanding of content?
If your answer is "No," is it because you lack enough access to technology? Is it because you don't feel ready? Or do you feel ready, but need additional support in your classroom? Depending on your answer, your path to tech integration may look different from someone else's. However varied access and readiness may be, tech integration can successfully occur in any classroom.

Getting Started
The first step in successful tech integration is recognizing the change that may need to happen inside of yourself and in your approach to teaching. When any teacher brings technology into the classroom, he or she will no longer be the center of attention. The level of refocused attention will, of course, depend on the amount and the type of technology (e.g., mobile device, e-reader, laptop, interactive whiteboard) being brought into the classroom. However, this does not mean that the teacher is no longer essential to the learning process. While students may be surrounded by technology at home, it is dangerous to assume that they know how to use it for learning -- this is commonly referred to as the "myth of the digital native," and you can read more about it in this Edutopia blog post: " Digital Native vs. Digital Citizen? Examining a Dangerous Stereotype ." Most students still need a guide to help them use digital tools effectively for learning and collaboration.
Integrating Technology Across the Access Spectrum
As discussed in the What is Successful Technology Integration? section, how we define "technology integration" depends on the kinds of technology available and how much access one has to technology. This definition also depends on who is using the technology. For instance, in a classroom with only an interactive whiteboard and one computer, learning will still remain teacher centered and integration will revolve around teacher needs, which are not necessarily student needs. Still, there are ways to use an interactive whiteboard to make it a tool for your students. Even with one computer in the room, there are ways to integrate that one machine into your classroom and still make sure that you and your students are indeed doing things that you couldn't do before, not just doing the same things you did before in a quicker, more efficient way.

Below you will find a quick overview with suggestions of what kinds of tools and activities are best matched with various levels of technology access. All of the resources linked to are either free or offer free versions.
If your class has an interactive whiteboard and projector:
- Try interactive websites such as BrainPOP .
- Dig in to Scholastic's whiteboard activities page .
- Show online videos related to the lessons.
- Explore virtual math manipulatives .
- Check out the native software that came with the board.
- Use the videoconferencing tool Skype to connect beyond the classroom.
If there is only one computer in your room:
- All of the above, plus…
- Assign one student to be the class scribe and take notes.
- Start a collaborative class blog.
- Check out the Skype an Author Network website.
- Try Voicethread , a collaborative multimedia conversation tool.
- Let students access review or intervention materials on a rotating schedule.
- Curate resources for students via a Livebinder .
- Build a Google Site to house class content.
- Encourage skills practice, research, or the creation of collaborative stories using Google Docs .
- Record Screencasts for providing onscreen instruction.
- Find more free resources and ideas from this Eduptopia blog post .
If you have a pod of three to five computers in the classroom or access to a library with a pod of computers:
- Encourage individual student blogging using Kidblog .
- Have students create digital stories using Voicethread .
- Explore student-created multimedia presentations using Microsoft PowerPoint, LibreOffice , Prezi , or Google Docs .
- Use Edmodo , Schoology , or Moodle to manage course content, assignments, and assessments.
- Get the students to create cartoons using ToonDoo .
- Have students make videos using Windows Movie Maker or Animoto .
- Build websites with students using Weebly or Wikispaces .
If you have access to a laptop cart or a computer lab:
- Enable students to work through course content at their own pace through the use of screencasts, e-books, and other digital media.
- Use Poll Everywhere or Socrative to poll students.
- Start live class discussions with TodaysMeet .
- Explore enhanced digital note taking with Evernote .
If your students have 1:1 laptops or netbooks:
- All of the above, whenever you want, for however long you like (especially if students take their laptops or netbooks home).
If you have access to a handful of mobile devices:
- Have students create videos using the Animoto app
- Record group discussions using a voice recording app.
- Have students record themselves reading aloud for fluency checks.
- Assign student-created comics using the Puppet Pals app .
- Offer e-books for required readings.
- Upload and access course content using the Edmodo or Schoology apps.
- Conduct research.
- Foster skills practice using apps specific to subject area.
- Collaborate using apps like Whiteboard .
If your students have 1:1 mobile devices:
- Use them as multifunction devices (e.g., e-book readers, calculators, platforms for taking notes).
- Try out a tool like Nearpod to project information onto student devices.
- Check out mobile apps for student polling from Poll Everywhere or Socrative .
Getting to "Seamless" Integration
To begin to move your tech integration to the point where it is "seamless," consider these questions:
- What skills are applied to nearly all tools (e.g., saving a file, naming a file, finding a file, logging in and out of accounts)? Have your students mastered these basic skills?
- How many different tools will you introduce this year? How many is too many?
- How will technology help your students better understand content -- will it push them to a deeper understanding that could not have been achieved without technology?
- What level of integration do you want in your classroom by the end of the school year? What specific steps must you take to achieve that goal? What is a realistic goal based on time and resources?
For more on levels of technology access and what that means for tech integration, read this blog post: " What Does 'Technology Integration' Mean? "
You can also check out the outstanding Technology Integration Matrix produced by the Arizona K12 Center. It provides guidance on different levels of tech integration based on readiness and current practice, and offers links to sample lessons.
Tips for Shared Hardware
In schools that are not 1:1, sharing resources can be a huge challenge. Here are some quick tips for sharing resources effectively:
- Hold an introductory session with your students when introducing a new tool.
- Use the tool yourself first before putting your students in front of it.
- Have a plan for collecting student work.
- Communicate with other colleagues that may want to use the resources as well.
- Manage time with the resources wisely. Set goals for work completion with your students.
- Communicate with your administration about how and when you will be using shared technology.
Get more details about these six tips from this blog post: " Six Tips for Teachers: How to Maximize Shared Resources ."
Creating a Professional-Development Plan
Once you have discovered what level of access you have and what possibilities this access affords you, it is time to address your own comfort level with the technology that is in your classroom. This can be achieved through self-assessment and/or the use of a fellow teacher or an instructional coach in your school or district. Once you know your comfort level, then you can begin to build a professional-development plan for yourself. This can be done alone, as part of your "grade team," or as part of your school or district's personal-growth plan. You can also begin to seek out professional-development opportunities online and outside of your district or school to begin to connect with other educators exploring the same challenges and seeking solutions. For more resources for taking professional development into your own hands, check out our DIY Professional Development page .
It doesn't matter what your comfort level is with technology in your classroom -- without a continuous professional-development plan, you will never be as effective as you can be. Many schools and districts have made the mistake of placing technology into classrooms without a comprehensive plan for training teachers. Often, this technology sits unused or underused. If you are a teacher in a situation where technology has been "thrown" at you with no professional development, be thankful for the new tool(s) that you have at your fingertips -- and then do your best to learn about how they can transform and improve your teaching and have a positive effect on student learning. You can do this either on your own or by asking for help from your colleagues, mentors, or professional learning community.
Unlike many other aspects of teaching, technology changes constantly. Just as in any industry, it is vital that educators stay current with new trends and developments in both pedagogy and new technologies. If you have a tech-integration specialist at your school, then use this person to your full advantage, as they are the front line for the tools you have or may want to bring into your classroom.
Hardware and Equipment
While hardware and software vary across classrooms, schools, and districts, one thing can be guaranteed across the board: technology, no matter what kind it is, will fail.
This inevitable part of tech integration is often the number-one fear of classroom teachers everywhere. Whether you are taking the steps to integrate technology into your classroom on your own or as part of a schoolwide or district initiative, this fear must be the first hurdle to overcome.
Here are some basic tips for when technology goes awry:
- Have a nontechnology backup plan.
- Just as we always tell our students that failure is OK, that we learn from failure, and that failure is part of the learning process, so must we, as adults, follow our own advice.
- Model troubleshooting with your students.
- Report the problem (and know to whom this reporting should be done).
- Ask for help. Have someone who knows how to fix the problem show you how for next time.
Using Technology for Feedback and Assessment
One of the most exciting aspects of bringing technology into your classroom -- and into your students' hands -- is the enhanced opportunity for timely and meaningful feedback.
Quick Checks: If you want to know if your students grasp enough of a particular concept before you move on, you can use tools such as Poll Everywhere , Socrative , or Mentimeter to get a quick snapshot of the class. By creating a short quiz or open-ended response question using one of these tools and having your students use an internet-enabled device to answer, you can get quick and easy feedback that will help inform your instruction.
Personalized Feedback: Through the use of course-management tools such as Edmodo , Schoology , or Moodle , it is now possible for teachers to provide personalized feedback quickly and efficiently to their students. All three tools provide the ability for teachers to leave personalized comments and notes on student work, and they provide a messaging service for students who may want to send emails with questions or concerns about the course.
Screencasts can also provide personalized feedback on student work. A teacher can record his or her computer screen while viewing student work, pointing out areas for improvement and areas where a student has excelled. Some great tools for this are Screencast-O-Matic and Jing .
In addition, Evernote is a powerful note-taking tool that can be accessed through any Internet-enabled device through a web browser or the mobile app. It allows users to record audio notes, and it can be a great way to provide personalized feedback to students. Teachers can share these recordings, which are embedded in notes created through the app or website, with students through email. This can be a great way to keep students updated on their progress or to provide feedback on a particular assignment asynchronously. Because the feedback is recorded, students can also rewind and relisten for better comprehension or to refer back to if they like.
Please note, all of these kinds of tools require that students have access to Internet-enabled devices on a regular basis and that they hand in their work digitally.
For more on using technology to provide feedback to students, you can read this blog post: " Using Tech Tools to Provide Timely Feedback ."
The Role of Digital Citizenship
Our students are constantly immersed in technology, yet that does not mean that they know how to use it for learning. We also cannot assume that they know how to use it responsibly either. Just as we teach our children how to handle bullies on the playground, or as we admonish a student for copying someone's work and handing it in as his or her own, we must take the time to explicitly teach about cyberbullying, copyright, plagiarism, digital footprint, and proper conduct online.
Of course, what we teach and how we teach it depend on grade level. We probably wouldn't teach first graders about the nitty-gritty details of copyright law, but we might teach them what kinds of information are safe or unsafe to share online. Likewise, while we may quickly review safe and unsafe information with high school students, we are more likely to focus on digital footprint and plagiarism.
It is worth your time to spend some time early in the year setting expectations for online conduct, use of information found online, and staying safe when using digital tools. For more on teaching digital citizenship, you can visit BrainPOP , Common Sense Media , or Edutopia's Digital Citizenship Resource Roundup .
Since it's clear that tech integration is here to stay, it is not a question of whether teachers integrate technology into their classrooms, but rather how to do it best. By taking small steps, teachers can begin to reap the benefits that technology can bring to their teaching and to student learning. This process does not have to be painful, and no one will become a tech-integration whiz overnight. However, even with limited access, with careful planning, some risk taking, and an open mind, teachers can successfully use technology to enhance their teaching and bring learning to life for their students.
Continue to the next section of the guide, Workshop Activities .
This guide is organized into six sections:
- Introduction
- Why Integrate Technology?
- What Is Tech Integration?
- Workshop Activities
- Resources for Tech Integration
REALIZING THE PROMISE:
Leading up to the 75th anniversary of the UN General Assembly, this “Realizing the promise: How can education technology improve learning for all?” publication kicks off the Center for Universal Education’s first playbook in a series to help improve education around the world.
It is intended as an evidence-based tool for ministries of education, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, to adopt and more successfully invest in education technology.
While there is no single education initiative that will achieve the same results everywhere—as school systems differ in learners and educators, as well as in the availability and quality of materials and technologies—an important first step is understanding how technology is used given specific local contexts and needs.
The surveys in this playbook are designed to be adapted to collect this information from educators, learners, and school leaders and guide decisionmakers in expanding the use of technology.
Introduction
While technology has disrupted most sectors of the economy and changed how we communicate, access information, work, and even play, its impact on schools, teaching, and learning has been much more limited. We believe that this limited impact is primarily due to technology being been used to replace analog tools, without much consideration given to playing to technology’s comparative advantages. These comparative advantages, relative to traditional “chalk-and-talk” classroom instruction, include helping to scale up standardized instruction, facilitate differentiated instruction, expand opportunities for practice, and increase student engagement. When schools use technology to enhance the work of educators and to improve the quality and quantity of educational content, learners will thrive.
Further, COVID-19 has laid bare that, in today’s environment where pandemics and the effects of climate change are likely to occur, schools cannot always provide in-person education—making the case for investing in education technology.
Here we argue for a simple yet surprisingly rare approach to education technology that seeks to:
- Understand the needs, infrastructure, and capacity of a school system—the diagnosis;
- Survey the best available evidence on interventions that match those conditions—the evidence; and
- Closely monitor the results of innovations before they are scaled up—the prognosis.
RELATED CONTENT

Podcast: How education technology can improve learning for all students

To make ed tech work, set clear goals, review the evidence, and pilot before you scale
The framework.
Our approach builds on a simple yet intuitive theoretical framework created two decades ago by two of the most prominent education researchers in the United States, David K. Cohen and Deborah Loewenberg Ball. They argue that what matters most to improve learning is the interactions among educators and learners around educational materials. We believe that the failed school-improvement efforts in the U.S. that motivated Cohen and Ball’s framework resemble the ed-tech reforms in much of the developing world to date in the lack of clarity improving the interactions between educators, learners, and the educational material. We build on their framework by adding parents as key agents that mediate the relationships between learners and educators and the material (Figure 1).
Figure 1: The instructional core
Adapted from Cohen and Ball (1999)
As the figure above suggests, ed-tech interventions can affect the instructional core in a myriad of ways. Yet, just because technology can do something, it does not mean it should. School systems in developing countries differ along many dimensions and each system is likely to have different needs for ed-tech interventions, as well as different infrastructure and capacity to enact such interventions.
The diagnosis:
How can school systems assess their needs and preparedness.
A useful first step for any school system to determine whether it should invest in education technology is to diagnose its:
- Specific needs to improve student learning (e.g., raising the average level of achievement, remediating gaps among low performers, and challenging high performers to develop higher-order skills);
- Infrastructure to adopt technology-enabled solutions (e.g., electricity connection, availability of space and outlets, stock of computers, and Internet connectivity at school and at learners’ homes); and
- Capacity to integrate technology in the instructional process (e.g., learners’ and educators’ level of familiarity and comfort with hardware and software, their beliefs about the level of usefulness of technology for learning purposes, and their current uses of such technology).
Before engaging in any new data collection exercise, school systems should take full advantage of existing administrative data that could shed light on these three main questions. This could be in the form of internal evaluations but also international learner assessments, such as the Program for International Student Assessment (PISA), the Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS), and/or the Progress in International Literacy Study (PIRLS), and the Teaching and Learning International Study (TALIS). But if school systems lack information on their preparedness for ed-tech reforms or if they seek to complement existing data with a richer set of indicators, we developed a set of surveys for learners, educators, and school leaders. Download the full report to see how we map out the main aspects covered by these surveys, in hopes of highlighting how they could be used to inform decisions around the adoption of ed-tech interventions.
The evidence:
How can school systems identify promising ed-tech interventions.
There is no single “ed-tech” initiative that will achieve the same results everywhere, simply because school systems differ in learners and educators, as well as in the availability and quality of materials and technologies. Instead, to realize the potential of education technology to accelerate student learning, decisionmakers should focus on four potential uses of technology that play to its comparative advantages and complement the work of educators to accelerate student learning (Figure 2). These comparative advantages include:
- Scaling up quality instruction, such as through prerecorded quality lessons.
- Facilitating differentiated instruction, through, for example, computer-adaptive learning and live one-on-one tutoring.
- Expanding opportunities to practice.
- Increasing learner engagement through videos and games.
Figure 2: Comparative advantages of technology
Here we review the evidence on ed-tech interventions from 37 studies in 20 countries*, organizing them by comparative advantage. It’s important to note that ours is not the only way to classify these interventions (e.g., video tutorials could be considered as a strategy to scale up instruction or increase learner engagement), but we believe it may be useful to highlight the needs that they could address and why technology is well positioned to do so.
When discussing specific studies, we report the magnitude of the effects of interventions using standard deviations (SDs). SDs are a widely used metric in research to express the effect of a program or policy with respect to a business-as-usual condition (e.g., test scores). There are several ways to make sense of them. One is to categorize the magnitude of the effects based on the results of impact evaluations. In developing countries, effects below 0.1 SDs are considered to be small, effects between 0.1 and 0.2 SDs are medium, and those above 0.2 SDs are large (for reviews that estimate the average effect of groups of interventions, called “meta analyses,” see e.g., Conn, 2017; Kremer, Brannen, & Glennerster, 2013; McEwan, 2014; Snilstveit et al., 2015; Evans & Yuan, 2020.)
*In surveying the evidence, we began by compiling studies from prior general and ed-tech specific evidence reviews that some of us have written and from ed-tech reviews conducted by others. Then, we tracked the studies cited by the ones we had previously read and reviewed those, as well. In identifying studies for inclusion, we focused on experimental and quasi-experimental evaluations of education technology interventions from pre-school to secondary school in low- and middle-income countries that were released between 2000 and 2020. We only included interventions that sought to improve student learning directly (i.e., students’ interaction with the material), as opposed to interventions that have impacted achievement indirectly, by reducing teacher absence or increasing parental engagement. This process yielded 37 studies in 20 countries (see the full list of studies in Appendix B).
Scaling up standardized instruction
One of the ways in which technology may improve the quality of education is through its capacity to deliver standardized quality content at scale. This feature of technology may be particularly useful in three types of settings: (a) those in “hard-to-staff” schools (i.e., schools that struggle to recruit educators with the requisite training and experience—typically, in rural and/or remote areas) (see, e.g., Urquiola & Vegas, 2005); (b) those in which many educators are frequently absent from school (e.g., Chaudhury, Hammer, Kremer, Muralidharan, & Rogers, 2006; Muralidharan, Das, Holla, & Mohpal, 2017); and/or (c) those in which educators have low levels of pedagogical and subject matter expertise (e.g., Bietenbeck, Piopiunik, & Wiederhold, 2018; Bold et al., 2017; Metzler & Woessmann, 2012; Santibañez, 2006) and do not have opportunities to observe and receive feedback (e.g., Bruns, Costa, & Cunha, 2018; Cilliers, Fleisch, Prinsloo, & Taylor, 2018). Technology could address this problem by: (a) disseminating lessons delivered by qualified educators to a large number of learners (e.g., through prerecorded or live lessons); (b) enabling distance education (e.g., for learners in remote areas and/or during periods of school closures); and (c) distributing hardware preloaded with educational materials.
Prerecorded lessons
Technology seems to be well placed to amplify the impact of effective educators by disseminating their lessons. Evidence on the impact of prerecorded lessons is encouraging, but not conclusive. Some initiatives that have used short instructional videos to complement regular instruction, in conjunction with other learning materials, have raised student learning on independent assessments. For example, Beg et al. (2020) evaluated an initiative in Punjab, Pakistan in which grade 8 classrooms received an intervention that included short videos to substitute live instruction, quizzes for learners to practice the material from every lesson, tablets for educators to learn the material and follow the lesson, and LED screens to project the videos onto a classroom screen. After six months, the intervention improved the performance of learners on independent tests of math and science by 0.19 and 0.24 SDs, respectively but had no discernible effect on the math and science section of Punjab’s high-stakes exams.
One study suggests that approaches that are far less technologically sophisticated can also improve learning outcomes—especially, if the business-as-usual instruction is of low quality. For example, Naslund-Hadley, Parker, and Hernandez-Agramonte (2014) evaluated a preschool math program in Cordillera, Paraguay that used audio segments and written materials four days per week for an hour per day during the school day. After five months, the intervention improved math scores by 0.16 SDs, narrowing gaps between low- and high-achieving learners, and between those with and without educators with formal training in early childhood education.
Yet, the integration of prerecorded material into regular instruction has not always been successful. For example, de Barros (2020) evaluated an intervention that combined instructional videos for math and science with infrastructure upgrades (e.g., two “smart” classrooms, two TVs, and two tablets), printed workbooks for students, and in-service training for educators of learners in grades 9 and 10 in Haryana, India (all materials were mapped onto the official curriculum). After 11 months, the intervention negatively impacted math achievement (by 0.08 SDs) and had no effect on science (with respect to business as usual classes). It reduced the share of lesson time that educators devoted to instruction and negatively impacted an index of instructional quality. Likewise, Seo (2017) evaluated several combinations of infrastructure (solar lights and TVs) and prerecorded videos (in English and/or bilingual) for grade 11 students in northern Tanzania and found that none of the variants improved student learning, even when the videos were used. The study reports effects from the infrastructure component across variants, but as others have noted (Muralidharan, Romero, & Wüthrich, 2019), this approach to estimating impact is problematic.
A very similar intervention delivered after school hours, however, had sizeable effects on learners’ basic skills. Chiplunkar, Dhar, and Nagesh (2020) evaluated an initiative in Chennai (the capital city of the state of Tamil Nadu, India) delivered by the same organization as above that combined short videos that explained key concepts in math and science with worksheets, facilitator-led instruction, small groups for peer-to-peer learning, and occasional career counseling and guidance for grade 9 students. These lessons took place after school for one hour, five times a week. After 10 months, it had large effects on learners’ achievement as measured by tests of basic skills in math and reading, but no effect on a standardized high-stakes test in grade 10 or socio-emotional skills (e.g., teamwork, decisionmaking, and communication).
Drawing general lessons from this body of research is challenging for at least two reasons. First, all of the studies above have evaluated the impact of prerecorded lessons combined with several other components (e.g., hardware, print materials, or other activities). Therefore, it is possible that the effects found are due to these additional components, rather than to the recordings themselves, or to the interaction between the two (see Muralidharan, 2017 for a discussion of the challenges of interpreting “bundled” interventions). Second, while these studies evaluate some type of prerecorded lessons, none examines the content of such lessons. Thus, it seems entirely plausible that the direction and magnitude of the effects depends largely on the quality of the recordings (e.g., the expertise of the educator recording it, the amount of preparation that went into planning the recording, and its alignment with best teaching practices).
These studies also raise three important questions worth exploring in future research. One of them is why none of the interventions discussed above had effects on high-stakes exams, even if their materials are typically mapped onto the official curriculum. It is possible that the official curricula are simply too challenging for learners in these settings, who are several grade levels behind expectations and who often need to reinforce basic skills (see Pritchett & Beatty, 2015). Another question is whether these interventions have long-term effects on teaching practices. It seems plausible that, if these interventions are deployed in contexts with low teaching quality, educators may learn something from watching the videos or listening to the recordings with learners. Yet another question is whether these interventions make it easier for schools to deliver instruction to learners whose native language is other than the official medium of instruction.
Distance education
Technology can also allow learners living in remote areas to access education. The evidence on these initiatives is encouraging. For example, Johnston and Ksoll (2017) evaluated a program that broadcasted live instruction via satellite to rural primary school students in the Volta and Greater Accra regions of Ghana. For this purpose, the program also equipped classrooms with the technology needed to connect to a studio in Accra, including solar panels, a satellite modem, a projector, a webcam, microphones, and a computer with interactive software. After two years, the intervention improved the numeracy scores of students in grades 2 through 4, and some foundational literacy tasks, but it had no effect on attendance or classroom time devoted to instruction, as captured by school visits. The authors interpreted these results as suggesting that the gains in achievement may be due to improving the quality of instruction that children received (as opposed to increased instructional time). Naik, Chitre, Bhalla, and Rajan (2019) evaluated a similar program in the Indian state of Karnataka and also found positive effects on learning outcomes, but it is not clear whether those effects are due to the program or due to differences in the groups of students they compared to estimate the impact of the initiative.
In one context (Mexico), this type of distance education had positive long-term effects. Navarro-Sola (2019) took advantage of the staggered rollout of the telesecundarias (i.e., middle schools with lessons broadcasted through satellite TV) in 1968 to estimate its impact. The policy had short-term effects on students’ enrollment in school: For every telesecundaria per 50 children, 10 students enrolled in middle school and two pursued further education. It also had a long-term influence on the educational and employment trajectory of its graduates. Each additional year of education induced by the policy increased average income by nearly 18 percent. This effect was attributable to more graduates entering the labor force and shifting from agriculture and the informal sector. Similarly, Fabregas (2019) leveraged a later expansion of this policy in 1993 and found that each additional telesecundaria per 1,000 adolescents led to an average increase of 0.2 years of education, and a decline in fertility for women, but no conclusive evidence of long-term effects on labor market outcomes.
It is crucial to interpret these results keeping in mind the settings where the interventions were implemented. As we mention above, part of the reason why they have proven effective is that the “counterfactual” conditions for learning (i.e., what would have happened to learners in the absence of such programs) was either to not have access to schooling or to be exposed to low-quality instruction. School systems interested in taking up similar interventions should assess the extent to which their learners (or parts of their learner population) find themselves in similar conditions to the subjects of the studies above. This illustrates the importance of assessing the needs of a system before reviewing the evidence.
Preloaded hardware
Technology also seems well positioned to disseminate educational materials. Specifically, hardware (e.g., desktop computers, laptops, or tablets) could also help deliver educational software (e.g., word processing, reference texts, and/or games). In theory, these materials could not only undergo a quality assurance review (e.g., by curriculum specialists and educators), but also draw on the interactions with learners for adjustments (e.g., identifying areas needing reinforcement) and enable interactions between learners and educators.
In practice, however, most initiatives that have provided learners with free computers, laptops, and netbooks do not leverage any of the opportunities mentioned above. Instead, they install a standard set of educational materials and hope that learners find them helpful enough to take them up on their own. Students rarely do so, and instead use the laptops for recreational purposes—often, to the detriment of their learning (see, e.g., Malamud & Pop-Eleches, 2011). In fact, free netbook initiatives have not only consistently failed to improve academic achievement in math or language (e.g., Cristia et al., 2017), but they have had no impact on learners’ general computer skills (e.g., Beuermann et al., 2015). Some of these initiatives have had small impacts on cognitive skills, but the mechanisms through which those effects occurred remains unclear.
To our knowledge, the only successful deployment of a free laptop initiative was one in which a team of researchers equipped the computers with remedial software. Mo et al. (2013) evaluated a version of the One Laptop per Child (OLPC) program for grade 3 students in migrant schools in Beijing, China in which the laptops were loaded with a remedial software mapped onto the national curriculum for math (similar to the software products that we discuss under “practice exercises” below). After nine months, the program improved math achievement by 0.17 SDs and computer skills by 0.33 SDs. If a school system decides to invest in free laptops, this study suggests that the quality of the software on the laptops is crucial.
To date, however, the evidence suggests that children do not learn more from interacting with laptops than they do from textbooks. For example, Bando, Gallego, Gertler, and Romero (2016) compared the effect of free laptop and textbook provision in 271 elementary schools in disadvantaged areas of Honduras. After seven months, students in grades 3 and 6 who had received the laptops performed on par with those who had received the textbooks in math and language. Further, even if textbooks essentially become obsolete at the end of each school year, whereas laptops can be reloaded with new materials for each year, the costs of laptop provision (not just the hardware, but also the technical assistance, Internet, and training associated with it) are not yet low enough to make them a more cost-effective way of delivering content to learners.
Evidence on the provision of tablets equipped with software is encouraging but limited. For example, de Hoop et al. (2020) evaluated a composite intervention for first grade students in Zambia’s Eastern Province that combined infrastructure (electricity via solar power), hardware (projectors and tablets), and educational materials (lesson plans for educators and interactive lessons for learners, both loaded onto the tablets and mapped onto the official Zambian curriculum). After 14 months, the intervention had improved student early-grade reading by 0.4 SDs, oral vocabulary scores by 0.25 SDs, and early-grade math by 0.22 SDs. It also improved students’ achievement by 0.16 on a locally developed assessment. The multifaceted nature of the program, however, makes it challenging to identify the components that are driving the positive effects. Pitchford (2015) evaluated an intervention that provided tablets equipped with educational “apps,” to be used for 30 minutes per day for two months to develop early math skills among students in grades 1 through 3 in Lilongwe, Malawi. The evaluation found positive impacts in math achievement, but the main study limitation is that it was conducted in a single school.
Facilitating differentiated instruction
Another way in which technology may improve educational outcomes is by facilitating the delivery of differentiated or individualized instruction. Most developing countries massively expanded access to schooling in recent decades by building new schools and making education more affordable, both by defraying direct costs, as well as compensating for opportunity costs (Duflo, 2001; World Bank, 2018). These initiatives have not only rapidly increased the number of learners enrolled in school, but have also increased the variability in learner’ preparation for schooling. Consequently, a large number of learners perform well below grade-based curricular expectations (see, e.g., Duflo, Dupas, & Kremer, 2011; Pritchett & Beatty, 2015). These learners are unlikely to get much from “one-size-fits-all” instruction, in which a single educator delivers instruction deemed appropriate for the middle (or top) of the achievement distribution (Banerjee & Duflo, 2011). Technology could potentially help these learners by providing them with: (a) instruction and opportunities for practice that adjust to the level and pace of preparation of each individual (known as “computer-adaptive learning” (CAL)); or (b) live, one-on-one tutoring.
Computer-adaptive learning
One of the main comparative advantages of technology is its ability to diagnose students’ initial learning levels and assign students to instruction and exercises of appropriate difficulty. No individual educator—no matter how talented—can be expected to provide individualized instruction to all learners in his/her class simultaneously . In this respect, technology is uniquely positioned to complement traditional teaching. This use of technology could help learners master basic skills and help them get more out of schooling.
Although many software products evaluated in recent years have been categorized as CAL, many rely on a relatively coarse level of differentiation at an initial stage (e.g., a diagnostic test) without further differentiation. We discuss these initiatives under the category of “increasing opportunities for practice” below. CAL initiatives complement an initial diagnostic with dynamic adaptation (i.e., at each response or set of responses from learners) to adjust both the initial level of difficulty and rate at which it increases or decreases, depending on whether learners’ responses are correct or incorrect.
Existing evidence on this specific type of programs is highly promising. Most famously, Banerjee et al. (2007) evaluated CAL software in Vadodara, in the Indian state of Gujarat, in which grade 4 students were offered two hours of shared computer time per week before and after school, during which they played games that involved solving math problems. The level of difficulty of such problems adjusted based on students’ answers. This program improved math achievement by 0.35 and 0.47 SDs after one and two years of implementation, respectively. Consistent with the promise of personalized learning, the software improved achievement for all students. In fact, one year after the end of the program, students assigned to the program still performed 0.1 SDs better than those assigned to a business as usual condition. More recently, Muralidharan, et al. (2019) evaluated a “blended learning” initiative in which students in grades 4 through 9 in Delhi, India received 45 minutes of interaction with CAL software for math and language, and 45 minutes of small group instruction before or after going to school. After only 4.5 months, the program improved achievement by 0.37 SDs in math and 0.23 SDs in Hindi. While all learners benefited from the program in absolute terms, the lowest performing learners benefited the most in relative terms, since they were learning very little in school.
We see two important limitations from this body of research. First, to our knowledge, none of these initiatives has been evaluated when implemented during the school day. Therefore, it is not possible to distinguish the effect of the adaptive software from that of additional instructional time. Second, given that most of these programs were facilitated by local instructors, attempts to distinguish the effect of the software from that of the instructors has been mostly based on noncausal evidence. A frontier challenge in this body of research is to understand whether CAL software can increase the effectiveness of school-based instruction by substituting part of the regularly scheduled time for math and language instruction.
Live one-on-one tutoring
Recent improvements in the speed and quality of videoconferencing, as well as in the connectivity of remote areas, have enabled yet another way in which technology can help personalization: live (i.e., real-time) one-on-one tutoring. While the evidence on in-person tutoring is scarce in developing countries, existing studies suggest that this approach works best when it is used to personalize instruction (see, e.g., Banerjee et al., 2007; Banerji, Berry, & Shotland, 2015; Cabezas, Cuesta, & Gallego, 2011).
There are almost no studies on the impact of online tutoring—possibly, due to the lack of hardware and Internet connectivity in low- and middle-income countries. One exception is Chemin and Oledan (2020)’s recent evaluation of an online tutoring program for grade 6 students in Kianyaga, Kenya to learn English from volunteers from a Canadian university via Skype ( videoconferencing software) for one hour per week after school. After 10 months, program beneficiaries performed 0.22 SDs better in a test of oral comprehension, improved their comfort using technology for learning, and became more willing to engage in cross-cultural communication. Importantly, while the tutoring sessions used the official English textbooks and sought in part to help learners with their homework, tutors were trained on several strategies to teach to each learner’s individual level of preparation, focusing on basic skills if necessary. To our knowledge, similar initiatives within a country have not yet been rigorously evaluated.
Expanding opportunities for practice
A third way in which technology may improve the quality of education is by providing learners with additional opportunities for practice. In many developing countries, lesson time is primarily devoted to lectures, in which the educator explains the topic and the learners passively copy explanations from the blackboard. This setup leaves little time for in-class practice. Consequently, learners who did not understand the explanation of the material during lecture struggle when they have to solve homework assignments on their own. Technology could potentially address this problem by allowing learners to review topics at their own pace.
Practice exercises
Technology can help learners get more out of traditional instruction by providing them with opportunities to implement what they learn in class. This approach could, in theory, allow some learners to anchor their understanding of the material through trial and error (i.e., by realizing what they may not have understood correctly during lecture and by getting better acquainted with special cases not covered in-depth in class).
Existing evidence on practice exercises reflects both the promise and the limitations of this use of technology in developing countries. For example, Lai et al. (2013) evaluated a program in Shaanxi, China where students in grades 3 and 5 were required to attend two 40-minute remedial sessions per week in which they first watched videos that reviewed the material that had been introduced in their math lessons that week and then played games to practice the skills introduced in the video. After four months, the intervention improved math achievement by 0.12 SDs. Many other evaluations of comparable interventions have found similar small-to-moderate results (see, e.g., Lai, Luo, Zhang, Huang, & Rozelle, 2015; Lai et al., 2012; Mo et al., 2015; Pitchford, 2015). These effects, however, have been consistently smaller than those of initiatives that adjust the difficulty of the material based on students’ performance (e.g., Banerjee et al., 2007; Muralidharan, et al., 2019). We hypothesize that these programs do little for learners who perform several grade levels behind curricular expectations, and who would benefit more from a review of foundational concepts from earlier grades.
We see two important limitations from this research. First, most initiatives that have been evaluated thus far combine instructional videos with practice exercises, so it is hard to know whether their effects are driven by the former or the latter. In fact, the program in China described above allowed learners to ask their peers whenever they did not understand a difficult concept, so it potentially also captured the effect of peer-to-peer collaboration. To our knowledge, no studies have addressed this gap in the evidence.
Second, most of these programs are implemented before or after school, so we cannot distinguish the effect of additional instructional time from that of the actual opportunity for practice. The importance of this question was first highlighted by Linden (2008), who compared two delivery mechanisms for game-based remedial math software for students in grades 2 and 3 in a network of schools run by a nonprofit organization in Gujarat, India: one in which students interacted with the software during the school day and another one in which students interacted with the software before or after school (in both cases, for three hours per day). After a year, the first version of the program had negatively impacted students’ math achievement by 0.57 SDs and the second one had a null effect. This study suggested that computer-assisted learning is a poor substitute for regular instruction when it is of high quality, as was the case in this well-functioning private network of schools.
In recent years, several studies have sought to remedy this shortcoming. Mo et al. (2014) were among the first to evaluate practice exercises delivered during the school day. They evaluated an initiative in Shaanxi, China in which students in grades 3 and 5 were required to interact with the software similar to the one in Lai et al. (2013) for two 40-minute sessions per week. The main limitation of this study, however, is that the program was delivered during regularly scheduled computer lessons, so it could not determine the impact of substituting regular math instruction. Similarly, Mo et al. (2020) evaluated a self-paced and a teacher-directed version of a similar program for English for grade 5 students in Qinghai, China. Yet, the key shortcoming of this study is that the teacher-directed version added several components that may also influence achievement, such as increased opportunities for teachers to provide students with personalized assistance when they struggled with the material. Ma, Fairlie, Loyalka, and Rozelle (2020) compared the effectiveness of additional time-delivered remedial instruction for students in grades 4 to 6 in Shaanxi, China through either computer-assisted software or using workbooks. This study indicates whether additional instructional time is more effective when using technology, but it does not address the question of whether school systems may improve the productivity of instructional time during the school day by substituting educator-led with computer-assisted instruction.
Increasing learner engagement
Another way in which technology may improve education is by increasing learners’ engagement with the material. In many school systems, regular “chalk and talk” instruction prioritizes time for educators’ exposition over opportunities for learners to ask clarifying questions and/or contribute to class discussions. This, combined with the fact that many developing-country classrooms include a very large number of learners (see, e.g., Angrist & Lavy, 1999; Duflo, Dupas, & Kremer, 2015), may partially explain why the majority of those students are several grade levels behind curricular expectations (e.g., Muralidharan, et al., 2019; Muralidharan & Zieleniak, 2014; Pritchett & Beatty, 2015). Technology could potentially address these challenges by: (a) using video tutorials for self-paced learning and (b) presenting exercises as games and/or gamifying practice.
Video tutorials
Technology can potentially increase learner effort and understanding of the material by finding new and more engaging ways to deliver it. Video tutorials designed for self-paced learning—as opposed to videos for whole class instruction, which we discuss under the category of “prerecorded lessons” above—can increase learner effort in multiple ways, including: allowing learners to focus on topics with which they need more help, letting them correct errors and misconceptions on their own, and making the material appealing through visual aids. They can increase understanding by breaking the material into smaller units and tackling common misconceptions.
In spite of the popularity of instructional videos, there is relatively little evidence on their effectiveness. Yet, two recent evaluations of different versions of the Khan Academy portal, which mainly relies on instructional videos, offer some insight into their impact. First, Ferman, Finamor, and Lima (2019) evaluated an initiative in 157 public primary and middle schools in five cities in Brazil in which the teachers of students in grades 5 and 9 were taken to the computer lab to learn math from the platform for 50 minutes per week. The authors found that, while the intervention slightly improved learners’ attitudes toward math, these changes did not translate into better performance in this subject. The authors hypothesized that this could be due to the reduction of teacher-led math instruction.
More recently, Büchel, Jakob, Kühnhanss, Steffen, and Brunetti (2020) evaluated an after-school, offline delivery of the Khan Academy portal in grades 3 through 6 in 302 primary schools in Morazán, El Salvador. Students in this study received 90 minutes per week of additional math instruction (effectively nearly doubling total math instruction per week) through teacher-led regular lessons, teacher-assisted Khan Academy lessons, or similar lessons assisted by technical supervisors with no content expertise. (Importantly, the first group provided differentiated instruction, which is not the norm in Salvadorian schools). All three groups outperformed both schools without any additional lessons and classrooms without additional lessons in the same schools as the program. The teacher-assisted Khan Academy lessons performed 0.24 SDs better, the supervisor-led lessons 0.22 SDs better, and the teacher-led regular lessons 0.15 SDs better, but the authors could not determine whether the effects across versions were different.
Together, these studies suggest that instructional videos work best when provided as a complement to, rather than as a substitute for, regular instruction. Yet, the main limitation of these studies is the multifaceted nature of the Khan Academy portal, which also includes other components found to positively improve learner achievement, such as differentiated instruction by students’ learning levels. While the software does not provide the type of personalization discussed above, learners are asked to take a placement test and, based on their score, educators assign them different work. Therefore, it is not clear from these studies whether the effects from Khan Academy are driven by its instructional videos or to the software’s ability to provide differentiated activities when combined with placement tests.
Games and gamification
Technology can also increase learner engagement by presenting exercises as games and/or by encouraging learner to play and compete with others (e.g., using leaderboards and rewards)—an approach known as “gamification.” Both approaches can increase learner motivation and effort by presenting learners with entertaining opportunities for practice and by leveraging peers as commitment devices.
There are very few studies on the effects of games and gamification in low- and middle-income countries. Recently, Araya, Arias Ortiz, Bottan, and Cristia (2019) evaluated an initiative in which grade 4 students in Santiago, Chile were required to participate in two 90-minute sessions per week during the school day with instructional math software featuring individual and group competitions (e.g., tracking each learner’s standing in his/her class and tournaments between sections). After nine months, the program led to improvements of 0.27 SDs in the national student assessment in math (it had no spillover effects on reading). However, it had mixed effects on non-academic outcomes. Specifically, the program increased learners’ willingness to use computers to learn math, but, at the same time, increased their anxiety toward math and negatively impacted learners’ willingness to collaborate with peers. Finally, given that one of the weekly sessions replaced regular math instruction and the other one represented additional math instructional time, it is not clear whether the academic effects of the program are driven by the software or the additional time devoted to learning math.
The prognosis:
How can school systems adopt interventions that match their needs.
Here are five specific and sequential guidelines for decisionmakers to realize the potential of education technology to accelerate student learning.
1. Take stock of how your current schools, educators, and learners are engaging with technology .
Carry out a short in-school survey to understand the current practices and potential barriers to adoption of technology (we have included suggested survey instruments in the Appendices); use this information in your decisionmaking process. For example, we learned from conversations with current and former ministers of education from various developing regions that a common limitation to technology use is regulations that hold school leaders accountable for damages to or losses of devices. Another common barrier is lack of access to electricity and Internet, or even the availability of sufficient outlets for charging devices in classrooms. Understanding basic infrastructure and regulatory limitations to the use of education technology is a first necessary step. But addressing these limitations will not guarantee that introducing or expanding technology use will accelerate learning. The next steps are thus necessary.
“In Africa, the biggest limit is connectivity. Fiber is expensive, and we don’t have it everywhere. The continent is creating a digital divide between cities, where there is fiber, and the rural areas. The [Ghanaian] administration put in schools offline/online technologies with books, assessment tools, and open source materials. In deploying this, we are finding that again, teachers are unfamiliar with it. And existing policies prohibit students to bring their own tablets or cell phones. The easiest way to do it would have been to let everyone bring their own device. But policies are against it.” H.E. Matthew Prempeh, Minister of Education of Ghana, on the need to understand the local context.
2. Consider how the introduction of technology may affect the interactions among learners, educators, and content .
Our review of the evidence indicates that technology may accelerate student learning when it is used to scale up access to quality content, facilitate differentiated instruction, increase opportunities for practice, or when it increases learner engagement. For example, will adding electronic whiteboards to classrooms facilitate access to more quality content or differentiated instruction? Or will these expensive boards be used in the same way as the old chalkboards? Will providing one device (laptop or tablet) to each learner facilitate access to more and better content, or offer students more opportunities to practice and learn? Solely introducing technology in classrooms without additional changes is unlikely to lead to improved learning and may be quite costly. If you cannot clearly identify how the interactions among the three key components of the instructional core (educators, learners, and content) may change after the introduction of technology, then it is probably not a good idea to make the investment. See Appendix A for guidance on the types of questions to ask.
3. Once decisionmakers have a clear idea of how education technology can help accelerate student learning in a specific context, it is important to define clear objectives and goals and establish ways to regularly assess progress and make course corrections in a timely manner .
For instance, is the education technology expected to ensure that learners in early grades excel in foundational skills—basic literacy and numeracy—by age 10? If so, will the technology provide quality reading and math materials, ample opportunities to practice, and engaging materials such as videos or games? Will educators be empowered to use these materials in new ways? And how will progress be measured and adjusted?
4. How this kind of reform is approached can matter immensely for its success.
It is easy to nod to issues of “implementation,” but that needs to be more than rhetorical. Keep in mind that good use of education technology requires thinking about how it will affect learners, educators, and parents. After all, giving learners digital devices will make no difference if they get broken, are stolen, or go unused. Classroom technologies only matter if educators feel comfortable putting them to work. Since good technology is generally about complementing or amplifying what educators and learners already do, it is almost always a mistake to mandate programs from on high. It is vital that technology be adopted with the input of educators and families and with attention to how it will be used. If technology goes unused or if educators use it ineffectually, the results will disappoint—no matter the virtuosity of the technology. Indeed, unused education technology can be an unnecessary expenditure for cash-strapped education systems. This is why surveying context, listening to voices in the field, examining how technology is used, and planning for course correction is essential.
5. It is essential to communicate with a range of stakeholders, including educators, school leaders, parents, and learners .
Technology can feel alien in schools, confuse parents and (especially) older educators, or become an alluring distraction. Good communication can help address all of these risks. Taking care to listen to educators and families can help ensure that programs are informed by their needs and concerns. At the same time, deliberately and consistently explaining what technology is and is not supposed to do, how it can be most effectively used, and the ways in which it can make it more likely that programs work as intended. For instance, if teachers fear that technology is intended to reduce the need for educators, they will tend to be hostile; if they believe that it is intended to assist them in their work, they will be more receptive. Absent effective communication, it is easy for programs to “fail” not because of the technology but because of how it was used. In short, past experience in rolling out education programs indicates that it is as important to have a strong intervention design as it is to have a solid plan to socialize it among stakeholders.

Beyond reopening: A leapfrog moment to transform education?
On September 14, the Center for Universal Education (CUE) will host a webinar to discuss strategies, including around the effective use of education technology, for ensuring resilient schools in the long term and to launch a new education technology playbook “Realizing the promise: How can education technology improve learning for all?”
file-pdf Full Playbook – Realizing the promise: How can education technology improve learning for all? file-pdf References file-pdf Appendix A – Instruments to assess availability and use of technology file-pdf Appendix B – List of reviewed studies file-pdf Appendix C – How may technology affect interactions among students, teachers, and content?
About the Authors
Alejandro j. ganimian, emiliana vegas, frederick m. hess.
- Media Relations
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Become an Insider
Sign up today to receive premium content.

The Evolution of Technology in K–12 Classrooms: 1659 to Today

Alexander Huls is a Toronto-based writer whose work has appeared in The New York Times , Popular Mechanics , Esquire , The Atlantic and elsewhere.
In the 21st century, it can feel like advanced technology is changing the K–12 classroom in ways we’ve never seen before. But the truth is, technology and education have a long history of evolving together to dramatically change how students learn.
With more innovations surely headed our way, why not look back at how we got to where we are today, while looking forward to how educators can continue to integrate new technologies into their learning?
DISCOVER: Special education departments explore advanced tech in their classrooms.
Using Technology in the K–12 Classroom: A History
1659: magic lantern.
- Inventor: Christiaan Huygens
- A Brief History: An ancestor of the slide projector, the magic lantern projected glass slides with light from oil lamps or candles. In the 1680s, the technology was brought to the education space to show detailed anatomical illustrations, which were difficult to sketch on a chalkboard.
- Interesting Fact: Huygens initially regretted his creation, thinking it was too frivolous.
1795: Pencil
- Inventor: Nicolas-Jacques Conté
- A Brief History : Versions of the pencil can be traced back hundreds of years, but what’s considered the modern pencil is credited to Conté, a scientist in Napoleon Bonaparte’s army. It made its impact on the classroom, however, when it began to be mass produced in the 1900s.
- Interesting Fact: The Aztecs used a form of graphite pencil in the 13th century.
1801: Chalkboard
- Inventor: James Pillans
- A Brief History: Pillans — a headmaster at a high school in Edinburgh, Scotland — created the first front-of-class chalkboard, or “blackboard,” to better teach his students geography with large maps. Prior to his creation, educators worked with students on smaller, individual pieces of wood or slate. In the 1960s, the creation was upgraded to a green board, which became a familiar fixture in every classroom.
- Interesting Fact: Before chalkboards were commercially manufactured, some were made do-it-yourself-style with ingredients like pine board, egg whites and charred potatoes.
1888: Ballpoint Pen
- Inventory: John L. Loud
- A Brief History: John L. Loud invented and patented the first ballpoint pen after seeking to create a tool that could write on leather. It was not a commercial success. Fifty years later, following the lapse of Loud’s patent, Hungarian journalist László Bíró invented a pen with a quick-drying special ink that wouldn’t smear thanks to a rolling ball in its nib.
- Interesting Fact: When ballpoint pens debuted in the U.S., they were so popular that Gimbels, the department store selling them, made $81 million in today’s money within six months.
LEARN MORE: Logitech Pen works with Chromebooks to combine digital and physical learning.
1950s: Overhead Projector
- Inventor: Roger Appeldorn
- A Brief History: Overhead projects were used during World War II for mission briefings. However, 3M employee Appeldorn is credited with creating not only a projectable transparent film, but also the overhead projectors that would find a home in classrooms for decades.
- Interesting Fact: Appeldorn’s creation is the predecessor to today’s bright and efficient laser projectors .
1959: Photocopier
- Inventor: Chester Carlson
- A Brief History: Because of his arthritis, patent attorney and inventor Carlson wanted to create a less painful alternative to making carbon copies. Between 1938 and 1947, working with The Haloid Photographic Company, Carlson perfected the process of electrophotography, which led to development of the first photocopy machines.
- Interesting Fact: Haloid and Carlson named their photocopying process xerography, which means “dry writing” in Greek. Eventually, Haloid renamed its company (and its flagship product line) Xerox .
1967: Handheld Calculator
- Inventor: Texas Instruments
- A Brief History: As recounted in our history of the calculator , Texas Instruments made calculators portable with a device that weighed 45 ounces and featured a small keyboard with 18 keys and a visual display of 12 decimal digits.
- Interesting Fact: The original 1967 prototype of the device can be found in the Smithsonian Institution’s National Museum of American History .
1981: The Osborne 1 Laptop
- Inventor: Adam Osborne, Lee Felsenstein
- A Brief History: Osborne, a computer book author, teamed up with computer engineer Felsenstein to create a portable computer that would appeal to general consumers. In the process, they provided the technological foundation that made modern one-to-one devices — like Chromebooks — a classroom staple.
- Interesting Fact: At 24.5 pounds, the Osborne 1 was about as big and heavy as a sewing machine, earning it the current classification of a “luggable” computer, rather than a laptop.
1990: World Wide Web
- Inventor: Tim Berners-Lee
- A Brief History: In the late 1980s, British scientist Berners-Lee created the World Wide Web to enable information sharing between scientists and academics. It wasn’t long before the Web could connect anyone, anywhere to a wealth of information, and it was soon on its way to powering the modern classroom.
- Interesting Fact: The first web server Berners-Lee created was so new, he had to put a sign on the computer that read, “This machine is a server. DO NOT POWER IT DOWN!”
Click the banner to access customized K–12 technology content when you sign up as an Insider.

What Technology Is Used in Today’s K–12 Classrooms?
Technology has come so far that modern classrooms are more technologically advanced than many science labs were two decades ago. Students have access to digital textbooks, personal devices , collaborative cloud-based tools , and interactive whiteboards . Emerging technologies now being introduced to K–12 classrooms include voice assistants, virtual reality devices and 3D printers.
Perhaps the most important thing about ed tech in K–12 isn’t what the technology is, but how it’s used.
How to Integrate Technology into K–12 Classrooms
The first step to integrating technology into the K–12 classroom is figuring out which solution to integrate , given the large variety of tools available to educators. That variety comes with benefits — like the ability to align tech with district objectives and grade level — but also brings challenges.
“It’s difficult to know how to choose the appropriate digital tool or resource,” says Judi Harris, professor and Pavey Family Chair in Educational Technology at the William & Mary School of Education. “Teachers need some familiarity with the tools so that they understand the potential advantages and disadvantages.”

Judi Harris Professor and Pavey Family Chair in Educational Technology, William and Mary School of Education
K–12 IT leaders should also be careful not to focus too much on technology implementation at the expense of curriculum-based learning needs. “What districts need to ask themselves is not only whether they’re going to adopt a technology, but how they’re going to adopt it,” says Royce Kimmons, associate professor of instructional psychology and technology at Brigham Young University.
In other words, while emerging technologies may be exciting, acquiring them without proper consideration of their role in improving classroom learning will likely result in mixed student outcomes. For effective integration, educators should ask themselves, in what ways would the tech increase or support a student’s productivity and learning outcomes? How will it improve engagement?
Integrating ed tech also requires some practical know-how. “Teachers need to be comfortable and confident with the tools they ask students to use,” says Harris.
Professional development for new technologies is crucial, as are supportive IT teams, tech providers with generous onboarding programs and technology integration specialists. Harris also points to initiatives like YES: Youth and Educators Succeeding, a nonprofit organization that prepares students to act as resident experts and classroom IT support.
KEEP READING: What is the continued importance of professional development in K–12 education?
But as educational technology is rolled out and integrated, it’s important to keep academic goals in sight. “We should never stop focusing on how to best understand and help the learner to achieve those learning objectives,” says Harris.
That should continue to be the case as the technology timeline unfolds, something Harris has witnessed firsthand during her four decades in the field. “It’s been an incredible thing to watch and to participate in,” she notes. “The great majority of teachers are extremely eager to learn and to do anything that will help their students learn better.”

- Professional Development
Related Articles

Learn from Your Peers
What can you glean about security from other IT pros? Check out new CDW research and insight from our experts.
Copyright © 2024 CDW LLC 200 N. Milwaukee Avenue , Vernon Hills, IL 60061 Do Not Sell My Personal Information
This site belongs to UNESCO's International Institute for Educational Planning

IIEP Learning Portal

Search form
- issue briefs
- Improve learning
Information and communication technology (ICT) in education
Information and communications technology (ict) can impact student learning when teachers are digitally literate and understand how to integrate it into curriculum..
Schools use a diverse set of ICT tools to communicate, create, disseminate, store, and manage information.(6) In some contexts, ICT has also become integral to the teaching-learning interaction, through such approaches as replacing chalkboards with interactive digital whiteboards, using students’ own smartphones or other devices for learning during class time, and the “flipped classroom” model where students watch lectures at home on the computer and use classroom time for more interactive exercises.
When teachers are digitally literate and trained to use ICT, these approaches can lead to higher order thinking skills, provide creative and individualized options for students to express their understandings, and leave students better prepared to deal with ongoing technological change in society and the workplace.(18)
ICT issues planners must consider include: considering the total cost-benefit equation, supplying and maintaining the requisite infrastructure, and ensuring investments are matched with teacher support and other policies aimed at effective ICT use.(16)
Issues and Discussion
Digital culture and digital literacy: Computer technologies and other aspects of digital culture have changed the ways people live, work, play, and learn, impacting the construction and distribution of knowledge and power around the world.(14) Graduates who are less familiar with digital culture are increasingly at a disadvantage in the national and global economy. Digital literacy—the skills of searching for, discerning, and producing information, as well as the critical use of new media for full participation in society—has thus become an important consideration for curriculum frameworks.(8)
In many countries, digital literacy is being built through the incorporation of information and communication technology (ICT) into schools. Some common educational applications of ICT include:
- One laptop per child: Less expensive laptops have been designed for use in school on a 1:1 basis with features like lower power consumption, a low cost operating system, and special re-programming and mesh network functions.(42) Despite efforts to reduce costs, however, providing one laptop per child may be too costly for some developing countries.(41)
- Tablets: Tablets are small personal computers with a touch screen, allowing input without a keyboard or mouse. Inexpensive learning software (“apps”) can be downloaded onto tablets, making them a versatile tool for learning.(7)(25) The most effective apps develop higher order thinking skills and provide creative and individualized options for students to express their understandings.(18)
- Interactive White Boards or Smart Boards : Interactive white boards allow projected computer images to be displayed, manipulated, dragged, clicked, or copied.(3) Simultaneously, handwritten notes can be taken on the board and saved for later use. Interactive white boards are associated with whole-class instruction rather than student-centred activities.(38) Student engagement is generally higher when ICT is available for student use throughout the classroom.(4)
- E-readers : E-readers are electronic devices that can hold hundreds of books in digital form, and they are increasingly utilized in the delivery of reading material.(19) Students—both skilled readers and reluctant readers—have had positive responses to the use of e-readers for independent reading.(22) Features of e-readers that can contribute to positive use include their portability and long battery life, response to text, and the ability to define unknown words.(22) Additionally, many classic book titles are available for free in e-book form.
- Flipped Classrooms: The flipped classroom model, involving lecture and practice at home via computer-guided instruction and interactive learning activities in class, can allow for an expanded curriculum. There is little investigation on the student learning outcomes of flipped classrooms.(5) Student perceptions about flipped classrooms are mixed, but generally positive, as they prefer the cooperative learning activities in class over lecture.(5)(35)
ICT and Teacher Professional Development: Teachers need specific professional development opportunities in order to increase their ability to use ICT for formative learning assessments, individualized instruction, accessing online resources, and for fostering student interaction and collaboration.(15) Such training in ICT should positively impact teachers’ general attitudes towards ICT in the classroom, but it should also provide specific guidance on ICT teaching and learning within each discipline. Without this support, teachers tend to use ICT for skill-based applications, limiting student academic thinking.(32) To support teachers as they change their teaching, it is also essential for education managers, supervisors, teacher educators, and decision makers to be trained in ICT use.(11)
Ensuring benefits of ICT investments: To ensure the investments made in ICT benefit students, additional conditions must be met. School policies need to provide schools with the minimum acceptable infrastructure for ICT, including stable and affordable internet connectivity and security measures such as filters and site blockers. Teacher policies need to target basic ICT literacy skills, ICT use in pedagogical settings, and discipline-specific uses. (21) Successful implementation of ICT requires integration of ICT in the curriculum. Finally, digital content needs to be developed in local languages and reflect local culture. (40) Ongoing technical, human, and organizational supports on all of these issues are needed to ensure access and effective use of ICT. (21)
Resource Constrained Contexts: The total cost of ICT ownership is considerable: training of teachers and administrators, connectivity, technical support, and software, amongst others. (42) When bringing ICT into classrooms, policies should use an incremental pathway, establishing infrastructure and bringing in sustainable and easily upgradable ICT. (16) Schools in some countries have begun allowing students to bring their own mobile technology (such as laptop, tablet, or smartphone) into class rather than providing such tools to all students—an approach called Bring Your Own Device. (1)(27)(34) However, not all families can afford devices or service plans for their children. (30) Schools must ensure all students have equitable access to ICT devices for learning.
Inclusiveness Considerations
Digital Divide: The digital divide refers to disparities of digital media and internet access both within and across countries, as well as the gap between people with and without the digital literacy and skills to utilize media and internet.(23)(26)(31) The digital divide both creates and reinforces socio-economic inequalities of the world’s poorest people. Policies need to intentionally bridge this divide to bring media, internet, and digital literacy to all students, not just those who are easiest to reach.
Minority language groups: Students whose mother tongue is different from the official language of instruction are less likely to have computers and internet connections at home than students from the majority. There is also less material available to them online in their own language, putting them at a disadvantage in comparison to their majority peers who gather information, prepare talks and papers, and communicate more using ICT. (39) Yet ICT tools can also help improve the skills of minority language students—especially in learning the official language of instruction—through features such as automatic speech recognition, the availability of authentic audio-visual materials, and chat functions. (2)(17)
Students with different styles of learning: ICT can provide diverse options for taking in and processing information, making sense of ideas, and expressing learning. Over 87% of students learn best through visual and tactile modalities, and ICT can help these students ‘experience’ the information instead of just reading and hearing it. (20)(37) Mobile devices can also offer programmes (“apps”) that provide extra support to students with special needs, with features such as simplified screens and instructions, consistent placement of menus and control features, graphics combined with text, audio feedback, ability to set pace and level of difficulty, appropriate and unambiguous feedback, and easy error correction. (24)(29)
Plans and policies
- India [ PDF ]
- Detroit, USA [ PDF ]
- Finland [ PDF ]
- Alberta Education. 2012. Bring your own device: A guide for schools . Retrieved from http://education.alberta.ca/admin/technology/research.aspx
- Alsied, S.M. and Pathan, M.M. 2015. ‘The use of computer technology in EFL classroom: Advantages and implications.’ International Journal of English Language and Translation Studies . 1 (1).
- BBC. N.D. ‘What is an interactive whiteboard?’ Retrieved from http://www.bbcactive.com/BBCActiveIdeasandResources/Whatisaninteractivewhiteboard.aspx
- Beilefeldt, T. 2012. ‘Guidance for technology decisions from classroom observation.’ Journal of Research on Technology in Education . 44 (3).
- Bishop, J.L. and Verleger, M.A. 2013. ‘The flipped classroom: A survey of the research.’ Presented at the 120th ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition. Atlanta, Georgia.
- Blurton, C. 2000. New Directions of ICT-Use in Education . United National Education Science and Culture Organization (UNESCO).
- Bryant, B.R., Ok, M., Kang, E.Y., Kim, M.K., Lang, R., Bryant, D.P. and Pfannestiel, K. 2015. ‘Performance of fourth-grade students with learning disabilities on multiplication facts comparing teacher-mediated and technology-mediated interventions: A preliminary investigation. Journal of Behavioral Education. 24.
- Buckingham, D. 2005. Educación en medios. Alfabetización, aprendizaje y cultura contemporánea, Barcelona, Paidós.
- Buckingham, D., Sefton-Green, J., and Scanlon, M. 2001. 'Selling the Digital Dream: Marketing Education Technologies to Teachers and Parents.' ICT, Pedagogy, and the Curriculum: Subject to Change . London: Routledge.
- "Burk, R. 2001. 'E-book devices and the marketplace: In search of customers.' Library Hi Tech 19 (4)."
- Chapman, D., and Mählck, L. (Eds). 2004. Adapting technology for school improvement: a global perspective. Paris: International Institute for Educational Planning.
- Cheung, A.C.K and Slavin, R.E. 2012. ‘How features of educational technology applications affect student reading outcomes: A meta-analysis.’ Educational Research Review . 7.
- Cheung, A.C.K and Slavin, R.E. 2013. ‘The effectiveness of educational technology applications for enhancing mathematics achievement in K-12 classrooms: A meta-analysis.’ Educational Research Review . 9.
- Deuze, M. 2006. 'Participation Remediation Bricolage - Considering Principal Components of a Digital Culture.' The Information Society . 22 .
- Dunleavy, M., Dextert, S. and Heinecke, W.F. 2007. ‘What added value does a 1:1 student to laptop ratio bring to technology-supported teaching and learning?’ Journal of Computer Assisted Learning . 23.
- Enyedy, N. 2014. Personalized Instruction: New Interest, Old Rhetoric, Limited Results, and the Need for a New Direction for Computer-Mediated Learning . Boulder, CO: National Education Policy Center.
- Golonka, E.M., Bowles, A.R., Frank, V.M., Richardson, D.L. and Freynik, S. 2014. ‘Technologies for foreign language learning: A review of technology types and their effectiveness.’ Computer Assisted Language Learning . 27 (1).
- Goodwin, K. 2012. Use of Tablet Technology in the Classroom . Strathfield, New South Wales: NSW Curriculum and Learning Innovation Centre.
- Jung, J., Chan-Olmsted, S., Park, B., and Kim, Y. 2011. 'Factors affecting e-book reader awareness, interest, and intention to use.' New Media & Society . 14 (2)
- Kenney, L. 2011. ‘Elementary education, there’s an app for that. Communication technology in the elementary school classroom.’ The Elon Journal of Undergraduate Research in Communications . 2 (1).
- Kopcha, T.J. 2012. ‘Teachers’ perceptions of the barriers to technology integration and practices with technology under situated professional development.’ Computers and Education . 59.
- Miranda, T., Williams-Rossi, D., Johnson, K., and McKenzie, N. 2011. "Reluctant readers in middle school: Successful engagement with text using the e-reader.' International journal of applied science and technology . 1 (6).
- Moyo, L. 2009. 'The digital divide: scarcity, inequality and conflict.' Digital Cultures . New York: Open University Press.
- Newton, D.A. and Dell, A.G. 2011. ‘Mobile devices and students with disabilities: What do best practices tell us?’ Journal of Special Education Technology . 26 (3).
- Nirvi, S. (2011). ‘Special education pupils find learning tool in iPad applications.’ Education Week . 30 .
- Norris, P. 2001. Digital Divide: Civic Engagement, Information Poverty, and the Internet Worldwide . Cambridge, USA: Cambridge University Press.
- Project Tomorrow. 2012. Learning in the 21st century: Mobile devices + social media = personalized learning . Washington, D.C.: Blackboard K-12.
- Riasati, M.J., Allahyar, N. and Tan, K.E. 2012. ‘Technology in language education: Benefits and barriers.’ Journal of Education and Practice . 3 (5).
- Rodriquez, C.D., Strnadova, I. and Cumming, T. 2013. ‘Using iPads with students with disabilities: Lessons learned from students, teachers, and parents.’ Intervention in School and Clinic . 49 (4).
- Sangani, K. 2013. 'BYOD to the classroom.' Engineering & Technology . 3 (8).
- Servon, L. 2002. Redefining the Digital Divide: Technology, Community and Public Policy . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers.
- Smeets, E. 2005. ‘Does ICT contribute to powerful learning environments in primary education?’ Computers and Education. 44 .
- Smith, G.E. and Thorne, S. 2007. Differentiating Instruction with Technology in K-5 Classrooms . Eugene, OR: International Society for Technology in Education.
- Song, Y. 2014. '"Bring your own device (BYOD)" for seamless science inquiry in a primary school.' Computers & Education. 74 .
- Strayer, J.F. 2012. ‘How learning in an inverted classroom influences cooperation, innovation and task orientation.’ Learning Environment Research. 15.
- Tamim, R.M., Bernard, R.M., Borokhovski, E., Abrami, P.C. and Schmid, R.F. 2011. ‘What forty years of research says about the impact of technology on learning: A second-order meta-analysis and validation study. Review of Educational Research. 81 (1).
- Tileston, D.W. 2003. What Every Teacher Should Know about Media and Technology. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
- Turel, Y.K. and Johnson, T.E. 2012. ‘Teachers’ belief and use of interactive whiteboards for teaching and learning.’ Educational Technology and Society . 15(1).
- Volman, M., van Eck, E., Heemskerk, I. and Kuiper, E. 2005. ‘New technologies, new differences. Gender and ethnic differences in pupils’ use of ICT in primary and secondary education.’ Computers and Education. 45 .
- Voogt, J., Knezek, G., Cox, M., Knezek, D. and ten Brummelhuis, A. 2013. ‘Under which conditions does ICT have a positive effect on teaching and learning? A call to action.’ Journal of Computer Assisted Learning. 29 (1).
- Warschauer, M. and Ames, M. 2010. ‘Can one laptop per child save the world’s poor?’ Journal of International Affairs. 64 (1).
- Zuker, A.A. and Light, D. 2009. ‘Laptop programs for students.’ Science. 323 (5910).
Related information
- Information and communication technologies (ICT)

- Evolution Technology Classroom
The Evolution of Technology in the Classroom

Purdue Online
Technology has always been at the forefront of human education. From the days of carving figures on rock walls to today, when most students are equipped with several portable technological devices at any given time, technology continues to push educational capabilities to new levels. In looking at where educational methods and tools have come from to where they are going in the future, technology’s importance in the classroom is evident now more than ever.
A History of Classroom Technology: The Primitive Classroom
In the Colonial years, wooden paddles with printed lessons, called Horn-Books, were used to assist students in learning verses. Over 200 years later, in 1870, technology advanced to include the Magic Lantern, a primitive version of a slide projector that projected images printed on glass plates. By the time World War I ended, around 8,000 lantern slides were circulating through the Chicago public school system. By the time the Chalkboard came around in 1890, followed by the pencil in 1900, it was clear that students were hungry for more advanced educational tools.
- Radio in the 1920s sparked an entirely new wave of learning; on-air classes began popping up for any student within listening range.
- Next came the overhead projector in 1930, followed by the ballpoint pen in 1940 and headphones in 1950.
- Videotapes arrived on the scene in 1951, creating a new and exciting method of instruction.
- The Skinner Teaching Machine produced a combined system of teaching and testing, providing reinforcement for correct answers so that the student can move on to the next lesson.
- The photocopier (1959) and handheld calculator (1972) entered the classrooms next, allowing for mass production of material on the fly and quick mathematical calculations.
- The Scantron system of testing, introduced by Michael Sokolski n 1972, allowed educators to grade tests more quickly and efficiently.
The pre-computer years were formative in the choices made for computers in the years following. Immediate response-type systems (video, calculator, Scantron) had become necessary, and quick production of teaching materials, using the photocopier, had become a standard. The U.S. Department of Education reports that high school enrollment was only 10% in 1900, but by 1992 had expanded to 95%. The number of students in college in 1930 was around 1 million, but by 2012 had grown to a record 21.6 million. Teachers needed new methods of instruction and testing, and students were looking for new ways to communicate, study, and learn.
The Entrance and Significance of Personal Computers
Although the first computers were developed in the ‘30s, everyday-use computers were introduced in the ‘80s. The first portable computer, in 1981, weighed 24 pounds and cost $1,795. When IBM introduced its first personal computer in 1981, the educational world knew that it was on the verge of greatness. Time magazine named The Computer its “Man of the Year” in 1982, and aptly so: the foundation of immediate learning capabilities had been laid. Time declared, “it is the end result of a technological revolution that has been in the making for four decades and is now, quite literally, hitting home.”
- Toshiba released its first mass-market consumer laptop in 1985 (the T1100), and Apple’s infamous Mac (which later evolved into the Powerbook) was available starting in 1984.
- In 1990, The World Wide Web was given life when a British researcher developed Hyper Text Markup Language, or HTML, and when the National Science Foundation (NSF) removed restrictions on the commercial use of the Internet in 1993, the world exploded into a frenzy of newfound research and communication methods.
- The first Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs) were released by Apple Computer Inc. in 1993, and with that, computers were a part of every day, if not every moment. By 2009, 97% of classrooms had one or more computers , and 93% of classroom computers had Internet access. For every 5 students, there was one computer. Instructors stated that 40% of students used computers often in their educational methods, in addition to interactive whiteboards and digital cameras. College students nowadays are rarely without some form of computer technology: 83% own a laptop, and over 50% have a Smartphone.
The Future of Technology in the Classroom
It seems like years since MySpace, first introduced in 2003, Facebook (2004) and Twitter (2007) have changed both the communication and business worlds. Instant connectivity has branched out from merely a tool of personal communication, to a platform for educational instruction and outreach. Social media is now being recognized as an accepted form of instruction in some instances, and groups such as Scholastic Teachers provide excellent support and tips for instructors. Many instructors use social media to communicate directly with their students, or to form forum-style groups for students to communicate with each other, and the method seems to be proving valuable in providing one-on-one attention to student’s questions and concerns.
With the classroom having already evolved into a hotbed of technological advances, what can the future possibly hold that could further educational proficiencies even more?
- Biometrics, a technology that recognizes people based on certain physical or behavioral traits, is on the technological horizon. The science will be used to recognize the physical and emotional disposition of students in the classroom, altering course material to tailor to each individual’s needs based on biometric signals.
- A second up-and-coming technology is Augmented Reality (AR) glasses , rumored to be on Google’s release list, and this technology could be a whole new world for education. AR Glasses (or even contact lenses) will layer data on top of what we naturally see, to allow for a real-world learning experience. For example, a student wearing AR Glasses could potentially sit at his desk and have a conversation with Thomas Edison about invention. It was Edison, after all, who said that “Books will soon be obsolete in schools. Scholars will soon be instructed through the eye.”
- Multi-touch surfaces are commonly used through equipment such as the iPhone, but the technology could become more relevant to education through entirely multi-touch surfaces, such as desks or workstations. This could allow students to collaborate with other students, even those around the world, and videos and other virtual tools could be streamed directly to the surface.
Educators and the Evolution of Technology in the Classroom
With the evolution of technology, educational capabilities are growing and changing every day. The Internet is a vast electronic library of information, and both research and instruction can be achieved through a click of the mouse. With these advances come new responsibilities to the instructor and therefore increase the value of a Master of Science in Education in Learning Design and Technology . As technology advances, an educator’s abilities will grow by leaps and bounds, and without the knowledge of these changes and capabilities, an instructor has a good chance of being left behind.
A career in education requires hard work and dedication, but, for the diligent educator, can prove very rewarding. For those who are serious about success in the education field, staying well-informed of current and changing technologies is imperative. As the world of technology evolves, the learning environment, both on-campus and online, will equally progress, and the need for teachers who are educated in technology and design will continue to grow.
Learn more about the online MSEd in Learning Design and Technology at Purdue University today and help redefine the way in which individuals learn. Call (877) 497-5851 to speak with an admissions advisor or click here to request more information.
- Learning Design and Technology
About the Author
- Communication
- Health Sciences
- Student Advice
Most Popular Posts
- How Has Technology Changed Education?
- What Do Instructional Designers Do?
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
What 126 studies say about education technology
Press contact :.

Previous image Next image
In recent years, there has been widespread excitement around the transformative potential of technology in education. In the United States alone, spending on education technology has now exceeded $13 billion . Programs and policies to promote the use of education technology may expand access to quality education, support students’ learning in innovative ways, and help families navigate complex school systems.
However, the rapid development of education technology in the United States is occurring in a context of deep and persistent inequality . Depending on how programs are designed, how they are used, and who can access them, education technologies could alleviate or aggravate existing disparities. To harness education technology’s full potential, education decision-makers, product developers, and funders need to understand the ways in which technology can help — or in some cases hurt — student learning.
To address this need, J-PAL North America recently released a new publication summarizing 126 rigorous evaluations of different uses of education technology. Drawing primarily from research in developed countries, the publication looks at randomized evaluations and regression discontinuity designs across four broad categories: (1) access to technology, (2) computer-assisted learning or educational software, (3) technology-enabled nudges in education, and (4) online learning.
This growing body of evidence suggests some areas of promise and points to four key lessons on education technology.
First, supplying computers and internet alone generally do not improve students’ academic outcomes from kindergarten to 12th grade, but do increase computer usage and improve computer proficiency. Disparities in access to information and communication technologies can exacerbate existing educational inequalities. Students without access at school or at home may struggle to complete web-based assignments and may have a hard time developing digital literacy skills.
Broadly, programs to expand access to technology have been effective at increasing use of computers and improving computer skills. However, computer distribution and internet subsidy programs generally did not improve grades and test scores and in some cases led to adverse impacts on academic achievement. The limited rigorous evidence suggests that distributing computers may have a more direct impact on learning outcomes at the postsecondary level.
Second, educational software (often called “computer-assisted learning”) programs designed to help students develop particular skills have shown enormous promise in improving learning outcomes, particularly in math. Targeting instruction to meet students’ learning levels has been found to be effective in improving student learning, but large class sizes with a wide range of learning levels can make it hard for teachers to personalize instruction. Software has the potential to overcome traditional classroom constraints by customizing activities for each student. Educational software programs range from light-touch homework support tools to more intensive interventions that re-orient the classroom around the use of software.
Most educational software that have been rigorously evaluated help students practice particular skills through personalized tutoring approaches. Computer-assisted learning programs have shown enormous promise in improving academic achievement, especially in math. Of all 30 studies of computer-assisted learning programs, 20 reported statistically significant positive effects, 15 of which were focused on improving math outcomes.
Third, technology-based nudges — such as text message reminders — can have meaningful, if modest, impacts on a variety of education-related outcomes, often at extremely low costs. Low-cost interventions like text message reminders can successfully support students and families at each stage of schooling. Text messages with reminders, tips, goal-setting tools, and encouragement can increase parental engagement in learning activities, such as reading with their elementary-aged children.
Middle and high schools, meanwhile, can help parents support their children by providing families with information about how well their children are doing in school. Colleges can increase application and enrollment rates by leveraging technology to suggest specific action items, streamline financial aid procedures, and/or provide personalized support to high school students.
Online courses are developing a growing presence in education, but the limited experimental evidence suggests that online-only courses lower student academic achievement compared to in-person courses. In four of six studies that directly compared the impact of taking a course online versus in-person only, student performance was lower in the online courses. However, students performed similarly in courses with both in-person and online components compared to traditional face-to-face classes.
The new publication is meant to be a resource for decision-makers interested in learning which uses of education technology go beyond the hype to truly help students learn. At the same time, the publication outlines key open questions about the impacts of education technology, including questions relating to the long-term impacts of education technology and the impacts of education technology on different types of learners.
To help answer these questions, J-PAL North America’s Education, Technology, and Opportunity Initiative is working to build the evidence base on promising uses of education technology by partnering directly with education leaders.
Education leaders are invited to submit letters of interest to partner with J-PAL North America through its Innovation Competition . Anyone interested in learning more about how to apply is encouraged to contact initiative manager Vincent Quan .
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- J-PAL Education, Technology, and Opportunity Initiative
- Education, Technology, and Opportunity Innovation Competition
- Article: "Will Technology Transform Education for the Better?"
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab
- Department of Economics
Related Topics
- School of Humanities Arts and Social Sciences
- Education, teaching, academics
- Technology and society
- Computer science and technology
Related Articles

J-PAL North America calls for proposals from education leaders

J-PAL North America’s Education, Technology, and Opportunity Innovation Competition announces inaugural partners

New learning opportunities for displaced persons

J-PAL North America announces new partnerships with three state and local governments

A new way to measure women’s and girls’ empowerment in impact evaluations
Previous item Next item
More MIT News
A new way to spot life-threatening infections in cancer patients
Read full story →

Technique improves the reasoning capabilities of large language models

A creation story told through immersive technology
With programmable pixels, novel sensor improves imaging of neural activity

Featured video: Researchers discuss queer visibility in academia

Scientists preserve DNA in an amber-like polymer
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
Technology in Education: An Overview

- Share article
Technology is everywhere in education: Public schools in the United States now provide at least one computer for every five students. They spend more than $3 billion per year on digital content. Led by the federal government, the country is in the midst of a massive effort to make affordable high-speed Internet and free online teaching resources available to even the most rural and remote schools. And in 2015-16, for the first time, more state standardized tests for the elementary and middle grades will be administered via technology than by paper and pencil.
To keep up with what’s changing (and what isn’t), observers must know where to look.
There’s the booming ed-tech industry, with corporate titans and small startups alike vying for a slice of an $8 billion-plus yearly market for hardware and software. Much attention is also paid to the “early adopters”—those districts, schools, and teachers who are making the most ingenious and effective uses of the new tools at their disposal.
But a significant body of research has also made clear that most teachers have been slow to transform the ways they teach, despite the influx of new technology into their classrooms. There remains limited evidence to show that technology and online learning are improving learning outcomes for most students. And academics and parents alike have expressed concerns about digital distractions, ways in which unequal access to and use of technology might widen achievement gaps, and more.
State and federal lawmakers, meanwhile, have wrestled in recent years with the reality that new technologies also present new challenges. The rise of “big data,” for example, has led to new concerns about how schools can keep sensitive student information private and secure.
What follows is an overview of the big trends, opportunities, and concerns associated with classroom technology. Links to additional resources are included in each section for those who would like to dig deeper.
What Is Personalized Learning?
Many in the ed-tech field see new technologies as powerful tools to help schools meet the needs of ever-more-diverse student populations. The idea is that digital devices, software, and learning platforms offer a once-unimaginable array of options for tailoring education to each individual student’s academic strengths and weaknesses, interests and motivations, personal preferences, and optimal pace of learning.
In recent years, a group of organizations including the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Michael and Susan Dell Foundation, and EDUCAUSE have crafted a definition of “personalized learning” that rests on four pillars:
- Each student should have a “learner profile” that documents his or her strengths, weaknesses, preferences, and goals;
- Each student should pursue an individualized learning path that encourages him or her to set and manage personal academic goals;
- Students should follow a “competency-based progression” that focuses on their ability to demonstrate mastery of a topic, rather than seat time; and,
- Students’ learning environments should be flexible and structured in ways that support their individual goals.
How does technology support that vision?
In many schools, students are given district-owned computing devices or allowed to bring their own devices from home. The idea is that this allows for “24-7” learning at the time and location of the student’s choosing.
Learning management systems, student information systems, and other software are also used to distribute assignments, manage schedules and communications, and track student progress.
And educational software and applications have grown more “adaptive,” relying on technology and algorithms to determine not only what a student knows, but what his or her learning process is, and even his or her emotional state.
For all the technological progress, though, implementation remains a major challenge. Schools and educators across the country continue to wrestle with the changing role of teachers, how to balance flexible and “personalized” models with the state and federal accountability requirements they still must meet, and the deeper cultural challenge of changing educators’ long-standing habits and routines.
Despite the massive investments that many school systems are making, the evidence that digital personalized learning can improve student outcomes or narrow achievement gaps at scale remains scattered, at best.
Additional resources:
- Taking Stock of Personalized Learning (Education Week special report)
- A Working Definition of Personalized Learning
- Why Ed Tech Is Not Transforming How Teachers Teach
What Is 1-to-1 Computing?
Increasingly, schools are moving to provide students with their own laptop computer, netbook, or digital tablet. Schools purchased more than 23 million devices for classroom use in 2013 and 2014 alone. In recent years, iPads and then Chromebooks (inexpensive Web-based laptops) have emerged as the devices of choice for many schools.
Video: Creating a Digital Culture

The two biggest factors spurring the rise in 1-to-1 student computing have been new mandates that state standardized tests be delivered online and the widespread adoption of the Common Core State Standards.
Generally, the hope is that putting devices in the hands of students will help with some or all of the following goals:
- Allowing teachers and software to deliver more personalized content and lessons to students, while allowing students to learn at their own pace and ability level;
- Helping students to become technologically skilled and literate and thus better prepared for modern workplaces;
- Empowering students to do more complex and creative work by allowing them to use digital and online applications and tools;
- Improving the administration and management of schools and classrooms by making it easier to gather information on what students know and have done;
- Improving communications among students, teachers, and parents.
Despite the potential benefits, however, many districts have run into trouble when attempting to implement 1-to-1 computing initiatives. Paying for the devices can be a challenge, especially as the strategy of issuing long-term bonds for short-term technology purchases has come into question. Many districts have also run into problems with infrastructure (not enough bandwidth to support all students accessing the Internet at the same time) and deployment (poor planning in distributing and managing thousands of devices.)
The most significant problem for schools trying to go 1-to-1, though, has been a lack of educational vision. Without a clear picture of how teaching and learning is expected to change, experts say, going 1-to-1 often amounts to a “spray and pray” approach of distributing many devices and hoping for the best.
Some critics of educational technology also point to a recent study by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, which found that countries where 15-year old students use computers most in the classroom scored the worst on international reading and math tests.
- Learn More About 1-to-1 Computing
- Hard Lessons Learned in Ambitious L.A. iPad Initiative
- Chromebooks Gaining Popularity in School Districts
What Is Blended Learning?
In its simplest terms, blended learning combines traditional, teacher-to-student lessons with technology-based instruction.
Many schools and districts use a “rotation” model, which is often viewed as an effective means of providing students with more personalized instruction and smaller group experiences. In some cases, saving money (through larger overall class sizes, for example) is also a goal. The basic premise involves students rotating between online and in-person stations for different parts of the day. There are many versions of this approach, however: Do students stay in the classroom or go to a computer lab?
Does online instruction cover core content, or is it primarily for remediation? Are all students doing the same thing online, or do different students have different software and learning experiences?
Video: At Blended Learning School, Students on Flexible Schedules

One big trend for schools involves trying to make sure that what happens online is connected with what happens during face-to-face interactions with teachers. That could involve giving teachers a say in selecting the software that students use, for example, or making a concerted effort to ensure online programs provide teachers with data that is useful in making timely instructional decisions.
Another trend involves boosting students’ access to the Internet outside of school. Robust blended learning programs involve “anytime, anywhere” access to learning content for students—a major challenge in many communities.
Perhaps the biggest hurdle confronting educators interested in blended learning, though, is the lack of a solid research base. As of now, there is still no definitive evidence that blended learning works (or doesn’t.) While some studies have found encouraging results with specific programs or under certain circumstances, the question of whether blended learning positively impacts student learning still has a mostly unsatisfactory answer: “It depends.”
- Blended Learning: Breaking Down Barriers (Education Week special report)
- Blended Learning Research: The 7 Studies You Need to Know
- Learn More About Blended Learning
What Is the Status of Tech Infrastructure and the E-Rate?
The promise of technology in the classroom is almost entirely dependent on reliable infrastructure. But in many parts of the country, schools still struggle to get affordable access to high-speed Internet and/or robust wireless connectivity.
A typical school district network involves multiple components. In 2014, the Federal Communications Commission established connectivity targets for some of the pieces:
- A connection to the broader Internet provided by an outside service provider to the district office (or another central district hub). Target: 100 megabits per second per 1,000 students in the short-term, and 1 Gigabit per second per 1,000 students in the long-term.
- A “Wide Area Network” that provides network connections between the district’s central hub and all of its campuses, office buildings, and other facilities. Target: Connections capable of delivering 10 Gigabits per second per 1,000 students.
- “Local Area Networks” that provide connections within a school, including the equipment necessary to provide Wi-Fi service inside classrooms. Target: The FCC recommended a survey to determine a suitable measure. Many school-technology advocates call for internal connections that support 1-to-1 computing.
To support schools (and libraries) in building and paying for these networks, the FCC in 1996 established a program known as the E-rate. Fees on consumers’ phone bills fund the program, which has paid out more than $30 billion since its inception.
In 2014, the commission overhauled the E-rate, raising the program’s annual spending cap from $2.4 billion to $3.9 billion and prioritizing support for broadband service and wireless networks. The changes were already being felt as of Fall 2015; after steadily declining for years, the number of schools and libraries applying for E-rate funds for wireless network equipment skyrocketed, with nearly all of the applicants expected to receive a portion of the $1.6 billion in overall wireless-related requests.

As part of the E-rate overhaul, the FCC also approved a series of regulatory changes aimed at leveling the playing field for rural and remote schools, which often face two big struggles: accessing the fiber-optic cables that experts say are essential to meeting the FCC’s long-term goals, and finding affordable rates.
Infrastructure in some contexts can also be taken to include learning devices, digital content, and the policies and guidelines that govern how they are expected to be used in schools (such as “responsible use policies” and “digital citizenship” programs aimed to ensure that students and staff are using technology appropriately and in support of learning goals.)
Another big—and often overlooked—aspect of infrastructure is what’s known as interoperability. Essentially, the term refers to common standards and protocols for formatting and handling data so that information can be shared between software programs. A number of frameworks outline data interoperability standards for different purposes. Many hope to see the field settle on common standards in the coming years.
Additional Resources:
- The Typical School Network (EducationSuperHighway)
- The E-rate Overhaul in 4 Easy Charts
- Reversing a Raw Deal: Rural Schools Still Struggle to Access Affordable High Speed Internet (Education Week special series)
How Is Online Testing Evolving?
The biggest development on this front has been states’ adoption of online exams aligned with the Common Core State Standards. During the 2014-15 school year, 10 states (plus the District of Columbia) used exams from the Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers (PARCC), and 18 states used exams from the Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, all of which were delivered primarily online. Many of the other states also used online assessments.
The 2015-16 school year will be the first in which more state-required summative assessments in U.S. middle and elementary schools will be delivered via technology rather than paper and pencil, according to a recent analysis by EdTech Strategies, an educational technology consulting firm.
Beyond meeting legislative mandates, perceived benefits include cost savings, ease of administration and analysis, and the potential to employ complex performance tasks.
But some states—including Florida, Minnesota, Montana, and Wisconsin—have experienced big problems with online tests, ranging from cyber attacks to log-in problems to technical errors. And there is growing evidence that students who take the paper-and-pencil version of some important tests perform better than peers who take the same exams online, at least in the short term.
Nevertheless, it appears likely that online testing will continue to grow—and not just for state summative assessments. The U.S. Department of Education, for example, is among those pushing for a greater use of technologically enhanced formative assessments that can be used to diagnose students’ abilities in close to real time. In the department’s 2016 National Education Technology Plan, for example, it calls for states and districts to “design, develop, and implement learning dashboards, response systems, and communication pathways that give students, educators, families, and other stakeholders timely and actionable feedback about student learning to improve achievement and instructional practices.”
- PARCC Scores Lower for Students Who Took Exams on Computers
- Map: The National K-12 Testing Landscape
- Pencils Down: The Shift to Online and Computer-Based Testing (EdTech Strategies)
- Online Testing Glitches Causing Distrust in Technology
- U.S. Ed-Tech Plan Calls Attention to ‘Digital-Use Divide’
How Are Digital Materials Used in Classrooms?
Digital instructional content is the largest slice of the (non-hardware) K-12 educational technology market, with annual sales of more then $3 billion. That includes digital lessons in math, English/language arts, and science, as well as “specialty” subjects such as business and fine arts. The market is still dominated by giant publishers such as Houghton Mifflin Harcourt and Pearson, who have been scrambling to transition from their print-centric legacy products to more digital offerings.
But newcomers with one-off products or specific areas of expertise have made inroads, and some apps and online services have also gained huge traction inside of schools.
As a result, many schools use a mix of digital resources, touting potential benefits such as greater ability to personalize, higher engagement among students, enhanced ability to keep content updated and current, and greater interactivity and adaptivity (or responsiveness to individual learners).
Still, though, the transition to digital instructional materials is happening slowly, for reasons that range from the financial (for districts that haven’t been able to purchase devices for all students, for example) to the technical (districts that lack the infrastructure to support every student being online together.) Print still accounts for about 70 percent of pre-K-12 instructional materials sales in the United States.
- Learn More About Digital Curriculum
- Digital Content Providers Ride Wave of Rising Revenues
- K-12 Print Needs Persist Despite Digital Growth
What Are Open Educational Resources?
Rather than buying digital instructional content, some states and districts prefer using “open” digital education resources that are licensed in such a way that they can be freely used, revised, and shared. The trend appears likely to accelerate: The U.S. Department of Education, for example, is now formally encouraging districts to move away from textbooks and towards greater adoption of OER.

New York and Utah have led the way in developing open educational resources and encouraging their use by schools. The K-12 OER Collaborative, which includes 12 states and several nonprofit organizations, is working to develop OER materials as well.
Proponents argue that OER offer greater bang for the buck, while also giving students better access to a wider array of digital materials and teachers more flexibility to customize instructional content for individual classrooms and students. Some also believe OER use encourages collaboration among teachers. Concerns from industry and others generally focus on the quality of open materials, as well as the challenges that educators face in sifting through voluminous one-off resources to find the right material for every lesson.
- What is OER? (Creative Commons)
- Districts Put Open Educational Resources to Work
- Calculating the Return on Open Educational Resources
How Are Virtual Education and Distance Learning Doing?
One technology trend that has come under increasing scrutiny involves full-time online schools, particularly cyber charters. About 200,000 students are enrolled in about 200 publicly funded, independently managed online charter schools across 26 states.
But such schools were found to have an “overwhelming negative impact” on student learning in a comprehensive set of studies released in 2015 by a group of research organizations, including Stanford University’s Center for Research on Education Outcomes at Stanford University.
That research did not cover the more than two dozen full-time online schools that are state-run, however, nor did it cover the dozens more that are run by individual school districts. Thousands upon thousands of students who are enrolled in traditional brick-and-mortar schools also take individual courses online. Five states—Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Michigan, and Virginia—now require students to have some online learning to graduate. Other states, such as Utah, have passed laws encouraging such options for students.
For many students, especially those in rural and remote areas, online and distance learning can offer access to courses, subjects, and teachers they might otherwise never be able to find. Such opportunities can also benefit advanced and highly motivated students and those with unusual schedules and travel requirements, and be a useful tool to keep schools running during snow days.
But so far, achieving positive academic outcomes at scale via online learning has proven difficult, and many observers have expressed concerns about the lack of accountability in the sector, especially as relates to for-profit managers of online options.
- Learn More About Remote/Virtual Learning
- Cyber Charters Have ‘Overwhelming Negative Impact’
Education Issues, Explained
How to Cite This Article Herold, B. (2016, February 5). Technology in Education An Overview. Education Week. Retrieved Month Day, Year from https://www.edweek.org/technology/technology-in-education-an-overview/2016/02
Sign Up for EdWeek Tech Leader
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

How Important Is Technology in Education? Benefits, Challenges, and Impact on Students
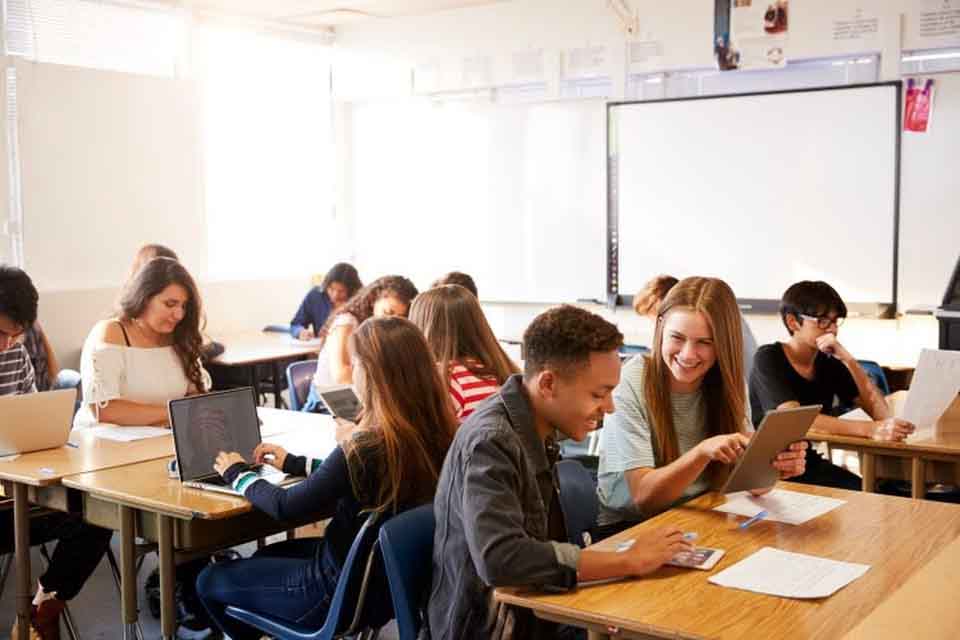

Many of today’s high-demand jobs were created in the last decade, according to the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE). As advances in technology drive globalization and digital transformation, teachers can help students acquire the necessary skills to succeed in the careers of the future.
How important is technology in education? The COVID-19 pandemic is quickly demonstrating why online education should be a vital part of teaching and learning. By integrating technology into existing curricula, as opposed to using it solely as a crisis-management tool, teachers can harness online learning as a powerful educational tool.
The effective use of digital learning tools in classrooms can increase student engagement, help teachers improve their lesson plans, and facilitate personalized learning. It also helps students build essential 21st-century skills.
Virtual classrooms, video, augmented reality (AR), robots, and other technology tools can not only make class more lively, they can also create more inclusive learning environments that foster collaboration and inquisitiveness and enable teachers to collect data on student performance.
Still, it’s important to note that technology is a tool used in education and not an end in itself. The promise of educational technology lies in what educators do with it and how it is used to best support their students’ needs.
Educational Technology Challenges
BuiltIn reports that 92 percent of teachers understand the impact of technology in education. According to Project Tomorrow, 59 percent of middle school students say digital educational tools have helped them with their grades and test scores. These tools have become so popular that the educational technology market is projected to expand to $342 billion by 2025, according to the World Economic Forum.
However, educational technology has its challenges, particularly when it comes to implementation and use. For example, despite growing interest in the use of AR, artificial intelligence, and other emerging technology, less than 10 percent of schools report having these tools in their classrooms, according to Project Tomorrow. Additional concerns include excessive screen time, the effectiveness of teachers using the technology, and worries about technology equity.
Prominently rising from the COVID-19 crisis is the issue of content. Educators need to be able to develop and weigh in on online educational content, especially to encourage students to consider a topic from different perspectives. The urgent actions taken during this crisis did not provide sufficient time for this. Access is an added concern — for example, not every school district has resources to provide students with a laptop, and internet connectivity can be unreliable in homes.
Additionally, while some students thrive in online education settings, others lag for various factors, including support resources. For example, a student who already struggled in face-to-face environments may struggle even more in the current situation. These students may have relied on resources that they no longer have in their homes.
Still, most students typically demonstrate confidence in using online education when they have the resources, as studies have suggested. However, online education may pose challenges for teachers, especially in places where it has not been the norm.
Despite the challenges and concerns, it’s important to note the benefits of technology in education, including increased collaboration and communication, improved quality of education, and engaging lessons that help spark imagination and a search for knowledge in students.
The Benefits of Technology in Education
Teachers want to improve student performance, and technology can help them accomplish this aim. To mitigate the challenges, administrators should help teachers gain the competencies needed to enhance learning for students through technology. Additionally, technology in the classroom should make teachers’ jobs easier without adding extra time to their day.
Technology provides students with easy-to-access information, accelerated learning, and fun opportunities to practice what they learn. It enables students to explore new subjects and deepen their understanding of difficult concepts, particularly in STEM. Through the use of technology inside and outside the classroom, students can gain 21st-century technical skills necessary for future occupations.
Still, children learn more effectively with direction. The World Economic Forum reports that while technology can help young students learn and acquire knowledge through play, for example, evidence suggests that learning is more effective through guidance from an adult, such as a teacher.
Leaders and administrators should take stock of where their faculty are in terms of their understanding of online spaces. From lessons learned during this disruptive time, they can implement solutions now for the future. For example, administrators could give teachers a week or two to think carefully about how to teach courses not previously online. In addition to an exploration of solutions, flexibility during these trying times is of paramount importance.
Below are examples of how important technology is in education and the benefits it offers to students and teachers.
Increased Collaboration and Communication
Educational technology can foster collaboration. Not only can teachers engage with students during lessons, but students can also communicate with each other. Through online lessons and learning games, students get to work together to solve problems. In collaborative activities, students can share their thoughts and ideas and support each other. At the same time, technology enables one-on-one interaction with teachers. Students can ask classroom-related questions and seek additional help on difficult-to-understand subject matter. At home, students can upload their homework, and teachers can access and view completed assignments using their laptops.
Personalized Learning Opportunities
Technology allows 24/7 access to educational resources. Classes can take place entirely online via the use of a laptop or mobile device. Hybrid versions of learning combine the use of technology from anywhere with regular in-person classroom sessions. In both scenarios, the use of technology to tailor learning plans for each student is possible. Teachers can create lessons based on student interests and strengths. An added benefit is that students can learn at their own pace. When they need to review class material to get a better understanding of essential concepts, students can review videos in the lesson plan. The data generated through these online activities enable teachers to see which students struggled with certain subjects and offer additional assistance and support.
Curiosity Driven by Engaging Content
Through engaging and educational content, teachers can spark inquisitiveness in children and boost their curiosity, which research says has ties to academic success. Curiosity helps students get a better understanding of math and reading concepts. Creating engaging content can involve the use of AR, videos, or podcasts. For example, when submitting assignments, students can include videos or interact with students from across the globe.
Improved Teacher Productivity and Efficiency
Teachers can leverage technology to achieve new levels of productivity, implement useful digital tools to expand learning opportunities for students, and increase student support and engagement. It also enables teachers to improve their instruction methods and personalize learning. Schools can benefit from technology by reducing the costs of physical instructional materials, enhancing educational program efficiency, and making the best use of teacher time.
Become a Leader in Enriching Classrooms through Technology
Educators unfamiliar with some of the technology used in education may not have been exposed to the tools as they prepared for their careers or as part of their professional development. Teachers looking to make the transition and acquire the skills to incorporate technology in education can take advantage of learning opportunities to advance their competencies. For individuals looking to help transform the education system through technology, American University’s School of Education online offers a Master of Arts in Teaching and a Master of Arts in Education Policy and Leadership to prepare educators with essential tools to become leaders. Courses such as Education Program and Policy Implementation and Teaching Science in Elementary School equip graduate students with critical competencies to incorporate technology into educational settings effectively.
Learn more about American University’s School of Education online and its master’s degree programs.
Virtual Reality in Education: Benefits, Tools, and Resources
Data-Driven Decision Making in Education: 11 Tips for Teachers & Administration
Helping Girls Succeed in STEM
BuiltIn, “Edtech 101”
EdTech, “Teaching Teachers to Put Tech Tools to Work”
International Society for Technology in Education, “Preparing Students for Jobs That Don’t Exist”
The Journal, “How Teachers Use Technology to Enrich Learning Experiences”
Pediatric Research, “Early Childhood Curiosity and Kindergarten Reading and Math Academic Achievement”
Project Tomorrow, “Digital Learning: Peril or Promise for Our K-12 Students”
World Economic Forum, “The Future of Jobs Report 2018”
World Economic Forum, “Learning through Play: How Schools Can Educate Students through Technology”
Request Information
for Education
- Google Classroom
- Google Workspace Admin
- Google Cloud
Where teaching and learning come together
Google Classroom helps educators create engaging learning experiences they can personalize, manage, and measure. Part of Google Workspace for Education, it empowers educators to enhance their impact and prepare students for the future.
- Contact sales
- Sign in to Classroom
150M people worldwide use Google Classroom
Google Classroom is designed with feedback from the educational community, influencing the development of new features that let educators focus on teaching and students focus on learning.
Enrich and personalize learning
Drive student agency with tools that meet students where they are – and build skills for their future.
Premium features that inspire new ways of teaching and learning
Power student potential.
Create interactive assignments, even from existing PDFs, that provide real-time feedback and individual guidance with prompts and hints with the help of AI.
Help students develop literacy skills
Assign differentiated reading activities using the Classroom integration with Read Along, a fun, speech-based tool from Google that helps students independently build their reading skills, while giving educators insight into their progress.
Reinforce concepts with self-paced learning
Assign interactive questions for YouTube videos, giving students real-time feedback as they move through a lesson, while viewing insights into their performance.

Enhance lessons with popular integrations
Easily find, add, use and grade content with add-ons from popular EdTech tools, right within Classroom.
Make learning more personal and foster student agency
Support differentiated instruction.
Customize classwork for every student and support them with real-time feedback and easy communication tools.
Foster academic integrity
Encourage original thinking and identify potential plagiarism with originality reports that compare student work against billions of web pages and over 40 million books.
Make learning accessible and inclusive
Help students customize their learning environment to reduce barriers to learning.
Prepare students for the future
Encourage organization and time management skills with interactive to-do lists, automatic due dates, and industry-leading productivity tools.
- Explore all features
Amplify instruction with tools that simplify everyday tasks
Boost instructional time with tools purpose-built for teaching, productivity, and collaboration.
Premium features that elevate teaching
Support originality with plagiarism detection.
Help students integrate citations and avoid unintentional plagiarism with unlimited originality reports and a school-owned repository of past work.
Streamline lesson planning
Create a link to your class, then share it with peers in your organization, so they can easily preview, select, and import high-quality classwork into their classes.
Inform instruction with data-driven insights
Classroom analytics provide educators with insights and visibility into how students turn in, perform on, and engage with assignments, so educators can make informed decisions about the best way to provide support.
Simplify and connect grading workflows
Sync gradebooks to seamlessly manage and export grades from Classroom to your school’s SIS – available for PowerSchool (coming soon), Infinite Campus, Skyward SMS, Skyward Qmlativ, and Follett Aspen. Educators can customize grading periods (e.g., quarters, semesters, terms) and grading scales (e.g., letter, numeric) in their class settings to align to their school’s grading structure or system, reduce errors for SIS grade export and allow educators to more easily filter and analyze assignments.
Tools designed for seamless teaching
Save time on everyday tasks.
Assign, grade, and provide feedback across multiple classes, and even on the go with iOS and Android versions of the Classroom app.
Elevate communication, collaboration, and connection
Connect with students and parents instantly with embedded chat and meeting tools while leveraging built-in chat and comment features to leave students feedback as they’re working.
Grade more efficiently
Assess student progress with customizable rubrics that students can see, and save time with efficient feedback and grade export tools.
Get creative with hundreds of apps
Hundreds of EdTech apps integrate with Classroom to spark creativity and enable more opportunities for learning.
Operate with solutions designed to gain visibility, insights, and control
Create learning environments that are easier to manage and support educators and students with connected, safer tools.
Premium features to support your organization and foster stronger learning outcomes
Make data-driven decisions.
Gain visibility into everything from class performance to individual student assignment completion with Classroom analytics (coming soon), or export Classroom logs to BigQuery to analyze adoption, engagement, and more.
Distribute high-quality class templates to educators
Easily share high-quality class templates so educators in your organization can preview and import classwork into their own classes.
Virtually visit classes to support teachers and students
Designated education leaders and staff can temporarily access classes to support educators, manage substitute teachers, see information for guardian conversations, and more.
Manage classes at scale
Create classes automatically and sync class lists from your student information system (SIS) with Clever .
A secure, reliable, and extensible platform for school communities of all sizes
Benefit from industry-leading privacy and security.
Classroom uses the same infrastructure as other Google Workspace products, meeting rigorous privacy standards with regular third-party audits. Access a centralized Admin console with controlled entry and insights into performance and security.
Stay flexible and reliable
Scale your school community with a global network with full-stack security and 99% uptime.
Extend and scale Classroom
Integrate with your student information system (SIS) and customize Classroom to work for your unique needs with APIs.
Support staff and enhance collaboration
Empower educators with instructional resources , professional development programs , and online training courses , available at no cost.
Level up your Classroom with apps
Discover a world of apps that seamlessly integrate with Chromebooks and Google Workspace for Education.
- Explore App Hub
How Classroom can make a difference for you
Education leaders, it administrators.
Classroom can be learned in minutes and serves all types of learners and educators, regardless of their tech savviness. Empower educators, and encourage adoption and proficiency with new tools and techniques, with a broad range of resources.
- Get a quick overview of the benefits of Classroom
- Read customer stories
- Explore trainings and resources for educators
- 40+ ways to use Google Workspace for Education paid editions
- Learn about sustainability in Google for Education products
Teachers can immediately set up classes, easily create coursework, distribute it to the whole class, and grade it efficiently and transparently.
- Find an educator community
- Download the Classroom user guide
- View product guides
Admins have as much control as they need while they access and analyze their data for insights and choose from a range of upgrade options for additional capabilities to fit their specific needs.
- Get started with the paid editions of Workspace for Education
- View product demos
- Explore 40+ ways to use Google Workspace for Education paid editions
- Learn more about Google for Education security and privacy
- Guardian's Guide to Google Classroom
Need more information about Classroom?
- Visit the Help Center
Bring all of your tools together with Google Workspace for Education
Google Workspace for Education empowers your school community with easy-to-use tools that elevate teaching, learning, collaboration, and productivity – all on one secure platform.
- Explore Google Workspace for Education
150 million users
Active around the world, ready to transform your school, you're now viewing content for a different region..
For content more relevant to your region, we suggest:
Sign up here for updates, insights, resources, and more.
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
How technology is reinventing education.

New advances in technology are upending education, from the recent debut of new artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots like ChatGPT to the growing accessibility of virtual-reality tools that expand the boundaries of the classroom. For educators, at the heart of it all is the hope that every learner gets an equal chance to develop the skills they need to succeed. But that promise is not without its pitfalls.
“Technology is a game-changer for education – it offers the prospect of universal access to high-quality learning experiences, and it creates fundamentally new ways of teaching,” said Dan Schwartz, dean of Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE), who is also a professor of educational technology at the GSE and faculty director of the Stanford Accelerator for Learning . “But there are a lot of ways we teach that aren’t great, and a big fear with AI in particular is that we just get more efficient at teaching badly. This is a moment to pay attention, to do things differently.”
For K-12 schools, this year also marks the end of the Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) funding program, which has provided pandemic recovery funds that many districts used to invest in educational software and systems. With these funds running out in September 2024, schools are trying to determine their best use of technology as they face the prospect of diminishing resources.
Here, Schwartz and other Stanford education scholars weigh in on some of the technology trends taking center stage in the classroom this year.
AI in the classroom
In 2023, the big story in technology and education was generative AI, following the introduction of ChatGPT and other chatbots that produce text seemingly written by a human in response to a question or prompt. Educators immediately worried that students would use the chatbot to cheat by trying to pass its writing off as their own. As schools move to adopt policies around students’ use of the tool, many are also beginning to explore potential opportunities – for example, to generate reading assignments or coach students during the writing process.
AI can also help automate tasks like grading and lesson planning, freeing teachers to do the human work that drew them into the profession in the first place, said Victor Lee, an associate professor at the GSE and faculty lead for the AI + Education initiative at the Stanford Accelerator for Learning. “I’m heartened to see some movement toward creating AI tools that make teachers’ lives better – not to replace them, but to give them the time to do the work that only teachers are able to do,” he said. “I hope to see more on that front.”
He also emphasized the need to teach students now to begin questioning and critiquing the development and use of AI. “AI is not going away,” said Lee, who is also director of CRAFT (Classroom-Ready Resources about AI for Teaching), which provides free resources to help teach AI literacy to high school students across subject areas. “We need to teach students how to understand and think critically about this technology.”
Immersive environments
The use of immersive technologies like augmented reality, virtual reality, and mixed reality is also expected to surge in the classroom, especially as new high-profile devices integrating these realities hit the marketplace in 2024.
The educational possibilities now go beyond putting on a headset and experiencing life in a distant location. With new technologies, students can create their own local interactive 360-degree scenarios, using just a cell phone or inexpensive camera and simple online tools.
“This is an area that’s really going to explode over the next couple of years,” said Kristen Pilner Blair, director of research for the Digital Learning initiative at the Stanford Accelerator for Learning, which runs a program exploring the use of virtual field trips to promote learning. “Students can learn about the effects of climate change, say, by virtually experiencing the impact on a particular environment. But they can also become creators, documenting and sharing immersive media that shows the effects where they live.”
Integrating AI into virtual simulations could also soon take the experience to another level, Schwartz said. “If your VR experience brings me to a redwood tree, you could have a window pop up that allows me to ask questions about the tree, and AI can deliver the answers.”
Gamification
Another trend expected to intensify this year is the gamification of learning activities, often featuring dynamic videos with interactive elements to engage and hold students’ attention.
“Gamification is a good motivator, because one key aspect is reward, which is very powerful,” said Schwartz. The downside? Rewards are specific to the activity at hand, which may not extend to learning more generally. “If I get rewarded for doing math in a space-age video game, it doesn’t mean I’m going to be motivated to do math anywhere else.”
Gamification sometimes tries to make “chocolate-covered broccoli,” Schwartz said, by adding art and rewards to make speeded response tasks involving single-answer, factual questions more fun. He hopes to see more creative play patterns that give students points for rethinking an approach or adapting their strategy, rather than only rewarding them for quickly producing a correct response.
Data-gathering and analysis
The growing use of technology in schools is producing massive amounts of data on students’ activities in the classroom and online. “We’re now able to capture moment-to-moment data, every keystroke a kid makes,” said Schwartz – data that can reveal areas of struggle and different learning opportunities, from solving a math problem to approaching a writing assignment.
But outside of research settings, he said, that type of granular data – now owned by tech companies – is more likely used to refine the design of the software than to provide teachers with actionable information.
The promise of personalized learning is being able to generate content aligned with students’ interests and skill levels, and making lessons more accessible for multilingual learners and students with disabilities. Realizing that promise requires that educators can make sense of the data that’s being collected, said Schwartz – and while advances in AI are making it easier to identify patterns and findings, the data also needs to be in a system and form educators can access and analyze for decision-making. Developing a usable infrastructure for that data, Schwartz said, is an important next step.
With the accumulation of student data comes privacy concerns: How is the data being collected? Are there regulations or guidelines around its use in decision-making? What steps are being taken to prevent unauthorized access? In 2023 K-12 schools experienced a rise in cyberattacks, underscoring the need to implement strong systems to safeguard student data.
Technology is “requiring people to check their assumptions about education,” said Schwartz, noting that AI in particular is very efficient at replicating biases and automating the way things have been done in the past, including poor models of instruction. “But it’s also opening up new possibilities for students producing material, and for being able to identify children who are not average so we can customize toward them. It’s an opportunity to think of entirely new ways of teaching – this is the path I hope to see.”
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
How technology is shaping learning in higher education
About the authors.
This article is a collaborative effort by Claudio Brasca, Charag Krishnan , Varun Marya , Katie Owen, Joshua Sirois, and Shyla Ziade, representing views from McKinsey’s Education Practice.
The COVID-19 pandemic forced a shift to remote learning overnight for most higher-education students, starting in the spring of 2020. To complement video lectures and engage students in the virtual classroom, educators adopted technologies that enabled more interactivity and hybrid models of online and in-person activities. These tools changed learning, teaching, and assessment in ways that may persist after the pandemic. Investors have taken note. Edtech start-ups raised record amounts of venture capital in 2020 and 2021, and market valuations for bigger players soared.
A study conducted by McKinsey in 2021 found that to engage most effectively with students, higher-education institutions can focus on eight dimensions of the learning experience. In this article, we describe the findings of a study of the learning technologies that can enable aspects of several of those eight dimensions (see sidebar “Eight dimensions of the online learning experience”).
Eight dimensions of the online learning experience
Leading online higher-education institutions focus on eight key dimensions of the learning experience across three overarching principles.
Seamless journey
Clear education road map: “My online program provides a road map to achieve my life goals and helps me structure my day to day to achieve steady progress.”
Seamless connections: “I have one-click access to classes and learning resources in the virtual learning platform through my laptop or my phone.”
Engaging teaching approach
Range of learning formats: “My program offers a menu of engaging courses with both self-guided and real-time classes, and lots of interaction with instructors and peers.”
Captivating experiences: “I learn from the best professors and experts. My classes are high quality, with up-to-date content.”
Adaptive learning: “I access a personalized platform that helps me practice exercises and exams and gives immediate feedback without having to wait for the course teacher.”
Real-world skills application: “My online program helps me get hands-on practice using exciting virtual tools to solve real-world problems.”
Caring network
Timely support: “I am not alone in my learning journey and have adequate 24/7 support for academic and nonacademic issues.”
Strong community: “I feel part of an academic community and I’m able to make friends online.”
In November 2021, McKinsey surveyed 600 faculty members and 800 students from public and private nonprofit colleges and universities in the United States, including minority-serving institutions, about the use and impact of eight different classroom learning technologies (Exhibit 1). (For more on the learning technologies analyzed in this research, see sidebar “Descriptions of the eight learning technologies.”) To supplement the survey, we interviewed industry experts and higher-education professionals who make decisions about classroom technology use. We discovered which learning tools and approaches have seen the highest uptake, how students and educators view them, the barriers to higher adoption, how institutions have successfully adopted innovative technologies, and the notable impacts on learning (for details about our methodology, see sidebar “About the research”).
Double-digit growth in adoption and positive perceptions
Descriptions of the eight learning technologies.
- Classroom interactions: These are software platforms that allow students to ask questions, make comments, respond to polls, and attend breakout discussions in real time, among other features. They are downloadable and accessible from phones, computers, and tablets, relevant to all subject areas, and useful for remote and in-person learning.
- Classroom exercises: These platforms gamify learning with fun, low-stakes competitions, pose problems to solve during online classes, allow students to challenge peers to quizzes, and promote engagement with badges and awards. They are relevant to all subject areas.
- Connectivity and community building: A broad range of informal, opt-in tools, these allow students to engage with one another and instructors and participate in the learning community. They also include apps that give students 24/7 asynchronous access to lectures, expanded course materials, and notes with enhanced search and retrieval functionality.
- Group work: These tools let students collaborate in and out of class via breakout/study rooms, group preparation for exams and quizzes, and streamlined file sharing.
- Augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR): Interactive simulations immerse learners in course content, such as advanced lab simulations for hard sciences, medical simulations for nursing, and virtual exhibit tours for the liberal arts. AR can be offered with proprietary software on most mobile or laptop devices. VR requires special headsets, proprietary software, and adequate classroom space for simultaneous use.
- AI adaptive course delivery: Cloud-based, AI-powered software adapts course content to a student’s knowledge level and abilities. These are fully customizable by instructors and available in many subject areas, including business, humanities, and sciences.
- Machine learning–powered teaching assistants: Also known as chatbot programs, machine learning–powered teaching assistants answer student questions and explain course content outside of class. These can auto-create, deliver, and grade assignments and exams, saving instructors’ time; they are downloadable from mobile app stores and can be accessed on personal devices.
- Student progress monitoring: These tools let instructors monitor academic progress, content mastery, and engagement. Custom alerts and reports identify at-risk learners and help instructors tailor the content or their teaching style for greater effectiveness. This capability is often included with subscriptions to adaptive learning platforms.
Survey respondents reported a 19 percent average increase in overall use of these learning technologies since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. Technologies that enable connectivity and community building, such as social media–inspired discussion platforms and virtual study groups, saw the biggest uptick in use—49 percent—followed by group work tools, which grew by 29 percent (Exhibit 2). These technologies likely fill the void left by the lack of in-person experiences more effectively than individual-focused learning tools such as augmented reality and virtual reality (AR/VR). Classroom interaction technologies such as real-time chatting, polling, and breakout room discussions were the most widely used tools before the pandemic and remain so; 67 percent of survey respondents said they currently use these tools in the classroom.
About the research
In November 2021, McKinsey surveyed 634 faculty members and 818 students from public, private, and minority-serving colleges and universities over a ten-day period. The survey included only students and faculty who had some remote- or online-learning experience with any of the eight featured technologies. Respondents were 63 percent female, 35 percent male, and 2 percent other gender identities; 69 percent White, 18 percent Black or African American, 8 percent Asian, and 4 percent other ethnicities; and represented every US region. The survey asked respondents about their:
- experiences with technology in the classroom pre-COVID-19;
- experiences with technology in the classroom since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic; and
- desire for future learning experiences in relation to technology.
The shift to more interactive and diverse learning models will likely continue. One industry expert told us, “The pandemic pushed the need for a new learning experience online. It recentered institutions to think about how they’ll teach moving forward and has brought synchronous and hybrid learning into focus.” Consequently, many US colleges and universities are actively investing to scale up their online and hybrid program offerings .
Differences in adoption by type of institution observed in the research
- Historically Black colleges and universities (HBCUs) and tribal colleges and universities made the most use of classroom interactions and group work tools (55 percent) and the least use of tools for monitoring student progress (15 percent).
- Private institutions used classroom interaction technologies (84 percent) more than public institutions (63 percent).
- Public institutions, often associated with larger student populations and course sizes, employed group work and connectivity and community-building tools more often than private institutions.
- The use of AI teaching-assistant technologies increased significantly more at public institutions (30 percent) than at private institutions (9 percent), though overall usage remained comparatively higher at private institutions.
- The use of tools for monitoring student progress increased by 14 percent at private institutions, versus no growth at public institutions.
Some technologies lag behind in adoption. Tools enabling student progress monitoring, AR/VR, machine learning–powered teaching assistants (TAs), AI adaptive course delivery, and classroom exercises are currently used by less than half of survey respondents. Anecdotal evidence suggests that technologies such as AR/VR require a substantial investment in equipment and may be difficult to use at scale in classes with high enrollment. Our survey also revealed utilization disparities based on size. Small public institutions use machine learning–powered TAs, AR/VR, and technologies for monitoring student progress at double or more the rates of medium and large public institutions, perhaps because smaller, specialized schools can make more targeted and cost-effective investments. We also found that medium and large public institutions made greater use of connectivity and community-building tools than small public institutions (57 to 59 percent compared with 45 percent, respectively). Although the uptake of AI-powered tools was slower, higher-education experts we interviewed predict their use will increase; they allow faculty to tailor courses to each student’s progress, reduce their workload, and improve student engagement at scale (see sidebar “Differences in adoption by type of institution observed in the research”).
While many colleges and universities are interested in using more technologies to support student learning, the top three barriers indicated are lack of awareness, inadequate deployment capabilities, and cost (Exhibit 3).
Students want entertaining and efficient tools
More than 60 percent of students said that all the classroom learning technologies they’ve used since COVID-19 began had improved their learning and grades (Exhibit 4). However, two technologies earned higher marks than the rest for boosting academic performance: 80 percent of students cited classroom exercises, and 71 percent cited machine learning–powered teaching assistants.
Although AR/VR is not yet widely used, 37 percent of students said they are “most excited” about its potential in the classroom. While 88 percent of students believe AR/VR will make learning more entertaining, just 5 percent said they think it will improve their ability to learn or master content (Exhibit 5). Industry experts confirmed that while there is significant enthusiasm for AR/VR, its ability to improve learning outcomes is uncertain. Some data look promising. For example, in a recent pilot study, 1 “Immersive biology in the Alien Zoo: A Dreamscape Learn software product,” Dreamscape Learn, accessed October 2021. students who used a VR tool to complete coursework for an introductory biology class improved their subject mastery by an average of two letter grades.
Faculty embrace new tools but would benefit from more technical support and training
Faculty gave learning tools even higher marks than students did, for ease of use, engagement, access to course resources, and instructor connectivity. They also expressed greater excitement than students did for the future use of technologies. For example, while more than 30 percent of students expressed excitement for AR/VR and classroom interactions, more than 60 percent of faculty were excited about those, as well as machine learning–powered teaching assistants and AI adaptive technology.
Eighty-one percent or more of faculty said they feel the eight learning technology tools are a good investment of time and effort relative to the value they provide (Exhibit 6). Expert interviews suggest that employing learning technologies can be a strain on faculty members, but those we surveyed said this strain is worthwhile.
While faculty surveyed were enthusiastic about new technologies, experts we interviewed stressed some underlying challenges. For example, digital-literacy gaps have been more pronounced since the pandemic because it forced the near-universal adoption of some technology solutions, deepening a divide that was unnoticed when adoption was sporadic. More tech-savvy instructors are comfortable with interaction-engagement-focused solutions, while staff who are less familiar with these tools prefer content display and delivery-focused technologies.
According to experts we interviewed, learning new tools and features can bring on general fatigue. An associate vice president of e-learning at one university told us that faculty there found designing and executing a pilot study of VR for a computer science class difficult. “It’s a completely new way of instruction. . . . I imagine that the faculty using it now will not use it again in the spring.” Technical support and training help. A chief academic officer of e-learning who oversaw the introduction of virtual simulations for nursing and radiography students said that faculty holdouts were permitted to opt out but not to delay the program. “We structured it in a ‘we’re doing this together’ way. People who didn’t want to do it left, but we got a lot of support from vendors and training, which made it easy to implement simulations.”

Reimagining higher education in the United States
Takeaways from our research.
Despite the growing pains of digitizing the classroom learning experience, faculty and students believe there is a lot more they can gain. Faculty members are optimistic about the benefits, and students expect learning to stay entertaining and efficient. While adoption levels saw double-digit growth during the pandemic, many classrooms have yet to experience all the technologies. For institutions considering the investment, or those that have already started, there are several takeaways to keep in mind.
- It’s important for administration leaders, IT, and faculty to agree on what they want to accomplish by using a particular learning technology. Case studies and expert interviews suggest institutions that seek alignment from all their stakeholders before implementing new technologies are more successful. Is the primary objective student engagement and motivation? Better academic performance? Faculty satisfaction and retention? Once objectives are set, IT staff and faculty can collaborate more effectively in choosing the best technology and initiating programs.
- Factor in student access to technology before deployment. As education technology use grows, the digital divide for students puts access to education at risk. While all the institution types we surveyed use learning technologies in the classroom, they do so to varying degrees. For example, 55 percent of respondents from historically Black colleges and universities and tribal colleges and universities use classroom interaction tools. This is lower than public institutions’ overall utilization rate of 64 percent and private institutions’ utilization rate of 84 percent. Similarly, 15 percent of respondents from historically Black colleges and universities and tribal colleges and universities use tools for monitoring student progress, while the overall utilization rate for both public and private institutions is 25 percent.
- High-quality support eases adoption for students and faculty. Institutions that have successfully deployed new learning technologies provided technical support and training for students and guidance for faculty on how to adapt their course content and delivery. For example, institutions could include self-service resources, standardize tools for adoption, or provide stipend opportunities for faculty who attend technical training courses. One chief academic officer told us, “The adoption of platforms at the individual faculty level can be very difficult. Ease of use is still very dependent upon your IT support representative and how they will go to bat to support you.”
- Agree on impact metrics and start measuring in advance of deployment. Higher-education institutions often don’t have the means to measure the impact of their investment in learning technologies, yet it’s essential for maximizing returns. Attributing student outcomes to a specific technology can be complex due to the number of variables involved in academic performance. However, prior to investing in learning technologies, the institution and its faculty members can align on a core set of metrics to quantify and measure their impact. One approach is to measure a broad set of success indicators, such as tool usage, user satisfaction, letter grades, and DFW rates (the percentage of students who receive a D, F, or Withdraw) each term. The success indicators can then be correlated by modality—online versus hybrid versus in-class—to determine the impact of specific tools. Some universities have offered faculty grants of up to $20,000 for running pilot programs that assess whether tools are achieving high-priority objectives. “If implemented properly, at the right place, and with the right buy-in, education technology solutions are absolutely valuable and have a clear ROI,” a senior vice president of academic affairs and chief technology officer told us.
In an earlier article , we looked at the broader changes in higher education that have been prompted by the pandemic. But perhaps none has advanced as quickly as the adoption of digital learning tools. Faculty and students see substantial benefits, and adoption rates are a long way from saturation, so we can expect uptake to continue. Institutions that want to know how they stand in learning tech adoption can measure their rates and benchmark them against the averages in this article and use those comparisons to help them decide where they want to catch up or get ahead.
Claudio Brasca is a partner in McKinsey’s Bay Area office, where Varun Marya is a senior partner; Charag Krishnan is a partner in the New Jersey office; Katie Owen is an associate partner in the St. Louis office, where Joshua Sirois is a consultant; and Shyla Ziade is a consultant in the Denver office.
The authors wish to thank Paul Kim, chief technology officer and associate dean at Stanford School of Education, and Ryan Golden for their contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Setting a new bar for online higher education

How to transform higher-education institutions for the long term

Technology in the Classroom: The Complete Guide
There has always been technology in the classroom, even if it hasn’t always been welcome. Take a brief look at the history of technology’s uneasy relationship with education. Then see some common modern additions to the classroom ranging from computers to smartphones. Then you won’t want to miss the advantages (and disadvantages) to modern EdTech. However, the advantages far outweigh the disadvantages, so we also provide a simplified implementation guide.
Continue reading to learn everything you always wanted to know about technology in the classroom.
There has always been technology in the classroom. From books to tablets or slates to interactive whiteboards, humans have used learning tools for as long as we have had formal education.
And while the technology itself changes, some things remain the same. Teachers teach, learners learn, and everyone is uncertain about the latest tech’s role in education. Luckily, we have put together this guide for you to see a more complete picture of how technology fits into the 21 st -century classroom.
A Brief History of Technology in the Classroom
Technology has always had an uneasy relationship with education.
There was a time when the only available method of storing information was in people’s memories. Learners would memorize what their elders said. Scholars would have long dialogs, which learners would also have to memorize. Information was passed down through oral traditions of songs, stories, or memorized lectures. This was education without any technology.
Then books showed up on the scene. Books allowed people to store knowledge externally without having to remember every fact. They were a permanent record of known information that could be passed down intact. It was a breakthrough in the storage and transmission of information, so naturally, people hated it.
Socrates famously criticized books (and writing in general) as a weakness saying to Plato, “This discovery of yours will create forgetfulness in the learners’ souls because they will not use their memories.” Of course, we know this because Plato wrote it down.
And so began a long history of the old guard resisting the latest technology in education. Each time new technology is introduced to schools and students, it’s the same story. Those educators who are set in their ways resist. Then they are overtaken by the younger generation trying out new things, finding the ones that work, and then implementing their new methods until something newer comes along. Rinse and repeat throughout the history of education.
- late 1700s – The slate provides students with a portable, personal writing surface.
- 1890s – The chalkboard appeared in classrooms, allowing larger class sizes.
- 1900s – Mass-produced pencils and paper allowed students to have permanent written records of their work.
- 1920s – Radio’s popularity leads to on-air classes.
- 1930s – Overhead projectors adopted.
- 1951 – Videotapes allow for audio and visual content.
- 1959 – Photocopiers allowed schools to mass-produce printed materials on site.
- 1980s – Personal computers are available to the average consumer.
- 1990 – The Internet brings about unprecedented access to information.
- 1991 – Interactive whiteboards become available.
- 2005 – Learning Management System (LMS) takes off as a viable teaching tool.
- 2012 – The iPad brings tablets into public perception.
Click here for a more complete timeline on the history of EdTech.
Types of Technology in the Classroom
While interesting, the history of EdTech probably doesn’t help your students very much in the here and now. What technology is available in the modern classroom? And what is it doing for education?
Both desktops and laptops continue to have places in modern classrooms. At many schools, laptops are issued to students to use throughout the school year. In general lessons, laptops are used primarily for note-taking, writing, and independent research. Depending on the material being presented, computers also present an opportunity for adding more media to lessons, gamification, and connectivity with either classmates or instructors.
More powerful desktops are usually saved for computer-specific courses and computer labs, but they also have their place in the classroom. (A desktop is often part of a resource center for younger grades where it’s not yet appropriate for each student to have their own laptop.)
But while computers have value in the classroom, it’s important to note that they have limitations. For example, research suggests that taking notes by hand may be more effective than typing (though this is not yet definitive ). And then there’s the potential for distraction in Internet-enabled laptops, but this could probably be said about windows on sunny days as well.
The bottom line is that computers are commonly found in classrooms, and they are likely to remain in one form or another.
Projectors have been used in classrooms in one form or another for well over 100 years. The modern classroom projector has come a long way from its single-slide ancestor, however.
In the classroom, a projector acts primarily as a display. (There are certainly interactive projectors, but those are covered more in the next section on interactive whiteboards.) And display data needs to come from somewhere, so most projectors will be paired with a computer or other device. Even smart projectors won’t be able to do much more than playing a video or slideshow without streaming from another device.
As an established classroom technology, projectors are popular for their relative simplicity, low cost to purchase, and their ability to project to very large screens. With the advent of lamp-free projectors, there is less maintenance and fewer calibration issues than older models. However, there are still issues with shadows and glare, and projectors don’t work as well in brightly-lit classrooms.
Does a projector sound like a good fit for your classroom? You may want to check this out: What to Look for When Purchasing an Education Projector
Interactive Whiteboards
Interactive whiteboards (IWBs) are also sometimes called interactive displays or even digital whiteboards. As a catch-all term, an IWB is any display that also responds real-time to actions on its surface, allowing it to act as a whiteboard. This includes both projector-based interactive displays (like these ) or interactive flat-panel displays (like ViewBoard ).
Due to their versatility, there is a global shift towards IWBs that is picking up momentum, especially interactive touch screen displays . The technology blends the best of multimedia and touch technologies with the familiar functions of a regular whiteboard. Therefore a teacher can show a video or search the Internet live, annotate the content, and then even share with students via their devices.
But despite the ever-growing list of features available for IWBs, there are still a few challenges ahead. They are certainly more expensive than an analog whiteboard, and it still requires extra effort to produce content for them. These tend to be the challenges for any new technology, however, and as interactive whiteboards become more accessible they will continue to grow in popularity.
More portable than even laptops but with large viewing screens, tablets seem to be custom-made for education. They are very powerful research tools and may serve as a replacement for heavy, expensive textbooks. Their touch screens also allow students to interact with digital content more intuitively than with a keyboard and mouse or trackpad.

While not as versatile as a PC, this may actually be to a tablet’s advantage as its more limited functions can reduce distraction. However, students do admit to multitasking more on tablets than in ebooks. And paper books still have a role to play, especially in young readers’ development. (See this article on how ebooks stack up to paper books .)
Smartphones
Smartphones are often overlooked as EdTech because they are so often the cause of distractions, but they are a valuable learning tool.

At its most basic, a smartphone is a student’s portal to their community of peers for support and the Internet for research. There are educational apps like Duolingo for self-study and Kahoot! for group learning activities. Plus a huge number of media-creation apps that produce everything from documents to polished videos. And in fact, a significant number of students already use their smartphones to do their homework.
So while phone distraction is a very real problem among students , educators should be careful not to throw the baby out with the bathwater. Even the evil smartphone can be a valuable bit of technology in the classroom when used correctly.
5 Advantages of Technology in the Classroom
Though there are many benefits to technology in the classroom , here is a short list of reasons why you might want to add more digital tech to your classes.
- Improves engagement and retention. Digital technology in the classroom opens up new media types not available on its analog versions. And there is potential for far more interactivity being built into digital education content.
- Accommodates multiple learning styles. EdTech is a great way to accommodate various learning styles and pace content for individual students. What’s more, effective classroom tech doubles as assistive technology for students with a range of special needs .
- Promotes collaboration. Technology has a unique ability to collaborate live on a task or project and to share information with peers faster than ever before. From huddle spaces to remote work, technology is able to break down barriers.
- Instant feedback for teachers. The same tools that allow students to share with their peers also allow students to share feedback with their teachers. This feedback could come in the form of answers, questions, or even suggestions for teaching improvements.
- Prepares students for the future. Technology – especially digital technology and its connectivity – is becoming increasingly entwined in daily life. Being able to deal with not only familiar tech but strange and new devices will be an important part of students’ future success.
5 Challenges of Technology in the Classroom
It would be dishonest to say that tech in the classroom is without its challenges – and even its dangers. However, the benefits far outweigh the disadvantages. Since there’s no such thing as a perfect system, it’s far more effective to be aware of some potential problems and work to reduce any negative impact.
- Distracts students. Smartphones have a bad reputation in classrooms and there have been strong cases for banning them in schools . However, this does students a disservice in many ways, including missing the opportunity to teach proper tech use.
- Requires management. New tech in the classroom means needing IT professionals to help set it up, maintain it, and support teachers and students in its use. But institutions can help maximize their technical support staff by finding a less resource-intensive solution. (Read 10 Reasons Education IT Administrators Love Interactive Touch Screen Displays .)
- Leads to tech disparity. Tech disparity refers to how much access students have to the necessary devices. In schools that expect students to use their personal devices, tech disparity is closely tied to income inequality. However, the problem can be reduced by schools providing the necessary devices, especially as part of a computer lab .
- Cost money. Nothing in this world is free. And buying cutting-edge electronics for a classroom is downright expensive. While there’s no way to avoid spending money modernizing a classroom, it is at least possible to maximize the total cost of ownership (TCO) by installing devices with longer lifespans and reduced maintenance.
- Less face time. Despite modern connectivity, it seems people are more disconnected than ever. Instead of communicating directly, many are instead choosing to filter all communications through their mobile devices. But there are lots of ways to inspire direct person-to-person communication, such as through tech-centric ways to promote engagement. Or get back to basics and having learners leave the tech behind and work together on group tasks the old-fashioned way.

Implementing Technology in the Classroom
So you’ve decided to add some technology to your classroom (or upgrade what’s already there). But that’s only the first step. What’s next? You’ll need to implement the changes or find someone to implement the changes for you .
Here are a few things to keep in mind as you are upgrading your classroom’s tech capabilities.

ViewSonic Education
Learning Solutions For the Future
Connectivity
We live in a connected world. As you are shopping around for new devices, be very aware of connectivity with your existing data network. Without connection, you miss out on the saving, sharing, and collaborating that define modern EdTech (and make up a huge part of its usefulness).
- How does the device connect with your network? Wireless? Cable?
- What kind of wireless connection does it use? Bluetooth? Wifi? Infrared?
- What kind of cable connection can it make? DisplayPort? HDMI? USB-C? Thunderbolt?
Integration
Beyond connecting your tech to the network, you have to make sure devices connect to each other. In a classroom setting, you want to be sure that students can also participate no matter what device they might be using.
The same applies to software solutions as well. Make sure all your tech gets along. There’s something to be said about working within a larger ecosystem of devices and software from the same solution provider: if it’s built together it’ll work together.
- What operating system does the solution require? Windows? Android? iOS? Device agnostic?
- How are you going to transmit data to learners? Email? Direct link? Direct file transfer?
- Does the device connect to cloud storage services? Does it store files locally?
Though users should absolutely be familiar with their tech’s best use practices, it’s unreasonable to expect everyone to know how to fix it. Maintenance is a specialized task for specialized staff. But unless you’re planning to hire new IT management for the new tech, it’s important to work within your team’s capabilities.
Make sure that whatever solutions you implement in your classroom are supported by your existing support structure. This includes setting up the necessary systems and maintaining them over time.
- Does your IT team already provide support for this solution?
- Does the solution provide adequate training for new IT staff?
- Is the solution user-friendly for end-users (reducing the need for frequent support)?
You may also want to check this out: 10 Reasons Education IT Administrators Love Interactive Touch Screen Displays
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is how much a device, software, etc. costs over its entire lifetime. This also includes all the hidden costs like maintenance, replacement parts, subscriptions, even electricity.
Even products that are inexpensive to buy initially may have significant long-term expenses. For example, an inkjet printer is often very inexpensive to buy. However, replacement ink cartridges can then be almost as expensive as a new printer.
It’s possible that a more expensive solution could save your school time, money, and frustration over the long run. Consider the following in addition to the listed price of your chosen solution – either hardware or software.
- What does support cost? Is there a free helpline? Can you do repairs in-house? Or do you need to hire the solutions licensed staff to do repairs or make changes?
- What is the lifespan of the product? What are the lifespans of replaceable parts?
- What other resources could this solution consume besides money (e.g. time, labor, etc.)?
- Is there a subscription in place for parts or services? What is the most cost-effective way to pay it (e.g. monthly, annually, lifetime, etc.)?
Classroom Design
Classroom design is a major factor when deciding on technological solutions. For example, most classrooms make in the last century or so assume a display of some sort at the front of the room. Until recently, it’s been a chalkboard or whiteboard, which also makes the room a good candidate for an interactive whiteboard of some kind.
In the case of large lecture halls, however, flat-panel interactive whiteboards like the ViewBoard are probably not the best option to reach the entire class. A projector might not be as efficient – or provide as many features – but it does feature a more scalable display size.
Here are some things to consider about your classroom when deciding on the best tech solution.
- How big is the room? What display will work best to reach the entire class?
- Who will be delivering the learning materials? Is it a teacher at the front of the room with a single large display? Students in huddle spaces with smaller group displays?
- Should the tech be focused on a resource station in the classroom? Should it be spread evenly throughout?
- Does the hardware need to be fixed in the classroom at all times? Or is a portable setup that can be shared among classrooms more practical?
And you can find another nice summary of implementing the latest tech in your classroom here: Your Educational Digital DNA – Get Ready for Edtech Innovation
Final Thoughts on Technology in the Classroom
Though technology in the classroom will never replace teachers, it is a valuable tool for improving learning outcomes and preparing students for a digital future. Like every advance in learning technology, there are fierce critics of adding more advanced EdTech into our schools. And their concerns are not entirely out of place, as there are still major challenges ahead as we attempt to better integrate modern connectivity to places of learning.
But the benefits of updating our classrooms with modern resources definitely outweigh the disadvantages. Technological solutions solve far more problems than they create. Between improved engagement, broader appeal to more students, and preparing learners for a digital future, it’s clear that more classrooms need to take advantage of EdTech solutions.
Want to read more about solutions for your classroom? Here’s a good primer: How to Build a Modern School – 6 Key Elements to Embed in Your Groundwork . Or go straight to ViewSonic’s education solutions to find out what we do for teachers and learners.
RELATED ARTICLES
Technology in the Classroom | May 23 2024
Creating Modern Classrooms: 3 Contemporary Approaches to Classroom Design
Discover how modern classroom design transforms education with adaptable, inclusive, and sustainable spaces where every student can thrive.
Education | Mar 14 2024
Introducing Multimedia Learning Design in Education – By Owen Matson, Ph.D.
Owen Matson, Ph.D. introduces multimedia learning in education and offers educators strategies to incorporate it into their teaching methods.
Professional Development | Jan 26 2024
Why Every Teacher Needs Their Community
Discover how teacher communities provide opportunities to learn, collaborate, and grow on an educational journey with like-minded peers.
Professional Development | Jan 18 2024
The Power of the ViewSonic Education Ecosystem
The ViewSonic Education Ecosystem blends hardware, software, and services to empower educators, enhance learning, and streamline operations.
SELECT YOUR REGION
Asia pacific & africa.
Larry Cuban on School Reform and Classroom Practice: Every Tech Tool in Classrooms Needs Ruthless Scrutiny (Jessica Grose) (Guest post by Jessica Grose)
- Computing, Technology, and Information Systems
Just as school boards and administrators evaluate carefully every item placed in classrooms from the size of windows to furniture to whiteboards to textbooks, so too should the ubiquitous technologies used daily–nay, hourly–such as cell phones and laptops (including software) be rigorouly assessed. New York Times r eporter Jessica Grose makes just that point in thi s article .
Educational technology in schools is sometimes described as a wicked problem — a term coined by a design and planning professor, Horst Rittel, in the 1960s , meaning a problem for which even defining the scope of the dilemma is a struggle, because it has so many interconnected parts that never stop moving.
When you have a wicked problem, solutions have to be holistic, flexible and developmentally appropriate. Which is to say that appropriate tech use for elementary schoolers in rural Oklahoma isn’t going to be the same as appropriate tech use in a Chicago high school.
I spent the past few weeks speaking with parents, teachers, public school administrators and academics who study educational technology. And while there are certainly benefits to using tech as a classroom tool, I’m convinced that when it comes to the proliferation of tech in K-12 education, we need “ a hard reset ,” as Julia Freeland Fisher of the Christensen Institute put it, concurring with Jonathan Haidt in his call for rolling back the “phone-based childhood.” When we recently spoke, Fisher stressed that when we weigh the benefits of ed tech, we’re often not asking, “What’s happening when it comes to connectedness and well-being?”
Well said. We need a complete rethink of the ways that we’re evaluating and using tech in classrooms; the overall change that I want to see is that tech use in schools — devices and apps — should be driven by educators, not tech companies.
In recent years, tech companies have provided their products to schools either free or cheap , and then schools have tried to figure out how to use those products. Wherever that dynamic exists, it should be reversed: Districts and individual schools should first figure out what tech would be most useful to their students, and their bar for “useful” should be set by available data and teacher experience. Only then should they acquire laptops, tablets and educational software.
As Mesut Duran — a professor of educational technology at the University of Michigan, Dearborn, and the author of “Learning Technologies: Research, Trends and Issues in the U.S. Education System” — told me, a lot of the technology that’s used in classrooms wasn’t developed with students in mind. “Most of the technologies are initially created for commercial purposes,” he said, “and then we decide how to use them in schools.”
In many cases, there’s little or no evidence that the products actually work, and “work” can have various meanings here: It’s not conclusive that tech, as opposed to hard-copy materials, improves educational outcomes. And sometimes devices or programs simply don’t function the way they’re supposed to. For example, artificial intelligence in education is all the rage, but then we get headlines like this one, in February, from The Wall Street Journal: “ We Tested an A.I. Tutor for Kids. It Struggled With Basic Math. ”
Alex Molnar, one of the directors of the National Educational Policy Center at the University of Colorado, Boulder, said that every school should be asking if the tech it’s using is both necessary and good. “The tech industry’s ethos is: If it’s doable, it is necessary. But for educators, that has to be an actual question: Is this necessary?” Even after you’ve cleared the bar of necessary, he said, educators should be asking, “Is doing it this way good, or could we do it another way that would be better? Better in the ethical sense and the pedagogical sense.”
With that necessary and good standard in mind, here are some specific recommendations that I’ve taken away from several discussions and a lot of reading. It’s unrealistic — and considering that we’re in a tech-saturated world, not ideal — to get rid of every last bit of educational technology. But we’re currently failing too many children by letting it run rampant.
At the State and Federal Levels: Privacy Protections and Better Evaluation
A complaint I heard from many public school parents who responded to my March 27 questionnaire and wanted a lower-tech environment for their kids is that they’re concerned about their children’s privacy. They couldn’t opt out of things like Google Classroom, they said, because in many cases, all of their children’s homework assignments were posted there. Molnar has a radical but elegant solution for this problem: “All data gathered must be destroyed after its intended purpose has been accomplished.” So if the intended purpose of a platform or application is grading, for example, the data would be destroyed at the end of the school year; it couldn’t be sold to a third party or used to further enhance the product or as a training ground for artificial intelligence.
Another recommendation — from a recent paper by the University of Edinburgh’s Ben Williamson, Molnar and the University of Colorado, Boulder’s Faith Boninger outlining the risks of A.I. in the classroom — is for the creation of an “independent government entity charged with ensuring the quality of digital educational products used in schools” that would evaluate tech before it is put into schools and “periodically thereafter.” Because the technology
is always evolving, our oversight of it needs to be, as well.
At the District Level: Centralize the Tech-Vetting Process
Stephanie Sheron is the chief of strategic initiatives for the Montgomery County Public Schools, the largest district in Maryland, and all the district’s technology departments report to her. She likened the tech landscape, coming out of the Covid-19 pandemic remote school period, to the “Wild West.” School districts were flooded with different kinds of ed tech in an emergency situation in which teachers were desperately trying to engage their students, and a lot of relief money was pouring in from the federal government. When the dust settled, she said, the question was, “Now what do we do? How do we control this? How do we make sure that we’re in alignment with FERPA and COPPA and all of those other student data privacy components?”
To address this, Sheron said, her district has secured grant funding to hire a director of information security, who will function as the hub for all the educational technology vending and evaluate new tech. Part of the standardization that the district has been undergoing is a requirement that to be considered, curriculum vendors must offer both digital and hard-copy resources. She said her district tried to look at tech as a tool, adding: “A pencil is a tool for learning, but it’s not the only modality. Same thing with technology. We look at it as a tool, not as the main driver of the educational experience.
At the Classroom Level: Ruthlessly Evaluate Every Tool
In my conversations with teachers, I’ve been struck by their descriptions of the cascade of tech use — that more tech is often offered as a solution to problems created by tech. For example, paid software like GoGuardian, which allows teachers to monitor every child’s screen, has been introduced to solve the problem of students goofing off on their laptops. But there’s a simple, free, low-tech solution to this problem that Doug Showley, a high school English teacher in Indiana I spoke to, employs: He makes all his students face their computer screens in his direction.
Every teacher who is concerned about tech use in his or her classroom should do a tech audit. There are several frameworks ; I like the worksheet created by Beth Pandolpho and Katie Cubano, the authors of “Choose Your Own Master Class: Urgent Ideas to Invigorate Your Professional Learning.” In the chapter “Balancing Technology Use in the Classroom,” they suggest that teachers list every tech tool they are using and evaluate its specific functions, asking, “Are these novel or duplicative?” They also encourage teachers to write out a defense of the tool and the frequency of use.
I like these questions because they make clear that the solutions are not going to be one size fits all.
Students Deserve Authentic Connection
As I close out this series, I want to return to what Fisher said about the importance of student connection and well-being. Of course academic outcomes matter. I want our kids to learn as much about as many different topics as they can. I care about falling test scores and think they’re an important piece of data.
But test scores are only one kind of information. A key lesson we should have learned from 2020 and ’21 is that school is about so much more than just academics. It’s about socialization, critical thinking, community and learning how to coexist with people who are different from you. I don’t know that all of these are things that can be tracked in a scientific way, which brings me back to the idea of tech in schools as a wicked problem: These aren’t easily measurable outcomes.
Jeff Frank, a professor of education at St. Lawrence University, expresses a sense that I’ve had very well in a paper , “Sounding the Call to Teach in a Social Media Age: Renewing the Importance of Philosophy in Teacher Education.” He says students are “hungry for experiences that make them feel alive and authentically connected to other people and to deeper sources of value. Though filtering and managing life through technologies offers safety, predictability and a sense of control, it also leads to life that can feel extremely small, constraining and lonely. Teaching can offer a powerful way to pierce this bubble.”
Ultimately, I believe the only way kids will be able to find that deeper meaning is through human relationships with their peers and teachers, no matter how shiny an A.I. tutor appears to be at first blush.
This blog post has been shared by permission from the author. Readers wishing to comment on the content are encouraged to do so via the link to the original post. Find the original post here:
The views expressed by the blogger are not necessarily those of NEPC.

Larry Cuban

Jessica Grose

TechBullion
The future of education: technology in the classroom.

In today’s rapidly evolving world, technology has become an omnipresent force reshaping every facet of our lives, including how we communicate, work, and learn. As advancements continue to redefine industries and societies, education stands at the forefront of this transformation. Traditional classrooms are increasingly integrating digital tools to enhance learning experiences, personalise education, and foster global connectivity. This article will highlight the broader impact of technology on education, exploring how these innovations are shaping a more dynamic and inclusive future for learners of all backgrounds.
Sneak Peek into Modern Classrooms: Latest Tech-Savvy Learning Practices!
As we peer into the future of education, it’s clear that digital tools are poised to redefine the learning landscape in profound ways. These tools are revolutionising how knowledge is accessed, absorbed, and applied. By integrating these technologies into classrooms, educators can cater to diverse learning styles, enhance engagement, and adapt curriculum in real-time to meet evolving educational needs. A few of these tech-savvy learning practices are discussed below:
Integration of Virtual Reality (VR) for Immersive Learning Experiences
VR technology transports students beyond the confines of traditional textbooks and classrooms, allowing them to explore historical landmarks, dive into scientific phenomena, or even simulate complex engineering projects—all within a virtual environment. For example, in biology classes, students can venture inside a virtual human body to observe biological processes at a cellular level, which is far more engaging and memorable than reading about it in a textbook .
This immersive approach not only enhances engagement and retention but also cultivates a deeper understanding of subjects by making abstract concepts tangible and interactive. By interacting with virtual models and environments, students can visualise complex concepts in ways that traditional methods cannot replicate, instilling curiosity and facilitating deeper learning experiences.
Gamification: Making Learning Fun and Engaging
Gamification makes learning enjoyable and motivating by integrating rewards, levels, and competition. For instance, in language learning, students earn points for correctly using new words in sentences, encouraging active practice. International students often face language barriers, especially when they are assigned homework tasks and ultimately they seek assignment writing help UK to avoid academic setbacks.
However, by providing immediate feedback and reinforcement, gamification bridges these gaps effectively, boosting students’ confidence and fluency as they progress through interactive levels and earn rewards for their achievements. This method not only enhances learning outcomes but also empowers students to overcome language challenges independently, creating a more inclusive and supportive learning environment overall.
Adaptive Learning Platforms Personalising Education
Adaptive learning platforms like ALEKS represent another leap forward, tailoring educational content and pacing to the individual needs of each student. By leveraging algorithms that analyse learning patterns and performance, these platforms provide personalised learning pathways. For example, in mathematics, an adaptive learning platform can assess a student’s proficiency level in various topics such as algebra or geometry.
Based on the assessment, the platform can then generate customised lessons and exercises that cater to the student’s strengths and weaknesses. If a student excels in algebra but struggles with geometry proofs, the platform can provide additional practice problems and tutorials specifically targeting geometry concepts. This personalised approach not only enhances the student’s understanding and mastery of the subject but also promotes a more efficient and engaging learning experience overall.
Collaborative Tools and Cloud-Based Platforms Transforming Collaboration
Collaborative tools like Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) and Microsoft Teams, along with cloud-based platforms such as Google Drive and OneDrive, are transforming the way students collaborate and interact both inside and outside the classroom. These technologies enable seamless communication and resource sharing among peers and educators, encouraging teamwork and facilitating project-based learning initiatives.
Such platforms not only enhance collaboration by allowing real-time editing and commenting on documents but also prepare students for the collaborative nature of modern workplaces, where remote teamwork and shared document management are increasingly commonplace. By familiarising students with these tools early on, educators equip them with essential skills for future professional success in a digital-driven world.
AI-Powered Tutoring Systems: Promoting Individualised Learning
AI-Powered Tutoring Systems such as Squirrel AI Learning and Carnegie Learning represent a cutting-edge approach to education, promoting individualised learning tailored to each student’s unique needs. These systems harness artificial intelligence algorithms to analyse student performance data and learning patterns.
For instance, in subjects like accounting, where students often struggle to find comprehensive dissertation topics, AI-powered platforms can streamline the search process. By analysing vast databases and student interests, these systems suggest relevant accounting dissertation topics that align with the student’s academic goals and research interests. This not only saves time but also ensures that students receive personalised guidance and support throughout their academic careers, ultimately enhancing their learning outcomes and scholarly achievements.
How Will Digital Tools Redefine Education in The Future?
As we look ahead to the future of education, the role of digital tools extends beyond mere enhancement; it represents a paradigm shift towards a more dynamic and learner-centric approach. These tools are catalysts for fostering creativity, critical thinking, and collaboration among students and educators alike. See how it’s going to influence future:
- Enhanced Accessibility and Inclusivity – Digital tools will break down barriers to education, providing flexible learning options for diverse learners regardless of location or physical ability, ensuring everyone has equal access to quality education.
- Global Connectivity and Remote Learning Opportunities – Digital tools facilitate seamless collaboration and knowledge sharing across borders, enabling students to participate in virtual classrooms, exchange ideas with peers worldwide, and access educational resources remotely.
- Data-Driven Insights for Continuous Improvement – By harnessing data analytics, educators can gain valuable insights into student progress and learning patterns, enabling them to refine teaching strategies, personalise interventions, and continuously enhance the educational experience.
In closing, the future of education stands at the intersection of innovation and opportunity, driven by the limitless potential of digital tools. By harnessing these tools effectively, educators can empower students to excel in a rapidly evolving world, ensuring that the future of education remains vibrant, adaptive, and filled with limitless possibilities for growth and achievement. It’s a future where learning knows no bounds, and the pursuit of knowledge is as exciting as it is transformative.

Recommended for you

Trending Stories

Best travel insurance for seniors 2024
Travel is an exciting adventure, but it also carries risks. As people age, they...

Harnessing Best Strategies for Crypto Success: An Interview with Charlie Rothkopf, Founder of CZR Fund
Earlier this year, entrepreneur Charlie Rothkopf announced the launch of his CZR Fund –...

Immediate Flare Erfahrungen 2024: Betrug oder echt – Fakten überprüft
Immediate Flare Erfahrungen 2024: Betrug oder echt – Fakten überprüft Immediate Flare ist ein...

Crypto Expert Levi Hails BlockDAG’s Keynote 2: Predicts Daily $5M Sales; Shiba Inu And Litecoin Show Bullish Trends
Delivering Keynote 2 from the Moon, BlockDAG captivated YouTube crypto analysts, especially Levi, who...

The Next Generation of Vending and Kiosk Technology for Your Business
With rapid advancements in technology reshaping industries, the evolution of vending machines and kiosks...

The Automated Future of Marketing: AI and ML Take the Reins
The world of marketing is in a state of transformation. Once considered a purely...

What Is Tubidy and How Does It Work for Music Downloads?
Tubidy, a popular music streaming and downloading platform in South Africa, offers an extensive...

Quantum Dexair Review 2024: Scam or Legit? – Scam Tested!
Quantum Dexair is a new trading system that has become popular among crypto traders...

South Korea Chip Prices Surge 42%, AI-Driven
The demand for AI and sales of high-bandwidth memory caused a 42.1% increase in...

10 Must-Have Event Services Technologies For A Successful Virtual Event
Virtual events have become increasingly popular, offering unique opportunities for global participation and engagement...

BlockDAG’s 1120% ROI Explosion Mesmerizes Crypto World As Litecoin Slump & Toncoin Skyrocket
BlockDAG is making waves in the crypto market with a stellar presale, accumulating over...

Know About IoT Sims: Power of the Internet
The Internet of Things is a unique way of transforming your world. Starting from...

What if the Other Driver Doesn’t Have Insurance?
As of 2022, approximately 14.0% of motorists, or about one in seven drivers, were...

Injex Finance Mainnet Goes LIVE: Revolutionizing DeFi Trading on Injective Network
As decentralized finance (DeFi) continues to evolve, liquidity aggregators have become crucial for traders...

Forex Day Trading: 5 Mistakes to Avoid
What is Forex? The term Forex (FX) stands for the Foreign Exchange Market, where currencies...

Analyst: No One Is Counting On A Cardano (ADA) Recovery Anymore; Retik Finance (RETIK) And Polygon (MATIC) Catch Attention As Alternatives
Cardano (ADA), once hailed as a promising blockchain platform with potential to revolutionize the...

The Future of Team Productivity: How Technology is Changing the Game
Introduction to team productivity and its importance Welcome to the exciting world of team...

RCO Finance (RCOF) Attracts Big Money, Outdoing RollBlock (RBLK) and Moonbag (MBAG)
Cryptocurrency token presales in 2024 are shaping up to be major opportunities for investors...

Transform Your Health: Top Health Benefits of Magnesium Citrate
Do you experience unexplained fatigue, sluggishness, or anxiety? These symptoms may indicate a deficiency...

BYD Tang EV Electric Cars – Revolutionizing the Road
The automotive world is rapidly shifting towards electric vehicles (EVs), and among the top...
Like Us On Facebook
Latest interview.

Earlier this year, entrepreneur Charlie Rothkopf announced the launch of his CZR Fund – an entity that blends Bitcoin investment with active...
Latest Press Release

Vanpowers Announces Inspiring Collaboration with Amputee Rider Jim Wilkes
Jim was told he’d never be able to ride again. But there’s no way he was leaving it at that! After grueling...
Pin It on Pinterest
More From Forbes
Move over, chatgpt: here are 5 ai education tools loved by teachers.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Move Over ChatGPT! Here Are 5 AI Education Tools Loved By Teachers
Artificial Intelligence is inspiring educators all over the world.
I reached out to teachers on LinkedIn, X, and Facebook to find out which AI tools are having the most impact in classrooms. The overwhelming response is testament to how much educators are loving their new AI workmates. After exploring the first round of popular tools, let’s take a look at five more.
While many educators are using leading AI chatbots such as ChatGPT and Google Gemini, platforms designed specifically for educators and students are offering more specialized functionality.
Here are five more AI tools making waves in classrooms worldwide:
- Magic School
Chat For Schools
Magic media in canva.
With insights from educators who are leveraging their potential, let’s explore them in more detail.
Five AI Tools For Educators
Magicschool.
MagicSchool is a generative AI platform designed to assist educators with various tasks such as lesson planning, writing assessments and creating individualized education plans. It offers over 60 tools to streamline various processes and aims to save teachers significant amounts of time each week. The platform also offers a suite of tools specifically designed for students to enhance their AI literacy and learning experience.
Paraiso Miami Swim Week Makes Waves
Wwe smackdown results winners and grades from glasgow scotland, robert plant alison krauss offer up magical evening on stage outside chicago.
Heather Brown, a K-5 math interventionist and STEAM teacher in Illinois, shared her enthusiasm: "I love that MagicSchool has so much of the prompting built in to help students truly engage with AI. The variety of ways it can be used is also incredible, from rap battles to research assistants to math review and beyond! The guidance it gives to students before proceeding into using AI is also a great starting point for teachers to talk about AI in a factual, unbiased way."
I use MagicSchool's tools when leading sessions with students to help them create AI bots for their own personal use. I'm constantly amazed by how they innovate, developing bots for themselves to help with studying, career guidance and even sleep management.
Poe is a versatile AI tool that allows students to create personal chatbots and explore different AI models. It allows customization of chatbot behavior and responses, providing a more tailored and interactive experience.
Jason Gulya, a professor of English at Berkeley College uses Poe in his classroom: "I currently teach my students to use Poe. It helps them to create their own personal chatbots. When they use it, they start to realize that AI isn't magic, but a technology that allows them to build useful solutions around their own problems and interests."
I received a lot of replies mentioning this tool. Chat for Schools by Skill Struck is tailored for K-12 classrooms, allowing students to engage with AI chatbots. Teachers can create custom tutors, monitor chat history and control the AI's usage to prevent cheating and ensure appropriate interactions. The platform also integrates features like sentiment analysis and reading level adjustments to enhance the educational experience.
Devan Miller, a career and technical education teacher in Florida, praised Chat For Schools: "It allows me to create tutors for specific aspects of content that I would like my students to practice and learn while allowing me to monitor my students' queries. The management system also flags anything that could prove to be inappropriate for school. It's an amazing resource that I recommend be used by teachers!"
Magic Media, an app in the Canva platform, enables users to create images, graphics and videos from simple text prompts. Teachers can generate high-quality visual content without requiring extensive design skills. Users can further enhance their creations using Canva’s editing tools, which offer options for adding animations, transitions and other effects to make the final product more dynamic and engaging.
Ainsley Messina, a technology integrator in New York City, shared her positive experience: "I love using Canva Magic Media tools with my 4th graders! These tools are fantastic for teaching students how AI can enhance photo editing and presentation creation. By using Magic Media, my students get an engaging introduction to the capabilities of AI, learning firsthand how it can be integrated into creative projects. It's also an excellent way to highlight the importance of detailed prompt writing, helping them understand how precise instructions can yield the best results. Overall, it's a fun and educational way to prepare them for the future of digital creativity."
Magic Media is just one of many AI tools in Canva. Educators can access these with a free premium account.
Udio is a new AI platform designed to generate custom music tracks based on user preferences. You simply type in what kind of song you would like, select the genre of music and wait around 1 minute for a unique 30 second song. Advanced features allow users to create full length songs, include their own lyrics and even generate a song from an audio input.
Pravin Kaipa, an education specialist at an elementary school in California, uses Udio with his special needs students: "My students and I love using Udio because we generate songs to help us memorize concepts or understand new ones, and we have created everything from mnemonics to remember the prime numbers under 10 to the differences between potential and kinetic energy. They also loved using it to create positive self-image theme songs that I play when they finish a big presentation."
Important Considerations For Educators
These five tools are just a few of the many platforms shared by educators around the world. To search for other AI platforms being used in education, many educators use the AI Educator Tools repository .
Before integrating any digital platform into your classroom, it is crucial to follow your organization's procedures regarding data protection. Always seek guidance from the people responsible for this in your school, college, or university.
The teachers I spoke to are saving many hours per week using tools such as the ones above. When integrated in a safe way, AI has the potential to transform the practices of any teacher.
This could be you.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
72% of U.S. high school teachers say cellphone distraction is a major problem in the classroom

New York Gov. Kathy Hochul recently announced that she will introduce legislation to ban smartphones in schools during her state’s 2025 legislative session. She cited the impact that social media and technology can have on youth, including leaving them “cut off from human connection, social interaction and normal classroom activity.”
Hochul’s legislative push comes as K-12 teachers in the United States face challenges around students’ cellphone use, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in fall 2023. One-third of public K-12 teachers say students being distracted by cellphones is a major problem in their classroom, and another 20% say it’s a minor problem.
Following news that New York Gov. Kathy Hochul is seeking to ban smartphones in schools, Pew Research Center published this analysis to examine how K-12 teachers and teens in the United States feel about cellphones, including the use of cellphones at school.
This analysis is based on two recent Center surveys, one of public K-12 teachers in the U.S. and the other of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17. More information about these surveys, including their field dates, sample sizes and other methodological details, is available at the links in the text.
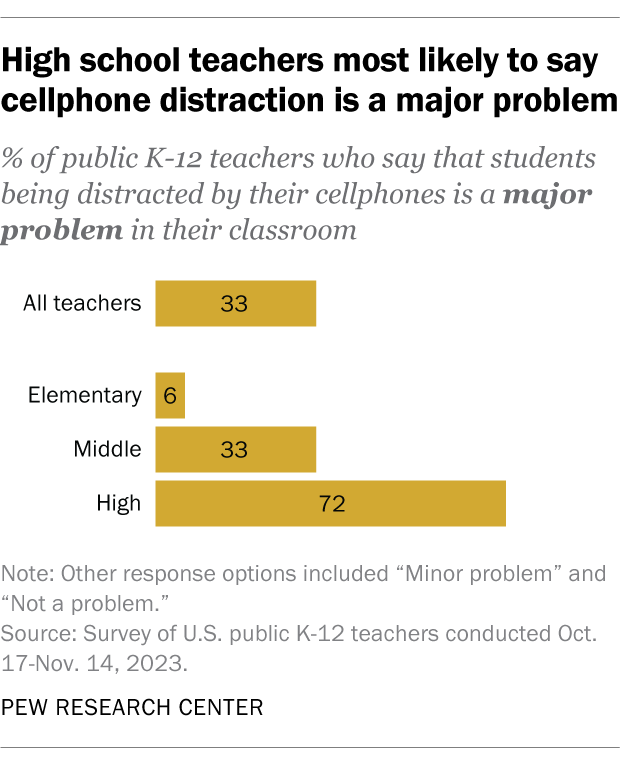
High school teachers are especially likely to see cellphones as problematic. About seven-in-ten (72%) say that students being distracted by cellphones is a major problem in their classroom, compared with 33% of middle school teachers and 6% of elementary school teachers.
Many schools and districts have tried to address this challenge by implementing cellphone policies , such as requiring students to turn off their phones during class or give them to administrators during the school day.
Overall, 82% of K-12 teachers in the U.S. say their school or district has a cellphone policy of some kind. Middle school teachers (94%) are especially likely to say this, followed by elementary (84%) and high school (71%) teachers.
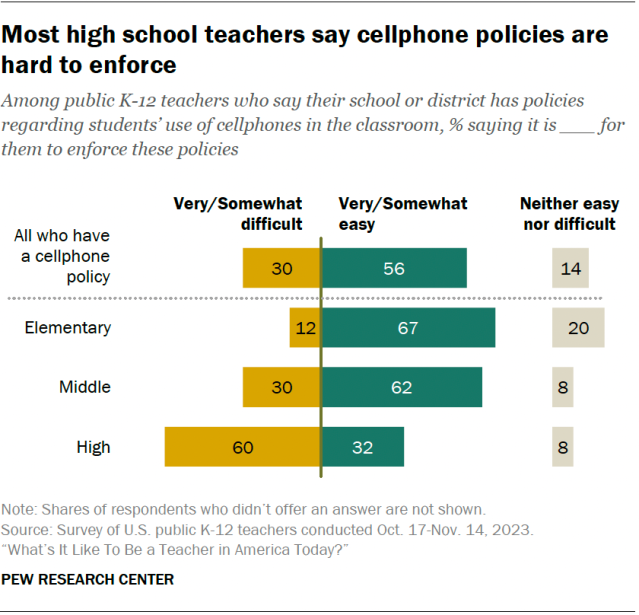
However, 30% of teachers whose schools or districts have cellphone policies say they are very or somewhat difficult to enforce. High school teachers are more likely than their peers to report that enforcing these policies is difficult. Six-in-ten high school teachers in places with a cellphone policy say this, compared with 30% of middle school teachers and 12% of elementary school teachers.
Our survey asked teachers about cellphones in general, whereas Hochul’s plan would apply only to smartphones. Even so, nearly all U.S. teenagers ages 13 to 17 – 95% – say they have access to a smartphone , according to a separate Center survey from 2023.
Even as some policymakers and teachers see downsides to smartphones, teens tend to view the devices as a more positive than negative thing in their lives overall.
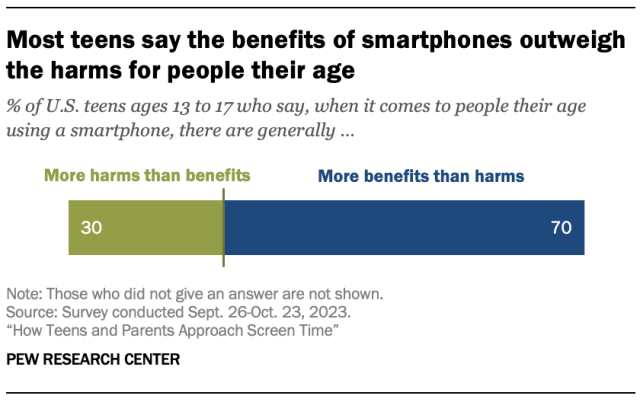
Seven-in-ten teens ages 13 to 17 say there are generally more benefits than harms to people their age using smartphones , while three-in-ten say the opposite. And 45% of teens say smartphones make it easier for people their age to do well in school, compared with 23% who say they make it harder. Another 30% say smartphones don’t affect teens’ success in school.
- Smartphones
Jenn Hatfield is a writer/editor at Pew Research Center .
U.S. public, private and charter schools in 5 charts
A quarter of u.s. teachers say ai tools do more harm than good in k-12 education, most americans think u.s. k-12 stem education isn’t above average, but test results paint a mixed picture, about 1 in 4 u.s. teachers say their school went into a gun-related lockdown in the last school year, about half of americans say public k-12 education is going in the wrong direction, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This comprehensive guide explains the positive impact of technology in the classroom and how to get the most from your classroom tech.
<p>Stanford Graduate School of Education Dean Dan Schwartz and other education scholars weigh in on what's next for some of the technology trends taking center stage in the classroom.</p>
Schools struggle to balance increasing use of ed-tech tools for teaching and learning with growing concerns about "tech fatigue."
In today's educational landscape, where technology plays such a pivotal role, integrating instructional strategies with technology is increasingly important. As an instructional technology resource teacher, I have a primary role of supporting teachers in effectively integrating technology into their classroom instruction.
Use of Educational Technology for Instruction in Public Schools: 2019—20. Schools were asked about the types of staff who work with teachers to bring technology into classes for teaching and learning. Fifty-seven percent reported that content specialists, or experts, from the school or district work with teachers for this purpose (table A-6).
Adoption & introduction of educational technology in the classroom is good for both students & educators. Learn how it works, why it's important & the benefits.
Learn more about the benefits of technology in the classroom and how it can be integrated in unique and effective ways.
Digital technology in the classroom refers to various software and gadgets meant to help students with particular accessibility needs. The most effective way to reduce the number of repetitive, time-consuming duties a teacher undertake is to use technology in the classroom.
The 2023 GEM Report on technology and education explores these debates, examining education challenges to which appropriate use of technology can offer solutions (access, equity and inclusion; quality; technology advancement; system management), while recognizing that many solutions proposed may also be detrimental.
Successful technology integration is more than just getting the tools into the classroom; here are some ideas on how to engage students and enliven your lessons with those tools. From our Technology Integration Professional Development Module.
Here are five specific and sequential guidelines for decisionmakers to realize the potential of education technology to accelerate student learning. 1. Take stock of how your current schools ...
Educational technology isn't new, but meaningfully integrating tech in a modern learning environment can be a significant challenge for educators today.
Integration of technology in education simply refers to the use of technology to enhance the student learning experience. Utilizing different types of technology in the classroom, including a virtual classroom, creates learners who are actively engaged with learning objectives. The implementation of technology also creates pathways for ...
Education news, analysis, and opinion about using technology in schools for teaching and learning.
Information and Communications Technology (ICT) can impact student learning when teachers are digitally literate and understand how to integrate it into curriculum. Schools use a diverse set of ICT tools to communicate, create, disseminate, store, and manage information.(6) In some contexts, ICT has also become integral to the teaching-learning interaction, through such approaches as replacing ...
The evolution of technology in the classroom includes where educational methods and tools have come from to where they are going in the future. Learn more.
Major advances in technology, especially digitaltechnology, are rapidly transforming the world.Information and communication technology (ICT) hasbeen applied for 100 years in education, ever sincethe popularization of radio in the 1920s. But it is the useof digital technology over the past 40 years that hasthe most significant potential to transform education.An education technology industry ...
Additionally, we need to examine the use of technology in teacher education. If we want current and future teachers to identify effective practices for using technology in their classrooms, we need to role model what that looks like.
To harness education technology's full potential, education decision-makers, product developers, and funders need to understand the ways in which technology can help — or in some cases hurt — student learning. ... Software has the potential to overcome traditional classroom constraints by customizing activities for each student ...
From blended learning to computerized testing, digital and online technologies are reshaping the classroom experience for students.
How important is technology in education? Learn how American University's School of Education can prepare you to serve as a leader in educational technology. ... Additionally, technology in the classroom should make teachers' jobs easier without adding extra time to their day. Technology provides students with easy-to-access information ...
Get started with Google Classroom, a central hub for tools and resources designed to help educators manage classrooms and enrich learning experiences.
New advances in technology are upending education, from the recent debut of new artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots like ChatGPT to the growing accessibility of virtual-reality tools that expand the boundaries of the classroom. For educators, at the heart of it all is the hope that every learner gets an equal chance to develop the skills they need to succeed.
The COVID-19 pandemic forced a shift to remote learning overnight for most higher-education students, starting in the spring of 2020. To complement video lectures and engage students in the virtual classroom, educators adopted technologies that enabled more interactivity and hybrid models of online and in-person activities.
There has always been technology in the classroom, so be ready for how EdTech is changing education with this in-depth guide.
Our education systems, however, focus on "teaching for the test" too often, eschewing curiosity and creativity. Tools like Interactive Digital Narratives and systems thinking and mapping can help us re-think how we educate minds for a complicated, multivariate world. Technological development and interconnectedness are advancing rapidly — and ...
Just as school boards and administrators evaluate carefully every item placed in classrooms from the size of windows to furniture to whiteboards to textbooks, so too should the ubiquitous technologies used daily-nay, hourly-such as cell phones and laptops (including software) be rigorouly assessed. New York Times reporter Jessica Grose makes just that point in this article.
In today's rapidly evolving world, technology has become an omnipresent force reshaping every facet of our lives, including how we communicate, work, and learn. As advancements continue to redefine industries and societies, education stands at the forefront of this transformation. Traditional classrooms are increasingly integrating digital tools to enhance learning experiences, personalise ...
Teachers are using AI tools beyond ChatGPT and Google Gemini, such as Canva, and MagicSchool, to enhance and personalize education for children around the world.
High school teachers are especially likely to see cellphones as problematic. About seven-in-ten (72%) say that students being distracted by cellphones is a major problem in their classroom, compared with 33% of middle school teachers and 6% of elementary school teachers. Many schools and districts have tried to address this challenge by ...