- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers

How to Write a Research Synopsis: Template, Examples, & More
Last Updated: May 9, 2024 Fact Checked
Research Synopsis Template
- Organizing & Formatting
- Writing Your Synopsis
- Reviewing & Editing
This article was reviewed by Gerald Posner and by wikiHow staff writer, Raven Minyard, BA . Gerald Posner is an Author & Journalist based in Miami, Florida. With over 35 years of experience, he specializes in investigative journalism, nonfiction books, and editorials. He holds a law degree from UC College of the Law, San Francisco, and a BA in Political Science from the University of California-Berkeley. He’s the author of thirteen books, including several New York Times bestsellers, the winner of the Florida Book Award for General Nonfiction, and has been a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize in History. He was also shortlisted for the Best Business Book of 2020 by the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 239,172 times.
A research synopsis describes the plan for your research project and is typically submitted to professors or department heads so they can approve your project. Most synopses are between 3,000 and 4,000 words and provide your research objectives and methods. While the specific types of information you need to include in your synopsis may vary depending on your department guidelines, most synopses include the same basic sections. In this article, we’ll walk you step-by-step through everything you need to know to write a synopsis for research.
Things You Should Know
- Begin your research synopsis by introducing the question your research will answer and its importance to your field.
- List 2 or 3 specific objectives you hope to achieve and how they will advance your field.
- Discuss your methodology to demonstrate why the study design you chose is appropriate for your research question.

Organizing Your Research Synopsis

- Find out what citation format you’re supposed to use, as well as whether you’re expected to use parenthetical references or footnotes in the body of your synopsis.
- If you have questions about anything in your guidelines, ask your instructor or advisor to ensure you follow them correctly.

- Title: the title of your study
- Abstract: a summary of your research synopsis
- Introduction: identifies and describes your research question
- Literature Review: a review of existing relevant research
- Objectives: goals you hope to accomplish through your study
- Hypotheses: results you expect to find through your research
- Methodology and methods: explains the methods you’ll use to complete your study
- References: a list of any references used in citations
Tip: Your synopsis might have additional sections, depending on your discipline and the type of research you're conducting. Talk to your instructor or advisor about which sections are required for your department.

- Keep in mind that you might not end up using all the sources you initially found. After you've finished your synopsis, go back and delete the ones you didn't use.
Writing Your Research Synopsis

- Your title should be a brief and specific reflection of the main objectives of your study. In general, it should be under 50 words and should avoid unneeded phrases like “an investigation into.”
- On the other hand, avoid a title that’s too short, as well. For example, a title like “A Study of Urban Heating” is too short and doesn’t provide any insight into the specifics of your research.

- The introduction allows you to explain to your reader exactly why the question you’re trying to answer is vital and how your knowledge and experience make you the best researcher to tackle it.
- Support most of the statements in your introduction with other studies in the area that support the importance of your question. For example, you might cite a previous study that mentions your problem as an area where further research needs to be done.
- The length of your introduction will vary depending on the overall length of your synopsis as well as the ultimate length of your eventual paper after you’ve finished your research. Generally, it will cover the first page or two of your synopsis.

- For example, try finding relevant literature through educational journals or bulletins from organizations like WHO and CDC.
- Typically, a thorough literature review discusses 8 to 10 previous studies related to your research problem.
- As with the introduction, the length of your literature review will vary depending on the overall length of your synopsis. Generally, it will be about the same length as your introduction.
- Try to use the most current research available and avoid sources over 5 years old.

- For example, an objective for research on urban heating could be “to compare urban heat modification caused by vegetation of mixed species considering the 5 most common urban trees in an area.”
- Generally, the overall objective doesn’t relate to solving a specific problem or answering a specific question. Rather, it describes how your particular project will advance your field.
- For specific objectives, think in terms of action verbs like “quantify” or “compare.” Here, you’re hoping to gain a better understanding of associations between particular variables.

- Specify the sources you used and the reasons you have arrived at your hypotheses. Typically, these will come from prior studies that have shown similar relationships.
- For example, suppose a prior study showed that children who were home-schooled were less likely to be in fraternities or sororities in college. You might use that study to back up a hypothesis that home-schooled children are more independent and less likely to need strong friendship support networks.

- Expect your methodology to be at least as long as either your introduction or your literature review, if not longer. Include enough detail that your reader can fully understand how you’re going to carry out your study.
- This section of your synopsis may include information about how you plan to collect and analyze your data, the overall design of your study, and your sampling methods, if necessary. Include information about the study setting, like the facilities and equipment that are available to you to carry out your study.
- For example, your research work may take place in a hospital, and you may use cluster sampling to gather data.

- Use between 100 and 200 words to give your readers a basic understanding of your research project.
- Include a clear statement of the problem, the main goals or objectives of your study, the theories or conceptual framework your research relies upon, and the methods you’ll use to reach your goals or objectives.
Tip: Jot down a few notes as you draft your other sections that you can compile for your abstract to keep your writing more efficient.
Reviewing and Editing Your Research Synopsis

- If you don’t have that kind of time because you’re up against a deadline, at least take a few hours away from your synopsis before you go back to edit it. Do something entirely unrelated to your research, like taking a walk or going to a movie.

- Eliminate sentences that don’t add any new information. Even the longest synopsis is a brief document—make sure every word needs to be there and counts for something.
- Get rid of jargon and terms of art in your field that could be better explained in plain language. Even though your likely readers are people who are well-versed in your field, providing plain language descriptions shows you know what you’re talking about. Using jargon can seem like you’re trying to sound like you know more than you actually do.
Tip: Free apps, such as Grammarly and Hemingway App, can help you identify grammatical errors as well as areas where your writing could be clearer. However, you shouldn't rely solely on apps since they can miss things.

- Reference list formatting is very particular. Read your references out loud, with the punctuation and spacing, to pick up on errors you wouldn’t have noticed if you’d just read over them.
- Compare your format to the one in the stylebook you’re using and make sure all of your entries are correct.

- Read your synopsis backward by starting on the last word and reading each word separately from the last to the first. This helps isolate spelling errors. Reading backward sentence by sentence helps you isolate grammatical errors without being distracted by the content.
- Print your synopsis and circle every punctuation mark with a red pen. Then, go through them and focus on whether they’re correct.
- Read your synopsis out loud, including the punctuation, as though you were dictating the synopsis.

- Have at least one person who isn’t familiar with your area of study look over your synopsis. If they can understand your project, you know your writing is clear. If any parts confuse them, then that’s an area where you can improve the clarity of your writing.

Expert Q&A
- If you make significant changes to your synopsis after your first or second round of editing, you may need to proofread it again to make sure you didn’t introduce any new errors. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://admin.umt.edu.pk/Media/Site/iib1/FileManager/FORMAT%20OF%20SYNOPSIS%2012-10-2018.pdf
- ↑ https://www.scientificstyleandformat.org/Tools/SSF-Citation-Quick-Guide.html
- ↑ https://numspak.edu.pk/upload/media/Guidelines%20for%20Synopsis%20Writing1531455748.pdf
- ↑ https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279917593_Research_synopsis_guidelines
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ https://www.cornerstone.edu/blog-post/six-steps-to-really-edit-your-paper/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jul 25, 2022
Did this article help you?
Wave Bubble
Aug 31, 2021

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
How to Write a Great Synopsis for Thesis
A synopsis is a structured outline of a research thesis and the steps followed to answer the research question. The goal of writing a synopsis is to clearly and thoroughly explain the need to investigate a certain problem using particular practical methods to conduct the study. One of the main components of this written work is an extensive literature review containing strong evidence that the proposed research is feasible.
Establishing the Background
A supervisor may ask you to write a synopsis for one or more reasons:
- to help you improve your critical thinking and writing skills
- to help you understand how to design a comprehensive synopsis
- to encourage you to write a comprehensive literature review to make sure that the research problem has not been answered yet
- to make you conduct a logical analysis of the steps that should be followed to meet the objectives of the research
A synopsis should be coherent in terms of research design. Thus, you should ensure that the research problem, aims, and research methods are logically linked and well-considered. Note that all synopses should contain answers for several crucial questions:
- Why should research on the proposed problem be undertaken?
- What is expected to be achieved?
- What has been done by other researchers on the proposed topic?
- How will the objectives of the study be achieved?
The Writing Process
Before proceeding, consider answering the following questions:
- Why am I going to study this topic?
- Why do I consider it to be important?
- Have I conducted an extensive literature review on the topic?
- What problem will the research help to solve?
- How do I incorporate previous studies on the topic?
The structure of a synopsis should correspond to the structure of qualifying research work, and the word count should be 2,500–3,000 words (Balu 38). The basic elements of a synopsis include a title page, contents page, an introduction, background, literature review, objectives, methods, experiments and results, conclusions, and references.
Introduction
As this comprises the first part of the main text, the introduction should convince readers that the study addresses a relevant topic and that the expected outcomes will provide important insights. Also, this section should include a brief description of the methods that will be used to answer the research question. Usually, the introduction is written in 1–3 paragraphs and answers the following questions:
- What is the topic of the research?
- What is the research problem that needs to be meaningfully understood or investigated?
- Why is the problem important?
- How will the problem be studied?
In this section, you should set the scene and better introduce the research topic by proving its scientific legitimacy and relevance. It is important to establish a clear focus and avoid broad generalizations and vague statements. If necessary, you may explain key concepts or terms. Consider covering the following points in this section:
- Discuss how the research will contribute to the existing scientific knowledge.
- Provide a detailed description of the research problem and purpose of the research.
- Provide a rationale for the study.
- Explain how the research question will be answered.
- Be sure to discuss the methods chosen and anticipated implications of the research.
Literature Review
A review of existing literature is an important part of a synopsis, as it:
- gives a more detailed look at scientific information related to the topic
- familiarizes readers with research conducted by others on a similar subject
- gives insight into the difficulties faced by other researchers
- helps identify variables for the research based on similar studies
- helps double-check the feasibility of the research problem.
When writing the literature review, do not simply present a list of methods researchers have used and conclusions they have drawn. It is important to compare and contrast different opinions and be unafraid to criticize some of them. Pay attention to controversial issues and divergent approaches used to address similar problems. You may discuss which arguments are more persuasive and which methods and techniques seem to be more valid and reliable. In this section, you are expected not to summarize but analyze the previous research while remembering to link it to your own purpose.
Identify the objectives of the research based on the literature review. Provide an overall objective related to the scientific contribution of the study to the subject area. Also include a specific objective that can be measured at the end of the research.
When writing this section, consider that the aim of the research is to produce new knowledge regarding the topic chosen. Therefore, the research methodology forms the core of your project, and your goal is to convince readers that the research design and methods chosen will rationally answer the research questions and provide effective tools to interpret the results correctly. It may be appropriate to incorporate some examples from your literature review into the description of the overall research design.
When describing the research methodology, ensure that you specify the approaches and techniques that will be used to answer the research question. In addition, be specific about applying the chosen methods and what you expect to achieve. Keep in mind that the methods section allows readers to evaluate the validity and feasibility of the study. Therefore, be sure to explain your decision to adopt specific methods and procedures. It is also important to discuss the anticipated barriers and limitations of the study and how they will be addressed. Specify what kind of contribution to the existing knowledge on the topic is expected, and discuss any ethical considerations that are relevant to the research.
Experiments and Results
Logically present and analyze the results of the study using tables or figures.
In this section, you should again state the significance of the research and summarize the study. Be sure to mention the study objectives and methods used to answer the research questions. Also, discuss how the results of the study contribute to the current knowledge on the problem.
A synopsis should contain a list of all references used. Make sure the references are formatted according to the chosen citation style and each source presented in this section is mentioned within the body of the synopsis.
The purpose of writing a synopsis is to show a supervisor a clear picture of a proposed project and allow him or her to find any gaps that have not been considered previously. A concisely written synopsis will help you gain approval to proceed with the actual research. While no rigid rules for writing this type of paper have been established, a synopsis should be constructed in a manner to help a supervisor understand the proposed research at first glance.
Balu, R. “Writing a Good Ph.D Research Synopsis.” International Journal of Research in Science and Technology, vol. 5, no. 4, 2015, pp. 38–48.
Unfortunately, your browser is too old to work on this site.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Summary – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Summary
Definition:
A research summary is a brief and concise overview of a research project or study that highlights its key findings, main points, and conclusions. It typically includes a description of the research problem, the research methods used, the results obtained, and the implications or significance of the findings. It is often used as a tool to quickly communicate the main findings of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or decision-makers.
Structure of Research Summary
The Structure of a Research Summary typically include:
- Introduction : This section provides a brief background of the research problem or question, explains the purpose of the study, and outlines the research objectives.
- Methodology : This section explains the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study. It describes the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Results : This section presents the main findings of the study, including statistical analysis if applicable. It may include tables, charts, or graphs to visually represent the data.
- Discussion : This section interprets the results and explains their implications. It discusses the significance of the findings, compares them to previous research, and identifies any limitations or future directions for research.
- Conclusion : This section summarizes the main points of the research and provides a conclusion based on the findings. It may also suggest implications for future research or practical applications of the results.
- References : This section lists the sources cited in the research summary, following the appropriate citation style.
How to Write Research Summary
Here are the steps you can follow to write a research summary:
- Read the research article or study thoroughly: To write a summary, you must understand the research article or study you are summarizing. Therefore, read the article or study carefully to understand its purpose, research design, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Identify the main points : Once you have read the research article or study, identify the main points, key findings, and research question. You can highlight or take notes of the essential points and findings to use as a reference when writing your summary.
- Write the introduction: Start your summary by introducing the research problem, research question, and purpose of the study. Briefly explain why the research is important and its significance.
- Summarize the methodology : In this section, summarize the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study. Explain the sample size, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Present the results: Summarize the main findings of the study. Use tables, charts, or graphs to visually represent the data if necessary.
- Interpret the results: In this section, interpret the results and explain their implications. Discuss the significance of the findings, compare them to previous research, and identify any limitations or future directions for research.
- Conclude the summary : Summarize the main points of the research and provide a conclusion based on the findings. Suggest implications for future research or practical applications of the results.
- Revise and edit : Once you have written the summary, revise and edit it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors. Make sure that your summary accurately represents the research article or study.
- Add references: Include a list of references cited in the research summary, following the appropriate citation style.
Example of Research Summary
Here is an example of a research summary:
Title: The Effects of Yoga on Mental Health: A Meta-Analysis
Introduction: This meta-analysis examines the effects of yoga on mental health. The study aimed to investigate whether yoga practice can improve mental health outcomes such as anxiety, depression, stress, and quality of life.
Methodology : The study analyzed data from 14 randomized controlled trials that investigated the effects of yoga on mental health outcomes. The sample included a total of 862 participants. The yoga interventions varied in length and frequency, ranging from four to twelve weeks, with sessions lasting from 45 to 90 minutes.
Results : The meta-analysis found that yoga practice significantly improved mental health outcomes. Participants who practiced yoga showed a significant reduction in anxiety and depression symptoms, as well as stress levels. Quality of life also improved in those who practiced yoga.
Discussion : The findings of this study suggest that yoga can be an effective intervention for improving mental health outcomes. The study supports the growing body of evidence that suggests that yoga can have a positive impact on mental health. Limitations of the study include the variability of the yoga interventions, which may affect the generalizability of the findings.
Conclusion : Overall, the findings of this meta-analysis support the use of yoga as an effective intervention for improving mental health outcomes. Further research is needed to determine the optimal length and frequency of yoga interventions for different populations.
References :
- Cramer, H., Lauche, R., Langhorst, J., Dobos, G., & Berger, B. (2013). Yoga for depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Depression and anxiety, 30(11), 1068-1083.
- Khalsa, S. B. (2004). Yoga as a therapeutic intervention: a bibliometric analysis of published research studies. Indian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 48(3), 269-285.
- Ross, A., & Thomas, S. (2010). The health benefits of yoga and exercise: a review of comparison studies. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 16(1), 3-12.
Purpose of Research Summary
The purpose of a research summary is to provide a brief overview of a research project or study, including its main points, findings, and conclusions. The summary allows readers to quickly understand the essential aspects of the research without having to read the entire article or study.
Research summaries serve several purposes, including:
- Facilitating comprehension: A research summary allows readers to quickly understand the main points and findings of a research project or study without having to read the entire article or study. This makes it easier for readers to comprehend the research and its significance.
- Communicating research findings: Research summaries are often used to communicate research findings to a wider audience, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the general public. The summary presents the essential aspects of the research in a clear and concise manner, making it easier for non-experts to understand.
- Supporting decision-making: Research summaries can be used to support decision-making processes by providing a summary of the research evidence on a particular topic. This information can be used by policymakers or practitioners to make informed decisions about interventions, programs, or policies.
- Saving time: Research summaries save time for researchers, practitioners, policymakers, and other stakeholders who need to review multiple research studies. Rather than having to read the entire article or study, they can quickly review the summary to determine whether the research is relevant to their needs.
Characteristics of Research Summary
The following are some of the key characteristics of a research summary:
- Concise : A research summary should be brief and to the point, providing a clear and concise overview of the main points of the research.
- Objective : A research summary should be written in an objective tone, presenting the research findings without bias or personal opinion.
- Comprehensive : A research summary should cover all the essential aspects of the research, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research summary should accurately reflect the key findings and conclusions of the research.
- Clear and well-organized: A research summary should be easy to read and understand, with a clear structure and logical flow.
- Relevant : A research summary should focus on the most important and relevant aspects of the research, highlighting the key findings and their implications.
- Audience-specific: A research summary should be tailored to the intended audience, using language and terminology that is appropriate and accessible to the reader.
- Citations : A research summary should include citations to the original research articles or studies, allowing readers to access the full text of the research if desired.
When to write Research Summary
Here are some situations when it may be appropriate to write a research summary:
- Proposal stage: A research summary can be included in a research proposal to provide a brief overview of the research aims, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
- Conference presentation: A research summary can be prepared for a conference presentation to summarize the main findings of a study or research project.
- Journal submission: Many academic journals require authors to submit a research summary along with their research article or study. The summary provides a brief overview of the study’s main points, findings, and conclusions and helps readers quickly understand the research.
- Funding application: A research summary can be included in a funding application to provide a brief summary of the research aims, objectives, and expected outcomes.
- Policy brief: A research summary can be prepared as a policy brief to communicate research findings to policymakers or stakeholders in a concise and accessible manner.
Advantages of Research Summary
Research summaries offer several advantages, including:
- Time-saving: A research summary saves time for readers who need to understand the key findings and conclusions of a research project quickly. Rather than reading the entire research article or study, readers can quickly review the summary to determine whether the research is relevant to their needs.
- Clarity and accessibility: A research summary provides a clear and accessible overview of the research project’s main points, making it easier for readers to understand the research without having to be experts in the field.
- Improved comprehension: A research summary helps readers comprehend the research by providing a brief and focused overview of the key findings and conclusions, making it easier to understand the research and its significance.
- Enhanced communication: Research summaries can be used to communicate research findings to a wider audience, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the general public, in a concise and accessible manner.
- Facilitated decision-making: Research summaries can support decision-making processes by providing a summary of the research evidence on a particular topic. Policymakers or practitioners can use this information to make informed decisions about interventions, programs, or policies.
- Increased dissemination: Research summaries can be easily shared and disseminated, allowing research findings to reach a wider audience.
Limitations of Research Summary
Limitations of the Research Summary are as follows:
- Limited scope: Research summaries provide a brief overview of the research project’s main points, findings, and conclusions, which can be limiting. They may not include all the details, nuances, and complexities of the research that readers may need to fully understand the study’s implications.
- Risk of oversimplification: Research summaries can be oversimplified, reducing the complexity of the research and potentially distorting the findings or conclusions.
- Lack of context: Research summaries may not provide sufficient context to fully understand the research findings, such as the research background, methodology, or limitations. This may lead to misunderstandings or misinterpretations of the research.
- Possible bias: Research summaries may be biased if they selectively emphasize certain findings or conclusions over others, potentially distorting the overall picture of the research.
- Format limitations: Research summaries may be constrained by the format or length requirements, making it challenging to fully convey the research’s main points, findings, and conclusions.
- Accessibility: Research summaries may not be accessible to all readers, particularly those with limited literacy skills, visual impairments, or language barriers.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- Current Students
- News & Press
- Exam Technique for In-Person Exams
- Revising for 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Introduction to 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Before the 24 Hour Take Home Exam
- Exam Technique for 24 Hour Take Home Exams
- Structuring a Literature Review
- Writing Coursework under Time Constraints
- Reflective Writing
- Writing a Synopsis
- Structuring a Science Report
- Presentations
- How the University works out your degree award
- Personal Extenuating Circumstances (PEC)
- Accessing your assignment feedback via Canvas
- Inspera Digital Exams
- Writing Introductions and Conclusions
- Paragraphing
- Reporting Verbs
- Signposting
- Proofreading
- Working with a Proofreader
- Writing Concisely
- The 1-Hour Writing Challenge
- Editing strategies
- Apostrophes
- Semi-colons
- Run-on sentences
- How to Improve your Grammar (native English)
- How to Improve your Grammar (non-native English)
- Independent Learning for Online Study
- Reflective Practice
- Academic Reading
- Strategic Reading Framework
- Note-taking Strategies
- Note-taking in Lectures
- Making Notes from Reading
- Using Evidence to Support your Argument
- Integrating Scholarship
- Managing Time and Motivation
- Dealing with Procrastination
- How to Paraphrase
- Quote or Paraphrase?
- How to Quote
- Referencing
- Artificial Intelligence and Academic Integrity
- Use and limitations of generative AI
- Acknowledging use of AI
- Numeracy, Maths & Statistics
- Library Search
- Search Techniques
- Keeping up to date
- Evaluating Information
- Managing Information
- Thinking Critically about AI
- Using Information generated by AI
- Digital Capabilities
- SensusAccess
- Develop Your Digital Skills
- Digital Tools to Help You Study

Learn how to prepare and write a synopsis assignment.
- Newcastle University
- Academic Skills Kit
- Assignment Types
A synopsis is a brief summary which gives readers an overview of the main points. In an academic context, this is usually a summary of a text (a journal article, book, report etc) but in some instances you might be writing a synopsis of a talk, film or other form of presentation. A synopsis is a neutral summary, objectively capturing the main points, rather than your own perspective or critique, and it focusses directly on the text you’re summarising rather than being a wider discussion of a topic, as an essay might be.
A synopsis aims to give the reader a full, if brief, account of the whole text so that they can follow its main points without having to read it themselves. It’s not a ‘trailer’ designed to tempt your audience to read the text itself, so you don’t have to worry about ‘hooking’ them in with hints and high points or ‘spoiling the ending’ - give the whole text equal coverage, including the conclusions. You could add some commentary which gives the reader a bit of context about the text, including the authors and circumstances it was written in (for example, if it is part of a debate, particular school of thought or its significance and what impact it’s had).
Writing a good synopsis is a skill, and there are a number of challenges:
- Separating the main points from the minor detail
- Knowing what to leave out as well as what to include
- Giving a sense of the overall narrative as well as listing the key points
- Covering the whole text within a small word limit
- Knowing how closely to stick to the original, especially in terms of the wording
- Whether to give all key points equal treatment, or cover some more briefly, even combining them
- Rephrasing things concisely without losing the meaning or misrepresenting it
- Not leaving out anything crucial to understanding the whole overall message
A good synopsis will allow the reader to feel as if they’d skimread the whole text themselves, understanding the overall gist and highlighting what they need to know. A poor synopsis will get bogged down in detail, giving a confused account of the whole story by just listing points, miss out major points or give an inaccurate or one-sided account or stick so closely to the original that it becomes plagiarism without demonstrating a real understanding by the person summarising it.
How to prepare a synopsis
Boiling down the key points and overall narrative of the original means good reading and note-taking skills which aim to identify and boil down key points to their essence. You could try some of the following approaches:
- Read the whole text, and afterwards, without re-reading, jot down your first initial summary in 50 words to capture its overall point. You can check it back for accuracy or anything you left out, but stick within ca 50 words
- Read the introduction and first line of each paragraph to get a sense of the overall structure and key points within it
- Highlight one sentence in each paragraph that you think is essential detail to understanding that section
- Alternatively, with a marker pen, cross out anything that isn’t essential to an understanding of the whole section or text
- Jot down only key words as a summary of each point rather than whole sentences
- Read each paragraph and summarise it without looking, in one sentence of your own
- Consider how many points you can make within your word count, and reduce or combine your list of summarised points down to this number
You could start small, identifying just keywords or sentences at first and then work them up into phrases, bullet points and sentences as a rough plan or draft, or you could start big with the original text and reduce each section, paragraph and sentence summary again and again until you have boiled it down to its essence.
When you start to prepare your first plan or draft, try to use your notes or memory and step away from the original as much as you can. You can go back and check it afterwards, but you need to create some distance to be able to create your own account and have confidence in the points you have identified as essential.
Writing a synopsis
The main decisions facing you as you write up your summary are about how closely to stick to the original in terms of structure and style, and how much attention to give to each point.
- You could begin your synopsis with a brief context, explaining who the authors are, the context and significance of their work, as well as anything you think might help the reader to understand the following summary
- The most common structure is to follow that of the original text, to give a sense of its narrative flow as well as the key points within it. You could choose to depart from it a little though, perhaps glossing over some points faster than others, combining two sections which go together or aren’t enough in their own right, possibly even changing the order a little where it helps to combine two similar points. Careful use of signposting language will help the reader clearly follow the structure (and note anywhere you’ve changed it from the original) so they can identify the bit you’re talking about in the original if they want to
- The style will naturally be strongly influenced by the original wording, but you should phrase it in your own words wherever possible. It’s harder to nibble away words from a much longer original than it is to start again and use your own concise phrasing, and you want to demonstrate your own understanding to the reader. You could use the odd original phrase or quotation here or there, but the synopsis needs to be more than a collage of quotations; it’s a thing in its own right rather than a cut-down version of the original
- You can also show your own response to the text in the way you use language to guide the reader to what you feel are the key points and (briefly) why. Your own voice doesn’t need to be very obvious in the synopsis, as it’s about the text rather than your reaction to it, but you have made analytical decisions about what is important, and might want to explain to the reader why these points are significant in understanding the whole
- What is the main purpose of this text? What did it aim to discover, explain or prove?
- Why was this research done? How significant is it?
- How was the research conducted? What kind of research is it?
- What were the three (or four, five) main things I should be aware of from this paper?
- What is their line of argument?
- What is their overall conclusion, recommendation, finding? Why is that important?
Managing word count
The trick to writing a concise synopsis which keeps within your word limit is not to start from the much bigger original text, but from your own boiled down notes. If you’re over the word count, you could start cutting out words that don’t seem essential, but if you go too far, you end up with a text which does not read well and doesn’t hang together. It might be better to remove whole sentences and perhaps whole points, than nibble away at words here and there.
Download this guide as a PDF
Learn how to prepare and write a synopsis assignment. **PDF Download**
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Research synopsis writing

Related Papers
International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Science Archive
Mohammed Ismael Rushdi
An abstract is like a movie trailer. People will only consider reading the rest of the manuscript if they find your abstract interesting. It is an outline/brief summary of your paper and your whole project. Keywords: , research, descriptive and informative research.
Langley, BC: Trinity Western University. …
Paul T P Wong
Shubham Mishra
Alex Galarosa
William Schafer
The abstract serves two major purposes: it helps a person decide whether to read the paper, and it provides the reader with a framework for understanding the paper if they decide to read it. Thus, your abstract should describe the most important aspects of the study within the word-limit provided by the journal. As appropriate for your research, try to include a statement of the problem, the people you studied, the dependent and independent variables, the instruments, the design, major findings, and conclusions. If pressed for space, concentrate on the problem and,
UncleChew Bah
Parlindungan Pardede
Amir siddiqui
Hira Qureshi
Synopsis is a short summary of your Ph.D thesis work. This paper suggests some ideas to motivate the young researchers for effectively writing the Ph.D synopsis with essential tips and tricks.This can act as a reference and help young researcher to going to write Ph.D synopsis.
RELATED PAPERS
International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics
Instiaty Abuhaerah
Genome announcements
IFTIKHAR AHMED
Revista de Saúde Pública
Sandhi Barreto
Fertility and Sterility
Valérie Sérazin
Jurnal Pengabdian Masyarakat MIPA dan Pendidikan MIPA
verena agustini
WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment
Lionel Catalan
Mariafrancesca Sgadari
Cognitio Estudos Revista Eletronica De Filosofia Issn 1809 8428
Monica Aiub
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Hwoon-yong Jung
Dr Jhilam Chattaraj
ACS Catalysis
Eloy del Río
European Radiology
Mirella Fraquelli
Clinical Chemistry
Gunnar Nordin
Revista de Administração
Maria de Fatima Bruno-Faria
Sir Syed Research Journal of Engineering & Technology
Quaderns de cine
Felipe Cabrerizo
Helminthologia
Rositsa Milcheva
Journal of Water and Health
panagiotis karanis
Australian Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Abhishek Saroj
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write a Synopsis
I. What is a Synopsis?
A synopsis is a brief summary that gives audiences an idea of what a composition is about. It provides an overview of the storyline or main points and other defining factors of the work, which may include style, genre, persons or characters of note, setting, and so on. We write synopses for all kinds of things—any type of fiction or nonfiction book, academic papers, journal and newspaper articles, films, TV shows, and video games, just to name a few!
The amount of detail and information revealed in a synopsis depends on its purpose. For instance, authors often need to provide a lengthy synopsis when proposing a book, article, or work to potential publishers or editors —in that case, a synopsis will include a full plot overview (which includes revealing the ending), signs of character progression, detailed explanation of theme and tone, and so on. This article will mainly focus on the short synopses you see every day on websites and other media outlets.
II. Example of a Synopsis
Here’s an example of a short synopsis of the story of Jack and Jill:
Jack and Jill is the story of a boy and a girl who went up a hill together. They went to fetch a pail of water, but unfortunately, their plan is disrupted when Jack falls and hits his head, and rolls back down the hill. Then, Jill falls too, and comes tumbling down after Jack.
As you can see, the synopsis outlines what happens in the story. It introduces the main characters and the main plot points without being overly detailed or wordy.
III. Importance of Synopses
Synopses are extremely valuable and necessary pieces of writing for authors, film makers, TV producers, academic writers, and many others.
- On one level, it’s what actually helps a book get published or a film or TV series get made—a successful, well-written synopsis can convince the person in charge of publication or production to bring a work to life
- On the other hand, synopses grab the attention of potential audiences and can convince them to read, watch, or listen
- Also, they help researchers find what they are looking for and decide if a piece is relevant to their field
Without them, audiences and readers would never know what something was about before reading or viewing it! Thus, the importance of synopses is twofold: it both helps works get made and then helps them reach the right audiences.
IV. Examples of Synopses in Literature
Example 1: synopsis of a novel.
When we want to choose a novel, it’s a common practice to read a synopsis of what it’s about. A short synopsis will give us just enough details to draw readers in and hopefully convince them to read the book! Here’s a brief synopsis from Cliff’s Notes of The Hunger Games :
In Suzanne Collins’ The Hunger Games, the Capitol forces each of Panem’s 12 districts to choose two teenagers to participate in the Hunger Games, a gruesome, televised fight to the death. In the 12th district, Katniss Everdeen steps in for her little sister and enters the Games, where she is torn between her feelings for her hunting partner, Gale Hawthorne, and the district’s other tribute, Peeta Mellark, even as she fights to stay alive. The Hunger Games will change Katniss’ life forever, but her acts of humanity and defiance might just change the Games, too.
Example 2: Synopsis of an Academic Paper
Sometimes, teachers, professors, publications, or editors want a synopsis of an academic paper, lecture, or article, which is more formally called an abstract (See Related Terms ). Like with a work of fiction, it gives a summary of the main points of the papers or article and provides a snapshot of what issues will be discussed. Synopses of these types of work are particularly important for scholars and anyone doing research, because when searching, they need to be able to know what an article is about and whether it is relevant to their work.
During his career, J.R.R. Tolkien gave a lecture on the classic Beowulf , which became one of the most respected and most-consulted academic sources on the poem to date. Here is a synopsis:
Before Tolkien, general scholarly opinion held…that while the poem might after all be unified, it was nevertheless unfortunate that the poet had chosen to tell stories about a hero, ogres, and a dragon, instead of detailing the wars in the North to which he often provocatively alludes. Tolkien’s lecture strongly and sometimes ironically defends the poet’s decision and the poem itself. The poet had every right to choose fantasy rather than history as his subject; in doing so he universalized his theme; his many allusions to events not recounted gave his work depth; most of all, the poem offered a kind of negotiation between the poet’s own firmly Christian world and the world of his pagan ancestors, on whom he looked back with admiration and pity.
This synopsis shares the main focus of Tolkien’s famous lecture and outlines its purpose for those who may be interested in it and can benefit from his research.
V. Examples of Synopses in Popular Culture
Example 1: synopsis of a tv series.
Giving the audience a written preview of a subject or storyline is a standard practice for TV producers. Before the series Gotham premiered, Warner Brothers released a detailed synopsis of exactly what the show would be about, which was particularly important because the audience would want to know how it would be placed amongst other Batman storylines. Here is a selection from its official synopsis:
Gotham is the origin story of the great DC Comics Super- Villains and vigilantes, revealing an entirely new chapter that has never been told. From executive producer/writer Bruno Heller (The Mentalist, Rome), this one-hour drama follows one cop’s rise through a dangerously corrupt city teetering on the edge of evil and chronicles the genesis of one of the most popular super heroes of our time. Brave, earnest and eager to prove himself, the newly minted detective Gordon (Ben McKenzie) is partnered with the brash, but shrewd police legend Harvey Bullock (Donal Logue), as the two stumble upon the city’s highest-profile case ever: the murder of local billionaires Thomas and Martha Wayne.
This is only one piece of the synopsis provided by Warner Brothers, but it’s a good sample of the bigger picture. It introduces the main theme and major characters, giving us a taste of what the series has in store.
Example 2: Synopsis of a Film
The job of a film synopsis is to build excitement and anticipation in the audience. Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them is a long-awaited addition to J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter universe and the release of this synopsis and trailer was big news in the world of popular culture. Here’s the synopsis:
Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them opens in 1926 as Newt Scamander has just completed a global excursion to find and document an extraordinary array of magical creatures. Arriving in New York for a brief stopover, he might have come and gone without incident…were it not for a No-Maj (American for Muggle) named Jacob, a misplaced magical case, and the escape of some of Newt’s fantastic beasts, which could spell trouble for both the wizarding and No-Maj worlds.
When a new film is announced, producers usually release a written synopsis like this, as well as an official trailer. Truly, a movie trailer is just a visual form of a synopses. But, a trailer builds even more anticipation in the audience than a written summary, because it gives a true peek at what will unfold on screen.
VI. Related Terms
An abstract is a brief summary of a scholarly work. It does the same things as a synopsis, but goes by a different term—“synopsis” is the preferred term for creative writing, films, and television, “while abstract” is the preferred term for formal or academic works. Overall, they have the same purpose.
An outline is shorter, less defined plan of what you’re going to include in a piece of writing. It’s usually written in the brainstorming phase, and just “outlines” general things that the work will include, and may change as you get farther in your work. An outline comes before a work is written, and a synopsis is written after a work is complete.
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, synopses are useful summaries that are written for the benefit of a potential reader or audience. It gives an overview and a “sneak peek” at a work, which lets them choose things that are interesting or useful to them personally and/or professionally.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.
Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.

Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
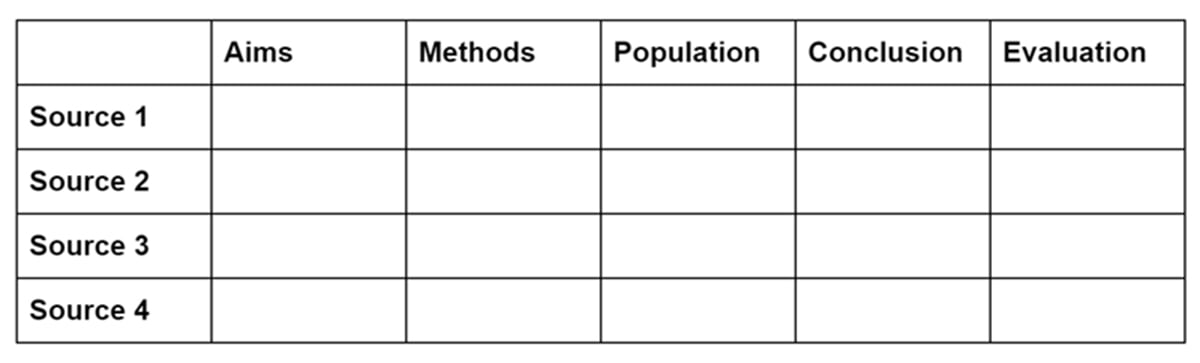
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.
Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
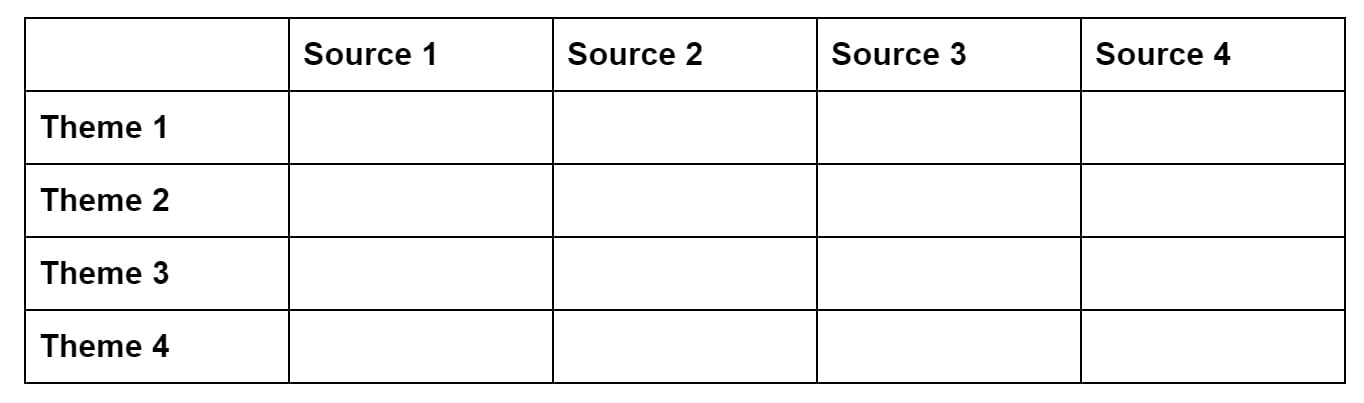
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
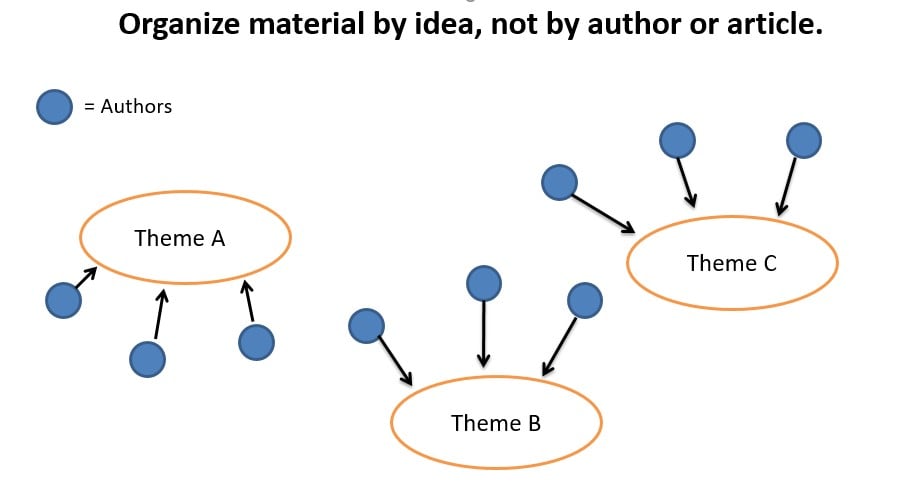
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay
Related Articles

Student Resources
How To Cite A YouTube Video In APA Style – With Examples

How to Write an Abstract APA Format

APA References Page Formatting and Example

APA Title Page (Cover Page) Format, Example, & Templates

How do I Cite a Source with Multiple Authors in APA Style?
How to Write a Psychology Essay
Looking to publish? Meet your dream editor, designer and marketer on Reedsy.
Find the perfect editor for your next book
1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Blog • Understanding Publishing
Posted on Sep 12, 2018
How to Write an Incredible Synopsis in 4 Simple Steps
Your novel is fully written, edited, and polished to perfection — you’re ready to pitch it to agents! But you’re missing a critical piece of persuasion: the synopsis. Even after putting together your entire book, you may have no idea how to write one, or even how to approach it.
Luckily, we’ve got answers for you. Read on for our best tips on writing a synopsis that’s clear, concise, captivating… and may even lead to an all-out agent battle over your novel!
What is a synopsis?
A synopsis is a summary of a book that familiarizes the reader with the plot and how it unfolds. Although these kinds of summaries also appear on the pages of school book reports and Wikipedia, this guide will focus on constructing one that you can send out to agents (and eventually publishers).
Your novel synopsis should achieve two things: firstly, it should convey the contents of your book, and secondly, it should be intriguing!
While you don’t need to pull out all the marketing stops at this stage, you should have a brief hook at the beginning and a sense of urgency underlying the text that will keep your reader going. It should make potential agents want to devour your whole manuscript — even though they’ll already know what happens.
While writing your synopsis, make sure that it includes:
- A complete narrative arc
- Your own voice and unique elements of your story
- The ending or resolution ( unlike in a blurb )
As for the ideal length for this piece, it varies from project to project. Some authors recommend keeping it to 500 words, while others might write thousands. However, the standard range is about one to two single-spaced pages (or two to five double-spaced pages). And if you're interested in knowing how to format the whole of your manuscript for submission, we recommend downloading this manuscript format template.

FREE RESOURCE
Manuscript Format Template
Get your manuscript ready for submission to agents and publishers.
You may also want to have an additional “brief” summary prepared for agents who specifically request a single page or less. Remember: as hard as it will be to distill all your hard work into that minimal space, it’s crucial to keep your synopsis digestible and agent-friendly.
How to write a novel synopsis in 4 steps

1. Get the basics down first
When it comes to writing a synopsis, substance is the name of the game. No matter how nicely you dress it up, an agent will disregard any piece that doesn’t demonstrate a fully fleshed out plot and strong narrative arc. So it stands to reason that as you begin writing, you should focus on the fundamentals.
Start with major plot points
Naturally, you want agents to be aware of your story's major plot points . So the best way to start summarizing your story is to create a list of those plot points, including:
- The inciting incident — what sparks the central conflict of your story?
- The events of the rising action — what happens in the interlude between the inciting incident and the climax, and how does this build tension?
- The height of the action, or climax , of your story — this one is the most important, as it should be the most exciting part of your book!
- The resolution or ending — again, unlike a blurb, a synopsis doesn’t need to dangle the carrot of an unknown ending to the reader; you can and should reveal your story’s ending here, as this brings the plot and narrative arc to a close.
Listing these points effectively maps out the action and arc of your story, which will enable the reader to easily follow it from beginning to end.
Include character motivations
The key here is not to get too deep into characterization, since you don’t have much room to elaborate. Instead, simply emphasize character motivations at the beginning and end of your synopsis — first as justification for the inciting incident, then again to bring home the resolution. For example:
Beginning: “Sally has spent the past twenty years wondering who her birth parents are [motivation]. When a mysterious man offers her the chance to find them, she spontaneously buys a ticket to Florence to begin her journey [inciting action].”
Ending: “She returns to the US with the man who was her father all along [resolution], safe in the knowledge that she’ll never have to wonder about him again [restated motivation].”
Also note how the text here is written in third person, present tense, as it should be regardless of the tense or POV of your actual book. Writing a synopsis in first or second person doesn’t really work because it’s not meant to be narrated — just summarized. Basically, the present tense works to engage the reader while the third person allows the story to be told smoothly.

Query Submissions Tracker
Stay organized on your journey to find the right agent or publisher.
2. Highlight what’s unique
Now it’s time to spice up your synopsis by highlighting the elements that make it unique. Agents need to know what’s so special about your book in particular — and moreover, is it special enough to get readers to pick it up? Below are some features you might employ to grab an agent’s attention and assure them of your book’s appeal.
Your writing voice is an essential tool here: it conveys your novel’s tone and is one of the most important factors in making your work stand out. However, it’s also one of the most difficult elements to evoke in such a small amount of space.
The best way to capture voice in a synopsis is through extremely deliberate word choice and sentence structure. So if you were Jane Austen, you’d use clever words to magnify your wit: “When Darcy proposes to her apropos of nothing, Elizabeth has the quite understandable reaction of rejecting him.” You may not be able to use all the elaborate prose of your novel, but your synopsis should still reflect its overall feeling.
Plot twists
Even though they’re one of the oldest tricks in the book, readers will never tire of juicy plot twists. If your novel contains one or more of these twists, especially at the climax, make sure your synopsis accentuates it. But don’t hint too much at the twist, as this will make it seem more dramatic when it comes; a couple of words in the intro will suffice as foreshadowing.
For instance, if you were writing a summary of Gone Girl , you might open with “Nick Dunne wakes up one morning to find that his wife, Amy, has apparently disappeared. ” This implies that she may not be as “gone” as we think she is, setting the stage for the later reveal.

Point of view
Another aspect that might set your book apart is a distinctive point of view . Since you’ll be giving your synopsis in third person, you can limit this inclusion to an introductory sentence: “This book is narrated from the point of view of a mouse.”
Although this strategy works best for books with a highly unusual point of view (such as The Book Thief by Markus Zusak, in which the story is told by Death), it can also be very helpful to remember for seemingly bog-standard narrators. If one of your characters narrates in first person, make sure to address their individual narrative quirks as well as any biases or limitations; highlighting an unreliable narrator can really add to your novel’s intrigue!
3. Edit for clarity and excess
Don’t shroud your synopsis in mystery; this is very frustrating to agents who just want to know what happens in your book! With that in mind, after you’ve written the bulk of your summary, it’s time to edit for clarity. You also may have to delete some text, so you can get it right in that couple-page sweet spot.
Editing for clarity
The paramount rule of synopses is a real doozy: tell, don’t show. It’s the opposite of that classic adage that writers have heard their whole lives, and it’s exactly what you need to write a successful synopsis.
As you return to what you’ve written, scan for sentences that are vague or unclear, especially toward the beginning. Many writers fall into the trap of trying to hook agents by opening with a sentence akin to the first murky line of a literary novel. Again, though you do want your intro to be intriguing, it has to cut to the chase pretty quickly.
When it comes to opening a synopsis, you need to think like Tolkien, not Tolstoy. “In a hole in the ground there lived a hobbit.” Crisp, clear, and to the point: one of the very few times you should tell, rather than show .
Editing excess words
If your synopsis is longer than a couple of pages at this point, you need make some serious cutbacks. Read through what you have, scrutinizing every sentence and word, even if you think you’ve chosen them carefully. Reduce any run-on sentences or subordinate clauses that unnecessarily lengthen your piece.
Finally, eliminate irrelevant details — anything that doesn’t lead to the next plot point or directly contribute to your voice or other distinctive elements. It’s unlikely you’ll have included any of these in the first place, but just in case they’ve slipped through, cut them. Save the frills for your book; remember, your synopsis is all about substance .
4. Make sure it flows
By the time it’s finished, your synopsis should read like a summary from an excellent book review — or at the very least SparkNotes or Shmoop. This means not only clearly and concisely hitting every important point, but also reading in a smooth manner, placing just the right amount of emphasis on the critical moments and unique aspects we’ve discussed.
Get test readers
A great way to ensure that your synopsis is paced precisely and flows well is to give it to test readers, either someone you know or a professional editor . You’ve spent way too much time with these words to be objective about them, so pay attention to what other people suggest: possible word substitutions, transitions, and which details to emphasize versus delete.
Use professional synopses as models
You don’t want to look at examples of other synopses too soon, otherwise yours will come out sounding formulaic and stale. That said, professional synopses can be a very valuable tool for refining toward the end of the process! Compare and contrast them to the synopsis you’ve written, and adapt any techniques or turns of phrase you feel would enhance it.
Here’s an example of a strong (albeit brief) synopsis of Great Expectations by Charles Dickens , courtesy of the Oxford Companion to English Literature:
Phillip Pirrip, more commonly known as “Pip,” has been brought up by his tyrannical sister, wife of the gentle Joe Gargery. He is introduced to the house of Miss Havisham who, half-crazed by the desertion of her lover on her bridal night, has brought up the girl Estella to use her beauty as a means of torturing men. Pip falls in love with Estella and aspires to become a gentleman.
Money and expectations of more wealth come to him from a mysterious source, which he believes to be Miss Havisham. He goes to London, and in his new mode of life meanly abandons the devoted Joe Gargery, a humble connection of whom he is now ashamed.
Misfortunes come upon him. His benefactor proves to be an escaped convict, Abel Magwich, whom he as a boy had helped. Pip’s great expectations fade away and he is penniless. Estella meanwhile marries his sulky enemy Bentley Drummle, by whom she is cruelly ill treated.
In the end, taught by adversity, Pip returns to Joe Gargery and honest labor. He and Estella, who has also learnt her lesson, are finally reunited.

This synopsis works well because it includes:
- The inciting incident (Pip moving in with Miss Havisham), the rising action (him being in London), the climax (returning to Joe Gargery), and the resolution (reuniting with Estella)
- Character motivations (Miss Havisham wants to punish all men because her fiancé betrayed her; Pip wants to become a gentleman so Estella will fall in love with him)
- A plot twist (Pip’s benefactor being a criminal — whom he knows from his childhood!)
- Distinctive voice (formal yet engaging, doesn’t detract from the plot) and smoothly written style (events are chronological and progress quickly)
Your synopsis is one of the biggest deciding factors in whether an agent wants to see more from you or not. No matter how chipper your query letter , the bottom line is that this summary tells agents (and later publishers) what they really need to know: what your book is about, what makes it unique, and most importantly, if they can sell it.

FREE COURSE
How to Write a Query Letter
Learn to grab agents’ attention with 10 five-minute lessons.
That’s why it’s vital that you make your synopsis airtight. Fortunately, if you’ve followed these steps, yours will be chock full of plot details with a touch of your own special writing sauce: a synopsis that any agent (hopefully) won’t be able to resist.
Many thanks to Reedsy editors (and former agents) Sam Brody and Rachel Stout for consulting on this piece!
Do you have any tips for writing an irresistible synopsis? Leave them in the comments below!
2 responses
Elizabeth Westra says:
12/09/2018 – 22:10
This looks interesting, and I will read every word, but this would be different for a picture book. You only get one page to query for many children's books.
Dorothy Potter Snyder says:
14/10/2018 – 20:11
I am curious if anyone has ideas on how translators can write a synopsis for agents / publishers of works in translation? Might there be something about why this author is important in his/her country of origin and literary tradition? Which authors more known to English language readers might relate to this author (they've never heard of before)?
Comments are currently closed.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

The 6 Best Ghostwriting Companies to Write Your Book
Learn which companies you can trust if you want to find a ghostwriter to write your next book.

How to Publish a Book For Free: The 7 Best Sites
If you want to publish your book without spending a single dime, check out this handy list of 7 free self-publishing services.

5 Ways to Save on Your Self-Publishing Budget
If you want to self-publish a book without breaking the bank, here are 5 tips to ensure you still get the best result possible.

30 Great Book Dedication Examples to Inspire Your Own
A list of 30 of the best book dedications in the business, that'll have you crying, laughing, and crying laughing.

Expository Writing: The Craft of Sharing Information
Expository writing is a fundamental part of how we learn and make sense of the world. Learn all about it in this post.

Additional Reviews: Query Critique December 2024
Additional critiques from Reedsy's December 2024 query letter session.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

Bring your publishing dreams to life
The world's best freelance editors, designers, and marketers are on Reedsy. Sign up for free and meet them TODAY.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
What Is a Synopsis? Definition & 15+ Examples
A synopsis, your literary passport, is the secret to whisking readers into the vibrant world you’ve crafted. As a condensed yet captivating summary, it teases the intriguing twists and turns of your story, inviting readers to embark on a journey filled with compelling characters, tantalizing plotlines, and unforgettable moments.
In the vast ocean of literature, a well-crafted synopsis is a beacon that guides readers to the shores of your imaginative landscape, promising an adventure they won’t want to miss.
So, make yourself comfortable and get ready to set sail on an enchanting literary voyage!
Table of Contents
Definition of Synopsis
A synopsis serves as a vital tool in the realm of storytelling, offering a condensed yet captivating glimpse into the heart of a work. This concise summary provides an overview of the main points , plot , or arguments , effectively piquing the curiosity of potential readers or viewers.
The power of a well-crafted synopsis lies in its ability to convey the essence of a story while preserving the allure of its hidden depths. Spanning various forms of writing — from novels to academic research — synopses bridge the gap between creators and their audience, acting as an enticing invitation to explore the full content.
Synopsis vs. Abstract
Although often used interchangeably, synopsis and abstract are distinct concepts with different purposes. A synopsis is a brief summary or condensed version of a piece of work, typically presenting the main points in a clear and concise manner. It is commonly used to outline a story , research paper , or report , providing potential readers with insight into the content.
An abstract , on the other hand, is a short and coherent overview of a research paper or scientific article, highlighting the objectives , methods , results , and conclusions . Abstracts help readers quickly determine whether the study is relevant to their interests and decide whether to read the entire paper.
Understanding the differences between a synopsis and an abstract is essential for effectively summarizing different forms of work and communicating their contents to appropriate audiences.
Purpose of Synopsis
A synopsis serves several vital functions in the writing process, regardless of whether the work is a novel , screenplay , or academic paper . Its primary objective is to convey the main points, key elements, or salient features of a written work in a clear, concise manner.
There are multiple reasons for creating a synopsis:
- Clarity and focus: A synopsis helps the writer to gain a clearer understanding of their story’s structure and main elements. This allows them to streamline the narrative, identify weaknesses, and sharpen their work’s focus.
- Assessment tool: For editors, agents, and publishers, a synopsis is a valuable tool to determine a work’s potential marketability and merit. A clear, engaging synopsis demonstrates the author’s storytelling abilities and allows the reader to quickly grasp the story’s key themes and plot points.
- Submission material: A well-written synopsis is often required when submitting a manuscript or screenplay to a publisher, agent, or film producer. As part of the submission package, the synopsis helps to pique the interest of the decision-maker, showcasing the story’s viability and the writer’s skill.
- Planning and organization: Writing a synopsis can facilitate the planning and organization of a written work, acting as a roadmap that helps guide the writer throughout the creative process. It can be particularly helpful for writers working on complex or intricate plots, assisting them in maintaining focus and preventing plot inconsistencies.
Elements of a Synopsis
A synopsis is a condensed summary of a work’s main points, plot, or argument. When writing one, it’s important to include several key elements in order to accurately convey the essence of the work.
The following are some essential components of a well-crafted synopsis:
- Characters: Introduce the main characters, including their names, roles, and key traits. This will provide context for the events and relationships described in the synopsis.
- Setting: Briefly describe the story’s setting, including the time period, location, and any relevant historical or cultural details. This helps to establish the overarching context of the work.
- Inciting incident: Identify the event or situation that serves as a catalyst for the story’s central conflict. This is often the moment when the protagonist is presented with a significant challenge or decision.
- Plot development: Summarize the main events and turning points in the story, giving special attention to any pivotal moments that drive the narrative forward. This may include conflicts, resolutions, and any character growth or development.
- Climax: Highlight the culmination of the story, where the central conflict reaches its peak, and the outcome becomes clear. This is typically the most intense and exciting part of the story.
- Resolution: Describe how the story concludes, including the outcomes for the main characters and any lasting implications or lessons. This offers a sense of closure for the reader.
When crafting a synopsis, it’s crucial to maintain a balance between providing enough detail for the reader to understand the work’s key elements without including unnecessary or overly descriptive information. A well-structured, concise synopsis serves as an invaluable tool for both authors and readers alike.
Characteristics of a Good Synopsis
Clarity and conciseness.
When writing a synopsis, it’s important to ensure that your language is clear and concise. This means using simple, easily understood words and phrases while avoiding jargon or overly complex sentence structures.
A synopsis should provide a summary of the work’s main ideas, themes, or events as efficiently as possible to keep the audience engaged.
For example:
- Use short sentences and simple words.
- Avoid ambiguous or vague phrases.
- Be specific about characters, events, and themes.
Focus and Main Themes
A quality synopsis should also focus on the central themes and main points of the work. This means highlighting the key aspects of the storyline, including major characters , conflicts , and turning points . Avoid getting bogged down in minor details that detract from the overall focus of the synopsis.
To maintain focus in your synopsis, consider the following:
- Summarize the work’s primary message or theme.
- Mention key characters and their roles.
- Identify crucial plot developments or conflicts.
Well-Organized Structure
Lastly, a successful synopsis should have a well-organized structure. This means arranging the information in a logical, easy-to-follow order that guides the reader through the critical points of the work. Use paragraphs to divide the synopsis into smaller segments, making it easier for your audience to read and understand.
Consider these tips when organizing your synopsis:
- Present information in chronological order, if applicable
- Group similar ideas together into paragraphs
- Use transitional phrases to connect ideas and maintain a smooth flow
Types of Synopsis
Academic synopsis.
An academic synopsis serves as a concise summary of a scholarly paper or published research. It outlines the objectives , methods , results , and conclusions of the study, providing readers with an overview of the content without delving into extensive detail.
This type of synopsis is crucial in helping other academics and researchers identify relevant literature for their studies.
Book Synopsis
A book synopsis highlights the main plot points , characters , and themes of a book. It is typically used by authors and publishers to market and promote the book to potential readers and appeal to literary agents or editors.
A well-written book synopsis should capture the tone , style , and essence of the book in a brief, compelling manner.
Film or Television Synopsis
Film or television synopses offer a brief overview of a movie or TV show’s plot , setting , and characters . They are often used for promotional purposes, appearing on official websites, DVD covers, or streaming platforms.
This type of synopsis should entice potential viewers by revealing enough information to spark interest without disclosing significant spoilers.
Play or Theater Synopsis
Similar to film and television synopses, a play or theater synopsis provides a succinct overview of a stage production’s story, main characters, and themes. It is used for marketing and promotion of the play or musical, often appearing in playbills, websites, and promotional materials.
An effective play or theater synopsis should engage potential audiences while remaining brief and informative.
Business Synopsis
A business synopsis offers a quick summary of a company’s goals, products or services, organizational structure, and financial performance. This type of synopsis is often found in annual reports, business plans, and investor presentations.
A well-written business synopsis can generate interest in the company and facilitate an understanding of its activities and objectives.
Scientific Synopsis
Scientific synopses typically accompany research articles or other scientific publications, serving as an abbreviated summary of the content. They convey the purpose , methodology , key findings , and implications of the research in a concise format.
This allows readers to quickly determine the relevance and significance of the study within their own fields of inquiry.
Examples of Synopsis
In literature, a synopsis is an essential tool for authors to pitch their stories to agents or publishers. They provide a clear and concise summary of the main events and characters in the story, giving readers the necessary information to understand the core elements.
Here are a few examples of synopses from different genres to help illustrate their structure and style:
- The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health Among Adolescents “This study investigates the relationship between social media usage and mental health in adolescents aged 13-18. Using a mixed-methods approach, including surveys and interviews, the research found that excessive social media use is correlated with increased levels of anxiety and depression in this age group. The findings suggest that implementing educational programs and setting guidelines for healthier social media habits could help mitigate these negative effects.”
- Exploring the Efficacy of Mindfulness-Based Interventions in Reducing Anxiety and Stress Among College Students “Our study examines the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions, such as meditation and yoga, in alleviating anxiety and stress among college students. Through a randomized controlled trial, we compare the outcomes of students participating in mindfulness programs to those in a control group. The results demonstrate that participants in the mindfulness interventions exhibit significantly lower levels of anxiety and stress, suggesting that such practices can be beneficial for the mental well-being of college students.”
- Urban Green Spaces and Public Health: An Analysis of Physical and Psychological Benefits in Major Cities “This interdisciplinary research explores the relationship between urban green spaces, such as parks and community gardens, and public health in major cities. By analyzing data from various sources, including epidemiological studies, surveys, and geographic information systems, we uncover a strong association between access to green spaces and improved physical and mental health outcomes. The findings highlight the importance of urban planning and investment in green spaces to promote healthier and more sustainable cities.”
- George Orwell’s 1984 : “In a dystopian future , the totalitarian regime of Oceania, led by the enigmatic Big Brother, controls every aspect of its citizens’ lives. Winston Smith, a low-ranking member of the ruling Party, becomes disillusioned with the oppressive regime and joins a forbidden love affair. As he secretly rebels against the system, Winston is drawn into a dangerous game of cat and mouse with the Thought Police.”
- Jane Austen’s Pride and Prejudice : “In early 19th-century England, the spirited Elizabeth Bennet navigates the complexities of love, family, and social expectations. When the wealthy and aloof Mr. Darcy enters her world, Elizabeth’s prejudices and Darcy’s pride must give way to mutual understanding as they discover the true nature of their feelings for one another.”
- F. Scott Fitzgerald’s The Great Gatsby : “Set in the Roaring Twenties, the story follows the mysterious Jay Gatsby as he pursues the elusive Daisy Buchanan, a woman from his past. Through the eyes of the narrator, Nick Carraway, we witness the opulence, decadence, and disillusionment of the Jazz Age, culminating in a tragic tale of love, wealth, and the American Dream.”
Film Synopsis
- The Godfather : “In this epic crime saga, the Corleone family, led by the powerful patriarch Vito Corleone, navigates the treacherous world of organized crime. When a rival gang threatens their empire, Vito’s youngest son Michael is reluctantly drawn into the family business, setting in motion a series of events that will test their loyalty, resolve, and capacity for violence.”
- The Shawshank Redemption : “Wrongly convicted for the murder of his wife, banker Andy Dufresne is sentenced to life in Shawshank State Penitentiary. Over the years, Andy forms an unlikely friendship with fellow inmate Red, using his intelligence and resourcefulness to transform the lives of those around him while secretly plotting his own escape.”
- Titanic : “In this tragic love story set against the backdrop of the ill-fated maiden voyage of the RMS Titanic, young aristocrat Rose and penniless artist Jack fall deeply in love despite the vast social divide between them. As the ship meets its doomed fate, the couple’s love is tested by disaster, fate, and the unrelenting forces of nature.”
Play Synopsis
- William Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet : “In the feuding city of Verona, young lovers Romeo and Juliet find themselves caught in a web of family strife and ancient grudges. Their desperate quest for happiness ultimately leads to a tragic climax, forcing the warring families to confront the senseless cycle of violence and revenge that has consumed them.”
- Arthur Miller’s Death of a Salesman : “Willy Loman, an aging salesman, struggles with the harsh reality of his failed dreams and the ever-changing world around him. As he clings to the American Dream, his relationships with his wife, Linda, and their two sons, Biff and Happy, unravel, revealing the painful truth about ambition, success, and the human condition.”
- Henrik Ibsen’s A Doll’s House : “In 19th-century Norway, Nora Helmer lives a seemingly idyllic life as a devoted wife and mother. When a secret from her past threatens to destroy her carefully constructed facade, Nora must confront societal expectations, gender roles, and her own awakening sense of self.”
- “Our company’s mission is to revolutionize the e-commerce industry by providing an innovative, user-friendly platform that connects buyers and sellers globally. Through advanced technology, seamless payment systems, and exceptional customer service, we aim to become the go-to online marketplace for a diverse range of products and services.”
- “This business plan outlines our strategy for launching a sustainable, eco-friendly clothing line that combines style, quality, and environmental responsibility. By using ethically sourced materials and partnering with fair trade suppliers, we aim to create a brand that resonates with environmentally conscious consumers and promotes a more sustainable fashion industry.”
- “Our startup aims to disrupt the food delivery market by offering a unique subscription service focused on providing healthy, gourmet meals prepared by local chefs. With a commitment to using fresh, locally-sourced ingredients and customizable meal options, we seek to revolutionize the way people experience home dining while supporting local businesses and promoting healthy lifestyles.”
- “In this groundbreaking study, we investigate the potential of CRISPR gene-editing technology to treat genetic disorders, focusing on the specific case of cystic fibrosis. Our research demonstrates the successful use of CRISPR in correcting the underlying genetic mutation, paving the way for future clinical trials and potential therapies.”
- “Our team explores the effects of climate change on polar ice caps, using satellite data and advanced modeling techniques to predict future sea level rise. Our findings highlight the urgent need for global action to mitigate the impacts of climate change on coastal communities and the world at large.”
- “This study examines the complex relationship between gut microbiota and human health, revealing how the balance of microorganisms in our digestive systems influences various aspects of our well-being, from immune function to mental health. Our research contributes to the growing body of knowledge in this field and underscores the importance of further exploration into the potential of probiotics and other targeted interventions.”
Importance of Synopsis
A synopsis serves as an essential tool for various individuals involved in the creative process.
To better understand its significance, consider the roles it plays in different contexts:
- For authors: A well-written synopsis can help authors showcase the key elements of their story in a concise and compelling manner. It allows them to demonstrate the structure, plot, and character development without sharing the entire work.
- For agents and publishers: A synopsis makes it easier for agents and publishers to evaluate a manuscript’s potential. By summarizing the story, they can quickly decide if it aligns with their market or genre preferences, saving time and effort.
- For readers: Synopses aid readers in selecting books that align with their interests. By providing a snapshot of the story, readers can make informed decisions without relying solely on cover art or book blurbs.
- For screenwriters and filmmakers: In the world of cinema, a synopsis is often the first step in pitching a story to producers or directors. It enables them to decide if the plot engages their attention and if it has the potential to be translated well to the screen.
Additionally, crafting a synopsis challenges creators to think critically about their work — practicing brevity , clarity , and refinement in storytelling. It encourages them to distill complex ideas into concise, engaging summaries, a vital skill in today’s information-driven society.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a compelling synopsis.
To write a compelling synopsis, start by identifying the most crucial elements of your work , such as the main characters , central conflicts , key events , or overarching themes . Focus on conveying these aspects in a clear, concise manner while avoiding excessive detail or spoilers.
Use engaging language and a narrative style that captures the tone and atmosphere of your work, drawing the reader or viewer into the world you’ve created.
Organize the information in a logical order , ensuring that the synopsis flows smoothly and coherently. Remember to tailor the content to your target audience, adapting the tone, style, and level of detail to suit their needs and expectations.
Lastly, infuse your synopsis with a sense of intrigue and curiosity that leaves the audience eager to explore the full content, creating a tantalizing invitation that they can’t resist.
What are the common mistakes to avoid in writing a synopsis?
When writing a synopsis, there are several common mistakes to avoid in order to create an engaging and effective summary.
One mistake is providing too much detail or revealing major spoilers, which can rob the reader or viewer of the excitement of discovering the twists and turns themselves.
Another pitfall is being overly vague or generic , which can make it difficult for the audience to grasp the essence of the work or understand what makes it unique.
Additionally, neglecting to mention key characters, main points, or central conflicts can leave the audience with an incomplete understanding of the material.
Finally, failing to tailor the tone and style to suit the intended audience may result in a synopsis that feels disconnected from their needs and expectations.
How long should a synopsis be?
The ideal length of a synopsis depends on the work being summarized and the context in which it will be used. Generally, a synopsis should be concise and focused, providing a clear overview of the material without delving into excessive detail.
For novels and plays, synopses typically span a few paragraphs, giving enough information to pique the interest of agents, publishers, or potential readers.
In the case of academic articles or research papers, synopses — often called abstracts — usually range between 150 to 300 words, adhering to guidelines set by the journal or field of study.
Ultimately, the goal is to craft a synopsis that effectively conveys the essence of the work in a succinct and engaging manner tailored to the intended audience and purpose.
In summary, a synopsis is a concise, simplified description of a piece of work, whether it’s a novel, film, or research study. They are beneficial for various purposes, such as helping readers decide if a work is worth their time and attention or providing a quick understanding of the key points.
Examples of synopses include book summaries, movie plot summaries, and abstracts for scholarly articles. When writing a synopsis, remember to focus on the main ideas and events while avoiding excessive detail or opinion. It is essential to maintain a neutral tone and convey accurate information regarding the work being summarized.
Utilizing various formatting tools, such as bullet points or tables, adds clarity and structure to the synopsis, enhancing its readability and effectiveness. By following these guidelines, one can successfully provide a useful, informative synopsis that serves its intended purpose.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
As you found this post useful...
Share it on social media!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?

Aerielle Ezra

Report Writing Guide
Report generator.

How is writing a report any different from writing an essay ?
- Article Writing Examples & Samples
- Memo Writing Examples & Samples
Unlike an ordinary essay, reports are lengthy and concise in form. They follow a formal structure and are used to convey the results or findings of a given study. Knowing how to write a report is essential in communication. You want to make sure that its target readers clearly understand the message being delivered. These types of documents are usually assessed based on its content, structure, format or layout, language, and referencing. Because of this, a writer must focus on the main purpose of the report, and how they may communicate in such a way that will cater its audience. You may also see writing templates & examples .
Although there are many ways to write a report, here are some basic steps to guide you through:
1. Determine What the Report Is about.
Understanding the subject of your report is the first and the most important step of the process. You need to determine what the assignment is asking from you, and what purpose does it serve. You may also see free writing examples .
In order to discover what the report is about, begin by reading the instructions or information given regarding the report, and proceed by asking yourself the following questions:
- What should the report be about? Identify what the main topic of the report is, and what must be tackled in its content. You may also like book writing examples & samples .
- What is needed? Determine what resources are needed, such as surveys or questionnaires, to complete the report.
- When is it due? Since most reports are academic-related, they often have a specific due date that will help you come up with a timeline for the research process. You may also check out script writing examples & samples .
- Who is its target audience or proponents? When it comes to report writing, you need to keep your audience in mind. This may consist of the general public, a customer or client, or of any specific demographic.
Once you have found the answers to these points, you can then identify the scope and limitations of the assignment.
2. Do Your Research.
The next step is to find the information needed to create the report. However, this would greatly depend on the type of report being written as well. You might be interested in tips for writing an effective essay .

For instance, a journalistic report would require facts about a given topic. This may involve gaining personal testimonies from significant individuals, observing certain people, activities, or events, or reading a published material. Ensure that the information gathered is relevant, appropriate, and reliable. What you have collected from this step will serve as a basis for the body of the report, along with its findings.
3. Decide on a Structure.
Reports generally follow a similar structure. A case study report , a status report , and an incident report all share a common purpose, yet they may slightly differ in terms of their length and tone.
Depending on the type of report being created, the standard structure of a report consists of the following parts:
- Summary or Abstract
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Terms of reference (Scope & Limitations)
- Conclusions
- Recommendations
- References or Bibliography
Each section of a report may also be composed of headings and subheadings that are used to break down complex ideas into specific details. You may also see what do you mean by writing skills?
4. Create a Draft.
By now, you should be able to draft the content of your report. Keep in mind that report writing involves a thorough process of learning, formal writing , and analyzing concepts and theories from the available references. With the information garnered from your sources, you can then proceed to the findings of your report.
The findings are typically the results drawn from your readings, experiments, observations, and interviews. Your research activity, which is found in the procedures or methodology section of the document, must be indicated to prove your findings are reliable. It’s also necessary to provide accurate descriptions of how the process was conducted and what materials were used. Depending on the type of report written, the findings may include photos, graphs, tables, or any visual representation that can help support your claims. You may also like essay writing examples & samples .
Any additional details that may complement information stated in the report — like spreadsheets, forms, and brochures — may be included in the appendices.
5. Analyze Your Findings and Form Conclusions.
This is the part where you need to examine what you have gathered, and interpret what you have found to draw conclusions. This may explain why a certain situation occurred, what this means for an entity, and what is likely to happen if this event continues (or discontinues). Remember, the conclusion shouldn’t serve as a mere summary rather, a collection of facts that explain the significant details of your findings and what it suggests. You wouldn’t need to provide an explanation for your results unless a discussion is asked from you. You may also see informative writing examples & samples .
6. Provide Recommendations.
Recommendations typically imply what the researchers think should happen next. This involves the succeeding actions that its readers, specifically those who asked for the report, should do or not do. For instance, students who write school reports often target the academe and its members. So as part of their recommendation, the authors would direct future researchers to enhance certain areas of the report that have not been thoroughly addressed. It’s important to include enough details for the readers to be guided in terms of what must be done and who should do it.
7. Formulate a Summary and Table of Contents.
For reports that do require an executive summary , remember to do this by the very end of the report writing. This must be kept brief and to-the-point, where a maximum of 100 words would be enough to carry out your message. It should provide readers with a gist of what the report is about, as well as a summary of the recommendations.
Once you have finalized each section of the report, you can then create a list of its contents. This should be arranged according to how the report is structured. You may also indicate the page number of each section to make it easier for readers to find what they’re looking for.
8. Compile Your References.
At the beginning of the report writing process, you may have collected information from a number of print and online sources to support your study. These references must be compiled and arranged by following the standard APA format once you have already completed your findings. Insert this section at the back portion of your report, or as indicated in the instructions given. Take note that this reference list may also serve as a basis for readers to determine the credibility of the said report. You may also see what is writing used for?
Before printing or submitting the report, it’s always advisable to proofread and recheck the document for any gaps. Make sure you have accomplished everything that needed to be done by reviewing the instructions and guidelines of the assignment, along with the proposed marking schedule. Terms, symbols, abbreviations, and illustrations used in the report must also be explained. Besides that, ensure that the format, numbering, headings, spelling, and grammar of your report are consistent and correct to avoid any problems. You may also like essay writing examples .

If you have enough time to spare, you may even prepare several drafts to review before finalizing your report. You can also have a friend or adviser check your report for assurance. When finished, remember to study the report, as you may be asked to present it in front of an audience. You may also check out summary writing examples and samples .
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a report on the impact of technology in the classroom on student learning outcomes
Prepare a report analyzing the trends in student participation in sports and arts programs over the last five years at your school.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Present a detailed research synopsis with these tips A research synopsis describes the plan for your research project and is typically submitted to professors or department heads so they can approve your project. Most synopses are between...
PDF | Guidelines I have written for students following my course on research planning at the University of Copenhagen, Useful for starting researchers | Find, read and cite all the research you ...
A synopsis is a structured outline of a research thesis and the steps followed to answer the research question. The goal of writing a synopsis is to clearly and thoroughly explain the need to investigate a certain problem using particular practical methods to conduct the study. One of the main components of this written work is an extensive literature review containing strong evidence that the ...
A research summary is a brief and concise overview of a research project or study that highlights its key findings, main points, and conclusions. It typically includes a description of the research problem, the research methods used, the results obtained, and the implications or significance of the findings.
This document provides guidelines for preparing a research synopsis (and indirectly of the final report of your work that will be presented at the end of your research program). The research synopsis is the plan for your research project. It provides the rationale for the research, the research objectives, the proposed methods for data collection and recording formats and/or questionnaires and ...
Writing a research project synopsis or protocol is a crucial step in initiating any research endeavor. It serves as a blueprint that outlines the objectives, methods and anticipated outcomes of ...
A well curated research summary represents you and your skills as knowledgeable about the information written in the research paper. To generate a concise, accurate, and a good research summary, you must stay attentive to the goals and purpose of a research summary.
A synopsis is a brief summary which gives readers an overview of the main points. In an academic context, this is usually a summary of a text (a journal article, book, report etc) but in some instances you might be writing a synopsis of a talk, film or other form of presentation. A synopsis is a neutral summary, objectively capturing the main ...
Synopsis is one of the first important research document you write for your PhD. A great synopsis is the one that delivers maximum information in minimum words.
The synopsis for a thesis is basically the plan for a research project, typically done when pursuing a doctorate. It outlines the focus areas and key components of the research in order to obtain approval for the research. Here is a listing of the sections that typically are a part of the synopsis. Do check with your guide/supervisor for those ...
Synopsis is a short summary of your Ph.D thesis work. This paper suggests some ideas to motivate the young researchers for effectively writing the Ph.D synopsis with essential tips and tricks.This can act as a reference and help young researcher to going to write Ph.D synopsis.
Learn how to write a summary of a source in five easy steps, with examples and tips to help you avoid plagiarism and improve your writing skills.
Learn how to write a research summary, including the structure and steps involved. Find useful writing tips and examples.
The research synopsis is the plan for your research project. It provides the rationale for the research, the research objectives, the proposed methods for data collection and recording formats and/or questionnaires and interview guides.
A synopsis example can make it easier to understand how to summarize a larger piece of work. Luckily, you can find several tailored examples with our list.
Clear definition and great examples of Synopsis. This article will show you the importance of Synopsis and how to use it. A synopsis is a brief summary that gives audiences an idea of what a composition is about.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly knowledge on a topic. Our guide with examples, video, and templates can help you write yours.
PDF | On Jan 27, 2021, Dr NIRAJ Kumar and others published How to Make the Research Synopsis as Ph.D. and PG. level | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you've read - you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Learn how to write a synopsis that could decide the fate of your book. In 4 steps, you'll know what makes a great synopsis and how to craft one yourself.
Synthesizing sources involves combining the work of other scholars to provide new insights. It's a way of integrating sources that helps situate your work in relation to existing research.
A synopsis is a brief summary or condensed version of a piece of work, typically presenting the main points in a clear and concise manner. It is commonly used to outline a story, research paper, or report, providing potential readers with insight into the content. An abstract, on the other hand, is a short and coherent overview of a research ...
Having trouble writing your report?Enhance your report writing skills with these simple steps.
Additionally, some scholars have investigated tourism-oriented vernacular landscape design, capitalizing on the burgeoning rural tourism industry (Mao 2021 ). In summary, research on vernacular landscapes covers a range of topics, mainly on issues about historical culture, heritage preservation, ecology, and tourism.