Romeo And Juliet Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on romeo and juliet.
Romeo and Juliet is the most famous love tragedy written by William Shakespeare. This is a story of love and fate. Furthermore, the basis of this tragic love story is the Old Italian tale translated into English in the sixteenth century. The story is about two young star-crossed lovers whose death results in reconcile between their feuding families. Moreover, Romeo and Juliet is among the most frequently performed plays by Shakespeare .


Lessons of Love from Romeo and Juliet
First of all, Romeo and Juliet teach us that love is blind. Romeo and Juliet belonged to two influential families. Furthermore, these two families were engaged in a big feud among themselves. However, against all odds, Romeo and Juliet find each other and fall in love. Most noteworthy, they are blind to the fact that they are from rival families. They strive to be together in spite of the threat of hate between their families.
Another important lesson is that love brings out the best in us. Most noteworthy, Romeo and Juliet were very different characters by the end of the story than in the beginning. Romeo was suffering from depression before he met Juliet. Furthermore, Juliet was an innocent timid girl. Juliet was forced into marriage against her will by her parents. After falling in love, the personalities of these characters changed in positive ways. Romeo becomes a deeply passionate lover and Juliet becomes a confident woman.
Life without love is certainly not worth living. Later in the story, Romeo learns that his beloved Juliet is dead. At this moment Romeo felt a heart-shattering moment. Romeo then gets extremely sad and drinks poison. However, Juliet was alive and wakes up to see Romeo dead. Juliet then immediately decides to kill herself due to this massive heartbreak. Hence, both lovers believed that life without love is not worth living.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Legacy of Romeo and Juliet
Romeo and Juliet is one of Shakespeare’s most popular plays. Furthermore, the play was very popular even in Shakespeare’s lifetime. Scholar Gary Taylor believes it as the sixth most popular of Shakespeare’s plays. Moreover, Sir William Davenant of the Duke’s Company staged Romeo and Juliet in 1662. The earliest production of Romeo and Juliet was in North America on 23 March 1730.
There were professional performances of Romeo and Juliet in the mid-19th century. In 19th century America, probably the most elaborate productions of Romeo and Juliet took place. The first professional performance of the play in Japan seems to be George Crichton Miln’s company’s production in 1890. In the 20th century, Romeo and Juliet became the second most popular play behind Hamlet.
There have been at least 24 operas based on Romeo and Juliet. The best-known ballet version of this play is Prokofiev’s Romeo and Juliet. Most noteworthy, Romeo and Juliet have a huge impact on literature. Romeo and Juliet made romance as a worthy topic for tragedy. Before Romeo and Juliet, romantic tragedy was certainly unthinkable.
Romeo and Juliet are probably the most popular romantic fictional characters. They have been an inspiration for lovers around the world for centuries. Most noteworthy, the story depicts the struggle of the couple against a patriarchal society. People will always consider Romeo and Juliet as archetypal young lovers.
Q1 State any one lesson of love from Romeo and Juliet?
A1 One lesson of love from Romeo and Juliet is that love brings out the best in us.
Q2 What makes Romeo and Juliet unique in literature?
A2 Romeo and Juliet made romance as a worthy topic for tragedy. This is what makes it unique.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


A Summary and Analysis of William Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet
By Dr Oliver Tearle (Loughborough University)
Although it was first performed in the 1590s, the first documented performance of Romeo and Juliet is from 1662. The diarist Samuel Pepys was in the audience, and recorded that he ‘saw “Romeo and Juliet,” the first time it was ever acted; but it is a play of itself the worst that ever I heard in my life, and the worst acted that ever I saw these people do.’
Despite Pepys’ dislike, the play is one of Shakespeare’s best-loved and most famous, and the story of Romeo and Juliet is well known. However, the play has become so embedded in the popular psyche that Shakespeare’s considerably more complex play has been reduced to a few key aspects: ‘star-cross’d lovers’, a teenage love story, and the suicide of the two protagonists.
In the summary and analysis that follow, we realise that Romeo and Juliet is much more than a tragic love story.
Romeo and Juliet : brief summary
After the Prologue has set the scene – we have two feuding households, Montagues and Capulets, in the city-state of Verona; and young Romeo is a Montague while Juliet, with whom Romeo is destined to fall in love, is from the Capulet family, sworn enemies of the Montagues – the play proper begins with servants of the two feuding households taunting each other in the street.
When Benvolio, a member of house Montague, arrives and clashes with Tybalt of house Capulet, a scuffle breaks out, and it is only when Capulet himself and his wife, Lady Capulet, appear that the fighting stops. Old Montague and his wife then show up, and the Prince of Verona, Escalus, arrives and chastises the people for fighting. Everyone leaves except Old Montague, his wife, and Benvolio, Montague’s nephew. Benvolio tells them that Romeo has locked himself away, but he doesn’t know why.
Romeo appears and Benvolio asks his cousin what is wrong, and Romeo starts speaking in paradoxes, a sure sign that he’s in love. He claims he loves Rosaline, but will not return any man’s love. A servant appears with a note, and Romeo and Benvolio learn that the Capulets are holding a masked ball.
Benvolio tells Romeo he should attend, even though he is a Montague, as he will find more beautiful women than Rosaline to fall in love with. Meanwhile, Lady Capulet asks her daughter Juliet whether she has given any thought to marriage, and tells Juliet that a man named Paris would make an excellent husband for her.
Romeo attends the Capulets’ masked ball, with his friend Mercutio. Mercutio tells Romeo about a fairy named Queen Mab who enters young men’s minds as they dream, and makes them dream of love and romance. At the masked ball, Romeo spies Juliet and instantly falls in love with her; she also falls for him.
They kiss, but then Tybalt, Juliet’s kinsman, spots Romeo and recognising him as a Montague, plans to confront him. Old Capulet tells him not to do so, and Tybalt reluctantly agrees. When Juliet enquires after who Romeo is, she is distraught to learn that he is a Montague and thus a member of the family that is her family’s sworn enemies.
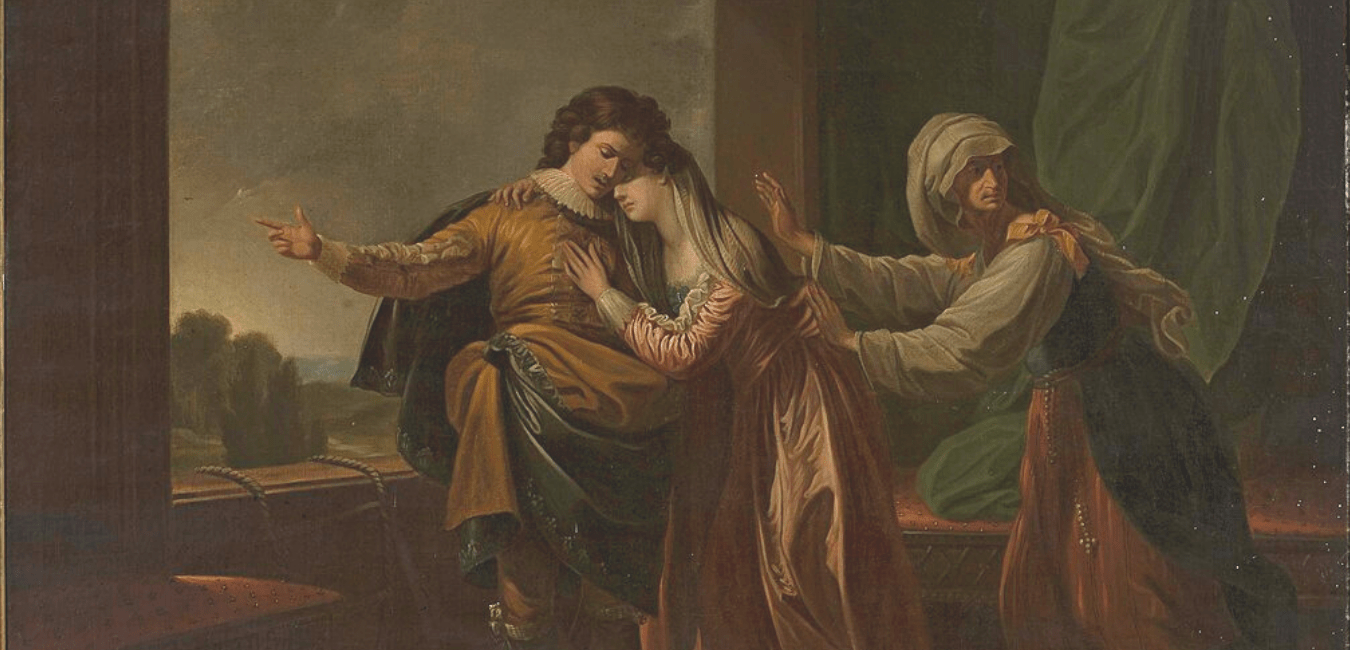
Romeo breaks into the gardens of Juliet’s parents’ house and speaks to her at her bedroom window. The two of them pledge their love for each other, and arrange to be secretly married the following night. Romeo goes to see a churchman, Friar Laurence, who agrees to marry Romeo and Juliet.
After the wedding, the feud between the two families becomes violent again: Tybalt kills Mercutio in a fight, and Romeo kills Tybalt in retaliation. The Prince banishes Romeo from Verona for his crime.
Juliet is told by her father that she will marry Paris, so Juliet goes to seek Friar Laurence’s help in getting out of it. He tells her to take a sleeping potion which will make her appear to be dead for two nights; she will be laid to rest in the family vault, and Romeo (who will be informed of the plan) can secretly come to her there.
However, although that part of the plan goes fine, the message to Romeo doesn’t arrive; instead, he hears that Juliet has actually died. He secretly visits her at the family vault, but his grieving is interrupted by the arrival of Paris, who is there to lay flowers. The two of them fight, and Romeo kills him.
Convinced that Juliet is really dead, Romeo drinks poison in order to join Juliet in death. Juliet wakes from her slumber induced by the sleeping draught to find Romeo dead at her side. She stabs herself.
The play ends with Friar Laurence telling the story to the two feuding families. The Prince tells them to put their rivalry behind them and live in peace.
Romeo and Juliet : analysis
How should we analyse Romeo and Juliet , one of Shakespeare’s most famous and frequently studied, performed, and adapted plays? Is Romeo and Juliet the great love story that it’s often interpreted as, and what does it say about the play – if it is a celebration of young love – that it ends with the deaths of both romantic leads?
It’s worth bearing in mind that Romeo and Juliet do not kill themselves specifically because they are forbidden to be together, but rather because a chain of events (of which their families’ ongoing feud with each other is but one) and a message that never arrives lead to a misunderstanding which results in their suicides.
Romeo and Juliet is often read as both a tragedy and a great celebration of romantic love, but it clearly throws out some difficult questions about the nature of love, questions which are rendered even more pressing when we consider the headlong nature of the play’s action and the fact that Romeo and Juliet meet, marry, and die all within the space of a few days.
Below, we offer some notes towards an analysis of this classic Shakespeare play and explore some of the play’s most salient themes.
It’s worth starting with a consideration of just what Shakespeare did with his source material. Interestingly, two families known as the Montagues and Capulets appear to have actually existed in medieval Italy: the first reference to ‘Montagues and Capulets’ is, curiously, in the poetry of Dante (1265-1321), not Shakespeare.
In Dante’s early fourteenth-century epic poem, the Divine Comedy , he makes reference to two warring Italian families: ‘Come and see, you who are negligent, / Montagues and Capulets, Monaldi and Filippeschi / One lot already grieving, the other in fear’ ( Purgatorio , canto VI). Precisely why the families are in a feud with one another is never revealed in Shakespeare’s play, so we are encouraged to take this at face value.
The play’s most famous line references the feud between the two families, which means Romeo and Juliet cannot be together. And the line, when we stop and consider it, is more than a little baffling. The line is spoken by Juliet: ‘Romeo, Romeo, wherefore art thou Romeo?’ Of course, ‘wherefore’ doesn’t mean ‘where’ – it means ‘why’.
But that doesn’t exactly clear up the whys and the wherefores. The question still doesn’t appear to make any sense: Romeo’s problem isn’t his first name, but his family name, Montague. Surely, since she fancies him, Juliet is quite pleased with ‘Romeo’ as he is – it’s his family that are the problem. Solutions have been proposed to this conundrum , but none is completely satisfying.
There are a number of notable things Shakespeare did with his source material. The Italian story ‘Mariotto and Gianozza’, printed in 1476, contained many of the plot elements of Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet . Shakespeare’s source for the play’s story was Arthur Brooke’s The Tragical History of Romeus and Juliet (1562), an English verse translation of this Italian tale.
The moral of Brooke’s tale is that young love ends in disaster for their elders, and is best reined in; Shakespeare changed that. In Romeo and Juliet , the headlong passion and excitement of young love is celebrated, even though confusion leads to the deaths of the young lovers. But through their deaths, and the example their love set for their parents, the two families vow to be reconciled to each other.
Shakespeare also makes Juliet a thirteen-year-old girl in his play, which is odd for a number of reasons. We know that Romeo and Juliet is about young love – the ‘pair of star-cross’d lovers’, who belong to rival families in Verona – but what is odd about Shakespeare’s play is how young he makes Juliet.
In Brooke’s verse rendition of the story, Juliet is sixteen. But when Shakespeare dramatised the story, he made Juliet several years younger, with Romeo’s age unspecified. As Lady Capulet reveals, Juliet is ‘not [yet] fourteen’, and this point is made to us several times, as if Shakespeare wishes to draw attention to it and make sure we don’t forget it.
This makes sense in so far as Juliet represents young love, but what makes it unsettling – particularly for modern audiences – is the fact that this makes Juliet a girl of thirteen when she enjoys her night of wedded bliss with Romeo. As John Sutherland puts it in his (and Cedric Watts’) engaging Oxford World’s Classics: Henry V, War Criminal?: and Other Shakespeare Puzzles , ‘In a contemporary court of law [Romeo] would receive a longer sentence for what he does to Juliet than for what he does to Tybalt.’
There appears to be no satisfactory answer to this question, but one possible explanation lies in one of the play’s recurring themes: bawdiness and sexual familiarity. Perhaps surprisingly given the youthfulness of its tragic heroine, Romeo and Juliet is shot through with bawdy jokes, double entendres, and allusions to sex, made by a number of the characters.
These references to physical love serve to make Juliet’s innocence, and subsequent passionate romance with Romeo, even more noticeable: the journey both Romeo and Juliet undertake is one from innocence (Romeo pointlessly and naively pursuing Rosaline; Juliet unversed in the ways of love) to experience.
In the last analysis, Romeo and Juliet is a classic depiction of forbidden love, but it is also far more sexually aware, more ‘adult’, than many people realise.
Discover more from Interesting Literature
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Type your email…
4 thoughts on “A Summary and Analysis of William Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet”
Modern reading of the play’s opening dialogue among the brawlers fails to parse the ribaldry. Sex scares the bejeepers out of us. Why? Confer “R&J.”
It’s all that damn padre’s fault!
- Pingback: A Summary and Analysis of William Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet
- Pingback: A Short Analysis of the ‘Two Households’ Prologue to Romeo and Juliet – Interesting Literature
Comments are closed.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

The Definitive Guide to Analysing Shakespeare’s ‘Romeo and Juliet’: Summary, Context, Themes & Characters

Thinking to yourself, “Notes, o notes, wherefore art my notes?” Well, if you’re struggling with your analysis of Romeo and Juliet for English, we’ve got your back with a summary featuring the key characters, context and themes!
On top of that, we’ve got a free example of an analysis table (also known as a TEE table ) and a sample paragraph on Romeo and Juliet for you to download!
So, let’s dive into our analysis of Romeo and Juliet!
Romeo and Juliet Summary Key Characters in Romeo and Juliet Context Themes Explored in Romeo and Juliet Analysis of Romeo and Juliet
Summary of Romeo and Juliet
Romeo and Juliet is a tragic love story by Shakespeare about two lovers who are not meant to be together as they come from feuding families.
To summarise it, Romeo of the Montagues and Juliet of the Capulets were born to be sworn enemies due to the life long conflict between their families. Yet, they embarked in a forbidden love together that led to their deaths, which finally reconciles the two families.
The play is set out in five acts and we’ll dive into more detail on what happens during each of the acts.
Access the Romeo and Juliet Downloadable Sample Paragraph and Examples of Analysis PDF here!
Act I of the play starts with a Chorus who introduces two powerful families in the City of Verona, Italy. These are the Montagues and Capulets, who have been on bad terms with one another for a long time.
The Capulets are holding a party for their daughter, Juliet, to meet Count Paris for an arranged marriage. Meanwhile, Romeo, the son of Montague, disguises himself and crashes the party with his friends in hopes of seeing Rosaline, his previous lover.
Instead, Romeo falls in love at first sight when he meets Juliet and the two become very attracted to each other.
However, Romeo and Juliet soon discover that they come from opposing families and realise their doomed love . At the same time, Tybalt who is Juliet’s cousin, recognises Romeo and drives Romeo and his friends out from the Capulet house.
In Act II, as Romeo’s friends were leaving the Capulet place, Romeo stays behind to find Juliet. Romeo sees Juliet in her window, and they confess their love for one another and agree to marry the next day .
Romeo runs to Friar Laurence, who agrees to help as he believes Romeo and Juliet’s marriage will end the feud between the Montagues and Capulets. With the help of Juliet’s nurse and Friar Laurence, Romeo and Juliet marry in secret.

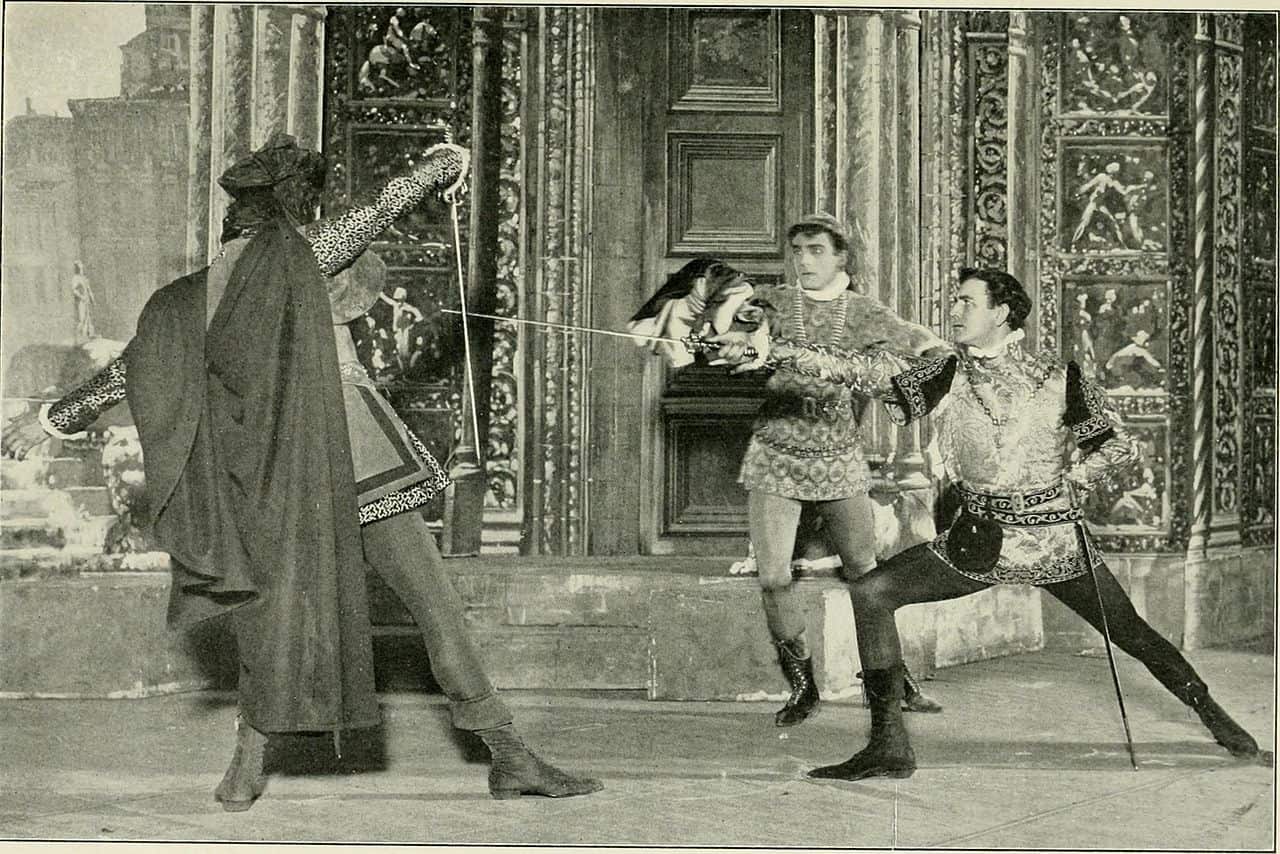
In Act III, Tybalt challenges Romeo to a fight. Romeo declines the fight and remains calm while being disrespected by Tybalt. This angers Romeo’s friend, Mercutio who starts a fight with Tybalt.
Romeo tries to stop the fight, but Mercutio is accidentally killed . Enraged, Romeo chases Tybalt down and kills him.
The Prince of Verona banishes Romeo for his crimes. Before Romeo leaves for Mantua, Friar Laurence helps Romeo and Juliet stay the night together.
Meanwhile, Lord Capulet arranges for Paris and Juliet to wed the next day. Juliet is upset because she does not want to marry Paris, and this angers her parents as they do not know about Juliet’s secret affair with Romeo.

In Act IV, Juliet asks Friar Lawrence for help and he gives her a sleeping potion that will make her appear dead . The next morning, the Capulet family finds Juliet in her bed and believes that she had died.
Friar Laurence sends a messenger to inform Romeo about Juliet’s plan and instructs Romeo to collect a sleeping Juliet from the Capulet house.
Act V is the most intense part of the story as the very important message did not reach Romeo in time due to the plague that delayed the messenger’s journey.
Instead, Romeo hears the news of Juliet’s death and buys himself poison. Romeo goes to Juliet’s tomb in the Capulet’s house, kills a grieving Paris, drinks the poison and dies before Juliet wakes up.
Friar Laurence enters but is too late. He tells Juliet what had happened and Juliet stabs herself from heartbreak.
Friar Laurence, the Prince, the Capulets and the Montague father come together and agree to make peace following the children’s death.
Romeo and Juliet Characters
In case you’ve missed anything, here is a list of the key characters in Romeo and Juliet who are pivotal to the plot.
Romeo Montague Romeo is the handsome son of the head of Montagues and is 16 years old. He is sensitive, though he can become quite impulsive when his emotions get the better of him. Unlike his friends, Romeo is not interested in violence but passionate about love. At the beginning of the play, Romeo was madly in love with Rosaline before falling in love with Juliet. Furthermore, Romeo shares his love for his own friends and family too, including Mercutio and Friar Laurence.
Juliet Capulet Juliet is the beautiful 13 year old daughter of the Capulet family. Juliet starts off as a naive girl who knows little about love but soon gains the courage to go against her father’s wishes to marry Romeo in secret instead of marrying Paris like her father wanted. She’s loyal and trusts Romeo wholeheartedly, choosing to support Romeo despite him killing off her cousin, Tybalt.
Friar Laurence Friar Laurence is a Franciscan friar who helps Romeo and Juliet. He is a nice man who is also skilled in herbs and potion making. He always has a plan to help Romeo and Juliet in hopes that their relationship will calm the tension between two families and bring peace.
Mercutio Mercutio is Romeo’s best friend and he is quite the character. He is loud, opinionated, and charismatic with a bombastic attitude that’s flowing in wit and sarcasm. He also has quite a hot temper. Unlike Romeo, Mercutio is highly hedonistic as he tries to convince Romeo to see love as a sexual pursuit.
Tybalt Tybalt is Juliet’s cousin from her mother’s side. He is often protective over his family and he acts aggressive and violent whenever he feels offended. He absolutely hates the Montagues.
Context of Romeo and Juliet
Shakespeare had written Romeo and Juliet based on the true love story from the 3rd century about two Italian lovers who come from the families Cappelletti and Montecchi . The play was written during the Renaissance period where there were great changes in religion, politics, science and the arts.
When the play was written, Europe had just undergone ‘The Reformation’, where it transitioned from being a traditional Catholic nation to a Protestant society. When Europe was a Catholic society, mortal sin such as bigamy (where you marry someone else while being married to one person) was punished severely.
However, as it progressed into a Protestant nation that broke free from the strict rules of Catholicism, society gained more freedom and less oppression . As people exercised more freedom, they explored notions of humanism which is a Renaissance concept of individual power over their own lives.

Fate and Destiny
Even so, the Elizabethan people still highly believed that their lives were tied to fate and destiny. If you think astrology is popular now, it was actually all the hype during the Elizabethan era!
Elizabethans would plan their whole lives based on astrology readings, including their love lives, travels and more depending on whether the stars favoured them.
As such, Elizabethans valued providentialism, the belief that they have no power in changing their fate as everything in their lives is already ‘predestined’ for them.

Family Values
Family values were also kept quite traditional, as the Elizabethan society remained patriarchal. This means that the father was always the head of the household while the women were left with no rights, properties or legal authority , though they can influence their husbands’ decisions.
Children were also used as property and often engaged in arranged marriages as part of a political or financial deal to gain wealth.
Romeo and Juliet may seem too young to be married but in the Elizabethan years, it was considered normal for people to marry young.
As such, love was perceived to be a dream for Elizabethans who often enter into arranged marriages. It is often restrained with little contact between “lovers”, and the only expressions of love come in gifts, letters and poems.
This is perhaps why the Elizabethan audience were so enticed by Romeo and Juliet’s passionate love for one another , as this was rarely seen in their society.

Appreciation for Theatre
That being said, plays were highly popular in the Elizabethan theatres. Here is where the rich and poor gather in rowdy crowds to watch plays.
Poorer people stood near the stages while richer people watched from stands above. As such, Shakespearean plays became really popular in this era , as there was a great appreciation for the arts across all groups from all backgrounds.

Romeo and Juliet Themes
Here are three key themes from Romeo and Juliet. Feel free to look to these for inspiration when you’re planning to write your thesis and topic sentences in your essay .
Fate VS Free Will
Shakespeare lived in a transition period where people were starting to gain their own freedom to live their lives, yet were still tied to the notions of fate and destiny. You can see this with his characters, Romeo and Juliet, who try to exercise their free will by choosing to be with one another despite their opposing family history.
Yet, it is Romeo and Juliet’s own actions and decisions that ultimately led to their doomed fate. This reinforces the Elizabethan belief that fate and destiny govern our lives, even when we try to control it ourselves.
Some key quotes that explore this idea include:
| Quote | Link to Fate VS Free Will |
|---|---|
| The term “star-crossed lovers” is used to show that Romeo and Juliet’s relationship is controlled by fate, symbolised as a “star”. | |
| This line from Romeo reveals that he foresees his tragic fate that has been planned from the start, even before he meets Juliet. | |
| This line from Romeo shows his attempt to use his free will to overcome his fate. |
Love VS Conflict
It would be nice to say that “love conquers all” in Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet, but it’s not as simple as that.
Love and conflict coexist within this text. The love between Romeo and Juliet is seen as a sign of hope to bring peace to the ongoing feud between the Montagues and Capulets.
However, the conflict between families grew so violent that it had caused the deaths of their beloved children and the love between them. Ultimately, Shakespeare shows us that love affects conflict, and conflict affects love.
Here are some quotes that allow you to explore this a bit deeper:
| Quote | Link to Love VS Conflict |
|---|---|
| This line from Romeo reveals that his love is as passionate as the hatred the families have for each other. | |
| Juliet realises that the Romeo she loves is ironically from the family that she is supposed to hate. | |
| This line from Juliet reveals that the conflict between the two families have caused her and Romeo to suffer so much, that it made her see death as being “restorative”. |
The Freedom of Youth Rebellion
Have you ever wanted to do whatever you felt like, without your parents butting in?
If that’s a yes from you, you’ll probably be able to relate to Romeo and Juliet. These two are also young teenagers who rebel against their parents’ wishes and express their individuality through their love for one another.
However, an excess of youthful spirit can also lead to dire consequences, as Romeo and Juliet’s unbridled passion for one another led to their unfortunate end.
Here are some key quotes that relate to this theme:
| Quote | Link to the Freedom of Youth Rebellion |
|---|---|
| This line from Romeo reveals that he values love unlike his friends and family who harbour hate for the other family. | |
| Romeo explains that his love for Juliet gives him “light wings” to climb over “stony limits” that may be set by their parents’ strife. | |
| Juliet describes her love for Romeo as “boundless as the sea”, reiterating the notion that their youthful love surpasses all limitations and sets her free. |
If none of these themes resonate with you, here are some other ideas that you may find interesting:
- External conflict VS internal conflict
- The conflict between independence VS family obligation
- The consequences of unbridled emotions
How to Analyse Romeo and Juliet in 3 Steps
Students often jump right into answering the question when writing their thesis for their essays. Many don’t realise that it is only after you’ve analysed your text that you can write an amazing thesis that not only answers the question, but proves that you really do know the text inside out.
Let’s go through the three simple steps you can take to analyse Romeo and Juliet and ace that essay!
Step 1: Select your example(s)
You may be thinking to yourself, “There’s lots happening in Romeo and Juliet so where do I even start?”
A great place to start is to look for an example with a technique . This technique can offer a deeper insight into the text, which will help you form an in-depth analysis.
Here are two quotes we have selected to focus on the theme of fate VS free will:
“It is the east, and Juliet is the sun”
“I defy you, stars!”
Step 2: Identify your technique(s)
Students often fall into the trap of listing every technique they can find or using highly complicated techniques in hopes of getting a good mark. This is not true!
It is better to find a technique which allows you to talk about your theme in more depth and build your argument throughout your essay.
Techniques that provide a deeper understanding of the text include symbols, metaphors, recurring motifs, allegories, connotations and similes. Try to avoid using surface level techniques such as alliteration or repetition.
The three techniques found in the quotes above include simile, symbolism and allusion to astrology.
If you can, try to find a few techniques within one quote to help you kill two birds with one stone!
Step 3: Write the analysis
When you’re writing an analysis, try not to list out every technique you can find in the quote. It is very important to explain what the effect of the technique is and how that relates to your argument.
An example of listing out techniques looks like this:
Simile is used as Romeo refers to Juliet as the metaphorical “Sun” and uses the symbolism of astrology as he “def(ies) you, stars” to allude to fate versus free will.
To avoid this, we need to go into how each of these techniques support our argument.
First of all, the simile of Juliet being like the “Sun” reveals Romeo’s love for Juliet that transcends beyond their families’ feud. The symbol of the “Sun” is also important to emphasise the fated doom between the two star crossed lovers.
The allusion to astrology in “I defy you, stars!” shows how fate governs Romeo and Juliet’s relationship. Once we put these techniques together, our analysis will look like:
Shakespeare’s simile in Romeo’s description of Juliet as the “Sun” reveals their perception that their love can transcend beyond the boundaries of their families’ strife. Yet, the symbolism of the “Sun” reminds the audience that Romeo and Juliet still remain as “star crossed lovers” who are destined to die despite their efforts to overcome their fated doom. As Romeo proclaims “I defy you, stars” before submitting to his fate, the astrological allusion reinforces how destiny continues to govern their lives, reinstating the Elizabethan belief that fate will always overpower free will.

You’ve made it to the end! Find another sample analysis paragraph of Romeo and Juliet here !
Need some help with your essay analysis of other texts aside from Romeo and Juliet?
Check out other texts we’ve created guides for below:
- Lord of the Flies
- Photograph 51
- In Cold Blood
- The Meursault Investigation
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- The Book Thief
- Away by Michael Gow
- Blade Runner
- Fahrenheit 451
We’ve also got a bunch of articles specifically on plays by Shakespeare which you can have a read through below:
- A Midsummer Night’s Dream
- The Merchant of Venice
- Much Ado About Nothing
- King Richard III
- The Tempest
Are you looking for some extra help with your analysis of Romeo and Juliet?
We have an incredible team of tutors and mentors.
We can help you master your analysis of Romeo and Juliet by taking you through the summary, context, key characters and themes. We’ll also help you ace your upcoming English assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home or online!
We’ve supported over 8,000 students over the last 11 years , and on average our students score mark improvements of over 20%!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational tutor and mentor, get in touch today or give us a ring on 1300 267 888!
Kate Lynn Law graduated in 2017 with an all rounders HSC award and an ATAR of 97.65. Passionate about mentoring, she enjoys working with high school students to improve their academic, work and life skills in preparation for the HSC and what comes next. An avid blogger, Kate had administered a creative writing page for over 2000 people since 2013, writing to an international audience since her early teenage years.
- Topics: ✏️ English , ✍️ Learn
Related Articles
The extensive guide to analysing shakespeare’s ‘the tempest’: summary, context, characters & themes, important quotes you should pay attention to in the merchant of venice, the ultimate guide to shakespeare for hsc english, 45,861 students have a head start....
Get exclusive study content & advice from our team of experts delivered weekly to your inbox!

Looking for English Support?
Discover how we can help you!

We provide services in

- TOP CATEGORIES
- AS and A Level
- University Degree
- International Baccalaureate
- Uncategorised
- 5 Star Essays
- Study Tools
- Study Guides
- Meet the Team
Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare
Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare

Published: 1590s
Country: United Kingdom
Publisher: Thomas Creede
Romeo and Juliet is probably the most famous literary love story in the world. Even people who’ve never read or seen the play know the names of the two main characters. When Shakespeare wrote the play more than 400 years ago, arranged marriages were far more common than romantic love and would continue to be so for a long time.
The play takes a radical, and modern, approach to male/female relationships, without being sentimental. It is after all a tragedy. What destroys the two lovers is not the hasty, impulsive nature of their love, but the fact that, because of the loathing their two families have for one another, they are never allowed to love freely or openly.
The play continues to resonate in the 21st century, because human beings still create seemingly unbreakable barriers of class, creed, race, or sexuality between their children, and Juliet’s words still echo: “‘Tis but thy name that is my enemy.”
More on Romeo and Juliet
- ACTS - Read our detailed act by act breakdown to get an understanding of the plot, and then look at some exemplar essays to help you generate your own ideas.
- CHARACTERS - Find out all about the characters that Shakespeare created by reading our character analysis and essays on each characters.
- THEMES - Fate, love and hate- get to know the key themes in Romeo and Juliet to give you ideas for your own essays.
Romeo and Juliet Essays
Have a read of these hand picked essays to give you some ideas and inspiration for your coursework.

How does Shakespeare use imagery in his play Romeo and Juliet to intensify the drama, create atmosphere and illuminate the central themes?
By using a variety of metaphors, dramatic irony, use of figurative language and his explanation of poetic forms he conveys meaning and character excellently.

Although centuries old Romeo and Juliet is still relevant today. Do you agree or disagree with this statement?
Although centuries old Romeo and Juliet is still relevant today. Do you agree or disagree with this statement? I strongly agree with this statement the reason being,


How Does Shakespeare Use The Idea Of Opposition As A Dramatic Device In 'Romeo and Juliet'? What Are The Effects Of These Techniques?
Shakespeare uses an immense amount of opposition in the play, 'Romeo and Juliet'; this creates dramatic impact. The oppositions have a major effect on the...

Romeo and juliet- Themes
Themes Shakespeare uses a number of methods and themes to illustrate the atmosphere in this play. He uses the methods and themes to make the play more effective and motivating.

Examine the role of women in Romeo and Juliet, and explore the role of women in 16th century society
Women had a specific place in society, and they were expected to conform to expectations of their positions. Women were owned by their husbands, and had little...

William Shakespeare wrote Romeo and Juliet in the 16th century
Not every Montague shared in the intense hatred for caplets. Romeo Montague was quite the opposite; he was infatuated with Rosaline, a Capulet. However Rosaline...

- Ask LitCharts AI
- Discussion Question Generator
- Essay Prompt Generator
- Quiz Question Generator

- Literature Guides
- Poetry Guides
- Shakespeare Translations
- Literary Terms
Romeo and Juliet
William shakespeare.

Ask LitCharts AI: The answer to your questions
| . Read our . |
In Renaissance-era Verona, Italy, two noble families, the Montagues and Capulets, are locked in a bitter and ancient feud whose origin no one alive can recall. After a series of public brawls between both the nobles and the servants of the two families, which shed blood and disturb the peace in Verona’s city streets, Prince Escalus , the ruler of Verona, declares that anyone in either family involved in any future fighting will be put to death.
Every year, the Capulets throw a masquerade ball. The Montagues are, of course, not invited. As Capulet and Lady Capulet fuss over the arrangements for the party, ensuring that everything is perfect for their friends and guests, they hope that their daughter Juliet will fall in love with the handsome count Paris at the ball. At 13, Juliet is nearly of marriageable age, and the Capulets believe that marrying Paris would allow their daughter to ascend the social ladder in Verona. During the party, two Montagues, 16-year-old Romeo and his cousin Benvolio , along with their bawdy, quick-tongued friend Mercutio , a kinsmen of Prince Escalus, crash the affair. Romeo attends the party reluctantly, and only because he is hoping to see Rosaline , a young woman he has been hopelessly in love with—and unsuccessfully pursuing—for quite some time. His lack of romantic success has made him noticeably forlorn as of late, much to the chagrin of his friends, who nonetheless poke fun at their lovesick friend’s melodramatic state. Tybalt , a hot-blooded member of House Capulet, notices the intrusion of the Montagues and recognizes them in spite of their masks—but when he draws his rapier and begins approaching them to provoke a fight, Capulet urges Tybalt not to embarrass their family.
When the masked Romeo spots Juliet from across the room, he instantly falls in love with her. Juliet is equally smitten. The two of them speak, exchanging suggestive jokes, and then kiss. As the party ends, Romeo and Juliet, pulled away from one another to attend to their friends and family, separately discover who the other truly is. Both are distraught—Juliet laments that her “only love [has] sprung from [her] only hate.” As the party winds down and Romeo’s friends prepare to leave, Romeo breaks off from them, jumps an orchard wall, and hides in the dark beneath Juliet’s bedroom window. She emerges onto her balcony and bemoans her forbidden love for Romeo, wishing aloud that he could “be some other name.” Romeo jumps out from his hiding place and tells Juliet that he’d do anything for her—he is determined to be with her in spite of the obstacles they face. Romeo and Juliet exchange vows of love, and Romeo promises to call upon Juliet tomorrow so they can hastily be married.
The next day, Romeo visits a kindly but philosophical friar, Friar Laurence , in his chambers. He begs Friar Laurence to marry him to his new love, Juliet. Friar Laurence urges Romeo to slow down and take his time when it comes to love: “these violent delights,” he predicts, “have violent ends.” But Romeo insists he and Juliet know what they’re doing. Friar Laurence comes around, realizing that a marriage between Romeo and Juliet could end their parents’ age-old feud. Later that day, Benvolio and Mercutio encounter Tybalt, who is furious that the Montagues crashed the Capulet party. Tybalt has, in a letter, challenged Romeo to a duel, and Mercutio and Benvolio are worried about the impulsive Romeo rising to the skilled Tybalt’s challenge. When Romeo shows up to find Tybalt, Benvolio, and Mercutio exchanging verbal barbs and teetering on the edge of a fight, Romeo does all he can to resist dueling with Tybalt. He and Juliet have just hastily visited Friar Laurence’s chambers together and are now married. Romeo doesn’t want to fight Tybalt, who is now technically his kinsman—but he knows he can’t reveal the truth to Tybalt, either. Before Romeo can explain his reasons for hesitating, Mercutio disgustedly steps in and challenges Tybalt to a duel himself. Romeo tries to separate them, but Tybalt stabs and kills Mercutio under Romeo's arm. Mercutio dies from his wounds, cursing both the Montagues and the Capulets and invoking “a plague [on] both houses.” In a miserable, mournful rage, Romeo kills Tybalt, then declares himself “fortune’s fool.” Benvolio urges him to hurry from the square. The prince and the citizens’ watch arrive, along with the elders of House Capulet and House Montague. Benvolio tells Prince Escalus what has unfolded, and the prince decides to banish Romeo to Mantua rather than sentence him to death.
Back at the Capulet manse, Juliet dreamily awaits the arrival of Romeo, whom she believes is hurrying from church so that they can spend their wedding night together. Juliet’s reveries are shattered with her nurse enters and informs her that Romeo has slain Tybalt and been banished from Verona. Juliet is furious with Romeo for killing Tybalt, but at the same time, her love for him is so profound that she admits she’d rather he lived than Tybalt. Juliet bids her nurse to go find Romeo and bring him to her, letting him know that she still wants to see him in spite of his actions. The nurse heads to Friar Laurence’s chambers, where the miserable, embarrassed, and angry Romeo is hiding. Though Romeo laments his fate to Friar Laurence, the friar urges Romeo to see that he is lucky to be alive, and promises to find a way to bring him back to Verona from exile in Mantua soon enough. The nurse arrives and summons Romeo to Juliet’s chambers—he happily follows her, and Friar Laurence urges Romeo to head straight to Mantua in the morning and await word from a messenger.
The death of Tybalt affects Capulet deeply. He decides to marry Juliet to Paris immediately, to cheer both Juliet and himself up. Juliet and Romeo bid each another farewell as the dawn breaks the next morning, and though Juliet says she has a terrible feeling she’ll never see Romeo again, she urges him to hurry on to Mantua. Lady Capulet enters Juliet’s chambers just after Romeo leaves to find her daughter weeping. Believing Juliet is still sad over Tybalt’s death, Lady Capulet delivers the news that Juliet will soon be married to Paris. Juliet refuses, and Lady Capulet urges Juliet to tell her father of her decision. Capulet enters, and, when Juliet stubbornly and angrily refutes the arrangement he’s made for her, Capulet threatens to disown her. Lady Capulet sides with her husband, and even the nurse advises Juliet to marry Paris and forget Romeo.
Juliet rushes to Friar Laurence in a rage, threatening to kill herself if he cannot devise a plan to get her out of the marriage to Paris. Friar Laurence, sensing Juliet’s deep pain, quickly comes up with a scheme: he gives her a vial of potion that, once drunk, will make it seem like she's dead—but will really only put her to sleep for about 40 hours. Juliet will be laid to rest in the Capulet tomb, and once she wakes up there, Friar Laurence will collect her and hide her until Romeo returns from Mantua. The friar promises to get news of the plan to Romeo so that he can hurry back home. Juliet takes the vial and returns home with it. Though she is afraid the potion might either kill her or not work at all, Juliet drinks it and immediately falls unconscious. The next morning the Capulet household wakes to discover that Juliet has seemingly died. As Capulet and Lady Capulet dramatically mourn their daughter’s loss, Friar Laurence chides them for their tears—in life, he says, they sought Juliet’s social “promotion.” Now that she is in heaven, she has received the highest promotion of all.
In Mantua, Romeo’s servant Balthasar approaches and tells him that Juliet has died. Romeo is devastated—he plans to “deny [the] stars” and return to Verona. Before leaving Mantua, however, he visits the shop of a local apothecary who sells forbidden poisons . If Juliet really is dead, Romeo plans to drink the vial of poison and kill himself inside her tomb. Back in Verona, Friar Laurence learns that his brother in the cloth, Friar John , has failed to deliver the letter about Juliet’s feigned “death” to Romeo—Romeo has no idea that Juliet is really alive. Friar Laurence hurries to the Capulet crypt to try to head off any calamity. At the gravesite, however, trouble is brewing: Paris has arrived with his page, intending to scatter flowers around Juliet’s tomb. Romeo and Balthasar approach, and Paris hides to see who has come to the crypt. Romeo takes up some tools and begins to break open the Capulet tomb. The astonished, offended Paris steps forward to stop him. The two duel, and Romeo kills Paris. Romeo succeeds in opening Juliet’s tomb, and brings Paris’s corpse down into it with him.
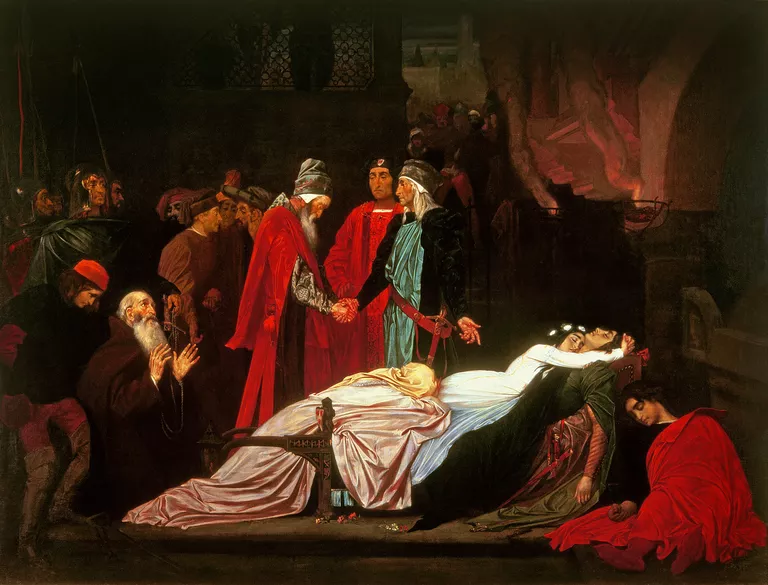
As Romeo looks upon Juliet, he notes that her cheeks and lips still seem flushed with blood—but, believing she is dead, resolves to drink the poison after a final kiss. Romeo drinks the vial and dies. Friar Laurence arrives to find a terrible scene before him. Juliet wakes, and Friar Laurence urges her to follow him without looking at the bodies. As sounds of the citizens’ watch approach, however, Friar Laurence flees, begging Juliet to follow him so he can install her in a nunnery. Instead, Juliet stays behind with Romeo’s corpse. Seeing the poison in his hand, she tries to drink a drop from his lips, but Romeo has left none for her. Instead, she pulls Romeo’s dagger from his hip and uses it to kill herself. Several watchmen arrive and bring Friar Laurence, Balthasar, Prince Escalus, and Paris’s page to the crypt to investigate what has happened. As the truth unravels, the elders of House Montague and Capulet arrive. Prince Escalus tells them that their hatred has killed their children. “All,” the prince says, “are punished.” The Capulets and Montagues agree to end their feud and erect statues of each other’s children in the town square.

- Quizzes, saving guides, requests, plus so much more.
Romeo and Juliet
By william shakespeare.
- Romeo and Juliet Summary
Romeo and Juliet is set in Verona, Italy, where there is an ongoing feud between the Montague and Capulet families. The play opens with servants from both houses engaged in a street brawl that eventually draws in the family patriarchs and the city officials, including Prince Escalus . The Prince ends the conflict by issuing a decree that prohibits any further fighting at the risk of great punishment.
Meanwhile, Romeo , a young man from the Montague house, laments his unrequited love for a woman named Rosaline, who has vowed to remain chaste for the rest of her life. Romeo and his friend Benvolio happen to stumble across a Capulet servant, Peter , who is trying to read a list of invitees to a masked party at the Capulet house that evening. Romeo helps Peter read the list and decides to attend the party because Rosaline will be there. He plans to wear a mask so that he will nobody will recognize him as a Montague.
Romeo arrives at the Capulets' party in costume. He falls in love with young Juliet Capulet from the moment he sees her. However, Juliet's cousin Tybalt recognizes Romeo and wants to kill him on the spot. Lord Capulet intervenes, insisting that Tybalt not disturb the party because it will anger the Prince. Undeterred, Romeo quietly approaches Juliet and confesses his love for her. After exchanging loving words, they kiss.
Afterwards, Juliet's Nurse tells Romeo that Juliet is a Capulet, which upsets the smitten youngster. Meanwhile, Juliet is similarly distraught when she finds out that Romeo is a Montague. Later that night, Romeo climbs the garden wall into Juliet's garden. Juliet emerges on her balcony and speaks her private thoughts out loud. She wishes Romeo could shed his name and marry her. Upon hearing her confession, Romeo appears and tells Juliet that he loves her. She warns him to be true in his love, and he swears by his own self that he will be. Before they part, they agree that Juliet will send her Nurse to meet Romeo at nine o'clock the next day, at which point he will set a place for them to be married.
The Nurse carries out her duty, and tells Juliet to meet Romeo at the chapel where Friar Laurence lives and works. Juliet meets Romeo there, and the Friar marries them in secret.
Benvolio and Mercutio (another one of Romeo's friends) are waiting on the street later that day when Tybalt arrives. Tybalt demands to know where Romeo is so that he can challenge him to a duel, in order to punish him for sneaking into the party. Mercutio is eloquently vague, but Romeo happens to arrive in the middle of the verbal sparring. Tybalt challenges him, but Romeo passively resists fighting, at which point Mercutio jumps in and draws his sword on Tybalt. Romeo tries to block the two men, but Tybalt cuts Mercutio and runs away, only to return after he hears that Mercutio has died. Angry over his friend's death, Romeo fights with Tybalt and kills him. Then, he decides to flee. When Prince Escalus arrives at the murder scene, he banishes Romeo from Verona forever.
The Nurse tells Juliet the sad news about what has happened to Tybalt and Romeo. Juliet is heart-broken, but she realizes that Romeo would have been killed if he had not fought Tybalt. She sends her Nurse to find Romeo and give him her ring.
That night, Romeo sneaks into Juliet's room, and they consummate their marriage. The next morning, he is forced to leave when Juliet's mother arrives. Romeo travels to Mantua, where he waits for someone to send news about Juliet or his banishment.
During Romeo and Juliet's only night together, however, Lord Capulet decides that Juliet should marry a young man named Paris , who has been asking for her hand. Lord and Lady Capulet tell Juliet of their plan, but she refuses, infuriating her father. When both Lady Capulet and the Nurse refuse to intercede for the girl, she insists that they leave her side.
Juliet then visits Friar Laurence, and together they concoct a plan to reunite her with Romeo. The Friar gives Juliet a potion that will make her seem dead for at least two days, during which time Romeo will come to meet her in the Capulet vault. The Friar promises to send word of the plan to Romeo.
Juliet drinks the Friar's potion that night. The next morning, the day of Juliet and Paris' wedding, her Nurse finds her "dead" in bed. The whole house decries her suicide, and Friar Laurence insists they quickly place her into the family vault.
Unfortunately, Friar John has been unable to deliver the letter to Romeo informing him of the plan, so when Romeo's servant brings him news in Mantua that Juliet has died, Romeo is heart-broken. He hurries back to Verona, but first, buys poison from an Apothecary and writes a suicide note detailing the tragic course of events. As soon as Friar Laurence realizes that his letter never made it to Romeo's hands, he rushes to the Capulet tomb, hoping to arrive before Romeo does.
Romeo arrives at the Capulet vault and finds it guarded by Paris, who is there to mourn the loss of his betrothed. Paris challenges Romeo to a duel, and Romeo kills him quickly. Romeo then carries Paris' body into the grave and sets it down. Upon seeing Juliet's "dead" body lying in the tomb, Romeo drinks the poison, gives her a last kiss - and dies.
Friar Laurence arrives to the vault just as Juliet wakes up. He tries to convince her to flee, but upon seeing Romeo's dead body, she takes her own life as well.
The rest of the town starts to arrive at the tomb, including Lord Capulet and Lord Montague . Friar Laurence explains the whole story, and Romeo's letter confirms it. The two families agree to settle their feud and form an alliance despite the tragic circumstances.

Romeo and Juliet Questions and Answers
The Question and Answer section for Romeo and Juliet is a great resource to ask questions, find answers, and discuss the novel.
Can you find verbal irony in the play? Where?
One example of verbal irony would be Romeo's reference to the poison he has purchased as a "sweet medicine". A cordial is a sweet liquor or medicine.
Come, cordial and not poison, go with me To Juliet's grave; for there must I use thee.
What do we learn about Mercutio in queen man speech?
The whole speech is based on pagan Celtic mythology. Mercutio’s speech is laced with sexual innuendo. The words “queen” and “mab” refer to whores in Elizabethan England. As his speech goes on we notice the subtext get increasingly sexual...
What does Romeo fear as he approaches Capulet house? What literary device would this be an example of?
Romeo feels something bad is going to happen.
I fear too early, for my mind misgives Some consequence yet hanging in the stars
Looks like foreshadowing to me!
Study Guide for Romeo and Juliet
Romeo and Juliet study guide contains a biography of William Shakespeare, literature essays, a complete e-text, quiz questions, major themes, characters, and a full summary and analysis.
- About Romeo and Juliet
- Romeo and Juliet Video
- Character List
Essays for Romeo and Juliet
Romeo and Juliet essays are academic essays for citation. These papers were written primarily by students and provide critical analysis of Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare.
- Unity in Shakespeare's Tragedies
- Fate in Romeo and Juliet
- Romeo and Juliet: Under the Guise of Love
- The Apothecary's Greater Significance in Romeo and Juliet
- Romeo and Juliet: Two Worlds
Lesson Plan for Romeo and Juliet
- About the Author
- Study Objectives
- Common Core Standards
- Introduction to Romeo and Juliet
- Relationship to Other Books
- Bringing in Technology
- Notes to the Teacher
- Related Links
- Romeo and Juliet Bibliography
E-Text of Romeo and Juliet
Romeo and Juliet e-text contains the full text of Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare.
- List of Characters
Wikipedia Entries for Romeo and Juliet
- Introduction
Share this page
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
Romeo and Juliet
Synopsis and plot overview of shakespeare's romeo and juliet.
- In this section
TL;DR (may contain spoilers): The classic story of boy meets girl; girl's family hates boy's family; boy's family hates girl's family; boy kills girl's cousin; boy and girl kill themselves.
Romeo and Juliet Summary
An age-old vendetta between two powerful families erupts into bloodshed. A group of masked Montagues risk further conflict by gatecrashing a Capulet party. A young lovesick Romeo Montague falls instantly in love with Juliet Capulet, who is due to marry her father’s choice, the County Paris. With the help of Juliet’s nurse, the women arrange for the couple to marry the next day, but Romeo’s attempt to halt a street fight leads to the death of Juliet’s own cousin, Tybalt, for which Romeo is banished. In a desperate attempt to be reunited with Romeo, Juliet follows the Friar’s plot and fakes her own death. The message fails to reach Romeo, and believing Juliet dead, he takes his life in her tomb. Juliet wakes to find Romeo’s corpse beside her and kills herself. The grieving family agree to end their feud.
- Read our Romeo and Juliet Character Summaries .
More detail: 2 minute read
Romeo and Juliet begins as the Chorus introduces two feuding families of Verona: the Capulets and the Montagues. On a hot summer's day, the young men of each faction fight until the Prince of Verona intercedes and threatens to banish them. Soon after, the head of the Capulet family plans a feast. His goal is to introduce his daughter Juliet to a Count named Paris who seeks to marry Juliet.
Montague's son Romeo and his friends (Benvolio and Mercutio) hear of the party and resolve to go in disguise. Romeo hopes to see his beloved Rosaline at the party. Instead, while there, he meets Juliet and falls instantly in love with her. Juliet's cousin Tybalt recognises the Montague boys and forces them to leave just as Romeo and Juliet discover one another.

Romeo lingers near the Capulet house to talk with Juliet when she appears in her window. The pair declare their love for one another and intend to marry the next day. With the help of Juliet's Nurse, the lovers arrange to marry when Juliet goes for confession at the cell of Friar Laurence. There, they are secretly married (talk about a short engagement).
Parting is such sweet sorrow that I shall say goodnight till it be morrow — Romeo and Juliet, Act 2 Scene 2
Following the secret marriage, Juliet's cousin Tybalt sends a challenge to Romeo. Romeo refuses to fight, which angers his friend Mercutio who then fights with Tybalt. Mercutio is accidentally killed as Romeo intervenes to stop the fight. In anger, Romeo pursues Tybalt, kills him, and is banished by the Prince.
Juliet is anxious when Romeo is late to meet her and learns of the brawl, Tybalt's death, and Romeo's banishment. Friar Laurence arranges for Romeo to spend the night with Juliet before he leaves for Mantua. Meanwhile, the Capulet family grieves for Tybalt, so Lord Capulet moves Juliet's marriage to Paris to the next day. Juliet’s parents are angry when Juliet doesn't want to marry Paris, but they don't know about her secret marriage to Romeo.

A pair of star-crossed lovers — Romeo and Juliet, Prologue
Friar Laurence helps Juliet by providing a sleeping draught that will make her seem dead. When the wedding party arrives to greet Juliet the next day, they believe she is dead. The Friar sends a messenger to warn Romeo of Juliet's plan and bids him to come to the Capulet family monument to rescue his sleeping wife.
Ready to test your knowledge? Have a go at our multiple choice Romeo and Juliet Quiz
The vital message to Romeo doesn't arrive in time because the plague is in town (so the messenger cannot leave Verona). Hearing from his servant that Juliet is dead, Romeo buys poison from an Apothecary in Mantua. He returns to Verona and goes to the tomb where he surprises and kills the mourning Paris. Romeo takes his poison and dies, while Juliet awakens from her drugged coma. She learns what has happened from Friar Laurence, but she refuses to leave the tomb and stabs herself. The Friar returns with the Prince, the Capulets, and Romeo's lately widowed father. The deaths of their children lead the families to make peace, and they promise to erect a monument in Romeo and Juliet's memory.

Romeo and Juliet Animated Summary - 3-Minute Shakespeare
To watch more animated play summaries visit our 3-Minute Shakespeare pages
For additional reading, see our blogs on Romeo and Juliet
Discover more of Shakespeare's romantic lines: Shakespeare Quotes on Love
Help keep Shakespeare's story alive
Read more play summaries, learn about william shakespeare, shakespeare's birthplace, anne hathaway's cottage, shakespeare's new place.
We use essential and non-essential cookies that improve the functionality and experience of the website. For more information, see our Cookies Policy.
Necessary cookies
Necessary cookies ensure the smooth running of the website, including core functionality and security. The website cannot function properly without these cookies.
Analytics cookies
Analytical cookies are used to determine how visitors are using a website, enabling us to enhance performance and functionality of the website. These are non-essential cookies but are not used for advertising purposes.
Advertising cookies
Advertising cookies help us monitor the effectiveness of our recruitment campaigns as well as enabling advertising to be tailored to you through retargeting advertising services. This means there is the possibility of you seeing more adverts from the Shakespeare Birthplace Trust on other websites that you visit.
- Save settings Minimise
Website navigation
A Modern Perspective: Romeo and Juliet
By Gail Kern Paster
Does Romeo and Juliet need an introduction? Of all Shakespeare’s plays, it has been the most continuously popular since its first performance in the mid-1590s. It would seem, then, the most direct of Shakespeare’s plays in its emotional impact. What could be easier to understand and what could be more moving than the story of two adolescents finding in their sudden love for each other a reason to defy their families’ mutual hatred by marrying secretly? The tragic outcome of their blameless love (their “misadventured piteous overthrows”) seems equally easy to understand: it results first from Tybalt’s hotheaded refusal to obey the Prince’s command and second from accidents of timing beyond any human ability to foresee or control. Simple in its story line, clear in its affirmation of the power of love over hate, Romeo and Juliet seems to provide both a timeless theme and universal appeal. Its immediacy stands in welcome contrast to the distance, even estrangement, evoked by other Shakespeare plays. No wonder it is often the first Shakespeare play taught in schools—on the grounds of its obvious relevance to the emotional and social concerns of young people.
Recent work by social historians on the history of private life in western European culture, however, offers a complicating perspective on the timelessness of Romeo and Juliet. At the core of the play’s evident accessibility is the importance and privilege modern Western culture grants to desire, regarding it as deeply expressive of individual identity and central to the personal fulfillment of women no less than men. But, as these historians have argued, such conceptions of desire reflect cultural changes in human consciousness—in ways of imagining and articulating the nature of desire. 1 In England until the late sixteenth century, individual identity had been imagined not so much as the result of autonomous, personal growth in consciousness but rather as a function of social station, an individual’s place in a network of social and kinship structures. Furthermore, traditional culture distinguished sharply between the nature of identity for men and women. A woman’s identity was conceived almost exclusively in relation to male authority and marital status. She was less an autonomous, desiring self than any male was; she was a daughter, wife, or widow expected to be chaste, silent, and, above all, obedient. It is a profound and necessary act of historical imagination, then, to recognize innovation in the moment when Juliet impatiently invokes the coming of night and the husband she has disobediently married: “Come, gentle night; come, loving black-browed night, / Give me my Romeo” ( 3.2.21 –23).
Recognizing that the nature of desire and identity is subject to historical change and cultural innovation can provide the basis for rereading Romeo and Juliet. Instead of an uncomplicated, if lyrically beautiful, contest between young love and “ancient grudge,” the play becomes a narrative that expresses an historical conflict between old forms of identity and new modes of desire, between authority and freedom, between parental will and romantic individualism. Furthermore, though the Chorus initially sets the lovers as a pair against the background of familial hatred, the reader attentive to social detail will be struck instead by Shakespeare’s care in distinguishing between the circumstances of male and female lovers: “she as much in love, her means much less / To meet her new belovèd anywhere” ( 2. Chorus. 11 –12, italics added). The story of “Juliet and her Romeo” may be a single narrative, but its clear internal division is drawn along the traditionally unequal lines of gender.
Because of such traditional notions of identity and gender, Elizabethan theatergoers might have recognized a paradox in the play’s lyrical celebration of the beauty of awakened sexual desire in the adolescent boy and girl. By causing us to identify with Romeo and Juliet’s desire for one another, the play affirms their love even while presenting it as a problem in social management. This is true not because Romeo and Juliet fall in love with forbidden or otherwise unavailable sexual partners; such is the usual state of affairs at the beginning of Shakespearean comedy, but those comedies end happily. Rather Romeo and Juliet’s love is a social problem, unresolvable except by their deaths, because they dare to marry secretly in an age when legal, consummated marriage was irreversible. Secret marriage is the narrative device by which Shakespeare brings into conflict the new privilege claimed by individual desire and the traditional authority granted fathers to arrange their daughters’ marriages. Secret marriage is the testing ground, in other words, of the new kind of importance being claimed by individual desire. Shakespeare’s representation of the narrative outcome of this desire as tragic—here, as later in the secret marriage that opens Othello —may suggest something of Elizabethan society’s anxiety about the social cost of romantic individualism.
The conflict between traditional authority and individual desire also provides the framework for Shakespeare’s presentation of the Capulet-Montague feud. The feud, like the lovers’ secret marriage, is another problem in social management, another form of socially problematic desire. We are never told what the families are fighting about or fighting for; in this sense the feud is both causeless and goal-less. The Chorus’s first words insist not on the differences between the two families but on their similarity: they are two households “both alike in dignity.” Later, after Prince Escalus has broken up the street brawl, they are “In penalty alike” ( 1.2.2 ). Ironically, then, they are not fighting over differences. Rather it is Shakespeare’s careful insistence on the lack of difference between Montague and Capulet that provides a key to understanding the underlying social dynamic of the feud. Just as desire brings Romeo and Juliet together as lovers, desire in another form brings the Montague and Capulet males out on the street as fighters. The feud perpetuates a close bond of rivalry between these men that even the Prince’s threat of punishment cannot sever: “Montague is bound as well as I,” Capulet tells Paris ( 1.2.1 ). Indeed, the feud seems necessary to the structure of male-male relations in Verona. Feuding reinforces male identity—loyalty to one’s male ancestors—at the same time that it clarifies the social structure: servants fight with servants, young noblemen with young noblemen, old men with old men. 2
That the feud constitutes a relation of desire between Montague and Capulet is clear from the opening, when the servants Gregory and Sampson use bawdy innuendo to draw a causal link between their virility and their eagerness to fight Montagues: “A dog of that house shall move me to stand,” i.e., to be sexually erect ( 1.1.12 ). The Montagues seem essential to Sampson’s masculinity since, by besting Montague men, he can lay claim to Montague women as symbols of conquest. (This, of course, would be a reductive way of describing what Romeo does in secretly marrying a Capulet daughter.) The feud not only establishes a structure of relations between men based on competition and sexual aggression, but it seems to involve a particularly debased attitude toward women. No matter how comic the wordplay of the Capulet servants may be, we should not forget that the sexual triangle they imagine is based on fantasized rape: “I will push Montague’s men from the wall and thrust his maids to the wall” ( 1.1.18 –19). Gregory and Sampson are not interested in the “heads” of the Montague maidens, which might imply awareness of them as individuals. They are interested only in their “maidenheads.” Their coarse view of woman as generic sexual object is reiterated in a wittier vein by Mercutio, who understands Romeo’s experience of awakened desire only as a question of the sexual availability of his mistress: “O Romeo, that she were, O, that she were / An open-arse, thou a pop’rin pear” ( 2.1.40 –41).
Feuding, then, is the form that male bonding takes in Verona, a bonding which seems linked to the derogation of woman. But Romeo, from the very opening of the play, is distanced both physically and emotionally from the feud, not appearing until the combatants and his parents are leaving the stage. His reaction to Benvolio’s news of the fight seems to indicate that he is aware of the mechanisms of desire that are present in the feud: “Here’s much to do with hate, but more with love” ( 1.1.180 ). But it also underscores his sense of alienation: “This love feel I, that feel no love in this” ( 187 ). He is alienated not only from the feud itself, one feels, but more importantly from the idea of sexuality that underlies it. Romeo subscribes to a different, indeed a competing view of woman—the idealizing view of the Petrarchan lover. In his melancholy, his desire for solitude, and his paradox-strewn language, Romeo identifies himself with the style of feeling and address that Renaissance culture named after the fourteenth-century Italian poet Francesco Petrarca or Petrarch, most famous for his sonnets to Laura. By identifying his beloved as perfect and perfectly chaste, the Petrarchan lover opposes the indiscriminate erotic appetite of a Gregory or Sampson. He uses the frustrating experience of intense, unfulfilled, and usually unrequited passion to refine his modes of feeling and to enlarge his experience of self.
It is not coincidental, then, that Shakespeare uses the language and self-involved behaviors of the Petrarchan lover to dramatize Romeo’s experience of love. For Romeo as for Petrarch, love is the formation of an individualistic identity at odds with other kinds of identity: “I have lost myself. I am not here. / This is not Romeo. He’s some other where” ( 1.1.205 –6). Petrarchan desire for solitude explains Romeo’s absence from the opening clash and his lack of interest in the activities of his gang of friends, whom he accompanies only reluctantly to the Capulet feast: “I’ll be a candle holder and look on” ( 1.4.38 ). His physical isolation from his parents—with whom he exchanges no words in the course of the play—further suggests his shift from traditional, clan identity to the romantic individualism prefigured by Petrarch.
Shakespeare’s comic irony is that such enlargement of self is itself a mark of conventionality, since Petrarchism in European literature was by the late sixteenth century very widespread. A more cutting irony is that the Petrarchan lover and his sensual opponent (Sampson or Gregory) have more in common than is first apparent. The Petrarchan lover, in emphasizing the often paralyzing intensity of his passion, is less interested in praising the remote mistress who inspires such devotion than he is in displaying his own poetic virtuosity and his capacity for self-denial. Such a love—like Romeo’s for Rosaline—is founded upon frustration and requires rejection. The lover is interested in affirming the uniqueness of his beloved only in theory. On closer look, she too becomes a generic object and he more interested in self-display. Thus the play’s two languages of heterosexual desire—Petrarchan praise and anti-Petrarchan debasement—appear as opposite ends of a single continuum, as complementary discourses of woman, high and low. Even when Paris and old Capulet, discussing Juliet as prospective bride, vary the discourse to include a conception of woman as wife and mother, she remains an object of verbal and actual exchange.
In lyric poetry, the Petrarchan mistress remains a function of language alone, unheard, seen only as a collection of ideal parts, a center whose very absence promotes desire. Drama is a material medium, however. In drama, the Petrarchan mistress takes on embodiment and finds an answering voice, like Juliet’s gently noting her sonneteer-pilgrim’s conventionality: “You kiss by th’ book” ( 1.5.122 ). In drama, the mistress may come surrounded by relatives and an inconveniently insistent social milieu. As was noted above, Shakespeare distinguishes sharply between the social circumstances of adolescent males and females. Thus one consequence of setting the play’s domestic action solely within the Capulet household is to set Juliet, the “hopeful lady” of Capulet’s “earth” ( 1.2.15 ), firmly into a familial context which, thanks to the Nurse’s fondness for recollection and anecdote, is rich in domestic detail. Juliet’s intense focus upon Romeo’s surname—“What’s Montague? . . . O, be some other name” ( 2.2.43 , 44 )—is a projection onto her lover of her own conflicted sense of tribal loyalty. Unlike Romeo, whose deepest emotional ties are to his gang of friends, and unlike the more mobile daughters of Shakespearean comedy who often come in pairs, Juliet lives isolated and confined, emotionally as well as physically, by her status as daughter. Her own passage into sexual maturity comes first by way of parental invitation to “think of marriage now” ( 1.3.75 ). Her father invites Paris, the man who wishes to marry Juliet, to attend a banquet and feast his eyes on female beauty: “Hear all, all see, / And like her most whose merit most shall be” ( 1.2.30 –31). Juliet, in contrast, is invited to look only where her parents tell her:
I’ll look to like, if looking liking move.
But no more deep will I endart mine eye
Than your consent gives strength to make it fly.
( 1.3.103 –5)
The logic of Juliet’s almost instant disobedience in looking at, and liking, Romeo (rather than Paris) can be understood as the ironic fulfillment of the fears in traditional patriarchal culture about the uncontrollability of female desire, the alleged tendency of the female gaze to wander. Petrarchism managed the vexed question of female desire largely by wishing it out of existence, describing the mistress as one who, like the invisible Rosaline of this play, “will not stay the siege of loving terms, / Nor bide th’ encounter of assailing eyes” ( 1.1.220 –21). Once Romeo, in the Capulet garden, overhears Juliet’s expression of desire, however, Juliet abandons the conventional denial of desire—“Fain would I dwell on form; fain, fain deny / What I have spoke. But farewell compliment” ( 2.2.93 –94). She rejects the “strength” implied by parental sanction and the protection afforded by the Petrarchan celebration of chastity for a risk-taking experiment in desire that Shakespeare affirms by the beauty of the lovers’ language in their four scenes together. Juliet herself asks Romeo the serious questions that Elizabethan society wanted only fathers to ask. She challenges social prescriptions, designed to contain erotic desire in marriage, by taking responsibility for her own marriage:
If that thy bent of love be honorable,
Thy purpose marriage, send me word tomorrow,
By one that I’ll procure to come to thee,
Where and what time thou wilt perform the rite,
And all my fortunes at thy foot I’ll lay
And follow thee my lord throughout the world.
( 2.2.150 –55)
The irony in her pledge—an irony perhaps most obvious to a modern, sexually egalitarian audience—is that Romeo here is following Juliet on an uncharted narrative path to sexual fulfillment in unsanctioned marriage. Allowing her husband access to a bedchamber in her father’s house, Juliet leads him into a sexual territory beyond the reach of dramatic representation. Breaking through the narrow oppositions of the play’s two discourses of woman—as either anonymous sexual object (for Sampson and Gregory) or beloved woman exalted beyond knowing or possessing (for Petrarch)—she affirms her imaginative commitment to the cultural significance of desire as an individualizing force:
Come, civil night,
Thou sober-suited matron all in black,
And learn me how to lose a winning match
Played for a pair of stainless maidenhoods.
Hood my unmanned blood, bating in my cheeks,
With thy black mantle till strange love grow bold,
Think true love acted simple modesty.
( 3.2.10 –16)
Romeo, when he is not drawn by desire deeper and deeper into Capulet territory, wanders into the open square where the destinies of the play’s other young men—and in part his own too—are enacted. Because the young man’s deepest loyalty is to his friends, Romeo is not really asked to choose between Juliet and his family but between Juliet and Mercutio, who are opposed in the play’s thematic structure. Thus one function of Mercutio’s anti-Petrarchan skepticism about the idealization of woman is to offer resistance to the adult heterosexuality heralded by Romeo’s union with Juliet, resistance on behalf of the regressive pull of adolescent male bonding—being “one of the guys.” This distinction, as we have seen, is in part a question of speaking different discourses. Romeo easily picks up Mercutio’s banter, even its sly innuendo against women. Mercutio himself regards Romeo’s quickness at repartee as the hopeful sign of a return to a “normal” manly identity incompatible with his ridiculous role as lover:
Why, is not this better now than groaning for love? Now art thou sociable, now art thou Romeo, now art thou what thou art, by art as well as by nature. For this driveling love is like a great natural that runs lolling up and down to hide his bauble in a hole.
( 2.4.90 –95)
Implicit here is a central tenet of traditional misogyny that excessive desire for a woman is effeminizing. For Mercutio it is the effeminate lover in Romeo who refuses shamefully to answer Tybalt’s challenge: “O calm, dishonorable, vile submission!” he exclaims furiously ( 3.1.74 ). Mercutio’s death at Tybalt’s hands causes Romeo temporarily to agree, obeying the regressive emotional pull of grief and guilt over his own part in Mercutio’s defeat. “Why the devil came you between us?” Mercutio asks. “I was hurt under your arm” ( 3.1.106 –8). Why, we might ask instead, should Mercutio have insisted on answering a challenge addressed only to Romeo? Romeo, however, displaces blame onto Juliet: “Thy beauty hath made me effeminate / And in my temper softened valor’s steel” ( 3.1.119 –20).
In terms of narrative structure, the death of Mercutio and Romeo’s slaying of Tybalt interrupt the lovers’ progress from secret marriage to its consummation, suggesting the incompatibility between romantic individualism and adolescent male bonding. The audience experiences this incompatibility as a sudden movement from comedy to tragedy. Suddenly Friar Lawrence must abandon hopes of using the love of Capulet and Montague as a force for social reintegration. Instead, he must desperately stave off Juliet’s marriage to Paris, upon which her father insists, by making her counterfeit death and by subjecting her to entombment. The legal finality of consummated marriage—which was the basis for Friar Lawrence’s hopes “to turn your households’ rancor to pure love” ( 2.3.99 )—becomes the instrument of tragic design. It is only the Nurse who would allow Juliet to accept Paris as husband; we are asked to judge such a prospect so unthinkable that we then agree imaginatively to Friar Lawrence’s ghoulish device.
In terms of the play’s symbolic vocabulary, Juliet’s preparations to imitate death on the very bed where her sexual maturation from girl- to womanhood occurred confirms ironically her earlier premonition about Romeo: “If he be marrièd, / My grave is like to be my wedding bed” ( 1.5.148 –49). Her brief journey contrasts sharply with those of Shakespeare’s comic heroines who move out from the social confinement of daughterhood into a freer, less socially defined space (the woods outside Athens in A Midsummer Night’s Dream , the Forest of Arden in As You Like It ). There they can exercise a sanctioned, limited freedom in the romantic experimentation of courtship. Juliet is punished for such experimentation in part because hers is more radical; secret marriage symbolically is as irreversible as “real” death. Her journey thus becomes an internal journey in which her commitment to union with Romeo must face the imaginative challenge of complete, claustrophobic isolation and finally death in the Capulet tomb.
It is possible to see the lovers’ story, as some critics have done, as Shakespeare’s dramatic realization of the ruling metaphors of Petrarchan love poetry—particularly its fascination with “death-marked love” ( Prologue. 9 ). 3 But, in pondering the implications of Shakespeare’s moving his audience to identify with this narrative of initiative, desire, and power, we also do well to remember the psychosocial dynamics of drama. By heightening their powers of identification, drama gives the members of an audience an embodied image of the possible scope and form of their fears and desires. Here we have seen how tragic form operates to contain the complex play of desire/identification. The metaphors of Petrarchan idealization work as part of a complex, ambivalent discourse of woman whose ultimate social function is to encode the felt differences between men and women on which a dominant male power structure is based. Romeo and Juliet find a new discourse of romantic individualism in which Petrarchan idealization conjoins with the mutual avowal of sexual desire. But their union, as we have seen, imperils the traditional relations between males that is founded upon the exchange of women, whether the violent exchange Gregory and Sampson crudely imagine or the normative exchange planned by Capulet and Paris. Juliet, as the daughter whose erotic willfulness activates her father’s transformation from concerned to tyrannical parent, is the greater rebel. Thus the secret marriage in which this new language of feeling is contained cannot here be granted the sanction of a comic outcome. When Romeo and Juliet reunite, it is only to see each other, dead, in the dim confines of the Capulet crypt. In this play the autonomy of romantic individualism remains “star-crossed.”
- The story of these massive shifts in European sensibility is told in a five-volume study titled A History of Private Life , gen. eds. Philippe Ariès and Georges Duby (Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1987–91). The study covers over three millennia in the history of western Europe. For the period most relevant to Romeo and Juliet, see vol. 3, Passions of the Renaissance (1989), ed. Roger Chartier, trans. Arthur Goldhammer, pp. 399–607.
- The best extended discussion of the dynamic of the feud is Coppélia Kahn, Man’s Estate: Masculine Identity in Shakespeare (Berkeley: University of California Press, 1981), pp. 83ff.
- Nicholas Brooke, Shakespeare’s Early Tragedies (London: Methuen, 1968), pp. 82ff.
Stay connected
Find out what’s on, read our latest stories, and learn how you can get involved.

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center

What are some examples of film adaptations of Romeo and Juliet ?
- How did Shakespeare die?
- Why is Shakespeare still important today?

Romeo and Juliet
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Internet Shakespeare Editions - Romeo and Juliet
- Shakespeare Birthplace Trust - Romeo and Juliet
- Theatre Database - Romeo and Juliet
- Lit2Go - "Romeo and Juliet"
- Folger Shakespeare Library - Romeo and Juliet
- Shakespeare Online - Romeo and Juliet: Analysis by Act and Scene
- PlayShakespeare.com - Romeo and Juliet Overview
- Internet Archive - "Romeo and Juliet"
- Romeo and Juliet - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
What is Romeo and Juliet about?
Romeo and Juliet is about a young hero and heroine whose families, the Montagues and the Capulets, respectively, are ferocious enemies. Romeo and Juliet ’s passionate star-crossed love leads to their demise, which ultimately serves to pacify the relationship between their families.
What is Romeo and Juliet based on?
Shakespeare’s principal source for the plot of Romeo and Juliet was The Tragicall Historye of Romeus and Juliet , a long narrative poem written in 1562 by the English poet Arthur Brooke , who had based his poem on a French translation of a tale by the Italian writer Matteo Bandello .
Where is Romeo and Juliet set?
Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet is set in Verona , Italy.
How is Romeo and Juliet still relevant today?
The characters of Romeo and Juliet have been continuously depicted in literature, music, dance, and theatre. The premise of the young hero and heroine whose families are enemies is so appealing that Romeo and Juliet have become, in the modern popular imagination, the representative type of star-crossed lovers.
Some of the most distinct film adaptations of Romeo and Juliet are Franco Zeffirelli ’s 1968 version of the same name, which notably cast actors similar in age to the play’s young protagonists; Baz Luhrmann ’s visually vibrant 1996 Romeo + Juliet ; and the 2013 zombie romantic comedy Warm Bodies . Learn more.
Recent News

Romeo and Juliet , play by William Shakespeare , written about 1594–96 and first published in an unauthorized quarto in 1597. An authorized quarto appeared in 1599, substantially longer and more reliable. A third quarto, based on the second, was used by the editors of the First Folio of 1623. The characters of Romeo and Juliet have been depicted in literature , music, dance, and theatre. The appeal of the young hero and heroine—whose families, the Montagues and the Capulets, respectively, are implacable enemies—is such that they have become, in the popular imagination, the representative type of star-crossed lovers.
Shakespeare’s principal source for the plot was The Tragicall Historye of Romeus and Juliet (1562), a long narrative poem by the English poet Arthur Brooke , who had based his poem on a French translation of a tale by the Italian Matteo Bandello .

Shakespeare sets the scene in Verona , Italy . Juliet and Romeo meet and fall instantly in love at a masked ball of the Capulets, and they profess their love when Romeo, unwilling to leave, climbs the wall into the orchard garden of her family’s house and finds her alone at her window. Because their well-to-do families are enemies, the two are married secretly by Friar Laurence . When Tybalt, a Capulet, seeks out Romeo in revenge for the insult of Romeo’s having dared to shower his attentions on Juliet, an ensuing scuffle ends in the death of Romeo’s dearest friend, Mercutio . Impelled by a code of honour among men, Romeo kills Tybalt and is banished to Mantua by the Prince of Verona, who has been insistent that the family feuding cease . When Juliet’s father, unaware that Juliet is already secretly married, arranges a marriage with the eminently eligible Count Paris, the young bride seeks out Friar Laurence for assistance in her desperate situation. He gives her a potion that will make her appear to be dead and proposes that she take it and that Romeo rescue her. She complies. Romeo, however, unaware of the friar’s scheme because a letter has failed to reach him, returns to Verona on hearing of Juliet’s apparent death. He encounters a grieving Paris at Juliet’s tomb, reluctantly kills him when Paris attempts to prevent Romeo from entering the tomb, and finds Juliet in the burial vault. There he gives her a last kiss and kills himself with poison. Juliet awakens, sees the dead Romeo, and kills herself. The families learn what has happened and end their feud.
For a discussion of this play within the context of Shakespeare’s entire corpus, see William Shakespeare: Shakespeare’s plays and poems .
Romeo And Juliet Essay Questions

Romeo And Juliet Lesson Summary and Explanation in English Class 12th
Back to: Karnataka Board Class 12th English Guide and Notes
Table of Contents
Introduction
William Shakespeare was an English dramatist, poet, artist, and playwright, broadly viewed as the best writer in the English language. The story ‘Romeo and Juliet’ is a tragic love story of two lovers Romeo and Juliet who belong to respectable families of Verona that is the Montagues and the Capulets. Both the families had grudges against each other and have been fighting each other as sworn enemies for a long time.
Meanwhile, Paris, a young relative of Prince Escalus falls in love with the fourteen-year-old Julies and wishes to marry her. Lord Capulet thinks she’s too young to marry but reveals that he won’t go against the marriage if Paris can win Juliet’s consent. Meanwhile, Romeo falls in love with Rosaline who doesn’t love him back. The Capulet family organizes a private party and makes a servant in charge of the guest list.
Explanation
He compares Juliet’s beauty to nature. Romeo says that even the bright light of a torch would look dull before the brightness of Juliet. It looks like she hangs on the cheek of the night. Romeo says that the beauty of Juliet is like a jewel that is hung in the ear of an African woman.
Romeo says Juliet is too beautiful to belong to Earth. Juliet’s beauty is so vast that she cannot die and be buried in the Earth. The earth cannot contain her beauty. He further says Juliet is like white snow which is flying with other common people who belong to the species of crows.
Romeo just wishes to express that Juliet belongs to the divine world and living among ordinary and common people. Romeo proposes to find the place where Juliet stood and wants to touch her blessed hand and make his own rude hand blessed. Romeo further asks a question of whether he ever loved before. He feels this is true love. Romeo, think she has never seen a beautiful woman like Juliet before this night.
Background II
Romeo’s friend. Getting back from the wedding Juliet’s brother starts a fight with Romeo because of his interference at the ball. Mercutio, another friend of Romeo gets killed by Tybalt, and aroused by the death of his dearest friend Romeo kills Tybalt. Juliet unaware of the situation wait for Romeo’s arrival at her father’s orchard and becomes impatient as anytime Romeo could arrive but this will be the first time he’ll come as her husband. This monologue is popularly known as ‘Juliet’s invocation to the night’.
Juliet is inviting the night. The night she is inviting is none other than Romeo himself. Juliet compares Romeo tonight. Juliet calls Romeo a day in the night. Juliet sees the night as a bird with wings on which Romeo would ride and come as a ‘New Snow’. Juliet calls the night a gentle night and a ‘Black – Browed Night’. Juliet wants nothing from the night except her love Romeo.
The two Stanzas in the poem, one by Romeo and the other by Juliet, highlight the intensity of love of the young lovers. This intensity of love is brought out by using the contrasting imagery of night and day, black and white, bright jewel and dark surface, snowy dove, etc.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
500+ Words Essay on Romeo And Juliet. Romeo and Juliet is the most famous love tragedy written by William Shakespeare. This is a story of love and fate. Furthermore, the basis of this tragic love story is the Old Italian tale translated into English in the sixteenth century. The story is about two young star-crossed lovers whose death results ...
Romeo goes to see a churchman, Friar Laurence, who agrees to marry Romeo and Juliet. After the wedding, the feud between the two families becomes violent again: Tybalt kills Mercutio in a fight, and Romeo kills Tybalt in retaliation. The Prince banishes Romeo from Verona for his crime. Juliet is told by her father that she will marry Paris, so ...
Act IV. In Act IV, Juliet asks Friar Lawrence for help and he gives her a sleeping potion that will make her appear dead.The next morning, the Capulet family finds Juliet in her bed and believes that she had died. Friar Laurence sends a messenger to inform Romeo about Juliet's plan and instructs Romeo to collect a sleeping Juliet from the Capulet house.
Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare. Published: 1590s. Country: United Kingdom. Publisher: Thomas Creede. Romeo and Juliet is probably the most famous literary love story in the world. Even people who've never read or seen the play know the names of the two main characters. When Shakespeare wrote the play more than 400 years ago, arranged ...
Romeo and Juliet exchange vows of love, and Romeo promises to call upon Juliet tomorrow so they can hastily be married. The next day, Romeo visits a kindly but philosophical friar, Friar Laurence, in his chambers. He begs Friar Laurence to marry him to his new love, Juliet. Friar Laurence urges Romeo to slow down and take his time when it comes ...
Romeo and Juliet is a tragic play by William Shakespeare about two ill-fated teenagers who fall in love despite the bloody feud between their families, the Montagues and the Capulets. Romeo meets ...
Romeo, a Montague, moping for the love of Rosaline at the beginning of the play, falls in love with Juliet at a ball give by Capulet, her father. That Juliet feels the same about him he discovers ...
Romeo notes this distinction when he continues: Arise, fair sun, and kill the envious moon, Who is already sick and pale with grief. That thou, her maid, art fair more fair than she (ll.4-6 ...
Romeo and Juliet is set in Verona, Italy, where there is an ongoing feud between the Montague and Capulet families. The play opens with servants from both houses engaged in a street brawl that eventually draws in the family patriarchs and the city officials, including Prince Escalus. The Prince ends the conflict by issuing a decree that prohibits any further fighting at the risk of great ...
Master Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet using Absolute Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet essay, plot summary, quotes and characters study guides. Plot Summary: A quick plot review of Romeo and Juliet including every important action in the play. An ideal introduction before reading the original text. Commentary: Detailed description of each act with ...
Good. 2 pages / 707 words. In Shakespeare's play, Romeo and Juliet, Shakespeare explores the tragic lives and deaths of the two "star-crossed lovers". Both Romeo and Juliet are unable to escape their dreadful destiny, even though the strength of their love. While fate plays a significant role in the tragic...
A young lovesick Romeo Montague falls instantly in love with Juliet Capulet, who is due to marry her father's choice, the County Paris. With the help of Juliet's nurse, the women arrange for the couple to marry the next day, but Romeo's attempt to halt a street fight leads to the death of Juliet's own cousin, Tybalt, for which Romeo is ...
Rather Romeo and Juliet's love is a social problem, unresolvable except by their deaths, because they dare to marry secretly in an age when legal, consummated marriage was irreversible. Secret marriage is the narrative device by which Shakespeare brings into conflict the new privilege claimed by individual desire and the traditional authority ...
Romeo and Juliet, play by William Shakespeare, written about 1594-96 and first published in an unauthorized quarto in 1597.An authorized quarto appeared in 1599, substantially longer and more reliable. A third quarto, based on the second, was used by the editors of the First Folio of 1623. The characters of Romeo and Juliet have been depicted in literature, music, dance, and theatre.
fate. This essay will explore the themes of love, fate, and conflict in Romeo and Juliet, and how they contribute to the play's enduring appeal. One of the central themes in Romeo and Juliet is the powerful and transformative nature of love. The love between Romeo and Juliet is portrayed as pure and passionate, transcending the boundaries of
Romeo And Juliet Essay Questions Crafting an essay on the subject of "Romeo and Juliet Essay Questions" can present a considerable challenge. The complexity lies not only in the intricacies of Shakespearean language but also in the depth of themes explored in the play. Addressing questions related to the characters, their motivations, the socio-cultural context, and the tragedy itself requires ...
Explanation. He compares Juliet's beauty to nature. Romeo says that even the bright light of a torch would look dull before the brightness of Juliet. It looks like she hangs on the cheek of the night. Romeo says that the beauty of Juliet is like a jewel that is hung in the ear of an African woman. Romeo says Juliet is too beautiful to belong ...