Essay on Mahatma Gandhi – Contributions and Legacy of Mahatma Gandhi
500+ words essay on mahatma gandhi.
Essay on Mahatma Gandhi – Mahatma Gandhi was a great patriotic Indian, if not the greatest. He was a man of an unbelievably great personality. He certainly does not need anyone like me praising him. Furthermore, his efforts for Indian independence are unparalleled. Most noteworthy, there would have been a significant delay in independence without him. Consequently, the British because of his pressure left India in 1947. In this essay on Mahatma Gandhi, we will see his contribution and legacy.


Contributions of Mahatma Gandhi
First of all, Mahatma Gandhi was a notable public figure. His role in social and political reform was instrumental. Above all, he rid the society of these social evils. Hence, many oppressed people felt great relief because of his efforts. Gandhi became a famous international figure because of these efforts. Furthermore, he became the topic of discussion in many international media outlets.
Mahatma Gandhi made significant contributions to environmental sustainability. Most noteworthy, he said that each person should consume according to his needs. The main question that he raised was “How much should a person consume?”. Gandhi certainly put forward this question.
Furthermore, this model of sustainability by Gandhi holds huge relevance in current India. This is because currently, India has a very high population . There has been the promotion of renewable energy and small-scale irrigation systems. This was due to Gandhiji’s campaigns against excessive industrial development.
Mahatma Gandhi’s philosophy of non-violence is probably his most important contribution. This philosophy of non-violence is known as Ahimsa. Most noteworthy, Gandhiji’s aim was to seek independence without violence. He decided to quit the Non-cooperation movement after the Chauri-Chaura incident . This was due to the violence at the Chauri Chaura incident. Consequently, many became upset at this decision. However, Gandhi was relentless in his philosophy of Ahimsa.
Secularism is yet another contribution of Gandhi. His belief was that no religion should have a monopoly on the truth. Mahatma Gandhi certainly encouraged friendship between different religions.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Legacy of Mahatma Gandhi
Mahatma Gandhi has influenced many international leaders around the world. His struggle certainly became an inspiration for leaders. Such leaders are Martin Luther King Jr., James Beve, and James Lawson. Furthermore, Gandhi influenced Nelson Mandela for his freedom struggle. Also, Lanza del Vasto came to India to live with Gandhi.

The awards given to Mahatma Gandhi are too many to discuss. Probably only a few nations remain which have not awarded Mahatma Gandhi.
In conclusion, Mahatma Gandhi was one of the greatest political icons ever. Most noteworthy, Indians revere by describing him as the “father of the nation”. His name will certainly remain immortal for all generations.
Essay Topics on Famous Leaders
- Mahatma Gandhi
- APJ Abdul Kalam
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Swami Vivekananda
- Mother Teresa
- Rabindranath Tagore
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
- Subhash Chandra Bose
- Abraham Lincoln
- Martin Luther King
FAQs on Mahatma Gandhi
Q.1 Why Mahatma Gandhi decided to stop Non-cooperation movement?
A.1 Mahatma Gandhi decided to stop the Non-cooperation movement. This was due to the infamous Chauri-Chaura incident. There was significant violence at this incident. Furthermore, Gandhiji was strictly against any kind of violence.
Q.2 Name any two leaders influenced by Mahatma Gandhi?
A.2 Two leaders influenced by Mahatma Gandhi are Martin Luther King Jr and Nelson Mandela.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

How Mahatma Gandhi changed political protest
His non-violent resistance helped end British rule in India and has influenced modern civil disobedience movements across the globe.

Widely referred to as Mahatma, meaning great soul or saint in Sanskrit, Gandhi helped India reach independence through a philosophy of non-violent non-cooperation.
He’s been called the “father of India” and a “great soul in beggar’s garb." His nonviolent approach to political change helped India gain independence after nearly a century of British colonial rule. A frail man with a will of iron, he provided a blueprint for future social movements around the world. He was Mahatma Gandhi, and he remains one of the most revered figures in modern history.
Born Mohandas Gandhi in Gujarat, India in 1869, he was part of an elite family. After a period of teenage rebellion, he left India to study law in London. Before going, he promised his mother he’d again abstain from sex, meat, and alcohol in an attempt to re-adopt strict Hindu morals.

A portrait of Gandhi as a young man.
In 1893, at the age of 24, the new attorney moved to the British colony of Natal in southeastern Africa to practice law. Natal was home to thousands of Indians whose labor had helped build its wealth, but the colony fostered both formal and informal discrimination against people of Indian descent. Gandhi was shocked when he was thrown out of train cars, roughed up for using public walkways, and segregated from European passengers on a stagecoach.
In 1894, Natal stripped all Indians of their ability to vote. Gandhi organized Indian resistance , fought anti-Indian legislation in the courts and led large protests against the colonial government. Along the way, he developed a public persona and a philosophy of truth-focused, non-violent non-cooperation he called Satyagraha .
Gandhi brought Satyagraha to India in 1915, and was soon elected to the Indian National Congress political party. He began to push for independence from the United Kingdom, and organized resistance to a 1919 law that gave British authorities carte blanche to imprison suspected revolutionaries without trial. Britain responded brutally to the resistance, mowing down 400 unarmed protesters in the Amritsar Massacre .

A map of Gandhi’s 1930 protest march against a law compelling Indians to purchase British salt.
Now Gandhi pushed even harder for home rule, encouraging boycotts of British goods and organizing mass protests. In 1930, he began a massive satyagraha campaign against a British law that forced Indians to purchase British salt instead of producing it locally. Gandhi organized a 241-mile-long protest march to the west coast of Gujarat, where he and his acolytes harvested salt on the shores of the Arabian Sea. In response, Britain imprisoned over 60,000 peaceful protesters and inadvertently generated even more support for home rule.

Children in Rajkot, Gujarat, where Gandhi spent most of his boyhood, dressed as the legendary activist to celebrate what would have been his 144th birthday in 2013. This year will mark Gandhi’s 150th birthday.
By then, Gandhi had become a national icon, and was widely referred to as Mahatma, Sanskrit for great soul or saint. Imprisoned for a year because of the Salt March, he became more influential than ever. He protested discrimination against the “untouchables,” India’s lowest caste, and negotiated unsuccessfully for Indian home rule. Undeterred, he began the Quit India movement , a campaign to get Britain to voluntarily withdraw from India during World War II. Britain refused and arrested him yet again.
Huge demonstrations ensued, and despite the arrests of 100,000 home rule advocates by British authorities, the balance finally tipped toward Indian independence. A frail Gandhi was released from prison in 1944, and Britain at last began to make plans to withdraw from the Indian subcontinent. It was bittersweet for Gandhi, who opposed the partition of India and attempted to quell Hindu-Muslim animosity and deadly riots in 1947.
India finally gained its independence in August 1947. But Gandhi only saw it for a few months; a Hindu extremist assassinated him on January 30, 1948. Over 1.5 million people marched in his massive funeral procession.

Ascetic and unflinching, Gandhi changed the face of civil disobedience around the world. Martin Luther King, Jr. drew on his tactics during the Civil Rights Movement, and the Dalai Lama was inspired by his teachings, which are still heralded by those who seek to inspire change without inciting violence.
But though his legacy still resonates, others wonder whether Gandhi should be revered. Among some Indian Hindus, he remains controversial for his embrace of Muslims. Others question whether he did enough to challenge the Indian caste system. He has also been criticized for supporting racial segregation between black and white South Africans and making derogatory remarks about black people. And though he supported women’s rights in some regards, he also opposed contraception and invited young women to sleep in his bed naked as a way of testing his sexual self-control.
Mohandas Gandhi the man was complex and flawed. However, Mahatma Gandhi the public figure left an indelible mark on the history of India and on the exercise of civil disobedience worldwide. “After I am gone, no single person will be able completely to represent me,” he said . “But a little bit of me will live in many of you. If each puts the cause first and himself last, the vacuum will to a large extent be filled.”
Related Topics
- LAW AND LEGISLATION
- HISTORY AND CIVILIZATION
You May Also Like

Who gets to claim the ‘world’s richest shipwreck’?

Lincoln was killed before their eyes. Then their own horror began.

What made Oxford's medieval students so murderous?

Meet the ruthless king who unified the Kingdom of Hawai'i

Was Manhattan really sold to the Dutch for just $24?
- Environment
- Paid Content
- Photography
- Perpetual Planet
History & Culture
- History & Culture
- History Magazine
- Mind, Body, Wonder
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Your US State Privacy Rights
- Children's Online Privacy Policy
- Interest-Based Ads
- About Nielsen Measurement
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Nat Geo Home
- Attend a Live Event
- Book a Trip
- Inspire Your Kids
- Shop Nat Geo
- Visit the D.C. Museum
- Learn About Our Impact
- Support Our Mission
- Advertise With Us
- Customer Service
- Renew Subscription
- Manage Your Subscription
- Work at Nat Geo
- Sign Up for Our Newsletters
- Contribute to Protect the Planet
Copyright © 1996-2015 National Geographic Society Copyright © 2015-2024 National Geographic Partners, LLC. All rights reserved
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Mahatma Gandhi Essay

Important Essay on Mahatma Gandhi for Students in English
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, often called the 'Father of the Nation' , was a leader who fought for India's freedom from British rule. He believed in non-violence. Every year on October 2nd, Mahatma Gandhi's birthday is celebrated as Gandhi Jayanti to honor his efforts in freeing India.
English Essay on Mahatma Gandhi
Rabindranath Tagore was the first to call Gandhiji 'Mahatma,' which means 'Great Soul' in Sanskrit. His wise ideas and beliefs led people to respect and call him 'Mahatma Gandhi.' His dedication to the country and efforts to turn his ideas into reality make Indians around the world very proud of him .
According to Mahatma Gandhi’s biography, he was born on October 2, 1869 , in Porbandar, a coastal town in the present-day Indian state of Gujarat. He grew up in a Hindu family and ate basic vegetarian meals. His dad, Karamchand Uttamchand Gandhi, was an important leader in Porbandar State. In South Africa, he was the first to lead a peaceful protest movement, setting him apart from other demonstrators. Mahatma Gandhi also introduced the idea of Satyagraha, a nonviolent approach to opposing unfairness. He devoted 20 years of his life to battling discrimination in South Africa.
His idea of 'Ahimsa,' which means not hurting anyone, was widely admired and followed by many influential people worldwide. He became an indomitable figure who couldn't be defeated in any situation. Mahatma Gandhi initiated the 'Khadi Movement' to encourage the use of fabrics like khadi or jute. This movement was a crucial part of the larger 'Non-co-operation Movement,' which advocated for Indian goods and discouraged foreign ones. Gandhi strongly supported agriculture and encouraged people to engage in farming. He inspired Indians to embrace manual labor and emphasized self-reliance, urging them to provide for their needs and lead simple lives. He began weaving cotton clothes using the Charkha to reduce dependence on foreign goods and promote Swadeshi products among Indians.
During the fight for India's freedom, Gandhiji faced imprisonment several times along with his followers, but his main goal was always the freedom of his motherland. Even when he was in prison, he never chose the path of violence.
Mahatma Gandhi made significant contributions to various social issues. His efforts against 'untouchability' while he was in Yerwada Jail, where he went on a hunger strike against this ancient social evil, greatly helped uplift the oppressed community in modern times. He also emphasized the importance of education, cleanliness, health, and equality in society.
These qualities defined him as a person with a great soul and justified his transformation from Gandhi to Mahatma. He led many freedom movements, including the "Quit India Movement," which was highly successful. His death was a huge loss to the forces of peace and democracy, leaving a significant void in the nation's life.
Gopal Krishna Gokhale, a prominent Indian nationalist leader, significantly influenced Mahatma Gandhi's political ideology and leadership approach. Gandhi considered him his political teacher.
Mahatma Gandhi played a crucial role in India's fight for freedom from British rule. His life was dedicated to serving his country and its people, and he became an international symbol of Indian leadership. Even today, he continues to inspire and motivate young people worldwide with his values and principles.
Gandhi Ji was known for his strong sense of discipline. He emphasized the importance of self-discipline in achieving significant goals, a principle he applied in promoting his philosophy of Ahimsa (non-violence). Through his own life, he demonstrated that rigorous discipline can lead to the realization of any objective, provided we remain committed and dedicated. These qualities established him as a revered and respected leader whose influence extends far beyond his lifetime. His ideals continue to resonate not only in India but also around the world.

FAQs on Mahatma Gandhi Essay
1. What were the different movements that Gandhi started in order to bring Independence to India?
In order to bring freedom, Gandhi started the Satyagraha movement in 1919, the non-cooperation movement in 1921, and Civil Disobedience movement in 1930 and Quit India movement in 1942.
2. Who killed Mahatma Gandhi?
A young man named Nathuram Godse killed Mahatma Gandhi when he was going to attend an evening prayer meeting.
3. Why is Gandhi known as the ‘Father of the Nation’?
Mahatma Gandhi is known as the ‘Father of the Nation’ because he laid the true foundation of independent India with his noble ideals and supreme sacrifice.
4. How do we commemorate Mahatma Gandhi’s contribution for our Nation?
His birthday on 2 nd October is celebrated as a National Holiday across the nation in order to commemorate his great contributions and sacrifices for the country’s independence.
5. What are the things we should learn from Mahatma Gandhi?
There are various things one can learn from Gandhiji. The principles that he followed and preached his entire generation and for generations to come are commendable. He believed in ‘Ahimsa’ and taught people how any war in the world can be won through non-violence. To simply state one can learn the following principles from Gandhiji -
Nonviolence,
Respect for elders,
Essay on Mahatma Gandhi
Here we have shared the Essay on Mahatma Gandhi in detail so you can use it in your exam or assignment of 150, 250, 400, 500, or 1000 words.
You can use this Essay on Mahatma Gandhi in any assignment or project whether you are in school (class 10th or 12th), college, or preparing for answer writing in competitive exams.
Topics covered in this article.
Essay on Mahatma Gandhi in 150-250 words
Essay on mahatma gandhi in 300-400 words, essay on mahatma gandhi in 500-1000 words.
Mahatma Gandhi, also known as Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, was a prominent leader in India’s struggle for independence from British rule. Born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, Gujarat, Gandhi played a pivotal role in shaping India’s history and inspiring movements for civil rights and freedom across the world.
Gandhi advocated for nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience as powerful tools to challenge injustice and oppression. He promoted the principles of truth, nonviolence, and peaceful coexistence. Through his leadership, he mobilized millions of Indians in the fight for independence, employing methods such as boycotts, protests, and fasting.
Gandhi’s philosophy of Satyagraha, or truth force, emphasized the power of love, compassion, and moral courage in bringing about social and political change. His commitment to social equality, religious harmony, and the upliftment of the marginalized sections of society continues to inspire generations.
Gandhi’s influence extended beyond India’s struggle for independence. He became an iconic figure and a source of inspiration for civil rights movements and leaders worldwide. His principles of nonviolence, justice, and equality remain relevant in today’s world, where peaceful resistance and social justice continue to be essential aspirations.
In conclusion, Mahatma Gandhi’s life and teachings have left an indelible impact on India and the world. His unwavering commitment to nonviolence, truth, and social justice continues to inspire people to strive for a better, more equitable world. Gandhi’s legacy serves as a reminder that even in the face of adversity, change can be achieved through peaceful means and the power of moral conviction.
Mahatma Gandhi, born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, Gujarat, was a renowned leader and a key figure in India’s struggle for independence from British rule. Fondly known as the “Father of the Nation,” Gandhi left an indelible mark on the world with his philosophy of nonviolence and principles of truth, justice, and equality.
Gandhi’s journey as a leader began in South Africa, where he fought against racial discrimination faced by the Indian community. It was during this time that he developed his concept of Satyagraha, a nonviolent method of resistance that emphasized the power of truth and moral courage. Gandhi firmly believed in nonviolence as a means to achieve social and political change, and he employed it effectively throughout his life.
In India, Gandhi played a pivotal role in leading the Indian National Congress and mobilizing the masses in the fight against British colonial rule. He led numerous campaigns, including the famous Salt March in 1930, where he and his followers marched to the Arabian Sea to produce salt in defiance of the British monopoly. His emphasis on nonviolent resistance, civil disobedience, and peaceful protests inspired millions of Indians to join the struggle for independence.
Beyond India’s fight for freedom, Gandhi’s influence transcended borders. His philosophy of nonviolence inspired movements and leaders around the world, including Martin Luther King Jr., Nelson Mandela, and Aung San Suu Kyi. Gandhi’s teachings emphasized the power of love, compassion, and moral courage in bringing about lasting change. He believed in the unity of all humanity and the importance of harmonious coexistence.
Gandhi’s principles of truth, nonviolence, and social justice remain relevant in today’s world. His emphasis on simplicity, self-reliance, and communal harmony serve as guiding principles for addressing contemporary challenges such as inequality, conflict, and environmental degradation.
In conclusion, Mahatma Gandhi’s life and teachings continue to resonate with people across the globe. His philosophy of nonviolence, his unwavering commitment to truth and justice, and his emphasis on the upliftment of the marginalized are a testament to his visionary leadership. Gandhi’s legacy is a reminder that change can be achieved through peaceful means and the power of moral conviction. His ideals inspire us to strive for a more just, compassionate, and equitable world.
Title: Mahatma Gandhi – The Father of Indian Independence and Champion of Nonviolence
Introduction :
Mahatma Gandhi, born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, Gujarat, was a visionary leader and a prominent figure in India’s struggle for independence from British rule. Fondly referred to as the “Father of the Nation,” Gandhi left an indelible mark on the world with his philosophy of nonviolence and principles of truth, justice, and equality. This essay delves into the life, teachings, and impact of Mahatma Gandhi, highlighting his role as a transformative leader and his enduring legacy as a symbol of peace, nonviolence, and social change.
Early Life and Formative Years
Mahatma Gandhi was born into a middle-class family and received his education in law in London. However, it was during his years in South Africa, where he practiced law, that he encountered racial discrimination and injustice faced by the Indian community. These experiences deeply influenced Gandhi’s outlook and ignited his commitment to fight against oppression and injustice.
Philosophy of Nonviolence and Satyagraha
Gandhi developed a unique philosophy of nonviolence, which he termed Satyagraha or truth force. He believed that nonviolence was not a sign of weakness but a powerful force capable of bringing about profound social and political change. Gandhi advocated for peaceful resistance to injustice, using methods such as civil disobedience, fasting, and peaceful protests to challenge oppressive systems. He firmly believed that by embracing nonviolence, individuals and societies could achieve lasting transformation and justice.
Leadership in the Indian Independence Movement
Gandhi emerged as a prominent leader in the Indian National Congress and spearheaded the struggle for independence from British rule. He emphasized the importance of Swaraj, or self-rule, and called for the empowerment of the Indian masses. Gandhi organized numerous campaigns and movements, including the famous Salt March in 1930, where he and his followers walked 240 miles to the Arabian Sea to protest the British monopoly on salt production. Through his leadership, Gandhi mobilized millions of Indians, cutting across lines of caste, religion, and socio-economic backgrounds, in the fight for freedom.
Principles of Truth and Simplicity
Gandhi’s teachings were rooted in the principles of truth and simplicity. He emphasized the importance of leading an honest and authentic life and believed that truth could conquer any adversity. Gandhi practiced what he preached, adopting a simple lifestyle, wearing homespun cloth (khadi) to promote self-sufficiency, and advocating for economic self-reliance.
Legacy and Impact
Mahatma Gandhi’s impact extended far beyond India’s struggle for independence. His philosophy of nonviolence inspired civil rights movements and leaders around the world, including Martin Luther King Jr., Nelson Mandela, and Aung San Suu Kyi. Gandhi’s commitment to truth, justice, and equality continues to inspire individuals and communities in their pursuit of social change. His principles of nonviolence and peaceful resistance remain relevant in addressing contemporary challenges, such as conflict resolution, human rights, and environmental sustainability.
Conclusion :
Mahatma Gandhi’s life and teachings continue to inspire generations. His philosophy of nonviolence, his unwavering commitment to truth and justice, and his emphasis on equality and social change make him a transformative figure in the history of India and the world. Gandhi’s legacy serves as a reminder that change can be achieved through peaceful means and the power of moral conviction. His ideals inspire us to strive for a more just, compassionate, and equitable world, and his influence continues to shape the path towards peace and social transformation.
Related Posts

Essential Elements of Valid Contract (Explained With Examples)

What is World Population? Main Causes, Effects, Top 20 Countries

Essay on Mahatma Gandhi [100, 150, 200, 300, 500 Words]
Essay on Mahatma Gandhi in English: In this article, you are going to read short and long essays on Mahatma Gandhi in English (100, 150, 200-250, 300, and 500 words). This article will be also helpful for you If you are looking for a speech on Mahatma Gandhi or Paragraph on Mahatma Gandhi in English. We’ve written this article for students of all classes (nursery to class 12). So, let’s get started.
Table of Contents
Short Essay on Mahatma Gandhi 100 Words
Mahatma Gandhi was one of the greatest leaders of our country. He was born in Porbandar, India, on October 2, 1869. His father Karamchand Gandhi was the Dewan and his mother Putlibai was a pious lady. Gandhiji went to England to become a barrister. In 1893 he went to South Africa and worked for the rights of our people.
He returned to India in 1915 and joined the freedom struggle. He started many political movements like Non-cooperation movement, Salt Satyagraha, Quit India Movement to fight against the British. Gandhiji worked for the ending of the caste system and the establishment of Hindu-Muslim unity. He was killed by Nathuram Godse On January 30, 1948.

Mahatma Gandhi Essay in English 150 Words
Mahatma Gandhi was a great leader. His full name was Mohandas and Gandhi. He was born on October 2, 1869 at Porbandar. His father was a Diwan. He was an average student. He went to England and returned as a barrister.
In South Africa, Gandhiji saw the bad condition of the Indians. There he raised his voice against it and organised a movement.
In India, he started the non-cooperation and Satyagraha movements to fight against the British Government. He went to jail many times. He wanted Hindu-Muslim unity. In 1947, he got freedom for us.
Gandhiji was a great social reformer. He worked for Dalits and lower-class people. He lived a very simple life. He wanted peace. He believed in Ahimsa.
On January 30, 1948, he was shot dead. We call him ‘Bapu’ out of love and respect. He is the Father of the Nation.

Also Read: 10 Lines on Mahatma Gandhi
Essay on Mahatma Gandhi 200-250 Words
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, freedom activist, and politician. Gandhiji was born on October 2, 1869 at Porbandar, Gujarat. His father Karamchand Gandhi was the Chief Minister (diwan) of Porbandar state. His mother Putlibai was a religious woman.
He went to England to study law at the age of 18 years. After his return to India, he started a practice as a lawyer in the Bombay High Court. He went to South Africa and started practicing law. There he protested against the injustice and harsh treatment of the white people towards the native Africans and Indians.
He returned to India in 1915 and started to take interest in politics. Mahatma Gandhi used the ideals of truth and non-violence as weapons to fight against British colonial rule. He worked for the upliftment of Harijans. He fought against untouchability and worked for Hindu-Muslim unity.
Through his freedom movements like Non-cooperation movement, Khilafat movement, and civil disobedience movement he fought for freedom against the British imperialists. 1942, he launched the Quit India movement to end the British rule. At last, India got freedom in 1947 at his initiative.
People affectionately call him ‘Bapu’ and the ‘Father of the Nation’. He was shot dead in 1948 by the Hindu fanatic Nathuram Godse. Gandhiji’s life is a true inspiration for all of us.

Mahatma Gandhi Essay in English 300 Words
Mahatma Gandhi was born at Porbandar in Gujarat on 2nd October, 1869. His father was the Diwan of the State. His name was Karam Chand Gandhi. Mahatma Gandhi’s full name was Mohan Das Karamchand Gandhi. His mother’s name was Putali Bai. Mahatma Gandhi went to school first at Porbandar then at Rajkot. Even as a child, Mahatma never told a lie. He passed his Matric examination at the age of 18.
Mohan Das was married to Kasturba at the age of thirteen. Mahatma Gandhi was sent to England to study law and became a Barrister. He lived a very simple life even in England. After getting his law degree, he returned to India.
Mr. Gandhi started his law practice. He went to South Africa in the course of a law suit. He saw the condition of the Indians living there. They were treated very badly by the white men. They were not allowed to travel in 1st class on the trains, also not allowed to enter certain localities, clubs, and so on. Once when Gandhiji was travelling in the 1st class compartment of the train, he was beaten and thrown out of the train. Then Mahatma decided to unite all Indians and started the Non-violence and Satyagrah Movement. In no time, the Movement picked up.
Mahatma Gandhi returned to India and joined Indian National Congress. He started the Non-violence, Non-cooperation Movements here also. He travelled all over India, especially the rural India to see the conditions of the poor.
Mahatma Gandhi started Satyagrah Movement to oppose the Rowlatt Act and there was the shoot-out at Jalian-Wala-Bagh. The Act was drawn after many people were killed. He then started the Salt Satyagraha and Quit India Movements. And finally, Gandhiji won freedom for us. India became free on 15th August, 1947. He is called as “Father of the Nation”. Unfortunately, Gandhiji was shot on 30 January 1948 by a Hindu extremist Nathuram Godse.
Also Read: Gandhi Jayanti Speech 10 Lines
Mahatma Gandhi Essay in English 500 Words
Introduction:.
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi was a politician, social activist, writer, and leader of the Indian national movement. He is a figure known all over the world. His name is a household word in India, rather, in all the world round. His creed of non-violence has placed him on the same par with Buddha, Sri Chaitanya, and Jesus Christ.
Family & Education:
Mahatma Gandhi was born in the small town of Porbandar in the Kathiwad state on October 2, 1869. His father Karamchand Gandhi was the prime minister of Rajkot State and his mother Putlibai was a pious lady. Her influence shaped the future life of Mahatma Gandhi.
He was sent to school at a very early age, but he was not a very bright student. After his Matriculation Examination, he went to England to study law and returned home as a barrister. He began to practice law in Bombay but he was not very successful.
Life in South Africa:
In 1893 Gandhiji went to South Africa in connection with a case. He found his own countrymen treated with contempt by the whites. Gandhiji started satyagraha against this color hated. It was a non-violent protest, yet hundreds were beaten up and thousands were sent to jail. But Gandhiji did not buzz an inch from his faith in truth and non-violence and at last, he succeeded in his mission. He was awarded the title of Mahatma.
Fight for India’s Independence:
In 1915 Gandhiji came back to India after twenty long years in South Africa. He joined the Indian National congress and championed the cause of India’s freedom movement. He asked people to unite for the cause of freedom. He used the weapons of truth and non-violence to fight against the mighty British.
The horrible massacre at Jalianwalabag in Punjab touched him and he resolved to face the brute force of the British Government with moral force. In 1920 he launched the Non-cooperation movement to oppose British rule in India.
He led the famous Dandi March on 12th March 1930. This march was meant to break the salt law. And as a result of this, the British rule in India had already started shaking and he had to go to London for a Round Table Conference in 1931. But this Conference proved abortive and the country was about to give a death blow to the foreign rule.
In 1942 Gandhiji launched his final bout for freedom. He started the ‘Quit India’ movement. At last, the British Government had to quit India in 1947, and India was declared a free country on August 15, 1947.
Social Works:
Mahatma Gandhi was a social activist who fought against the evils of society. He found the Satyagraha Ashram on the banks of the Sabarmati river in Gujarat. He preached against untouchability and worked for Hindu-Muslim unity. He fought tirelessly for the rights of Harijans.
Conclusion:
Mahatma Gandhi, the father of the nation was a generous, god-loving, and peace-loving person. But unfortunately, he was assassinated by Nathuram Godse on 30th January 1948 at the age of 78. To commemorate Gandhiji’s birth anniversary Gandhi Jayanti is celebrated every year on October 2. Gandhiji’s teachings and ideologies will continue to enlighten and encourage us in the future.
Read More: 1. Essay on Swami Vivekananda 2. Essay on Subhash Chandra Bose 3. Essay on Mother Teresa 4. Essay on APJ Abdul Kalam 5. Essay on Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan
Related Posts
Apj abdul kalam essay in english | 100, 200, 300, 500 words, blood donation essay in english | 150, 200, 300 words, my mother essay in english 10 lines [5 sets], essay on mother teresa in english for students [300 words], leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

https://studynlearn.com/
Essay on mahatma gandhi: biography of mahatma gandhi | 800+ words.

Mahatma Gandhi, one of the most influential figures of the 20th century, is widely regarded as the Father of the Nation in India. He was a freedom fighter, political leader, and spiritual teacher who dedicated his life to nonviolent resistance and social justice. In this essay on Mahatma Gandhi biography in English, we will explore his life, legacy, and achievements. From his humble beginnings in Porbandar, Gujarat, to his leadership in India's independence movement, Gandhi's teachings and philosophy have had a profound impact on social and political movements around the world. This essay will delve into his life's work and highlight the enduring legacy of this remarkable individual.
In this article, we have shared 800+ words essay on mahatama gandhi, including all the birth, childhood, marriage and education of Mahatma Gandhi.
Essay On Mahatma Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi is also known as Mahatma Gandhi is considered to be the father of this country. In the fight for independence against British rule, he was the leader of the nationalist movement. He was an Indian lawyer, political ethicist, anti-colonial nationalist, writer, and a kind-hearted person.
Birth and Childhood
Mahatma Gandhi was born on October 2, the year 1869 in a place named Porbandar, Gujrat in northwest India. He was born in a Hindu Modh family. His father Karamchand Gandhi was a political figure and also the chief minister of Porbandar. His mother named Putlibai Gandhi was the fourth wife of his father, previous wives died during childbirth. Gandhi was born in a vaishya family that's why from an early age of life he learned a lot of things such as non-injury to living beings, tolerance and vegetarianism.
In May 1883, he was 13 years old when he got married to a girl named Kasturba Makhanji, who was also 13 years old, this marriage was arranged by their parents. They together had four sons, Harilal (1888), Manilal (1892), Ramdas (1897), Devdas (1900).
In this essay on Mahatma Gandhi, let's know about Mahatma Gandhi's education Porbandar did not have enough chance of education, all the children in school used to write in dust with their fingers. However, he was lucky that his father became the chief minister of another city named Rajkot. He was average in education. At the age of 13, he lost a year at school due to marriage. He was not a shining student in the classroom or playground, but he always obeyed the given order by elders.
That's why like other kids he did not go through all the teenage life. He wanted to eat meat but never did because of their parent's beliefs. In the year of 1887, Gandhi passed the matriculation examination from the University of Bombay and joined a college in Bhavnagar named Samaldas College. It was clear for him by then that if he has to maintain his family tradition and become a high office working person in the state of Gujarat, he would have to become a barrister.
At the age of 18, he was offered to continue his studies in London and he was not very happy at Samaldas College so he accepted the offer and sailed to London in September 1888. After reaching London, He was having difficulty understanding the culture and understanding the English language. Some days after arrival he joined a Law college named Inner Temple which was one of the four London law colleges.
The transformation of changing life from a city to India studying in a college in England was not easy for him but he took his study very seriously and started to brush up his English and Latin. His vegetarianism became a very problematic subject for him as everyone around him as eating meat and he started to feel embarrassed.
Some of his new friends in London said some of the things like not eating meat will make him weak physically and mentally. But eventually, he found a vegetarian restaurant and a book that helped him understand the reason to become a vegetarian. From childhood, he wanted to eat meat himself but never did because of his parents but now in London, he was convinced that he finally embraced vegetarianism and never again thought of eating meat.
After some time he became an active member of the society called London vegetarian society and started to attend all the conferences and journals. In England not only Gandhi met Food faddists but also met some men and women who had vast knowledge about Bhagavad-Gita, Bible, Mahabharata, etc. From them, he learned a lot about Hinduism, Buddhism, Christianity and many others.
Many people he met were rebels not supporting the Victorian establishment from these people Gandhi slowly absorbed politics, personality, and more importantly ideas. He passed his study from England and became a Barrister but there was some painful news was waiting for him back at home in India. In January 1891 Gandhi's mother died while Gandhi was still in London.
He came back to India in July 1891 and started to begin the legal career but he lost his very first case in India. He soon realized that the legal profession was heavily overcrowded and he changed his path. He then was offered to be a teacher in Bombay high school but he turned it down and returned to Rajkot. With the dream of living a good life, he started to draft petitions for litigants which soon ended with the dissatisfaction of a local British officer.
Fortunately in the year 1893, he got an offer to go to Natal, South Africa and work there in an Indian firm for 1 year as it was a contract basis.
Civil Right Movement in Africa
South Africa was waiting with a lot of challenges and opportunities for him. From there he started to grow a new leaf. In South Africa 2 of his four sons were born. He had to face many difficulties there too. Once he as advocating for his client and he had to flee from the court because he was so nervous, he wasn't able to talk properly. But the bigger problem was waiting for him, as he had to face racial discrimination in South Africa.
In the journey from Durban to Pretoria, he faced a lot from, being asked to take off the turban in a court to travel on a car footboard to make room for European passenger but he refused. He was beaten by a taxi driver and thrown out of a first-class compartment but these instances made him strong and gave him the strength to fight for justice.
He started to educate others about their rights and duties. When he learned about a bill to deprive Indians of the right to vote, it was that time when others begged him to take up the fight on behalf of them. Eventually at the age of 25 in July 1894 he became a proficient political campaigner.
He drafted petitions and got them signed by hundreds of compatriots. He was not able to stop the bill but succeeded in drawing the attention of the public in Natal, England, and India. He then built many societies in Durban. He planted the seed, spirit of solidarity in the Indian community.
Very well known newspapers of that time such as The Times of London and The Statesman and Englishman of Calcutta were writing about him from this his success could be measured. He began to wear white Indian dhoti in this time-period which later became his trademark. He started a non-violent protest against tax also known as "Satyagraha" where he led a march with more than 2000 people and later he was arrested and for nine-month he was in prison.
His contribution to India's Freedom struggle and Achievements
Back in India, in the year of 1919, the British started to arrest and imprison anyone they suspect of sedition that's when Gandhi stood up and started non-violent disobedience. Gandhi's goal about Indian's independence got cleared after a tragic incident when more than 20000 protesters were getting open fired by the British army in the city of Amritsar.
400 people were killed and 1000 injured. He started the mass boycotts of British goods and institutions and told everyone to stop working for the British. In 1992 he was again got arrested and got a 6-year prison sentence. In 1930 he started the salt march and a very well known campaign of walking 390km to the Arabian Sea shores.
The salt act protesters around 60,000 including Gandhi were imprisoned. At the time of World War II, Gandhi started his campaign if Quit India to banish British rule from the country, he was again arrested and sent to prison with many other well-known leaders of Indian Congress. He met King George V on behalf of the Indian National Congress, but there was not that much progress.
After the End of the war, Britain's government was changed and this time progress was made they were willing to discuss independence for India but a tragic event followed by it partition of the country into India and Pakistan. In 1947 India gained independence. In the year of 1948, a Hindu extremist killed Gandhi. In this essay on Mahatma Gandhi, learn about the contributions made by Mahatma Gandhi!
What he was famous for?
He was known for his silent protest, disobedience campaign in India, Satyagraha, and passive resistance. His death made India mourn for 13 days, His birthday 2nd October is celebrated as a national holiday in India.
Why he was called Mahatma?
The title Mahatma means "great- soul". It is a title that was given to him by Rabindranath Tagore but he thinks he is not worthy of this title so he never accepted it.
Books dedicated to him or written by him
He was a writer from an early age, he liked writing books and there are many books written by him. Some of the most famous of them is Autobiography of Gandhi, The Essential Gandhi, Hind Swaraj and other writings, the words of Gandhi, Satyagraha in South Africa, and many more.
Many writers have written about Mahatma Gandhi some of them are Great Soul by Joseph Lelyveld, Gandhi Before India by Ramachandra Guha, The Good Boatman by Rajmohan Gandhi, Gandhi: Prisoner of hope by Judith M. Brown, etc.
While writing an essay on mahatma gandhi you can include books dedicated to him or his autobiographies.
Mahatma Gandhi Struggled very much from his early life but regardless of all the suffering, he made his way. And he is a very important part of our history of independence. We hope we have covered all the detail in this essay on Mahatma Gandhi for you to write a perfect essay!
Short Essay On Mahatma Gandhi Biography In English
Mahatma Gandhi, also known as Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, was a prominent Indian leader who played a pivotal role in India's struggle for independence. This essay on Mahatma Gandhi biography in English will explore his life, legacy, and achievements.
Gandhi was born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, Gujarat. After studying law in London, he moved to South Africa, where he fought against discrimination faced by the Indian community. His experiences in South Africa would later shape his philosophy of nonviolent resistance or Satyagraha.
Returning to India in 1915, Gandhi became a prominent leader in India's independence movement. He advocated for nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience against British colonial rule. His leadership and vision played a crucial role in India's eventual independence in 1947.
Gandhi's teachings have had a profound impact on social and political movements around the world. His message of nonviolent resistance has inspired many leaders, including Martin Luther King Jr. and Nelson Mandela. He was a spiritual leader who believed in the power of love and compassion to bring about social change.
In addition to his political achievements, Gandhi was also an advocate for social justice and equality. He fought against caste discrimination, championed the rights of women, and promoted communal harmony.
In conclusion, Mahatma Gandhi was a remarkable individual whose life and teachings continue to inspire people around the world. His philosophy of nonviolent resistance, his leadership in India's independence movement, and his advocacy for social justice and equality make him a true hero of our time. This essay on Mahatma Gandhi biography in English is a testament to his enduring legacy.
Read More- APJ Abdul Kalam Essay | Biography | 800+ Words
- May,13 2021
Leave your comment
Reply comment.

- Students' Projects
- Mahatma Gandhi - Father of the Nation
Mahatma Gandhi Essay in English
Mahatma Gandhi is popularly known as 'Father of Nation', was a great Indian freedom warrior. He played a major role in uprooting British rule from Indian soil and followed 'Ahimsa', the non-violence.

Table of Contents
Mahatma Gandhi Essay in English: Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi who is known by the name, Mahatma Gandhi is popularly called as Father of Nation. His contributions towards the freedom struggle and to making India free from the rule of the British Raj are immense and could not be put into simple words. To pay tribute to his efforts in the freedom struggle and to his ideologies we celebrate Gandhi Jayanti on the 2nd of October every year. Schools and colleges celebrate and commemorate this special day by conducting competitions on writing Gandhi Jayanti Essay and arranging a patriotic Gandhi Jayanti speech . This day is declared to be a Public and Bank Holiday across the Nation. In this essay, you can find information on his contribution and legacy.
In this essay, we have provided insights into Gandhiji’s birth, movements and campaigns led by him, his contributions to the freedom struggle, ideologies and principles followed by him and much more. He has great thoughts, ideologies and principles and so people called him Mahatma which means ‘great soul’ in Sanskrit. He always followed the principle of ‘Ahimsa’ which is non-violence in attaining freedom from British reign. Read ahead to this essay on Mahatma Gandhi to gather more information on our father of the nation.
Gandhiji’s Childhood
Mahatma Gandhi was born on 2nd October 1869 in Porbandar, Gujarat, and played a pivotal role in India’s struggle for independence through nonviolent civil disobedience. He was raised in an affluent Hindu Family. He was interested in pursuing law and therefore he went to England to study the same and soon became a Barrister. He was born to Karamchand Gandhi (Father of Mahatma Gandhi), the dewan of Porbandar. Growing up with principles of dharma and ahimsa (non-violence) helped Gandhi to walk on the emergence of freedom. To practice the law, he went to South Africa where he was deeply annoyed by the Europeans’ rule against South Africans where there were racial and color discrimination issues.
Campaigns and Movements led by Gandhiji
Gandhiji developed a concept of a Non-violent Movement called ‘Satyagraha’ and he united Indians who had settled in South Africa from different religions, communities or languages. When he returned to India, he saw British people dominating Indians, cruelly. But Gandhiji followed a non-violent method in uprooting Britishers from Indian soil. His concept of ‘Ahimsa’, not to injure anyone is highly appreciable.
Therefore he started several movements such as the Khadi movement to make use of fibres such as Jute or Khadi and weaved the same using a chakra. He started with the Non-Co-operation movement to make use of Indian Swadeshi goods and stopped the use of foreign goods. A major breakthrough movement is the ‘Quit India Movement’ to put an end to the British Colonial rule in India.
Central to Gandhi’s ideology was the concept of ahinsa, or nonviolence, which he believed could transform society. His campaigns, such as the Salt Satyagraha and Dandi March, were iconic examples of peaceful resistance. Mahatma Gandhi’s ability to mobilize the masses without resorting to violence showcased the potency of his principles.
Dandi March or Salt Satyagraha: This is a non-violent civil disobedience campaign led by Gandhiji in the year 1930 to resist the payment of taxes levied on salt which was available free of cost to the common people. He led a campaign starting from Sabarmati Ashram along with his followers to reach Dandi and there at a seashore he took a lump of salty mud and boiled it, thereby, producing illegal salt.
Mahatma Gandhi in Freedom Struggle
Mahatma Gandhi Ji played a major and very important role in the freedom struggle of India. He was imprisoned several times but he didn’t give up the efforts and pace of freedom fighting. He had driven off the ‘Untouchability’ issue while he got imprisoned in Yerwada Jail and went on fast for several days. He also stressed the need and importance of education, cleanliness, health, and equality in society.
In the year 1915, Mahatma Gandhi returned back to India and joined the Indian National Congress Party and demanded ‘Purn Swaraj’, which means complete independence from British rule. Satyagraha was announced by him, which created a major revolt which was the massacre of Amritsar. He also started the Civil disobedience Movement which involved the oppression of British rule by strictly not adhering to the laws and orders imposed by the Britishers. Then Martial law was imposed, which was an important aspect of the Indian Independence movement.
Gandhi’s impact reverberated globally, influencing civil rights movements and inspiring leaders like Martin Luther King Jr. and Nelson Mandela. Despite criticism and challenges, he remained steadfast in his convictions, leaving an indelible mark on the world as a symbol of peace, justice, and the enduring power of nonviolence.
Principles of Gandhiji
Mahatma Gandhi, a key figure in India’s struggle for independence, advocated principles of non-violence, truth, and self-discipline. He believed in Ahinsa, the idea that one should avoid causing harm to others, both physically and verbally. Truthfulness, or Satya, was another core principle, emphasizing the importance of honesty in all aspects of life. Gandhi also promoted self-discipline, encouraging individuals to control their desires and lead a simple life. His physiology extended to the concept of Sarvodaya, meaning the welfare of all. Gandhi’s teachings emphasized the power of love, compassion, and tolerance, fostering unity among diverse communities. Through these principles, he aimed to create a society where individuals worked collectively for the common good, breaking free from the shackles of oppression and injustice.
On the whole, Mahatma Gandhi ji was a man of simplicity but his ideologies had no boundaries. He is highly revered and respected even now after a number of decades because of his fame, ethics, and values. As Indians, let us all try to follow the principle of Mahatma Gandhi and enlighten our lives to achieve bigger goals.
Sharing is caring!
Mahatma Gandhi Essay: FAQ's
Q1. who is called as 'mahatma'.
Ans. Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, was known in the name of 'Mahatma' by Rabindranath Tagore which means great soul in sanskrit.
Q2. Where was Gandhiji born?
Ans. Gandhiji was born on 2nd October 1869 in Porbandar, Gujarat.
Q3. What are the famous movements initiated by Gandhiji?
Ans. Gandhiji had started various movements for freedom struggle in a non-violent manner, which are satyagraha, khadi movement, non-cooperative movement, Quit India movement, Civil disobedience movement .
Q4. When is Gandhi Jayanti celebrated?
Ans. Gandhi Jayanti is celebrated on 2nd of October every year, as a remembrance of Gandhiji's birthdate.
As Team Lead- Content Writer, I take on leadership within our content creation team, overseeing the development of error-free educational content. My primary responsibility is to produce and analyse high-quality content educating and informing the aspirants about upcoming government exams published on our website. I have more than 6 years experience in content writing wherein 3.5 years of experience in ed-tech content writing.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Board Result 2024
- RBSE Class 8th Result 2024
- RBSE Class 5th Result 2024
- RBSE Class 10th Result 2024
- RBSE Class 10th Toppers 2024
- Plus One Result 2024 Out
- Maharashtra SSC Result 2024
CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 English Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus
CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 10 English Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Science Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 SST Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Hindi Syllabus
- CUET Exam Analysis 2024
- CUET Answer Key 2024
- CUET Admit Card 2024
- NEET Result 2024
- NEET OMR Response Sheet 2024
- NEET Rank Predictor 2024
- NEET Question Paper 2024
- NEET Answer Key 2024
Latest Posts
Important exams.
- JEE Mains 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- NIMCET 2024
- AP EAMCET 2024
- TS EAMCET 2024
- AP ECET 2024
- TS ECET 2024
- TS PGECET 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- AP Polycet 2024
- TS Polycet 2024
- JEECUP 2024
- Bihar Polytechnic 2024
- Jharkhand Polytechnic 2024
- Responsible Disclosure Program
- Cancellation & Refunds
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Mahatma Gandhi – 200, 400, 600 Words

- Updated on
- May 3, 2024

Born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, Gujarat, Mahatma Gandhi was a proponent of non-violence and truth, earning him the title of a truth messenger. Coming from a well-to-do family, he was known by his full name, Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi. Although he was a reserved and diligent student, he ventured to England for legal studies and later became a barrister upon his return to India, practising law in the Bombay High Court.
However, Gandhi’s true calling lay beyond the legal profession. During his time in South Africa , he allied with the locals and initiated the non-violent Satyagraha movement , aimed at challenging the oppression imposed by Europeans . Eventually, he returned to India and took a leading role in the struggle for India’s independence from British rule.
Deeply moved by the suffering of his fellow Indians, he launched the Non-Cooperation Movement and the Quit India Movement, advocating non-violent resistance against the British.
We have provided some essays on Mahatma Gandhi below that will be useful for speech delivery, essay writing, or speech-providing competitions. After reading these essays on Babu, you will get knowledge about his life and beliefs, his teachings, the role he played in the independence movement and why he is regarded as the most revered leader in the world.
Table of Contents
- 1 Essay on Mahatma Gandhi (200 Words)
- 2.1 Birth and Childhood
- 2.2 Marriage and Education
- 2.3 Civil Rights Movement in Africa
- 3.1.1 Champaran and Kheda Agitations
- 3.1.2 Non-cooperation Movement
- 3.1.3 Salt Satyagraha or Salt March
- 3.1.4 Quit India Movement
- 3.2.1 Champion Against Racial Discrimination in South Africa
- 3.2.2 The Icon of India’s Freedom Struggle
- 3.2.3 Eradicating Social Evils
- 3.3 Demise
- 4 Simple Essay on Mahatma Gandhi
Quick Read: How to Calculate Percentage in ICSE Board Class 10?
Also Read: How to Write an Essay in English
Also Read: Speech on Republic Day for Class 12th
Essay on Mahatma Gandhi (200 Words)
Mahatma Gandhi, who was born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, India, struggled and gave up things he valued to free India from British oppression. All throughout his life, he was guided by nonviolent beliefs.
One of the greatest political figures in history, Mahatma Gandhi is revered and held in the highest regard in India as the “father of the nation.” His legacy will live on forever, inspiring future generations with his words and example.
Bapu struggled greatly and gave up a lot of his personal possessions in his quest to free India from British tyranny, but he never wavered from his nonviolent beliefs.
His legal career took him to South Africa, where he fought against racial injustice. He married Kasturba at the age of thirteen and continued his schooling in London.
Gandhi used nonviolence in a number of movements during India’s war for independence, including the Champaran and Kheda agitations, the Non-cooperation Movement, the Salt March, and the Quit India Movement . His influence was felt all around the world, motivating figures like Nelson Mandela and Martin Luther King Jr .
Gandhi made contributions to secularism, environmental sustainability, and social transformation. His legacy is firmly based on his nonviolence (Ahimsa) ideology. On January 30, 1948, he was murdered, yet his influence lives on, earning him the title of renowned “Father of the Nation and Bapu” in India’s history.
Also Read: Essay on Peer Pressure
Essay on Mahatma Gandhi (400 Words)
Mahatma Gandhi stands as one of the greatest political icons in history, with Indians holding him in the highest esteem and revering him as the “father of the nation.” His name and teachings will undoubtedly remain immortal, continuing to inspire generations to come.
Throughout his efforts, Mahatma Gandhi endured great hardship and made significant personal sacrifices in his mission to liberate India from British rule, all while steadfastly adhering to non-violent principles.
Let’s dive deeper into his life:
Birth and Childhood
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, which is now part of the state of Gujarat, India.
His father, Karamchand Gandhi, held the position of Chief Minister (diwan) in Porbandar during that period. Gandhi’s mother, Putlibai, was a deeply devout and charitable woman.
As a young boy, Gandhi embodied his mother’s qualities, inheriting her strong values, ethical principles, and spirit of self-sacrifice.
Marriage and Education
At the tender age of 13, Mohandas entered into marriage with Kasturba Makanji. In 1888, they welcomed a baby boy before he set sail for London to pursue further studies. In 1893, he ventured to South Africa to continue his law practice, where he encountered severe racial discrimination imposed by the British.
A significant incident that profoundly impacted the young Gandhi was when he was forcibly evicted from a first-class train compartment solely due to his race and skin colour.
Civil Rights Movement in Africa
Having endured discrimination and humiliation due to his race and colour, Gandhi made a resolute pledge to combat and confront racial discrimination against immigrants in South Africa. In 1894, he established the Natal Indian Congress and embarked on a relentless crusade against racial prejudice. Gandhi passionately advocated for the civil rights of immigrants in South Africa, devoting approximately two decades to this endeavour.
Mahatma Gandhi’s influence has reached far and wide, touching the lives of numerous international leaders across the globe. Leaders like Martin Luther King Jr. , James Bevel, and James Lawson found inspiration in his struggle and adopted his principles. Nelson Mandela, in his quest for freedom, was also deeply influenced by Gandhi’s teachings, while Lanza del Vasto even chose to reside in India to be close to him.
The impact of Mahatma Gandhi’s legacy is evident in the recognition he received from the United Nations. They have honoured him by designating 2nd October as the “International Day of Nonviolence.” Additionally, many countries observe 30th January as the School Day of Nonviolence and Peace to commemorate his ideals.
Throughout his life, Mahatma Gandhi received numerous awards and accolades, making his contribution widely acknowledged. Almost every nation has bestowed honours upon him, with only a few exceptions.
Also Read: Essay on Education System
Essay on Mahatma Gandhi (600 Words)
Mahatma Gandhi, who was born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, Gujarat, advocated for truth and non-violence, giving him the moniker “truth messenger.” He was referred to by his full name, Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, and he came from a wealthy family.
Let’s dive deep into the life of Mahatma Gandhi in this essay.
Role of Mahatma Gandhi in India’s Freedom Struggle
The significance of non-violence in India’s freedom struggle gained prominence with the involvement of Mahatma Gandhi. While there were parallel violent movements against British rule, the peaceful nature of non-violence made it a powerful way to demand complete independence.
Mahatma Gandhi utilized non-violence in every movement against the British government, and some of the most notable non-violent movements were as follows:
Champaran and Kheda Agitations
In 1917, Mahatma Gandhi organized a non-violent protest against the British-imposed indigo cultivation and fixed pricing, leading to the acceptance of farmers’ demands. Similarly, in 1918, he led peaceful protests against the British administration for tax relief during a famine in the Kheda region, resulting in the suspension of revenue collection.
Non-cooperation Movement
Sparked by the Jallianwala Bagh massacre and harsh British policies in 1920, this movement promoted the boycott of British products and services. Indians withdrew from British-run institutions and civil services, significantly affecting British administration without resorting to violence.
Salt Satyagraha or Salt March
In 1930, Mahatma Gandhi led the famous 26-day non-violent march to Dandi, Gujarat, protesting the salt monopoly imposed by the British. Breaking the salt laws and promoting local salt production, the Salt March gained international attention and strengthened the foundation of Independent India.
Quit India Movement
Launched on August 8, 1942, the Quit India Movement demanded the British to leave India. Despite being in the midst of World War II, the non-violent civil disobedience movement intensified the pressure on the British government and paved the way for India’s eventual independence.
These non-violent movements, led by Mahatma Gandhi, wielded the power of truth and non-violence as their weapons against British rule. The effectiveness of non-violence garnered international attention and exposed the oppressive policies of the British government to the world.
Accomplishments
Mahatma Gandhi, a man on a mission, not only played a crucial role in India’s fight for independence but also made significant contributions to eradicate various social evils. His accomplishments can be summarized as follows:
Champion Against Racial Discrimination in South Africa
Witnessing the racial discrimination in South Africa deeply affected Mahatma Gandhi, motivating him to take a stand against it. He courageously challenged the law that denied voting rights to non-European individuals and became a prominent civil rights activist fighting for the rights of immigrants in South Africa.
The Icon of India’s Freedom Struggle
As a prominent leader of the Indian independence movement, Mahatma Gandhi adopted a liberal approach, advocating peaceful and nonviolent protests against British rule. His leadership in movements like the Champaran Satyagraha, Civil Disobedience Movement, Salt March, and Quit India Movement garnered global attention and shook the foundation of British rule in India.
Eradicating Social Evils
Gandhi Ji dedicated himself to rooting out various social evils prevalent in society at that time. He initiated campaigns to ensure equal rights for the untouchables and uplift their status in society. Additionally, he championed women’s empowerment, promoted education, and vehemently opposed child marriage, leaving a lasting impact on Indian society.
Demise
After India gained independence in 1947, Mahatma Gandhi’s life came to a tragic end when he was assassinated by a Hindu activist named Nathuram Godse on January 30, 1948.
Throughout his life, he devoted himself to the service of the motherland, leaving a profound impact on the nation. His teachings and actions illuminated our path to true freedom from British rule.
Also Read: Essay On Subhash Chandra Bose
Simple Essay on Mahatma Gandhi
Here is a short and simple essay on Mahatma Gandhi for school students:
Also Read: National Safe Motherhood Day 2023
A. Mahatma Gandhi, also known as Gandhiji or Bapu, emerged as a prominent leader during India’s struggle for independence from British rule. He firmly advocated non-violence, civil disobedience, and passive resistance as effective means to achieve social and political transformation.
A. Mahatma Gandhi was born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, a town located in present-day Gujarat, India.
A. His full name was Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi.
A. Gandhi played a pivotal role in India’s freedom struggle, leading various non-violent movements and campaigns against British rule, including the Non-Cooperation Movement, Salt Satyagraha, and Quit India Movement.
Explore more interesting essay topics
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu.
Abhishek Kumar Jha
Abhishek Kumar Jha is a professional content writer and marketer, having extensive experience in delivering content in journalism and marketing. He has written news content related to education for prominent media outlets, garnering expansive knowledge of the Indian education landscape throughout his experience. Moreover, he is a skilled content marketer, with experience in writing SEO-friendly blogs. His educational background includes a Postgraduate Diploma in English Journalism from the prestigious Indian Institute of Mass Communication (IIMC), Dhenkanal. By receiving an education from a top journalism school and working in the corporate world with complete devotion, he has honed the essential skills needed to excel in content writing.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in


Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
India’s Struggle for Independence: Indian Freedom Movement
Last updated on April 8, 2024 by ClearIAS Team

In the 6-part framework to study modern Indian History , we have so far covered:
- India in 1750 .
- British Expansion .
- The changes introduced by the British .
- Popular Uprisings and Revolts against the British
- Socio-religious movements in India .
In this article (6th part), we discuss the emergence of Indian nationalism and India’s struggle for independence.
Table of Contents
Indian Nationalism
India has been unified under many empires in its history like the Mauryan Empire and Mughal empire. A sense of oneness has been there for ages – even though most of the centralised administration in India didn’t last long.
With the end of Mughal rule, India broke into hundreds of princely states. The British – which were instrumental in the fall of the Mughal Empire – held control over the princely states and created the British Indian Empire .
However, most Indians were extremely dissatisfied with the exploitative foreign rule.
The educated Indians realised that the British always gave priority to their colonial interests and treated India only as a market.

They advocated for the political independence of India.
Foundation of Indian National Congress (INC) in 1885
The late nineteenth century witnessed the emergence of many political organisations in British India.
Indian National Congress (also known as Congress Party) founded in 1885 was the most prominent one.
Initially, its aim was to create a platform for civic and political dialogue between Indians and the British Raj and thus obtain a greater share of government for educated Indians.
Later, under the leaders like Mahatma Gandhi , Jawarhal Nehru , Subhas Chandra Bose , and Sardar Vallabhai Patel , the Congress party played a central role in organising mass movements against the British.
Partition of Bengal (1905)
Indian nationalism was gaining in strength and Bengal was the nerve centre of Indian nationalism in the early 1900s.
Lord Curzon, the Viceroy (1899-1905), attempted to ‘dethrone Calcutta’ from its position as the centre from which the Congress Party manipulated throughout Bengal, and indeed, the whole of India.

The decision to partition Bengal into two was in the air from December 1903.
Congress party – from 1903 to mid-1905 – tried moderate techniques of petitions, memoranda, speeches, public meetings and press campaigns. The objective was to turn to public opinion in India and England against the partition.
However, Viceroy Curzon 1905 formally announced the British Government’s decision for the partition of Bengal on 19 July 1905. The partition took effect on 16 October 1905.
The partition was meant to foster another kind of division – on the basis of religion. The aim was to place Muslim communalists as a counter to the Congress. Curzon promised to make Dacca the new capital.
This resulted in a lot of discontent among the Indians. Many considered this as a policy of ‘Divide and Rule’ by the British.
This triggered a self-sufficiency movement popularly known as the Swadeshi movement.
Also read: Dr. Rajendra Prasad: Architect of the Indian Republic
The Swadeshi Movement (1905-1908)
From conservative moderation to political extremism, from terrorism to incipient socialism, from petitioning and public speeches to passive resistance and boycott, all had their origins in the movement.
Swadeshi is a conjunction of two Sanskrit words: swa (“self”) and desh (“country”).
The movement popularised the use and consumption of indigenous products. Indians started ditching British goods for Indian products.
Women, students, and a large section of the urban and rural population of Bengal and other parts of India became actively involved in politics for the first time with Swadeshi Movement.
The message of Swadeshi and the boycott of foreign goods soon spread to the rest of the country.
The militant nationalists led by Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Bipin Chandra Pal, Lajpat Rai and Aurobindo Ghosh were in favour of extending the movement to the rest of India and carrying it beyond the programme of just Swadeshi and boycott to a full-fledged political mass struggle. For them, the aim was Swaraj.
In 1906, the Indian National Congress at its Calcutta Session presided over by Dadabhai Naoroji, declared that the goal of the Indian National Congress was ‘self-government or Swaraj like that of the United Kingdom or the Colonies.
There were differences in the ideologies of the congressmen who were popularly known by the names Moderates and the Extremists. They had differences of opinion regarding the pace of the movement and the techniques of struggle to be adopted. This came to a head in the 1907 Surat session of the Congress where the party split (the two factions re-joined later).
This period also saw a breakthrough in Indian art, literature, music, science and industry.
It was, perhaps, in the cultural sphere that the impact of the Swadeshi Movement was most marked. The songs composed at that time by Rabindranath Tagore, Rajani Kanta Sen etc became the moving spirit for nationalists of all hues.
In art, this was the period when Abanindranath Tagore broke the domination of Victorian naturalism over Indian art and sought inspiration from the rich indigenous traditions of Mughal, Rajput and Ajanta paintings.
In science, Jagdish Chandra Bose, Prafulla Chandra Ray, and others pioneered original research that was praised the world over.
The Swadeshi period also saw the creative use of traditional popular festivals and melas as a means of reaching out to the masses. The Ganapati and Shivaji festivals, popularized by Tilak, became a medium for Swadeshi propaganda not only in Western India but also in Bengal.
Another important aspect of the Swadeshi Movement was the great emphasis given to self-reliance or ‘Atmasakti’in various fields meant the re-asserting of national dignity, honour and confidence.
Self-reliance also meant an effort to set up Swadeshi or indigenous enterprises. The period saw a mushrooming of Swadeshi textile mills, soap and match factories etc.
One of the major features of the programme of self-reliance was Swadeshi or National Education. In 1906, the National Council of Education was established. The vernacular medium was given stress from the primary to university level.
Corps of volunteers (or samitis as they were called) were another major form of mass mobilization widely used by the Swadeshi Movement. The Swadesh Bandhab Samiti set up by Ashwini Kumar Dutt was the most well-known volunteer organization of them all.
Reasons for the failure of the Swadeshi Movement
- The main drawback of the Swadeshi Movement was that it was not able to garner the support of the mass. The British use of communalism to turn the Muslims against the Swadeshi Movement was to a large extent responsible for this.
- During the Swadeshi phase, the peasantry was not organized around peasant demands. The movement was able to mobilize the peasantry only in a limited way.
- By mid-1908 repression took the form of controls and bans on public meetings, processions and the press.
- The internal squabbles, and especially, the split in the Congress (1907), the apex all-India organization, weakened the movement.
- The Swadeshi Movement lacked an effective organization and party structure.
- Lastly, the movement declined because of the very logic of mass movements itself — they cannot be sustained endlessly.
However, the movement made a major contribution in taking the idea of nationalism, in a truly creative fashion, to many sections of the people. The peasant participation in the Swadeshi Movement even though less, marked the very beginnings of modern mass politics in India.
Also read: Ghadar Party
The Split in the Congress (1907)
The main public leaders of the two wings, Tilak (of the Extremists) and Gokhale (of the Moderates) were aware of the dangers of disunity in the nationalist ranks.
A split was avoided in 1906 by choosing Dadabhai Naoroji as president of INC in the Calcutta session. Also, four compromise resolutions on the Swadeshi, Boycott, National Education, and Self-Government demands were passed. However, the hope of a united Congress was short-lived.
The Extremists wanted to extend the Swadeshi and the Boycott Movement from Bengal to the rest of the country but the Moderators opposed it.
The Extremists were fumed by the rumours that the Moderates wanted to scuttle the four Calcutta resolutions. This created friction among them which led to the split at the Congress session was held on 26 December 1907 at Surat, on the banks of the river Tapti.
The Indian National Congress split in December 1907. By 1907, the Moderate nationalists had exhausted their historical role. They failed to meet the demands of the new stage of the national movement and even failed to attract the younger generation.
Almost at the same time, revolutionary terrorism made its appearance in Bengal.
Britain’s policy towards INC
- The British had been suspicious of the National Congress from its inception but they were not overtly hostile either.
- In 1888 Viceroy Dufferin ridiculed INC as representing only the elite — ‘a microscopic minority’.
- Lord Curzon said: “The Congress is tottering to its fall, and one of my greatest ambitions while in India is to assist it to a peaceful demise.”
- The intimidating policies of the British towards INC changed once the Swadeshi and Boycott Movement began. The strengthening of the militant nationalist trend alarmed the British.
- A new policy, known as the policy of the carrot and the stick was invoked. It was three-pronged. It was described as a policy of r epression-conciliation-suppression .
- The Extremists were repressed, though mildly in the first stage. The purpose is to frighten the Moderates. The British also tried to pacify Moderates through some concessions and promises if they disassociated themselves from the Extremists. However, the British always wanted to suppress Extremists.
Minto-Morley constitutional reforms (1909)
The Government of India which was headed by Lord Minto as Viceroy and John Morley as the Secretary of State offered fresh reforms in the Legislative Councils. They began discussions with Moderates within Indian National Congress regarding this. However, when the decision was taken, not just Moderates but the country as a whole were disappointed.
Major Provisions:
- The Indian Councils Act of 1909 increased the number of elected members (but most of them were still indirectly elected) in the Imperial Legislative Council and the provincial legislative councils.
- An Indian was to be appointed a member of the Governor-General’s Executive Council.
- The Act permitted members to introduce resolutions; it also increased their power to ask questions.
- Voting on separate budget items was allowed.
The real purpose of the Morley-Minto Reforms was to divide the nationalist ranks and encourage the growth of Muslim communalism. For the latter, they introduced the system of separate electorates under which Muslims could only vote for Muslim candidates in constituencies specially reserved for them.
The Ghadar Movement (1914)
The outbreak of the First World War in 1914 gave impetus to the nationalist feelings of Indians. The Home Rule League by Lokmanya Tilak and Annie Besant were formed during First World War.
At the same time, a revolutionary movement gained popularity – The Ghadar Movement. (Note: The word Ghadar means ‘revolt’)
The Ghadar Movement was an international political movement founded by expatriate Indians to overthrow British rule in India.
The early membership was composed mostly of Punjabi Indians who lived and worked on the West Coast of the United States and Canada. The movement later spread to India and Indian diasporic communities around the world.
The main leader initially was Bhagwan Singh, a Sikh priest who had worked in Hong Kong and the Malay States.
Later Har Dayal took leadership and played a crucial role in the Ghadar movement. He issued a Yugantar Circular praising the attack on the Viceroy. He urged Indians in the USA not to fight against the US but use their freedom in the US to fight the British.
The Ghadar militants toured extensively, visiting mills and farms where most of the Punjabi immigrant labour worked. The Yugantar Ashram became the home and headquarters and refuge of these political workers.
Komagatamaru Incident
- The Komagata Maru incident involved the Japanese steamship Komagata Maru, on which a group of people from British India attempted to immigrate to Canada in April 1914. Most of the ship passengers were denied entry and forced to return to Calcutta (present-day Kolkata). There, the Indian Imperial Police attempted to arrest the group leaders. A riot ensued, and they were fired upon by the police, resulting in the deaths of 22 people.
- British Government passed orders that no passenger be allowed to disembark anywhere on the way — not even at the places from where they had joined the ship — but only at Calcutta.
- It triggered off a wave of resentment and anger among the Indian community and became the occasion for anti-British mobilization.
- A number of Ghadar leaders, like Barkatullah and Tarak Nath Das, used the inflammatory passions surrounding the Komagata Maru incident as a rallying point and successfully brought many disaffected Indians in North America into the party’s fold.
Ghadar’s weakness
- Ghadar leaders completely underestimated the extent of preparation needed at every level — organizational, ideological, strategic, tactical, and financial — that was necessary before an armed revolt could be organized.
- An almost non-existent organizational structure; the Ghadar Movement was sustained more by the enthusiasm of the militants than by their effective organization.
- The movement failed to generate an effective and sustained leadership that was capable of integrating the various aspects of the movement. Har Dayal’s ideas did not form a structured vision but remained a shifting amalgam of various theories that attracted him from time to time.
- Lacking a mass base, despite the remarkable heroism of the individual revolutionaries who operated in small secret groups, the movement could not withstand suppression by the strong colonial state.
- The Ghadar Movement came to an abrupt end with the arrest of Har Dayal.
The Home Rule Movement (1916-1918)
The Home Rule Movement under the leadership of Annie Besant and Bal Gangadhar Tilak was an important political movement that set the stage for India’s struggle for independence.
Annie Besant, who was a proponent of Free Thought, Radicalism, Fabianism and Theosophy, had come to India in 1893 to work for the Theosophical Society.
In 1914, she decided to enlarge the sphere of her activities. She started a movement for Home Rule on the lines of the Irish Home Rule League.
She realized that she needs the cooperation of both Moderates and Extremists. In the annual session of the Congress 1915, it was decided that the Extremists be allowed to rejoin the Congress along with the Moderates.
Tilak set up the Home Rule League in the Bombay Province.
The two leagues worked in different areas.
Tilak promoted the Home Rule campaign which linked the question of Swaraj with the demand for the formation of linguistic states and education in the vernacular medium.
Members of Gokhale’s Servants of India Society, though not permitted to become members of the League, encouraged the demand for Home Rule by undertaking lecture tours and publishing pamphlets.
During the Lucknow session of the Congress in December 1916, the famous Congress-League Pact was declared. Both Tilak and Annie Besant had played a role in bringing about this agreement between the Congress and the League, much against the wishes of many important leaders, including Madan Mohan Malaviya. This pact is popularly known as the Lucknow Pact where separate electorates for Muslims were accepted.
The turning point in the home rule movement came with the decision of the Government of Madras in 1917 to place Mrs Besant and her associates, B.P. Wadia and George Arundale, under arrest.
Montague Declaration was introduced by the British government as a sign of a conciliatory effort. Henceforth, Home Rule or self-government movement was not treated as a seditious activity. However, this did not mean that the British were ready to grant self-government.
In 1920 All India Home Rule League changed its name to Swarajya Sabha.
The main achievement of the Home Rule Movement was that it created a generation of ardent nationalists who formed the backbone of the national movement. In the later years, under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi , the Indian freedom struggle entered its truly mass phase.
Champaran movement in Bihar (1917)
Mahatma Gandhi, after his struggle against apartheid in South Africa (racial discrimination against blacks) for almost twenty years, returned to India in 1915. On Gokhale’s advice, he spent a year travelling around British India to understand the problems of Indians.
He initially maintained a distance from political affairs, including the Home Rule Movement that was gathering momentum at this time.
Mahatma Gandhi began his experiments with Satyagraha against the oppressive European indigo planters at Champaran in Bihar in 1917.
Champaran issue had actually begun in the early 19th century when European planters made agreements with Indian farmers that forced them to cultivate indigo on the 3/20th of their holdings (known as the Tinkathia system).
Resistance kept surfacing within planters and cultivators, because of the exploitation measures adopted by the British behind the indigo cultivation.
In 1908 Raj Kumar Shukla, a local man persuaded Gandhiji to come to Champaran to investigate the problem. Gandhi reached Champaran but faced resistance from the Commissioner who ordered him to immediately leave the district. Gandhiji refused. He preferred to take the punishment for his defiance of the law. This step was unusual because even Home Rule leaders used to obey the Government.
The British Indian government didn’t want to create a controversy and ordered the local Government to retreat. They allowed Gandhiji to proceed with his enquiry and even nominated him as one of the enquiry members of the Government.
Meanwhile, Gandhiji started investigating the grievances of peasants along with Brij Kishore, Rajendra Prasad and other members of the Bihar intelligentsia. J.B. Kripalani toured the villages and recorded the statements of peasants.
Gandhiji had little difficulty in convincing the Commission that the Tinkathia system needed to be abolished and that the peasants should be compensated for the illegal enhancement of their dues. The Commission founder planters guilty of exploitation.
The commission of enquiry decided to make refunds to the peasants. Gandhi asked for 50%. But the representative of planters offered to refund to the extent of 25%. In order to break the deadlock, Gandhiji agreed to a 25 per cent refund to the farmers. For Gandhi, it was not the money but the principles that were of utmost importance. In his belief, the submission of British landlords was more significant than the percentage of refunds.
Ahmedabad Satyagraha in Gujarat (1918)
In Ahmedabad, a dispute was brewing between workers and mill owners over the question of a ‘plague bonus’.
The employers wanted to withdraw the bonus once the epidemic had passed but the workers insisted it stay.
The British Collector asked Gandhiji to work out a compromise. Gandhiji persuaded the mill owners and the workers to agree to arbitration.
The workers demanded a 50% wage hike while the mill owners offered only a twenty per cent wage hike. They threatened to dismiss all workers who did not accept it.
Gandhiji advised the workers to go on strike. He himself started fasting for workers.
Gandhiji was peculiar in that workers should get at least a thirty-five per cent increase in wages.
Finally, the strike was withdrawn after mill owners agreed to a thirty-five per cent increase the workers had demanded.
Anasuya Behn was one of the main lieutenants of Gandhiji in this struggle.
Kheda Satyagraha in Gujarat (1918)
The Kheda district of Gujarat was on the verge of famine owing to the failure of the crops.
The yield had been so low that the cultivators were unable to pay the revenue. But the government insisted that the cultivators should pay the tax.
Gandhi saw the justice of the cause of the cultivators. Enquiries by members of the Servants of India Society and Vithalbhai Patel too confirmed the genuineness of the peasants’ case.
Gandhiji advised the withholding of tax payments, and asked the peasants to ‘fight unto death against such a spirit of vindictiveness and tyranny’.
The peasants of Kheda, already deprived because of plague, high prices and drought, were showing signs of weakness when Gandhiji came to know that the Government had issued secret instructions directing that revenue should be recovered only from those peasants who could pay.
The Government said that if well-to-do cultivators paid up the poorer section would be granted suspension. This was agreed to and the campaign ended.
The Kheda Satyagraha marked the beginning of an awakening among the peasants of Gujarat, the beginning of their true political education. In addition, it gave the educated public workers the chance to establish contact with the actual life of the peasants.
Rowlatt Satyagraha (1919)
During the First World War of 1914-18, the British instituted censorship of the press and permitted detention without trial.
The Anarchical and Revolutionary Crimes Act of 1919, popularly known as the Rowlatt Act, was passed by the Imperial Legislative Council in Delhi on 18 March 1919, indefinitely extending the emergency measures of preventive indefinite detention, incarceration without trial and judicial review enacted in the Defence of India Act 1915 during the First World War.
It was enacted in light of a perceived threat from revolutionary nationalists to organisations of re-engaging in similar conspiracies as during the war which the Government felt the lapse of the Defence of India Act would enable.
This act was passed on the recommendations of the Sedition Committee chaired by Sir Sidney Rowlatt.
Gandhiji launched Satyagraha against the inhuman Rowlatt Act.
The protests were particularly intense in the Punjab Gandhiji was detained while proceeding there.
Jallianwala Bagh massacre (1919)
The passage of the Rowlatt Act in 1919 resulted in large-scale political unrest throughout India.
A large peaceful crowd had gathered at the Jallianwala Bagh in Amritsar, Punjab to protest against the arrest of pro-Indian independence leaders Dr. Saifuddin Kitchlew and Dr. Satya Pal.
In response to the public gathering, the British Brigadier-General R. E. H. Dyer surrounded the Bagh with his soldiers.
General Dyer ordered his troops to open fire on the nationalist meeting killing hundreds. The brutality at Jallianwala Bagh stunned the entire nation.
This event caused many moderate Indians to abandon their previous loyalty to the British and become nationalists distrustful of British rule.
Non-cooperation Movement (1920)
Gandhiji called for a campaign of “non-cooperation” with British rule. Indians who wished colonialism to end were asked to stop attending schools, colleges, and law courts. They were asked to not pay taxes. In sum, they were asked to adhere to a “renunciation of all voluntary association with the British Government”.
Gandhiji said that if non-cooperation was effectively carried out India would win swaraj within a year.
When Congress met for its annual session at Nagpur, C.R. Das moved the main resolution on non-cooperation. Many groups of revolutionary terrorists, especially in Bengal, also pledged support to the movement.
The goal of the Congress, by this time, changed from the attainment of self-government by constitutional means to the attainment of Swaraj by peaceful means.
Khilafat Movement (1919-24)
The Khilafat movement was a political protest campaign launched by Muslims of British India to restore the caliph of the Ottoman Caliphate, who was considered the leader of the Muslims.
To further broaden the Indian freedom struggle, Gandhiji joined hands with the Khilafat Movement.
The movement collapsed by late 1922 when Turkey gained a more favourable diplomatic position and moved towards Nationalism. By 1924, Turkey abolished the role of the caliph.
However, the tremendous participation of Muslims in the Non-Cooperation Movement and the maintenance of communal unity, despite the Malabar developments, was in itself no mean achievement.
Chauri Chaura incident (1922)
On 4 February 1922, at Chauri Chaura (a place in modern Uttar Pradesh), the British police opened fire at a large group of people who were participating in the Non-cooperation movement.
In retaliation, the demonstrators attacked and set fire to a police station, killing all of its occupants. The incident led to the death of three civilians and 22 policemen.
Mahatma Gandhi, who was strictly against violence, halted the non-cooperation movement on the national level on 12 February 1922, as a direct result of the Chauri Chaura incident.
In spite of Gandhi’s decision, 19 arrested demonstrators were sentenced to death and 14 to imprisonment for life by the British colonial authorities.
Motilal Nehru, C.R. Das, Jawaharlal Nehru, Subhas Bose, and many others recorded their disagreement on Gandhiji’s views.
Bardoli Satyagraha in Gujarat (1928)
In January 1926, the officer charged with the duty of reassessment of the land revenue demand of the taluq had recommended a 30% increase over the existing assessment.
The Congress leaders were quick to protest against the increase and set up the Bardoli Inquiry Committee to go into the issue.
In July 1927, the Government reduced the enhancement to 21.97 per cent. But the concessions were too meagre and came too late to satisfy anybody.
The constitutionalist leaders now began to advise the peasants to resist by paying only the current amount and withholding the enhanced amount.
Gradually as the limitations of constitutional leadership became more apparent, Vallabhbhai Patel was invited to lead the campaign.
The government ignored Vallabhai’s request which resulted in the start of Bardoli Satyagraha.
The no-tax movement was launched in Bardoli taluq of Surat district in Gujarat in 1928.
The main mobilization was done through extensive propaganda via meetings, speeches, pamphlets, and door-to-door persuasion. Special emphasis was placed on the mobilization of women and many women activists were recruited for the purpose.
Members of the Bombay Legislative Council like K.M. Munshi and Lalji Naranji, the representatives of the Indian Merchants Chamber, resigned their seats.
The government was forced to conduct an inquiry. The inquiry was done by a judicial officer, Broomfield, and a revenue officer, Maxwell. They came to the conclusion that the increase had been unjustified. The government later reduced the enhancement to 6.03 per cent.
The boycott of the Simon Commission (1927)
On 8 November 1927, an all-white, Simon Commission was appointed to recommend whether India was ready for further constitutional reforms.
Indian National Congress boycott Simon Commission because no Indian was present in the commission. There were protests in many places.
In Lahore, Lala Lajpat Rai, the hero of the extremist days and the most revered leader of Punjab was hit. He succumbed to the injuries in November 1928.
Bhagat Singh and his comrades sought to avenge the death of Lala Lajpat Rai. They killed the white police official, Saunders, in December 1928.
Jawaharlal Nehru and Subhas Bose emerged as the leaders during the Simon Commission boycott movement.
Nehru Report (1928) and the attempt to draft the Indian Constitution
Britain did not acknowledge the right of Indians to frame their own constitution.
British policy, until almost the end of the Raj, was that the timing and nature of Indian constitutional development were to be decided exclusively by the British Parliament, but it was assumed that Indians would be consulted as appropriate.
In December 1927, at its Madras session, the Indian National Congress took two major decisions in response to the setting up the Simon Commission: first, it decided to not cooperate with the Commission; second, it set up an All Parties Conference to draft a Constitution for India.
The committee of the All Parties Conference to draft the Constitution was chaired by Motilal Nehru with his son Jawaharlal Nehru acting as a secretary. There were nine other members in this committee.
The report submitted by the committee in 1928 was called the Nehru Report – which was actually a memorandum to appeal for dominion status and a federal set-up of government for the constitution of India.
The Nehru Report also rejected the principle of separate communal electorates on which previous constitutional reforms had been based. Seats would be reserved for Muslims at the Centre and in provinces in which they were in a minority, but not in those where they had a numerical majority.
The Nehru Report also recommended universal adult suffrage, equal rights for women, freedom to form unions, and dissociation of the state from religion in any form.
However, Jinnah withdrew his support to the report and proposed his ‘Fourteen Points’ which were basically a reiteration of his objections to the Nehru Report.
Young and radical nationalists led by Jawaharlal Nehru had objections to the Nehru Report of Motilal Nehru. Their slogan was ‘Complete Independence.’
Purna Swaraj or Complete Independence Campaign (1929)
In the Lahore session in 1929, Jawaharlal Nehru was made the President of INC. He declared ‘Purna Swaraj’ or Complete Independence as the only honourable goal Indians could strive for.
On the banks of the river Ravi, at midnight on 31 December 1929, the tricolour flag of Indian independence was hosted.
The first task that the Congress set itself in the new year was that of organizing all over the country public meetings at which the Independence Pledge would be read out and collectively affirmed on 26 January.
Civil Disobedience Movement and Dandi March (1930)
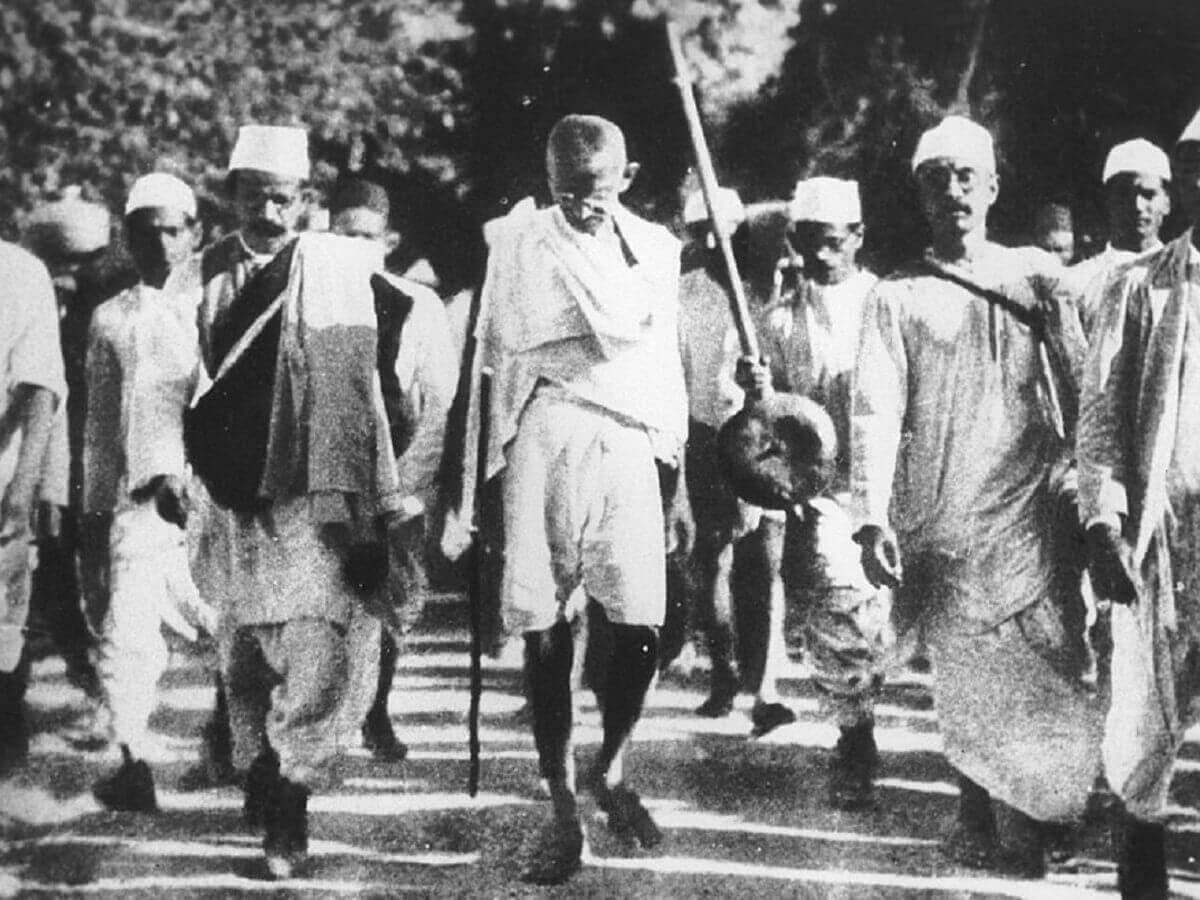

The Lahore Session of Congress (1929) authorized the Working Committee to launch a programme of civil disobedience including non-payment of taxes.
Gandhi’s ultimatum to Lord Irwin, stating the minimum demands in the form of 11 points, had been ignored, and there was now only one way out: civil disobedience. Gandhi selected salt as his main tool of disobedience.
In every Indian household, salt was indispensable; yet people were forbidden from making salt even for domestic use, compelling them to buy it from shops at a high price. The state monopoly over salt was deeply unpopular. By making salt his target, Gandhiji hoped to mobilise a wider discontent against British rule.
Gandhi, along with a band of seventy-eight members of the Sabarmati Ashram started to march from Ahmedabad to the coast at Dandi. There he broke the salt laws by collecting salt from the beach.
On 6 April 1930, by picking up a handful of salt, Gandhi inaugurated the Civil Disobedience Movement – a movement that was to remain unsurpassed in the history of the Indian national movement for the country-wide mass participation it unleashed.
Like other parts of India, the civil disobedience movement was also launched in North-West Frontier Province (Khyber–Pakhtoonkhwa). The local Congress sought help from the Khudai Khidmatgars, the most popular socio-political organization in the province.
Khan Abdul Gaffar Khan’s Khudai Khidmatgars, popularly known as the Red Shirts, played an extremely active role in the Civil Disobedience Movement.
The city came under the control of the masses for at least a week and the soldiers of the Garhwali regiment refused to fire at the unarmed crowds of Peshwar demonstrations.
Nehru’s arrest on 14th April was followed by public protests in Madras, Calcutta and Karachi.
The Salt March was notable for at least three reasons:
- It was this event that first brought Mahatma Gandhi to world attention.
- It was the first nationalist activity in which women participated in large numbers. Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay had persuaded Gandhi for this issue.
- It was the Salt March that forced upon the British the realisation that their Raj would not last forever, and that they would have to devolve some power to the Indians.
Gandhi-Irwin Pact (1931) and the Round Table Conferences (1930-32)
British convened a series of “Round Table Conferences” in London to discuss constitutional reforms in India.
The first meeting was held in November 1930. However, without the pre-eminent political leader in India, it was an exercise in futility.
Gandhi was released from jail in January 1931. In the following month, he had several long meetings with the Viceroy. These culminated in what was called the “Gandhi-Irwin Pact’.
The terms of the agreement included the immediate release of all political prisoners not convicted for violence, the remission of all fines not yet collected, the return of confiscated lands not yet sold to third parties, and lenient treatment for those government employees who had resigned. The Government also conceded the right to make salt for consumption to villages along the coast. They also gave the right to peaceful and non-aggressive picketing.
The Congress’s demand for a public inquiry into police excesses was not accepted, but Gandhiji’s insistent request for an inquiry was recorded in the agreement.
Congress, on its part, agreed to discontinue the Civil Disobedience Movement (CDM).
A second Round Table Conference was held in London in the latter part of 1931. Here, Gandhiji represented the Congress. Gandhi opposed the demand for separate electorates for “lower castes”. For him, separate electorates to the “Untouchables” will ensure their bondage in perpetuity. He thought this would prevent their integration into mainstream society and permanently segregate them from other caste Hindus.
But Ambedkar was in favour of separate electorates for depressed classes. He believed it is the only path for a community so handicapped to succeed in the struggle for life against the organised tyranny of higher castes.
During the second Round Table Conference in London, Winston Churchill, leader of the right wing, strongly objected to the British Government negotiating on terms of equality with the ‘seditious fakir’. He demanded a strong government in India.
The discussions with Gandhi failed as the British Government refused to concede the basic Indian demand for freedom. Gandhiji resumed Civil Disobedience after reaching back
The government launched its strike against the national movement by arresting Gandhi. British government promulgated ordinances that gave the authorities unlimited power – the ‘Civil Martial Law.’ Civil liberties no longer existed and the authorities could seize people and property at will.
In 1934 the inevitable decision to withdraw Civil Disobedience Movement was taken by Gandhi.
However, many political activists were not in favour of stopping the movement. They included Jawaharlal Nehru who was critical of Gandhiji’s decisions regarding the timing of the withdrawal of CDM.
The support that the movement had garnered from the poor and the illiterate, both in the town and in the country, was remarkable indeed.
Nevertheless, the participation of Muslims in the Civil Disobedience Movement was certainly nowhere near that of the Non-cooperation movement 1920-22.
For Indian women, the movement was the most liberating experience to date and can truly be said to have marked their entry into the public space.
The Communal Award (1932)
After the Third Round Table Conference, in November 1932, the then Prime Minister of Britain Ramsay McDonald gave an order which is known as the Communal Award.
It was part of Britain’s policy of ‘Divide and Rule.
The award granted separate electorates in British India for the Forward Caste, Lower Caste, Muslims, Buddhists, Sikhs, Indian Christians, Anglo-Indians, Europeans and Untouchables (Dalits) etc.
The Congress Party was unhappy at the extension of communal representation but became particularly outraged at the British offer of separate-electorate seats for “depressed classes”.
Gandhi viewed the McDonald Award as a nefarious British plot to wean more than 50 million Hindus away from their higher-caste brothers and sisters.
The idea of a separate electorate for Muslims had been accepted by Congress as far back as 1916 as a part of the compromise with the Muslim League. Hence, Congress took the position it was opposed to separate electorates but not in favour of changing the Award without the consent of the minorities.
Gandhi demanded that the representatives of the Depressed Classes should be elected if possible by the universal, common franchise. At the same time, he did not object to the demand for a larger number of reserved seats for the Depressed Classes. He went on a fast unto death on 20 September 1932 to enforce his demand.
In the end, political leaders succeeded in bringing an agreement, known as the Poona Pact.
In this pact, the idea of separate electorates for the Depressed Classes was abandoned but the seats reserved for them in the provincial legislatures and Central Legislature were increased.
After being released from prison Gandhiji shifted to Satyagraha Ashram at Wardha after abandoning Sabarmati Ashram at Ahmedabad for he had vowed in 1930 not to return to Sabarmati till Swaraj was won.
Government of India Act (1935)
The growing demand for constitutional reforms in India led the British Parliament to enact the Government of India Act 1935.
The Act promised some form of representative government.
The Act provided the establishment of an All-India Federation based on the union of British Indian provinces and the Princely States.
Defence and foreign affairs would remain outside the control of the federal legislature, while the Viceroy would retain special control over other subjects.
Governors, appointed by the British Government, retained special powers. They could veto legislative and administrative measures, especially those concerning minorities, the rights of civil servants, law and order, and British business interests.
The Governor also had the power to take over and indefinitely run the administration of a province.
The Act of 1935 was condemned and unanimously rejected by Congress. The Congress demanded the convening of a Constituent Assembly elected on the basis of adult franchise to frame a constitution for an independent India.
Resignation of Congress ministries (1939)
Congress won the elections to the provincial assemblies held in February 1937. Its election manifesto reaffirmed its total rejection of the 1935 Act.
One of the first acts of the Congress Government was to release thousands of political prisoners and to cancel deportation orders on political workers.
The difference between the Congress provinces and the non-Congress provinces of Bengal and Punjab was most apparent in this realm. In the latter, especially in Bengal, civil liberties continued to be curbed and they never released prisoners.
However, Congress could not attempt a complete overhaul of the agrarian structure by completely eliminating the Zamindari system .
Later the Second World War broke out. Mahatma Gandhi and Jawaharlal Nehru promised Congress support to the war effort if the British, in return, promised to grant India independence once hostilities ended. The offer was refused. Gandhi withdrew support to the British in War.
The Congress ministries resigned in October and November 1939, in protest against Viceroy Lord Linlithgow’s action of declaring India to be belligerent in the Second World War without consulting the Indian people.
The resignations brought the Left and the Right in Congress closer because of a common policy on the question of participation in the war.
Crisis at Tripuri (1939)
Subhas Bose had been a unanimous choice as the President of Congress in 1938. In 1939, he decided to stand again — this time as the spokesperson of militant politics and radical groups.
However, with the blessings of Gandhiji, Sardar Patel, Rajendra Prasad, J.B. Kripalani other leaders put up Pattabhi Sitaramayya as a candidate for the post.
Bose accused Patel and other top leaders of Congress as ‘rightists’. He openly accused them of working for a compromise with the Government on the question of the federation. Bose had, therefore, appealed to Congressmen to vote for a leftist and ‘a genuine anti-federationist.’
Nevertheless, in reality, the difference between ‘right’ and ‘left’ was not very vivid within the Congress and most Congressmen were anti-federationist.
Subhas Bose won the election on 29 January on the popularity of his militant politics but only by a narrow margin – 1580 votes against 1377.
But the election of Bose brought the brewing crisis to a head at the Tripuri session of the Congress.
Gandhiji declared that Sitaramayya’s defeat was ‘more mine than his.
Bose argued in his presidential address at Tripuri for a programme of immediately giving the British Government a six-month ultimatum to grant the national demand for independence and of launch a mass civil disobedience movement if it failed to do so.
Subhas Bose believed that the Congress was strong enough to bunch an immediate struggle and that the masses were ready for such a struggle.
However, Gandhi’s perceptions were very different. Gandhi believed the time was not yet ripe for an ultimatum because neither Congress nor the masses were yet ready for struggle.
The internal strife reached its climax at the Tripuri session of the Congress, held from 8 to 12 March 1939.
Bose had completely misjudged his support and the meaning of his majority in the presidential election. Congressmen had voted for him not because they wanted to have him as the supreme leader of the national movement – but mainly because of his policies and militant politics. They were not willing to reject Gandhi’s leadership or his views.
Bose resigned from the presidency. This led to the election of Rajendra Prasad in his place.
Subsequently, Subhas Bose and his followers formed the Forward Bloc as a new party within Congress.
As Bose planned a protest against an AICC resolution, the Working Committee removed Bose from the presidentship of the Bengal Provincial Congress Committee and debarred him from holding any Congress office for three years.
Individual Satyagraha (1940)
Gandhiji decided to initiate a limited satyagraha on an individual basis by a few selected individuals in every locality. The demand of a satyagrahi was for the freedom of speech to preach against participation in the War.
The satyagrahi would beforehand inform the district magistrate of the time and place where he or she was going to make the anti-war speech. If the Government did not arrest a satyagrahi, he or she would not only repeat the performance but move into the villages and start a trek towards Delhi, thus participating in a movement that came to be known as the ‘Delhi Chalo’ (onwards to Delhi) movement.
Vinoba Bhave was to be the first satyagrahi on 17 October 1940 and Jawaharlal Nehru the second.
Individual Satyagraha served a dual purpose — (1) it gave expression to the Indian people’s strong political feelings, (2) it gave the British Government another opportunity to peacefully accept the Indian demands.
Cripps Mission (1942)
The Cripps Mission was a failed attempt in late March 1942 by the British government to secure full Indian cooperation and support for their efforts in World War II.
The mission was headed by a senior minister Sir Stafford Cripps, traditionally sympathetic to Indian self-rule.
However, he was also a member of the coalition War Cabinet led by Prime Minister Winston Churchill, who had long been the leader of the movement to block Indian independence.
Churchill was persuaded to send Sir Stafford Cripps, to India to try and forge a compromise with Gandhiji and the Congress.
The Declaration promised India Dominion Status and a constitution-making body after the War. He proposed that the Constitutional Assembly members would be elected by the provincial assemblies and nominated by the rulers in the case of the princely states.
At that time, the demand for a separate nation for Muslims – Pakistan – also got momentum.
The Pakistan demand was accommodated by the provision that any province which was not prepared to accept the new constitution would have the right to sign a separate agreement with Britain regarding its future status.
Talks broke down, when, Congress objected to the provision for Dominion Status rather than full independence.
Congress insisted that if it was to help the British defend India from the Axis powers, then the Viceroy had first to appoint an Indian as the Defence Member of his Executive Council.
After the failure of the Cripps Mission, Mahatma Gandhi decided to launch the “Quit India” campaign also known as the ‘August Revolution’.
Quit India Movement (1942)
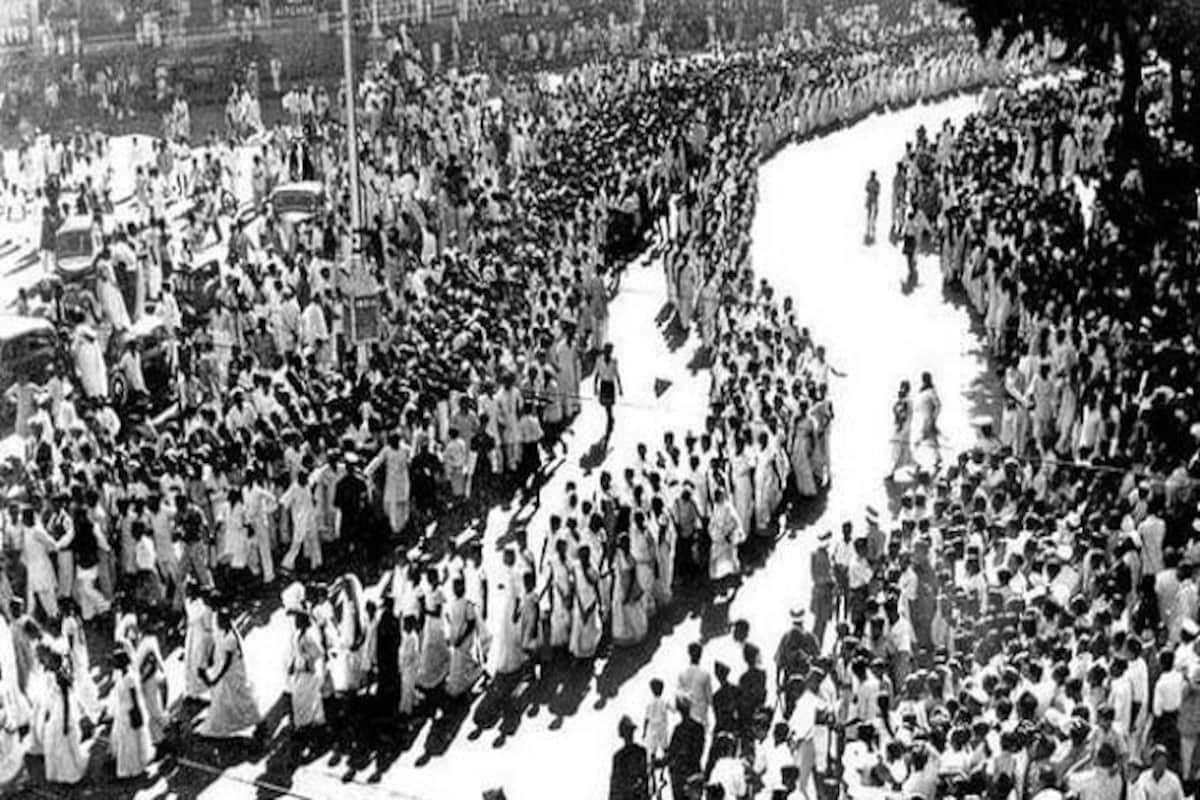

The Quit India Movement was launched at the Bombay session of the All India Congress Committee by Mahatma Gandhi on 8 August 1942, during World War II, demanding an end to British rule in India.
In this struggle, the common people of the country demonstrated unparalleled heroism and militancy.
However, the repression that they faced was the most brutal that had ever been used against the national movement.
At the historic August meeting at Gowalia Tank in Bombay, Gandhiji was particular about complete freedom and no more piece-meal approach from the British.
He proclaimed: ‘Do or Die’ – which meant either free India or die in the attempt.
Gandhi asked government servants to openly declare their allegiance to congress and not to resign.
In the meantime, underground networks were consolidated in various parts of the country. The prominent members of underground activities were Achyut Patwardhan, Aruna Asaf Ali, Ram Manohar Lohia, and Sucheta Kripalani.
The pattern of activity of the underground movement was that of organizing the disruption of communications by blowing up bridges, cutting telegraph and telephone wires, and derailing trains.
Congress Radio operated clandestinely from different locations in Bombay city, whose broadcast could be heard as far as Madras. Usha Mehta was an important member of the small group that ran the Congress Radio.
A significant feature of the Quit India Movement was the emergence of what came to be known as parallel governments in some parts of the country. Satara (Maharashtra) emerged as the base of the longest-lasting and most effective parallel government.
A significant feature of peasant activity was its total concentration on attacking symbols of British authority and a total lack of any incidents of anti-zamindar violence.
In February 1943, Gandhiji declared the fast in Aga Khan Palace where he was held in detention, as this was his answer to the Government which had been constantly exhorting him to condemn the violence of the people in the Quit India Movement. Gandhiji not only refused to condemn the people’s resort to violence but unequivocally held the Government responsible for it.
The resignation of the three Indian members of the Viceroy’s Executive Council, M.S. Aney, N.R. Sarkar and H.P. Mody, who never wished Gandhi to suffer, made a severe blow to the British.
Finally, the Congress leaders were released to participate in the Simla Conference in June 1945. That marked the end of the phase of confrontation that had existed since August 1942.
Simla Conference (1945) and the Wavell Plan
The Simla Conference of 1945 was a meeting between the Viceroy of India (Lord Wavell) and the major political leaders of British India at the Viceregal Lodge in Simla.
Wavell proposed a separate representation of Muslims within a united India. Talks, however, stalled on the issue of the selection of Muslim representatives. The All-India Muslim League claimed to be the sole representative of Indian Muslims. The Indian National Congress opposed this claim as the Congress had more Muslims in its support than the Muslim League.
This scuttled the conference, and perhaps the last viable opportunity for a united, independent India.
On 14 June 1945 Lord Wavell announced a plan for a new Executive Council in which all members except the Viceroy and the Commander in Chief would be Indians. This executive council was to be a temporary measure until a new permanent constitution could be agreed upon and come into force.
RIN Mutiny (1946)
The Royal Indian Navy (RIN) revolt started in February 1946 at Mumbai when the naval ratings on HMIS Talwar protested against the poor quality of food and racial discrimination by British officers.
From the initial flashpoint in Mumbai, the revolt spread and found support throughout India, from Karachi to Kolkata, and ultimately came to involve over 20,000 sailors in 78 ships and shore establishments.
Karachi was a major centre, second only to Bombay. Sympathetic strikes took place in military establishments in Madras, Vishakhapatnam, Calcutta, Delhi, Cochin, Jamnagar, the Andamans, Bahrain and Aden.
A revolt in the armed forces, even if soon suppressed, had a great liberating effect on the minds of people.
The naval mutiny proved to be the last nail in the coffin of British colonial aspirations in India.
India was seen to be on the brink of a revolution. The mutiny witnessed the demoralization of British officials and the changing loyalties of Indian officials.
However, communal unity evident in the RIN revolt was limited despite the Congress, League and Communist flags being jointly hoisted on the ships’ masts. Muslim ratings went to the League to seek advice on future action for Pakistan.
The Indian National Congress and the Muslim League condemned the mutiny, while the Communist Party of India was the only party that supported the rebellion.
The mutiny was suppressed by British troops and Royal Navy warships.
The revolt was called off following a meeting between the President of the Naval Central Strike Committee (NCSC), M. S. Khan, and Sardar Vallabhai Patel who had been sent to Bombay to settle the crisis.
Mountbatten Plan (1947)
The legislature representatives of the Indian National Congress, the Muslim League, and the Sikh community came to an agreement with Lord Mountbatten on what has come to be known as the 3 June Plan or Mountbatten Plan. This plan was the last plan for independence.
The plan announced by the Viceroy Mountbatten on 3 June 1947 included these principles:
- The principle of the partition of British India was accepted by the British Government.
- Successor governments would be given dominion status.
- Autonomy and sovereignty to both countries.
- The successor governments could make their own constitution
- The Princely States were given the right to join either Pakistan or India, based on two major factors: Geographical contiguity and the people’s wishes.
The Mountbatten plan led to the enactment of the India Independence Act of 1947.
India Independence Act (1947)
The Indian Independence Act of 1947 passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom divided British India into two new independent dominions; the Dominion of India ( later to become the Republic of India ) and the Dominion of Pakistan ( later to become the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ).
This Act received Royal Assent on 18 July 1947.
India and Pakistan became independent on August 15th, 1947.
India continues to celebrate August 15th as her Independence day, while Pakistan chose to celebrate August 14th as her Independence day as per their cabinet decisions.
Learn more about India’s Struggle for Independence
Hope you liked the mega article on the Indian freedom struggle.
This article on India’s struggle for independence is the 6th part of the article series on Modern Indian History. Click the link to read the 6-part framework to study modern Indian History . This is an easy-to-learn approach to mastering the history of modern India as a story.
Apart from the 6-part approach, we have also published many other articles on Indian History , which can be accessed from the ClearIAS Study materials section.
If you loved this article, please subscribe to ClearIAS and share this post with your friends.
Books referred to prepare this article on India’s Struggle for Independence
- NCERT Books Class 6-12
- History Of Modern India by Bipan Chandra
- India’s struggle for independence by Bipan Chandra
- Modern Indian History by Sonali Bansal and Snehil Tripathi

Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
February 6, 2022 at 9:52 am
Pls allowed to download in pdf form
February 7, 2022 at 11:38 am
@Zizoo – There is a ‘Print PDF’ button that you can use to download the article as a PDF.
July 29, 2023 at 1:02 pm
“India’s Struggle for Independence” on ClearIAS is a comprehensive and enlightening read. The blog beautifully captures the essence of India’s journey towards freedom, providing valuable historical context and key insights. It’s an essential resource for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of India’s rich and inspiring struggle for independence.
December 5, 2023 at 1:49 am
Please provide download option
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
Take ClearIAS Mock Exams: Analyse Your Progress
Analyse Your Performance and Track Your All-India Ranking
Ias/ips/ifs online coaching: target cse 2025.

Are you struggling to finish the UPSC CSE syllabus without proper guidance?

Honoring the Freedom Fighters of India
Ai generator.
Good morning, respected teachers, parents, and my dear friends!
Today, we gather to celebrate a day of immense significance in our nation’s history— Indian Independence Day . As we rejoice in the freedom we enjoy today, it is essential to remember and honor the countless freedom fighters who sacrificed everything for our independence.
The Struggle for Independence
The journey to independence was long and arduous. For nearly two centuries, our ancestors faced oppression under British rule. They endured immense hardships, but their spirit remained unbroken. Their courage and determination laid the foundation for the freedom we now cherish.
Remembering the Heroes
Mahatma Gandhi: Known as the father of our nation, Mahatma Gandhi led the freedom struggle with his principles of non-violence and civil disobedience. His leadership inspired millions to join the fight for justice and equality.
Jawaharlal Nehru: Our first Prime Minister, Jawaharlal Nehru, was a central figure in Indian politics before and after independence. His vision for a modern, progressive India guided the nation during its early years of freedom.
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel: Often referred to as the Iron Man of India, Sardar Patel played a crucial role in unifying the princely states and integrating them into a single nation. His efforts were vital in building a strong, united India.
Subhas Chandra Bose: A charismatic leader and fierce patriot, Subhas Chandra Bose led the Indian National Army and inspired many with his rallying cry, “Give me blood, and I will give you freedom.”
Bhagat Singh, Rajguru, and Sukhdev: These young revolutionaries sacrificed their lives for the cause of independence. Their bravery and martyrdom became symbols of resistance against British rule.
The Unsung Heroes
While we remember the well-known leaders, it is equally important to honor the unsung heroes whose contributions were just as significant. These individuals, often working behind the scenes, played vital roles in organizing protests, spreading awareness, and mobilizing the masses. Their efforts, though not always recognized, were crucial in building the momentum needed to achieve independence.
The Legacy of Sacrifice
The freedom fighters faced tremendous challenges, including imprisonment, torture, and even death. Yet, they remained steadfast in their commitment to the cause. Their sacrifices are a testament to their love for the country and their unwavering belief in the principles of justice and equality.
Our Responsibility
As we celebrate Independence Day, let us remember that the best way to honor our freedom fighters is to uphold the values they fought for. We must strive to build a nation that is just, inclusive, and prosperous. It is our duty to ensure that the hard-won freedom is preserved and that the rights of every citizen are respected.
In conclusion, let us bow our heads in respect and gratitude for the countless freedom fighters who laid down their lives for our independence. Their legacy lives on in our hearts, and it is our responsibility to carry forward their dream of a free and prosperous India.
Thank you for your attention. Jai Hind!
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Advertisement
Supported by
Is Nonviolent Resistance Past Its Prime?
In “We Refuse,” Kellie Carter Jackson explores the many forms of activism that oppressed people have resorted to and offers a more nuanced picture of their lives.
- Share full article

By Linda Villarosa
Linda Villarosa is the author of “Under the Skin: The Hidden Toll of Racism on American Lives and on the Health of Our Nation,” a 2023 Pulitzer Prize finalist.
WE REFUSE: A Forceful History of Black Resistance, by Kellie Carter Jackson
In his 1958 memoir “ Stride Toward Freedom ,” the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. laid out a series of principles — courage, friendship, spiritual transformation and so on — for combating racism and other forms of oppression. Inspired by Mahatma Gandhi and Jesus Christ, King urged that the acceptance of suffering, even violence, without retaliation put one in accord with the universe and armed just people with the power to defeat hate.
The practitioners of nonviolence fought with “the weapon of love,” King wrote, and their method became a foundational tactic for many civil rights activists. Think of the 1950s and ’60s, when young men and women were shoved and spit on for sitting at lunch counters. Ideally, they simply waited out the assault without so much as raising a hand. Underlying this strategy is the hope, in King’s words, that “unearned suffering is redemptive” and can open the door to understanding.
Since the civil rights era, iterations of King’s nonviolent approach have remained the most familiar, acceptable and celebrated forms of opposition to racial oppression. You can see the roots of King’s philosophy of nonviolence in the marches and hashtags in the summer of 2020 after the killings of George Floyd, Breonna Taylor and many others.
But is this singular approach the best that activists can do, even when fine-tuned for different generations or movements? Where do they look for other models? In her compelling and often counterintuitive new book, “We Refuse,” Kellie Carter Jackson, a professor of Africana studies, argues that the usual chronicles of this resistance are both narrow and watered down. “Our culture’s fixation on nonviolence has caused us to miss entire histories of Black responses to white supremacy,” she writes. “Nonviolence on its own is not at all expansive enough to rectify the harm that has been caused by racism.”
Her book warns against the dangers of misremembering the past and offers a broader and more nuanced picture of resistance through the frame of refusal. It is “a halting hand, a pointed finger waving from side to side or a powerful raised fist. It is a barrier that prevents oppressed people from being consumed.”
She divides her exploration into five categories — revolution, protection, force, flight and joy. Her chapter on revolution centers on the Haitian Revolution. Beginning with a revolt of enslaved people in 1791, the uprising lasted 13 bloody years and led to the end of colonial rule in Haiti. The fighting inspired people from Brazil to Philadelphia to agitate for freedom and equality. In 1807, a nervous American government passed an act to make the international slave trade illegal.
Carter Jackson believes revolutions don’t always involve fatalities, but they must result in forfeiture and equitable redistribution of wealth and other resources. “At the core of revolution is structural change, not violence,” she writes.
Her chapter on protection covers the ingenuity of the Underground Railroad, and the chapter on flight presents the Great Migration as a mass abandonment by six to eight million Black Southerners who took their “skills, genius and artistry” with them. These concepts overlap and intersect. “Sometimes revolutions involve force,” Carter Jackson writes. “Sometimes flight is motivated by protection. Sometimes flight and force are joyful.”
The book is most effective in unearthing the stories of little-known, everyday rebellions, especially from the lives of Black women. These histories have been at best under-told, if not lost altogether. Her chapter on force, which builds upon her more academic book “Force and Freedom: Black Abolitionists and the Politics of Violence,” is by far the sharpest, most convincing and surprising.
Force, a remedy of last resort, states Carter Jackson, can be a strike, a boycott, a vote — or it can be armed self-defense. She begins the chapter with the story of her grandmother, Reader Carter, who died in Detroit in 2003. When going through her belongings after her death, the family was shocked to open a night stand drawer and find a tiny .22 pistol — fully loaded: “Almost in unison, we bellowed, ‘Grandma has a gun!’”
Reader grew up in rural Louisiana in the 1930s before she became part of the Great Migration and went north. Carter Jackson remembers stories of the men in Louisiana, including her grandmother’s brothers, who spent weekends in jail to protect themselves from being lynched. “The white men in town used to get drunk on weekends and hang Black folks,” Carter Jackson’s grandmother explained, “so if you were already in jail, you were safe.” To Reader Carter, guns were force, “a bulwark against a hostile white supremacist world.”
Throughout the chapter, Carter Jackson offers a catalog of Black history heroes who owned guns, often unexpectedly so. In 1906, the scholar W.E.B. Du Bois, who was teaching in Georgia and had considered himself a pacifist, bought a double-barreled shotgun and two dozen rounds of shells after a riot in Atlanta that left lynching victims hanging from lampposts. “If a white mob had stepped on the campus,” he wrote, “I would without hesitation have sprayed their guts over the grass.”
“Few know better the utility of guns for Black liberation than Black women,” Carter Jackson writes. Though the image of Harriet Tubman hugging a rifle endures as one of the most indelible in Black history, many other notable Black women owned guns. “A Winchester rifle should have a place of honor in every Black home,” the crusading journalist Ida B. Wells wrote, “and it should be used for that protection which the law refuses to give.”
Decades later, the voting rights activist Fannie Lou Hamer explained that she kept “a shotgun in every corner of my bedroom, and the first cracker even look like he wants to throw some dynamite on my porch won’t write his mama again.” Even the paragon of civil disobedience, Rosa Parks, sometimes had her kitchen table covered with guns, Carter Jackson writes, “in case of an emergency.”
Black women used guns to stop trouble, Carter Jackson asserts, not start it. “Rarely were guns fatal,” she says. “Instead, they nearly always served as warnings — bullets fired in the air to quickly quell the violent desires of the mob.”
Is Carter Jackson advocating armed resistance at the next protest? Her book is not an instruction manual for activists. But she does suggest that every era gets the protest movement it needs and deserves. History — complicated, cleareyed and unrepentant — is her warning and her weapon of choice.
WE REFUSE : A Forceful History of Black Resistance | By Kellie Carter Jackson | Seal Press | 291 pp. | $30
Explore More in Books
Want to know about the best books to read and the latest news start here..
John S. Jacobs was a fugitive, an abolitionist — and the brother of the canonical author Harriet Jacobs. Now, his own fierce autobiography has re-emerged .
Don DeLillo’s fascination with terrorism, cults and mass culture’s weirder turns has given his work a prophetic air. Here are his essential books .
Jenny Erpenbeck’s “ Kairos ,” a novel about a torrid love affair in the final years of East Germany, won the International Booker Prize , the renowned award for fiction translated into English.
Kevin Kwan, the author of “Crazy Rich Asians,” left Singapore’s opulent, status-obsessed, upper crust when he was 11. He’s still writing about it .
Each week, top authors and critics join the Book Review’s podcast to talk about the latest news in the literary world. Listen here .

Essay on Freedom Fighters of India
Students are often asked to write an essay on Freedom Fighters of India in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Freedom Fighters of India
Introduction.
Freedom fighters of India are the brave souls who fought for India’s independence. They stood against the British rule, sacrificing their lives for the nation’s freedom.
Famous Freedom Fighters
Mahatma Gandhi, Subhash Chandra Bose, and Bhagat Singh are some famous freedom fighters. They led various movements and inspired many to join the struggle.
Mahatma Gandhi
Mahatma Gandhi, known for his non-violence, led the Dandi March and Quit India Movement. His teachings continue to inspire millions.
Subhash Chandra Bose
Subhash Chandra Bose, known as Netaji, led the Indian National Army. He believed in the power of youth and unity.
Bhagat Singh
Bhagat Singh, a young revolutionary, believed in action. He was executed at a young age but his courage still inspires.
The Freedom fighters of India are our national heroes. Their sacrifices and struggles led to India’s independence. We owe our freedom to them.
250 Words Essay on Freedom Fighters of India
The essence of freedom fighters.
India’s struggle for independence is marked by the valiant efforts of numerous freedom fighters. These individuals, propelled by an unflinching desire for emancipation, challenged the British Raj, inspiring millions with their courage and determination.
Significant Figures
Mahatma Gandhi, the pioneer of non-violence and civil disobedience, remains a global symbol for peaceful resistance. His leadership in the Dandi March and Quit India Movement significantly weakened the British hold.
Subhas Chandra Bose, with his “Give me blood, and I’ll give you freedom” motto, led the Indian National Army, challenging British forces on the battlefield. His contribution underlines the diversity of approaches in the struggle for independence.
Unsung Heroes
While these figures are widely recognized, many unsung heroes also contributed immensely. Bhagat Singh, a revolutionary socialist, is celebrated for his acts of defiance, notably the Central Legislative Assembly bombing. His execution at a young age ignited a nationwide outcry, fuelling the demand for independence.
Rani Padmini and Kittur Rani Chennamma demonstrated unparalleled bravery, symbolizing women’s significant role in the freedom struggle. Their stories serve as reminders of the multifaceted fight for independence.
Legacy and Influence
India’s freedom fighters’ legacy transcends national boundaries, inspiring liberation movements worldwide. Their philosophies of non-violence, civil disobedience, and self-rule continue to influence global political thought.
In conclusion, India’s freedom fighters, through their courage, resilience, and sacrifice, have left an indelible mark on history. They serve as a beacon of inspiration, reminding us of the price of freedom and the importance of preserving it.
500 Words Essay on Freedom Fighters of India
India’s struggle for independence is a saga of the valor of its freedom fighters. Their sacrifices, determination, and unwavering pursuit of liberation from the British rule are the cornerstones of Indian history. This essay aims to shed light on some of these brave souls who played pivotal roles in shaping India’s destiny.
Mahatma Gandhi: The Apostles of Non-Violence
Mahatma Gandhi is universally recognized as the leader of India’s freedom struggle. His philosophy of non-violence, or “Ahimsa,” and civil disobedience shook the foundations of the British Empire. Gandhi’s non-violent protests, including the Salt March and Quit India movement, garnered international attention and put pressure on the British, leading to India’s independence.
Subhash Chandra Bose: The Proponent of Armed Struggle
Subhash Chandra Bose, fondly known as Netaji, believed that freedom could not be achieved without an armed struggle. He formed the Forward Bloc and later the Azad Hind Fauj (Indian National Army) with the help of the Axis powers during World War II. His famous slogan, “Give me blood, and I will give you freedom,” continues to inspire millions of Indians.
Bhagat Singh: The Symbol of Youth Power
Bhagat Singh was a charismatic revolutionary whose actions stirred the youth of India. His execution at a young age by the British authorities for his involvement in the Lahore Conspiracy Case sparked outrage and ignited a nationwide protest. His writings and ideas, especially on socialism, continue to influence Indian political thought.
Rani Padmini and Rani Laxmi Bai: Women Freedom Fighters
The role of women in India’s freedom struggle is also noteworthy. Rani Padmini of Mewar and Rani Laxmi Bai of Jhansi fought valiantly against foreign invasions. Their courage underlines the fact that the struggle for freedom was not just a man’s fight.
The freedom fighters of India came from diverse backgrounds and ideologies, but their goal was singular – to secure India’s independence. Their sacrifices serve as a beacon, illuminating the path of resilience, unity, and patriotism. As we enjoy the fruits of their labor, it becomes our responsibility to honor their memory and uphold the values they fought for. The story of these freedom fighters is not just a part of history; it is a legacy that continues to shape India’s present and future.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Election in India
- Essay on Education in India
- Essay on Diversity in India
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Tushar Gandhi slams PM Modi’s Gandhiji statement: Who is the real ignoramus?
P rime Minister Narendra Modi’s statement about Mahatma Gandhi and leveraging his legacy, has set the cat amongst the poll pigeons. The opposition and Mahatma Gandhi’s great-grandson Tushar Gandhi cleaved into Modi after the PM reportedly stated that the 1982 Richard Attenborough’s film ‘Gandhi’ was largely responsible for Bapuji’s recognition and past leaders had failed to promote or leverage his legacy. The PM had reportedly stated, “the first time the Gandhi film was made, there was curiosity about who he is. If the world knows about Martin Luther King, South Africa’s Nelson Mandela, Gandhi wasn’t any less than them.”
Tushar Gandhi, Mahatma Gandhiji’s great grandson reacted, “I burst out laughing when I heard PM Narendra Modi’s statement about Mahatma Gandhi. I was in Benares and amidst all the buzz there, this gave me some moments of mirth.” Tushar Gandhi pointed out that there were contradictions within Modi’s statement itself. He said, “The PM said Bapuji was not as popular as Martin Luther King and Nelson Mandela. In fact, Martin Luther King’s civil rights movement was inspired by Gandhiji’s non-violence/Satyagraha ideology. Nelson Mandela is reported to have said to felt Gandhi’s presence in his cell at Robben Island.” Tushar Gandhi called Modi “ignorant” and added, “World leaders knew about Gandhi much before the Richard Attenborough film in 1982. Yet, how can one argue intellectually with an ignoramus?” He also accused the PM of using such utterances as, “diversions as he cannot answer the opposition and this is to move the focus away from the rule of inefficiency.”
The other side
Yet, Modi has his supporters who have hit back. Vishal Tibrewala RSS swayamsevak said, “The PM has actually spoken very highly of Gandhiji. Yet, it is the ignorant who will never understand this.” Vineet Jindal Supreme Court advocate stated, “The accountability of ensuring that the world knows about Mahatma Gandhi rings true, considering that the Indian Government made no significant efforts at the time to share his vision, values, and virtues. Gandhi, a pivotal figure in India’s struggle for freedom, epitomised true values and non-violence, foundational to humanity.
While Gandhi’s endeavours gained him recognition internationally, it was Richard Attenborough’s film ‘Gandhi’ that truly brought him to the global stage. Indian leaders of the time should have been proactive in spreading Gandhi’s ideas, yet they often exploited his name for political gain. Merely assuming Gandhi’s popularity was sufficient for global propagation overlooks our responsibility. India, blessed with such a legendary figure, failed to adequately promote Gandhi’s ideals to the world in the past.”
Shaina NC, BJP spokesperson, slammed back, “History is created by selfless service to society. Modiji has dedicated his life to the service of all Indians and proved his worth by his work. Tushar Gandhi is nothing to talk about other than his surname.”
Year the film Gandhi was made


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500+ Words Essay on Mahatma Gandhi. Essay on Mahatma Gandhi - Mahatma Gandhi was a great patriotic Indian, if not the greatest. He was a man of an unbelievably great personality. He certainly does not need anyone like me praising him. Furthermore, his efforts for Indian independence are unparalleled. Most noteworthy, there would have been a ...
Mahatma Gandhi's role in India's freedom struggle was transformative. His non-violent approach, ability to mobilize the masses, and vision for Swaraj were instrumental in shaping the course of India's freedom struggle. His philosophies have left an indelible mark on India's ethos and continue to inspire movements for civil rights and ...
Gandhi organized Indian resistance, fought anti-Indian legislation in the courts and led large protests against the colonial government. Along the way, he developed a public persona and a ...
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, often called the 'Father of the Nation', was a leader who fought for India's freedom from British rule.He believed in non-violence. Every year on October 2nd, Mahatma Gandhi's birthday is celebrated as Gandhi Jayanti to honor his efforts in freeing India.. English Essay on Mahatma Gandhi. Rabindranath Tagore was the first to call Gandhiji 'Mahatma,' which means ...
Mahatma Gandhi, also known as Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, was a prominent leader in India's struggle for independence from British rule. Born on October 2, 1869, in Porbandar, Gujarat, Gandhi played a pivotal role in shaping India's history and inspiring movements for civil rights and freedom across the world.
Essay on Mahatma Gandhi in English (100, 150, 200, 300, 500 words). Mahatma Gandhi essay in English. ... He returned to India in 1915 and joined the freedom struggle. He started many political movements like Non-cooperation movement, Salt Satyagraha, Quit India Movement to fight against the British. ... popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi was an ...
Mahatma Gandhi (born October 2, 1869, Porbandar, India—died January 30, 1948, Delhi) was an Indian lawyer, politician, social activist, and writer who became the leader of the nationalist movement against the British rule of India. As such, he came to be considered the father of his country.
Conclusion. Mahatma Gandhi, my favourite freedom fighter, was more than just a political leader. He was a social reformer, a philosopher, and a beacon of hope for millions. He embodied the spirit of resilience and showed the world the power of non-violence and truth. His life and principles continue to inspire and guide us in our quest for ...
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (ISO: Mōhanadāsa Karamacaṁda Gāṁdhī; 2 October 1869 - 30 January 1948) was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule.He inspired movements for civil rights and freedom across the world.
Essay On Mahatma Gandhi. ... His contribution to India's Freedom struggle and Achievements. Back in India, in the year of 1919, the British started to arrest and imprison anyone they suspect of sedition that's when Gandhi stood up and started non-violent disobedience. Gandhi's goal about Indian's independence got cleared after a tragic incident ...
Gandhi was a performance manager for the country and a supremely practical leader for change. Mahatma Gandhi believed that truth, tolerance, sacrifice, joy, and the nonviolent rejection of tyranny ...
With the outbreak of World War II, the nationalist struggle in India entered its last crucial phase.Gandhi hated fascism and all it stood for, but he also hated war. The Indian National Congress, on the other hand, was not committed to pacifism and was prepared to support the British war effort if Indian self-government was assured. Once more Gandhi became politically active.
The Direct Action Day called by Jinnah on 16 August 1946 leads to riots and Hindus and Muslims dead in their hundreds. Kasturba, Gandhi's lifelong companion, dies, leaving him bereft. Despite all the privations, setbacks, and tragedies he has had to endure, the last year of his life sees Gandhi at his greatest—courting danger, death, and ...
Mahatma Gandhi led the national freedom struggle against the British rule. The most unique thing about this struggle was that it was completely nonviolent. Mohan Das Karamchand Gandhi was born on 2nd October, 1869 at Porbandar in Gujarat. After finishing his early education in India, he sailed to England in 1891 and qualified as Barrister.
Mahatma Gandhi Essay in English: Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi who is known by the name, Mahatma Gandhi is popularly called as Father of Nation. His contributions towards the freedom struggle and to making India free from the rule of the British Raj are immense and could not be put into simple words. To pay tribute to his efforts in the freedom ...
1 Essay on Mahatma Gandhi (200 Words) 2 Essay on Mahatma Gandhi (400 Words) 2.1 Birth and Childhood. 2.2 Marriage and Education. 2.3 Civil Rights Movement in Africa. 2.4 Legacy. 3 Essay on Mahatma Gandhi (600 Words) 3.1 Role of Mahatma Gandhi in India's Freedom Struggle. 3.1.1 Champaran and Kheda Agitations.
Vipin Gaur: Mahatma Gandhi's Political Philosophy on Freedom Struggle in India 299 • The Election Commission should be in charge of the elections at every stage. The issues of the legislative, executive, and judicial branches should be handled by the Vigilance.
In the later years, under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi, the Indian freedom struggle entered its truly mass phase. Champaran movement in Bihar (1917) Mahatma Gandhi, after his struggle against apartheid in South Africa (racial discrimination against blacks) for almost twenty years, returned to India in 1915.
Mahatma Gandhi: The Torchbearer of Non-Violence. Mahatma Gandhi, often referred to as the 'Father of the Nation,' was instrumental in India's struggle for freedom. His philosophy of non-violence (Ahimsa) and civil disobedience shook the roots of the mighty British Empire.
Introduction to Mahatma Gandhi. Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, fondly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was born on October 2, 1869. He is revered as the "Father of the Nation" for his significant contributions to India's freedom struggle. Gandhi's philosophy of non-violence (ahimsa) and civil disobedience (satyagraha) became the cornerstone of the ...
Start your answer by briefly introducing the role of Mahatma Gandhi in freedom struggle. Discuss how his ideologies and tactics shape the course of India's struggle for independence. Conclude accordingly. Introduction. Mahatma Gandhi played a pivotal role in the Indian independence movement against British colonial rule. He emerged as a leading ...
They endured immense hardships, but their spirit remained unbroken. Their courage and determination laid the foundation for the freedom we now cherish. Remembering the Heroes. Mahatma Gandhi: Known as the father of our nation, Mahatma Gandhi led the freedom struggle with his principles of non-violence and civil disobedience. His leadership ...
Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in a recent TV interview, stated that Mahatma Gandhi was unknown to the world until Ben Kingsley's Gandhi (1982) movie. The statement comes ahead of the last phase of ...
Central to Chavez's approach was nonviolent resistance, inspired by the teachings of Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. Embracing the principles of civil disobedience and peaceful protest, he led strikes, boycotts, and marches to challenge the injustices perpetrated against farmworkers.
500 Words Essay on Indian Freedom Struggle ... Mahatma Gandhi's arrival on the political scene in 1915 marked a paradigm shift in the freedom struggle. His philosophy of Satyagraha (truth and firmness) and Ahimsa (non-violence) galvanized the masses. The non-cooperation movement (1920-22), Civil Disobedience Movement (1930-34), and Quit India ...
They both moulded their people's struggle for justice and freedom on Bapu's practice of non-violent Satyagraha. Senior leaders of the Civil Rights Movement in the US came to India and were trained ...
Her book warns against the dangers of misremembering the past and offers a broader and more nuanced picture of resistance through the frame of refusal. It is "a halting hand, a pointed finger ...
1d. P rime Minister and Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) leader Narendra Modi said in an interview that nobody knew the Father of the Nation in post-colonial India—Mahatma Gandhi—until a movie was ...
Mahatma Gandhi is universally recognized as the leader of India's freedom struggle. His philosophy of non-violence, or "Ahimsa," and civil disobedience shook the foundations of the British Empire. Gandhi's non-violent protests, including the Salt March and Quit India movement, garnered international attention and put pressure on the ...
Prime Minister Narendra Modi's statement about Mahatma Gandhi and leveraging his legacy, has set the cat amongst the poll pigeons. ... a pivotal figure in India's struggle for freedom ...