
Bell Ringers
Teaching literary analysis in middle school.
My literary analysis resources have basically been seven or eight years in the making.
I don’t know about you, but when I first realized I needed to be teaching literary analysis to a bunch of twelve and thirteen year-olds, I didn’t even know where to begin.
I had been teaching upper elementary in the three years prior, and we had done some on-demand literary analysis reading responses, but really digging into a literary analysis essay overwhelmed me.
Truth be told, my teaching strengths at the time were primarily reading and math. I had always had to dig deep to find my writing teacher voice.
But, I was now a seventh and eighth grade ELA teacher who could no longer hope her students picked up some writing skills along the way.
So I did what any good teacher would do…. I Googled how to teach…
I think I Googled something like, “Examples of middle school literary analysis essays.”
Nothing showed up in Google.
Then I Googled, “How do you teach literary analysis essays?”
I was able to find an example of a college-level literary analysis essay…
… and that was about it.
Because I couldn’t really find what I was looking for, I began creating and practicing each step of the literary analysis essay before I taught it.
This also created a ton of exemplars for my students.

I broke down each area of a literary analysis essay into lessons, chunks, chart papers, reference materials, and writing examples.
In the beginning, it was to get my brain wrapped around things, but not surprisingly it was exactly what my students needed too.
I literally learned how to write a literary analysis essay in front of them.
I would type my rough drafts as they were working and I could stop them as I came to struggles.
My mini-lessons were based on challenges I was having and again, not surprisingly the same challenges they were having.
I could also make reference pages (like the ones in your freebie) as we went along in the unit, because I could see what terms and concepts they needed constant reminders and help with.
Want to know what happened?
My student’s ELA proficiency scores increased 45% in one year and almost 70% in just two years. Those are not typos.
>> CLICK HERE << to download the FREE Literary Analysis Reference Booklet.

- Read more about: Middle School Reading , Middle School Writing
You might also like...
4 Station Ideas for Middle School ELA Skills

How to Plan Your Narrative Writing Unit

3 Independent Reading Strategies for Middle School
Get your free middle school ela pacing guides with completed scopes and sequences for the school year..

My ELA scope and sequence guides break down every single middle school ELA standard and concept for reading, writing, and language in 6th, 7th, and 8th grade. Use the guides and resources exactly as is or as inspiration for you own!
Meet Martina

I’m a Middle School ELA teacher committed to helping you improve your teaching & implement systems that help you get everything done during the school day!
Let's Connect
Member login.
PRIVACY POLICY
TERMS OF USE
WEBSITE DISCLAIMERS
MEMBERSHIP AGREEEMENT
© The Hungry Teacher • Website by KristenDoyle.co • Contact Martina
EL Education Curriculum
You are here.
- ELA 2019 G7:M3:U2:L9
Write a Literary Argument Essay: Draft Introduction
In this lesson, daily learning targets, ongoing assessment.
- Technology and Multimedia
Supporting English Language Learners
Materials from previous lessons, new materials, closing & assessments, you are here:.
- ELA 2019 Grade 7
- ELA 2019 G7:M3
- ELA 2019 G7:M3:U2
Like what you see?
Order printed materials, teacher guides and more.
How to order
Help us improve!
Tell us how the curriculum is working in your classroom and send us corrections or suggestions for improving it.
Leave feedback
Focus Standards: These are the standards the instruction addresses.
- W.7.1a, L.7.1a
Supporting Standards: These are the standards that are incidental—no direct instruction in this lesson, but practice of these standards occurs as a result of addressing the focus standards.
- RL.7.1, RL.7.2, W.7.4, W.7.5, W.7.10, L.7.6
- I can write an introduction for my essay giving context on the Harlem Renaissance, acknowledging a counterclaim, and clearly stating the main claim of the piece. ( W.7.1a )
- Opening A: Entrance Ticket: Unit 2, Lesson 9 ( L.7.1a )
- Work Time A: Annotated, color-coded model argument essay introduction ( W.7.1a )
- Work Time B: Language Dive: Model Essay, Main Claim note-catcher ( W.7.1a, W.7.1c, L.7.1a )
- Closing and Assessment A: Introductory Paragraph of Pair Argument Essay ( W.7.1a )
| Agenda | Teaching Notes |
|---|---|
| A. Engage the Learner – (5 minutes)
A. The Painted Essay®: Sort and Color-Code the Parts of an Introduction – (15 minutes) B. Language Dive: Model Essay, Main Claim – (10 minutes)
A. Pair Writing: Draft an Introduction – (15 minutes)
A. Explain Clauses in Proof Paragraph 1: Students complete Homework: Explain Clauses: Proof Paragraph 1 to explain the function of clauses in a Proof Paragraph of the Model Argument Essay. B. Independent Research Reading: Students read for at least 20 minutes in their independent research reading text. Then they select a prompt and write a response in their independent reading journal. | – Opening A: On an entrance ticket, students explain the function of the phrases in the main claim sentence of their pair essay. – Work Time A: Students use the Painted Essay® structure to more closely analyze a model introduction to note how it effectively introduces the topic and previews what is to follow. – Work Time B: Students participate in a Language Dive, analyzing the meaning of the model argument essay’s focus statement. – Closing and Assessment A: Students work in pairs to draft their introductions, introducing the topic with appropriate context and previewing what is to follow in a clear focus statement.
).
|
- Ensure there is a copy of Entrance Ticket: Unit 2, Lesson 9 at each student's workspace.
- Prepare Organize the Model: Introduction strips (one strip per pair) for Work Time A.
- Strategically pair students for work in Opening A with at least one strong reader per pair.
- Cut apart the introduction paragraph strips and organize them using envelopes or paperclips so that each pair will have one set.
- Review the Argument Writing checklist to become familiar with what will be required of students over the remainder of the unit.
- Post the learning targets and applicable anchor charts (see Materials list).
Tech and Multimedia
- Continue to use the technology tools recommended throughout previous modules to create anchor charts to share with families; to record students as they participate in discussions and protocols to review with students later and to share with families; and for students to listen to and annotate text, record ideas on note-catchers, and word-process writing.
Supports guided in part by CA ELD Standards 7.I.A.1, 7.I.B.5, 7.I.B.6, 7.I.B.7, 7.I.B.8, 7.I.C.11, 7.I.C.12, 7.II.A.1, 7.II.B.3, and 7.II.B.4.
Important Points in the Lesson Itself
- To support ELLs, this lesson includes the use of manipulatives to understand the key structures of an argument essay introduction. Also, the collaboration of writing a pair essay supports students in expressing their ideas in writing.
- ELLs may find it challenging to generate language for writing their introduction. In addition to the supports below, encourage students to use oral processing and their home-language to assist them in articulating their ideas.
- context (A)
- dependent clause, independent clause, phrase (DS)
(A): Academic Vocabulary
(DS): Domain-Specific Vocabulary
- Domain-specific word wall (one for display; from Module 1, Unit 1, Lesson 1, Work Time B)
- Close Readers Do These Things anchor chart (one for display; from Module 1, Unit 1, Lesson 4, Opening A)
- Academic word wall (one for display; from Module 1, Unit 1, Lesson 1, Opening A)
- Criteria of an Effective Argument Essay anchor chart (one for display; from Module 3, Unit 2, Lesson 8, Work Time A)
- Paint an Essay lesson plan (for teacher reference) (from Module 1, Unit 2, Lesson 7, Closing and Assessment A)
- Model Argument Essay: "Strength from the Past" (example for teacher reference) (from Module 3, Unit 2, Lesson 8, Work Time A)
- Vocabulary log (one per student; from Module 1, Unit 1, Lesson 2, Opening A)
- The Painted Essay® template (one per student and one for display; from Module 1, Unit 2, Lesson 7, Closing and Assessment A)
- Model Argument Essay: “Strength from the Past” (one per student and one for display; from Module 3, Unit 2, Lesson 8, Work Time A)
- Directions for Pair Argument Essay (one per student; from Module 3, Unit 2, Lesson 8, Closing and Assessment A)
- Argument Essay Writing Plan graphic organizer (one per student; from Module 3, Unit 2, Lesson 8, Closing and Assessment A)
- Argument Essay Writing Plan graphic organizer ▲
- Texts and Artwork from Module 3, Units 1 and 2: Shuffle Along , “Lift Every Voice and Sing,” The Harp , “Calling Dreams,” “Hope,” “I Shall Return,” Ethiopia Awakening, African Phantasy: Awakening , “The Negro Speaks of Rivers,” “His Motto,” and “The Boy and the Bayonet”
- Independent reading journal (one per student; begun in Module 1, Unit 1, Lesson 6, Work Time B)
- Organize the Model: Introduction strips (for teacher reference)
- Language Dive Guide: Model Argument Essay, Main Claim (answers for teacher reference)
- Language Dive: Model Argument Essay, Main Claim Sentence Chunk Chart (answers for teacher reference)
- Language Dive: Model Argument Essay, Main Claim note-catcher (for teacher reference)
- Argument Writing checklist (example for teacher reference)
- Entrance Ticket: Unit 2, Lesson 9 (one per student)
- Organize the Model: Introduction strips (one strip per pair)
- Colored pencils (red, yellow, blue, green; one of each per student)
- Language Dive: Model Argument Essay, Main Claim sentence chunk strips (one per pair of students)
- Language Dive: Model Argument Essay, Main Claim note-catcher (one per student)
- Argument Writing checklist (one per student and one to display)
- Lined paper (one per student)
- Online or print dictionaries (including ELL and home language dictionaries)
- Homework: Explain Clauses in Proof Paragraph 1
Each unit in the 6-8 Language Arts Curriculum has two standards-based assessments built in, one mid-unit assessment and one end of unit assessment. The module concludes with a performance task at the end of Unit 3 to synthesize students' understanding of what they accomplished through supported, standards-based writing.
| Opening |
|---|
| . , , and to the with translations in home languages where appropriate, and invite students to add the word to their . to review with students the word (background information necessary for understanding a topic). Record on the with translations in home languages, where appropriate, and invite students to record words in their vocabulary logs. |
| Work Time | Levels of Support |
|---|---|
| . Tell students that each pair has been given only one part of the introduction and later they will find the other parts to create a complete introduction. Explain that there are three parts to this introduction: context, acknowledgment of the counterclaim, and main claim. Each pair needs to find pairs with the other two parts of the introduction. Next, have the whole group work together to arrange all three parts of the introduction in an order that makes sense. and color code their strips. and to underline each part of the introduction in the correct color: red for the context, yellow for Point 1, blue for Point 2, dark yellow for Point 3, and green for the rest of the main claim of the piece. as necessary.
. Refer to as necessary. |
|
| and the poems "The Negro Speaks of Rivers" and "Lift Every Voice and Sing" most clearly demonstrate the theme of finding strength and hope by looking back to the past." | , , and . |
| Closing | Levels of Support |
|---|---|
| and . Also, display and distribute copies of the , and remind students that they used similar checklists in Modules 1 and 2 when they wrote informative essays. The specific characteristics will change for this essay, but they will work as a class to determine these new specific characteristics. Point out the following characteristics on the checklist: I have an introduction that gives readers the context they need to understand the topic or text.” I state my claim clearly, and my writing stays focused.” I fairly acknowledge claims that are different from my own.”
, , “Calling Dreams,” “Hope,” “I Shall Return,” , , and . Invite students to work in their pairs using the Model Argument Essay, the Criteria of an Effective Argument Essay anchor chart, and the Argument Writing Checklist to write an introduction. Remind students to refer to the domain-specific and academic word walls and as needed, especially for the definitions they provide while giving context in the introduction. | into simpler language that their peers who need heavier support can understand. Rephrasing the criteria ensures that students comprehend the writing expectations. that their peers who need lighter support rephrased. Translating or rephrasing the criteria ensures that students comprehend the writing expectations. |
| Homework |
|---|
| to explain the function of clauses in a Proof Paragraph of the Model Argument Essay. . |
Copyright © 2013-2024 by EL Education, New York, NY.
Get updates about our new K-5 curriculum as new materials and tools debut.
Help us improve our curriculum..
Tell us what’s going well, share your concerns and feedback.
Terms of use . To learn more about EL Education, visit eleducation.org
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on January 30, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 14, 2023.
Literary analysis means closely studying a text, interpreting its meanings, and exploring why the author made certain choices. It can be applied to novels, short stories, plays, poems, or any other form of literary writing.
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis , nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Before beginning a literary analysis essay, it’s essential to carefully read the text and c ome up with a thesis statement to keep your essay focused. As you write, follow the standard structure of an academic essay :
- An introduction that tells the reader what your essay will focus on.
- A main body, divided into paragraphs , that builds an argument using evidence from the text.
- A conclusion that clearly states the main point that you have shown with your analysis.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: reading the text and identifying literary devices, step 2: coming up with a thesis, step 3: writing a title and introduction, step 4: writing the body of the essay, step 5: writing a conclusion, other interesting articles.
The first step is to carefully read the text(s) and take initial notes. As you read, pay attention to the things that are most intriguing, surprising, or even confusing in the writing—these are things you can dig into in your analysis.
Your goal in literary analysis is not simply to explain the events described in the text, but to analyze the writing itself and discuss how the text works on a deeper level. Primarily, you’re looking out for literary devices —textual elements that writers use to convey meaning and create effects. If you’re comparing and contrasting multiple texts, you can also look for connections between different texts.
To get started with your analysis, there are several key areas that you can focus on. As you analyze each aspect of the text, try to think about how they all relate to each other. You can use highlights or notes to keep track of important passages and quotes.
Language choices
Consider what style of language the author uses. Are the sentences short and simple or more complex and poetic?
What word choices stand out as interesting or unusual? Are words used figuratively to mean something other than their literal definition? Figurative language includes things like metaphor (e.g. “her eyes were oceans”) and simile (e.g. “her eyes were like oceans”).
Also keep an eye out for imagery in the text—recurring images that create a certain atmosphere or symbolize something important. Remember that language is used in literary texts to say more than it means on the surface.
Narrative voice
Ask yourself:
- Who is telling the story?
- How are they telling it?
Is it a first-person narrator (“I”) who is personally involved in the story, or a third-person narrator who tells us about the characters from a distance?
Consider the narrator’s perspective . Is the narrator omniscient (where they know everything about all the characters and events), or do they only have partial knowledge? Are they an unreliable narrator who we are not supposed to take at face value? Authors often hint that their narrator might be giving us a distorted or dishonest version of events.
The tone of the text is also worth considering. Is the story intended to be comic, tragic, or something else? Are usually serious topics treated as funny, or vice versa ? Is the story realistic or fantastical (or somewhere in between)?
Consider how the text is structured, and how the structure relates to the story being told.
- Novels are often divided into chapters and parts.
- Poems are divided into lines, stanzas, and sometime cantos.
- Plays are divided into scenes and acts.
Think about why the author chose to divide the different parts of the text in the way they did.
There are also less formal structural elements to take into account. Does the story unfold in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? Does it begin in medias res —in the middle of the action? Does the plot advance towards a clearly defined climax?
With poetry, consider how the rhyme and meter shape your understanding of the text and your impression of the tone. Try reading the poem aloud to get a sense of this.
In a play, you might consider how relationships between characters are built up through different scenes, and how the setting relates to the action. Watch out for dramatic irony , where the audience knows some detail that the characters don’t, creating a double meaning in their words, thoughts, or actions.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Your thesis in a literary analysis essay is the point you want to make about the text. It’s the core argument that gives your essay direction and prevents it from just being a collection of random observations about a text.
If you’re given a prompt for your essay, your thesis must answer or relate to the prompt. For example:
Essay question example
Is Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” a religious parable?
Your thesis statement should be an answer to this question—not a simple yes or no, but a statement of why this is or isn’t the case:
Thesis statement example
Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” is not a religious parable, but a story about bureaucratic alienation.
Sometimes you’ll be given freedom to choose your own topic; in this case, you’ll have to come up with an original thesis. Consider what stood out to you in the text; ask yourself questions about the elements that interested you, and consider how you might answer them.
Your thesis should be something arguable—that is, something that you think is true about the text, but which is not a simple matter of fact. It must be complex enough to develop through evidence and arguments across the course of your essay.
Say you’re analyzing the novel Frankenstein . You could start by asking yourself:
Your initial answer might be a surface-level description:
The character Frankenstein is portrayed negatively in Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
However, this statement is too simple to be an interesting thesis. After reading the text and analyzing its narrative voice and structure, you can develop the answer into a more nuanced and arguable thesis statement:
Mary Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
Remember that you can revise your thesis statement throughout the writing process , so it doesn’t need to be perfectly formulated at this stage. The aim is to keep you focused as you analyze the text.
Finding textual evidence
To support your thesis statement, your essay will build an argument using textual evidence —specific parts of the text that demonstrate your point. This evidence is quoted and analyzed throughout your essay to explain your argument to the reader.
It can be useful to comb through the text in search of relevant quotations before you start writing. You might not end up using everything you find, and you may have to return to the text for more evidence as you write, but collecting textual evidence from the beginning will help you to structure your arguments and assess whether they’re convincing.
To start your literary analysis paper, you’ll need two things: a good title, and an introduction.
Your title should clearly indicate what your analysis will focus on. It usually contains the name of the author and text(s) you’re analyzing. Keep it as concise and engaging as possible.
A common approach to the title is to use a relevant quote from the text, followed by a colon and then the rest of your title.
If you struggle to come up with a good title at first, don’t worry—this will be easier once you’ve begun writing the essay and have a better sense of your arguments.
“Fearful symmetry” : The violence of creation in William Blake’s “The Tyger”
The introduction
The essay introduction provides a quick overview of where your argument is going. It should include your thesis statement and a summary of the essay’s structure.
A typical structure for an introduction is to begin with a general statement about the text and author, using this to lead into your thesis statement. You might refer to a commonly held idea about the text and show how your thesis will contradict it, or zoom in on a particular device you intend to focus on.
Then you can end with a brief indication of what’s coming up in the main body of the essay. This is called signposting. It will be more elaborate in longer essays, but in a short five-paragraph essay structure, it shouldn’t be more than one sentence.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
Some students prefer to write the introduction later in the process, and it’s not a bad idea. After all, you’ll have a clearer idea of the overall shape of your arguments once you’ve begun writing them!
If you do write the introduction first, you should still return to it later to make sure it lines up with what you ended up writing, and edit as necessary.
The body of your essay is everything between the introduction and conclusion. It contains your arguments and the textual evidence that supports them.
Paragraph structure
A typical structure for a high school literary analysis essay consists of five paragraphs : the three paragraphs of the body, plus the introduction and conclusion.
Each paragraph in the main body should focus on one topic. In the five-paragraph model, try to divide your argument into three main areas of analysis, all linked to your thesis. Don’t try to include everything you can think of to say about the text—only analysis that drives your argument.
In longer essays, the same principle applies on a broader scale. For example, you might have two or three sections in your main body, each with multiple paragraphs. Within these sections, you still want to begin new paragraphs at logical moments—a turn in the argument or the introduction of a new idea.
Robert’s first encounter with Gil-Martin suggests something of his sinister power. Robert feels “a sort of invisible power that drew me towards him.” He identifies the moment of their meeting as “the beginning of a series of adventures which has puzzled myself, and will puzzle the world when I am no more in it” (p. 89). Gil-Martin’s “invisible power” seems to be at work even at this distance from the moment described; before continuing the story, Robert feels compelled to anticipate at length what readers will make of his narrative after his approaching death. With this interjection, Hogg emphasizes the fatal influence Gil-Martin exercises from his first appearance.
Topic sentences
To keep your points focused, it’s important to use a topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph.
A good topic sentence allows a reader to see at a glance what the paragraph is about. It can introduce a new line of argument and connect or contrast it with the previous paragraph. Transition words like “however” or “moreover” are useful for creating smooth transitions:
… The story’s focus, therefore, is not upon the divine revelation that may be waiting beyond the door, but upon the mundane process of aging undergone by the man as he waits.
Nevertheless, the “radiance” that appears to stream from the door is typically treated as religious symbolism.
This topic sentence signals that the paragraph will address the question of religious symbolism, while the linking word “nevertheless” points out a contrast with the previous paragraph’s conclusion.
Using textual evidence
A key part of literary analysis is backing up your arguments with relevant evidence from the text. This involves introducing quotes from the text and explaining their significance to your point.
It’s important to contextualize quotes and explain why you’re using them; they should be properly introduced and analyzed, not treated as self-explanatory:
It isn’t always necessary to use a quote. Quoting is useful when you’re discussing the author’s language, but sometimes you’ll have to refer to plot points or structural elements that can’t be captured in a short quote.
In these cases, it’s more appropriate to paraphrase or summarize parts of the text—that is, to describe the relevant part in your own words:
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The conclusion of your analysis shouldn’t introduce any new quotations or arguments. Instead, it’s about wrapping up the essay. Here, you summarize your key points and try to emphasize their significance to the reader.
A good way to approach this is to briefly summarize your key arguments, and then stress the conclusion they’ve led you to, highlighting the new perspective your thesis provides on the text as a whole:
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, August 14). How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved August 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/literary-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write a narrative essay | example & tips, what is your plagiarism score.
Reading Worksheets, Spelling, Grammar, Comprehension, Lesson Plans
7th Grade Writing
For seventh graders, this Common Core area helps students gain mastery of writing skills by working collaboratively and producing written texts, understanding syntax and vocabulary, and organizing their ideas. Among the complete standards for this grade, seventh graders will be asked to: use precise language for written work, including formal style, use appropriate technology to publish writing and to collaborate on written projects, demonstrate keyboarding skill, go through the process of writing, editing and revision for their written work, conduct short research projects to answer a question, quote or paraphrase the data and conclusions of supporting texts while avoiding plagiarism and using proper citation, use evidence from literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research.
Abraham Lincoln Bio Poem

Your students will write a bio poem about Abraham Lincoln.
Back to School Diamante Poem

Teach your students a fun way to write diamante poems using our new back to school worksheet.
Bio Poem: My Mother

A fun Mother’s Day bio poem activity for your students!
Bio Poem: Pilgrim

A biography poem, also called a bio poem, is a short poem which describes a person or thing. This printable Thanksgiving Activity guides students through creating a bio poem about Pilgrims.
Bio Poem: Someone You Know

Students will write a bio poem about someone they know using the format set in this worksheet.
Christmas Tree Bio Poem

A biography poem, also called a bio poem, is a short poem which describes a person or thing. Sometimes writing a bio pem can be tricky! This printable Christmas Activity guides students through creating a bio poem about a Christmas tree.
Correct the Transition Words Mistakes – Worksheet

Have your students revise sentences and correct transition word mistakes with this educational writing activity.
Diamante Poem: Antonyms

Students write an antonym diamante poem in the space provided.
Diamante Poem: Synonyms

A diamante poem takes its name from the shape it makes: a diamond. Diamante poems were introduced in 1969 by Iris Tiedt. Students write a synonym diamante poem in the space provided.
Edgar Allan Poe; Journalist Trickster

Students read about one of Edgar Allan Poe’s hoaxes when he was a journalist. Each student then write’s their own hoax!
Edgar Allan Poe: Secrets in Poetry

Students read from Edgar Allan Poe’s “An Enigma” and decipher the name of the woman’s whose name is hidden within the text.
Father’s Day Bio Poem: My Father

Enhance your students’ writing skills with this fun Father’s Day Biography Poem activity.
Fourth of July Bio Poem: America

Encourage your students to learn about America with this Fourth of July Biography Poem activity.
George Washington Bio Poem

Your students will write a bio poem about George Washington.
George Washington’s List of Rules

When George Washington was a young boy, he made a list of rules for himself. Students choose one of the rules and write what it means.
Halloween Bio Poem Activity: Ghost

Create a bio poem about your own personal ghost with our fun Halloween printable activity!
Main Idea Organizer

Teach your students how to organize their writing with this helpful Main Idea Organizer. Students will be asked to complete the worksheet by writing their own main idea, three details, and a summary. This will help your students better understand how to organize their ideas for writing in the future, especially when writing an essay!

Newspaper Reporter: An Interview With President Lincoln

Your student is now an official reporter and their task is to interview President Abraham Lincoln! Students write three questions they would ask him and what his replies would be.
Transition Words: Complete the Sentence

Enhance your students’ writing skills with this “Complete the Sentence” transition words activity.
Using Transition Words

In this worksheet, your students will learn how to properly use transition words in a sentence.
How To Complete Your 7th Grade Literary Essay Successfully
Do you need to write a literary essay for your school in a given deadline? Do you think it is difficult to complete your paper on the given date because you have many assignments to tackle? Are you wondering how to write a literary essay because you do not have any experience with such papers? Do you wish you had some expert tips on writing a literary essay without any mistakes? Do you think it would be easier if you had a sample that you could follow for your paper? Do you struggle with the structure, format, approach, tone, and style for your paper? Do you face issues in writing a certain section of your paper?
It is usual for students to think about such questions and situations because they want to compose a great paper. They do not wish to risk their grade or commit a mistake that ruins the overall impression of their assignment. If you are in 7th grade then you would have some experience in writing essay assignments. You might be new to literary papers or this specific style but the traditional format and structure of the paper will stay the same. You need to start with an introduction, explain your major arguments in the body, and summarize your paper in the conclusion of your paper.
A literary paper talks about the theme, central idea, or main theory in a book, novel, or a piece of literature. You need to take a book, novel, play or any literary writing and read it a several times before presenting its focus to your readers. It is very important while writing such papers that you stay objective and neutral. You may have to consider the background of the author, the life story and events from his life that inspired him for such a writing, the social and economic settings of his time, the political situation, and other important things that contribute to this particular writing.
To write a literary essay, you need to understand the style and purpose of this paper very clearly. You should read expert written papers and see how professional writers attempt such an assignment. You can use expert papers to follow the style, structure, tone, approach, and format for your paper. You need to gather relevant and fresh data to support your stance in the paper.
Writing Ideas
- Persuasive cause&effect paper topics
- Paper on technology in an hour
- How to train essay writing
- The selection of an essay agency
- Getting sample expository essays
- What makes a proper custom essay
- Template informative paper on speech
- Getting essay samples about studies
- Starting an evaluation paper
- Getting template visual analysis essays
- Crafting an essay on friendship: idioms
- Sample reaction education papers
- In search of a great essay writer
- Getting paper introduction templates
- Working with essay agencies
- Looking for a writing company
- Silence against violence: essay tips
- How to pick an expert in essay writing
- The selection of a good writing agency
- Finding APA persuasive essay samples
- Hints on argumentative essay intro
- Grade 8 comparative essay samples
- How to find a proper writer
- Who can write papers fast?
- Crafting an APA graduate essay
Inspiring Tips:
- Persuasive essay sample
- Illustration paper
- Admission essays
- Application paper tips
Writing guides:
- Essay writing
Easy Solutions:
- Problem solution paper
- School games essay tips
- Essay hints: environment
Essay Types:
- Descriptive essay
- Literary paper
- Informative paper
- Expository essays
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript. Click here for instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your web browser.
- CommonLit is a nonprofit that has everything teachers and schools need for top-notch literacy instruction: a full-year ELA curriculum, benchmark assessments, and formative data. Browse Content Who We Are About
Jump to navigation
- Inside Writing
- Teacher's Guides
Student Models
- Writing Topics
- Minilessons
- Shopping Cart
- Inside Grammar
- Grammar Adventures
- CCSS Correlations
- Infographics
Student Writing Models
How do I use student models in my classroom?

When you need an example written by a student, check out our vast collection of free student models. Scroll through the list, or search for a mode of writing such as “explanatory” or “persuasive.”
Jump to . . .
Explanatory writing.
- How Much I Know About Space Explanatory Paragraph
- My Favorite Pet Explanatory Paragraph
- Sweet Spring Explanatory Paragraph
Narrative Writing
- A Happy Day Narrative Paragraph
- My Trip to Mexico Narrative Paragraph
Creative Writing
- Happy Easter Story Paragraph
- Leaf Person Story
Research Writing
- Parrots Report
- If I Were President Explanatory Paragraph
- My Dad Personal Narrative
- The Horrible Day Personal Narrative
Response to Literature
- One Great Book Book Review
- A Fable Story
- Ant Poem Poem
- The Missing Coin Story
- Winter Words Poem
- Horses Report
- Ladybugs Report
- How to Make Boiled Eggs How-To
Persuasive Writing
- Plastic, Paper, or Cloth? Persuasive Paragraph
- The Funny Dance Personal Narrative
- The Sled Run Personal Narrative
- Hello, Spring! Poem
- Cheetahs Report
Business Writing
- Dear Ms. Nathan Email
- My Favorite Place to Go Description
- My Mother Personal Essay
- Rules Personal Essay
- Shadow Fort Description
- Adopting a Pet from the Pound Editorial
- Letter to the Editor Letter to the Editor
- Ann Personal Narrative
- Grandpa, Chaz, and Me Personal Narrative
- Indy’s Life Story Personal Narrative
- Jet Bikes Personal Narrative
- The Day I Took the Spotlight Personal Narrative
- A Story of Survival Book Review
- Chloe’s Day Story
- Did You Ever Look At . . . Poem
- Dreams Poem
- I Am Attean Poem
- Sloppy Joes Poem
- The Civil War Poem
- The Haunted House Story
- The Terror of Kansas Story
- When I Was Upside Down Poem
- Deer Don’t Need to Flee to Stay Trouble-Free! Report
- Height-Challenged German Shepherd Report
- Friendship Definition
- What Really Matters News Feature
- Cheating in America Problem-Solution
- Hang Up and Drive Editorial
- Musical Arts Editorial
- Summer: 15 Days or 2 1/2 Months? Editorial
- A Cowboy's Journal Fictionalized Journal Entry
- Giving Life Personal Narrative
- The Great Paw Paw Personal Narrative
- The Racist Warehouse Personal Narrative
- Limadastrin Poem
- The Best Little Girl in the World Book Review
- How the Stars Came to Be Story
- Linden’s Library Story
- My Backyard Poem
- The Call Poem
- I Am Latvia Research Report
- Mir Pushed the Frontier of Space Research Report
- The Aloha State Research Report
- The Incredible Egg Observation Report
- Unique Wolves Research Report
- Dear Dr. Larson Email
Personal Writing
- A Lesson to Learn Journal
- Caught in the Net Definition
- From Bed Bound to Breaking Boards News Feature
- If Only They Knew Comparison-Contrast
- Save the Elephants Cause-Effect
- Student Entrepreneur Reaches for Dreams of the Sky News Feature
- Internet Plagiarism Problem-Solution
- Mosquito Madness Pet Peeve
- Anticipating the Dream Personal Narrative
- Huddling Together Personal Narrative
- H’s Hickory Chips Personal Narrative
- It’s a Boy! Personal Narrative
- My Greatest Instrument Personal Narrative
- Snapshots Personal Narrative
- Take Me to Casablanca Personal Narrative
- The Boy with Chris Pine Blue Eyes Personal Narrative
- The Climb Personal Narrative
- The House on Medford Avenue Personal Narrative
- Adam’s Train of Ghosts Music Review
- Diary of Gaspard Fictionalized Journal Entry
- My Interpretation of The Joy Luck Club Literary Analysis
- Mama’s Stitches Poem
- The KHS Press Play
- Rosa Parks Research Report
- The Killer Bean Research Report
- Mid-Project Report on History Paper Email
- Vegetarian Lunch Options at Bay High Email
MYP English A
Welcome to our class wiki for english language a.
These are some of the works we will read this year. We will also read a collection of short stories, and you will have a go at writing your own! See the pages on the drop down menu above for more details.
See below for Writing Tips.

Link to the Purple Duck here…

Writing Tips
Need help planning that literary essay? Use this scaffold. This is what we use with Grade 6 and 7 students to introduce you to the structure of a literary essay.
MYP Generic Essay Scaffold
Not happy with your Criterion C marks? Here are some exercises to improve your writing.
Comma Rules
Commas in Clauses
Punctuation
Semi Colons
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.

Infographics for GCSE results, 2024 (accessible)
Published 22 August 2024
Applies to England

© Crown copyright 2024
This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3.0 except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: [email protected] .
Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
This publication is available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/infographic-gcse-results-2024/infographics-for-gcse-results-2024-accessible
GCSE outcomes across all subjects, for all ages, at grade 4/C and above, 2017 to 2024 — England only
| Year | Percentage at grade 4/C or above |
|---|---|
| 2017 | 66.1% |
| 2018 | 66.6% |
| 2019 | 67.0% |
| 2020 | 75.9% |
| 2021 | 76.9% |
| 2022 | 73.0% |
| 2023 | 67.8% |
| 2024 | 67.4% |
Note: There were no summer exams in 2020 or 2021.
GCSE grades 7/A and above, 2019 to 2024 by region — England only
| Region | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North East | 16.4% | 22.0% | 24.5% | 22.4% | 17.6% | 17.8% |
| North West | 18.6% | 23.5% | 25.9% | 23.1% | 18.6% | 18.6% |
| Yorkshire and the Humber | 17.8% | 22.3% | 24.4% | 22.4% | 18.2% | 18.3% |
| West Midlands | 18.1% | 23.0% | 25.3% | 22.8% | 18.4% | 18.5% |
| East Midlands | 18.3% | 23.0% | 25.1% | 22.5% | 18.5% | 18.3% |
| Eastern region | 20.5% | 25.9% | 28.5% | 26.2% | 21.9% | 21.4% |
| South West | 20.4% | 26.1% | 29.1% | 25.3% | 20.8% | 21.2% |
| South East | 23.5% | 29.0% | 31.9% | 29.2% | 24.4% | 24.7% |
| London | 25.7% | 31.4% | 34.5% | 32.6% | 28.4% | 28.5% |
All grade 9s in all subjects taken in 2024, 16-year-olds — England only
| Number of GCSEs taken | Number of students |
|---|---|
| 7 | 95 |
| 8 | 145 |
| 9 | 340 |
| 10 | 545 |
| 11 or more | 145 |
| Total | 1,270 |
Of students receiving grade 9 in all subjects they took this year, 35% were male and 65% were female.
Note: Numbers of students have been rounded to the nearest 5.
Number of GCSEs taken in 2024, by 16-year-olds, in England
| Number of GCSEs taken | Number of students | Percentage of students |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8,715 | 1.3% |
| 2 | 13,815 | 2.1% |
| 3 | 11,460 | 1.7% |
| 4 | 12,780 | 1.9% |
| 5 | 21,270 | 3.2% |
| 6 | 45,850 | 6.9% |
| 7 | 103,940 | 15.6% |
| 8 | 167,330 | 25.1% |
| 9 | 189,285 | 28.4% |
| 10 | 81,460 | 12.2% |
| 11 | 11,030 | 1.7% |
| 12 or more | 390 | 0.1% |
| Total | 667,340 | 100% |
Note: Numbers of students have been rounded to the nearest 50. Because of roundings, percentages may not add up to 100%.
Average number of GCSEs taken by 16-year-olds, from 2019 to 2024 — England only
| Year | Average number of GCSEs |
|---|---|
| 2019 | 7.90 |
| 2020 | 7.87 |
| 2021 | 7.85 |
| 2022 | 7.78 |
| 2023 | 7.81 |
| 2024 | 7.81 |
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
Blog The Education Hub
https://educationhub.blog.gov.uk/2024/08/20/gcse-results-day-2024-number-grading-system/
GCSE results day 2024: Everything you need to know including the number grading system

Thousands of students across the country will soon be finding out their GCSE results and thinking about the next steps in their education.
Here we explain everything you need to know about the big day, from when results day is, to the current 9-1 grading scale, to what your options are if your results aren’t what you’re expecting.
When is GCSE results day 2024?
GCSE results day will be taking place on Thursday the 22 August.
The results will be made available to schools on Wednesday and available to pick up from your school by 8am on Thursday morning.
Schools will issue their own instructions on how and when to collect your results.
When did we change to a number grading scale?
The shift to the numerical grading system was introduced in England in 2017 firstly in English language, English literature, and maths.
By 2020 all subjects were shifted to number grades. This means anyone with GCSE results from 2017-2020 will have a combination of both letters and numbers.
The numerical grading system was to signal more challenging GCSEs and to better differentiate between students’ abilities - particularly at higher grades between the A *-C grades. There only used to be 4 grades between A* and C, now with the numerical grading scale there are 6.
What do the number grades mean?
The grades are ranked from 1, the lowest, to 9, the highest.
The grades don’t exactly translate, but the two grading scales meet at three points as illustrated below.
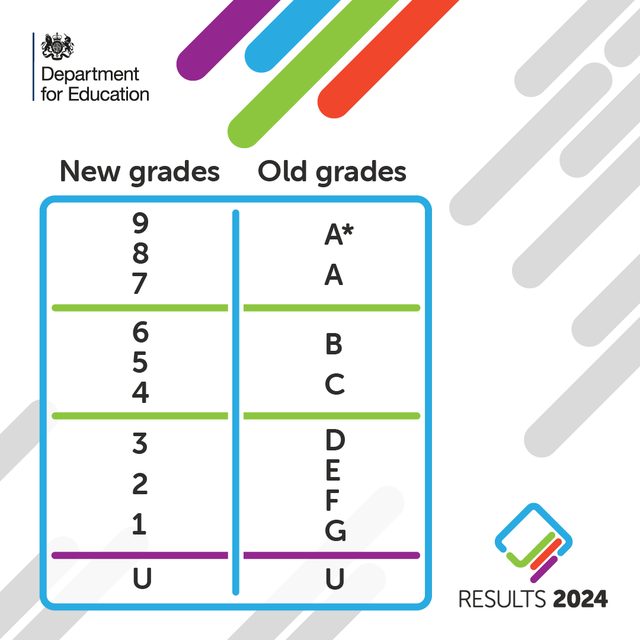
The bottom of grade 7 is aligned with the bottom of grade A, while the bottom of grade 4 is aligned to the bottom of grade C.
Meanwhile, the bottom of grade 1 is aligned to the bottom of grade G.
What to do if your results weren’t what you were expecting?
If your results weren’t what you were expecting, firstly don’t panic. You have options.
First things first, speak to your school or college – they could be flexible on entry requirements if you’ve just missed your grades.
They’ll also be able to give you the best tailored advice on whether re-sitting while studying for your next qualifications is a possibility.
If you’re really unhappy with your results you can enter to resit all GCSE subjects in summer 2025. You can also take autumn exams in GCSE English language and maths.
Speak to your sixth form or college to decide when it’s the best time for you to resit a GCSE exam.
Look for other courses with different grade requirements
Entry requirements vary depending on the college and course. Ask your school for advice, and call your college or another one in your area to see if there’s a space on a course you’re interested in.
Consider an apprenticeship
Apprenticeships combine a practical training job with study too. They’re open to you if you’re 16 or over, living in England, and not in full time education.
As an apprentice you’ll be a paid employee, have the opportunity to work alongside experienced staff, gain job-specific skills, and get time set aside for training and study related to your role.
You can find out more about how to apply here .
Talk to a National Careers Service (NCS) adviser
The National Career Service is a free resource that can help you with your career planning. Give them a call to discuss potential routes into higher education, further education, or the workplace.
Whatever your results, if you want to find out more about all your education and training options, as well as get practical advice about your exam results, visit the National Careers Service page and Skills for Careers to explore your study and work choices.
You may also be interested in:
- Results day 2024: What's next after picking up your A level, T level and VTQ results?
- When is results day 2024? GCSEs, A levels, T Levels and VTQs
Tags: GCSE grade equivalent , gcse number grades , GCSE results , gcse results day 2024 , gsce grades old and new , new gcse grades
Sharing and comments
Share this page, related content and links, about the education hub.
The Education Hub is a site for parents, pupils, education professionals and the media that captures all you need to know about the education system. You’ll find accessible, straightforward information on popular topics, Q&As, interviews, case studies, and more.
Please note that for media enquiries, journalists should call our central Newsdesk on 020 7783 8300. This media-only line operates from Monday to Friday, 8am to 7pm. Outside of these hours the number will divert to the duty media officer.
Members of the public should call our general enquiries line on 0370 000 2288.
Sign up and manage updates
Follow us on social media, search by date.
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | ||
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | |
Comments and moderation policy
GCSE results 2024: English and maths pass rate down

GCSE results have been released today across England, revealing that the percentage of students achieving pass grades in English and maths has fallen compared with last year - and that the gap between top grades achieved in private and state schools has increased.
The results are broadly similar to those of 2023 overall, with similar proportions of both top grades and students achieving a grade 4 or better.
However, there was a marked drop in the pass rate for English language GCSEs, which has mostly been driven by results for candidates aged 17 or over who were resitting the qualification.
Around four in five students aged 17 who took English language failed to achieve a grade 4 or better this year. (You can find our in-depth subject-by-subject breakdown here .)
Speaking in a Joint Council for Qualifications (JCQ) briefing this morning, Claire Thomson, AQA’s director of regulation and compliance, said the drop in pass rates was “largely around the 17-year-olds and over who are skewing the distributions. If you look at just the 16-year-olds, they are very stable with minimal movement over the years.
“The 17-and-over cohort has grown and come back over pre-pandemic levels, which is altering the results.”

Ofqual told examiners to proceed with “back to normal” grading standards this year after the two-step process to return to pre-pandemic grading was completed last year.
For 2024, examiners were asked to ensure the standard of work was comparable to 2023.
The 2023 GCSE results had seen a fall in the proportion of top grades awarded from 2022, bringing grade distribution more in line with 2019 levels. The proportion of top grades remained slightly above 2019 levels.
This year, examiners were asked by Ofqual to “bear in mind any residual impact of disruption on performance”.
Below are the key takeaways from this year’s GCSE results:
- GCSE grade spread similar to 2023
- English language resit passes down
- Private and state top grades gap increases
- Regions gap remains stable
- Gender gap narrows slightly
- Results in Wales and Northern Ireland
1. Grade spread similar to last year
Overall this year, 67.4 per cent of entries were awarded a grade 4/C or above. This is only slightly lower than last year, when 67.8 per cent of entries received a grade 4 or above.
In 2019, before the Covid-19 pandemic, 67 per cent received a grade 4 or above.
For the higher grades, the overall proportion of entries achieving a grade 7/A or higher was 21.7 per cent. This is very similar to 2023, when it was 21.6 per cent.
And finally, in 2024, a very slightly higher proportion of entries managed to achieve grade 9 (5 per cent). In 2023 and 2019, 4.9 per cent and 4.5 per cent of overall entries got a grade 9 respectively.
2. English language resit passes down
Pass rates for English and maths GCSEs were down on last year. However, this was in part because of a marked drop in the number of students aged 17 or over who did achieve a grade 4 in English language.
Overall in English language, 61.6 per cent achieved a grade 4/C or higher, compared with 64.2 per cent in 2023 and 61.8 per cent in 2019.
The pass rate in English language for candidates who were 17 or older was 20.9 per cent this year in England - down from 25.9 per cent last year.
The results only for 16-year-old candidates saw 71.2 per cent of entries awarded grade 4 or above - very slightly down from 71.6 per cent last year.
The percentage of students achieving the grade they need to pass in maths (4) has fallen this year to 59.6 per cent. Last year, 61 per cent of students achieved grade 4 in maths.
The results for 16-year-old entries show that 72 per cent of students achieved grade 4 in maths this year, slightly down from 72.3 per cent last year.
For entries among students who are aged 17 or over, 17.4 per cent of entries achieved grade 4 or above - up from 16.4 per cent last year.
Overall, 40.4 per cent of entries failed to achieve grade 4 in maths, and 38.4 per cent in English language.
In English literature, 73.7 per cent of entries received a grade 4 or above, very slightly down from 73.9 per cent last year. However, this was still slightly above the last set of pre-pandemic results, as 73.4 per cent passed in 2019.
Last summer’s GCSE results saw an increase in the number of students failing to achieve a pass mark for English and maths, and therefore an increase in those having to resit in November.
However, less than a quarter of the students who took GCSE maths in November 2023 passed - meaning the majority failed their resits .
Leaders across the sector have called for reform to the GCSE resit system, as many students currently never pass. Earlier this week, Professor Alan Smithers, director of the Centre for Education and Employment Research at the University of Buckingham, said that the current system is “soul-destroying” , and called on the government to make a change.
Paul Whiteman, general secretary of the NAHT school leaders’ union, said that the current GCSE resit policy for English and maths “must be scrapped”. “Those students who haven’t achieved the required grade are forced into repeated resits that are demotivating and can lead to disengagement with their learning,” he said.
Instead, Mr Whiteman said alternative qualifications in maths and English would be a more positive way for some students to demonstrate their achievements.
3. Private and state top grades gap increases
This year has also seen the gap between entries from academies and independent schools grow for achieving the top grades. Nearly half of entries from private schools achieved a grade 7/A or above (48.4 per cent), compared with 21.2 per cent of academies - a 27.2 percentage point gap.
Last year, there was a 26.5 percentage point gap between the proportion of entries from academies (21 per cent) and entries from independent schools (47.5 per cent) being awarded a grade 7 or above.
At secondary comprehensives, 19.4 per cent of entries achieved the top grades.
Statistics for independent schools also include city training colleges.

There was a slightly larger gap in 2023 between secondary comprehensive entries hitting the top grades (19.3 per cent) and independent schools of 28.2 percentage points.
However, the gap between school types was slightly lower in 2024 than in 2019, when there was a 27.5 percentage point between academies and independent schools and a 29.3 percentage point gap between comprehensive and private schools.
Schools minister Catherine McKinnell congratulated students and teachers on their achievements today but added: “While this is a moment to celebrate, I am deeply concerned about the inequalities in our education system with where you live and what type of school you attend still being too big an influence on your opportunities.”
4. Regions gap remains stable
The attainment gap between the North and South of England has also remained very similar to last year in terms of top grades.
The proportion of entries achieving a grade 7/A or above was lowest in the North East at 17.8 per cent. This is compared with London, where 28.5 per cent of entries made the grade 7/A.

Last year, the North East also saw the lowest proportion of top grades, with 17.6 per cent achieving a grade 7 or above. London remained the highest, with 28.4 per cent of entries being awarded those top grades.
That 10.8 percentage point gap was up from 9.3 percentage points in 2019. It has remained constant this year at 10.7 percentage points.
Senior leaders said earlier this year they were concerned about Year 11 exam readiness as absence remained high this spring term.
Absence has been particularly high among the most disadvantaged students. There is a higher proportion of disadvantaged students in the North.
Last week, education secretary Bridget Phillipson pledged to turn around “baked-in” educational inequalities and accused the previous government of leaving a legacy of regional “disparities” in exam outcomes and an attainment gap between private school students and their peers in state schools.
Pepe Di’Iasio, general secretary of the Association of School and College Leaders, said that the results show “significant differences” in regional outcomes for GCSEs in England.
“This suggests that relative levels of prosperity and socioeconomic disadvantage continue to play a huge part in educational outcomes,” he said. “Addressing these gaps must be a key priority for the new government working alongside the education sector.”
He added that “funding and teacher shortages, combined with post-pandemic issues around mental health, behaviour and attendance, have made circumstances particularly challenging”.
5. Gender gap narrows slightly
For 2024, the gender gap very slightly narrowed with 70.8 per cent of entries from girls achieving a grade 4/C or above compared with 64.1 per cent of boys - a 6.7 percentage point gap.
Last year, 71.3 per cent of all entries from girls achieved a grade 4 or above, compared with 64.4 per cent of entries from boys - a gap of 6.9 percentage points.
This 6.9 percentage point gap was narrower than in 2019, when 71.4 per cent of girls achieved a grade 4 or above compared with 62.7 per cent of boys.
Entries from girls were also more likely to receive top grades, with 24.4 per cent being awarded a grade 7/A, compared with 18.9 per cent of boys this year.
This was a slight narrowing of the gap from last year, when there was a 5.8 percentage point gap between girls and boys getting the top GCSE grades.
Girls continue to get more grade 9s than boys at 5.8 per cent of entries compared with 4.2 per cent.

The Education Policy Institute (EPI) highlighted recently that the gender gap that has seen girls generally attain higher for many years has been narrowing since the pandemic.
Up to 2023, this narrowing has not only been driven by some increases in attainment for boys at key stage 4, but also some falls in attainment for girls.
6. Wales and Northern Ireland: slight rise in top grades
In Northern Ireland, 31 per cent of GCSE students achieved a grade A/7 or above in 2024, compared with 30.5 per cent in 2019. Meanwhile, 82.7 per cent of exam entries received a grade C/4 or above, similar to the 82.2 per cent of entries in 2019.
In Wales, 19.2 per cent of students achieved an A/7 or above, compared with 18.4 per cent in 2019. This year, 62.2 per cent of exam entries received a C/4 or above - only slightly lower than the 62.8 per cent of entries that achieved this in 2019.

- GCSE results 2024: how did each subject perform?
- GCSE resits: everything you need to know
- How much does attendance really affect GCSE results?
- Government ‘should rethink soul-destroying resits’
- Concern over exams’ impact on student mental health
For the latest education news and analysis delivered every weekday morning, sign up for the Tes Daily newsletter
topics in this article


IMAGES
COMMENTS
1. "Somewhere outside, a war was raging. But it was far away- a bad dream- leaving us untouched". 2. "I played the harmonica while my parents danced. In our dream we believed the world to be good". 3. "Often, to keep from losing hope, I touched the harmonica, cold inside my pocket". 4.
Literary Analysis Writing Unit 7th grade Professional Develop Module Handouts Common Core Literary Analysis Writing Unit - Handouts for PD Module Page 1 ... Literary Essay Mentor Texts: The Other Side, By Jacqueline Woodson Baseball in April and Other Stories, By Gary Soto Every Living Thing, By Cynthia Rylant
But, I was now a seventh and eighth grade ELA teacher who could no longer hope her students picked up some writing skills along the way. So I did what any good teacher would do…. I Googled how to teach… I think I Googled something like, "Examples of middle school literary analysis essays." Nothing showed up in Google.
7th Grade Literary Texts "The War of the Wall" by Toni Cade Bambara (7th grade) In this short story, the narrator and their friends are upset when a stranger comes to paint a mural on a wall in their beloved neighborhood. ... This engaging personal essay helps students explore the perspective of someone who feels they need to change themselves ...
Lucy Calkins: Literary Essays Texts: Whole Group Classroom Short Texts for Modeling: (writing inside the story, close reading, characters, conversational prompts, provocative ideas, thesis, framing essay, stories as evidence, summaries, lists, craftmanship, polishing) Spaghetti by Cynthia Rylant (referenced in Units of Study Lessons)
A. Analyze a Model - W.7.1 (20 minutes) Review appropriate learning target relevant to the work to be completed in this section of the lesson: "I can identify the parts of a model argument essay and explain the purpose of each.". Distribute and display the Model Argument Essay: "Strength from the Past.".
7th Grade - Literary Essay Preface The following unit supports and aligns to the Common Core State Standards. This research-based work is the outcome of a collective effort made by numerous secondary teachers from around the state of Michigan. Michigan Association of
ELA 2019 G7:M3:U2:L8 Write a Literary Argument Essay: Analyze a Model Write a Literary Argument Essay: Draft Proof Paragraph 1 ELA 2019 G7:M3:U2:L10. In this Lesson. Daily Learning Targets; Ongoing Assessment; ... Use the Grade 7 Writing Process Checklist to assess students' writing abilities in Closing and Assessment A (see the Tools Page).
The Literary Analysis Task requires students to read two literary texts that are purposely paired. Students read the texts, answer questions for each text and for the texts as a pair, and then write an analytic essay. The 2015 blueprint for grade 7 Literary Analysis Task includes six Evidence-Based Selected Response/Technilogy-
Classic Literature: If. Help your students improve their reading skills with this activity set about Rudyard Kipling's poem "If". Grade Levels: 6th - 8th Grade, Grades K-12. CCSS Code (s): RL.5, RL.6, RL.7, RL.8. 1. Free, printable ELA Common Core Standards Worksheets for 7th grade literature skills. Use activities in class or home.
The Literary Essay is an insightful, critical interpretation of a literary work. It is not a summary of plot, character or other elements of fiction in any given literary work. …allows you, the writer, to provide your own understanding of the literary work in a properly structured format. In order to be complete, your essay must include the ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
rade 7 Literature Mini-Assessment "From the Wave" by Thom GunnThis grade 7 mi. i-assessment is based on the poem "From the Wave" by Thom Gunn. This text is considered to be a text worthy of students' time to. ead and also meets the expectations for text complexity at grade 7. Assessments aligned to the Common Core State S.
Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap. City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative. Table of contents. Example 1: Poetry. Example 2: Fiction. Example 3: Poetry. Attribution. The following examples are essays where student writers focused on close-reading a literary work.
Teaching how to write a literary analysis satisfies the following ELA Common Core Standards. RL.9-10.1 Cite strong and thorough textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text. L.9-10.2 Determine a theme or central idea of a text and analyze in detail its development over the ...
Grade 7 ELA Writing - Argumentative BACKGROUND and PURPOSE . The WY-TOPP ELA test has a Writing portion for grades 3, 5, 7, and 9. Each writing test contains one or more passages that relate to a prompt. Students are required to read passages associated with a topic, and then write a response based on a prompt. This type of text-based
Using Transition Words. In this worksheet, your students will learn how to properly use transition words in a sentence. Grade Levels: 4th and 5th Grade, 6th - 8th Grade, Grades K-12. CCSS Code (s): W.5.2.c, W.6.2.c, W.7.2.c. 2. Free, printable ELA Common Core Standards Worksheets for 7th grade writing skills. Use activities in class or home.
If you are in 7th grade then you would have some experience in writing essay assignments. You might be new to literary papers or this specific style but the traditional format and structure of the paper will stay the same. You need to start with an introduction, explain your major arguments in the body, and summarize your paper in the ...
The first unit in 7th grade engages students with diverse protagonists and universal experiences that provide opportunities for students to build empathy. Reading comprehension lessons challenge students to consider their role in creating community for others through collaborative discussion. Middle school students will easily relate to and ...
Adopting a High Quality Instructional Material like CommonLit 360 curriculum accelerates student growth with grade-level rigor and built-in support. Get a quote to roll out EdReports-green curriculum today! Dismiss Announcement CommonLit is a nonprofit that has everything teachers and schools need for top-notch literacy instruction: a full-year ...
7th grade humanities: Home Writing Notes Reading Notes > Social Studies Notes ... remember you can use the sentence starters that you learned during the literary essay unit! ... and rebuttals in your essay: Handout with examples of rebuttal approaches: counterclaim_rebuttal_handout.docx: File Size: 144 kb: File Type: docx: Download File ...
Student Models. When you need an example written by a student, check out our vast collection of free student models. Scroll through the list, or search for a mode of writing such as "explanatory" or "persuasive.".
Need help planning that literary essay? Use this scaffold. This is what we use with Grade 6 and 7 students to introduce you to the structure of a literary essay. MYP Generic Essay Scaffold. Not happy with your Criterion C marks? Here are some exercises to improve your writing. Adjectives.
GCSE grades 7/A and above, 2019 to 2024 by region — England only; All grade 9s in all subjects taken in 2024, 16-year-olds — England only; Number of GCSEs taken in 2024, by 16-year-olds, in ...
The shift to the numerical grading system was introduced in England in 2017 firstly in English language, English literature, and maths. By 2020 all subjects were shifted to number grades. This means anyone with GCSE results from 2017-2020 will have a combination of both letters and numbers.
Group 1: Language A: literature. English A: literature paper 1 and marking notes (first assessment 2021) [512KB] English A paper 2 [197KB] Group 2: Language acquisition: Language B. English B HL specimen paper 2 audio [84,3 MB] English B SL specimen paper 2 audio [61,7 MB] English B specimen papers and markschemes (first assessment 2020) [2.1MB]
For English literature, 73.7 per cent of overall entries achieved a grade 4/C or higher - down slightly from 73.9 per cent in 2023 but up slightly from 73.4 per cent in 2019. In literature, 20.1 per cent achieved a grade 7/A or above, and 15.6 per cent in language.
Overall, 40.4 per cent of entries failed to achieve grade 4 in maths, and 38.4 per cent in English language. In English literature, 73.7 per cent of entries received a grade 4 or above, very slightly down from 73.9 per cent last year. However, this was still slightly above the last set of pre-pandemic results, as 73.4 per cent passed in 2019.